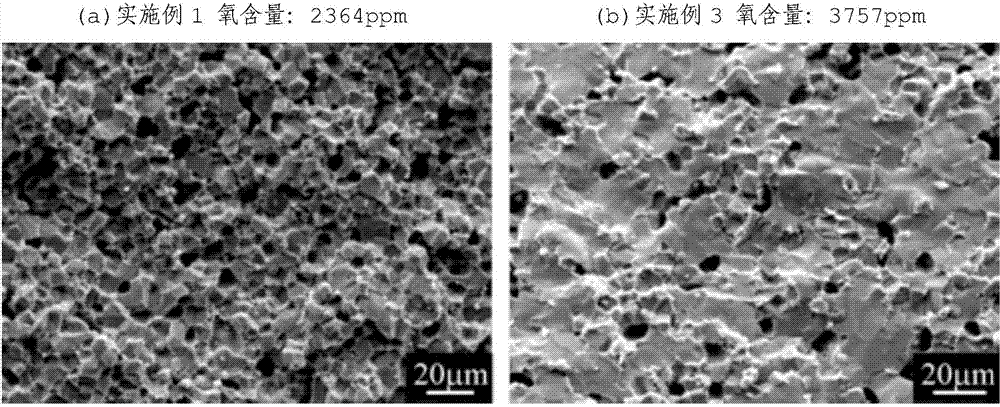
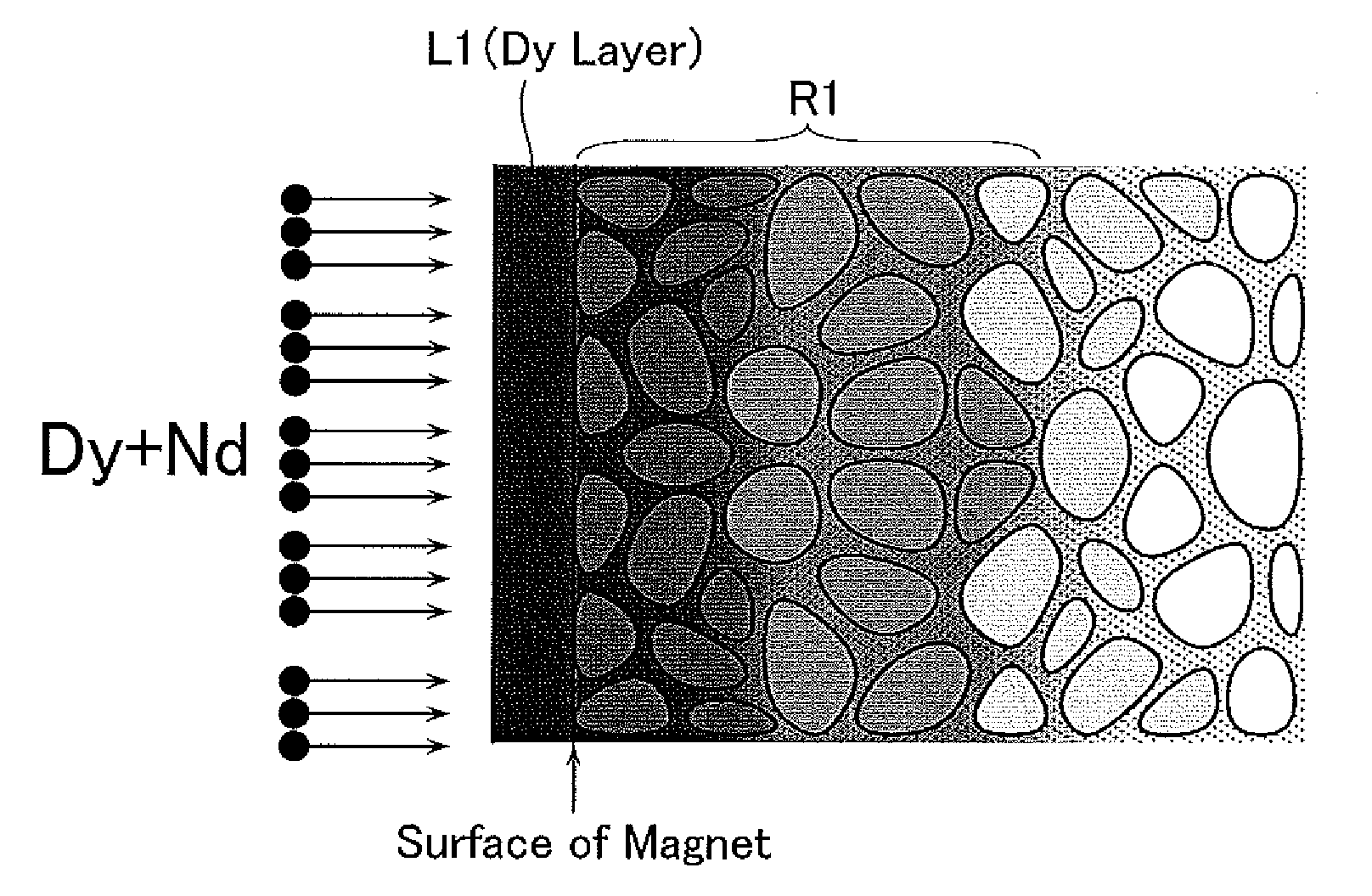
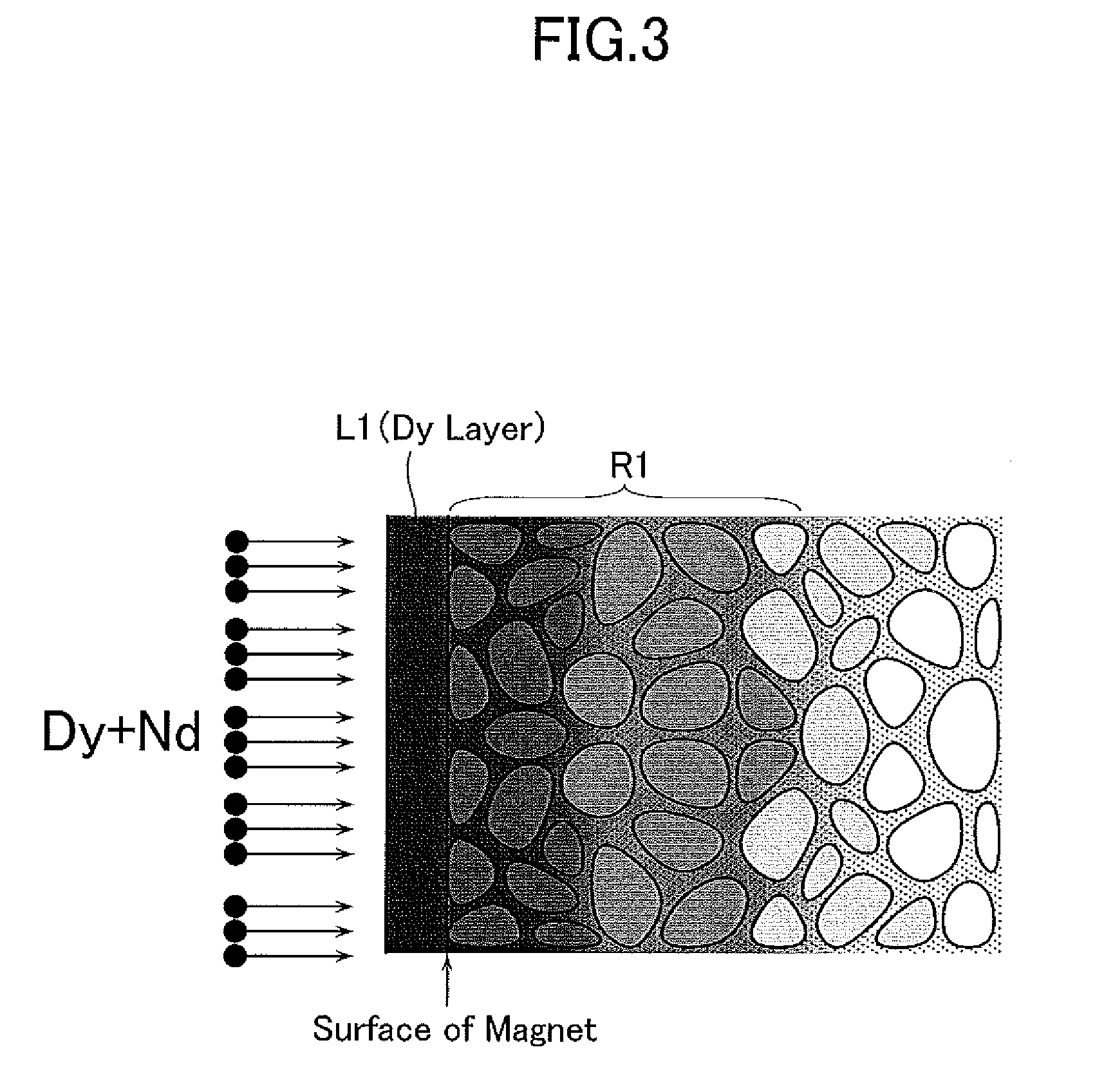
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1044 results about "Sintered magnets" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation of Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Material
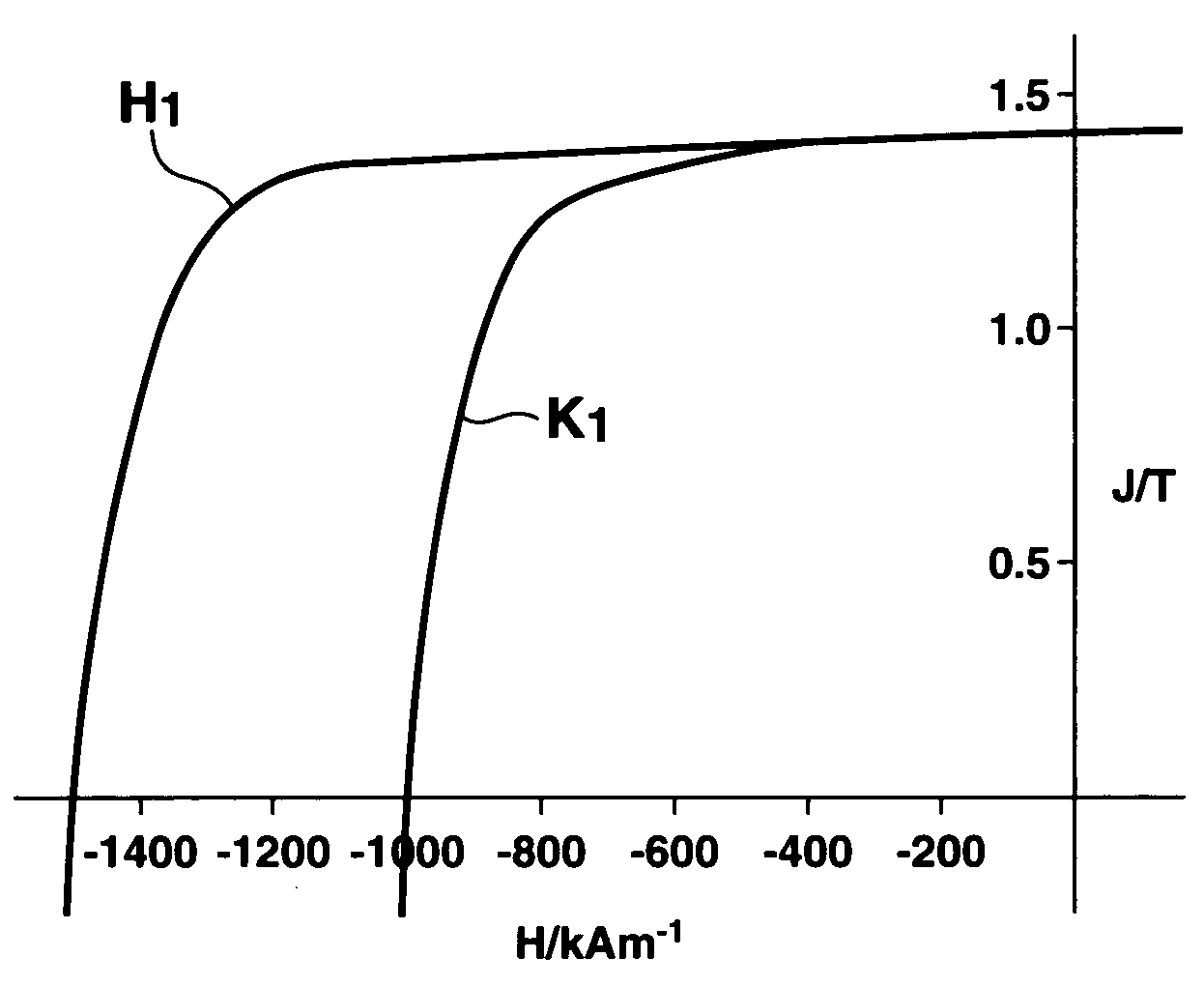
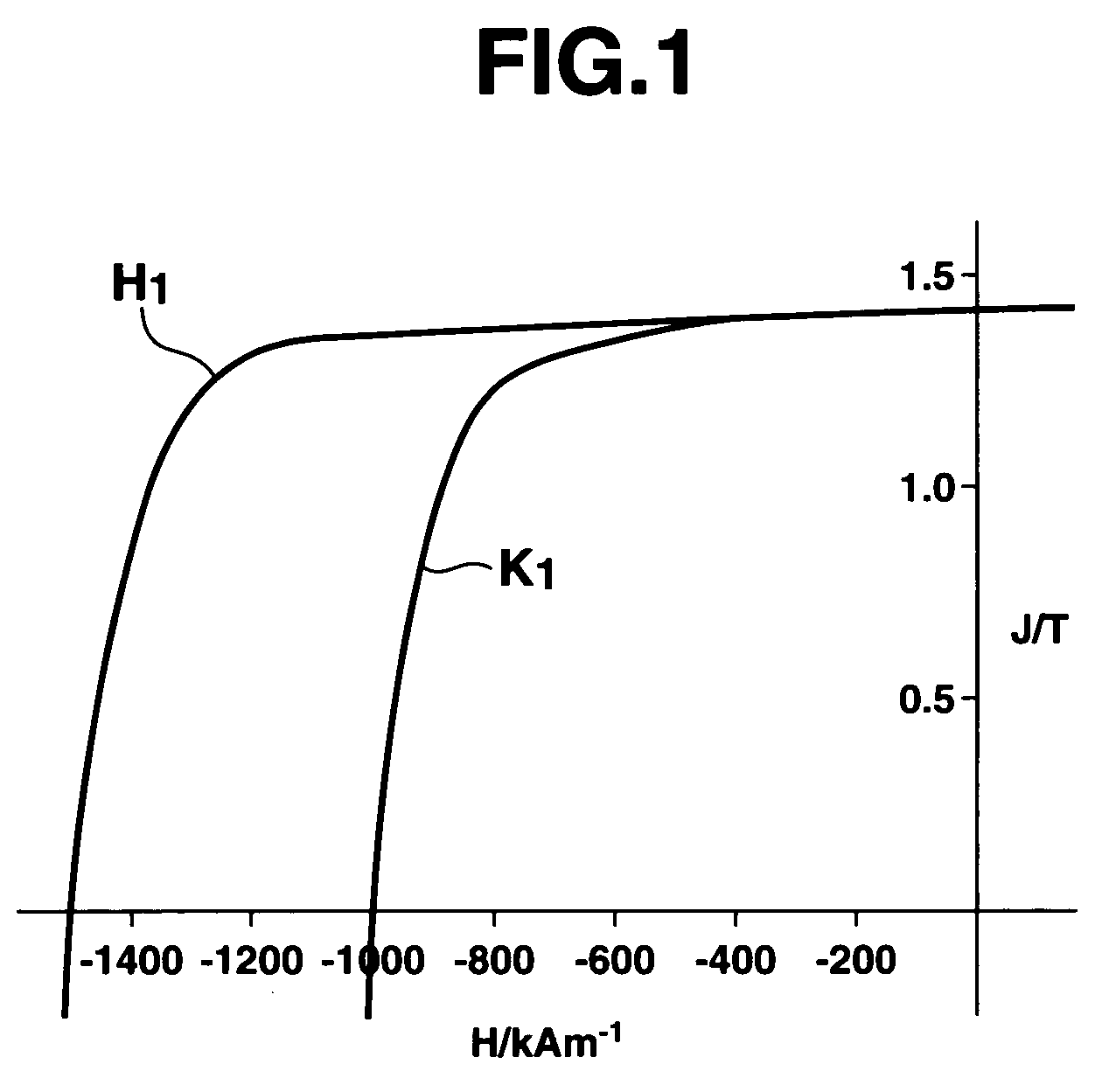
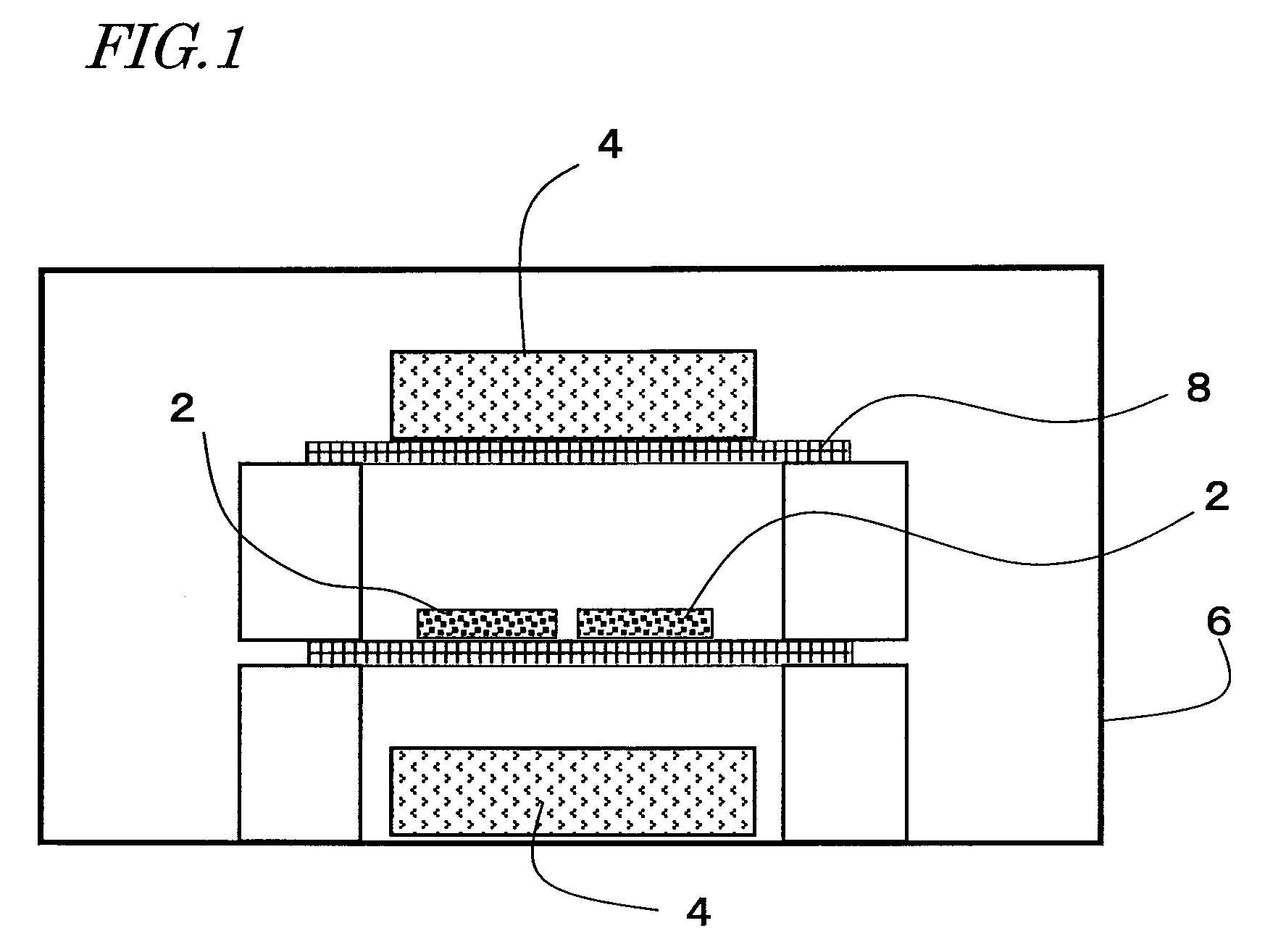
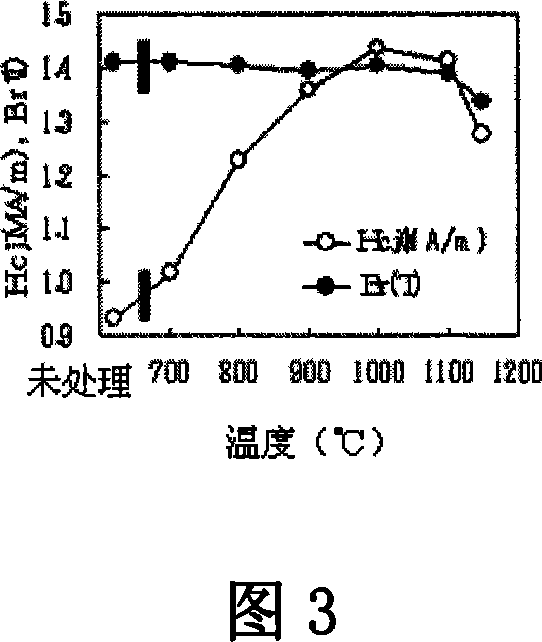
ActiveUS20080245442A1Improve remanenceImprove coercive forceElectric discharge tubesPermanent magnetsRare-earth elementRemanence
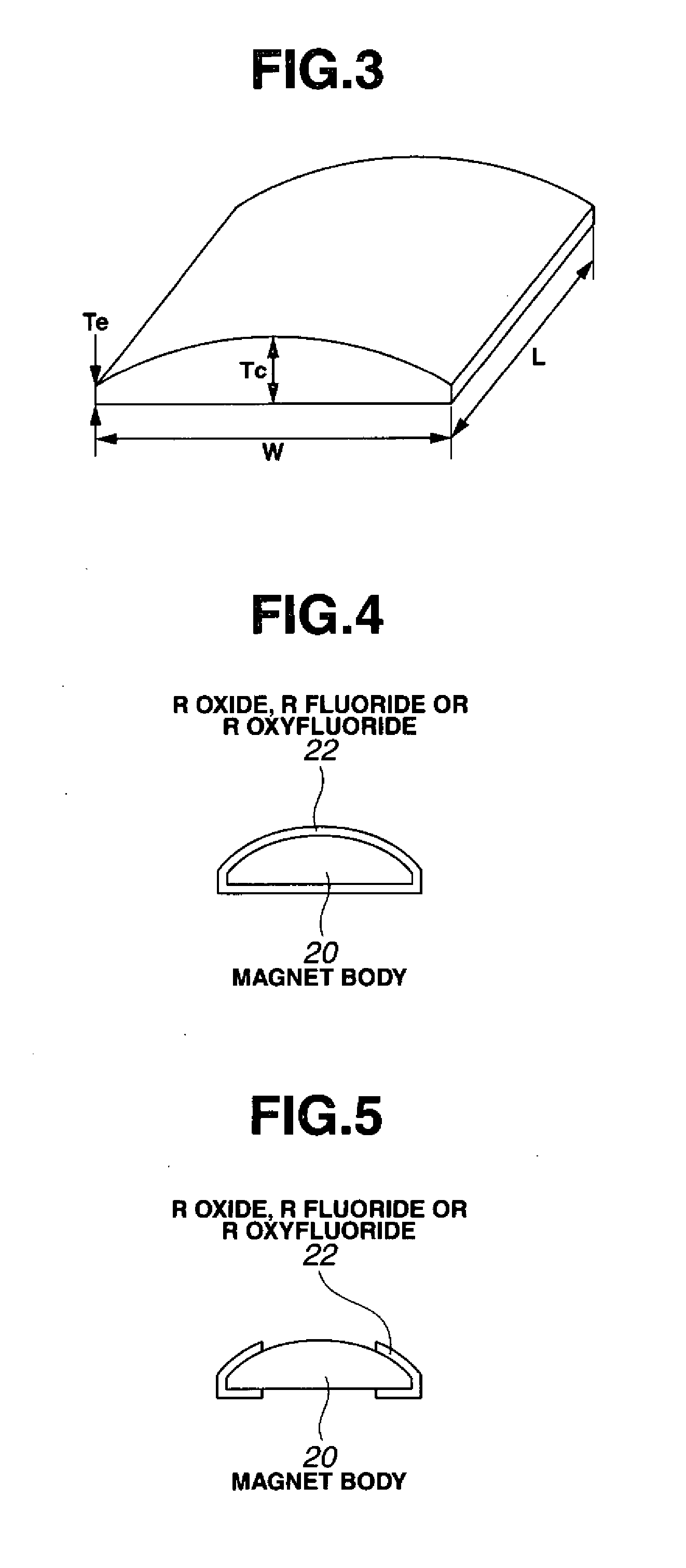
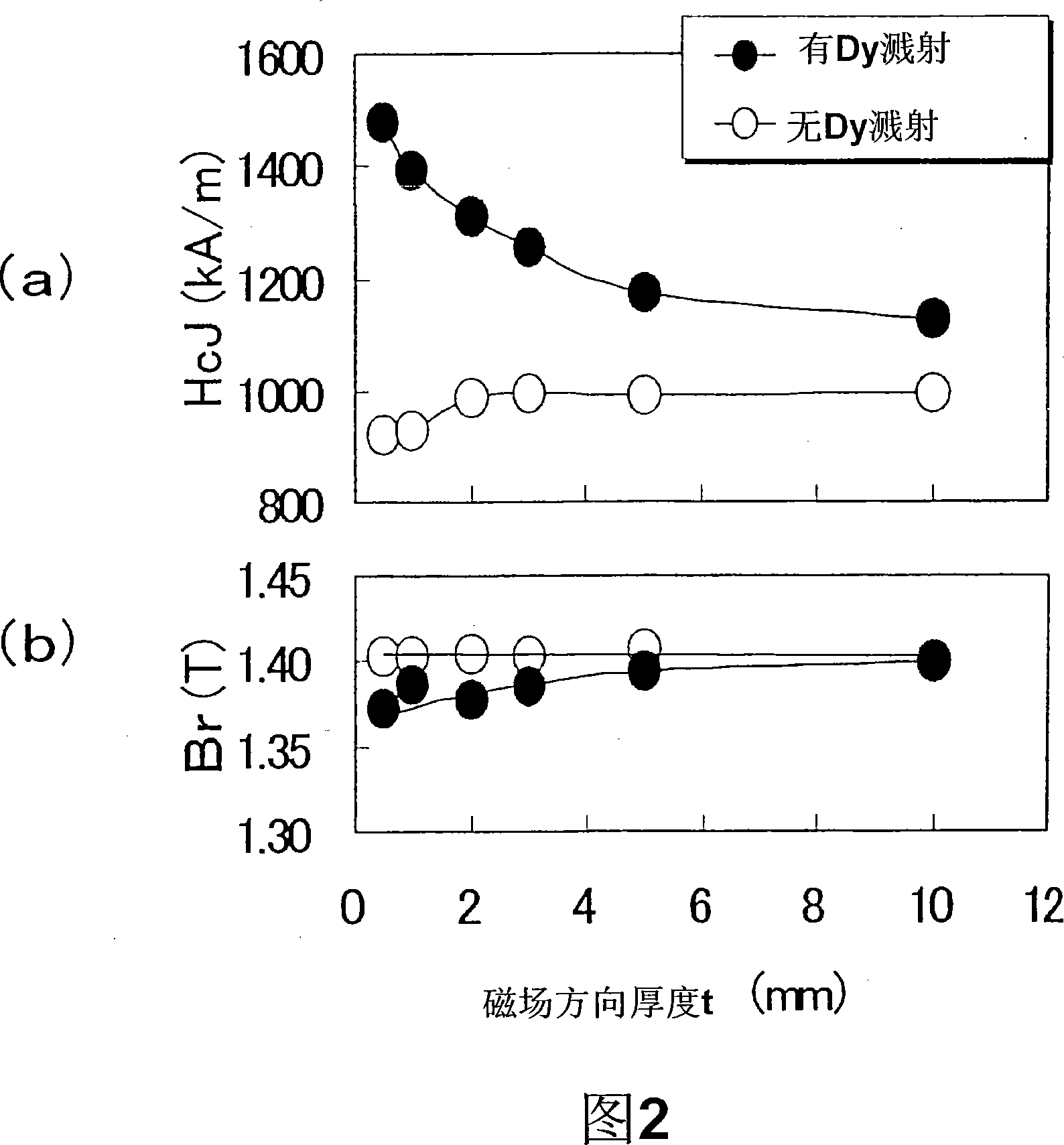
A method for preparing a rare earth permanent magnet material comprising the steps of:disposing a powder comprising one or more members selected from an oxide of R2, a fluoride of R3, and an oxyfluoride of R4 wherein R2, R3 and R4 each are one or more elements selected from among rare earth elements inclusive of Y and Sc on a sintered magnet form of a R1—Fe—B composition wherein R1 is one or more elements selected from among rare earth elements inclusive of Y and Sc, andheat treating the magnet form and the powder at a temperature equal to or below the sintering temperature of the magnet in vacuum or in an inert gas.The invention offers a high performance, compact or thin permanent magnet having a high remanence and coercivity at a high productivity.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
R-Fe-B Rare Earth Sintered Magnet and Method for Producing Same
ActiveUS20080286595A1Decrease in remanence Br minimizedCoercivity HcJ can be increasedInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementMetallurgy
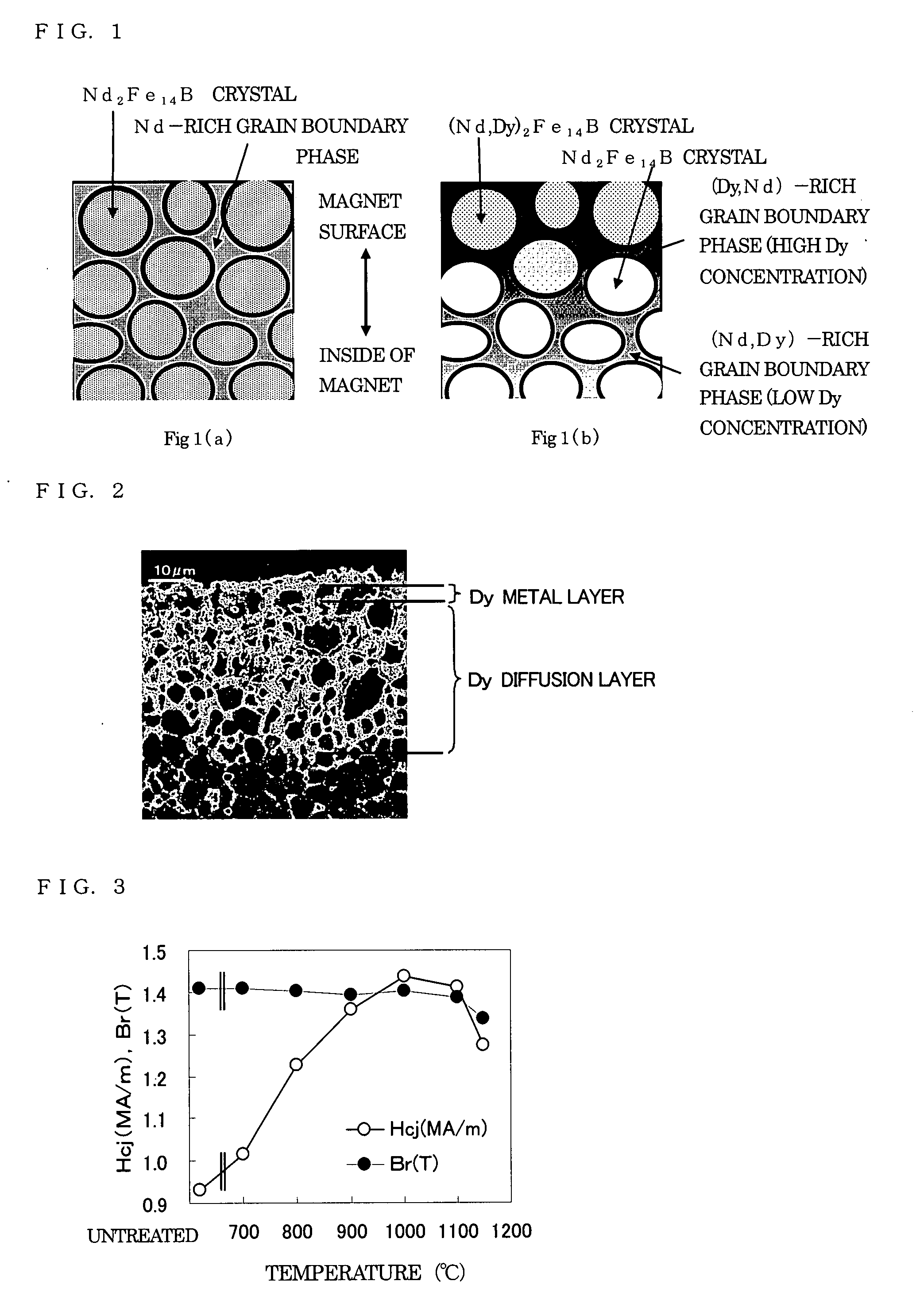
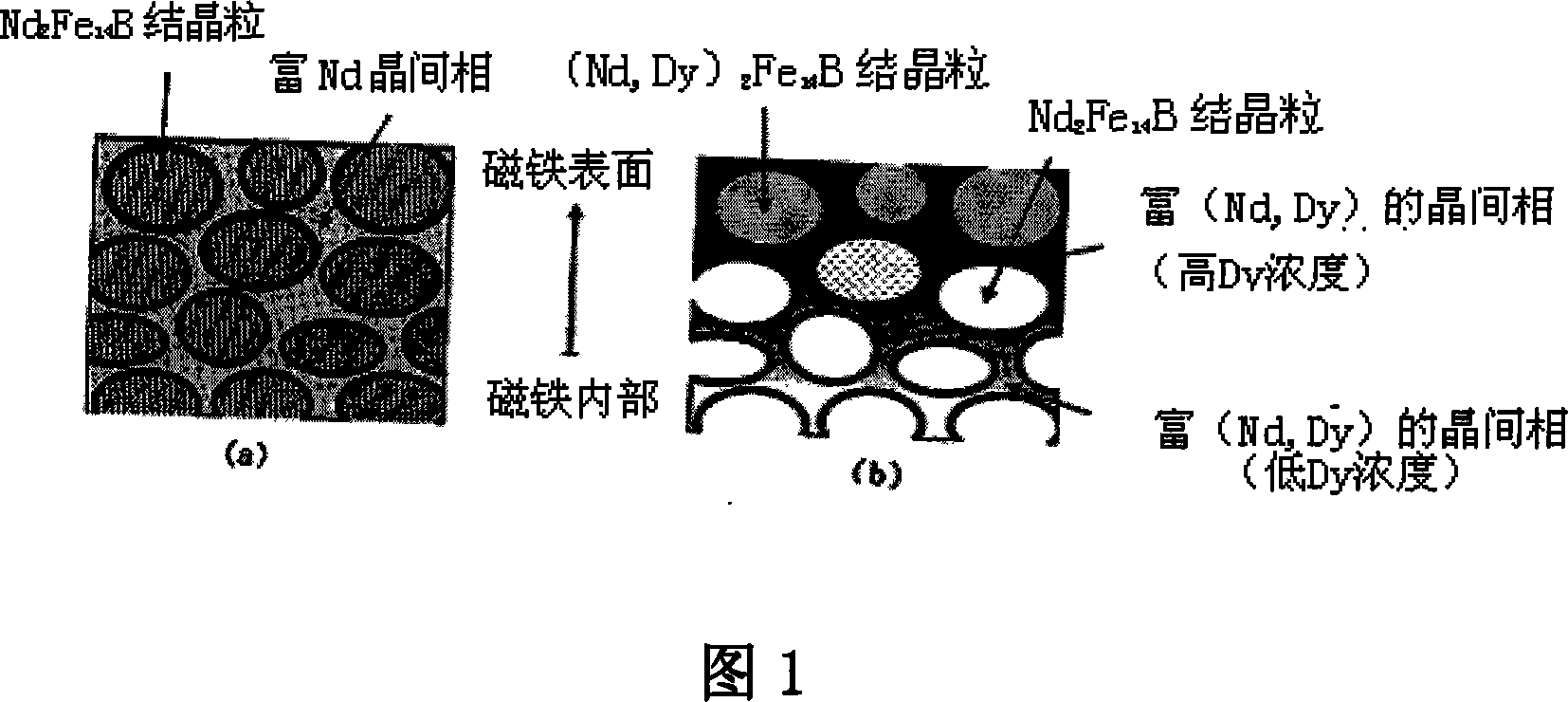
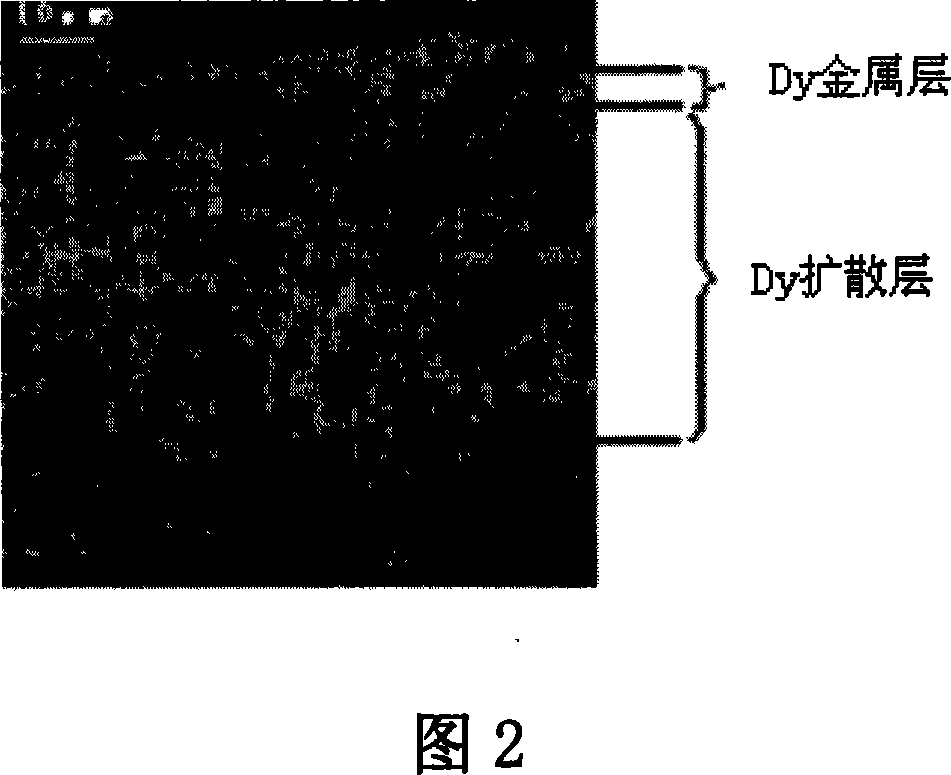
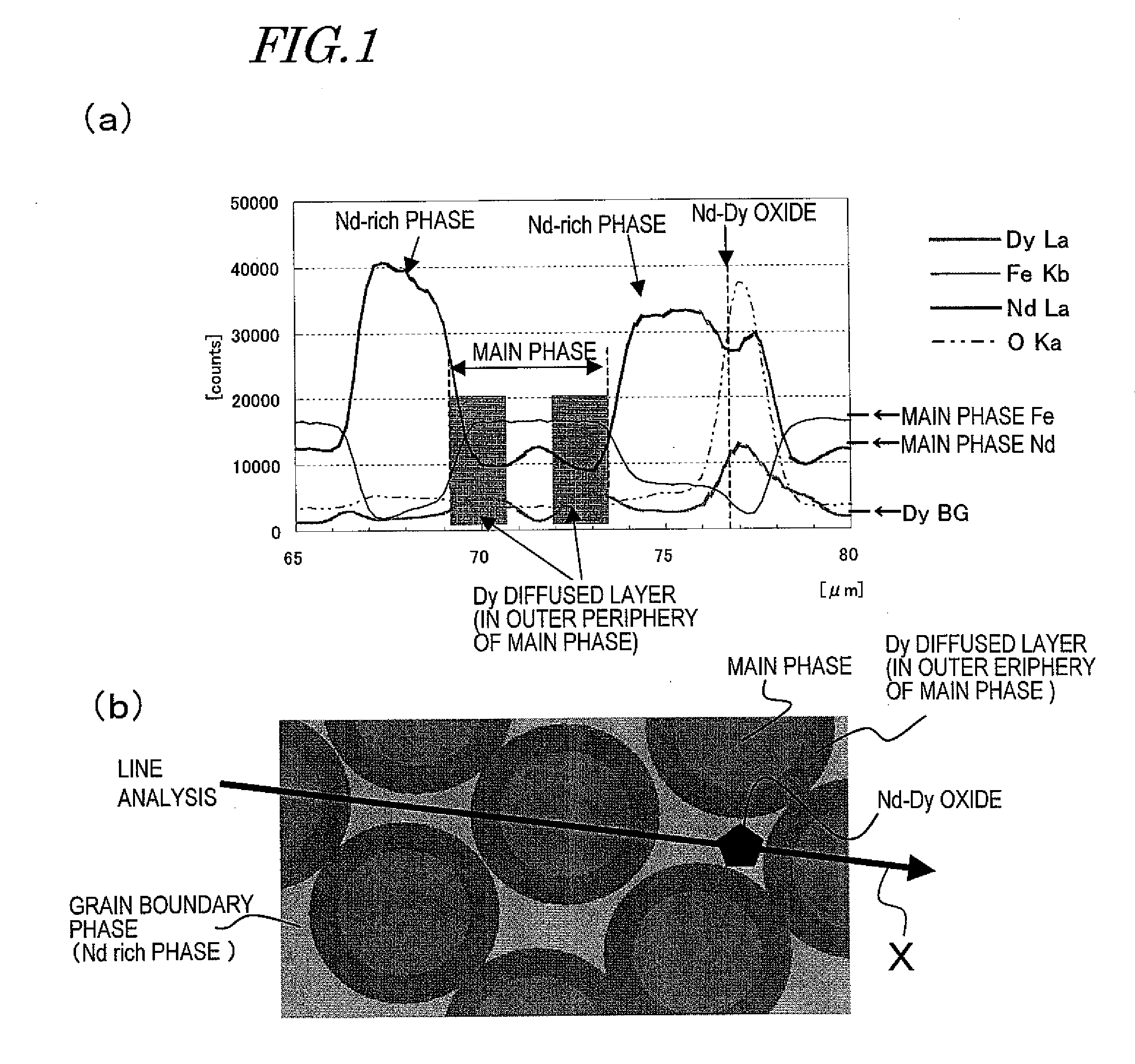
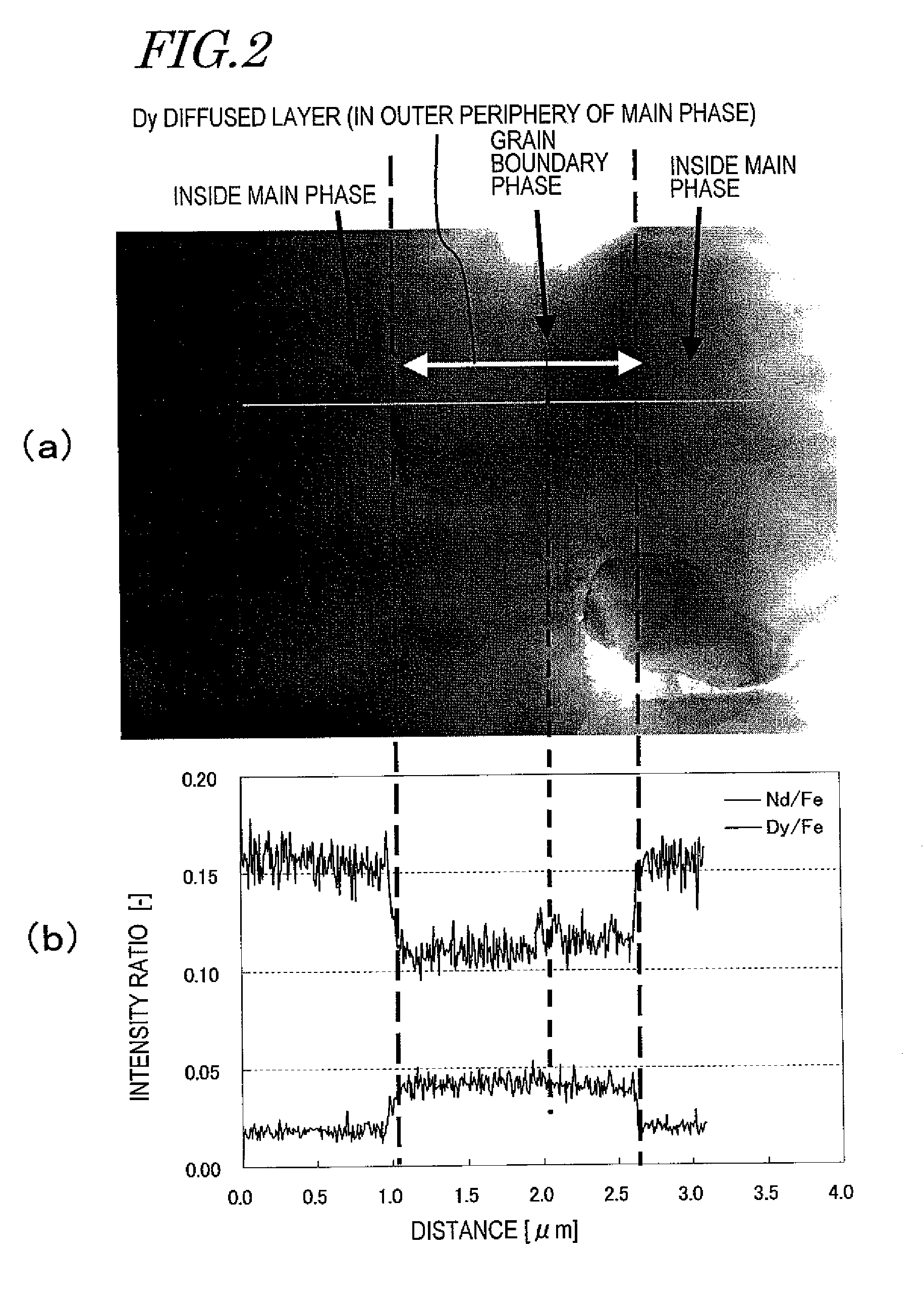
In a method for producing an R—Fe—B based rare-earth sintered magnet according to the present invention, first, provided is an R—Fe—B based rare-earth sintered magnet body including, as a main phase, crystal grains of an R2Fe14B type compound that includes a light rare-earth element RL, which is at least one of Nd and Pr, as a major rare-earth element R. Thereafter, the sintered magnet body is heated while a heavy rare-earth element RH, which is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Dy, Ho and Tb, is supplied to the surface of the sintered magnet body, thereby diffusing the heavy rare-earth element RH into the rare-earth sintered magnet body.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Alloy for r-t-b-based rare earth sintered magnet, process of producing alloy for r-t-b-based rare earth sintered magnet, alloy material for r-t-b-based rare earth sintered magnet, r-t-b-based rare earth sintered magnet, process of producing r-t-b-based rare earth sintered magnet, and motor
InactiveUS20140132377A1Improve coercive forceSuppression amountPermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementSintered magnets
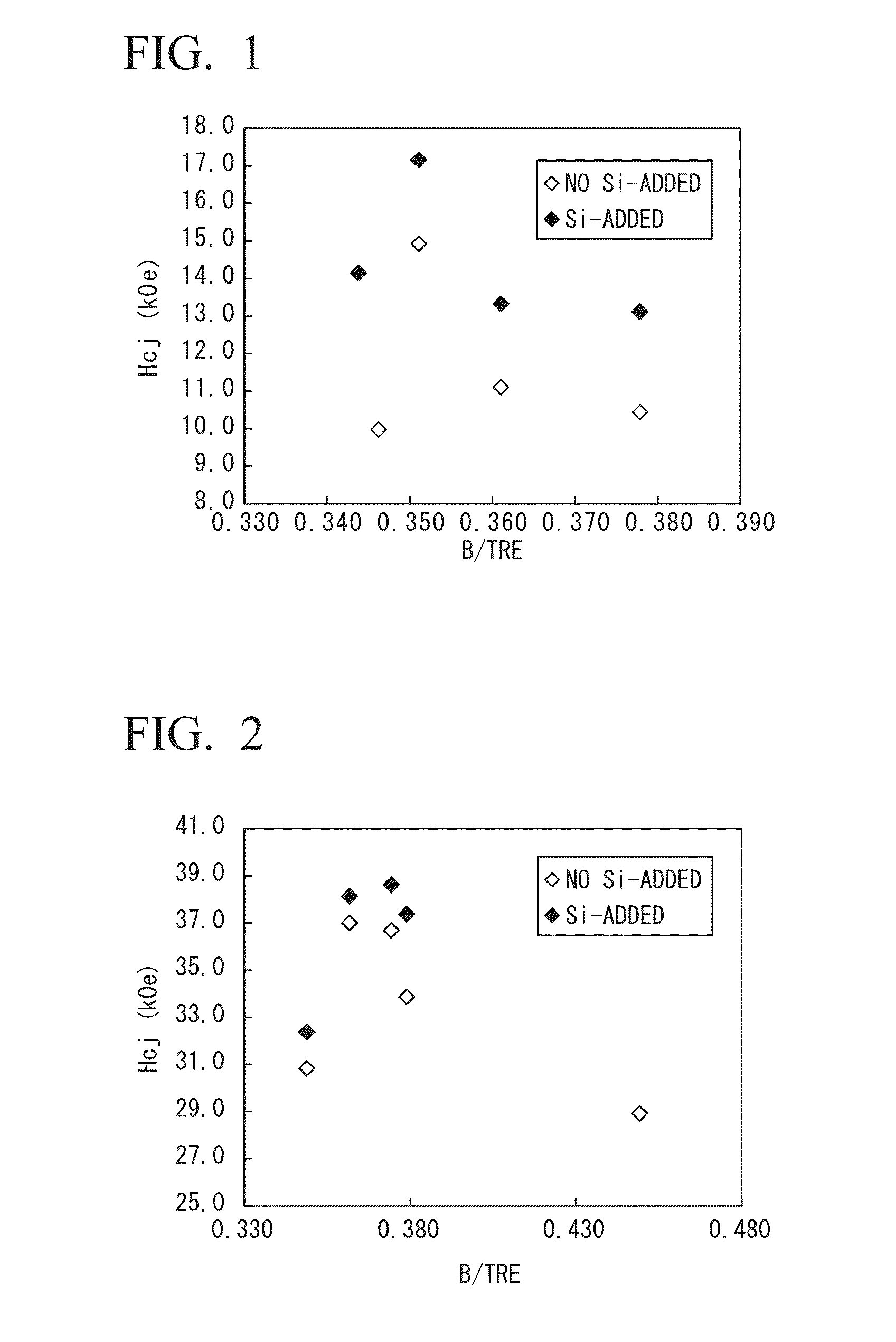
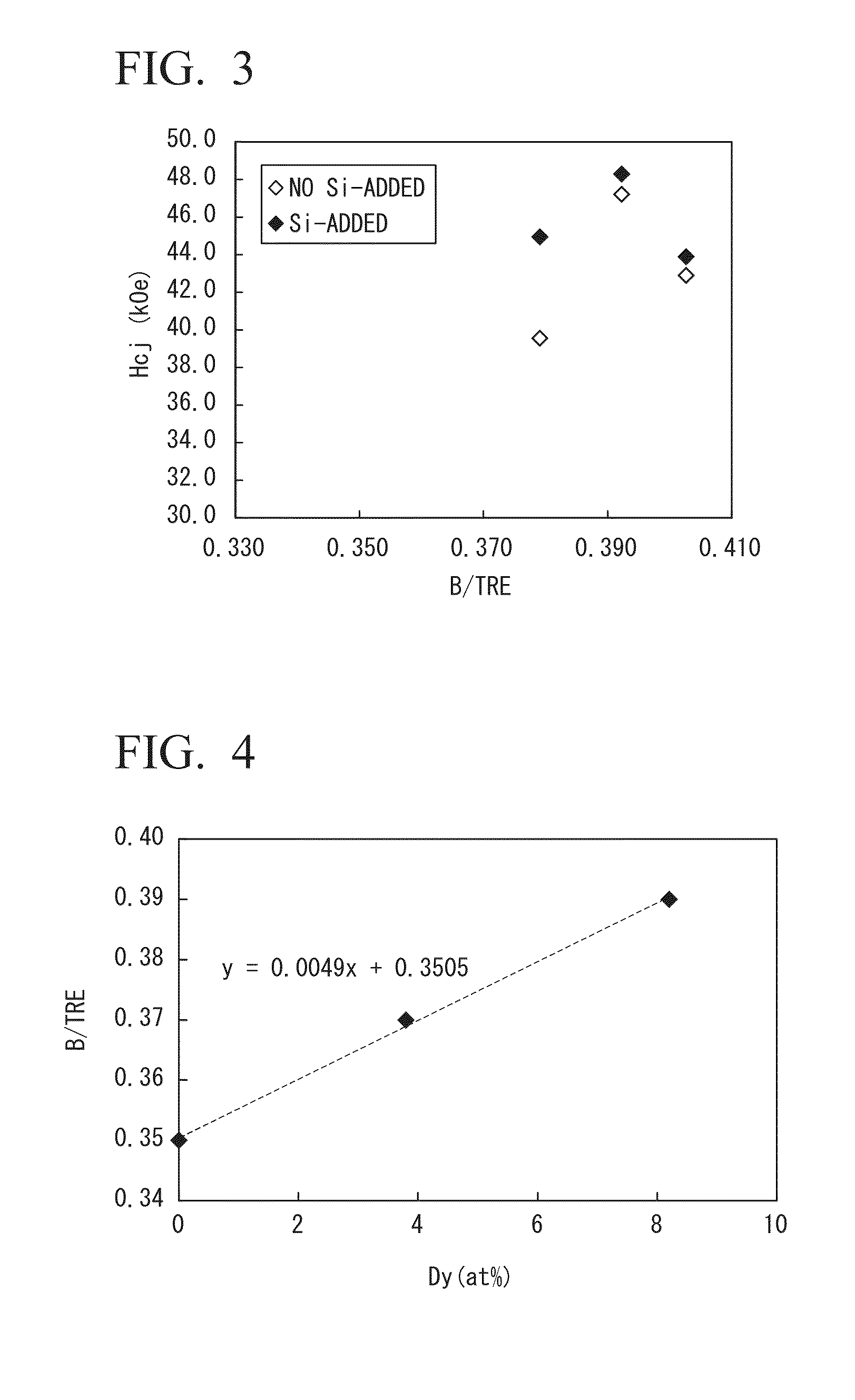
An alloy for R-T-B-based rare earth sintered magnets which contains R which is a rare earth element; T which is a transition metal essentially containing Fe; a metallic element M containing one or more metals selected from Al, Ga and Cu; B and inevitable impurities, in which R accounts for 13 at % to 15 at %, B accounts for 4.5 at % to 6.2 at %, M accounts for 0.1 at % to 2.4 at %, T accounts for balance, a proportion of Dy in all rare earth elements is in a range of 0 at % to 65 at %, and the following Formula 1 is satisfied,0.0049Dy+0.34≦B / TRE≦0.0049Dy+0.36 Formula 1wherein Dy represents a concentration (at %) of a Dy element, B represents a concentration (at %) of a boron element, and TRE represents a concentration (at %) of all the rare earth elements.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Method for preparing rare earth permanent magnet material
ActiveUS20070240789A1Improve performanceMinimizing contentInorganic material magnetismPermanent magnet manufactureRare-earth elementSintered magnets
A rare earth permanent magnet material is prepared by covering a sintered magnet body of R1—Fe—B composition wherein R1 is a rare earth element, with a powder comprising at least 30% by weight of an alloy of R2aTbMcAdHe wherein R2 is a rare earth element, T is Fe and / or Co, and M is Al, Cu or the like, and having an average particle size up to 100 μm, and heat treating the powder-covered magnet body at a suitable temperature, for causing R2, T, M and A in the powder to be absorbed in the magnet body.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method of preparing micro-structured powder for bonded magnets having high coercivity and magnet powder prepared by the same
InactiveUS20050081959A1Reduce manufacturing costSimplified mass productionInorganic material magnetismRare earthGrain boundary
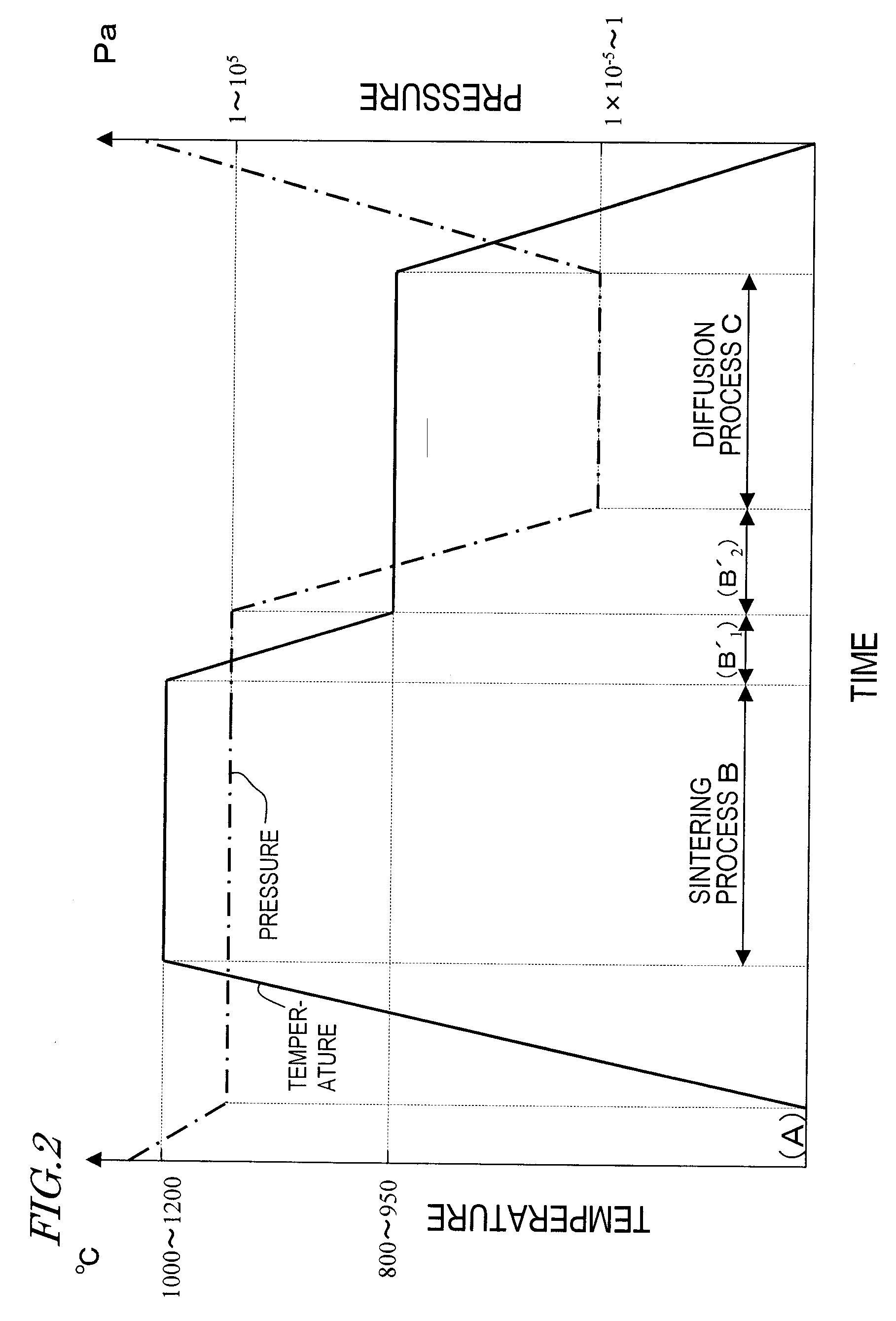
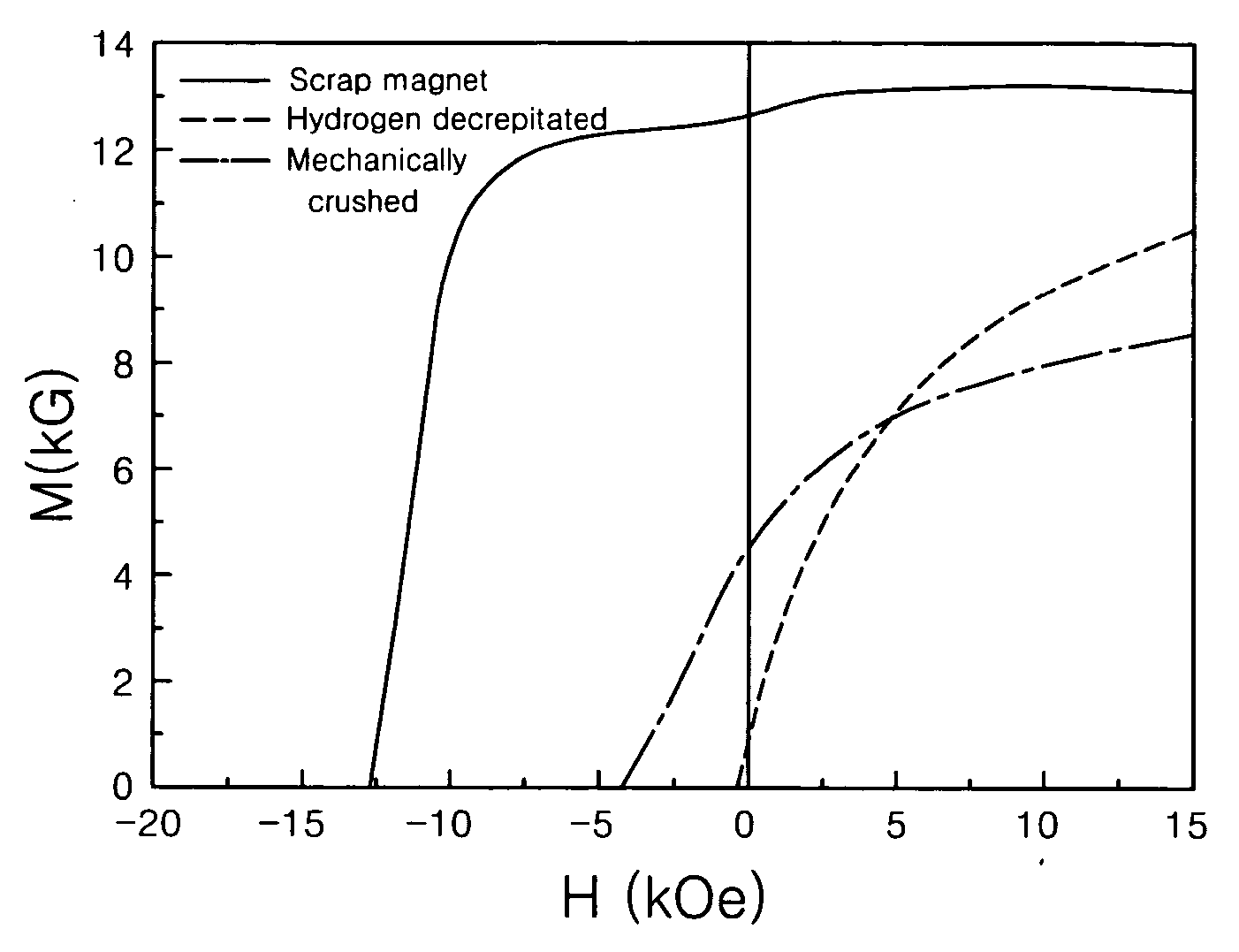
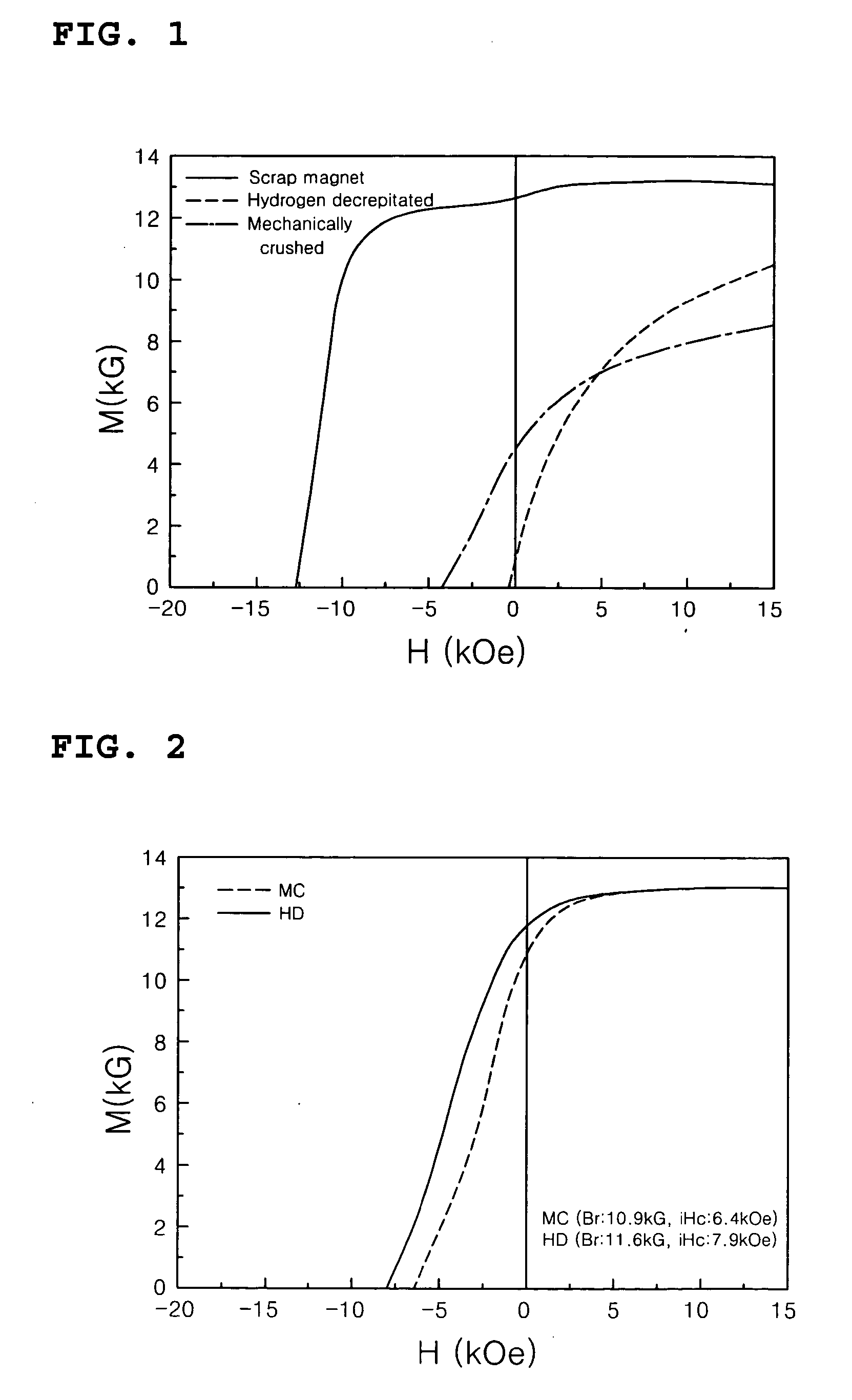
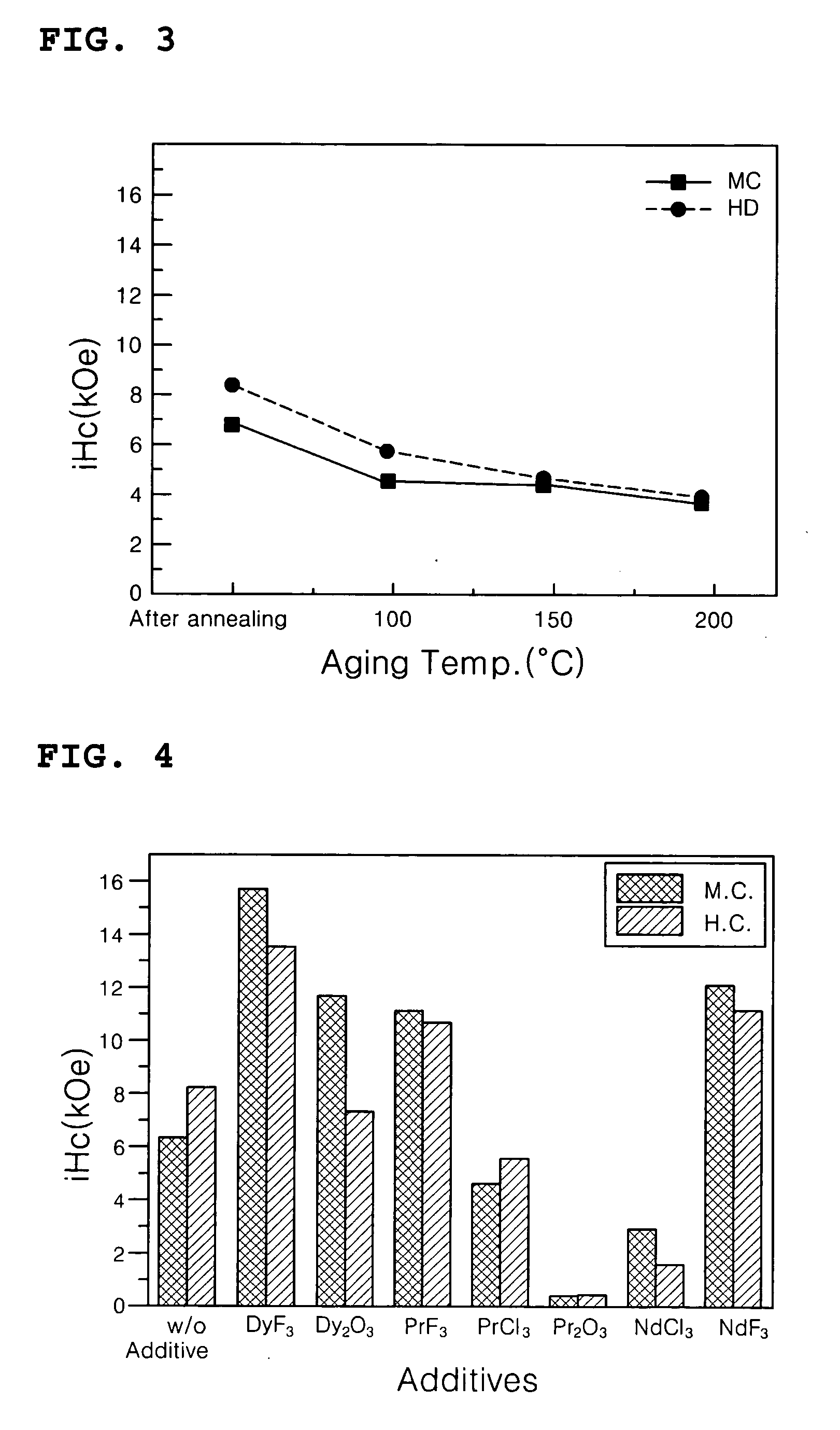
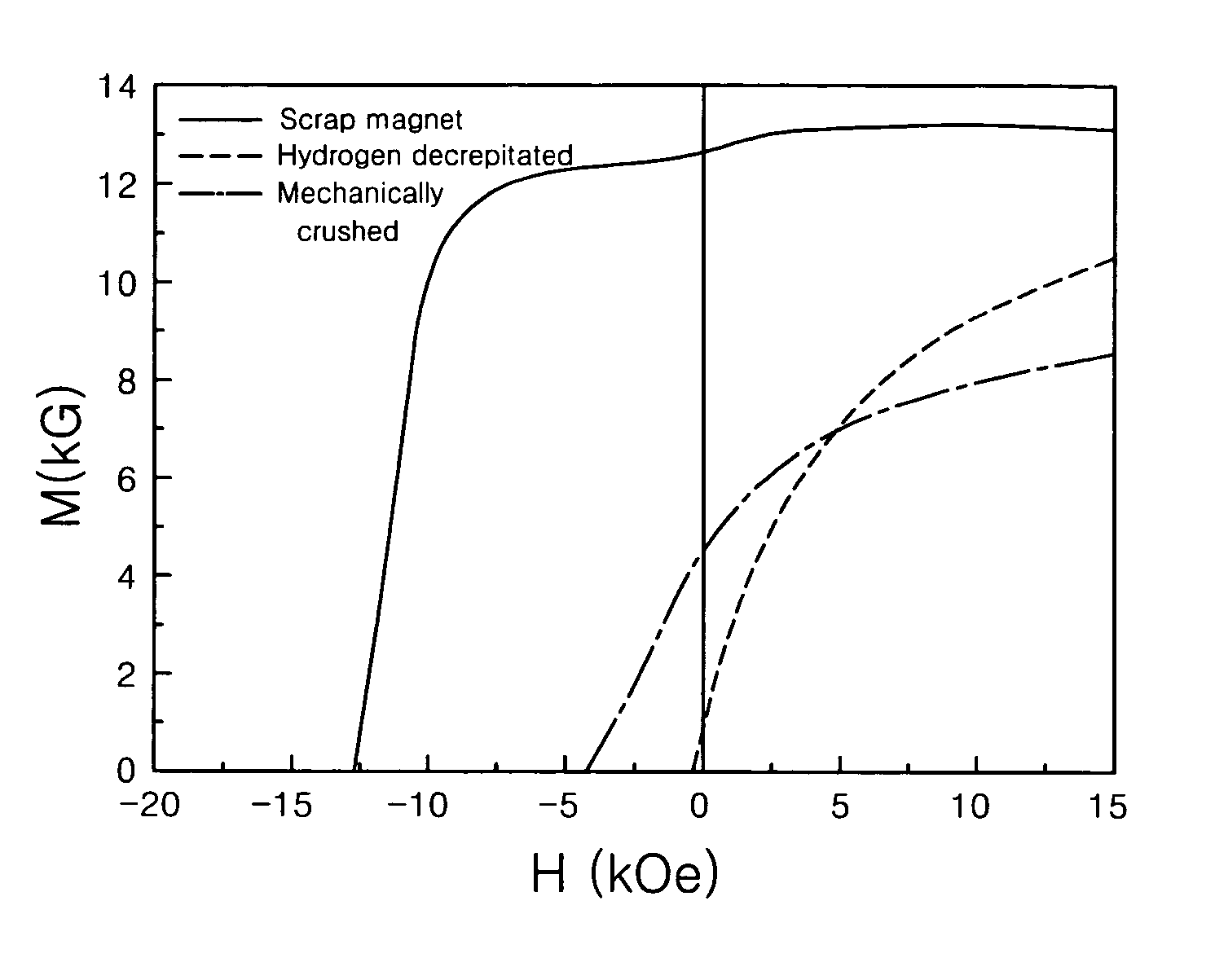
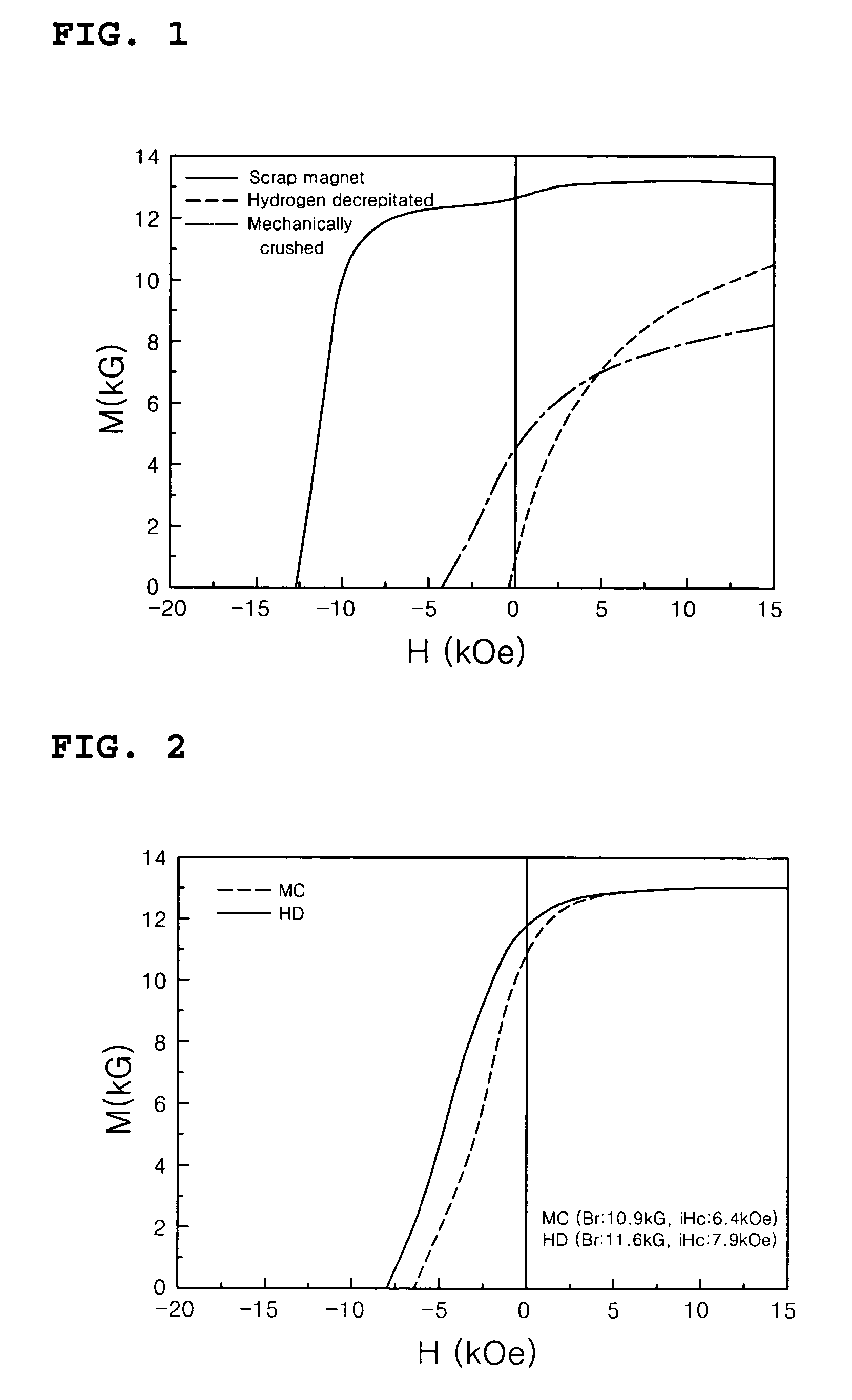
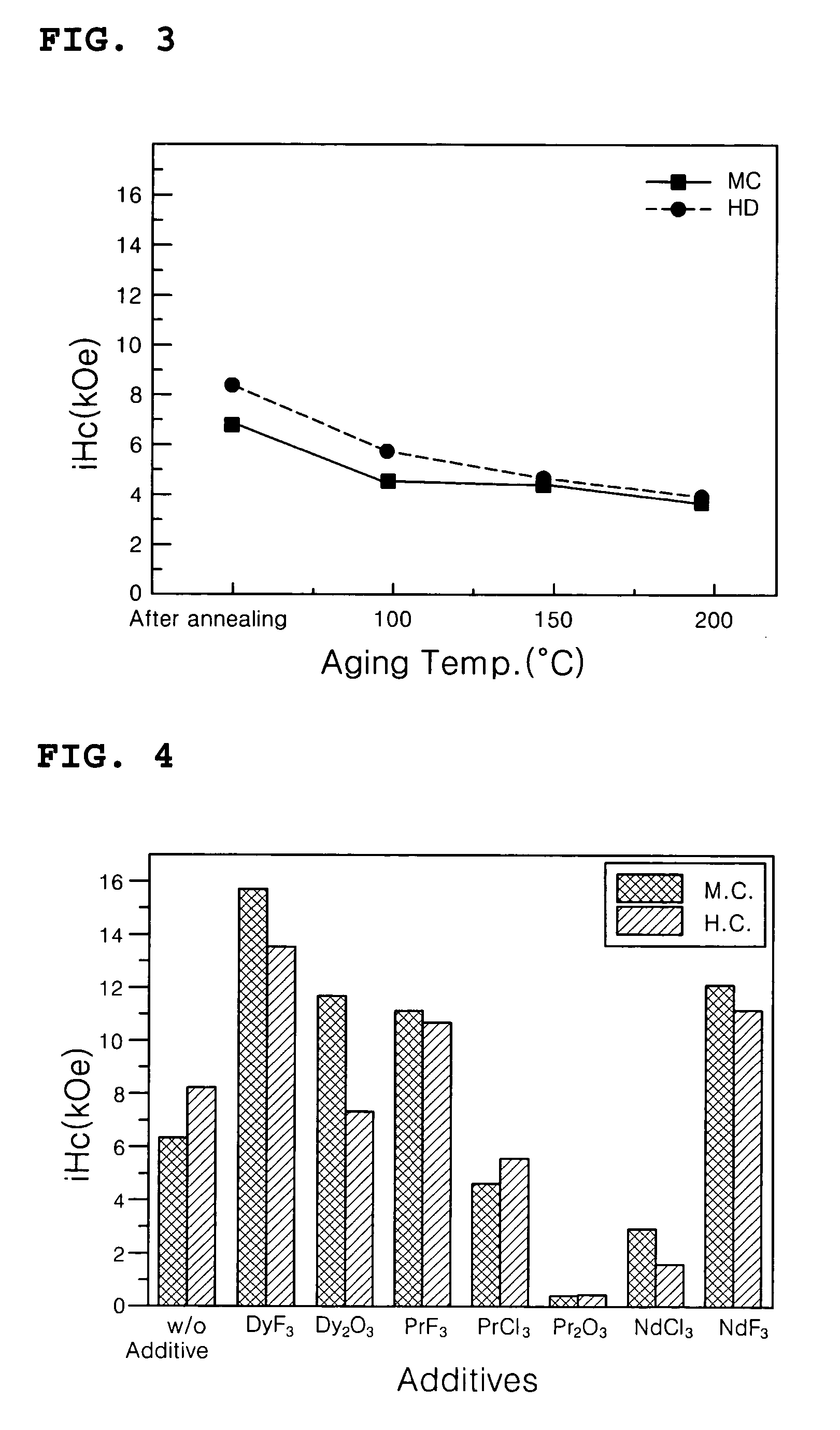
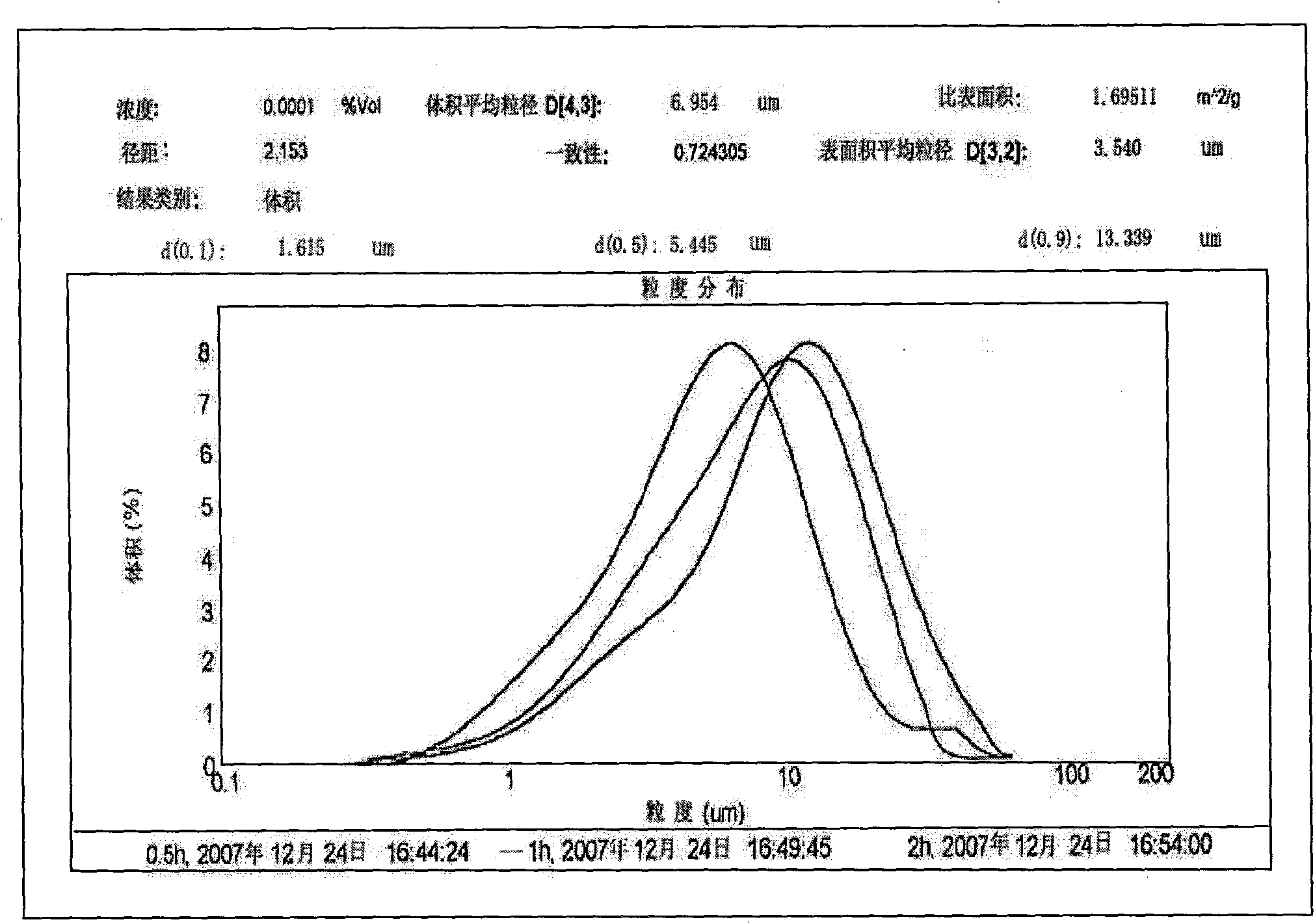
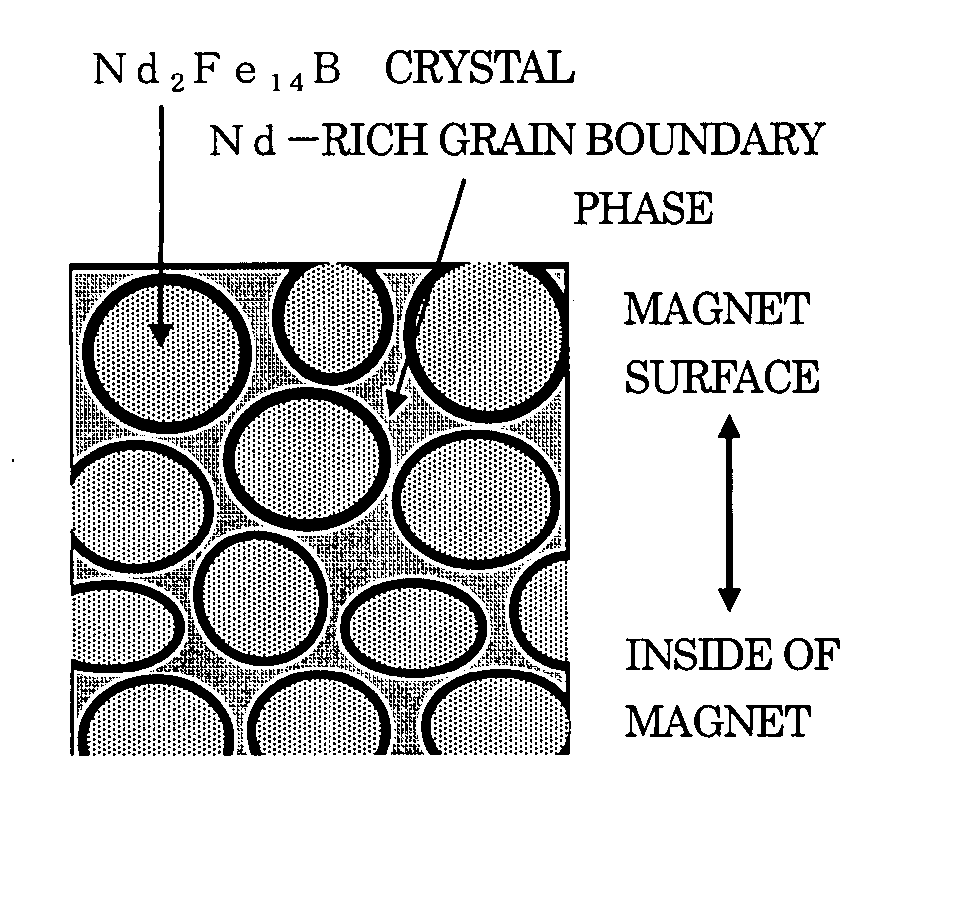
Disclosed is a method of preparing a micro-structured powder for bonded magnets having high coercivity, which is advantageous in terms of low preparation costs by recycling magnet scraps, simplified mass production, minimal environmental contamination by such a recycling process, and the preparation of stable anisotropic powders having high coercivity. Further, a magnet powder prepared by the above method is provided. The current method is characterized in that R—Fe—B type anisotropic sintered magnets or scraps thereof are crushed to prepare 50-500 μm sized magnet powders, which are then mixed with 1-10 wt % of rare earth fluoride (RF3) powders and thermally treated at high temperatures (500-1100° C.) in a vacuum or an inert gas, to cause the change of matrix-near surface and grain boundary of the powders. Thus obtained powders include a matrix phase having R2Fe14B crystal structure, a R-rich grain boundary phase containing rare earth fluoride, and other phases, in which the matrix phase has an average grain size of 1-20 μm, and the powders have an average size of 50-500 μm with superior magnetic characteristics of (BH)max≧20 MGOe and iHc≧5 kOe.
Owner:JAHWA ELECTRONICS
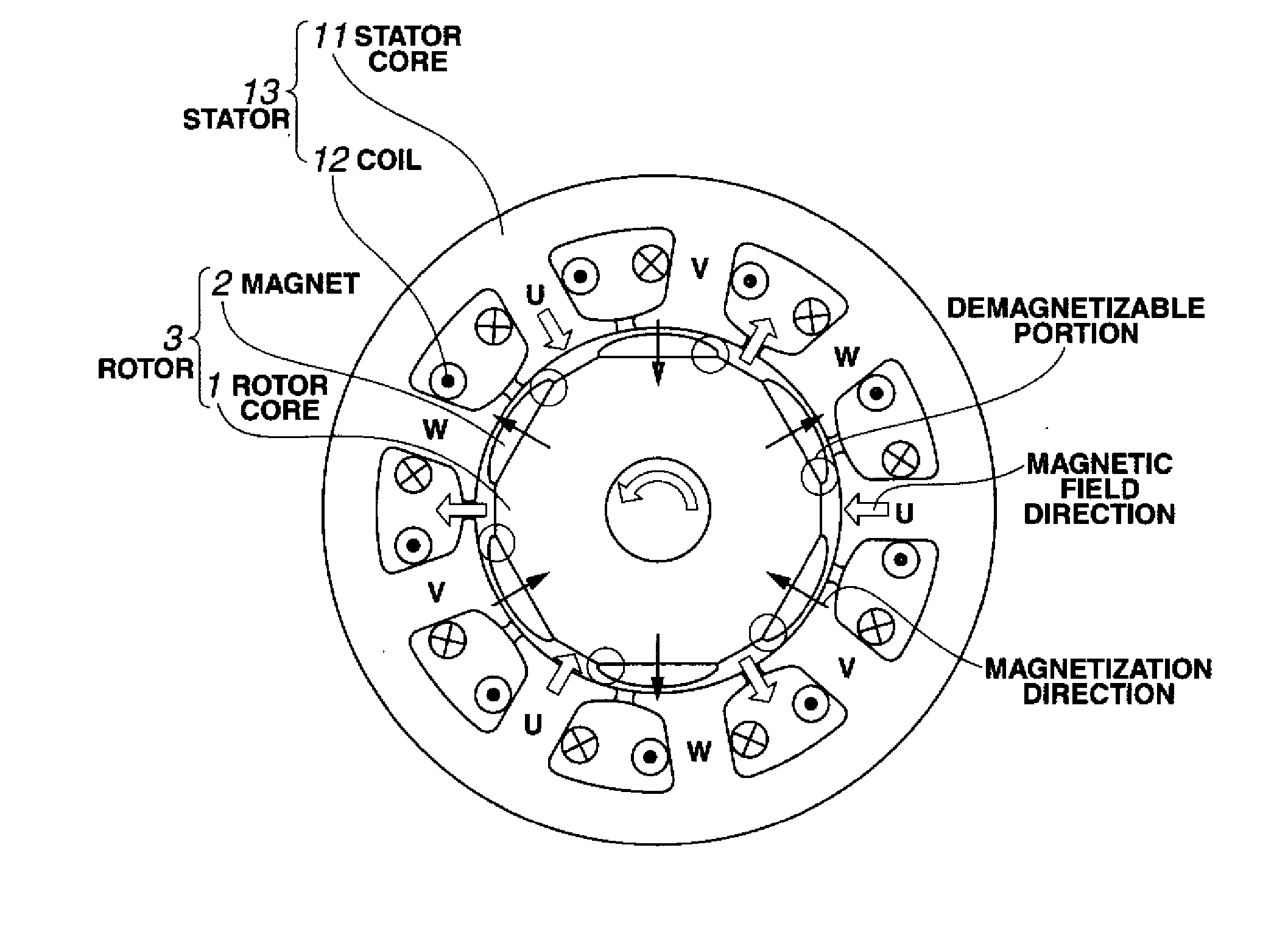
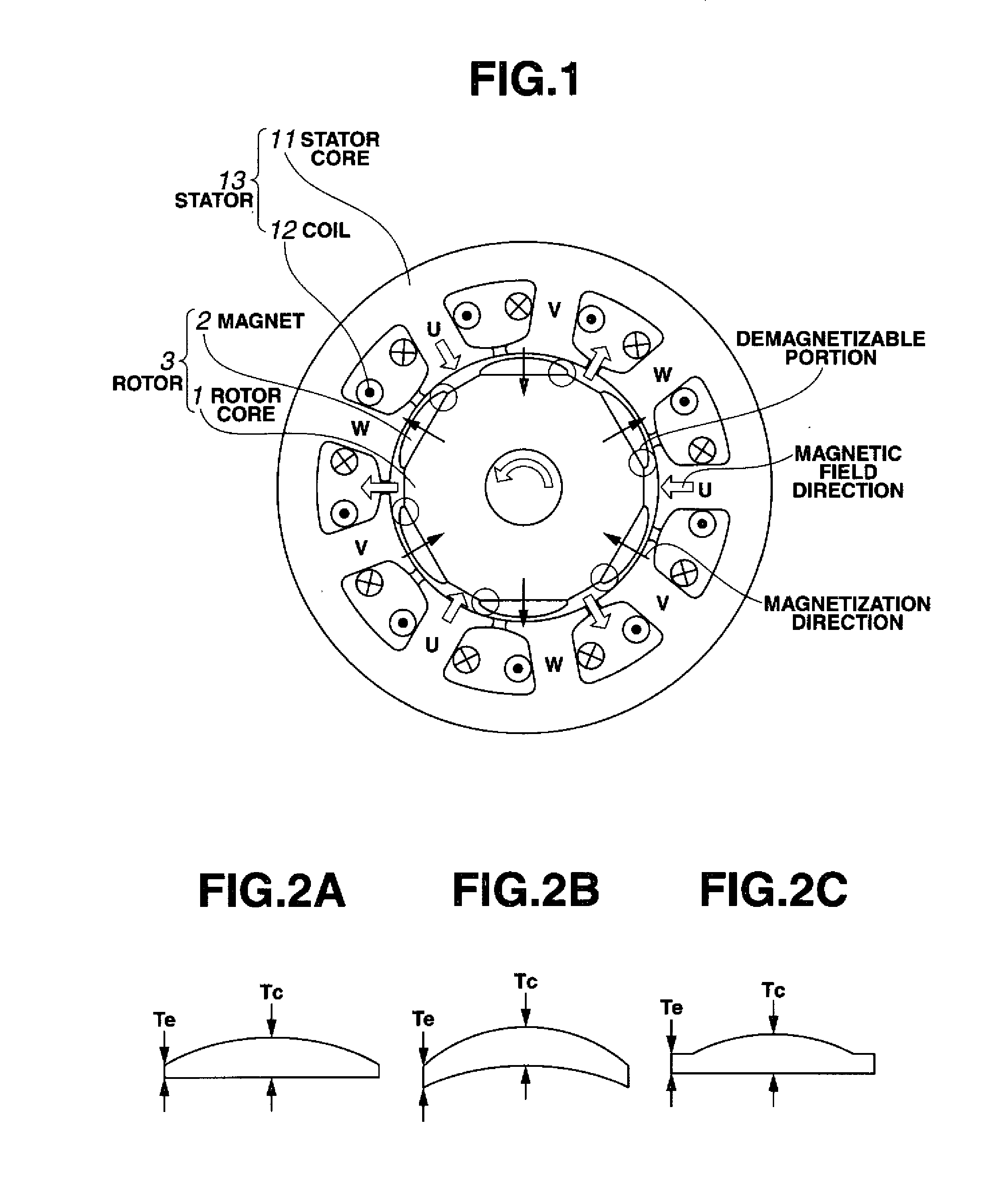
Permenent magnet rotating machine
ActiveUS20080054736A1Improve remanenceImprove coercive forceMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesRare-earth elementSintered magnets
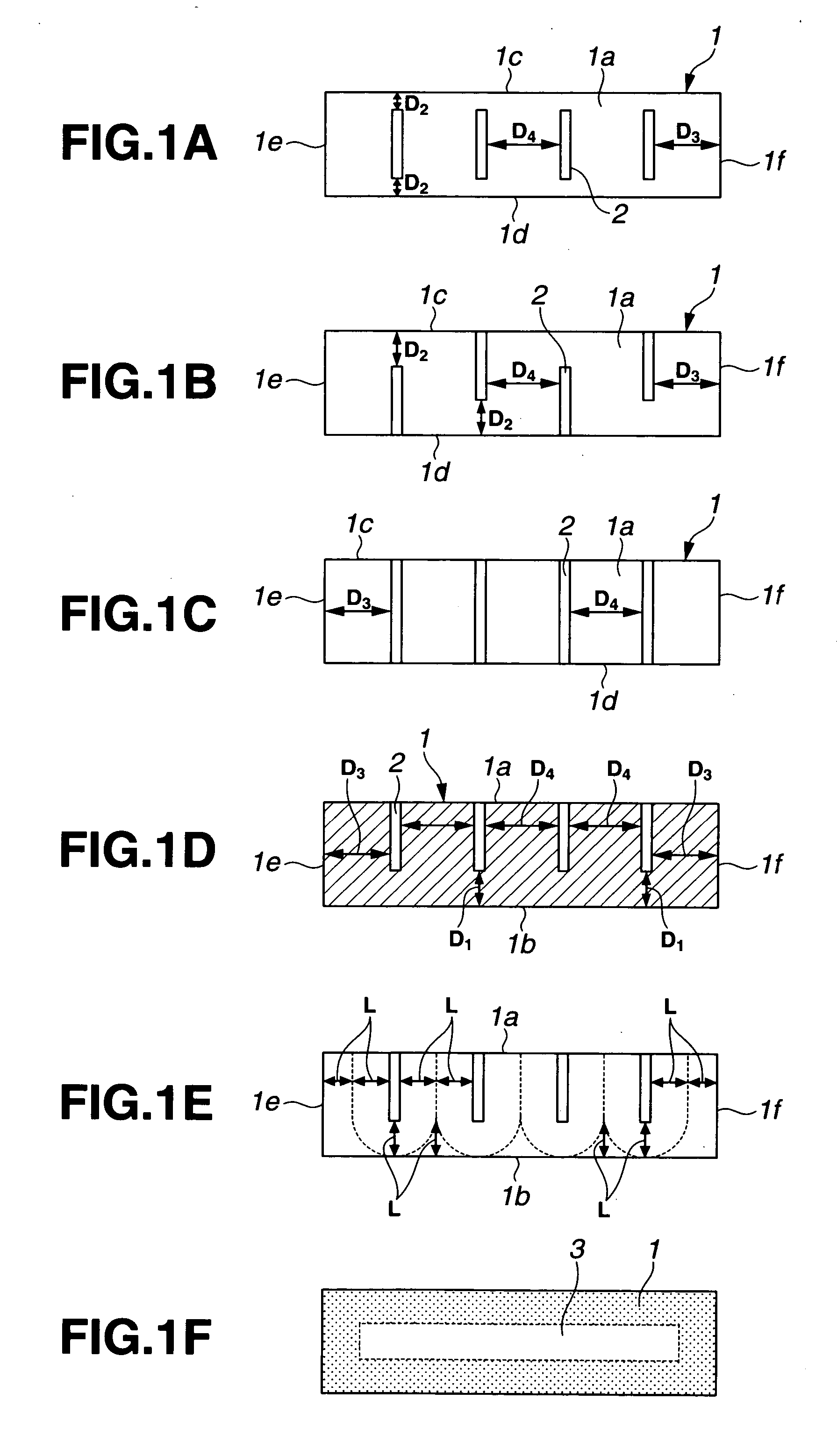
In a rotating machine comprising a rotor including a rotor core and a plurality of permanent magnet segments, and a stator including a stator core and windings, the permanent magnet segment is obtained by disposing a powder comprising an R2 oxide, R3 fluoride or R4 oxyfluoride on a sintered magnet body of R1—Fe—B composition, wherein R1 to R4 are rare earth elements, and heat treating the powder-covered magnet body. The permanent magnet segment of a cross-sectional shape which is tapered from the center toward opposed ends has a higher coercive force at the ends than at the center.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Rare earth permanent magnet, making method, and permanent magnet rotary machine
ActiveUS20070017601A1Minimized eddy currentImprove remanenceMagnetic circuitInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementSintered magnets
A rare earth permanent magnet is prepared from a sintered magnet body of a R1—Fe—B composition wherein R1 is a rare earth element inclusive of Y and Sc, by forming a plurality of slits in a surface of the magnet body, disposing a powder on the magnet body surface, the powder comprising an oxide of R2, a fluoride of R3, or an oxyfluoride of R4 wherein each of R2, R3, and R4 is a rare earth element, and heat treating the magnet body and the powder below the sintering temperature in vacuum or in an inert gas.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Magnetoplumbite permanent magnetic ferrite and method of producing the same
InactiveCN101552069AIncrease the degree of substitutionGuaranteed stabilityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRemanenceMetallurgy
The present invention relates to a magnet powder formula of hexagonal type magnetoplumbite permanent magnetic ferrite, sintered magnet and method of producing the same. The invention provides a sintered permanent magnetic ferrite and magnet powder capable of acquiring remanence of more than 4500 Gs and Intrinsic coercivity of more than 5000 Oe at the same time, pointing to problems of unable to acquire high magnetic property and high Intrinsic coercivity at the same time in prior technology, and method of producing the same. major formula of the invention is a permanent magnetic ferrite powder containing hexagonal type magnetoplumbite permanent magnetic ferrite of the following formula as main phase: A[1-x-y]Ca[x]R[y]Fe[2n-z]M[z]O[19], A represents Sr or Sr and Ba, R represents at least one of La, Pr, Nd or Bi, and La is needed; M represents at least one of Co, Ni and Zn, and Co is needed; x, y, z represents addition percentage of each main metal elements.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
R-Fe-B rare earth sintered magnet and method for producing same
ActiveCN101331566AEfficient replacementReduce flux densityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementSintered magnets
In a method for producing an R-Fe-B rare earth sintered magnet, there is firstly prepared an R-Fe-B rare earth sintered magnet body which contains, as the main phase, R2Fe14B compound crystal grains containing a light rare earth element RL (at least one of Nd and Pr) as a main rare earth element R, and then a heavy rare earth element RH is diffused into the rare earth sintered magnet body from the surface thereof by heating the sintered magnet body while supplying the heavy rare earth element RH (at least one substance selected from the group consisting of Dy, Ho and Tb) to the surface of the sintered magnet body.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Ferrite magnetic material, ferrite sintered magnet, and motor
InactiveUS20150170811A1Improve magnetic propertiesImprove performanceInorganic material magnetismCobalt compoundsSintered magnetsCrystal structure
A ferrite magnetic material and ferrite sintered magnet composed thereof have a ferrite having a hexagonal crystal structure as a main component. A composition ratio of a metallic element included in the main component is represented by: RxA1-x(Fe12-yCoy)z. R is at least one element selected from La, Ce, Pr, Nd and Sm and at least includes La. A is at least two elements selected from Ca, Sr and Ba and at least includes Ca and Sr. Si component and either or both of Al component and Cr component are included as a sub-component. When a sum of Al content and a value obtained by dividing Cr content by four and a value obtained by calculating the formula [(R+A)−(Fe+Co) / 12] / Si where R, A, Fe, Co and Si indicate values of each atom % thereof are defined as L and G, respectively, L and G have to be values within a predetermined region.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method for preparing heavy rare earth hydride nano-particle doped sintered NdFeB permanent magnet
ActiveCN101521069AImprove coercive forceNot easily oxidizedInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementDehydrogenation
The invention discloses a method for preparing a heavy rare earth hydride nano-particle doped sintered NdFeB permanent magnet, which belongs to the technical field of magnetic materials. The prior preparation method improves the coercive force and the temperature stability of magnets by adding heavy rare earth elements, namely terbium or dysprosium into master alloy, but the method can cause the residual magnetism of the magnets, the reduction of magnetic energy product and the increase of manufacturing cost. The method adopts heavy rare earth terbium hydride and dysprosium hydride nano-powder doping technology to prepare the sintered NdFeB permanent magnet with high coercive force and excellent magnetic property. The method comprises the following steps: preparing NdFeB powder by a rapidly solidified flake process and a hydrogen decrepitation process; preparing the terbium hydride or the dysprosium hydride nano-powder by physical vapor deposition technology; mixing the two powders, and performing magnetic field orientation and press forming; and performing dehydrogenation treatment, sintering and heat treatment on a green compact at different temperatures, and obtaining the sintered magnet. The coercive force of the magnet prepared by the method is higher than that of the prior sintered magnet with the same ingredients; and compared with the sintered magnet with the equivalent coercive force, the proportion of the terbium and dysprosium needed by the magnet prepared by the method is remarkably reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Rare earth sintered magnet and process for producing the same
ActiveCN101006534APhenomena that promote grain boundary diffusionEfficient replacementLiquid applicationPermanent magnetsRare-earth elementSintered magnets
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Method for preparing rare-earth system sintered magnet
InactiveUS6187259B1Improve magnetic propertiesEasy to produceInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureChemical reactionSintered magnets
The object of the present invention is to provide rare-earth system sintered magnets such as R-Fe-B system or R-Co system having excellent magnetic properties, unique configuration of a small size, thin wall thickness and intricate geometry. With the method for preparing the present invention, a granulation of alloy powders can be achieved easily, a chemical reaction between rare-earth system and binder substances can be suppressed, so that the residual oxygen and carbon levels in the sintered products can be reduced. Moreover, by this production method, the flowability and lubricant capability during the forming process can be improved. The dimension accuracy and productivity are also enhanced. A certain type of binder is added to rare-earth alloy powders and kneaded into a slurry state. The slurry is then formed into granulated powders by spray-dryer equipment. The thus granulated powders are molded, and sintered through a powder metallurgy technique.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Oxide magnetic material, ferrite particles, bonded magnet, sintered magnet, process for producing the same, and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS6402980B1Excellent magnetic propertiesIncrease valueMagnetic materials for record carriersInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementSintered magnets
The present invention provides an oxide magnetic material, which includes a primary phase of a hexagonal ferrite containing metallic elements Ca, R, Fe and M, where M represents at least one element selected from the group including Co, Ni and Zn, and R represents at least one element selected from the group including Bi and rare earth elements including Y, with La being essentially included in R; wherein the proportions of the metallic elements Ca, R, Fe and M with respect to the total amount of the metallic elements are from 1 to 13 atomic % for Ca, from 0.05 to 10 atomic % for R, from 80 to 95 atomic % for Fe, and from 1 to 7 atomic % for M. The present invention also provides ferrite particles, a bonded magnet, a sintered magnet, a process for producing them, and a magnetic recording medium, which contain the oxide magnetic material.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method of preparing micro-structured powder for bonded magnets having high coercivity and magnet powder prepared by the same
InactiveUS7163591B2Improve coercive forceReduce manufacturing costInorganic material magnetismRare earthContamination
Disclosed is a method of preparing a micro-structured powder for bonded magnets having high coercivity, which is advantageous in terms of low preparation costs by recycling magnet scraps, simplified mass production, minimal environmental contamination by such a recycling process, and the preparation of stable anisotropic powders having high coercivity. Further, a magnet powder prepared by the above method is provided. The current method is characterized in that R—Fe—B type anisotropic sintered magnets or scraps thereof are crushed to prepare 50–500 μm sized magnet powders, which are then mixed with 1–10 wt % of rare earth fluoride (RF3) powders and thermally treated at high temperatures (500–1100° C.) in a vacuum or an inert gas, to cause the change of matrix-near surface and grain boundary of the powders. Thus obtained powders include a matrix phase having R2Fe14B crystal structure, a R-rich grain boundary phase containing rare earth fluoride, and other phases, in which the matrix phase has an average grain size of 1–20 μm, and the powders have an average size of 50–500 μm with superior magnetic characteristics of (BH)max≧20 MGOe and iHc≧5 kOe.
Owner:JAHWA ELECTRONICS
Method for preparing rare earth permanent magnet material
ActiveUS20090226339A1Inorganic material magnetismSolid state diffusion coatingRare-earth elementPowder mixture
A method for preparing a rare earth permanent magnet material is characterized by comprising the steps of disposing a powder mixture on a surface of a sintered magnet body of R1—Fe—B composition wherein R1 is at least one element selected from rare earth elements inclusive of Sc and Y, the powder mixture comprising a powder containing at least 0.5% by weight of M which is at least one element selected from Al, Cu, and Zn and having an average particle size equal to or less than 300 μm and a powder containing at least 30% by weight of a fluoride of R2 which is at least one element selected from rare earth elements inclusive of Sc and Y and having an average particle size equal to or less than 100 μm, and heat treating the magnet body having the powder disposed on its surface at a temperature equal to or below the sintering temperature of the magnet body in vacuum or in an inert gas, for causing at least one of M and R2 in the powder mixture to be absorbed in the magnet body. The invention provides an R—Fe—B sintered magnet with high performance and a minimized amount of Tb or Dy used.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Samarium-cobalt sintered magnet material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101882494ALower temperature coefficient of remanenceLower flux temperature coefficientMagnetic materialsRare earthCobalt
The invention discloses a 2:17 type samarium-cobalt sintered magnet material and a preparation method thereof. The 2:17 type samarium-cobalt sintered magnet material comprises the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 10 to 25 percent of samarium, 45 to 55 percent of cobalt, 10 to 20 percent of iron, 3 to 9 percent of copper, 1 to 3 percent of zirconium and 5 to 15 percent of at least one heavy rear earth element. Due to the selection and the proportion of the raw materials and the innovation of the sintering process, a microstructure of the magnet material is optimized, and the aims of reducing the temperature coefficient of a magnet and simultaneously maintaining higher magnetic energy product of the magnet are fulfilled, wherein the magnetic energy product of the prepared magnet is 14 to 25 MGsOe, the residual magnetism temperature coefficient is about -0.005 to -0.03 percent per DEG C, and a lower magnetic flux temperature coefficient is maintained in an environment at the temperature of between -35 and 300 DEG C.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
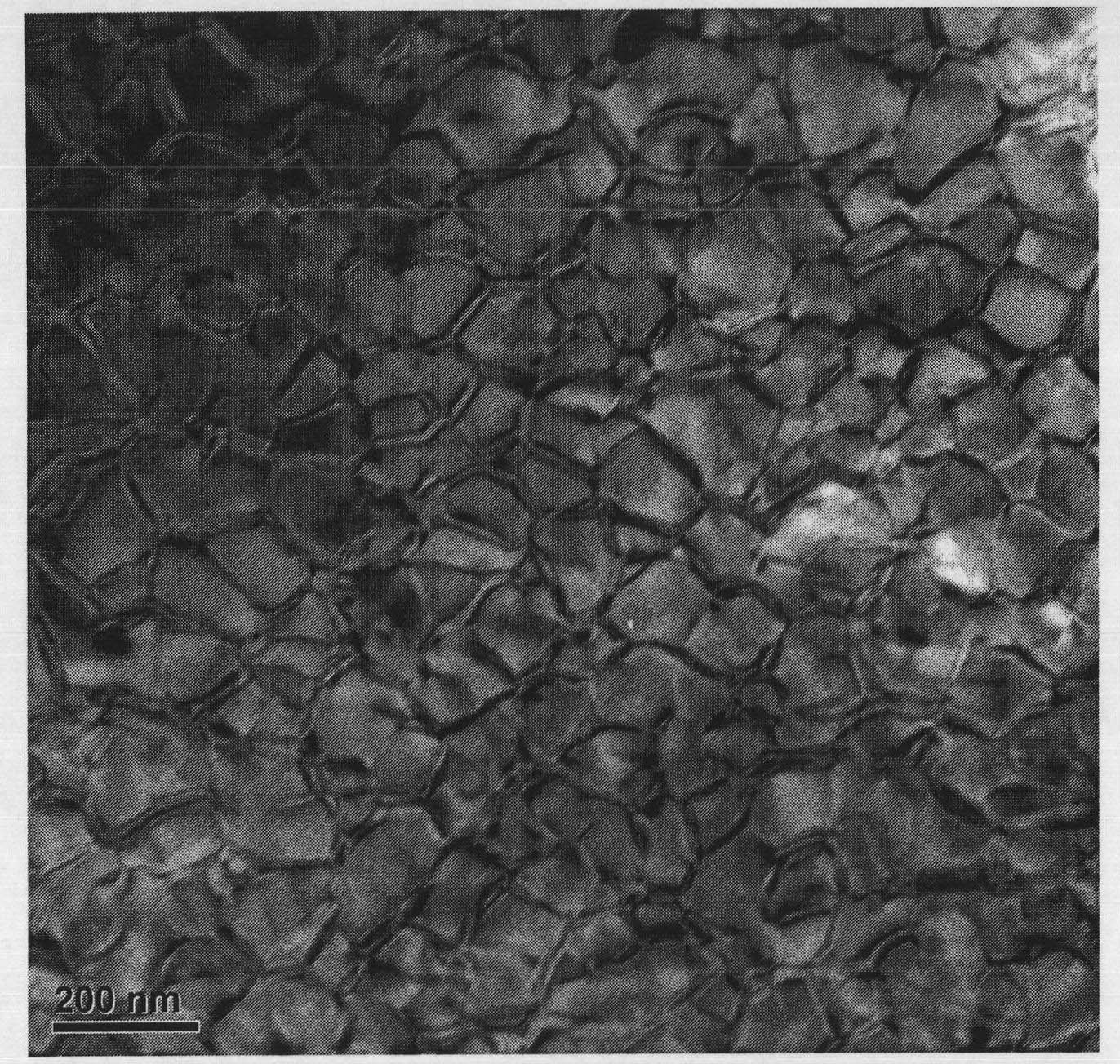
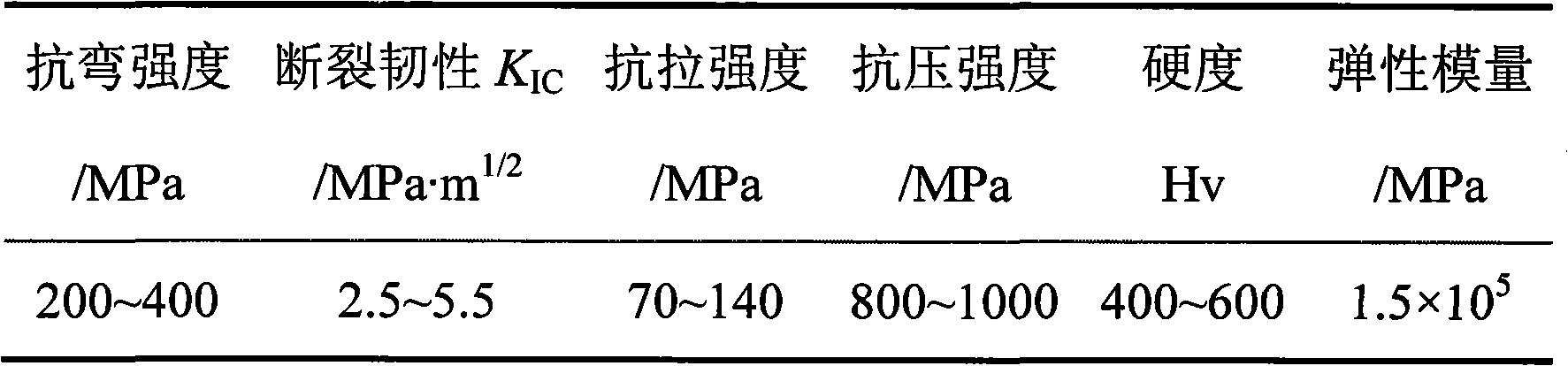
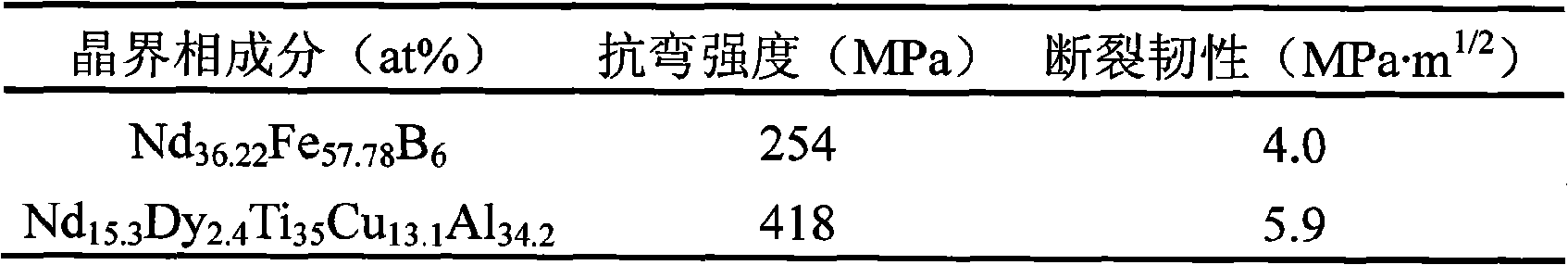
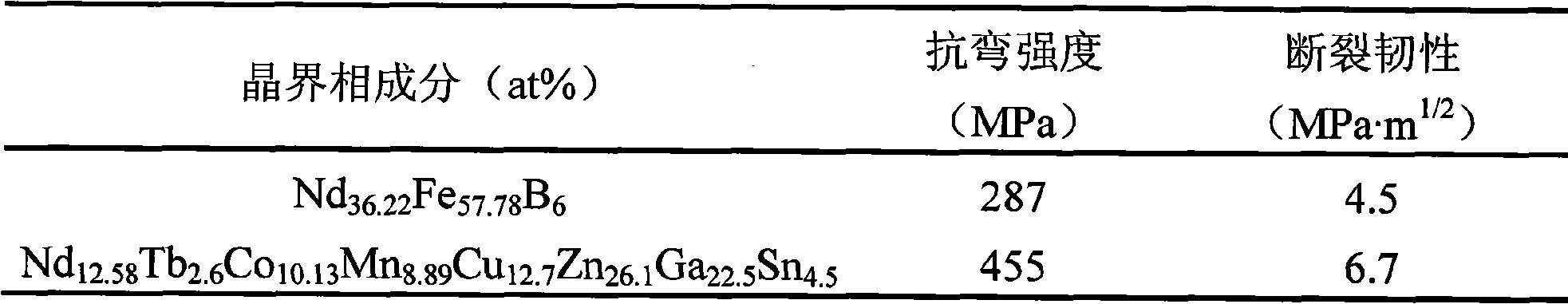
High-strength tenacity agglomeration neodymium-iron-boron magnet reconstructed by crystal boundary phase and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101325109AImprove toughnessLow melting pointMagnetic materialsSintered magnetsGrain boundary
The invention discloses a high-obdurability Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet reconstructed by the grain boundary phase and the preparation method thereof. The Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet comprises the component of NdeFe100-e-f-gBfMg, wherein, e is more than or equal to 6 and less than or equal to 24, f is more than or equal to 5.3 and less than or equal to 6.4, and g is more than or equal to 0.01 and less than or equal to 6, and M is one or more elements of Dy, Tb, Pr, Sm, Ce, Yb, Co, Ni, Mn, Nb, Ta, Zr, Si, Ti, Mo, Ag, Au, Mg, Cu, Al, Zn, Ga, Bi, Sn and In; the preparation method comprises the following steps: main phase alloy and grain boundary phase alloy are respectively prepared into powder, and then the powder is intensively mixed; the mixed powder is pressed into the molded blank in the magnetic field; and the sintered magnet is obtained in a high-vacuum sintering oven. Through the restruction of the grain boundary phase component, the solution grain boundary phase alloy with low smelting point and high strength ductility is achieved, the obdurability of the grain boundary phase is enhanced on the basis that the magnetic property is guaranteed, thereby the high ductility of the magnet is enhanced, and the process is simple, the cost is low, and the magnet is suitable for the mass production, thereby the double-alloy method combined with the grain boundary restruction can be used for preparing the Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet with high obdurability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Sintered magnet
ActiveUS20150170810A1Improve coercive forceUse amount of heavy rare earth elements is reducedPermanent magnetsMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementSintered magnets
A sintered magnet of a preferred embodiment has a composition comprising: R (R is a rare earth element that must contain any one of Nd and Pr.): 29.5 to 33.0 mass %; B: 0.7 to 0.95 mass %; Al: 0.03 to 0.6 mass %; Cu: 0.01 to 1.5 mass %; Co: 3.0 mass % or less (provided that 0 mass % is not included.); Ga: 0.1 to 1.0 mass %; C: 0.05 to 0.3 mass %; O: 0.03 to 0.4 mass %; and Fe and other elements: a balance, and wherein a content of heavy rare earth elements in total is 1.0 mass % or less, and wherein the following relations are satisfied: 0.29<[B] / ([Nd]+[Pr])<0.40 and 0.07<([Ga]+[C]) / [B]<0.60, where [Nd], [Pr], [B], [C] and [Ga] represent the numbers of atoms of Nd, Pr, B, C and Ga, respectively.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
R-Fe-B sintered magnet
ActiveUS7090730B2Improve coercive forceInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementSintered magnets
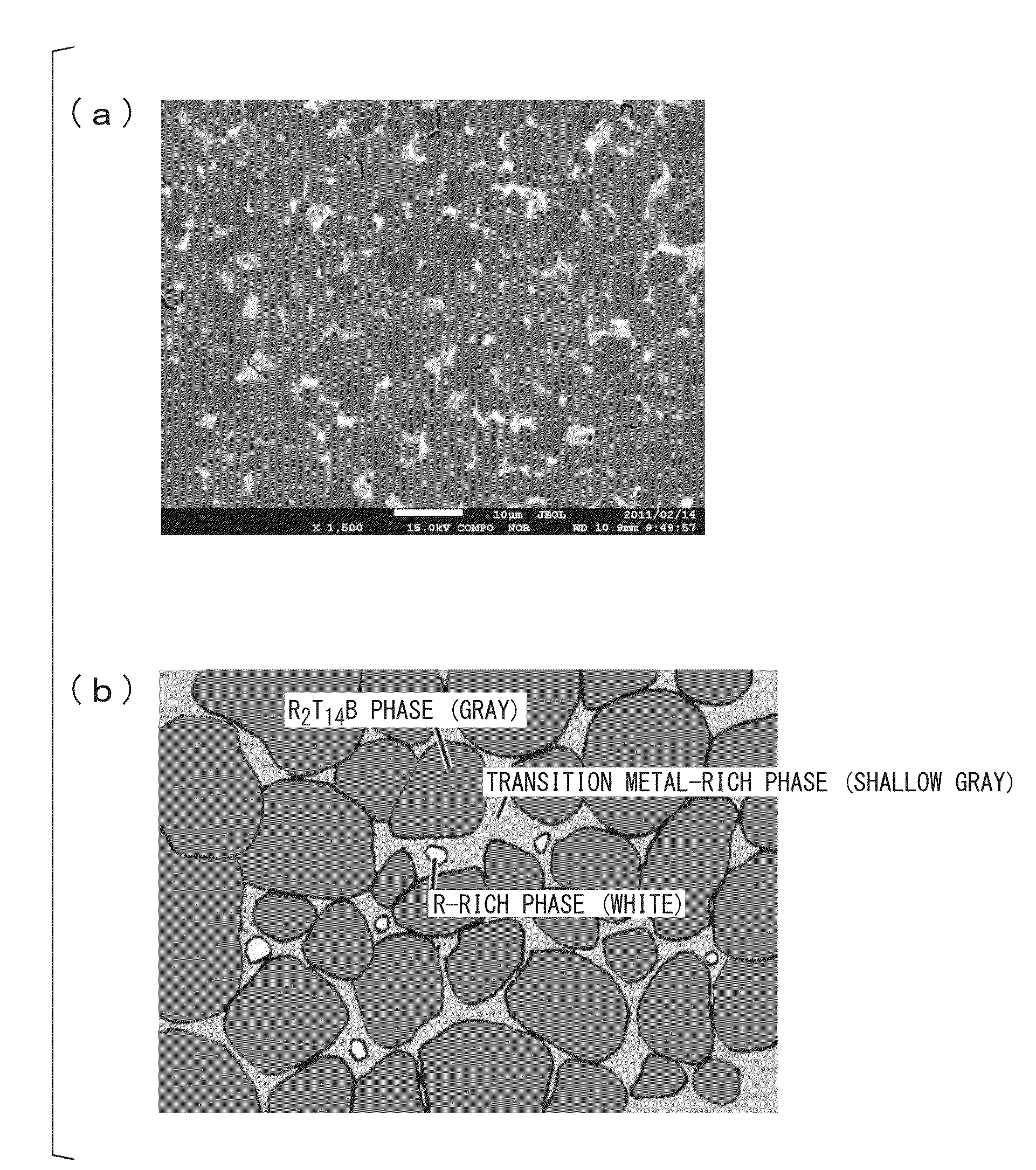
An R—Fe—B base sintered magnet having a composition of 12–17 at % of R (wherein R stands for at least two of yttrium and rare earth elements and essentially contains Nd and Pr), 0.1–3 at % of Si, 5–5.9 at % of B, 0–10 at % of Co, and the balance of Fe, containing a R2(Fe,(Co),Si)14B intermetallic compound primary phase and at least 1% by volume of an R—Fe(Co)—Si grain boundary phase, and being free of a B-rich phase exhibits a coercive force of at least 10 kOe despite a reduced content of heavy rare earth.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
R-t-b-type sintered magnet and method for production thereof
ActiveUS20110025440A1Increase in coercivityImprove remanencePermanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureSintered magnetsOxygen content
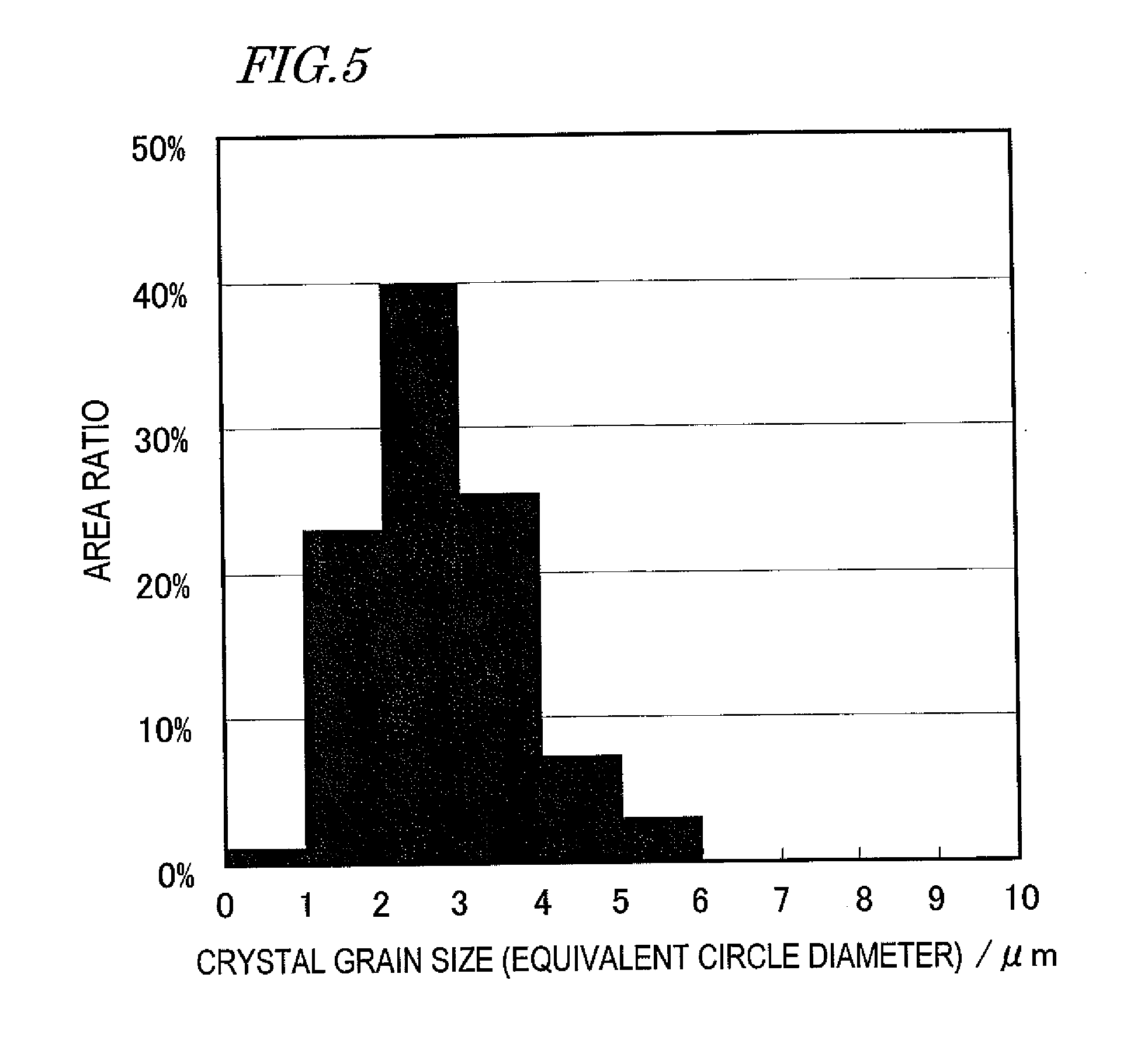
An R-T-B based sintered magnet according to the present invention has a composition including: 27.3 mass % to 29.5 mass % of R; 0.92 mass % to 1 mass % of B; 0.05 mass % to 0.3 mass % of Cu; 0.02 mass % to 0.5 mass % of M; and T as the balance, and has an oxygen content of 0.02 mass % to 0.2 mass %. The main phase of the sintered magnet is an R2T14B type compound. The crystal grain size of the main phase is represented by an equivalent circle diameter of 8 μm or less. And crystal grains with equivalent circle diameters of 4 μm or less account for at least 80% of the overall area of the main phase.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Preparation of rare earth permanent magnet material
ActiveUS20110150691A1Improve remanenceImprove coercive forceElectric discharge tubesPermanent magnetsRare-earth elementRemanence
A method for preparing a rare earth permanent magnet material comprises the steps of: disposing a powder comprising one or more members selected from an oxide of R2, a fluoride of R3, and an oxyfluoride of R4 wherein R2, R3 and R4 each are one or more elements selected from among rare earth elements inclusive of Y and Sc on a sintered magnet form of a R1—Fe—B composition wherein R1 is one or more elements selected from among rare earth elements inclusive of Y and Sc, and then heat treating the magnet form and the powder at a temperature equal to or below the sintering temperature of the magnet in vacuum or in an inert gas. The result high performance, compact or thin permanent magnet has a high remanence and coercivity at a high productivity.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Nd-Fe-B Magnetic with Modified Grain Boundary and Process for Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080006345A1Improve coercive forceEasy to demagnetizeInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureReduction treatmentViewpoints
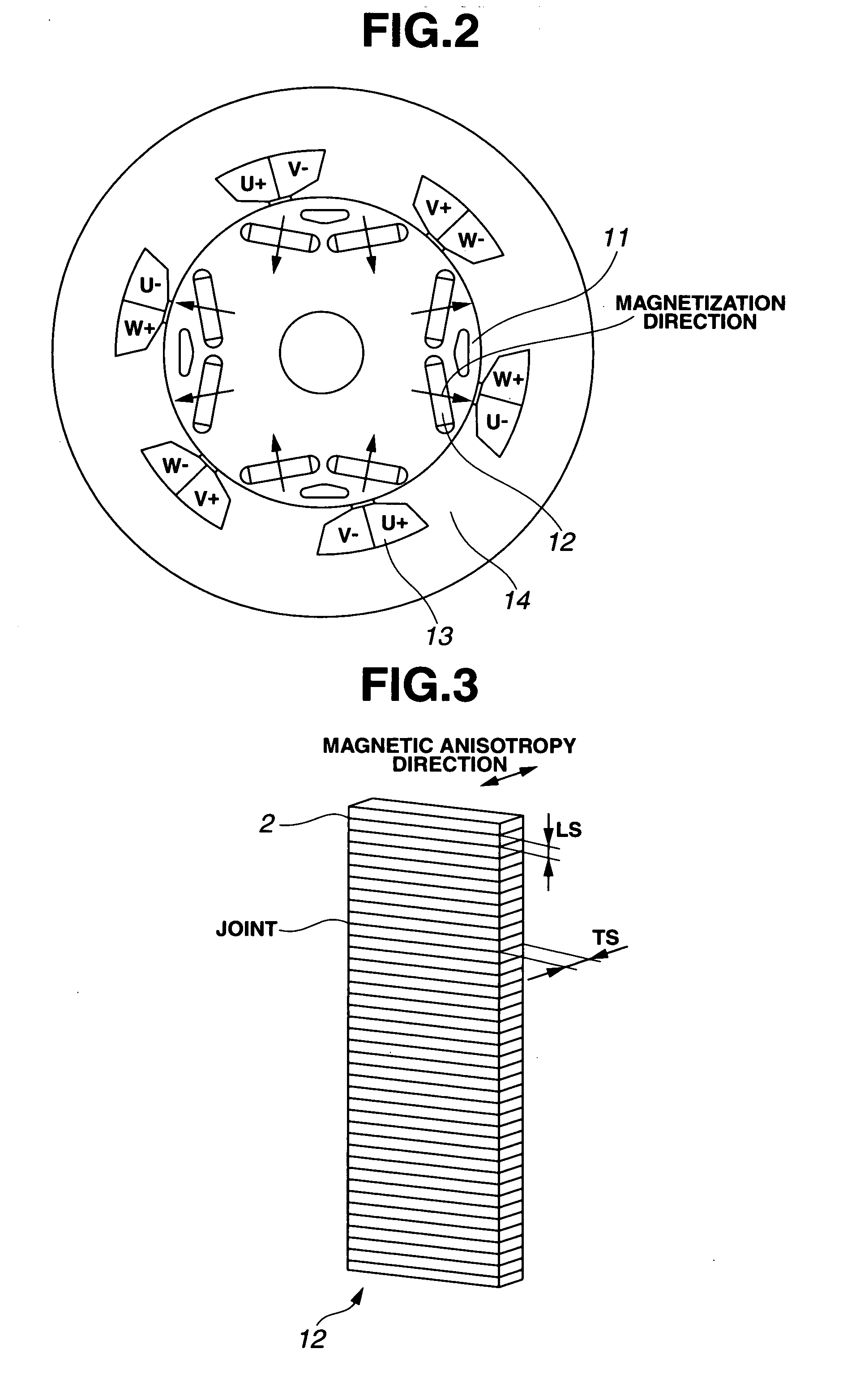
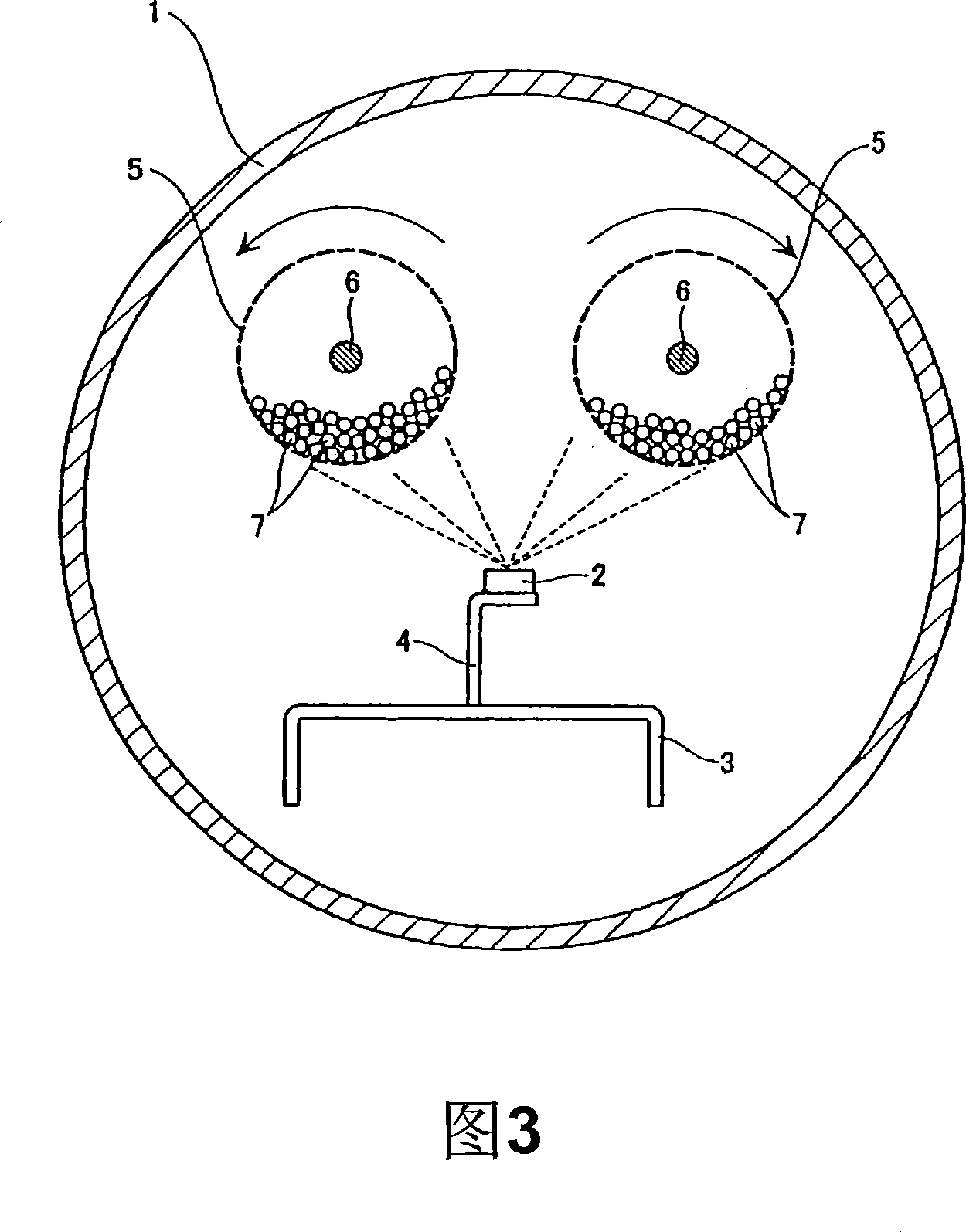
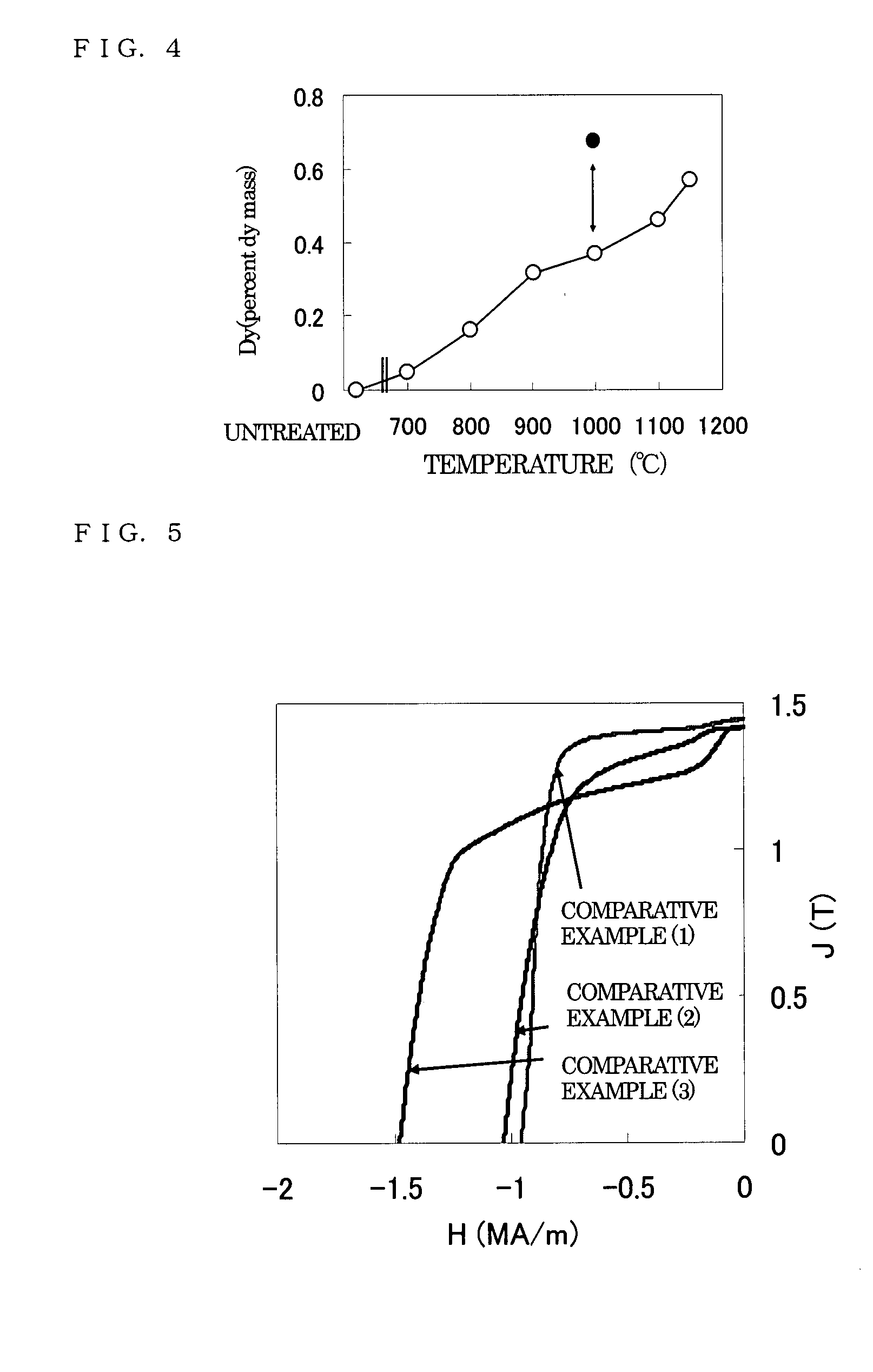
[Problem] In known methods, an improvement of the coercive force is realized by allowing the Dy metal or the like to present selectively in crystal grain boundary portions of a sintered magnet. However, since these are based on a physical film formation method, e.g., sputtering, through the use of a vacuum vessel, there is a mass productivity problem in the case where large amounts of magnet is treated. Furthermore, there is a magnet cost problem from the viewpoint that, for example, an expensive, high-purity Dy metal or the like must be used as a raw material for film formation. [Solving Means] A method for modifying grain boundaries of a Nd—Fe—B base magnet characterized by including the step of allowing an M metal component to diffuse and penetrate from a surface of a Nd—Fe—B base sintered magnet body having a Nd-rich crystal grain boundary phase surrounding principal Nd2Fe14B crystals to the grain boundary phase through a reduction treatment of a fluoride, an oxide, or a chloride of an M metal element (where M is Pr, Dy, Tb, or Ho).
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Mixed rare earth sintering permanent magnet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104715876AImprove coercive forceReduce extractionPermanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureSintered magnetsRare earth
The present invention provides a mixed rare earth sintered permanent magnet and preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the mixed rare earth sintered permanent magnet prepares the sintered permanent magnet by more than two kinds of alloys. The preparation method of the mixed rare earth sintered permanent magnet of the present invention may produce a sintered magnet with a magnetic energy product such as 2-45 MGOe and optional performance by adjusting proportions of each alloy according to need. A stable main phase of R2Fe14B can be formed by multi-alloy process. Because the permanent magnet is prepared directly by the mixed rare earth, steps of extraction, separation and purification for preparing a single rare earth can be partly saved on one hand, the cost is greatly saved and the environment is protected; the comprehensive utilization of the rare earth resource can be maximized on the other hand.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONG KE SAN HUAN HI TECH +1
Method for preparing high performance sintered neodymium-iron-boron air stream millby hydrogenation
InactiveCN101051544AImprove powder output efficiencyIncrease the coercive force of the magnetInorganic material magnetismNitrogen gasCrusher
The method includes steps: (1) using casting technique to produce ingot of Nd-Fe-B alloy, or using quick hardening technique to produce quick hardening slices; (2) using hydrogen explosion technique or crusher to crash alloy of ingot or quick hardening slices into coarse powder; (3) through airflow grinding machine to produce fine powder from coarse powder; and mixed compressed gas from nitrogen and hydrogen is adopted by the airflow grinding machine; (4) mixing fine powder, gasoline, and antioxidant evenly by blender so as to obtain mixed powder; (5) molded blanks are pressed from mixed powder under 1.2-2.0T magnetic field; (6) molded blanks are sintered inside high vacuum sintering furnace at deg.C 1050-1120 for 2-4h; and through temper of heat treatment 2-4h at deg.C 500-650 so as to produce sintered magnet. Comparing with traditional technique, the invention produces magnet with high coercive force, and fine powder in high efficiency, is suitable to batch production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Permanent magnet and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20090322459A1Low costImprove magnetic propertiesVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSintered magnetsRare earth
A permanent magnet is provided which has formed a Dy, Tb film on a surface of an iron-boron-rare earth sintered magnet of a predetermined shape, with diffusion thereof into grain boundary phases, having a higher coercive force. The method of manufacturing a permanent magnet includes a film-forming step of evaporating metal evaporating material containing at least one of Dy and Tb and adhering evaporated metal atoms to a surface of the iron-boron-rare earth sintered magnet, and a diffusing step of performing heat treatment to diffuse metal atoms adhered to the surface into grain boundary phases of the sintered magnet. The metal evaporating material contains at least one of Nd and Pr.
Owner:ULVAC INC
R-t-b system sintered magnet
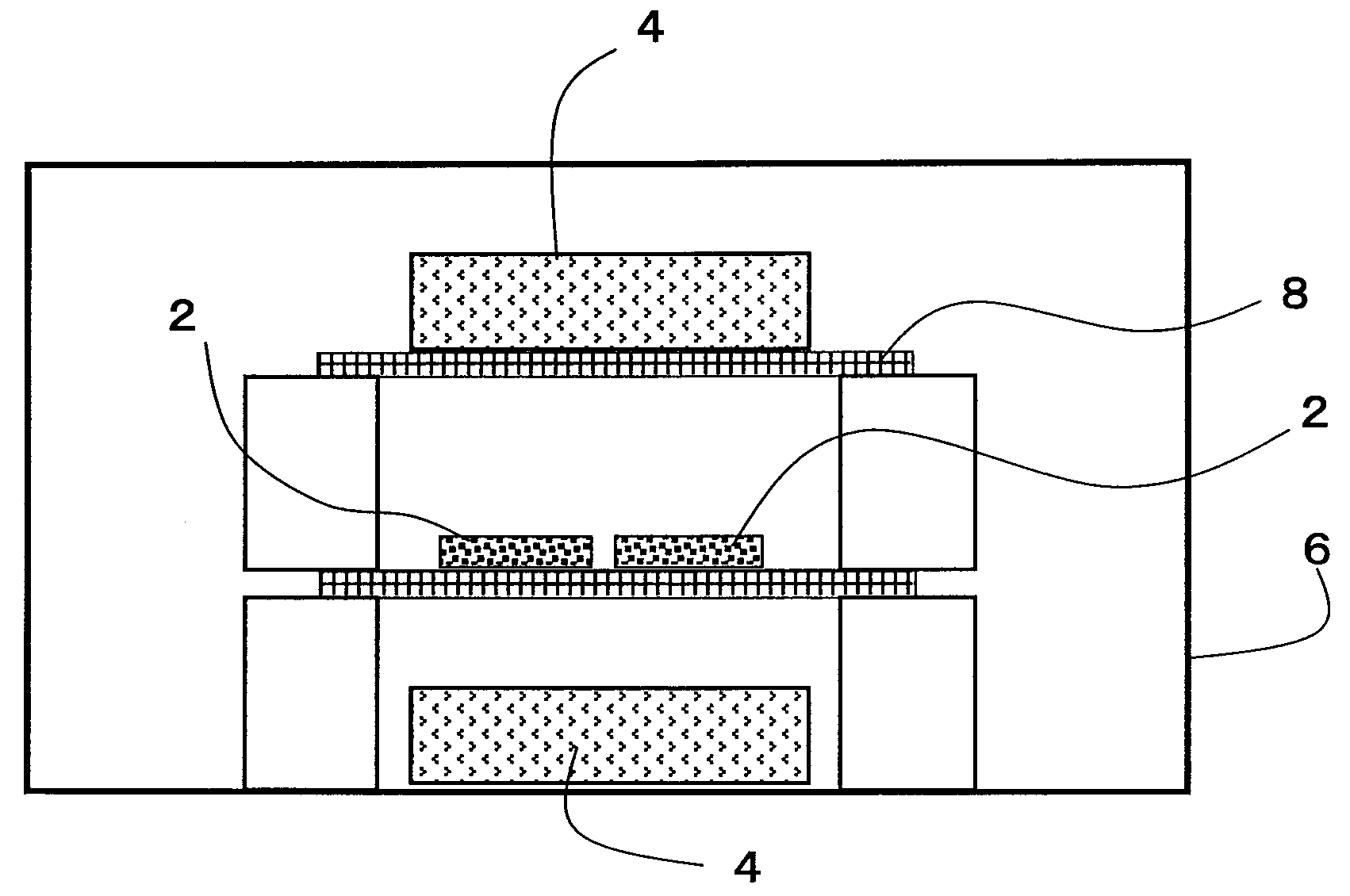
ActiveUS20090019969A1High Remanent Flux DensityImprove coercive forceInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementShortest distance
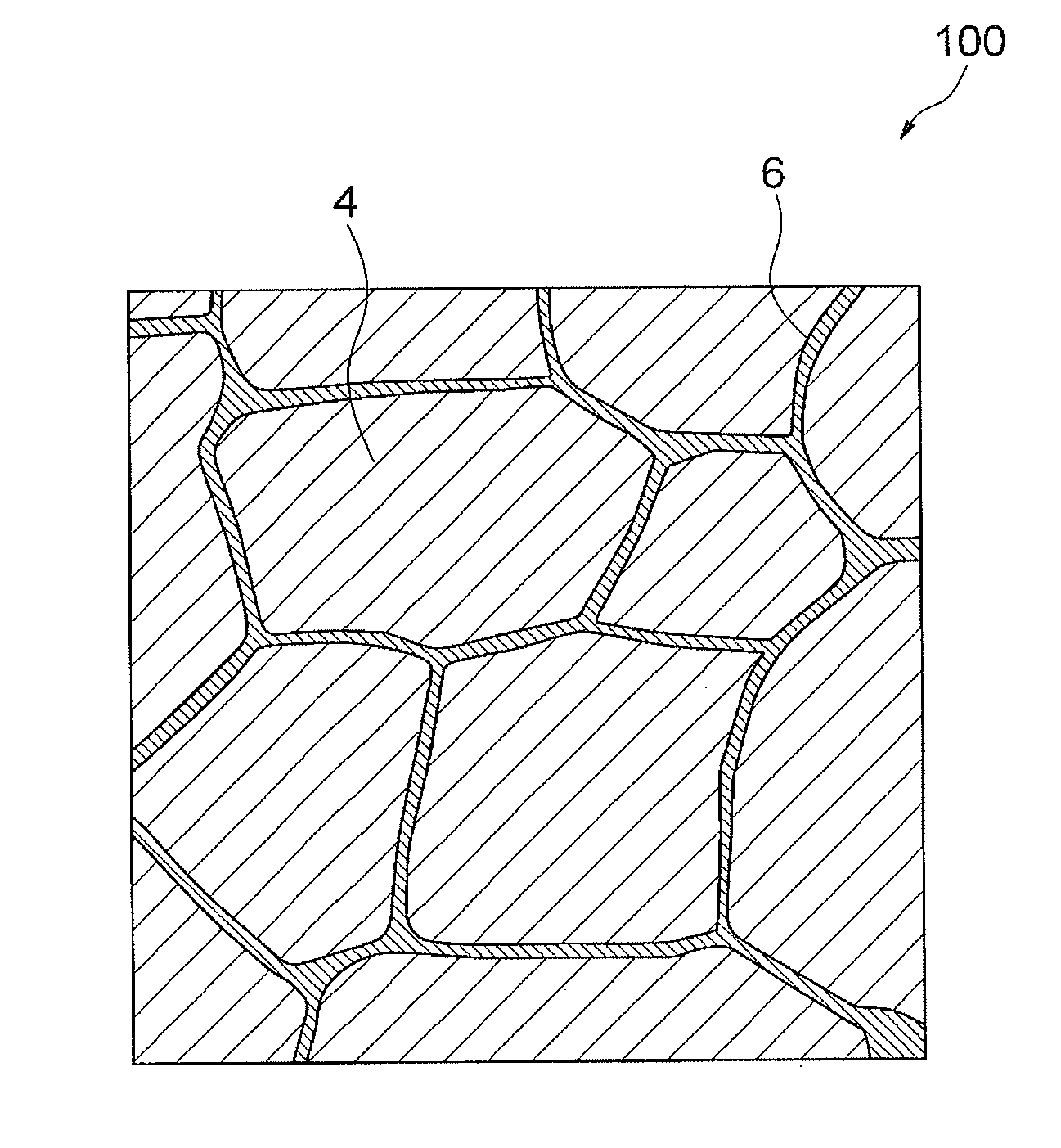
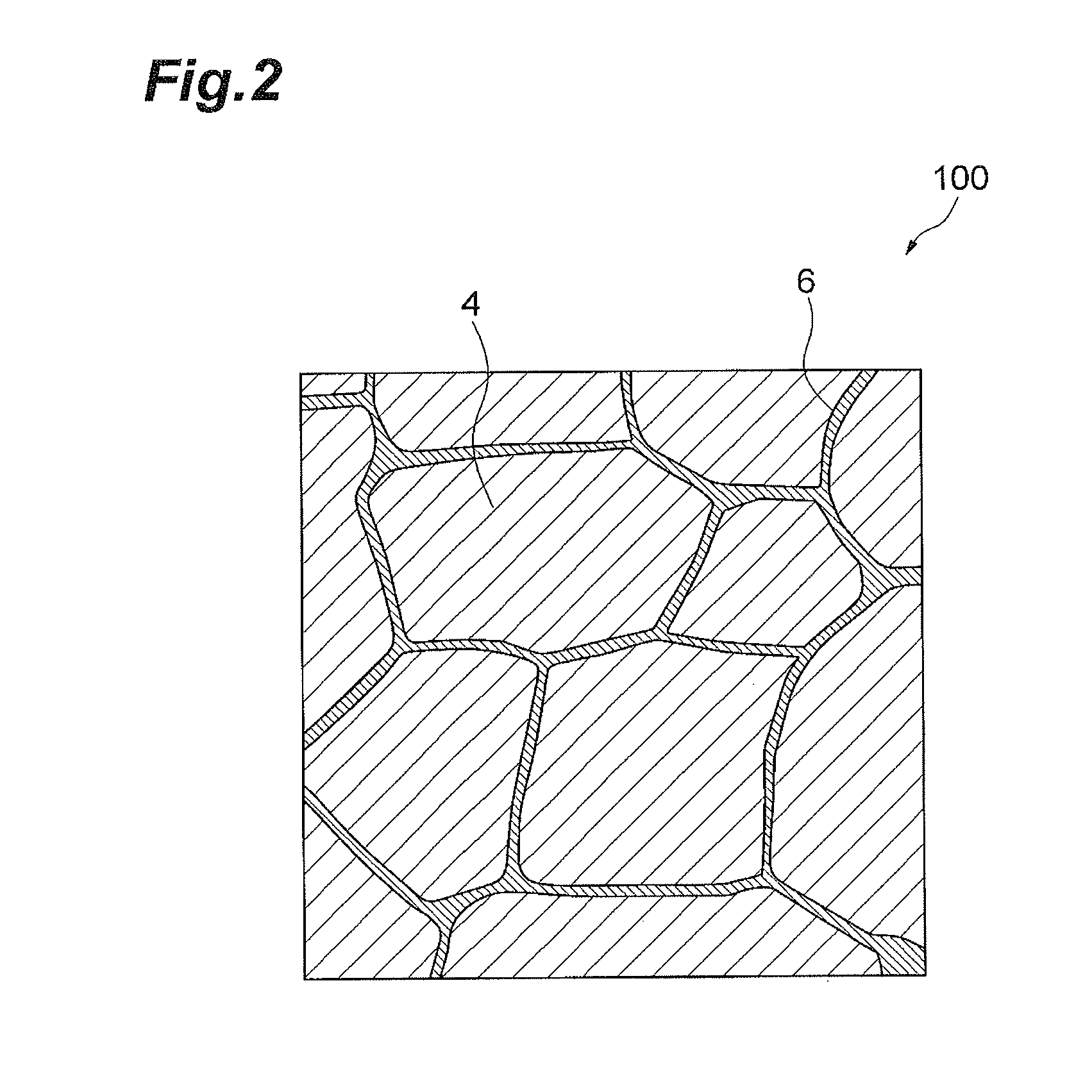
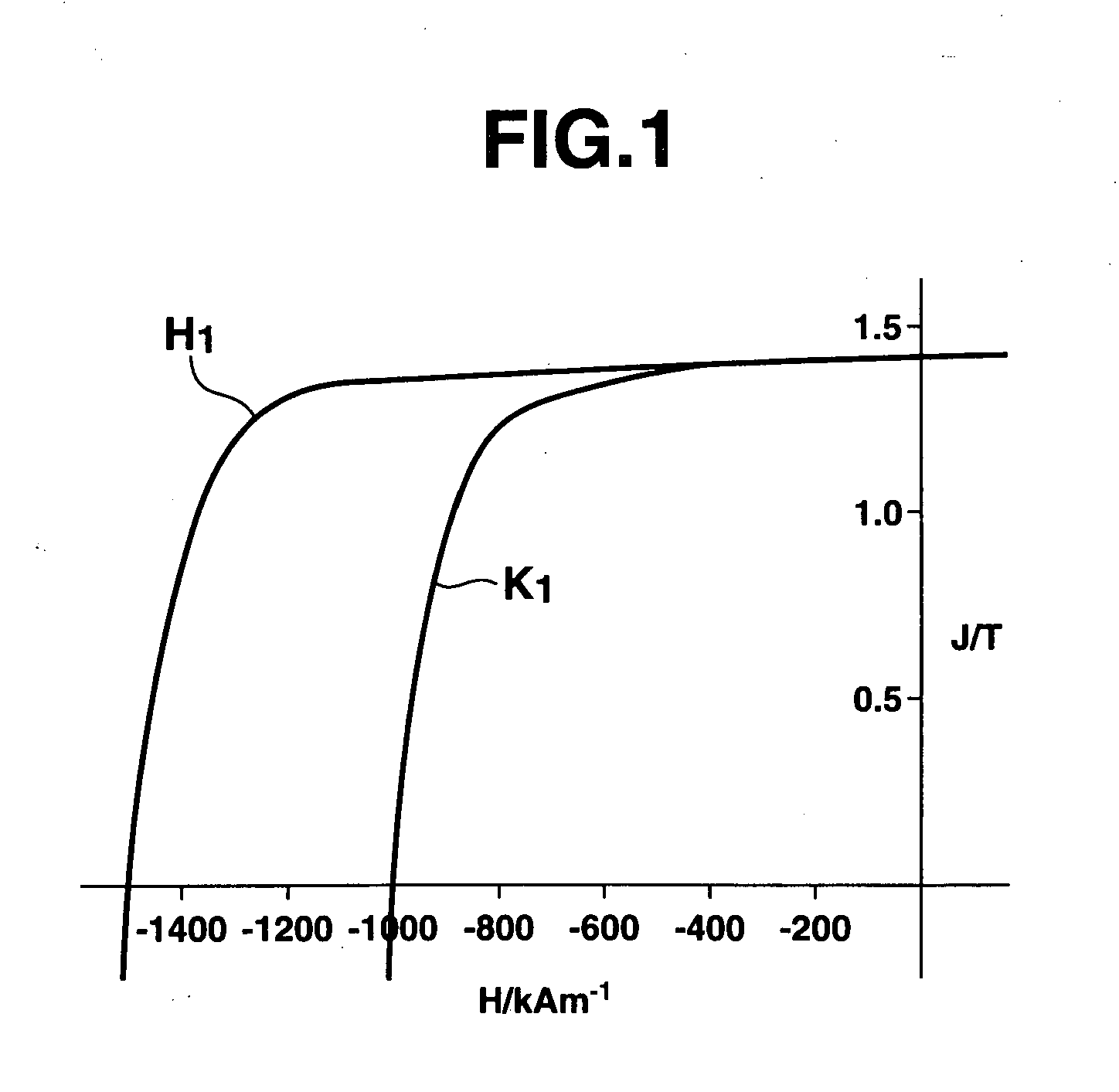
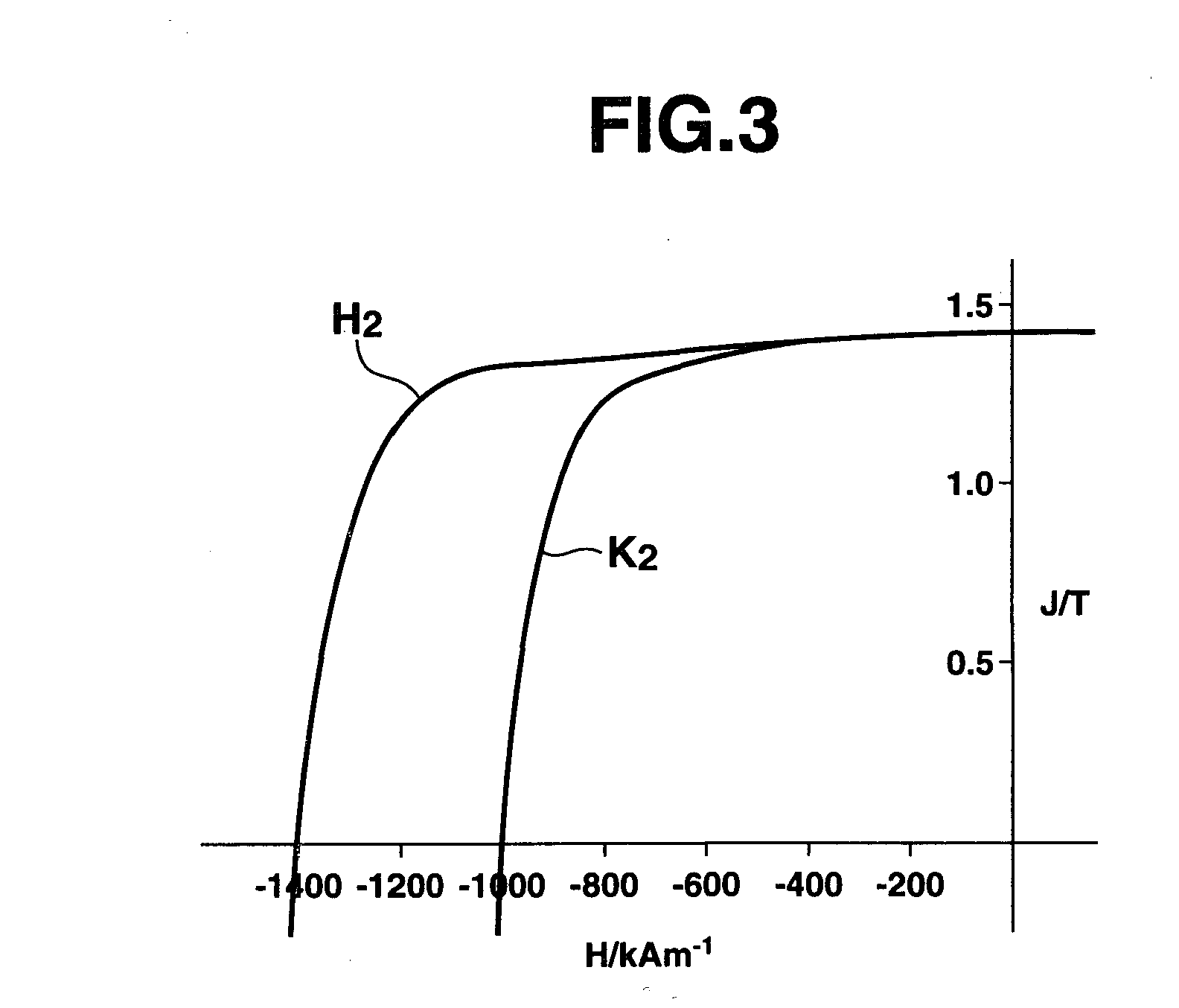
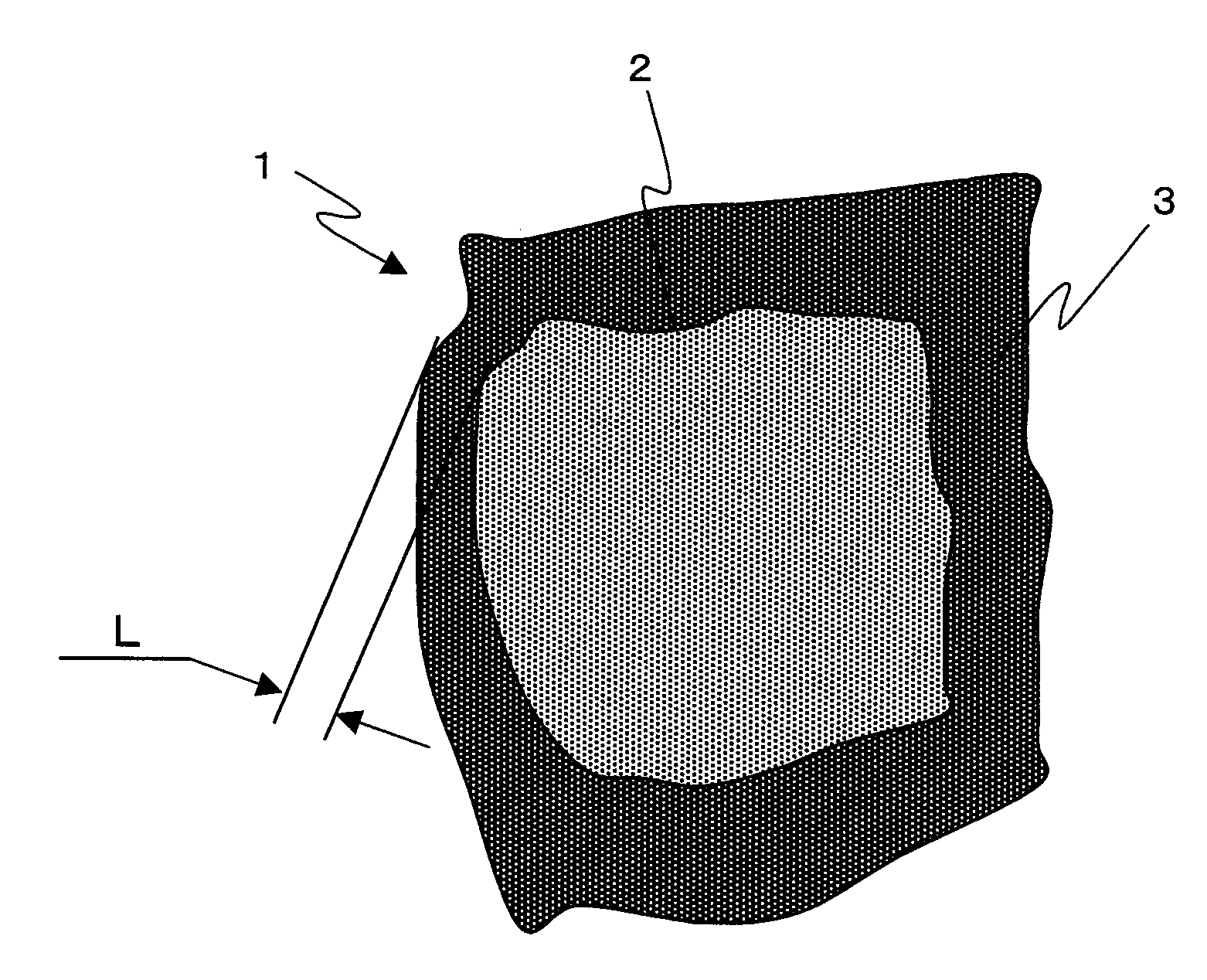
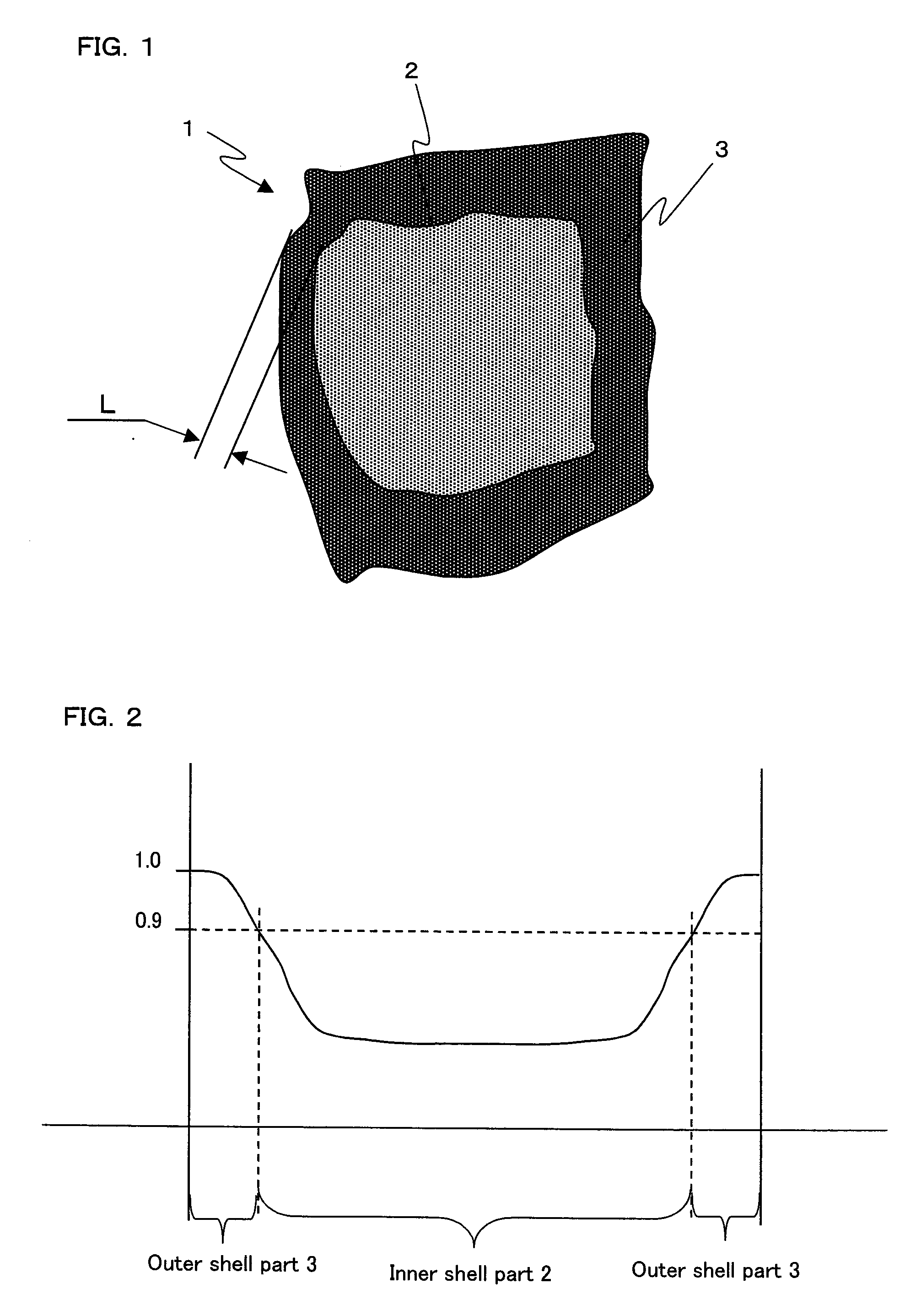
An R-T-B system sintered magnet is provided which achieves both a high residual magnetic flux density and a high coercive force. The R-T-B system sintered magnet comprises main-phase grains 1 each having a core-shell structure comprising an inner shell part 2 and an outer shell part 3 surrounding the inner shell part 2, wherein the concentration of the heavy rare earth element in the inner shell part 2 is lower by 10% or more than the concentration of the heavy rare earth element in the periphery of the outer shell part 3, and (L / r)ave falls within a range from 0.03 to 0.40 in the main-phase grains 1 each comprising the inner shell part 2 and the outer shell part 3, wherein L represents the shortest distance from the periphery of the main phase grain 1 to the inner shell part 2, r represents the equivalent diameter of the main phase grain 1, and (L / r)ave represents the average value of L / r for the main-phase grains 1 present in the sintered body and having the core-shell structure.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Nd-fe-b magnet with modified grain boundary and process for producing the same
InactiveCN101076870AIncrease the coercive forceEasy to demagnetizeInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureReduction treatmentSintered magnets
In the conventional process, a coercitivity increase is realized by effecting selective presence of, for example, Dy metal in crystal grain boundary zones of sintered magnet. However, as this process employs a physical film forming technique using a vacuum vessel, such as sputtering, there has been a difficulty in mass productivity in the performing of vast quantities of magnet treatment. Further, from the viewpoint, for example, that an expensive high-purity Dy metal or the like must be employed as a film forming material, there has been a drawback in magnet cost. There is provided a method of modifying the grain boundary of Nd-Fe-B magnet, characterized in that a fluoride, oxide or chloride of metal element M (M: Pr, DY, Tb or Ho) is subjected to reduction treatment so that there is effected diffusion infiltration of the metal element M from the surface of Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet having an Nd rich crystal grain boundary phase surrounding the circumferential part of Nd2Fe14B main crystal into the grain boundary phase.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
R-Fe-B TYPE RARE EARTH SINTERED MAGNET AND PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION OF THE SAME
ActiveUS20100182113A1Improve concentrationPermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementSintered magnets
In an R—Fe—B based rare-earth sintered magnet according to the present invention, at a depth of 20 μm under the surface of its magnet body, crystal grains of an R2Fe14B type compound have an (RL1-xRHx)2Fe14B (where 0.2≦x≦0.75) layer with a thickness of 1 nm to 2 μm in their outer periphery. In this case, the light rare-earth element RL is at least one of Nd and Pr, and the heavy rare-earth element RH is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Dy, Ho and Tb.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
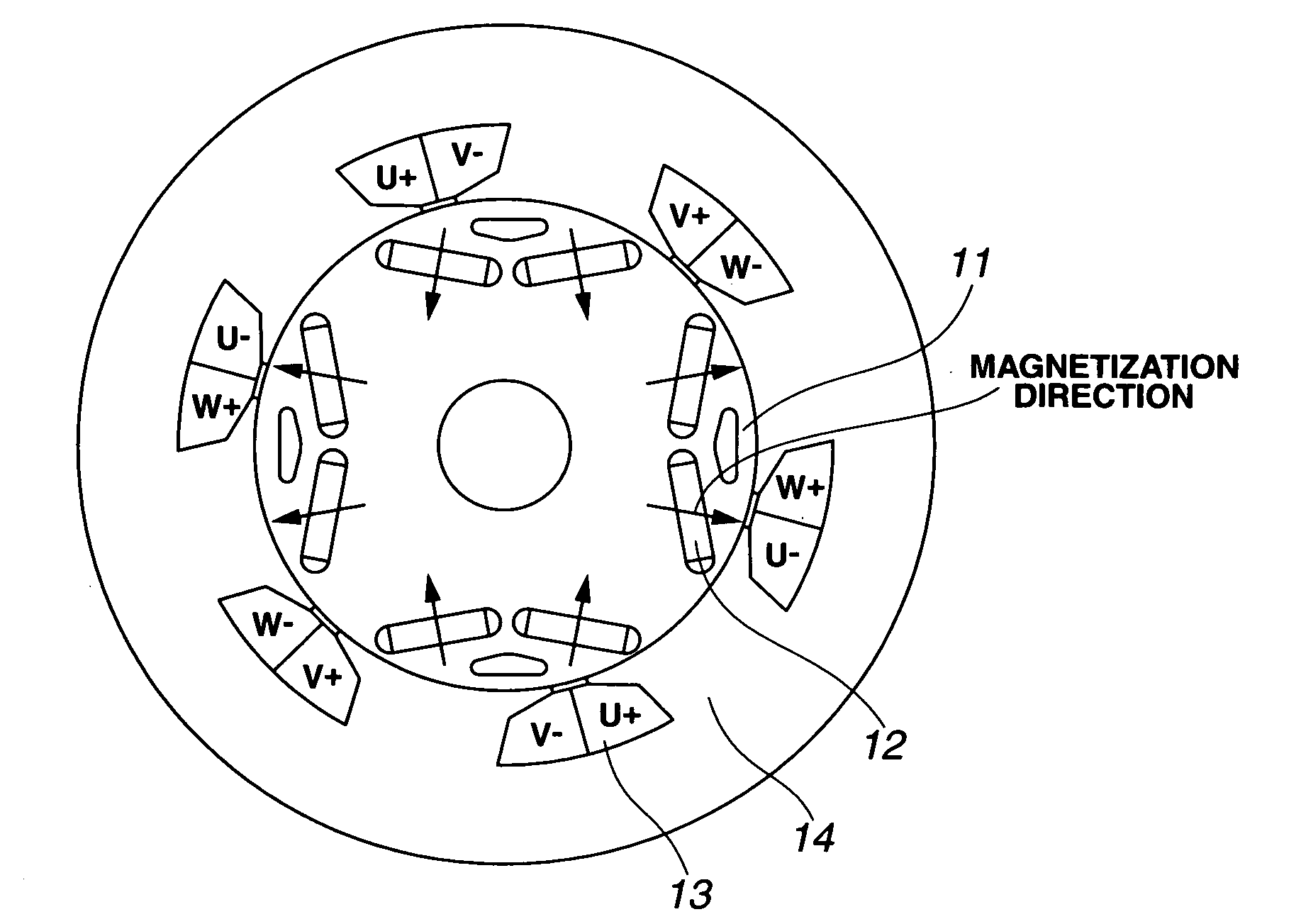
Rare earth permanent magnet, making method, and permanent magnet rotary machine
ActiveUS7559996B2Improve remanenceEffective absorptionMagnetic circuitPermanent magnetsRare-earth elementSintered magnets
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com