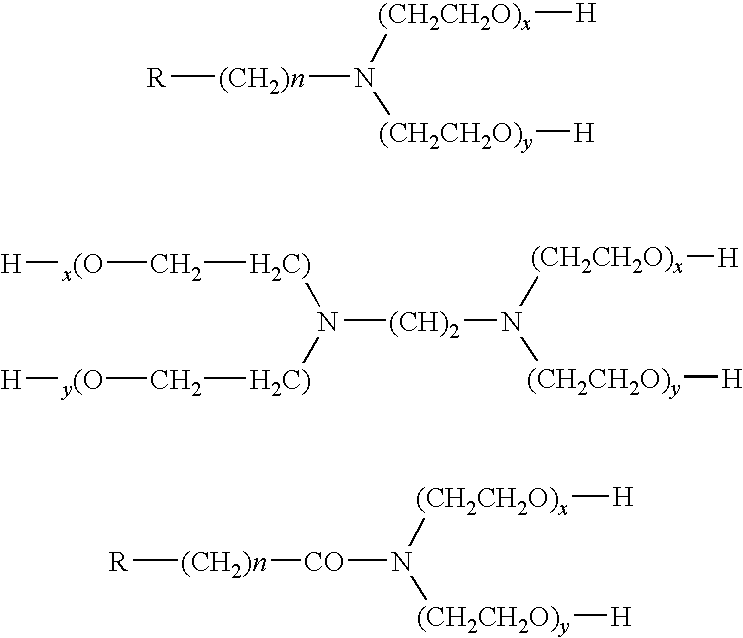
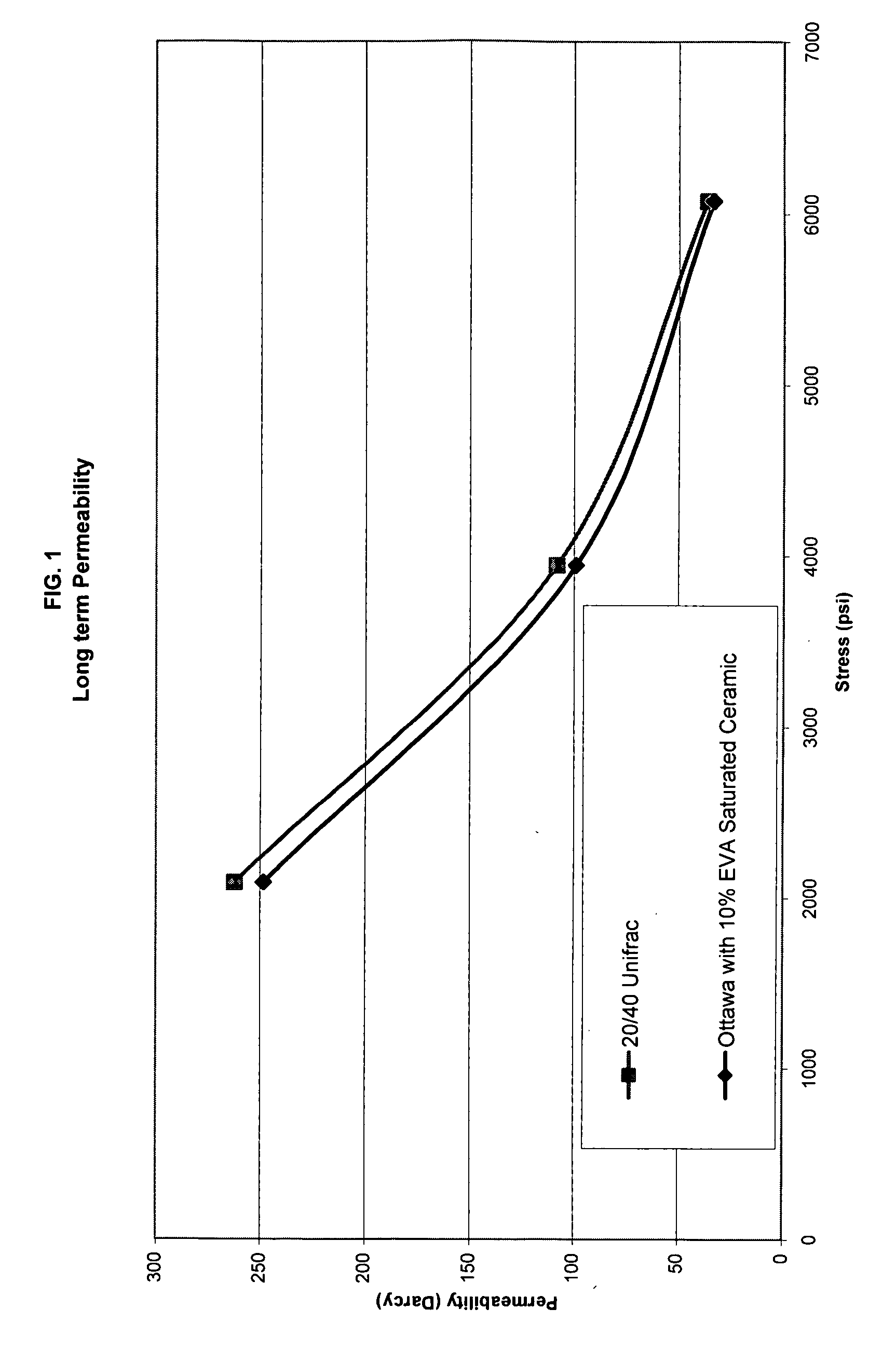
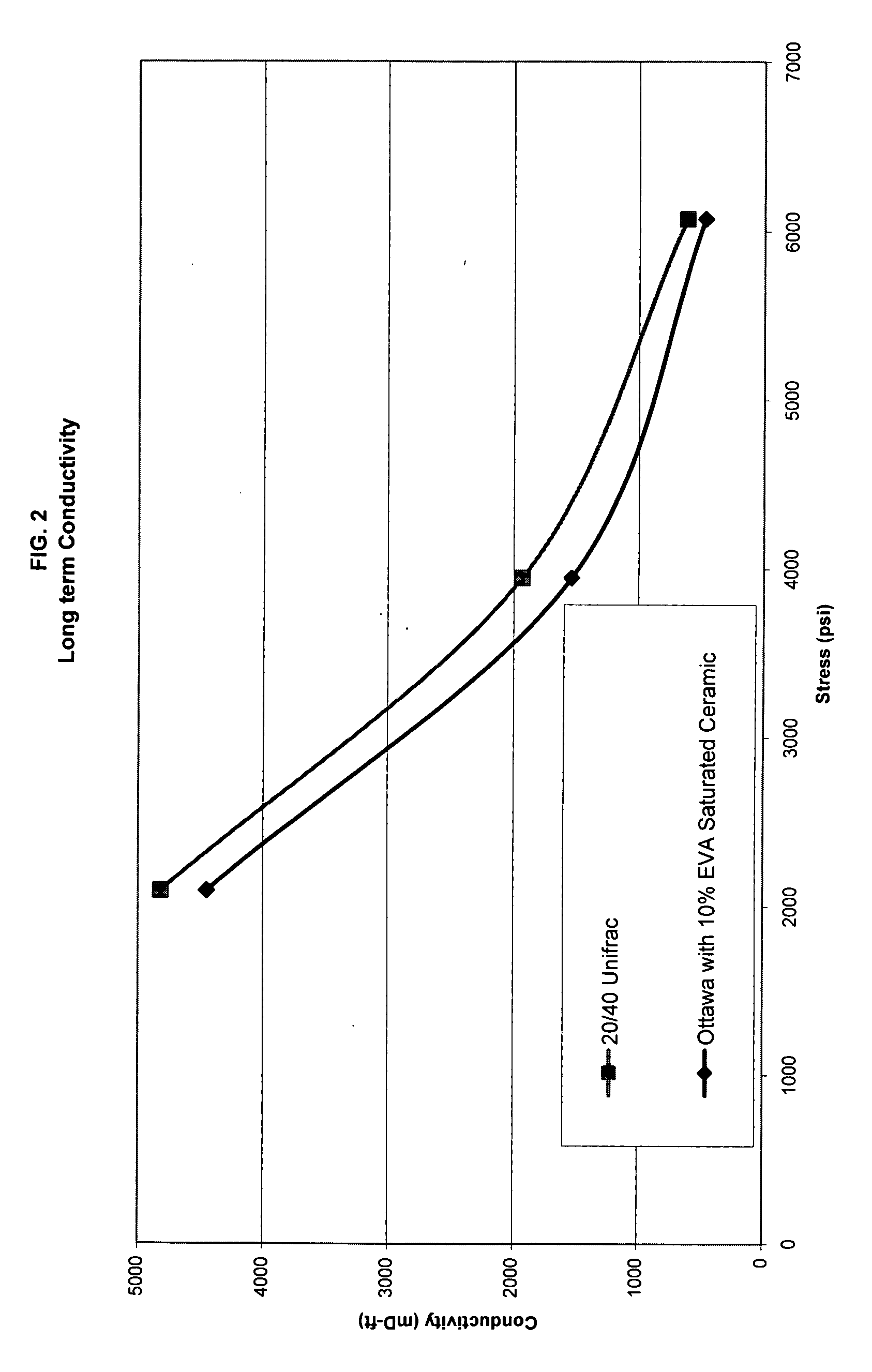
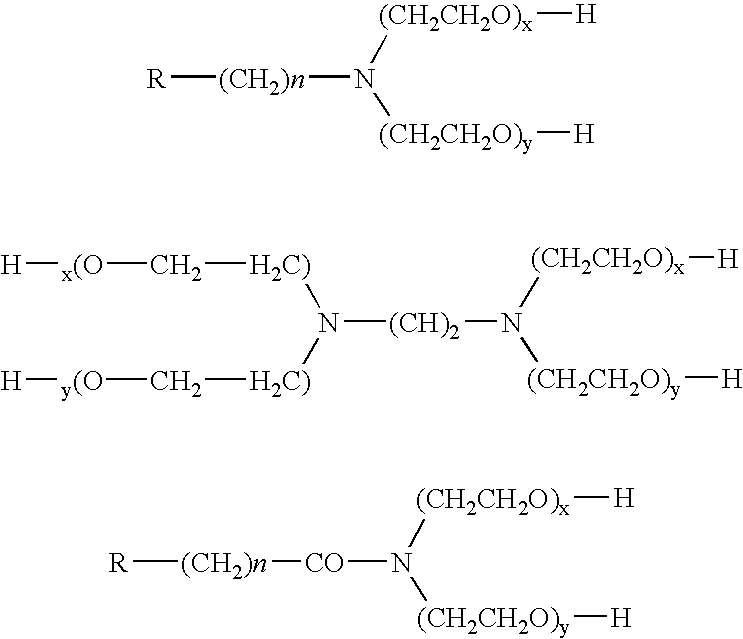
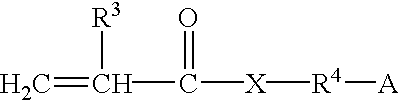
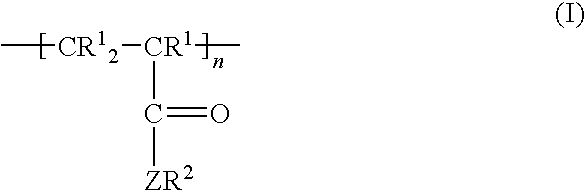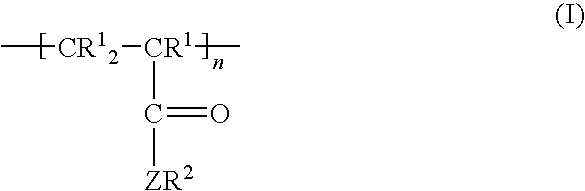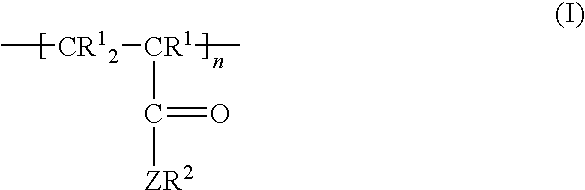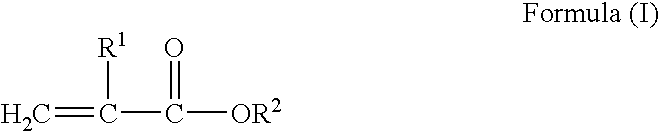Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1546 results about "Water in oil" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
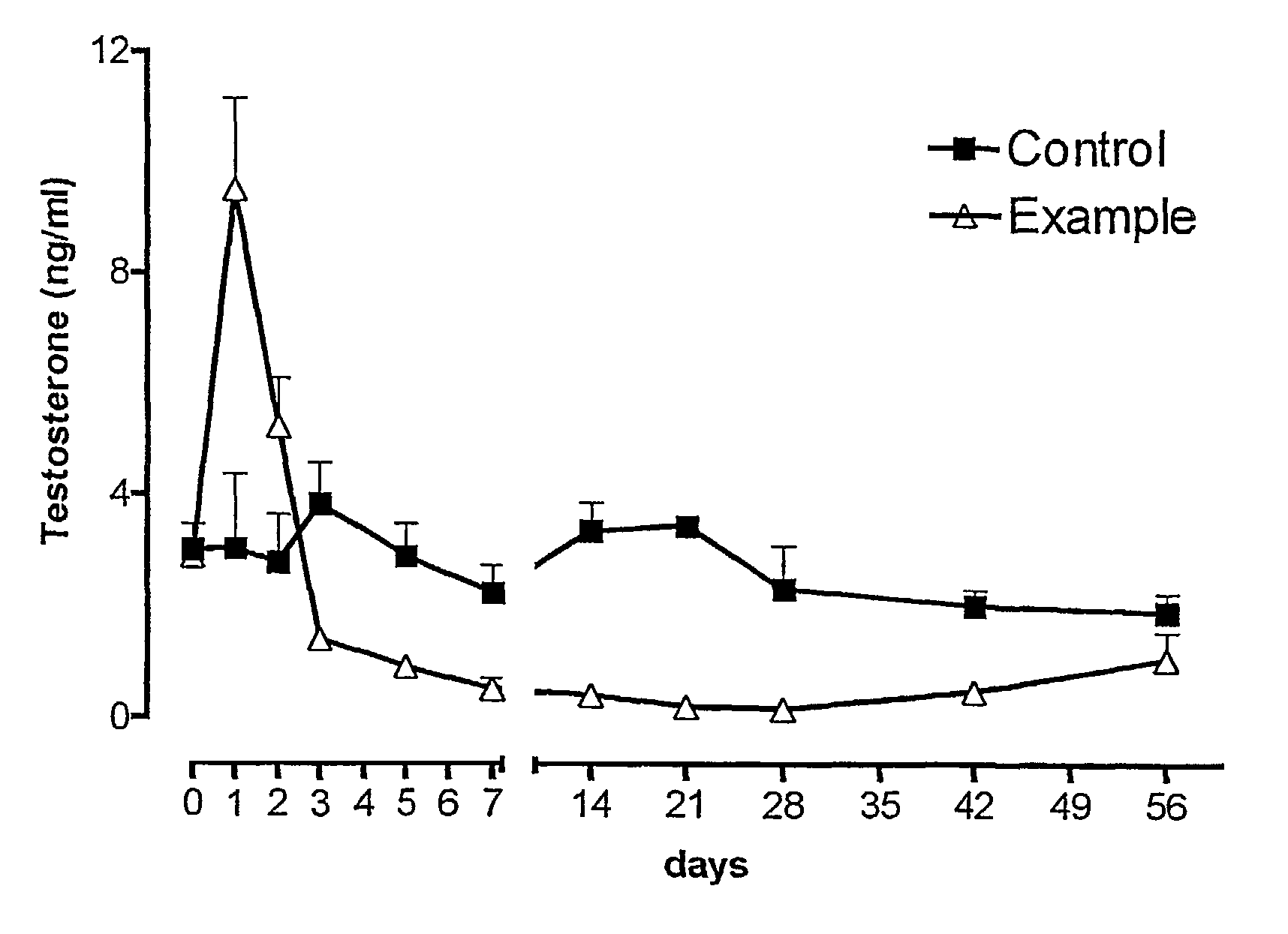
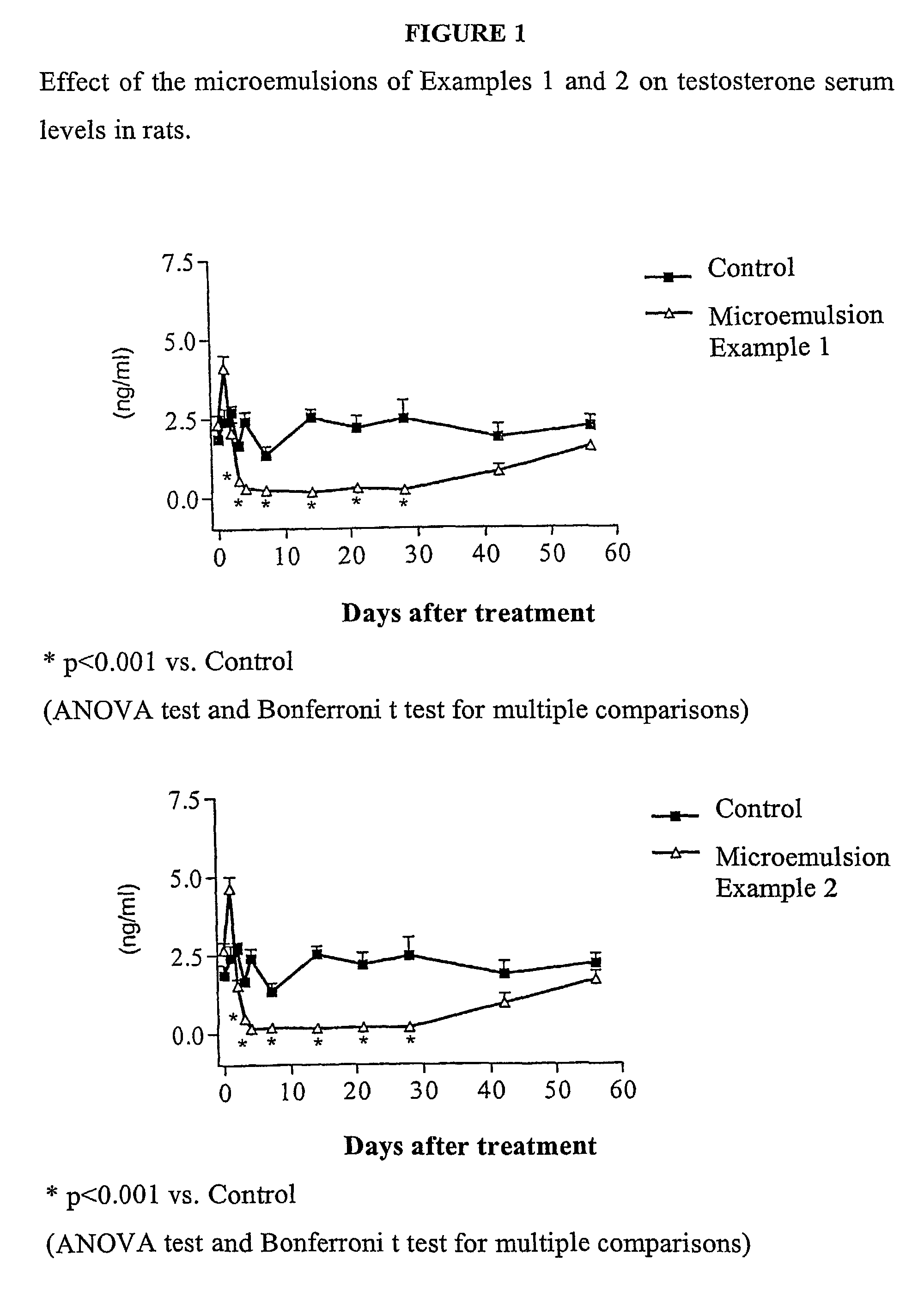
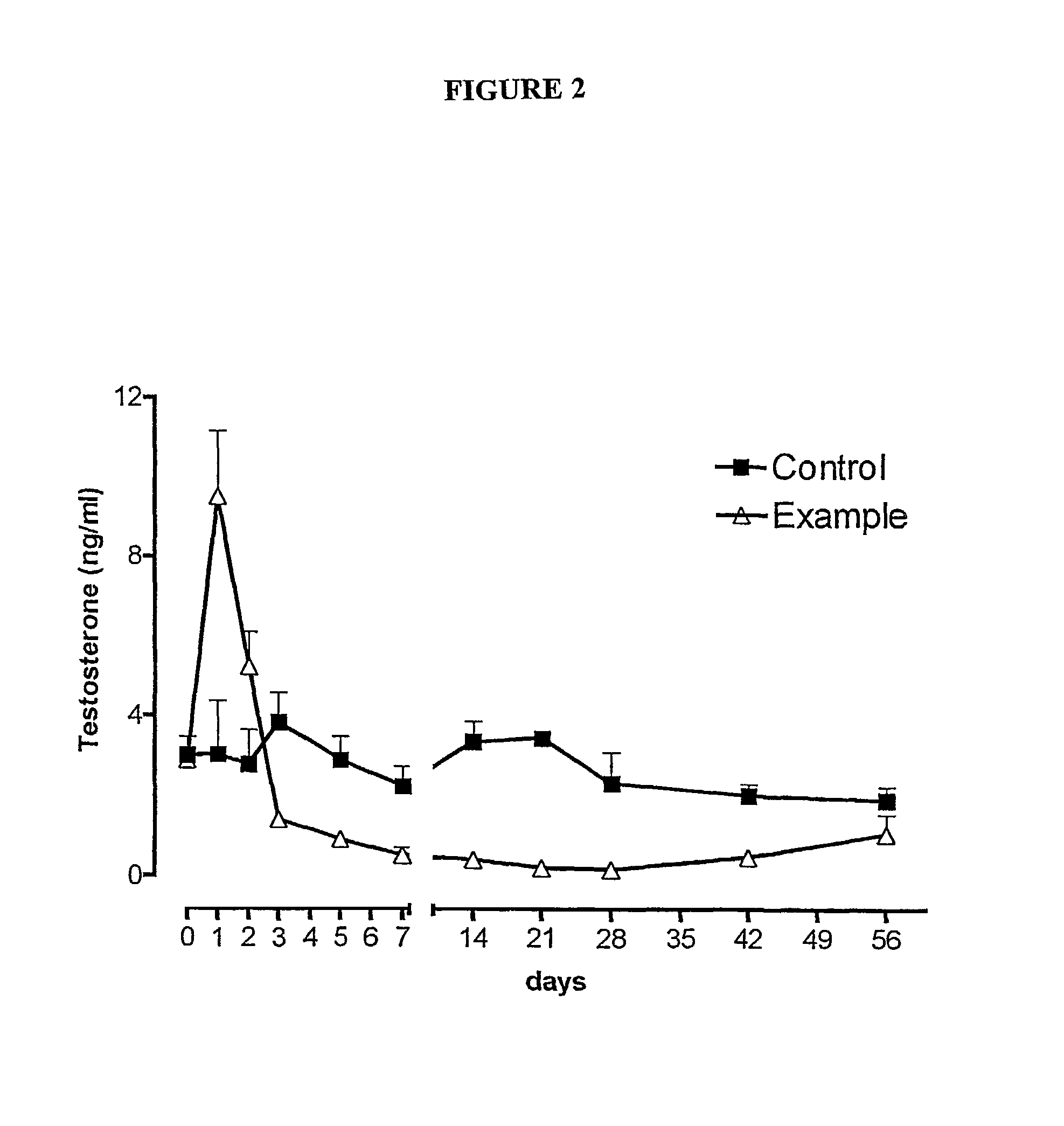
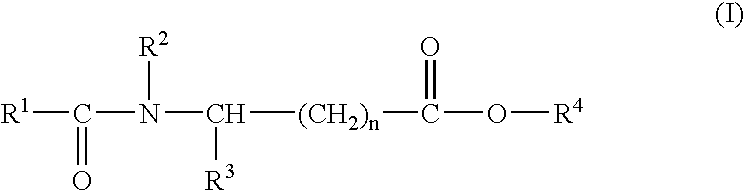
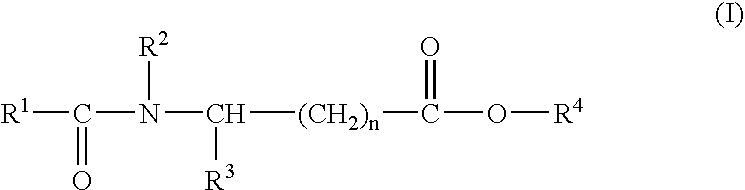
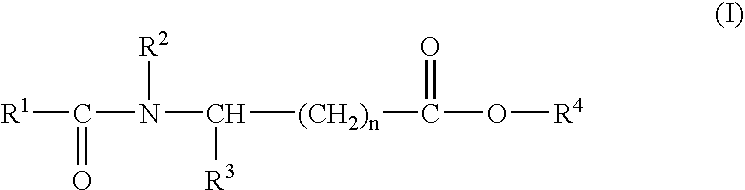
Sustained release pharmaceutical compositions for the parenteral administration of hydrophilic compounds
InactiveUS7157099B2Easy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsParenteral nutritionBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Owner:ITALFARMACO SPA
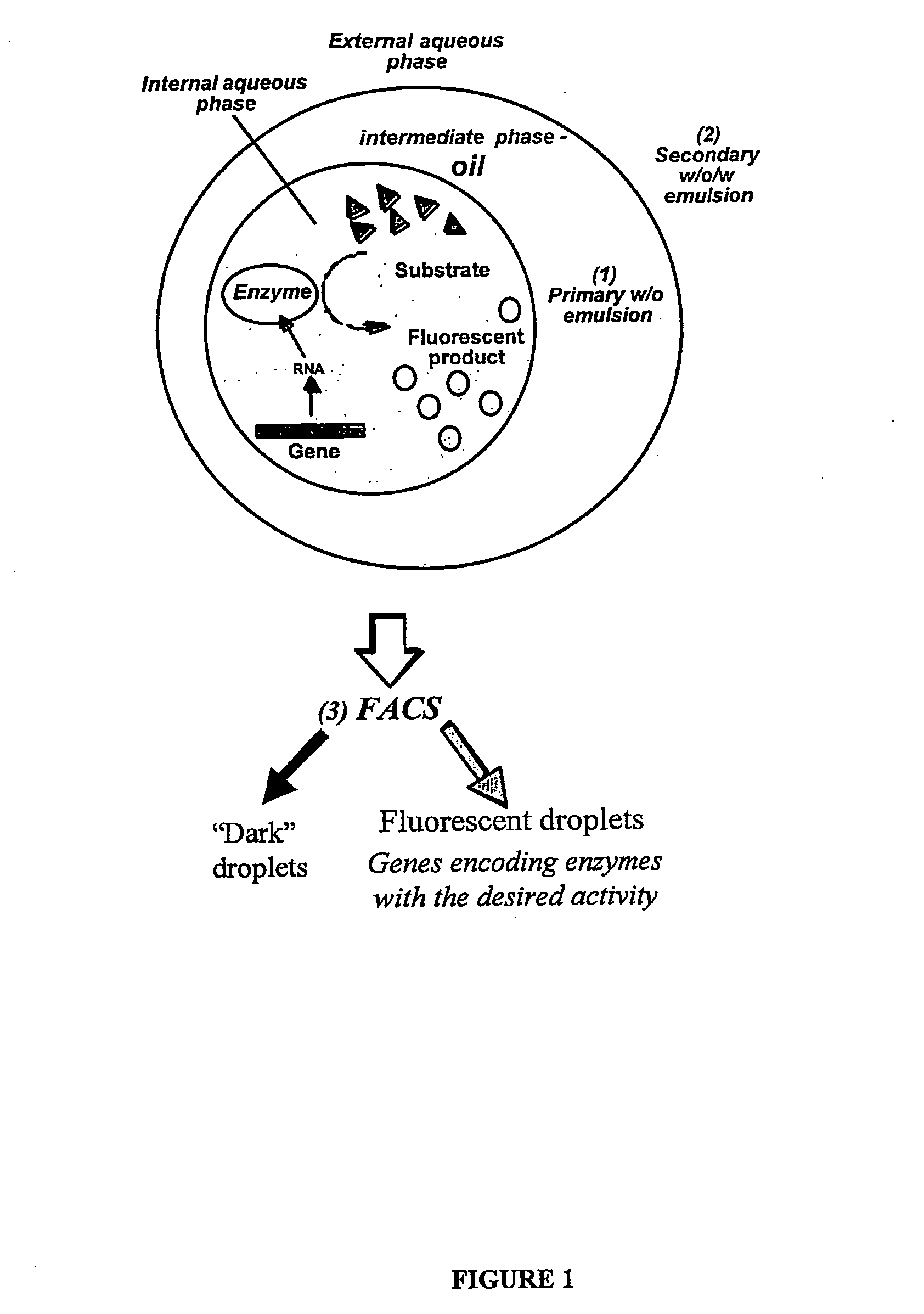
Compositions and methods for in vitro sorting of molecular and cellular libraries
InactiveUS20070077572A1Emulsion stabilizationWide potentialPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell biologyIn vitro system
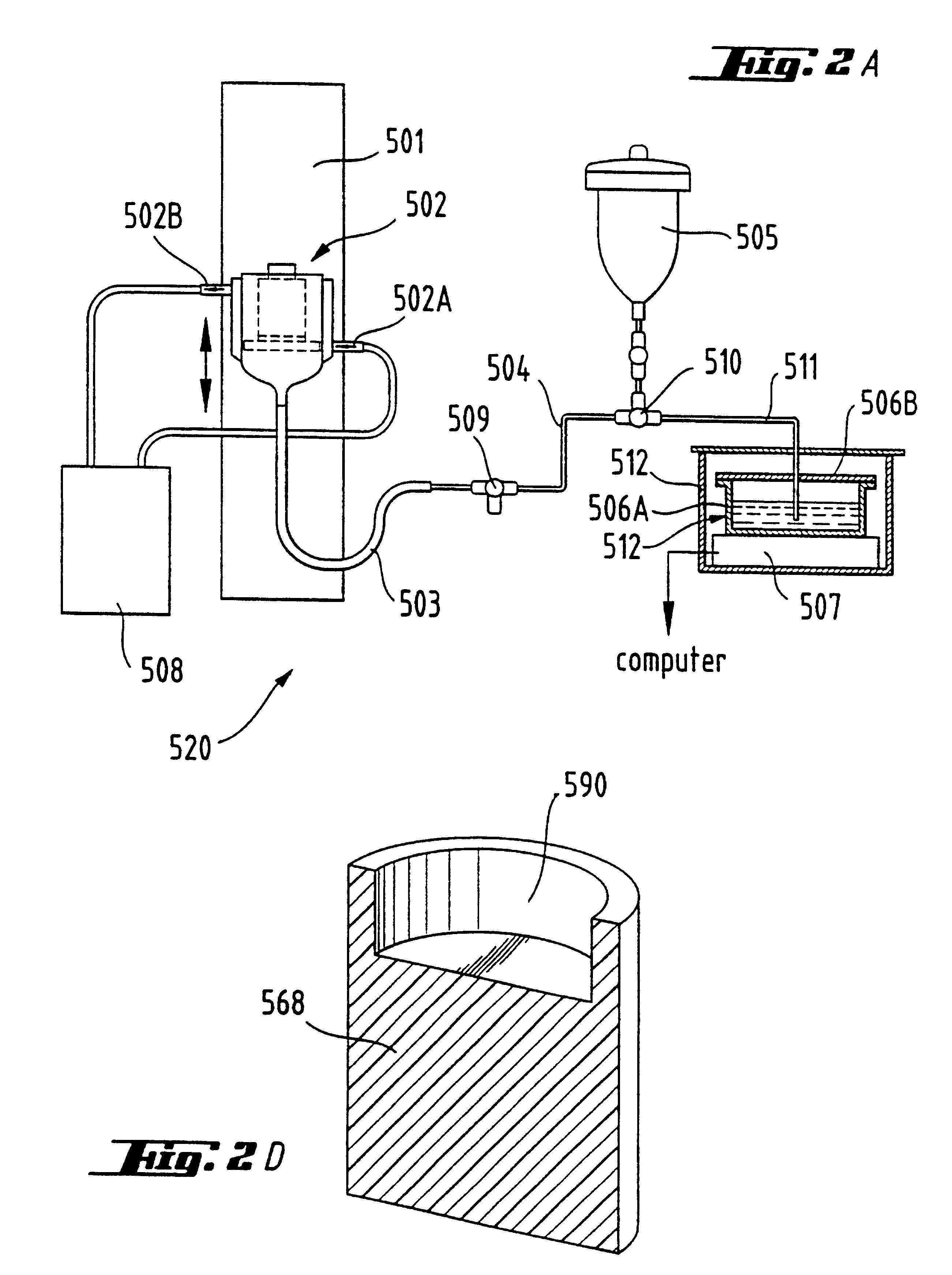
The present invention provides an in vitro system for compartmentalization of molecular or cellular libraries and provides methods for selection and isolation of desired molecules or cells from the libraries. The library includes a plurality of distinct molecules or cells encapsulated within a water-in-oil-in-water emulsion. The emulsion includes a continuous external aqueous phase and a discontinuous dispersion of water-in-oil droplets. The internal aqueous phase of a plurality of such droplets comprises a specific molecule or cell that is within the plurality of distinct molecules or cells of the library.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL +2
Absorbent articles with distribution materials positioned underneath storage material
An absorbent article having an ultimate fluid storage region and a fluid distribution region, positioned between the ultimate storage region and the garment oriented surface of the article, in fluid communication with the ultimate fluid storage region, the ultimate fluid storage region includes a material which has: (1) a Capillary Sorption Desorption Capacity at 100 cm (CSDC 100) of at least 10 g / g; (2) a Capillary Sorption Desorption Capacity at 0 cm (CSDC 0) higher than the CSDC 100; (3) a Loosely Bound Liquid Capacity (LBLC); and (4) a Capillary Sorption Desorption Release Height when 50% of the LBLC are released (CSDRH 50) less than 60 cm. Further, the liquid distribution layer material has a Capillary Sorption Absorption Height at 30% of its maximum capacity (CSAH 30) of at least 35 cm. Distribution material can be foam materials, particularly those derived from high internal phase water-in-oil emulsions.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Directed Evolution and Selection Using in Vitro Compartmentalization
InactiveUS20080004436A1Easy to adjustImprove concentrationSugar derivativesDNA preparationWater in oil emulsionGenetic element
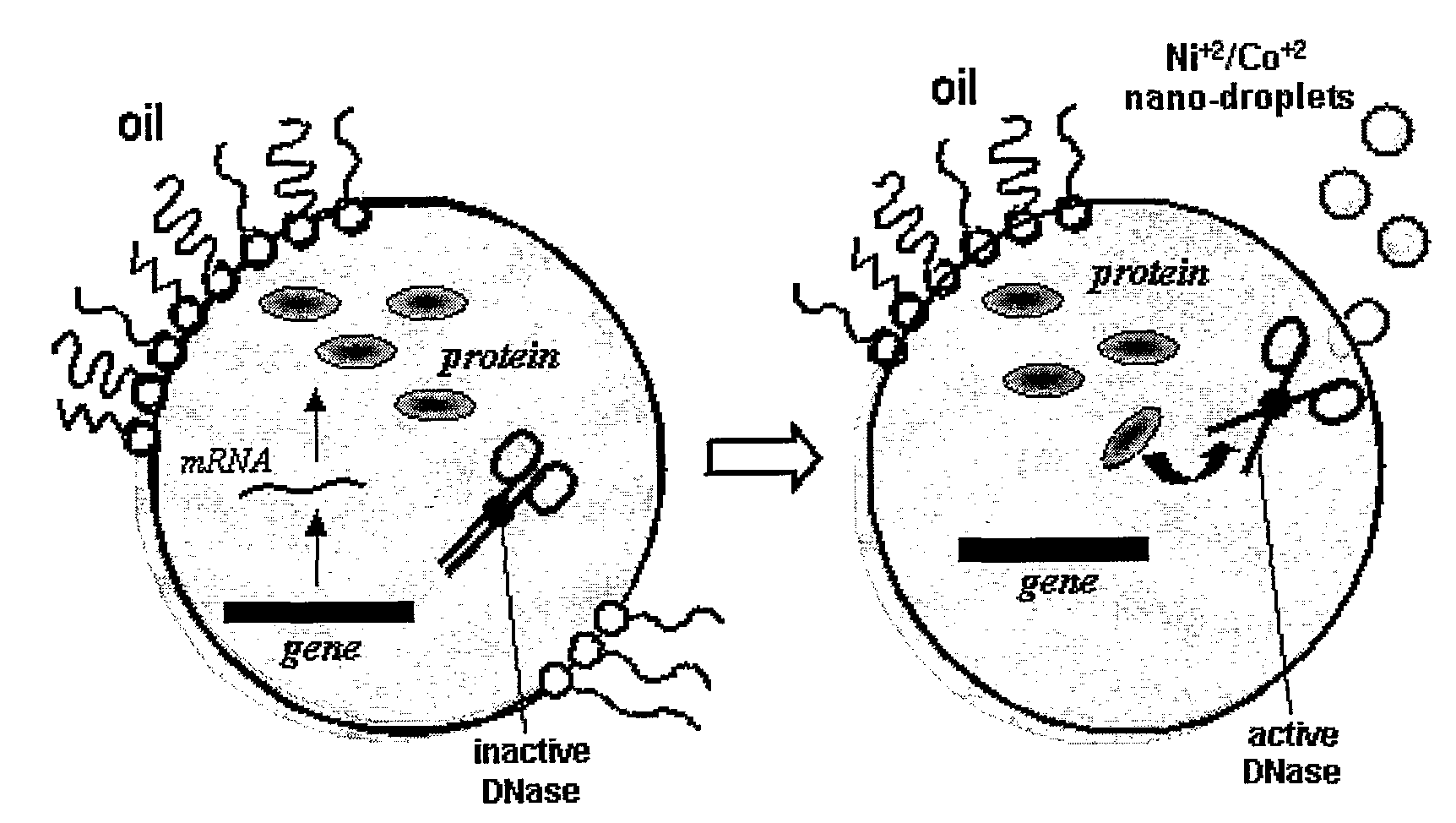
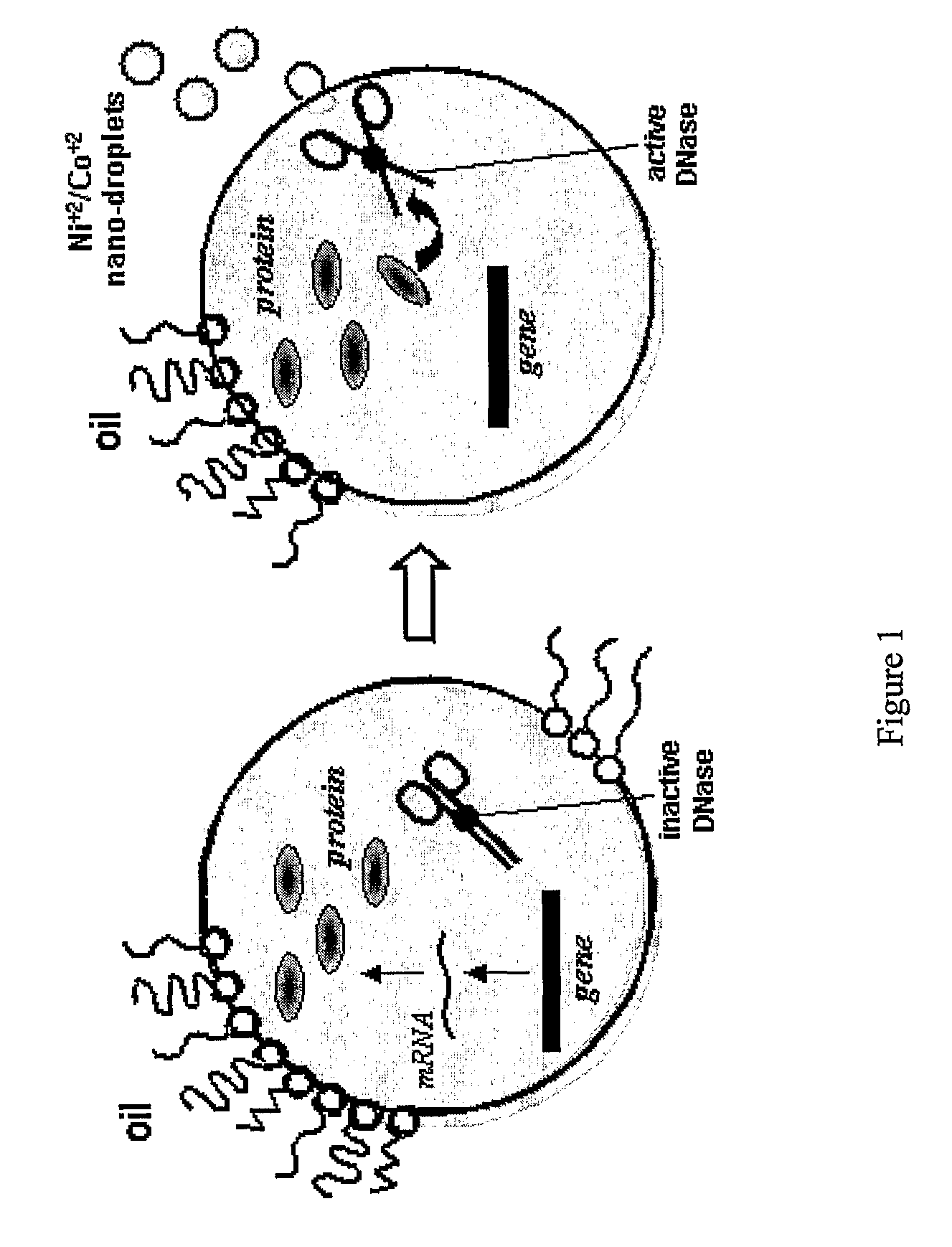
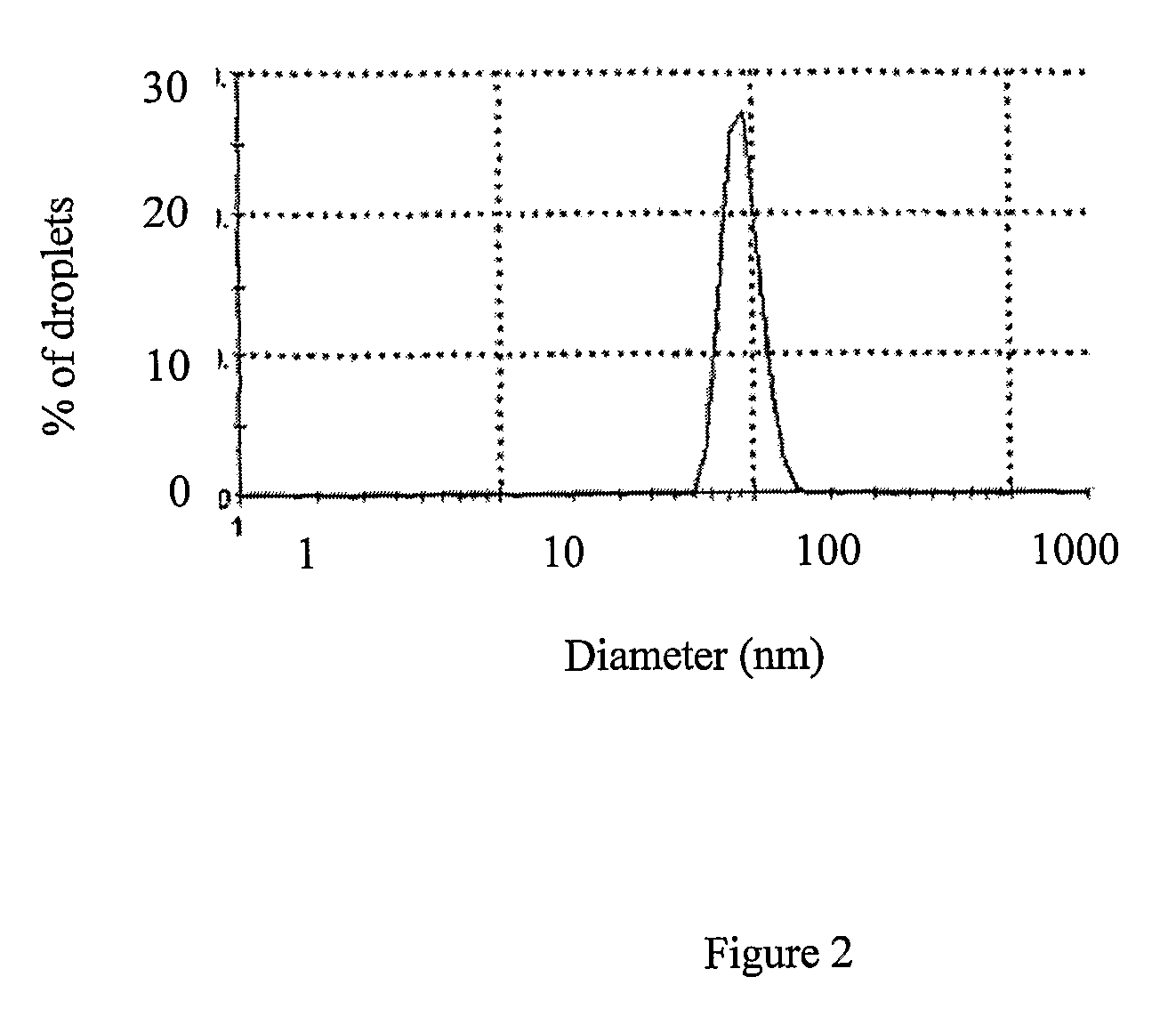
The present invention is related to the field of compartmentalized libraries of genetic elements and the selection of biologically active molecules and the genes encoding same from said libraries. The selection assay of the invention utilizes water-in-oil emulsions and is particularly advantageous in applications in the field of directed-evolution, as exemplified herein for selection of protein inhibitors of DNA nucleases.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Storage stable compositions of biological materials
Storage stable compositions of biological materials, including bioactive biological materials are provided in the form of a water-in-oil emulsion, comprising:(a) cellular material selected from living and / or dormant prokaryotic and / or eukaryotic cells and tissues, the cellular material being compatible with water-in-oil emulsions;(b) one or more oils selected from vegetable oils and fish oils;(c) an oil-soluble nonionic polymeric surfactant having a molecular weight of from about 2500 to about 15000; and(d) water.The compositions may also contain a thickener such as a hydrophobic fumed silica or bentonite.Compositions may be used for various purposes, depending on the contained biological material. Specific examples include compositions containing Fusarium lateritium control of Eutypa lata in plant wounds made by cutting or pruning, and compositions containing Lagenidium giganteum for control of mosquitoes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Foams made by photopolymerization of emulsions
InactiveUS6573305B1High mechanical strengthFilm/foil adhesivesOptical articlesWater in oil emulsionPolymer chemistry
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Antibacterial nano fiber material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101358382ANo side effects on the human bodyContinuous and stable releaseFilament/thread formingMacromolecular non-active ingredientsFiberSide effect
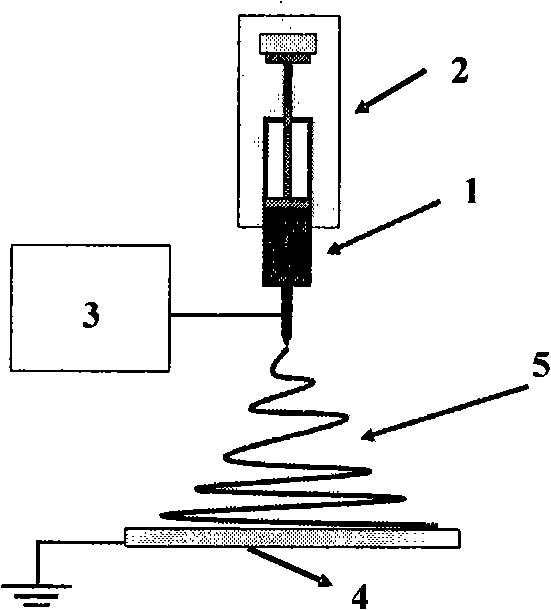
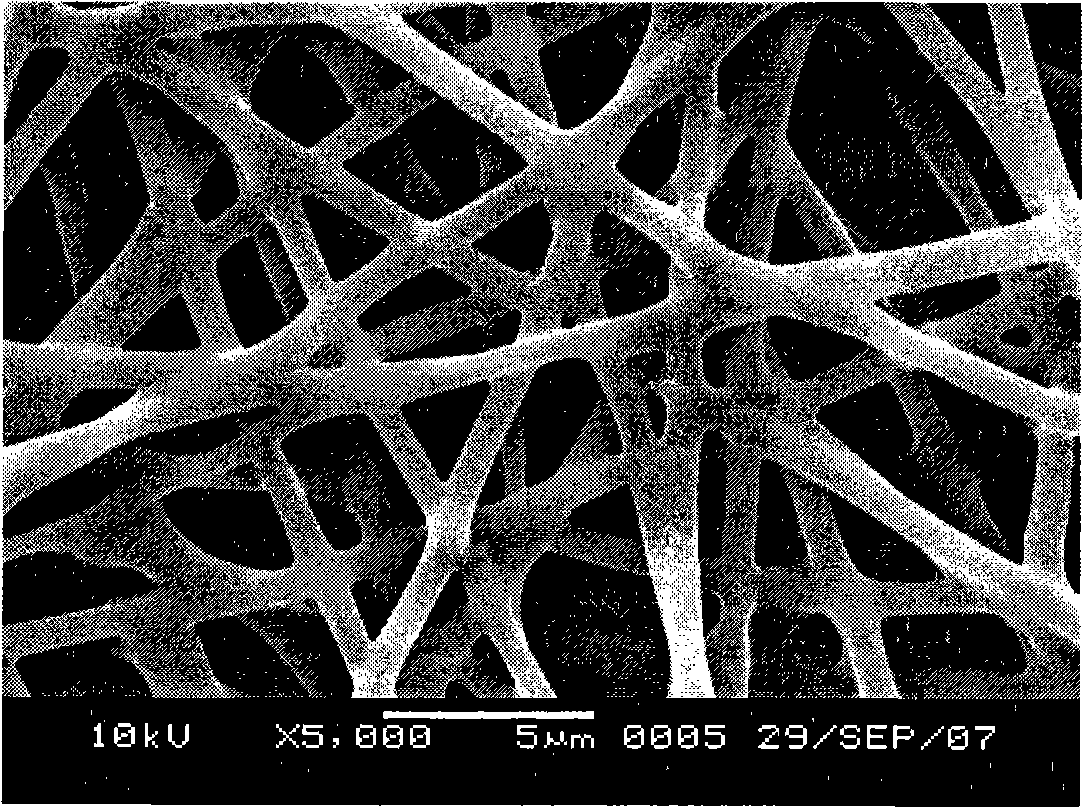
The invention relates to an antibacterium nano fiber material and a preparation method thereof; the material comprises polymer superfine fiber and antibacterial agent, and the weight ratio is 60 to 98: 2 to 40; the preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) the antibacterial agent is dissolved in distilled water to prepare solution; the polymer superfine fiber is dissolved in methylene dichloride or chloroform organic solvent, emulsifier is added to be mixed evenly, to obtain solution which is dispersed evenly; (2) the two types of solution are mixed to obtain even water-in-oil W / O latex, and then electrostatic spinning is conducted to the latex, to obtain the antibacterium nano fiber material. The nano fiber material has good ventilation property and filterability, still has bacteriostasis and sterilization functions for a long time after stably releasing the antibacterial agent, has simple preparation method, adopts the biodegradable and bioabsorbable polymer as carrier materials, can be absorbed by the human body after fully releasing, is not left, does not need secondary operation and has no side effect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
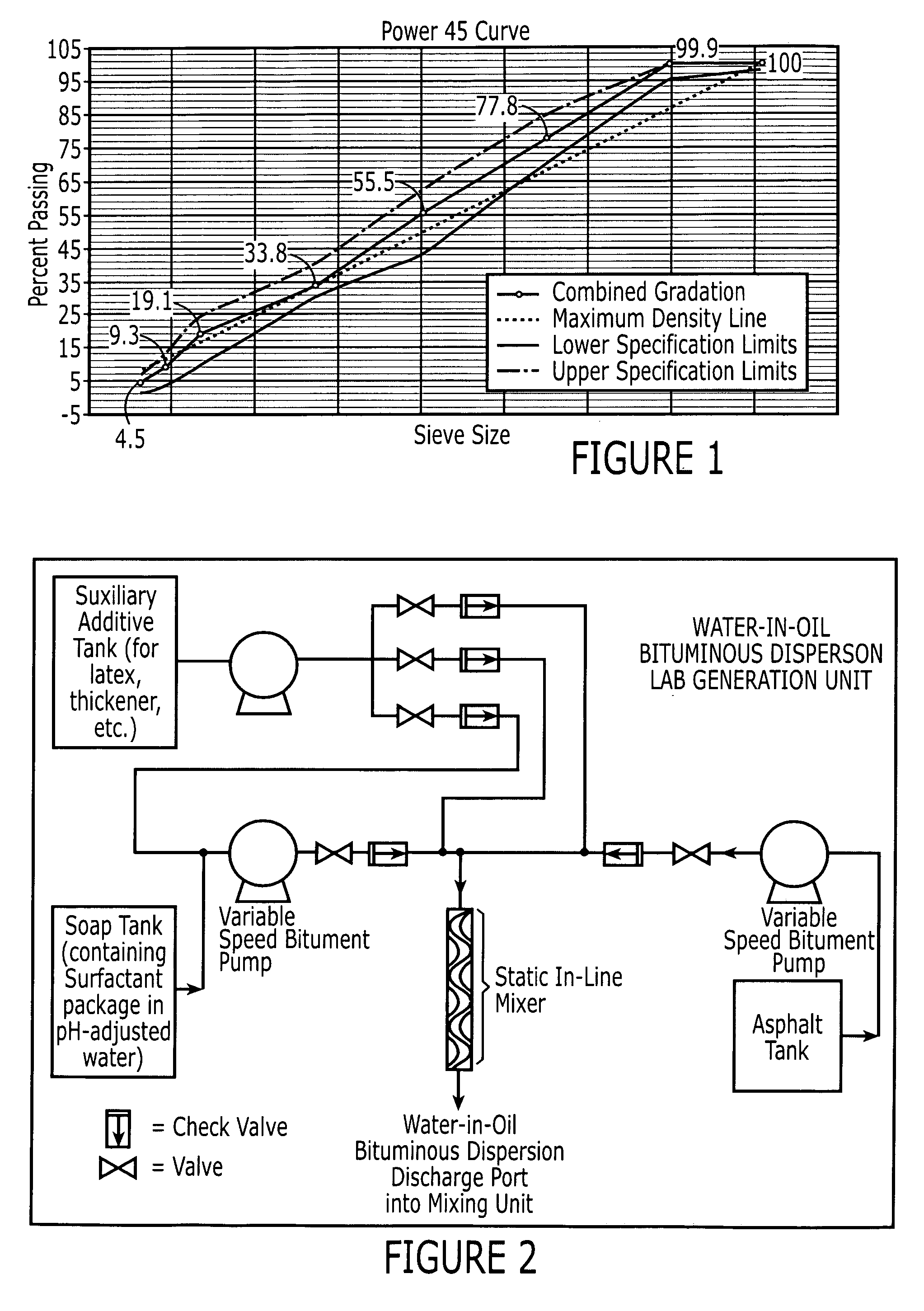
Water-in-oil bituminous dispersions and methods for producing paving compositions from the same
ActiveUS20070082983A1Low viscosityAccelerated strength developmentProductsIn situ pavingsSolvent freeSURFACTANT BLEND
There is provided a method for making bituminous compositions comprising water-in-oil bituminous dispersion and aggregate by the steps of: preparing a solvent-free, water-in-oil bituminous dispersion comprising: (1) bitumen, in an amount from about 75.0% to about 95.0% by total weight of the bitumen dispersion; (2) a surfactant in an amount from about 0.05% to about 2.0% by total weight of the bitumen dispersion; and (3) water in an amount to complete the water-in-oil bituminous dispersion, and producing the bituminous composition having a temperature from about 50° C. to about 120° C. by mixing: (1) the water-in-oil bituminous dispersion of step (A), having a temperature from about 75° C. to about 95° C., in an amount from about 2.0% to about 10.0% by total weight of the bituminous composition, and (2) aggregate, having a temperature from about 60° C. to about 140° C., in an amount from about 90.0% to about 98.0% by total weight of the bituminous composition.
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
Water-in-oil emulsions and methods
The present invention provides a process for delivery of water nanoclusters of diameter less than about one nanometer to the skin to yield high epidermal permeability and improved delivery of water to within the outer layer of human skin. This invention provides effective water-cluster-based formulations for a broad range of stable water / oil nanoemulsion configurations.
Owner:HYDROELECTRON VENTURES
Method of using water-in-oil emulsion to remove oil base or synthetic oil base filter cake
ActiveUS7481273B2Improve breathabilityHighly efficient in breakingCleaning apparatusScale removal and water softeningParticulatesParaffin wax
Fluid producing or injecting wells may be treated with a water-in-oil emulsion for the removal or inhibition of unwanted particulates, including pipe dope, asphaltenes and paraffins. In addition, such emulsions are effective in the displacement of oil base drilling muds and / or residues from such muds from wells. The emulsion may also be used to break the interfacial and / or rheological properties of oil base mud and synthetic oil base mud filter cakes, and act as a demulsifier to break the water-in-oil emulsion present in such oil base and synthetic oil base muds. The water-in-oil emulsions may optionally contain a dispersing agent as well as a surfactant.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Microemulsions for use in food and beverage products
ActiveUS20070087104A1Acceptable tasteImprove bioavailabilityEdible oils/fats with aqeous phaseFood gradeBeta-Carotene
Oil-in-water microemulsions which can be used to incorporate lipophilic water-insoluble materials, such as beta-carotene, into food and beverage compositions are disclosed. The microemulsions utilize a ternary food grade emulsifier system which incorporates a low HLB emulsifier, a medium HLB emulsifier, and a high HLB emulsifier. The microemulsions of the present invention allow for the incorporating of water-insoluble materials in an effective and easy-to-process manner while providing formulational flexibility and without significantly affecting the taste of the underlying food or beverage product. Food and beverage products including the microemulsions are also disclosed. Finally, the method of preparing the microemulsions is described. The invention also encompasses water-in-oil microemulsions for use in incorporating water-soluble materials into food and beverage products. Finally, the invention encompasses concentrate compositions used for making those microemulsions.
Owner:WILD FLAVORS INC
Water-in-oil emulsions with ethylene oxide groups, compositions, and methods
Water-in-oil emulsions, compositions, and methods that include a vinyl polymer that includes ethylene oxide-containing side chains and alkyl-Y-containing side chains, wherein Y is O or NR, wherein R is H or CH3, and wherein the alkyl group of the alkyl-Y-containing side chain has at least 4 carbon atoms on average in a cyclic, branched-, or straight-chain configuration and optionally including one or more heteroatoms.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Water-in-oil bituminous dispersions and methods for producing paving compositions from the same
ActiveUS7297204B2Low viscosityHighly preventive effectProductsIn situ pavingsSolvent freeSURFACTANT BLEND
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
Porous composites containing hydrocarbon-soluble well treatment agents and methods for using the same
Composites containing a hydrocarbon-soluble well treatment agent may be supplied to a well using a porous particulate. Such well treatment agents may for example inhibit the formation of paraffins, salts, gas hydrates, asphaltenes and / or other deleterious processes such as emulsification (both water-in-oil and oil-in-water). Further, other well treatment agents include foaming agents, oxygen scavengers, biocides and surfactants as well as other agents wherein slow release into the production well is desired.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Porous composites containing hydrocarbon-soluble well treatment agents and methods for using the same
Composites containing a hydrocarbon-soluble well treatment agent may be supplied to a well using a porous particulate. Such well treatment agents may for example inhibit the formation of paraffins, salts, gas hydrates, asphaltenes and / or other deleterious processes such as emulsification (both water-in-oil and oil-in-water). Further, other well treatment agents include foaming agents, oxygen scavengers, biocides and surfactants as well as other agents wherein slow release into the production well is desired.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Water-in-oil type emulsified composition
Water-in-oil type emulsified compositions with a high silicone oil content which are excellent in emulsification stability and whose sticky feeling has been improved may be obtained by incorporating a specific (A) N-long chain acyl neutral amino acid ester, (B) a silicone oil, and (C) water therein.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Composite particles and method for preparing
A method for producing composite particles using a supercritical fluid extraction technique on an emulsion. First and second materials (for example; a polymer and a biologically active material) are dissolved or suspended in a preferably solvent to form a solution or dispersion. The solution or dispersion is emulsified in a polar solvent to form an oil-in-water or water-in-oil-in-water emulsion. The emulsion is contacted with a supercritical fluid to extract the solvent. Removal of the solvent by the supercritical fluid from the emulsion supersaturates at least the first material in the solution causing the first material to precipitate out of the solution as composite particles that include both the first and second materials.
Owner:FERRO CORP
Preparation of porous particles with multiple markers
Porous particles are prepared using a first water-in-oil emulsion comprising a first marker material in a first aqueous phase that is dispersed in a first oil phase containing a polymer and a first organic solvent, and a second water-in-oil emulsion comprising a second marker material in a second aqueous phase that is dispersed in a second oil phase. The first and second marker materials are detectably different. The two water-in-oil emulsions can be used to form a third water-in-oil emulsion containing distinct droplets of the first and second aqueous phases. This third water-in-oil emulsion is dispersed in a third aqueous phase containing a surface stabilizing agent to form a water-in-oil-in-water emulsion containing droplets of the third water-in-oil emulsion. The organic solvents are removed from the water-in-oil-in-water emulsion to form porous particles comprising first and second discrete pores that are isolated from each other. The first marker material is present within the first discrete pores, and the second marker material is present within the second discrete pores.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
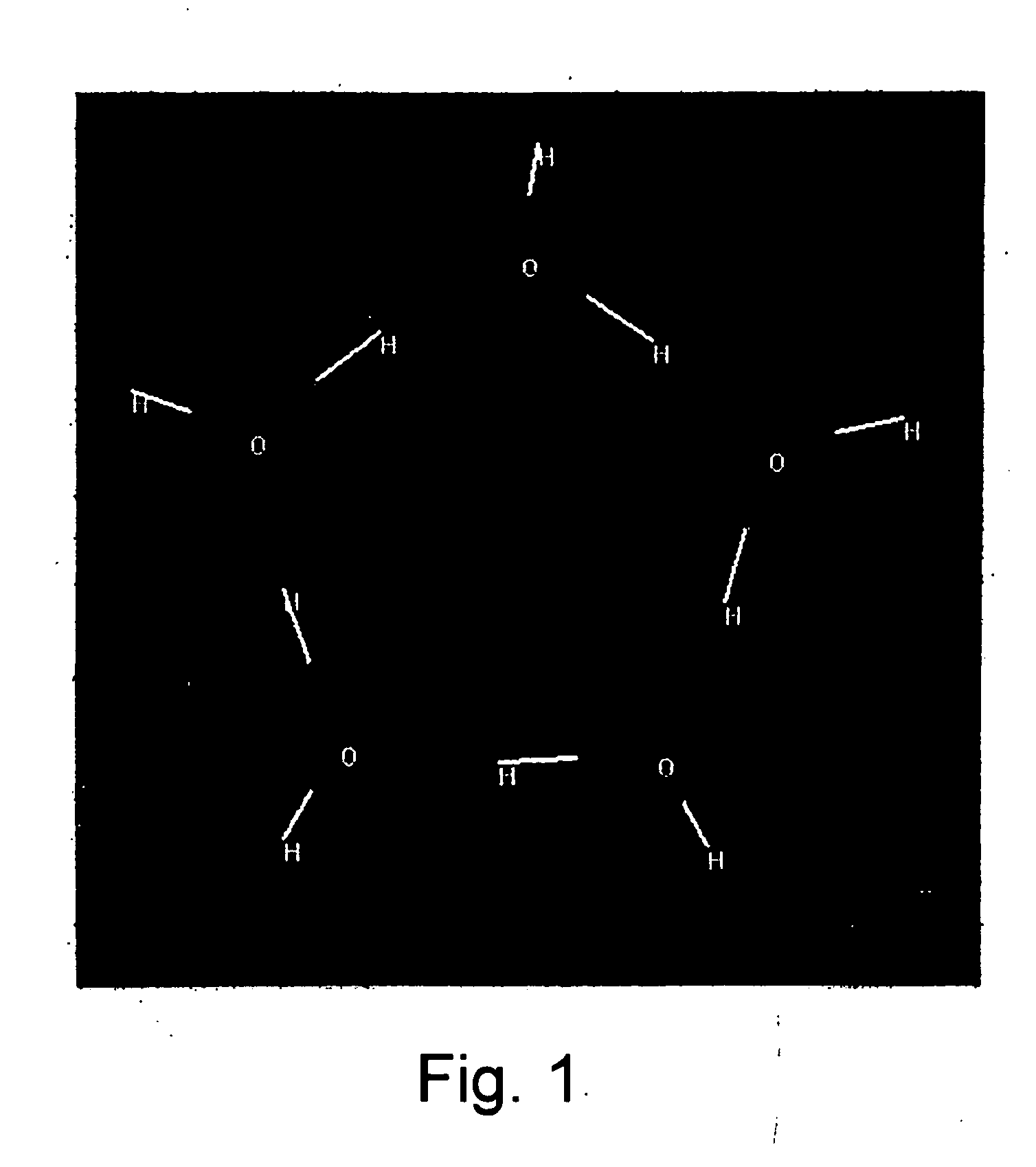
Stable water-in-oil-in-water multiple emulsion system produced by hydrodynamic dual stabilization and a method for preparation thereof
InactiveUS20060188463A1Much-improved stabilityImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsHydrogenWater in oil
The present invention relates to a water-in-oil-in-water multiple emulsion system and a method for preparation thereof, characterized by hydrodynamically stabilizing the multiple emulsion system by using hydrodynamic dual stabilization (HDS) technology. The HDS technology hydrophobizes water molecules in the internal aqueous phase by using a hydrogen bonding inhibitor and by improving the aggregating force between water molecules in the internal aqueous phase by using a water molecule aggregating agent.
Owner:AMOREPACIFIC CORP
Water-in-oil polymer emulsion containing microparticles
InactiveUS7531600B1Predictable and convenient and efficient preparationEasily metered into the fluid.Sludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater treatment compoundsPolymer scienceFracturing fluid
A storage stable water-in-oil emulsion composition that includes 5% to 99% by weight of a water-in-oil emulsion polymer including a polymer or copolymer containing repeat units from an acrylamide monomer; 0.1% to 10% by weight of one or more inorganic microparticles; 0.5% to 90% by weight of a carrier solvent; and 0 to 90% by weight of a fluidizing agent. The compositions can be used to treat aqueous systems including paper processing, sludge dewatering and for fracturing fluids for subterranean formations.
Owner:KROFF CHEM
Water-in-oil microemulsions for oilfield applications
A well treatment microemulsion includes an oil external phase, an internal aqueous phase and a hydrophilic surfactant. The surfactant has a hydrophile lipophile balance of between 8-18. The oil external phase may include d-Limonene, xylenes, light mineral oil, or kerosene. The surfactant is configured to emulsify the water of the internal aqueous phase into the oil of the external (continuous) phase. The surfactant may include polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan tristearate, polyoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil, polyoxyethylene sorbitan monostearate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate or mixtures therebetween. The use of hydrophilic surfactants to emulsify an internal aqueous phase within an oil external microemulsion produces unexpected and beneficial results.
Owner:PNC BANK NAT ASSOC
Method for displacing oil base drilling muds and/or residues from oil base drilling mud using water-in-oil emulsion
ActiveUS7188676B2Improve breathabilityEfficacious in displacingCleaning apparatusFluid removalParticulatesParaffin wax
Fluid producing wells may be treated with a water-in-oil emulsion for the removal or inhibition of unwanted solid particulates, including pipe dope, asphaltenes and paraffins. Such emulsions are of particular applicability in the displacement of oil base drilling muds and / or residues from such muds from producing wells. The water-in-oil emulsions may optionally contain a dispersing agent as well as a surfactant.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Microfluidic device and method for preparing microgel by using microfluidic device
ActiveCN105641743ASuitable for industrial mass productionStable capillary forceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolyvinyl alcoholChemistry
The invention provides a microfluidic device and a method for preparing microgel by using the microfluidic device. The method comprises the steps of (1) taking a solution containing live cells or bioactive molecules, a photocuring agent and a hydrogel prepolymer as an internal phase, taking a mixed solution containing oil and an surfactant as an intermediate phase, and taking a polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution as an external phase; (2) respectively conveying the internal phase, the intermediate phase and the external phase into a corresponding microchannel of the microfluidic device through a micro pump or a micro injector to form a monodispersed water-in-oil-in-water double emulsion; (3) enabling the monodispersed water-in-oil-in-water double emulsion in the step (2) to pass through an output channel of the microfluidic device, and collecting the monodispersed water-in-oil-in-water double emulsion in the step (2) into a collection vessel filled with an aqueous solution, thus obtaining the microgel immobilizing with the live cells or the bioactive molecules. The preparation of the microgel immobilizing with cells by a one-step method is realized, the obtained microgel is controllable in size, and narrow in size distribution, and meanwhile the survival rate of cells is maintained.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUA NOVA BIOTECH LTD
Method for modifying biomass cracked oil to modified bio-oil by quality-improving of esterification and etherification
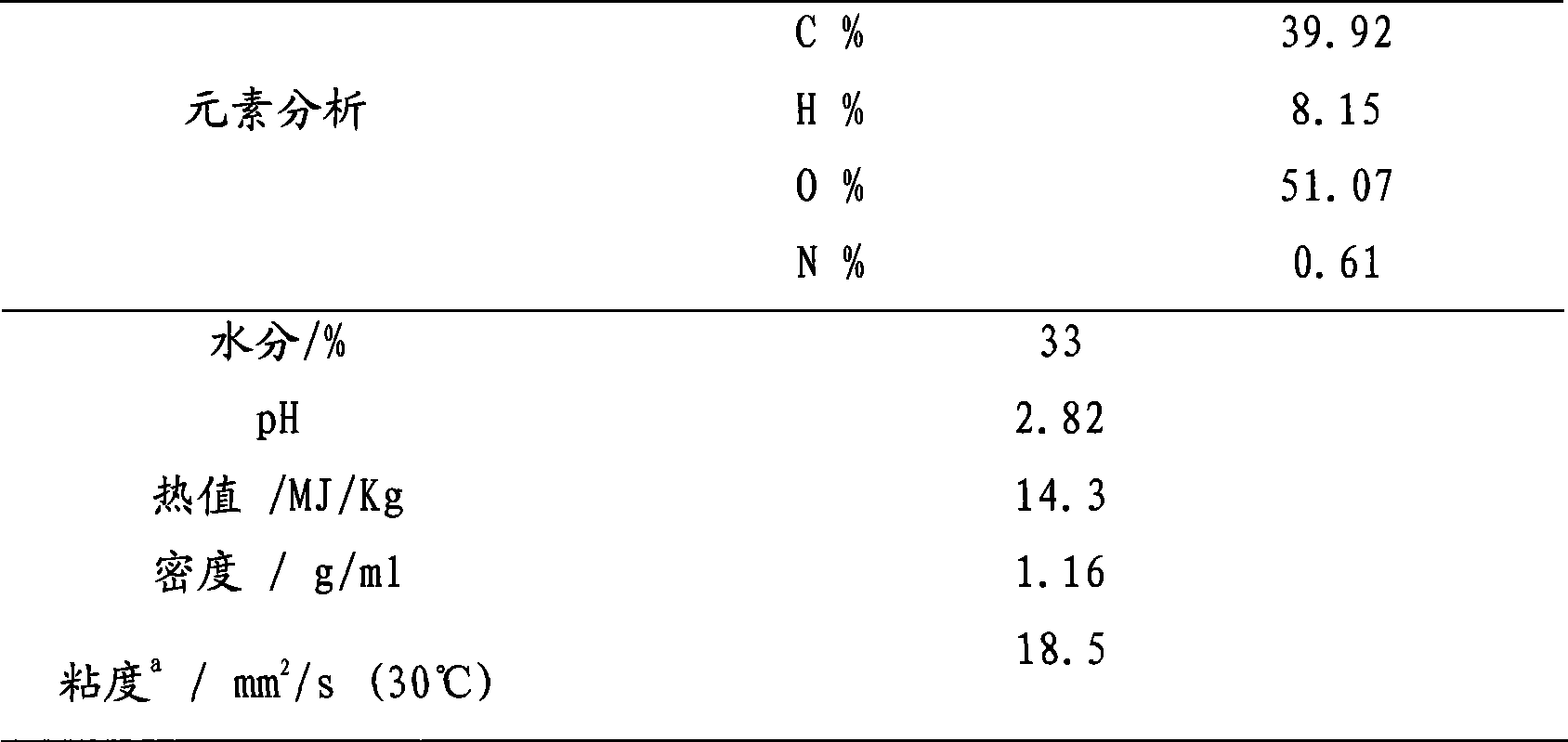
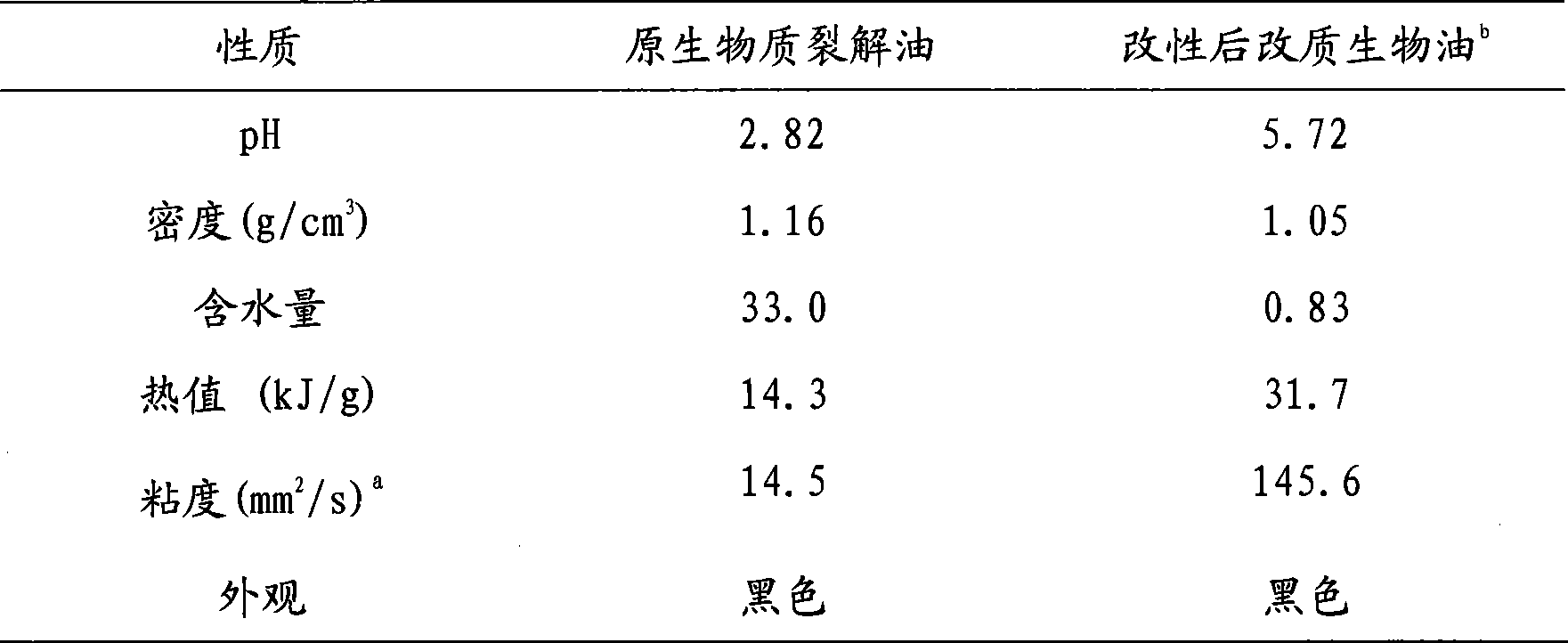
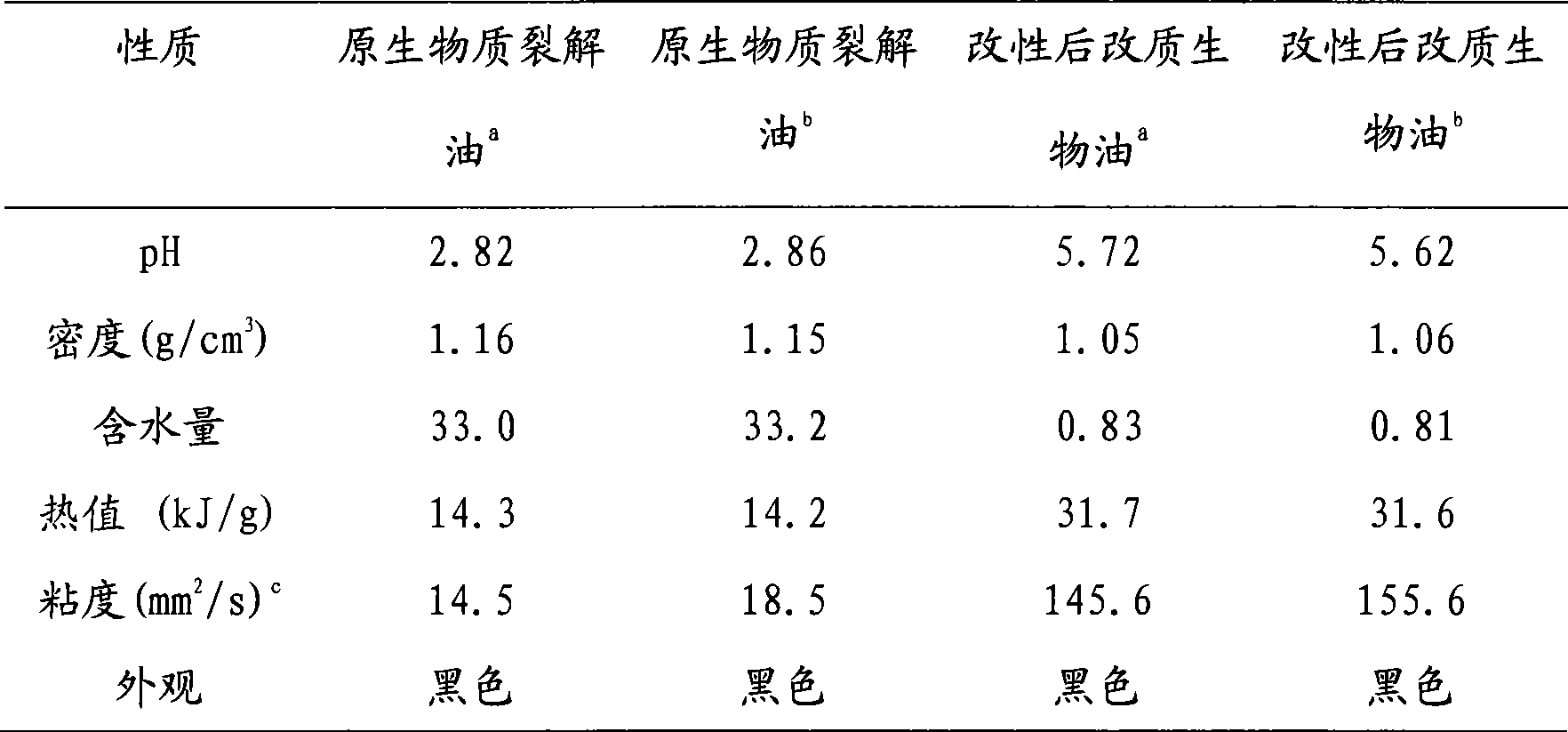
InactiveCN101381611AImprove conversion rateIncrease the rate of etherification reactionLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionViscous liquidAlcohol
The invention discloses a method for modifying biomass cracking oil to modified biomass oil through esterification, etherification and quality-improvement. The method comprises the following: step one, according to the proportion that the mass ratio of biomass cracking oil to benzyl chloride to alkaline solution to low-carbon alcohol is 100 to 80-100 to 40-80 to 10-20; and the biomass cracking oil, the low-carbon alcohol, the benzyl chloride and the alkaline solution are added into a reaction kettle, are heated at the temperature of between 90 and 110 DEG C to an infinite reflux state and react for 5 to 8 hours. Step two, after the infinite reflux reaction is finished, the mixture is cooled, condensed and layered; the lower layer is clear and transparent aqueous solution; black oil phase on the upper layer is separated, and is distilled under the condition that the temperature is 80 DEG C and the pressure is 10 kilopascal; low-carbon alcohol and water in oil phase are removed; the residual mixture is distilled under the condition that the temperature is between 130 and 150 DEG C and the pressure is 10 kilopascal; the unreacted benzyl chloride is reclaimed to obtain a product of black viscous liquid; and according to the proportion that the mass ratio of the product to ethanol is 3 to 1, the black viscous liquid is diluted and dissolved to obtain the modified biomass oil of which the PH value is between 5 and 7, the density is between 1.0 and 1.1 g / cm<3>, the water content is between 0.5 and 1.0 percent, the thermal value is between 25.0 and 35.0 kJ / g and the viscidity is between 135 and 150 mm<2> / s.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Process for preparing thermally stable oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions
InactiveUS20100022421A1Improve thermal stabilityEnhanced saline stabilityTransportation and packagingMixingAlcoholWell drilling
A method for preparing a thermally stable well servicing fluid in the form of an oil-in-water (O / W) macroemulsion, a water-in-oil (W / O) macroemulsion or a water-in-oil (W / O) microemulsion at the well drilling location is provided. The servicing fluid is prepared by mixing a hydrocarbon phase, a water phase and a surfactant phase to obtain either an O / W macroemulsion, a W / O macroemulsion or a W / O microemulsion. The surfactant phase comprises a first surfactant and / or a second surfactant. The first surfactant comprises a fatty acid mixture and a hygroscopic first additive. The second surfactant comprises a C4-C6 alcohol. Whether or not an O / W macroemulsion, W / O macroemulsion or a W / O microemulsion is produced is determined by the concentration of the phases, the first surfactant, the second surfactant and the timing upon which the first additive, water phase and second surfactant are introduced to the mixture.
Owner:INTREVEP SA
Compositions for treating a well penetrating a subterranean formation and uses thereof
ActiveUS20060042796A1Excellent particle suspension capacityPrevent redepositionCleaning apparatusFluid removalWater in oilParaffin wax
Fluid producing wells may be treated with a water-in-oil emulsion for the removal or inhibition of unwanted solid particulates, including pipe dope, asphaltenes and paraffins. Such emulsions are of particular applicability in the displacement of oil base drilling muds and / or residues from such muds from producing wells. The water-in-oil emulsions may optionally contain a dispersing agent as well as a surfactant.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Use in cosmetics of a reverse latex of nitrogenous salts of polyacrylate, novel latices, process for their preparation and cosmetic compositions incorporating them
Use of a composition having an oil phase, an aqueous phase, at least one emulsifier of water-in-oil (W / O) type and at least one emulsifier of oil-in-water (O / W) type, in the form of a reverse latex comprising from 20% to 70% by weight, and preferably from 25% to 40% by weight, of an anionic polyelectrolyte, the anionic polyelectrolyte being based on partially neutralized acrylic acid, which may be branched and / or crosslinked, to prepare a cosmetic, dermopharmaceutical or pharmaceutical composition. Novel lattices, process for their preparation and cosmetic, dermopharmaceutical or pharmaceutical composition incorporating them.
Owner:SOC DEXPLOITATION DE PROD POUR LES IND CHEM SEPPIC
Slickwater fracturing fluid drag reducer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103013488AImprove stabilityReduce system complexity indexDrilling compositionFunctional monomerFracturing fluid
The invention discloses drag reducer which can be applied to slickwater fracturing fluid and a method for preparing drag reducer. The method includes: adding organic salt into acrylamide and functional monomer aqueous solution to prepare an aqueous phase, adding the aqueous phase into an oil phase system consisting of surfactant and base oil under the condition of high-speed stirring to form a stable W / O (water in oil) type microemulsion system, feeding nitrogen for dispersing oxygen, and adding initiator for polymerization to form a branchless long chain structure. The polymer microemulsion is a transparent or semitransparent thermodynamic stable system, can be quickly swelled into water and is directly usable. Adding a small quantity of the drag reducer during fluid transport can improve flow quantity and reduce energy consumption to some extent, and the drag reduction effect can reach 30%-65% when the drag reducer is compared with clear water. The drag reducer has the advantages of high stability, dissolving speed and dissolving performance, convenience in use, remarkable drag reduction effects and the like and is applicable to the slickwater fracturing technology, and excellent yield increasing effects are obtained after the drag reducer is applied to field fracturing operations.
Owner:CHENGDU BAICHUN PETROLEUM TECH +1
Nanometer composite porous gel microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102617769APharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicroballoon preparationMicrospherePickering emulsion
The invention relates to a nanometer composite porous gel microsphere and a preparation method thereof, which are characterized in that the nanometer composite porous gel microsphere is prepared by the steps of using double Pickering emulsion (O / W / O) as a template, using a water-soluble polymerizable monomer and an initiator as aqueous phase, and adding hydrophilic moderate nanometer particles in the aqueous phase to form oil-in-water type emulsion through emulsification; adding hydrophobic nanometer particles in outer oil phase, adding colostrums into a dispersing agent of the outer oil phase to perform emulsification once again to obtain water-in-oil and oil-in-water type double Pickering emulsion. An aqueous monomer of intermediate phase of the obtained double Pickering emulsion is polymerized to obtain the nanometer composite porous gel microsphere. By means of the preparation method, a large amount of independent gel microspheres with holes insides can be simply prepared. Due to the fact that the functionalization of the nanometer particles can further endow special responsiveness of the microsphere, the nanometer composite porous gel microsphere has wide application prospect in drug encapsulation, targeted slow release, cell culture and other fields.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Water-in-oil emulsions with anionic groups, compositions, and methods
Water-in-oil emulsions, compositions, and methods that include a vinyl polymer having a pKa of less than 4 that includes anionic group-containing side chains and alkyl-Y-containing side chains, wherein Y is O or NR, wherein R is hydrogen or methyl, and wherein the alkyl group of the alkyl-Y-containing side chain has at least 4 carbon atoms on average in a cyclic, branched-, or straight-chain configuration and optionally including one or more heteroatoms.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com