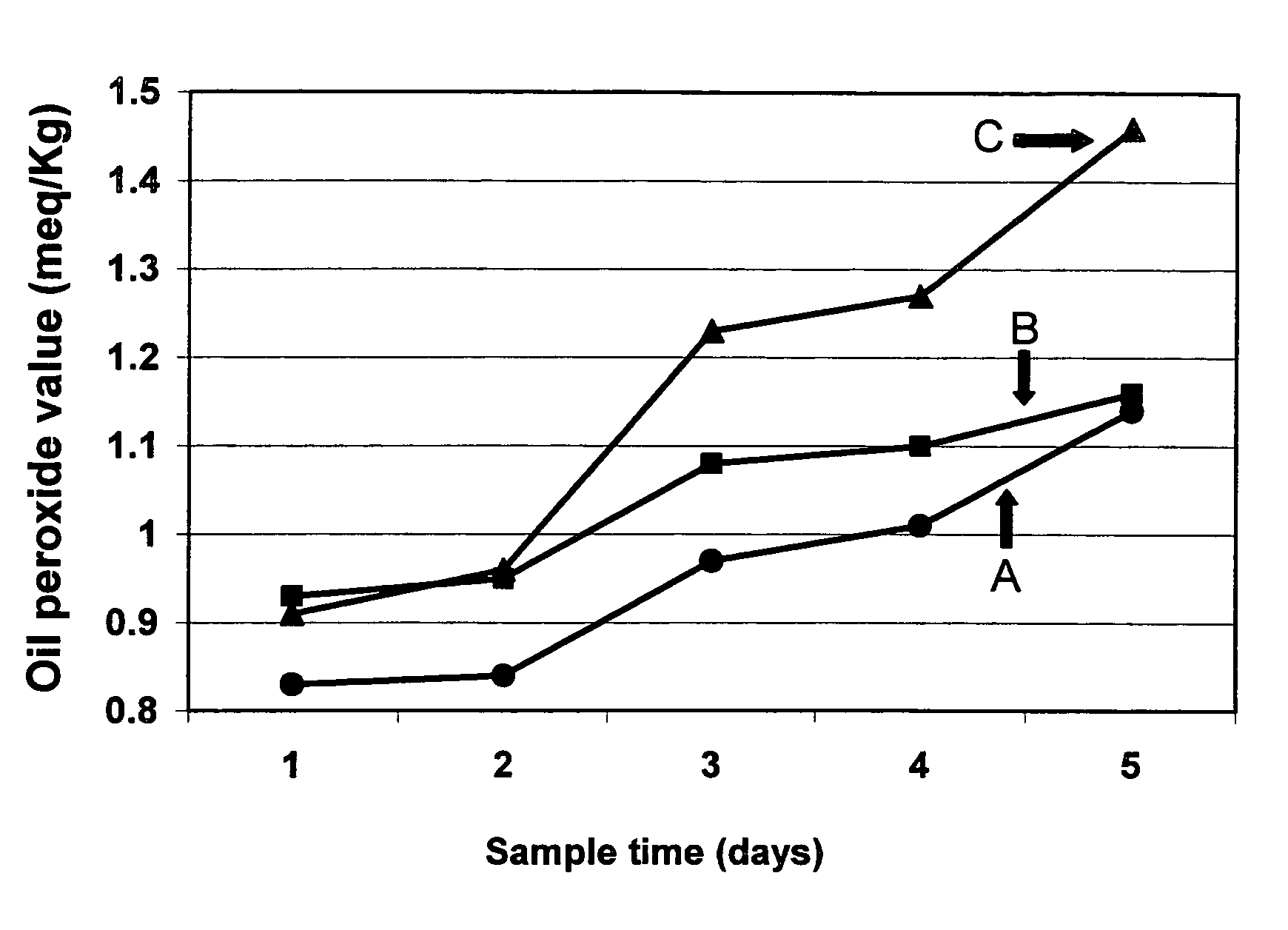
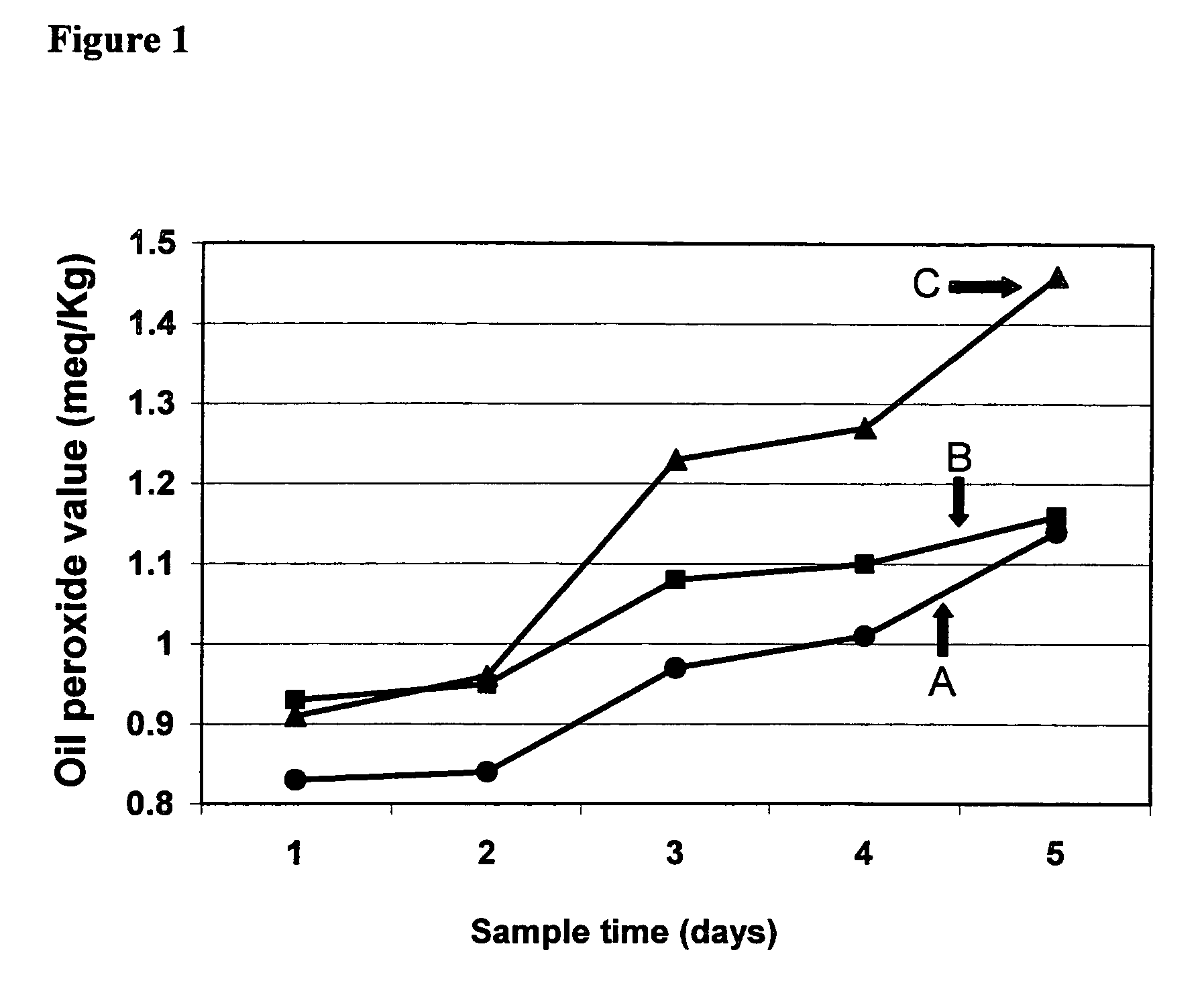
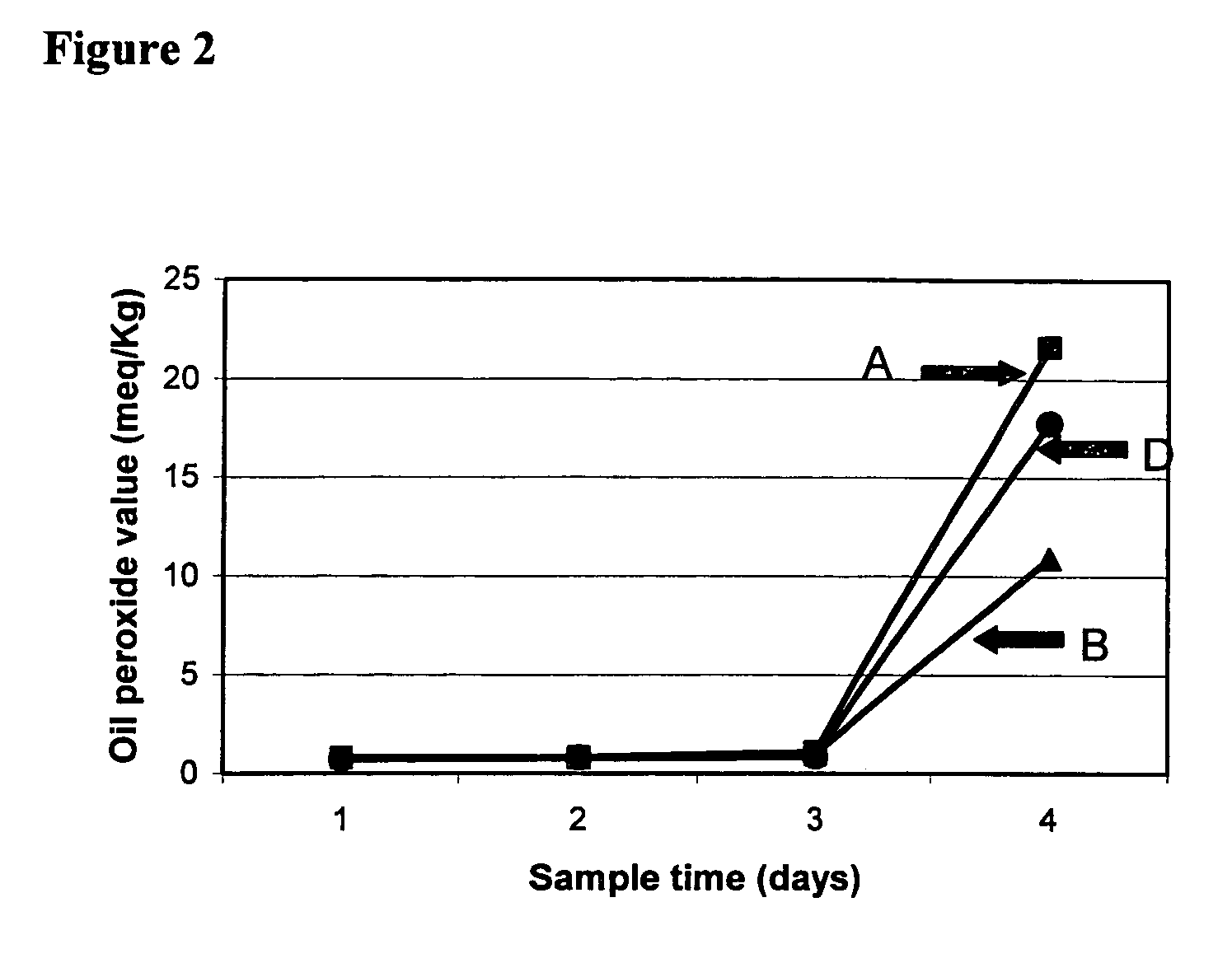
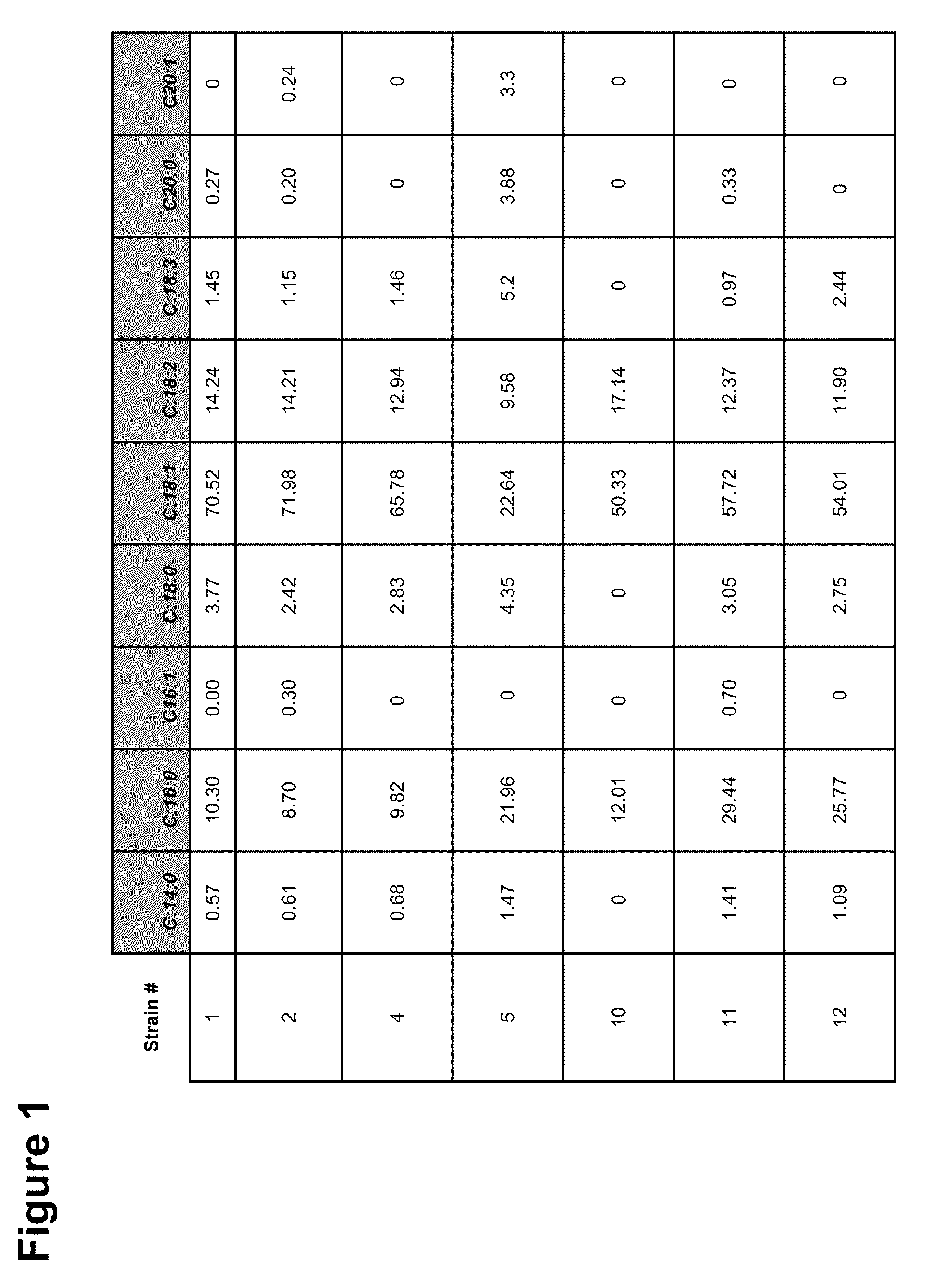
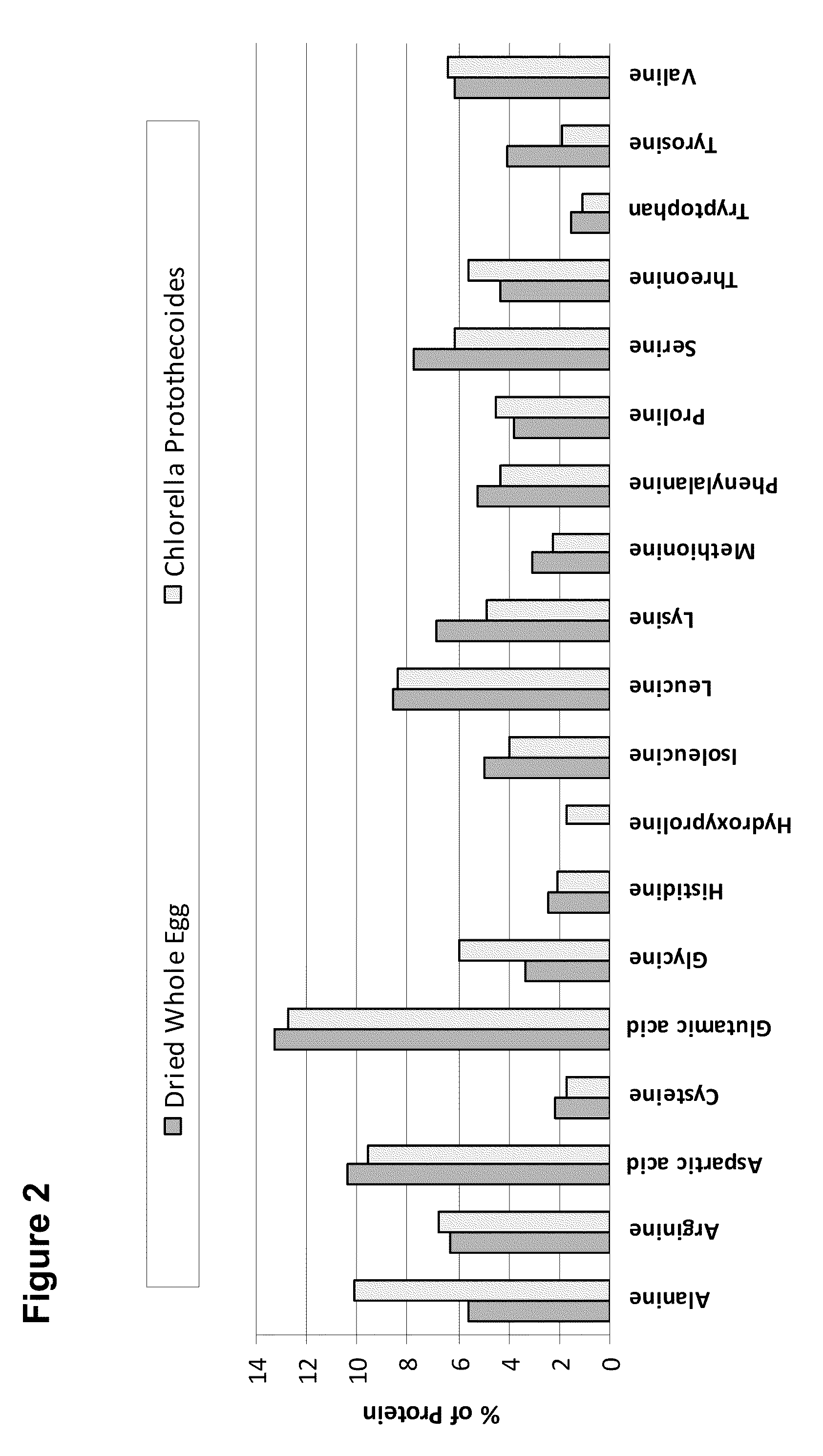
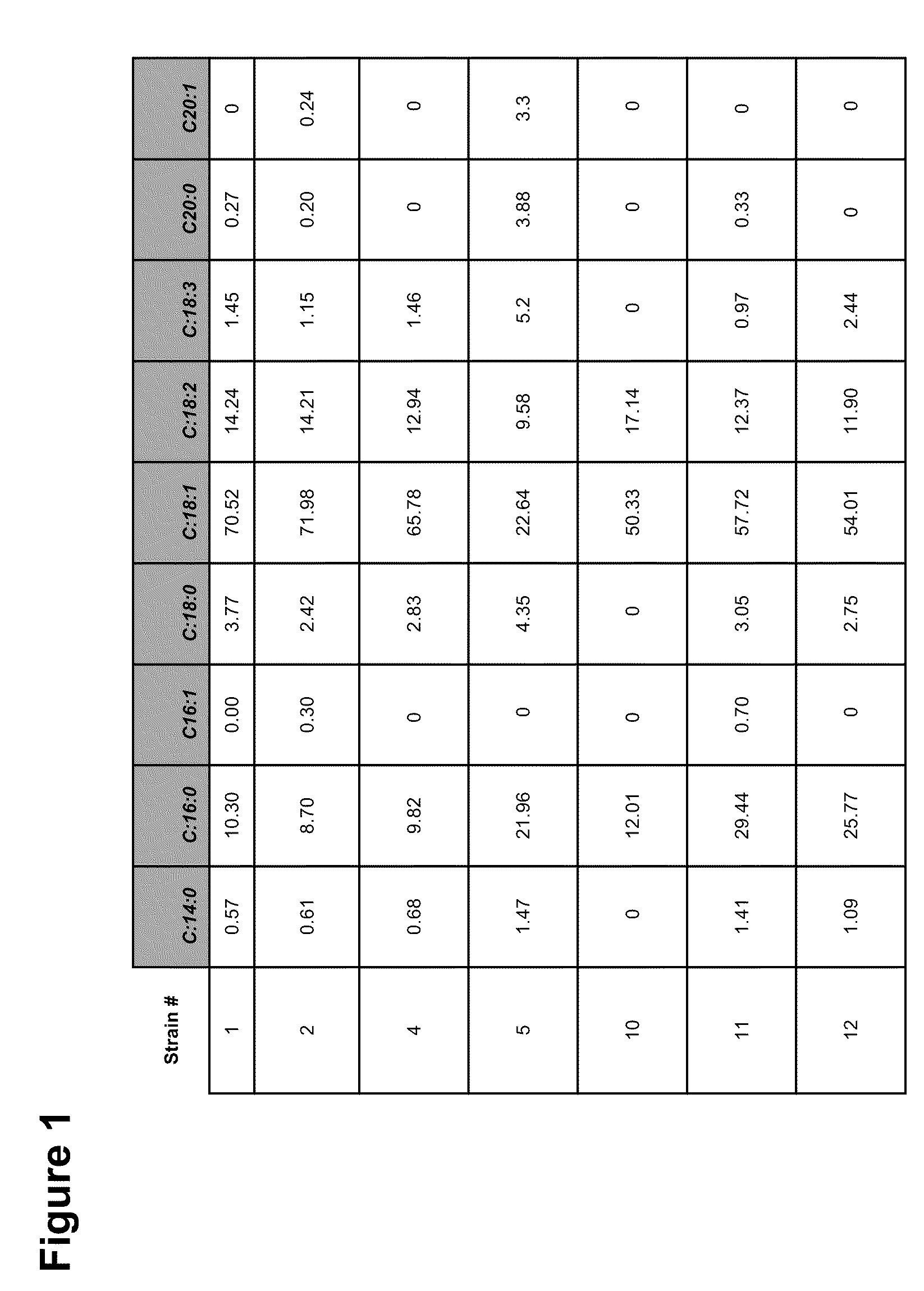
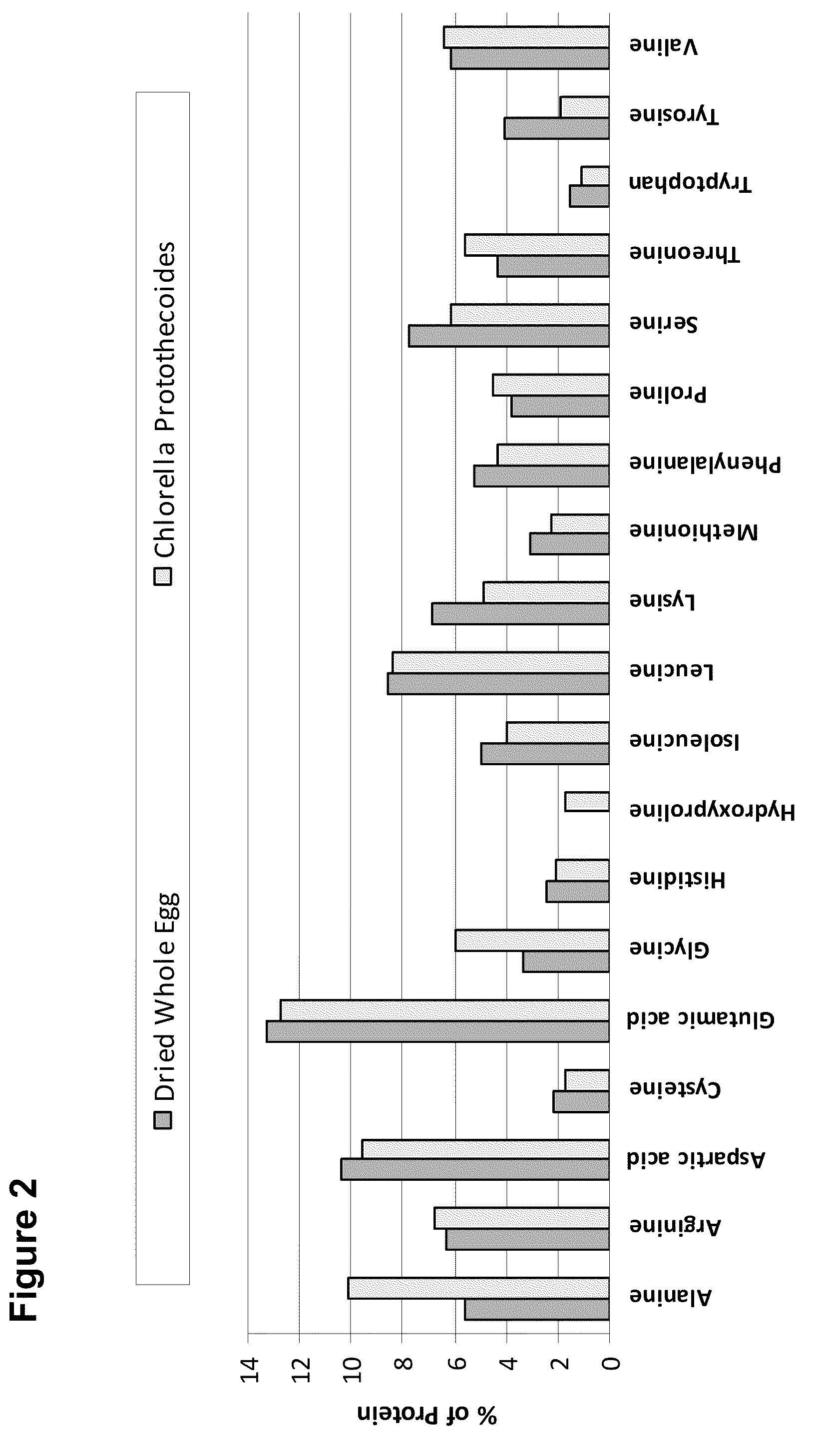
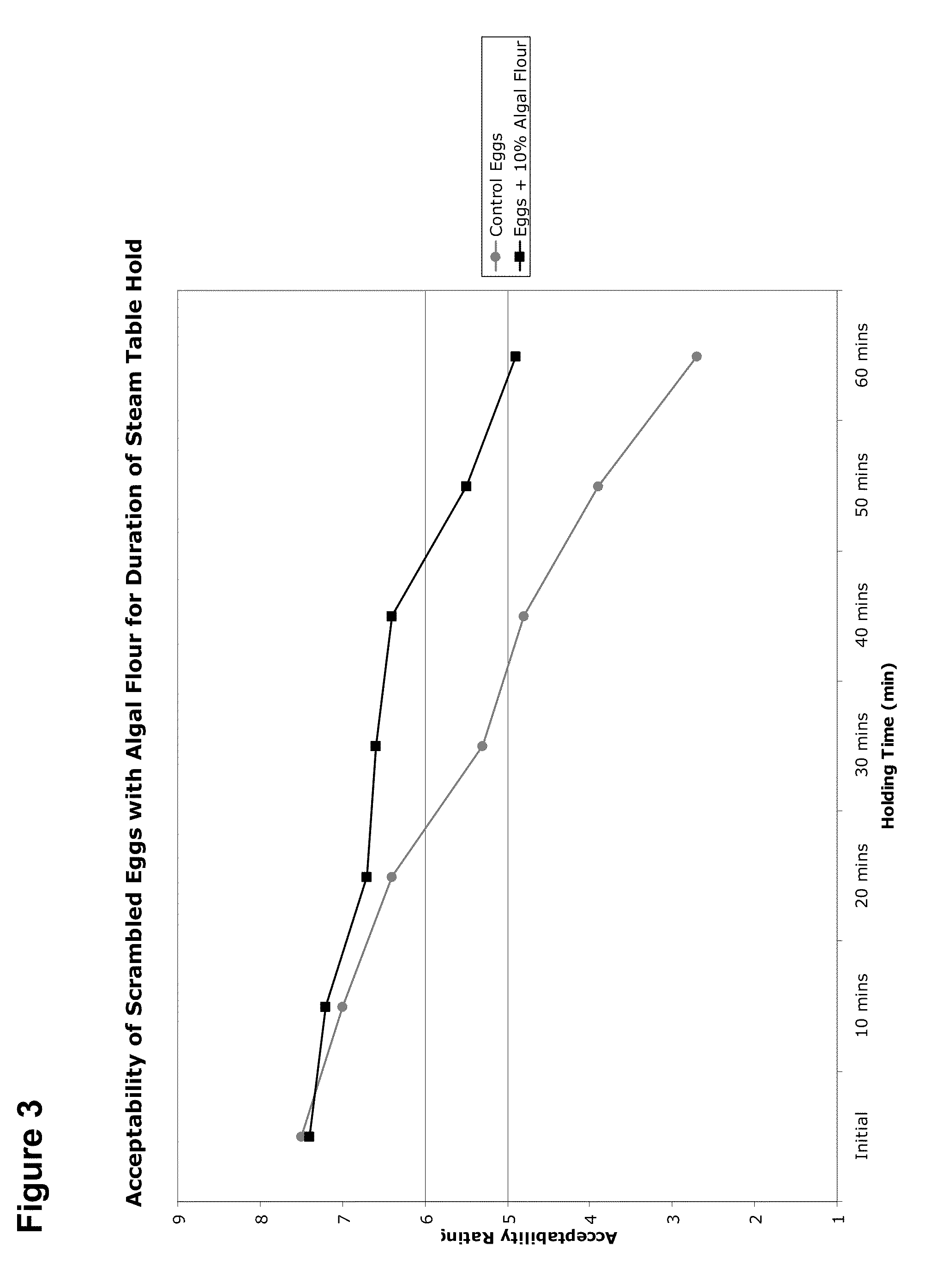
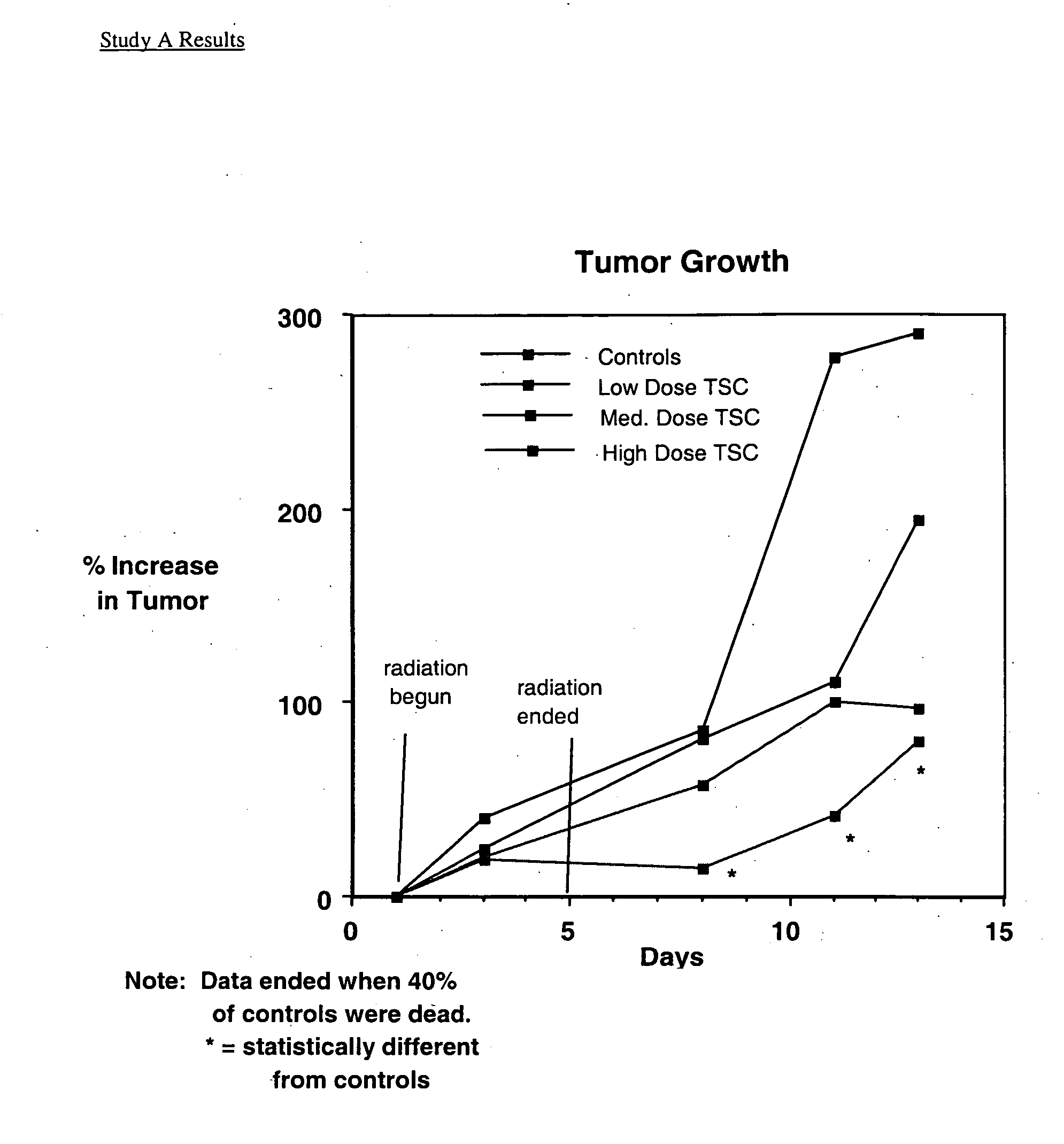
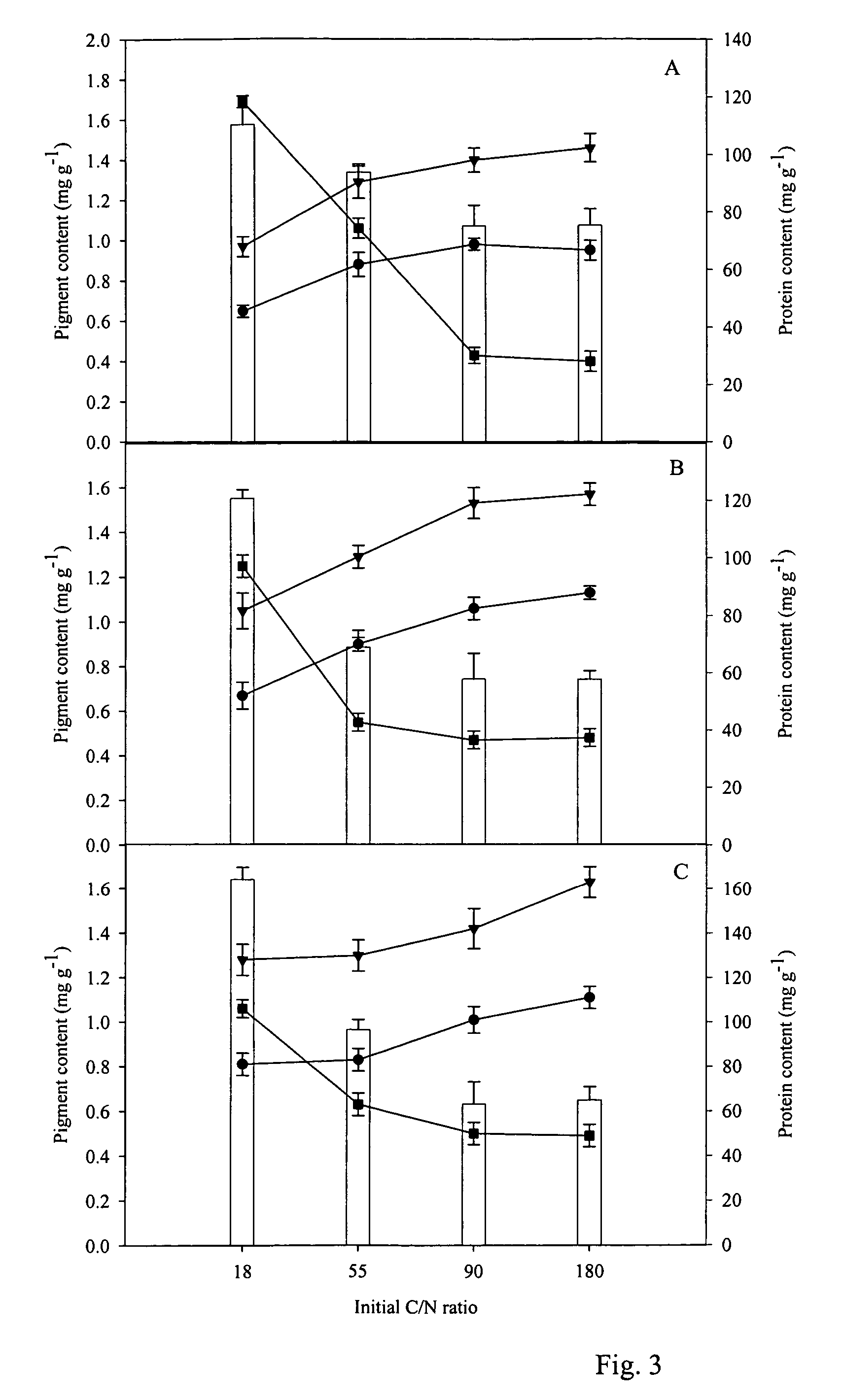
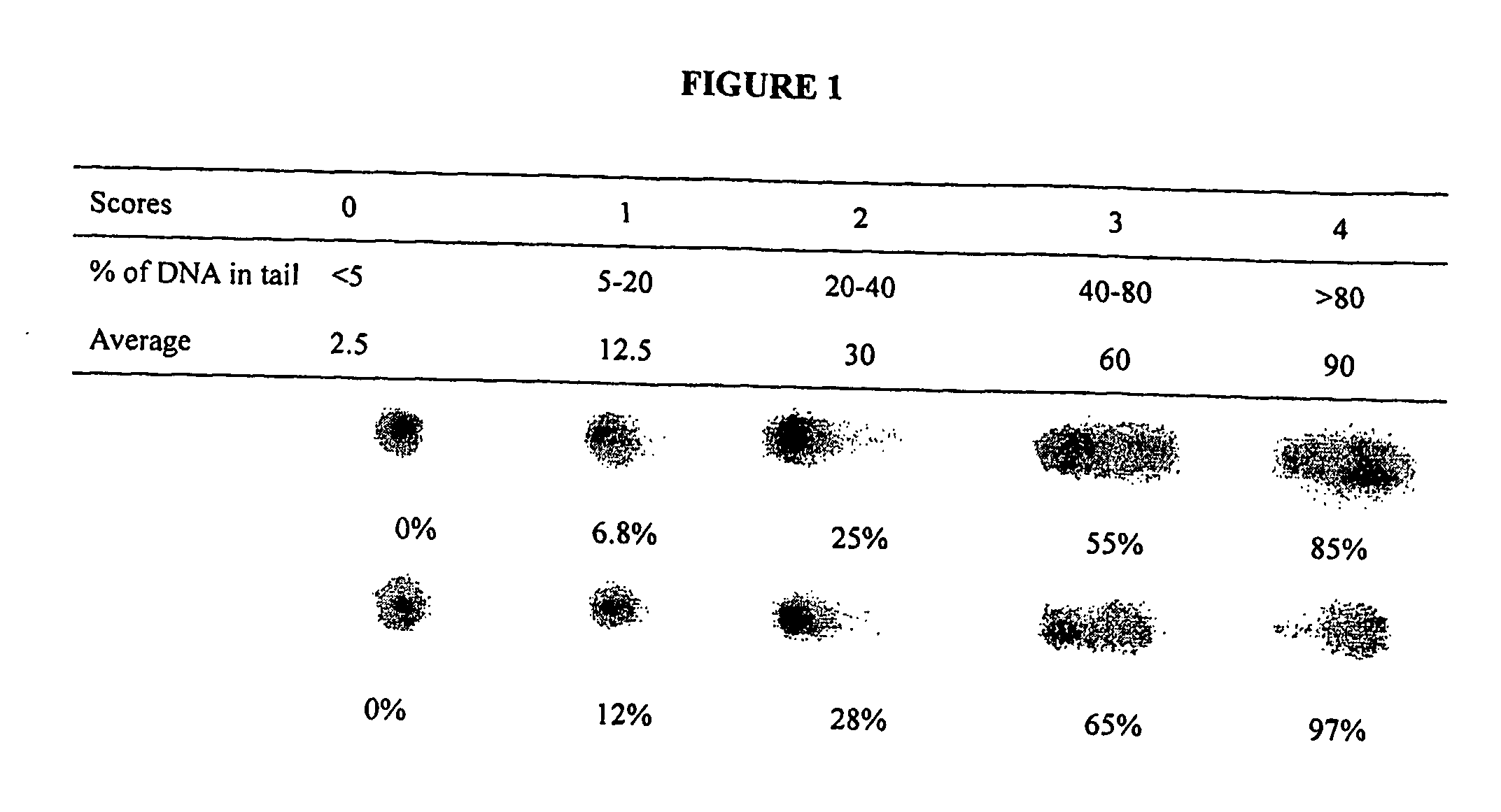
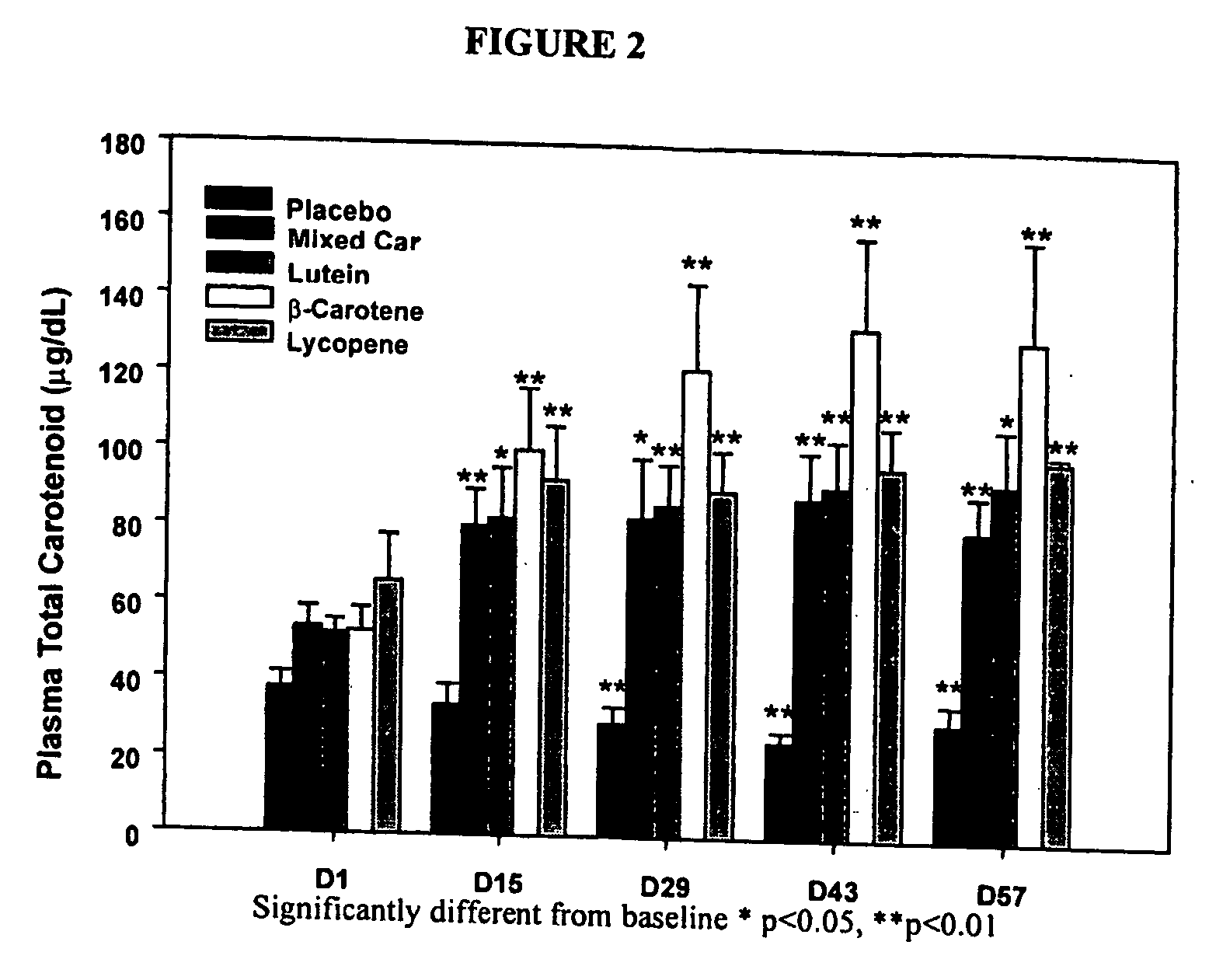
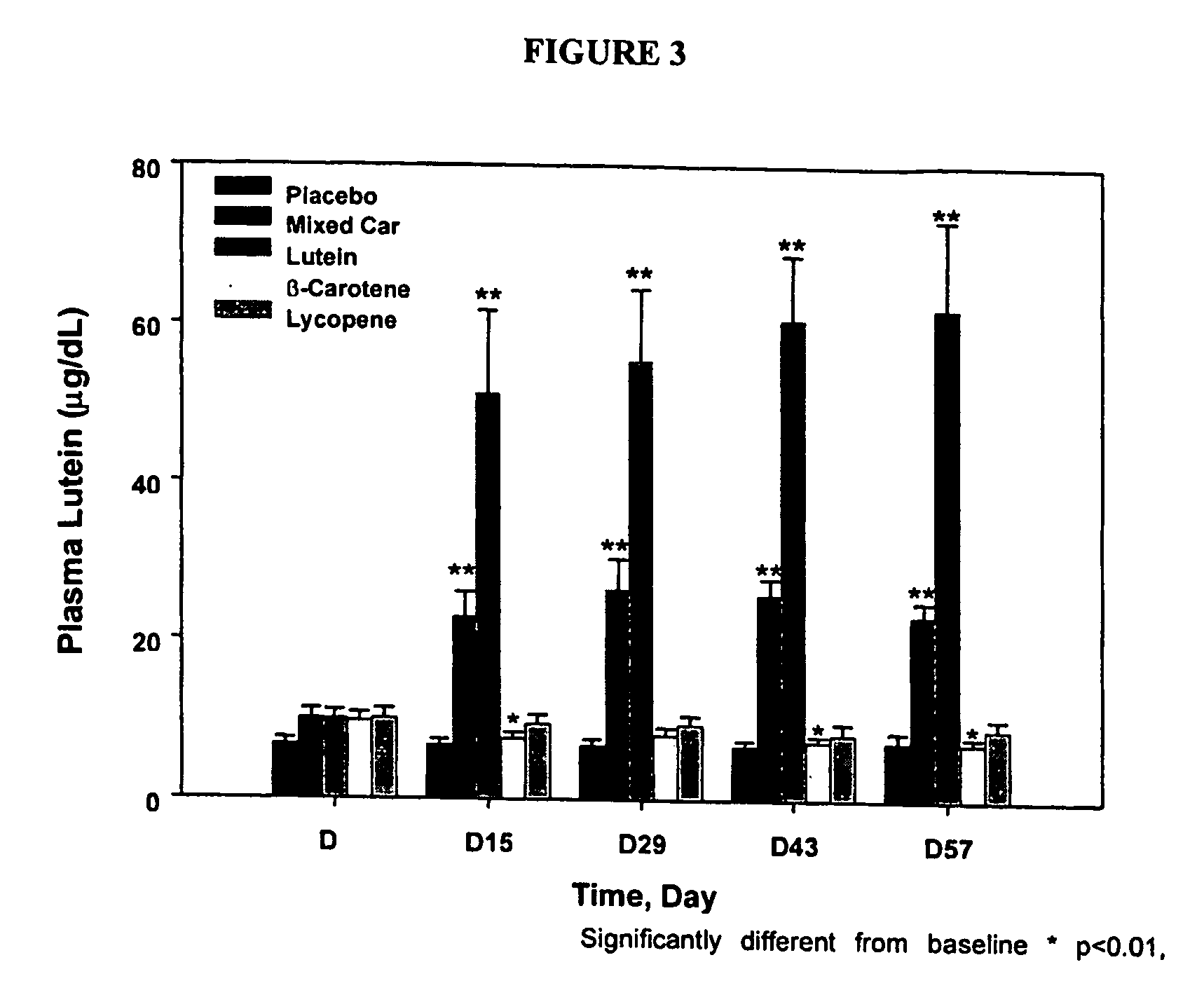
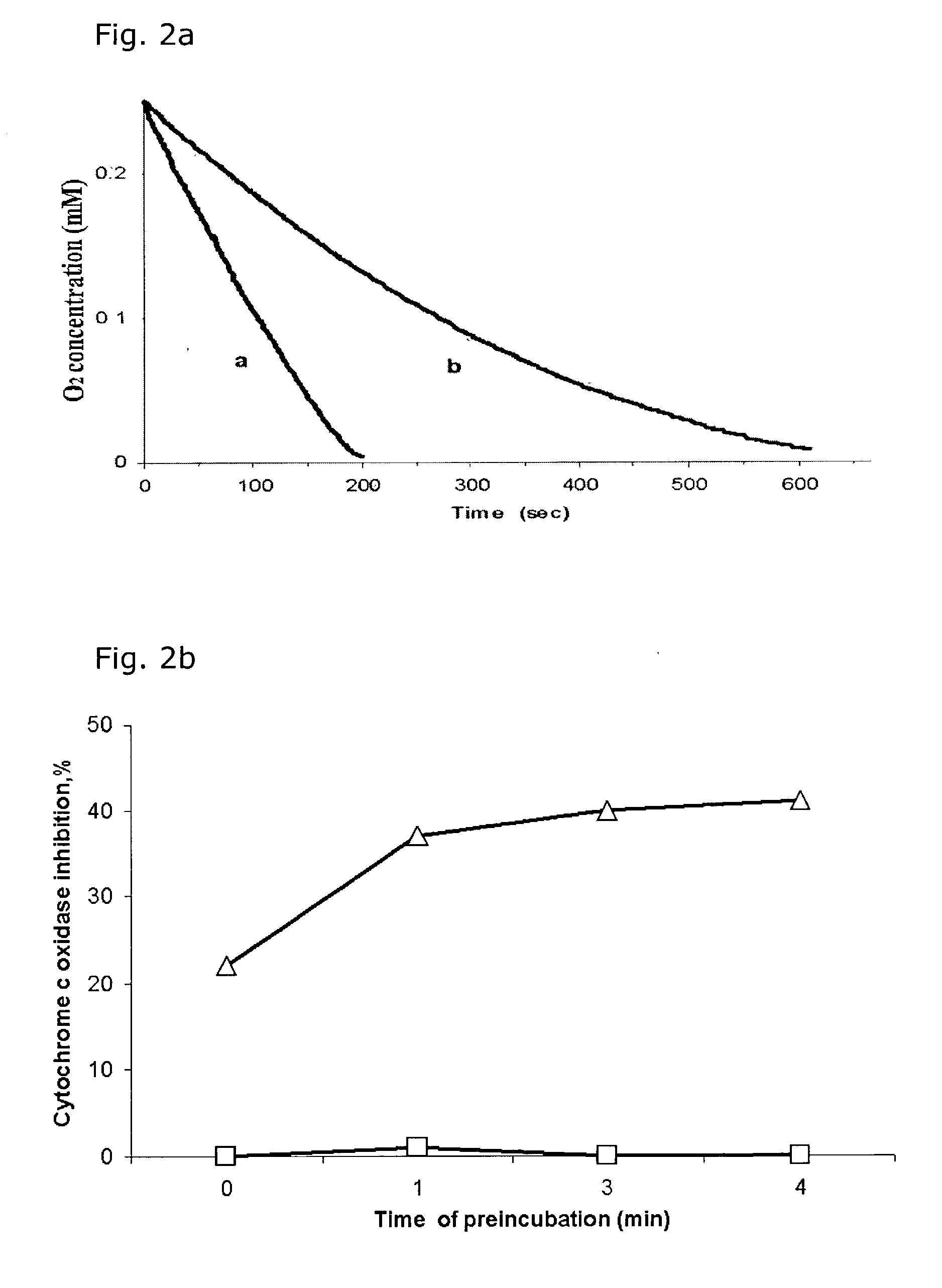
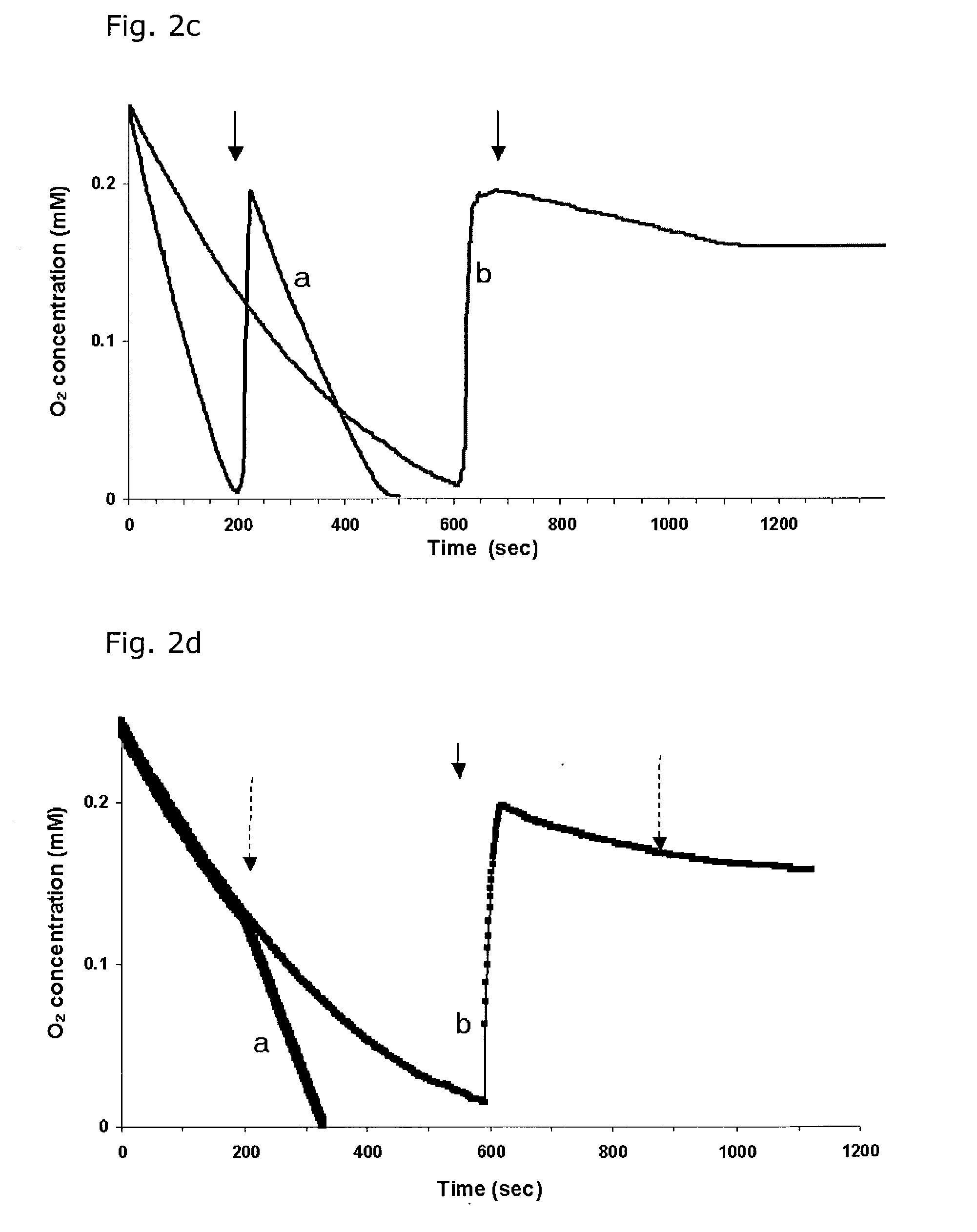
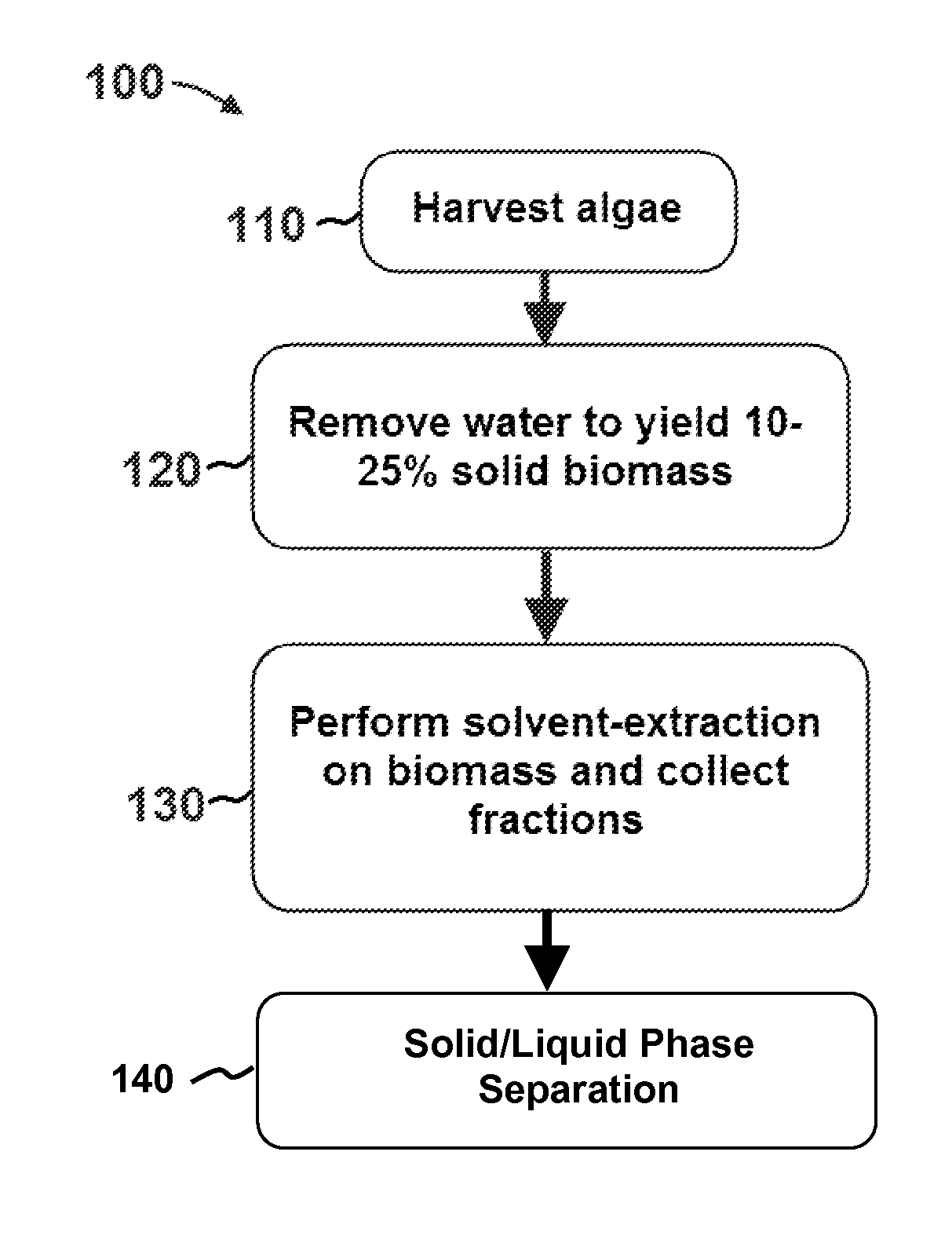
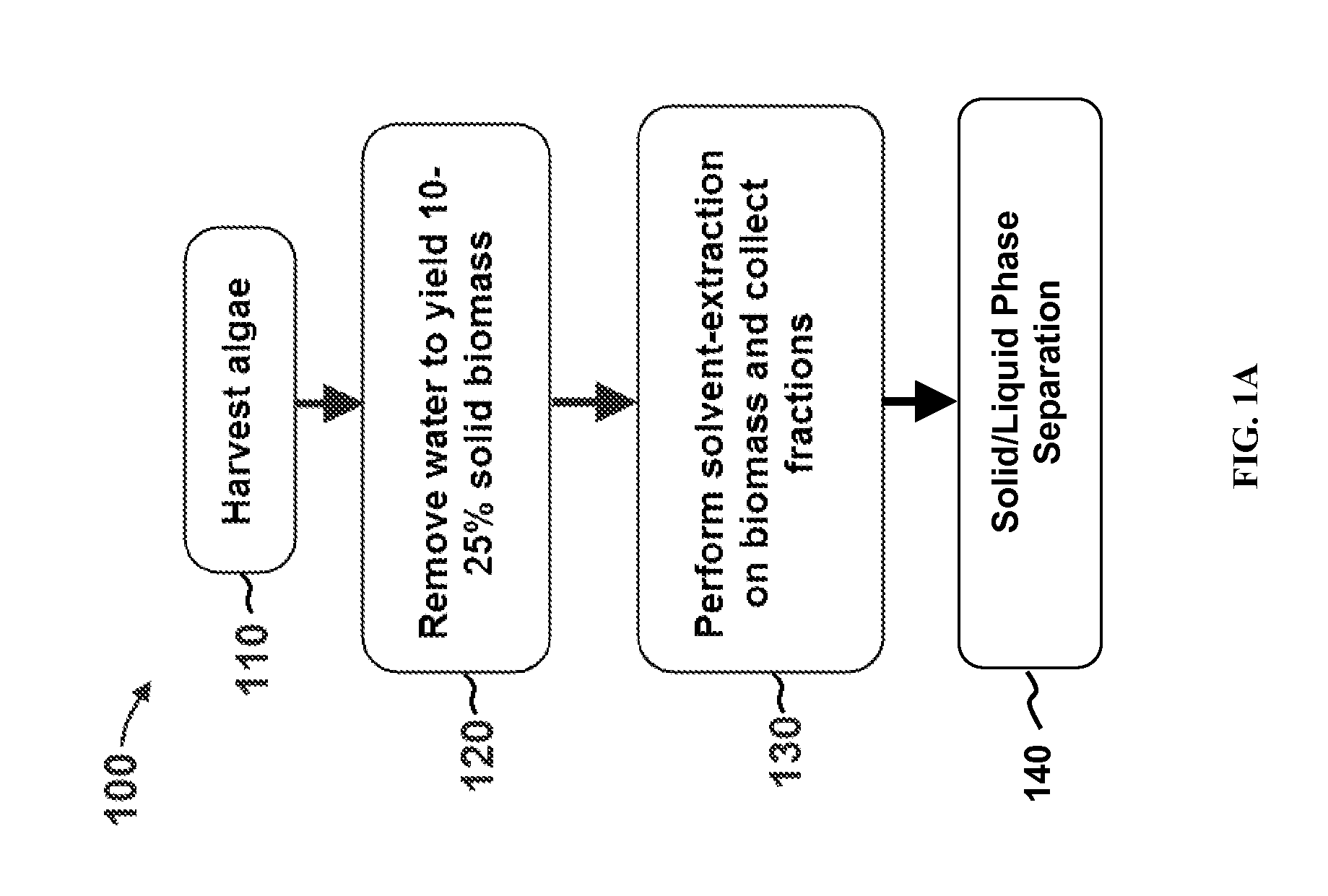
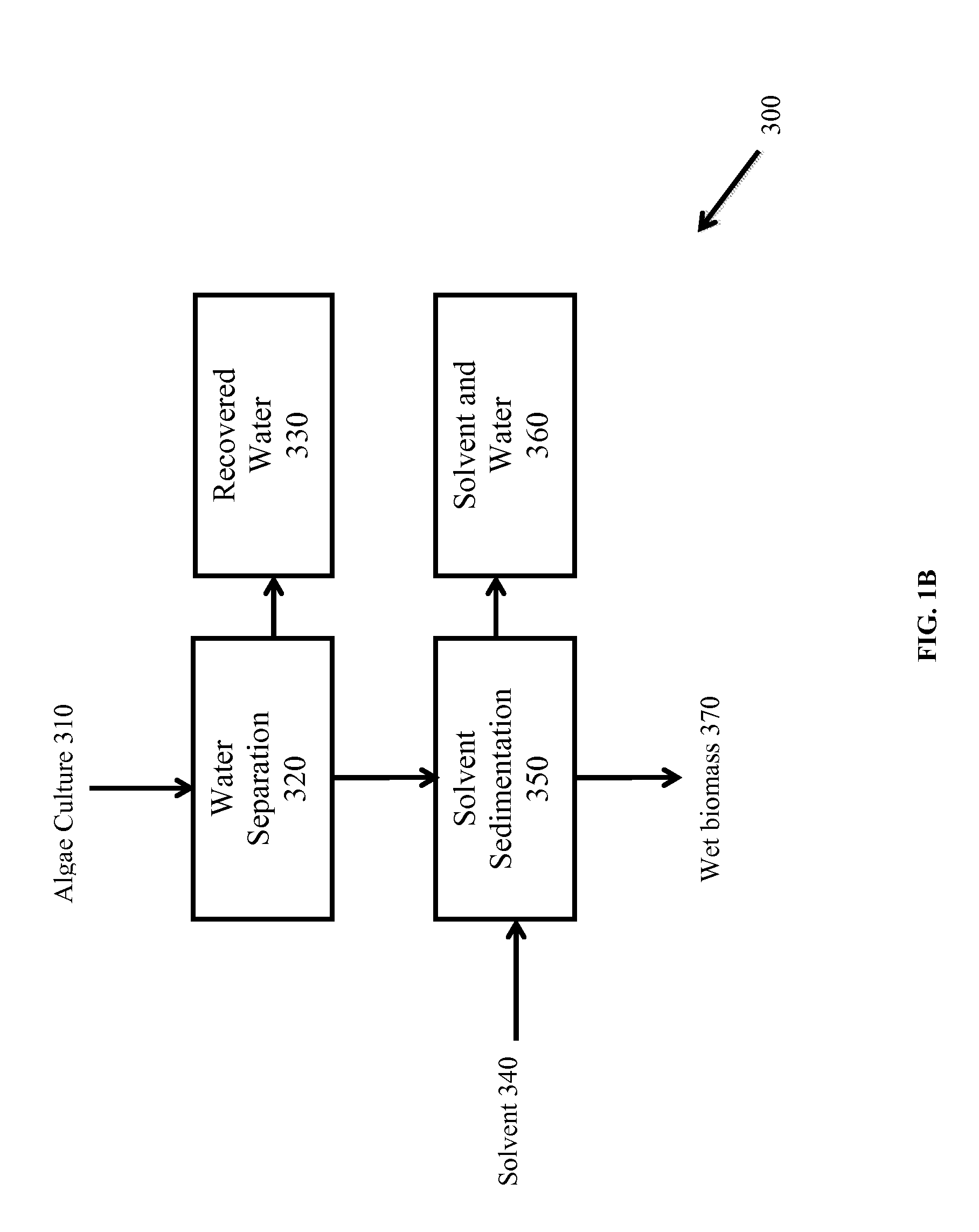
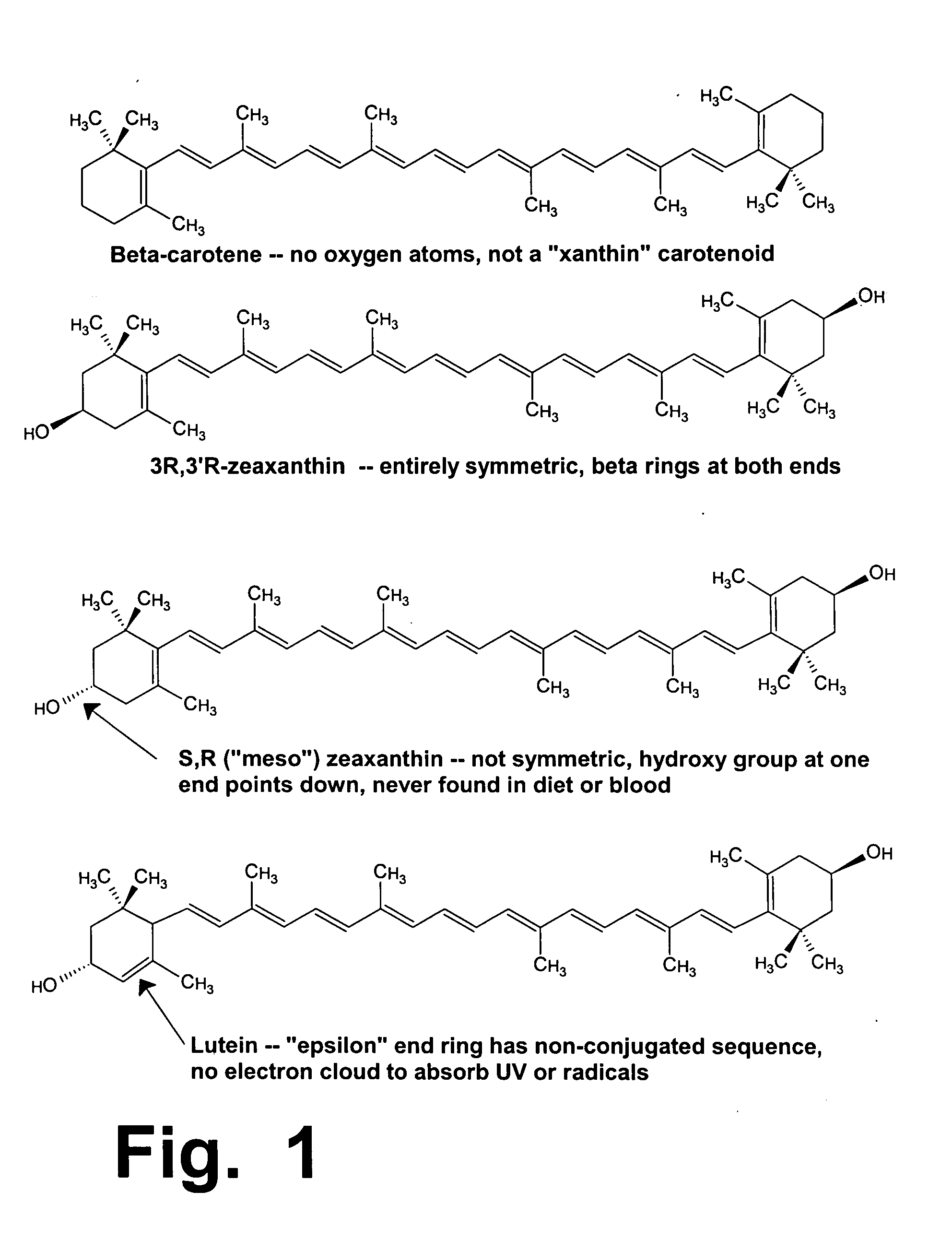
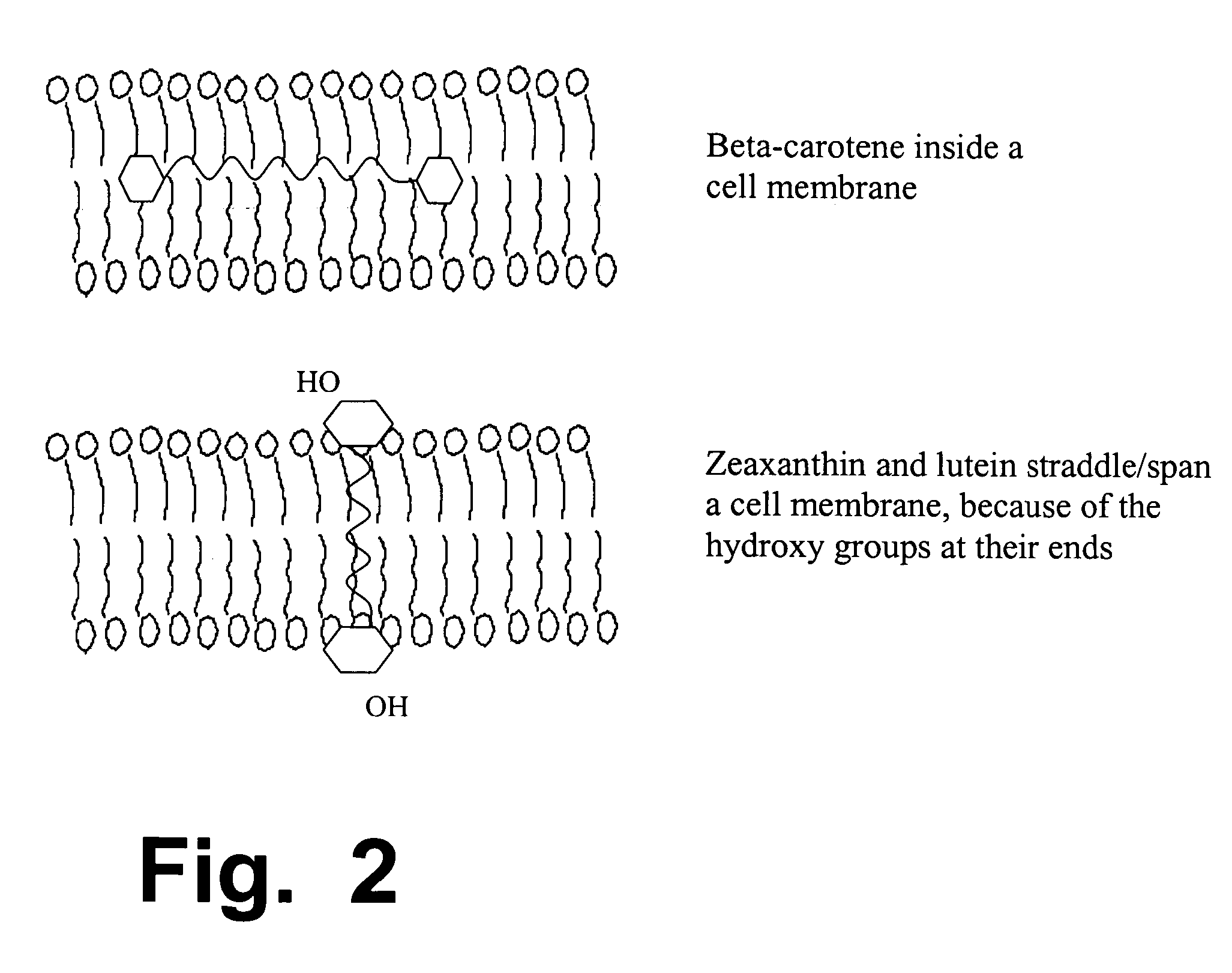
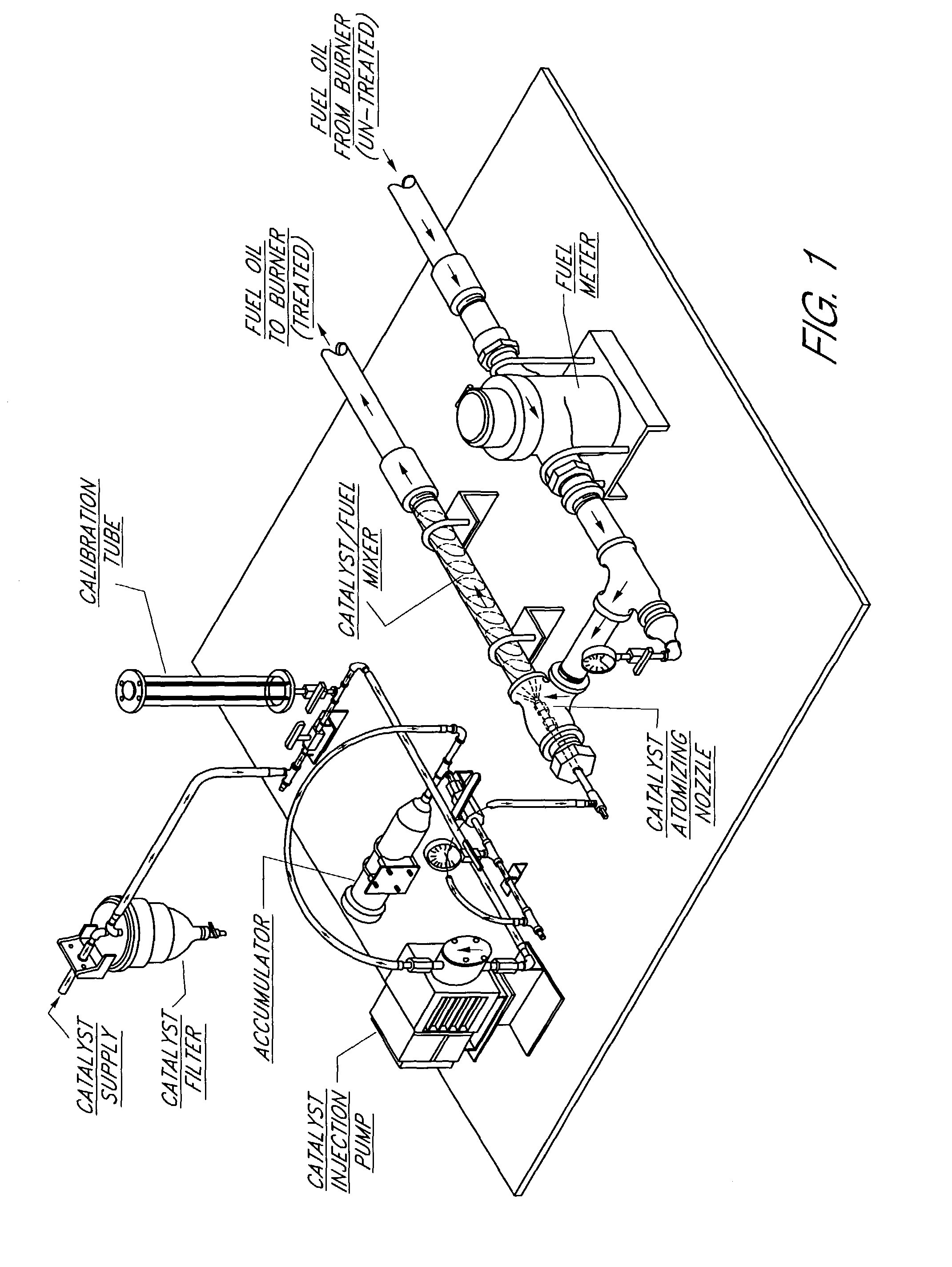
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4276 results about "Carotene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
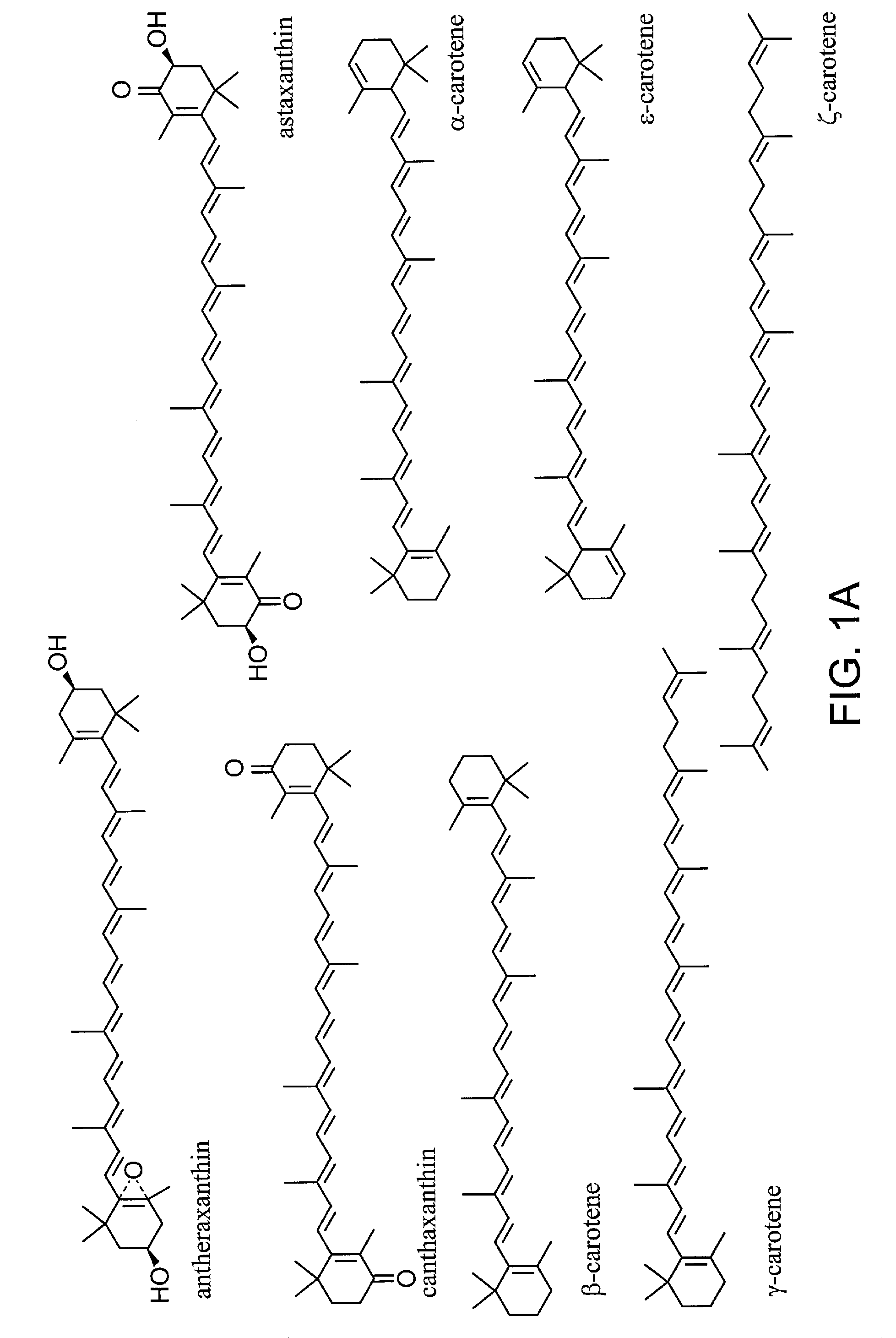
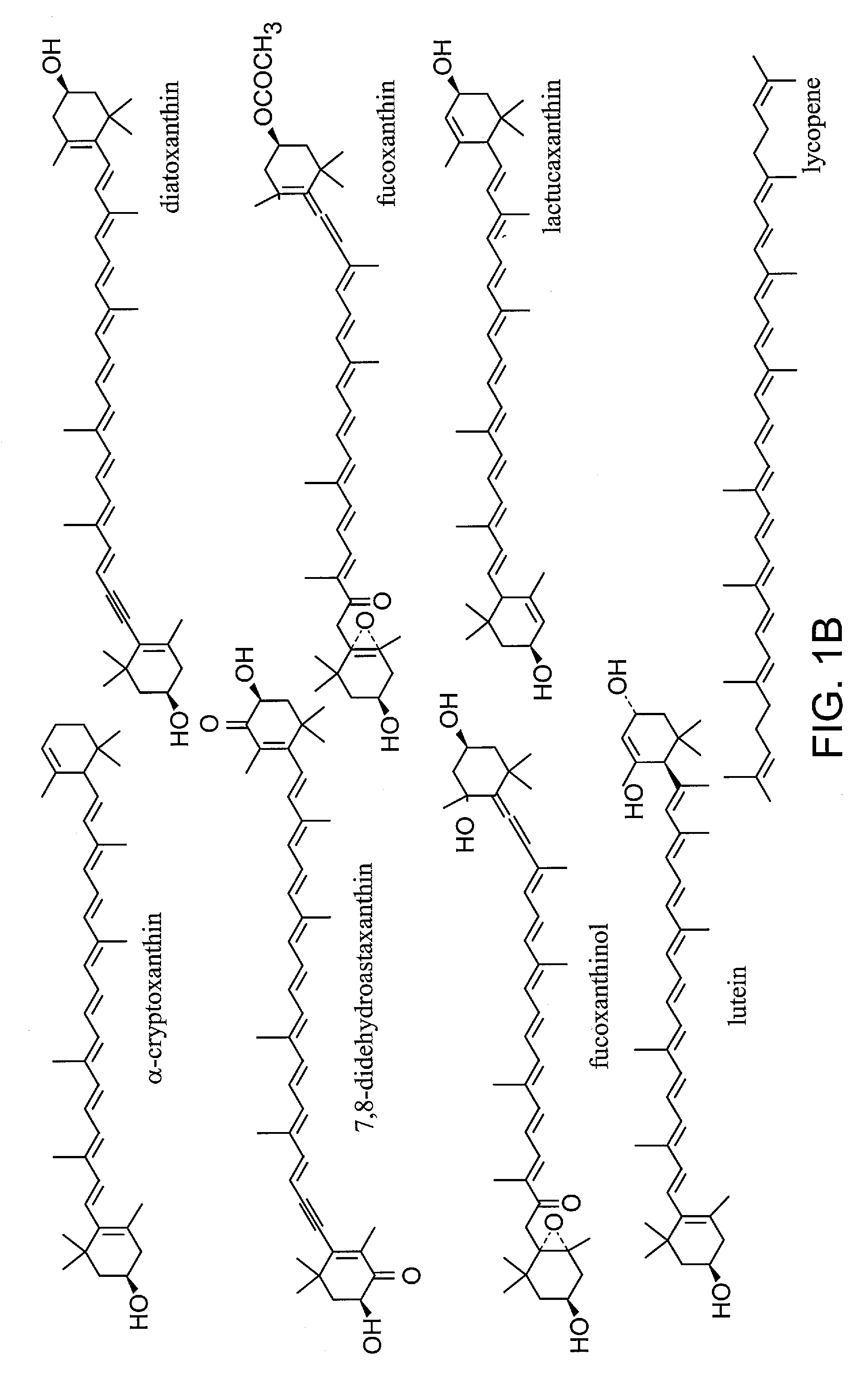
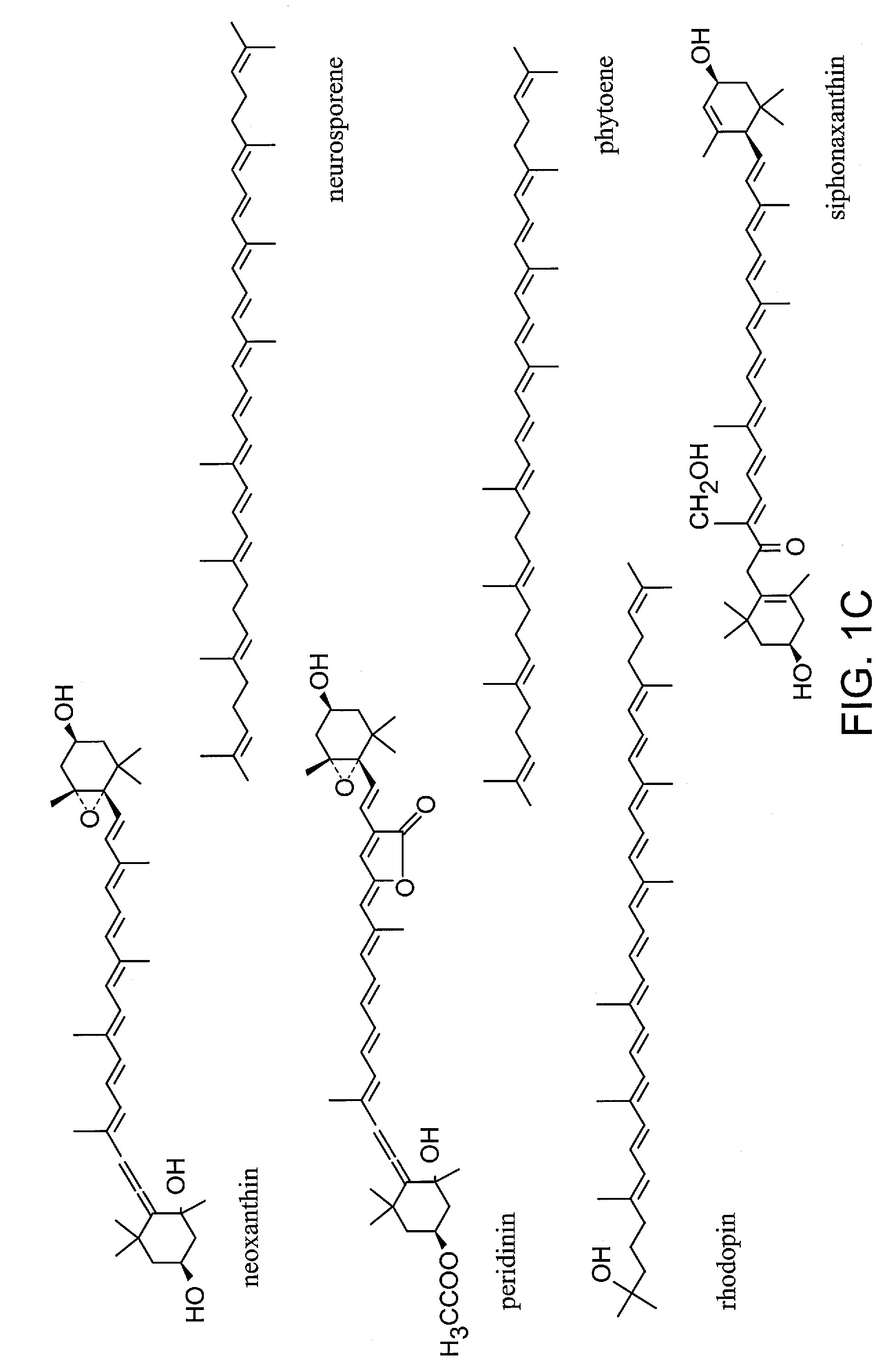
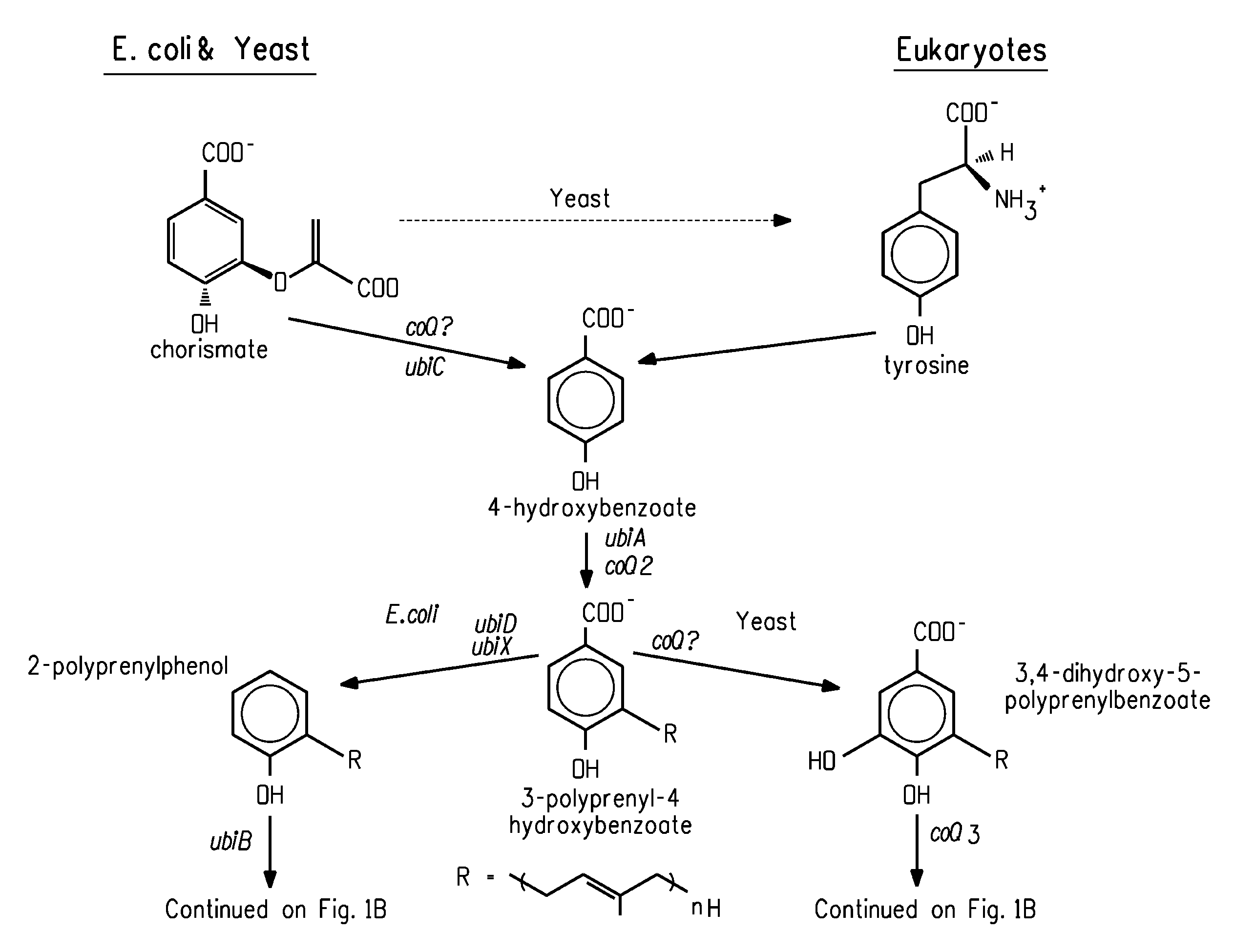
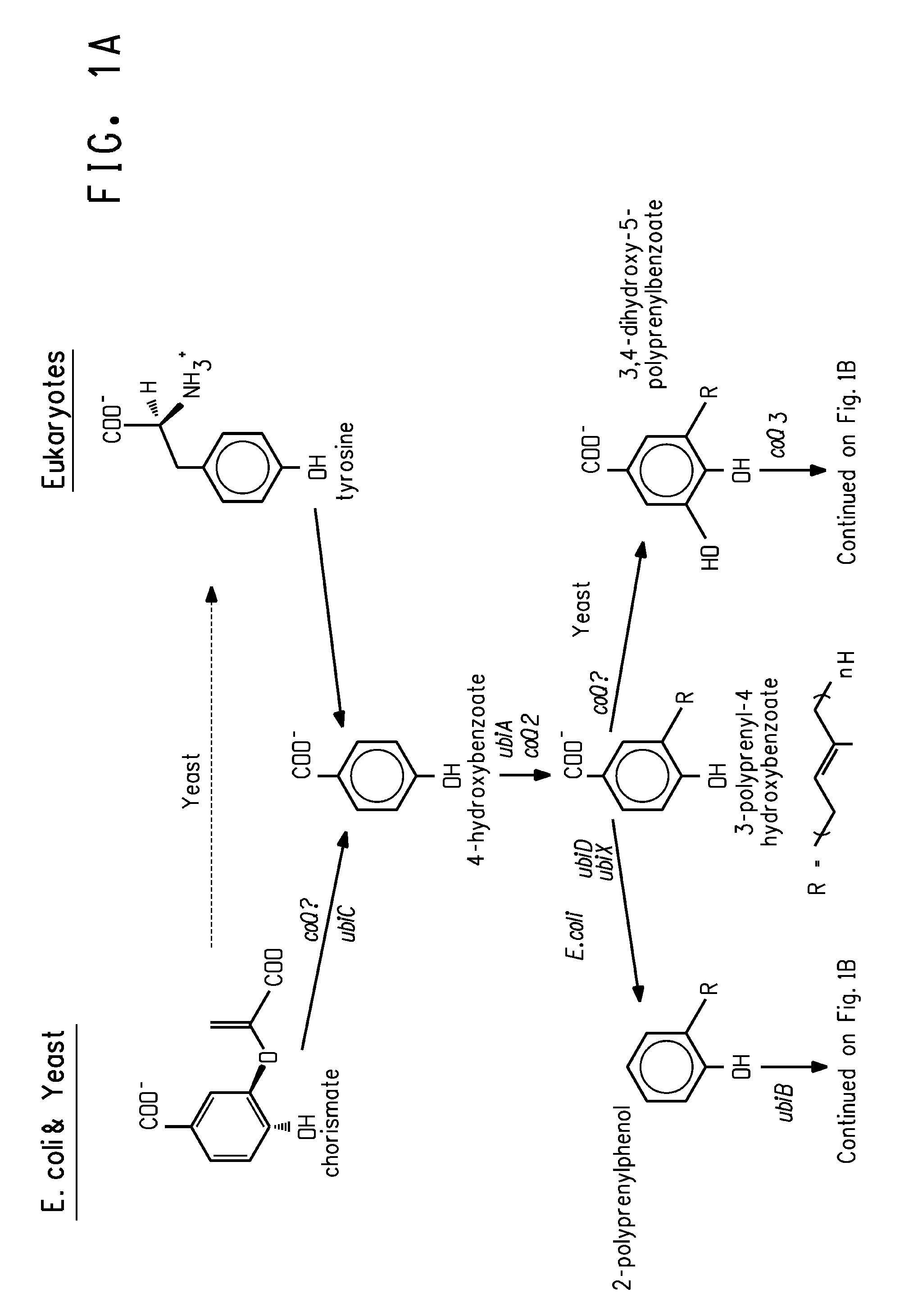
The term carotene (also carotin, from the Latin carota, "carrot") is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C₄₀Hₓ, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals (with the exception of some aphids and spider mites which acquired the synthesizing genes from fungi). Carotenes are photosynthetic pigments important for photosynthesis. Carotenes contain no oxygen atoms. They absorb ultraviolet, violet, and blue light and scatter orange or red light, and (in low concentrations) yellow light.
Microparticles for Oral Delivery
The invention provides microbeads containing oil-associated biologically active compounds and methods for their manufacture and use. The microbeads consist of a soluble complex of non-digestible polymer and emulsifier with oil-associated biologically active compounds embedded in a matrix of digestible polymer. The disclosed microbead complex protects the biologically active compounds, such as vitamins, fish oil and carotenoids, from oxidation, taste and odor degradation. The disclosed microbeads also provide protection from the stomach digestive distraction, and allows for the delivery of the biologically active compounds in the intestine.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Process for extraction and purification of lutein, zeaxanthin and rare carotenoids from marigold flowers and plants
InactiveUS6262284B1Oxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationBeta-CaroteneBeta-cryptoxanthin
A process for simultaneously extracting, saponifying, and isolating lutein and zeaxanthin, and a mixture of several rare carotenoids in high purity from plants without the use of harmful organic solvents. Lutein crystals containing 5% zeaxanthin were obtained from the dried petals of Marigold flowers Tagete erecla while zeaxanthin was isolated and purified from the berries of Lycium Chinese Mill (LCM berries). Similarly, this process has been employed to isolate and purify a mixture of lutein, beta-carotene, neoxanthin, violaxanthin, and lutein epoxide from green plants, preferably, kale, collard green, and spinach. These plants, to a lesser extent, also serve as a source of several rare carotenoids such as alpha-cryptoxanthin (Marigolds) and beta-cryptoxanthin (LCM berries). The purified carotenoids isolated by this process are free from impurities and serve as a safe source of nutritional supplement for human consumption as well as providing a suitable and effective color additive for human foods.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Soaps Produced from Oil-Bearing Microbial Biomass and Oils
ActiveUS20090305942A1Improve efficiencyLow costSoap detergents with organic compounding agentsBiofuelsMicroorganismMicrobial oil
Soap and cosmetic products can be made from oil-bearing microbial biomass via the alkaline hydrolysis of glycerolipids and fatty acid esters to fatty acid salts. The saponified microbial oils / lipids can be combined with a variety of additives to produce compositions for use as soaps and other cosmetic products, which may also contain other constituents of the biomass, including unsaponified oils, glycerol and carotenoids, among others.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Nutritional formula containing select carotenoid combinations
ActiveUS20050208179A1Improving stability of powderImprove stabilityMilk preparationFruit and vegetables preservationBeta-CaroteneLutein
Disclosed are nutritional formulas, including reconstitutable powders, comprising carbohydrate, protein and a lipid component containing a polyunsaturated fatty acid; and from about 0.25 to about 10 ppm, by weight of the total oil content of the infant formula, of a combination of lutein, lycopene, and beta-carotene with preferred weight ratios of the lutein to beta-carotene of from about 0.0196:1 to about 59:1, the lycopene to beta-carotene of from about 0.00805:1 to about 114:1, and the lutein to lycopene of from about 0.0117:1 to about 108:1. Also disclosed are methods of providing nutrition using the disclosed formulas. The nutritional formulas provide improved product stability and color characteristics.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Nutritional formula containing select carotenoid combinations
ActiveUS7090879B2Improve stabilityImproves antioxidant stabilityMilk preparationFruit and vegetables preservationBeta-CaroteneLutein
Disclosed are nutritional formulas, including reconstitutable powders, comprising carbohydrate, protein and a lipid component containing a polyunsaturated fatty acid; and from about 0.25 to about 10 ppm, by weight of the total oil content of the infant formula, of a combination of lutein, lycopene, and beta-carotene with preferred weight ratios of the lutein to beta-carotene of from about 0.0196:1 to about 59:1, the lycopene to beta-carotene of from about 0.00805:1 to about 114:1, and the lutein to lycopene of from about 0.0117:1 to about 108:1. Also disclosed are methods of providing nutrition using the disclosed formulas. The nutritional formulas provide improved product stability and color characteristics.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Microalgae-Based Beverages
InactiveUS20100297295A1Great tasteLower levelMilk preparationDough treatmentEmulsionAdditive ingredient
The invention provides novel beverages and raw materials for the manufacture thereof, such beverage and raw materials containing microalgae of various species with varying components. Attributes of the microalgal biomass used in the invention include nutrition-providing materials such as carotenoids, dietary fiber, tocotrienols and tocopherols, and varying lipid compositions, particularly low levels of saturated lipids. Attributes of the microalgal biomass used in the invention include structural attributes such as improved mouth feel compared to alternative milk products such as soy milk and rice milk. The novel beverages provide delivery systems for high nutrition materials found in microalgae. The invention provides a new category of finished beverages based on microalgae (such as refrigerated and shelf stable liquids and emulsions) as well as compositions for augmenting properties of current beverages through inclusion of novel microalgae-based materials as ingredients.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Reduced Pigmentation Microalgae Strains and Products Therefrom
InactiveUS20100297292A1Reduced colorationIncrease rangeMilk preparationDough treatmentHypopigmentationCarotenoid
The invention provides unique and novel strains of microalgae that have been subjected to non-transgenic methods of mutation sufficient to reduce the coloration of biomass produced by the strains. Biomass produced from such strains can be used in the manufacture of baked goods, gluten free foods, beverages, high lipid algal flours, and other foods. Pigments such as carotenoids and chlorophyll can be undesirable for consumer acceptance when incorporated into foods such as mayonnaise, yogurt, and white sauces that are not traditionally associated with colors such as yellow, red, orange and green. Some pigments, such as chlorophyll, can also create undesirable taste profiles. Use of reduced pigment microalgal biomass expands the range of food products that can be manufactured with healthy lipid profiles. High protein containing biomass of the invention, also reduced in pigmentation, is also incorporated into products such as meat analogues, nutritional bars and meal replacement beverages. The reduced pigmentation microalgae also allow for incorporation of higher amounts of biomass into certain food products that could otherwise be achieved using highly pigmented microalgal biomass. Methods of generating novel reduced pigment microalgae are disclosed herein. The strains provided by the invention are also useful in the manufacture of healthy, neutral colored extracted triglyceride oils.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Production of carotenoids in oleaginous yeast and fungi
ActiveUS7851199B2Improve oilinessAlter their carotenoid-producing capabilitiesSenses disorderFungiYeastCarotenoid
The present invention provides systems for producing engineered oleaginous yeast or fungi that express carotenoids.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Trans carotenoids, their synthesis, formulation and uses
The invention relates to trans carotenoid compounds and salts thereof as well as compositions thereof, methods for making them, and uses thereof. These compounds are useful in improving diffusivity of oxygen between red blood cells and body tissues in mammals including humans.
Owner:DIFFUSION PHARMA LLC
Method and synergistic composition for treating attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder
InactiveUS6541043B2Minimize side effectsBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsBeta-CaroteneBetaine
A composition and method for treating Attention Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is provided which can be used both with and without ethical drugs now used to treat ADHD. The composition contains dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE), omega 3-fatty acids, betaine, oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPC), folic acid, vitamins C, E, B12, B6, B5 and beta-carotene and minerals (calcium, magnesium, zinc and selenium). Ethical drugs such as amphetamines, methylphenidate HCl and pemoline are known to control ADHD, but each has significant side effects when used in their therapeutic dose. When combining the composition with such ethical drugs, the amount of the ethical drug can be lowered below a level which causes undesirable side effects which is an important feature. Preferred compositions contain one or more of lecithin, choline, 5-hydroxytryptophan, tyrosine, Reishi Extract, Kava Extract, Gingko, Ginseng and St. John's Wort.
Owner:PHILIP C LANG
Composition and method for reducing the risk or progression of cardiovascular, glaucoma, tardive dyskinesia and other diseases
InactiveUS20040087479A1Reduce riskShorten the progressBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBeta-CaroteneAdditive ingredient
Elevated levels of homocysteine have been implicated as an important risk factor for cardiovascular and other diseases. A composition for decreasing levels of plasma homocysteine and a method for administering the composition are provided, the composition containing dextromethorphan (DM), folic acid and vitamins B6 and B12. The composition provides a synergistic therapeutic effect so that lower amounts of the above ingredients may be employed to minimize any undesirable side effects caused by the use of high levels of a component such as DM. Preferred compositions for cardiovascular diseases further include lecithin, vitamin E, betacarotene, procyanidins / flavonoids, trimethylglycine, garlic oil and minerals. Other compositions for treating glaucoma include bilberry, bioflavonoids and beta-carotene and for treating tardive dyskinesia include an antioxidant such a grape seed extract and pine bark extract, lecithin and oligomeric proanthocyanidins. The compositions may be administered using any suitable means such as orally or intravenous.
Owner:SOSNOWSKI ROBERT E +1
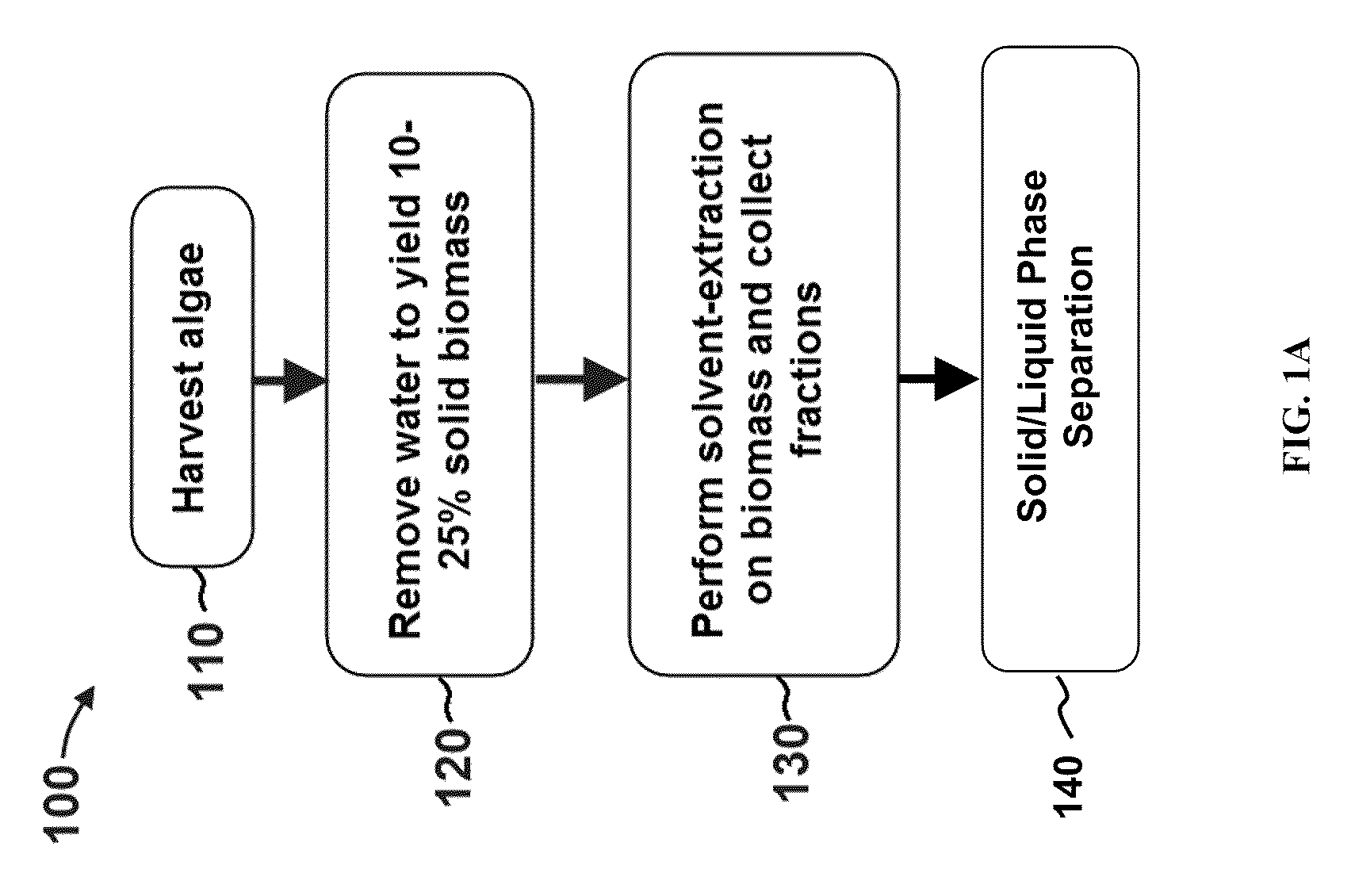
Methods of producing biofuels, chlorophylls and carotenoids
InactiveUS20110263886A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationWater insolubleBiofuel
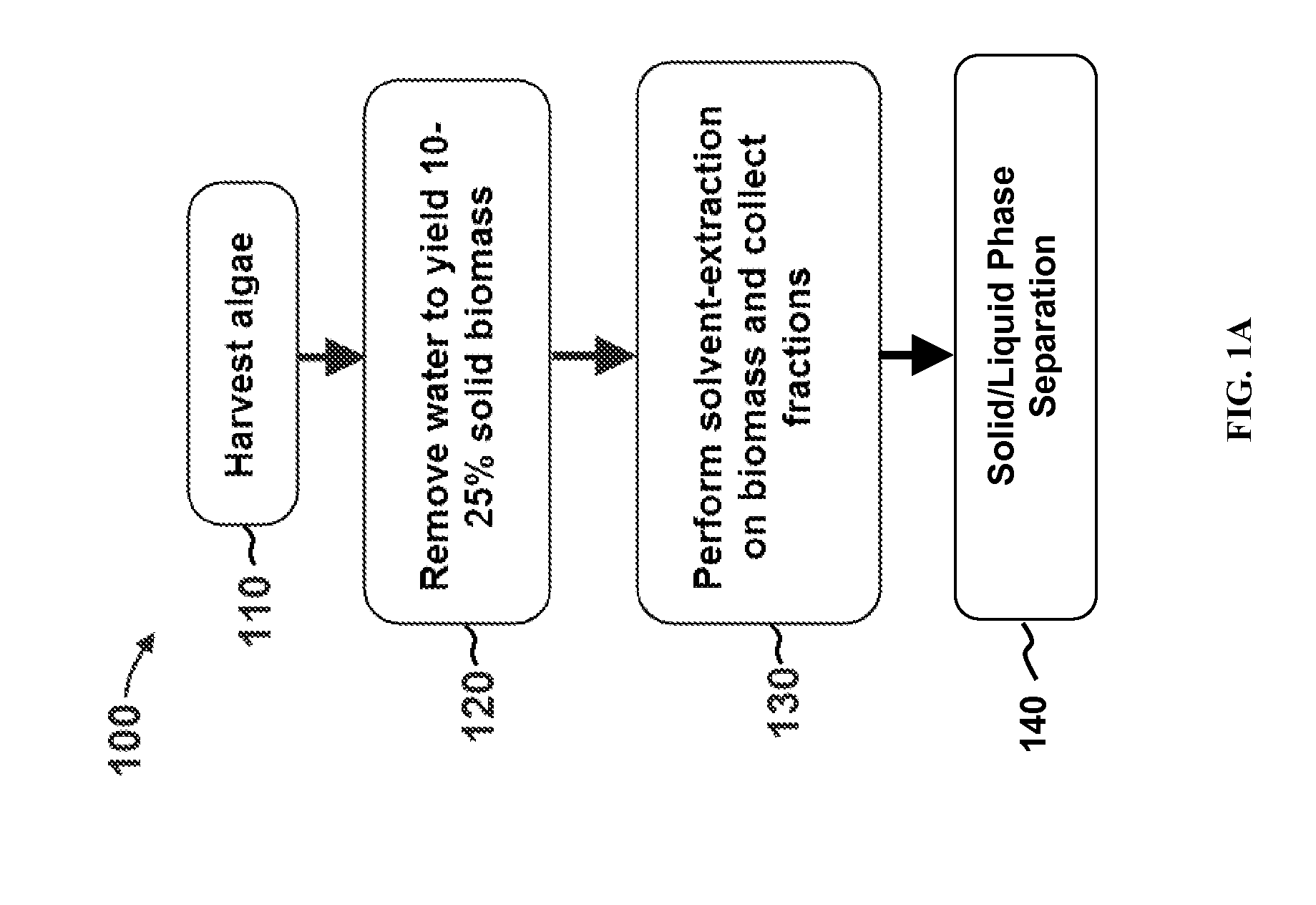
A method for producing biofuels along with valuable food and neutraceutical products is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids along with carotenoids and chlorophylls from the algal biomass, and separation of the carotenoids and chlorophylls using adsorption or membrane diafiltration or other methods. The remaining neutral lipids are esterified with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising omega-3 fatty acids esters and remaining carotenoids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
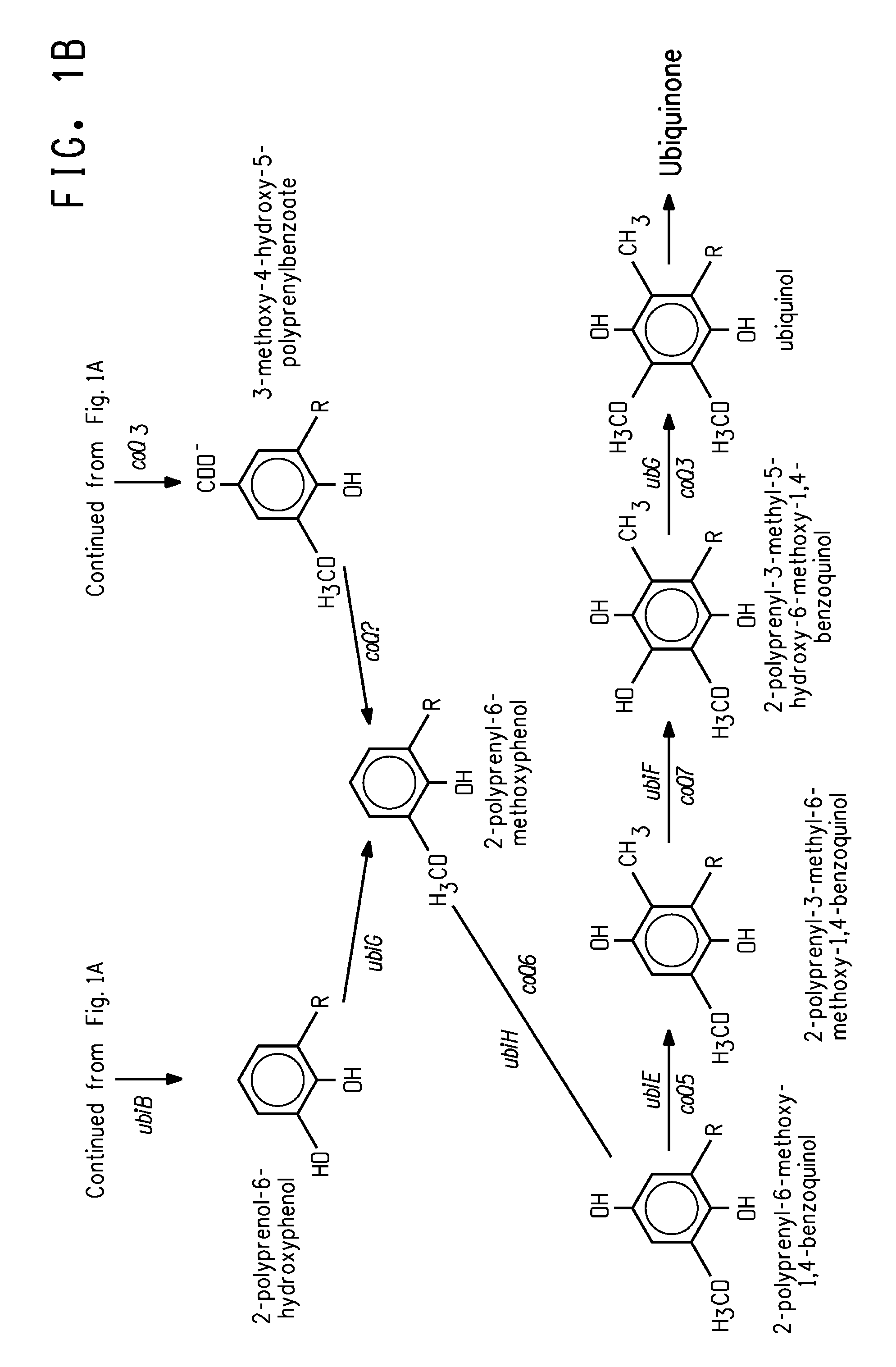
Coenzyme Q10 Production in a Recombinant Oleaginous Yeast
Engineered strains of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica capable of co-producing coenzyme Q10 and at least one ω-3 / ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid are provided. The strains may also be engineered to co-produce at least one C40 carotenoid. Methods of using the antioxidant products obtained (e.g., biomass and / or pigmented oils) in food and feed applications are also provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
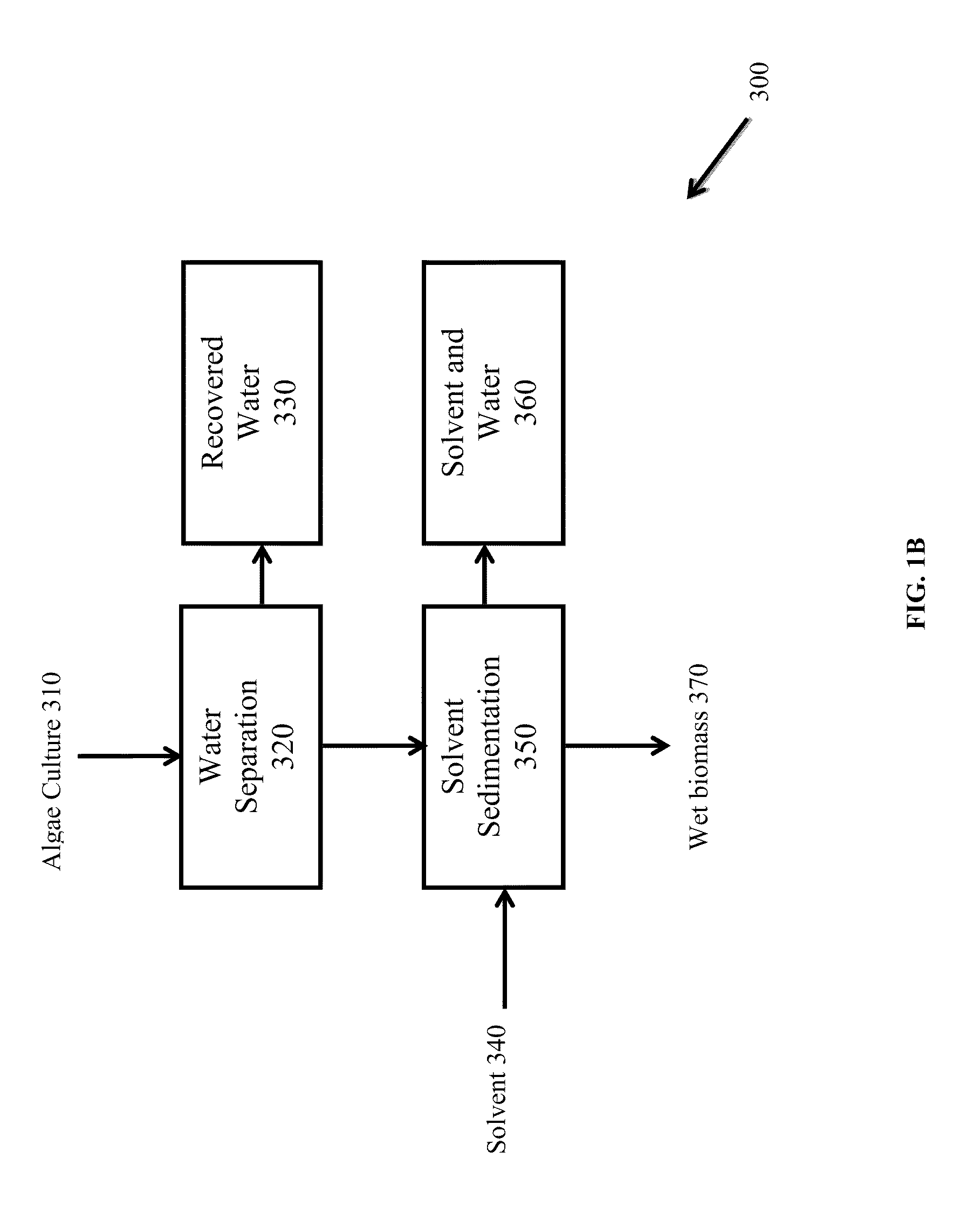
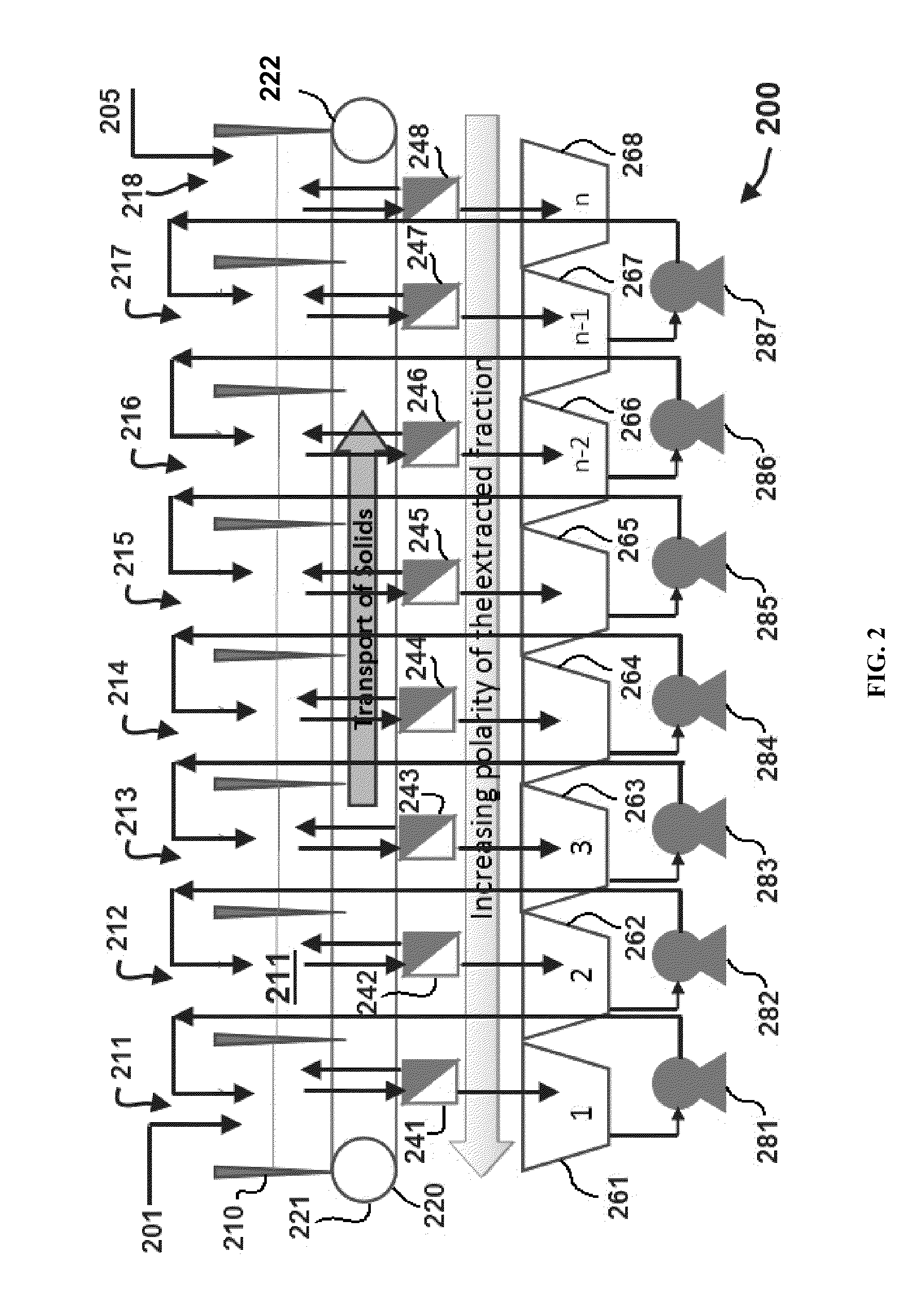
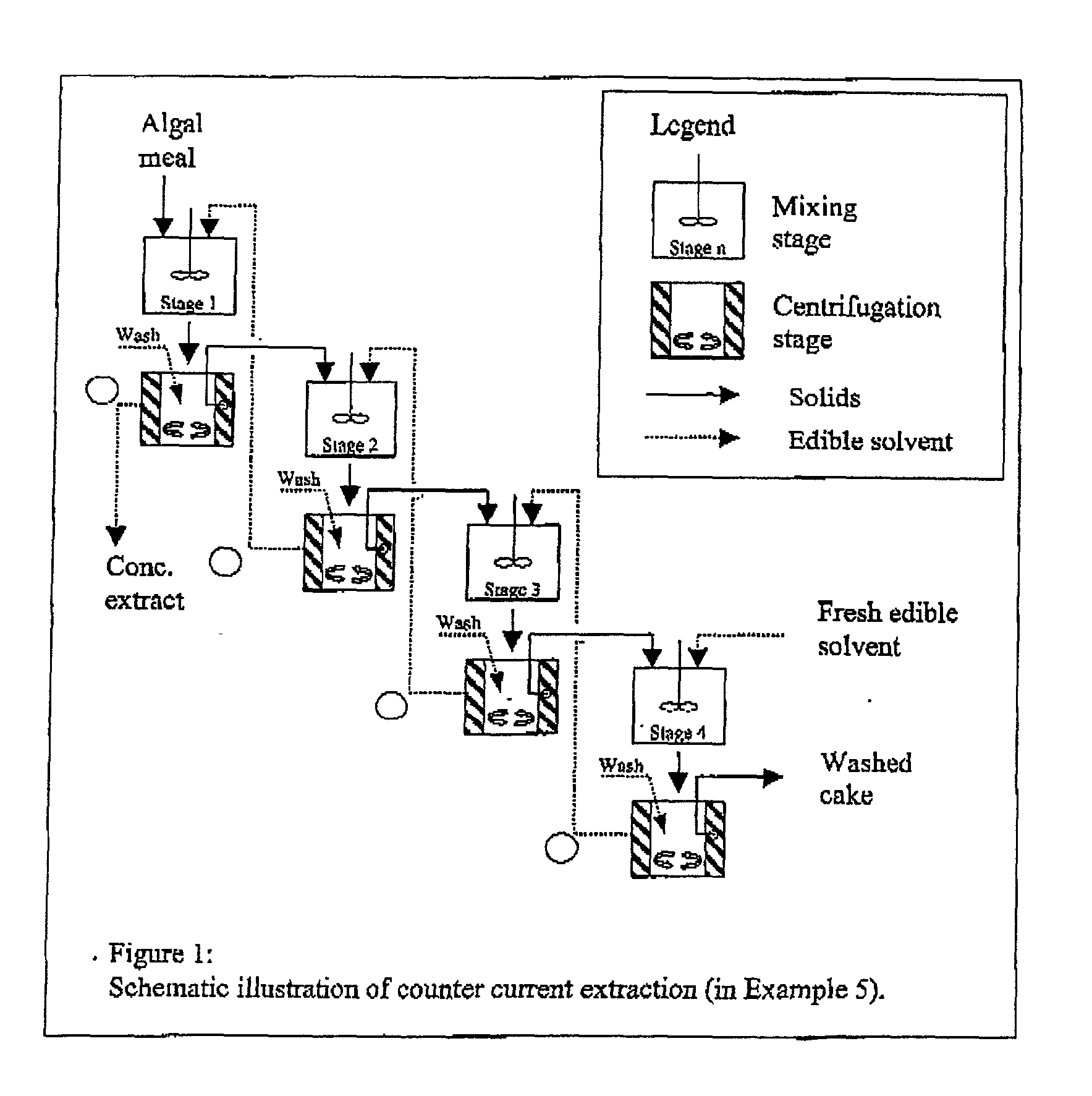
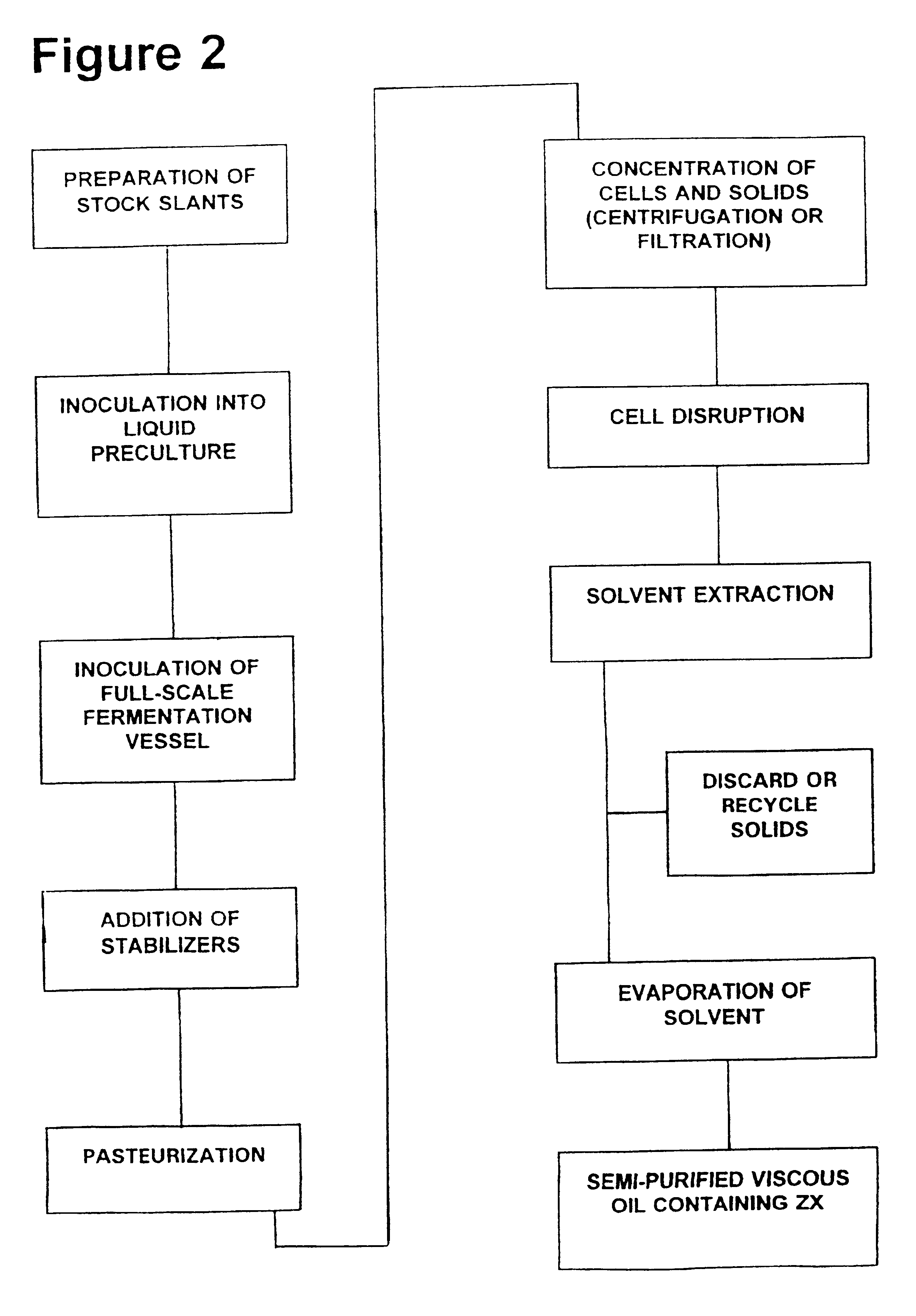
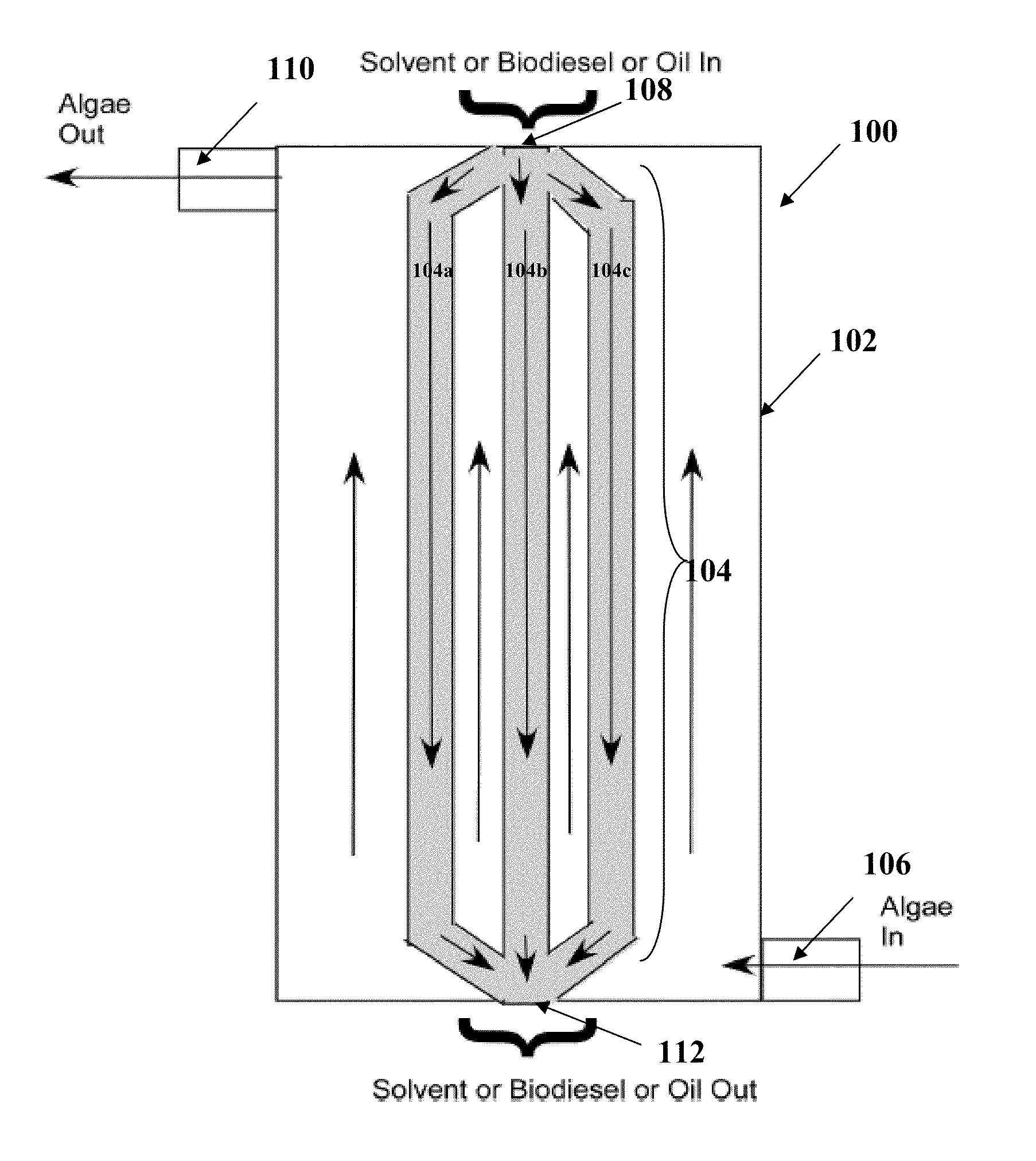
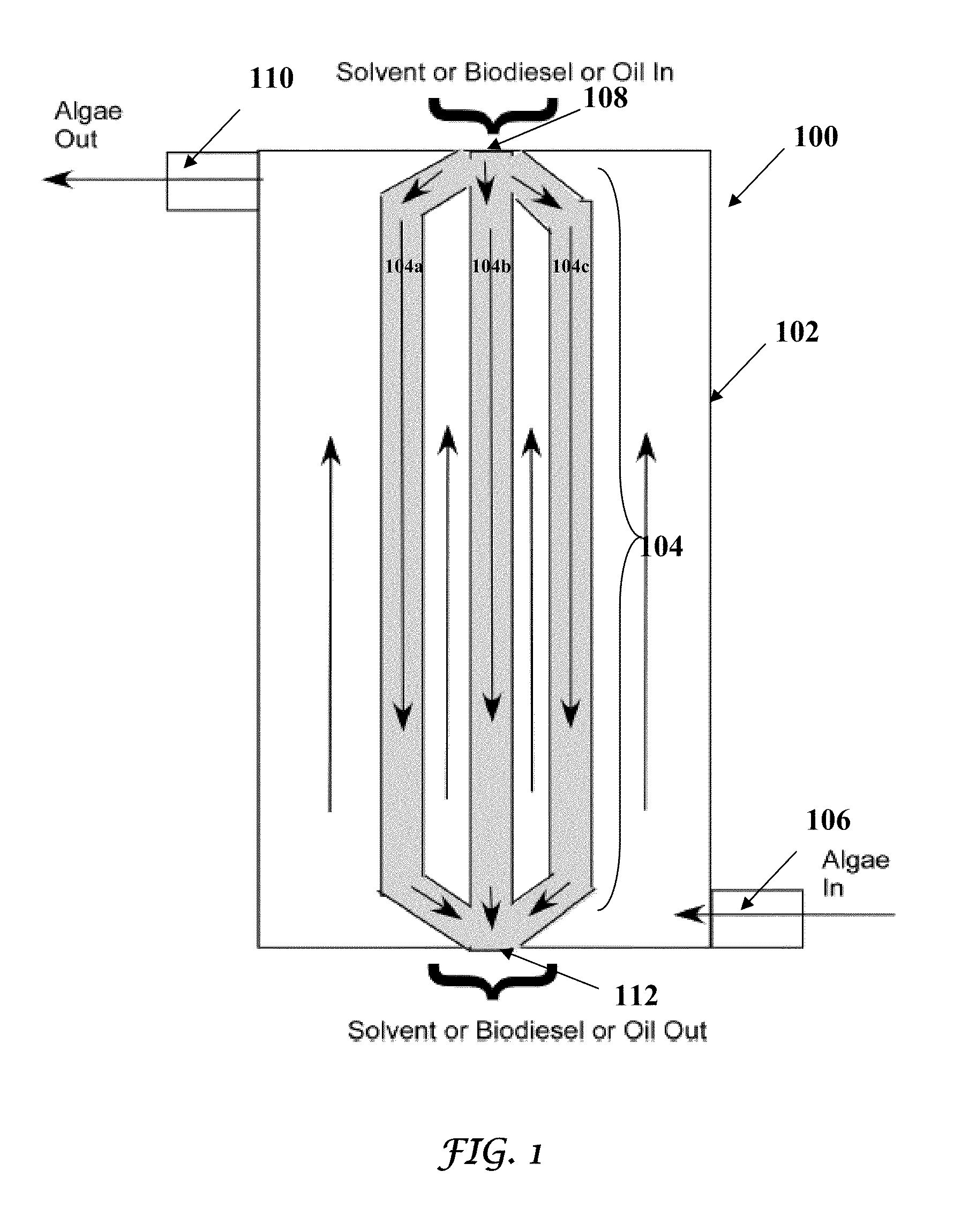
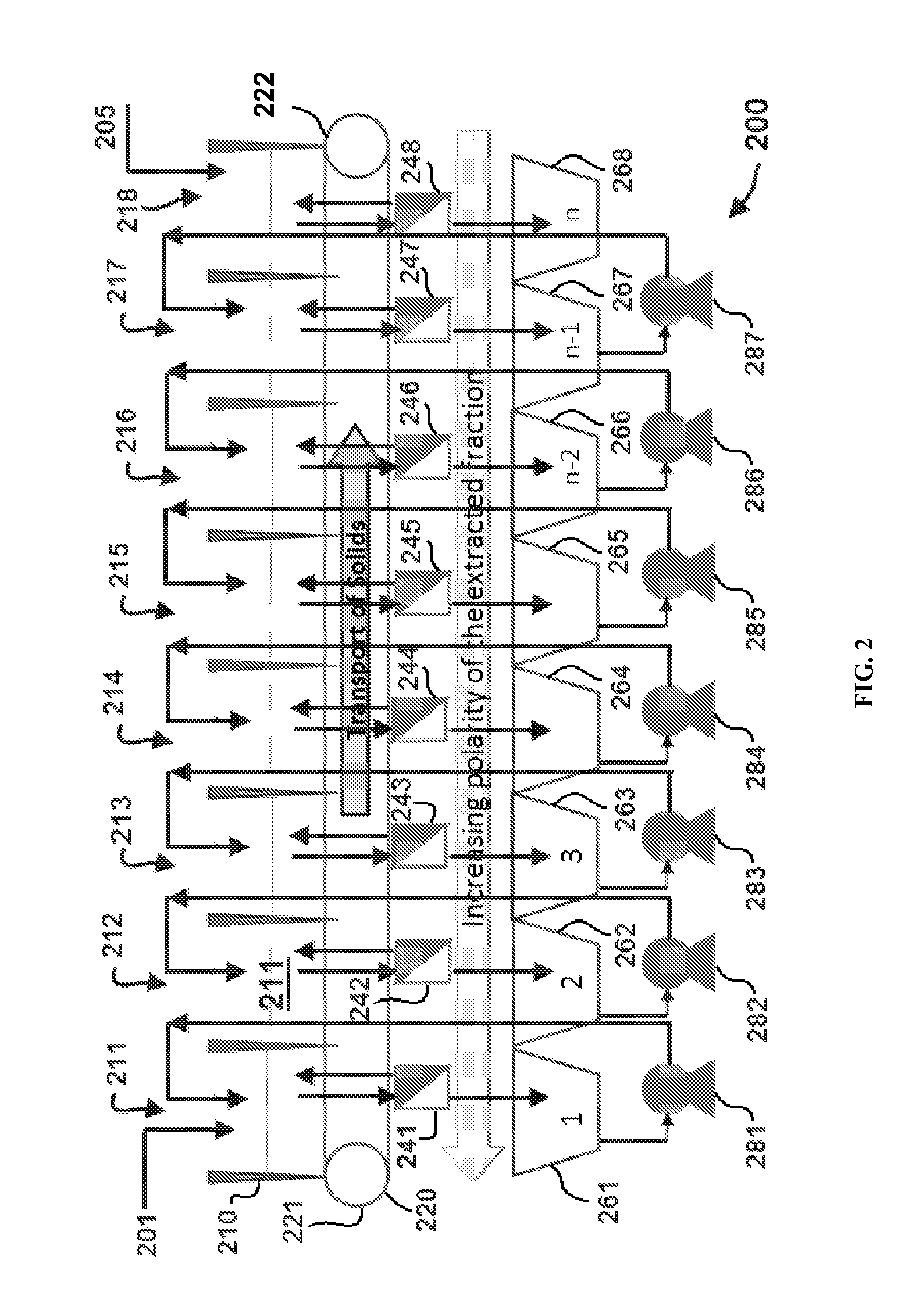
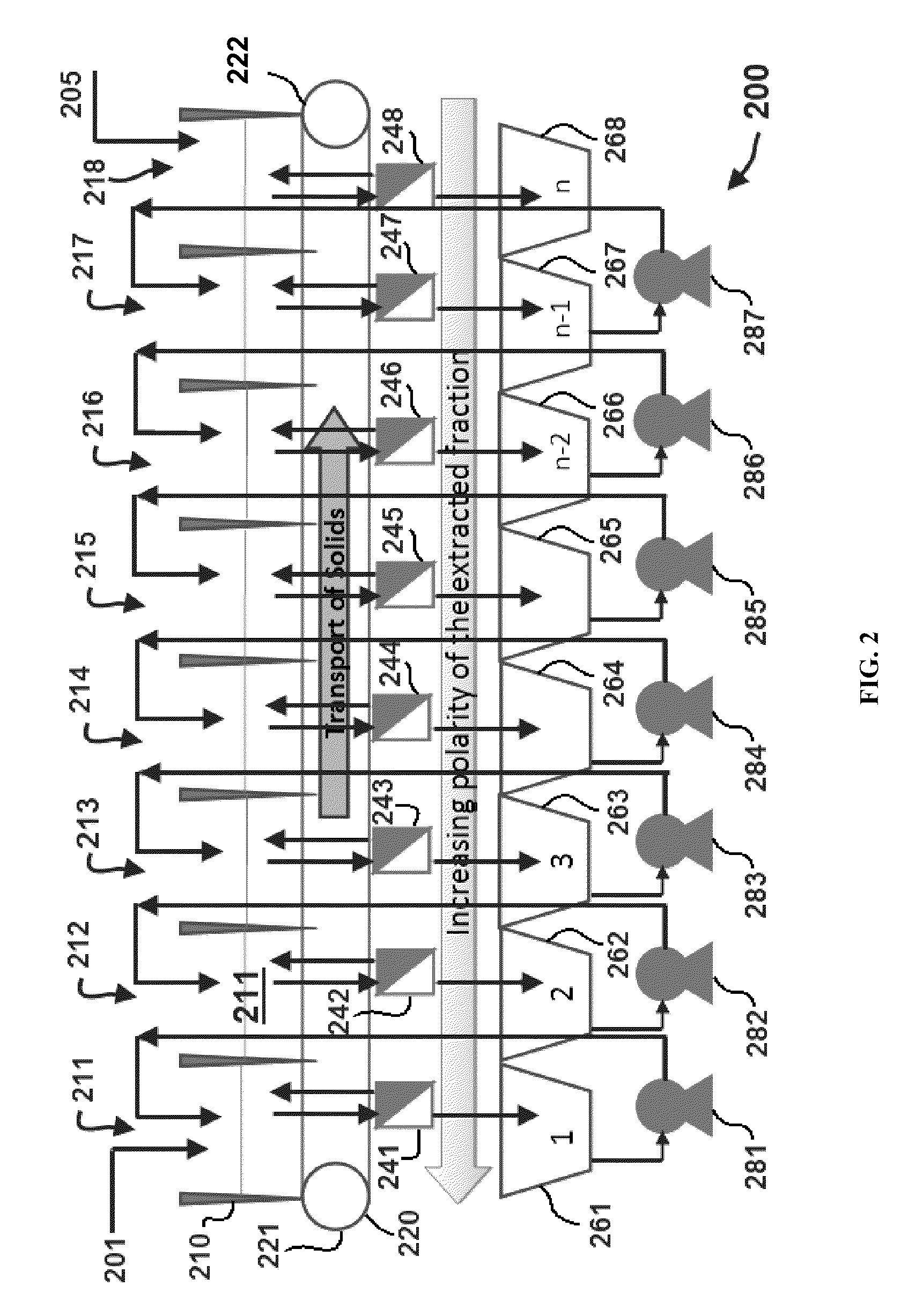
Edible solvent extraction of carotenoids from microorganisms
InactiveUS20030054070A1Efficient extractionEnriching carotenoid contentLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbonsParticulatesAnimal food
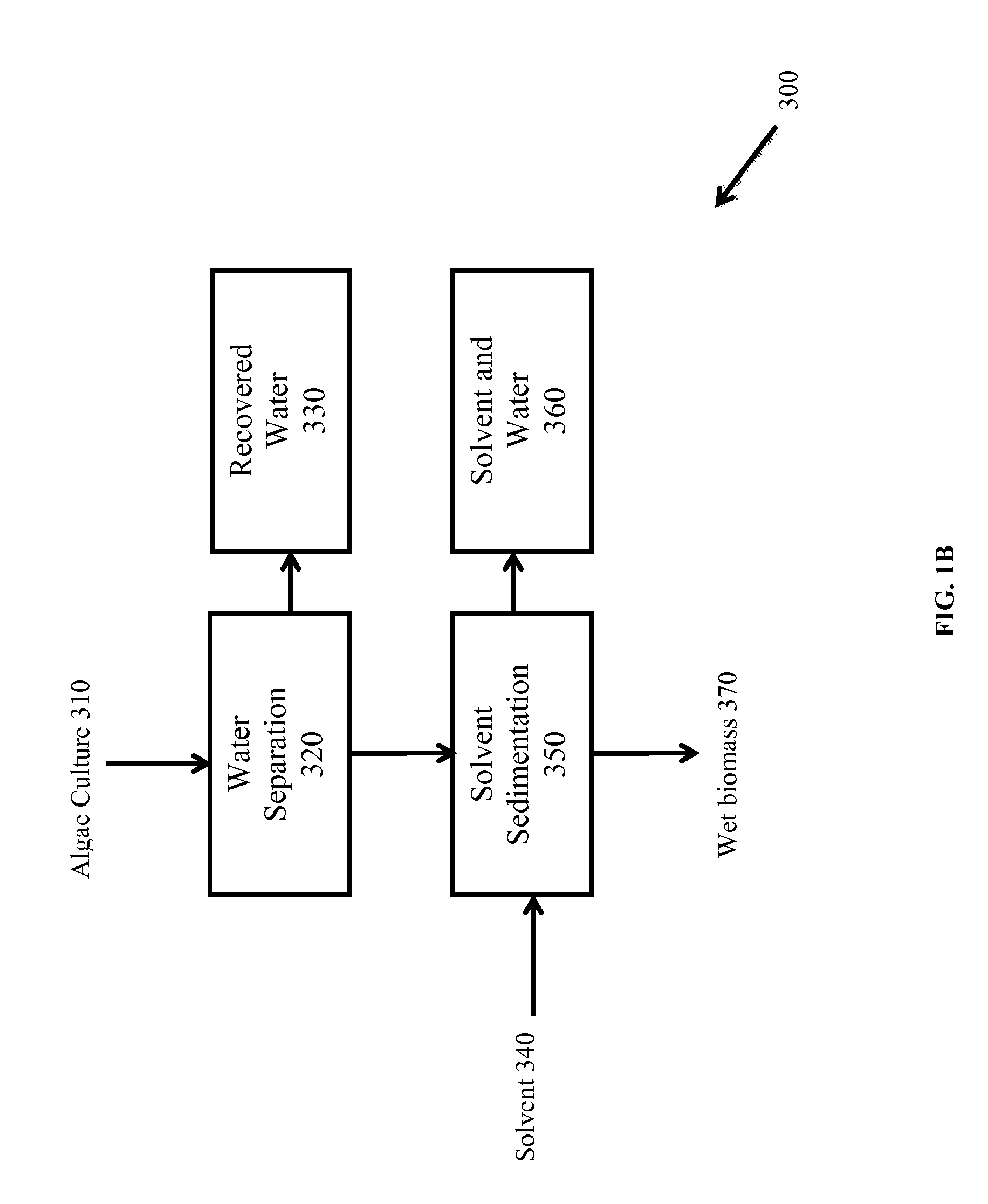
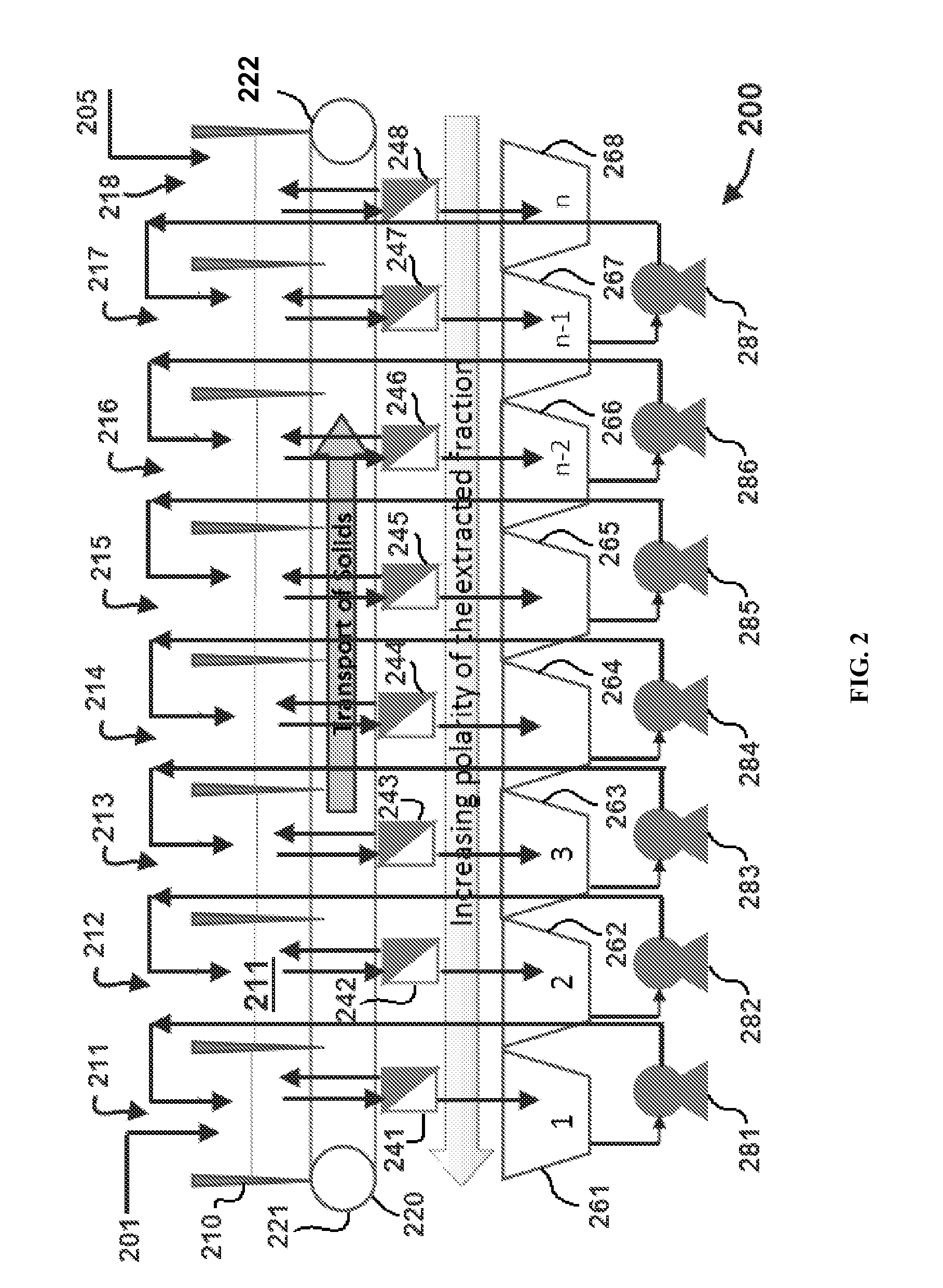
A process for extracting carotenoids from a carotenoid-containing starting material produced by microorganisms is described. Said starting material is admixed with edible solvent to effectuate the transfer of carotenoids. Separation of the carotenoid-enriched edible solvent is improved by the formation of a "cake", composed of said carotenoid-containing particulate solids, and, as required, a certain quantity of suitable filtration aid to modify the cake's consistency. Mechanical aids accelerate the separation of the carotenoid-enriched edible solvent. Said mixture may be hydrated to aid the removal of solids and gums from the carotenoid containing edible solvent. The carotenoid-enriched edible solvent is filtered though said cake to reduce the particulate load including any undesirable microbial load. A counter-current process increases the carotenoid concentration of the extract. The carotenoid-enriched edible solvent can be used as an ingredient in human and animal foodstuffs and dietary supplements for the possible prevention and treatment of illnesses and diseases.
Owner:AQUSRCH
Nutritional supplement for treatment of ocular diseases
A nutritional supplement composition that promotes visual health and reduces or reverses visual acuity loss by a reduced Vitamin E content from standard supplements with the addition of taurine, omega-3 fatty acids, and non proform Vitamin A carotenoids including lutein and zeaxanthin. The essential ingredients of the nutritional or dietary supplements are Vitamin C, no more than 300 IUs of Vitamin E, Vitamin A at least a portion of which is provided in the form of a proform Vitamin A carotenoid, omega-3 fatty acids, and non proform Vitamin A carotenoids including lutein and / or zeaxanthin. The essential ingredients are provided in a form suitable of oral ingestion or other forms of administration in one or more doses per day.
Owner:PAUL JR EDWARD L
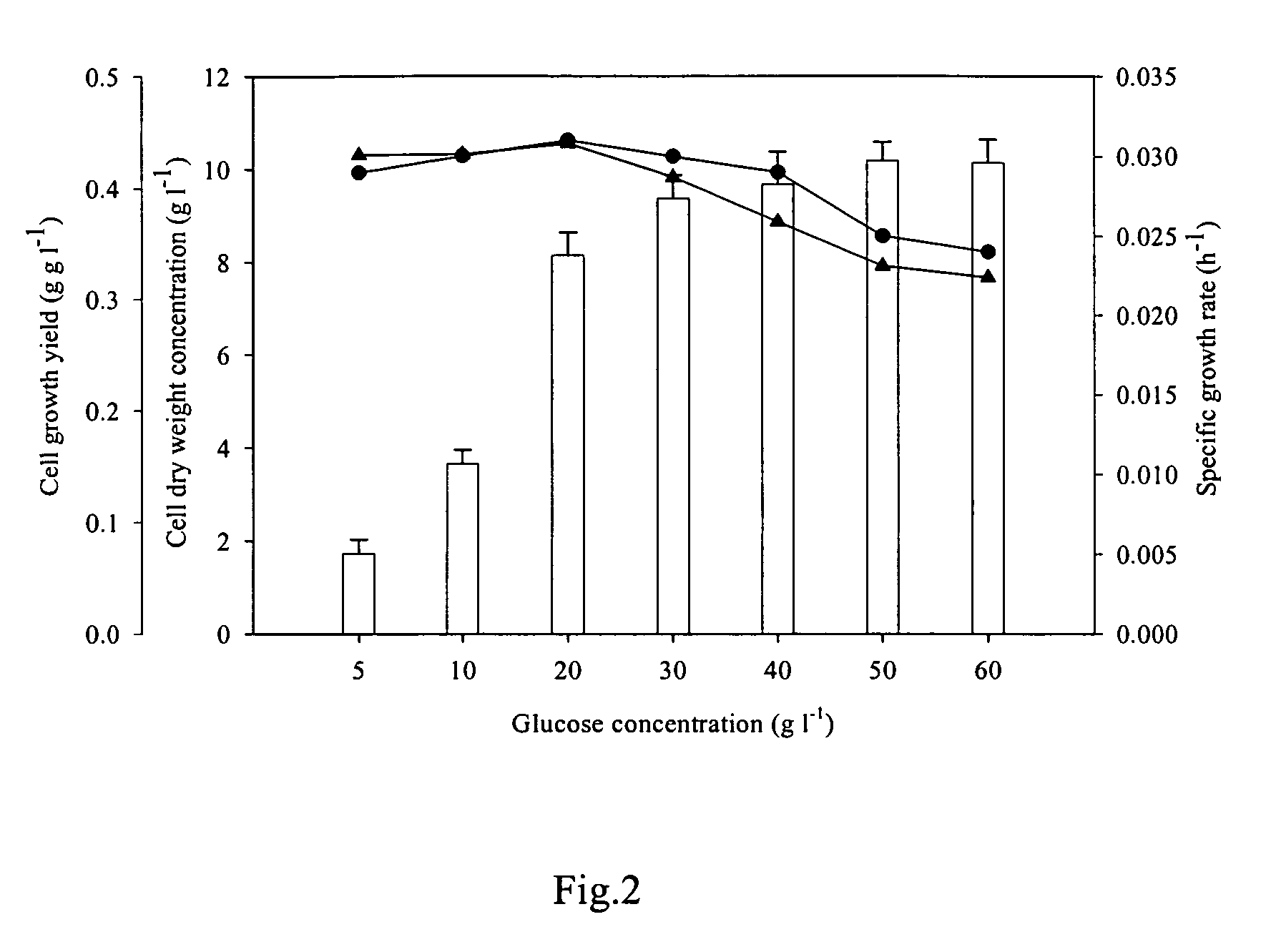
Methods for production of astaxanthin from the green microalgae Chlorella in dark-heterotrophic cultures
A method for producing the high-value ketocarotenoid astaxanthin by the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis in dark-heterotrophic cultures shows excellent growth and high-yield astaxanthin production on glucose-supplemented media in the dark. The specific growth rate and astaxanthin yield can be as high as 0.031 h−1, and 10.3 mg l−1, respectively, which are the highest so far reported in heterotrophic algal cultures. The light-independent astaxanthin-producing ability of Chlorella zofingiensis can be employed for commercial production of astaxanthin using industrial fermenters.
Owner:HONG KONG UNIV OF
Synergistic effect of compositions comprising carotenoids selected from lutein, beta-carotene and lycopene
InactiveUS20070082044A1Improve antioxidant capacitySlow effectCosmetic preparationsBiocideDiseaseAntioxidant capacity
The methods of the invention can be used to protect against lymphocyte DNA damage and free-radical associated disorders in a subject. The methods of the present invention can be used to increase the antioxidant capacity in both the aqueous and lipid compartments, decrease DNA oxidation, decrease lipid peroxidation, and increase antioxidant nutrient levels in the circulation. The protective effect of the physiologic dose of the mixed carotenoid supplement is rapid, consistent and cumulative.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
Optical method and apparatus for determining status of agricultural products
InactiveUS7215420B2Improve efficiencyAutomation of quality controlRadiation pyrometryComponent separationBeta-CaroteneLycopene
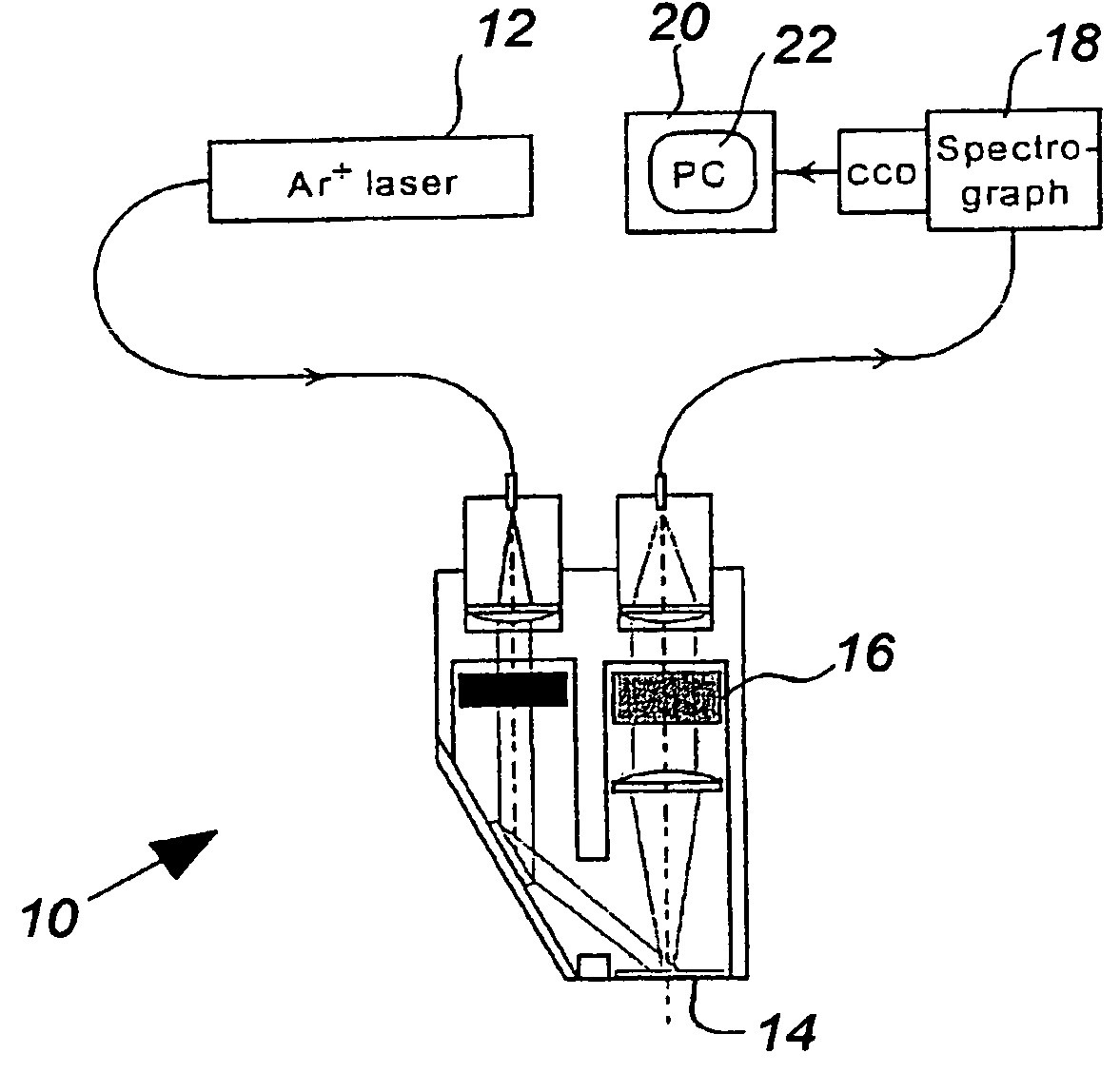
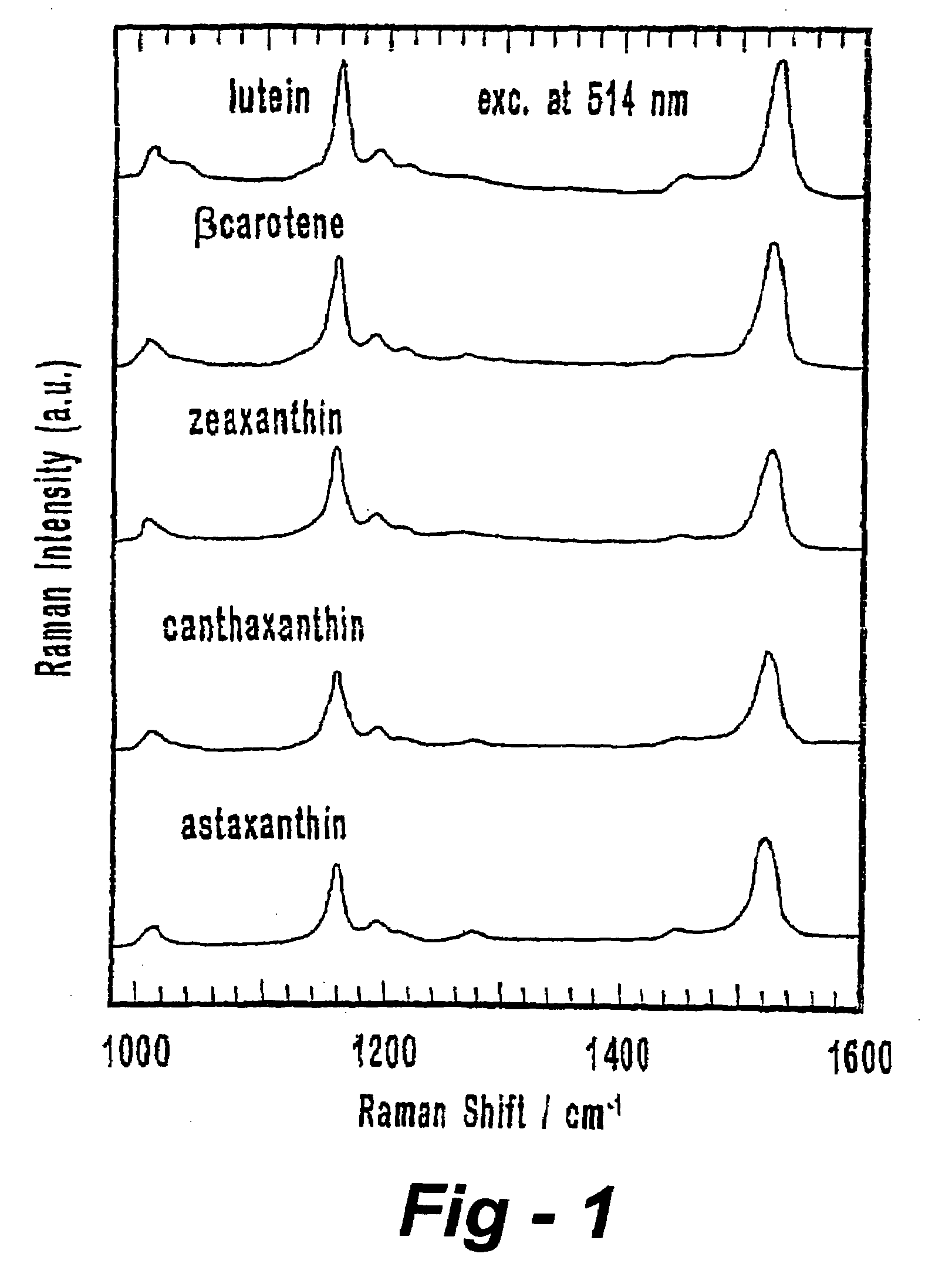
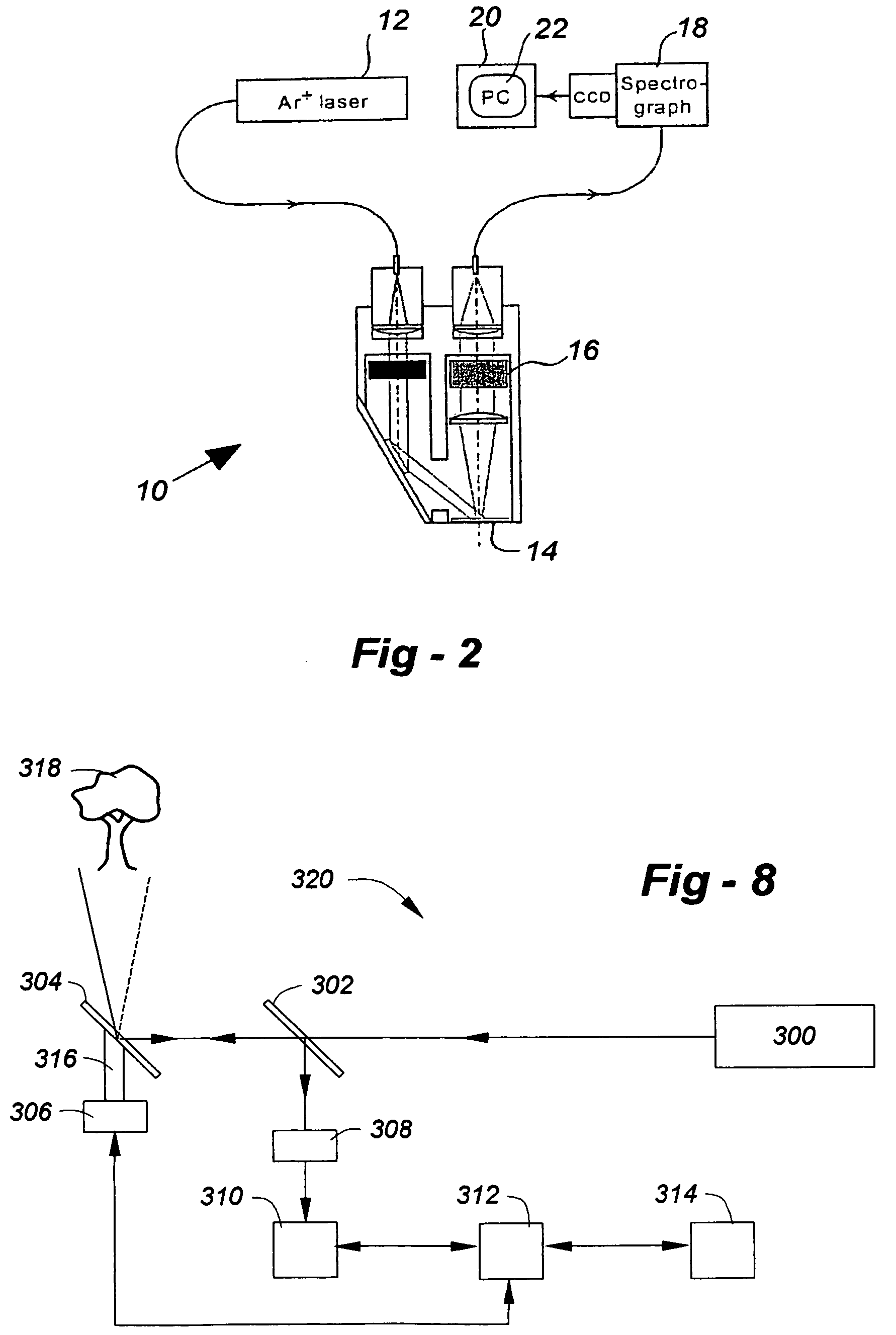
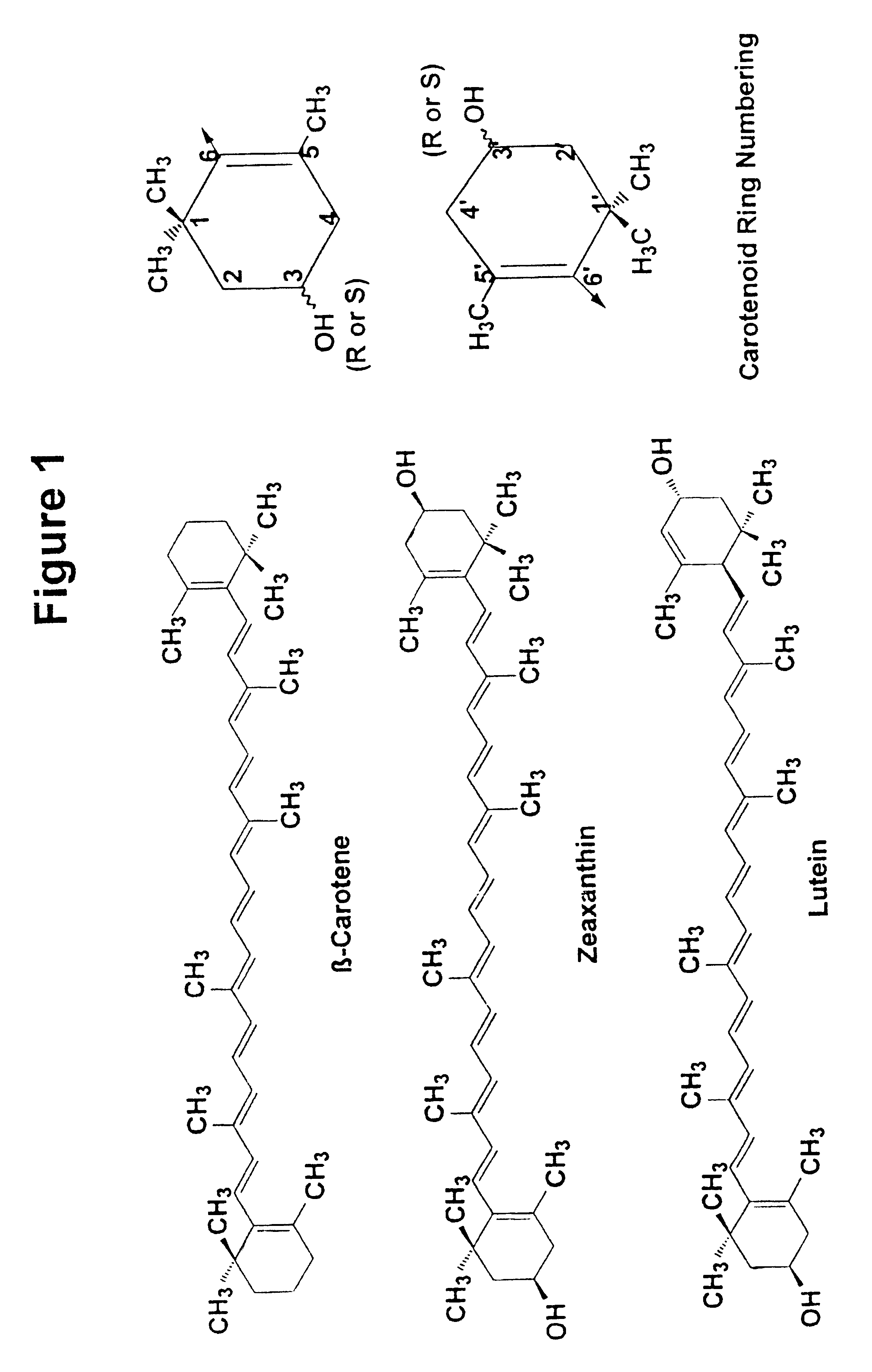
A spectroscopic method, preferably Raman scattering, is used to rapidly determine the general health or stress status of living plants and plant products, including agricultural crops, forests, and harvested fruits and vegetables. In the preferred embodiments, carotenoid levels are used to provide an indication of oxidative deterioration. Based upon the results of the analysis, further action may or may not be taken, for example, in terms of choosing, picking, harvesting or sorting the agricultural product in accordance with the carotenoid level. Concentration levels of an analyte substance can be determined relative to an external standard, to each other, or relative to another substance in the item being analyzed. Carotenoids such as lycopene, beta-carotene, lutein, violaxanthin, neoxanthin, antheraxanthin, and zeaxanthin are determined according to the invention, through other plant components may be analyzed such as other terpenes, polyenes, chlorophyll, proteins, starches, sugars, overall nitrogen levels, flavonoids, and vitamins. The hardware associated with the invention may be field portable or mounted on a piece of equipment such as a harvester or sorter.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Zeaxanthin formulations for human ingestion
InactiveUSRE38009E1Low costPrevent macular degenerationPowder deliverySenses disorderSolventCarotene
Preparations are disclosed containing the 3R-3'R stereoisomer of zeaxanthin as a sole detectable isomer, packaged for oral ingestion by humans as a therapeutic drug or nutritional supplement. Zeaxanthin is a yellow carotenoid pigment found in the macula (in the center of the human retina), which helps protect retinal cells against phototoxic damage. The pure R-R stereoisomer can be prepared by fermenting cells, such as Flavobacterium multivorum (ATCC 55238), which do not create any detectable quantity of the undesired and potentially toxic S-S or S-R isomers, and which do not synthesize any other carotenoids. The R-R isomer can be concentrated, in large quantities and at low cost, into a viscous oily fluid containing about 5 to 20% zeaxanthin, by means of a simple solvent extraction process. This oily fluid can be mixed with a carrier such as vegetable oil and enclosed within a digestible capsule, comparable to a conventional capsule containing Vitamin E. Alternately, a zeaxanthin fluid can be added to various types of foods, such as margarine, dairy products, syrup, cookie dough, and certain types of meat preparations which are not subjected to harsh cooking. Additional purification steps can also be used to purify zeaxanthin to a granular or powdered state which contains nearly pure zeaxanthin. Such processing can be used to create formulations such as ingestible tablets, and particulate formulations that can be added to soups, salads, drinks, or other foods. Preferred stabilizers and anti-oxidants are also disclosed herein. When consumed by humans in any of these modes, the purified R-R stereoisomer of zeaxanthin can help treat and prevent macular degeneration, one of the leading causes of blindness and vision loss, especially among the elderly.
Owner:ZEAVISION LLC
Isolation of carotenoid crystals
InactiveUS7015014B2Reduce usageIncrease carotenoid contentOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMicroorganismAnti solvent
The present invention relates to a crystalline carotenoid compound, such as β-carotene, with a purity of at least 95% and with substantially no solvent enclosed in the crystal lattice. The present invention further describes a process to prepare such a highly pure crystalline carotenoid compound from microbial biomass, without the use of a solvent extraction and / or an anti-solvent crystallization process.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Non-Dispersive Process for Insoluble Oil Recovery From Aqueous Slurries
ActiveUS20110174734A1Efficient separationEliminate the problemFatty acid chemical modificationFatty acids production/refiningBiodieselBeta-Carotene
The development and application of a novel non-polar oil recovery process utilizing a non-dispersive solvent extraction method to coalesce and recover oil from a bio-cellular aqueous slurry is described herein. The process could apply to recovery of algal oil from a lysed algae slurry, recovery of Omega fatty acids from a bio-cellular aqueous feed, recovery of Beta-carotene from a bio-cellular aqueous feed and for the removal from produced water in oil production and similar type applications. The technique of the present invention utilizes a microporous hollow fiber (MHF) membrane contactor. The novel non-polar oil recovery process described herein can be coupled to a collecting fluid (a non-polar solvent such as heptane, a biodiesel mixture or the previously extracted oil) that is circulated through the hollow fiber membrane. In cases where the biodiesel mixture or the previously extracted oil is used the solvent recovery step (e.g. distillation) can be eliminated.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
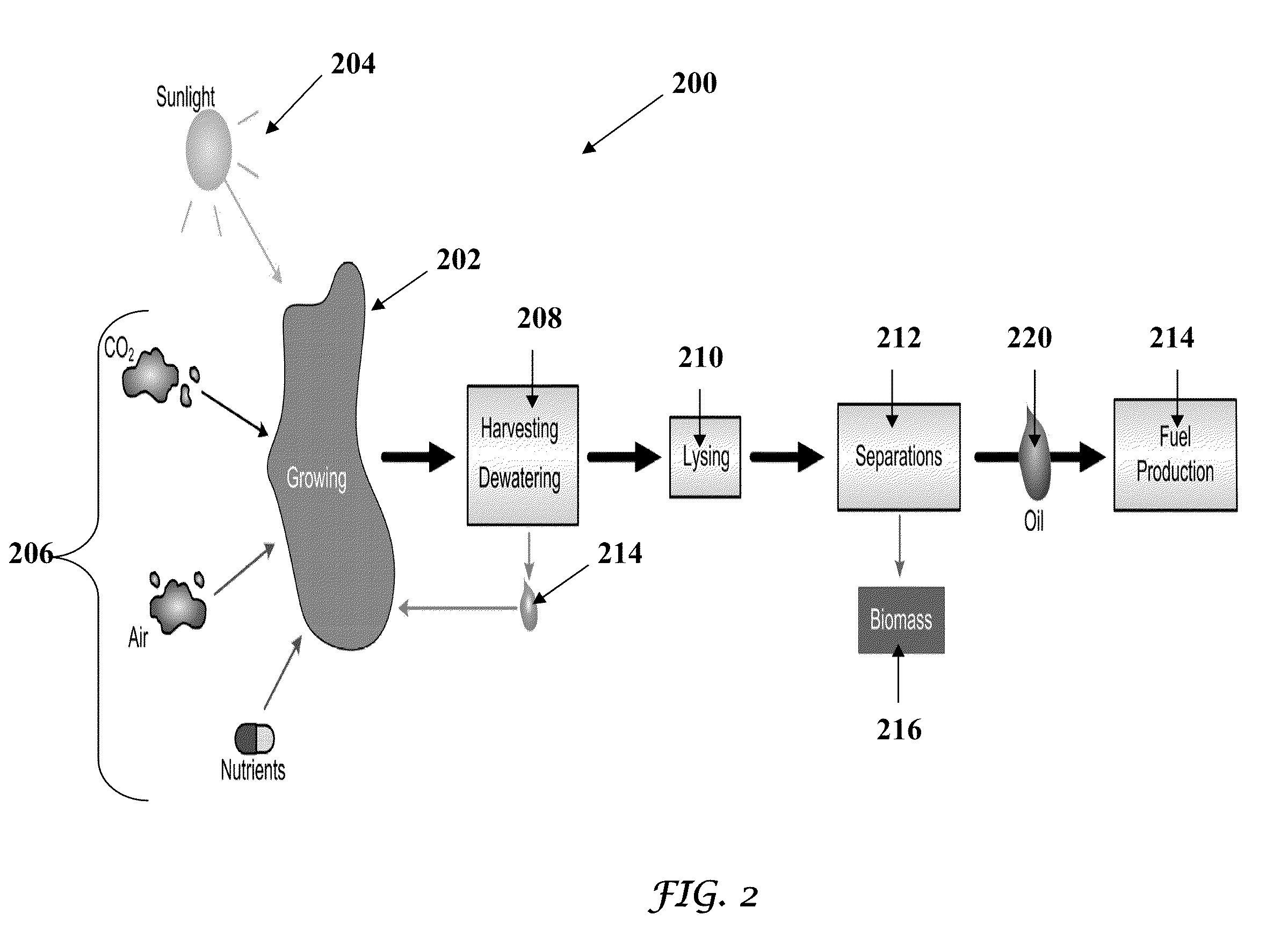
Methods of and Systems for Producing Biofuels
A method for producing biofuels is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids from the algal biomass, and esterifying the neutral lipids with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising carotenoids and omega-3 fatty acids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Composition for the treatment and/or prevention of macular degeneration, method for its manufacture, and its use for treating the eye
Negatively charged phospholipids, as well as compositions including negatively charged phospholipids and possibly carotenoids and / or antioxidants, for treating the eye are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, a composition comprising at least one negatively charged phospholipid except cardiolipin is used to treat age-related macular degeneration. Methods for producing the negatively charged phospholipids, as well as methods for producing the compositions including negatively charged phospholipids and possibly carotenoids and / or antioxidants for treating age-related macular degeneration, are also disclosed.
Owner:MULTIGENE BIOTECH
Method for producing docosahexenoic acid by fermenting schizochytrium
ActiveCN101519676AIncrease productionYield securityMicroorganism based processesFermentationDiseaseBeta-Carotene
The invention relates to a method for producing triglyceride type docosahexenoic acid fat by industrially fermenting schizochytrium. The method comprises the following step: the docosahexenoic acid fat is prepared by fermenting the schizochytrium taken as the strain with the a culture medium with microelements; wherein the culture medium with the microelements comprises a carbon source, a nitrogen source, inorganic salt and microelements, and the microelements comprise at least one of biotin, chlorophyll, beta-carotene, vitaminB1, vitaminB6 and vitaminB12. The prepared docosahexenoic acid fat does not need to be further chemically modified and can be directly used by people needing DHA, including infants, pregnant women, breast feeding women or patients who suffer from diseases due to insufficient DHA and need to supplement DHA. The invention has the advantages of high DHA content, high purity, safe and reliable quality, low production cost, stable production and almost no EPA; and the environmental-friendly, safe and high-content triglyceride type DHA fat can be produced with low cost at a large scale.
Owner:湖北福星生物科技有限公司
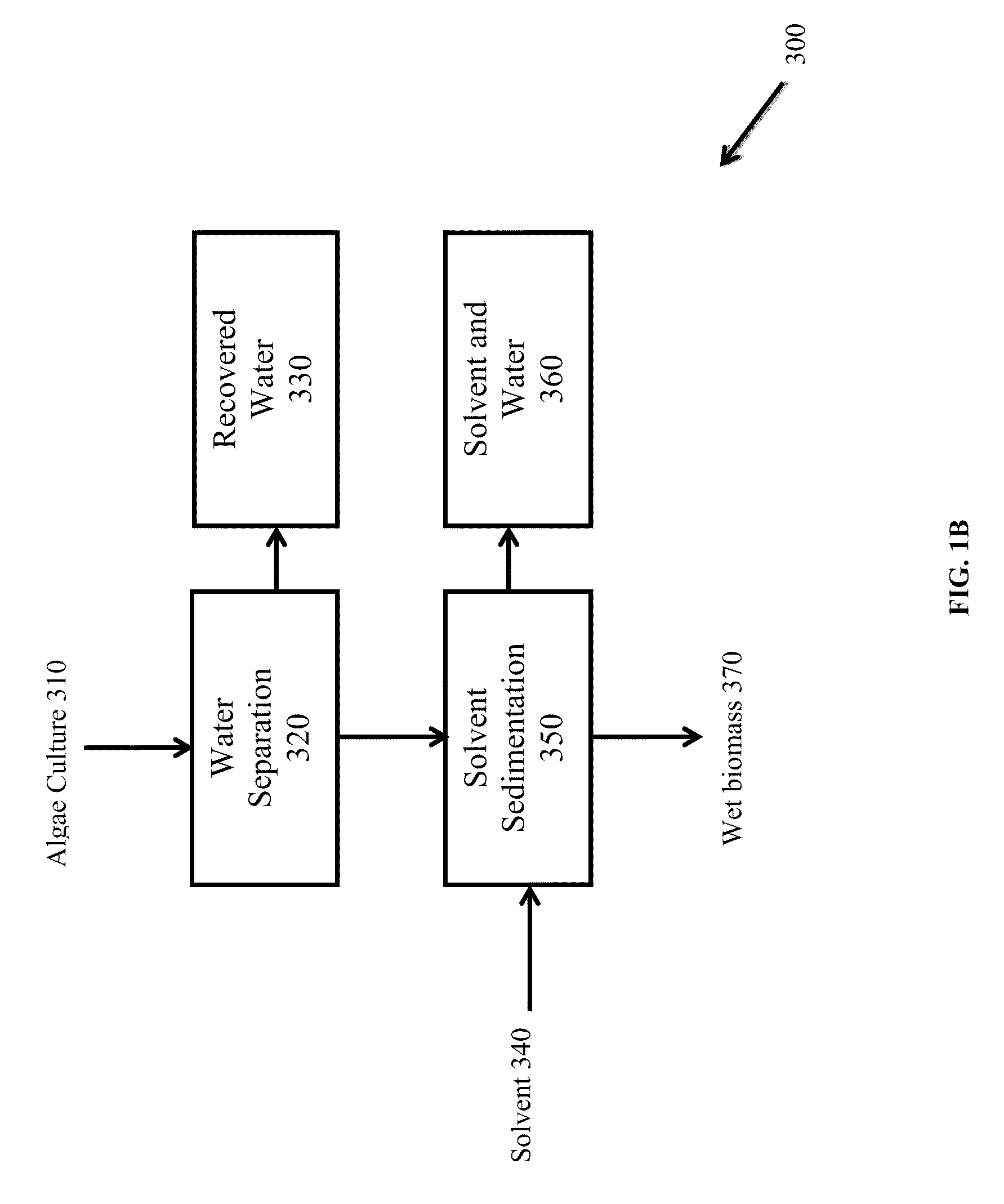
Methods of and Systems for Isolating Nutraceutical Products from Algae
A method of isolating nutraceuticals products from algae is provided. A method of isolating carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil from algae includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass and adding a first ethanol fraction to the algal biomass. The method also includes separating a first substantially solid biomass fraction from a first substantially liquid fraction comprising proteins and combining the first substantially solid biomass fraction with a second ethanol fraction. The method further includes separating a second substantially solid biomass fraction from a second substantially liquid fraction comprising polar lipids and combining the second substantially solid biomass fraction with a third ethanol solvent fraction. The method also includes separating a third substantially solid biomass fraction from a third substantially liquid fraction comprising neutral lipids, wherein the third substantially solid biomass fraction comprises carbohydrates and separating the neutral lipids into carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Ocular formulations with neuroprotectants to reduce Alzheimer and neurotoxic risks created by large zinc dosages
InactiveUS20060039954A1Reduce riskIncreased riskBiocideInorganic active ingredientsBeta-CaroteneClinical trial
Formulations marketed to elderly consumers for preventing or treating age-related eye diseases such as macular degeneration are modified in various four ways, compared to the formulations tested in the first “Age-Related Eye Disease Study” (AREDS-1) clinical trial. Zinc dosages are substabtially reduced, to reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease and other neurotoxic damage in the brains of elderly people, and zeaxanthin is substituted for a substantial portion of any beta-carotene. Additional useful agents are also disclosed.
Owner:GIERHART DENNIS L +2
Method and composition for using organic, plant-derived, oil-extracted materials in resid fuel additives for reduced emissions
InactiveUS7141083B2Reduce pollutant emissionsAvoid equipmentSolid fuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCombustionEngineering
A resid fuel additive is provided that includes a plant oil extract, β-carotene, and jojoba oil. The additive may be added to any resid fuel to reduce emissions of undesired components during combustion of the fuel. A method for preparing the additive is also provided.
Owner:AQ
Methods of producing biofuels, chlorophylls and carotenoids
InactiveUS8115022B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationWater insolubleBiofuel
A method for producing biofuels along with valuable food and neutraceutical products is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids along with carotenoids and chlorophylls from the algal biomass, and separation of the carotenoids and chlorophylls using adsorption or membrane diafiltration or other methods. The remaining neutral lipids are esterified with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising omega-3 fatty acids esters and remaining carotenoids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Methods of and systems for isolating nutraceutical products from algae
A method of isolating nutraceuticals products from algae is provided. A method of isolating carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil from algae includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass and adding a first ethanol fraction to the algal biomass. The method also includes separating a first substantially solid biomass fraction from a first substantially liquid fraction comprising proteins and combining the first substantially solid biomass fraction with a second ethanol fraction. The method further includes separating a second substantially solid biomass fraction from a second substantially liquid fraction comprising polar lipids and combining the second substantially solid biomass fraction with a third ethanol solvent fraction. The method also includes separating a third substantially solid biomass fraction from a third substantially liquid fraction comprising neutral lipids, wherein the third substantially solid biomass fraction comprises carbohydrates and separating the neutral lipids into carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
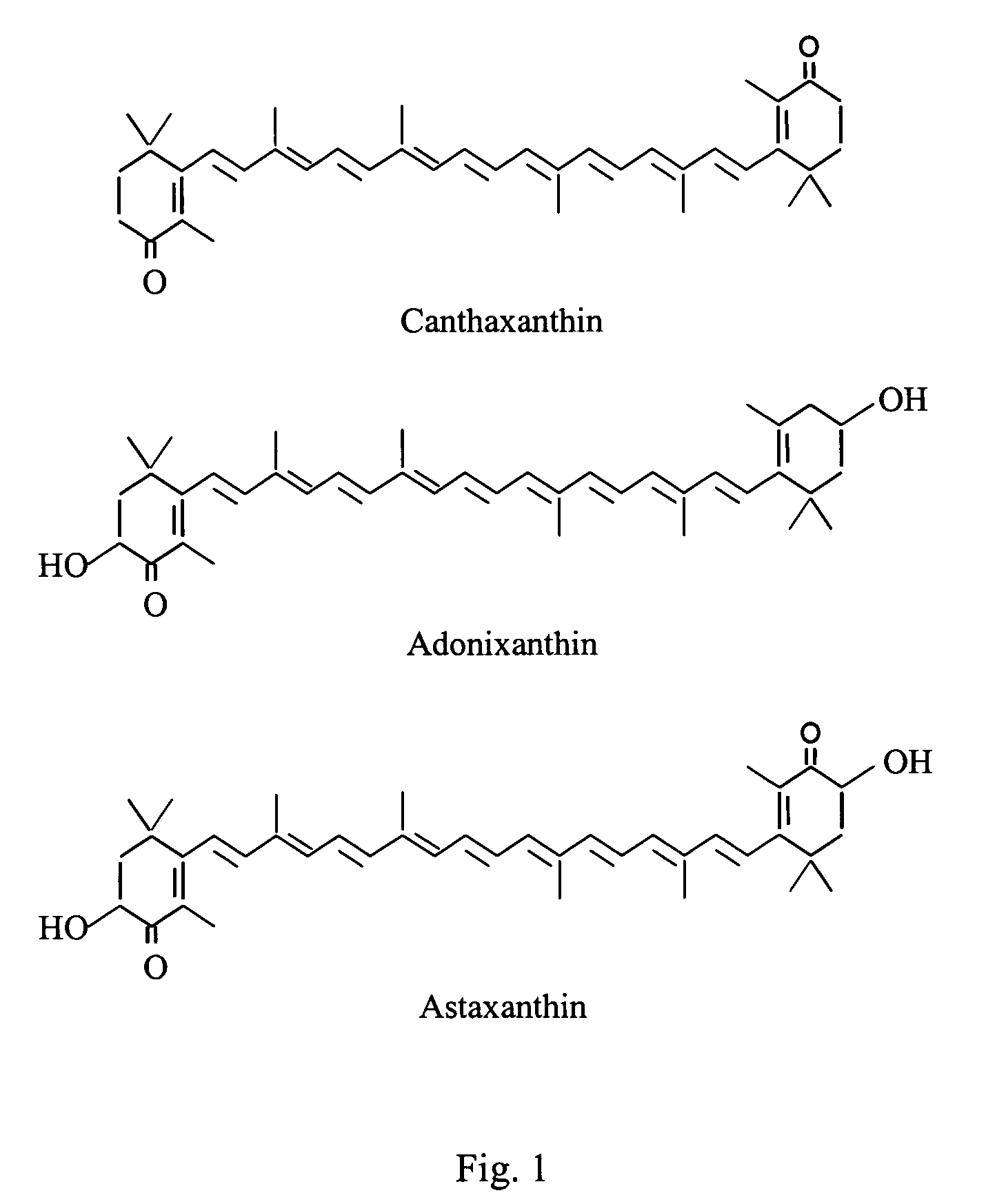
Method for retarding and ameliorating fever blisters and canker sores
Astaxanthin is a potent antioxidant, over 500 times more powerful than Vitamin E and 10 times stronger than other carotenoids such as zeaxanthin, lutein, canthaxanthin and beta-carotene. Astaxanthin has also been shown to enhance and modulate the immune system and diminish the damaging effects of UVA sunlight. Disclosed is a method for retarding and ameliorating fever blisters (cold sores) and canker sores. The method comprises administering a source of astaxanthin in a therapeutically effective amount to prevent, retard and ameliorate fever blisters and canker sores. The astaxanthin may be administered orally, topically, or in a combination of oral and topical dosage.
Owner:CYANOTECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com