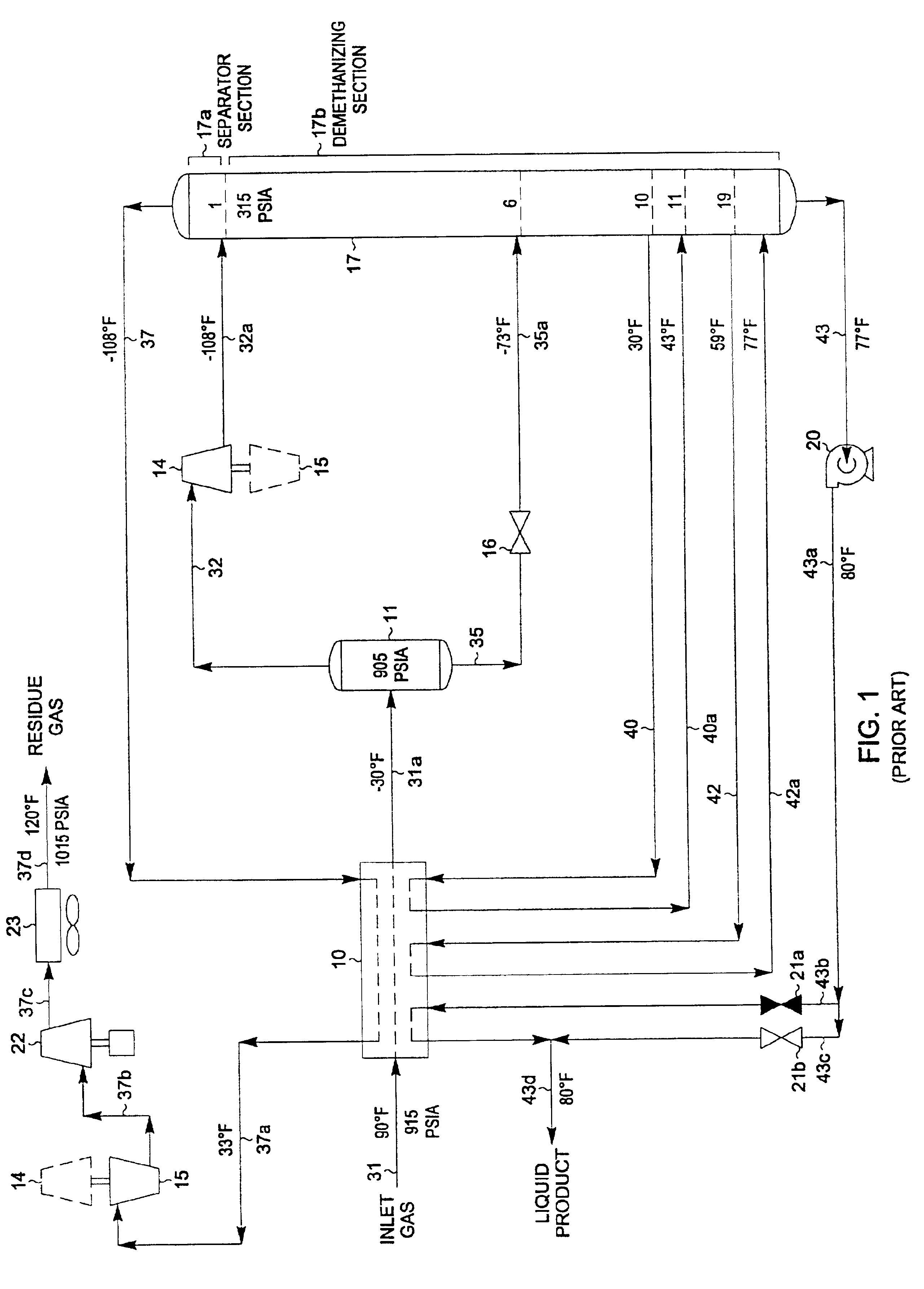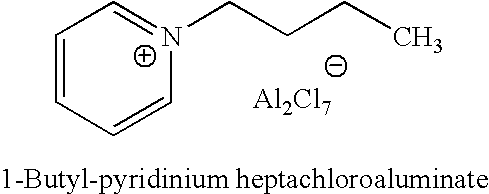Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2670results about "Hydrocarbon purification/separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
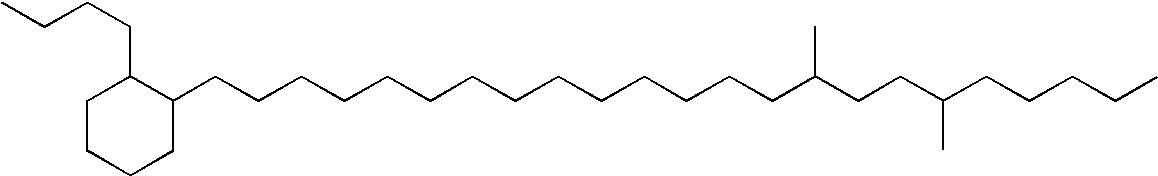
Premium synthetic lubricant base stock having at least 95% non-cyclic isoparaffins
InactiveUS6080301ARefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationParaffin waxAlkane
A premium synthetic lubricating oil base stock having a high VI and low pour point is made by hydroisomerizing a Fischer-Tropsch synthesized waxy, paraffinic feed wax and then dewaxing the hydroisomerate to form a 650-750 DEG F.+ dewaxate. The waxy feed has an initial boiling point in the range of about 650-750 DEG F., from which it continuously boils up to at least 1050 DEG F. and has a T90-T10 temperature difference of at least 350 DEG F. The feed is preferably hydroisomerized without any pretreatment, other than optional fractionation. The 650-750 DEG F.+ dewaxate is fractionated into two or more base stocks of different viscosity.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
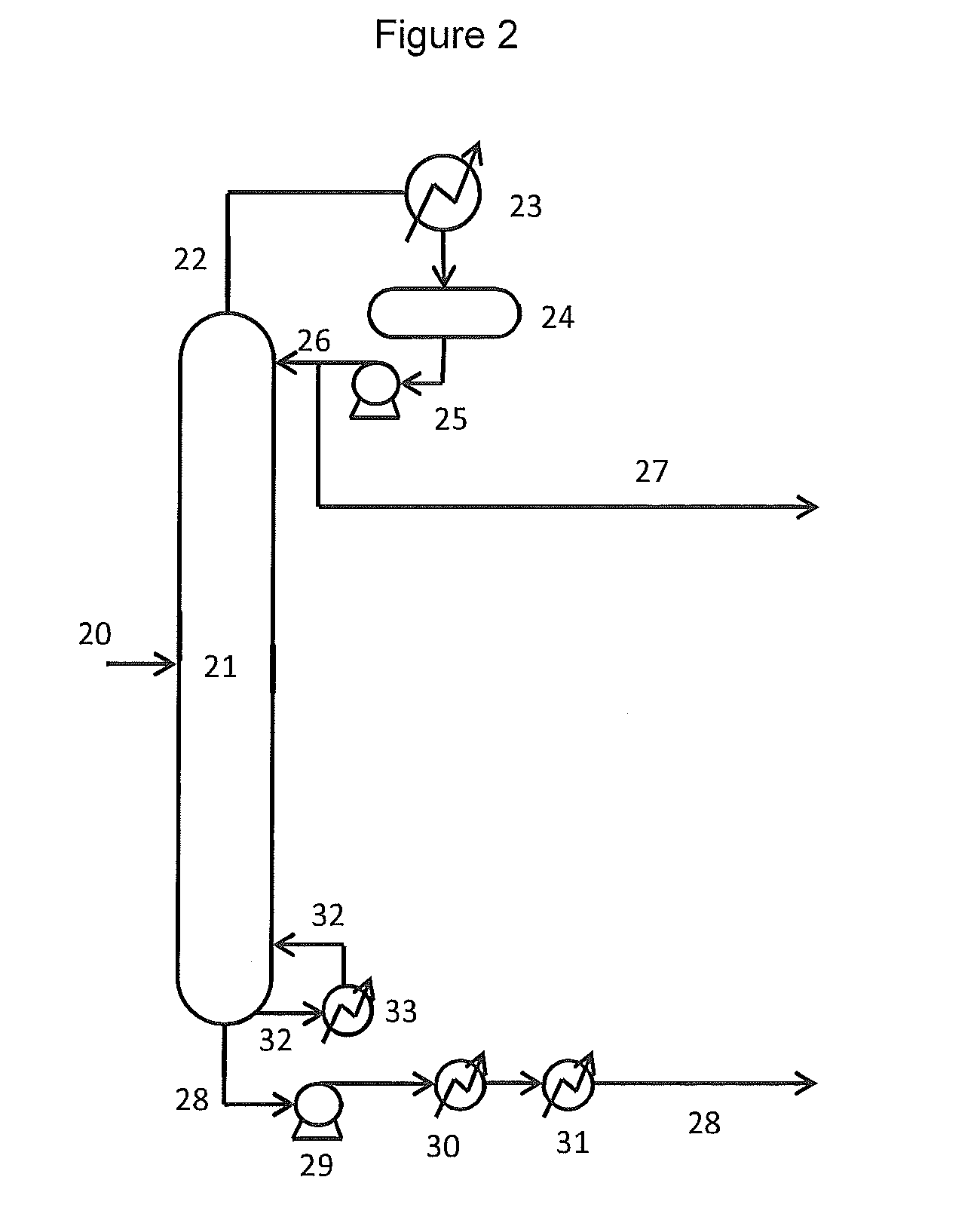
Hydrocarbon gas processing
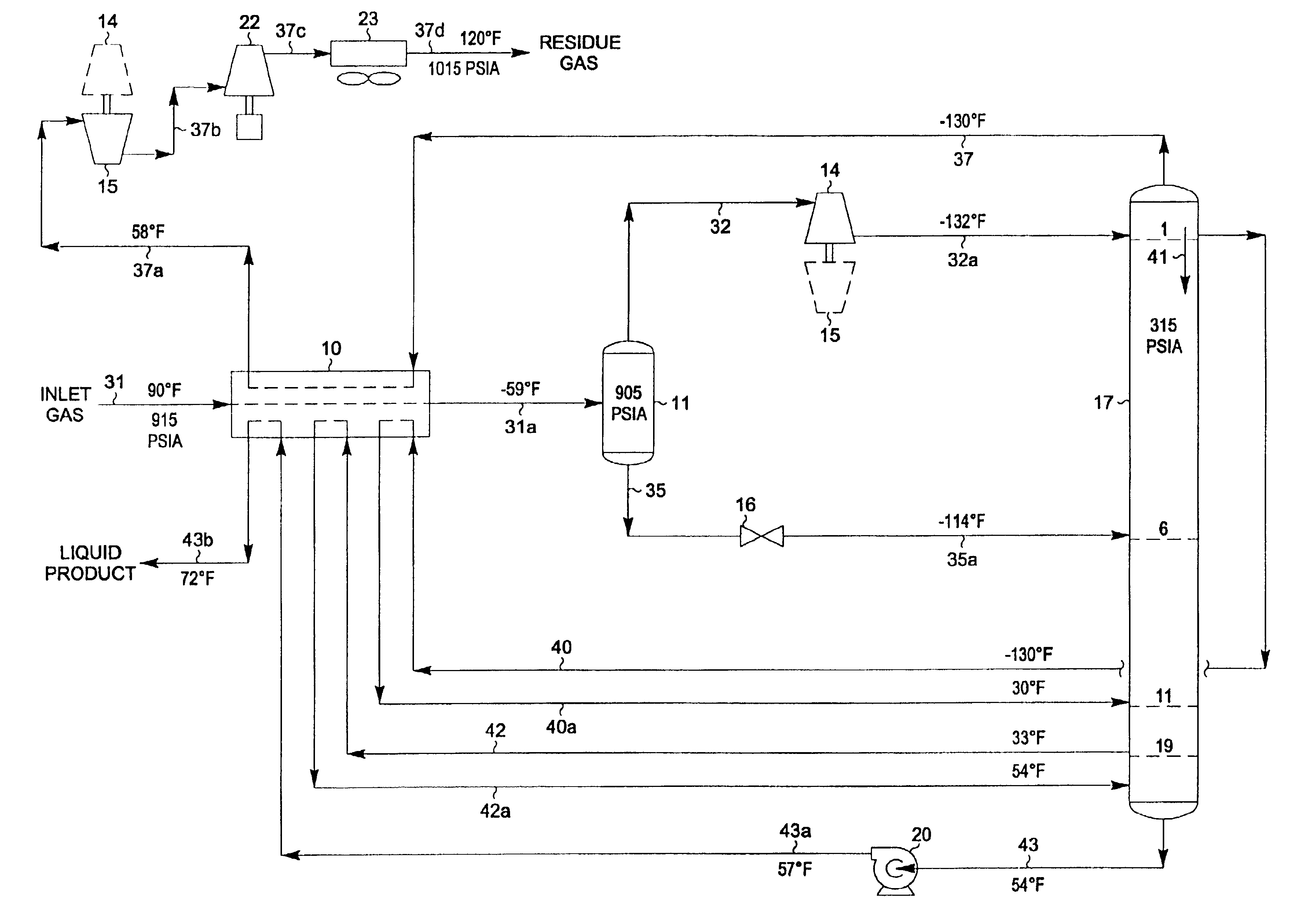
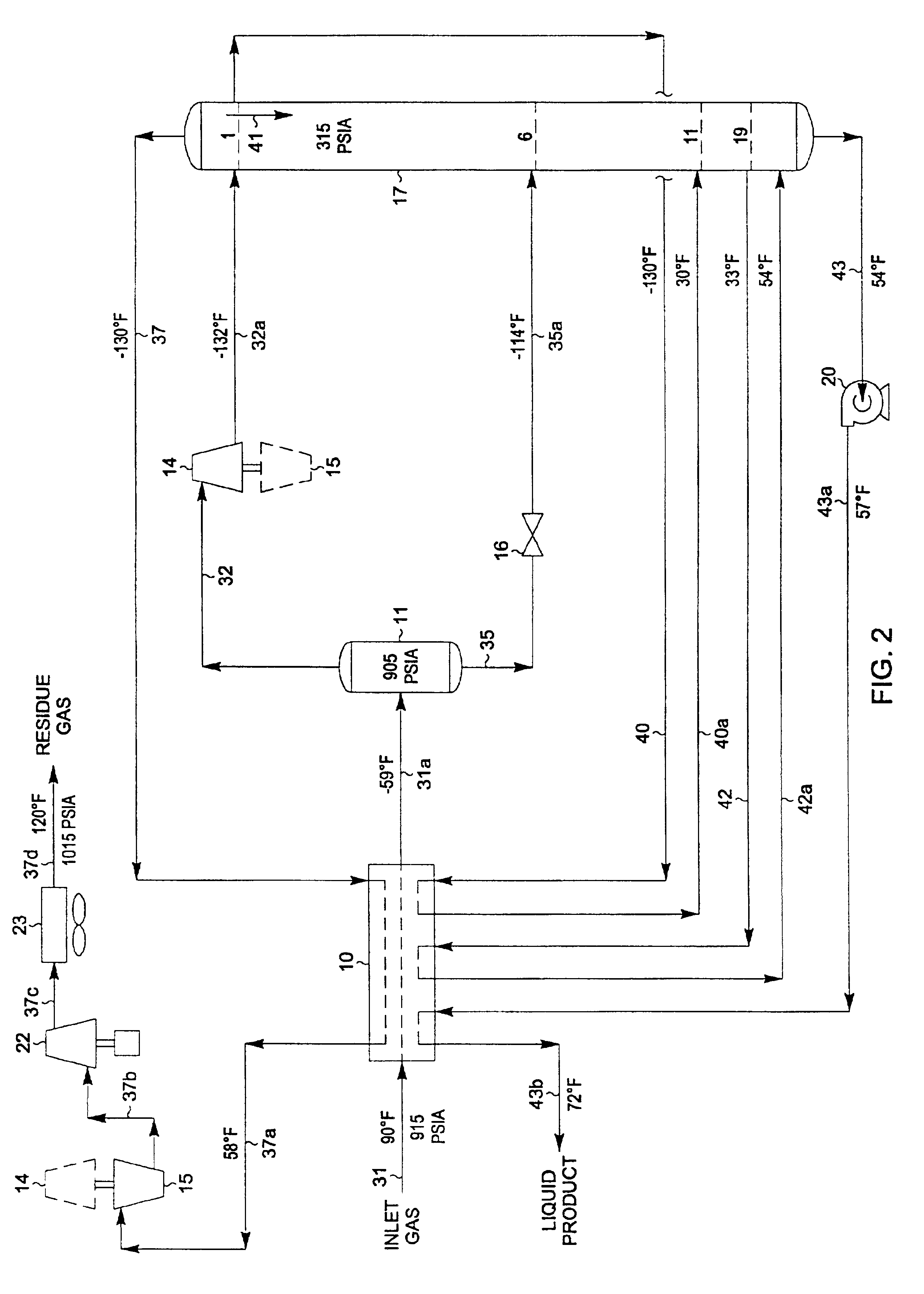
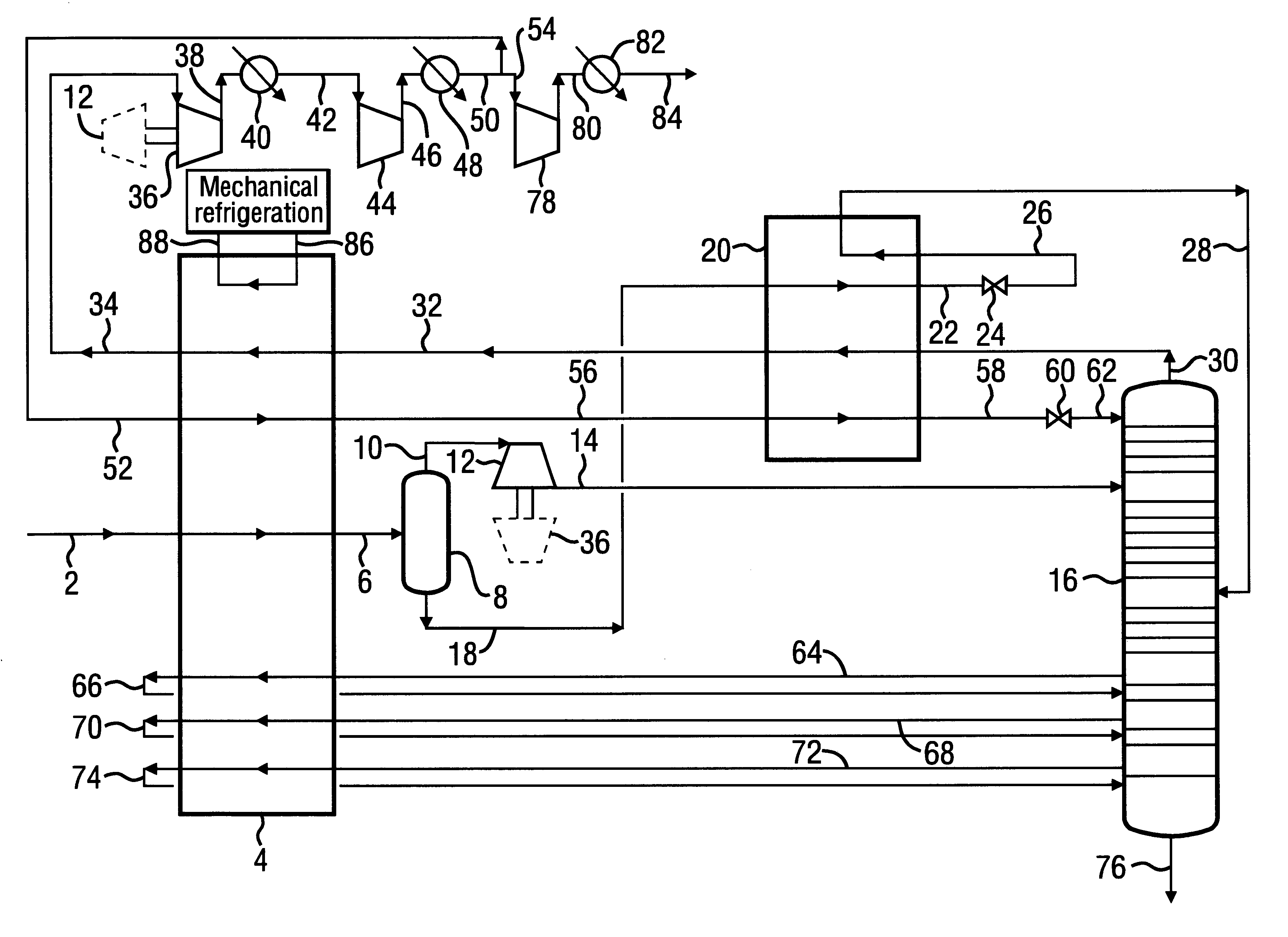
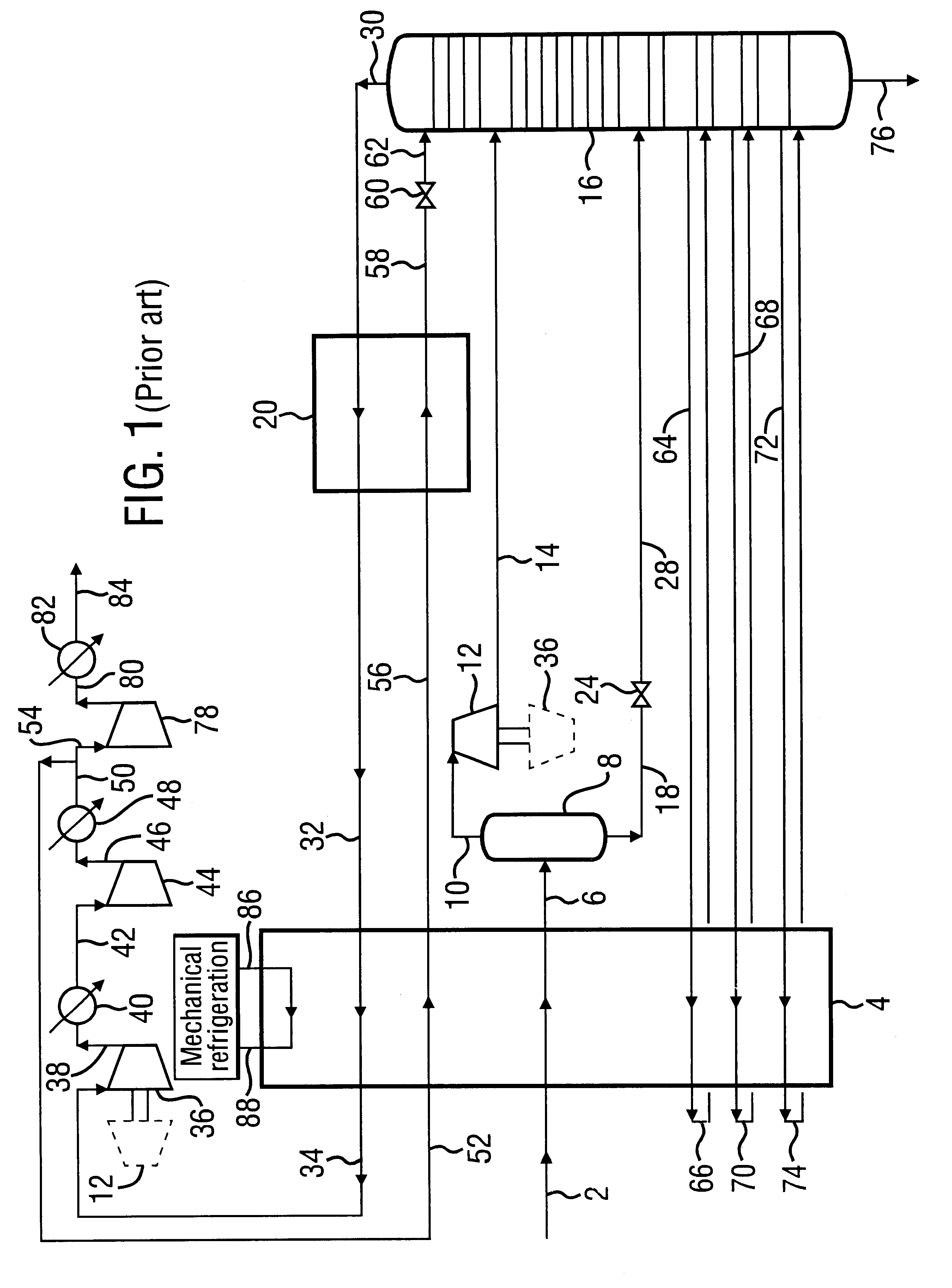
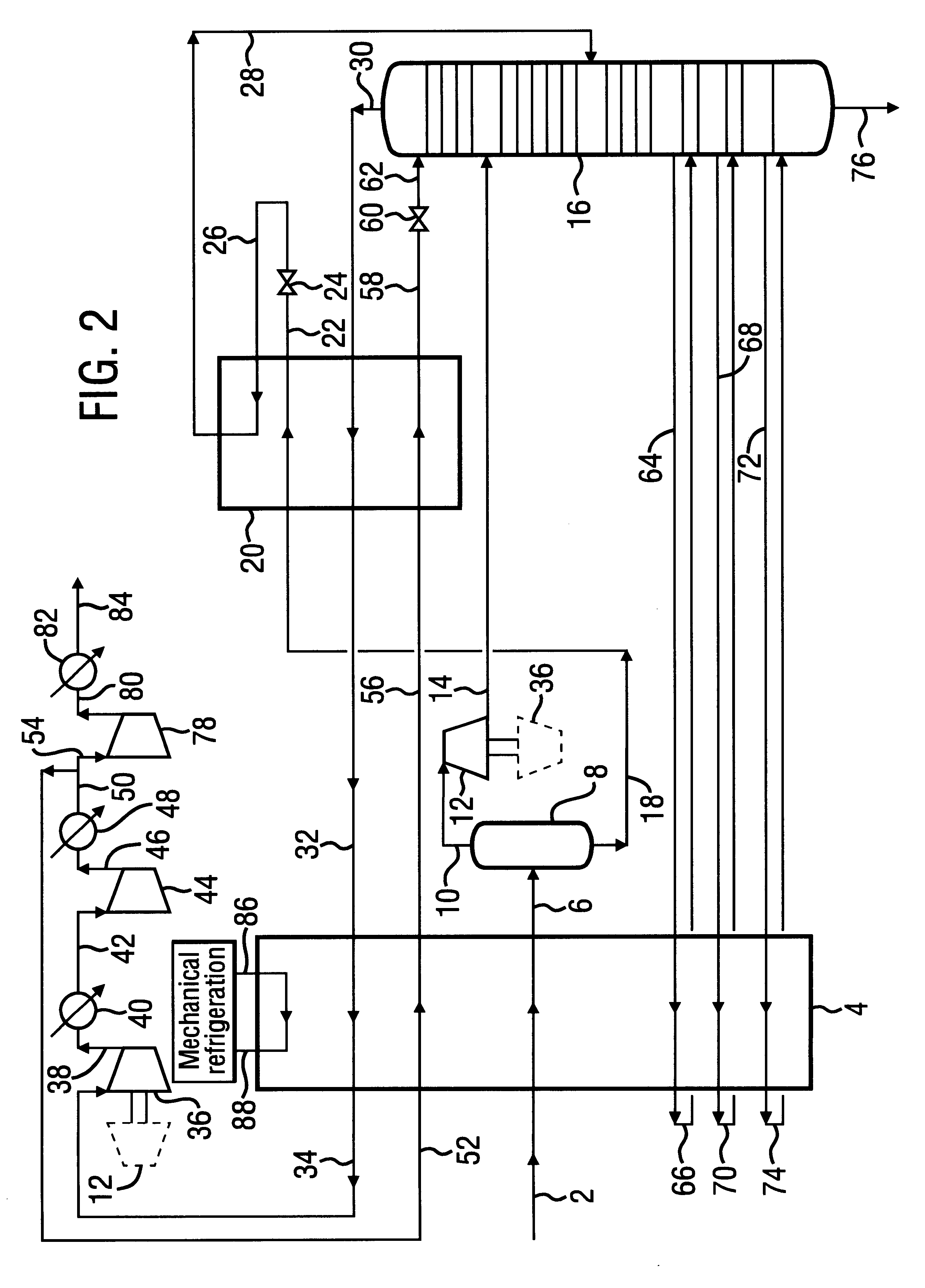
A process for the recovery of ethane, ethylene, propane, propylene and heavier hydrocarbon components from a hydrocarbon gas stream is disclosed. In recent years, the preferred method of separating a hydrocarbon gas stream generally includes supplying at least portions of the gas stream to a fractionation tower having at least one reboiler, and often one or more side reboilers, to supply heat to the column by withdrawing and heating some of the tower liquids to produce stripping vapors that separate the more volatile components from the desired components. The reboiler and side reboilers (if any) are typically integrated into the feed stream cooling scheme to provide at least a portion of the refrigeration needed to condense the desired components for subsequent fractionation in the distillation column. In the process disclosed, the tower reboiling scheme is modified to use one or more tower liquid distillation streams from a point higher in the column than is used in the conventional reboiling scheme, providing colder stream(s) for the reboiler(s) that allow more effective cooling of the feed streams and thereby improve the efficiency with which the desired components are recovered. In addition, the tower liquid streams withdrawn from a higher point in the column contain larger quantities of the more volatile components, which when vaporized provide better stripping of undesirable components like carbon dioxide without reducing the recovery of the desired components. The heated distillation stream is returned to a lower point on the fractionation tower that is separated from the withdrawal point by at least one theoretical stage.
Owner:UOP LLC
Hydroprocessing Microalgal Oils
InactiveUS20100170144A1Improve efficiencyLow costHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon purification/separationChemical treatmentAlkaline hydrolysis
Fuels and other valuable compositions and compounds can be made from oil extracted from microbial biomass and from oil-bearing microbial biomass via hydroprocessing and / or other chemical treatments, including the alkaline hydrolysis of glycerolipids and fatty acid esters to fatty acid salts.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Synthesis of liqiud fuels and chemicals from oxygenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080300434A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationHydrocarbon purification/separationFuranCarboxylic acid
Processes and reactor systems are provided for the conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbons to hydrocarbons, ketones and alcohols useful as liquid fuels, such as gasoline, jet fuel or diesel fuel, and industrial chemicals. The process involves the conversion of mono-oxygenated hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, furans, carboxylic acids, diols, triols, and / or other polyols, to C4+ hydrocarbons, alcohols and / or ketones, by condensation. The oxygenated hydrocarbons may originate from any source, but are preferably derived from biomass.
Owner:VIRENT
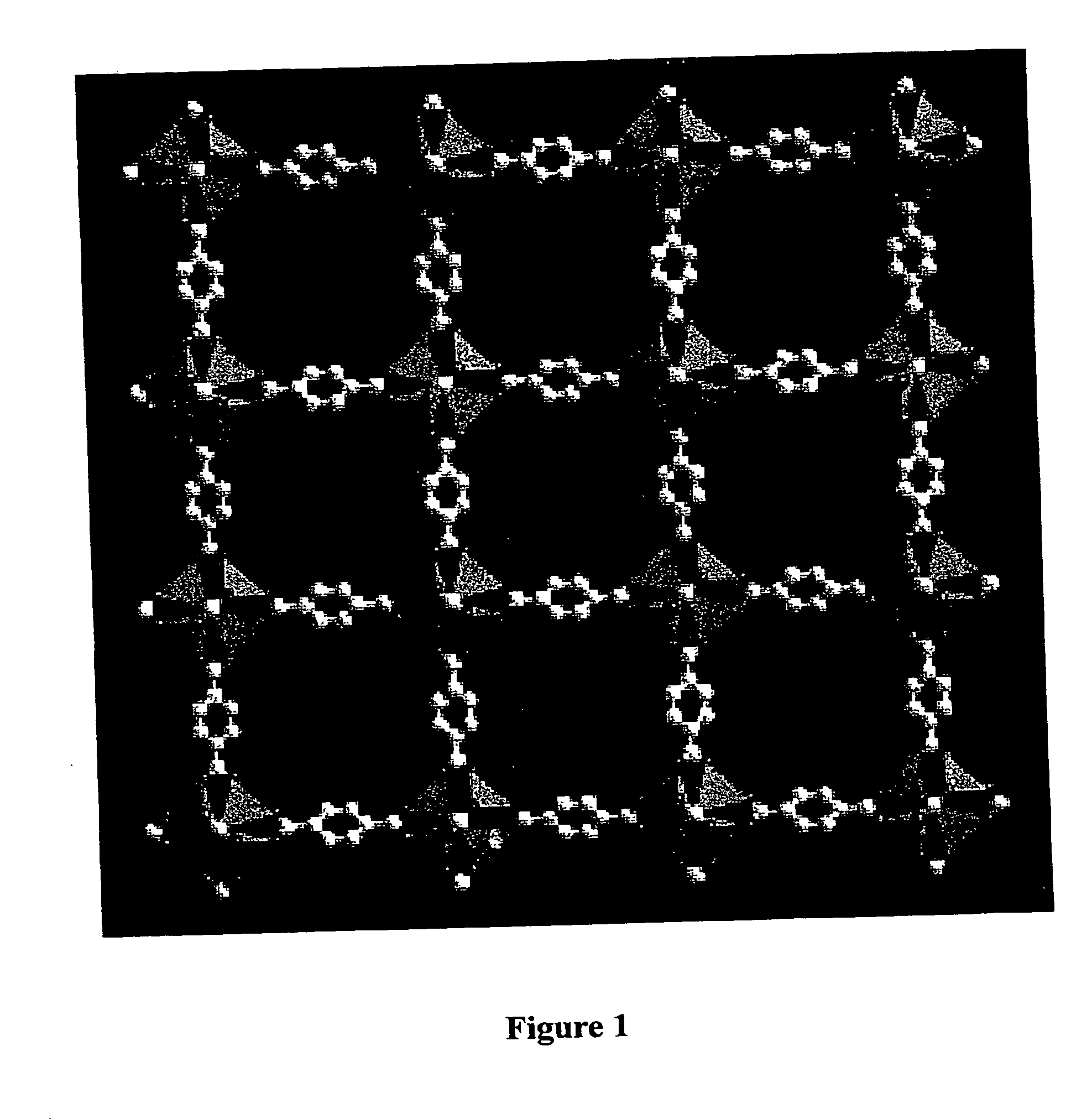
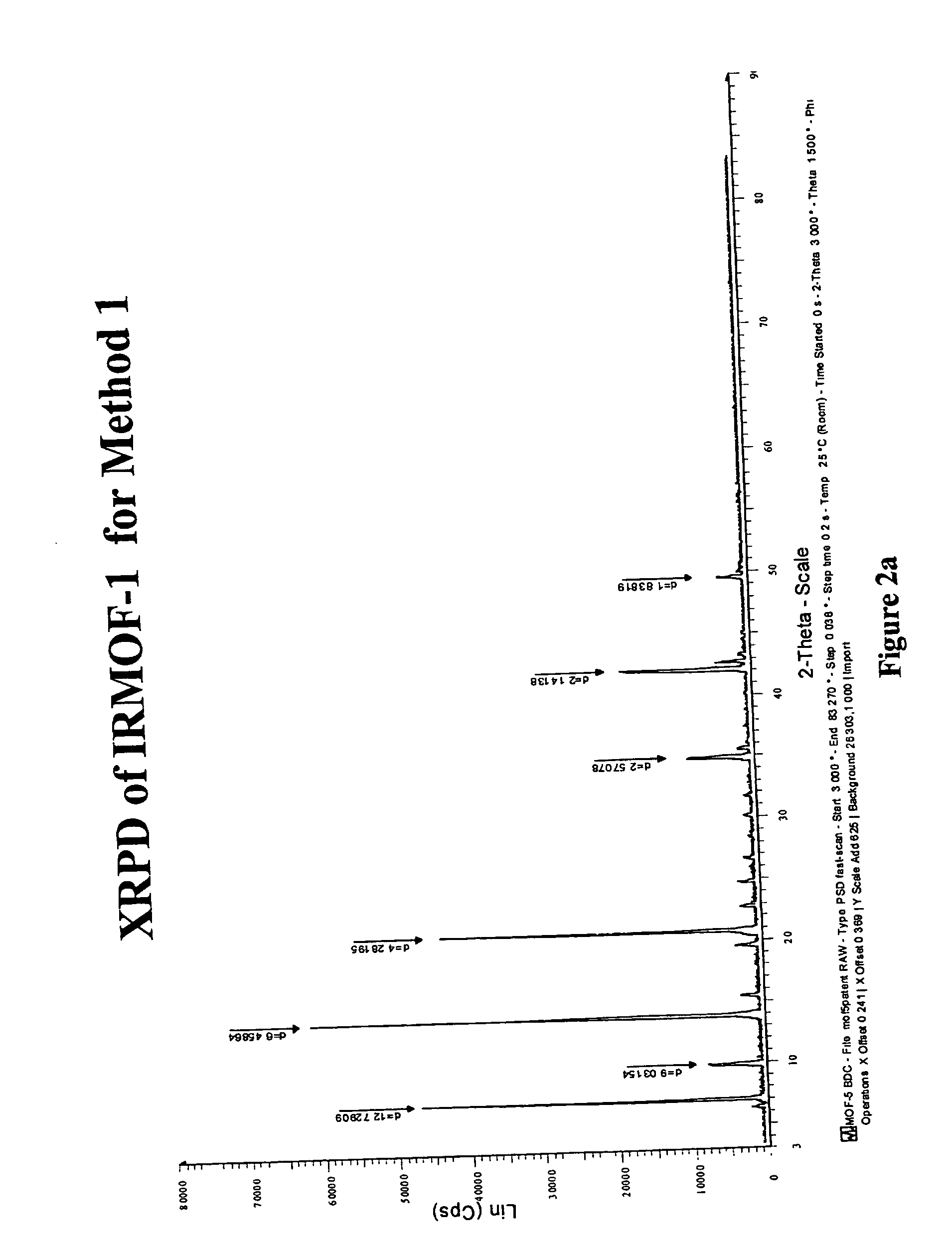
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS6930193B2High methane storage capacityIncrease storage capacityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsOrganic linkingSystems design
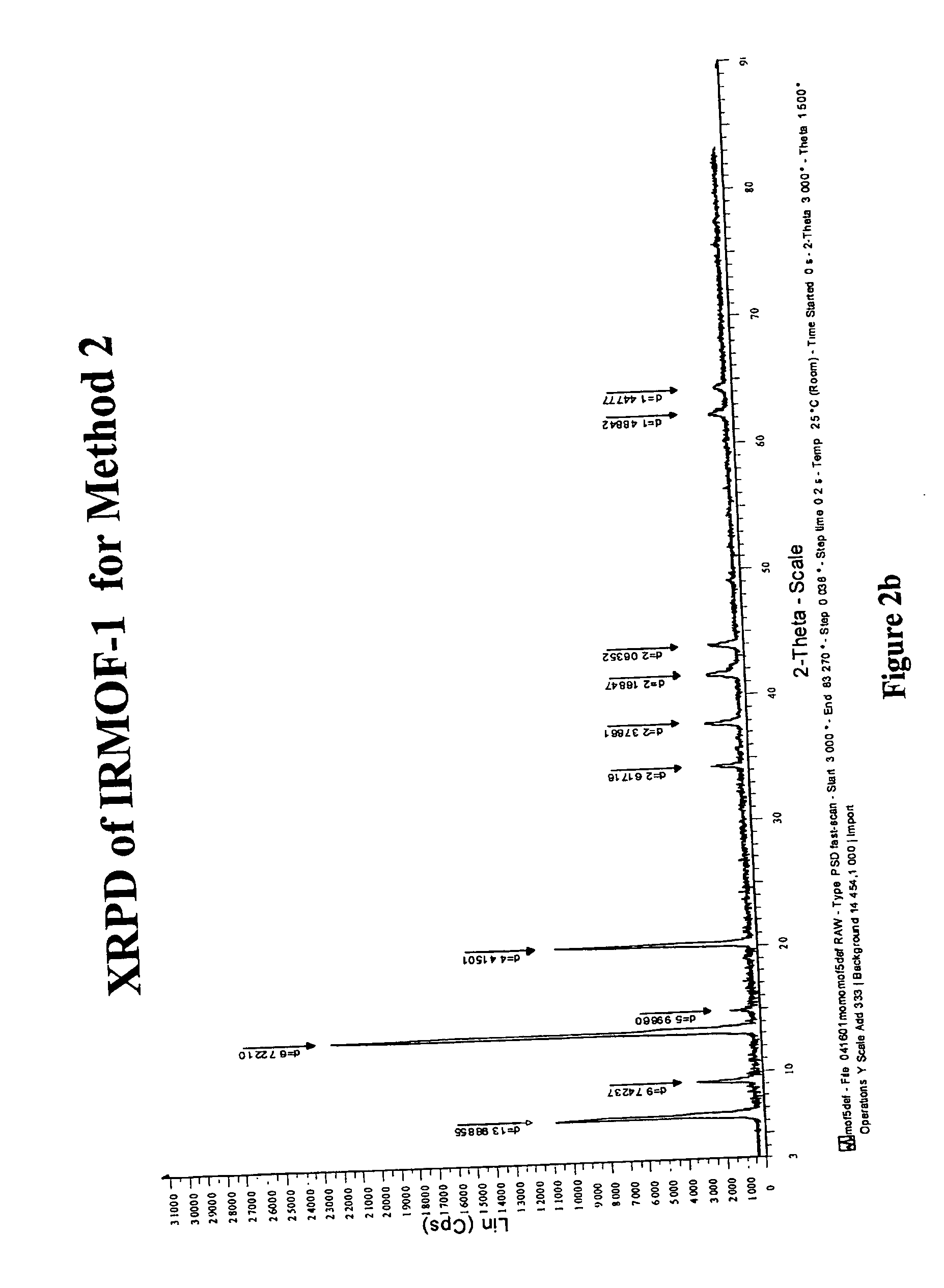
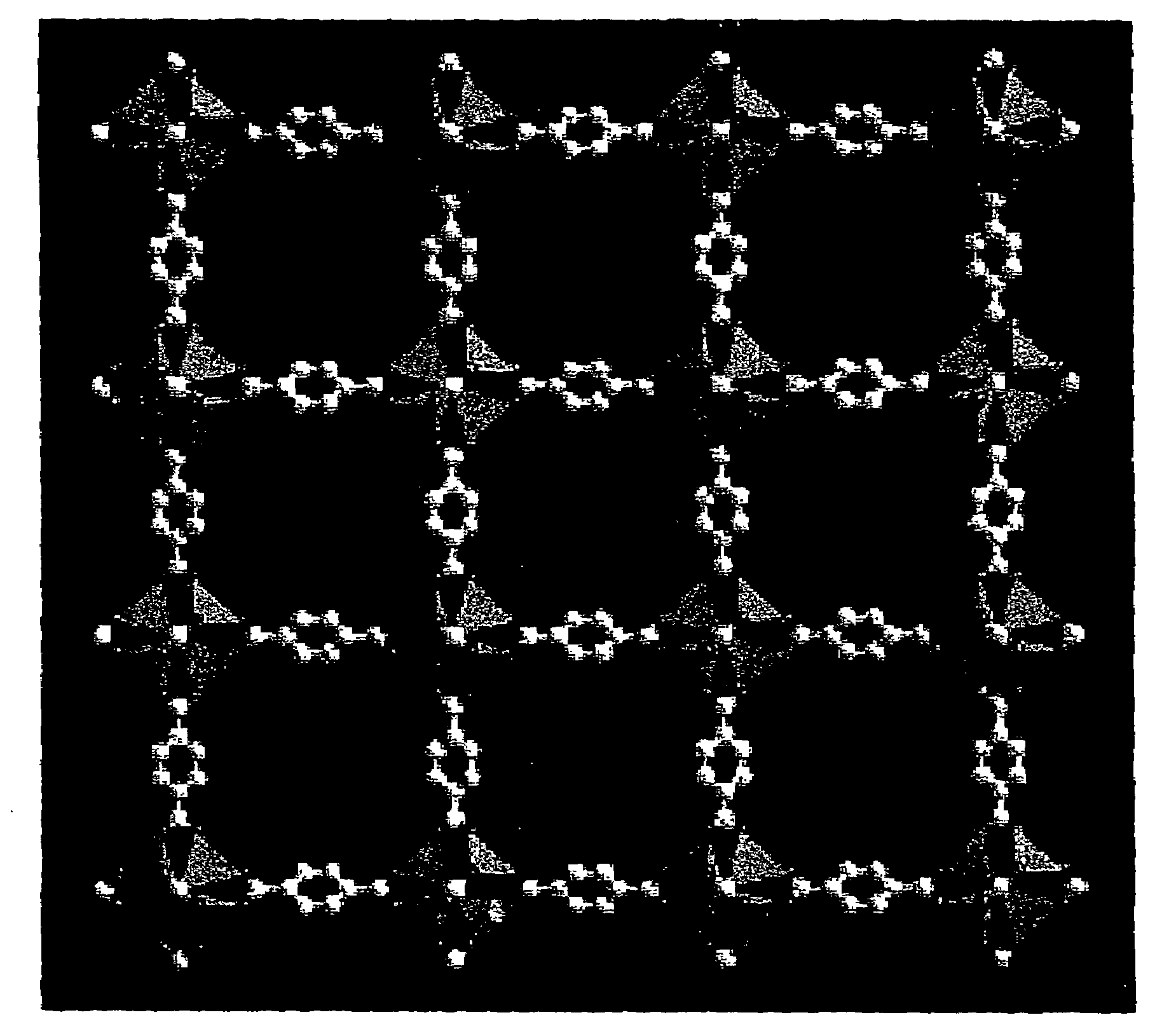
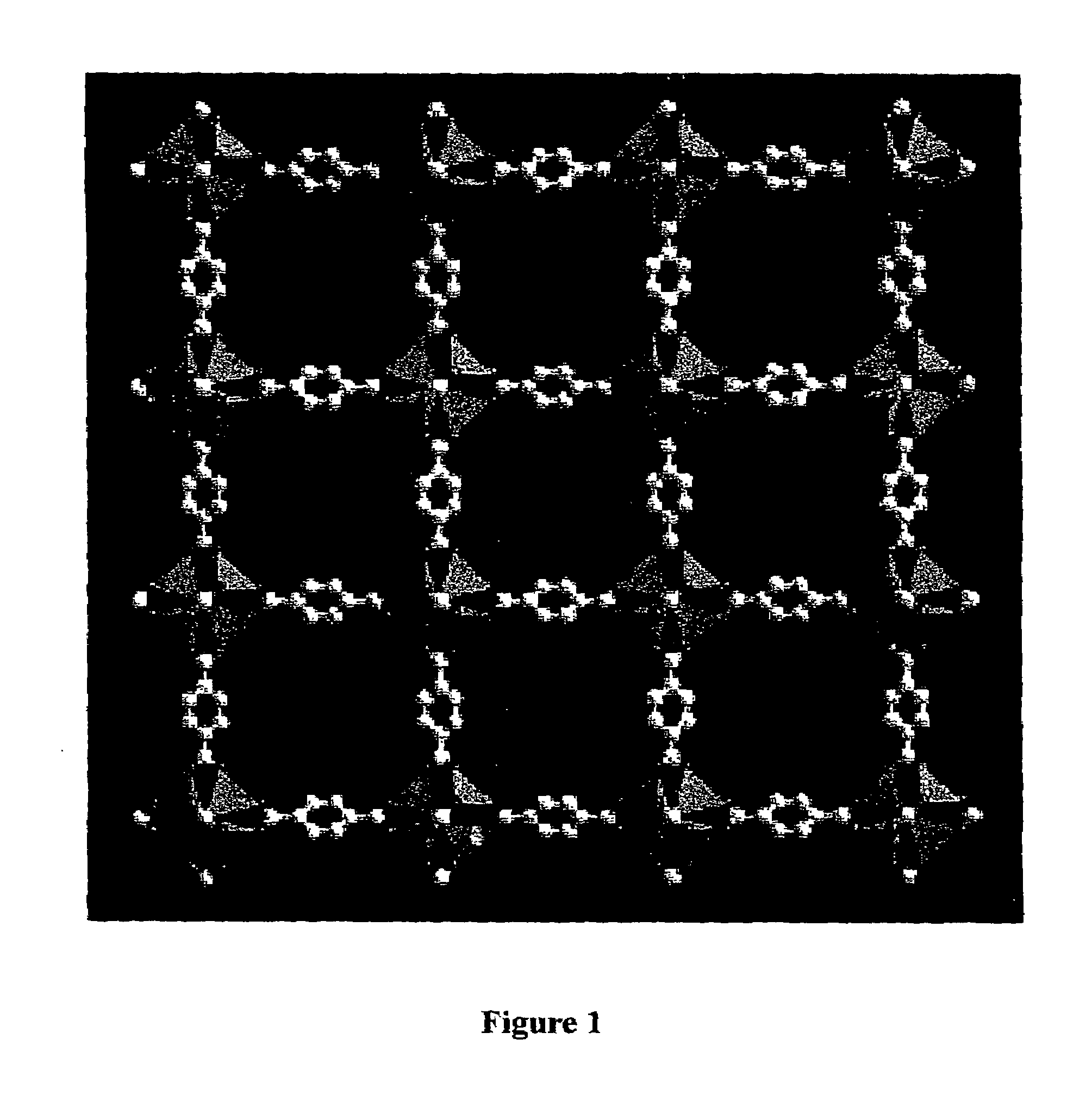
An isoreticular metal-organic framework (IRMOF) and method for systematically forming the same. The method comprises the steps of dissolving at least one source of metal cations and at least one organic linking compound in a solvent to form a solution; and crystallizing the solution under predetermined conditions to form a predetermined IRMOF. At least one of functionality, dimension, pore size and free volume of the IRMOF is substantially determined by the organic linking compound.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Grafted polymers as gas hydrate inhibitors
InactiveUS6867262B1Low ground water pollution classificationReduce security risksThermal non-catalytic crackingUsing liquid separation agentPolymerHydrate
Owner:BASF AG
Premium synthetic lubricants
InactiveUS6475960B1Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationAntioxidantBoiling point
Premium synthetic lubricants comprise a synthetic isoparaffinic hydrocarbon base stock and an effective amount of at least one, and typically a plurality of lubricant additives such as a detergent, dispersant, antioxidant, antiwear additive, pout point depresant, VI improver and the like. The base stock is derived from a waxy, paraffinic, Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon feed fraction having an initial boiling point in the range of about 650-750° F. and continuously boiling up to at least 1050° F., by a process which comprises hydroisomerizing the feed and dewaxing the isomerate. The waxy feed has a T90-T10 temperature difference of at least 350° F. and is preferably hydroisomerized without any pretreatment, other than optional fractionation. The lubricant may also contain hydrocarbonaceous and synthetic base stock material. Lubricants, such as fully formulated multigrade automotive crankcase and transmission oils formed by adding a suitable additive package to the isoparaffinic base stock have exhibited performance superior to similar fully formulated oils based on both PAO and conventional, petroleum derived base stocks.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS7196210B2Group 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSystems designMetal-organic framework
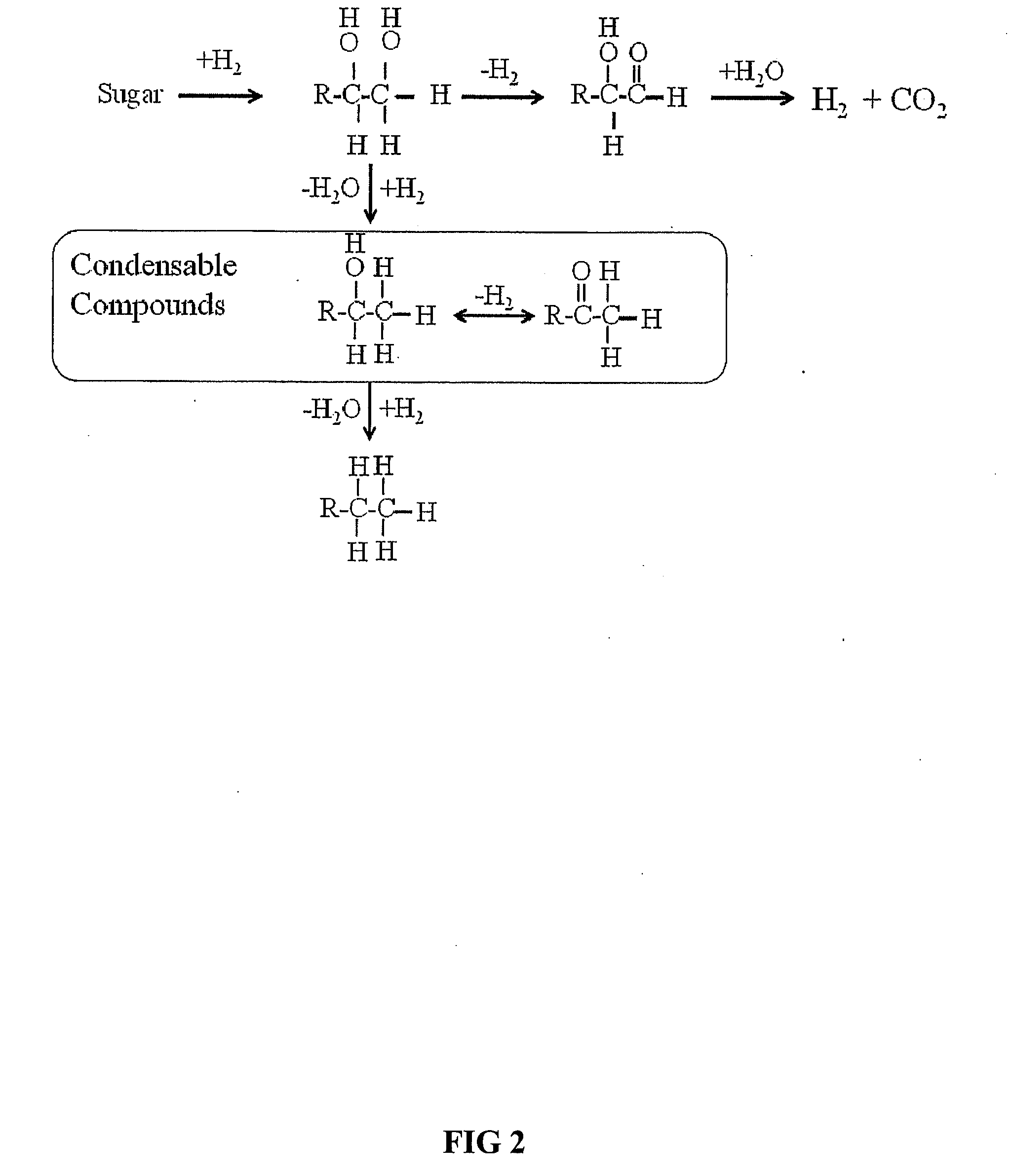
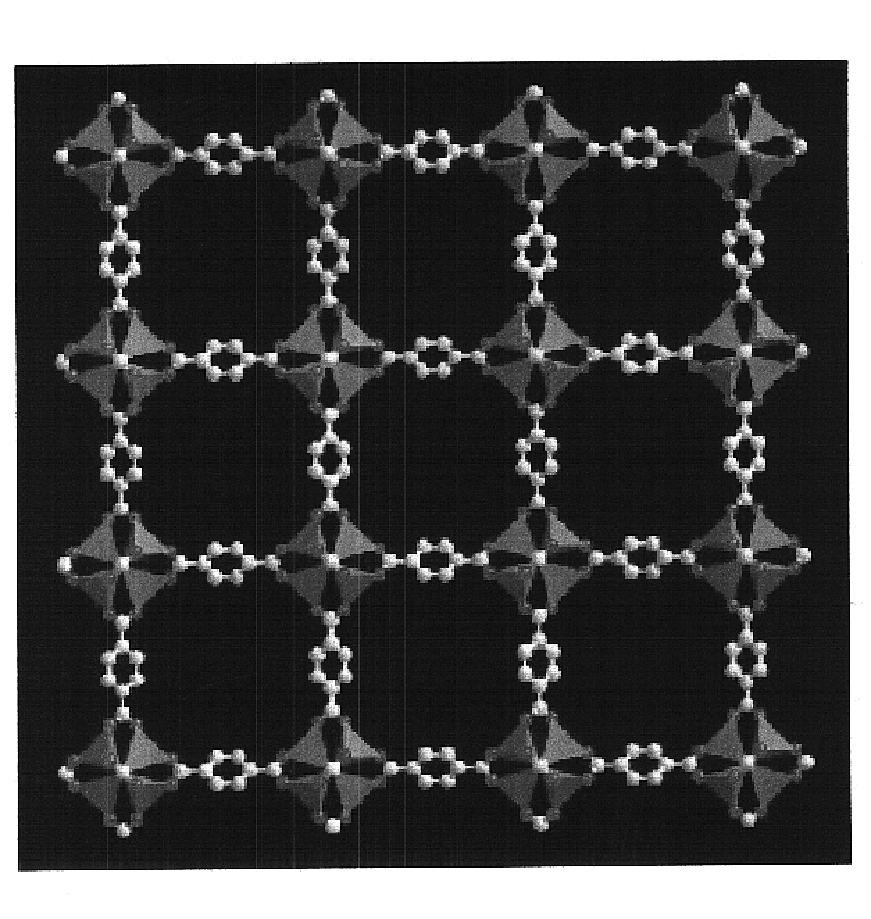
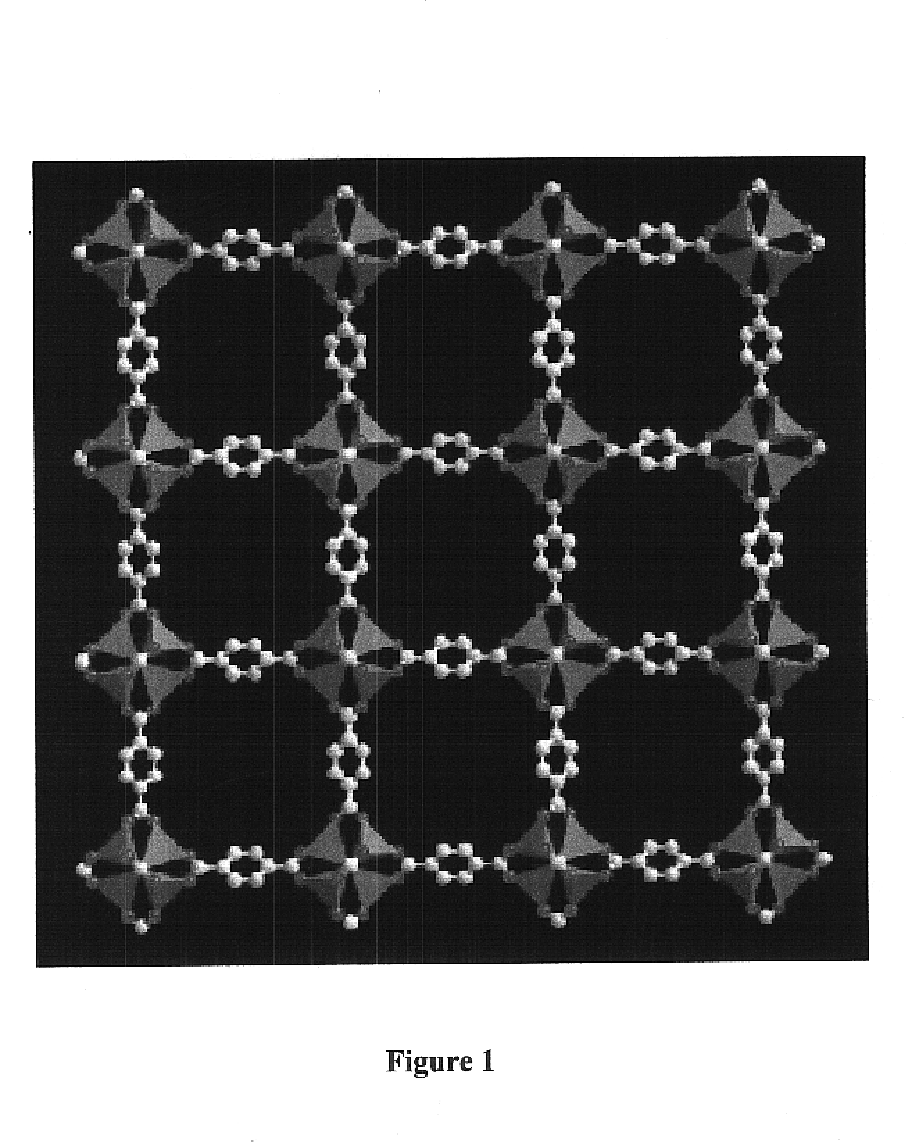
The ability to design and construct solid-state materials with pre-determined structures is a grand challenge in chemistry. An inventive strategy based on reticulating metal ions and organic carboxylate links into extended networks has been advanced to a point that has allowed the design of porous structures in which pore size and functionality can be varied systematically. MOF-5, a prototype of a new class of porous materials and one that is constructed from octahedral Zn—O—C clusters and benzene links, was used to demonstrate that its 3-D porous system can be functionalized with the organic groups, —Br, —NH2, —OC3H7, —OC5H11, —H4C2, and —H4C4, and its pore size expanded with the long molecular struts biphenyl, tetrahydropyrene, pyrene, and terphenyl. The ability to direct the formation of the octahedral clusters in the presence of a desired carboxylate link is an essential feature of this strategy, which resulted in the design of an isoreticular (having the same framework topology) series of sixteen well-defined materials whose crystals have open space representing up to 91.1% of the crystal volume, and homogeneous periodic pores that can be incrementally varied from 3.8 to 28.8 angstroms. Unlike the unpredictable nature of zeolite and other molecular sieve syntheses, the deliberate control exercised at the molecular level in the design of these crystals is expected to have tremendous implications on materials properties and future technologies. Indeed, data indicate that members of this series represent the first monocrystalline mesoporous organic / inorganic frameworks, and exhibit the highest capacity for methane storage (155 cm3 / cm3 at 36 atm) and the lowest densities (0.41 to 0.21 g / cm3) attained to date for any crystalline material at room temperature.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Production of Aviation Fuel from Biorenewable Feedstocks
ActiveUS20090158637A1Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationAlkaneVegetable oil
A process has been developed for producing aviation fuel from renewable feedstocks such as plant oils and animal fats and oils. The process involves treating a renewable feedstock by hydrogenating and deoxygenating to provide n-paraffins having from about 8 to about 24 carbon atoms. At least some of the n-paraffins are isomerized to improve cold flow properties. At least a portion of the paraffins are selectively cracked to provide paraffins meeting specifications for different aviation fuels such as JP-8.
Owner:UOP LLC
Gelled hydrocarbon compositions and methods for use thereof
InactiveUS6849581B1Improve stabilityAvoid stabilityOrganic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsOrganic baseOrganic fluid
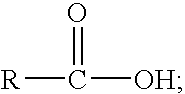
Gelled organic compositions and methods for using same. The gelled compositions may be liquid organic fluids, such as gelled liquid hydrocarbons, formed from a mixture of an organic-base fluid, a carboxylic acid, and one or more metal source compounds, such as a metal salt of carboxylic acid. The gelled compositions may be used in variety of applications including, but not limited to, oil field, pipeline and processing facility applications.
Owner:BJ SERVICES LLC +1
Preparation of olefins
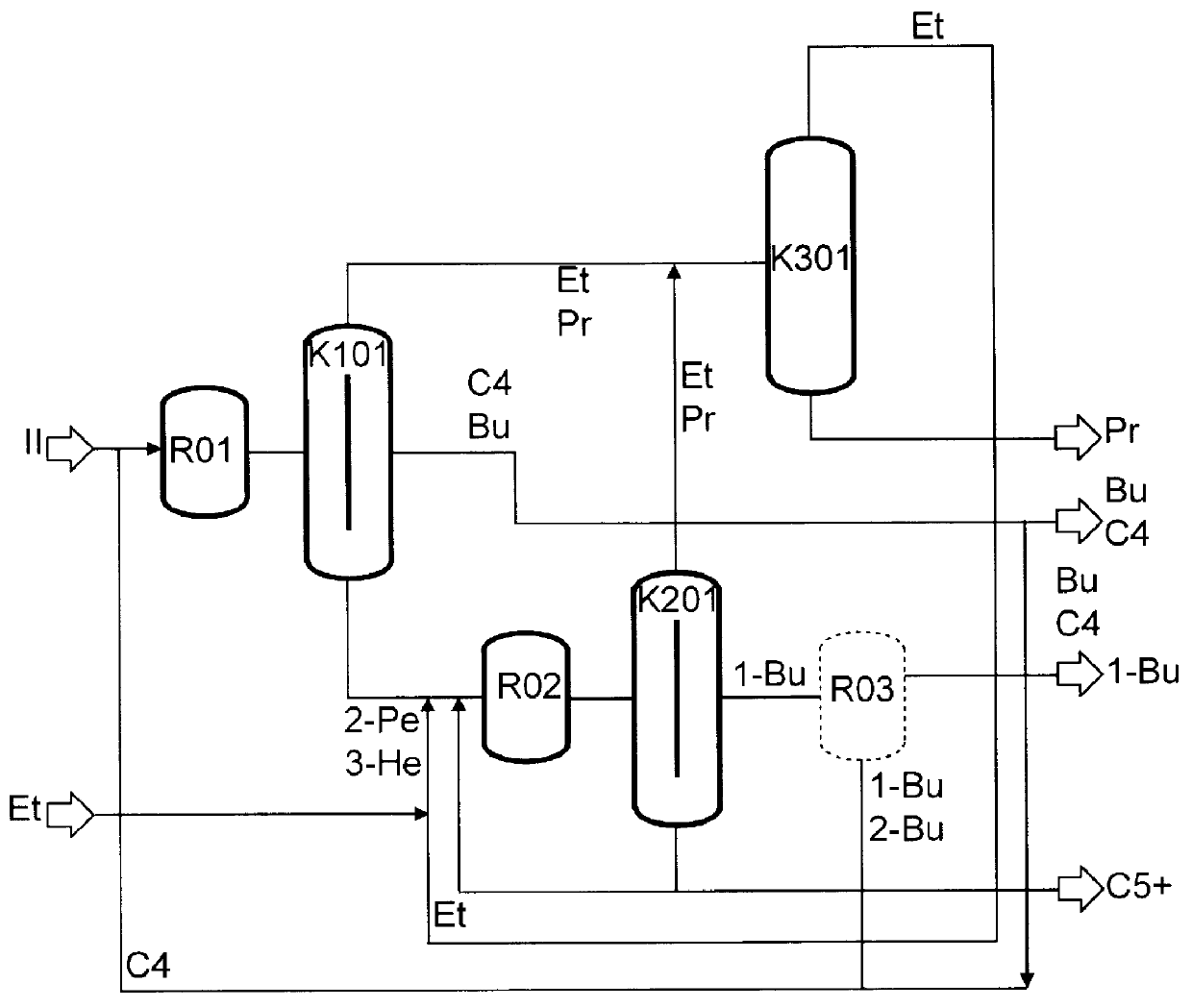
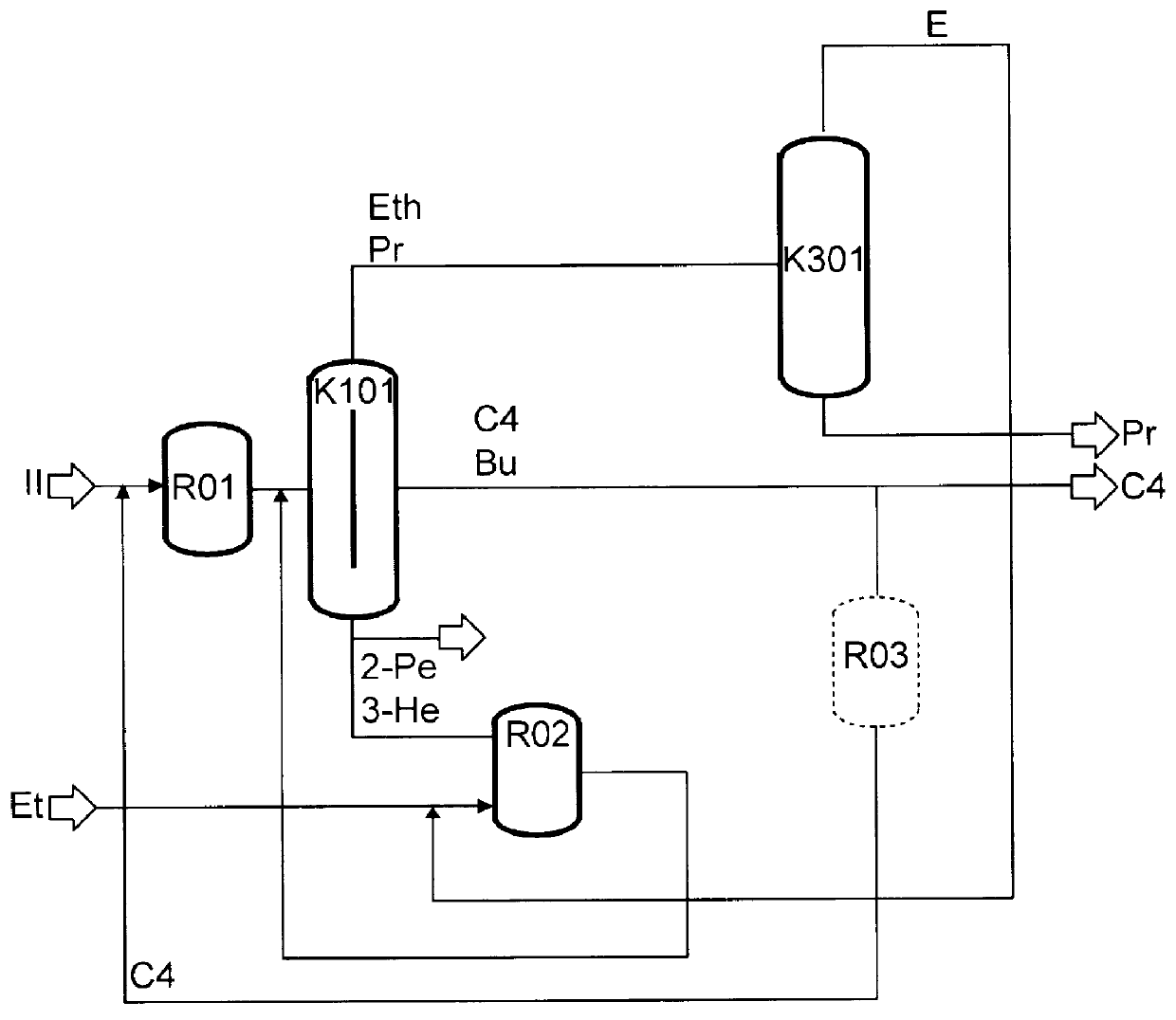
The preparation of olefins from steam cracker or refinery C4 streams is carried out by selective hydrogenation of butadienes and acetylenic impurities in the steam cracker or refinery C4 stream, with simultaneous or subsequent, at least partial isomerization of 1-butene to 2-butene, followed by removal of i-butene from the C4 stream by reaction with an alcohol to form an ether, followed by removal of oxygen-containing impurities from the C4 stream using adsorber materials, followed by two-stage metathesis of the butenes in the C4 stream by conversion of 1-butene and 2-butene present in the C4 stream into propene and 2-pentene and subsequent reaction of the 2-pentene with ethene in the presence of a metathesis catalyst to form propene and 1-butene. Optionally, butadiene may be removed from the C4 stream by extractive distillation in a preliminary step.
Owner:BASF AG
Palladium-silver bimetallic hydrogenation catalyst
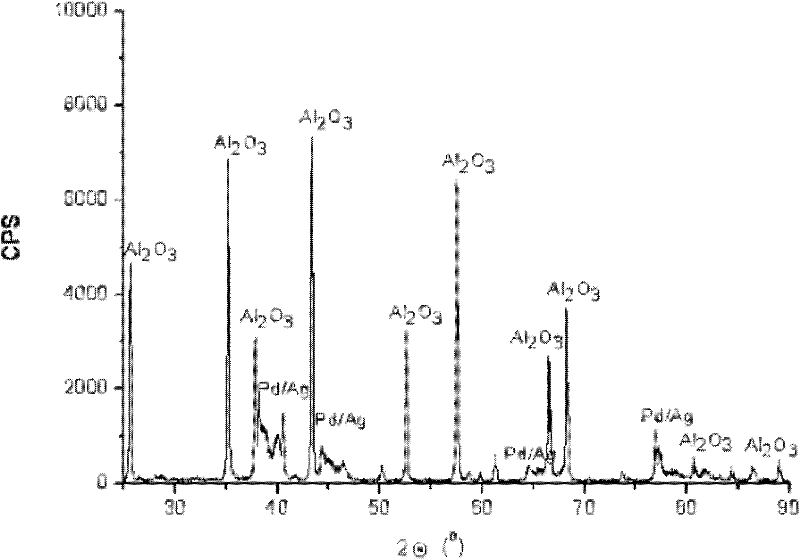
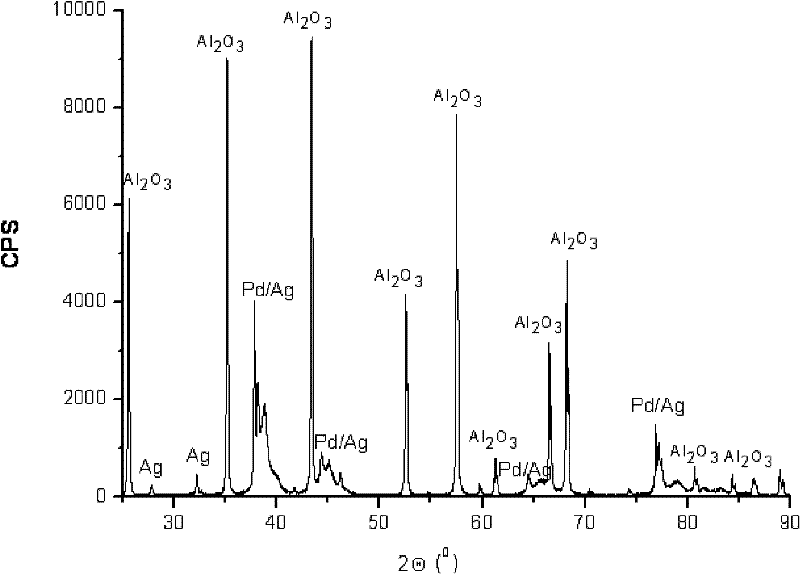
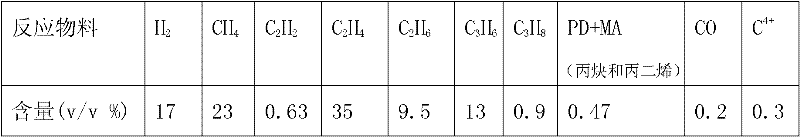
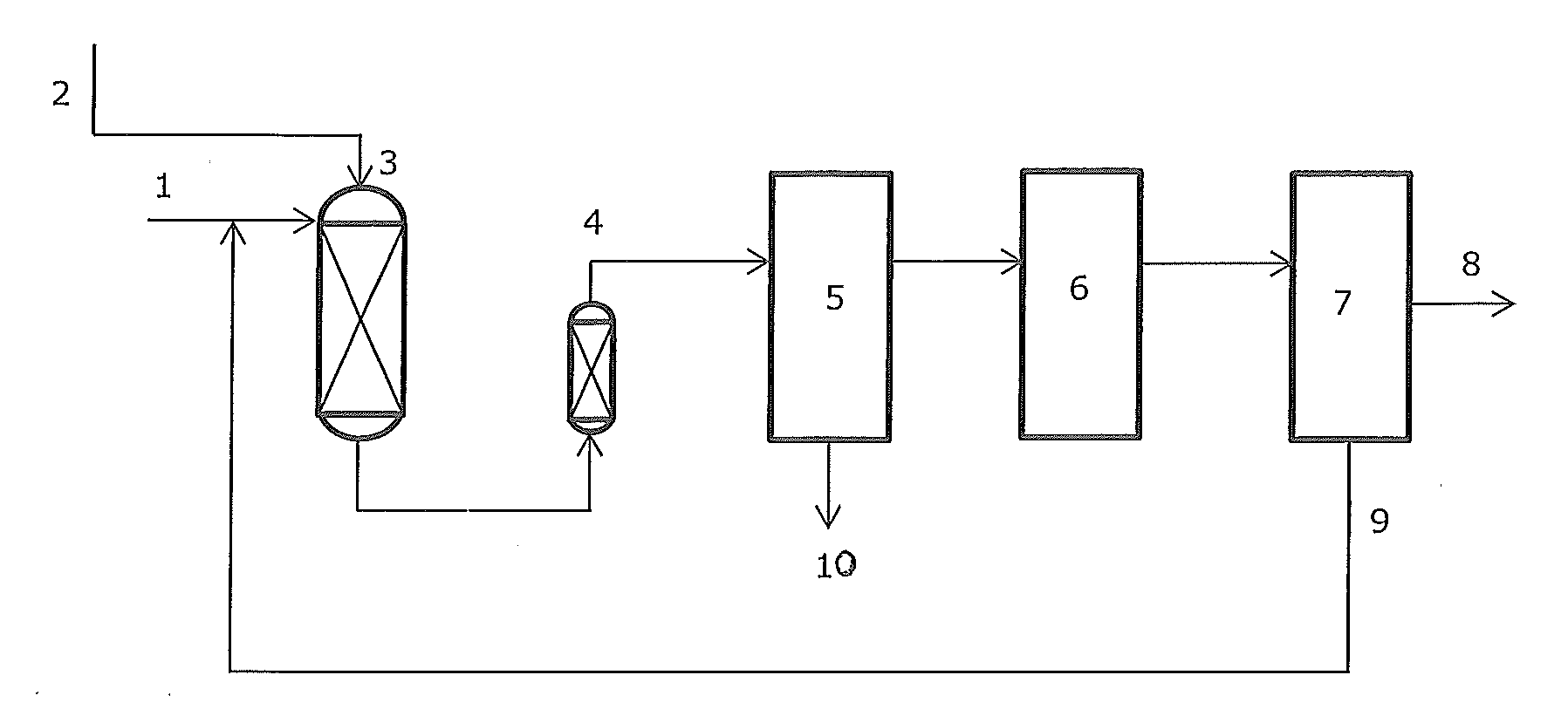
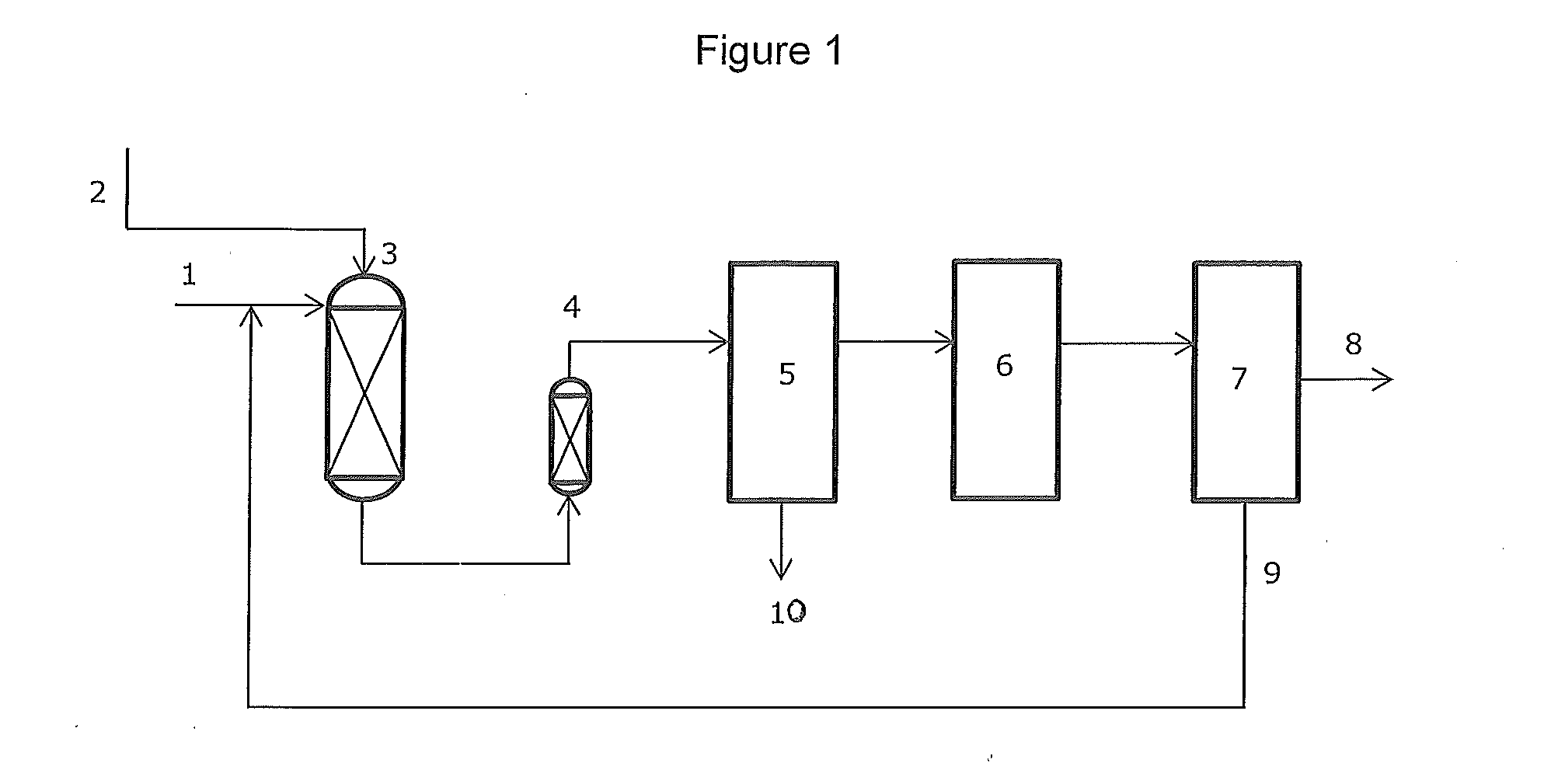
ActiveCN102205243AGood choiceImprove hydrogenation activityHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsHydrogenation processSolvation
The invention relates to a palladium-silver bimetallic hydrogenation catalyst, a carrier of which mainly contains Al2O3 and which is characterized by comprising, based on 100% of the catalyst weight, 0.01-0.4% of Pd, 0.02-0.2% of Ag, and has a specific surface area of 1-100m<2> / g. The catalyst is obtained through three steps of: first, preparing a functionalized-high-molecular / Al2O3 precursor, then preparing a Pd-Ag-high-molecular / Al2O3 precursor, and lastly roasting the precursors at 380-550 DEG C for 2-6h. The preparation method overcomes the influences of dipping liquid surface tensionand solvation effect on palladium-silver disperseness, and the prepared catalyst has excellent selectivity. The catalyst of the invention can be applied to selective hydrogenation process of fractions such as C2 and C3, and has a good hydrogenation activity, excellent selectivity and good hydrogenation stability.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Complex comprising oxidative dehydrogenation unit
ActiveUS20140249339A1Consumes lotThermal non-catalytic crackingSequential/parallel process reactionsAlkaneDehydrogenation
Oxidative dehydrogenation of paraffins to olefins provides a lower energy route to produce olefins. Oxidative dehydrogenation processes may be integrated with a number of processes in a chemical plant such as polymerization processes, manufacture of glycols, and carboxylic acids and esters. Additionally, oxidative dehydrogenation processes can be integrated with the back end separation process of a conventional steam cracker to increase capacity at reduced cost.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
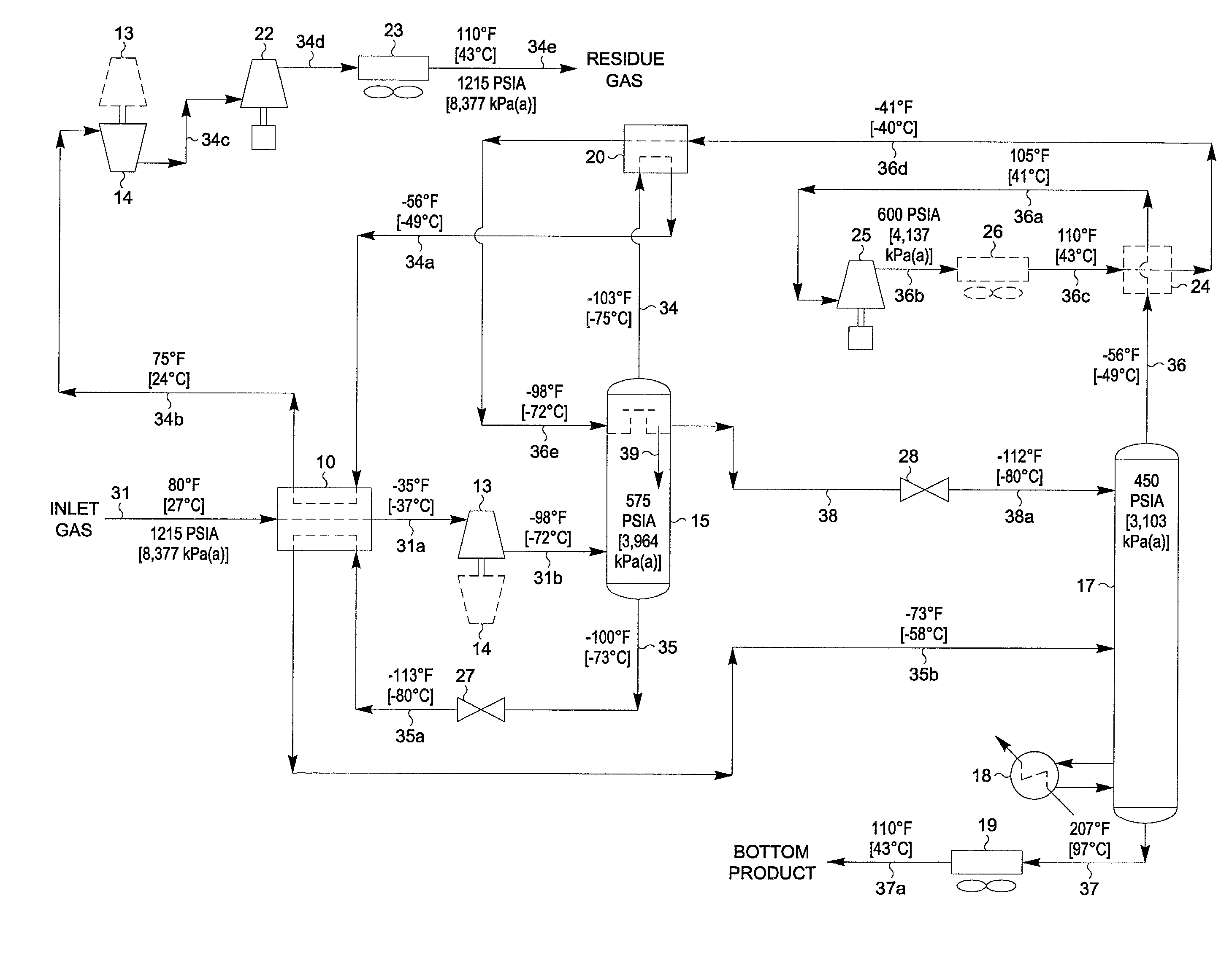
Hydrocarbon gas processing
A process for the recovery of propane, propylene and heavier hydrocarbon components from a hydrocarbon gas stream is disclosed. The stream is cooled and / or expanded to partially condense it, then separated to provide a first vapor stream. The first vapor stream is directed into a contacting device whereby vapors and liquids are formed. The liquids are directed to a distillation column operating at lower pressure wherein a second vapor stream is separated to recover a product containing the major portion of the C3 components and heavier hydrocarbon components. The second vapor stream is directed into heat exchange relation with the vapors to cool the second vapor stream and condense at least a part of it, forming a condensed stream. At least a portion of the condensed stream is directed to the contacting device to intimately contact the first vapor stream; the remaining portion (if any) of the condensed stream can be supplied to the distillation column as its top feed. The quantities and temperatures of the feeds to the contacting device and the distillation column are effective to maintain the overhead temperatures of the contacting device and the distillation column at temperatures whereby the major portion of the desired components is recovered.
Owner:ELCOR CORP
Composition of lubricating base oil with high monocycloparaffins and low multicycloparaffins
ActiveUS7083713B2Improve Oxidation StabilityHigh viscosity indexRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationCycloparaffinsBase oil
A composition of lubricating base oil having a weight percent of all molecules with at least one aromatic function less than 0.30, a weight percent of all molecules with at least one cycloparaffin function greater than 10, and a ratio of weight percent of molecules with monocycloparaffins to weight percent of molecules with multicycloparaffins greater than 15.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Premium synthetic lubricant base stock (Law734) having at least 95% noncyclic isoparaffins
A premium synthetic lubricating oil base stock having a high VI and low pour point is made by hydroisomerizing a Fischer-Tropsch synthesized waxy, paraffinic feed wax and then dewaxing the hydroisomerate to form a 650-750° F.+ dewaxate. The waxy feed has an initial boiling point in the range of about 650-750° F., from which it continuously boils up to at least 1050° F. and has a T90-T10 temperature difference of at least 350° F. The feed is preferably hydroisomerized without any pretreatment, other than optional fractionation. The 650-750° F.+ dewaxate is fractionated into two or more base stocks of different viscosity.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Base oil
ActiveUS20070135663A1Improve technical effectReduce fuel consumptionHydrocarbon purification/separationLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCarbon numberViscosity index
The invention relates to a new base stock material. Specifically the invention relates to a saturated hydrocarbon composition and particularly to a composition based on biological raw materials, to be used as a high-quality base oil or to be used as a component in the production of a base oil having a high viscosity index and good low temperature properties. The composition contains saturated hydrocarbons and has a narrow carbon number range.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Methods and compositions for producing olefins
Owner:LS9 INC +1
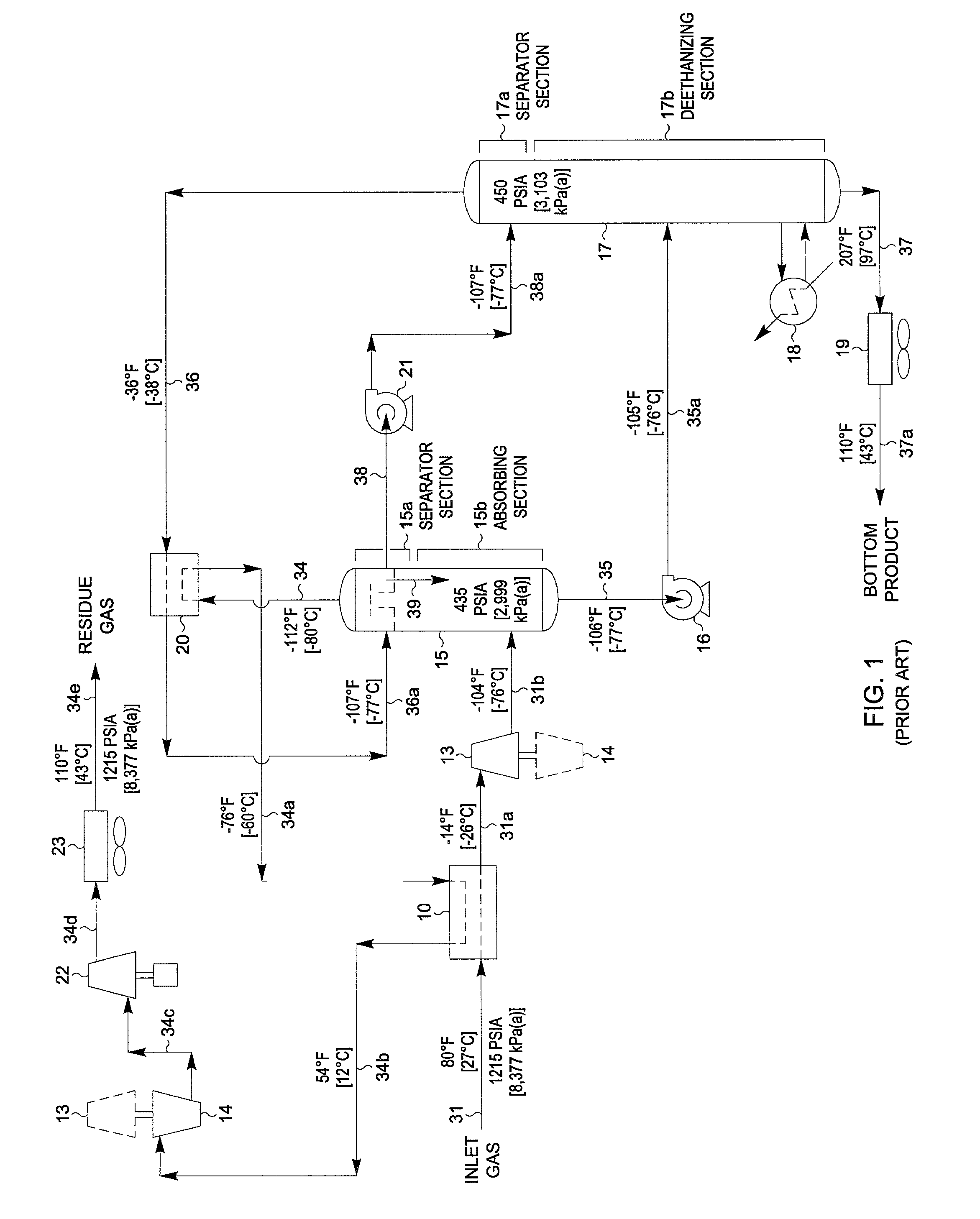
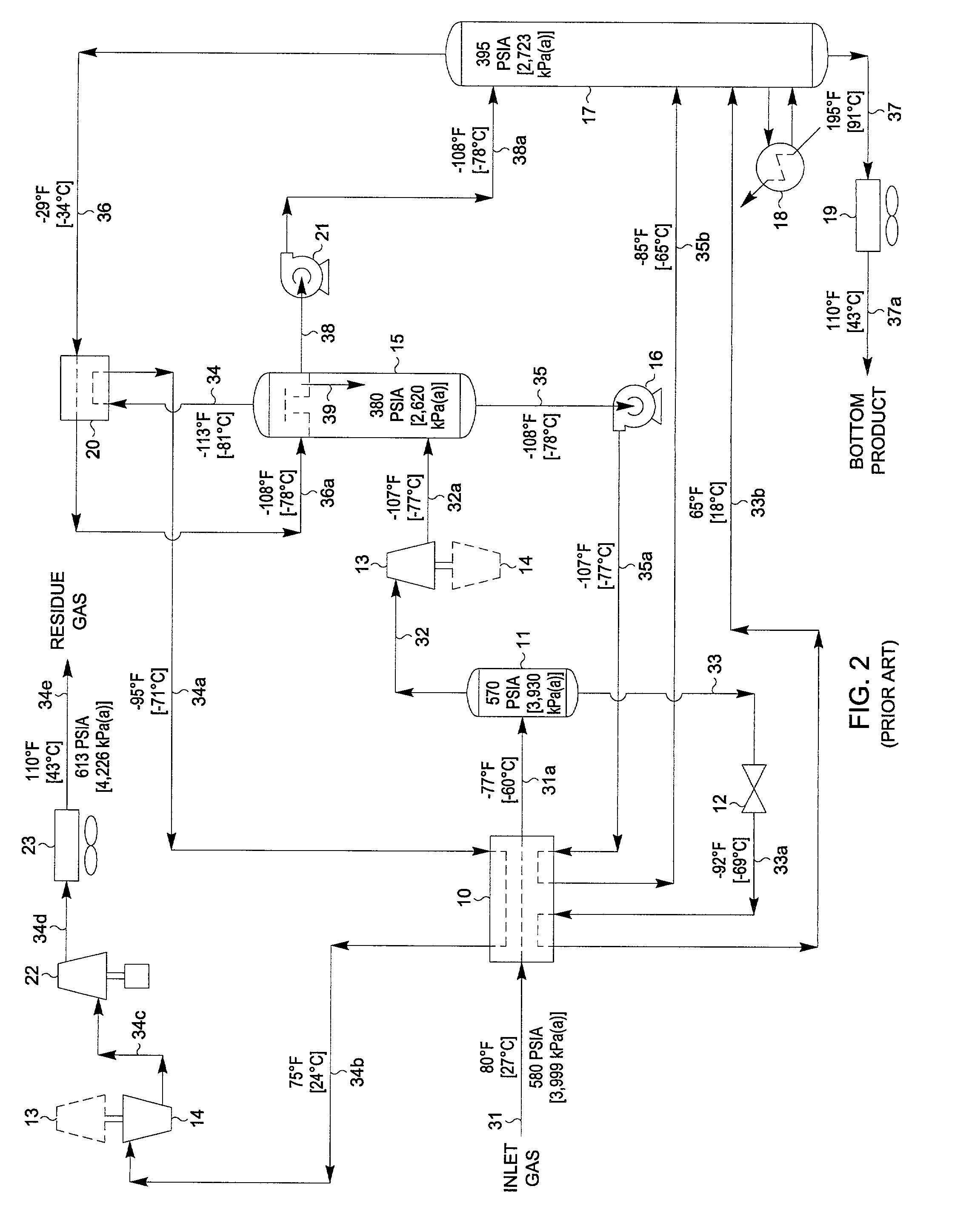
Hydrocarbon separation process and apparatus
InactiveUS6363744B2Reduce the temperaturePromote recoverySolidificationLiquefactionPhysical chemistryRefrigeration
A process is described for separating the heavier hydrocarbons from a gaseous hydrocarbon feed wherein a first separator is employed to separate partially condensed gaseous feed and wherein the vapour portion undergoes work expansion and is fed to a fractionation column. The liquid portion is subcooled in heat exchange with the overhead vapour from the fractionation column, expanded, evaporated to provide refrigeration at a low temperature level, and fed to the fractionation column. The rewarmed residual vapour is subsequently compressed to a pressure suitable for export, with a portion of the compressed gas being cooled, condensed and recycled back to reflux the top section of the fractionation column.Also described is a process wherein a first separator is employed to separate partially condensed gaseous feed and wherein the vapour portion undergoes work expansion and is fed to a high pressure wash column. The liquid portion is expanded and fed to the base of the high pressure wash column. Bottoms liquid from the wash column is subcooled in heat exchange with the overhead vapour from a fractionation column, expanded, evaporated to provide refrigeration at a low temperature level, and fed to the fractionation column. Vapour from the high pressure wash column is partially condensed, with the liquid portion used to provide reflux to the high pressure wash column and the fractionation column.The processes are especially applicable to recovery of ethane and heavier components from natural gas. Overall process power requirements are reduced, recovery of the desired heavy hydrocarbons is increased or both of these effects are realised.
Owner:COSTAIN OIL GAS & PROCESS
Catalyst and process for the selective hydrogenation of unsaturated compounds in hydrocarbon streams
InactiveUS6350717B1Maintain good propertiesHigh selectivityOrganic chemistry methodsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbonChemistry
A catalyst comprising at least one metal of the 10th group of the Periodic Table of the Elements and at least one metal of the 11th group of the Periodic Table of the Elements on an aluminum oxide support, wherein the metal or metals of the 10th group is or are essentially concentrated in an outer layer close to the surface of the catalyst particle, the metal or metals of the 11th group is or are distributed essentially uniformly over the volume of the catalyst particle and the weight ratio of the metal or metals of the 11th group to the metal or metals of the 10th group is not more than 1.95.
Owner:BASF AG
Acetylene hydrocarbon selective hydrogenation method
ActiveCN101434508AGood hydrogenation effectImprove hydrogenation activityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationButadiene DioxideUnsaturated hydrocarbon
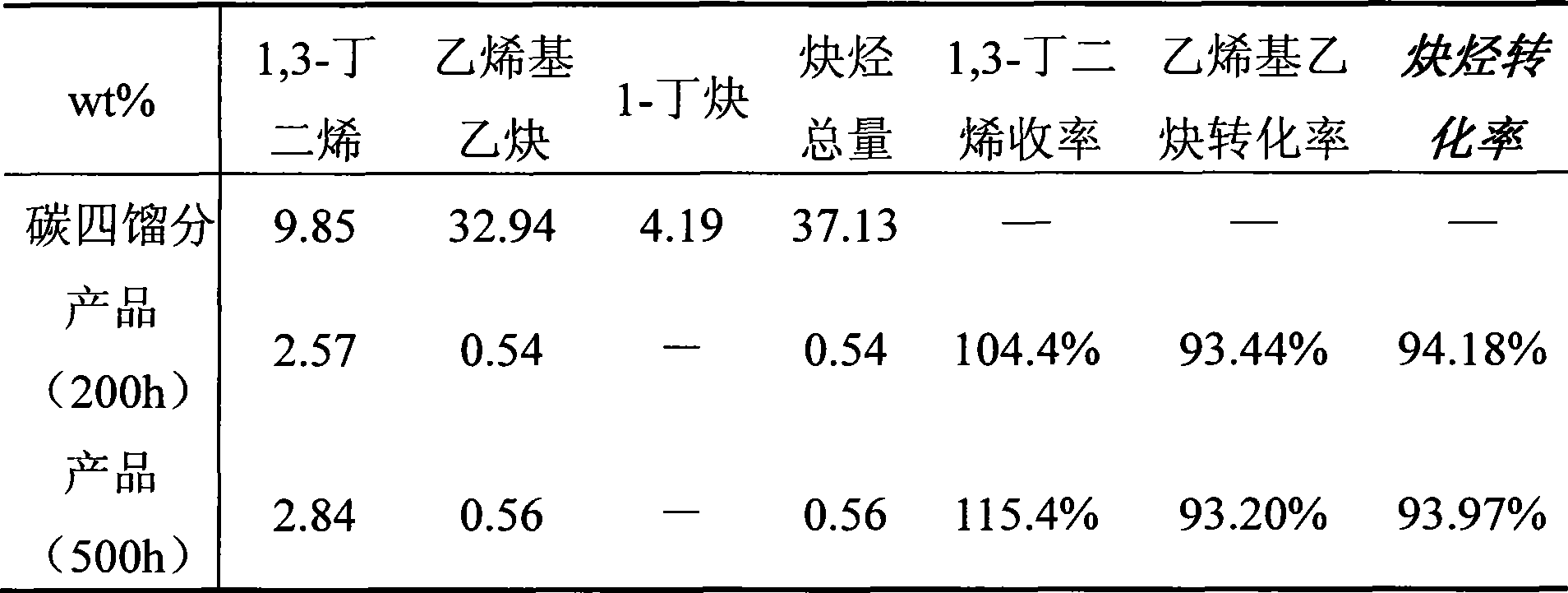
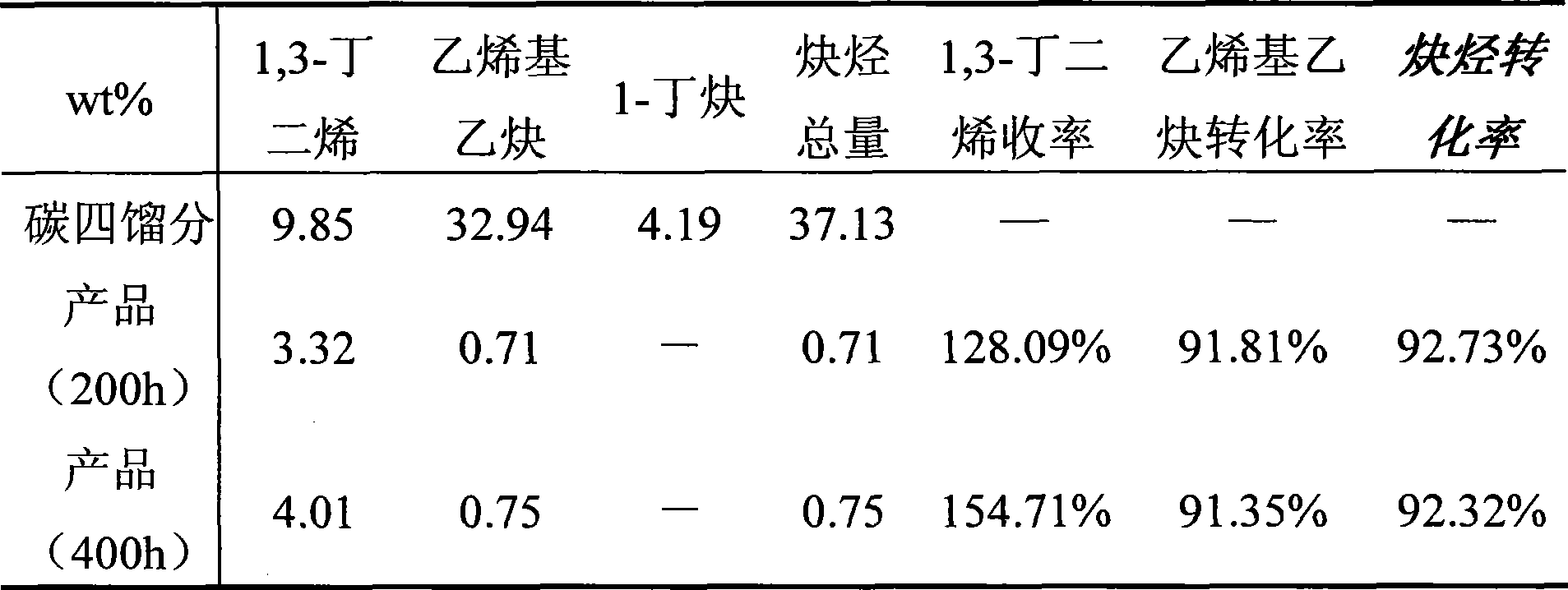
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation method of high unsaturated hydrocarbons in C4 fractions, which is characterized in that salvage stores which are rich in acetylene hydrocarbon and prepared by extracting butadiene are used as the material, and a fixed bed reactor is adopted to obtain 1, 3-budiene by selective hydrogenation under the existence of a catalyst. The adopted process conditions are as follows: the reaction temperature is between 30 DEG C and 90 DEG C, the reaction pressure is between 1.0 MPa and 4.0 MPa and the liquid space velocity is 7 to 20h<-1>. The catalyst is preferably a palladium system catalyst with alumina as a carrier, the specific surface is 50 to 150m<2> / g and the specific pore volume is 0.25 to 1.0ml / g. The method has remarkable good effects on reducing waste of resources and improving economic benefits by effectively utilizing the salvage stores rich in acetylene hydrocarbon and prepared by extracting butadiene.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Regeneration of acidic catalysts
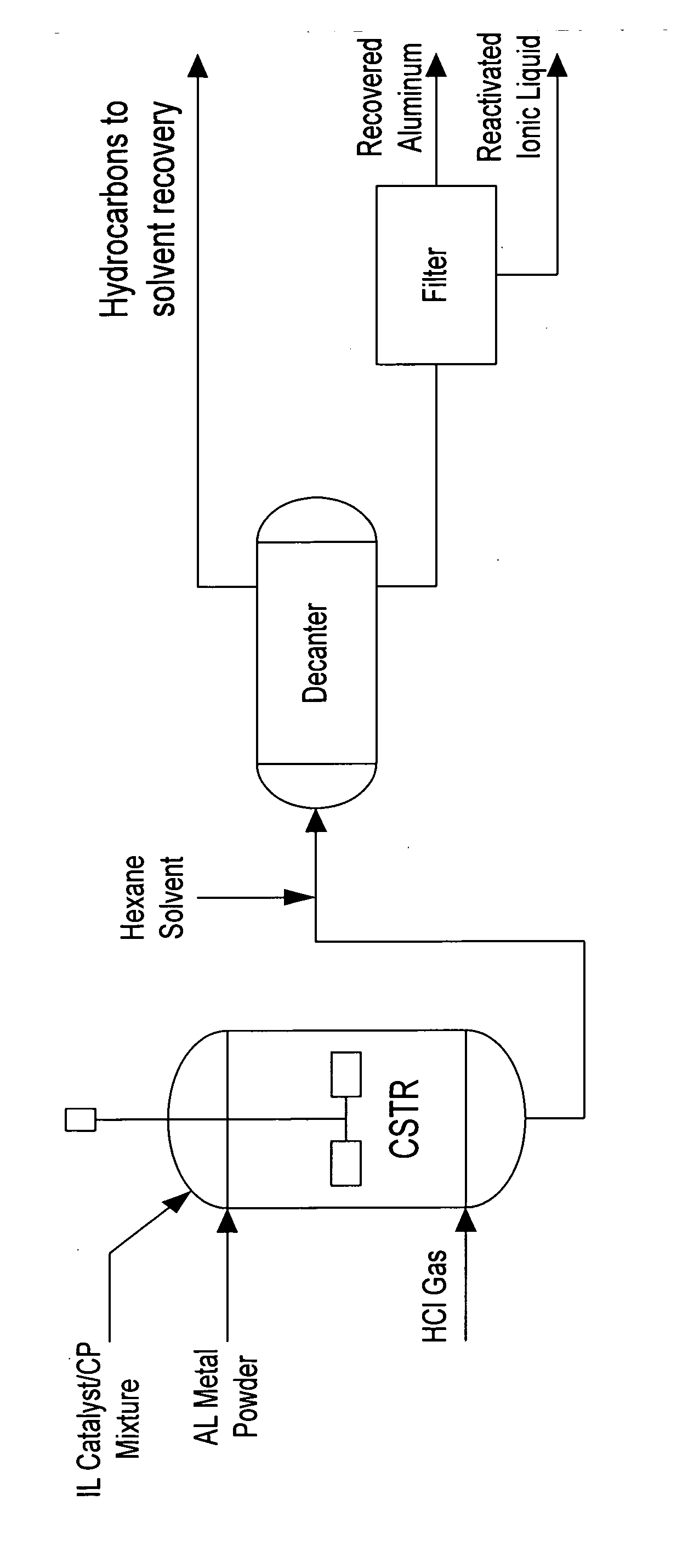
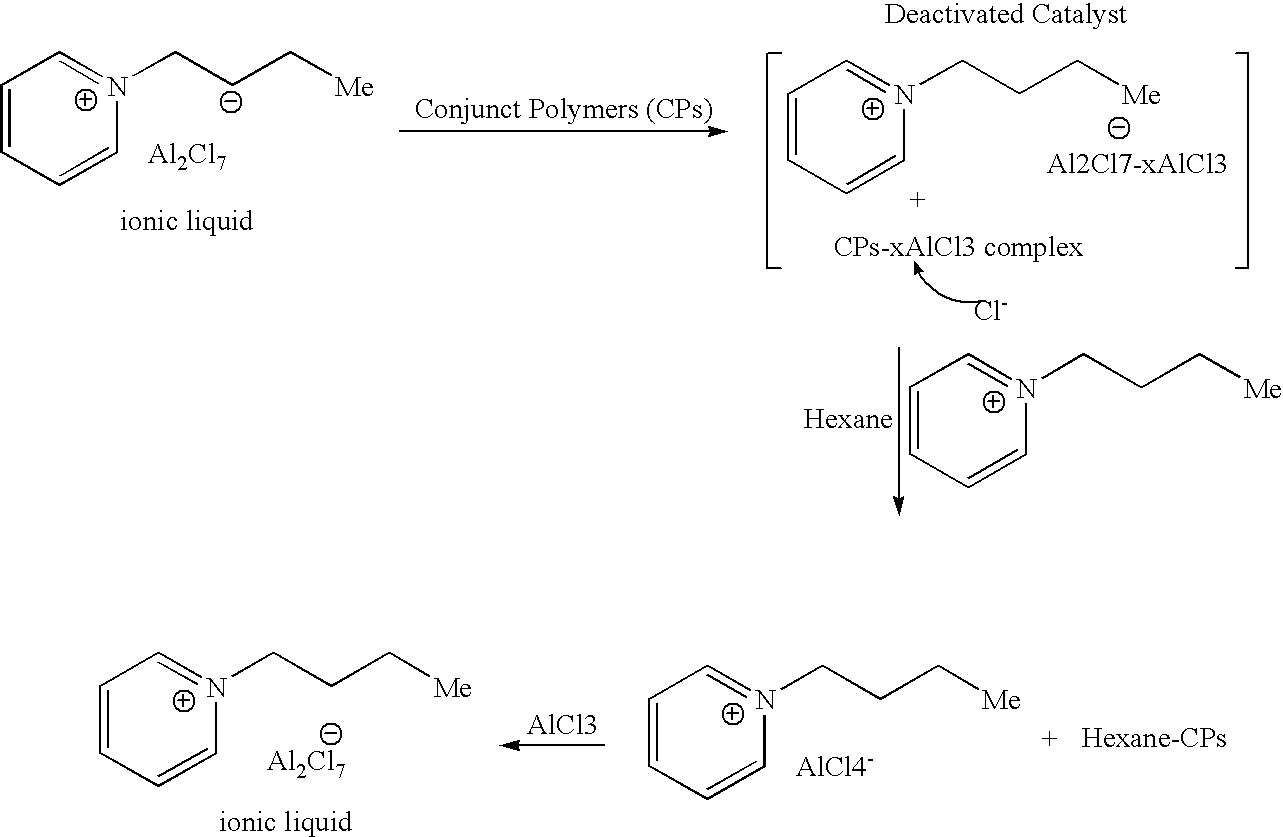
ActiveUS20070142213A1High activityChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationSulfur compoundsAlkyl transferIonic liquid
A process for regenerating a used acidic catalyst which has been deactivated by conjunct polymers by removing the conjunct polymers so as to increase the activity of the catalyst is disclosed. Methods for removing the conjunct polymers include hydrogenation, addition of a basic reagent and alkylation. The methods are applicable to all acidic catalysts and are described with reference to certain ionic liquid catalysts.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Combined cracking and selective hydrogen combustion for catalytic cracking
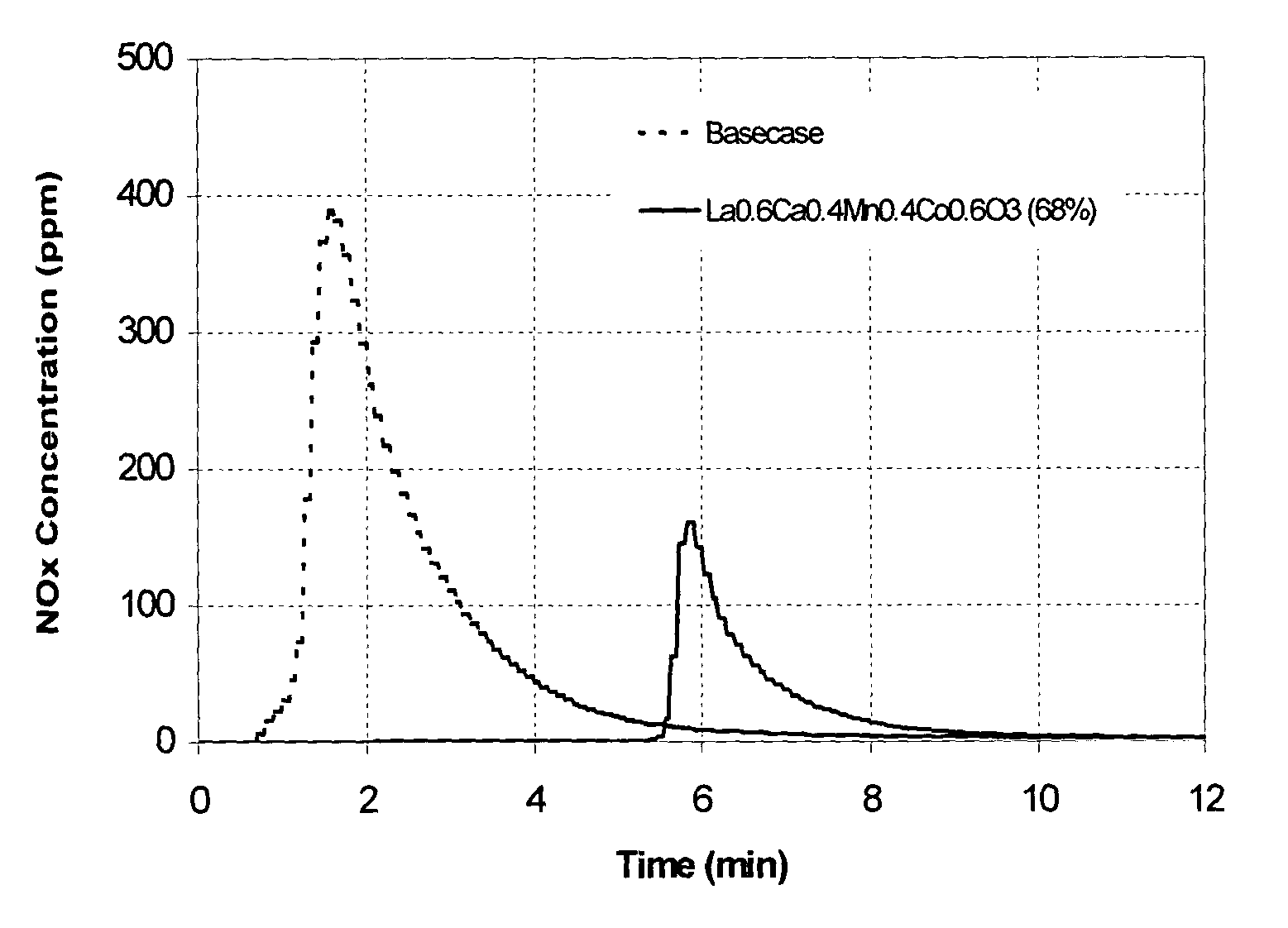
A catalyst system and process for combined cracking and selective hydrogen combustion of hydrocarbons are disclosed. The catalyst system contains at least one solid acid component and at least one metal-based component which consists of (a) oxygen and / or sulfur and (b) a metal combination selected from the group consisting of: i) at least one metal from Group 3 and at least one metal from Groups 4-15 of the Periodic Table of the Elements; ii) at least one metal from Groups 5-15 of the Periodic Table of the Elements, and at least one metal from at least one of Groups 1, 2, and 4 of the Periodic Table of the Elements; iii) at least one metal from Groups 1 and 2, at least one metal from Group 3, and at least one metal from Groups 4-15 of the Periodic Table of the Elements; and iv) two or more metals from Groups 4-15 of the Periodic Table of the Elements, wherein the at least one of oxygen and sulfur is chemically bound both within and between the metals and, optionally, (3) at least one of at least one support, at least one filler and at least one binder. The process is such that the yield of hydrogen is less than the yield of hydrogen when contacting the hydrocarbons with the solid acid component alone. Further the emissions of NOx from the regeneration cycle of the catalyst system are reduced.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for the production of gasolines with low sulfur contents
InactiveUS6692635B2Increase chanceMinimizing the octane lossHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationDecompositionGasoline
Process for the production of gasoline with a low sulfur content that comprises at least the following two stages:a) a hydrogenation stage of the unsaturated sulfur containing compounds,b) a decomposition stage of saturated sulfur containing compounds,and optionally a preliminary stage for pretreatment of the feedstock such as selective hydrogenation of dienes.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
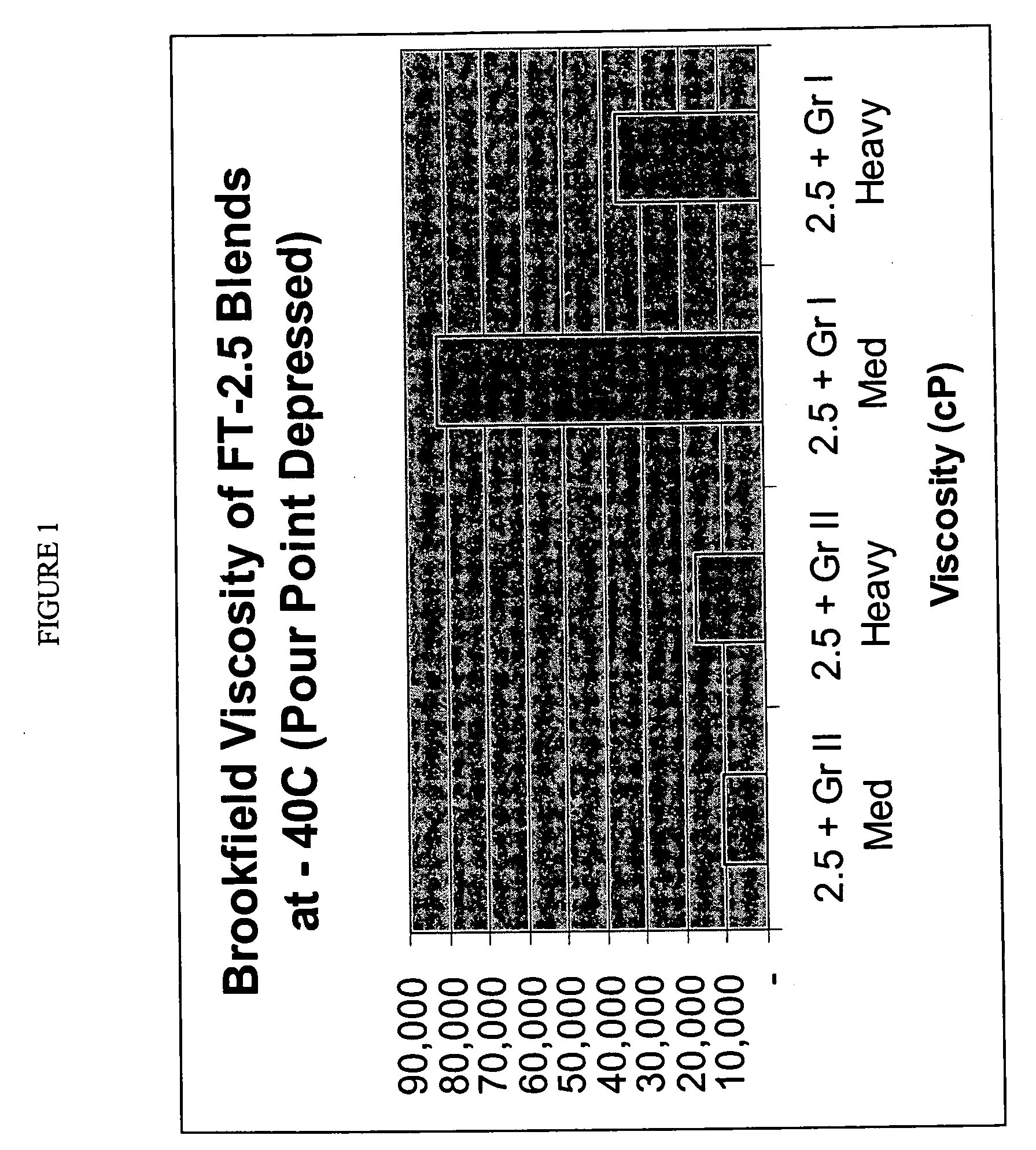
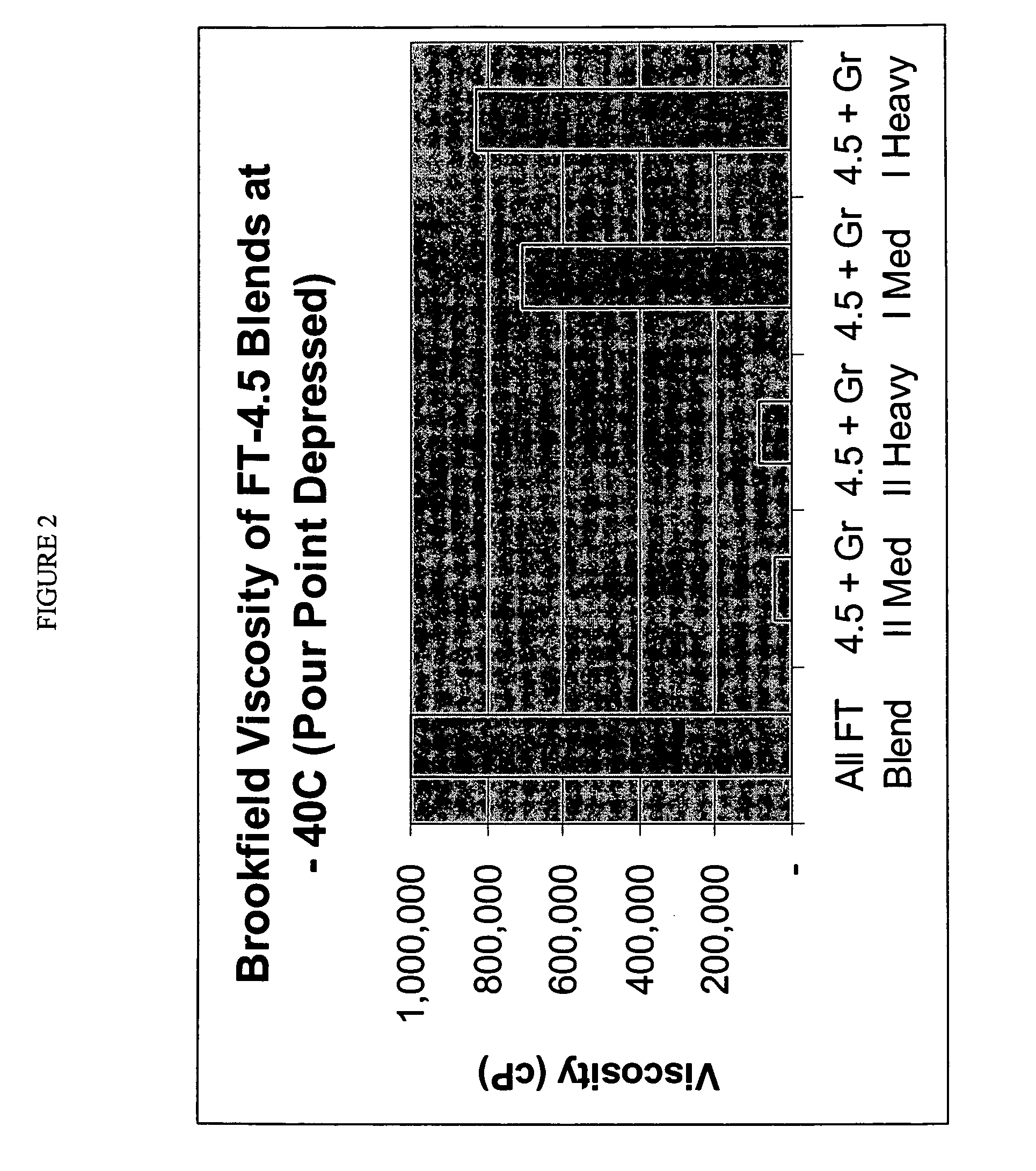
Processes for making lubricant blends with low brookfield viscosities
InactiveUS20050261146A1Improve low temperature performanceLow viscosityRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationParaffin waxSulfur
Lubricant blends and finished gear oils comprising a lubricant base oil fraction derived from highly paraffinic wax, a petroleum derived base oil, and a pour point depressant are provided. The lubricant base oil fraction derived from highly paraffinic wax comprises less than 0.30 weight percent aromatics, greater than 5 weight percent molecules with cycloparaffinic functionality, and a ratio of weight percent of molecules with monocycloparaffinic functionality to weight percent of molecules with multicycloparaffinic functionality greater than 15. The petroleum derived base oils comprises greater than 90 weight percent saturates and less than 300 ppm sulfur and is preferably selected from the group consisting of a Group II base oil, a Group III base oil, and mixtures thereof. These lubricant blends have surprising low Brookfield viscosities at −40° C.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS20050192175A1Catalyst protectionMolecular sieve catalystsSystems designMetal-organic framework
The ability to design and construct solid-state materials with pre-determined structures is a grand challenge in chemistry. An inventive strategy based on reticulating metal ions and organic carboxylate links into extended networks has been advanced to a point that has allowed the design of porous structures in which pore size and functionality can be varied systematically. MOF-5, a prototype of a new class of porous materials and one that is constructed from octahedral Zn—O—C clusters and benzene links, was used to demonstrate that its 3-D porous system can be functionalized with the organic groups, —Br, —NH2, —OC3H7, —OC5H11, —H4C2, and —H4C4, and its pore size expanded with the long molecular struts biphenyl, tetrahydropyrene, pyrene, and terphenyl. The ability to direct the formation of the octahedral clusters in the presence of a desired carboxylate link is an essential feature of this strategy, which resulted in the design of an isoreticular (having the same framework topology) series of sixteen well-defined materials whose crystals have open space representing up to 91.1% of the crystal volume, and homogeneous periodic pores that can be incrementally varied from 3.8 to 28.8 angstroms. Unlike the unpredictable nature of zeolite and other molecular sieve syntheses, the deliberate control exercised at the molecular level in the design of these crystals is expected to have tremendous implications on materials properties and future technologies. Indeed, data indicate that members of this series represent the first monocrystalline mesoporous organic / inorganic frameworks, and exhibit the highest capacity for methane storage (155 cm3 / cm3 at 36 atm) and the lowest densities (0.41 to 0.21 g / cm3) attained to date for any crystalline material at room temperature.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Composition of lubricating base oil with high monocycloparaffins and low multicycloparaffins
ActiveUS20050133408A1Improve Oxidation StabilityHigh viscosity indexHydrocarbon purification/separationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCycloparaffinsBase oil
A composition of lubricating base oil having a weight percent of all molecules with at least one aromatic function less than 0.30, a weight percent of all molecules with at least one cycloparaffin function greater than 10, and a ratio of weight percent of molecules with monocycloparaffins to weight percent of molecules with multicycloparaffins greater than 15.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Functional fluid and a process for the preparation of the functional fluid
A functional fluid for the removal of contaminates such as but not limited to, acid causing components in gas, sulfur components and carbon oxides from fluid streams, and removal and treatment of NOX & SOX from post combustion emissions. Also described is the manufacturing process to produce the functional fluid both in a batch atmospheric process system as well as a closed system capable of operating at above or below atmospheric conditions.
Owner:SPECIALIST PROCESS TECH
Process for improving the lubricating properties of base oils using a Fischer-Tropsch derived bottoms
InactiveUS20050098476A1High viscosityReduce pointsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationProcess engineeringBase oil
A method for improving the lubricating properties of a distillate base oil characterized by a pour point of 0 degrees C. or less and a boiling range having the 10 percent point falling between about 625 degrees F. and about 790 degrees F. and the 90 percent point falling between about 725 degrees F. and about 950 degrees F., the method comprises blending with said distillate base oil a sufficient amount of a pour point depressing base oil blending component to reduce the pour point of the resulting base oil blend at least 3 degrees C. below the pour point of the distillate base oil, wherein the pour point depressing base oil blending component is an isomerized Fischer-Tropsch derived bottoms product having a pour point that is at least 3 degrees C. higher than the pour point of the distillate base oil.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method for inhibiting the plugging of conduits by gas hydrates
A method for inhibiting hydrate formation in a hydrocarbon flow by adding an amount of a dendrimeric compound effective to inhibit formation of hydrates at conduit temperatures and pressures, and flowing the mixture containing the dendrimeric compound and any hydrates through the conduit. Preferably, a hyperbranched polyester amide is used as hydrate formation inhibitor compound.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com