Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7966 results about "Magnetic powder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
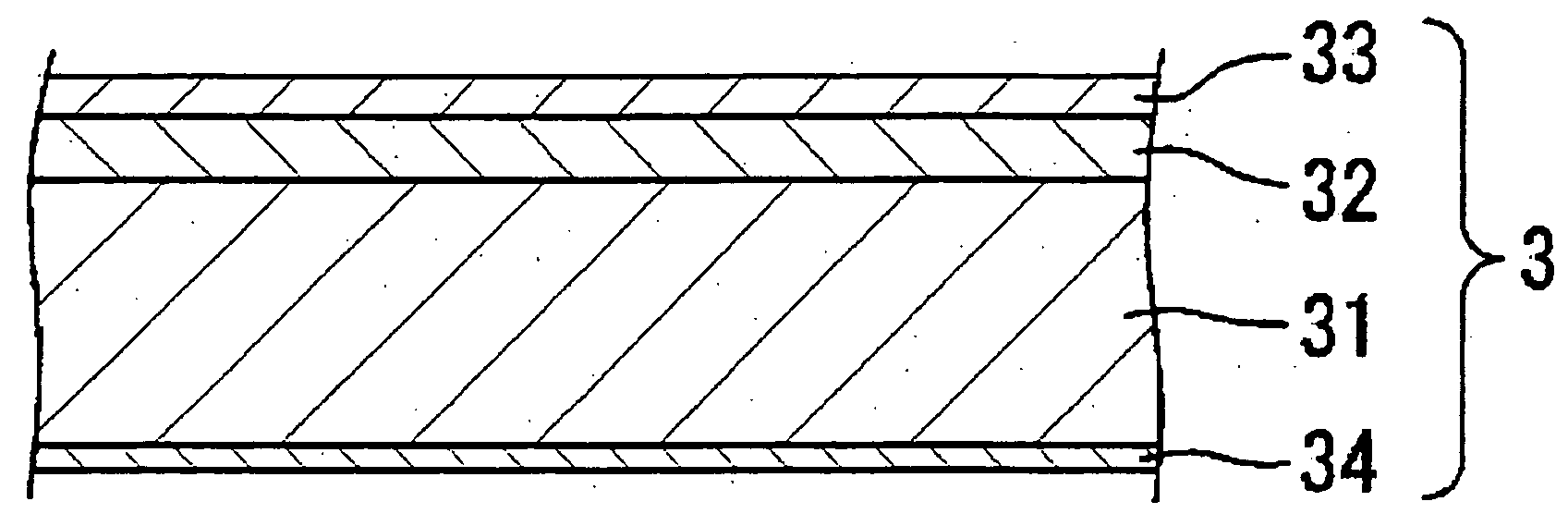
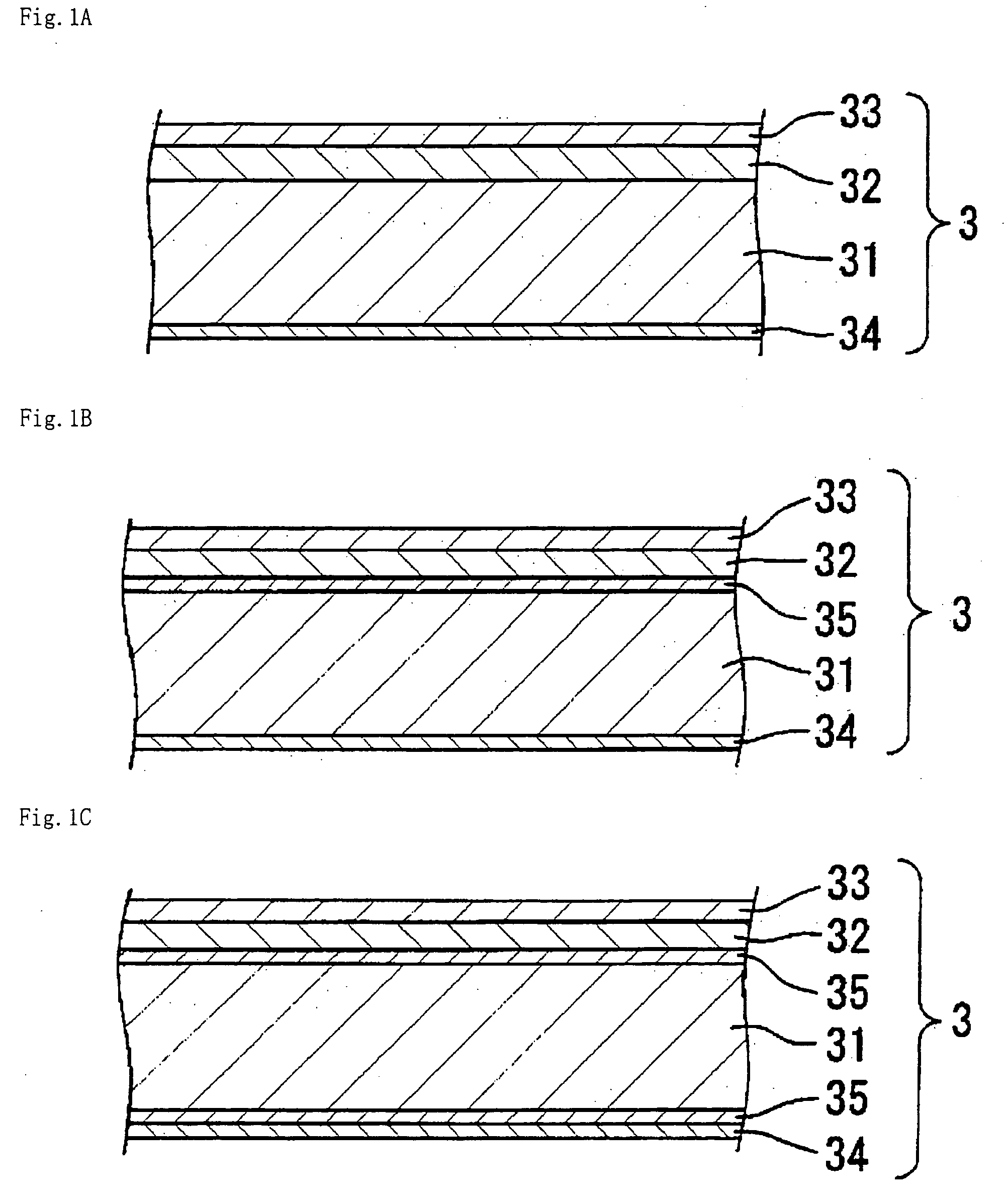
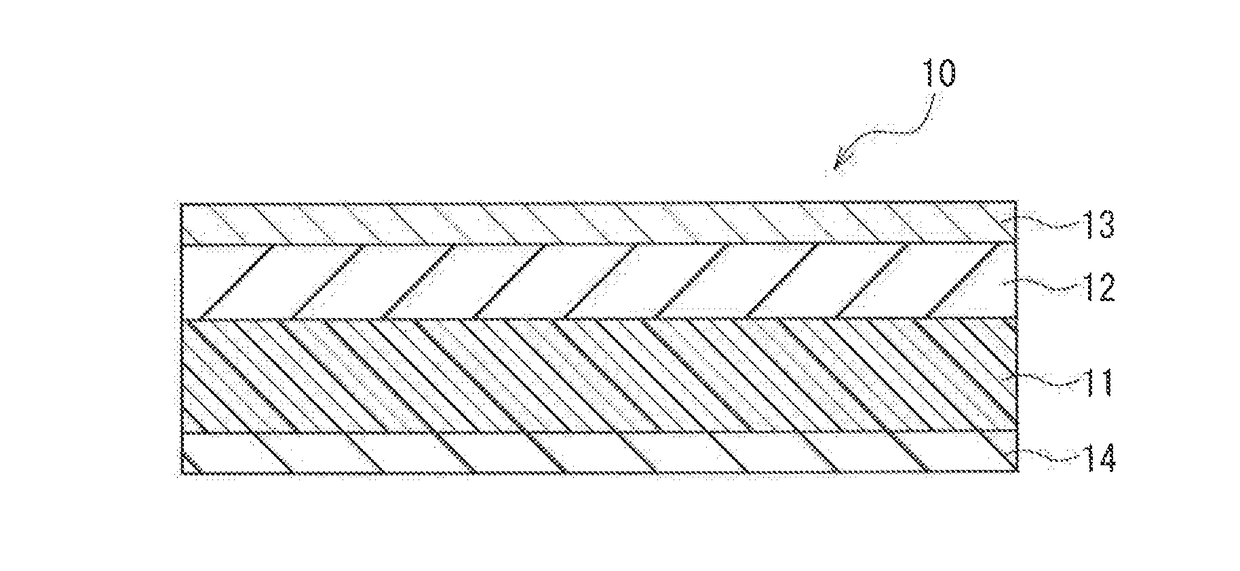
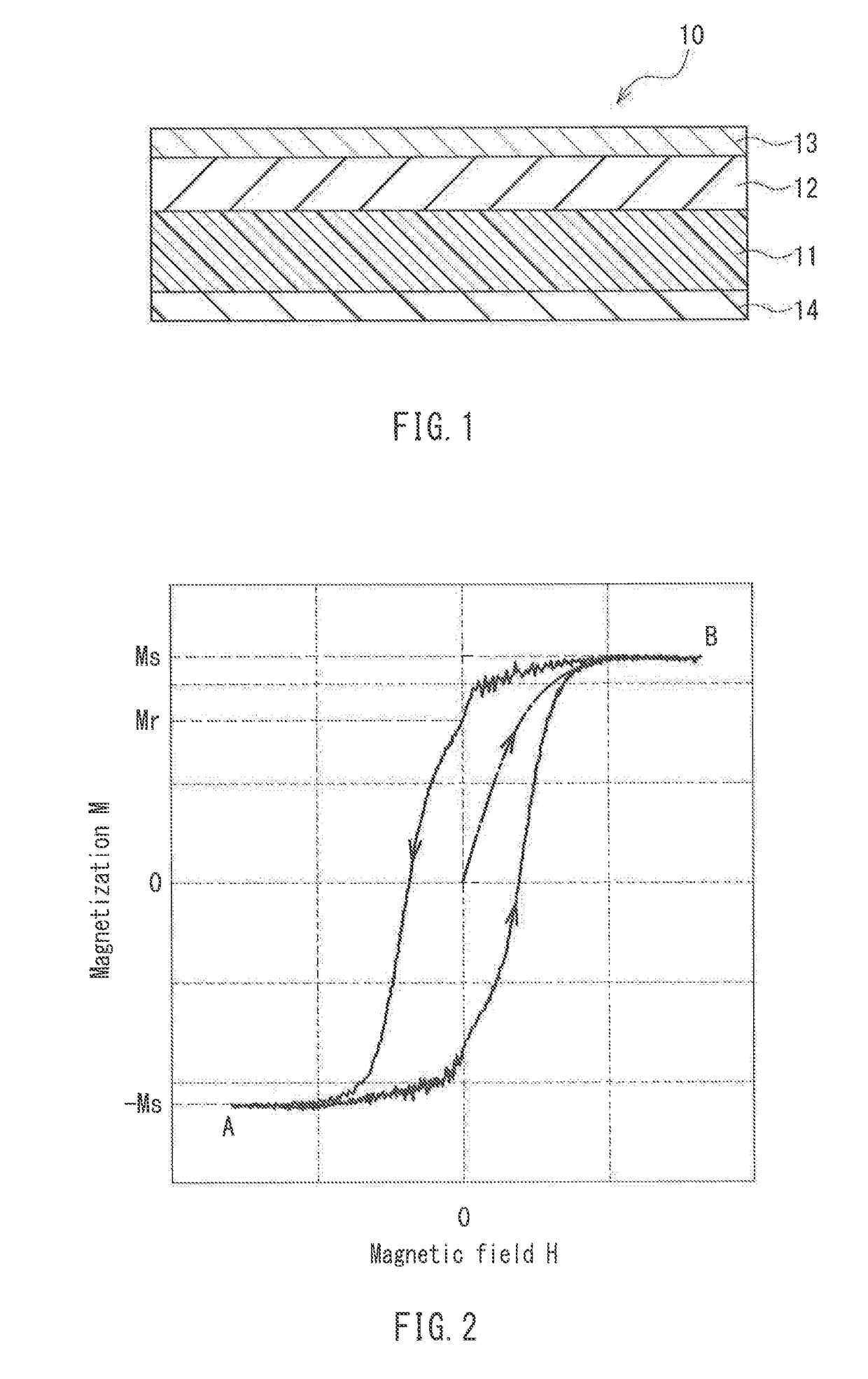
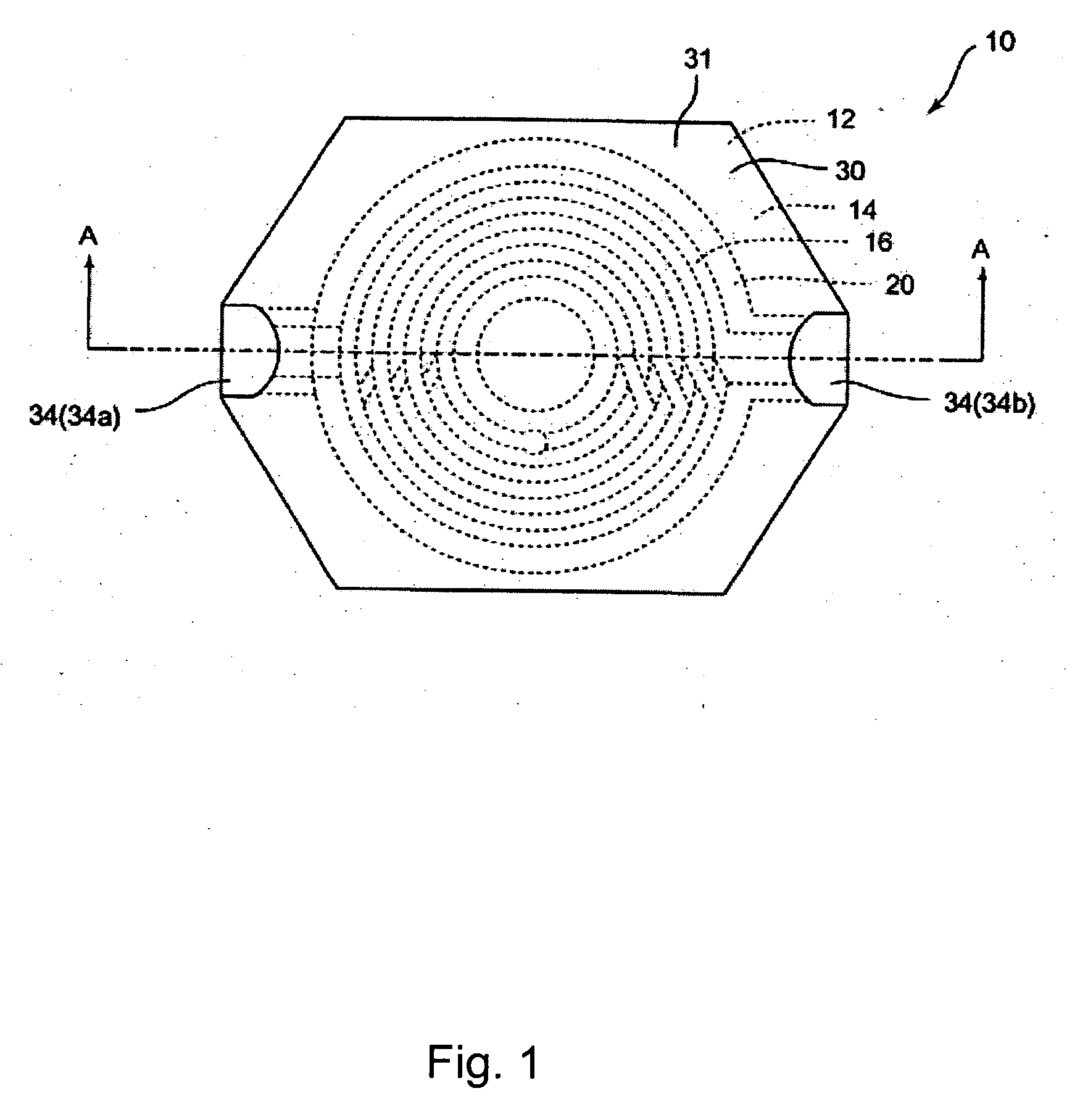
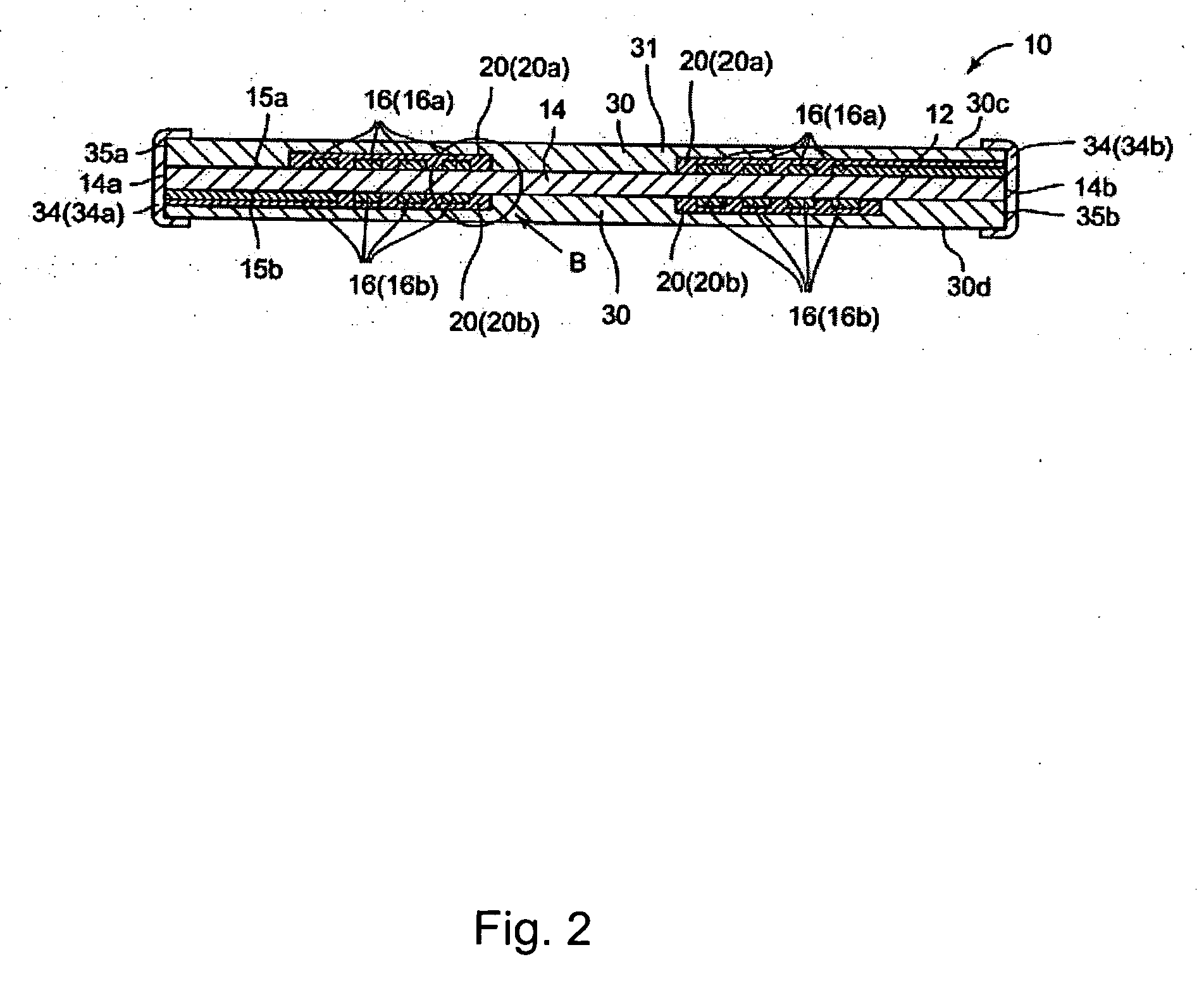
Magnetic recording medium
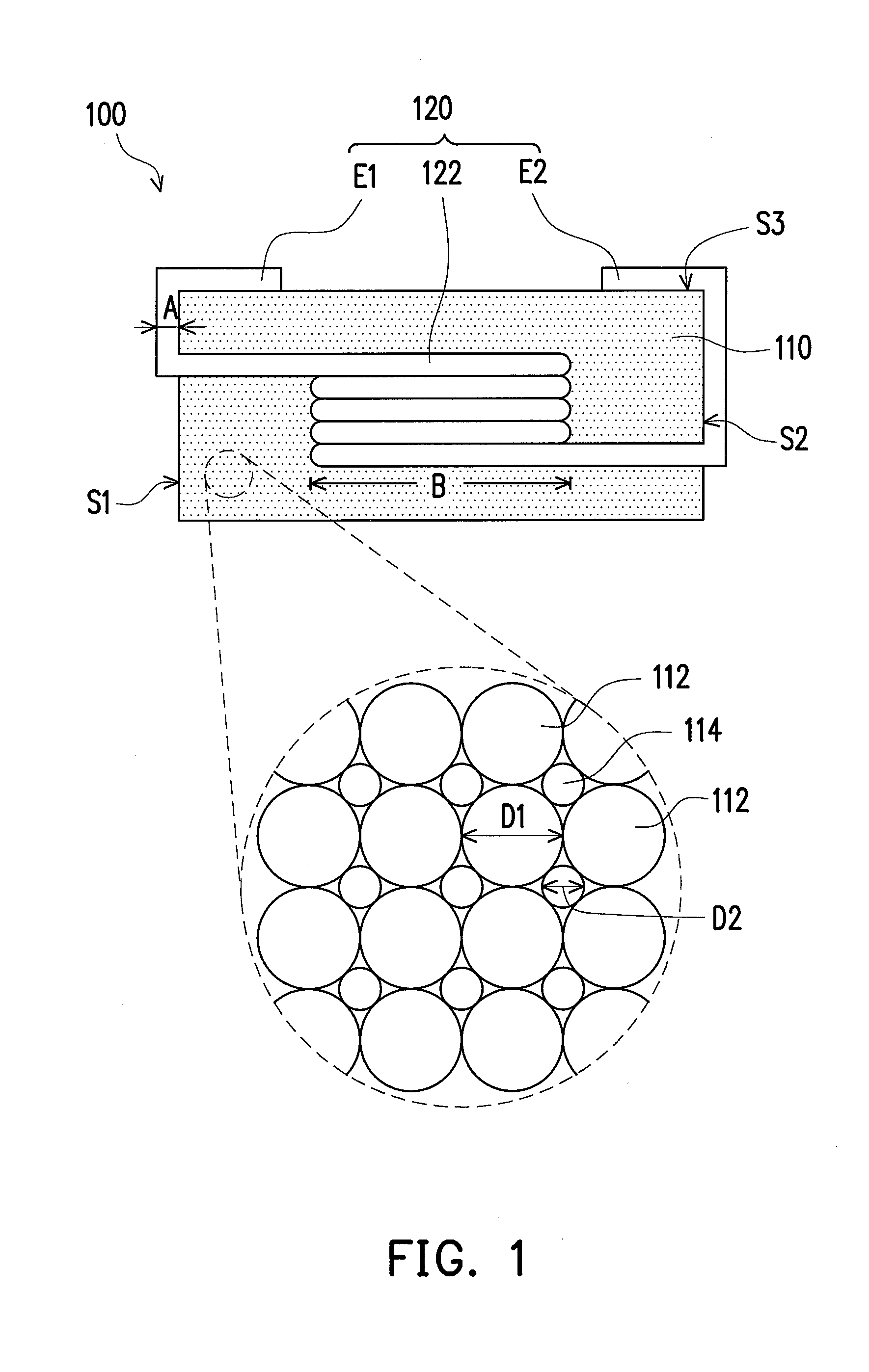
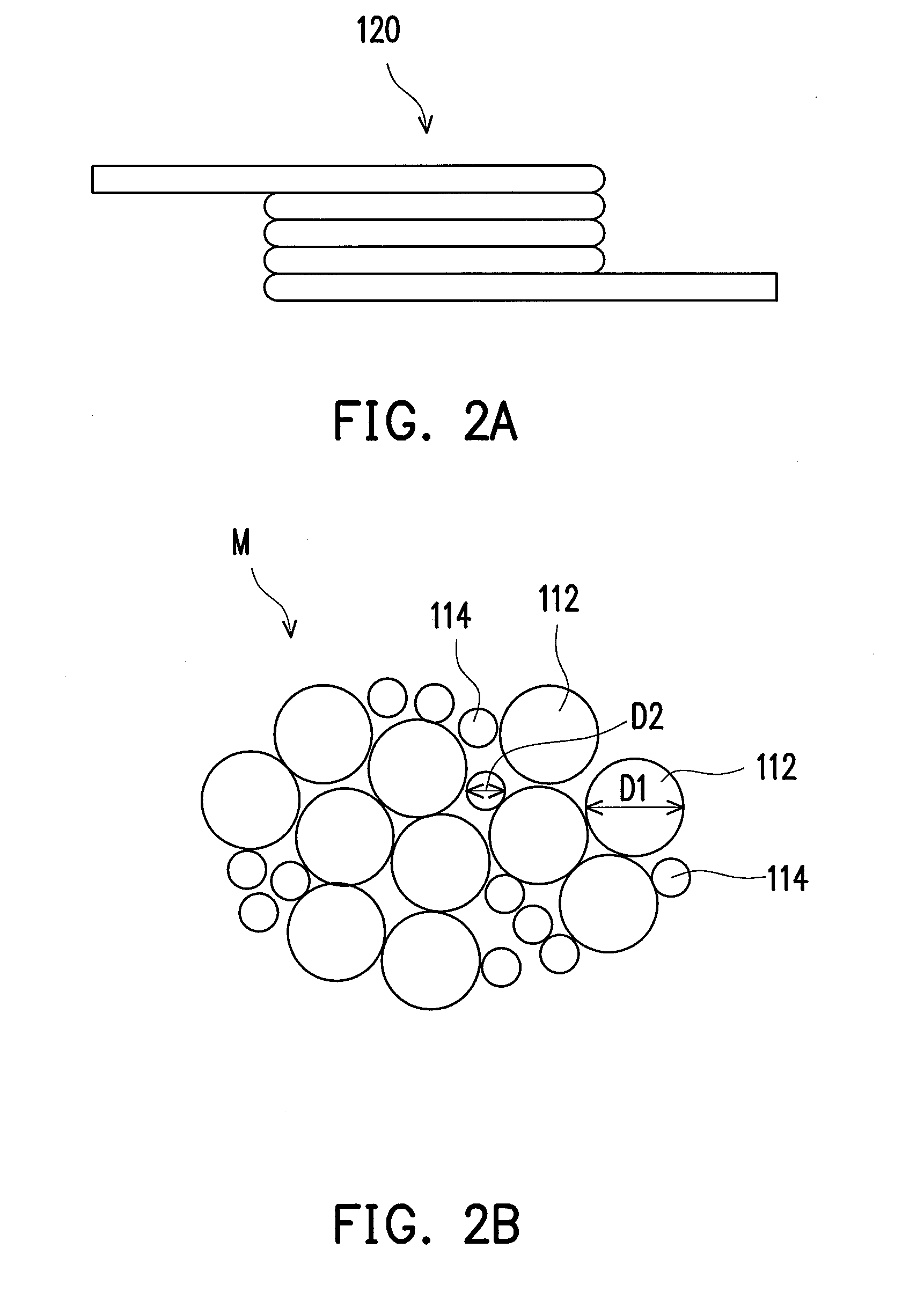
ActiveUS20120045664A1Superior recording/reproducing characteristicSuperior characteristic transportMaterials with ironRecord information storageNon magneticHexane
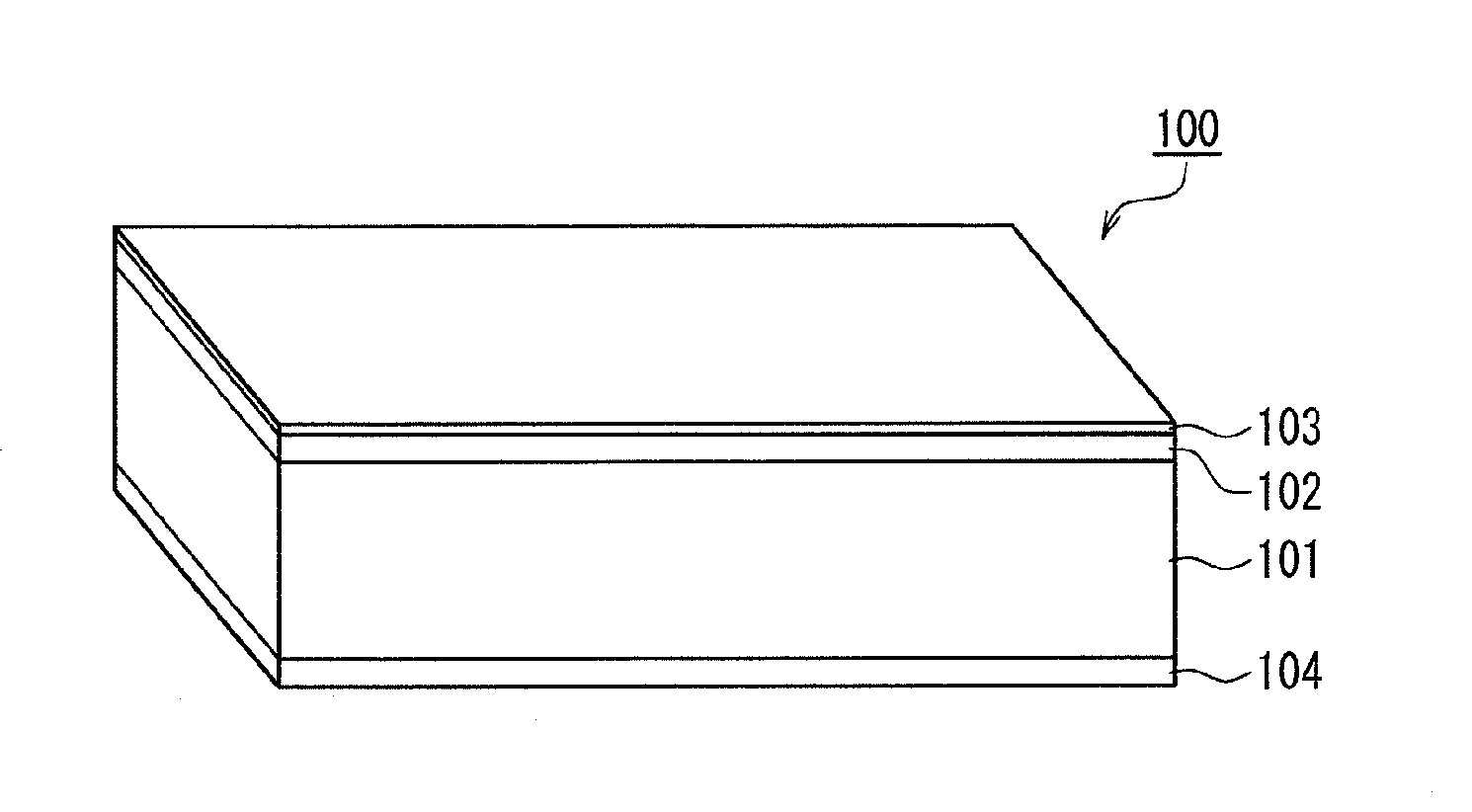
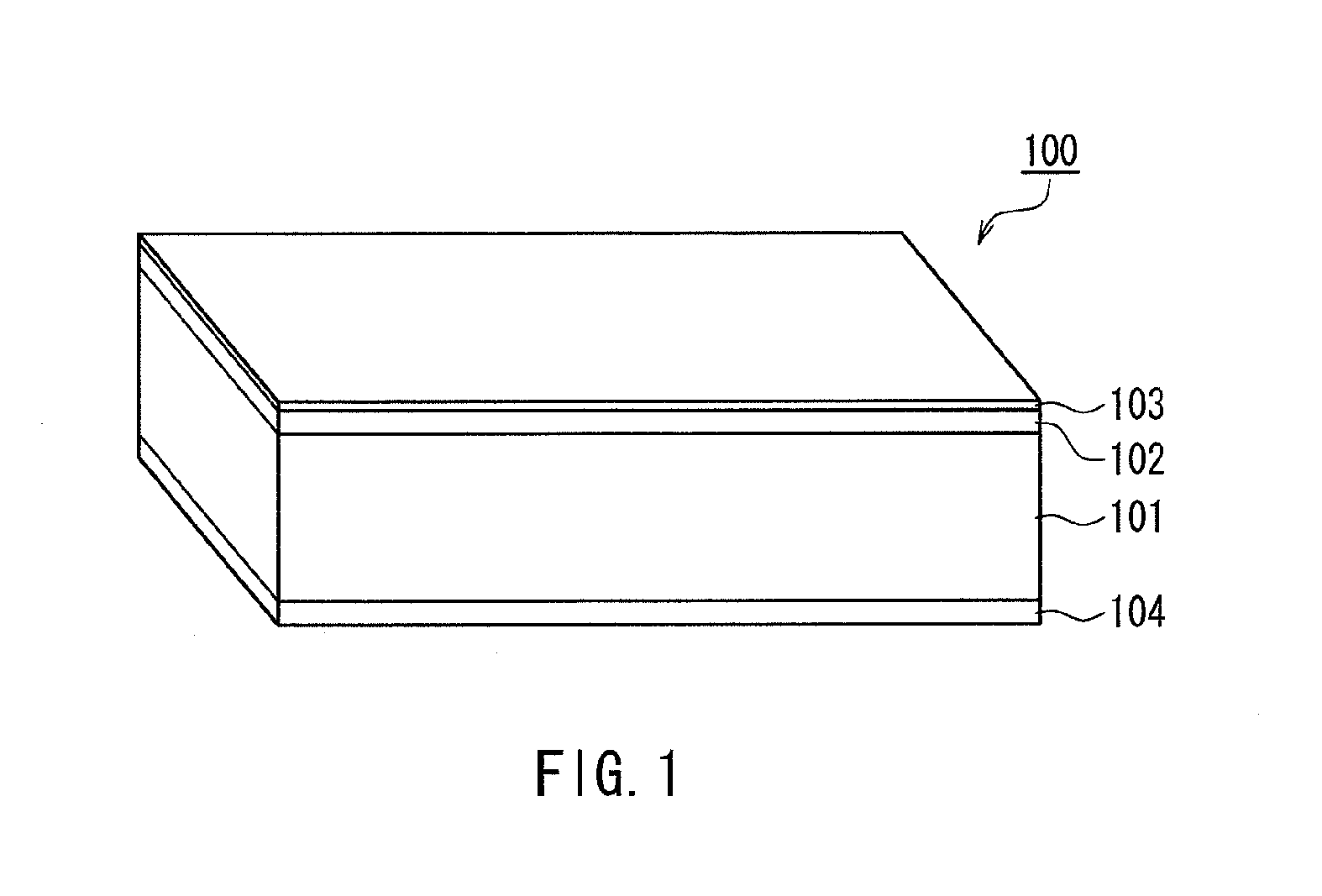
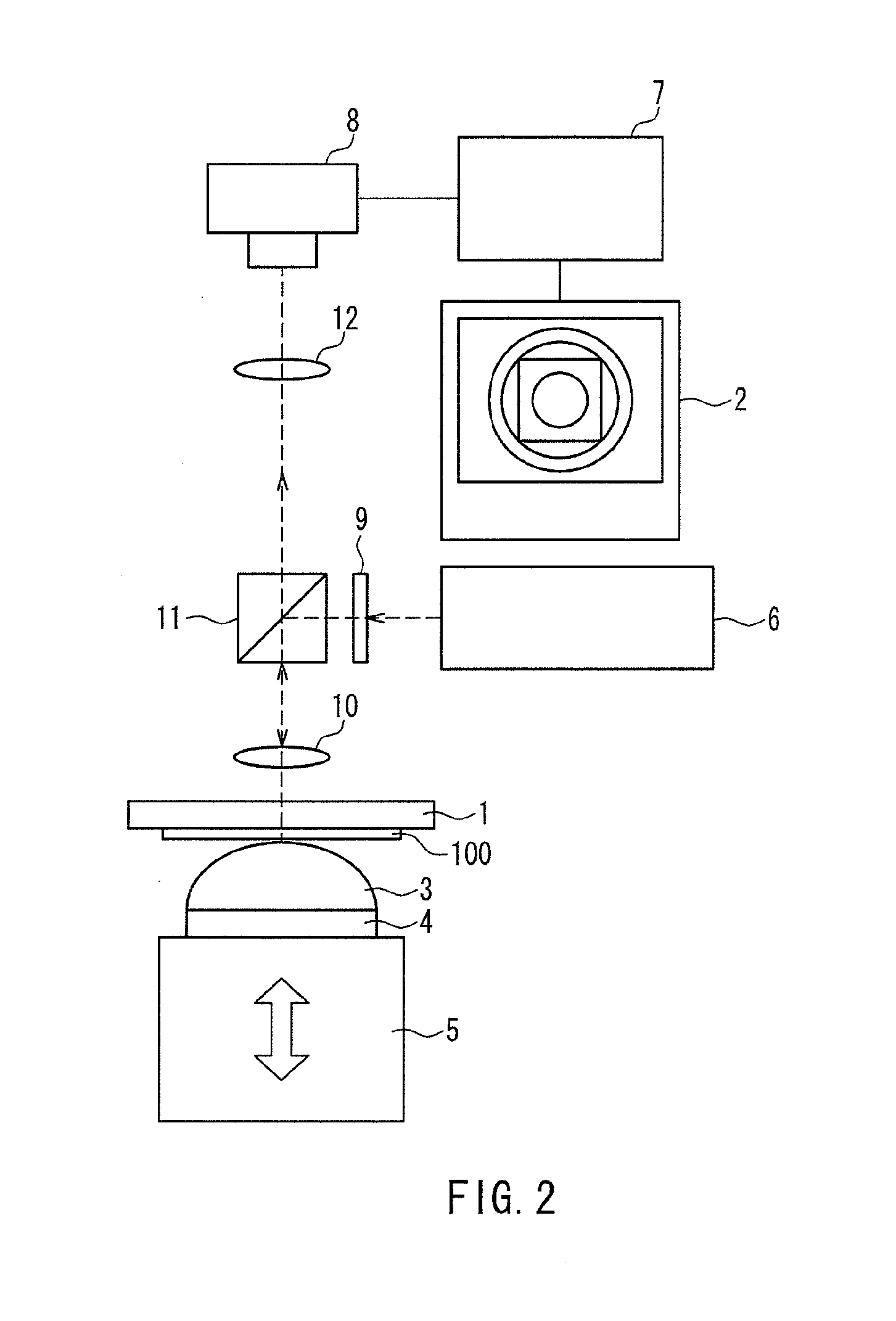
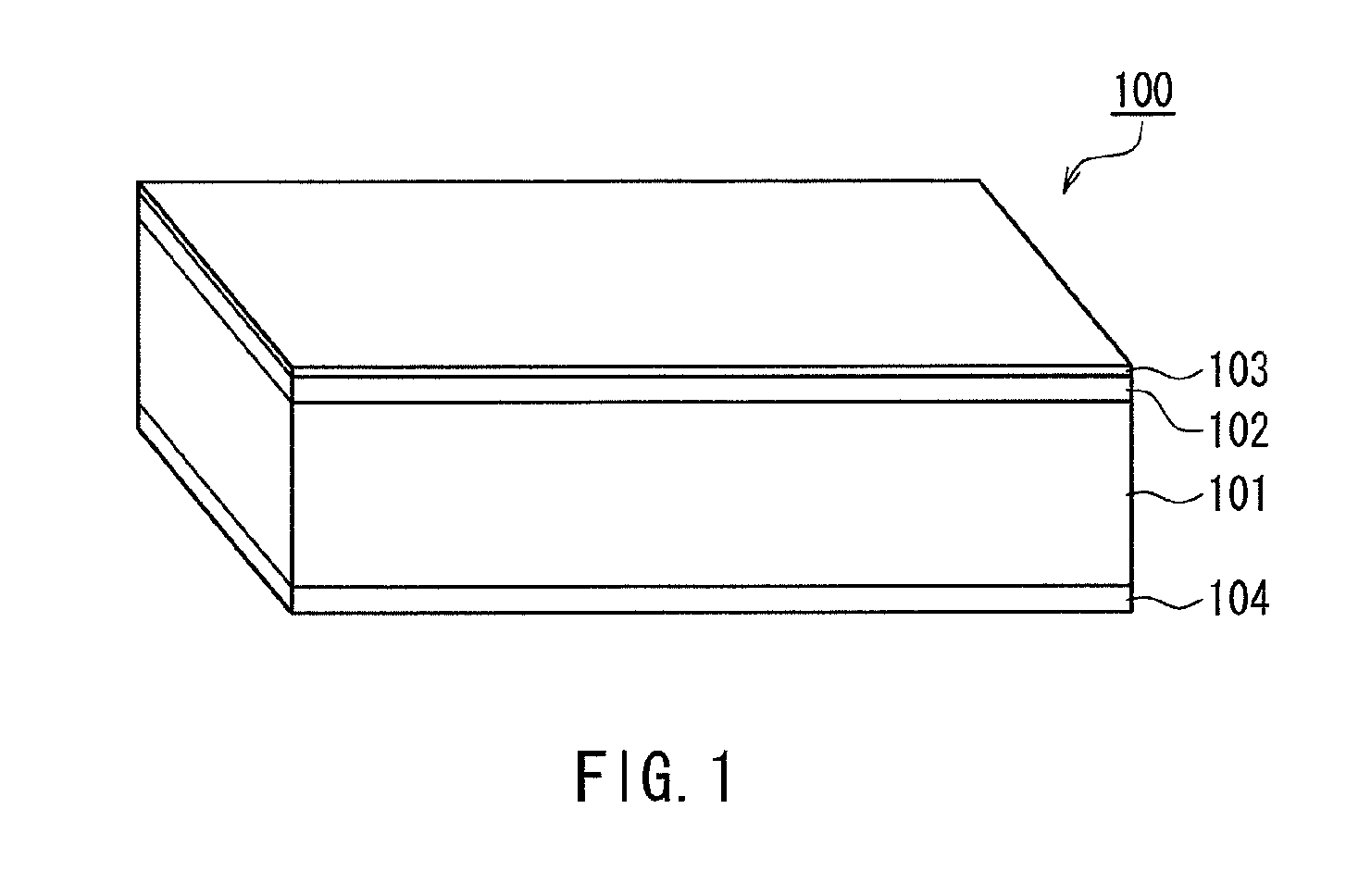
A magnetic recording medium of the present invention is a magnetic recording medium including a non-magnetic substrate; a non-magnetic layer that is formed on one of principal surfaces of the non-magnetic substrate and contains a non-magnetic powder, a binder, and a lubricant; and a magnetic layer that is formed on a principal surface of the non-magnetic layer opposite to the non-magnetic substrate and contains a magnetic powder and a binder. The magnetic powder has an average particle size between 10 inn and 35 nm inclusive. The lubricant is migratable to the magnetic layer and forms a lubricant layer on a surface of the magnetic layer when a pressure is applied to the magnetic layer. When spacing of the surface of the magnetic layer before and after washing the lubricant with n-hexane is measured with a TSA (Tape Spacing Analyzer), the value of the spacing after washing is 3 to 10 nm, and the value of the spacing before washing is 1 to 5 nm smaller than the value of the spacing after washing.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electronic device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20100289609A1Improve breathabilityPrevent oxidationTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInorganic material magnetismMagnetic powderHardness
An electronic device including a magnetic body and a wire is provided. The magnetic body has a first magnetic powder and a second magnetic powder mixed with the first magnetic powder. The Vicker's Hardness of the first magnetic powder is greater than that of the second magnetic powder and the mean particle diameter of the first magnetic powder is greater than that of the second magnetic powder.
Owner:CYNTEC
Hexagonal barium ferrite magnetic particle and method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20120177951A1Inhibit drop in thermal stabilityEnsure easeMagnetic materials for record carriersInorganic material magnetismBiological activationMaterials science
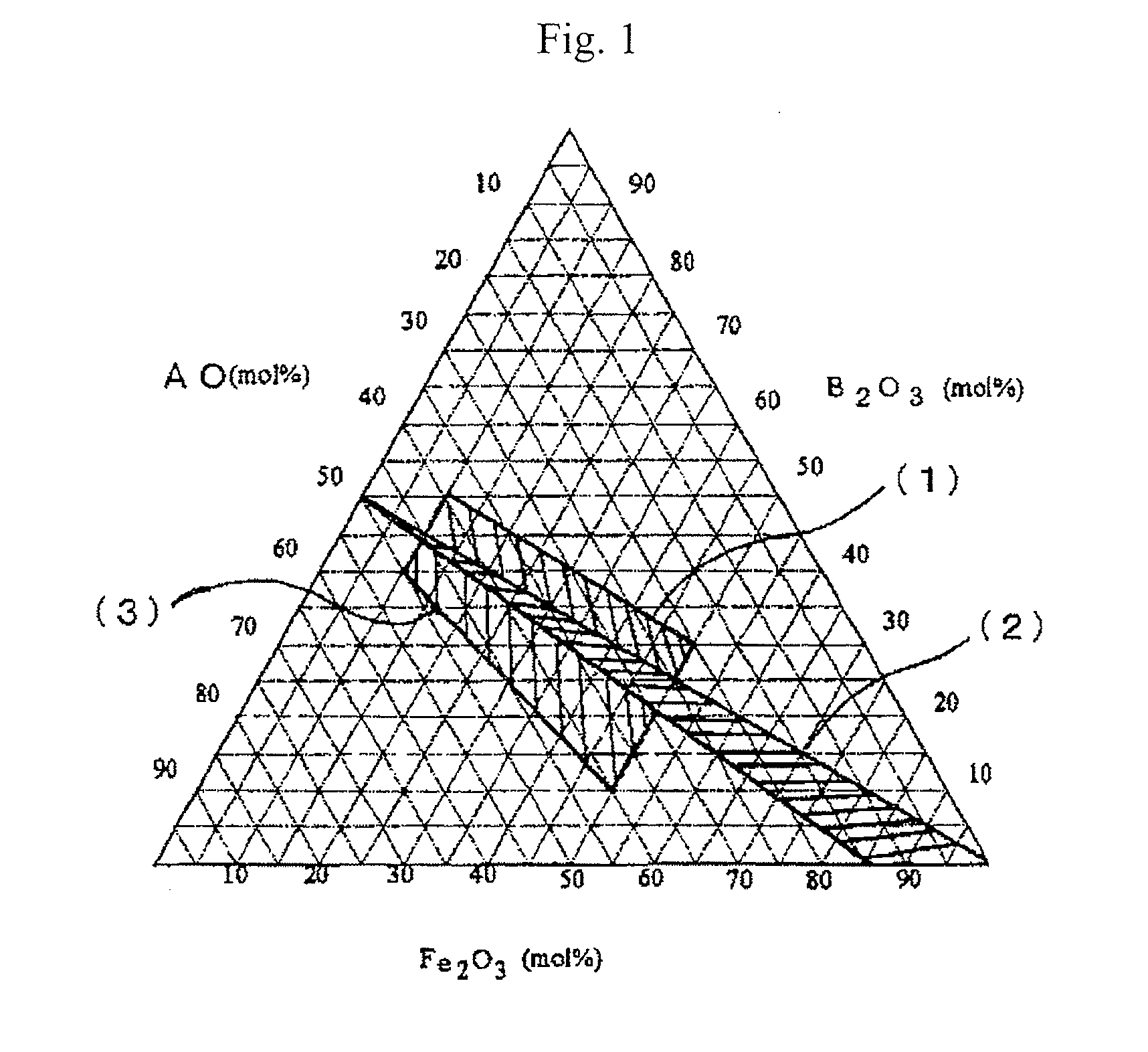
An aspect of the present invention relates to a hexagonal barium ferrite magnetic particle, wherein, relative to 100 atom percent of a Fe content, an Al content ranges from 1.5 to 15 atom percent, a combined content of a divalent element and a pentavalent element ranges from 1.0 to 10 atom percent, an atomic ratio of a content of the divalent element to a content of the pentavalent element is greater than 2.0 but less than 4.0, and an activation volume ranges from 1,300 to 1,800 nm3.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Iron nitride magnetic powder and magnetic recording medium comprising the same
InactiveUS20100035086A1Magnetic interactionIncreasing magnetic interactionRecord information storageInorganic material magnetismIron nitrideYttrium
A spherical or ellipsoidal iron nitride magnetic powder having a core comprising iron nitride including a Fe16N2 phase as a primary phase and an outer layer containing yttrium (Y) and aluminum (Al), in which an average particle size r of the iron nitride magnetic powder is 20 nm or less, an average diameter d of the core is 4 to 10 nm, and a ratio of r to d (r / d) is 2 to 3, and average content of yttrium and aluminum in the outer layer are from 0.9 to 5 atomic % and from 30 to 50 atomic %, respectively, each based on the total number of iron atoms in the iron nitride magnetic powder, and standard deviations of the contents of yttrium and aluminum are 0.6 atomic % or less and 17 atomic % or less, respectively.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape cartridge
InactiveUS20050153170A1Improved in performanceGood dimensional stabilityMaterials with ironLayered productsMagnetic tapeThermal expansion
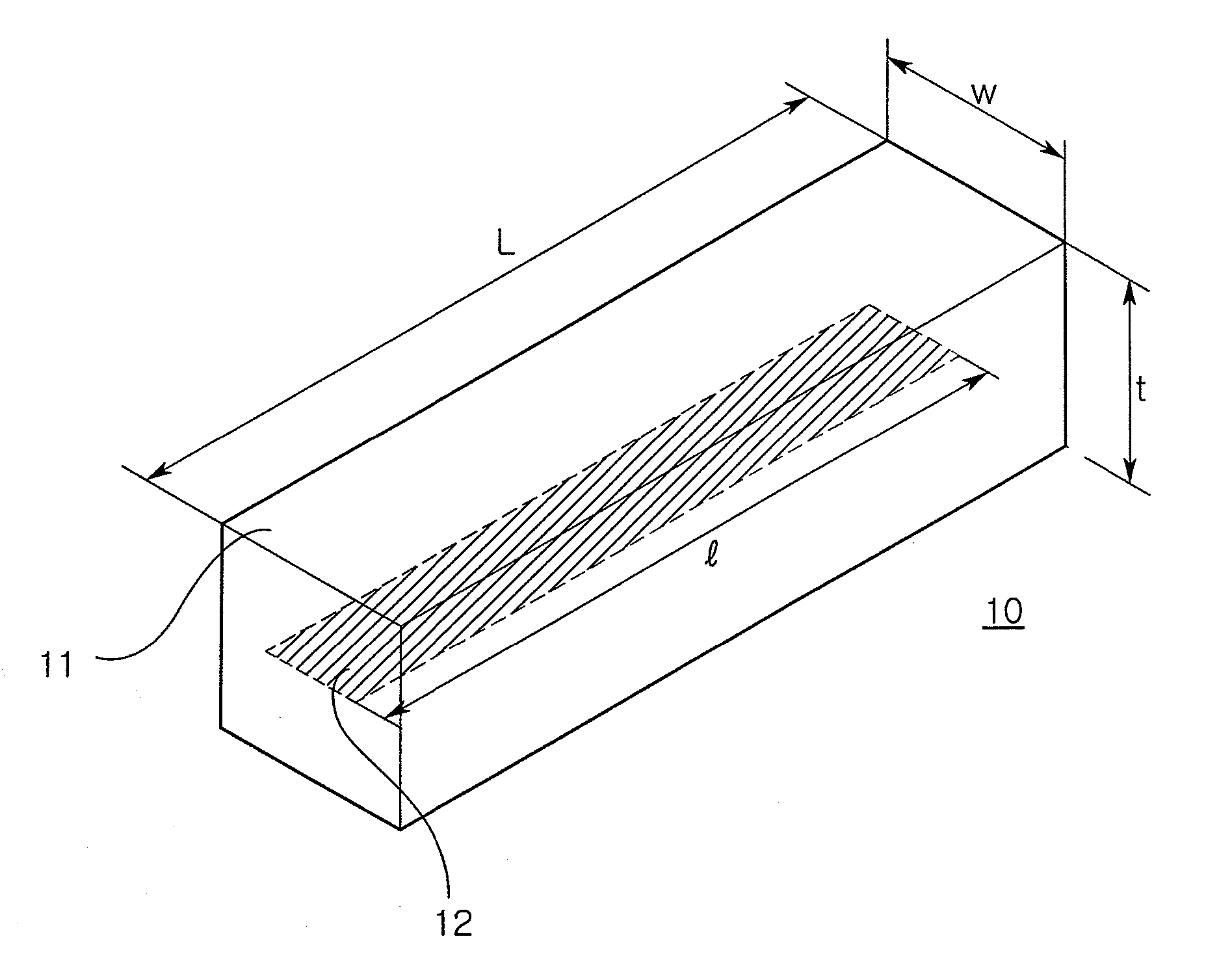
There is provided a magnetic tape comprising a non-magnetic support, and a primer layer and a magnetic layer both formed on a surface of the non-magnetic support, and a backcoat layer formed on the other surface of the non-magnetic support, wherein the magnetic layer contains magnetic powder which comprises needle-like iron-based magnetic particles, and has a thickness of 0.09 μm or less; and the primer layer contains non-magnetic powder which comprises plate-like non-magnetic oxide particles with an average particle size of 10 to 100 nm. Further, the thermal expansion coefficient of the magnetic layer in the tape widthwise direction is (0 to 8)×10−6 / ° C., and the humidity expansion coefficient of the magnetic layer in the tape widthwise direction is (0 to 10)×10−6 / % RH; and the amount of edge weave which is formed on either of the edges of the tape serving as the side of reference for the feeding of the tape is 0.8 μm or less. This magnetic tape is excellent in performance for recording / reproducing signals with short wavelengths and hardly causes a decrease in reproducing output due to off-track.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS9311946B2Superior recording/reproducing characteristic and transport characteristicFlat surfaceMaterials with ironRecord information storageNon magneticHexane
A magnetic recording medium of the present invention is a magnetic recording medium including a non-magnetic substrate; a non-magnetic layer that is formed on one of principal surfaces of the non-magnetic substrate and contains a non-magnetic powder, a binder, and a lubricant; and a magnetic layer that is formed on a principal surface of the non-magnetic layer opposite to the non-magnetic substrate and contains a magnetic powder and a binder. The magnetic powder has an average particle size between 10 nm and 35 nm inclusive. The lubricant is migratable to the magnetic layer and forms a lubricant layer on a surface of the magnetic layer when a pressure is applied to the magnetic layer. When spacing of the surface of the magnetic layer before and after washing the lubricant with n-hexane is measured with a TSA (Tape Spacing Analyzer), the value of the spacing after washing is 3 to 10 nm, and the value of the spacing before washing is 1 to 5 nm smaller than the value of the spacing after washing.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method of manufacturing hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder, magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120244387A1Good dispersionReduce dispersion loadMagnetic materials for record carriersIron organic compoundsMagnetic liquidsSolvent
An aspect of the present invention relates to a method of manufacturing hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder. The method of manufacturing hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder comprises wet processing hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles obtained following acid treatment in a water-based solvent to prepare an aqueous magnetic liquid satisfying relation (1) relative to an isoelectric point of the hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles: pH0−pH*≧2.5, wherein, pH0 denotes the isoelectric point of the hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles and pH* denotes a pH of the aqueous magnetic liquid, which is a value of equal to or greater than 2.0, adding a surface-modifying agent comprising an alkyl group and a functional group that becomes an anionic group in the aqueous magnetic liquid to the aqueous magnetic liquid to subject the hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles to a surface-modifying treatment, and removing the water-based solvent following the surface-modifying treatment to obtain hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
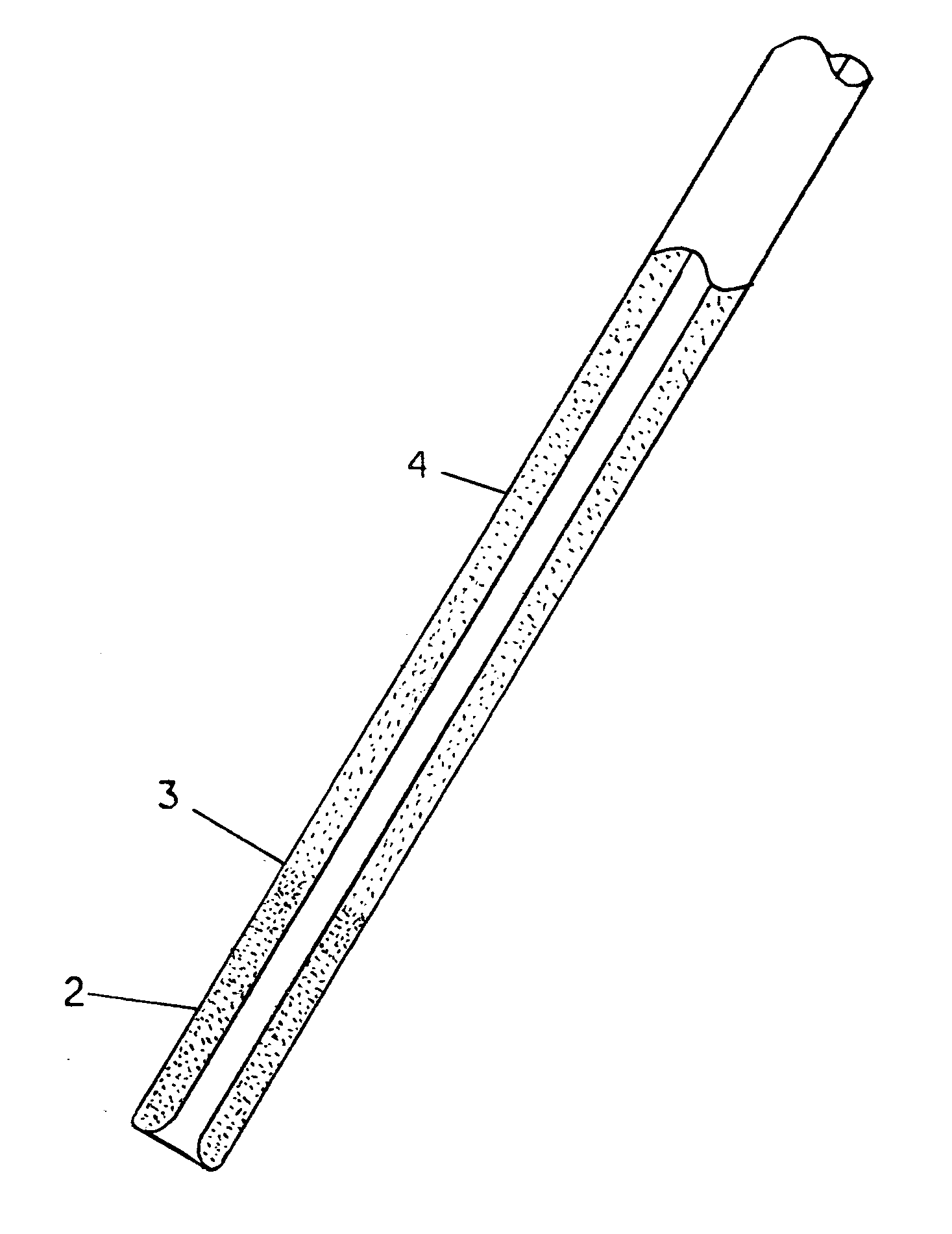
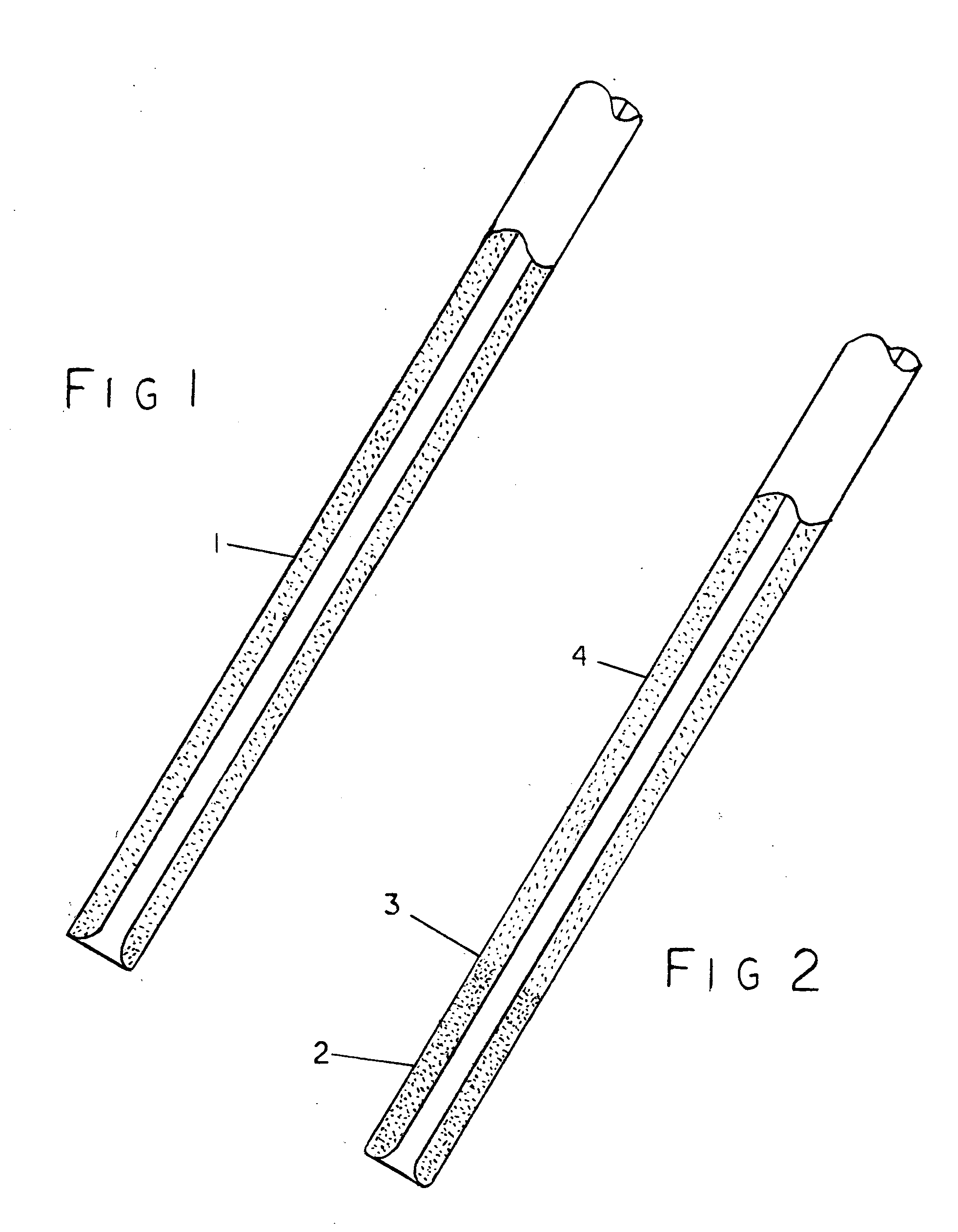
Vibrating, magnetically guidable catheter with magnetic powder commingled with resin, extruded as an integral part the catheter
InactiveUS20050245846A1Preventing accumulative adhesionLongitudinal stiffness is smallCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineUltimate tensile strength
A catheter that is produced in which magnetic powder is commingled and becomes an integral part of the catheter, which makes it not only guidable within the body by an external device, but can be made to vibrate at various speeds (cycles per second) and at varying intensities (voltages) to not only prevent its adhesion to vascular walls, but to render plaque into a viscous state, for easy suctioning from the body.
Owner:CASEY DON EWARD
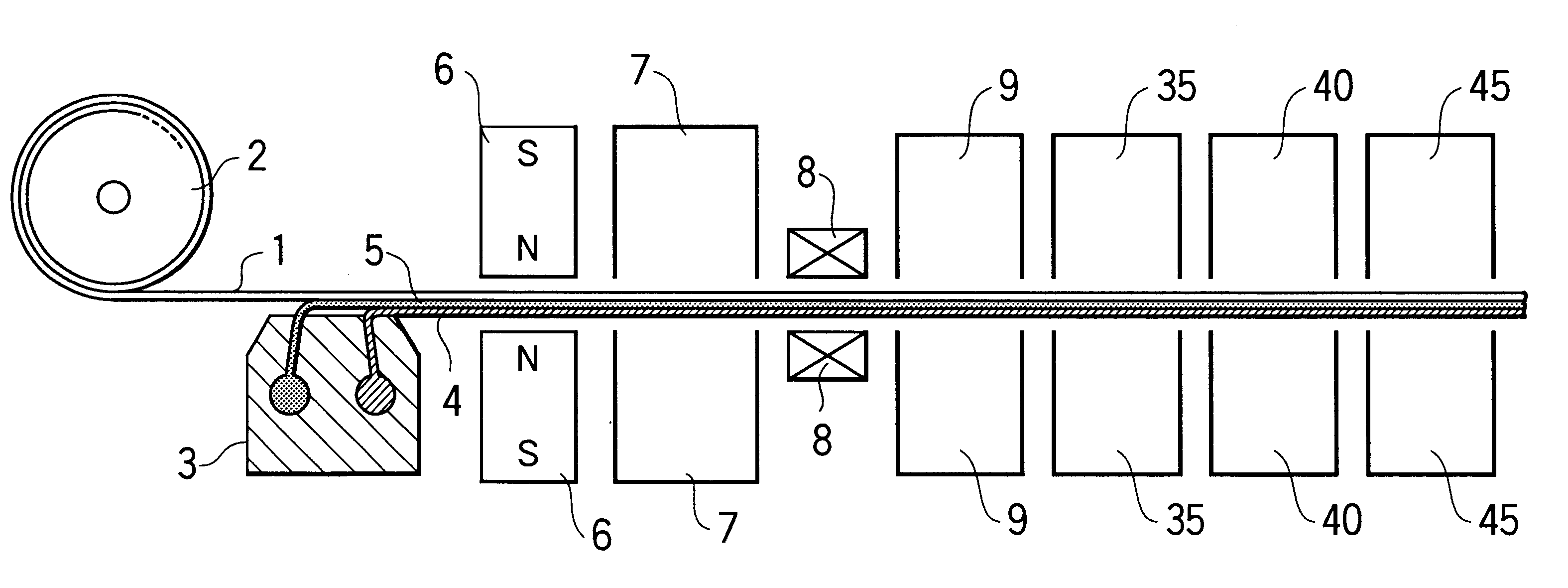
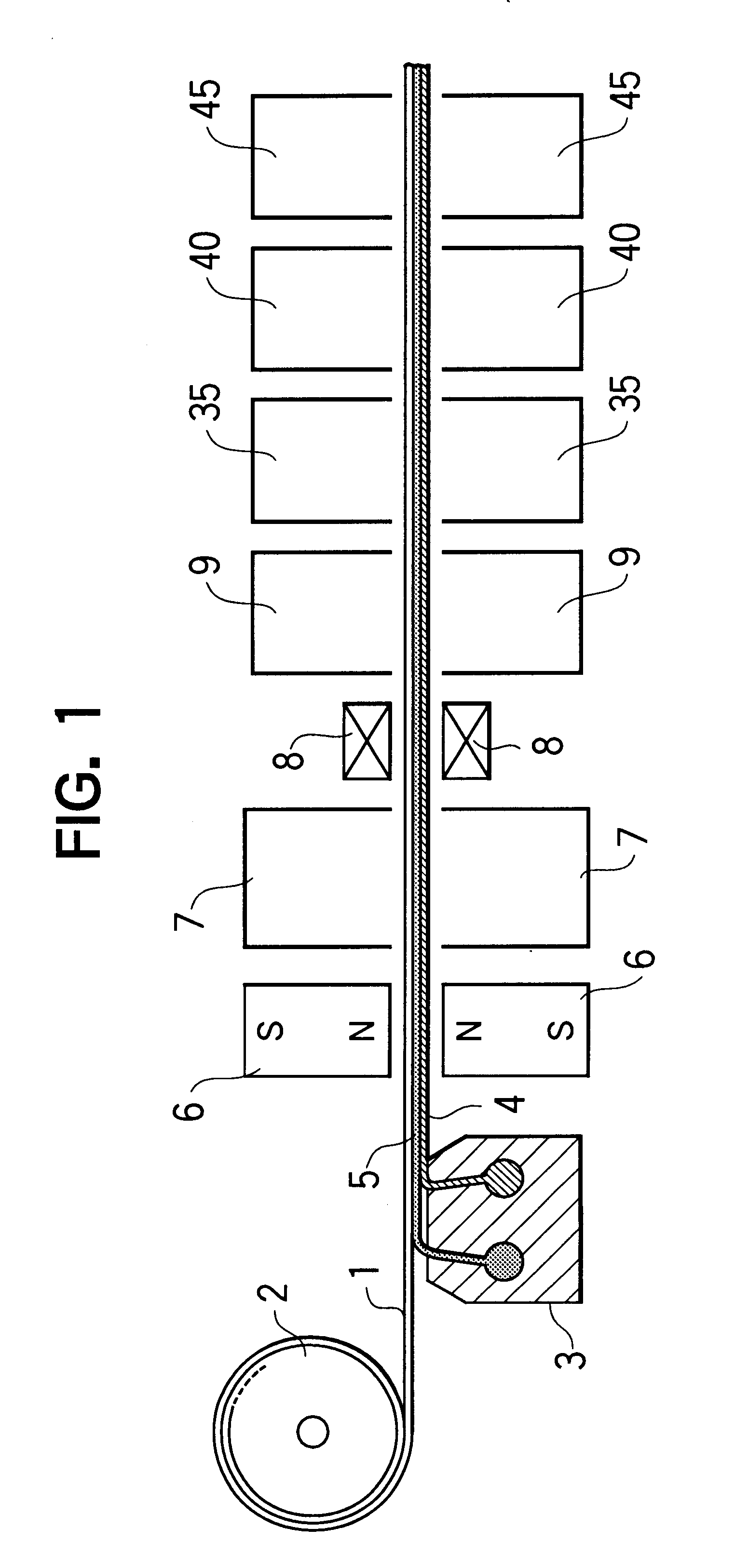
Method and apparatus for manufacturing magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS6261647B1Raise the ratioIncreased durabilityCoating by liquid dispersionMagnetic materialsEngineeringNon magnetic
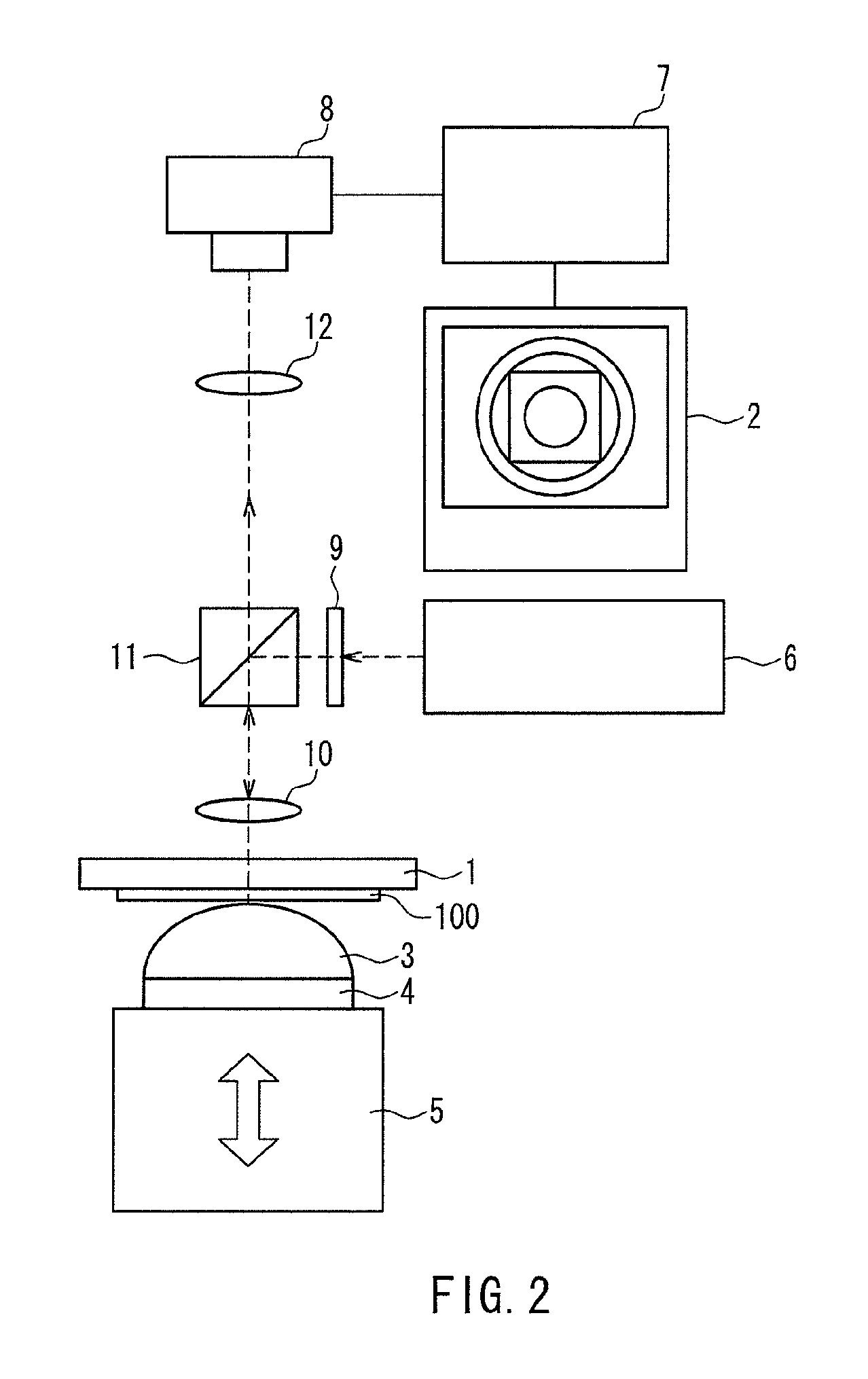
A method for manufacturing a magnetic recording medium includes steps of forming a magnetic layer containing magnetic powder particles on a web-like non-magnetic support being continuously transported in one direction and applying a magnetic field to the magnetic layer by a plurality of magnets in such a manner that an angle of the magnetic field applied to the magnetic layer to the transporting direction of the non-magnetic support in a plane perpendicular to a surface of the magnetic layer and parallel to the transporting direction of the non-magnetic support gradually increases in the transporting direction of the non-magnetic support, thereby orienting the magnetic powder particles in an oblique direction with respect to the surface of the magnetic layer. According to this method, it is possible to orient magnetic powder particles in a desired direction with respect to the surface of a magnetic layer and to manufacture a magnetic recording medium having a high squareness ratio without increasing the size of the apparatus.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Signal transmission cable with connector
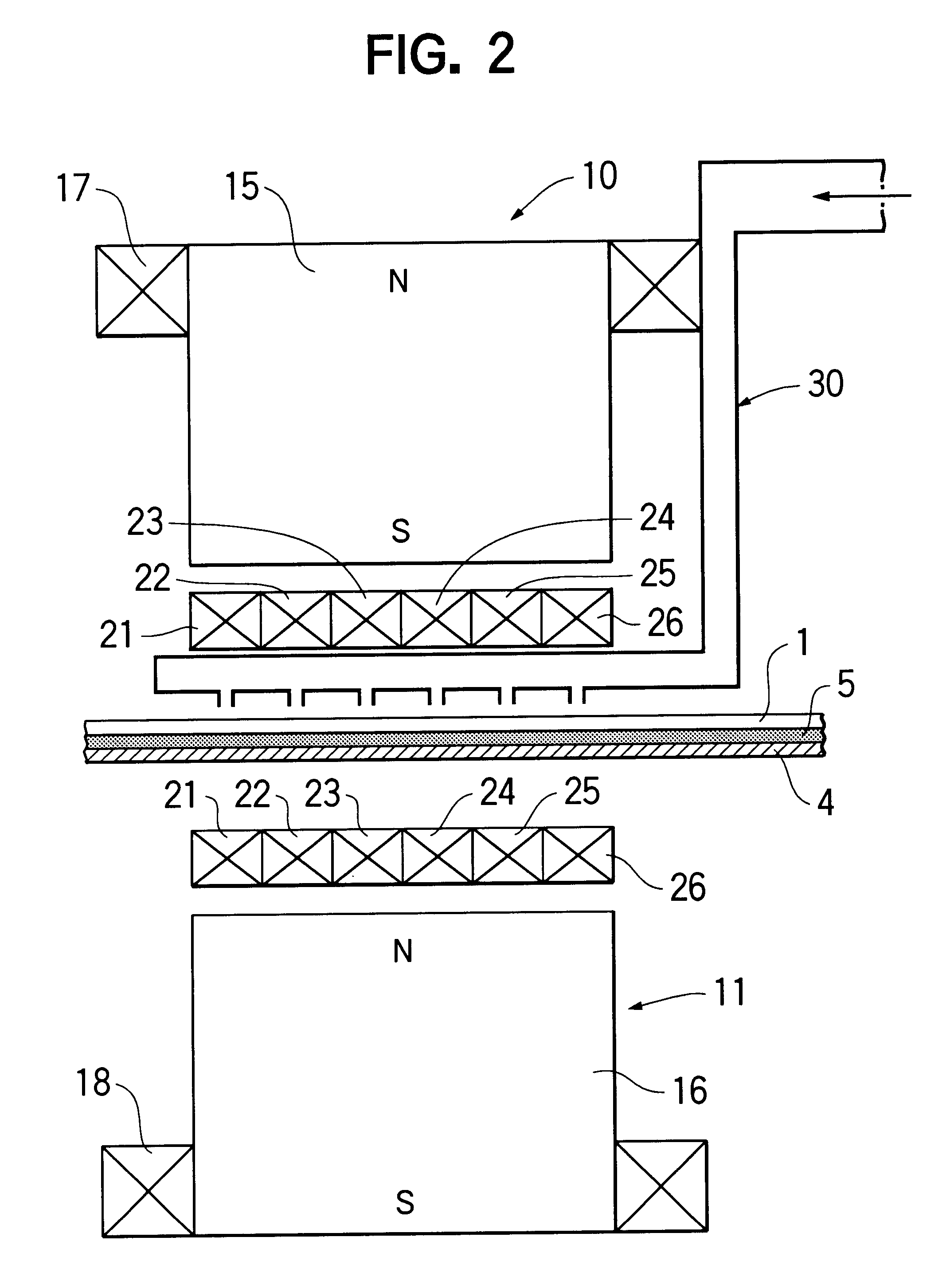
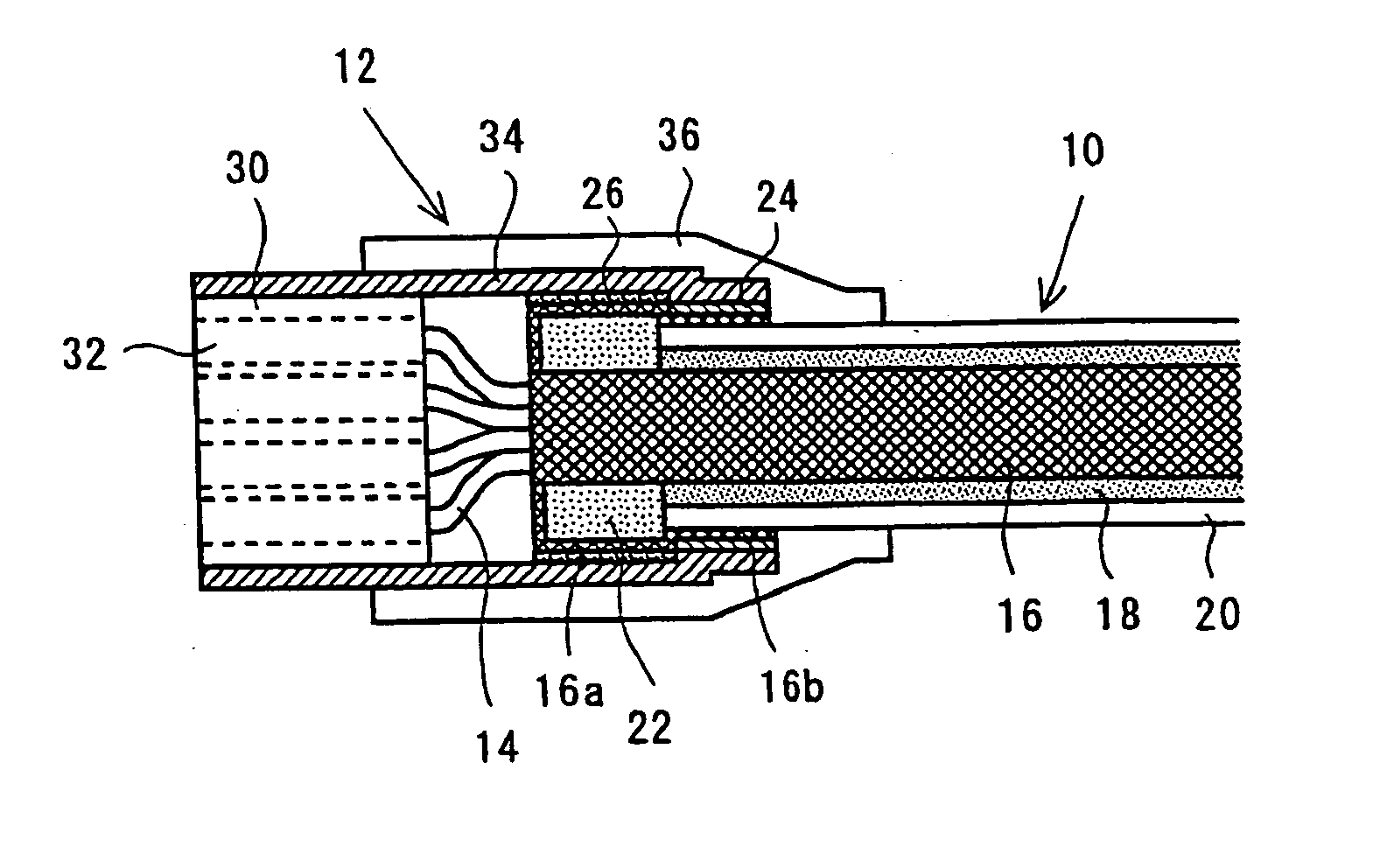
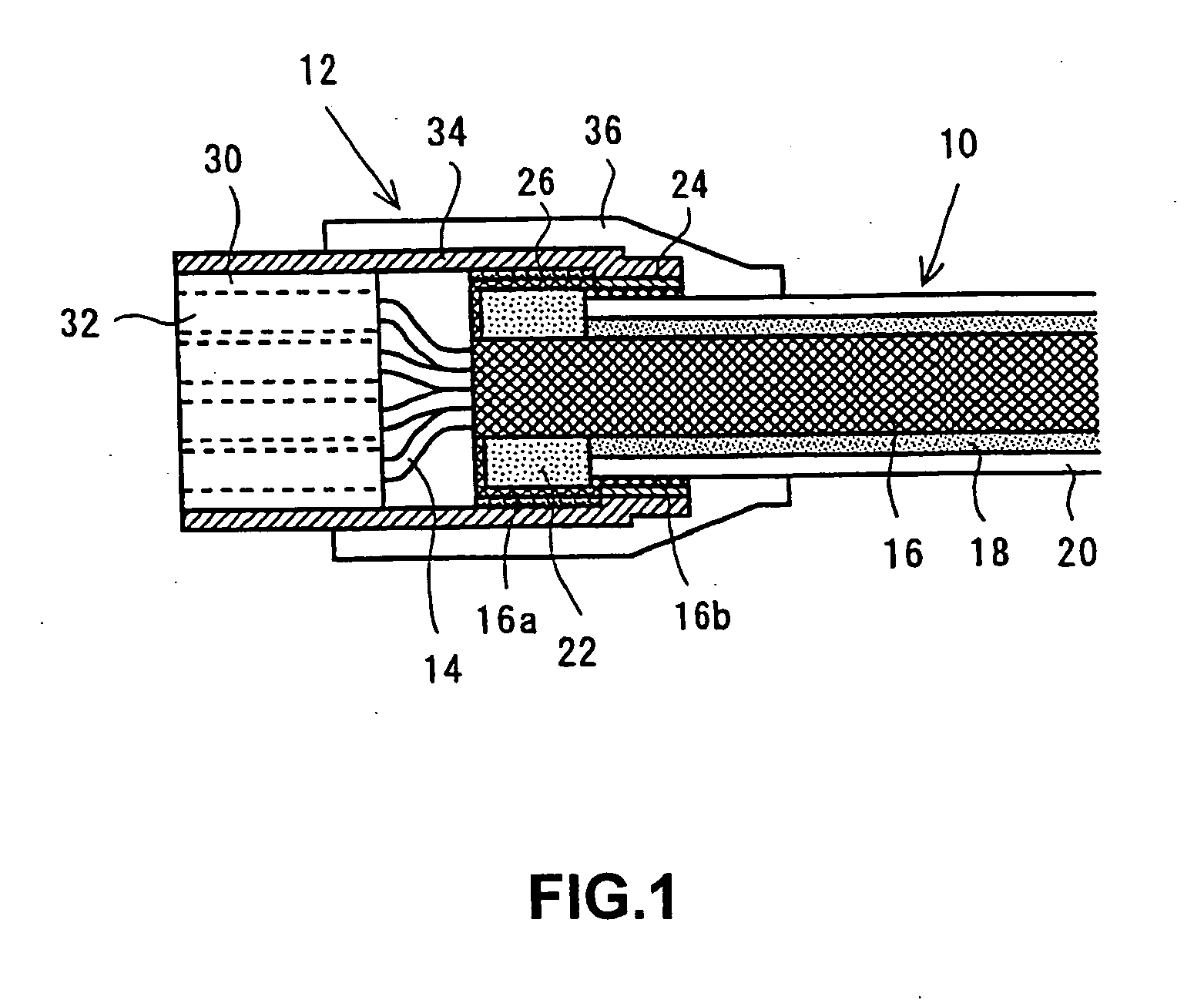
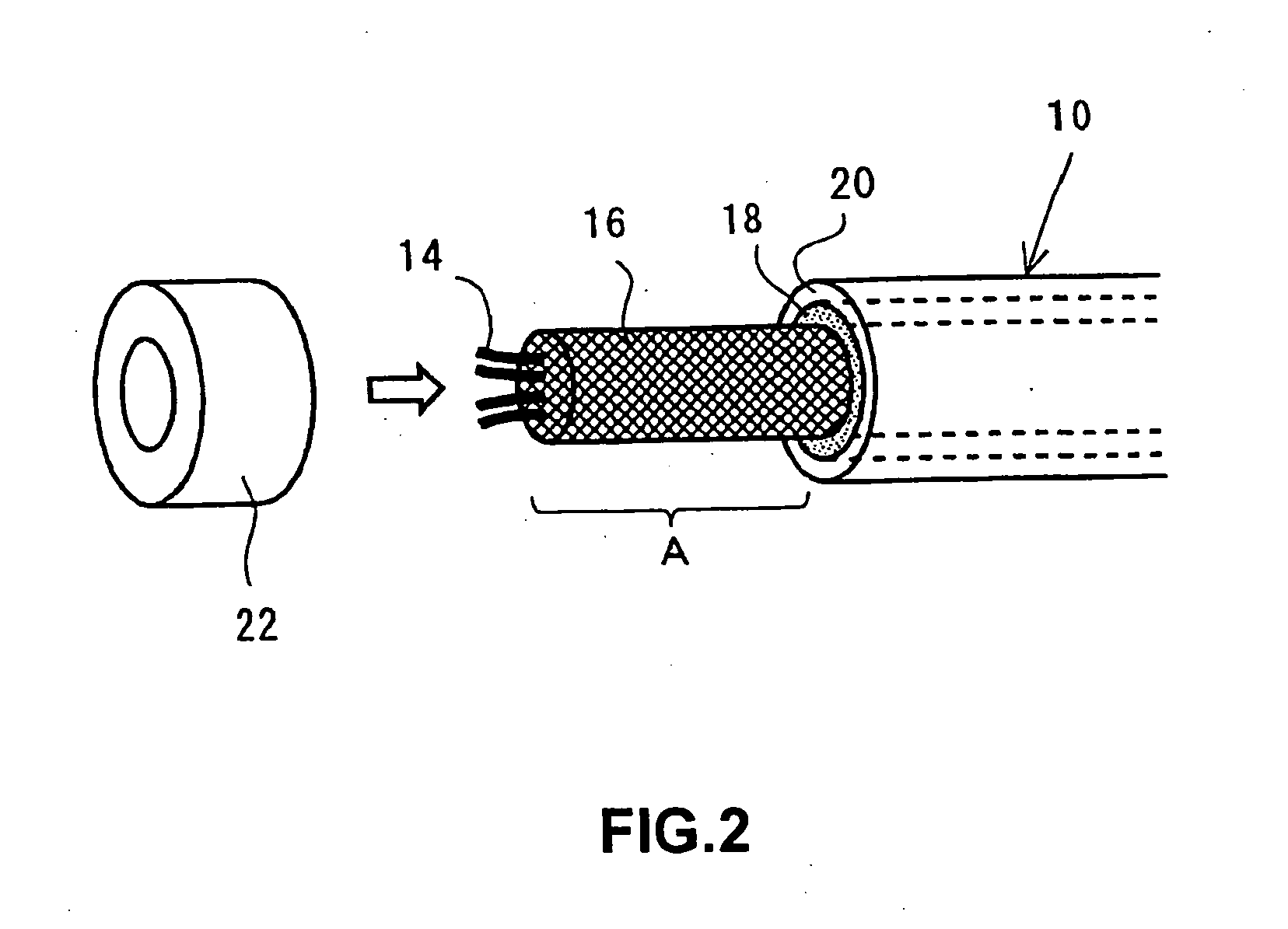
InactiveUS20050133245A1Sufficient common mode current suppression effectAppearance without damageElectrically conductive connectionsCoupling for high frequencyMagnetic coreMagnetic powder
Provided is a signal transmission cable with a connector, including: a shielded cable having a shielding layer and an insulating coating layer, which cover a periphery of a plurality of insulated wires, and a magnetic powder compound layer interposed between the shielding layer and the insulating coating layer; a connector which is electrically and mechanically connected to at least one end of the shielded cable, and which has a shielding metal cover extending from a housing part to a cable end, the housing part holding terminals to be connected to the insulated wires; and a closed magnetic path core which is fitted on a separated part of the insulating coating layer at the end of the shielded cable. The shielding layer is folded back so as to cover outside of the closed magnetic path core, an insulating tape is wound around the shielding layer in a peripheral portion of the closed magnetic path core, and a tip portion of the shielding layer is connected to the shielding metal cover in a state where the closed magnetic path core is housed in the shielding metal cover. Thus, a coil of one turn is formed.
Owner:FDK CORP
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20060035114A1High density recording performanceImprove reliability and durabilityMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageParticulatesHigh density
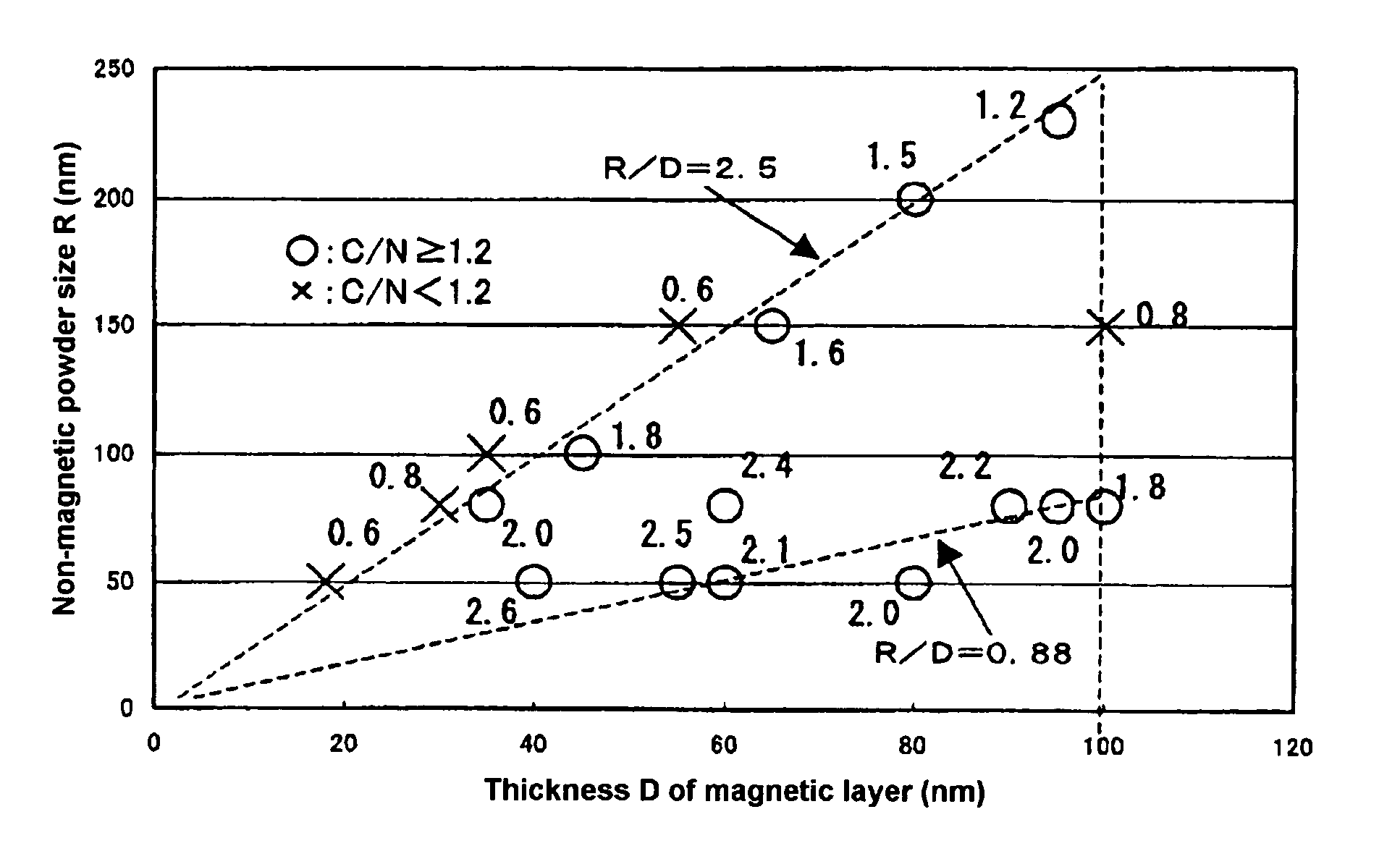
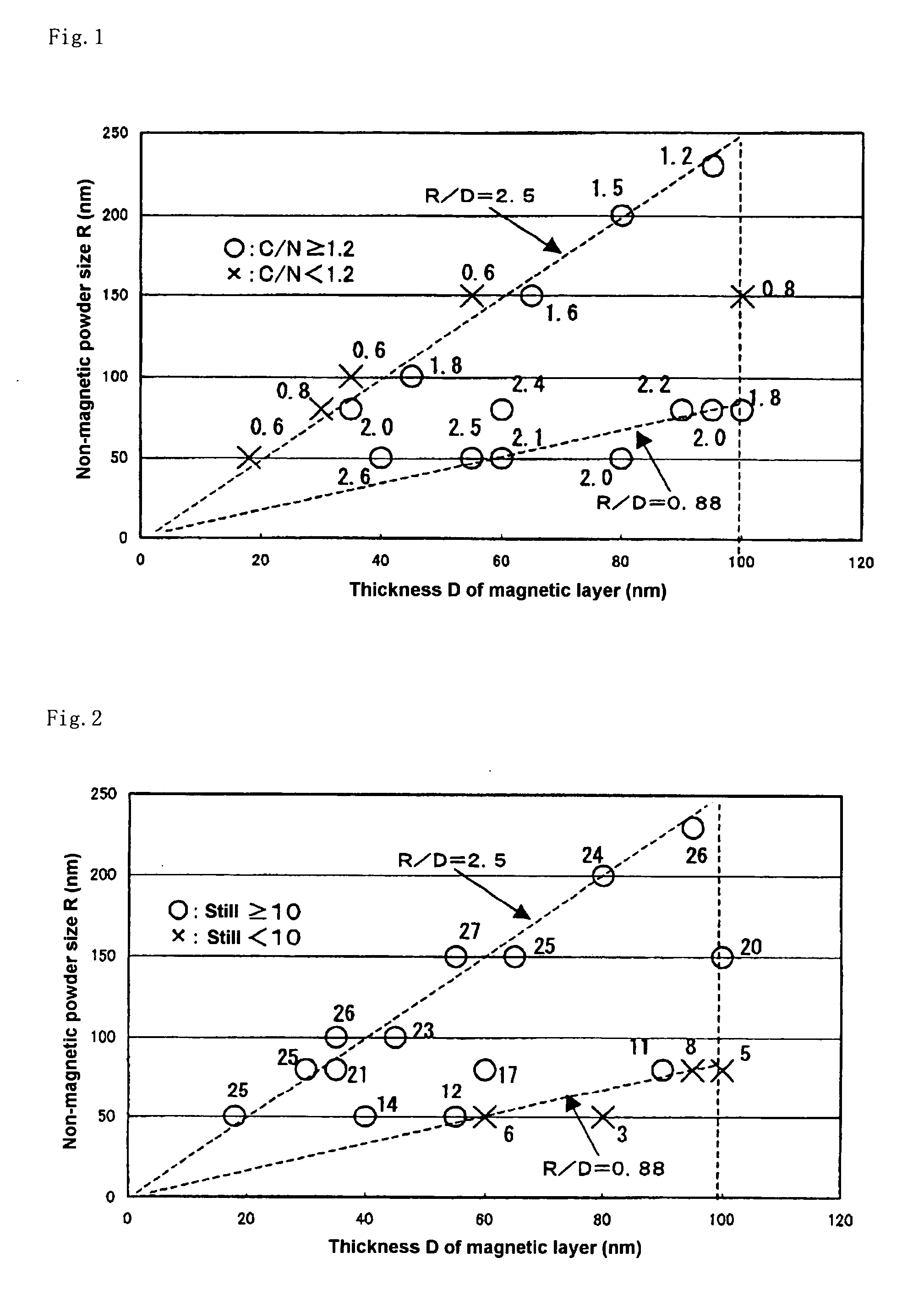
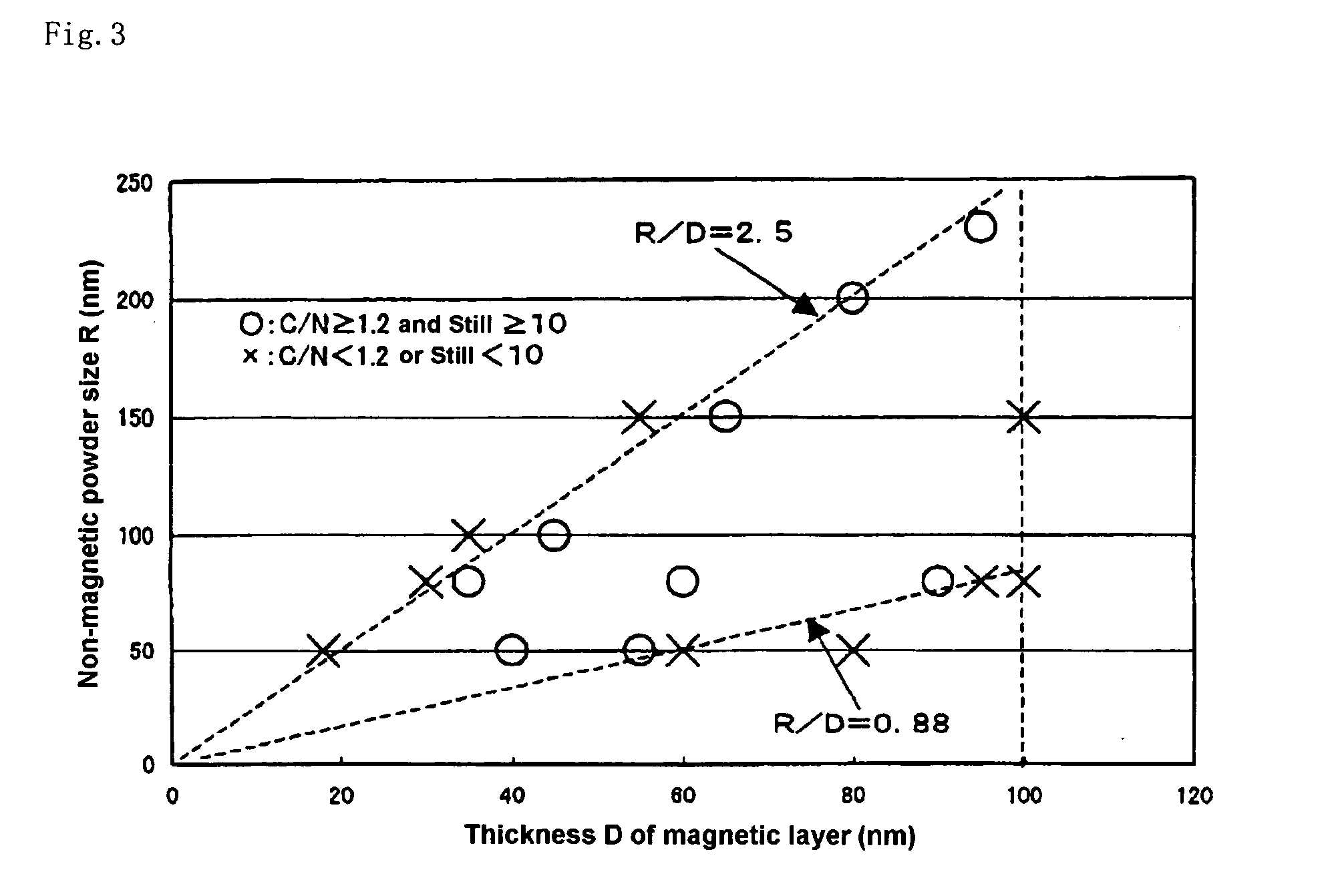
A magnetic recording medium with excellent high density recording performances and good durability comprising a non-magnetic substrate, a non-magnetic layer containing a non-magnetic powder and a binder formed on the non-magnetic substrate, and a magnetic layer having a thickness of less than 100 nm and containing a substantially particulate non-magnetic powder, a substantially particulate magnetic powder having an average particle size of less than 25 nm, and a binder, wherein an average particle size R of the non-magnetic powder contained in the magnetic layer and a thickness D of the magnetic powder satisfy the following relationship: 0.88≦R / D≦2.5.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20100227201A1Excellent reproduction outputReduced particle noiseRecord information storageMagnetic recordingMagnetiteMagnetization
A magnetic recording medium having a nonmagnetic substrate, and a soft magnetic layer and a ferromagnetic layer having a thickness of 5 to 150 nm formed in this order on the nonmagnetic substrate, in which, the ferromagnetic layer contains a spherical, ellipsoidal or plate-form ferromagnetic powder and a binder, and has an axis of easy magnetization substantially in a perpendicular direction, and the soft magnetic layer contains a spherical or ellipsoidal magnetite soft magnetic powder having a particle size of 30 nm or less, a rate of variation in particle size of 20% or less and a saturation magnetization of 10 to 60 Am2 / kg, and a binder.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Magnetic recording media
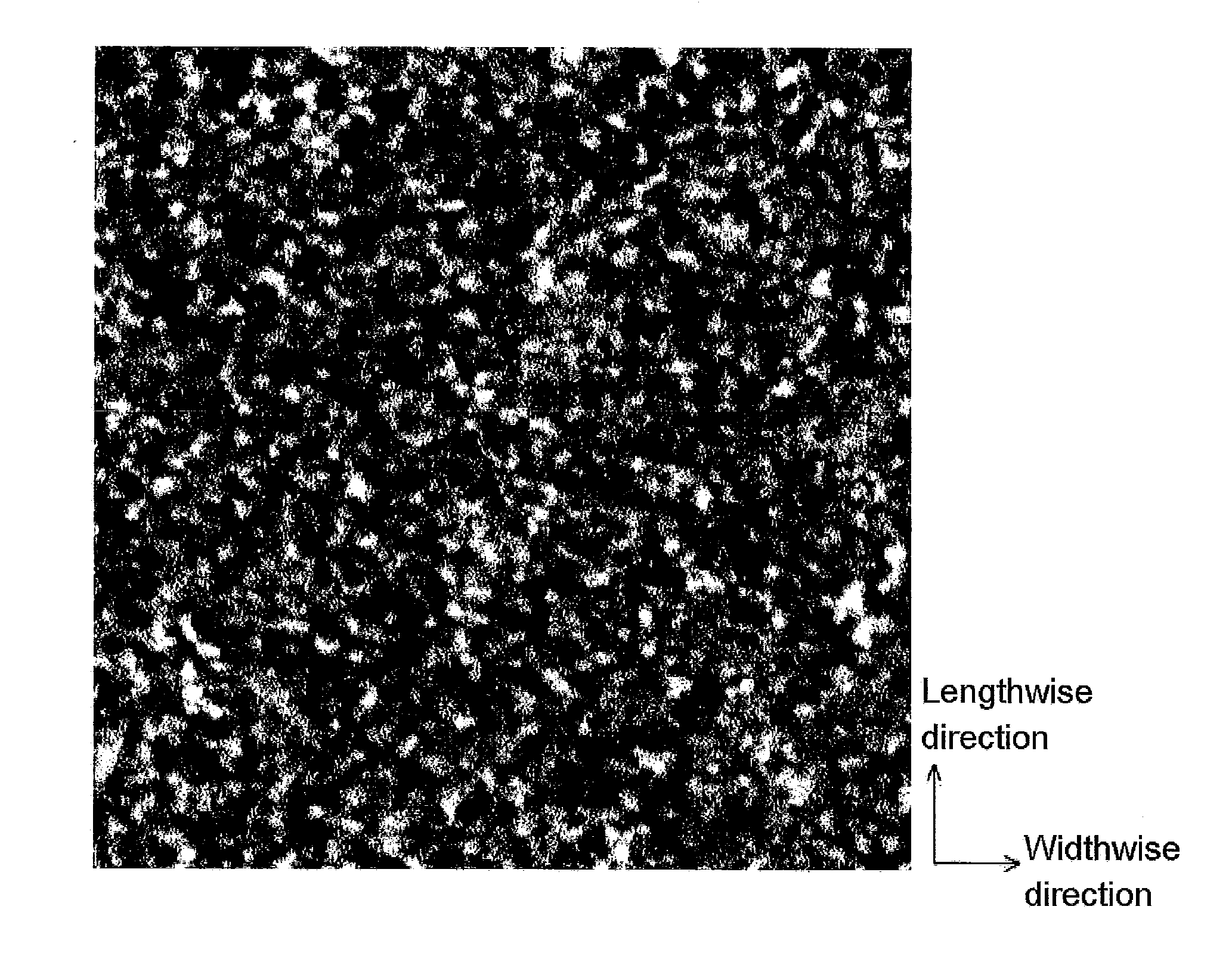
InactiveUS20110151281A1Medium noise is reducedSuitable for useRecord information storageMaterials with non-metallic substancesNon magneticMagnetic layer
A magnetic recording medium which has a non-magnetic substrate and a magnetic layer formed on the non-magnetic substrate, in which the magnetic layer contains magnetic powder with a particle size of 40 nm or less and a binder, an autocovariance length Ma of the magnetic layer in its lengthwise direction is 70 nm or less, an autocovariance length Mb of the magnetic layer in its widthwise direction is 80 nm or less, and a ratio Ma / Mb is from 0.80 to 1.20.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
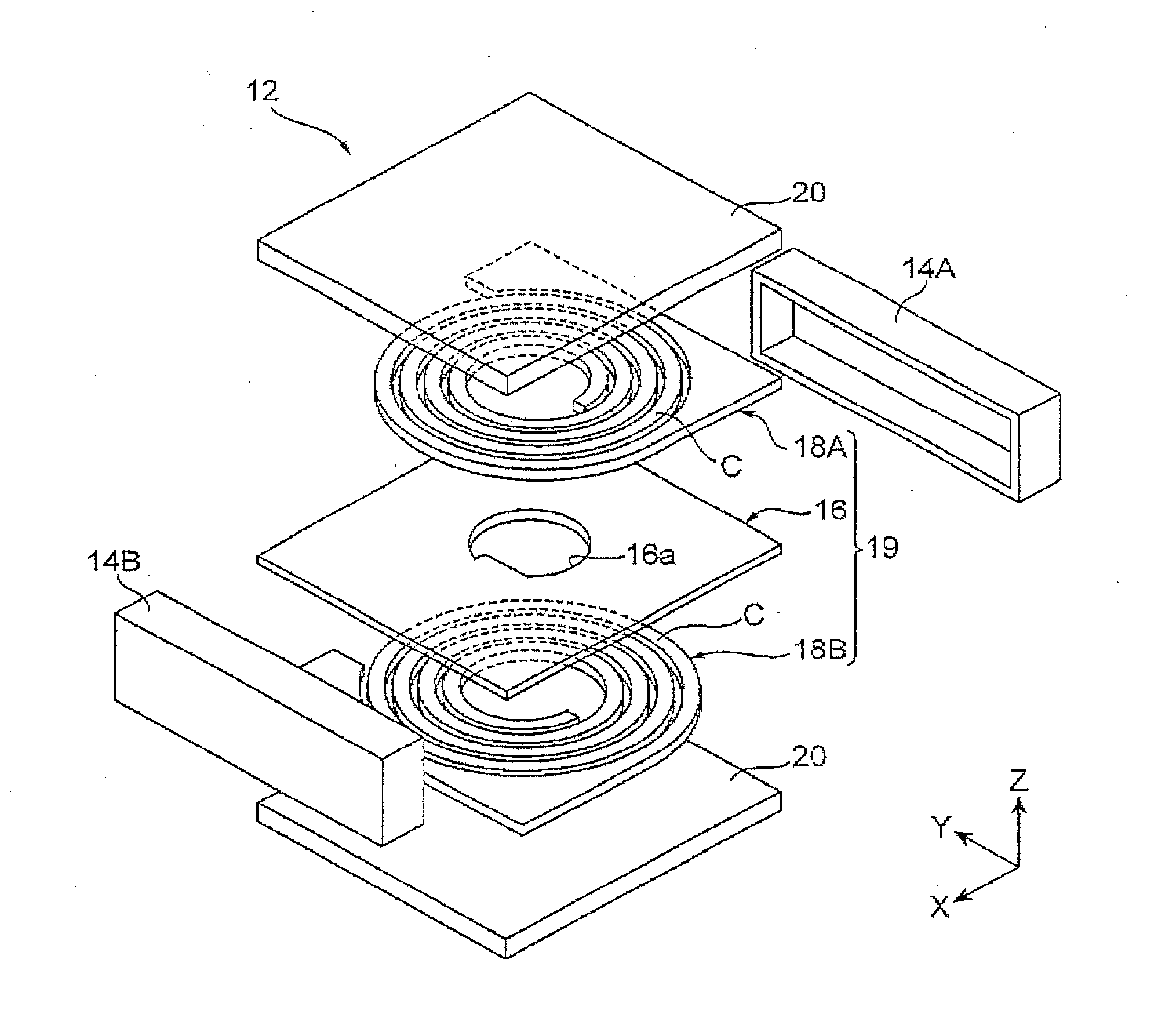
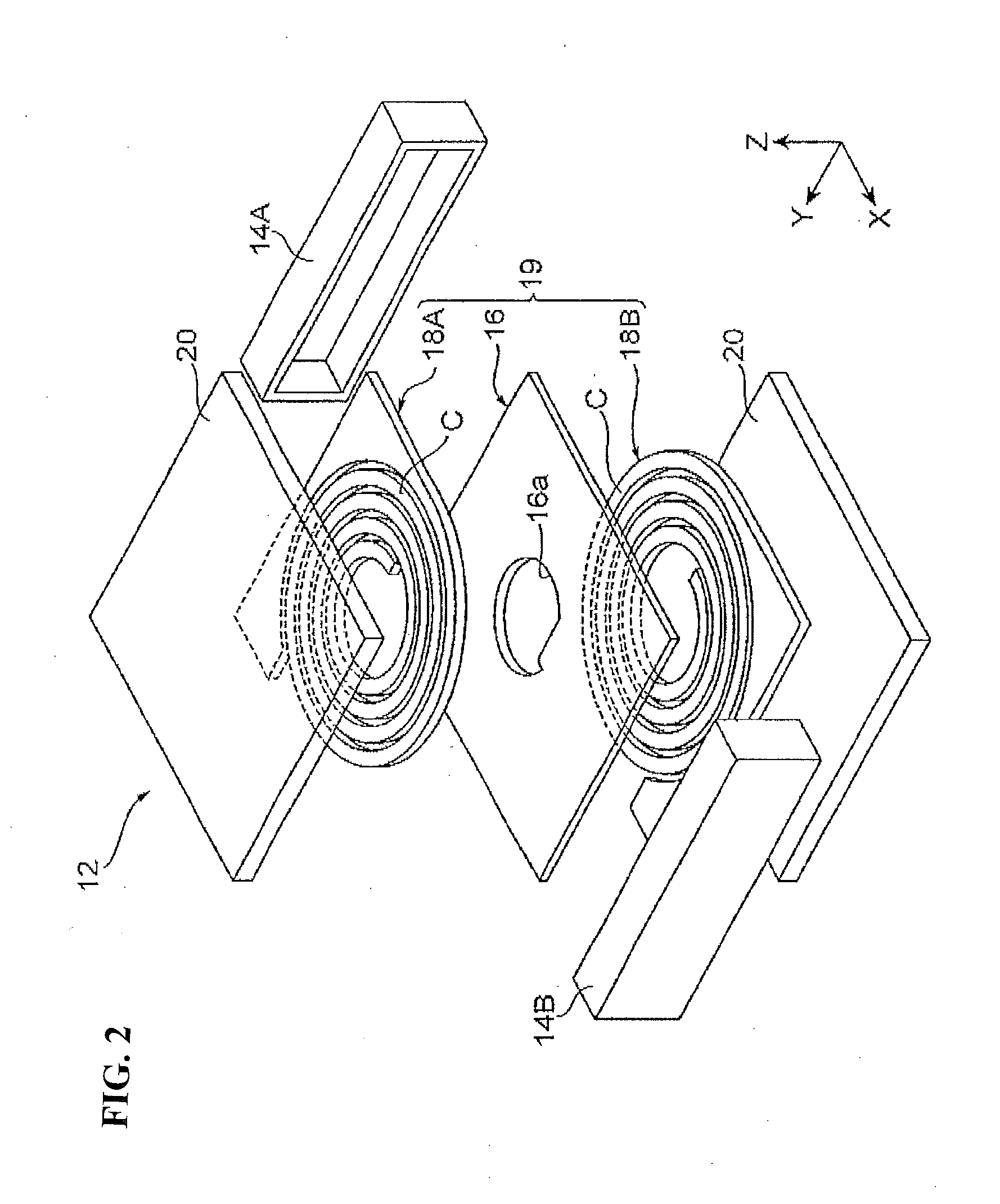
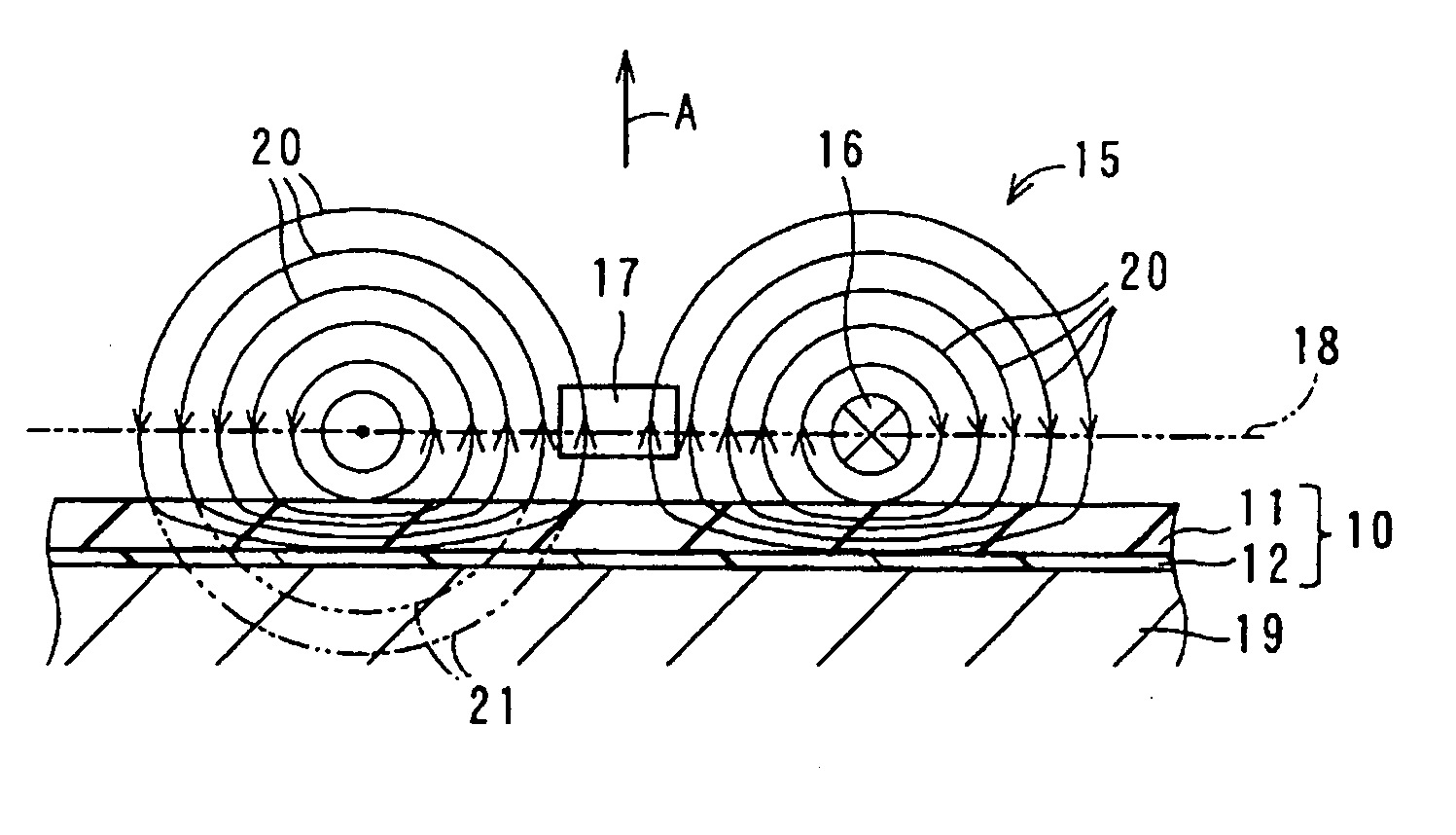
Planar coil element and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20130249664A1Easy to produceLow viscosityInorganic material magnetismTransformers/inductances detailsViscositySpherical form
In a planar coil element and a method for producing the same, a metal magnetic powder-containing resin containing an oblate or needle-like first metal magnetic powder contains a second metal magnetic powder having an average particle size (1 μm) smaller than that (32 μm) of the first metal magnetic powder, which significantly reduces the viscosity of the metal magnetic powder-containing resin. Therefore, the metal magnetic powder-containing resin is easy to handle when applied to enclose a coil unit, which makes it easy to produce the planar coil element.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
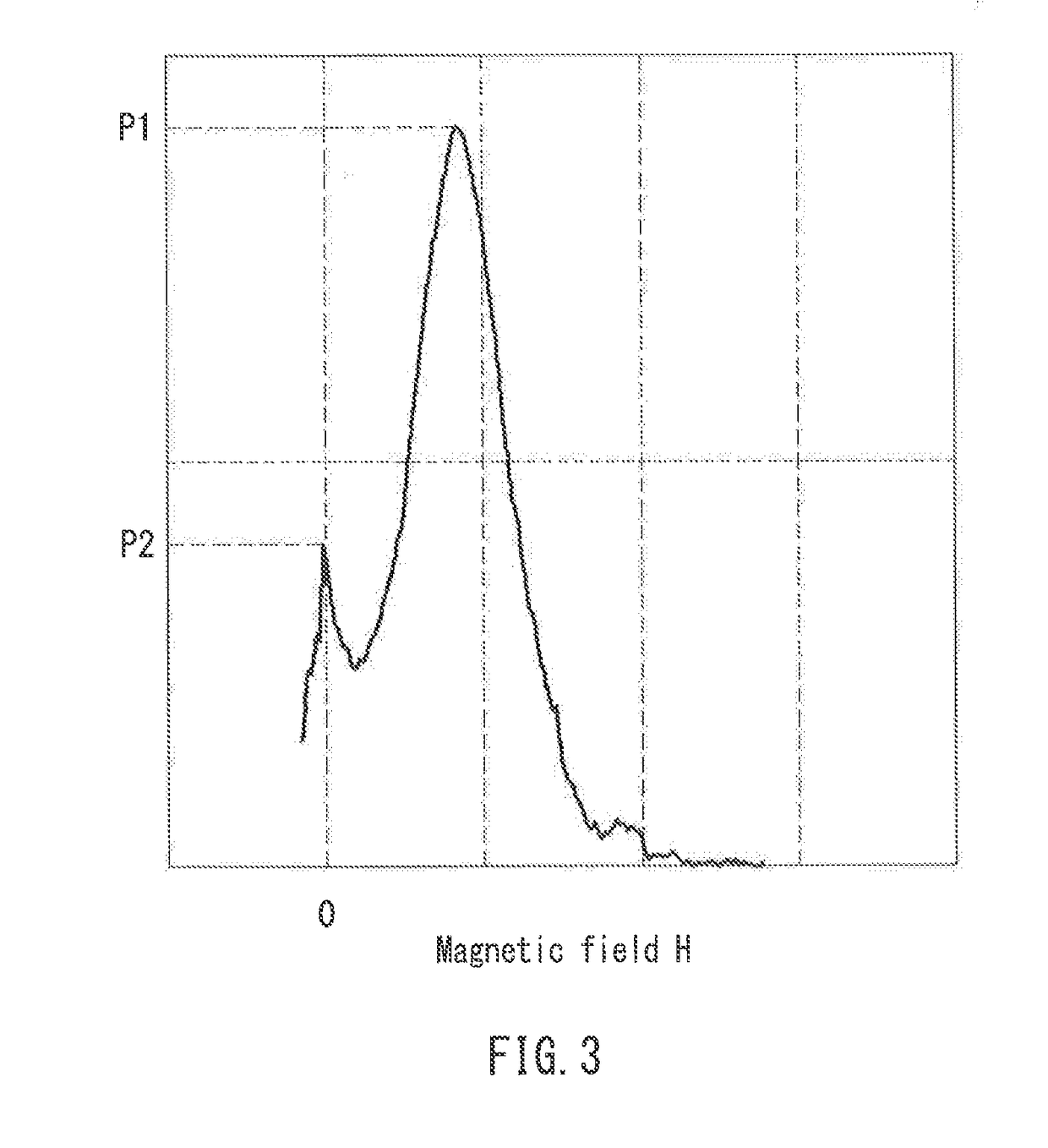
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20170221513A1Increased durabilityHigh outputProtective coatings for layersRecord information storageHysteresisNon magnetic
A magnetic recording medium of the present invention includes a non-magnetic substrate, and a magnetic layer containing a magnetic powder. The magnetic powder is constituted by an ε-iron oxide powder. The magnetic layer has a squareness in a thickness direction of 0.65 or more. In a differential curve obtained by differentiating a hysteresis curve in the thickness direction of the magnetic layer, two or more peaks are present. In a case where, out of peaks in the same direction among the above-described peaks, a local maximum of a largest peak in a magnetic field range of +500 oersted [Oe] or more is taken as P1 and a local maximum of a largest peak in a magnetic field range of −500 oersted [Oe] or more and less than +500 oersted [Oe] is taken as P2, a relationship below is satisfied:0.25≦P2 / P1≦0.60.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder for magnetic recording, method for producing hexagonal ferrite magnetic particles, and magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS9748026B2High coated film durabilityIncreased durabilityMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMaterials scienceMetal
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS6994925B2High outputRaise the ratioMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageNon magneticLength wave
To provide a magnetic recording medium which undergoes little effect of thermal fluctuation and provides a high short wavelength output and C / N ratio when reproduction is conducted using MR head, the magnetic recording medium includes a non-magnetic layer having a non-magnetic powder dispersed in a binder provided on a support and a magnetic layer having a ferromagnetic powder dispersed in a binder provided on the non-magnetic layer, wherein the ferromagnetic powder comprises a hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder having an average diameter of from 10 to 35 nm and a coercive force of from 135 to 400 kA / m; the magnetic layer has a coercive force of from 135 to 440 kA / m; and a product of an anisotropic magnetic field of the magnetic layer and an average particle volume of the hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder is from 1.2×106 to 2.4×106 kA / m·nm3.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Planar coil element
ActiveUS20130249662A1Improve permeabilitySmall particle sizeInorganic material magnetismTransformers/inductances detailsMetalMaterials science
In a planar coil element, the quantitative ratio of inclined particles to total particles of a first metal magnetic powder contained in a metal magnetic powder-containing resin provided in a through hole of a coil unit is higher than the quantitative ratio of inclined particles to total particles of the first metal magnetic powder contained in the metal magnetic powder-containing resin provided in other than the through hole, and many of particles of the first metal magnetic powder in the magnetic core are inclined particles whose major axes are inclined with respect to the thickness direction and the planar direction of a substrate. Therefore, the planar coil element has improved strength as compared to a planar coil element shown in FIG. 9A and has improved magnetic permeability as compared to a planar coil element shown in FIG. 9B.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic particle-based therapy
InactiveUS20060025713A1Reduce and decrease deleterious activityReduced activityEnergy modified materialsMedical devicesDiseaseHazardous substance
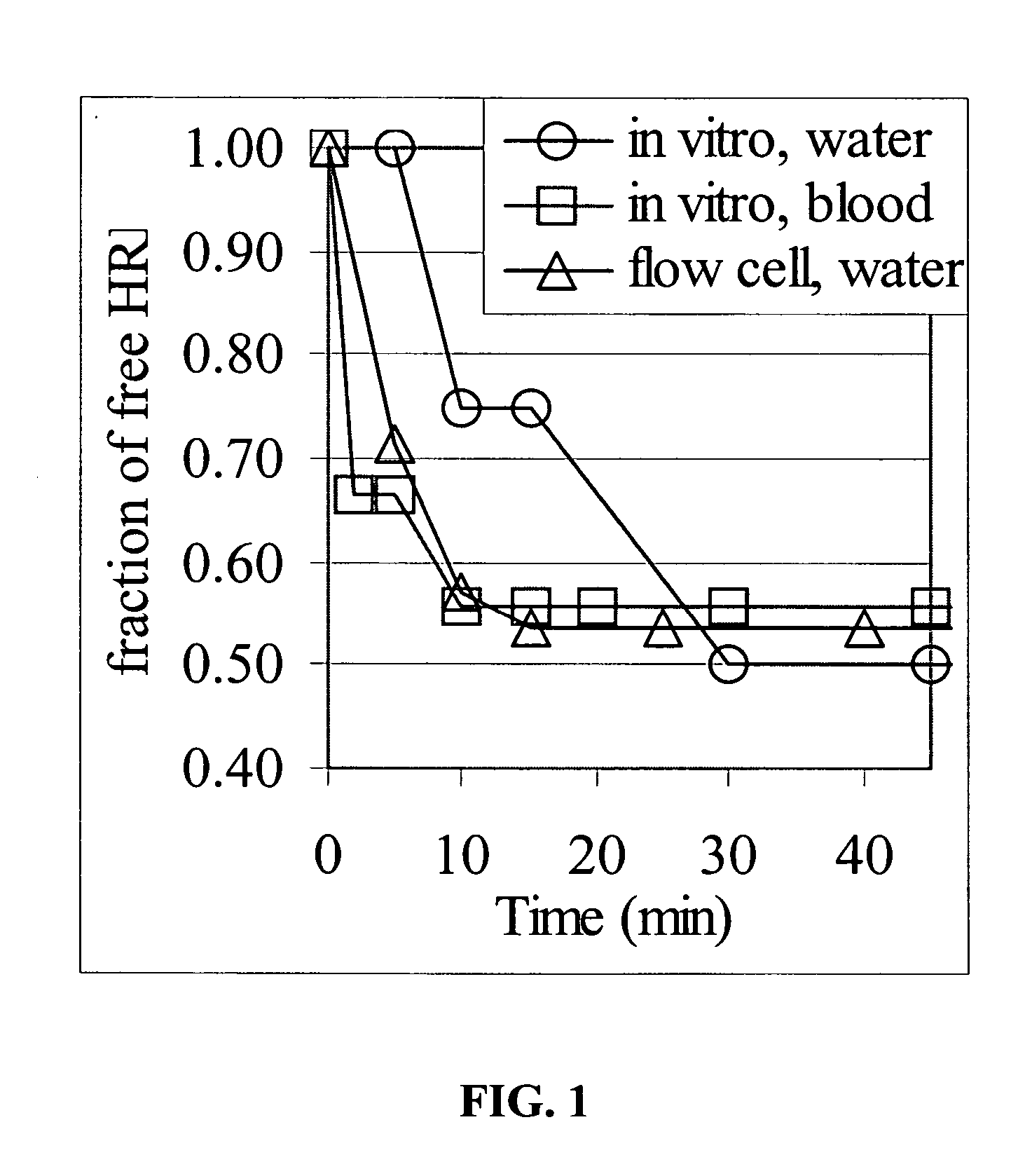
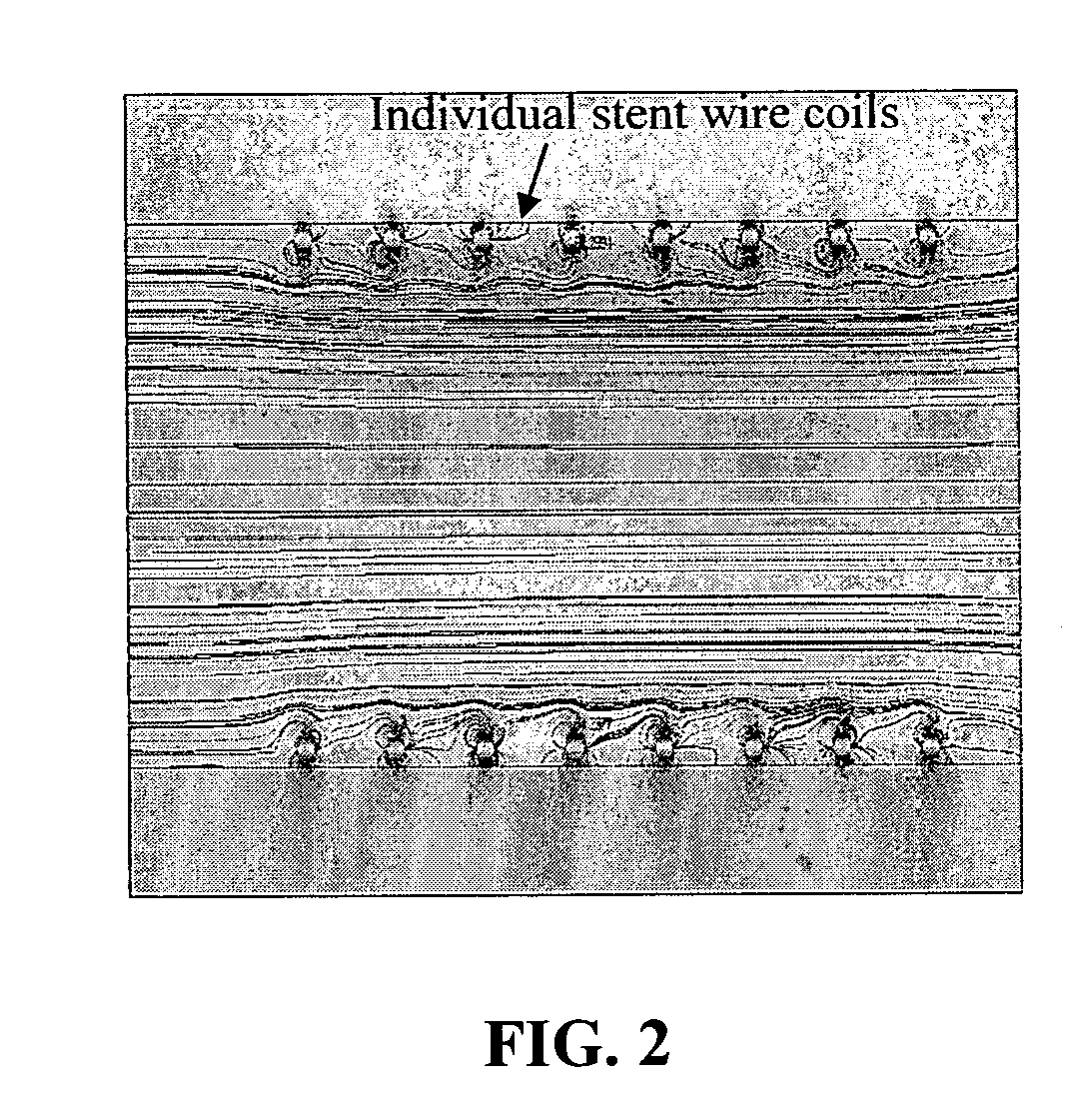
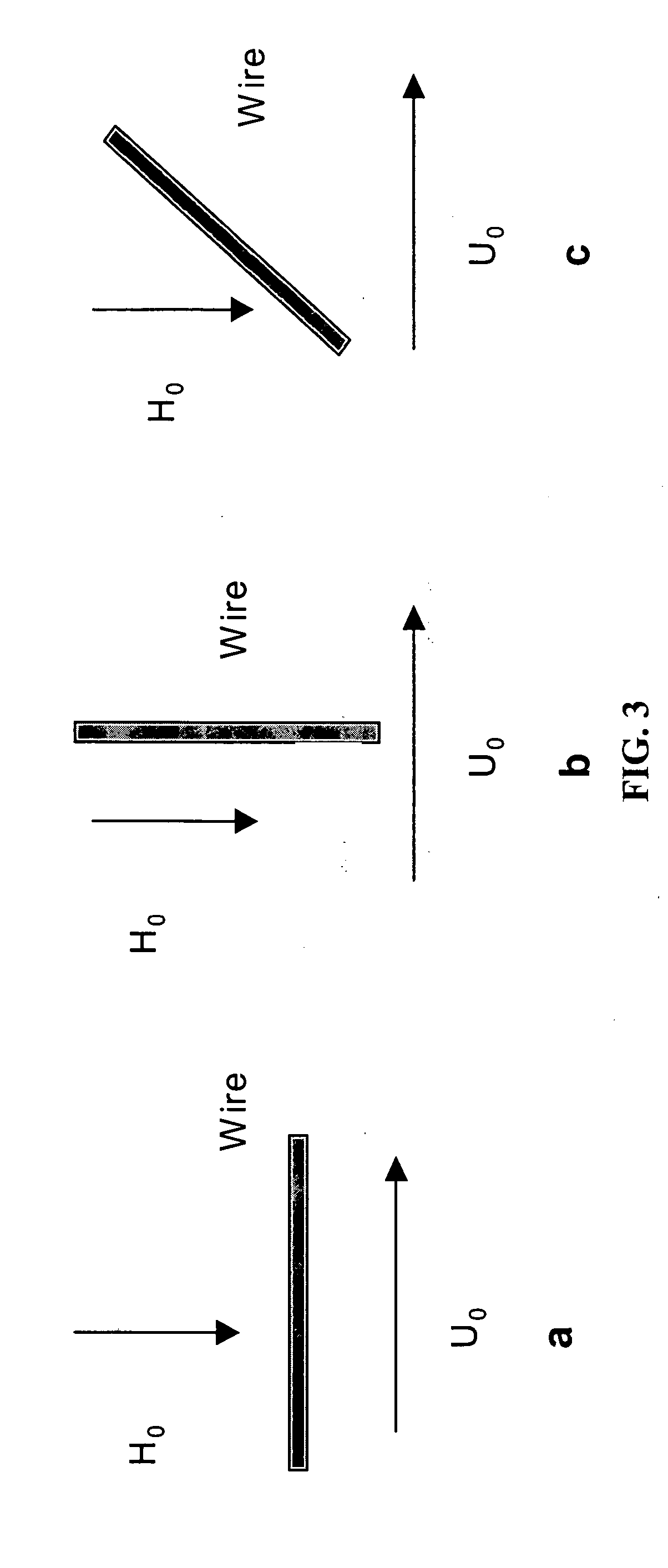
The invention provides materials and methods for the administration of an effectively magnetic medication or diagnostic reagent, or for the removal, sequestration, or effective conversion to a non-deleterious condition of a deleterious substance such as a toxin (e.g., biological, chemical, or radiological compound or composition) in vivo by administering a biocompatible magnetic particle to an organism in need, e.g., by delivery to the bloodstream, with the organism optionally having an internal magnetizable stent or magnetizable seed. The materials and methods are useful in the diagnosis and treatment of a variety of acute and chronic diseases, disorders and conditions afflicting man and other organisms, as well as for the removal of a variety of deleterious substances, including toxins, with the optional aid of an external magnetic generator and an optional magnetic filtration device.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Method for preparing magnetic filling with biological affinity, hydrophilicity and activity for water treatment
InactiveCN1522972AEasy to grow and compactGood compatibilitySustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentInjection molding machineInjection moulding
The present invention relates to a preparation method of biological affinity hydrophilic active magnetic seed filling material for treating water. It is characterized by that said method includes the following steps: mixing biological affinity substance, hydrophilic substance, magnetic powder and active carbon or magnetic powder and calcium carbonate in the high-molecular base material, and adding dispersion lubricating agent, uniformly stirring them, placing them into injection moulding machine, utilizing filling mould to make extrusion moulding and magnetizing, so as to obtain the invented filling material. It has biological affinity and hydrophilicity, at the same time can induce microbial activity and enzyme activity, and can raise oxygen utilization rate in water and water treatment efficiency.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Broad band antenna
InactiveUS20080055178A1Big decrease in gainRadiating elements structural formsElongated active element feedPolymer resinBroadband
A broad band antenna including: a body formed of a material having a relative permittivity of 2 to 20, a relative permeability of 1 to 10, and a magnetic loss tangent of 0.001 to 0.2, at a usable frequency; and at least one radiator disposed on the body. The material forming the body may be a composite material formed of a polymer resin mixed with a magnetic powder. The composite material may contain the magnetic powder by 90 wt % with respect to a total weight.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
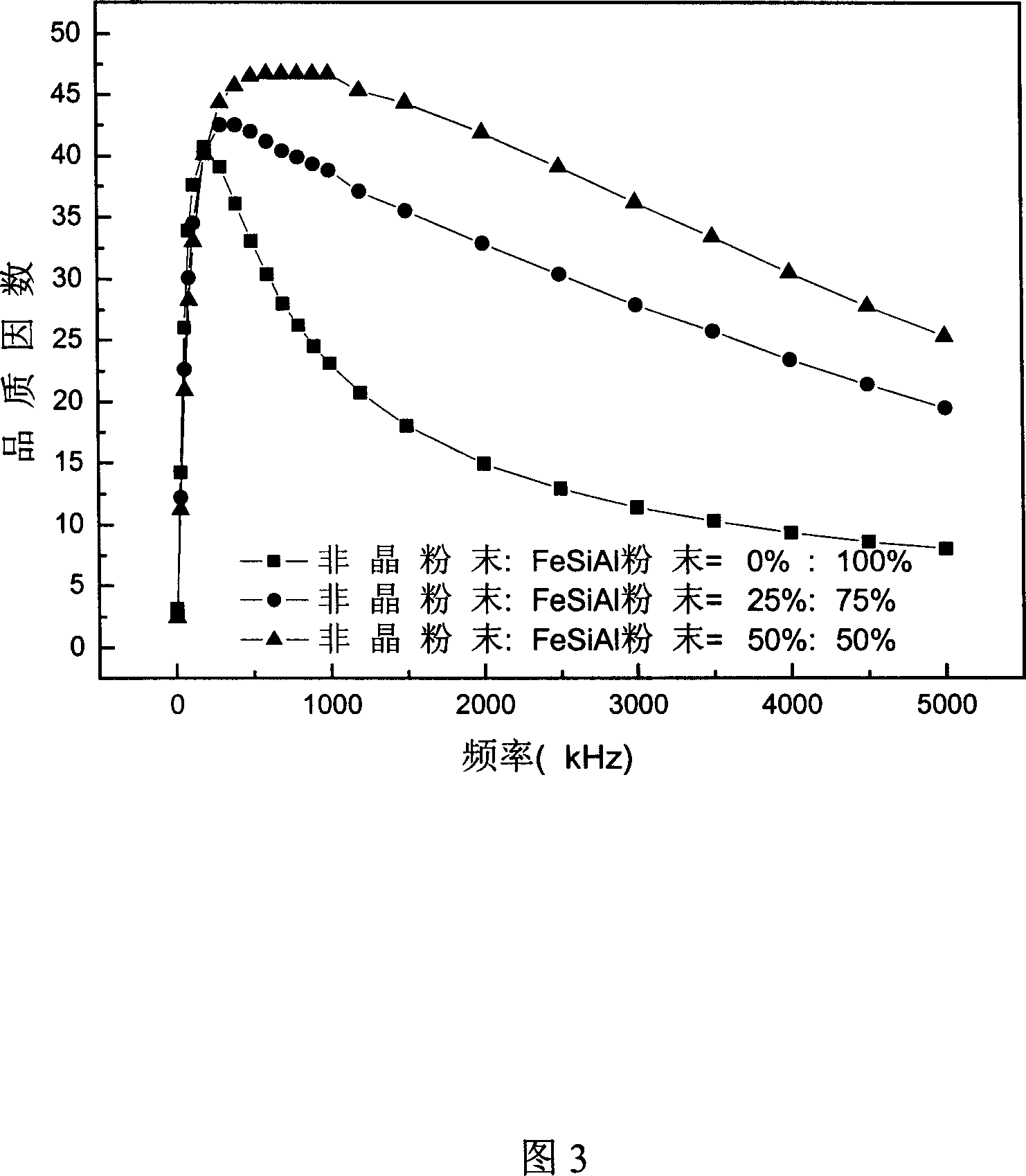
Composite powder, magnetic powder core for magnetic powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101118797AExcellent soft magnetic propertiesIncrease the amount of participationInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureAl powderIron powder
The present invention provides a magnetic powder core, composite powder used for the magnetic powder core, and a production method for the both. The composite powder is blended and formed by powder A and powder B, the content of which comprises 50-96wt percent of the powder A and 4-50wt percent of the powder B; wherein, the powder A is one out of iron powder, Fe-Si powder, Fe-Si-Al powder, Fe-based nanometer crystal powder, Fe-base amorphous powder, Fe-Ni powder and Fe-Ni-Mo powder; the powder B has different demand characteristics compared with the powder A and is selected from at least one out of iron powder, Fe-Si powder, Fe-Si-Al powder, Fe-based nanometer crystal powder, Fe-based amorphous powder, Fe-Ni powder and Fe-Ni-Mo powder. The powder B can be Fe-based soft magnetic amorphous powder as the insulating agent, which can reduce the wastage of magnetic powder core and make up for the declining magnetic conductivity of magnetic powder core caused by the traditional insulating agent. The excellent of soft magnetic properties of the insulating agent is utilized to improve frequency features of the magnetic powder core.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
Electromagnetic Interference Suppressor, Antenna Device and Electronic Information Transmitting Apparatus
InactiveUS20070252771A1High densitySuperior electromagnetic interference suppressing effectMagnetic/electric field screeningLayered productsElastomerVitrification
An electromagnetic interference suppressor of substantially unpressurized sheet form is obtained by applying and drying a magnetic paint, and comprises 30 to 80% by volume of soft magnetic powder and 20 to 70% by volume of a binder. The binder is an elastomer or a resin that a glass transition point and / or a softening point is 50° C. or more and a storage modulus (E′) is 107 Pa (JIS K 7244-1) or more in a state containing neither solvent nor filler at room temperature. This electromagnetic interference suppressor exerts a superior electromagnetic interference suppressing effect.
Owner:NITTA CORP
Method of preparing micro-structured powder for bonded magnets having high coercivity and magnet powder prepared by the same
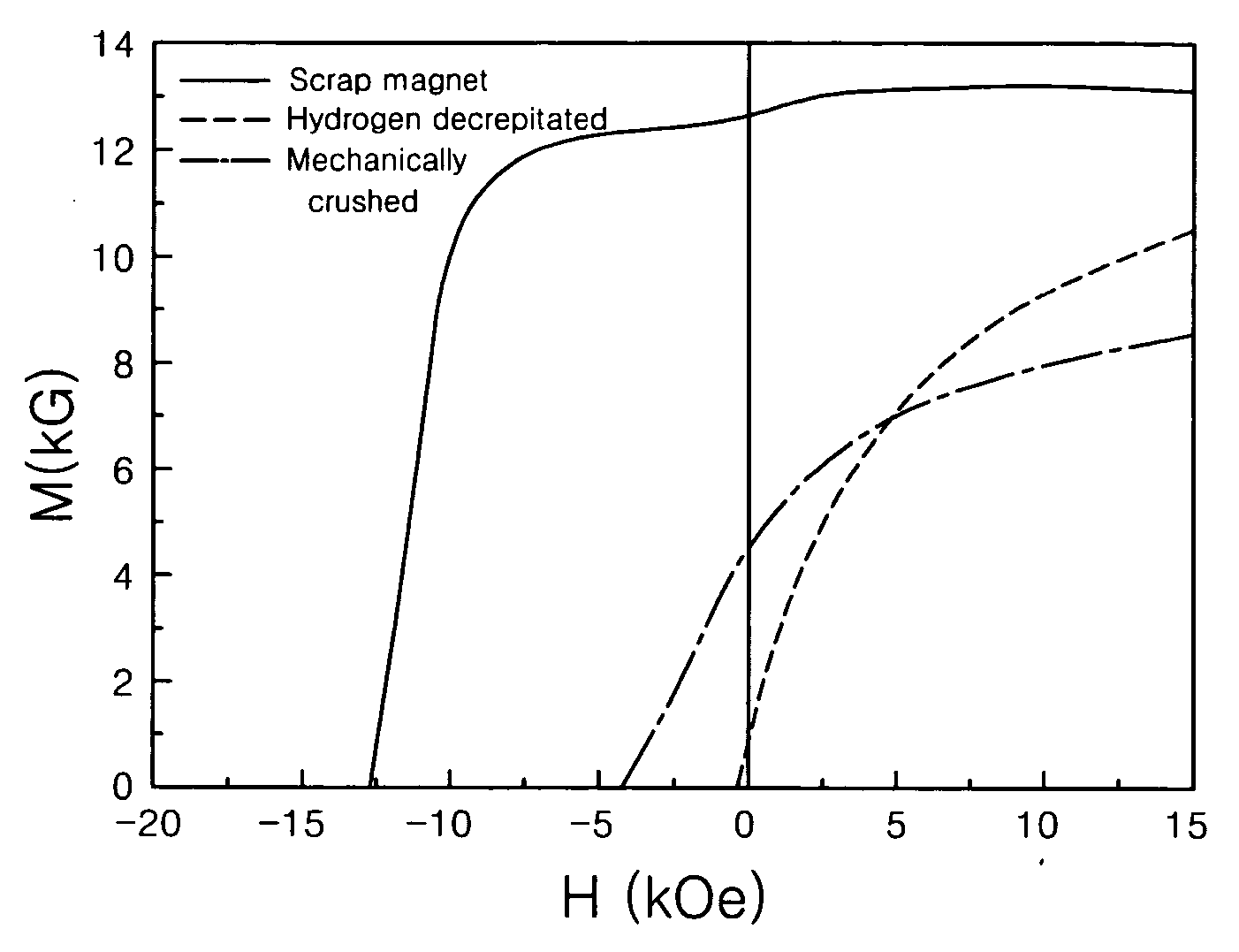
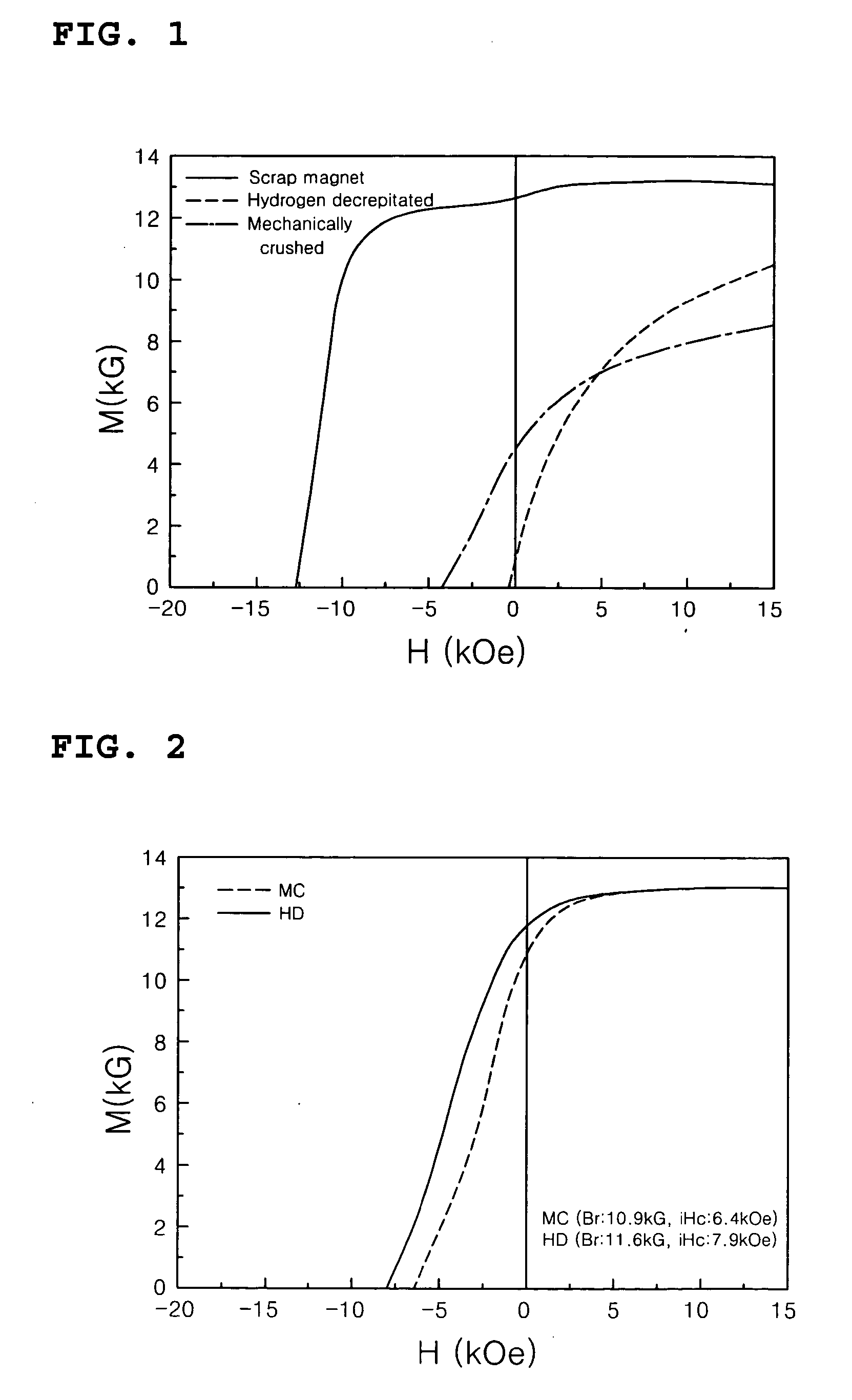
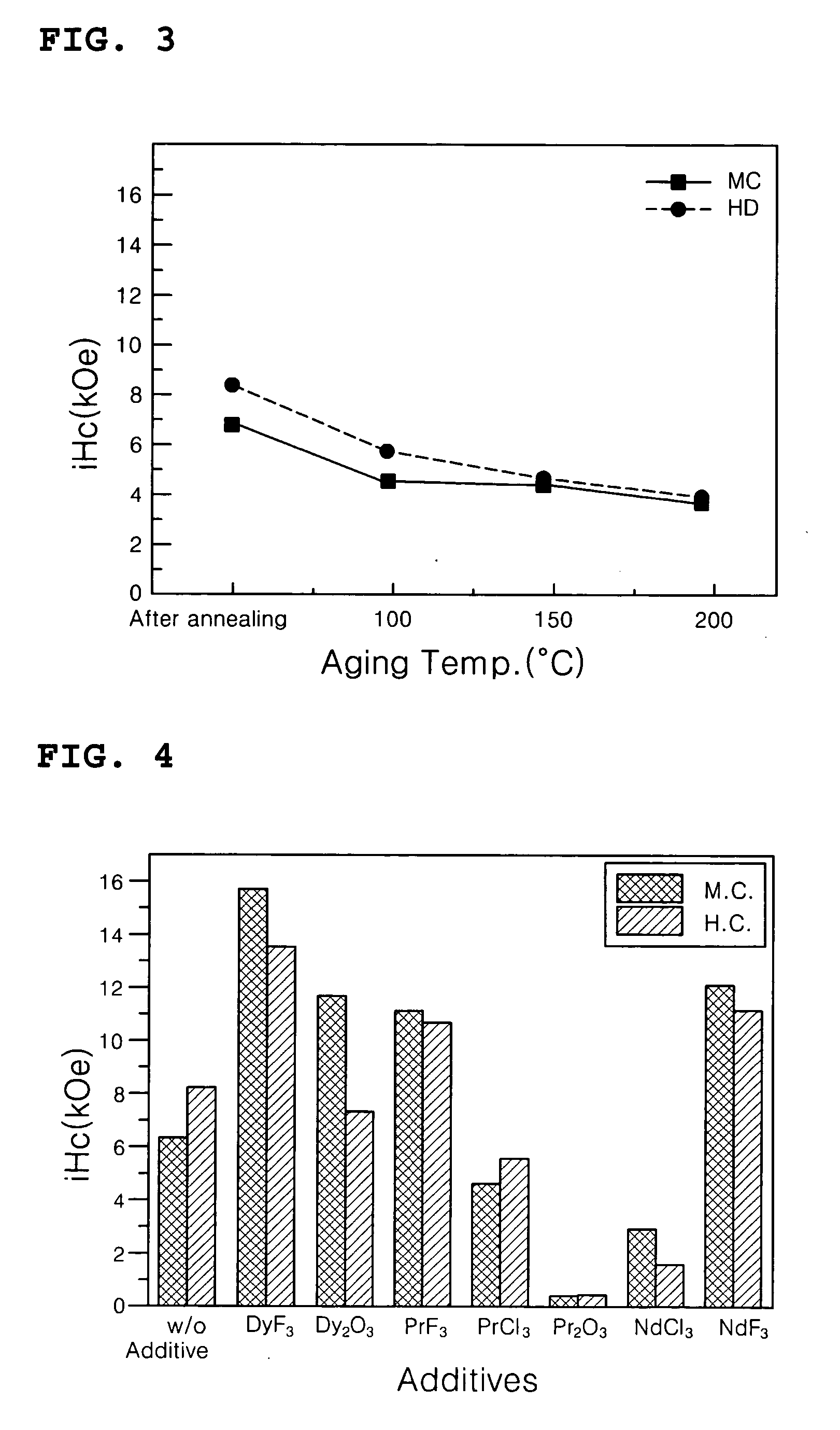
InactiveUS20050081959A1Reduce manufacturing costSimplified mass productionInorganic material magnetismRare earthGrain boundary
Disclosed is a method of preparing a micro-structured powder for bonded magnets having high coercivity, which is advantageous in terms of low preparation costs by recycling magnet scraps, simplified mass production, minimal environmental contamination by such a recycling process, and the preparation of stable anisotropic powders having high coercivity. Further, a magnet powder prepared by the above method is provided. The current method is characterized in that R—Fe—B type anisotropic sintered magnets or scraps thereof are crushed to prepare 50-500 μm sized magnet powders, which are then mixed with 1-10 wt % of rare earth fluoride (RF3) powders and thermally treated at high temperatures (500-1100° C.) in a vacuum or an inert gas, to cause the change of matrix-near surface and grain boundary of the powders. Thus obtained powders include a matrix phase having R2Fe14B crystal structure, a R-rich grain boundary phase containing rare earth fluoride, and other phases, in which the matrix phase has an average grain size of 1-20 μm, and the powders have an average size of 50-500 μm with superior magnetic characteristics of (BH)max≧20 MGOe and iHc≧5 kOe.
Owner:JAHWA ELECTRONICS
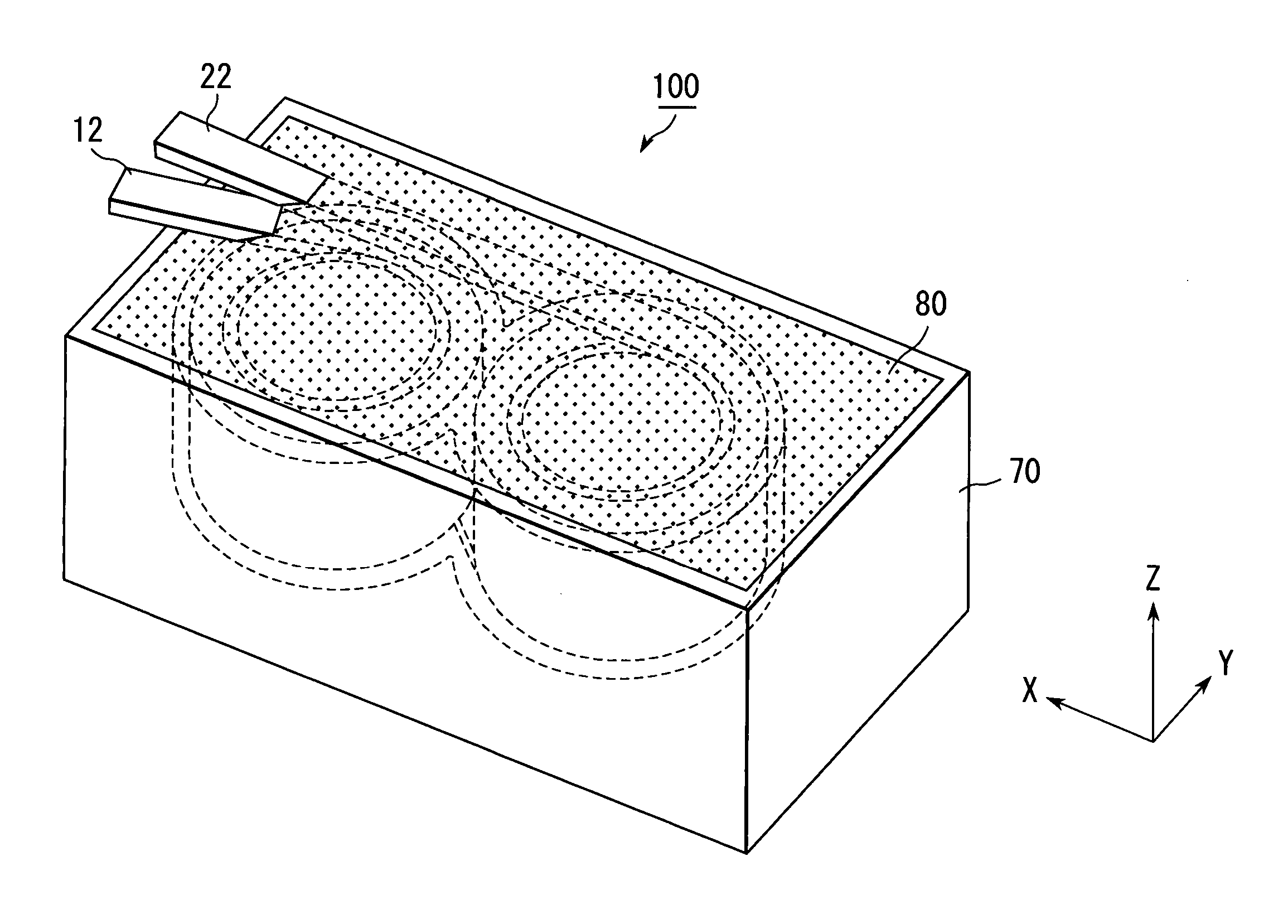
Coil component and fabricaiton method of the same
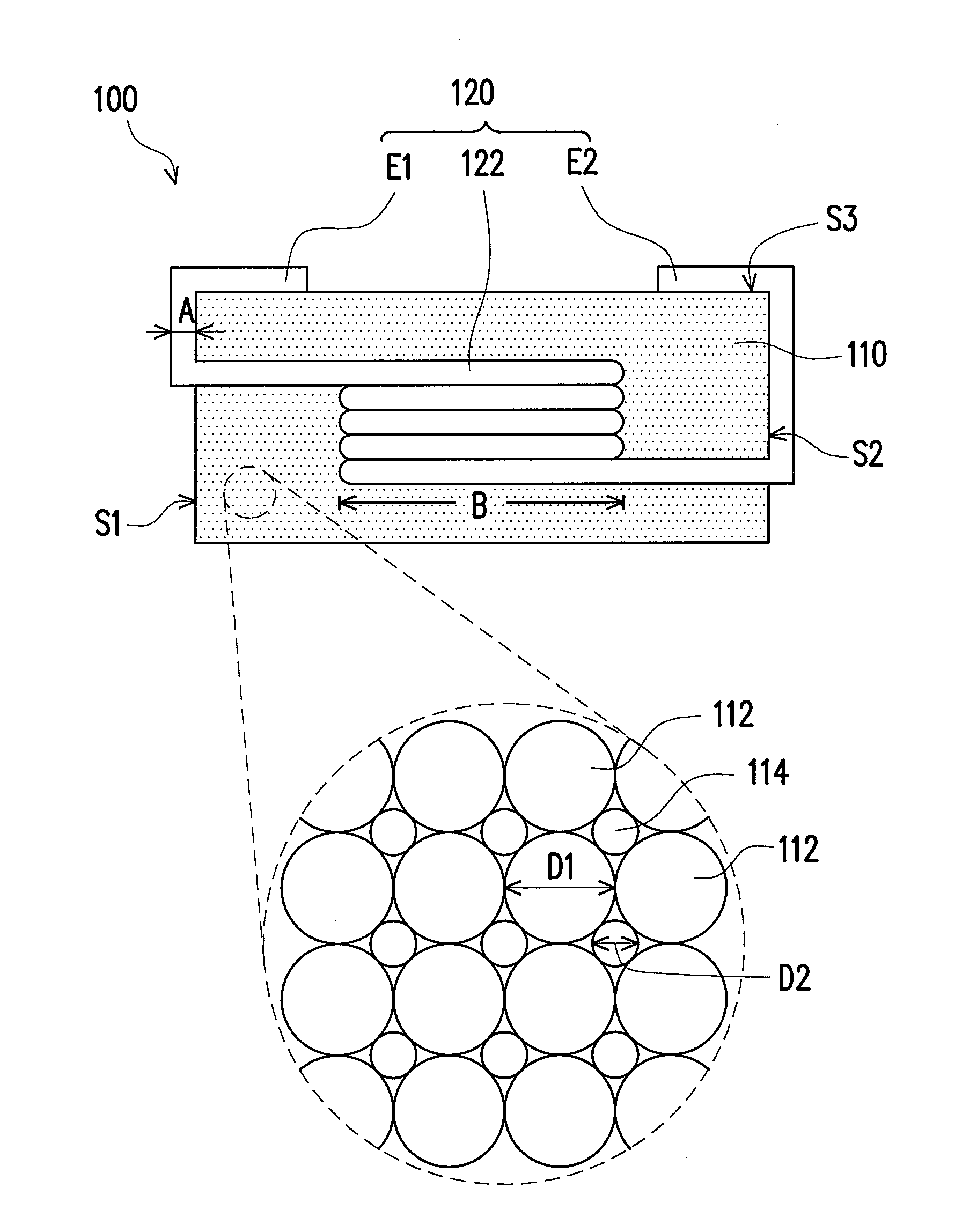
ActiveUS20050012581A1Suppress whineTransformers/inductances casingsInorganic material magnetismEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A coil component (100) comprises a coil-containing insulator enclosure and a magnetic core (80). The coil-containing insulator enclosure can be obtained by enclosing a coil (30), except for end portions (12, 22) of the coil (30), with an insulator (50), wherein the insulator (50) comprises at least first resin. The magnetic core (80) is made of a mixture of a second resin (82) and powder, which comprises at least magnetic powder (84). The coil-containing insulator enclosure is embedded in the magnetic core (80).
Owner:DENSO CORP 50 INTEREST +2
Surface-mounting coil component and method of producing the same
ActiveUS7209022B2Low costReduced durabilityTransformers/inductances casingsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsShear modulusSurface mounting
A surface-mounting choke coil has a resin coating material with magnetic powder which is filled a space between the upper flange and the lower flange of a drum-type ferrite core, while covering the circumferential of the winding. The resin coating material with magnetic powder has a glass transition temperature Tg of about −20° C. or lower, more preferably about −50° C. or lower in a course of transferring from a glass state to a rubber state during changing of shear modulus with respect to temperature as a physical property when hardening, and the thickness of the upper flange of the drum-type ferrite core is about 0.35 mm or less, and a value of a ratio L2 / L1 of an outer diameter L2 of the upper flange to a diameter L1 of the winding core of the drum-type ferrite core is about 1.9 or more.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
Inductor
InactiveUS20060214759A1Increase inductanceIncreasing the thicknessTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureElectrical conductorInsulation layer
An inductor that can be mounted on a flexible substrate and which also can be used in large-current signal lines or power lines. The inductor has a film-type coil formed by providing, in order, a heat-resistant resin film, a flexible conductor coil and insulation layer for covering the conductor coil. A compound magnet that combines magnetic powder and resin is disposed on one or both sides of the film-type coil, with the heat-resistant resin film, the insulation layer and the compound magnetic body being at least flexible.
Owner:SUMIDA CORP
Inorganic insulating adhesive for soft magentic metal powder core andits prepn process
InactiveCN101089108AInsulation hasNo generationInorganic material magnetismInorganic adhesivesAdhesiveOrganic matter
The present invention provides one kind of inorganic insulating adhesive for soft magnetic metal powder core. The inorganic insulating adhesive consists of SiO2, Al2O3, ZrO2, mica powder and water mixed together, and possesses both insulating and adhering functions. The present invention also provides the method of using the inorganic insulating adhesive in preparing soft magnetic metal powder core. Using the inorganic insulating adhesive can result in high magnetic performance of the magnetic metal powder core and enhanced mechanical strength, and the soft magnetic powder core without organic matter contained has no ageing and performance degradation caused by heat.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
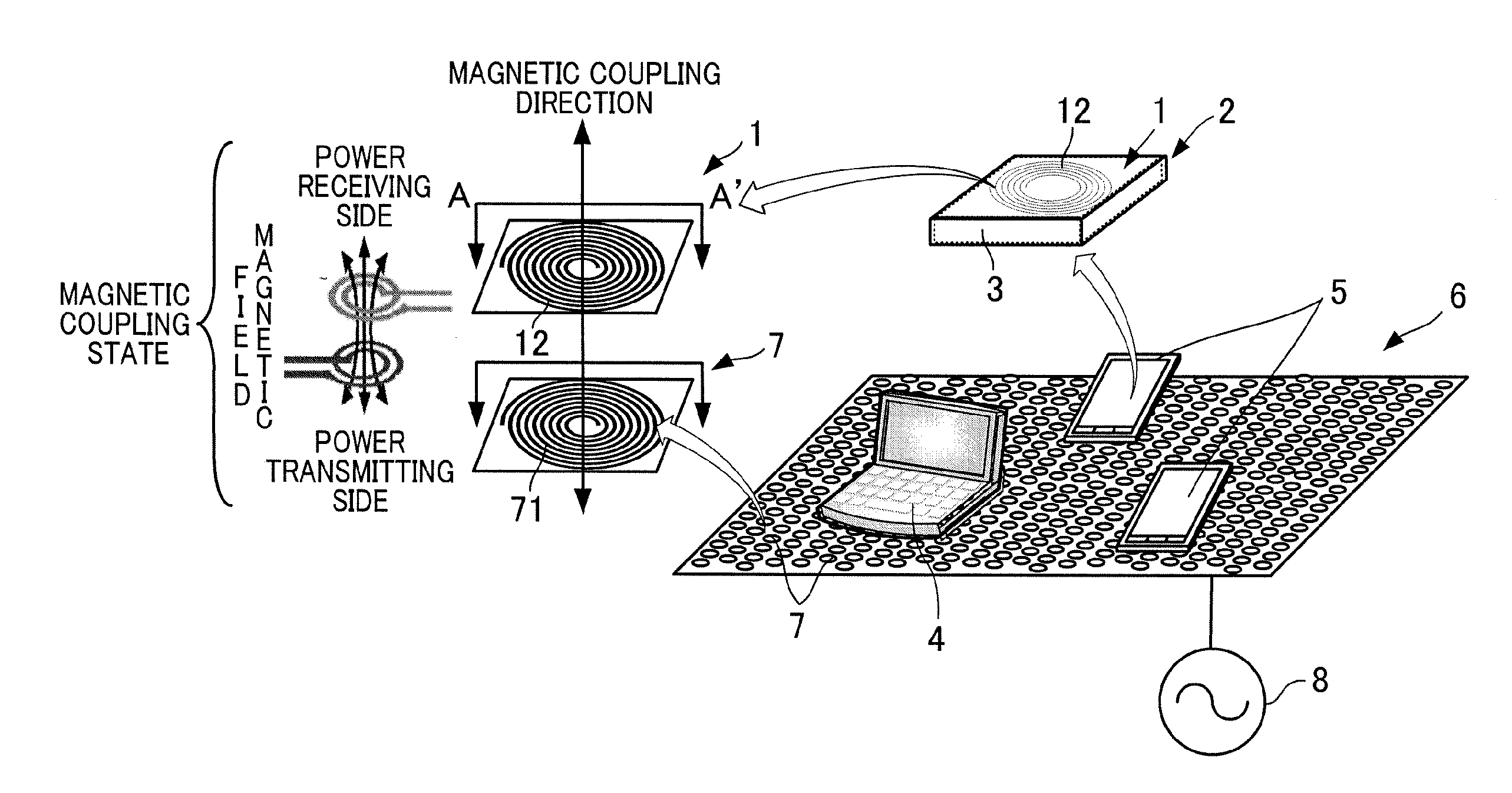
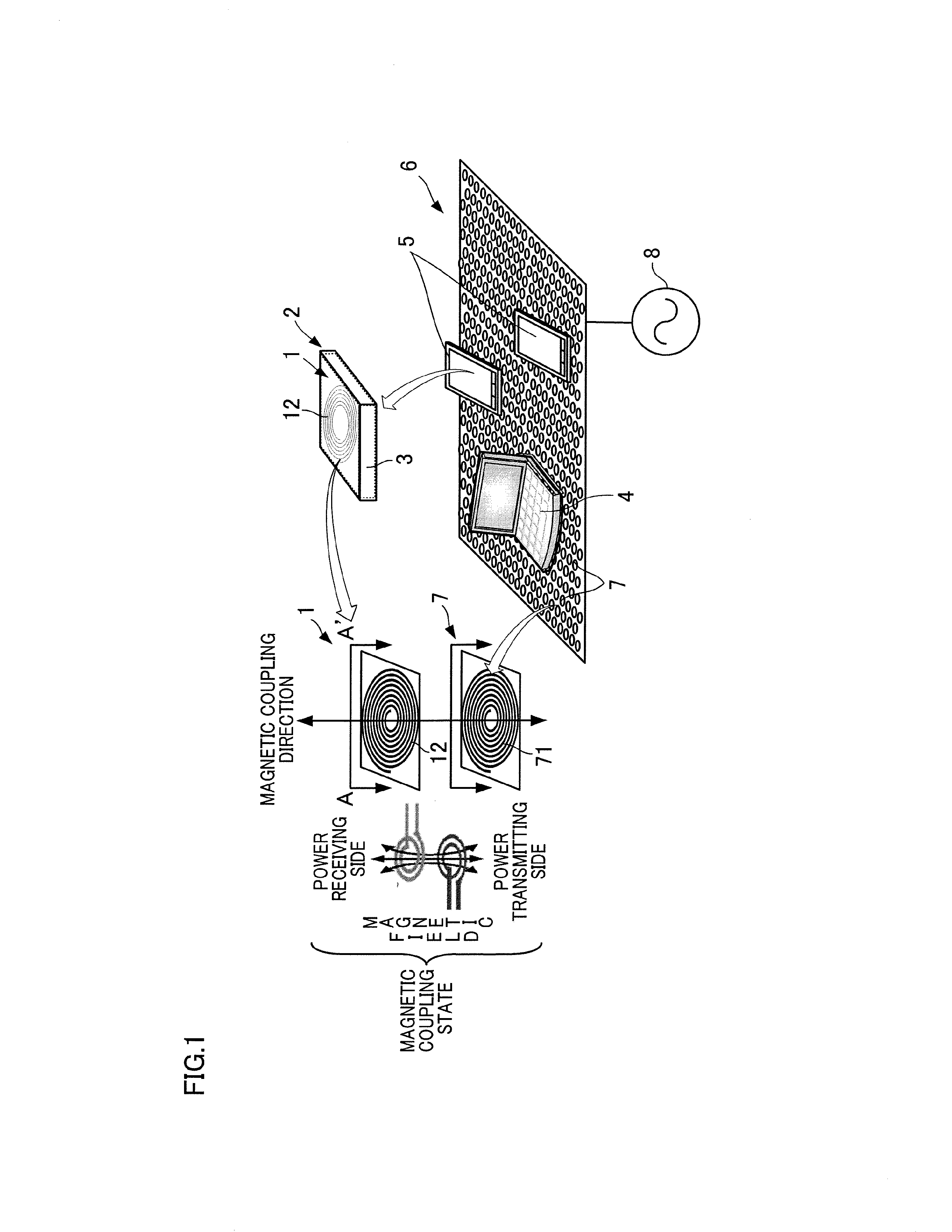
Mobile terminal power receiving module utilizing wireless power transmission and mobile terminal rechargable battery including mobile terminal power receiving module
InactiveUS20130175984A1Large capacityIncrease heat radiationNear-field transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric forceElectrical conductor
A mobile terminal power receiving module 1 which is housed together with a rechargeable battery 3 in a rechargeable battery pack 2 in a mobile terminal such as a smart phone 5, includes a sheet coil 13 in which a coil 12 constituted by conductors is formed on a flexible circuit board 11 as a circuit pattern and a magnetic sheet 14 made of resin in which magnetic powder is dispersed.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Magnetic toner, process for production thereof, and image forming method, apparatus and process cartridge using the toner
InactiveUS6465144B2Reduce wastePerformance and recoveryDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusMagnetizationX-ray
A magnetic toner includes: magnetic toner particles each comprising at least a binder resin and magnetic toner, and inorganic fine powder. The magnetic toner has an average circularity of at least 0.970, and a magnetization of 10-50 Am2 / kg at a magnetic field of 79.6 kA / m. The magnetic powder comprises at least magnetic iron oxide. The magnetic toner particles retain carbon in an amount of A and iron in an amount of B at surfaces thereof as measured by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, satisfying: B / A<0.001. The binder resin comprises a resin formed by polymerization of a monomer comprising at least styrene monomer. The magnetic toner has a residual styrene monomer content of less than 300 ppm, and contains at least 50% by number of toner particles satisfying a relationship of: D / C<=0.02, wherein C represents a volume-average particle size of the magnetic toner, and D represents a minimum distance between the surface of a magnetic toner particle and magnetic powder particles contained in the magnetic toner particle. Owing to the above features, the magnetic toner can exhibit good electrohotographic performances, including excellent chargeability and little transfer-residual toner, even in a cleanerless-mode image forming system.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com