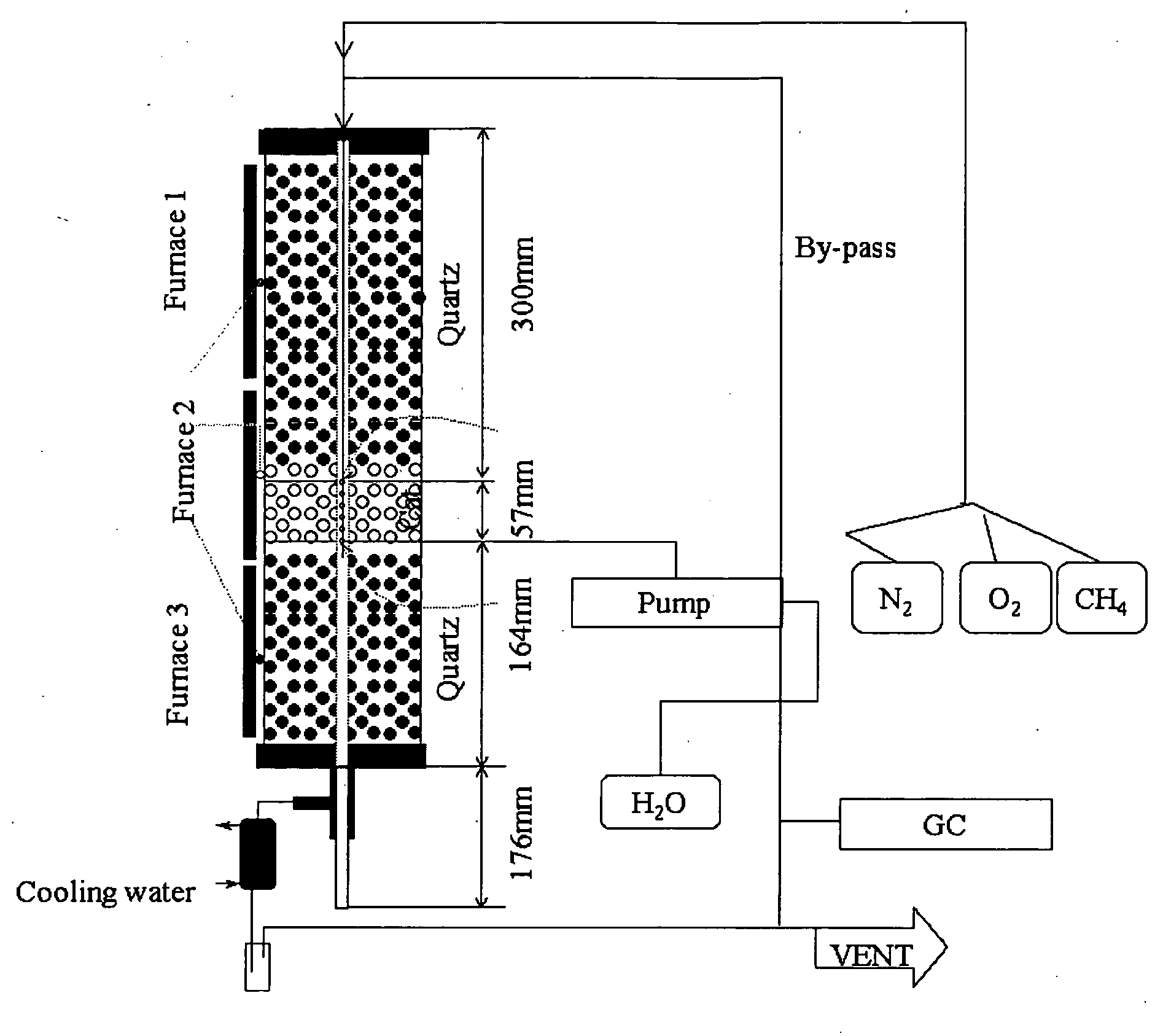
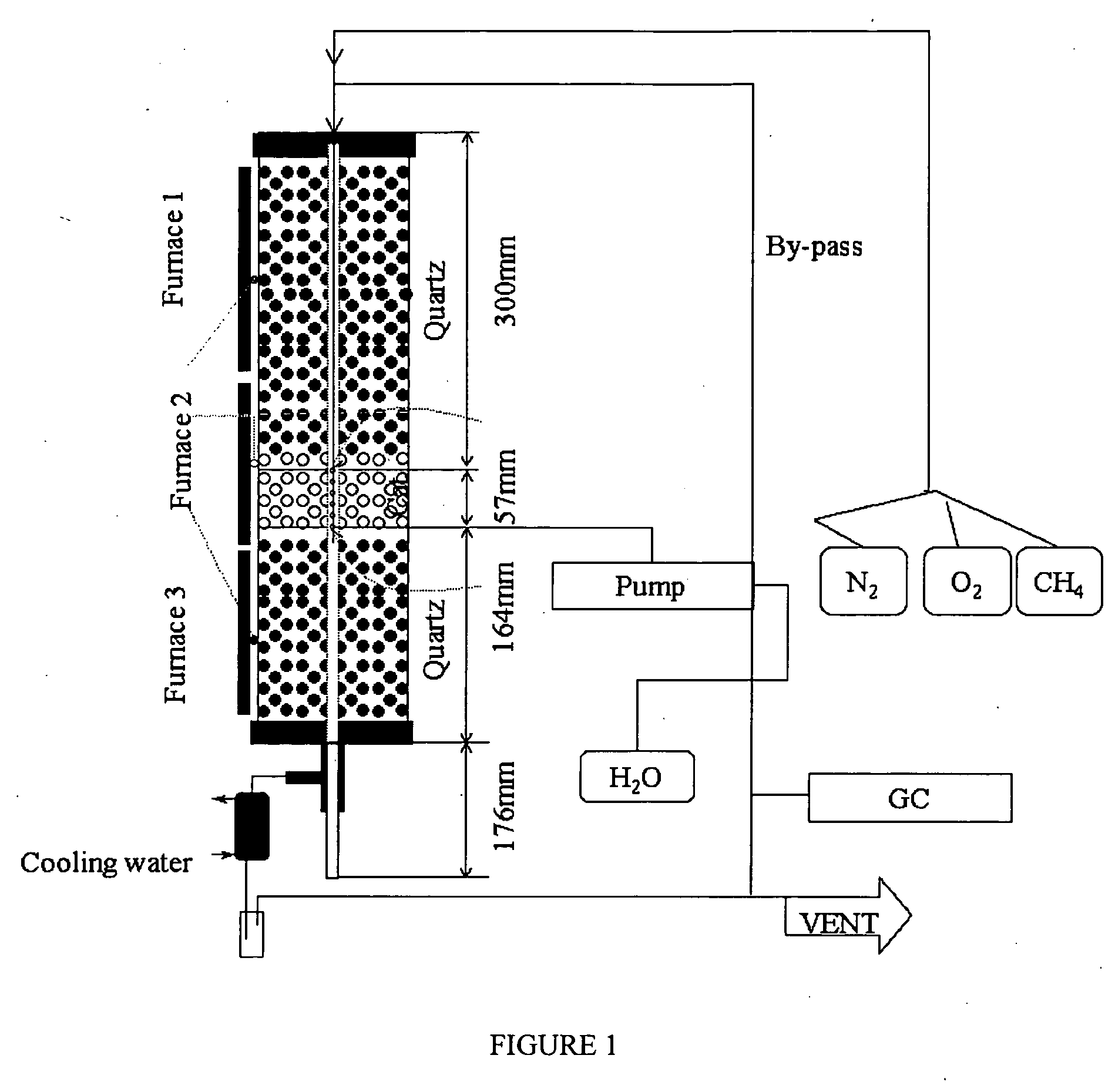
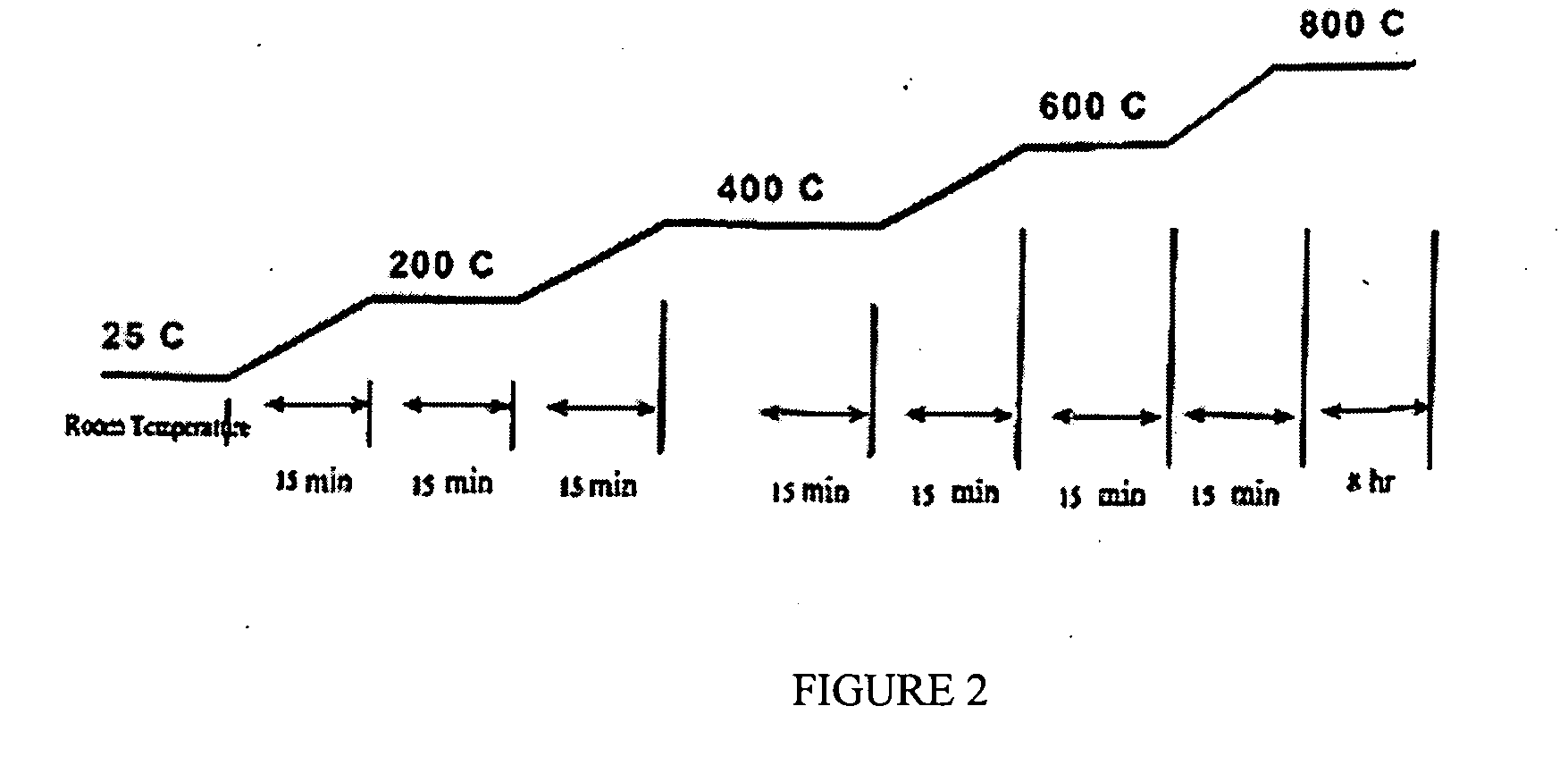
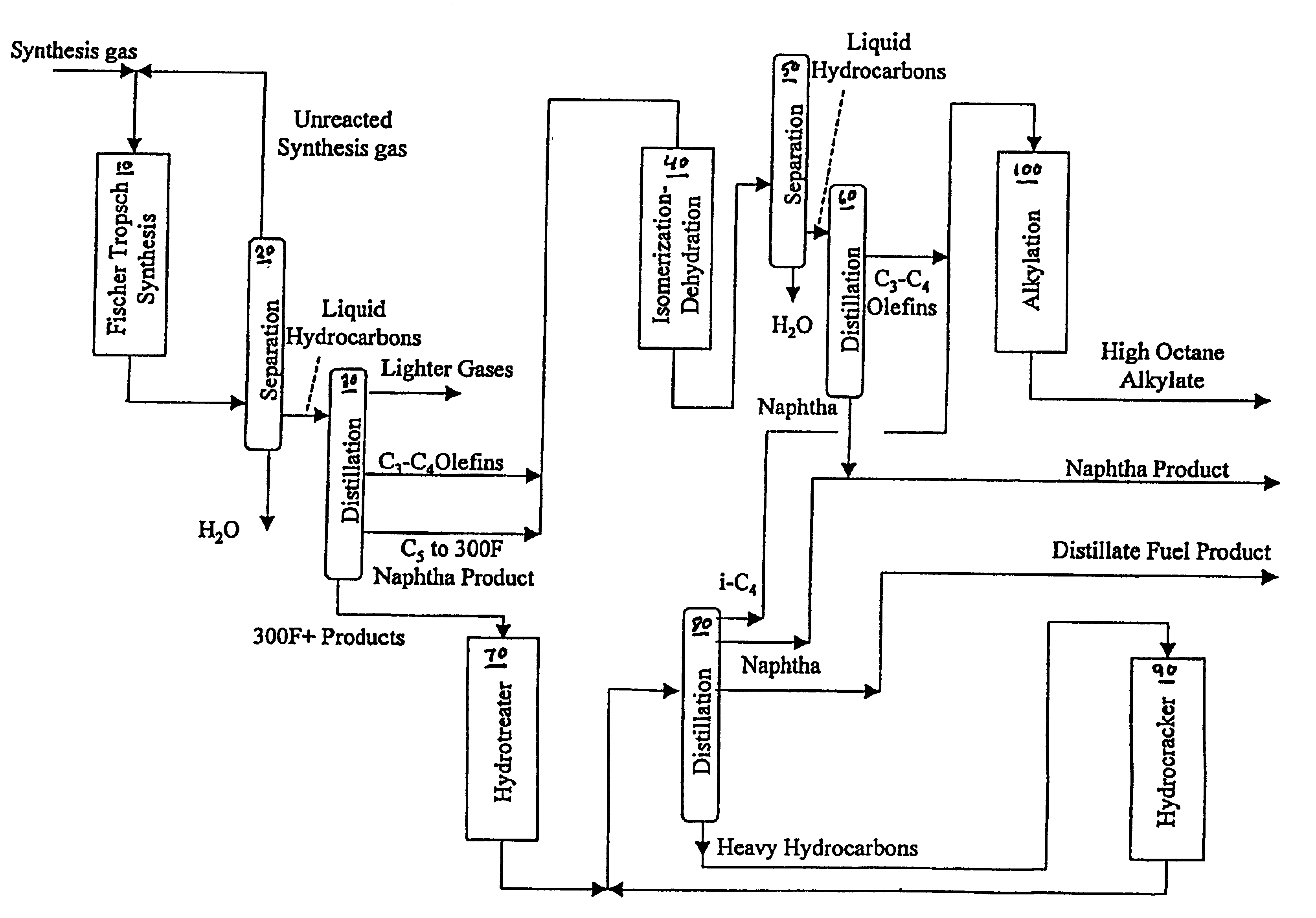
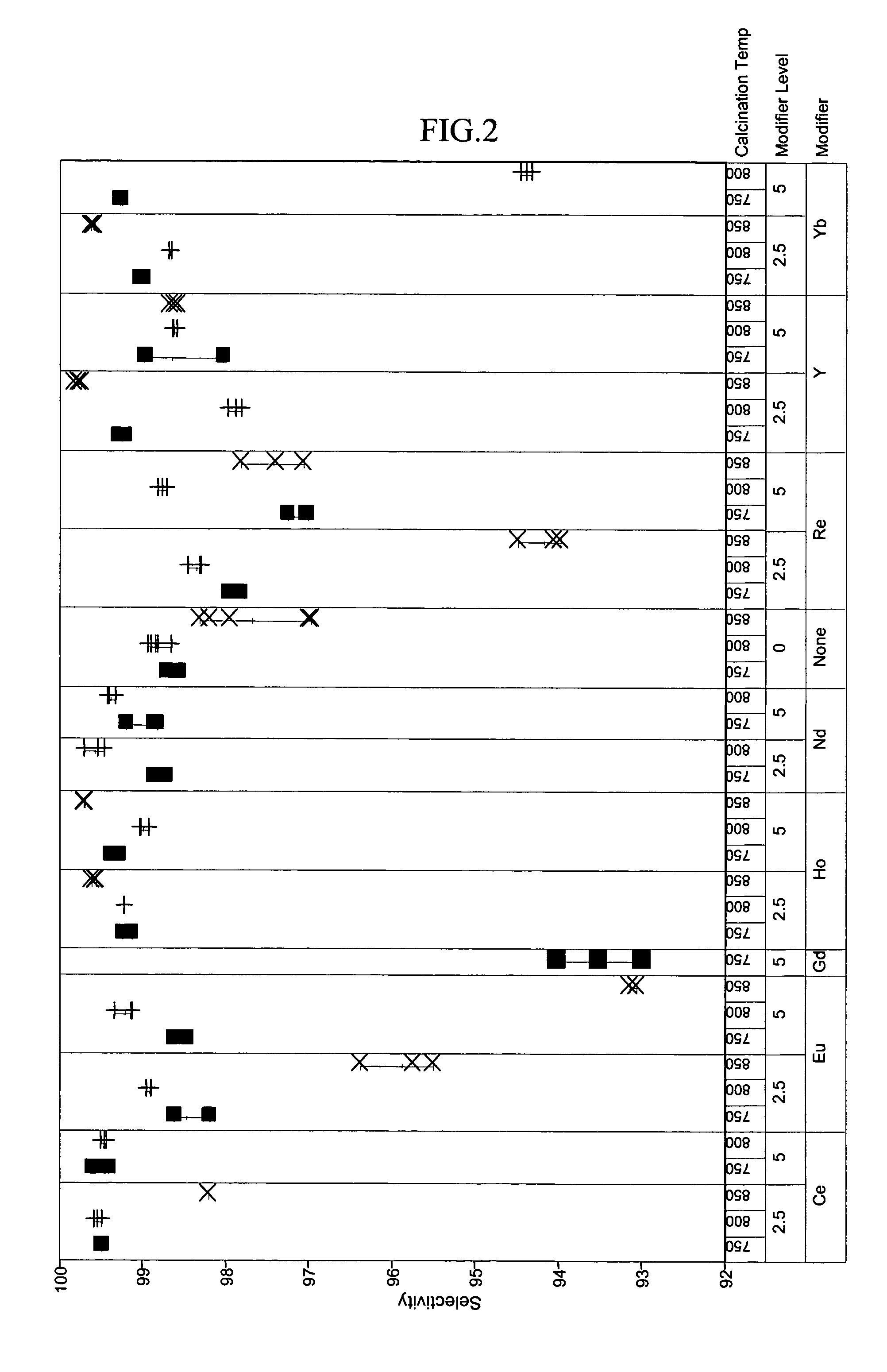
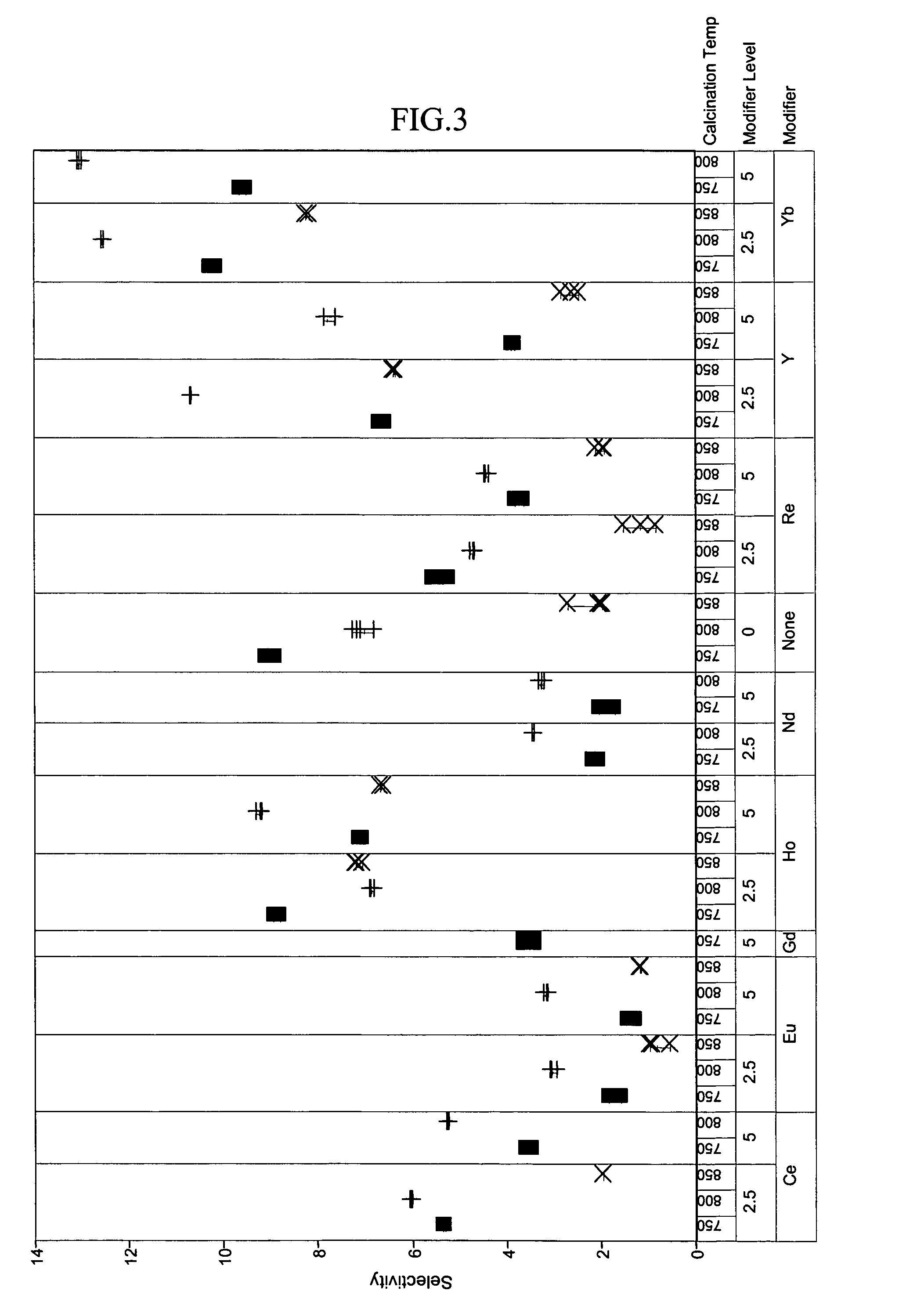
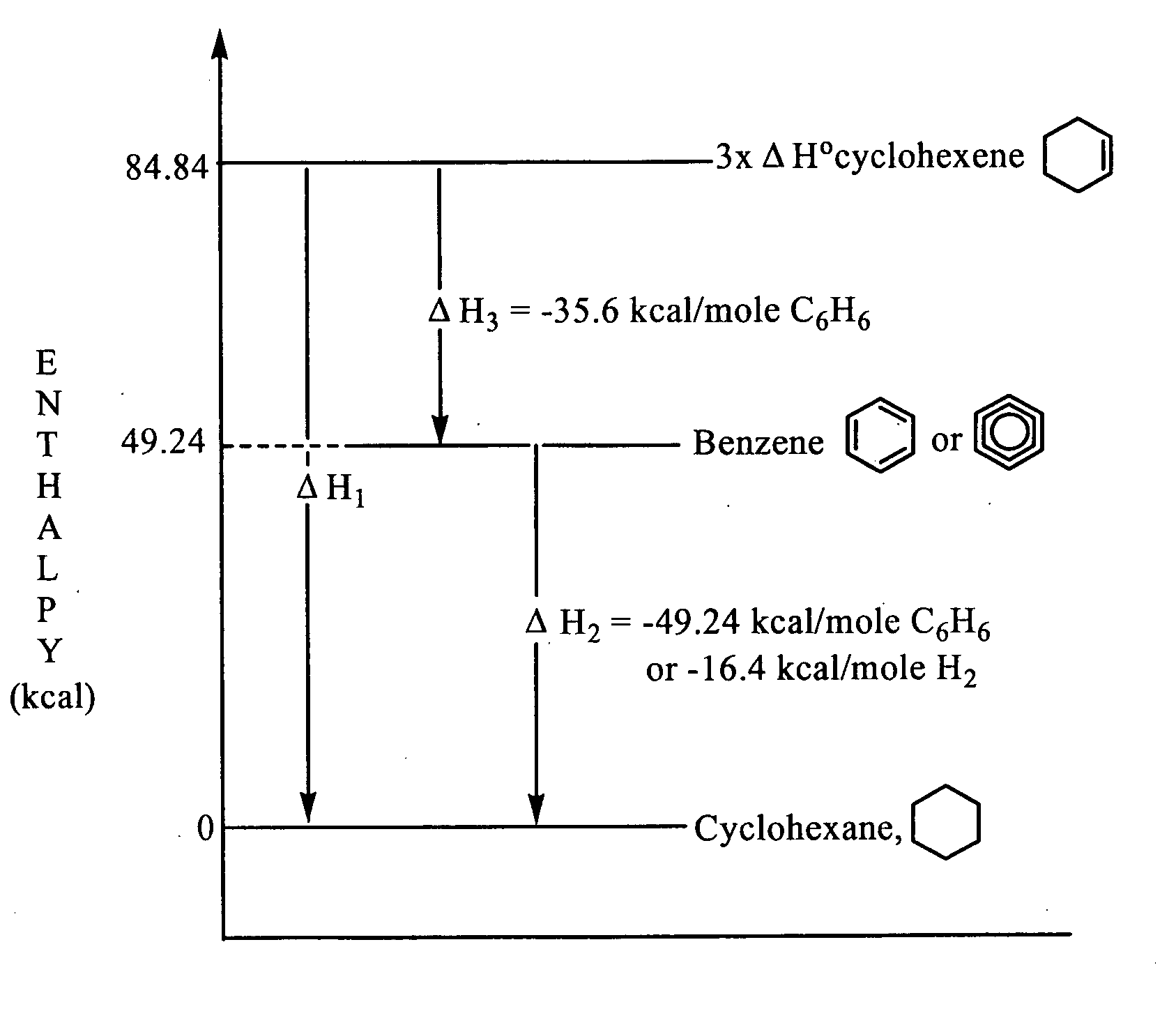
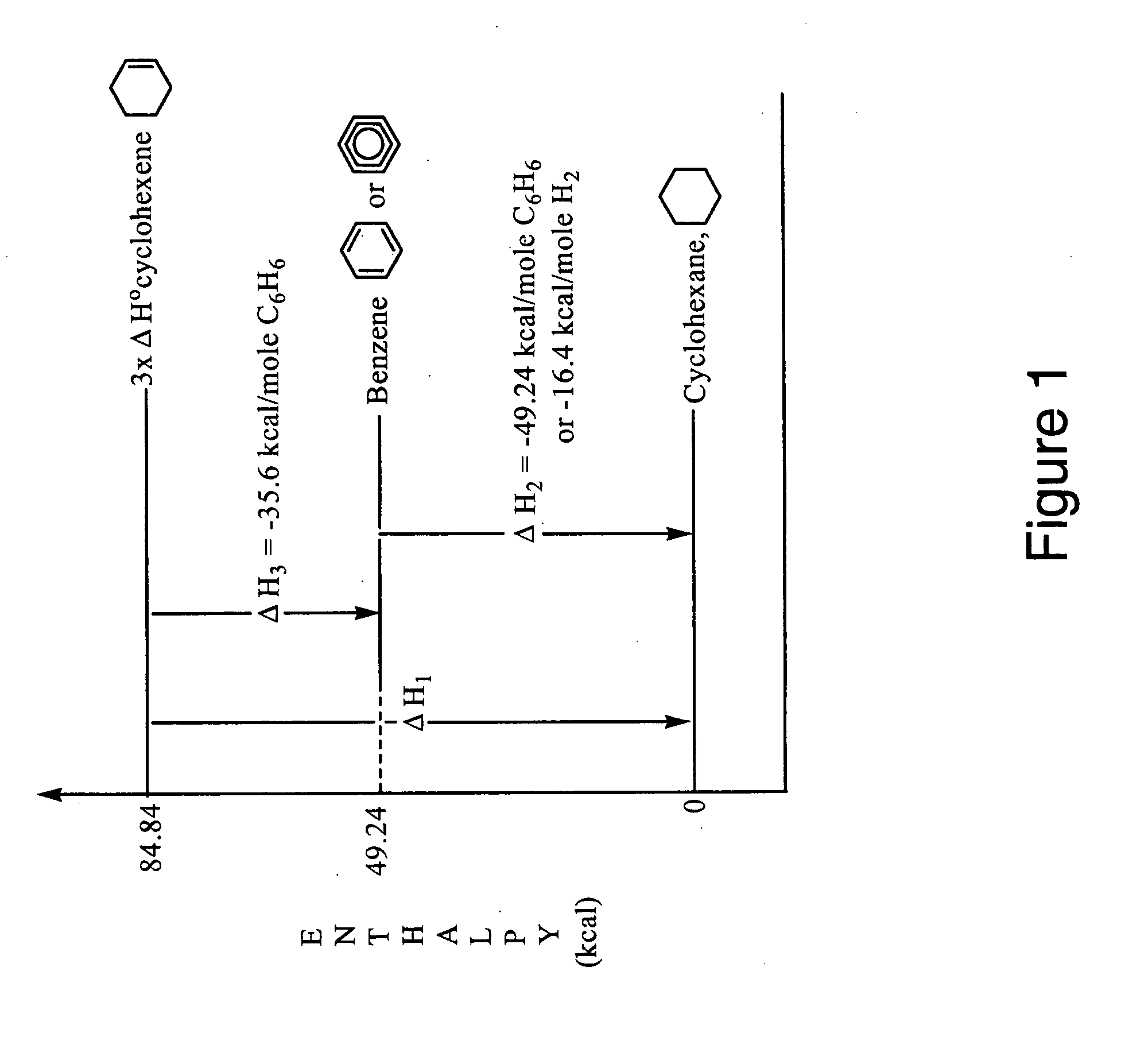
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1321results about "Catalytic naphtha reforming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
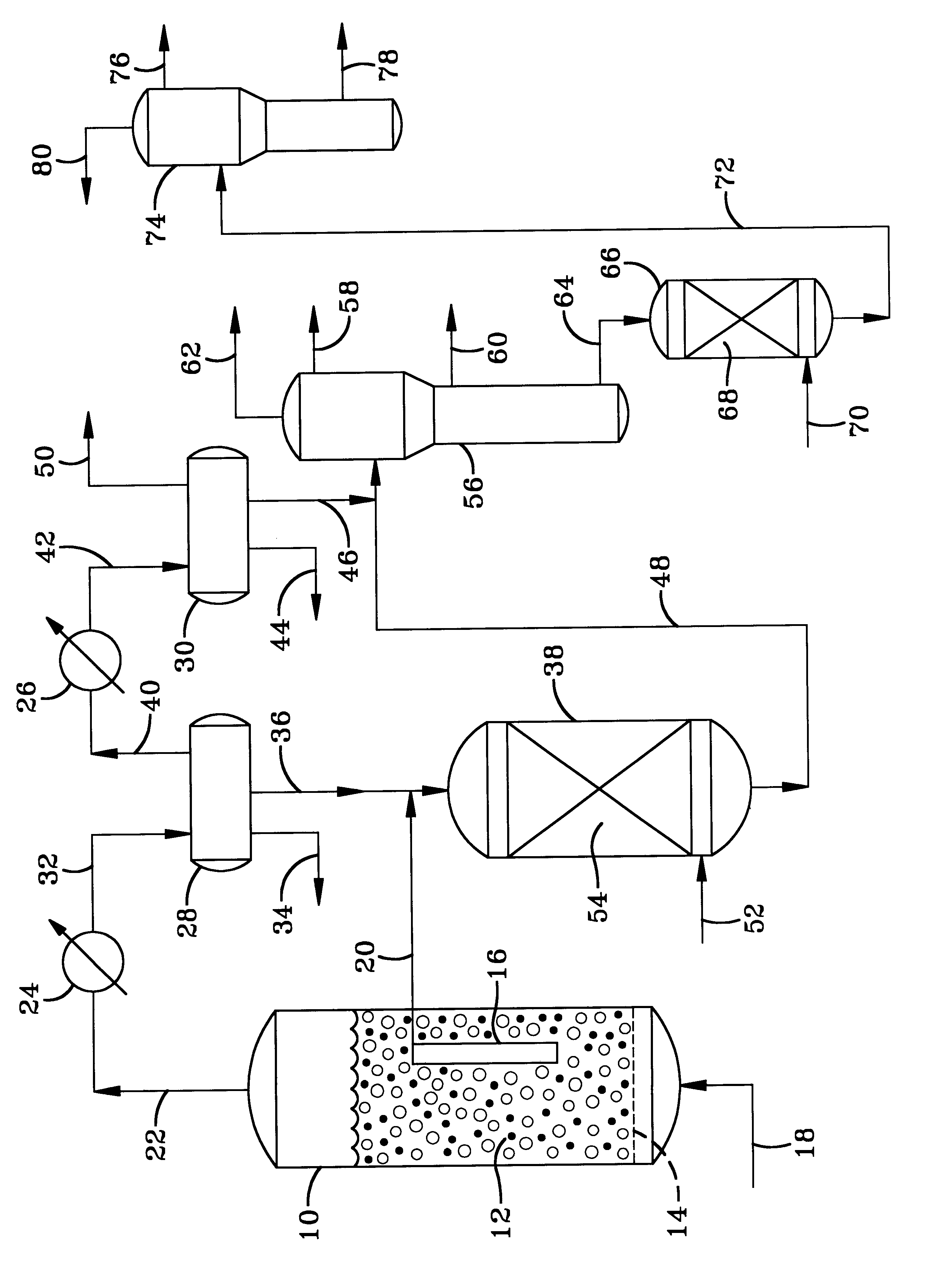
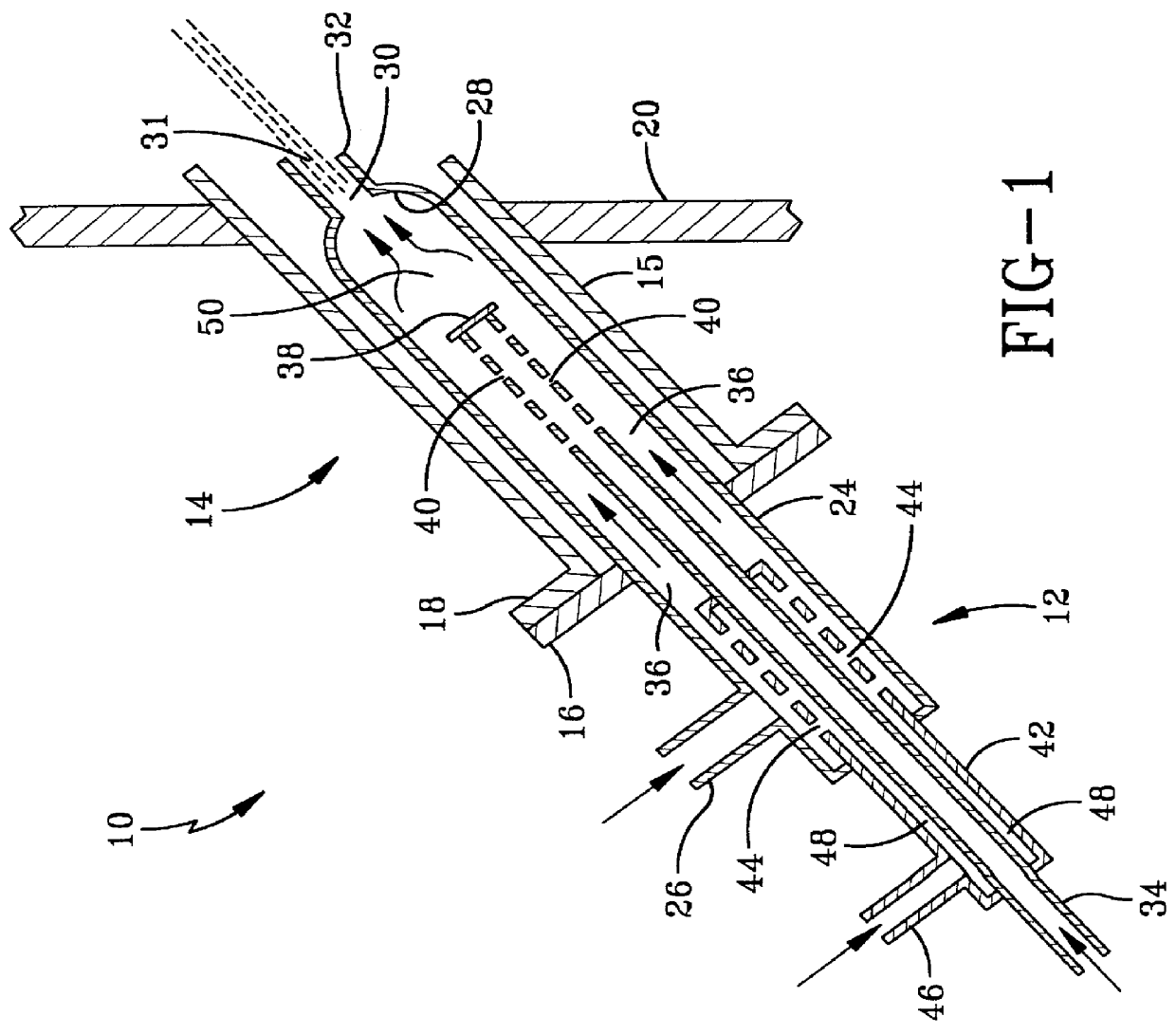
Pre-passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus, and passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus during the initial reacation
ActiveUS20100282645A1Reduce operational riskReduce contentThermal non-catalytic crackingPhysical/chemical process catalystsLiquid productReaction temperature
The present invention relates to a pre-passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus prior to the reaction, or a passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus during the initial reaction, comprising loading a reforming catalyst into the continuous reforming apparatus, starting the gas circulation and raising the temperature of a reactor, injecting sulfide into the gas at a reactor temperature ranging from 100-650° C., controlling the sulfur amount in the recycle gas within a range of 0.5-100×10−6 L / L so as to passivate the apparatus.The process of the present invention may also comprise the following steps:(1) loading a reforming catalyst into the continuous reforming apparatus, starting the gas circulation and raising the temperature of a reactor, feeding the reforming feedstock into the reaction system when the temperature of the reactor is increased to 300-460° C., introducing sulfide into the reaction system while or after the reforming feedstock is fed, controlling the ratio of the total sulfur amount introduced into the system to the reforming feedstock within the range of 0.5 μg / g-50 μg / g, reducing the content of sulfide introduced into the system when hydrogen sulfide concentration in the recycle gas reaches to 2.0 μL / L˜30 μL / L; and(2) maintaining the reforming reactor at a temperature of 460-490° C., controlling the ratio of the total sulfur amount introduced into the system to the reforming feedstock within the range of 0.2 μg / g-0.5 μg / g, adjusting the amount of the reforming feedstock to the design value of the apparatus, increasing the reforming reaction temperature to 490-545° C. according to the requirements on the octane number of the liquid product, and letting the reforming apparatus run under normal operating conditions.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
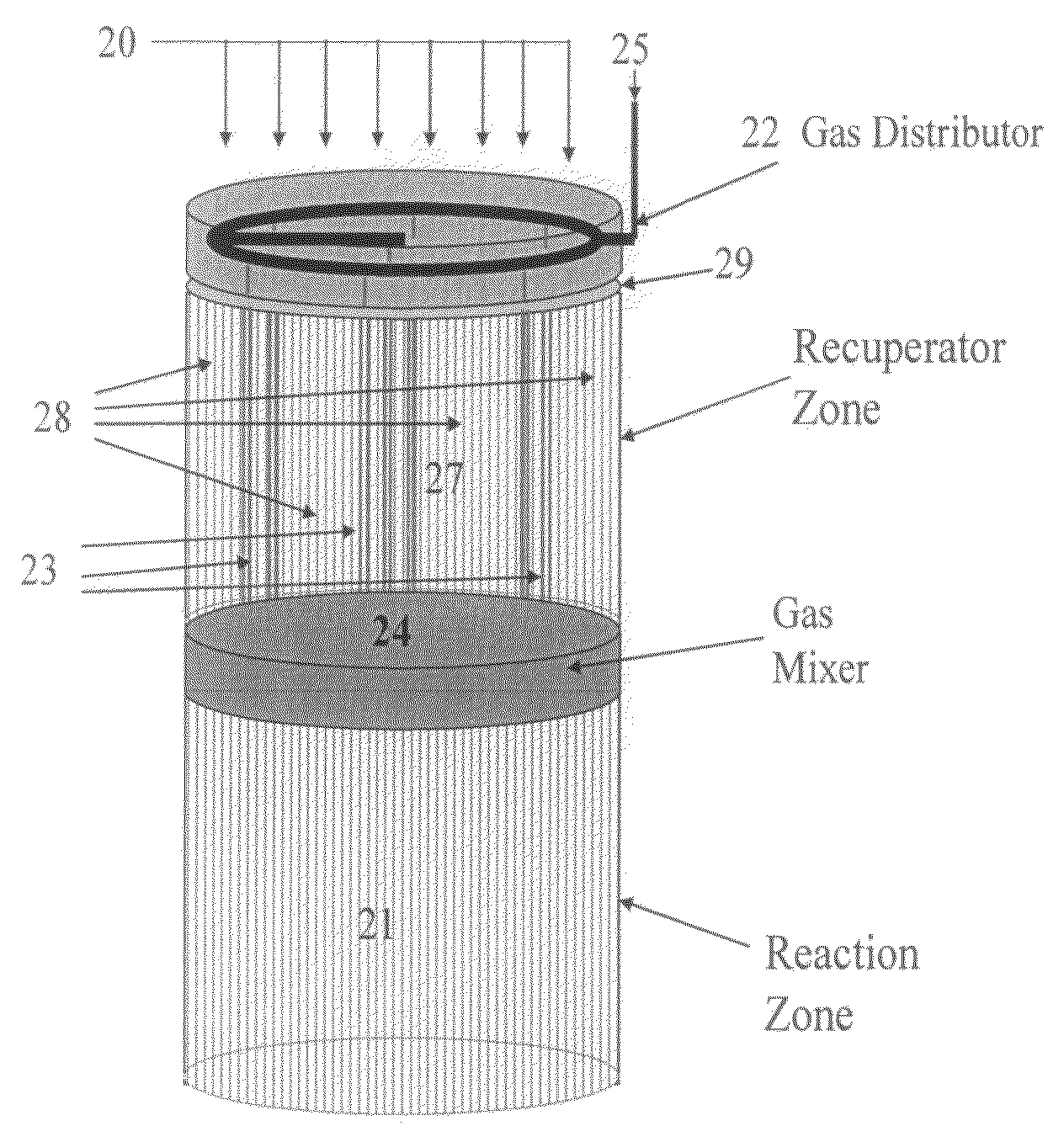
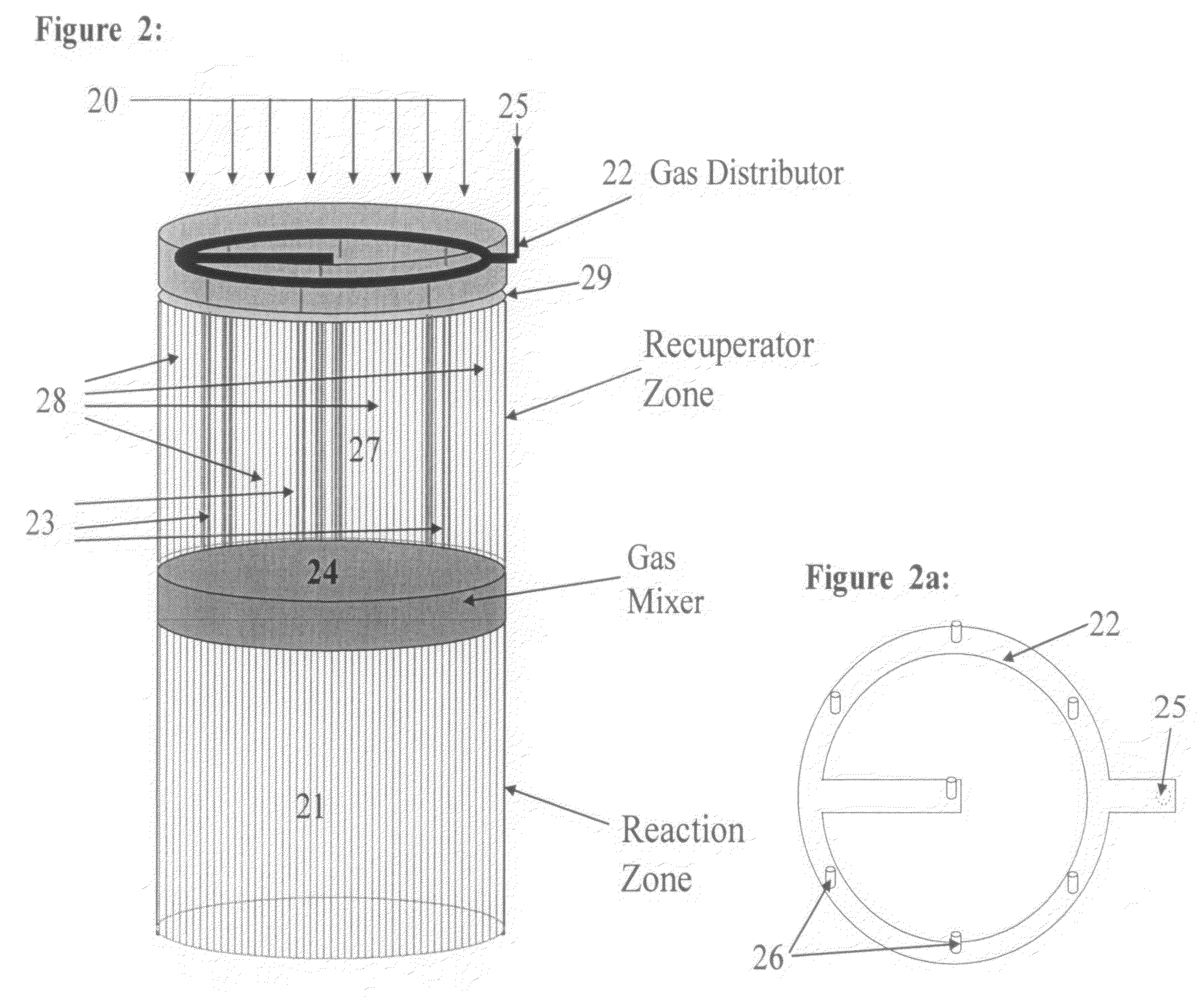
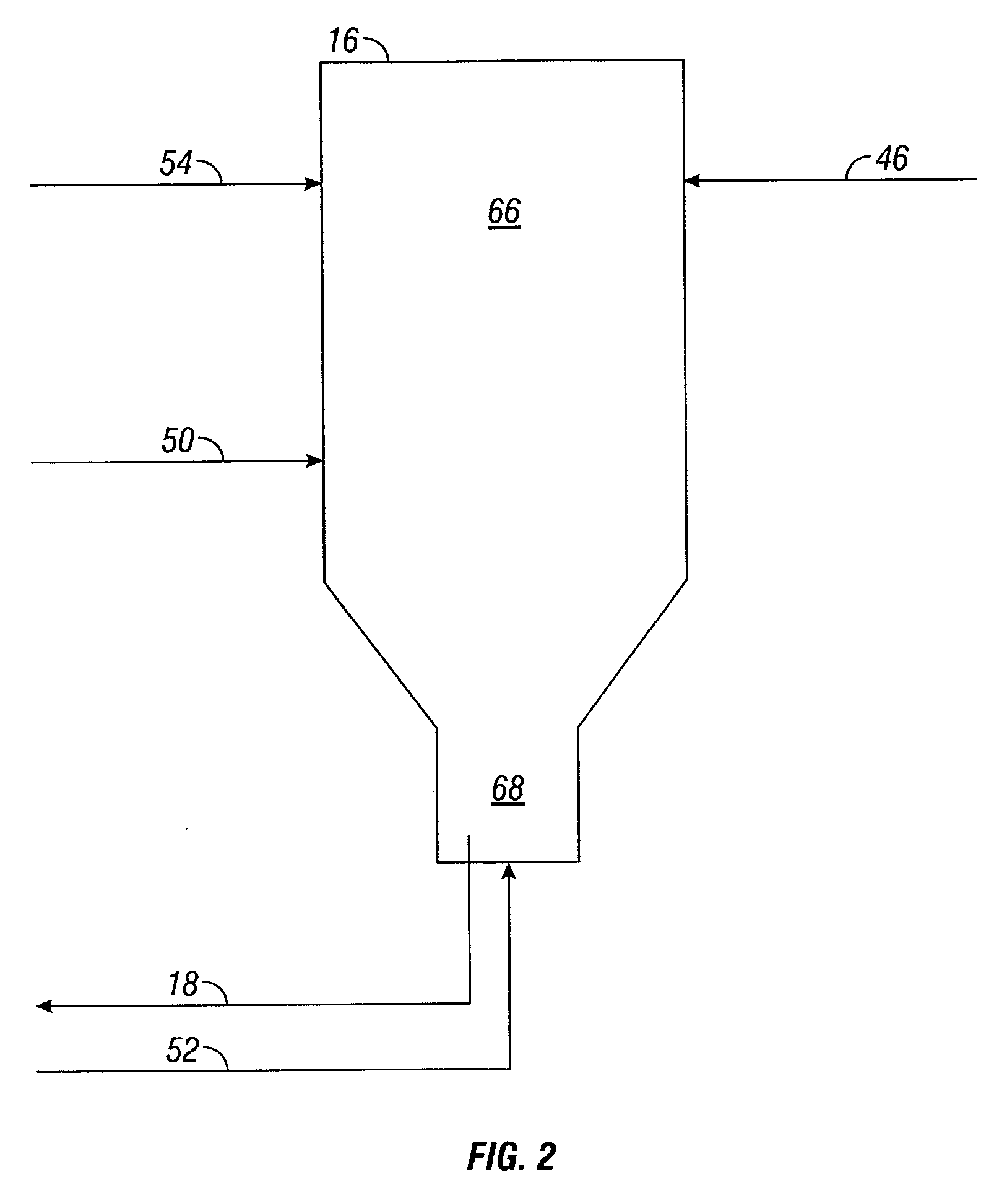
Controlled combustion for regenerative reactors with mixer/flow distributor
ActiveUS7815873B2Efficient transferEvenly distributedHydrocarbon by dehydrogenationFlow mixersReactor systemCombustion
The overall efficiency of a regenerative bed reverse flow reactor system is increased where the location of the exothermic reaction used for regeneration is suitably controlled. The present invention provides a method and apparatus for controlling the combustion to improve the thermal efficiency of bed regeneration in a cyclic reaction / regeneration processes. The process for thermal regeneration of a regenerative reactor bed entails(a) supplying the first reactant through a first channel means in a first regenerative bed and supplying at least a second reactant through a second channel means in the first regenerative bed,(b) combining said first and second reactants by a gas mixing means situated at an exit of the first regenerative bed and reacting the combined gas to produce a heated reaction product,(c) passing the heated reaction product through a second regenerative bed thereby transferring heat from the reaction product to the second regenerative bed.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
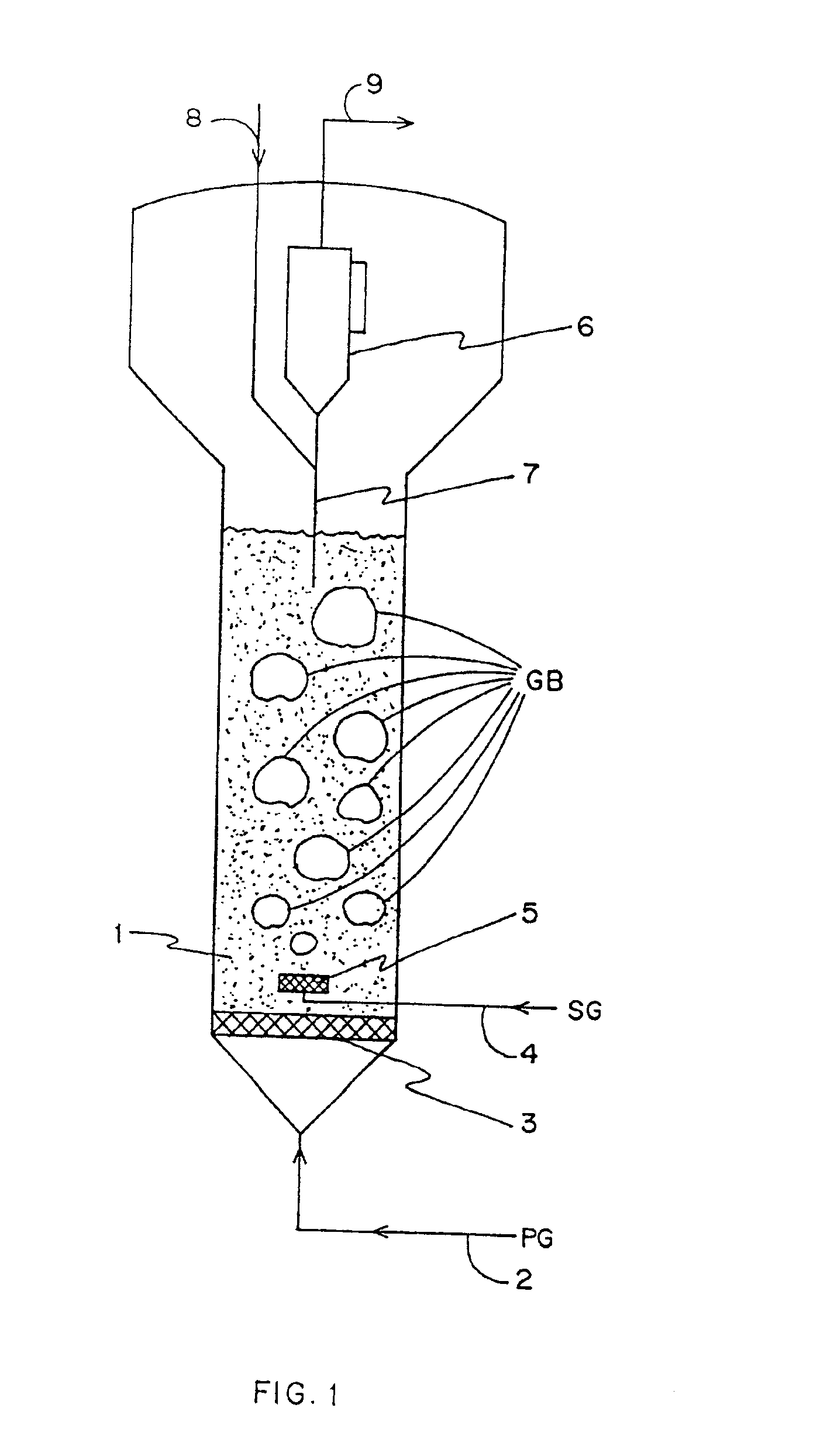
Method for gas-solid contacting in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor
InactiveUS6894183B2Eliminate and drastically reduce bypassEffective contactThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingForming gasSolid particle
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Process for reducing haze point in bright stock
InactiveUS6051129ASuperior lube oil yieldHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrogenHaze
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Catalyst and process of paraffin hydrocarbon conversion
InactiveUS20040077914A1Improve solubilityEasy to useHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationAlkanePtru catalyst
A catalyst composition and process for the conversion of linear and / or branched paraffin hydrocarbons based on the use of an ionic liquid catalyst in combination with a Brønsted Acid, which provides a catalytic composition with an increased activity compared with said ionic liquid. Under suitable reaction conditions this conversion is leading to paraffin hydrocarbon fraction with higher octane number.
Owner:HALDOR TOPSOE AS
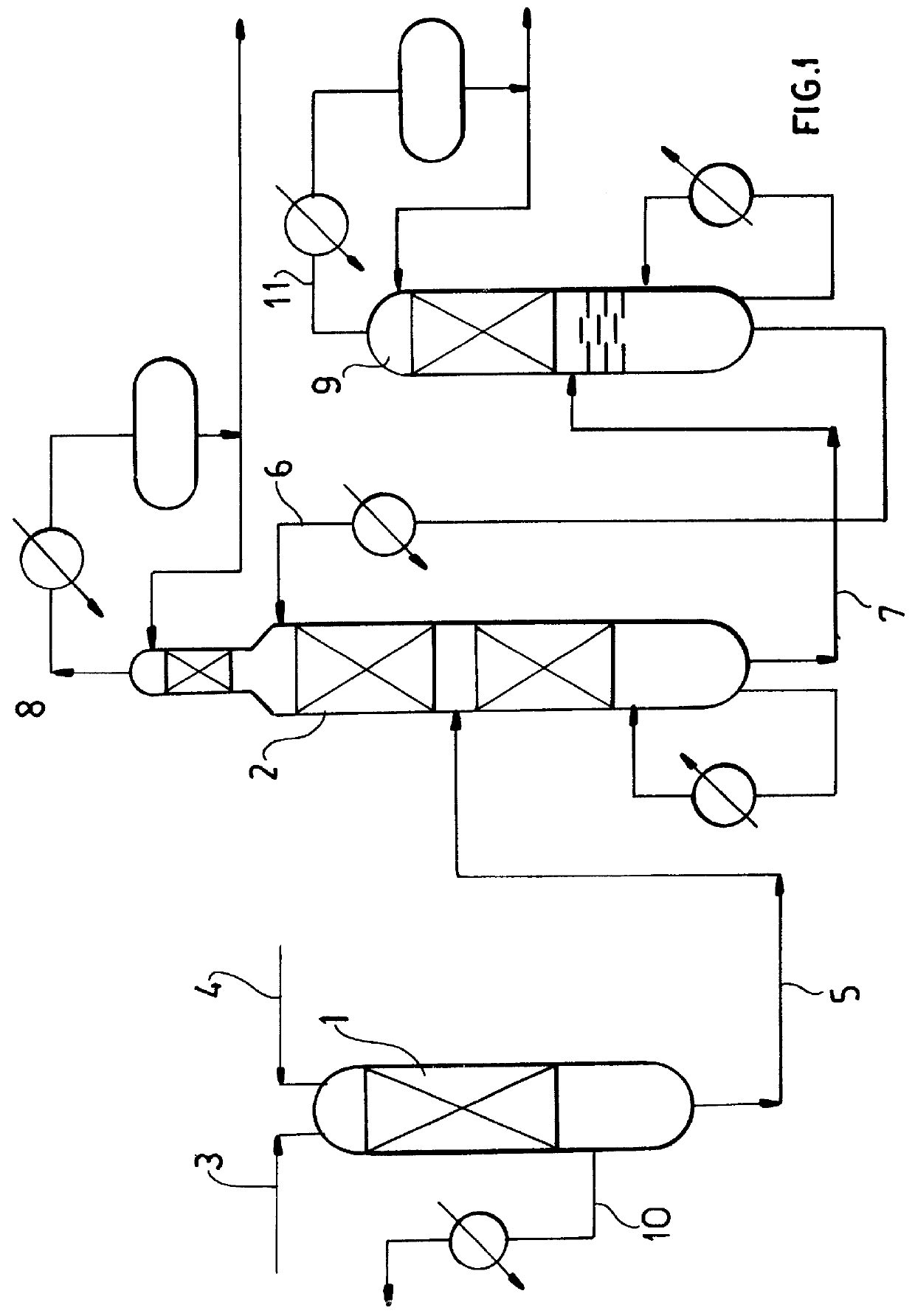
Device for injecting and mixing fluids in a downward-flow reactor
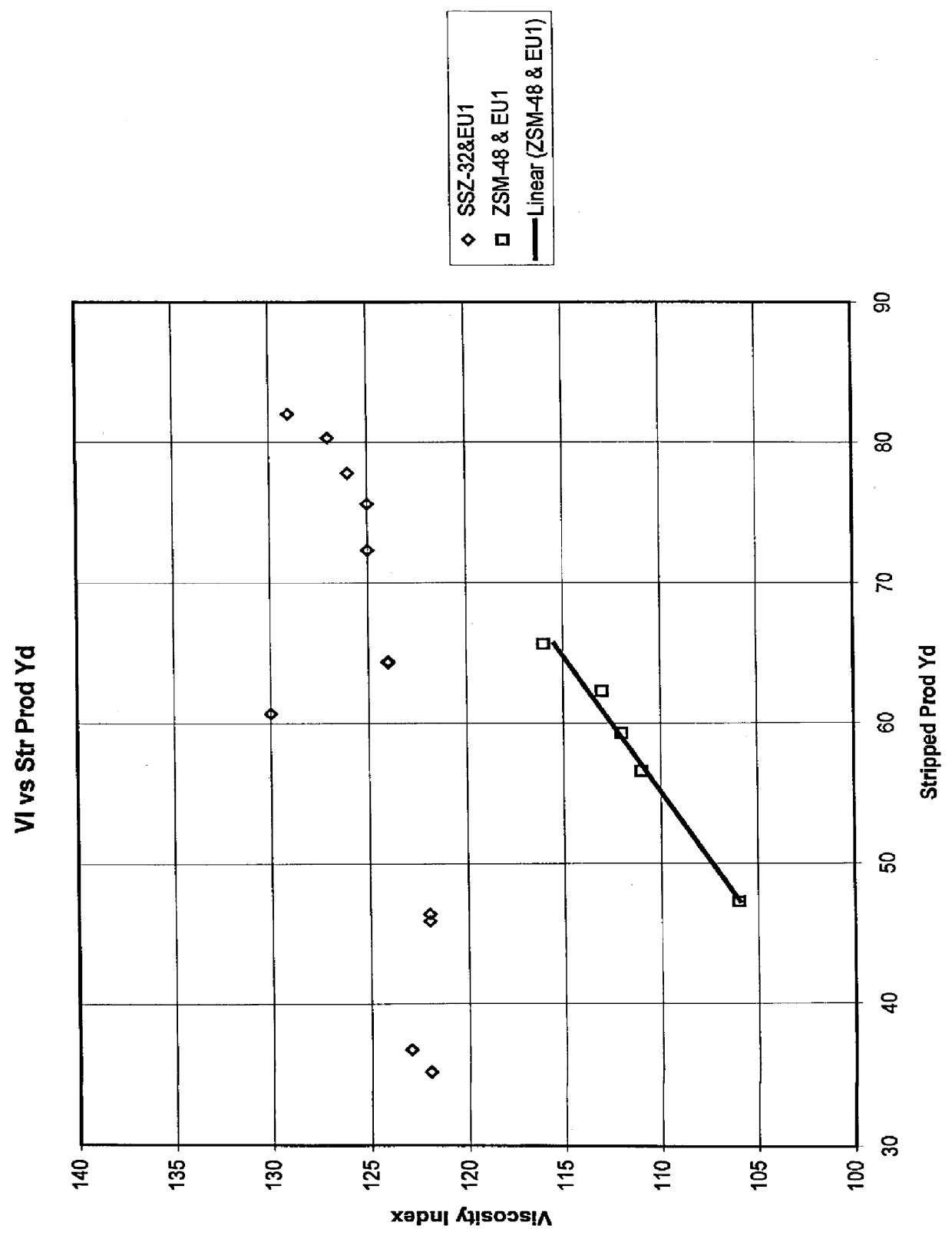
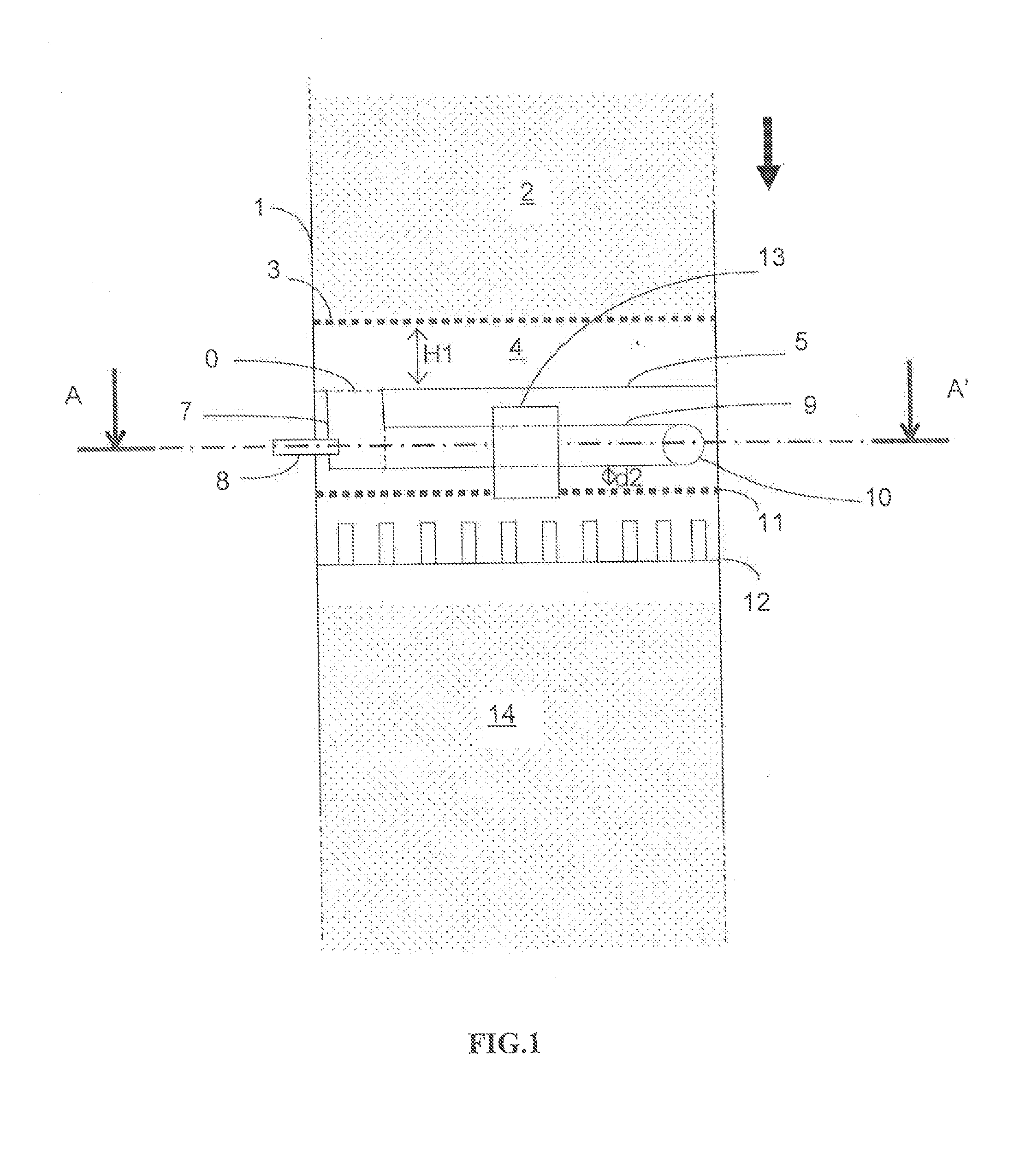
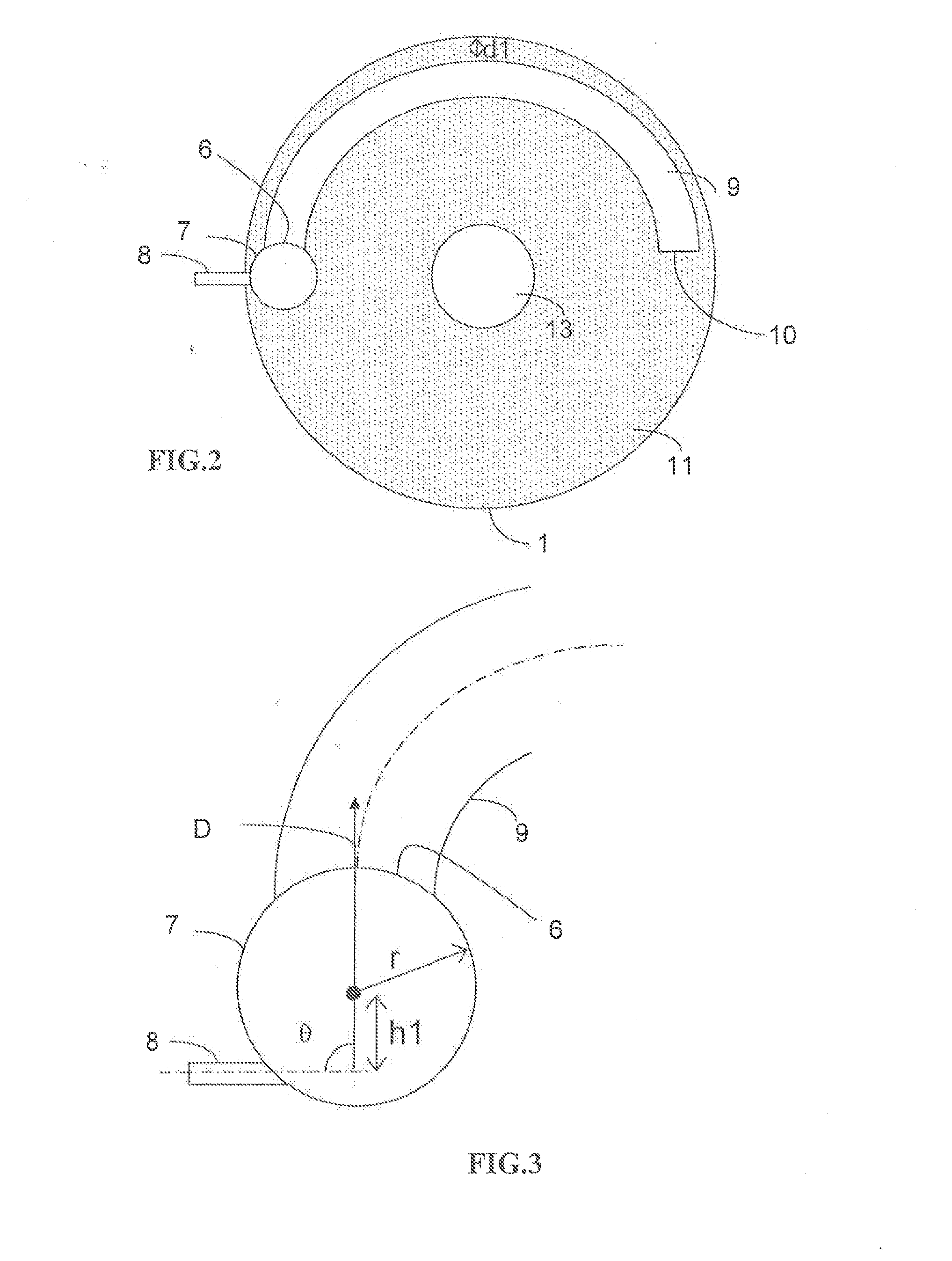
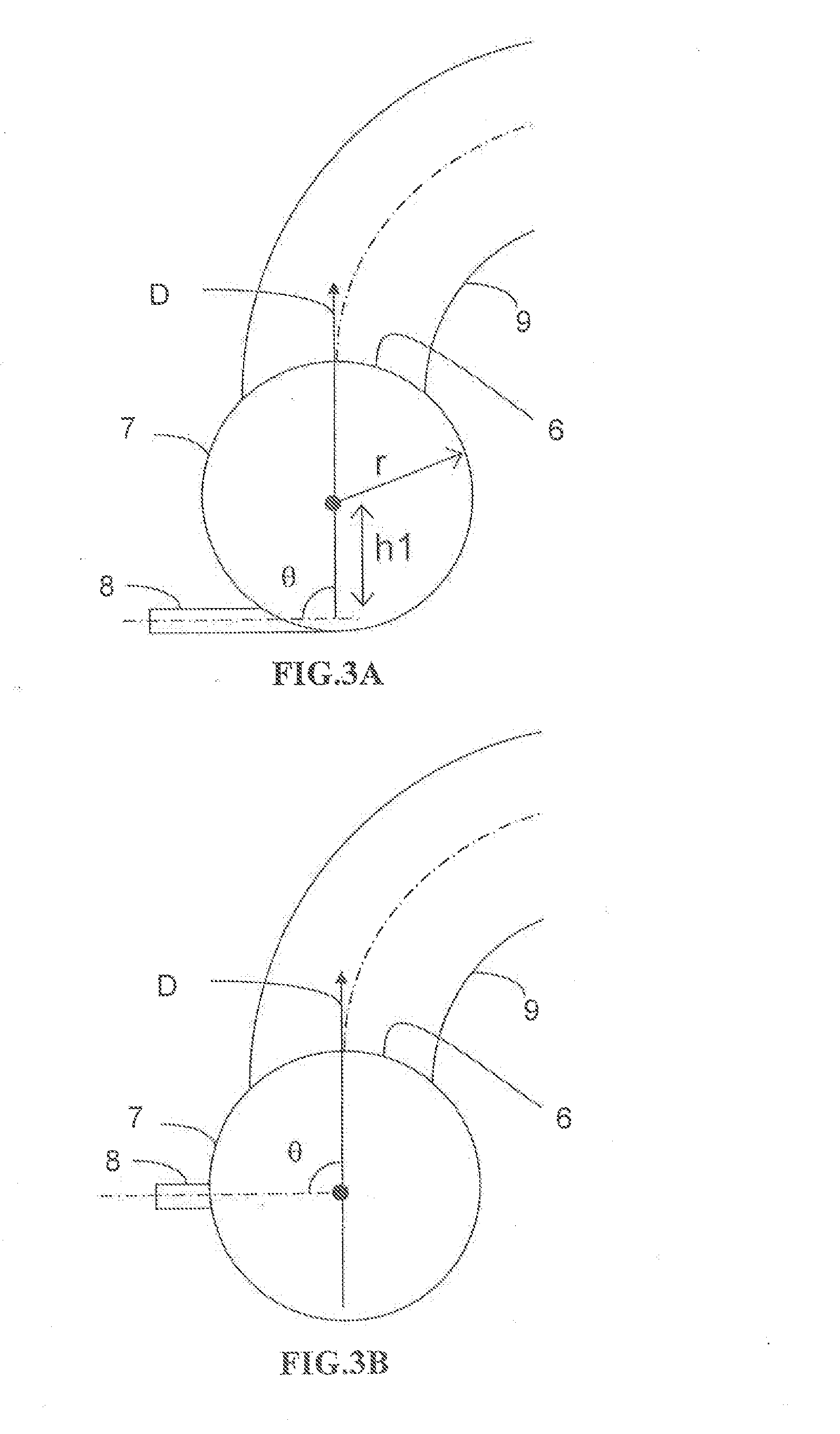
The catalytic reactor with downward flow comprises a chamber (1) containing at least two solid catalyst beds (2; 11) separated by an intermediate zone comprising an essentially horizontal collecting plate (5) communicating with a vertical collecting pipe (7) for receiving fluids collected by the collecting plate, with a means for injecting a quenching fluid (8) emptying into the collecting pipe. An annular mixing chamber (9) is located below the collecting plate (5). A predistribution plate (11) is arranged below the chamber (9).The injection means (8) comprises a tubular portion that empties into the collecting pipe (7) in such a way as to inject quenching fluid in a direction forming an angle θ between 45° and 135° with the direction D from the axis of the mixing chamber measured at its input end.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Isoparaffinic base stocks by dewaxing fischer-tropsch wax hydroisomerate over Pt/H-mordenite
A high VI and low pour point lubricant base stock is made by hydroisomerizing a high purity, waxy, paraffinic Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon fraction having an initial boiling point in the range of 650-750° F., followed by catalytically dewaxing the hydroisomerate using a dewaxing catalyst comprising a catalytic platinum component and an H-mordenite component. The hydrocarbon fraction is preferably synthesized by a slurry Fischer-Tropsch using a catalyst containing a catalytic cobalt component. This combination of the process, high purity, waxy paraffinic feed and the Pt / H-mordenite dewaxing catalyst, produce a relatively high yield of premium lubricant base stock.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
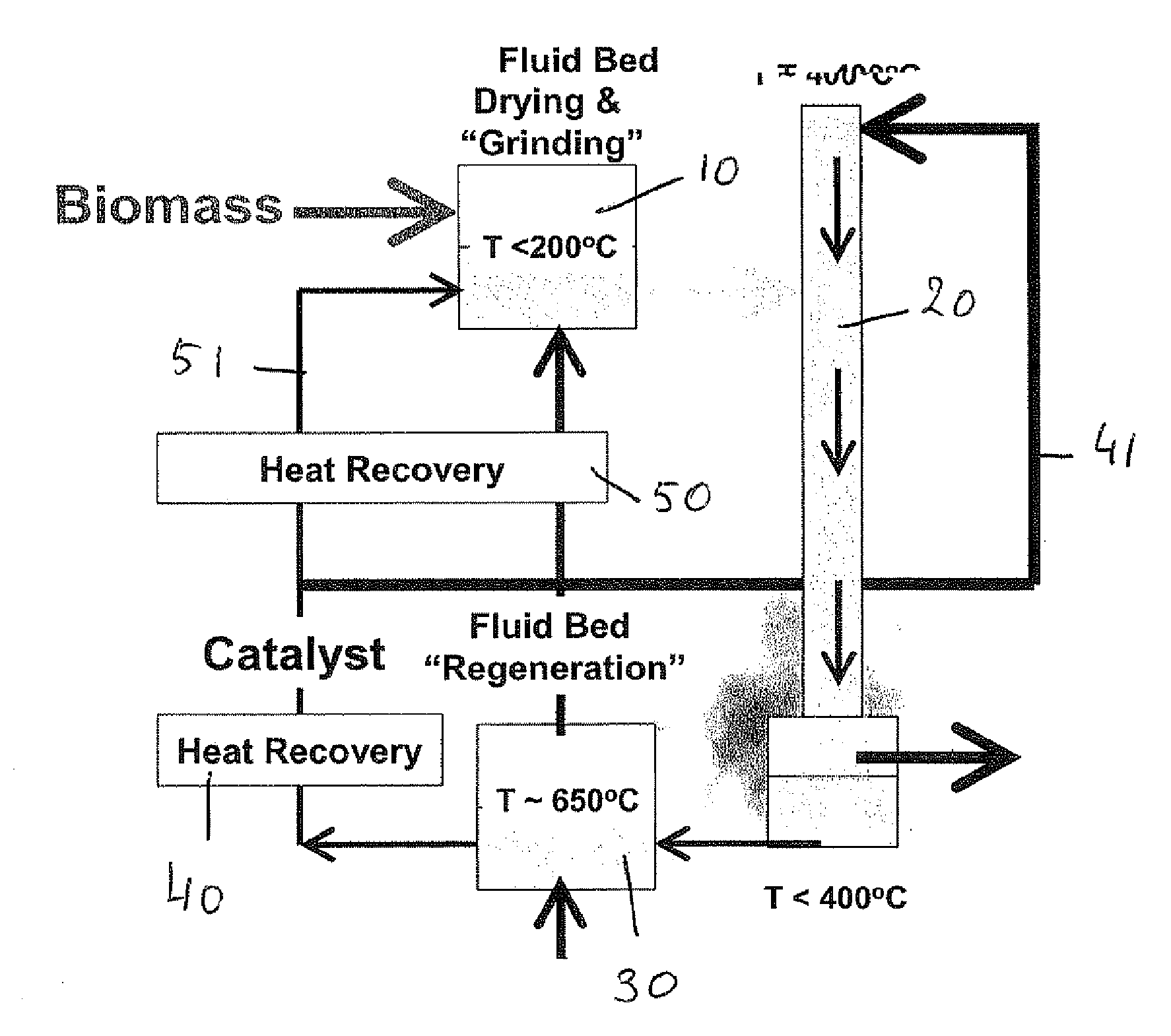
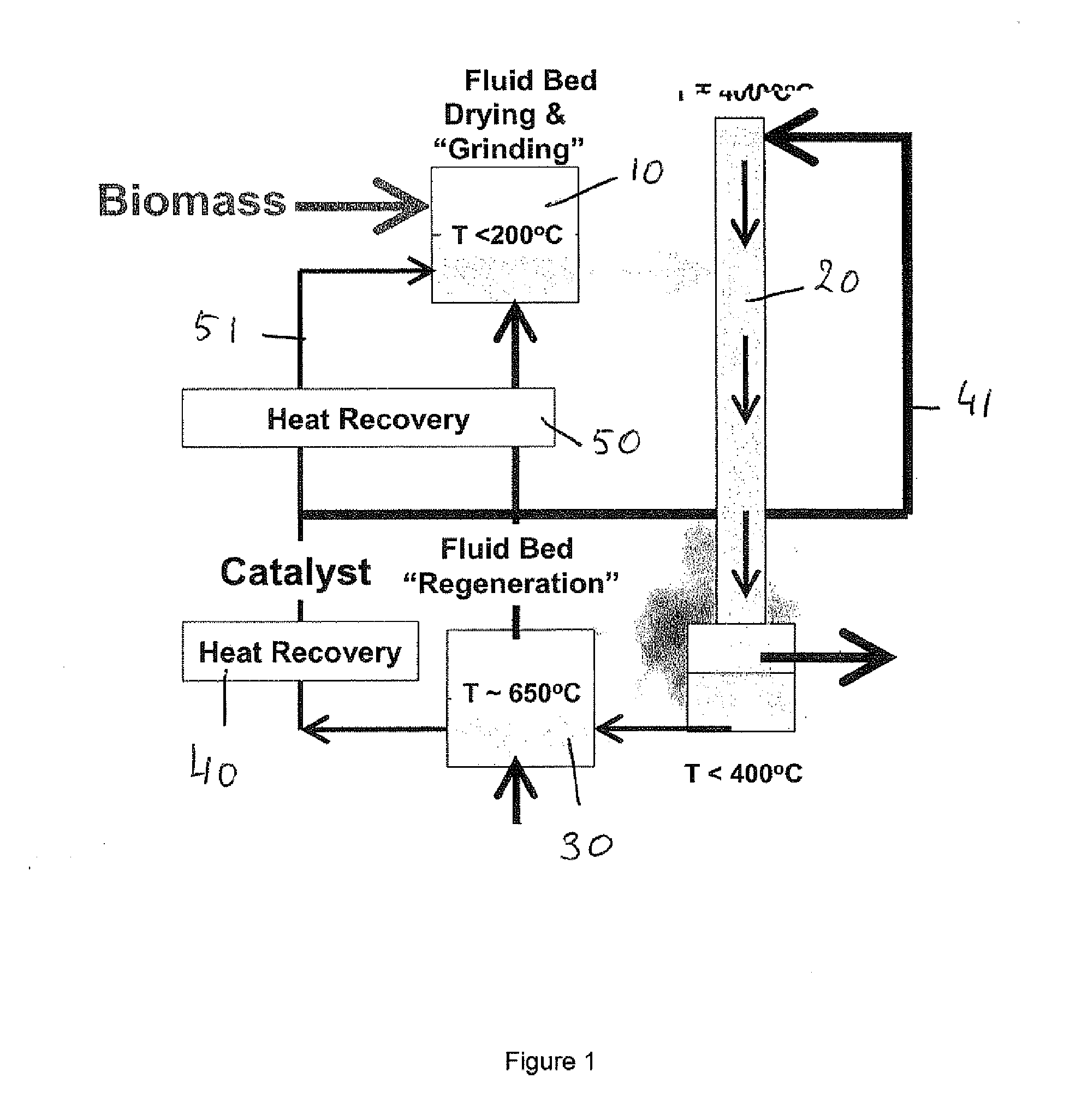
Process for converting carbon-based energy carrier material
InactiveUS20090308787A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
A process is disclosed process for converting a solid or highly viscous carbon-based energy carrier material to liquid and gaseous reaction products, said process comprising the steps of: a) contacting the carbon-based energy carrier material with a particulate catalyst material b) converting the carbon-based energy carrier material at a reaction temperature between 200° C. and 450° C., preferably between 250° C. and 350° C., thereby forming reaction products in the vapor phase. In a preferred embodiment the process comprises the additional step of: c) separating the vapor phase reaction products from the particulate catalyst material within 10 seconds after said reaction products are formed; In a further preferred embodiment step c) is followed by: d) quenching the reaction products to a temperature below 200° C.
Owner:MARD INC
Preparation of olefins
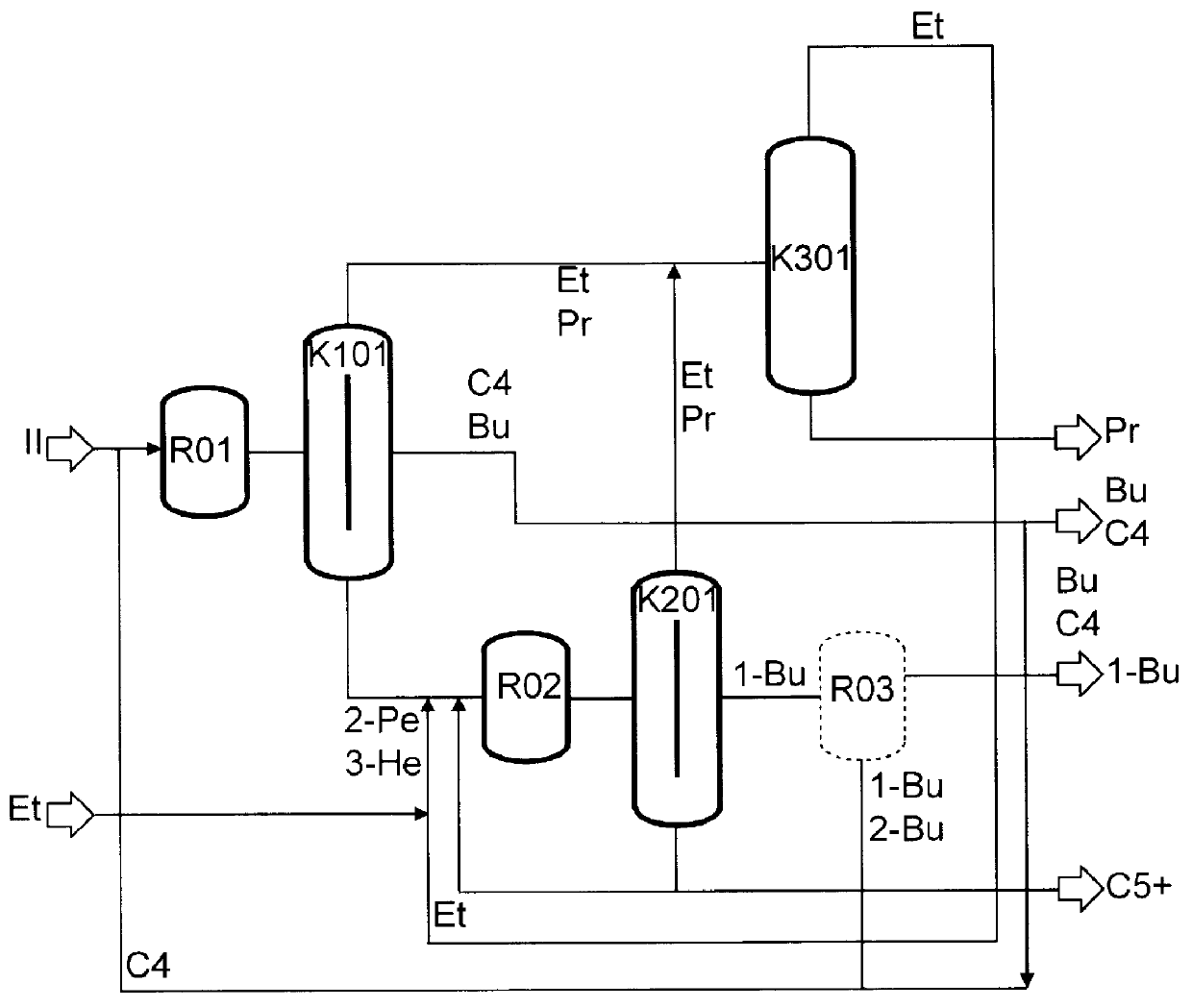
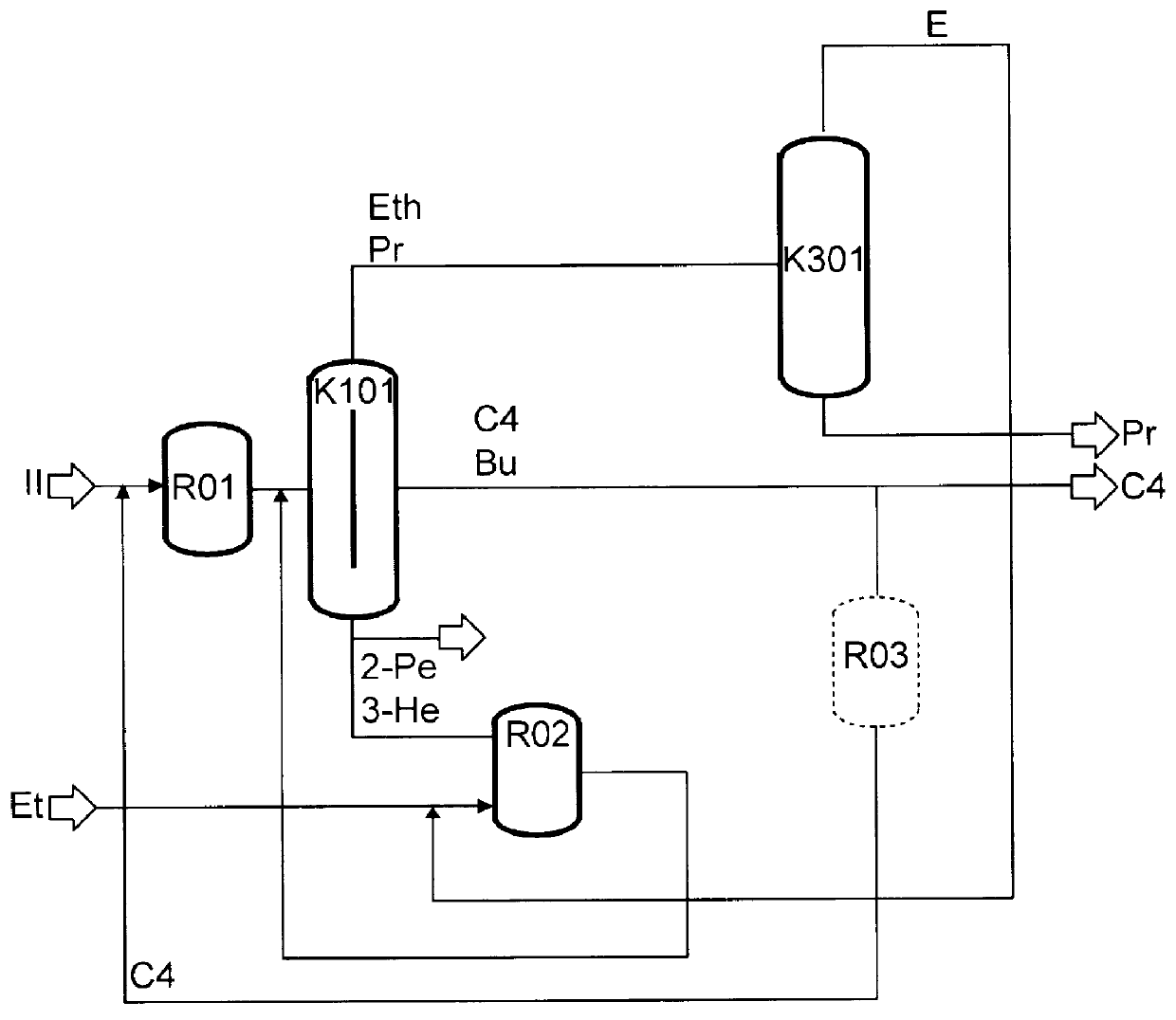
The preparation of olefins from steam cracker or refinery C4 streams is carried out by selective hydrogenation of butadienes and acetylenic impurities in the steam cracker or refinery C4 stream, with simultaneous or subsequent, at least partial isomerization of 1-butene to 2-butene, followed by removal of i-butene from the C4 stream by reaction with an alcohol to form an ether, followed by removal of oxygen-containing impurities from the C4 stream using adsorber materials, followed by two-stage metathesis of the butenes in the C4 stream by conversion of 1-butene and 2-butene present in the C4 stream into propene and 2-pentene and subsequent reaction of the 2-pentene with ethene in the presence of a metathesis catalyst to form propene and 1-butene. Optionally, butadiene may be removed from the C4 stream by extractive distillation in a preliminary step.
Owner:BASF AG
Method and apparatus for making a middle distillate product and lower olefins from a hydrocarbon feedstock
ActiveUS20060178546A1Yield maximizationCatalytic crackingCatalytic naphtha reformingPetroleum productGasoline
Disclosed is a process for making middle distillate and lower olefins. The process includes catalytically cracking a gas oil feedstock within a riser reactor zone by contacting under suitable catalytic cracking conditions within the riser reactor zone the gas oil feedstock with a middle distillate selective cracking catalyst that comprises amorphous silica alumina and a zeolite to yield a cracked gas oil product and a spent cracking catalyst. The spent cracking catalyst is regenerated to yield a regenerated cracking catalyst. Within an intermediate cracking reactor such as a dense bed reactor zone and under suitable high severity cracking conditions a gasoline feedstock is contacted with the regenerated cracking catalyst to yield a cracked gasoline product and a used regenerated cracking catalyst. The used regenerated cracking catalyst is utilized as the middle distillate selective catalyst.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Catalytic process for converting renewable resources into paraffins for use as diesel blending stocks
A process for converting renewable resources such as vegetable oil and animal fat into paraffins in a single step which comprises contacting a feed which is a renewable resources with hydrogen and a catalyst which comprises a non-precious metal and an oxide to produce a hydrocarbon product having a ratio of odd-numbered hydrocarbons to even-numbered hydrocarbons of at least 2:1.
Owner:REFINING TECH SOLUTIONS LLC
FCC feed injection using subcooled water sparging for enhanced feed atomization
Atomization of a high boiling point, hot liquid, such as a hydrocarbon feed oil for a fluid cat cracker, is enhanced by injecting subcooled water into the hot liquid, to form a two-phase fluid of the liquid and steam, upstream of the atomization. The hot liquid is at conditions of temperature and pressure effective for the injected, subcooled water to vaporize into steam, when the water contacts it. Typically this means that the hot liquid is hotter and at a lower pressure than the water. In an FCC process, the subcooled water is sparged into the flowing hot oil in a conduit in a riser feed injector. This produces a spray of hot oil in the riser reaction zone in which the oil drops are smaller and more uniformly distributed in the spray.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Low pressure process for the hydroconversion of heavy hydrocarbons
PCT No. PCT / US97 / 02409 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 19, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 19, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 14, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 29841 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 21, 1997This invention relates to a process of catalytic hydroconversion of a heavy hydrocarbon oil containing a substantial portion of components having an atmospheric boiling point above 565 DEG C. to give a product hydrocarbon oil containing components having a boiling point below about 565 DEG C. The process includes steps of mixing a heavy hydrocarbon oil with an oil soluble molybdenum compound, introducing the resulting mixture into a hydroconversion zone, introducing a reactor feed gas into the hydroconversion zone, and recovering the product hydrocarbon oil from the hydroconversion zone.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
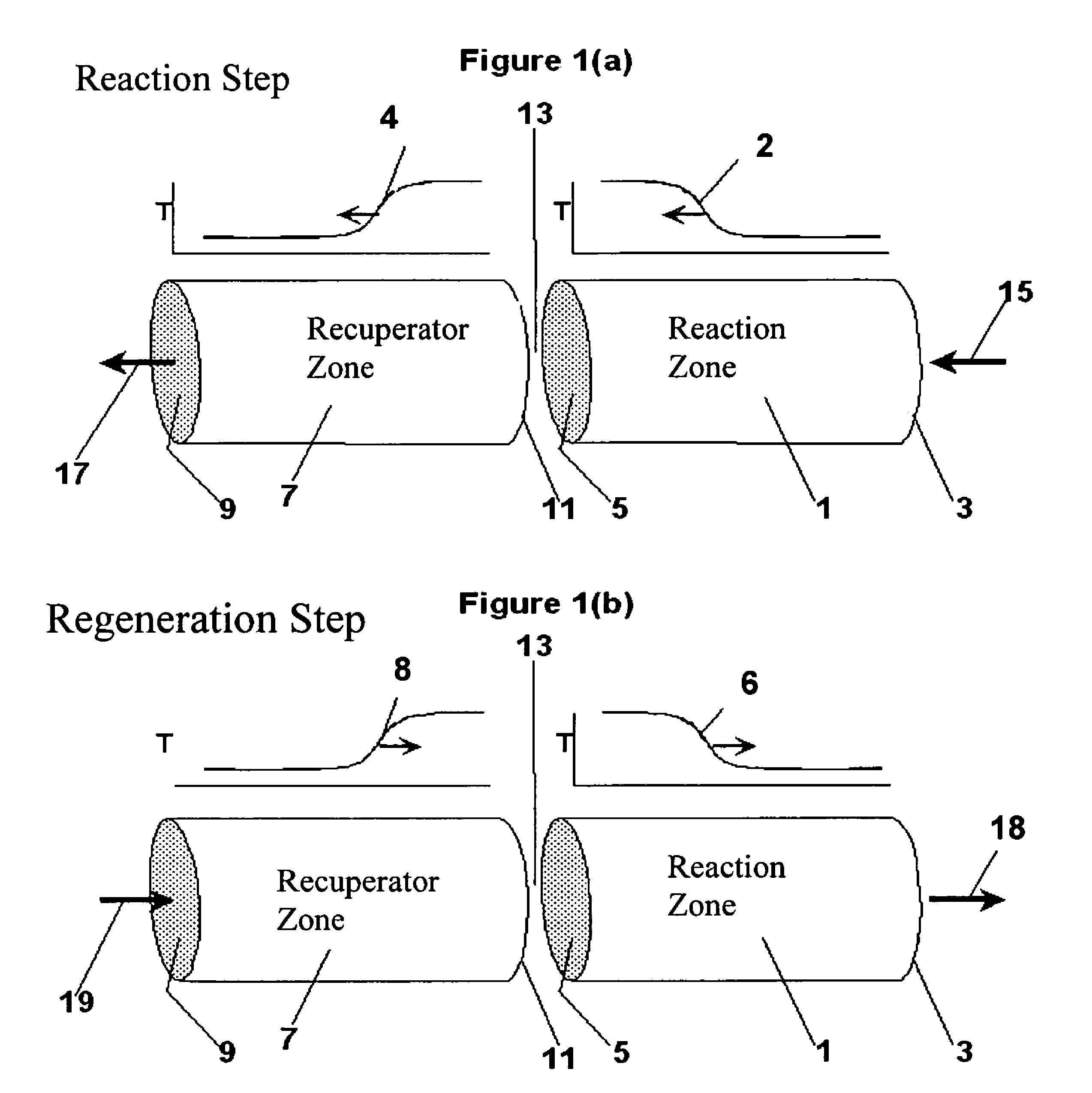
Controlled combustion for regenerative reactors
The overall efficiency of a regenerative bed reverse flow reactor system is increased where the location of the exothermic reaction used for regeneration is suitably controlled. The present invention provides a method and apparatus for controlling the combustion to improve the thermal efficiency of bed regeneration in a cyclic reaction / regeneration processes. The process for thermal regeneration of a regenerative reactor bed entails(a) supplying the first reactant through a first channel means in a first regenerative bed and supplying at least a second reactant through a second channel means in the first regenerative bed,(b) combining said first and second reactants by a gas mixing means situated at an exit of the first regenerative bed and reacting the combined gas to produce a heated reaction product,(c) passing the heated reaction product through a second regenerative bed thereby transferring heat from the reaction product to the second regenerative bed.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for generating pure benzene from reformed gasoline
InactiveUS6124514AReduce benzene contentAchieve separationThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingBenzeneExtractive distillation
A process is disclosed for generating pure aromatic compounds from a reformed gasoline which contains aromatic compounds, olefins, diolefin, and triolefins, which comprises the steps of: (a) selectively hydrogenating the olefins, diolefins and triolefins in the reformed gasoline to obtain a mixture of hydrogenated, non-aromatic compounds and aromatic compounds; and (b) separating the aromatic compounds from the hydrogenated, non-aromatic compounds in the mixture formed during step (a) by either extractive distillation, liquid-liquid extraction or both to obtain the pure aromatic compounds.
Owner:BASF AG
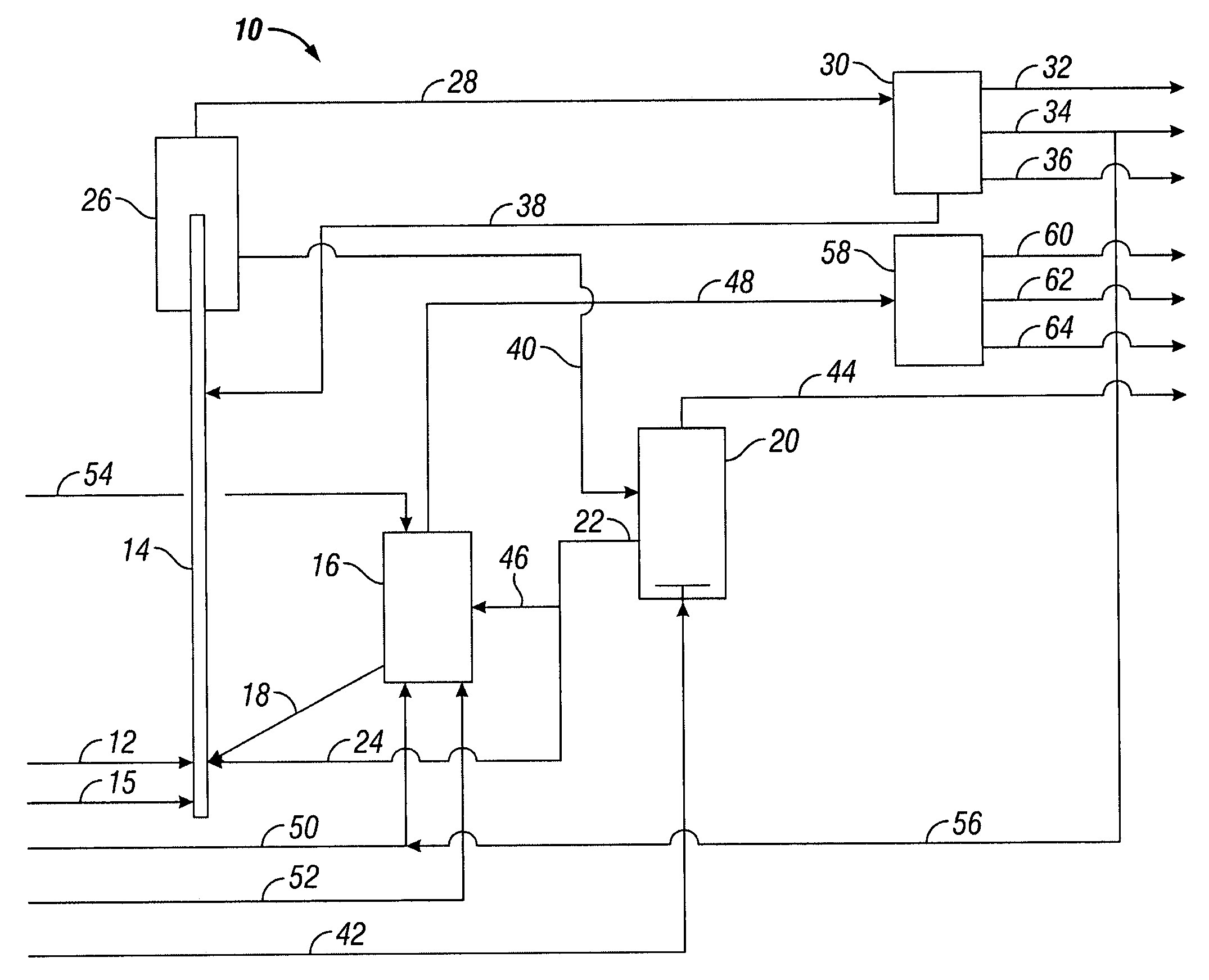
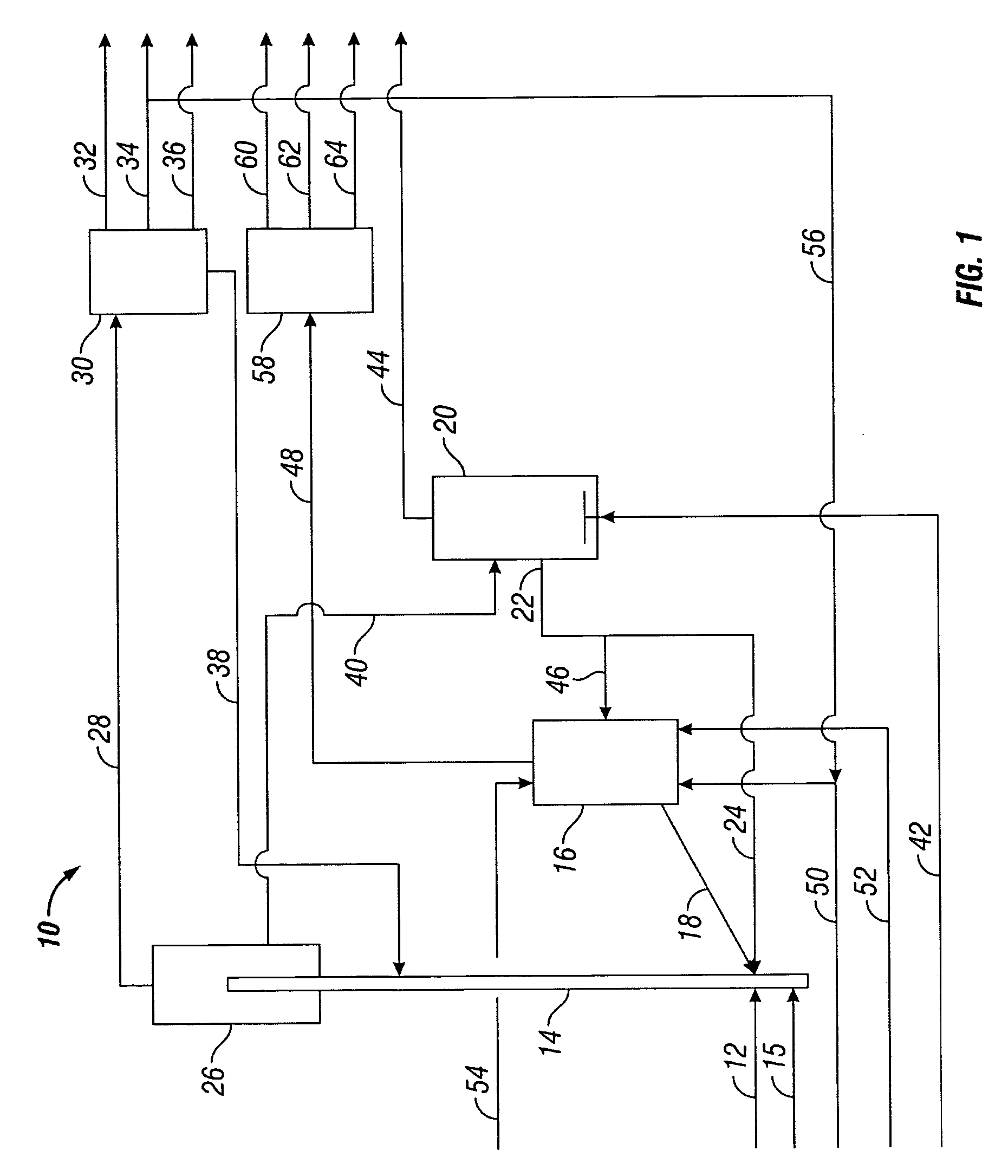
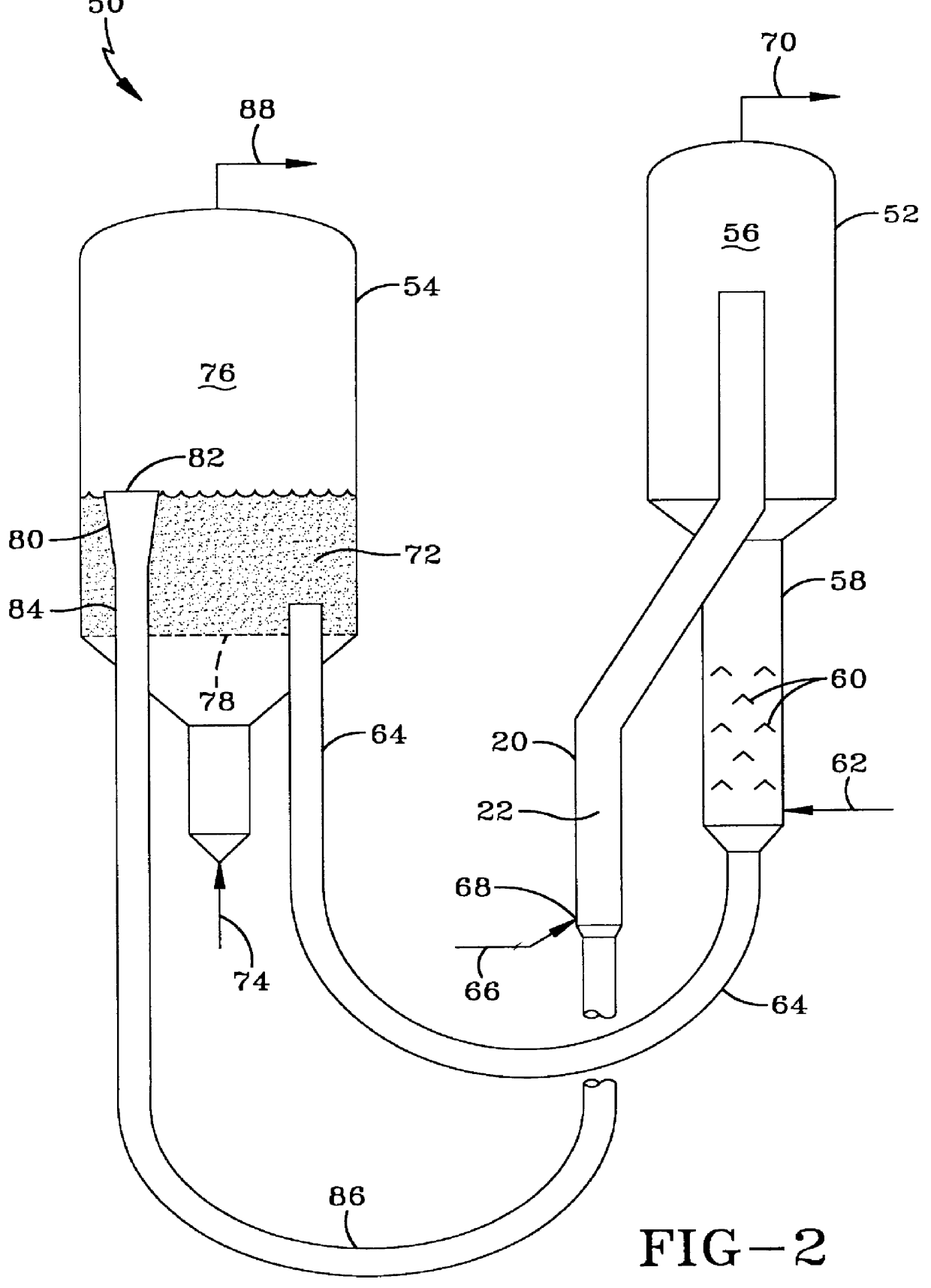
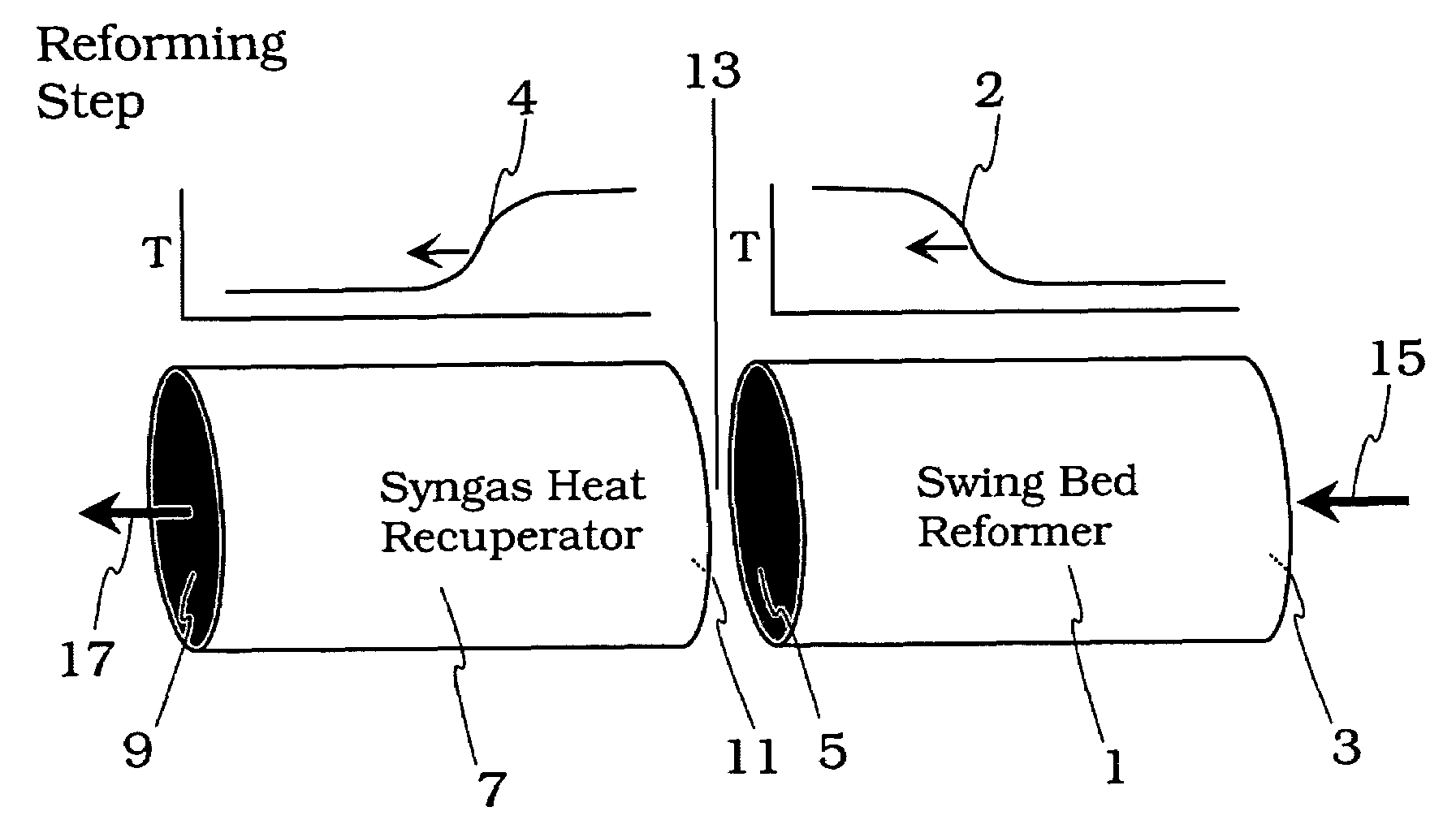
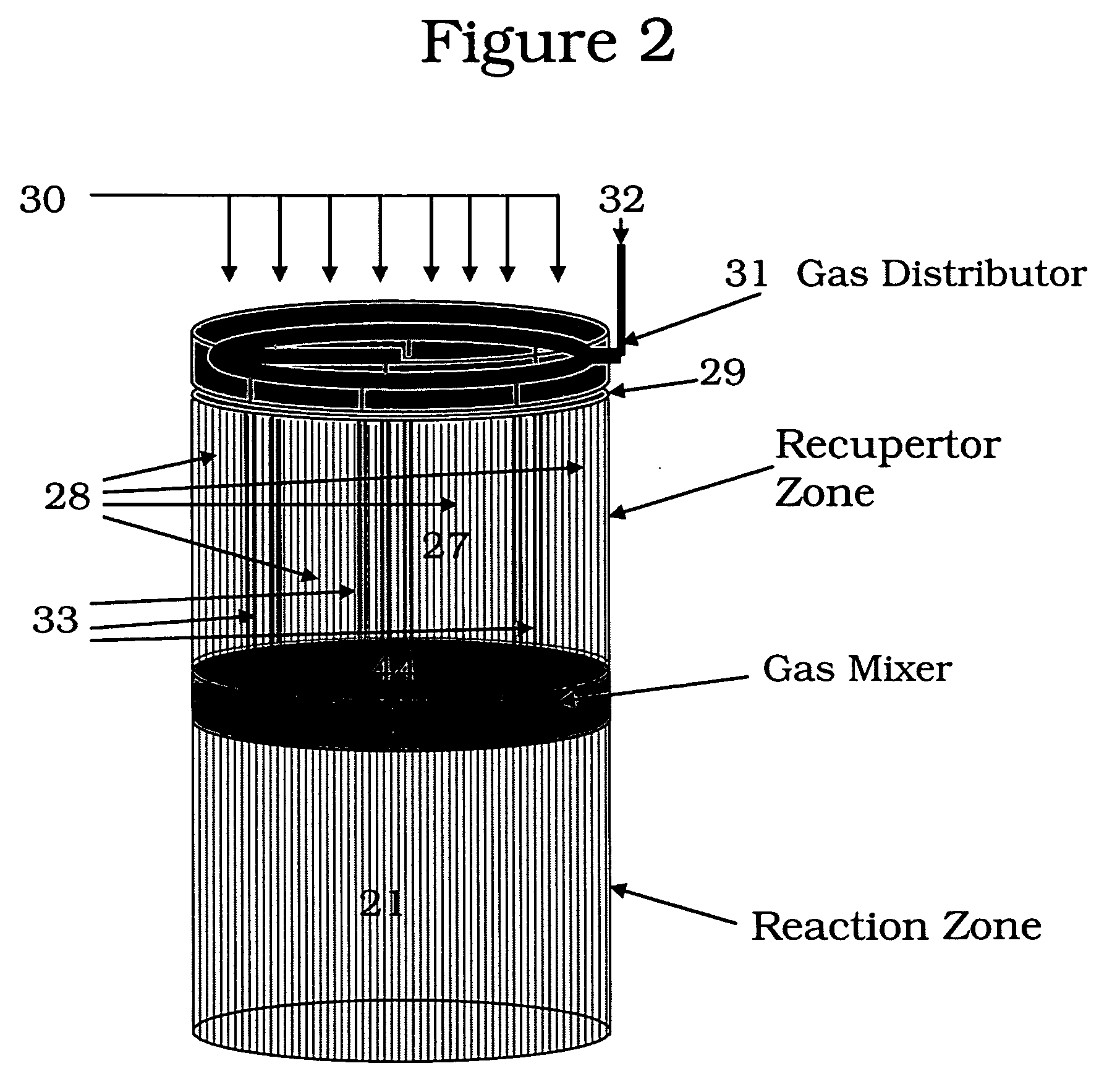
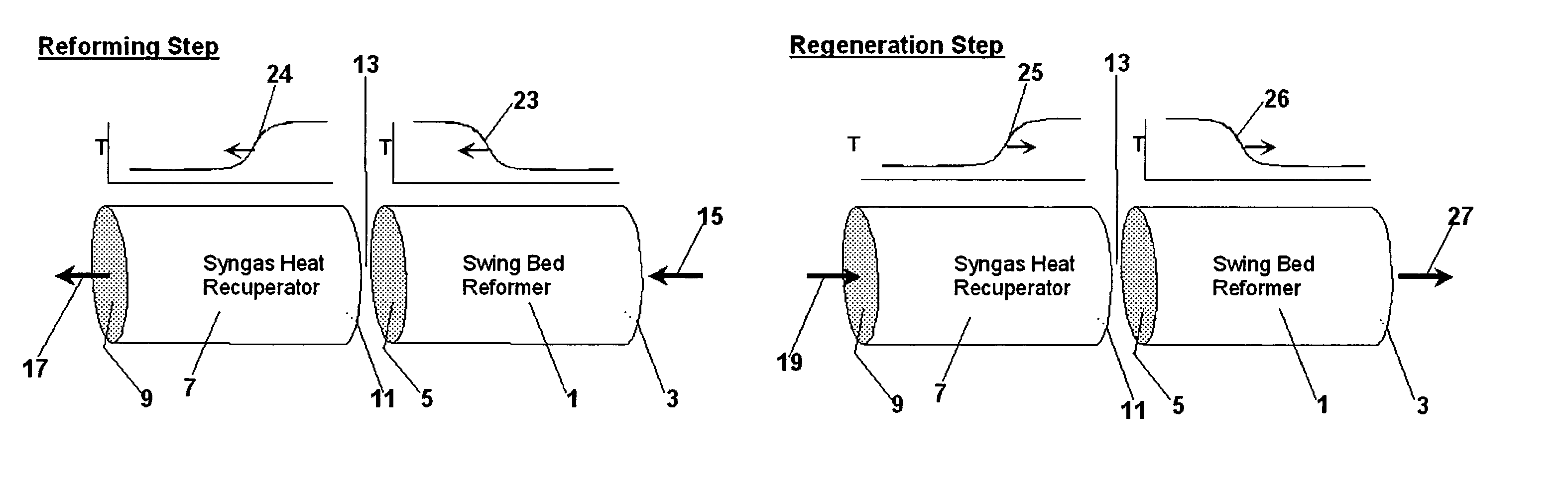
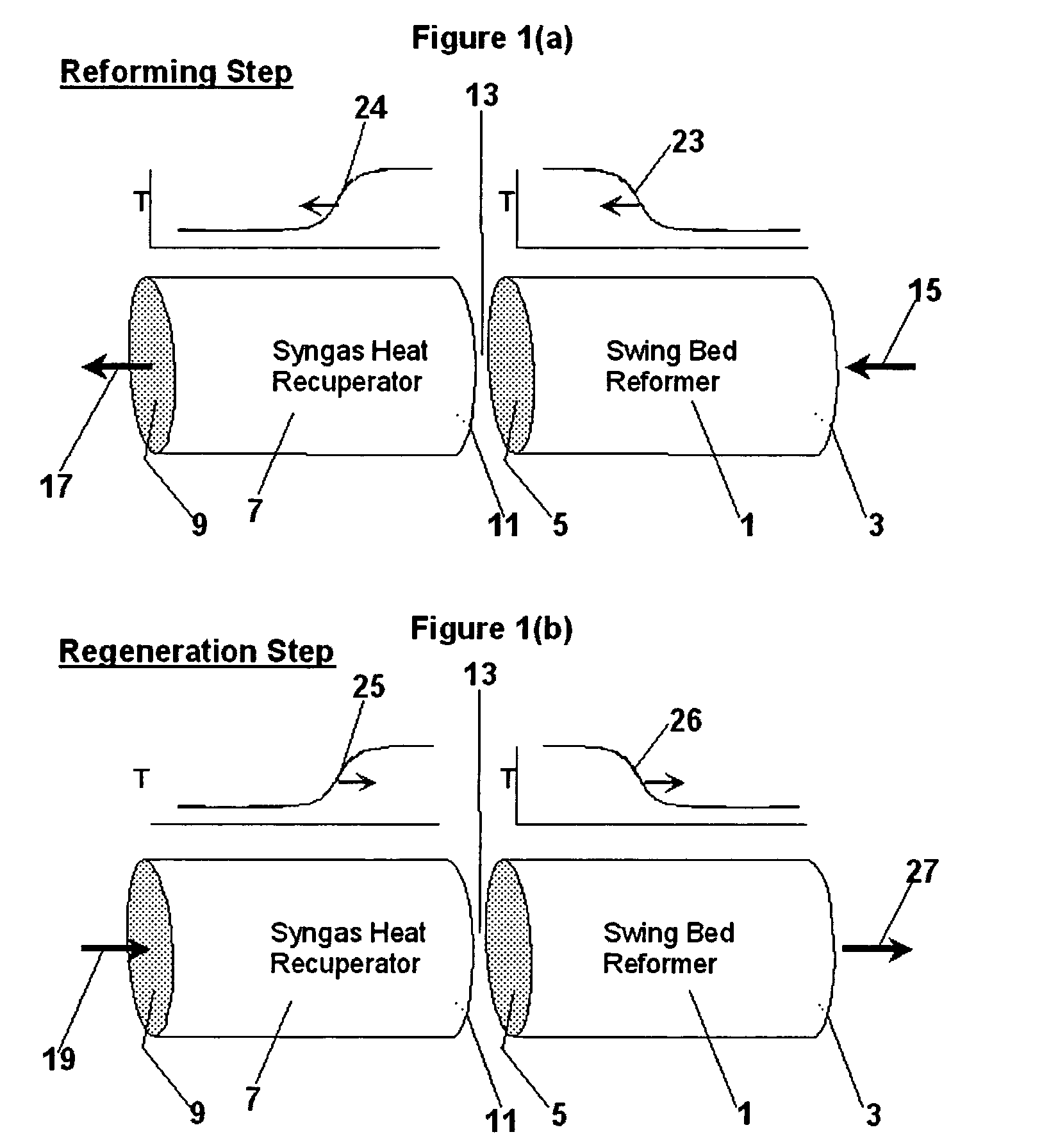
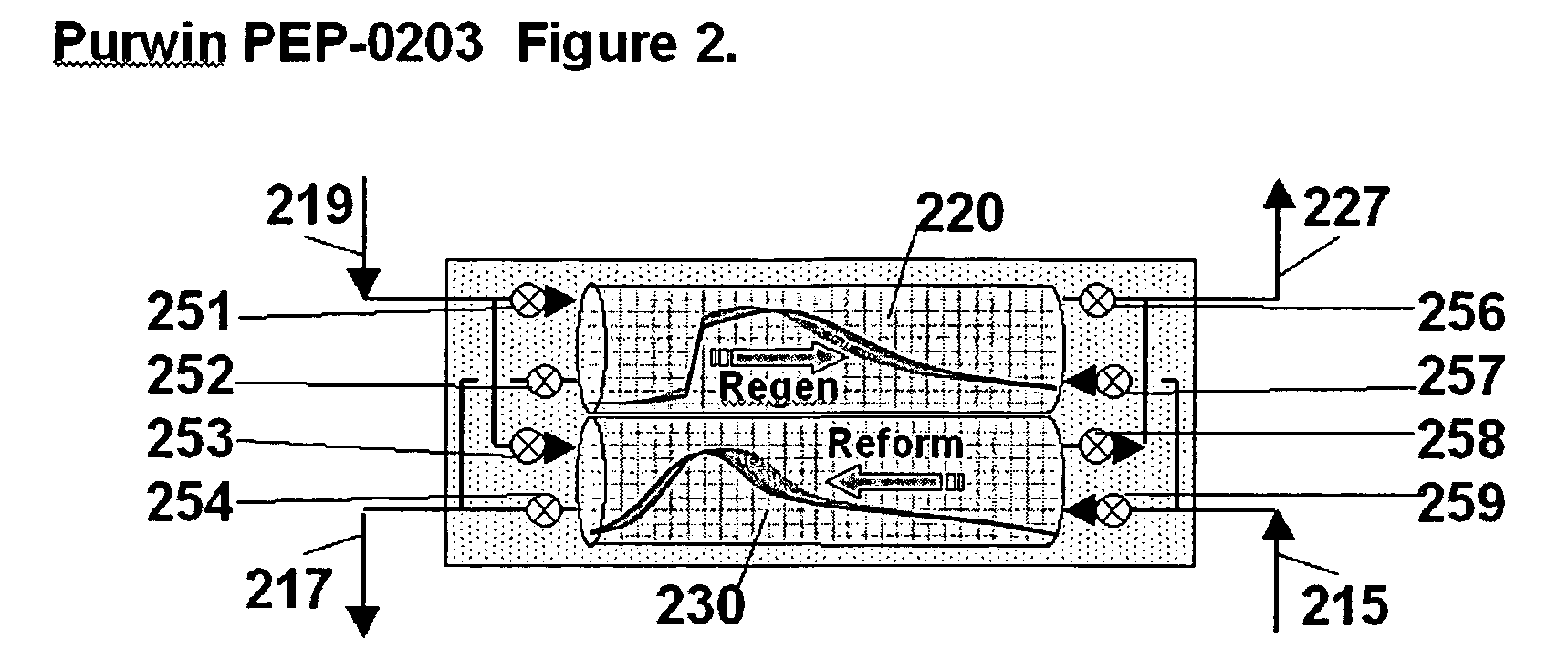
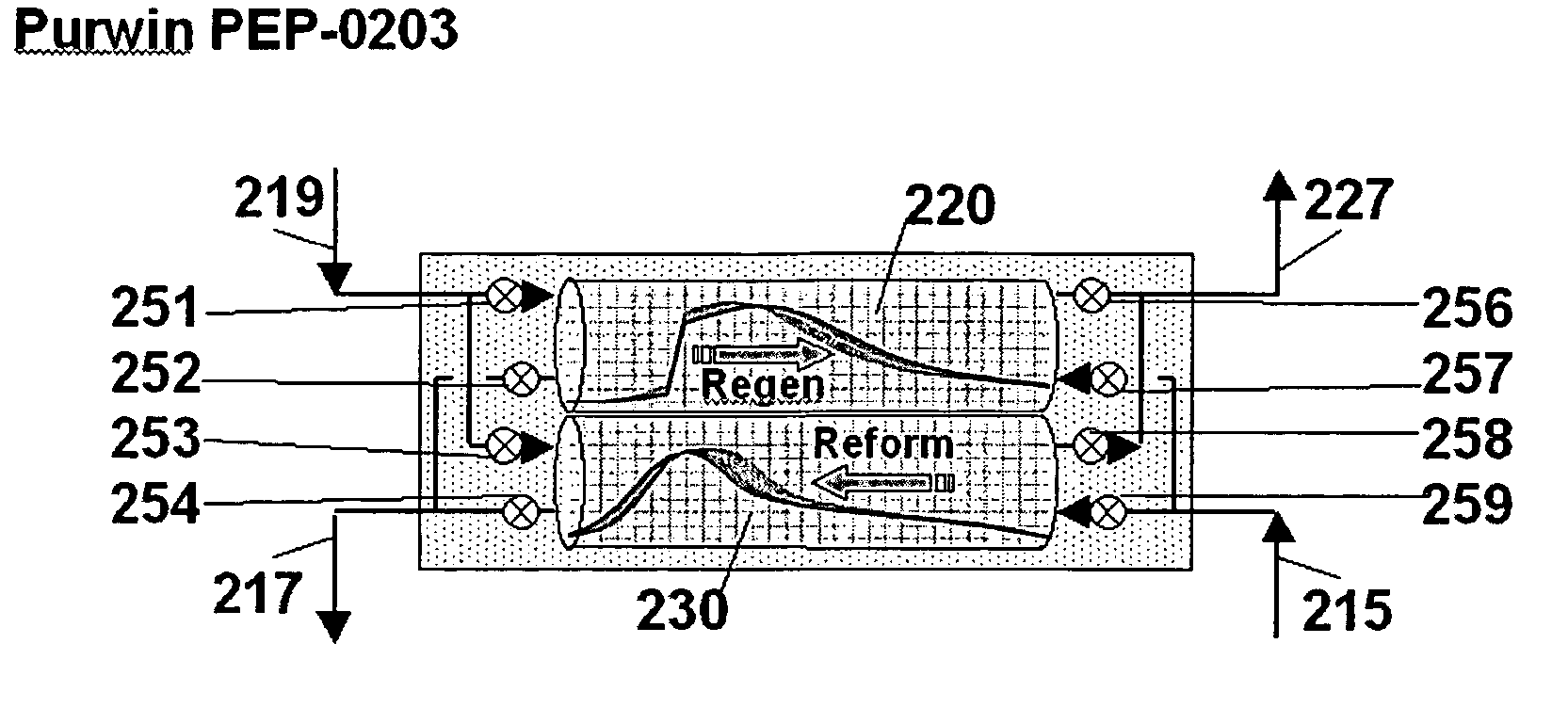
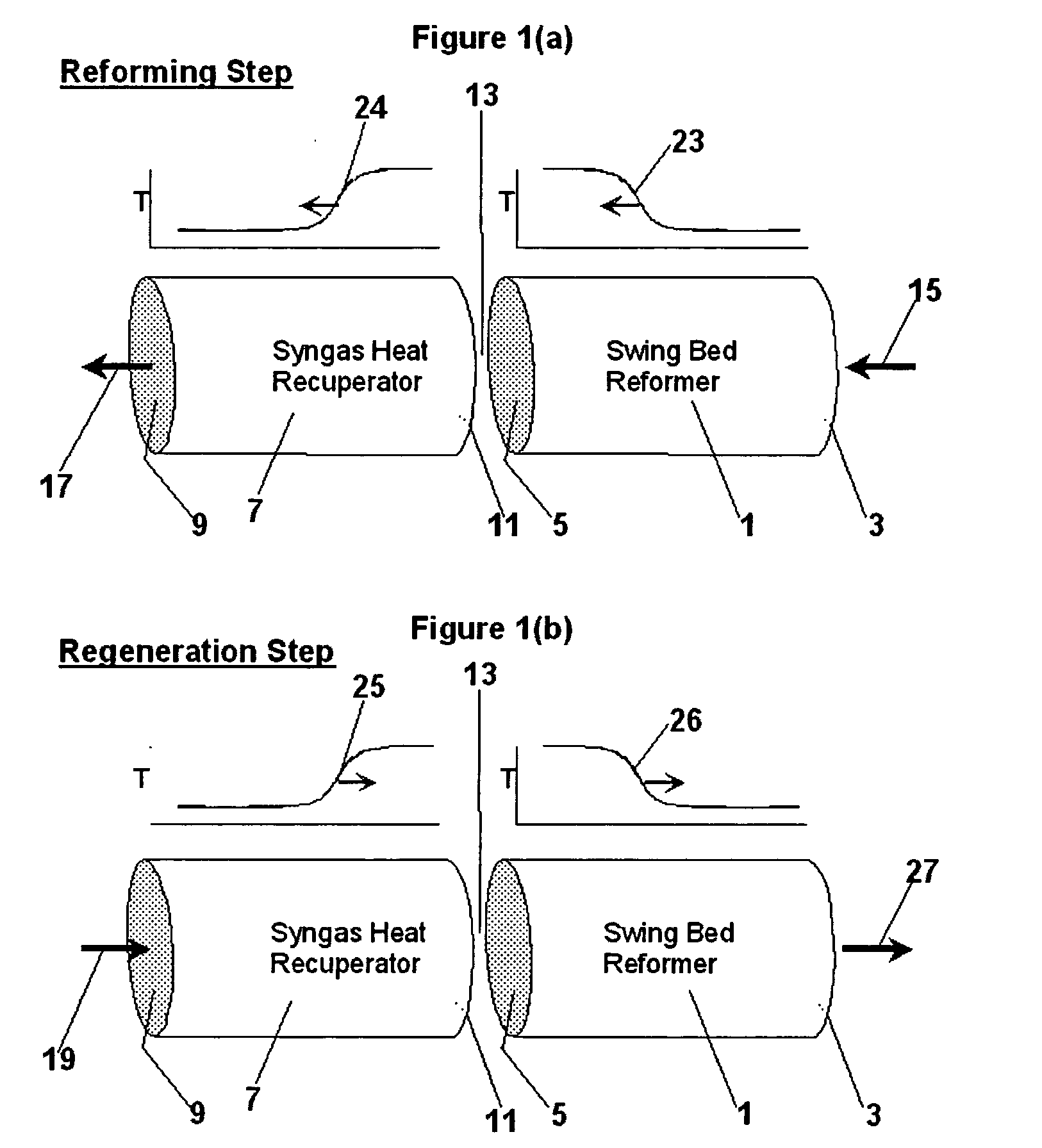
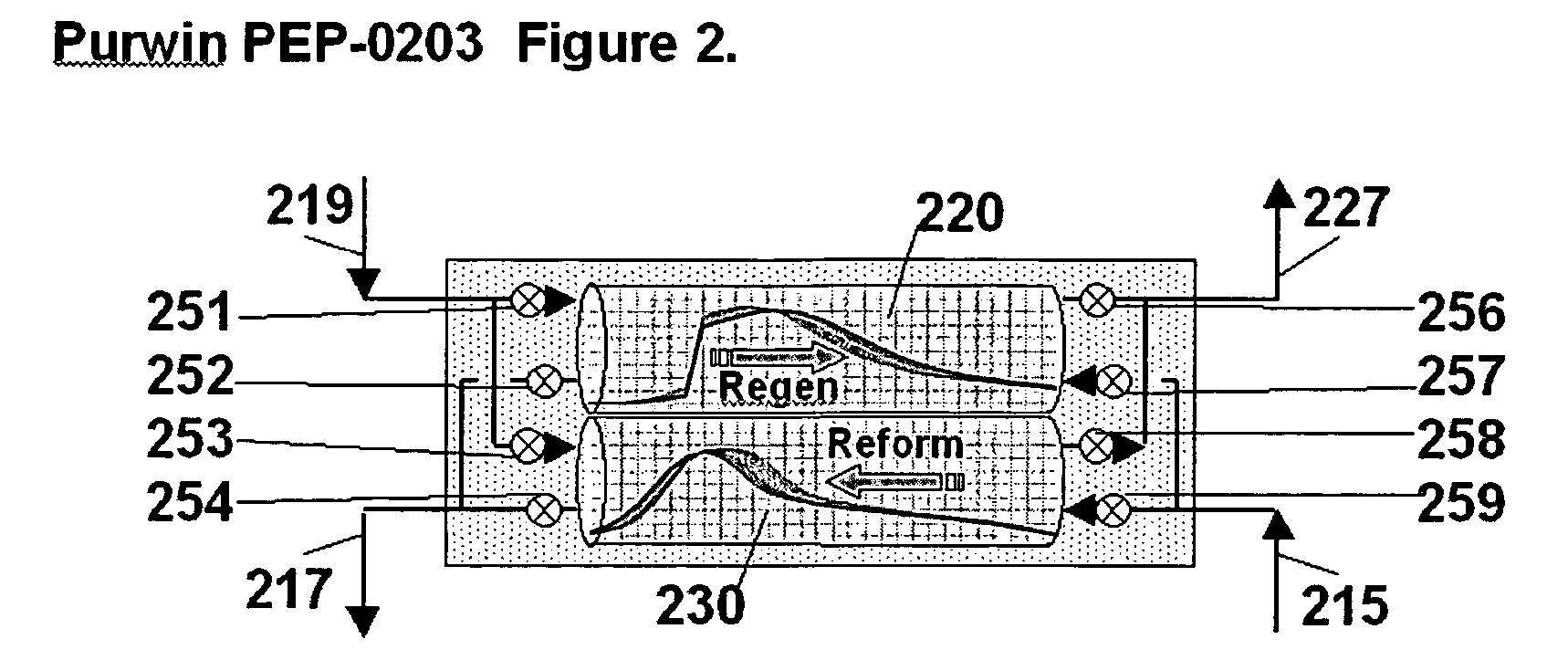
Pressure swing reforming for fuel cell systems
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Pressure swing reforming for fuel cell systems
ActiveUS20040175326A1Efficient productionImprove permeabilityHydrogenChemical industrySyngasFuel cells
The present invention provides an improvement in the process of producing hydrogen from hydrocarbon-containing streams. A cyclic reforming process, referred to as pressure swing reforming, provides an efficient means for producing a hydrogen containing synthesis gas for fuel cell applications. Pressure swing reforming may be integrated with shift reactions, preferential oxidation, and membrane separation, achieving thermal and material efficiencies relative to conventional hydrogen production. In one embodiment, at least some synthesis gas which is first produced in the pressure swing reforming process is combusted with air to provide the heat for the regeneration step of the pressure swing reforming process.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
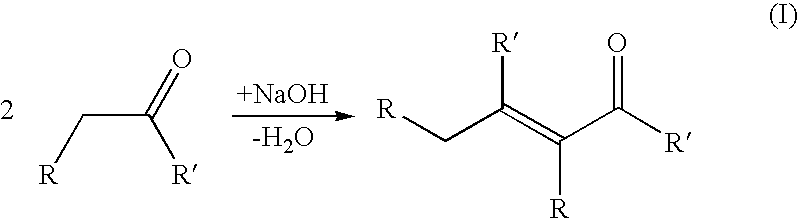
Process for producing a branched hydrocarbon component
InactiveUS20070135316A1Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationCatalytic naphtha reformingIsomerizationHydrodeoxygenation
The invention relates to a process for producing high-quality hydrocarbon base oil particularly of biological origin. The process of the invention comprises aldol condensation, hydrodeoxygenation, and isomerization steps. Aldehydes and / or ketones, preferably of biological origin are used as the feedstock.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Solid-acid isomerization catalyst and process
ActiveUS7041866B1Improve performanceImprove stabilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingAlkaneSulfation
A catalyst and process is disclosed to selectively upgrade a paraffinic feedstock to obtain an isoparaffin-rich product for blending into gasoline. The catalyst comprises a support of a sulfated oxide or hydroxide of a Group IVB (IUPAC 4) metal, a first component comprising at least one Group III A (IUPAC 13) component, and at least one platinum-group metal component which is preferably platinum.
Owner:UOP LLC
Catalyst and method for converting low molecular weight paraffinic hydrocarbons into alkenes and organic compounds with carbon numbers of 2 or more
InactiveUS20070083073A1Reduce the amount requiredPromotes oxidative couplingHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCarbon numberOxygen
A catalyst and process for formation of hydrocarbons having carbon numbers of two or greater, the result of both oxidative coupling of methane (“OCM”), and other reforming reactions of OCM end products. An OCM catalyst has a structure represented by formula ABTiO3, wherein A is samarium or tin, B is barium; the reforming catalysts a composition represented by formula XYZ, wherein X is a metal from Group IA, Group IIA or Group VIIIA, or not present, Y a metal from Group VA, Group VIA, Group VIIA or Group VIIIA, Z chosen from oxygen, silica, silicalite and alumina. The inventive catalyst comprises an OCM catalyst and a reforming catalyst blended together; when used in a reactor effects an increased yield of hydrocarbons having a carbon number greater than 2 (in excess of 27%-30%, first pass rate of methane conversion about 50%) than occurs under OCM conditions alone.
Owner:HRD CORP
Manufacture of high octane alkylate
InactiveUS6768035B2Hydrocarbon by isomerisationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAlcoholGasoline
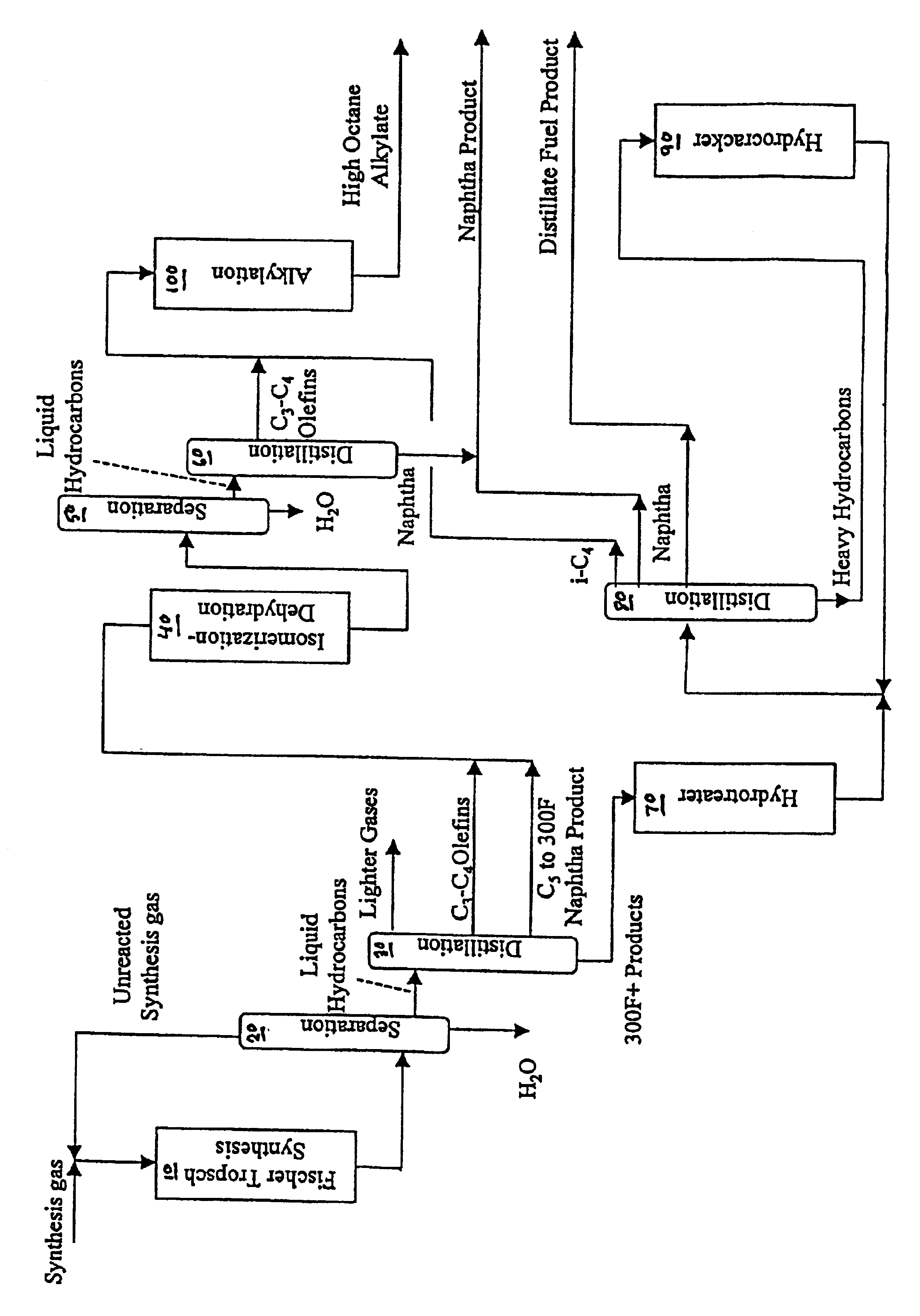
A Fischer-Tropsch C3-C4 olefin stream is simultaneously dehydrated and isomerized to convert alcohols to olefins and 1-butenes to 2-butenes and thereby lower the oxygenate content. Another Fischer-Tropsch fraction is hydrotreated and hydrocracked to provide an isobutane stream. The treated C3-C4 olefin stream having an oxygenate content less than 4000 ppm, is reacted with the isobutane stream to provide a highly branched, high octane isoparaffinic alkylate. The alkylate is useful as a blending component in motor gasoline.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method of using carbide and/or oxycarbide containing compositions
InactiveUS20020121460A1Facilitated DiffusionHigh porosityMaterial nanotechnologyHydrocarbon by isomerisationFluid phaseChemical reaction
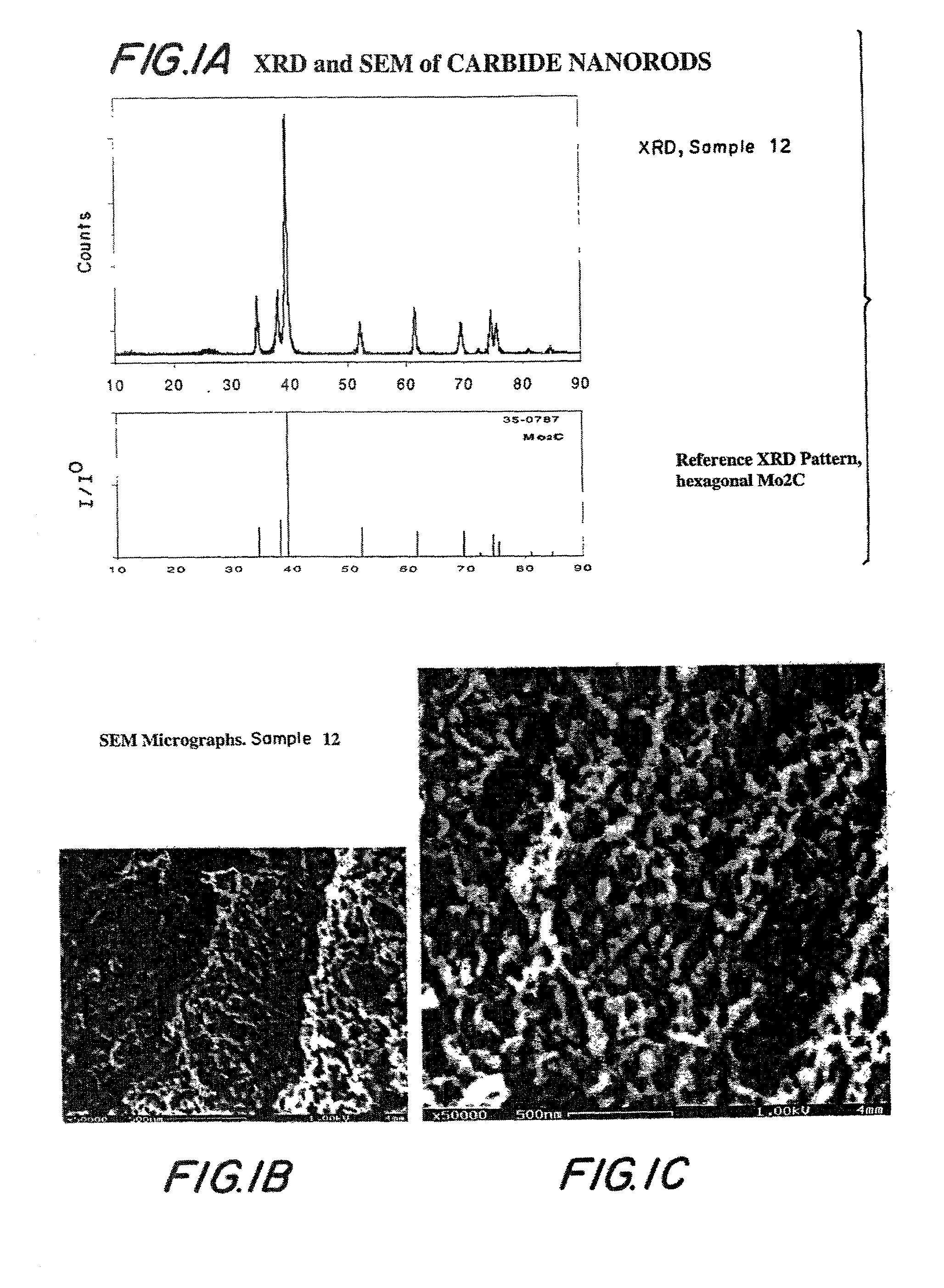
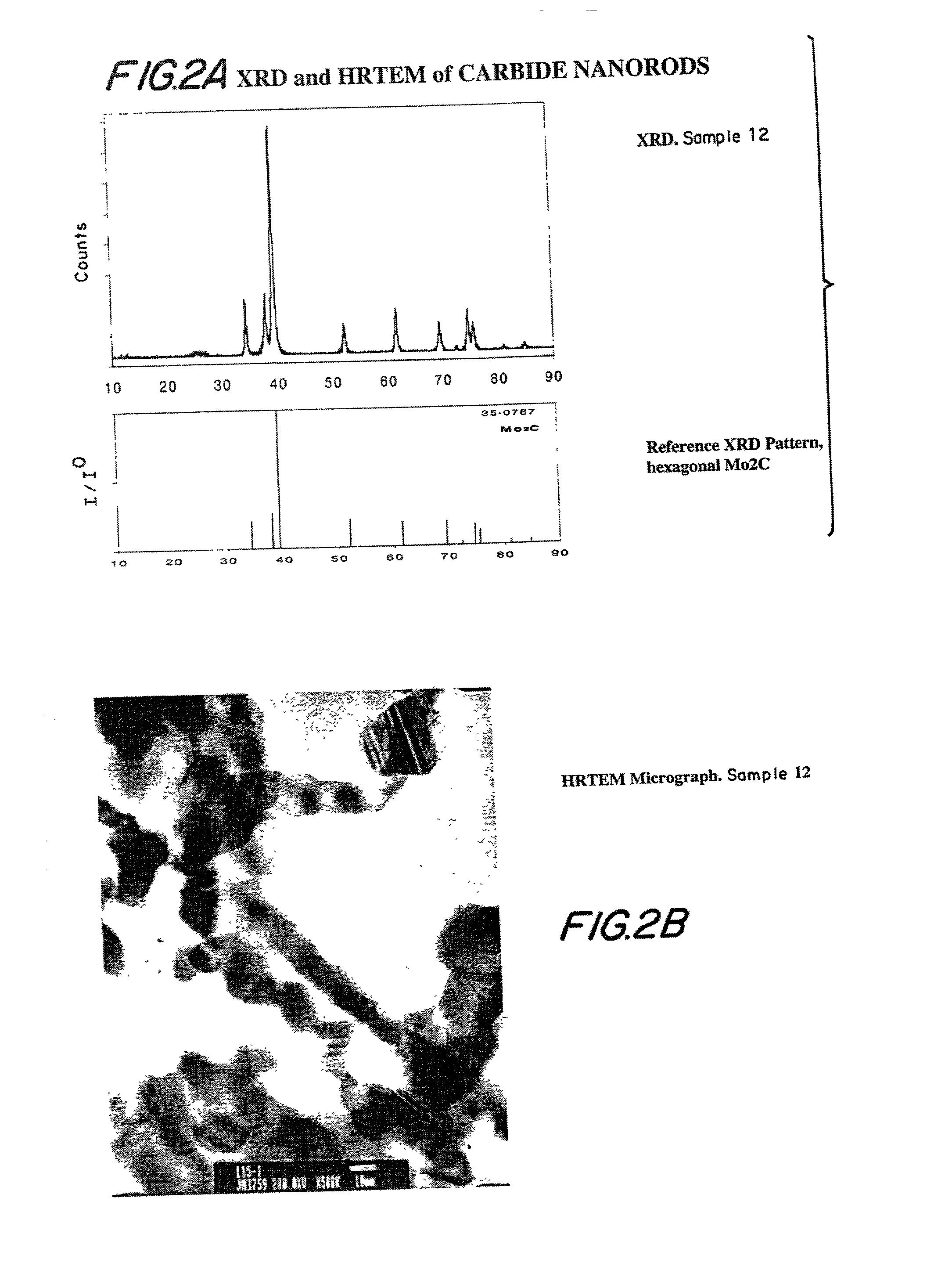
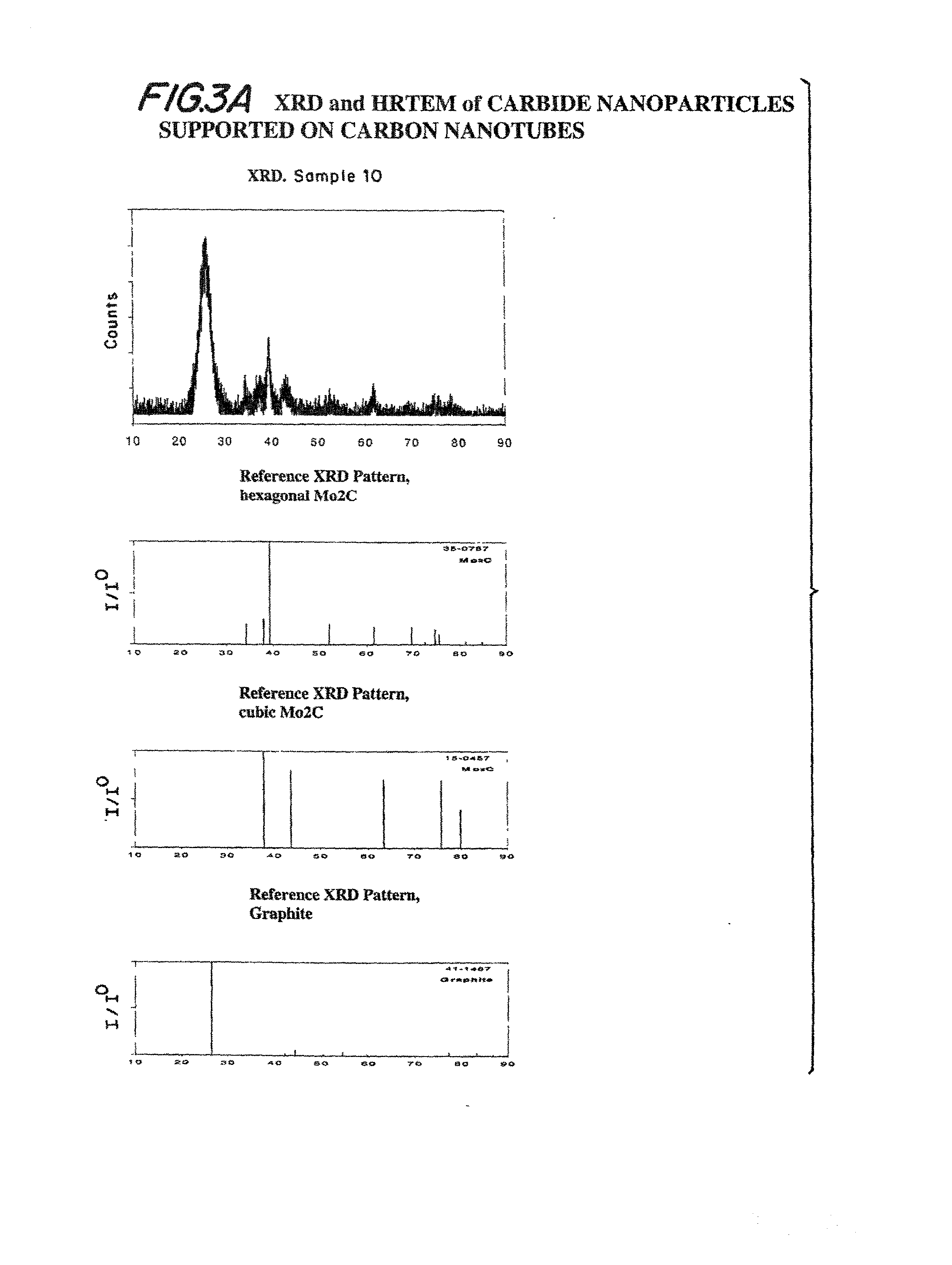
Compositions including carbide-containing nanorods and / or oxycarbide-containing nanorods and / or carbon nanotubes bearing carbides and oxycarbides and methods of making the same are provided. Rigid porous structures including oxycarbide-containing nanorods and / or carbide containing nanorods and / or carbon nanotubes bearing carbides and oxycarbides and methods of making the same are also provided. The compositions and rigid porous structures of the invention can be used either as catalyst and / or catalyst supports in fluid phase catalytic chemical reactions. Processes for making supported catalyst for selected fluid phase catalytic reactions are also provided.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Supported catalysts having a controlled coordination structure and methods for preparing such catalysts
ActiveUS7011807B2Reduce molecular weightReduce the possibilityHydrogen peroxideHydrogenHydrogenOrganic fluid
Supported reactive catalysts having a controlled coordination structure and methods for their production are disclosed. The supported catalysts of the present invention are useful for the preparation of hydrogen peroxide with high selectivity in addition to other chemical conversion reactions. The supported catalyst comprises catalyst particles having top or outer layer of atoms in which at least a portion of the atoms exhibit a controlled coordination number of 2. The catalyst and methods may be used for the concurrent in situ and ex situ conversion of organic compounds. In addition, a process is provided for catalytically producing hydrogen peroxide from hydrogen and oxygen feeds by contacting them with the catalysts of the invention and a suitable organic liquid solvent having a Solvent Selection Parameter (SSP) between 0.14×10−4 and 5.0×10−4.
Owner:BORAL IP HLDG
Isoparaffinic base stocks by dewaxing fischer-tropsch wax hydroisomerate over Pt/H-mordenite
A high VI and low pour point lubricant base stock is made by hydroisomerizing a high purity, waxy, paraffinic Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon fraction having an initial boiling point in the range of 650-750° F., followed by catalytically dewaxing the hydroisomerate using a dewaxing catalyst comprising a catalytic platinum component and an H-mordenite component. The hydrocarbon fraction is preferably synthesized by a slurry Fischer-Tropsch using a catalyst containing a catalytic cobalt component. This combination of the process, high purity, waxy paraffinic feed and the Pt / H-mordenite dewaxing catalyst, produce a relatively high yield of premium lubricant base stock.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Reforming process using high density catalyst
InactiveUS20060102520A1High densityIncreased pinning marginCatalytic naphtha reformingCatalyst activation/preparationMössbauer spectroscopyMass ratio
A catalyst and a process for using the catalyst are disclosed generally for the conversion of hydrocarbons. The catalyst has an increased average bulk density and a decreased mass ratio of platinum-group metal. The process using the catalyst obtains unexpected high activity and stability for the reforming of naphtha range hydrocarbons. Mössbauer spectroscopy is used to characterize the extent of tin association with platinum and determine an effective molar tin ratio appropriate for alumina supports with densities above 0.6 g / cc.
Owner:UOP LLC
Isomerization catalyst and processes
InactiveUS6977322B2Improve performanceImprove stabilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingAlkaneIsomerization
A catalyst and process is disclosed to selectively upgrade a paraffinic feedstock to obtain an isoparaffin-rich product for blending into gasoline. The catalyst comprises a support of a tungstated oxide or hydroxide of a Group IVB (IUPAC 4) metal, a first component of at least one lanthanide element, yttrium or mixtures thereof, which is preferably ytterbium or holmium, and at least one platinum-group metal component which is preferably platinum.
Owner:UOP LLC
Refining method of reforming aromatic oil
InactiveCN1618932AEfficient removalNo loss increaseCatalytic naphtha reformingOrganic chemistryChemistry
Owner:曹炳铖
Process for isomerization dewaxing of hydrocarbon streams
InactiveUS20030168379A1Yield maximizationReduce pointsMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationMolecular sieveIsomerization
A process for isomerization dewaxing of a hydrocarbon feed which includes contacting the hydrocarbon feed with a large pore size, small crystal size, crystalline molecular sieve and an intermediate pore size, small crystal size, crystalline molecular sieve to produce a dewaxed product with a reduced pour point and a reduced cloud point. In a preferred embodiment, the feed is contacted with the molecular sieves sequentially, first with the large pore sieve followed by the intermediate pore sieve.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Hydrogen storage by reversible hydrogenation of pi-conjugated substrates
ActiveUS20050002857A1Less energy expenditureEasy to separateCatalytic naphtha reformingVariable capacity gas holdersPartial hydrogenationDehydrogenation
Processes are provided for the storage and release of hydrogen by means of a substantially reversible catalytic hydrogenation of extended pi-conjugated substrates which include large polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with nitrogen heteroatoms, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with oxygen heteroatoms, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with alkyl, alkoxy, nitrile, ketone, ether or polyether substituents, pi-conjugated molecules comprising 5 membered rings, pi-conjugated molecules comprising six and five membered rings with nitrogen or oxygen hetero atoms, and extended pi-conjugated organic polymers. The hydrogen, contained in the at least partially hydrogenated form of the extended pi-conjugated system, can be facilely released for use by a catalytic dehydrogenation of the latter in the presence of a dehydrogenation catalyst which can be effected by lowering the hydrogen gas pressure, generally to pressures greater than 0.1 bar or raising the temperature to less than 250° C. or less, or by a combination of these two process parameters.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Production of fuels and lube oils from fischer-tropsch wax
Dewaxed fuel and lubricant base stocks are made by (a) producing a synthesis gas from natural gas, (b) reacting the H2 and CO in the gas in the presence of a cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalyst, at reaction conditions effective to synthesize a waxy hydrocarbon feed boiling in the fuel and lubricant oil ranges, which is hydrodewaxed in a first stage to produce a dewaxed fuel and a partially dewaxed lubricant fraction. The partially dewaxed lubricant fraction is separated into heavy and lower boiling fractions each of which is separately hydrodewaxed, to produce lubricant base stocks. A hydrodewaxing catalyst comprising a hydrogenation component, binder and solid acid component used to hydrodewax at least one, and preferably at least two of the waxy feed and partially dewaxed heavy and lower boiling lubricant fractions.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Popular searches
Hydrogen sulfides Hydrocarbon oils treatment products Transportation and packaging Indirect heat exchangers Treatment with hydrotreatment processes Hydrocarbon by hydrocarbon condensation Hydrogen/synthetic gas production Mixing gases with gases/vapours Naphtha treatment Hydrocarbon by hydrocarbon cracking
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com