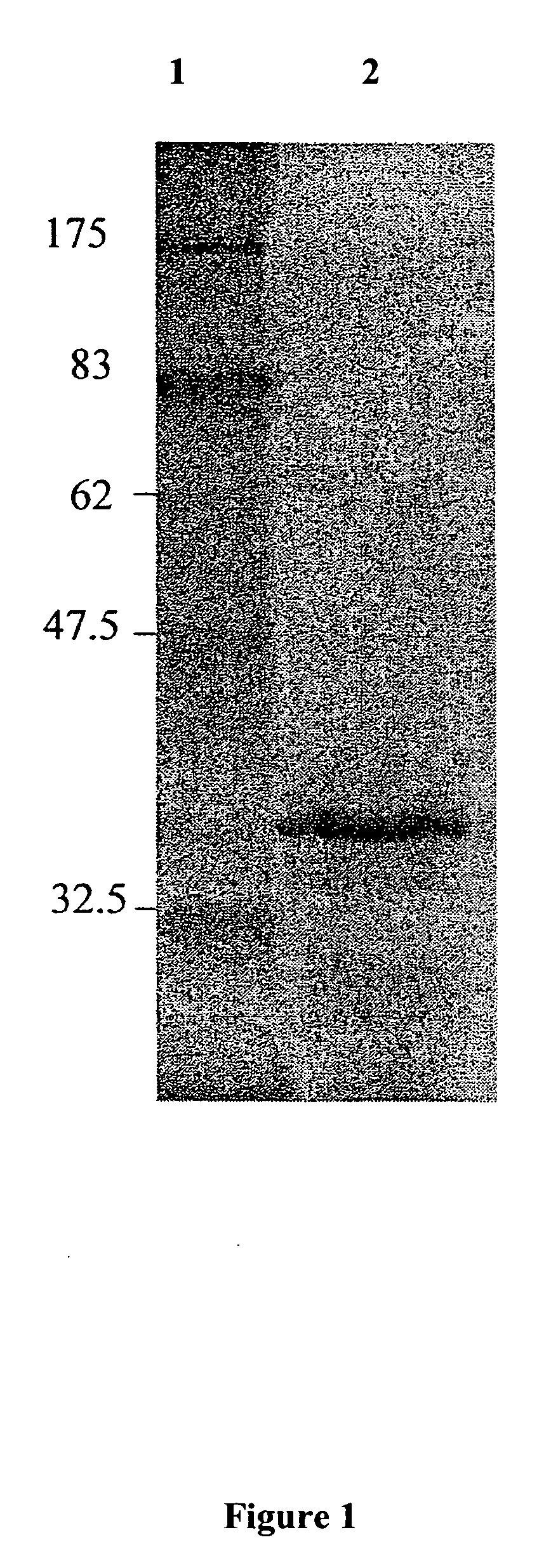
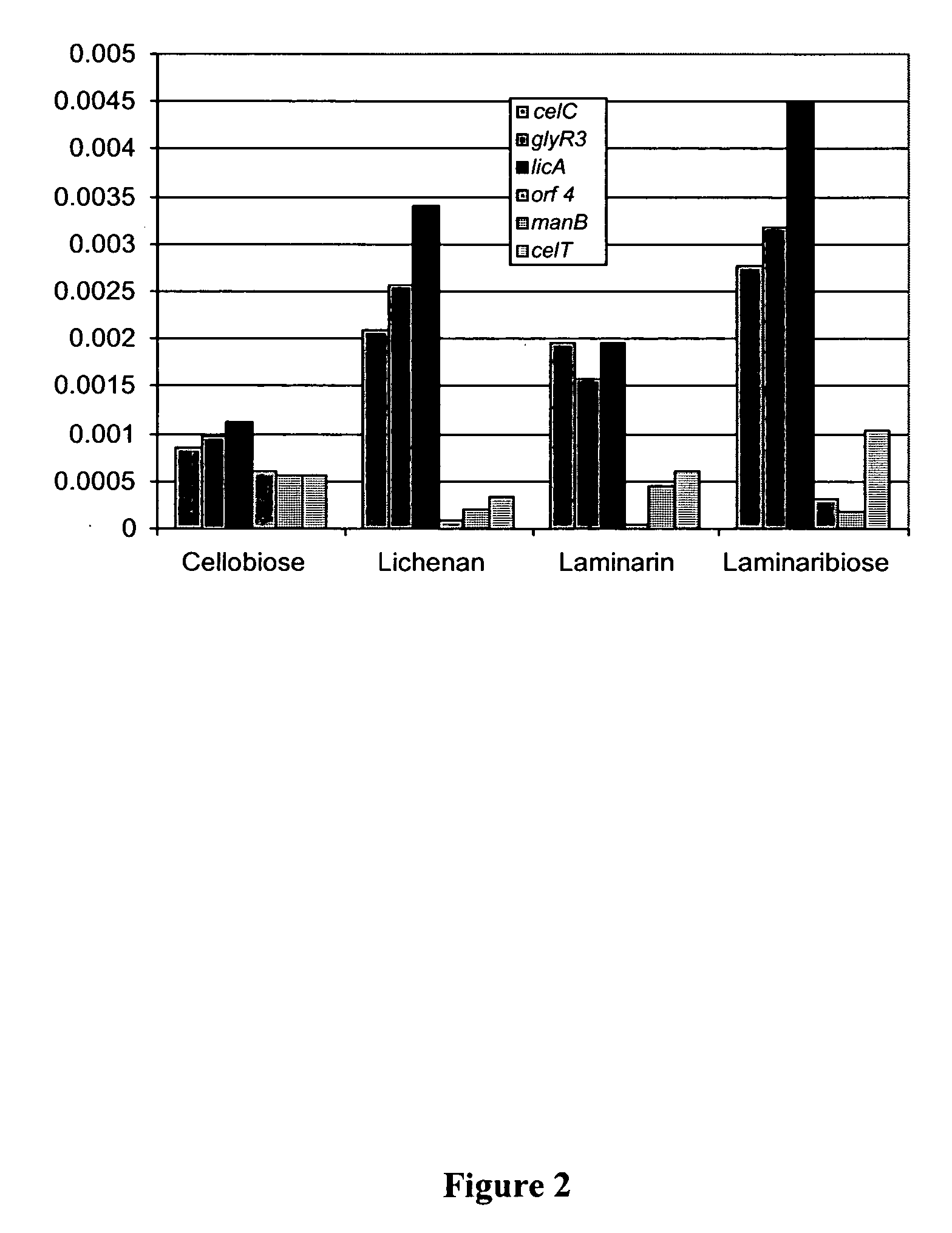
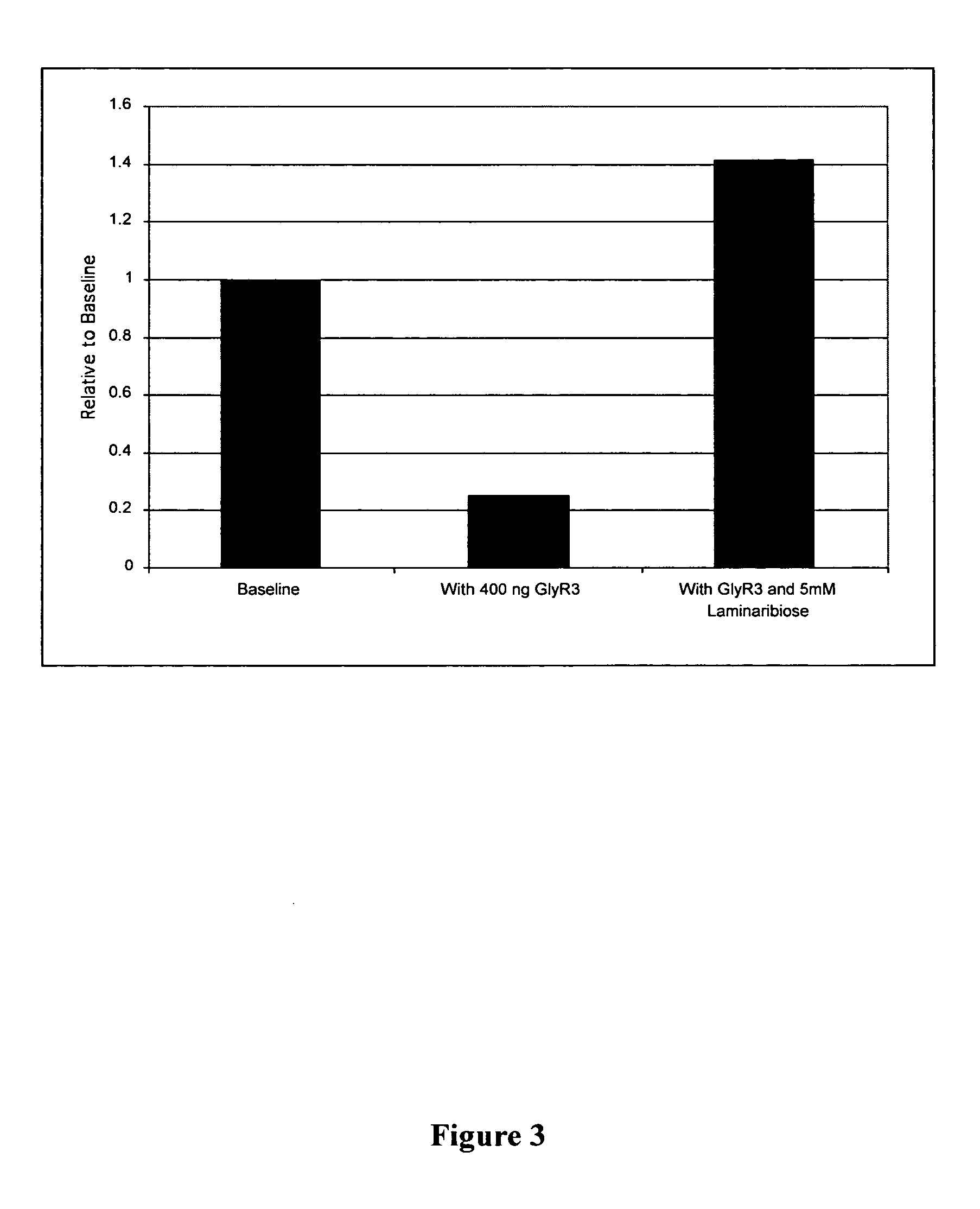
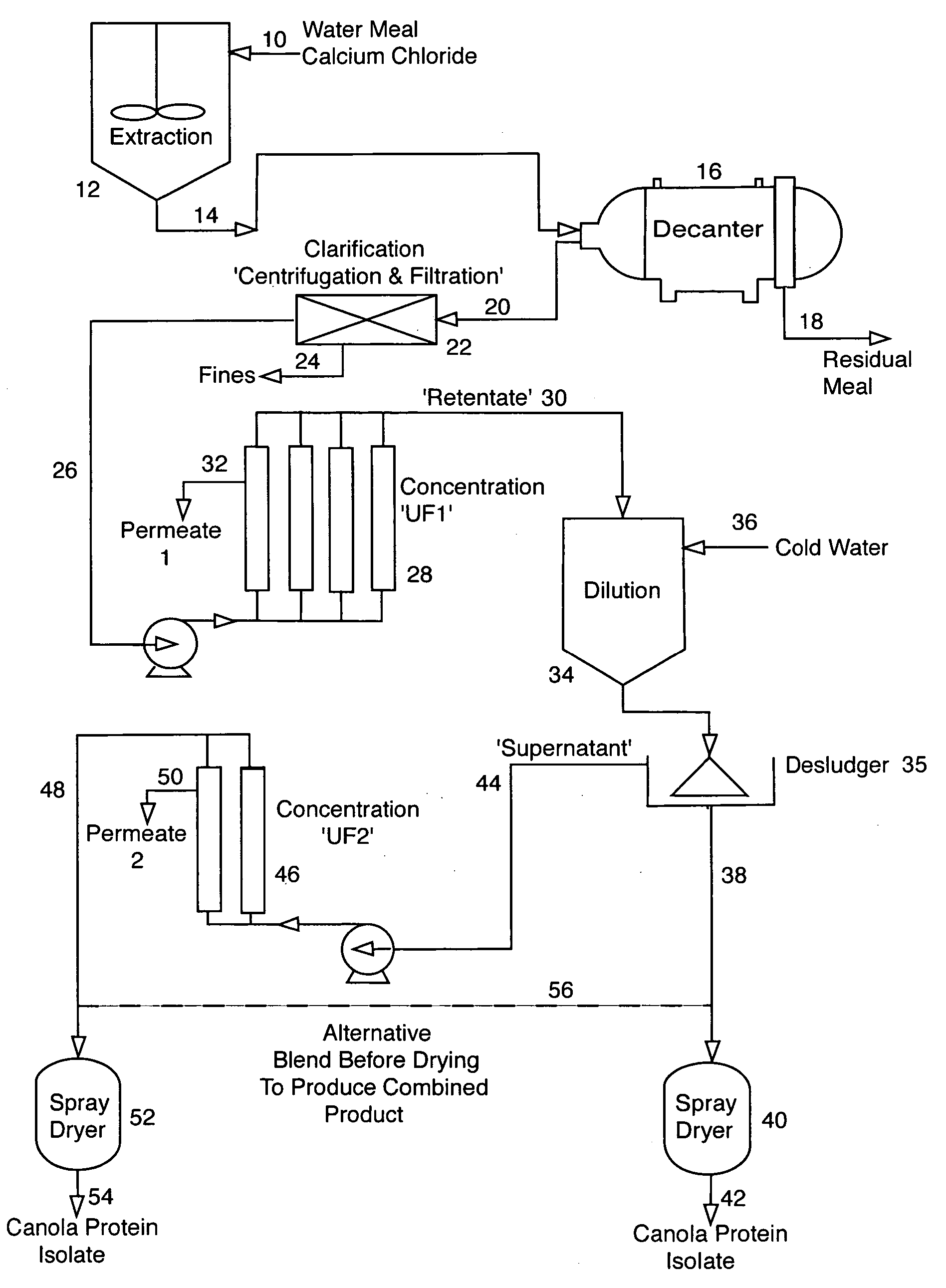
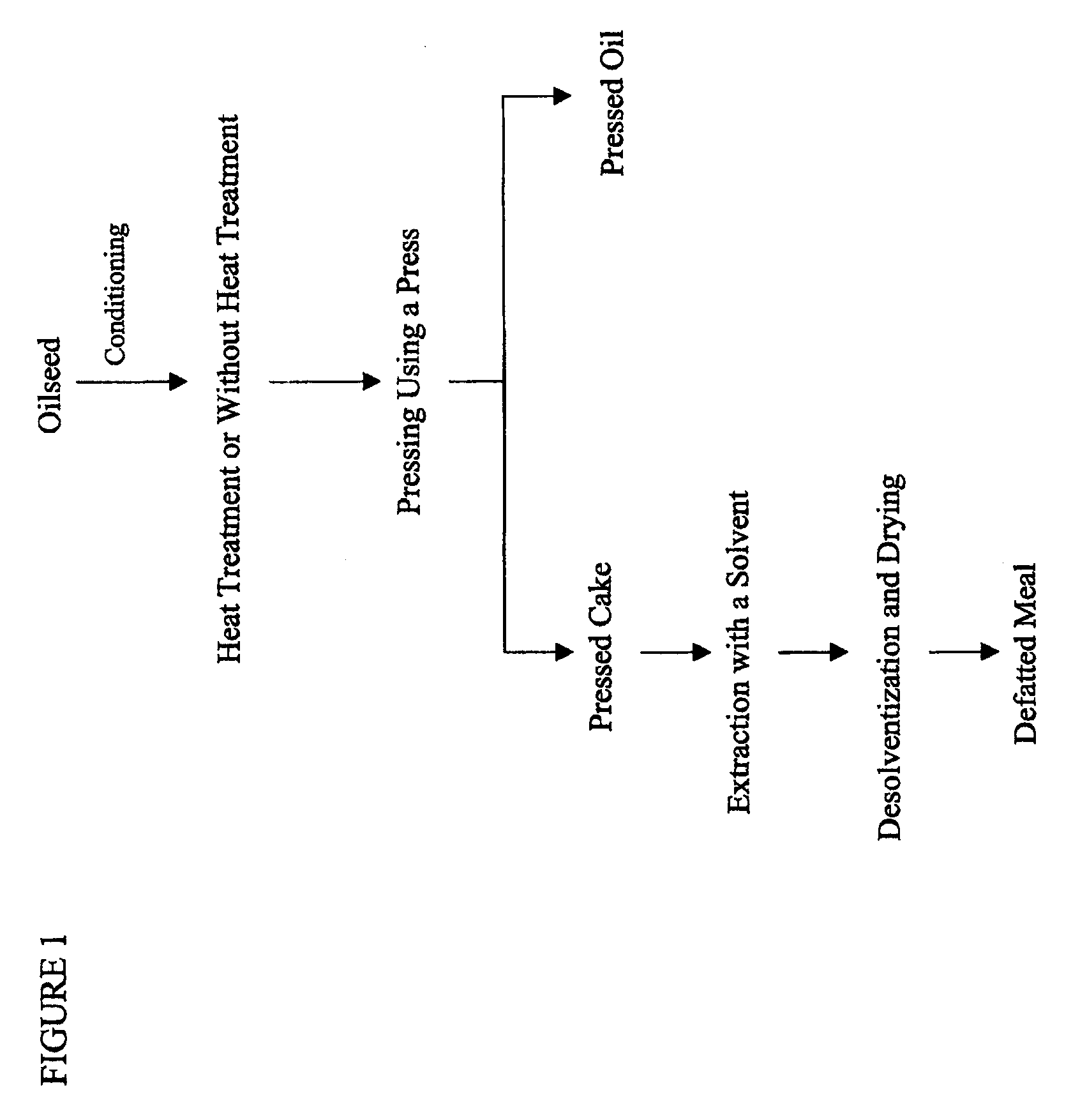
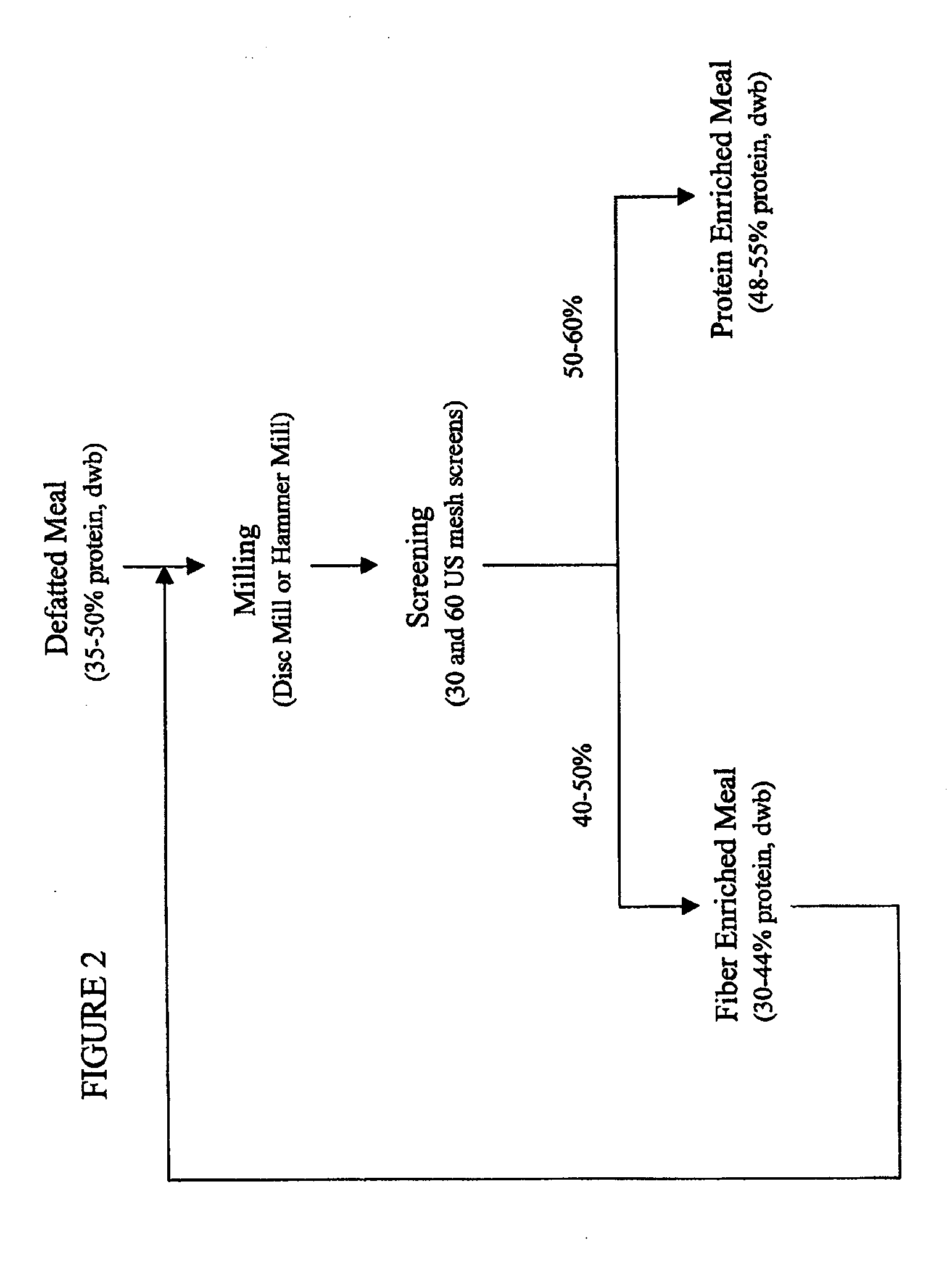
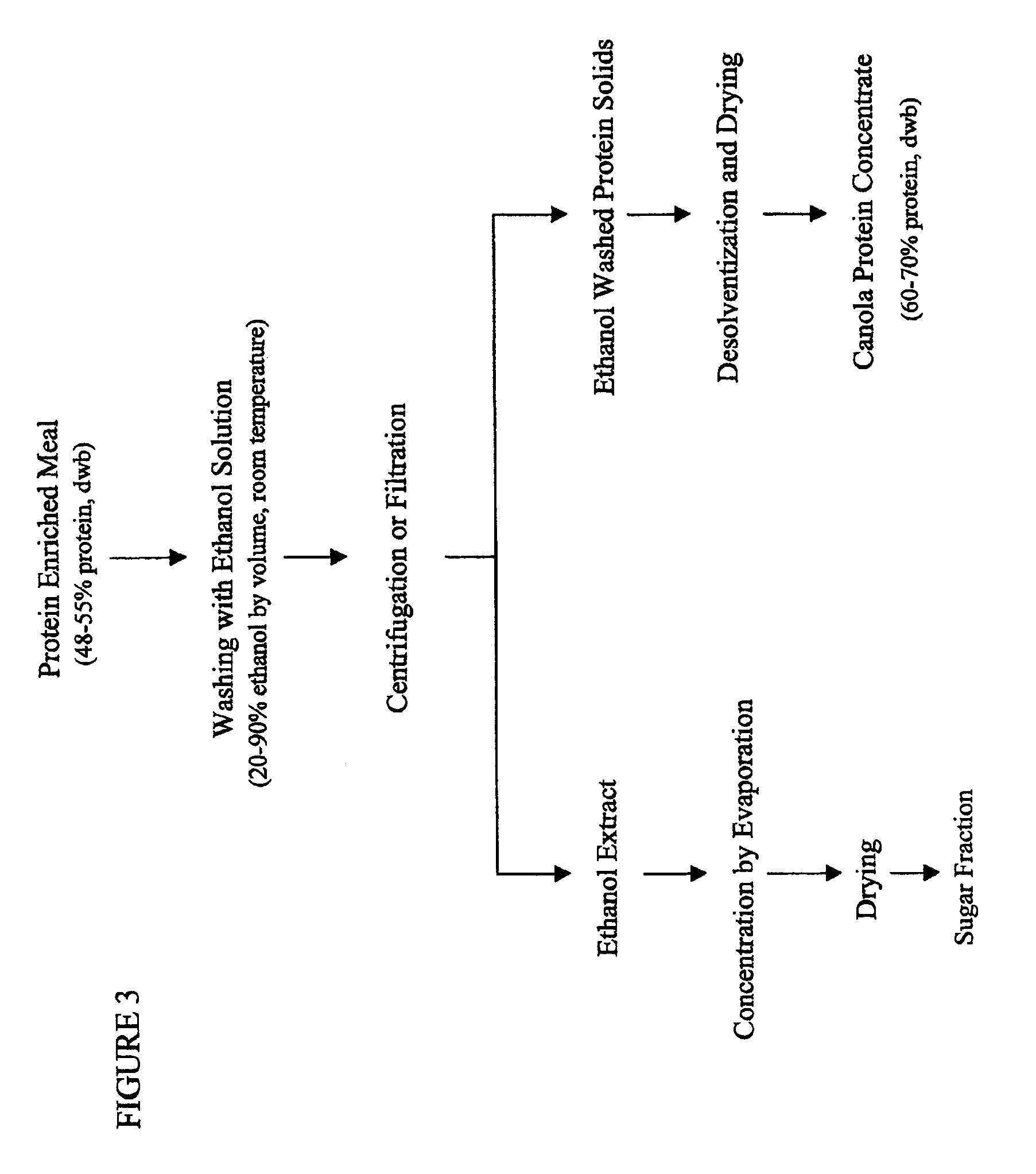
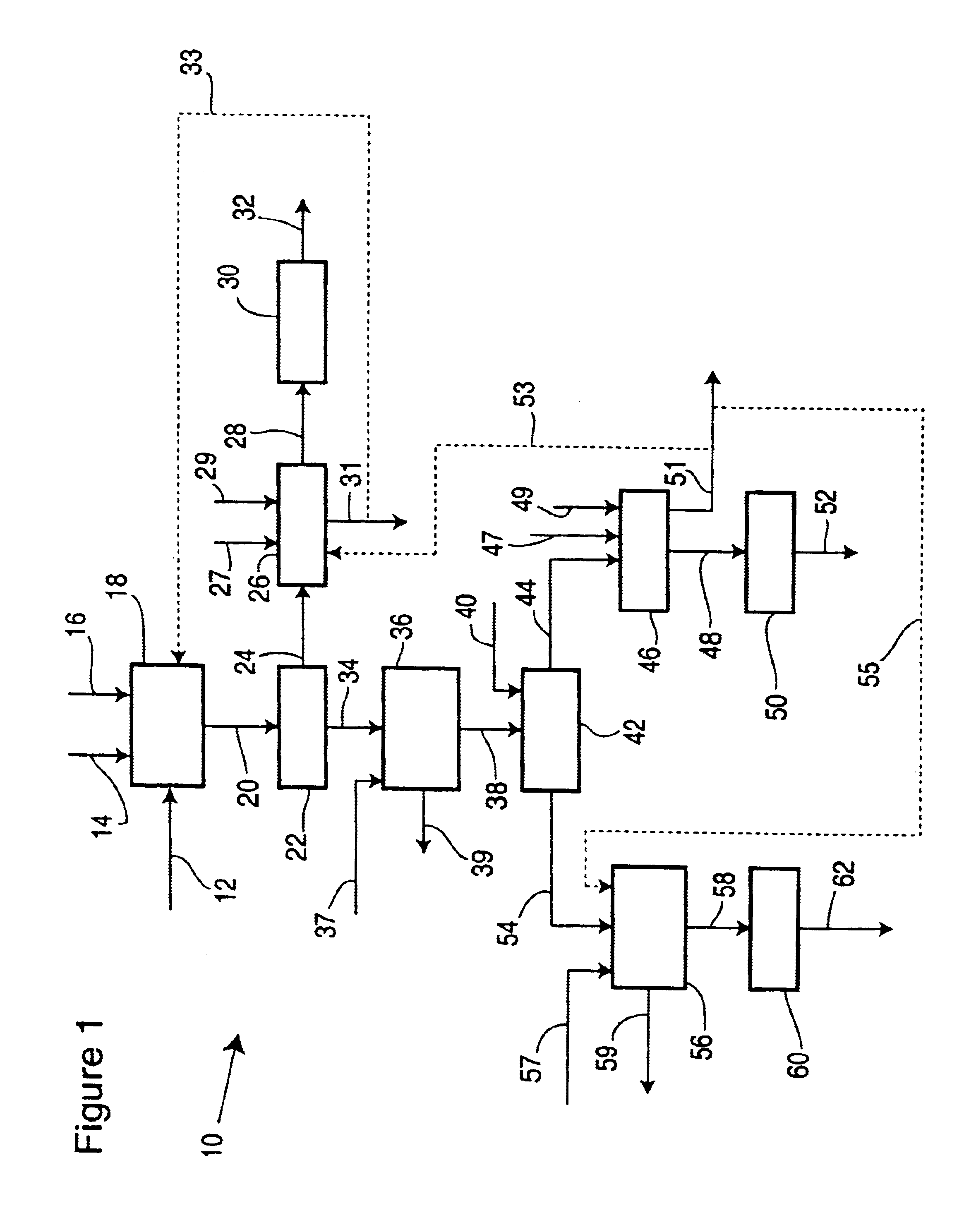
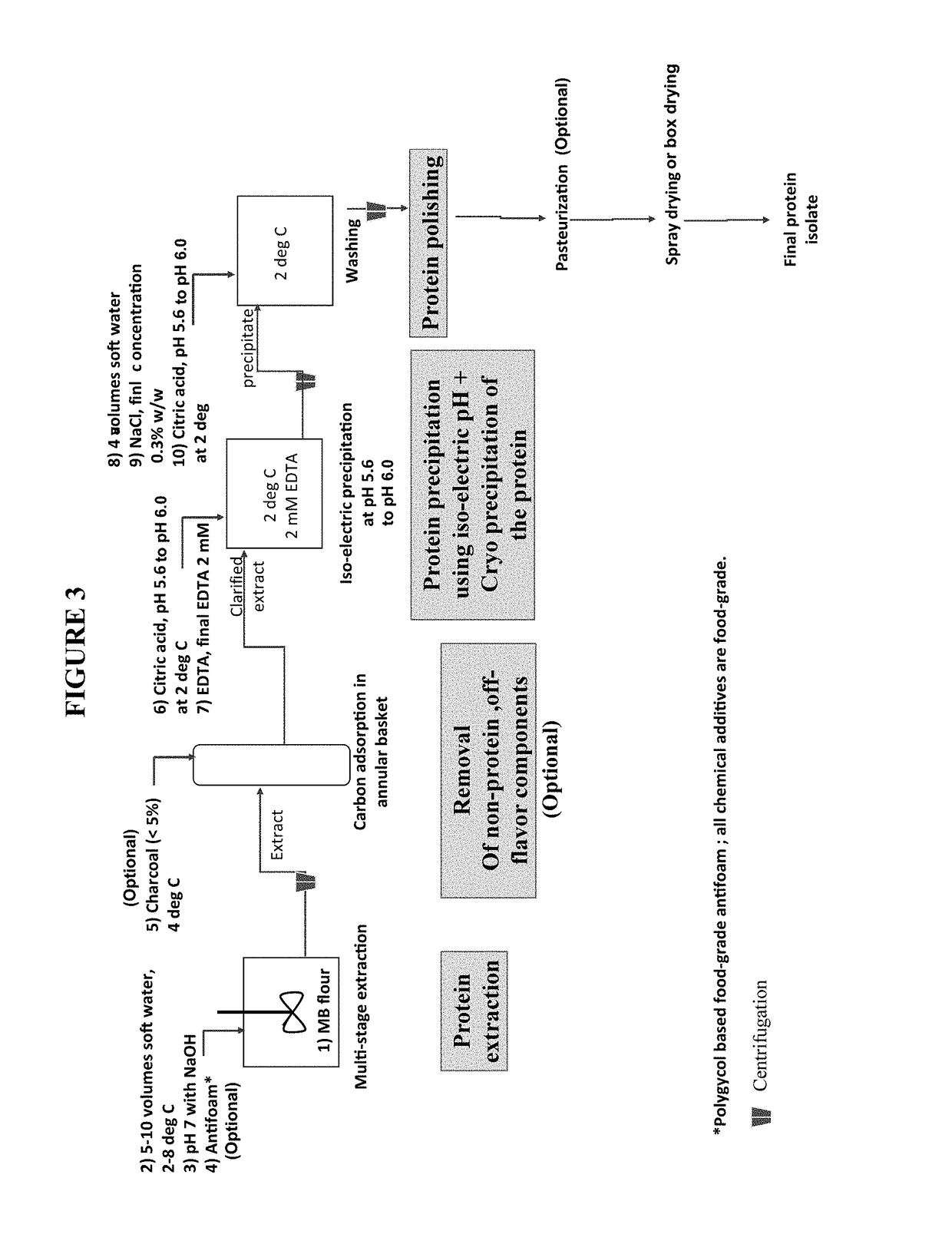
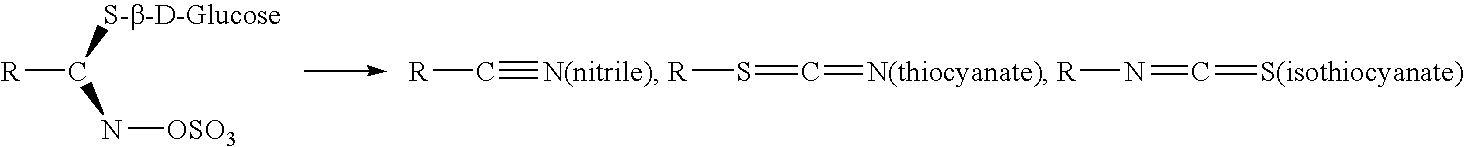Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
383 results about "Protein isolate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Promoters and proteins from Clostridium thermocellum and uses thereof
The present invention relates to an inducible and a high expression nucleic acid promoter isolated from Clostridium thermocellum. These promoters are useful for directing expression of a protein or polypeptide encoded by a nucleic acid molecule operably associated with the nucleic acid promoters. The present invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs including the C. thermocellum promoters, and expression vectors and hosts containing such nucleic acid constructs. The present invention also relates to protein isolated from Clostridium thermocellum, including a repressor protein. The present invention also provides methods of using the isolated promoters and proteins from Clostridium thermocellum, including methods for directing inducible in vitro and in vivo expression of a protein or polypeptide in a host, and methods of producing ethanol from a cellulosic biomass.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Protein isolation procedures for reducing phytic acid
ActiveUS20050255226A1Reduced phytic acid contentHigh nutritional valueBiocideProtein composition from vegetable seedsIsolation proceduresProtein isolate
Owner:BURCON NUTRASCI MB
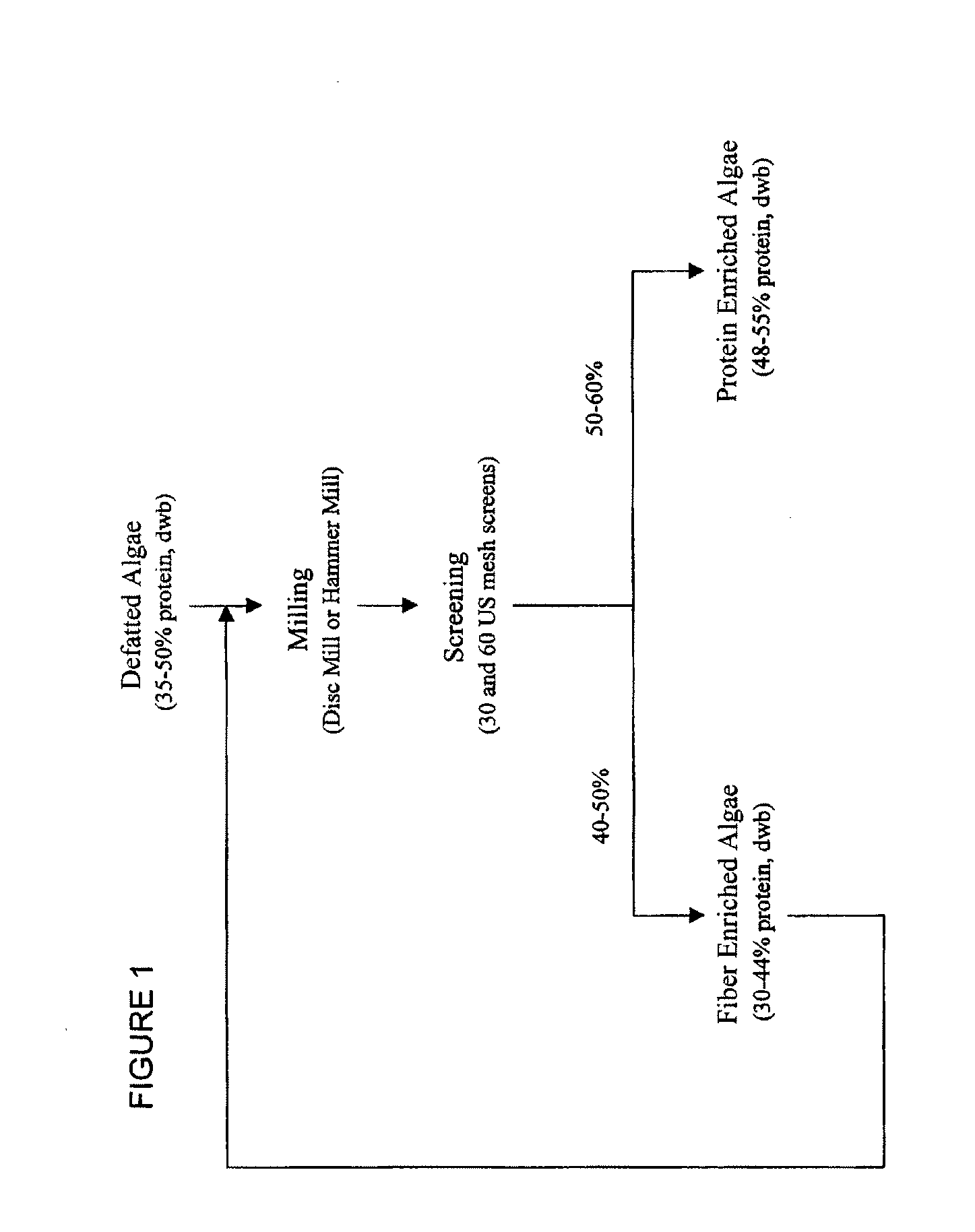
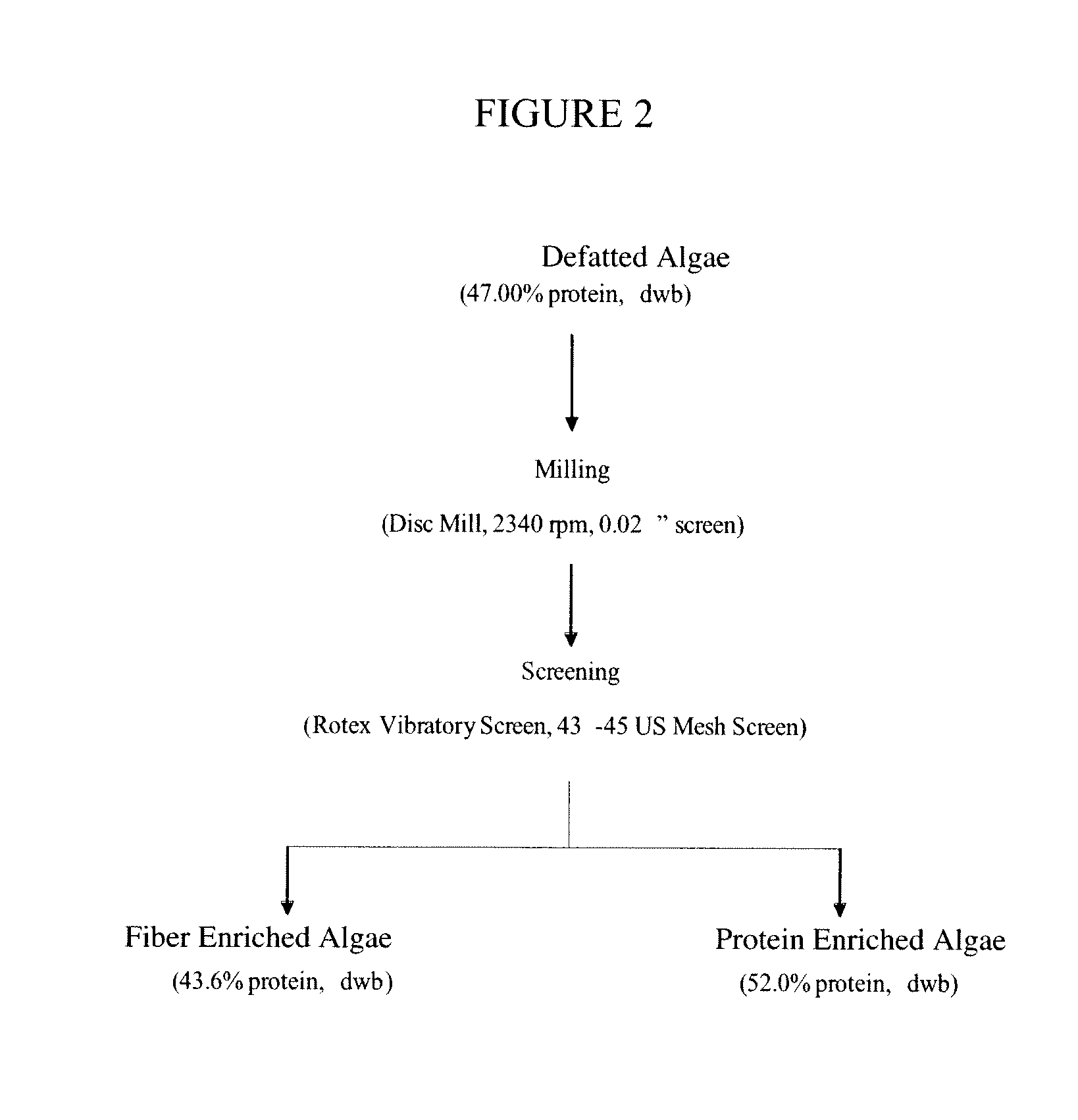
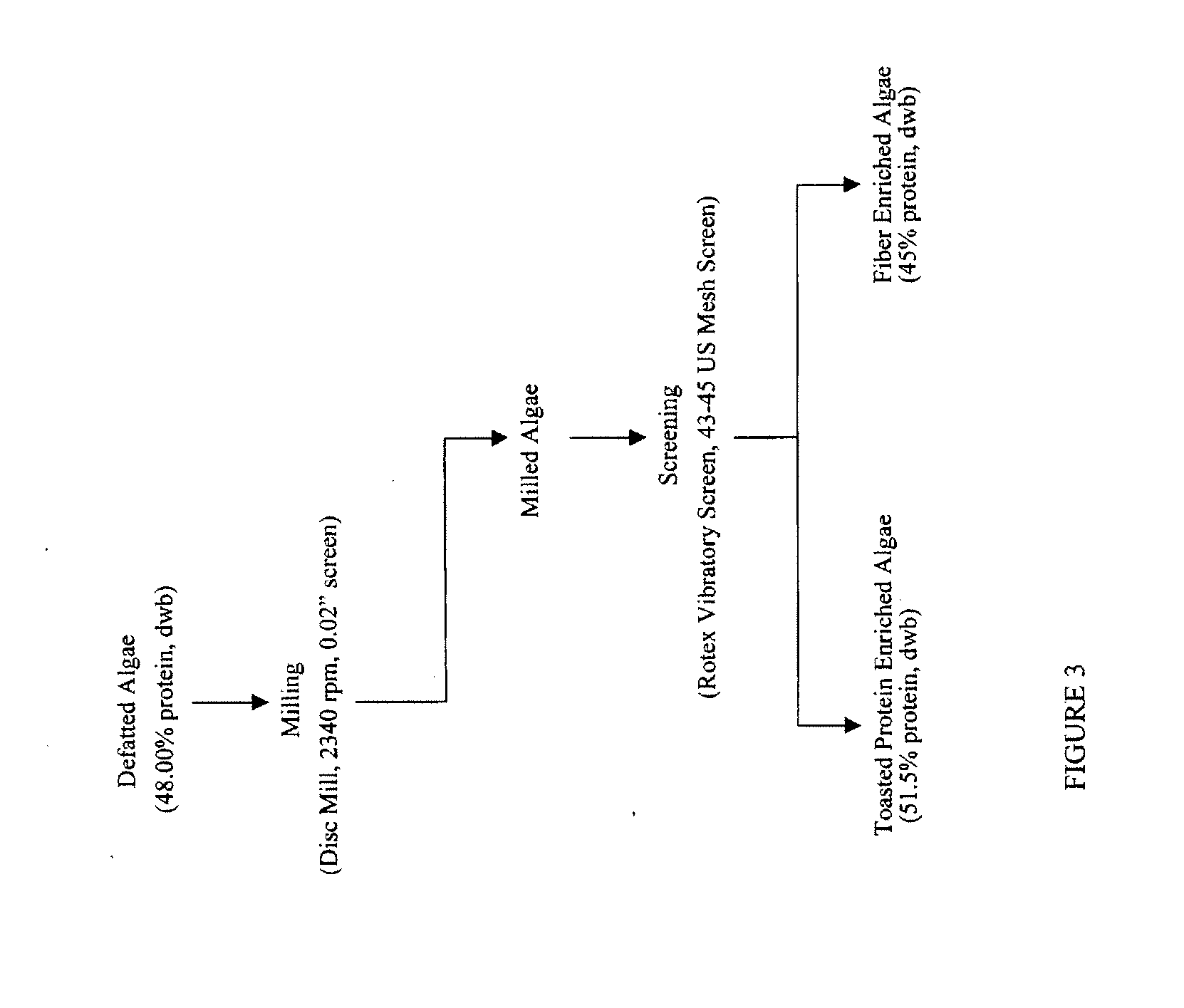
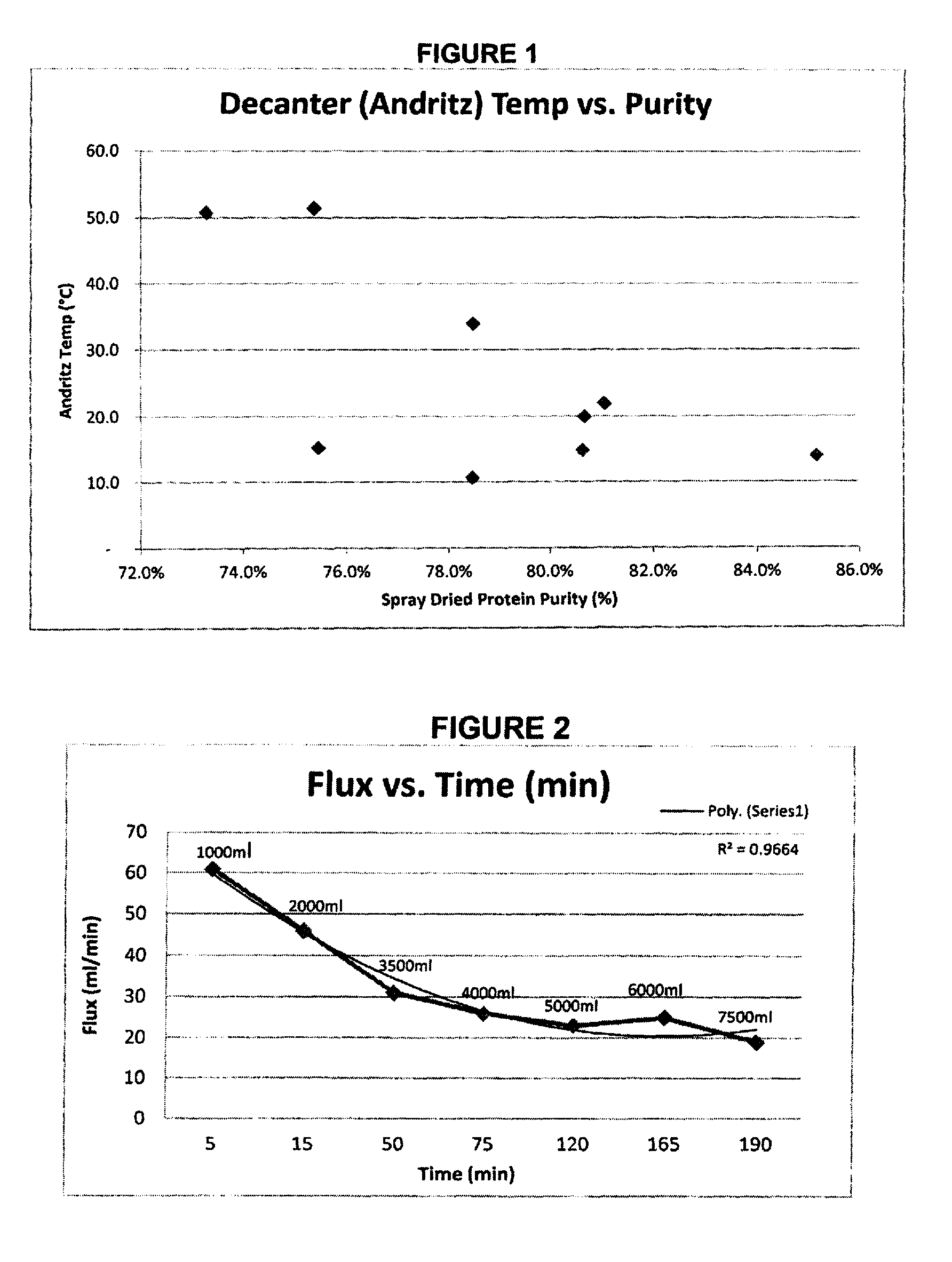
Protein concentrates and isolates, and processes for the production thereof from macroalgae and/or microalgae
InactiveUS20120021457A1Quality improvementPeptide preparation methodsFermentationFiberProtein isolate
Owner:SIEBTE PMI VERW
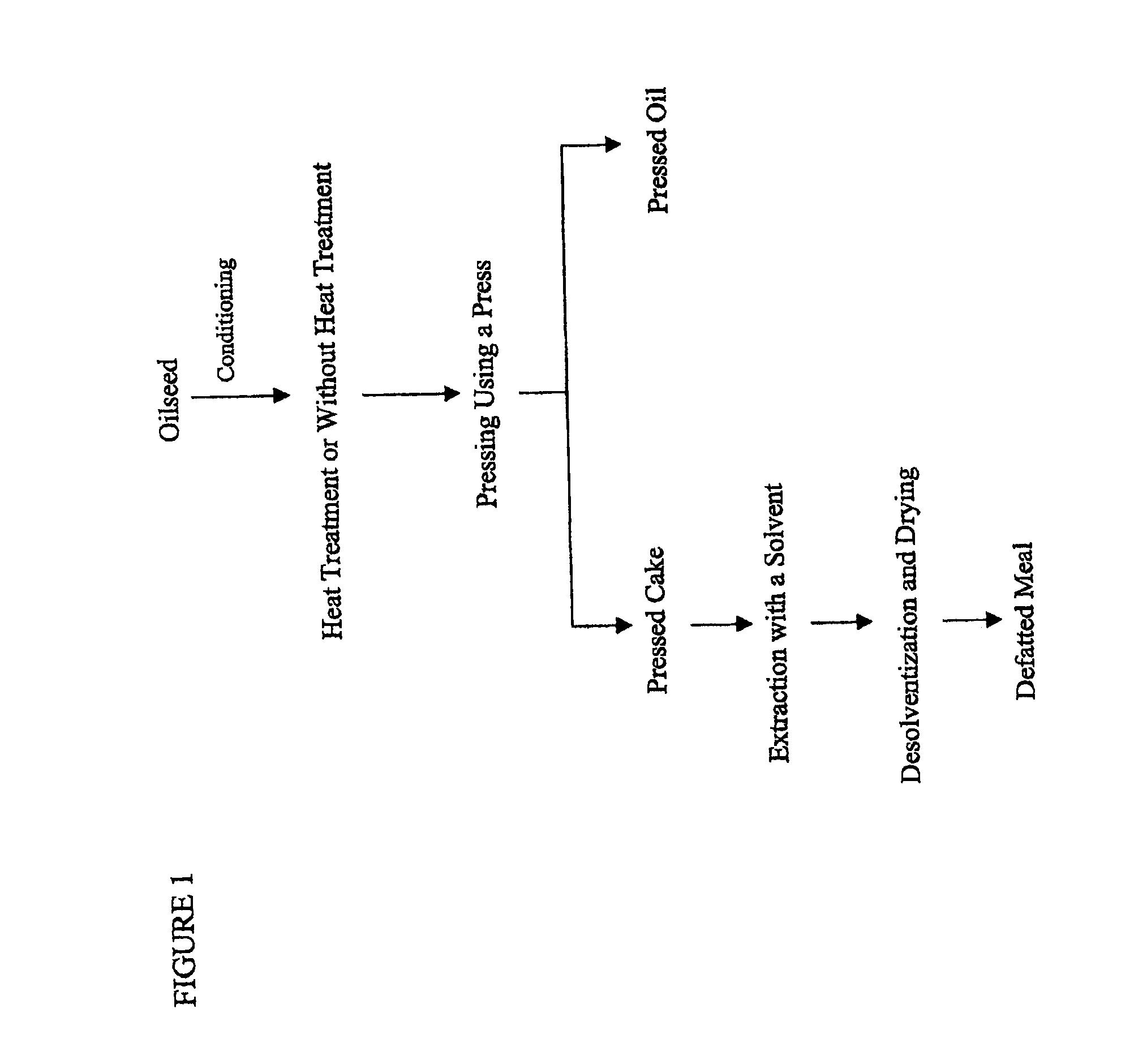
Aqueous process for preparing protein isolate and hydrolyzed protein from an oilseed
InactiveUS20120252065A1Peptide/protein ingredientsProtein composition from vegetable seedsProtein solutionPhytase
The present disclosure relates to an aqueous process for the preparation of a protein isolate and a hydrolyzed protein concentrate from an oilseed meal, optionally comprising:mixing an oilseed meal with an aqueous solvent to form a slurry;optionally treating the slurry with phytase y;separating the slurry with a solid / liquid separation to form:a liquid phase, comprising the aqueous solvent, soluble protein and oil; anda solid phase comprising insoluble protein;separating the liquid phase to form:an oil phase; andan aqueous protein phase;subjecting the aqueous protein phase to membrane filtration to obtain a protein solution; and drying the protein solution to obtain the protein isolatesubjecting the insoluble protein to enzymatic hydrolysis, andsubjecting the hydrolyzed protein to membrane filtration to obtain an amino acid and peptide solution; and drying the amino acid and peptide solution to obtain the hydrolyzed protein concentrate.
Owner:POS PILOT PLANT CORP +1
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding regulatory proteins
InactiveUS20050153402A1High yieldIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaBiological bodyAntisense nucleic acid
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated MR nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel MR proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing MR nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated MR proteins, mutated MR proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of MR genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
Colour reduction in canola protein isolate
InactiveUS20040077838A1Prevent oxidationHigh protein concentrationBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismBiotechnologyProtein isolate
Owner:BURCON NUTRASCI MB
Composition and method for making high-protein and low-carbohydrate food products
InactiveUS20050129823A1Effectively reducing the net carbohydrate total of the traditional productIncrease nutritionDough treatmentBaking mixturesAdditive ingredientProtein isolate
Conventional food compositions for use in making baked goods and extruded food products are improved by reducing the carbohydrate content. This is done by substituting the conventional flour in whole or in part by a combination of starch that is resistant to amylase digestion and / or from about 1-150 baker's percent of a first proteinaceous ingredient comprising at least about 70% by weight protein, and a second proteinaceous ingredient selected from the group consisting of (i) between about 0.5-100 baker's percent of a wheat protein isolate product; (ii), between about 0.5-100 baker's percent of a wheat protein concentrate product; (iii) between about 0.5-100 baker's percent of a devitalized wheat gluten product; (iv) between about 0.5-20 baker's percent of a fractionated wheat protein product; (v) between about 0.5-20 baker's percent of a deamidated wheat gluten product; (vi) between about 0.5-30 baker's percent of a hydrolyzed wheat protein product; and (vii) any combination of ingredients (i) to (vi).
Owner:MGP INGREDIENTS
Protein concentrates and isolates, and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS20090286961A1Protein composition from vegetable seedsDepsipeptidesInsoluble proteinProtein isolate
Protein concentrates and protein isolates, in addition to processes for the production of protein concentrates and protein isolates, are disclosed. In particular, the disclosure relates to a process for removing fiber from an oilseed meal, comprising:i) mixing an oilseed meal with a blending solvent, optionally water, saline solution, polysaccharide solution or protein containing solution, to form a mixture;ii) optionally adjusting the pH of the protein slurry to a pH of about 2 to about 10; andiii) separating the mixture to form a protein slurry comprising soluble and insoluble proteins and an insoluble fiber fraction.
Owner:SIEBTE PMI VERW
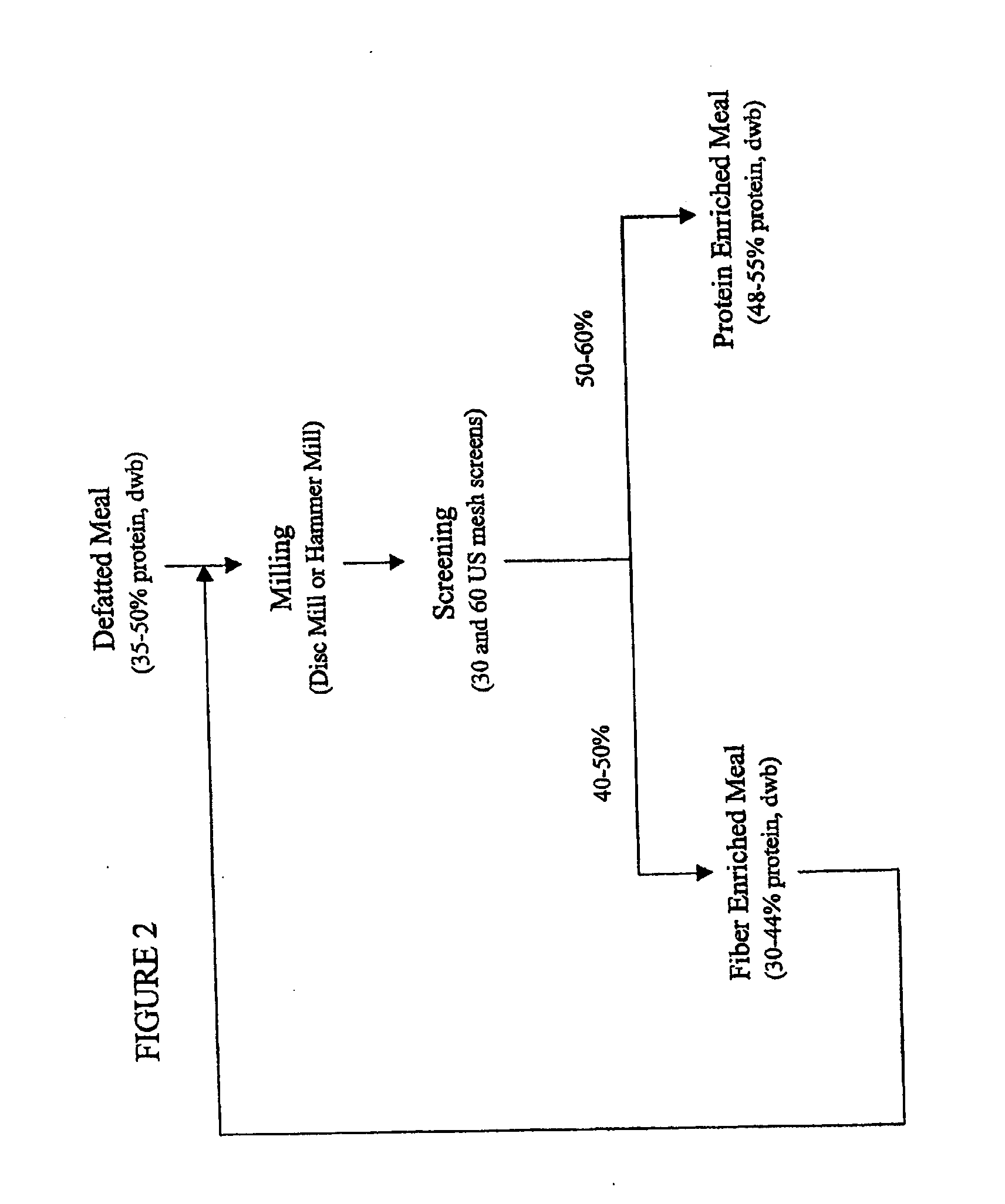
Production of high-quality protein isolates from defatted meals of Brassica seeds
The present invention provides a method for processing defatted oil seeds, comprising the steps of: (a) solubilizing at least a portion of the protein contained in the oil seeds to produce suspended residual solids and a first solution comprising protein, phenolic-protein complexes, and free phenolic compounds; (b) separating at least a portion of the free phenolic compounds from the first solution and recovering a free phenolic reduced solution; and (c) treating the free phenolic reduced solution to precipitate at least a portion of the protein as a precipitated protein isolate and recovering a treated solution containing a soluble protein isolate. Novel protein products are also disclosed. Food and drink products containing the novel protein products are also disclosed.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
High-protein, low-carbohydrate bakery products
InactiveUS20050013900A1Good source of nutritionLow glycemic indexMilk preparationDough treatmentResistant starchProtein isolate
A high-protein, low-carbohydrate bakery product comprising a first proteinaceous ingredient and a second proteinaceous ingredient selected from the group consisting of wheat protein isolate, wheat protein concentrate, devitalized wheat gluten, fractionated wheat protein, deamidated wheat gluten, hydolyzed wheat protein, and combinations thereof are provided. Preferred bakery products further comprise an amount of resistant starch which replaces a portion of digestible carbohydrate therein.
Owner:MGP INGREDIENTS
Protein isolate compositions and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070014914A1Diminution of its viscoelastic propertySugar food ingredientsFood ingredient as binding agentBiotechnologyParticulates
The various non-limiting embodiments of the present disclosure relate to a protein-based binder or coating system for particulate- and / or powder-type food systems, for example, to form nutritive ready-to-eat food bars, protein bars, snack pieces, or cereal clusters, where the binder comprises a modified wheat protein isolate. Other non-limiting embodiments relate to food compositions comprising a modified wheat protein isolate binder, and at least one of food particulates; powdered food ingredients, such as protein powders; and combinations thereof. In addition, methods for forming the various non-limiting embodiments of the food compositions and the modified wheat protein isolate binder systems are also disclosed.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Protein beverage and method of making the same
A protein beverage composition and a method of making it relate to a beverage including a protein essentially free of caseinate and derived from an aqueous protein isolate collected from membrane-filtration isolation of the protein and without substantial drying the protein beverage composition exhibits a pH ranging from about 2.0 to about 4.6. Substantial solubility of the protein is maintained in the beverage composition, and the protein beverage is essentially free of active microbes known to be harmful to human health, both at the time of packaging of the protein beverage and for a time period of at least one year after packaging.
Owner:NEXTPROTEINS INC
Protein engineering strategies to optimize activity of surface attached proteins
InactiveUS20100260465A1Without substantial loss of enzymatic activityHigh binding affinityHydrolasesTransferasesActive enzymeProtein isolate
Isolated and / or recombinant enzymes that include surface binding domains, surfaces with active enzymes bound to them and methods of coupling enzymes to surfaces are provided. Enzymes can include large and / or multiple surface coupling domains for surface coupling.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
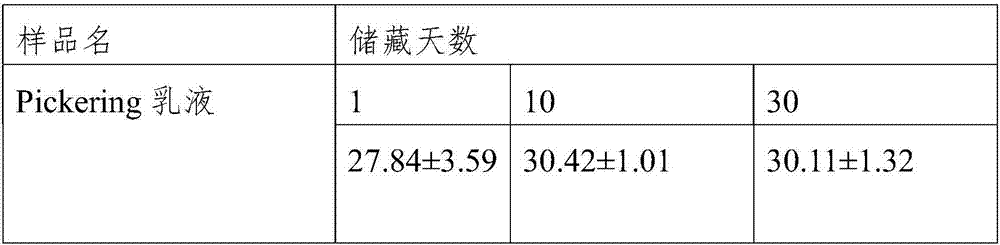
Pickering emulsion prepared from peanut protein isolate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107455550ALow costSimple and fast operationProtein composition from vegetable seedsVegetable proteins working-upProtein isolatePickering emulsion
The invention relates to a method for preparing a Pickering emulsion from peanut protein isolate, and the method comprises the following steps: preparing a peanut protein dispersion solution by taking a peanut protein isolate solution as a raw material; preparing a proteoglycan mixed dispersion solution from a polysaccharide solution and the peanut protein isolate dispersion solution; adding transglutaminase to the proteoglycan mixed dispersion solution, and preparing gel blocks by crosslinking reaction; preparing a microgel particle dispersion solution by taking the gel blocks as raw materials; and then adding the microgel particle dispersion solution to edible oil for preparing the Pickering emulsion. The method disclosed by the invention adopts high-speed shearing equipment, high-pressure homogenizing equipment and other common equipment for conducting granulation, and the Pickering emulsion prepared by high-speed shearing is not added with any inorganic materials in the preparation process, and has good biosafety and strong biocompatibility. The prepared Pickering can be stable at room temperature for more than 30 days, and can be used as a delivery system of fat-soluble and photosensitive active substances.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Bologna sausage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102038208AThe ratio of group allocation is reasonableBeautiful and fragrantFood preparationMonosodium glutamateFood additive
The invention relates to a bologna sausage. The bologna sausage comprises pork, chicken, emulsified skin, ice water, salt, sugar, monosodium glutamate, composite phosphate, modified starch, protein isolate, carrageenan, scallion powder, garlic powder, sodium erythorbate, potassium sorbate, a food additive, white wine, an edible pigment and sodium nitrite; and the raw materials are rolled, rubbed, salted, smoked, cooked and sterilized in turn after being mixed. The produced product has good color, aroma and taste, rich nutrition, low fat content and high protein content, and is convenient to eat and suitable for old people and children; and the preparation process is suitable for quick industrial production.
Owner:天津宝迪农业科技股份有限公司
Preparation of soy protein isolate
InactiveCN101372501AAdditional preparation stepsEasy to handlePeptide preparation methodsSolubilityLow activity
The invention provides a method for preparing separated soy protein and comprises the following steps: (1) the preparation of concentrated soybean albumen powder by vacuum drying alcoholic method; (2) solution preparation and heat treatment; (3) acid coprecipitate and neutrality adjustment; (4) instantaneous heating and sterilizing as well as sponging drying. The separated soy protein prepared by the method not only has the advantages of high solubility and high protein content of common protein isolate, but also has the advantages of low beanyflavor, light color, low activity of nutrition resistant substance, easy treatment on discharged sewage, and the like which are not possessed by common separated soy protein; therefore, the invention is an ideal preparation method for producing beverage type separated soy protein.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
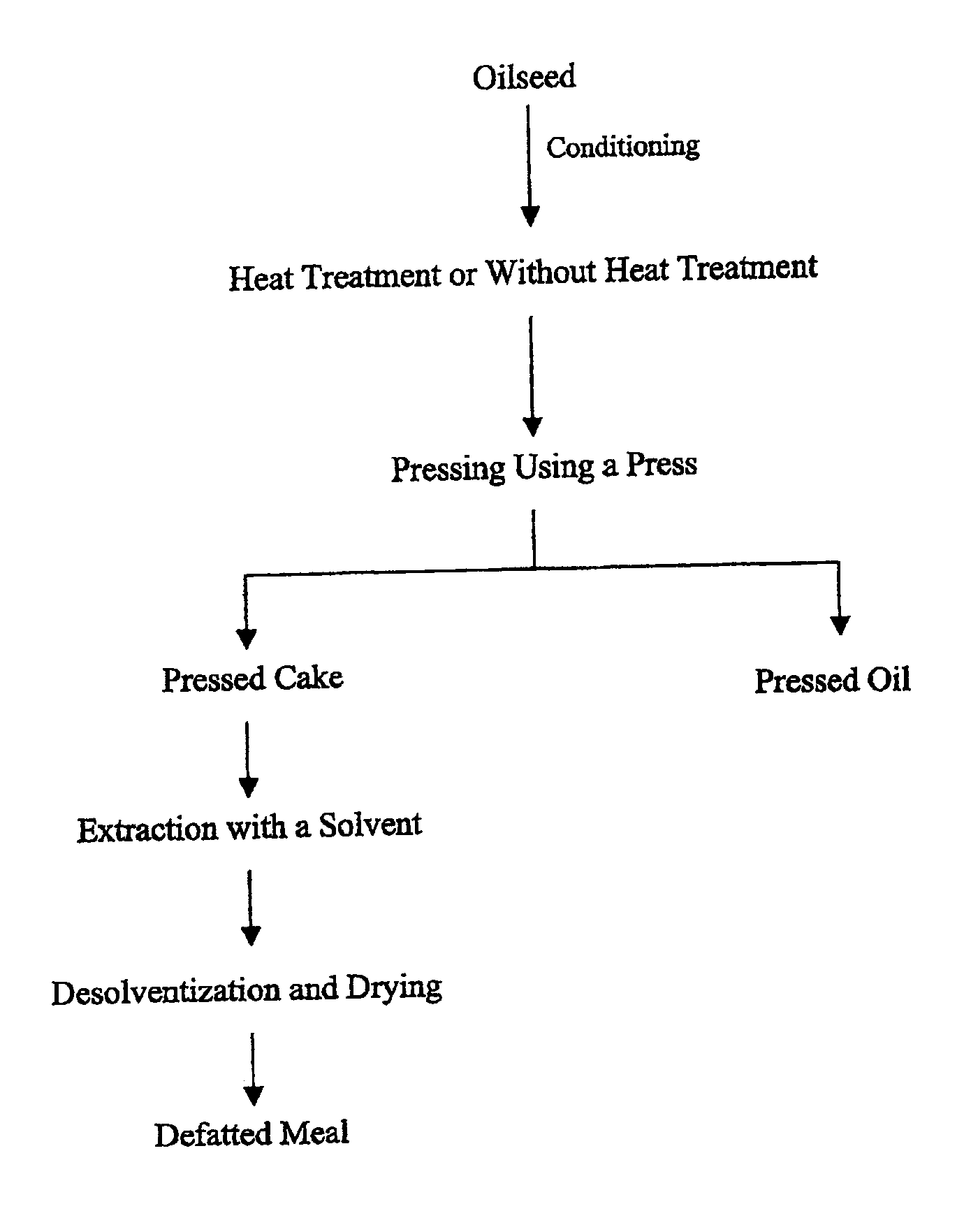
ITFM extraction of oil seeds
InactiveUS7156981B2Superior, high purity, bright proteinsIncrease in absorbable proteinHydrocarbon distillationEssential-oils/perfumesProtein insertionProtein isolate
A process for the producing edible protein-containing meal for human and animal consumption and high quality food grade oils from oil seed using iodotrifluoromathane as the solvent is shown. The meal has a significantly improved level of dietary available (absorbable) protein. The process involves the preparation of protein isolates by a procedure which is conducted at room temperature, thus decreases protein degradation and denaturing which is caused by elevated temperatures. The process also provides for extraction of substantially all oils and fats, which interfere with the formation of the protein micelle, from the protein meal providing a cleaner, purer product with high levels of absorbable protein. Such protein isolates can then be used as such or added to formulated foods in order to increase the total protein content of that food. The protein produced and the oils recovered have compositions which are also unique and unobtainable by prior processing methods.
Owner:BIO EXTRACTION INC
High-protein, reduced-carbohydrated flat bakery and other food products
InactiveUS20050031754A1Effectively reducing the “net” carbohydrate totalIncrease nutritionDough treatmentBaking mixturesAdditive ingredientProtein isolate
A high-protein, low-carbohydrate flat bakery product comprising a first proteinaceous ingredient and a second proteinaceous ingredient selected from the group consisting of wheat protein isolate, wheat protein concentrate, devitalized wheat gluten, fractionated wheat protein, deamidated wheat gluten, hydrolyzed wheat protein, and combinations thereof are provided. Preferred bakery products further comprise an amount of resistant starch which replaces a portion of digestible carbohydrate therein.
Owner:MGP INGREDIENTS
High-protein, reduced-carbohydrate bakery and other food products
InactiveUS20050037125A1Effectively reducing the “net” carbohydrate totalIncrease nutritionDough treatmentBaking mixturesProtein isolateAdditive ingredient
A high-protein, low-carbohydrate bakery product comprising a first proteinaceous ingredient and a second proteinaceous ingredient selected from the group consisting of wheat protein isolate, wheat protein concentrate, devitalized wheat gluten, fractionated wheat protein, deamidated wheat gluten, hydrolyzed wheat protein, and combinations thereof are provided. Preferred bakery products further comprise an amount of resistant starch which replaces a portion of digestible carbohydrate therein.
Owner:MGP INGREDIENTS
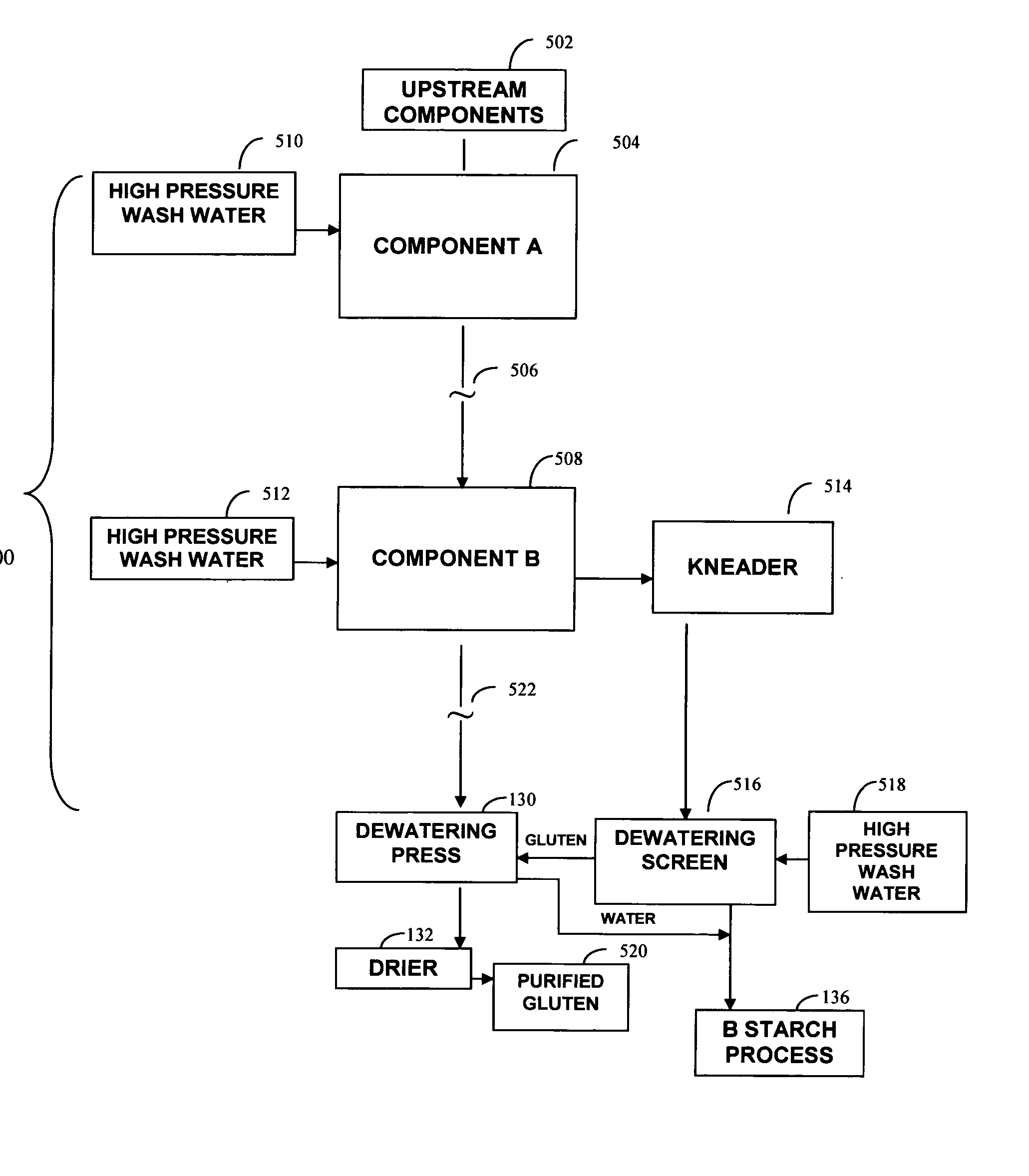
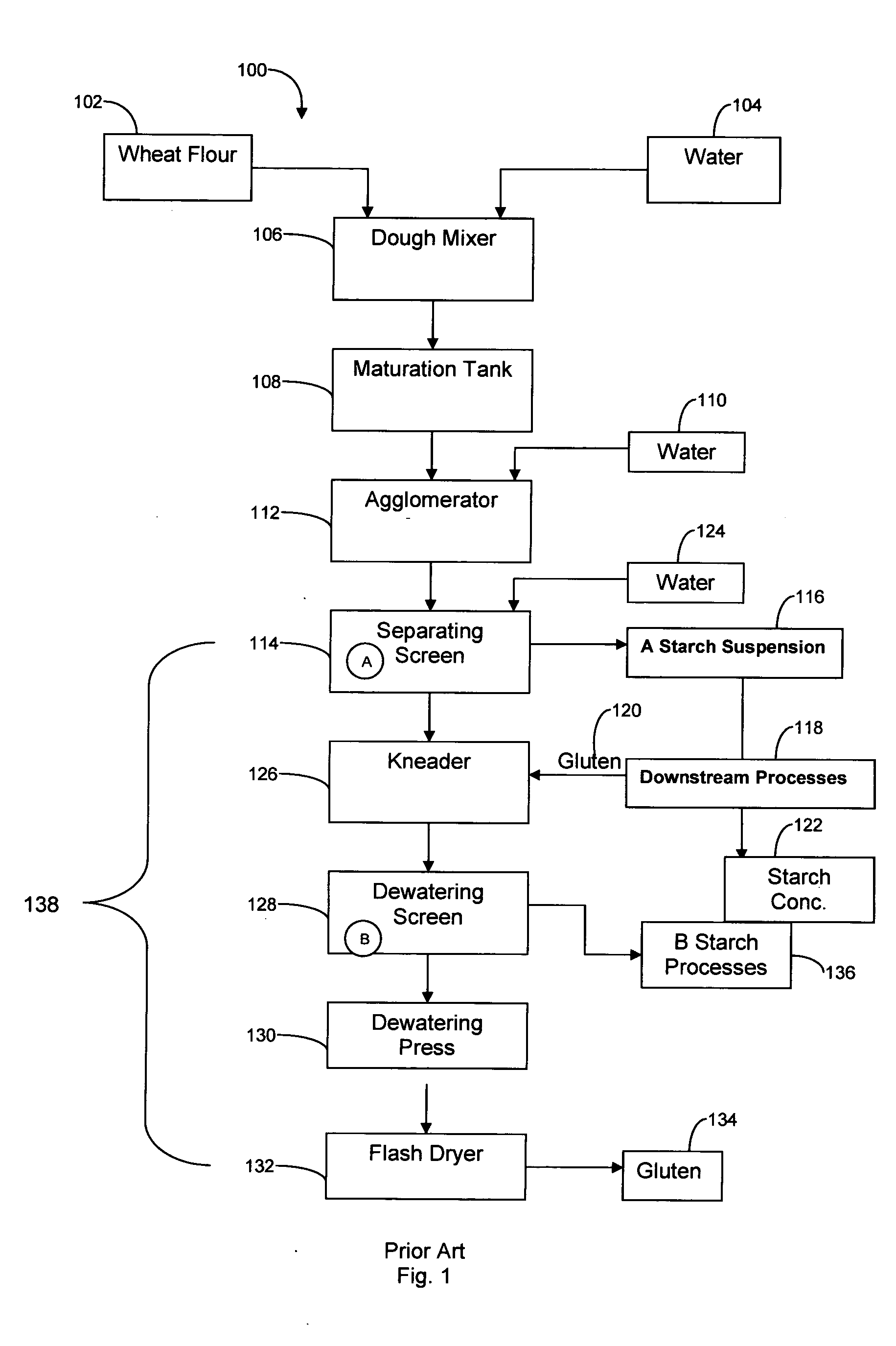
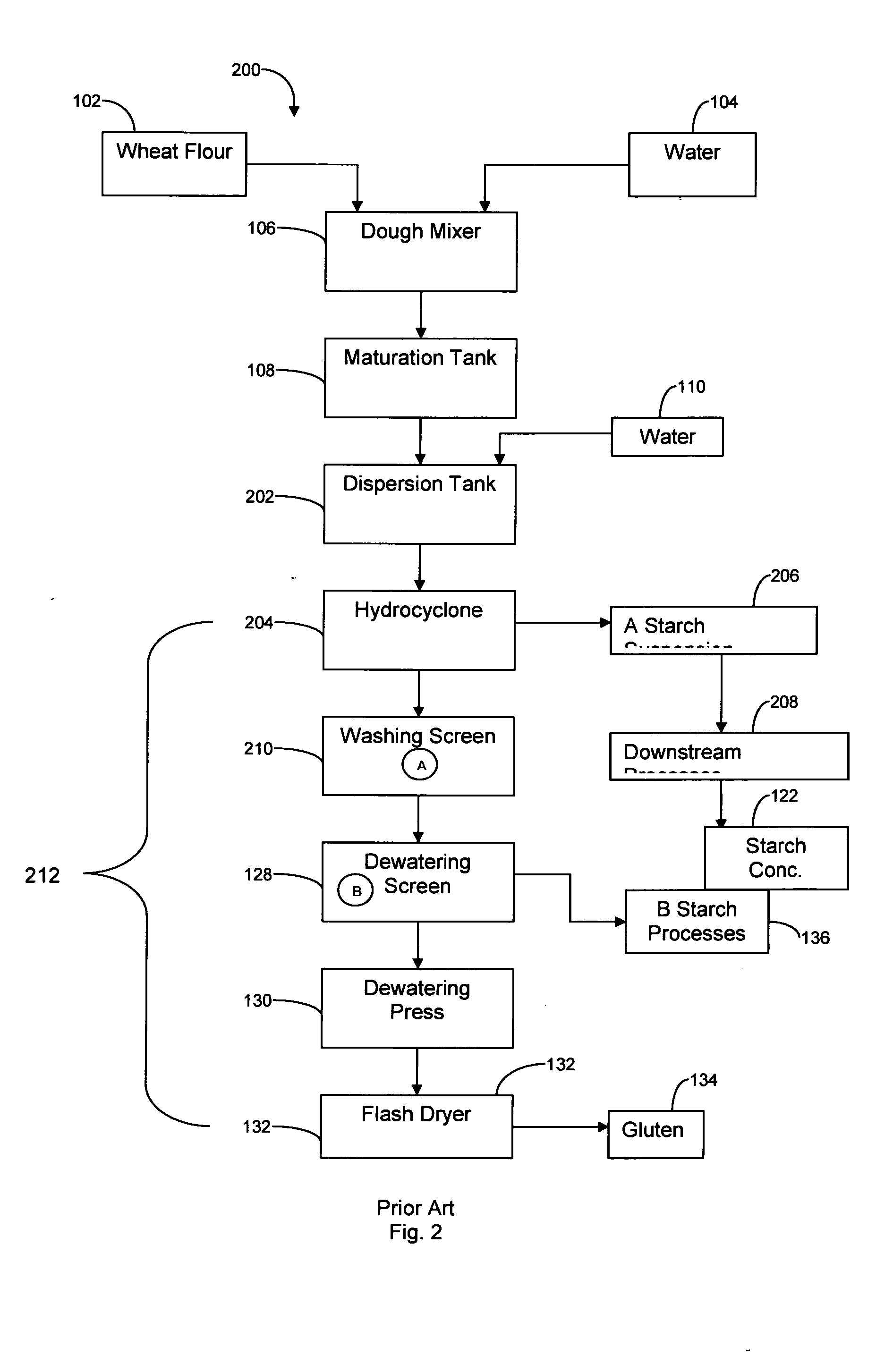
Wheat protein isolates and their modified forms and methods of making
ActiveUS20050287267A1Accurate descriptionDough treatmentBaking mixturesProcess equipmentProtein isolate
Process equipment for the separation of gluten from wheat starch including gluten process equipment configured to process gluten after the gluten is initially separated from A starch, the gluten processing equipment having a dewatering press configured to dewater gluten and modified gluten process equipment including at least one component selected from the group consisting of a high pressure water wash system located upstream of the dewatering press, a kneader located upstream of the dewatering press, a homogenizer located upstream of the dewatering press, a dispersion tank configured to precipitate fines downstream of the dewatering press, a solids-ejecting centrifuge downstream, and combinations thereof.
Owner:MGPI PROCESSING
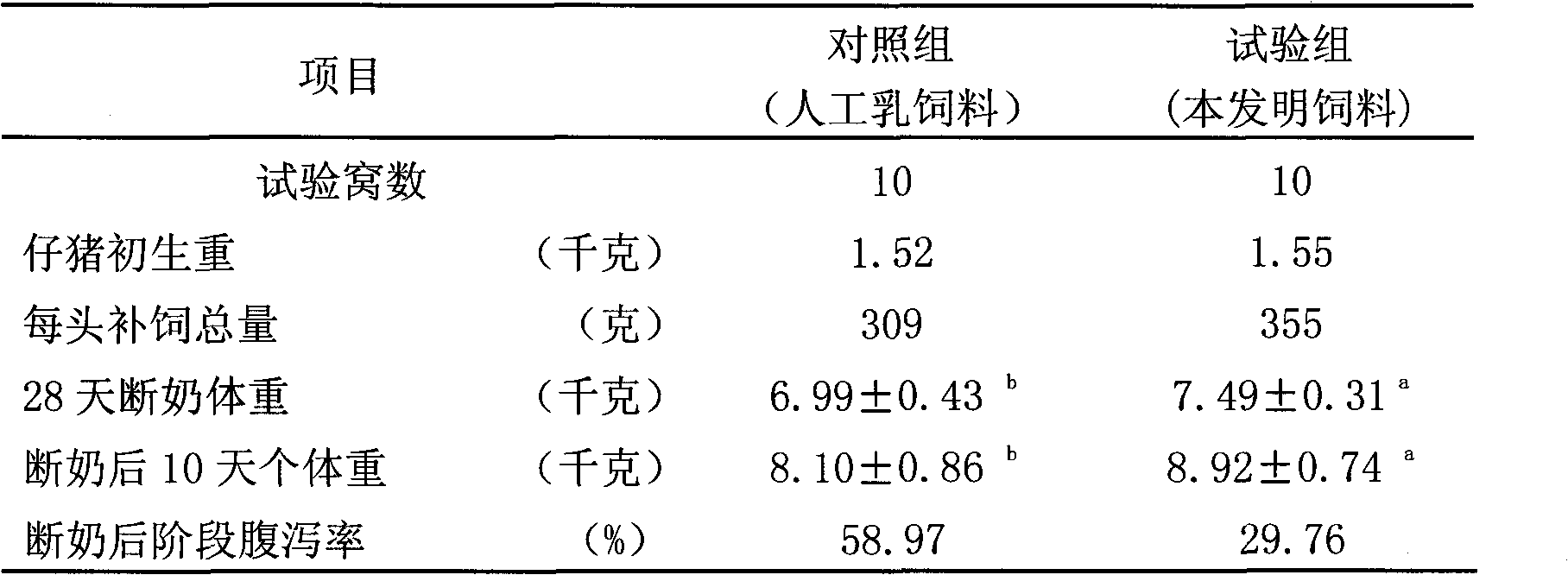
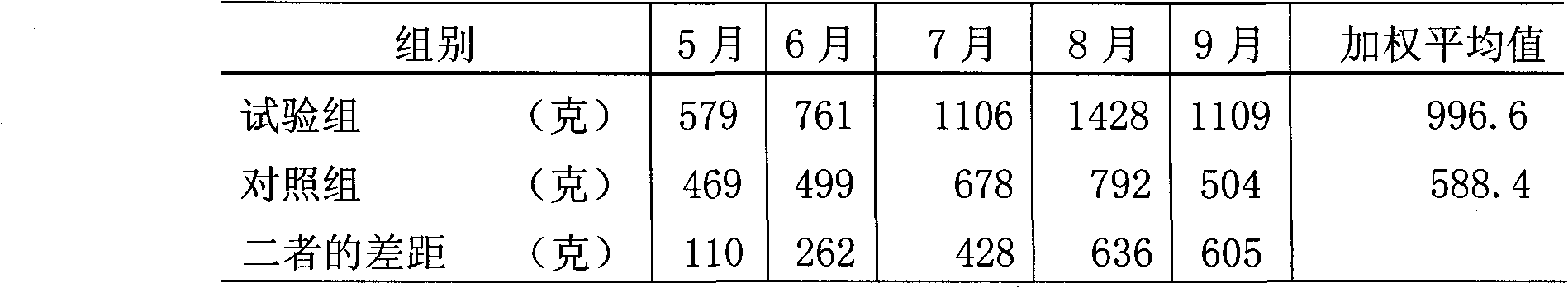
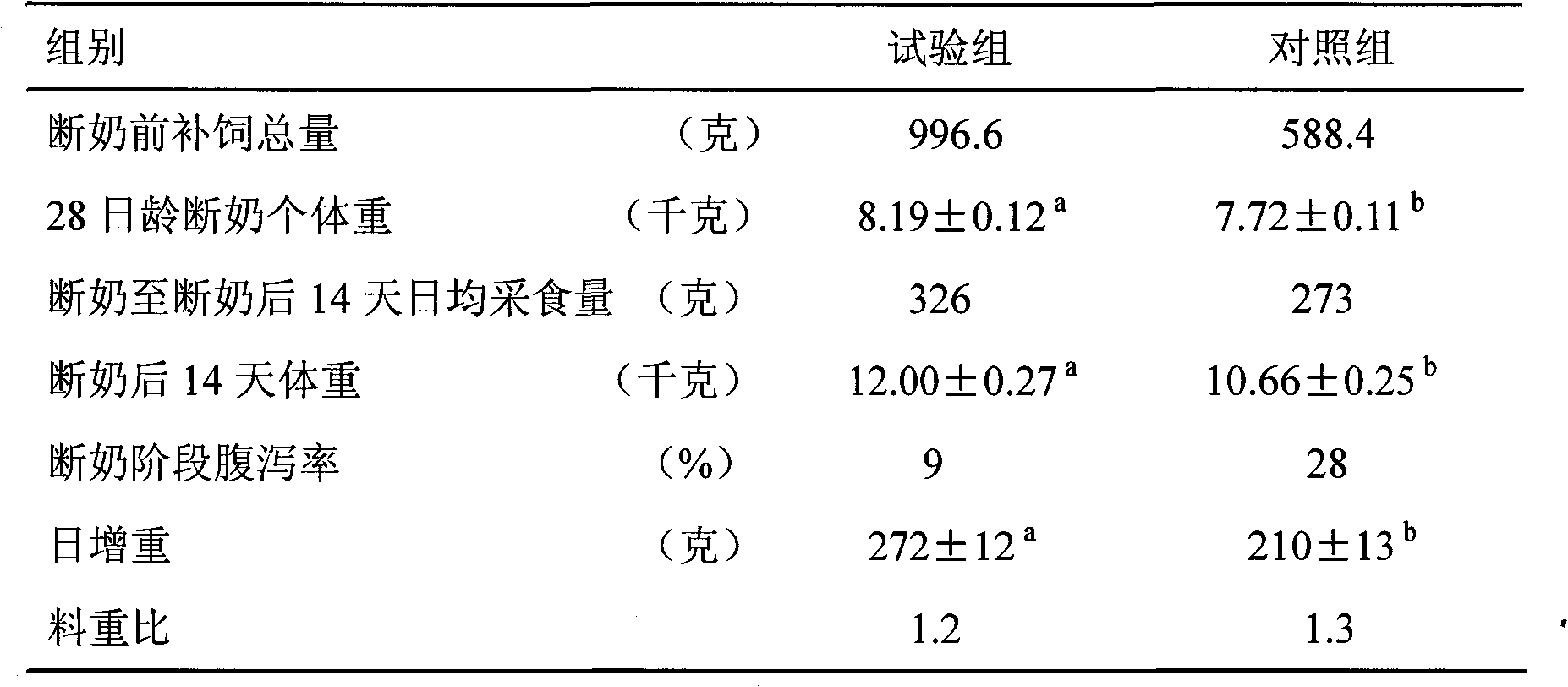
Plant-derived piglet feeding attractant
ActiveCN101803689AKeep the original scentIncrease weaning weightAnimal feeding stuffVegetable oilProtein isolate
The invention relates to a plant-derived piglet feeding attractant. The technical scheme adopted is as follows: the attractant comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 30 to 50 percent of puffed cereal, 10 to 20 percent of flour, 10 to 20 percent of fermented soybean meal, 3 to 5 percent of wheat protein isolate, 3 to 6 percent of milk powder, 5 to 10 percent of lactose, 0.5 to 1 percent of acidifier, 3 to 6 percent of vegetable oil, 1 to 2 percent of calcium additive, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of salt, 1.0 to 2.0 percent of amino acid, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of composite trace element, and 0.03 to 0.08 percent of composite vitamin. The plant-derived piglet feed attractant is applied to piglet feeding attraction, can effectively improve the feed intake before and after a piglet weans, improve the weight before weaning and the weight 14 days after weaning, reduce the diarrhoea rate of the piglet after weaning so that the weaned piglet effectively overcomes weaning stress, and has important significance in improving the piglet production performance and survival rate.
Owner:LIAONING WELLHOPE AGRI TECH
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system proteins
InactiveUS6884614B1Increase productionHigh yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesAntisense nucleic acidProtein isolate
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated PTS nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel PTS proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing PTS nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated PTS proteins, mutated PTS proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of PTS genes in this organism.
Owner:DAESANG
Method for extracting peanut protein
InactiveCN102048021AHigh extraction rateReduce extraction timeProtein composition from vegetable seedsAlcoholProtein isolate
The invention discloses a method for extracting peanut protein, which comprises the following steps of: uniformly dissolving low-denatured peanut protein powder in alkali, performing ultrasonic extraction, centrifuging, performing ultrasonic extraction again, mixing supernatant, performing acid precipitation, centrifuging, washing precipitates with alcohol for two times, washing the precipitates with water for three times, and freeze-drying to obtain peanut protein isolate powder. The method has the advantages of short extraction time and low production cost.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Protein concentrates and isolates, and processes for the production thereof
ActiveUS20100136173A1Quality improvementMilk preparationProtein composition from vegetable seedsFiberProtein isolate
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Protein beverage and method of making the same
InactiveUS20110183052A1Dough treatmentFood ingredient as anti-foaming agentSolubilityProtein isolate
A protein beverage composition and a method of making it relate to a beverage including a protein essentially free of caseinate and derived from an aqueous protein isolate collected from membrane-filtration isolation of the protein and without substantial drying, wherein the protein beverage composition exhibits a pH ranging from about 2.0 to about 4.6. Substantial solubility of the protein is maintained in the beverage composition, and the protein beverage is essentially free of active microbes known to be harmful to human health, both at the time of packaging of the protein beverage and for a time period of at least one year after packaging.
Owner:NEXTPROTEINS INC
Process of making a homogeneous cheese
A process of making cheese, e.g., a mozzarella variety cheese, is disclosed. It comprises the following steps: a) preparing a cheese curd; b) grinding the curd while in admixture with (i) an aqueous solution of at least one cheese emulsifying salt and (ii) at least one GRAS food additive in the form of a comminuted solid, to obtain an emulsifier / additive-impregnated ground curd; and c) converting the emulsifier / additive-impregnated curd into cheese either by (i) heating, kneading, and stretching the emulsifier / additive-impregnated ground curd to obtain a homogeneous mass of cheese, or (ii) pressing the emulsifier / additive-impregnated ground curd to obtain a homogeneous mass of cheese. Examples of suitable GRAS food additives include gums, stabilizers, dairy solids (e.g., non-fat dry milk or whey protein concentrate), cheese powders, non-dairy protein isolates, sodium chloride, native or modified food starches, colorants, and flavorants. The process is particularly useful when a proteinaceous GRAS food additive is used.
Owner:LEPRINO FOODS
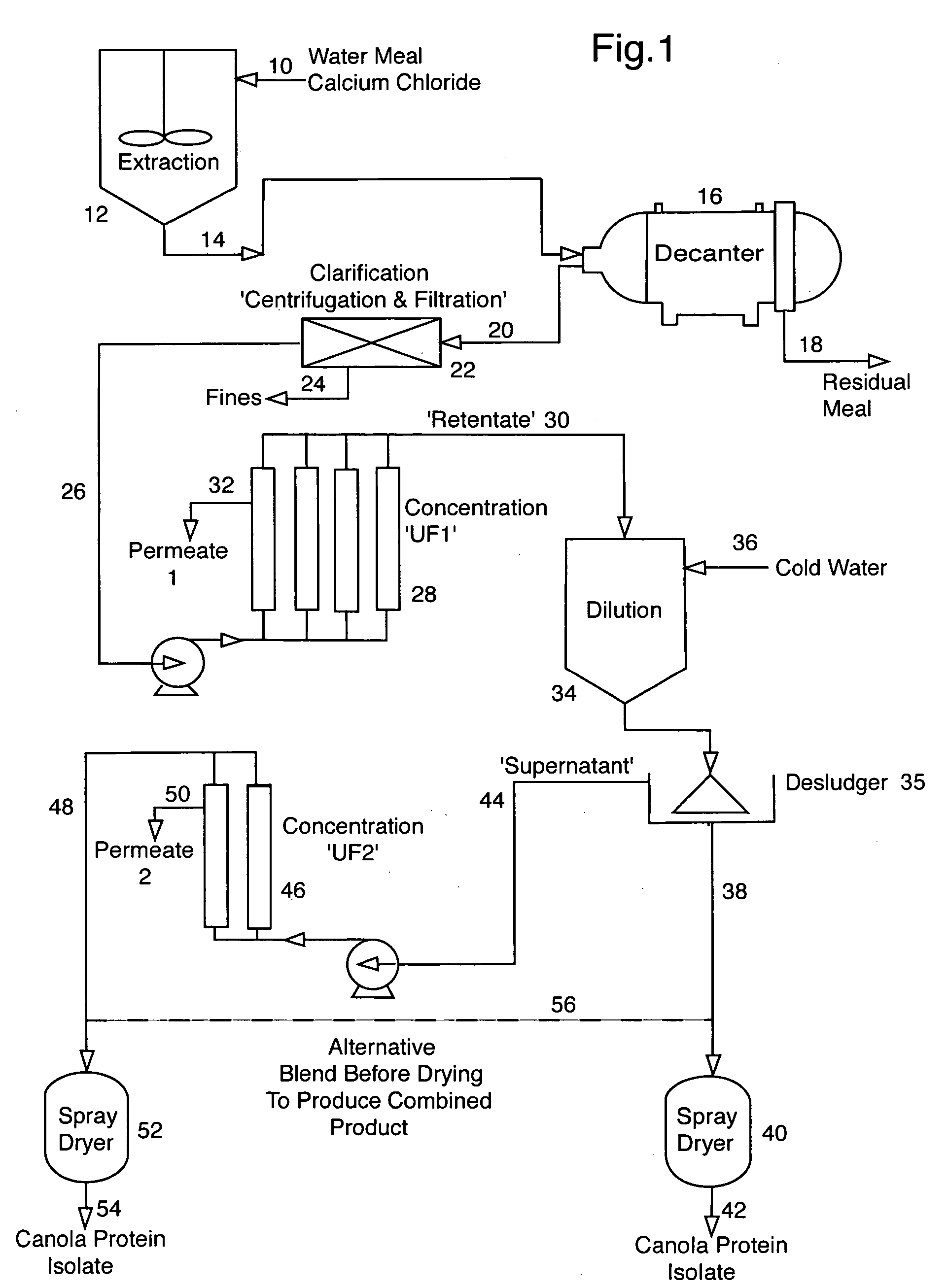
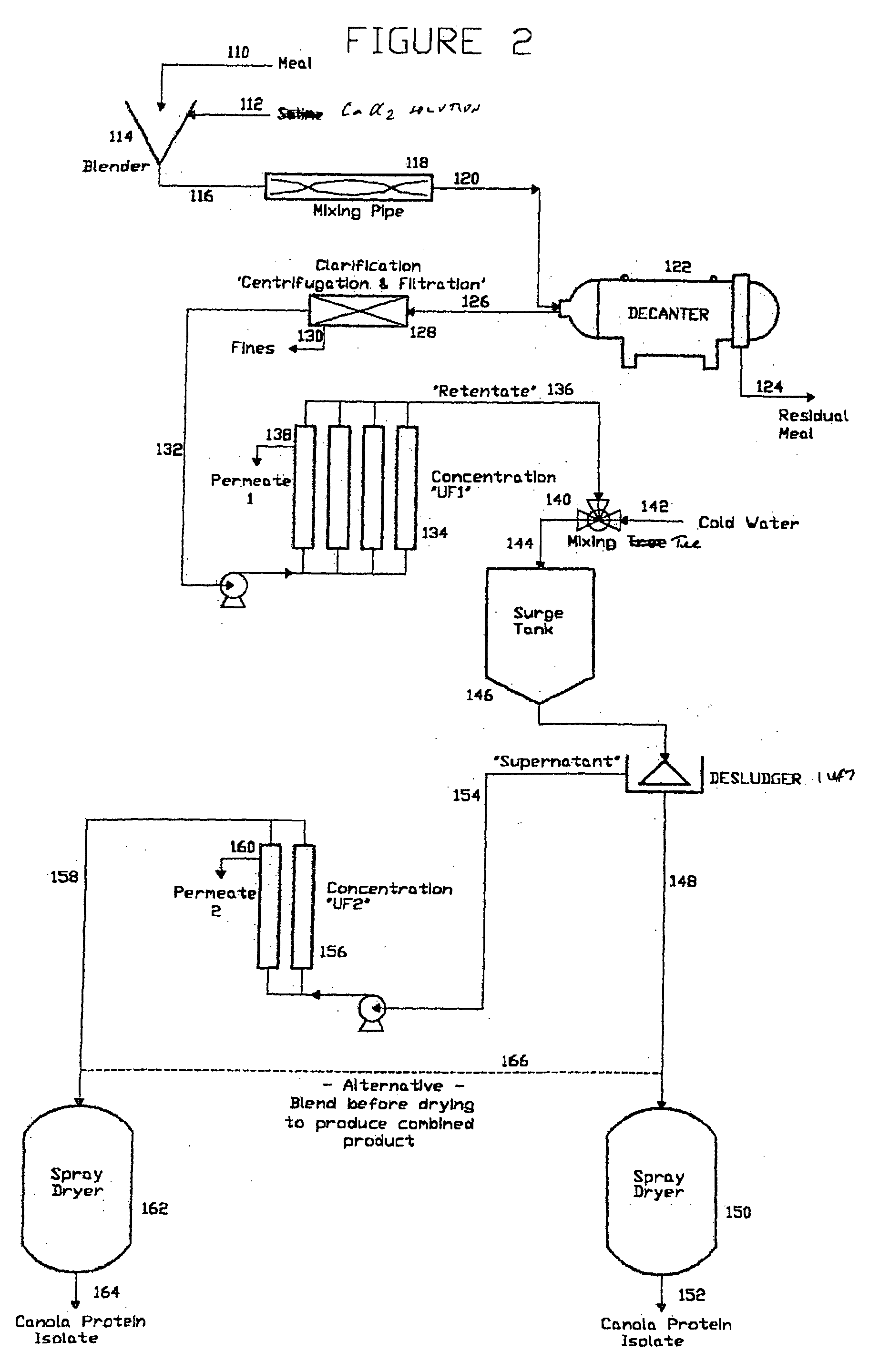
Soluble Canola Protein Isolate Production from PMM ("C307")
InactiveUS20100048875A1Low viscosityImprove performanceProtein composition from vegetable seedsDepsipeptidesProtein solutionProtein isolate
A soluble canola protein isolate is prepared from canola protein micellar mass by solubilizing the protein micellar mass in a calcium salt solution, preferably a calcium chloride solution, followed by dilution of the resulting canola protein solution. Following removal of the precipitate phytic acid, the aqueous canola protein solution is concentrated, optionally diafiltered, and acidified to a pH of about 2.5 to 4.0 to produce an acidified clear canola protein solution, which may be concentrated, subjected to a colour removal step and dried. The canola protein isolate so formed is soluble, transparent and heat stable in an acid aqueous environment and also is soluble at natural pH, without precipitation of protein.
Owner:BURCON NUTRASCI MB
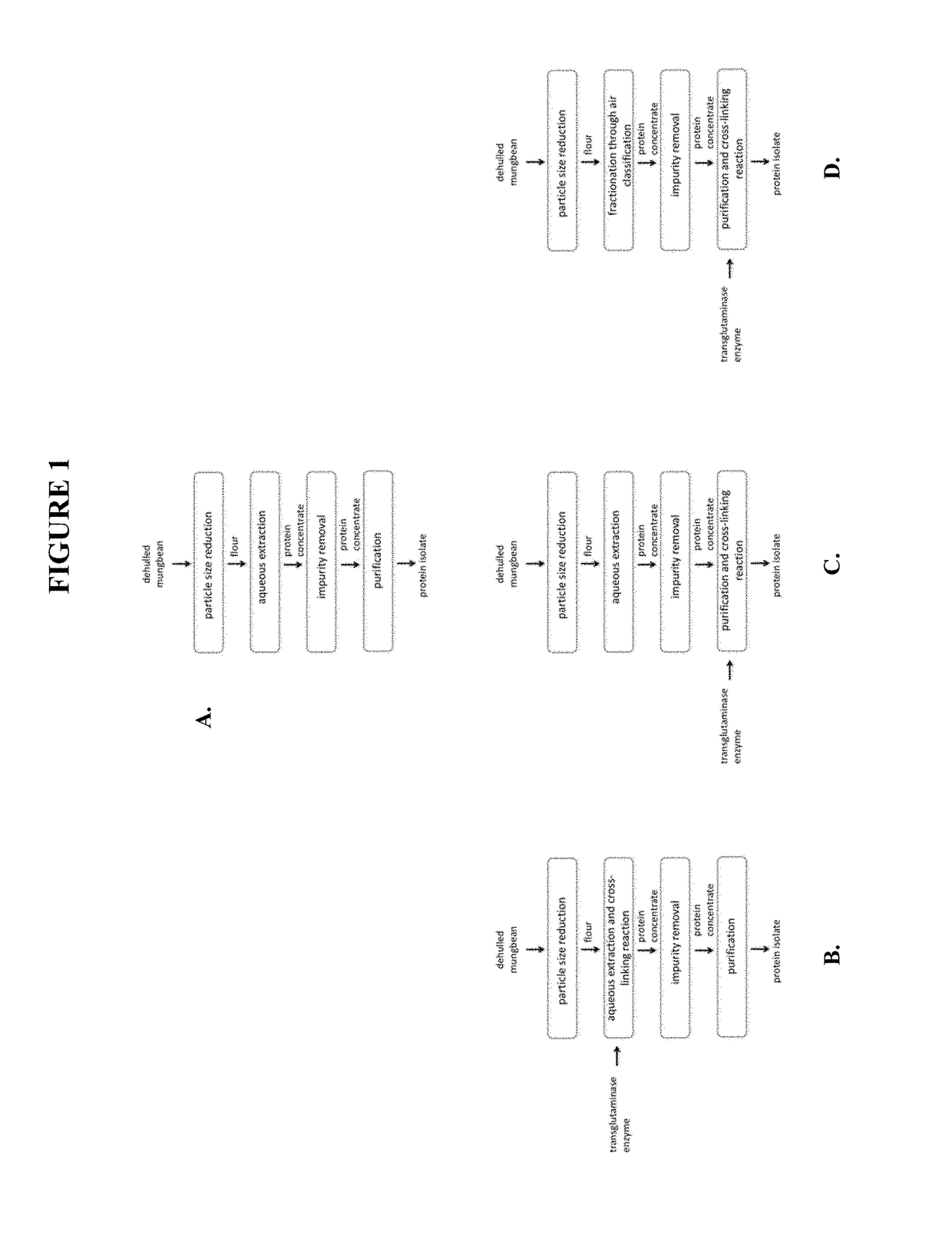
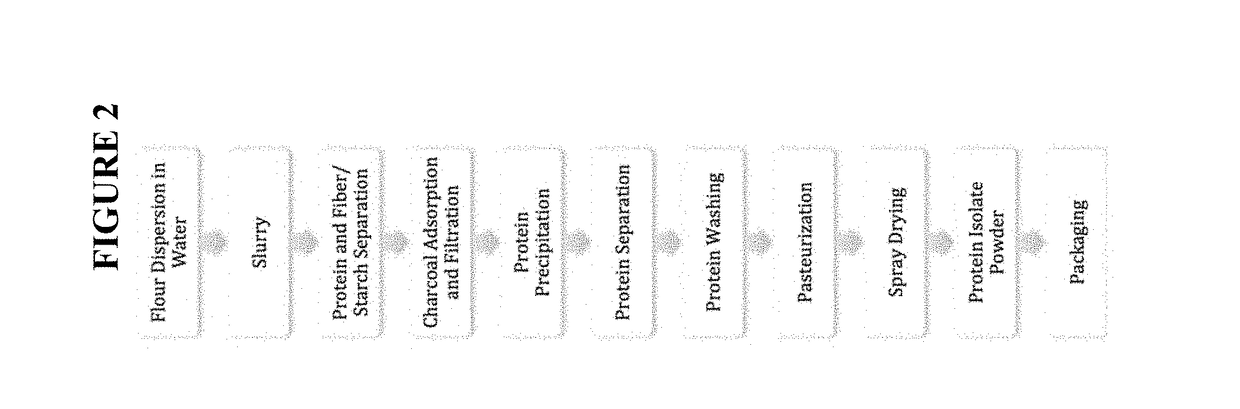
Functional mung bean-derived compositions
ActiveUS20170238590A1Reduced enzymatic activityReduced activityDough treatmentFrozen sweetsProtein isolateFiltration
Provided herein are methods for producing a mung bean protein isolate having high functionality for a broad range of food applications. In some embodiments, the methods for producing the isolate comprise one or more steps selected from: (a) extracting one or more mung bean proteins from a mung bean protein source in an aqueous solution, for example, at a pH between about 6.5-10.0; (b) purifying protein from the extract using at least one of two methods: (i) precipitating protein from the extract at a pH near the isoelectric point of a globulin-rich fraction, for example a pH between about 5.0-6.0; and / or (ii) fractionating and concentrating protein from the extract using filtration such as microfiltration, ultrafiltration or ion-exchange chromatography; and (c) recovering purified protein isolate.
Owner:JUST INC
Compositions for the treatment of cancer, and methods for testing and using the same
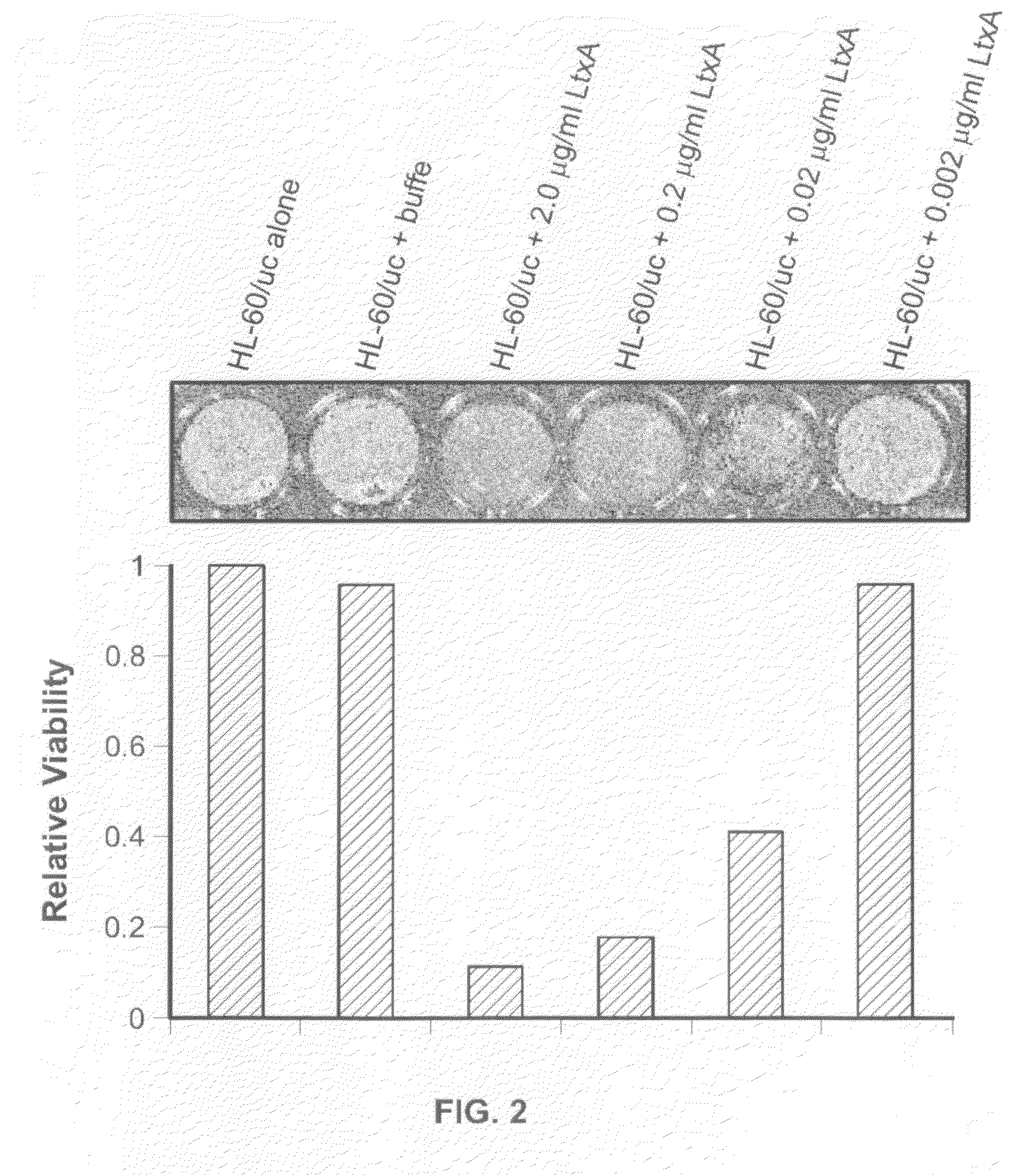
ActiveUS20090075883A1Rapidly and effectively determinedHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisBacteroidesProtein isolate
A composition comprising leukotoxin proteins isolated from a bacterium is provided. In this composition, greater than 85% of the leukotoxin proteins are chemically modified at a basic amino acid residue, and the proteins induce cell death in myeloid leukocytes, while remaining substantially non-toxic to lymphoid leukocytes, lymphocytes, and red blood cells. Also provided is a method of selectively inducing cell death in myeloid leukocytes. The method comprises contacting the myeloid leukocytes with a composition comprising leukotoxin proteins. These leukotoxin proteins may be isolated from the NJ4500 strain of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. A method of purifying leukotoxin protein from the NJ4500 strain of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans is also provided, as well as an assay that allows for the rapid determination of the activity of a given drug against leukemic cells either taken from a patient or derived from a cell line. The assay is performed in the presence of whole blood or serum.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
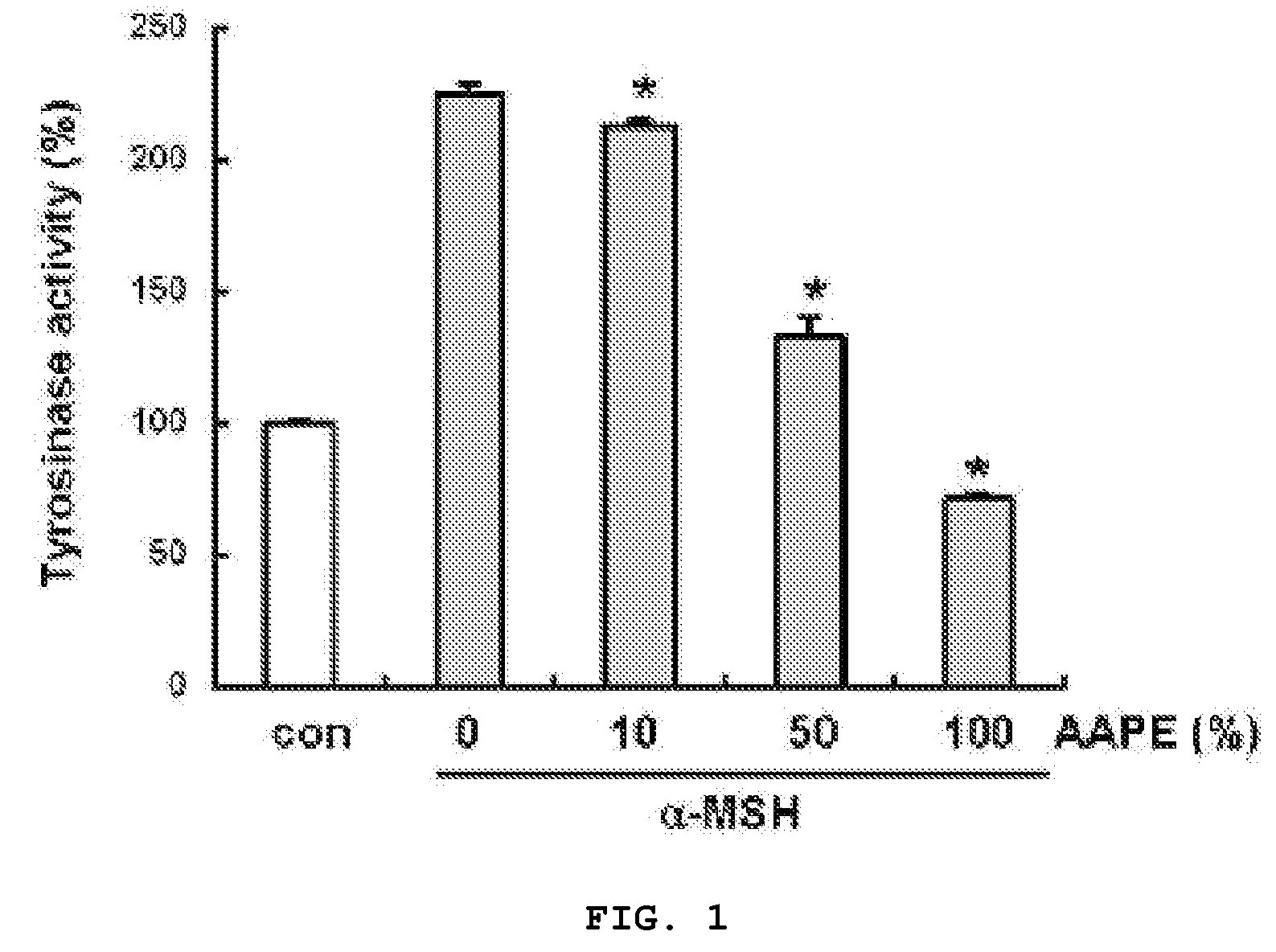
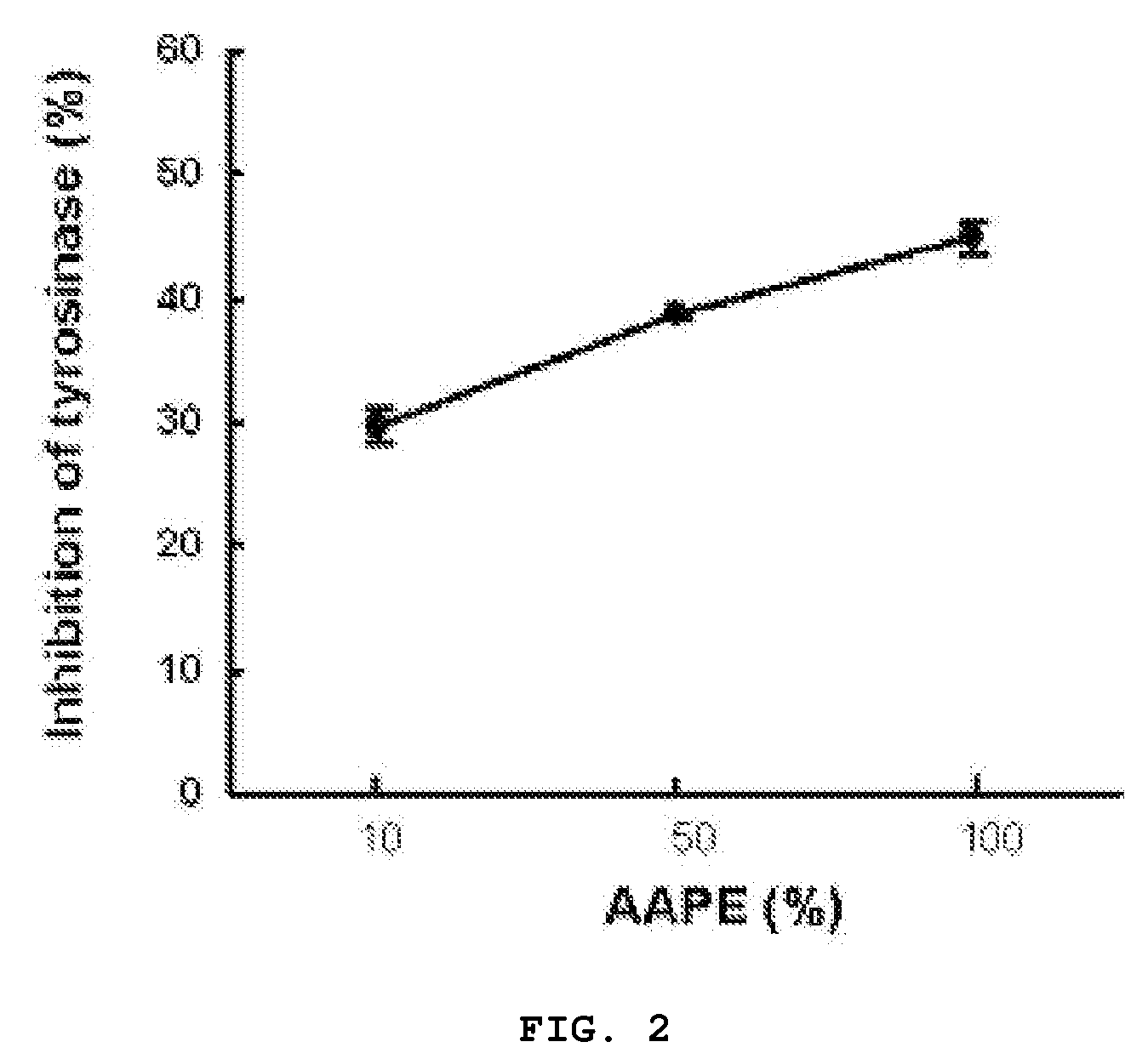
Composition and Method for Inhibition of Melanin Synthesis
InactiveUS20090035283A1Improve securityImprove effectivenessCosmetic preparationsBiocideSkin treatmentsProtein isolate
The present invention provides a whitening cosmetic composition comprising a stem cell, a culture medium thereof or a protein isolated from the culture medium and a method of whitening a skin which comprises administering to the skin an therapeutically effective amount of a stem cell, a culture medium thereof or a protein isolated from the culture medium.
Owner:PROSTEMICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com