Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1494results about "Oxygen-containing compound preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
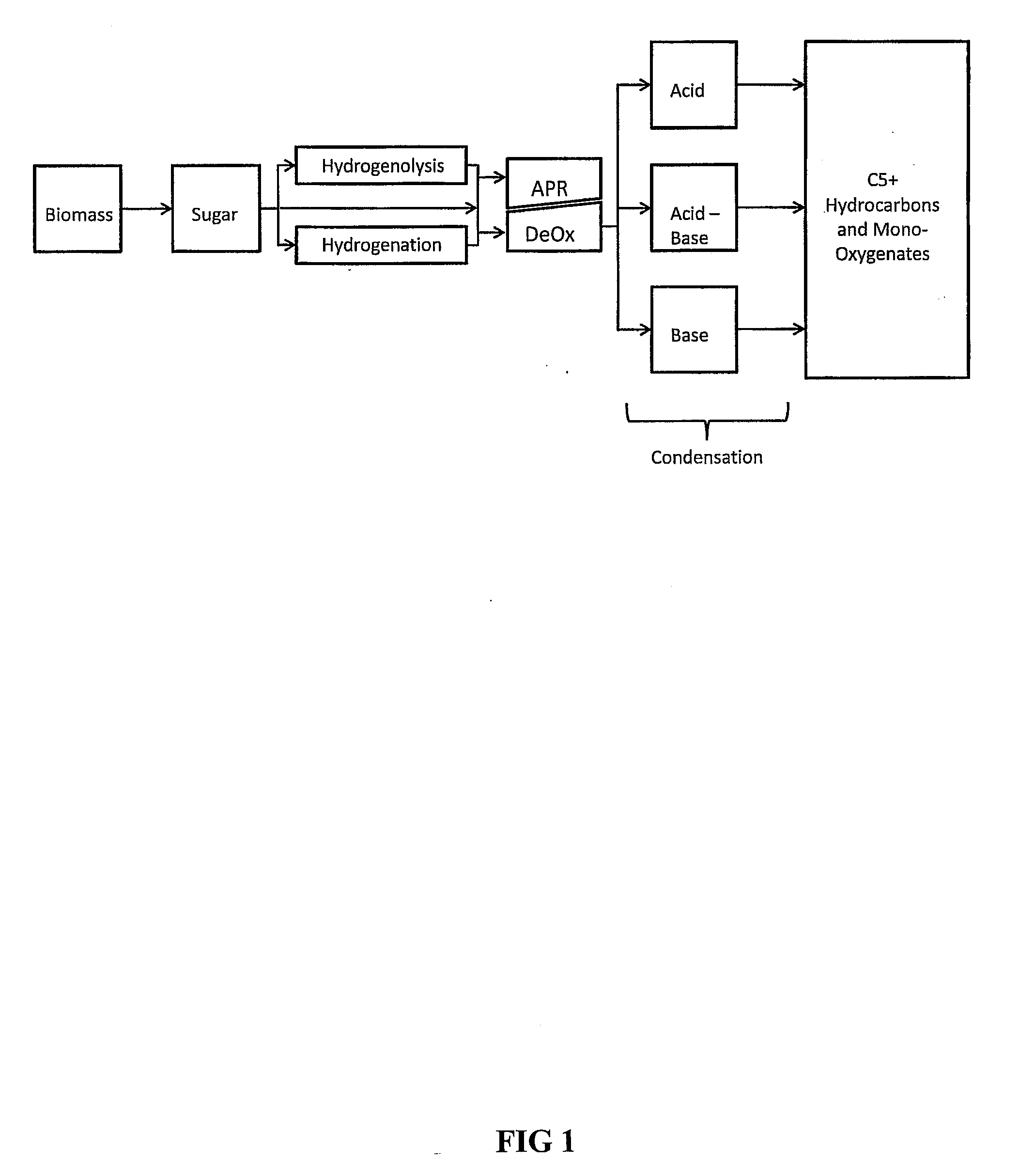
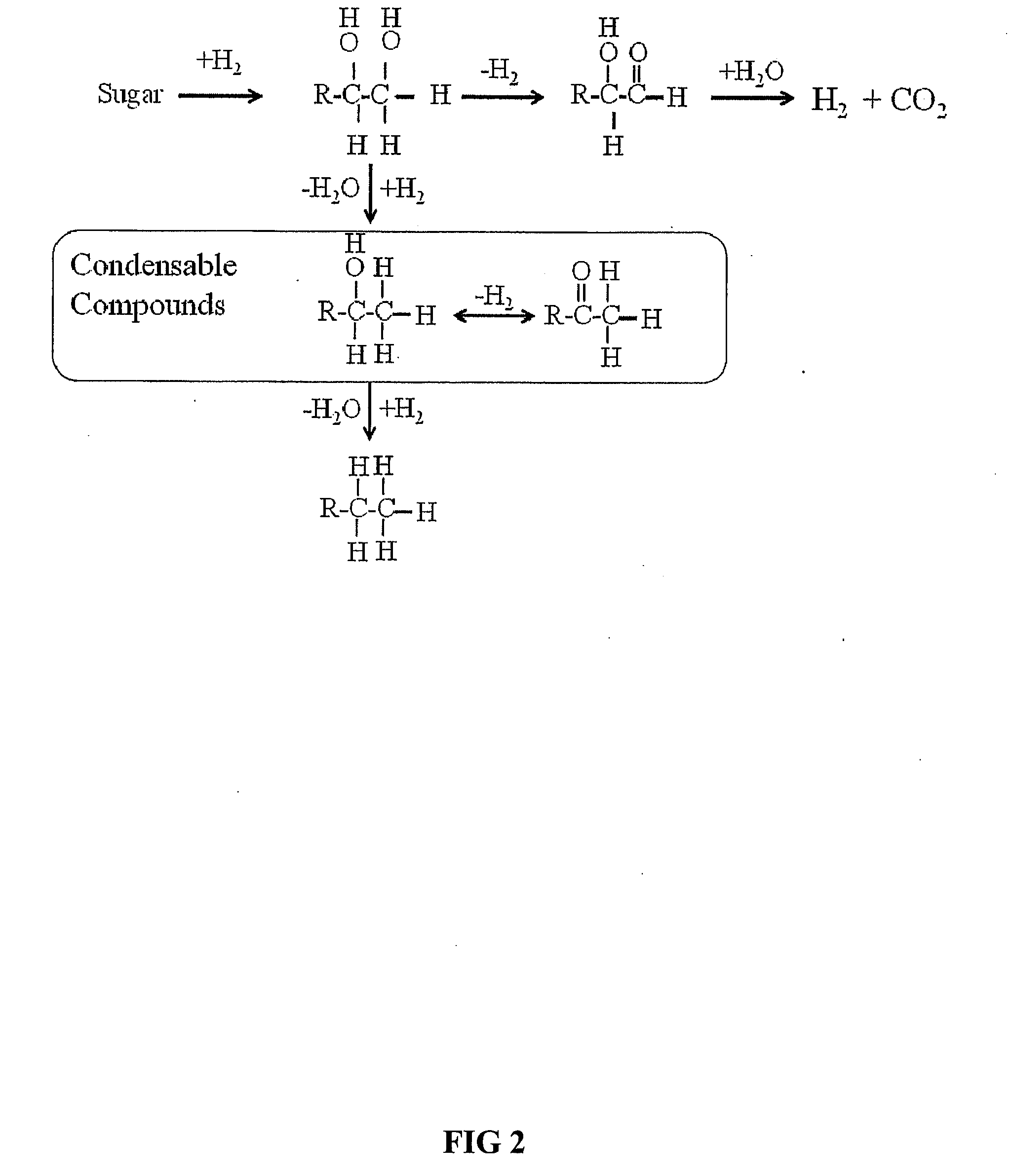
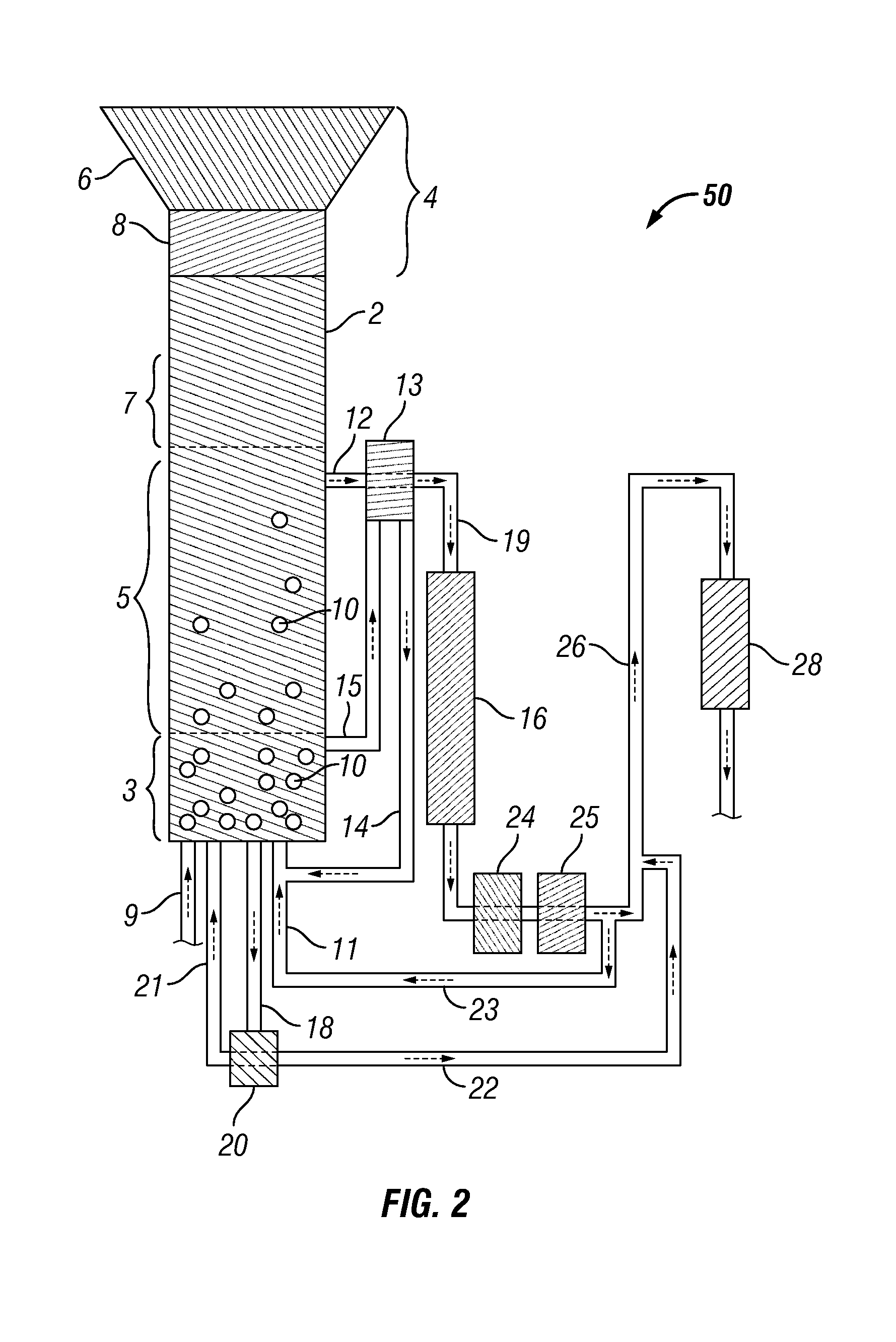
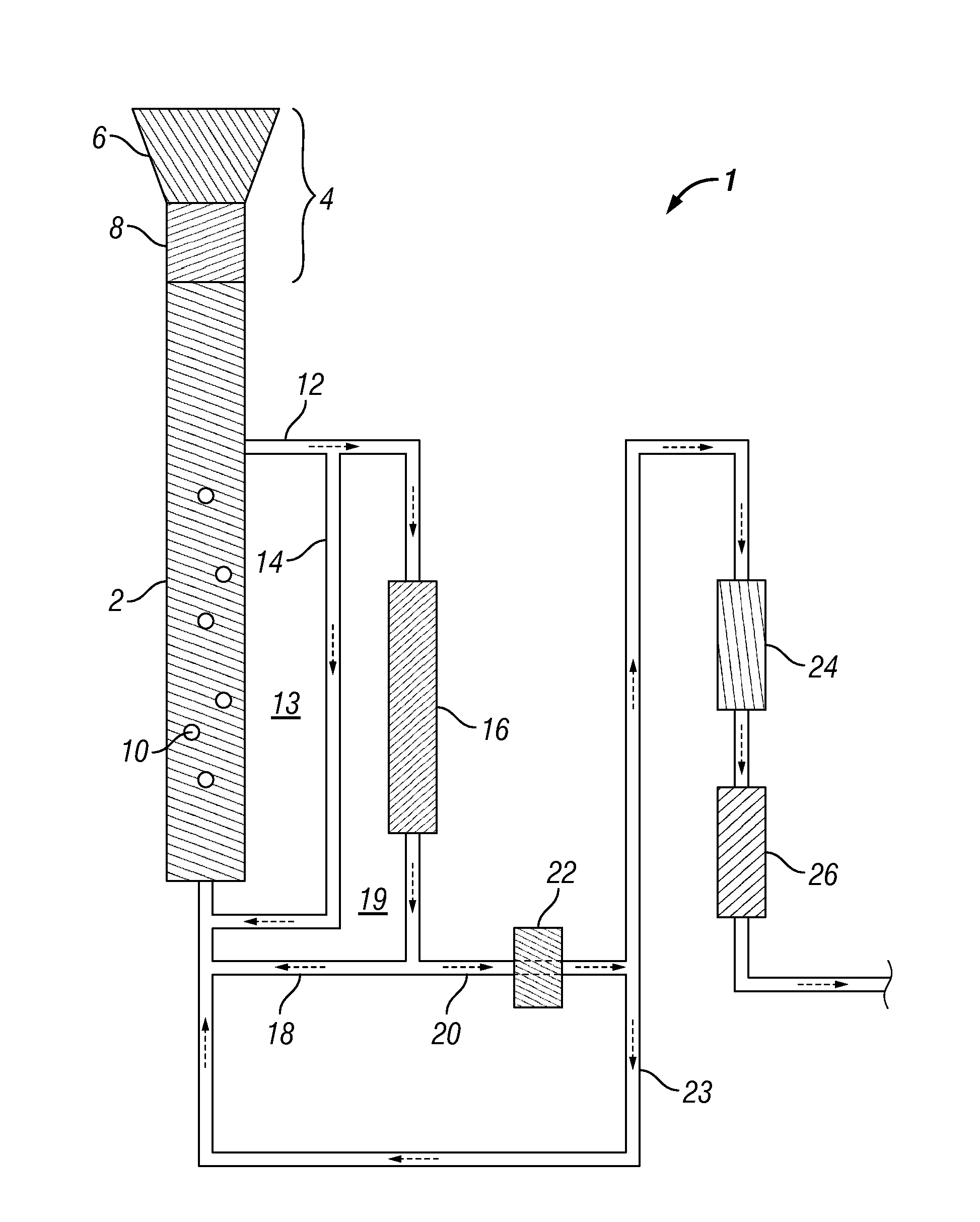
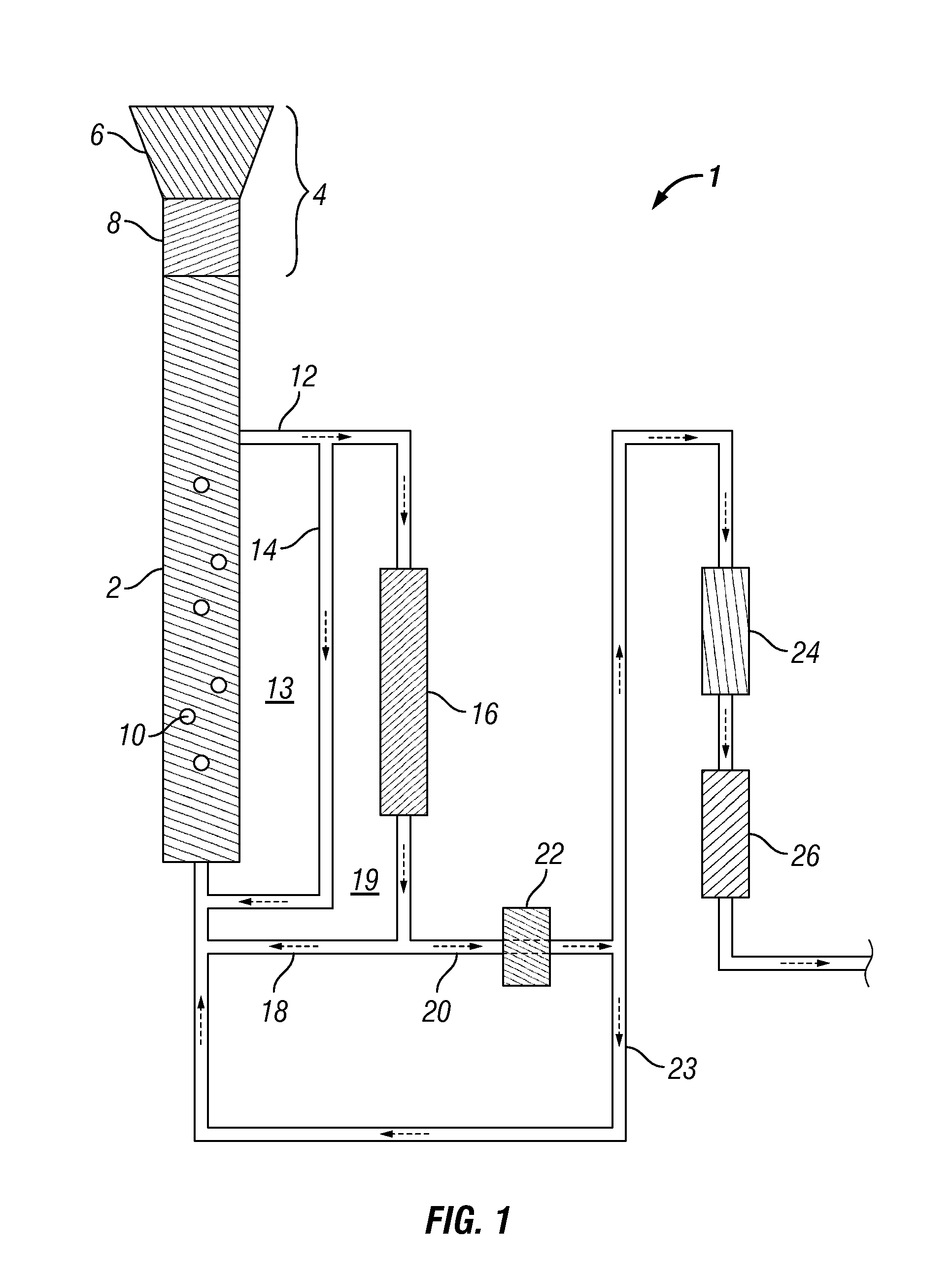
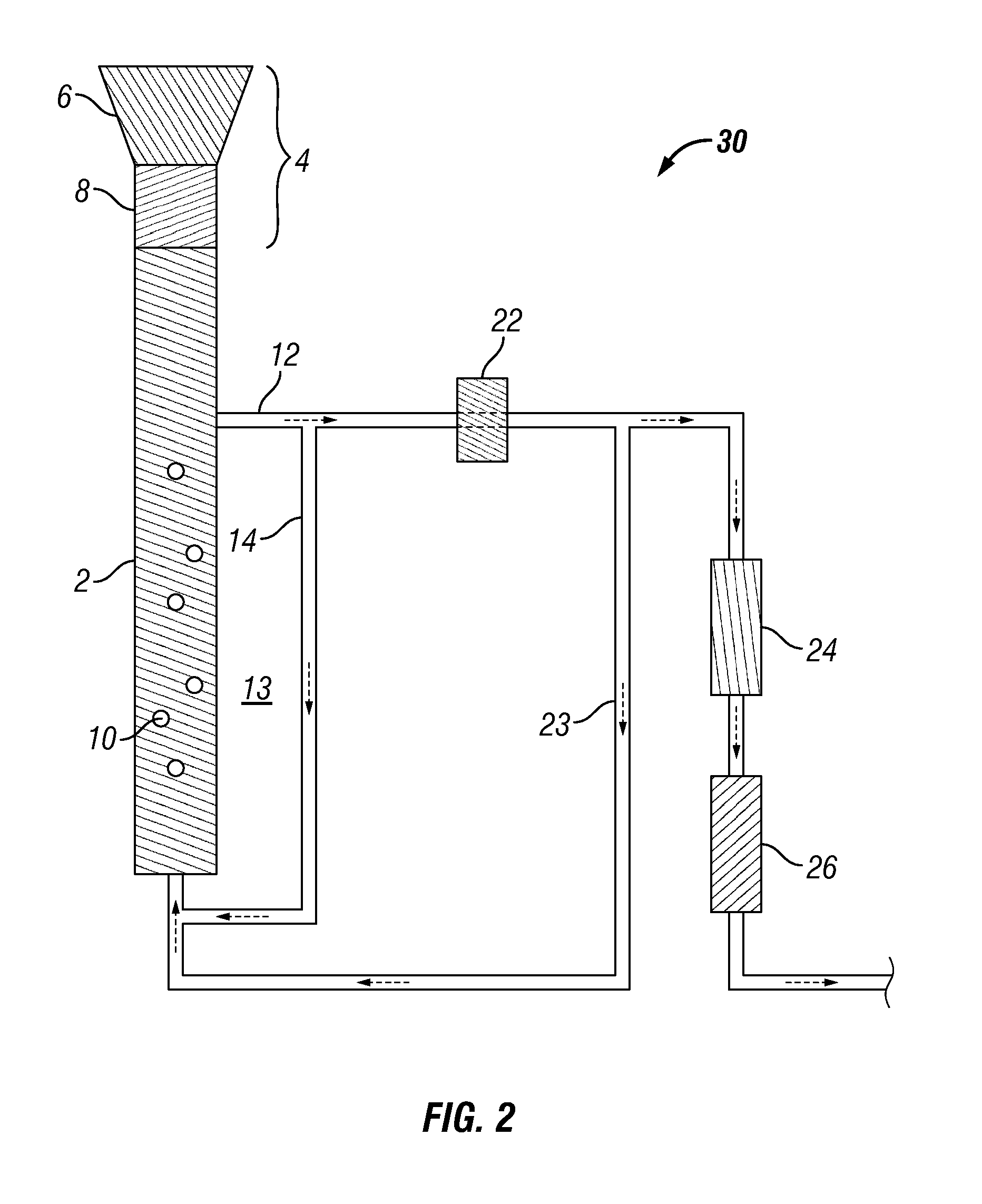
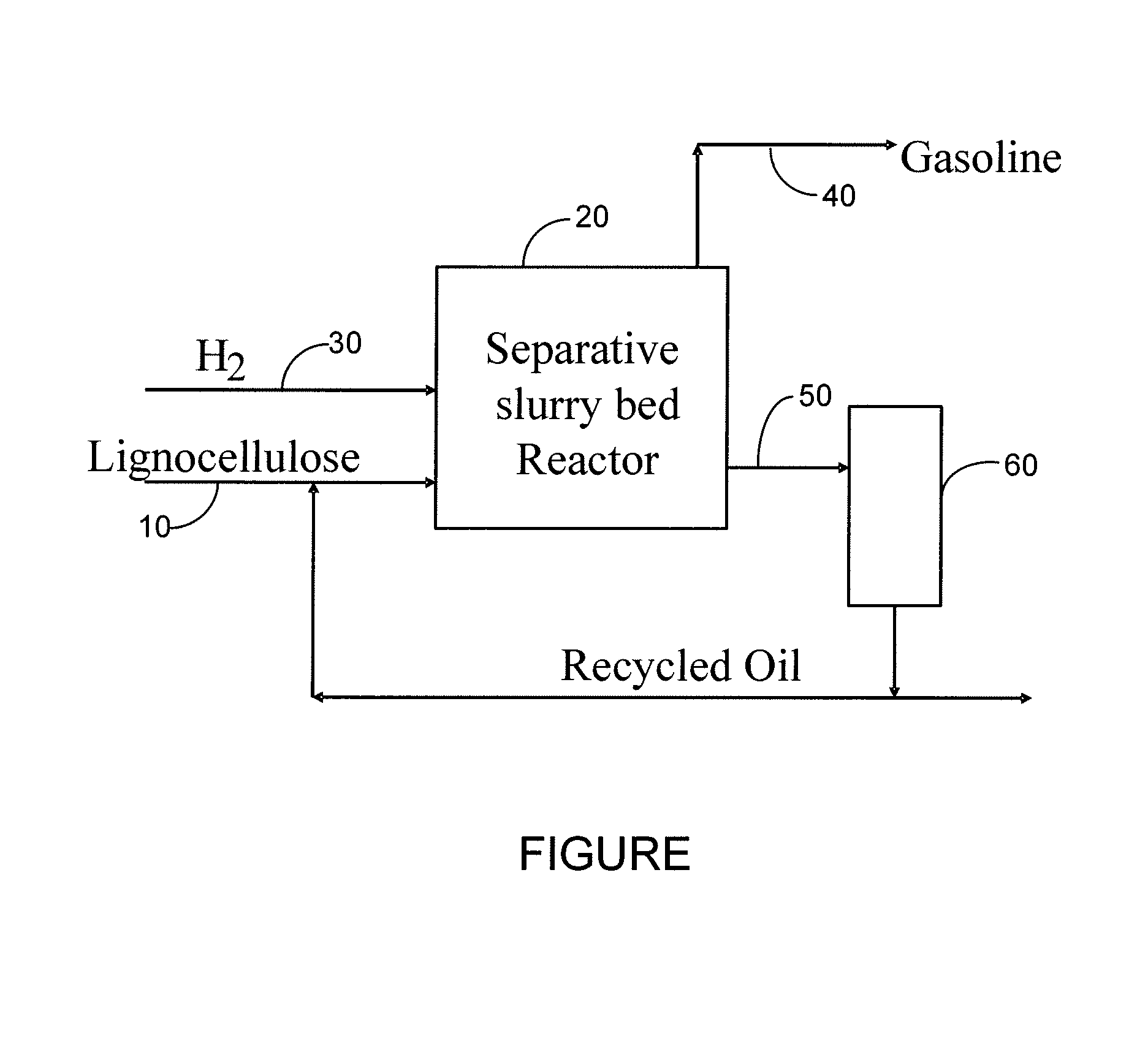
Synthesis of liquid fuels and chemicals from oxygenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080300435A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionFuranLiquid fuel
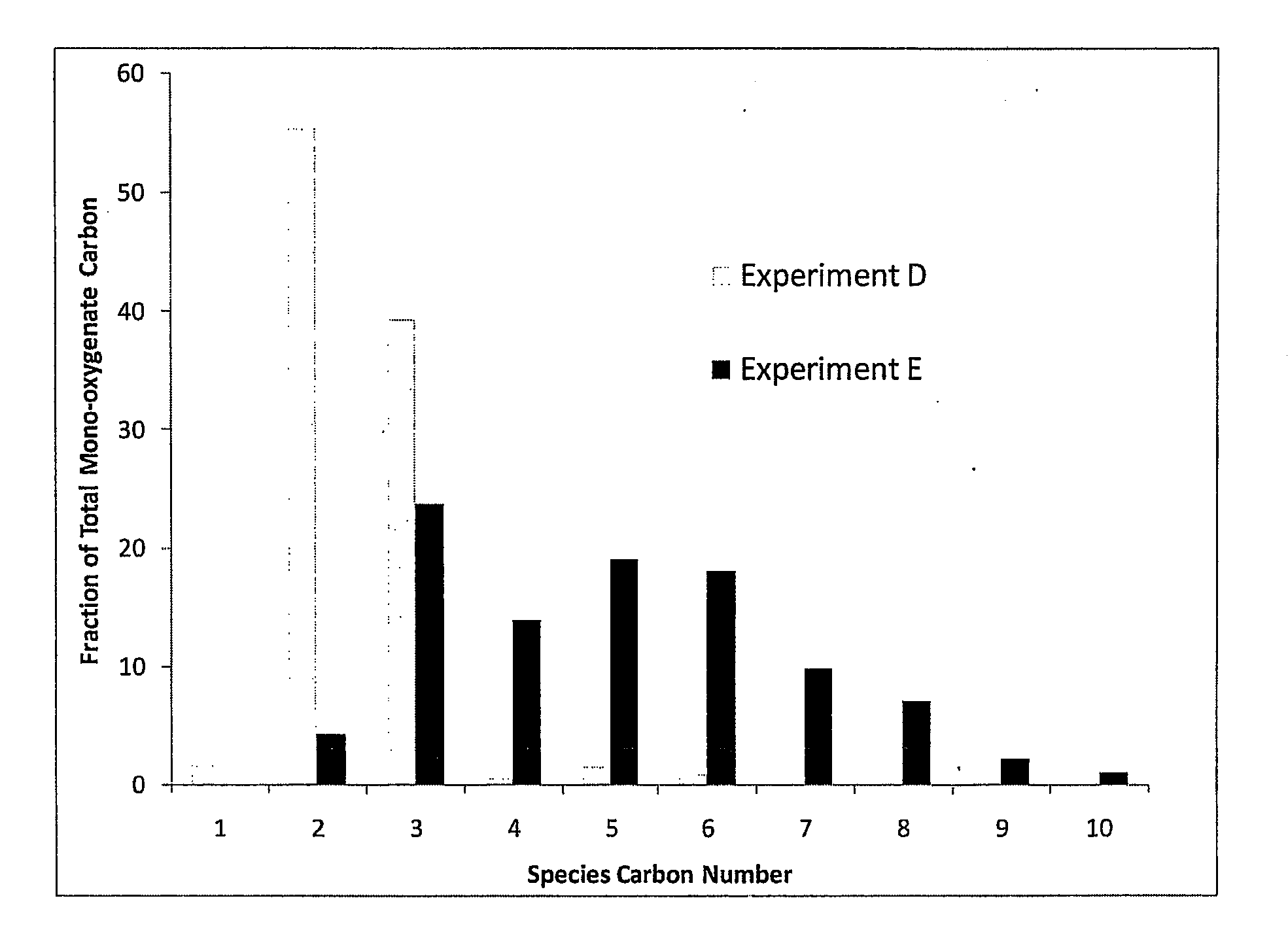
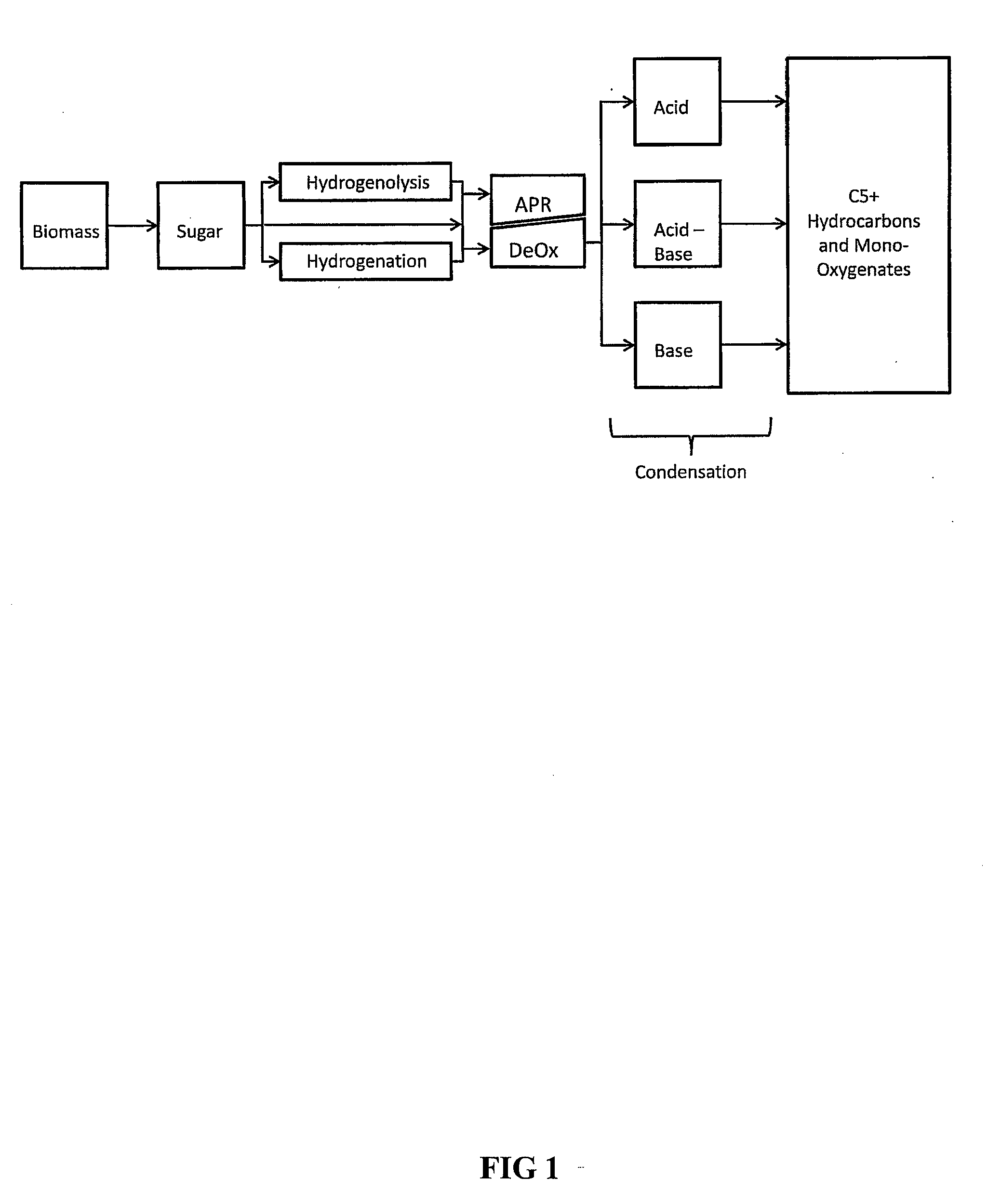
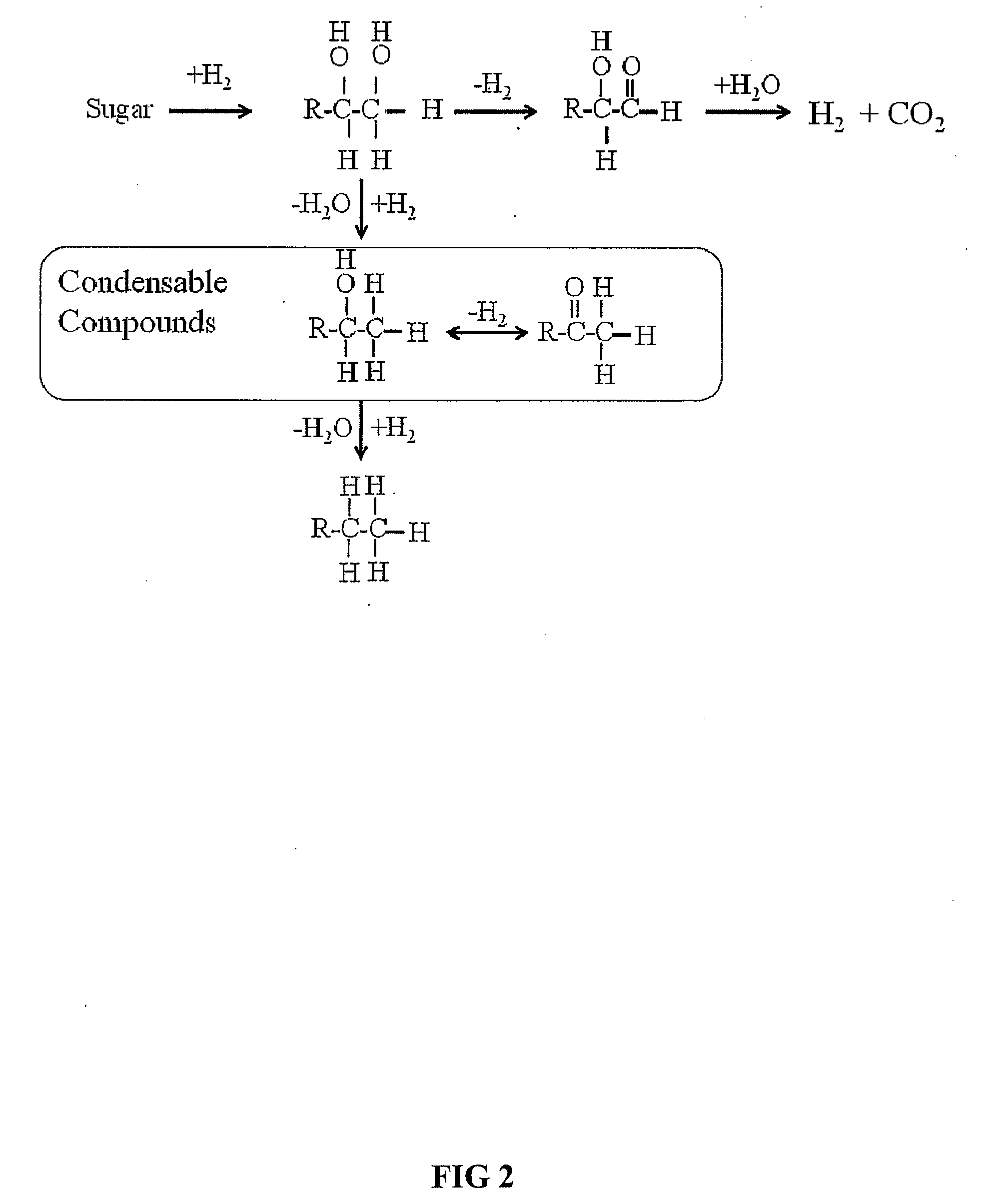
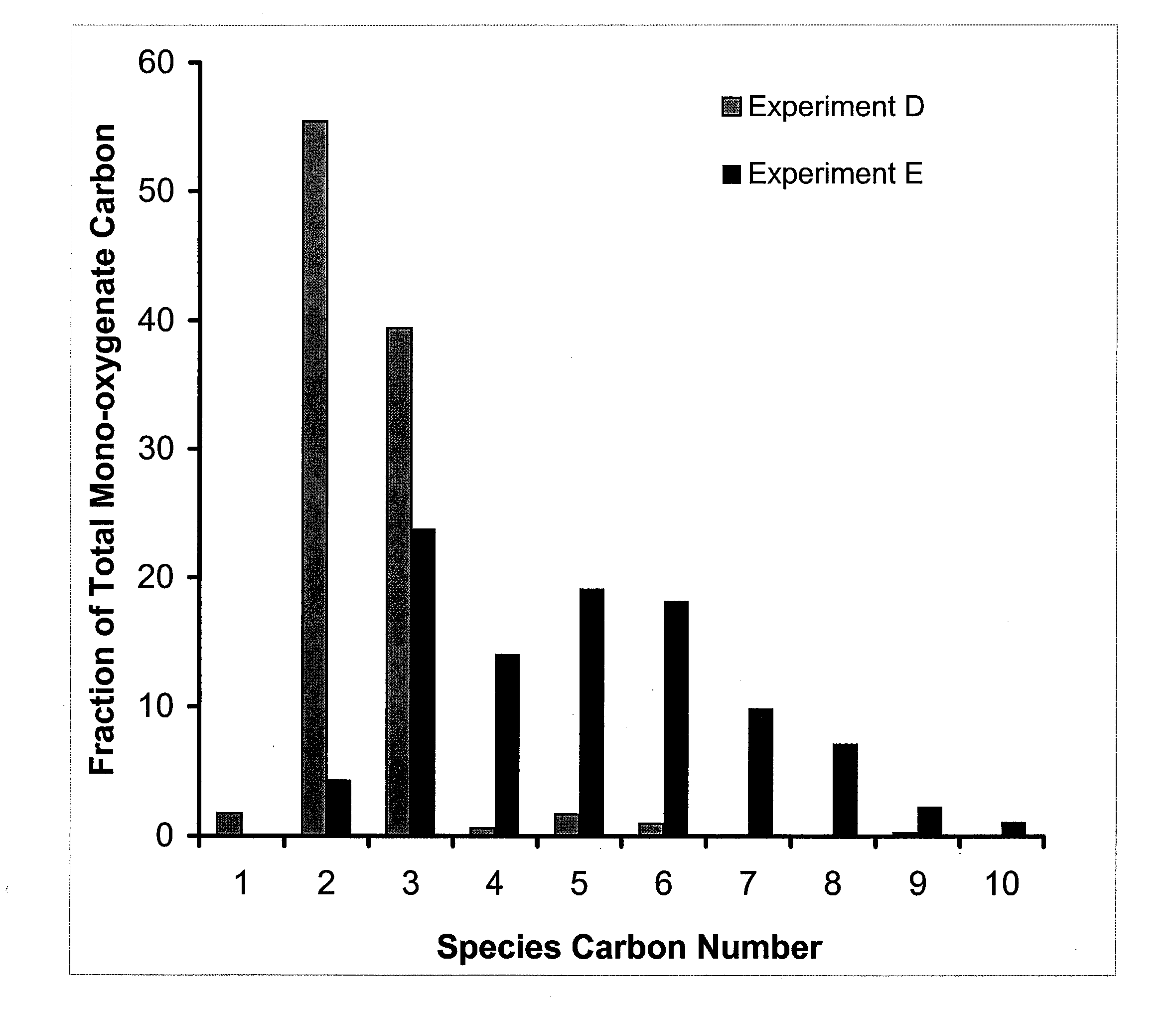
Processes and reactor systems are provided for the conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbons to hydrocarbons, ketones and alcohols useful as liquid fuels, such as gasoline, jet fuel or diesel fuel, and industrial chemicals. The process involves the conversion of mono-oxygenated hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, furans, carboxylic acids, diols, triols, and / or other polyols, to C4+ hydrocarbons, alcohols and / or ketones, by condensation. The oxygenated hydrocarbons may originate from any source, but are preferably derived from biomass.
Owner:VIRENT
Synthesis of liqiud fuels and chemicals from oxygenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080300434A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationHydrocarbon purification/separationFuranCarboxylic acid
Processes and reactor systems are provided for the conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbons to hydrocarbons, ketones and alcohols useful as liquid fuels, such as gasoline, jet fuel or diesel fuel, and industrial chemicals. The process involves the conversion of mono-oxygenated hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, furans, carboxylic acids, diols, triols, and / or other polyols, to C4+ hydrocarbons, alcohols and / or ketones, by condensation. The oxygenated hydrocarbons may originate from any source, but are preferably derived from biomass.
Owner:VIRENT
Integrate chemical processes for industrial utilization of seed oils
ActiveUS20050154221A1Easy to operateHigh olefin conversionFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOxygen-containing compound preparationPolyesterAmino esters
Integrated processes of preparing industrial chemicals starting from seed oil feedstock compositions containing one or more unsaturated fatty acids or unsaturated fatty acid esters, which are essentially free of metathesis catalyst poisons, particularly hydroperoxides; metathesis of the feedstock composition with a lower olefin, such as ethylene, to form a reduced chain olefin, preferably, a reduced chain α-olefin, and a reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester, preferably, a reduced chain α,Ω-unsaturated acid or ester. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be (trans)esterified to form a polyester polyolefin, which may be epoxidized to form a polyester polyepoxide. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reduction to produce an α,Ω-hydroxy acid or α,Ω-hydroxy ester, which may be (trans)esterified with a polyol to form an α,Ωpolyester polyol. Alternatively, the reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reductive amination to produce an α,Ω-amino acid or α,Ω-amino ester, which may be (trans)esterified to form an α,Ωpolyester polyamine.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Process for extraction and purification of lutein, zeaxanthin and rare carotenoids from marigold flowers and plants
InactiveUS6262284B1Oxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationBeta-CaroteneBeta-cryptoxanthin
A process for simultaneously extracting, saponifying, and isolating lutein and zeaxanthin, and a mixture of several rare carotenoids in high purity from plants without the use of harmful organic solvents. Lutein crystals containing 5% zeaxanthin were obtained from the dried petals of Marigold flowers Tagete erecla while zeaxanthin was isolated and purified from the berries of Lycium Chinese Mill (LCM berries). Similarly, this process has been employed to isolate and purify a mixture of lutein, beta-carotene, neoxanthin, violaxanthin, and lutein epoxide from green plants, preferably, kale, collard green, and spinach. These plants, to a lesser extent, also serve as a source of several rare carotenoids such as alpha-cryptoxanthin (Marigolds) and beta-cryptoxanthin (LCM berries). The purified carotenoids isolated by this process are free from impurities and serve as a safe source of nutritional supplement for human consumption as well as providing a suitable and effective color additive for human foods.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
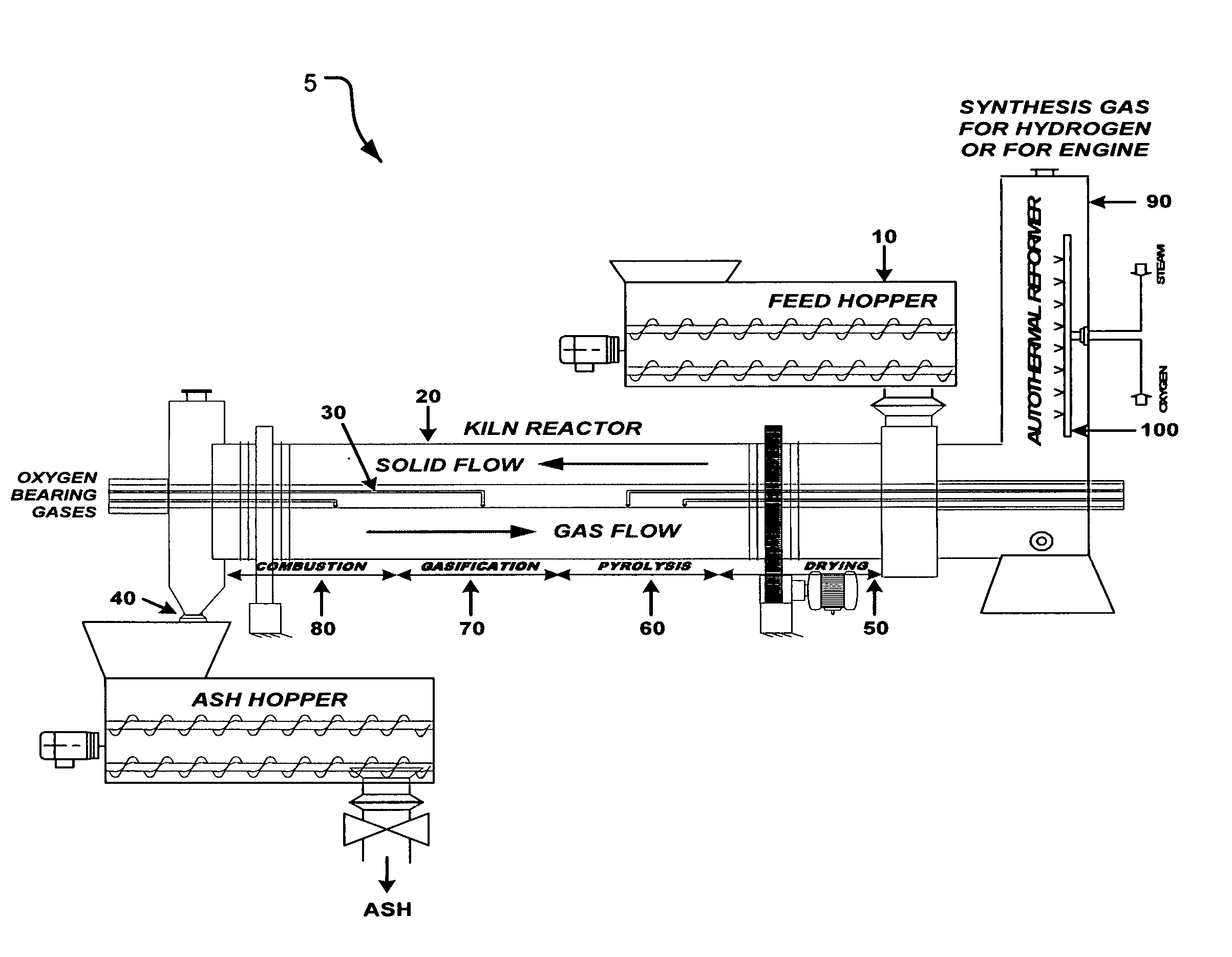
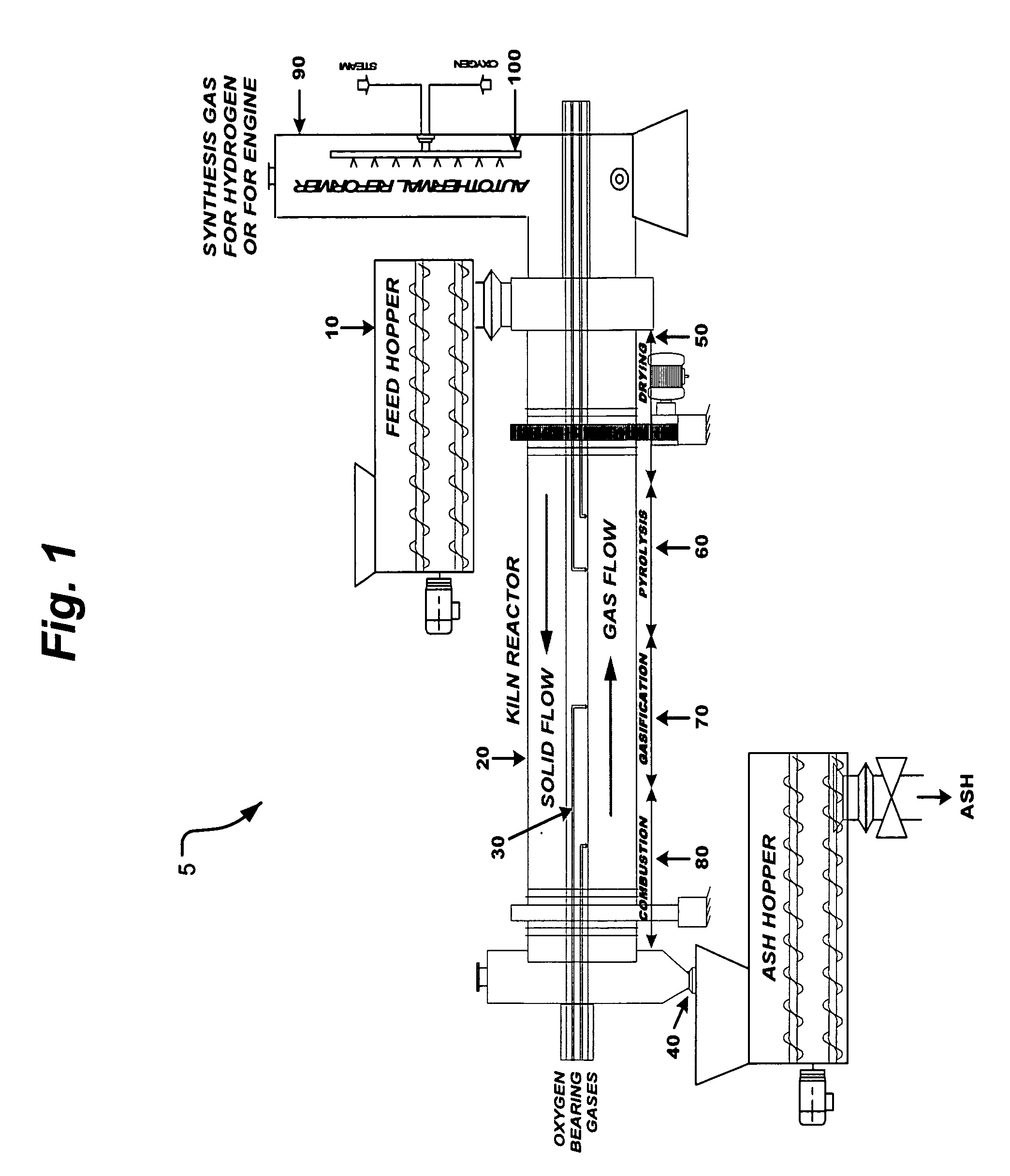
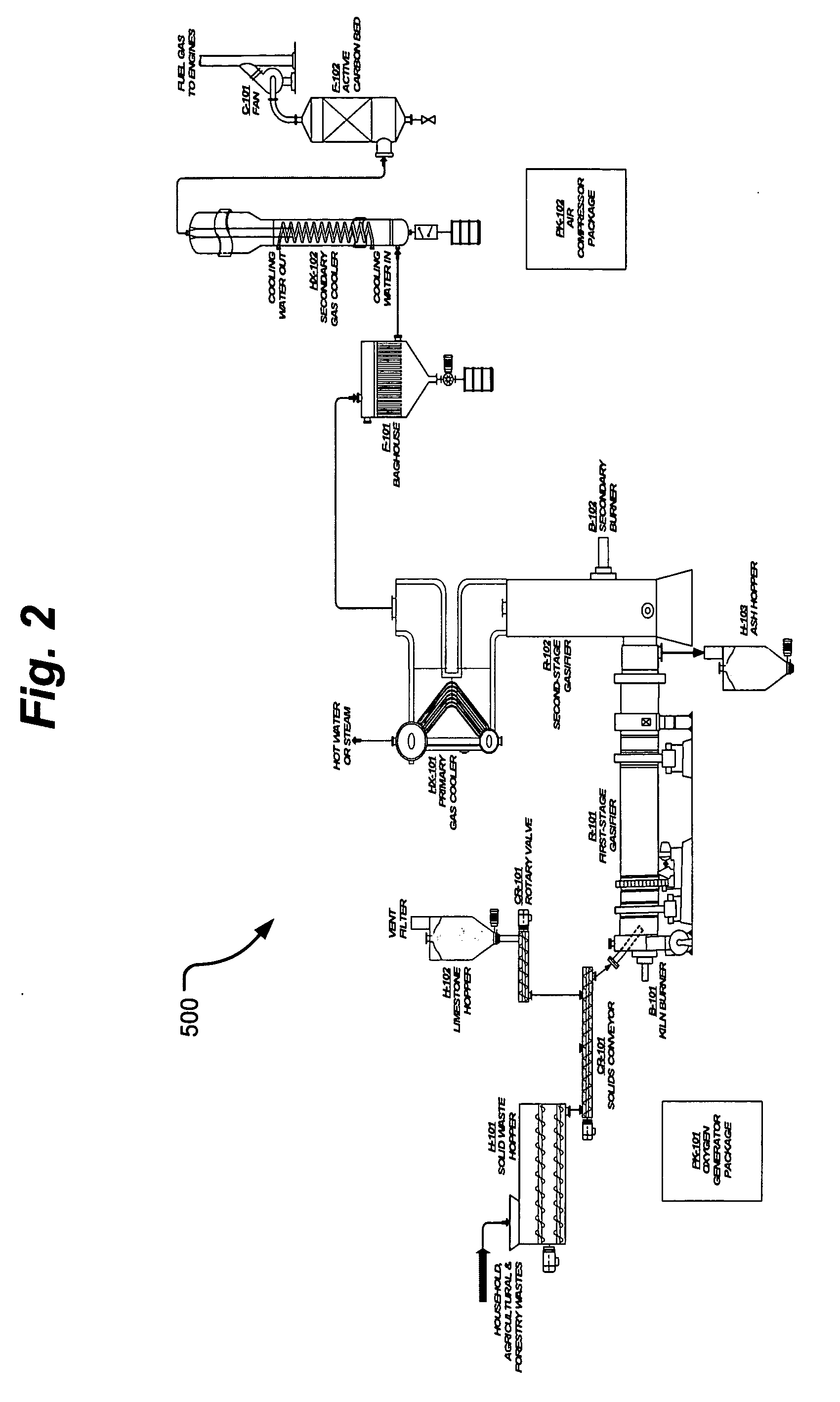
Process and apparatus for biomass gasification
InactiveUS20050095183A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationGasifier mechanical detailsForming gasTar
A waste-to-synthesis gas system including: a first gasifier for receiving biomass; a gas distributor for delivering reactant gas and oxygen into the first gasifier in a countercurrent direction to the biomass flow and to define a plurality of reaction regions including a drying region, a pyrolysis region, a gasification region and a combustion region; and, a second gasifier for receiving gases from the plurality of regions of the first gasifier and a gas distributor for delivering reactant gas and oxygen into the second gasifier in a concurrent direction to the flow of gases from the first gasifier. As a result, no carbon chars, oils or tars are expected to be present in the synthesis gas produced.
Owner:BIOMASS ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Specific Branched Aldehydes, Alcohols, Surfactants, and Consumer Products Based Thereon
ActiveUS20100137649A1Promote degradationImprove solubilityOxygen-containing compound preparationPreparation by oxo-reaction and reductionHydrogenAlcohol
A process for preparing a detergent alcohol mixture comprising the steps of providing one or more poly-branched poly-olefins, wherein the poly-branched poly-olefins must contain one non-branched terminal olefin and one or more additional branched olefins in the molecule; hydroformylating said poly-branched poly-olefins to produce a poly-branched olefin containing aldehyde product with one or more olefins or mixture thereof; reducing the aldehyde product of step (b) in the presence of hydrogen and a hydrogenation catalyst to form a poly-branched detergent alcohol mixture; and removing said poly-branched alcohol mixture from said catalyst and branched aldehydes, alcohols and surfactants produced from the products of this process.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Process for co-production of dialkyl carbonate and alkanediol
InactiveUS6207850B1Excellent regenerabilityImprove stabilityOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationCarbonateMetal
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
Method of installing an epoxidation catalyst in a reactor, a method of preparing an epoxidation catalyst, an epoxidation catalyst, a process for the preparation of an olefin oxide or a chemical derivable from an olefin oxide, and a reactor suitables for such a process
InactiveUS20070197801A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationCompound (substance)Alkene
The present invention relates to an improved epoxidation process and an improved epoxidation reactor. The present invention makes use of a reactor which comprises a plurality of microchannels. Such process microchannels may be adapted such that the epoxidation and optionally other processes can take place in the microchannels and that they are in a heat exchange relation with channels adapted to contain a heat exchange fluid. A reactor comprising such process microchannels is referred to as a “microchannel reactor”. The invention also provides a method of installing an epoxidation catalyst in a microchannel reactor. The invention also provides a method of preparing an epoxidation catalyst. The invention also provides an epoxidation catalyst. The invention also provides a certain process for the epoxidation of an olefin and a process for the preparation of a chemical derivable from an olefin oxide. The invention also provides a microchannel reactor.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Process for the synthesis of unsaturated alcohols
ActiveUS7176336B2Increase the number ofIncrease productionOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationPolymer scienceDecene
A process of preparing an unsaturated alcohol (olefin alcohol), such as, a homo-allylic mono-alcohol or homo-allylic polyol, involving protecting a hydroxy-substituted unsaturated fatty acid or fatty acid ester, such as methyl ricinoleate, derived from a seed oil, to form a hydroxy-protected unsaturated fatty acid or fatty acid ester; homo-metathesizing or cross-metathesizing the hydroxy-protected unsaturated fatty acid or fatty acid ester to produce a product mixture containing a hydroxy-protected unsaturated metathesis product; and deprotecting the hydroxy-protected unsaturated metathesis product under conditions sufficient to prepare the unsaturated alcohol. Preferably, methyl ricinoleate is converted by cross-metathesis or homo-metathesis into the homo-allylic mono-alcohol 1-decene-4-ol or the homo-allylic polyol 9-octadecene-7,12-diol, respectively.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Process for the carbonylation of epoxides
InactiveUS20050014977A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationLanthanideCobalt
The present invention pertains to a process for the carbonylation of an epoxide by reacting it with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst system containing two components, wherein the first component is a source of one or more metals selected from the group consisting of cobalt, ruthenium and rhodium, and the second component is a coordination complex of a tetrapyrrole compound with one or more of the metals belonging to the group consisting of groups IIIA and IIIB of the periodic system, lanthanides and actinides. The present invention also pertains a process for the preparation of a catalyst system.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Hydrodeoxygenation process
A process for producing a hydrocarbon from biomass. A feed stream having free fatty acids, fatty acid esters or combinations thereof is provided. The feed stream is heated in the presence of a first catalyst to produce a partially hydrodeoxygenated stream. The partially hydrodeoxygenated stream is heated in the presence of a second catalyst to produce an effluent stream containing the hydrocarbon.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
Methods and systems for processing lignin during hydrothermal digestion of cellulosic biomass solids
InactiveUS20140121419A1Easy to adaptOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationCelluloseAlcohol
Digestion of cellulosic biomass solids may be complicated by release of lignin therefrom. Methods for digesting cellulosic biomass solids may comprise: providing cellulosic biomass solids in a digestion solvent; at least partially converting the cellulosic biomass solids into a phenolics liquid phase comprising lignin, an aqueous phase comprising an alcoholic component derived from the cellulosic biomass solids, and an optional light organics phase; combining at least the phenolics liquid phase and the aqueous phase with one another, thereby forming a combined phase; and separating at least a portion of the alcoholic component from at least a portion of the combined phase.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Methods for production and processing of a glycol reaction product obtained from hydrothermal digestion of cellulosic biomass solids
InactiveUS20140121420A1Easy to adaptOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationCellulosePtru catalyst
Hydrothermal digestion of cellulosic biomass solids may be conducted such that a glycol reaction product is formed for subsequent processing. Processing of a glycol reaction product may include a drying operation conducted prior to condensation of the glycol reaction product into higher molecular weight compounds. Methods for digesting cellulosic biomass solids to form a glycol reaction product can comprise: providing cellulosic biomass solids and a slurry catalyst in a hydrothermal digestion unit, the slurry catalyst being capable of activating molecular hydrogen; heating the cellulosic biomass solids in the hydrothermal digestion unit in the presence of the slurry catalyst, a digestion solvent, and molecular hydrogen, thereby forming a liquor phase comprising soluble carbohydrates; and performing a first catalytic reduction reaction on the soluble carbohydrates within the hydrothermal digestion unit, thereby at least partially converting the soluble carbohydrates into a reaction product comprising a glycol.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Production of gasoline, diesel, naphthenes and aromatics from lignin and cellulosic waste by one step hydrocracking
ActiveUS20080076945A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationCelluloseNaphtha
A process for the conversion of biomass to a liquid fuel is presented. The process includes the production of diesel and naphtha boiling point range fuels by hydrotreating and hydrocracking of lignin in the biomass in a one step process.
Owner:UOP LLC
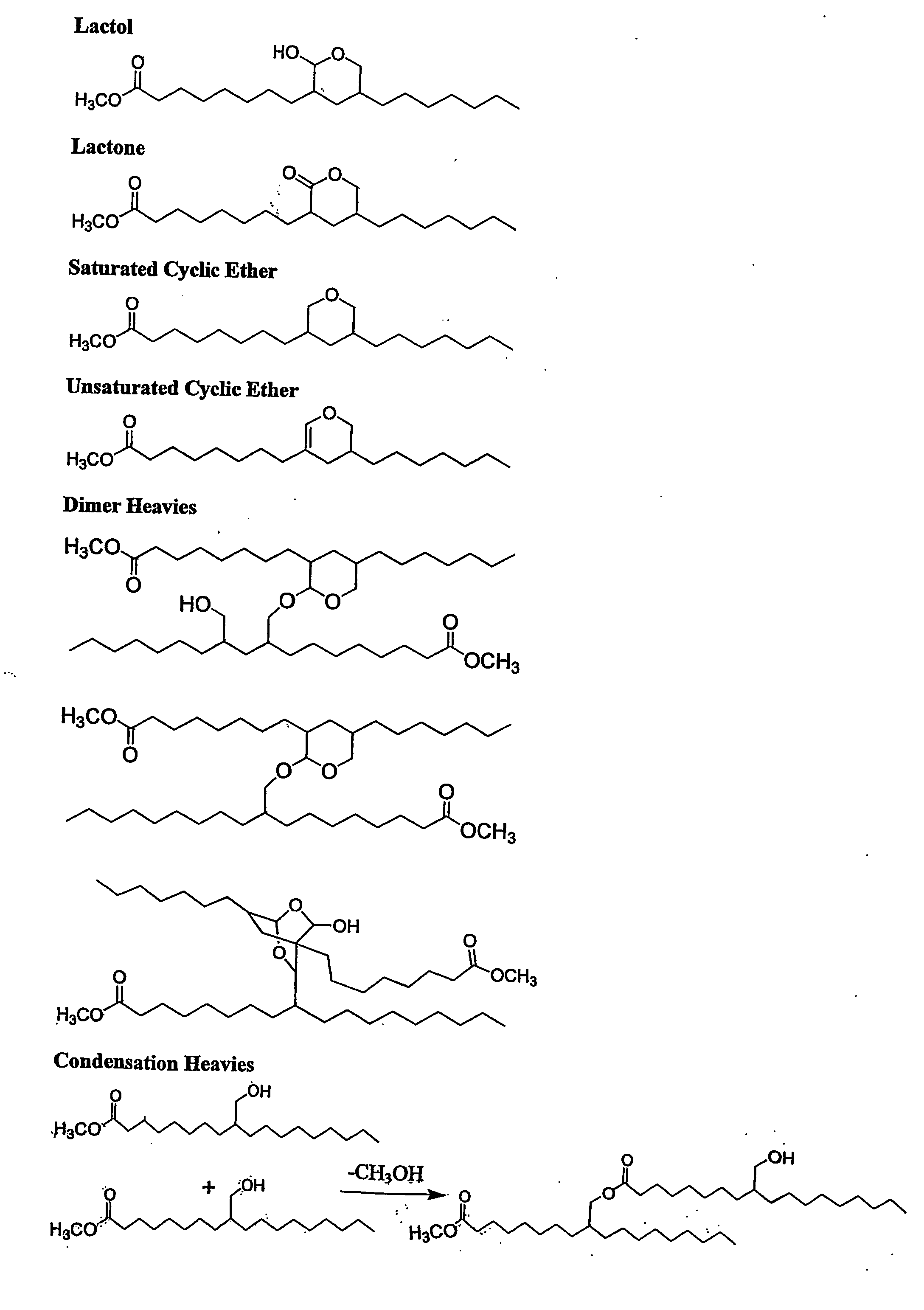
Aldehyde and alcohol compositions derived from seed oils
An aldehyde composition derived by hydroformylation of a transesterified seed oil and containing a mixture of formyl-substituted fatty acids or fatty acid esters having the following composition by weight: greater than about 10 to less than about 95 percent monoformyl, greater than about 1 to less than about 65 percent diformyl, and greater than about 0.1 to less than about 10 percent triformyl-substituted fatty acids or fatty acid esters, and having a diformyl to triformyl weight ratio of greater than about 5 / 1; preferably, greater than about 3 to less than about 20 percent saturates; and preferably, greater than about 1 to less than about 20 percent unsaturates. An alcohol composition derived by hydrogenation of the aforementioned aldehyde composition, containing a mixture of hydroxymethyl-substituted fatty acids or fatty acid esters having the following composition by weight: greater than about 10 to less than about 95 percent monoalcohol {mono(hydroxymethyl)}, greater than about 1 to less than about 65 percent diol {di(hydroxymethyl)}, greater than about 0.1 to less than about 10 percent triol, tri(hydroxmethyl)-substituted fatty acids or fatty acid esters; preferably greater than about 3 to less than about 35 percent saturates; and preferably, less than about 10 percent unsaturates. The alcohol composition can be converted into an oligomeric polyol for use in the manufacture of polyurethane slab stock flexible foams.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
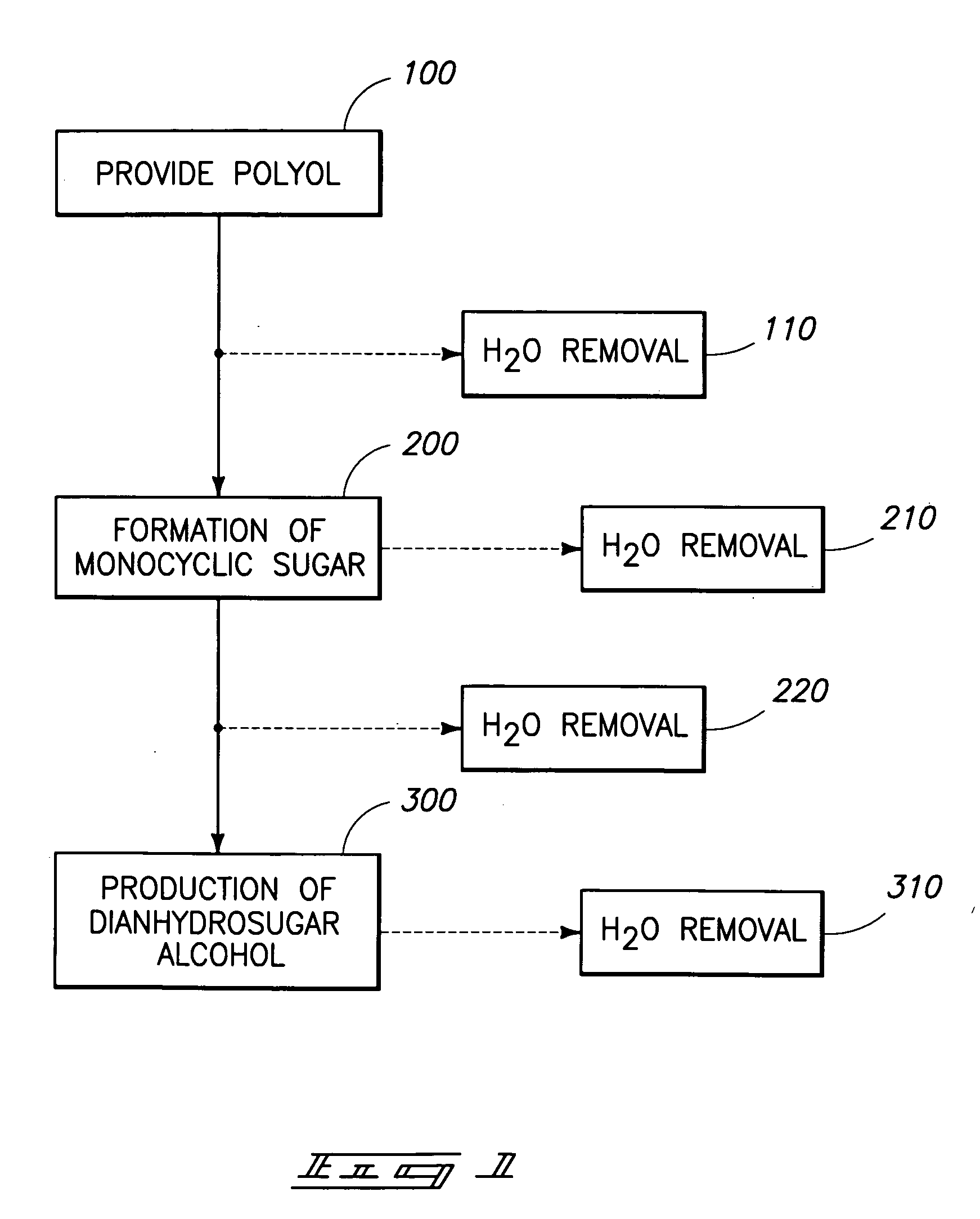
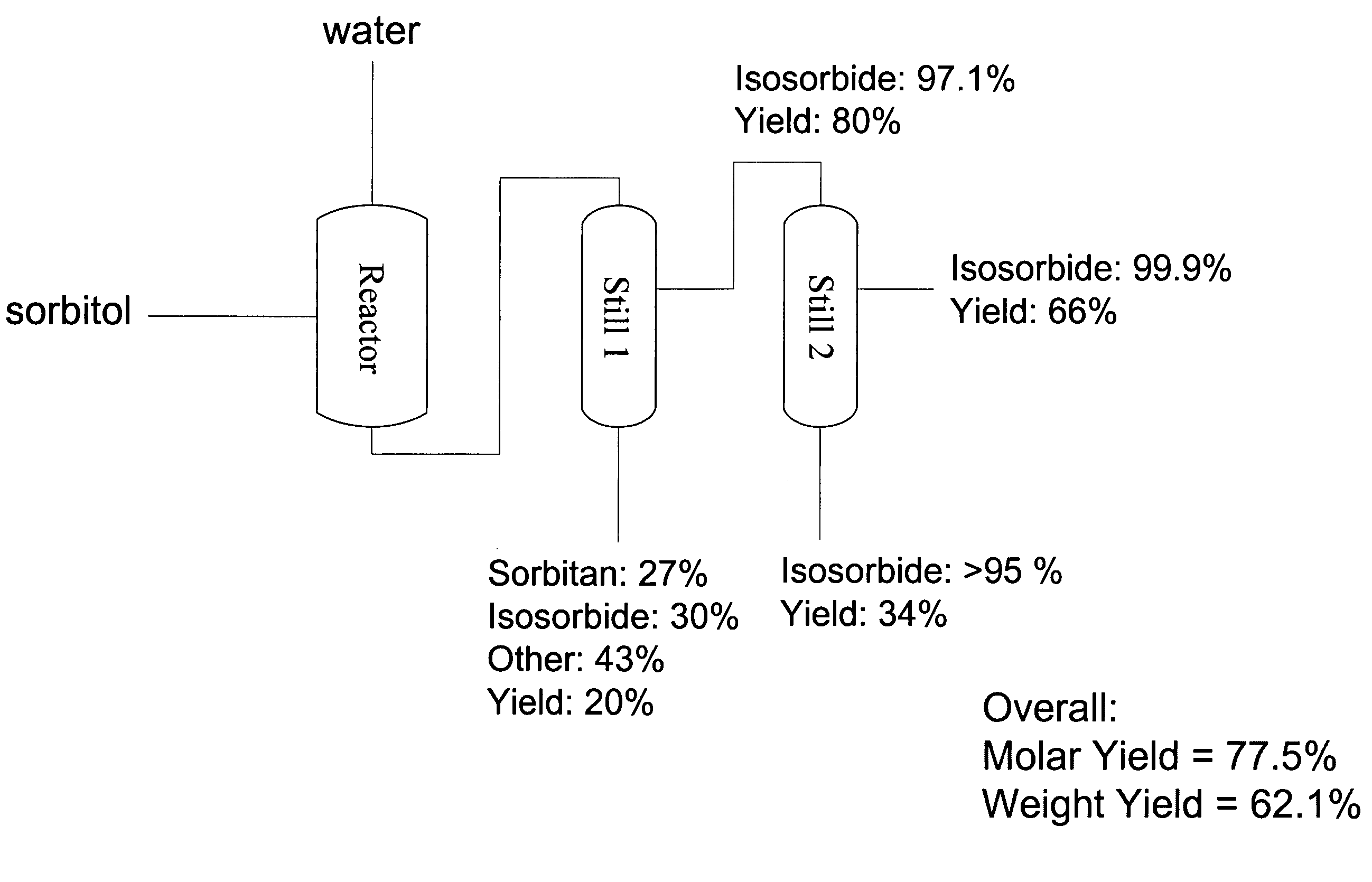
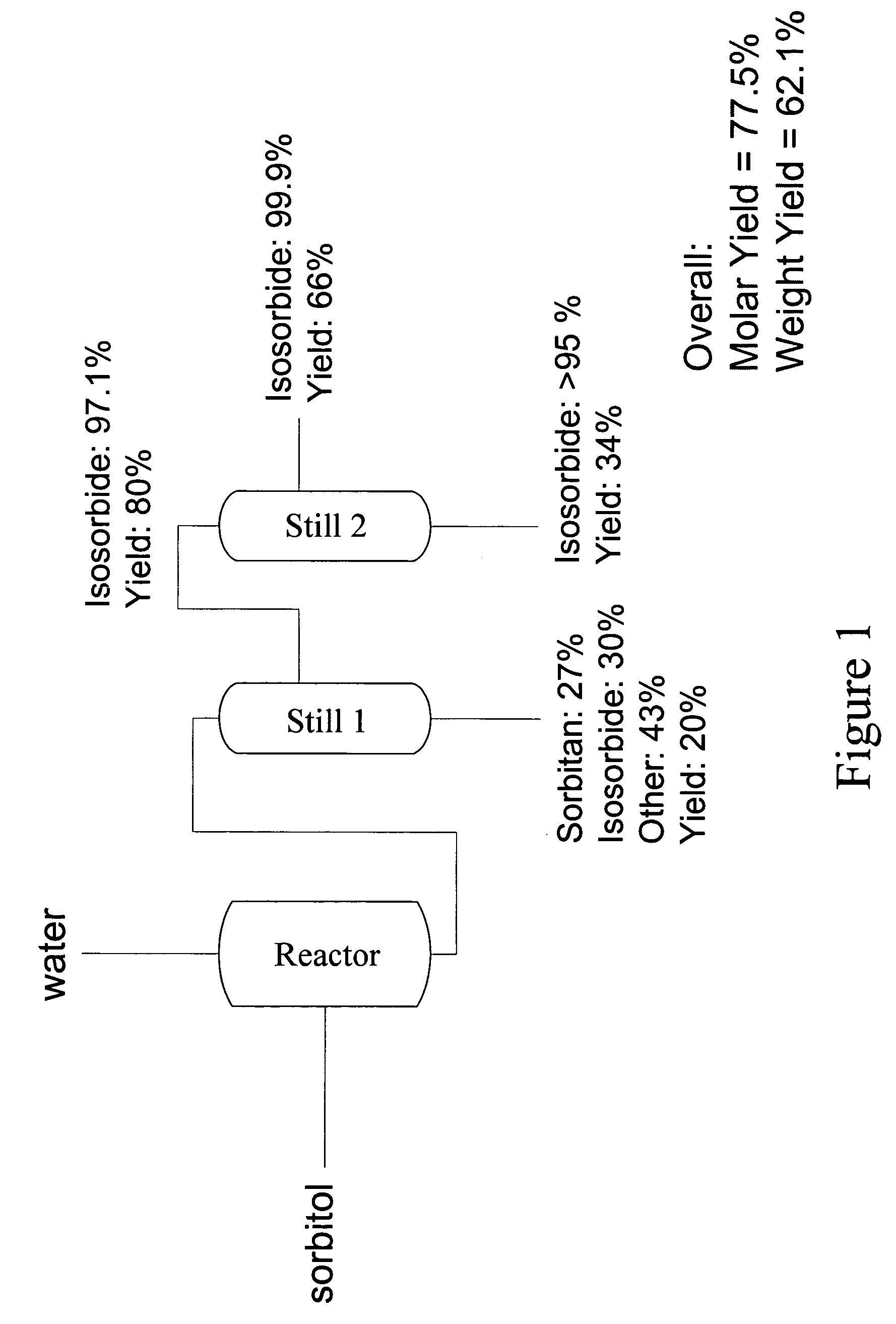
Method of forming a dianhydrosugar alcohol
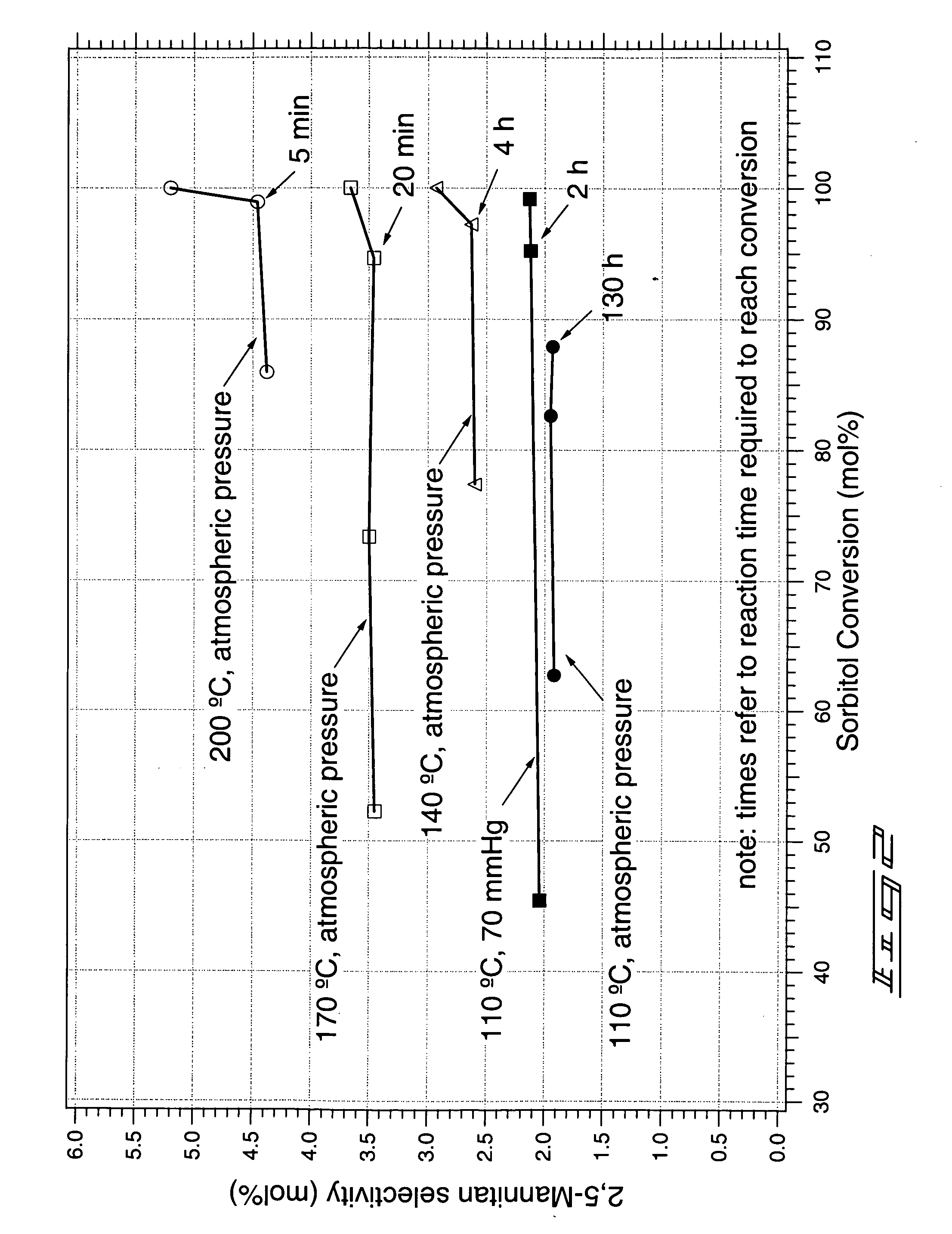
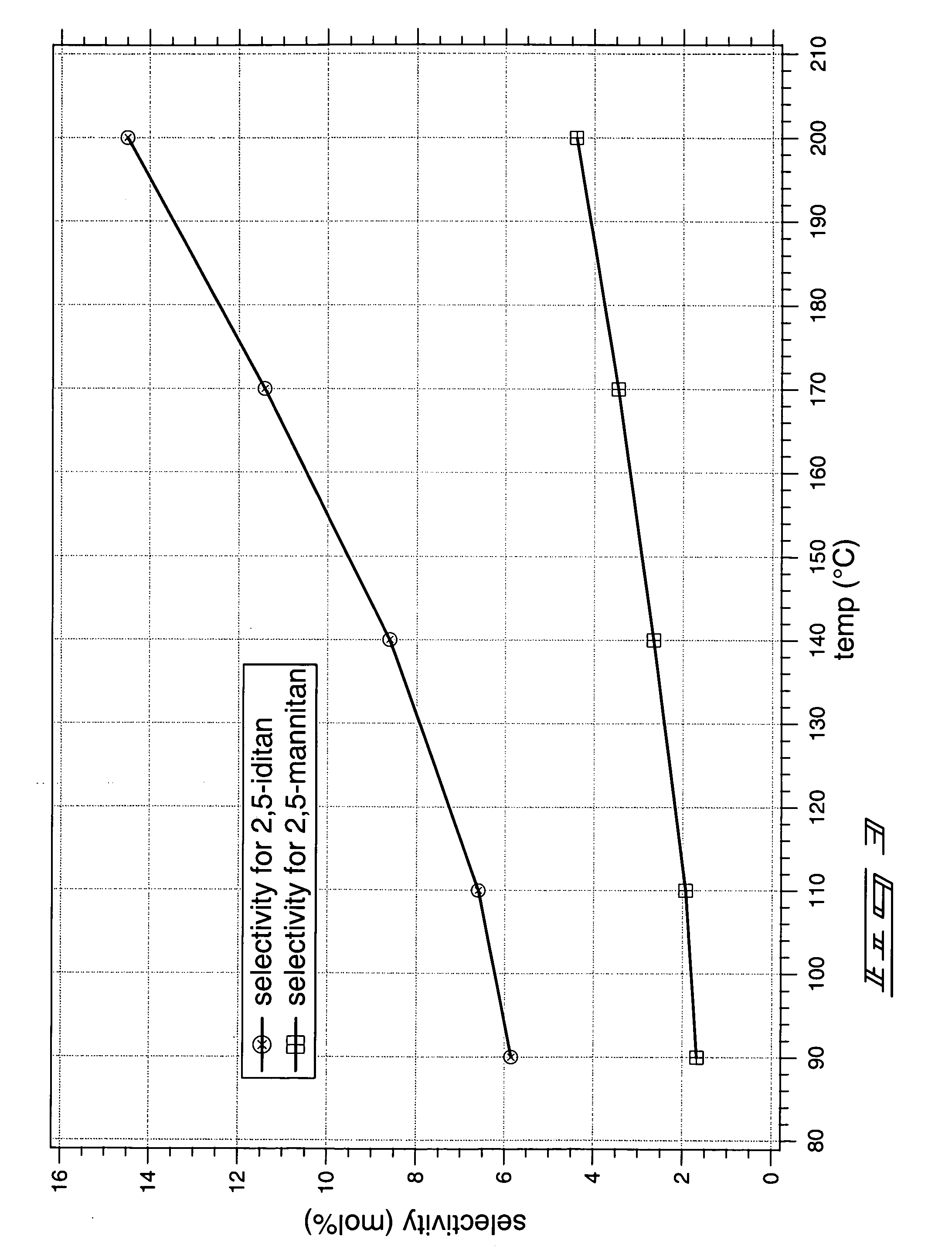
The invention includes methods of producing dianhydrosugars. A polyol is reacted in the presence of a first catalyst to form a monocyclic sugar. The monocyclic sugar is transferred to a second reactor where it is converted to a dianhydrosugar alcohol in the presence of a second catalyst. The invention includes a process of forming isosorbide. An initial reaction is conducted at a first temperature in the presence of a solid acid catalyst. The initial reaction involves reacting sorbitol to produce 1,4-sorbitan, 3,6-sorbitan, 2,5-mannitan and 2,5-iditan. Utilizing a second temperature, the 1,4-sorbitan and 3,6-sorbitan are converted to isosorbide. The invention includes a method of purifying isosorbide from a mixture containing isosorbide and at least one additional component. A first distillation removes a first portion of the isosorbide from the mixture. A second distillation is then conducted at a higher temperature to remove a second portion of isosorbide from the mixture.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Isolation of carotenoid crystals
InactiveUS7015014B2Reduce usageIncrease carotenoid contentOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMicroorganismAnti solvent
The present invention relates to a crystalline carotenoid compound, such as β-carotene, with a purity of at least 95% and with substantially no solvent enclosed in the crystal lattice. The present invention further describes a process to prepare such a highly pure crystalline carotenoid compound from microbial biomass, without the use of a solvent extraction and / or an anti-solvent crystallization process.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Two-stage dehydration of sugars
InactiveUS20070173651A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationSugar derivativesContinuous reactorAlcohol
The invention includes methods for producing dianhydrosugar alcohol by providing an acid catalyst within a reactor and passing a starting material through the reactor at a first temperature. At least a portion of the staring material is converted to a monoanhydrosugar isomer during the passing through the column. The monoanhydrosugar is subjected to a second temperature which is greater than the first to produce a dianhydrosugar. The invention includes a method of producing isosorbide. An initial feed stream containing sorbitol is fed into a continuous reactor containing an acid catalyst at a temperature of less than 120° C. The residence time for the reactor is less than or equal to about 30 minutes. Sorbitol converted to 1,4-sorbitan in the continuous reactor is subsequently provided to a second reactor and is dehydrated at a temperature of at least 120° C. to produce isosorbide.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Compounds that modulate PPAR activity and methods for their preparation
InactiveUS6875780B2BiocideOxygen-containing compound preparationAcute hyperglycaemiaHypertriglyceridemia
This invention relates to compounds that alter PPAR activity. The invention also relates to pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds, pharmaceutically acceptable compositions comprising the compounds or their salts, and methods of using them as therapeutic agents for treating or preventing dyslipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, obesity, hyperglycemia, atherosclerosis, hypertriglyceridemia and hyperinsulinemia in a mammal. The present invention also relates to methods for making the disclosed compounds.
Owner:WARNER-LAMBERT CO
Method of hydrocarbon preservation and environmental protection
InactiveUS7019182B2Preparation by oxidation reactionsOxygen-containing compound preparationLiquid productGas phase
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
Process for the production of anhydrosugar alcohols
A process is provided for the preparation of anhydrosugar alcohols. The process involves heating a sugar alcohol or a monoanhydrosugar alcohol starting material in the presence of an acid catalyst, and subsequent purification of the anhydrosugar alcohol. In some embodiments of the present invention, film evaporators are used in distillation and purification of the anhydrosugar alcohols. Anhydrosugar alcohols of very high purity are achieved in the practice of the present invention. In some embodiments of the present invention, very high purities of the anhydrosugar alcohols are achieved without the use of organic solvents.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Hydrodeoxygenation process
ActiveUS20090163744A1Increase costOxygen-containing compound preparationCoke ovensHydrodeoxygenationHydrocarbon
A process for producing a hydrocarbon from biomass. A feed stream having free fatty acids, fatty acid esters or combinations thereof is provided. The feed stream is heated in the presence of a first catalyst to produce a partially hydrodeoxygenated stream. The partially hydrodeoxygenated stream is heated in the presence of a second catalyst to produce an effluent stream containing the hydrocarbon.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
Extraction solvents derived from oil for alcohol removal in extractive fermentation
ActiveUS20110312044A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce decreaseFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOxygen-containing compound preparationSolventFatty alcohol
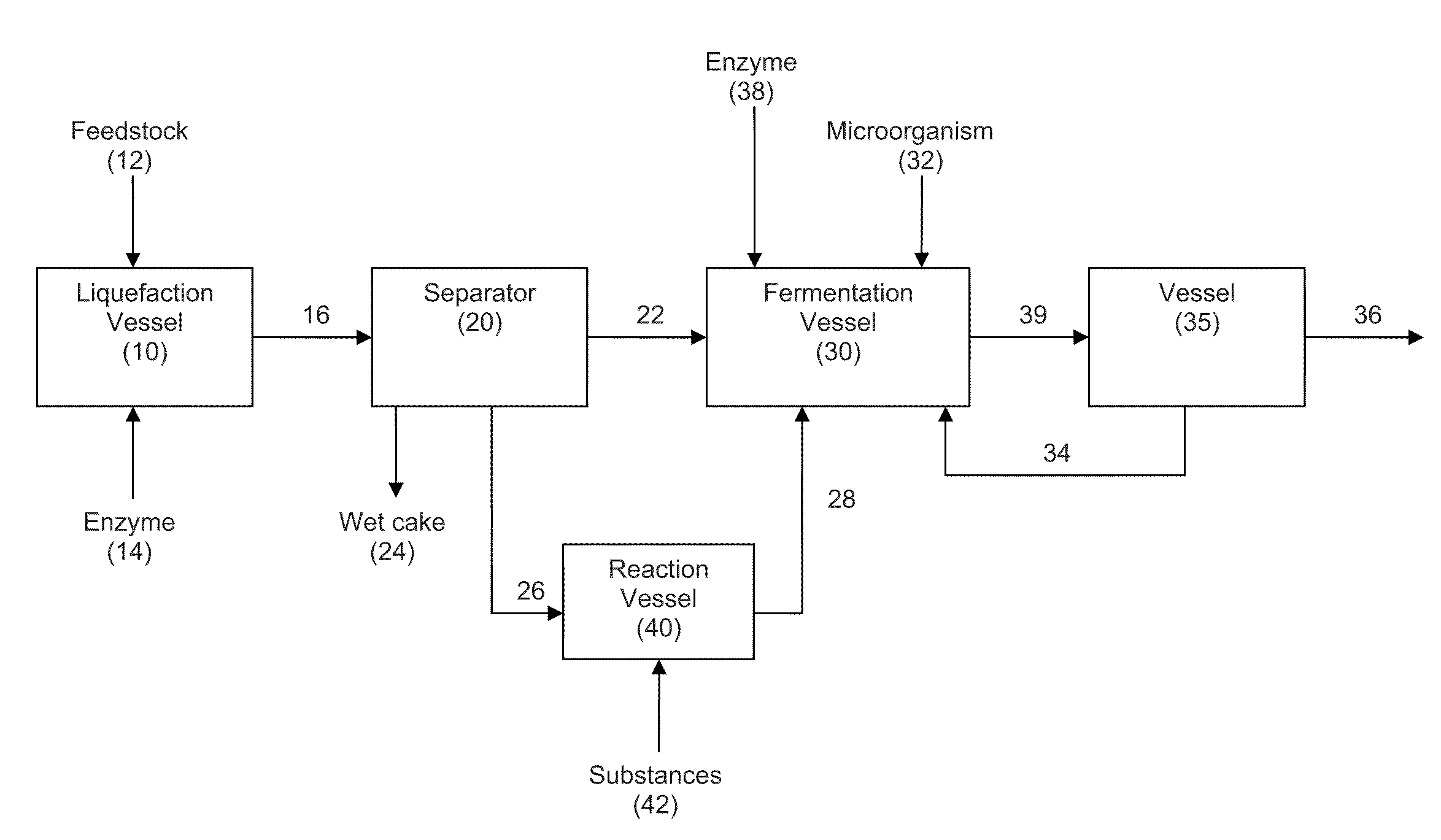
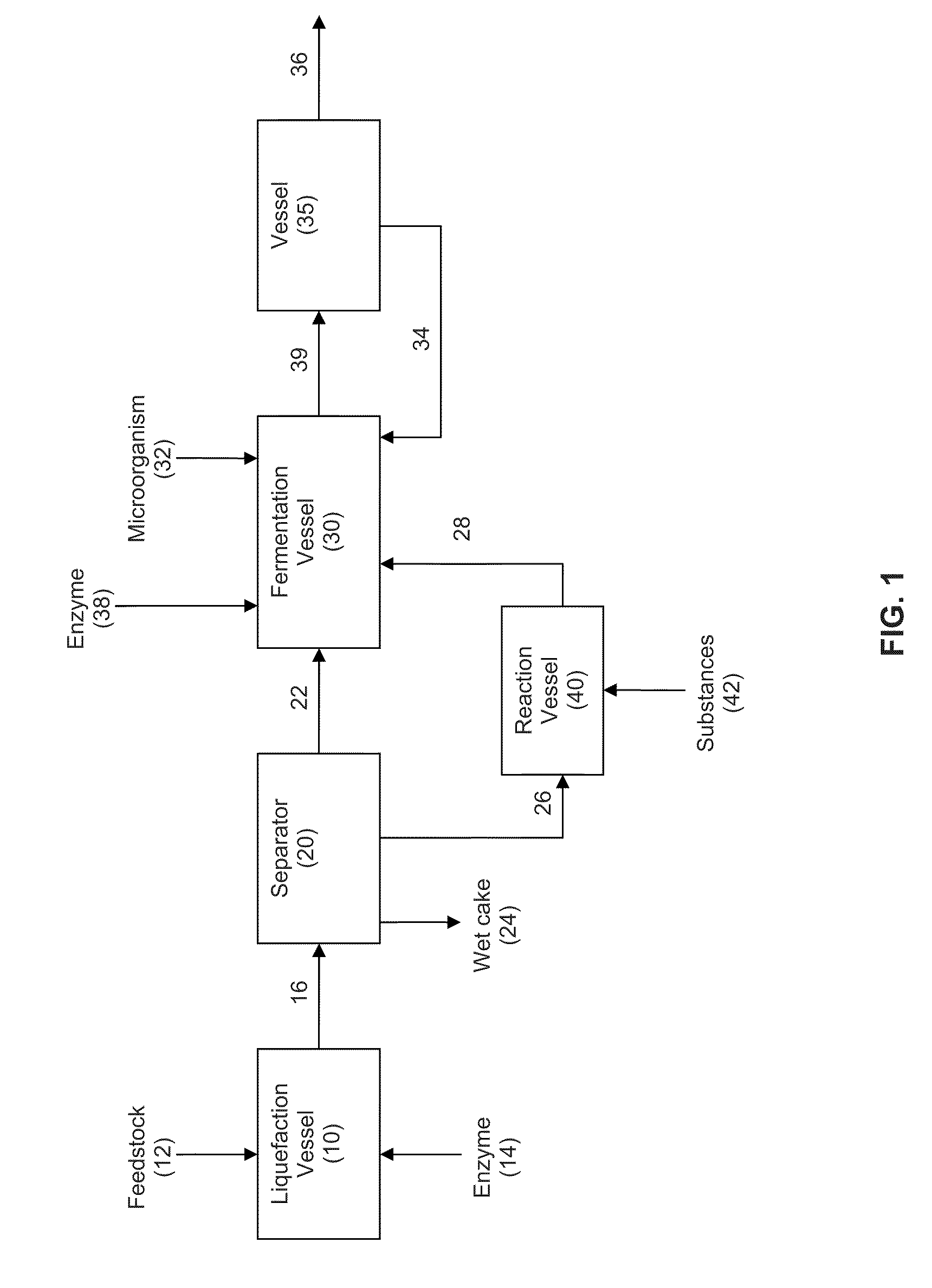
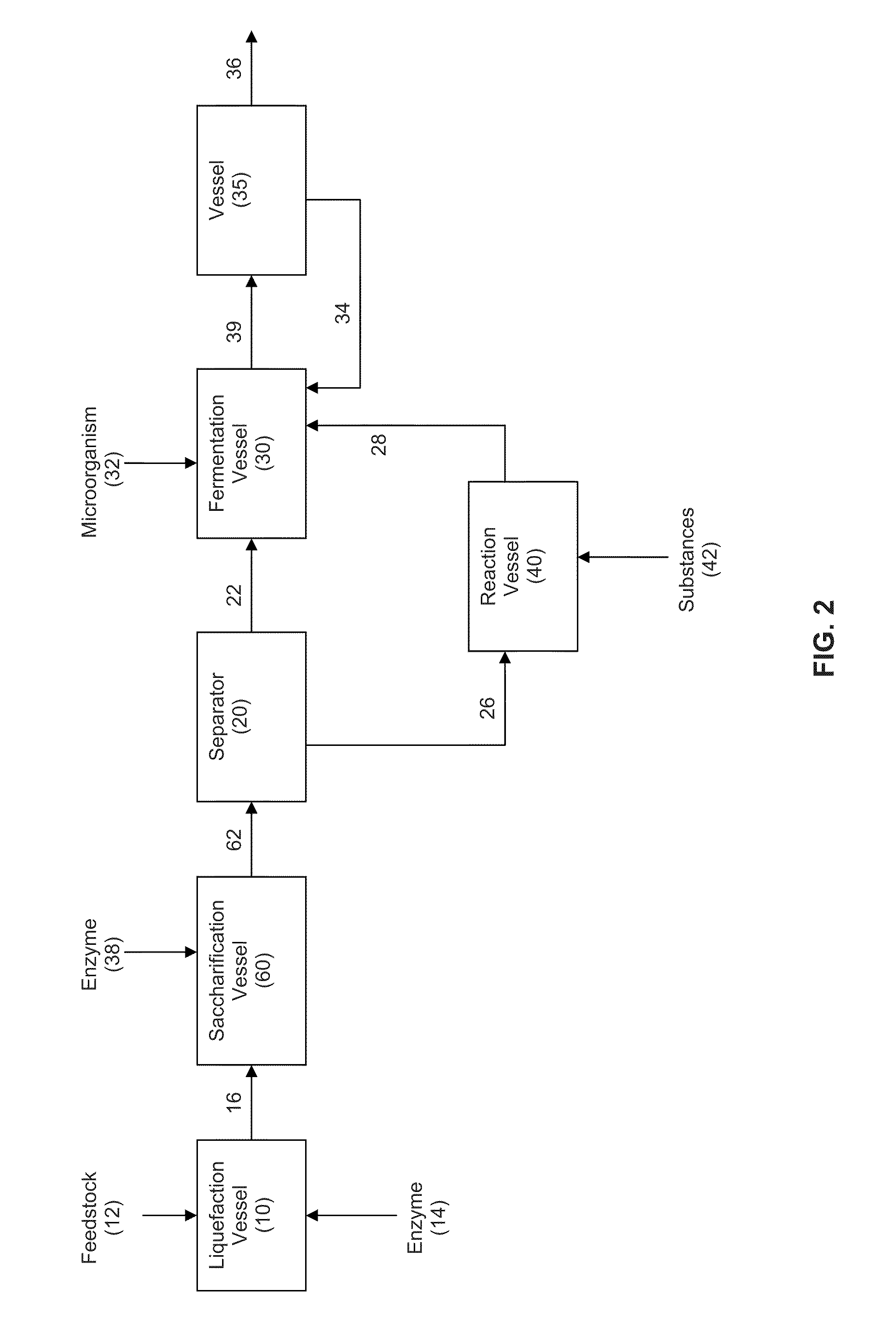
In an alcohol fermentation process, oil derived from biomass is chemically converted into an extractant available for in situ removal of a product alcohol such as butanol from a fermentation broth. The glycerides in the oil can be chemically converted into a reaction product, such as fatty acids, fatty alcohols, fatty amides, fatty acid methyl esters, fatty acid glycol esters, and hydroxylated triglycerides, and mixtures thereof, which forms a fermentation product extractant having a partition coefficient for a product alcohol greater than a partition coefficient of the oil of the biomass for the product alcohol. Oil derived from a feedstock of an alcohol fermentation process can be chemically converting into the fermentation product extractant. The oil can be separated from the feedstock prior to the feedstock being fed to a fermentation vessel, and the separated oil can be chemically converted to a fermentation product extractant, which can then contacted with a fermentation product comprising a product alcohol, whereby the product alcohol is separated from the fermentation product.
Owner:GEVO INC
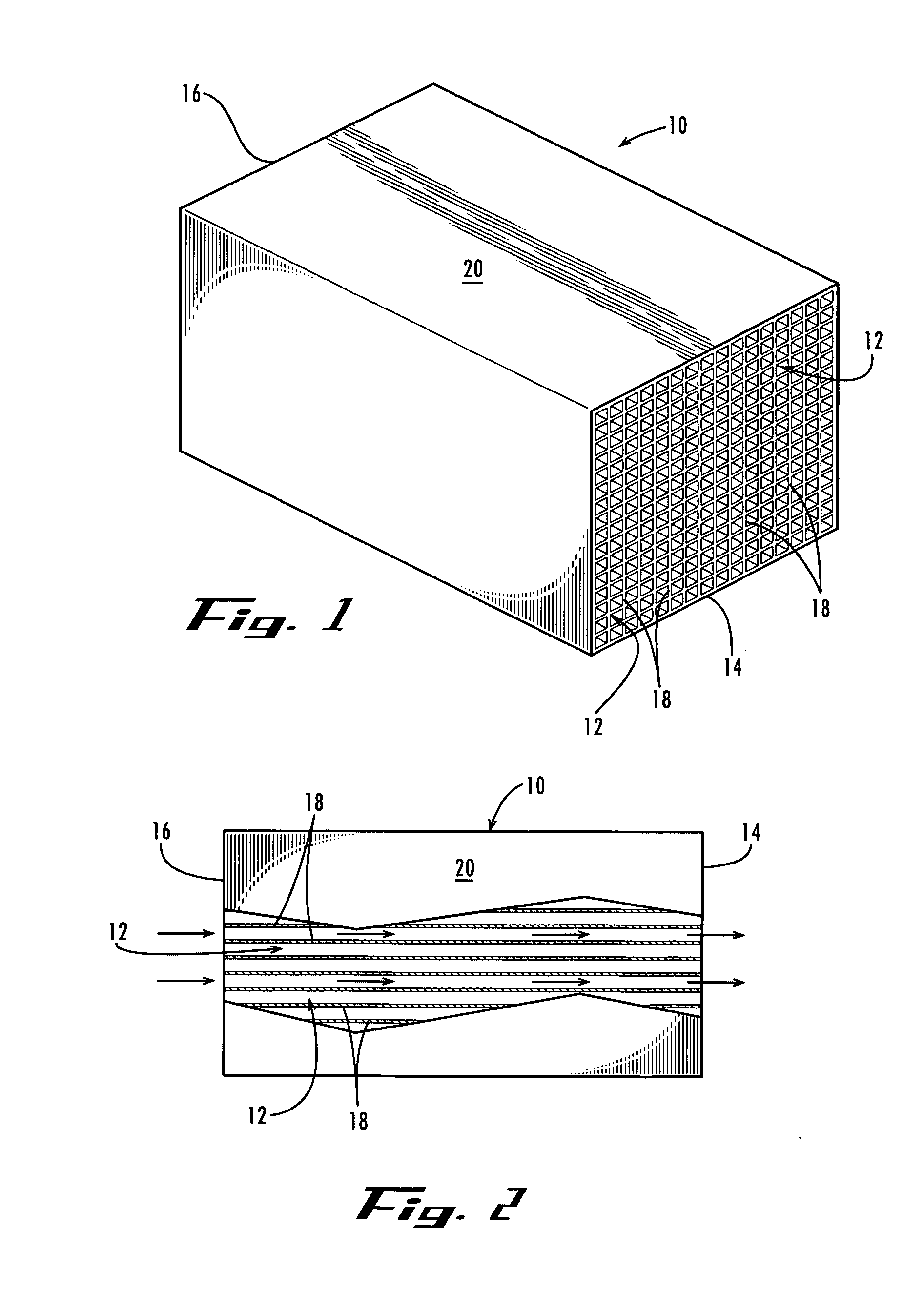
Activated carbon monolith catalyst, methods for making same, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060229476A1High activityHigh selectivityOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationActivated carbonSupport matrix
An activated carbon monolith catalyst comprising a finished self-supporting activated carbon monolith having at least one passage therethrough, and comprising a supporting matrix and substantially discontinuous activated carbon particles dispersed throughout the supporting matrix and at least one catalyst precursor on the finished self-supporting activated carbon monolith. A method for making, and a method for use, of such an activated carbon monolith catalyst in catalytic chemical reactions are also disclosed.
Owner:APPL TECH LLP
Method for producing ethylene glycol from polyhydroxy compound
ActiveUS20110046419A1High yieldHigh selectivityOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationIridiumHydrogen pressure
A method for producing ethylene glycol, including (a) adding a polyhydroxy compound and water to a sealed high-pressure reactor, (b) removing air and introducing hydrogen, and (c) allowing the polyhydroxy compound to react in the presence of a catalyst while stiffing. The catalyst includes a first active ingredient and a second active ingredient. The first active ingredient includes a transition metal of Group 8, 9, or 10 selected from iron, cobalt, nickel, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, iridium, and platinum, and / or a mixture thereof. The second active ingredient includes a metallic state of molybdenum and / or tungsten, or a carbide, nitride, or phosphide thereof. The method is carried out at a hydrogen pressure of 1-12 MPa, at a temperature of 120-300° C. for not less than 5 min in a one-step catalytic reaction. The efficiency, selectivity, and the yield of ethylene glycol are high. The preparation process is simple and the materials used are renewable.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of preparing ethylene glycol from cellulose
ActiveUS7960594B2High yieldHigh selectivityOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationCelluloseIridium
A method for preparing ethylene glycol from cellulose uses the cellulose as the feed for the reaction. The cellulose conversion is performed over catalysts which are composed of the metallic state, carbides, nitrides, or phosiphides of molybdenum or tungsten, and metallic cobalt, nickel, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, iridium, and platinum of the group 8, 9, or 10 transition metals. The catalytic conversion of cellulose is conducted at 120 to 300° C. and hydrogen pressure 1 to 12 MPa under the hydrothermal conditions to achieve the high efficiency, high selectivity, and high yield of ethylene glycol. Compared to the existing method of preparing ethylene glycol from ethylene, the method, using the renewable raw material for the reaction, is friendly to the environment, and has high atom economy.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for preparing ethylene glycol from polyhydroxy compounds
ActiveUS20120172633A1High yieldHigh selectivityOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationHydrogen pressureHeteropoly acid
This invention provides methods for producing ethylene glycol from polyhydroxy compounds such as cellulose, starch, hemicellulose, glucose, sucrose, fructose, fructan, xylose and soluble xylooligosaccharides. The methods uses polyhydroxy compounds as the reactant, a composite catalyst having active components comprising one or more transition metals of Groups 8, 9, or 10, including iron, cobalt, nickel, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, iridium, and platinum, as well as tungsten oxide, tungsten sulfide, tungsten hydroxide, tungsten chloride, tungsten bronze oxide, tungsten acid, tungstate, metatungstate acid, metatungstate, paratungstate acid, paratungstate, peroxotungstic acid, pertungstate, heteropoly acid containing tungsten. Reacting at a temperature of 120-300° C. and a hydrogen pressure of 1-13 MPa under hydrothermal conditions to accomplish one-step catalytic conversion. It realizes efficient, highly selective, high yield preparation of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol from polyhydroxy compounds. The advantage of processes disclosed in this invention include renewable raw material and high atom economy. At the same time, compared with other technologies that converts biomass raw materials into polyols, methods disclosed herein enjoy advantages including simple reaction process, high yield of targeted products, as well as easy preparation and low cost for the catalysts.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tungsten carbide catalysts, their preparation and application in synthesis of ethylene glycol from cellulose
ActiveUS20100255983A1Improve efficiencyHigh selectivityOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationHydrogen pressureCobalt
Tungsten carbide catalysts are used in preparation of ethylene glycol by hydrogenating degradation of cellulose. The catalyst includes tungsten carbide as main catalytic active component, added with small amount of one or more transition metals such as nickel, cobalt, iron, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium, platinum, and copper as the second metal, supported on one or more porous complex supports such as active carbon, alumina, silica, titanium dioxide, silicon carbide, zirconium oxide, for conversion of cellulose to ethylene glycol. The catalyst realizes high efficiency, high selectivity, and high yield in the conversion of cellulose to ethylene glycol at the temperature of 120-300° C., hydrogen pressure of 1-10 MPa, and hydrothermal conditions. Compared to the existing industrial synthetic method of ethylene glycol using ethylene as feedstock, the invention has the advantages of using renewable raw material resources, environment friendly process, and excellent atom economy.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quaternary phosphonium salt catalysts in catalytic hydrolysis of alkylene oxides
A process for the preparation of alkylene glycols by reacting an alkylene oxide with water in the presence of at least one ionic composition of a quaternary phosphonium cation of the general formula R1R2R3R4P+Whereby each of R1, R2, R3 and R4, independently, may be an alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, alkylaryl or arylalkyl group having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms, each of which may carry one or more substituents, or be attached to a polymer and an anion other than metalate or halogen.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method for production of ethylene oxide
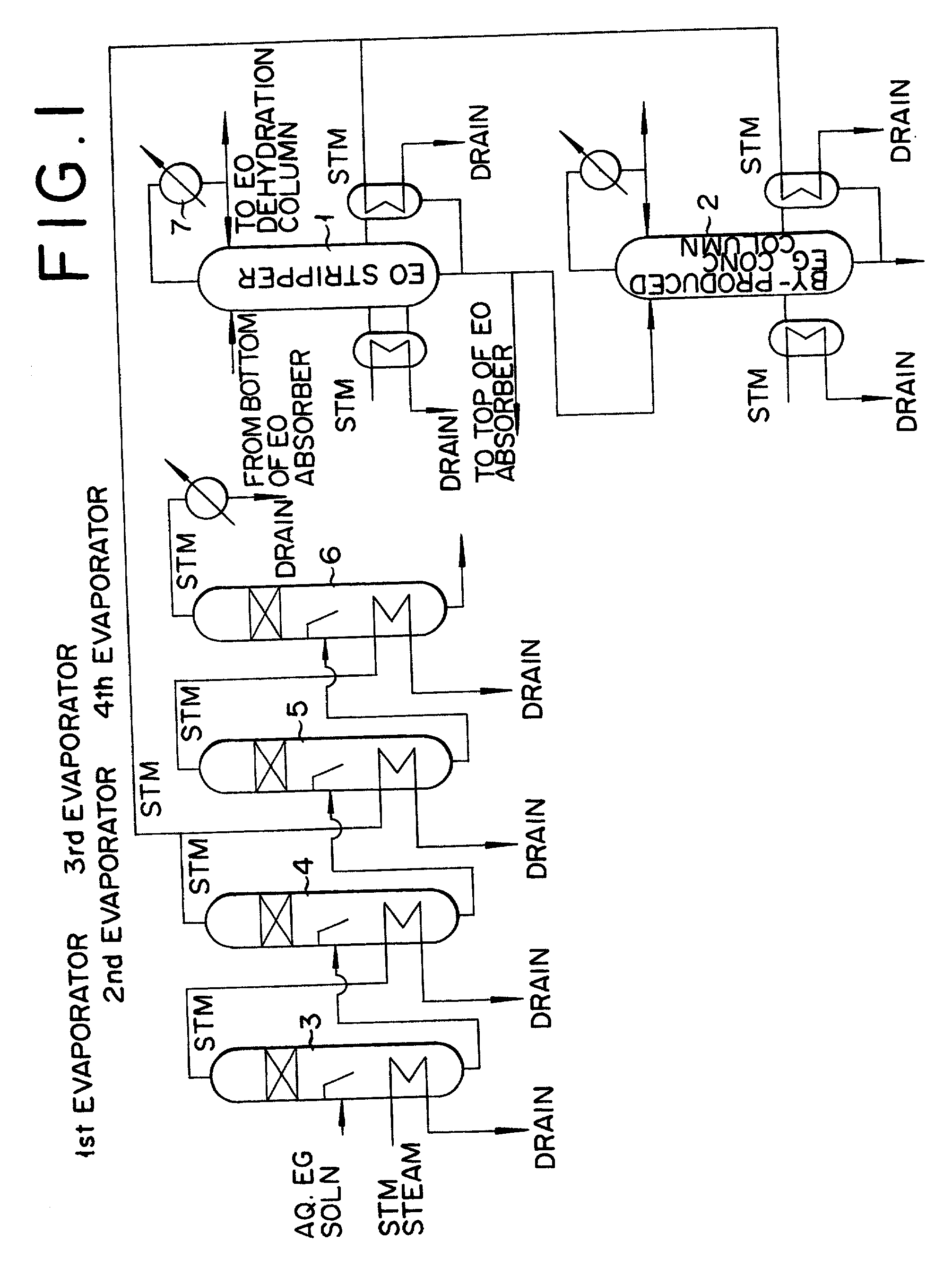
InactiveUS20020010378A1Efficient comprehensive utilizationEffective utilization can be attainedOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationEthylene oxideMultiple-effect evaporator
In a composite process for subjecting ethylene to catalytic gas phase oxidation thereby obtaining ethylene oxide and causing this ethylene oxide to react with water thereby obtaining ethylene glycol, a method for producing the ethylene glycol is provided which permits effective utilization of the energy at the step for dehydrating and concentrating the resultant aqueous ethylene glycol solution. In the production of ethylene glycol by the supply of the aqueous ethylene glycol solution to a concentrating treatment at the multi-effect evaporator, the method contemplated by this invention for the production of ethylene glycol comprises utilizing as the source of heating at least one specific step the steam generated in the multi-effect evaporator.
Owner:RECOVERYCARE COM +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com