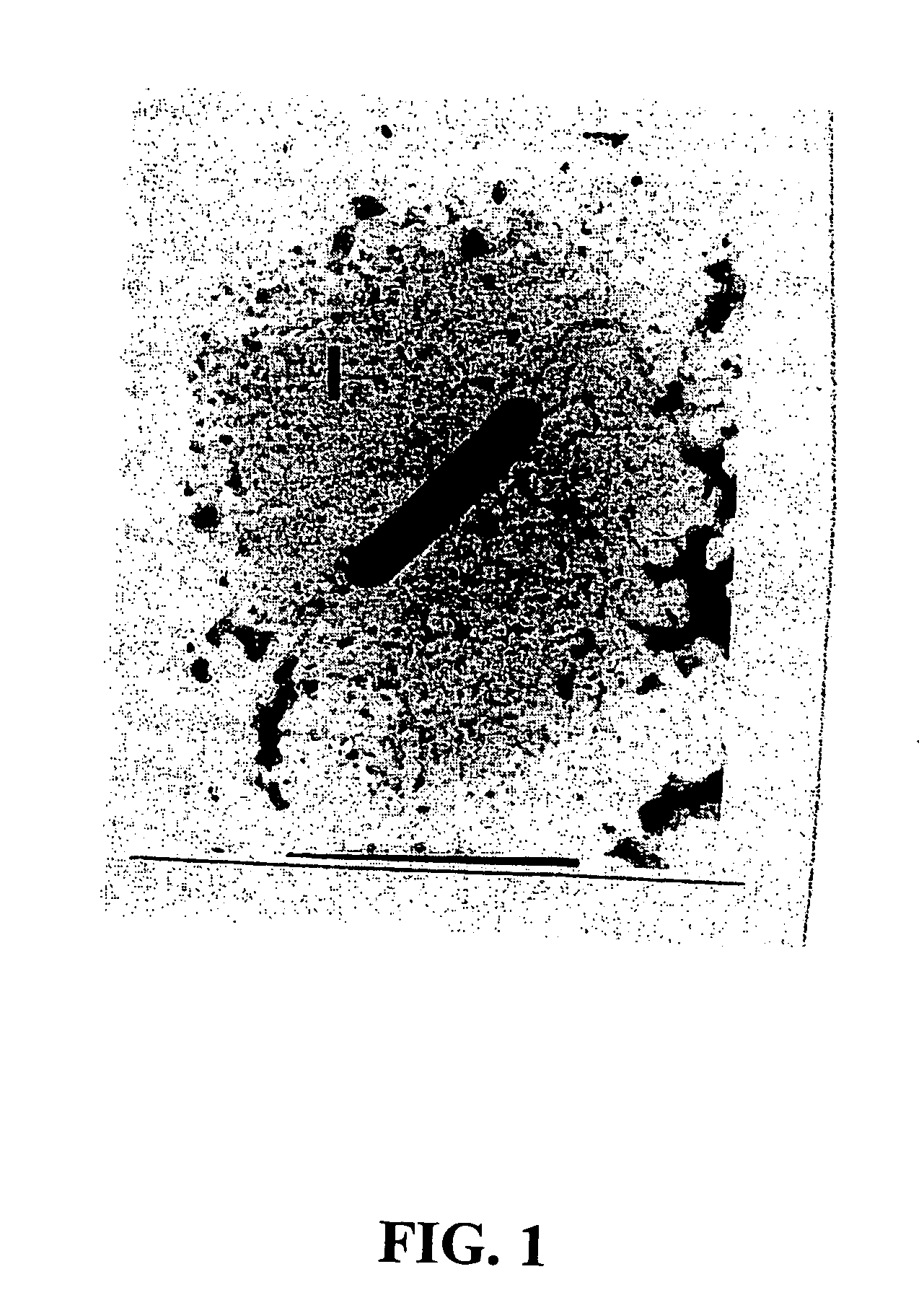
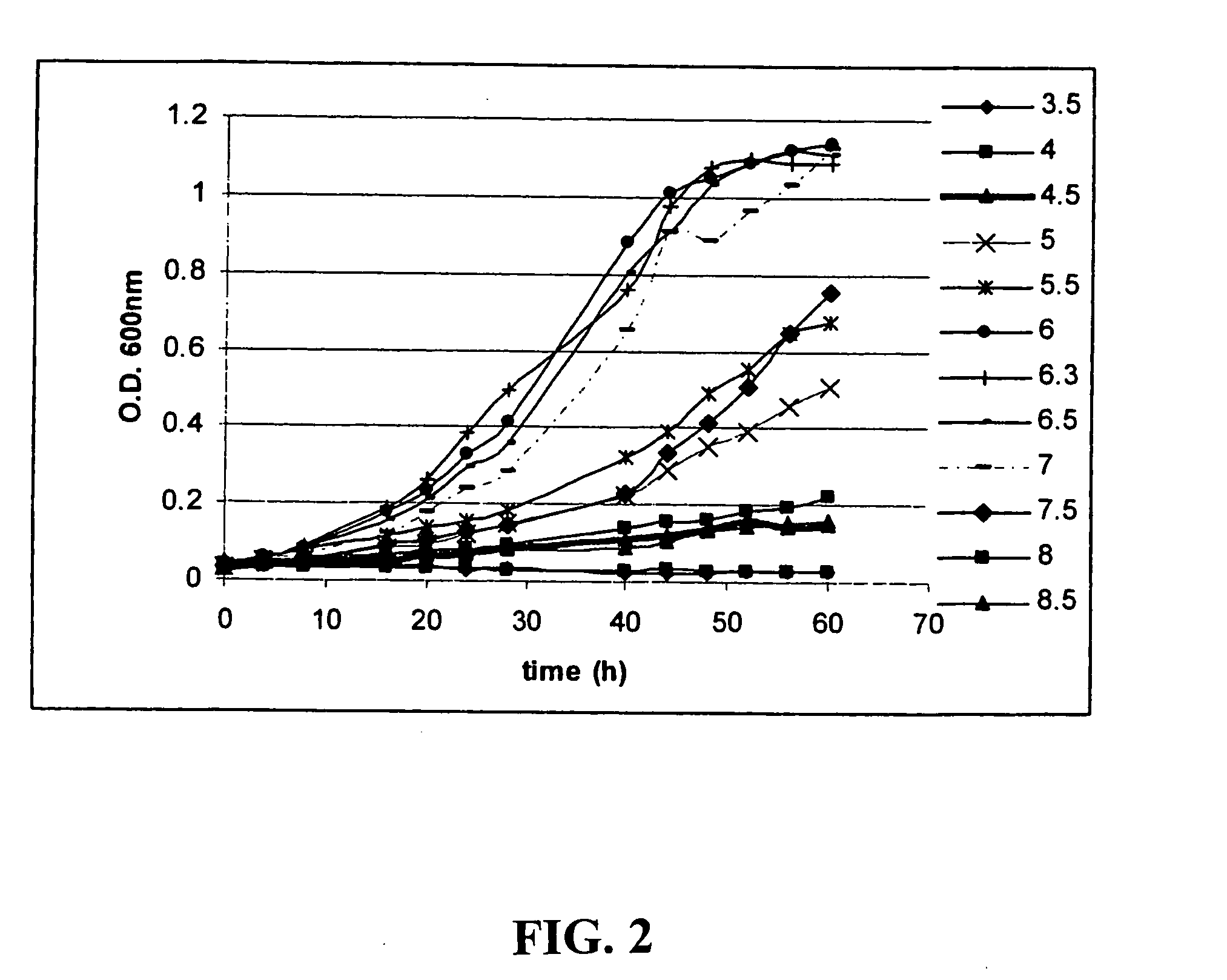
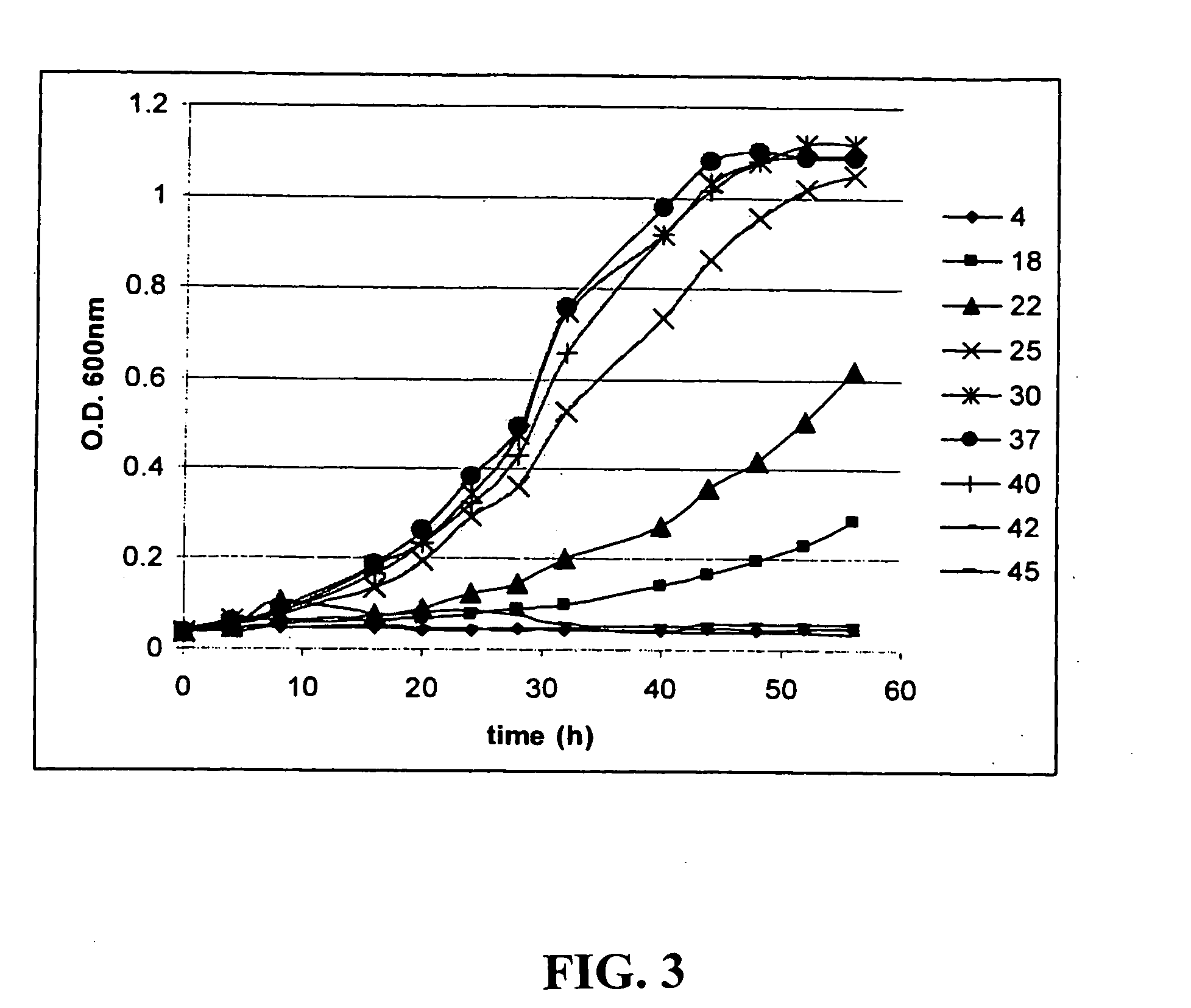
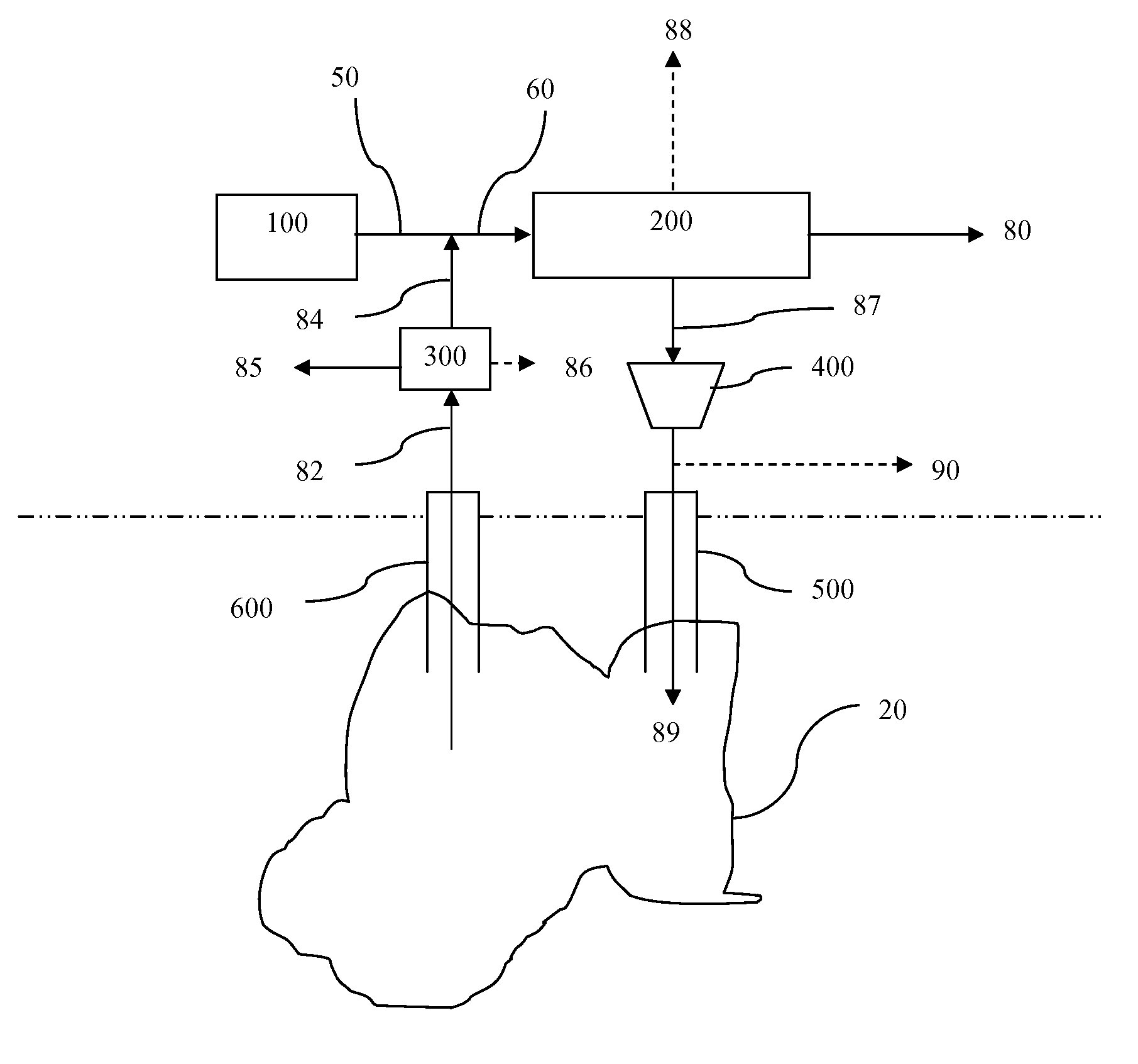
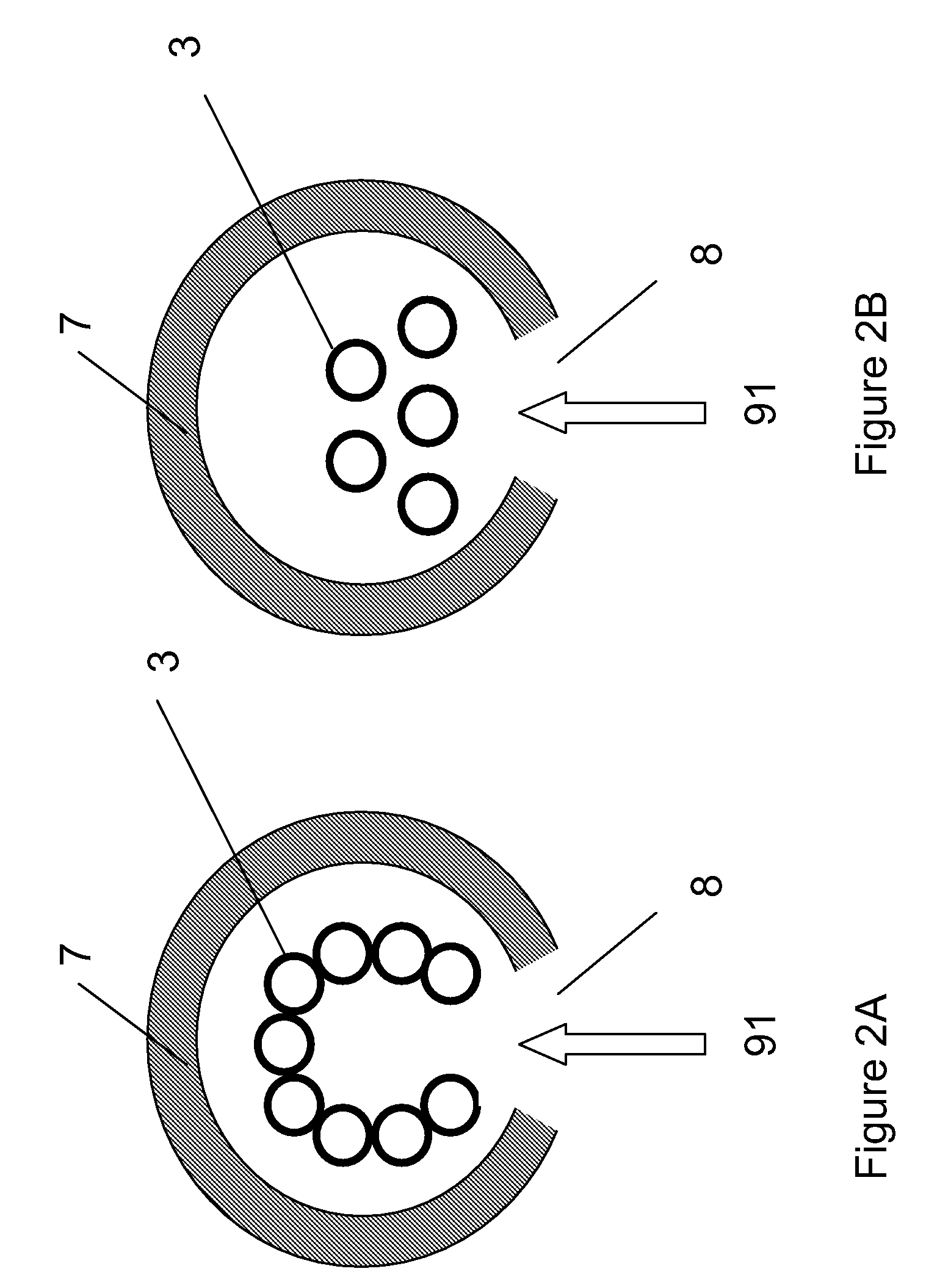
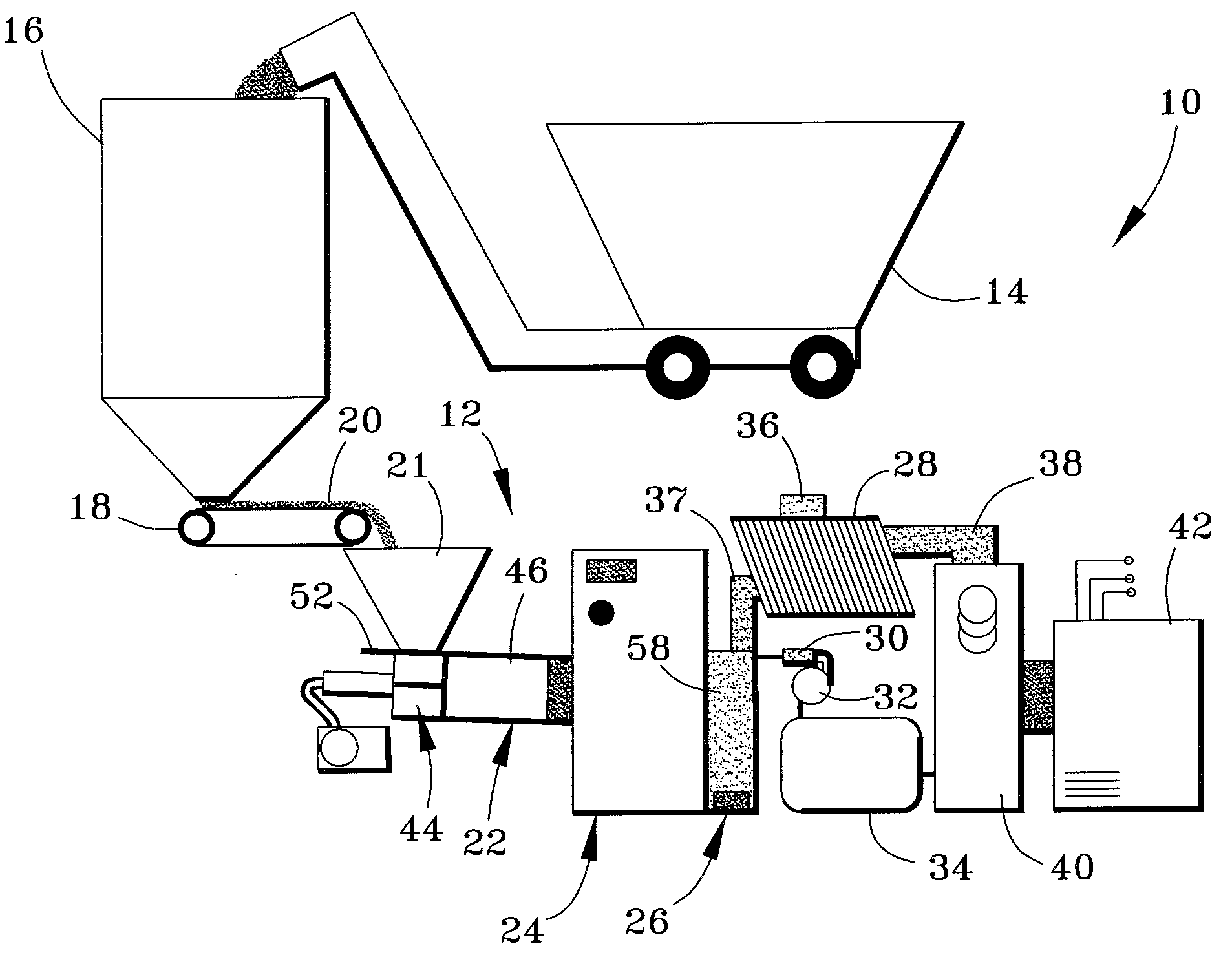
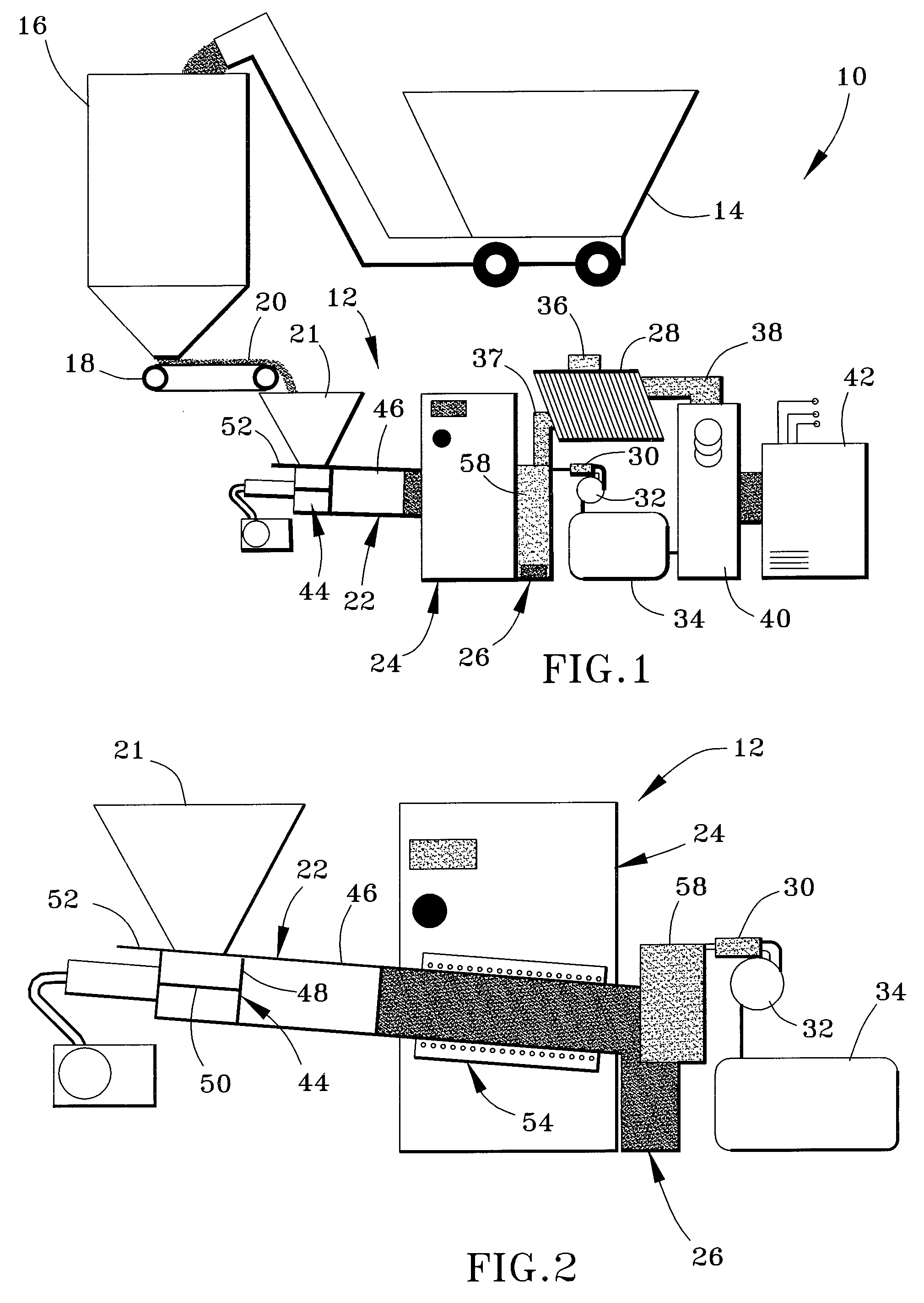
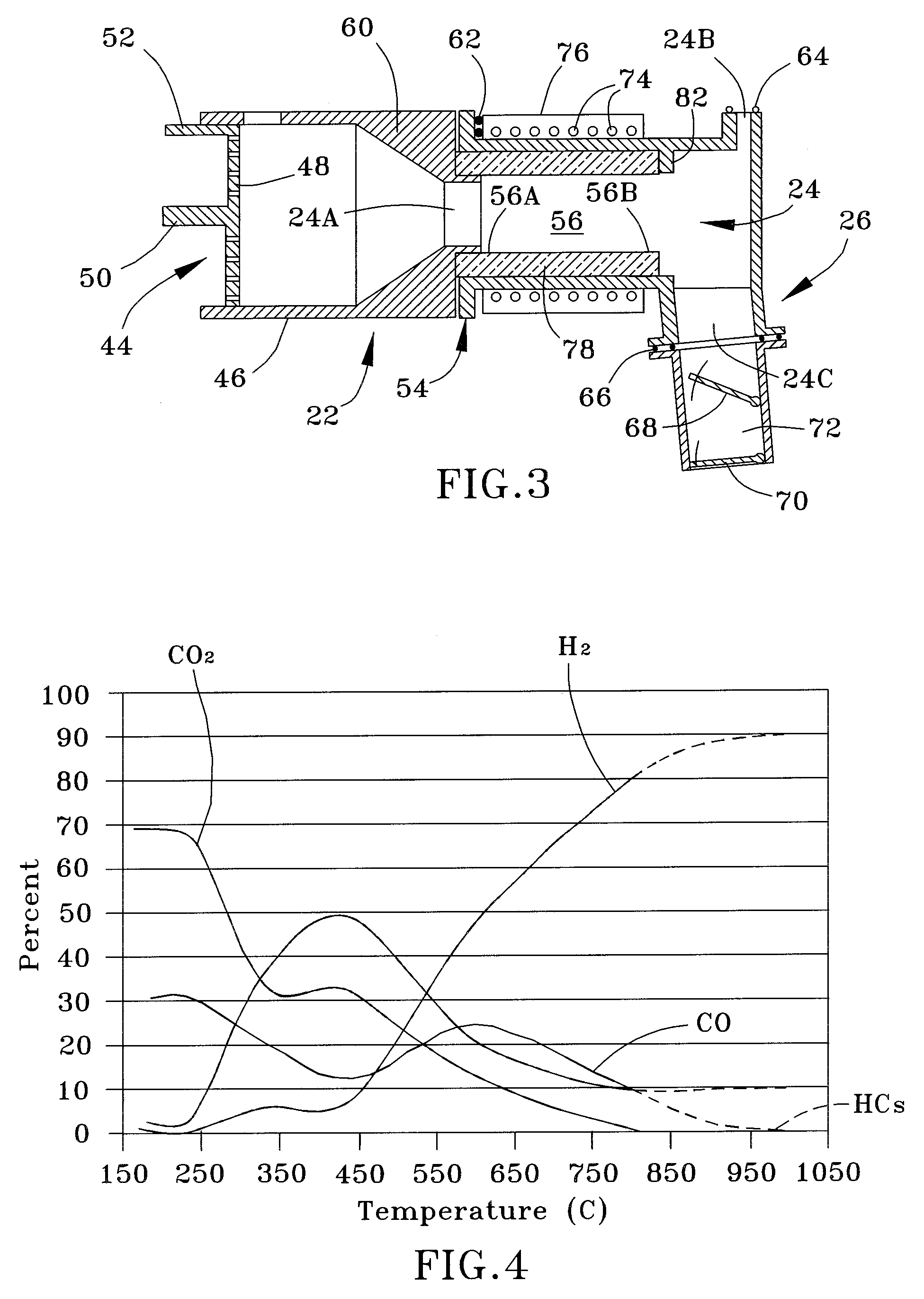
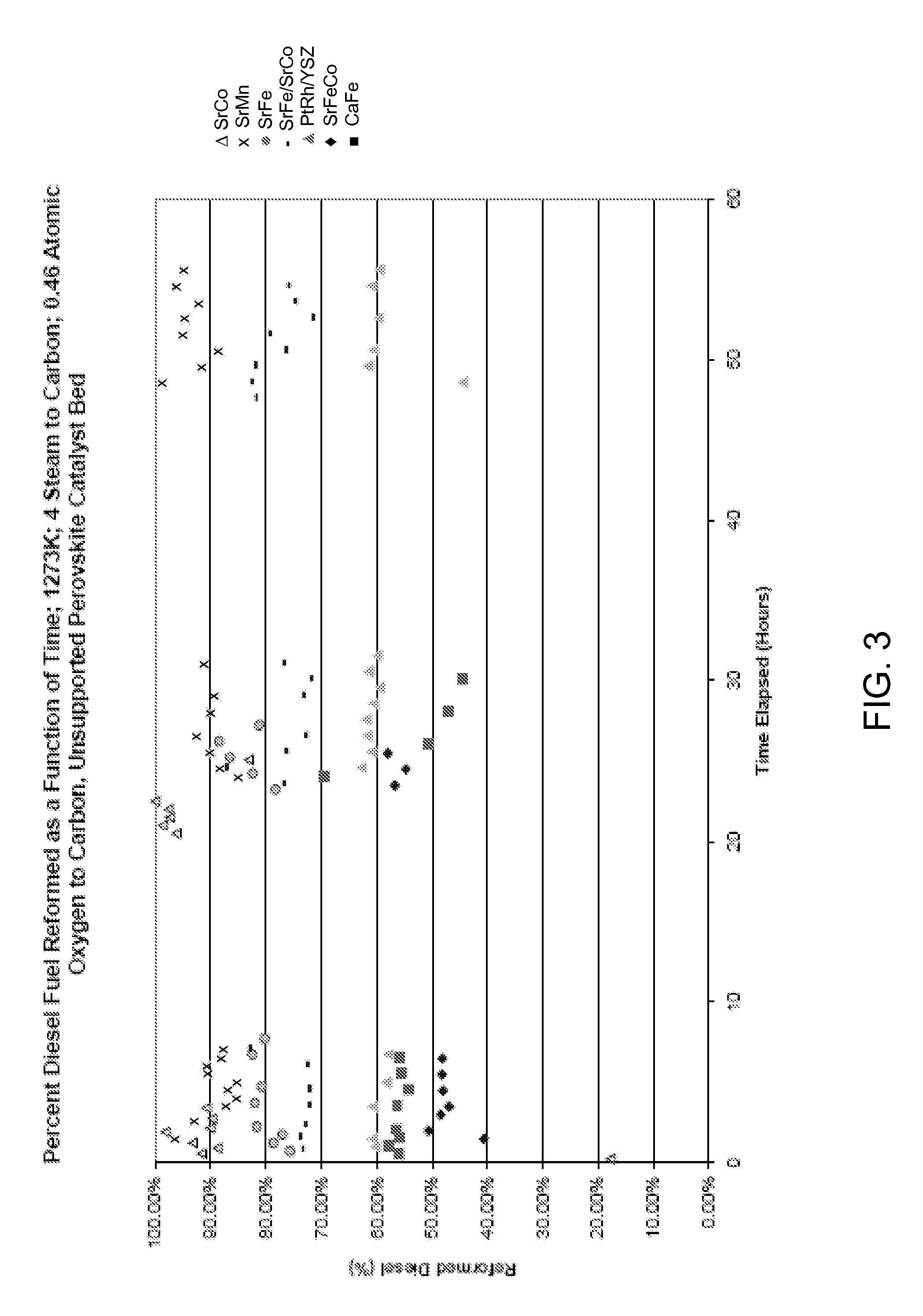
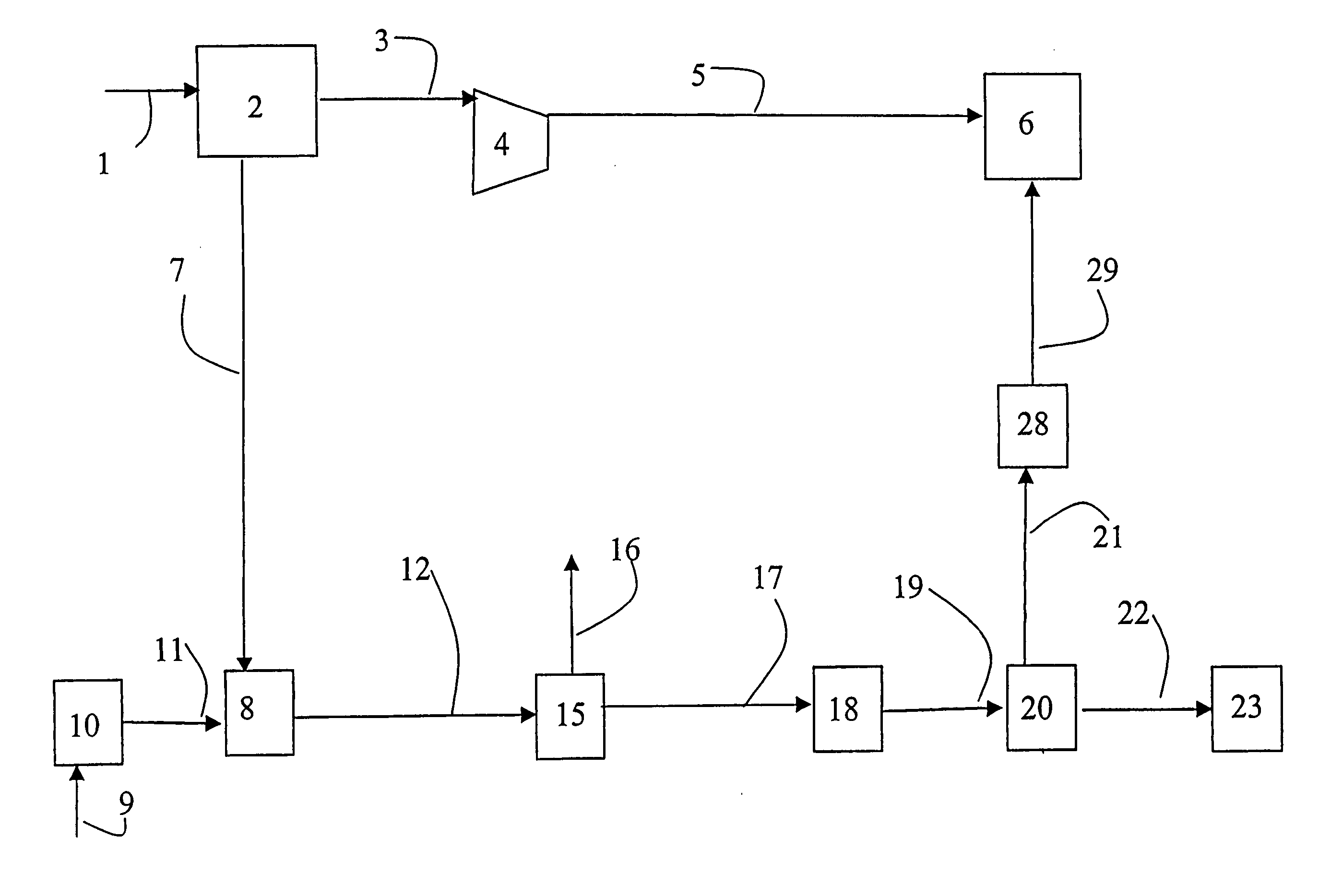
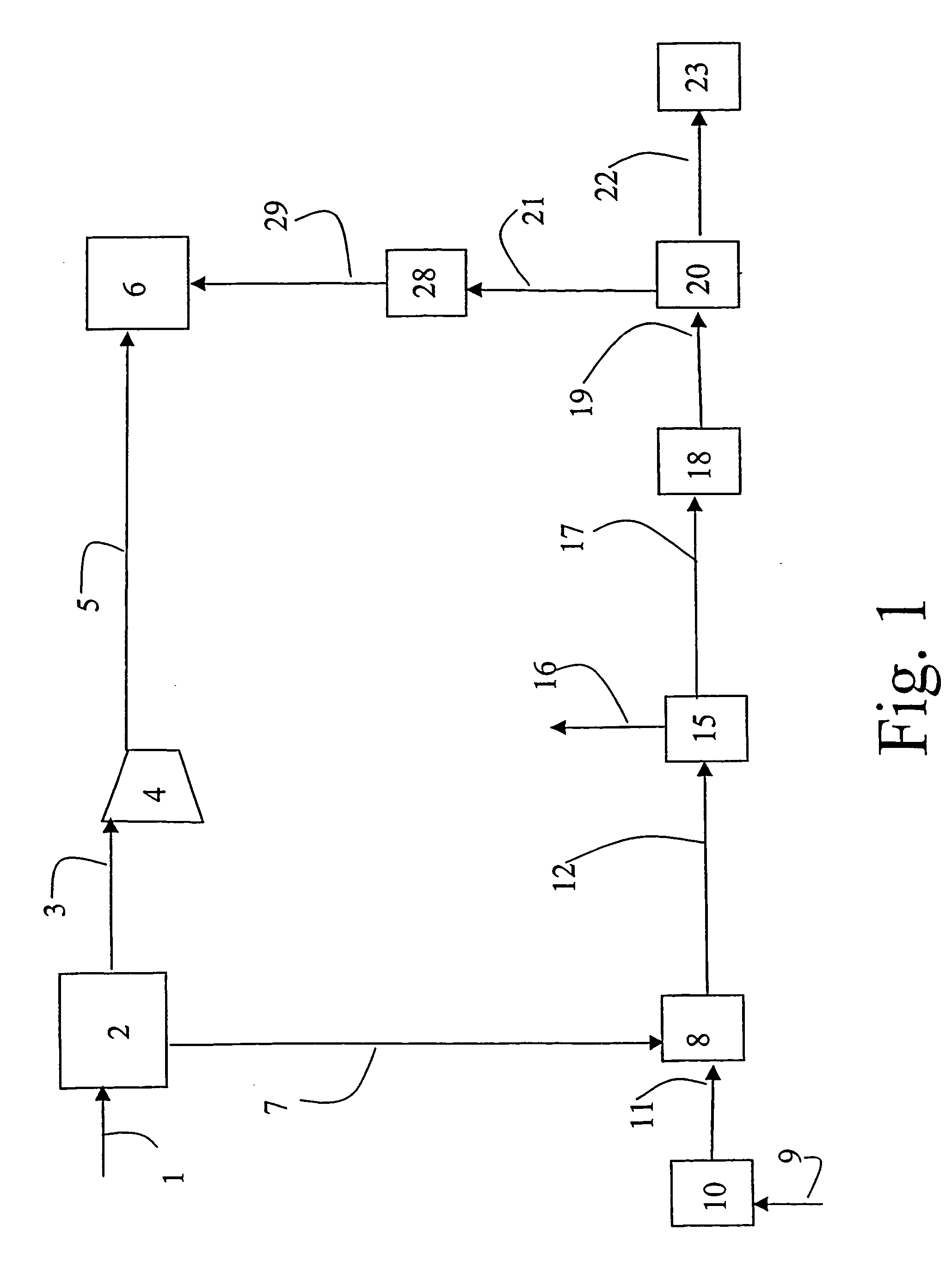
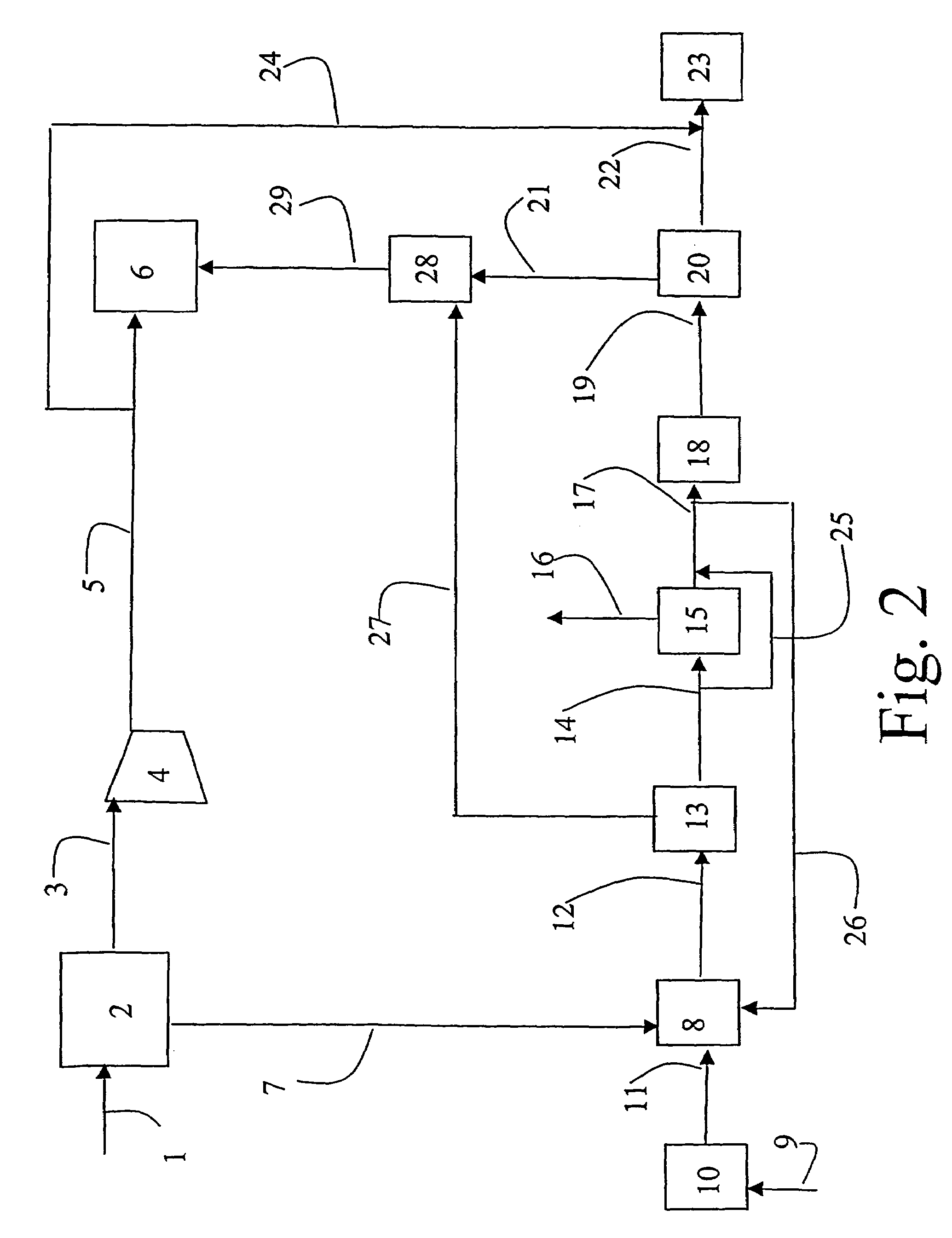
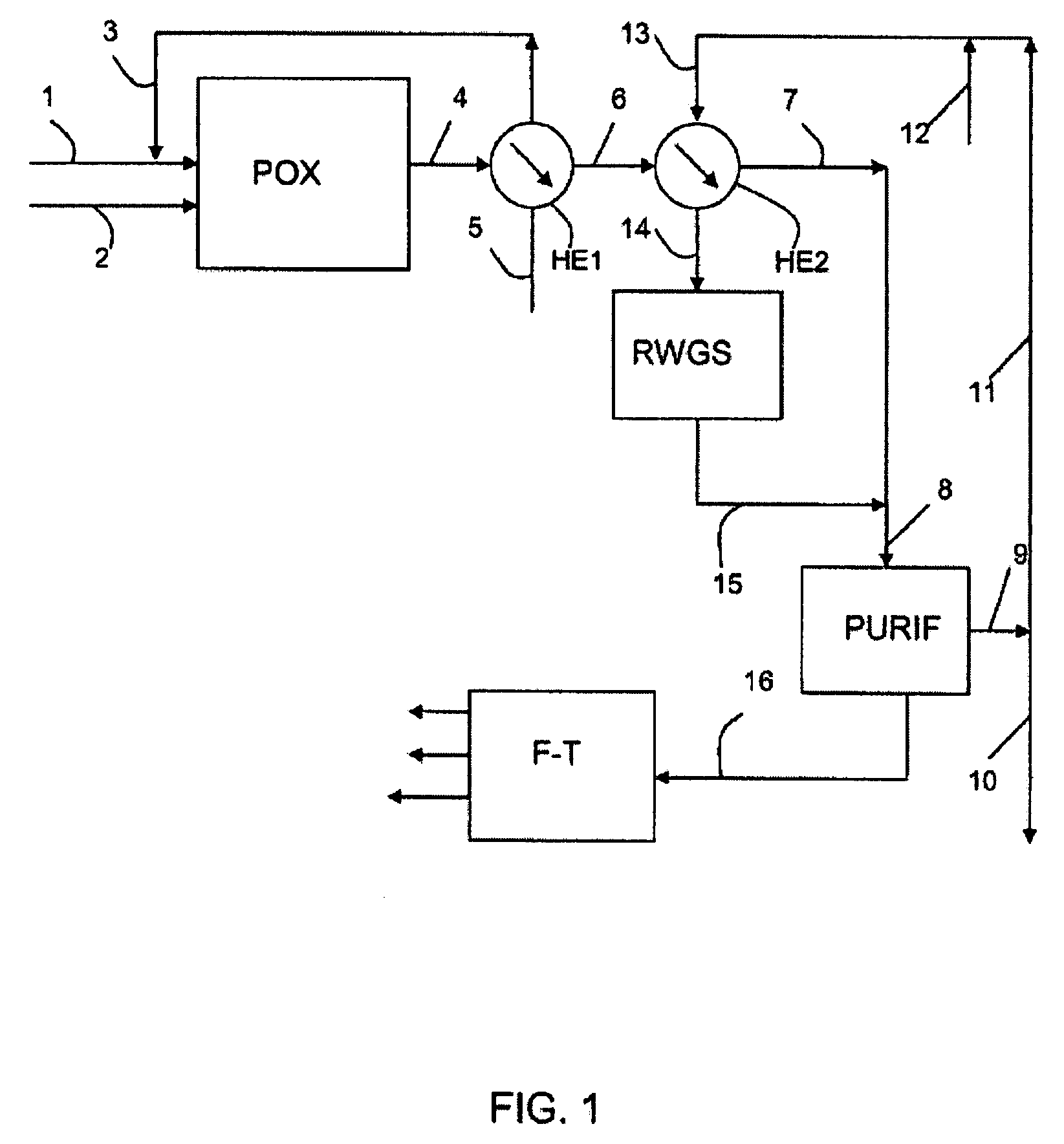
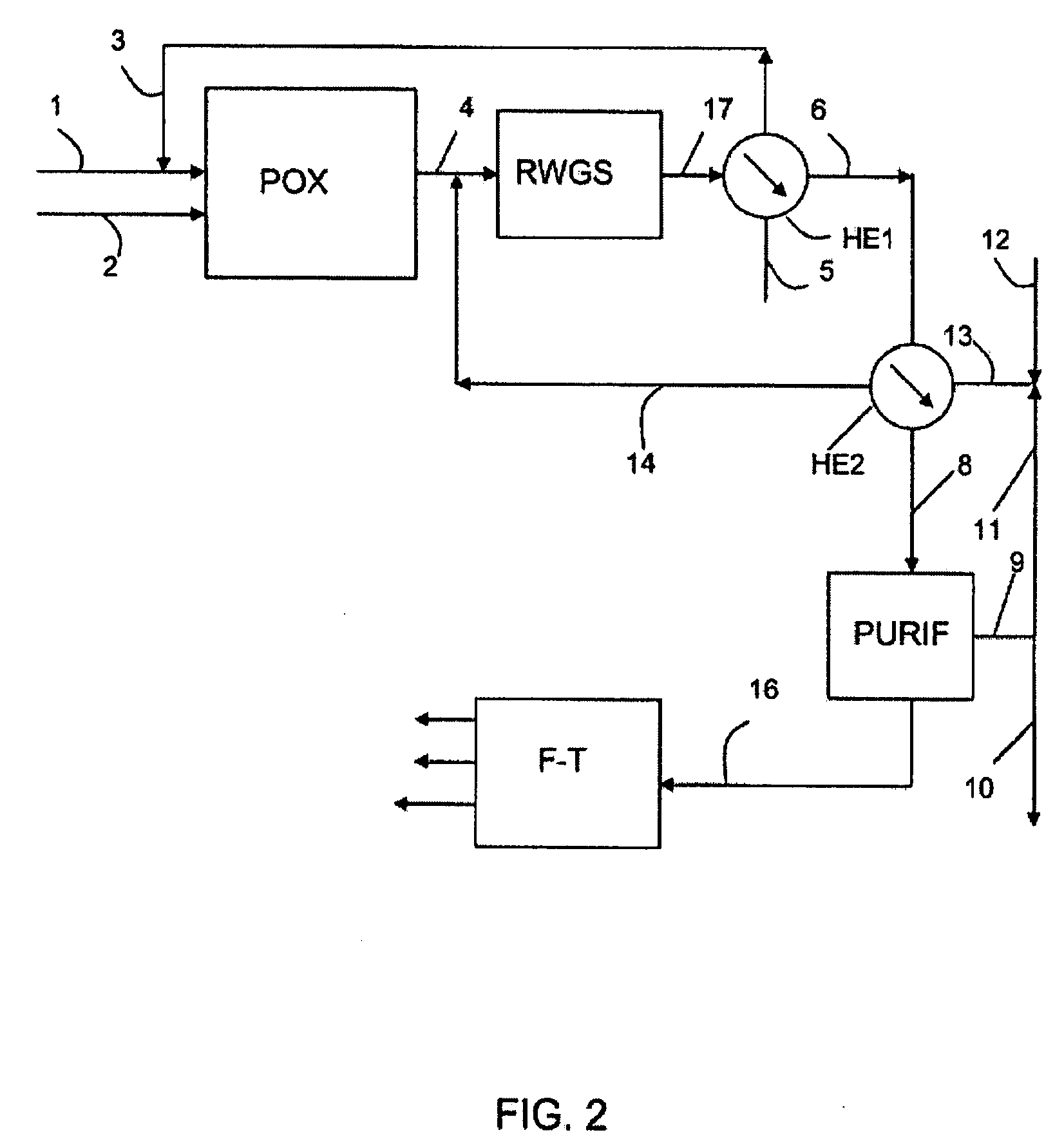
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5135 results about "Syngas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a fuel gas mixture consisting primarily of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and very often some carbon dioxide. The name comes from its use as intermediates in creating synthetic natural gas (SNG) and for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is usually a product of coal gasification and the main application is electricity generation. Syngas is combustible and can be used as a fuel of internal combustion engines. Historically, syngas has been used as a replacement for gasoline, when gasoline supply has been limited; for example, wood gas was used to power cars in Europe during WWII (in Germany alone half a million cars were built or rebuilt to run on wood gas). Syngas, however, has less than half the energy density of natural gas.
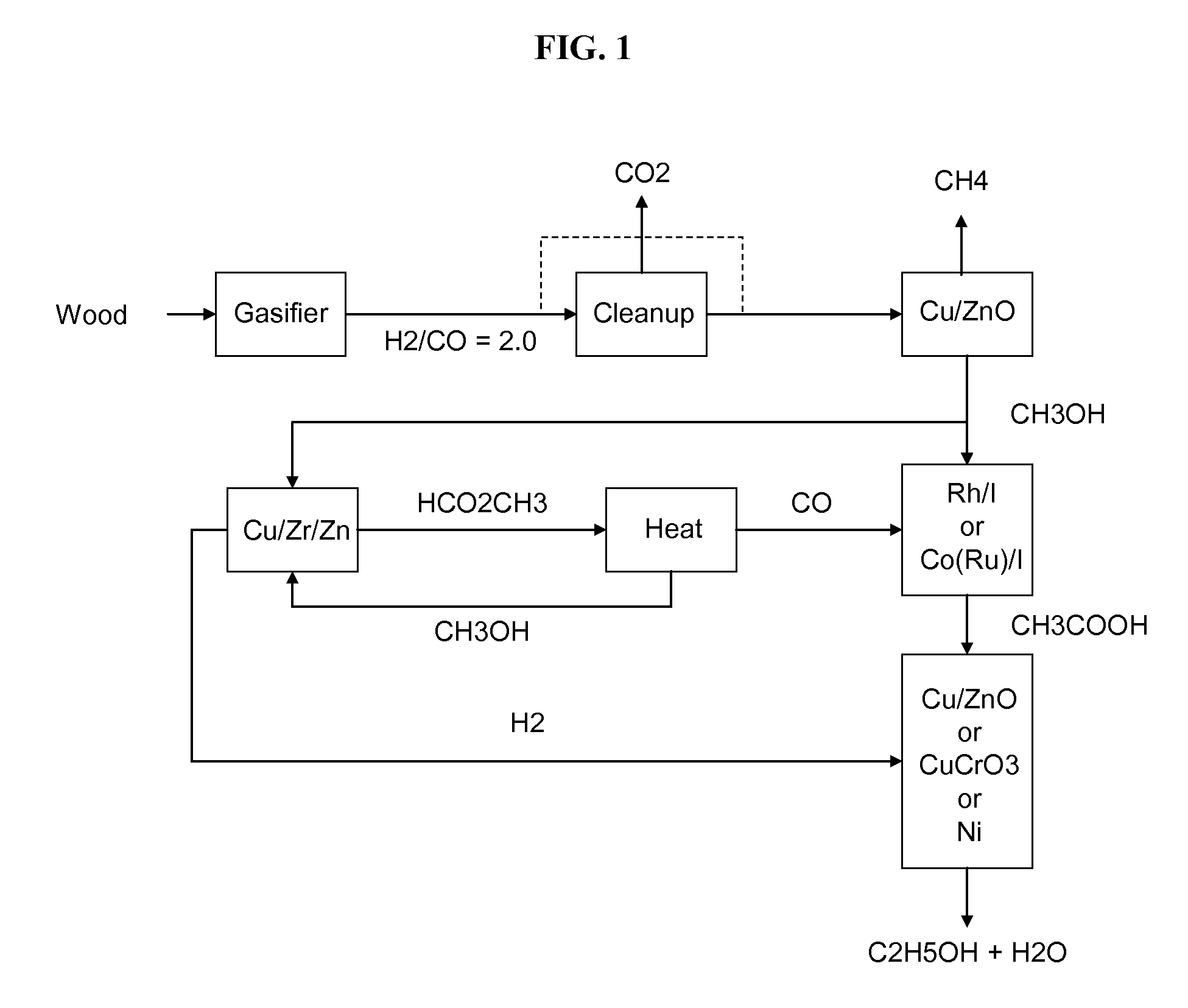
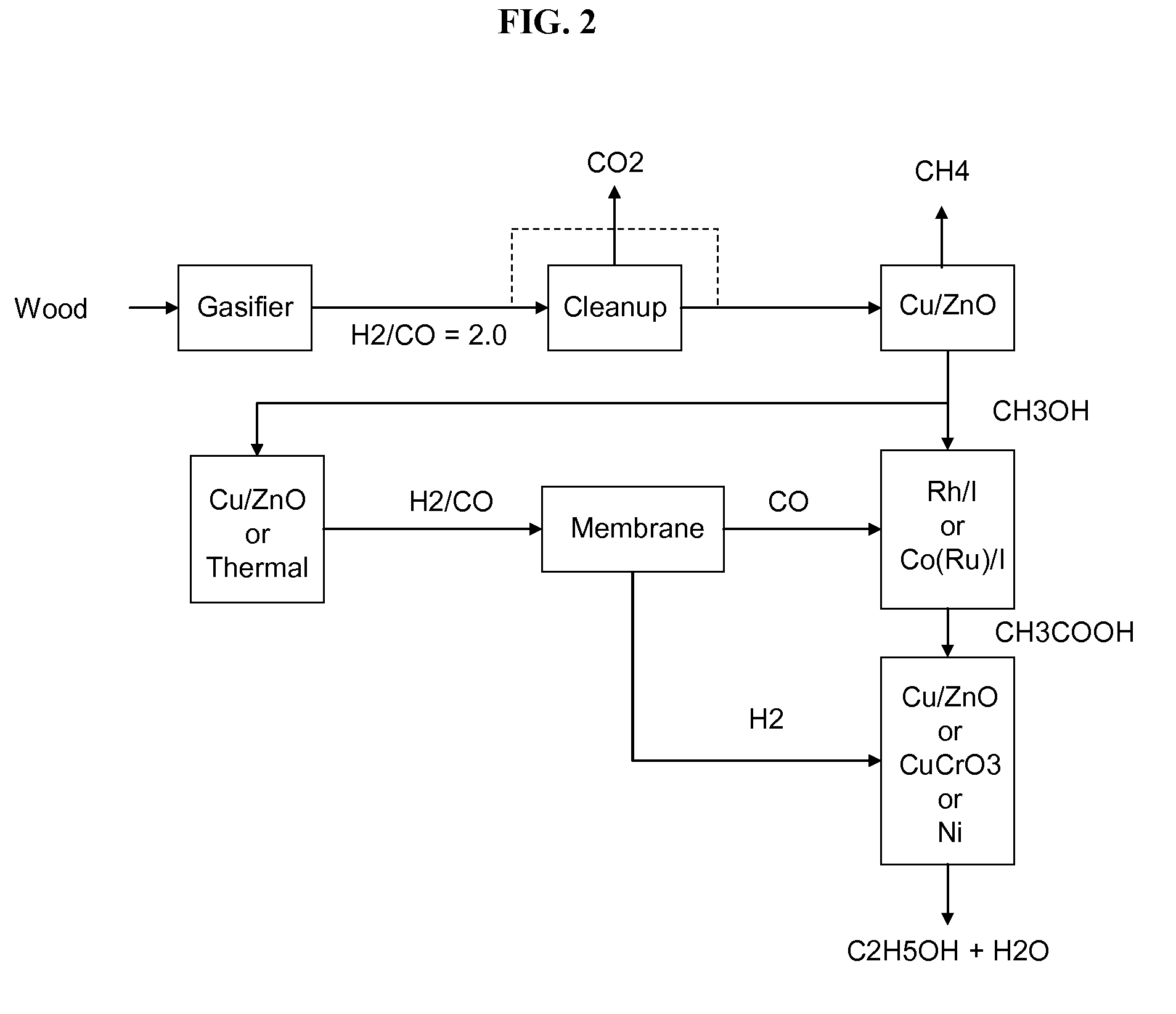
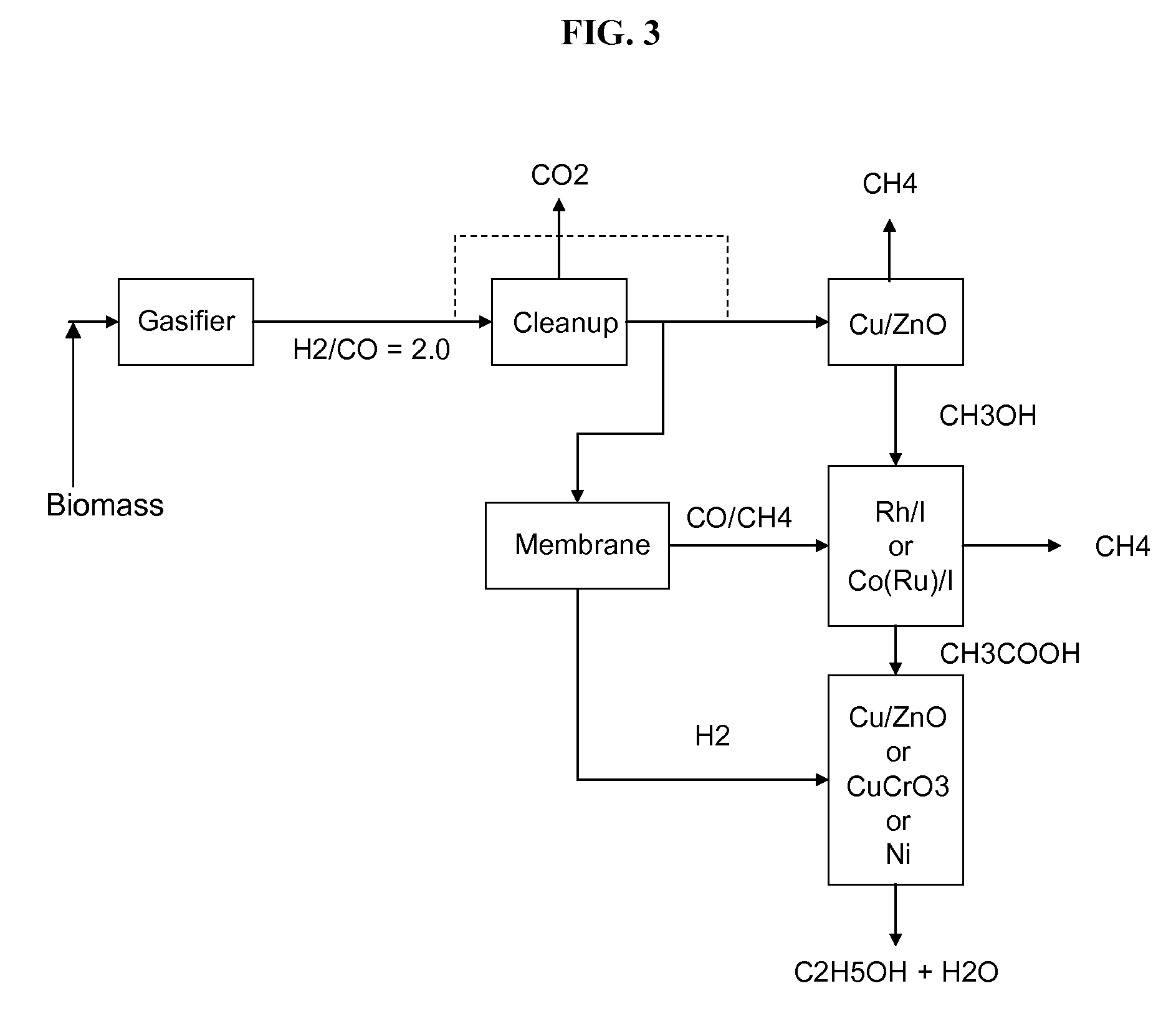
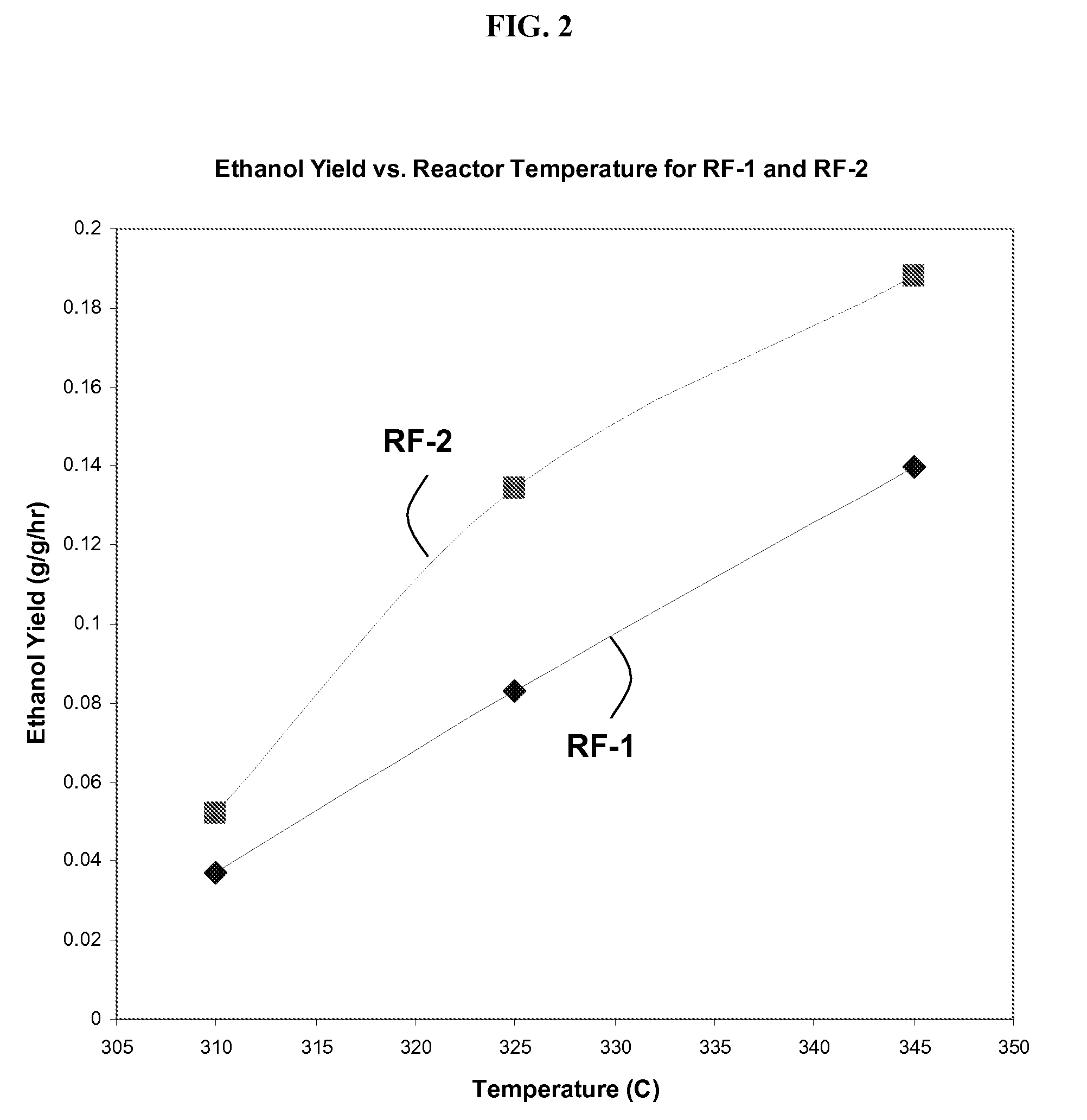
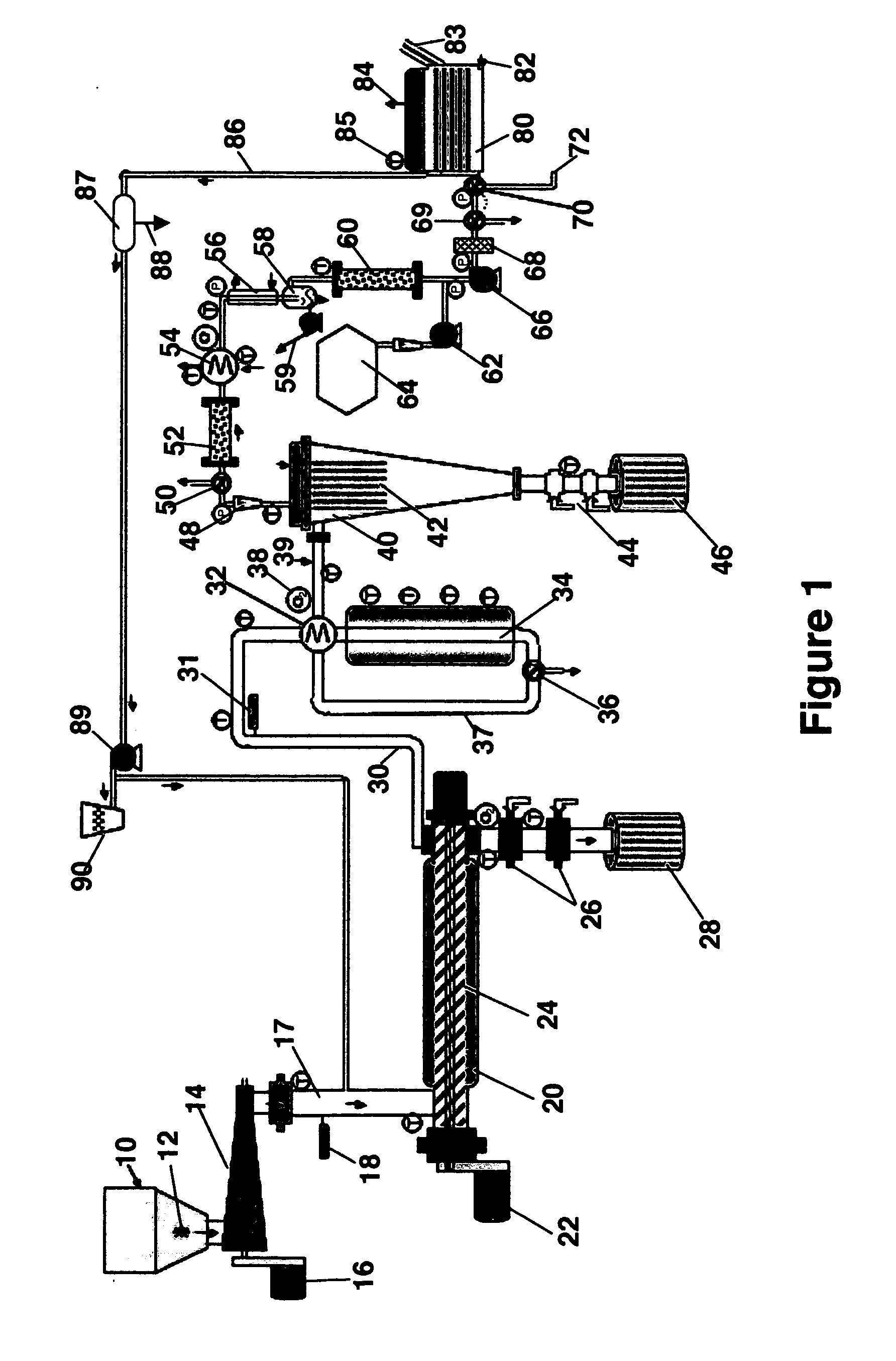
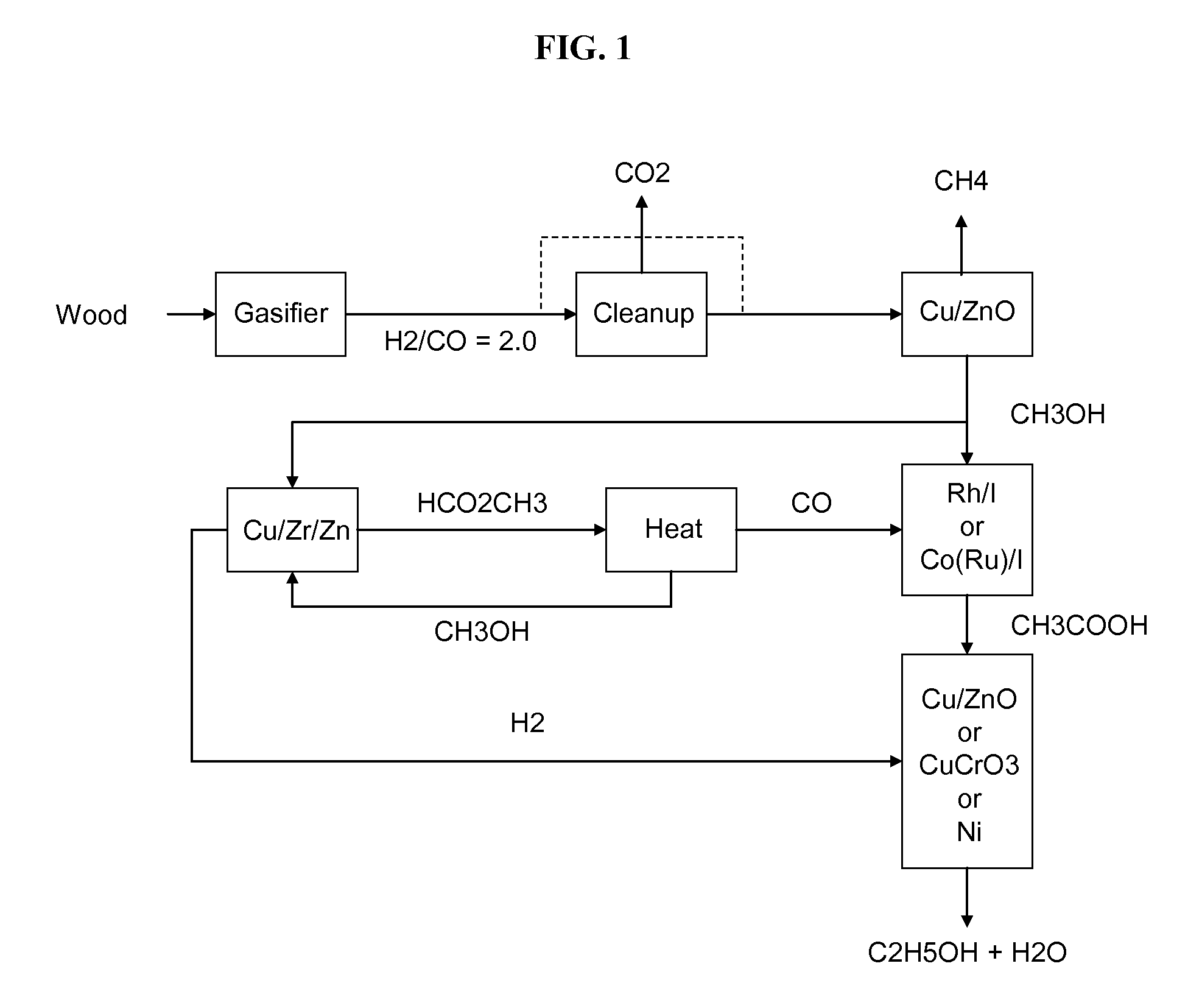
Methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from synthesis gas
The invention provides methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from syngas. As disclosed herein, syngas derived from cellulosic biomass (or other sources) can be catalytically converted into methanol, which in turn can be catalytically converted into acetic acid or acetates. Finally, the acetic acid or acetates can be reduced to ethanol according to several variations. In some embodiments, yields of ethanol from biomass can exceed 100 gallons per dry ton of biomass.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Indirect or direct fermentation of biomass to fuel alcohol
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium carboxidivorans, ATCC BAA-624, “P7”) is provided. P7 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P7 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium can transform waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P7 also catalyzes the production of acetate and butanol. Further, P7 is also capable of directly fermenting lignocellulosic materials to produce ethanol and other substances.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA +1
Cobalt-molybdenum sulfide catalyst materials and methods for ethanol production from syngas
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the chemical conversion of syngas to alcohols. The invention includes catalyst compositions, methods of making the catalyst compositions, and methods of using the catalyst compositions. Certain embodiments teach compositions for catalyzing the conversion of syngas into products comprising at least one C1-C4 alcohol, such as ethanol. These compositions generally include cobalt, molybdenum, and sulfur. Preferred catalyst compositions for converting syngas into alcohols include cobalt associated with sulfide in certain preferred stoichiometries as described and taught herein.
Owner:ALBEMARLE CORP
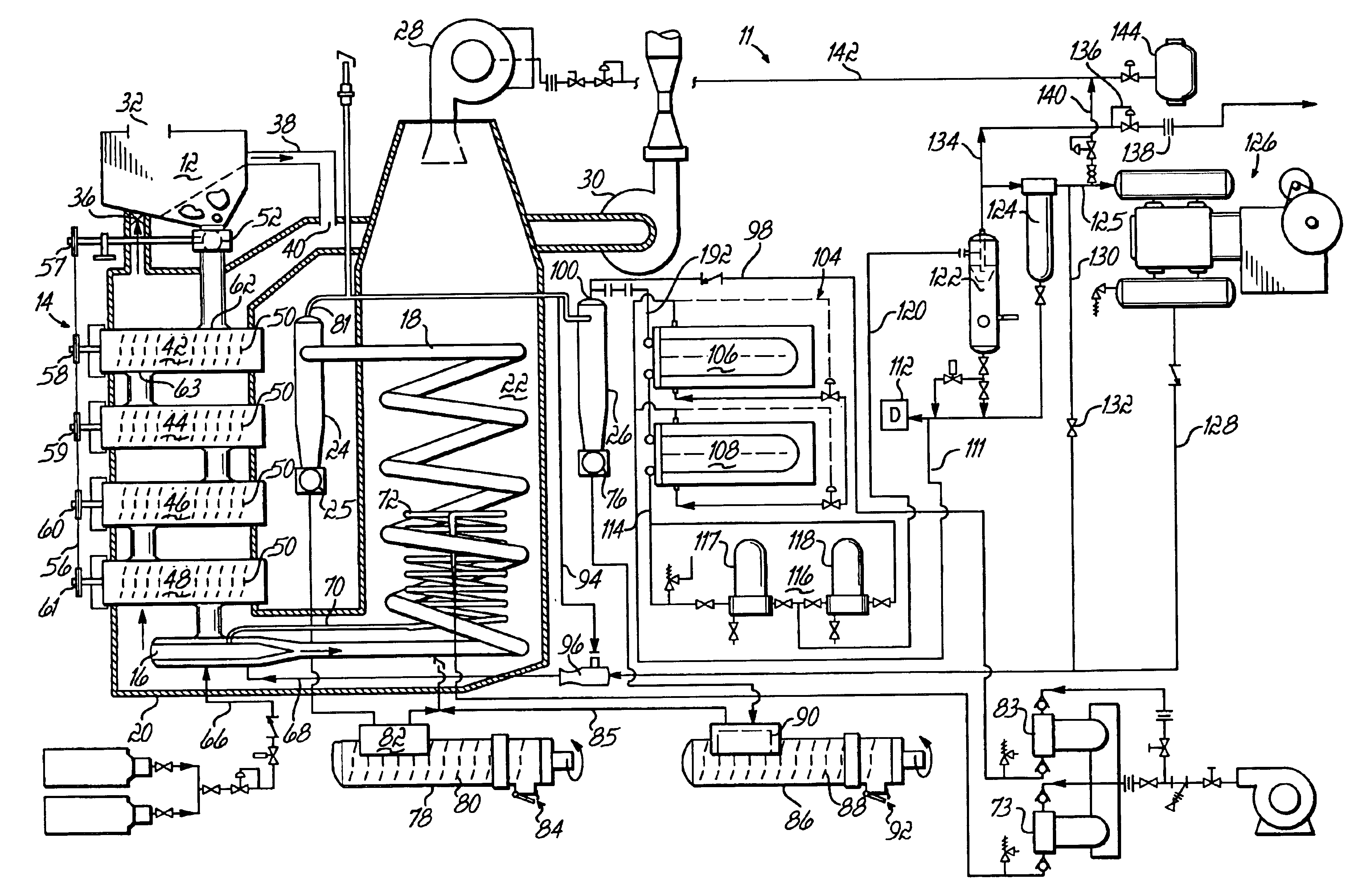
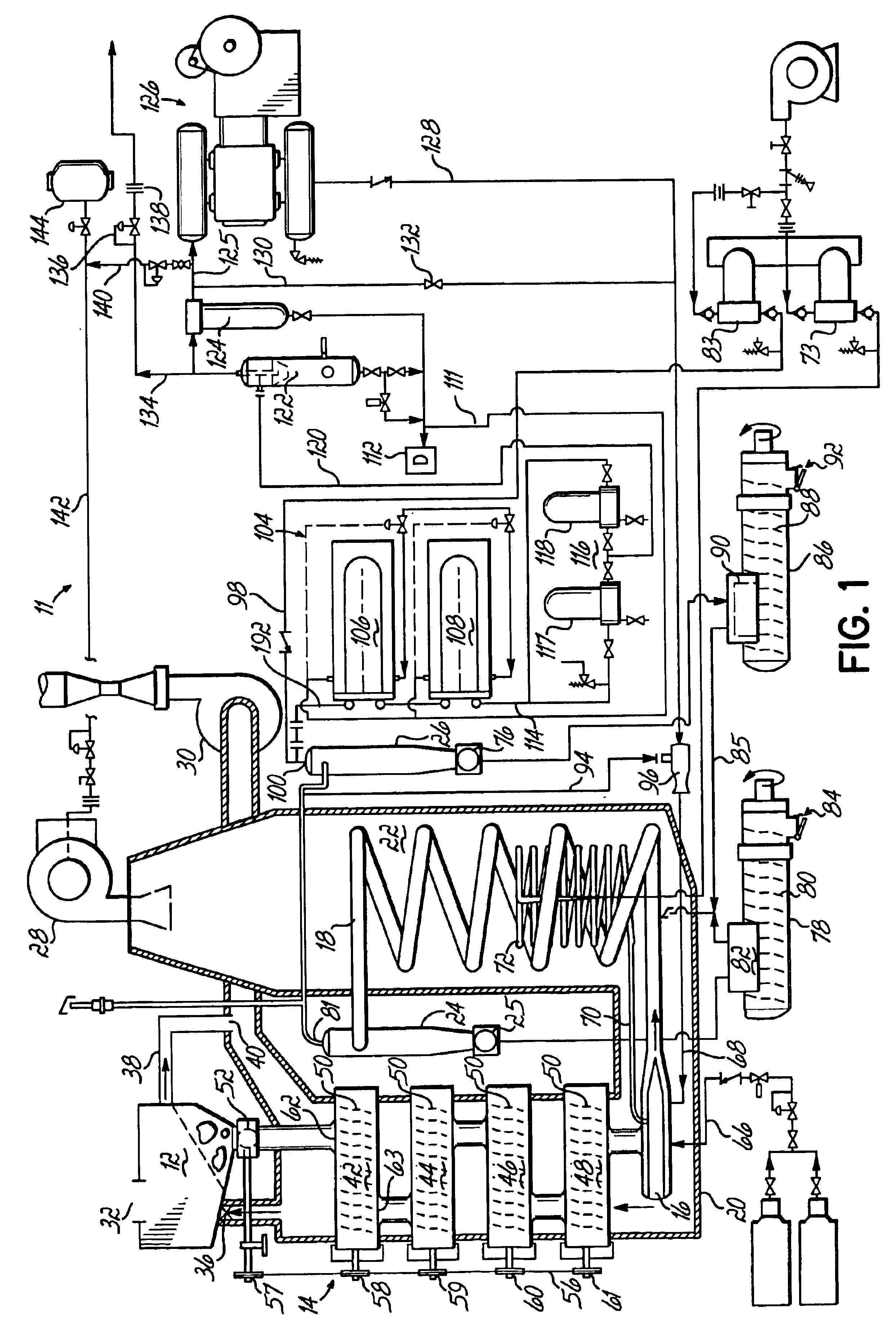
Method and apparatus for producing synthesis gas from carbonaceous materials
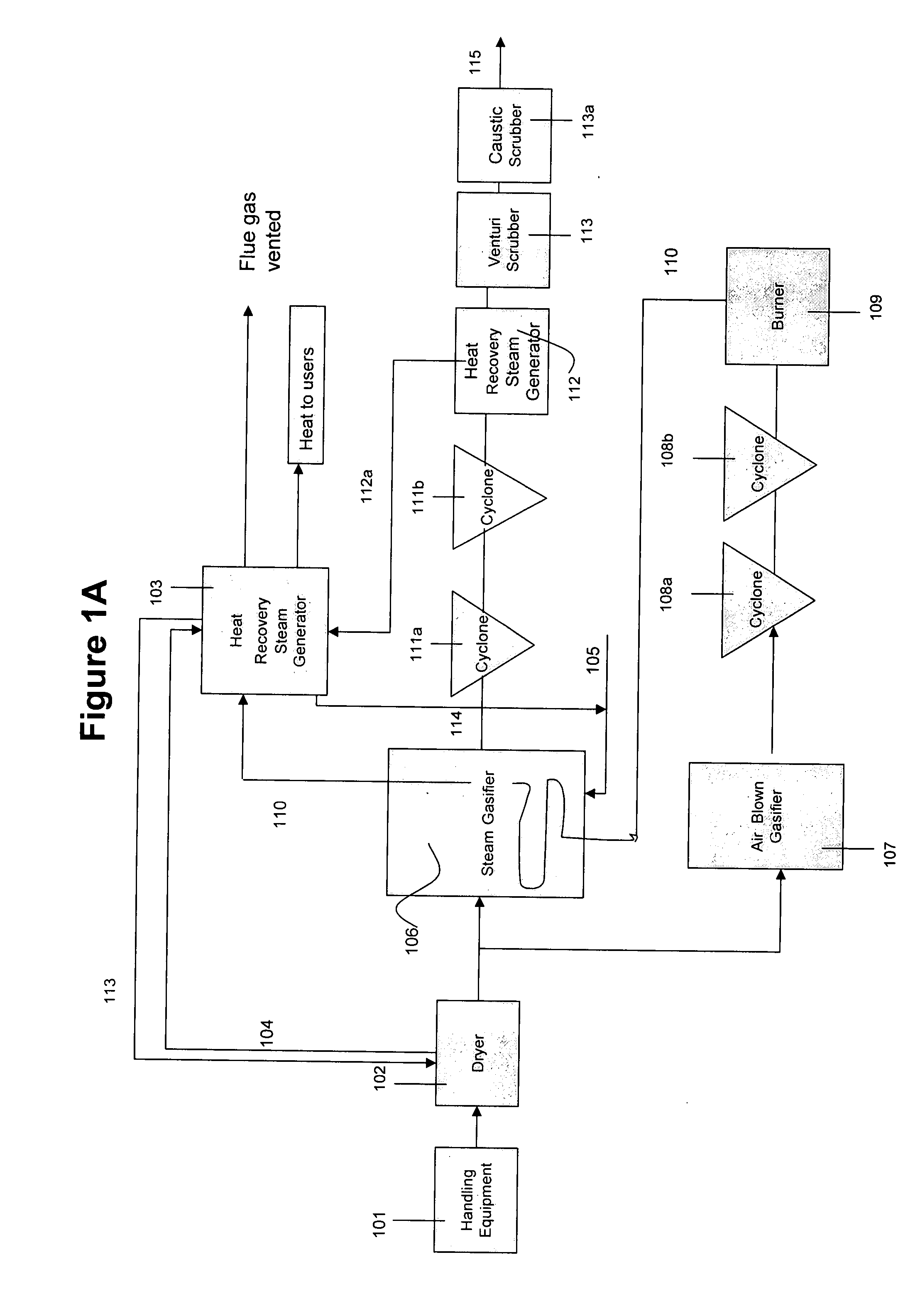
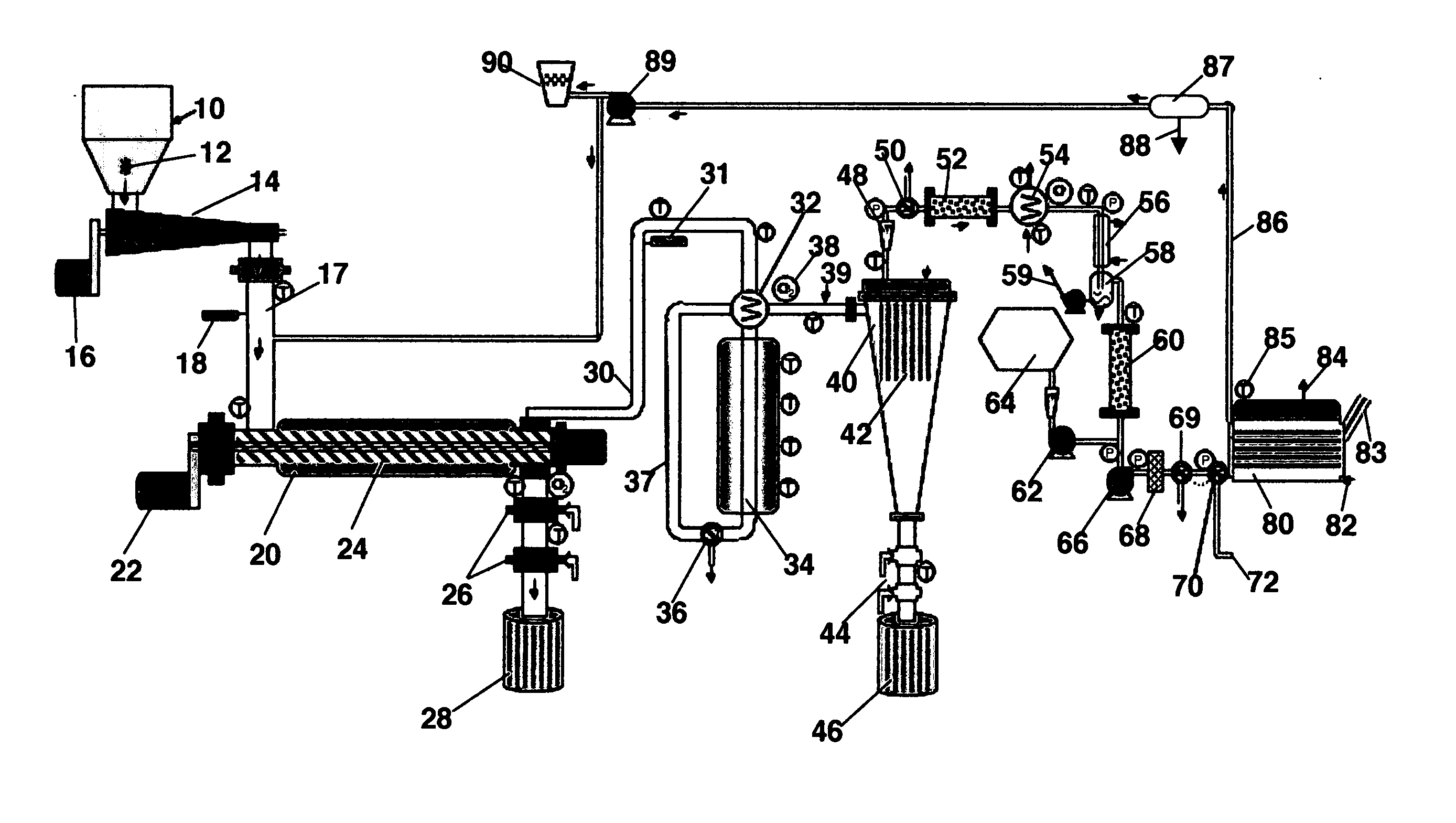
A method of producing syn gas from biomass or other carbonaceous material utilizes a controlled devolatilization reaction in which the temperature of the feed material is maintained at less than 450° F. until most available oxygen is consumed. This minimizes pyrolysis of the feed material. The method and apparatus utilizes the formed synthesis gas to provide the energy for the necessary gasification. This provides for a high purity syn gas and avoids production of slag.
Owner:JBK EXTRACTIONS
System and method for converting biomass to ethanol via syngas
A method and apparatus for synthesizing ethanol using synthetic routes via synthesis gas are disclosed. A method and apparatus for gasifying biomass, such as biomass, in a steam gasifier that employs a fluidized bed and heating using hot flue gases from the combustion of synthesis gas is described. Methods and apparatus for converting synthesis gas into ethanol are also disclosed, using stepwise catalytic reactions to convert the carbon monoxide and hydrogen into ethanol using catalysts including iridium acetate.
Owner:WOODLAND BIOFUELS
Pressure swing reforming
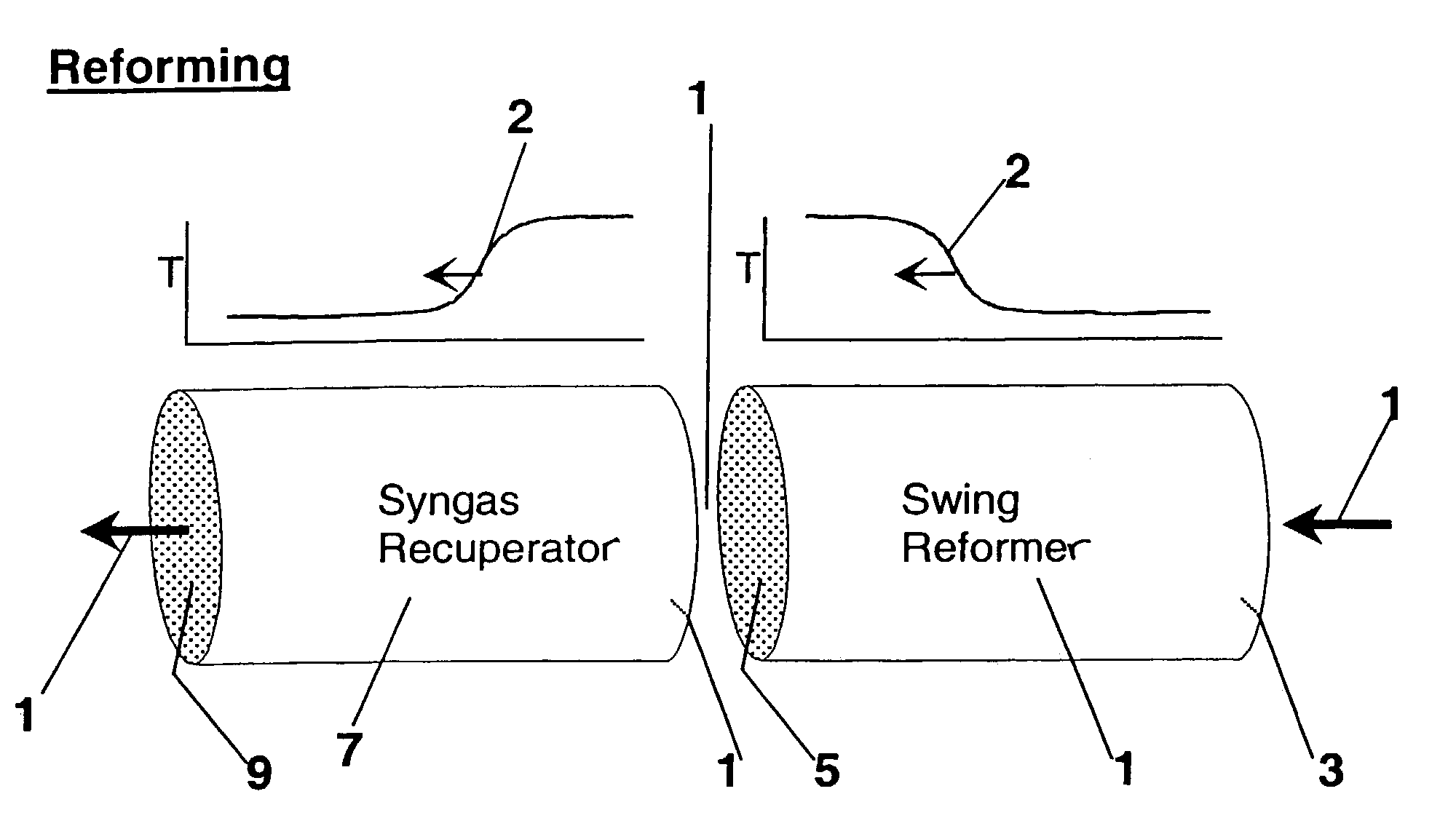
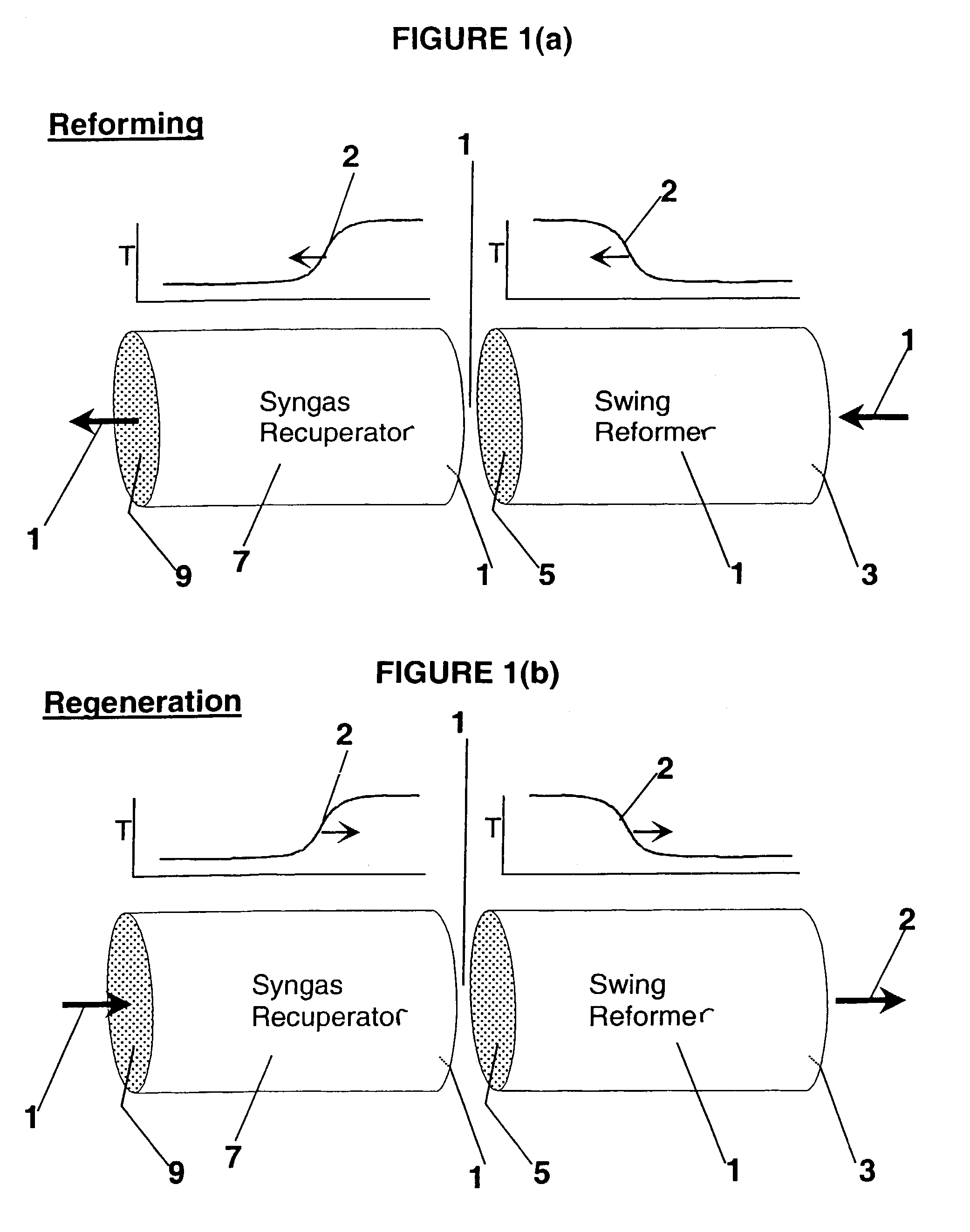
Synthesis gas is produced though a cyclic method where the first step of the cycle includes reforming a hydrocarbon feed over a catalyst to synthesis gas in a first zone of a bed and the second step reheats this first zone. A hydrocarbon feed is introduced to a bed along with CO2 and optionally steam where it is reformed into synthesis gas. The synthesis gas is collected at a second zone of the bed and an oxygen-containing gas is then introduced to this second zone of the bed and combusted with a fuel, thereby reheating the first zone to sufficient reforming temperatures. Additionally, a non-combusting gas can also be introduced to the second zone to move heat from the second zone to the first zone.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Hybrid catalyst system for exhaust emissions reduction
InactiveUS20060010857A1Improve efficiencySpeed up the conversion processHydrogenGas treatmentExhaust fumesEngineering
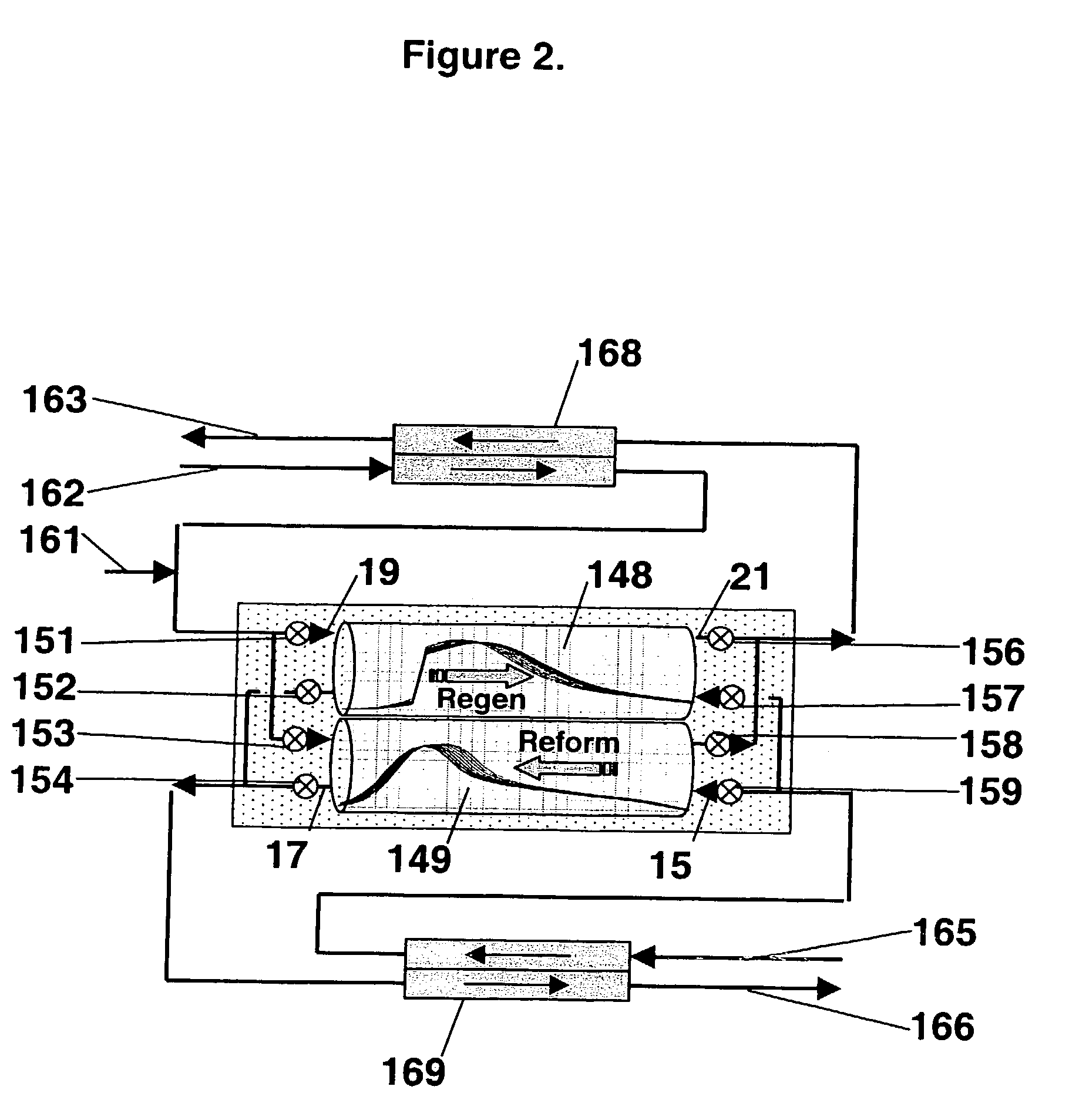
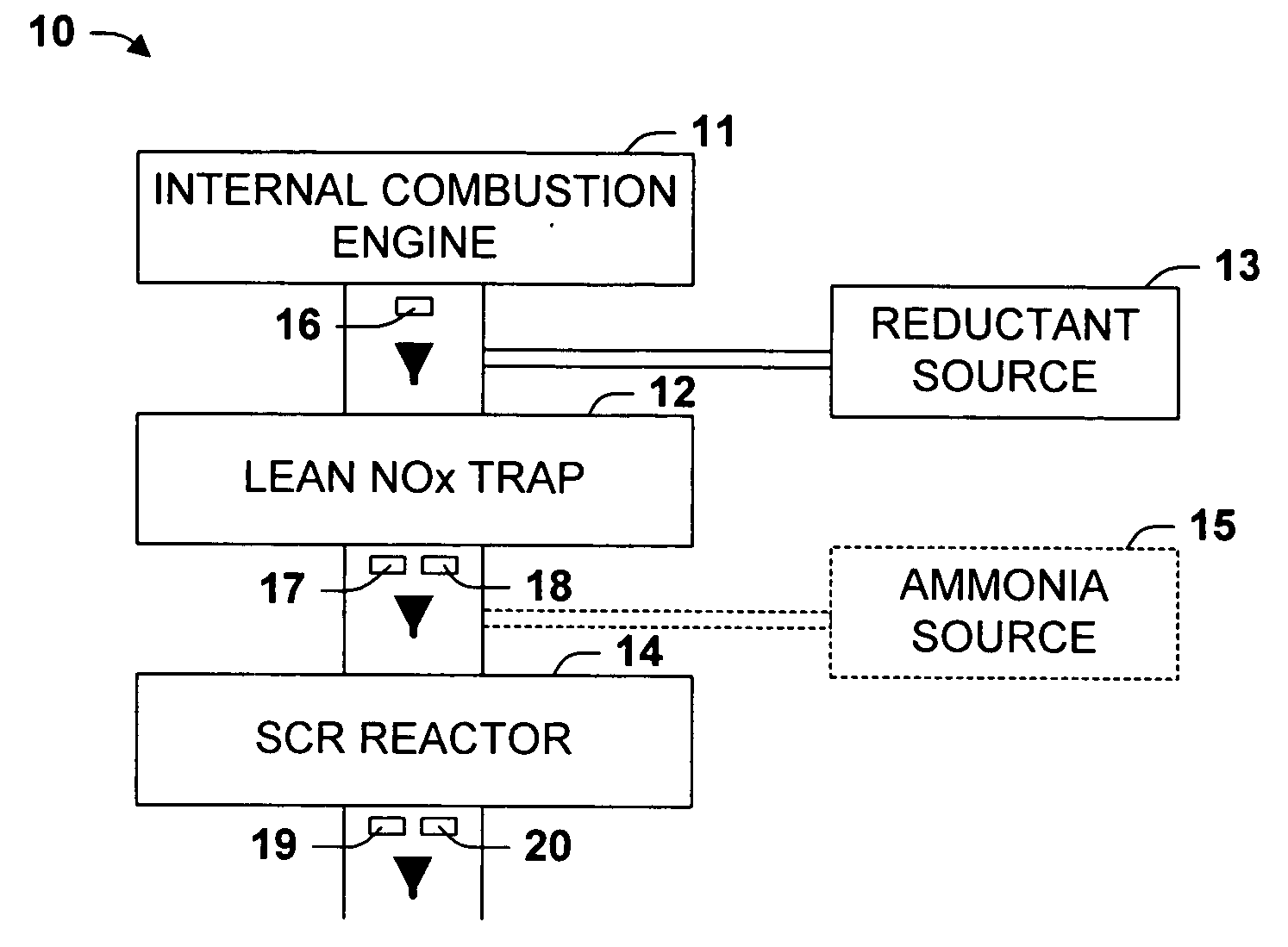
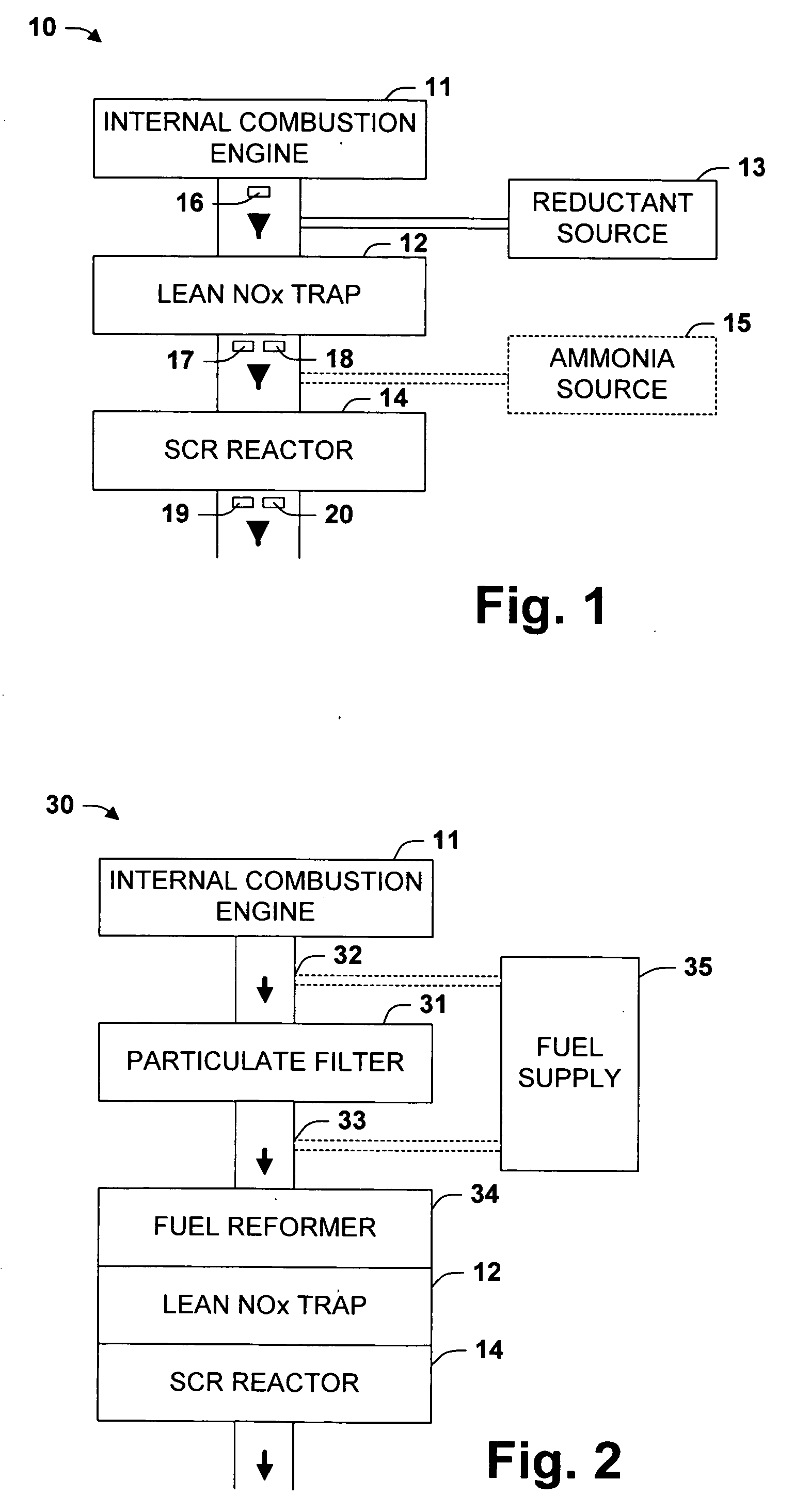
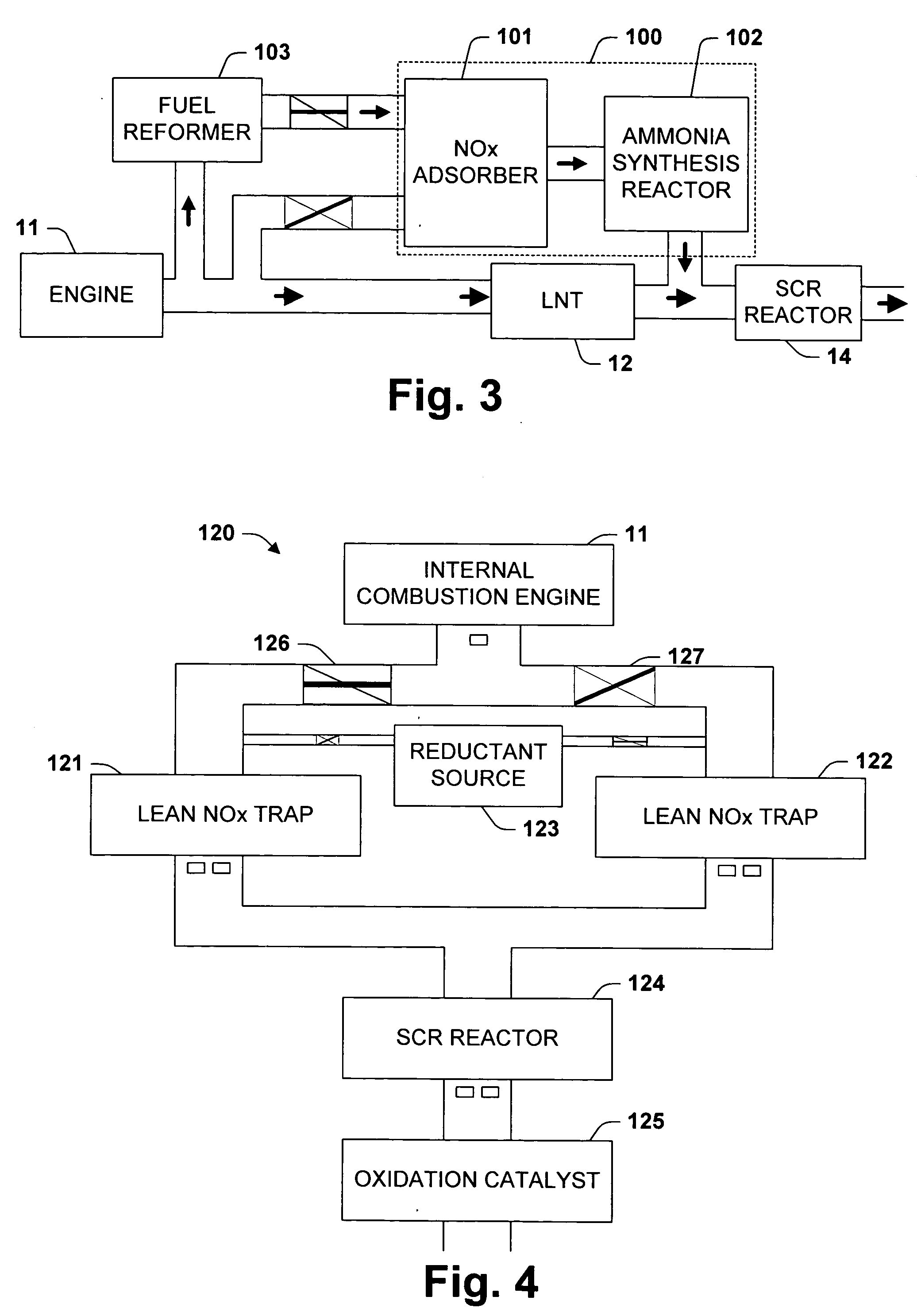
One aspect of the invention relates an exhaust treatment system having an SCR reactor following a NOx adsorber. Syn gas is used to regenerate the NOx adsorber. Another aspect relates to an LNT / SCR provided with an ammonia source separate from the LNT. A further aspect relates to a system comprising first and second LNTs and one or more SCRs downstream of the LNTs. A still further aspect relates to a device comprising first and second NOx adsorbers contained in a single housing. Another aspect relates to coating a surface of a moving part in an exhaust system with an oxidation catalyst to mitigate fouling. Additional aspects of the invention relate to strategies for controlling one or more of the time to initiate a regeneration cycle, the time to terminate a regeneration cycle, and the reductant injection rate during regeneration of LNT / SCR exhaust treatment systems.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
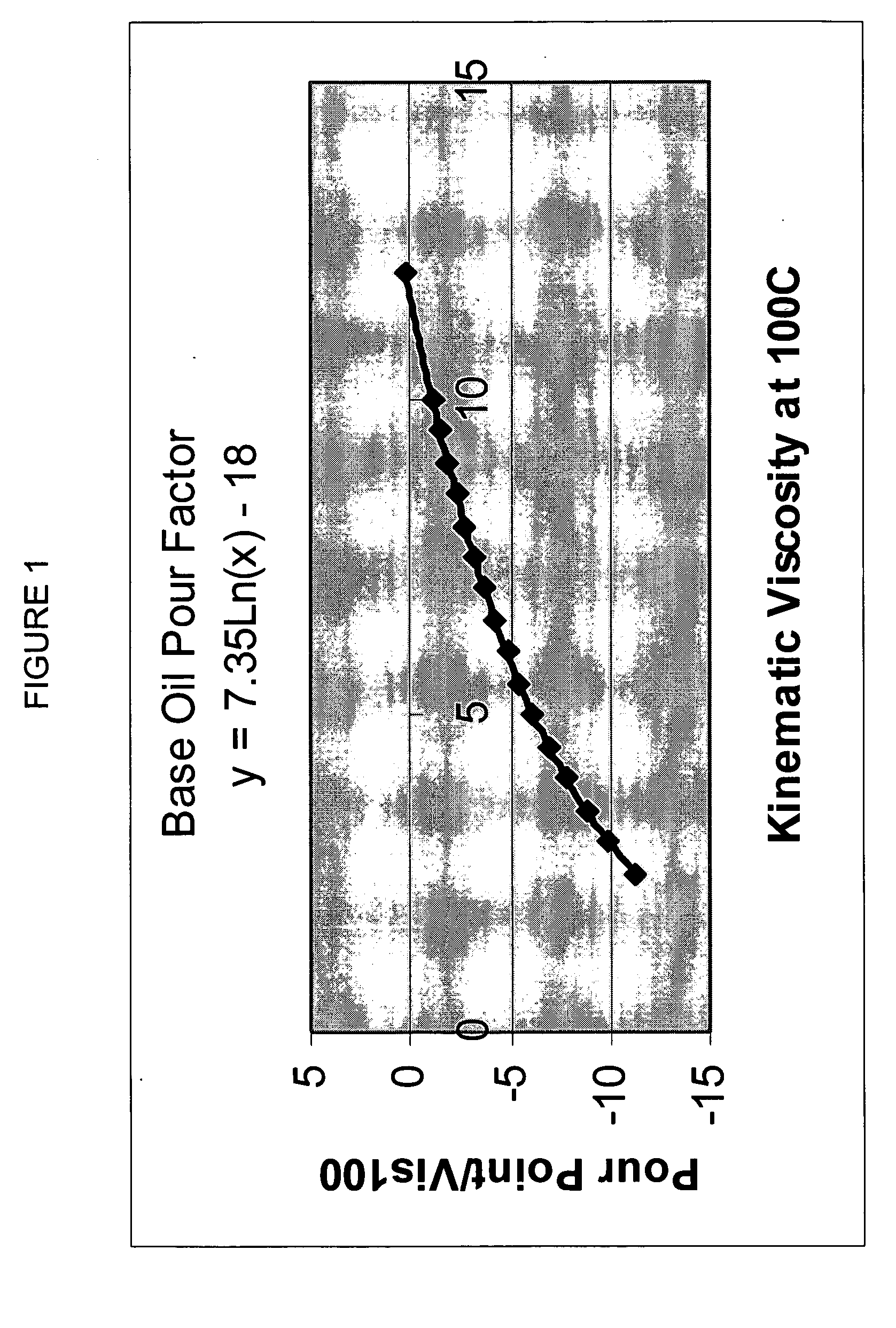
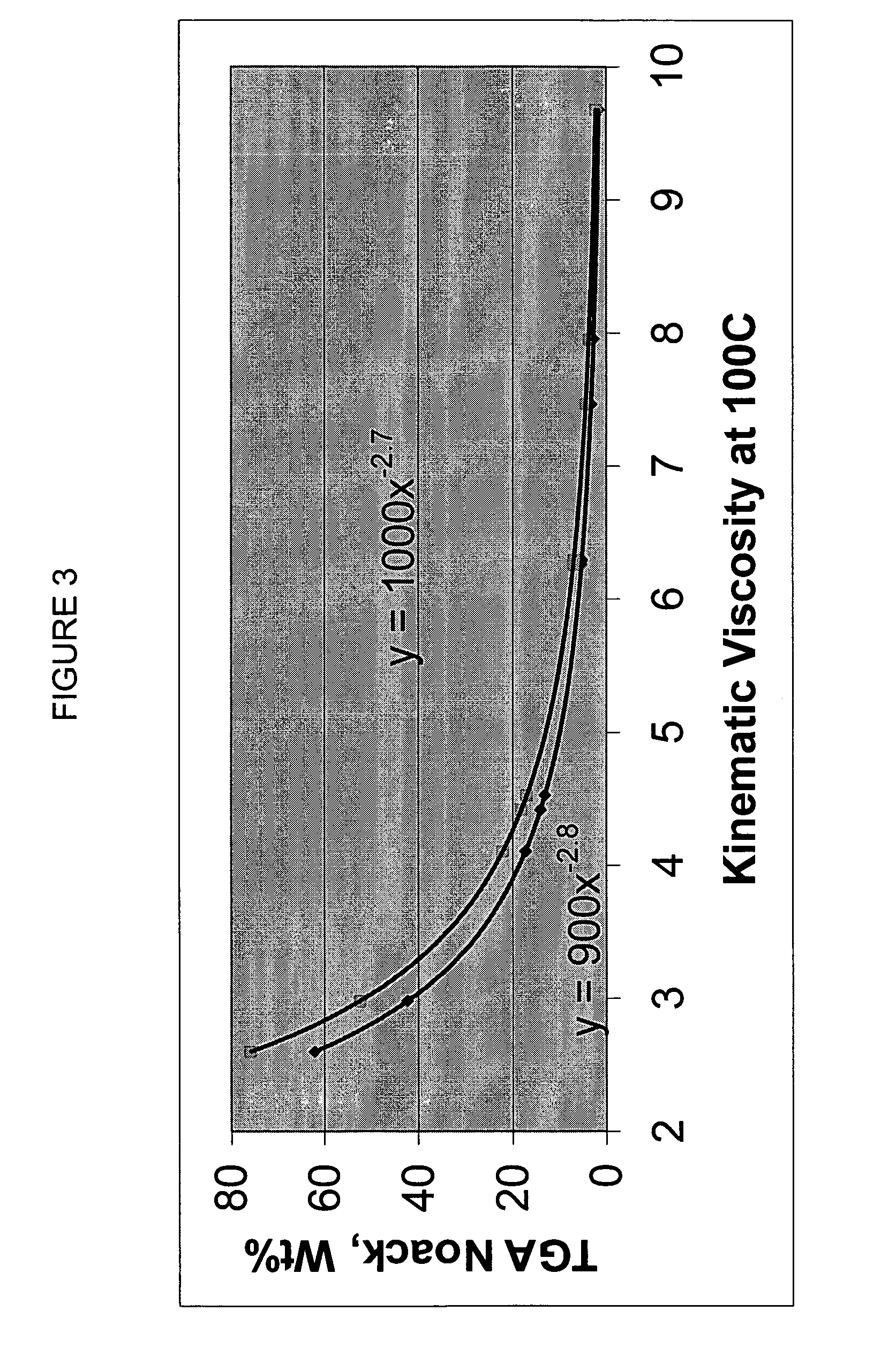
Process for manufacturing lubricating base oil with high monocycloparaffins and low multicycloparaffins
InactiveUS20050133409A1Improve Oxidation StabilityHigh viscosity indexTreatment with hydrotreatment processesAdditivesSyngasMolecular sieve
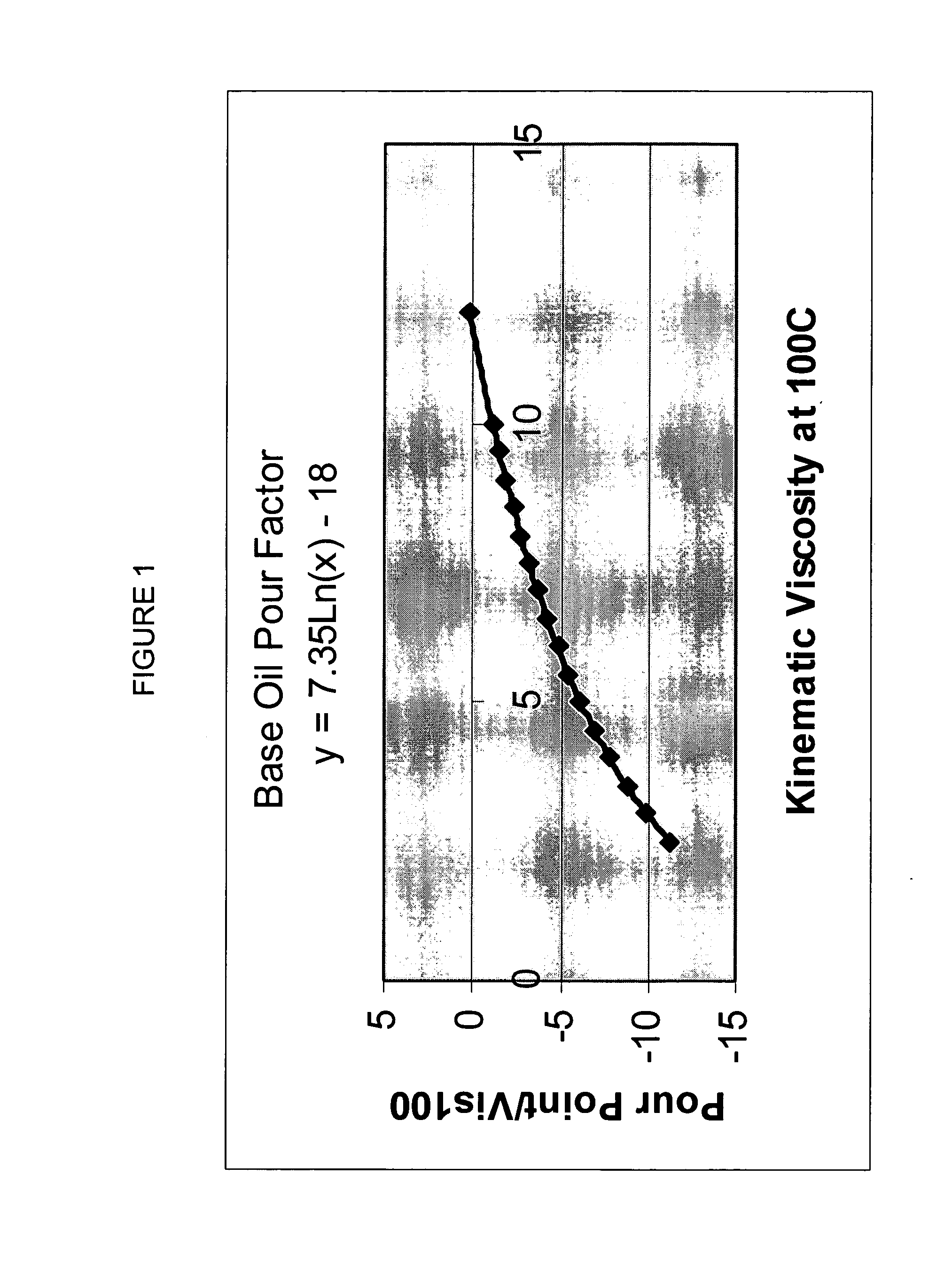
A process for manufacturing a lubricating base oil by: a) performing Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on syngas to provide a product stream; b) isolating from said product stream a substantially paraffinic wax feed having less than about 30 ppm total nitrogen and sulfur, and less than about 1 wt % oxygen; c) dewaxing said feed by hydroisomerization dewaxing using a shape selective intermediate pore size molecular sieve comprising a noble metal hydrogenation component, wherein the hydroisomerization temperature is between about 600° F. (315° C.) and about 750° F. (399° C.), to produce an is dimerized oil; and d) hydrofinishing said isomerized oil to produce a lubricating base oil having specific desired properties.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
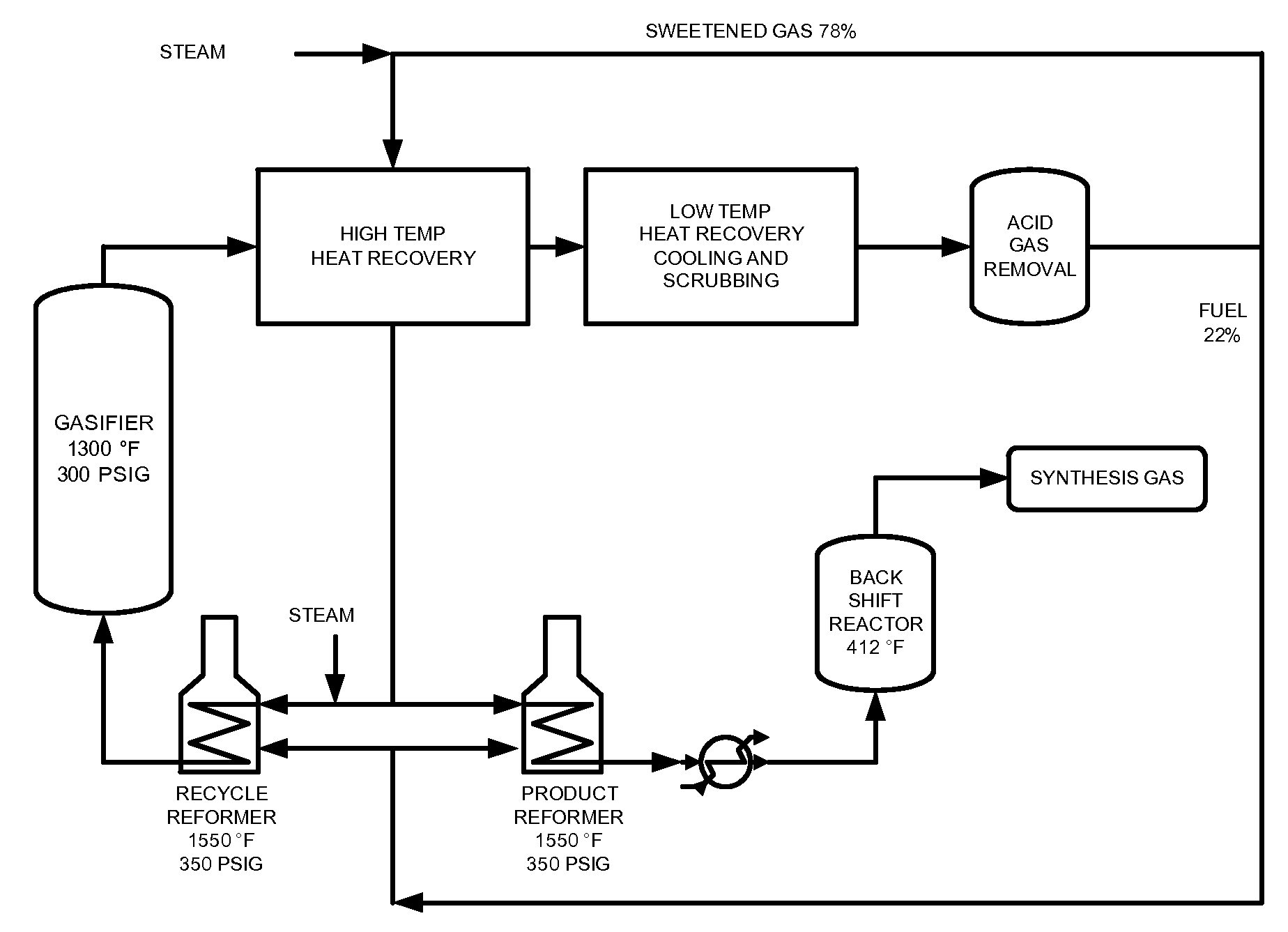
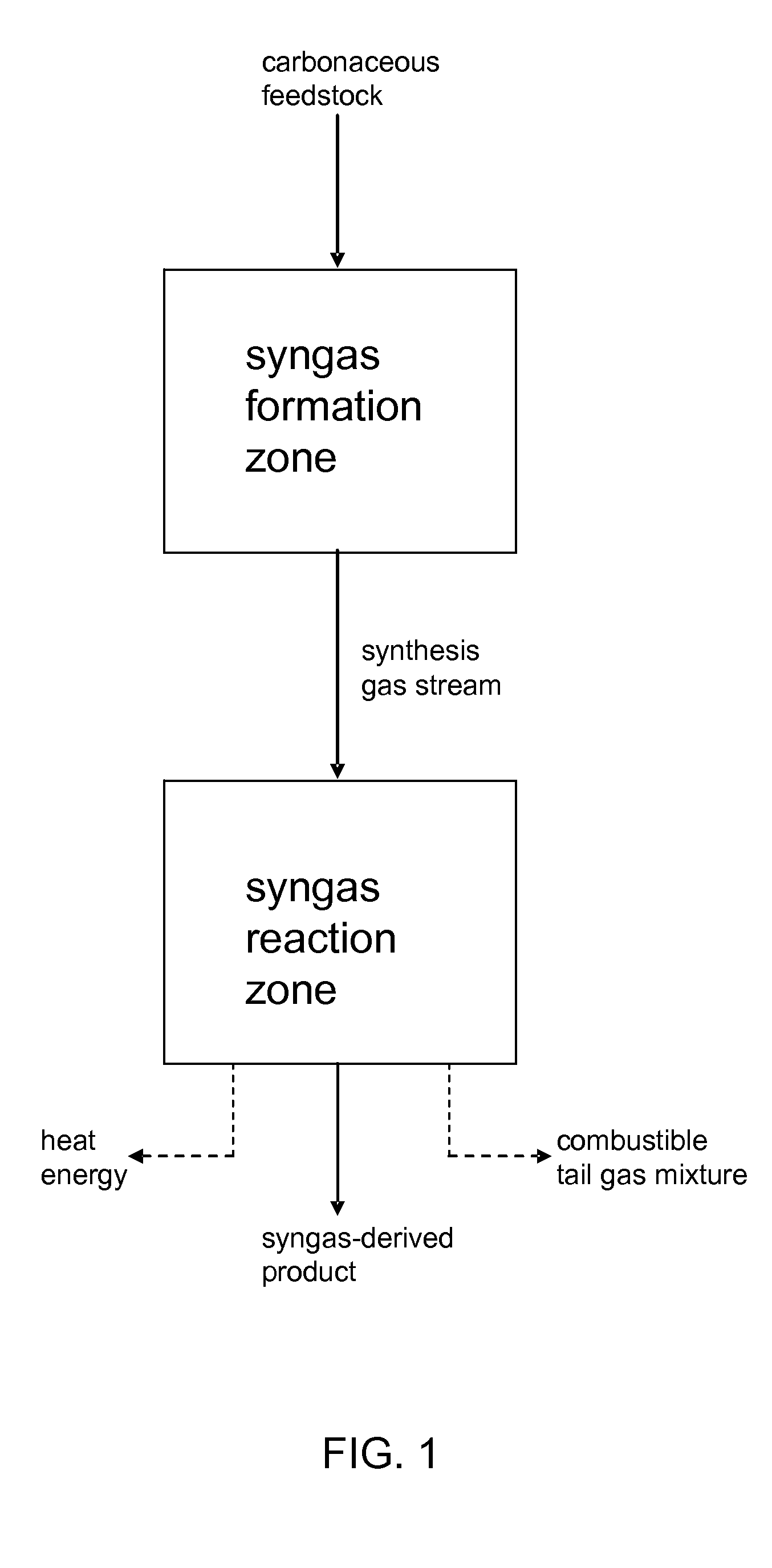
Processes for Making Synthesis Gas and Syngas-Derived Products
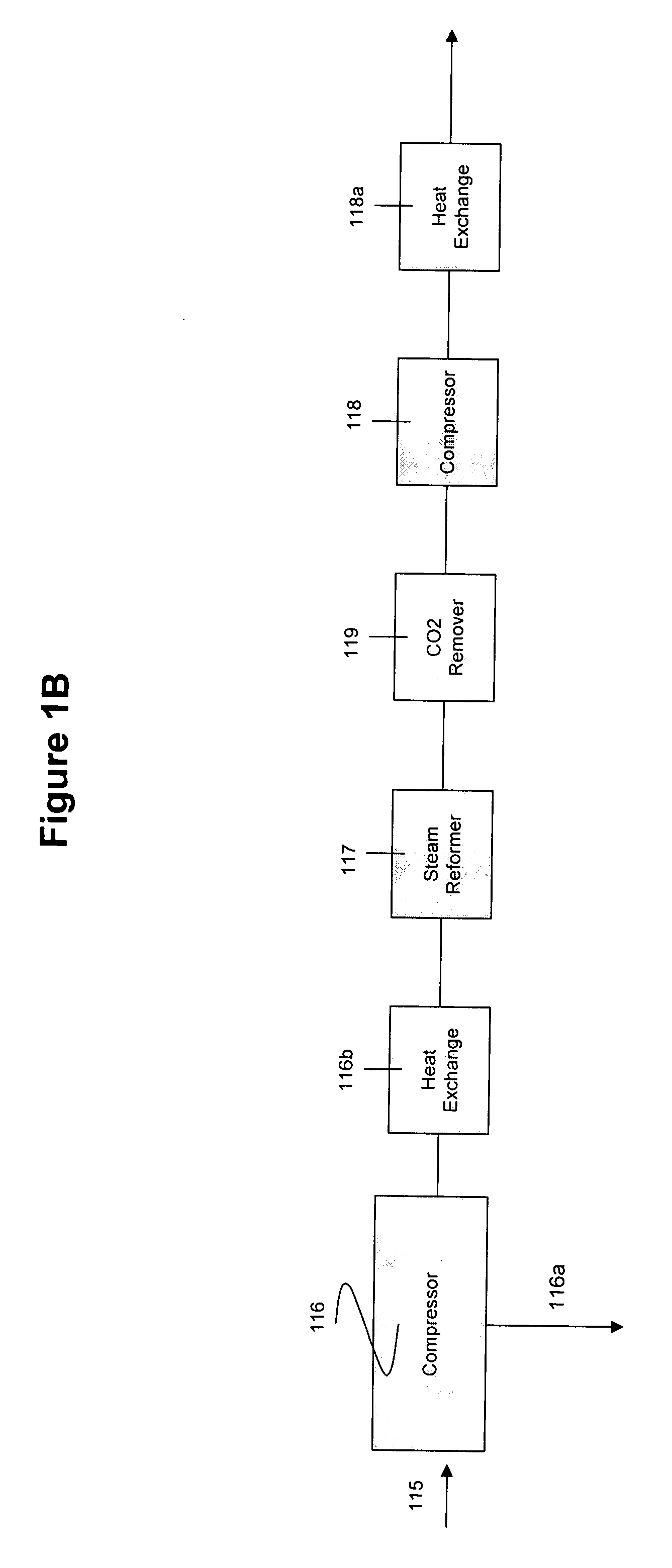
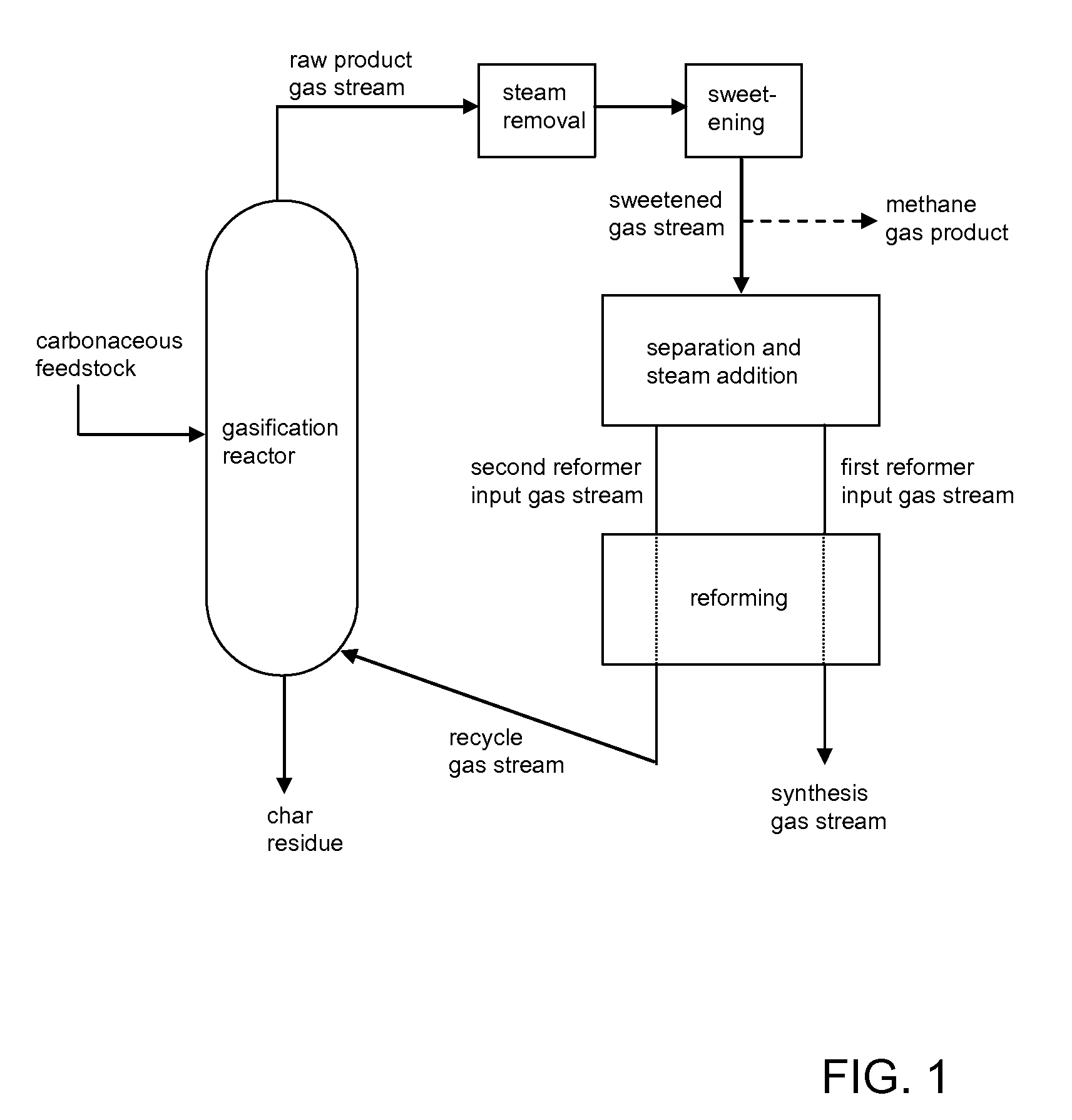
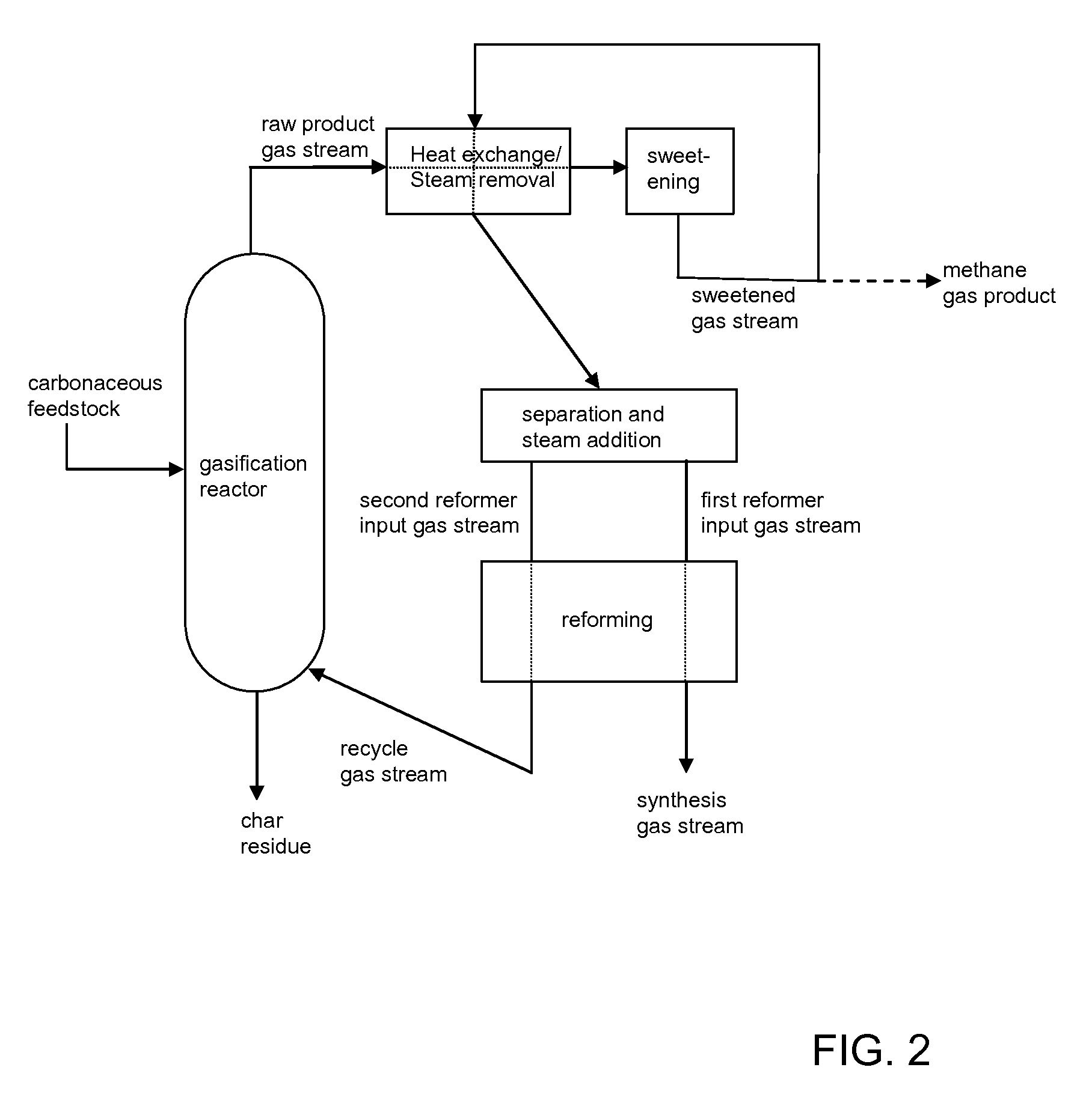
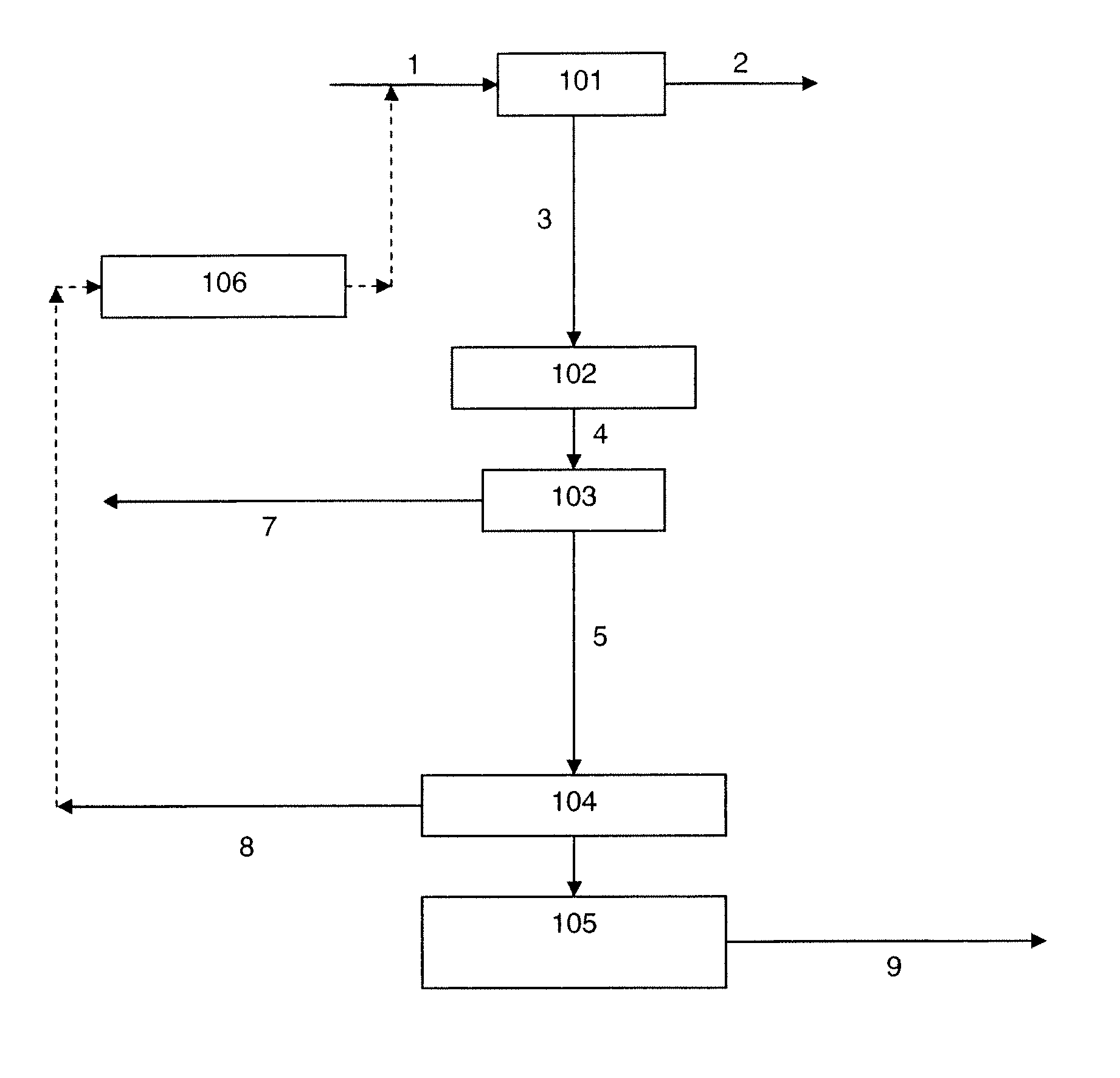
The present invention provides processes for making synthesis gas and processes for making syngas-derived products. For example, one aspect of the present invention provides a process for making a synthesis gas stream comprising hydrogen and carbon monoxide, the process comprising (a) providing a carbonaceous feedstock; (b) reacting the carbonaceous feedstock in a gasification reactor in the presence of steam and a gasification catalyst under suitable temperature and pressure to form a raw product gas stream comprising a plurality of gases comprising methane, hydrogen and carbon monoxide; (c) removing steam from and sweetening the raw product gas stream to form a sweetened gas stream; (d) separating and adding steam to the sweetened gas stream to form a first reformer input gas stream having a first steam / methane ratio; and a second reformer input stream having a second steam / methane ratio, in which the first steam / methane ratio is smaller than the second steam / methane ratio; (e) reforming the second reformer input stream to form a recycle gas stream comprising steam, carbon monoxide and hydrogen; (f) introducing the recycle gas stream to the gasification reactor; and (g) reforming the first reformer input stream to form the synthesis gas stream.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
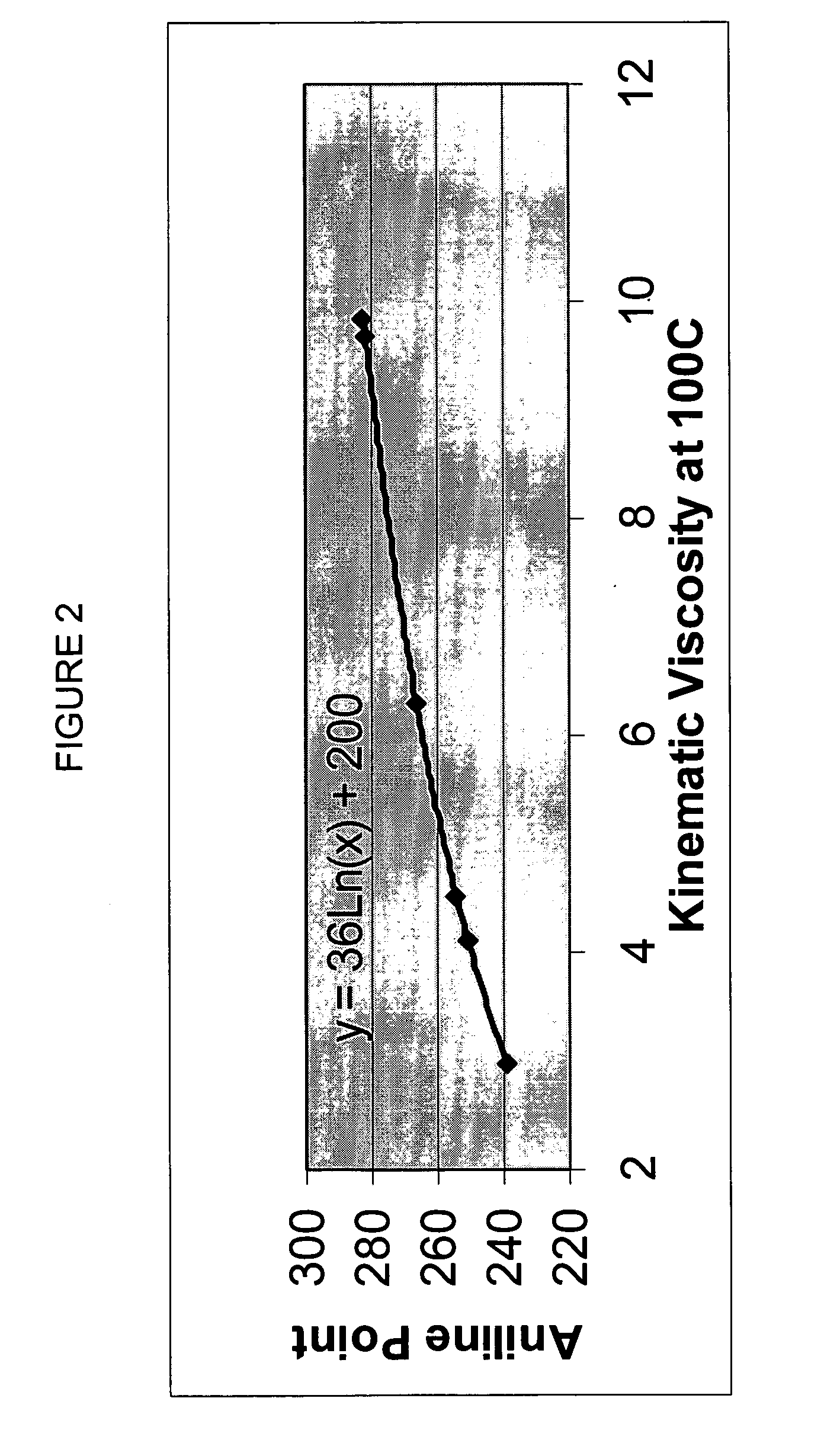
Finished lubricating comprising lubricating base oil with high monocycloparaffins and low multicycloparaffins
ActiveUS20050133407A1Improve Oxidation StabilityReduce wearRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionMolecular sieveWax
A process for manufacturing a finished lubricant by: a) performing Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on syngas to provide a product stream; b) isolating from said product stream a substantially paraffinic wax feed having less than about 30 ppm total nitrogen and sulfur, and less than about 1 wt % oxygen; c) dewaxing said feed by hydroisomerization dewaxing using a shape selective intermediate pore size molecular sieve comprising a noble metal hydrogenation component, wherein the hydroisomerization temperature is between about 600° F. (315° C.) and about 750° F. (399° C.), to produce an isomerized oil; and d) hydrofinishing said isomerized oil, whereby a lubricating base oil is produced having specific desired properties; and e) blending the lubricating base oil with at least one lubricant additive.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process and system for converting carbonaceous feedstocks into energy without greenhouse gas emissions
ActiveUS20070099038A1High hydrogen contentFuel cells groupingHydrogen separation using solid contactPetroleum cokePetroleum
The process of the invention converts carbonaceous feedstock such as coal, hydrocarbon oil, natural gas, petroleum coke, oil shale, carbonaceous-containing waste oil, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing military waste, carbonaceous-containing industrial waste, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing sewage sludge and municipal solid waste, carbonaceous-containing agricultural waste, carbonaceous-containing biomass, biological and biochemical waste, and mixtures thereof into electrical energy without the production of unwanted greenhouse emissions. The process uses a steam / CO2 reformer operating in the exit range of at least 700° to about 1600° C. (1300-2900°0 F.) to convert the carbonaceous feedstock and a greenhouse gas stream into a synthesis gas comprising mostly carbon monoxide and hydrogen that contains poisons and the compounds that poison fuel cells. The syngas is sent to an interface zone to remove these poisons and other fouling compounds that are electrochemically oxidized in an electricity-producing fuel cell into an exit gas comprising carbon dioxide and water.
Owner:RAVEN SR INC
Isolation and characterization of novel clostridial species
InactiveUS7704723B2High yieldReadily availableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSyngasAcetic acid
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium ragsdalei, ATCC BAA-622, “P11”) is provided. P11 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P11 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium transforms waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P11 also catalyzes the production of acetate.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
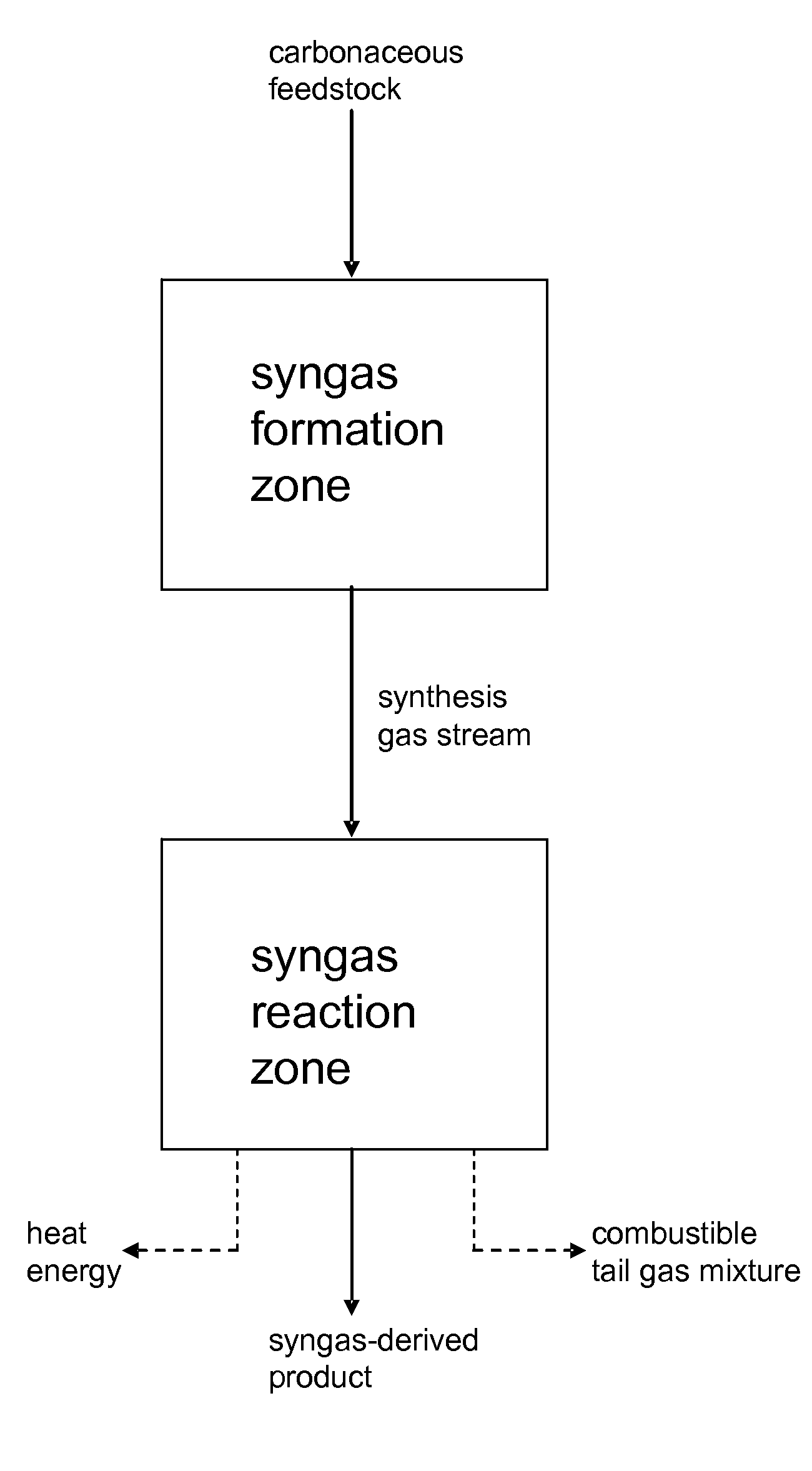
Processes for Making Syngas-Derived Products
The present invention provides processes for making syngas-derived products. For example, one aspect of the present invention provides a process for making a syngas-derived product, the process comprising (a) providing a carbonaceous feedstock; (b) converting the carbonaceous feedstock in a syngas formation zone at least in part to a synthesis gas stream comprising hydrogen and carbon monoxide; (c) conveying the synthesis gas stream to a syngas reaction zone; (d) reacting the synthesis gas stream in the syngas reaction zone to form the syngas-derived product and heat energy, a combustible tail gas mixture, or both; (e) recovering the syngas-derived product; and (f) recovering the heat energy formed from the reaction of the synthesis gas stream, burning the combustible tail gas mixture to form heat energy, or both.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from synthesis gas
InactiveUS20090318573A1Increased ethanol yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSyngasChemistry
The invention provides methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from syngas. As disclosed herein, syngas derived from cellulosic biomass (or other sources) can be catalytically converted into methanol, which in turn can be catalytically converted into acetic acid or acetates. Finally, the acetic acid or acetates can be reduced to ethanol according to several variations. In some embodiments, yields of ethanol from biomass can exceed 100 gallons per dry ton of biomass.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
System and process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbon
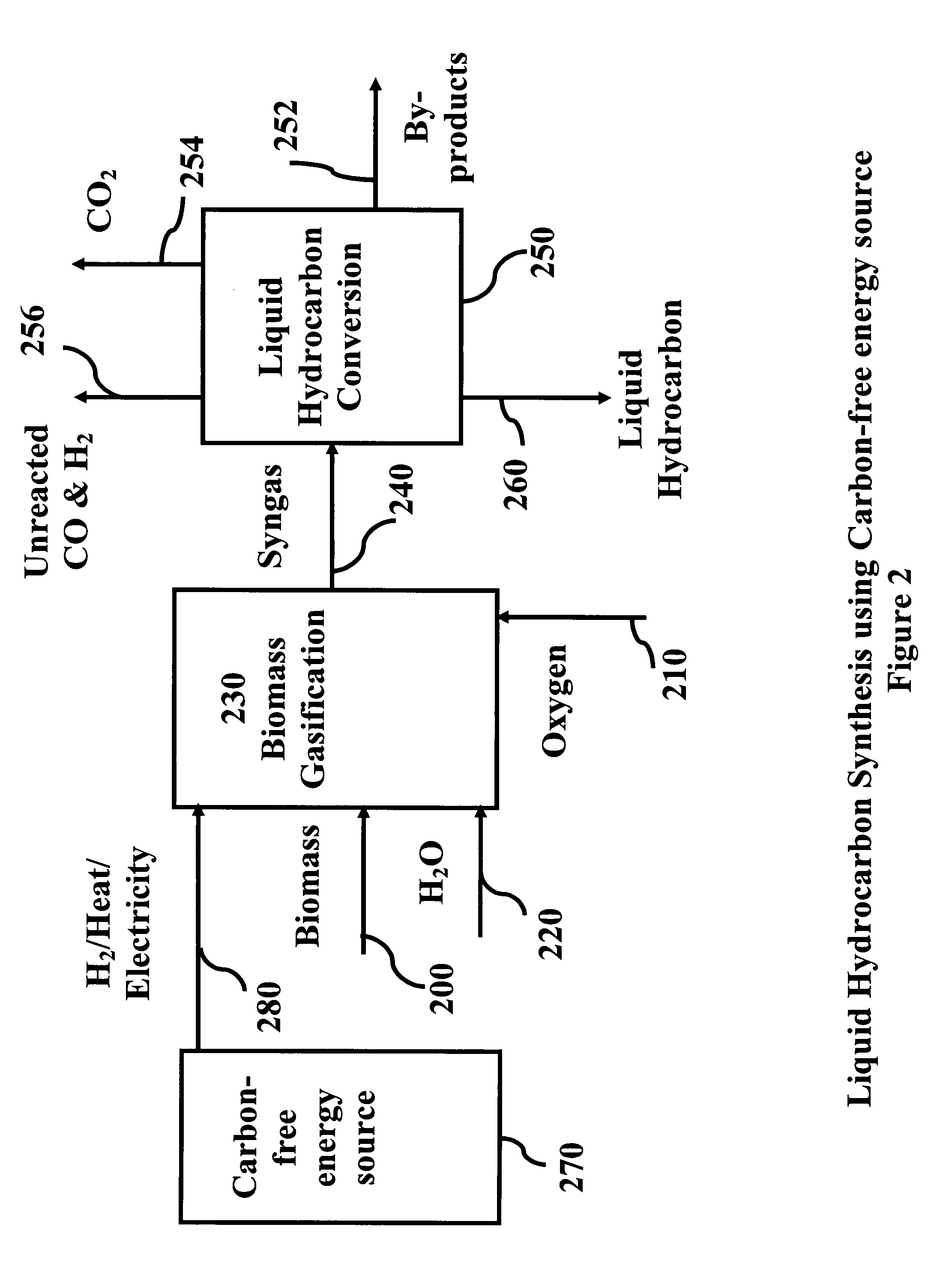
ActiveUS20080115415A1Improve carbon efficiencyReduce area requirementsMuffle furnacesCarbon compoundsOxygenElectrolysis of water
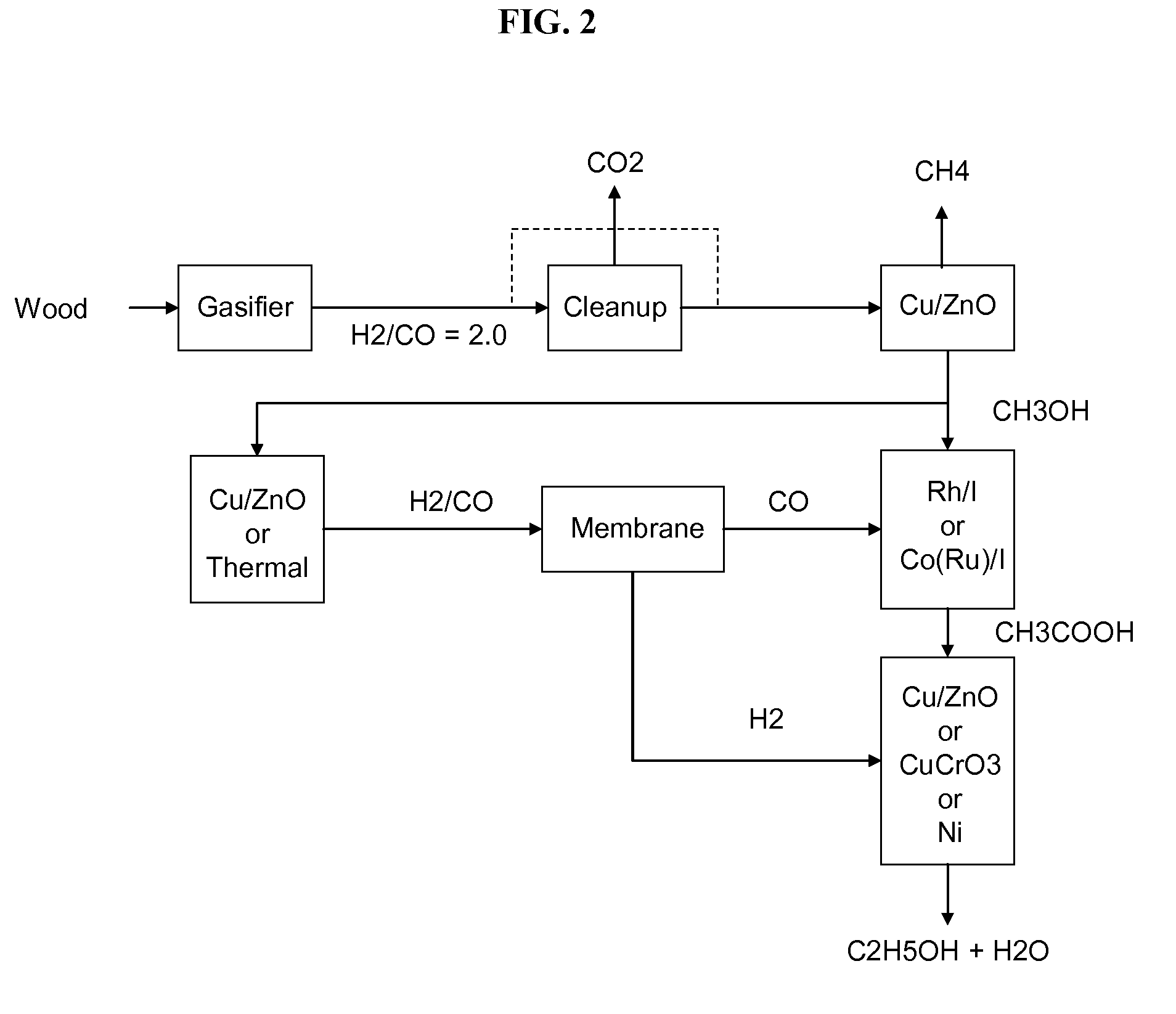
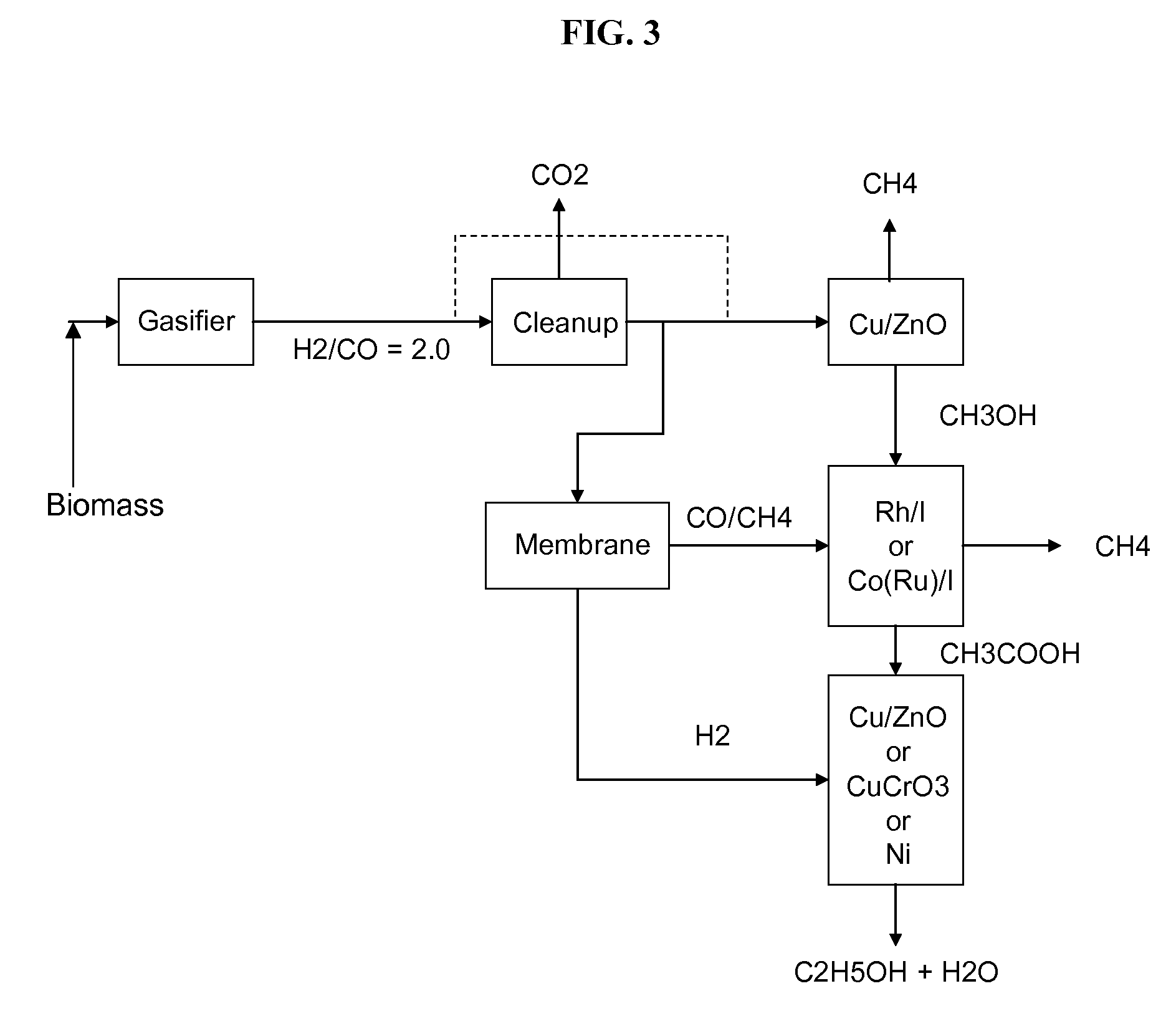
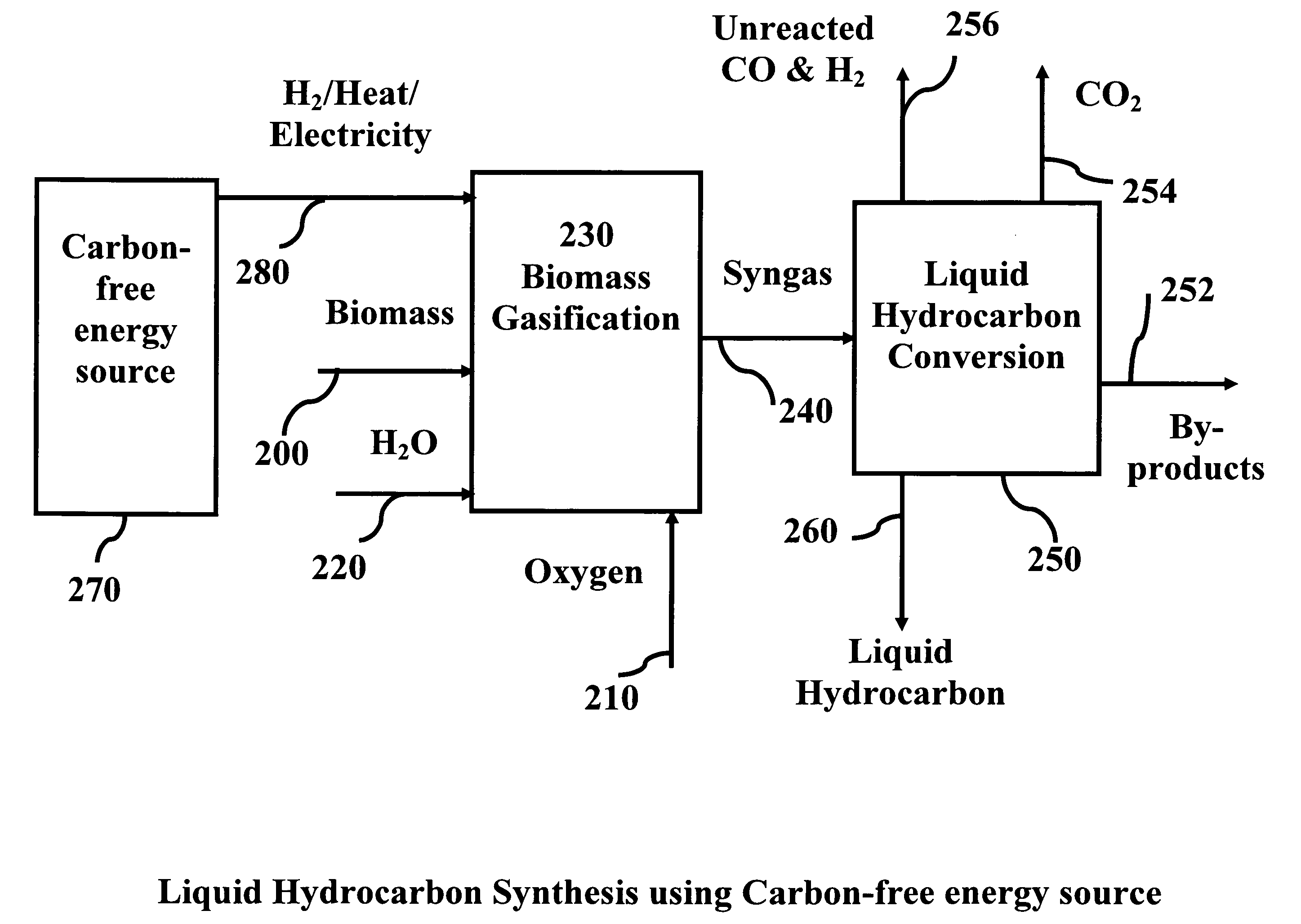
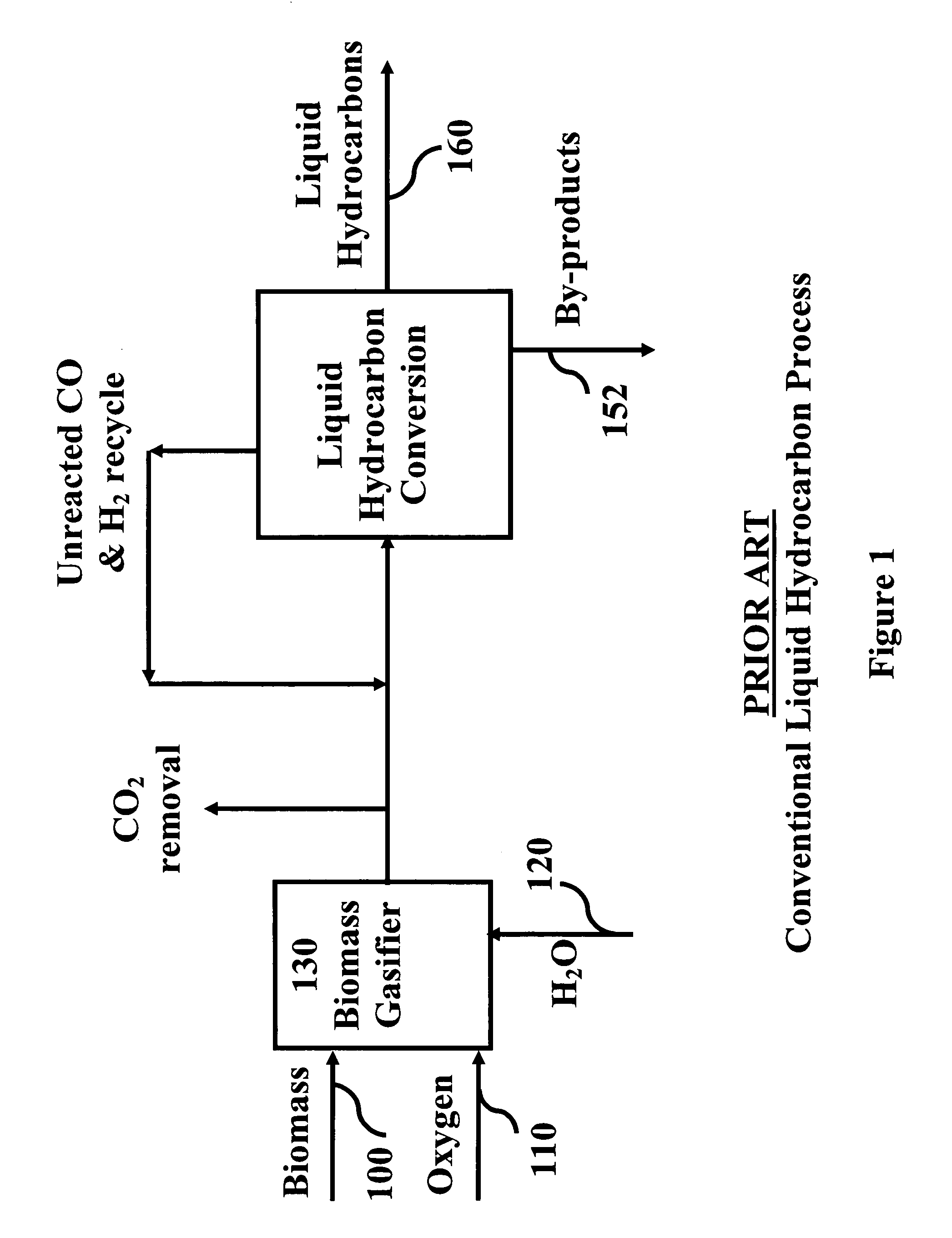
Production of synthetic liquid hydrocarbon fuel from carbon containing moieties such as biomass, coal, methane, naphtha as a carbon source and hydrogen from a carbon-free energy source is disclosed. The biomass can be fed to a gasifier along with hydrogen, oxygen, steam and recycled carbon dioxide. The synthesis gas from the gasifier exhaust is sent to a liquid hydrocarbon conversion reactor to form liquid hydrocarbon molecules. Unreacted CO & H2 can be recycled to the gasifier along with CO2 from the liquid hydrocarbon conversion reactor system. Hydrogen can be obtained from electrolysis of water, thermo-chemical cycles or directly by using energy from carbon-free energy sources.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for converting biomass into synthesis gas using a pressurized multi-stage progressively expanding fluidized bed gasifier followed by an oxyblown autothermal reformer to reduce methane and tars
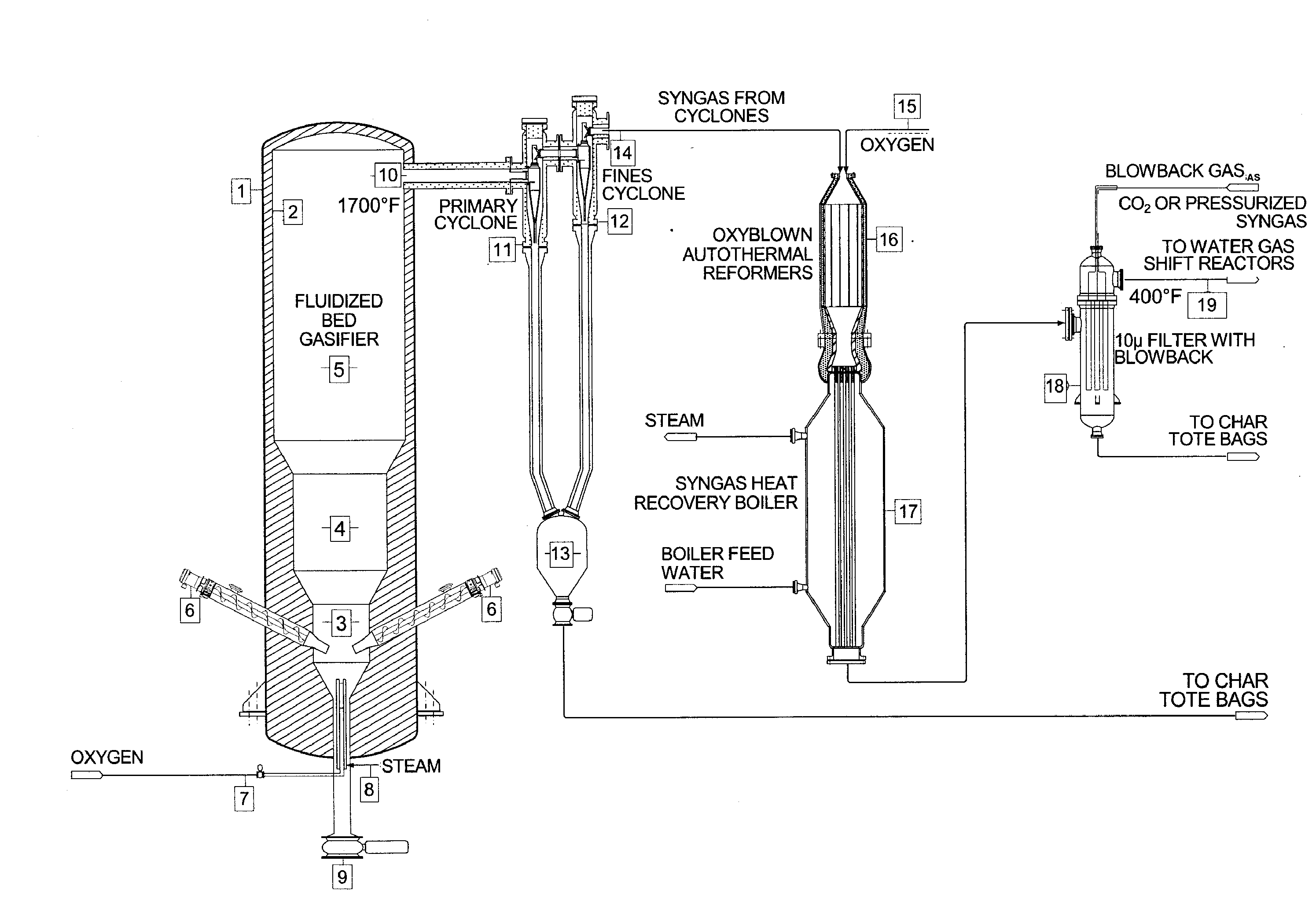
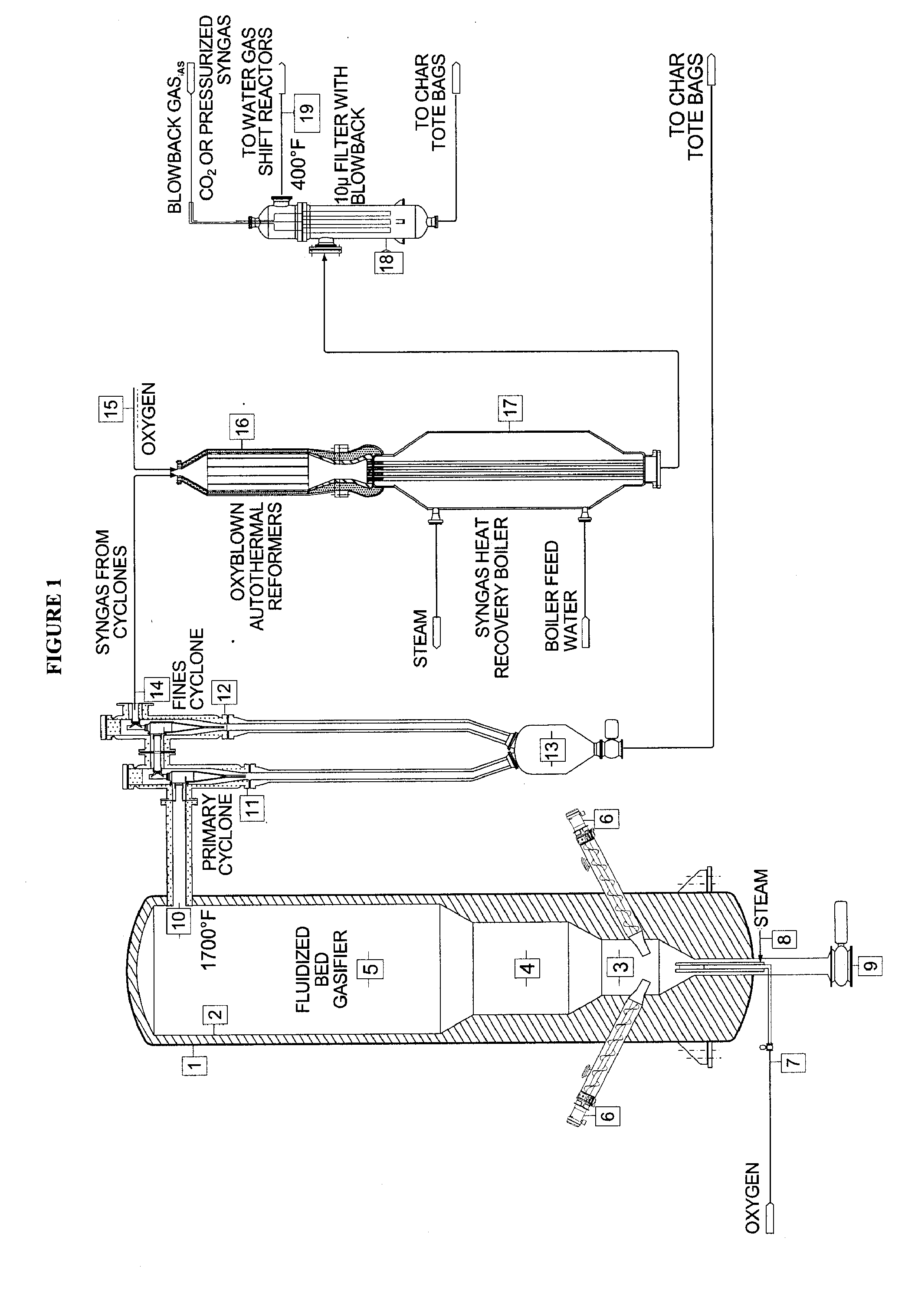
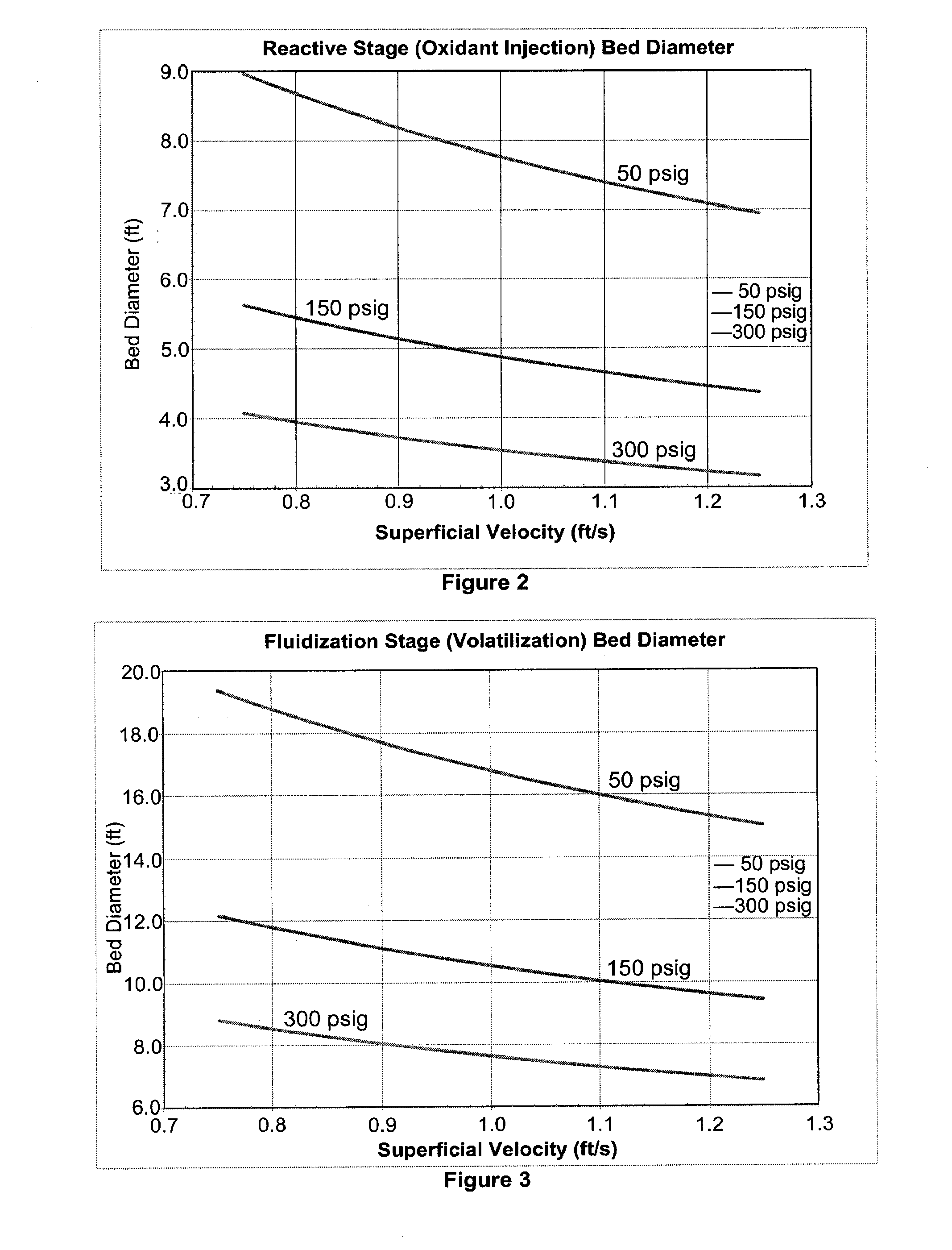
InactiveUS20100040510A1Lower Level RequirementsGasifier mechanical detailsCombustible gas catalytic treatmentSyngasFluidized bed gasifier
The invention provides systems and methods for converting biomass into syngas using a pressurized multi-stage progressively expanding fluidized bed gasifier to eliminate or reduce the formation of methane, volatiles such as BTX, and tars. The gasifier may include a reactive stage that may receive a biomass feed through a feed line and oxygen through an oxygen feed line. The gasifier may also include a fluidized bed section that may be configured to receive the reaction products from the first stage, mix them and perform fluidized bed activity. A gasifier may also have a disengagement section that may be configured to separate fluidized media and particulate matter from syngas product. A gasification system may also include oxyblown catalytic autothermal reactor and a cryogenic air separation unit.
Owner:SYNT
Isolation and characterization of novel clostridial species
InactiveUS20080057554A1High yieldReadily availableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacteroidesAcetic acid
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium ragsdalei, ATCC BAA-622, “P11”) is provided. P11 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P11 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium transforms waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P11 also catalyzes the production of acetate.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
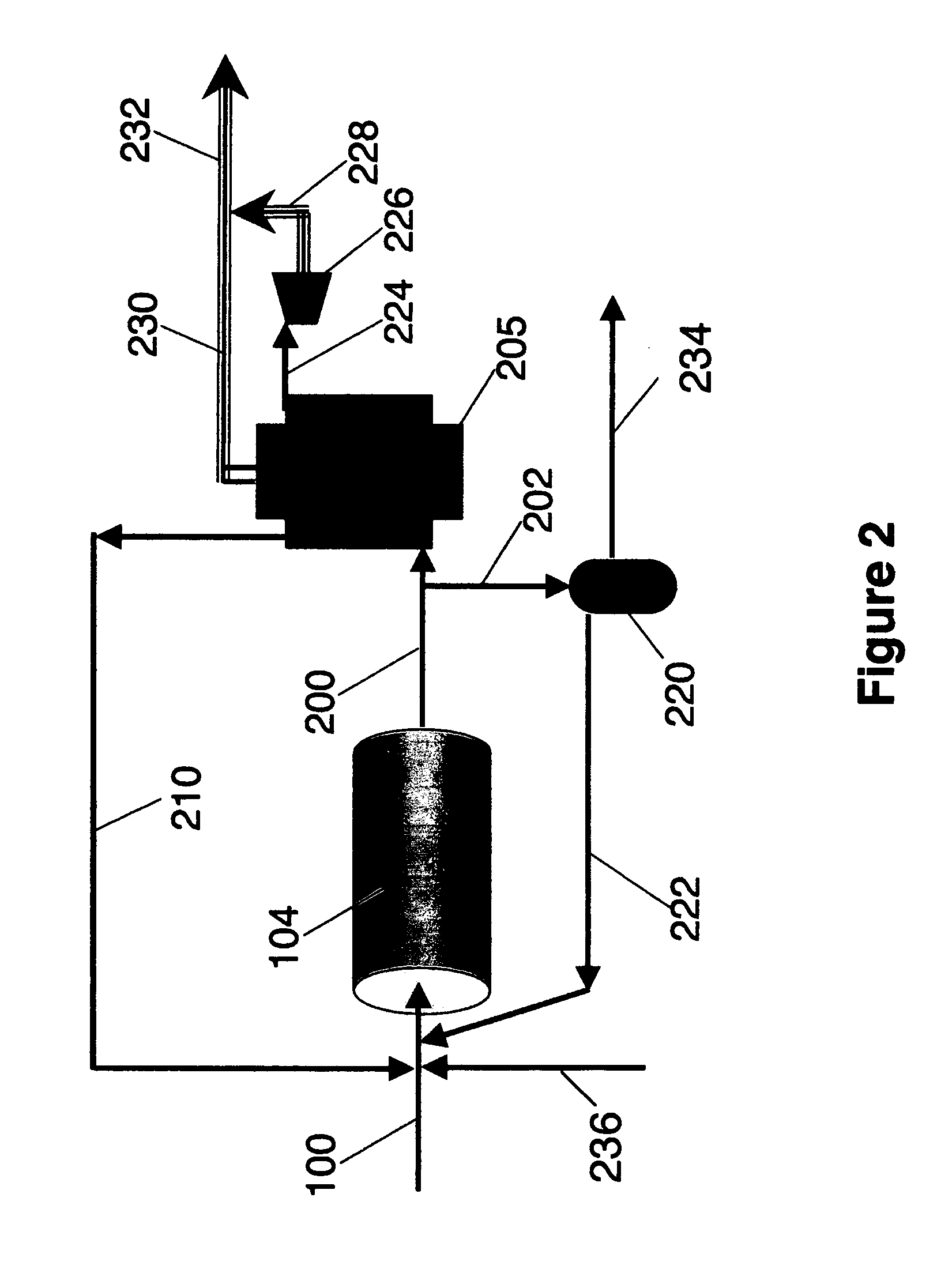
Integrated enhanced oil recovery process
ActiveUS20110088896A1Enhanced overall recoveryIncrease productionSolidificationLiquefactionGeneration processMethane
The present invention relates to an enhanced oil recovery process that is integrated with a synthesis gas generation process, such as gasification or methane reforming, involving combined capture and recycle of carbon dioxide from both processes.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Rapid solar-thermal conversion of biomass to syngas
ActiveUS20080086946A1Improve reaction kineticsWide rangeElectrical coke oven heatingSolar heating energySyngasReactor design
Methods for carrying out high temperature reactions such as biomass pyrolysis or gasification using solar energy. The biomass particles are rapidly heated in a solar thermal entrainment reactor. The residence time of the particles in the reactor can be 5 seconds or less. The biomass particles may be directly or indirectly heated depending on the reactor design. Metal oxide particles can be fed into the reactor concurrently with the biomass particles, allowing carbothermic reduction of the metal oxide particles by biomass pyrolysis products. The reduced metal oxide particles can be reacted with steam to produce hydrogen in a subsequent process step.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Process and system for syngas production from biomass materials
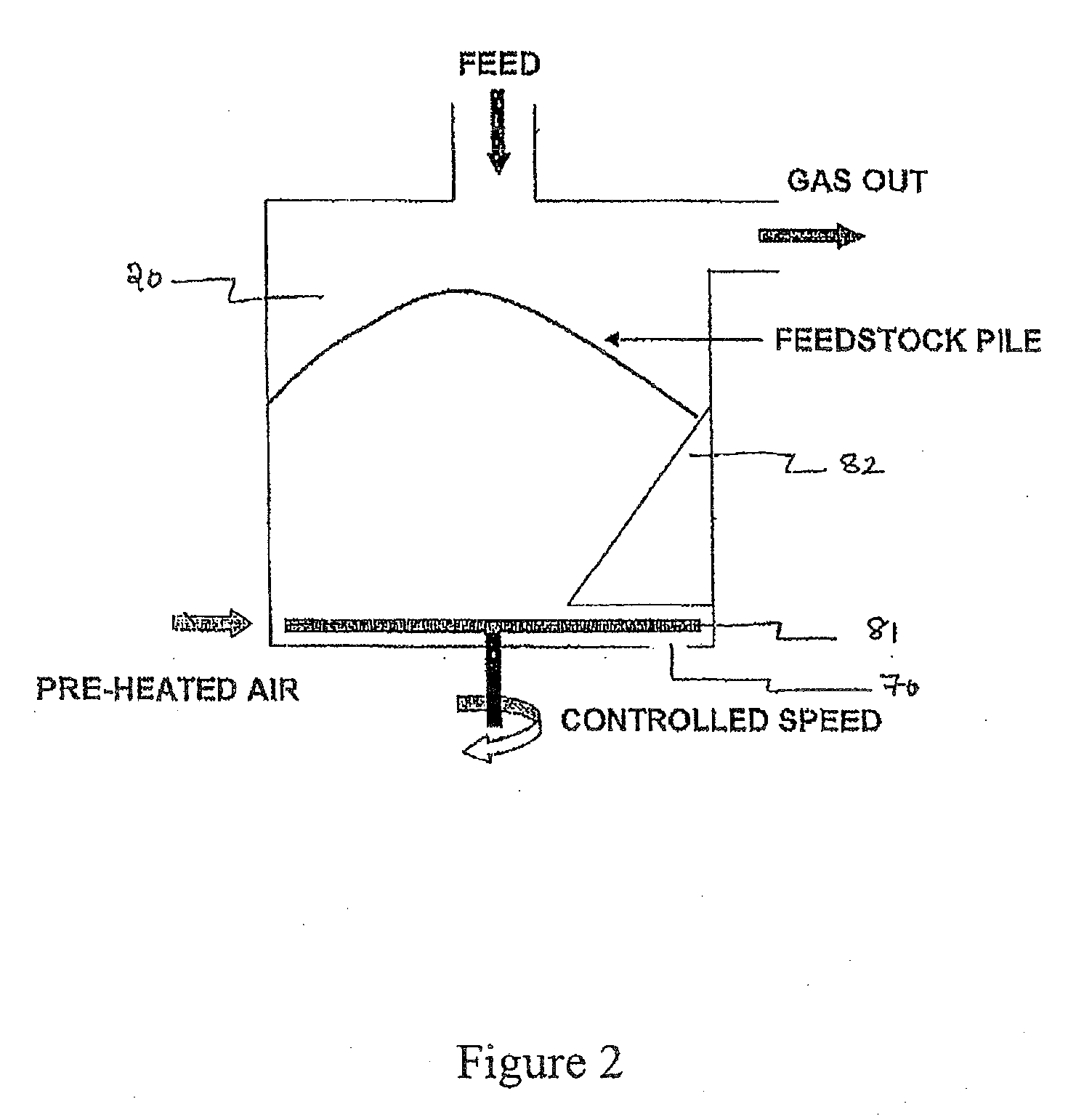
A process and system suitable for producing syngas from biomass materials. The process and system entail the compaction of a loose biomass material to remove air therefrom and form a compacted biomass material. The compacted biomass material is then introduced into a reactor and heated in the substantial absence of air so as not to combust the compacted biomass material. Instead, the compacted biomass material is heated to a temperature at which organic molecules within the compacted biomass material break down to form ash and gases comprising carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas. Thereafter, the carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas are released from the reactor, and the ash is removed from the reactor.
Owner:GREEN FORTRESS ENG INC
Gasification system with processed feedstock/char conversion and gas reformulation
ActiveUS20110036014A1Gasifier mechanical detailsEnergy based wastewater treatmentVitrificationSyngas
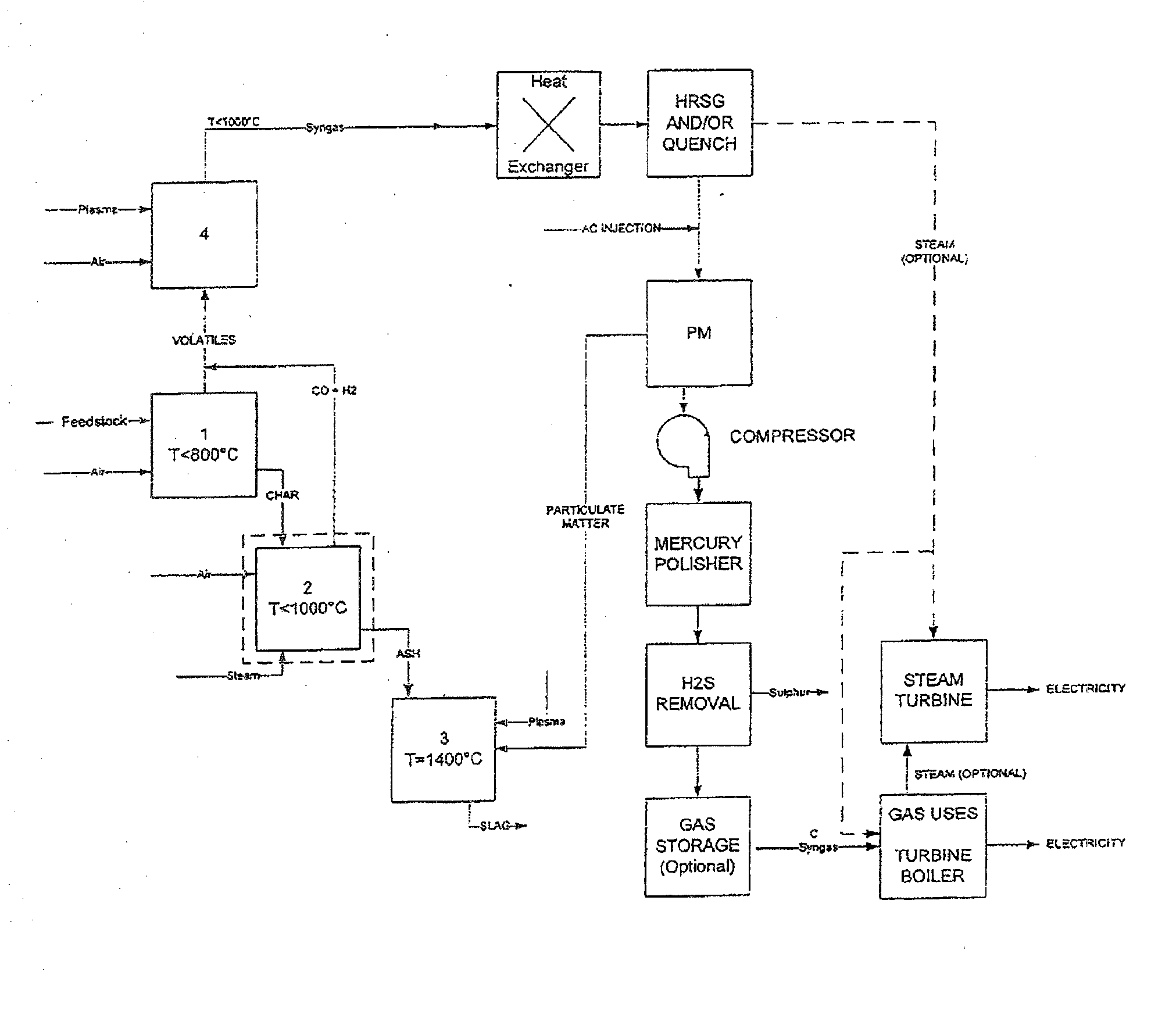
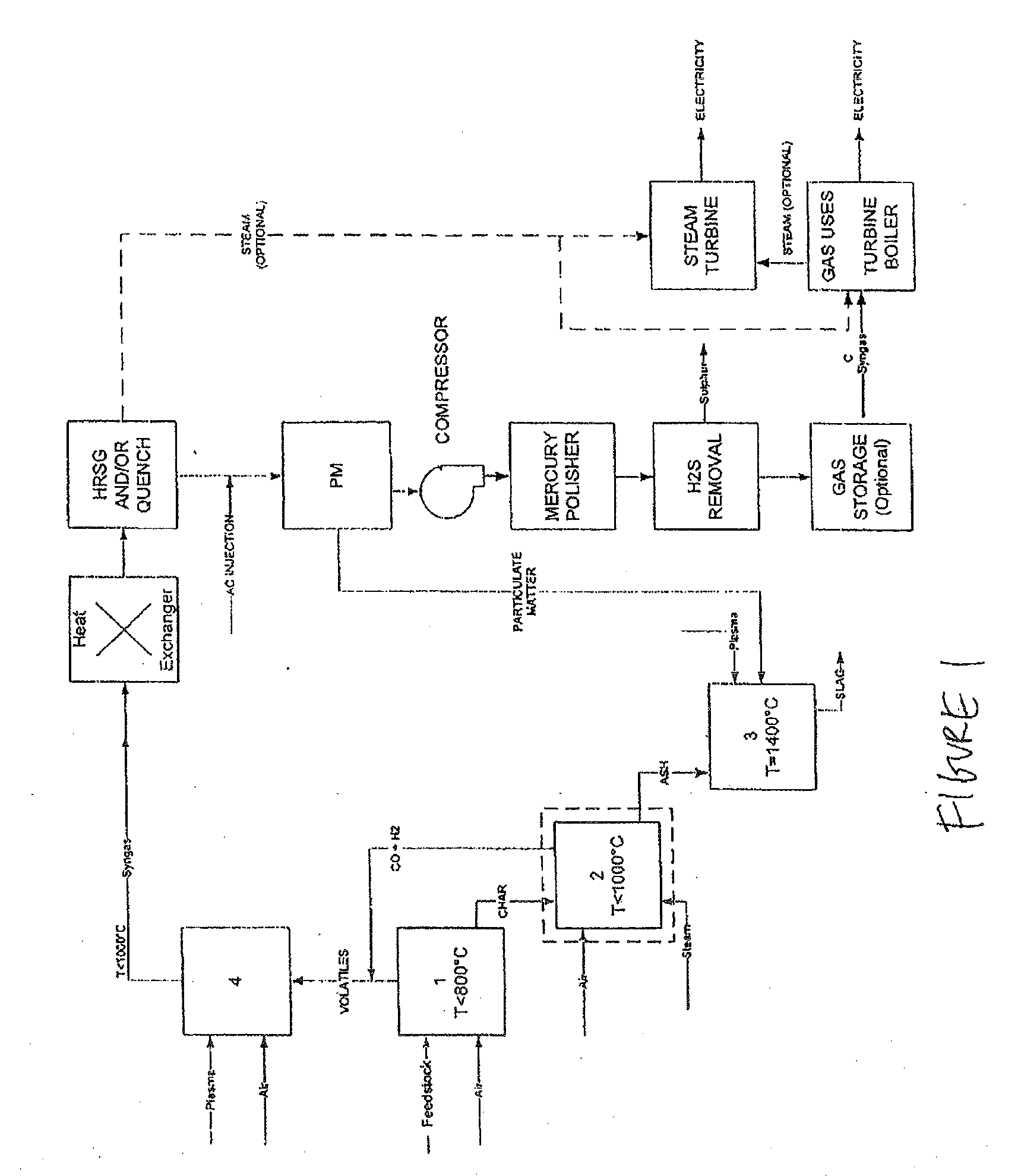
The invention provides a system designed for the complete conversion of carbonaceous feedstock into syngas and slag. The system comprises a primary chamber for the volatilization of feedstock generating a primary chamber gas (an offgas); a secondary chamber for the further conversion of processed feedstock to a secondary chamber gas (a syngas) and a residue; a gas-reformulating zone for processing gas generated within one or more of the chambers; and a melting chamber for vitrifying residue. The primary chamber comprises direct or indirect feedstock additive capabilities in order to adjust the carbon content of the feedstock. The system also comprises a control system for use with the gasification system to monitor and regulate the different stages of the process to ensure the efficient and complete conversion of the carbonaceous feedstock into a syngas product.
Owner:PLASCO CONVERSION TECH INC
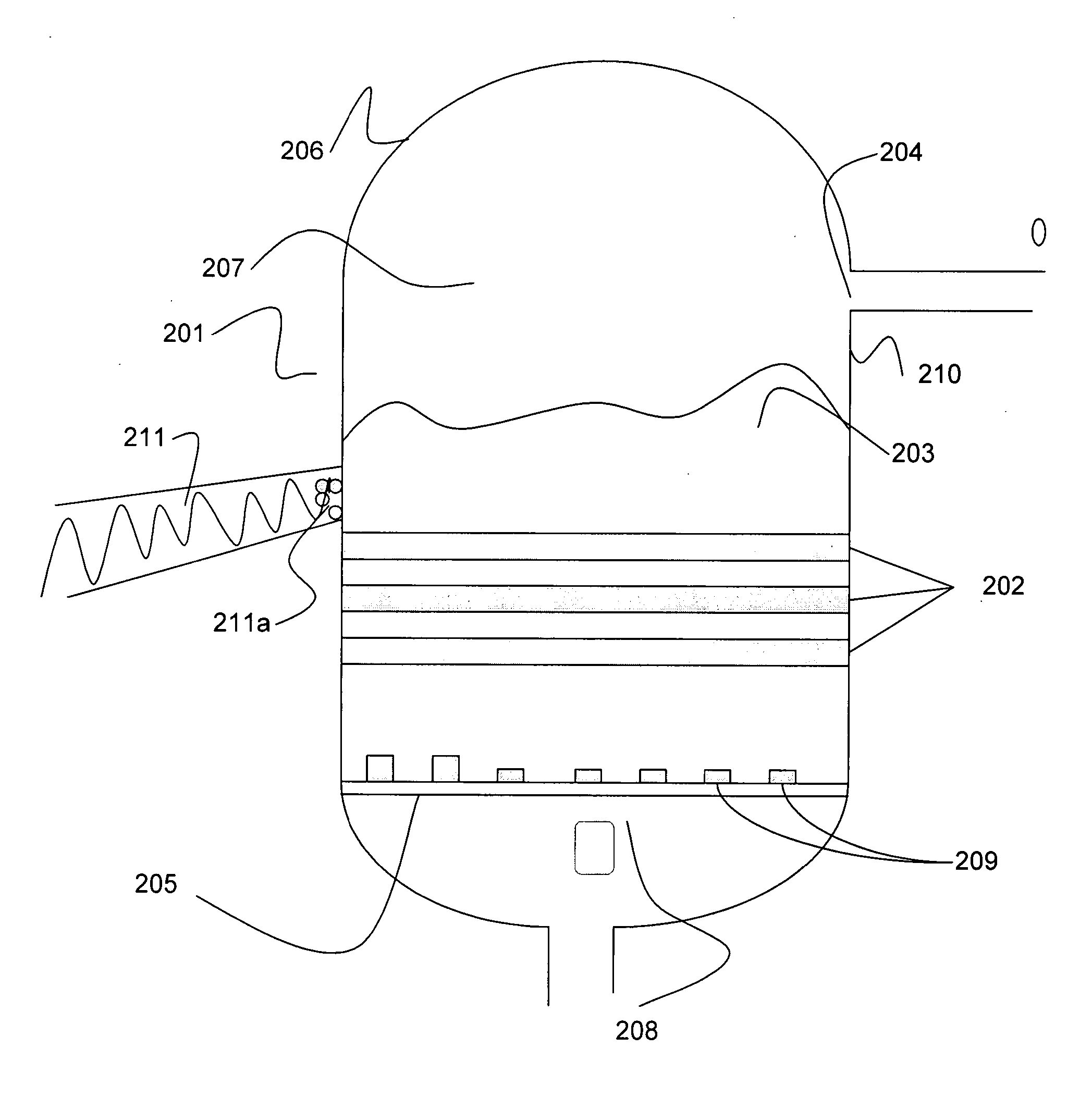
Separation of a sour syngas stream
A feed stream, comprising hydrogen sulphide (H2S), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen (H2) and, optionally, carbon monoxide (CO), is separated into at least a CO2 product stream and an H2 or H2 and CO product stream. The stream is separated using a pressure swing adsorption system, an H2S removal system and a further separation system, which systems are used in series to separate the stream. The method has particular application in the separation of a sour (i.e. sulphur containing) syngas, as for example produced from the gasification of solid or heavy liquid carbonaceous feedstock.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Catalytic membrane reactor and method for production of synthesis gas
InactiveUS20080169449A1High oxygen fluxHydrogenSemi-permeable membranesSulfur containingPhotochemistry
A solid state membrane for a reforming reactor is disclosed which comprises at least one oxygen anion-conducting oxide selected from the group consisting of hexaaluminates, cerates, perovskites, and other mixed metal oxides that are able to adsorb and dissociate molecular oxygen. The membrane adsorbs and dissociates molecular oxygen into highly active atomic oxygen and allows oxygen anions to diffuse through the membrane, to provide high local concentration of oxygen to deter formation and deposition of carbon on reformer walls. Embodiments of the membrane also have catalytic activity for reforming a hydrocarbon fuel to synthesis gas. Also disclosed are a reformer having an inner wall containing the new membrane, and a process of reforming a hydrocarbon feed, such as a high sulfur-containing diesel fuel, to produce synthesis gas, suitable for use in fuel cells.
Owner:ELTRON RES
Method and plant or increasing oil recovery by gas injection
A method and a plant for simultaneous production of a gas for injection into an oil field and production of methanol, dimethyl ether and / or other oxygenated hydrocarbons or production of higher hydrocarbons from natural gas is disclosed. An air separation unit (ATR) for production of pure nitrogen for injection and pure oxygen for production of synthesis gas (“syngas”) by authermal reformation of a natural gas is an essential part of the method and plant.
Owner:DEN NORSKE STATS OLJESELSKAP AS
Methods and apparatus for producing syngas and alcohols
The present invention features methods and apparatus for the pyrolysis or torrefaction of a carbon-containing feedstock before it is converted to syngas. In some embodiments, biomass is first pretreated by torrefaction and / or pyrolysis, followed by devolatilization and / or steam reforming to produce syngas. Various mixtures of such pretreated biomass, combined with fresh biomass, can be employed to produce syngas. The syngas can be converted to alcohols, such as ethanol, or to other products.
Owner:RANGE FUELS INC
Integrated, high-efficiency processes for biomass conversion to synthesis gas
InactiveUS20100270505A1Increase temperatureHydrogenHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesSyngasPartial oxidation
The present invention provides several variations for converting biomass, and other carbon-containing feedstocks, into syngas. Some variations include pyrolyzing or torrefying biomass in a devolatilization unit to form a gas stream and char, and gasifying the char. Other variations include introducing biomass into a fluid-bed gasifier to generate a solid stream and a gas stream, followed by a partial-oxidation or reforming reactor to generate additional syngas from either, or both, of the solid or gas stream from the fluid-bed gasifier. Hot syngas is preferably subjected to heat recovery. The syngas produced by the disclosed methods may be used in any desired manner, such as conversion to liquid fuels (e.g., ethanol).
Owner:HAAKON LLC
Production of low sulfur syngas from natural gas with C4+/C5+ hydrocarbon recovery
Sour natural gas is processed to remove the sulfur compounds and recover C4+ / C5+ hydrocarbons by scrubbing the gas with an amine solution to remove most of the sulfur, followed cooling the gas to remove C4+ / C5+ hydrocarbons and more sulfur compounds as liquid condensate to produce a gas having less than 20 vppm of total sulfur. The condensate is sent to a fractionator to recover the C4+ / C5+ hydrocarbons. The sulfur and hydrocarbon reduced gas is contacted first with zinc oxide and then nickel, to produce a gas having less than 10 vppb of total sulfur which is passed into a synthesis gas generating unit to form a very low sulfur synthesis gas comprising a mixture of H2 and CO. This synthesis gas is useful for hydrocarbon synthesis with increased life of the hydrocarbon synthesis catalyst and greater hydrocarbon production from the hydrocarbon synthesis reactor. Contacting the synthesis gas with zinc oxide further reduces the sulfur content to below 3 vppb.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Gas separation by combined pressure swing and displacement purge
InactiveUS6902602B2Improve efficiencyAvoid pollutionGas treatmentIsotope separationSyngasAtmospheric air
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
System and method for extracting energy from agricultural waste
InactiveUS7169821B2Reduce decreaseMinimize negative impactBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingSyngasBiodiesel
Owner:BEST BIOFUELS LLC
Process for the production of synthesis gas with conversion of CO2 into hydrogen
ActiveUS7846979B2Useful thermal recovery on the gasification effluentCombustible gas chemical modificationProductsSteam reformingPartial oxidation
Process for the production of liquid hydrocarbons from a feedstock that comprises at least one elementary feedstock from the group of biomass, coal, lignite, petroleum residues, methane, and natural gas, comprising: at least one stage a) for gasification of the feedstock by partial oxidation and / or steam reforming to produce a synthesis gas SG; a stage b) for separating CO2 from SG and a portion of the effluent of the subsequent stage c); the mixing of a portion of the CO2 that is separated with a gas of an H2 / CO ratio of more than 3; a stage c) for partial conversion with hydrogen, thermal or thermocatalytic, of the CO2 that is present in said first mixture according to the reaction: CO2+H2→CO+H2O in a specific reaction zone that is separated from said gasification zone or zones; a stage d) for Fisher-Tropsch synthesis on a synthesis gas that comprises at least a portion of SG and at least a portion of the CO that is produced by the conversion of CO2 into hydrogen.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com