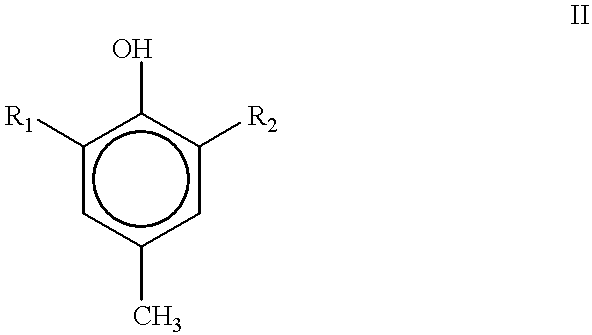
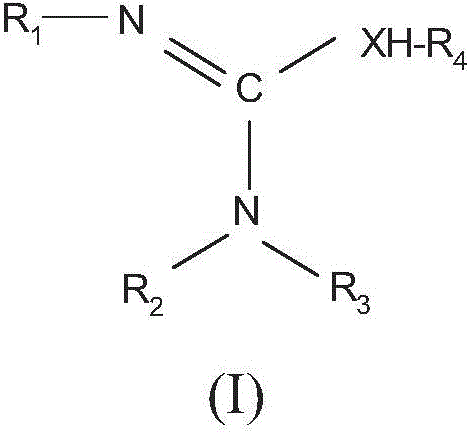
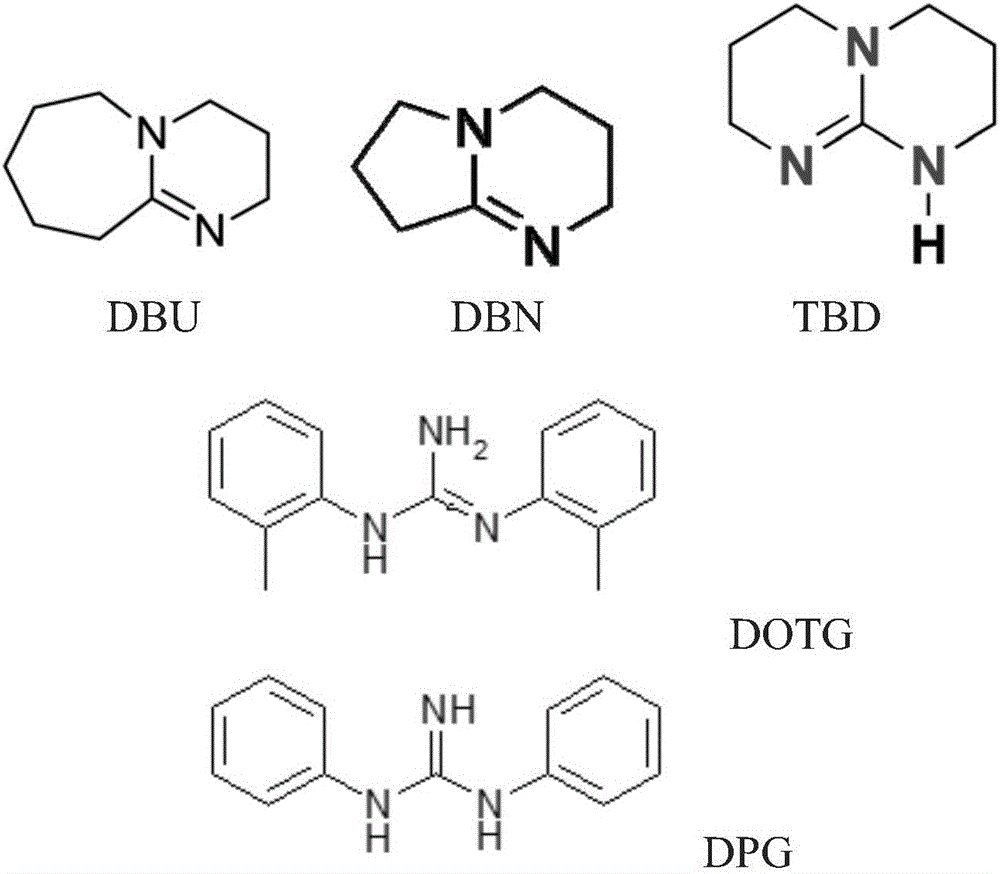
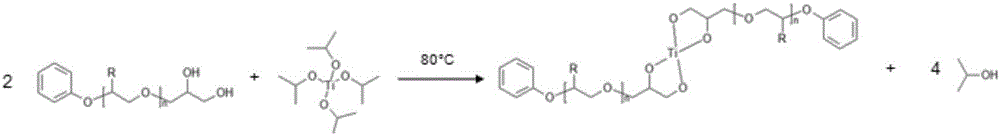
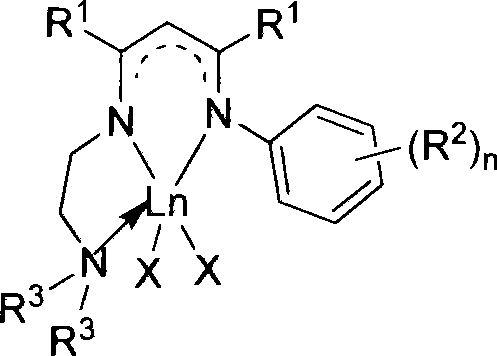
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Cyclic alkane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An alicyclic hydrocarbon with a saturated ring. Also called cycloparaffin. cycloalkane (ˌsaɪkləʊˈælkeɪn) n (Elements & Compounds) any saturated hydrocarbon similar to an alkane but having a cyclic molecular structure and the general formula CnH2n.
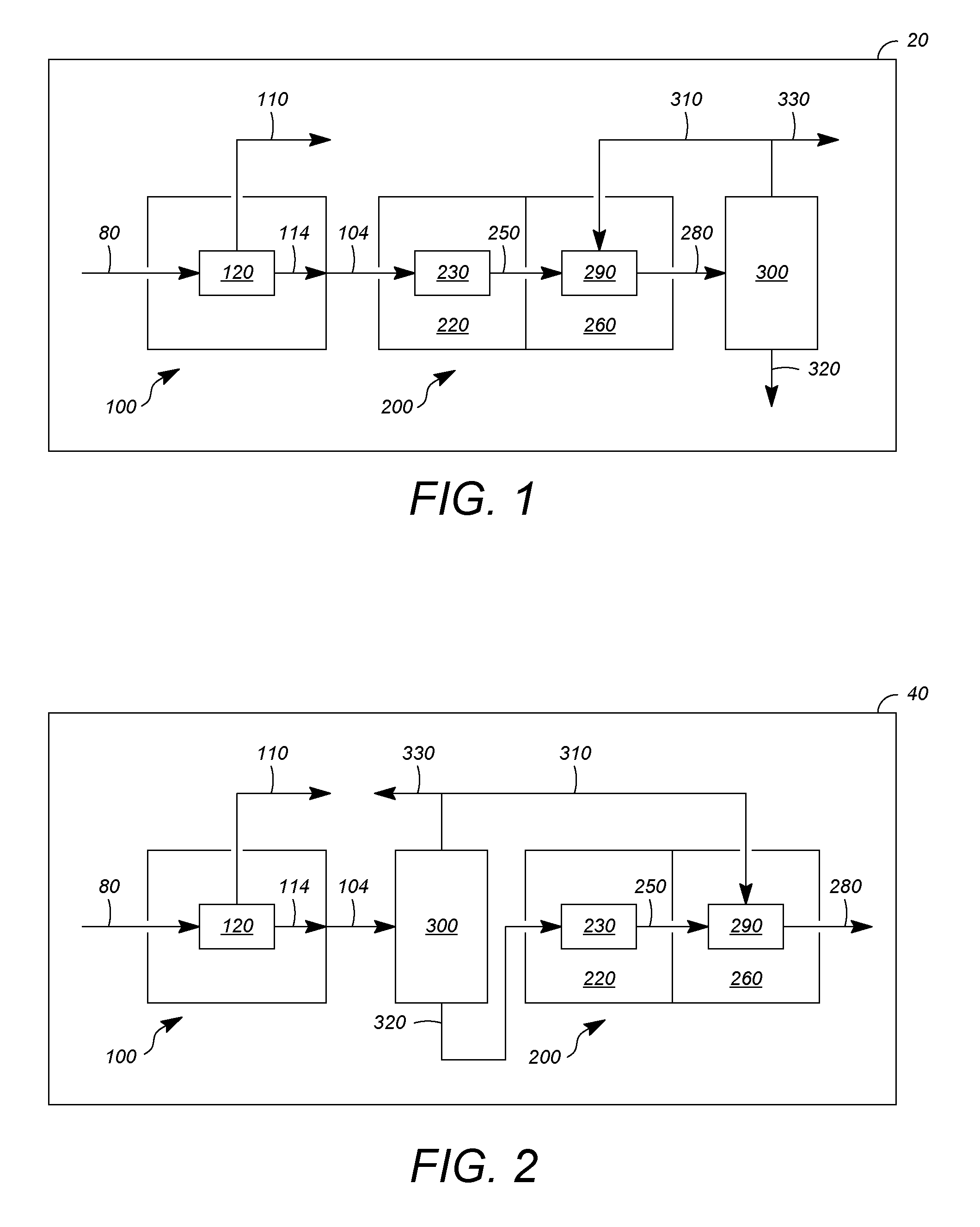
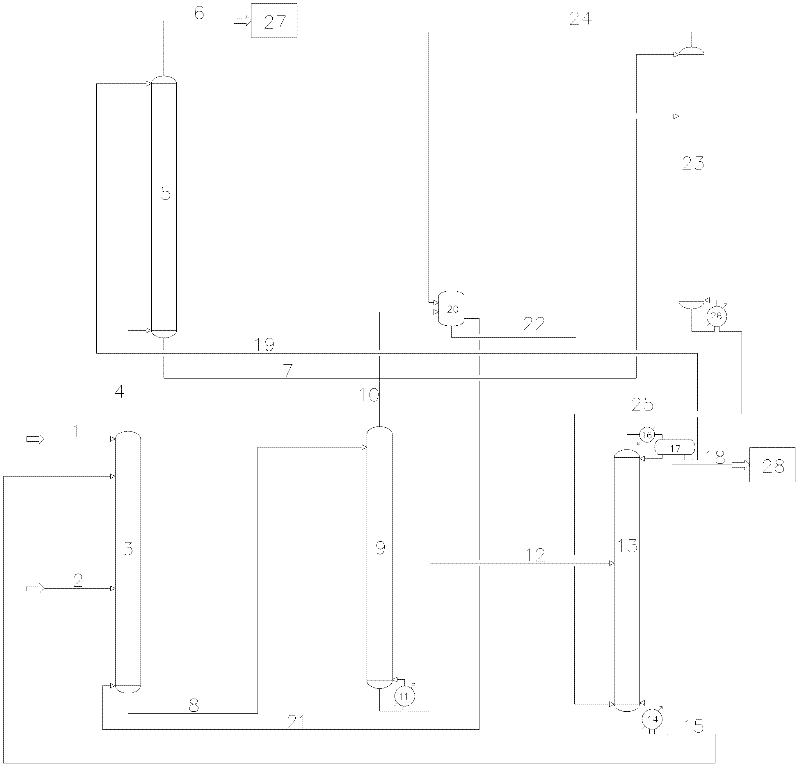
High octane number gasolines and their production using a process associating hydro-isomerization and separation
InactiveUS6338791B1Minimize cracksReduce the amount requiredRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCyclic alkaneIsomerization
The invention provides a high octane number gasoline pool comprises at least 2% of di-branched paraffins containing 7 carbon atoms, and a process for producing this gasoline pool by hydro-isomerizing a feed constituted by a C5 to C8 cut which comprises at least one hydro-isomerization section and at least one separation section, in which the hydro-isomerization section and at least one separation section, in which the hydro-isomerization section comprises at least one reactor. The separation section comprises at least one unit and produces at least two streams: a first stream which is rich in di- and tri-branched paraffins, and possibly in naphthenes and aromatic compounds which is sent to the gasoline pool; and in a first version of the process, a second stream is produced which is rich in straight-chain and mono-branched paraffins which is recycled to the inlet of the hydro-isomerization section, while in a second version of the process, a second flux is produced which is rich in straight-chain paraffins which is recycled to the inlet of a first hydro-isomerization section and a third stream is produced which is rich in mono-branched paraffins which is recycled to the inlet of a second hydroisomerization section.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
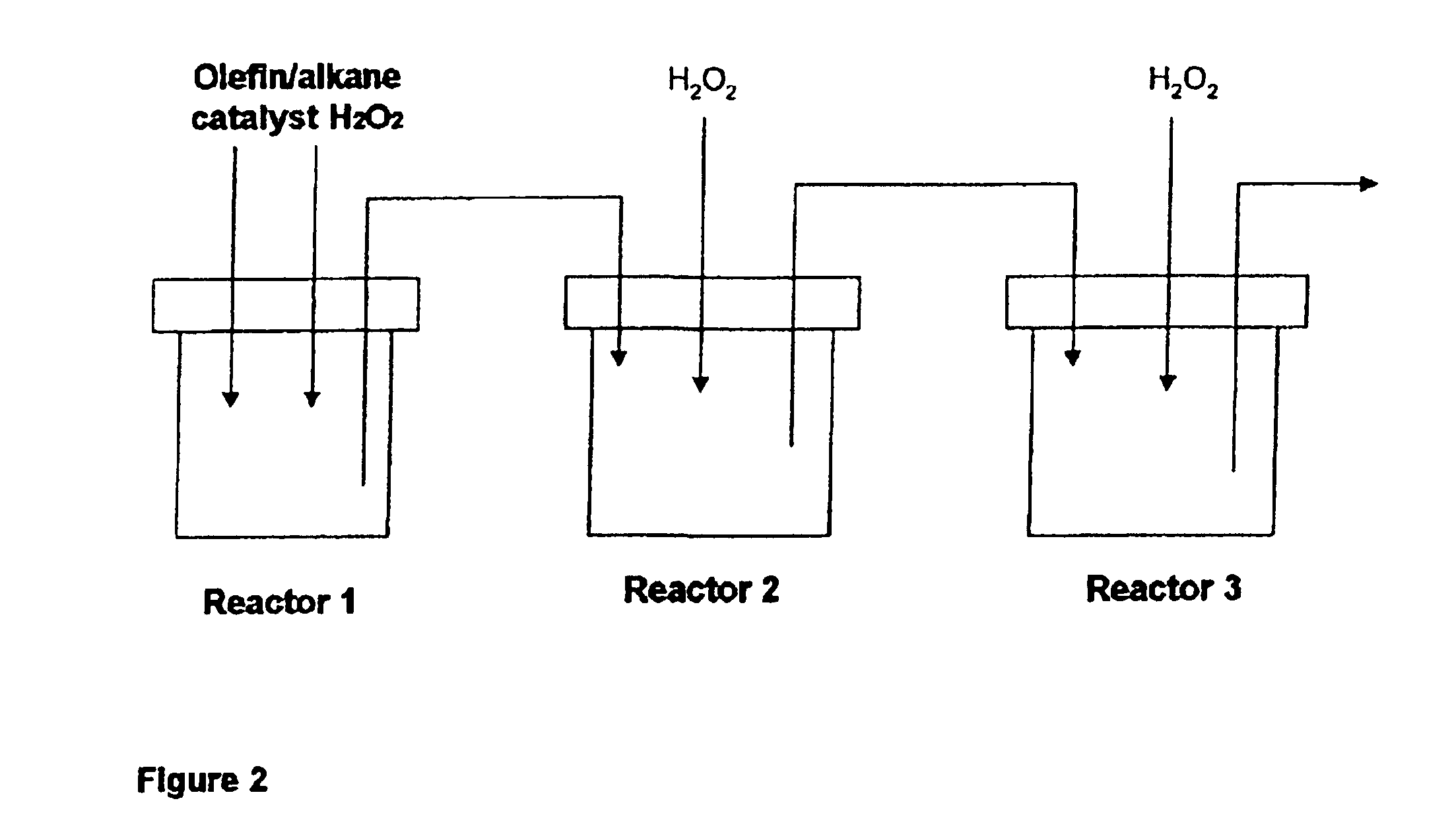
Process for the epoxidation of cyclic alkenes
ActiveUS6861540B2Increased space-time yieldContinuous operationOrganic chemistry methodsCyclic alkaneAlkene
The epoxidation of cyclic, at least monounsaturated alkenes is conducted by a process, which comprises conducting the epoxidation of a cyclic, at least monounsaturated alkene in the presence of an oxidant in a reaction medium that contains at least 1% by weight of the saturated cyclic alkane corresponding to the cyclic, at least monounsaturated alkene. In a preferred embodiment the reaction medium contains at least 2.5% by weight of the saturated cyclic alkane corresponding to the cyclic, at least monounsaturated alkene.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
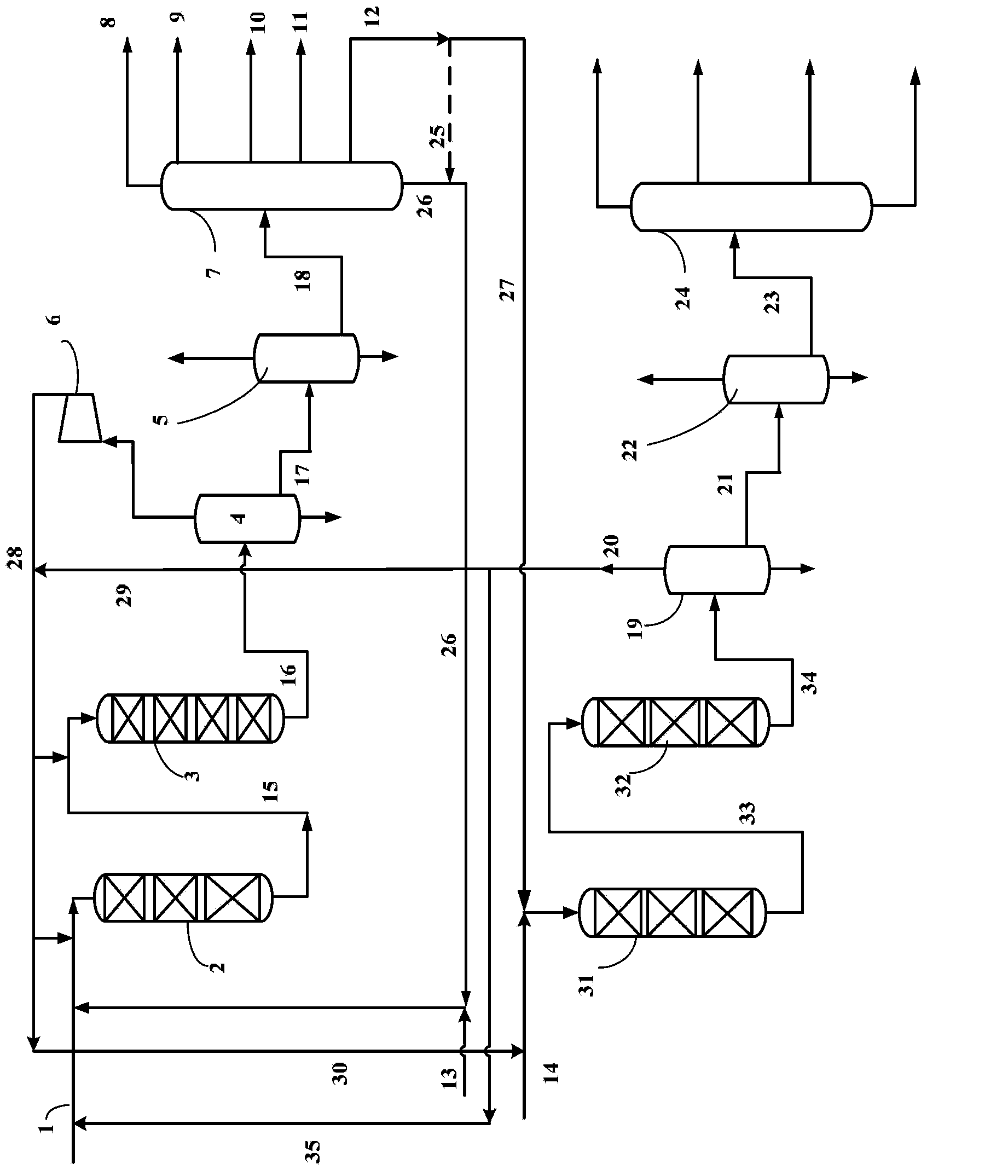
Method for producing aromatic hydrocarbon and ethylene by taking naphtha as raw material
The invention relates to a method for producing aromatic hydrocarbon and ethylene taking naphtha as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) contacting naphtha with a reforming catalyst in a catalytic reforming region to carry out a shallow catalytic reforming reaction in the presence of hydrogen at the pressure of 0.15-3.0 MPa, the temperature of 300-540 DEG C and the volume space velocity of 2.1-50 h<-1>, enabling the conversion rate of naphthenic hydrocarbon in the naphtha to be higher than 85wt%, and enabling the conversion rates from alkane to aromatic hydrocarbon and C4-hydrocarbon to be lower than 30wt%; (2) carrying out aromatic hydrocarbon separation on reformate produced by catalytic reforming in a first aromatic hydrocarbon separation region, so as to obtain aromatic hydrocarbon-rich cut fraction and alkane-rich cut fraction; (3) introducing the aromatic hydrocarbon-rich cut fraction and liquefied gas produced by the catalytic reforming into a steam cracking region, and carrying out a cracking reaction to produce ethylene. According to the method for producing the aromatic hydrocarbon and the ethylene taking naphtha as the raw material, the ethylene can be maximally produced when the naphtha is adequately utilized in a shallow catalytic reforming reaction manner.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Hydrocracking catalyst carrier containing beta molecular sieve and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103100427AHigh activityHigh selectivityCatalyst carriersMolecular sieve catalystsPtru catalystIsomerization
The invention discloses a hydrocracking catalyst carrier containing a beta molecular sieve, its preparation method and a hydrocracking catalyst with the carrier. The hydrocracking catalyst carrier contains a modified beta molecular sieve, amorphous silicon aluminum and alumina, wherein the modified beta molecular sieve is prepared by: subjecting a crystallized beta molecular sieve slurry directly to ammonium exchange and a template agent removal treatment, then first conducting a hydrothermal treatment, and performing an aluminum salt solution treatment, under the condition of maintaining a high beta molecular sieve crystallinity, removing part of non-framework aluminum uniformly, thus obtaining the beta molecular sieve with the characteristics of high Si / Al ratio, large specific surface area, appropriate acidity and acid distribution, and reasonable pore structure, etc. The modified beta molecular sieve especially has a suitable cracking effect and a very good isomerization effect on long-chain alkane and the long side chain alkyl of aromatic hydrocarbon and cyclane, and has a synergistic effect with amorphous silicon aluminum, so that the prepared hydrocracking catalyst has high activity, can produce maximum low condensation point diesel oil, and also can produce high quality hydrogenation tail oil as a byproduct.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Production of light olefins and aromatics
InactiveUS20100331590A1Increase the molar ratioIncrease valueCatalytic crackingHydrocarbonsCarbon numberCyclic alkane
Processes for the conversion of both straight- or branched-chain (e.g., paraffinic) as well as cyclic (e.g., naphthenic) hydrocarbons of a hydrocarbon feedstock into value added product streams are disclosed. The processes involve the use of both dehydrogenation and olefin cracking to produce both light olefins and aromatics in varying proportions depending on the feedstock composition and particular processing scheme. The processes are especially applicable to naphtha feedstocks comprising paraffins and naphthenes in the C5-C11 carbon number range.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process for methanol coupled catalytic cracking reaction of naphtha using a modified zsm-5 molecular sieve catalyst
ActiveUS20140051900A1Improving catalytic cracking efficiencyLow carbon olefinsCatalytic crackingLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCyclic alkaneNaphtha
The present invention provides a process for methanol coupled catalytic cracking reaction of naphtha using a modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst, comprising performing a co-feeding reaction of methanol and naphtha on the modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst to produce low carbon olefins and / or aromatic hydrocarbons. In the process, the modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst comprises, in term of weight percent, 25-80 wt % of a ZSM-5 molecular sieve, 15-70 wt % of a binder, and 2.2-6.0 wt % of lanthanum and 1.0-2.8 wt % of phosphorus loaded on the ZSM-5 molecular sieve. The naphtha comprises 63.8-89.5 wt % of saturated chain alkanes and 5.6-29.8 wt % of cyclic alkanes. The naphtha and methanol concurrently pass through the catalyst bed, which are reacted during contacting with the catalyst under a reaction condition of a reaction temperature of 550-670° C., a mass ratio of methanol to naphtha of 0.05-0.8, and a total mass space velocity of naphtha and methanol of 1.0-5 h−1.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electrical insulating oil with reduced gassing tendency
InactiveUS20020109127A1Reduce gasReduction tendencyLiquid organic insulatorsHydrocarbon distillationCyclic alkaneElectricity
An electrical oil having reduced gassing tendency includes a major amount of a paraffinic or naphthenic basestock and a blend of certain hindered phenols, especially a blend of 2,6-di-t-butyl phenol and 2,6-di-t-butyl cresol. A further enhanced gassing tendency can be provided to the electrical oil by including a tolyltriazole derivative.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Naphthenic hydrocarbon hydro-conversion catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101992120ALow cracking rateShort synthesis timeMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCyclic alkaneMolecular sieve
The invention discloses a naphthenic hydrocarbon hydro-conversion catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The naphthenic hydrocarbon hydro-conversion catalyst comprises a carrier active metal Pt, wherein a carrier consists of 10 to 90 weight percent of hydrogen-type Y-Beta composite molecular sieve, and an inorganic refractory oxide; and the active metal Pt content of the catalyst is 0.05 to 0.6 percent. The catalyst is prepared by an immersion method; and the obtained catalyst can be applied to hydro-conversion of various naphthenic hydrocarbon-containing raw materials andhas high conversion rate, high naphthenic hydrocarbon ring opening rate and low cracking rate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method of castor-oil plant based biological aircraft fuel
InactiveCN103320153AStable sourceNo pollution in the processLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBio-feedstockCyclic alkanePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of a castor-oil plant based biological aircraft fuel. According to the method, castor oil is selected as a raw material, an appropriate catalyst is prepared, and a hydrodeoxygenation reaction and a hydroisomerization reaction are carried out. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: hydrogen is blown into castor oil in the presence of a hydrodeoxygenation catalyst so as to generate n-alkanes; hydrogen is blown into n-alkanes in the presence of a hydroisomerization catalyst so as to isomerize to generate isoparaffin; and a fraction is subjected to fractionation so as to obtain the final product. The final product is the biological aircraft fuel which accords with usage requirements (such as American ASTMD7566 standard and the like). The obtained product castor-oil plant based biological aircraft fuel contains no alkene or napthene. By the adoption of the fuel, carbon formation of a motor is remarkably reduced. In addition, the fuel contains no sulfur compounds. When the fuel is in use, environmental pollution will not be caused. The castor-oil plant based biological aircraft fuel is an alternative for replacing a petrochemical aircraft fuel.
Owner:TIANJIN NANKAI UNIV CASTOR ENG SCI & TECH
Hydrocracking catalyst carrier and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103100430AHigh selectivityImprove product propertiesCatalyst carriersMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveCyclic alkane
The invention discloses a hydrocracking catalyst carrier and a preparation method thereof. The hydrocracking catalyst carrier comprises: a modified beta molecular sieve, a modified Y type molecular sieve and alumina. Specifically, the modified beta molecular sieve is prepared by: subjecting a crystallized beta molecular sieve slurry directly to ammonium exchange and a template agent removal treatment, then first conducting a hydrothermal treatment, and performing an aluminum salt solution treatment, under the condition of maintaining a high beta molecular sieve crystallinity, removing part of non-framework aluminum uniformly, thus obtaining the beta molecular sieve with the characteristics of high Si / Al ratio, large specific surface area, appropriate acidity and acid distribution, and reasonable pore structure, etc. The modified beta molecular sieve especially has a suitable cracking effect and a very good isomerization effect on long-chain alkane and the long side chain alkyl of aromatic hydrocarbon and cyclane, and has a synergistic effect with the Y type molecular sieve, so that the prepared hydrocracking catalyst can have very high catalytic activity and middle distillate selectivity. And the condensation point of diesel fraction is substantially reduced, and the product properties of middle distillate are improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Delivery of biologically-active agents using volatile, hydrophobic solvents
ActiveUS8852648B2Reduce inflammationReduce painAntibacterial agentsBiocideActive agentChlorofluorocarbon
A composition and method adapted for delivery of hydrophilic, biologically-active agents are disclosed. The composition can include a reverse microemulsion formed from at least one hydrophilic, biologically-active agent solubilized by a hydrophobic reverse emulsion surfactant in a non-stinging, volatile, hydrophobic solvent. The non-stinging, volatile, hydrophobic solvent is selected from the group consisting of volatile linear and cyclic siloxanes, volatile linear, branched, and cyclic alkanes, volatile fluorocarbons and chlorofluorocarbons, liquid carbon dioxide under pressure, and combinations thereof. The reverse microemulsion can be an optically clear solution.
Owner:ROCHAL TECH LLC
Hydrogenation method for producing lubricant basic oil with low pour point and high viscosity index
ActiveCN103627433AQuality improvementHigh viscosity indexTreatment with hydrotreatment processesLubricant compositionCyclic alkaneIsomerization
The invention discloses a hydrogenation method for producing lubricant basic oil with a low pour point and a high viscosity index. The hydrogenation method comprises the following steps: mixing raw material oil with hydrogen gas, then transporting the mixing to a hydro-cracking reaction unit, subjecting the reaction product which flows out from the hydro-cracking reaction unit to processes of separation and fractionation, recycling the obtained heavy tail oil fraction, then adding the heavy tail oil fraction into the hydro-cracking reaction unit, mixing the obtained tail oil fraction with hydrogen gas, and then transporting the mixture to a hydro-isomerization and pour-point reducing reaction unit to carry out hydro-isomerization reactions, pouring point reducing reactions, and hydrogenation saturation reactions so as to obtain the lubricant basic oil. The invention solves the problem that the quality of the lubricant basic oil cannot stay stable because the raw material quality turns bad, provides a hydrogenation method which can stably produce lubricant basic oil with an ultrahigh viscosity index; the obtained product has a high tail oil viscosity index, which can reach 140 or more, furthermore, the product is rich in chain alkane and mono-cyclic alkane and is a lubricant basic oil with a high viscosity index.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Laminate adhesive, stack using the same, and secondary battery
ActiveCN105658753AGood adhesivenessMeet moisture resistanceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesCell electrodesPolyolefinAdhesive
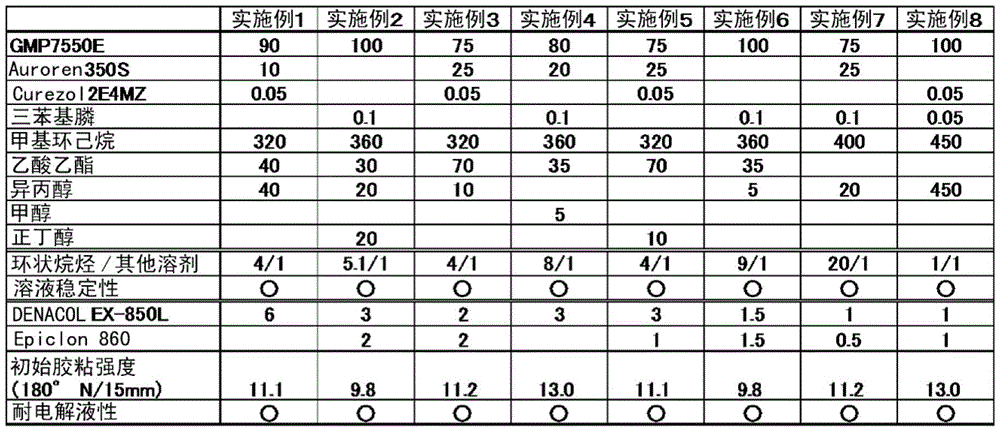
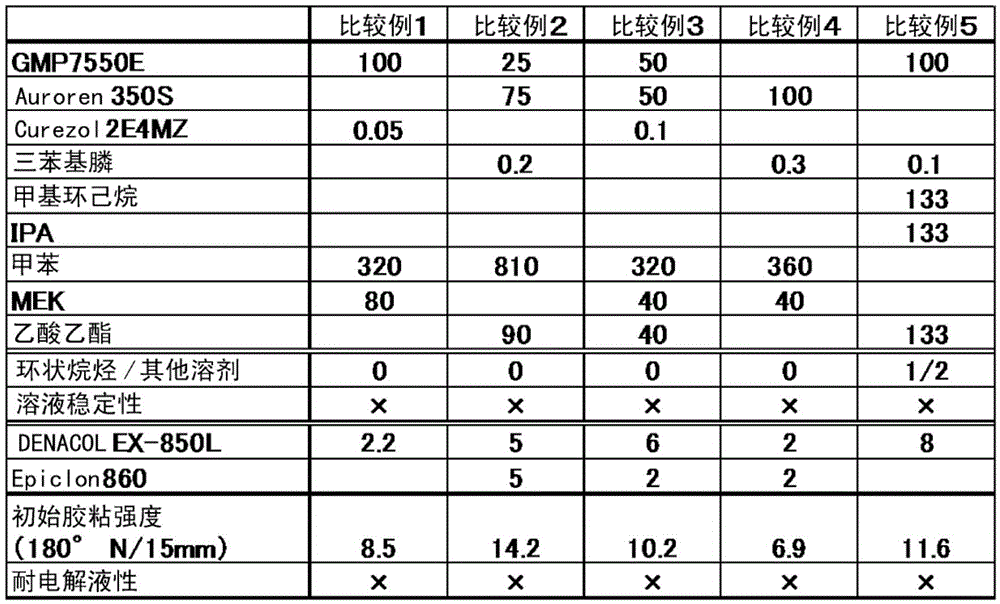
By providing a heretofore unknown laminate adhesive, the present invention addresses the problem of providing an adhesive composition for laminate stacks, which provides excellent adhesion between a metal layer and a plastic layer and satisfies moisture resistance, heat resistance, insulation performance, durability, etc., further combined with electrolyte resistance in low-temperature curing, without causing delamination over time. The present invention also addresses the problem of providing a stack using the adhesive composition, and a secondary battery. The above problems are solved with a laminate adhesive containing a non-chlorine polyolefin resin (A), an epoxy compound (B), and an organic solvent (C) essentially containing a cyclic alkane compound and containing an ester solvent or an alcohol solvent, wherein the organic solvent (C) is constituted such that the ratio of the mass parts of the cyclic alkane compound to the mass parts of other solvents is in the range of 1 / 1 to 20 / 1, inclusive.
Owner:DIC CORP
Synthetic base drilling fluid base oil
InactiveCN105505347ALow aromatic contentPromote degradationDrilling compositionCyclic alkanePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a base oil used during drilling operation, wherein the base oil is a synthetic base drilling fluid base oil with characteristics of environmental protection, low toxicity, high safety and low-temperature fluidity. According to the present invention, the synthetic base drilling fluid base oil is formed by mixing Fischer-Tropsch synthetic oil and non-conventional petroleum-derived fine chemical base oil, and contains at least 35% by mass of a variety of C9-C20 n-alkanes, at least 60% by mass of a variety of C9-C20 branched or cyclic alkanes, and less than 0.5% by mass of aromatic hydrocarbon, the kinematic viscosity of the synthetic base drilling fluid base oil at the temperature of 40 DEG C is 2-3 mm<2> / s, the pour point is -10 to -30 DEG C, and the flash point is 50-80 DEG C.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
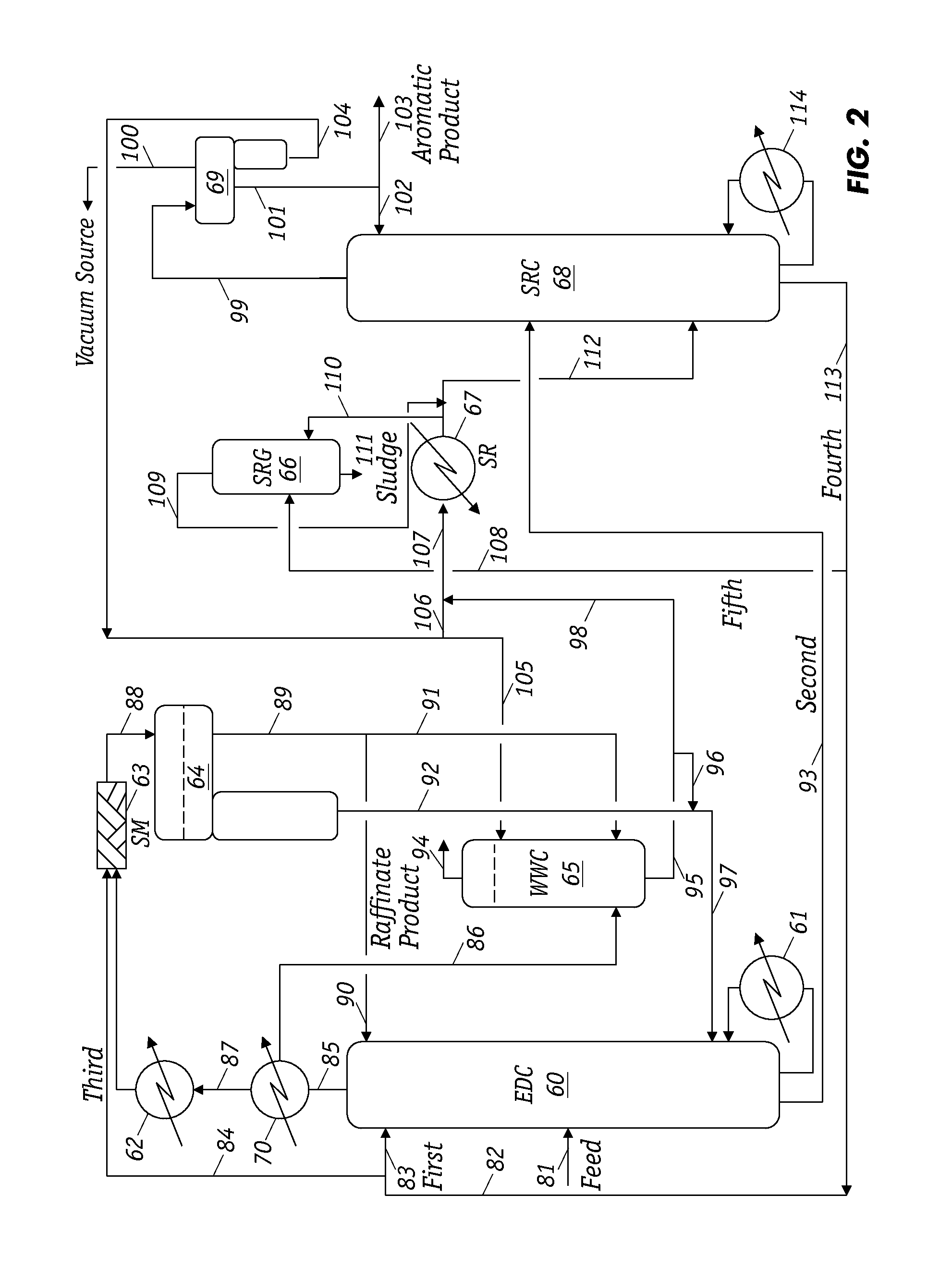
Extractive distillation for aromatics recovery
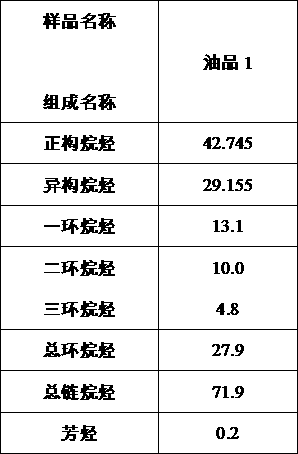
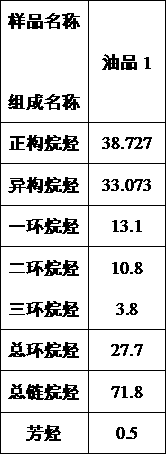
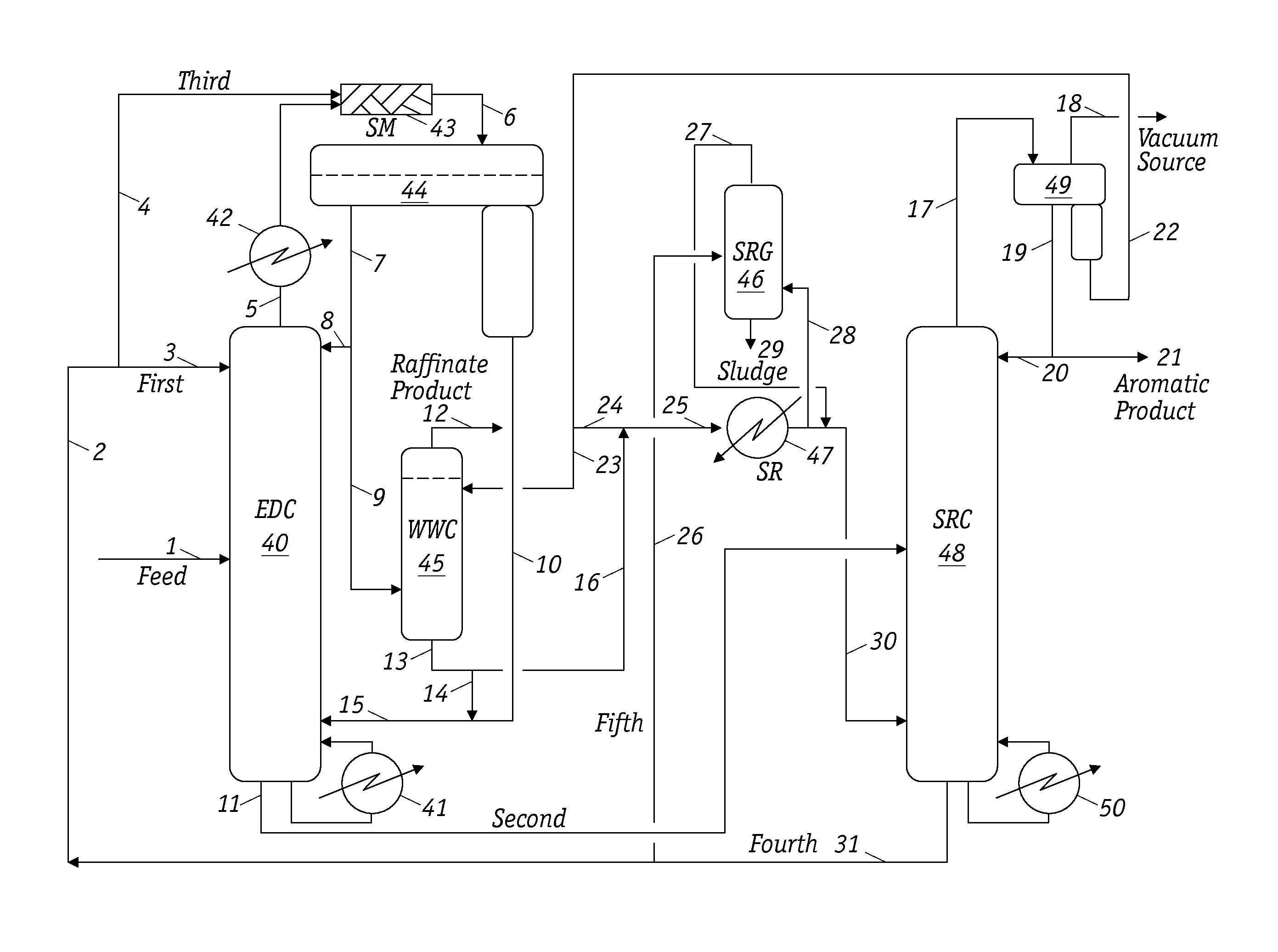
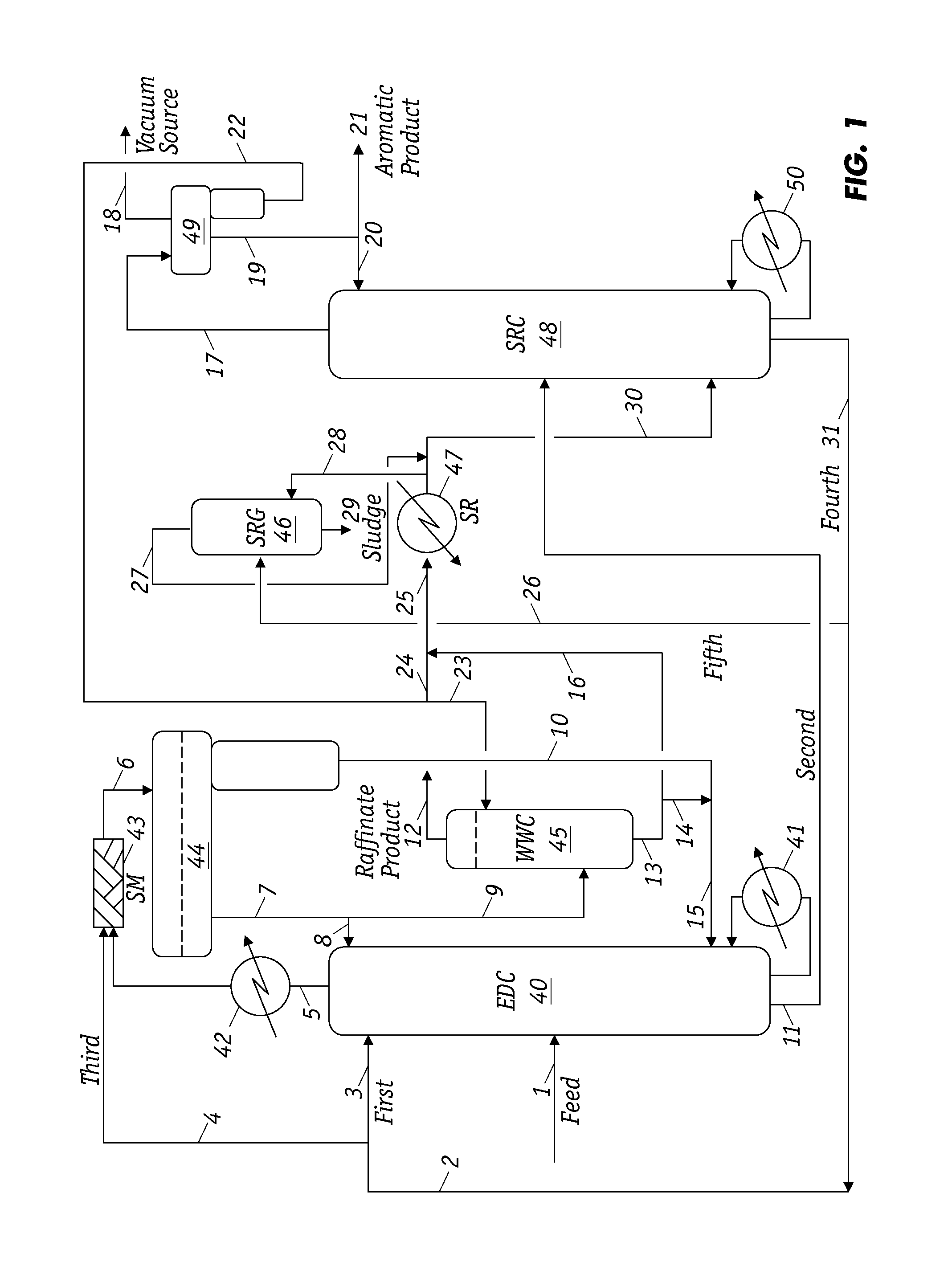
ActiveUS9221729B1Reducing naphthenes contentImprove the level ofDistillation purification/separationVapor condensationCyclic alkaneNarrow range
Extractive distillation for recovering aromatic hydrocarbons employs an extractive distillation column with a novel overhead system including a partial condenser. The process enables (i) efficient removal of heavy non-aromatics, particularly C8 naphthenic compounds, from the EDC bottom stream to increase the purity of aromatic products, especially of the mixed xylenes and (ii) reduction (or better control) of benzene loss to the raffinate product stream to maintain its quality as a gasoline blend stock and, as a result, enhance benzene recovery in the aromatic products. Feedstock includes a full-range feedstock, such as pyrolysis gasoline, or a narrow-range feedstock, such as reformate.
Owner:SHIN CHUANG TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing adamantine on solid acid catalyst
InactiveCN101125791AHigh reactivityEasy to separateHydrocarbon by isomerisationFixed bedReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing adamantane on solid-acid catalyst. The solid-acid catalyst is a solid-borne halide comprising chloride or bromide of aluminum, titanium, zinc or iron, etc., on carriers of mesopore Al2O3, Al2O3-SiO2 or silicon-aluminum molecular sieve, etc., uses tetrahydric dicyclopentadiene as raw material and synthesizes adamantane by isomerization reaction. Isomerization reaction is carried out in the mode of liquid-solid multiphase stirring reaction or fixed bed reaction and uses C6 to C10 linear paraffin or cyclane as solvent, the reaction temperature is 10 DEG C to 200 DEG C, reaction pressure is 0.5 to 5.0MPa in the atmosphere of H2 or N2. Reaction system does not need catalyst accelerato of HCl or HBr, etc., therefore, reaction equipment is not required to have great erosion-resistance. No separation process between catalyst and result is required after reaction and the method does not pollute the environment.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Direct conversion of biomass oxygenates to hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20130144098A1Hydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCyclic alkaneSingle pass
A single pass direct conversion of biomass derived oxygenates to longer chain hydrocarbons is described. The longer chain hydrocarbons include higher naphthene content which is quite useful in the distillate range fuels or more particularly, the jet and diesel range fuels. Naphthenes help the biomass derived hydrocarbons meet product specifications for jet and diesel while really helping cold flow properties.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Process for isomerizing a non-equilibrium alkylaromatic feed mixture and an aromatic production facility
ActiveUS20090182182A1High activityHigh selectivityHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystCyclic alkaneIsomerization
One exemplary embodiment can be a process for the isomerization of a non-equilibrium alkylaromatic feed mixture. The process can include contacting the non-equilibrium alkylaromatic feed mixture in a C8 isomerization zone. The C8 isomerization zone may include a first isomerization stage and a second isomerization stage. At the first isomerization stage, at least a portion of the non-equilibrium alkylaromatic feed mixture can be contacted at a first isomerization condition in a liquid phase in the substantial absence of hydrogen to obtain an intermediate stream. At the second isomerization stage, at least part of the intermediate stream and at least a part of a stream rich in at least one naphthene can be contacted at a second isomerization condition to obtain a concentration of at least one alkylaromatic isomer that is higher than a concentration of that at least one alkylaromatic isomer in the non-equilibrium alkylaromatic feed mixture.
Owner:UOP LLC
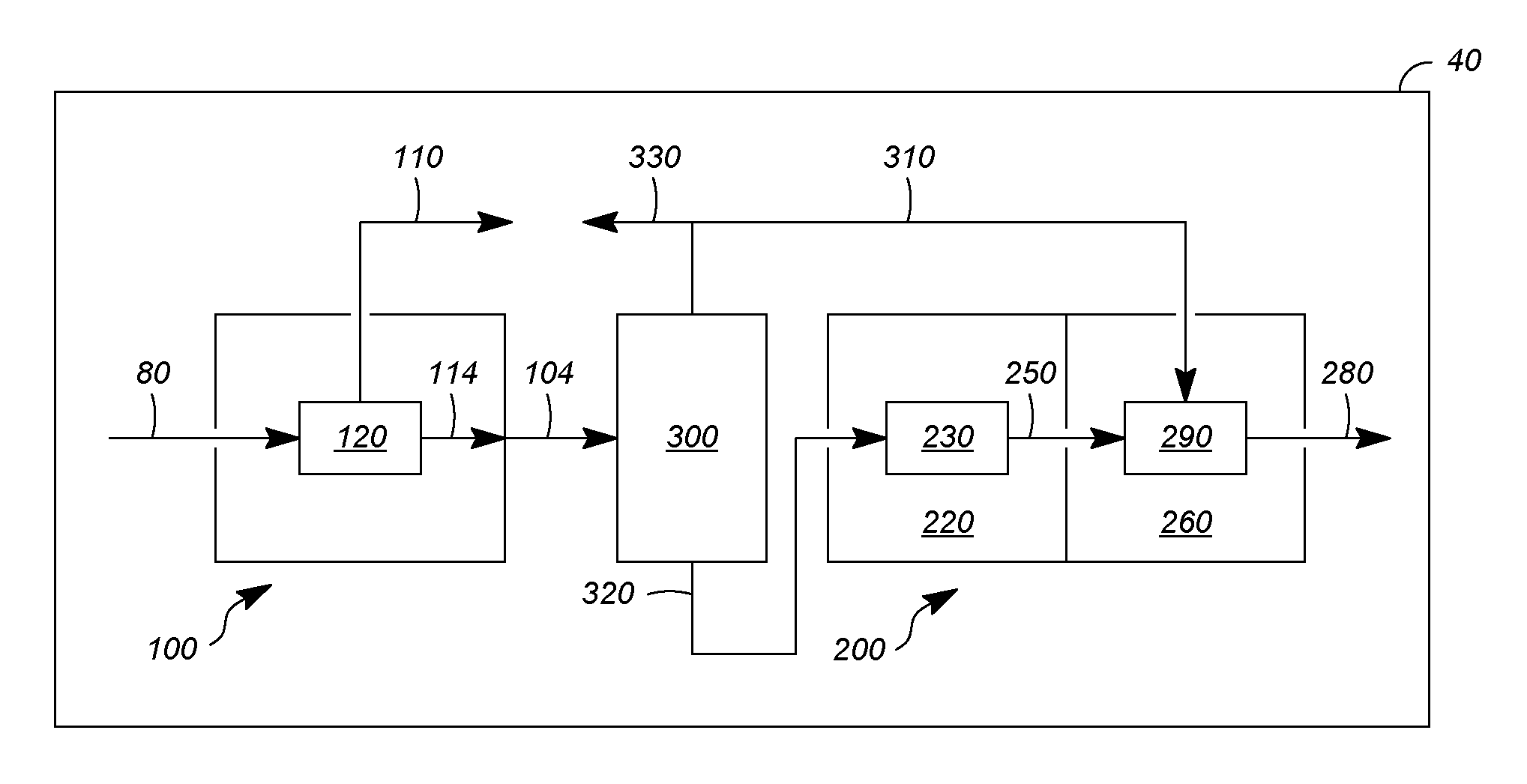
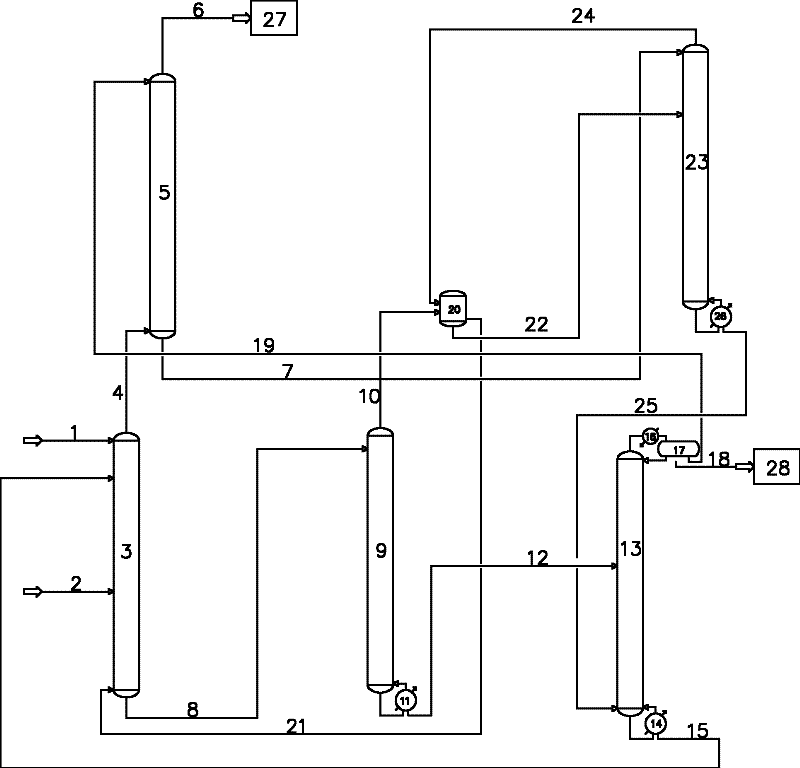
High octane number gasolines and their production using a process associating hydro-isomerzation and separation
InactiveUS20020175109A1Minimize cracksReduce the amount requiredRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonCatalytic naphtha reformingCyclic alkaneGasoline
The invention provides a high octane number gasoline pool comprises at least 2% of di-branched paraffins containing 7 carbon atoms, and a process for producing this gasoline pool by hydro-isomerising a feed constituted by a C5 to C8 cut which comprises at least one hydro-isomerisation section and at least one separation section, in which the hydro-isomerisation section comprises at least one reactor. The separation section comprises at least one unit and produces at least two streams: a first stream which is rich in di- and tri-branched paraffins, and possibly in naphthenes and aromatic compounds which is sent to the gasoline pool; and in a first version of the process, a second stream is produced which is rich in straight-chain and mono-branched paraffins which is recycled to the inlet of the hydro-isomerisation section, while in a second version of the process, a second flux is produced which is rich in straight-chain paraffins which is recycled to the inlet of a first hydro-isomerisation section and a third stream is produced which is rich in mono-branched paraffins which is recycled to the inlet of a second hydro-isomerisation section.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Laminating adhesive, laminate using the same, and secondary battery
InactiveUS20170088753A1Improve adhesionSatisfactory durabilityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesCell electrodesPolyolefinAdditive ingredient
It is an object to provide a novel laminating adhesive to thereby allow provision of a laminating adhesive composition for a laminate that provides good adhesion between a metal layer and a plastic layer, has satisfactory moisture barrier properties, heat resistance, insulation properties, durability, etc., also exhibits electrolyte resistance even after low-temperature curing, and does not undergo delamination over time. A laminate that uses the laminating adhesive composition and a secondary battery are also provided. The object is achieved by a laminating adhesive containing a non-chlorine-based polyolefin resin (A), an epoxy compound (B), and an organic solvent (C) including a cyclic alkane compound as an essential ingredient and further including an ester-based solvent or an alcohol-based solvent. In the organic solvent (C), the ratio, in parts by mass, of the cyclic alkane compound to the solvent other than the cyclic alkane compound is within the range of 1 / 1 to 20 / 1.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Method and device for optimizing naphtha
ActiveCN102517072AImprove the level ofSave resourcesNaphtha treatmentCatalytic reformingSeparation technology
The invention relates to a method and a device for optimizing naphtha. The method comprises the following steps of: separating the naphtha into raffinate oil rich in alkane and extracted oil rich in alkane and aromatic hydrocarbon by adopting an extracting method and using a composite solvent, and separating the extracted oil from the used extracting agent; and the feeding the separated and purified raffinate oil serving as a pyrolytic raw material into an ethylene pyrolysis device for pyrolysis, and feeding the extracted oil serving as a reforming raw material into a catalytic reforming device for reforming. Based on adsorptive separation and extracting separation of the naphtha raw material, a process flow for optimizing the naphtha is designed; by adopting the extracting separation technology, the naphtha is separated into the raffinate oil rich in the alkane and the extracted oil rich in the alkane and the aromatic hydrocarbon; and washing, stripping and rectification processes are sequentially performed, and the extracting agent is recycled. The invention saves resources, reduces energy consumption, is favorable for sustainable development and improving the level of the whole oil refining and ethylene industry, and has great economic benefits, environmental benefits and social benefits.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Optical systems and refractive index-matching compositions
InactiveUS6890619B2Reduce light absorptionLow toxicityOrganic compound preparationLayered productsSolid componentKetone
Optical systems such as, for example, optical switches, are disclosed comprising a solid component and a refractive index-matching liquid composition interfaced with the solid component. The liquid composition has a refractive-index that is substantially equal to that of the solid component. In one approach the liquid composition is a saturated cyclic compound consisting essentially of carbon and hydrogen and optionally oxygen such as, e.g., cyclic alkanes, alcohols or ketones. In another approach the liquid composition is benzene substituted with one or more electron-donating groups attached directly to the ring and one of more fluoro groups attached to the ring or to the electron-donating groups. In yet another approach the liquid composition is a combination comprising one or more of benzene or substituted benzene and optionally at least one of an alkane or substituted alkane having a boiling point less than about 130° C. Also disclosed are methods for preparing a liquid composition having a predetermined refractive index at a predetermined temperature and methods for transmitting optical signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Vinyl sulfonamide connector and application thereof
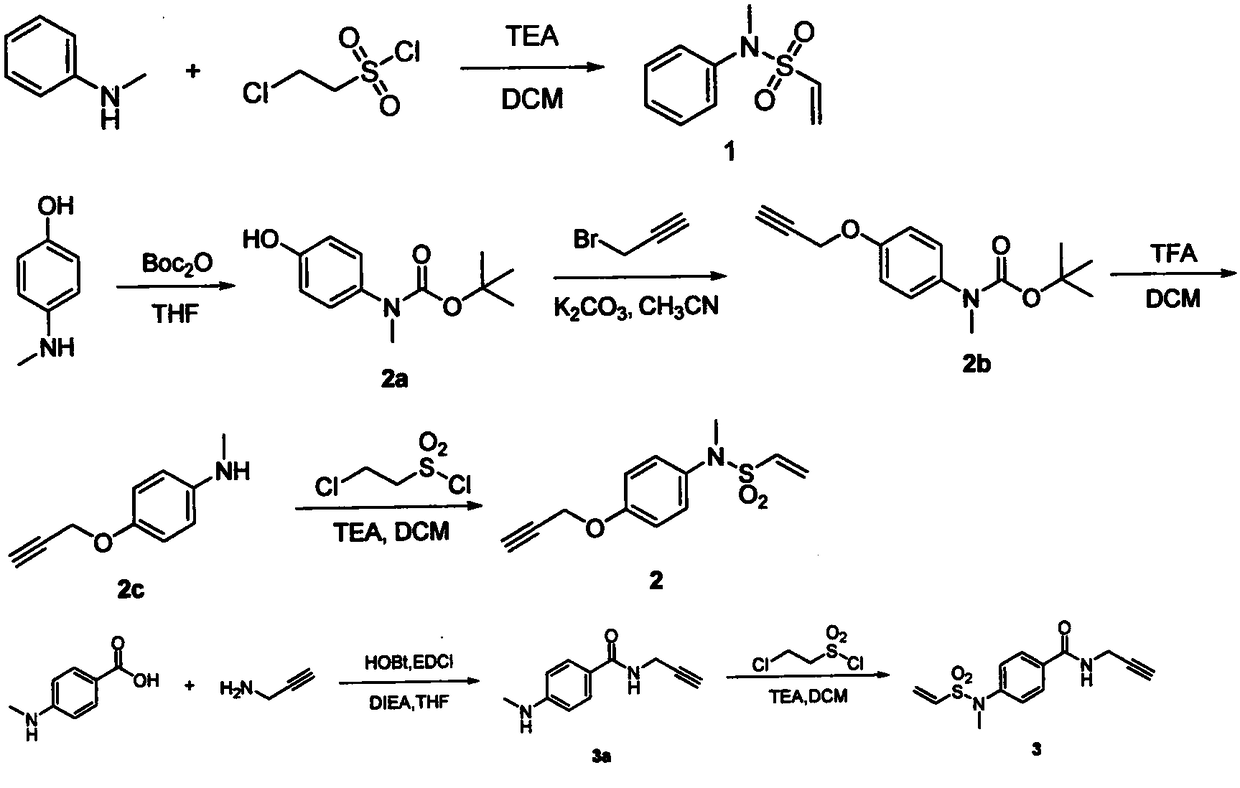
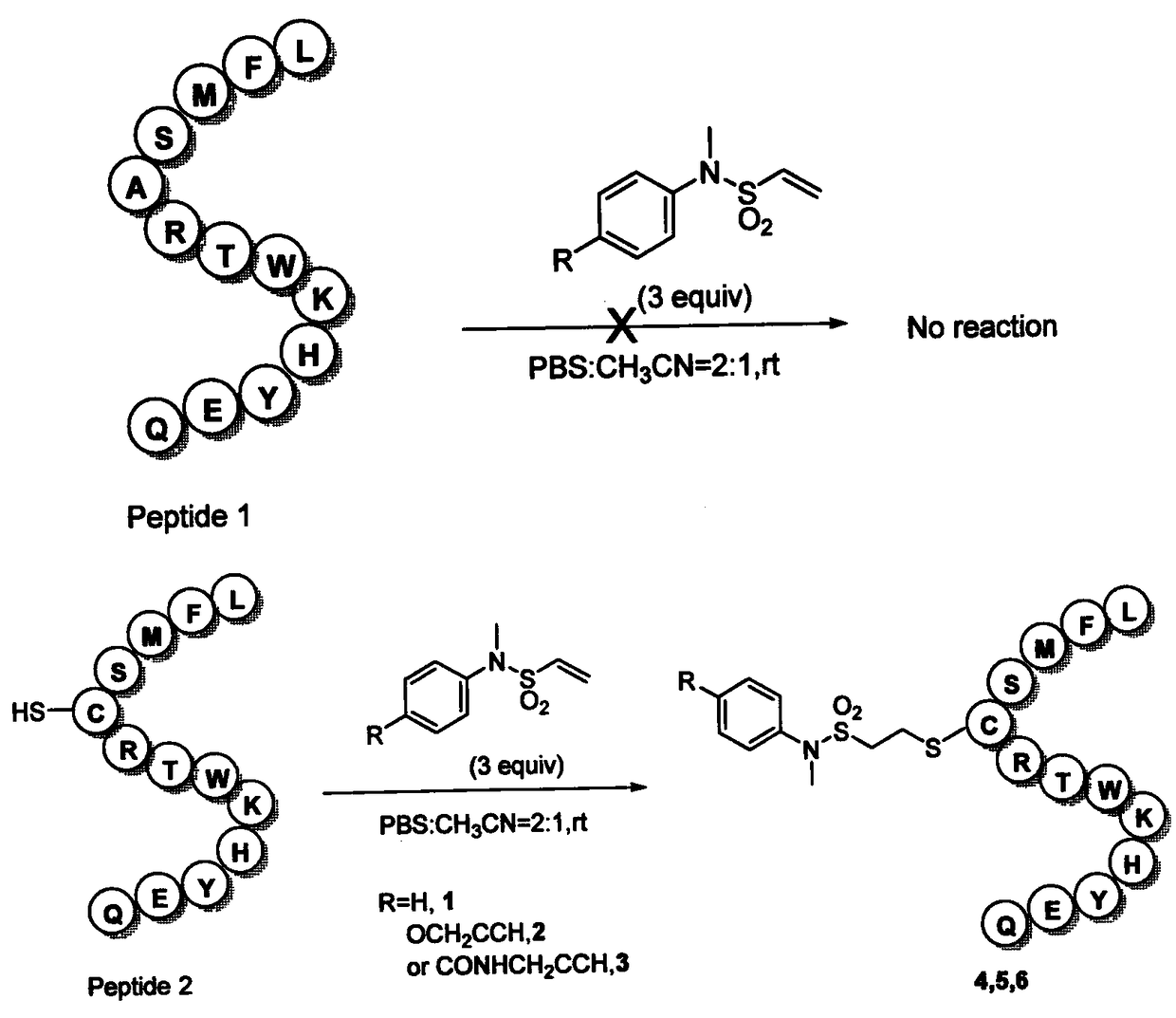
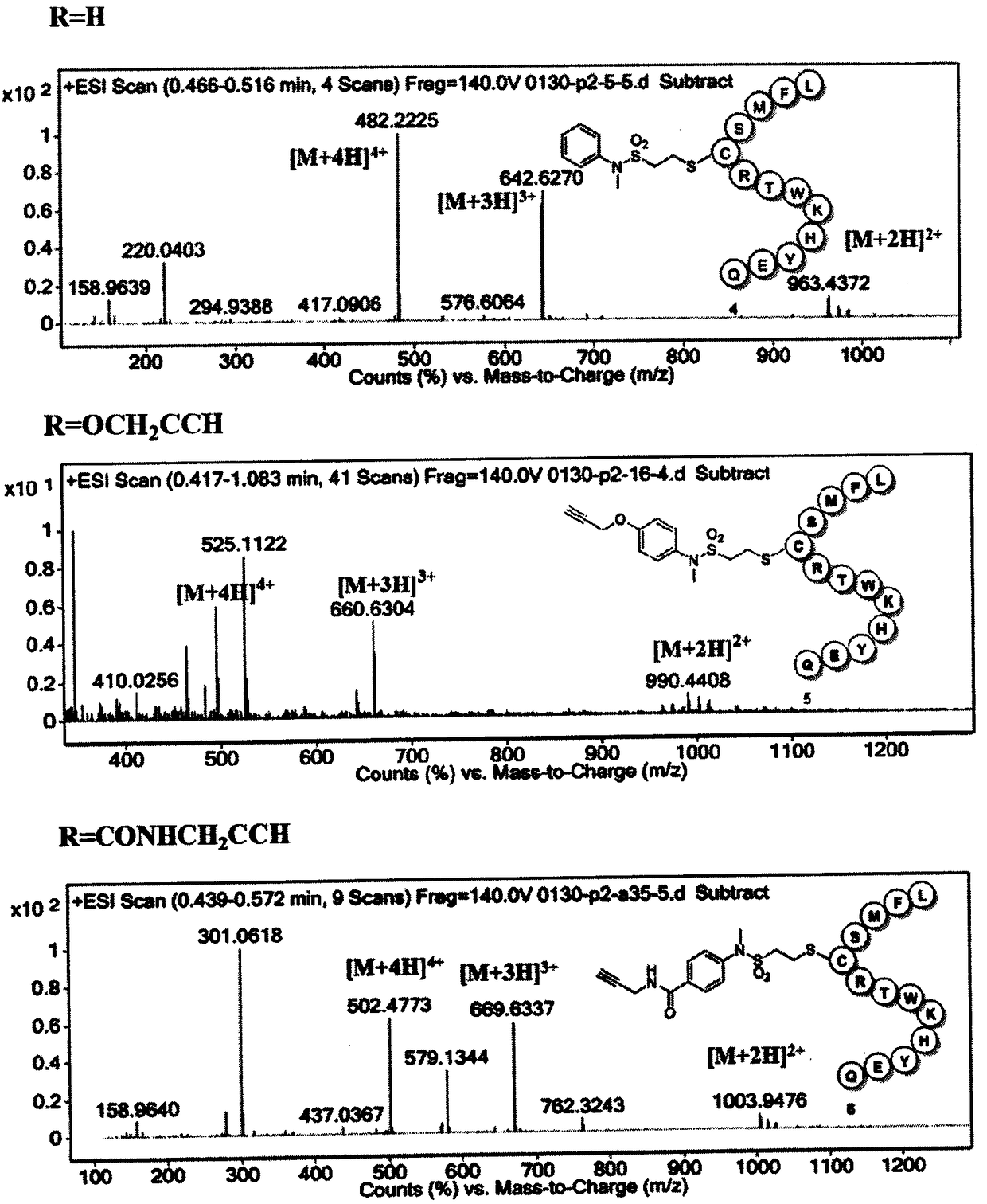
InactiveCN108530512AHigh selectivityImprove stabilityPeptide preparation methodsImmunoglobulinsCyclic alkaneVinyl sulfonamide
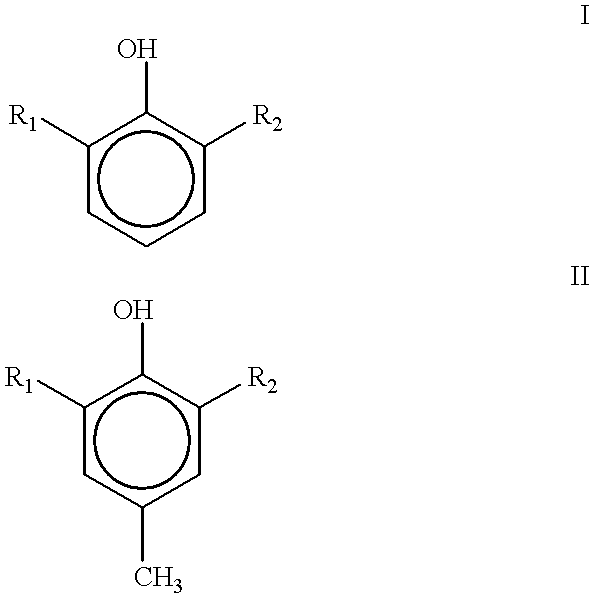
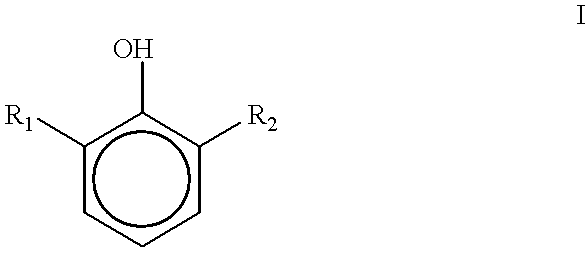
The invention provides a vinyl sulfonamide connector and application thereof. The structural formula of the vinyl sulfonamide connector is as shown in formula I, wherein X is selected from C or N; R is selected from one of or optional combination of hydrogen, amide, nitryl, hydroxyl, alkyl hydroxyl, aromatic hydroxyl, amino, alkyl amino, aromatic amino, sulfydryl, alkyl sulfydryl, aromatic sulfydryl, carboxylic acid, alkyl carboxylic acid, aromatic carboxylic acid, alkynyl, alkyl alkynyl, aromatic alkynyl, azide, alkyl azide, aromatic azide, carbonyl, alkyl carbonyl, aromatic carbonyl, aldehyde group, alkyl aldehyde group and aromatic aldehyde group; R1 is selected from one of or optional combination of hydrogen, linear, branched or cyclic alkane, acid, aldehyde group, linear carbonyl, benzyl or other aromatic benzyl and phenyl or other aromatic groups. The vinyl sulfonamide connector is high in selectivity and good in product stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Method for producing olefins and aromatic hydrocarbons with naphtha as raw material
ActiveCN104927915AEfficient use ofProduction maximizationHydrocarbonsTreatment with hydrotreatment processesCatalytic reformingCyclic alkane
A method for producing olefins and aromatic hydrocarbons with naphtha as a raw material comprises the steps: naphtha is subjected to liquid-liquid extraction, and an extract oil containing aromatic hydrocarbons and naphthenes and a raffinate oil containing alkanes and naphthenes are obtained, wherein the mass ratio of the naphthenes contained in the raffinate oil and the naphthenes contained in naphtha is 10-55%; the obtained raffinate oil is sent into a steam cracking zone and is subjected to a cracking reaction, obtained cracked gasline is hydrofined, and hydrofined cracked gasoline is obtained; the extract oil containing the aromatic hydrocarbons and the naphthenes is sent to a catalytic reforming zone and is subjected to a catalytic reforming reaction, and a reformed generated oil, a C3-C5 fraction and gas are obtained; and the obtained hydrofined cracked gasoline returns to the catalytic reforming zone to be used as a catalytic reforming raw material, or is mixed with naphtha and is subjected to liquid-liquid extraction, and the C3-C5 fraction obtained in the reforming reaction returns to the steam cracking zone and is subjected to a cracking reaction. The method can effectively utilize naphtha to produce more light-olefin aromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Pharmaceutical compounds
InactiveUS20150051199A1Inhibit functionPatient compliance is goodBiocideCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationCarbon atomHenipavirus Infections
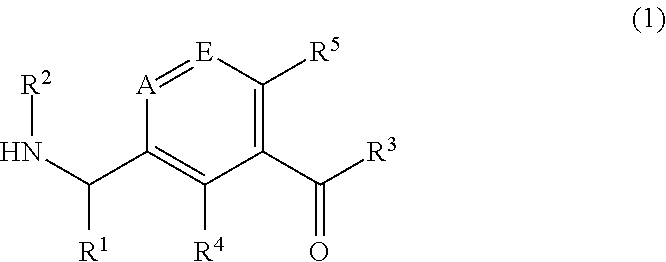
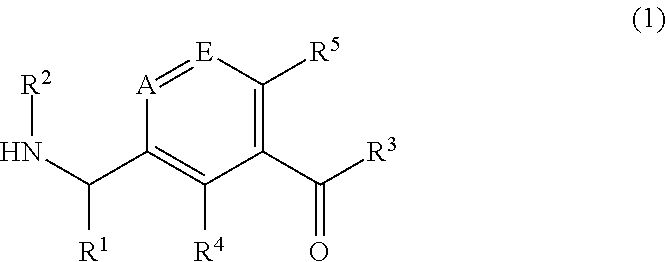
The invention provides compounds that are useful in the treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections. The compounds have the formula (1):or a salt, N-oxide, tautomer or stereoisomer thereof, wherein A is CH or N; E is CH or N;R1 is selected from:an optionally substituted acyclic C1-8 hydrocarbon group wherein one carbon atom of the acyclic C1-8 hydrocarbon group may optionally be replaced by O, S, NRc, S(O) or SO2, or two adjacent carbon atoms of the acyclic C1-8 hydrocarbon group may optionally be replaced by CONRc, NRcCO, NRcSO2 or SO2NRc provided that in each case at least one carbon atom of the acyclic C1-8 hydrocarbon group remains; andan optionally substituted monocyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic group of 3 to 7 ring members, of which 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4 are heteroatom ring members selected from O, N and S;R2 is hydrogen or X—R8;X is a C1-8 alkanediyl group wherein one carbon atom of the C1-8 alkanediyl group may optionally be bonded to a —CH2—CH2— moiety to form a cyclopropane-1,1-diyl group or two adjacent carbon atoms of the C1-8 alkanediyl group may optionally be bonded to a —(CH2)n moiety, where n is 1 to 5, to form a C3-7-cycloalkane-1,2-diyl group;R3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 10-membered monocyclic or bicyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring containing 0-3 heteroatom ring members selected from N, O and S;R4 is hydrogen or R4a wherein R4a is halogen; cyano; C1-4 alkyl; fluoro-1-4 alkyl; C1-4 alkoxy; fluoro-C1-4 alkoxy; hydroxy-C1-4 alkyl; or C1-2 alkoxy-C1-4 alkyl;R5 is hydrogen or R5a wherein R5a is selected from C1-2 alkyl optionally substituted with fluorine; C1-3 alkoxy optionally substituted with fluorine; halogen; cyclopropyl; and cyano;R8 is hydroxy or C(═O)NR10R11; provided that when R8 is hydroxy, there are at least two carbon atoms in line between the hydroxy group and the nitrogen atom to which X is attached;R10 is hydrogen or C1-4 alkyl; andR11 is hydrogen; amino-C2-4 alkyl or hydroxy-C2-4 alkyl;but excluding the compounds 1-(3-benzoylphenyl)-ethylamine and 1-(3-furan-2-oylcarbonylphenyl)-ethylamine.
Owner:ASTEX THERAPEUTICS LTD
Composition for manufacturing vitrimer resins of epoxy/anhydride type comprising a polyol
The present invention relates to a composition containing, besides a thermosetting resin of epoxy type and / or a hardener, at least one vitrimer effect catalyst and at least one polyol selected from linear, branched or cyclic alkanes containing at least two hydroxyl functions. This composition enables the manufacture of vitrimer resins, that is to say resins that can be deformed in the thermoset state. It also relates to an object obtained from this composition and also to a process for deforming this object.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Composition for manufacturing vitrimer resins of epoxy/anhydride type comprising polyol
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Nitrogen-containing ligand rare earth catalyst and application thereof in polyester synthesis
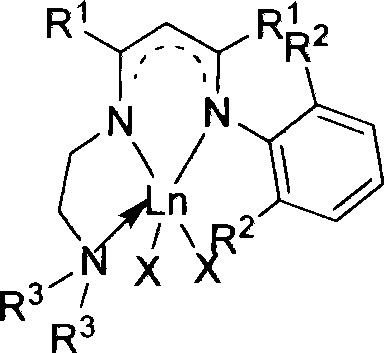
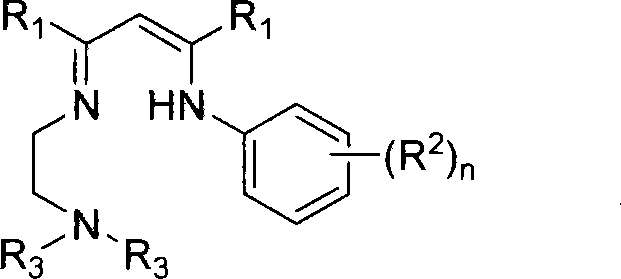
The invention relates to a new N-N-N tridentate ligand, relative rare-earth complex and relative application in the synthesis as poly-lactide acid or poly-caprolactone. The inventive ligand can be prepared from relative beta-diketone and amine via two-step condensation, the rare-earth complex can be prepared from the ligand with rare-earth alkyl compound or aamino-compound. The complex can catalyze lactide to open ring and polymerize to obtain polymer polyester, and catalyze caprolactone to polymerize. The formula of the complex is represented as above, wherein Ln is rare-earth metal ion as Y, Nd, Sm, Sc or the like, R1 is alkane of C1-10, R2 is alkane of C1-6, R2 is chain or cyclic alkane of C1-10, and X is alkyl, amido or alkoxy bonded with rare-earth ion.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Elastomer composition containing a softening agent
InactiveUS20040039108A1Good lookingGood moldabilityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsGranular deliveryElastomerCyclic alkane
An elastomer composition comprising a softening agent (A) comprising a naphthenic hydrocarbon and optionally at least one selected from the group consisting of an aromatic hydrocarbon and a paraffinic hydrocarbon, and an elastomer (B) comprising a crosslinkable elastomer, wherein said softening agent (A) has a ratio of an amount of the paraffinic hydrocarbon CP, and an amount of the naphthenic hydrocarbon CN, CP / CNN, which are specified by ASTM D2140-97, of not less than 0 and not more than 1.5, and an amount of the aromatic hydrocarbon CA of not less than 0% and not more than 5% based on an amount of hydrocarbons in the whole softening agent.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Process for isomerizing a non-equilibrium alkylaromatic feed mixture and an aromatic production facility
ActiveUS7932426B2Increased isomerizationQuantity minimizationHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystCyclic alkaneHydrogen
One exemplary embodiment can be a process for the isomerization of a non-equilibrium alkylaromatic feed mixture. The process can include contacting the non-equilibrium alkylaromatic feed mixture in a C8 isomerization zone. The C8 isomerization zone may include a first isomerization stage and a second isomerization stage. At the first isomerization stage, at least a portion of the non-equilibrium alkylaromatic feed mixture can be contacted at a first isomerization condition in a liquid phase in the substantial absence of hydrogen to obtain an intermediate stream. At the second isomerization stage, at least part of the intermediate stream and at least a part of a stream rich in at least one naphthene can be contacted at a second isomerization condition to obtain a concentration of at least one alkylaromatic isomer that is higher than a concentration of that at least one alkylaromatic isomer in the non-equilibrium alkylaromatic feed mixture.
Owner:UOP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com