Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11644results about "Flow mixers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
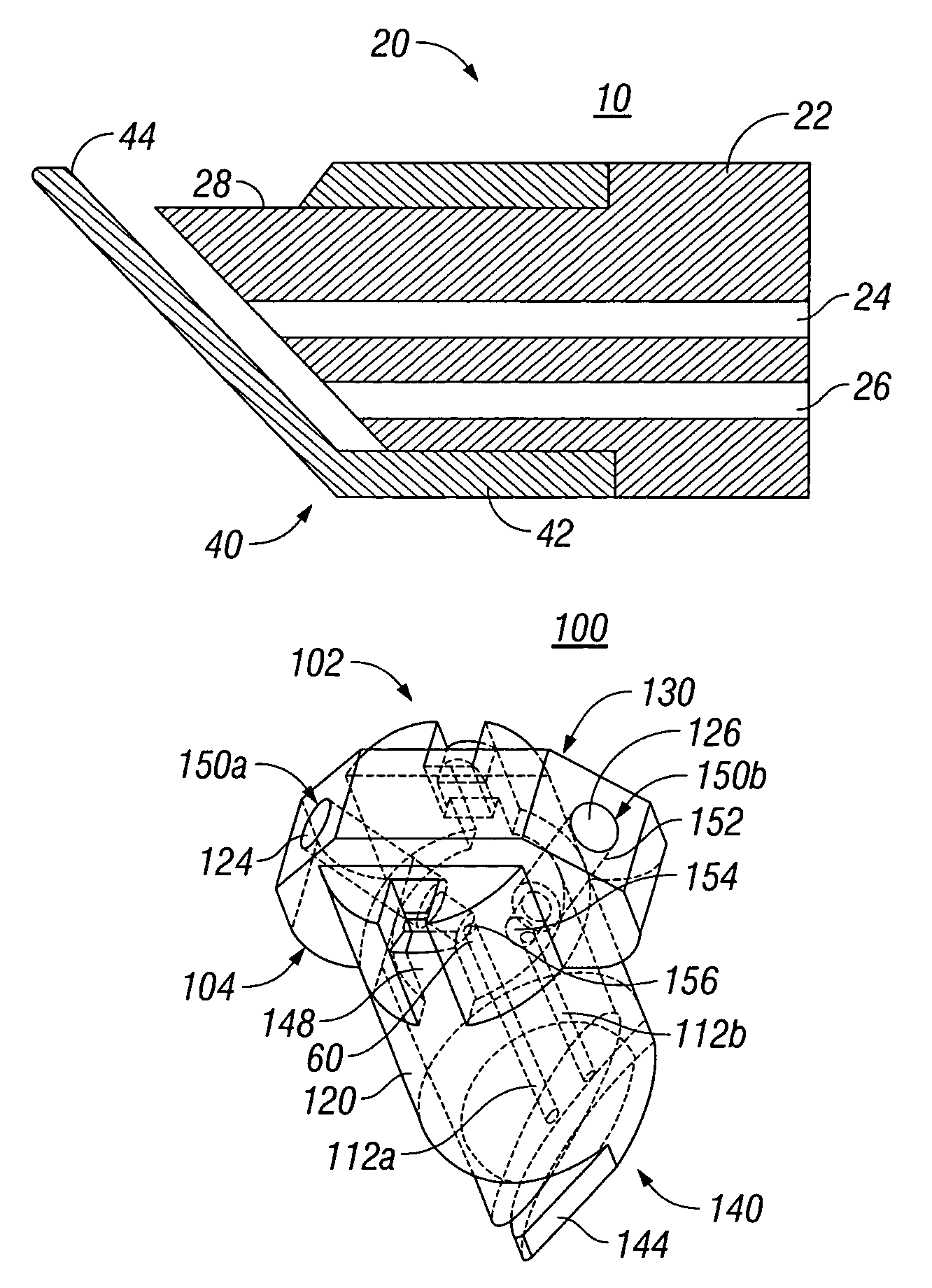
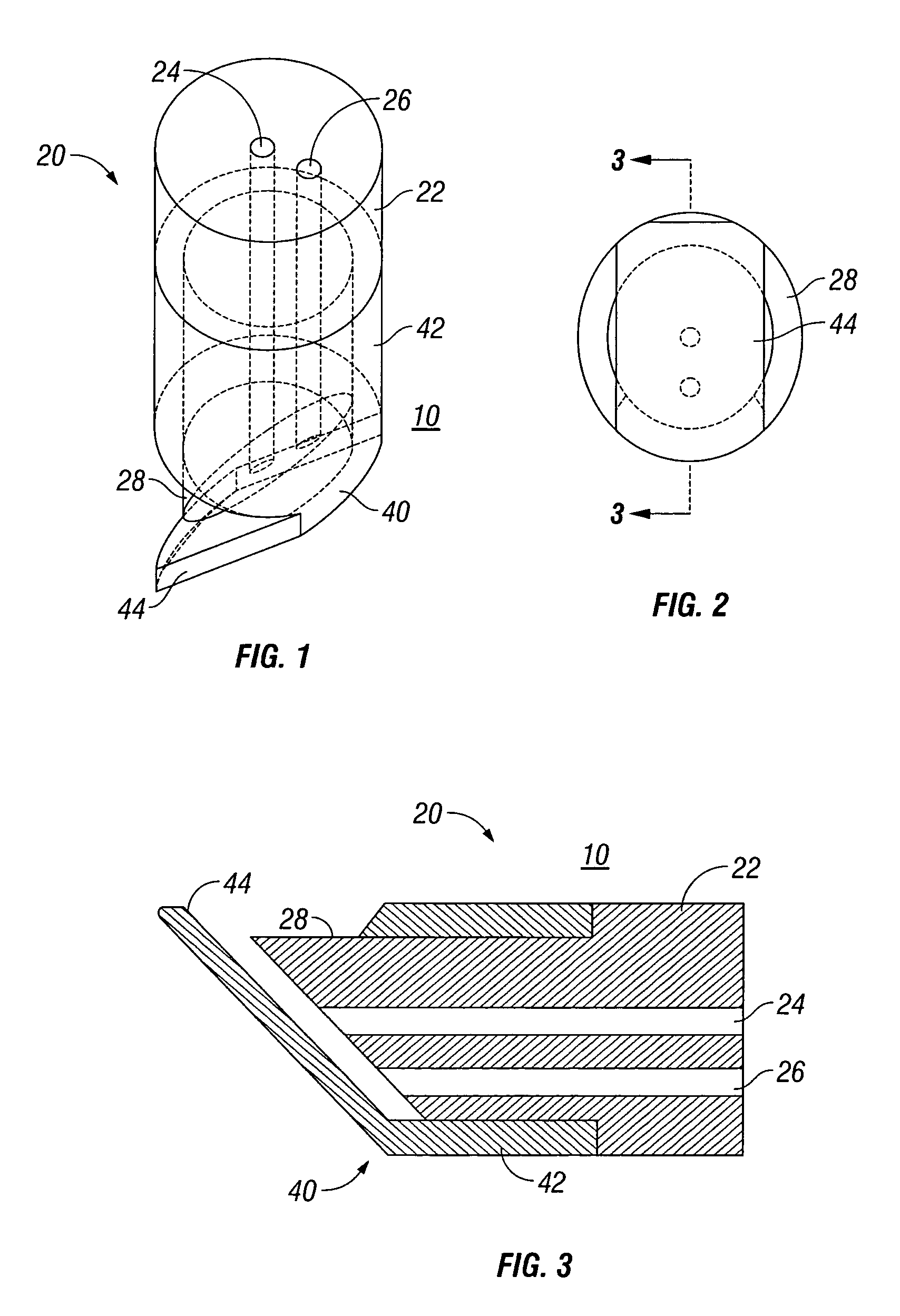
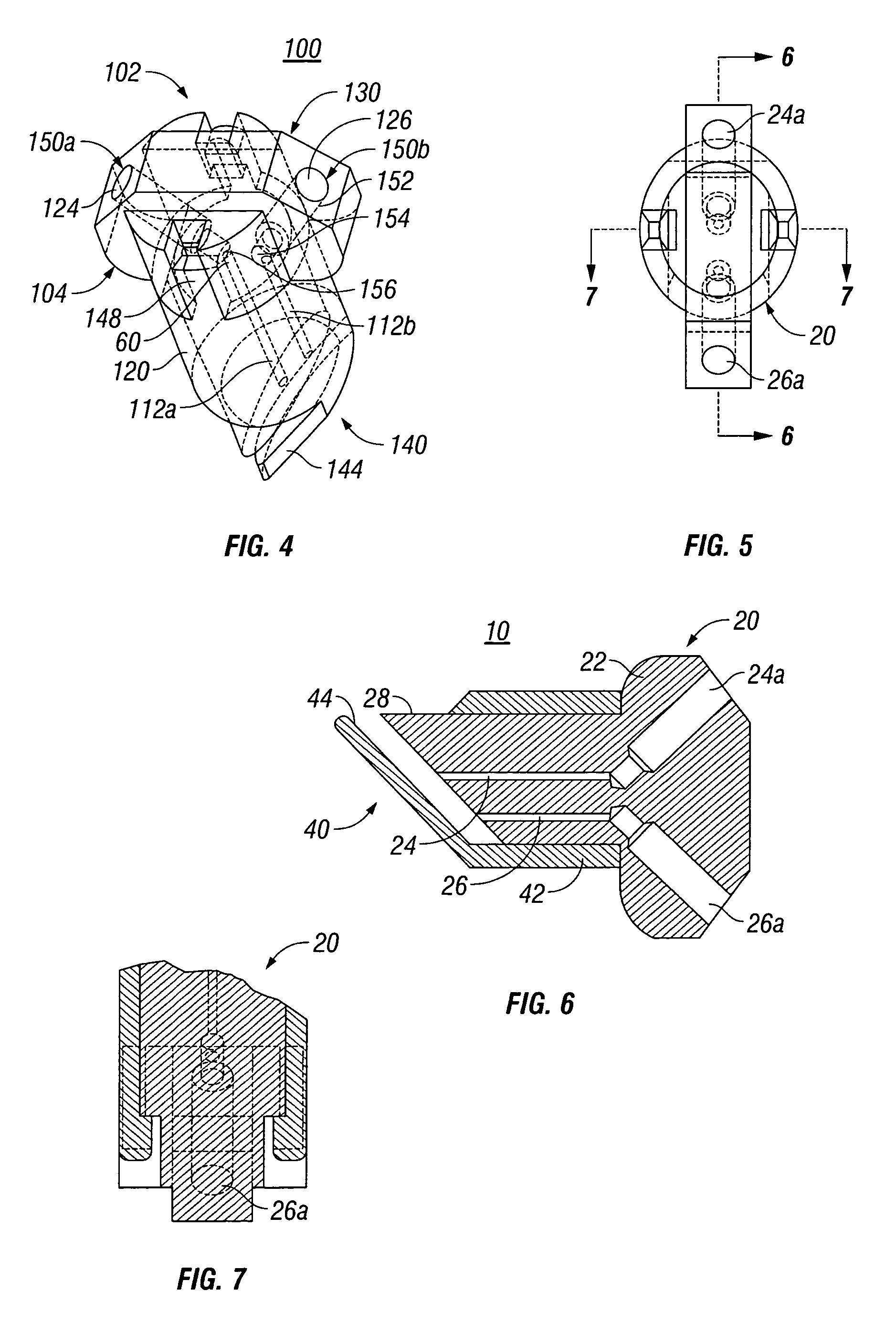
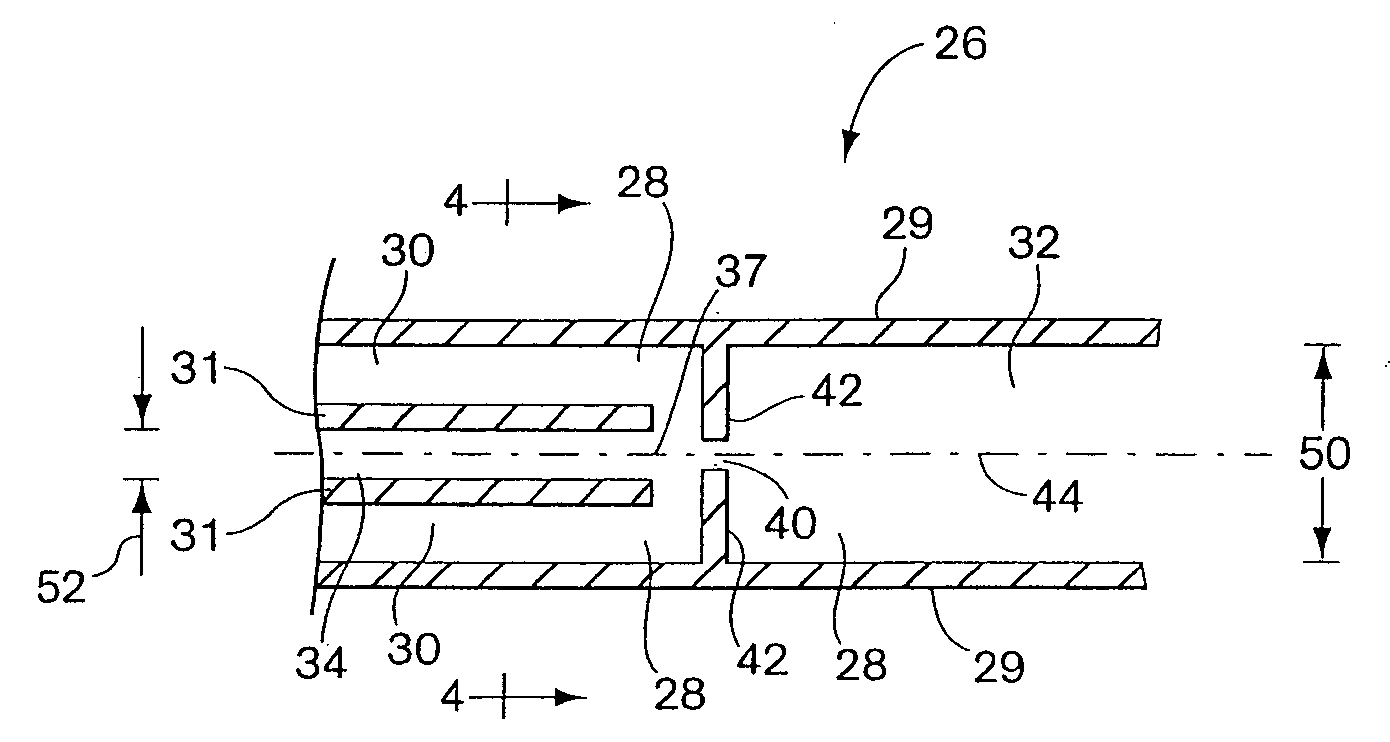
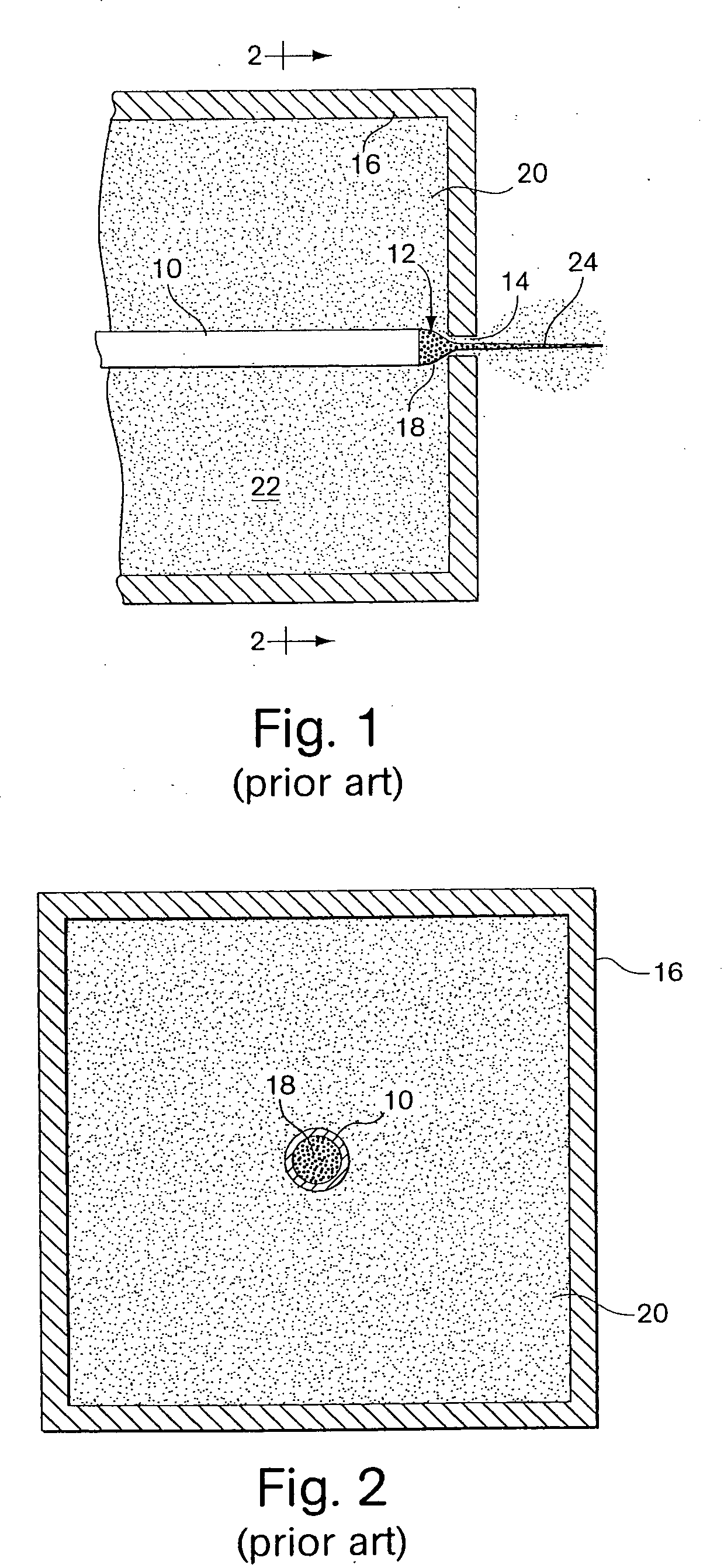
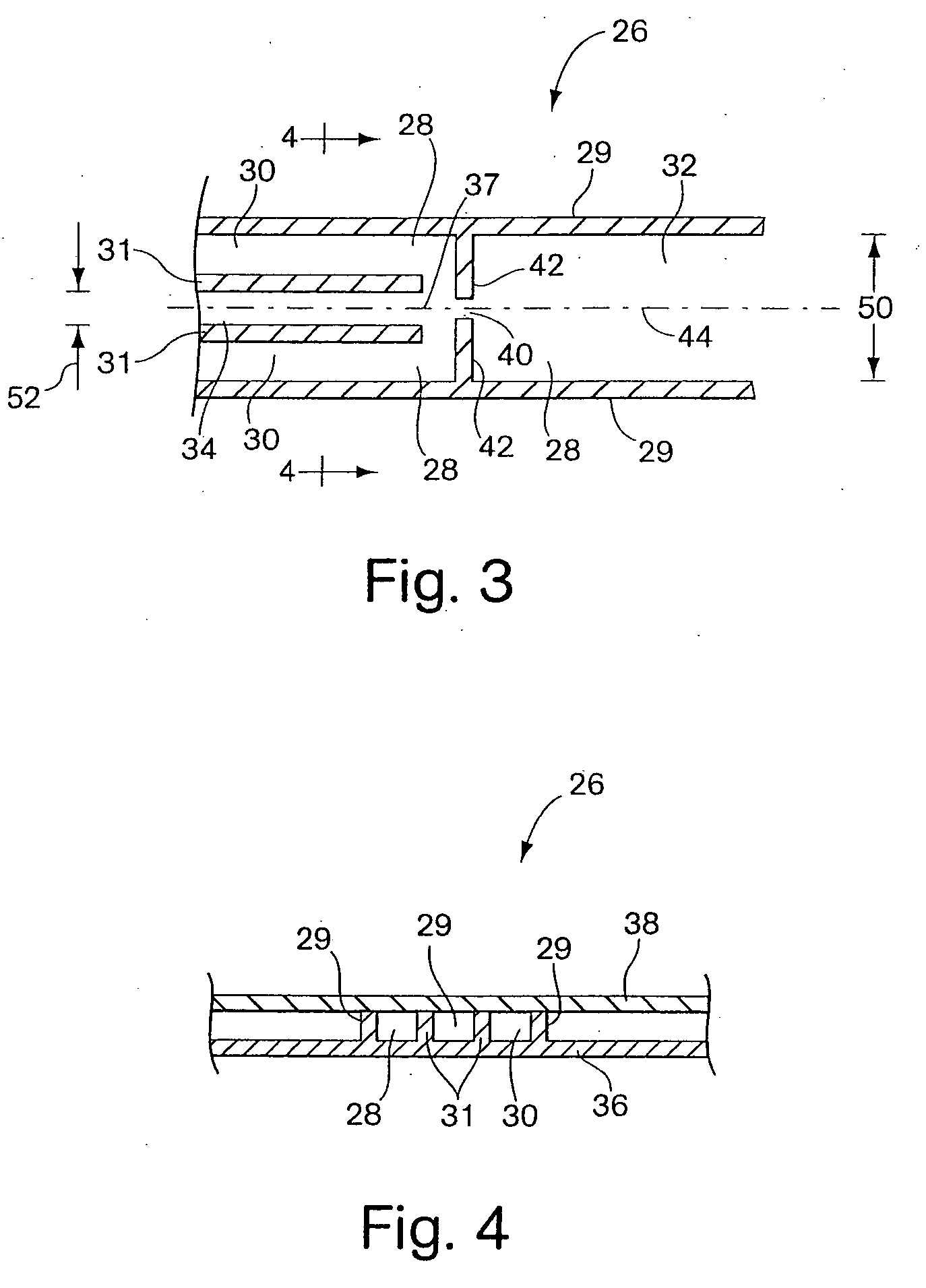
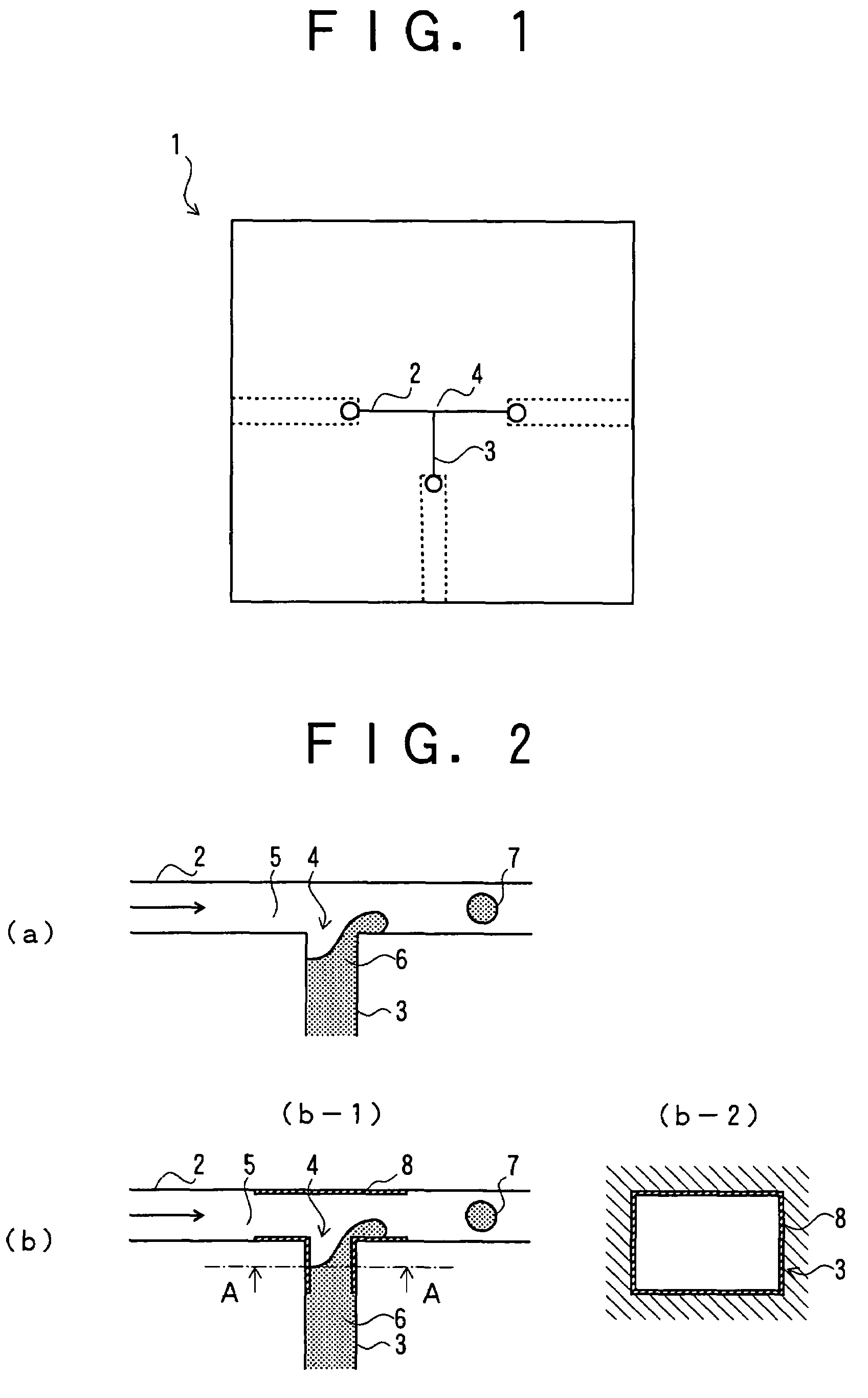
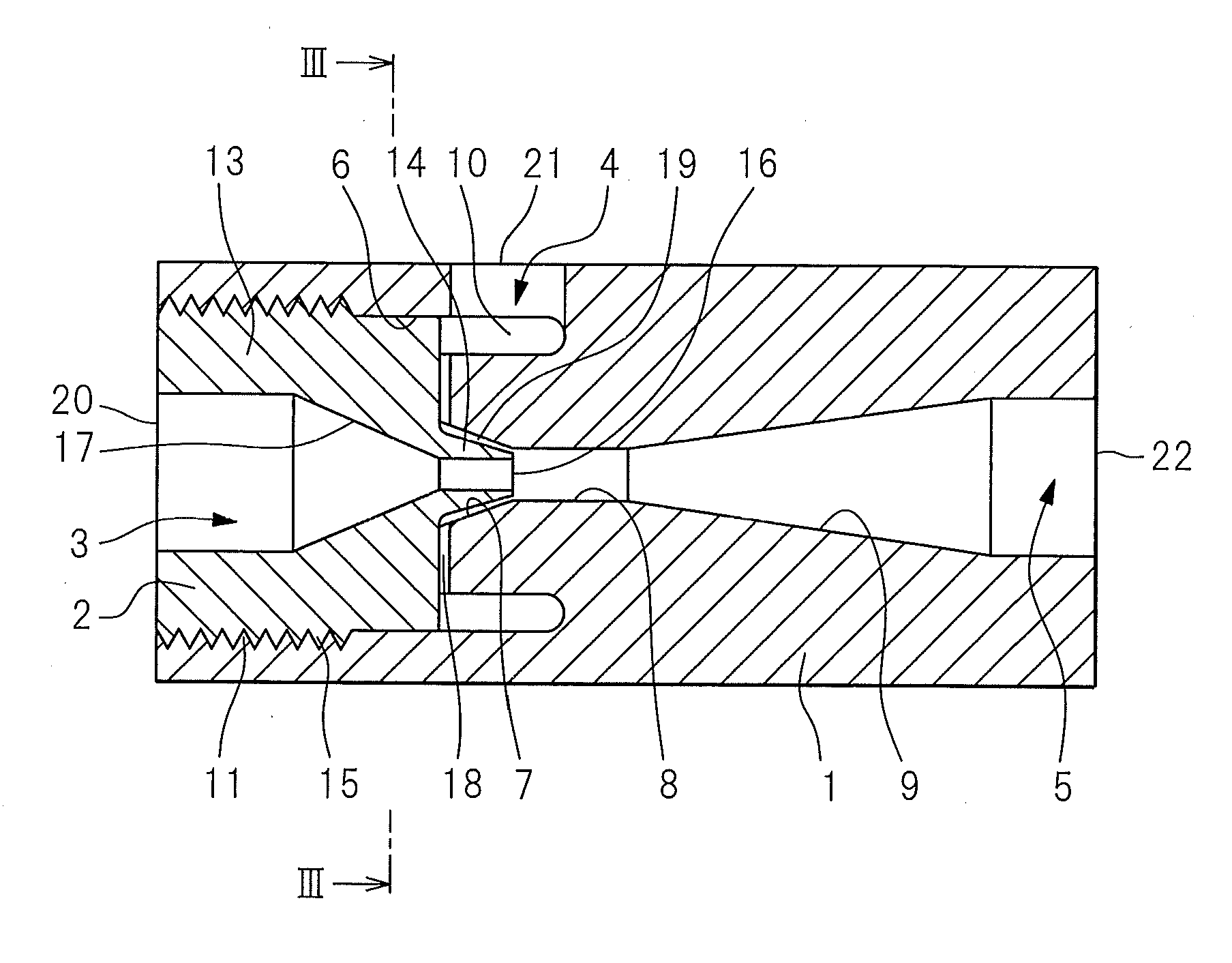
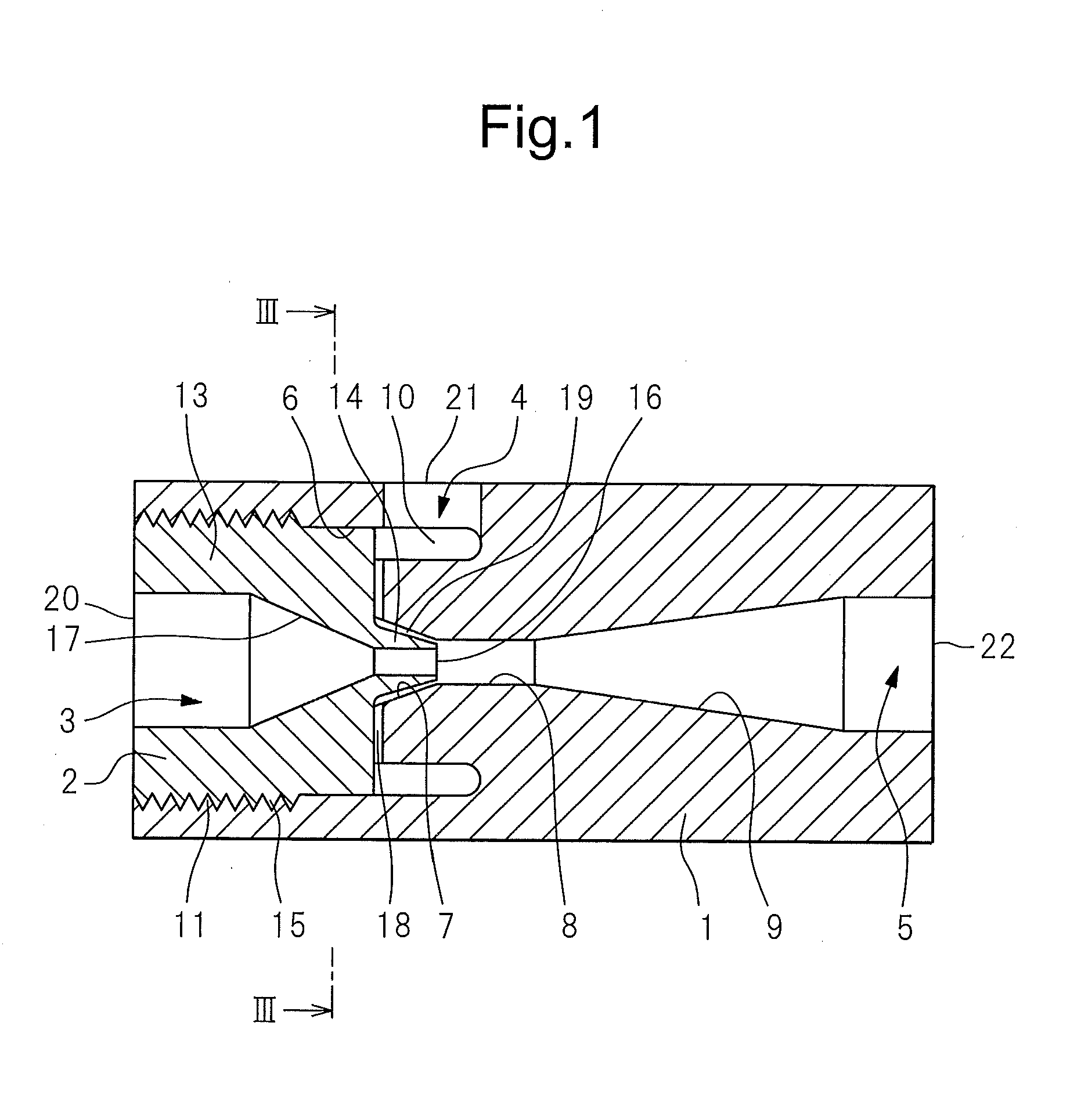
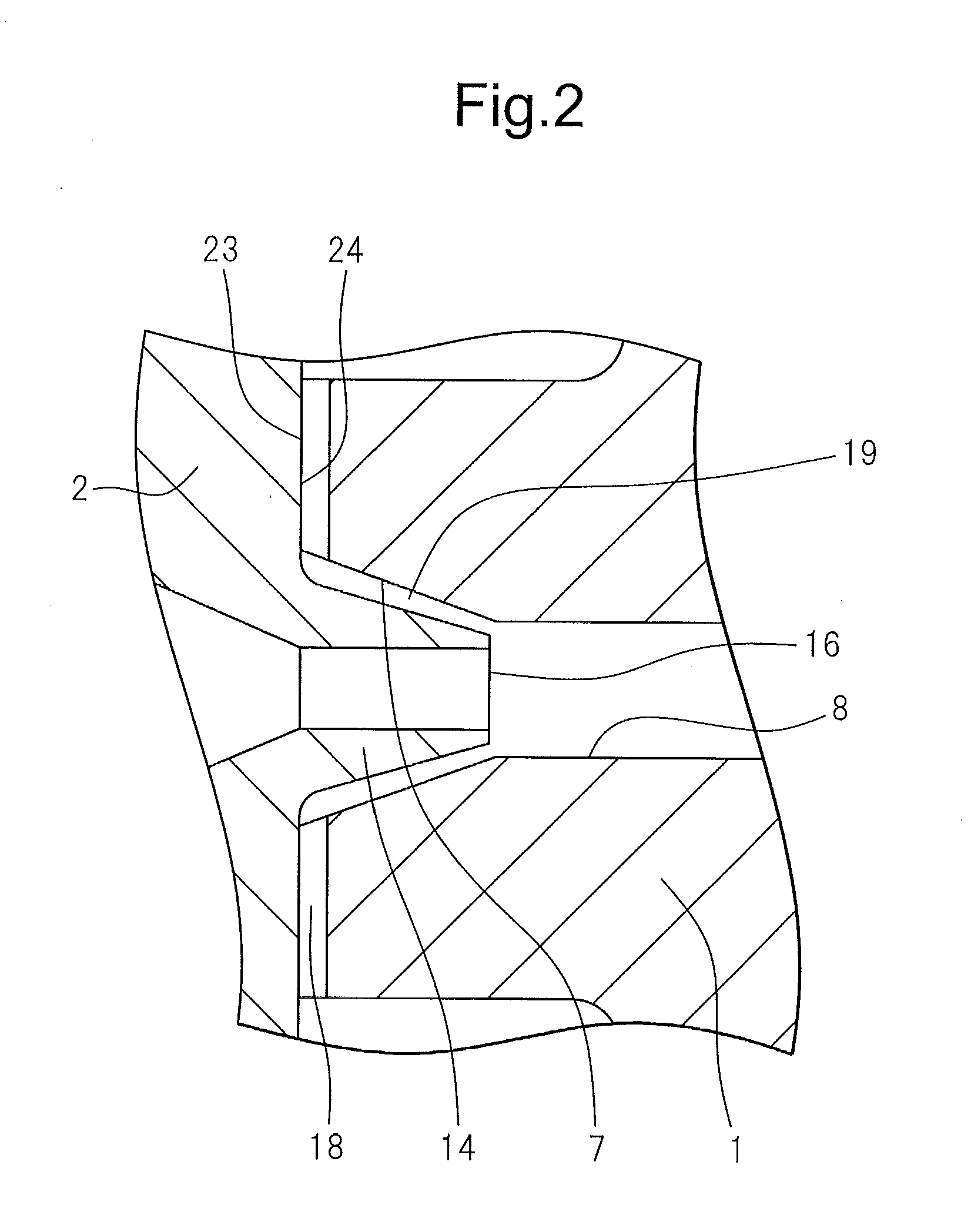
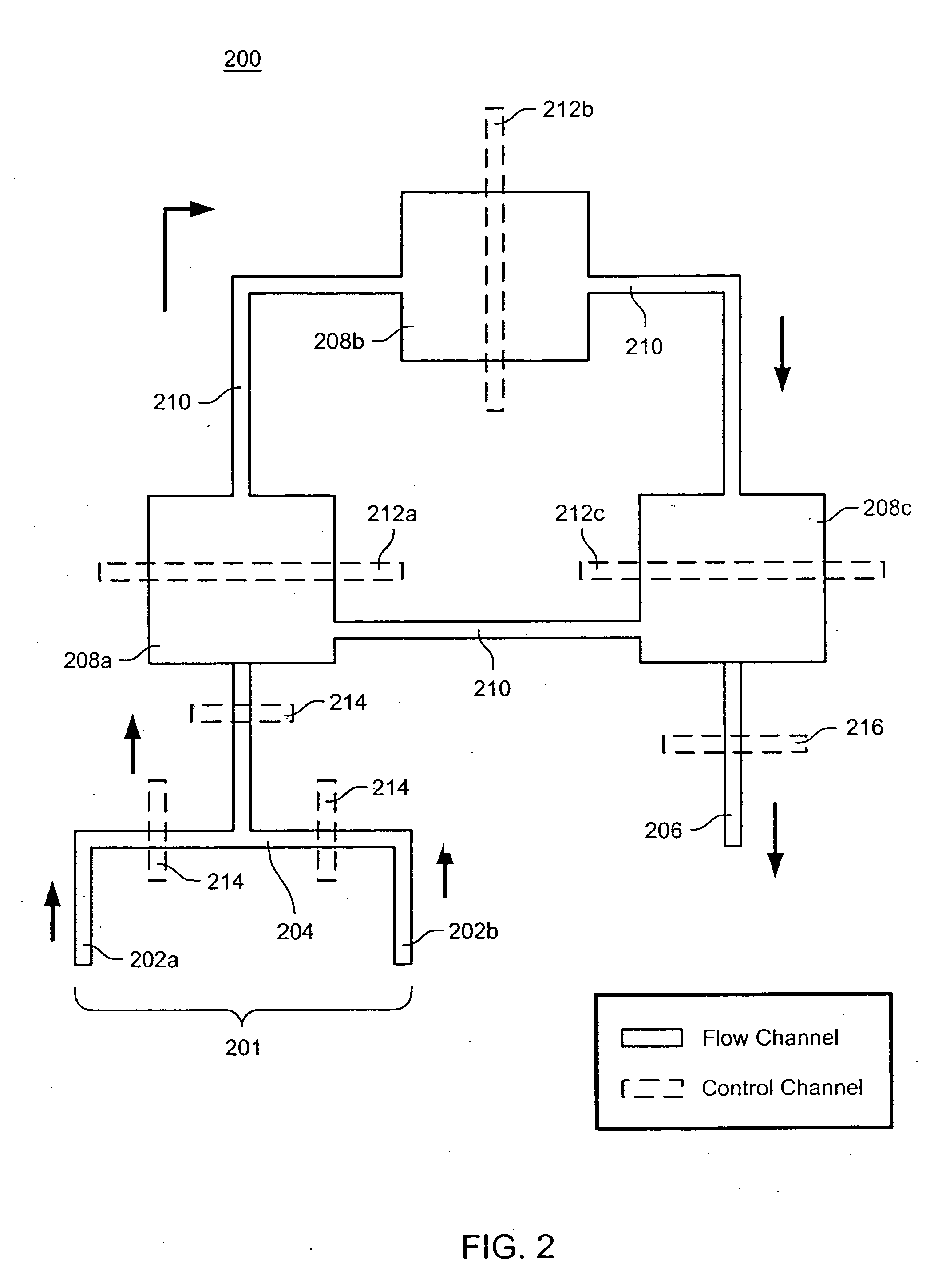
External mixer assembly
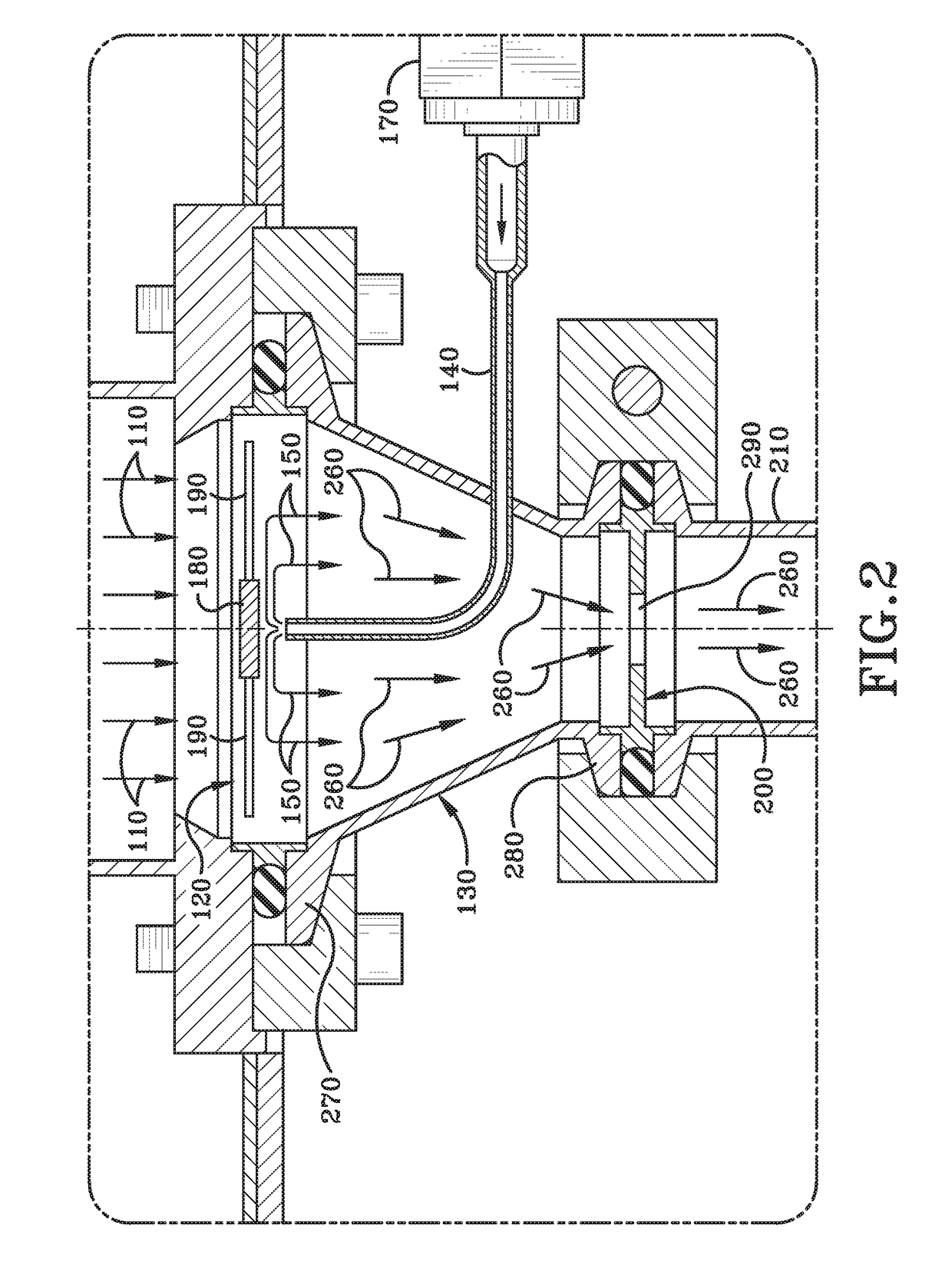
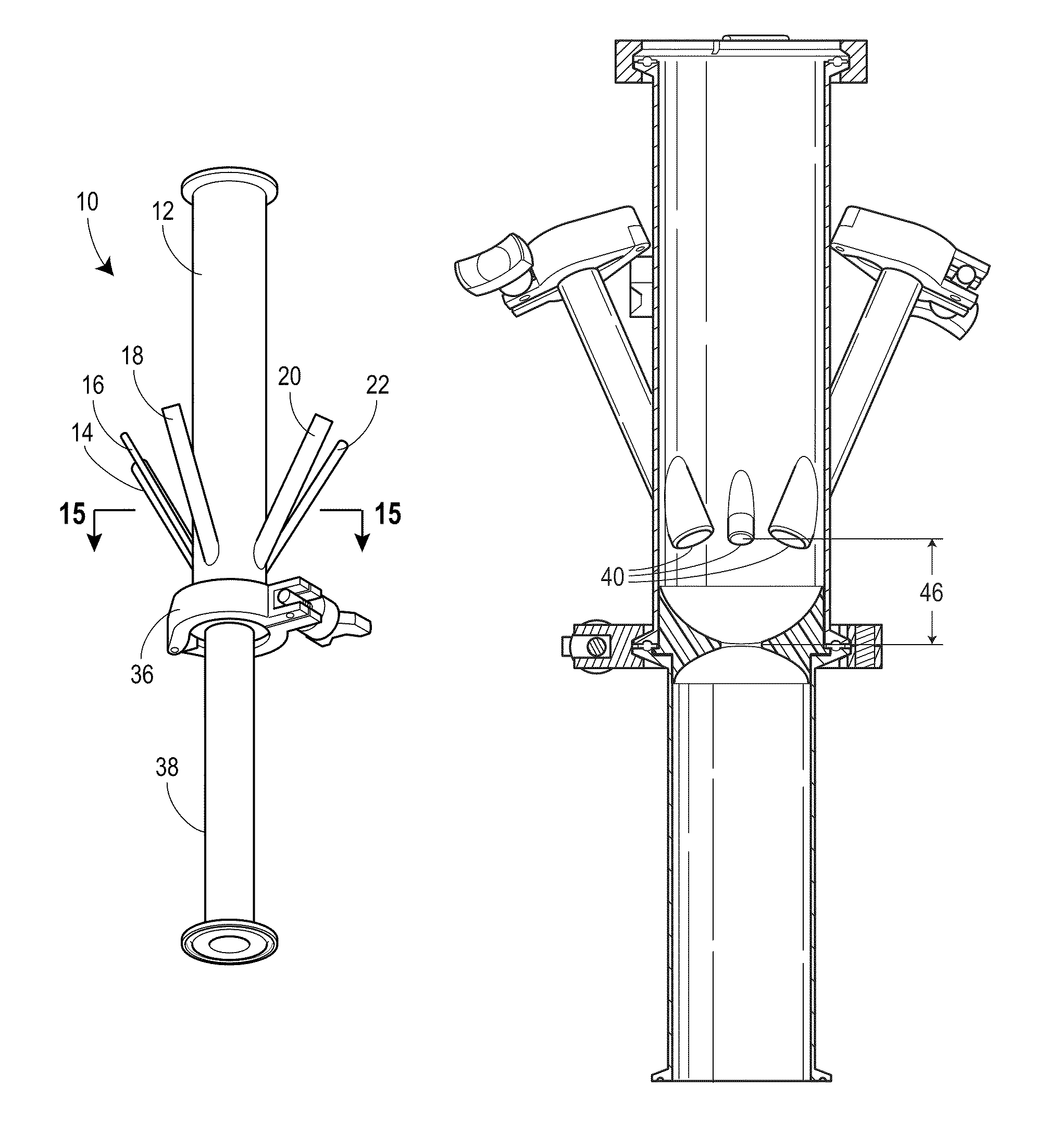
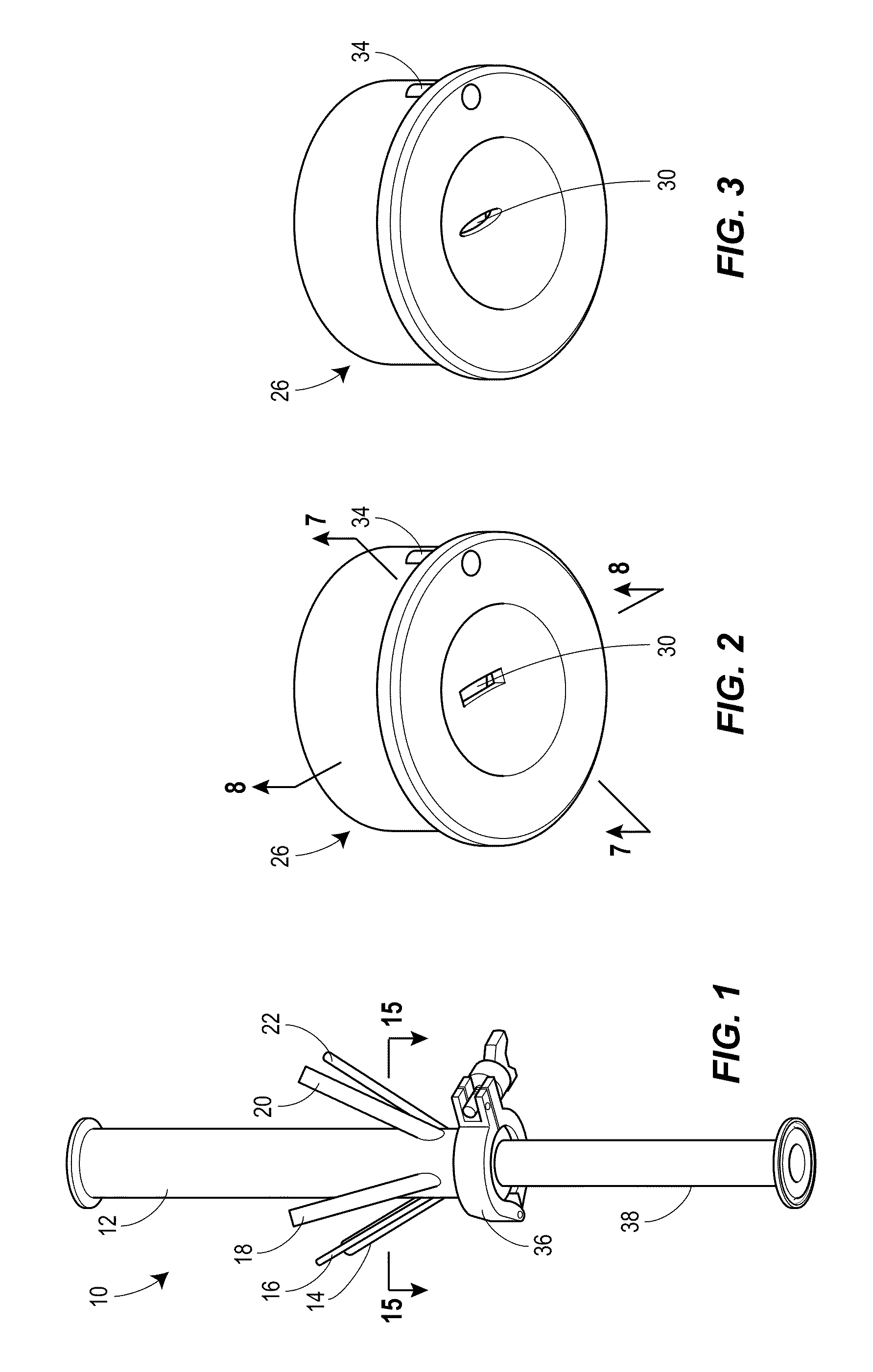
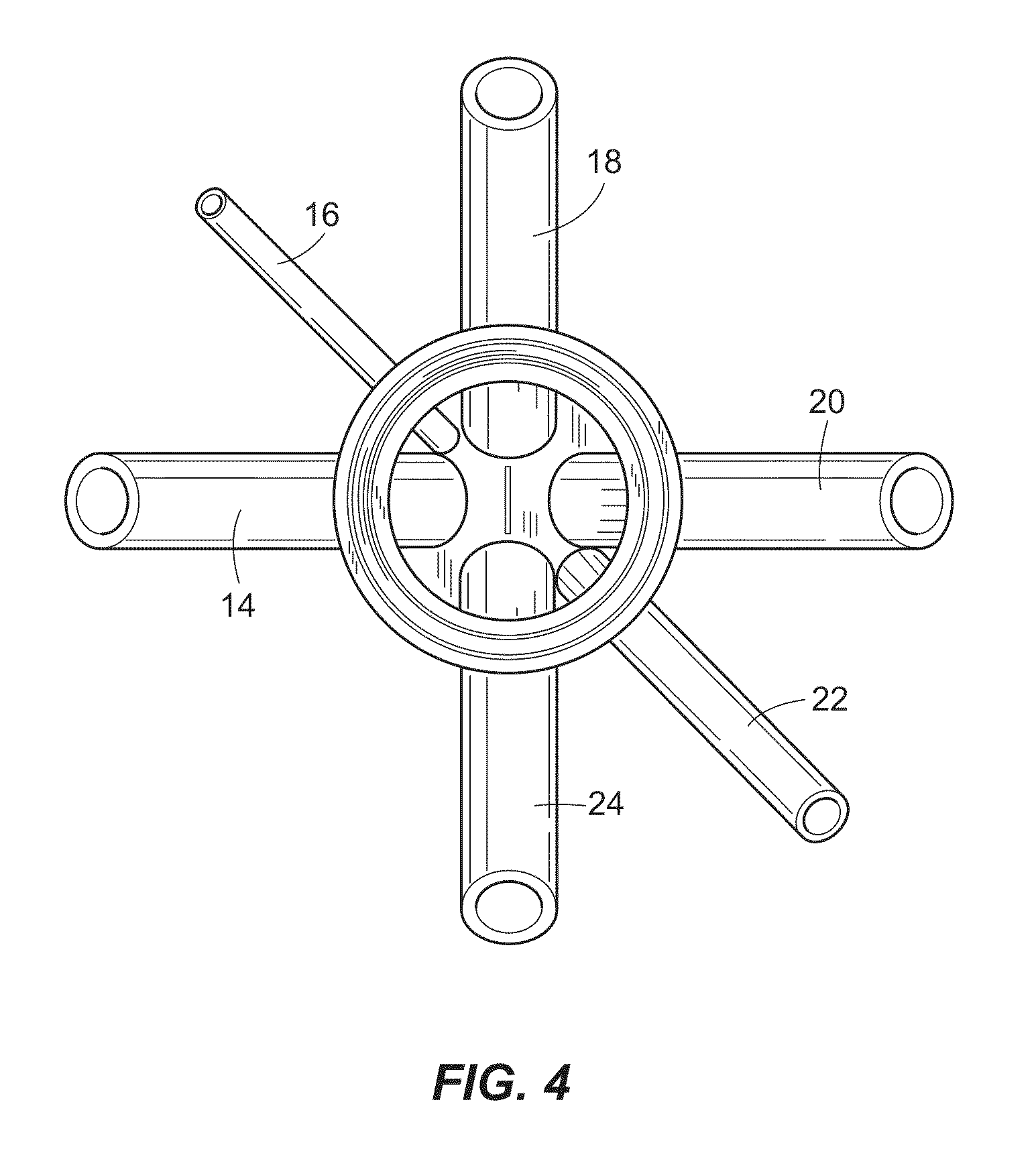
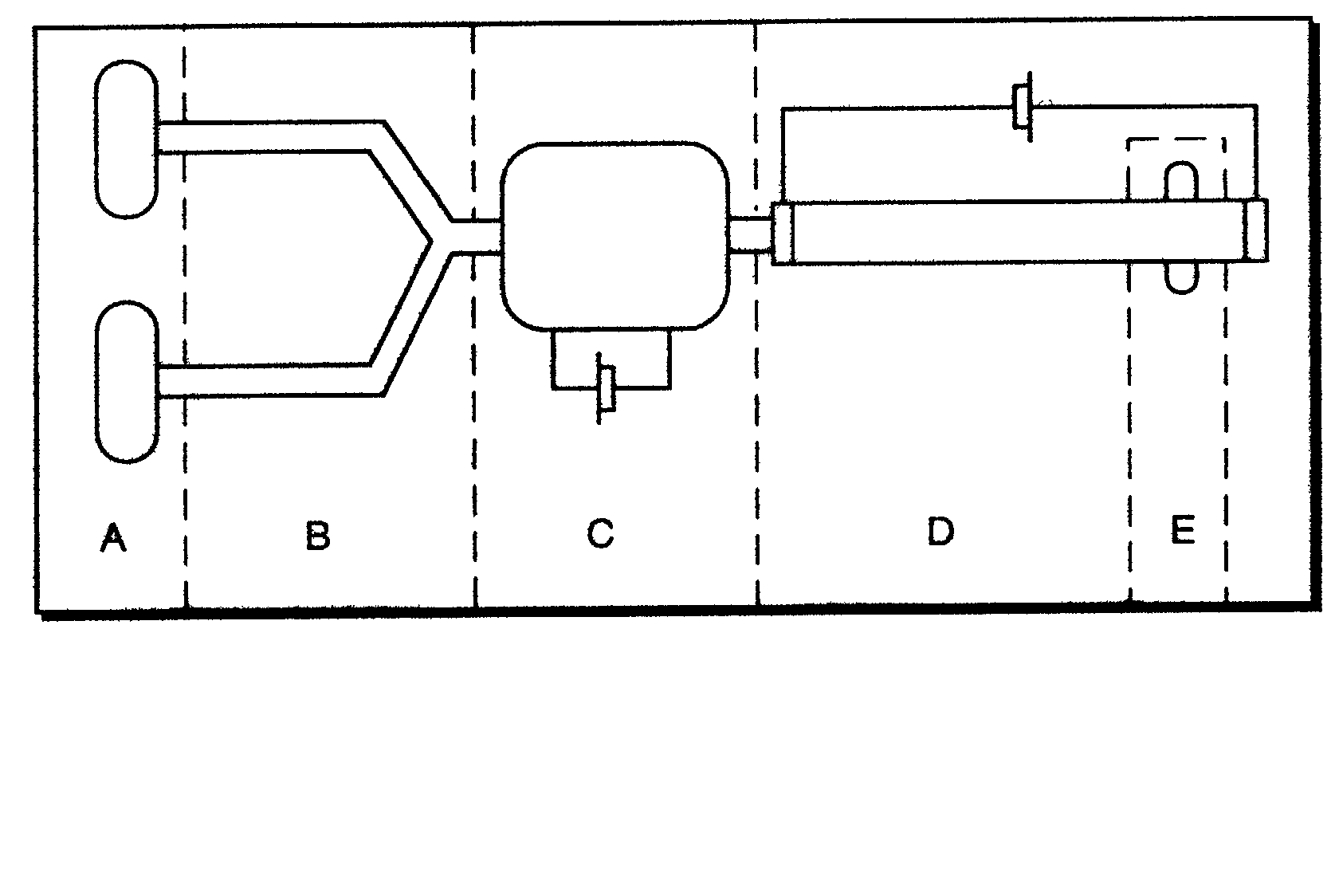
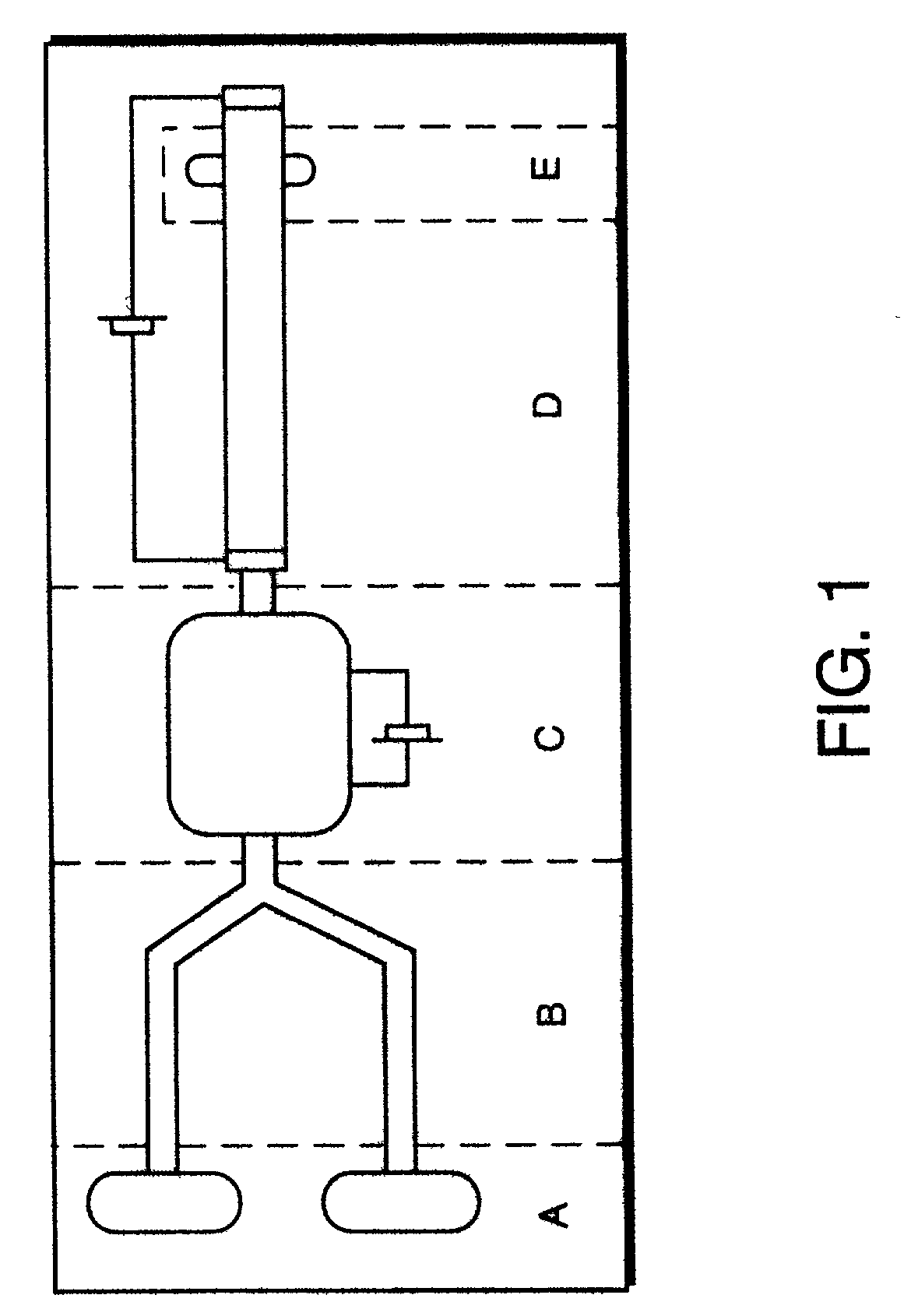
An external mixer assembly is provided which externally mixes and delivers a first and a second component of a biological adhesive to tissues or organs for sealing wounds, stopping bleeding and the like. The first and second components are mixed immediately after exiting from separate outlet ports disposed in fluid communication with component reservoirs. In on embodiment, the external mixer assembly includes a housing having a housing head for enclosing therein a first reservoir containing the first component, and a second reservoir containing the second component. The housing further includes a discharge nozzle defining a longitudinal axis for enclosing therein a conduit assembly having a first and a second conduit in communication with the first and second reservoir, respectively. A deflector assembly is connected to the discharge nozzle. The deflector assembly includes a deflector plate to provide a space for initial mixing of the first and second components. The deflector plate is oriented in generally parallel juxtaposed relation distal to the distal face of the discharge nozzle. The first and second components are preferably fibrinogen and thrombin which intermix to form a fibrin sealant.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
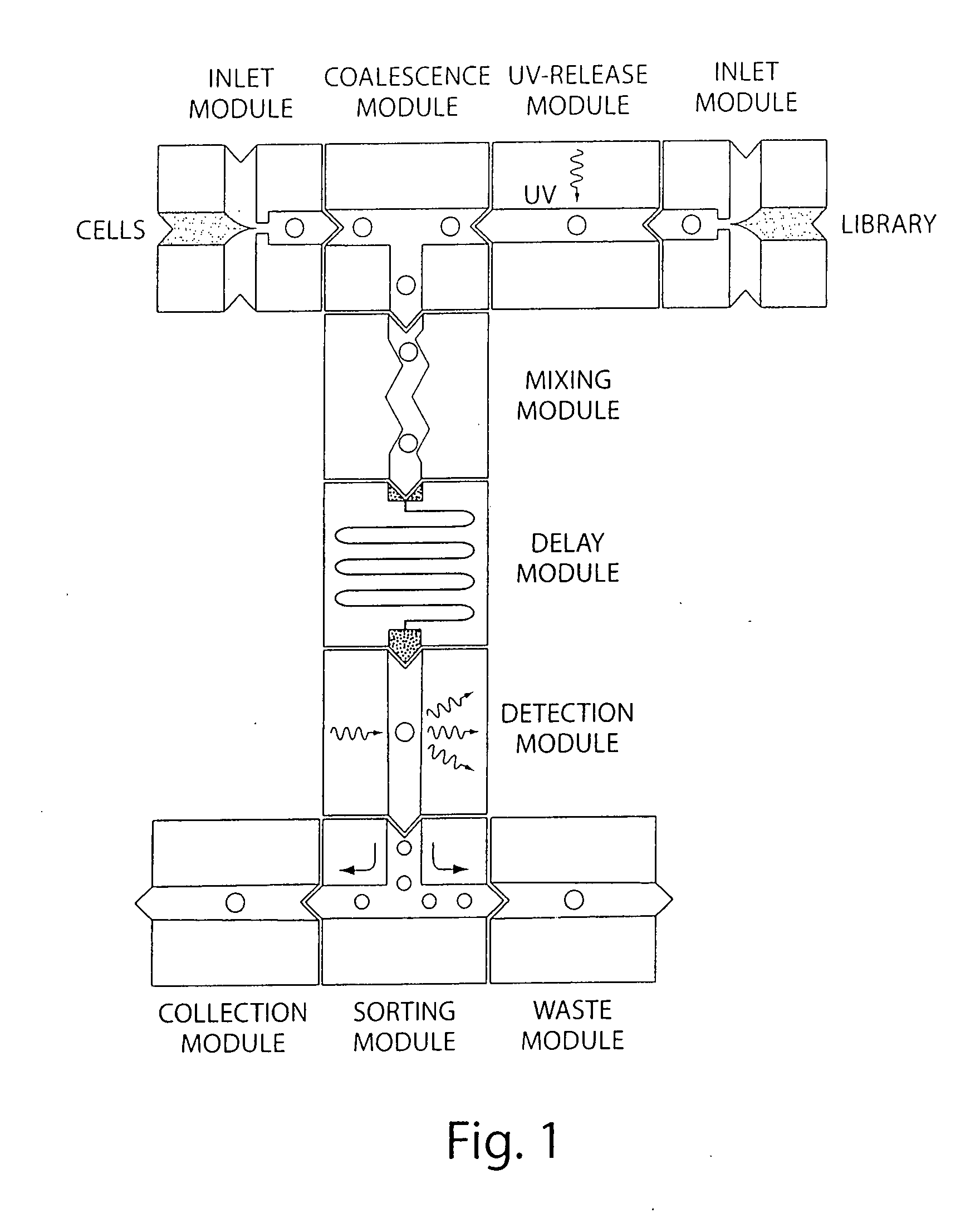
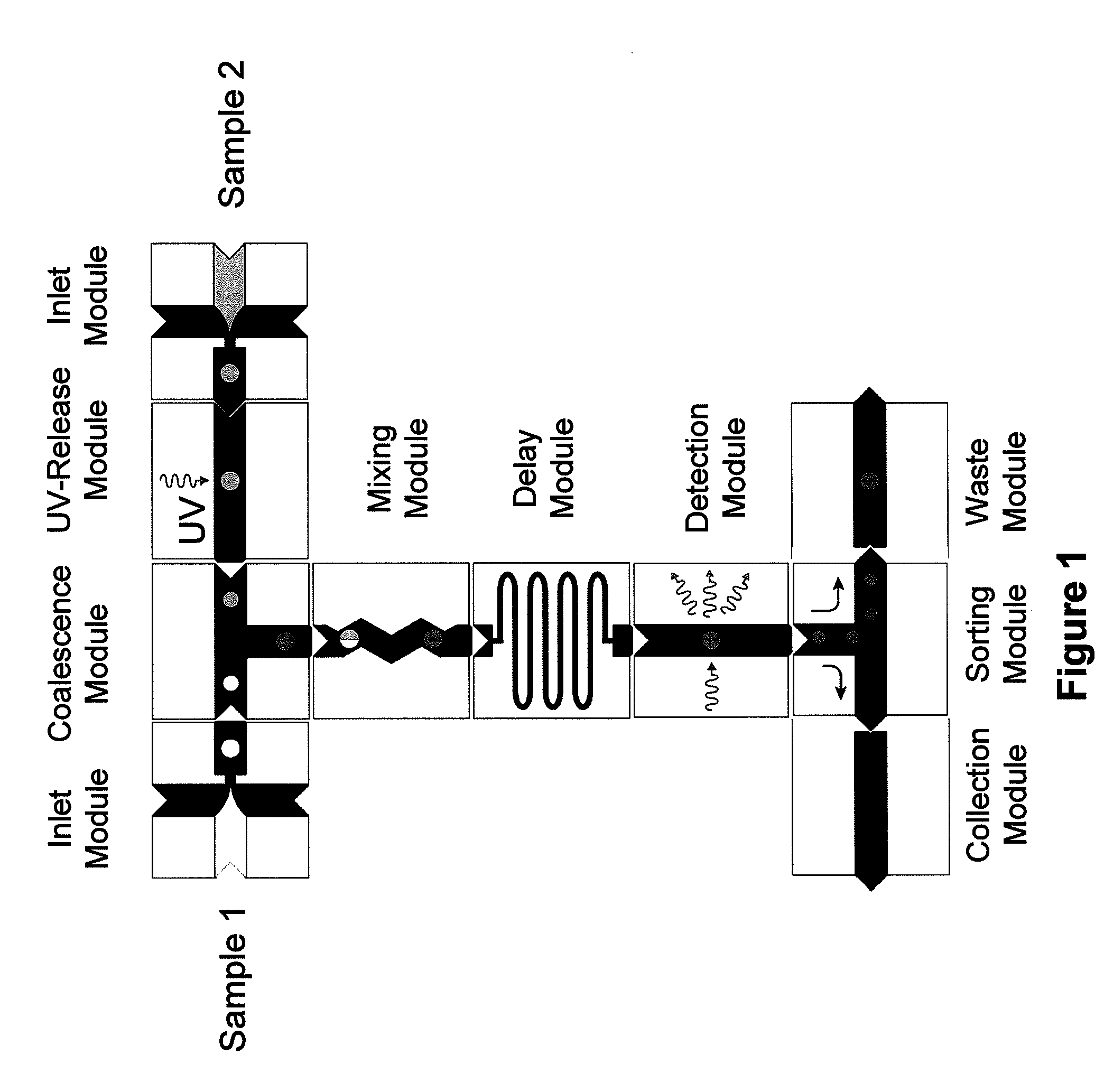
Microfluidic devices and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080014589A1Eliminates surface wettingDielectrophoresisLiquid separation by electricityComputer moduleBiomedical engineering
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Methods for producing droplets for use in capsule-based electrophoretic displays
Methods are provided for forming a dispersion of substantially uniform droplets. An internal phase that includes a plurality of particles suspended in a first fluid is provided and an external phase including a second fluid is provided. The internal phase is vibrated and the internal phase is applied to the external phase. Either the internal phase or a combination of the internal and external phases form a series of droplets or complex droplets of substantially uniform size.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
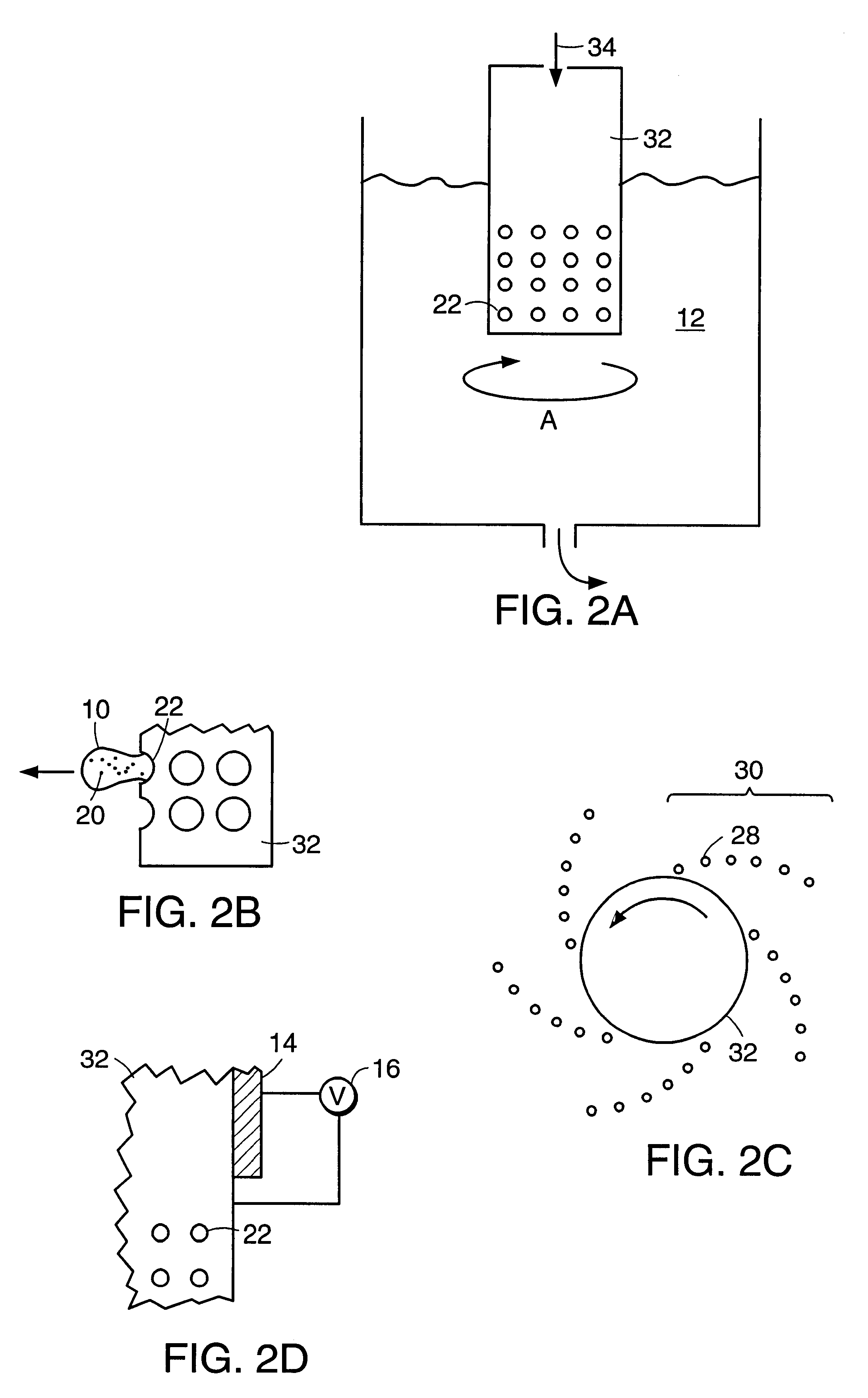
Nucleic acid amplification utilizing microfluidic devices
InactiveUS6960437B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRegulation temperatureEngineering
The present invention provides microfluidic devices and methods using the same in various types of thermal cycling reactions. Certaom devices include a rotary microfluidic channel and a plurality of temperature regions at different locations along the rotary microfluidic channel at which temperature is regulated. Solution can be repeatedly passed through the temperature regions such that the solution is exposed to different temperatures. Other microfluidic devices include an array of reaction chambers formed by intersecting vertical and horizontal flow channels, with the ability to regulate temperature at the reaction chambers. The microfluidic devices can be used to conduct a number of different analyses, including various primer extension reactions and nucleic acid amplification reactions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
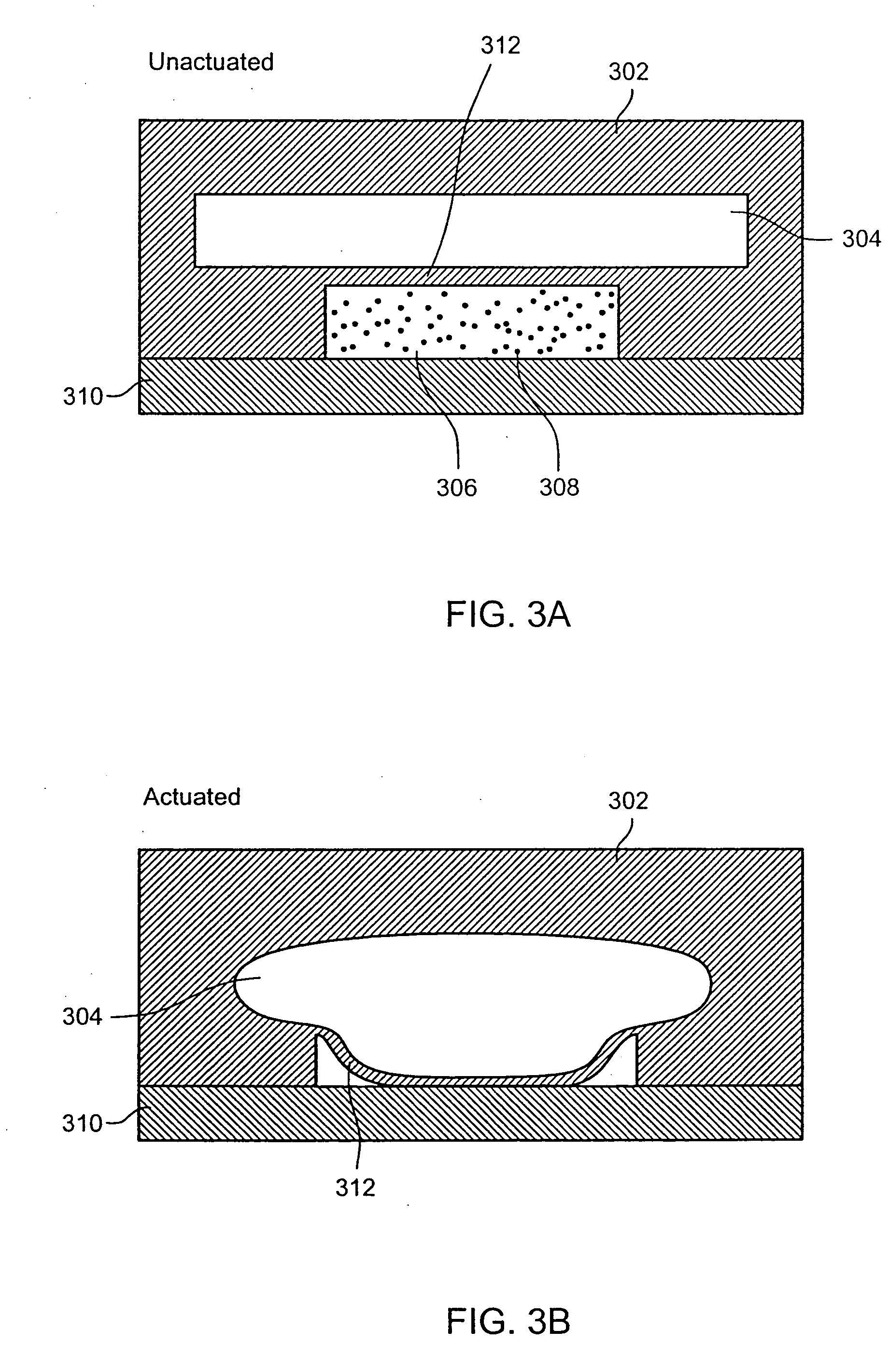
Non-planar microstructures for manipulation of fluid samples
This invention comprises an apparatus and method for the manipulation of materials, including particles, cells, macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids and other moieties, in fluid samples. The apparatus comprises an enclosed chamber on a chip having an internal microstructure with surface area substantially greater than the facial surface area of the internal structure. Generally the internal microstructure comprises a continuous network of channels, each of which has a depth substantially greater than its width. The network may comprise a single channel, a single channel with multiple branches, multiple channels, multiple channels with multiple branches, and any combination thereof. The internal structure may present an inert, non-reactive surface, or be coated with a reactive ligand, or be electrically conductive and optionally be coated with an electrical insulator. Discrete portions of the internal structure may differ in structural and surface properties. Multiple chips may be linked together to create a multiplexed array of chambers, optionally linked to other analytical devices.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Integrated active flux microfluidic devices and methods
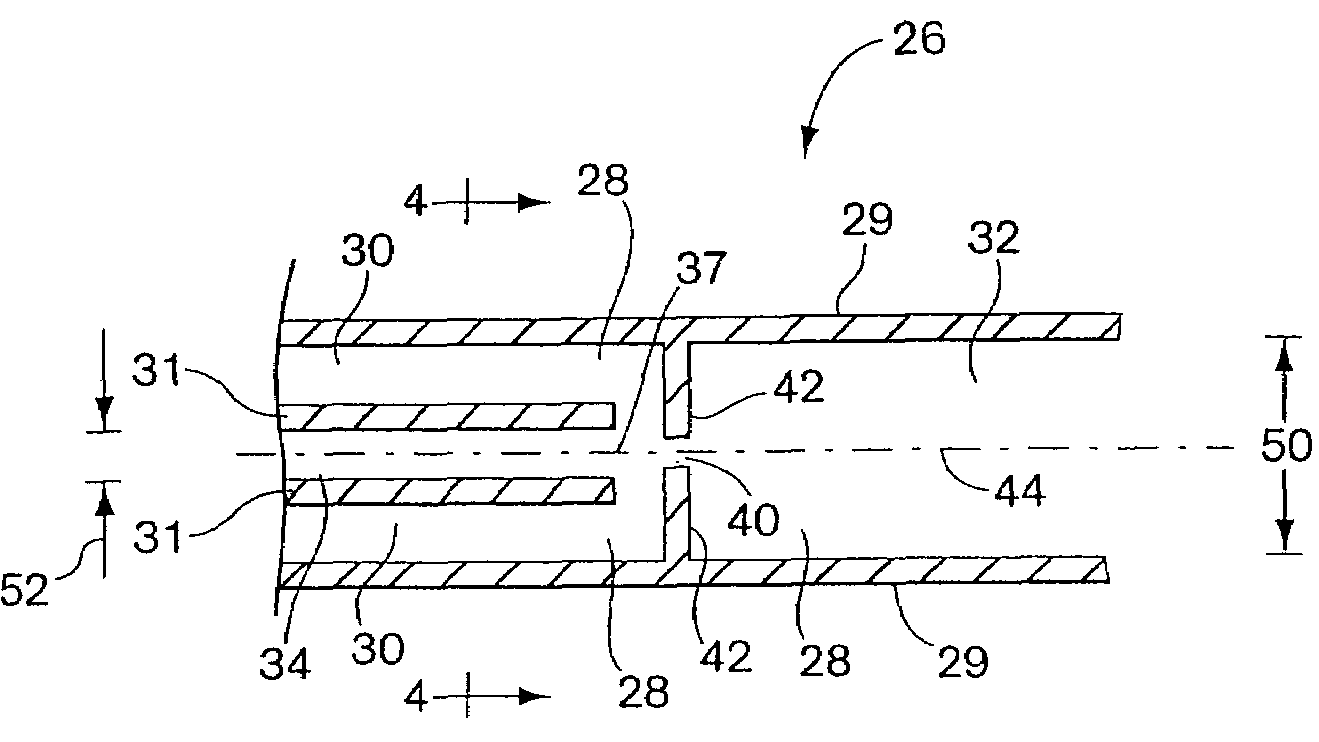
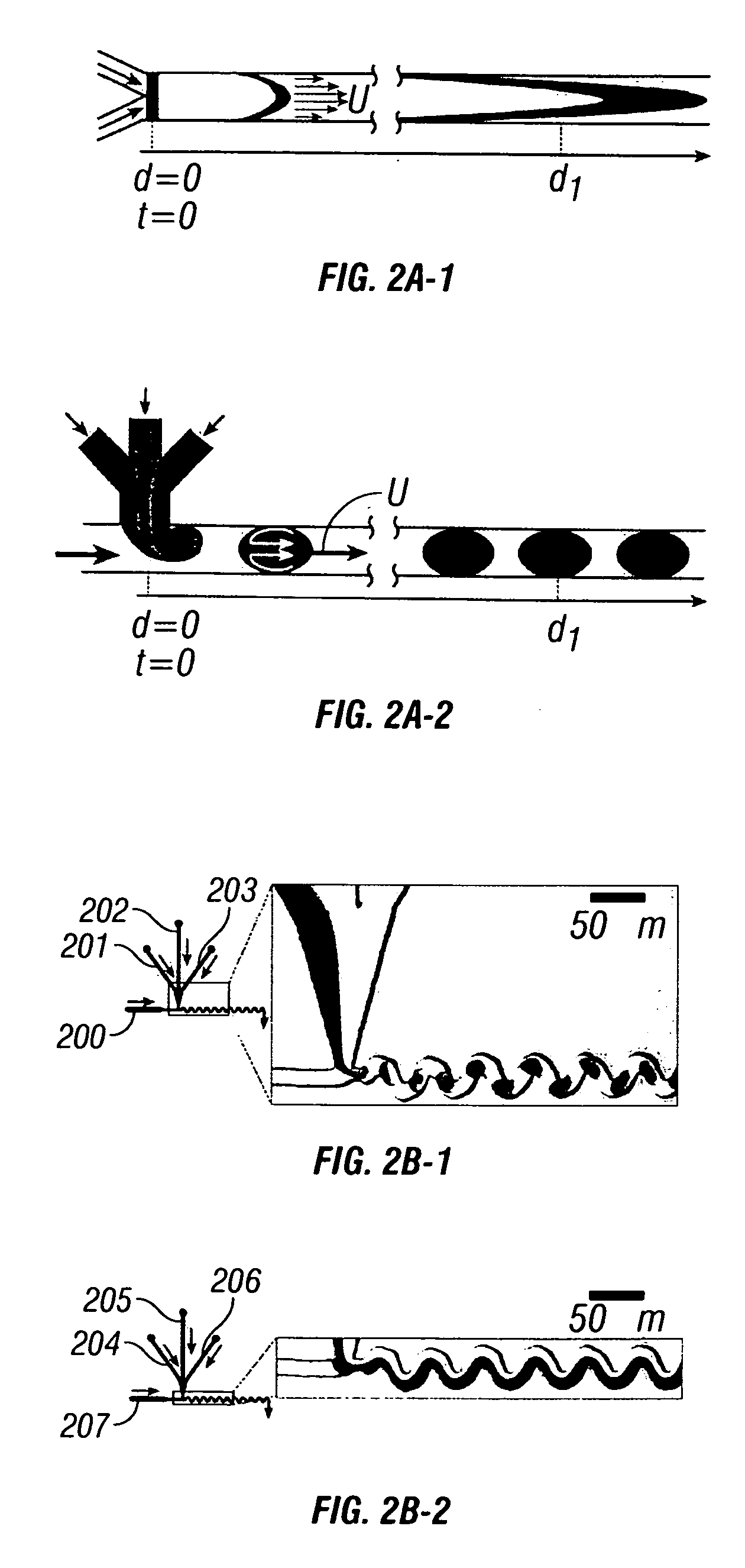
InactiveUS6767706B2Rapid and complete exposureQuick and accurate and inexpensive analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFlow mixersAntigenHybridization probe
The invention relates to a microfabricated device for the rapid detection of DNA, proteins or other molecules associated with a particular disease. The devices and methods of the invention can be used for the simultaneous diagnosis of multiple diseases by detecting molecules (e.g. amounts of molecules), such as polynucleotides (e.g., DNA) or proteins (e.g., antibodies), by measuring the signal of a detectable reporter associated with hybridized polynucleotides or antigen / antibody complex. In the microfabricated device according to the invention, detection of the presence of molecules (i.e., polynucleotides, proteins, or antigen / antibody complexes) are correlated to a hybridization signal from an optically-detectable (e.g. fluorescent) reporter associated with the bound molecules. These hybridization signals can be detected by any suitable means, for example optical, and can be stored for example in a computer as a representation of the presence of a particular gene. Hybridization probes can be immobilized on a substrate that forms part of or is exposed to a channel or channels of the device that form a closed loop, for circulation of sample to actively contact complementary probes. Universal chips according to the invention can be fabricated not only with DNA but also with other molecules such as RNA, proteins, peptide nucleic acid (PNA) and polyamide molecules.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
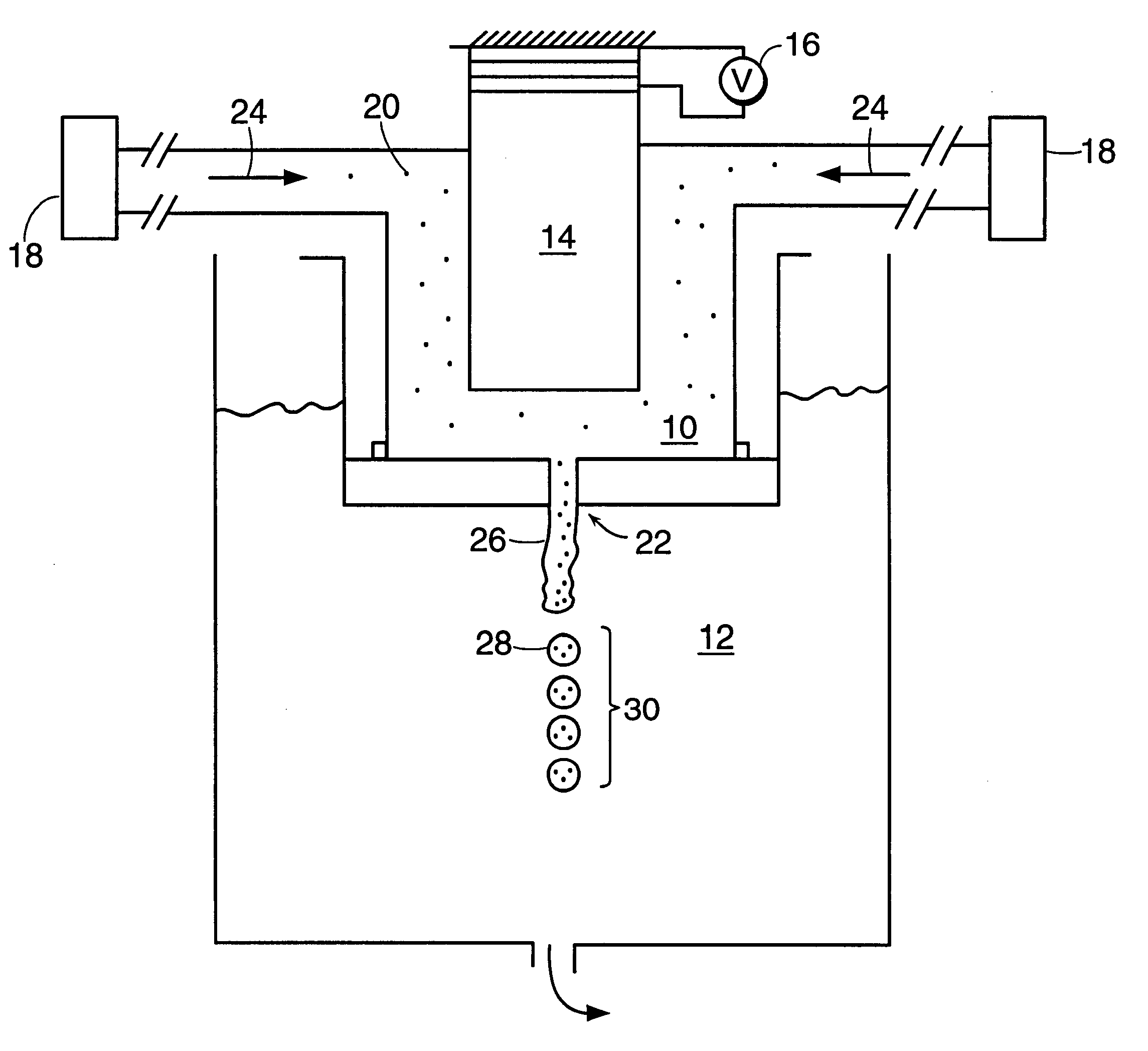
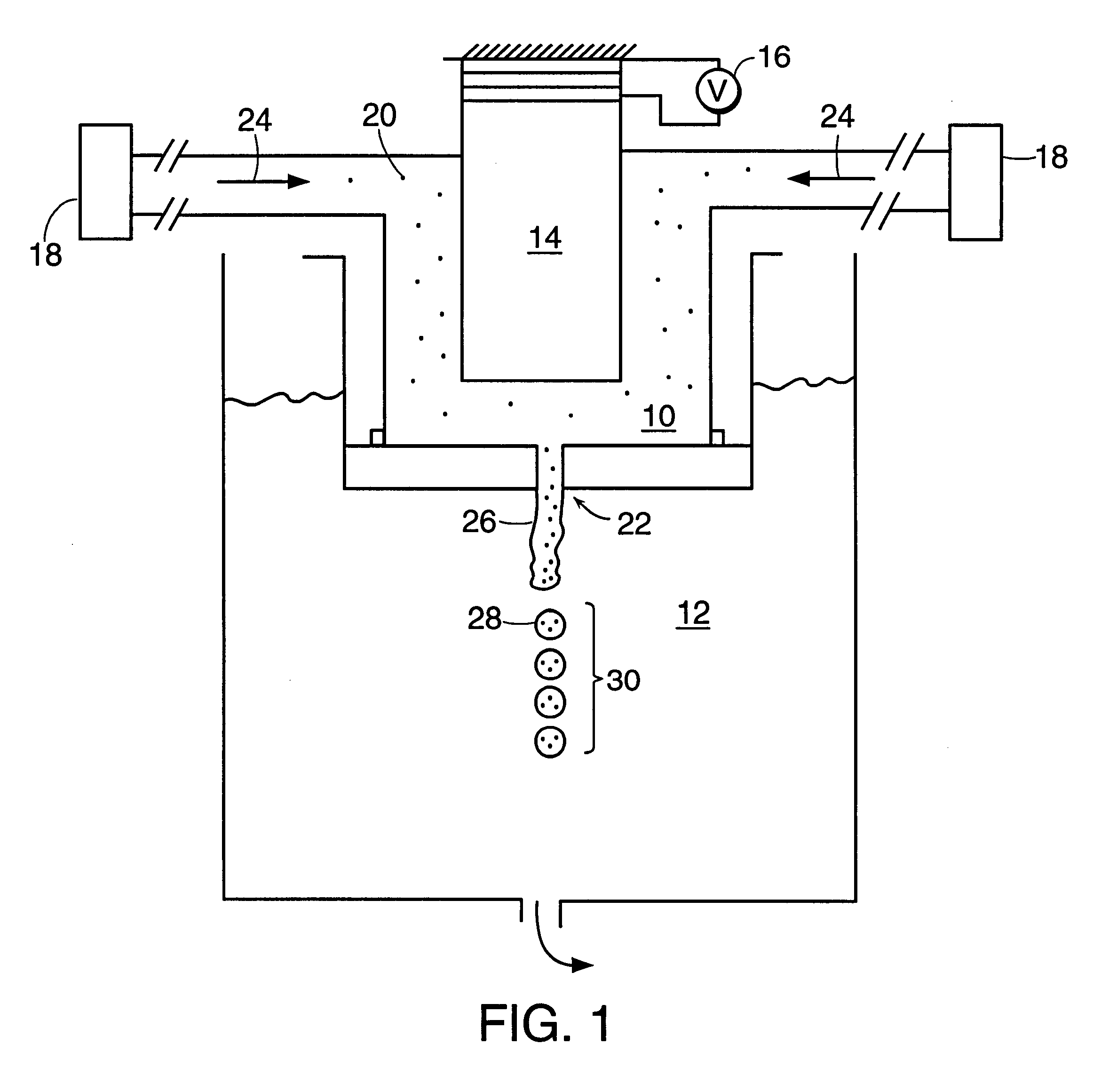
Method and apparatus for fluid dispersion
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO +1
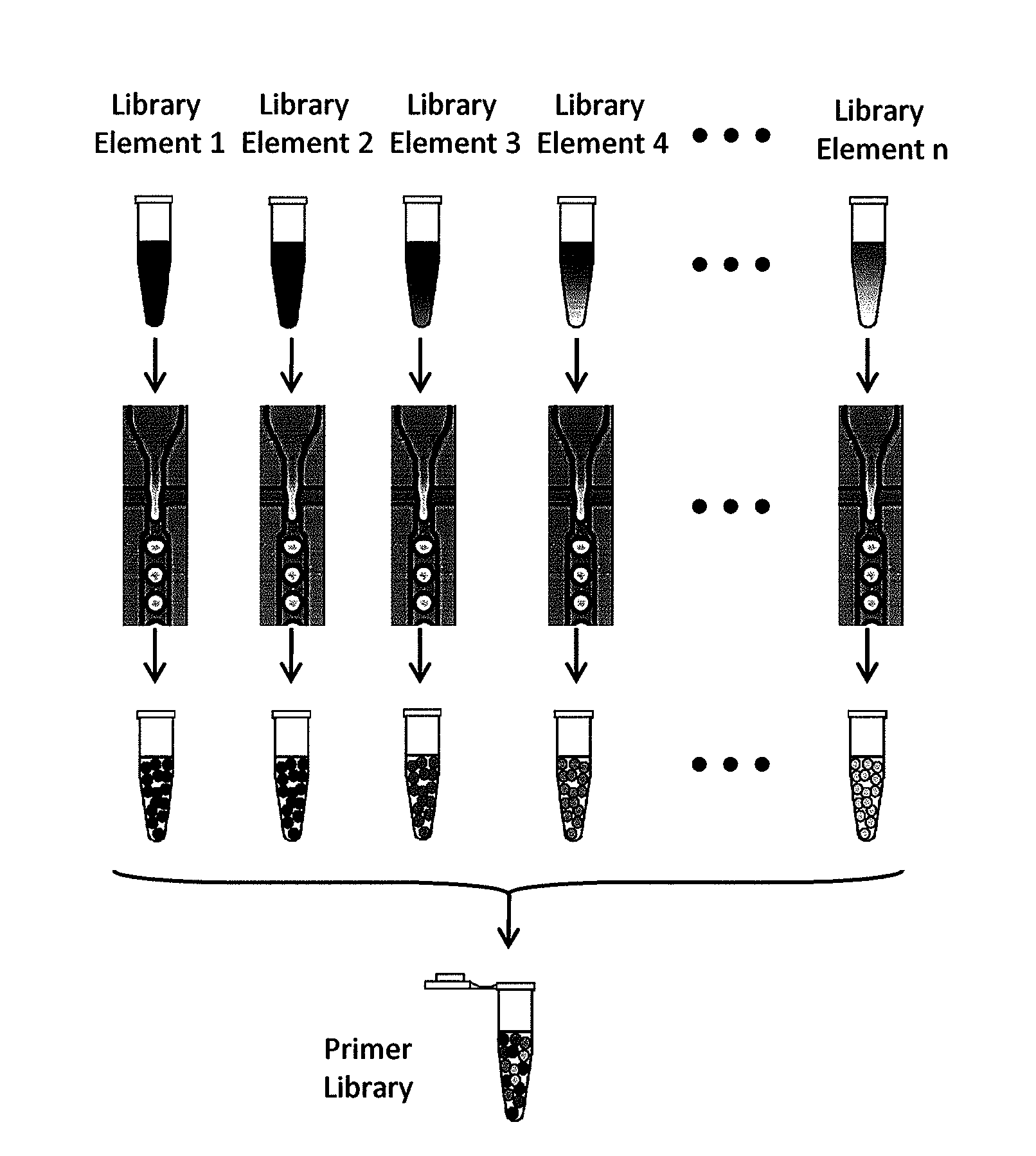
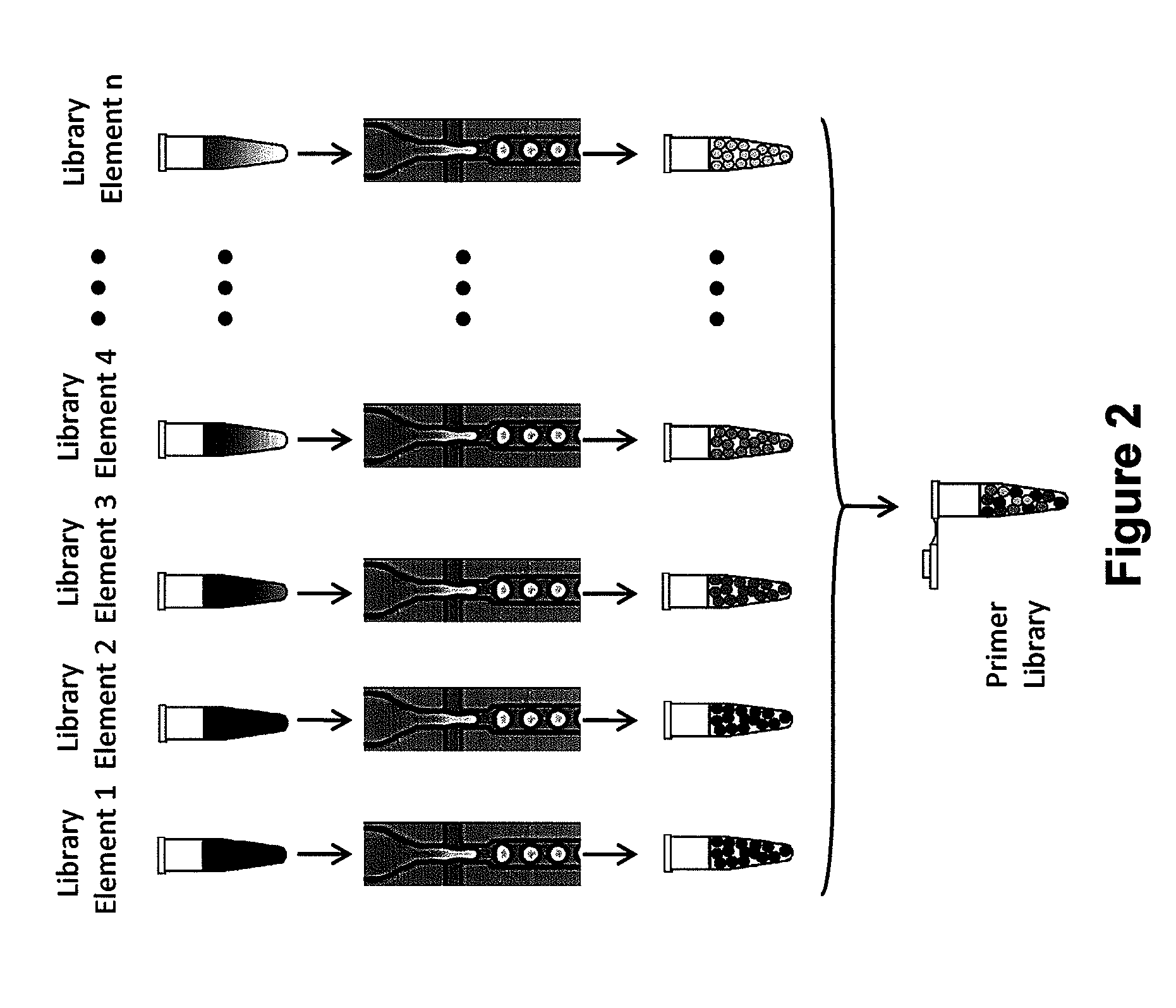
Droplet Libraries
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
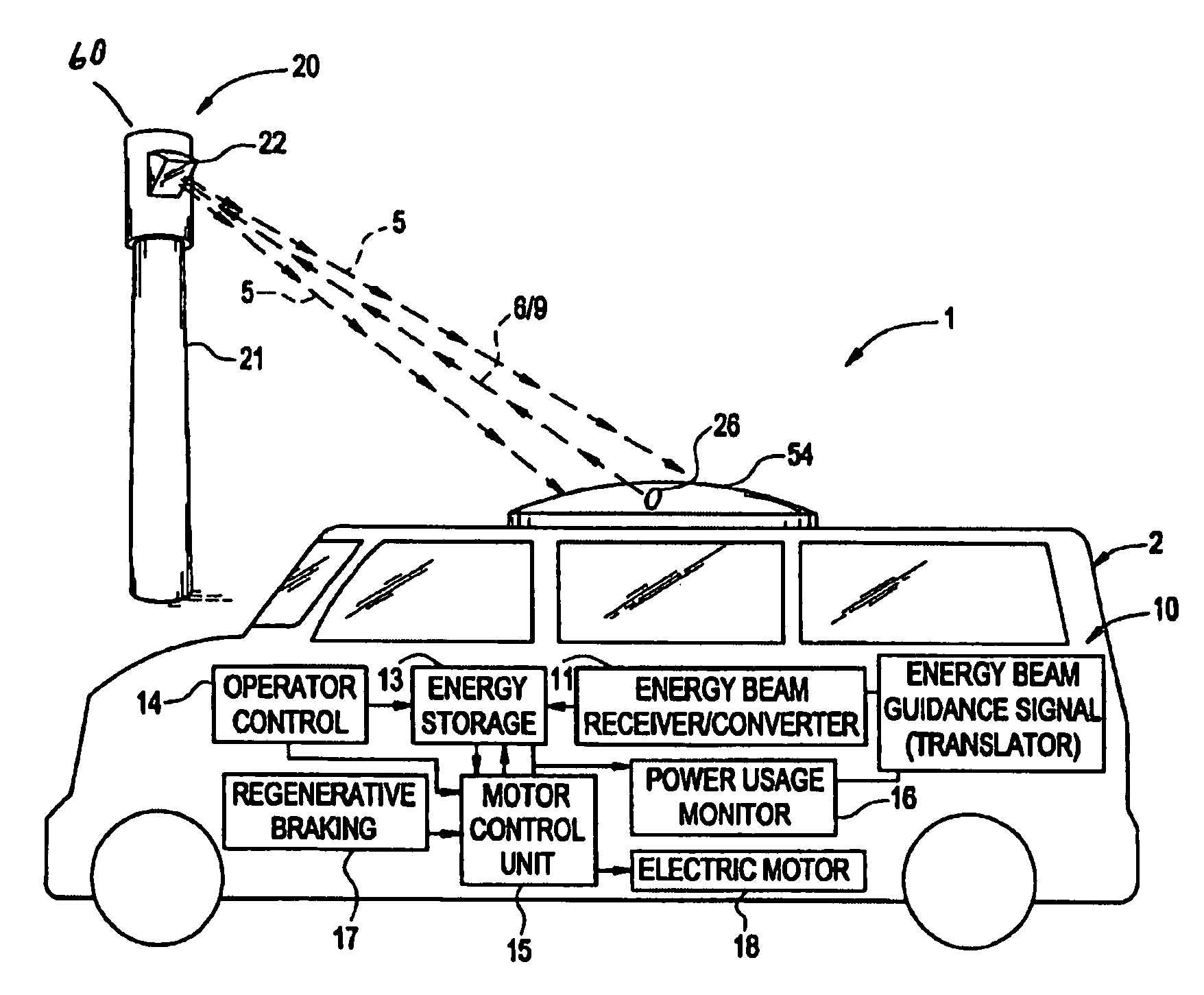
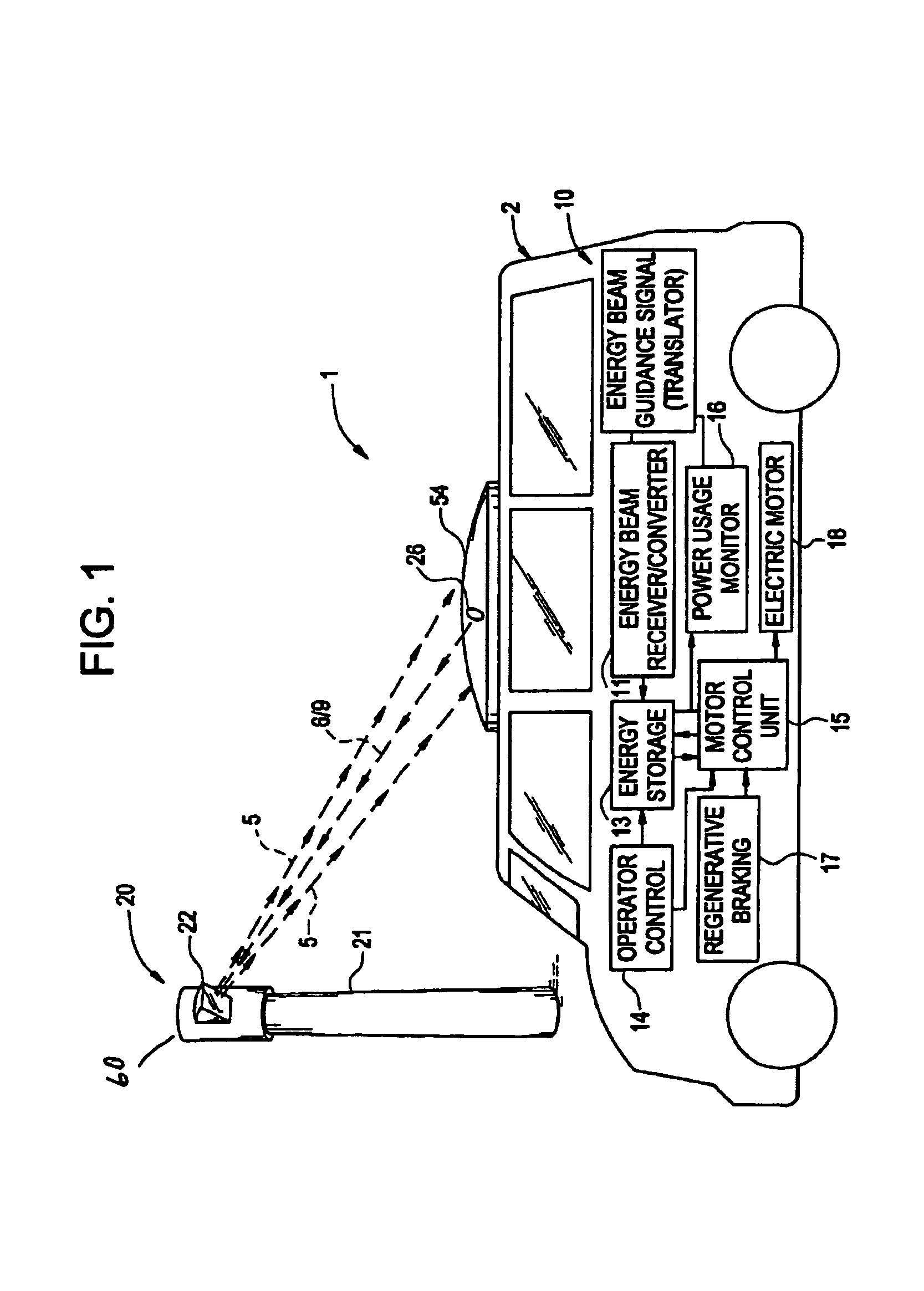
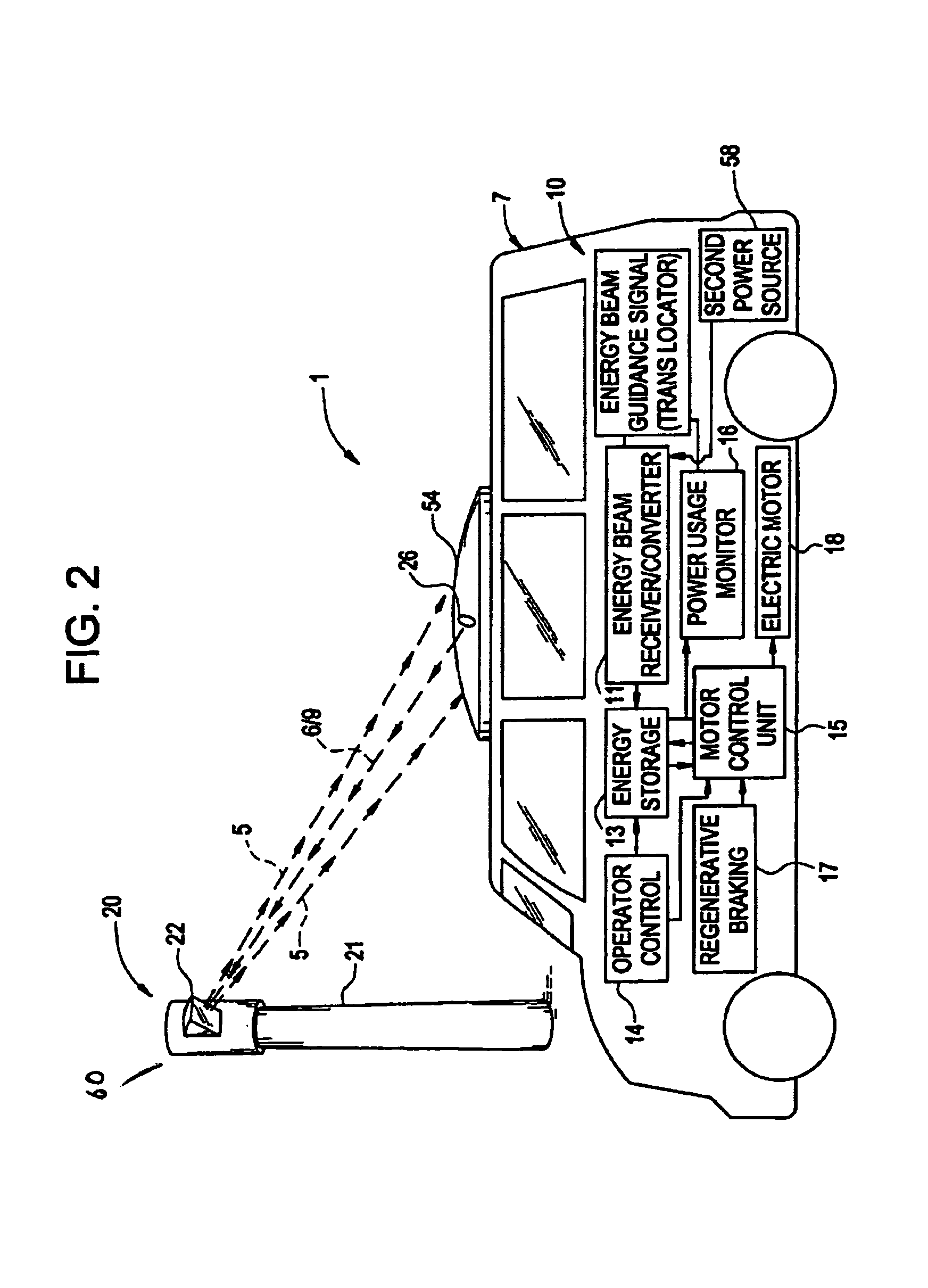
Remote power recharge for electronic equipment
InactiveUS7068991B2Batteries circuit arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
A conductorless charging and power system for electronic appliances and method for communicating power to a power receiver employing wireless energy transmission are disclosed. The remote charging system includes a power transmission unit, which transmits energy as a directional power beam, and a power receiver system that receives the transmitted energy. The power receiver system is preferably incorporated in an appliance and includes an energy receptor capable of receiving the wireless power beam and transferring the energy from the beam to an energy storage device included in the appliance. The power transmission unit receives and tracks a power request signal from the power receiver system to track the power receiver system location during energy transmission. Data streams may be incorporated into the wireless signals of the remote charging system, allowing the remote charging system to function as a communications pathway as well as a power delivery system.
Owner:PARISE RONALD J
Method and apparatus for fluid dispersion
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO +1
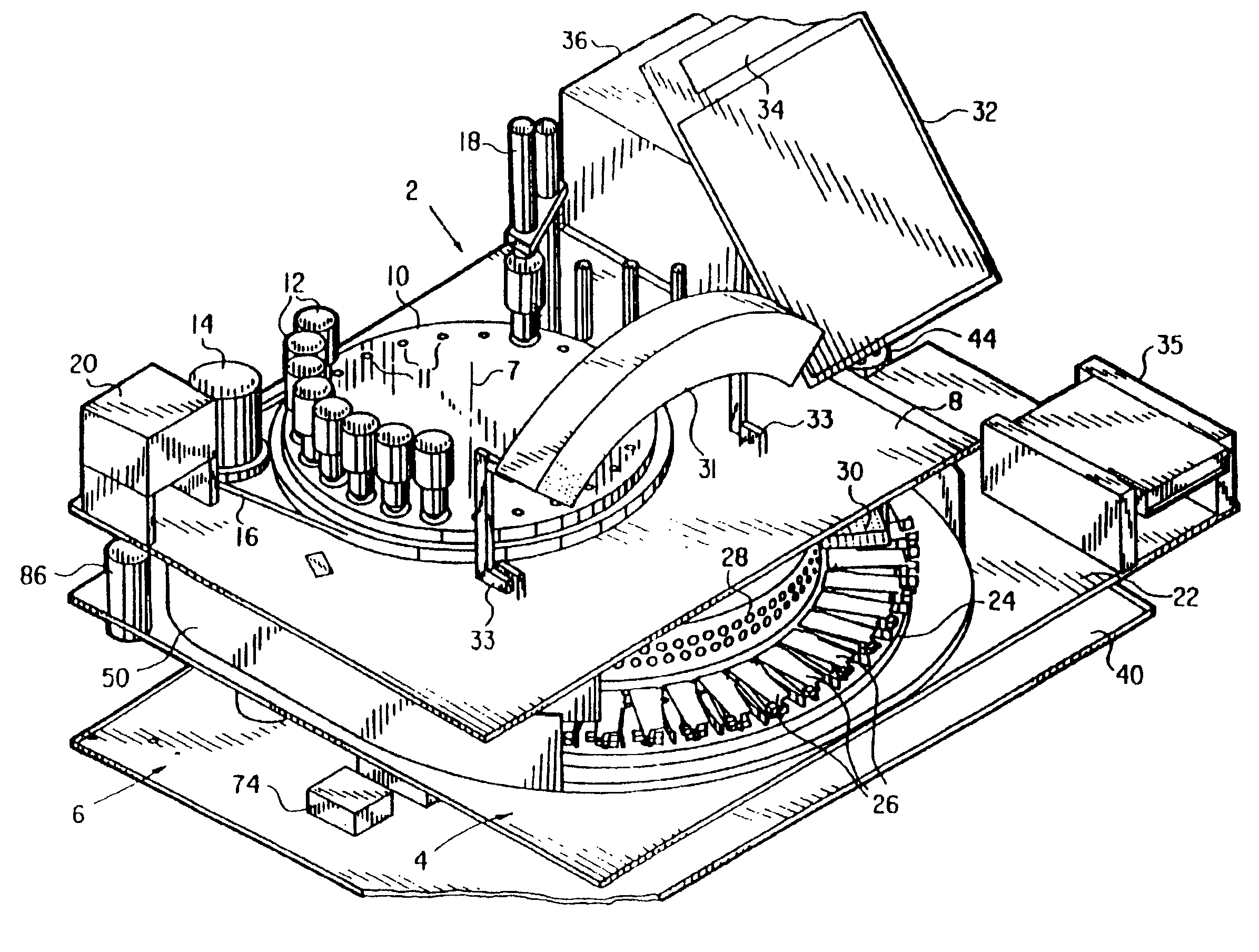
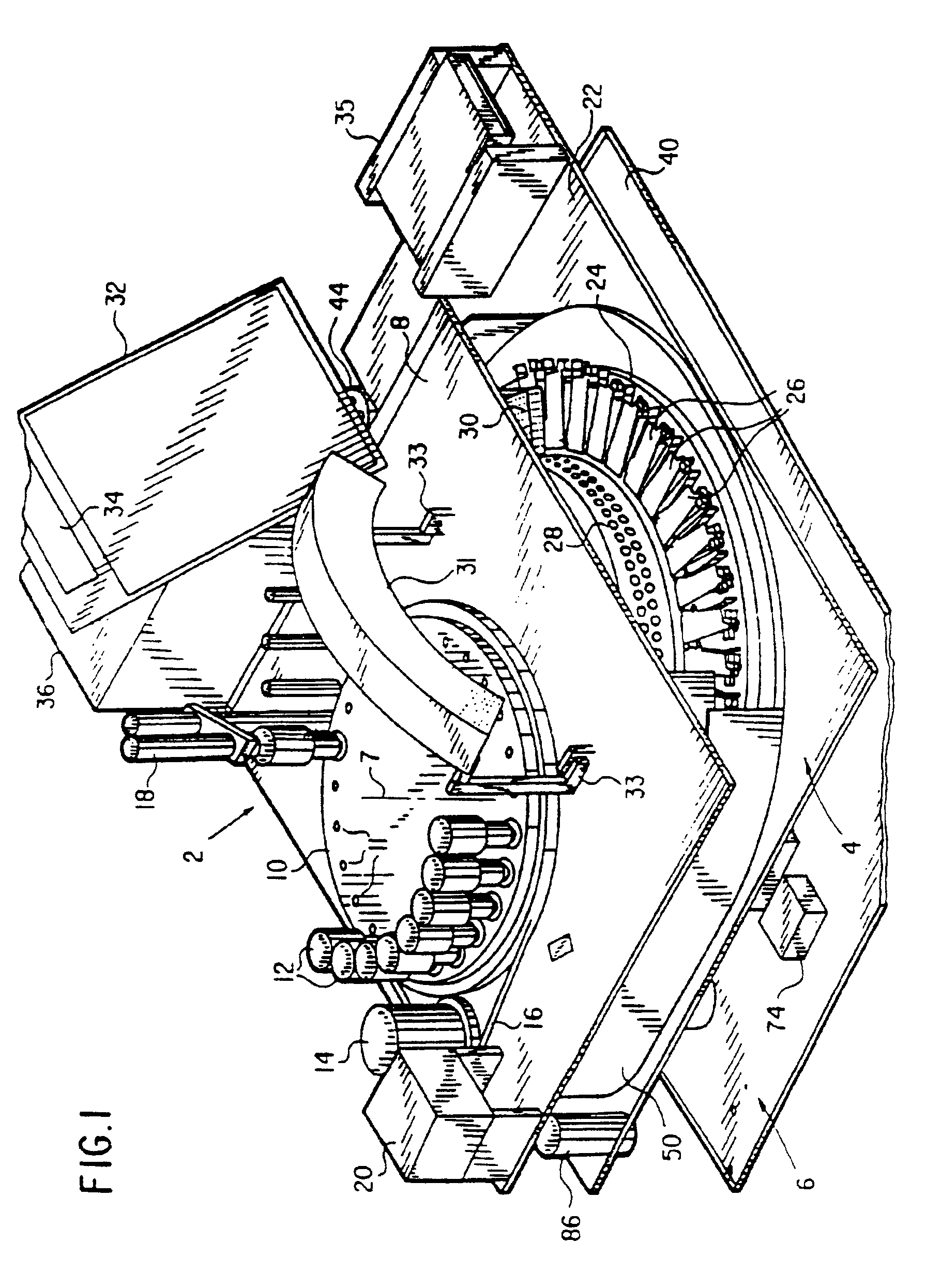
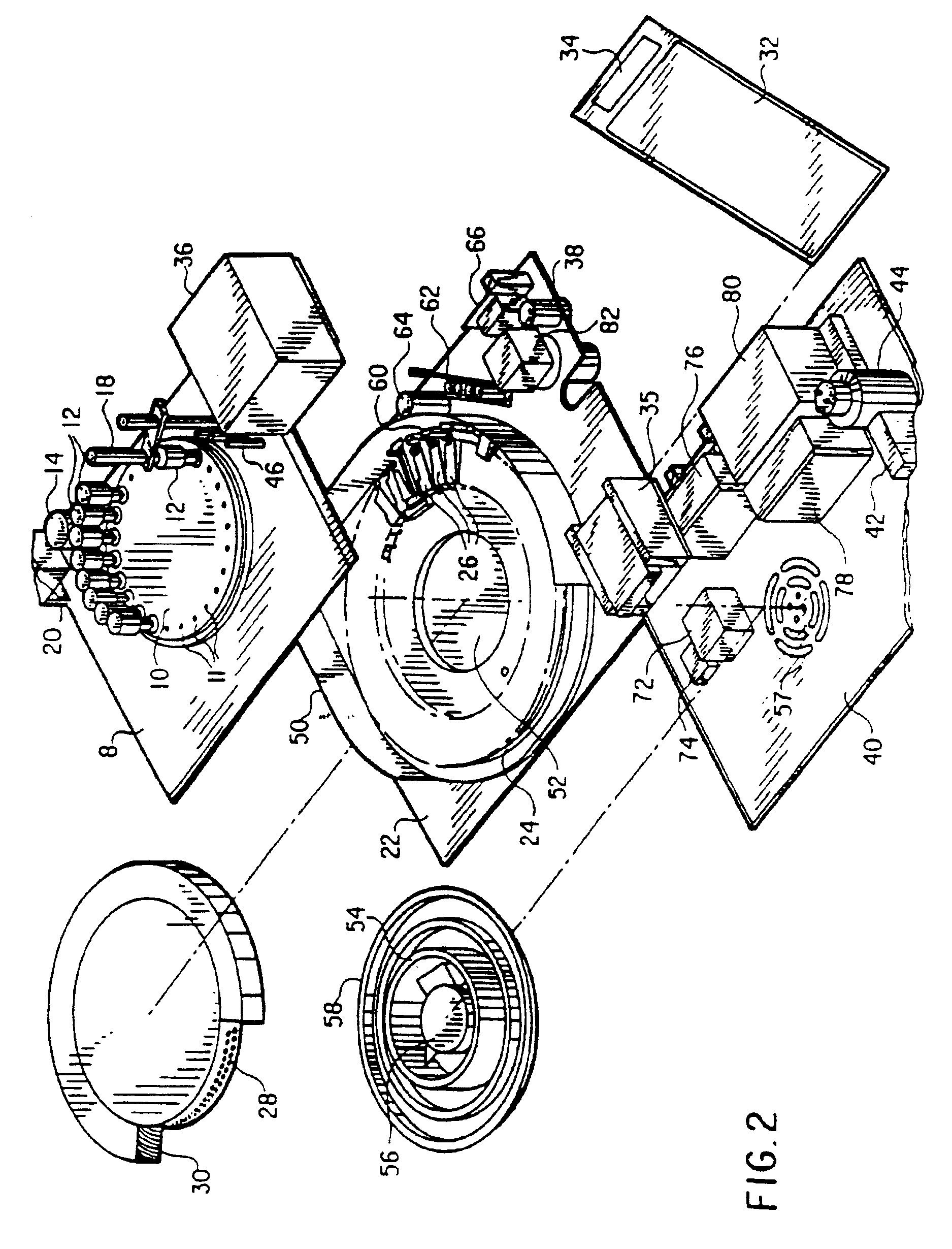
Automated biological reaction apparatus
An automated immunostaining apparatus having a reagent application zone and a reagent supply zone. The apparatus has a carousel slide support supporting a plurality of slide supports thereon, and drive means engaging the carousel slide support for consecutively positioning each of a plurality of slide supports in the reagent application zone. The apparatus also has a carousel reagent support having a plurality of reagent container supports thereon, and drive means engaging the carousel for rotating the carousel and positioning a preselected reagent container support in the reagent supply zone. The apparatus also has a reagent delivery actuator means positioned for engaging a reagent container positioned on a container support in the reagent delivery zone and initiating reagent delivery from the reagent container to a slide supported on a slide support in the reagent receiving zone.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
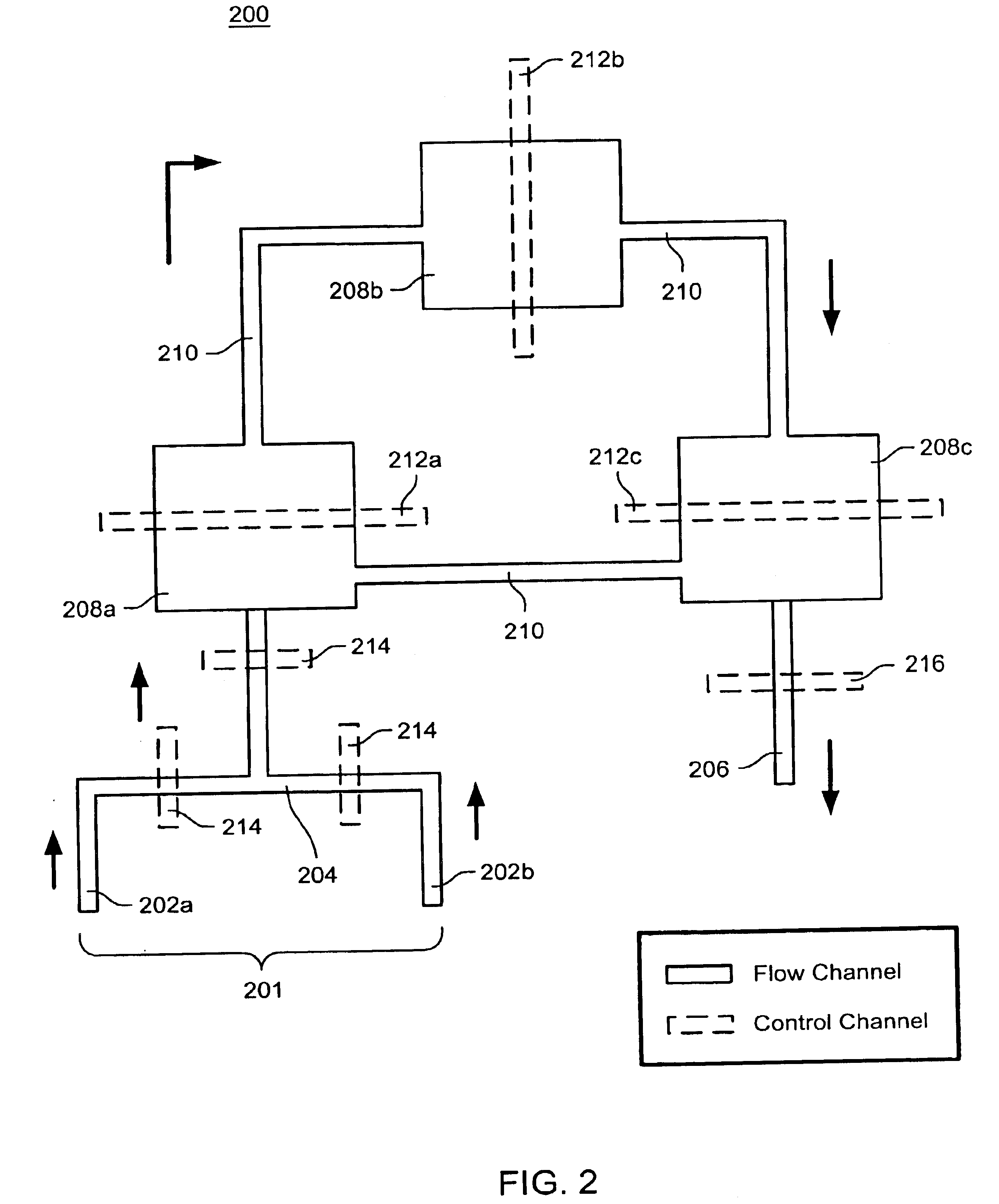
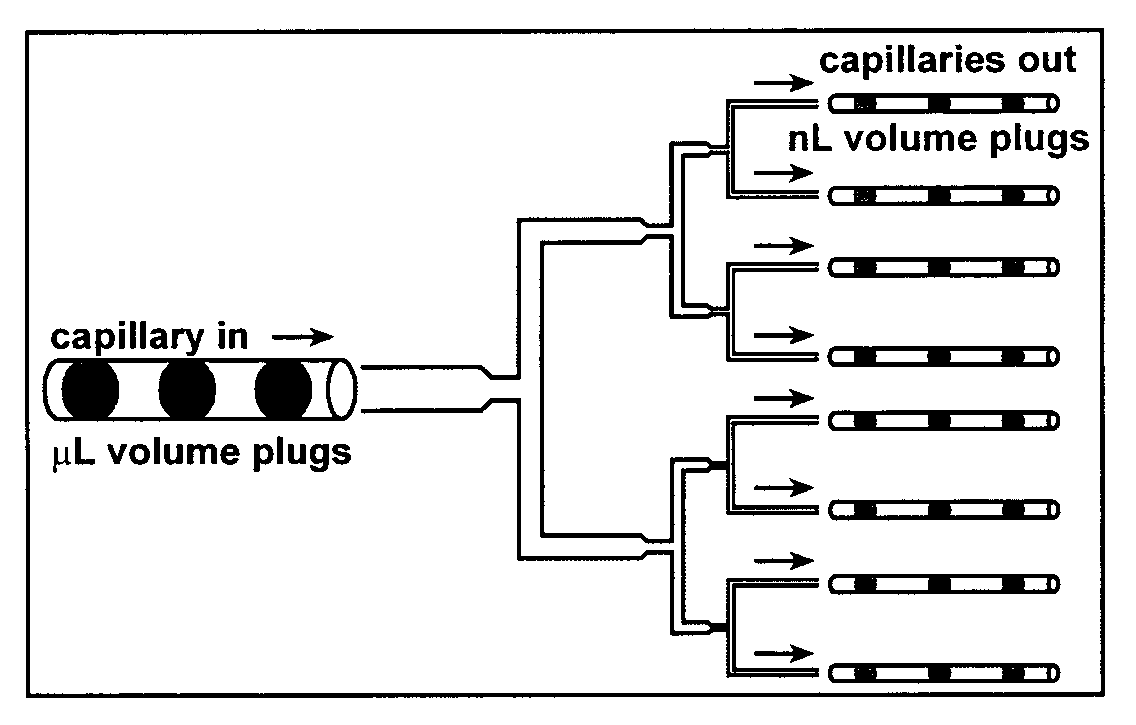
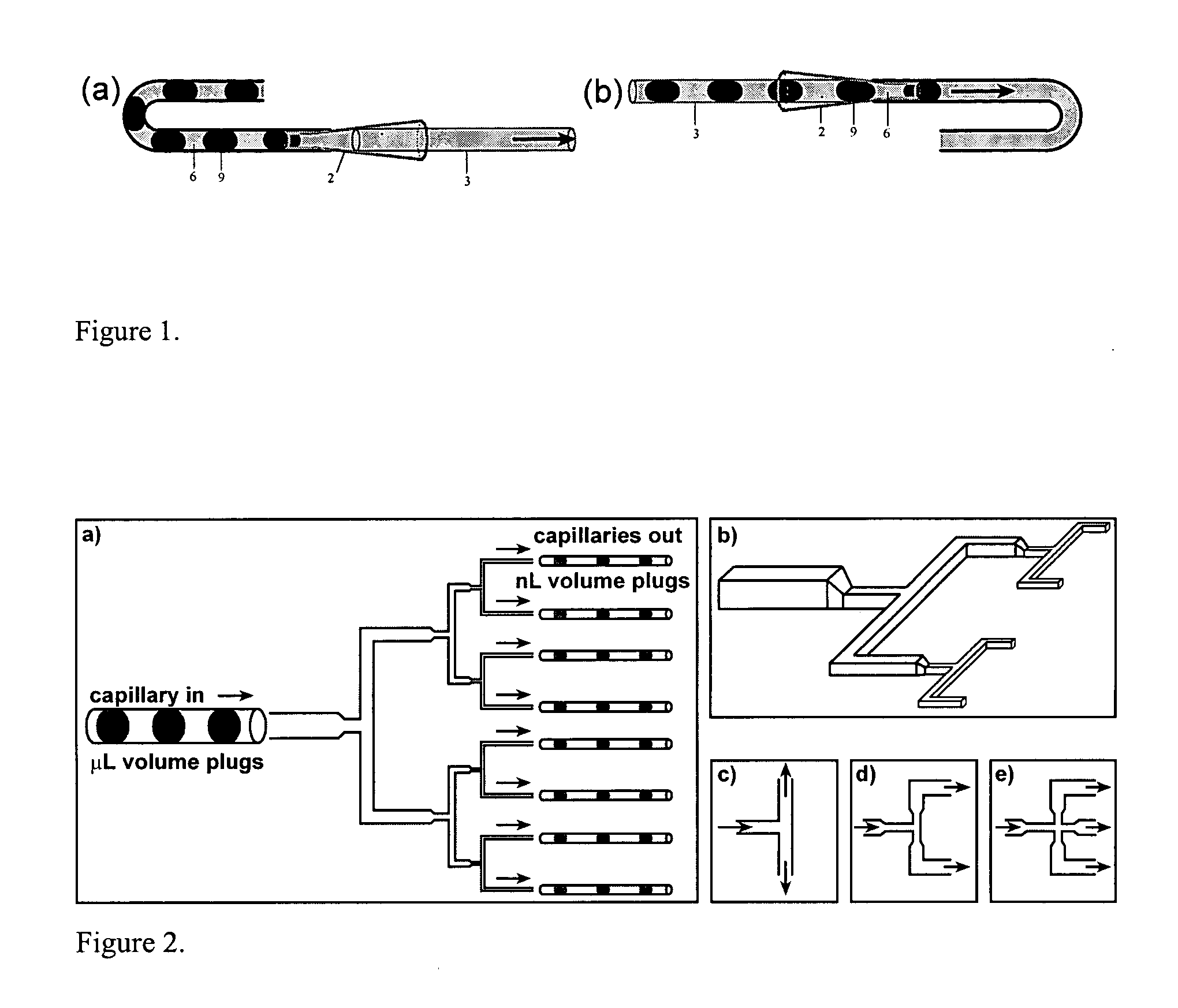
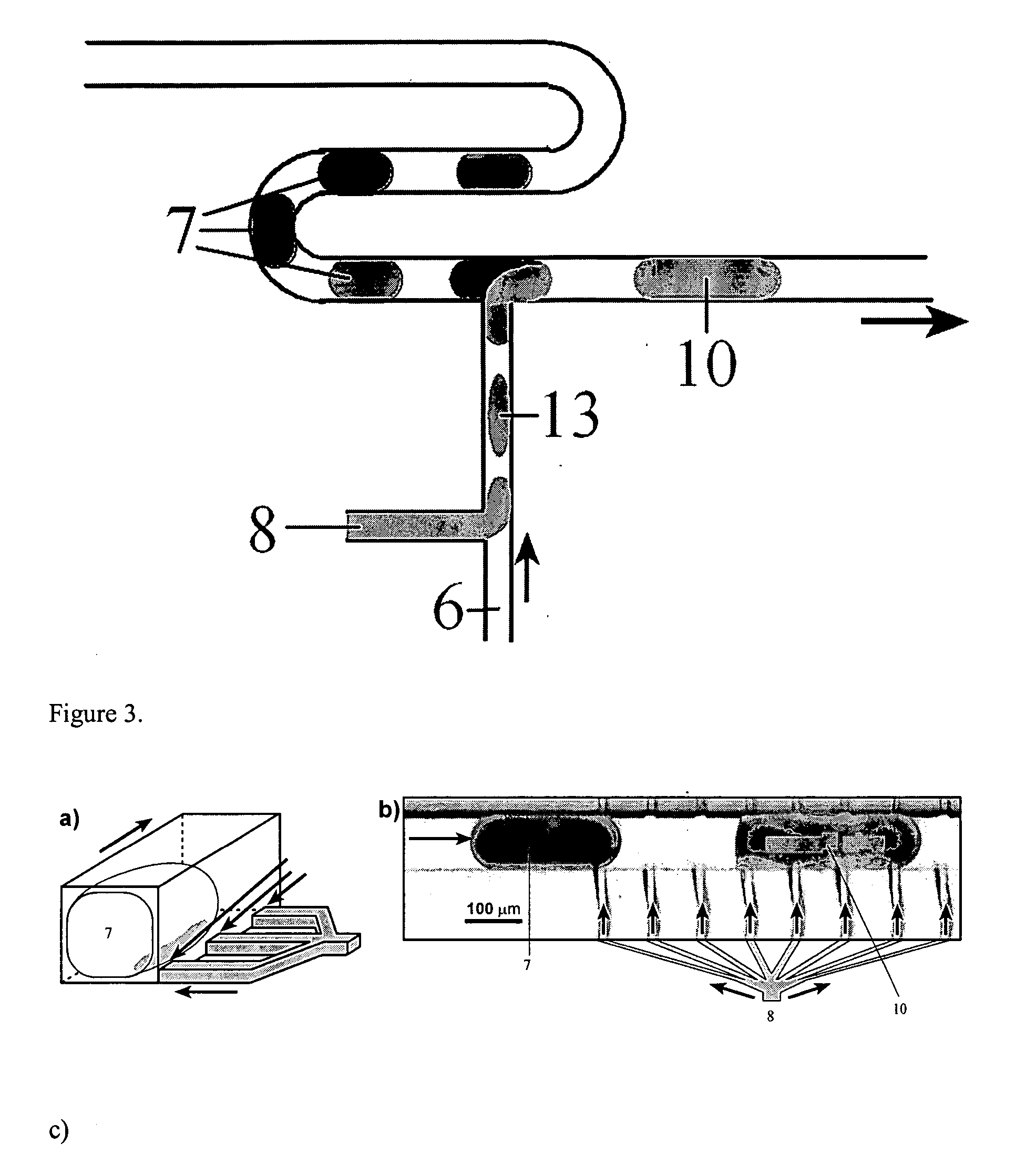
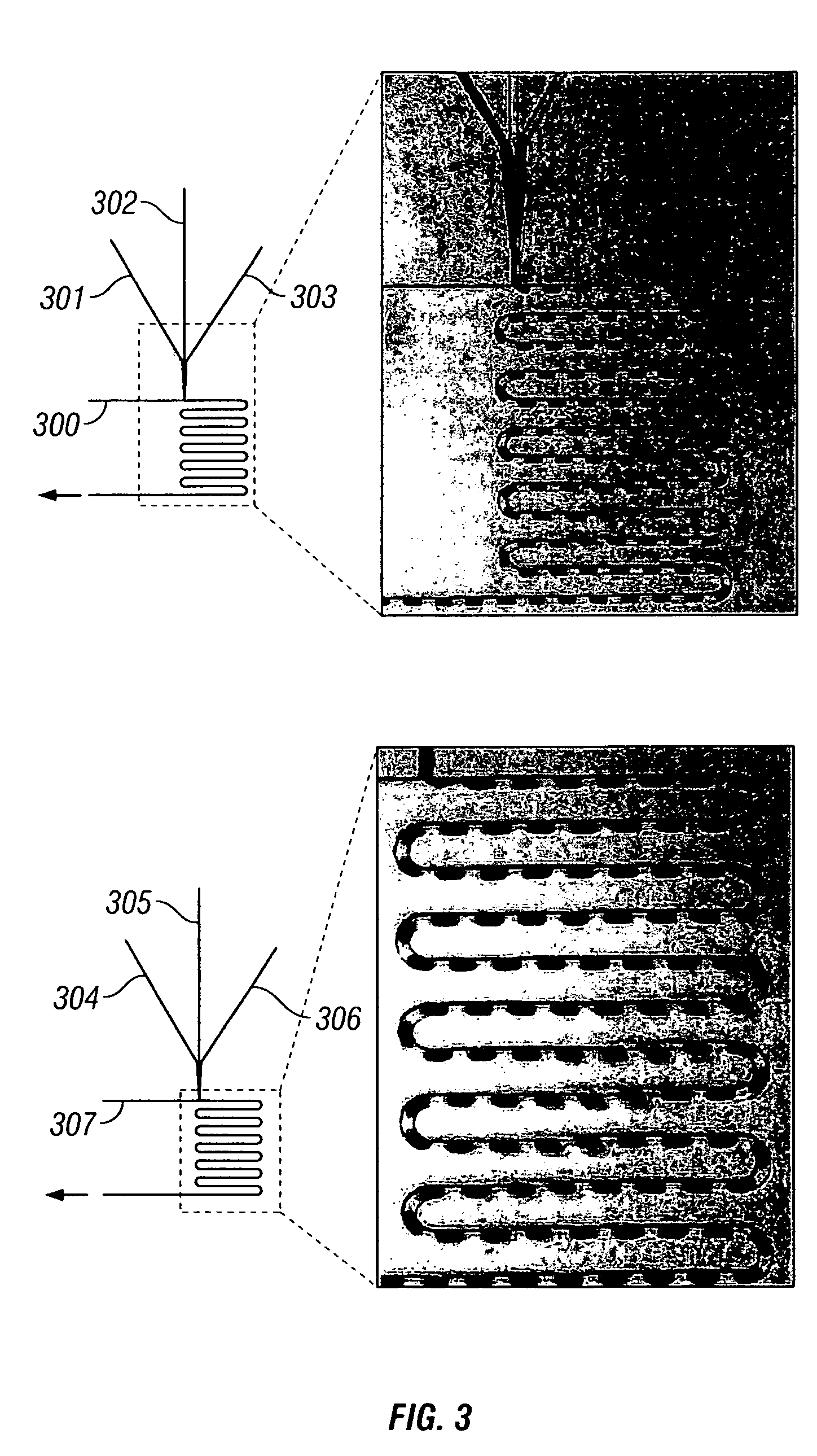
Device and method for pressure-driven plug transport and reaction
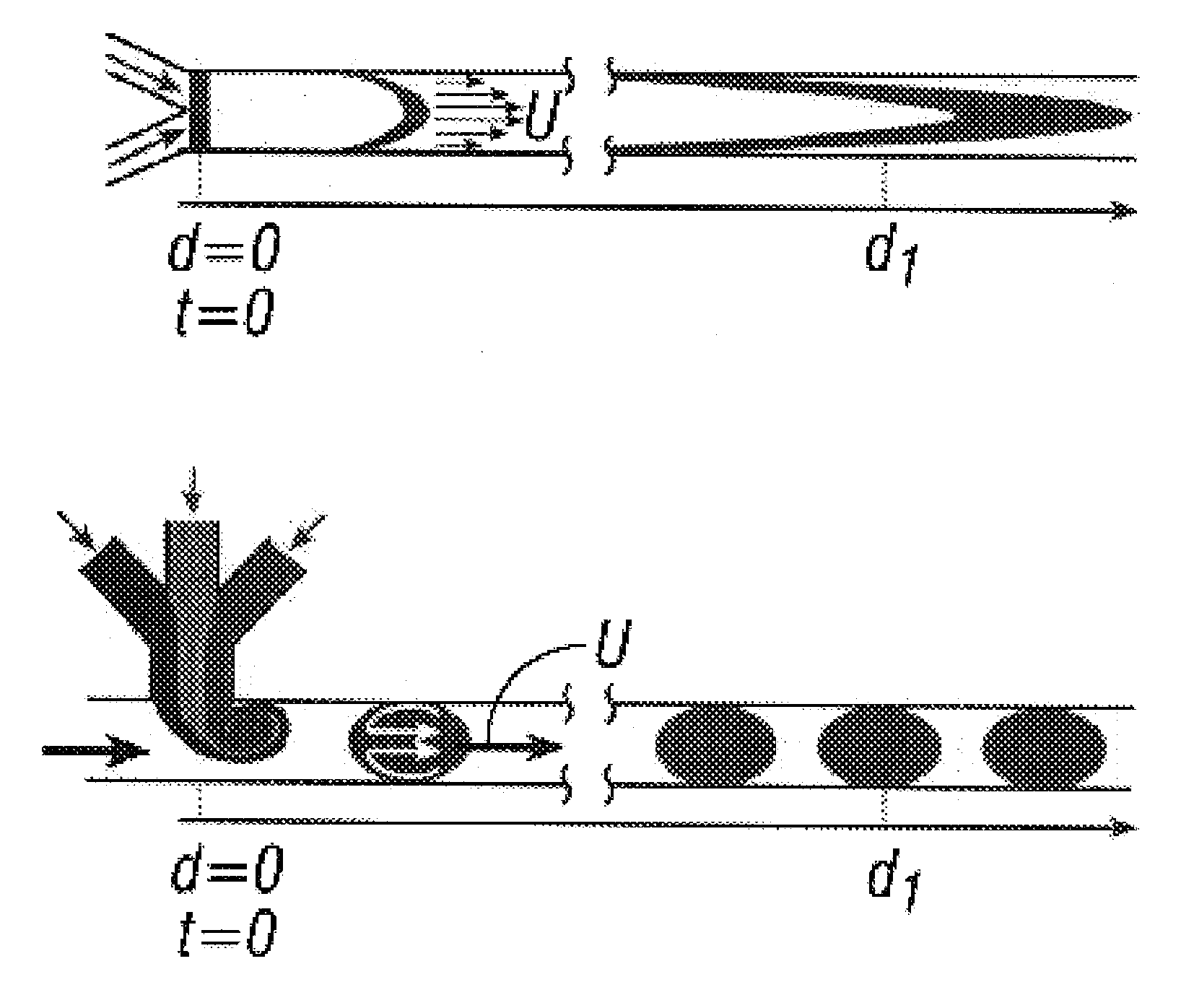
InactiveUS7129091B2Well mixedQuick mixMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsPressure.driveCarrier fluid
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
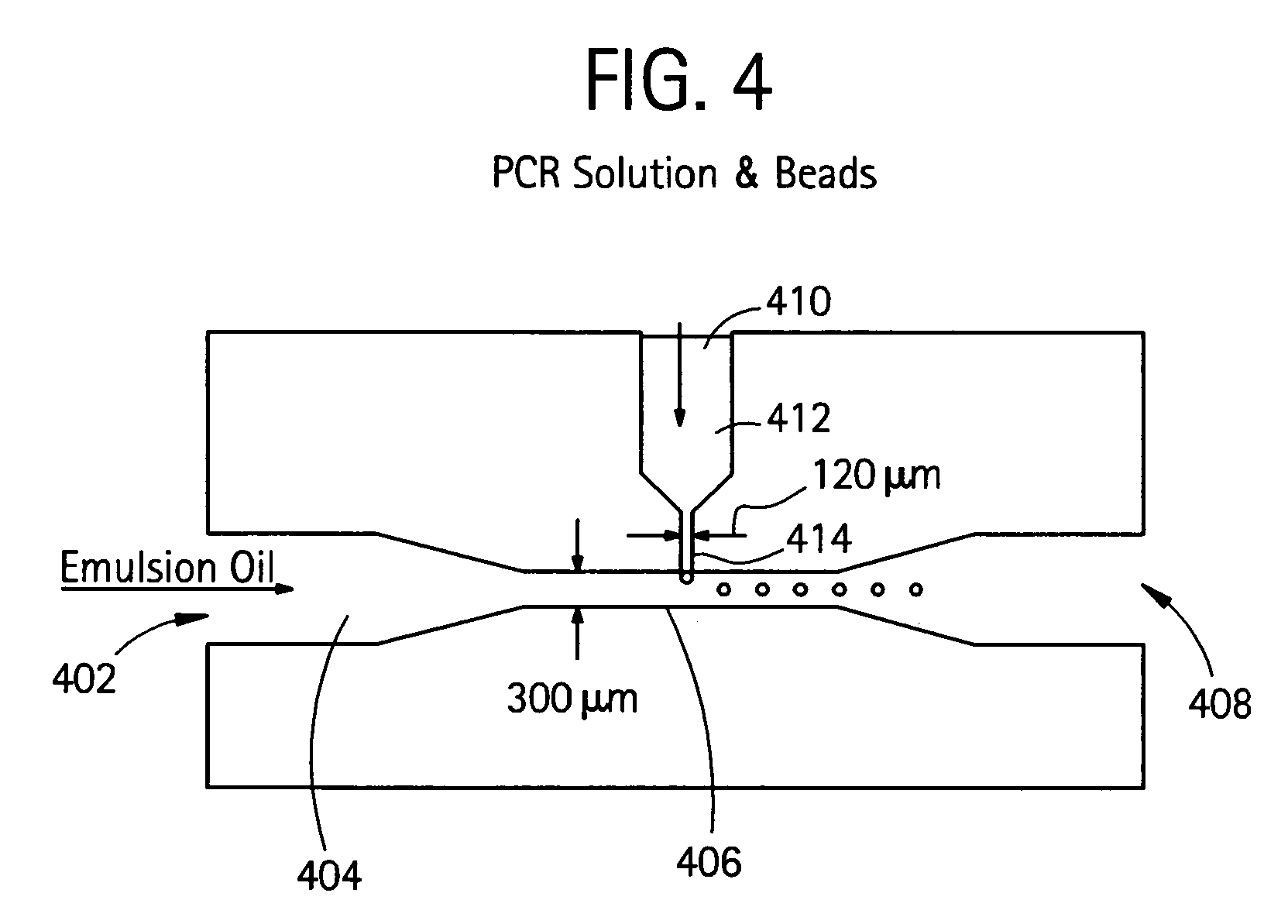
Nucleic acid amplification with continuous flow emulsion
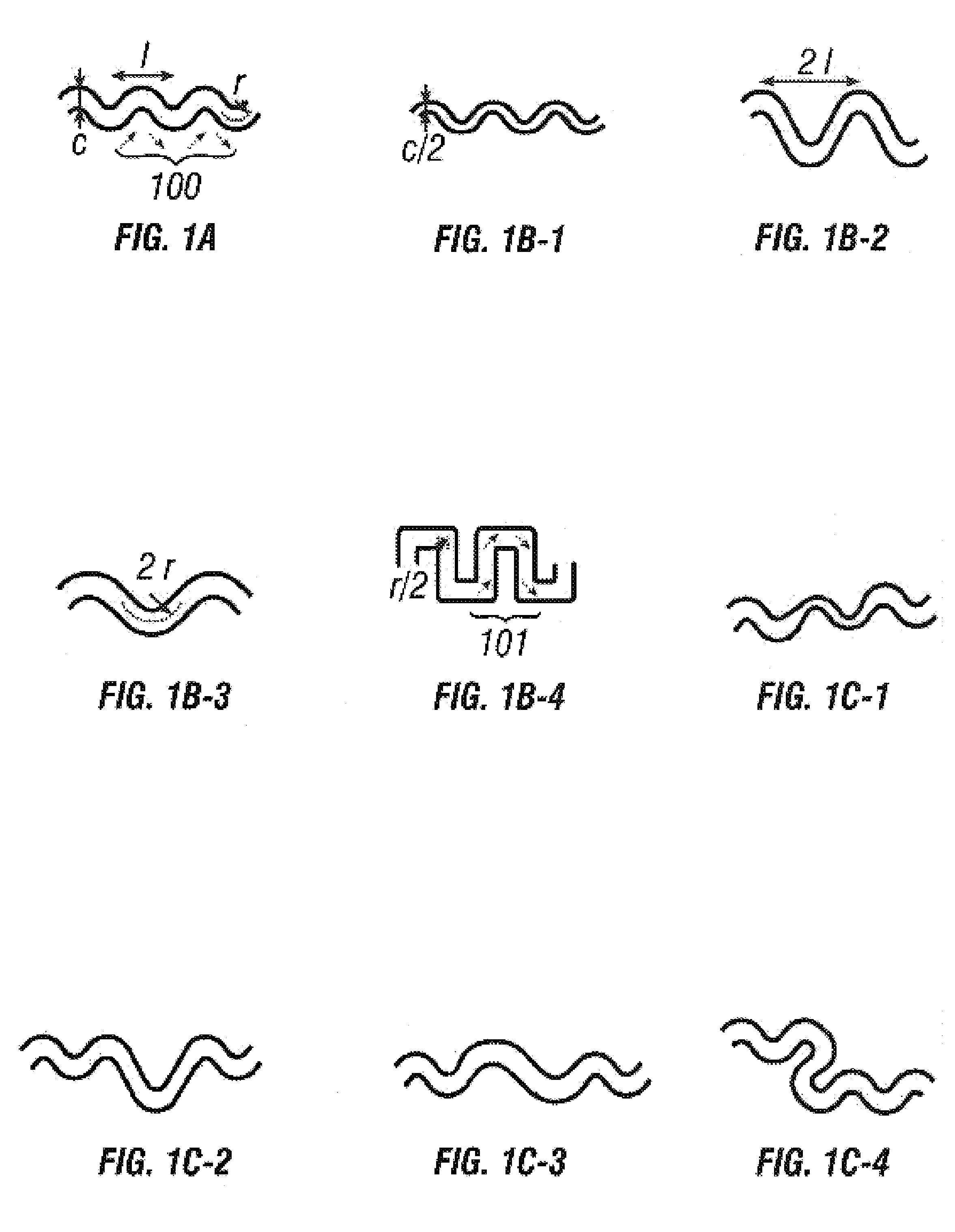
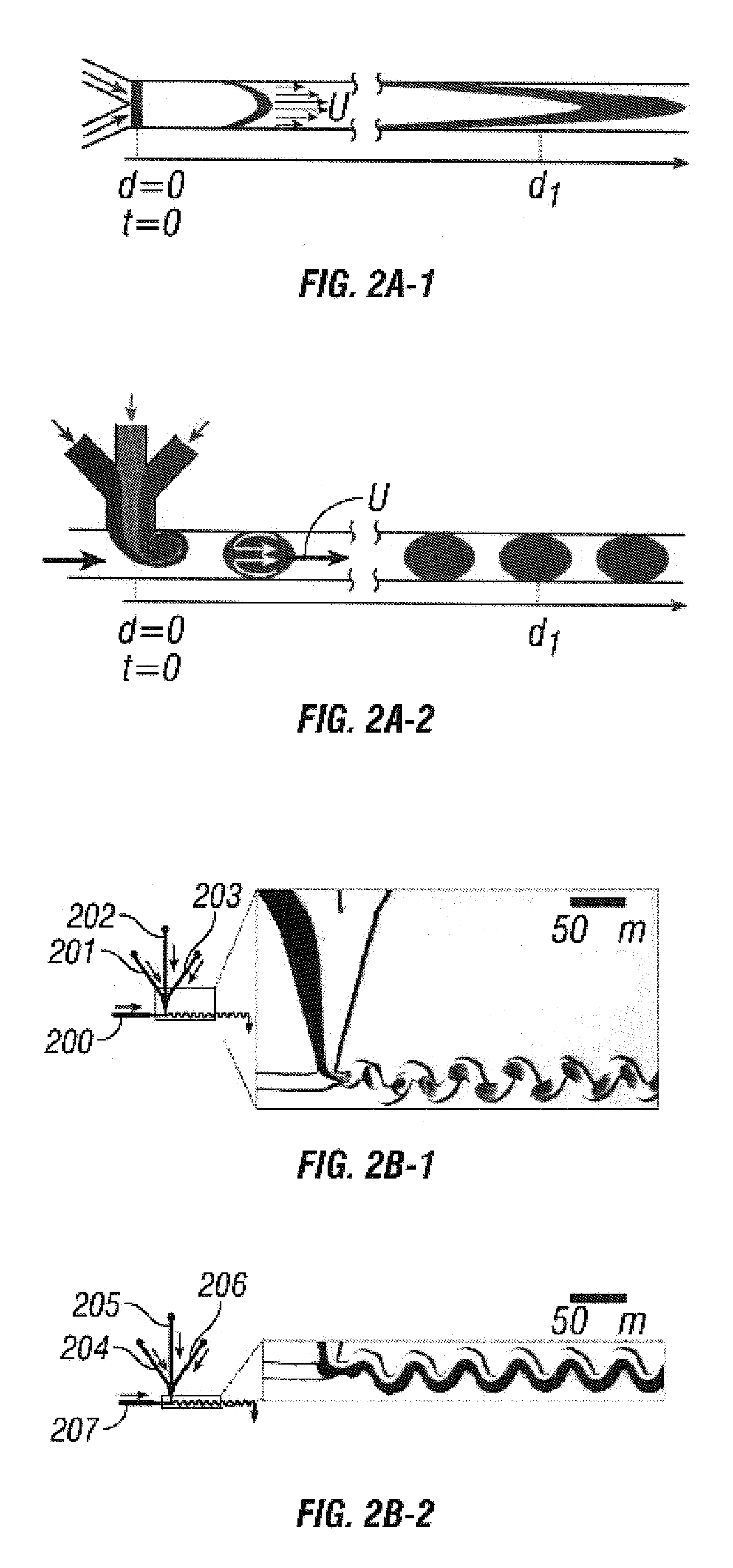
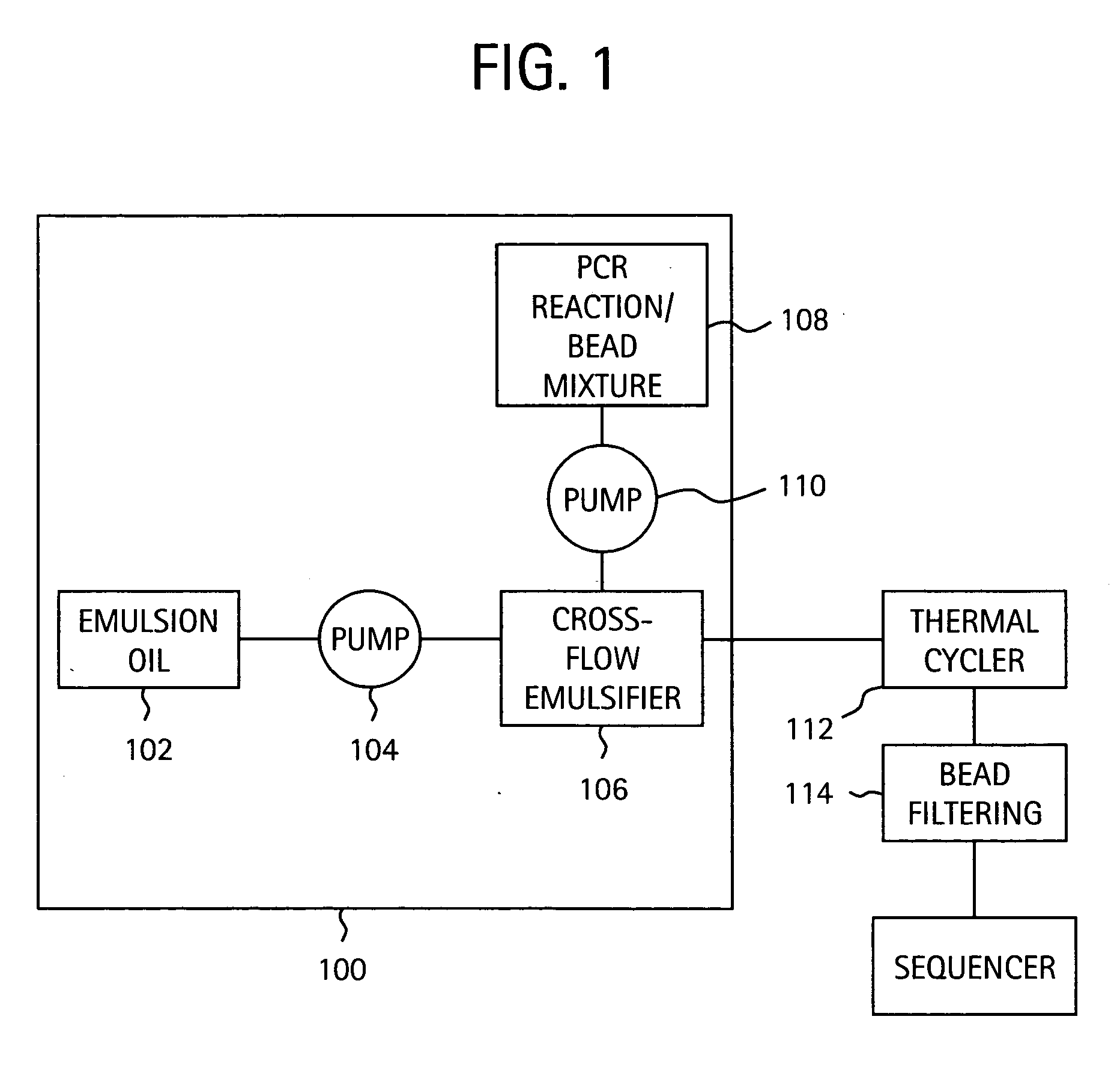
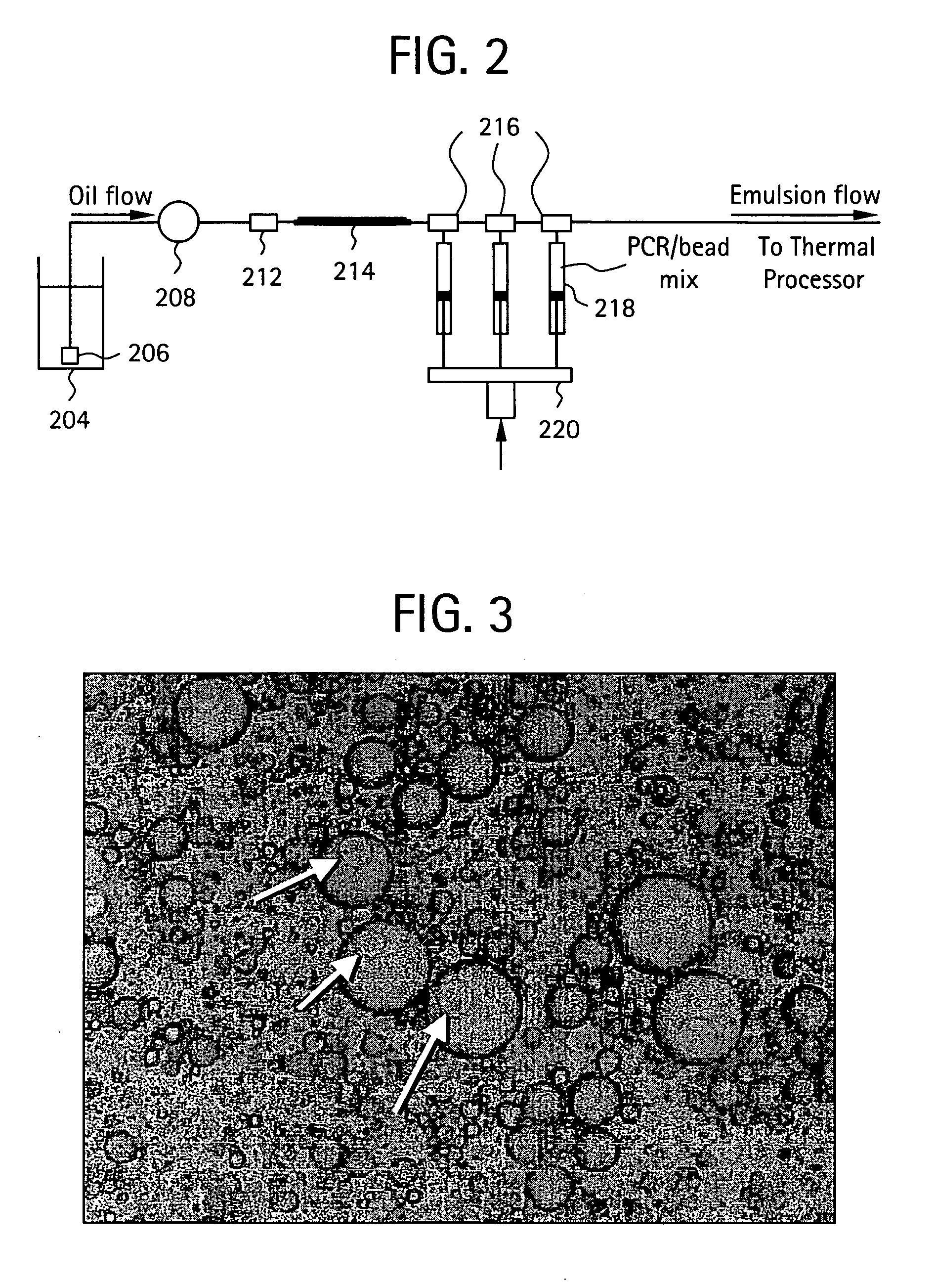
InactiveUS20050227264A1Rapid and economical mannerReduce nozzle cloggingHeating or cooling apparatusFlow mixersMicroreactorGenetic Materials
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods and devices / systems for amplifying genetic material and may include providing a water-in-oil emulsion in a continuous flow. The emulsion may include a plurality of water droplets comprising microreactors. Each of the plurality of microreactors may include a single bead capable of capturing a nucleic acid template, a single species nucleic acid template and sufficient reagents to amplify the copy number of the nucleic acid template. The method also includes flowing the emulsion across a first temperature zone and a second lower temperature zone to thermally process the microreactors to amplify the nucleic acid template by polymerase chain reaction.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
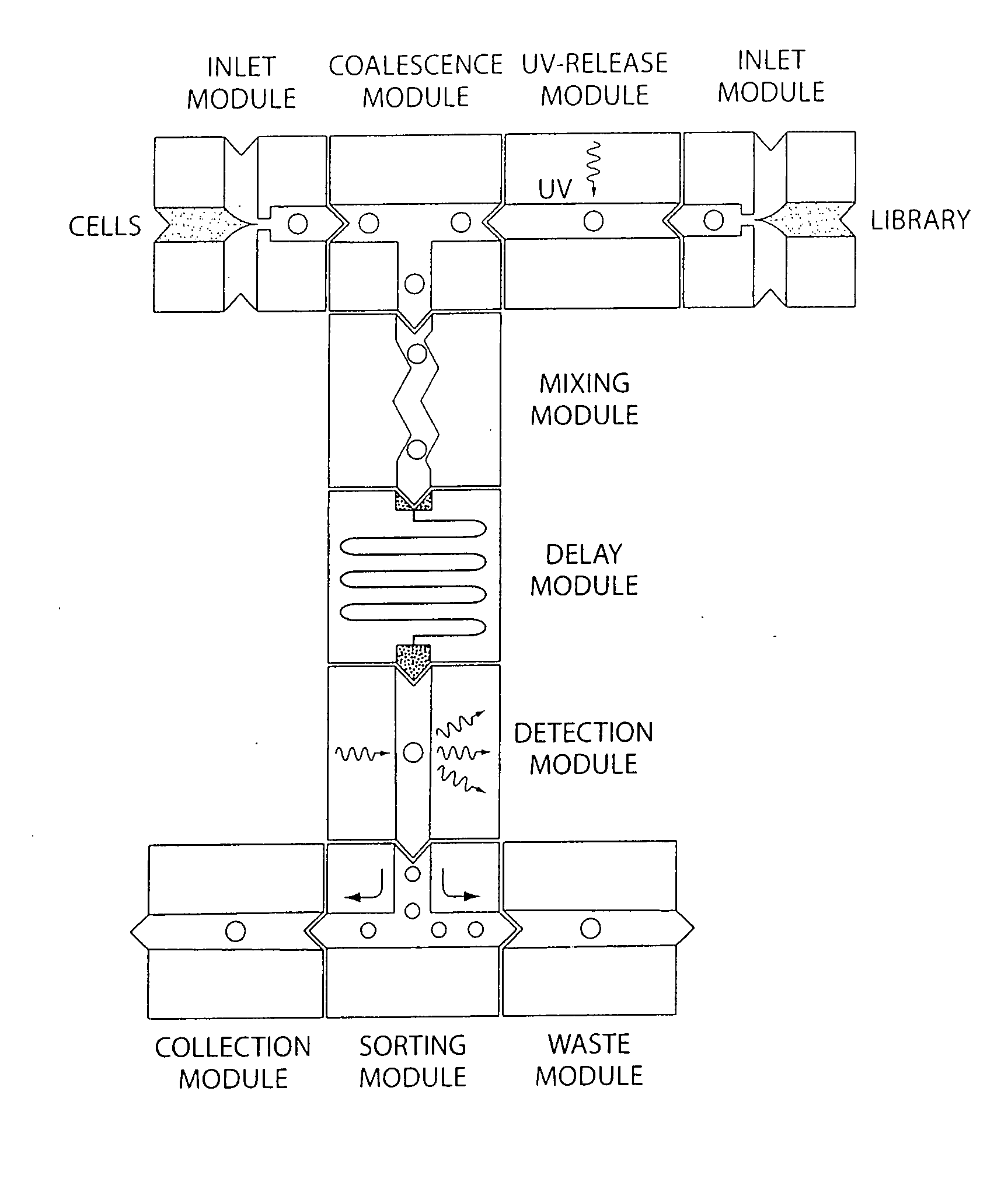
In vitro evolution in microfluidic systems
ActiveUS20060078888A1High activitySpeed up the processSequential/parallel process reactionsFlow mixersGene productGenetic element
The invention describes a method for isolating one or more genetic elements encoding a gene product having a desired activity, comprising the steps of: (a) compartmentalising genetic elements into microcapsules; and (b) sorting the genetic elements which express the gene product having the desired activity; wherein at least one step is under microfluidic control. The invention enables the in vitro evolution of nucleic acids and proteins by repeated mutagenesis and iterative applications of the method of the invention.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Compartmentalised screening by microfluidic control
InactiveUS20050221339A1Rapid and high-throughput screeningLow costCompound screeningSequential/parallel process reactionsCompound (substance)Drug development
The invention describes a method for the identification of compounds which bind to a target component of a biochemical system or modulate the activity of the target, comprising the steps of: a) compartmentalising the compounds into microcapsules together with the target, such that only a subset of the repertoire is represented in multiple copies in any one microcapsule; and b) identifying the compound which binds to or modulates the activity of the target; wherein at least one step is performed under microfluidic control. The invention enables the screening of large repertoires of molecules which can serve as leads for drug development.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
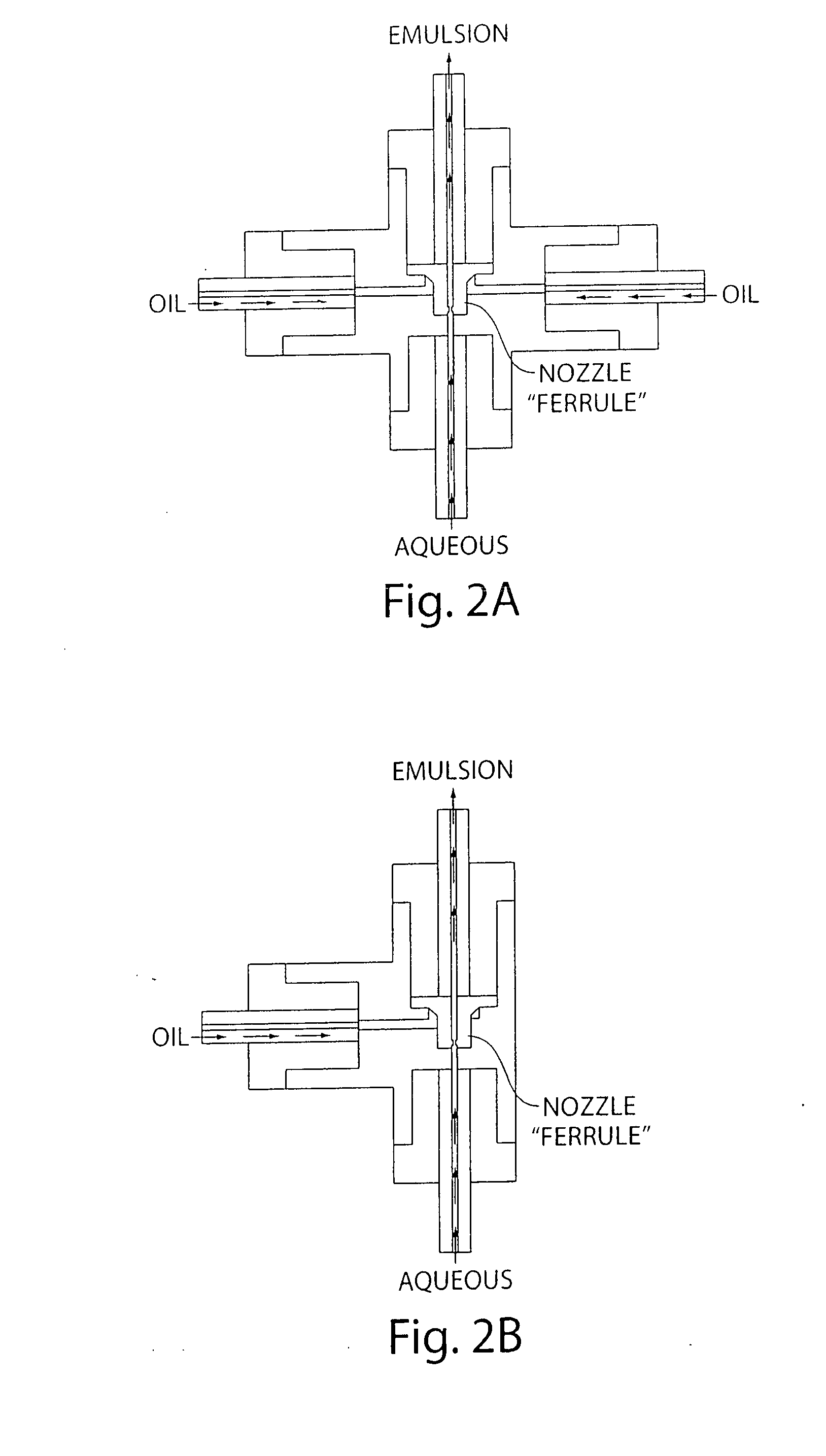
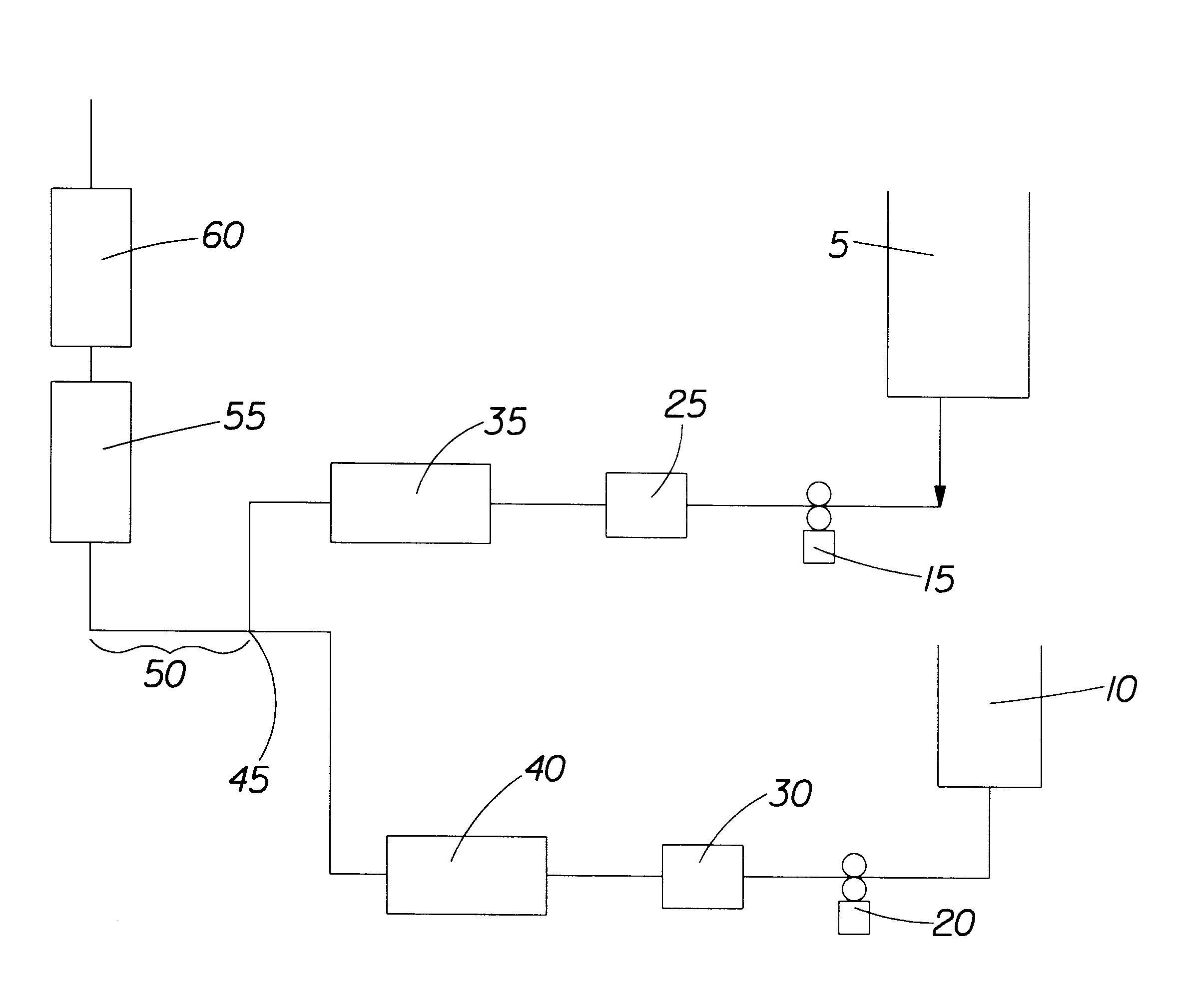
Process for producing emulsion and microcapsules and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS7268167B2Rapid productionSimple wayFlow mixersMixing methodsEmulsionMechanical engineering
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Apparatus and process for in-line preparation of HIPEs
A method of making high internal phase emulsions is described. The method forms high internal phase emulsion (HIPE) using a single pass through the static mixer. In alternative embodiments, the HIPE may be further processed to farther modify the size of dispersed phase droplets, to incorporate additional materials into the HIPE, to alter emulsion temperature, and the like.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
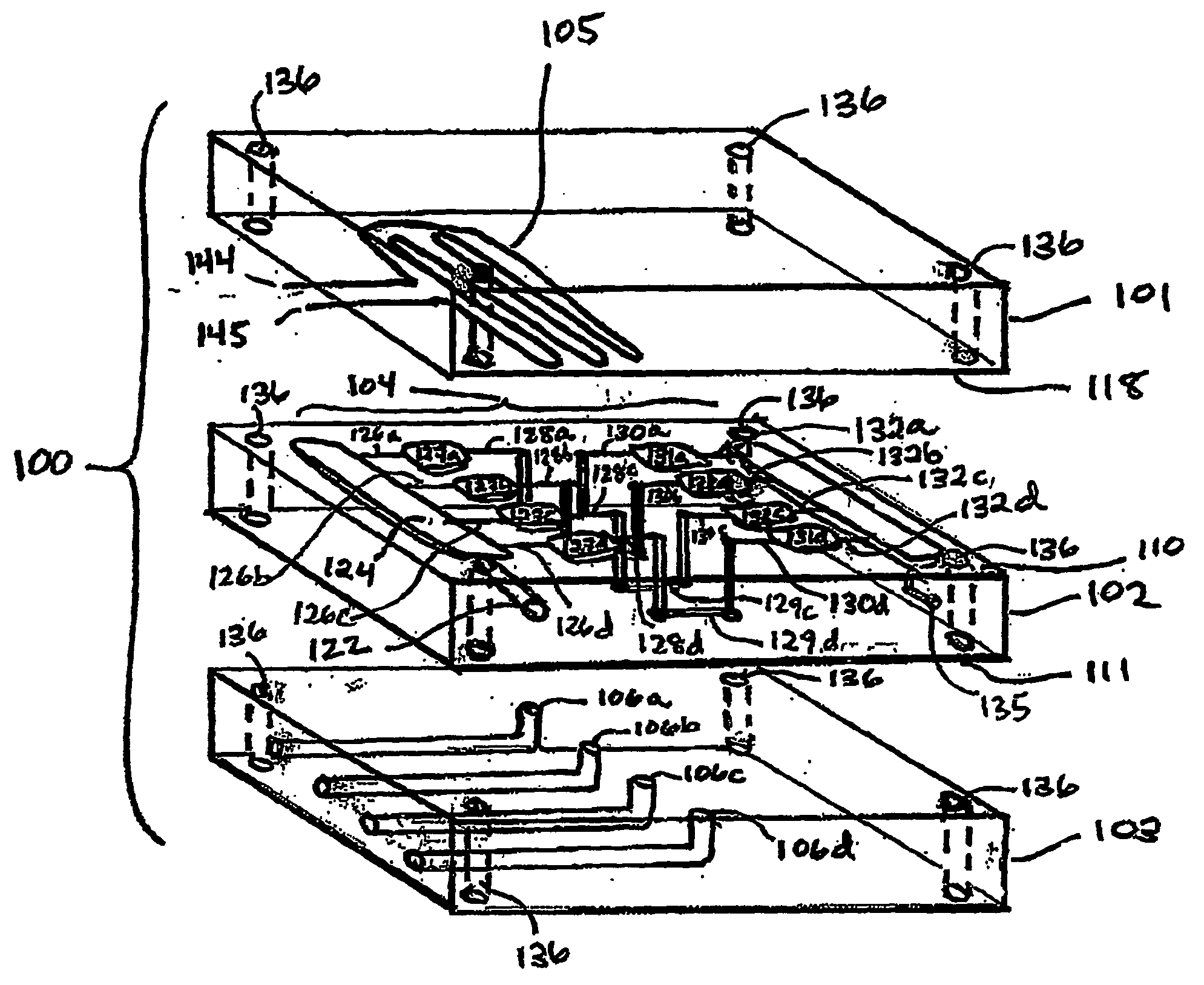
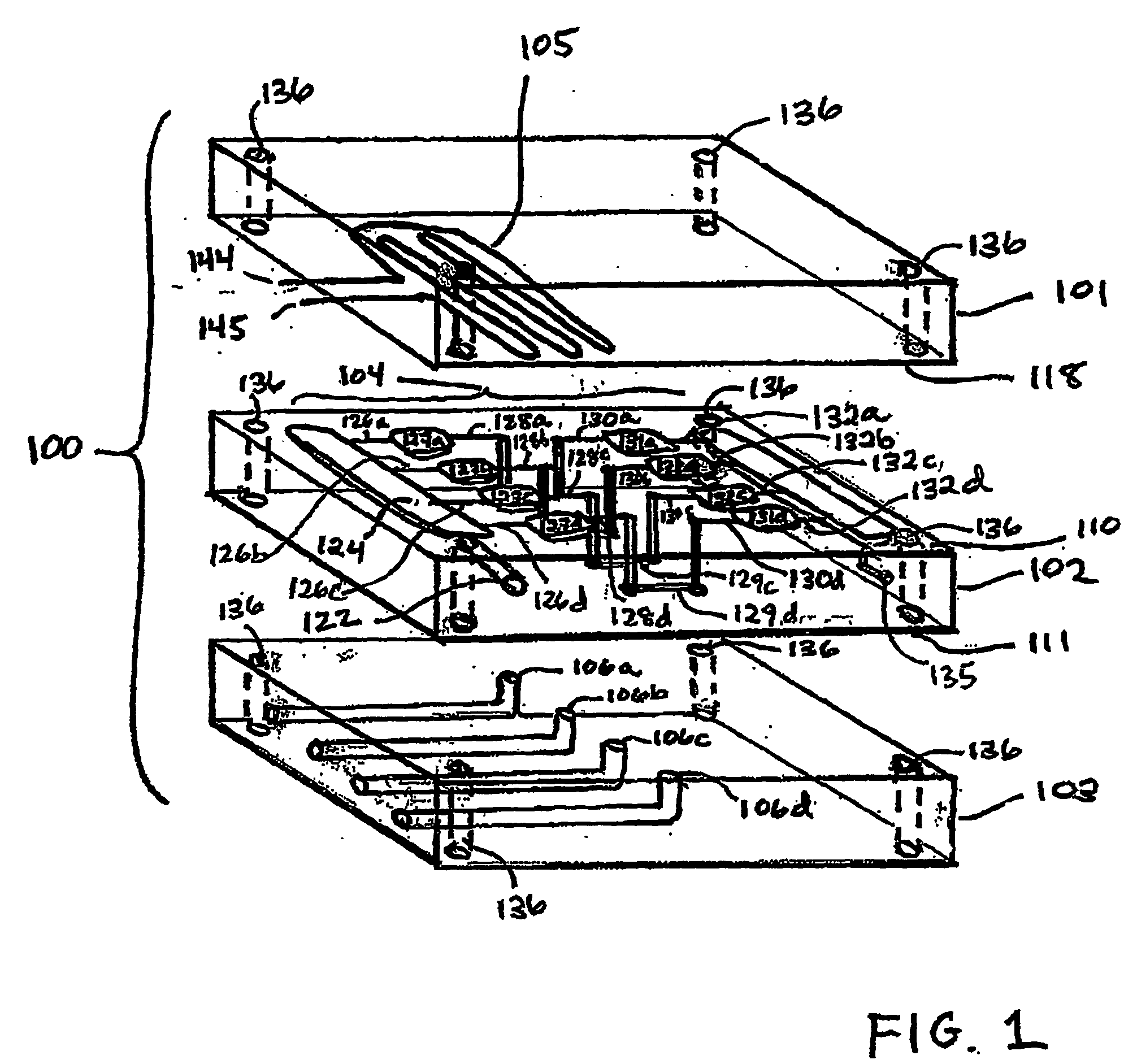
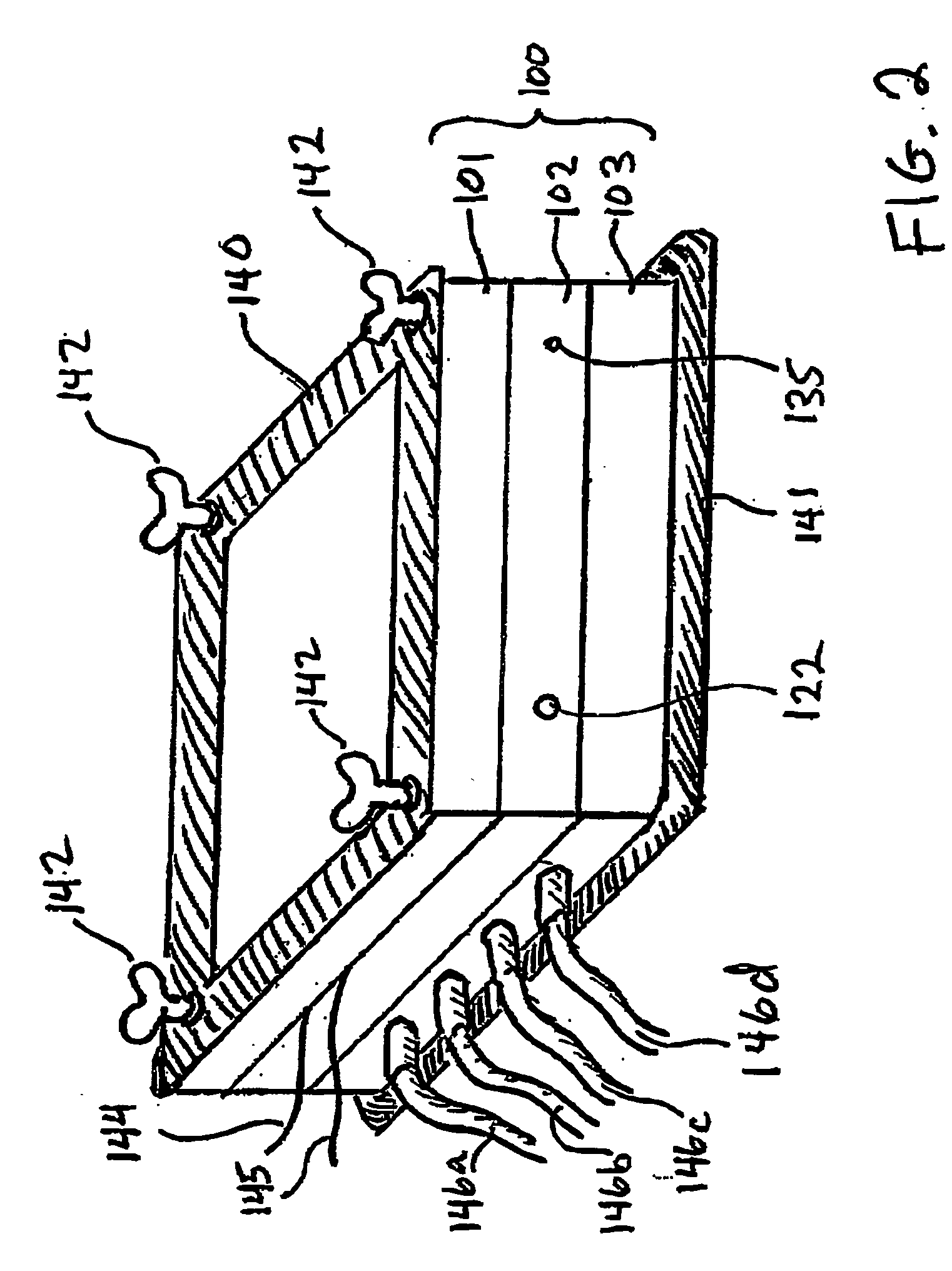
Three-dimensional microfluidics incorporating passive fluid control structures
InactiveUS20040109793A1Simple and effective and versatile controlShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersHeating or cooling apparatusFluid controlMicrofluidics
A three-dimensional microfluidic device (100) formed from a plurality of substantially planar layers (101, 102, 103) sealed together is disclosed
Owner:BIOMICRO SYST
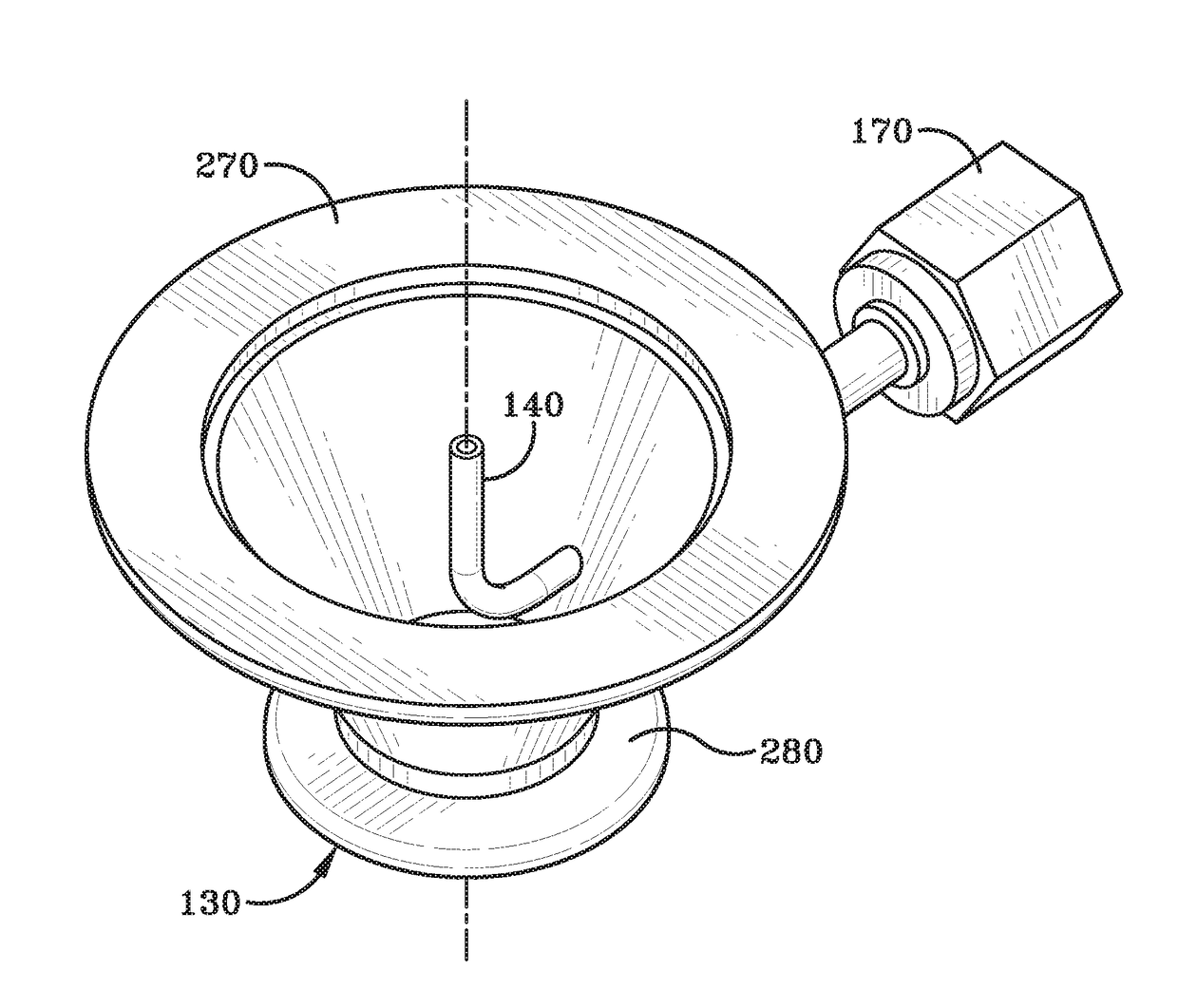
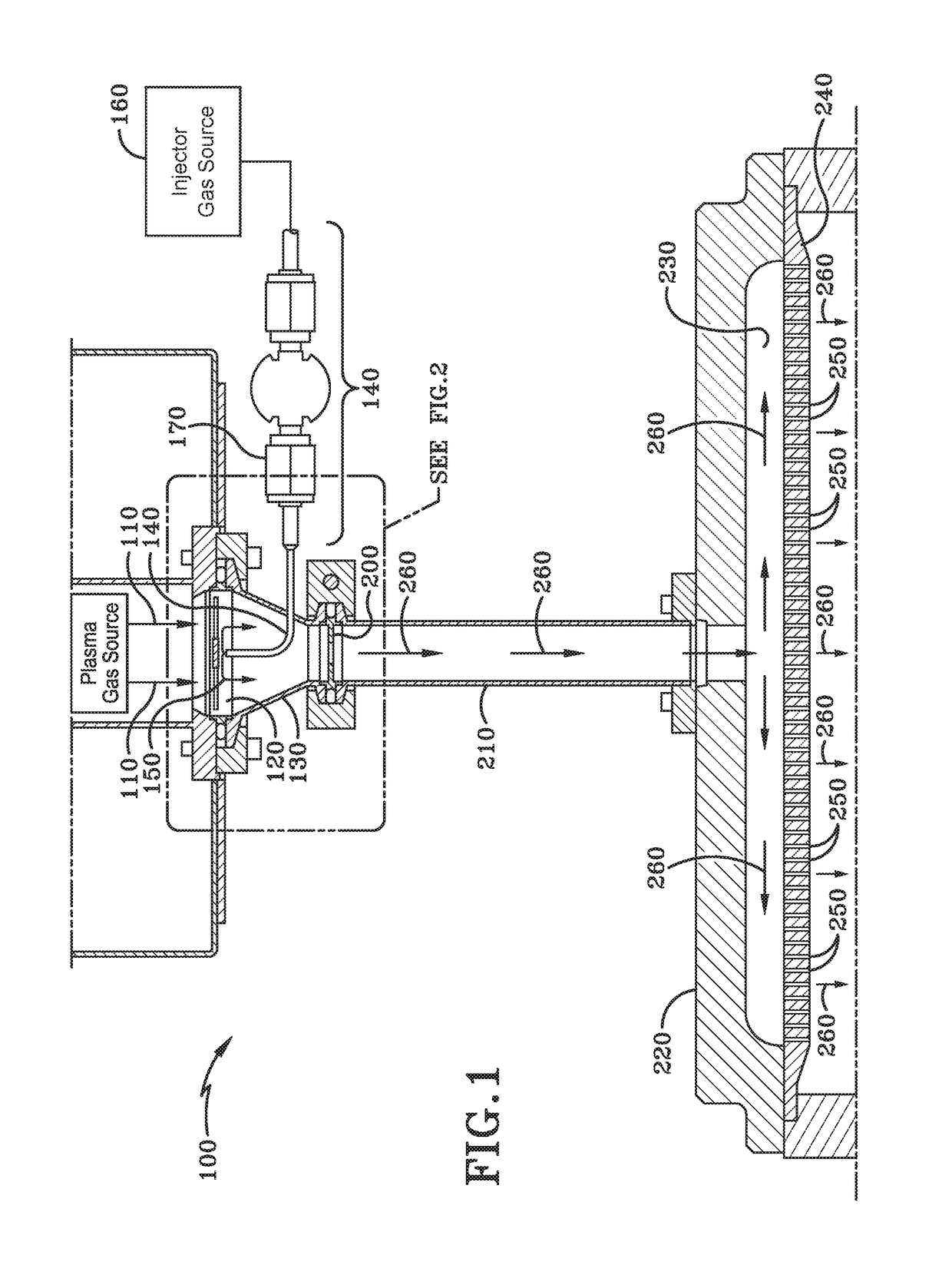
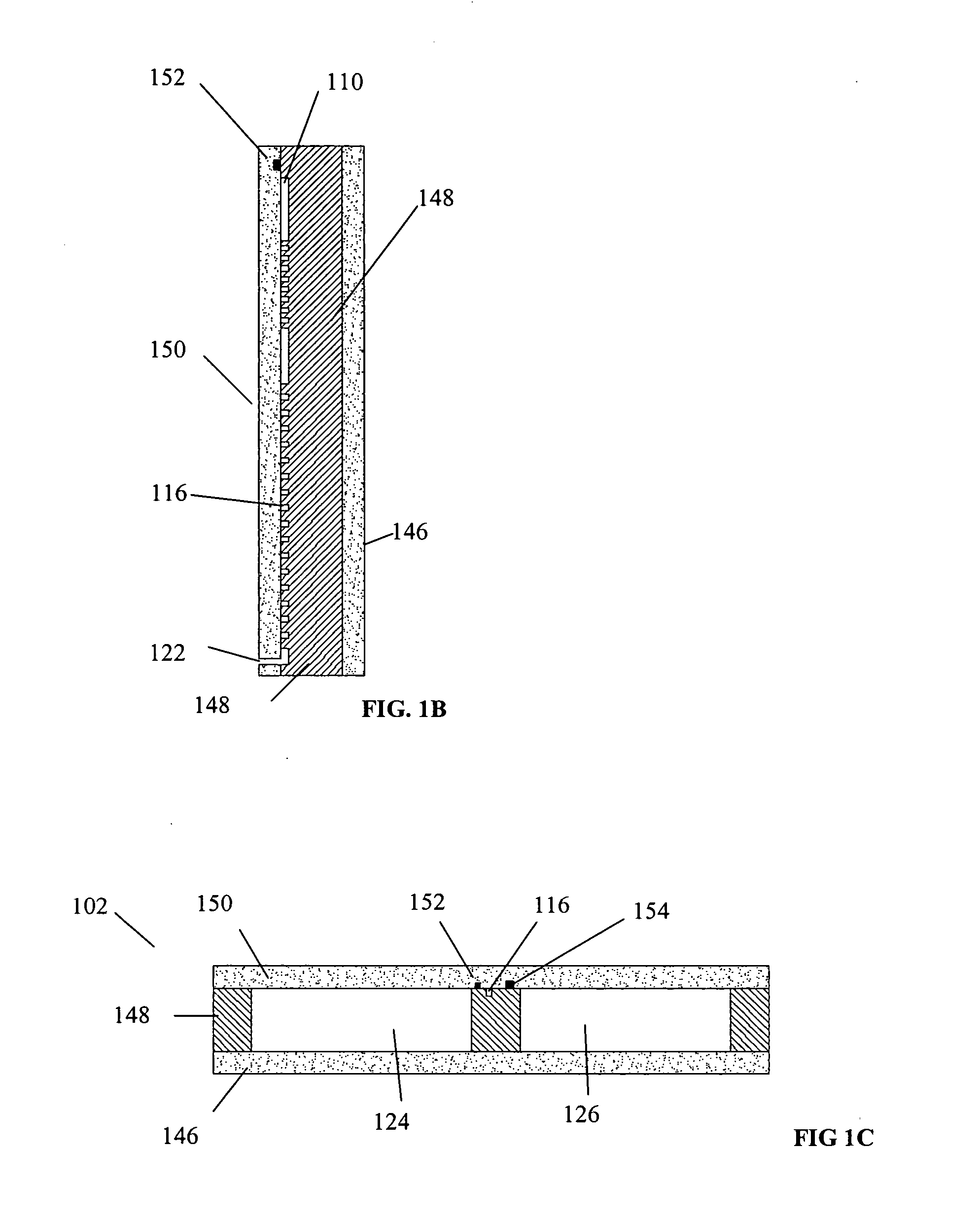
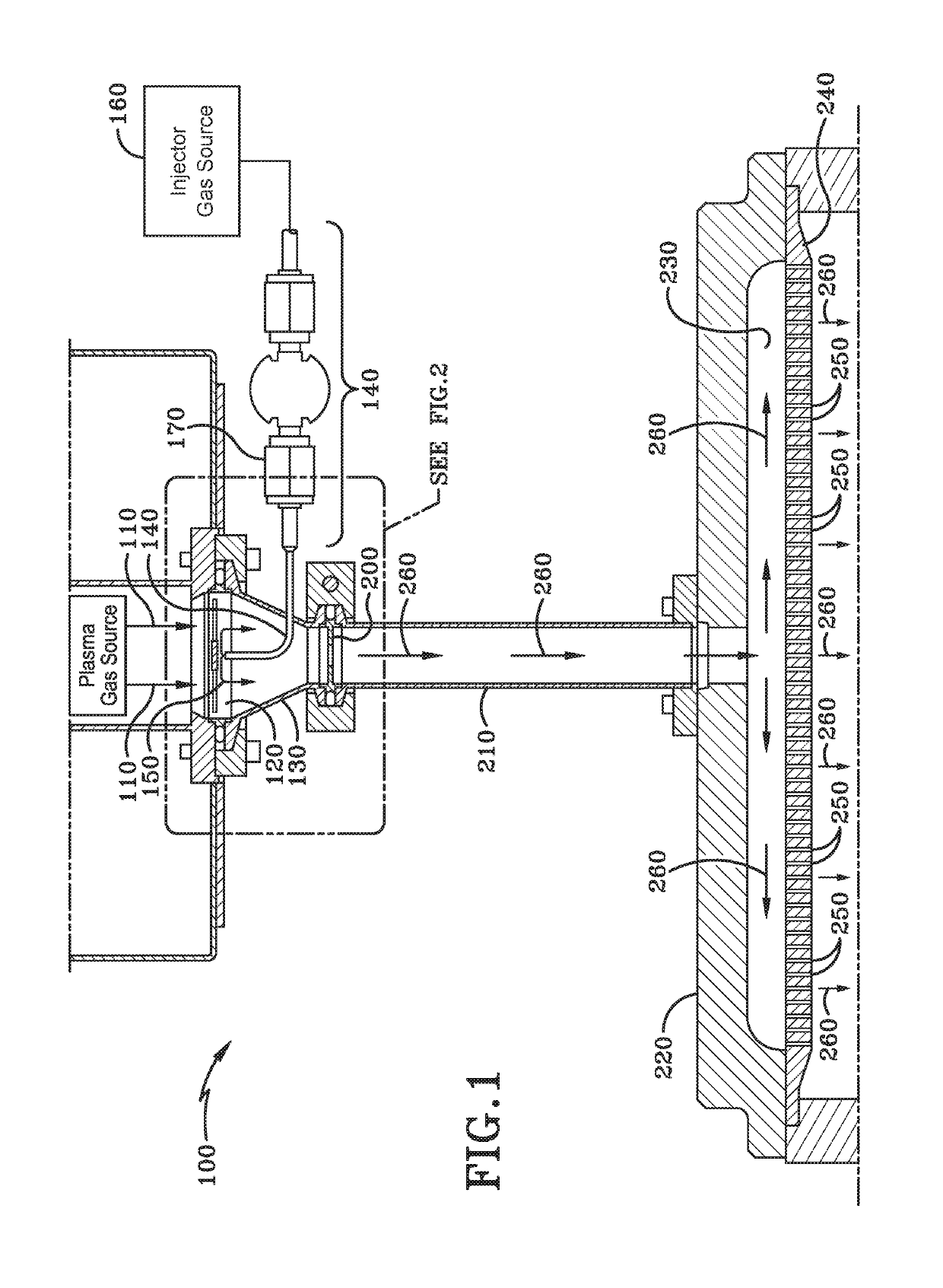
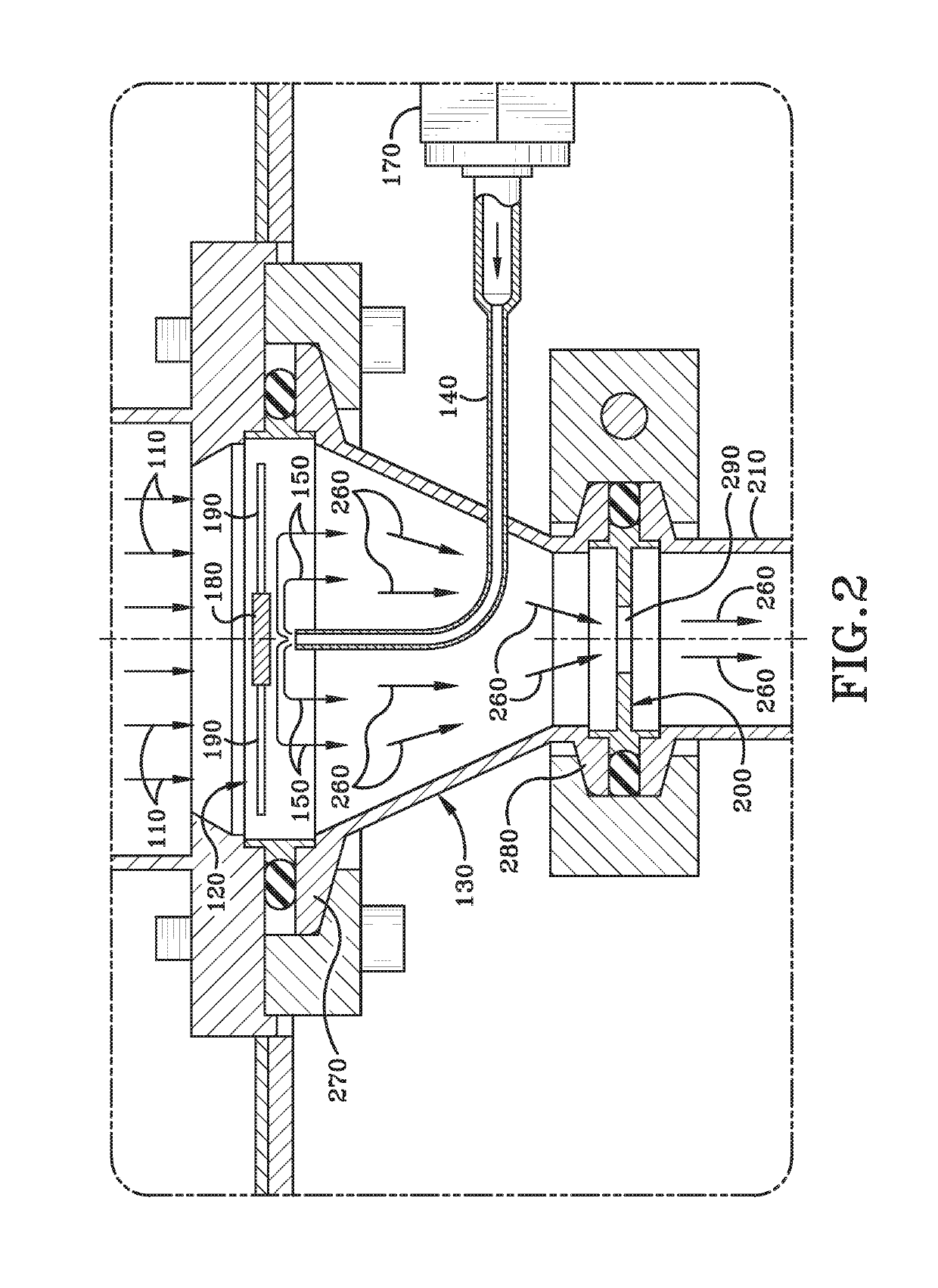
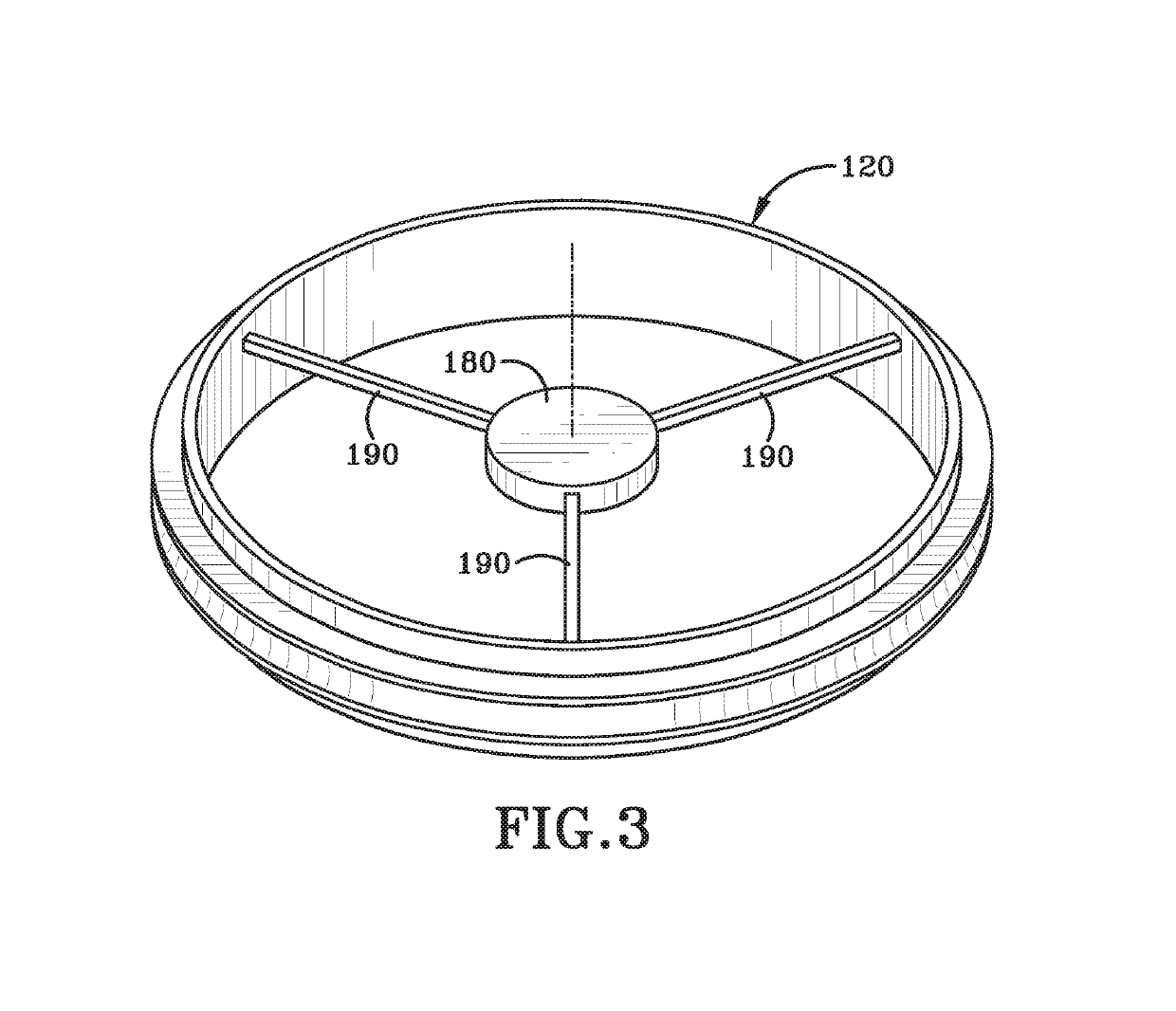
Counter flow mixer for process chamber
A counterflow mixing device for a process chamber is disclosed, comprising an injection tube that introduces a fluid in a manner counter to a flow of a post-plasma gas mixture traveling downward from a plasma source. The invention allows for proper mixing of the fluid as well as avoiding recombination of generated ions and radicals.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Semi-continuous feed production of liquid personal care compositions
ActiveUS9174178B2Shorten the timeReduce wasteFlow mixersTransportation and packagingPersonal careEngineering
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Microfluidic system
ActiveUS20060094119A1Rapid and economical reactionIncrease rangePolycrystalline material growthAnalysis using chemical indicatorsFemtoliterEngineering
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
Device and method for pressure-driven plug transport and reaction
InactiveUS20050272159A1Well mixedQuick mixMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsPressure.driveCarrier fluid
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Microfluidic chemical reactor for the manufacture of chemically-produced nanoparticles
InactiveUS20050129580A1Maintain propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthProcess functionNanoparticle
The present invention discloses microfluidic modules for making nanocrystalline materials in a continuous flow process. The microfluidic modules include one or more flow path with mixing structures and one or more controlled heat exchangers to process the nanocrystalline materials and reagents in the flow path. The microfluidic modules can be interconnected to form microfluidic reactors that incorporate one or more process functions such as nucleation, growth, and purification.
Owner:LAKE SHORE CRYOTRONICS INC
Counter flow mixer for process chamber
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
In-line-type fluid mixer
InactiveUS20120307588A1Reduce the cross-sectional areaHigh speedFlow mixersMixer accessoriesInlet channelEngineering
An in-line-type fluid mixer is provided, which includes a first channel-forming part defining a first inlet channel from a first inlet portion to a first passage portion; a second channel-forming part defining a second inlet channel from a second inlet portion to a second passage portion; a third channel-forming part defining an outlet channel having a sectional area that increases from a narrower portion through a flaring portion to an outlet portion, and being communicated with the first inlet channel and the second inlet channel, respectively, at an end of the narrow portion; and a whirling stream-generating part for generating a whirling stream in at least one of the first inlet channel and the second inlet channel.
Owner:ASAHI YUKIZAI KOGYO CO LTD
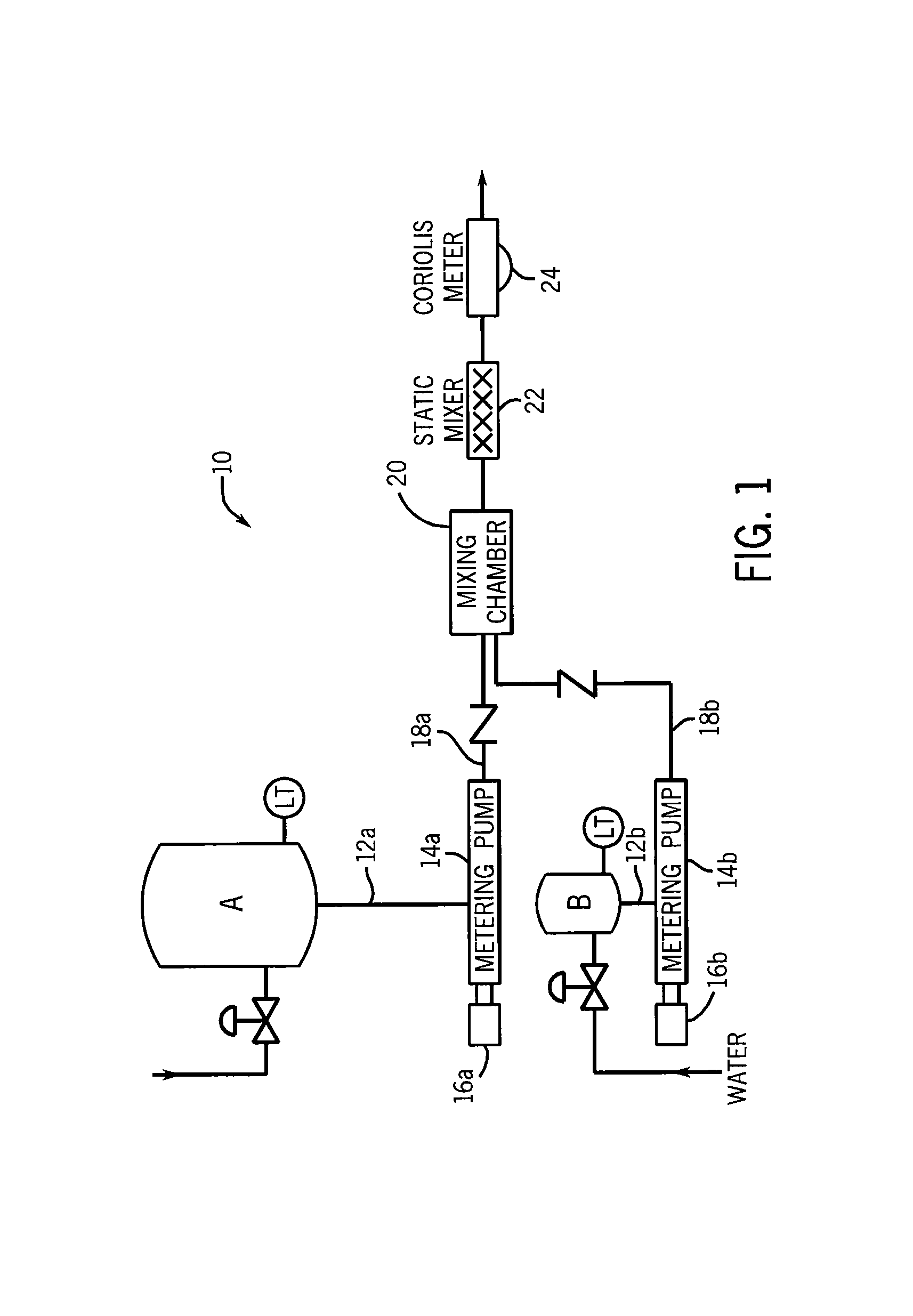
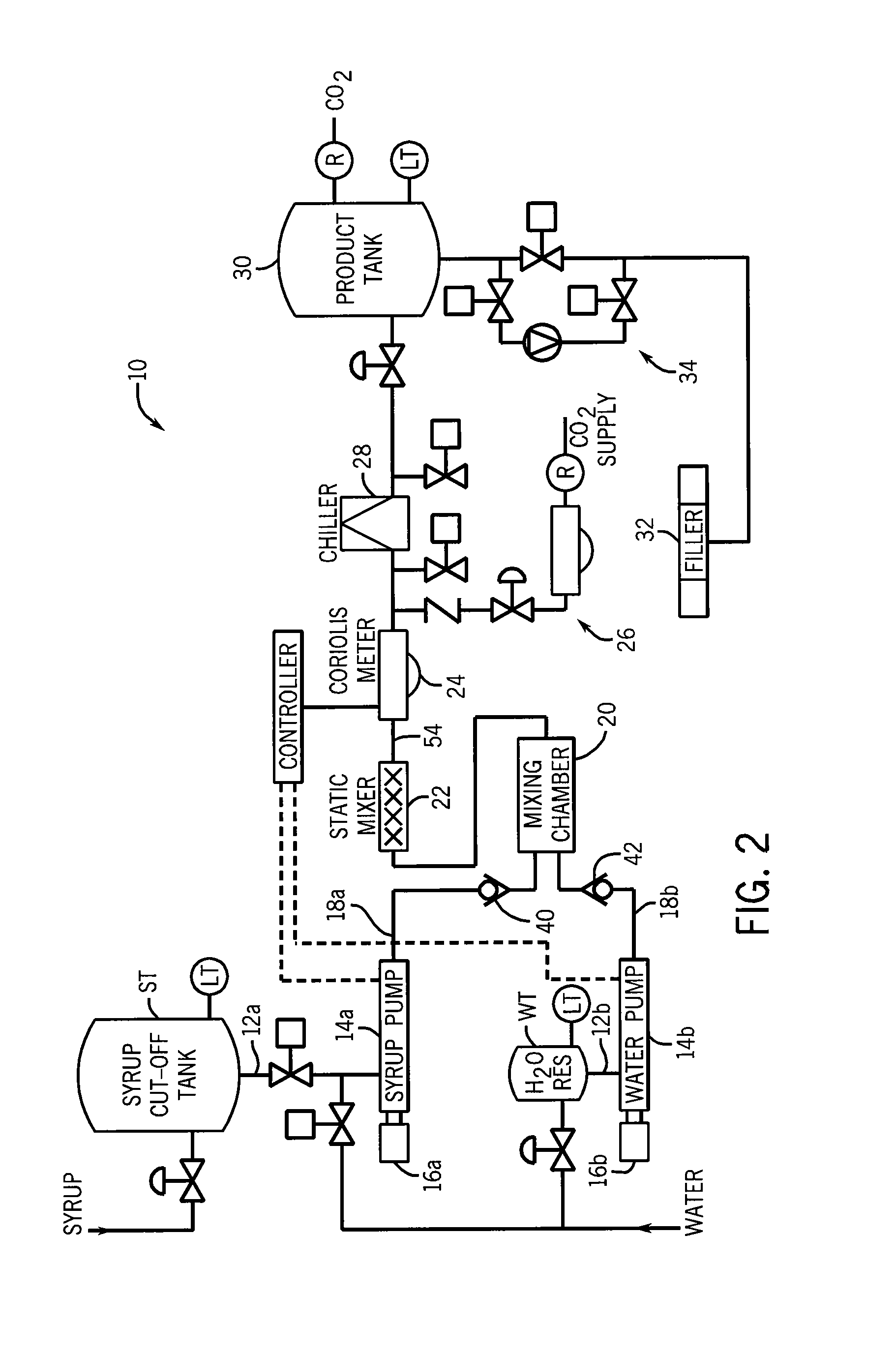
Fluid mixer using countercurrent injection
ActiveUS9004744B1Avoid many problemsEasy to controlFlow mixersTransportation and packagingEngineeringCheck valve
A method and apparatus for mixing fluids, such as beverage syrup and water, uses countercurrent injection to improve blending of the fluids. A mixing chamber has a first inlet through which a first fluid is fed to the mixing chamber, and a second inlet through which a countercurrent injection nozzle extends and is operative to inject a second fluid into a stream of the first fluid. The countercurrent injection nozzle is equipped with a check valve to control the flow of fluid into the mixing chamber. The mixing chamber may include additional inlets that may be fitted with countercurrent injection nozzles to permit the countercurrent injection of other fluid, such as flavorings, into the stream of the first fluid.
Owner:TECHNIBLEND LLC
Injectable gel implant for glaucoma treatment
InactiveUS20050277864A1Inhibit and slow effectEffective treatmentEye surgeryFlow mixersAqueous humorSchlemm's canal
Methods and implants for treating glaucoma in an eye are described. The implant includes an inlet section configured to be positioned in the anterior chamber of the eye and an outlet section in fluid communication with the inlet section. The outlet section is configured to be positioned in Schlemm's canal of the eye. The implant comprises a hydrogel and is configured to conduct aqueous humor from the anterior chamber to Schlemm's canal.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
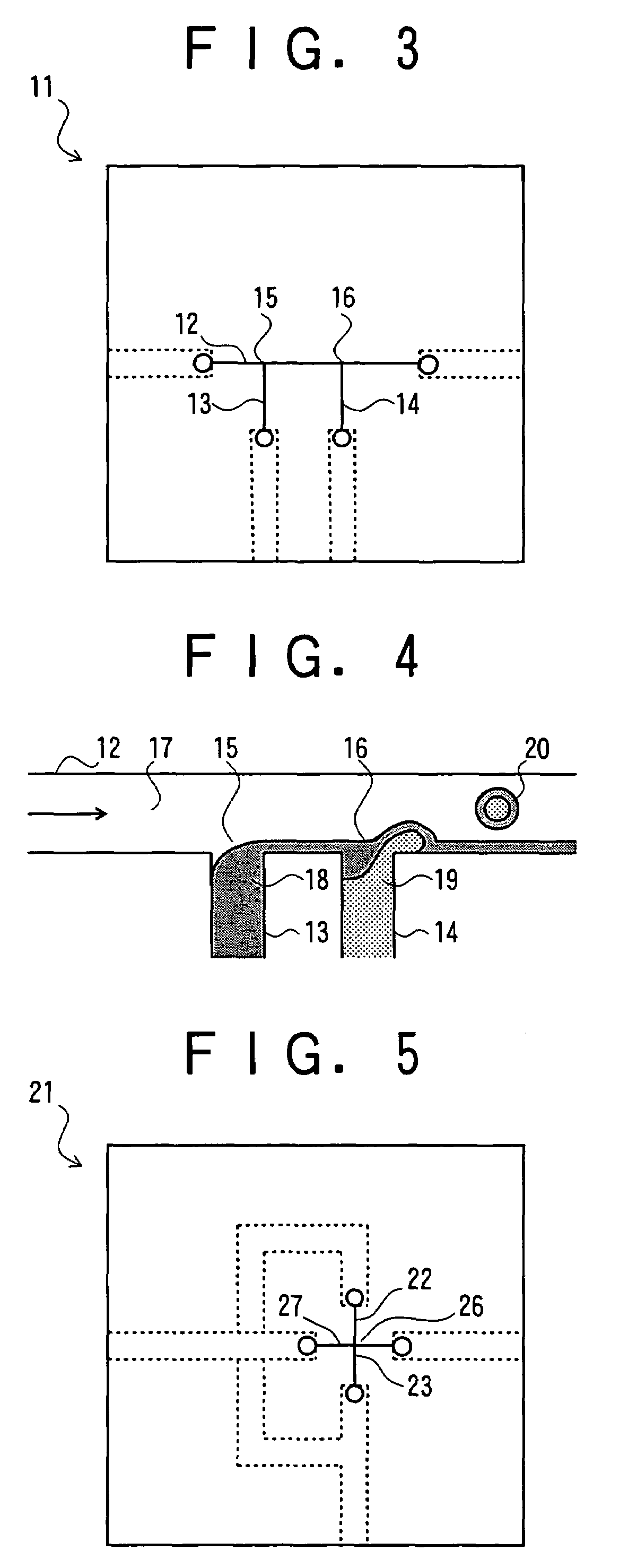
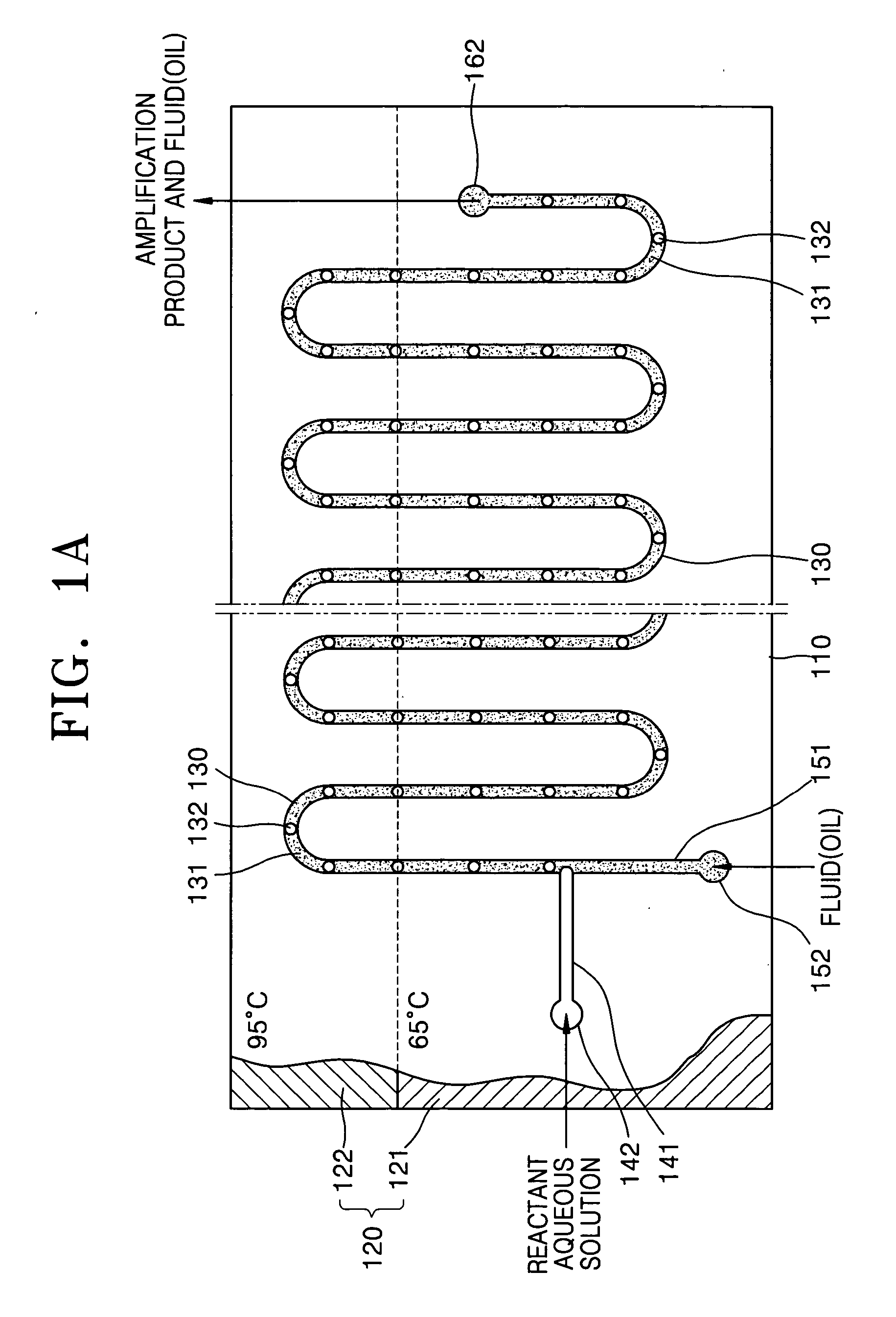
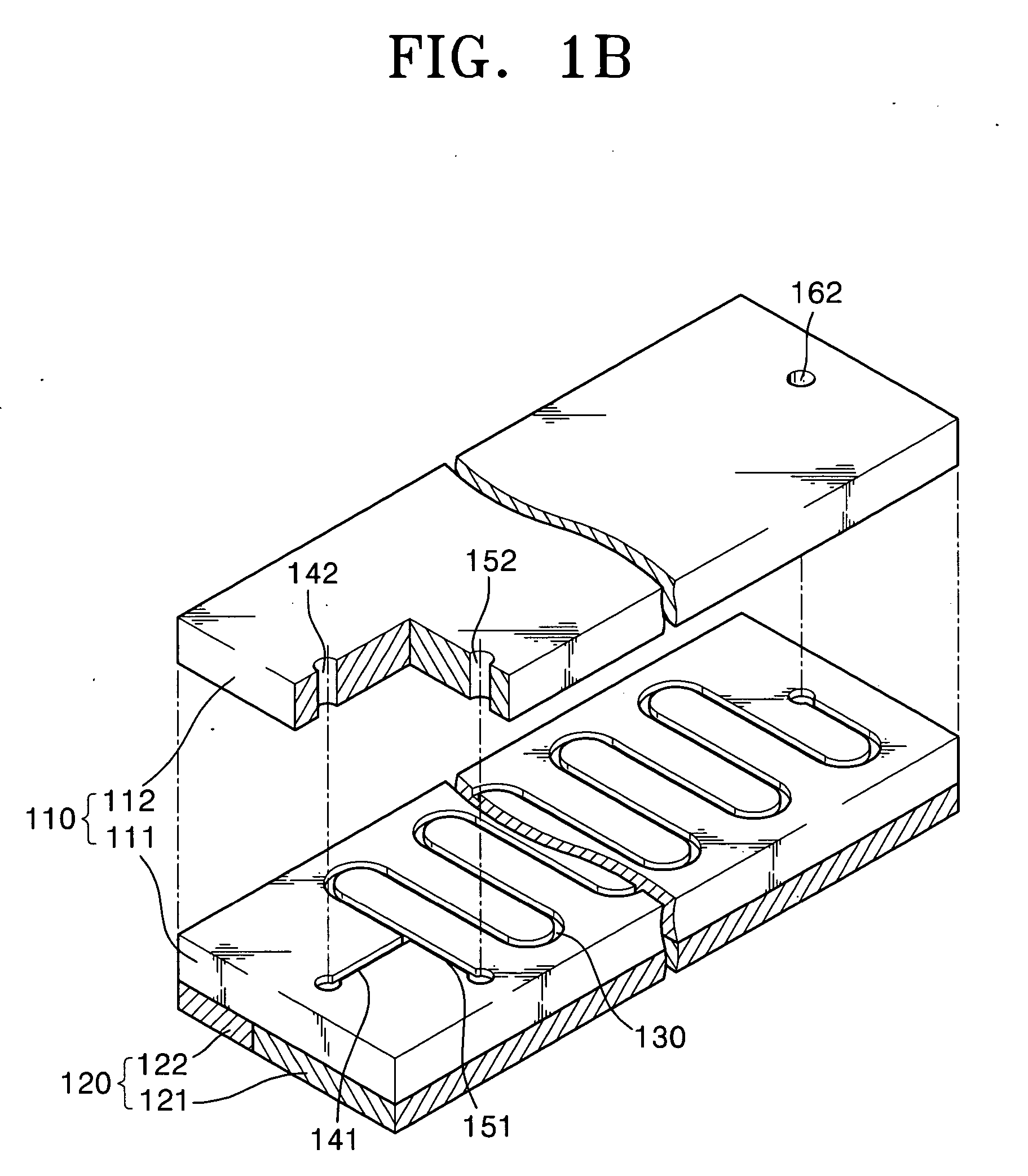
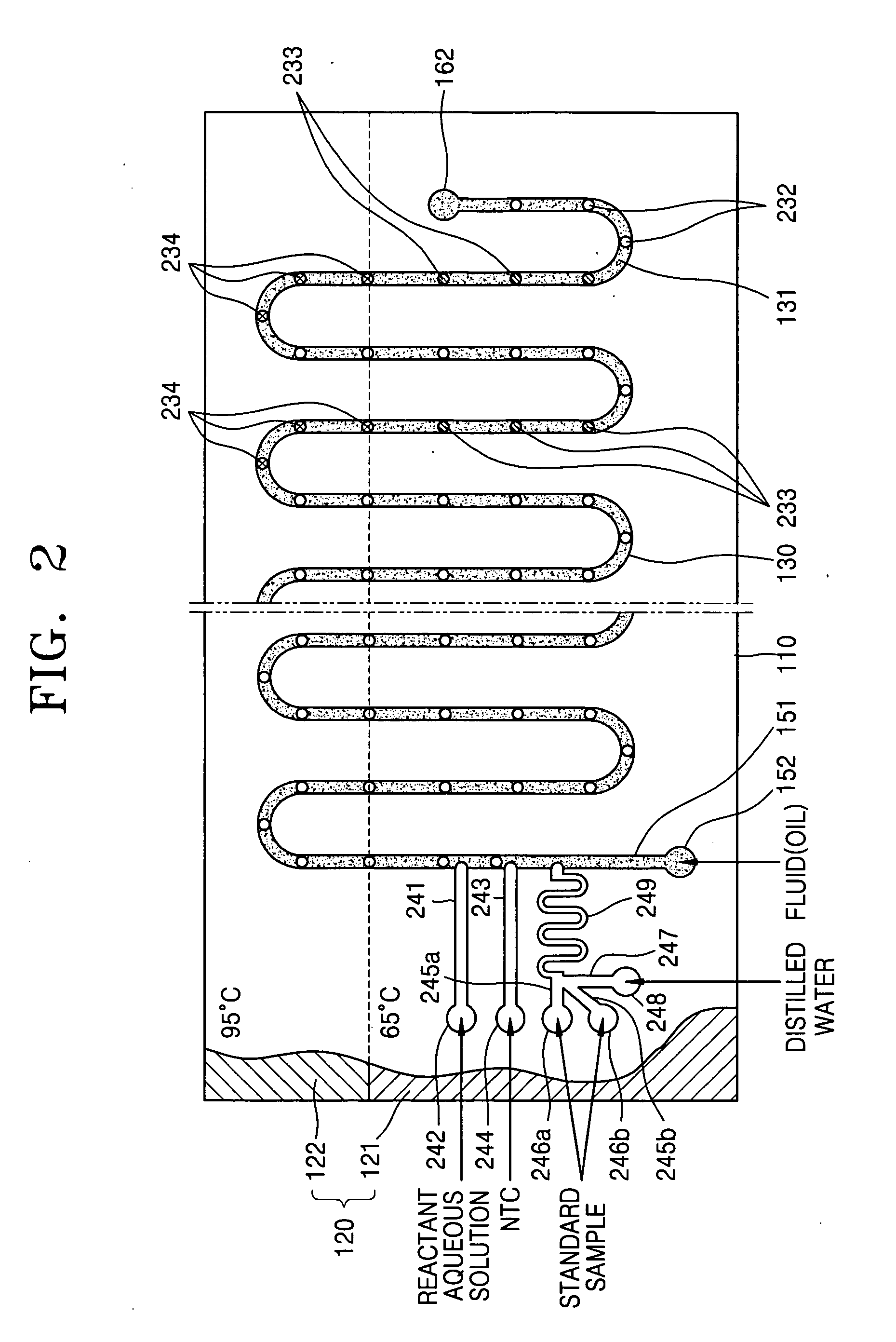
Method and apparatus for amplifying nucleic acids
ActiveUS20050202489A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsInlet channelAqueous solution
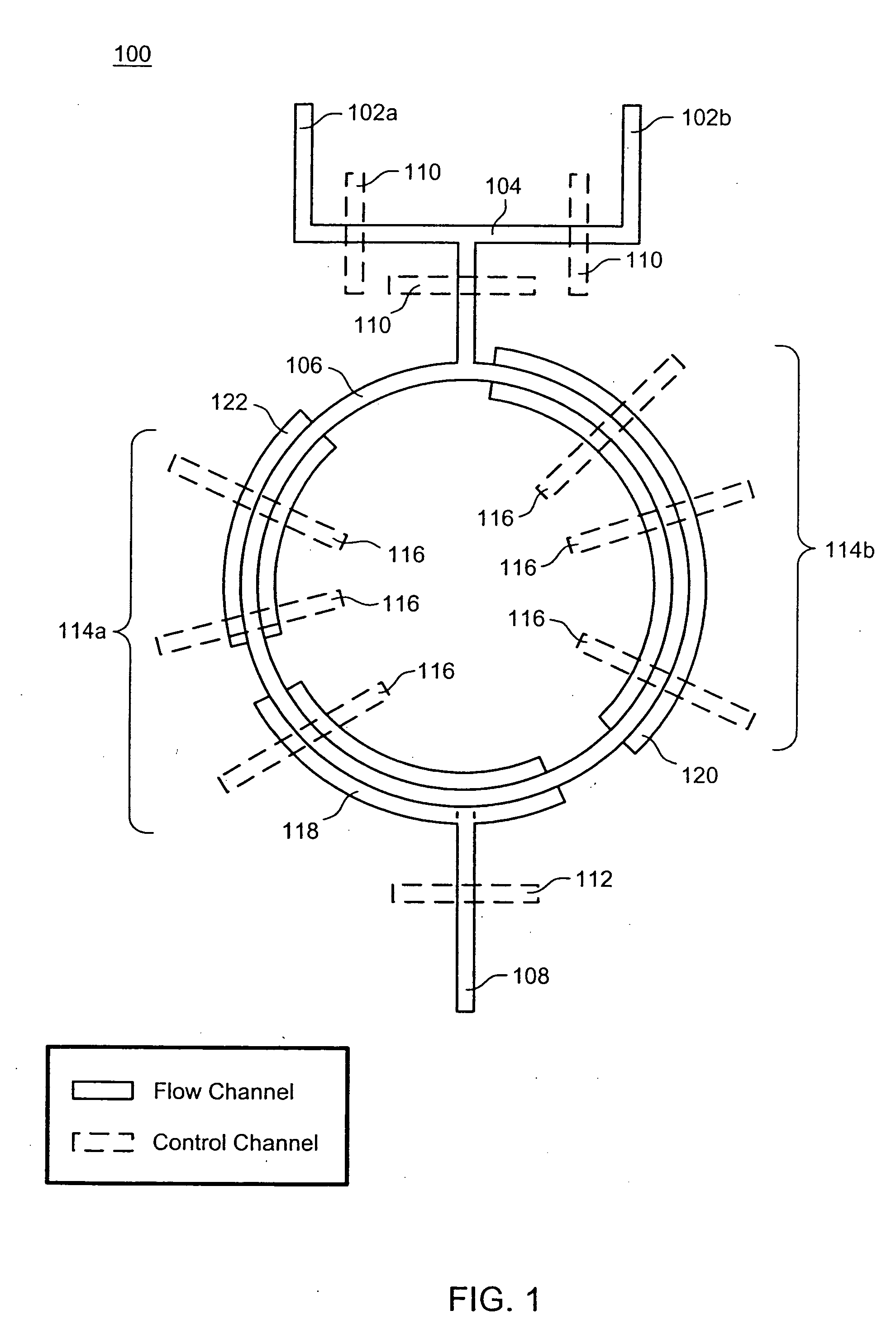
Provided are a method and apparatus for amplifying nucleic acids. The method includes introducing into a reaction vessel via different inlet channels a reactant aqueous solution containing reactants for nucleic acid amplification and a fluid that is phase-separated from the reactant aqueous solution and does not participate in amplification reaction, creating a plurality of reactant aqueous solution droplets surrounded by the fluid by contacting the reactant aqueous solution with the fluid in the reaction vessel, and amplifying the nucleic acids in the reactant aqueous solution droplets. The apparatus includes a substrate, a reaction vessel formed inside of the substrate, at least one first inlet channel formed inside the substrate, connected to an end of the reaction vessel, and allowing introduction of a reactant aqueous solution containing reactants for nucleic acid amplification into the reaction vessel, a second inlet channel formed inside the substrate, connected to the end of the reaction vessel, and allowing introduction of a fluid that is phase-separated from the reactant aqueous solution and does not participate in amplification reaction into the reaction vessel, and a heating unit installed on the substrate in such a way to thermally contact with the substrate and heating the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Compositions and methods for liquid metering in microchannels
InactiveUS20030070677A1Material nanotechnologyShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersElectrophoresisComputer module
The movement and mixing of microdroplets through microchannels is described employing microscale devices, comprising microdroplet transport channels, reaction regions, electrophoresis modules, and radiation detectors. Microdroplets are metered into defined volumes and are subsequently incorporated into a variety of biological assays. Electronic components are fabricated on the same substrate material, allowing sensors and controlling circuitry to be incorporated in the same device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
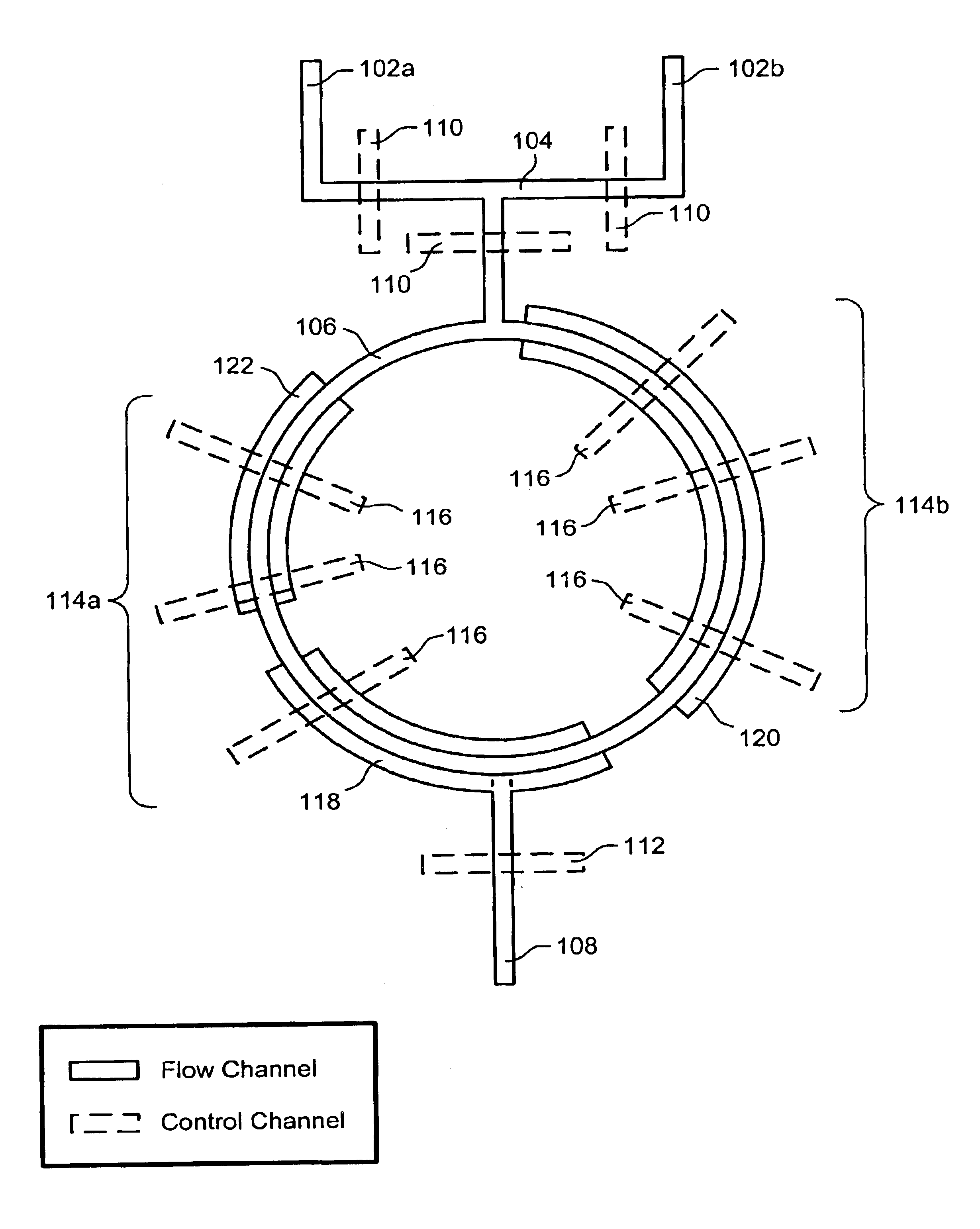
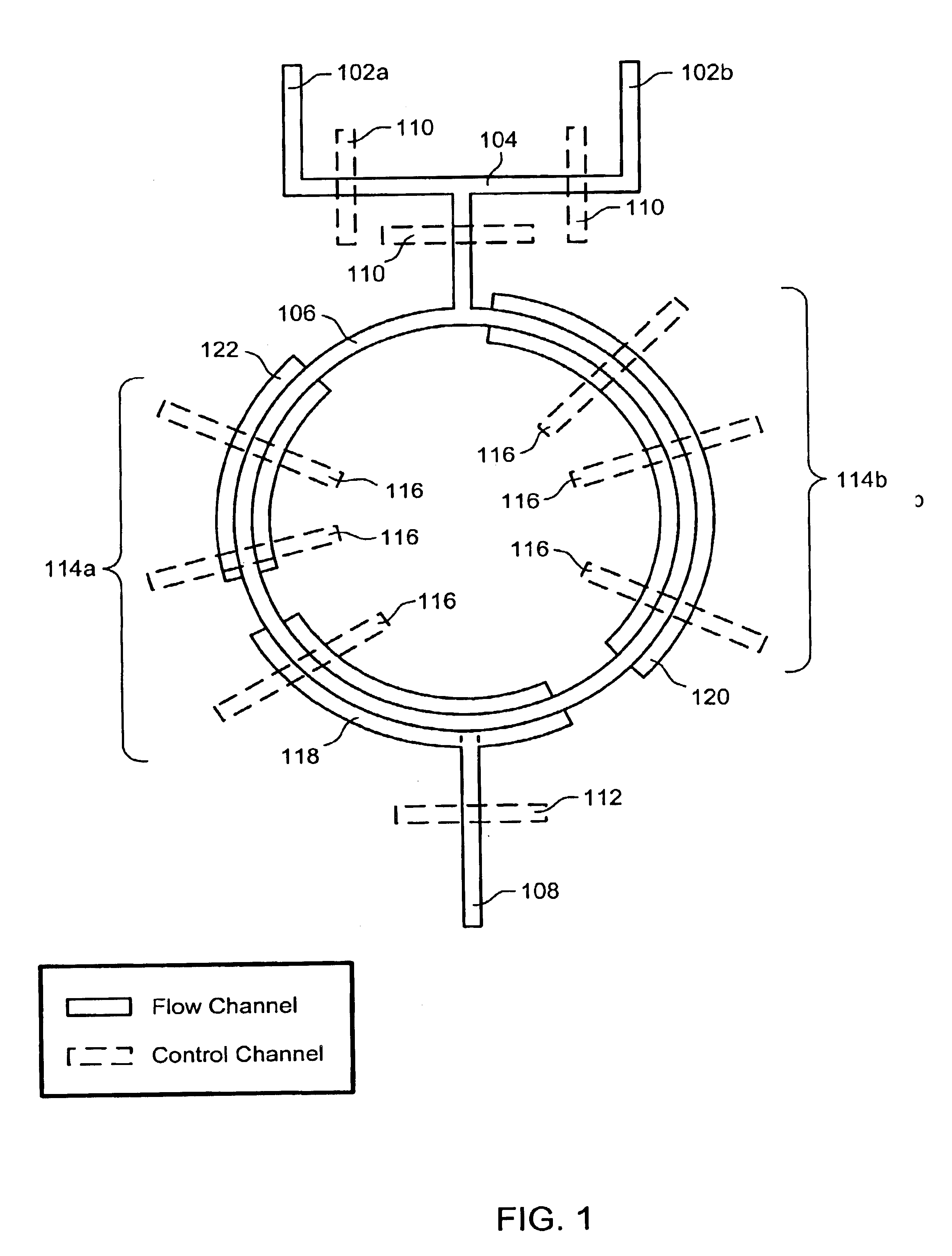
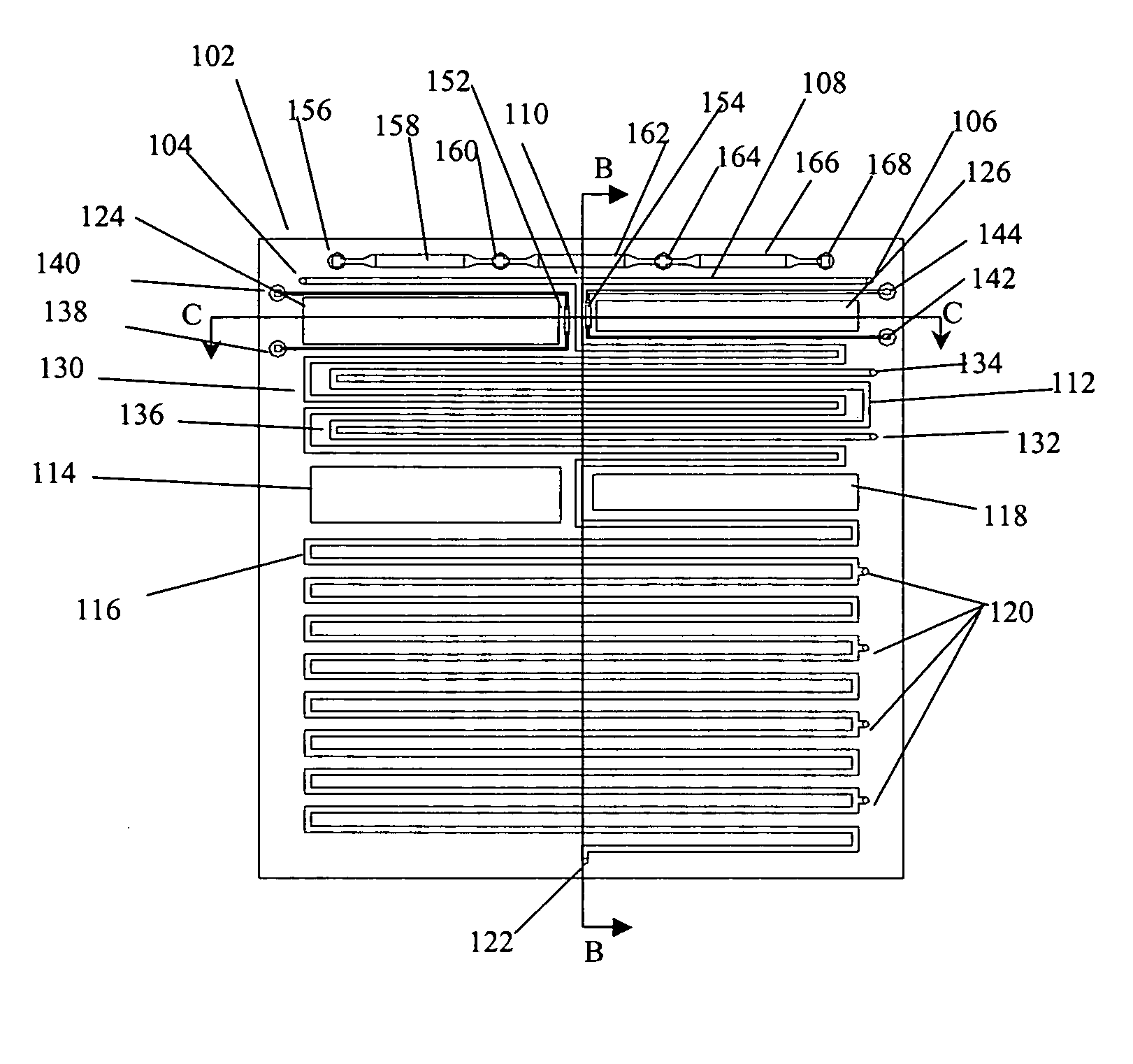
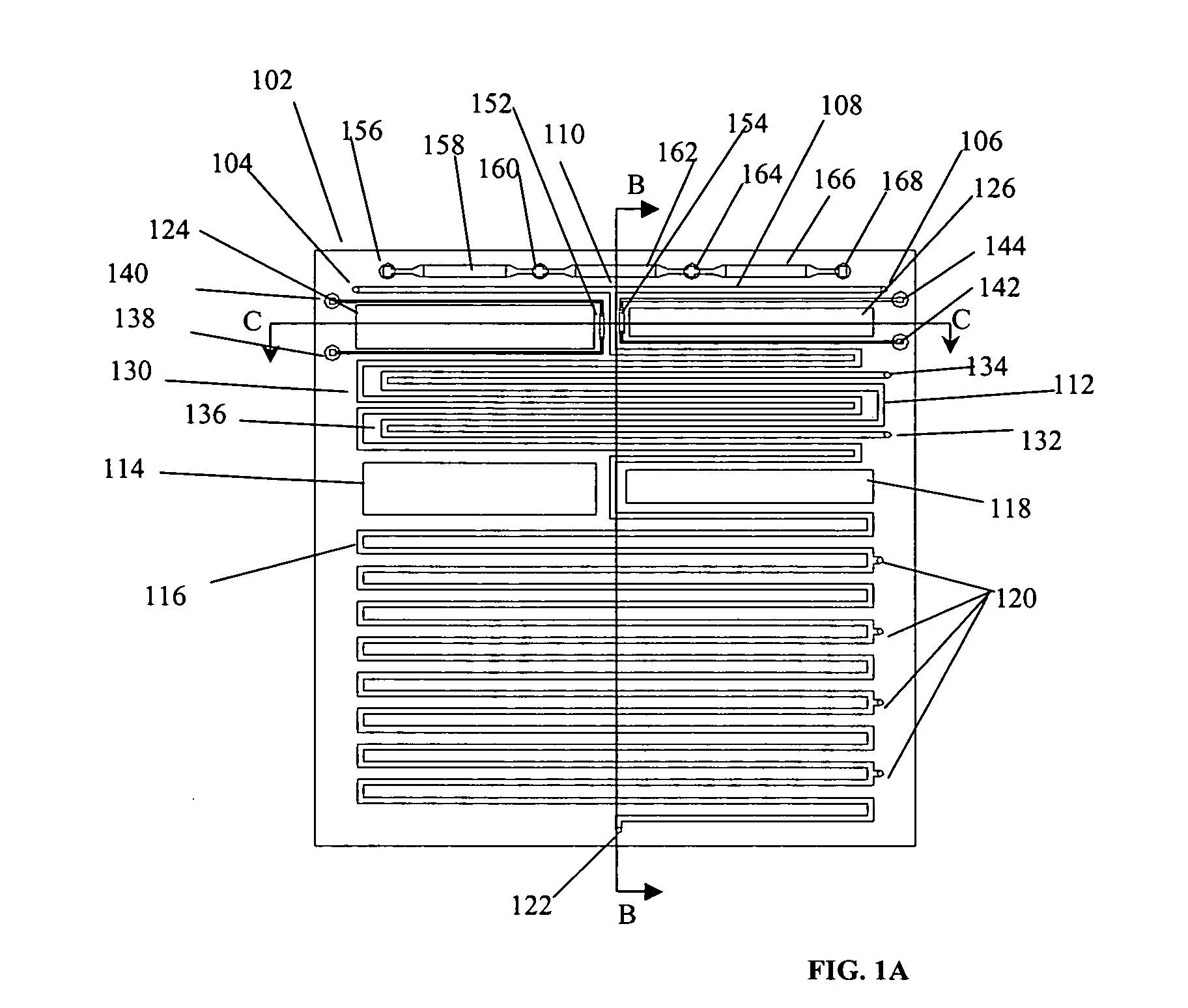
Nucleic acid amplification using microfluidic devices
InactiveUS20050221373A1Facilitate amplification reactionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusRegulation temperatureEngineering
The present invention provides microfluidic devices and methods using the same in various types of thermal cycling reactions. Certaom devices include a rotary microfluidic channel and a plurality of temperature regions at different locations along the rotary microfluidic channel at which temperature is regulated. Solution can be repeatedly passed through the temperature regions such that the solution is exposed to different temperatures. Other microfluidic devices include an array of reaction chambers formed by intersecting vertical and horizontal flow channels, with the ability to regulate temperature at the reaction chambers. The microfluidic devices can be used to conduct a number of different analyses, including various primer extension reactions and nucleic acid amplification reactions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com