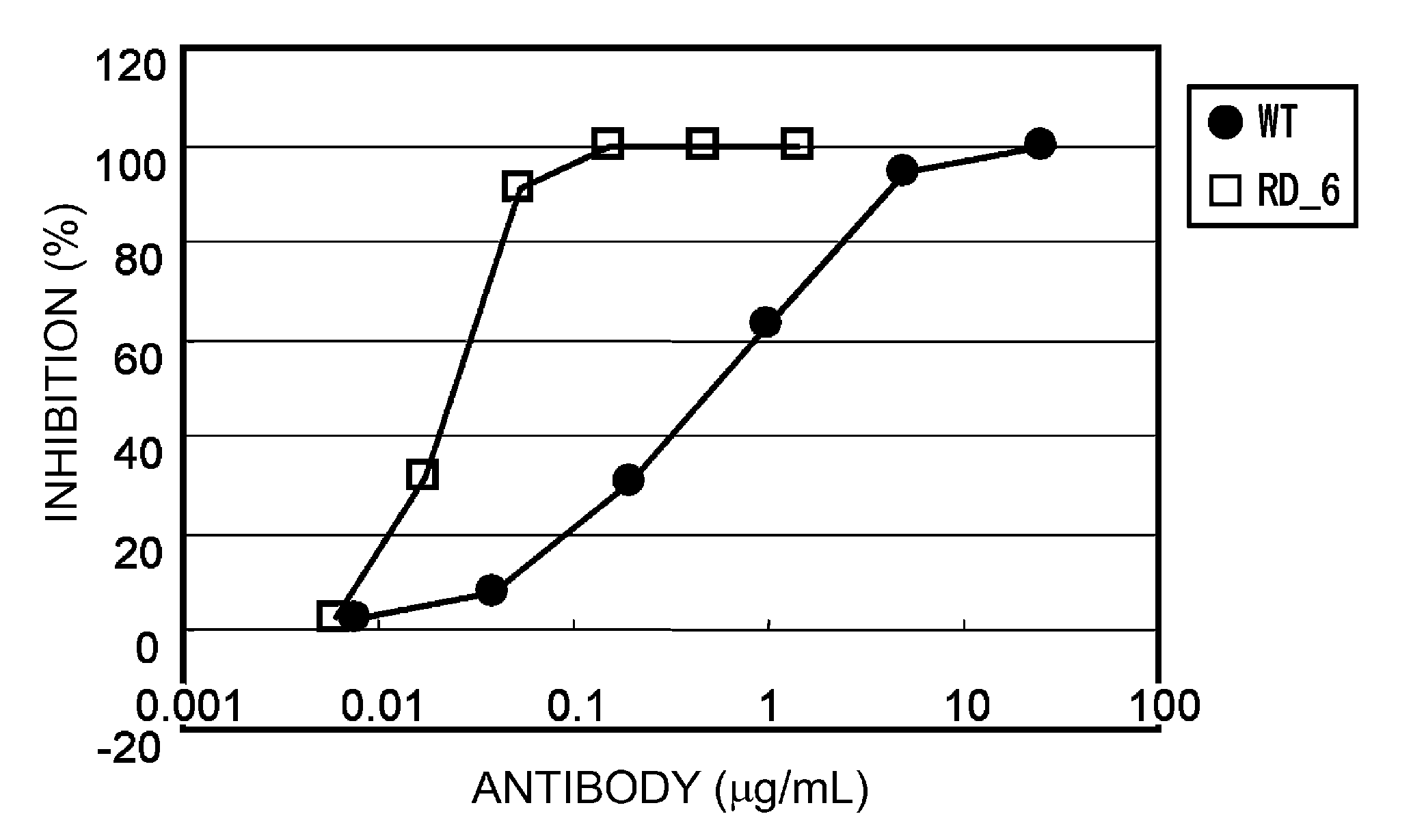
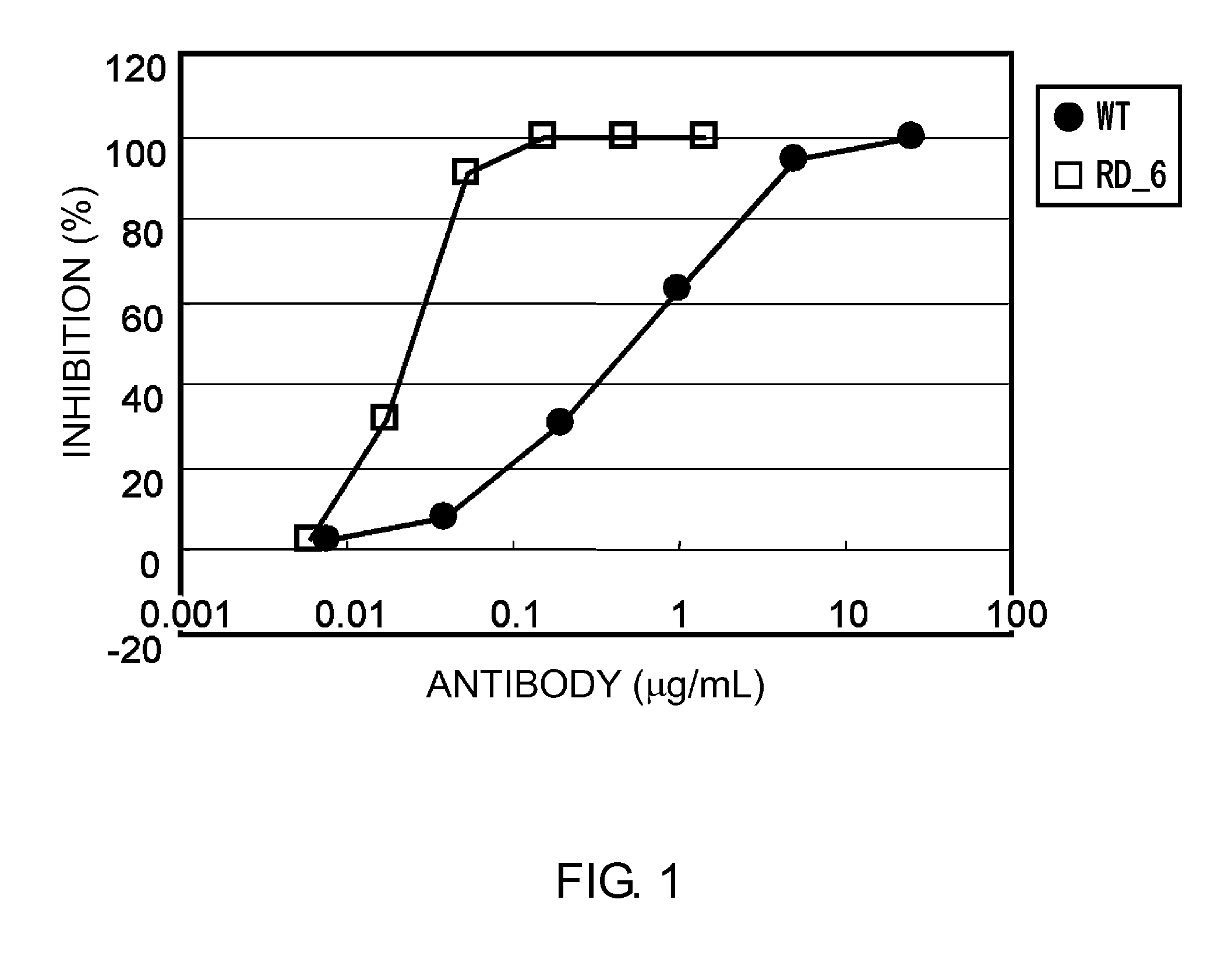
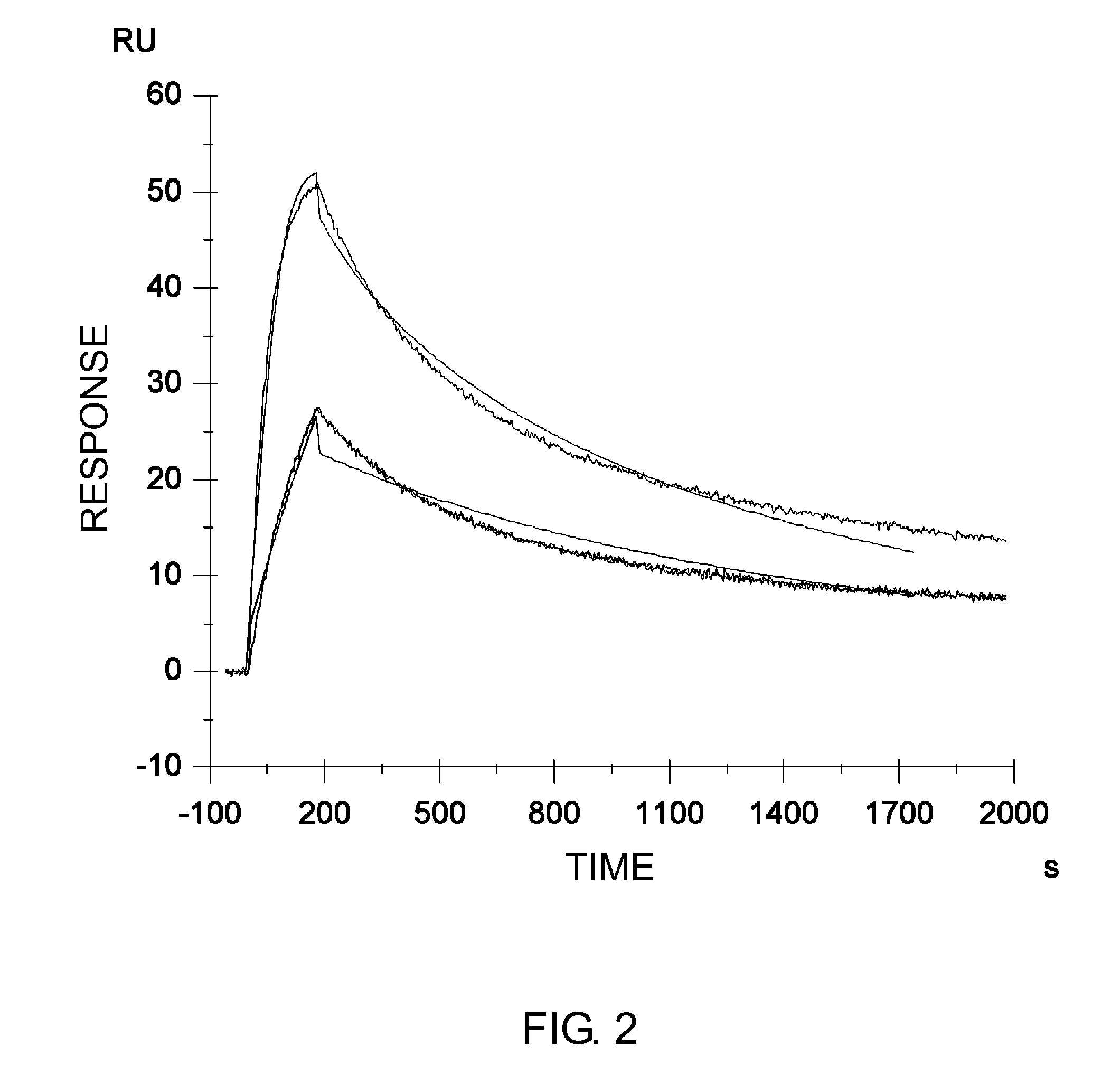
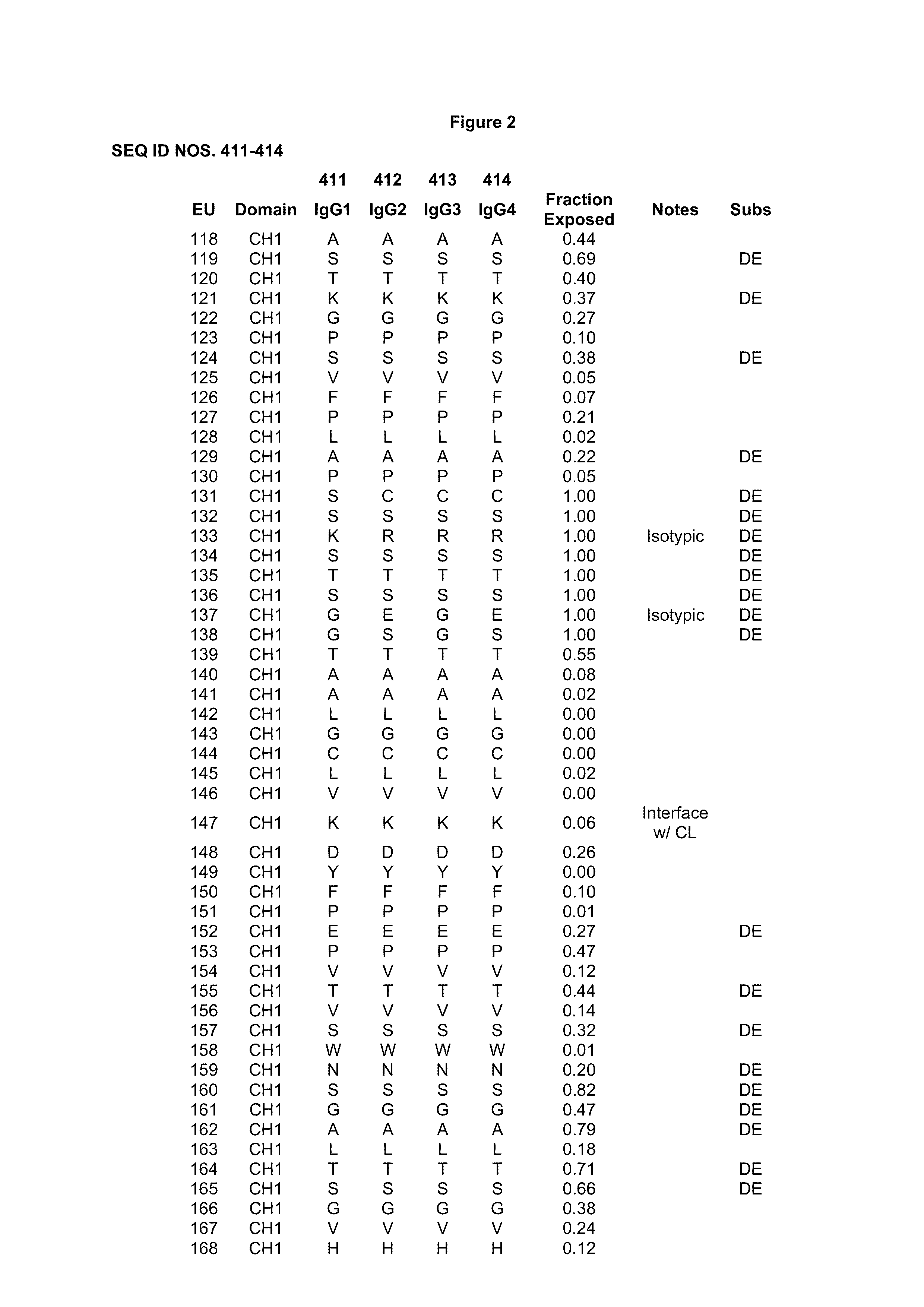
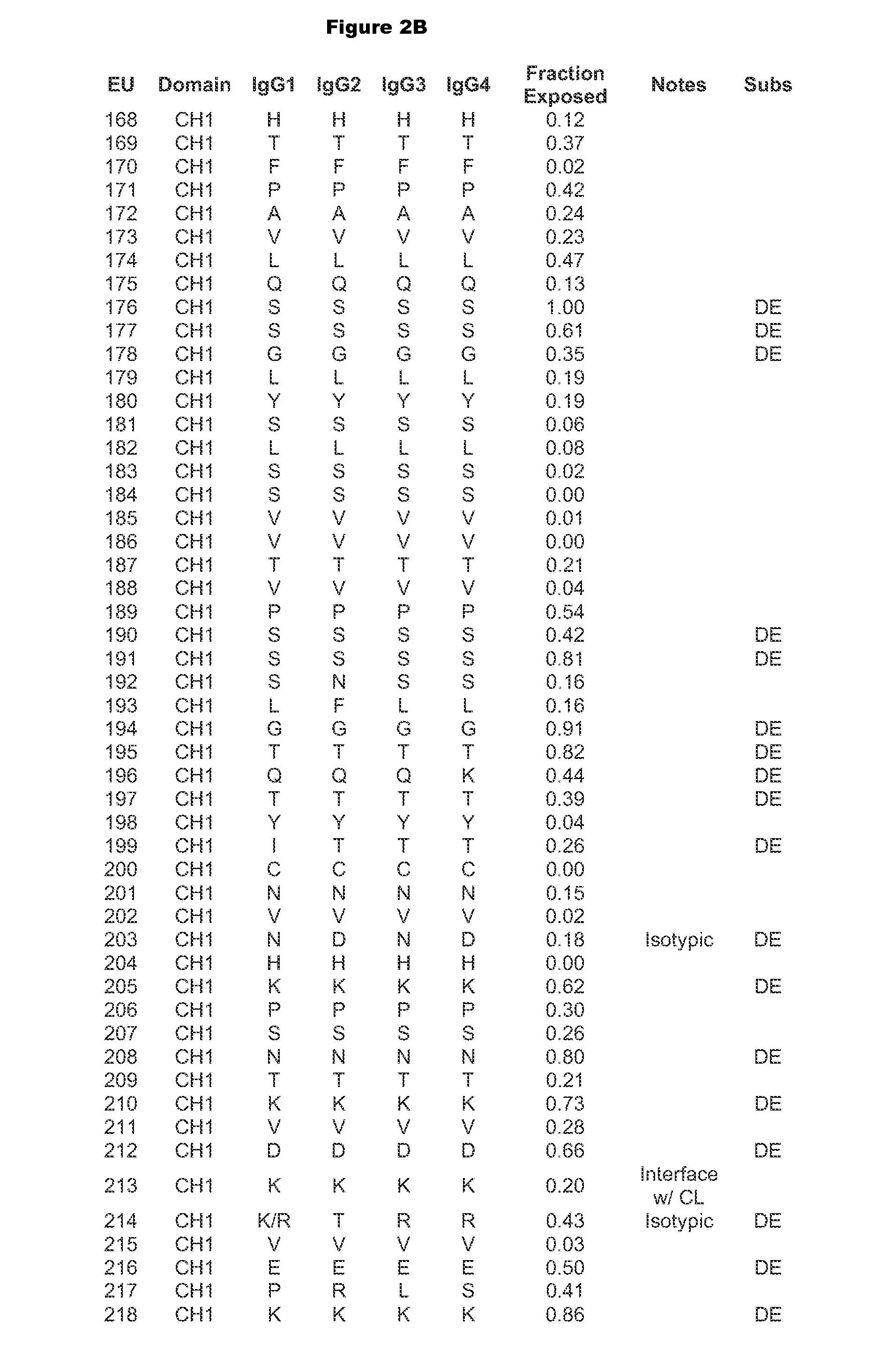
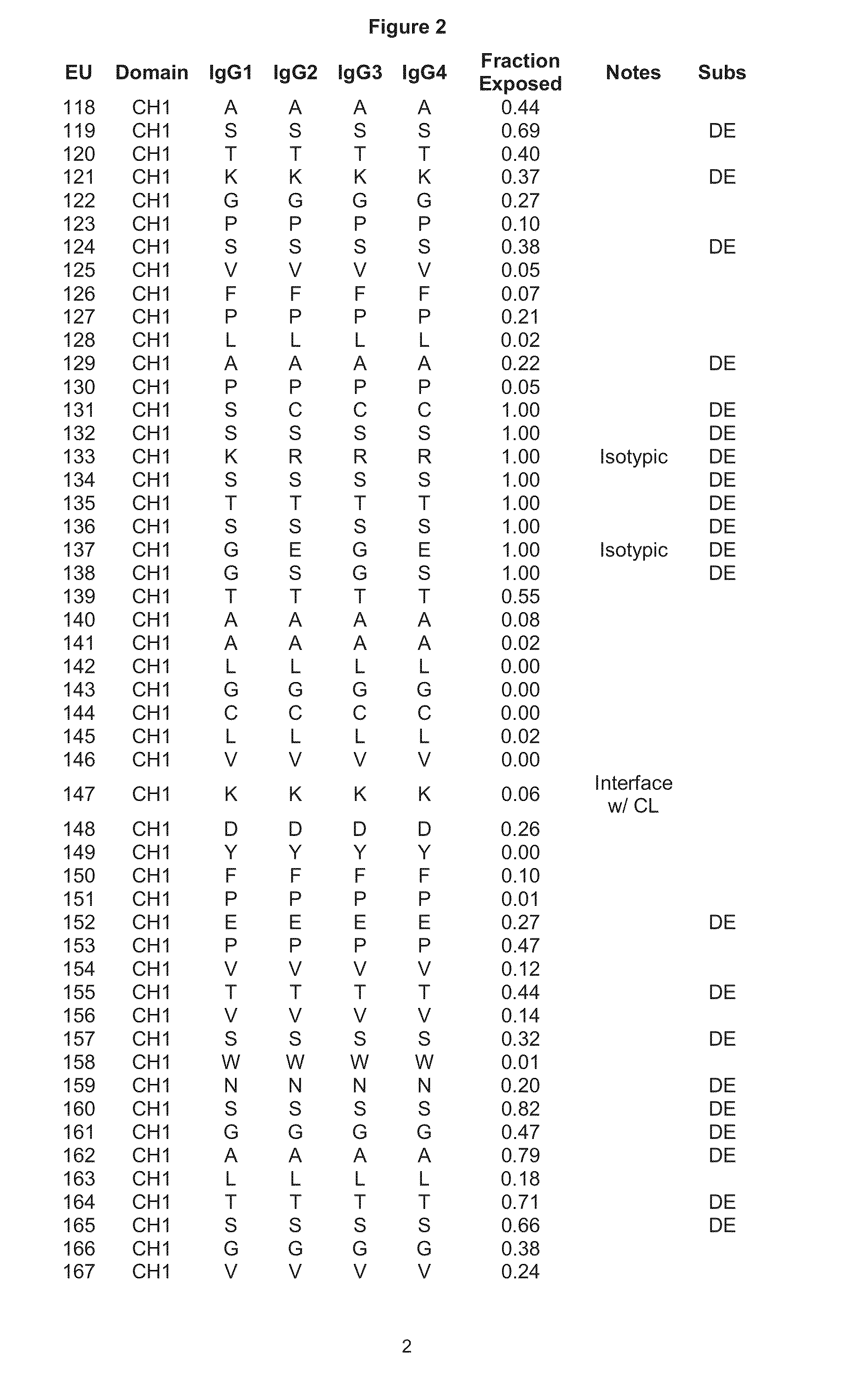
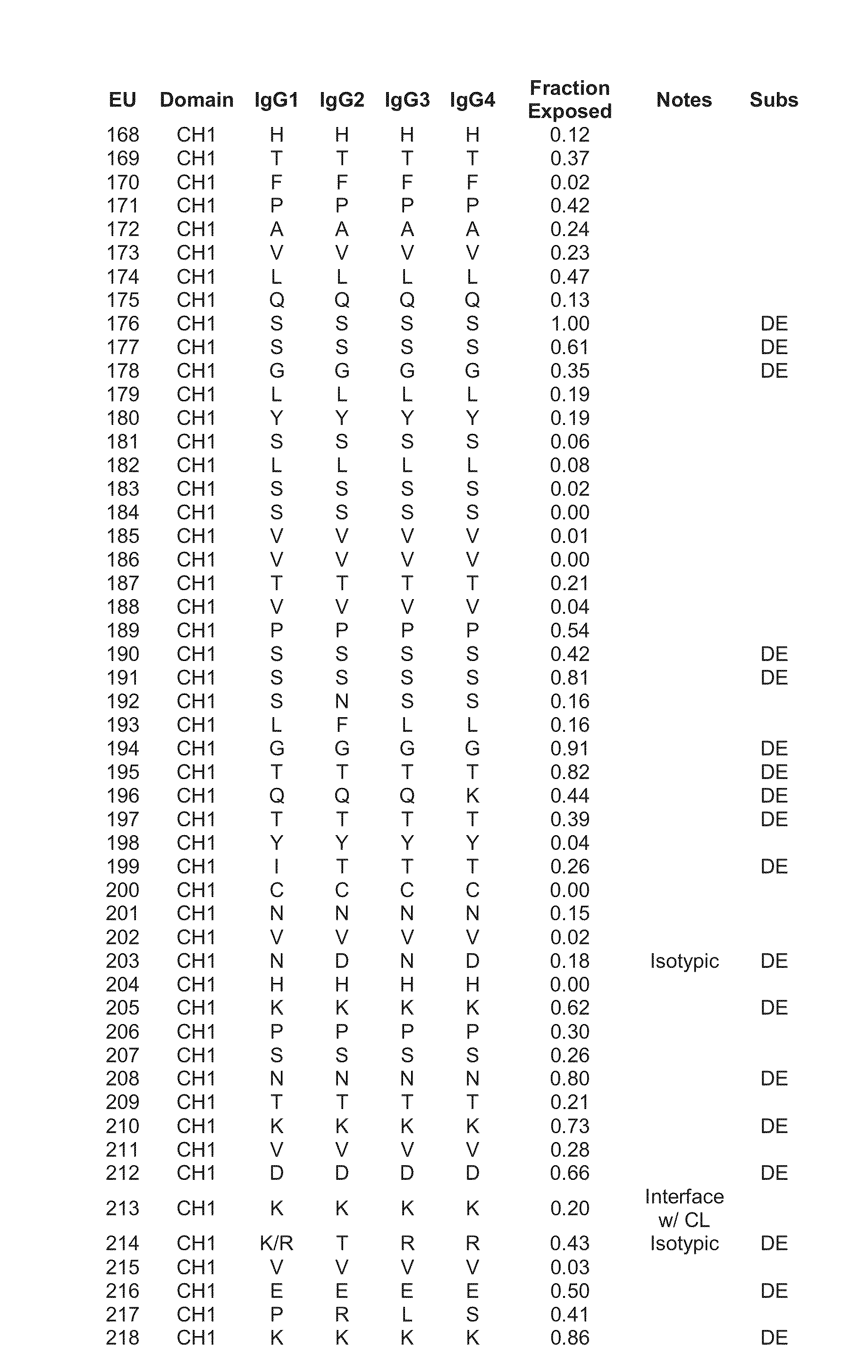
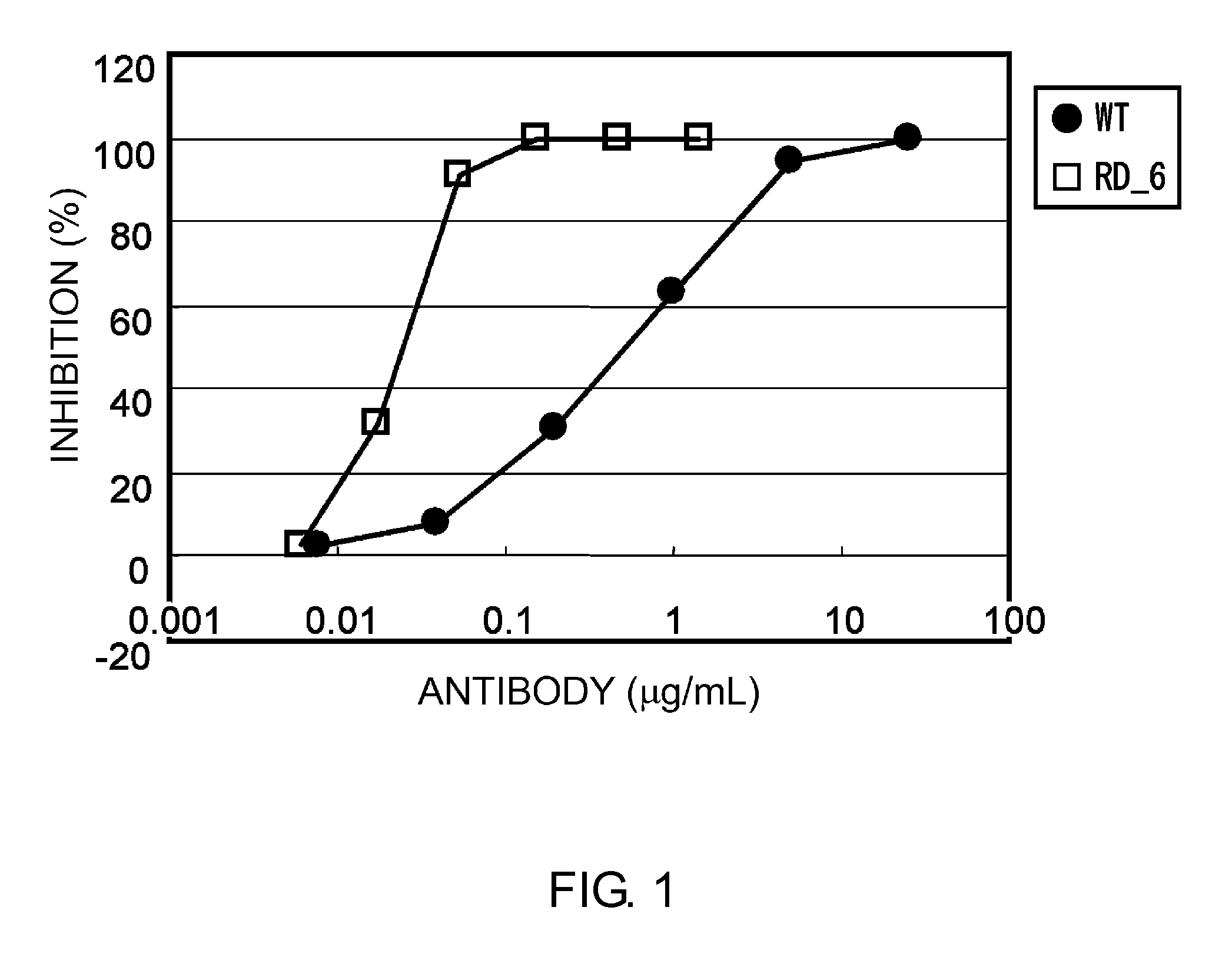
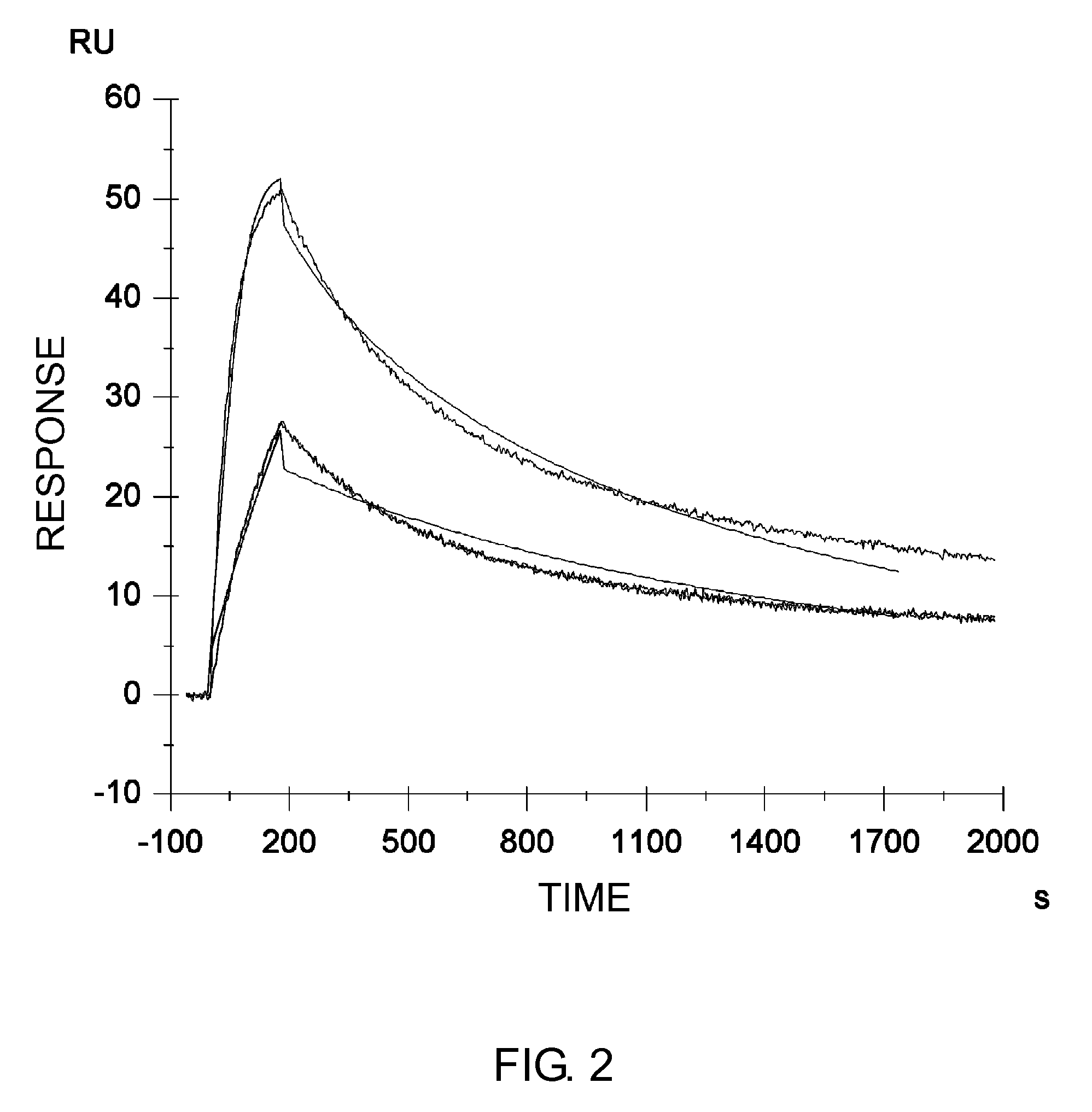
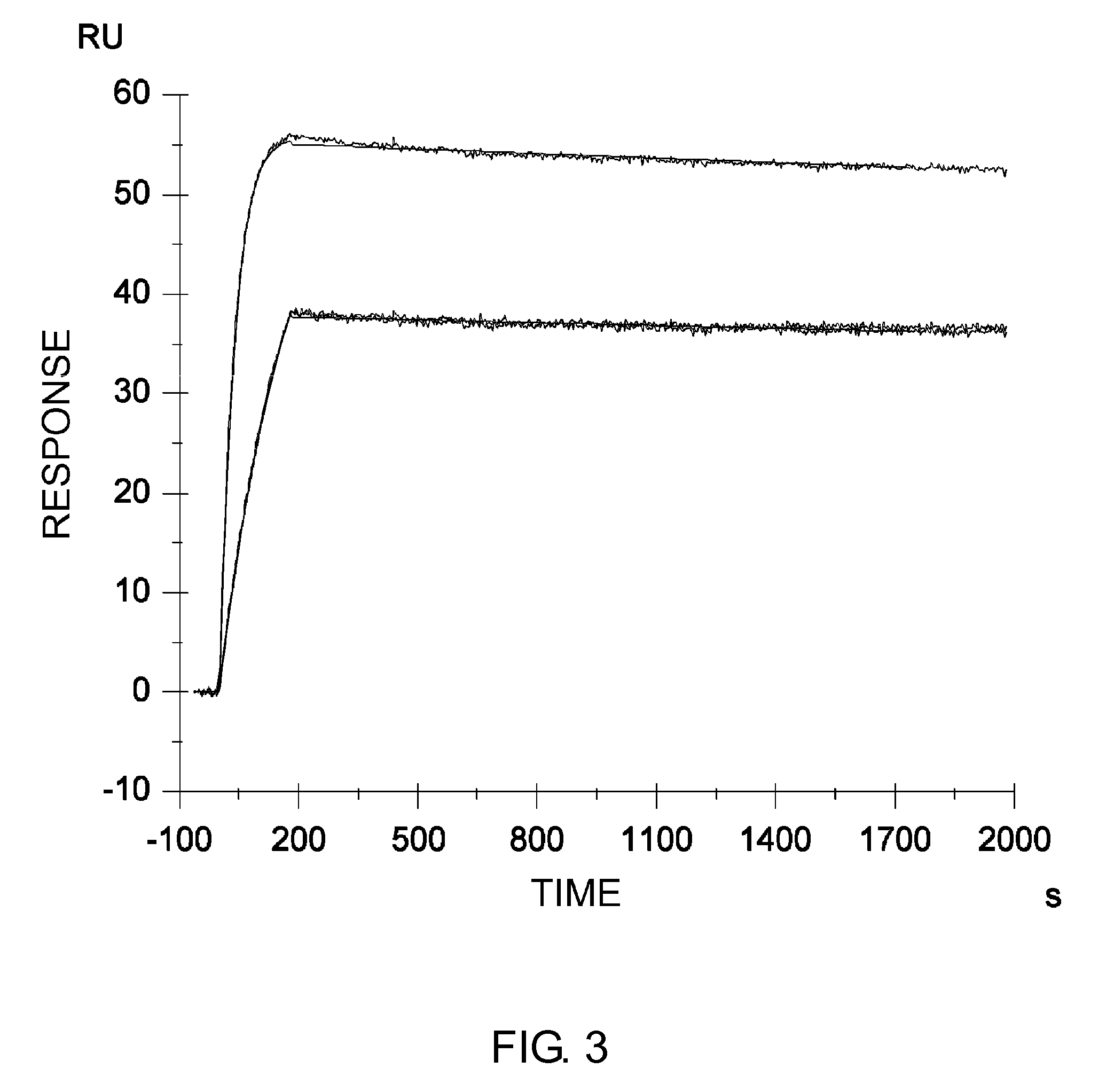
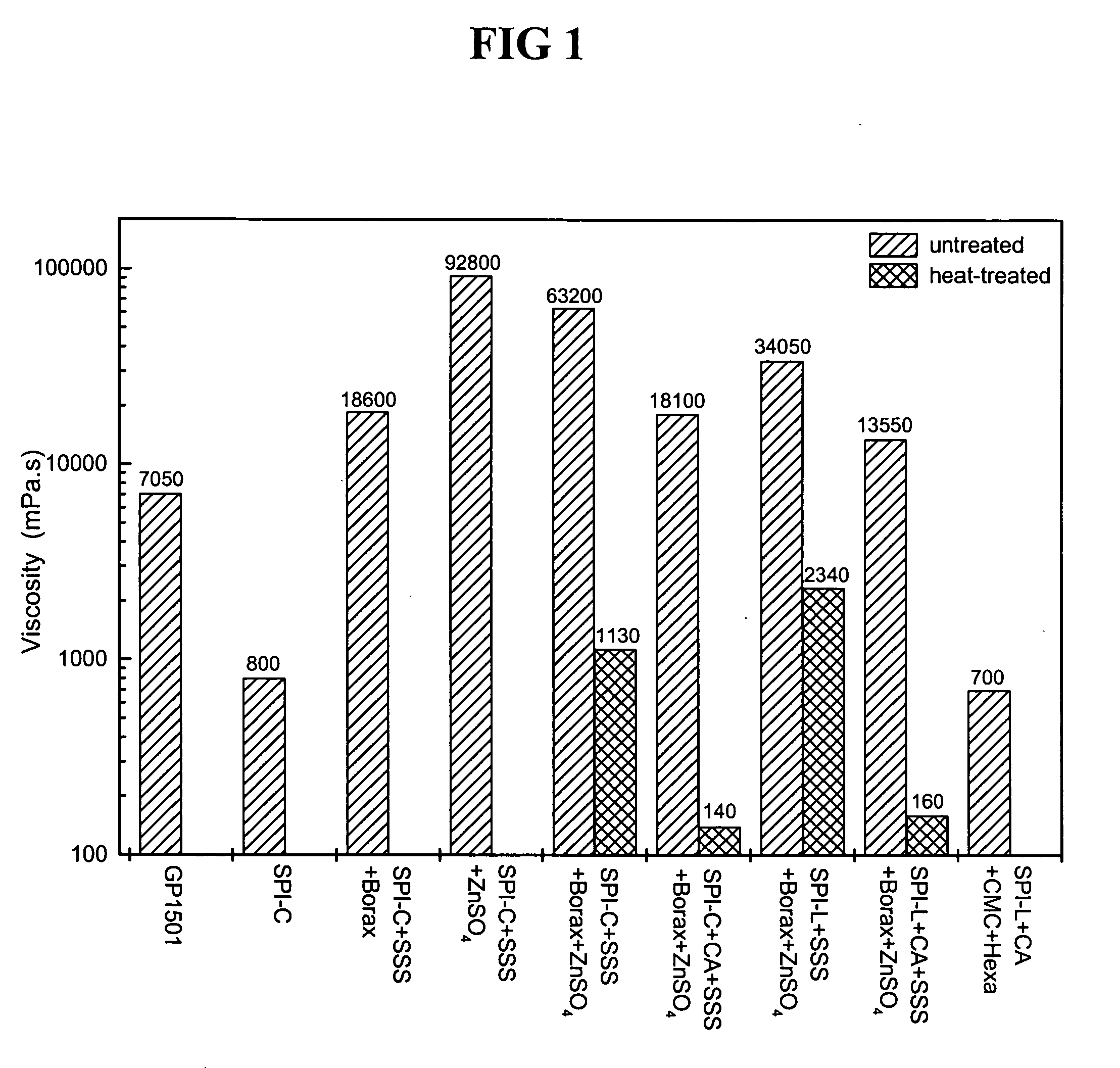
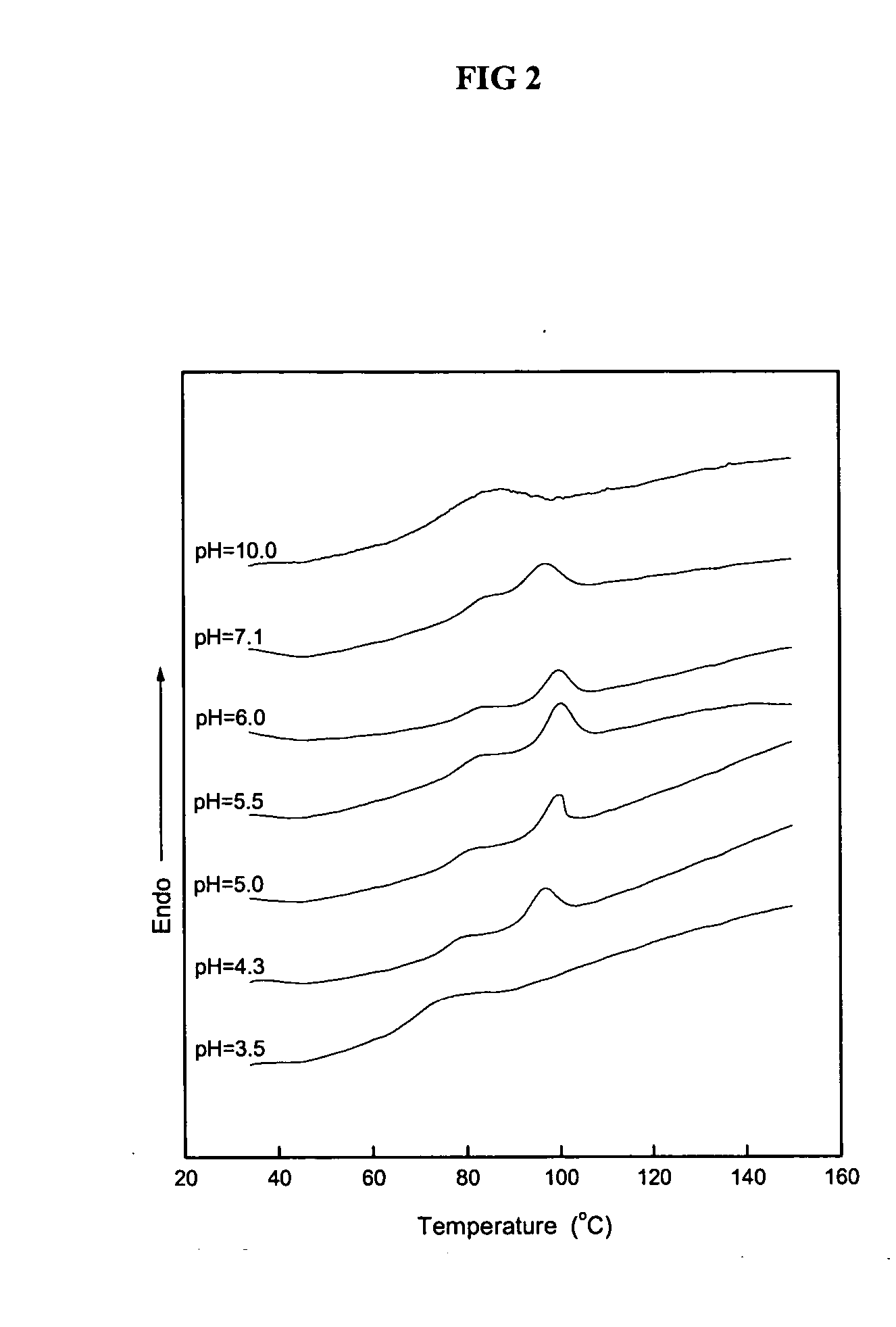
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1381 results about "Isoelectric point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
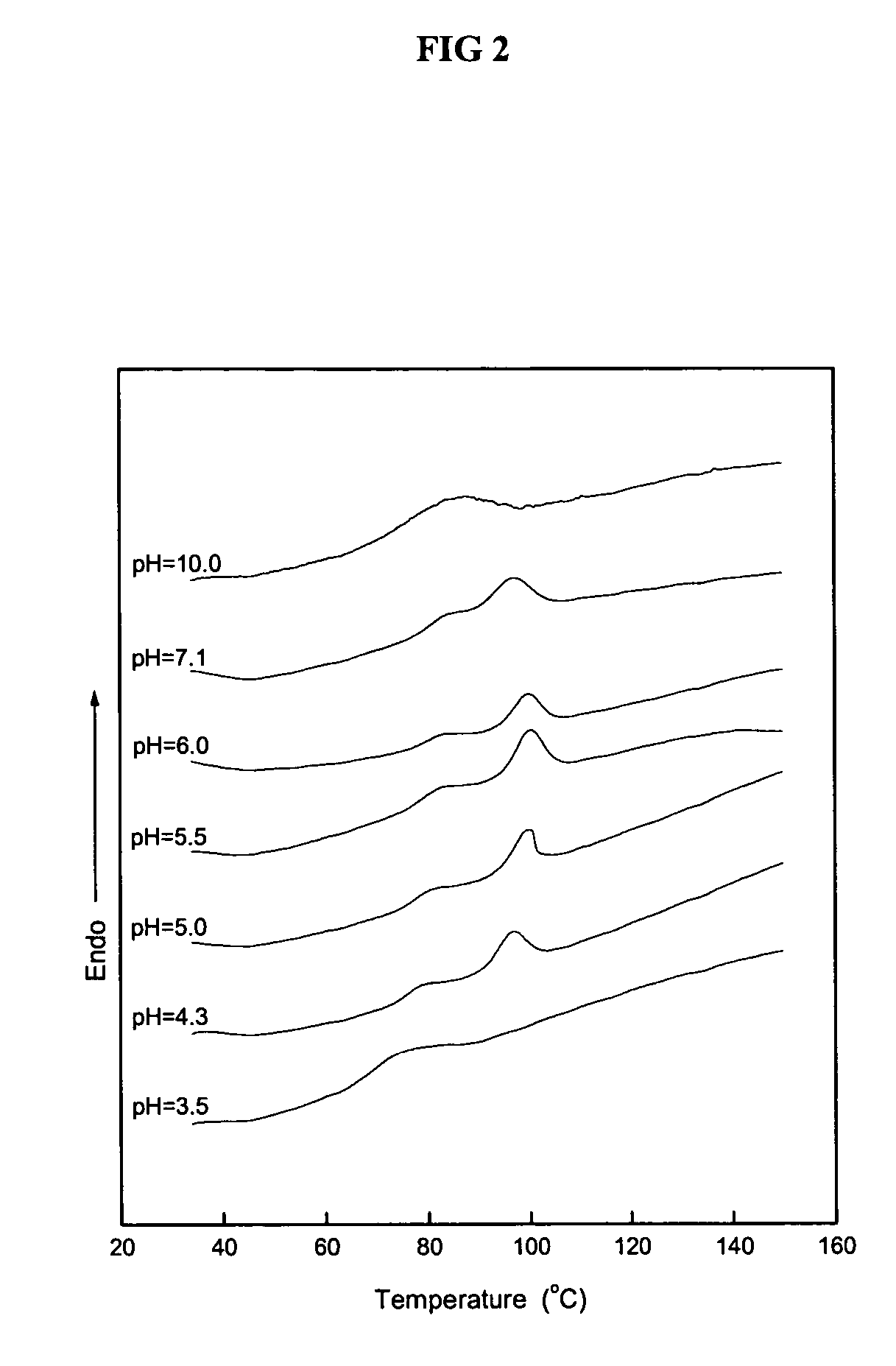
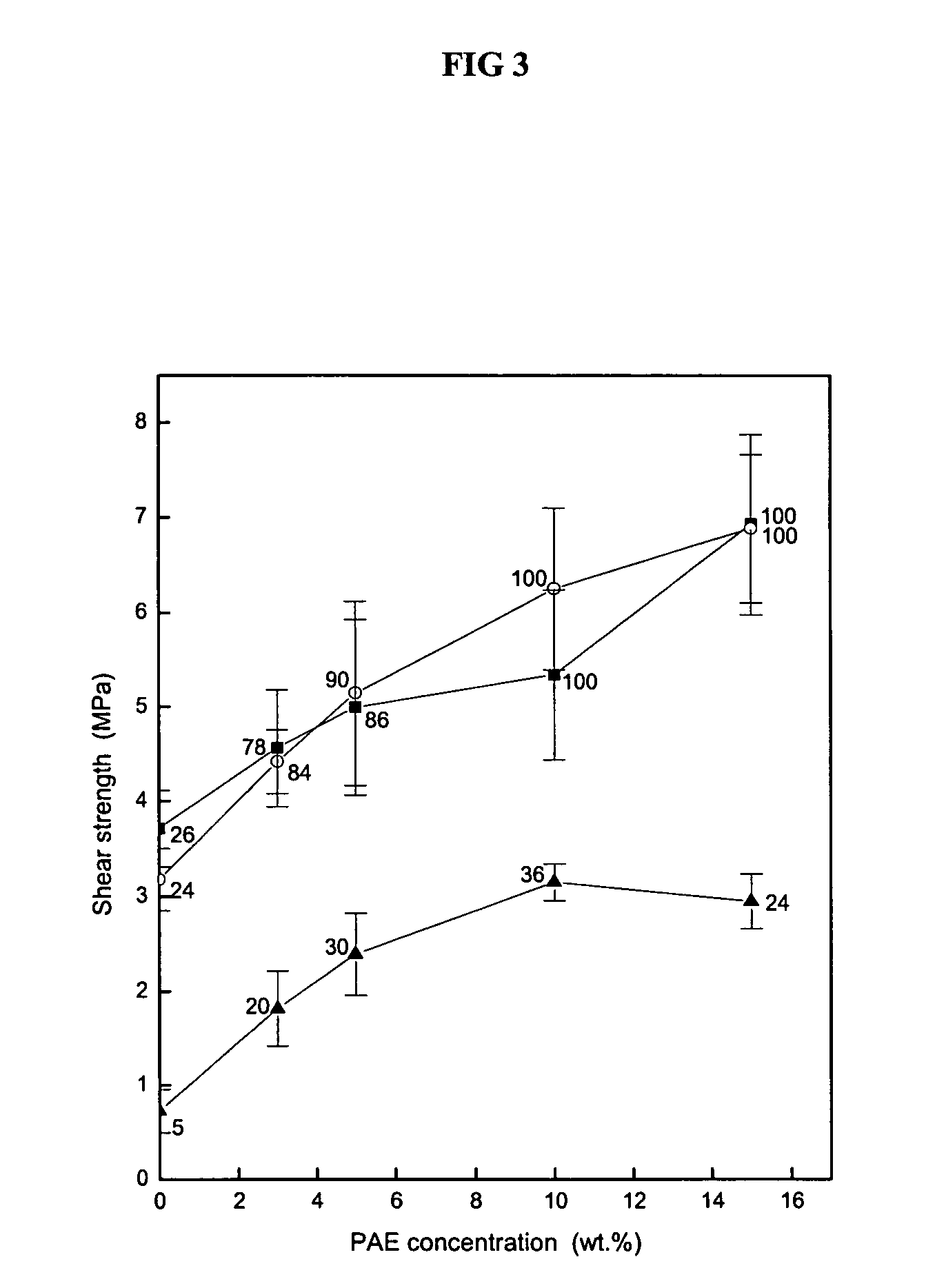
The isoelectric point (pI, pH(I), IEP), is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electrical charge or is electrically neutral in the statistical mean. The standard nomenclature to represent the isoelectric point is pH(I), although pI is also commonly seen, and is used in this article for brevity. The net charge on the molecule is affected by pH of its surrounding environment and can become more positively or negatively charged due to the gain or loss, respectively, of protons (H⁺).
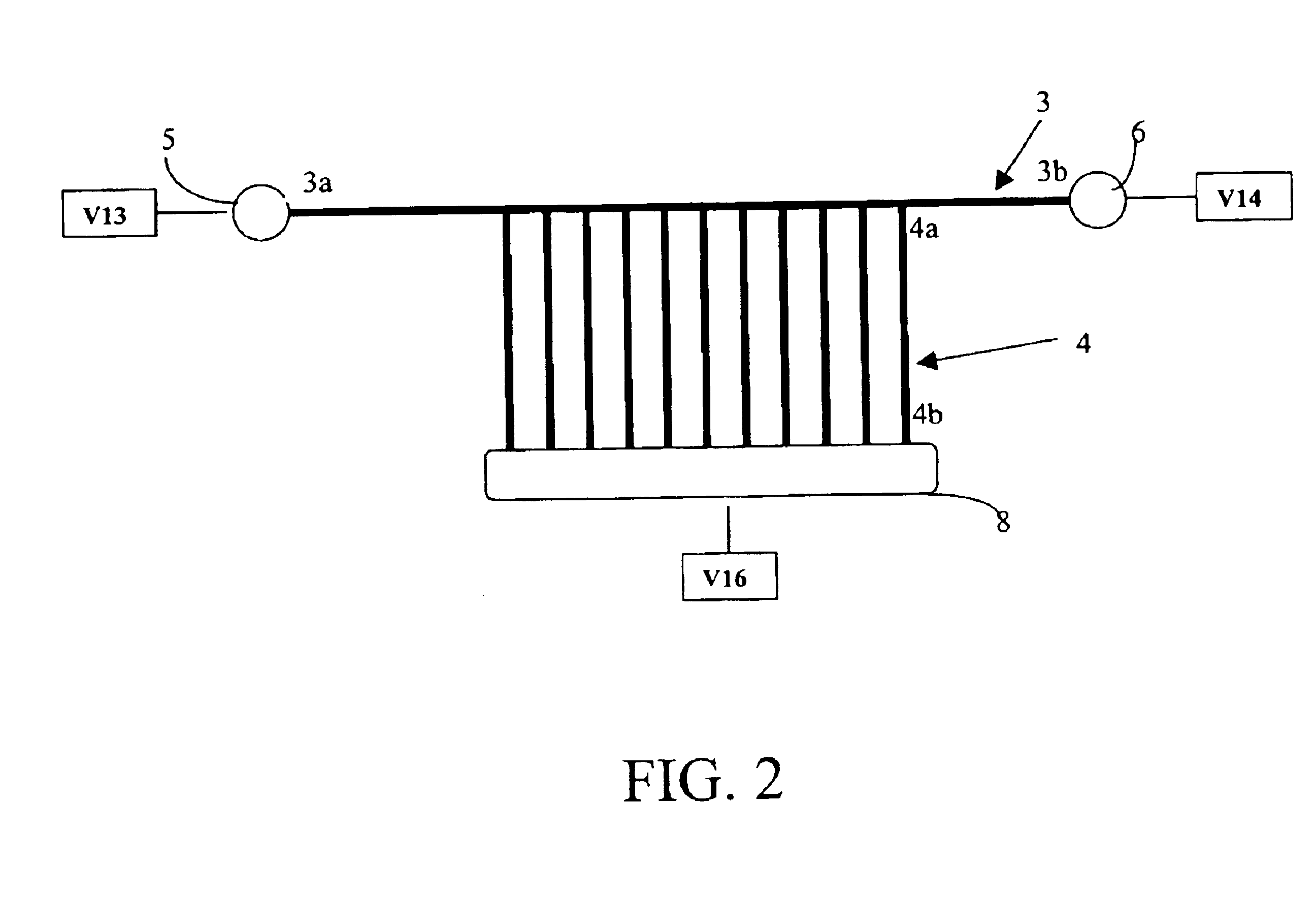
Methods of modifying antibodies for purification of bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS20090263392A1Efficient purificationFunction increaseSugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesBinding site
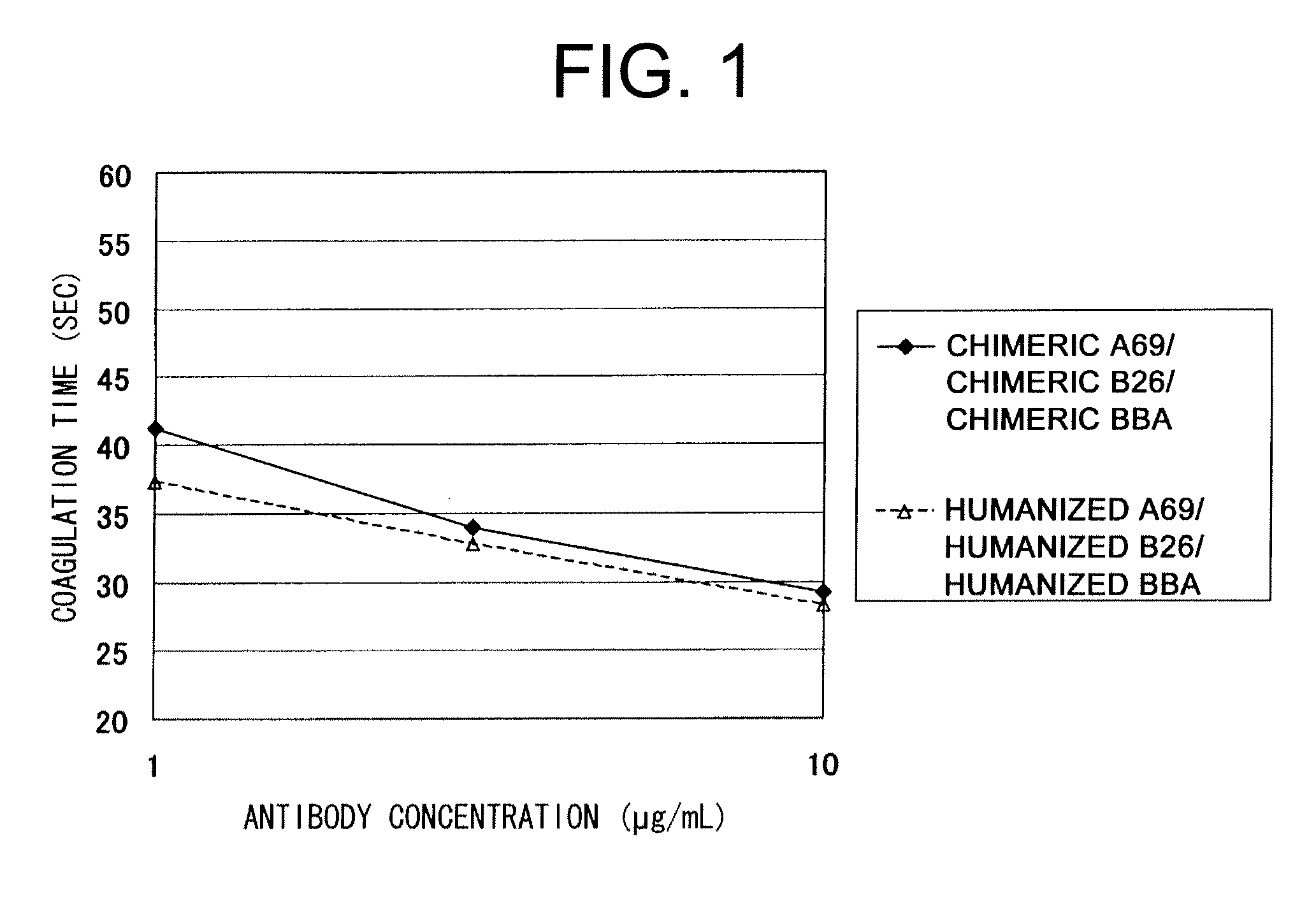
The present inventors devised methods for efficiently purifying bispecific antibodies using a chromatography column based on the difference in isoelectric points between the H chains of two types of antibodies, wherein the difference is introduced by modifying the amino acids present on the surface of the antibody variable regions of two types of antibodies that constitute a bispecific antibody. Furthermore, the inventors devised methods for efficiently purifying bispecific antibodies using a chromatography column by linking respective antigen binding sites (heavy chain variable regions) to the antibody constant regions having different isoelectric points, and then coexpressing these antibodies.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Antibodies with modified isoelectric points
ActiveUS20120028304A1Increased serum half-lifeMinimize the possibilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHalf-lifeBlood plasma
The invention relates generally to compositions and methods for altering the isoelectric point of an antibody, and in some cases, resulting in improved plasma pharmacokinetics, e.g. increased serum half-life in vivo.
Owner:XENCOR
Method of Modifying Isoelectric Point of Antibody Via Amino Acid Substitution in CDR
ActiveUS20110076275A1Enhanced antigen-neutralizing activityImprove retentionSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAmino acid substitution
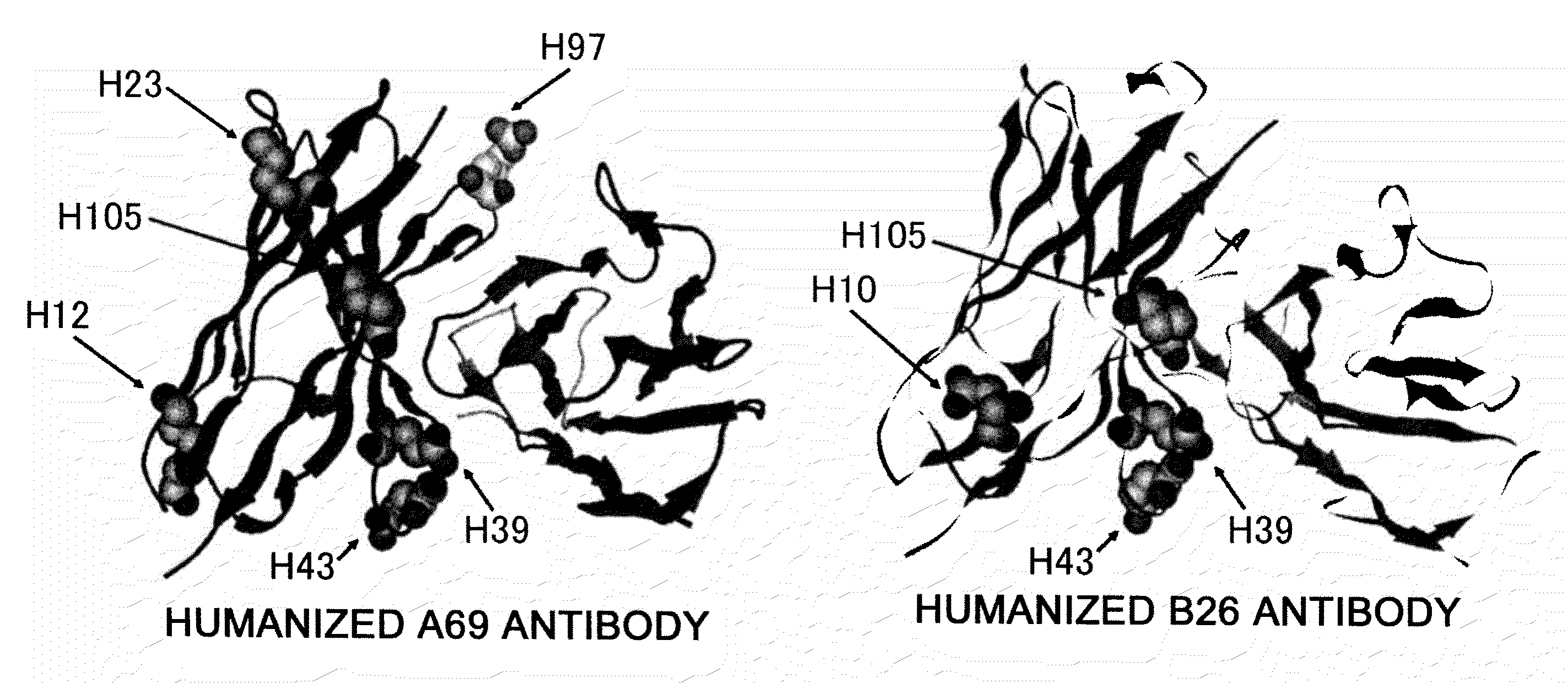
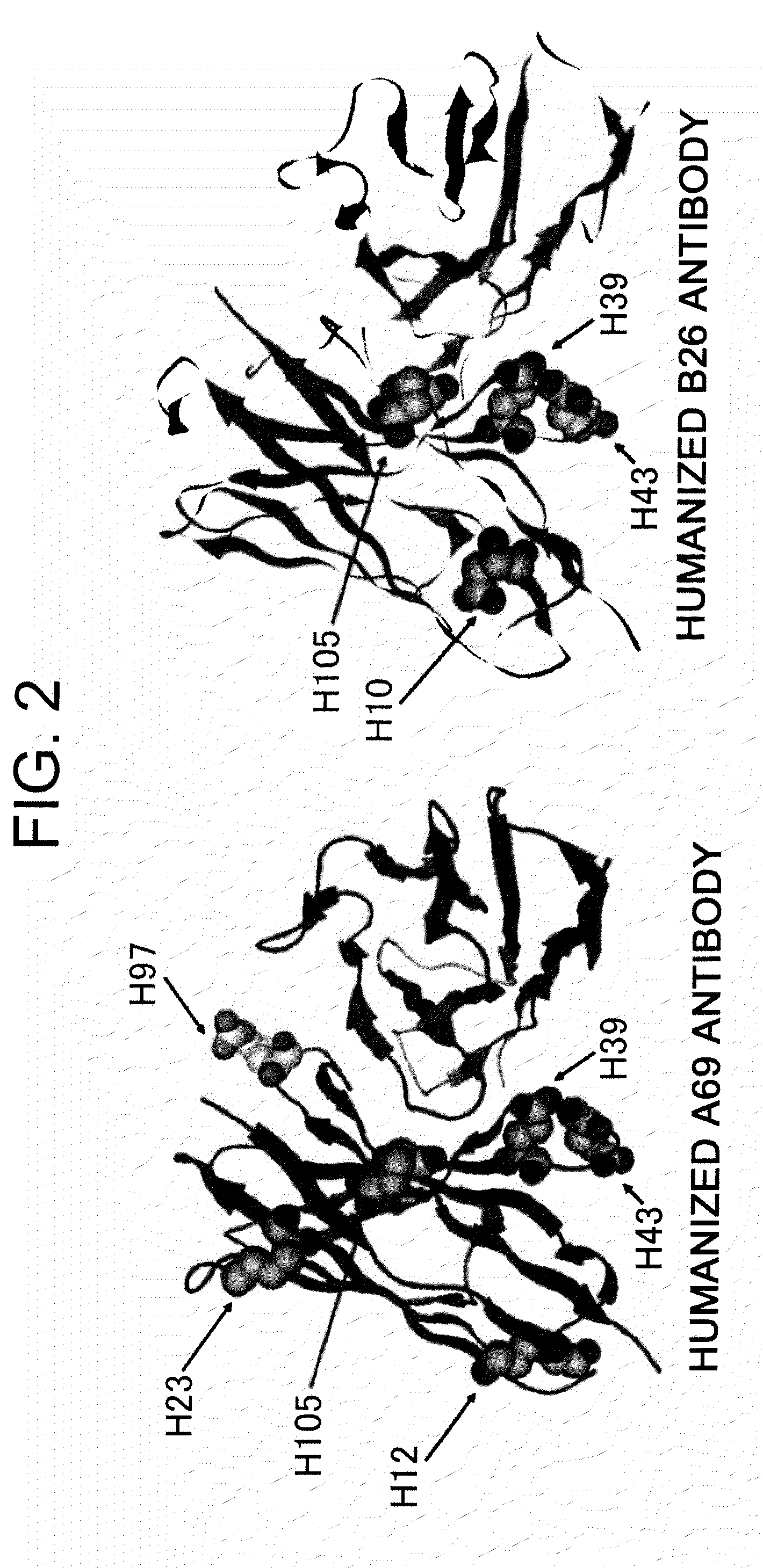
The present inventors provide methods for modifying the isoelectric point of an antibody while retaining its antigen-binding activity, comprising modifying the charge of at least one exposable amino acid residue on the surface of the complementarity determining region (CDR). The present invention also provides methods for purifying multispecific antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point, and methods for improving the plasma pharmacokinetics of antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point. The present invention further provides antibodies with a modified isoelectric point, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies as an active ingredient, and methods for producing the antibodies and compositions.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Method for Purifying Antibodies
ActiveUS20130171095A1Increased serum half-lifeMinimize the possibilityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsIsoelectric pointAntibody
The invention relates generally to compositions and methods for purifying the desired species from a mixture of desired heterodimer and contaminating homodimer immunoglobulin variants by modifying the isoelectric point(s) of the individual chains.
Owner:XENCOR
Method of manufacturing hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder, magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120244387A1Good dispersionReduce dispersion loadMagnetic materials for record carriersIron organic compoundsMagnetic liquidsSolvent
An aspect of the present invention relates to a method of manufacturing hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder. The method of manufacturing hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder comprises wet processing hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles obtained following acid treatment in a water-based solvent to prepare an aqueous magnetic liquid satisfying relation (1) relative to an isoelectric point of the hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles: pH0−pH*≧2.5, wherein, pH0 denotes the isoelectric point of the hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles and pH* denotes a pH of the aqueous magnetic liquid, which is a value of equal to or greater than 2.0, adding a surface-modifying agent comprising an alkyl group and a functional group that becomes an anionic group in the aqueous magnetic liquid to the aqueous magnetic liquid to subject the hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles to a surface-modifying treatment, and removing the water-based solvent following the surface-modifying treatment to obtain hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Antibodies with modified isoelectric points
ActiveUS8637641B2Increased serum half-lifeMinimize the possibilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesSerum igeHalf-life
The invention relates generally to compositions and methods for altering the isoelectric point of an antibody, and in some cases, resulting in improved plasma pharmacokinetics, e.g. increased serum half-life in vivo.
Owner:XENCOR INC
Enteric-coated multilayer encapsulated probiotic microcapsule and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1969889AGrowth inhibitionPromote formationMetabolism disorderBacteria material medical ingredientsAcid-fastSolubility
The invention discloses an enteric-solubility multilayer encysted bacterium microcapsule and making method in the biological agent technical domain, which is characterized by the following: adopting sodium alginate, calcium chloride and chitose as clad material of microcapsule; making lactic acid bacteria or bifidobacteria as core-clad material; proceeding ionic exchange for sodium alginate and calcium chloride; forming second clad on the surface of calcium alginate through different isoelectric points of calcium alginate and chitose; freezing at low temperature to obtain the product.
Owner:JINAN SYNBIOTICS BIOENG
Method of purifying protein
InactiveUS20060142549A1Efficient removalSerum immunoglobulinsColony-stimulating factorActive proteinDNA Contamination
Problems to be Solved: The present invention provides a simpler and less expensive method for purifying physiologically active proteins, especially antibodies, which can ensure removal of impurities such as DNA contaminants and viruses, and which can minimize a loss of physiologically active proteins. Means for Solving the Problems: A method for removing impurities in a physiologically active protein-containing sample, which comprises the following steps: 1) allowing the physiologically active protein-containing sample to be converted into an aqueous solution of low conductivity at a pH below the isoelectric point of the physiologically active protein; and 2) removing the resulting particles.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Antibodies with modified isoelectric points
ActiveUS20140249297A1Increased serum half-lifeMinimize the possibilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAntiendomysial antibodiesBlood plasma
The invention relates generally to compositions and methods for altering the isoelectric point of an antibody, and in some cases, resulting in improved plasma pharmacokinetics, e.g. increased serum half-life in vivo.
Owner:XENCOR INC
Process of making a water dispersible titanium dioxide pigment useful in paper laminates
The present invention relates to a process for making a titanium dioxide pigment having consisting of titanium dioxide and single layer of inorganic surface treatment consisting of aluminum phosphate wherein the pigment is characterized by and isoelectric point which is greater than pH 6 and a negative zeta potential of at a pH of 7.5 or more.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method of modifying isoelectric point of antibody via amino acid substitution in CDR
ActiveUS9096651B2Enhanced antigen-neutralizing activityGood treatment effectImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsComplementarity determining regionAmino acid substitution
Methods are described for modifying the isoelectric point of an antibody while retaining its antigen-binding activity, comprising modifying the charge of at least one exposable amino acid residue on the surface of the complementarity determining region (CDR). The disclosure also provides methods for purifying multispecific antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point, and methods for improving the plasma pharmacokinetics of antibodies with a modified isoelectric point. The disclosure further provides antibodies with a modified isoelectric point, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies as an active ingredient, and methods for producing the antibodies and compositions.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Adhesives from modified soy protein
InactiveUS20050166796A1Easy to determineEasy to findProtein adhesivesOil/fat/wax adhesivesEpoxyAdhesive
The, present invention provides useful adhesive compositions having similar adhesive properties to conventional UF and PPF resins. The compositions generally include a protein portion and modifying ingredient portion selected from the group consisting of carboxyl-containing compounds, aldehyde-containing compounds, epoxy group-containing compounds, and mixtures thereof. The composition is preferably prepared at a pH level at or near the isoelectric point of the protein. In other preferred forms, the adhesive composition includes a protein portion and a carboxyl-containing group portion.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Antibodies with modified isoelectric points and immunofiltering
InactiveUS20160068588A1Increased serum half-lifeMinimize the possibilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHalf-lifeBlood plasma
The invention relates generally to compositions and methods for altering the isoelectric point of an antibody, and in some cases, resulting in improved plasma pharmacokinetics, e.g. increased serum half-life in vivo.
Owner:XENCOR
Adhesives from modified soy protein
InactiveUS7416598B2Improve water resistanceStable structureProtein adhesivesOil/fat/wax adhesivesEpoxyAdhesive
The, present invention provides useful adhesive compositions having similar adhesive properties to conventional UF and PPF resins. The compositions generally include a protein portion and modifying ingredient portion selected from the group consisting of carboxyl-containing compounds, aldehyde-containing compounds, epoxy group-containing compounds, and mixtures thereof. The composition is preferably prepared at a pH level at or near the isoelectric point of the protein. In other preferred forms, the adhesive composition includes a protein portion and a carboxyl-containing group portion.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
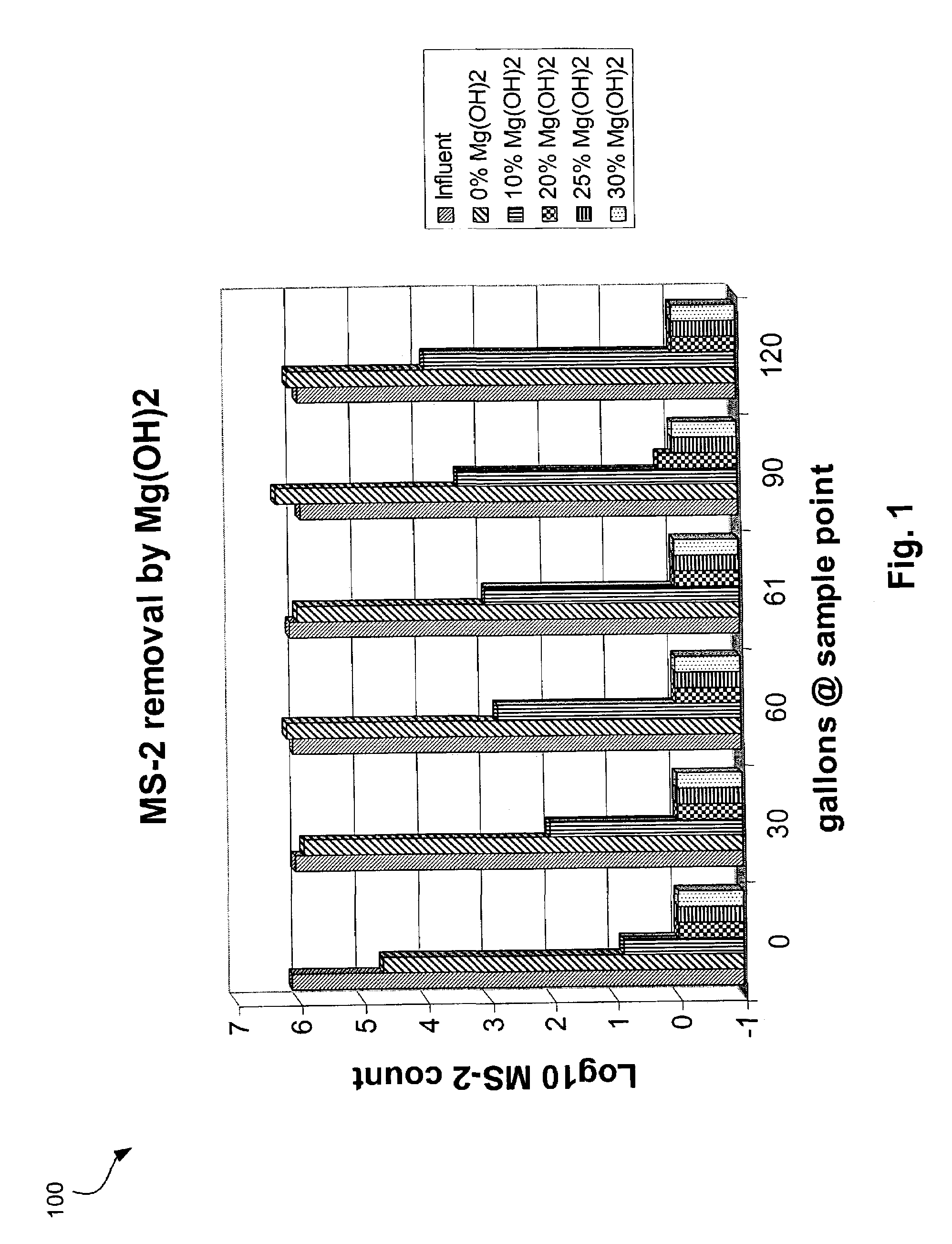
Microorganism-removing filter medium having high isoelectric material and low melt index binder
A filter medium capable of removing microorganisms from a fluid such as water. The filter medium includes particles of activated carbon, particles of a substantially insoluble inorganic material having an isoelectric point greater than the fluid being filtered. A low melt index binder, preferably with a melt index of less than about 1 gram per 10 minutes, binds the particles of activated carbon and particles of inorganic material, such that the binder will become tacky at elevated temperatures without becoming sufficiently liquid to substantially wet the particles of activated carbon and inorganic material.
Owner:COLOROX COMPANY THE
Cerium-zirconium composite metal oxide
ActiveUS7384888B2Increased durabilityIncrease capacityGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesMischmetalCerium
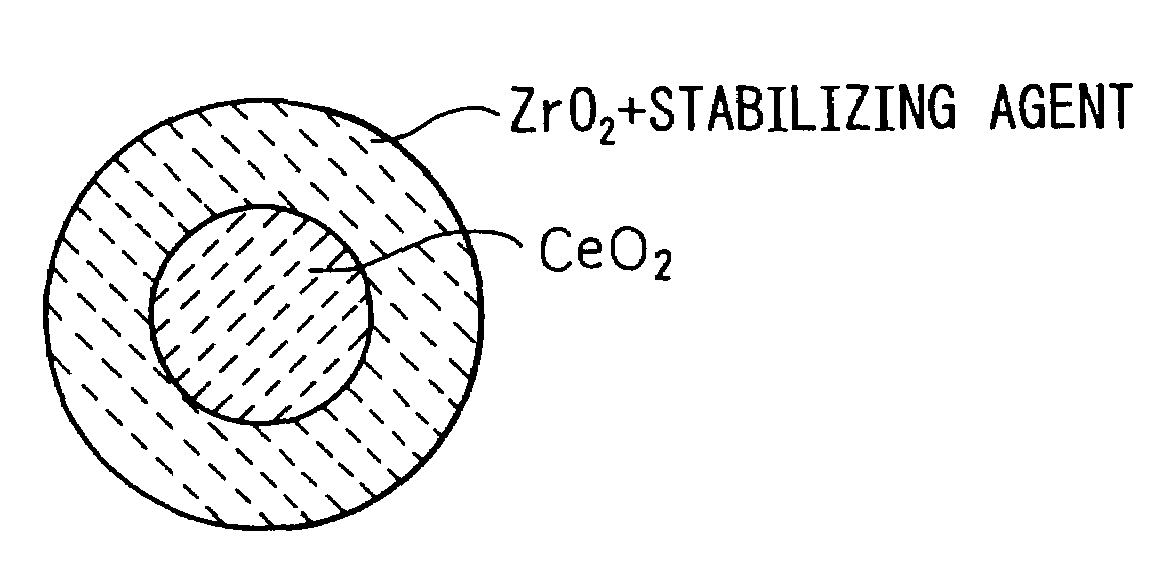
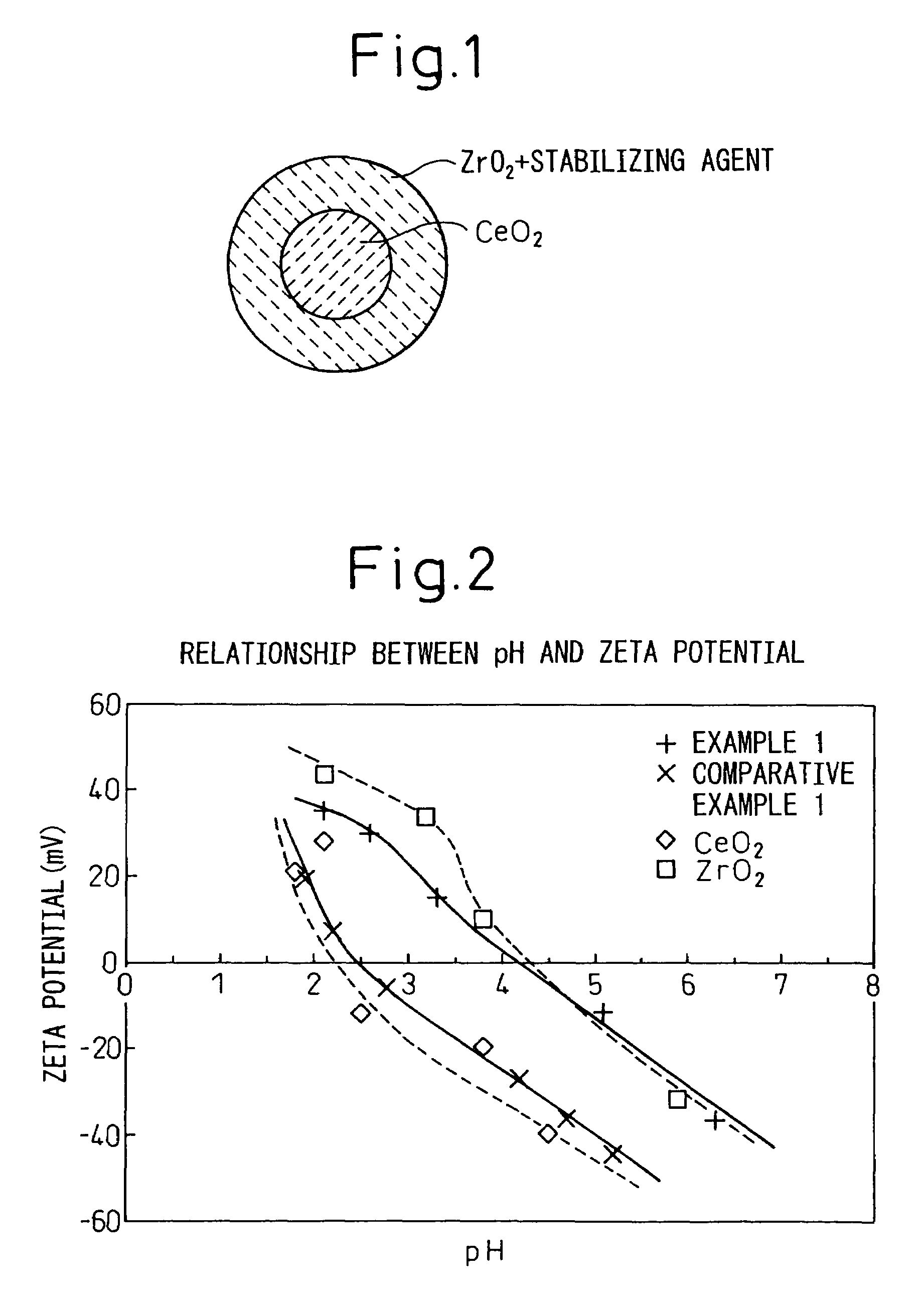
A cerium-zirconium composite metal oxide having improved durability at high temperature and a stable oxygen storage capacity is provided. The cerium-zirconium composite metal oxide is characterized in that the total mole number of Ce and Zr is at least 85% based on the total mole number of metal in the composite metal oxide, a molar ratio Ce / Zr is within a range from 1 / 9 to 9 / 1, and an isoelectric point of the composite metal oxide is more than 3.5. Preferably, the molar ratio Ce / Zr is within a range from 3 / 7 to 7 / 3 and the isoelectric point is within a range from 3.8 to 5.0, and the cerium-zirconium composite metal oxide contains a rare earth metal (excluding Ce) in a concentration of less than 15% by mole based on the total mole number of metal in the composite metal oxide. Also the present invention provides a cerium-zirconium composite metal oxide, characterized in that CeO2 forms a core surrounded by ZrO2.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20200126589A1Deterioration in electromagnetic conversionIncrease recording capacityMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageZeta potentialIonogram
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; a non-magnetic layer including a non-magnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including a ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic layer, in which a total thickness of the non-magnetic layer and the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.60 μm, an isoelectric point of a surface zeta potential of the magnetic layer is equal to or greater than 5.5, the magnetic layer includes an oxide abrasive, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
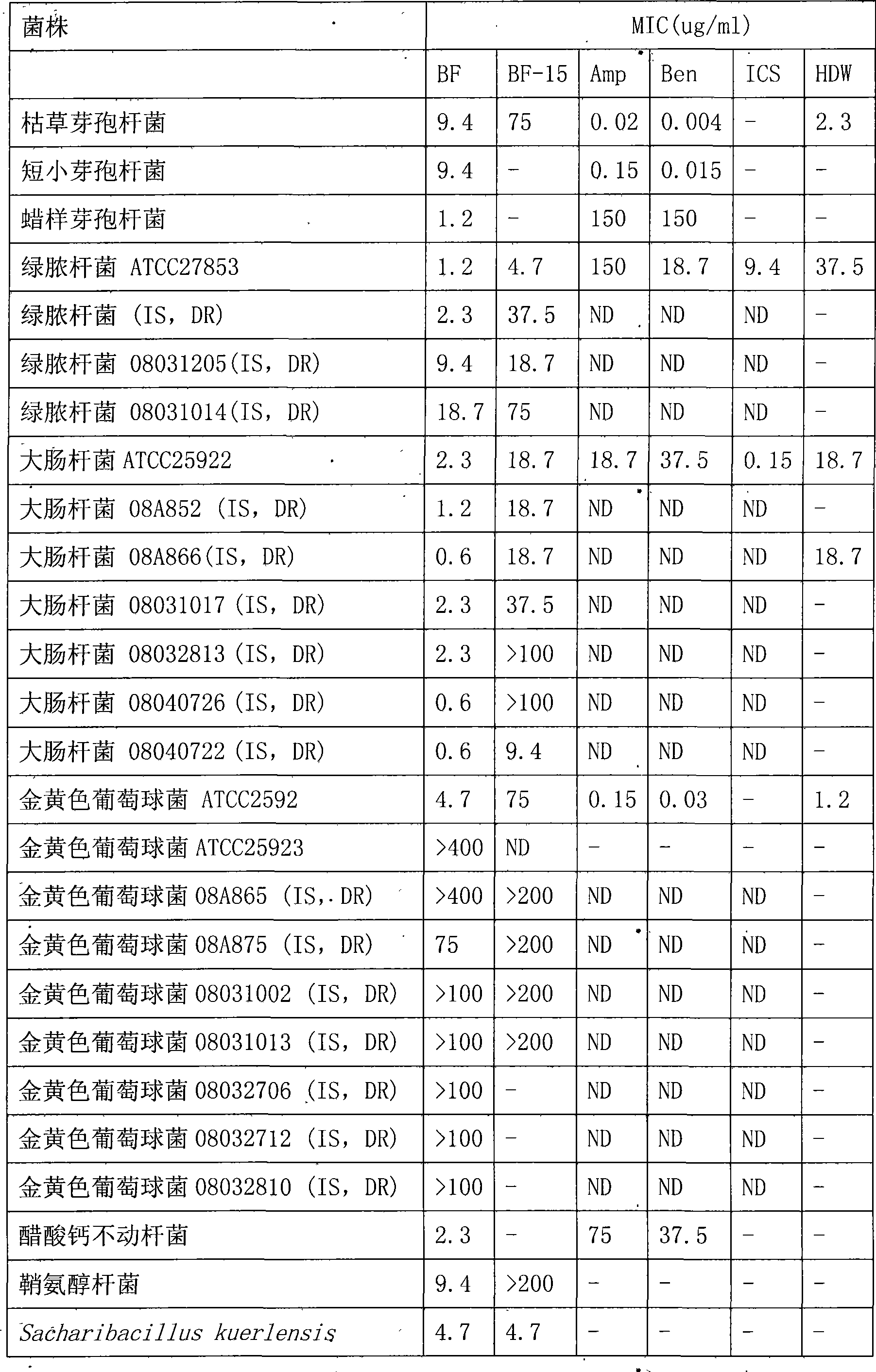
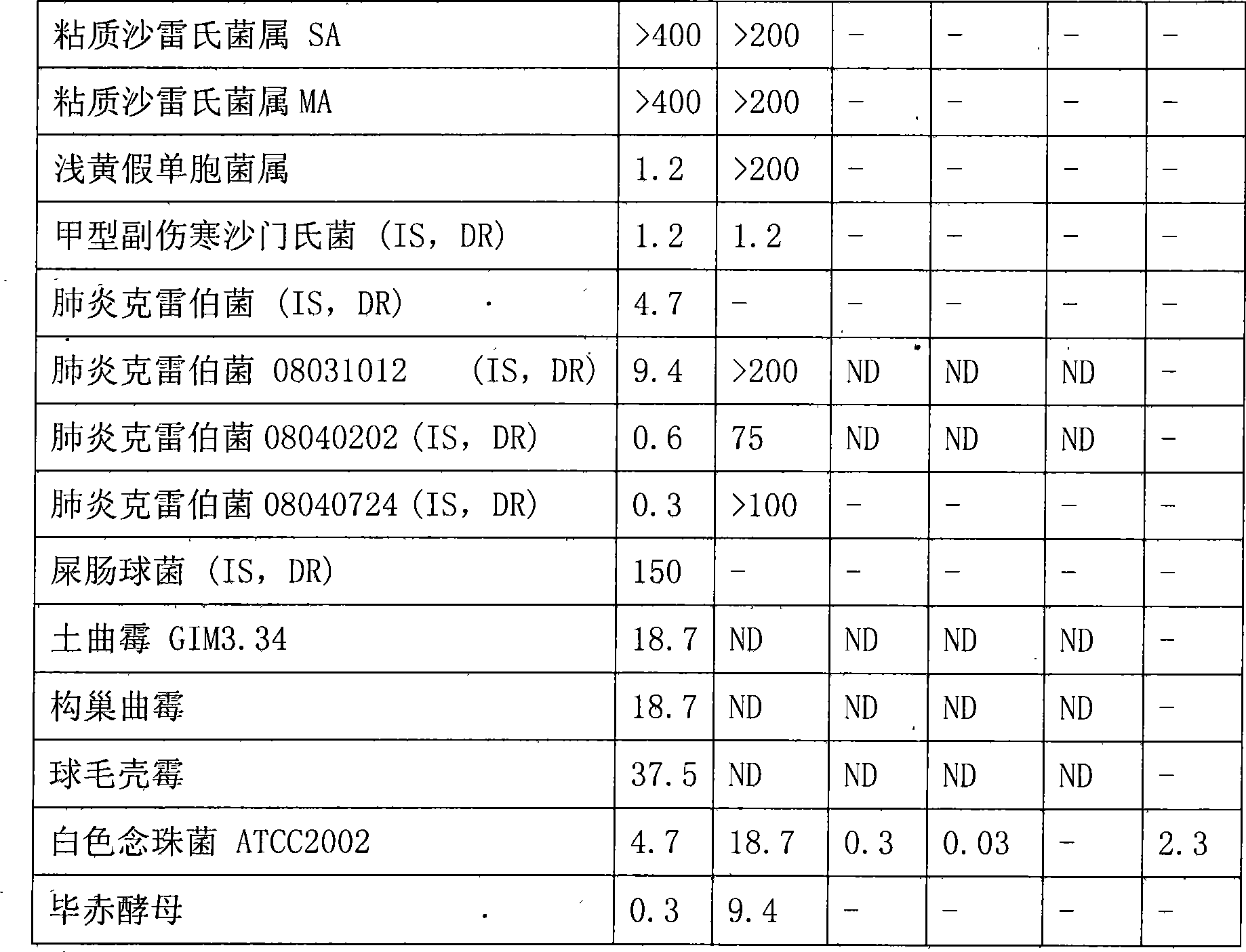
Bungarus fasciatus antibacterial peptide cathelicidin-BF, and genes and uses thereof
InactiveCN101412753ASmall molecular weightImprove the bactericidal effectFermentationAnimals/human peptidesArginineAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses cathelicidin-BF and a gene and application thereof, which belong to the field of biomedicine. The cathelicidin-BF is straight chain polypeptide and contains thirty amino acid residues, the molecular weight is 3,637.54Da, and the isoelectric point is 11.79. The complete sequence of the cathelicidin-BF is lysine-phenyl alanine-phenyl alanine-arginine-lysine-leucine- lysine-lysine-serine-valine-lysine-lysine-arginine-lactamine-lysine-glutamic acid-phenyl alanine- phenyl alanine-lysine-lysine-proline-arginine-valine-isoleucine-glycin-valine-serine-isoleucine- praline-phenyl alanine. The gene for encoding the cathelicidin-BF consists of 750 ribonucleotides, wherein 484th to 573rd ribonucleotides are used for encoding a mature peptide part. The cathelicidin-BF has small molecular weight, strong sterilization effect, and quick action time, and has quite strong killing function to a plurality of kinds of clinical drug-fast bacteria. In addition, the cathelicidin-BF also has the advantages of broad-spectrum antibiotics, salt independence and so on.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
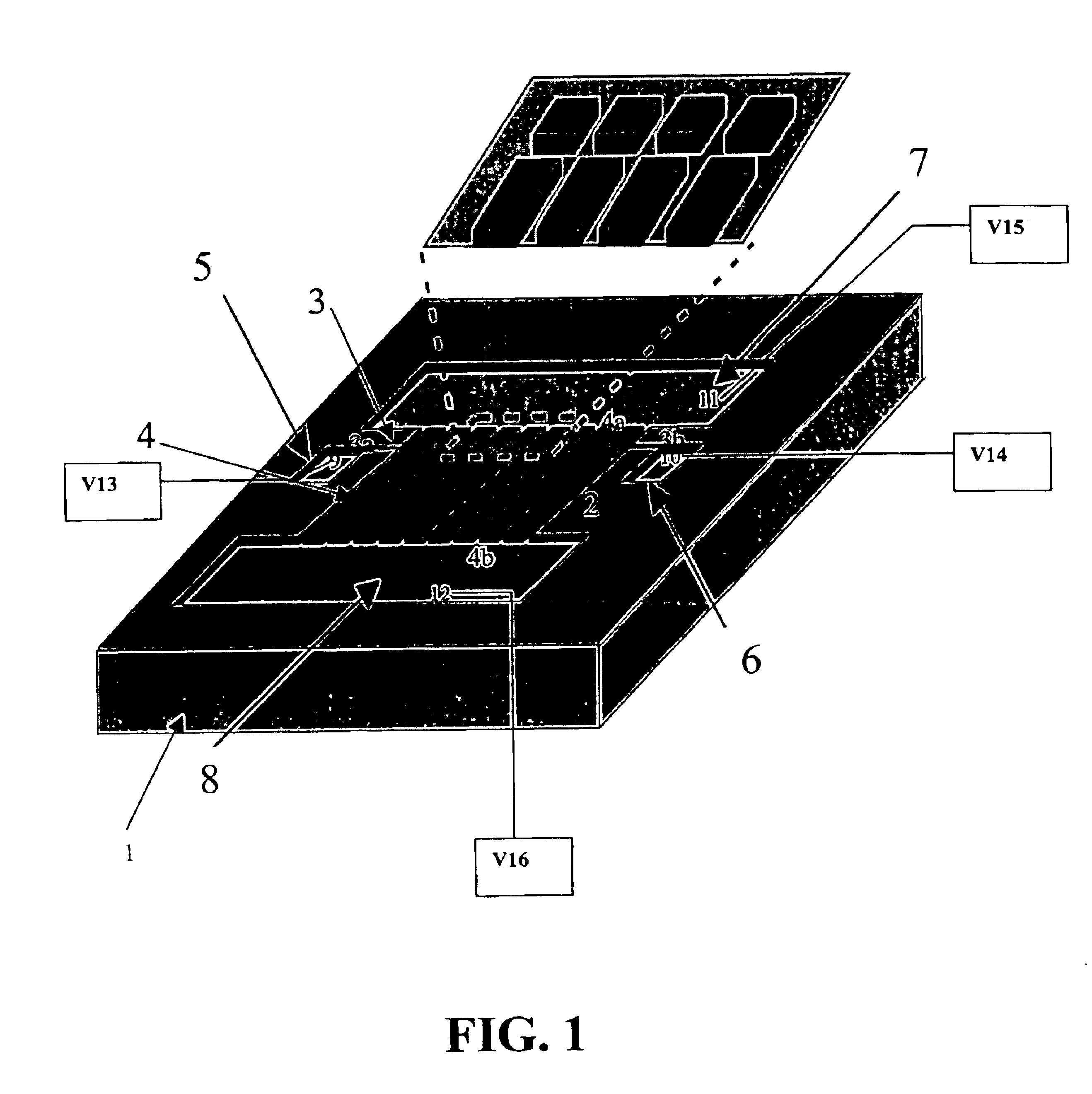
Plastic microfluidics enabling two-dimensional protein separations in proteome analysis
InactiveUS6974526B2Simple procedureHigh resolutionSludge treatmentFixed microstructural devicesElectricityMicrofluidics
The invention provides a microfluidic apparatus for performing 2-D biomolecular separations. The microfluidic 2-D device may include first and second planar substrates which include at least a first dimension microchannel extending in a first direction and an array of second dimension microchannels extending in a second direction, preferably, orthogonal to the first dimension. The ends of at least some of the microchannels are in fluid communication with a plurality of reservoirs. The substrates may further include a number of microchannels and reservoirs. The reservoirs are in electrical communication with a plurality of electrodes and voltage power sources. The device enables two dimensional separations of proteins and other biomolecules. According to another aspect of the invention, an isoelectric point based separation is enabled in a first dimension, and a size based separation in a second dimension.
Owner:CALIBRANT BIOSYST +1
Supported nano Au catalyst and method for preparing the same
InactiveCN1827213AEvenly dispersedEasy to adjust particle sizeCatalyst carriersOxygen compounds preparation by hydrocarbon oxidationActive componentGold particles
The invention discloses a carrier nanometer gold catalyst gold catalyst and relative preparing method. Said invention is formed by Au, Al, and Ti / Si, Ag, Cu, Ce, Fe, or Zn. Wherein, Au is the main active component of catalyst, whose mass percentage is 0.1-4.0%; Al is the carrier of catalyst, whose mass percentage is larger than 90%; Ti or Si is the agent of catalyst carrier, whose mass percentage is 0.01-1.0%; Ag, Cu, Ce, Fe, or Zn is used as the auxiliary active component of catalyst, whose mass percentage is 0.1-5.0%. The invention has the advantages that: the gold is distributed uniformly, and the graininess of attained gold particle can be adjusted easily; the catalyst has high stability; and it can apply the oxide carrier for carrying gold whose isoelectric point pH is less than 6 and made by coprecipitation method. The invention has be used to apply the cyclohexane to prepare the nadone and cyclohexanol, with better activity and selectivity, less used amount and recycle support.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
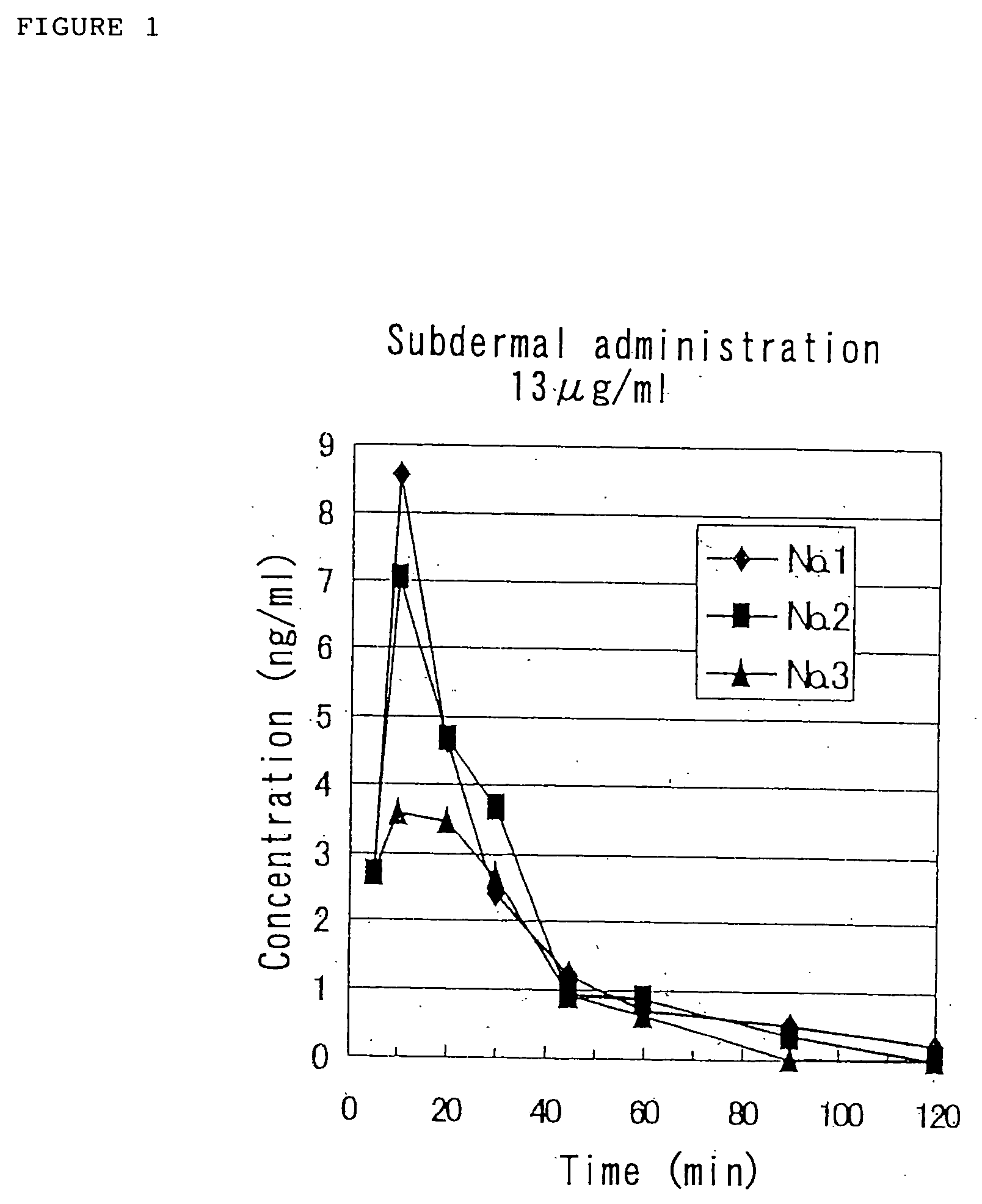
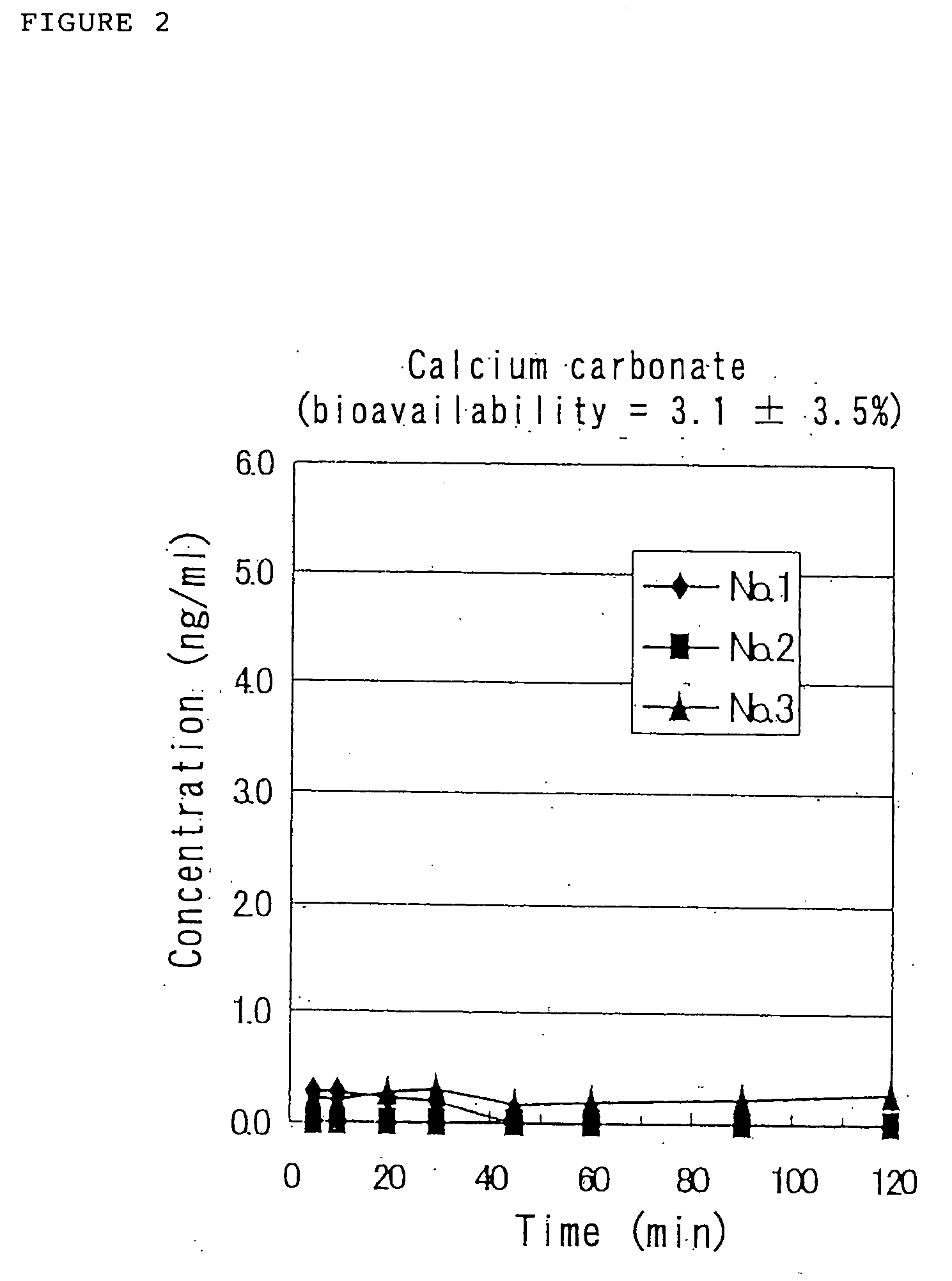
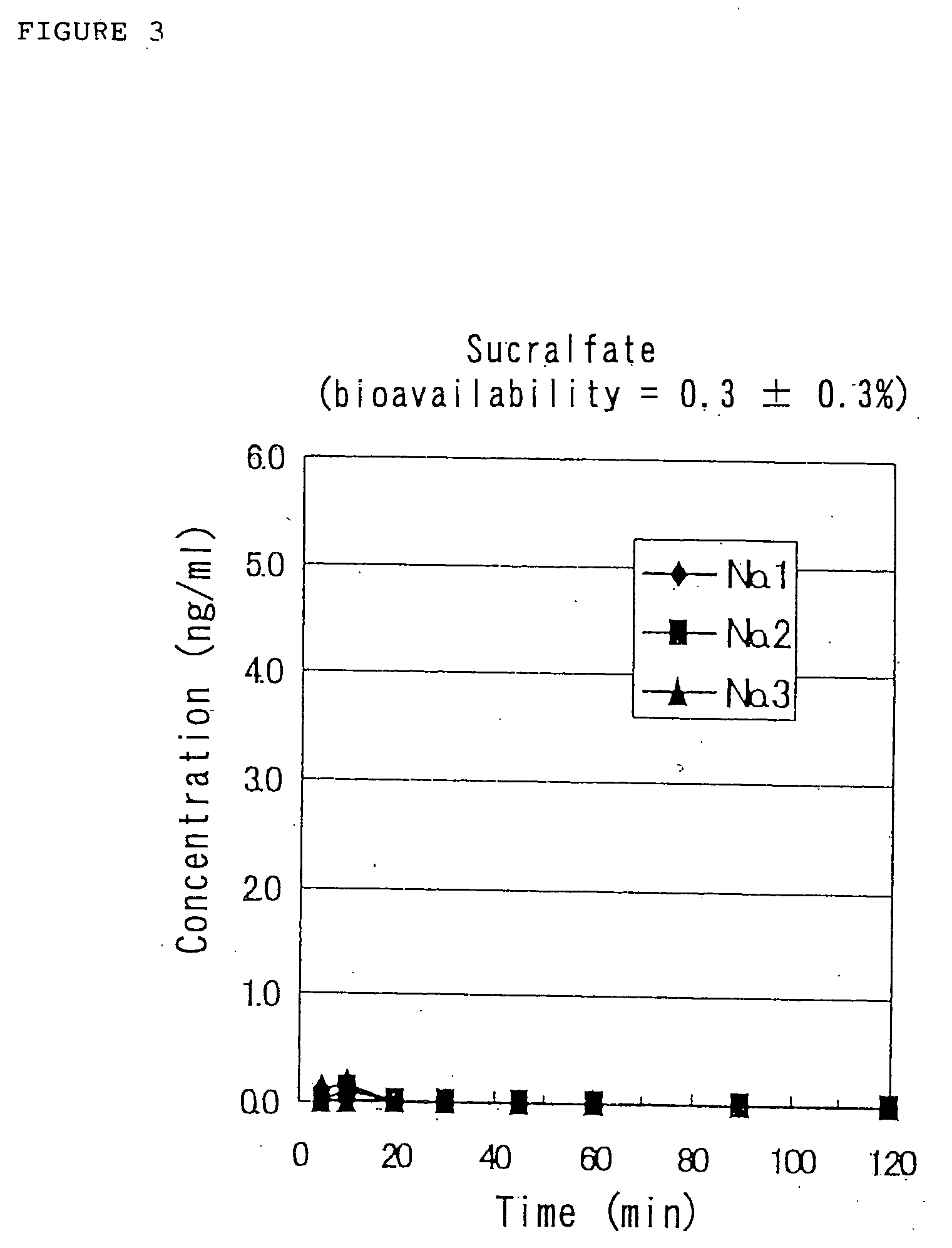
Medicinal compositions for nasal absorption
InactiveUS20050014681A1Evenly dispersedPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsZinc compoundsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
A pharmaceutical composition for nasal administration exhibits an improved bioavailability of a biologically active polypeptide, the active ingredient of the pharmaceutical composition. Specifically, the composition is prepared by uniformly dispersing and embedding a biologically active acidic polypeptide having an isoelectric point of 7 or lower on the surfaces of a polyvalent metal compound carrier with the help of an additive capable of dispersing and embedding the polypeptide on the surfaces of the carrier. The polyvalent metal compound carrier is a metal compound with a valent of 2 or higher that is either insoluble or little soluble in water, examples being aluminum compounds, calcium compounds, magnesium compounds, silicone compounds, iron compounds, and zinc compounds.
Owner:ASUBIO PHARMA
Oxides for Wound Healing and Body Repair
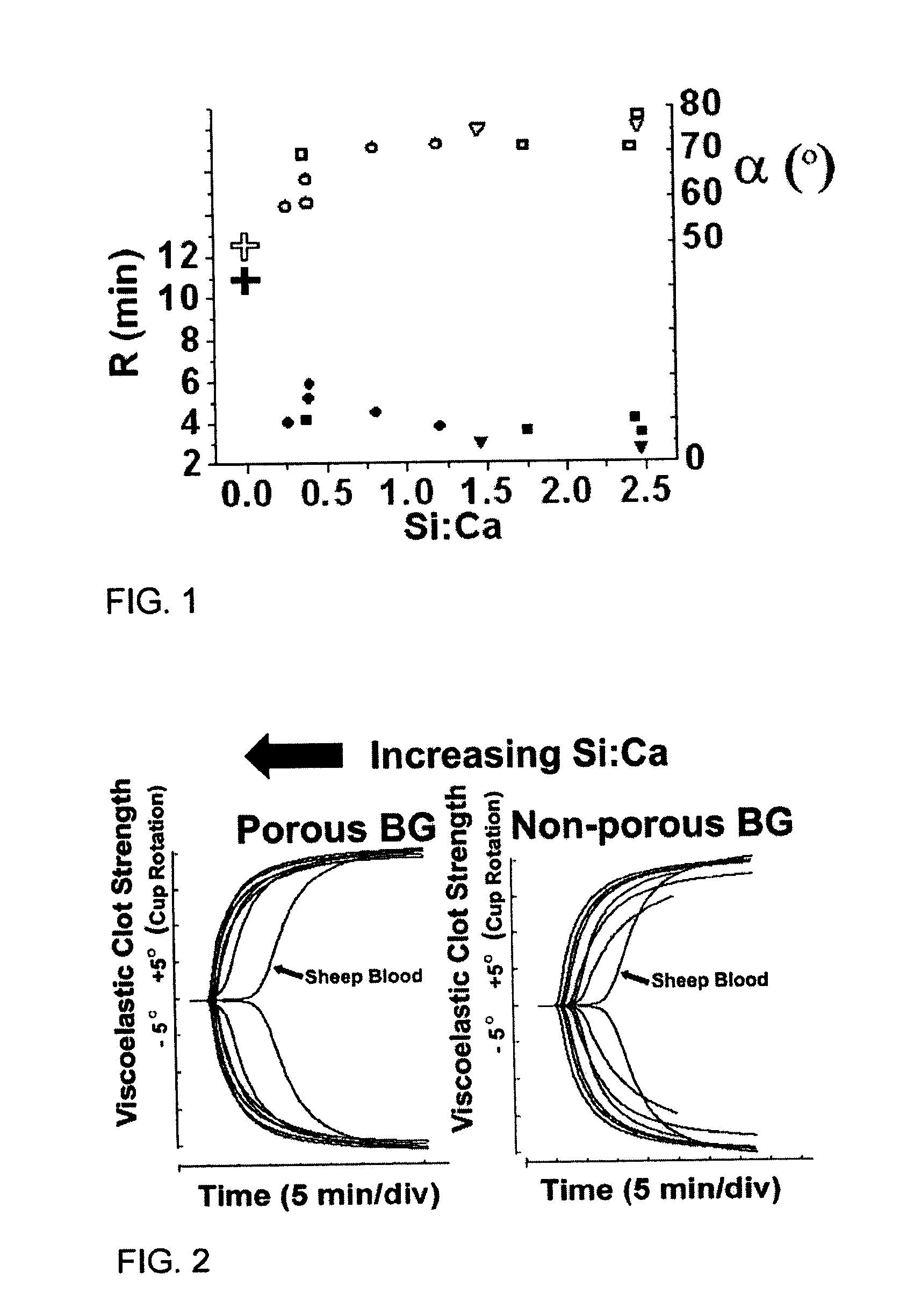
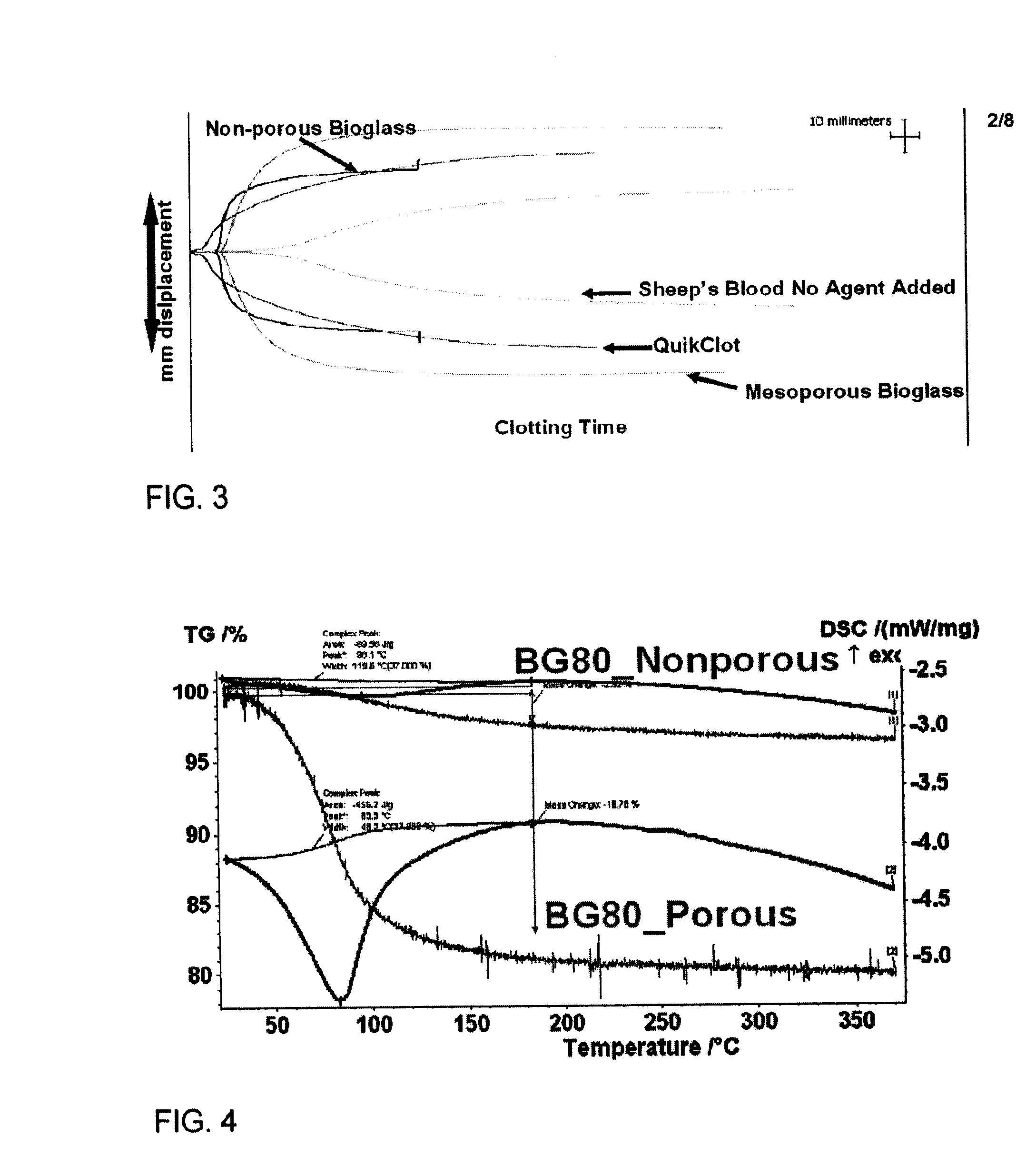
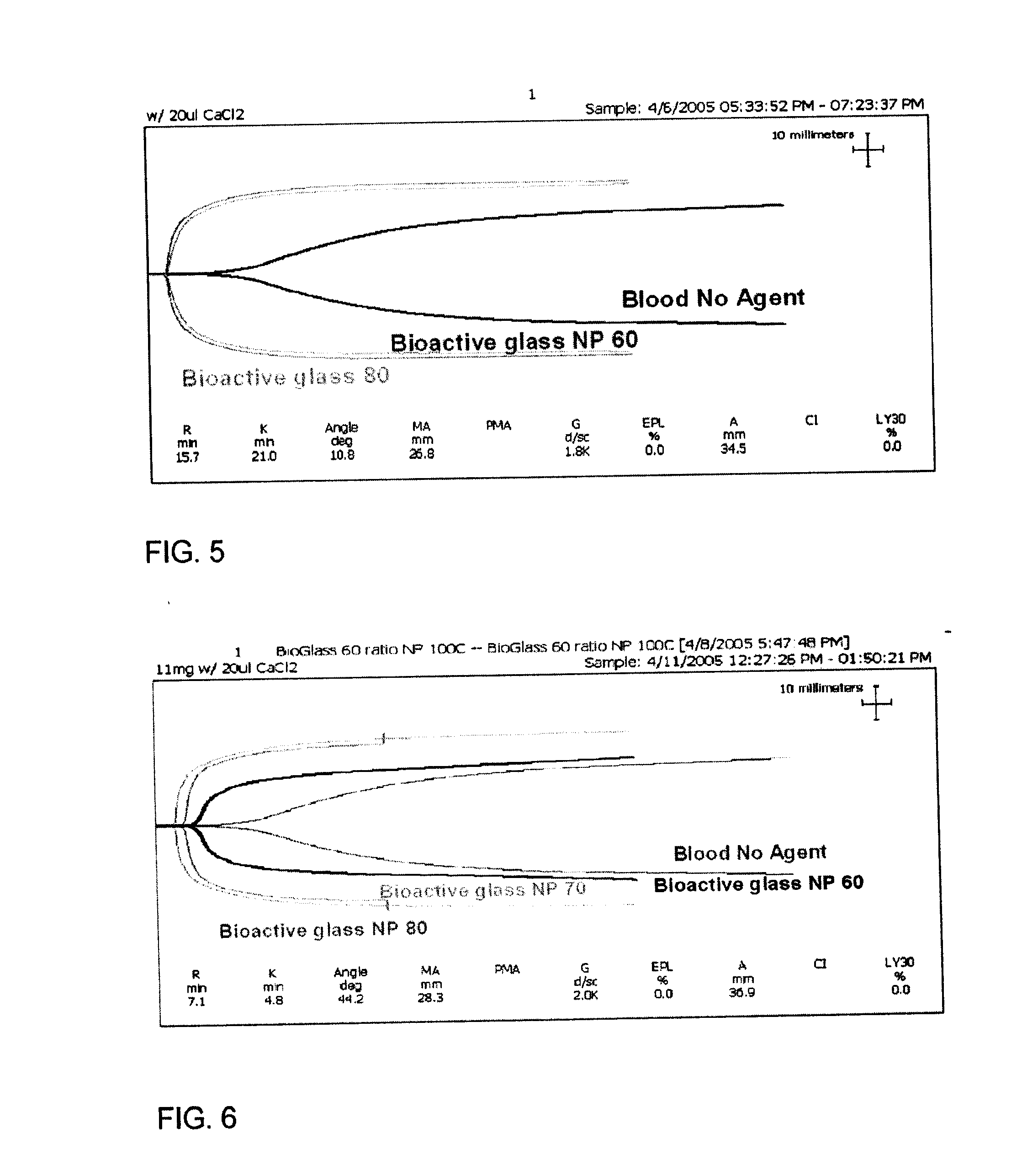
The invention provides a homogeneous composition comprising a hemostatically effective amount of a charged oxide, wherein the composition has an isoelectric point, as measured in calcium chloride, below 7.3 or above 7.4. Typically, the charged oxide is selected from the group consisting of silaceous oxides, titanium oxides, aluminum oxides, calcium oxides, zinc oxides, nickel oxides and iron oxides. In some embodiments, the composition further comprises a second oxide selected from the group consisting of calcium oxide, sodium oxide, magnesium oxide, zinc oxide, phosphorus oxide and alumina. In a typical embodiment of the invention, the charged oxide is silaceous oxide, the second oxide comprises calcium oxide and the ratio, by molar ratio, of silaceous oxide to calcium oxide is 0.25 to 15. Optionally, the composition further comprises phosphorous oxide. Also described are methods of making and using such compositions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for preparing metal oxide particles and an exhaust gas purifying catalyst
ActiveUS7314846B2Improve heat resistanceImprove abilitiesMaterial nanotechnologyZirconium compoundsSurface layerCerium(IV) oxide
The present invention relates to metal oxide particles having cores comprising larger molar amounts of zirconia than of ceria, and surface layers comprising larger molar amounts of ceria than of zirconia. Further, the present invention relates to a method for preparing the particles. The method comprises preparing a solution comprising zirconia sol and ceria sol, adjusting the pH of the solution within ±0.5 on the basis of the isoelectric point of zirconia, and aggregating zirconia and then aggregating ceria around the aggregated zirconia from the solution to make aggregates. Furthermore, the present invention relates to an exhaust gas purifying catalyst comprising the metal oxide particles, and a noble metal carried by the metal oxide particles.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
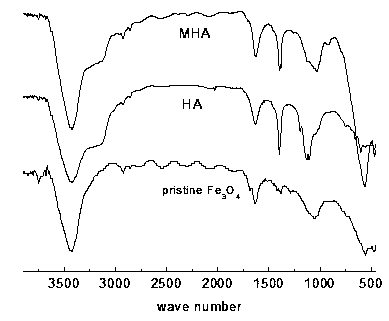
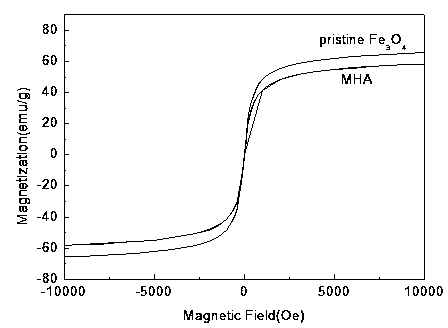
Magnetic humic acid nano material as well as preparation method and application of magnetic humic acid nano material
ActiveCN103752281AImprove removal efficiencyImprove recycling ratesOther chemical processesNanotechnologyDye absorptionNanoparticle
The invention discloses a magnetic humic acid nano material as well as a preparation method and application of the magnetic humic acid nano material. An isoelectric point of the magnetic humic acid nano material is negatively charged when the pH value is 3.2 and the pH value is more than 3.2-9.5; the magnetic induction intensity of magnetic humic acid is 62.88emu / g; the magnetic humic acid is in a torispherical form; the magnetic humic acid contains 22% of humic acid; the structure of the magnetic humic acid is formed by covering humic acid on the outer surface of a magnetic Fe3O4 crystal; in the magnetic humic acid nano material, the humic acid is connected to Fe3O4 mainly through coordination. The magnetic humic acid nanoparticle disclosed by the invention is low in price, environmentally-friendly, high in removal efficiency on cationic dye in wastewater, high in recovery rate and the like; and therefore, the magnetic humic acid nanoparticle can be widely used in dye absorption, water treatment, serving as an adsorbent and other fields, and has the excellent practicability.
Owner:克雷伯氏环保科技(苏州)有限公司
Selective placement of carbon nanotubes via coulombic attraction of oppositely charged carbon nanotubes and self-assembled monolayers
ActiveUS20130082233A1High densityReduce formationOrganic chemistryNanoinformaticsHigh densitySelf-assembled monolayer
A method of forming a structure having selectively placed carbon nanotubes, a method of making charged carbon nanotubes, a bi-functional precursor, and a structure having a high density carbon nanotube layer with minimal bundling. Carbon nanotubes are selectively placed on a substrate having two regions. The first region has an isoelectric point exceeding the second region's isoelectric point. The substrate is immersed in a solution of a bi-functional precursor having anchoring and charged ends. The anchoring end bonds to the first region to form a self-assembled monolayer having a charged end. The substrate with charged monolayer is immersed in a solution of carbon nanotubes having an opposite charge to form a carbon nanotube layer on the self-assembled monolayer. The charged carbon nanotubes are made by functionalization or coating with an ionic surfactant.
Owner:IBM CORP
Microorganism-removing filter medium having high isoelectric material and low melt index binder
ActiveUS7303683B2Improve antimicrobial effectiveness of filterProlong lifeApparatus sterilizationEnergy based wastewater treatmentActivated carbonMicroorganism
A filter medium capable of removing microorganisms from a fluid such as water. The filter medium includes particles of activated carbon, particles of a substantially insoluble inorganic material having an isoelectric point greater than the fluid being filtered. A low melt index binder, preferably with a melt index of less than about 1 gram per 10 minutes, binds the particles of activated carbon and particles of inorganic material, such that the binder will become tacky at elevated temperatures without becoming sufficiently liquid to substantially wet the particles of activated carbon and inorganic material. An antimicrobial material can be incorporated into the filter to prevent biofilm growth. The use of a biocidal material in combination with the high isoelectric point material provides a trap-and-kill mechanism for microorganism removal.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
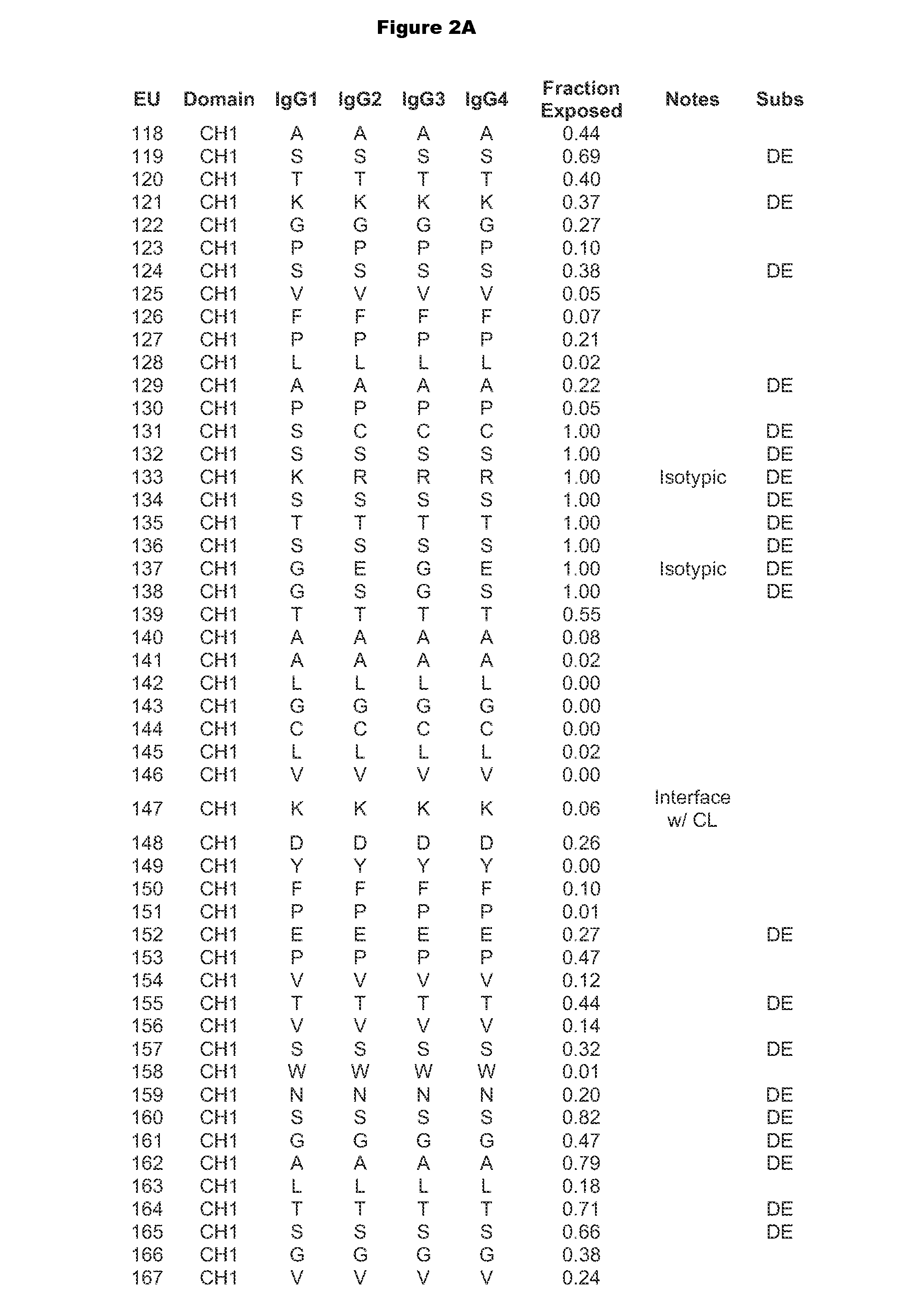
Process for preparing oat beta-glucans
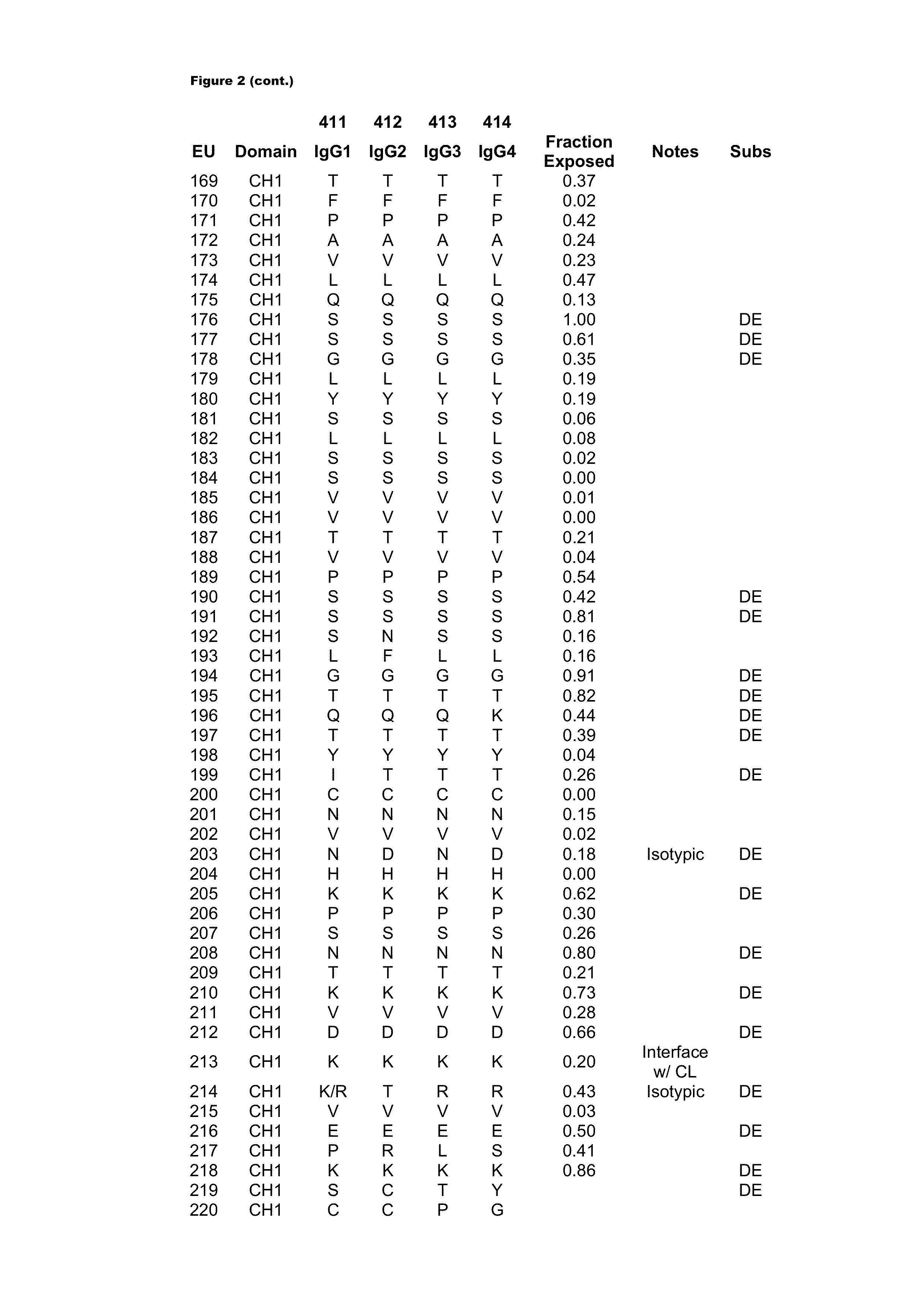
InactiveCN1966531APromote growthInhibition of reproductionEnzymesFermentationGlucanaseEthanol precipitation
This inventnion relates to a preparation method for high-efficiency prebiotics oat beta-glucan, belonging to the quintessential processing technologies of oat. The said method includes using oat bran as raw materials, crushing, microwave-assisted-extracting, adding amylase and glucoamylase, isoelectric-point-precipitating, centrifugating and separating, concentrating the supernatant, precipitating with ethanol, centrifugating and collecting the precipitation, solving with water, hydrolyzing with beta-glucanase, and spray-drying process to obtain the high-efficiency prebiotics oat beta-glucan with significantly enhanced intestinal and fecal bifidobacteria and actobacillus value-added effect. The method is scientifically and rationally designed, and of great significance in achieving the comprehensive utilization of resources oat and increasing its added value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing mixed type nucleotide feed addictive from yeast cell and application
InactiveCN101480220AHigh purityPromote growthAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsAnti stressPhosphodiesterase
The invention relates to a method for preparing a mixed-type nucleotide feed additive from yeast cells and applications of the feed additive, which belong to the technical field of the preparation of nucleotide feed additives from yeast cells. The method comprises the steps: using yeast cells as raw materials and combining a homogenization method and a salt method to break yeast cell walls ; separating the yeast cell walls, protein and other insoluble substances by centrifugation and fractional isoelectric crystallization; specially collecting RNA precipitates at special isoelectric points to obtain wet and crude nucleic acid with the purity of 70 percent; dissolving the wet and crude nucleic acid in water, using high-activity phosphodiesterase from malt roots to carry out a high-efficiency directional enzymatic reaction; directly spraying, drying and crushing the solution after the enzymatic reaction to obtain the mixed-type nucleotide feed additive product comprising the protein content lower than 10 percent and four monosomic nucleotides (AMP, GMP, CMP and UMP) larger than 60 percent. After the feed additive is applied to animal feed, the intestinal absorption function of animals can be notably improved, the growth of the animals is stimulated, and the immune function, the antiviral capability and the anti-stress capability of the animals are improved.
Owner:江苏省苏微微生物研究有限公司 +2
Protein appropriate for orientation-controlled immobilization and immobilization carrier on which the proteins are immobilized
InactiveUS20090299035A1Prepared efficiently and rapidlyFunction increasePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAcidic amino acidsIsoelectric point
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel protein having the following amino acid sequence altered for specifically and efficiently binding a protein to an immobilization carrier via the carboxy terminus. The protein is used for immobilizing a portion represented by R1-R2 on an immobilization carrier, comprising the amino acid sequence represented by the general formula R1-R2-R3-R4-R5 [wherein:the sequences are oriented from the amino terminal side to the carboxy terminal side;the sequence of the R1 portion is the sequence of a subject protein to be immobilized and contains neither a lysine residue nor a cysteine residue;the sequence of the R2 portion may be absent, but when the sequence of the R2 portion is present, the sequence of the R2 portion is a spacer sequence composed of amino acid residues other than lysine and cysteine residues;the sequence of the R3 portion is composed of two residues of amino acid represented by cysteine-X (where X denotes an amino acid residue other than lysine or cysteine);the sequence of the R4 portion may be absent, but when the sequence of the R4 portion is present, the sequence of the R4 portion contains neither a lysine residue nor a cysteine residue, but contains an acidic amino acid residue capable of acidifying the isoelectric point of the entire protein comprising the amino acid sequence represented by the general formula R1-R2-R3-R4-R5; andthe sequence of an R5 portion is an affinity tag sequence for protein purification.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
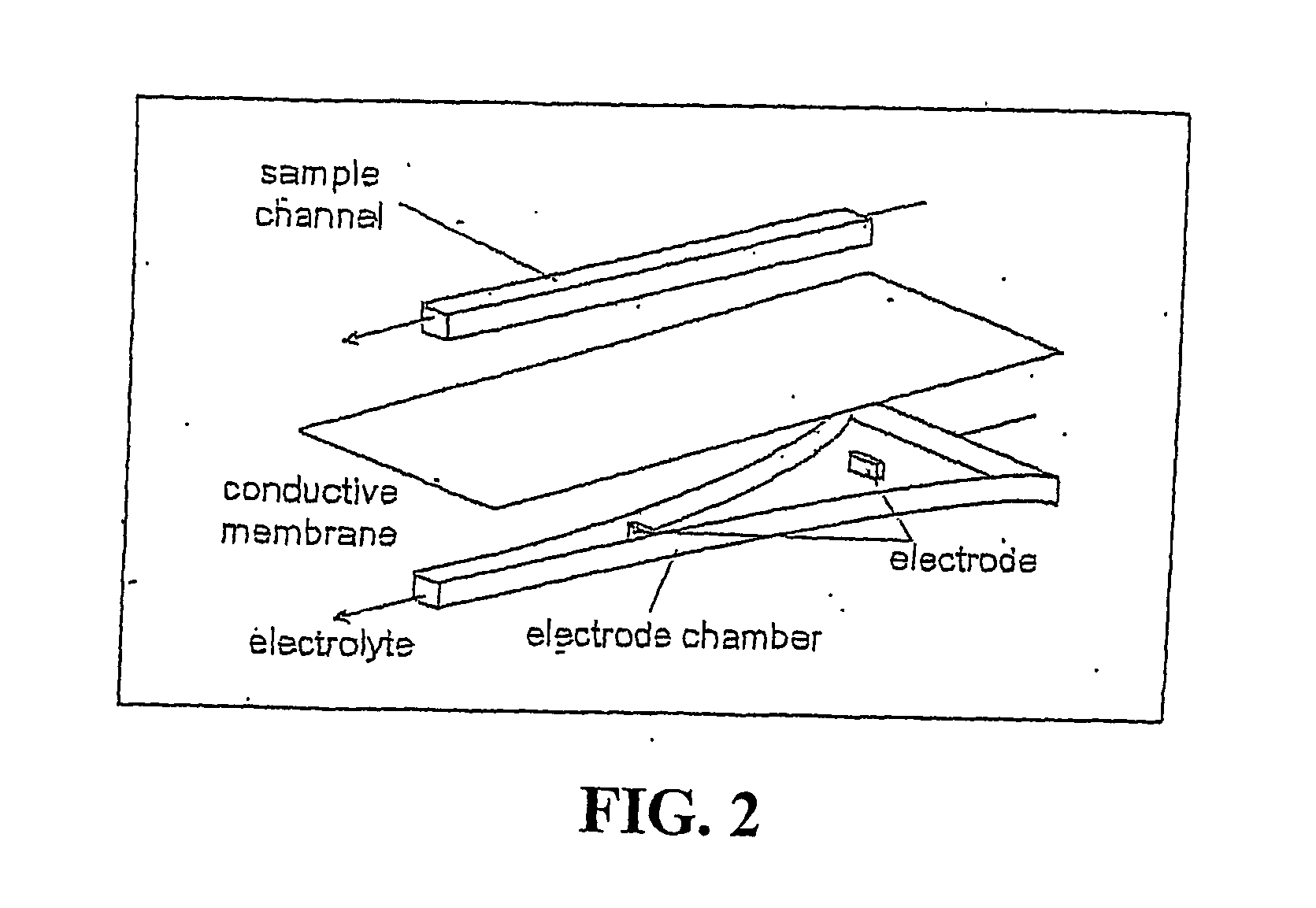
Method and apparatus determining the isoelectric point of charged analyte
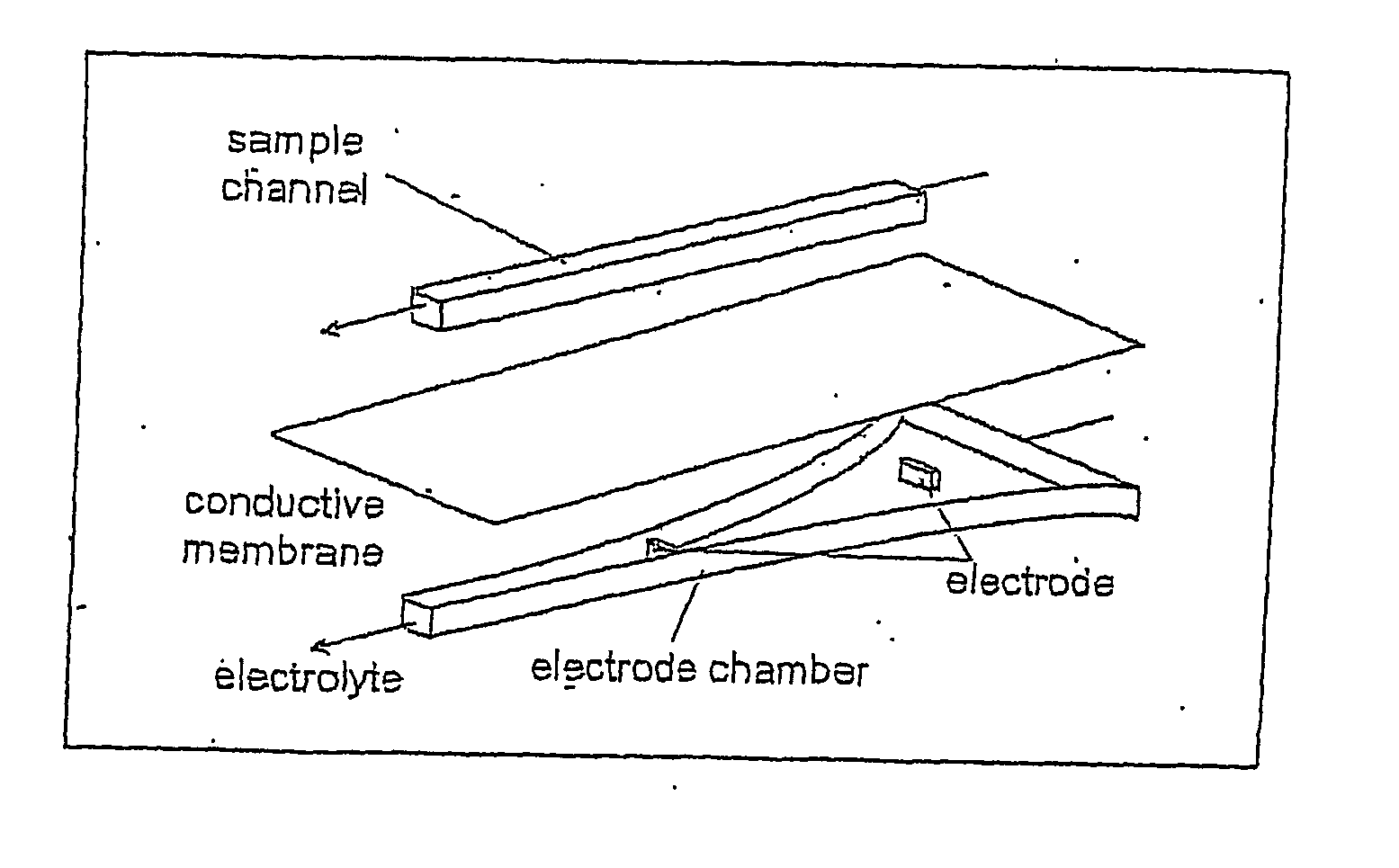
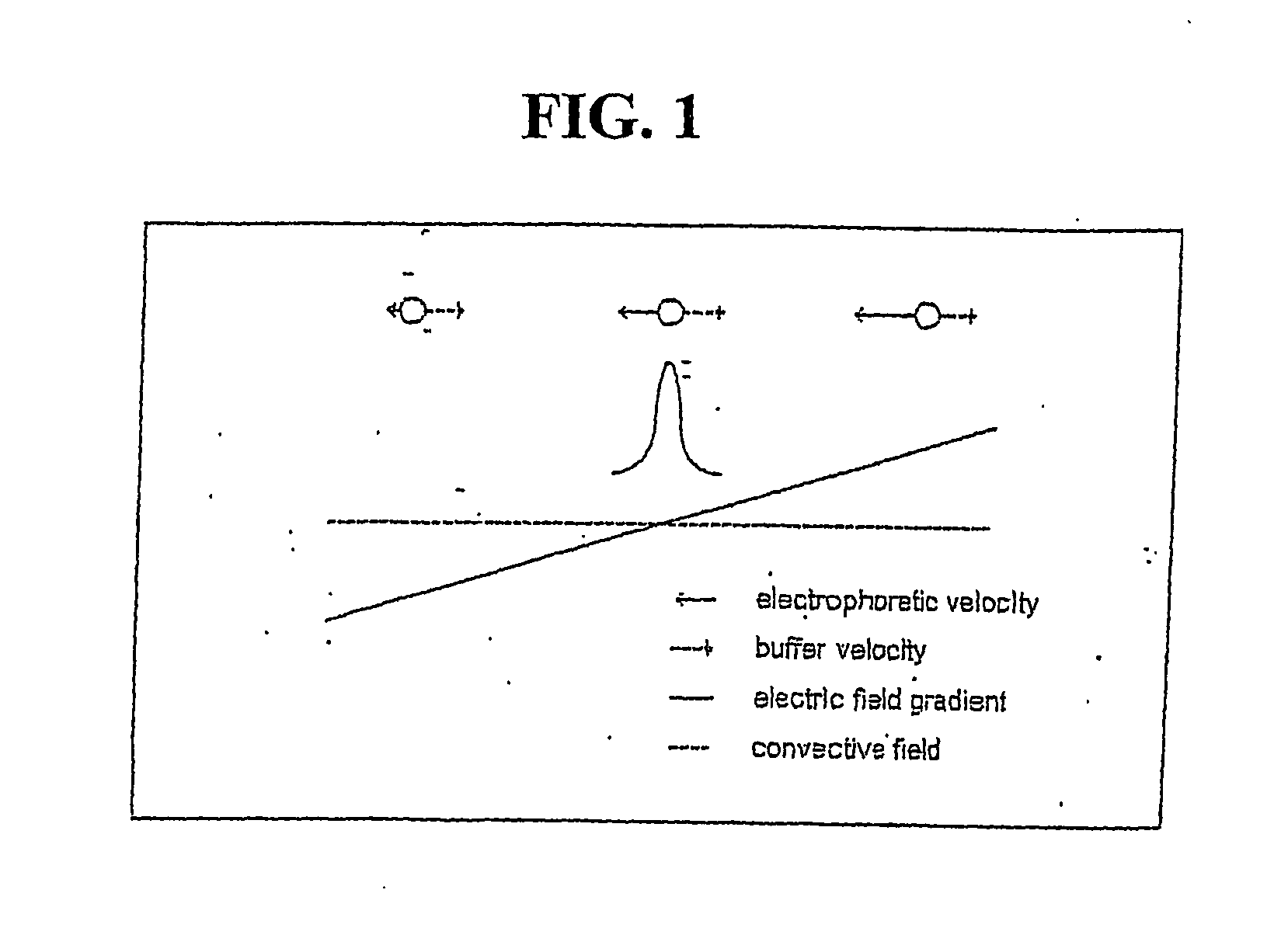
InactiveUS20070163884A1Readily apparentSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteCarrier fluid
Devices are provided for determining the isoelectric point of a charged analyte, comprising a titration chamber and an electrode chamber. The electrode chamber comprises at least two electrodes, for example, an electrode array. Either or both of the titration chamber and the electrode chamber may have a shaped geometry. The electrodes are operative, in conjunction with the shaped geometry of the chamber(s) where appropriate, to generate an electric field gradient in the titration chamber. Permeable material separates the titration chamber and the electrode chamber. A pH Sensor is located in the titration chamber for obtaining the pH of the first fluid. Certain preferred embodiments further include an analyte band detector for detecting the presence and optionally the location of a focused band of charged solute. Methods are provided for determining the isoelectric point of a charged analyte comprising introducing a carrier fluid comprising a Charge analyte into the titration chamber of a device as just described and applying an electric field gradient to focus the charged analyte into a focused band. The pH of the carrier fluid is incremented or adjusted to shift the location of the focused band of charged analyte, and the pH and location of the focused band of charged analyte are obtained for a plurality of locations and pH's and the isoelectric point is determined from such data.
Owner:PROTASIS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com