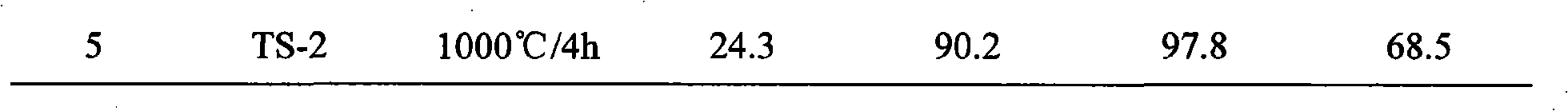Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
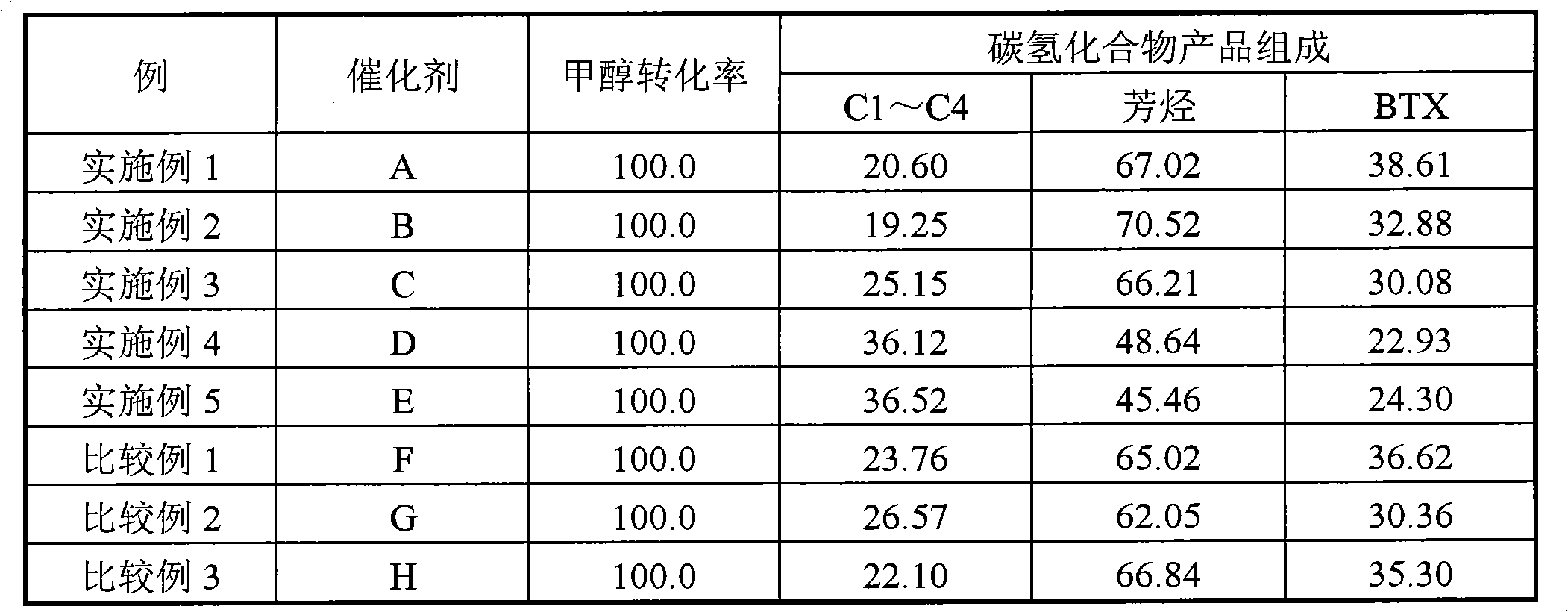
1357 results about "Space velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemical engineering and reactor engineering, space velocity refers to the quotient of the entering volumetric flow rate of the reactants divided by the reactor volume which indicates how many reactor volumes of feed can be treated in a unit time. It is commonly regarded as the reciprocal of the reactor space time. In industry, space velocity can be further defined by the phase of the reactants at given conditions. Special values for this measurement exist for liquids and gases, and for systems that use solid catalysts. By definition, space velocity can be expressed mathematically as SV ≡ υ0 / V. In this expression, υ0 represents the volumetric flow rate of the reactants entering the reactor and V represents the volume of the reactor itself. This expression is the reciprocal of the definition for the reactor space time, τ. However, the space time is measured at the conditions of the reactor entrance while the space velocity is often measured at a set of standard conditions, so the reported space velocity may be different from the reciprocal of the measured space time.
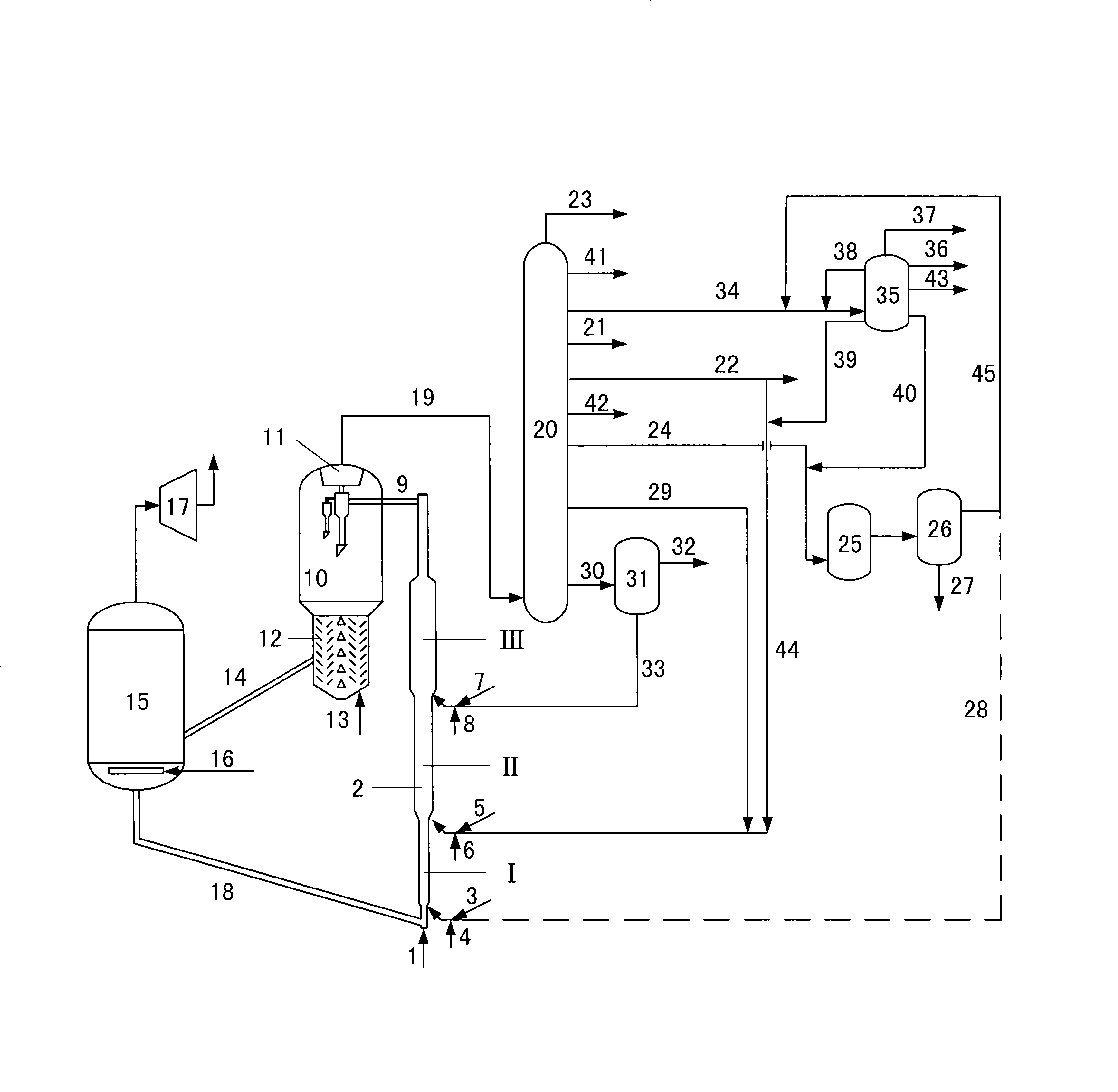
Process for preparing arene selectivity by enhancing methanol aromatizatian and process for preparation of catalyst thereof
ActiveCN101550051AImprove methodHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon condensationMolecular sieveFixed bed
The invention relates to a process for preparing arene selectivity by enhancing methanol aromatizatian. The process uses methanol as raw material, compositely modifies HZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst by active ions like Ga, Zn, Cu, Cr and Ag for catalyzing methanol aromatizatian, employs the fixed bed continuous process or the floating bed continuous process, wherein the reaction pressure is 0.1-3.5MPa; the reaction temperature is 380-500 DEG C; the space velocity of raw material liquid is 0.1-10.0 h; and N2 space velocity is 120-800 h. The advantages of the invention lie in collocation combination of mixing ion modification, and arene selectivity reaches to 70%.
Owner:TIANJI COAL CHEM IND GROUP +1
Method for preparing alcohol by acetic acid gas phase hydrogenation
ActiveCN102229520ALow reaction pressureReduce reaction energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationACETIC ACID LIQUIDGas phase
The invention relates to a method for preparing alcohol by acetic acid gas phase hydrogenation. A reaction system comprises acetic acid, hydrogen and a catalyst; the reaction temperature is 120-300 DEG C; the reaction pressure is 1.0-20.0MPa; the space velocity of acetic acid liquid is 0.5-10.5h<-1>; the molar ratio of H2 to acetic acid is 1-250; the catalyst takes activated carbon as a carrier; and main active components comprise one or two of transitional metals such as W and Mo. The addition agent is one of or more of precious metals such as Pd, Re, Pt, Rh and Ru and the like; and the acetic acid and the hydrogen can be converted into alcohol with high activity and selectivity under the action of the catalyst.
Owner:JIANGSU SOPO CHEM +1
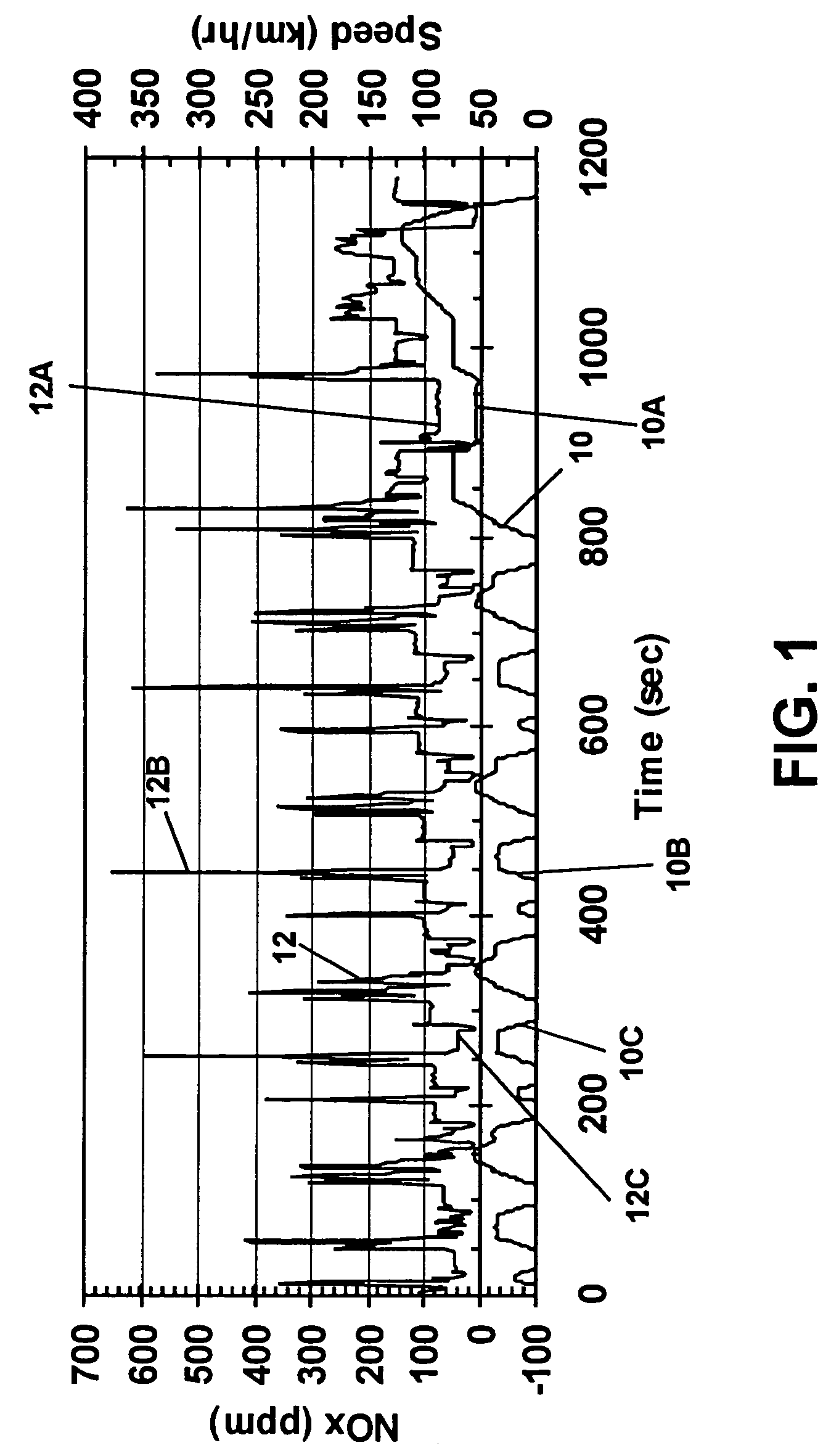
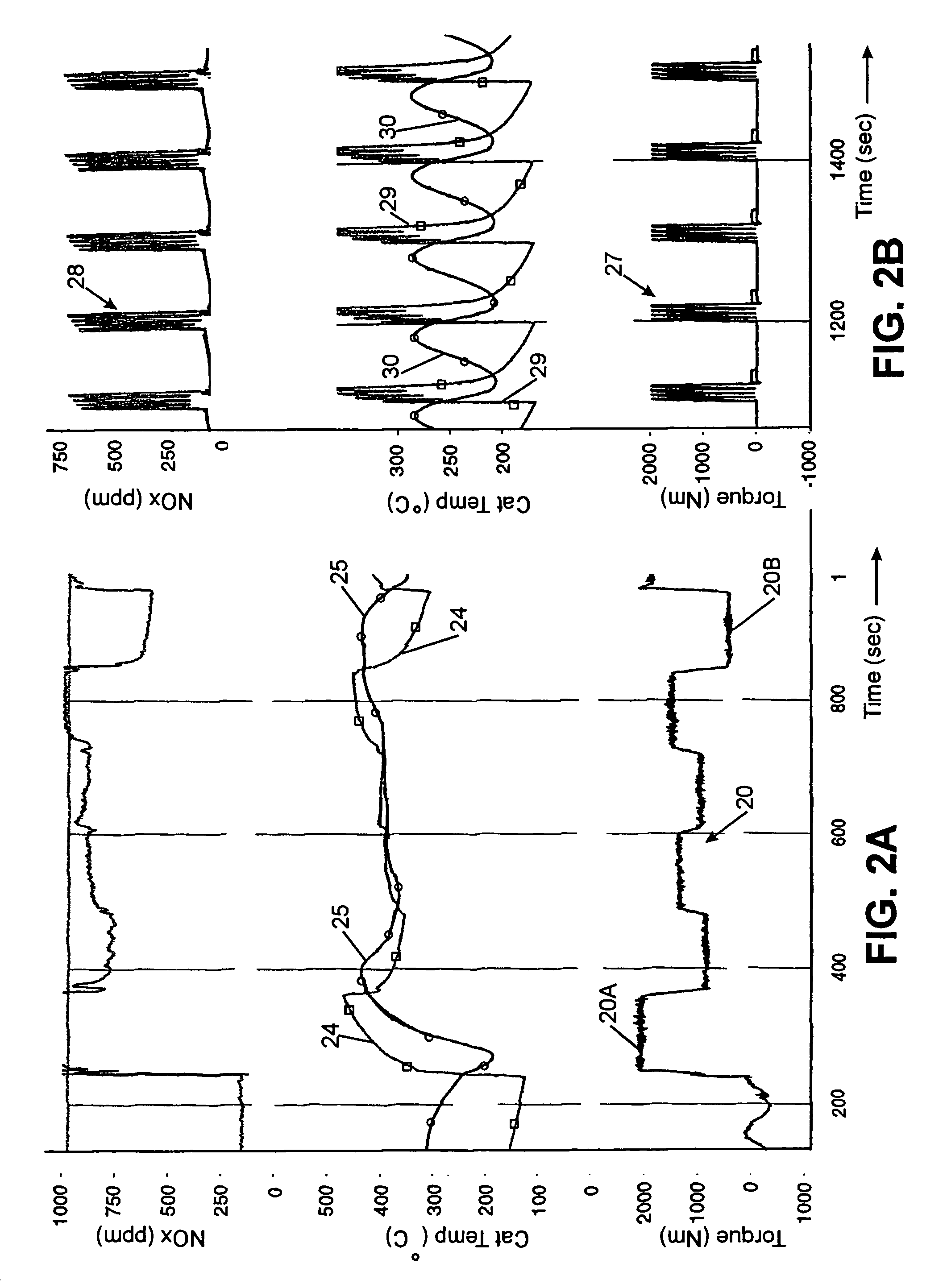
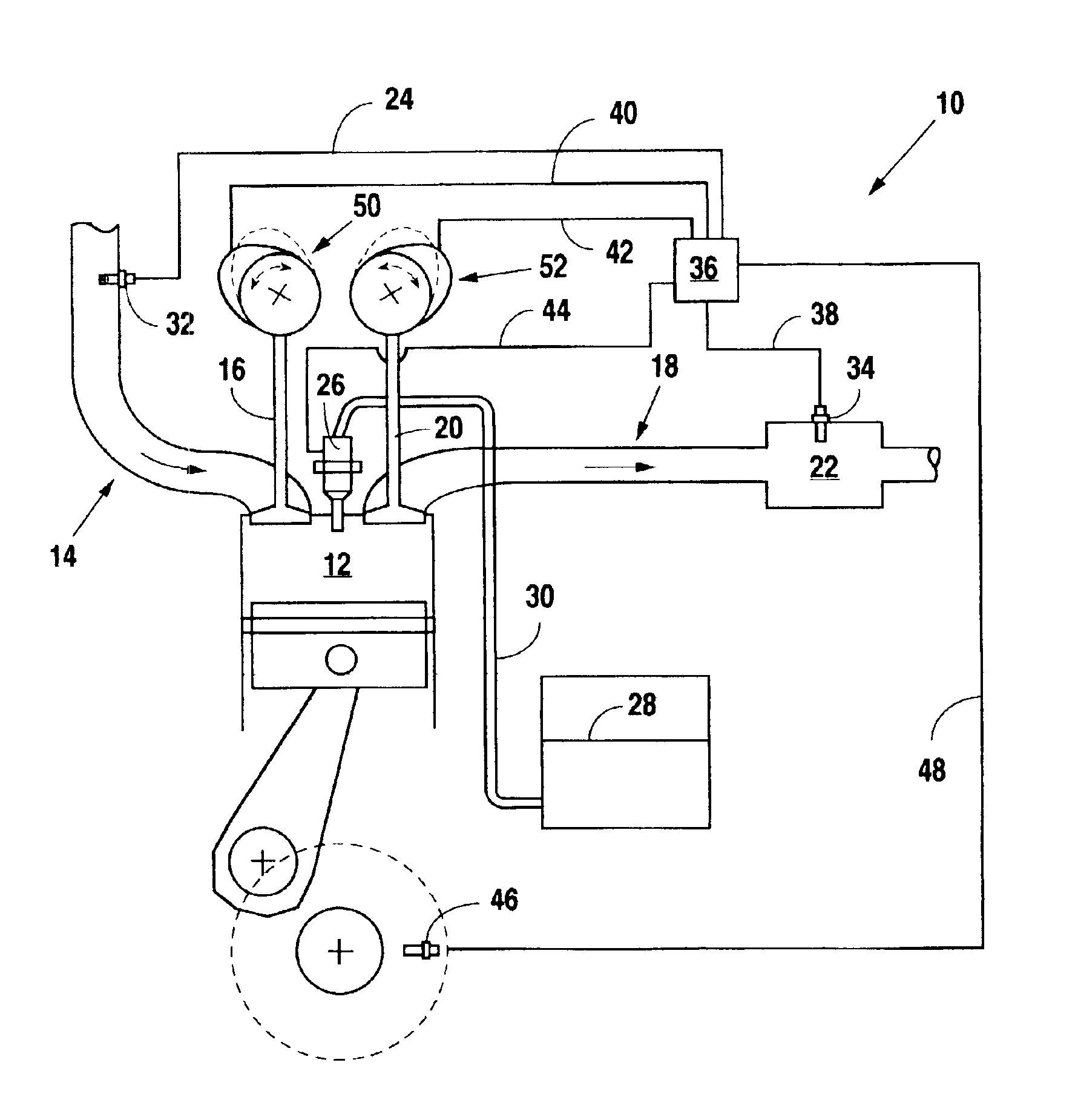
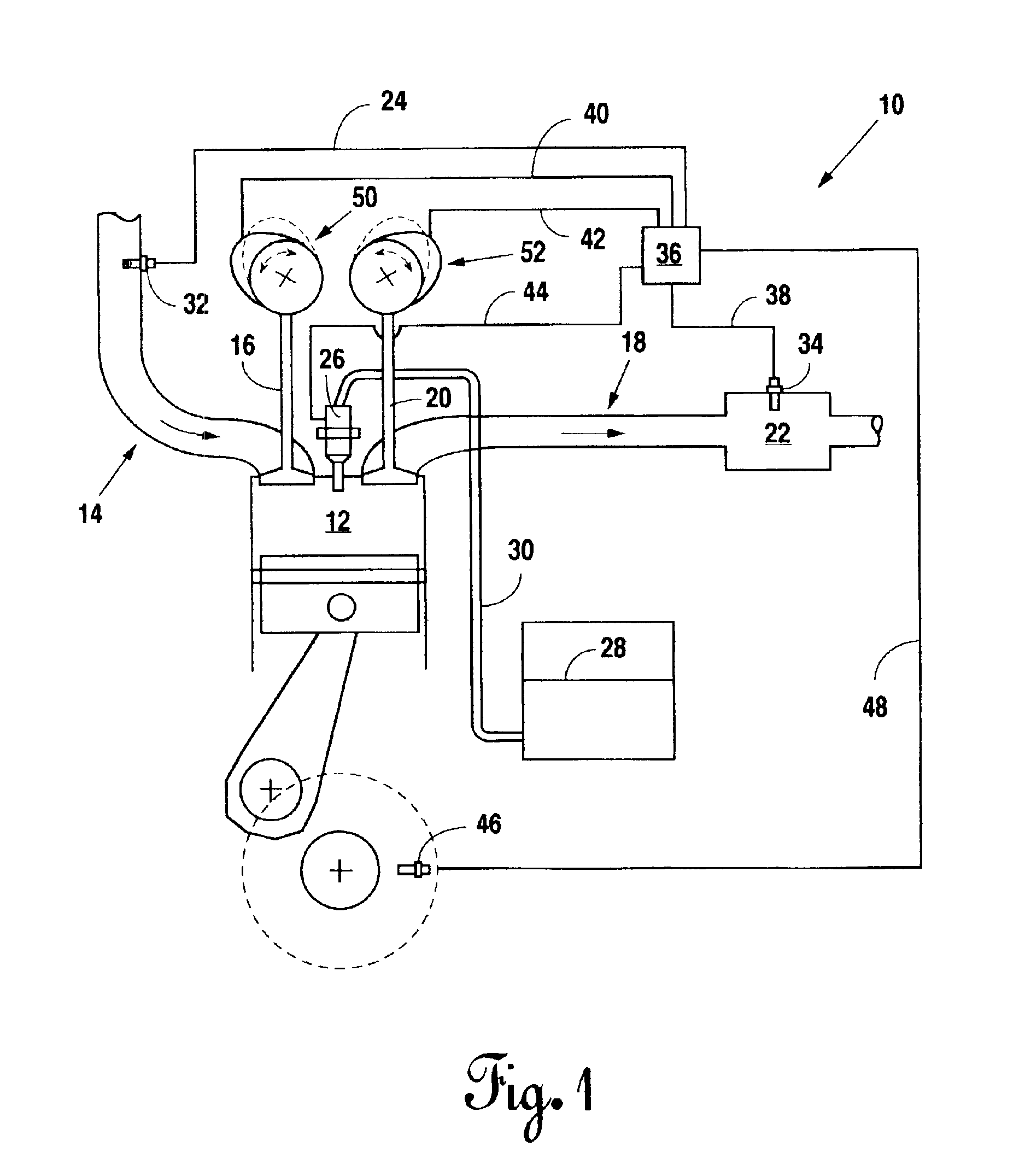
Control system for mobile NOx SCR applications
InactiveUS7150145B2Analogue computers for vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemSpace velocity
A diesel powered vehicle is provided with an SCR system which uses an external reducing reagent to convert NOx emissions in a manner which accounts for the effects of NOx transient emissions on the reducing catalyst. Actual NOx emissions produced by the engine are filtered using a variable NOx time constant in turn correlated to the reductant / NOx storage capacity of the reducing catalyst at its current temperature to account for changes in the SCR system attributed to NOx transient emissions. Catalyst temperature is filtered using a variable catalyst time constant corresponding to current space velocity of the exhaust gas to account for changes in the catalyst temperature attributed to NOx transient emissions. The reductant is metered on the basis of the filtered, corrected NOx concentration applied at a NSR ratio based, in turn, on the filtered, corrected reducing catalyst temperature.
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
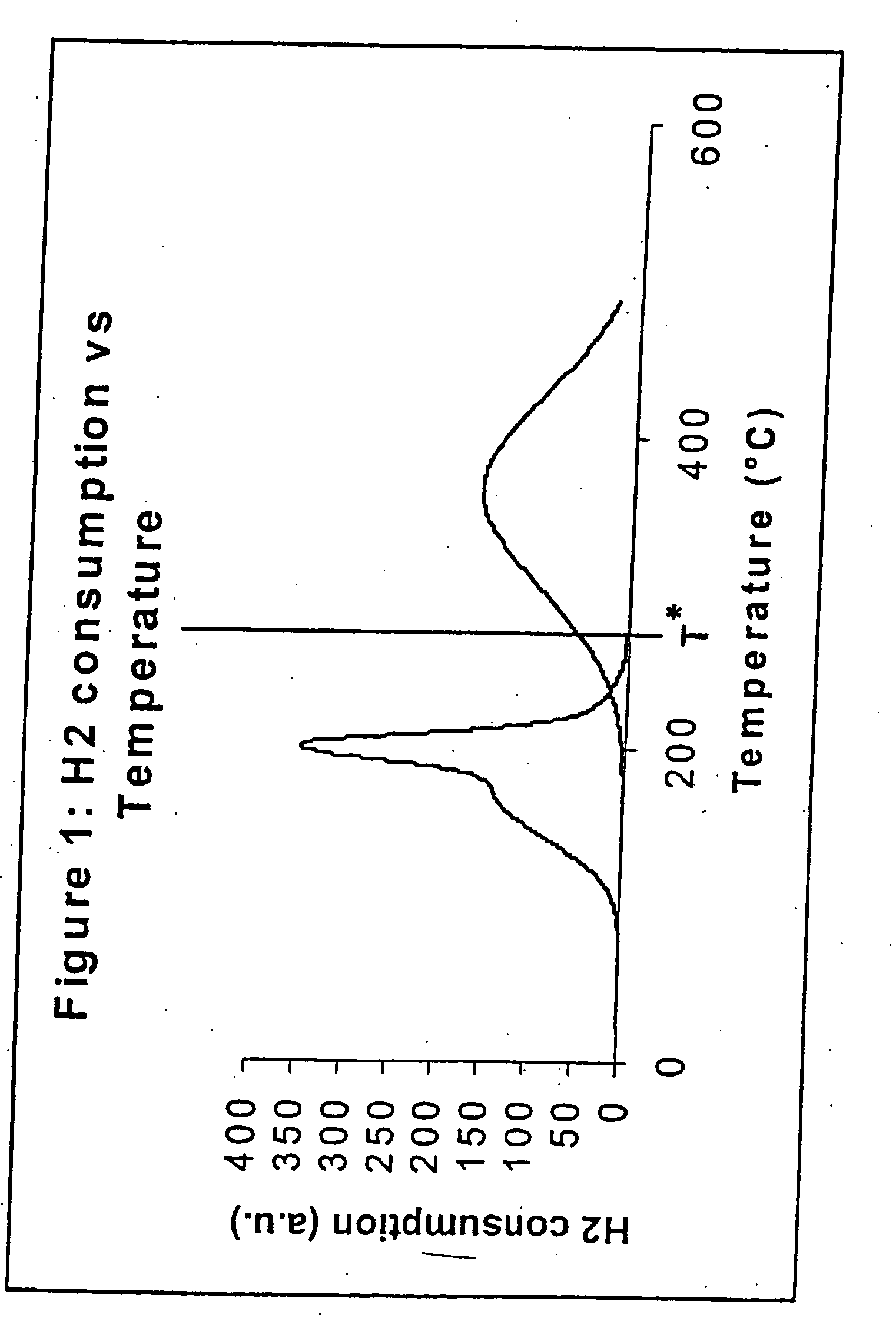
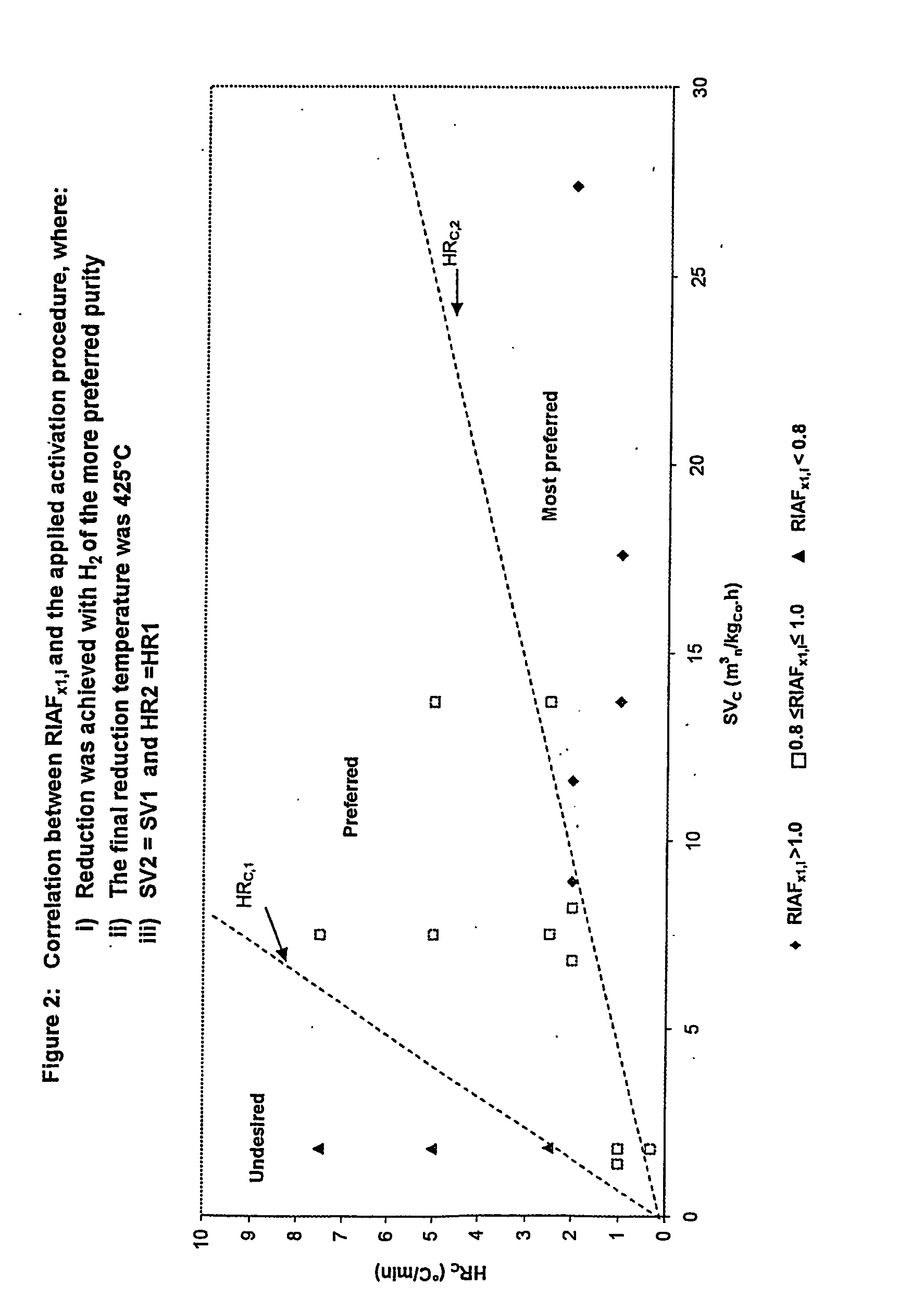
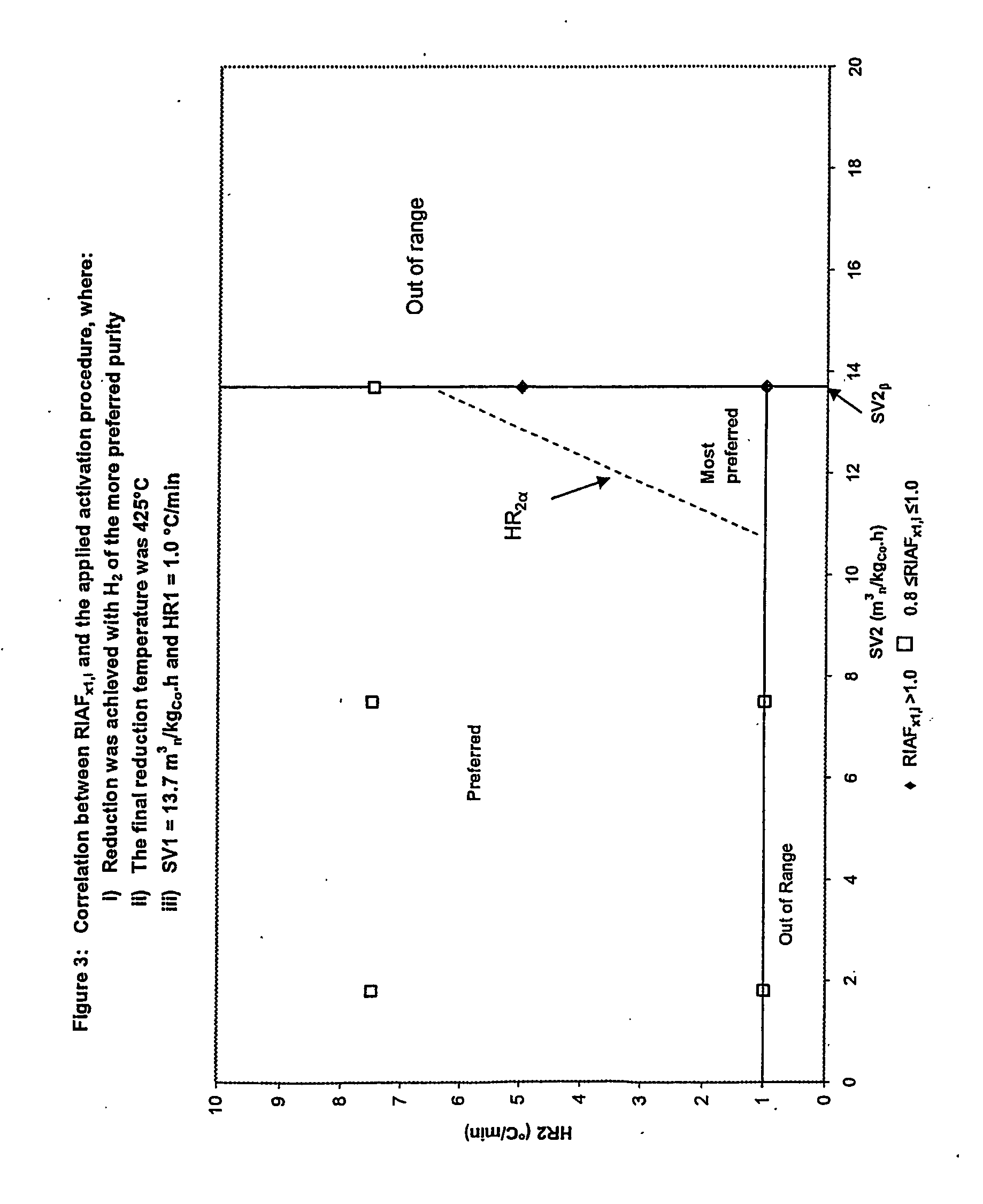
Process for activating cobalt catalysts
InactiveUS20050227866A1Improve reducibilityCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsParticulatesHydrogen
A particulate pre-reduction cobalt supported Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst precursor which comprises a catalyst support impregnated with cobalt, is treated with a pure hydrogen reducing gas, at a first specific feed gas space velocity, SV1, and at a first heating rate, HR1, to obtain a partially reduced precursor. The support contains reducible cobalt oxide in a calcined state and having a formula-unit in which each mole of cobalt atoms is associated with more than 4 / 3 moles of oxygen atoms and displaying a reducible cobalt oxide specific surface area at least equal to that of Co3O4 spinel. The partially reduced precursor is then treated with a pure hydrogen reducing gas, at a second specific feed gas space velocity, SV2, and at a second heating rate, HR2, to obtain an activated supported Fischer-Tropsch catalyst, with SV2≦SV1 and / or HR2≧HR1; however, when SV2=SV1, HR2≠HR1 and when HR2=HR1, SV2≠SV1.
Owner:SASOL TEKHNOLODZHI PROPRIEHJTEHRI LTD
Acetylene hydrocarbon selective hydrogenation method
ActiveCN101434508AGood hydrogenation effectImprove hydrogenation activityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationButadiene DioxideUnsaturated hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation method of high unsaturated hydrocarbons in C4 fractions, which is characterized in that salvage stores which are rich in acetylene hydrocarbon and prepared by extracting butadiene are used as the material, and a fixed bed reactor is adopted to obtain 1, 3-budiene by selective hydrogenation under the existence of a catalyst. The adopted process conditions are as follows: the reaction temperature is between 30 DEG C and 90 DEG C, the reaction pressure is between 1.0 MPa and 4.0 MPa and the liquid space velocity is 7 to 20h<-1>. The catalyst is preferably a palladium system catalyst with alumina as a carrier, the specific surface is 50 to 150m<2> / g and the specific pore volume is 0.25 to 1.0ml / g. The method has remarkable good effects on reducing waste of resources and improving economic benefits by effectively utilizing the salvage stores rich in acetylene hydrocarbon and prepared by extracting butadiene.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Catalytic conversion method of ethylene, propylene and aromatic hydrocarbon preparation
The invention discloses a catalytic conversion method for preparing ethylene, propylene and aromatic hydrocarbon. Hydrocarbon raw material with different cracking performances is contacted with a catalytic cracking catalyst, and cracking reaction is carried out in a fluidized bed reactor under the conditions that the temperature is 550 DEG C to 800 DEG C, the weight hourly space velocity is 0.1-800h<-1>, the reaction pressure is 0.10MPa to 1.0MPa, the weight ratio of the catalytic cracking catalyst and the raw material is 10-150, and the weight ratio of steam and the raw material is 0.15-1.0.Then a spent catalyst and reaction oil gas are separated, the spent catalyst returns to the reactor after regeneration, and the target products comprising low carbon olefin and the aromatic hydrocarbon are obtained by separating the reaction oil gas, wherein, fraction with the temperature to be 160 DEG C to 260 DEG C returns for catalytic cracking as circulating material, and the ethylene and the propylene are further obtained by cracking of ethane, propane, butane, and the steam entered. Low carbon olefin such as ethylene, propylene, and the like, is produced from heavy feedstock to the utmost extent in the method, and the yield of the ethylene and the propylene is over 20% by weight, in addition, the aromatic hydrocarbon such as toluene, xylene, and the like, are produced in an integrated way.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon through methanol transformation
ActiveCN102372535AHigh selectivityHigh catalytic activityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsMolecular sieveReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon through methanol transformation, and mainly solves the problems of complicated process flow and low selectivity of target products existing in the prior art. The problems are better solved by adopting the technical scheme that the method comprises the step of: reacting by taking methanol as a raw material and a mixture of HZSM-5 containing a metal element or oxide thereof and at least one of a HZSM-11 or HMCM-22 molecular sieve as an active main body of a catalyst under the condition that the reaction temperature is 320 to 480 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 0.1 to 3.0MPa and the weight hourly space velocity of the raw material is 0.5 to 6.0 h<-1>; and the method can be used for the industrial production of the aromatic hydrocarbon through methanol transformation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Dehydrogenation catalyst for feed gas containing carbon monoxide, preparation method and application method thereof
ActiveCN101543776AWide range of CO content requirementsGood choiceCarbon monoxideMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPlatinum saltsCerium
The invention discloses a dehydrogenation catalyst for feed gas containing carbon monoxide, a preparation method and an application method thereof. The catalyst takes alumina as a carrier, palladium and / or platinum as an active component and 2 to 4 MOxes as an additive, M is sodium, potassium, magnesium, titanium, zirconium, vanadium, manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, copper, molybdenum, tungsten or cerium, and components of the catalyst (calculated by carrier mass) are: 0.01 to 2 percent of the palladium and / or 0.01 to 1 percent of the platinum, and 1 to 2 percent of MOxes. The preparation method for the catalyst comprises the following steps that: firstly, an additive metal salt solution is used to impregnate the carrier; a palladium and / or platinum salt solution is used to impregnate the carrier after the carrier is dried and roasted; and the impregnated carrier is roasted at a temperature of between 450 and 850 DEG C to obtain the catalyst. Before the use, H2-N2 mixed gas containing more than 10 percent of hydrogen or pure hydrogen is activated by the catalyst at a temperature of between 450 and 650 DEG C. The catalyst can perform deep removal on less than 5 percent of hydrogen in the feed gas with the CO content of between 10 and 99 percent, the using temperature is between 100 and 300 DEG C, the space velocity is between 500 and 9,000h<-1>, the dehydrogenation rate is more than 99 percent, the content of outlet hydrogen is less than 100 ppm, and the loss of the carbon monoxide is less than 0.5 percent.
Owner:HAISO TECH
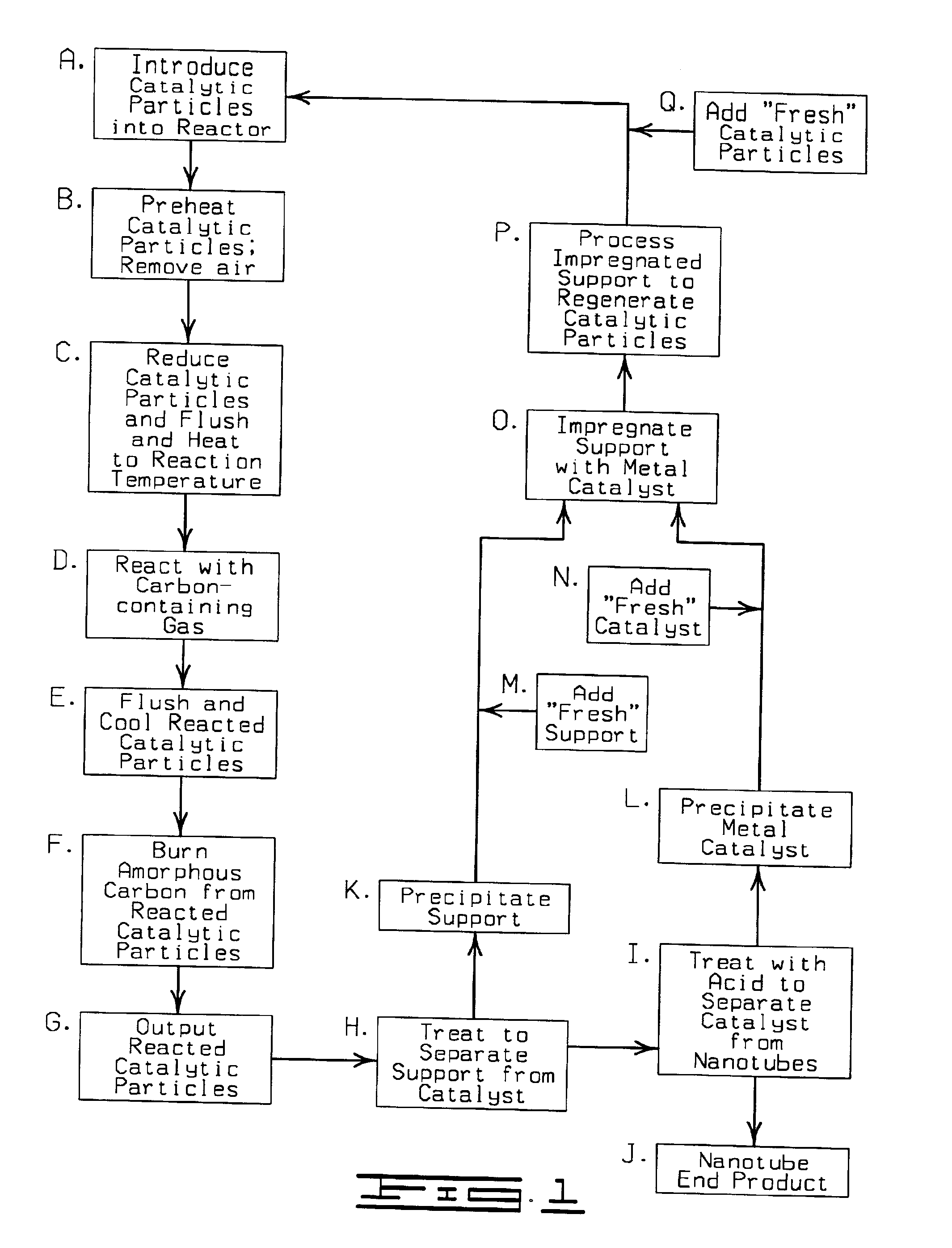
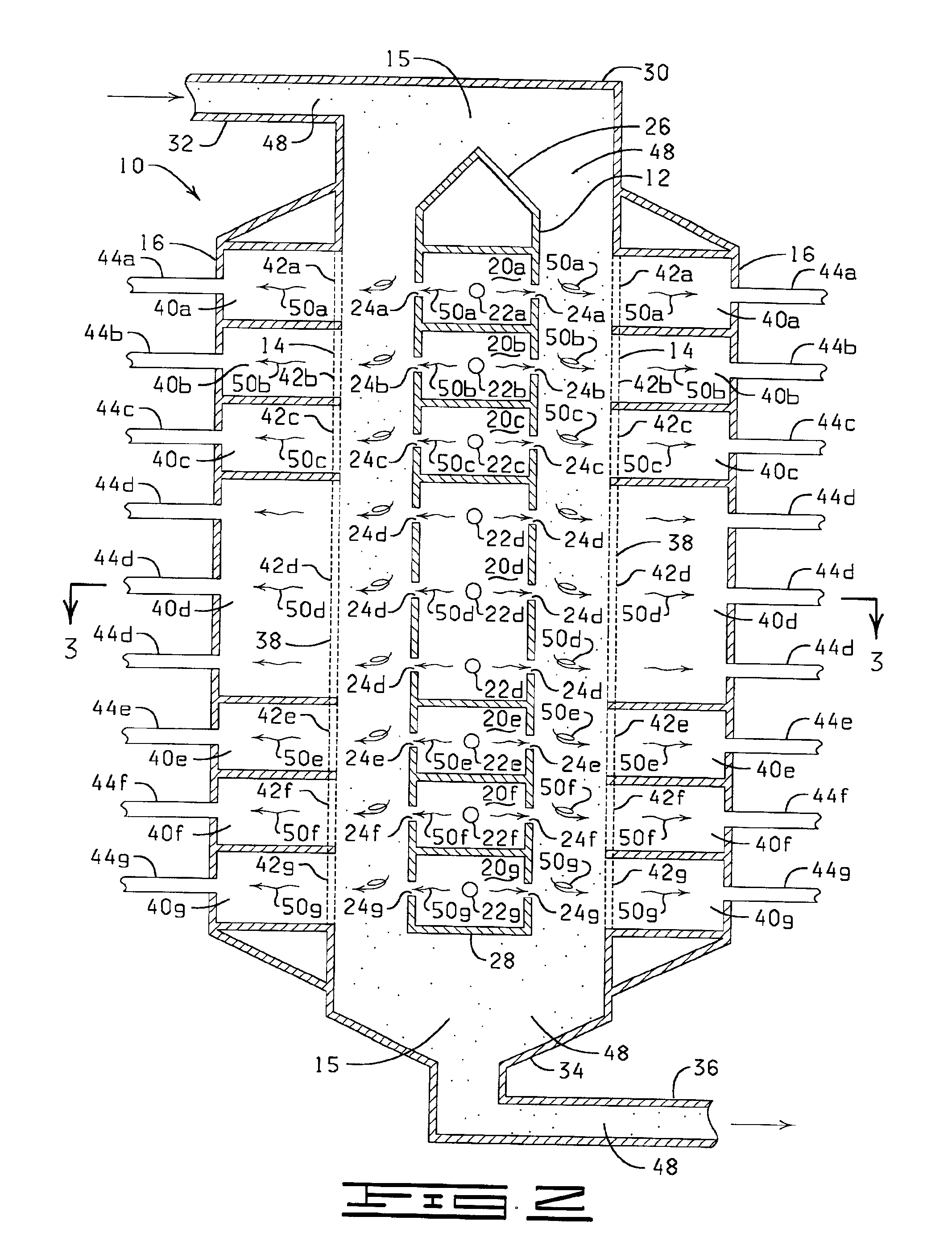
Process and apparatus for producing single-walled carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6919064B2Avoid defectsOptimize quantityMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst regeneration/reactivationParticulatesCarbon nanotube
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Method for producing aromatic hydrocarbons by methanol conversion
ActiveCN102372536AHigh selectivityHigh catalytic activityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsMolecular sieveActive component
The invention relates to a method for producing aromatic hydrocarbons by methanol conversion and mainly solves the problems of complex technological process and low selectivity of target products in the prior art. According to the invention, methanol is used as a raw material to react with a catalyst active component which is an HZSM-5 and HMCM-22 molecular sieve mixture containing rare earth metal or its oxide while the reaction temperature is 320-480 DEGC, the reaction pressure is 0.1-3.0MPa and weight hourly space velocity of the raw material is 0.5-6.0 h<-1>. The technical scheme greatly solves the problems and can be used in the industrial production of aromatic hydrocarbons by methanol conversion.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for producing light olefins and aromatics
ActiveUS20090288985A1High yield of propyleneTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCatalytic crackingPropeneXylene
A process for producing light olefins and aromatics, which comprises reacting a feedstock with a catalytic cracking catalyst in at least two reaction zones, wherein the reaction temperature of at least one reaction zone downstream of the first reaction zone is higher than that of the first reaction zone and its weight hourly space velocity is lower than that of the first reaction zone. The spent catalyst is separated from the reaction product vapor, regenerated and then returned to the reactor. The reaction product vapor is separated to obtain the desired products, light olefins and aromatics. This process efficiently produces light olefins such as propylene, ethylene, etc. from heavy feedstocks, wherein the yield of propylene exceeds 20% by weight, and produces aromatics such as toluene, xylene, etc. at the same time.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Supported active carbon catalytic material capable of eliminating formaldehyde at room temperature and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103071489AGood water vapor resistanceImprove overall lifespanOther chemical processesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActivated carbonWater vapor
The invention discloses a supported active carbon catalytic material capable of eliminating formaldehyde at room temperature. The catalytic material is characterized by comprising, by mass, 0.1 to 2% of a noble metal active component, 1 to 20% of a metal oxide and 78 to 98.9% of an active carbon supporter. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the supported active carbon catalytic material capable of eliminating formaldehyde at room temperature. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: pretreatment of active carbon; modification of active carbon; loading of the active component, and washing, filtering and drying so as to prepare the supported active carbon catalytic material capable of eliminating formaldehyde at room temperature. The catalytic material has the double functions of adsorption and catalytic oxidation at normal temperature during elimination of formaldehyde at room temperature; under the conditions of room temperature and a space velocity of 10000 / h, the removal rate of formaldehyde by the catalytic material is more than 98.2%, and formaldehyde becomes harmless H2O and CO through catalytic oxidation, thereby realizing green elimination of formaldehyde; moreover, the catalytic material has good resistance to water vapor and a long service life, and the preparation method for the material is simple and is easy to operate.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Supported noble metal catalyst for low-temperature catalytic oxidation benzene series and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a supported noble metal catalyst for low-temperature catalytically oxidizing benzene series (benzene, methylbenzene and dimethylbenzene) gas to CO2 and H2O. Active components of the noble metal catalyst are: at least one of Pd, Pt, Ag, Au and Rh; carrier is at least one of active carbon, red mud, molecular sieve, aluminum sesquioxide, titanium dioxide, manganese dioxide, zirconium dioxide, silicon dioxide, cerium dioxide, lanthanum sesquioxide, cobalt oxide, magnesium oxide, zinc oxide, calcium oxide and cupric oxide. Under general pressure, in atmosphere ambient, in fixed bed reactor, with a space velocity range from 10,000 to 100,000h<-1> and at a temperature range from 110 to 210 DEG C, the catalyst can be used for directly oxidizing 100 to 800ppm benzene series gas to CO2 and H2O without byproduct, which shows good low-temperature catalytic activity. The catalyst of the invention has the advantages of simple preparation, lower complete oxidation temperature, immunity to H2O, good stability and high practical value.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
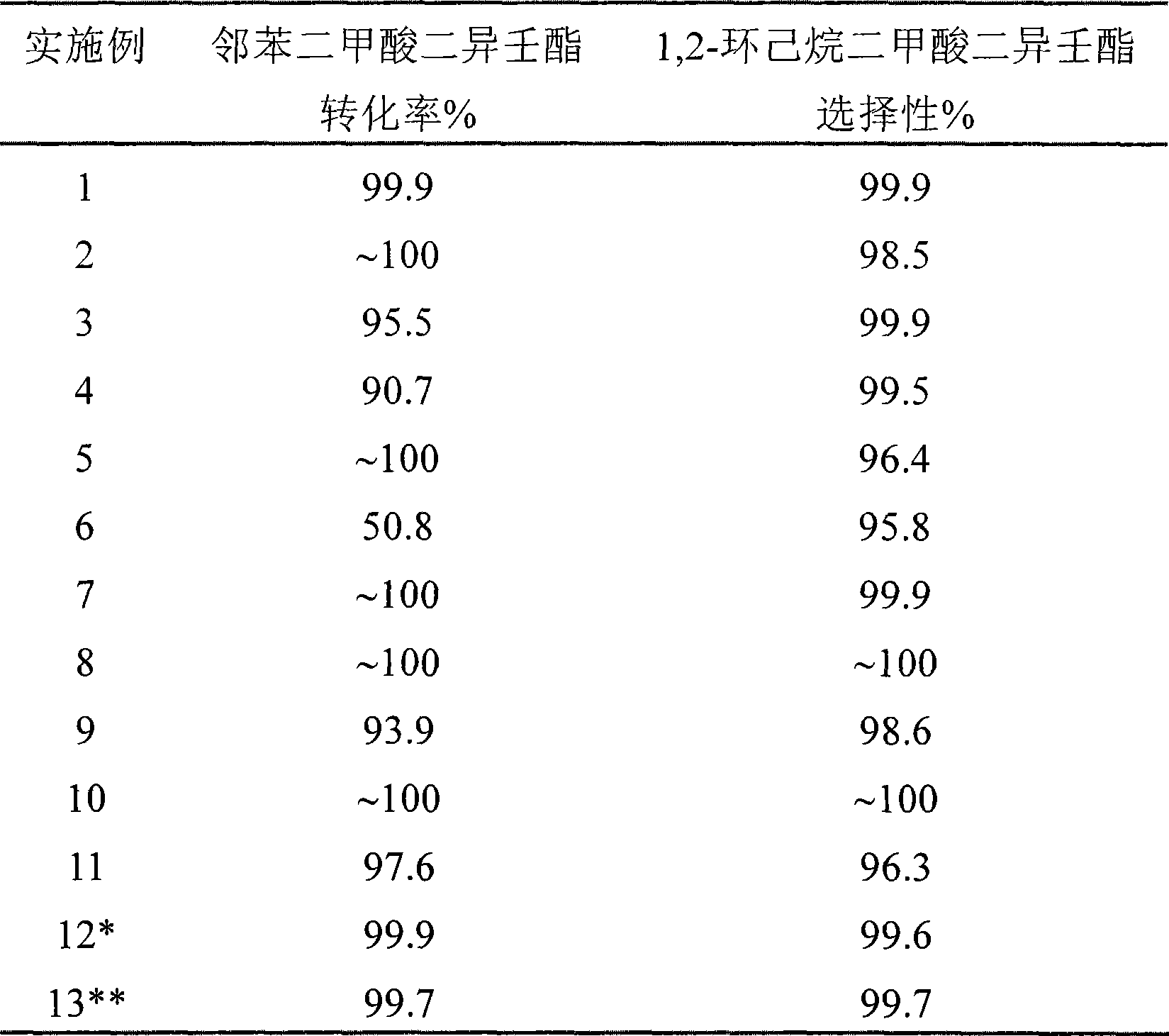
Method for preparing 1,2-cyclohexane cyclohexanedimethanol dibasic ester
ActiveCN101417950AHigh selectivityLow reaction pressureOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationReaction temperatureDibasic ester
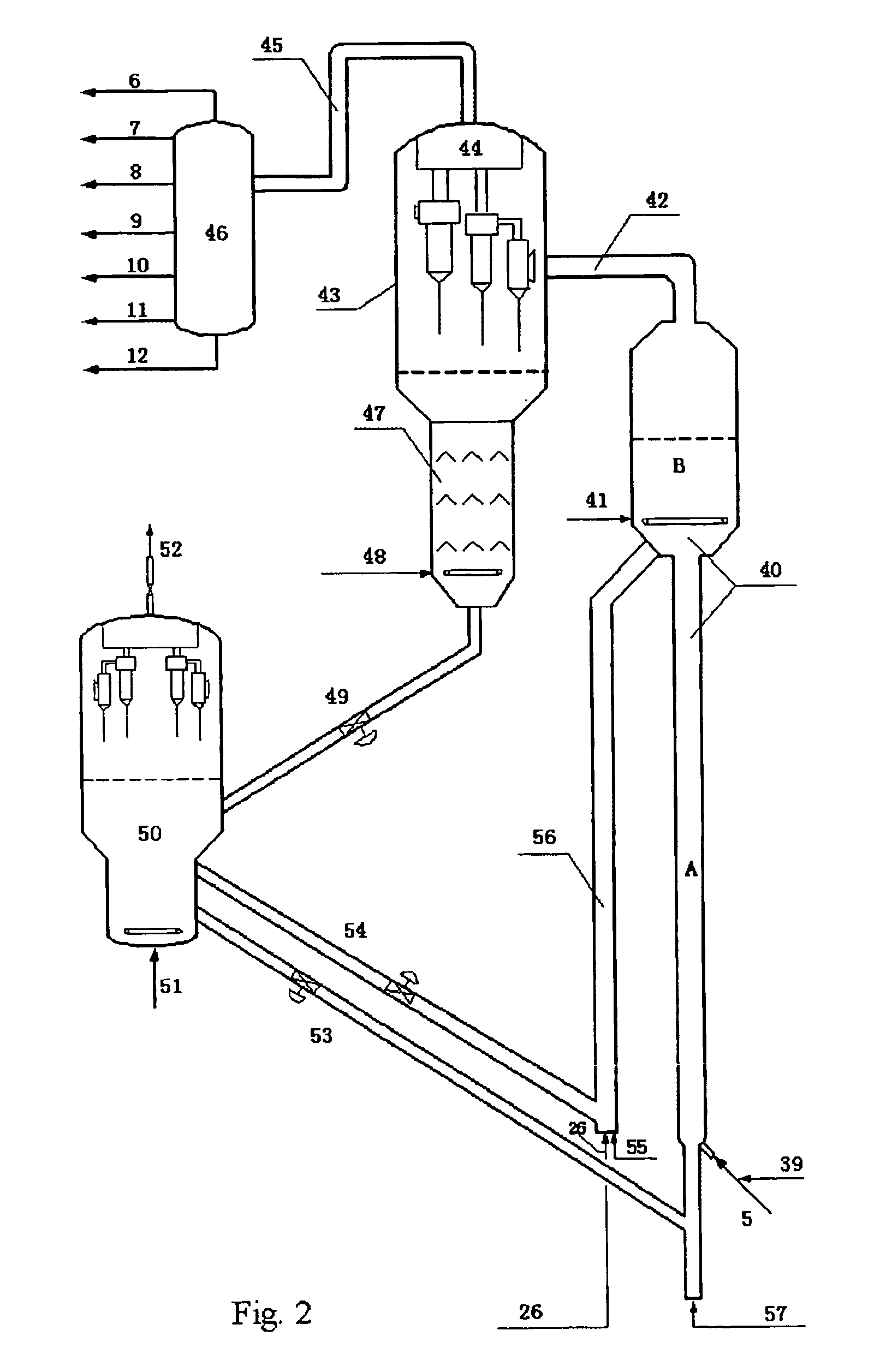
The invention relates to a method for preparing 1, 2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid ester of binary, comprising a reaction system composed by binary phthalate ester, hydrogen and a catalyst; the reaction temperature ranges from 100 to 250 DEG C; the reaction pressure ranges from 3.0 to 12.0 Mpa; the molar ratio of H2 and X ranges from 50 to 450; the liquid space velocity of binary phthalate ester ranges from 0.1 to 2.5 h<-1>; the catalyst uses Al2O3, ZrO2, TiO2 or SiO2-Al2O3 as vehicle, and load active component can be Ru, Pt, Pd, Rh, Fe, Co, Ni and Cu; the binary phthalate ester is diisonynol phthalate, diisooctyl phthalate or dibutyl phthalate; the product 1, 2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid ester of binary is 1, 2-cyclohexane diisononyl dimethyl ester, 1, 2-cyclohexane diisooctyl dimethyl ester or 1, 2-cyclohexane dibutyl dimethyl ester.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalyst for pressurized oxidative coupling of methane to prepare ethylene and its prepn.
InactiveCN1389293AHigh content of active ingredientsNo diluent requiredHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon condensationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActive componentSpace velocity
The present invention discloses a catalyst for methane oxidative coupling polymerization to prepare ethylene under the condition of pressurization, and said catalyst uses SiO2 as support, and its active component is formed from Mn2O3, Na2WO4 and SnO2, and its active component content is 10 wt%-20 wt%. Under the condition of no dilution gas, 0.6 MPa and high space velocity it can obtain 33.0% of methane conversion rate and 24.1% of C2 hydrocarbon yield.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing propylene from methanol
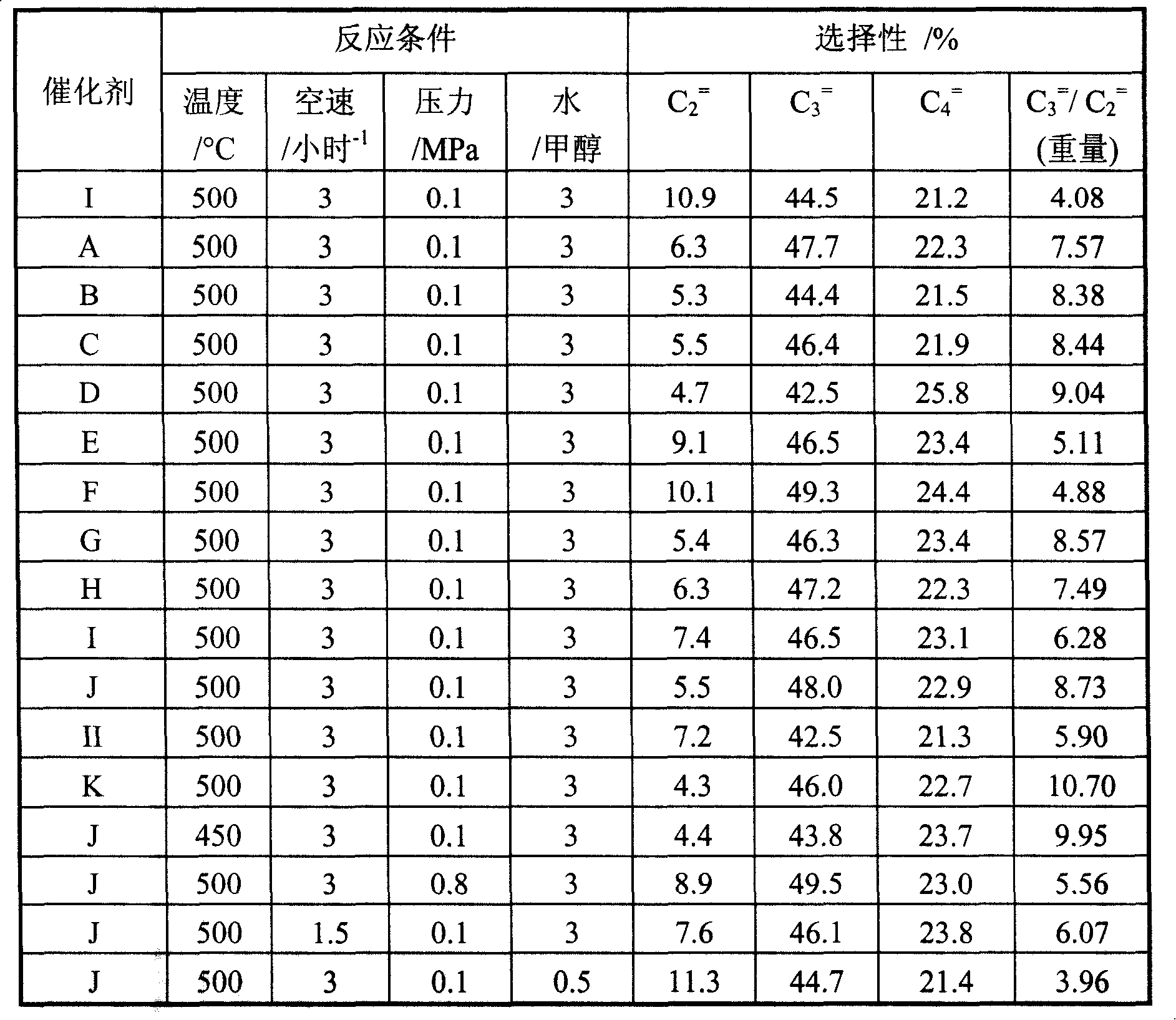
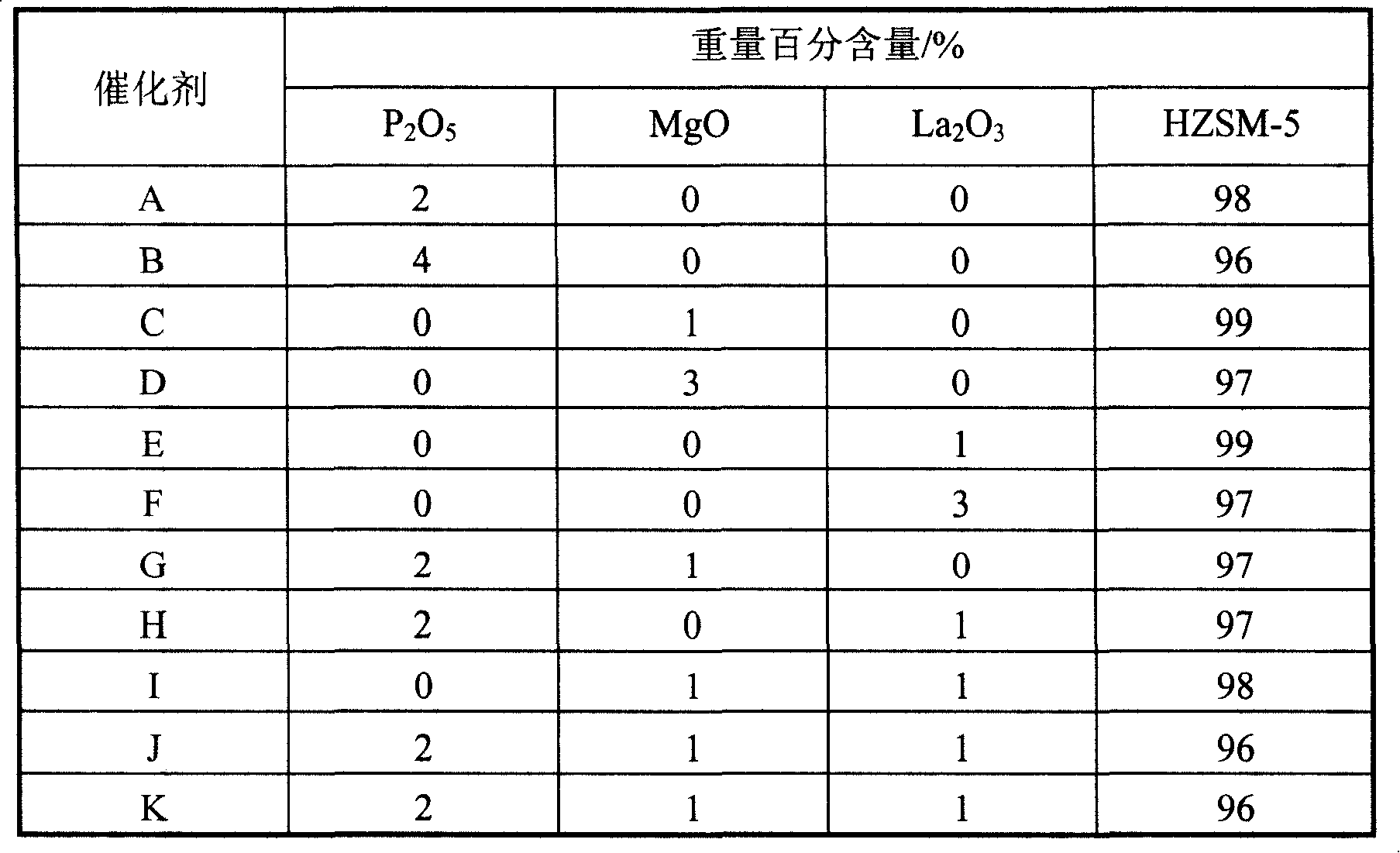
ActiveCN101239875AHigh selectivityHigh weight ratioMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsSpace velocityZSM-5
The invention relates to a method for preparing propylene from methanol, which mainly solves problems of the prior art, such as low weight ratio of propylene / ethylene and low propylene selectivity. The invention solves the problems by using the methanol / water mixing liquid as material, contacting the material with a catalyst under conditions of 400-550 DEG C, 0.1-1Mpa, 1-5 hour<-1> of methanol weight hourly space velocity and 0.2-5:1 of water / methanol weight ratio, reacting and generating an effluent containing propylene, wherein the catalyst contains following componets by weight percent: a) 0-10% P of P2O5; b) 0-10% Mg of MgO; c) 0-10% La of La2O3; d) and the rest ZSM-5 molecular sieve, wherein the dosage of a, b, and c can not be zero at the same time. Thereby, the invention is useful in industrial production of propylene from methanol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for the manufacture of methymercaptan
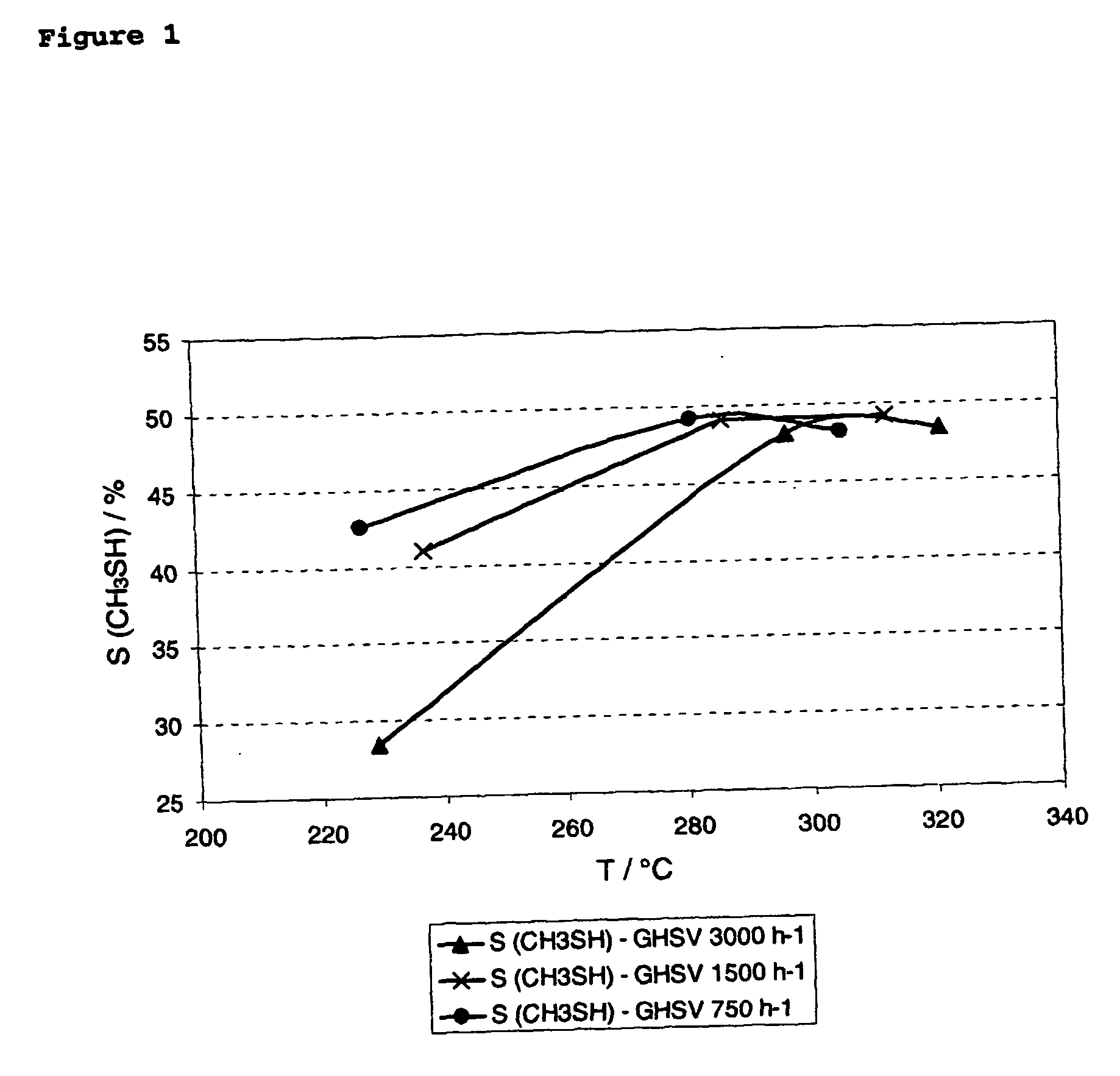
InactiveUS20070213564A1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationThiol preparationSpace velocityOrganic chemistry
The present invention refers to a continuous process for the manufacture of methyl mercaptan using Mo-O—K-based catalysts. It is further described that the total selectivity of methylmercaptan can be increased by at least 1% by lowering the total gas hourly space velocity. The invention further refers to a process for the preparation of a solid, preformed catalyst system.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method for preparing catalyst for preparing synthesis gas by reforming methane and carbon dioxide
InactiveCN101637726ALow costHigh catalytic activityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNickel saltCerium
The invention relates to a method for preparing a catalyst for preparing synthesis gas by reforming methane and carbon dioxide, which comprises the following steps: soaking a carrier into a mixed solution of cerium(III) nitrate and lanthanum nitrate, and drying and roasting the soaked carrier for 2 to 10 hours to obtain a modified carrier (A); soaking the (A) into a soluble nickel salt solution orsoaking the (A) into a chloroplatinic acid solution, and drying and roasting the soaked carrier to obtain (B) or (C); soaking the (B) into the chloroplatinic acid solution or soaking the (C) into thesoluble nickel salt solution, and drying and roasting the soaked carrier to obtain a catalyst precursor, or soaking the modified carrier into a mixed solution of the soluble nickel salt solution andthe chloroplatinic acid, and drying and roasting the soaked carrier to obtain a catalyst precursor; and reducing the precursor in hydrogen and nitrogen mixed gas to obtain the catalyst. The catalyst has the advantages of low cost, good catalytic activity under the reaction condition of large space velocity, high selectivity for H2 and CO, and good sintering resistance and carbon deposition resistance.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
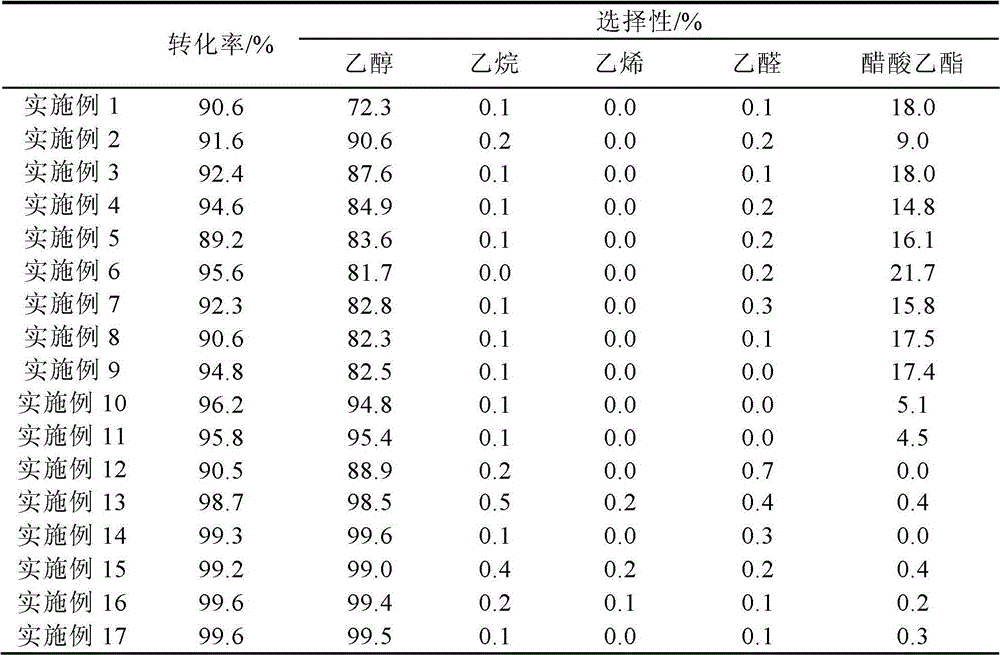
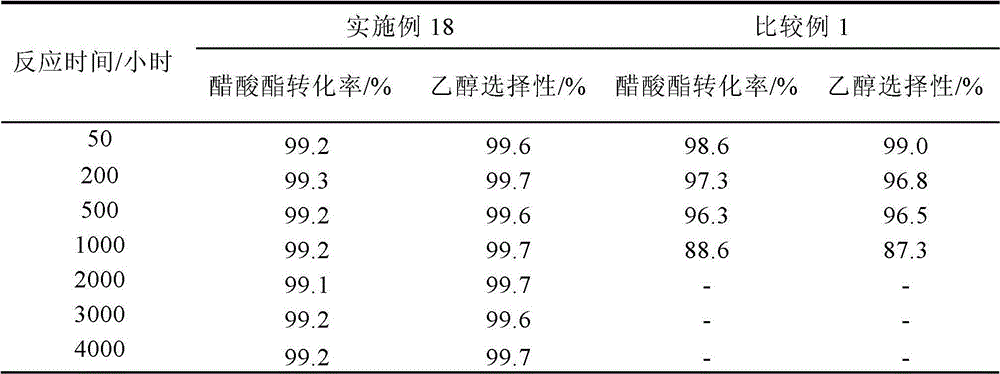
Catalyst for preparing ethanol from acetic ester hydrogenation, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102872878AEasy to prepareHigh activityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationHydrogenCopper oxide
The invention relates to a catalyst for preparing ethanol from acetic ester hydrogenation, a preparation method and an application thereof. The main catalytic components of the catalyst are copper or copper oxide with a content of 30 wt%-75 wt%; an auxiliary agent is one or more of La2O3, ZrO2, CeO2, Fe2O3, NiO, MgO, MnO, Al2O3 and K2O, with a content of 1wt%-40 wt%; a carrier is zinc oxide with a content of 20 wt%-65 wt%. In a relatively low hydrogen ester ratio and relatively large liquid hourly space velocity, the catalyst has a conversion rate of acetate larger than 99% and a selectivity of ethanol larger than 99%. Besides, the catalyst has good stability, can reduce cost greatly, and obtains higher production gains. The catalyst is simple in preparation method; the raw materials of the catalyst have wide sources and low cost; and the preparation process of the catalyst is environment-friendly, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI GRP CO
Preparation method for catalyst for synthesizing oxalic ester by gas-phase
ActiveCN101543784ALow costCatalyst activation/preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionGas phaseReaction temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method for a catalyst for synthesizing oxalic ester by gas-phase. The catalyst takes alpha-alumina as a carrier, palladium as an active component and 2 MOxes as an additive, M is magnesium, titanium, zirconium, vanadium, manganese, iron, nickel, copper, zinc, molybdenum or tungsten, and components of the catalyst (calculated by carrier mass) are: 0.01 to 0.75 percent of the palladium and 0.1 to 20 percent of MOxes. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: firstly, an additive metal salt solution is used to impregnate the carrier, and a palladium salt solution is used to impregnate the carrier to obtain the catalyst after the carrier is dried and roasted. Before the use, pure hydrogen or H2-N2 mixed gas is activated by the catalyst at a temperature of between 150 and 450 DEG C. The catalyst can be used for synthesizing oxalic ester by the carbonylation of CO and nitrous acid ester, the using reaction temperature of the catalyst is between 70 and 150 DEG C, and the reaction space velocity is between 500 and 9,000h<-1>. The catalyst has higher reaction activity and selectivity; and the catalyst has low cost.
Owner:HAISO TECH
Modified no-adhesive ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst and its prepn process
InactiveCN1974007ASimple preparation processLow costMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsAlcoholWater vapor
The present invention belongs to the field of material synthesis technology, and is especially modified no-adhesive ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst and its preparation process and application in catalyzing the dewatering of dilute alcohol solution to prepare ethylene. The catalyst is prepared with no-adhesive ZSM-5 zeolite as basic material and through one modification process combining high temperature water vapor and acid treatment. The catalyst has high content of effective component ZSM-5 zeolite, high molecule diffusion, high crystallization degree, opened channels and great specific surface area. In catalyzing the dewatering of dilute alcohol solution to prepare ethylene, the catalyst has high catalytic activity, low reaction solution ethanol concentration, low reaction temperature, high ethanol converting rate, high ethylene selectivity and high space velocity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Biomass quick cracked oil water vapour catforming hydrogen production method
InactiveCN101318622AExtended service lifeSolve the phenomenon of carbon depositionHydrogenCatalytic reformingGas phase
The invention discloses a method by adopting biomass fast pyrolysis oil which carries out two sections of fixed bed reactors and water vapor catalytic reforming for producing hydrogen; the two sections of fixed bed reactors are connected in series, the natural dolomite which is relatively cheap and easily available is taken as catalyst in water vapor reforming reaction at the first section of fixed bed reactor, while the second fixed bed reactor adopts Ni / Mgo as catalyst to further improve the purity and yield of the target product gas. Comparatively high temperature and comparatively high S / C (more than 12) are extremely important for the effective transformation of the biomass pyrolysis oil in the first fixed bed reactor. However, for any temperature point, low mass space velocity can facilitate the increasing of the yield of any gas product and the total gas phase transformation ratio of the biomass oil is increased accordingly. The Ni / MgO catalyst is extremely effective in the purification stage, when S / CH4 is not less than 2 and the temperature is not lower than 800 DEG C, the transformation ratio of methane can reach 100 %. Low mass space velocity can facilitate effective transformation of methane; when mass space velocity is not higher than 3600h<-1>, the potential hydrogen yield can reach 81.1%.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for synthesizing isooctyl nitrate and microchannel reactor
ActiveCN101462962AAvoid production accidentsLow costNitric acid ester preparationSynthesis methodsSolvent
The invention relates to the synthesis of isooctyl nitrate; in particular to a synthesis method of isooctyl nitrate and a microchannel reactor. Isooctyl alcohol is taken as raw material and an acid mixture of nitric acid and sulphuric acid is taken as nitrating agent, and the raw material and the nitrating agent are pumped into the microchannel reactor at normal temperature and pressure to carry out direct esterification. The process needs no catalyst or solvent, makes full use of the efficient heat and mass transfer capability of the microchannel as well as the characteristic of direct amplification and adopts two microreactors, of which one is a single-channel microreactor and the other is a multichannel microreactor; liquid hourly space velocity in the microreactor is 3000-10000h<-1>, the once-through conversion ratio of isooctyl alcohol is higher than 99% and the yield coefficient of isooctyl nitrate is higher than 98%. The process has high operation safety and high selectivity and can realize approximate isothermal operation in the reaction. The reactor is small in volume, is easy to integrate and amplify and space-time productive rate is high, thus being significant for strengthening and guaranteeing the safe production of isooctyl nitrate.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Titanium-silicon molecular sieve/tripolite composite catalyst and preparation
InactiveCN101264453AImprove catalytic performanceHigh selectivityOrganic oxidationMolecular sieve catalystsFixed bedLanthanum
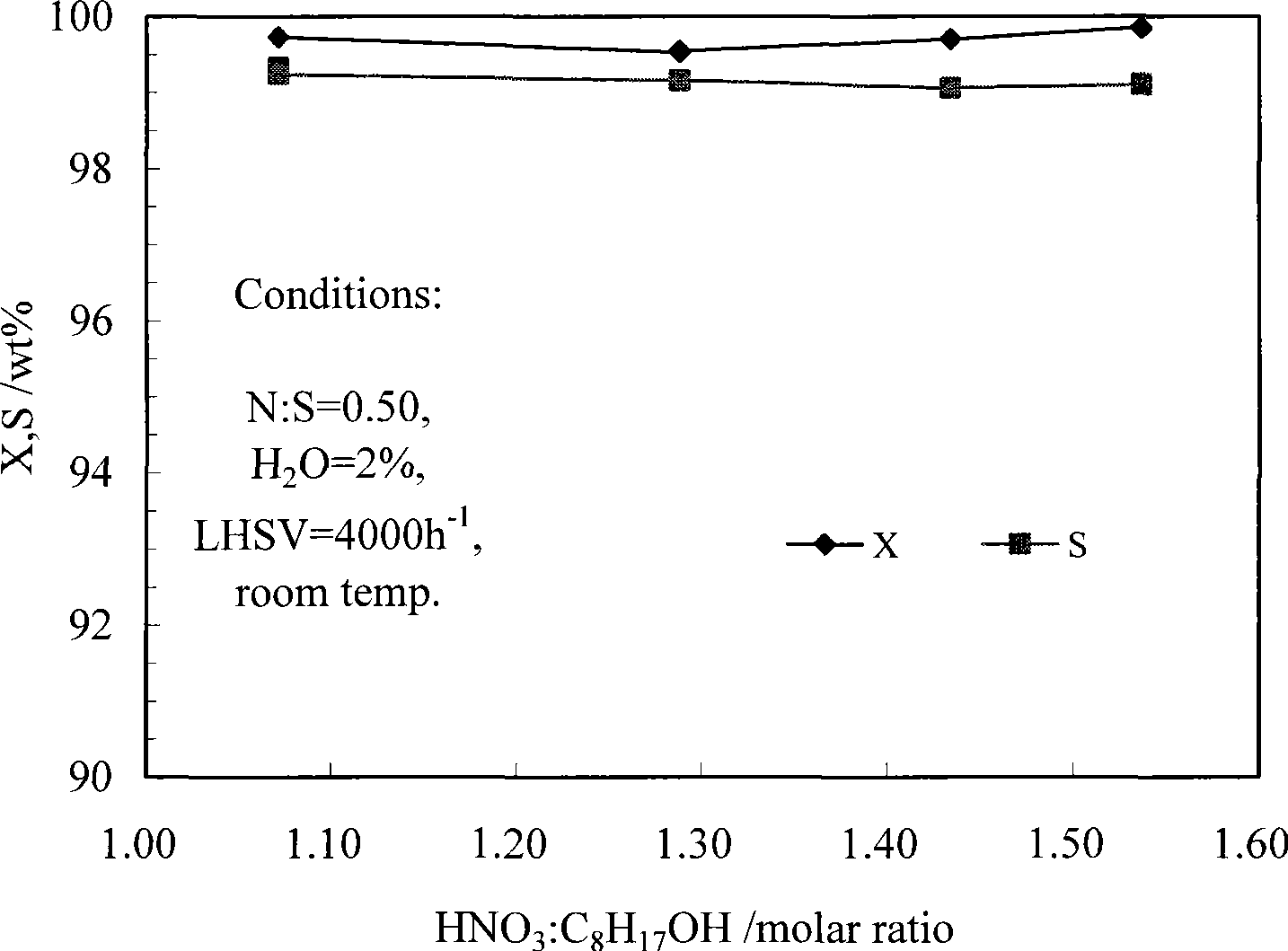
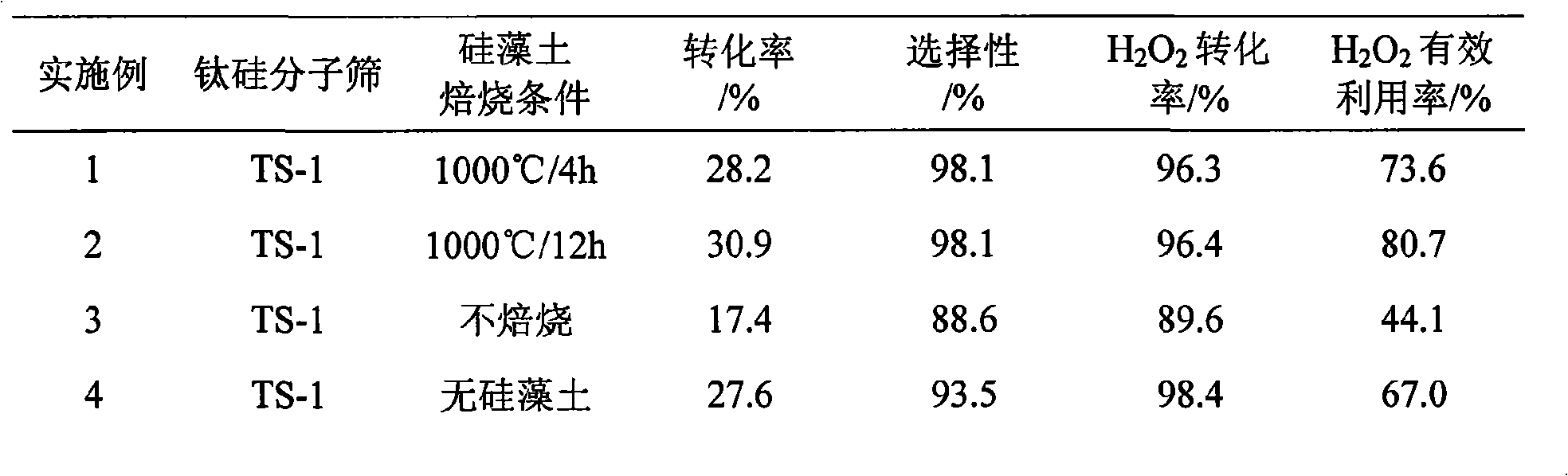
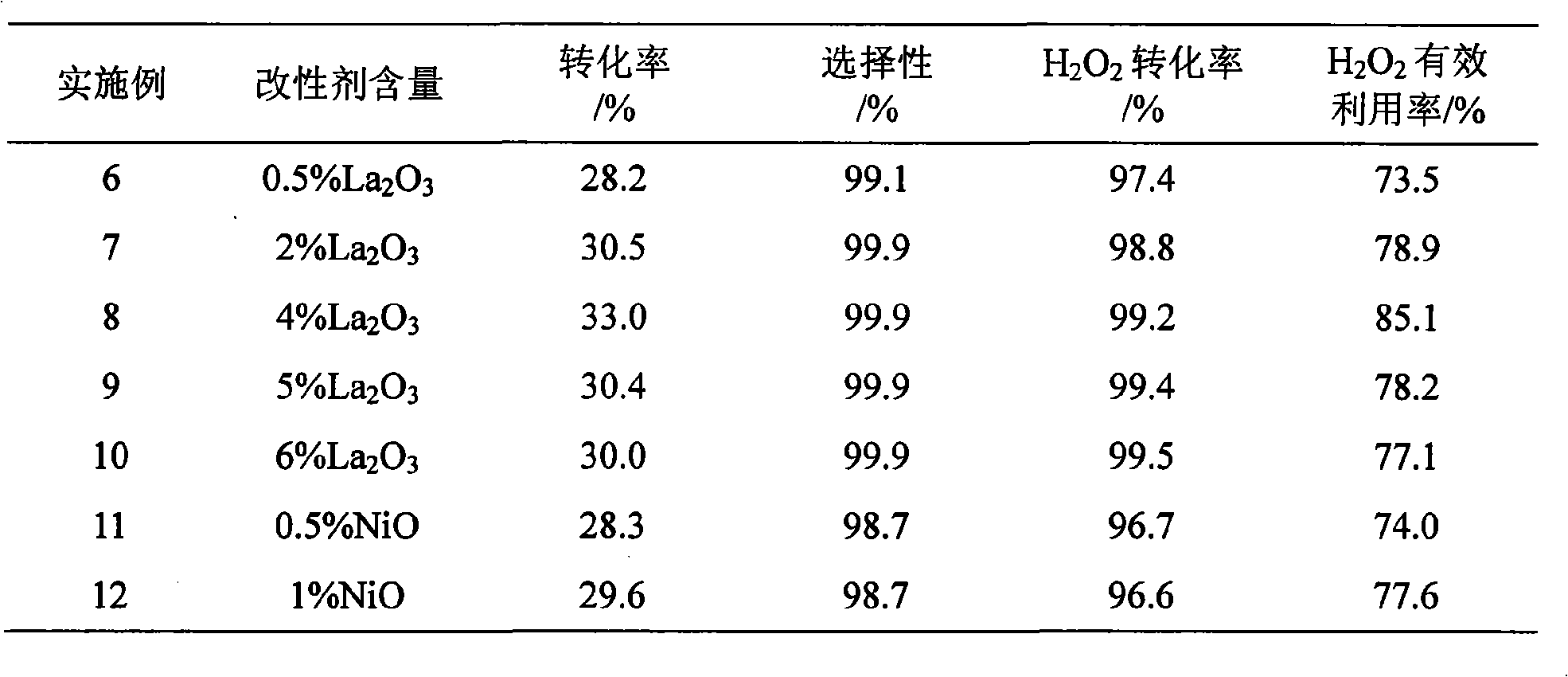
The invention discloses a Ti-Si molecular sieve / diatomite composite catalyst and a preparation method thereof, which is characterized in that: the catalyst is formed by compounding Ti-Si molecular sieve (such as TS-1 and TS-2) and diatomite with particular chemical property which is treated in a particular way, and is modified chemically by transition metal oxide after molding; the preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) after being treated with acid solution and alkaline solution, the diatomite needs heat treatment in high temperature to obtain particular chemical property; (2) the molding Ti-Si molecular sieve / diatomite composite catalyst is modified chemically by transition metal oxide (such as lanthanum and nickel). The composite catalyst can be used as the catalyst of selective oxidation reaction of the organic compound (such as the catalytic hydroxylation reaction of phenol) on fixed bed liquidoid, which uses hydrogen peroxide as the oxidant. The Ti-Si molecular sieve / diatomite composite catalyst has the advantages of high catalytic activity, high stability, long service life and easy separation, recovery and regeneration of the catalyst. When using the catalyst in the hydroxylation reaction of phenol of fixed bed liquidoid, under the reaction conditions of 84 DEG C, atmospheric pressure and 8.46h<-1> space velocity, the conversion rate of phenol is greater than 33%, the selectivity of diphenol reaches 99.9%, and the effective use rate of hydrogen peroxide is greater than 85%.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
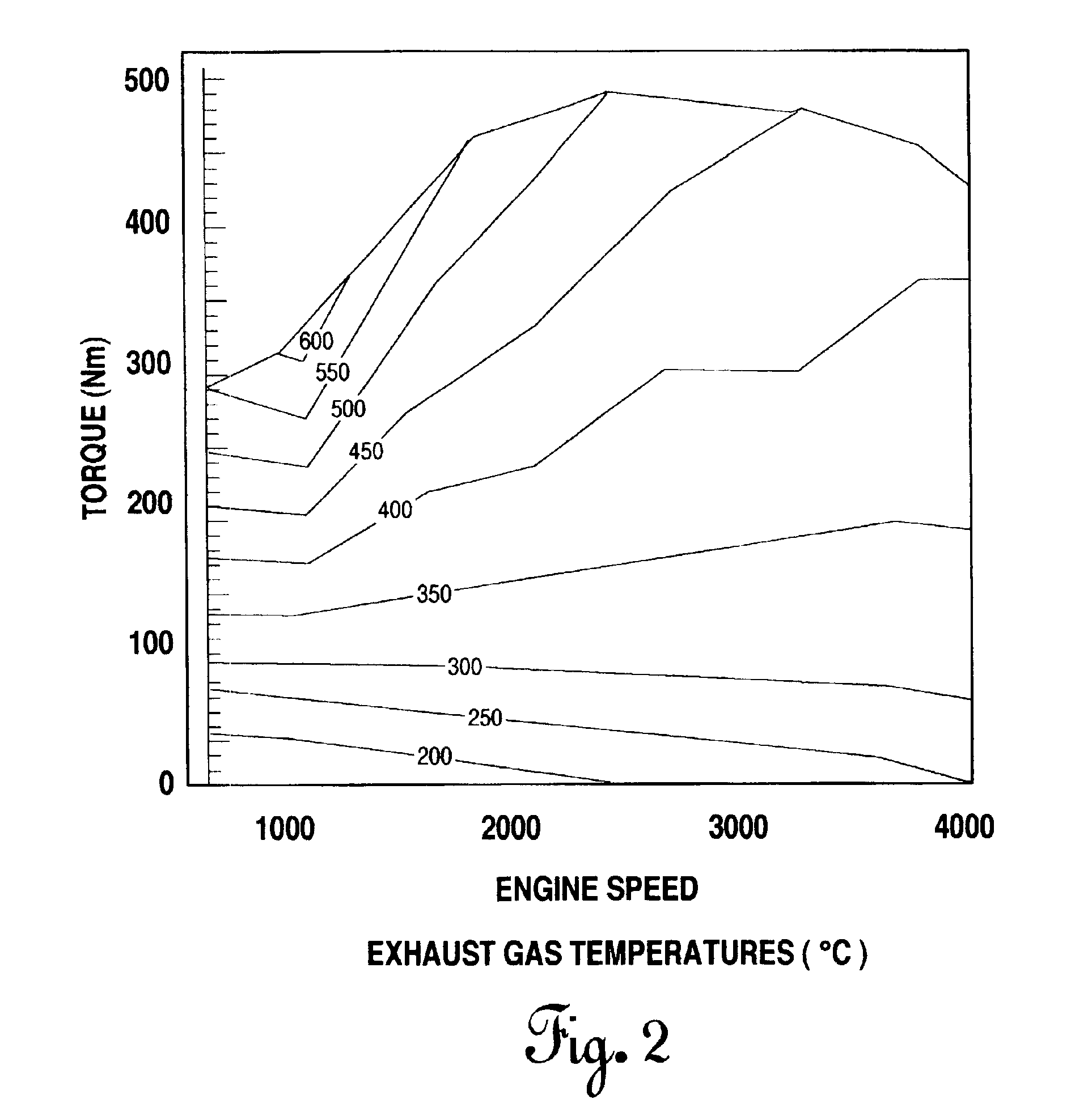
Use of a variable valve actuation system to control the exhaust gas temperature and space velocity of aftertreatment system feedgas
InactiveUS6948310B2Maintain temperatureValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveVariable valve timing
A method for controlling the temperature and / or space velocity of exhaust gas passing through an aftertreatment device disposed in the exhaust system of a diesel engine provides an optimal environment for efficient conversion of NOx and undesirable emissions during transient and steady state engine operation. The method includes controlling intake and / or exhaust valve timing, either singly or in combination with fuel injection timing and selective individual cylinder cutout, in response to sensed engine operating parameters.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Multiple catalyst system and its use in a high hydrocarbon space velocity process for preparing unsaturated aldehydes and acids
InactiveUS20060161019A1Improve concentrationIncrease with space velocityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation by oxidationGas phaseAcrolein
The present invention relates to a multiple catalyst system for preparing unsaturated aldehydes and acids from reactive hydrocarbons at high reactive hydrocarbon space velocity conditions. The present invention also relates to a process for preparing unsaturated aldehydes and acids from reactive hydrocarbons using the multiple catalyst system at high reactive hydrocarbon space velocity conditions. In one embodiment, the multiple catalyst system is utilized in a vapor phase catalytic oxidation reaction process which produces acrolein and acrylic acid from propylene at high reactive hydrocarbon space velocity conditions.
Owner:DECOURCY MICHAEL STANLEY +3
Method used for preparing methyl acetate via carbonylation of dimethyl ether
ActiveCN103896769AExtend your lifeControl temperature distributionPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionHydrogenReaction temperature
Provided is a method for preparing methyl acetate by dimethyl ether carbonylation, comprising passing a feed gas including dimethyl ether, carbon monoxide and optional hydrogen through a reactor filled with a mordenite and / or ferrierite molecular sieve based catalyst and reacting at a reaction temperature of 190-320°C, a reaction pressure of 0.5-20.0 MPa and a gas space velocity of 500-5000 h-1 so as to prepare methyl acetate, wherein the molar ratio of dimethyl ether to carbon monoxide is DME / CO=1 / 1-1 / 15, the molar ratio of hydrogen to carbon monoxide is H2 / CO=0-10 / 1, and the feed gas is distributed into each catalyst bed layer in a segmental feeding manner. A feed gas including dimethyl ether and carbon monoxide is uniformly distributed into each catalyst bed layer via a gas distributor, in a segmental feeding manner, which can remarkably improve the conversion rate of dimethyl ether, effectively control or adjust the temperature distribution of a catalyst bed layer, avoid the appearance of a hot spot, and prolong the service life of a catalyst.
Owner:YANCHANG ZHONGKE (DALIAN) ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Loaded mercury-free catalyst for vinyl chloride preparation by hydrochlorination of acetylene and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102416323ASimple compositionEasy to preparePreparation by halogen halide additionCatalyst activation/preparationHydrogenActive component
The invention discloses a loaded mercury-free catalyst for vinyl chloride preparation by hydrochlorination of acetylene and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst comprises precious metals / active carbon. The load capacity of the active components in the catalyst on a carrier is 0.1-3 wt%. The catalyst is prepared by carrier pretreatment and dipping, and a test for acetylene hydrochlorination activity is performed under a condition with a raw material gas space velocity of 120 h-1, a raw material gas ratio of V(HCl):V(C2H2) of 1.15, a normal pressure, and a reaction temperature of 160 DEG C. The advantages of the invention are that: the catalyst has good environmental benefits; the catalyst has a simple composition, and high catalytic activity; the acetylene conversion rate is more than 96%; the selectivity is high; the vinyl chloride selectivity is up to above 98%.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Pyrolysis gasoline cut fraction section selective hydrogenation method
ActiveCN101429453AImprove hydrogenation performanceImprove hydrogenation activityRefining by selective hydrogenationAlkaline earth metalCerium
The invention relates to a first-stage selectivity hydrogenation method for pyrolysis gasoline fractions, which uses palladium series hydrogenation catalyst which is used after being reduced. The first-stage selectivity hydrogenation method for the pyrolysis gasoline fractions is characterized in that the hydrogenation technological conditions are as follows: the volume space velocity of a liquid is less than or equal to 5h<-1>, the inlet temperature of a reactor is between 28 and 120 DEG C, the reaction pressure is more than or equal to 2.4 MPa, and the hydrogen / oil volume ratio is between 50 and 500; the palladium series hydrogenation catalyst takes theta-type alumina or theta and alpha mixed crystal type alumina giving priority to theta type as a carrier, takes metallic palladium as an active ingredient, and contains 0.2 to 0.5 weight percent of the active ingredient-the palladium, 2 to 8 weight percent of auxiliary agent-lanthanum and / or cerium, and 2 to 8 weight percent of alkaline earth element as calculated by 100 weight percent of the catalyst; and the catalyst can still be used by regeneration after being subjected to coking and deactivation. Under the condition of the application method and the technological conditions, the catalyst has good hydrogenation performance, and particularly still has good hydrogenation activity and stability when hydrogenation raw materials contain trace water and colloids.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Ammonia decomposition catalysts and their production processes, as well as ammonia treatment method
InactiveUS20110176988A1Efficient decompositionSimple and easy mannerGas treatmentNitrogen preparationDecompositionIron group
The ammonia decomposition catalyst of the present invention is a catalyst for decomposing ammonia into nitrogen and hydrogen, including a catalytically active component containing at least one kind of transition metal selected from the group consisting of molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and nickel, preferably including: (I) a catalytically active component containing: at least one kind selected from the group consisting of molybdenum, tungsten, and vanadium; (II) a catalytically active component containing a nitride of at least one kind of transition metal selected from the group consisting of molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and nickel; or (III) a catalytically active component containing at least one kind of iron group metal selected from the group consisting of iron, cobalt, and nickel, and at least one metal oxide, thereby making it possible to effectively decompose ammonia into nitrogen and hydrogen at relatively low temperatures and at high space velocities to obtain high-pure hydrogen.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com