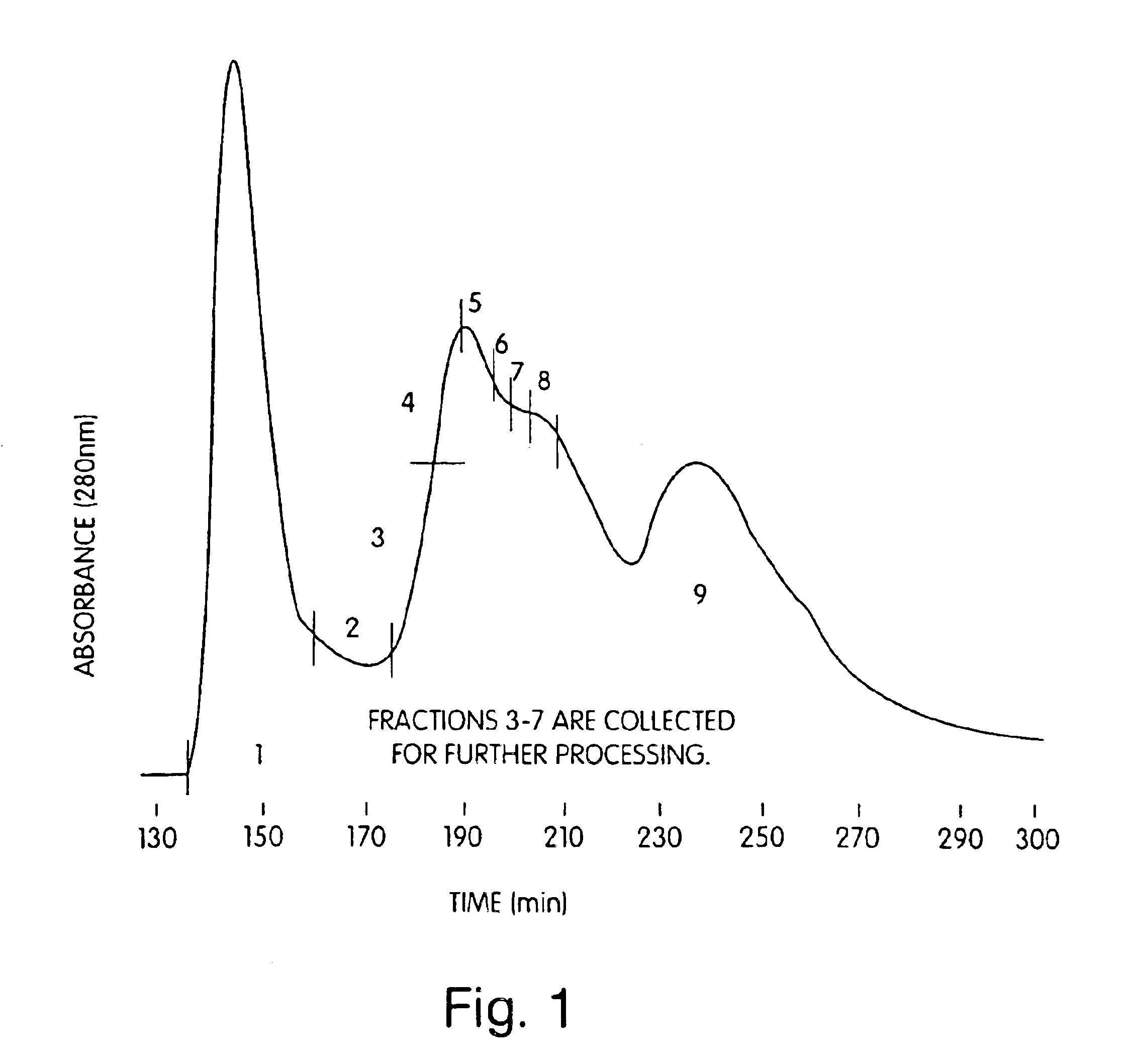
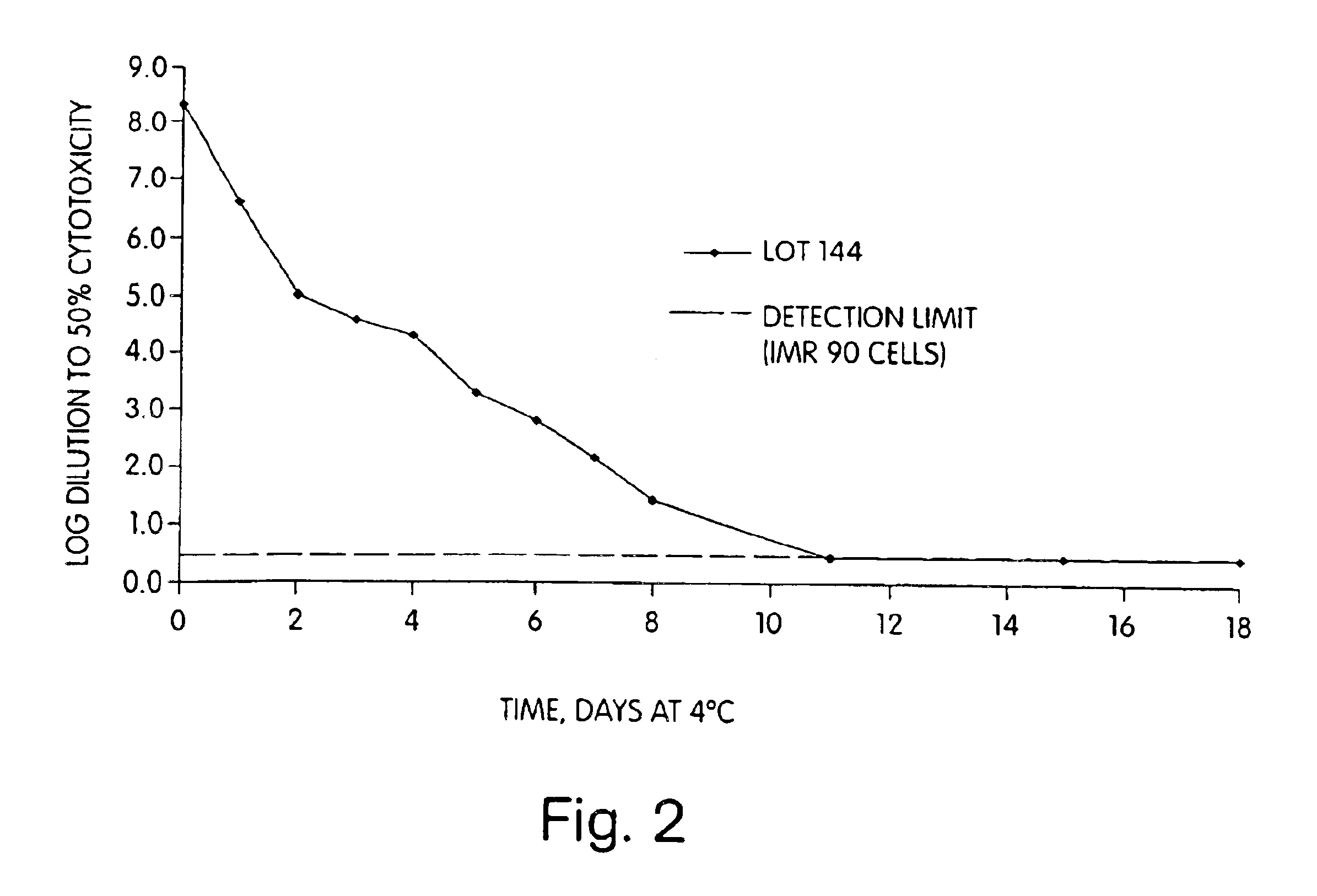
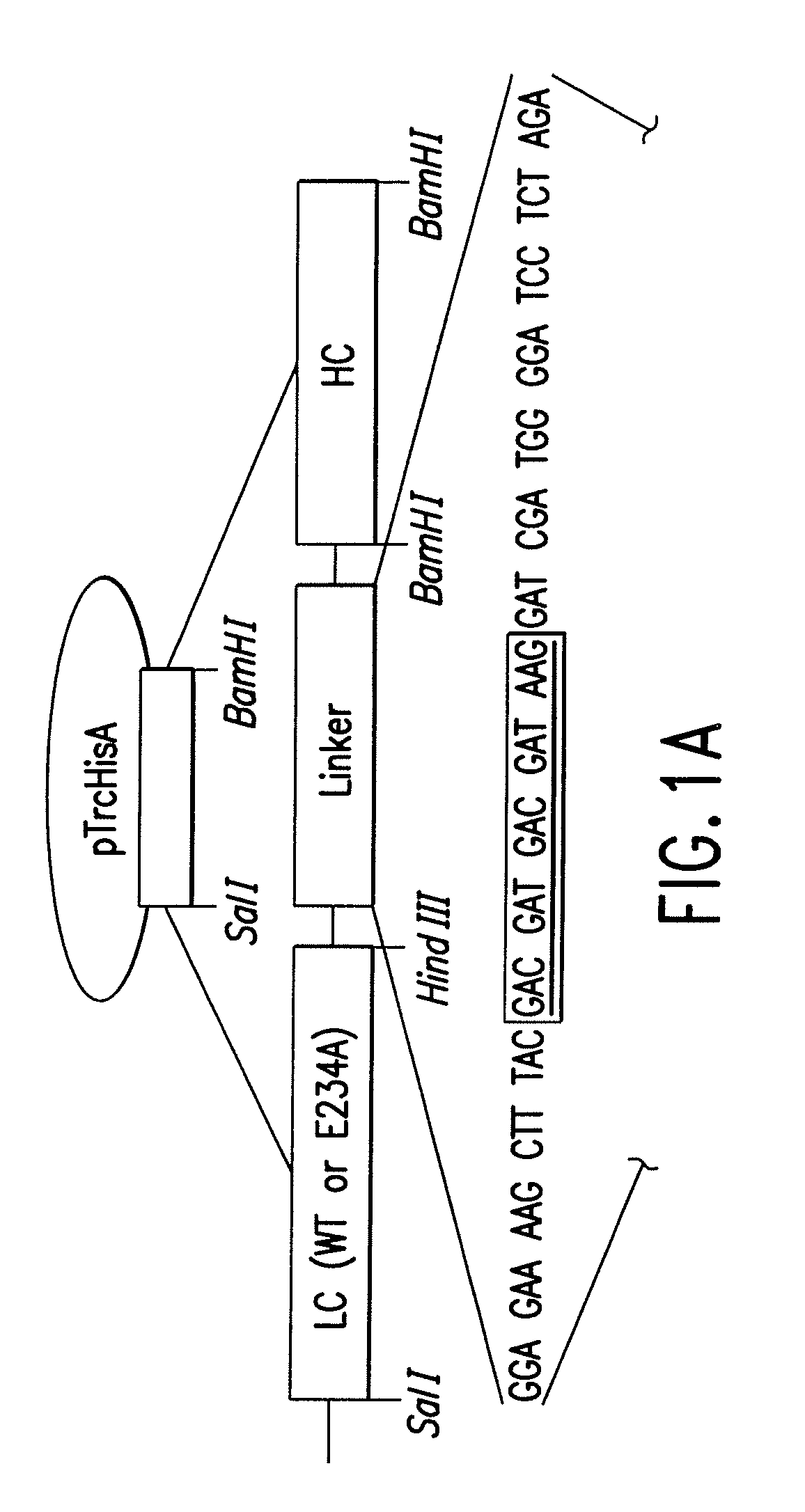
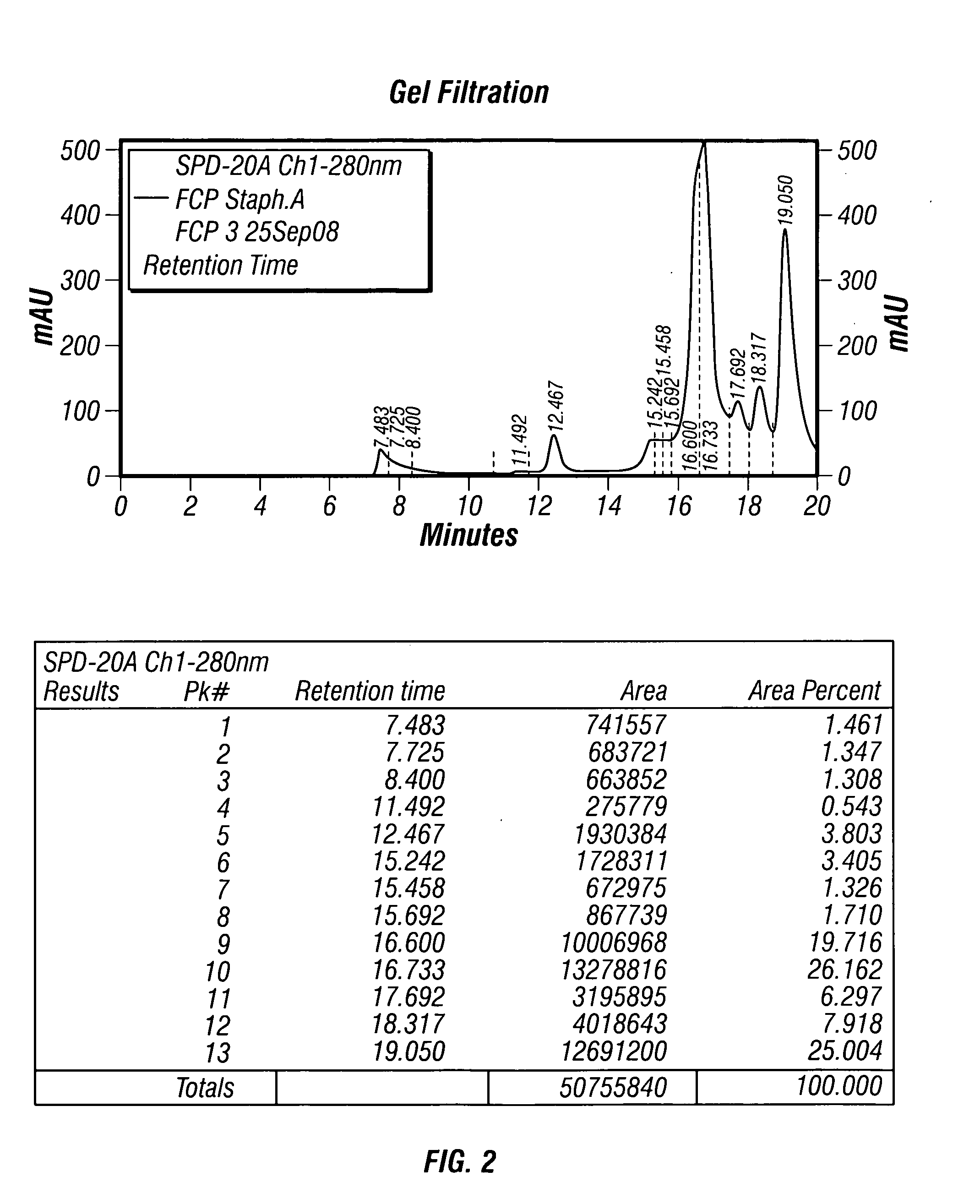
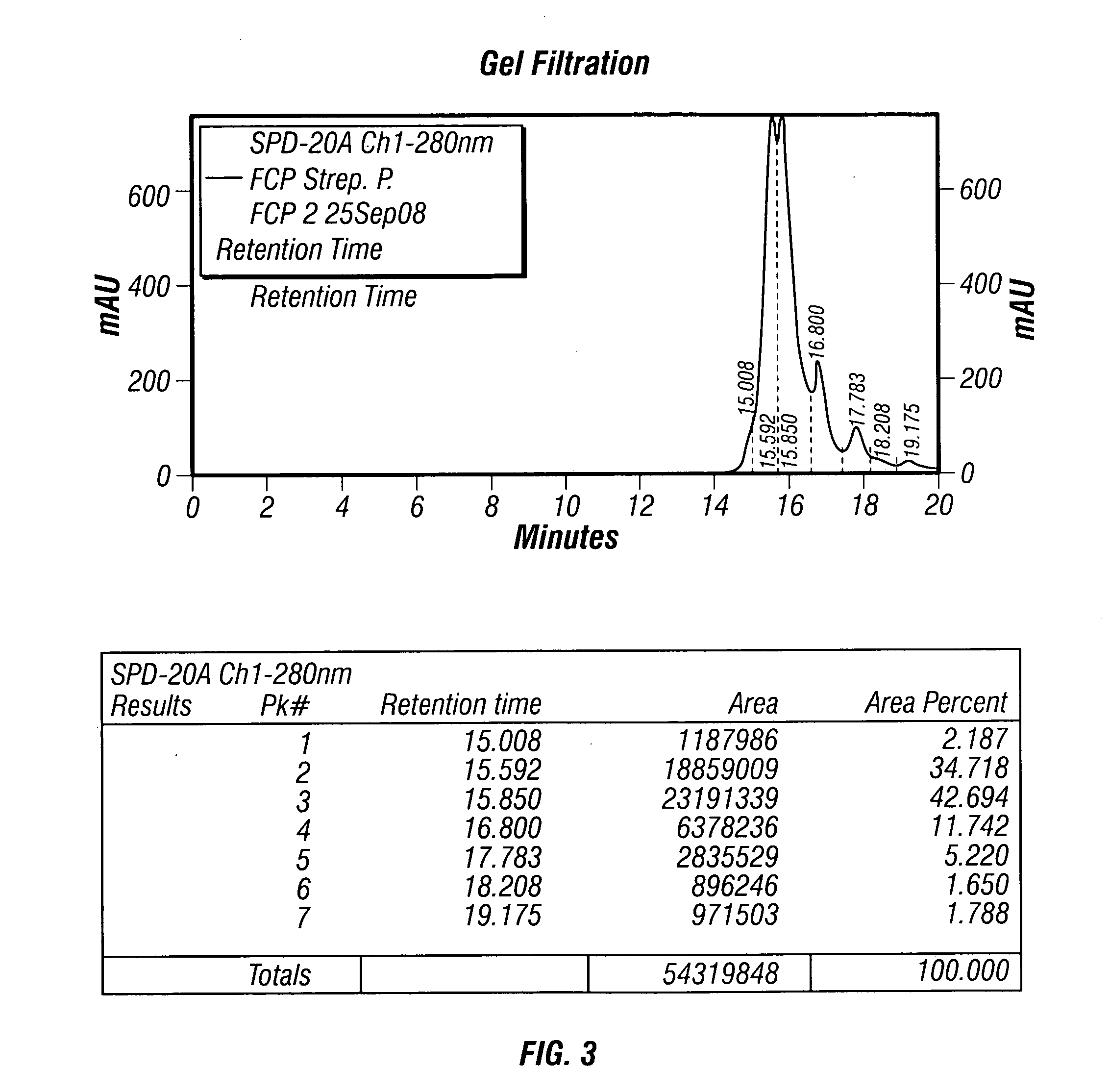
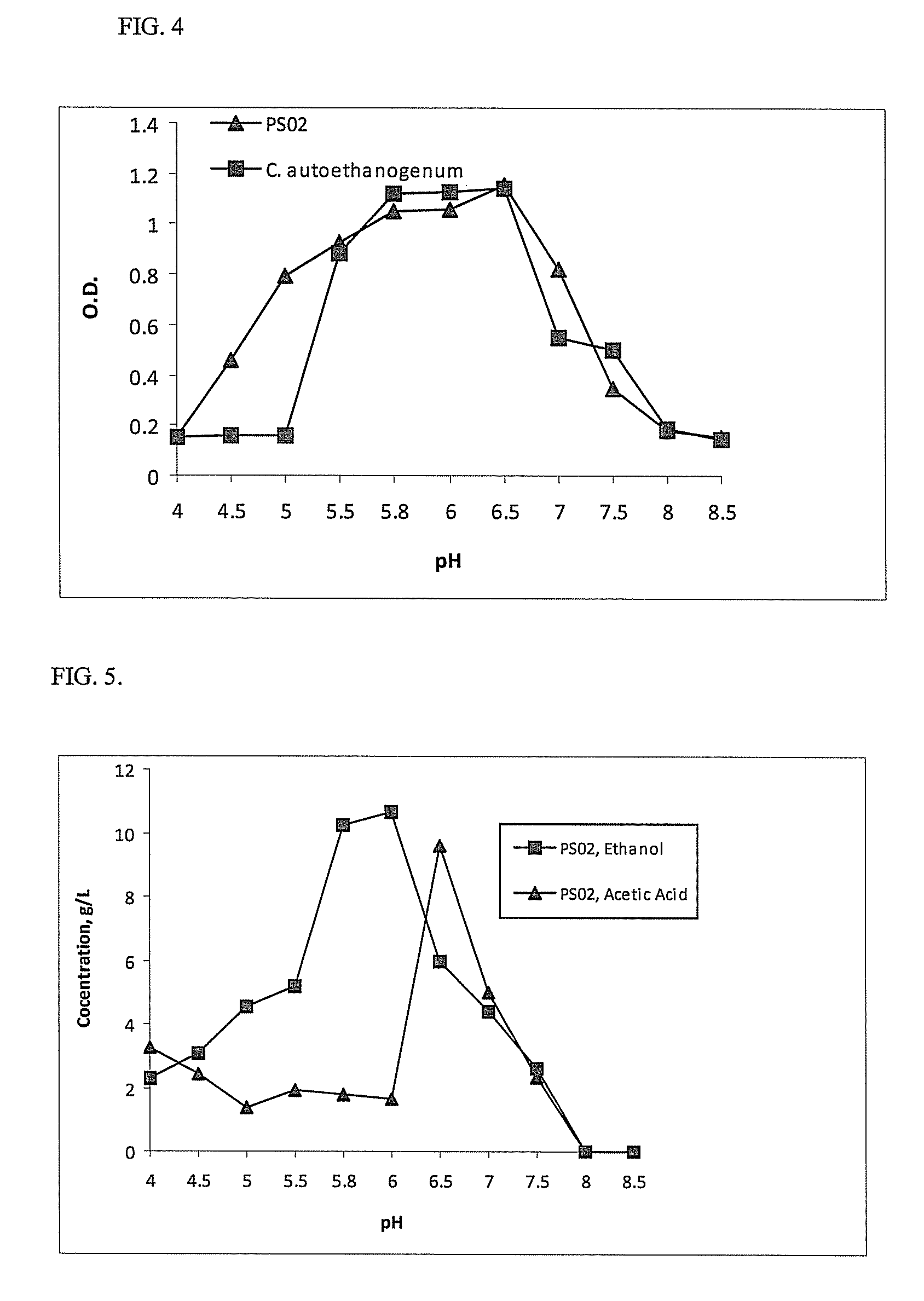
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
415 results about "Clostridium thermocellum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
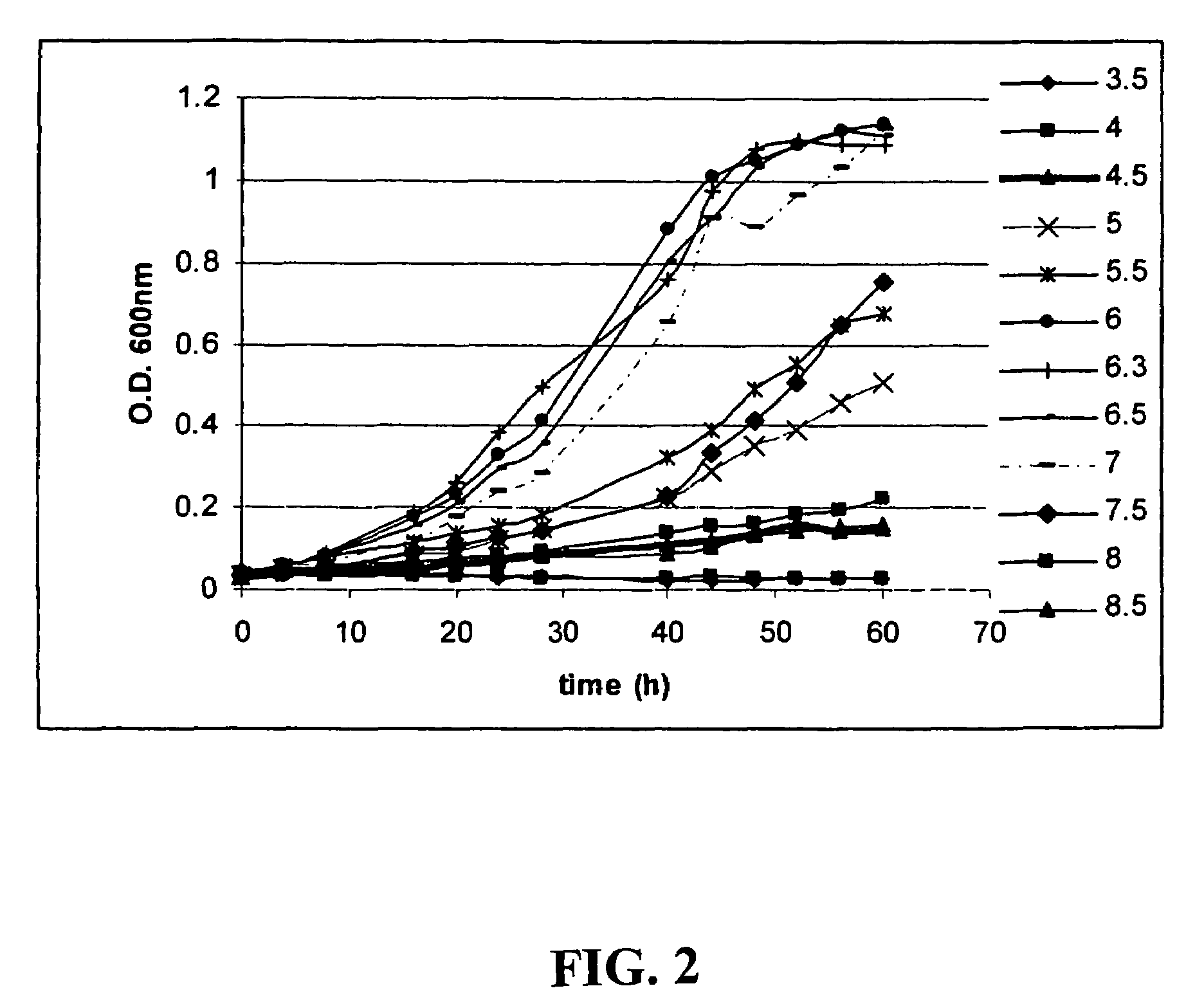
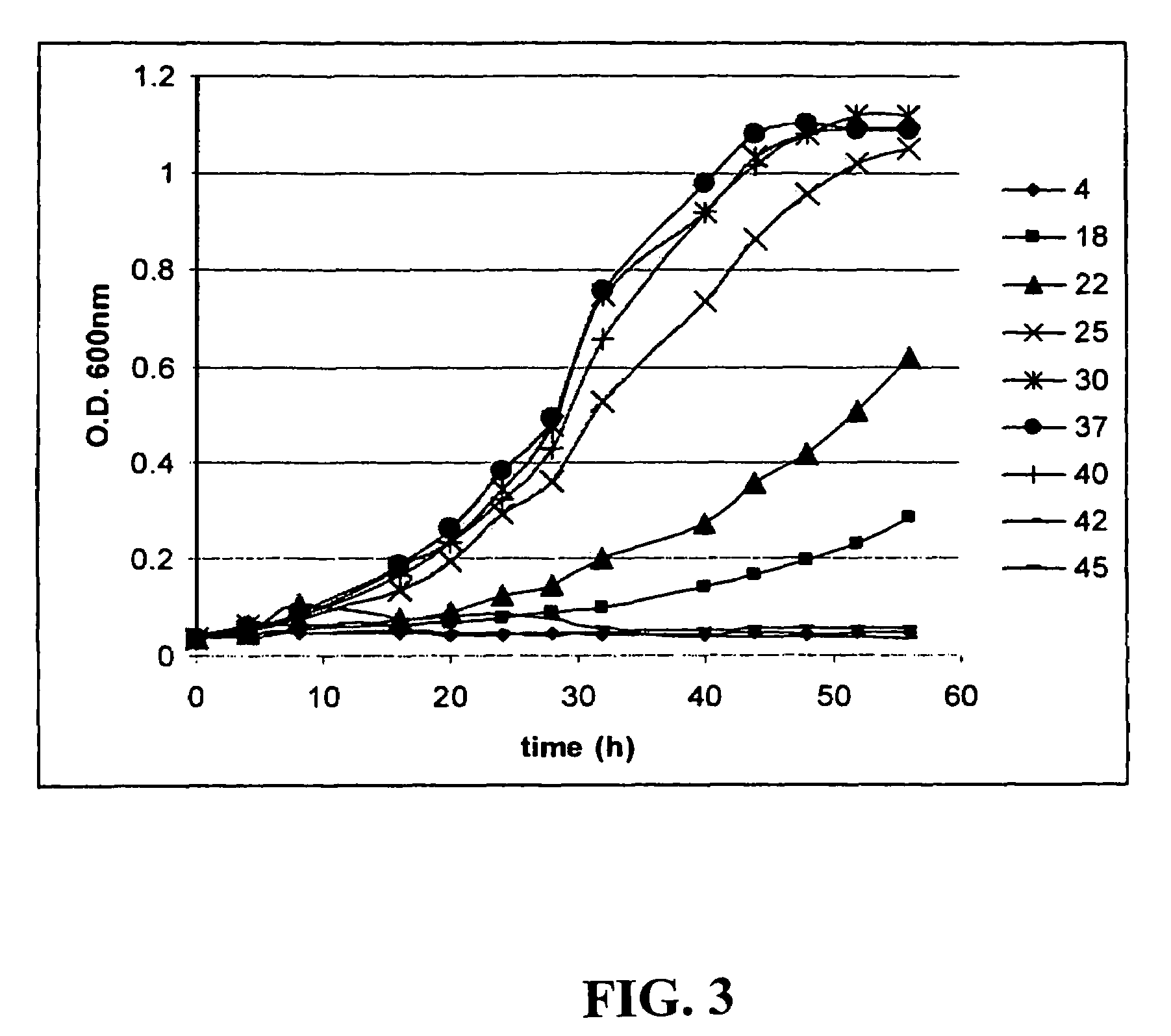
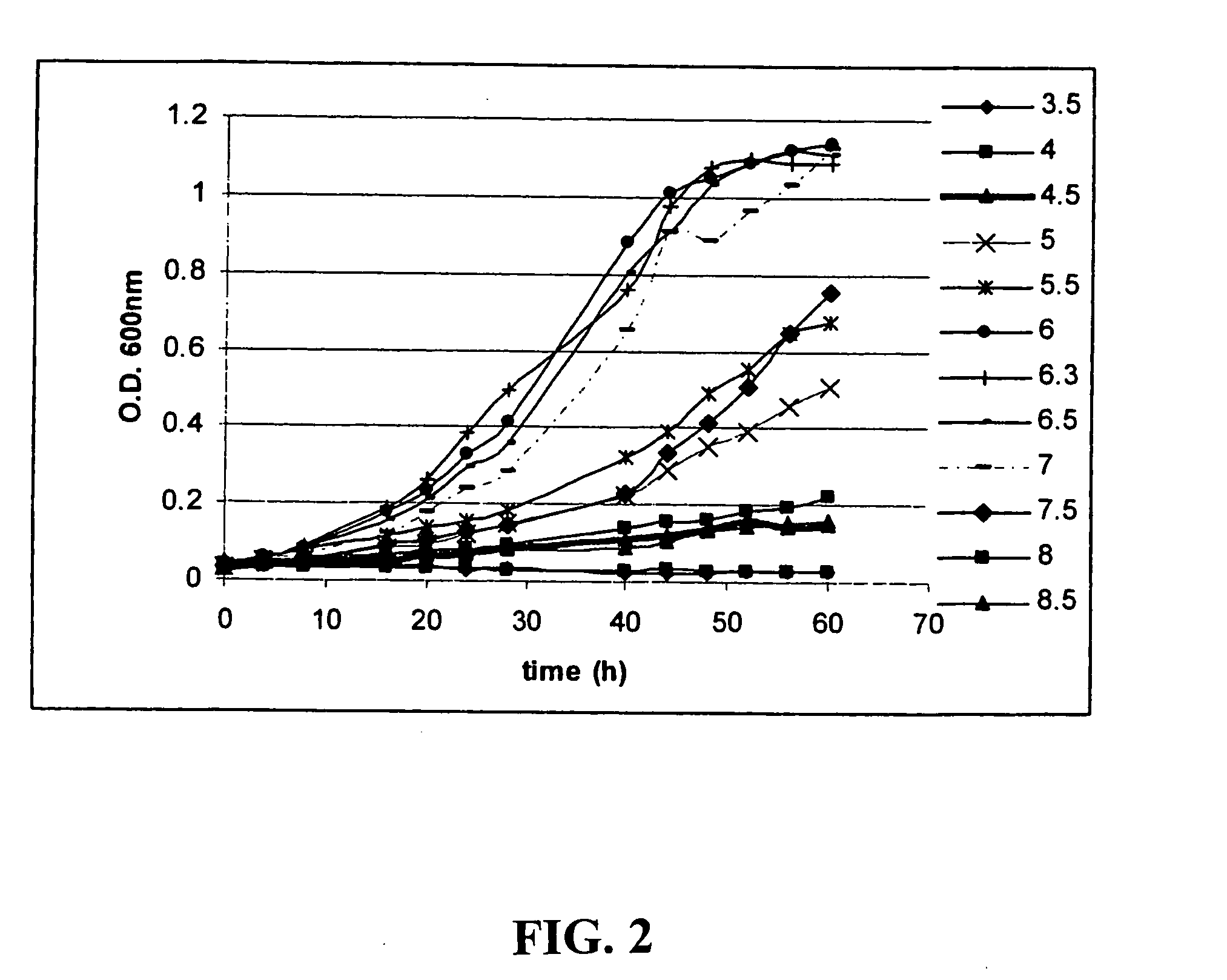
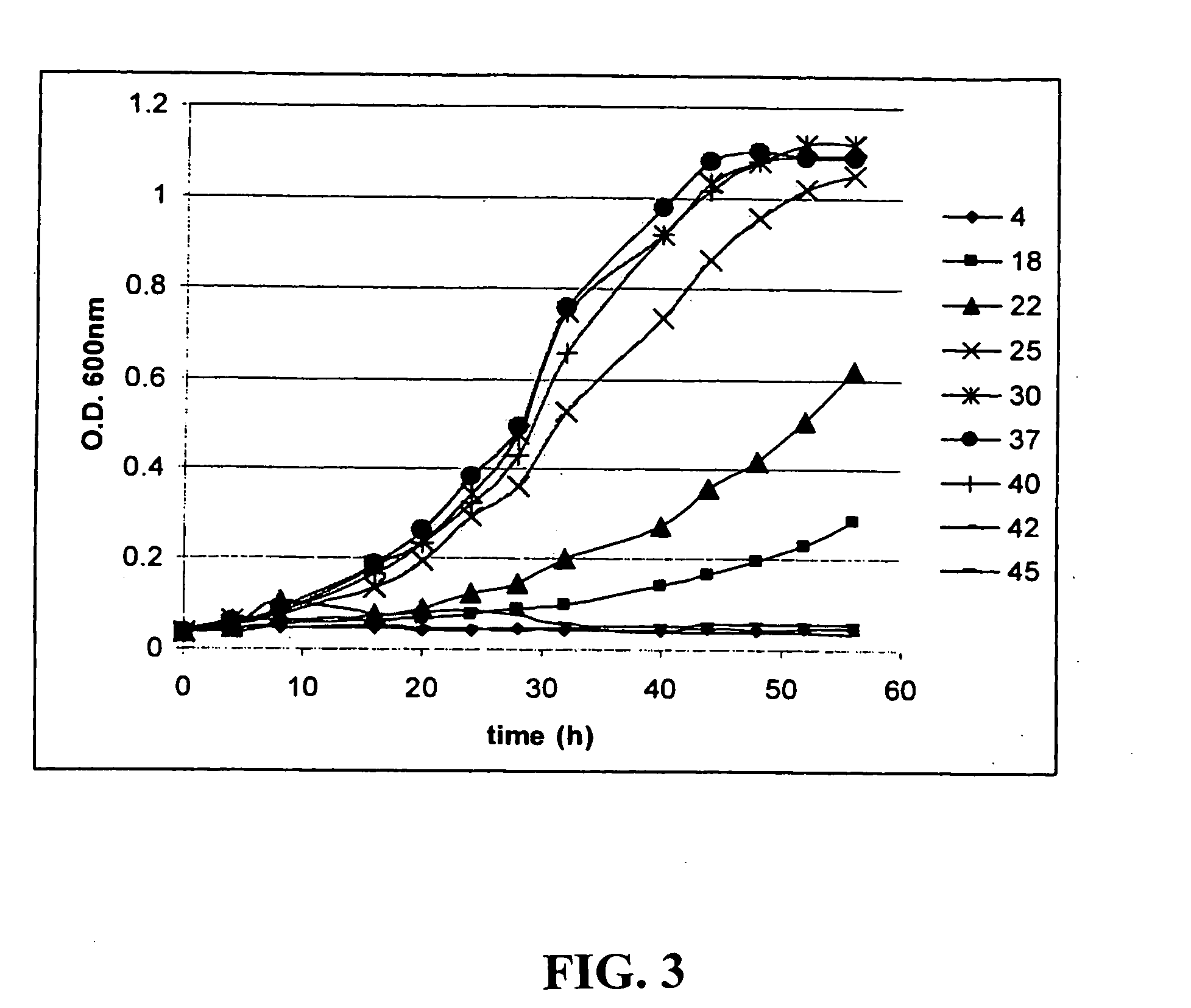
Clostridium thermocellum is an anaerobic, thermophilic bacterium. C. thermocellum has garnered research interest due to its cellulolytic and ethanologenic abilities, being capable of directly converting a cellulosic substrate into ethanol by consolidated bioprocessing. This makes it useful in converting biomass into a usable energy source. The degradation of the cellulose is carried out in the bacterium by a large extracellular cellulase system called a cellulosome, which contains nearly 20 catalytic subunits. The cellulase system of the bacterium significantly differs from fungal cellulases due to its high activity on crystalline cellulose, being able to completely solubilize crystalline sources of cellulose, such as cotton. However, there are some shortfalls in applying the organism to practical applications due to it having low ethanol yield, at least partially due to branched fermentation pathways that produce acetate, formate, and lactate along with ethanol. There is also evidence of inhibition due to the presence of hydrogen and due to agitation. Some recent research has been directed to optimizing the ethanol-producing metabolic pathway in hopes of creating more efficient biomass conversion.
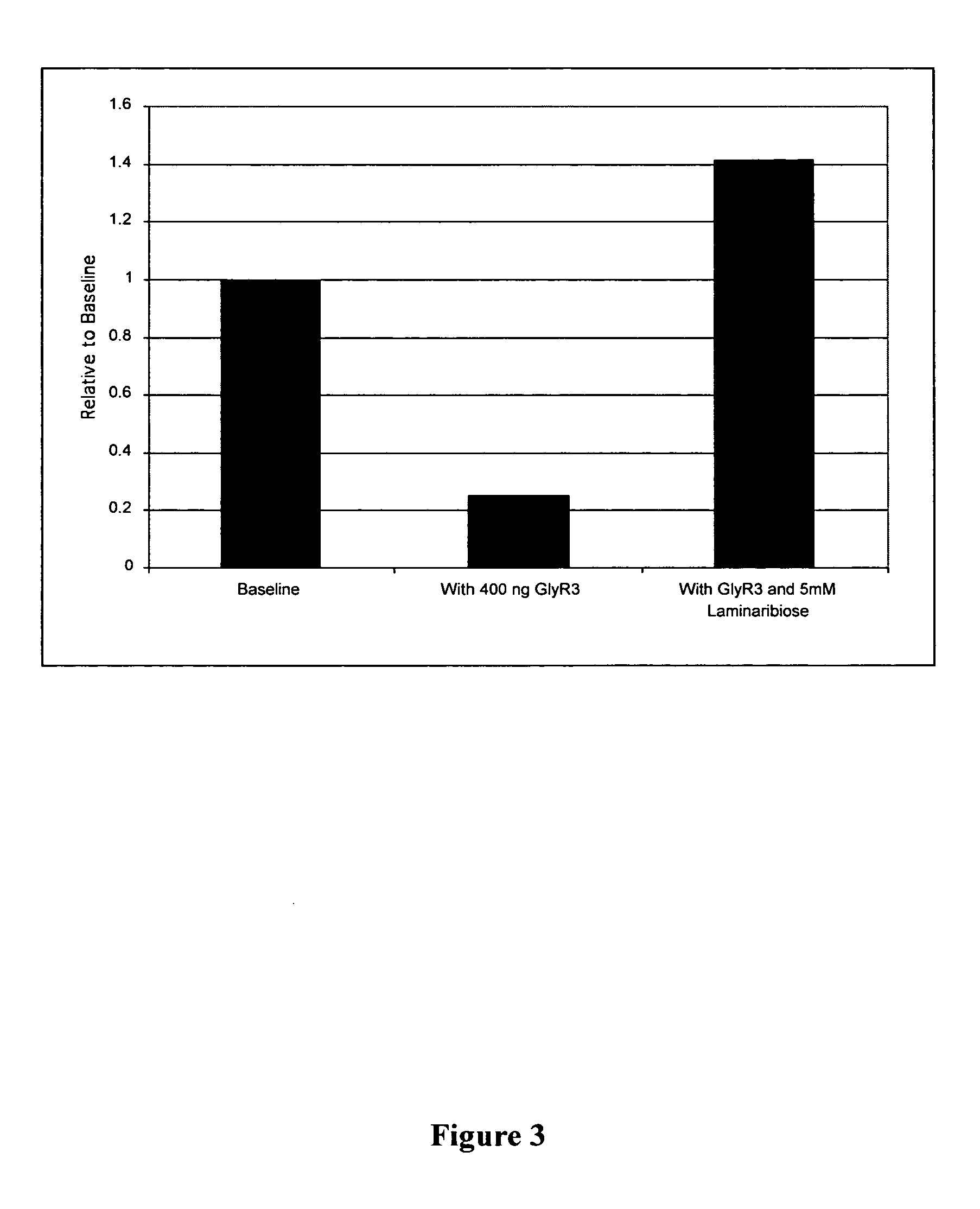
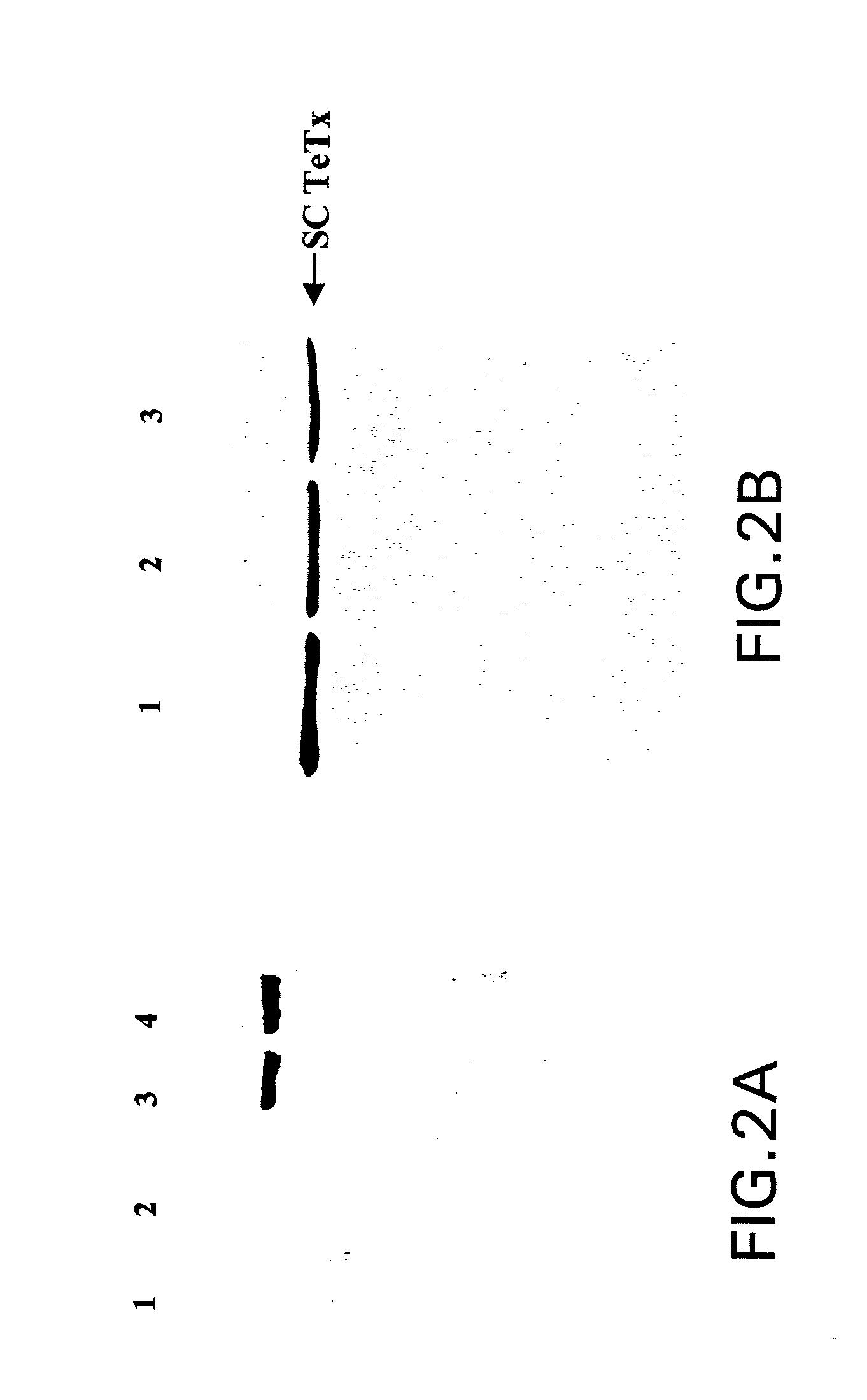
Clostridial toxin derivatives able to modify peripheral sensory afferent functions
InactiveUS6395513B1Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsClostridial toxinProjection neuron
The invention relates to an agent specific for peripheral sensory afferents. The agent may inhibit the transmission of signals between a primary sensory afferent and a projection neuron by controlling the release of at least one neurotransmitter or neuromodulator from the primary sensory afferent. The agent may be used in or as a pharmaceutical for the treatment of pain, particularly chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
Isolation and characterization of novel clostridial species
InactiveUS7704723B2High yieldReadily availableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSyngasAcetic acid
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium ragsdalei, ATCC BAA-622, “P11”) is provided. P11 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P11 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium transforms waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P11 also catalyzes the production of acetate.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Activatable clostridial toxins
InactiveUS20080032931A1Minimize security riskEnhanced efficiency and rateHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsClostridial toxinSaxitoxin
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Isolation and characterization of novel clostridial species
InactiveUS20080057554A1High yieldReadily availableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacteroidesAcetic acid
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium ragsdalei, ATCC BAA-622, “P11”) is provided. P11 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P11 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium transforms waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P11 also catalyzes the production of acetate.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Topically applied clostridium botulinum toxin compositions and treatment methods
InactiveUS20030113349A1Efficient use ofBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsChromhidrosisSeborrheic dermatitis
Hyperactive glandular conditions are treated using topically formulated botulinum toxin compositions. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, topical botulinum preparations are applied directly to the skin by a patient as needed to suppress his or her hyperhidrosis, bromhidrosis, chromhidrosis, nevus sudoriferous, acne, seborrhiec dermatitis or other glandular condition. In other embodiments, topical botulinum toxins are applied with the aid of mechanical, electrical, and / or chemical transdermal delivery enhancers.
Owner:COLEMAN WILLIAM P III
Fret protease assays for botulinum serotype A/E toxins
InactiveUS7208285B2Used to determineDecreased acceptor fluorescence intensityBacteriaSugar derivativesFluorophoreReceptor for activated C kinase 1
The present invention provides clostridial toxin substrates useful in assaying for the protease activity of any clostridial toxin, including botulinum toxins of all serotypes as well as tetanus toxins. A clostridial toxin substrate of the invention contains a donor fluorophore; an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence that includes a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor and where, under the appropriate conditions, resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Conjugates of galactose-binding lectins and clostridial neurotoxins as analgesics
InactiveUS7052702B1Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderBacteriaGalactose binding lectinProtein translocation
A class of novel agents that are able to modify nociceptive afferent function is provided. The agents may inhibit the release of neurotransmitters from discrete populations of neurones and thereby reduce or preferably prevent the transmission of afferent pain signals from peripheral to central pain fibers. They comprise a galactose-binding lectin linked to a derivative of a clostridial neurotoxin. The derivative of the clostridial neurotoxin comprises the L-chain, or a fragment thereof, which includes the active proteolytic enzyme domain of the light (L) chain, linked to a molecule or domain with membrane translocating activity. The agents may be used in or as pharmaceuticals for the treatment of pain, particularly chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
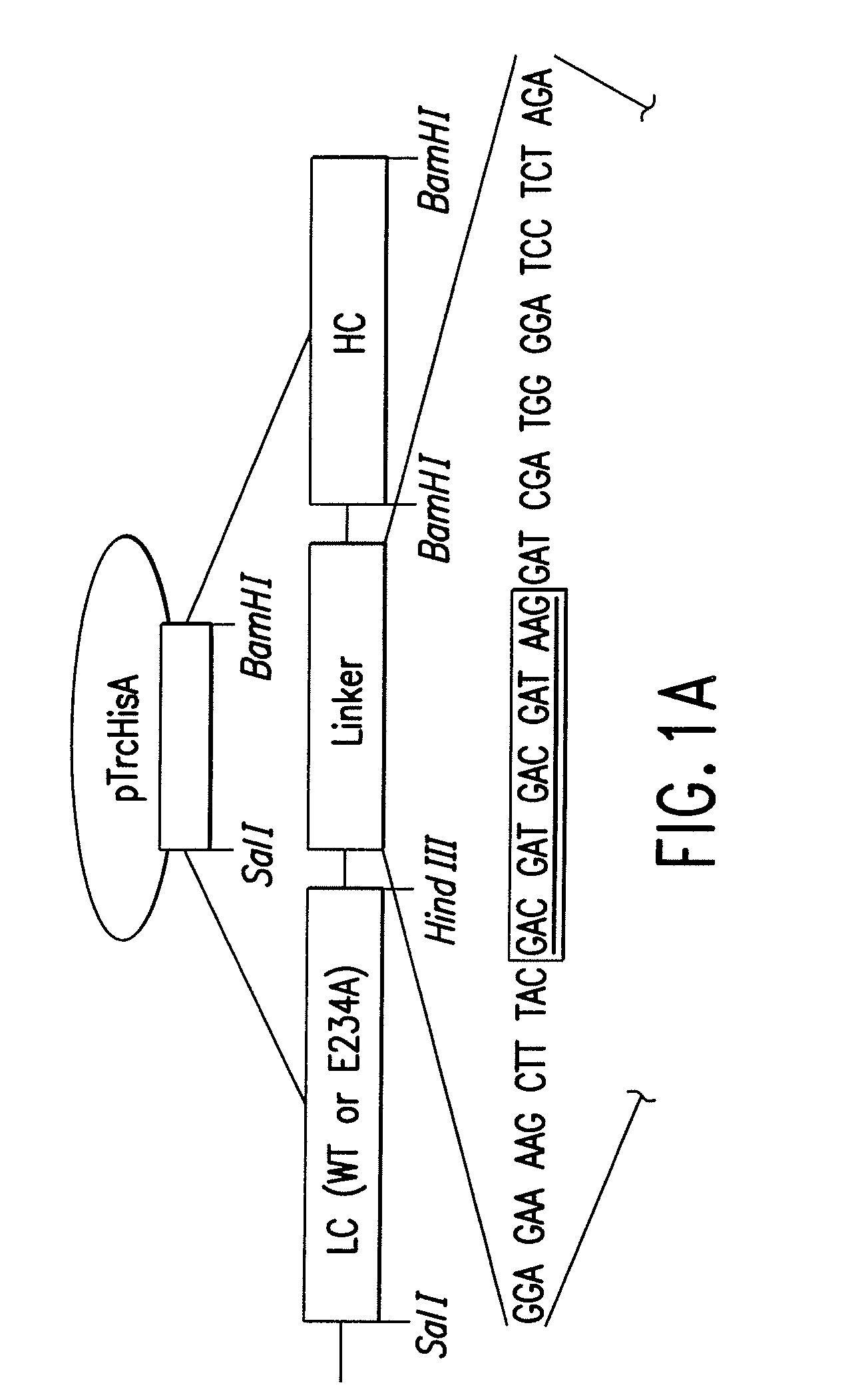
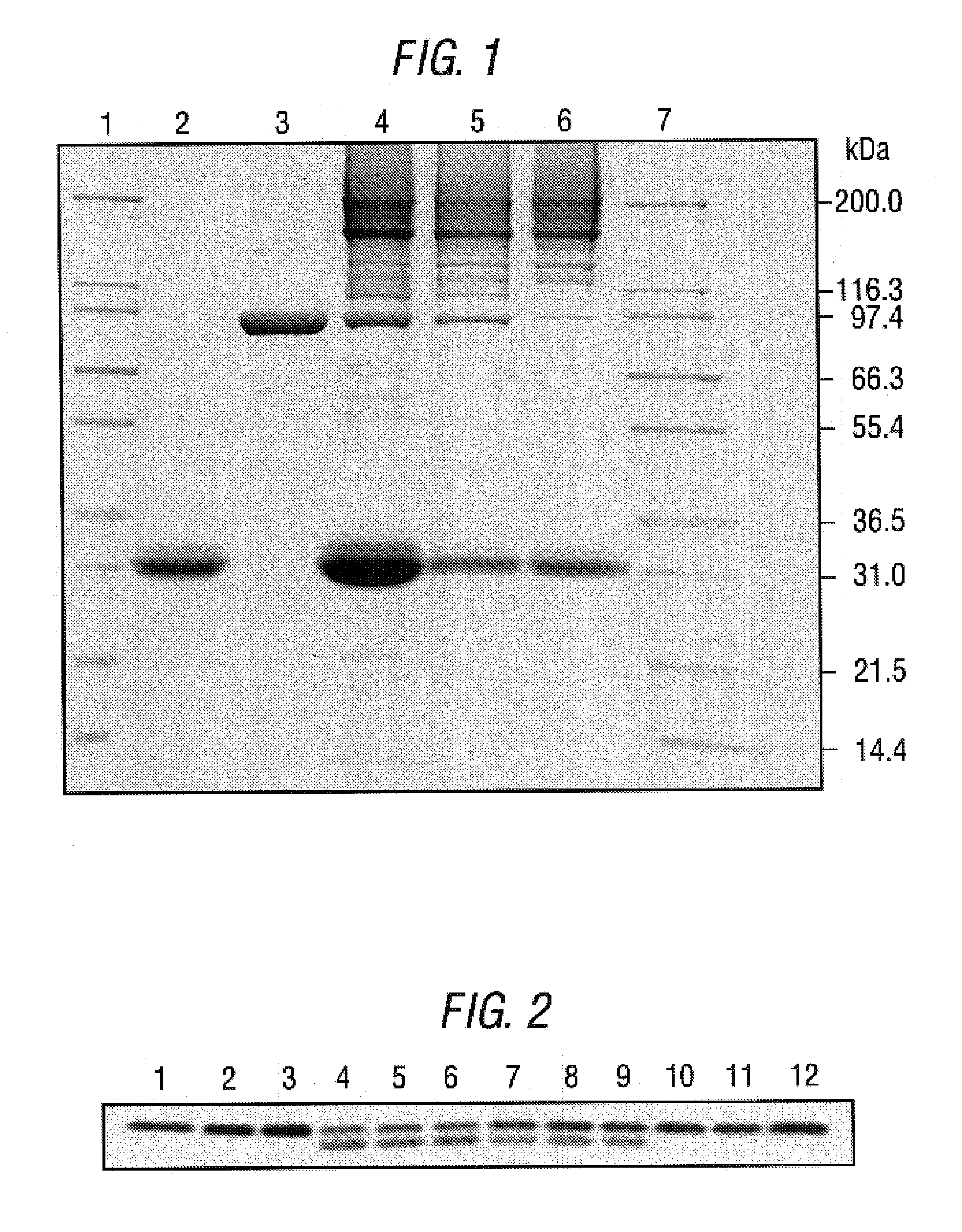
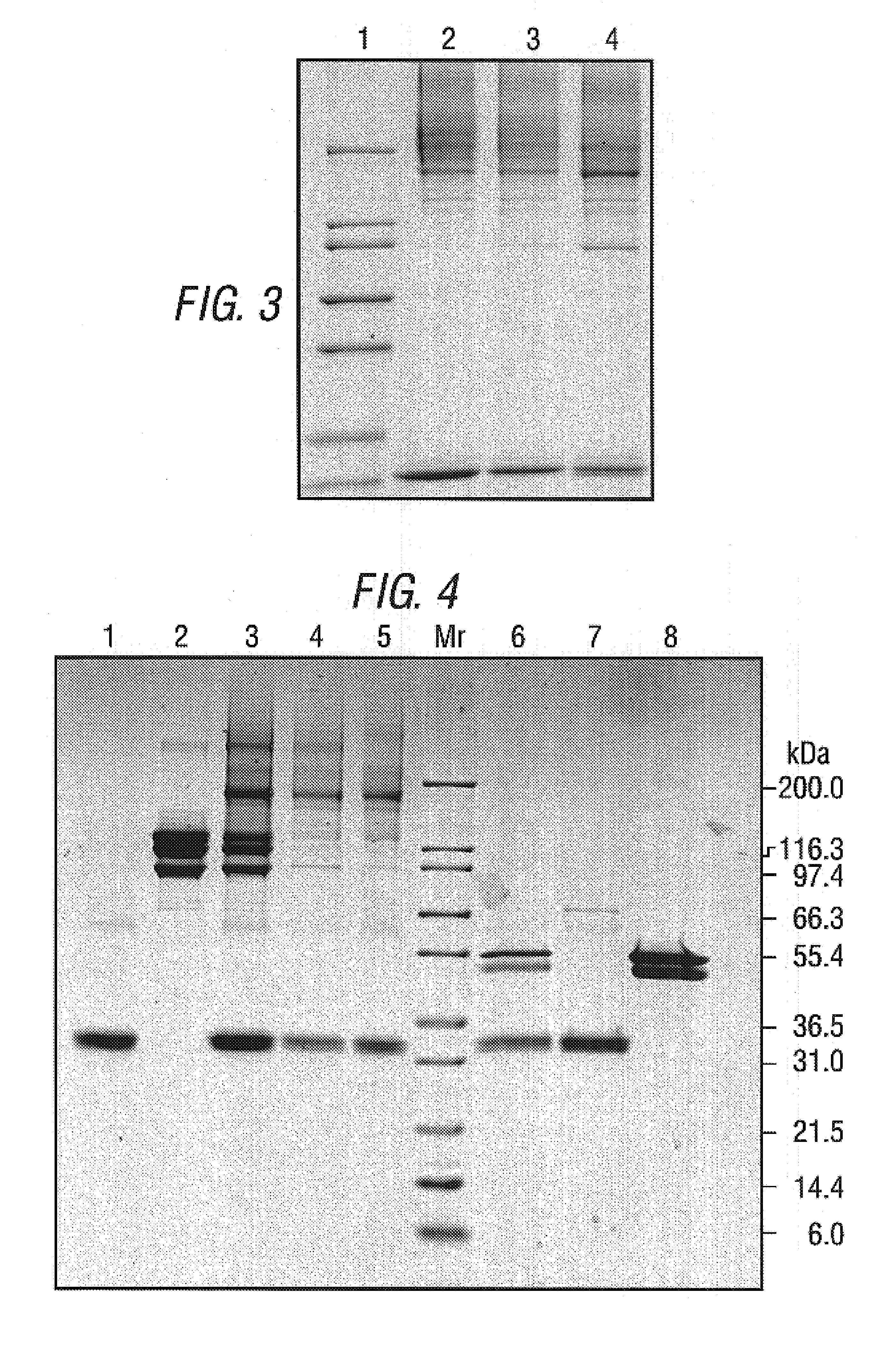
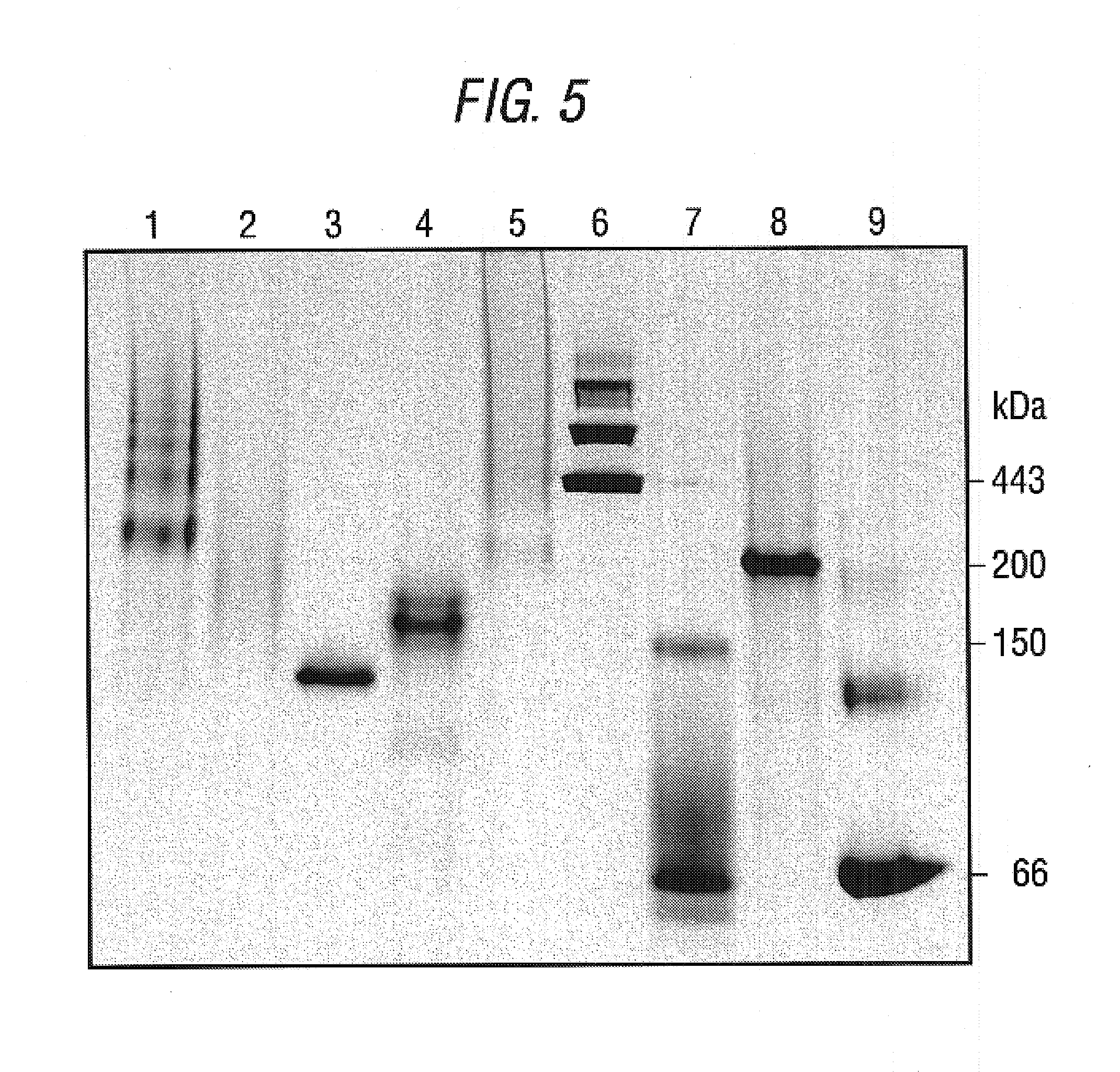
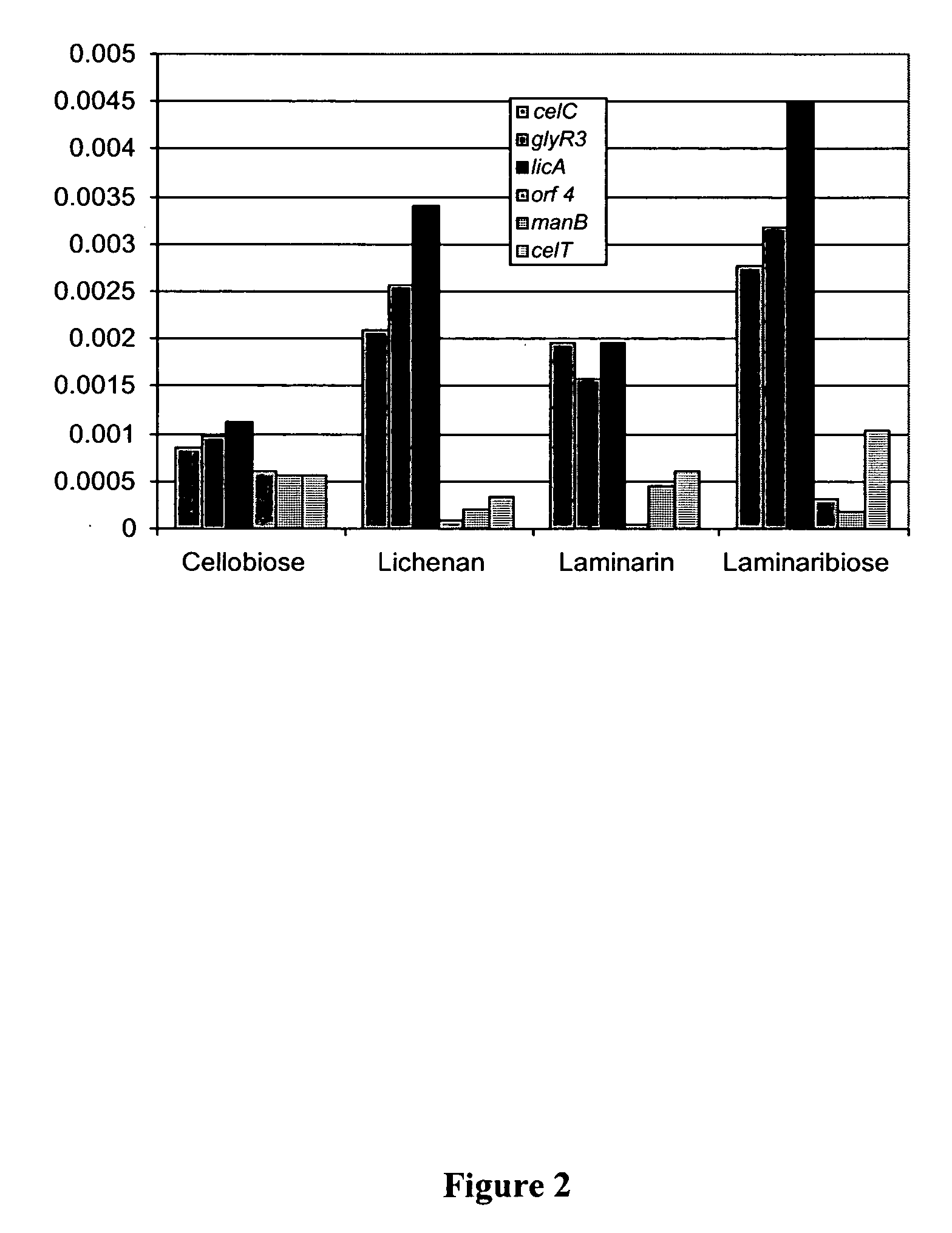
Promoters and proteins from Clostridium thermocellum and uses thereof
The present invention relates to an inducible and a high expression nucleic acid promoter isolated from Clostridium thermocellum. These promoters are useful for directing expression of a protein or polypeptide encoded by a nucleic acid molecule operably associated with the nucleic acid promoters. The present invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs including the C. thermocellum promoters, and expression vectors and hosts containing such nucleic acid constructs. The present invention also relates to protein isolated from Clostridium thermocellum, including a repressor protein. The present invention also provides methods of using the isolated promoters and proteins from Clostridium thermocellum, including methods for directing inducible in vitro and in vivo expression of a protein or polypeptide in a host, and methods of producing ethanol from a cellulosic biomass.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
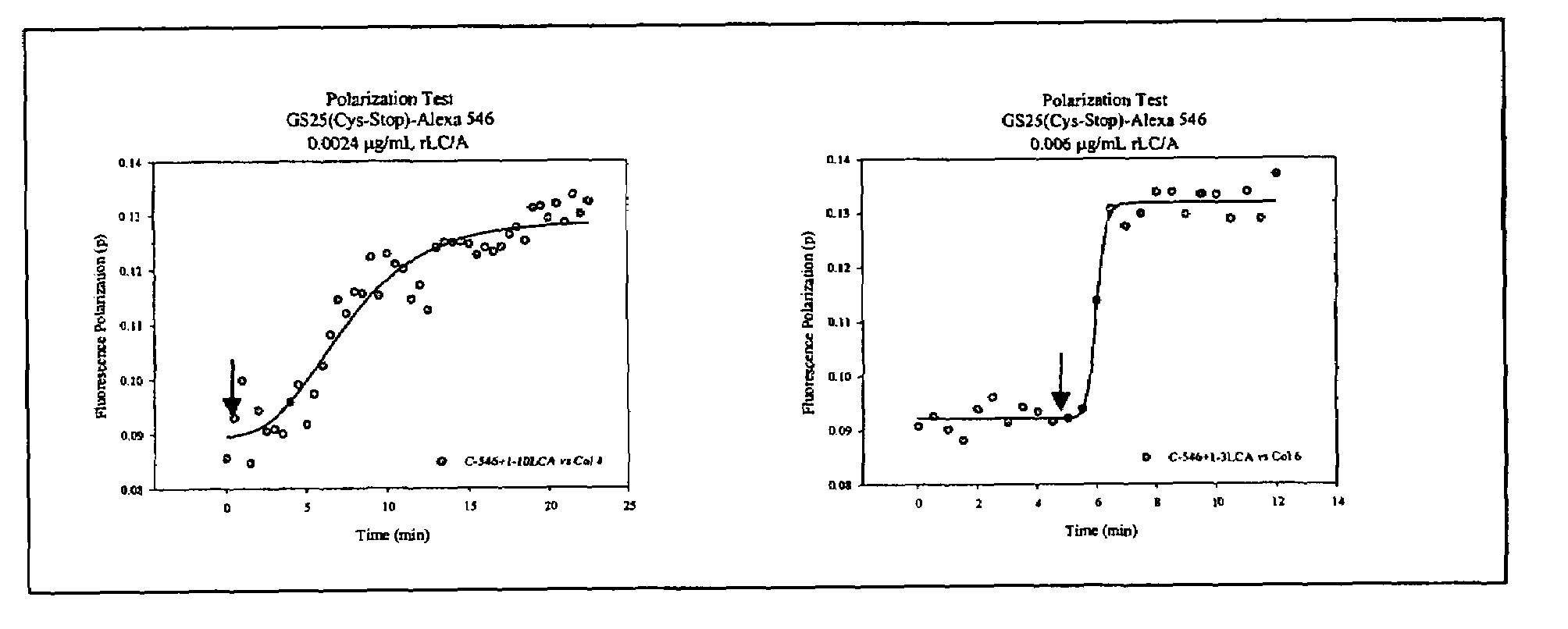
Fluorescence polarization assays for determining clostridial toxin activity
The present invention provides a method of determining the presence or activity of a clostridial toxin by (a) treating with a sample, under conditions suitable for clostridial toxin protease activity, a clostridial toxin substrate which includes a fluorophore; a bulking group; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site that intervenes between the fluorophore and the bulking group; (b) exciting the fluorophore with plane polarized light; and (c) determining fluorescence polarization of the treated substrate relative to a control substrate, where a change in fluorescence polarization of the treated substrate as compared to fluorescence polarization of the control substrate is indicative of the presence or activity of the clostridial toxin.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Active immunization against clostridium difficile disease
InactiveUS6969520B2Prevent relapseImmune responseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseasePassive Immunizations
The invention provides active and passive immunization methods for preventing and treating Clostridium difficile infection, which involve percutaneous administration of C. difficile toxin-neutralizing polyclonal immune globulin, C. difficile toxoids, or combinations thereof. Also provided by the invention are C. difficile toxoids, C. difficile toxin-neutralizing polyclonal immune globulin, and methods of identifying subjects that produce C. difficile toxin-neutralizing polyclonal immune globulin.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR BIOLOGICS CO
Activatable clostridial toxins
InactiveUS20090018081A1Long duration of therapyOvercome resistanceHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsClostridial toxinNucleic acid
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
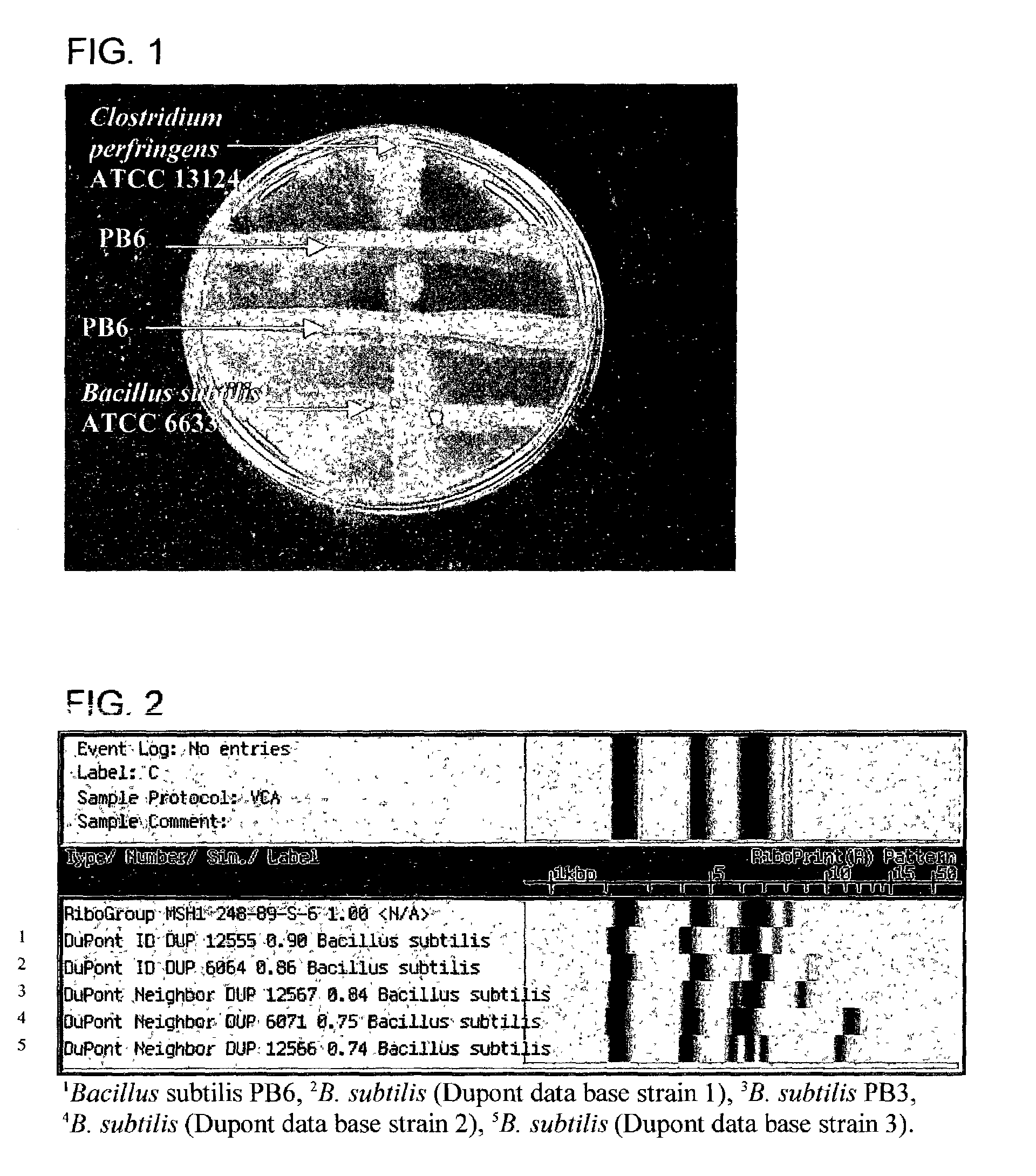
Antimicrobial compounds from Bacillus subtilis for use against animal and human pathogens
ActiveUS7247299B2Enhanced inhibitory effectRetain viabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacillus perfringensClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Antimicrobial compounds from Bacillus subtilis for use against animal and human pathogens. A novel strain of Bacillus subtilis was isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of poultry and was found to produce a factor or factors that have excellent inhibitory effects on Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium difficile, Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. The factor(s) retain full viability and antimicrobial activity after heat treatment. The invention provides a method of treatment of pathogenic microorganisms including C. perfringens.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Clostridial toxin derivatives able to modify peripheral sensory afferent functions
InactiveUS20030049264A1Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderHydrolasesClostridial toxinMedicine
The invention relates to an agent specific for peripheral sensory afferents. The agent may inhibit the transmission of signals between a primary sensory afferent and a projection neutron by controlling the release of at least one neurotransmitter or neuromodulator from the primary sensory afferent. The agent may be used in or as a pharmaceutical for the treatment of pain, particularly chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
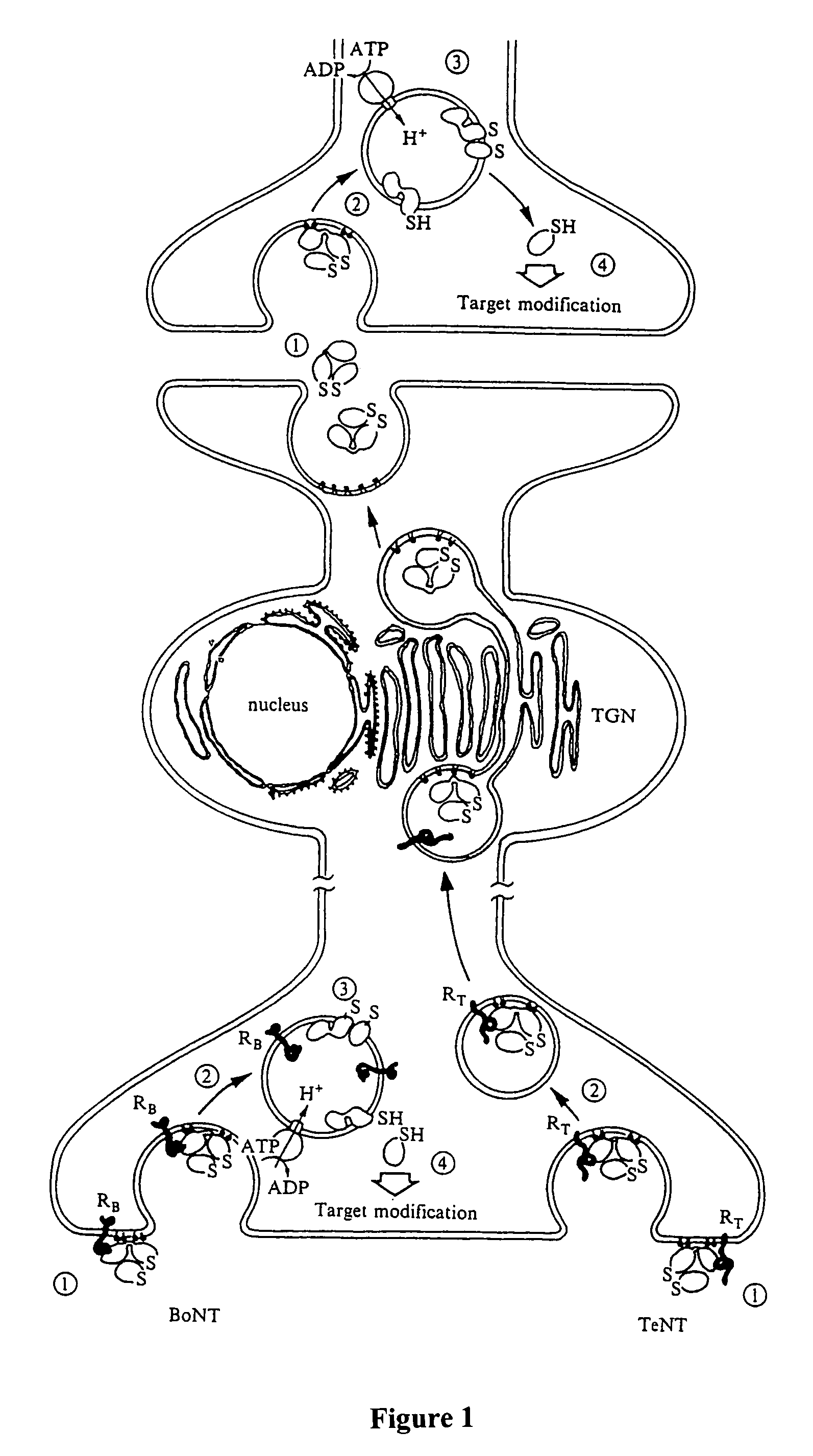
Modified clostridial neurotoxins with altered biological persistence
InactiveUS20020127247A1Increase and decrease persistenceIncrease or decrease stabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseToxin
The present invention discloses modified neurotoxins with altered biological persistence. In one embodiment, the modified neurotoxins are derived from Clostridial botulinum toxins. Such modified neurotoxins may be employed in treating various conditions, including but not limited to muscular disorders, hyperhidrosis, and pain.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Conjugates of galactose-binding lectins and clostridial neurotoxins as analgesics
InactiveUS7452543B2Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderBacteriaGalactose binding lectinProtein translocation
A class of novel agents that are able to modify nociceptive afferent function is provided. The agents may inhibit the release of neurotransmitters from discrete populations of neurones and thereby reduce or preferably prevent the transmission of afferent pain signals from peripheral to central pain fibers. They comprise a galactose-binding lectin linked to a derivative of a clostridial neurotoxin. The derivative of the clostridial neurotoxin comprises the L-chain, or a fragment thereof, which includes the active proteolytic enzyme domain of the light (L) chain, linked to a molecule or domain with membrane translocating activity. The agents may be used in or as pharmaceuticals for the treatment of pain, particular chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY
Affinity purified human polyclonal antibodies and methods of making and using them
The present invention describes a method for treating, removing or preventing a bacterial infection, which method comprises administering to a human suffering, suspected of suffering or at risk of suffering from Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infection, a Streptococcus infection, Escherichia coli (E. coli) infection, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) infection, Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) infection, Enterococcus faecium (E. faecium) infection and / or Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) infection, an effective amount of human polyclonal antibodies affinity purified from a human blood sample with an antigenic preparation comprising cellular and / or secreted antigen(s) from bacterial cells selected from S. aureus, a Streptococcus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, E. faecium, C. difficile or a combination thereof, and optionally, wherein said affinity purified human polyclonal antibodies are purified (e.g., as made more concentrated as compared to the starting or unpurified material) relative to the same human polyclonal antibodies in the unpurified or non-affinity-purified human blood sample, e.g., intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) sample, and / or also optionally, wherein said affinity purified human polyclonal antibodies are specific for the bacterial antigens used in the affinity purification, and / or further optionally wherein the affinity purified human polyclonal antibodies are substantially free of human antibodies that specifically bind to non-bacterial antigens in the human blood sample. Pharmaceutical compositions for treating bacterial infections, comprising an effective amount of human polyclonal antibodies affinity purified from a human blood sample with an antigenic preparation comprising cellular and / or secreted antigen(s) from S. aureus, Streptococcus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, E. faecium, C. difficile or a combination thereof, are also provided.
Owner:SCANTIBODIES LAB
Ethanologenic Clostridium species, Clostridium coskatii
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Compositions relating to a mutant clostridium difficile toxin and methods thereof
ActiveUS20120269841A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin BNucleotide
In one aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic composition that includes a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin A and / or a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin B. Each mutant toxin includes a glucosyltransferase domain having at least one mutation and a cysteine protease domain having at least one mutation, relative to the corresponding wild-type C. difficile toxin. The mutant toxins may further include at least one amino acid that is chemically crosslinked. In another aspect, the invention relates to antibodies or binding fragments thereof that binds to said immunogenic compositions. In further aspects, the invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences that encode any of the foregoing, and methods of use of any of the foregoing compositions.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Soluble recombinant botulinum toxin proteins
The present invention includes recombinant proteins derived from Clostridium botulinum toxins. In particular, soluble recombinant Clostridium botulinum type A, type B and type E toxin proteins are provided. Methods which allow for the isolation of recombinant proteins free of significant endotoxin contamination are provided. The soluble, endotoxin-free recombinant proteins are used as immunogens for the production of vaccines and antitoxins. These vaccines and antitoxins are useful in the treatment of humans and other animals at risk of intoxication with clostridial toxin.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Oxazolidinone piperazinyl derivatives as potential antimicrobials
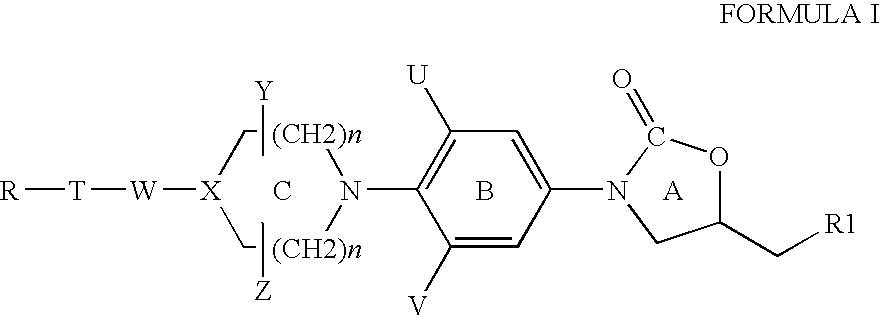
InactiveUS6956040B2High antibacterial activityTreatment safetyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAcid-fastGram
The present invention relates to certain substituted phenyl piperazinyl oxazolidinones, for example, to those having the structure of Formula I with the variables as defined within, and to processes for the synthesis of the same. This invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of the present invention as antimicrobials. The compounds are useful antimicrobial agents, effective against a number of human and veterinary pathogens, including gram-positive aerobic bacteria such as multiply-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci as well as anaerobic organisms such as Bacterioides spp. and Clostridia spp. species, and acid fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium spp.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
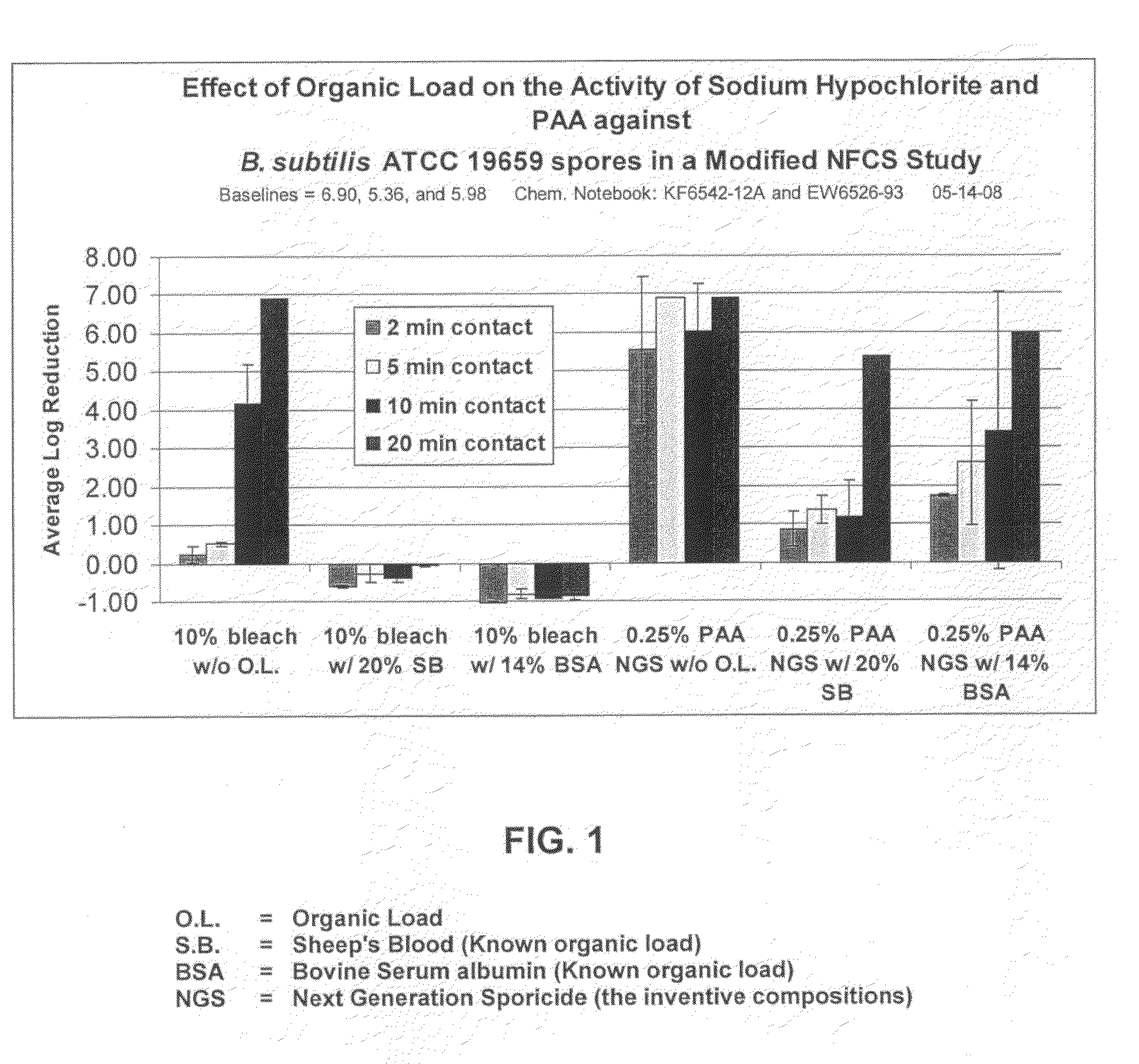
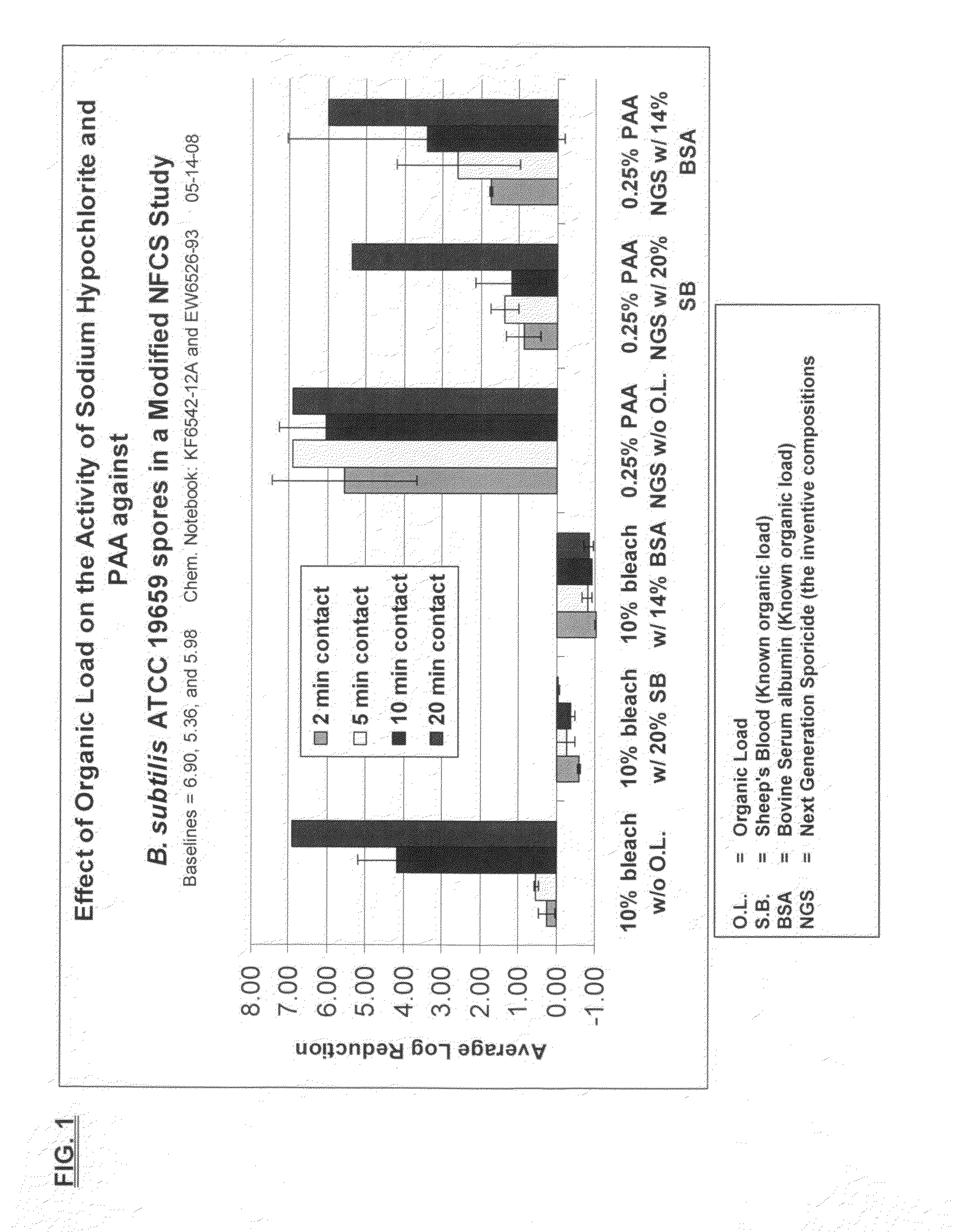
Low odor, hard surface sporicide
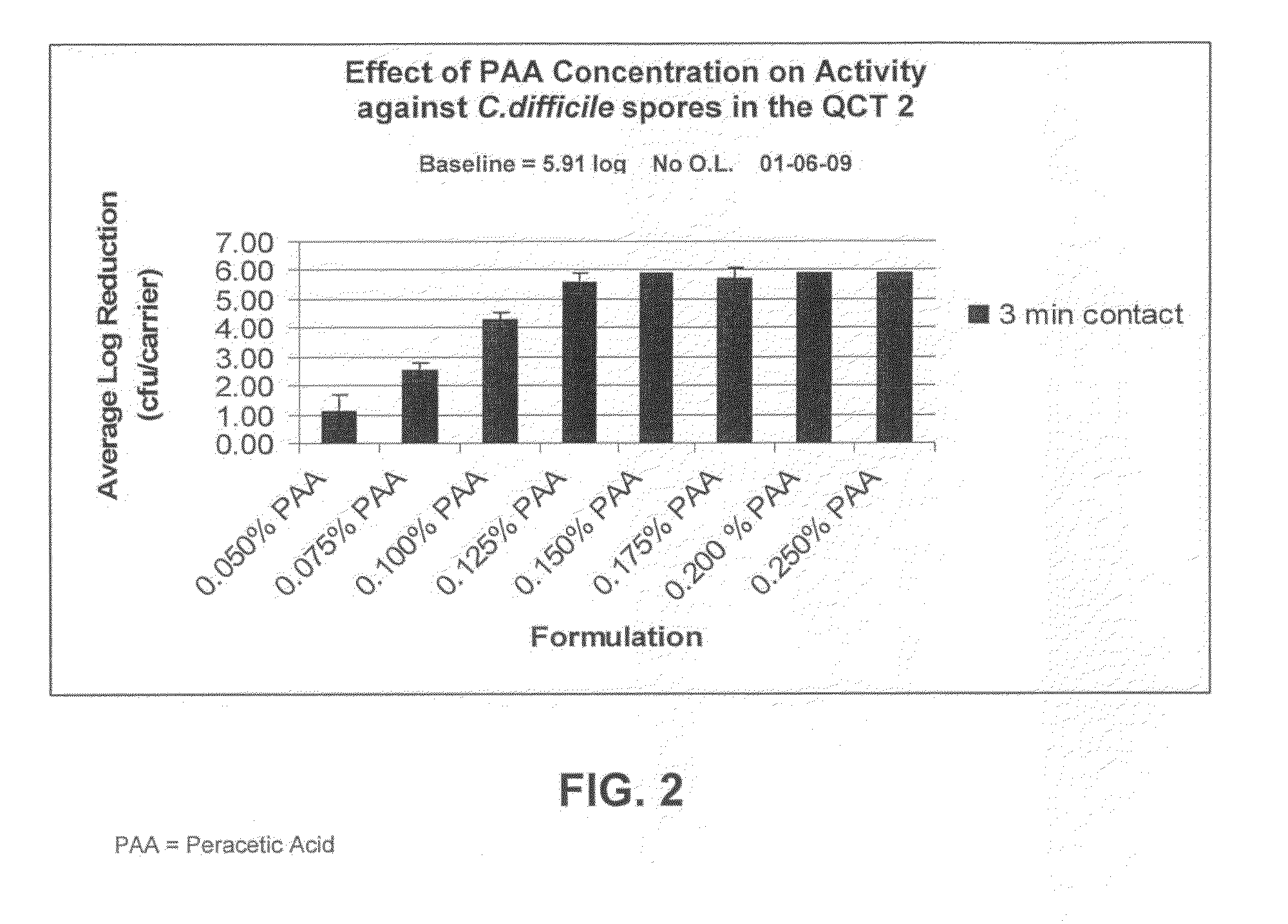
ActiveUS20100196503A1Safer and easy to handleSafer and easy to and transportBiocidePeroxide active ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin BNuclear chemistry
A low odor, liquid disinfectant composition comprising multiple components, which, upon mixing, provide an aqueous solution comprising low levels of peracetic acid for use in decontaminating articles and surfaces contaminated with bacteria, viruses, fungi and other biological contaminants such as spores, including, but not limited to, Clostridium difficile (C.diff). The disinfectant composition is prepared just prior to use by combining two or more separately packaged components.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
Low odor, hard surface sporicides and chemical decontaminants
ActiveUS20100196505A1Safer and easy to handleSafer and easy to and transportInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideClostridium difficile (bacteria)Clostridium sporogenes
A low odor, liquid disinfectant composition comprising multiple components, which, upon mixing, provide an aqueous solution comprising low levels of peracetic acid for use in decontaminating articles and surfaces contaminated with bacteria, viruses, fungi and other chemical and biological contaminants including, but not limited to, spores, such as Clostridium difficile (C. diff), Clostridium sporogenes, and anthrax, mouse parvo virus, and mustard, nerve and other chemical and biological warfare agents. The disinfectant composition is prepared just prior to use by combining two or more separately packaged components, one component which is an acetyl donor comprising TAED or DAMA, and the other component which is a hydrogen peroxide solution.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
Synthesis of human secretory IgA for the treatment of Clostridium difficile associated diseases
A composition for treating a subject is provided. The composition includes dimeric or polymeric secretory IgA therapeutic. Formulating agents are mixed with the dimeric or polymeric secretory IgA to yield a dosing form of a capsule, tablet, and a suppository. A process for manufacturing a medicament for the treatment of C. difficile associated disease in a human is also provided wherein dimeric or polymeric IgA is modified with secretory component to form a dimeric or polymeric secretory IgA therapeutic. The dimeric or polymeric secretory IgA therapeutic is then mixed with formulating agents to create a capsule, tablet, or suppository dosing form. The therapeutic is amenable to enrobement directly through microencapsulation or the dosing form is coated with an enteric coating. A method of C. difficile treatment with the therapeutic is also provided that is amenable to supplementation with concurrent or prior antibiotic administration.
Owner:SIMON MICHAEL R
Genetically engineered clostridial genes, proteins encoded by the engineered genes, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100196421A1Optimization propertiesOptimized therapeuticAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderEngineered geneticGenetically engineered
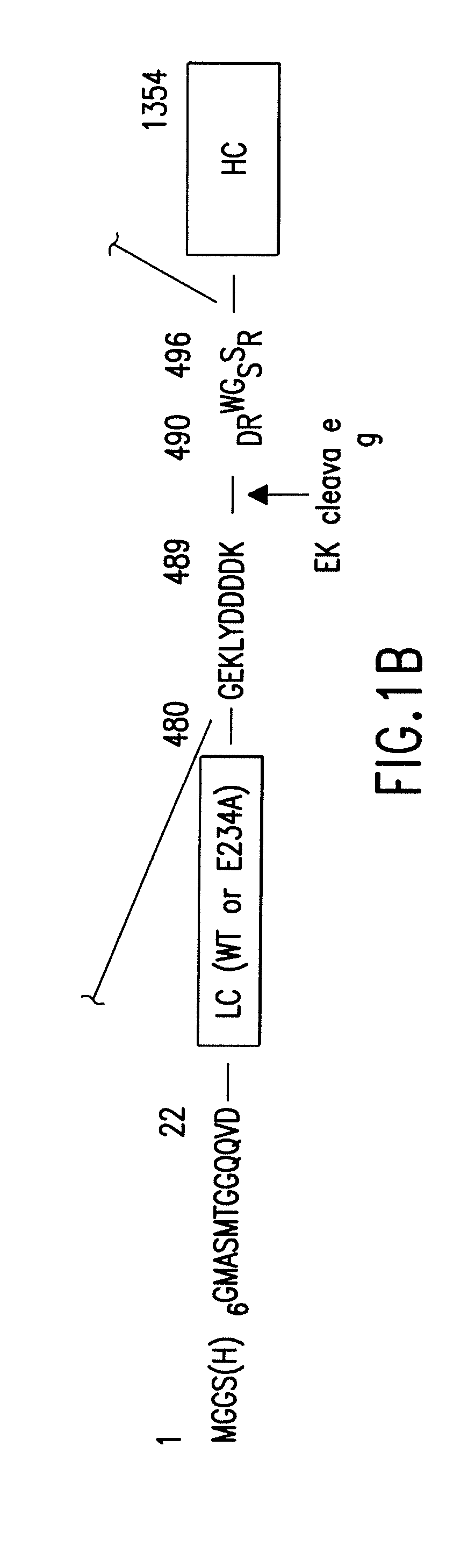
The present invention relates to an isolated Clostridial neurotoxin propeptide having a light chain region, a heavy chain region, where the light and heavy chain regions are linked by a disulfide bond, and an intermediate region connecting the light and heavy chain regions. An isolated nucleic acid molecule encoding a Clostridial neurotoxin propeptide is also disclosed. Also disclosed is an isolated, physiologically active Clostridial neurotoxin produced by cleaving a Clostridial neurotoxin propeptide, a vaccine or antidote thereof, and methods of immunizing against or treating for toxic effects of Clostridial neurotoxins. Methods of expressing recombinant physiologically active Clostridial neurotoxins are also disclosed. Also disclosed is a chimeric protein having a heavy chain region of a Clostridial neurotoxin and a protein with therapeutic functionality. A treatment method is also disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
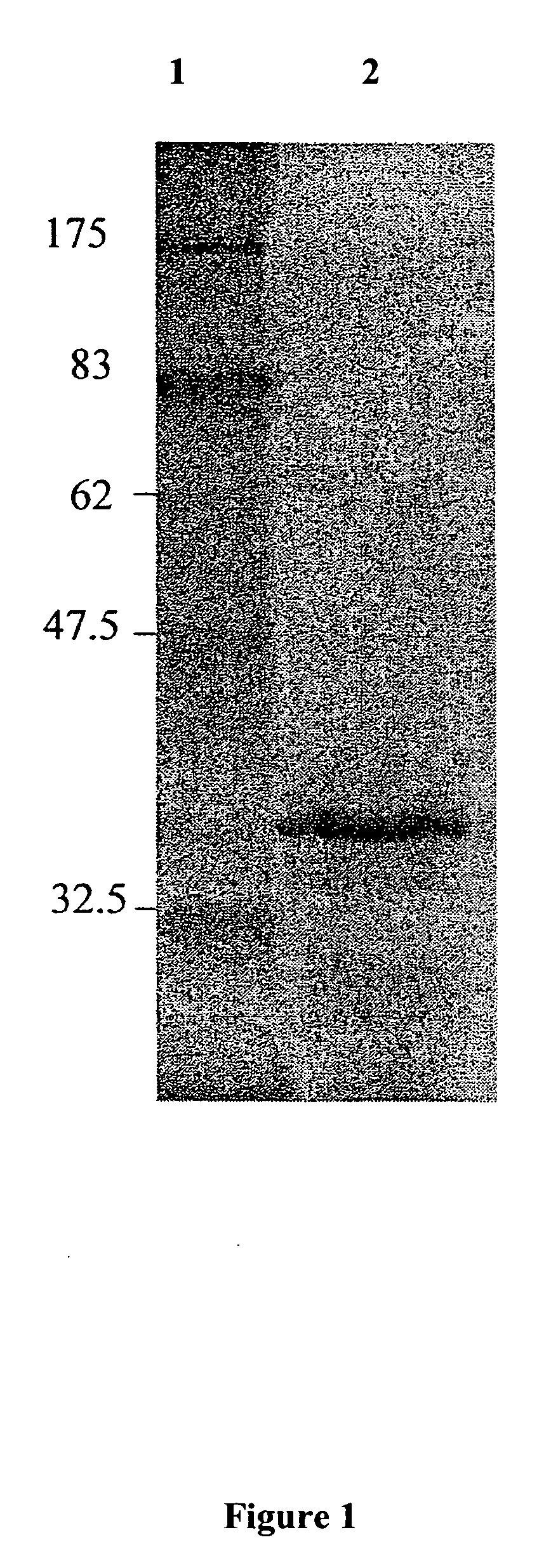
Thermostable cellulase and methods of use
A Clostridium thermocellum thermostable cellulase enzyme with both endocellulase activity and exocellulase activity that is able to degrade cellulose in the absence of scaffolding and other cellulosomic proteins is provided. The use of the enzyme to degrade cellulosic materials to soluble sugars is also provided.
Owner:BRUMM PHIL
Novel dihydrogen bond deep-eutectic solvent and method for pretreating rice straws through combination of solvent and sodium carbonate
InactiveCN107760739ALow costEasy to synthesizeBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesHydrolysateSolvent
The invention discloses a novel dihydrogen bond deep-eutectic solvent and a method for pretreating rice straws through combination of the solvent and sodium carbonate; straw hydrolysate after enzymolysis can be used for clostridium fermentation to synthesize bio-butanol. The deep-eutectic solvent provided by the invention is the novel dihydrogen bond deep-eutectic solvent which is synthesized by stirring choline chloride, formic acid and acetic acid at a molar ratio of 1:1:1 at the temperature of 30 DEG C; the solvent can be used for reducing the contents of lignin and hemicellulose in a lignocellulose raw material, so that the accessibility of cellulose in the lignocellulose raw material. The solvent and the sodium carbonate are combined to pretreat the rice straws, and enzyme hydrolysisis performed on the pretreated rice straws with cellulose, so as to obtain the hydrolysate containing 4.28g / L of total reducing sugar; the yield of glucose is 80%; in addition, the hydrolysate has noobvious inhibiting effect on the growth of microorganisms such as clostridium and the like, and the yield of butanol is 13.73g.L<-1>. The dihydrogen bond deep-eutectic solvent is an environment-friendly solvent which is simple in synthesis and convenient to use and has good application and development prospects in pretreatment of the lignocellulose raw material.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Healthcare facility disinfecting system
ActiveUS8551399B2Effectively eliminating aerosolized pathogensLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsEscherichia coliClostridium difficile toxin B
A system and process for disinfecting rooms such as health care facility rooms with an oxygen / ozone mixture is described, which is effective to combat “superbugs” such as Clostridium difficile (C. difficile); E. coli; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE). In preferred embodiments, hydrogen peroxide is additionally used. The system and process is effective to destroy bacteria deposited on surfaces as biofilm, and, accompanied by physical agitation such as jet nozzle outlets, is effective to disinfect carpet, drapery and similar absorbent and porous surfaces.
Owner:DD STEROZONE LLC +1
Multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and detection method for clostridium difficile toxin genes
ActiveCN103361434AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium difficile infectionsClostridium difficile toxin B
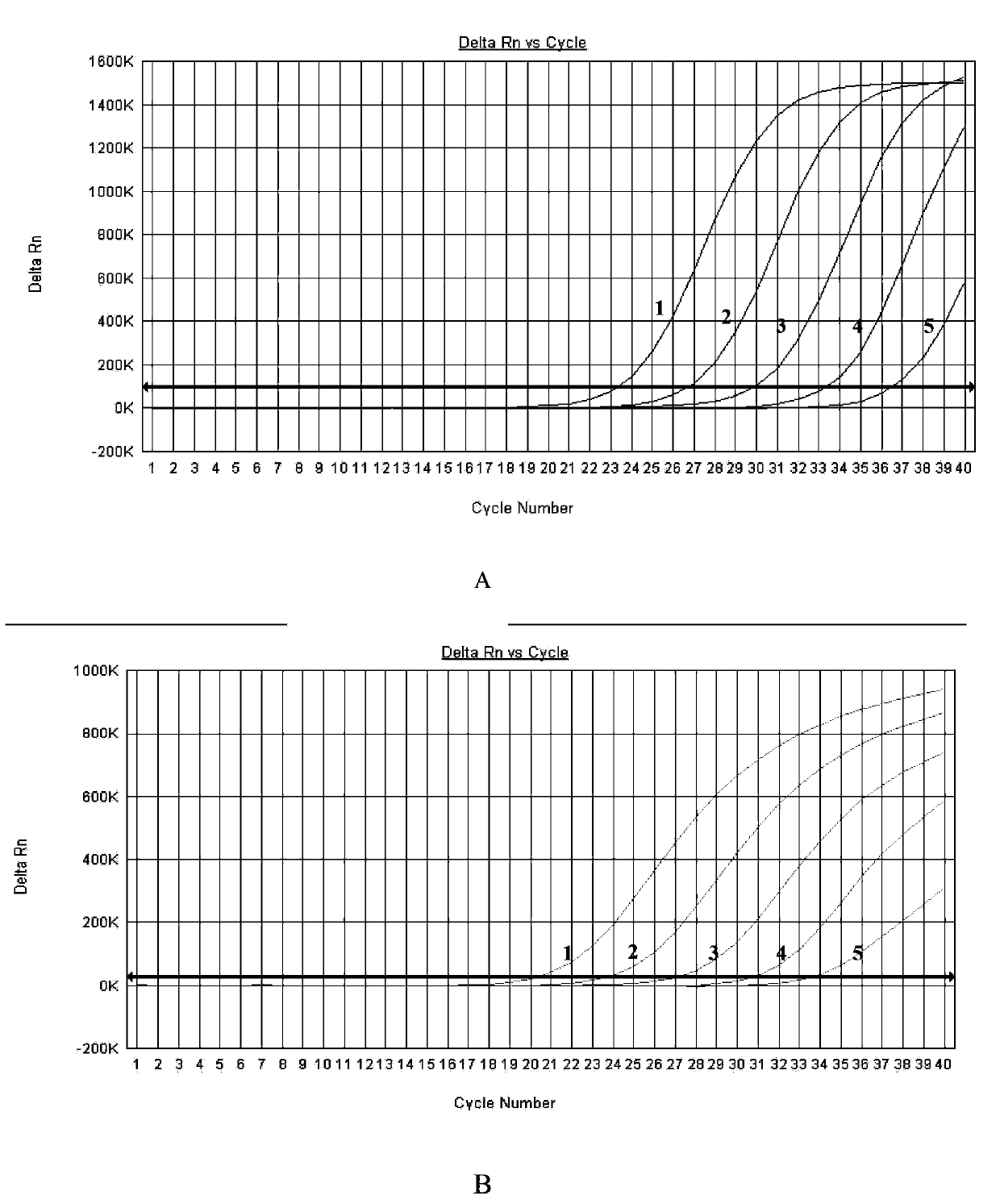
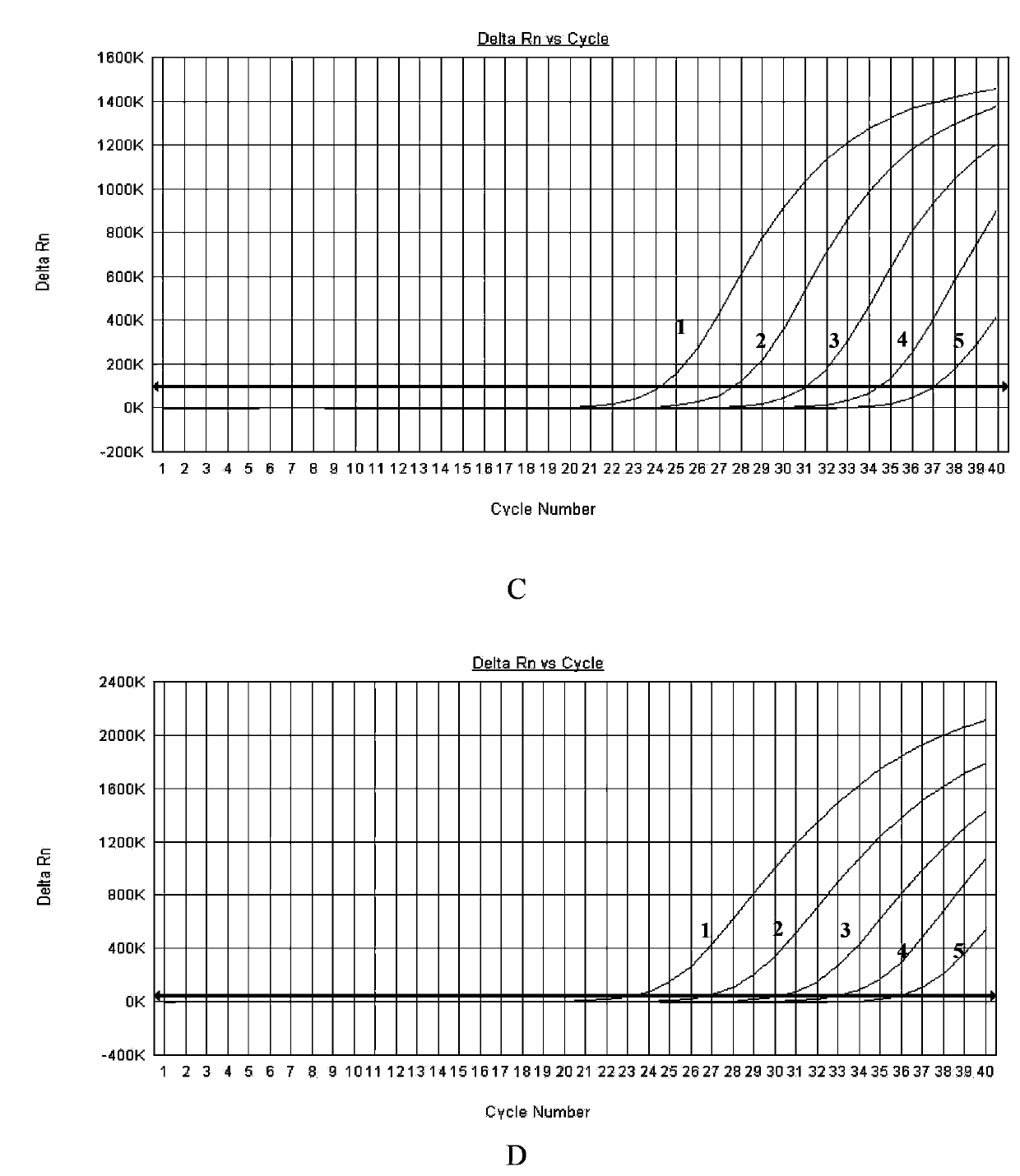
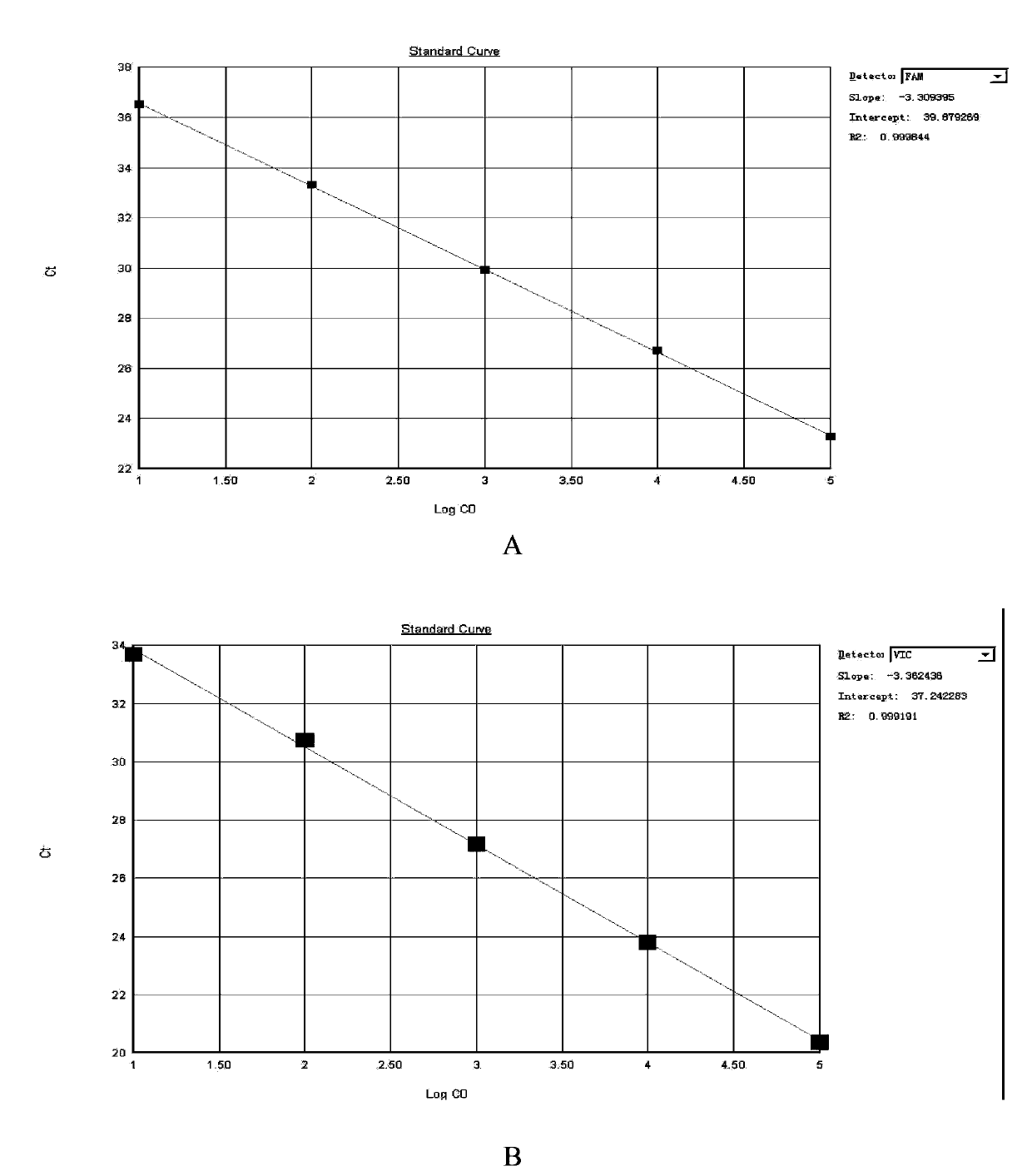
A provided multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit for clostridium difficile toxin genes mainly comprises specific primers, probes and a PCR reaction reagent, and the specific primers and the probes respectively consist of specific primers and probes of clostridium difficile toxin A (tcdA), toxin B (tcdB), binary toxin A (cdtA) and binary toxinB (cdtB). The beneficial effects of the invention comprise: the fast, sensitive and specific multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and a detection method are provided for the clostridium difficile toxin genes, and a foundation is provided for distinguishing between toxigenic strains and avirulent strains of clostridium difficile, and early diagnosis on infection of clostridium difficile.
Owner:杭州海基生物技术有限公司
Vaccine against clostridium perfringens
There is provided a vaccine for controlling Clostridium perfringens in animals, and particularly necrotic enteritis in poultry. The vaccine may comprise a C. perfringens antigenic polypeptide or variant thereof, a nucleic acid encoding the C. perfringens antigenic polypeptide or variant thereof, or a recombinant cell producing the C. perfringens antigenic polypeptide or variant thereof.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
Growth medium for clostridium histolyticum
The present invention provides improved media for the cultivation of Clostridium histolyticum and culture supernatants for the biotechnological production of collagenase enzymes. The nutrient media according to the invention comprise one or more peptones from a non-mammalian source, preferably plant-derived peptones. The media can additionally comprise fish gelatin. The invention provides media, culture supernatants comprising Clostridium histolyticum collagenase, and methods to produce said collagenase.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com