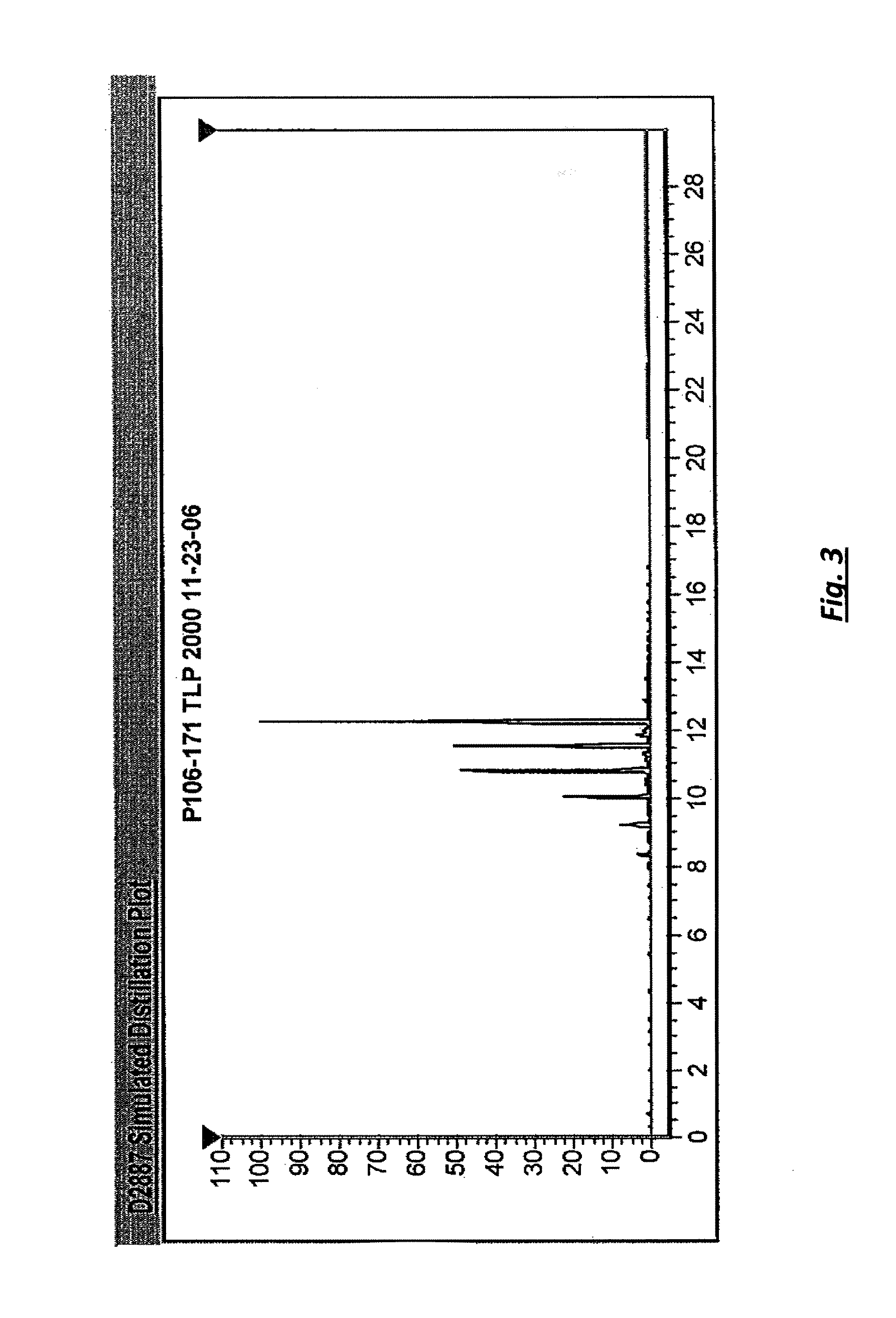
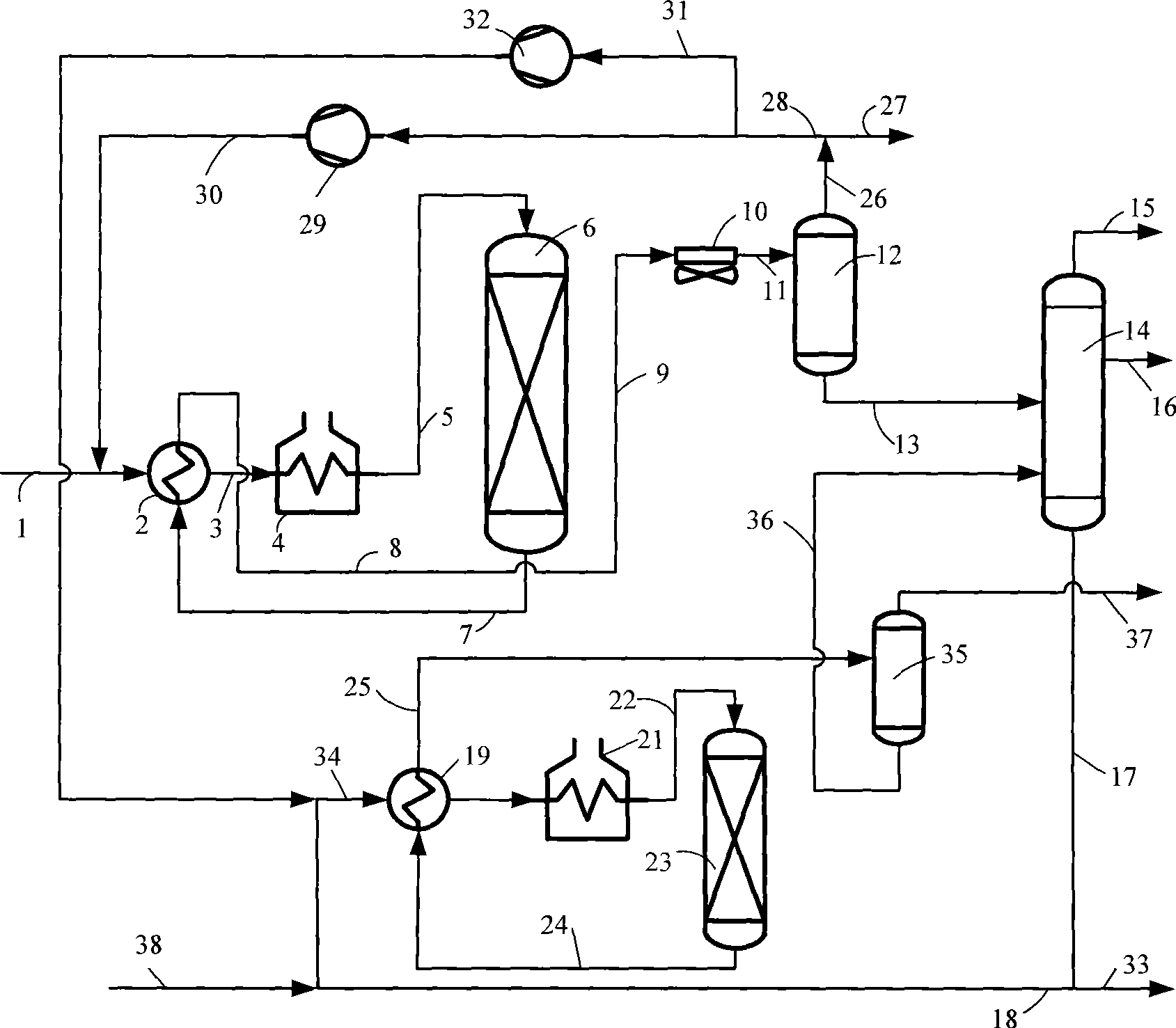
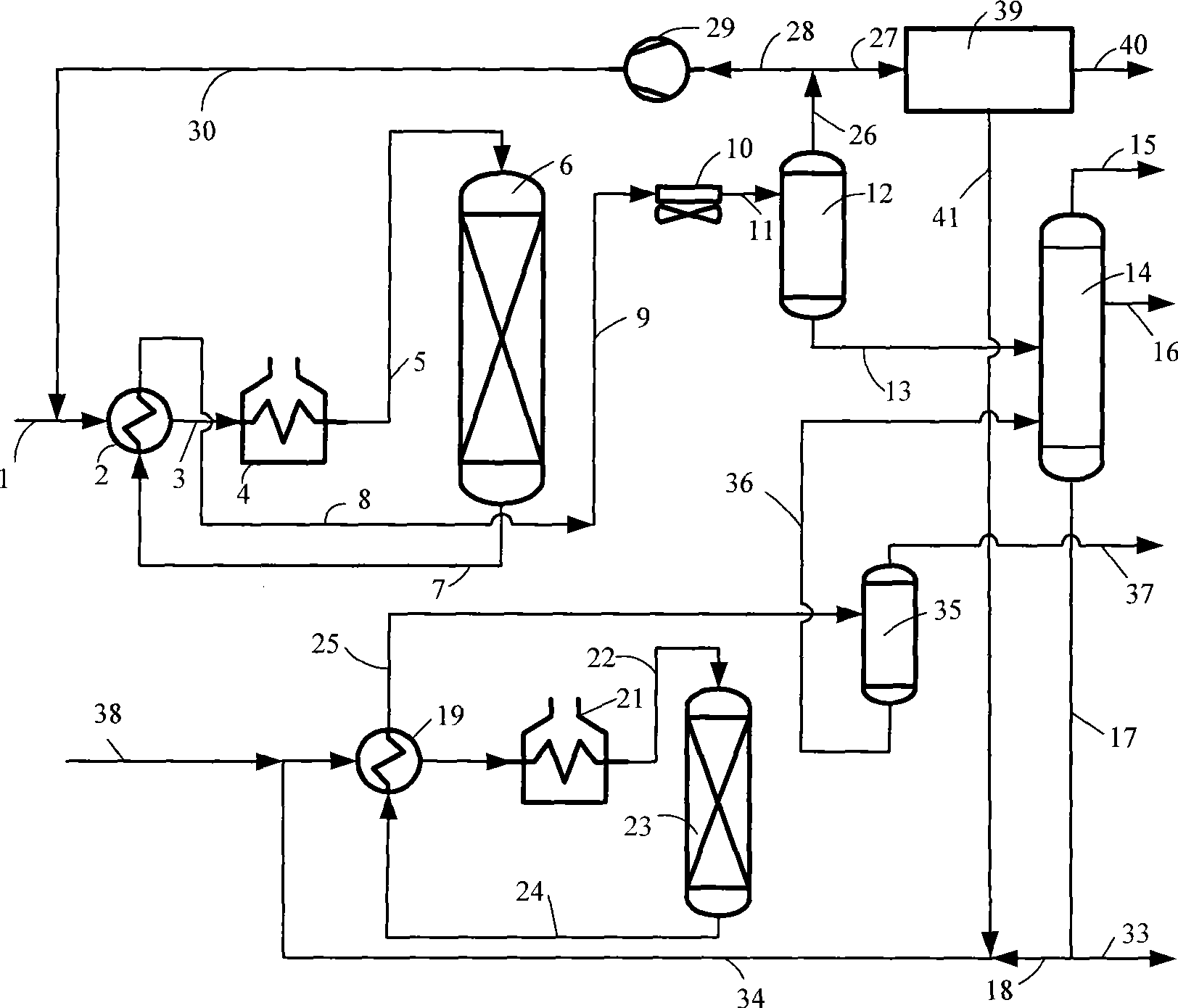
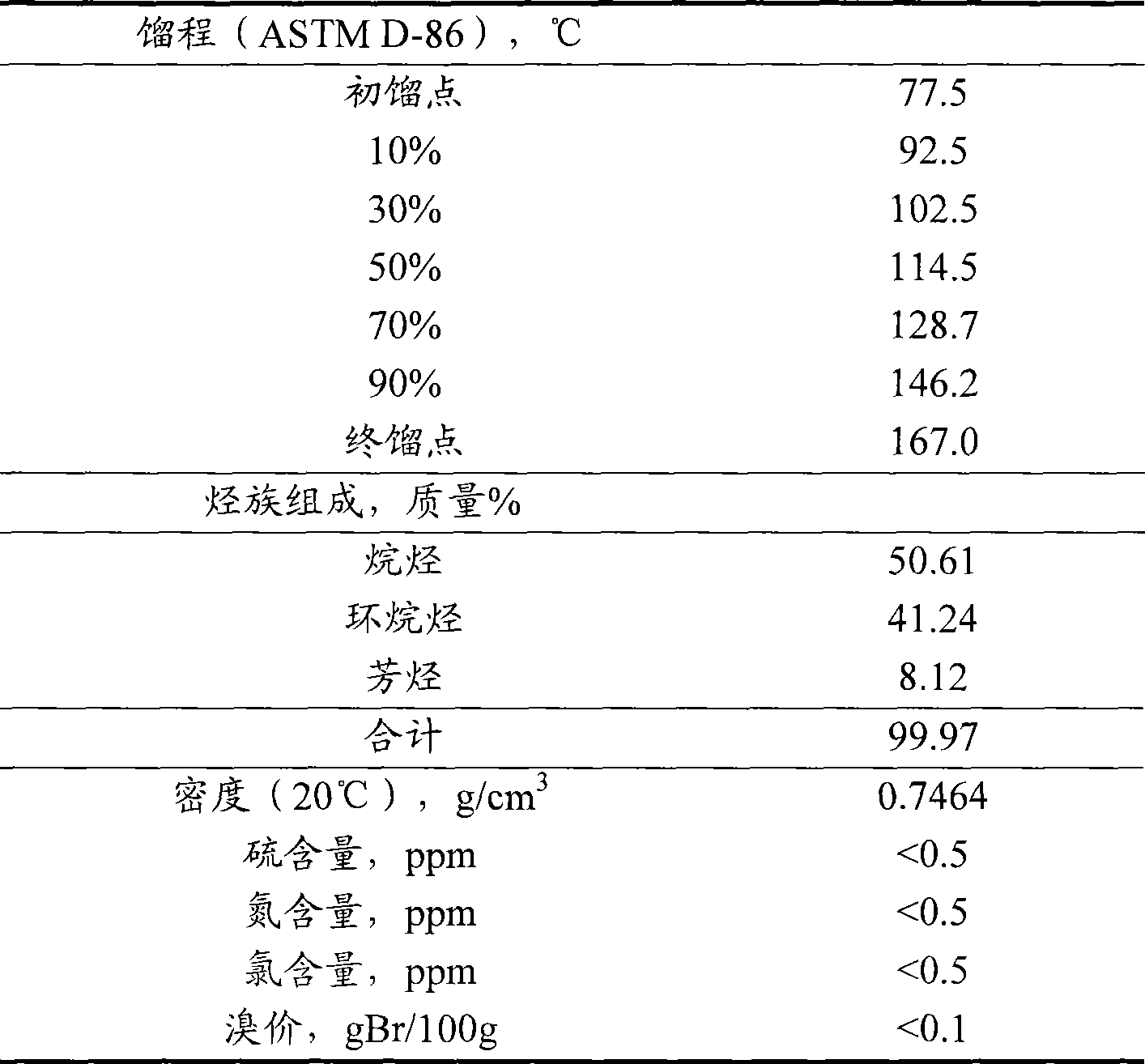
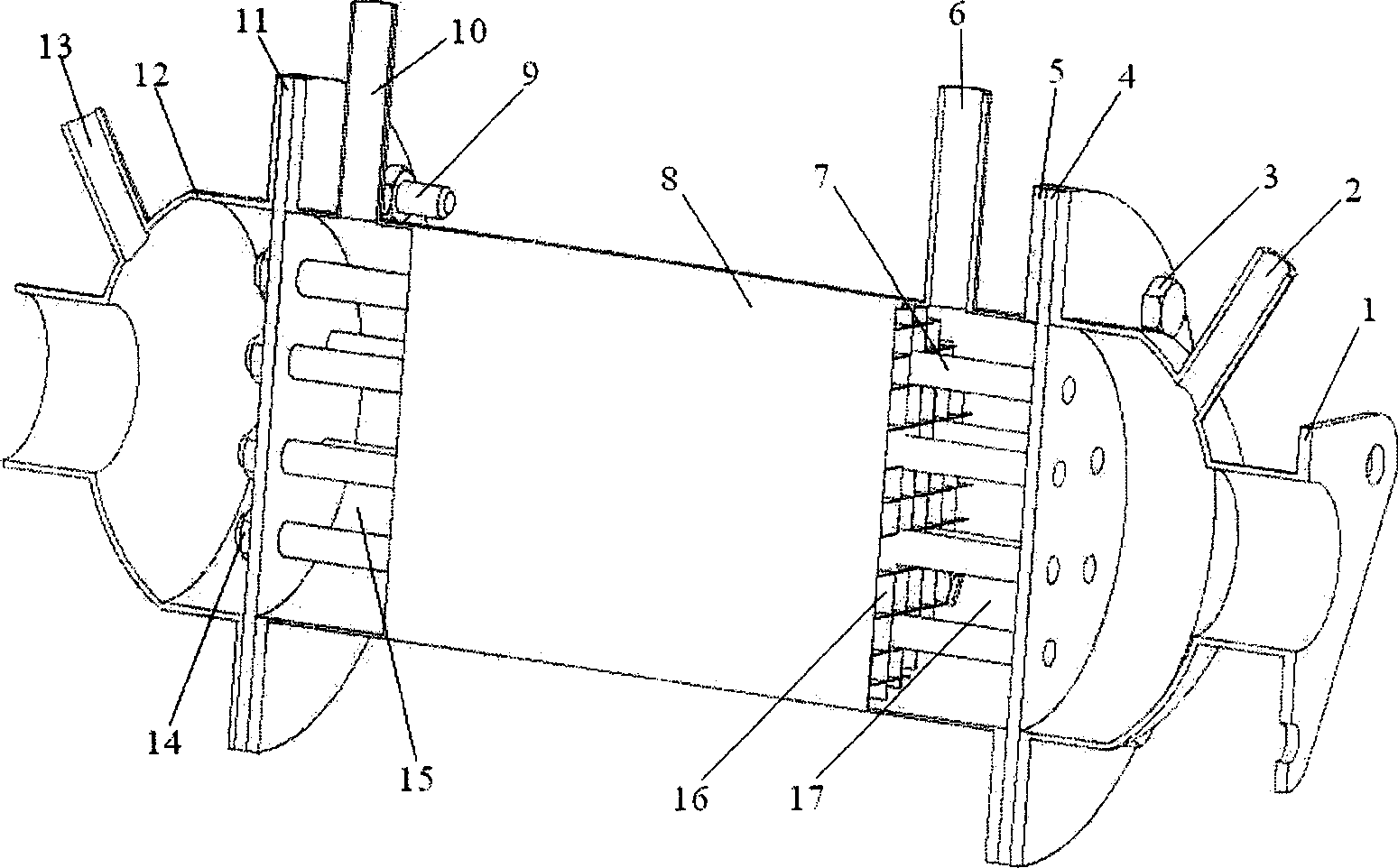
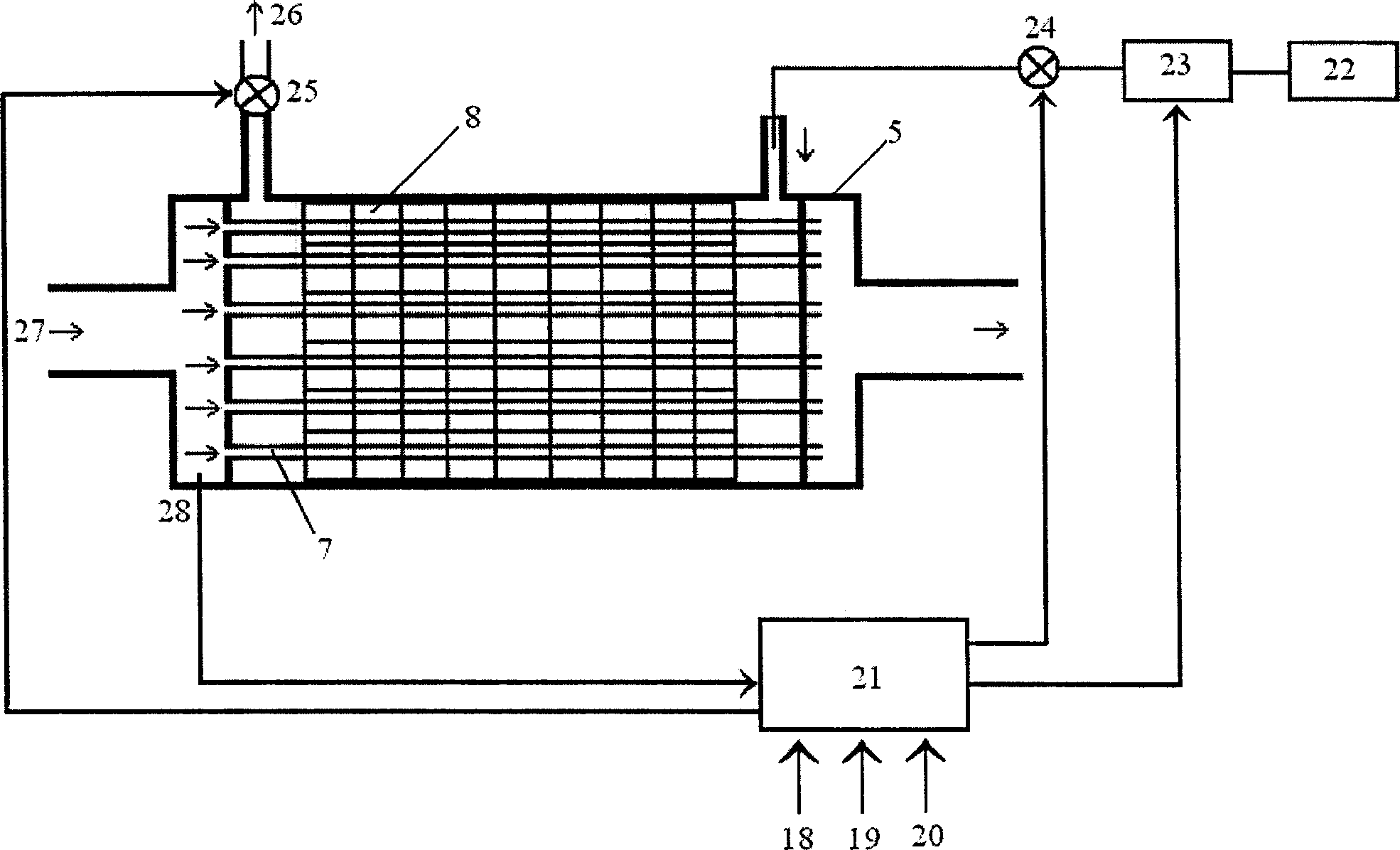
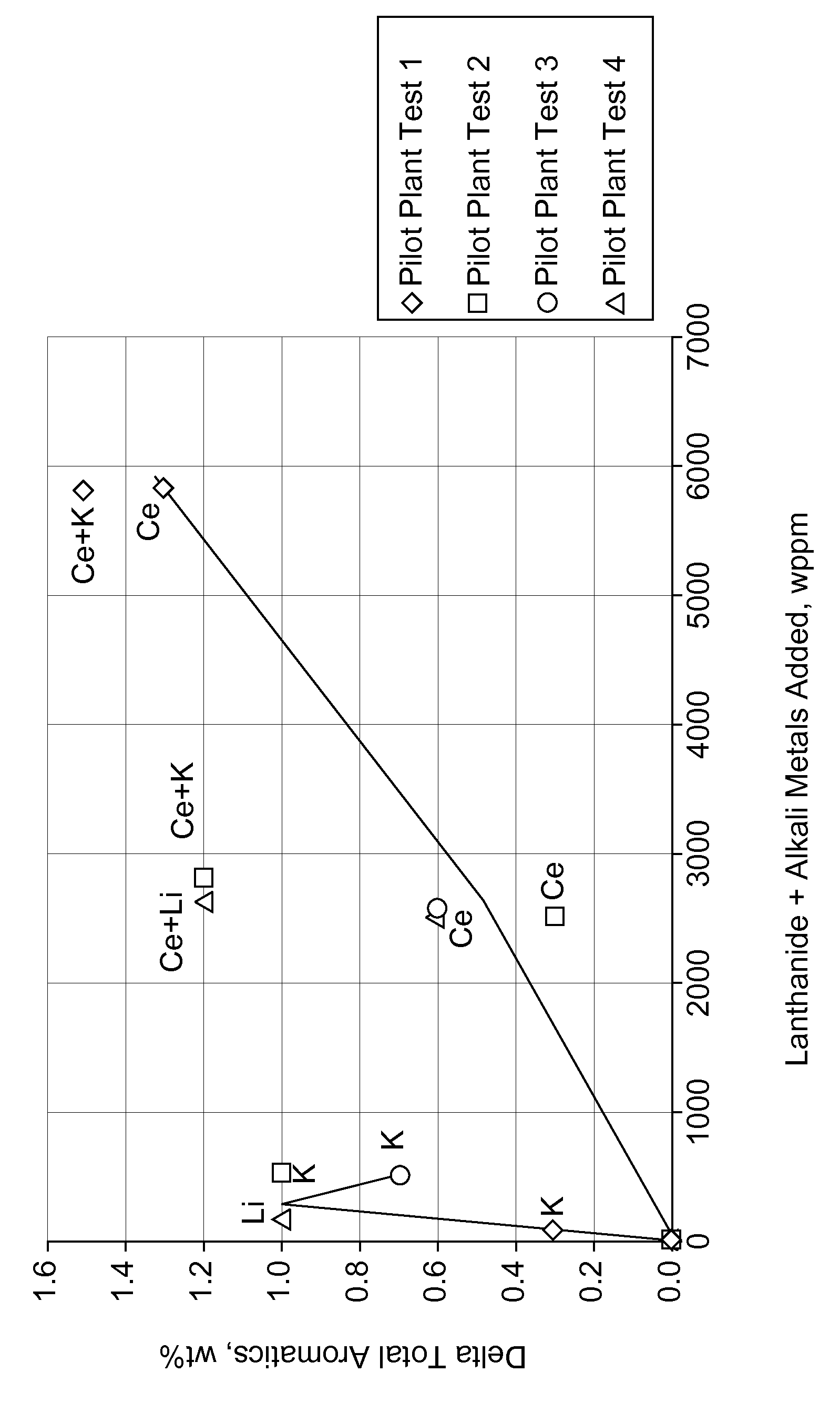
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
890 results about "Catalytic reforming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Catalytic reforming is a chemical process used to convert petroleum refinery naphthas distilled from crude oil (typically having low octane ratings) into high-octane liquid products called reformates, which are premium blending stocks for high-octane gasoline. The process converts low-octane linear hydrocarbons (paraffins) into branched alkanes (isoparaffins) and cyclic naphthenes, which are then partially dehydrogenated to produce high-octane aromatic hydrocarbons. The dehydrogenation also produces significant amounts of byproduct hydrogen gas, which is fed into other refinery processes such as hydrocracking. A side reaction is hydrogenolysis, which produces light hydrocarbons of lower value, such as methane, ethane, propane and butanes.
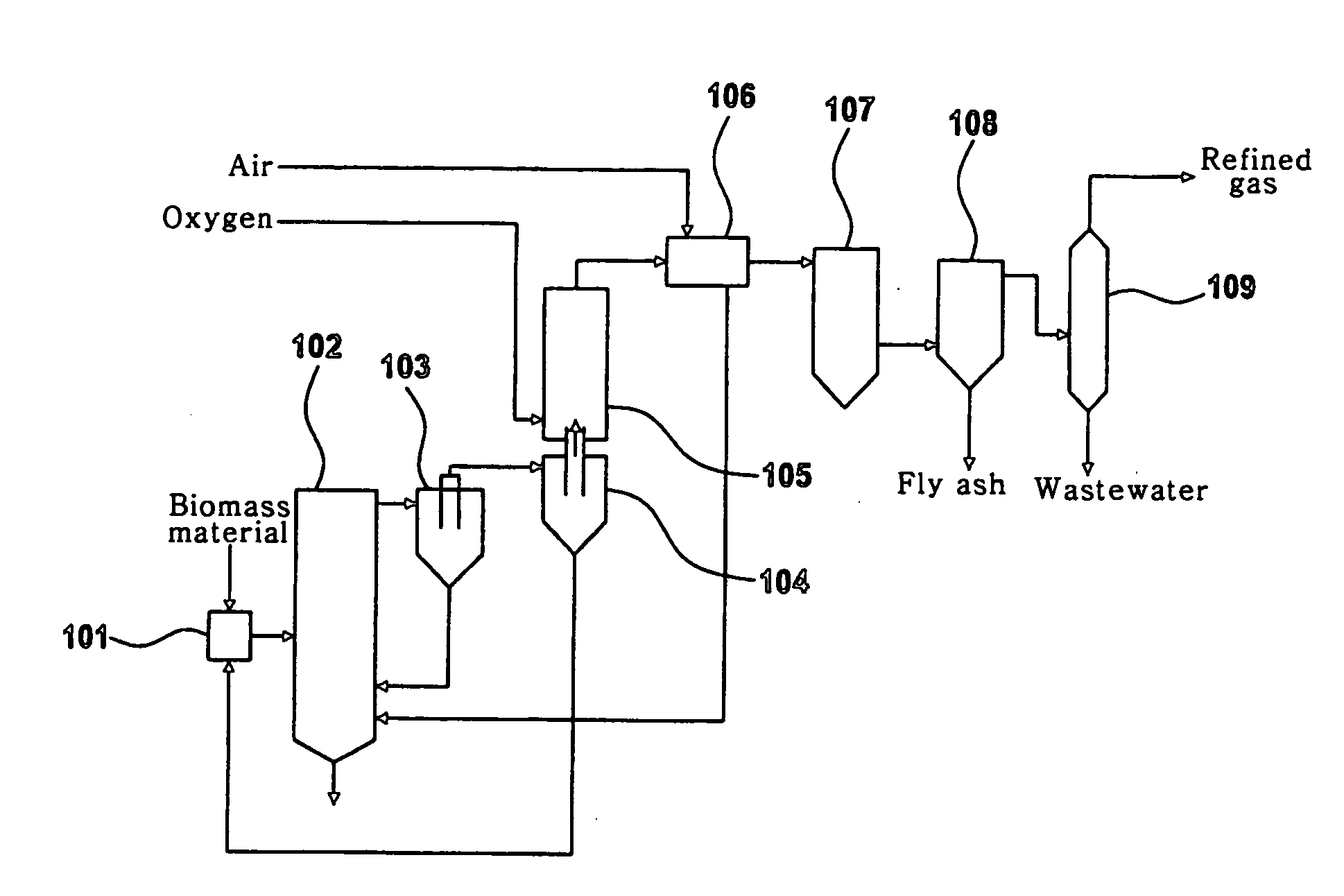
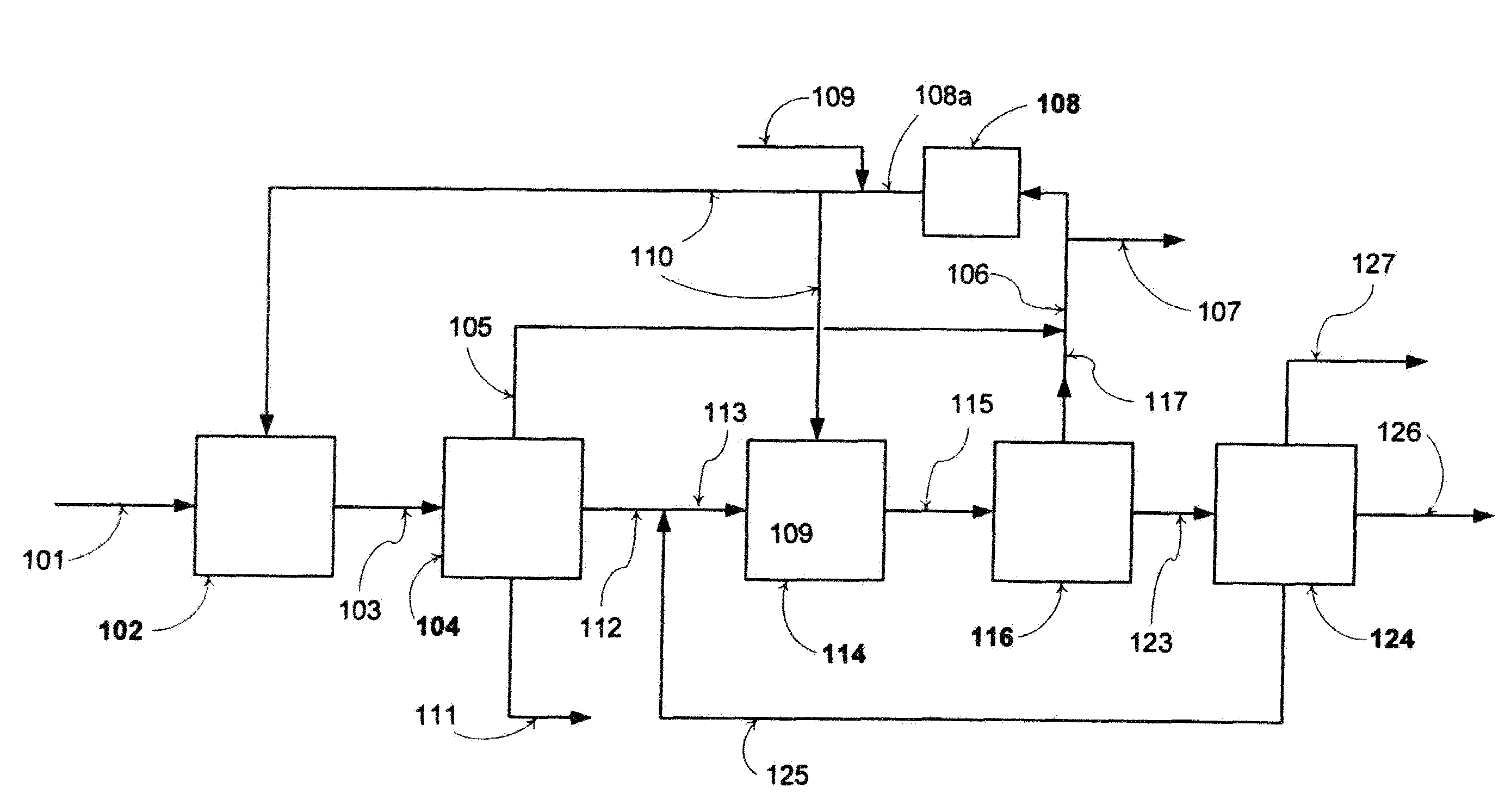
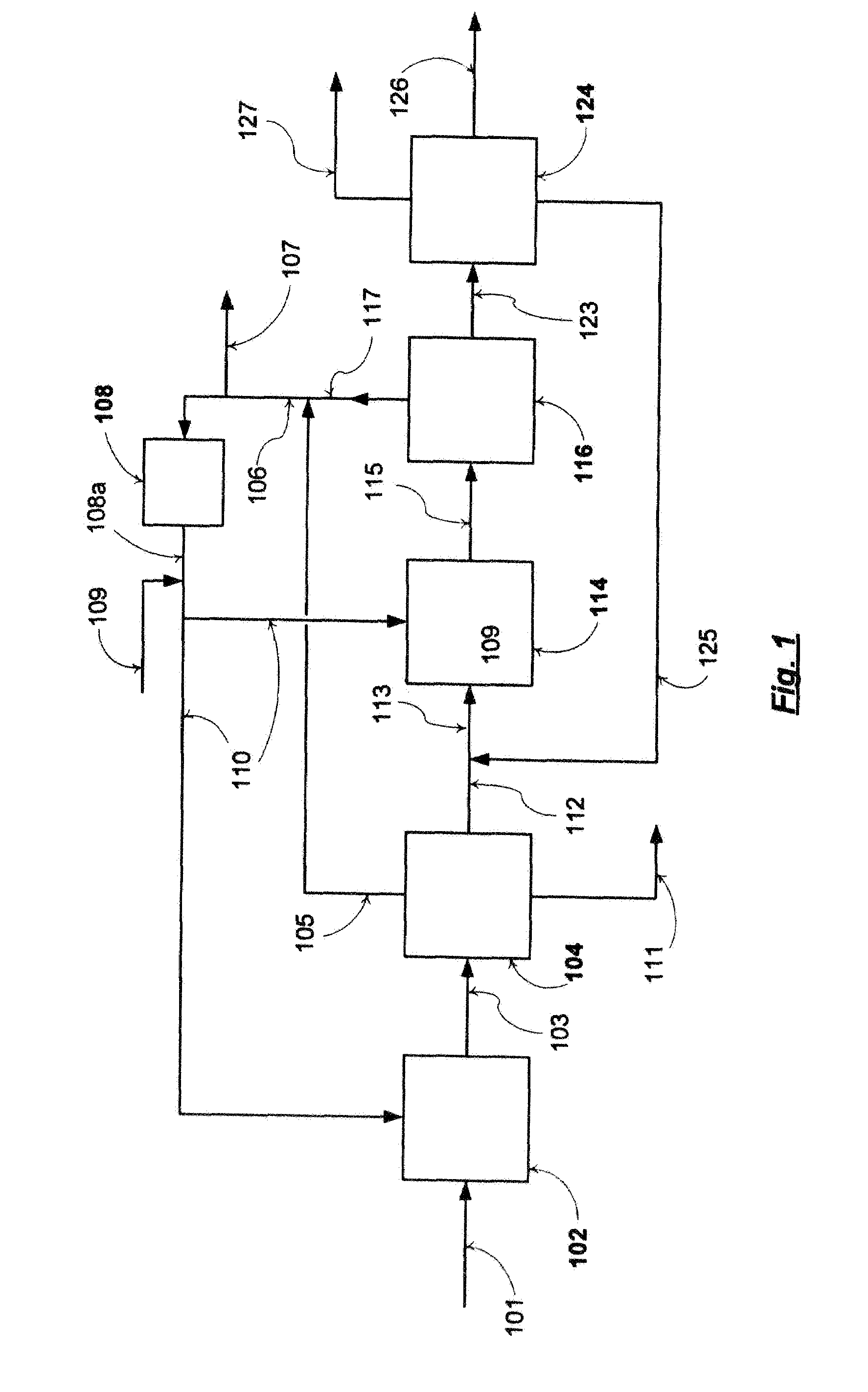
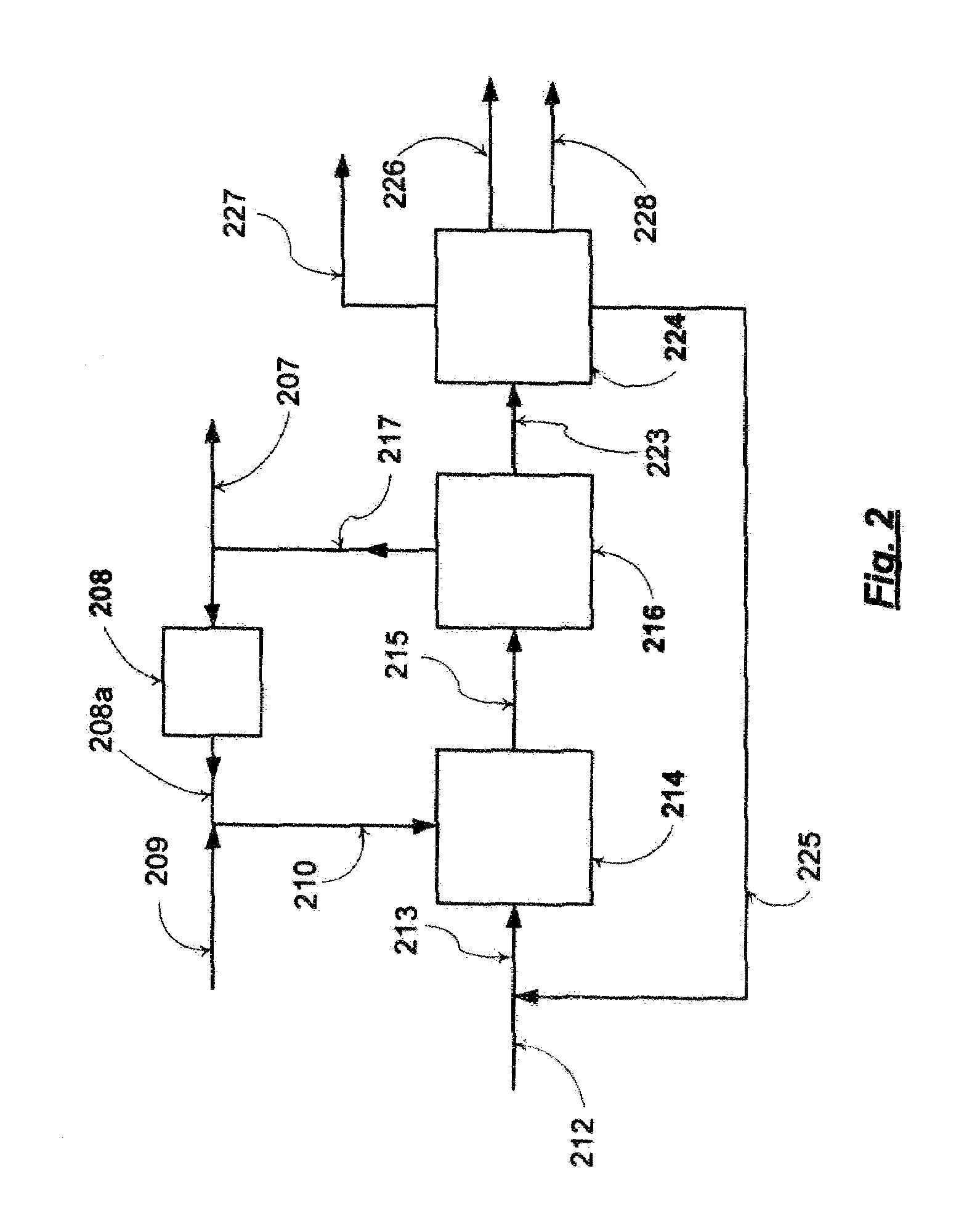
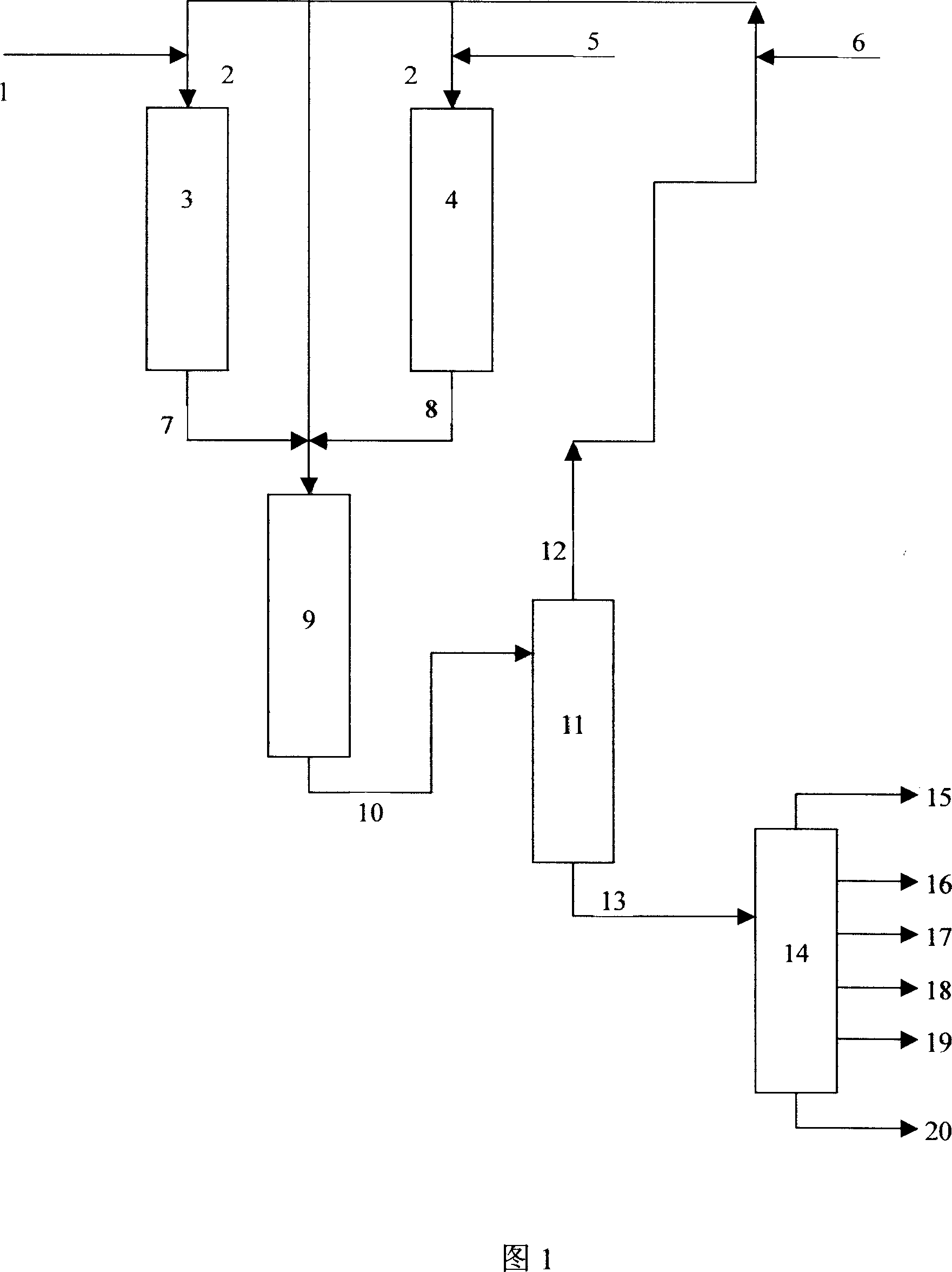
Method for preparing hydrogen-riched gas by solid fuel catalytic gasification
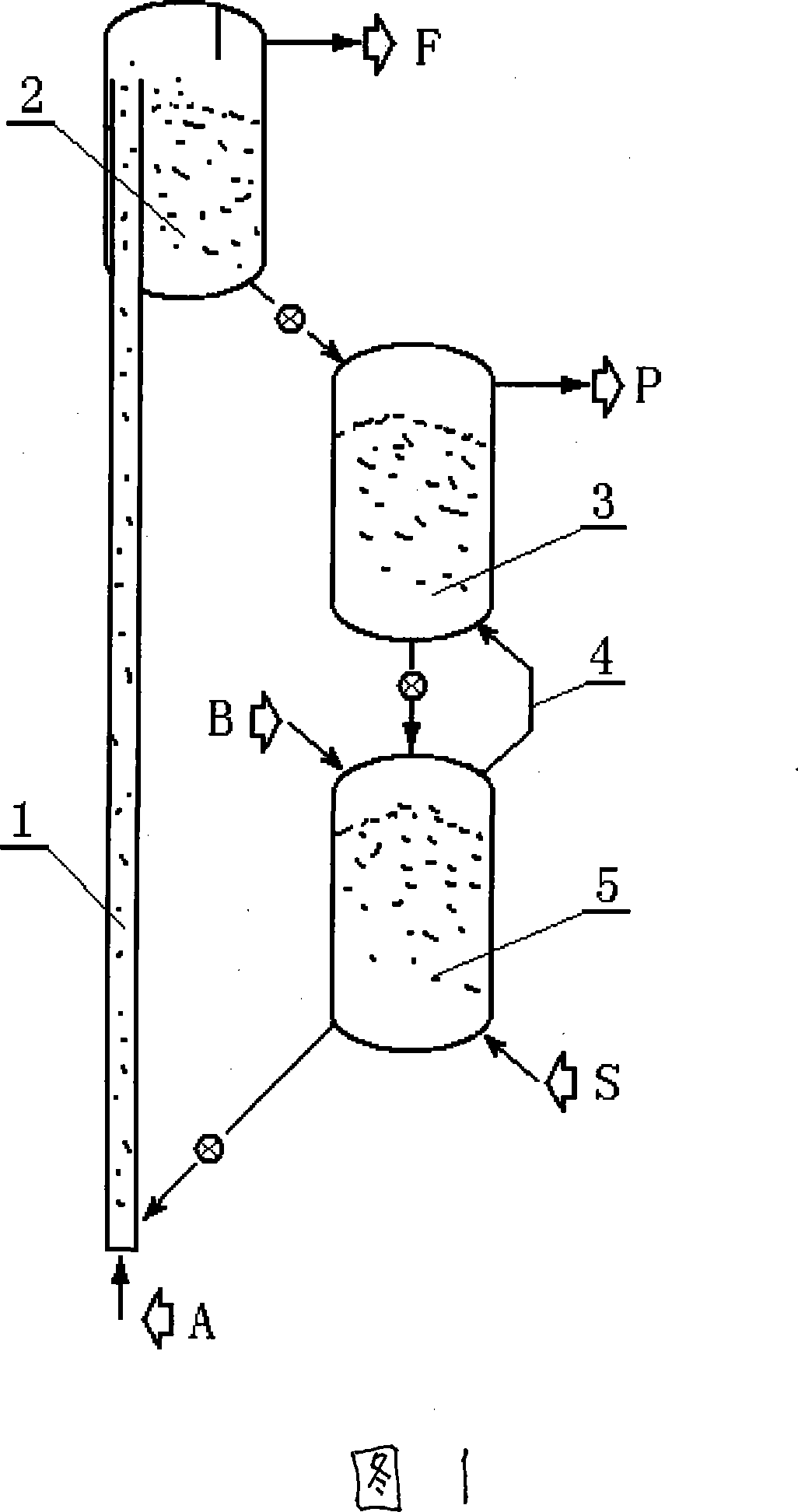
InactiveCN101045524AReasonable temperature distributionReduce the temperatureDirect heating destructive distillationHydrogen productionCatalytic reformingHeat carrier
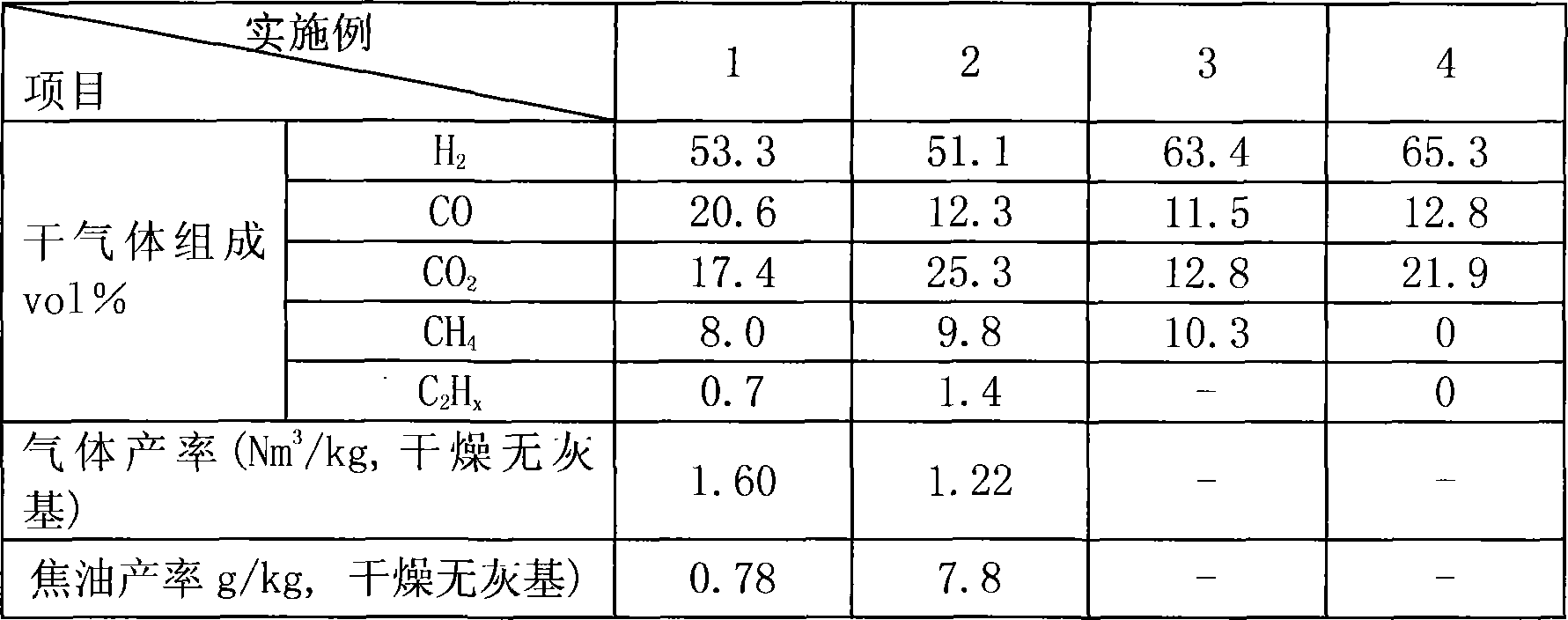
A process for preparing the H2-enriched gas by catalytic gasification of solid fuel features that the solid catalyst used also as the heat carrier is circulating through riser combustion reactor, solid catalyst storage tank, catalytic reforming reactor and pyrolyzing reactor. In said pyrolyzing reactor, the biomass or coal and the solid heat carrier (catalyst) take part in fast pyrolytic reaction. Its resultant and the water steam take part in catalytic decomposing and reforming reaction to generate H2-enriched gas or synthetic gas.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Highly heat integrated reformer for hydrogen production
InactiveUS20100178219A1Improve distributionEasy to introduceCatalytic gas-gas reactionHydrogenCatalytic reformingSteam reforming
Described herein is a highly heat integrated steam reformer / combustor assembly that can be used in a fuel processor for hydrogen production from a fuel source. The assembly comprises a reforming section and a combustion section separated by a wall. Catalyst able to induce the reforming reactions is coated on the wall facing the reforming section. Catalyst able to induce the combustion reactions is coated on the wall facing the combustion section. A steam and fuel mixture is supplied to the reforming section where it is reformed to product hydrogen. A fuel and air mixture is supplied to the combustion section where it is combusted to supply the heat for the reformer. Catalytic combustion takes place on the combustion catalyst coated on one side of the wall while catalytic reforming takes place on the reforming catalyst coated on the other side of the wall. Heat transfer is very facile and efficient across the wall. Multiple such assemblies can be bundled to form reactors of any size.
Owner:HELBIO HYDROGEN & ENERGY PRODN SYST
Compact fuel gas reformer assemblage
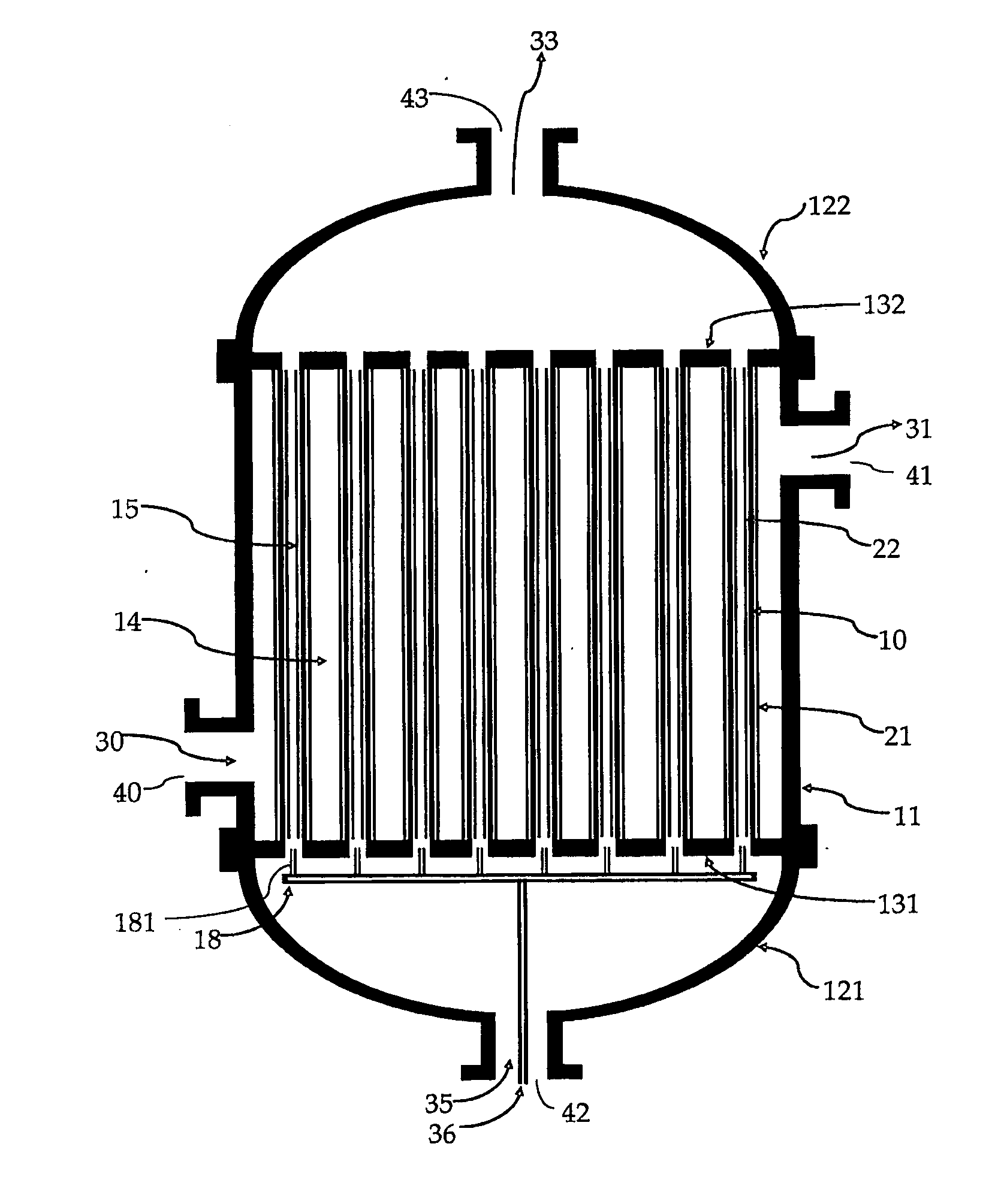
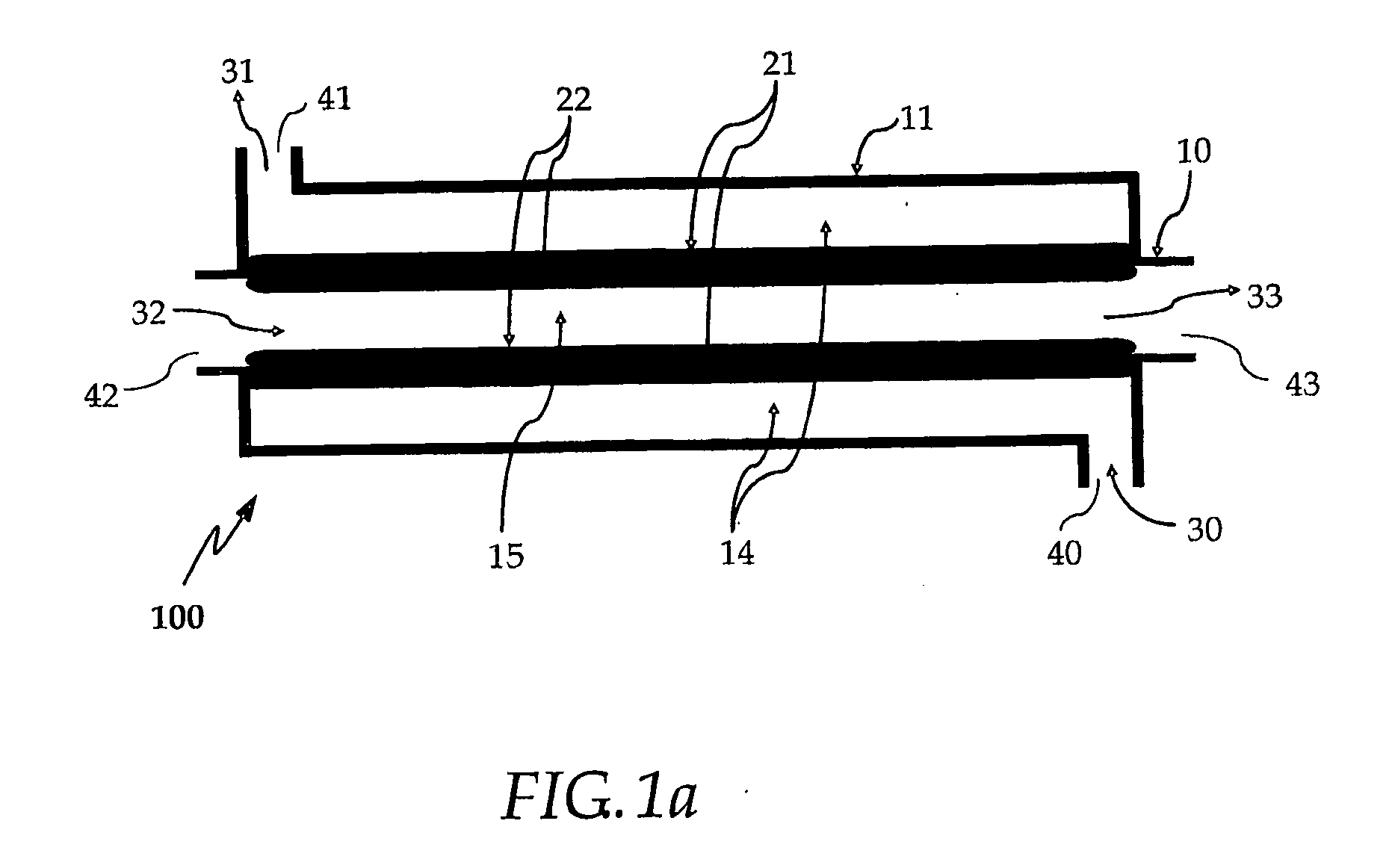
InactiveUS6203587B1Improve heat transfer performanceReduce the temperatureSemi-permeable membranesHydrogen separation using solid contactFuel cellsForming gas
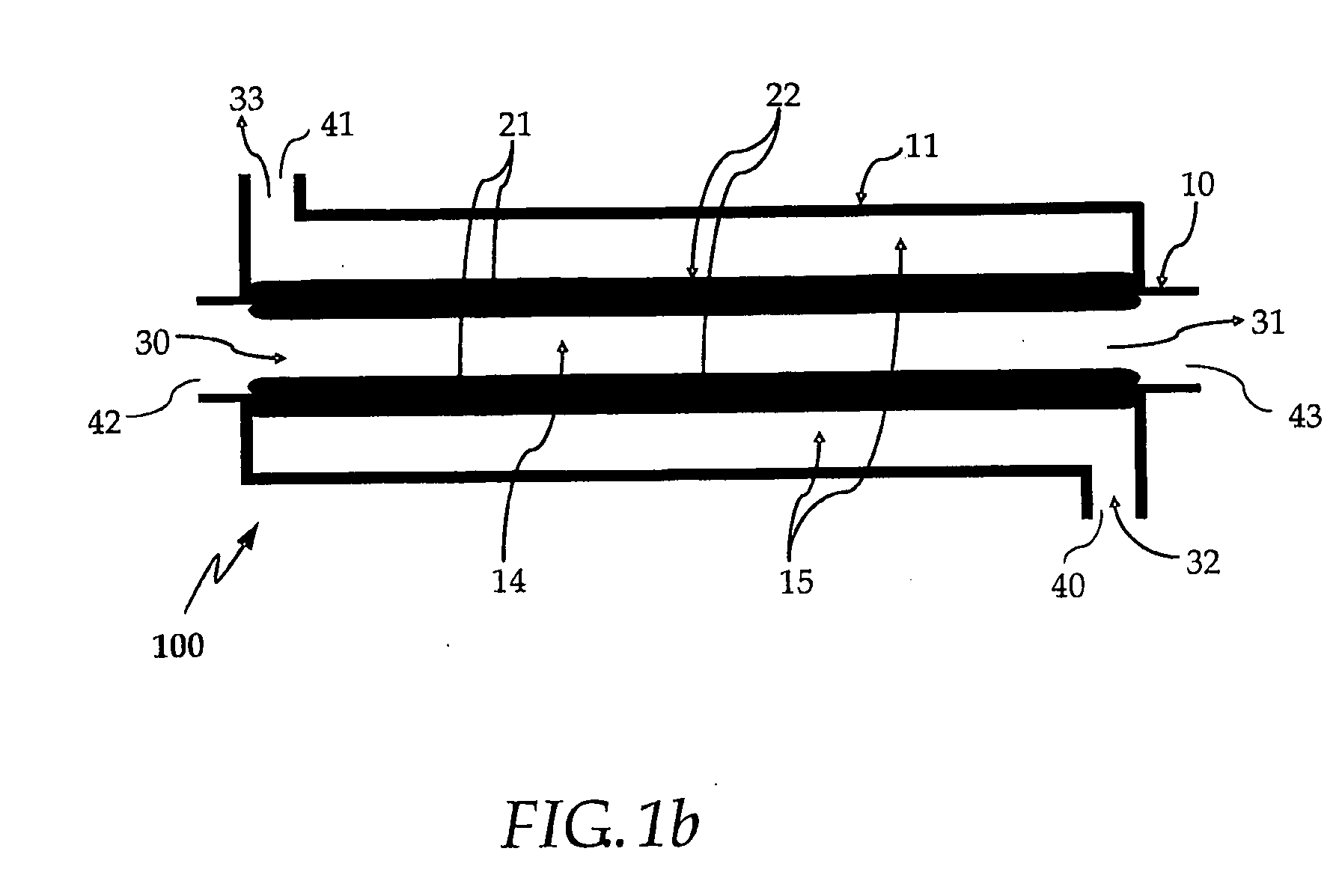
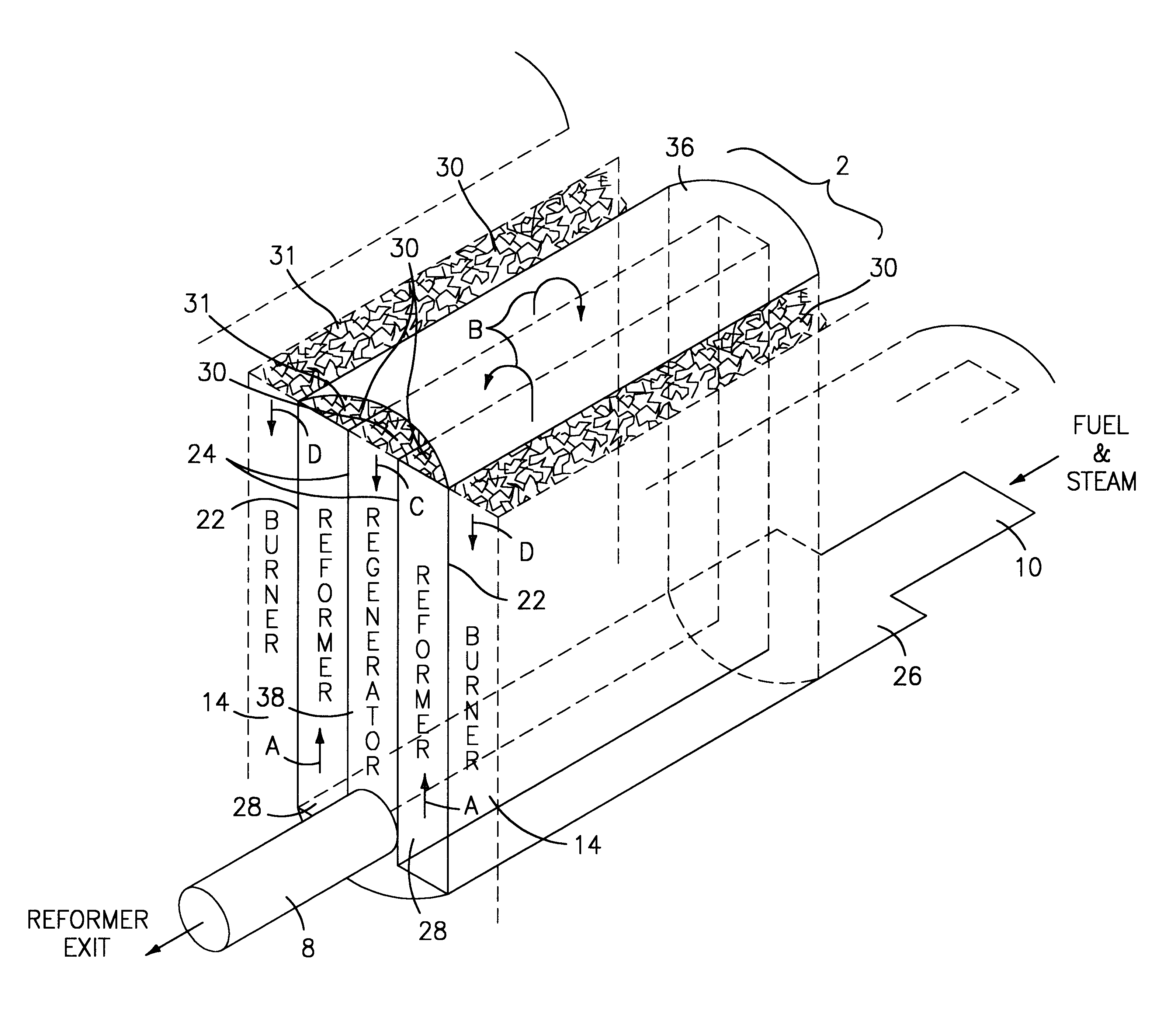
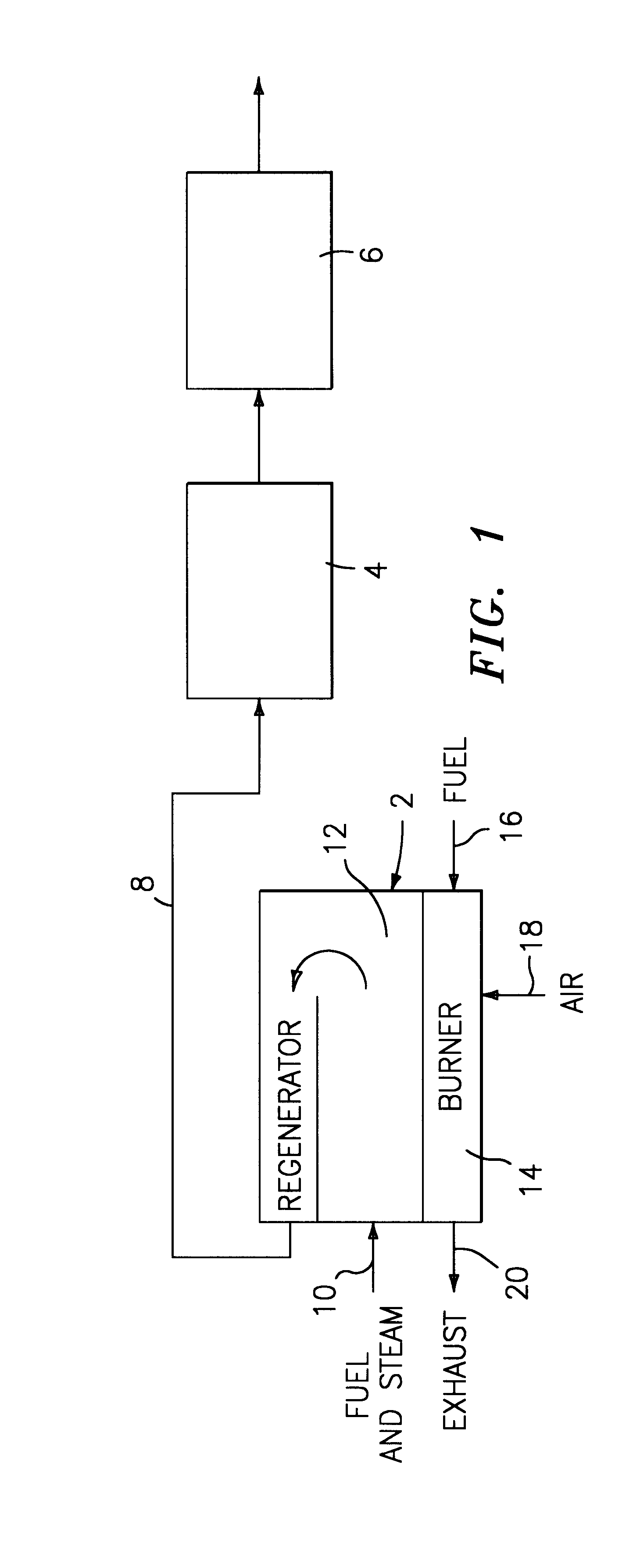
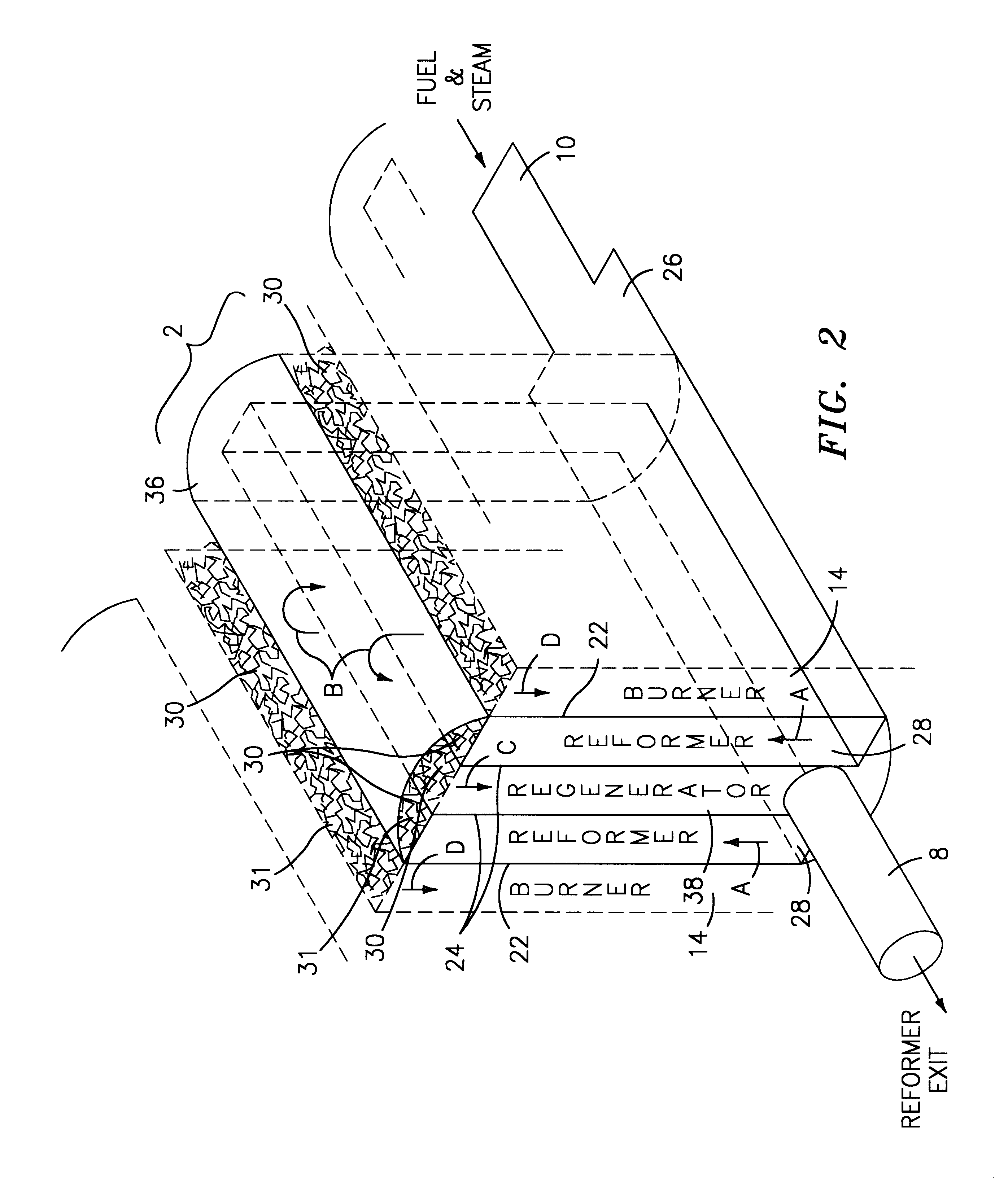
A fuel gas reformer assemblage for use in a fuel cell power plant is formed from a composite plate assembly which includes spaced-apart divider plates with interposed monolithic open cell sponge-like members which form gas passages. The monolithic members have a lattice of internal open cells which are both laterally and longitudinally interconnected so as to provide for a diffuse gas flow. The entire surface area of the monolithic components is wash coated with a porous alumina layer, and selected areas of the wash coat are also catalyzed. The reformer assemblage is constructed from a series of repeating sub-assemblies, each of which includes a core of separate regenerator / heat exchanger gas passages. The core in each sub-assembly is sandwiched between a pair of reformer gas passage skins, which complete the subassembly. Adjacent reformer gas / regenerator / reformer gas passage sub-assemblies in the composite plate assembly are separated from each other by burner gas passages. The regenerator / heat exchanger gas passages and the reformer gas passages in each sub-assembly are connected by gas flow return manifolds which form a part of each sub-assembly. The fuel gases flow in one end of the assemblage, through the reformer gas passages, and then reverse their direction of flow in the return manifolds so as to exit the reformer assemblage through the regenerator gas flow passages. The burner gases flow in one end of the reformer assemblage and out the other end.
Owner:INT FUEL CELLS
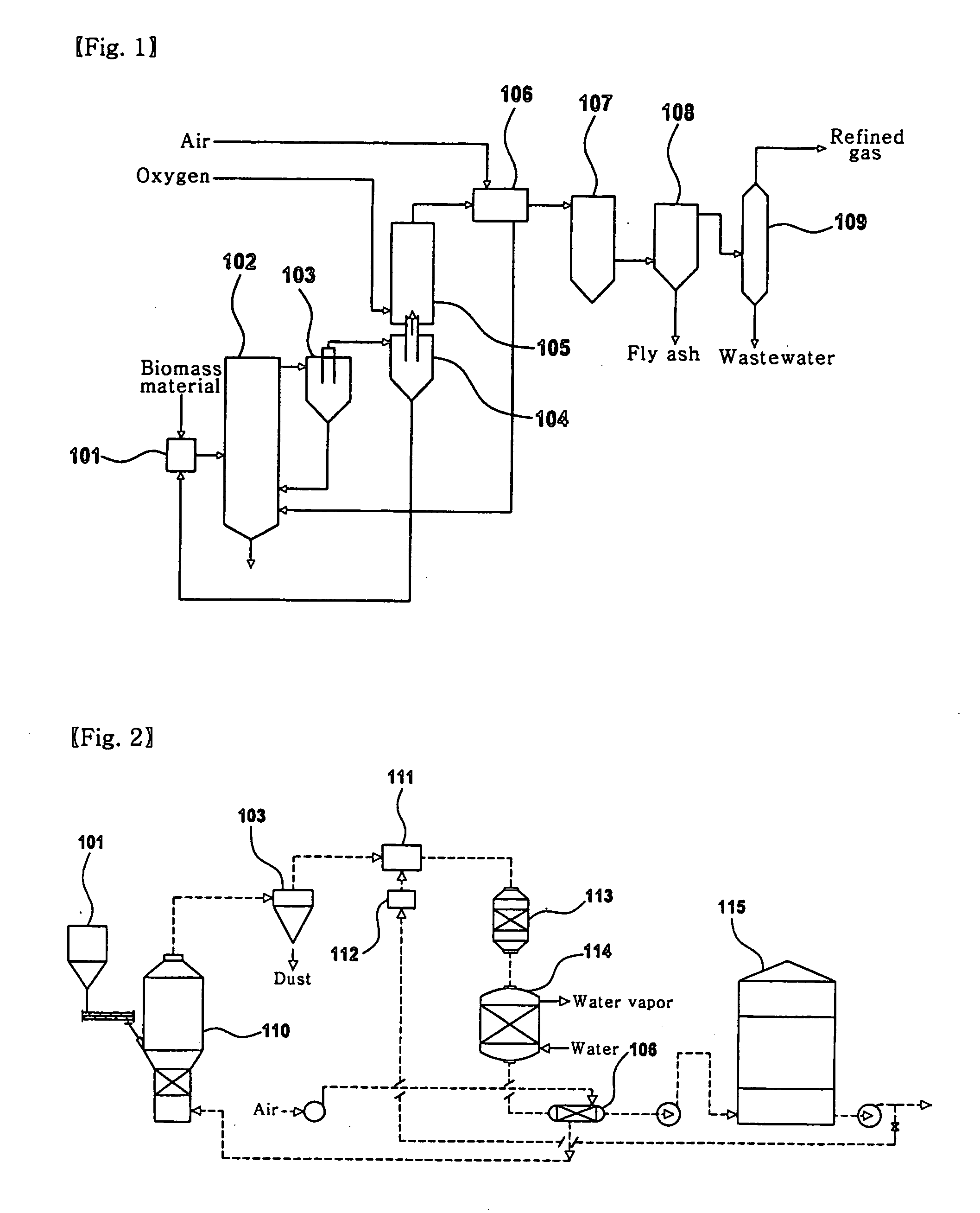
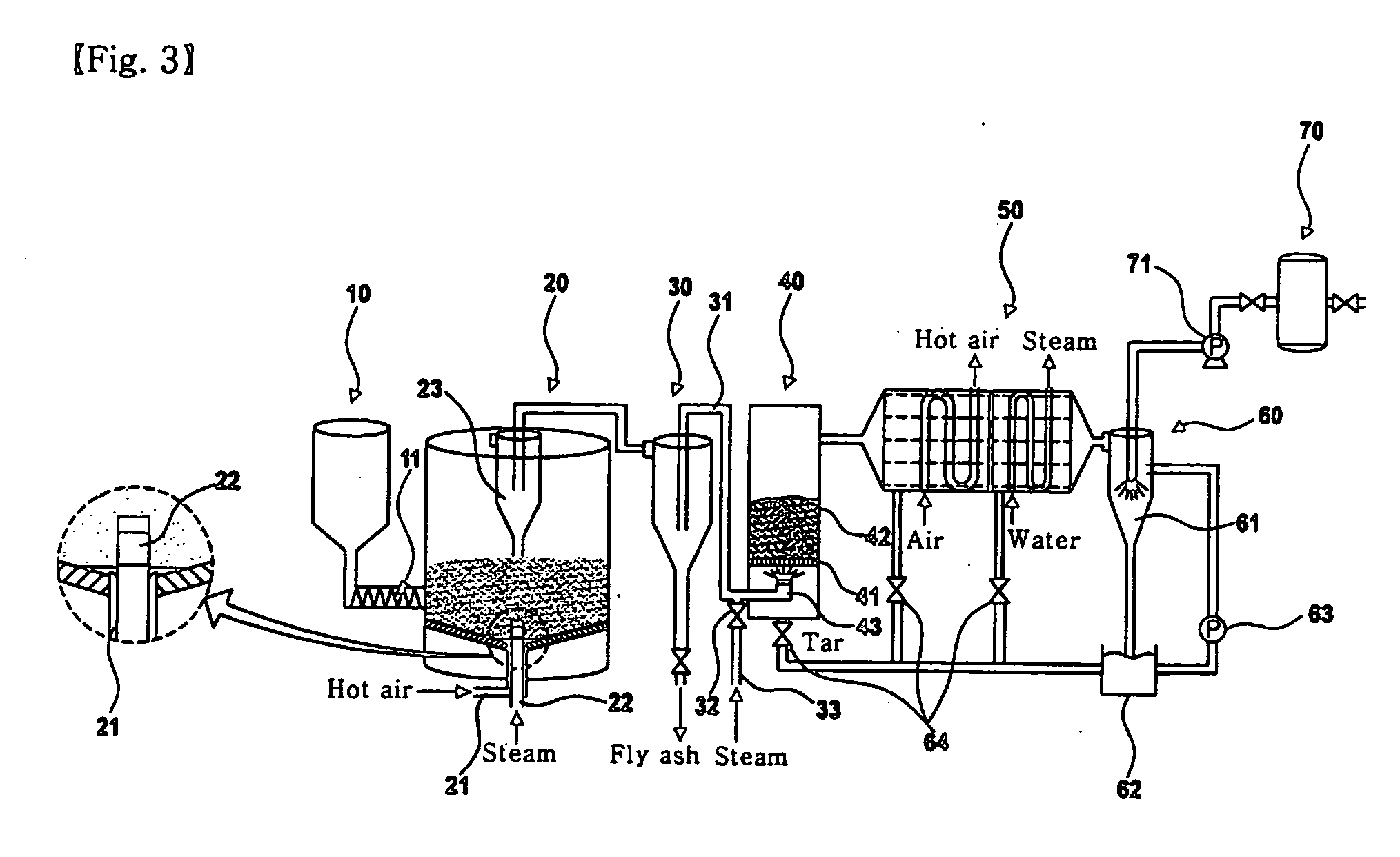
Apparatus of catalytic gasification for refined biomass fuel at low temperature and the method thereof
InactiveUS20070094929A1Low production costCompactCombustible gas catalytic treatmentLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCatalytic reformingFluidized bed
Disclosed is a gasification technique for converting biomass, which is difficult to treat, into clean gas fuel able to be burned in a cogeneration system. The gasification technique includes first stage fluidized-bed catalytic gasification, and second stage gasification of tar and catalytic reforming to convert nitrogen in tar, and HCN in a flammable gas into NH3, unlike conventional gasification techniques. In addition, since the temperature of a total gasification process is lower than a melting point of ash, powdery ash is generated and thus easily treated. Also, little heat is released due to the low process temperature, and therefore, a compact reactor may be designed to produce gas having a high caloric value. Further, the generated tar is recovered and reused in other processes, and the gas fuel contains a small amount of ammonia.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
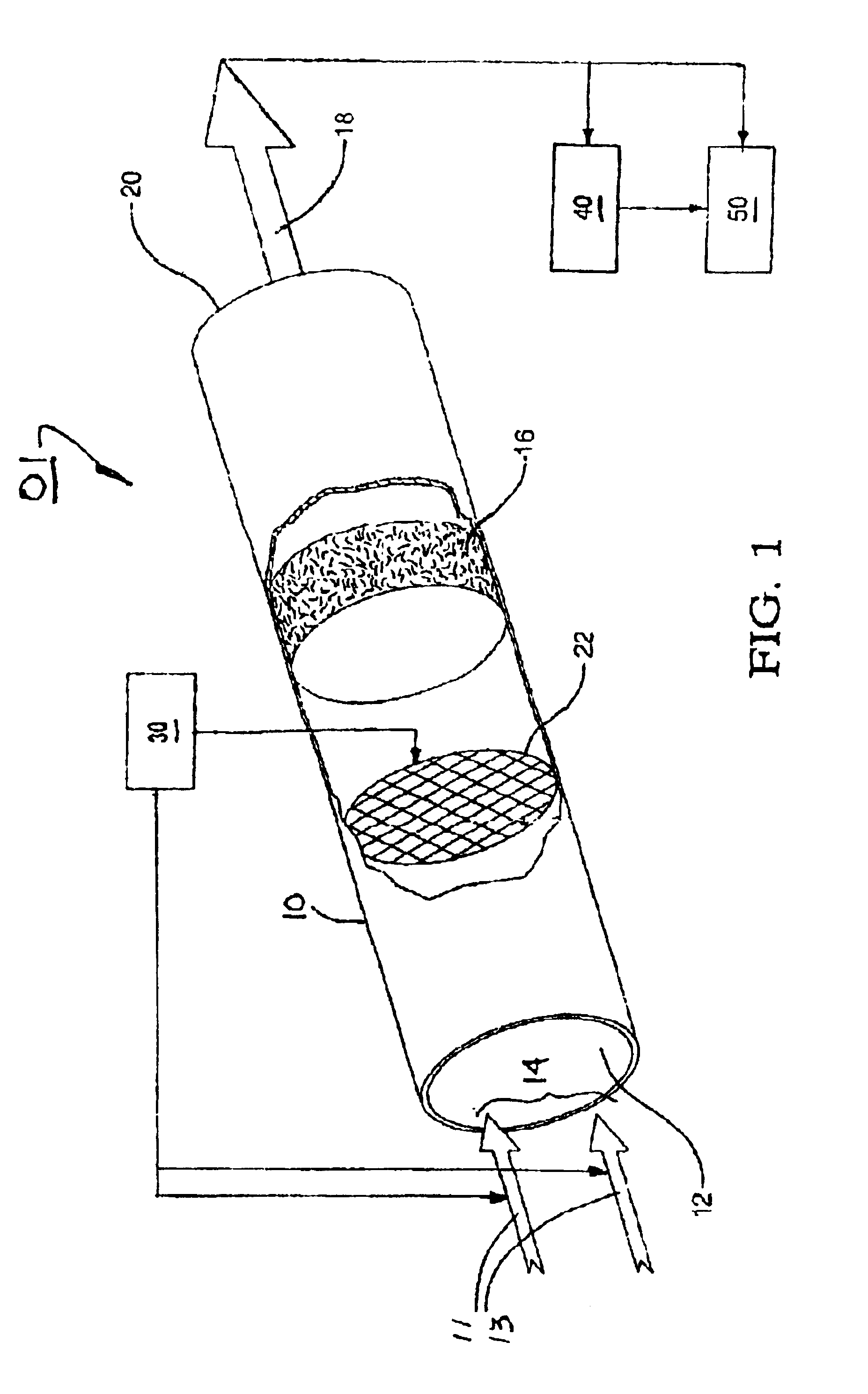
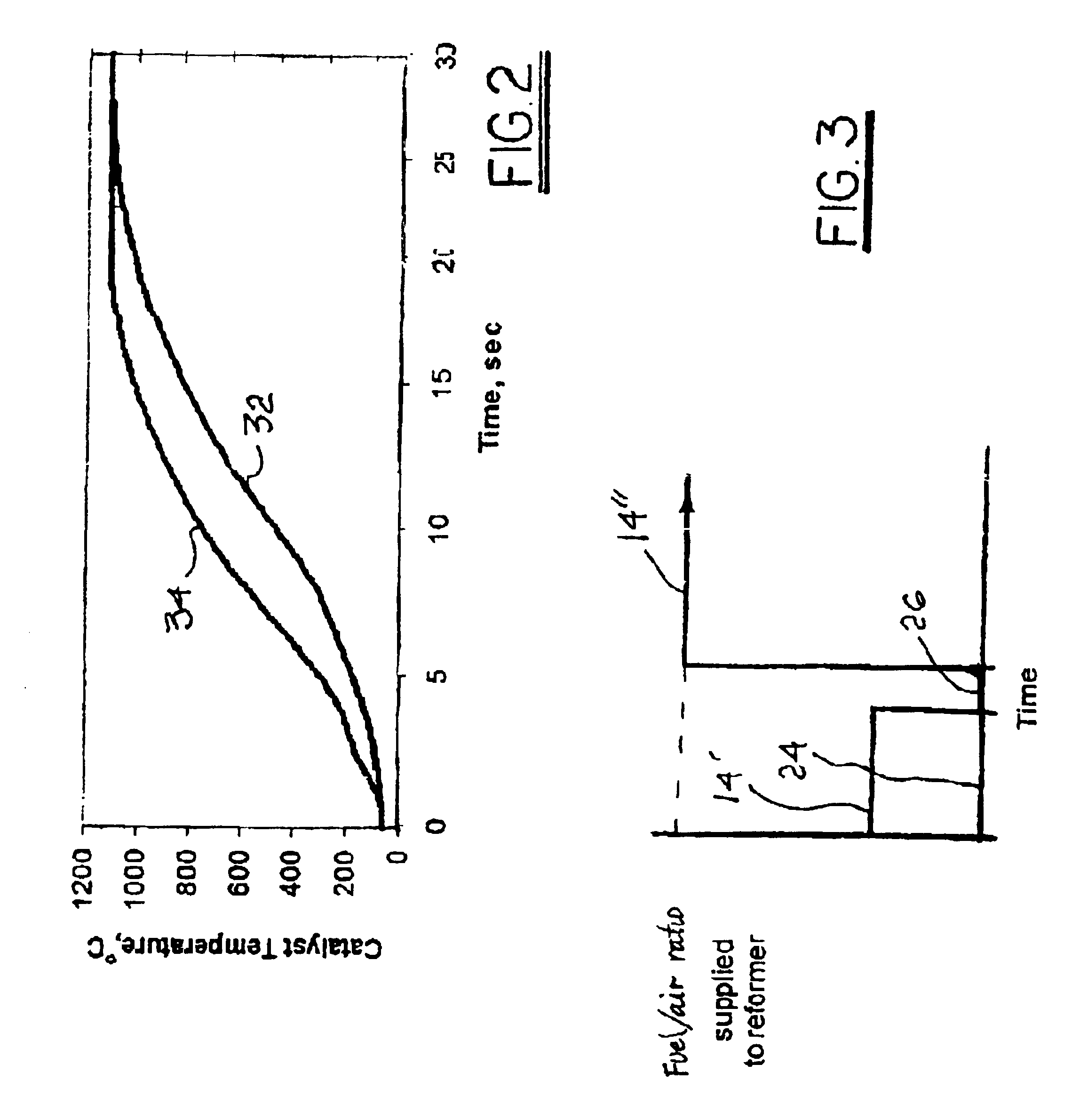
Method for starting a fast light-off catalytic fuel reformer
InactiveUS6869456B2Optimize reformate yieldStart fastCombination devicesHydrogenCatalytic reformingControl system
A method for starting a fast light-off catalytic reformer for producing hydrogen-rich reformate fuel from hydrocarbon fuel and air, the reformer having means for receiving flows of fuel and air, a reforming catalyst for reforming the fuel and air mixture, and an ignition device. A control system selects fuel and air flow rates to form a lean fuel / air mixture and operates the ignition device to ignite the lean mixture to produce hot exhaust gases that flow over and heat the reforming catalyst for a first length of time. Fuel flow is then stopped temporarily for a second length of time, and further ignition is terminated. Fuel flow is then restarted and adjusted to provide a rich fuel / air mixture which is directed to the heated catalyst for reforming into reformate fuel. Air flow may also be adjusted in setting the lean and / or rich fuel / air mixtures.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Method for preparing synthetic gas by three-phase type biomass pyrolysis-gasification-catalytic reforming
ActiveCN102424359AImprove conversion utilizationHigh yieldHydrogenWaste based fuelCatalytic reformingChemical industry
The invention belongs to the technical field of energy chemical industry. The process for preparing synthetic gas by biomass pyrolysis and gasification is divided into three steps of biomass low-temperature pyrolysis, coke or semi-coke high-temperature gasification and crude synthetic gas / tar catalytic reforming. The three reaction steps are successively and continuously carried out in three relatively independent spaces of an upper pyrolysis hearth, a lower gasification hearth and a catalyst bed inside the same gasification reaction device so as to finally obtain the high-quality synthetic gas. The method provided by the invention has high carbon conversion rate, produces no secondary pollution and is simple to realize. In addition, required biomass is rich in reserves and can be regenerated, thus realizing integrated sustainable utilization of resource, energy and environment.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +1
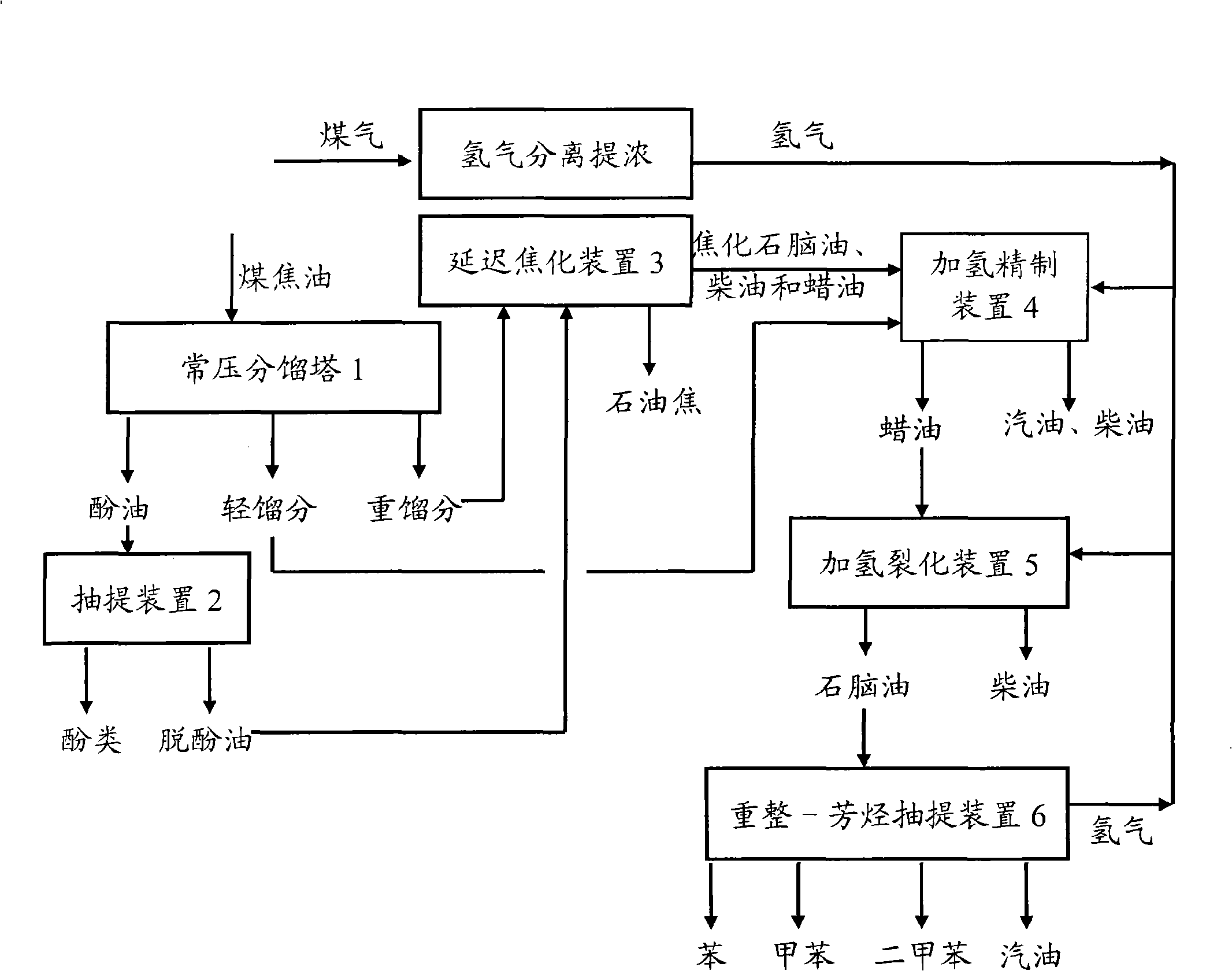
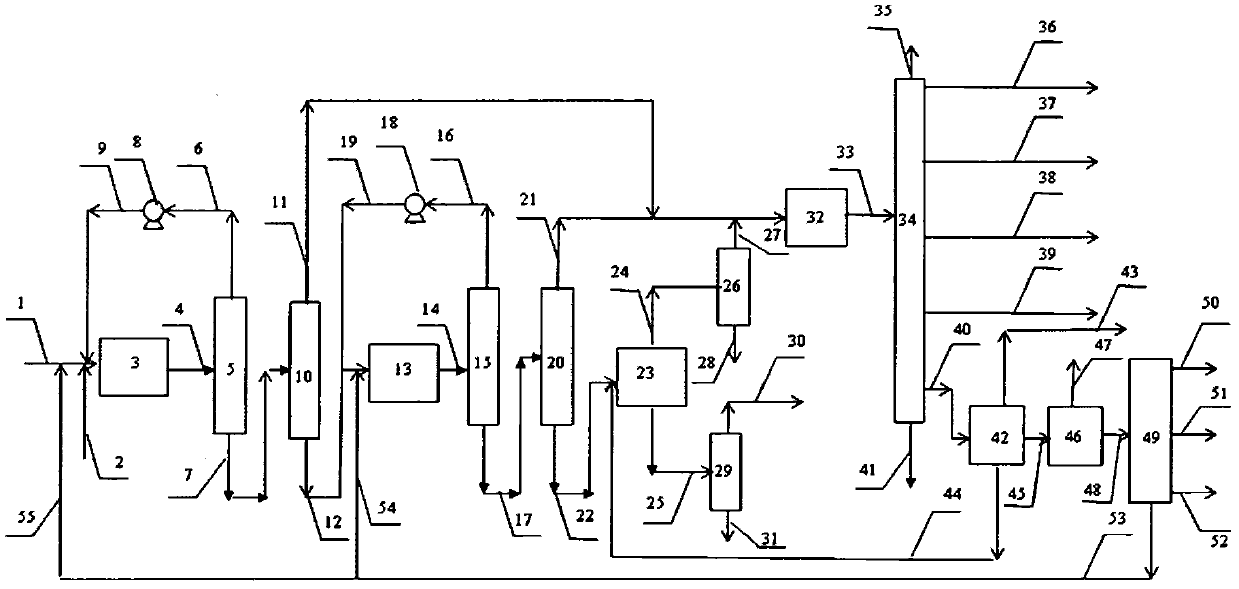
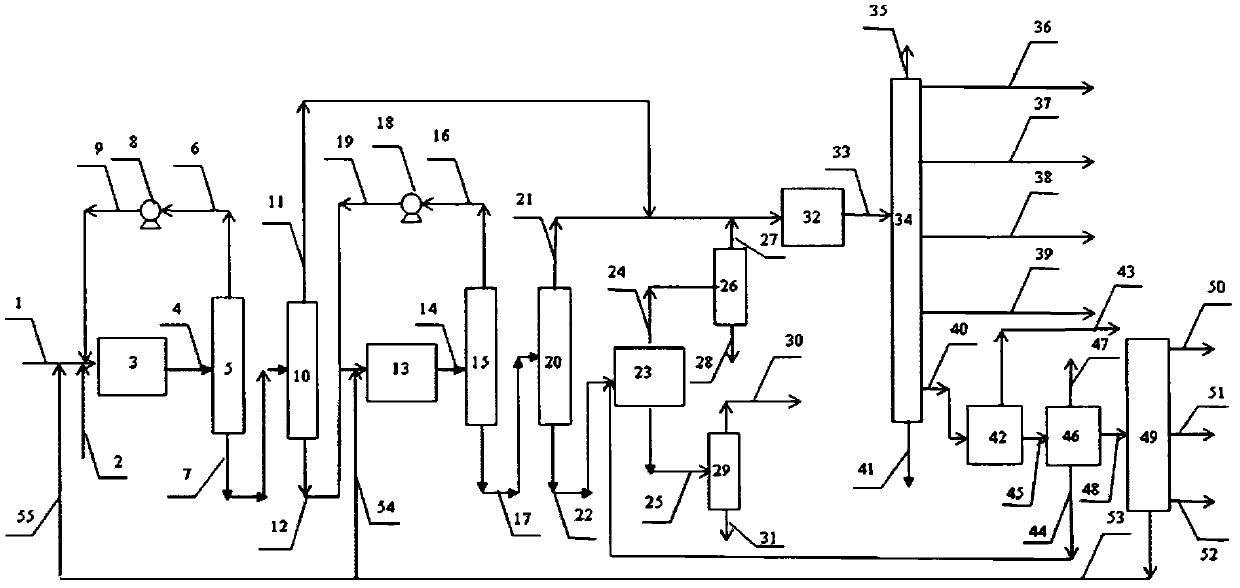
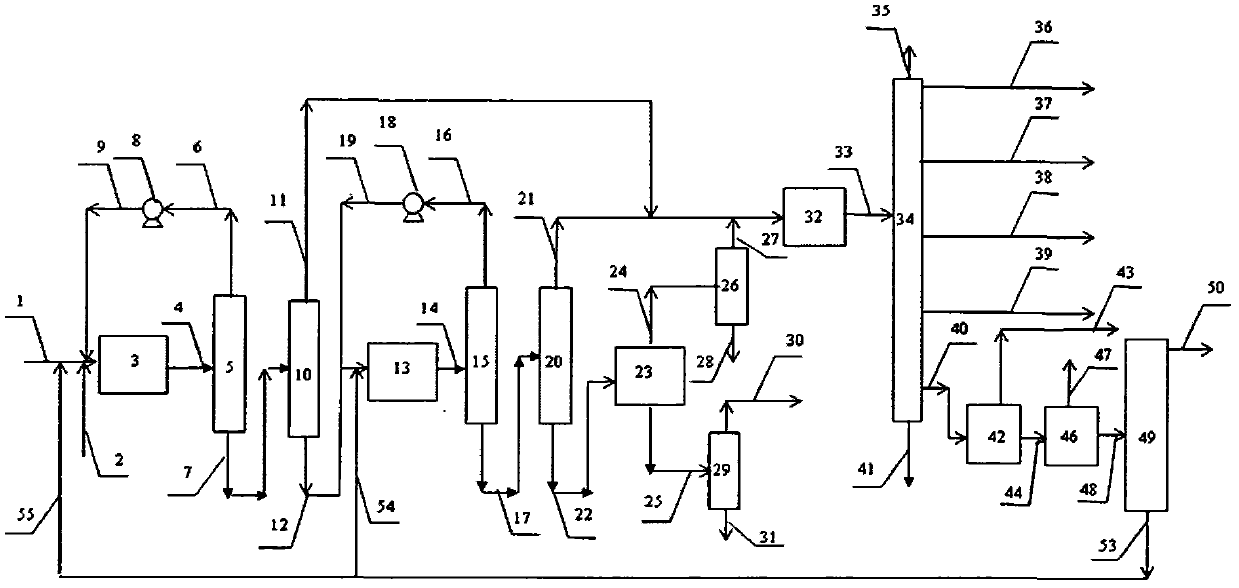
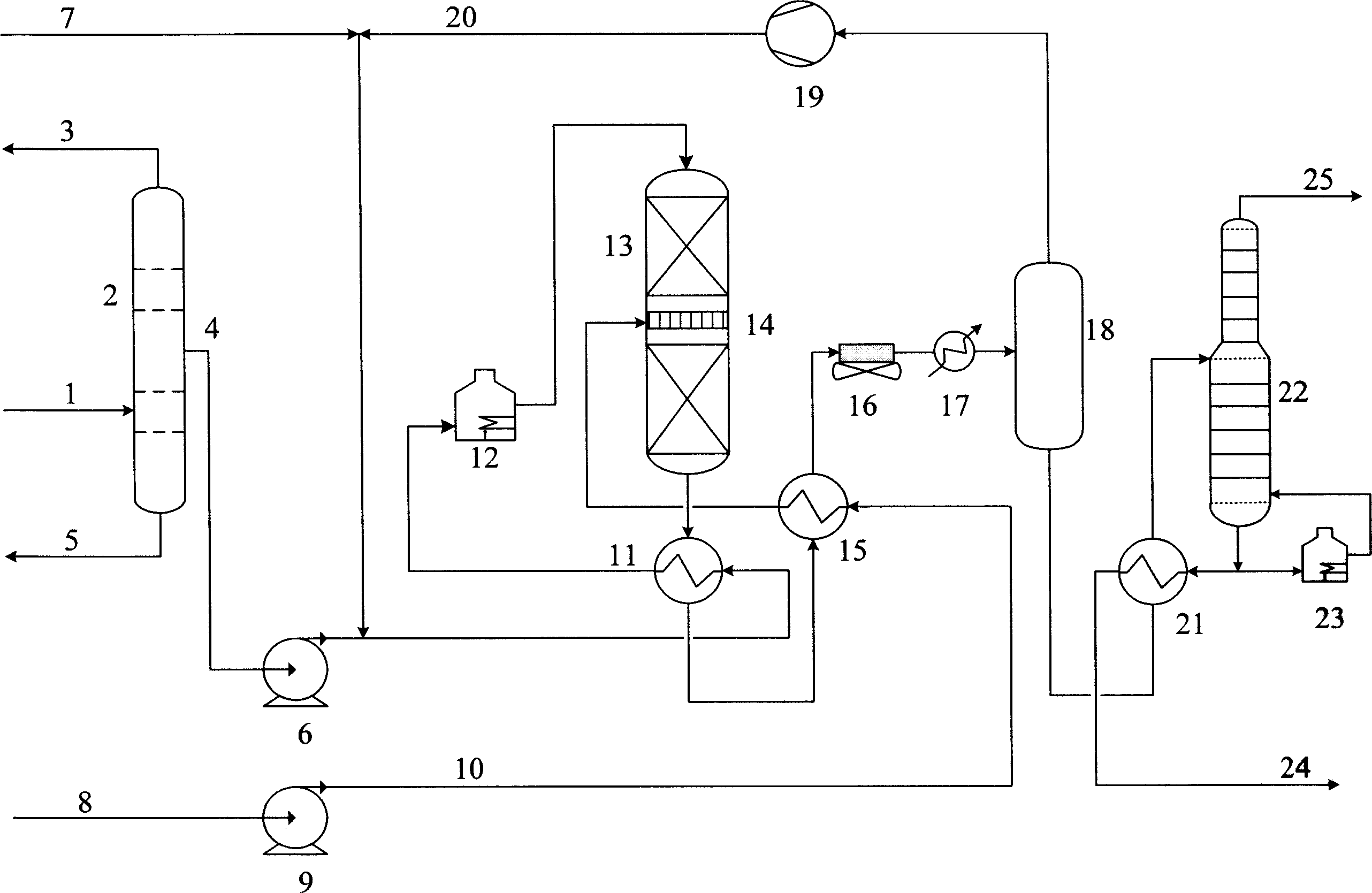
Medium and low temperature coal tar deep processing method
InactiveCN101538482AImprove performanceEfficient use ofThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic naphtha reformingCatalytic reformingFractionation
The invention discloses a medium and low temperature coal tar deep processing method. Medium and low temperature coke material is pretreated and fractionated to obtain light fraction, carbolic oil and heavy fraction, dephenolization treatment is carried out on the carbolic oil to obtain phenols product and dephenolized oil, the dephenolized oil and the above heavy fraction carry out pyrogenetic reaction jointly to obtain various carbonized products, wherein carbonized naphtha, at least one of carbonized diesel oil and carbonized wax oil is mixed with the light fraction obtained by material fractionation to carry out hydrofining and hydrocracking reaction, hydrogenated naphtha obtained by hydrocracking carries out catalytic reforming-aromatics extraction to obtain benzene, toluol, xylene, solvent oil and other products. Compared with the prior art, gasoline fraction and diesel oil fraction obtained by the inventive method are clean and stable in properties. In addition, the invention can produce a plurality of chemical products with high added value, truly realizes the effective utilization of medium and low temperature coal tar, and greatly improves the service life of devices.
Owner:胜帮科技股份有限公司
Biomass quick cracked oil water vapour catforming hydrogen production method
InactiveCN101318622AExtended service lifeSolve the phenomenon of carbon depositionHydrogenCatalytic reformingGas phase
The invention discloses a method by adopting biomass fast pyrolysis oil which carries out two sections of fixed bed reactors and water vapor catalytic reforming for producing hydrogen; the two sections of fixed bed reactors are connected in series, the natural dolomite which is relatively cheap and easily available is taken as catalyst in water vapor reforming reaction at the first section of fixed bed reactor, while the second fixed bed reactor adopts Ni / Mgo as catalyst to further improve the purity and yield of the target product gas. Comparatively high temperature and comparatively high S / C (more than 12) are extremely important for the effective transformation of the biomass pyrolysis oil in the first fixed bed reactor. However, for any temperature point, low mass space velocity can facilitate the increasing of the yield of any gas product and the total gas phase transformation ratio of the biomass oil is increased accordingly. The Ni / MgO catalyst is extremely effective in the purification stage, when S / CH4 is not less than 2 and the temperature is not lower than 800 DEG C, the transformation ratio of methane can reach 100 %. Low mass space velocity can facilitate effective transformation of methane; when mass space velocity is not higher than 3600h<-1>, the potential hydrogen yield can reach 81.1%.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
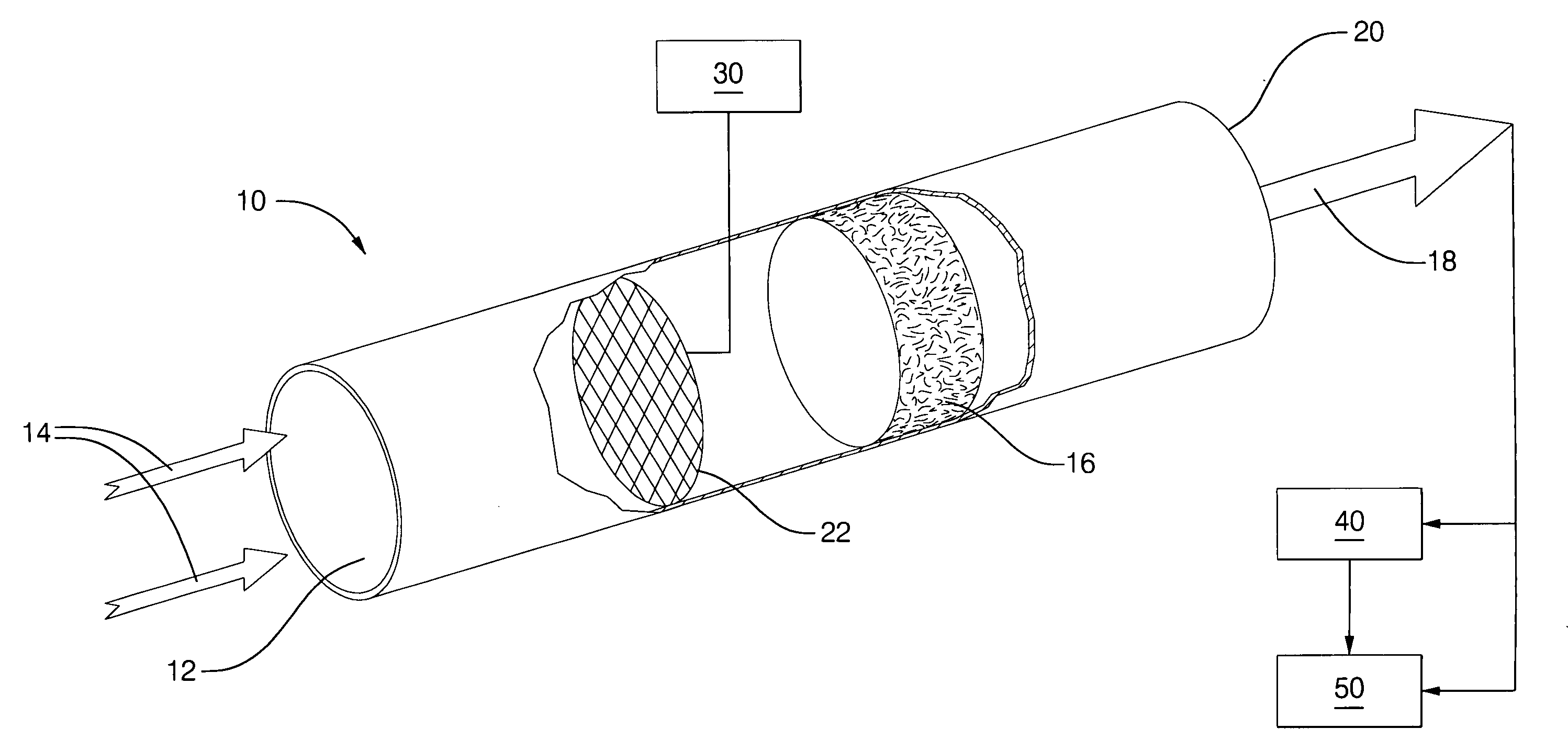
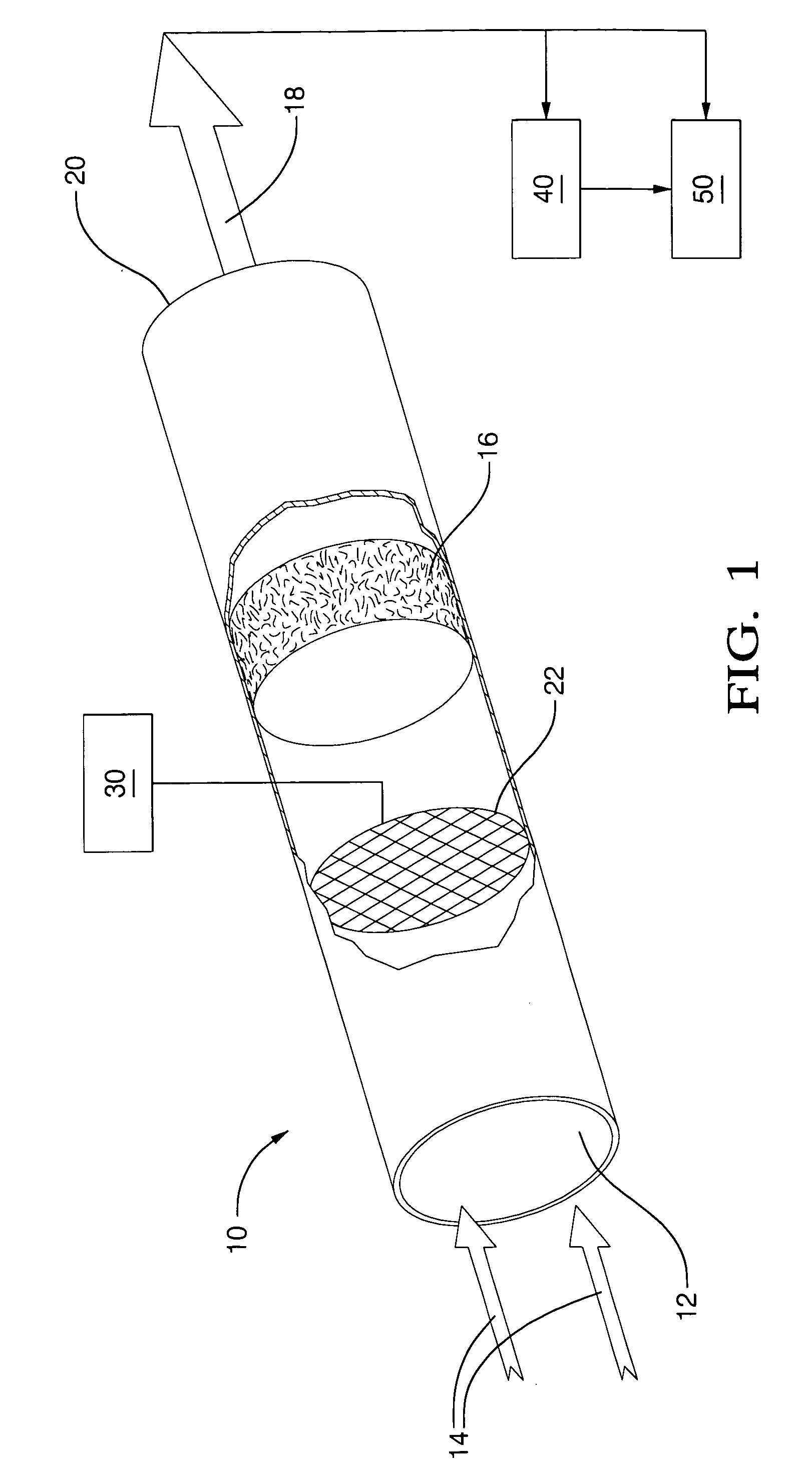
Fast light-off catalytic reformer
InactiveUS6887436B1Optimize reformate yieldHeating fastCombination devicesHydrogenCatalytic reformingOn board
A fast light-off catalytic reformer and method includes at least one preferably substantially cylindrical reactor tube having an inlet for receiving a flow of fuel and a flow of air, a reforming catalyst disposed within the reactor tube for converting the fuel and air to a reformate stream, and an outlet for discharging the produced reformate stream. An ignition device disposed within the reactor tube initiates an exothermic reaction between the fuel and air. Heat generated thereby provides fast light-off of the reforming catalyst. An associated control system selects fuel and air flow delivery rates and operates the ignition device to achieve fast light-off of the reforming catalyst at start-up and to maintain the catalyst at a temperature sufficient to optimize reformate yield. The rapid production of high yields of reformate is particularly suitable for use in an on-board reforming strategy for meeting SULEV emissions with spark-ignition engines, especially with larger, higher emitting vehicles.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
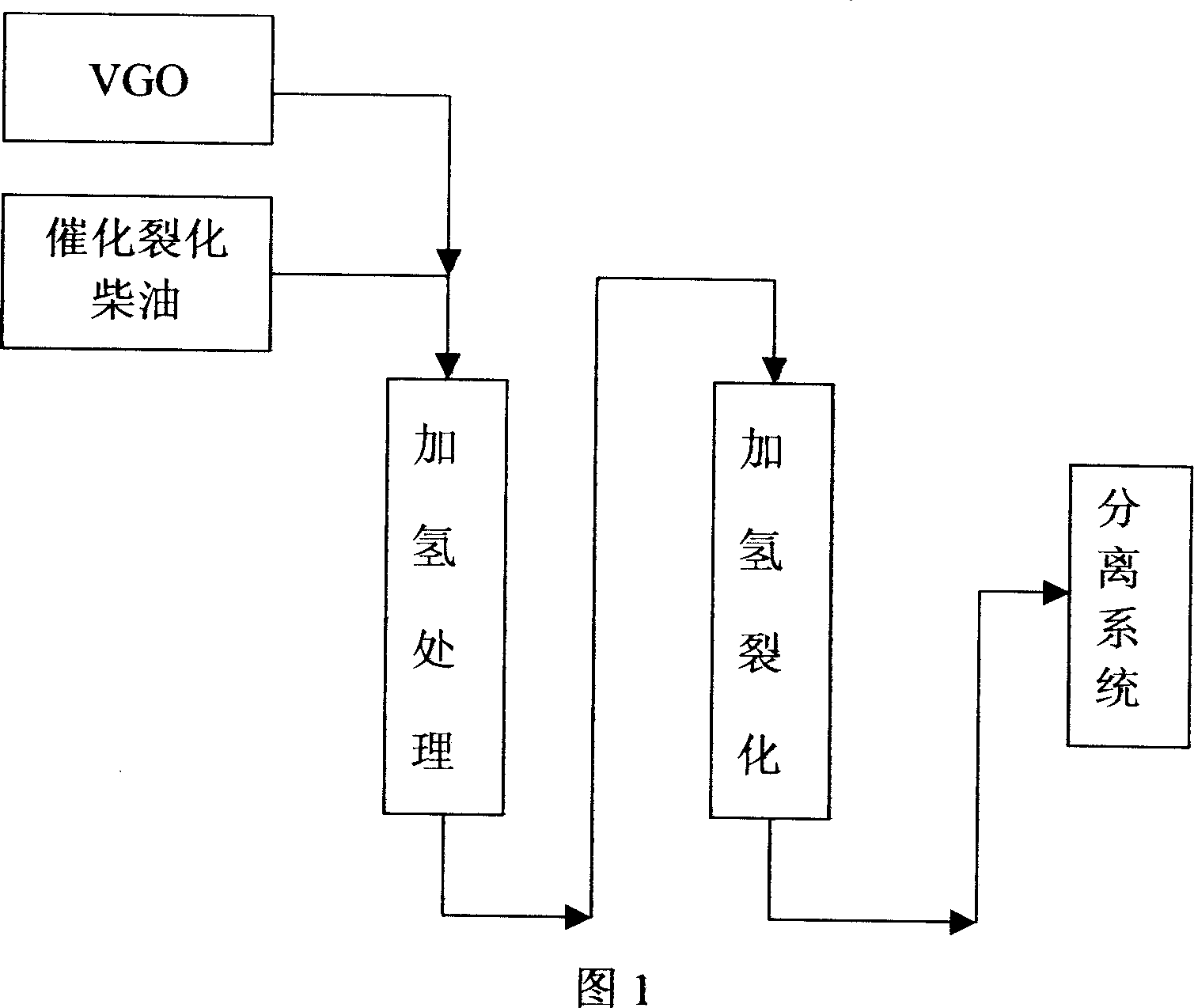
Hydrocracking method for producing chemical raw material
ActiveCN1955257AHigh yieldIncrease the potential content of aromaticsHydrocarbon oil crackingHexadecaneCatalytic reforming
This invention relates to a hydrocracking preparation of chemical materials production. Poor quality catalytic cracking Diesel and heavy hydrocracking material is mixed according to a proportion, and then hydrogenation and hydrocracking are conducted. The yield of heavy naphtha reaches 40wt% by controlling operating conditions, making sure the yield of tail oil 20wt%. The quality features of this poor quality catalytic cracking Diesel are high density, high content of aromatic hydrocarbon and low value of hexadecane. The density of the poor quality catalytic cracking diesel oil is above 0.95g / ml, and the aromatic hydrocarbon is over 90wt% and the value of hexadecane is under 20. Comparing with present technology, this invention combines poor quality catalytic cracking diesel and VGO organicly. High quality chemical material is effectively transformed with obtaining low BMCI value of tail oil, which is high quality material for ethylene preparation by steam cracking.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Process and apparatus for removing sulfur from hydrocarbons
ActiveUS7005058B1Reduce operating expensesDelay capital expenditureRefining to eliminate hetero atomsCatalytic reformingBoiling point
Disclosed is an apparatus and process for controlling the sulfur content of effluent from a hydrocarbon fractionation column. The effluent includes a low boiling stream, a middle boiling stream and a high boiling stream. Either of the feed or the low boiling stream may be subjected to a mercaptan removal treatment such as thioetherification or mercaptan oxidation treatment. The high boiling stream is subjected to hydrotreatment which will rid the high boiling stream of almost all organic sulfur compounds. The middle boiling stream may be subjected to a sulfur treatment complex which may comprise a sulfur removal unit and / or a catalytic reforming unit which may already be present in the refinery. Control valves govern the flow of adding the middle boiling stream to the low boiling stream and the high boiling stream in response to the sulfur concentration of the overhead stream downstream of the mercaptan removal treatment.
Owner:UOP LLC
Biorenewable naphtha composition and methods of making same
The present invention generally relates to a method for producing a naphtha product from a renewable feedstock. The method includes hydrotreating the renewable feedstock to produce a hydrotreating unit heavy fraction that includes n-paraffins, and hydrocracking the hydrotreating unit heavy fraction to produce a hydrocracking unit product that includes the naphtha product. The method also includes separating the naphtha fraction and optionally recycling the hydrocracking unit heavy fraction through the hydrocracking unit. The present invention also relates to a biorenewable naphtha product suitable for use as feed stock for steam crackers and catalytic reforming units, and for use as fuel, or fuel blend stock.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
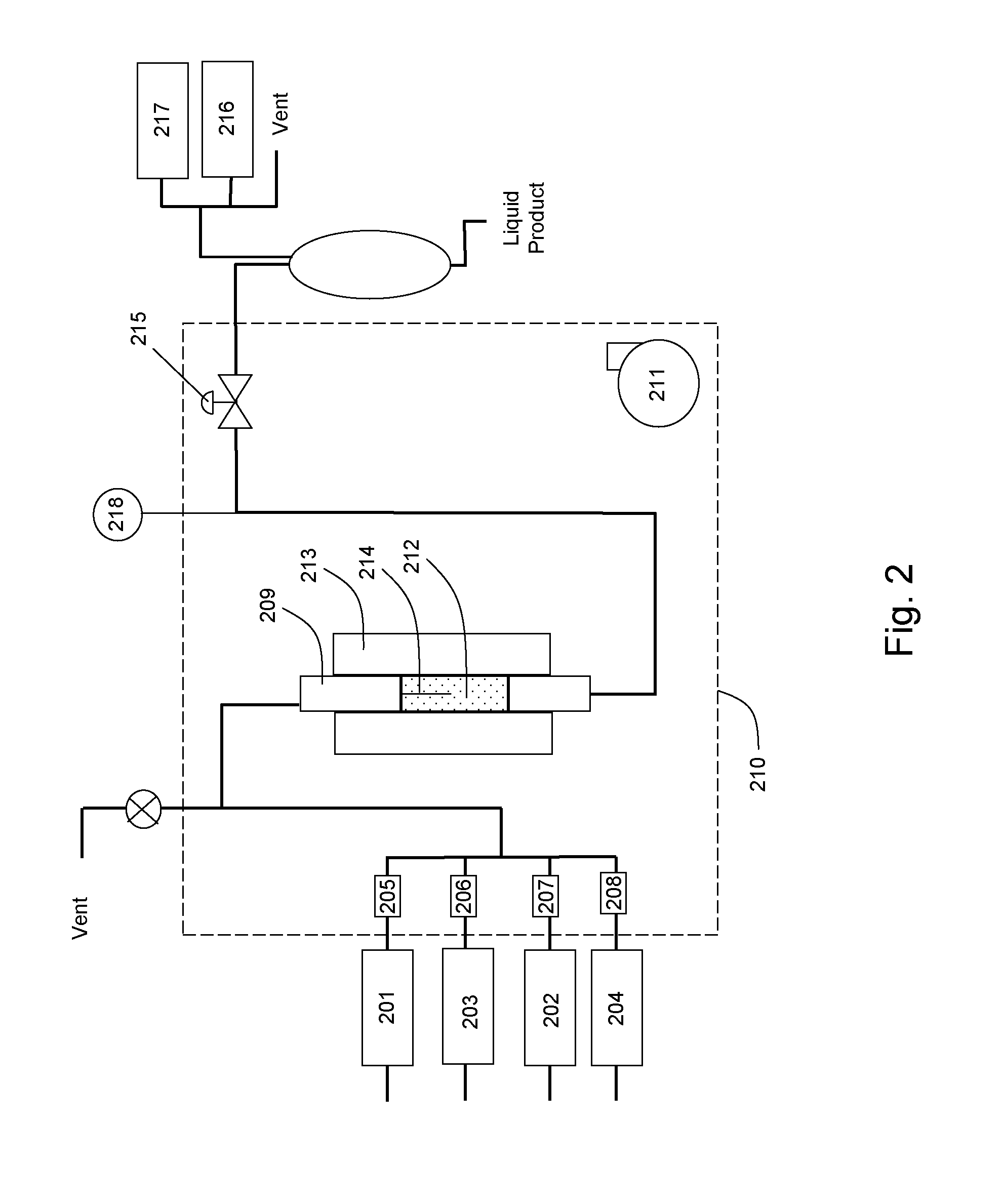
Benzin naphtha catalytic reforming method
ActiveCN101376823AImprove conversion rateGood choiceCatalytic naphtha reformingReforming process control/regulationLiquid productCatalytic reforming
The invention relates to a naphtha catalytic reforming method which includes the steps as follows: the naphtha is pumped into the reactor of a catalytic reforming device; gas-liquid separation is carried out on the reformed product for separating gas components, the light component of C8<-> as well as the heavy component of C9<+>; then a light aromatics reaction is carried out on the heavy component of C9<+> under the existence of a light aromatics catalyst; the hydrogen used by the light aromatics reaction is from the circulated hydrogen generated from a reforming device; then gas-liquid separation is carried out on the product after the light aromatics reaction; the liquid returns to the liquid product distilling system of the reforming device. The method can fully utilize the heavy component of C9<+> and convert the heavy component into light aromatic hydrocarbon, improve the aromatic hydrocarbon yield or the yield of the reformed gasoline during the whole process and improve the character of the gasoline.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing chloroethylene by catalytic reforming
InactiveCN101817723ASolve the problem of high temperature energy consumptionSolve pollutionPhysical/chemical process catalystsHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationCatalytic reformingActivated carbon
The invention discloses a method for preparing chloroethylene by catalytic reforming, which relates to a method for preparing the chloroethylene. The method comprises: a step of preparing a catalyst by using active carbon as a carrier, in which a barium salt is used as a catalyst, the active carbon is used as the catalyst carrier, and the barium salt is dissolved in water, absorbed by the active carbon and dried to obtain the catalyst carried by the active carbon; and a step of synthesizing the chloroethylene, in which acetylene gas and dichloroethane vapour are mixed and introduced to a reactor containing the catalyst carried by the active carbon to react, the reaction effluent is cooled to room temperature, unreacted dichloroethane is condensed to be separated out, and the remaining gas is compressed and frozen to give liquid chloroethylene. In the invention, a mercury free catalyst is adopted, the mercury pollution of the chloroethylene production industry is eliminated, and the reaction is performed spontaneously with little energy consumption.
Owner:ZHONGKE YIGONG SHANGHAI CHEM TECH CO LTD
Method for revamping fixed-bed catalytic reformers
InactiveUS20050274648A1Avoids major expenseQuality improvementCatalytic naphtha reformingBed hydrotreatment processes apparatusCatalytic reformingThermodynamics
A fixed-bed catalytic reformer unit is converted to moving bed reactor / cyclic regenerator operation by re-using the fixed bed reactors of the original unit as regenerator vessels operated in cyclic regeneration mode in a new catalyst regeneration section. A flow connection, suitably a liftpipe, is provided to convey spent catalyst from the spent catalyst outlet of a new moving bed reactor section to the converted regenerator section, together with a flow connection for regenerated catalyst from the regenerator section to the regenerated catalyst inlet of the new moving bed reactor section. A flow control distributor directs spent catalyst sequentially to each of the regenerator vessels to carry out the regeneration with regeneration gas. Each regenerator vessel is cycled through a fill, regeneration, discharge sequence to maintain a continuous flow of catalyst to and from the reactor section.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for catalytic reforming
A process for catalytic reforming of a hydrocarbon feed stream containing H2O, CO2, CH4 and CO at levels such that the H2O / CH4 is less than 0.8 and the CO2 / CH4 is greater than 0.5 and the feed stream further contains quantities of sulfur compounds up to about 20 ppm. The catalyst used in this process contains from about 0.5 percent to about 25 percent by weight of a calcium compound additive, from about 2 percent to about 30 percent by weight nickel, and from about 25 percent to about 98 percent by weight of an aluminum compound carrier, wherein substantially all of the calcium is combined with the alumina. The reforming process can be utilized to produce syngas, especially low hydrogen to carbon monoxide ratio syngas for applications such as iron ore reduction.
Owner:SUD CHEM INC
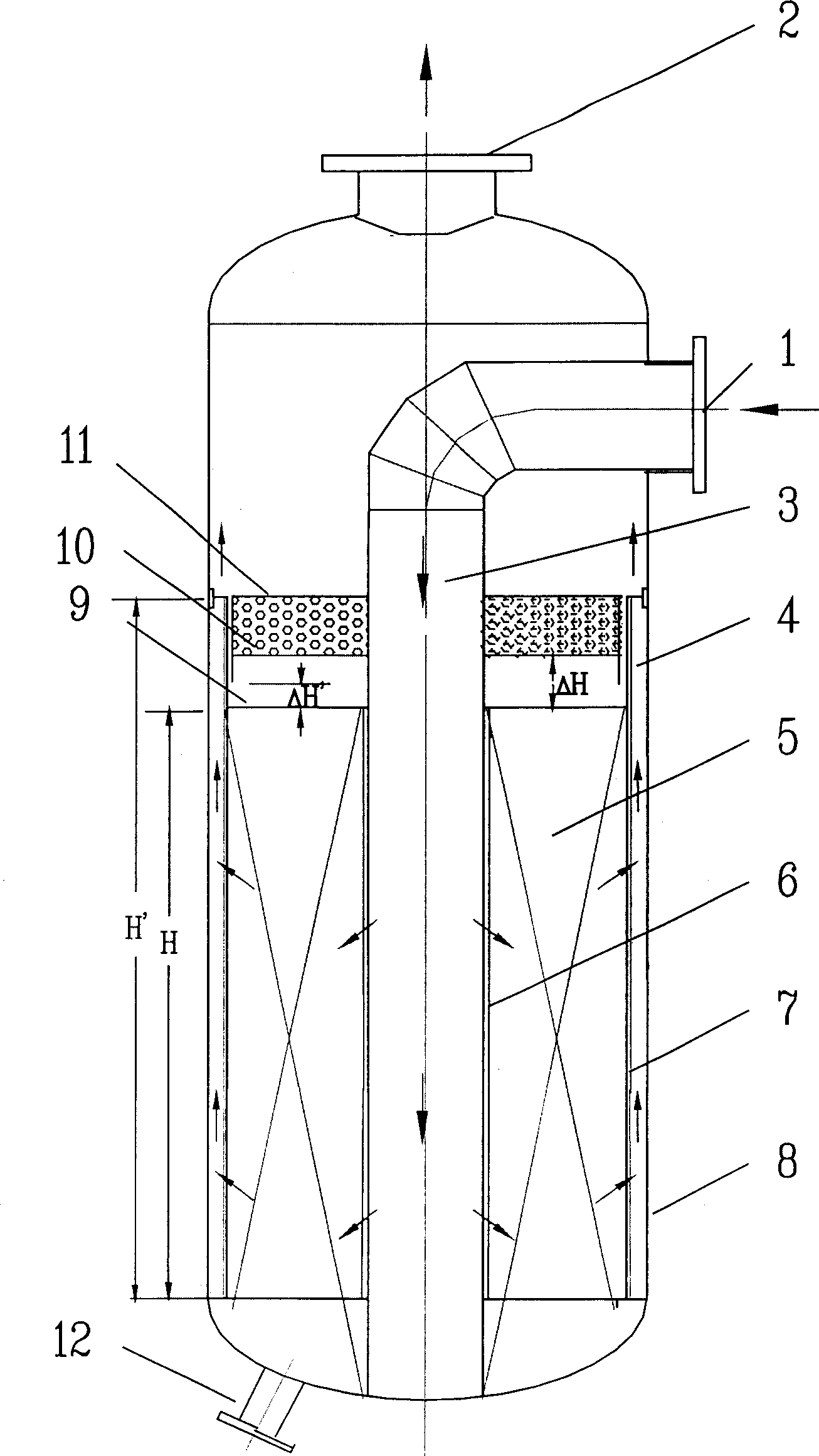
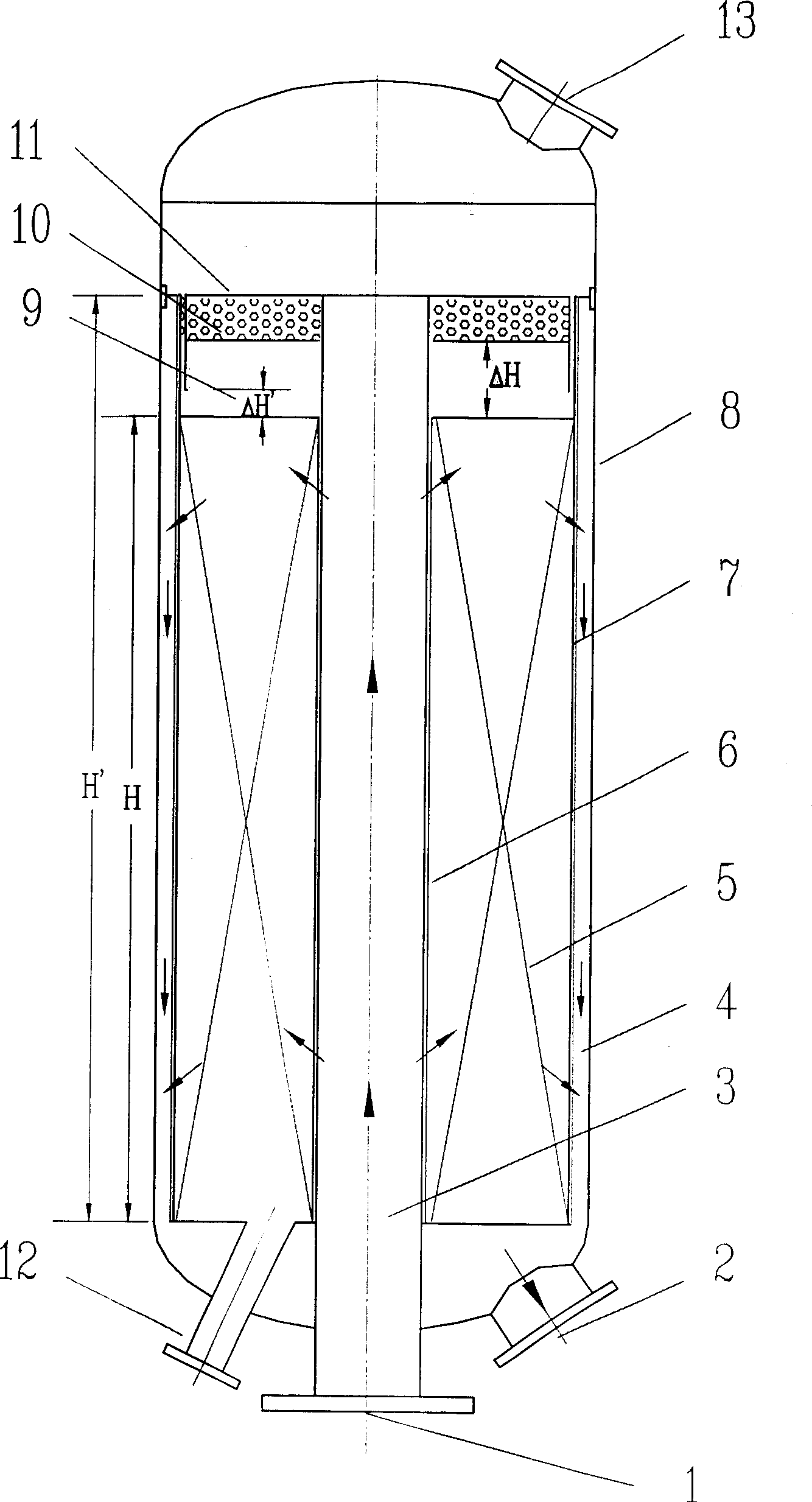
Continuous catalytic reforming reactor
InactiveCN1454970AReduce flow rateAvoid "sticking to the wall"Catalytic naphtha reformingCatalytic reformingEngineering
The present invention discloses a continuous catalytic reforming moving bed radial reactor. Said reactor adopts a circular container with catalytic bed as reaction equipment, the reactant inlet is positioned in the upper end of said reaction equipment, and its outlet is positioned in lower end of said reaction equipment, said catalytic bed is formed from external porous wall and internal porous wall cylinder in which the catalyst is filled. Said catalyst can be continuously flowed from top to bottom by means of gravity, at the same time the reaction material can be centrifugally flowed from centre toward exterior in the reaction equipment, and can be concurrently flowed from top to bottom in the distributary channel and collecting channel. Said invention is a Z-type centrifugal radial moving bed reactor, and its structure is simple and catalyst utilization rate is high.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
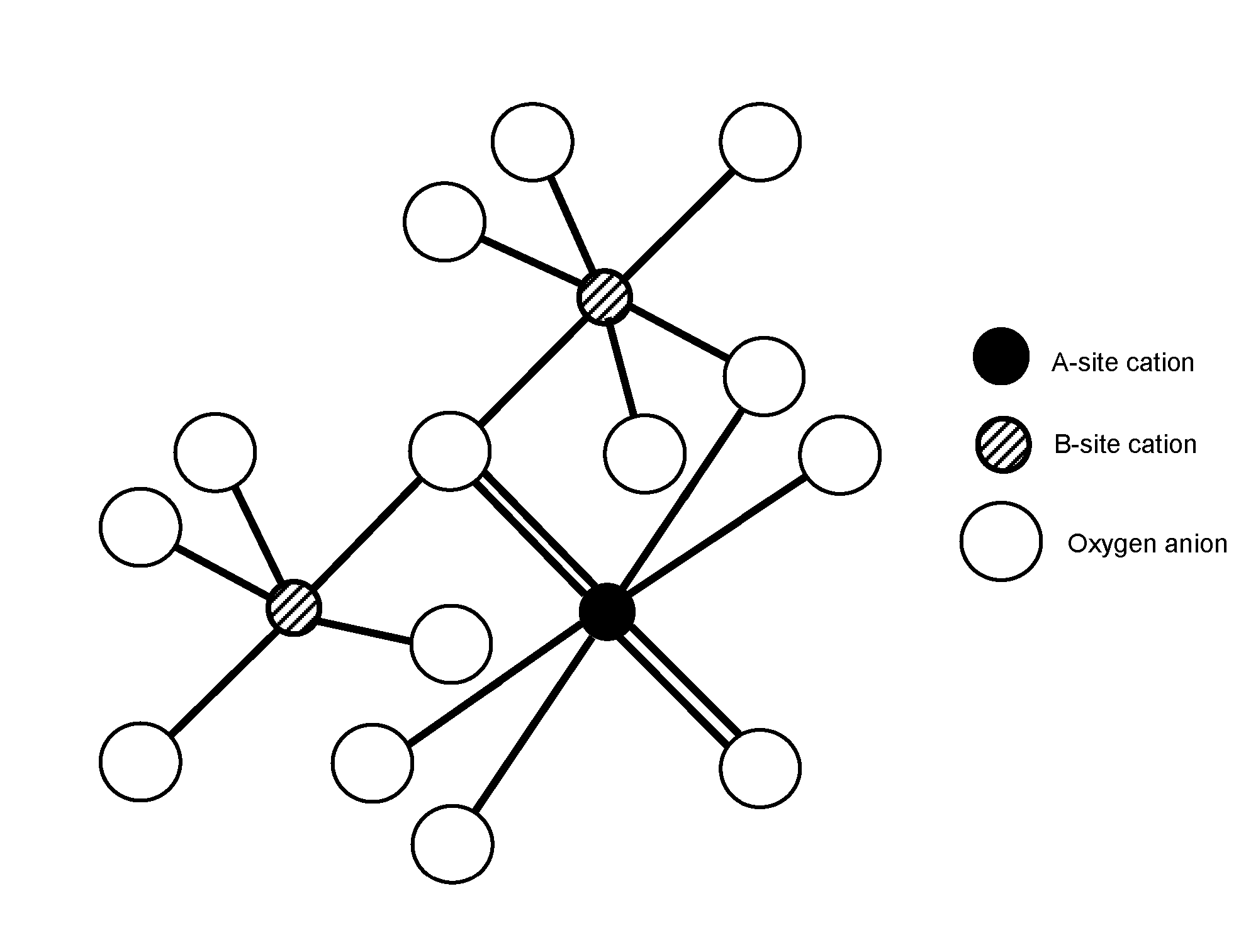
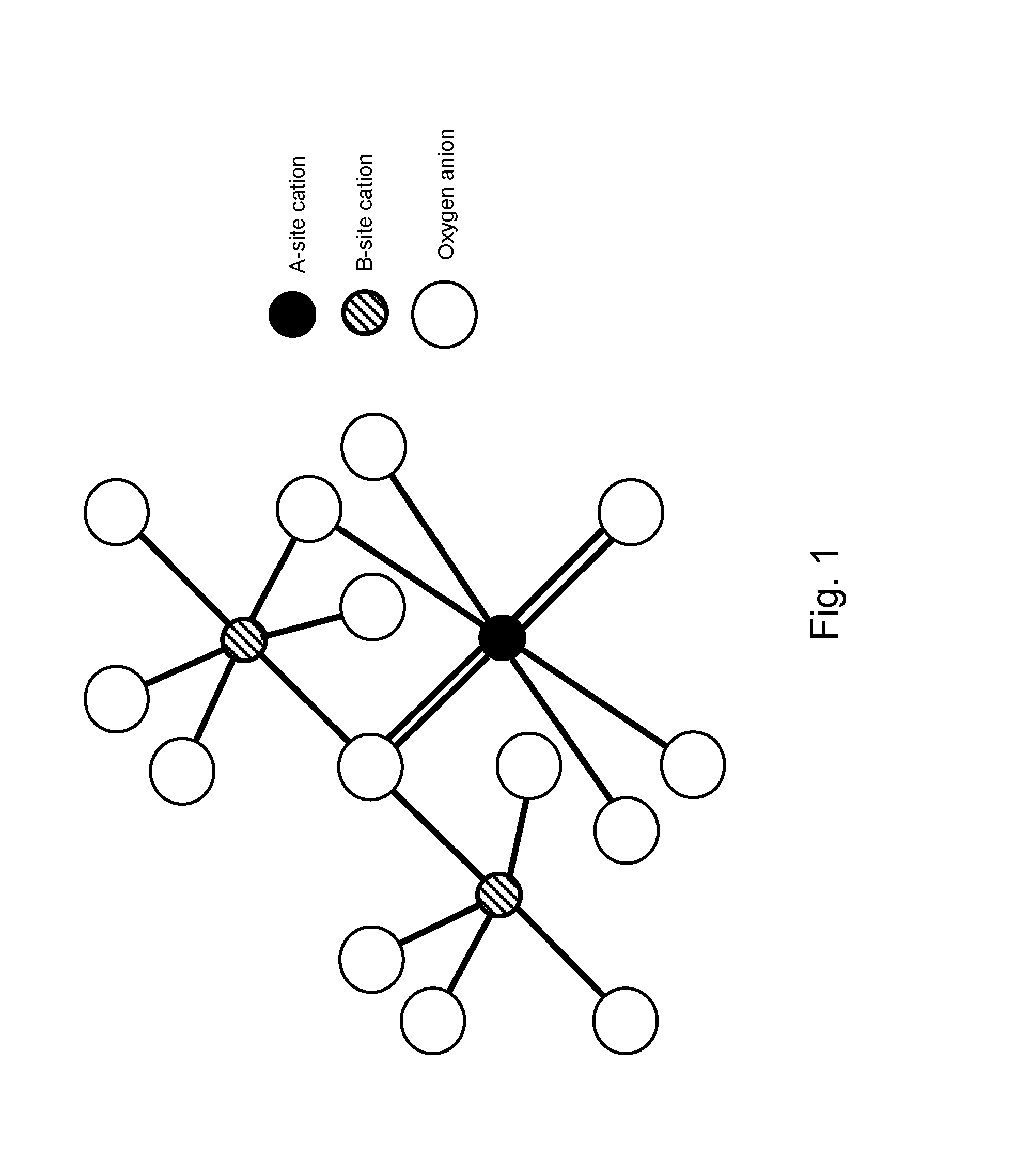
Pyrochlore-type catalysts for the reforming of hydrocarbon fuels
ActiveUS8133463B1Reducing metal sinteringReduce catalyst deactivationHydrogenHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCatalytic reformingFuel cells
A method of catalytically reforming a reactant gas mixture using a pyrochlore catalyst material comprised of one or more pyrochlores having the composition A2-w-xA′wA″xB2-y-zB′yB″zO7-Δ. Distribution of catalytically active metals throughout the structure at the B site creates an active and well dispersed metal locked into place in the crystal structure. This greatly reduces the metal sintering that typically occurs on supported catalysts used in reforming reactions, and reduces deactivation by sulfur and carbon. Further, oxygen mobility may also be enhanced by elemental exchange of promoters at sites in the pyrochlore. The pyrochlore catalyst material may be utilized in catalytic reforming reactions for the conversion of hydrocarbon fuels into synthesis gas (H2+CO) for fuel cells, among other uses.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
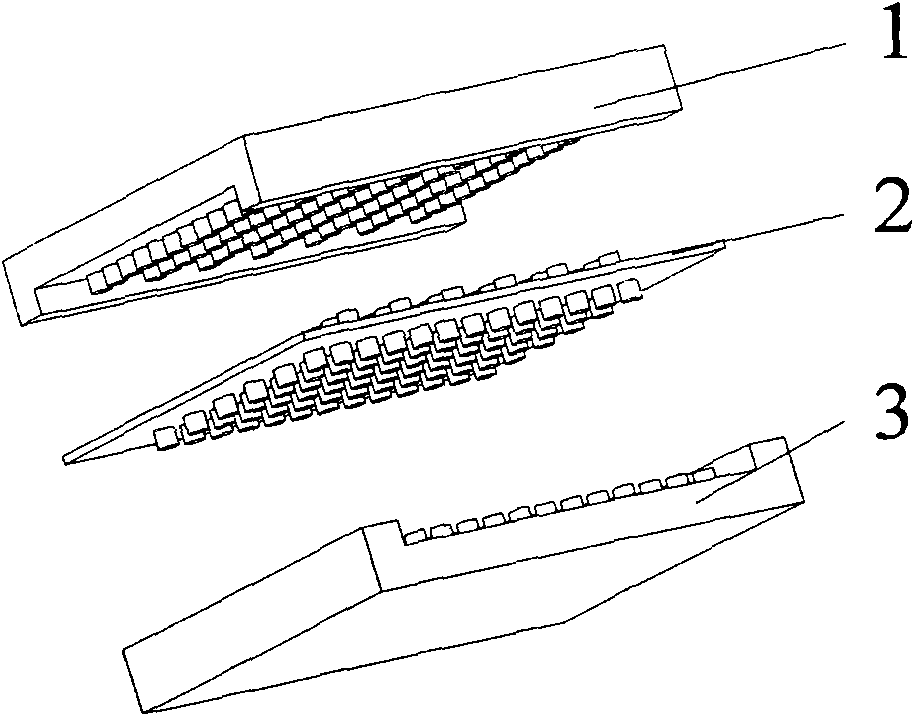
Self-heating type alcohol reforming hydrogen production micro channel reactor with micro-lug boss array structure
The invention discloses a self-heating type alcohol reforming hydrogen production micro channel reactor with the micro-lug boss array structure. Three layers of platy reaction carriers are all provided with micro-lug boss array structures; an upper layer and a lower layer are single-side micro-lug boss array structures; a middle layer is a double-side micro-lug boss array structure; the micro-lug bosses are arranged in the mode of parallel array; the three layers are cascaded to form a reaction channel with an inlet of 90 degrees; both ends of the channel are respectively provided with connector lugs; the gas inlet is provided with a detachable adapter and an outlet is provided with a fixed-type adapter. An upper layer channel is a catalytic reforming hydrogen production channel, and a lower layer channel is a combustion channel. The two layers of channel structures both adopt an open structural type being beneficial for the sediment of the catalytic coating. Fuel gases such as hydrogen and the like are combusted in the combustion channel and generate lot of heat which is transferred into the catalytic reforming hydrogen production channel by the middle layer of the reactor so as to meet the requirement of the steam reforming hydrogen production reaction; the reactor can produce hydrogen in a self-heating type. The invention increases the specific volume of the reactor and increases the yield of the alcohol reforming hydrogen production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
New method for preparing fuel oil by co-pyrolysis of biomass and waste plastic
ActiveCN102618312ARenewableOvercoming and mitigating pollution problemsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCatalytic reformingLiquid product
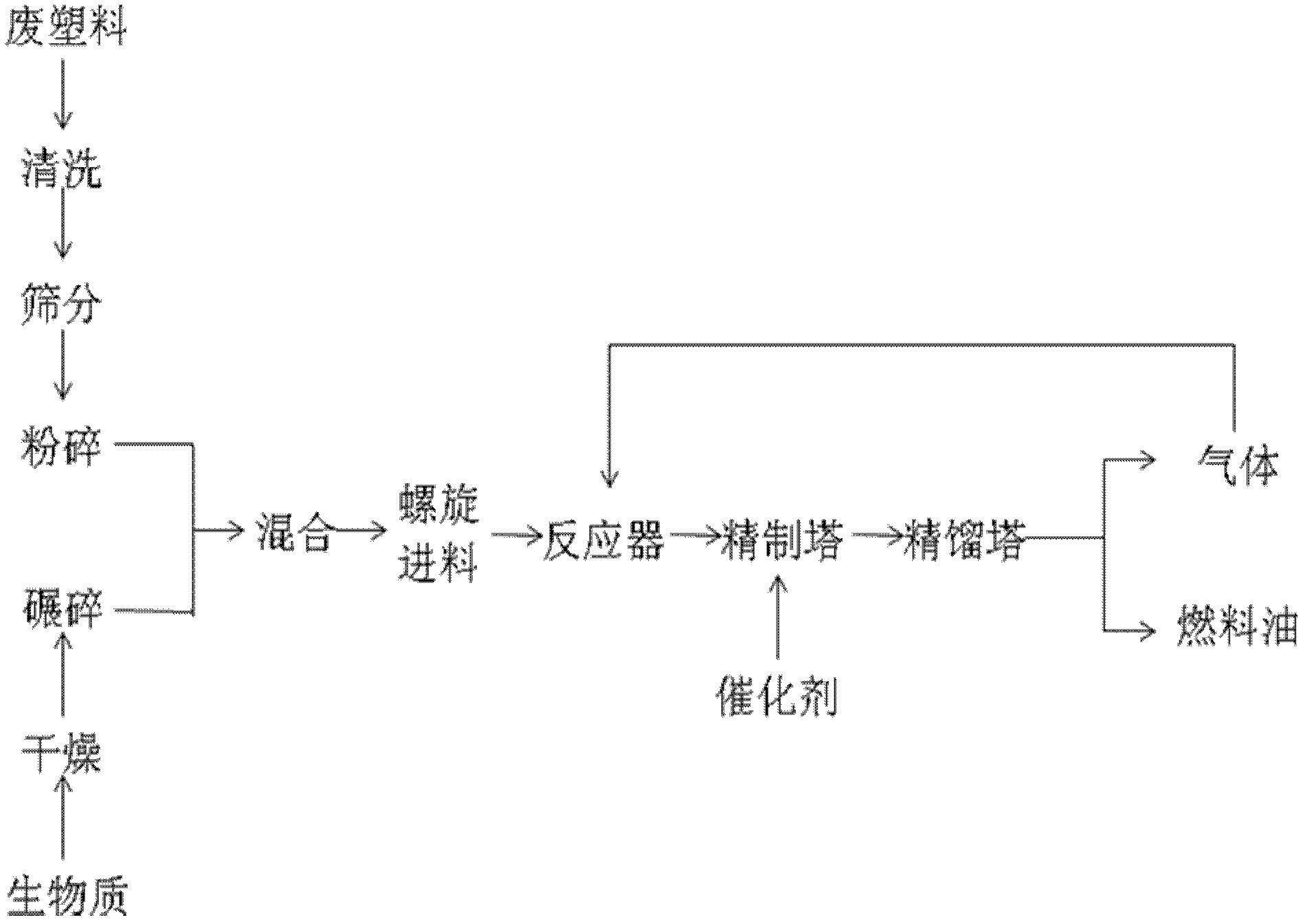
The invention discloses a new method for preparing fuel oil by co-pyrolysis of biomass and waste plastic, belonging to the field of solid waste disposal and utilization technology and biomass energy. The method comprises the following steps: mixing evenly the biomass and the waste plastic according to a certain ratio; placing the mixture in a pyrolysis reactor; heating the mixture to the needed pyrolysis temperature for a pyrolytic reaction; introducing the gas generated from the pyrolysis into a refined reaction tower for catalytic reforming; carrying out rectification on the reformed liquid product to obtain fuel oil with different cut fractions; and returning a small quantity of the combustible gas and the residues to the pyrolysis reactor for burning and being used as supplementary heat source. In the method, the biomass and the waste plastic are comprehensively utilized in co-pyrolysis and synergetic promotion is generated by the biomass and the waste plastic, so that the oil productivity and the oil quality are improved. The novel method not only resolves the environmental problems caused by white pollution, but also relieves the energy crisis caused by petrochemical resource exhaustion, thereby having wide application prospect and being able to generate huge social and economic benefits.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Catalyst having an improved crush strength and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS8263518B2Aluminium compoundsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsCatalytic reformingReaction zone
A method of preparing a catalyst comprising selecting a zeolite having a mean particle size of equal to or less than about 6 microns, blending the zeolite with a binder and water to form a paste, shaping the paste into a bound zeolite support, adding a metal to the bound zeolite support to form a metalized catalyst support, and adding at least one halide to the metalized catalyst support to form the catalyst. A catalytic reforming process for converting hydrocarbons to aromatics comprising: contacting a catalyst comprising a silica bound zeolite, a Group VIII metal supported thereby, and at least one halide with a hydrocarbon feed in a reaction zone under reforming conditions and recovering aromatics from the reaction zone, wherein the silica bound zeolite comprises a zeolite having a mean particle size of equal to or less than about 6 microns and a median particle size of equal to or less than about 5 microns.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Production of Gasoline From Fermentable Feedstocks
ActiveUS20100159553A1Easy to separateImprove isolationElectrolysis componentsBacteriaCatalytic reformingBiodiesel
Compositions and methods for forming hexane, and, optionally, gasoline and / or components of a gasoline composition, from fermentable sugars are disclosed. The sugars are fermented using a bacteria or yeast that predominantly forms butyric acid. The butyric acid is subjected to Kolbe or photo-Kolbe electrolysis to form hexane. The hexane can be subjected to catalytic, reforming and / or isomerization steps to form higher octane products, which are or can be included in gasoline compositions. In one aspect, the fermentable sugars are derived from lignocellulosic materials such as wood products, switchgrass, or agricultural wastes. These materials are delignified to form lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose. The cellulose and hemicellulose are depolymerized to form glycose and xylose, either or both of which can be fermented by the bacteria. The lignin can be used to generate heat energy and / or electric energy for use in one or more process steps, such as the fermentation, product isolation, Kolbe electrolysis, catalytic reforming and / or isomerization steps. Alternatively, the lignin can be converted to synthesis gas, which can then be subjected to Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, or converted to methanol and / or ethanol. Thus, the methods described herein can convert biomass to a fuel composition or fuel additive, which can be used in a conventional gasoline engine, unlike traditional fuels such as ethanol or biodiesel.
Owner:CPS BIOFUELS INC
Catalytic reforming and catalytic dehydrogenation centrifugal type fixed bed radial reactor
InactiveCN1546217AAvoid heat lossUniform axial temperatureCatalytic crackingChemical/physical processesCatalytic reformingFixed bed
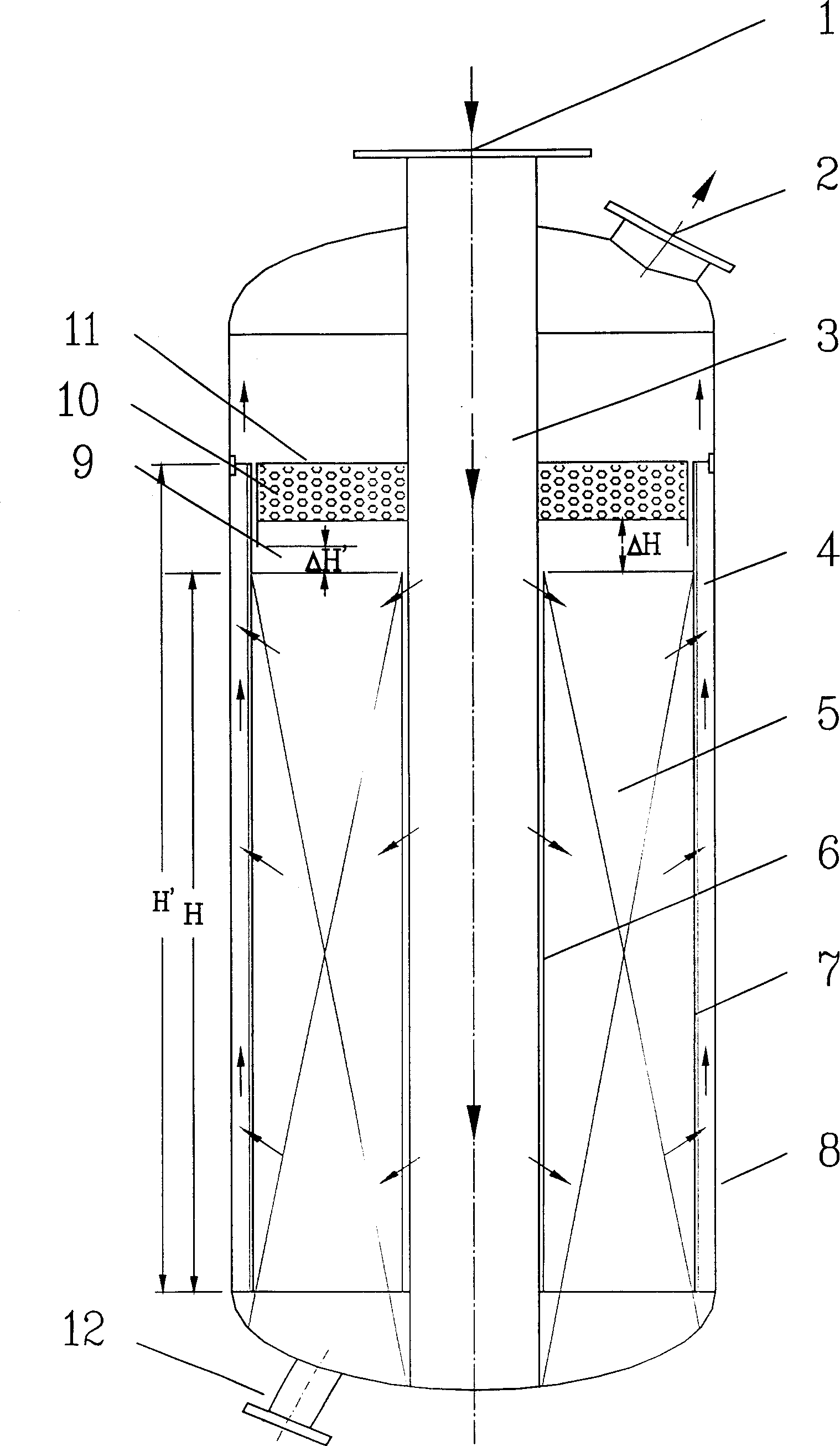
The invention discloses a kind of fixed bed reactor for catalytic reforming and dehydrogenation, the reactor uses a round pressure container which has a catalytic bed. The inlet and the outlet is at one side of the container, the catalytic bed is made up of outer multi-hole wall and round inner multi-hole wall, catalyst is filled in them, there has a cover sealing structure on the catalyst, the round inner multi-hole wall can uses variable hole-rate or zone structure. The reacting gas in the device flows centrifugally, the gas in the centre inner barrel and multi-hole outer barrel flow reversely.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biorenewable naphtha
InactiveUS20090300971A1Hydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystCatalytic reformingNaphtha
The present invention generally relates to a method for producing a naphtha product from a renewable feedstock. The method includes hydrotreating the renewable feedstock to produce a hydrotreating unit heavy fraction that includes n-paraffins, and hydrocracking the hydrotreating unit heavy fraction to produce a hydrocracking unit product that includes the naphtha product. The method also includes separating the naphtha fraction and optionally recycling the hydrocracking unit heavy fraction through the hydrocracking unit. The present invention also relates to a biorenewable naphtha product suitable for use as feed stock for steam crackers and catalytic reforming units, and for use as fuel, or fuel blend stock.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
Method for producing aromatic hydrocarbon and ethylene by taking naphtha as raw material
The invention relates to a method for producing aromatic hydrocarbon and ethylene taking naphtha as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) contacting naphtha with a reforming catalyst in a catalytic reforming region to carry out a shallow catalytic reforming reaction in the presence of hydrogen at the pressure of 0.15-3.0 MPa, the temperature of 300-540 DEG C and the volume space velocity of 2.1-50 h<-1>, enabling the conversion rate of naphthenic hydrocarbon in the naphtha to be higher than 85wt%, and enabling the conversion rates from alkane to aromatic hydrocarbon and C4-hydrocarbon to be lower than 30wt%; (2) carrying out aromatic hydrocarbon separation on reformate produced by catalytic reforming in a first aromatic hydrocarbon separation region, so as to obtain aromatic hydrocarbon-rich cut fraction and alkane-rich cut fraction; (3) introducing the aromatic hydrocarbon-rich cut fraction and liquefied gas produced by the catalytic reforming into a steam cracking region, and carrying out a cracking reaction to produce ethylene. According to the method for producing the aromatic hydrocarbon and the ethylene taking naphtha as the raw material, the ethylene can be maximally produced when the naphtha is adequately utilized in a shallow catalytic reforming reaction manner.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Hydrocracking method
ActiveCN1955260ALow BMCIIncrease the molar ratio of silicon to aluminumTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHexadecaneCatalytic reforming
This invention discloses a hydrocracking method.It includes that the heavy distillate oil and poor quality catalytic cracking diesel refining separately by hydrogenation, and the mixture enters into hydrocracking reactivator, then its cracking products is conducted gas liquid separation. Light naphtha, heavy naphtha, aviation kerosene, diesel oil and end oil will be obtained by distillating the liquid phase. The density of the poor quality catalytic cracking diesel oil is above 0.9g / ml, and the aromatic hydrocarbon is over 60wt% and the value of hexadecane is under 30. It is a adequate utilization of catalytic cracking craft to produce High aromatic hydrocarbon heavy naphtha and high quality end oil with heavy distillate oil and poor quality catalytic cracking diesel, which can be separately used as catalytic reforming material and making ethylene material by steam cracking method. High aromatic hydrocarbon heavy naphtha in this invention will produce a large amount of reforming hydrogen after catalytic reforming treatment, which can be used in the process of hydrocracking to make this preparation more ecnomical and reasonable.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Hydrogenation method for producing catalytic reforming raw material
The invention is a hydrogenating method for producing catalytic reforming raw materials, cutting secondary processed gasoline as light gasoline fractions, medium gasoline fractions and heavy gasoline fractions, where the medium gasoline fraction and hydrogen gas together enter in first reacting region to react by the action of hydrofining catalyst, the resultant effluent is not separated but directly mixes with virgin naphtha to enter in second reacting region so as to react by the action of hydrofining catalyst, the corresponding resultant effluent is cooled and separated, where the extracted hydrogen-rich gas is recycled and the extracted liquid enters in a distilling dehydrating tower and is purified to obtain naphtha. And it can process secondary gasoline with high sulfur, nitrogen and alkene contents, and provides qualified raw material with sulfur and nitrogen contents both less than 0.5 mug / g for catalytic reforming.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
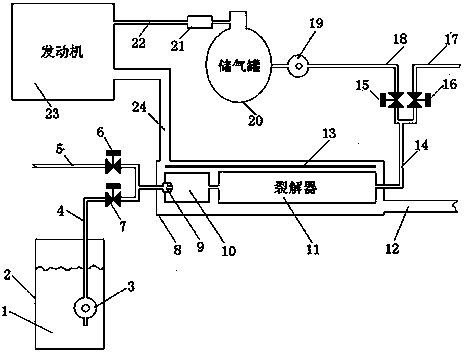
Hydrogen engine system
InactiveCN103352777AAvoid poisoningAvoid failureInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCatalytic reformingAlcohol
A hydrogen engine system is a low-carbon engine system which takes hydrogen-enriched gas produced by using alcohol cracking as fuel. The hydrogen engine system comprises a fuel storage tank and a fuel conveying device, a fuel heating gasifying and cracking device, a hydrogen-enriched gas compressor and an exhaust discharging pipe, wherein the fuel storage tank is connected with the fuel conveying device and then connected to the fuel heating gasifying and cracking device; fuel passes through the hydrogen-enriched gas compressor and is then input into an automobile engine to do work; the fuel heating gasifying and cracking device is installed inside a high-temperature chamber formed by an exhaust discharging device. The hydrogen engine system rarely changes an original gasoline-fueled automobile, keeps a function that the original automobile uses gasoline as fuel, and has unchanged dynamic performance; when an engine is started through cold start and no alcohol is supplied or a storage battery is low in power in the running process, common gasoline can be still used for driving the automobile or heating up a cracker to reach heat and temperature which are required by catalytic reforming hydrogen production, so that the hydrogen engine system has a good development prospect.
Owner:GUANGXI DIKAI SCI & TECH
Methanol catalytically reforming hydrogen producing apparatus utilizing afterheat of internal combustion engine and its control method
InactiveCN1887691AImprove conversion rateHigh hydrogen production rateHydrogenHydrogenExternal combustion engine
The present invention relates to internal combustion engine afterheat utilizing technology, and is especially methanol catalytically reforming hydrogen producing apparatus utilizing afterheat of internal combustion engine and its control method. The apparatus includes mainly methanol aqua gasifying cavities in the front part, middle part and back part of the reformer casing, catalytically reacting cavity and reformed gas product cavity. In the middle part inside the reformer casing, there are porous honeycomb ceramic with inside catalytically reacting cavity; and the inner wall of the catalytically reacting cavity has set honeycomb pores with reforming catalyst coated to the inner wall. One heat exchange pipe penetrates the porous honeycomb ceramic axially. The present invention has integrated heat exchange pipe and porous honeycomb ceramic, and possesses compact structure, high heat exchange efficiency, high hydrogen rate and other advantages.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Catalyst for conversion of hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20130261363A1High yieldCatalytic naphtha reformingCatalyst activation/preparationCatalytic reformingIridium
One embodiment is a catalyst for catalytic reforming of naphtha. The catalyst can have a noble metal including one or more of platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, osmium, and iridium, an alkali or alkaline-earth metal, a lanthanide-series metal, and a support. Generally, an average bulk density of the catalyst is about 0.300 to about 1.00 gram per cubic centimeter. The catalyst has a platinum content of less than about 0.375 wt %, a tin content of about 0.1 to about 2 wt %, a potassium content of about 100 to about 600 wppm, and a cerium content of about 0.1 to about 1 wt %. The lanthanide-series metal can be distributed at a concentration of the lanthanide-series metal in a 100 micron surface layer of the catalyst less than two times a concentration of the lanthanide-series metal at a central core of the catalyst.
Owner:UOP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com