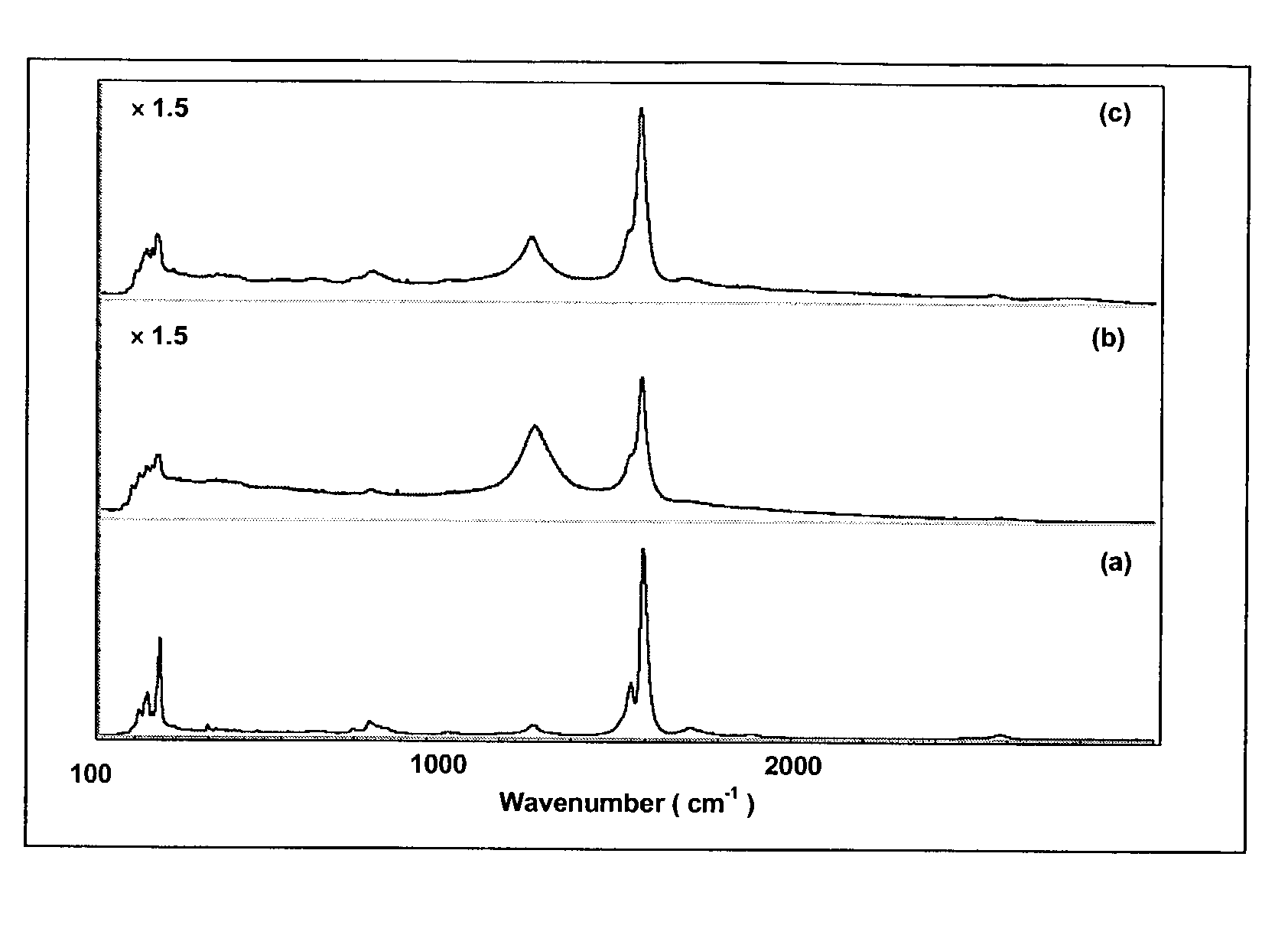
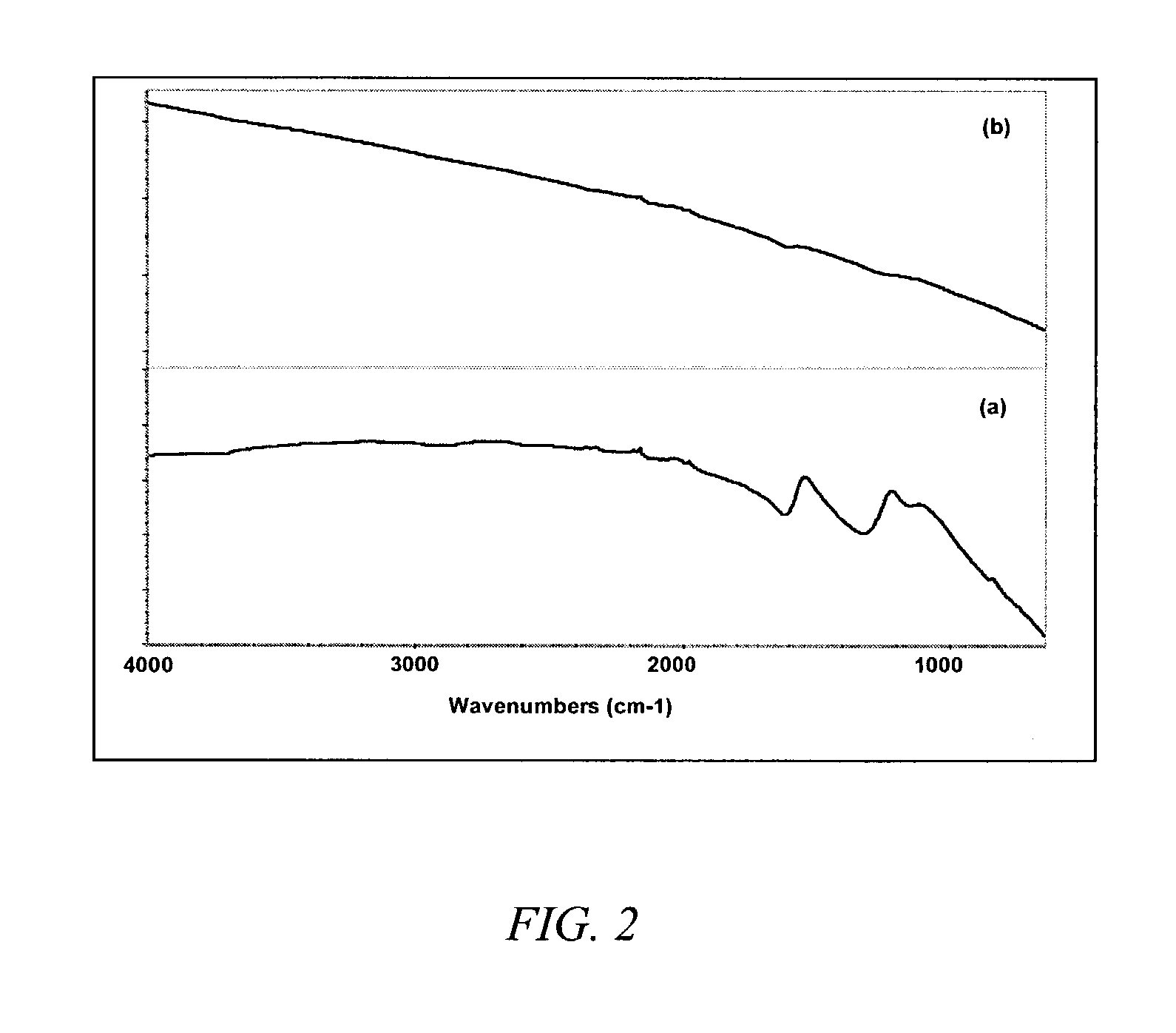
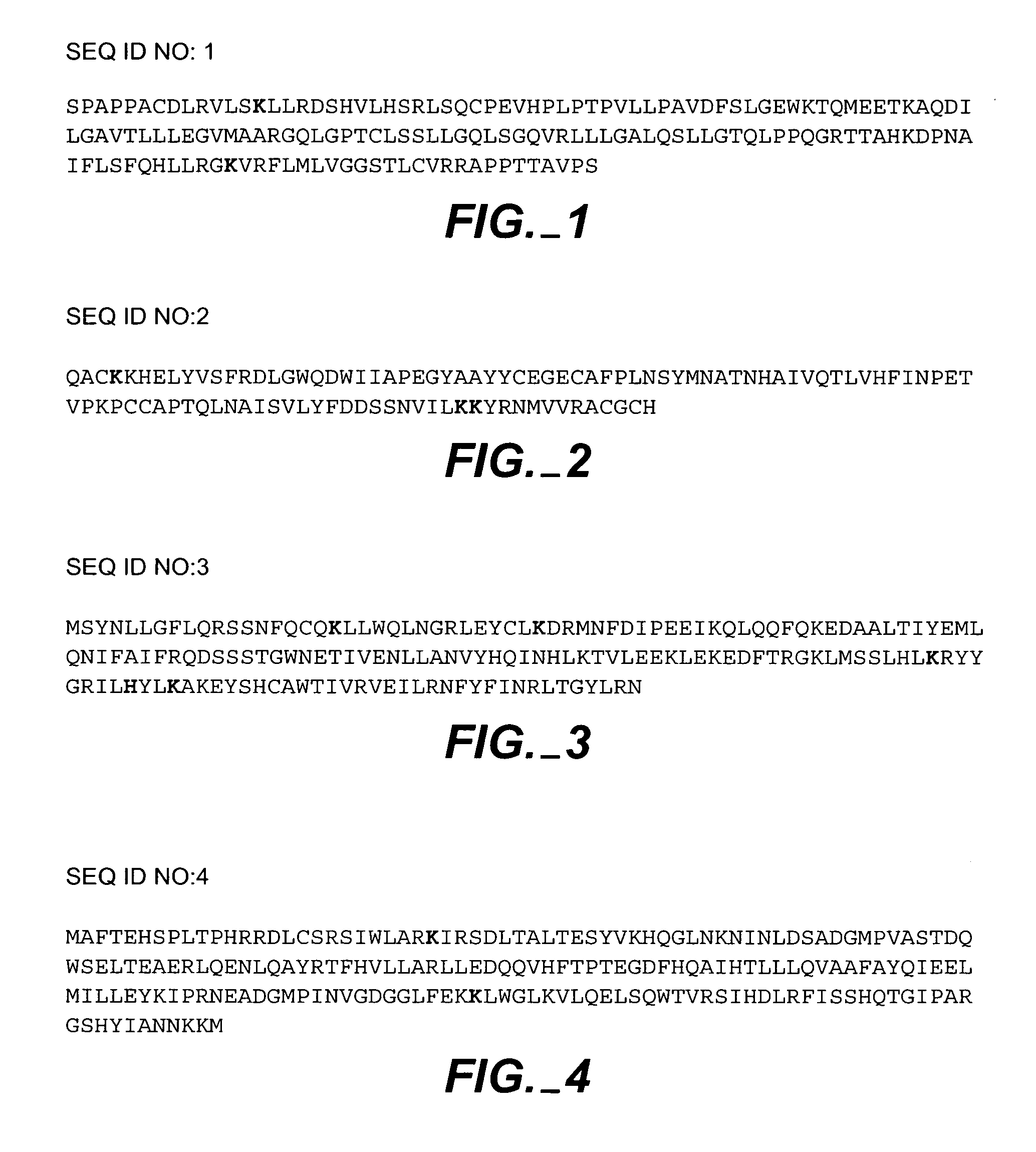
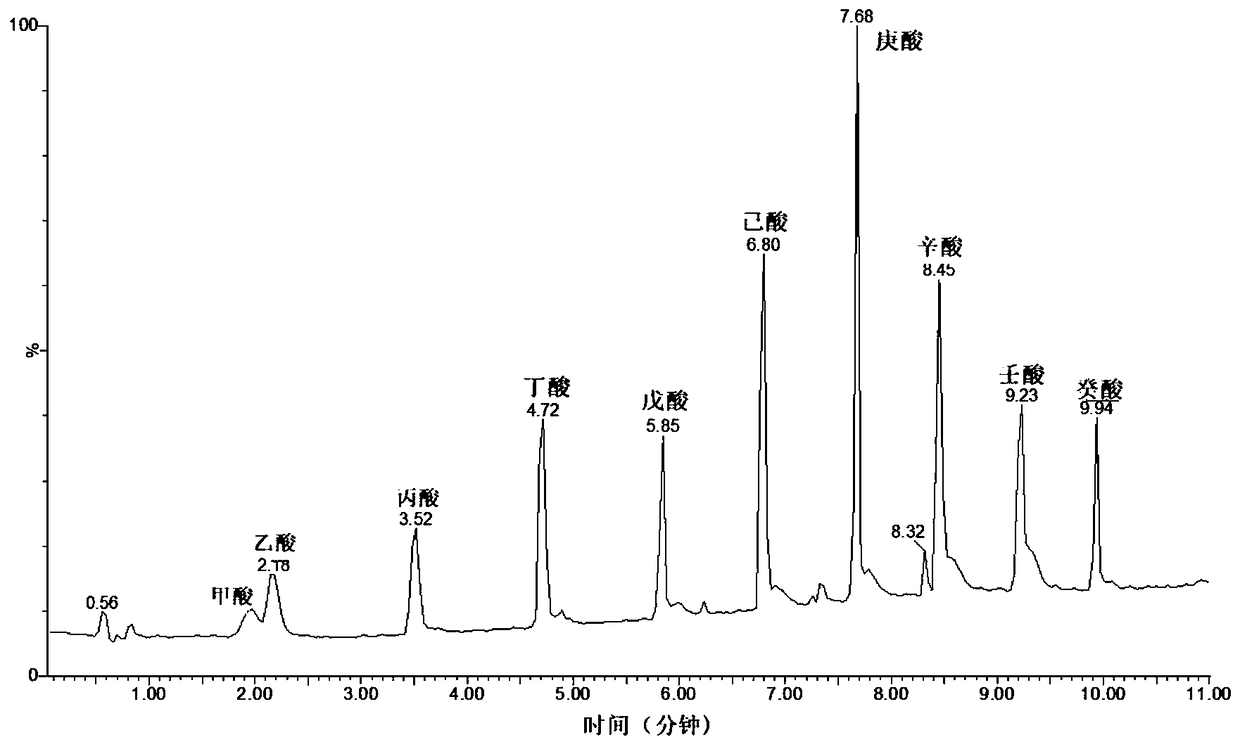
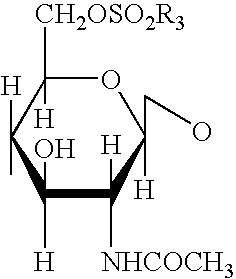
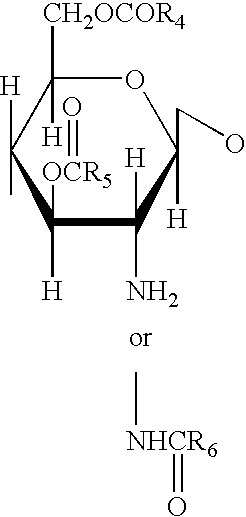
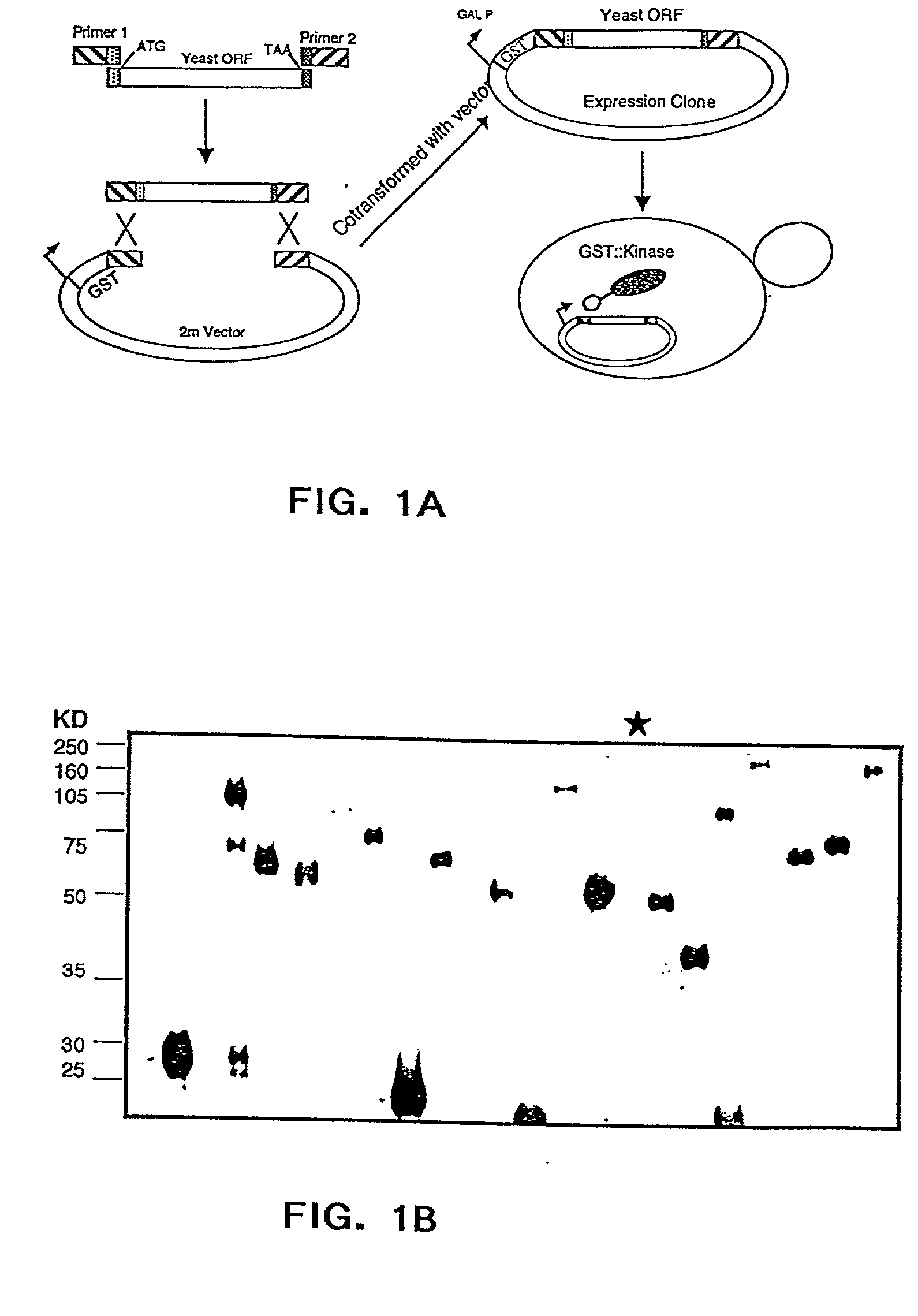
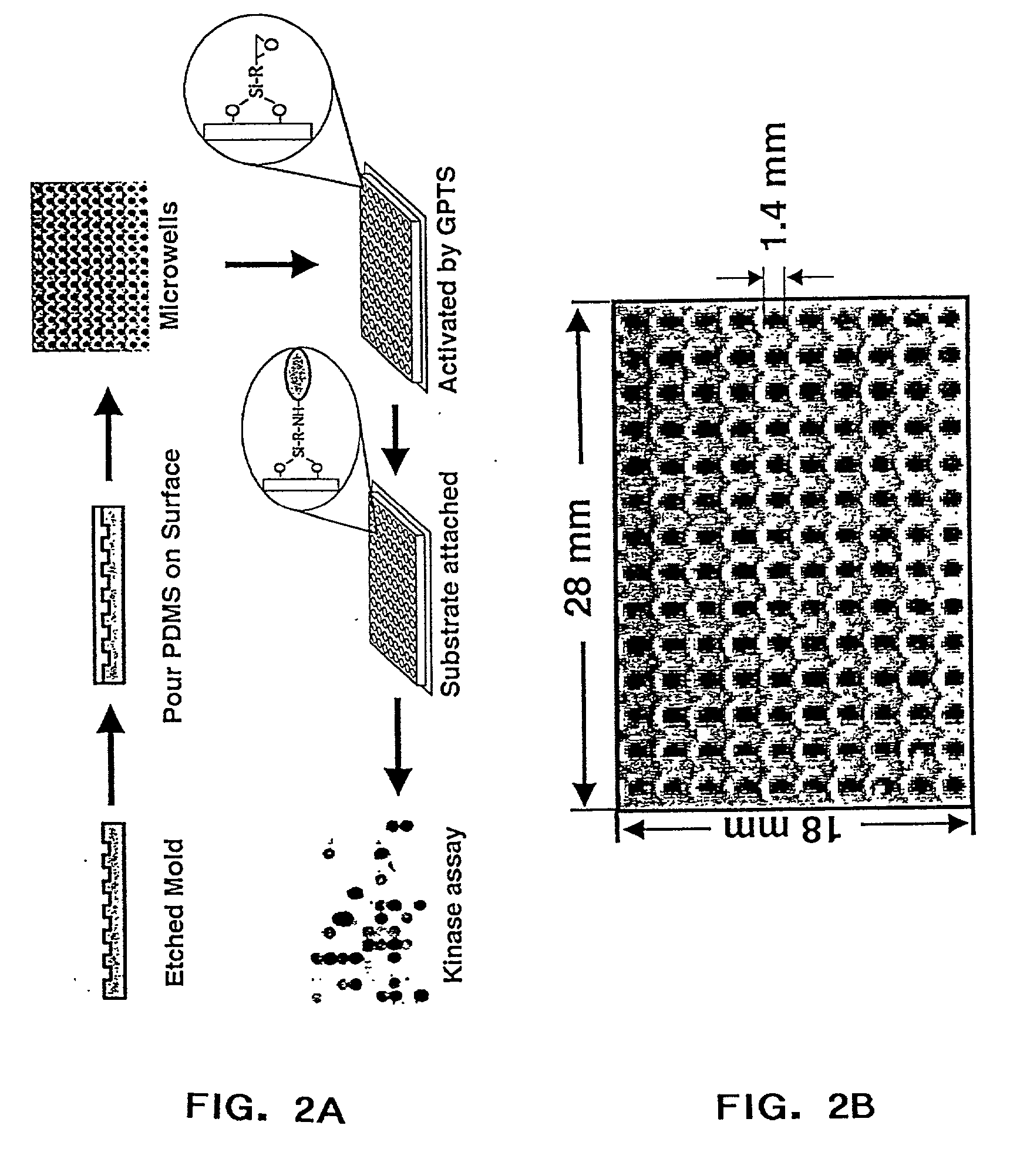
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2114 results about "Derivatization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
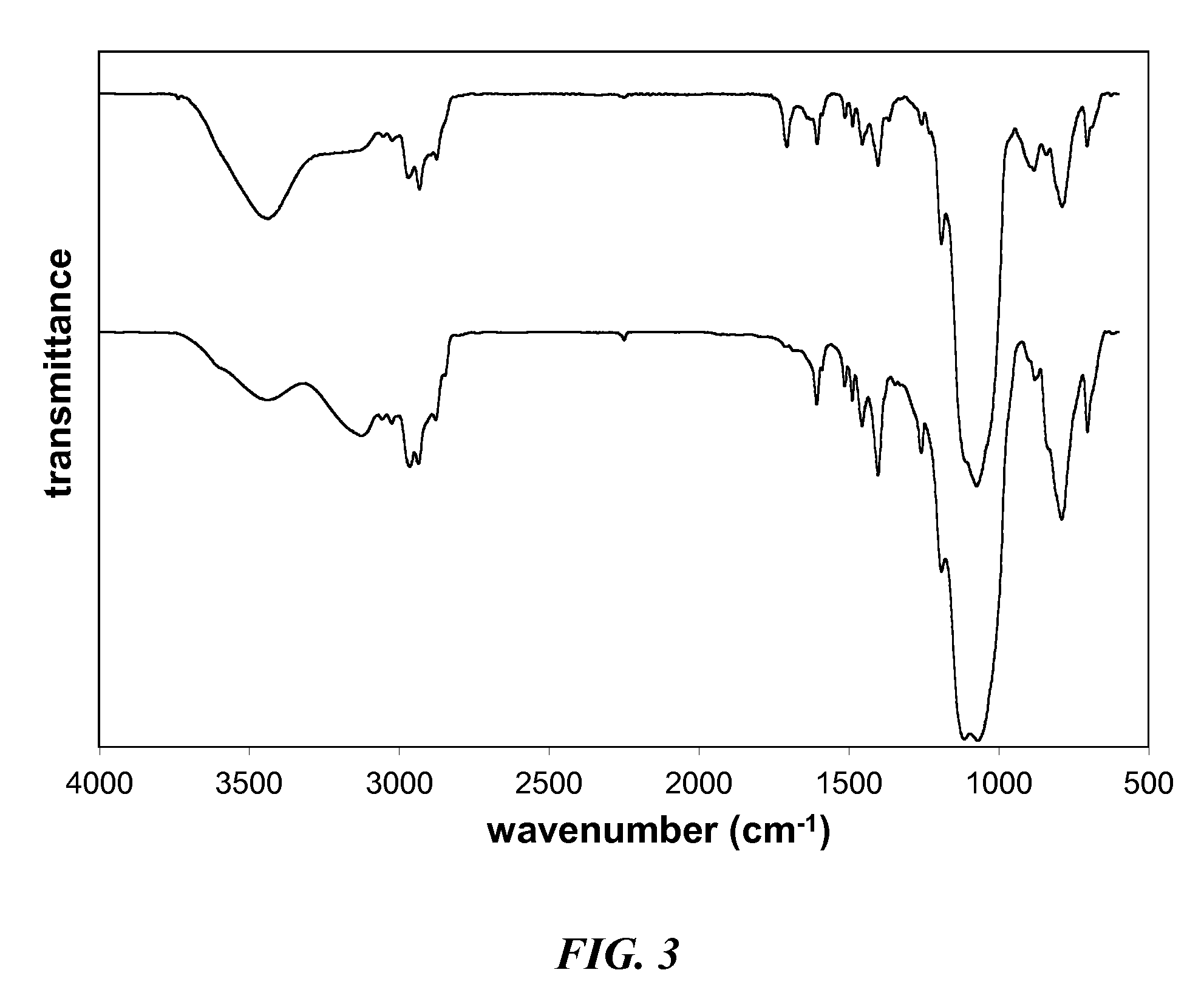
Derivatization is a technique used in chemistry which transforms a chemical compound into a product (the reaction's derivate) of similar chemical structure, called a derivative. Generally, a specific functional group of the compound participates in the derivatization reaction and transforms the educt to a derivate of deviating reactivity, solubility, boiling point, melting point, aggregate state, or chemical composition. Resulting new chemical properties can be used for quantification or separation of the educt.
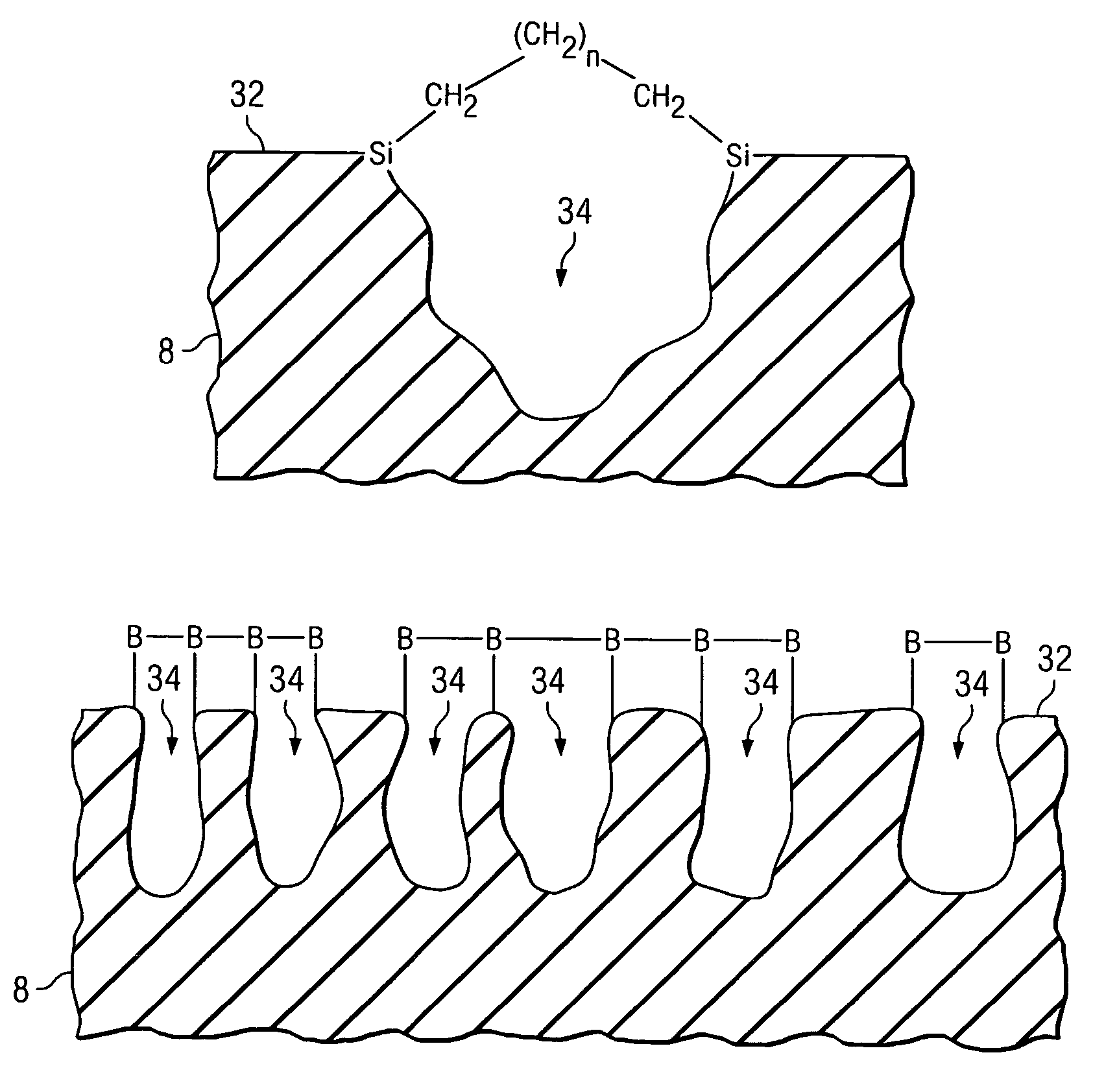
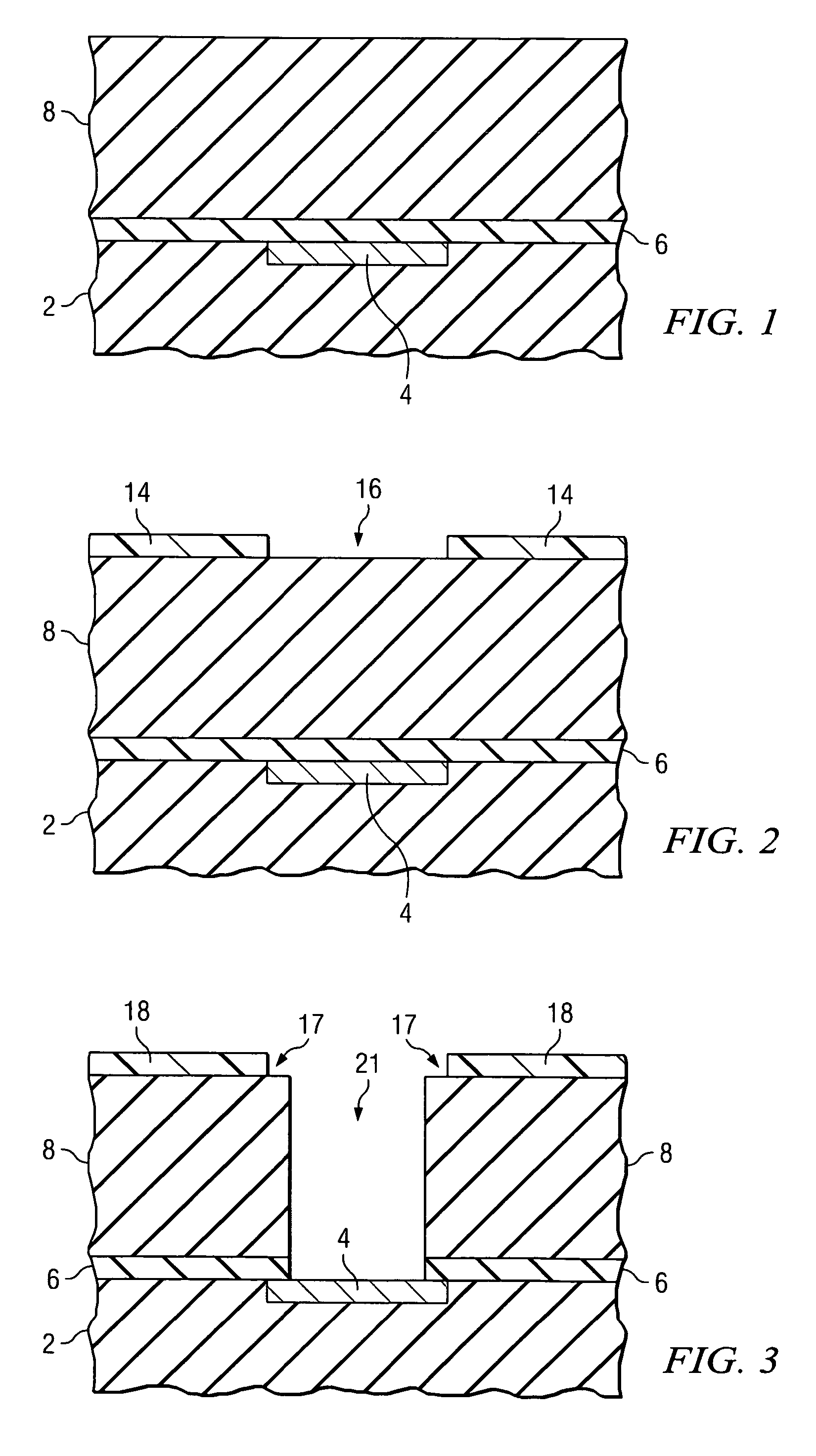
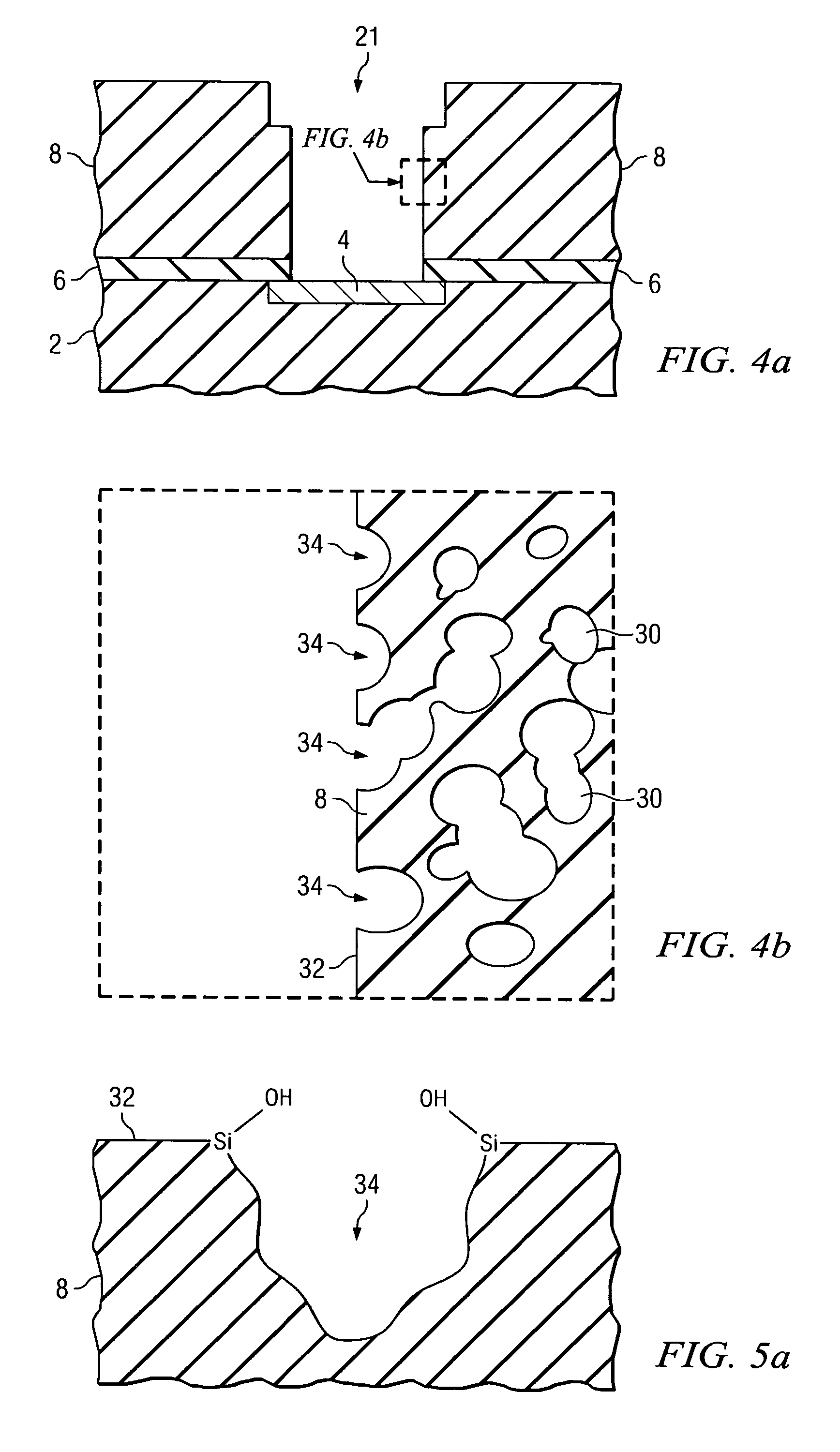
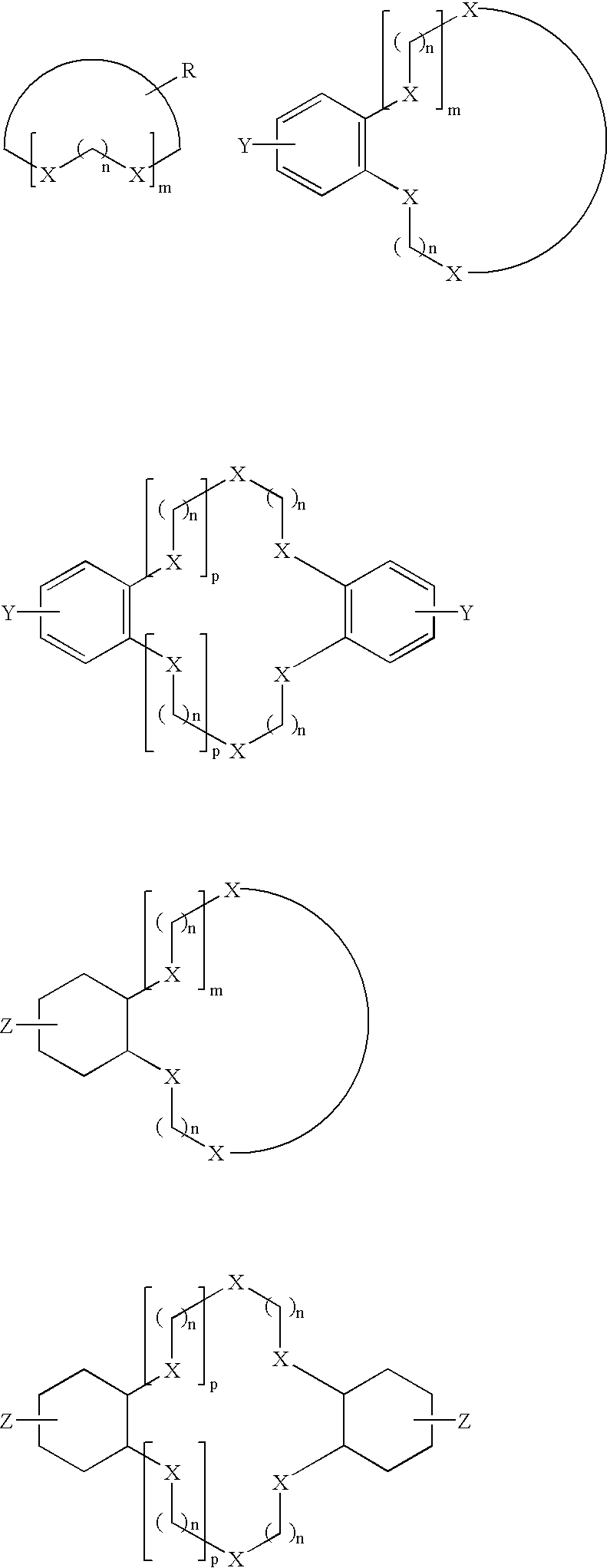
Using polydentate ligands for sealing pores in low-k dielectrics
InactiveUS7163900B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCross-linkDerivatization
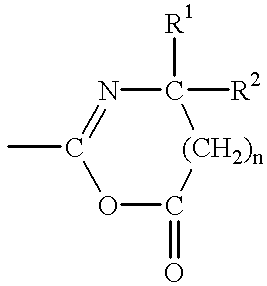
In preferred embodiments, a polydentate pore-sealing ligand is used to seal or repair pores damaged by plasma processing. The polydentate ligand includes bidentate ligands corresponding to the general formula X—CH2—(CH2)n—CH2—X or X—Si(CH3)2—(CH2)n—Si(CH3)2—X. The polydentate ligand also includes tridendate ligands corresponding to the general formula X—CH2—(CH2)m(CXH)(CH2)o—CH2—X or X—Si(CH3)2—(CH2)m(CXH)(CH2)o—Si(CH3)2—X. Alternative embodiments may include single or multiply branched polydentate ligands. Other embodiments include ligands that are cross-linked after attachment to the dielectric. Still other embodiments include a derivatization reaction wherein silanol groups formed by plasma damage are removed and favorable dielectric properties are restored.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
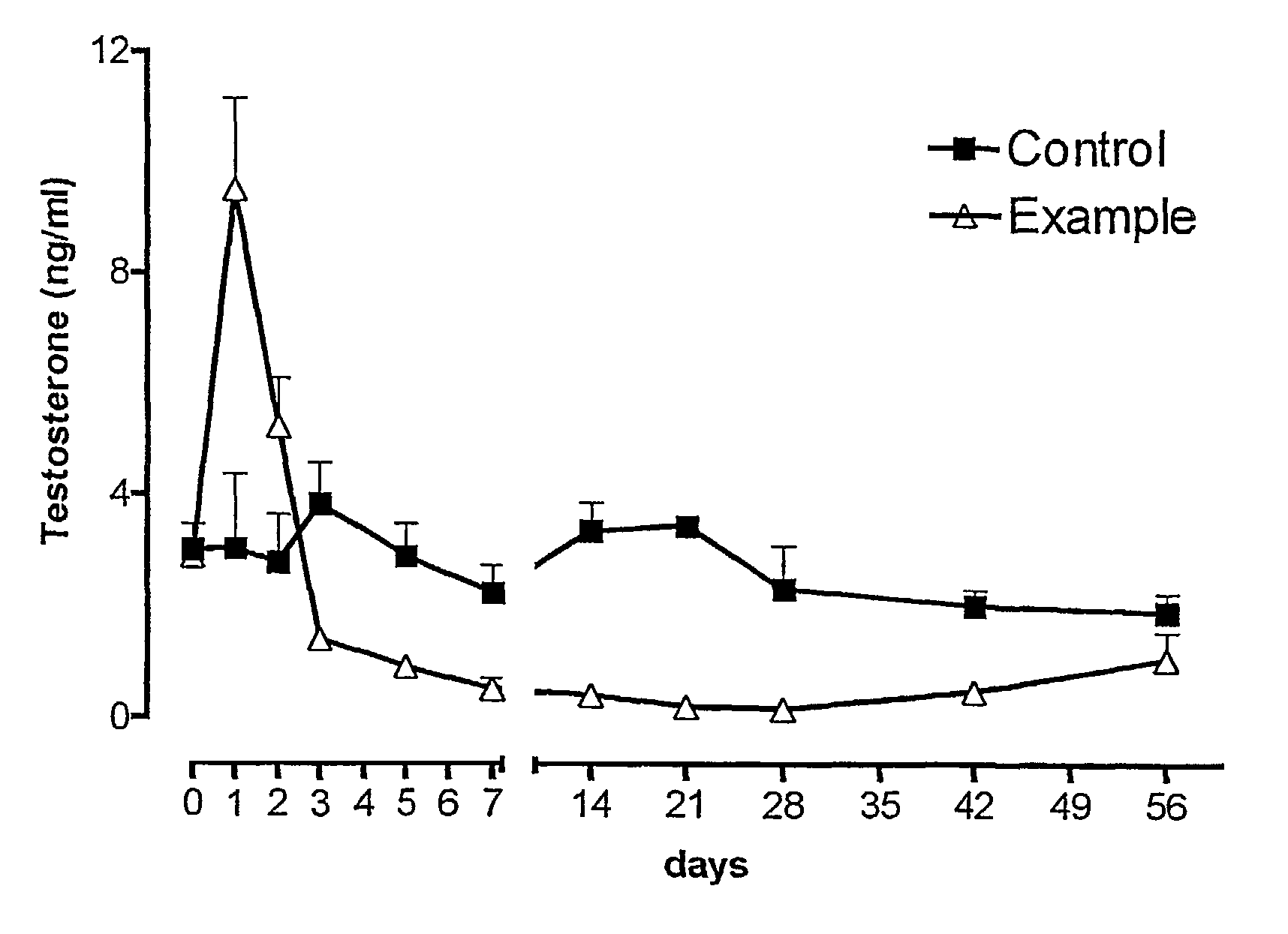
Sustained release pharmaceutical compositions for the parenteral administration of hydrophilic compounds
InactiveUS7157099B2Easy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsParenteral nutritionBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Owner:ITALFARMACO SPA
Novel recombinant proteins with N-terminal free thiol
InactiveUS20050170457A1Extended half-lifeIncreases circulating serum half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureCysteine thiolateHalf-life
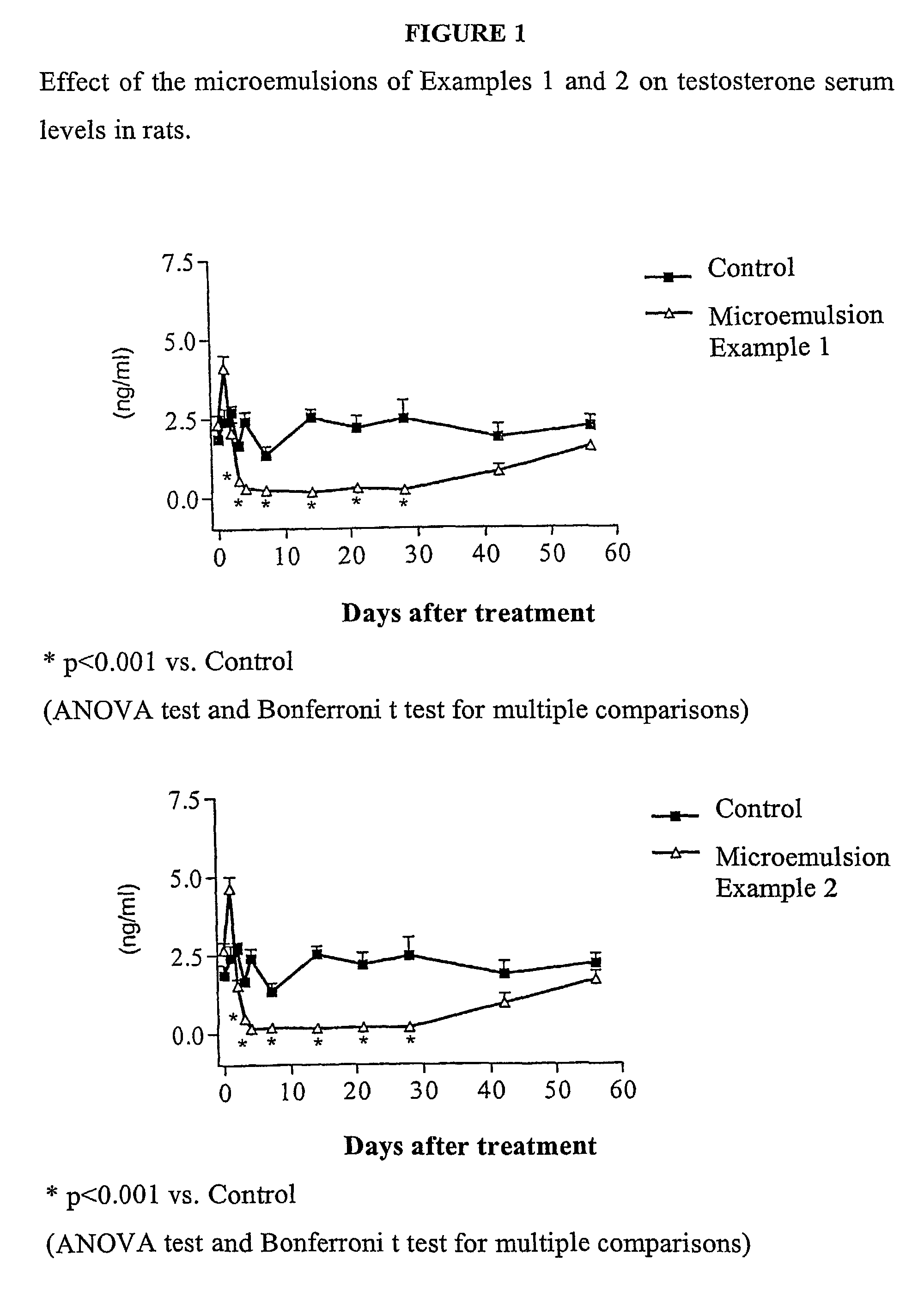
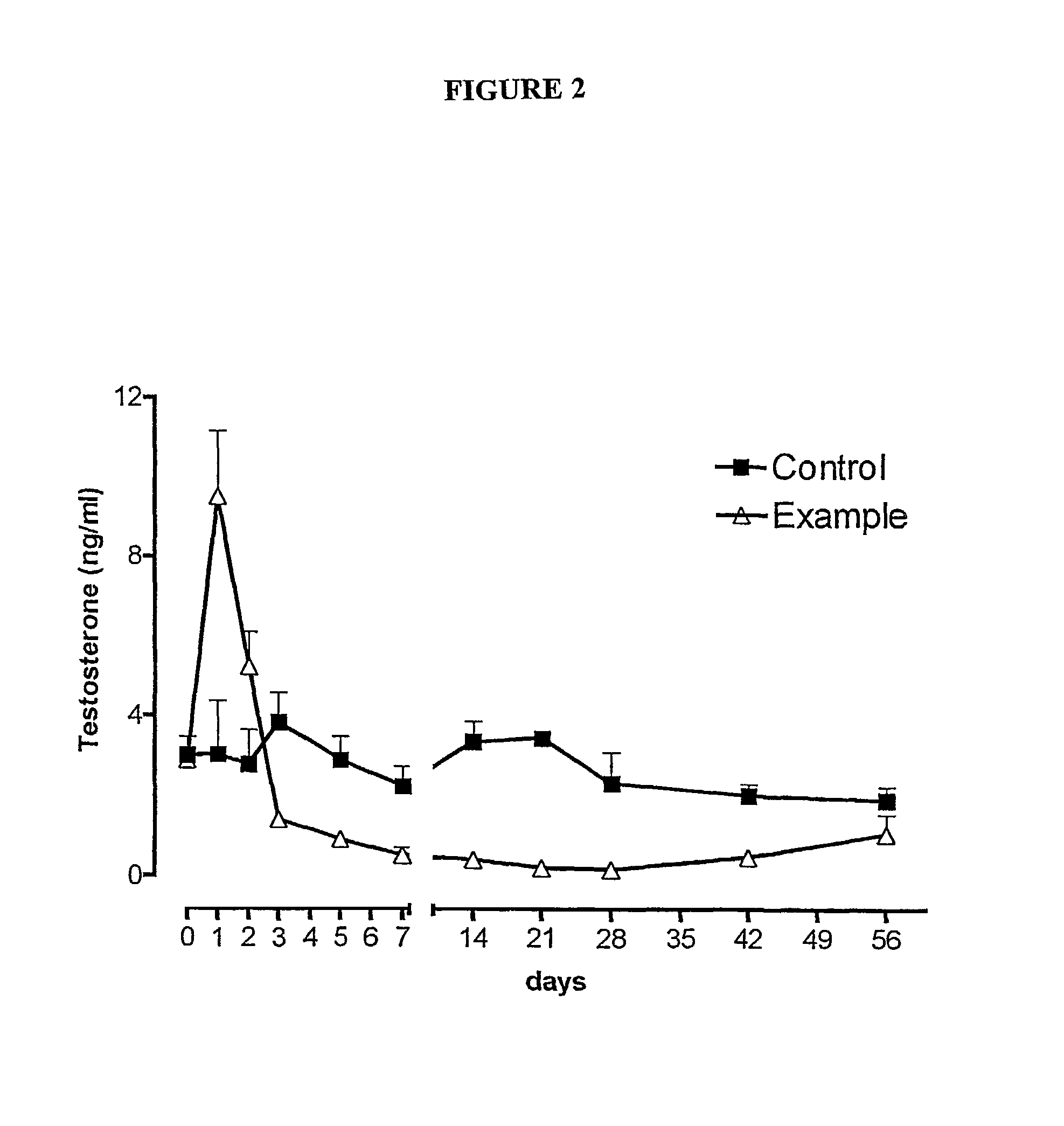
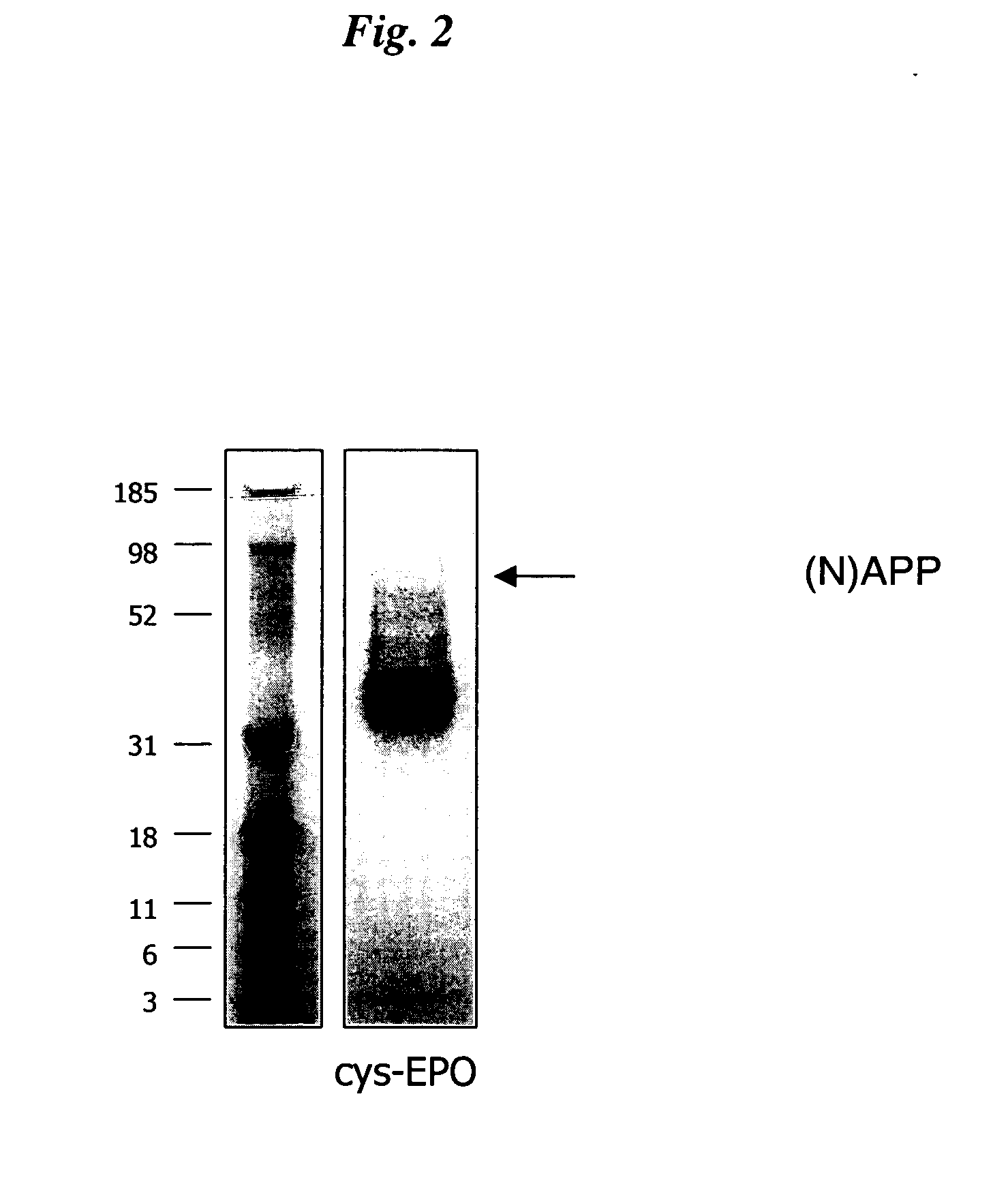
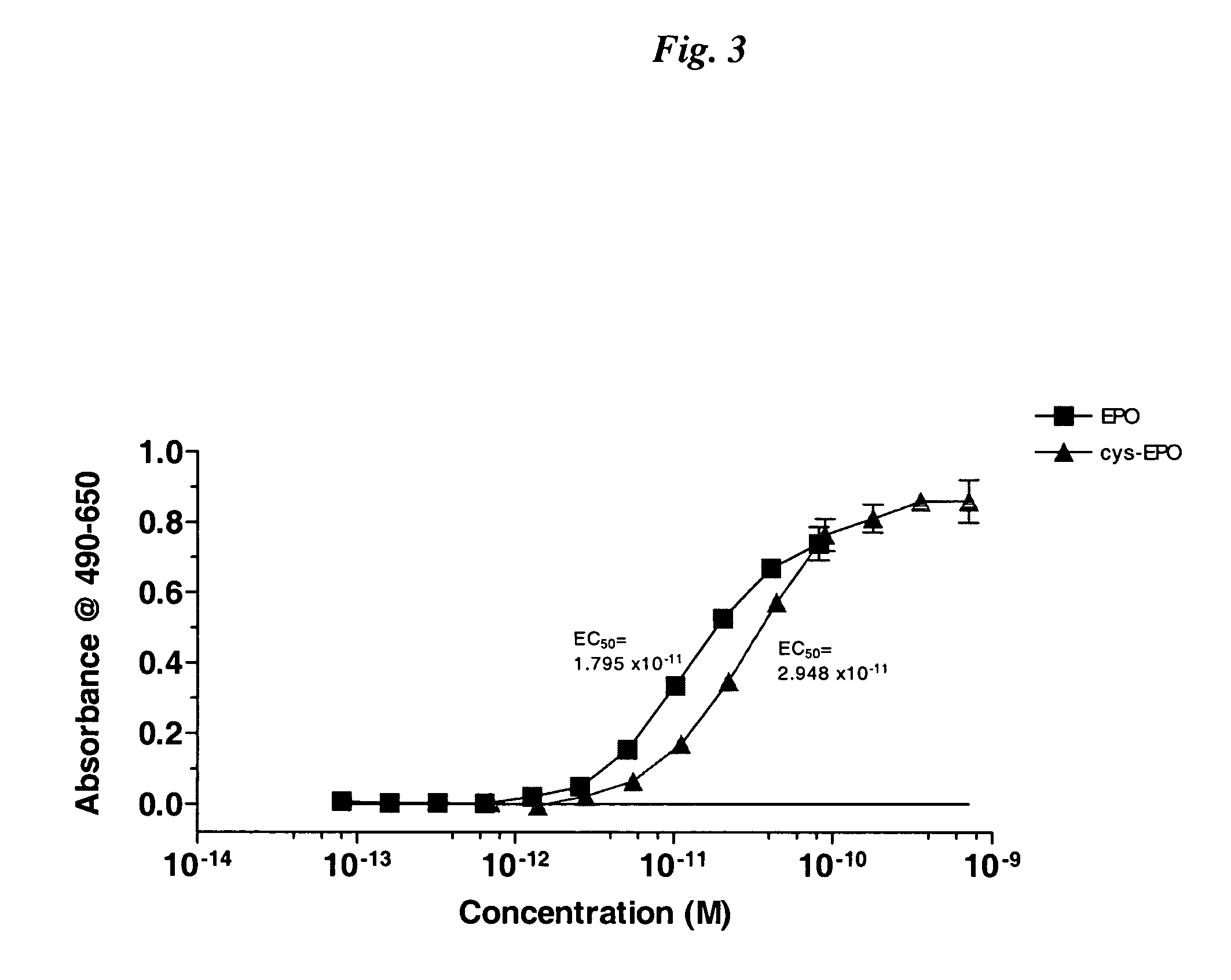
The present invention relates to novel modified proteins having N-terminal free thiols that can be produced by recombinant methods and are ready for further chemical derivatization. In particular, the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds having altered biochemical, physiochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. More particularly, one embodiment of the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds of the formula: (M)n-X-A-cys-EPO (I) where EPO is an erythropoeitin moiety selected from erythropoietin or an erythropoietin variant having at least one amino acid different from the wild-type human EPO, or any pharmaceutical acceptable derivatives thereof having biological properties of causing bone marrow cells to increase production of red blood cells; cys represents the amino acid cysteine and occurs at position −1 relative to the amino acid sequence of the erythropoietin moiety; A indicates the structure of the residual moiety used to chemically attach X to the thiol group of −1Cys; X is a water soluble polymer such as a polyalkylene glycol or other polymer; M is an organic molecule (including peptides and proteins) that increases the circulating half-life of the construct; and N is an integer from 0 to 15.
Owner:CENTOCOR
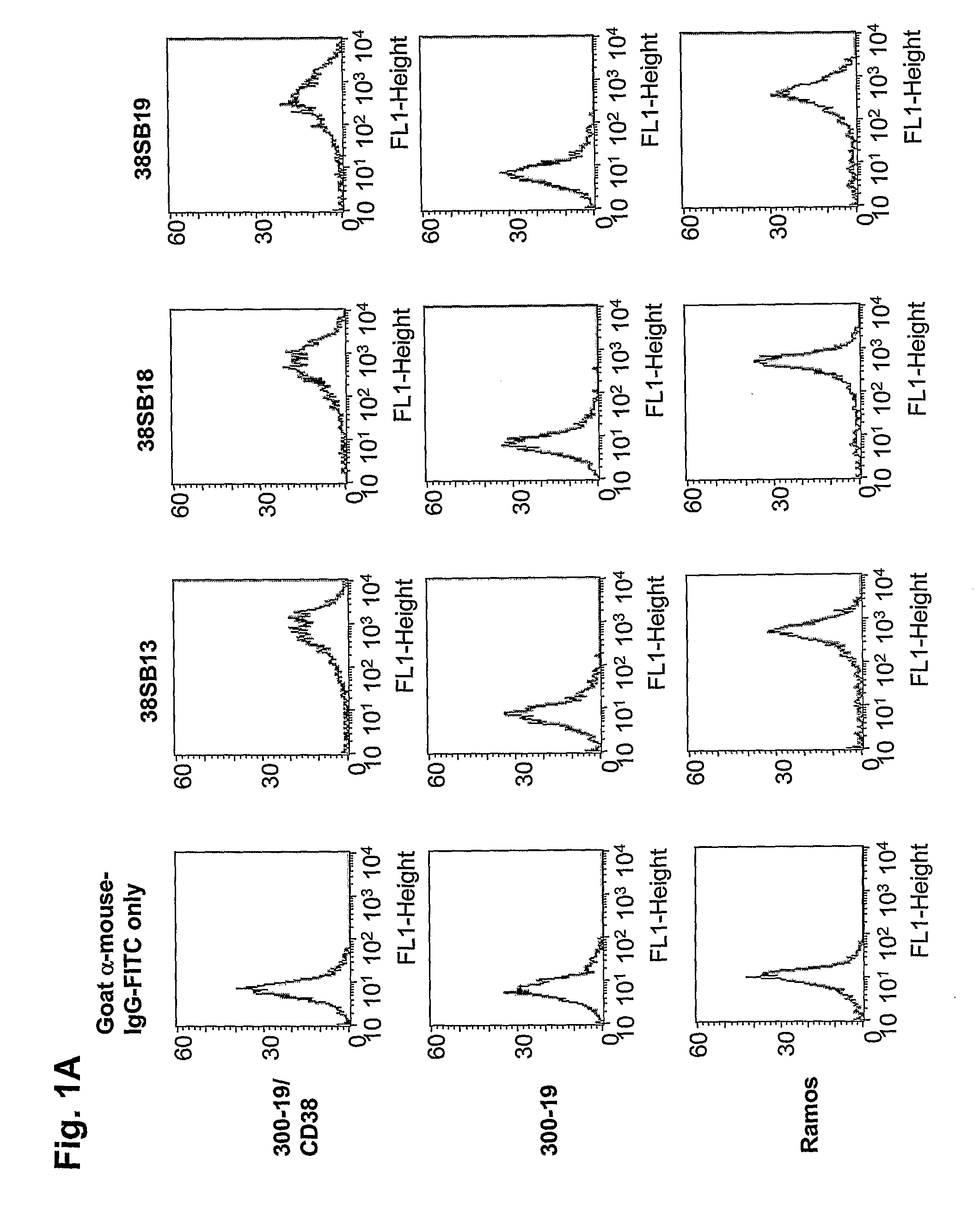
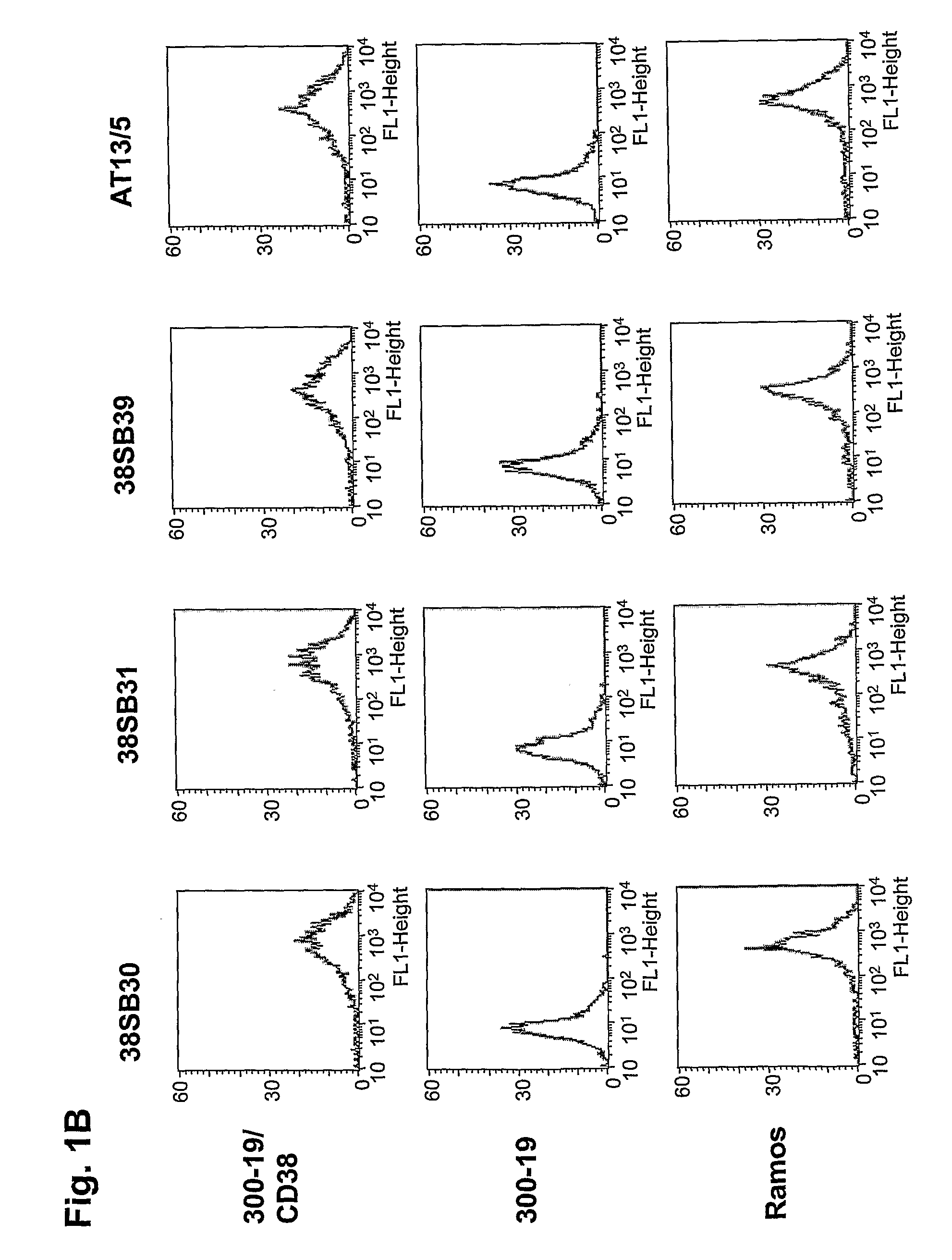
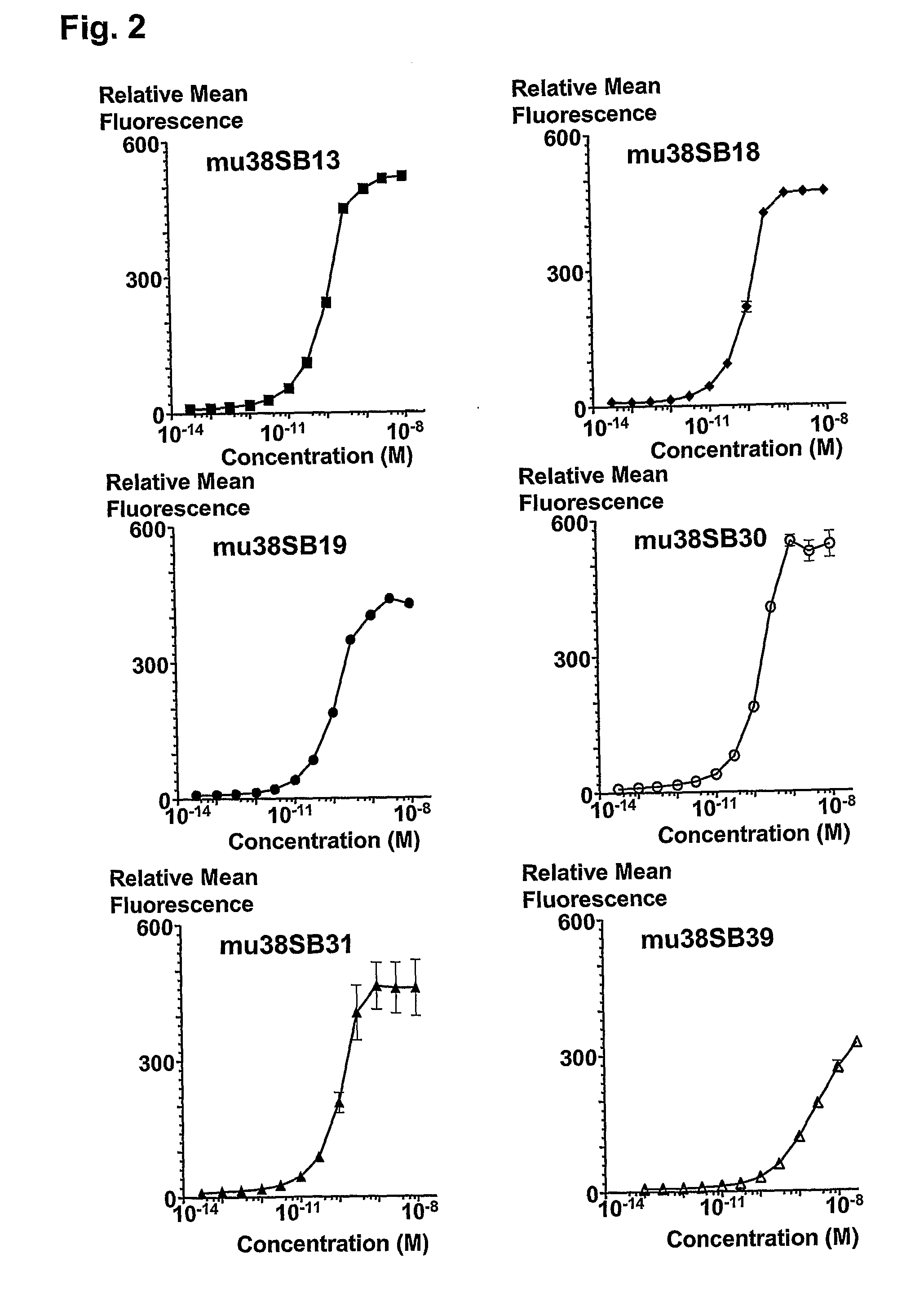
Novel Anti-cd38 antibodies for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20090304710A1Improve propertiesLess immunogenicSenses disorderAntipyreticComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody fragments
Antibodies, humanized antibodies, resurfaced antibodies, antibody fragments, derivatized antibodies, and conjugates of same with cytotoxic agents, which specifically bind to CD38, are capable of killing CD38+ cells by apoptosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and / or complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Said antibodies and fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of tumors that express CD38 protein, such as multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, or acute lymphocytic leukemia, or the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, erythematosus, and asthma. Said derivatized antibodies may be used in the diagnosis and imaging of tumors that express elevated levels of CD38. Also provided are cytotoxic conjugates comprising a cell binding agent and a cytotoxic agent, therapeutic compositions comprising the conjugate, methods for using the conjugates in the inhibition of cell growth and the treatment of disease, and a kit comprising the cytotoxic conjugate. In particular, the cell binding agent is a monoclonal antibody, and epitope-binding fragments thereof, that recognizes and binds the CD38 protein.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS US LLC
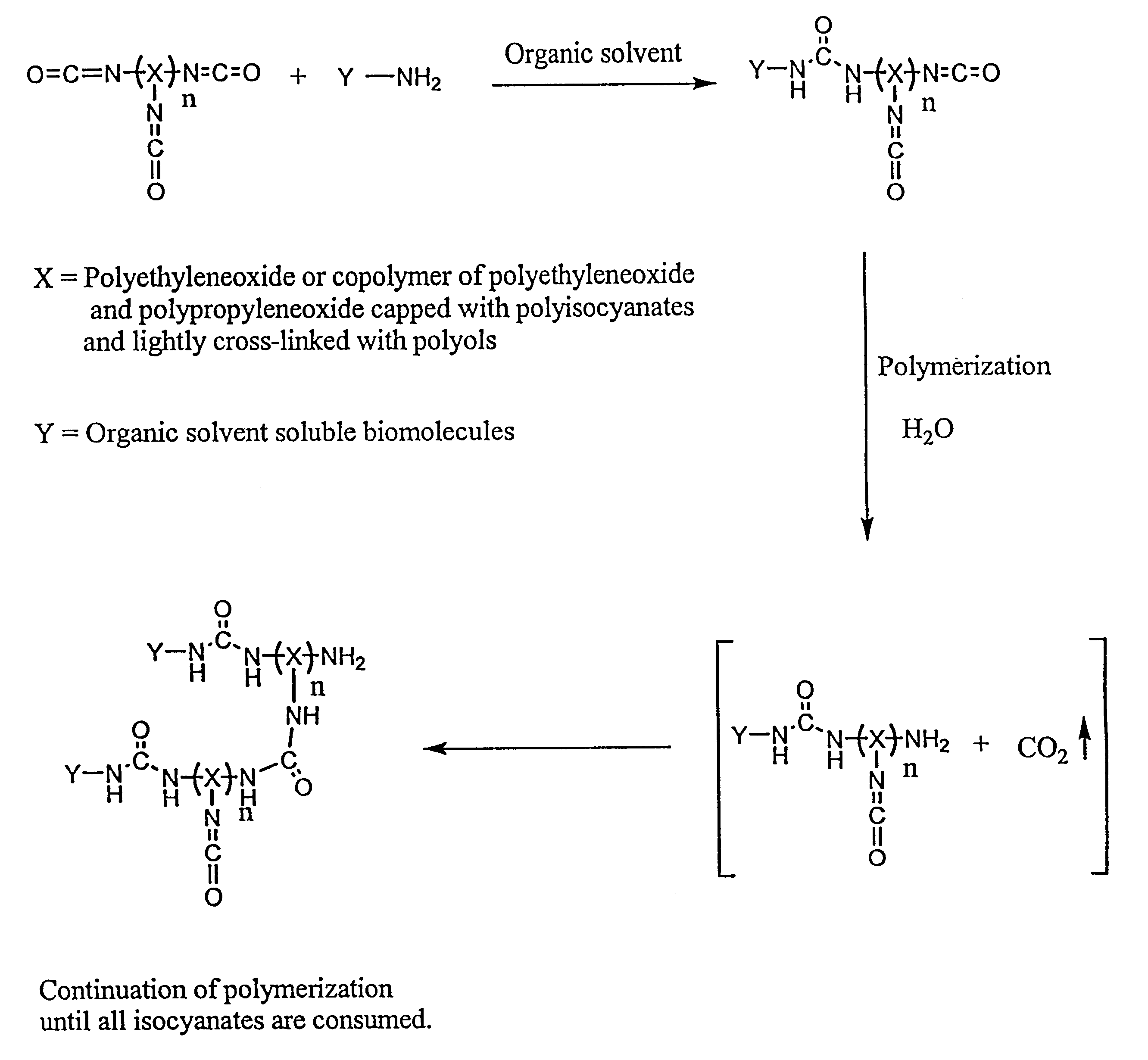
Method of making biochips and the biochips resulting therefrom
InactiveUS6174683B1Rapid and simple and cost-effective methodHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSodium bicarbonateSolid substrate
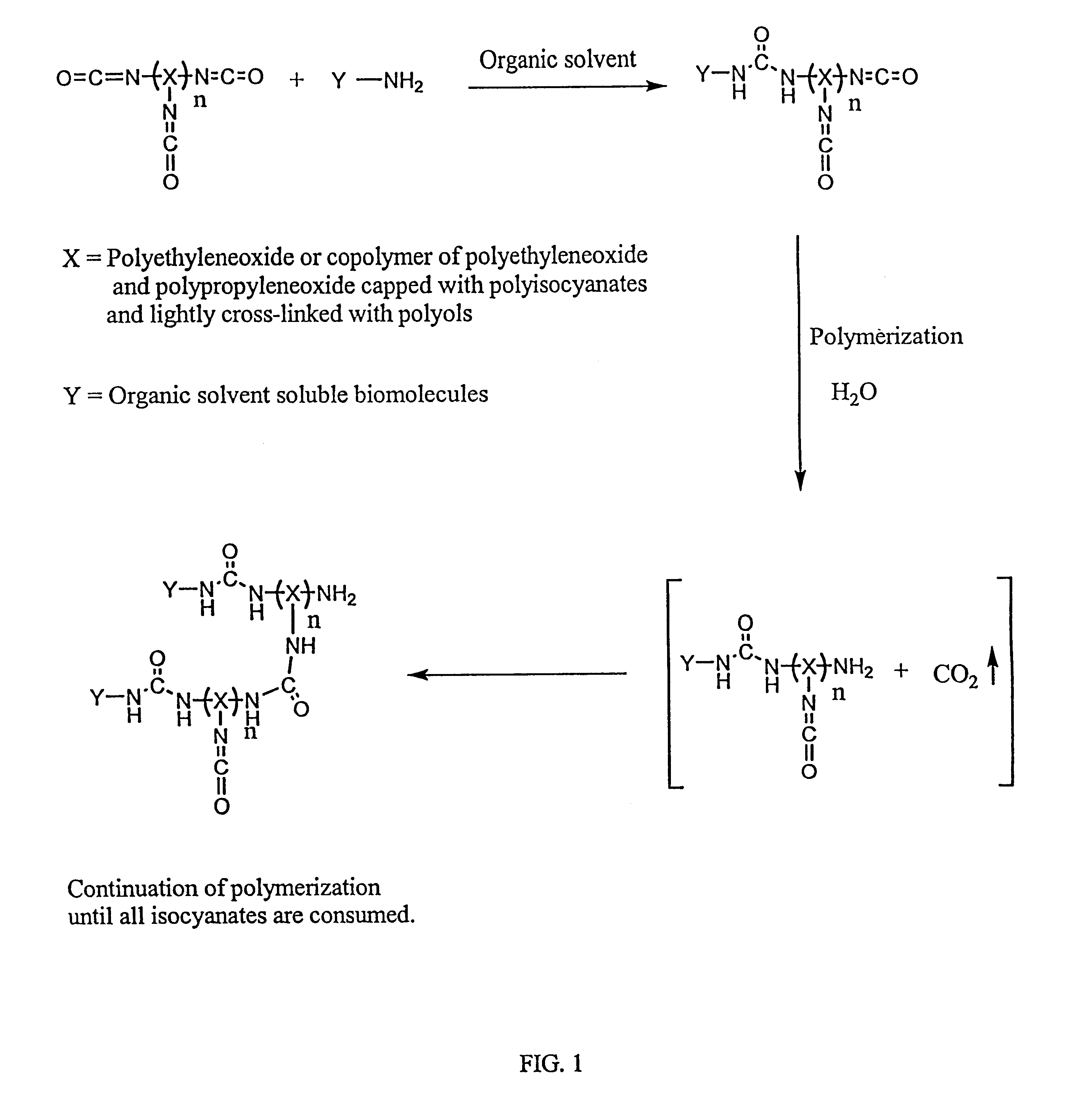
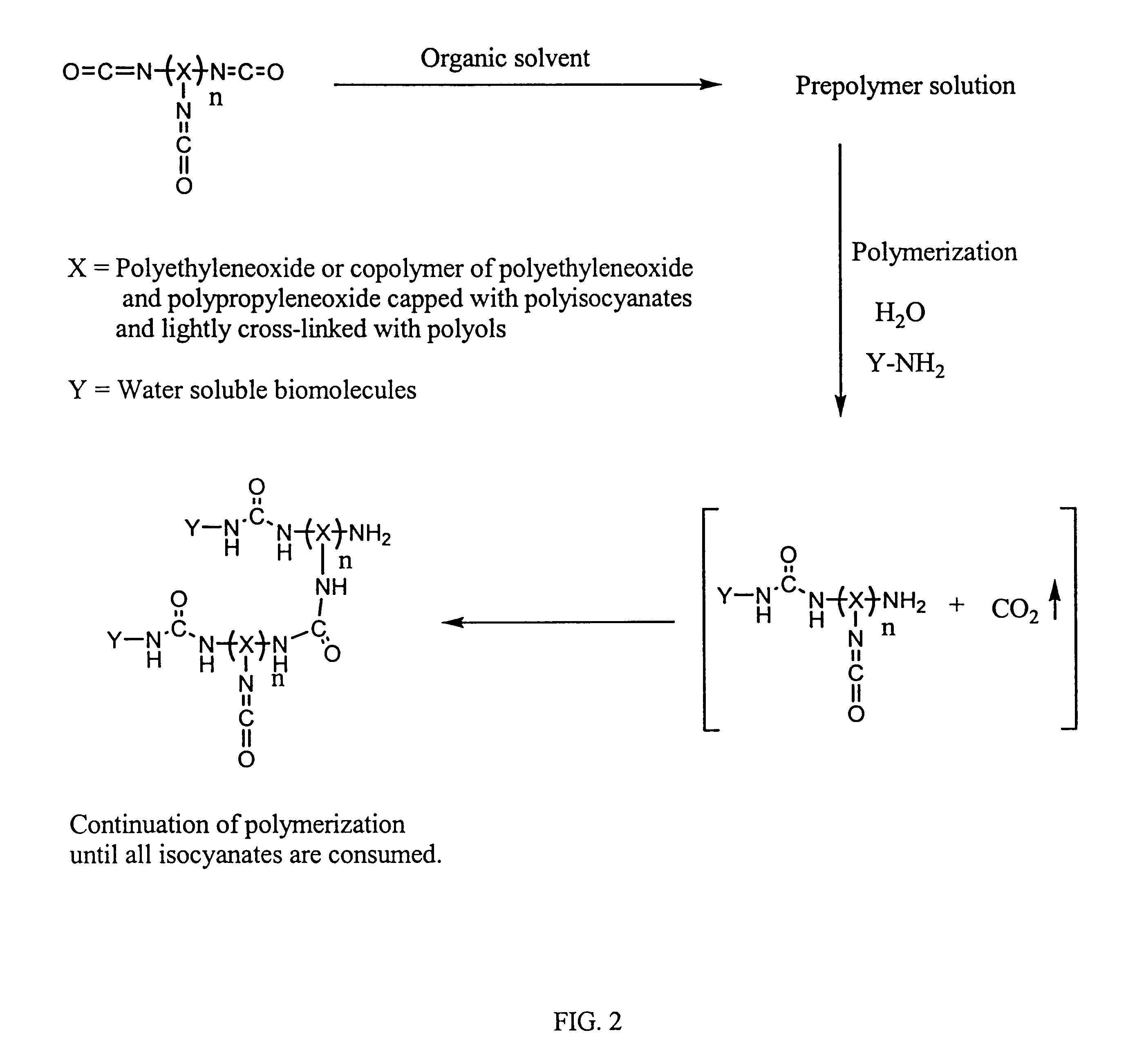
Methods for preparing a biochip are provided herein wherein the biomolecular probe to be used with the biochip is alternatively bound to a hydrogel prepolymer prior to or simultaneously with polymerization of the prepolymer. In particularly preferred embodiments, a polyurethane-based hydrogel prepolymer is derivatized with an organic solvent soluble biomolecule, such as a peptide nucleic acid probe in aprotic, organic solvent. Following derivatization of the prepolymer, an aqueous solution, for example sodium bicarbonate, preferably buffered to a pH of about 7.2 to about 9.5, is added to the derivatized prepolymer solution to initiate polymerization of the hydrogel. Alternatively, a water soluble biomolecule, such as DNA or other oligonucleotide, is prepared in an aqueous solution and added to the polyurethane-based hydrogel prepolymer such that derivatization and polymerization occur, essentially, simultaneously. While the hydrogel is polymerizing, it is microspotted onto a solid substrate, preferably a silanated glass substrate, to which the hydrogel microdroplet becomes covalently bound. Most preferably the hydrogel microdroplets are at least about 30 mum thick, for example about 50 mum to about 100 mum thick. The resulting biochips are particularly useful for gene discovery, gene characterization, functional gene analysis and related studies.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
Reversible pegylated drugs
ActiveUS20060171920A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeProvide benefitsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphate9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl
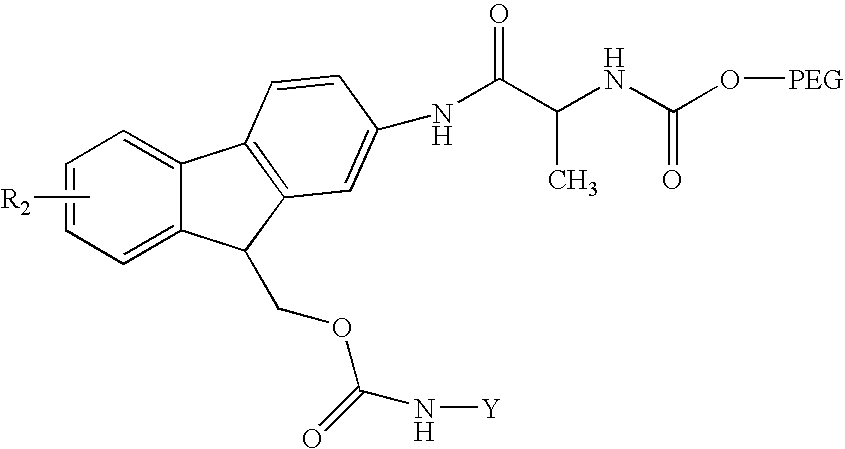
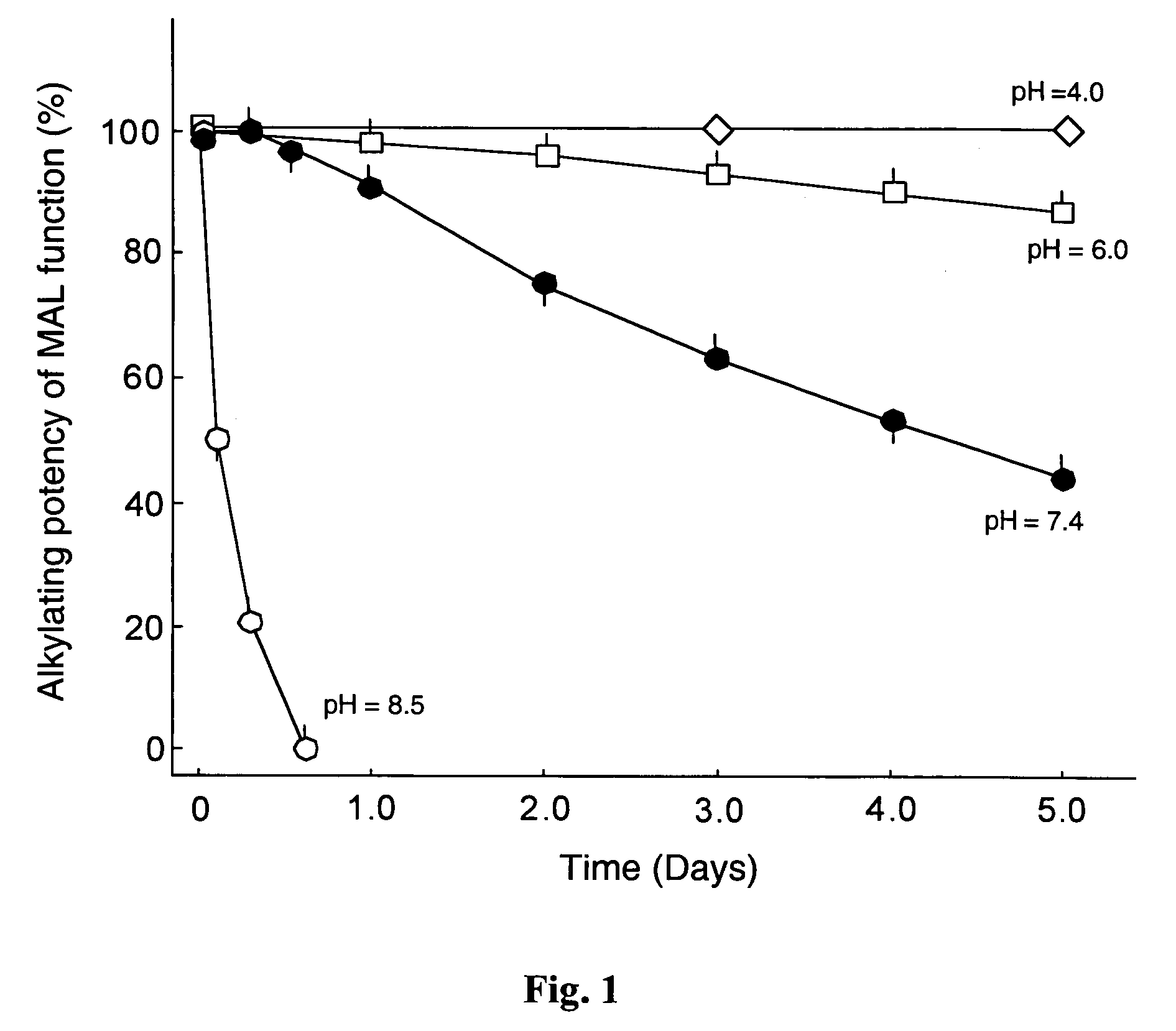
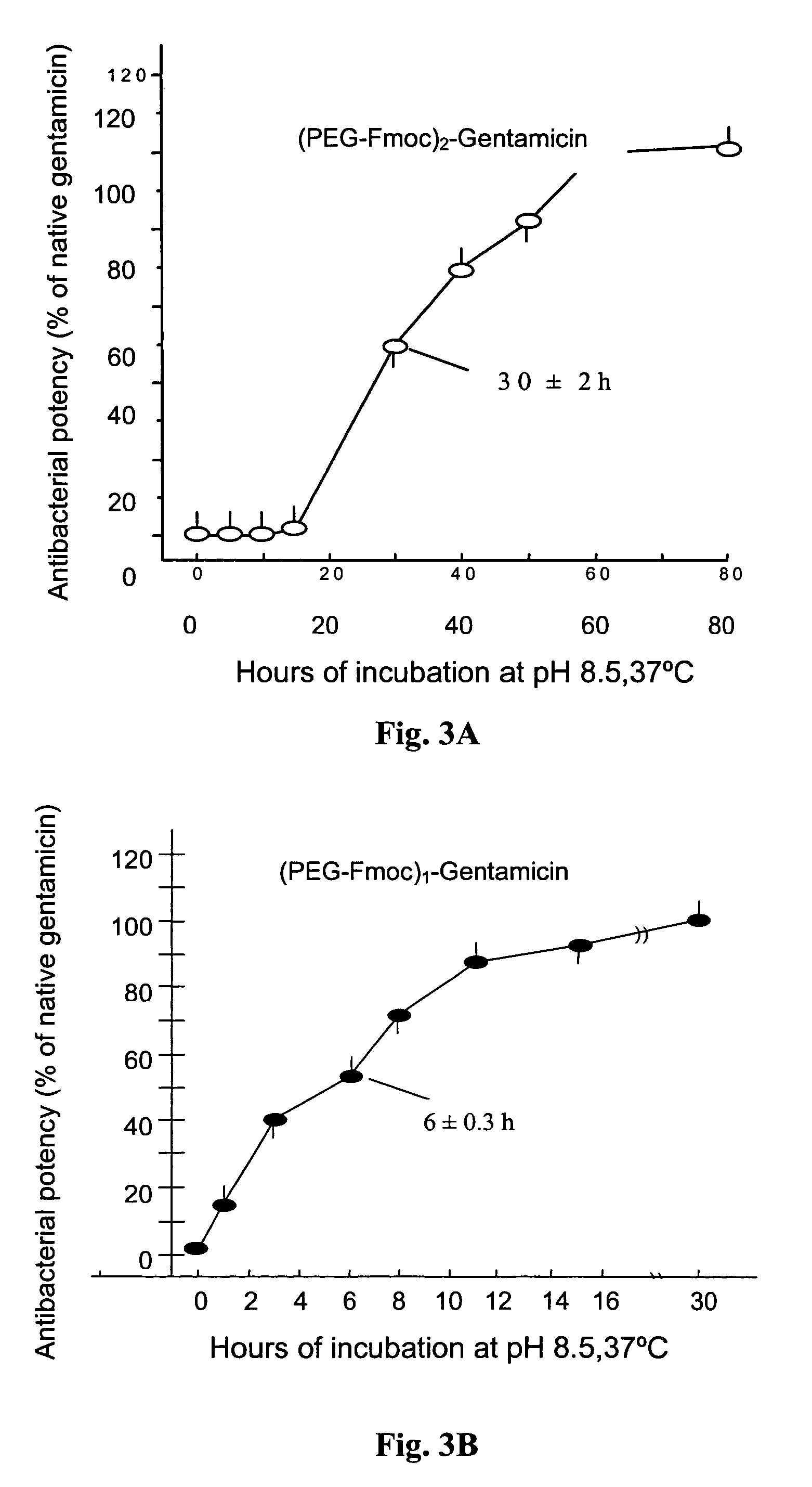
Reversible pegylated drugs are provided by derivatization of free functional groups of the drug selected from amino, hydroxyl, mercapto, phosphate and / or carboxyl with groups sensitive to mild basic conditions such as 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) or 2-sulfo-9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (FMS), to which group a PEG moiety is attached. In these pegylated drugs, the PEG moiety and the drug residue are not linked directly to each other, but rather both residues are linked to different positions of the scaffold Fmoc or FMS structure that is highly sensitive to bases and is removable under physiological conditions. The drugs are preferably drugs containing an amino group, most preferably peptides and proteins of low or medium molecular weight. Similar molecules are provided wherein a protein carrier or another polymer carrier replaces the PEG moiety.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Reversible pegylated drugs
ActiveUS7585837B2Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeLoss of biological and pharmacological potenciesAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphate9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl
Reversible pegylated drugs are provided by derivatization of free functional groups of the drug selected from amino, hydroxyl, mercapto, phosphate and / or carboxyl with groups sensitive to mild basic conditions such as 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) or 2-sulfo-9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (FMS), to which group a PEG moiety is attached. In these pegylated drugs, the PEG moiety and the drug residue are not linked directly to each other, but rather both residues are linked to different positions of the scaffold Fmoc or FMS structure that is highly sensitive to bases and is removable under physiological conditions. The drugs are preferably drugs containing an amino group, most preferably peptides and proteins of low or medium molecular weight. Similar molecules are provided wherein a protein carrier or another polymer carrier replaces the PEG moiety.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Antagonist antibody for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20100047257A1High degreeStrong cytotoxicitySugar derivativesBiological material analysisSynovial sarcomaAntibody fragments
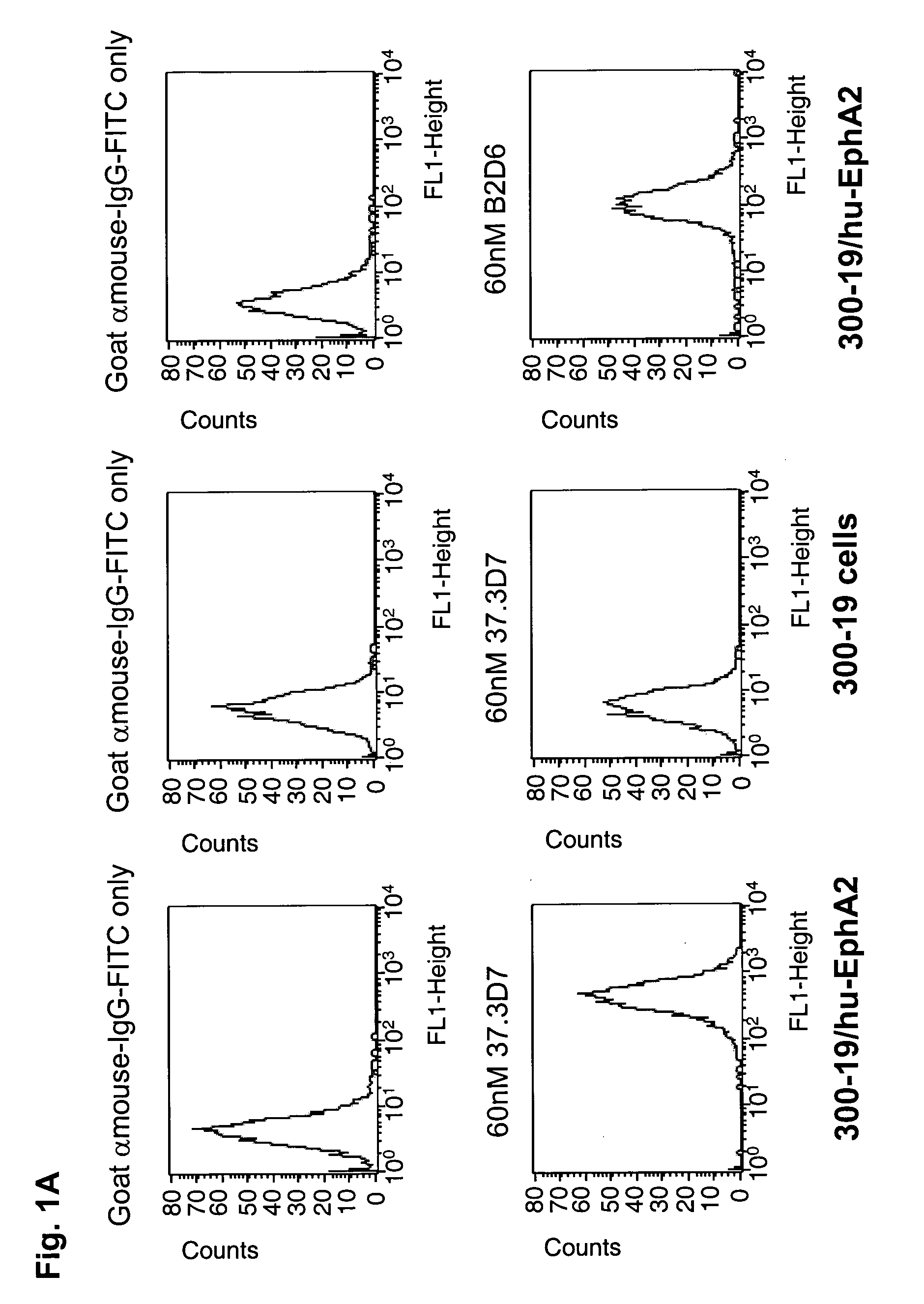
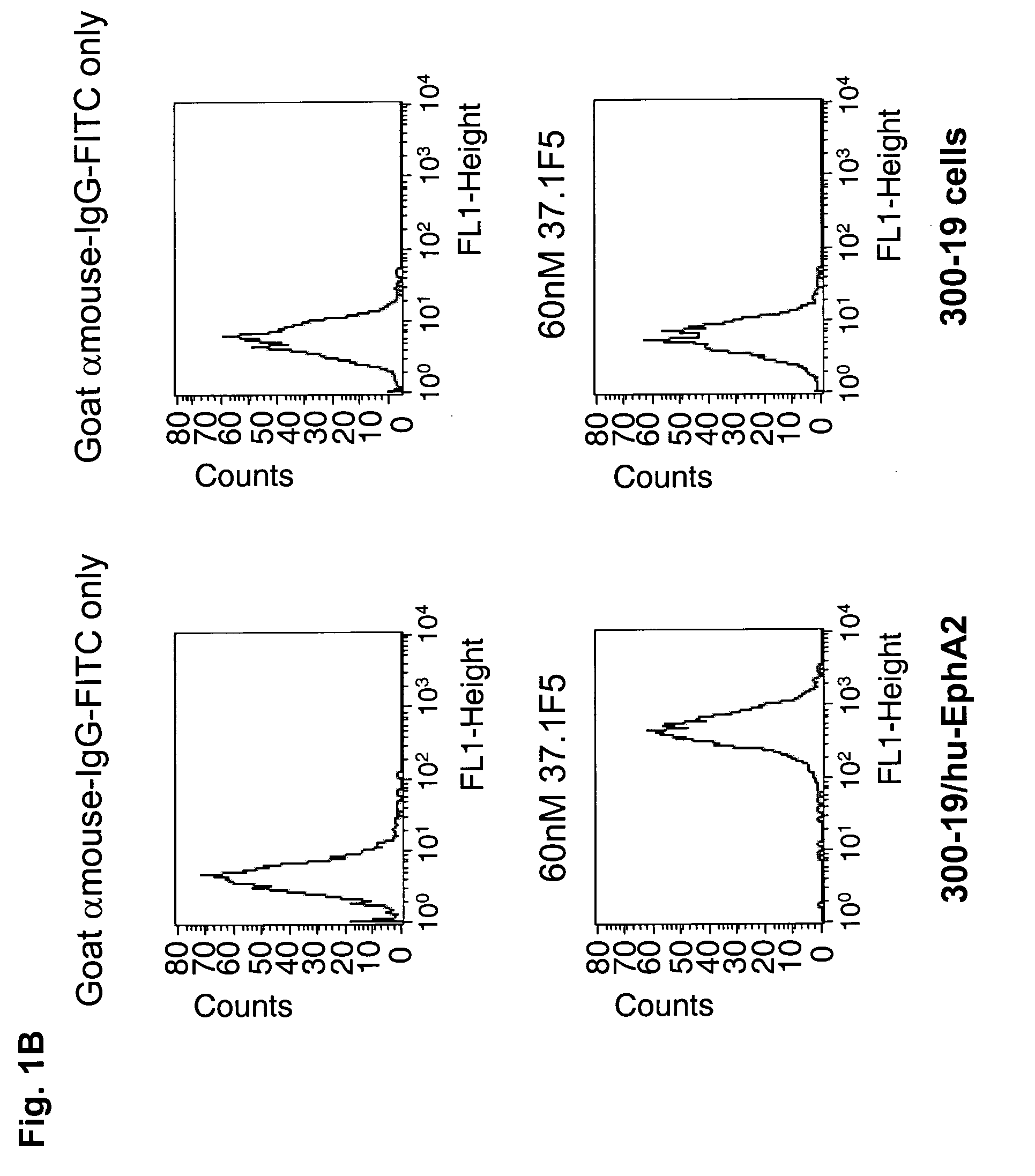
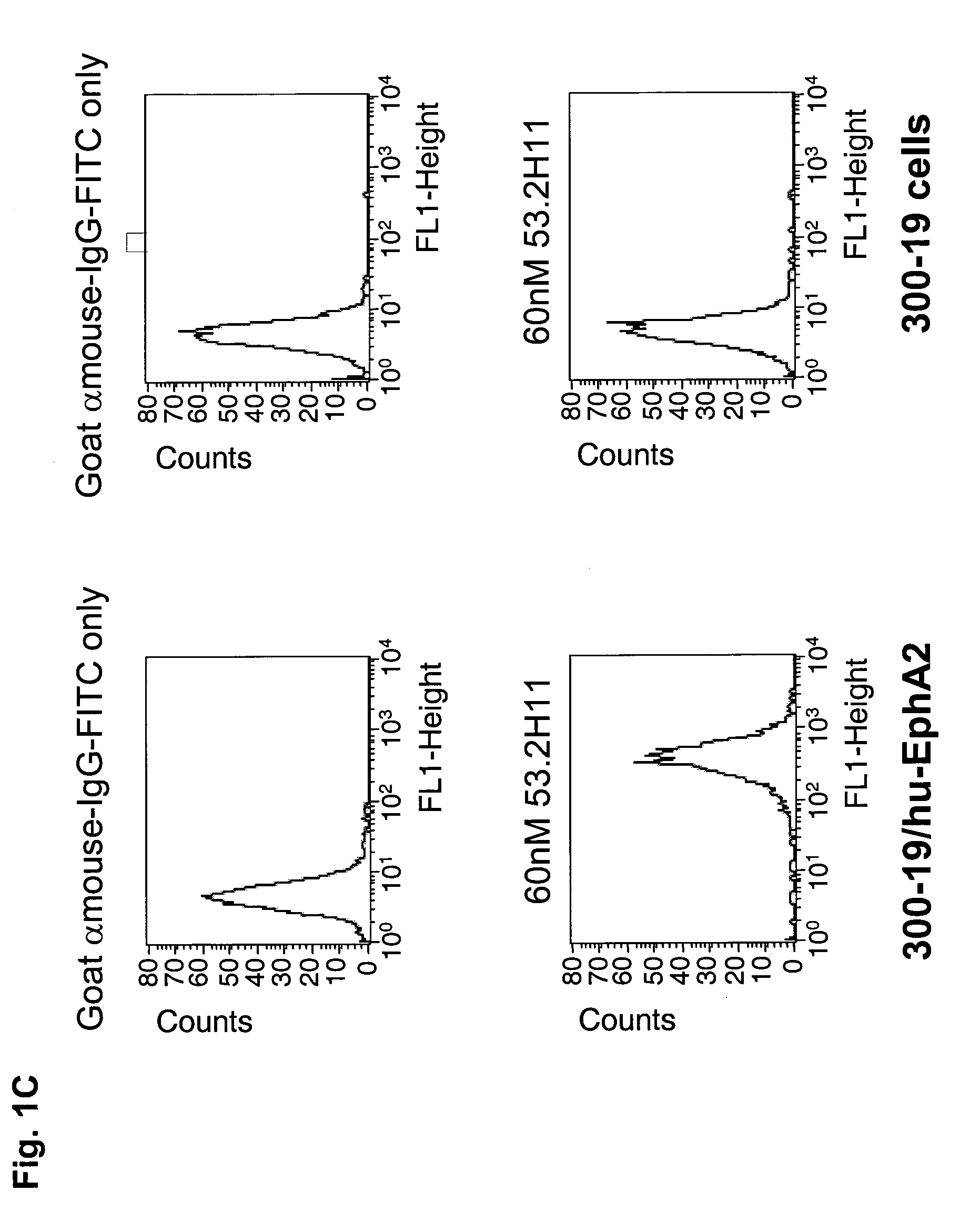
Antibodies, humanized antibodies, resurfaced antibodies, antibody fragments, derivatized antibodies, and conjugates of same with cytotoxic agents, which specifically bind to, and inhibit A class of Eph receptors, antagonize the effects of growth factors on the growth and survival of tumor cells, and which have minimal agonistic activity or are preferentially devoid of agonist activity. Said antibodies and fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of tumors that express elevated levels of A class of Eph receptors, such as breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, ovarian carcinoma, synovial sarcoma and pancreatic cancer, and said derivatized antibodies may be used in the diagnosis and imaging of tumors that express elevated levels of A class of Eph receptors. Also provided are cytotoxic conjugates comprising a cell binding agent and a cytotoxic agent, therapeutic compositions comprising the conjugate, methods for using the conjugates in the inhibition of cell growth and the treatment of disease, and a kit comprising the cytotoxic conjugate are disclosed are all embodiments of the invention. In particular, the cell binding agent is a monoclonal antibody, and epitope-binding fragments thereof, that recognizes and binds the A class of Eph receptors.
Owner:SANOFI SA
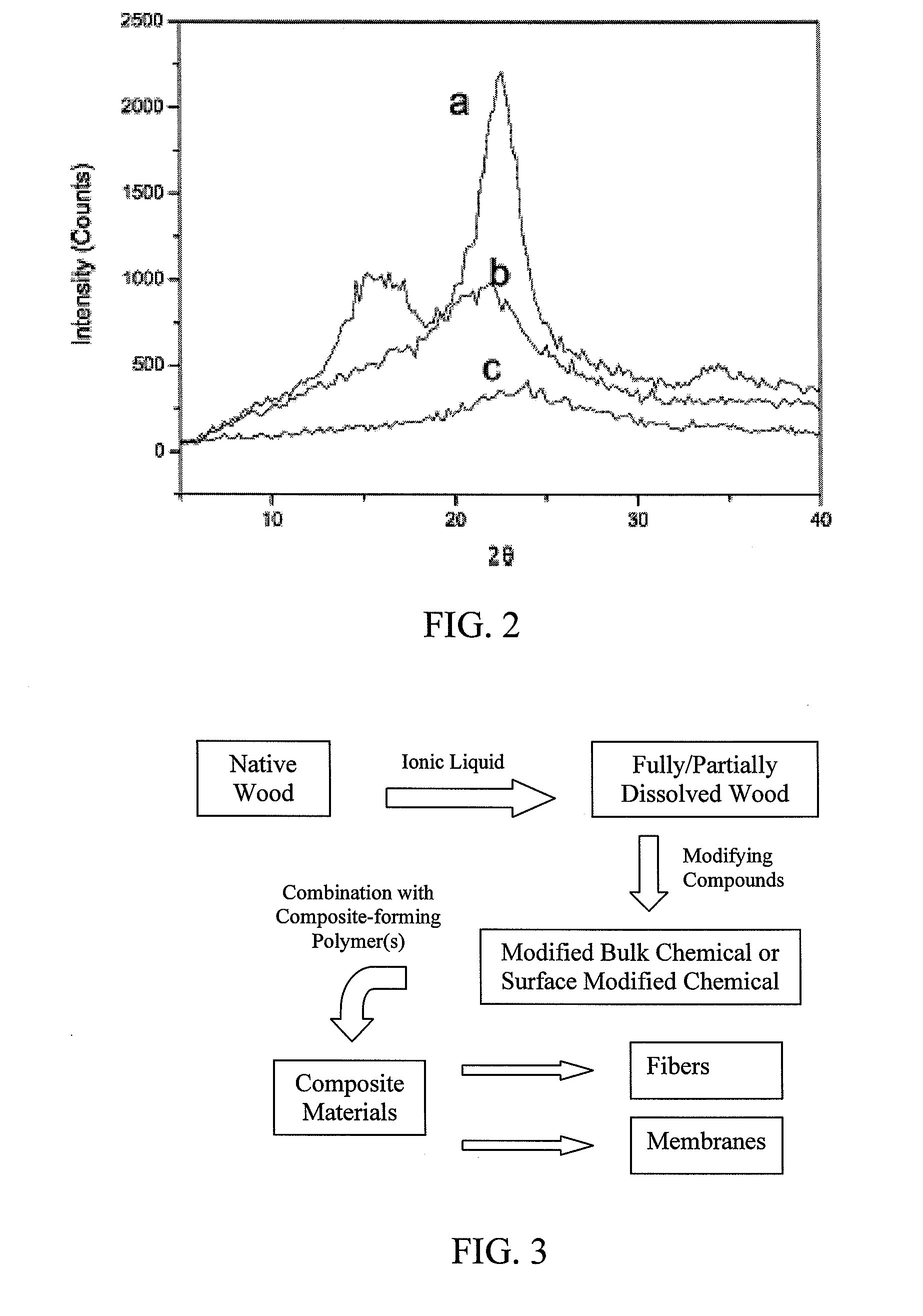
Polymer derivatives and composites from the dissolution of lignocellulosics in ionic liquids
The present invention provides wood derivatives and composite materials prepared by first solvating a lignocellulosic material using an ionic liquid. The solvated lignocellulosic material can be derivatized to incorporate functional groups, particularly groups that facilitate later combination with polymer materials, including non-polymer polymers. The polymeric materials can be combined with the derivatized lignocellulosic material in solution, or the derivatized lignocellulosic material can be isolated and later combined with the polymeric material in a melt. The invention encompasses a variety of wood derivatives, composites, and nanocomposites useful for preparing multiple types of products, including membranes, fibers, and formed parts.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Treatment of arthritis and other musculoskeletal disorders with crosslinked hyaluronic acid
InactiveUS20070203095A1Reduce frequencyFast pain reliefBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCarboxyl radical
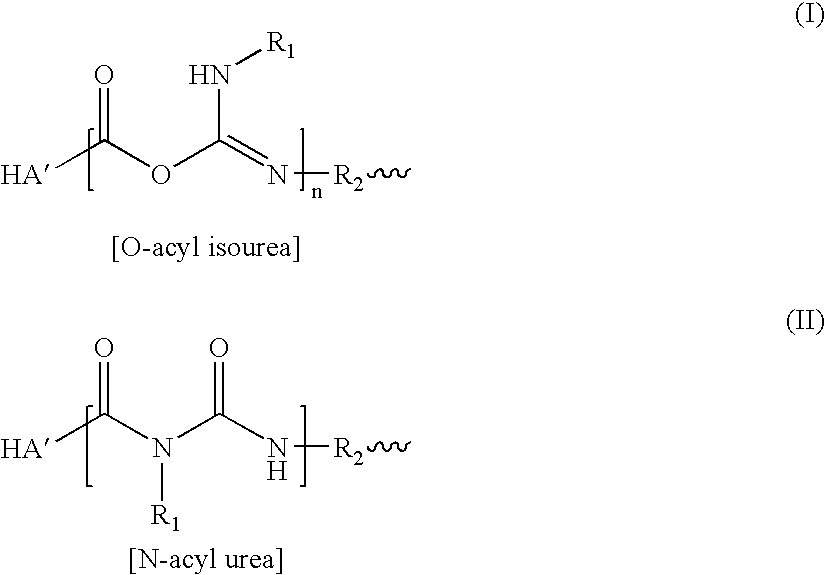
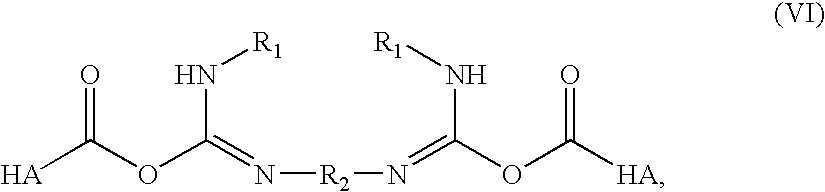
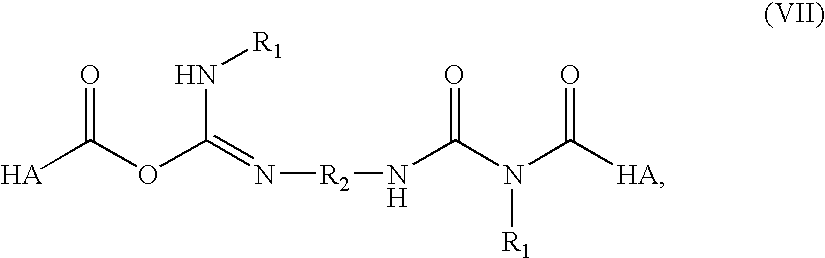
A method of treating a subject having a musculoskeletal disorder includes administering to a subject's articular site in need thereof an effective amount of a hyaluronic acid (HA) composition. In one embodiment, the HA composition includes an HA derivative, wherein carboxyl functionalities of the hyaluronic acid derivative are each independently derivatized to include an N-acylurea or 0-acyl isourea, or both N-acylurea and 0-acyl isourea. In another embodiment, the HA composition includes a crosslinked HA gel that is prepared by reacting an uncrosslinked HA with a biscarbodiimide in the presence of pH buffer in a range of between about 4 and about 8. The composite can optionally include at least one second bioactive agent other than the HA derivative, such as a steroid.
Owner:ANIKA THERAPEUTICS INC
Swellable sol-gels, methods of making, and use thereof
The present invention relates to a method of making a swellable sol-gel composition that involves the use of a bridged silane precursor. The resulting sol-gel includes residual silanols, which are derivatized with a reagent having at least one silanol-reactive group and at least one alkyl group; and the sol-gel is then dried. Sol-gels of the invention are demonstrated to swell up to about 8-10 times their original volume in the presence of a non-polar sorbate. The sol-gel compositions can be used in a sorbate-activated actuator or in a detector for non-polar sorbates. The sol-gel compositions can further be used to take up non-polar sorbates for purposes of chemical remediation, extraction from aqueous systems or vapor, and chemical sensing.
Owner:WOOSTER TECH GRP +1
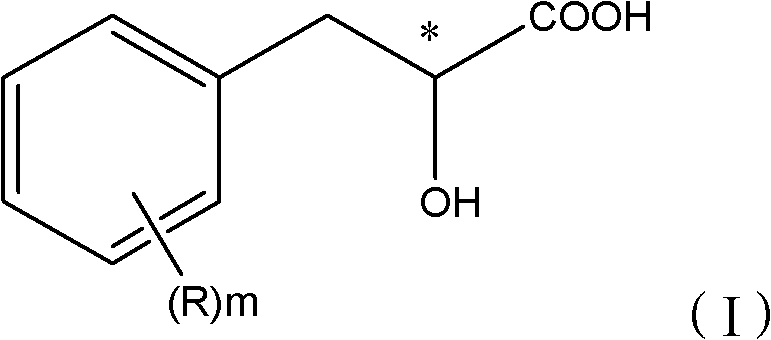
Method for screening stereoselective alpha-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase
InactiveCN102660631AOvercoming time-consuming and laboriousOvercoming demandsMicrobiological testing/measurementWater bathsAlpha hydroxy acid
The invention provides a method for screening stereoselective alpha-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase, comprising the following steps: (1) dissolving a sample to be detected containing alpha-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase in a buffer with pH of 6-9, adding an alpha-hydroxy acid chiral monomer as a substrate, and carrying out conversion reaction in water-bath at 20-50 DEG C; and (2) after the conversion reaction, adding the conversion solution in an FeCl3 developer solution to conduct color development reaction for 5-30 min, when the color development reaction finishes, judging the result according to the color appeared in the reaction solution. The method has no need to carry out derivatization on the substrate which is intend to screen, can rapidly identify the dehydrogenase activity and optical selectivity of the selected microbe by using simple colourimetry, has the advantages of simple screening flow, fast speed, low request for devices, strong versatility and the like, and offers great conveniences to the obtainment of optically pure products by using racemic mandelic acid and related derivatives as substrates to carry out resolution through biological enzymatic method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for cutting single-wall carbon nanotubes through fluorination
InactiveUS7029646B2Shorten the lengthHigh voltageMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureFlat panel displayDerivatization
A method for cutting single-wall carbon nanotubes involves partially fluorinating single-wall carbon nanotubes and pyrolyzing the partially fluorinated nanotubes in an inert atmosphere or vacuum up to about 1000° C. The nanotubes are optionally purified before cutting. The partial fluorination involves fluorinating the nanotubes to a carbon-fluorine stoichiometry of CFx, where x is up to about 0.3. The invention also relates to the derivatization of fluorinated and cut single-wall carbon nanotubes. The single-wall carbon nanotubes can be cut to any length depending on the fluorination and pyrolysis conditions. Short nanotubes are useful in various applications, such as field emitters for flat panel displays and as “seeds” for further nanotube growth.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Generating protein pro-drugs using reversible PPG linkages
InactiveUS20050079155A1Reduce and block activityEliminate side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectProtecting group
The invention relates to methods for modulating the side effects, including immunogenicity, of a protein therapeutic via derivatization with a protein protecting group using reversible or labile linkages.
Owner:XENCOR
Quantitative detecting method for various metabolites in biological sample, and metabolic chip
ActiveCN109298115AFast contentContent quicklyComponent separationMass spectrometric analysisMetaboliteDerivatization
The invention discloses a quantitative detecting method for various metabolic components in a biological sample, and a metabolic chip used for the quantitative detecting method. The quantitative detecting method is characterized in that the biological sample is subjected to derivatization treatment, and the biological sample subjected to derivatization is detected through liquid chromatography andmass spectrometry combination; and during derivatization treatment, 3-nitrophenylhydrazine serves as a derivatization reagent, and 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethly carbodiimide serves as a derivatization reaction catalyst. According to the quantitative detecting method, high-sensitivity detection can be achieved, and a plurality of level-crossing metabolic components can be covered during detection, and the quantitative detecting method is simple, fast and suitable for being applied to clinical and scientific research testing. The metabolic chip comprises a chip carrier microtitration plateand related reagents, and thus the multiple level-crossing metabolites such as amino acid, phenols, phenyl or benzyl derivatives, indole, organic acid, fatty acid, sugar and bile acid in the biological samples can be subjected to quantitative detection on the same microtitration plate.
Owner:麦特绘谱生物科技(上海)有限公司
Fluorescence proximity assay
InactiveUS20030059850A1Easy to operateEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingColloidFluorophore
The present invention provides binding assays, referred to here as fluorescence proximity assays or FPA. The inventions detect binding of target molecules in a sample to a molecular probe or probes that specifically bind or hybridize to those molecules. In particular, the molecular probes are immobilized to a bead or particle, such as colloidal gold, the reflects fluorescent energy from a fluorophore. The derivatized beads are contacted to a sample of fluorescently labeled target molecules, and binding of the target is indicated by an increase in the fluorescent signal. Kits are also provided that contain materials and reagents to performing a fluorescence proximity assay.
Owner:STANLEY MEDICAL RES HLDG
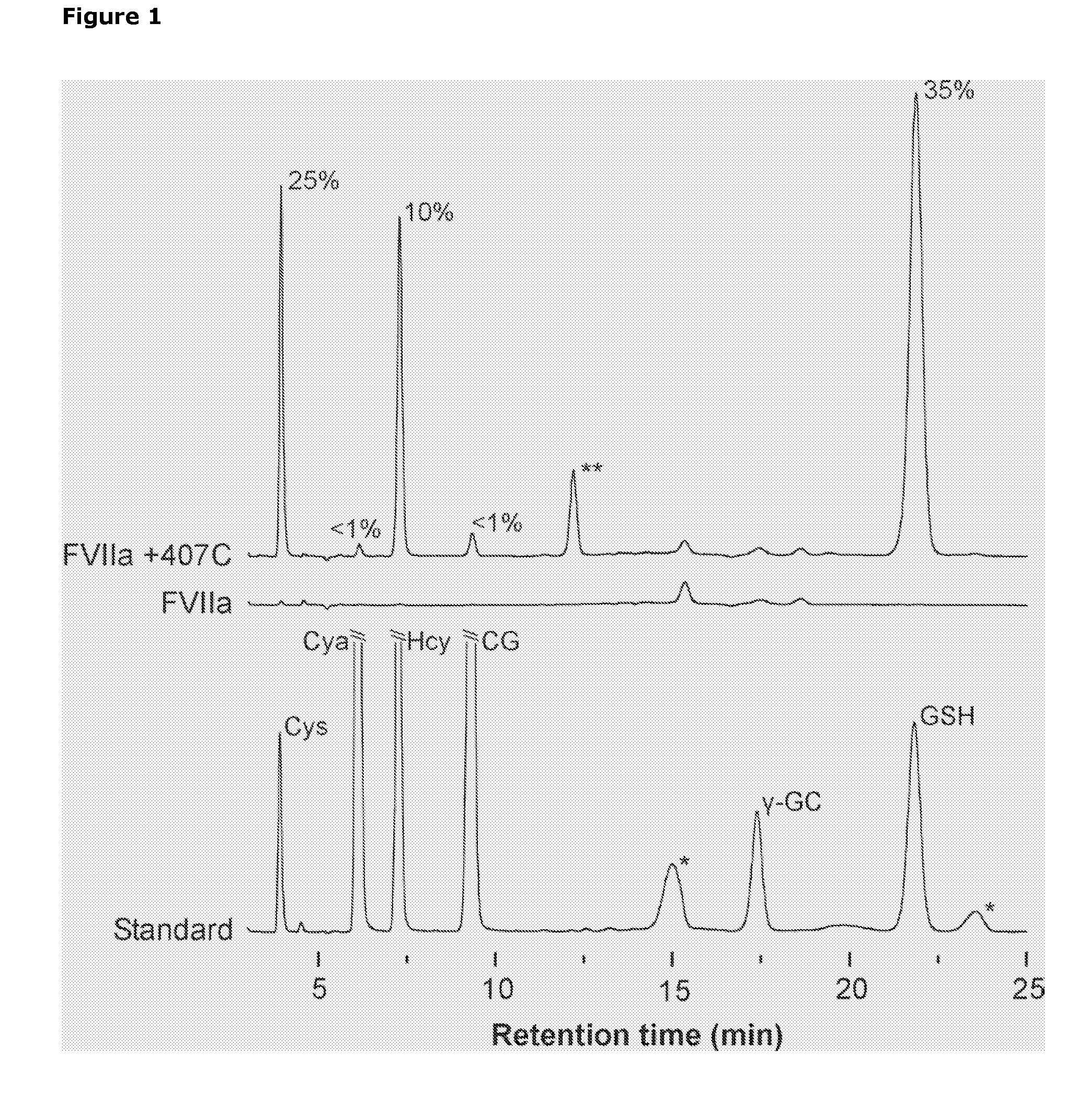
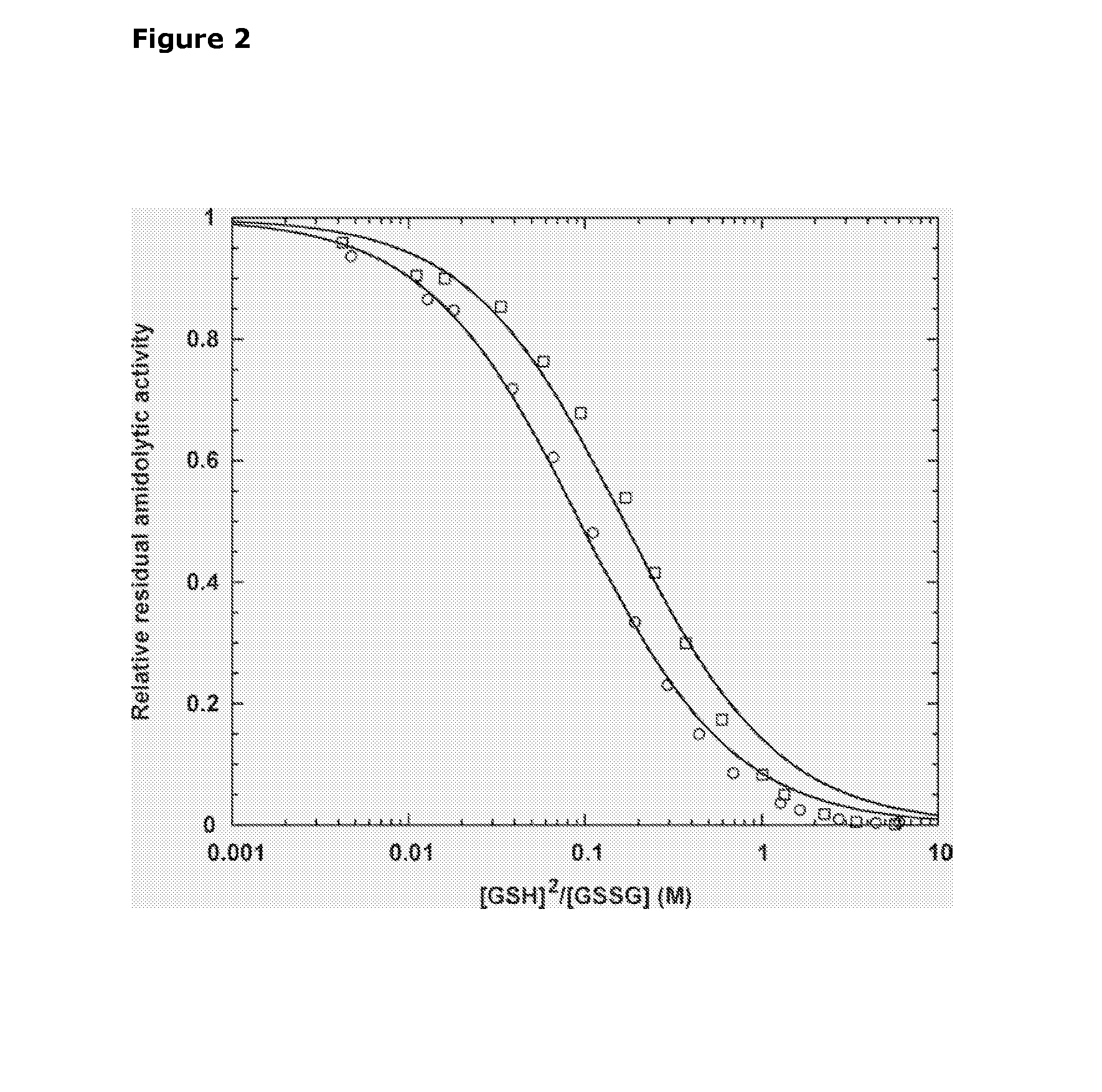
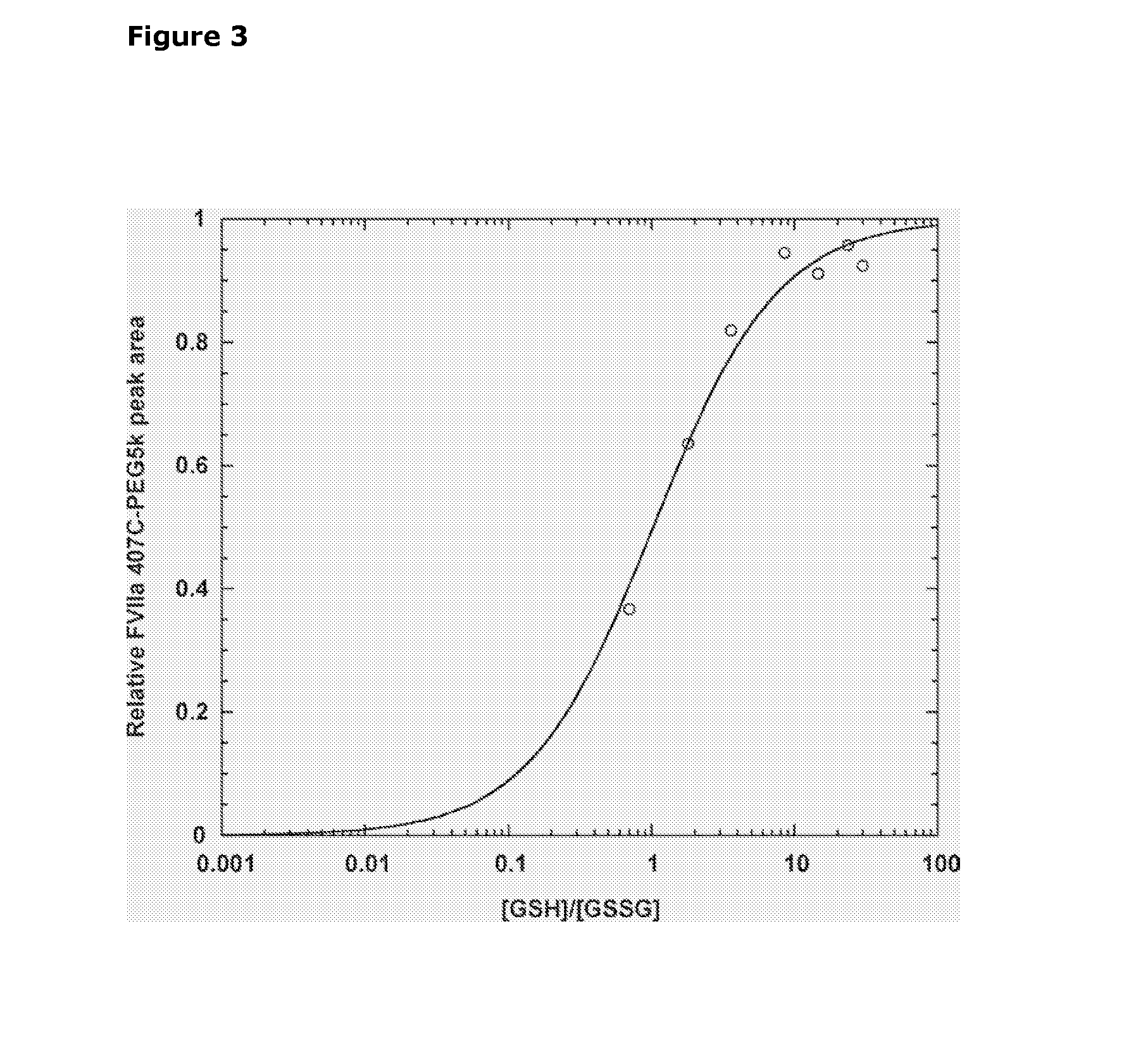
Selective Reduction and Derivatization of Engineered Proteins Comprising at Least One Non-Native Cysteine
InactiveUS20080200651A1Reduce decreasePeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsRedoxDerivatization
The present invention relates to method for selective reduction and derivatization of recombinantly prepared engineered proteins comprising at least one non-native cysteine, wherein the reduction reaction is conducted in the presence of a redox buffer or in the presence of a triarylphosphine reducing agent.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Laser based enhanced generation of photoacoustic pressure waves in dental and medical treatments and procedures
A laser tip, and method for the use thereof, is described for utilization in medical and dental applications. Specifically, a tip with an increased photoacoustic wave emission capability is formed by beveling the tip and further enhanced by stripping the adjacent sheath. Preferably, this conic and / or stripped tip section is surface modified, for example, by texturing, derivatization or metalization. In the field of endodontics the tip is inserted into a solution that has been introduced into a root canal and the pulsed laser is fired. The resulting generation of an enhanced photoacoustic wave propagates through the solution. These photoacoustic waves turbulently clean the interior of the root and lateral canal systems and / or causes cell lysis and dissolution of inorganics in biotic systems.
Owner:PIPSTEK LLC
Bioactive chip mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6887713B2Identification and/or quantificationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementTime informationSurface layer
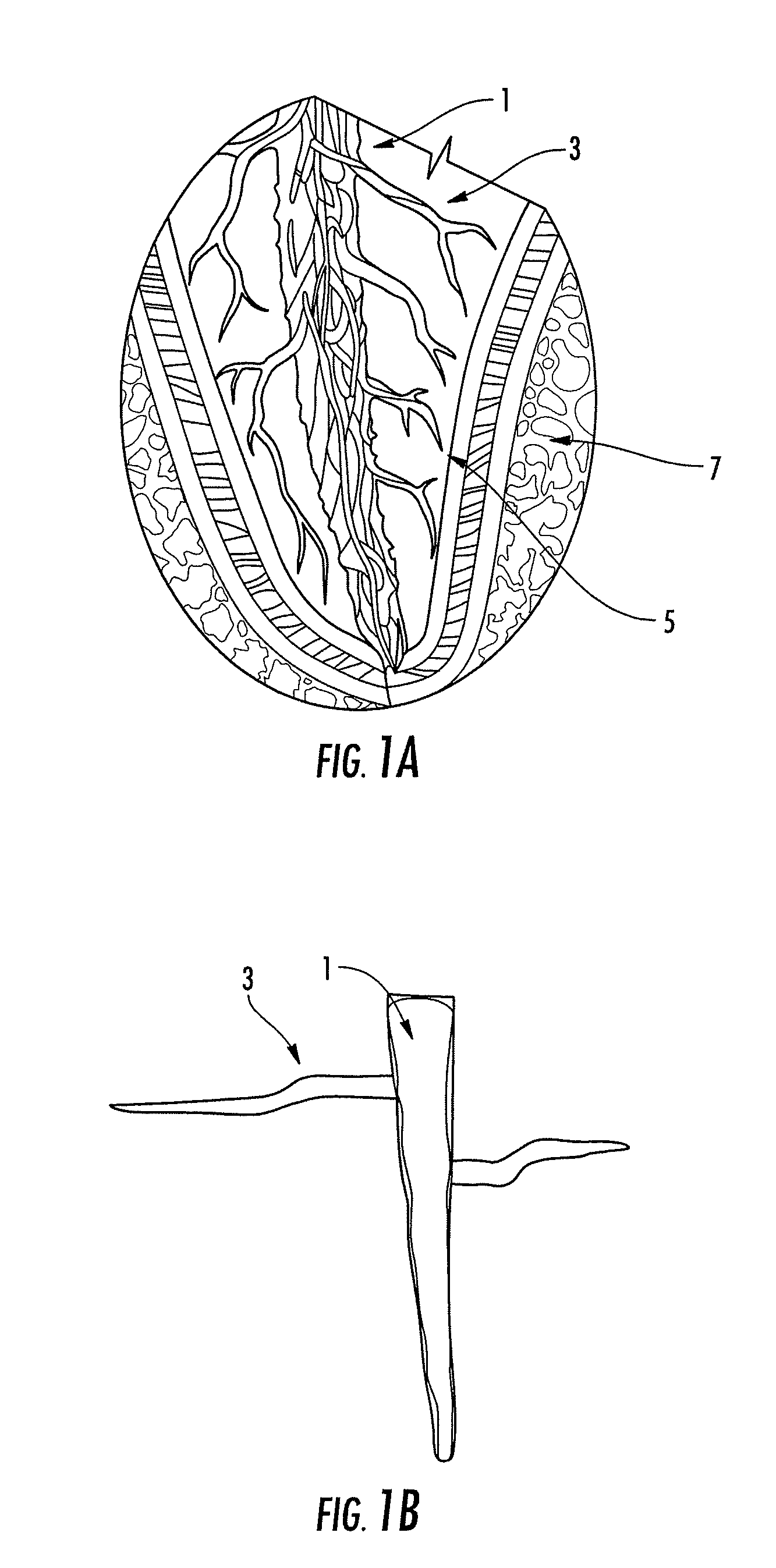
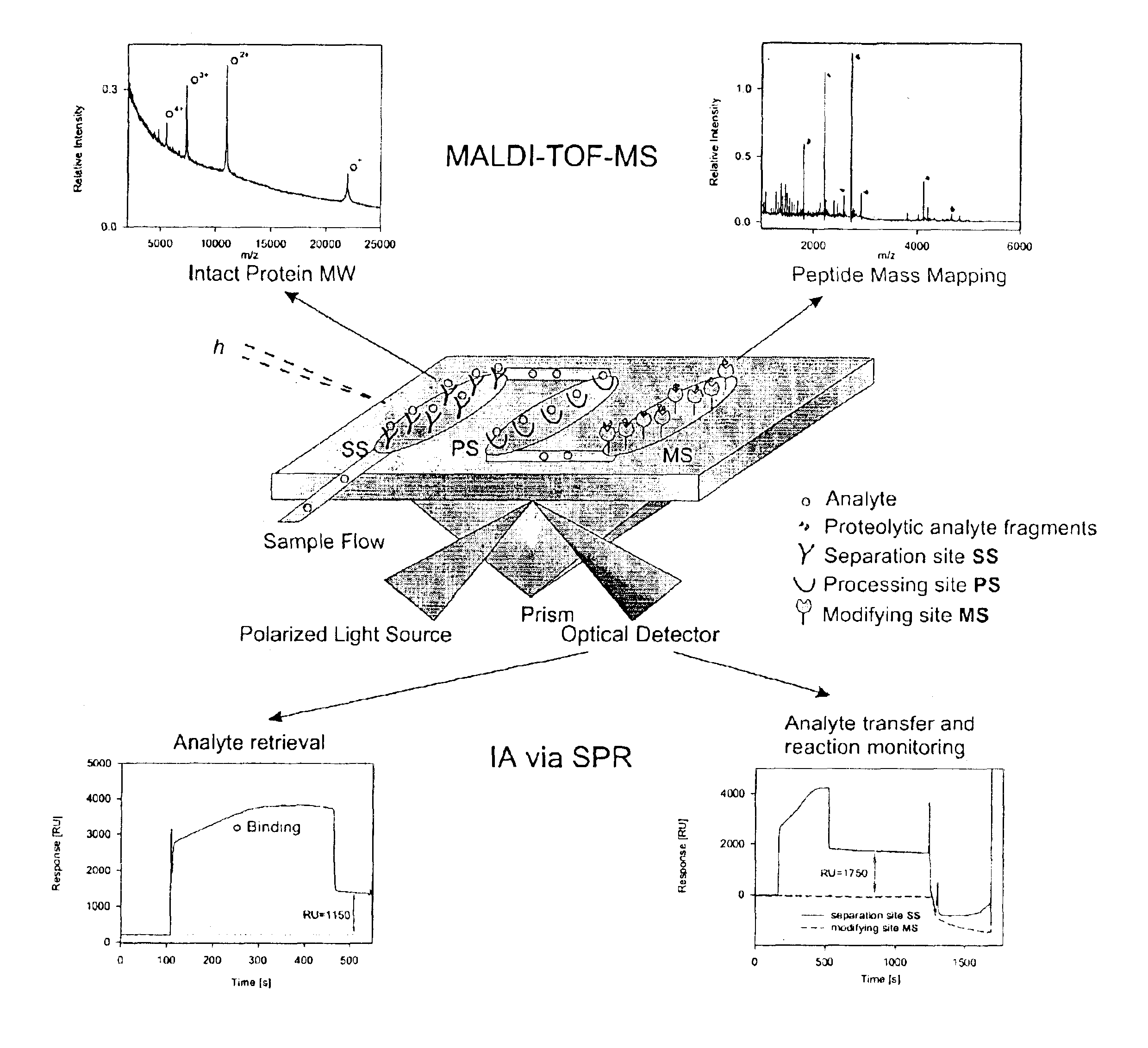
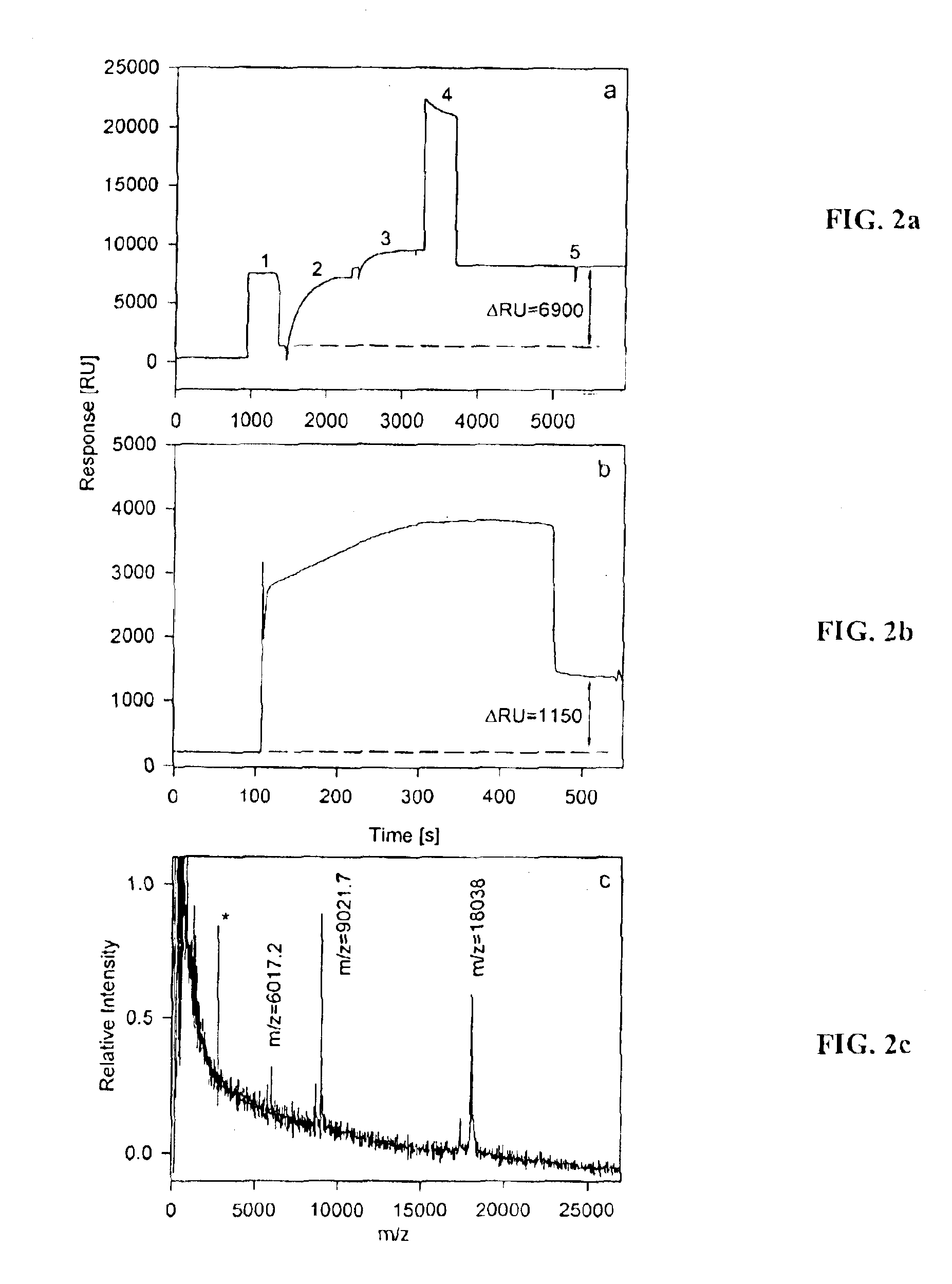
The present invention is directed to a bioactive probe or chip (BC) that allows for the isolation of analytes, such as biomolecules, followed by modification or bioreaction on these said analytes. More specifically, the present invention relates to various methods and apparatuses that include the BC and further include characterization and identification technologies, such as Bioactive Chip Mass Spectrometry (BCMS). Within the context of the present invention, BC provides a method and device for the capture and subsequent modifying, such as digestion or derivatization, of an analyte. Further, real-time information regarding a variety of molecular interactions may be provided by techniques such as interaction analysis (IA). Finally, the variety of molecules are localized and concentrated thereby aiding in the identification and / or quantification of the molecules by techniques such as mass spectroscopy. In one embodiment, a method for performing the modification, or bioreaction, of biomolecules is disclosed. Preferably, the method involves capturing an analyte present within a sample by an interactive surface layer located in a separation site; washing unwanted portions of the sample from the surroundings of the captured analyte; transferring the captured analyte from the separation site to a modifying site; modifying or bioreacting the analyte to create a modified or bioreacted analyte. The modified analyte may then be subsequently characterized and / or identified by techniques such as mass spectrometry.
Owner:INTRINSIC BIOPROBES
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising poly-beta-1->4-N-acetylglucosamine
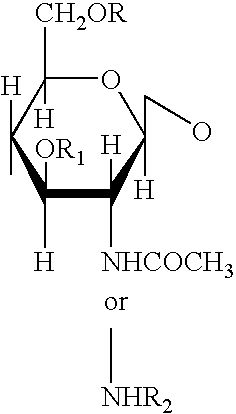
InactiveUS6743783B1Easy to produceHigh molecular weightOrganic active ingredientsBiocideN-AcetylglucosamineSugar
The present invention relates to a purified, easily produced poly-beta-1->4-N-acetylglucosamine (p-GlcNAc) polysaccharide species. The p-GlcNAc of the invention is a polymer of high molecular weight whose constituent monosaccharide sugars are attached in a beta-1->4 conformation, and which is free of proteins, and substantially free of single amino acids, and other organic and inorganic contaminants. In addition, derivatives and reformulations of p-GlcNAc are described. The present invention further relates to methods for the purification of the p-GlcNAc of the invention from microalgae, preferably diatom, starting sources. Still further, the invention relates to methods for the derivatization and reformulation of the p-GlcNAc. Additionally, the present invention relates to the uses of pure p-GlcNAc, its derivatives, and / or its reformulations.
Owner:MARINE POLYMER TECH
Methods and compositions for enhancing guar hydration rates and performing guar derivitization reactions
One embodiment of the present invention provides a method of treating guar splits comprising exposing guar splits to a treatment chemical to create treated guar splits; and then, without first washing the treated guar splits, grinding the treated guar splits; and, then drying the ground, treated guar splits. Another embodiment of the present invention provides a method of treating a portion of a subterranean formation comprising providing a treatment fluid comprising a viscosifying agent wherein the viscosifying agent comprises ground, treated guar splits made by the following method: exposing guar splits to a treatment chemical to create treated guar splits; and then, without first washing the treated guar splits, grinding the treated guar splits; and, then drying the ground, treated guar splits; placing the treatment fluid into a portion of a subterranean formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Protein chips for high throughput screening of protein activity
InactiveUS20030207467A1Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsChemical reaction
The present invention relates to protein chips useful for the large-scale study of protein function where the chip contains densely packed reaction wells. The invention also relates to methods of using protein chips to assay simultaneously the presence, amount, and / or function of proteins present in a protein sample or on one protein chip, or to assay the presence, relative specificity, and binding affinity of each probe in a mixture of probes for each of the proteins on the chip. The invention also relates to methods of using the protein chips for high density and small volume chemical reactions. Also, the invention relates to polymers useful as protein chip substrates and methods of making protein chips. The invention further relates to compounds useful for the derivatization of protein chip substrates.
Owner:YALE UNIV
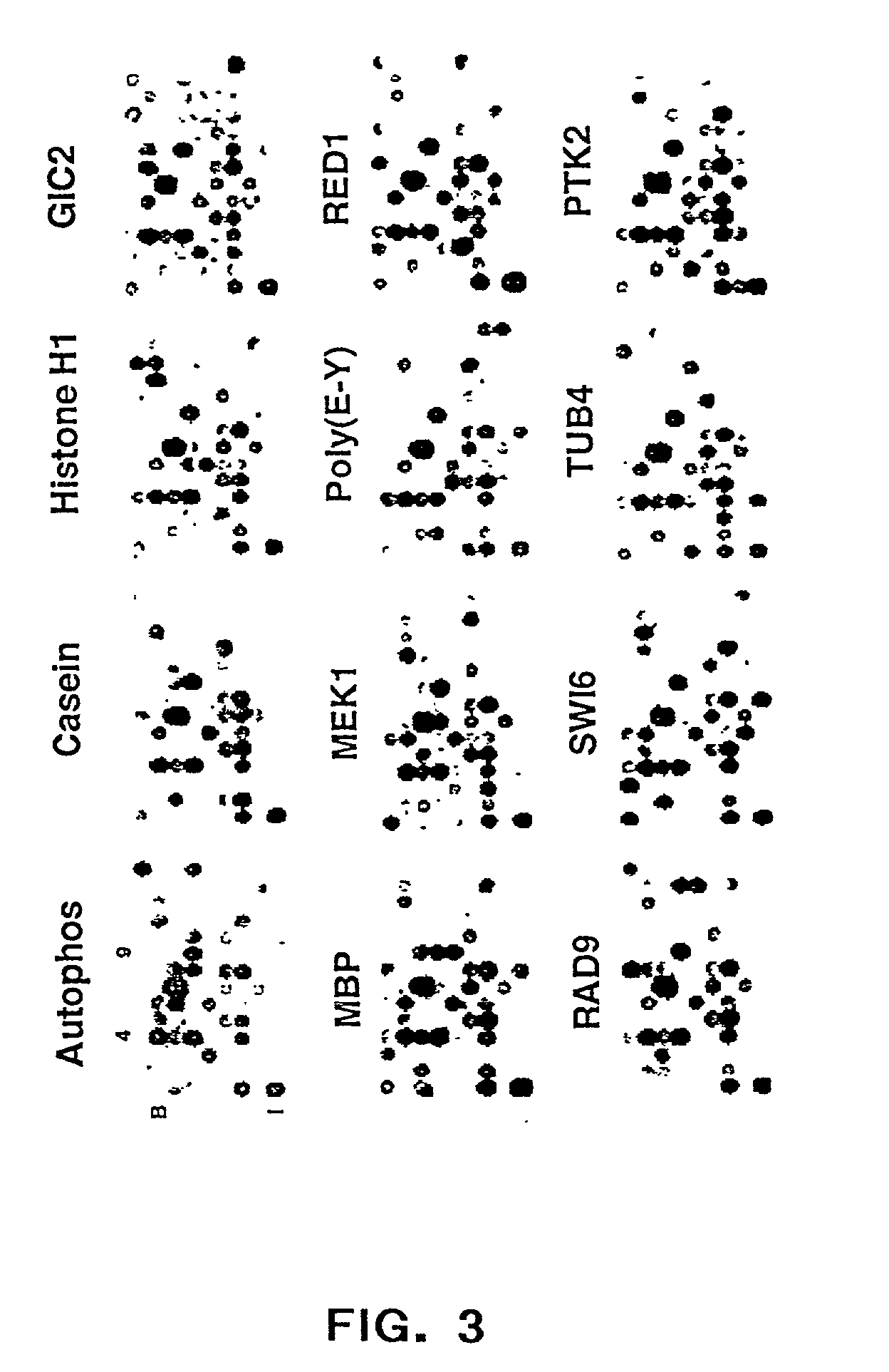
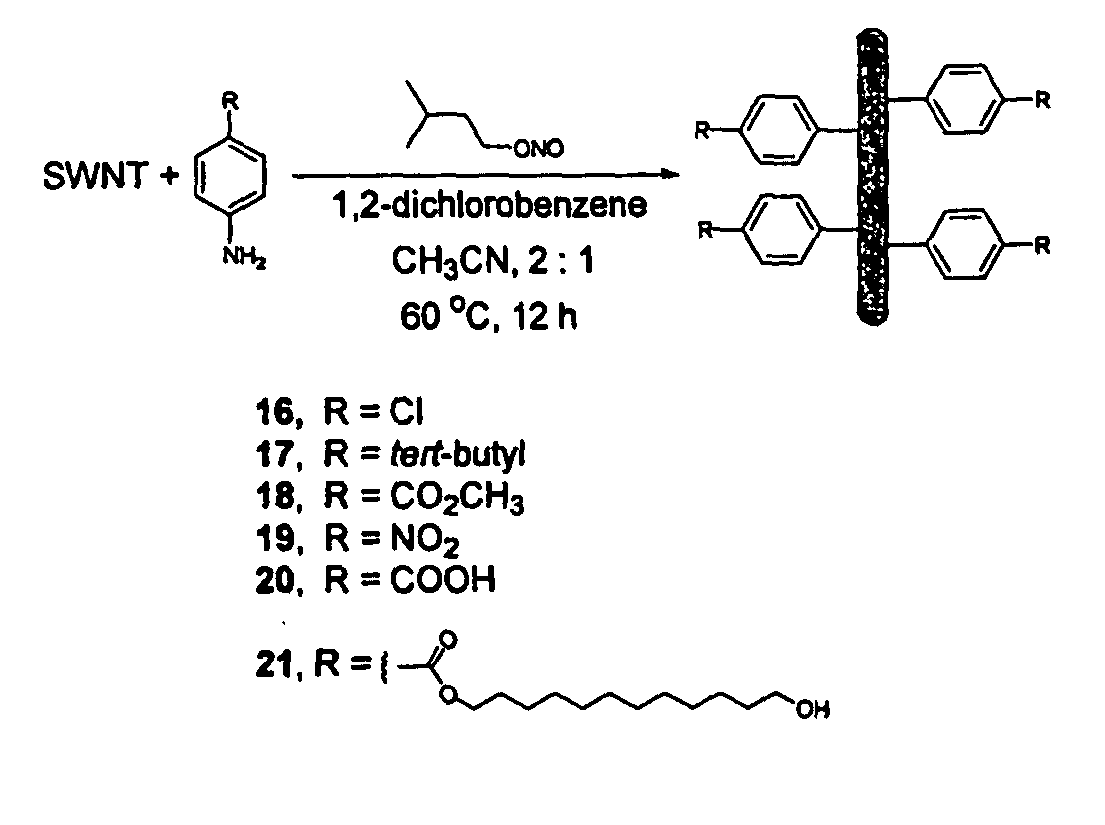
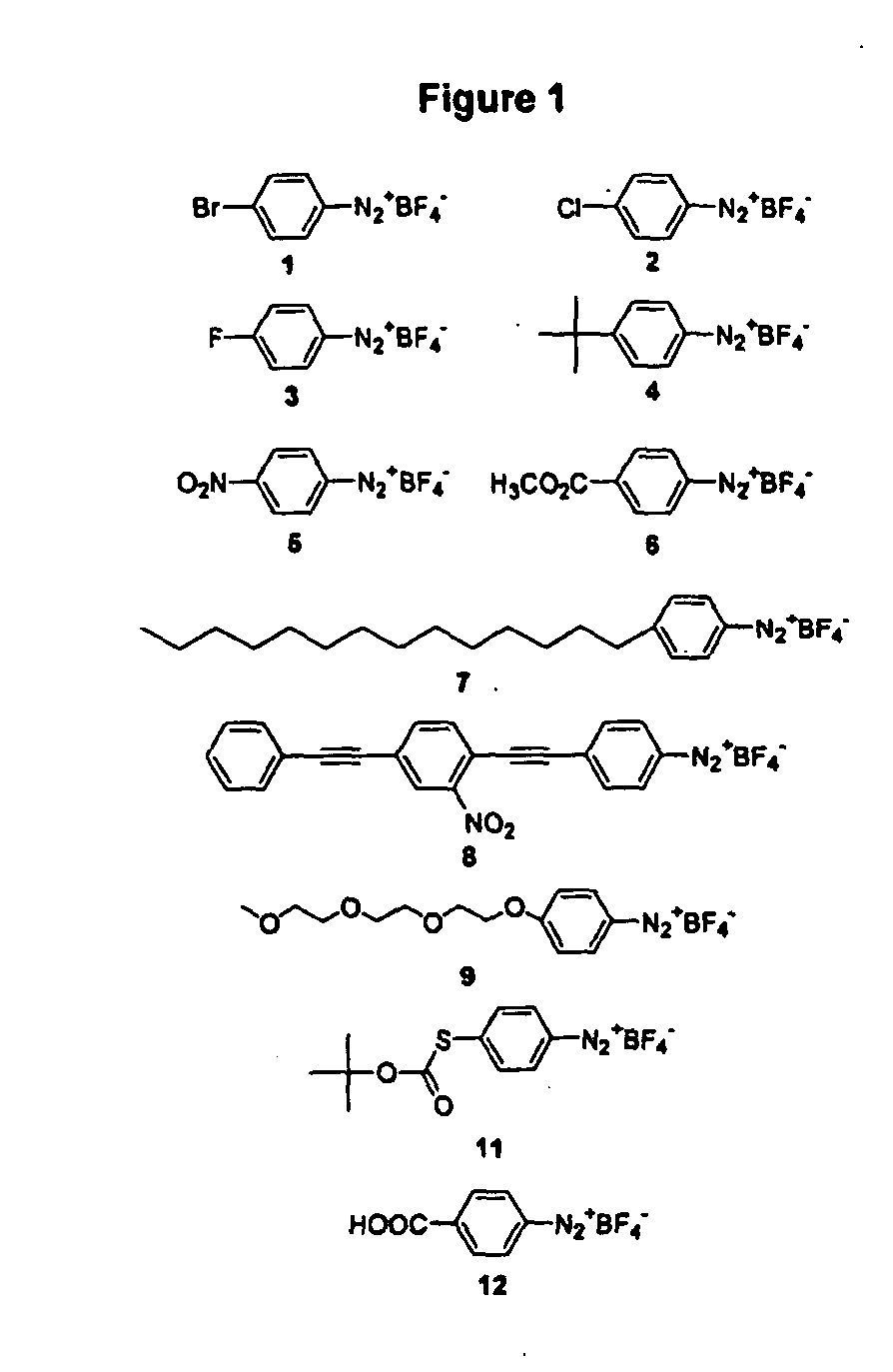
Carbon nanotubes derivatized with diazonium species
InactiveUS20050207963A1Advantage of scalabilityMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentElectrochemistryOrganic compound
Owner:RICE UNIV
Flow-controlled magnetic particle manipulation
InactiveUS7892856B2Increase concentrationSensitive highBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical physicsTest sample
Inventive methods and apparatus are useful for collecting magnetic materials in one or more magnetic fields and resuspending the particles into a dispersion medium, and optionally repeating collection / resuspension one or more times in the same or a different medium, by controlling the direction and rate of fluid flow through a fluid flow path. The methods provide for contacting derivatized particles with test samples and reagents, removal of excess reagent, washing of magnetic material, and resuspension for analysis, among other uses. The methods are applicable to a wide variety of chemical and biological materials that are susceptible to magnetic labeling, including, for example, cells, viruses, oligonucleotides, proteins, hormones, receptor-ligand complexes, environmental contaminants and the like.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
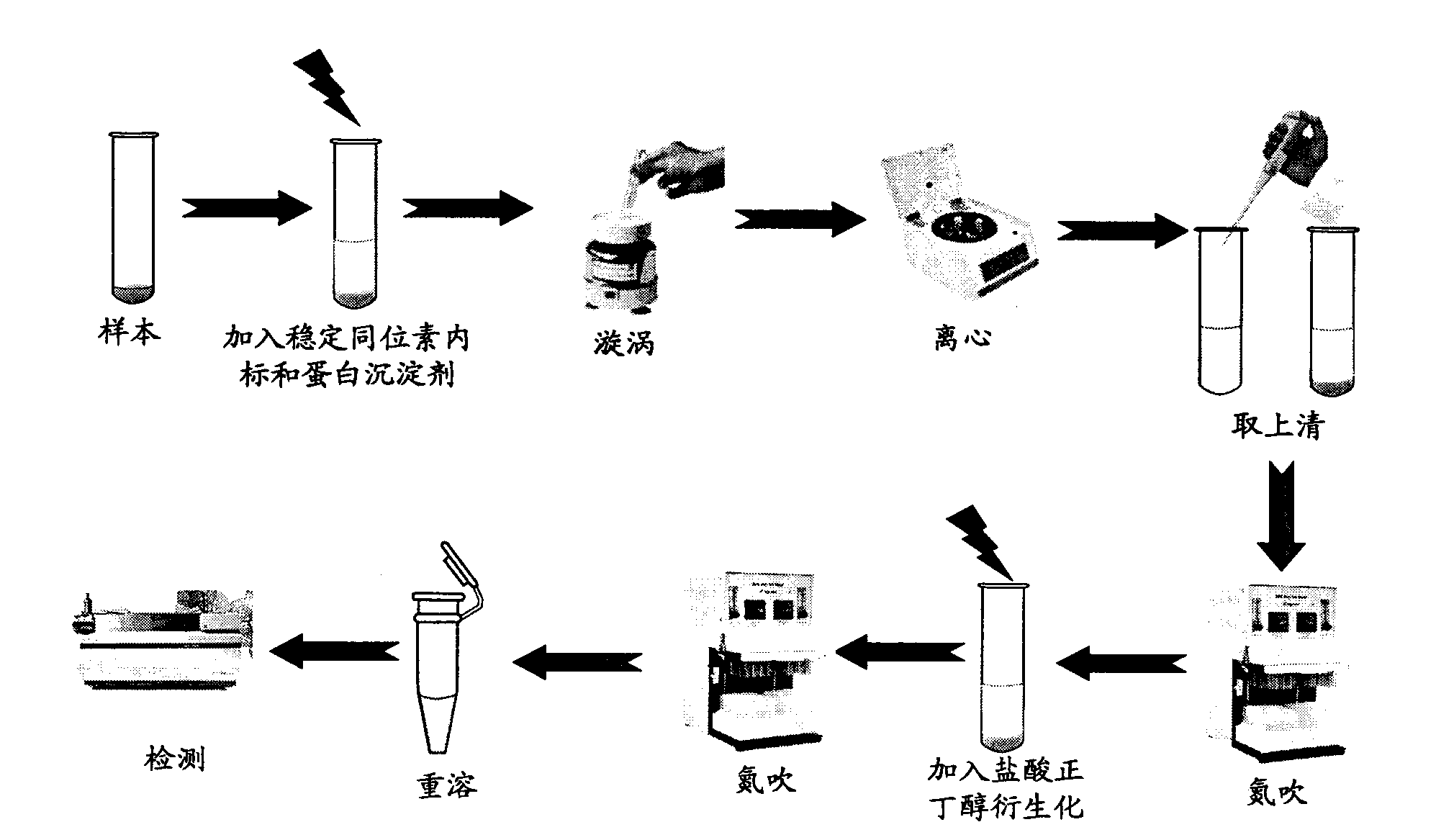
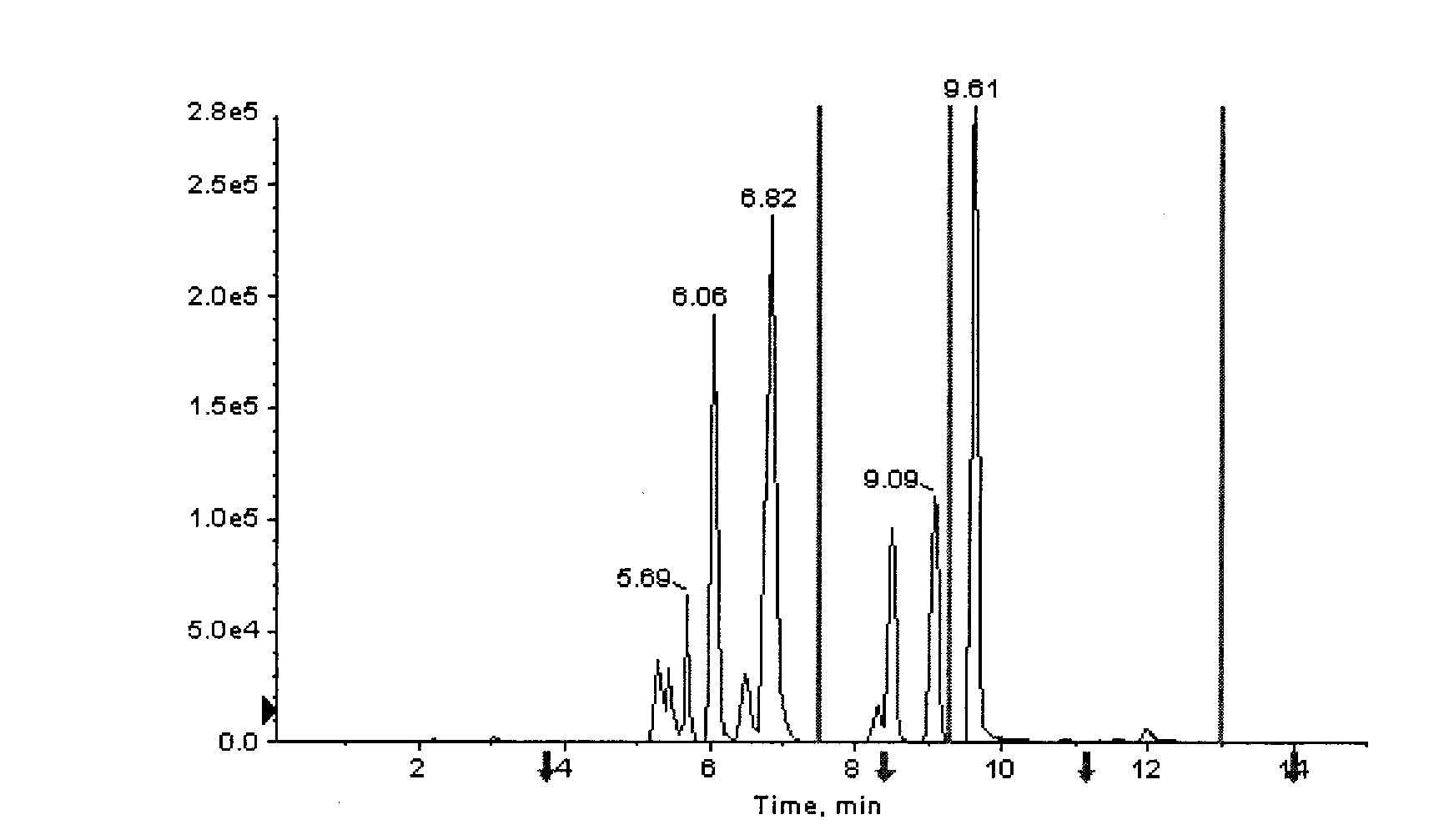
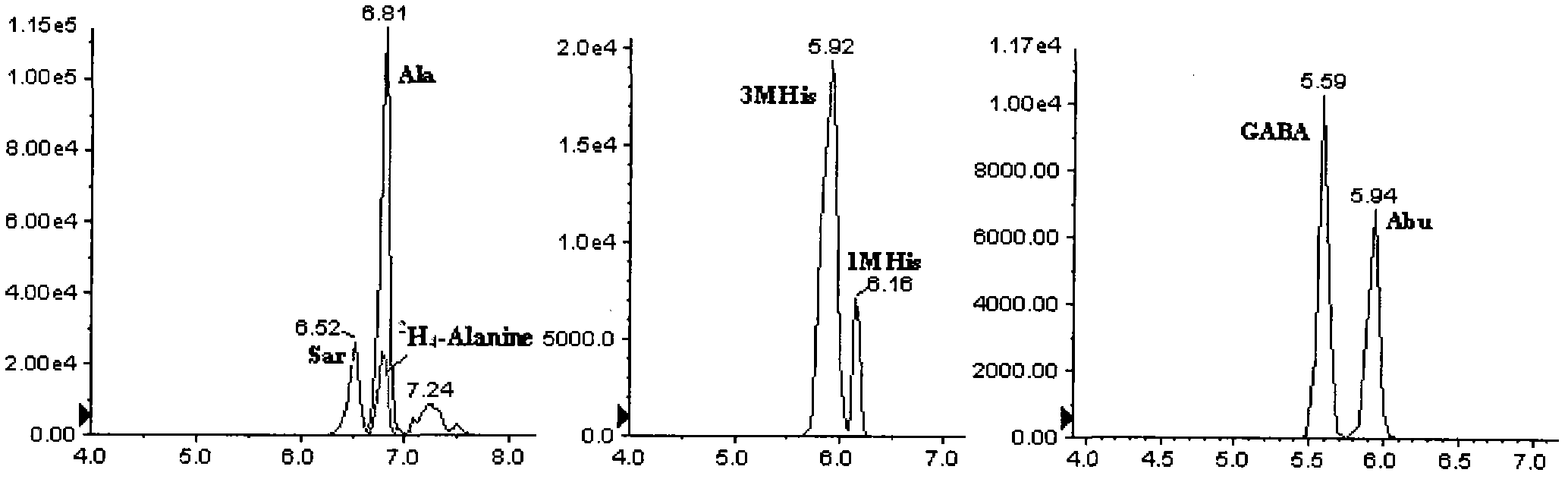
A simultaneous quantitative detection method of 30 amino acids and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103163226AImprove detection qualityRealize localizationComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansStable Isotope LabelingReversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography
The invention provides a high-sensitivity and high-throughput kit for simultaneous quantitative detection of 30 amino acids and a preparation method thereof. According to the kit, after extraction treatment of amino acids in a complex sample by using organic solvents, precipitating by using methanol, adding stable isotope-labeled amino acid internal labels, performing derivatization treatment by using hydrochloric acid and n-butanol, drying and redissolving, carrying out reversed-phase chromatography gradient separation by adopting C18 bonded phase silica gel as a stationary phase and acetonitrile-water containing heptafluorobutyric acid and formic acid as a mobile phase, and carrying out quantitative detection by adopting a mass spectrometer. The kit of the invention has the advantages that detection sensitivity can reach 10ng / ml, and all methodological indexes can meet the requirements of quantitative detections of amino acids in clinical examinations, industrial productions and scientific researches.
Owner:刘丽宏 +2
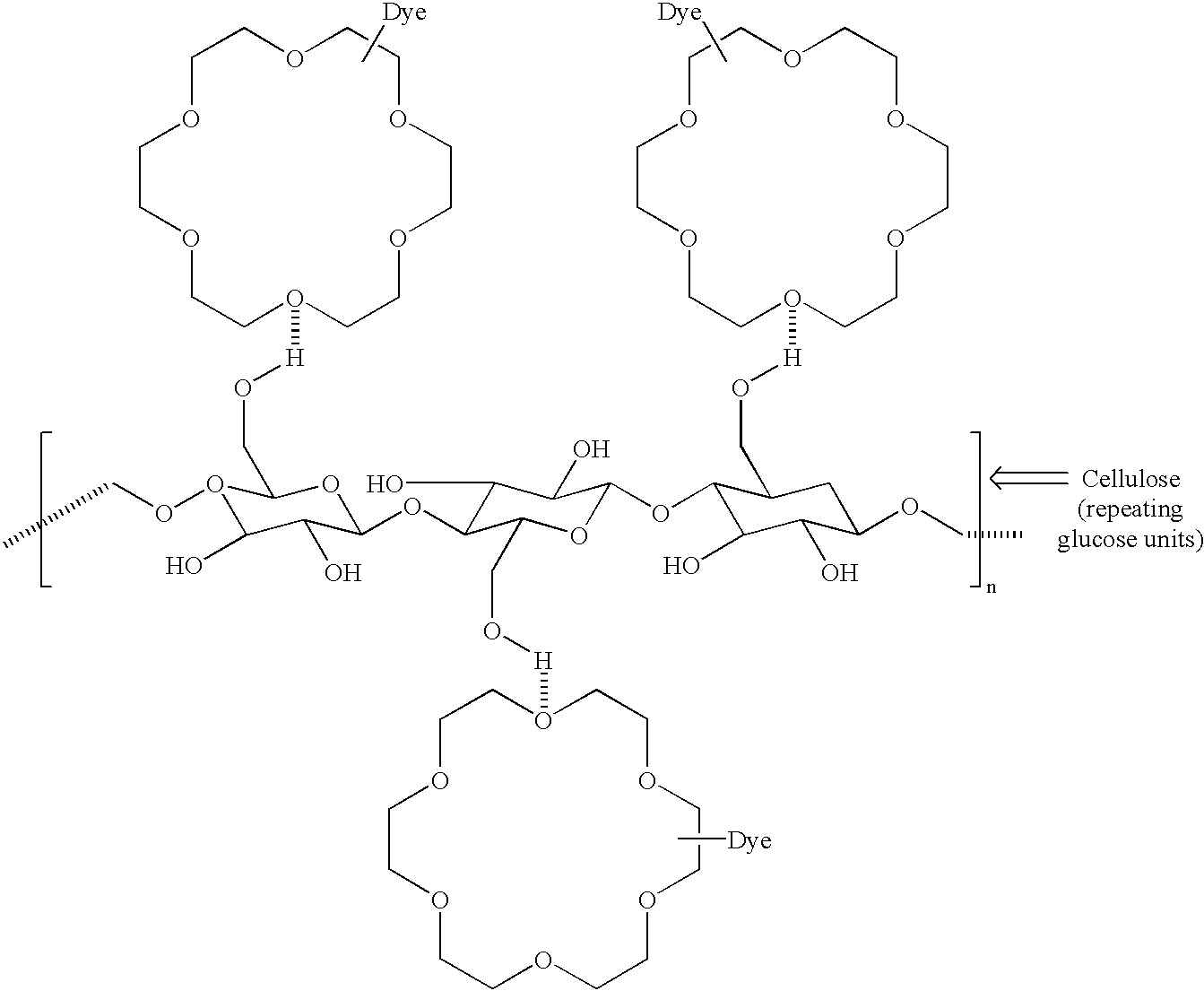
Derivatization of dyes/pigments with crown ethers and inkjet printing fluids containing the same
InactiveUS20020144626A1Improved lightfastnessImproved smearfastnessInksOrganic dyesDisperse dyeOrganic solvent
An inkjet ink is provided that employs one or more water-soluble colorants or water-insoluble colorants, such as solvent dyes, disperse dyes, or pigments. The colorant, whether water-soluble or water-insoluble, is derivatized with one or more crown ethers to render the water-insoluble colorants soluble in water and in water-miscible organic solvents commonly employed in inkjet printing, particularly thermal inkjet printing, and to impart improved properties to the colorants, such as lightfastness, smearfastness, and waterfastness. The inkjet ink comprises a vehicle and at least one crown ether derivatized colorant. The resulting inkjet ink evidences improved print quality properties, compared to inkjet inks containing colorants that are not so derivatized.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
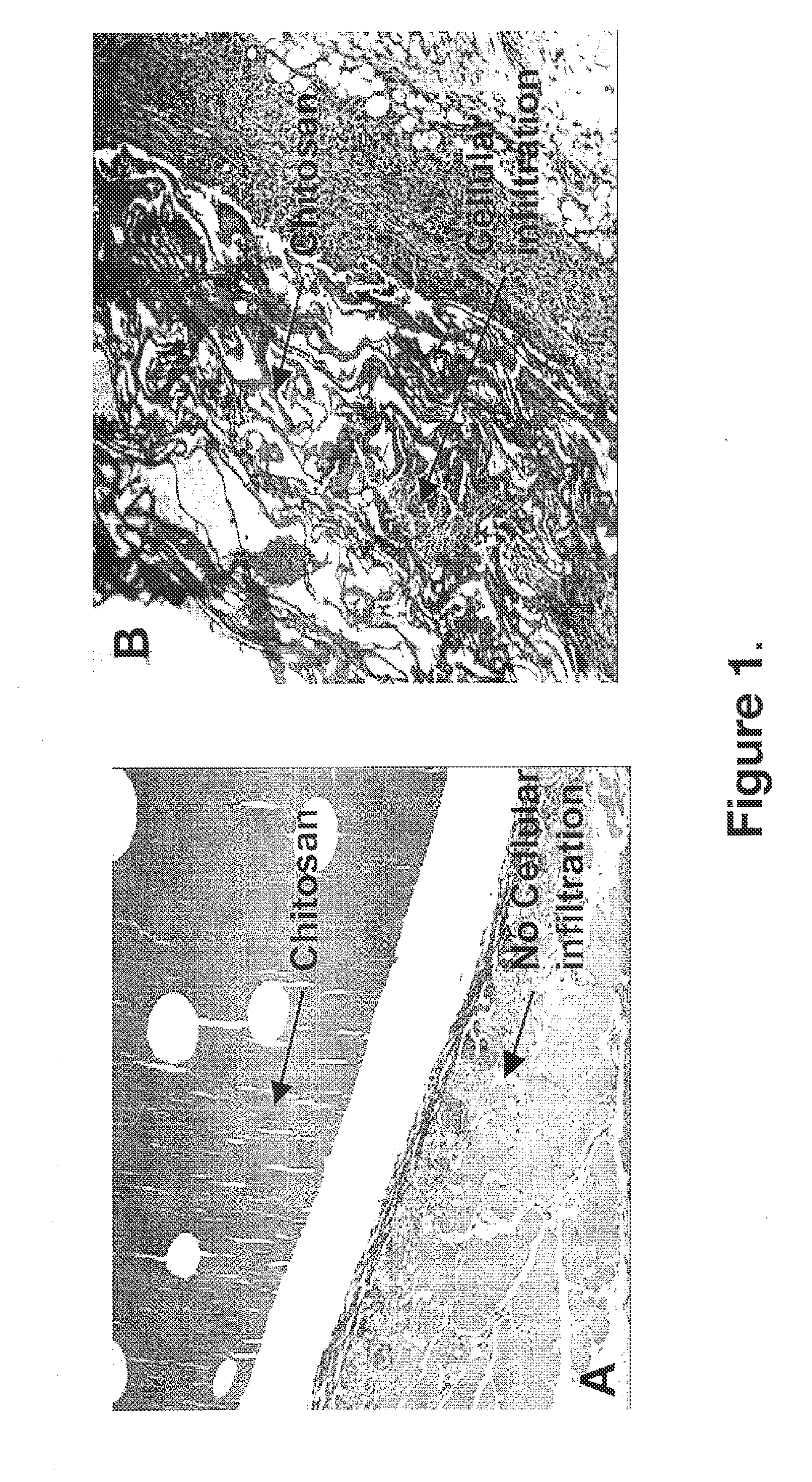
Biocompatible and bioabsorbable derivatized chitosan compositions
ActiveUS20140275291A1Reduces unnecessary riskQuick controlCompounds screening/testingBiocideCrosslinked chitosanChemical composition
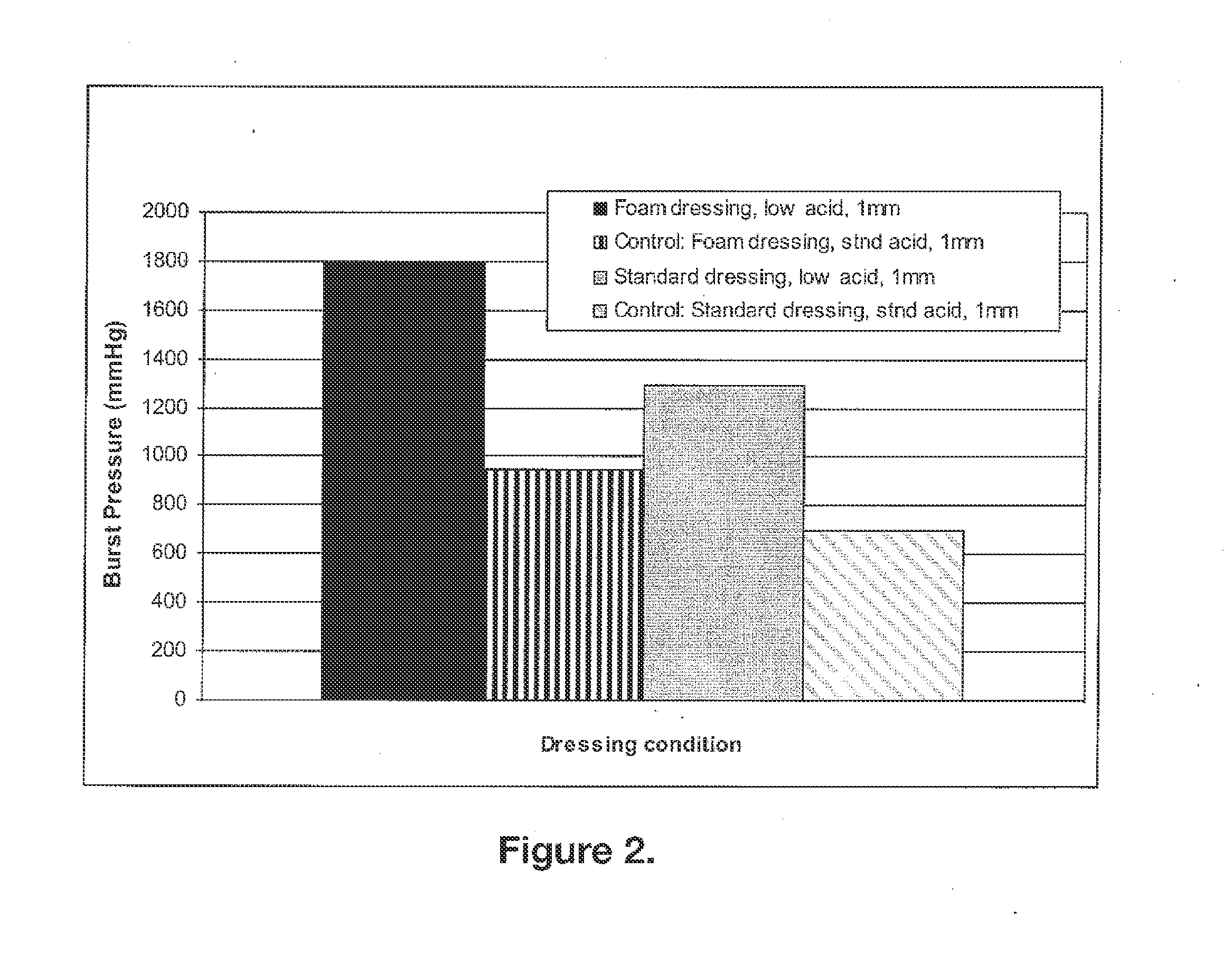
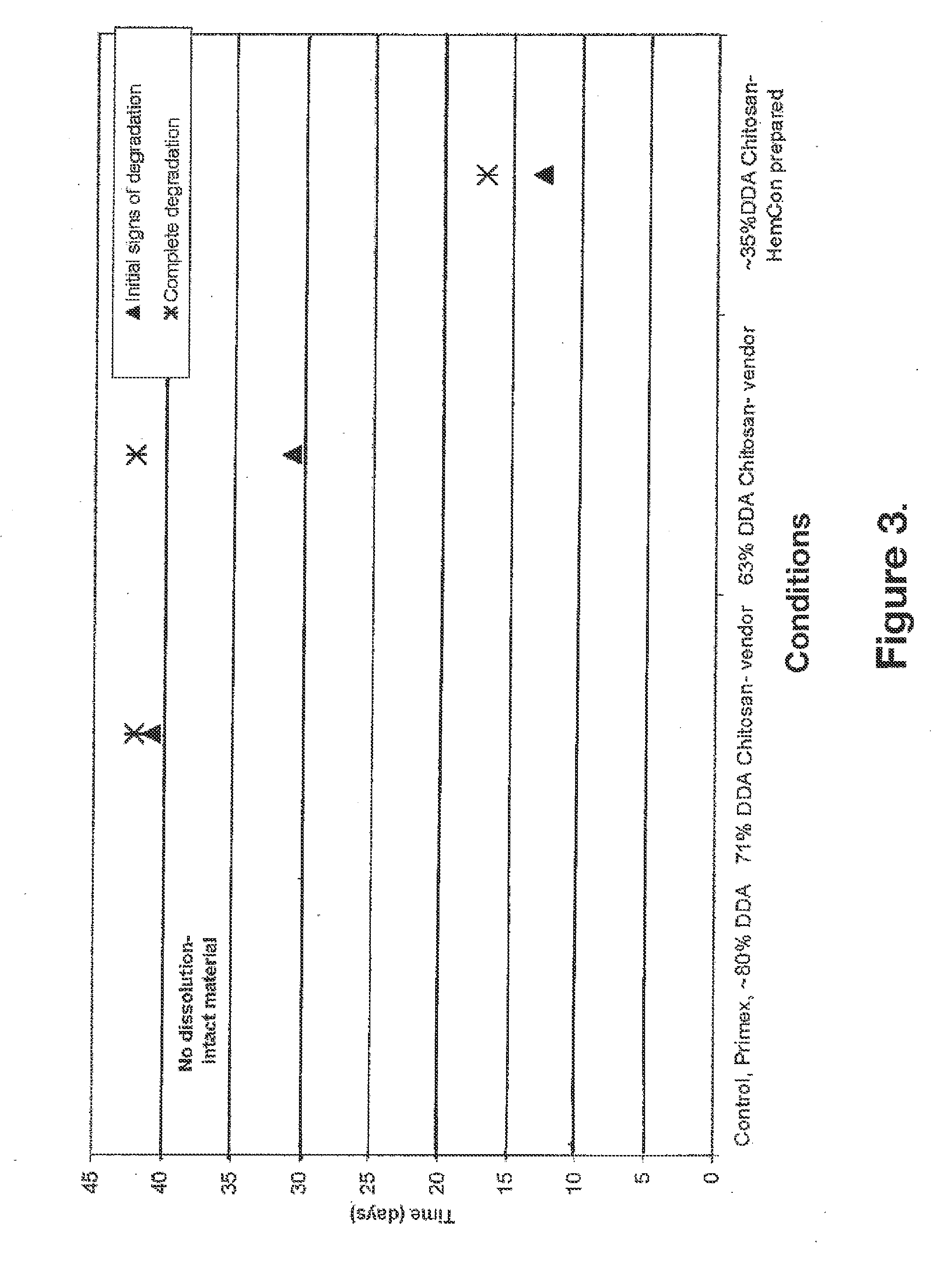
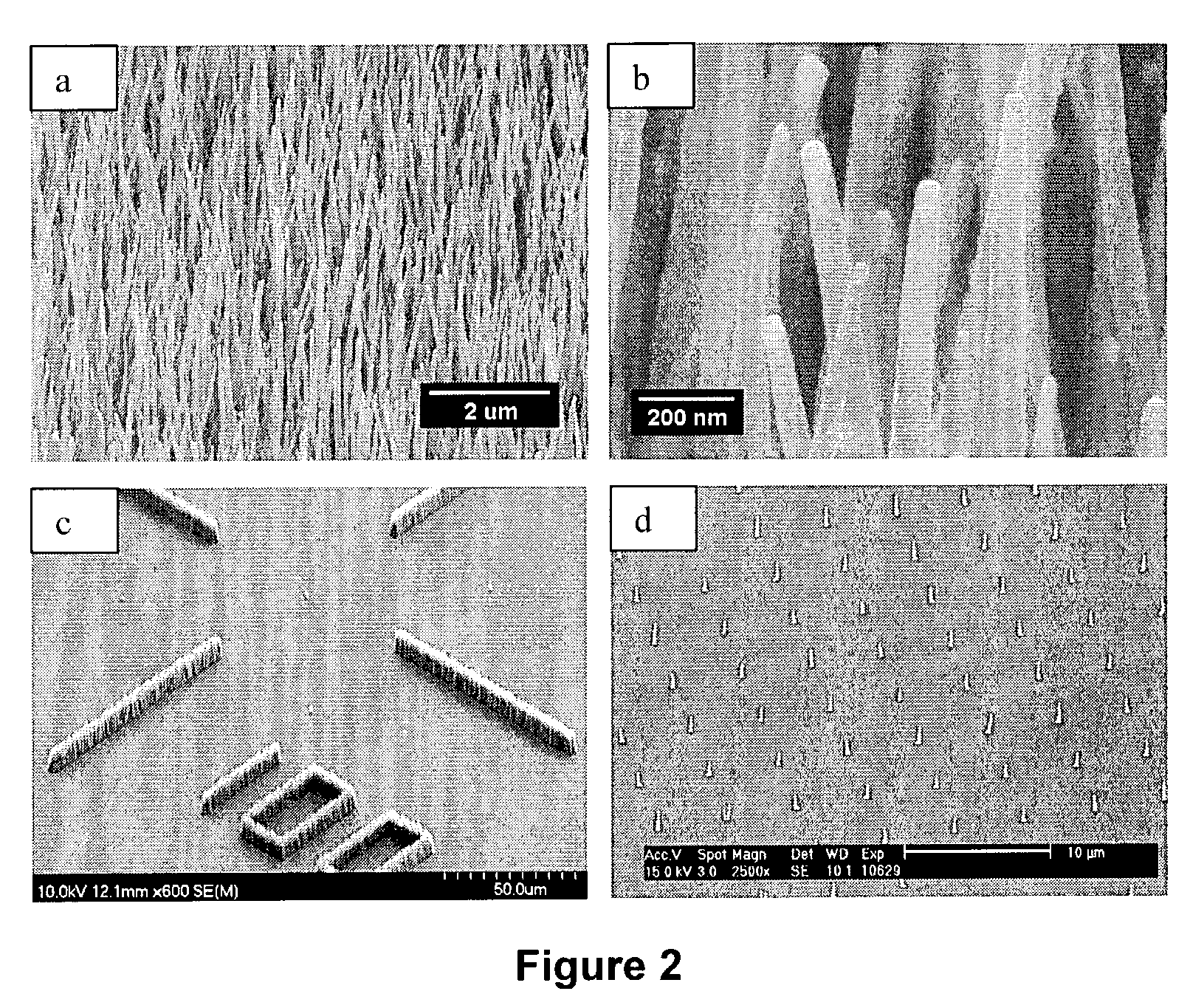
The invention relates to biocompatible, bioabsorbable derivatized non-crosslinked chitosan compositions optionally crosslinked to gelatin / collagen by 1-ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) for biomedical use and methods of making and testing such compositions, including a modified acute systemic toxicity test. The compositions comprise derivatized chitosan reacetylated to a degree of N-deacetylation (DDA) of between about 15% and 40%. The compositions are typically bioabsorbed in about 90 days or less and can be made to bioabsorb at differing rates of speed. The compositions are initially soluble in aqueous solution below pH 6.5. The compositions have an acid content that can be adjusted between about 0% (w / w) and about 8% (w / w) to customize the composition for uses that require and / or tolerate differing levels of cytotoxicity, adhesion, composition cohesion, and cell infiltration into the composition.
Owner:TRICOL BIOMEDICAL INC
Nanoengineered membranes for controlled transport
InactiveUS7641863B2Small scaleEasy to mergeMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesFiberCarbon fibers
A nanoengineered membrane for controlling material transport (e.g., molecular transport) is disclosed. The membrane includes a substrate, a cover defining a material transport channel between the substrate and the cover, and a plurality of fibers positioned in the channel and connected to and extending away from a surface of the substrate. The fibers are aligned perpendicular to the surface of the substrate, and have a width of 100 nanometers or less. The diffusion limits for material transport are controlled by the separation of the fibers. In one embodiment, chemical derivatization of carbon fibers may be undertaken to further affect the diffusion limits or affect selective permeability or facilitated transport. For example, a coating can be applied to at least a portion of the fibers. In another embodiment, individually addressable carbon nanofibers can be integrated with the membrane to provide an electrical driving force for material transport.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method for cell selection utilizing azlactone-functional supports
InactiveUS6379952B1High purityHigh yieldMicroorganism separationArtificial cell constructsAntigenCell selection
Azlactone-functional supports are used to provide cell selection from a mixture such as bone marrow or peripheral blood having a desired target cell population. An azlactone-functional support is derivatized by covalently coupling to the support a biologically active substance that binds the target cells. A mixture containing the target cells is contacted with the derivatized support to bind the target cells to the biologically active substance, and unbound remaining mixture is removed from the support. Bound cells may be eluted from the support to obtain purified target cells. Biologically active substances include antibodies, lectins, proteins, antigens and avidin. The biologically active substance may directly or indirectly bind cells in the mixture. Indirect binding may be through a second, intermediary biologically active substance that is bifunctional. The azlactone-functional support is provided by incorporating an azlactone moiety into a base polymer support that has been selected by prescreening base polymer supports with a cell mixture to identify a base polymer support having minimal nonspecific binding of cells in the mixture.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
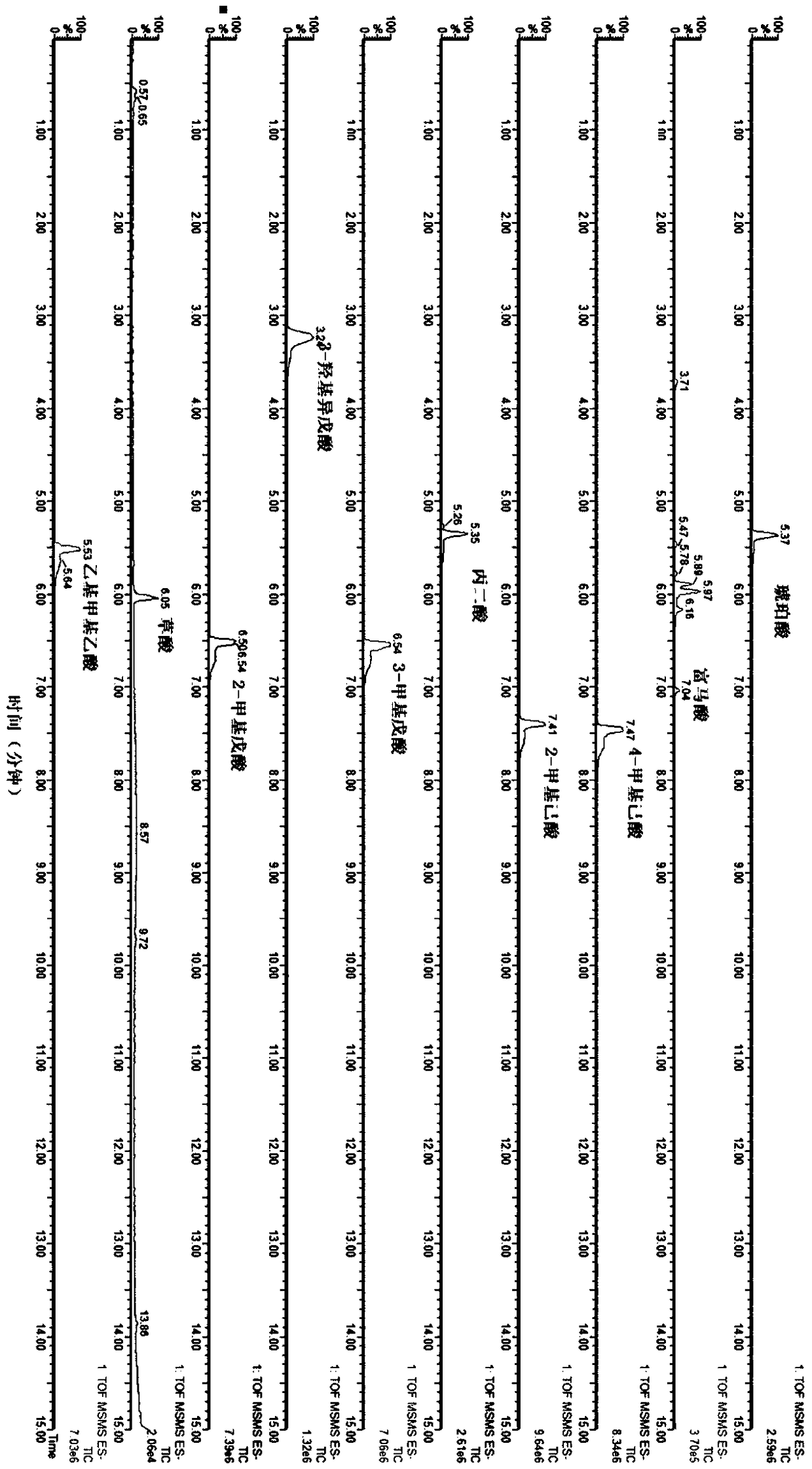
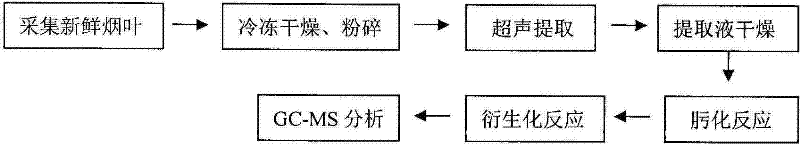
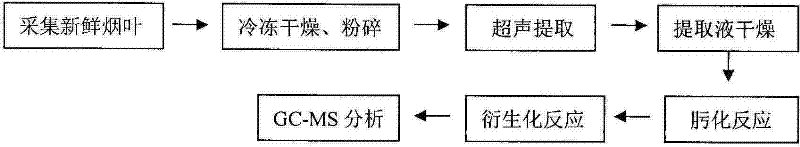
Method for detecting secondary metabolites in fresh tobacco leaves by using derivatization GC-MS
A method for detecting secondary metabolites in fresh tobacco leaves by using a derivatization GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer) is characterized by comprising the steps: quickly collecting new tobacco leaves and quickly freezing the new tobacco leaves by using liquid nitrogen on the site, crushing the tobacco leaves after removing the moisture in the tobacco leaves by means of freeze drying, extracting the secondary metabolites from tobacco powder by using a solvent, drying the extracted liquid supernatant, then performing oximation reaction and silane derivatization on the dried extractive, and finally performing analysis by the GC-MS. The method has the prominent advantages that firstly, a method suitable for extracting the secondary metabolites in the fresh tobacco leaves is developed. As the area of the tobacco leaves is larger, the secondary metabolites are not uniformly distributed in the whole tobacco leaves, and the tobacco leaves are not applicable to the punching sampling technique. However, according to a tobacco leave collection and extraction method provided by the invention, the collection period and the metabolite composition of the tobacco leaves at the collected part can be truly reflected. Secondly, most of the important metabolites of the tobacco leaves such as saccharides, amino acids, organic acids, terpene alcohols in the fresh tobacco leaves can be simultaneously detected, and the method has the characteristics of high throughput detection.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com