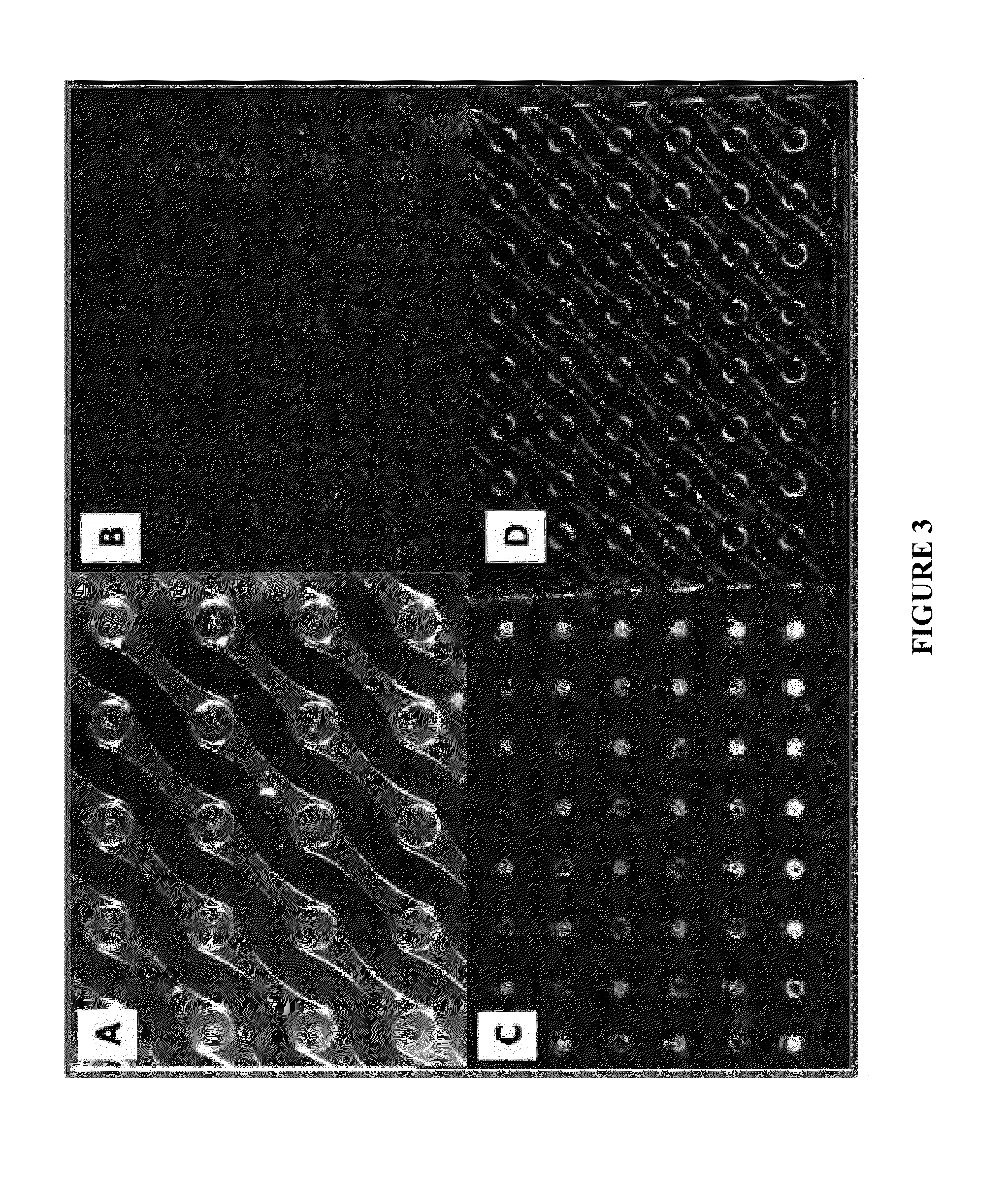
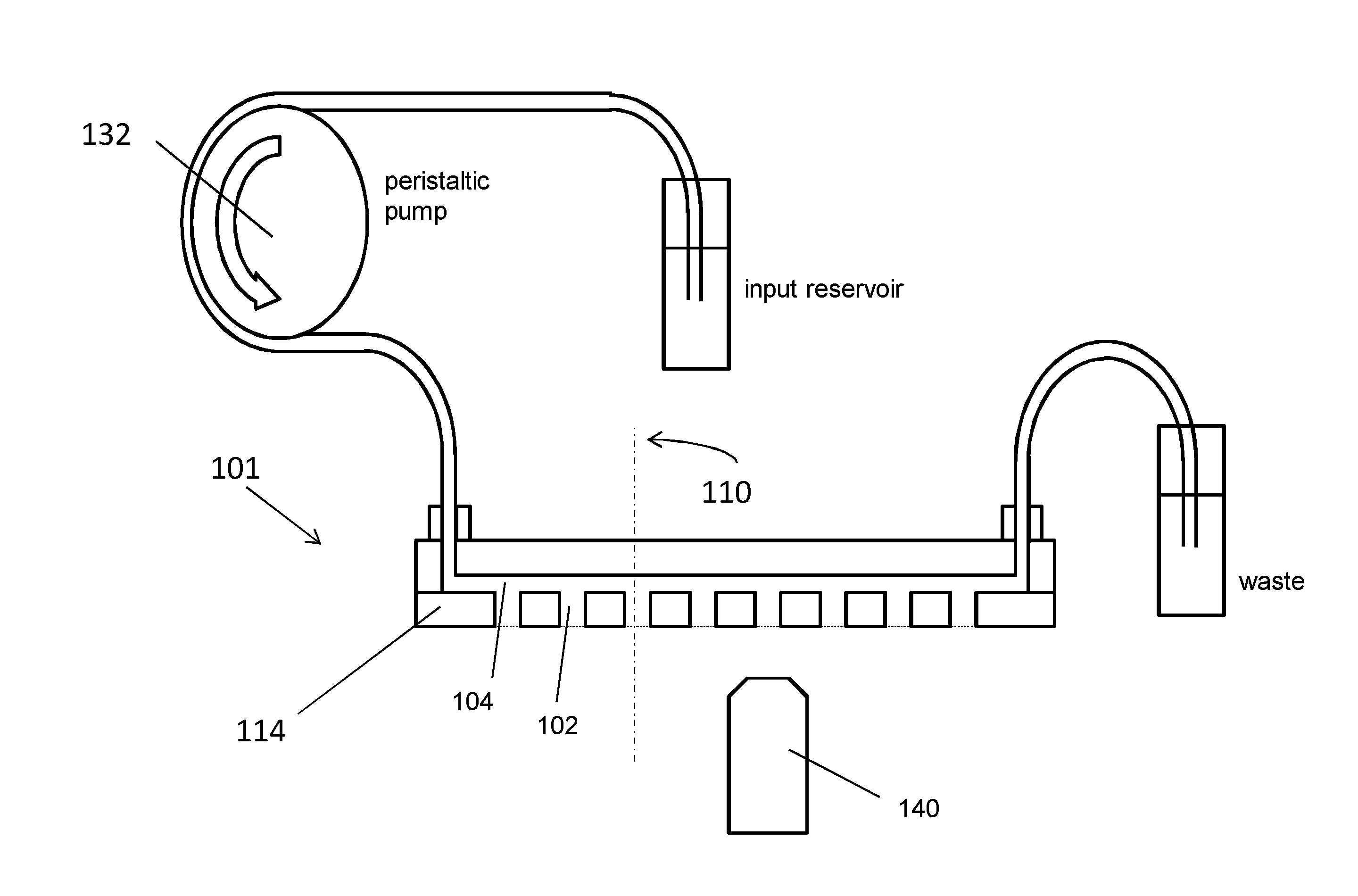
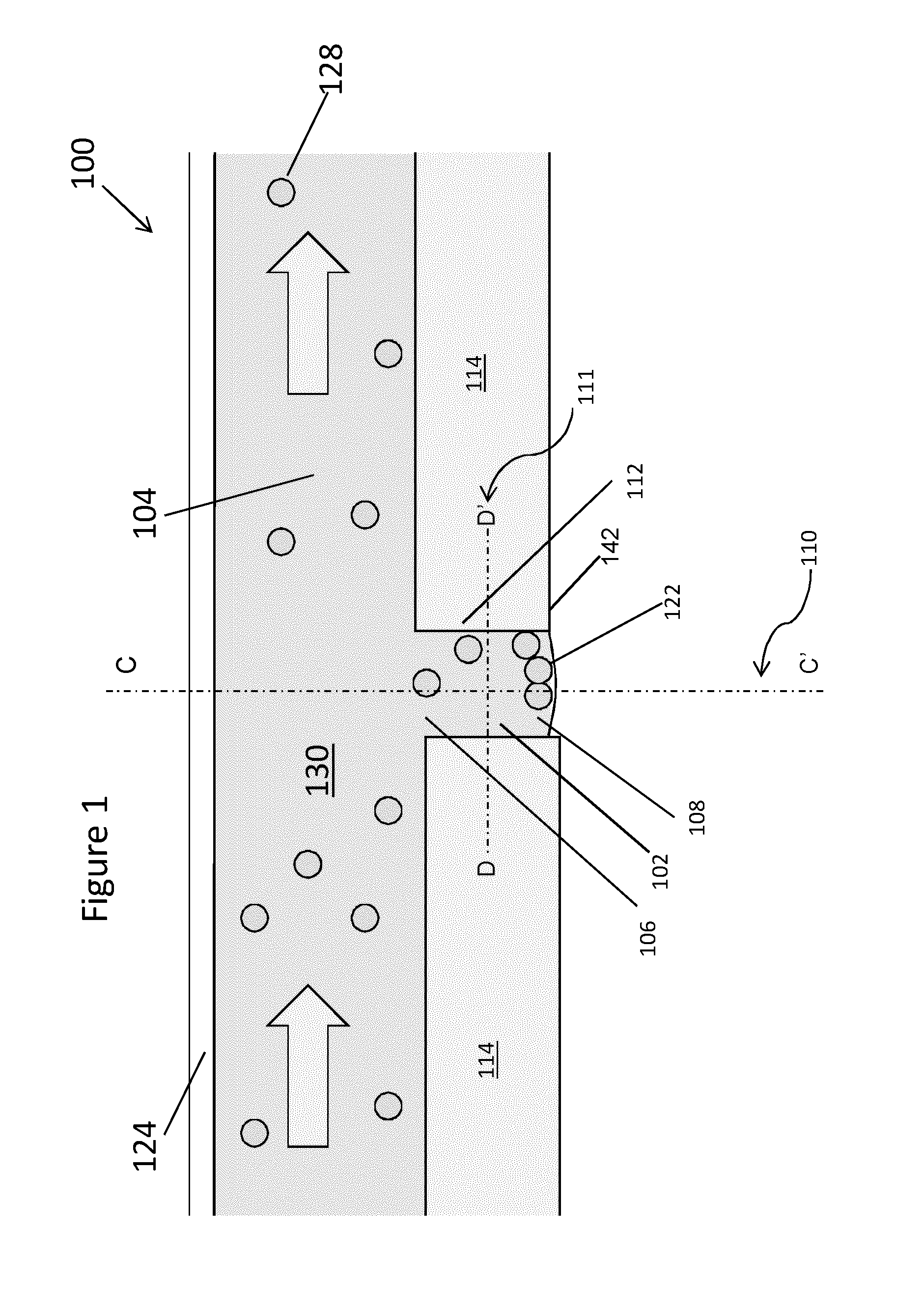
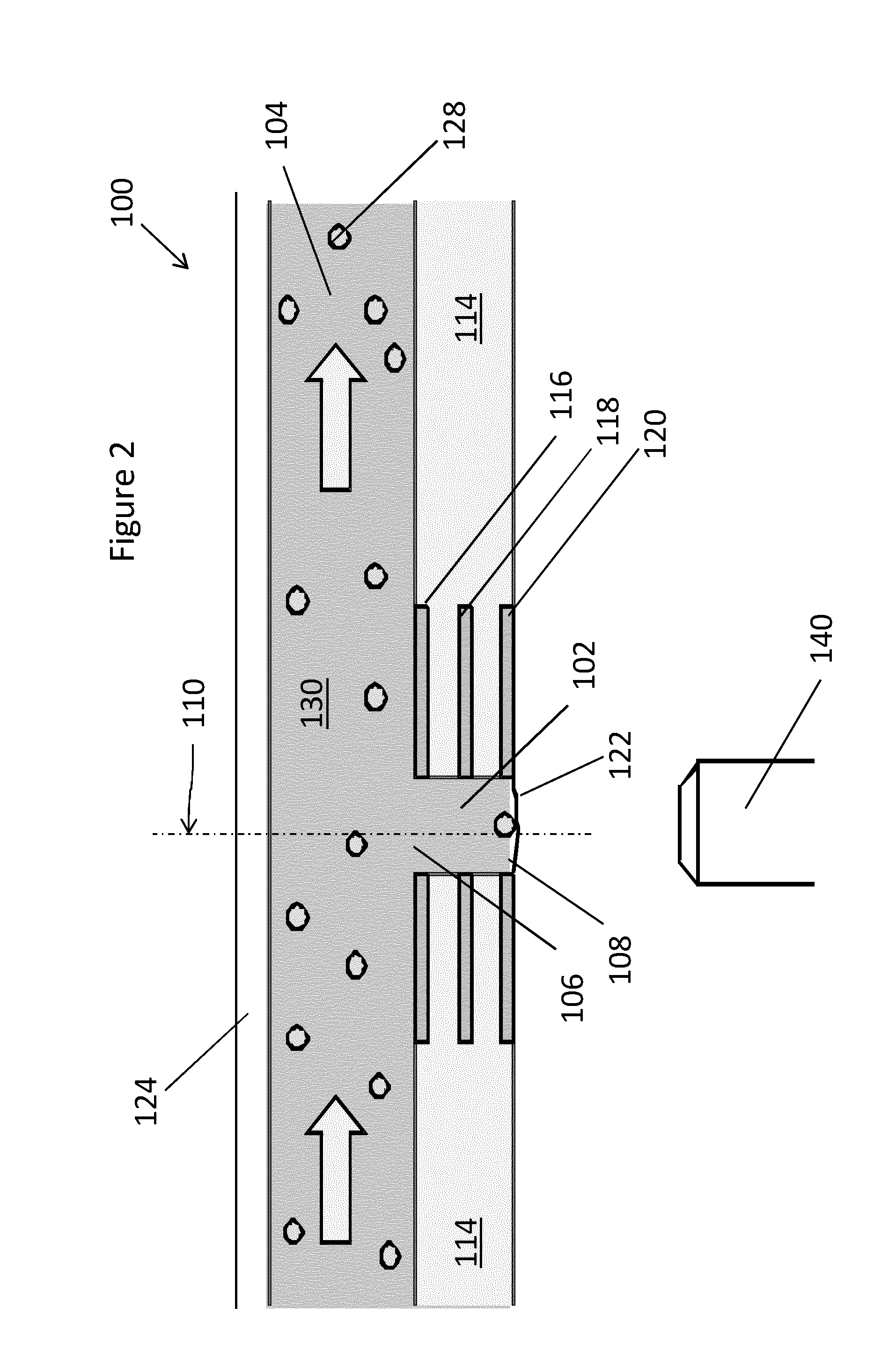
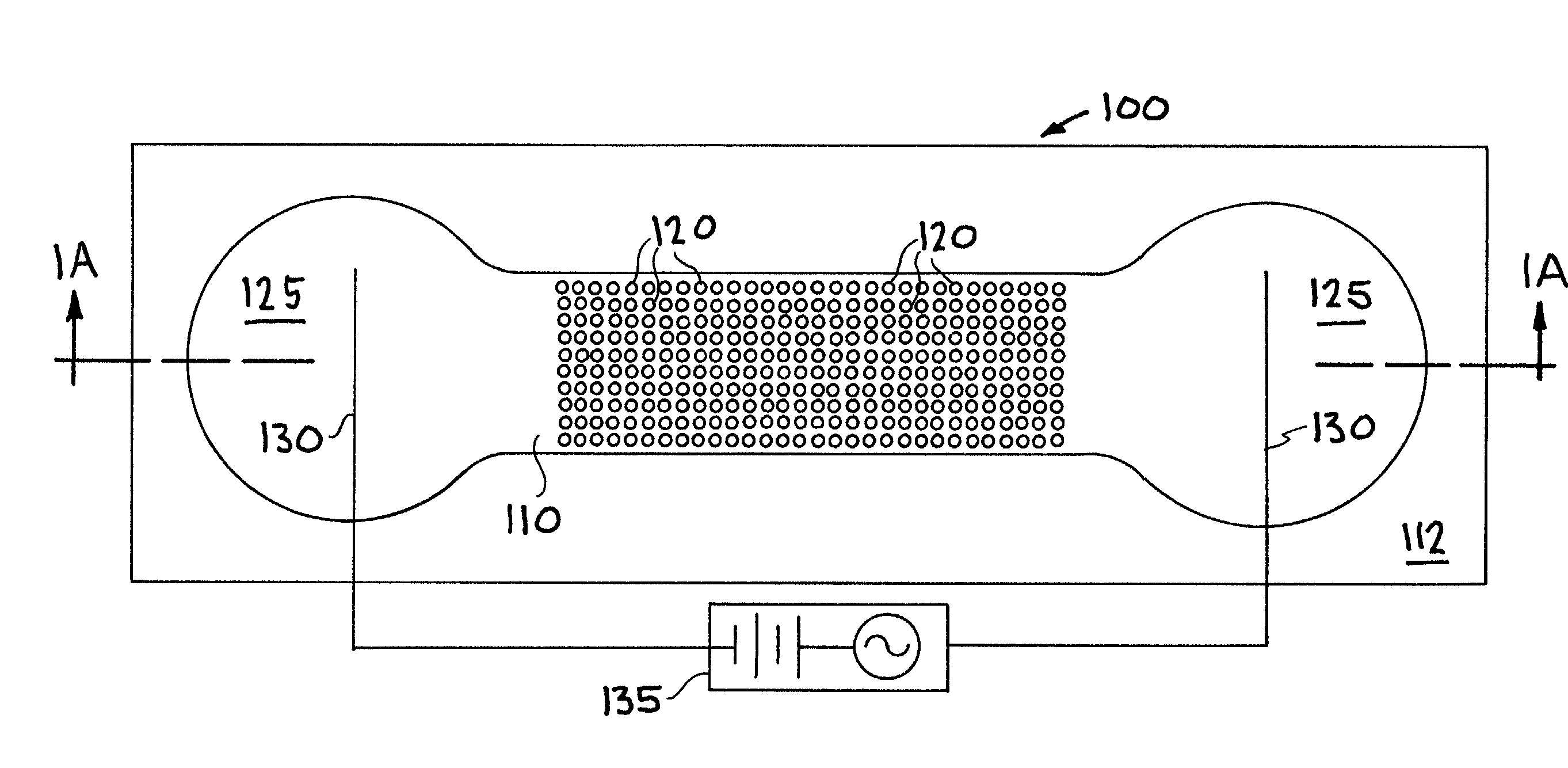
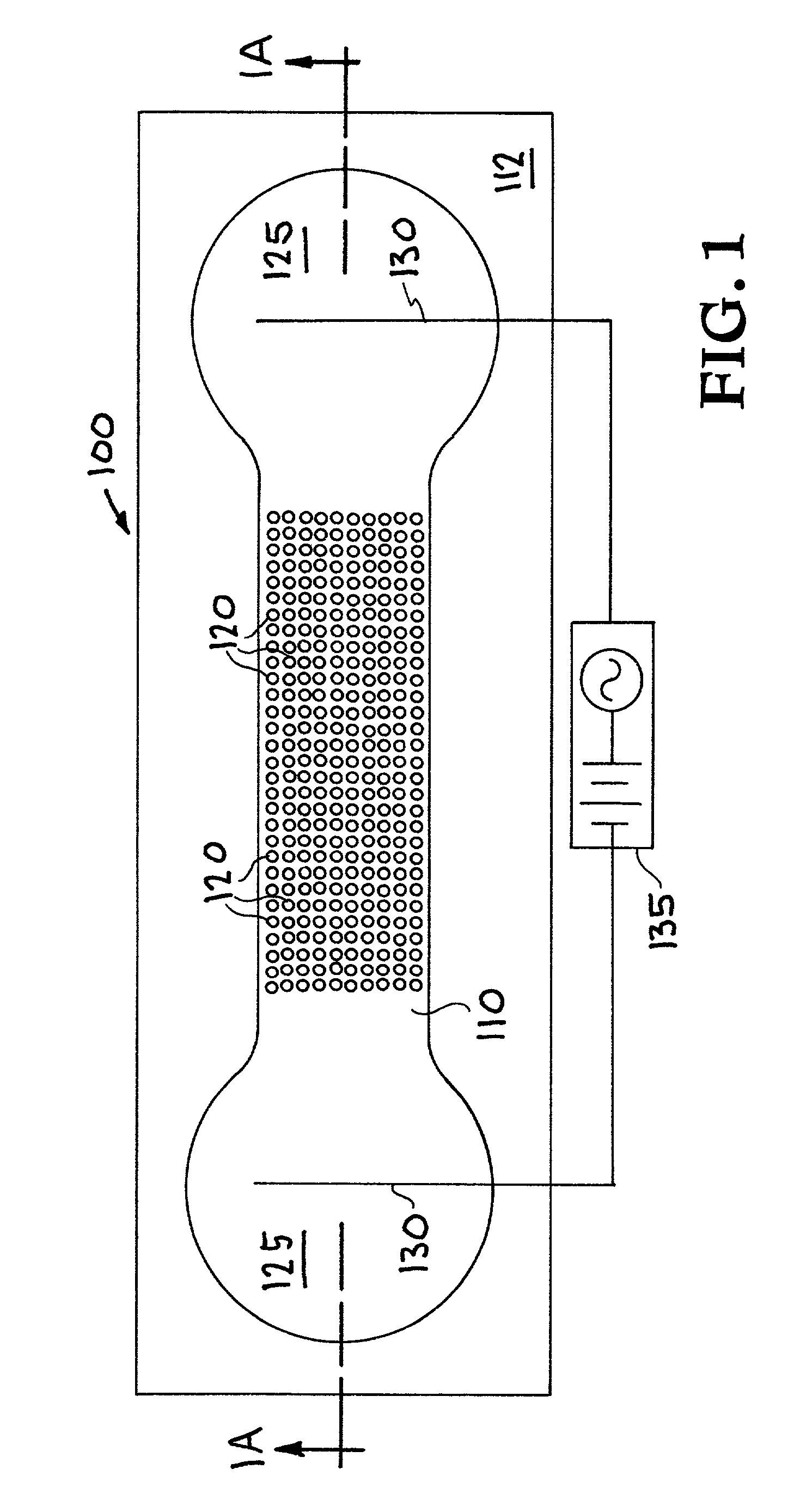
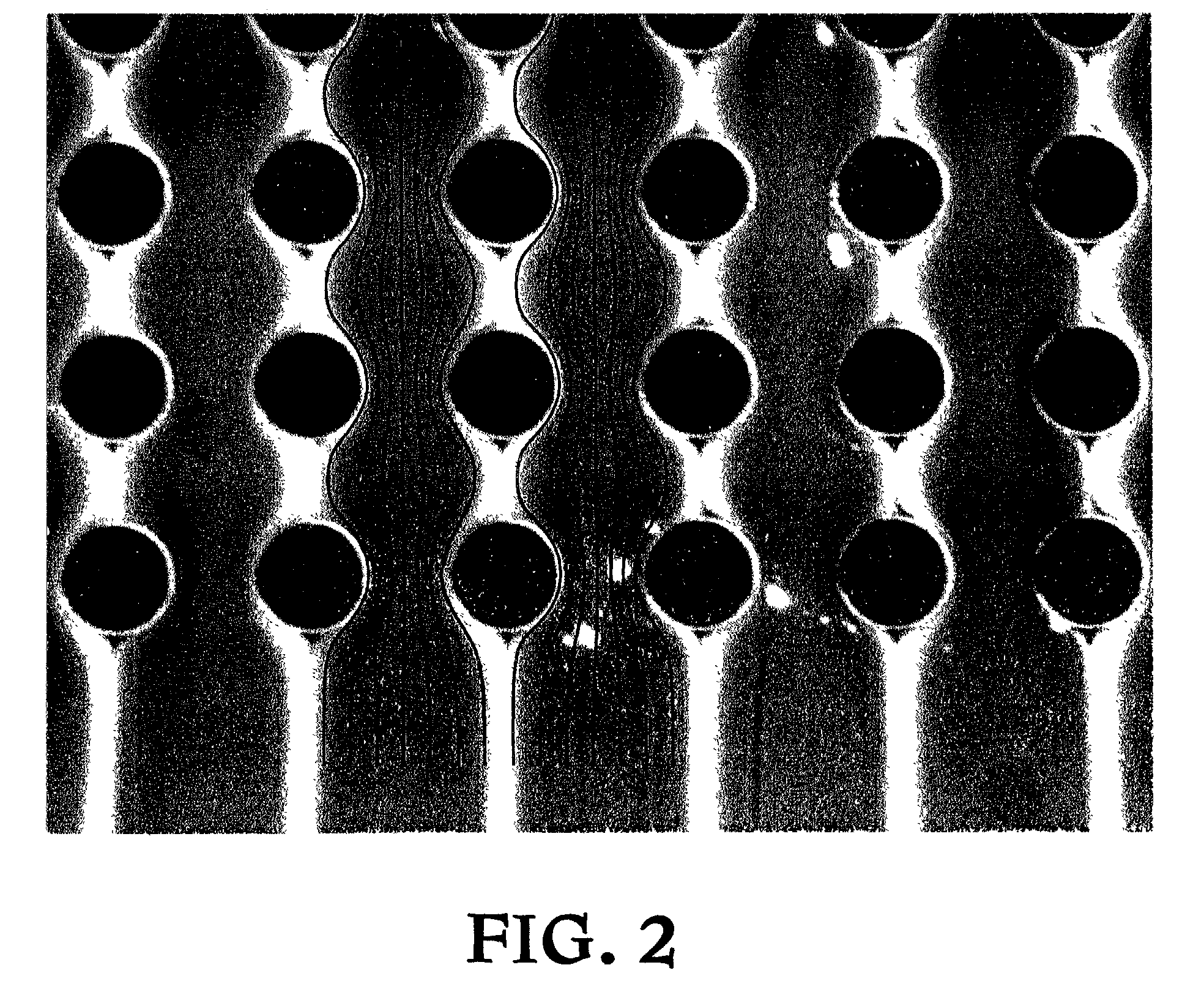
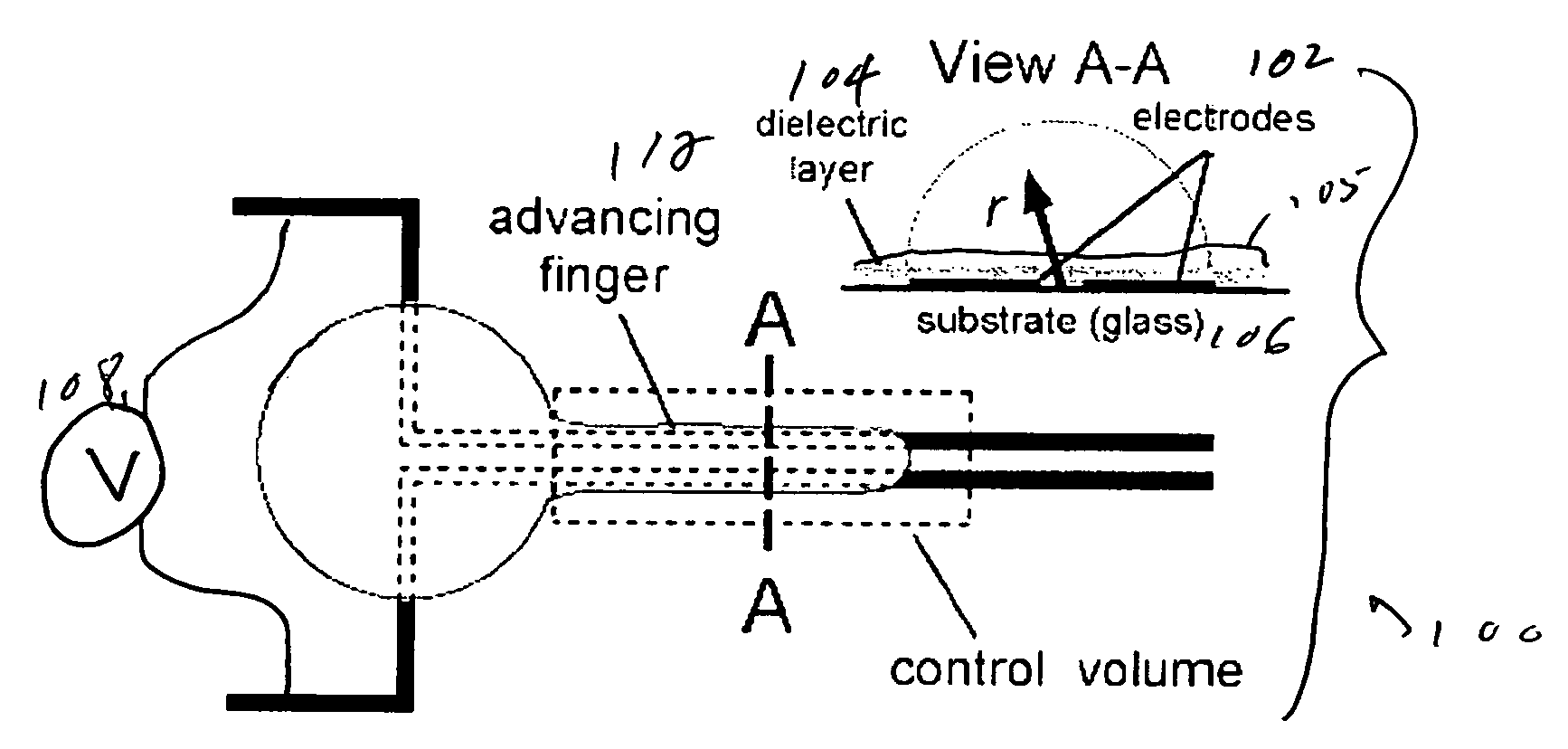
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
352results about "Dielectrophoresis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
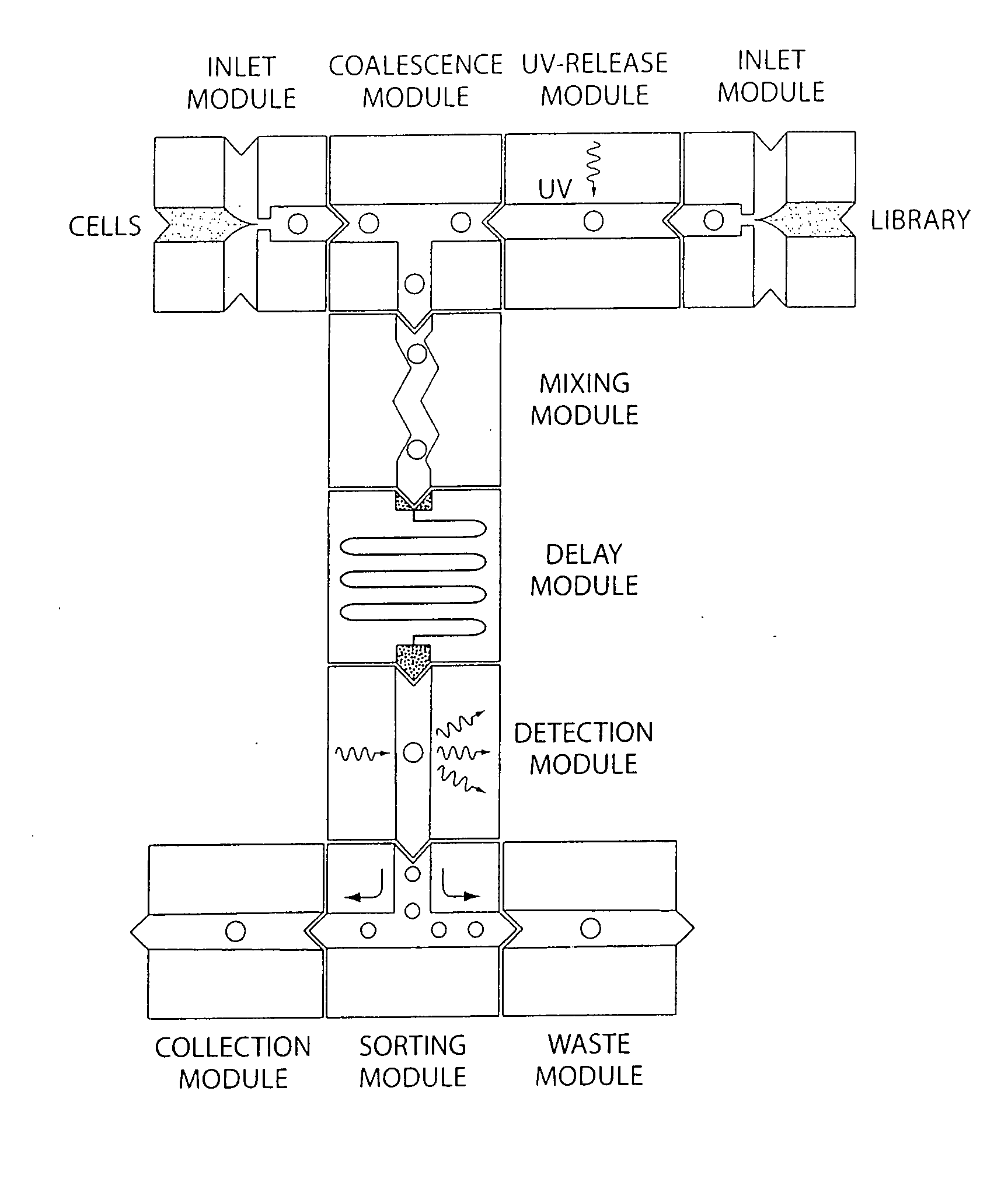
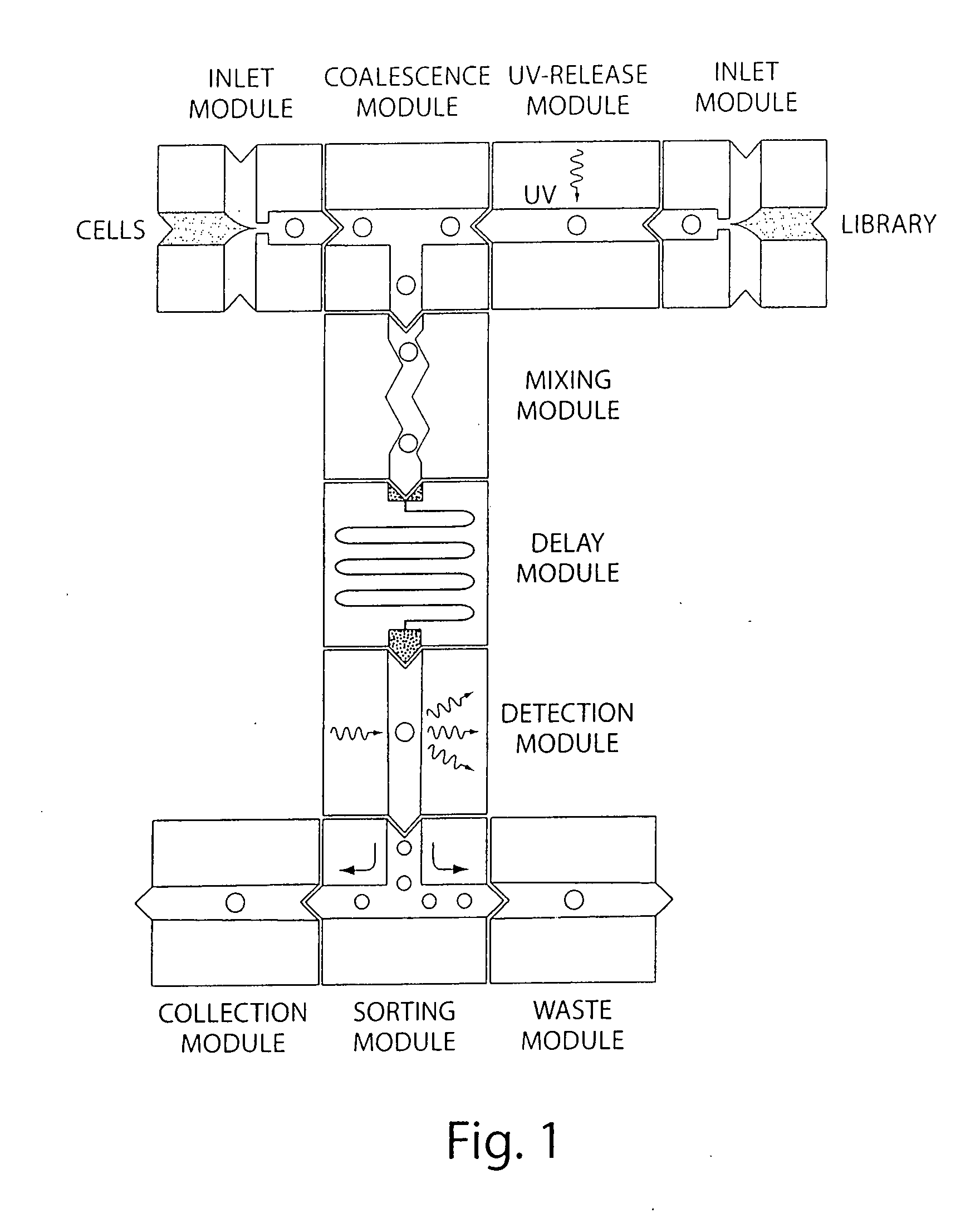
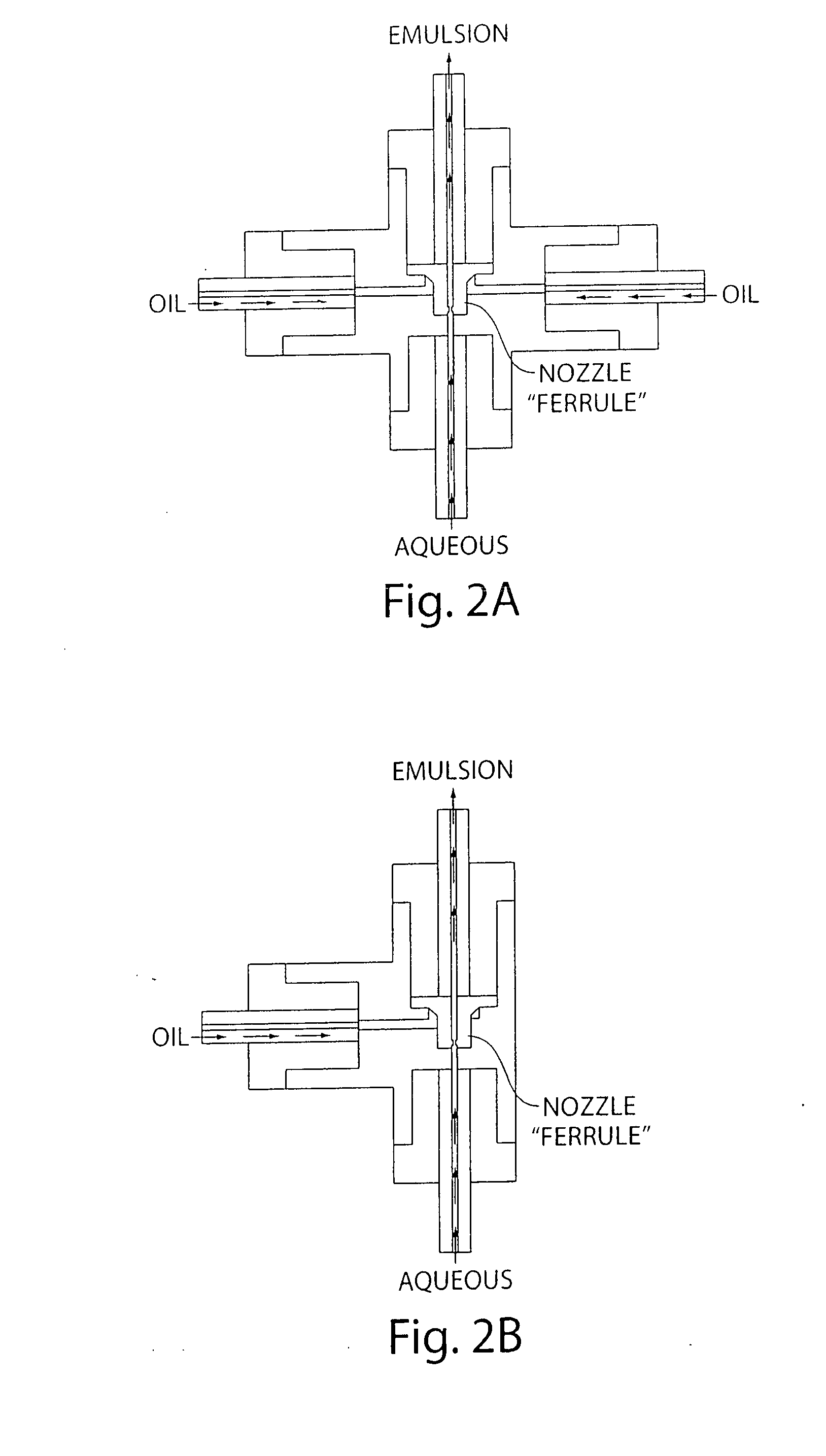
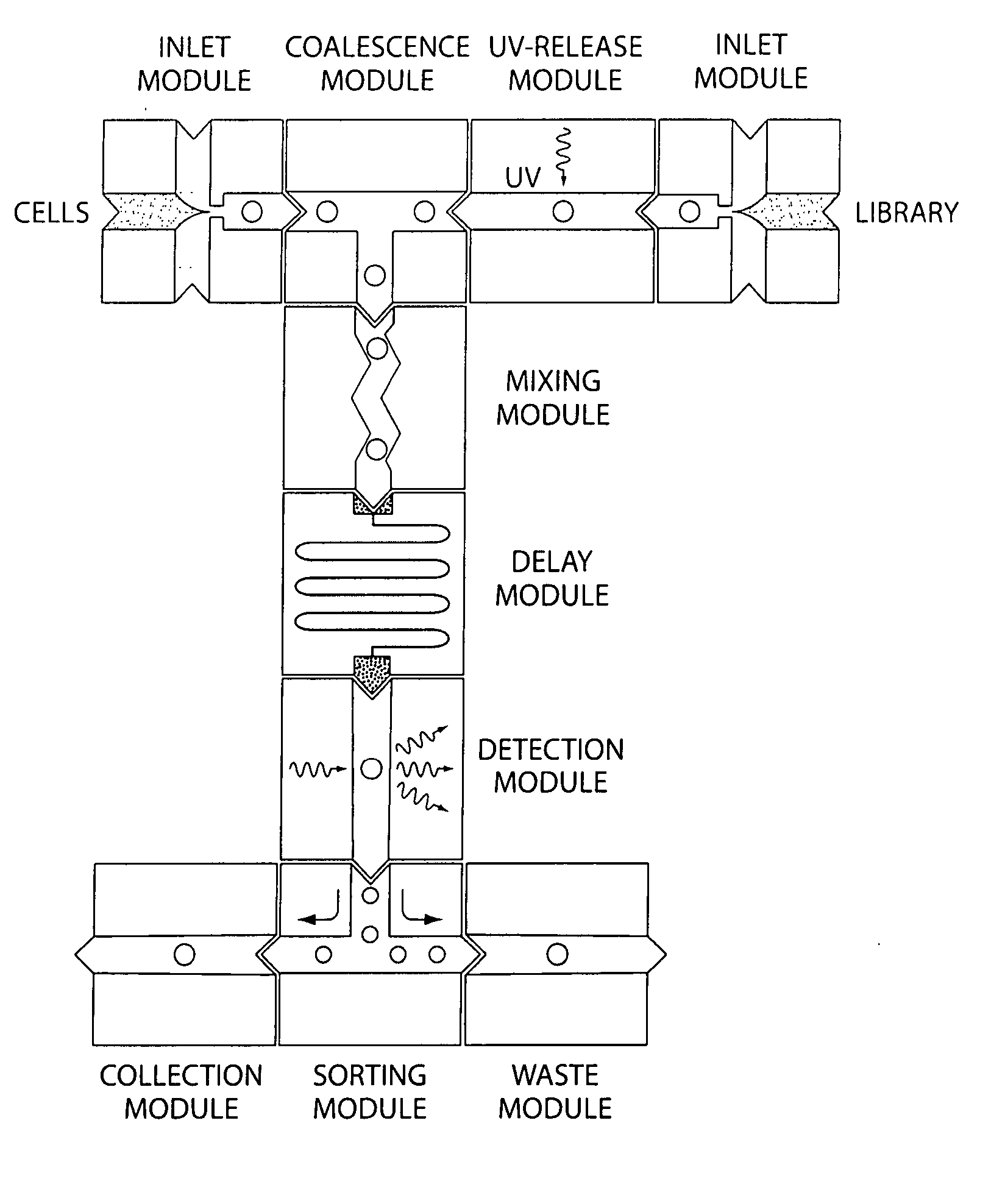
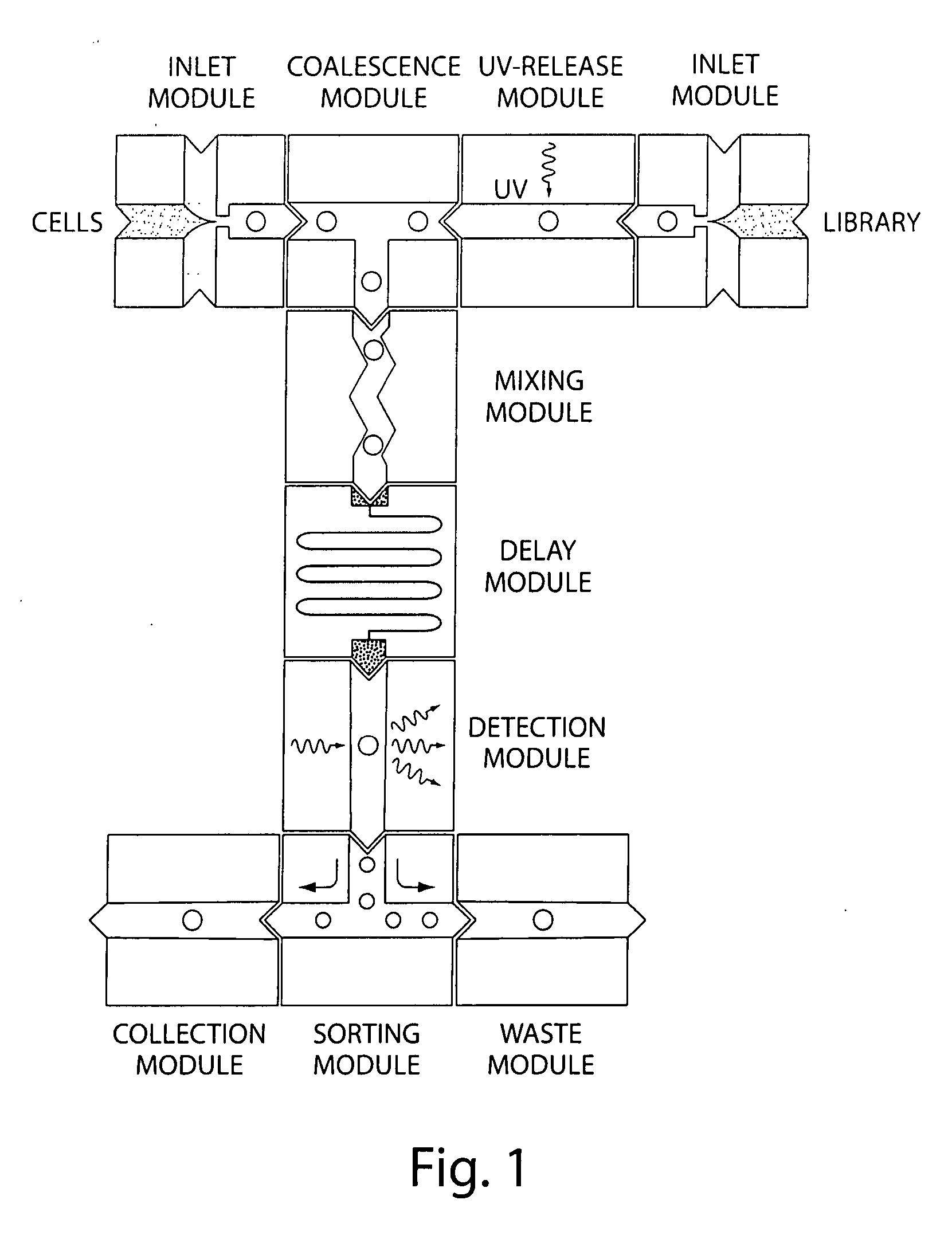
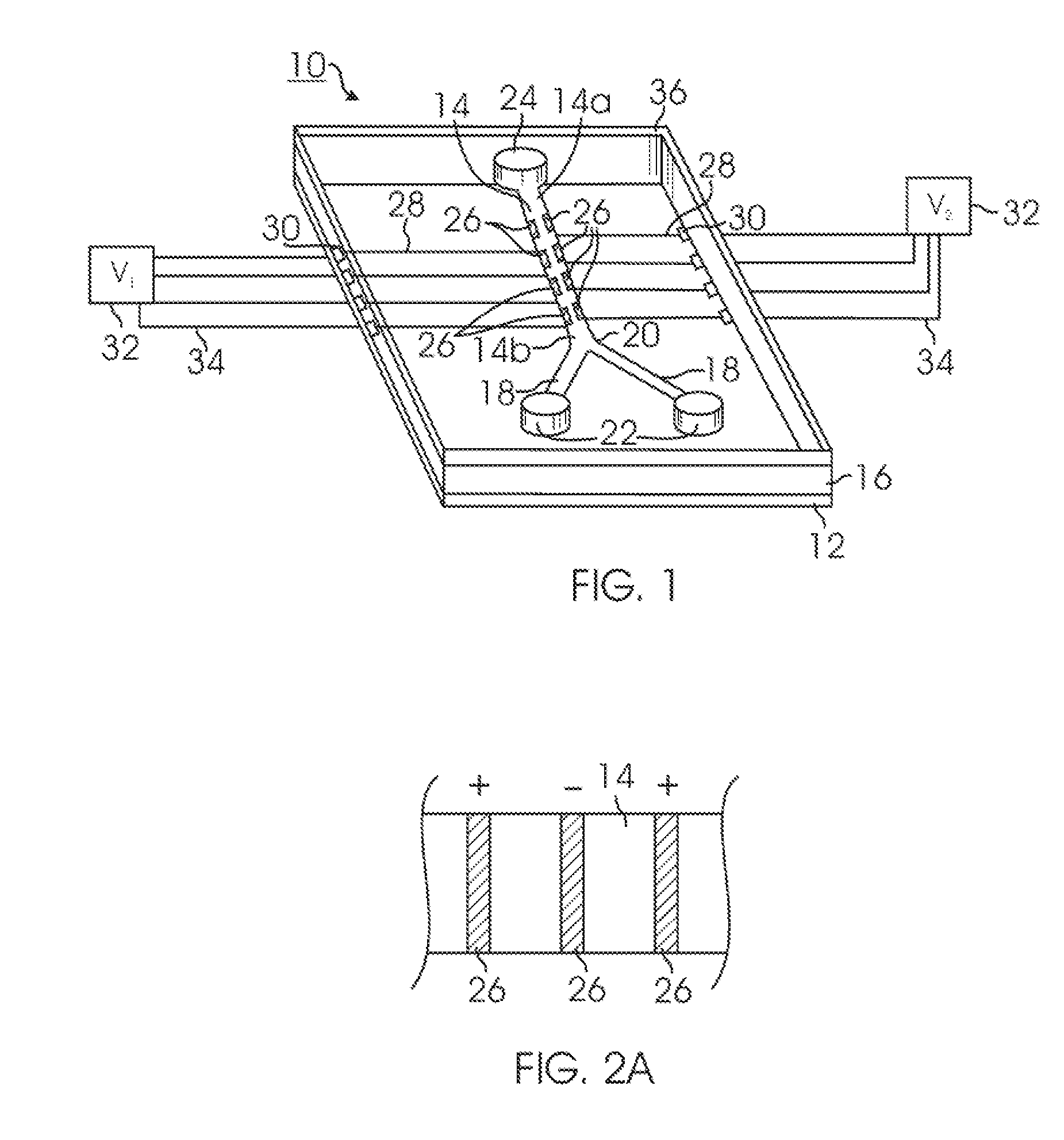
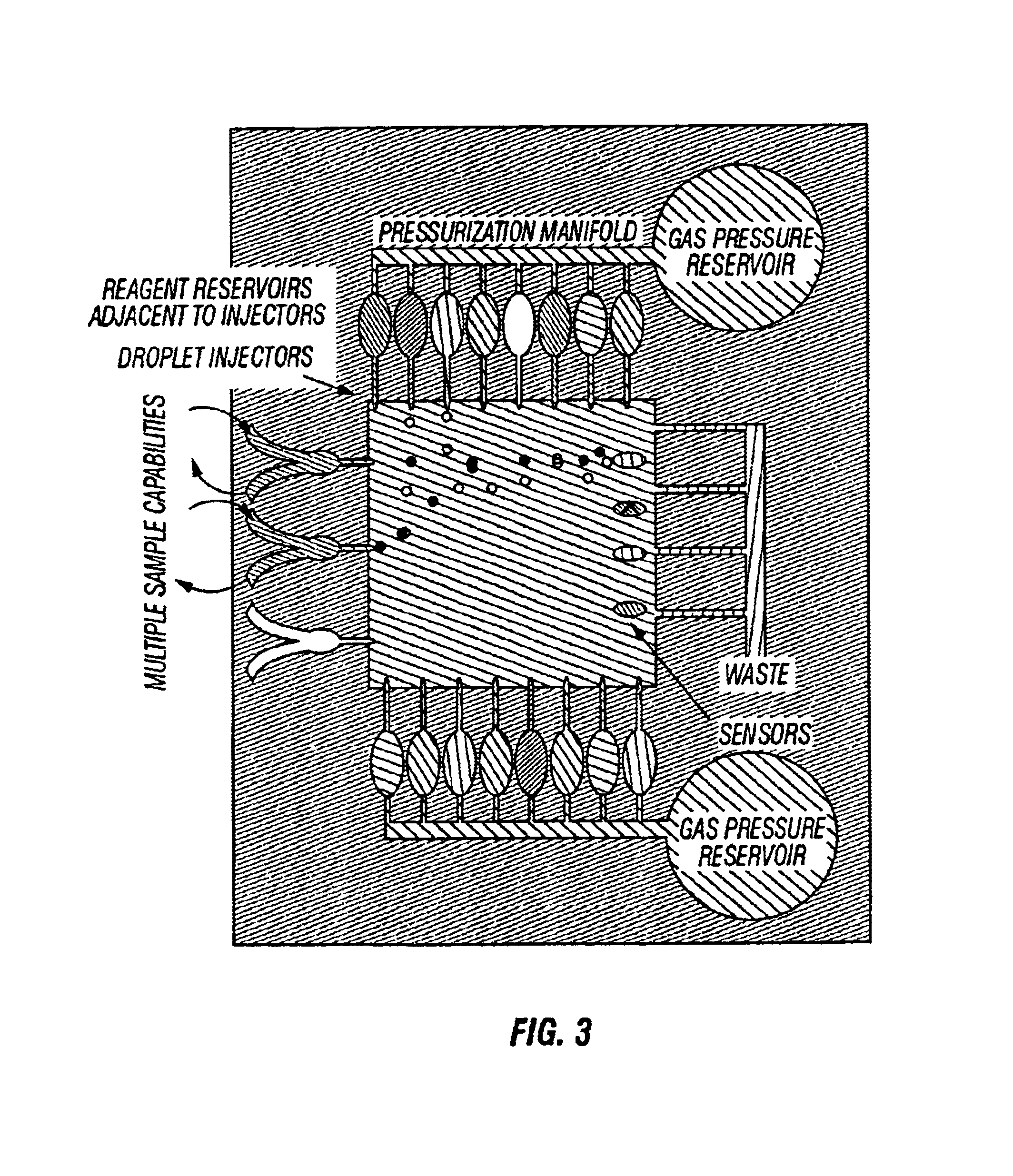
Microfluidic devices and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080014589A1Eliminates surface wettingDielectrophoresisLiquid separation by electricityComputer moduleBiomedical engineering
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
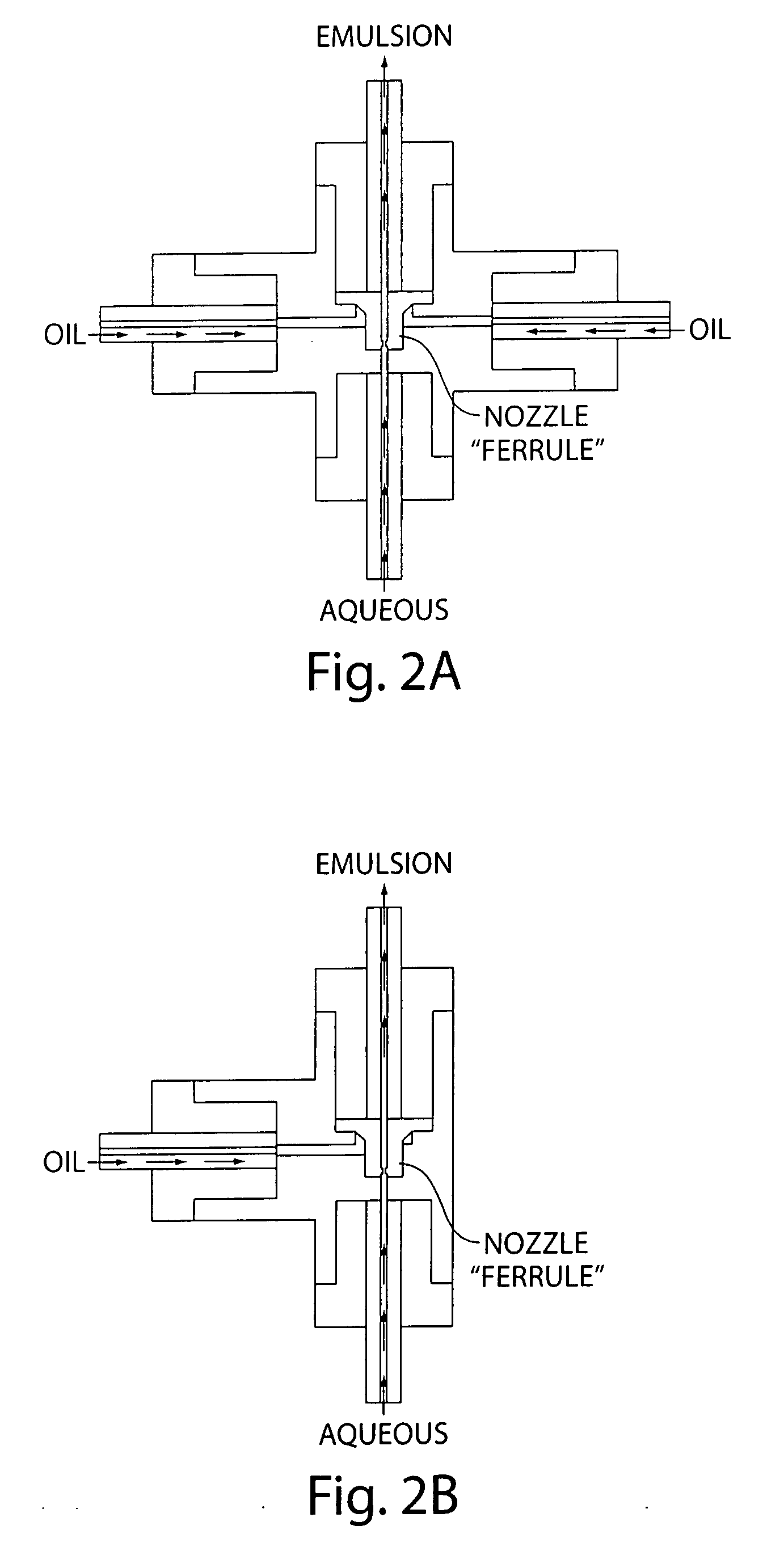
Microfluidic devices
InactiveUS20080003142A1Quickly and effectively and inexpensivelyDielectrophoresisHeating or cooling apparatusEngineering
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
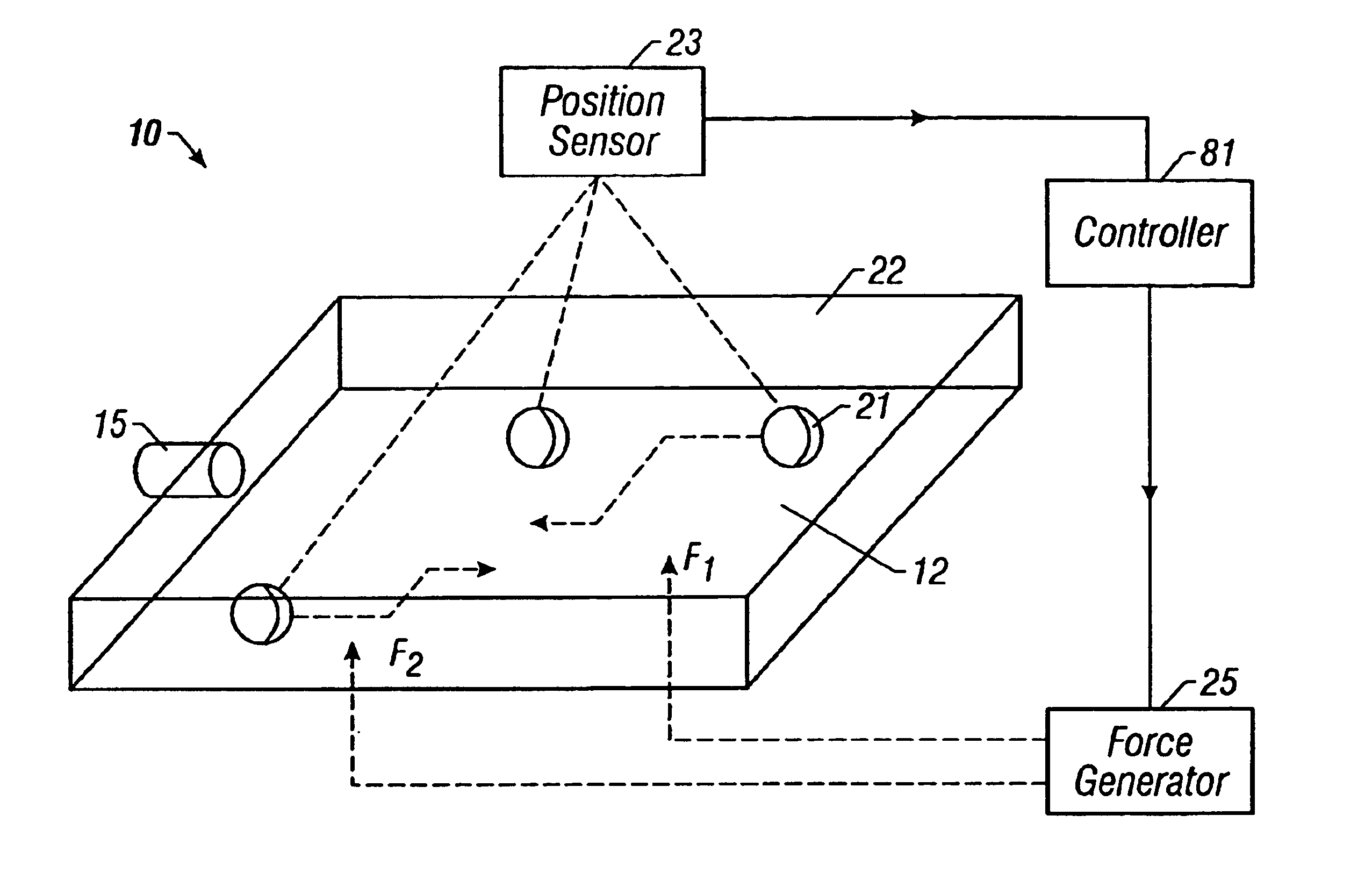
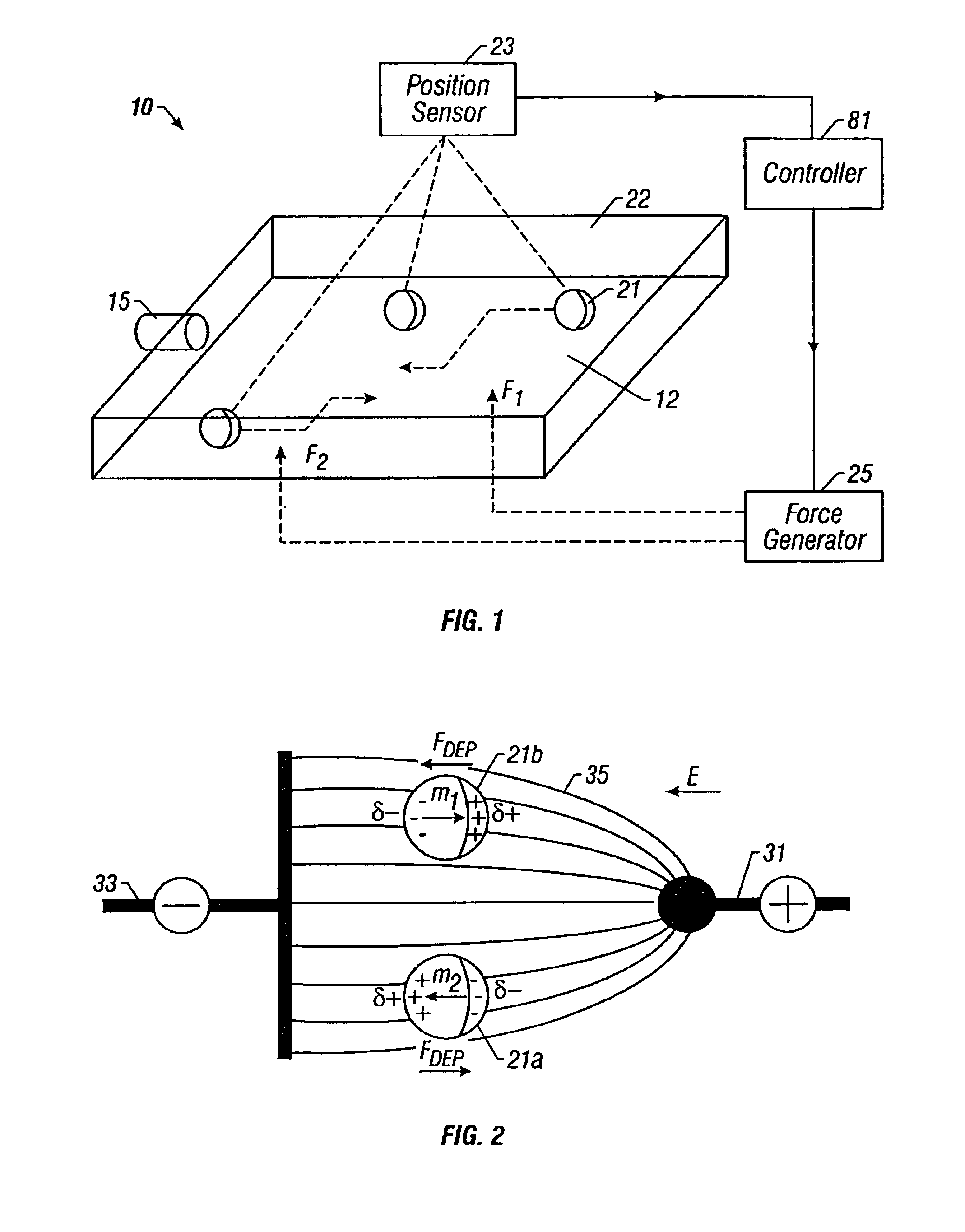
Method and apparatus for programmable fluidic processing
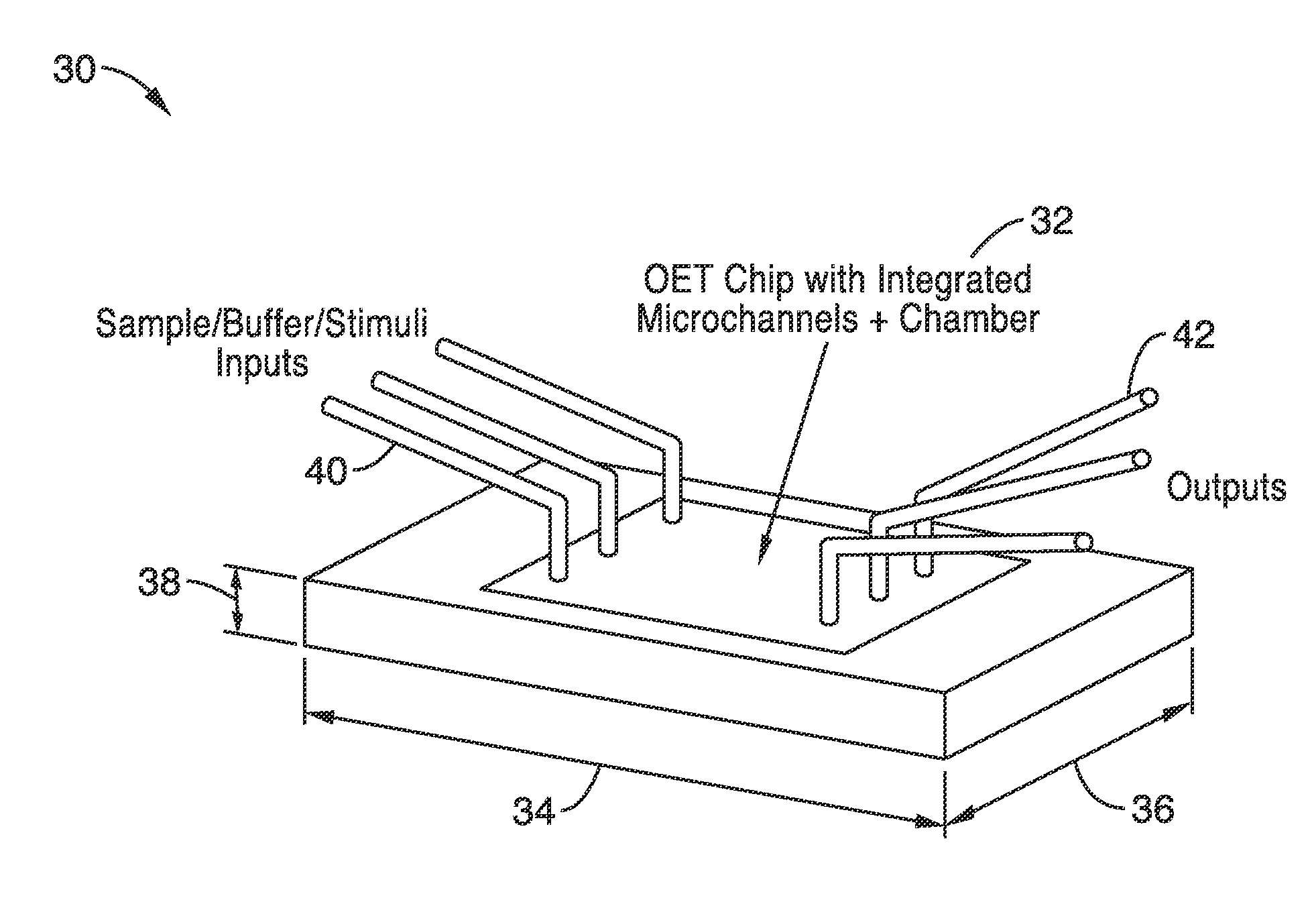
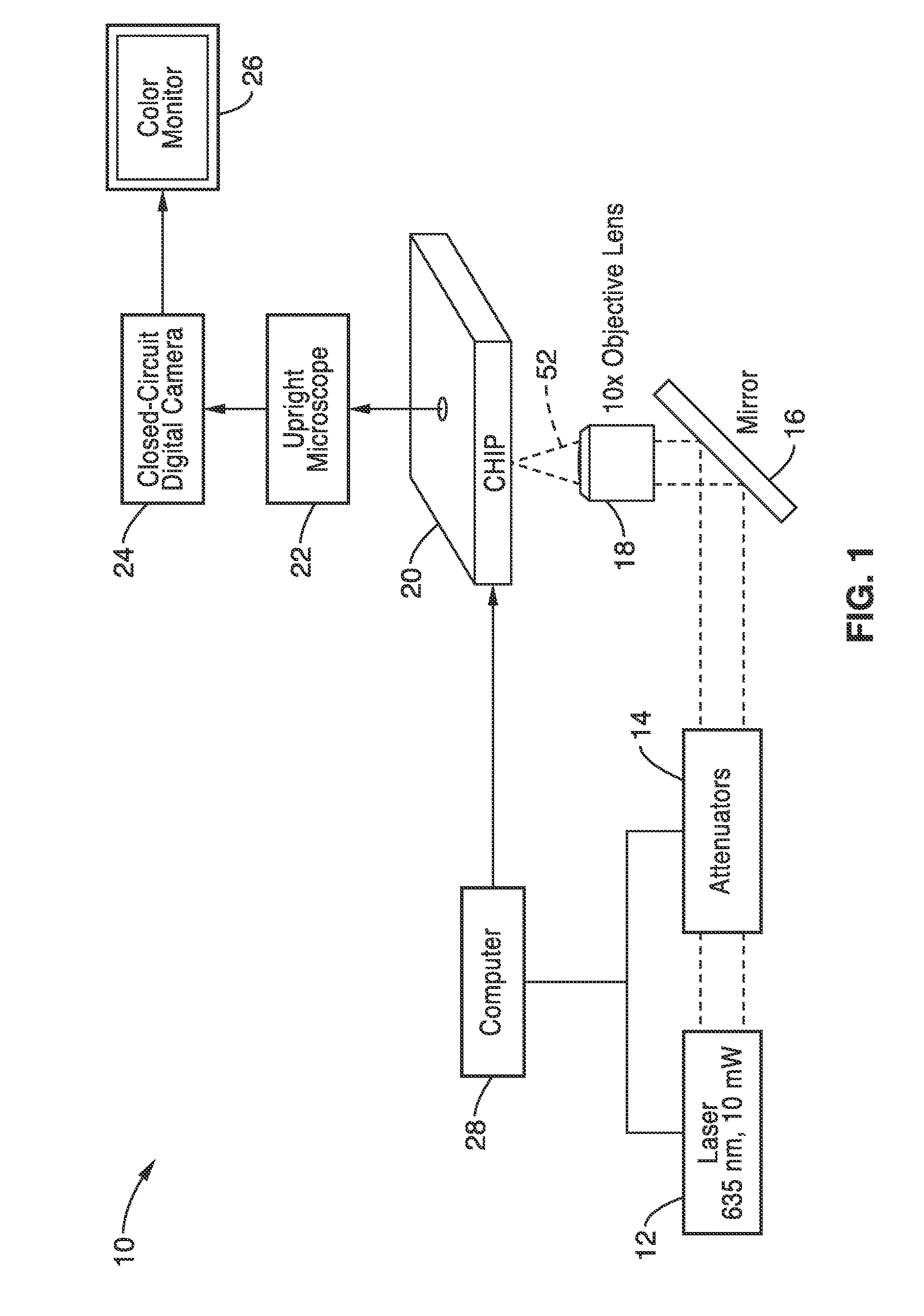
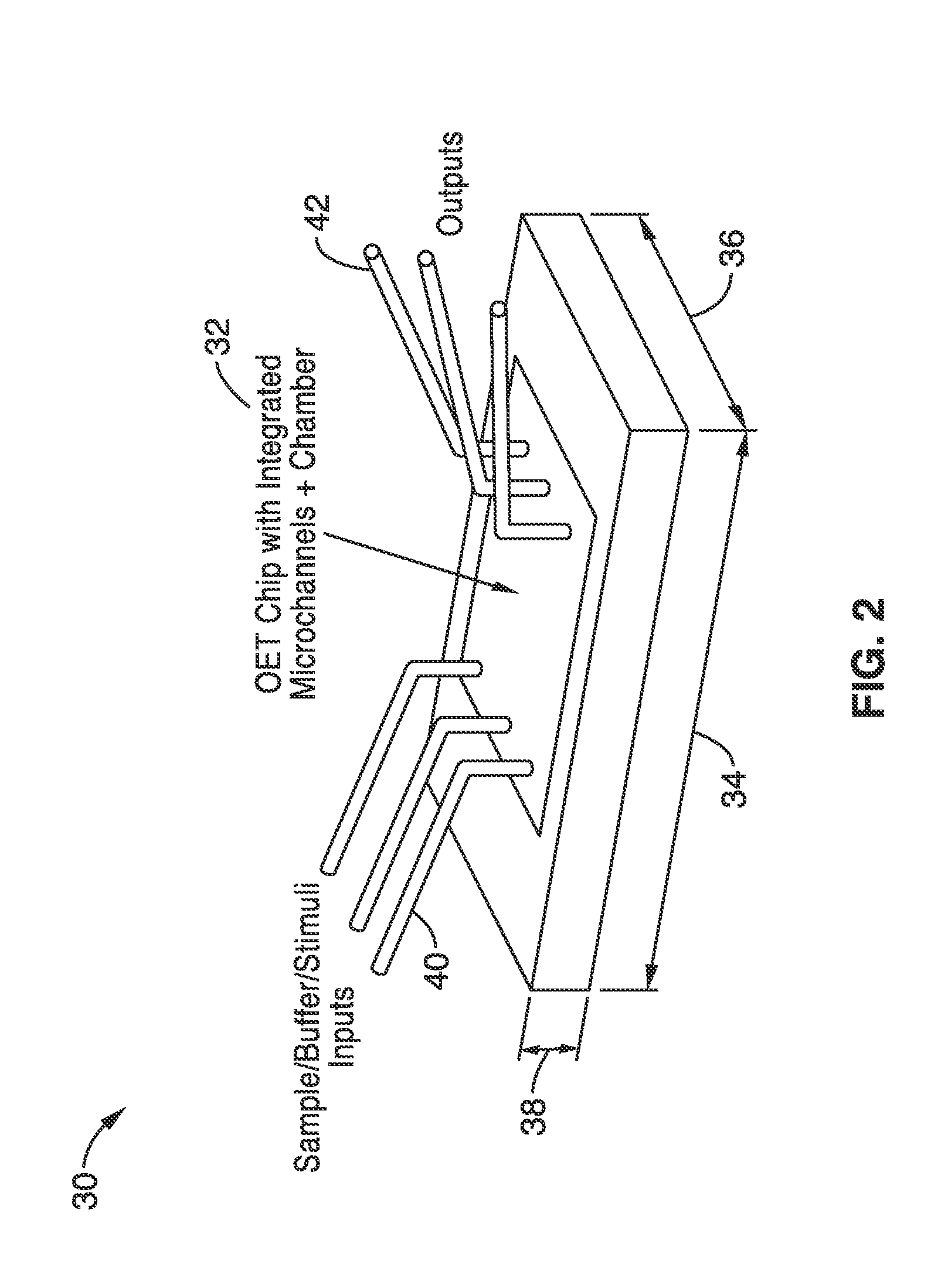
A method and apparatus for microfluidic processing by programmably manipulating a packet. A material is introduced onto a reaction surface and compartmentalized to form a packet. A position of the packet is sensed with a position sensor. A programmable manipulation force is applied to the packet at the position. The programmable manipulation force is adjustable according to packet position by a controller. The packet is programmably moved according to the programmable manipulation force along arbitrarily chosen paths.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
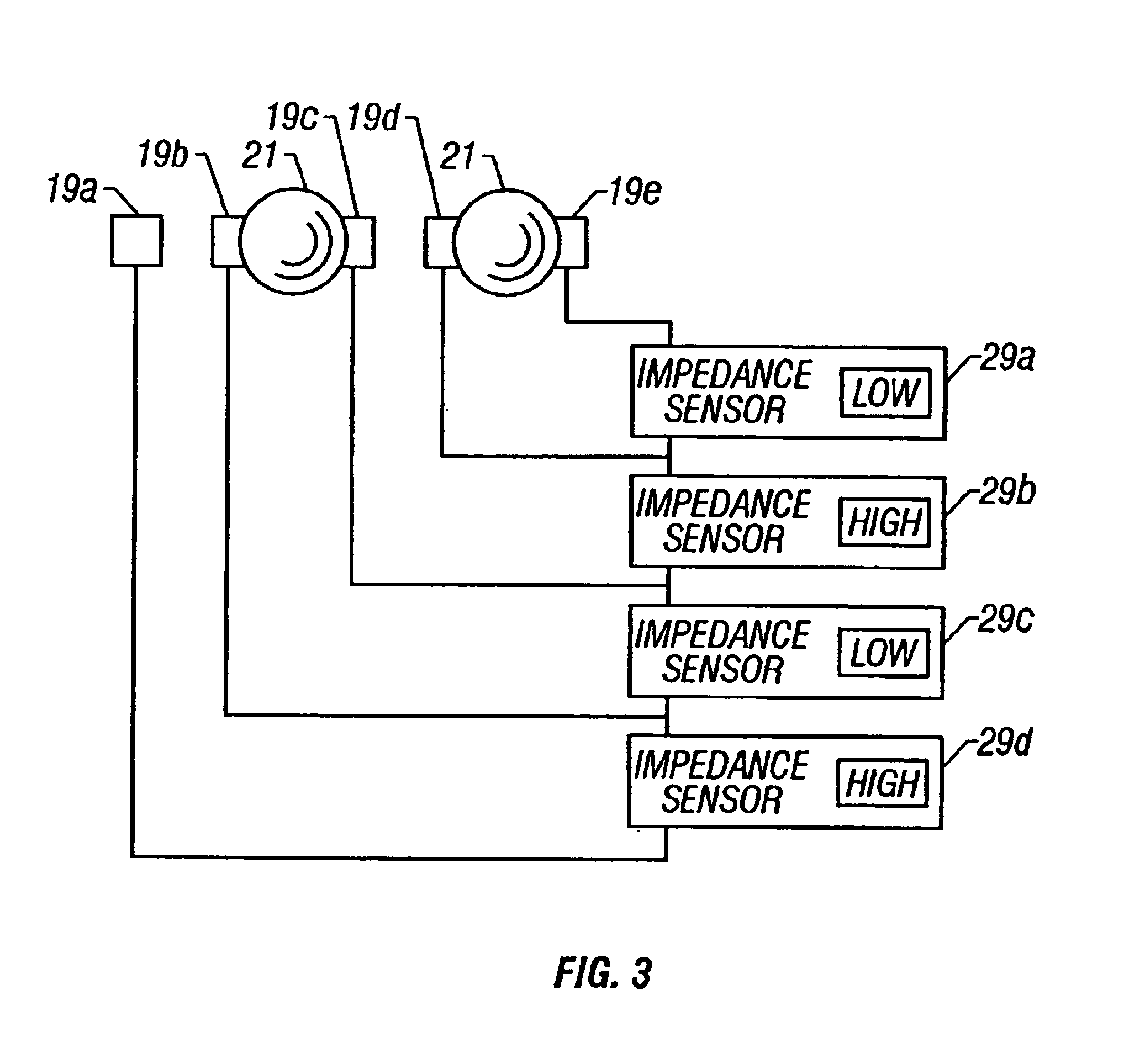
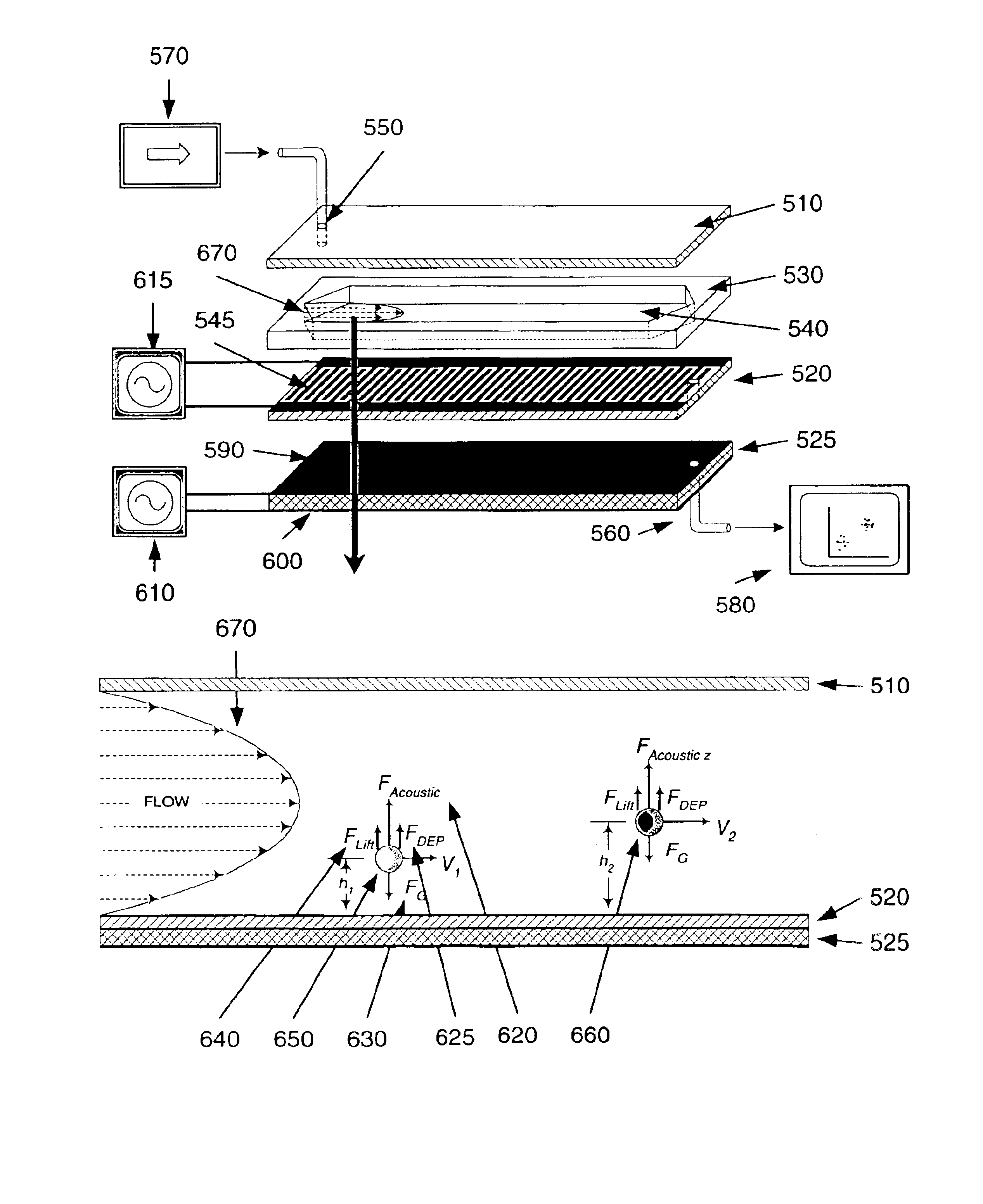
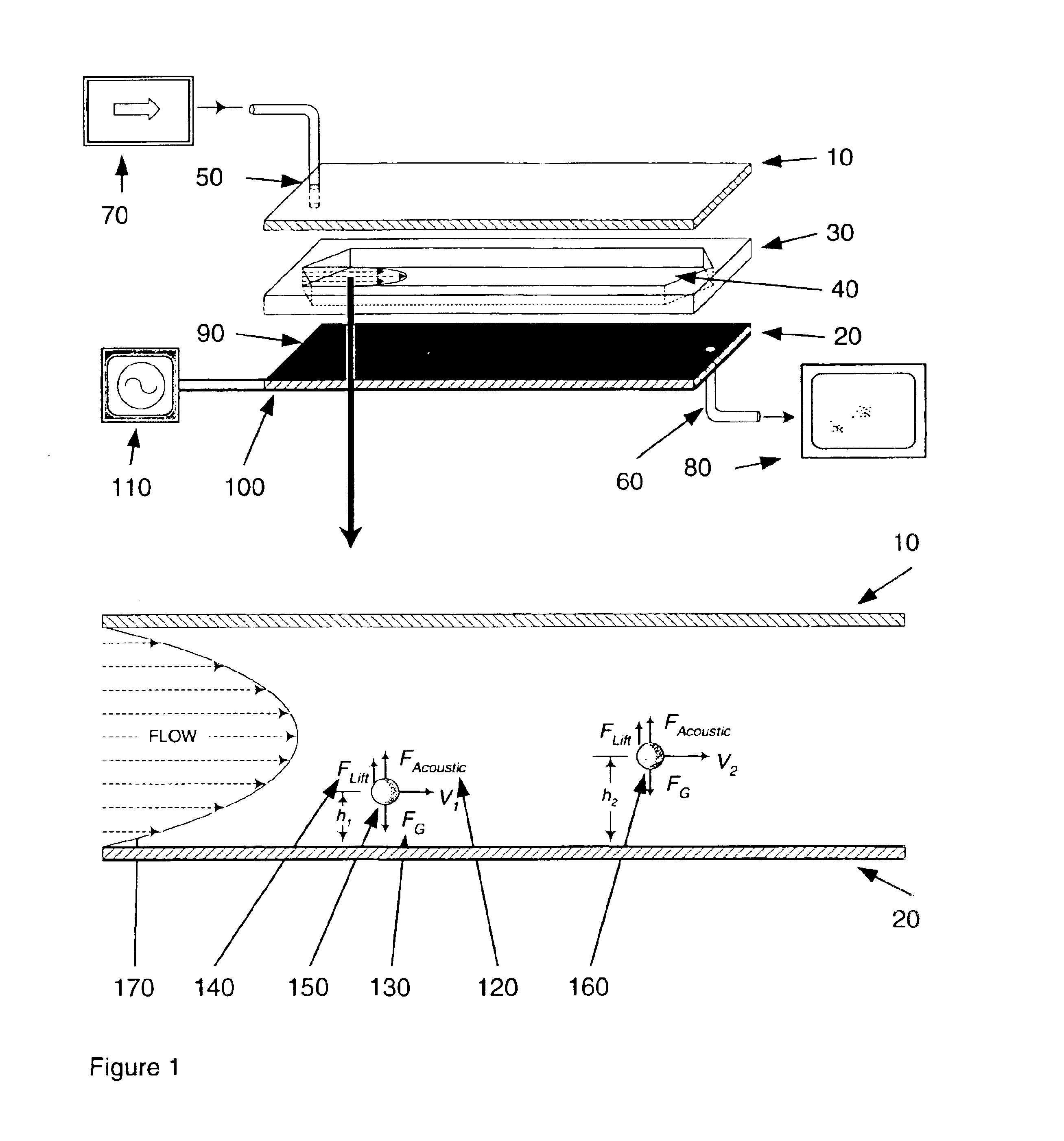
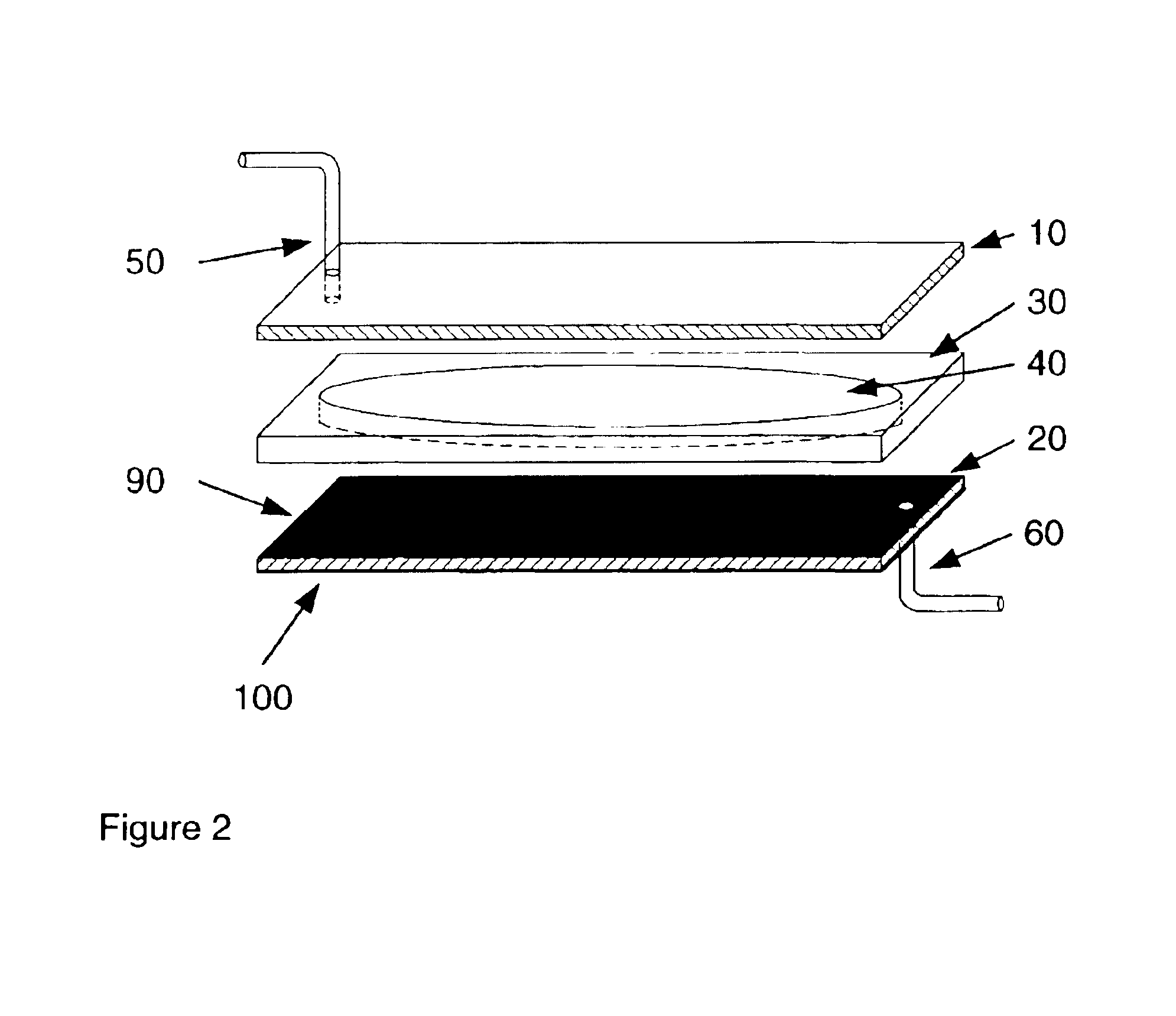
Apparatuses and methods for field flow fractionation of particles using acoustic and other forces
InactiveUS6881314B1Easy to separateEfficient separationDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsElectrophoresisDielectrophoretic force
This invention relates generally to the field of field-flow-fractionation. In particular, the invention provides apparatuses and methods for the discrimination of matters utilizing acoustic force, or utilizing acoustic force with electrophoretic or dielectrophoretic force, in field flow fractionation.
Owner:AVIVA BIOISCI CORP +2
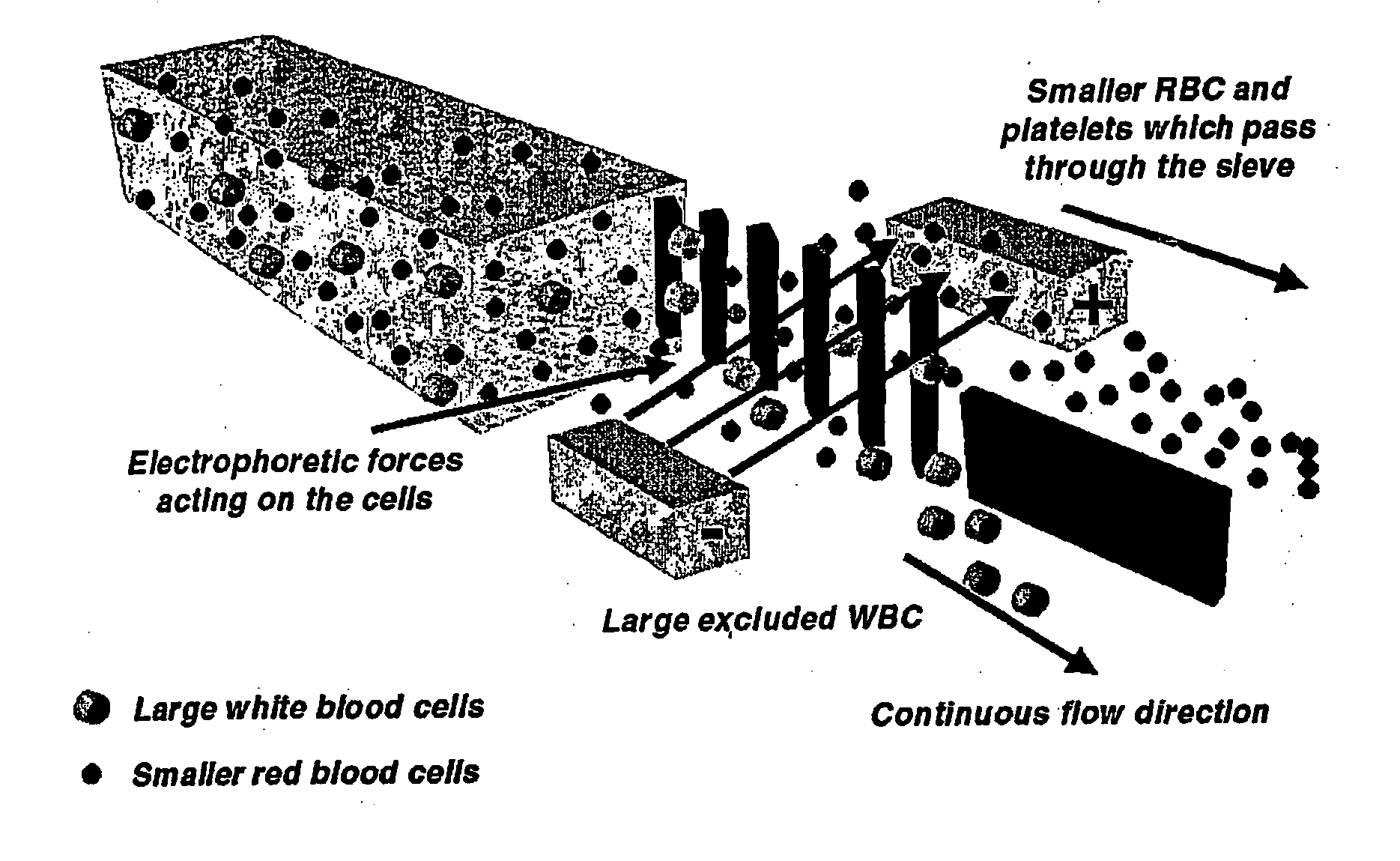
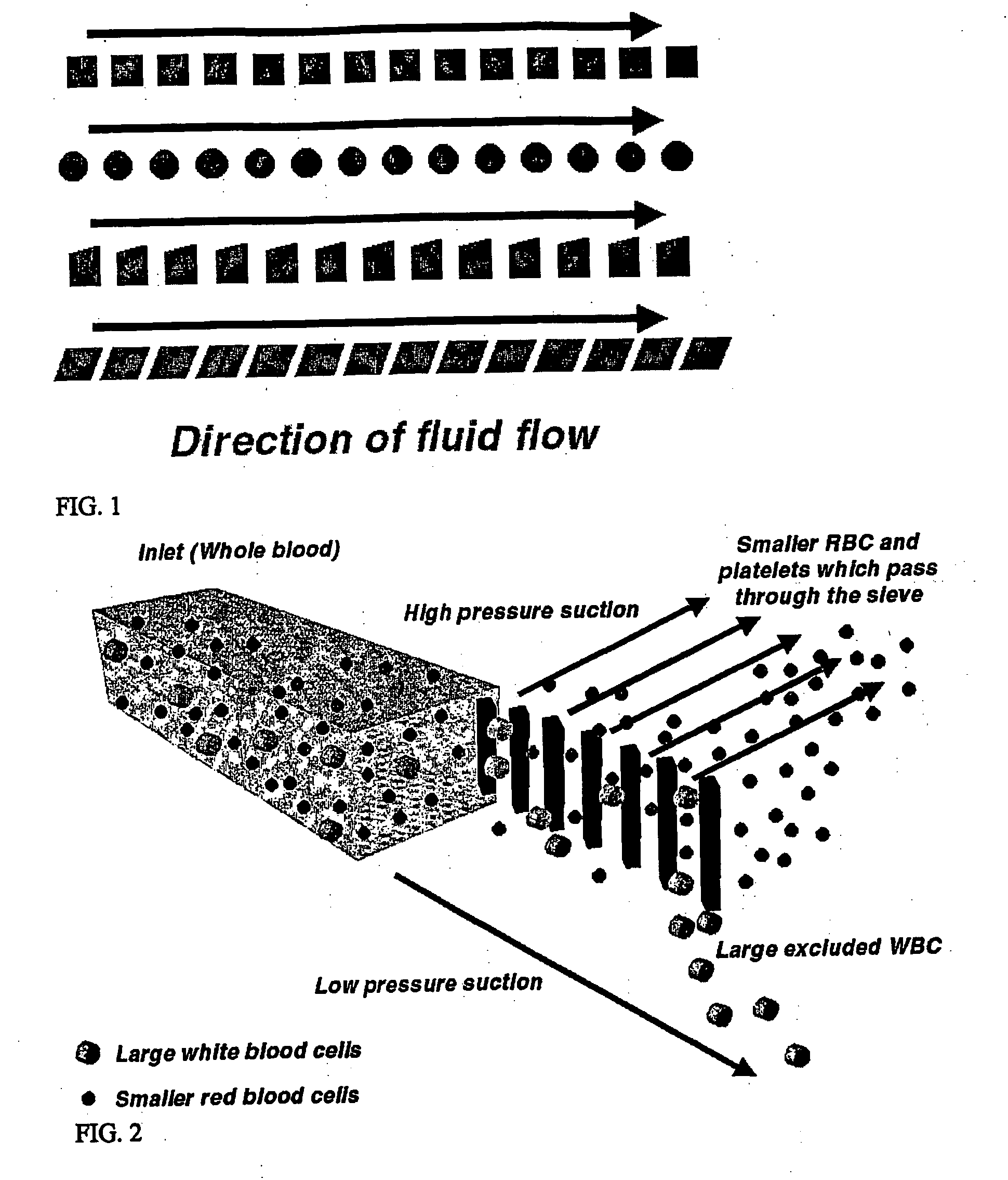
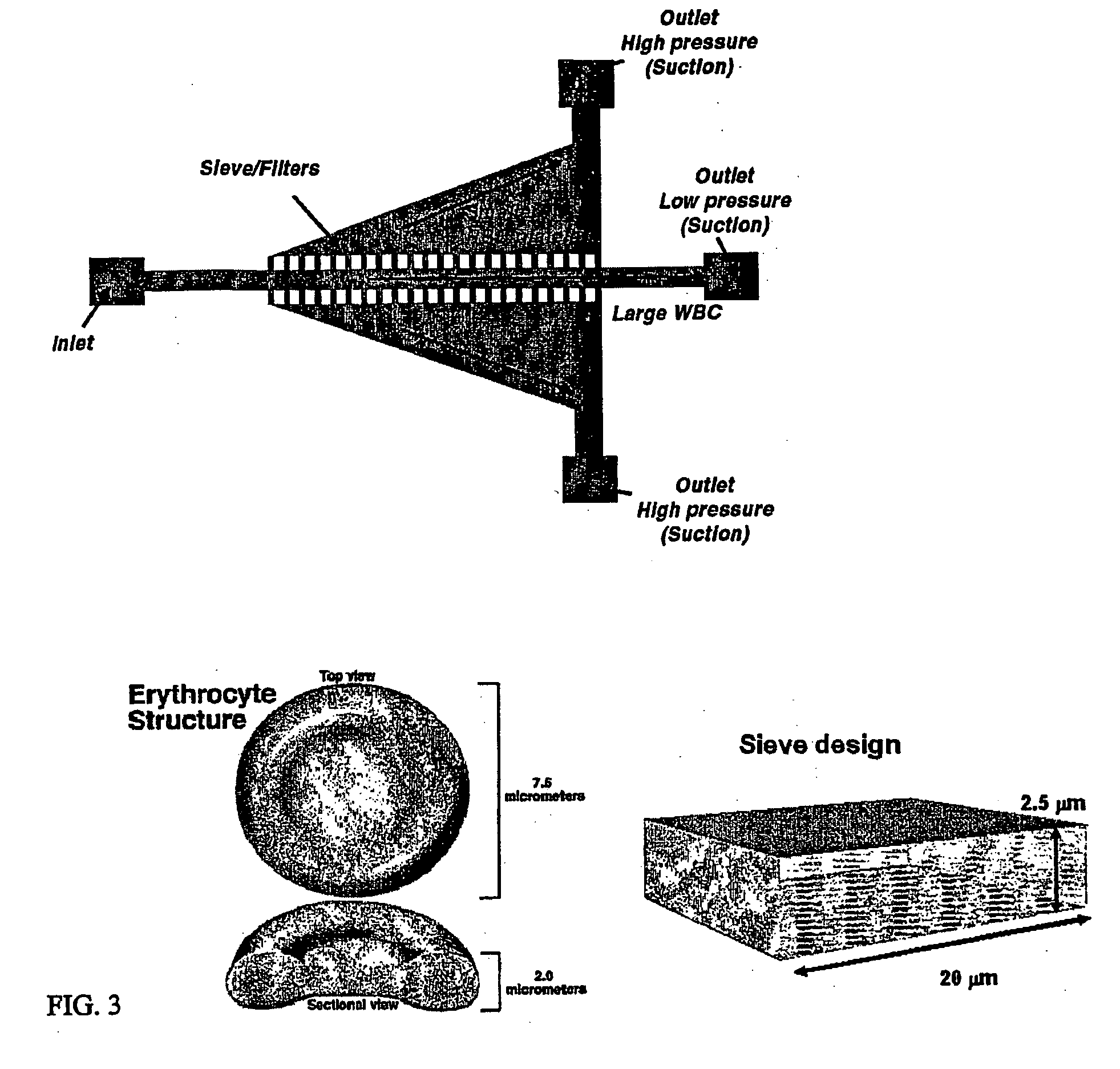
Microfluidic systems for size based removal of red blood cells and platelets from blood
The invention features devices and methods for enriching a sample in one or more desired particles. An exemplary use of these devices and methods is for the enrichment of cells, e.g., white blood cells in a blood sample. In general, the methods of the invention employ a device that contains at least one sieve through which particles of a given size, shape, or deformability can pass. Devices of the invention have at least two outlets, and the sieve is placed such that a continuous flow of fluid can pass through the device without passing through the sieve. The devices also include a force generator for directing selected particles through the sieve. Such force generators employ, for example, diffusion, electrophoresis, dielectrophoresis, centrifugal force, or pressure-driven flow.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
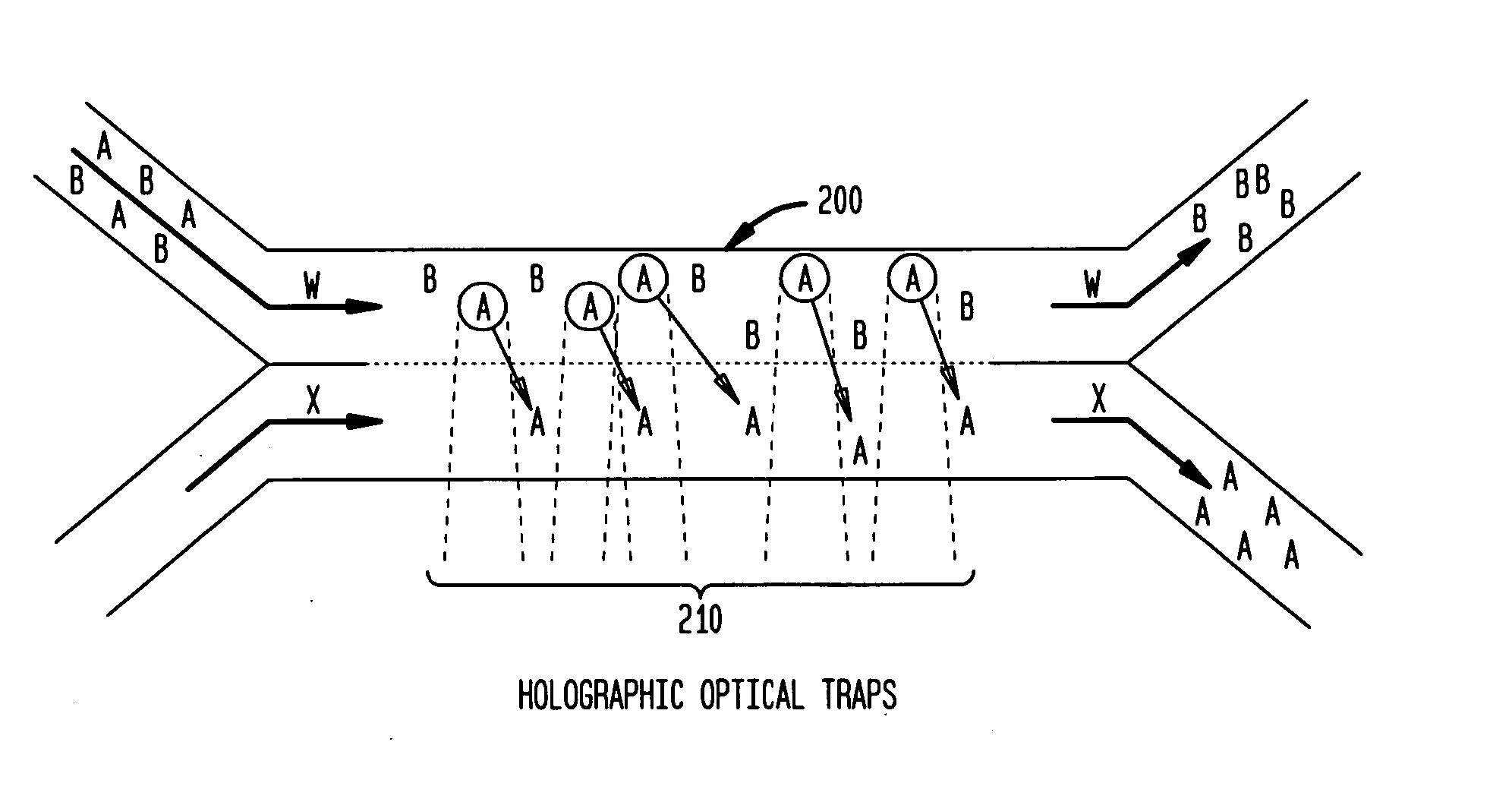
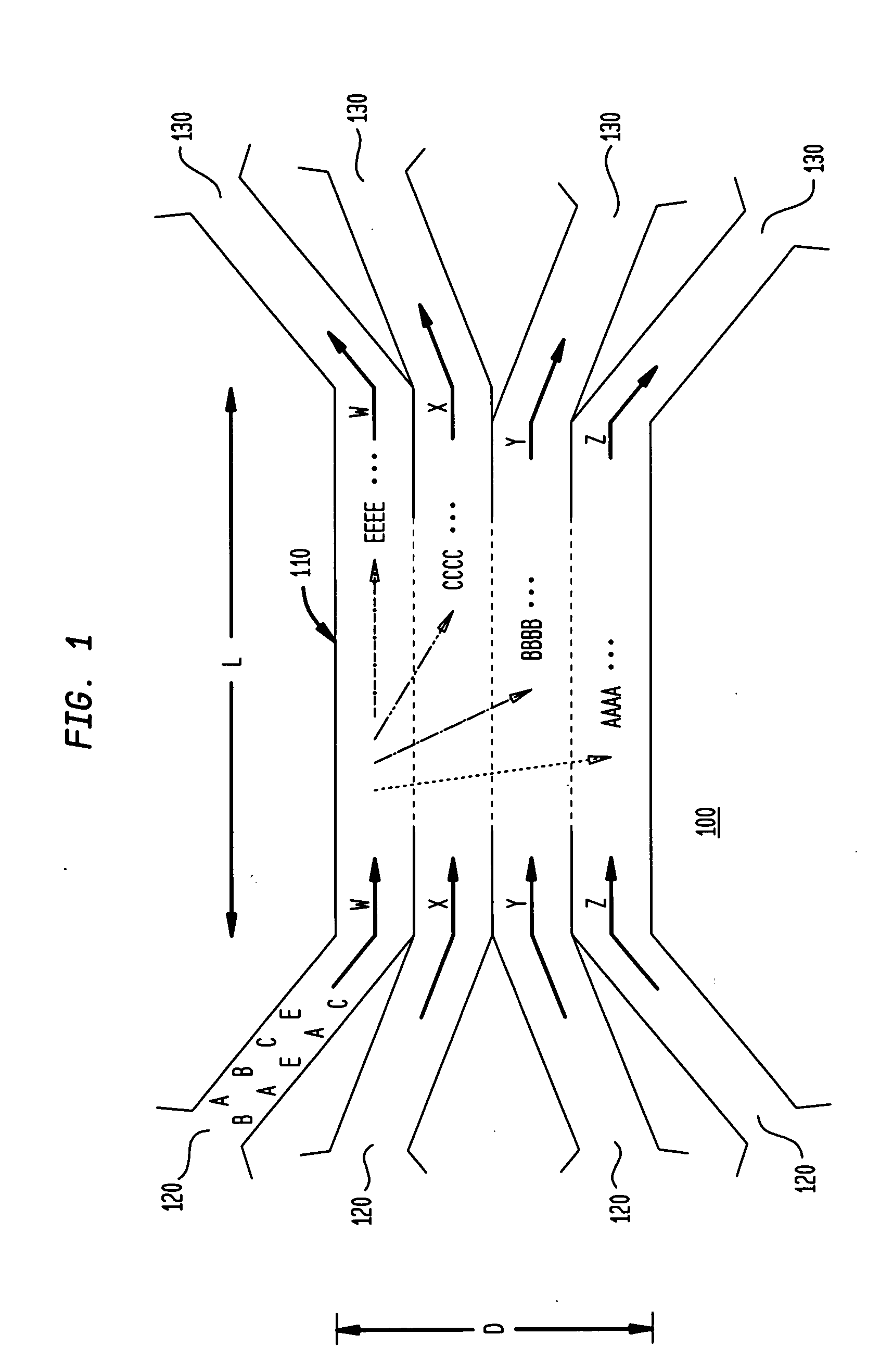
Multiple laminar flow-based particle and cellular separation with laser steering
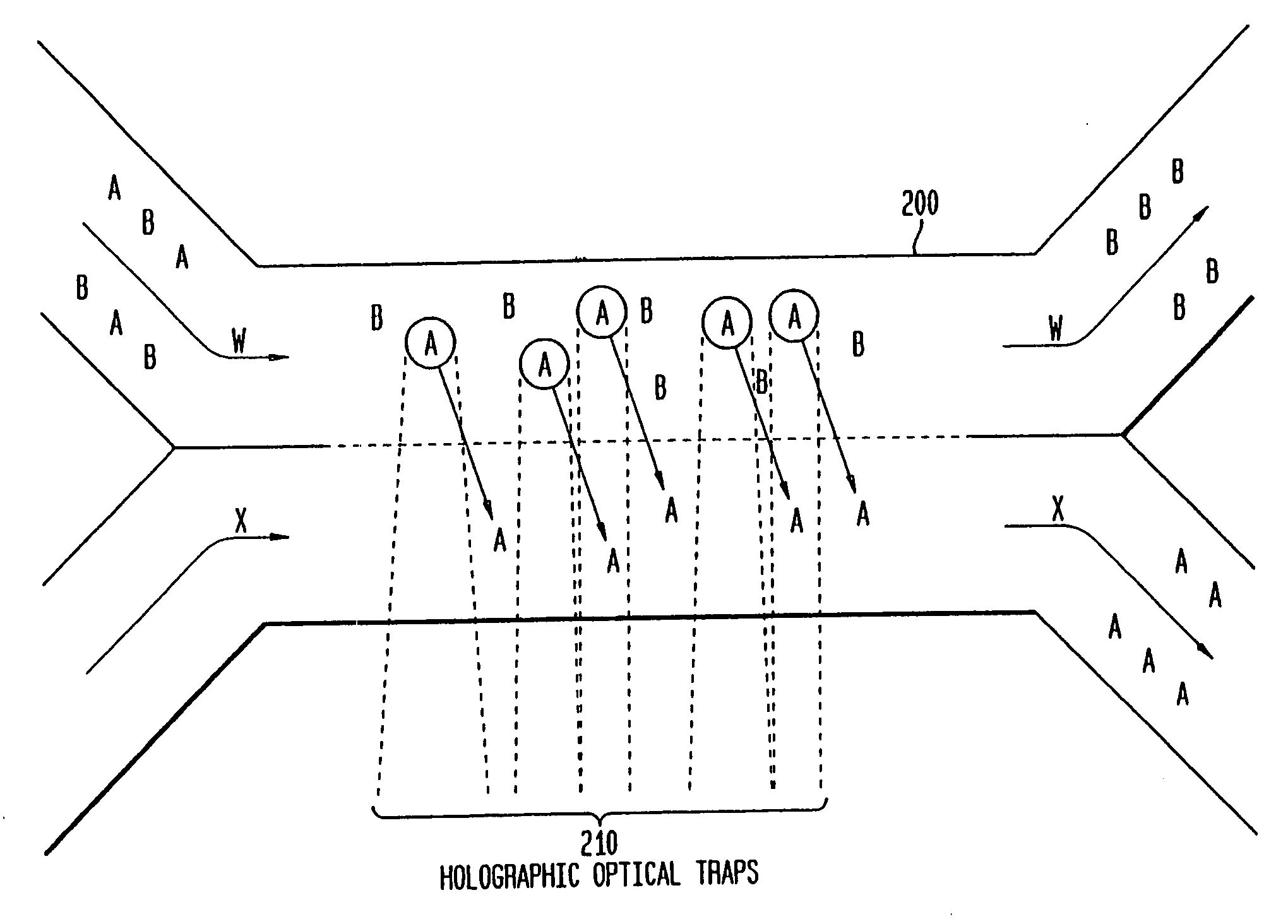
InactiveUS20050121604A1Save a lot of timeImprove throughputDielectrophoresisLaser detailsCellular componentBlood component
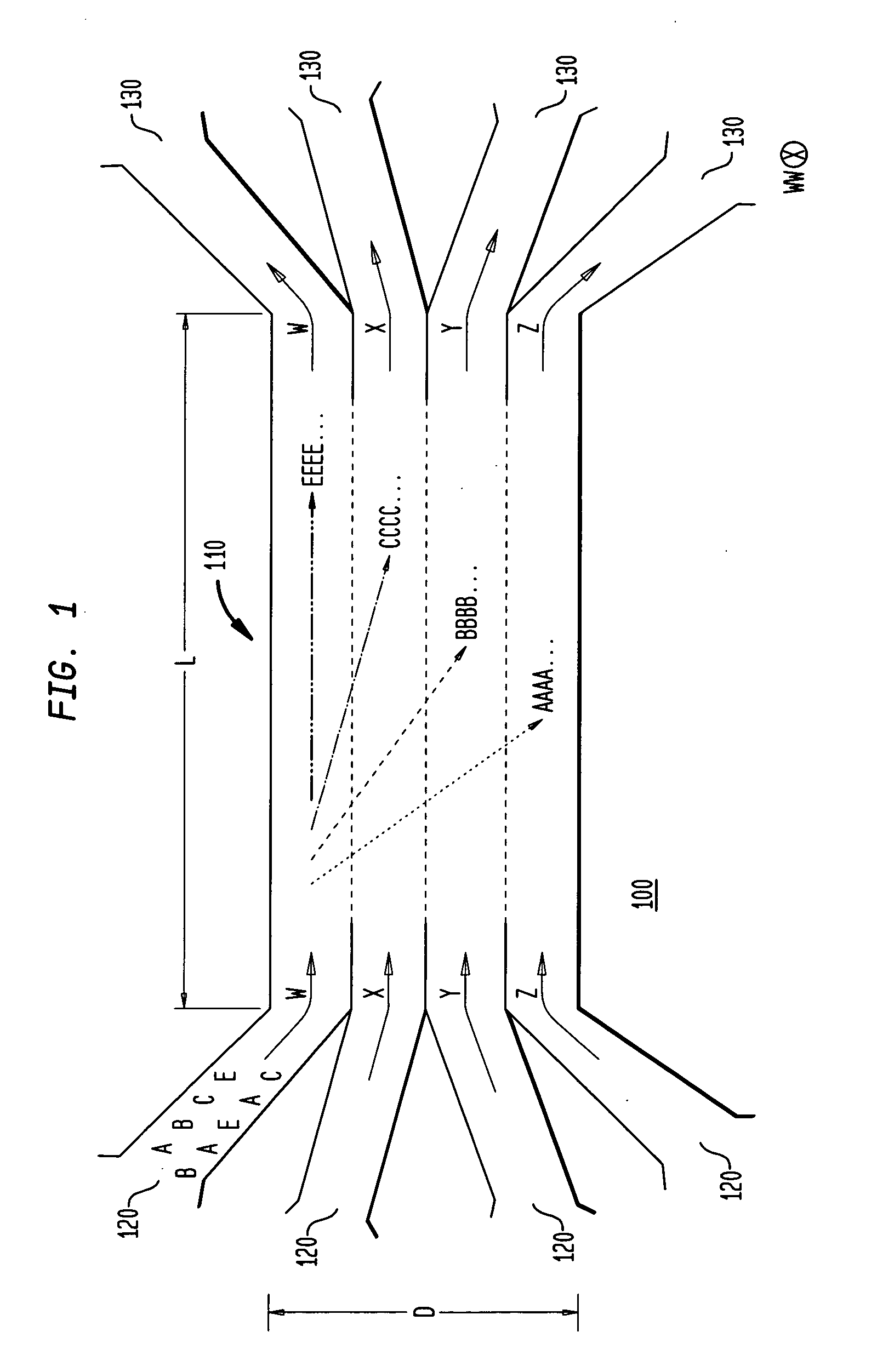
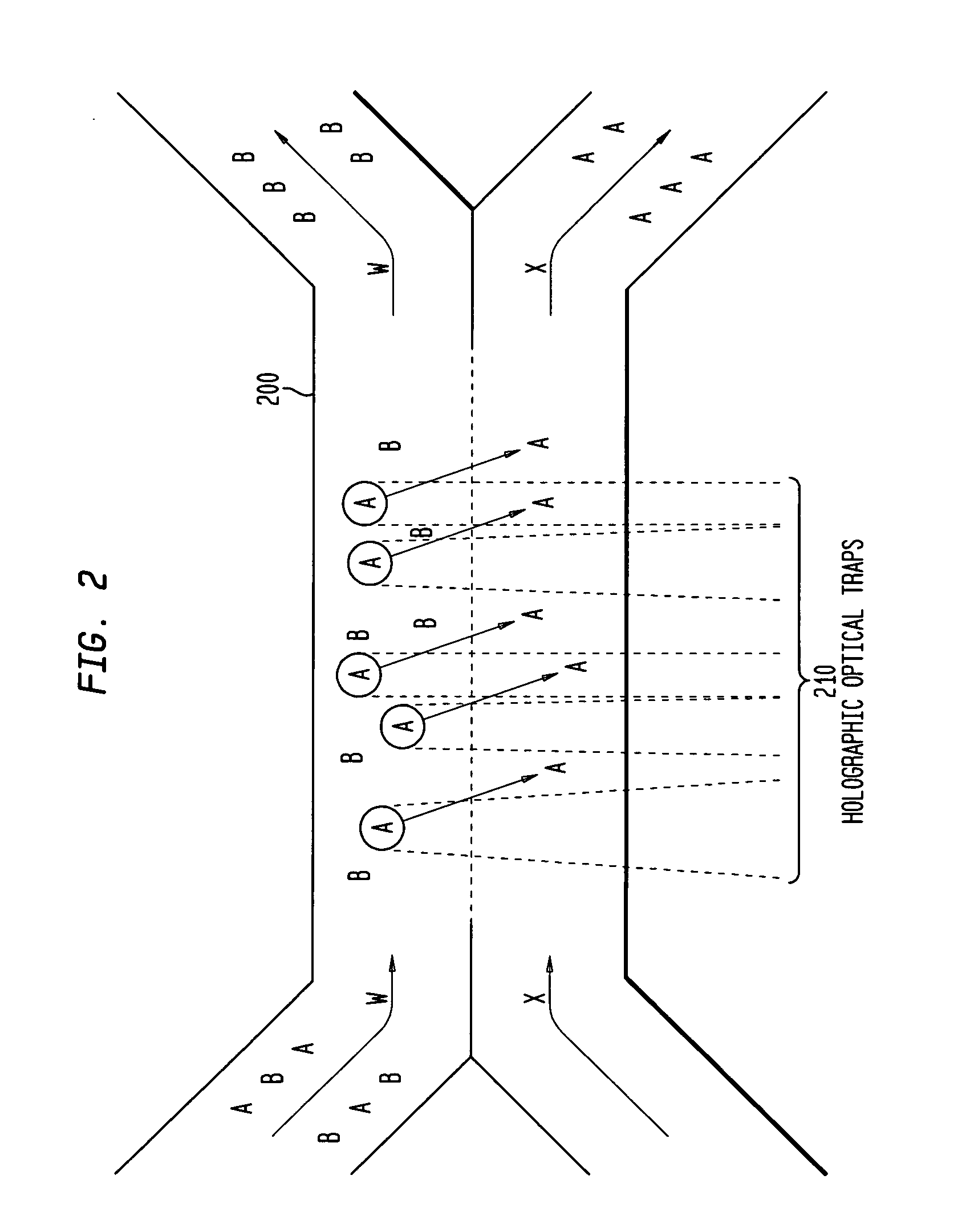
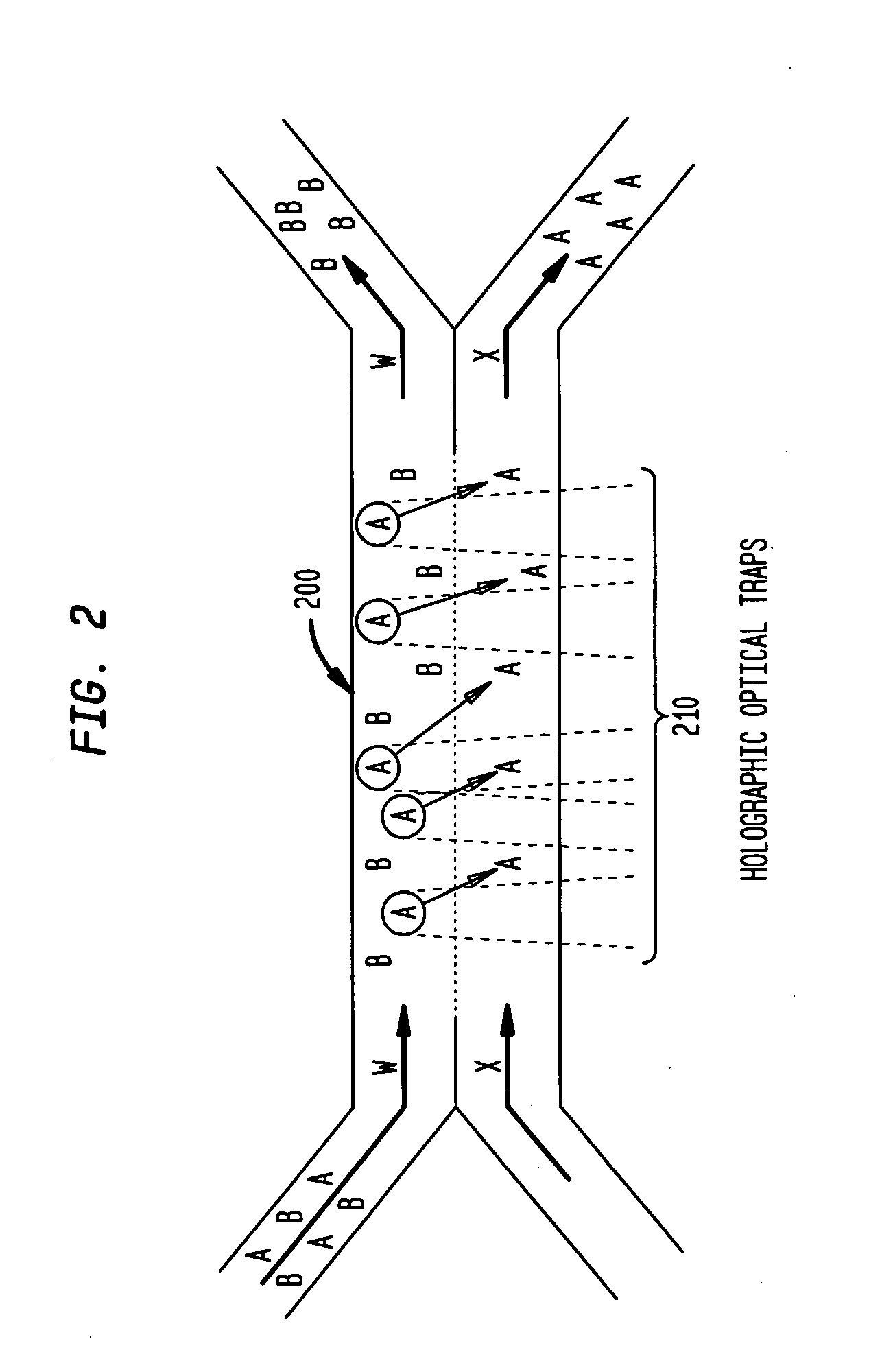
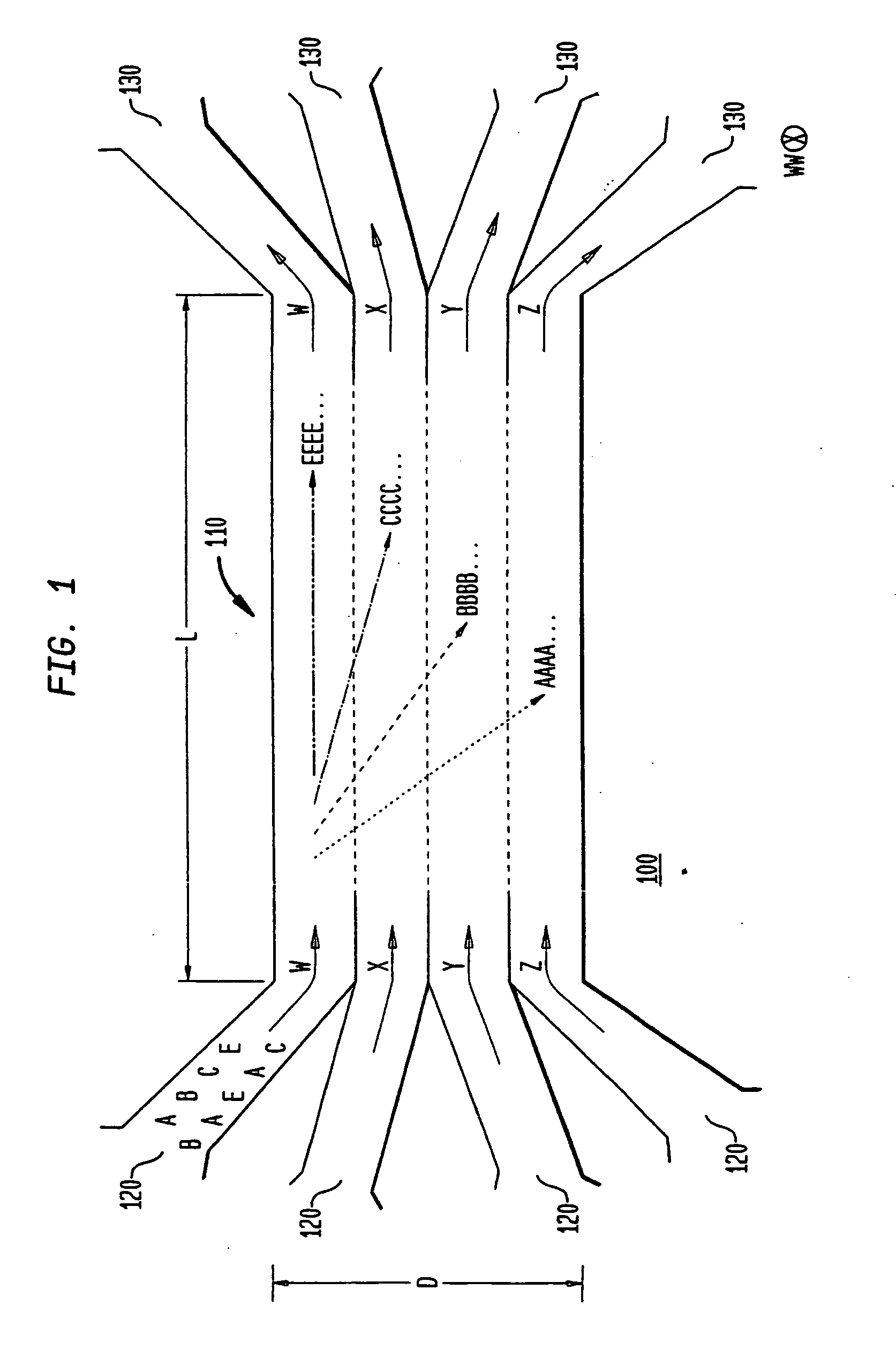
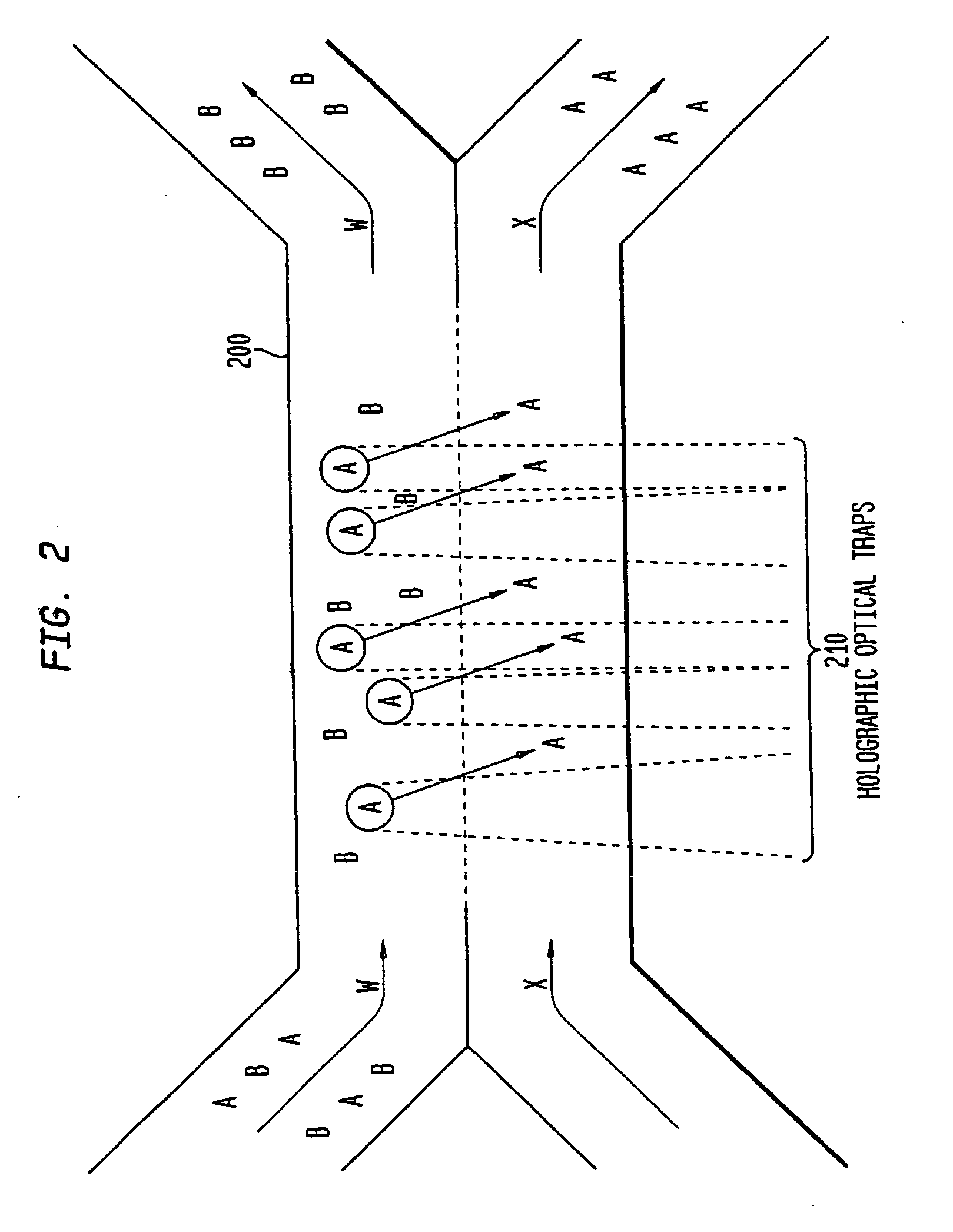
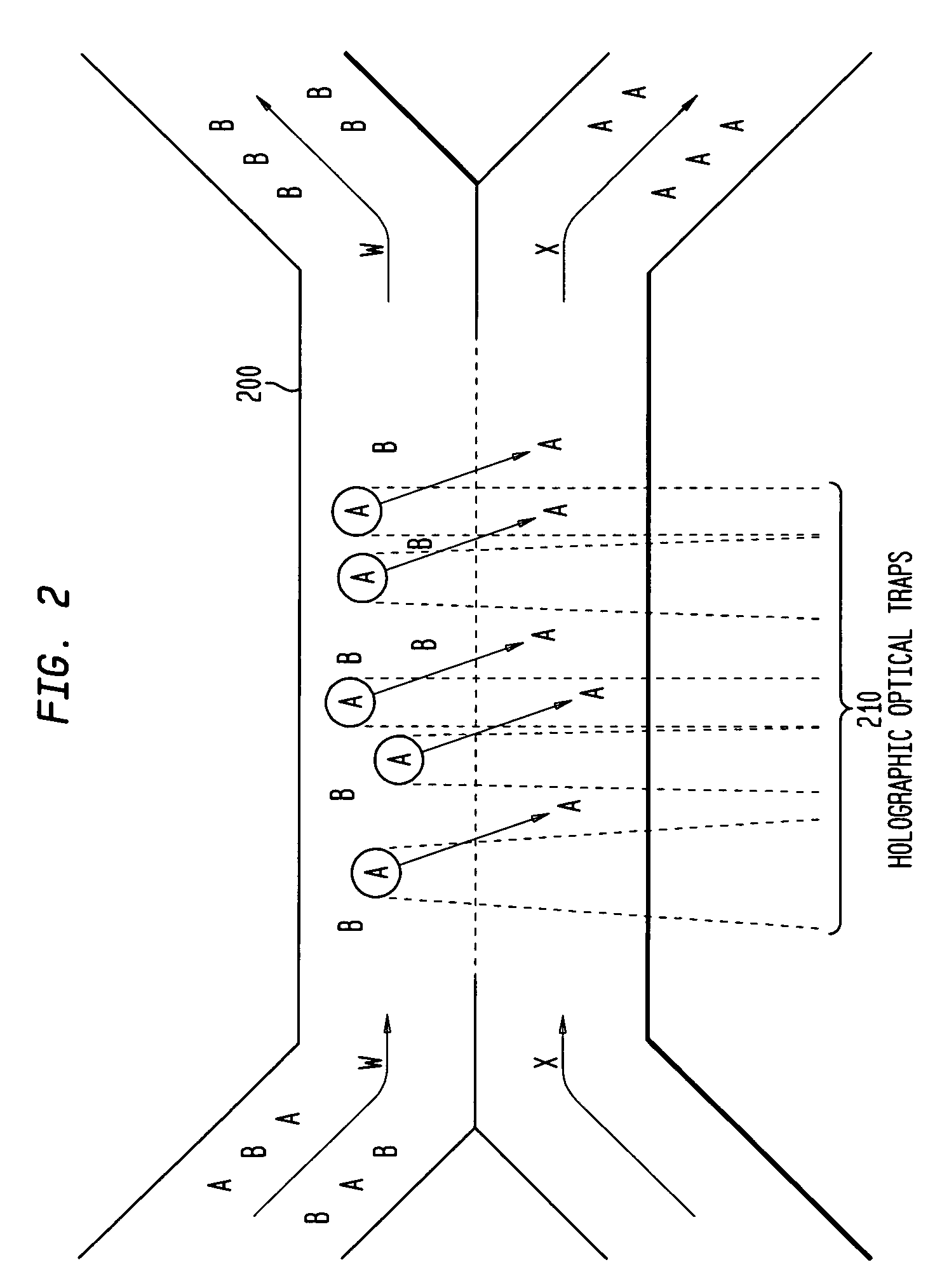
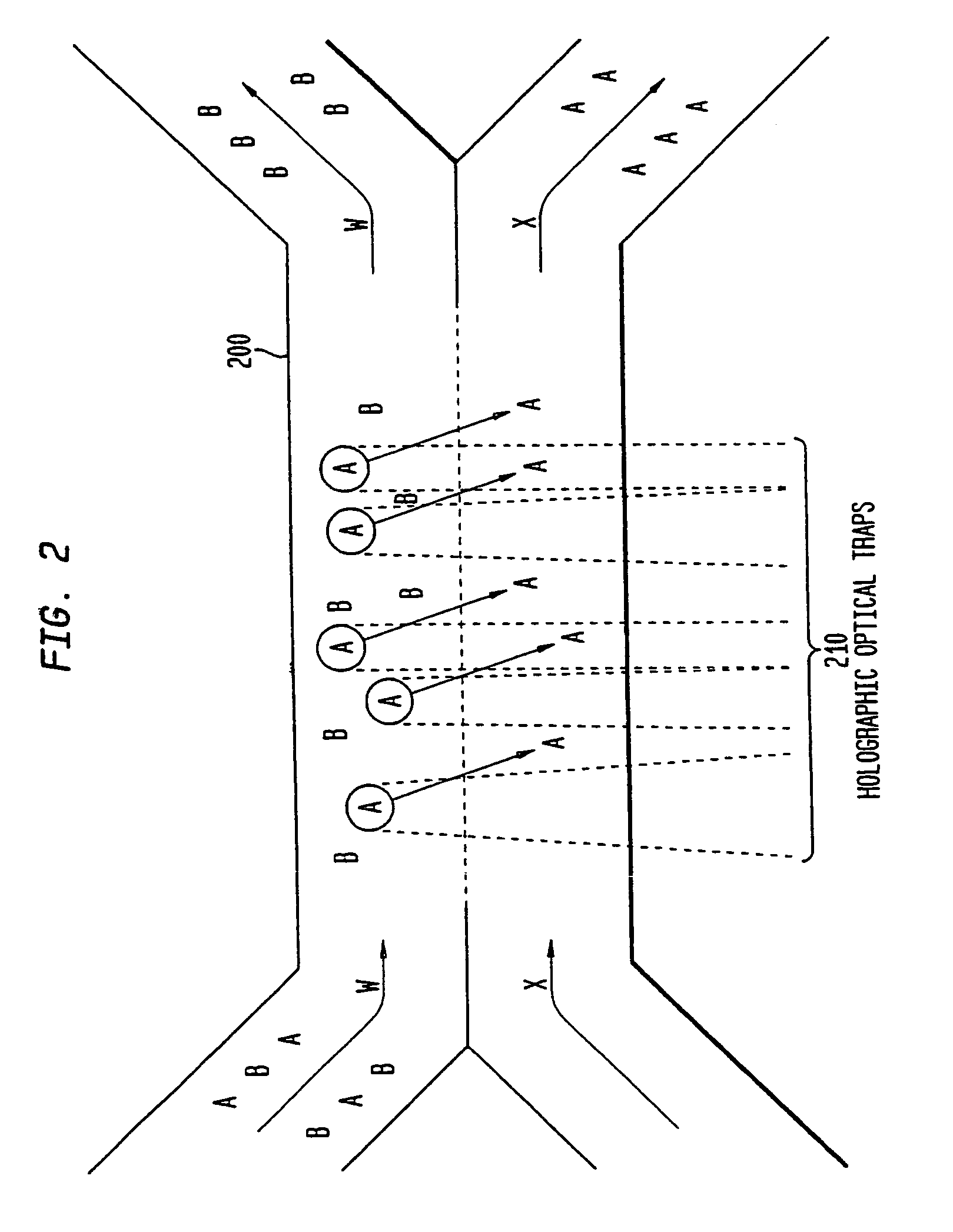
The invention provides a method, apparatus and system for separating blood and other types of cellular components, and can be combined with holographic optical trapping manipulation or other forms of optical tweezing. One of the exemplary methods includes providing a first flow having a plurality of blood components; providing a second flow; contacting the first flow with the second flow to provide a first separation region; and differentially sedimenting a first blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components into the second flow while concurrently maintaining a second blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components in the first flow. The second flow having the first blood cellular component is then differentially removed from the first flow having the second blood cellular component. Holographic optical traps may also be utilized in conjunction with the various flows to move selected components from one flow to another, as part of or in addition to a separation stage.
Owner:PREMIUM GENETICS UK
Bead Incubation and Washing on a Droplet Actuator
The present invention relates to bead incubating and washing on a droplet actuator. Methods for incubating magnetically responsive beads that are labeled with primary antibody, a sample (i.e., analyte), and secondary reporter antibodies on a magnet, on and off a magnet, and completely off a magnet are provided. Also provided are methods for washing magnetically responsive beads using shape-assisted merging of droplets. Also provided are methods for shape-mediated splitting, transporting, and dispensing of a sample droplet that contains magnetically responsive beads. The apparatuses and methods of the invention provide for rapid time to result and optimum detection of an analyte in an immunoassay.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Microscale sorting cytometer
InactiveUS20050175981A1Increase field strengthHigh strengthDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsElectrophoresisDielectrophoresis
The present invention provides a device and methods of use thereof in microscale cell sorting. This invention provides sorting cytometers, which trap individual cells within vessels following exposure to dielectrophoresis, allow for the assaying of trapped cells, such that a population is identified whose isolation is desired, and their isolation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
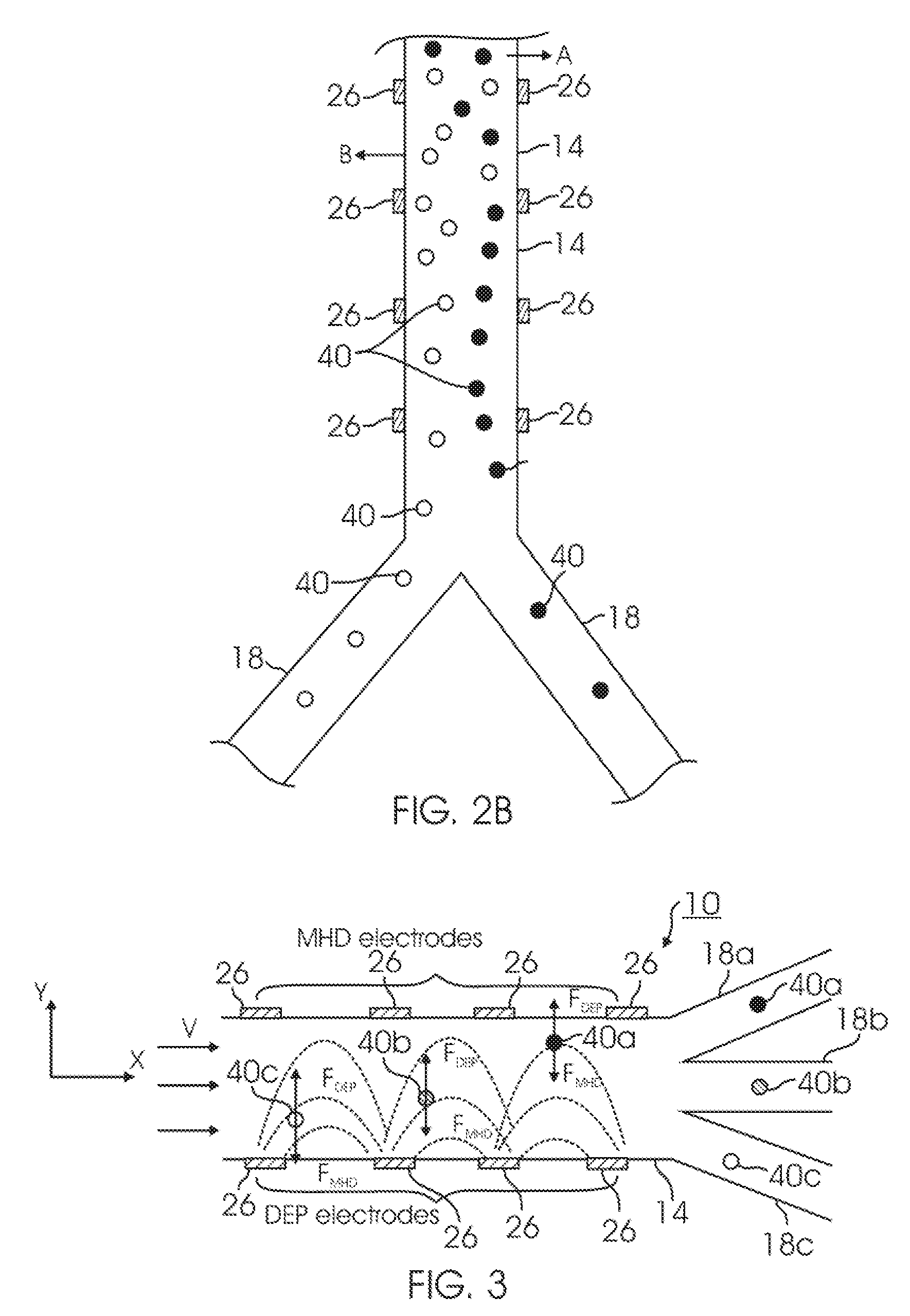
Dielectrophoresis devices and methods therefor
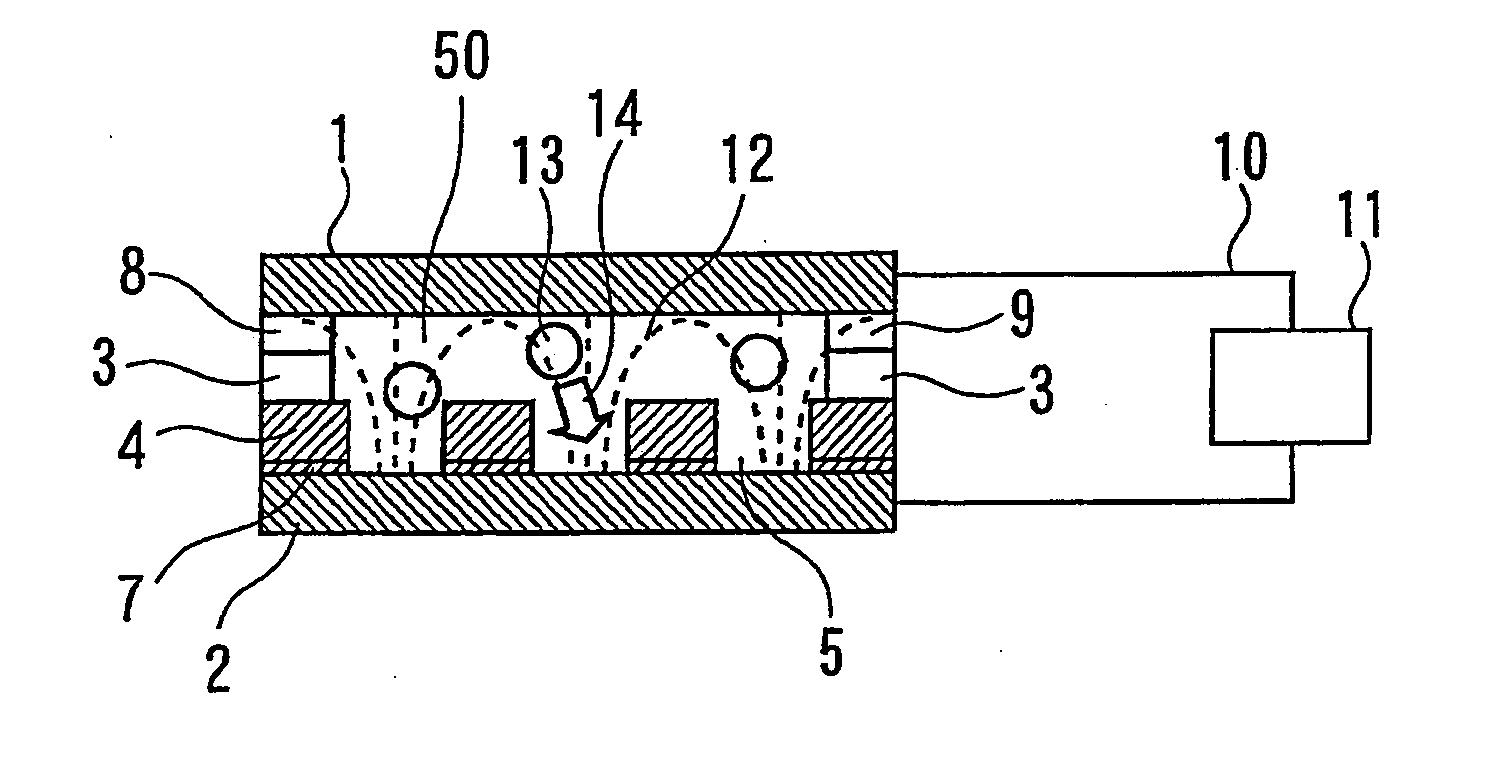
InactiveUS20120085649A1Easy maintenanceAvoid contactDielectrophoresisSludge treatmentSample integrityElectrophoresis
Devices and methods for performing dielectrophoresis are described. The devices contain a sample channel which is separated by physical barriers from electrode channels which receive electrodes. The devices and methods may be used for the separation and analysis of particles in solution, including the separation and isolation of cells of a specific type. As the electrodes do not make contact with the sample, electrode fouling is avoided and sample integrity is better maintained.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
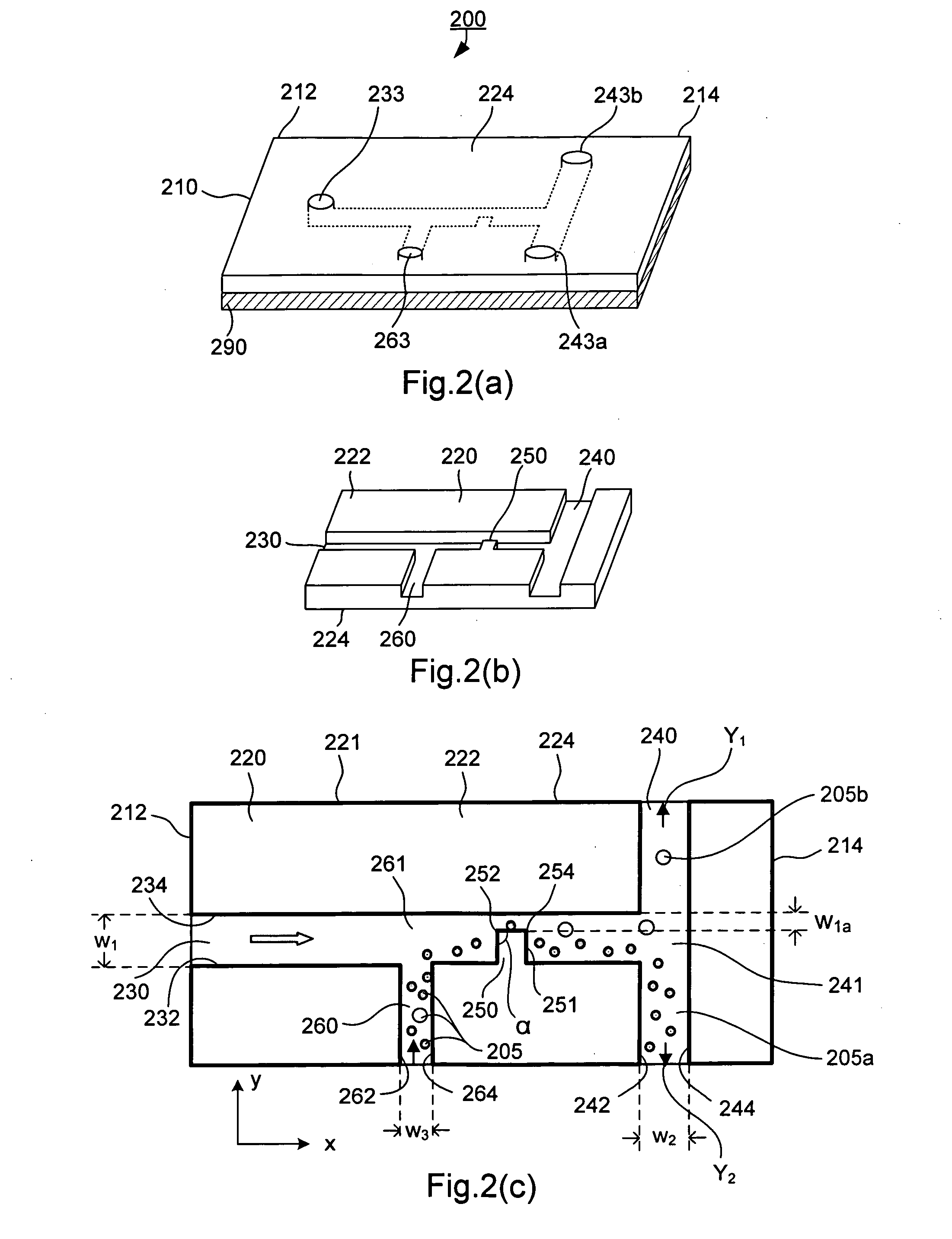
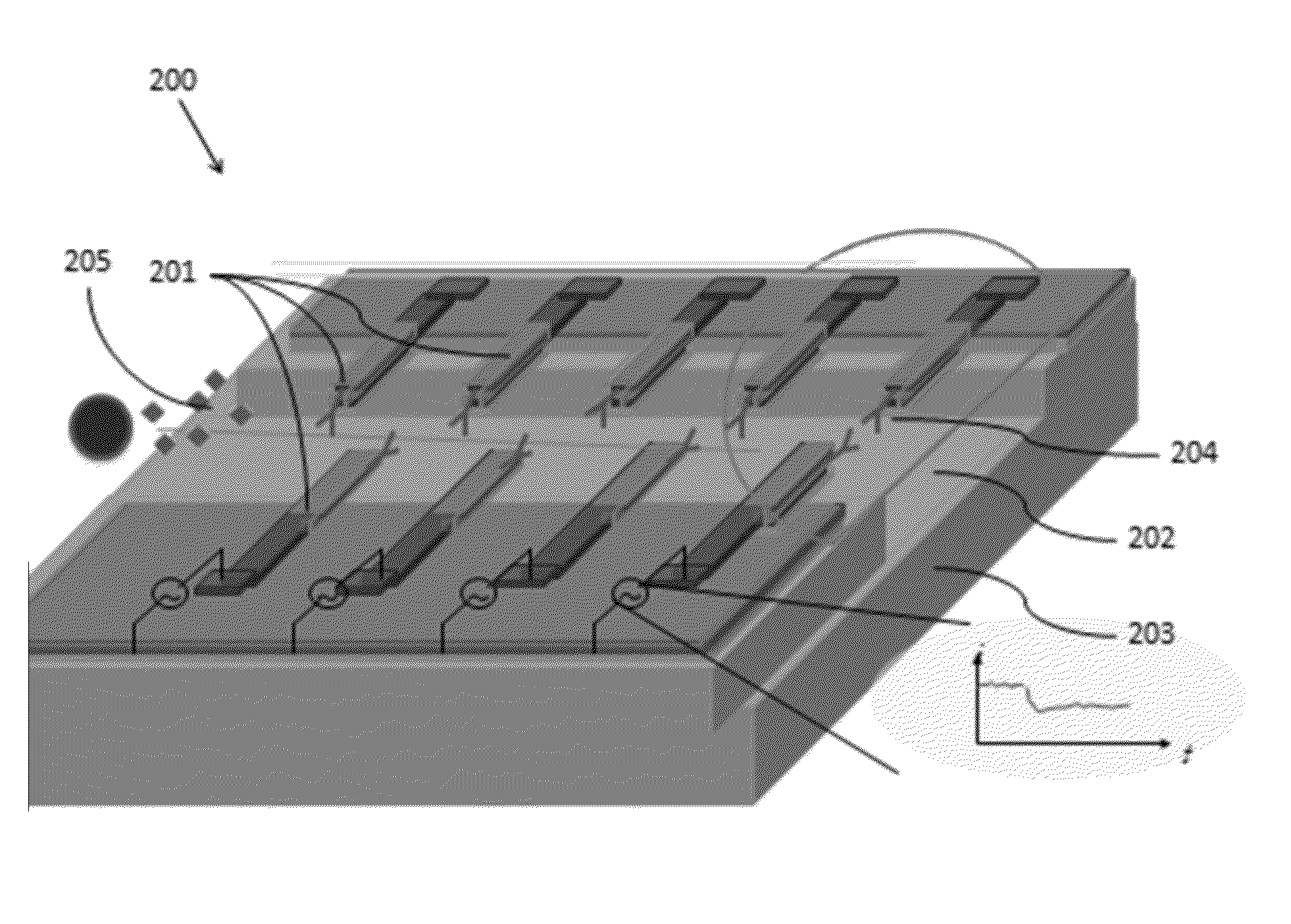
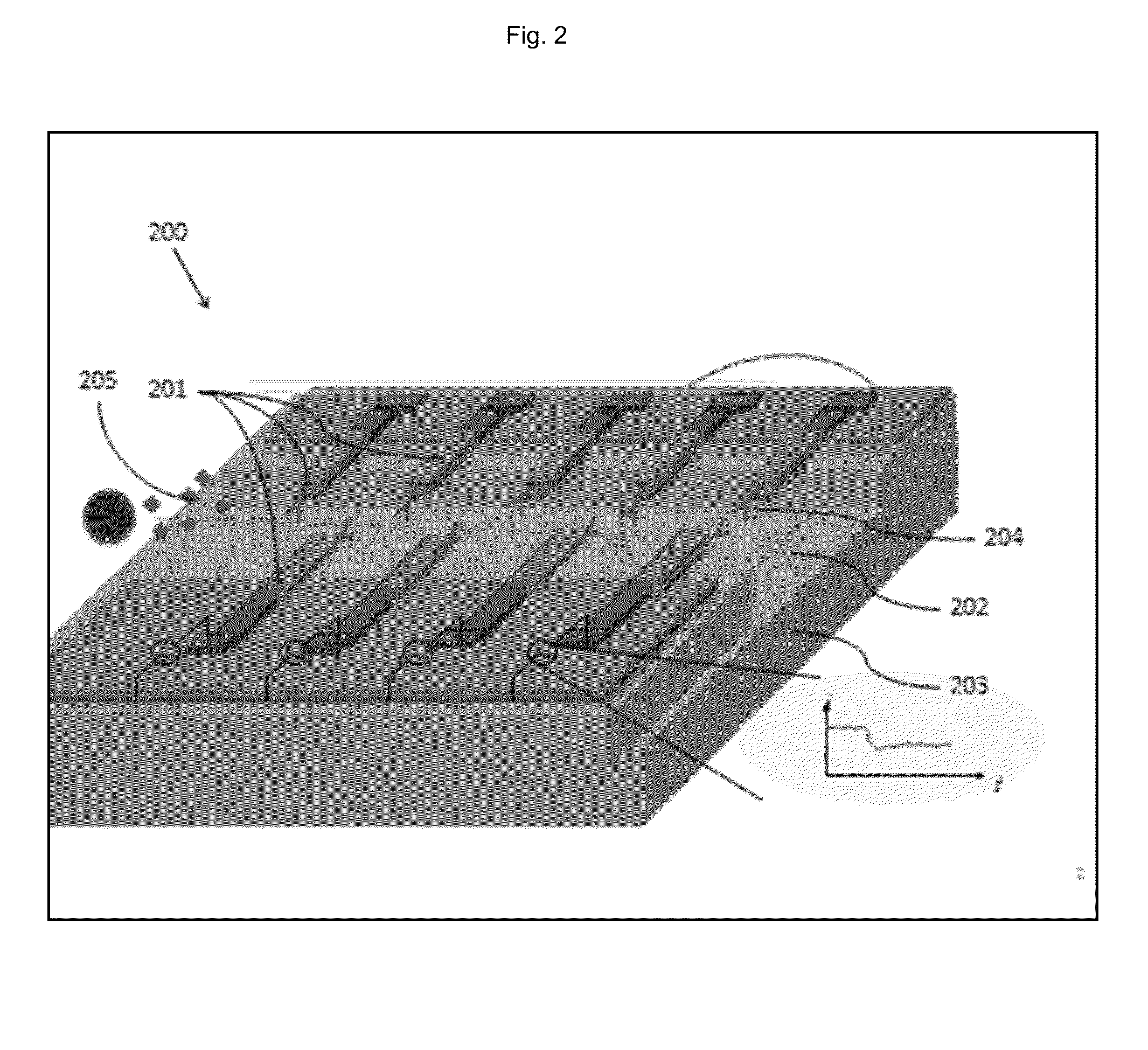
Microfluidic device for cell and particle separation
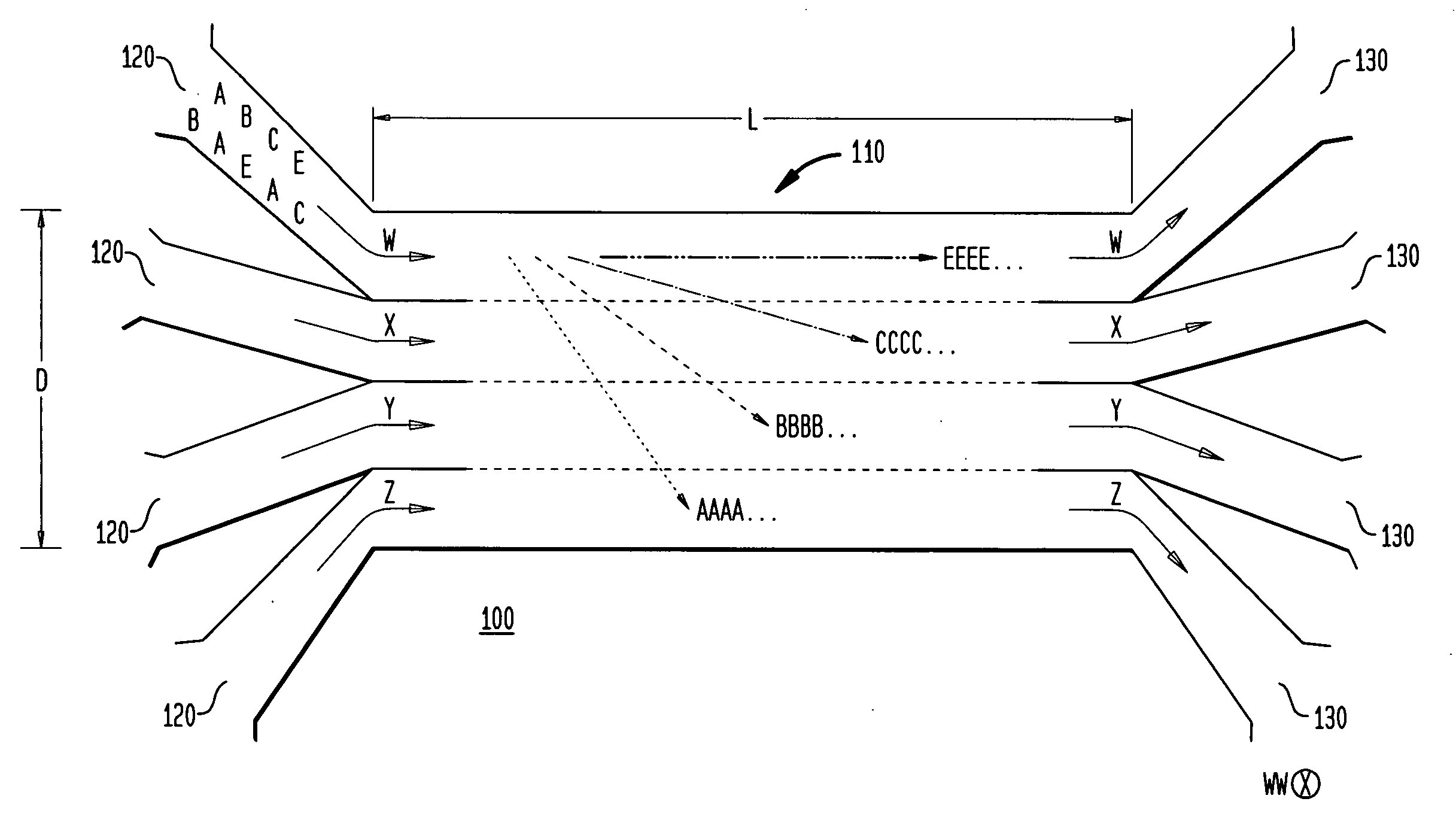
A microfluidic separation device includes a microchannel formed in a substrate and being defined at least by a bottom surface, a first side wall, and second side wall. Fluid containing particles or cells is flowed through the microchannel from an upstream end to a downstream end. The downstream end terminates in a plurality of branch channels. A plurality of vertically-oriented electrodes are disposed on the first wall and on the second wall opposite to the first wall. A voltage source is connected to the plurality of opposing electrodes to drive the electrodes. The opposing, vertically-oriented electrodes may be used to focus a heterogeneous population of particles or cells for subsequent downstream separation via additional electrodes placed on one of the side walls. Alternatively, the opposing, vertically-oriented electrodes may be used to spatially separate a heterogeneous population of particles or cells for later collection in one or more of the branch channels.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multiple laminar flow-based rate zonal or isopycnic separation with holographic optical trapping of blood cells and other static components
ActiveUS20050061962A1Improve throughputSave a lot of timeDielectrophoresisOther blood circulation devicesCellular componentBlood component
The invention provides a method and apparatus for separating blood into components, may be expanded to include other types of cellular components, and can be combined with holographic optical manipulation or other forms of optical tweezing. One of the exemplary methods includes providing a first flow having a plurality of blood components; providing a second flow; contacting the first flow with the second flow to provide a first separation region; and differentially sedimenting a first blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components into the second flow while concurrently maintaining a second blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components in the first flow. The second flow having the first blood cellular component is then differentially removed from the first flow having the second blood cellular component. Holographic optical traps may also be utilized in conjunction with the various flows to move selected components from one flow to another, as part of or in addition to a separation stage.
Owner:ABS GLOBAL
Methods and devices for sorting cells and other biological particulates
ActiveUS20120118740A1Accurately and systematically assessAccurate identificationDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsParticulatesEmbryo
An optical pattern-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and separation methods are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells and selection based on traits correlated with the DEP response. Embodiments of the apparatus use DEP electric field patterns in combination with microfluidic laminar flows to measure response, separate, segregate and extract particles from heterogeneous mixtures according to the relative response of the particles to one or more DEP fields without damaging living cells. The methods are particularly suited for selecting and extracting the best sperm and embryo candidates based on fitness for use with existing artificial reproduction procedures and excluding defective or non-viable gametes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
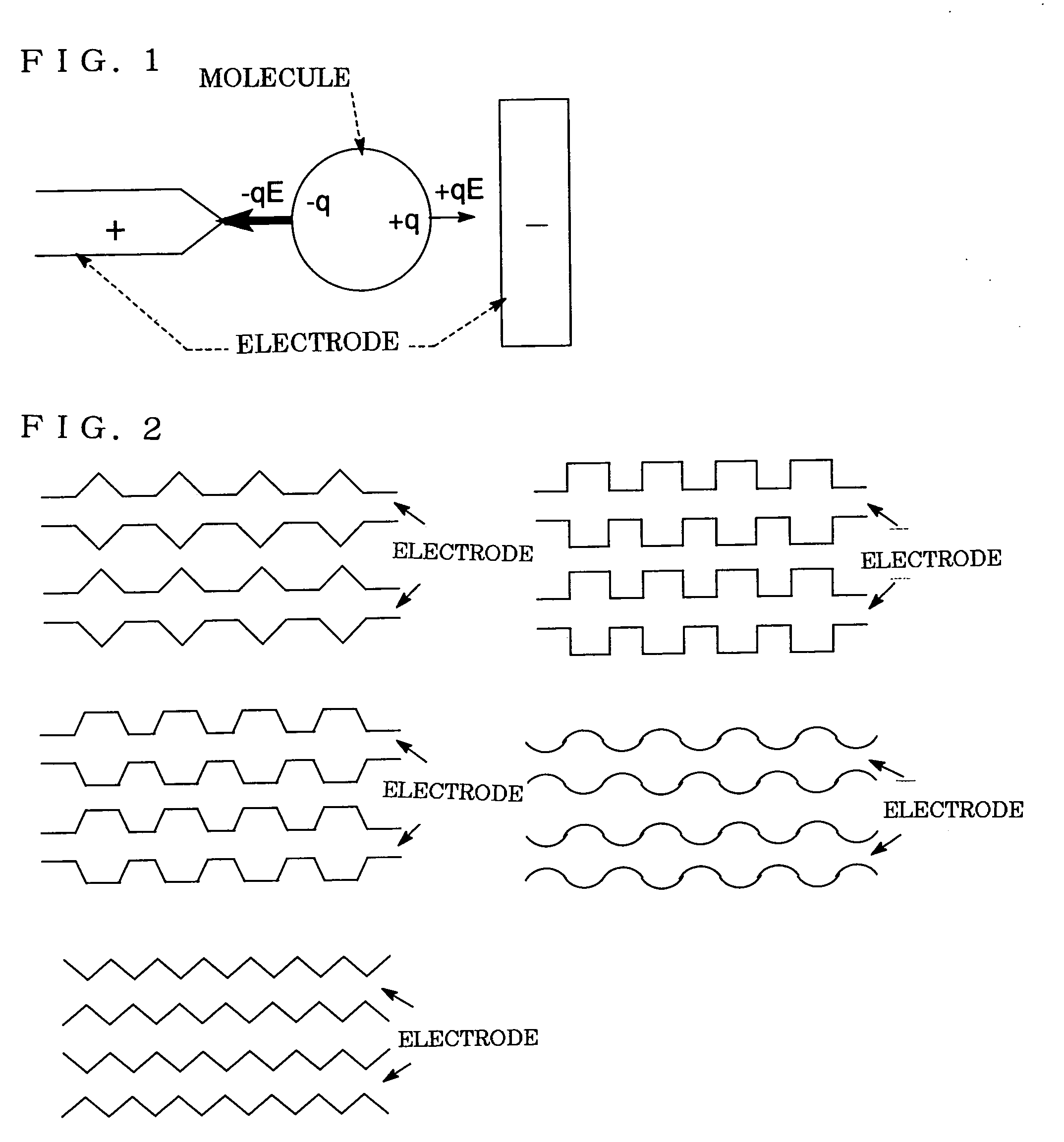
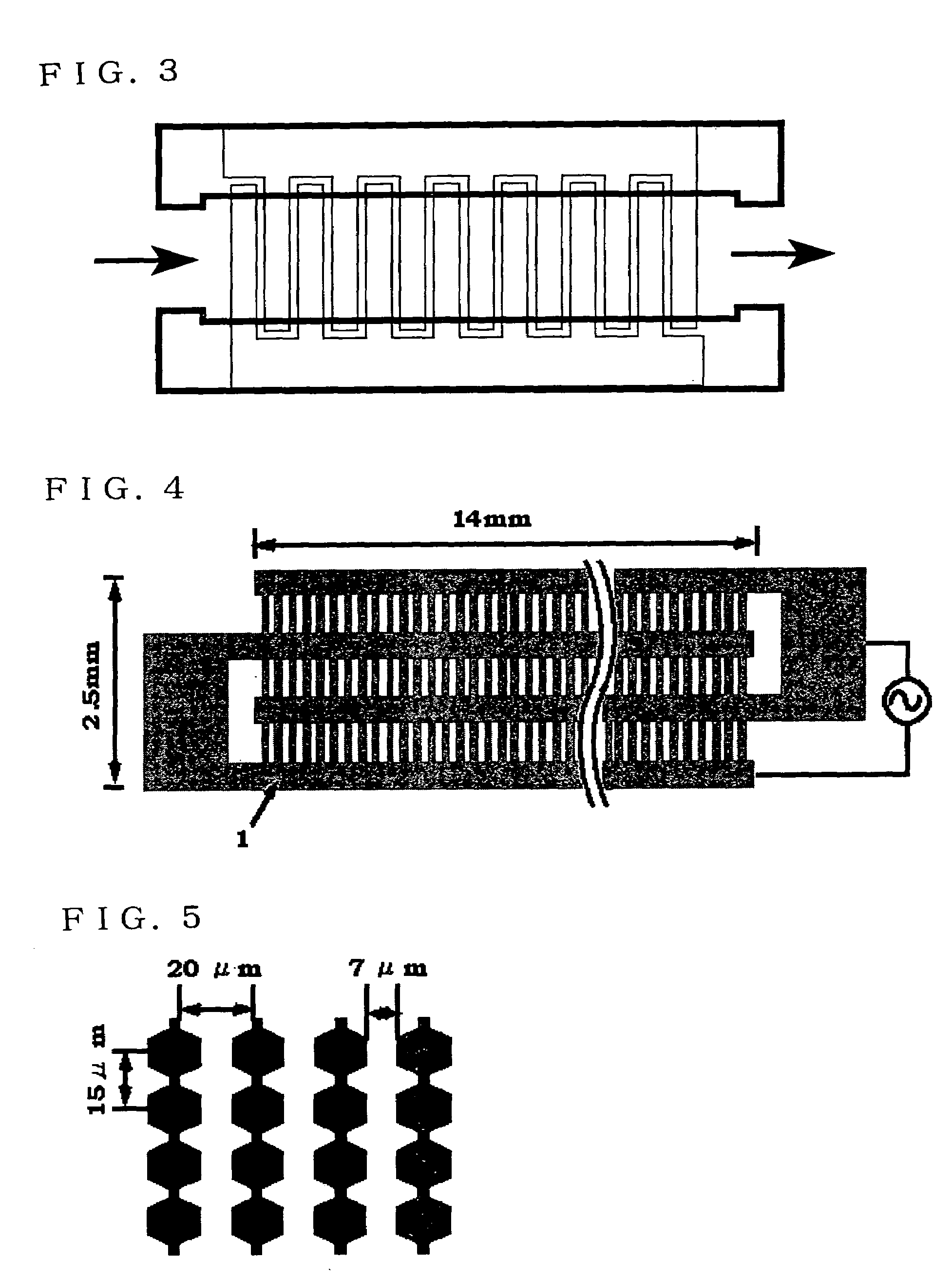
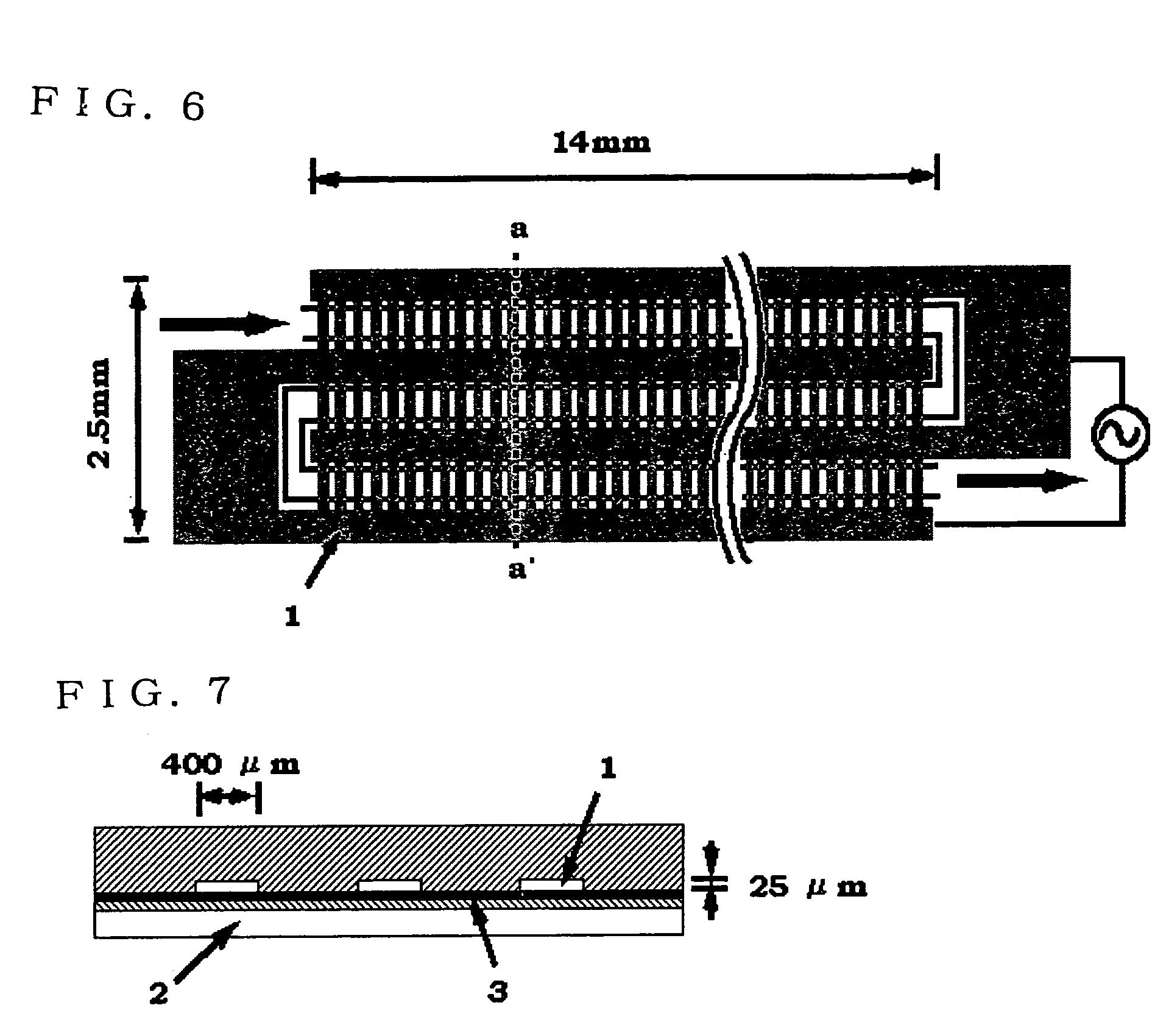
Method for separating substances using dielectrophoretic forces
InactiveUS7198702B1Rapidly and readily separatingDielectrophoresisSludge treatmentElectrical field strengthDielectrophoretic force
The present invention has an object of providing a method by which two kinds or more of molecules can be separated each other by using dielectrophoretic forces. The present invention comprises two methods. The first method is a method comprising forming a complex substance of a “specific molecule” containing in a sample, and a “substance capable of changing dielectrophoretic properties of the specific molecule”, which binds to the “specific molecule” contained therein, and thereby separating the complex substance and the molecules other than the specific molecule in the sample from each other. The second method is a method comprising placing a solution in which two kinds or more of molecules are dissolved under a strong electric field strength, that is, under a nonuniform electric field having an electric field strength of 500 KV / m or higher, by using dielectrophoretic forces.
Owner:WAKO PURE CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES
Multiple laminar flow-based particle and cellular separation with laser steering
ActiveUS20090032449A1Improve throughputSave a lot of timeDielectrophoresisMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCellular componentBlood component
The invention provides a method, apparatus and system for separating blood and other types of cellular components, and can be combined with holographic optical trapping manipulation or other forms of optical tweezing. One of the exemplary methods includes providing a first flow having a plurality of blood components; providing a second flow; contacting the first flow with the second flow to provide a first separation region; and differentially sedimenting a first blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components into the second flow while concurrently maintaining a second blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components in the first flow. The second flow having the first blood cellular component is then differentially removed from the first flow having the second blood cellular component. Holographic optical traps may also be utilized in conjunction with the various flows to move selected components from one flow to another, as part of or in addition to a separation stage.
Owner:ABS GLOBAL
Nucleic acid sample preparation
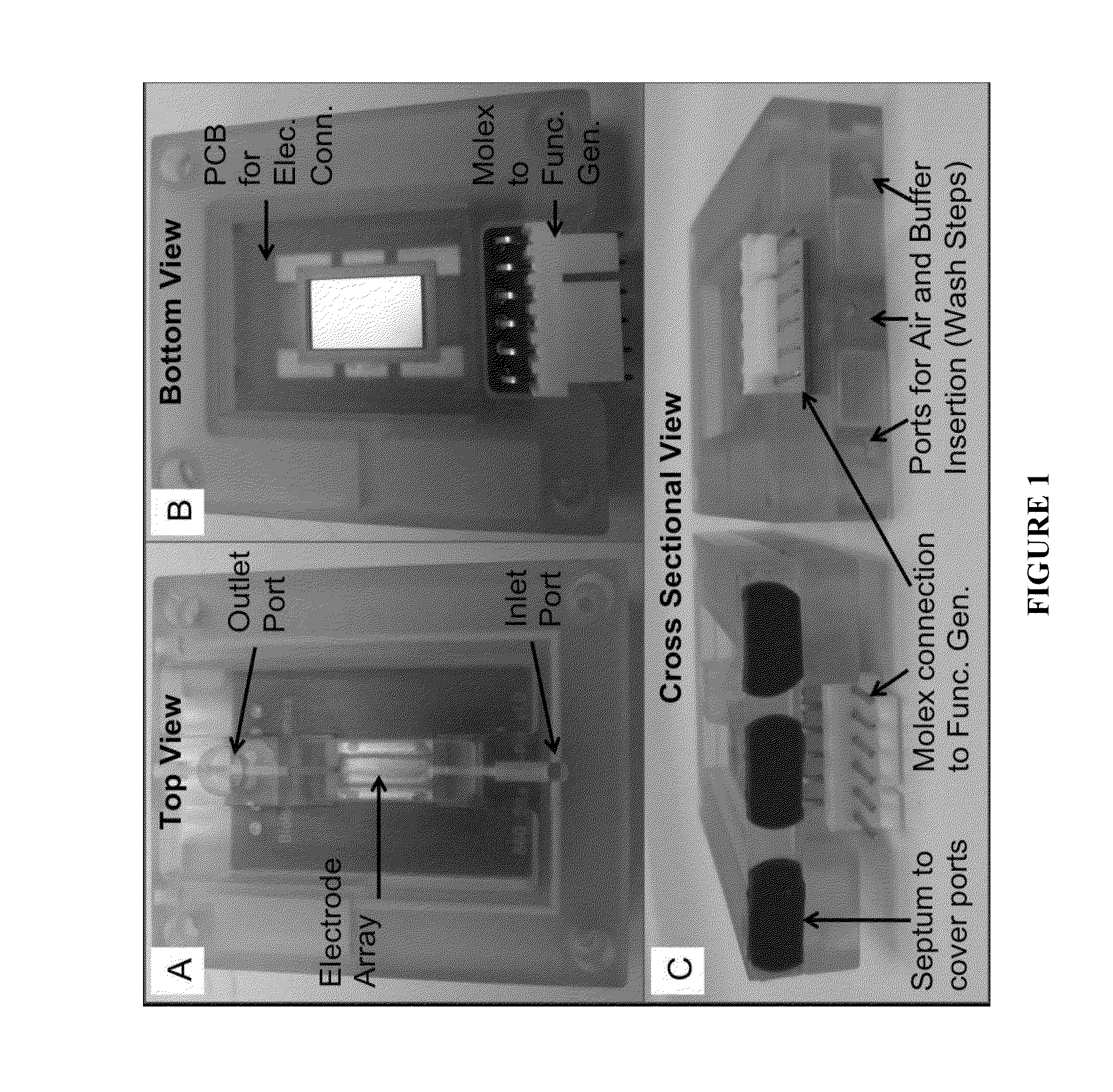
ActiveUS20130273640A1Highly purified nucleic acidsAmenable to multiplexed and high-throughput operationDielectrophoresisHeating or cooling apparatusBiologyNucleic acid
The present invention includes methods, devices and systems for isolating a nucleic acid from a fluid comprising cells. In various aspects, the methods, devices and systems may allow for a rapid procedure that requires a minimal amount of material and / or results in high purity nucleic acid isolated from complex fluids such as blood or environmental samples.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL DYNAMICS INC
Microanalysis of cellular function
ActiveUS20130261021A1Rapid and efficient testingRapid and efficient timingDielectrophoresisLibrary screeningAntibody-Secreting CellsGranular cell
An inverted microwell (102) provides rapid and efficient microanalysis system (100) and method for screening of biological particles (128), particularly functional analysis of cells on a single cell basis. The use of an inverted open microwell system (102) permits identification of particles, cells, and biomolecules that may be combined to produce a desired functional effect also functional screening of secreted antibody therapeutic activity as well as the potential to recover cells and fluid, and optionally expand cells, such as antibody secreting cells, within the same microwell.
Owner:CELLPLY SRL
Multiple laminar flow-based particle and cellular separation with laser steering
InactiveUS7118676B2Save a lot of timeImprove throughputDielectrophoresisOther blood circulation devicesCellular componentBlood component
Owner:PREMIUM GENETICS UK
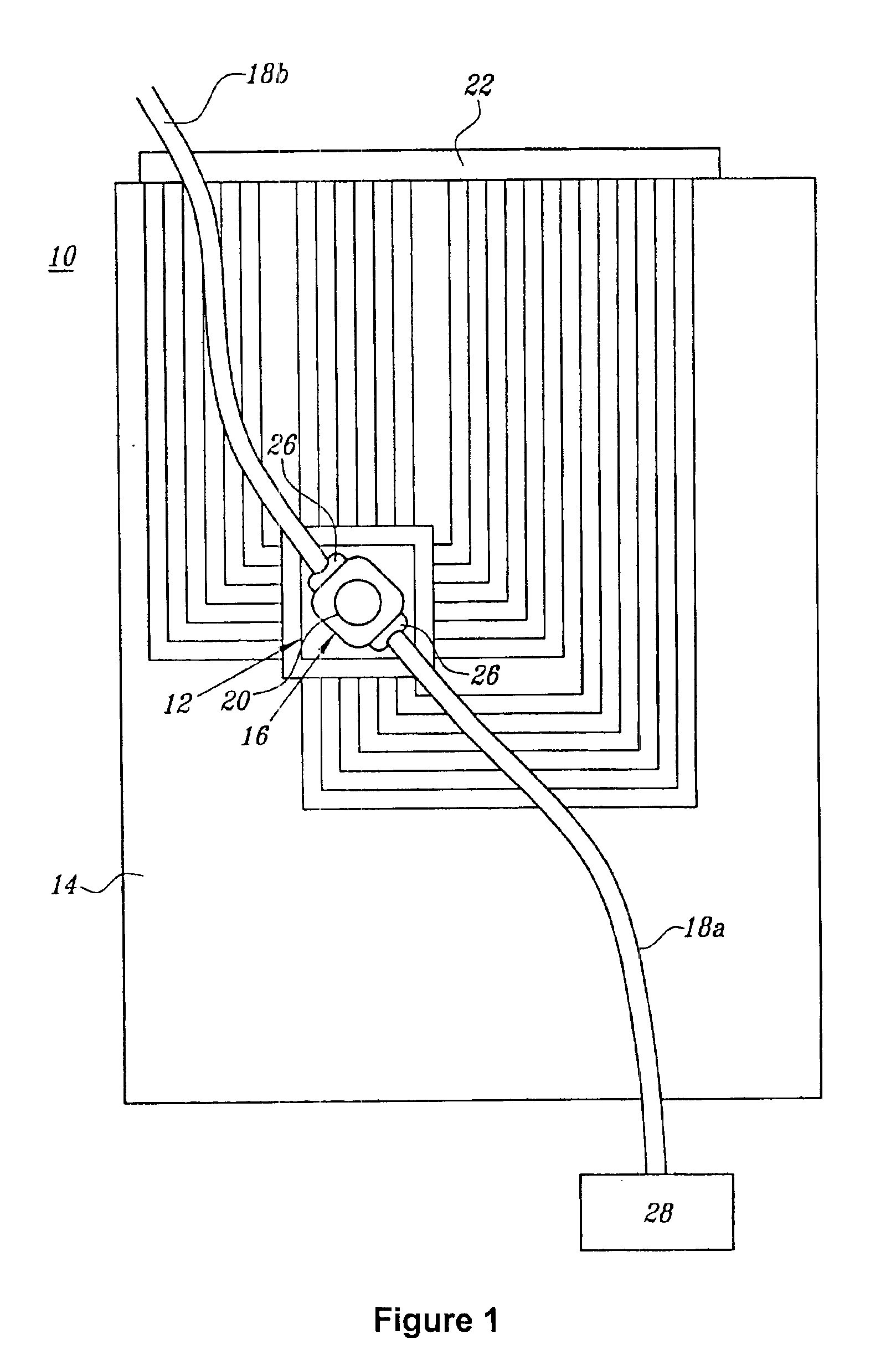
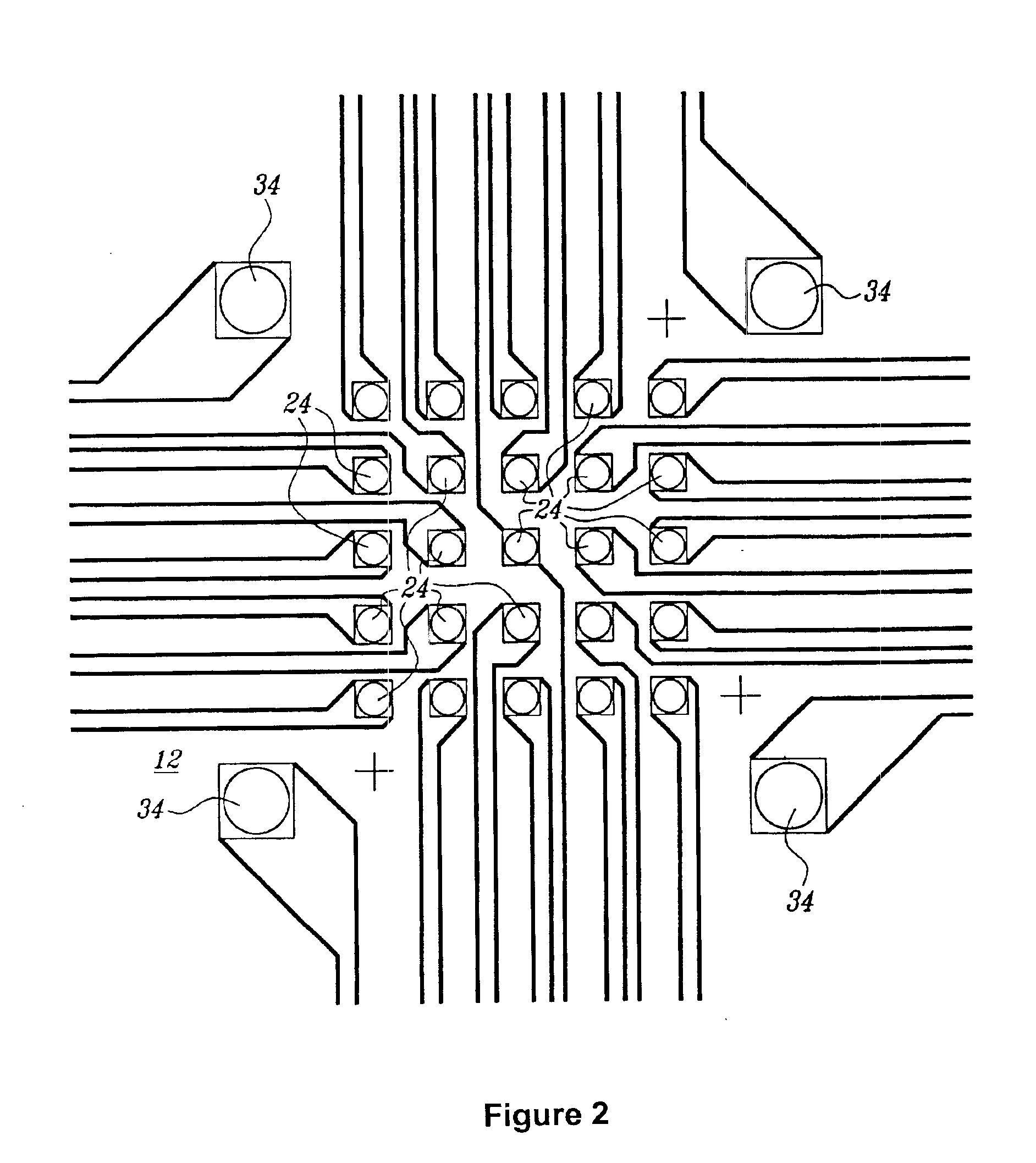
Insulator-Based DEP with Impedance Measurements for Analyte Detection
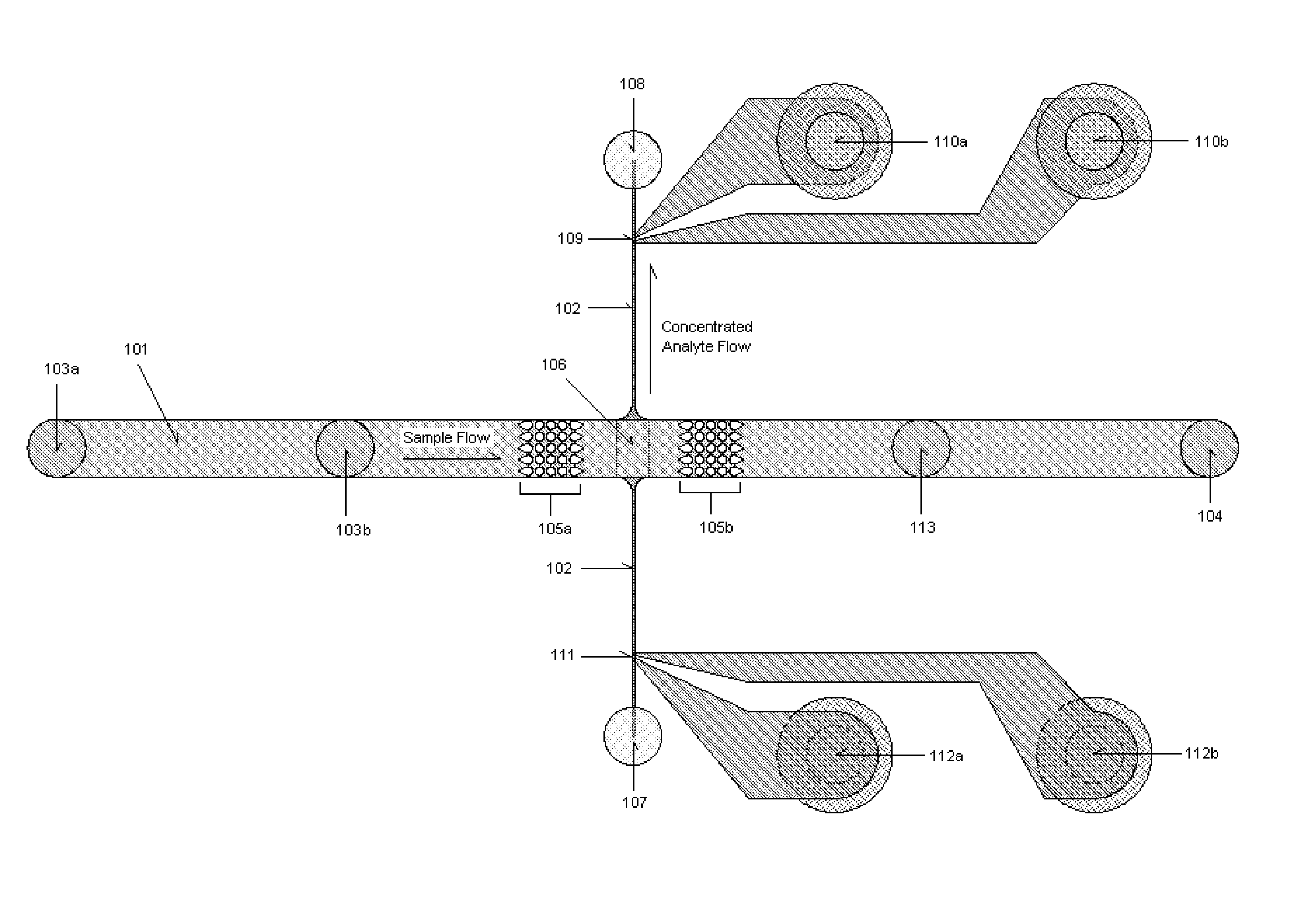
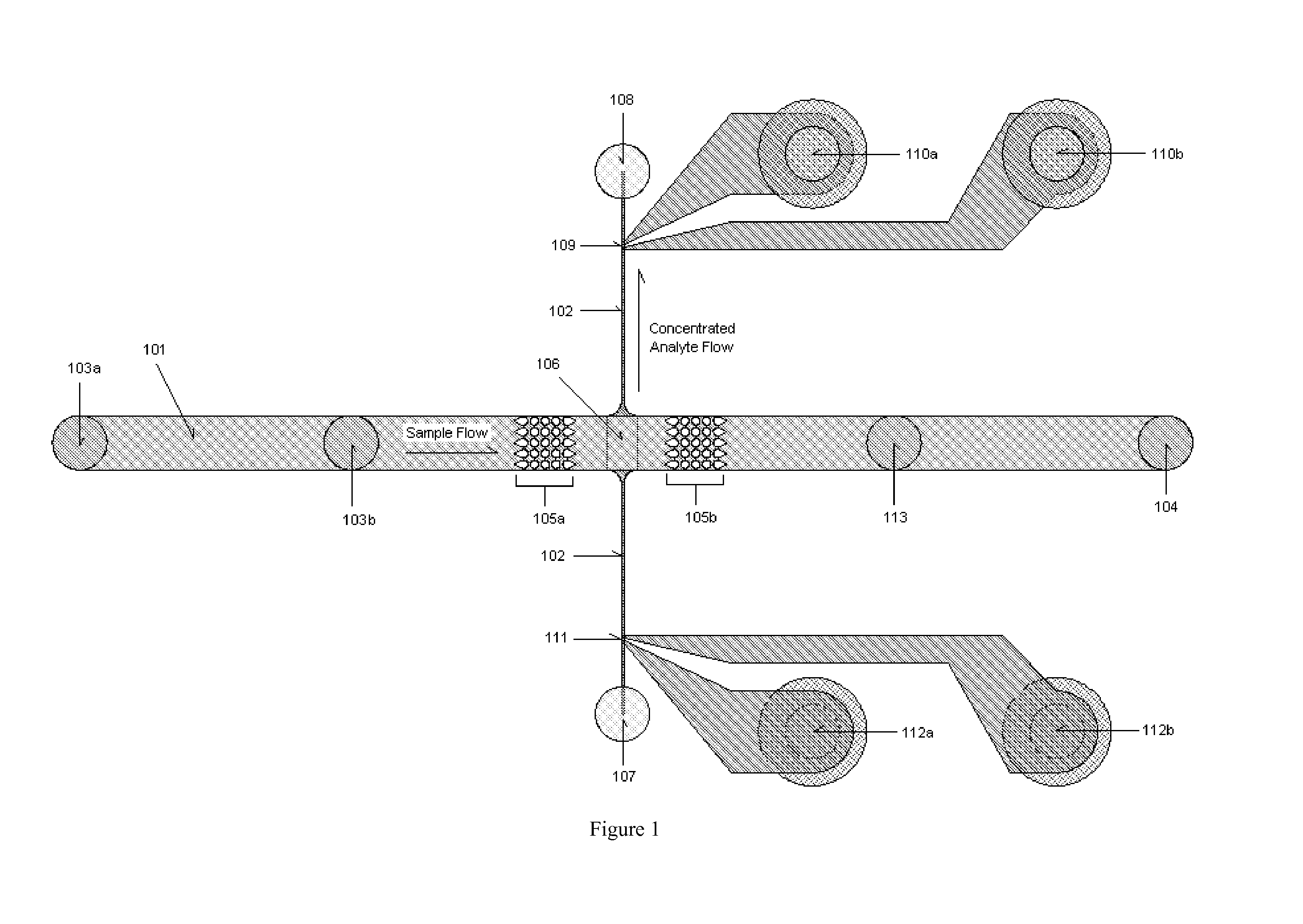
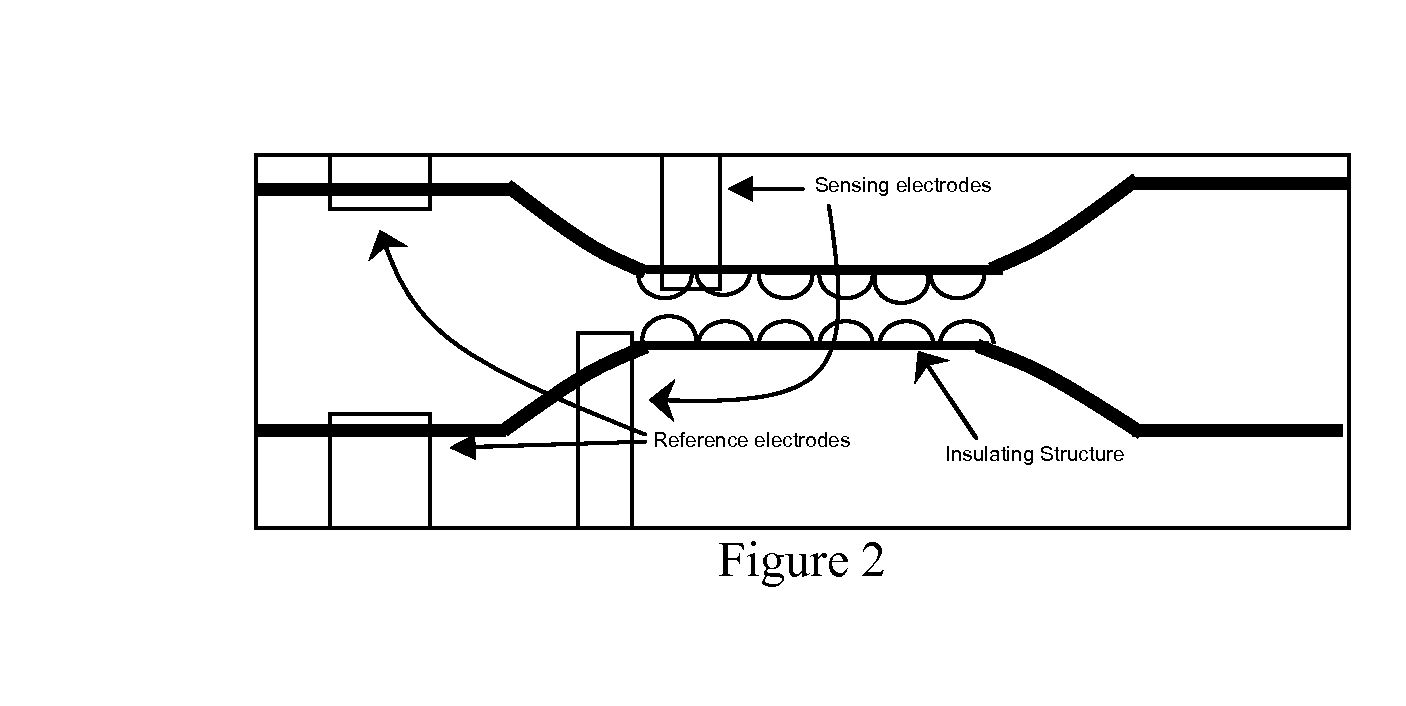
Disclosed herein are microfluidic devices for assaying at least one analyte specie in a sample comprising at least one analyte concentration area in a microchannel having insulating structures on or in at least one wall of the microchannel which provide a nonuniform electric field in the presence of an electric field provided by off-chip electrodes; and a pair of passivated sensing electrodes for impedance detection in a detection area. Also disclosed are assay methods and methods of making.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
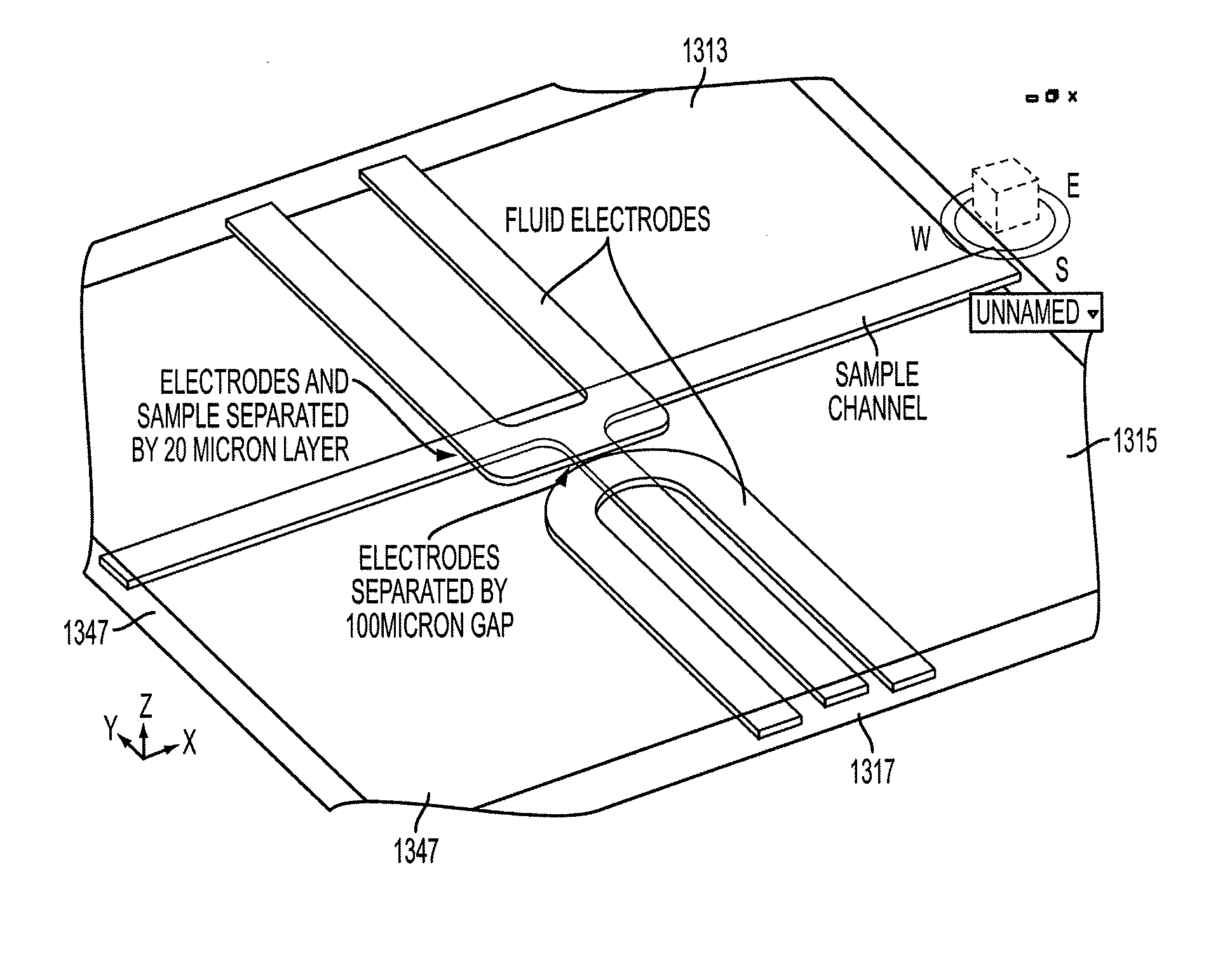
Devices and methods for contactless dielectrophoresis for cell or particle manipulation
ActiveUS20100224493A1Easy maintenanceAvoid contactDielectrophoresisSludge treatmentChemical physicsSample integrity
Devices and methods for performing dielectrophoresis are described. The devices contain sample channel which is separated by physical barriers from electrode channels which receive electrodes. The devices and methods may be used for the separation and analysis of particles in solution, including the separation and isolation of cells of a specific type. As the electrodes do not make contact with the sample, electrode fouling is avoided and sample integrity is better maintained.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Programmable fluidic processors
ActiveUS20060114296A1Meet needsDielectrophoresisTransportation and packagingContact freeComputer science
Disclosed are apparatuses, systems, and methods for programmable fluidic processors. In one embodiment, the invention involves manipulating droplets across a reaction surface of the processor substantially contact-free of any surfaces. The reaction surface and the electrodes of the processor may include a coating repelling the droplets. Further, the present invention provides for a suitable suspending medium for repelling droplets away from fixed surfaces.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Dielectrophoretic systems without embedded electrodes
InactiveUS7014747B2Mitigate mass transfer effectMinimize changesDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsChemical physicsElectrophoresis
Method and apparatus for dielectrophoretic separation of particles in a fluid based using array of insulating structures arranged in a fluid flow channel. By utilizing an array of insulating structures, a spatially inhomogeneous electric field is created without the use of the embedded electrodes conventionally employed for dielectrophoretic separations. Moreover, by using these insulating structures a steady applied electric field has been shown to provide for dielectrophoresis in contrast to the conventional use of an alternating electric field. In a uniform array of posts, dielectrophoretic effects have been produced flows having significant pressure-driven and electrokinetic transport. Above a threshold applied electric field, filaments of concentrated and rarefied particles appear in the flow as a result of dielectrophoresis. Above a higher threshold applied voltage, dielectrophoresis produces zones of highly concentrated and immobilized particles. These patterns are strongly influenced by the angle of the array of insulating structures with respect to the mean applied electric field and the shape of the insulating structures.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
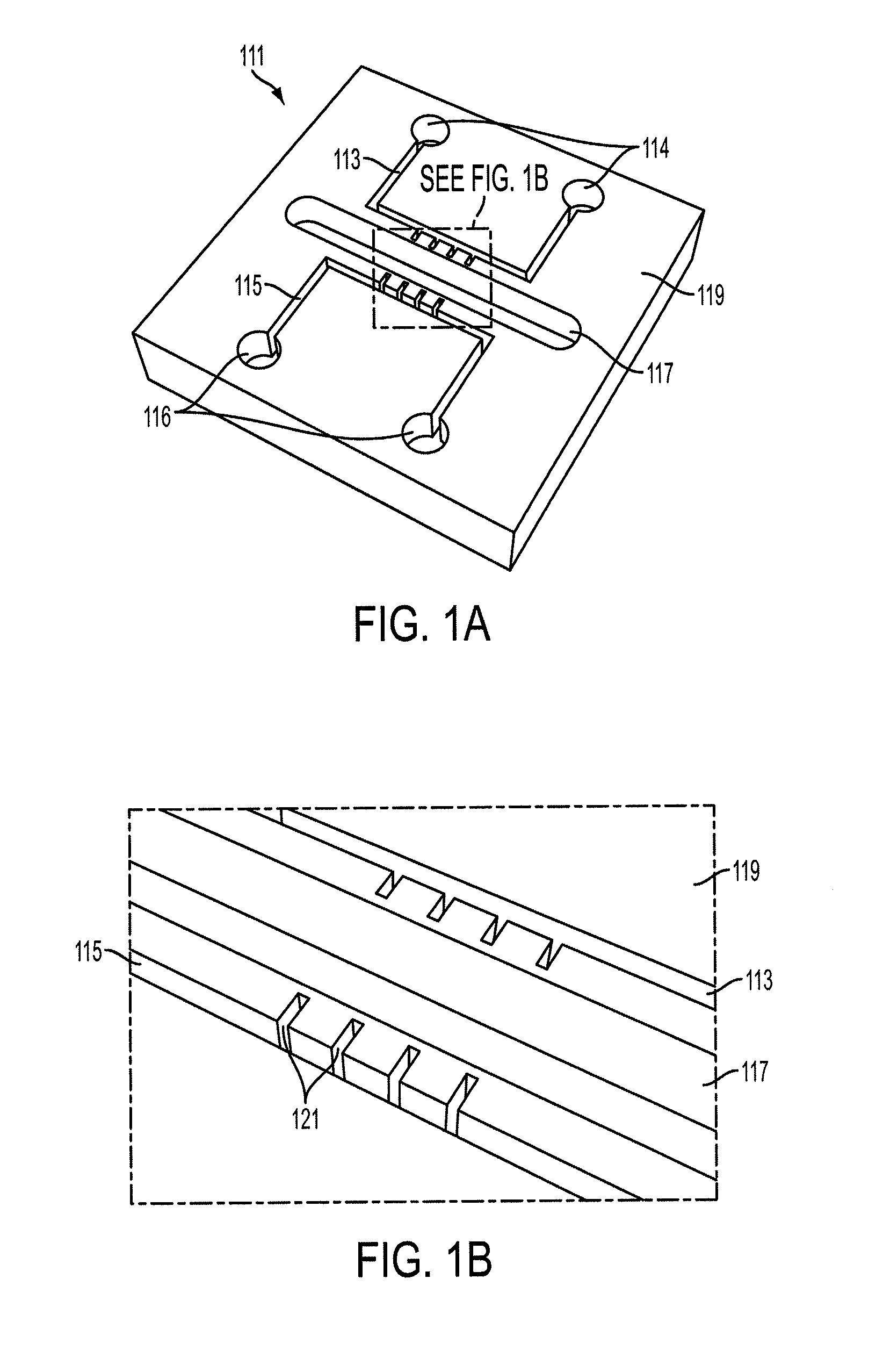
Rapid flow fractionation of particles combining liquid and particulate dielectrophoresis
Rapid, size-based, deposition of particles from liquid suspension is accomplished using a nonuniform electric field created by coplanar microelectrode strips patterned on an insulating substrate. The scheme uses the dielectrophoretic force both to distribute aqueous liquid containing particles and, simultaneously, to separate the particles. Size-based separation is found within nanoliter droplets formed along the structure after voltage removal. Bioparticles or macromolecules of similar size can also be separated based on subtle differences in dielectric property, by controlling the frequency of the AC current supplied to the electrodes.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
DC-dielectrophoresis microfluidic apparatus, and applications of same
The present invention relates to an apparatus and methods of separating particles or cells according to their sizes, wherein the size of each of the particles or cells is characterized by a corresponding diameter. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of providing a microchannel structure having at least one channel that is defined by a first sidewall and a second, opposite sidewall and has an insulating protrusion formed on one of the first sidewall and the second, opposite sidewall, introducing a plurality of particles or cells in a liquid medium into the at least one channel, and generating a non-uniform electrical field in the at least one channel such that when the plurality of particles or cells passes by the insulating protrusion, the plurality of particles or cells each receives a dielectrophoretic force proportional to its diameters, thereby being separable according to their sizes. The method further has the step of collecting particles or cells after the separation of particles or cells.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
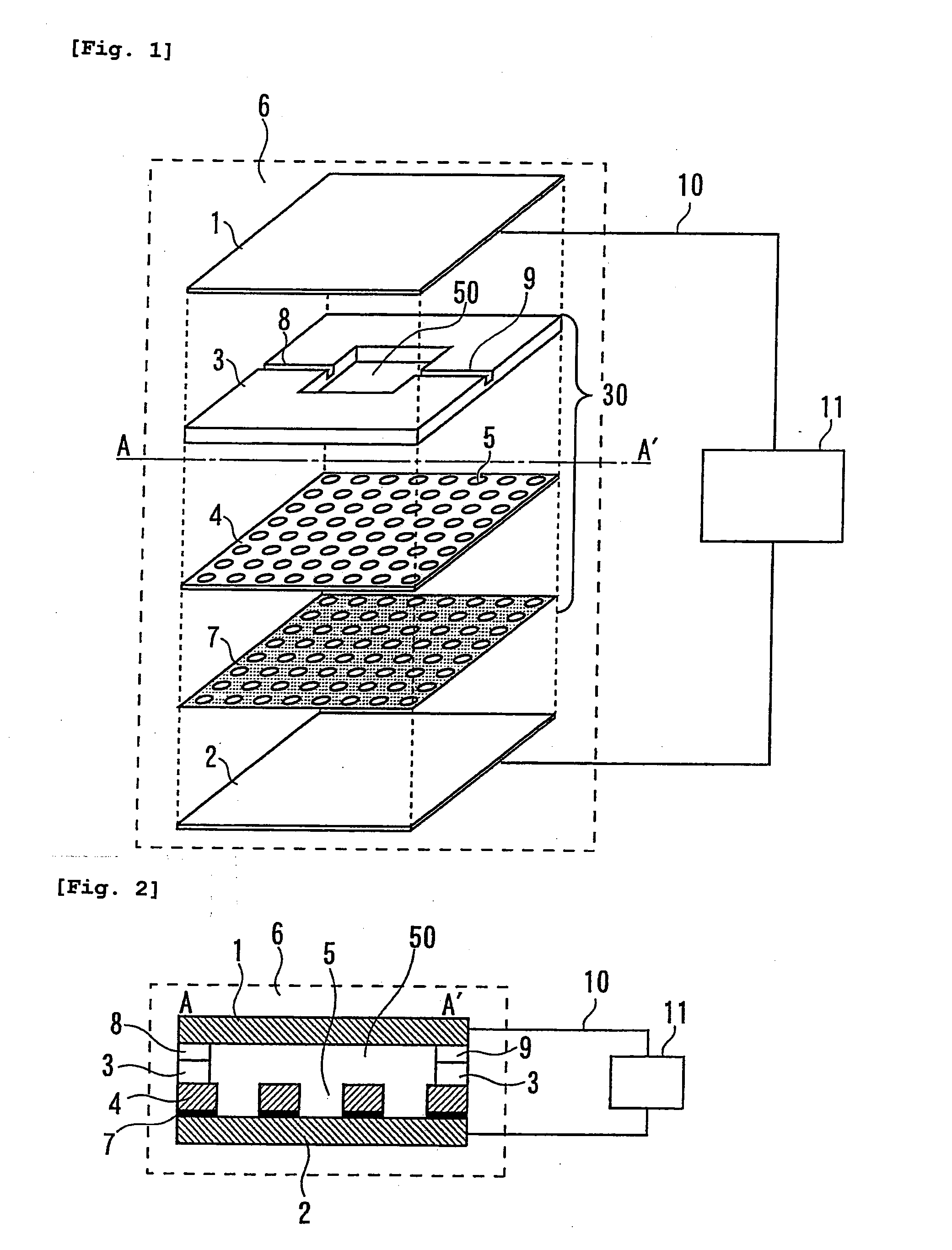
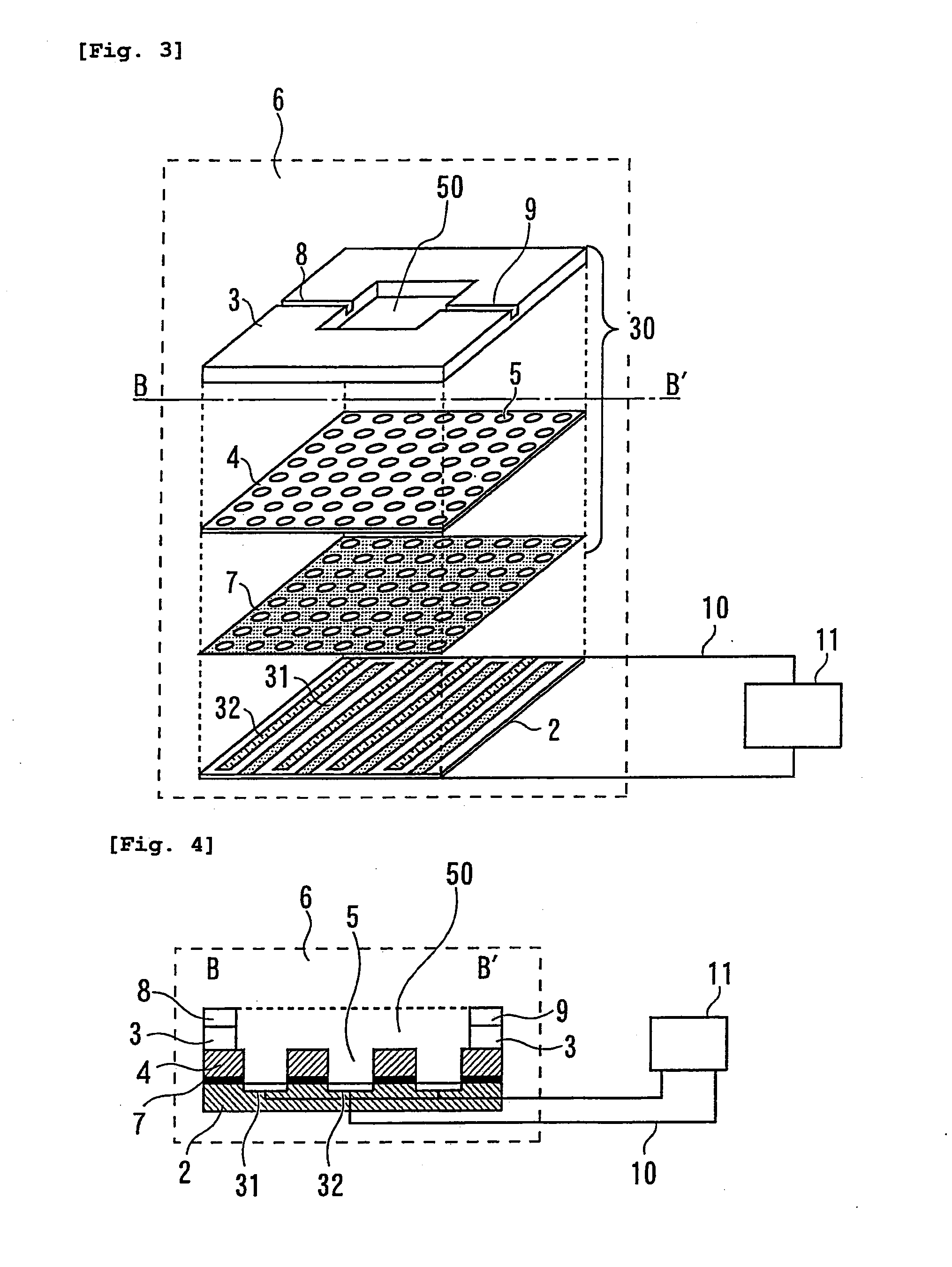
Biological sample immobilizing apparatus
InactiveUS20130118905A1Analyze moreEasy to getDielectrophoresisSludge treatmentHigh densityElectrophoresis
A biological sample immobilizing apparatus is provided, comprising a holding unit which holds a biological sample, a pair of electrodes which allows a dielectrophoretic force to act on the biological sample to move the biological sample to the holding unit, and a power source which applies an AC voltage to the pair of electrodes. Accordingly, a plurality of components contained in the biological sample can be conveniently separated into individuals one by one and respective genes thereof can be analyzed one by one quickly and simultaneously, while providing a high density and being miniaturized.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
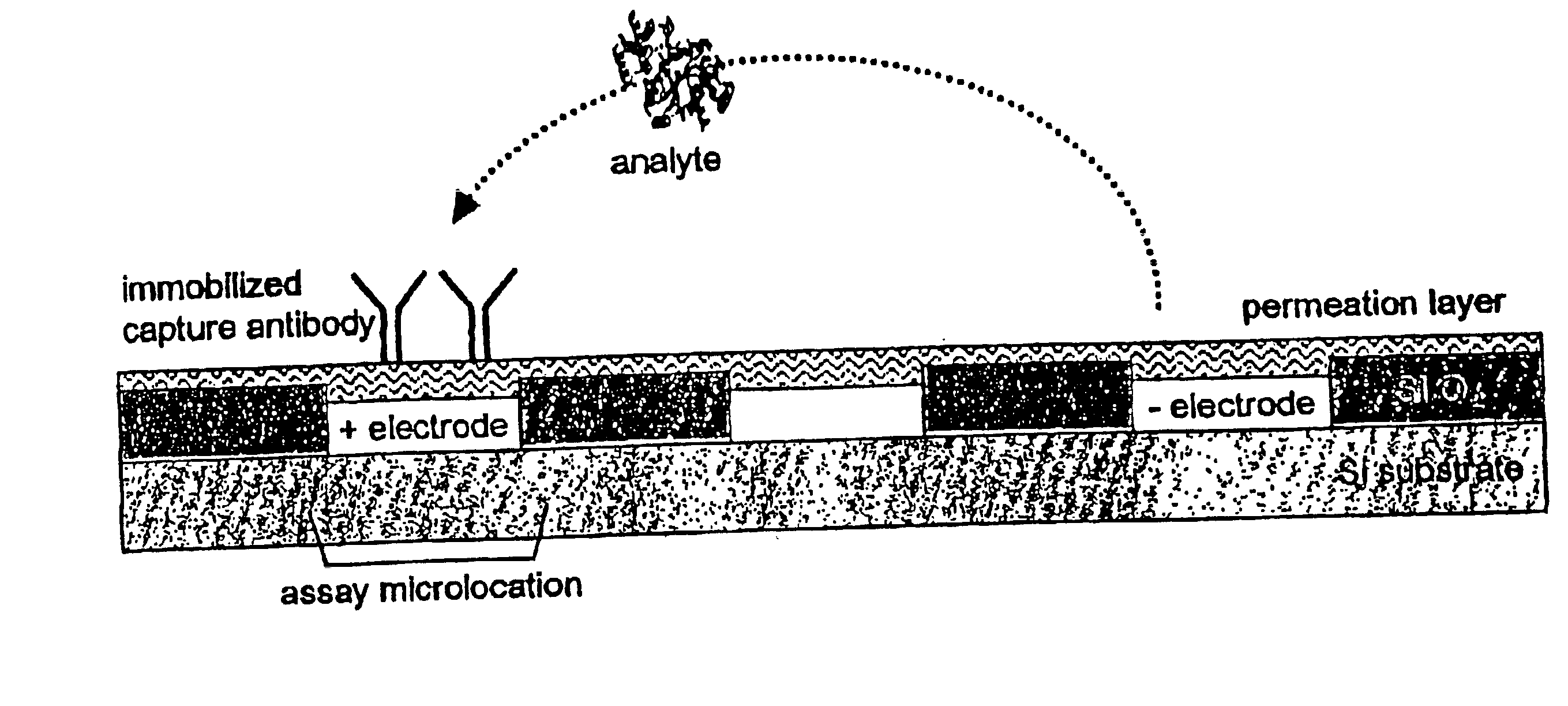
Dielectrophoretic separation and immunoassay methods on active electronic matrix devices
InactiveUS6887362B2Reduce the amount requiredDone quickly and efficientlyDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsAssayMedical product
This invention relates to devices and methods for performing active, multi-step molecular and biological sample preparation and diagnostic analyses employing immunochemical techniques. It relates generally to bioparticle separation, bioparticle enrichment, and electric field-mediated immunochemical detection on active electronic matrix devices utilizing AC and DC electric fields. More specifically, the invention relates to devices and methods for sample preparation / manipulation, immunoimmobilization, and immunoassays, all of which can be conducted on one or more active electronic chip devices within a single system. These manipulations are useful in a variety of applications, including, for example, detection of pathogenic bacteria and biological warfare agents, point-of-care diagnostics, food or medical product quality control assays, and other biological assays.
Owner:GAMIDA FOR LIFE +1
Multiphase non-linear electrokinetic devices
This invention provides devices and apparatuses comprising the same and methods of use thereof for efficient pumping and / or mixing of relatively small volumes of fluid, wherein the fluid contains a sample within an inner fluid phase dispersed in an outer phase. Such devices utilize nonlinear electrokinetics as a primary mechanism for driving fluid flow and / or mixing the fluid. Methods of cellular analysis, drug delivery and others, utilizing the devices are described.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Multiple laminar flow-based particle and cellular separation with laser steering
InactiveUS7699767B2Save a lot of timeImprove throughputDielectrophoresisMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCellular componentBlood component
The invention provides a method, apparatus and system for separating blood and other types of cellular components, and can be combined with holographic optical trapping manipulation or other forms of optical tweezing. One of the exemplary methods includes providing a first flow having a plurality of blood components; providing a second flow; contacting the first flow with the second flow to provide a first separation region; and differentially sedimenting a first blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components into the second flow while concurrently maintaining a second blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components in the first flow. The second flow having the first blood cellular component is then differentially removed from the first flow having the second blood cellular component. Holographic optical traps may also be utilized in conjunction with the various flows to move selected components from one flow to another, as part of or in addition to a separation stage.
Owner:ABS GLOBAL
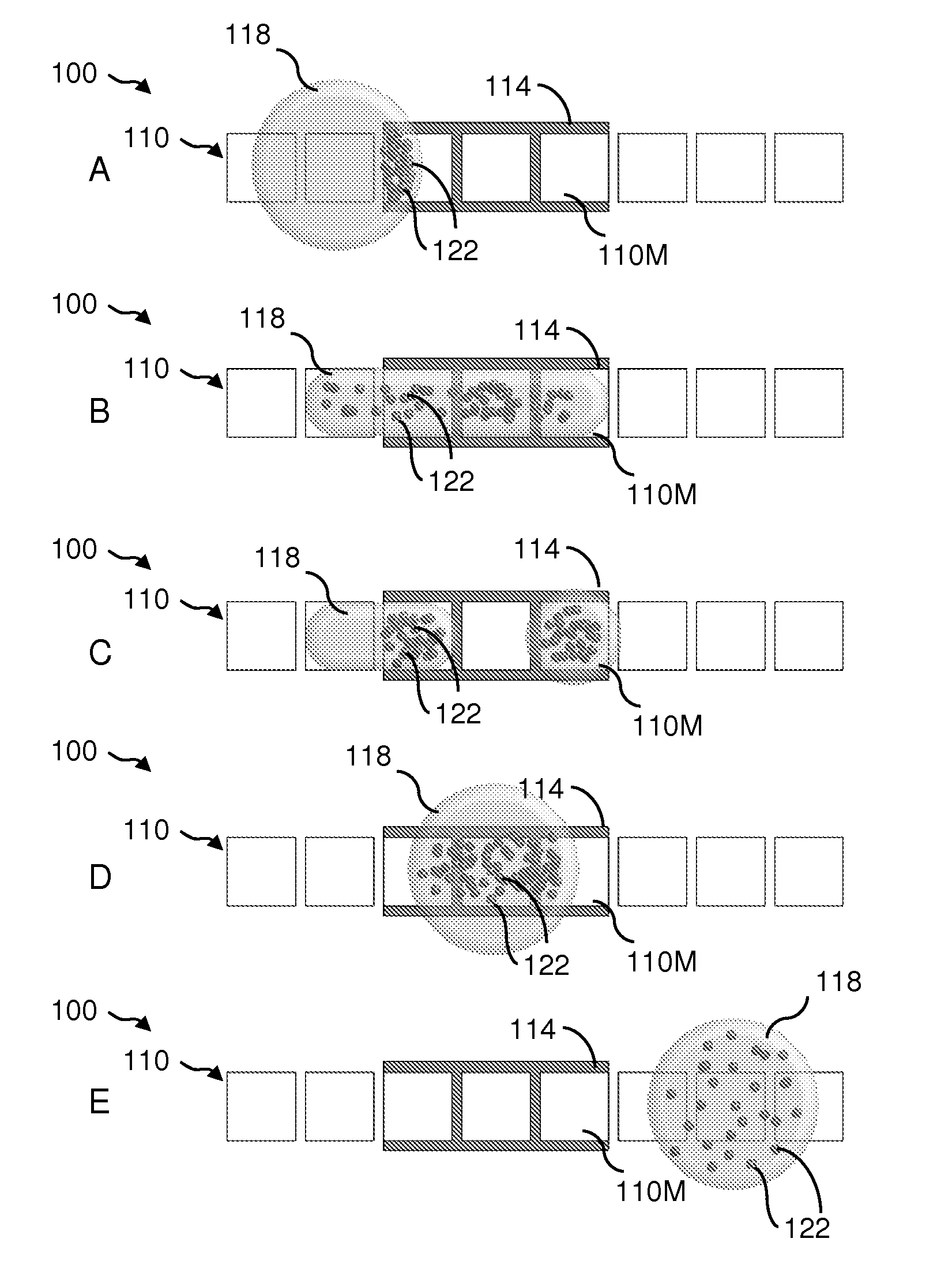
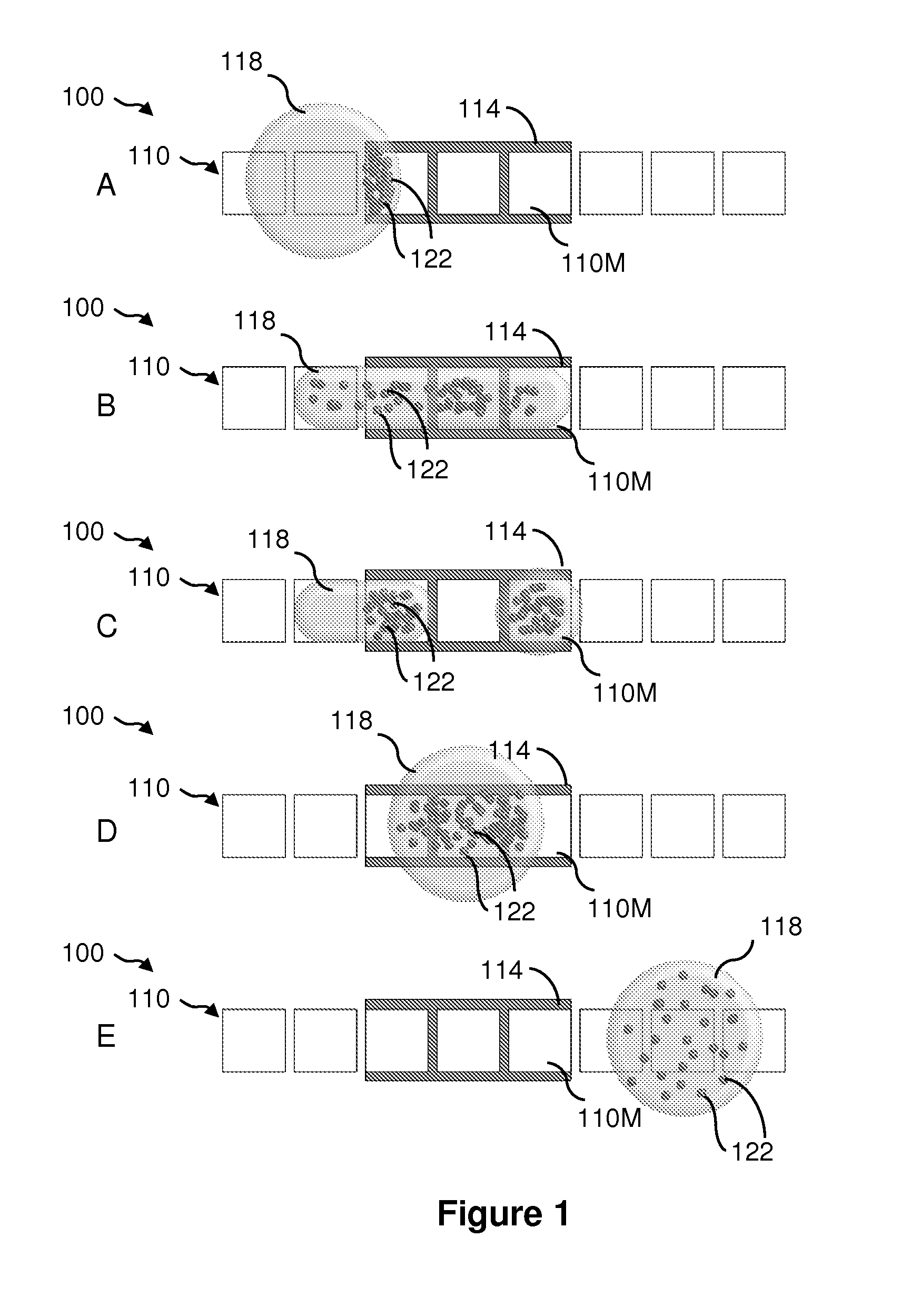
Methods and compositions for separating or enriching cells
InactiveUS20140008210A1Aid in diagnosis and prognosisImprove efficiencyDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsSurface reactionSputtering
The present invention provides a filtration chamber comprising a microfabricated filter enclosed in a housing, wherein the surface of said filter and / or the inner surface of said housing are modified by vapor deposition, sublimation, vapor-phase surface reaction, or particle sputtering to produce a uniform coating; and a method for separating cells of a fluid sample, comprising: a) dispensing a fluid sample into the filtration chamber disclosed herein; and b) providing fluid flow of the fluid sample through the filtration chamber, wherein components of the fluid sample flow through or are retained by the filter based on the size, shape, or deformability of the components.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Apparatus and method for fluid injection
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods and systems for electronic sequencing
ActiveUS20130096013A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsDielectrophoresisComputational biologyDNA sequencing
Owner:SEQUENCING HEALTH INC
Popular searches
Flow mixers Volume/mass flow measurement Chemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactors Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elements Isotope separation Biomass after-treatment Fluid speed measurement Optical light guides DNA preparation Water/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fields
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com