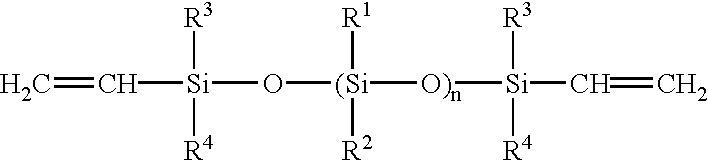
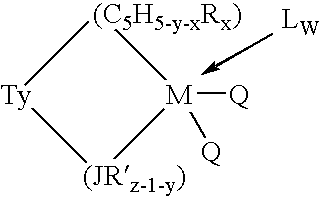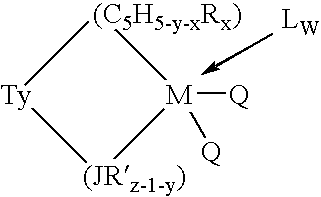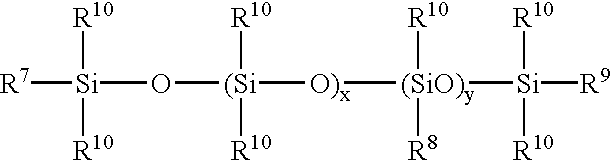Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3596 results about "Hydride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
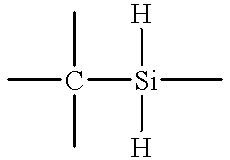
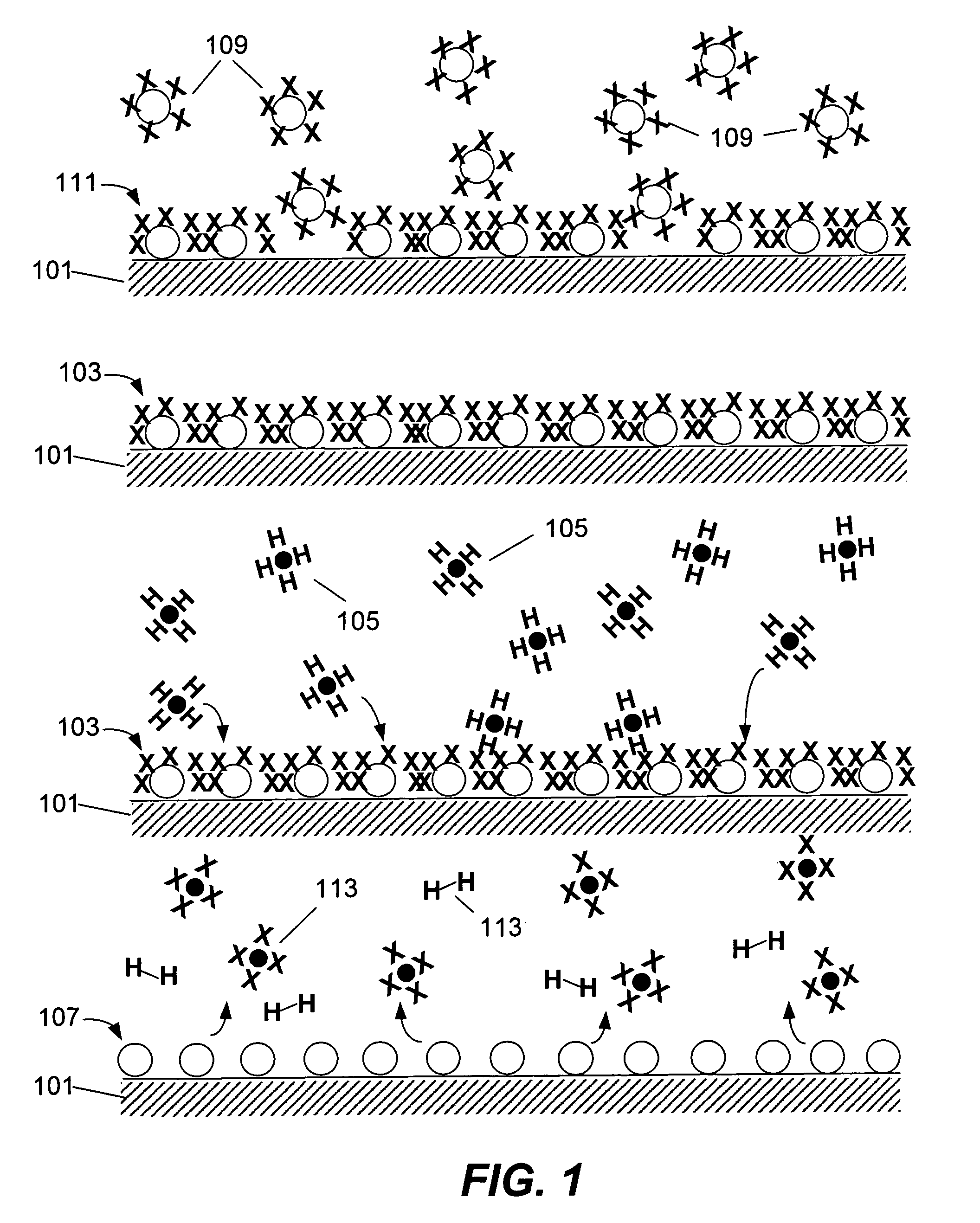
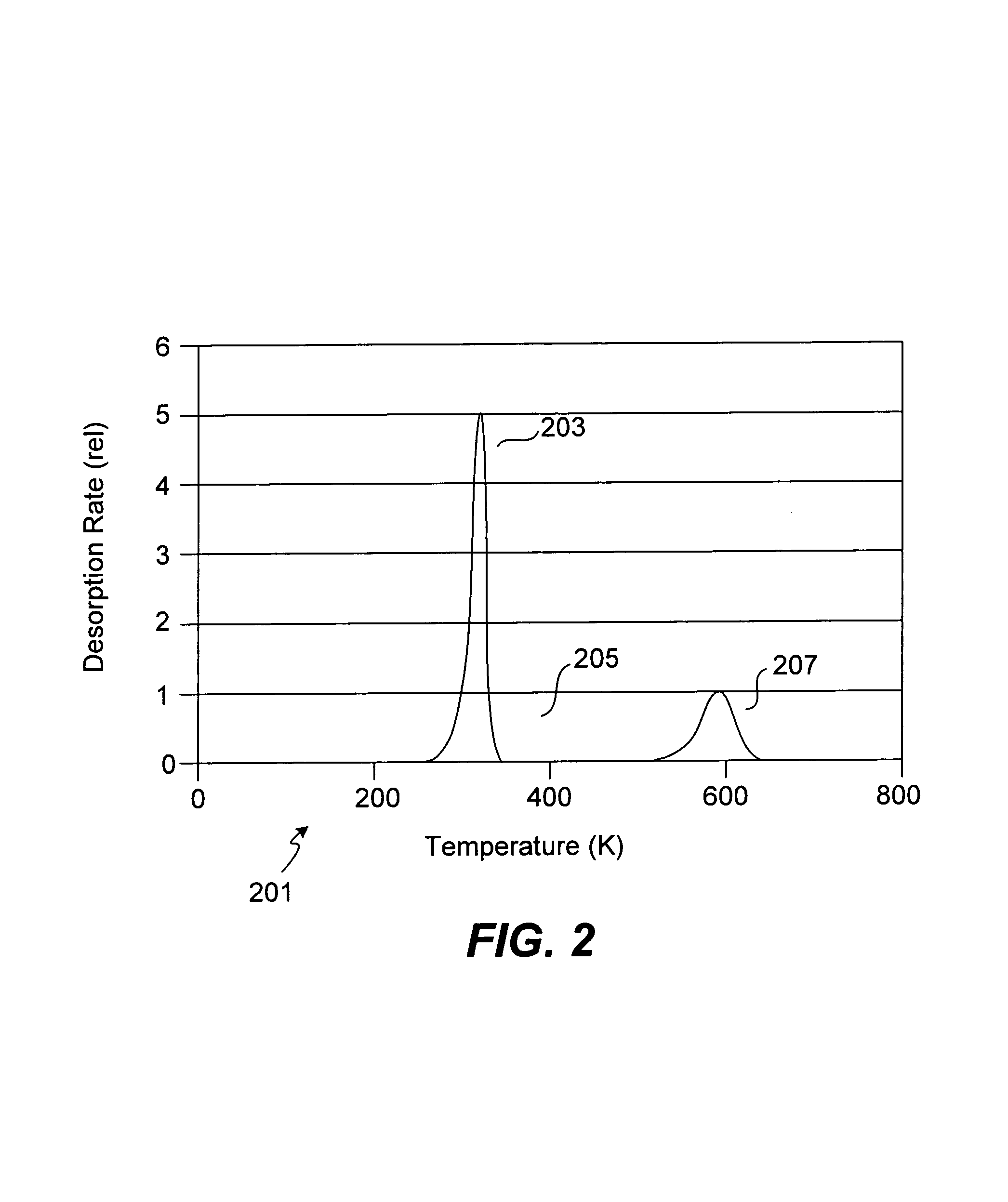
In chemistry, a hydride is the anion of hydrogen, H⁻, or more commonly it is a compound in which one or more hydrogen centres have nucleophilic, reducing, or basic properties. In compounds that are regarded as hydrides, the hydrogen atom is bonded to a more electropositive element or groups. Compounds containing hydrogen bonded to metals or metalloids may also be referred to as hydrides. Common examples are ammonia (NH₃), methane (CH₄), ethane (C₂H₆) (or any other hydrocarbon), and Nickel hydride (NiH), used in NiMH rechargeable batteries.
Precursor source mixtures
A precursor source mixture useful for CVD or ALD of a film comprising: at least one precursor composed of an element selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr, Be, Mg, Ti, Zr, Hf, Sc, Y, La, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Re, Fe, Ru, Os, Co, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Hg, B, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, As, P, Sb and Bi, to which is bound at least one ligand selected from the group consisting of hydride, alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkenyl, aryl, alkyne, carbonyl, amido, imido, hydrazido, phosphido, nitrosyl, nitryl, nitrate, nitrile, halide, azide, alkoxy, siloxy, silyl, and halogenated, sulfonated or silyated derivatives thereof, which is dissolved, emulsified or suspended in an inert liquid selected from the group consisting of aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, acids, phenols, esters, amines, alkylnitrile, halogenated hydrocarbons, silyated hydrocarbons, thioethers, amines, cyanates, isocyanates, thiocyanates, silicone oils, nitroalkyl, alkylnitrate, and mixtures thereof. The precursor source mixture may be a solution, emulsion or suspension and may consist of a mixture of solid, liquid and gas phases which are distributed throughout the mixture.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
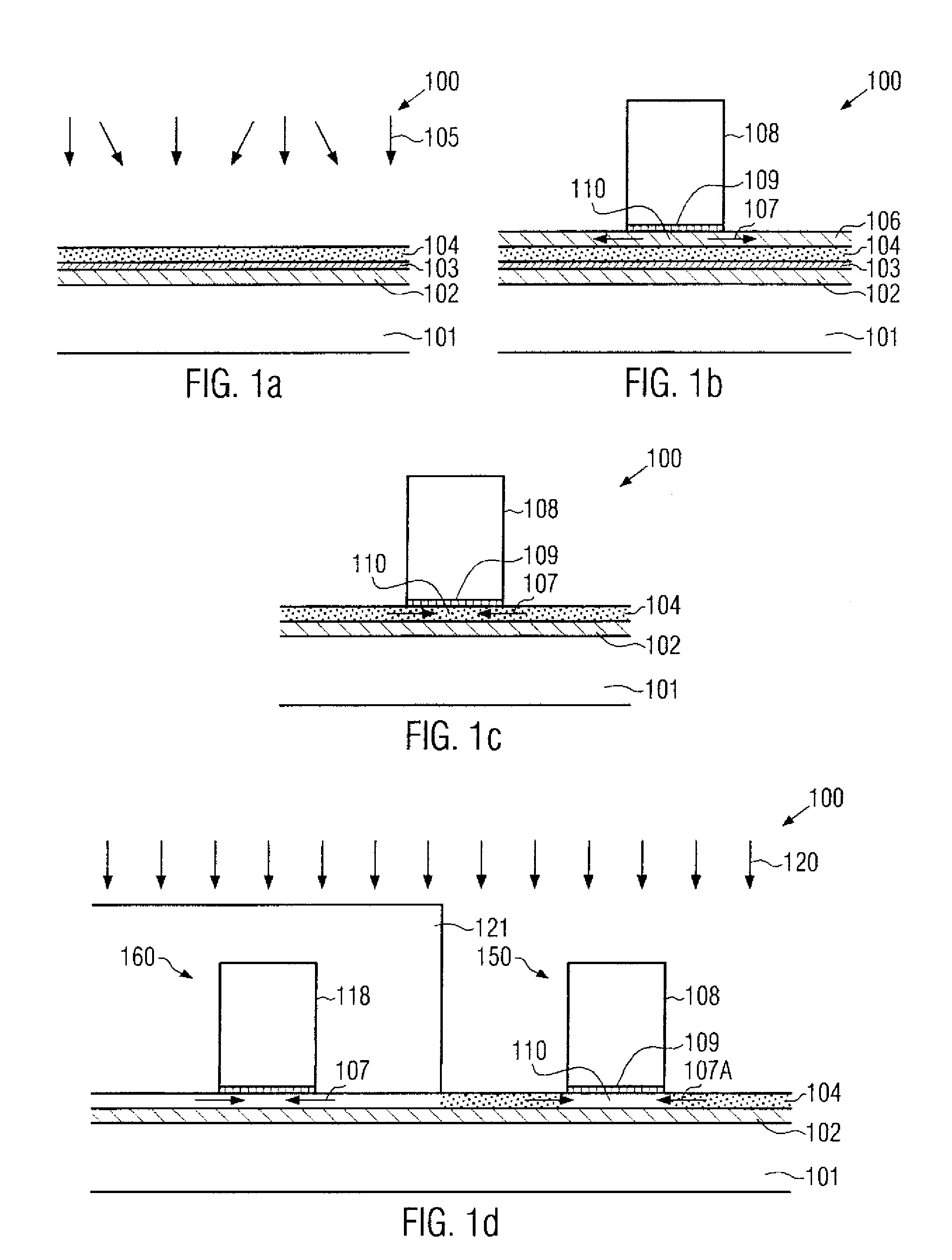
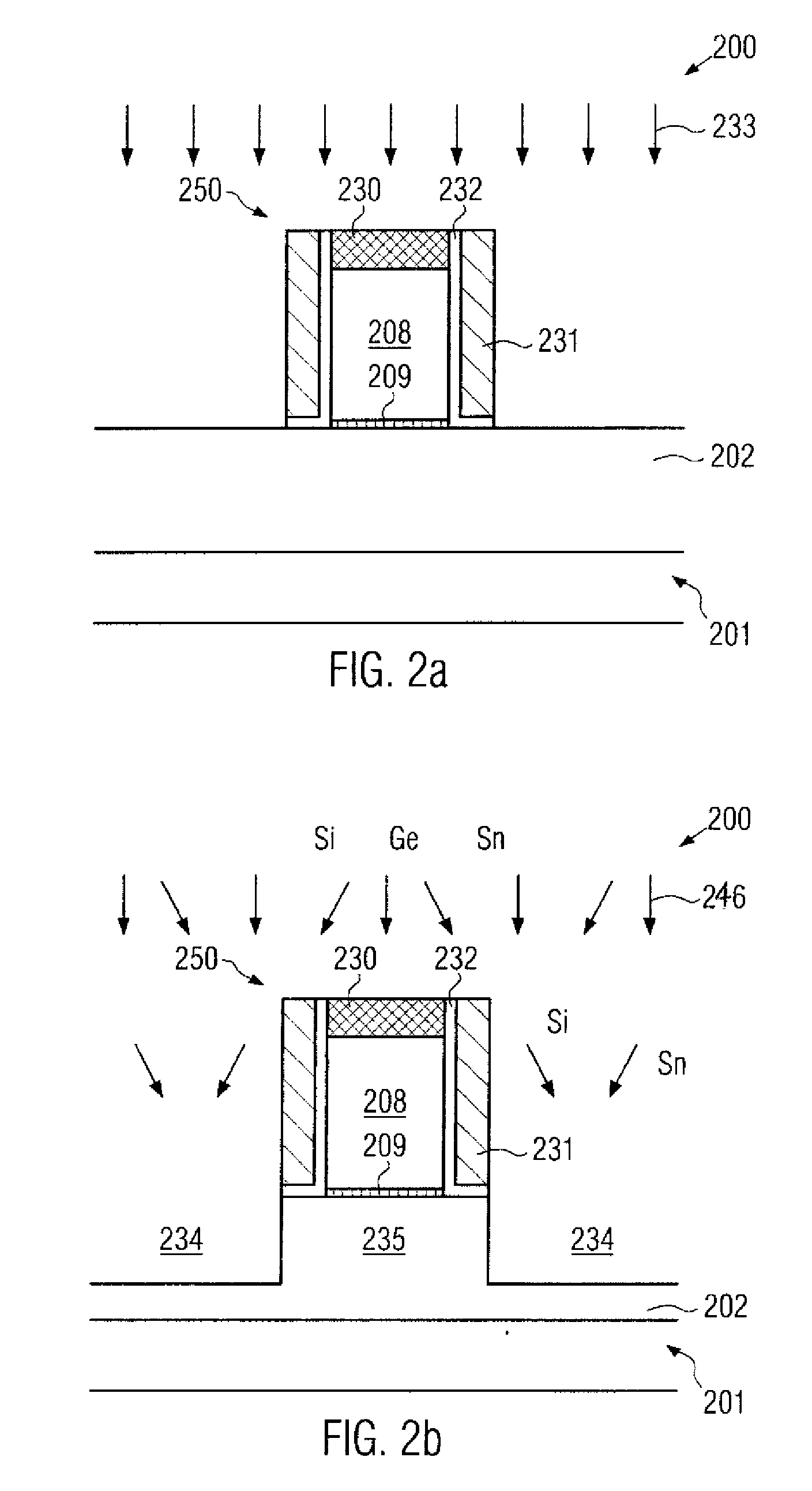
Technique for strain engineering in si-based transistors by using embedded semiconductor layers including atoms with high covalent radius
By incorporating an atomic species of increased covalent radius, which may at least partially substitute germanium, a highly efficient strain mechanism may be provided, in which the risk of stress relief due to germanium conglomeration and lattice defects may be reduced. The atomic species of increased radius, such as tin, may be readily incorporated by epitaxial growth techniques on the basis of tin hydride.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
CVD nanoporous silica low dielectric constant films
InactiveUS6171945B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilicon oxideGradual increase
A method and apparatus for depositing nano-porous low dielectric constant films by reaction of a silicon hydride containing compound or mixture optionally having thermally labile organic groups with a peroxide compound on the surface of a substrate. The deposited silicon oxide based film is annealed to form dispersed microscopic voids that remain in a nano-porous silicon oxide based film having a foam structure. The nano-porous silicon oxide based films are useful for filling gaps between metal lines with or without liner or cap layers. The nano-porous silicon oxide based films may also be used as an intermetal dielectric layer for fabricating dual damascene structures. Preferred nano-porous silicon oxide based films are produced by reaction of 1,3,5-trisilanacyclohexane, bis(formyloxysilano)methane, or bis(glyoxylylsilano)methane and hydrogen peroxide followed by a cure / anneal that includes a gradual increase in temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus, system, and method for generating a gas from solid reactant pouches
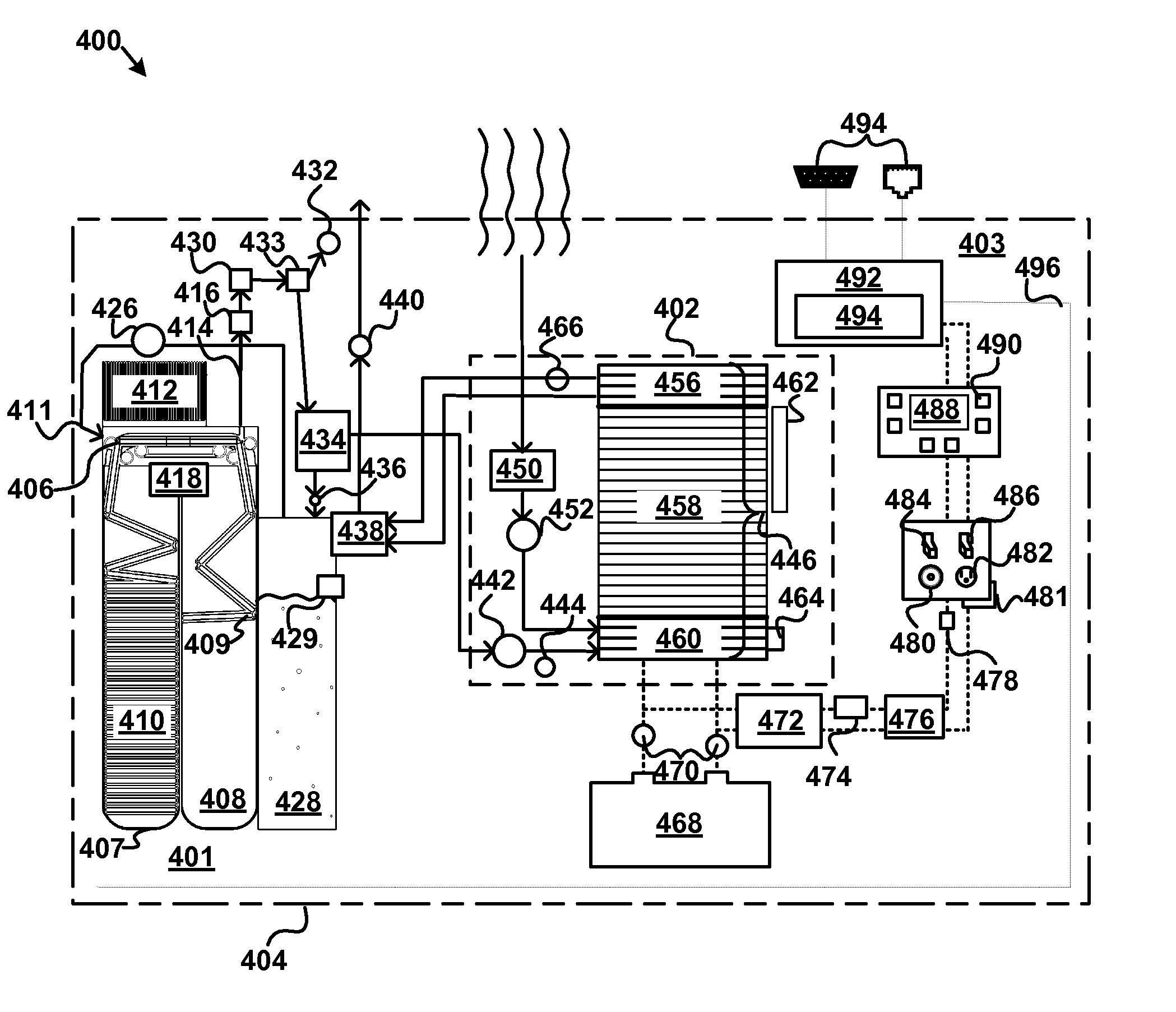
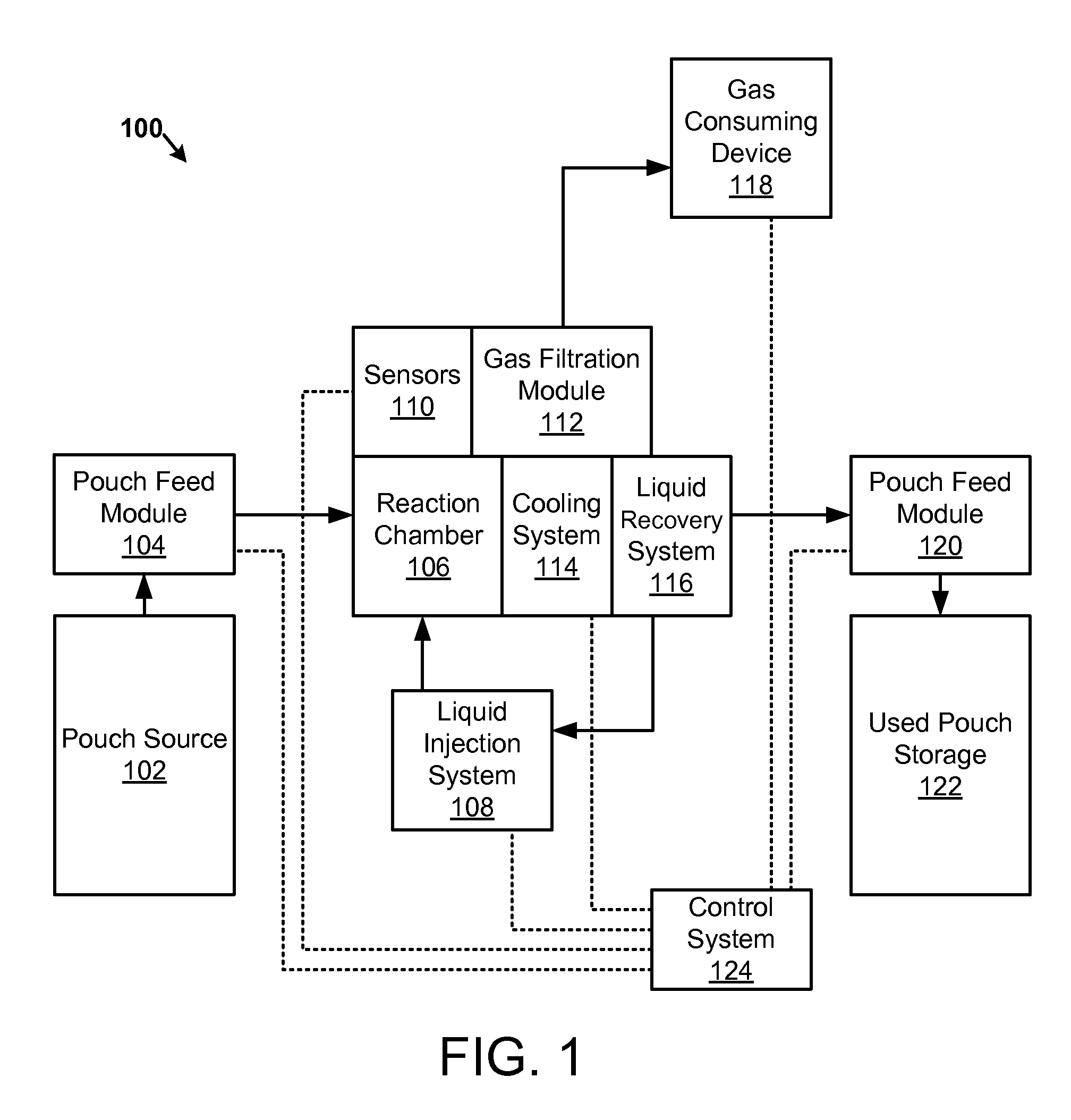
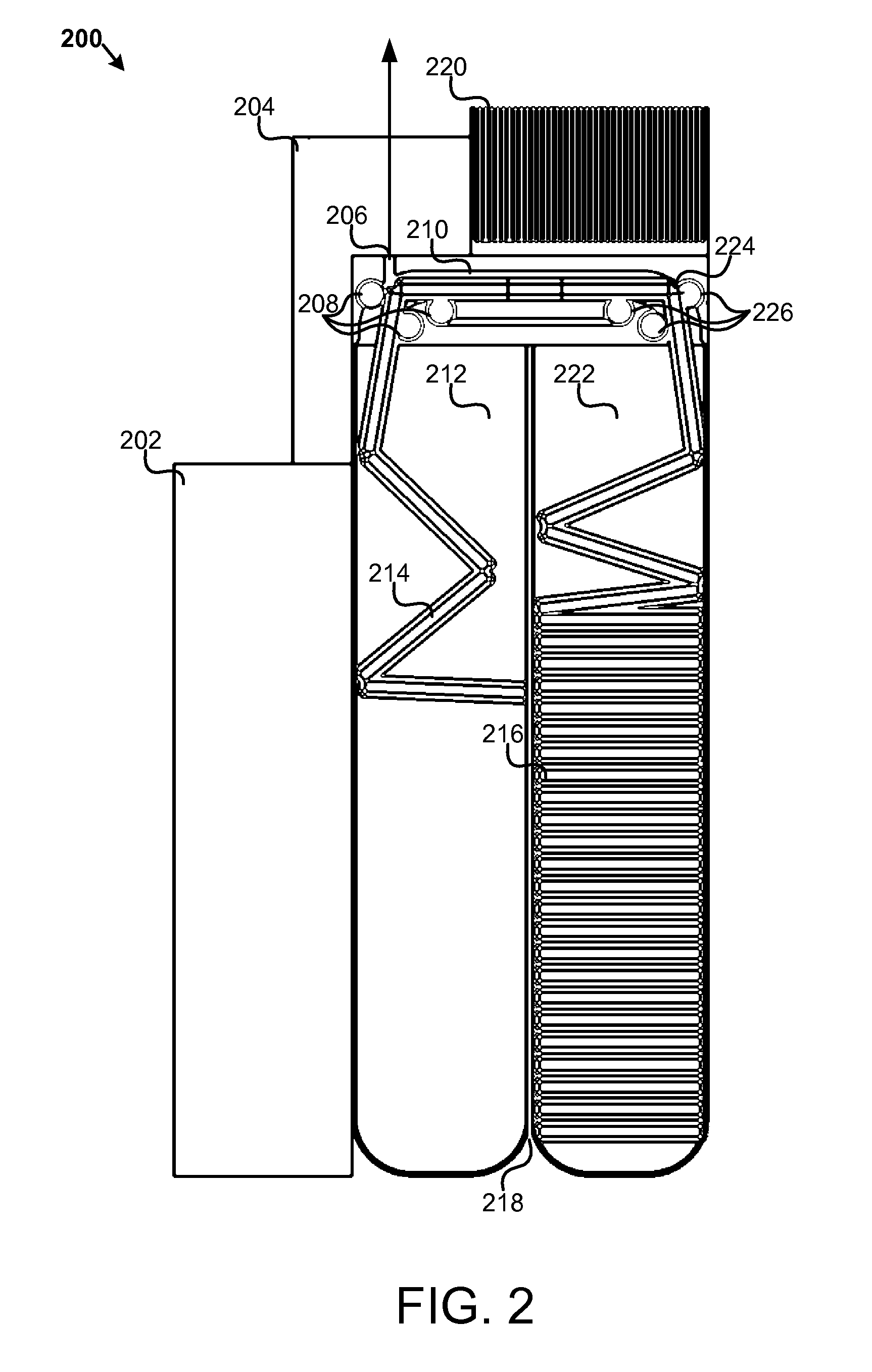
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for generating a gas. One or more liquid permeable pouches each define a cavity that contains a solid anhydrous reactant, such as a chemical hydride. A reaction chamber made of a heat, chemical and / or pressure resistant material receives the one or more pouches from a pouch feeder that transfers the one or more pouches into the reaction chamber successively at a feed rate. One or more liquid sources inject a liquid reactant into the reaction chamber so that the liquid reactant contacts a portion of the one or more pouches. The one or more liquid sources inject the liquid reactant at an injection rate that corresponds to the feed rate. A gas outlet releases a gas, such as hydrogen, oxygen, ammonia, borazine, nitrogen, or a hydrocarbon, that is produced by a reaction between the solid reactant and the liquid reactant.
Owner:TRULITE INC
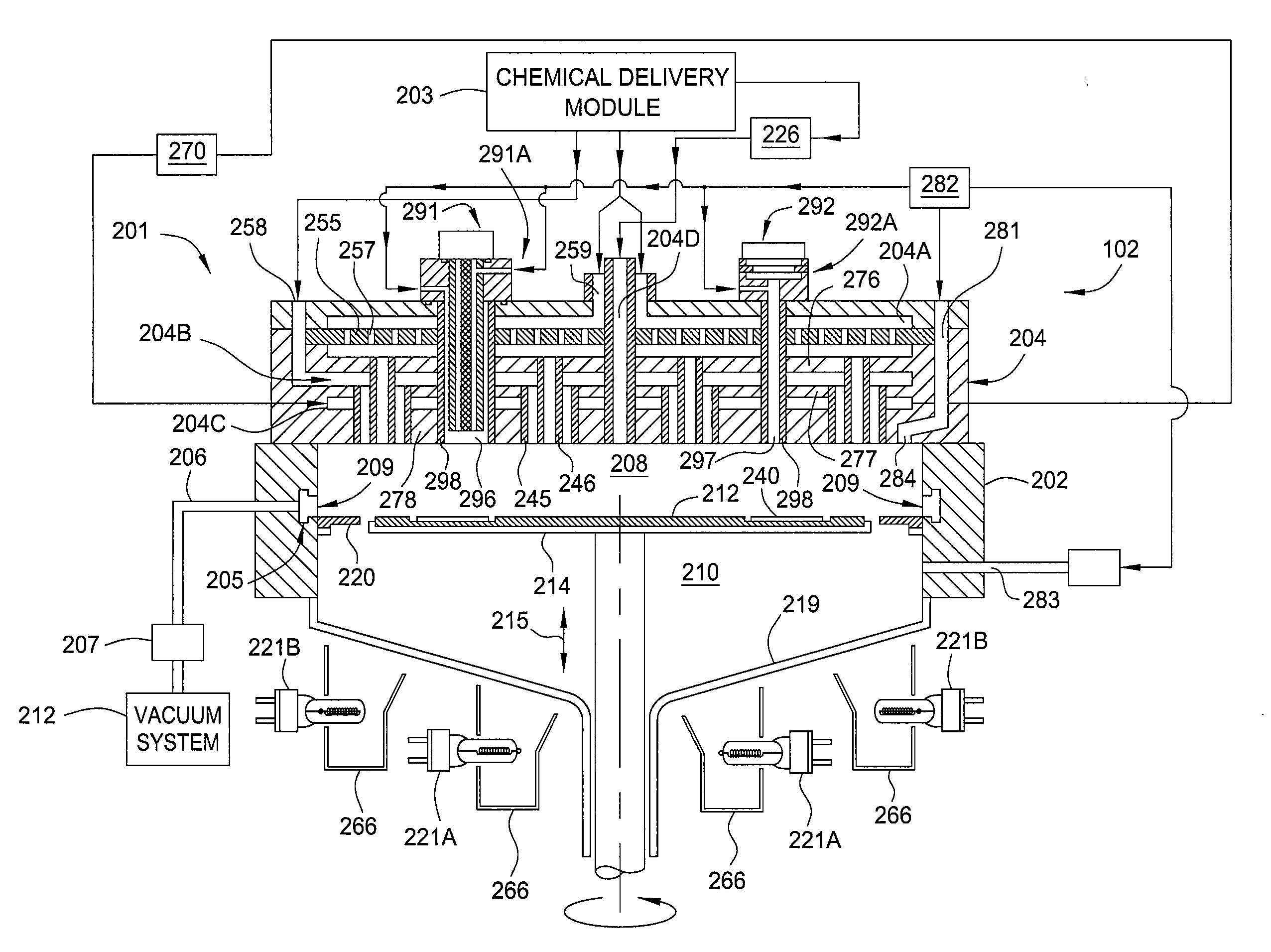
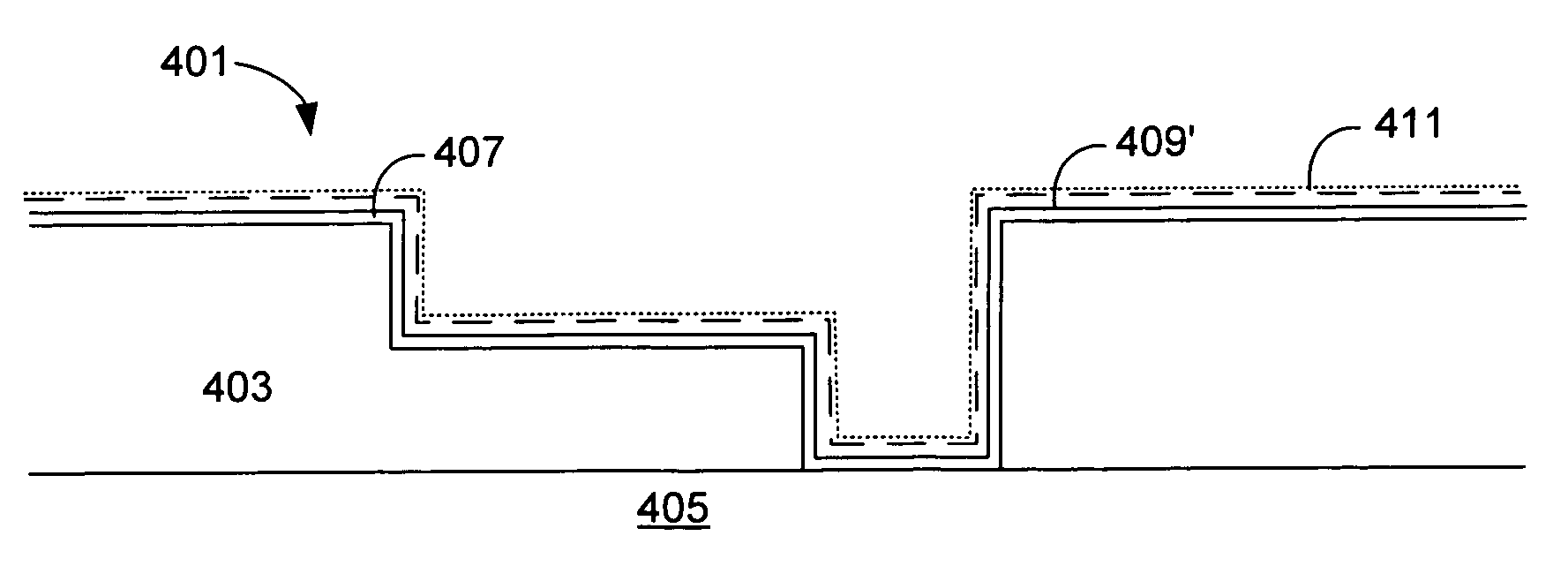
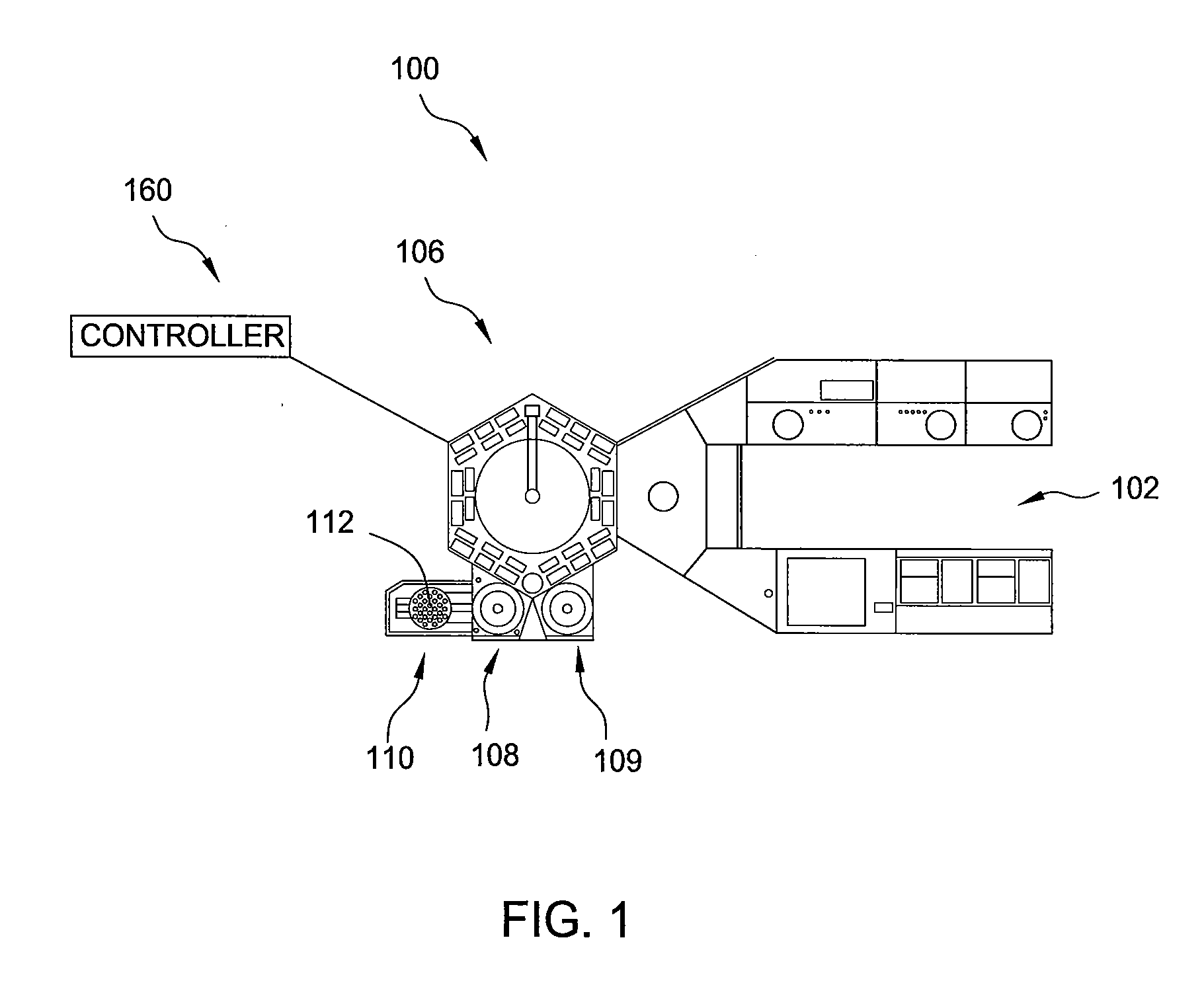
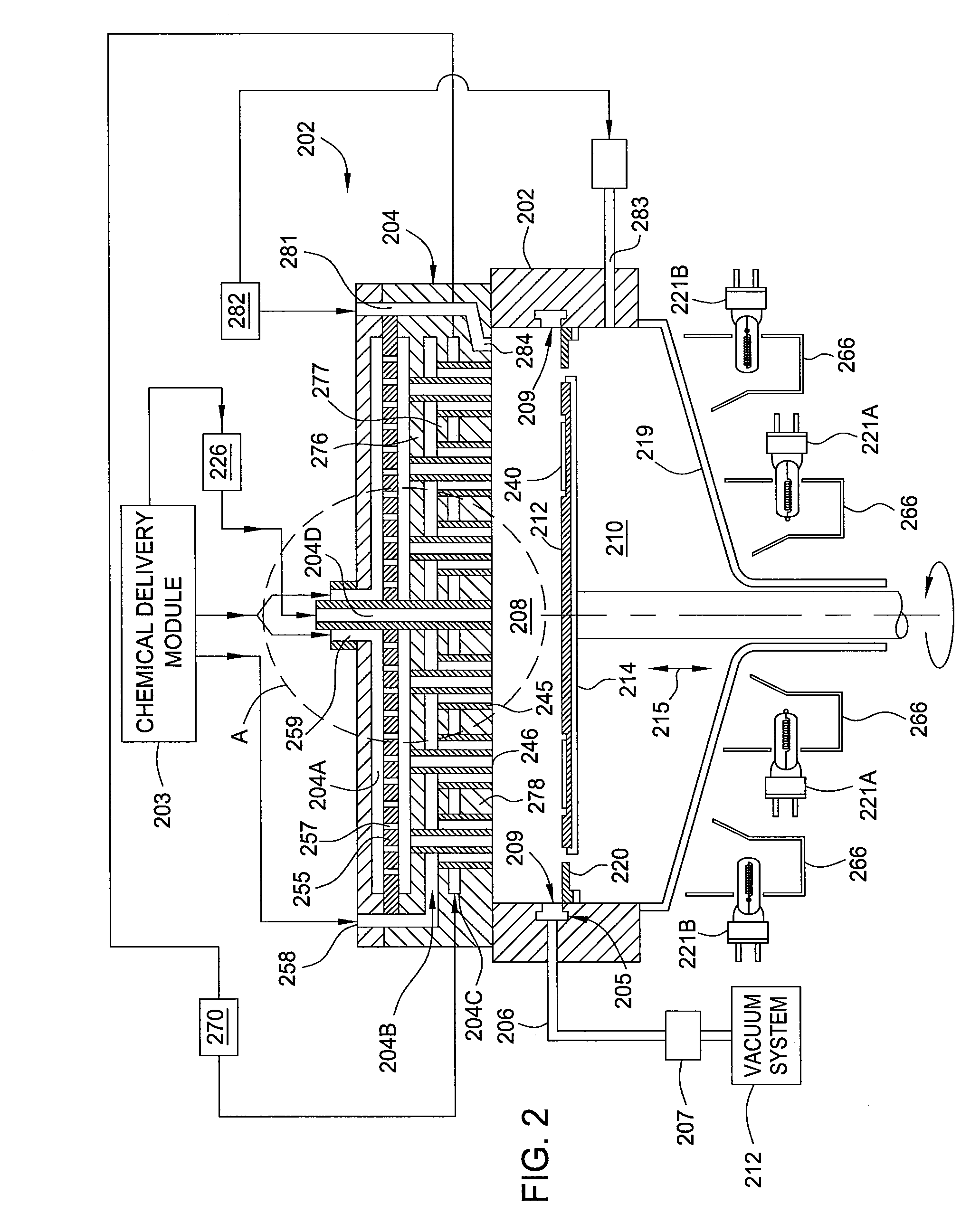
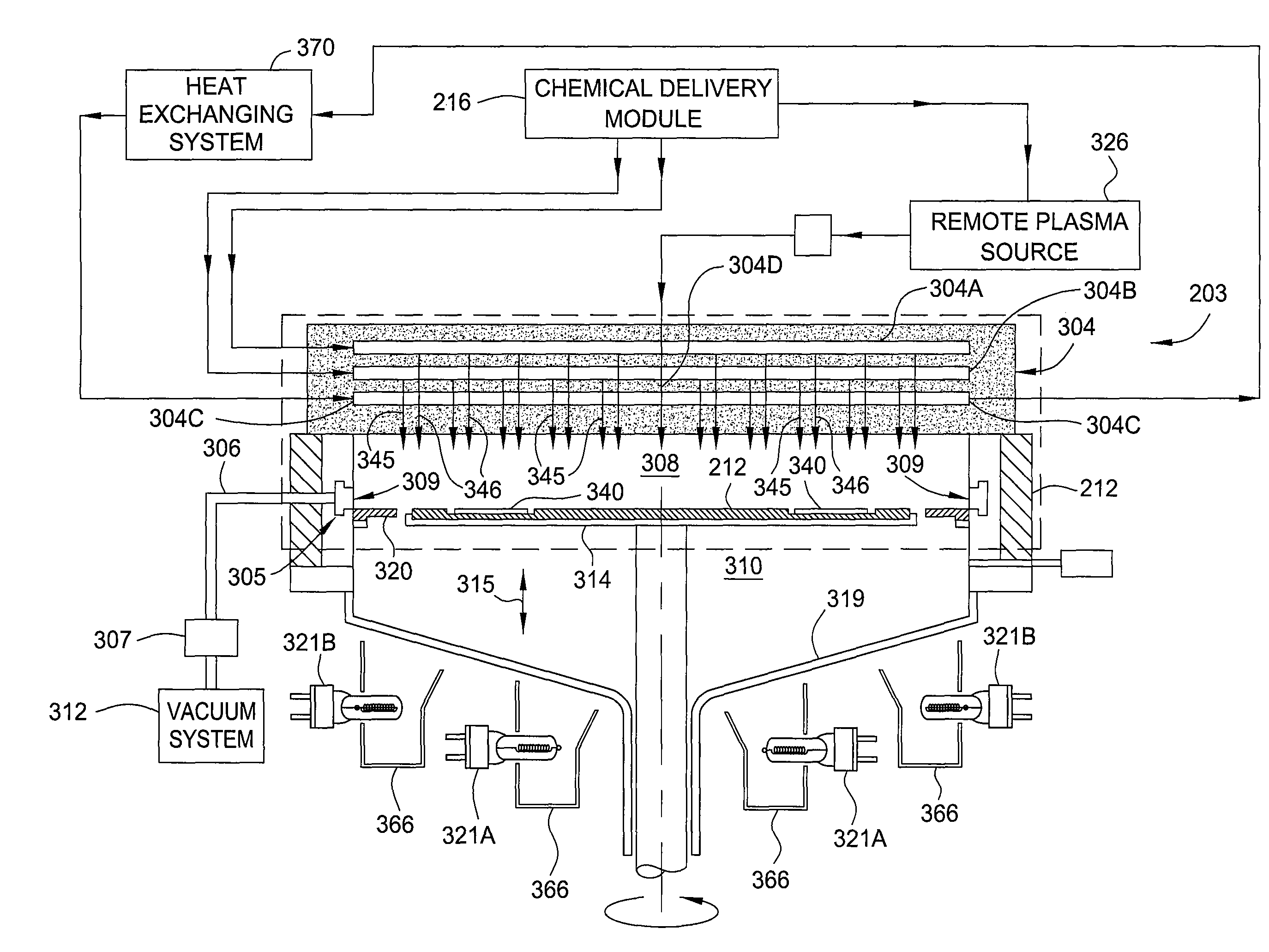
Showerhead assembly with metrology port purge
InactiveUS20110253044A1Avoid depositionLiquid surface applicatorsSpray nozzlesOptical measurementsChemical vapor deposition
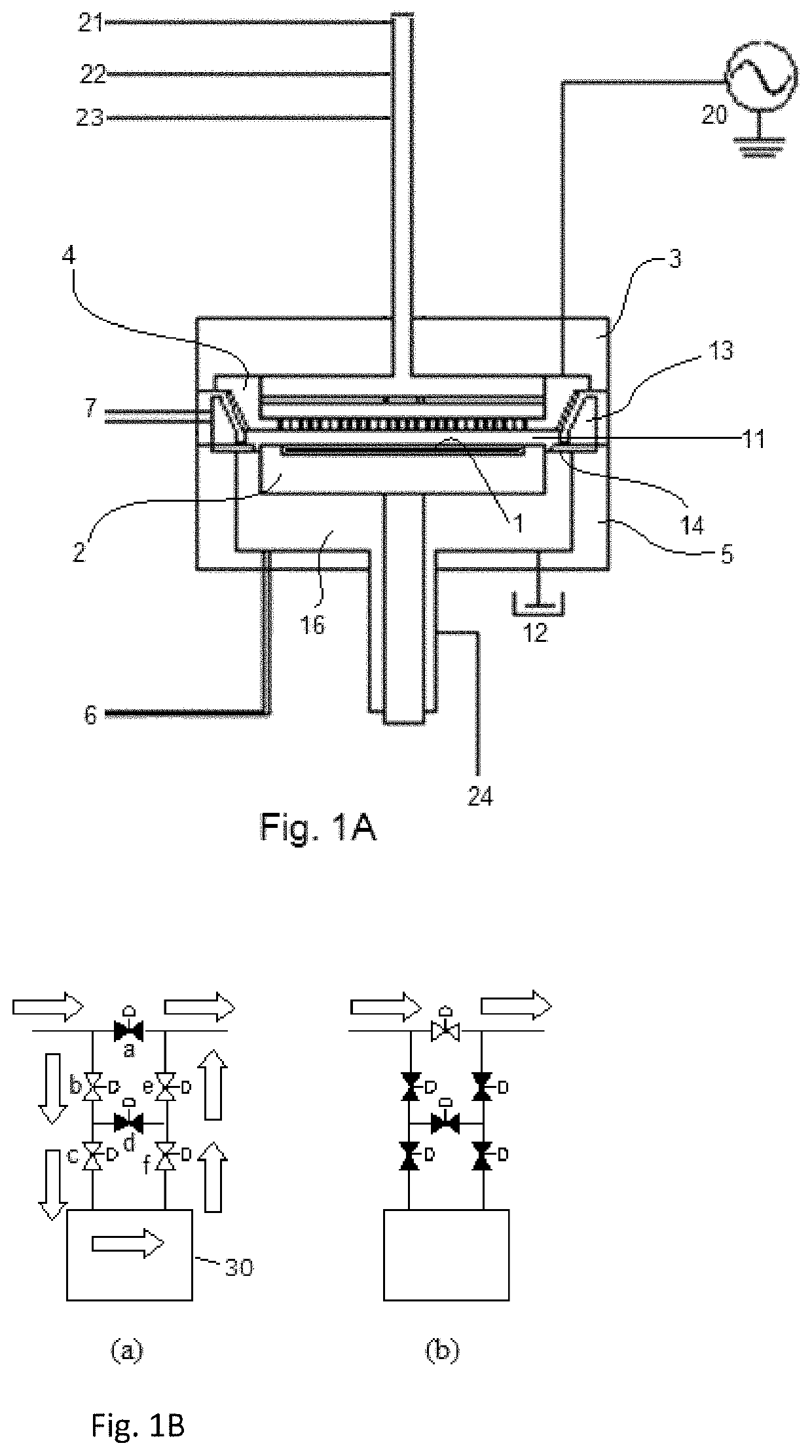
A method and apparatus that may be utilized for chemical vapor deposition and / or hydride vapor phase epitaxial (HVPE) deposition are provided. In one embodiment, the apparatus is a processing chamber that includes a showerhead with separate inlets and channels for delivering separate processing gases into a processing volume of the chamber without mixing the gases prior to entering the processing volume. In one embodiment, the showerhead includes metrology ports with purge gas assemblies configured and positioned to deliver a purge gas to prevent deposition thereon. In one embodiment, the metrology port is configured to receive a temperature measurement device, and the purge gas assembly is a concentric tube configuration configured to prevent deposition on components of the temperature measurement device. In one embodiment, the metrology port has a sensor window and is configured to receive an optical measurement device, and the purge gas assembly and sensor window are configured to prevent deposition on the sensor window.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Aluminum-free monocyclopentadienyl metallocene catalysts for olefin polymerization
ActiveUS7163907B1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetallocenesPolymer sciencePolyolefin
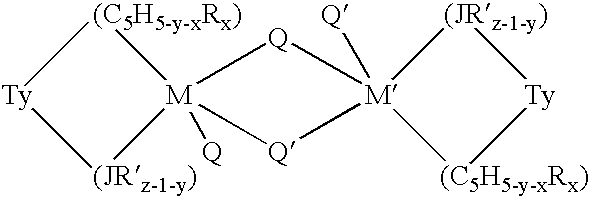
This invention relates to a catalyst system for the production of polyolefins comprising:(A) a Group IV B transition metal component represented by one of the two general formulaewherein(C5H5-y-xRx) is a cylopentadienyl ring(JR′z-l-y) is a heteroatom ligand in which J is an element with a coordination number of three from Group V-A or an element with a coordination number of two rom Group VI-A of the Periodic Table of Elements,each Q is independently, hydride, C1—C20 hydrocarbyl radicals, substituted hydrocarbyl radials wherein one or more hydrogen atoms is replaced by an electron withdrawing group, or C1—C20 hydrocarbyl-substituted metalloid radicals wherein the metalloid is selected from the group consisting of germanium and silicon, provided that Q is not a substituted or unsubstituted cyclopentadienyl ring, or both Q together may be an alkylidene, olefin, acetylene or a cyclometallated hydrocarbyl;“y” is 0 or 1; when “y” is 1, T is a covalent bridging group containing a Group IV-A or V-A element;L is a neutral Lewis base; and “w” is a number from 0 to 3;(B) an activator compound comprising (1) a cation; and (2) a compatible noncoordinating anion.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Method of selectively depositing a thin film material at a semiconductor interface
InactiveUS20070108404A1Detergent mixture composition preparationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice formMetal silicide
Embodiments of the invention provide processes to form a high quality contact level connection to devices formed on a substrate. In one embodiment, a method for depositing a material on a substrate is provided which includes exposing the substrate to a buffered oxide etch solution to form a silicon hydride layer during a pretreatment process, depositing a metal silicide layer on the substrate, and depositing a first metal layer (e.g., tungsten) on the metal silicide layer. The buffered oxide etch solution may contain hydrogen fluoride and an alkanolamine compound, such as ethanolamine diethanolamine, or triethanolamine. The metal silicide layer may contain cobalt, nickel, or tungsten and may be deposited by an electroless deposition process. In one example, the substrate is exposed to an electroless deposition solution containing a solvent and a complexed metal compound.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Lanthanide-based catalyst composition for producing cis-1,4-polydienes
InactiveUS7008899B2Easy to processHigh viscosityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPtru catalystLanthanide
A catalyst composition that is the combination of or the reaction product of ingredients comprising (a) a lanthanide compound, (b) an organoaluminum hydride, and (c) a tin halide compound.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Method of forming conformal silicon carbide film by cyclic CVD
ActiveUS20200118815A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbide siliconSilanes
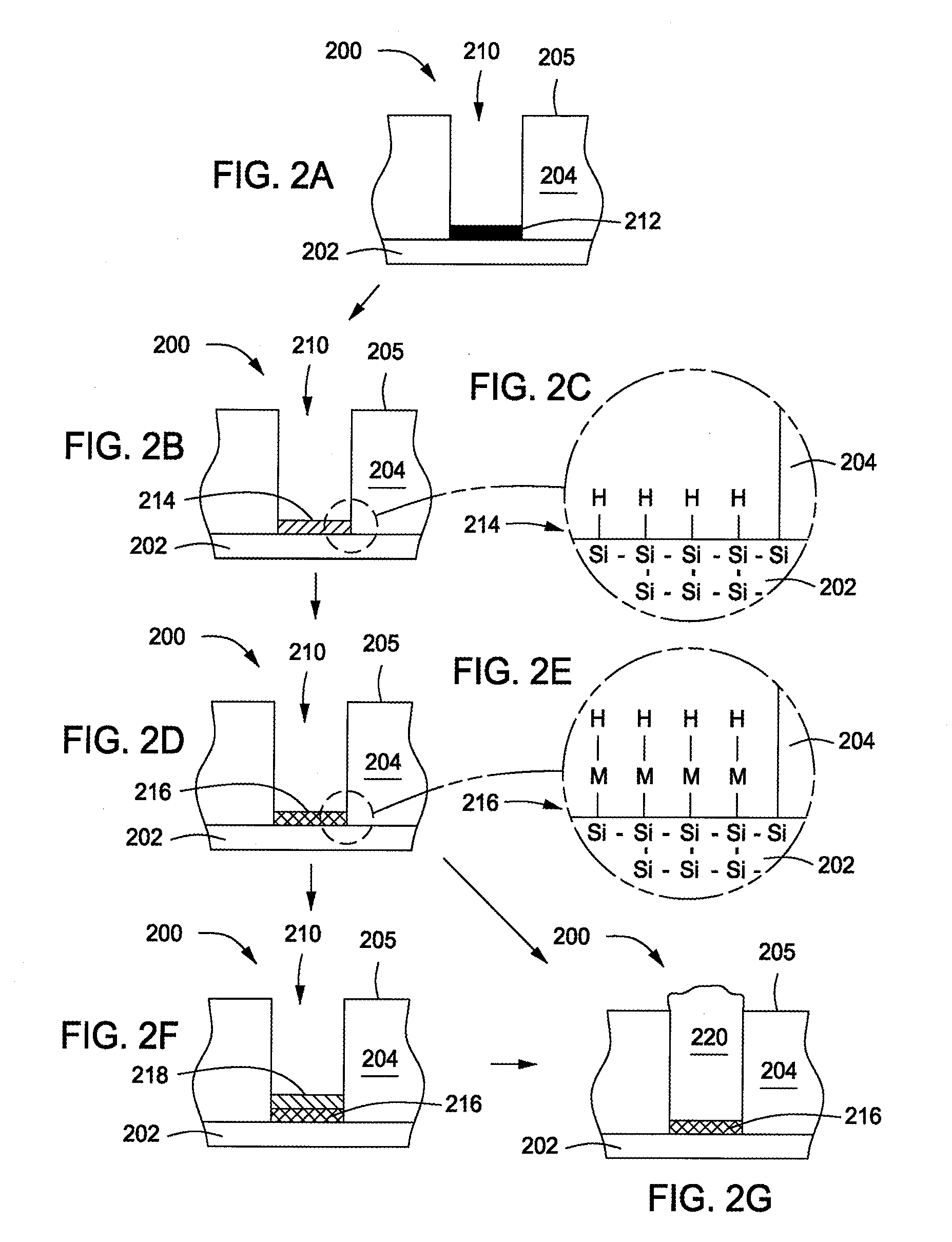
A method of forming, on a substrate having a recess pattern, a silicon carbide film having a reflective index of 2.3 or higher as measured at 633 nm, includes (i) supplying an organosilane precursor in a pulse to a reaction space where the substrate is placed, which precursor has a formula of RSiH3 wherein R is a hydrocarbon-containing moiety including at least one unsaturated bond; (ii) continuously supplying a plasma-generating gas to the reaction space, which plasma-generating gas is selected from the group consisting of inert gases and hydride gases; (iii) continuously applying RF power to the reaction space to generate a plasma which excites the precursor; and (iv) repeating steps (i) through (iii), thereby forming a silicon carbide film on the substrate, which silicon carbide film has a reflective index of 2.3 or higher as measured at 633 nm.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
ALD of tantalum using a hydride reducing agent
InactiveUS7144806B1Reducing hydrideSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenTantalum nitride
An ALD method deposits conformal tantalum-containing material layers on small features of a substrate surface. The method includes the following principal operations: depositing a thin conformal and saturated layer of tantalum-containing precursor over some or all of the substrate surface; using an inert gas or hydrogen plasma to purge the halogen byproducts and unused reactants; reducing the precursor to convert it to a conformal layer of tantalum or tantalum-containing material; using another purge of inert gas or hydrogen plasma to remove the halogen byproducts and unused reactants; and repeating the deposition / reduction cycles until a desired tantalum-containing material layer is achieved. An optional step of treating each newly formed surface of tantalum containing material with a nitrogen-containing agent can be added to create varying amounts of tantalum nitride.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
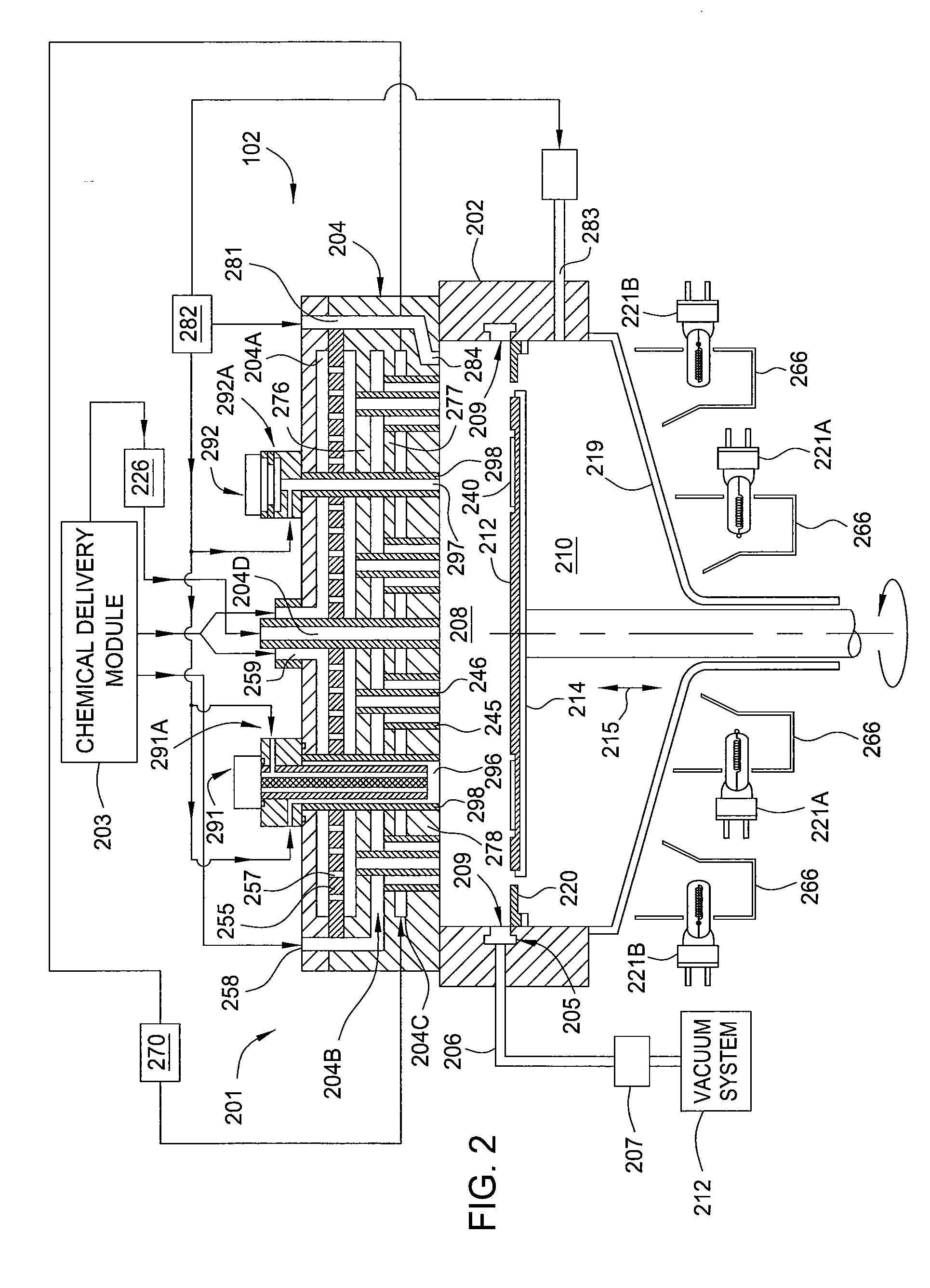
Multiple precursor concentric delivery showerhead
InactiveUS20110256692A1Simple methodSpray nozzlesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor depositionVapor phase
A method and apparatus that may be utilized for chemical vapor deposition and / or hydride vapor phase epitaxial (HVPE) deposition are provided. In one embodiment, the apparatus provides a processing chamber that includes a showerhead with separate inlets and channels for delivering separate processing gases into a processing volume of the chamber without mixing the gases prior to entering the processing volume. In one embodiment, a plurality of concentric tube assemblies are disposed within the showerhead to separately deliver a first gas from a first gas channel and a second gas from a second gas channel into the processing volume of the chamber. In one embodiment, the showerhead further includes a heat exchanging channel through which the plurality of concentric tube assemblies is disposed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Atomic layer deposition of tungsten material
InactiveCN101308794ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseNucleation
An implementing mode of the invention provides an improved technology for depositing materials containing tungsten. The technology utilizes an infusion technology and a gaseous phase deposition technology, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD), to provide tungsten-containing materials with obviously improved surface evenness and yield. In one implementing mode, a method for forming tungsten-containing materials on a substrate is provided. The method comprises deposing a substrate, which contains a bottom coating deposited thereon, in a technological chamber; exposing the substrate orderly in a precursor of tungsten and reducing gases so as to deposit a tungsten nucleation layer on the bottom coating, during the ALD technology; and depositing a tungsten block layer on the tungsten nucleation layer. The invention is characterized in that the reducing gases comprise a hydrogen gas / hydride flow ratio of 40:1, 100:1, 500:1, 800: 1, 1000:1 or more, and comprise hydride such as diborane, silicane or silicoethane.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
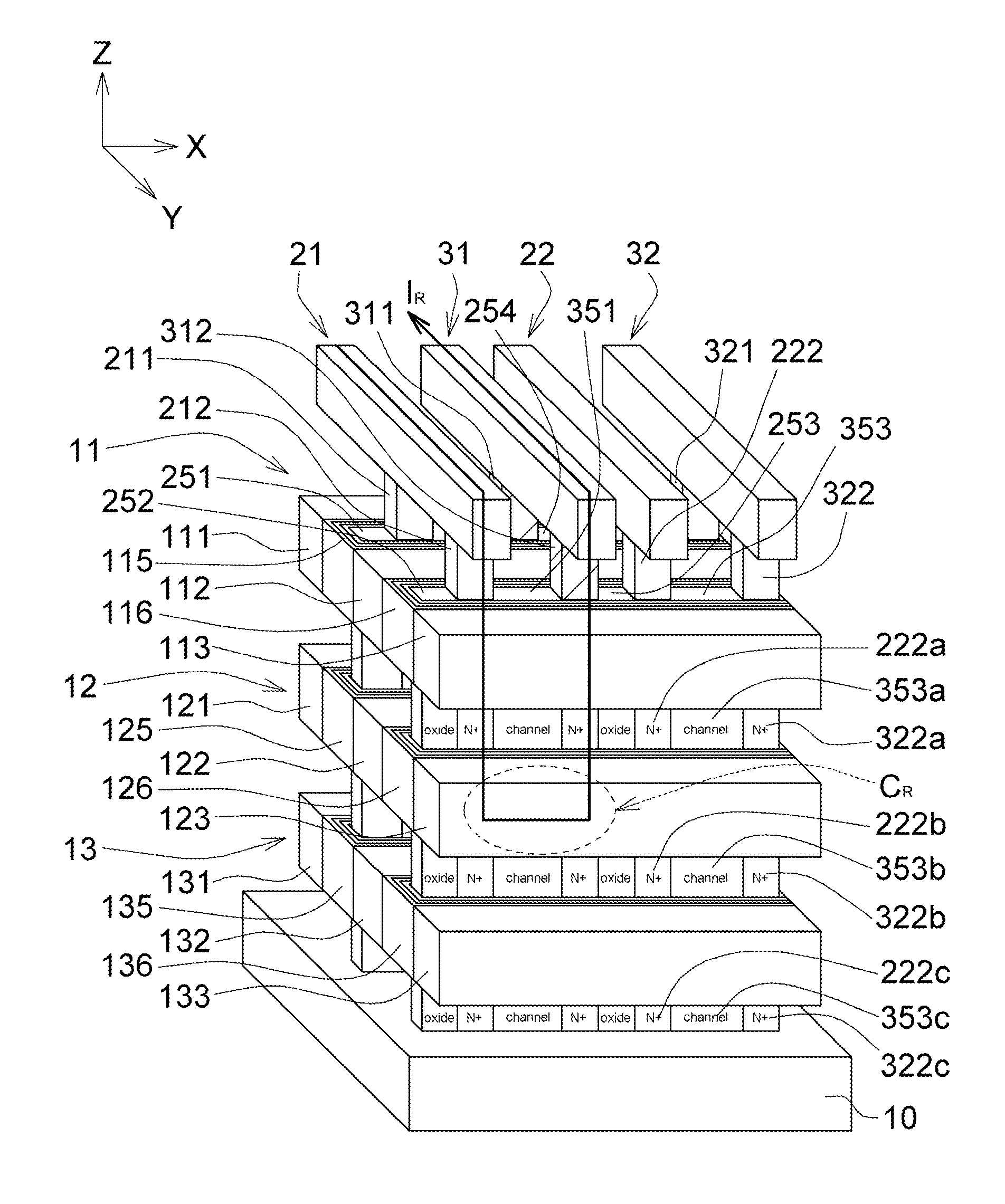
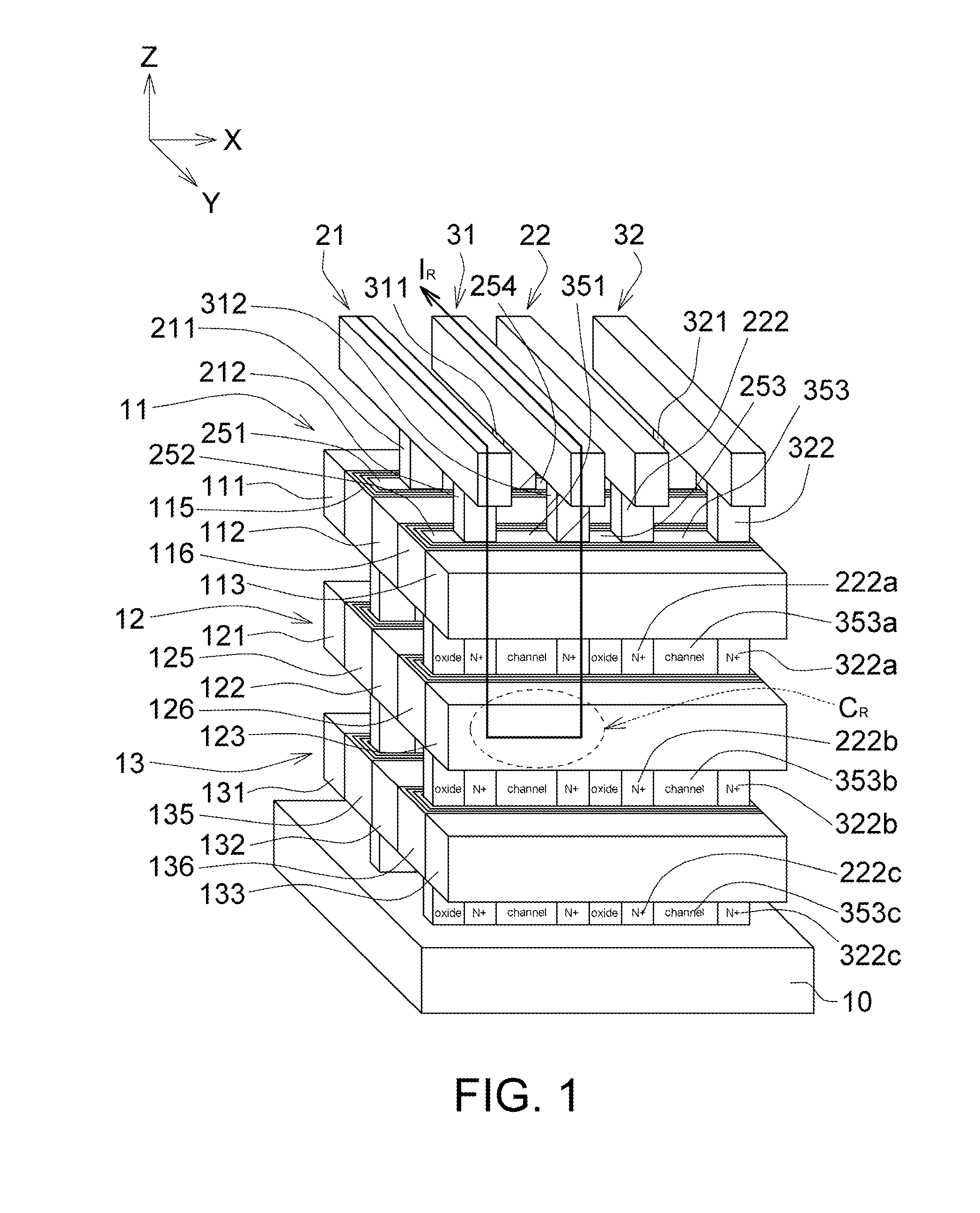
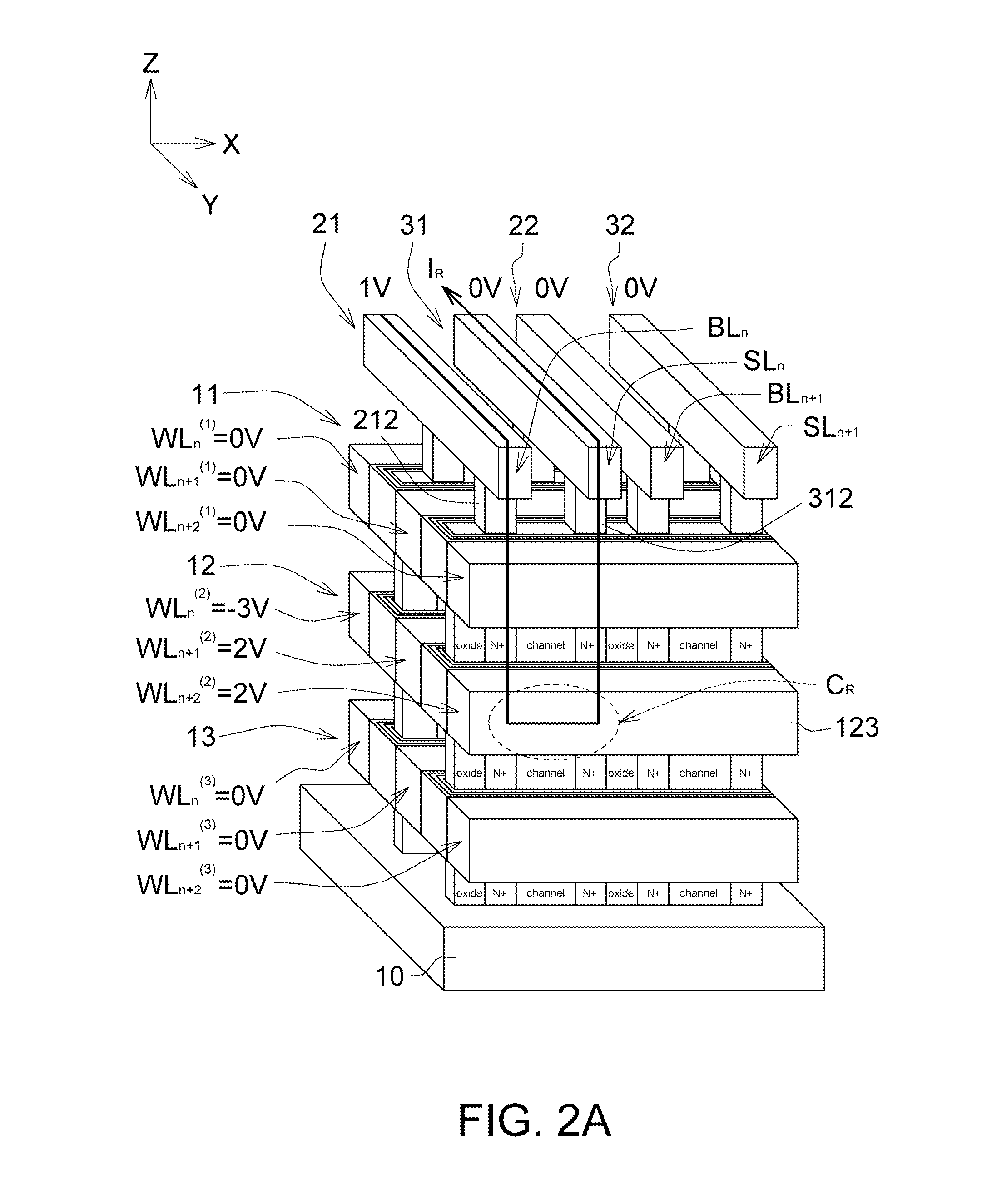
Three-dimensional stacked and-type flash memory structure and methods of manufacturing and operating the same hydride
A 3D stacked AND-type flash memory structure comprises several horizontal planes of memory cells arranged in a three-dimensional array, and each horizontal plane comprising several word lines and several of charge trapping multilayers arranged alternately, and the adjacent word lines spaced apart from each other with each charge trapping multilayer interposed between; a plurality of sets of bit lines and source lines arranged alternately and disposed vertically to the horizontal planes; and a plurality of sets of channels and sets of insulation pillars arranged alternatively, and disposed perpendicularly to the horizontal planes, wherein one set of channels is sandwiched between the adjacent sets of bit lines and source lines.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
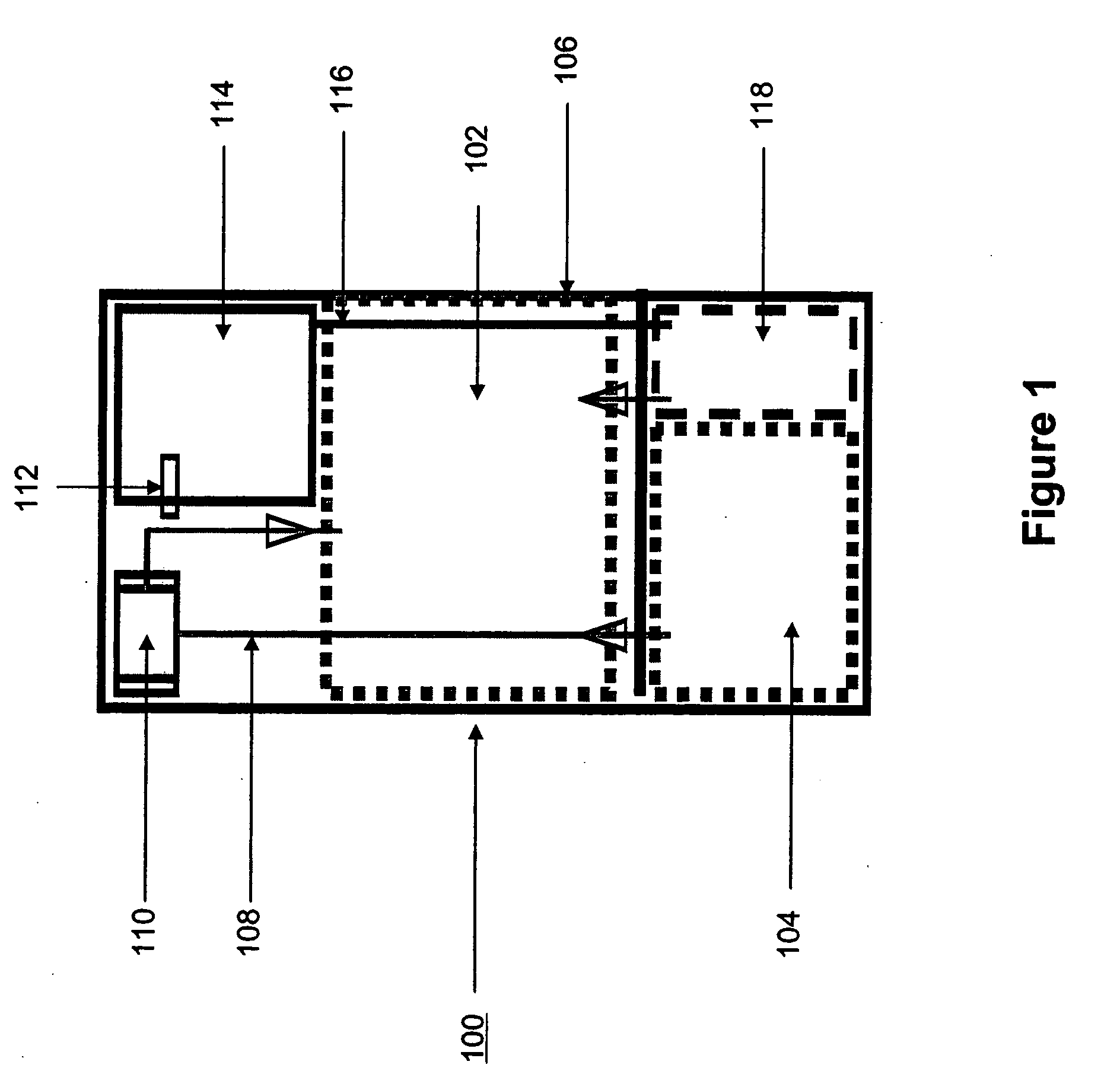
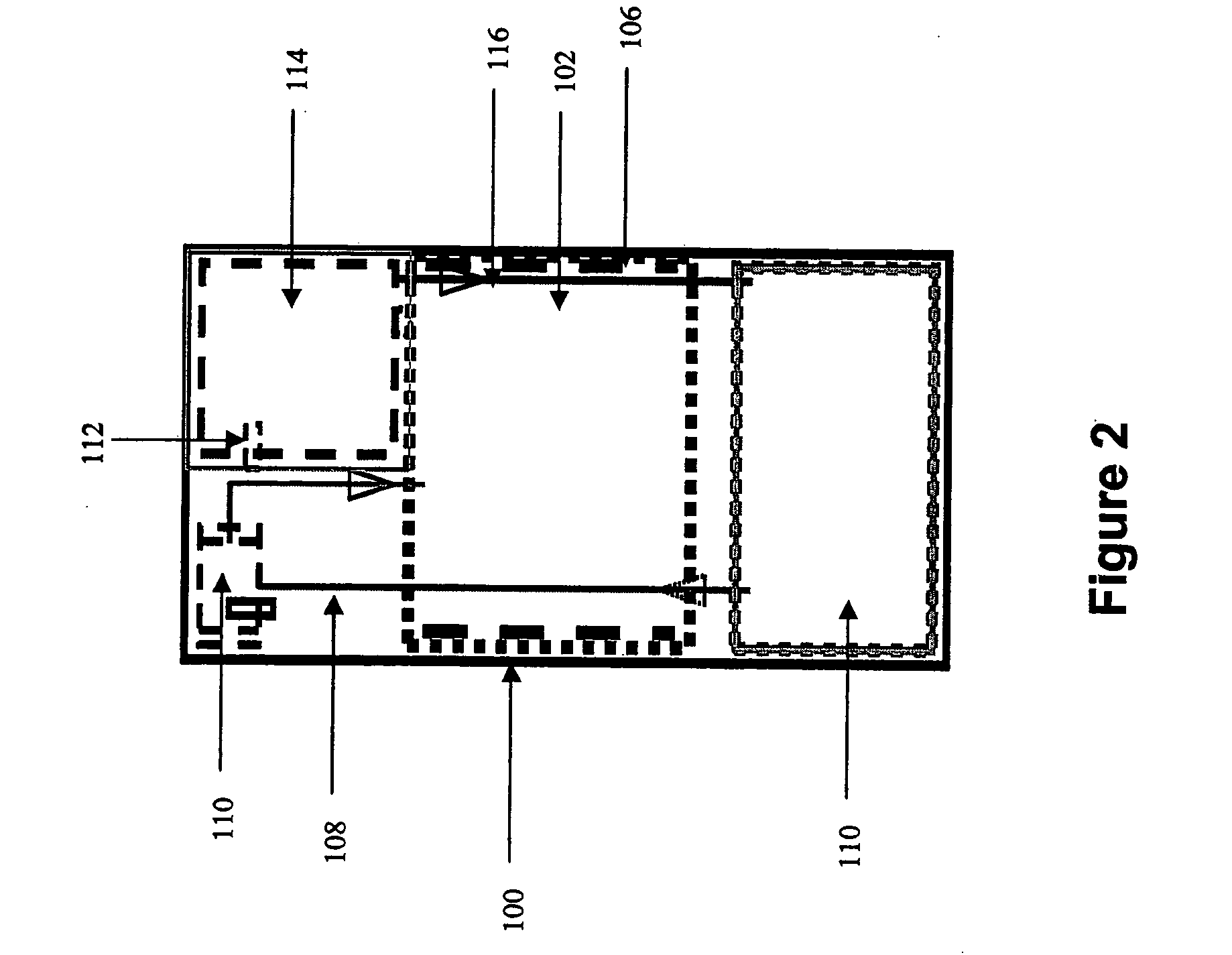
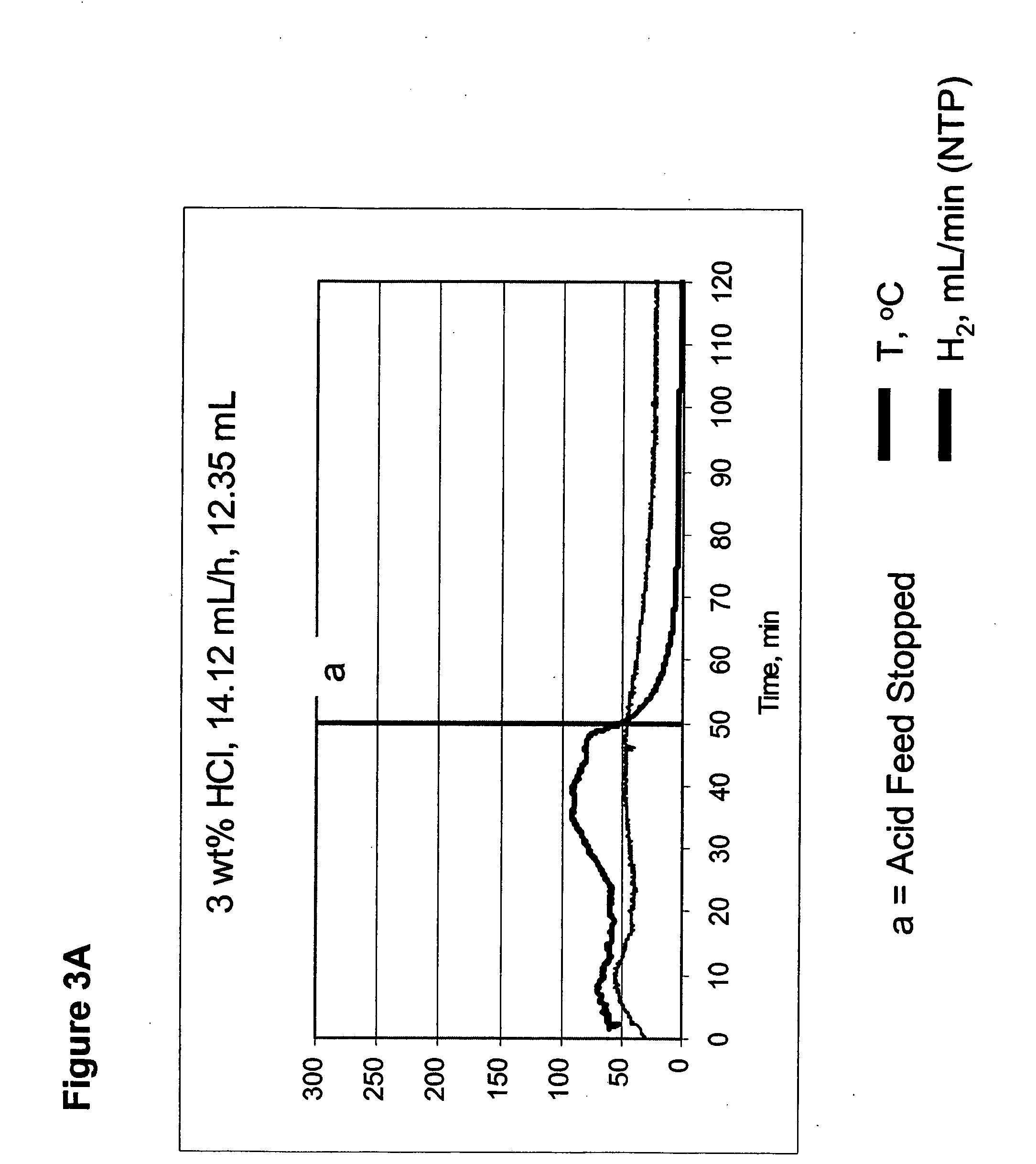
Systems and methods for hydrogen generation from solid hydrides
InactiveUS20050238573A1Regulate rateReactant parameters controlHydrogen productionO-Phosphoric AcidAlkaline earth metal
A system is disclosed for hydrogen generation based on hydrolysis of solid chemical hydrides with the capability of controlled startup and stop characteristics wherein regulation of acid concentration, acid feed rate, or a combination of both control the rate of hydrogen generation. The system comprises a first chamber for storing a solid chemical hydride and a second chamber for storing an acidic reagent. The solid chemical hydride is a solid metal borohydride having the general formula MBH4, where M is selected from the group consisting of alkali metal cations, alkaline earth metal cations, aluminum cation, zinc cation, and ammonium cation. The acidic reagent may comprise inorganic acids such as the mineral acids hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and phosphoric acid, and organic acids such as acetic acid, formic acid, maleic acid, citric acid, and tartaric acid, or mixtures thereof.
Owner:MILLENNIUM CELL
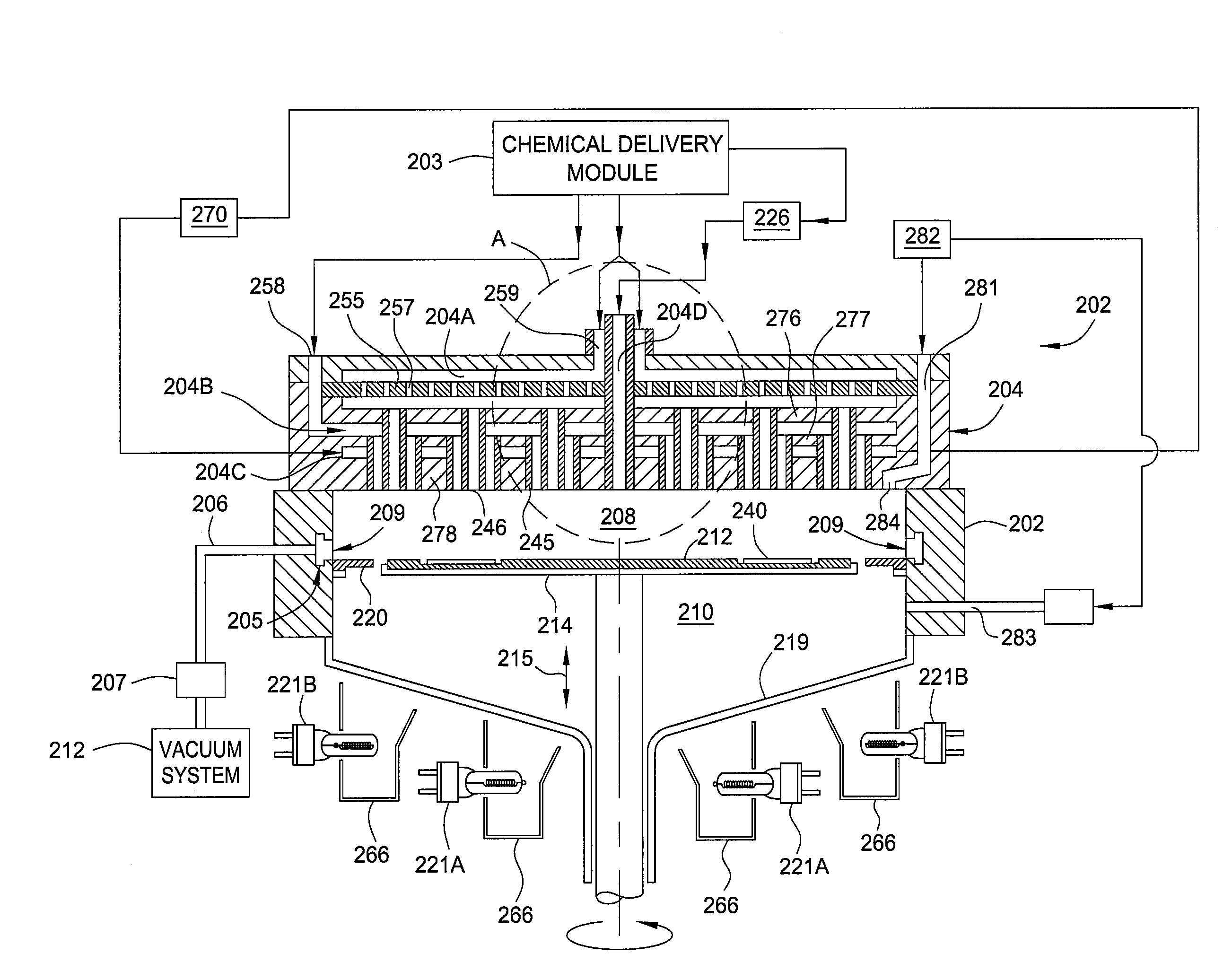
Decontamination of mocvd chamber using nh3 purge after in-situ cleaning
InactiveUS20100273291A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition processChemical vapor deposition
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to methods and apparatus for removing unwanted deposition build-up from one more interior surfaces of a substrate processing chamber after a substrate is processed in a chamber to form, for example, Group III-V materials by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) deposition processes and / or hydride vapor phase epitaxial (HVPE) deposition processes. In one embodiment, a method for removing unwanted deposition build-up from one or more interior surfaces of a substrate processing chamber is provided. The method comprises depositing one or more Group III containing layers over a substrate disposed in the substrate processing chamber, transferring the substrate out of the substrate processing chamber, and pulsing a halogen containing gas into the substrate processing chamber to remove at least a portion of the unwanted deposition build-up from one or more interior surfaces of the substrate processing chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
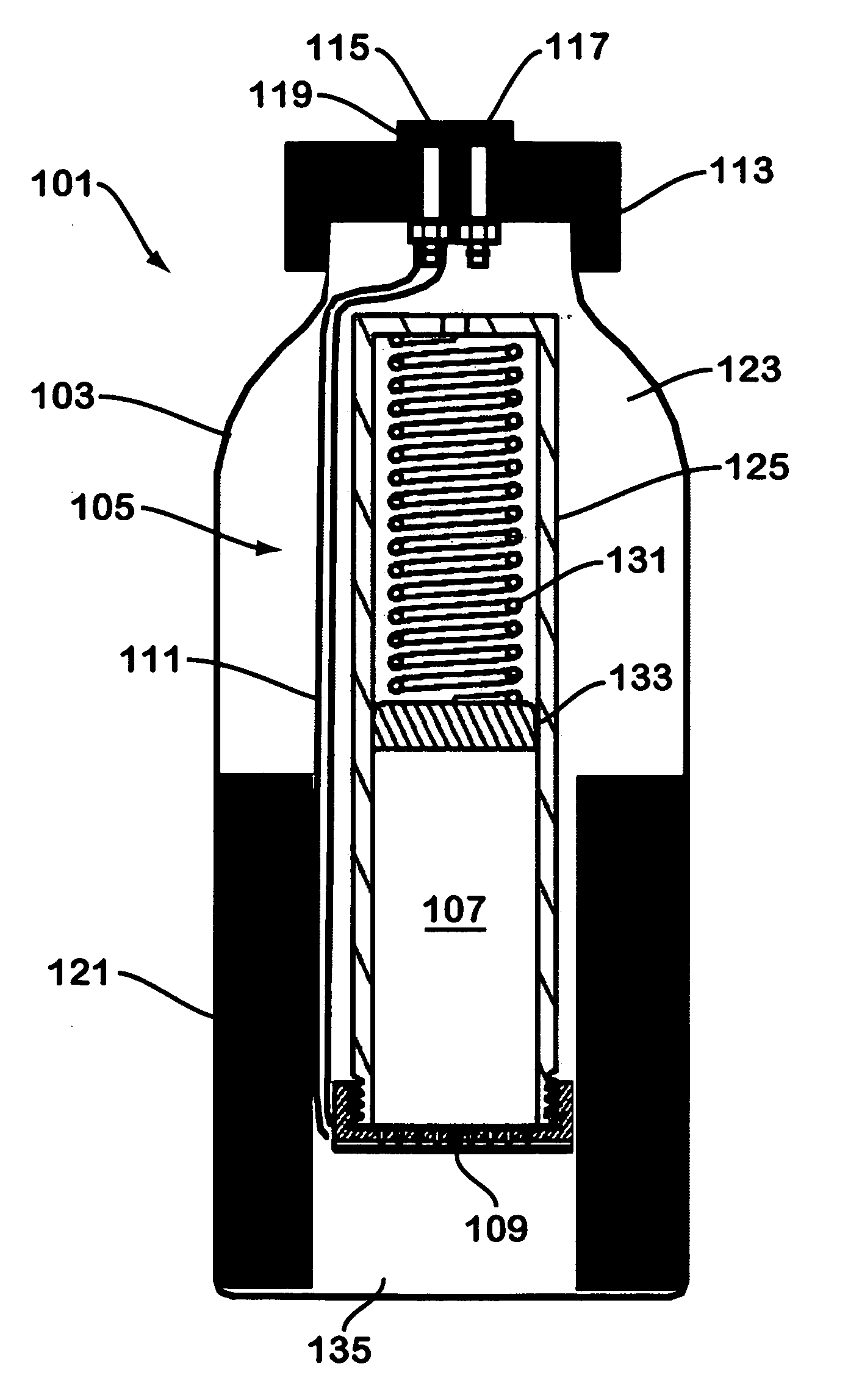
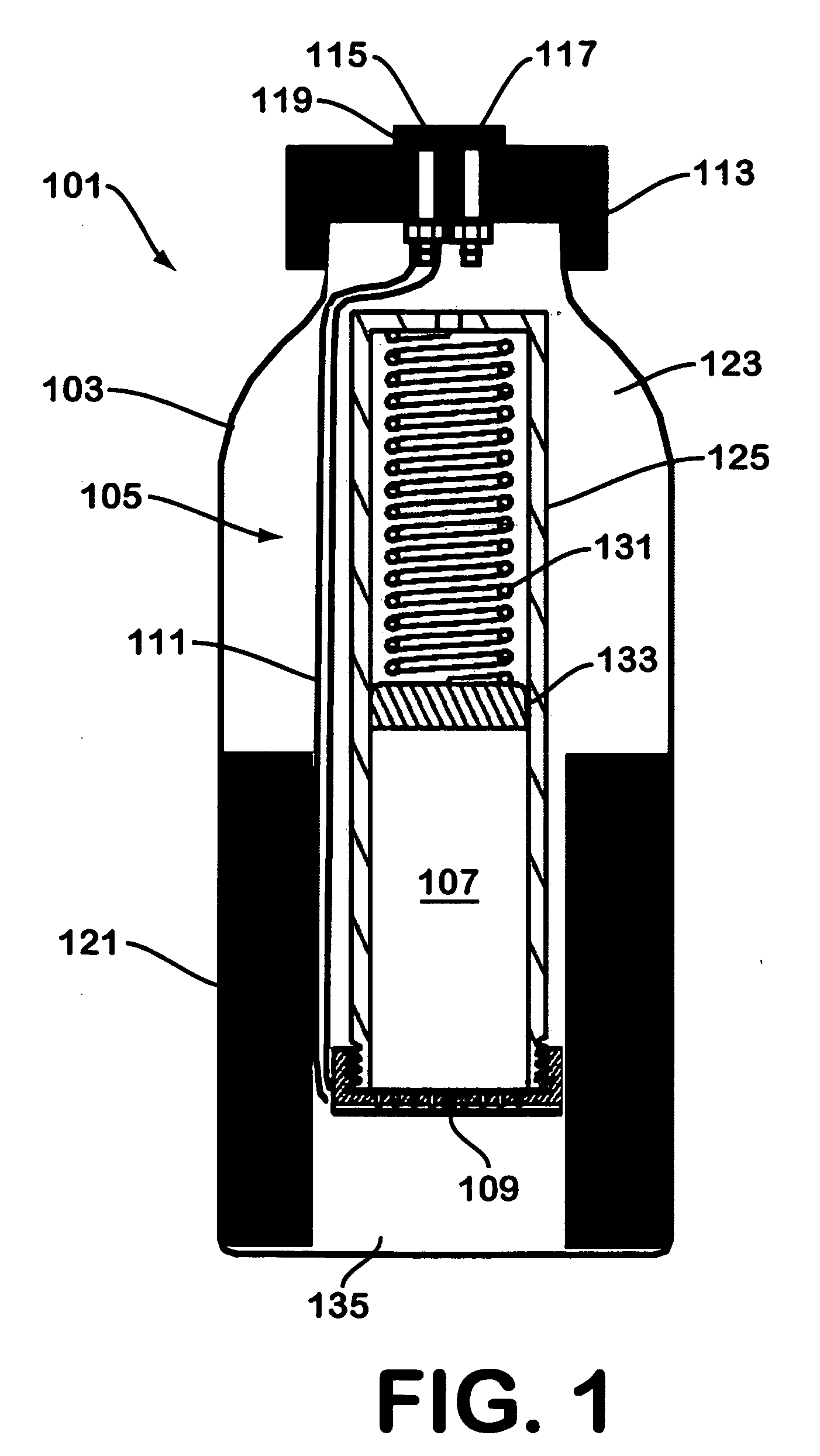
Solid chemical hydride dispenser for generating hydrogen gas
InactiveUS20070020172A1Molybdeum compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsCompound (substance)Hydrogen evolution
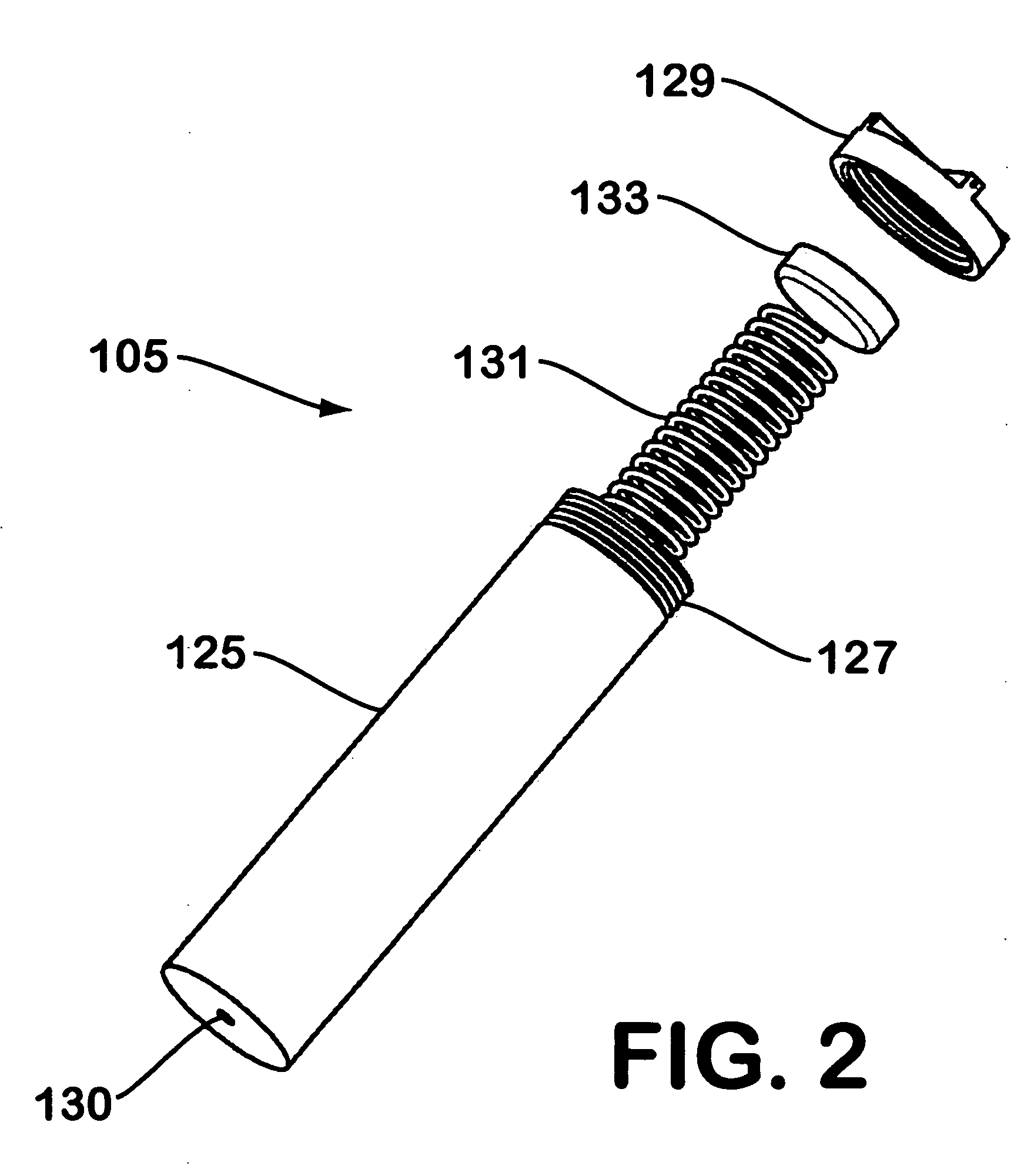
A device for generating hydrogen gas is provided. The device (101) comprises a first hydrogen-containing composition (107) that reacts with a second composition to evolve hydrogen gas; a dispenser (105) adapted to apply the first composition to a first porous member (109); and a conduit (111) adapted to supply the second composition to the first porous member. In a preferred embodiment, the first composition is selected from the group consisting of hydrides, borohydrides and boranes, the second composition is water, and the dispenser is spring-loaded and is charged with the first composition. As the first composition reacts with water at the interface to evolve hydrogen gas, the dispenser forces the reaction product across the interface and out of the dispenser, where it will not interfere with the progress of the hydrogen evolution reaction.
Owner:LYNNTECH POWER SYST
Bulk polymerization process for producing polydienes
ActiveUS7094849B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHalogenBulk polymerization
A method of producing cis-1,4-polydienes, the method comprising the step of contacting conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst system in the presence of less than 20% by weight of organic solvent based on the total weight of monomer, organic solvent, and resulting polymer, where the lanthanide-based catalyst system is the combination of or reaction product of (a) a lanthanide compound, (b) an organoaluminum hydride, (c) a trihydrocarbylaluminum, and (d) a halogen-containing compound.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Photoacid generator
InactiveUS7550246B2Improve solubilitySensitive highPhotosensitive materialsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsIridiumPhotoacid
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Ion implantation device and a method of semiconductor manufacturing by the implantation of boron hydride cluster ions
InactiveUS20060097193A1Improve productivityLow costTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMolecular clusterDevice material
An ion implantation device and a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device is described, wherein ionized boron hydride molecular clusters are implanted to form P-type transistor structures. For example, in the fabrication of Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) devices, the clusters are implanted to provide P-type doping for Source and Drain structures and for Polygates; these doping steps are critical to the formation of PMOS transistors. The molecular cluster ions have the chemical form BnHx+ and BnHx− where 10
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Process for the preparation and purification of thiol-containing maytansinoids
InactiveUSRE39151E1Reduce process complexityAllows scalabilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryLithiumThiol
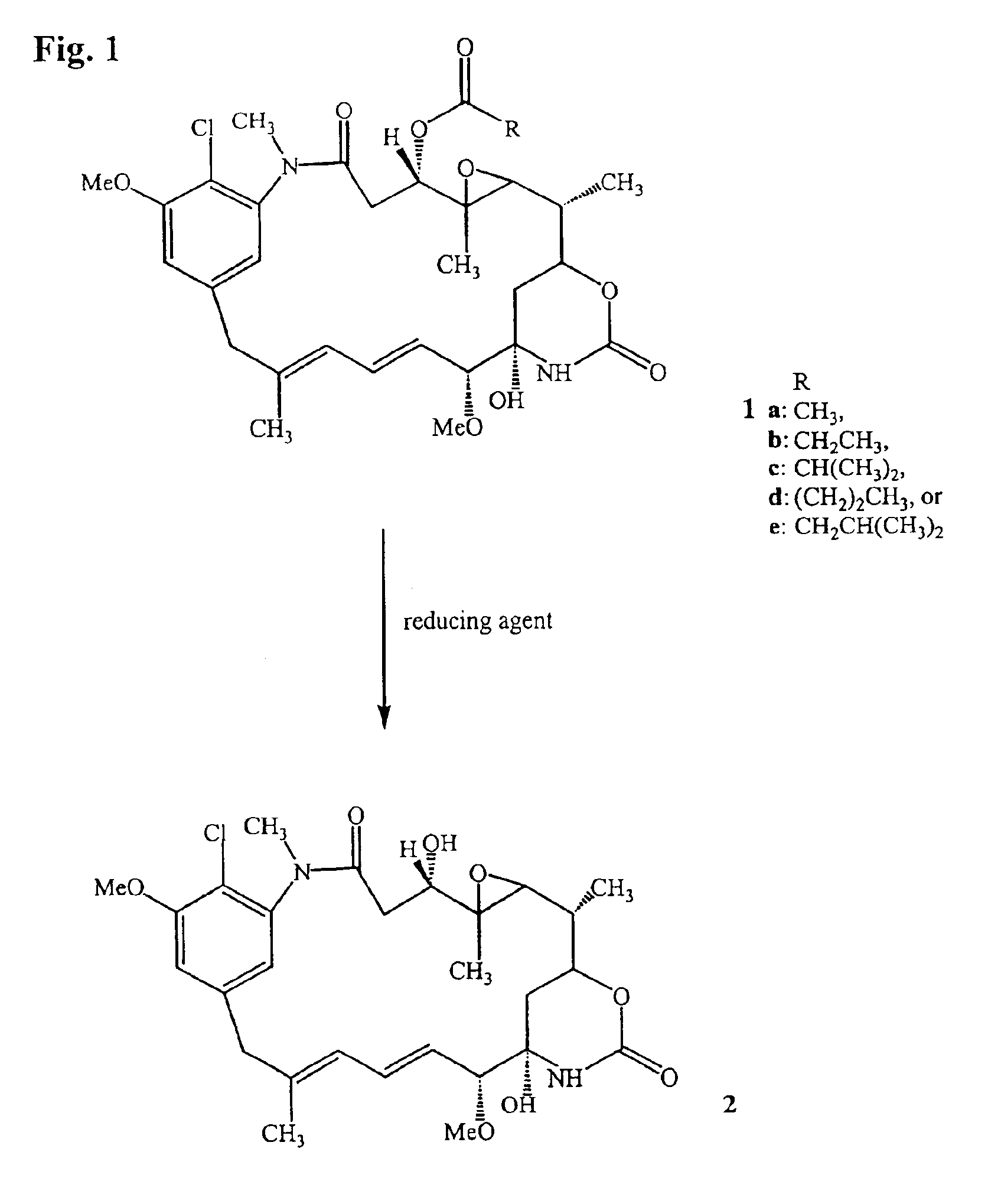
The present invention provides a process for the preparation and purification of thiol-containing maytansinoids comprising the steps of: (1) reductive hydrolysis of a maytansinoid C-3 ester with a reducing agent selected from the group consisting lithium trimethoxyaluminum hydride (LiAl (OMe)3H), lithium triethoxyaluminum hydride (LiAl(OEt)3H), lithium tripropoxyaluminum hydride (LiAl (OPr)3H), sodium trimethoxyaluminum hydride (NaAl (OMe)3H), sodium triethoxyaluminum hydride (NaAl(OEt)3H) and sodium tripropoxyaluminum hydride (NaAl(OPr)3H) to yield a maytansinol; (2) purifying the maytansinol to remove side products when present; (3) esterifying the purified maytansinol with a carboxylic acid to yield a mixture of an L- and a D-aminoacyl ester of maytansinol; (4) separating the L-aminoacyl ester of maytansinol from the reaction mixture in (3); (5) reducing the L-aminoacyl ester of maytansinol to yield a thiol-containing maytansinoid; and (5) purifying the thiol-containing maytansinoid.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
Active metal/aqueous electrochemical cells and systems
InactiveUS7645543B2Degree of flexibilityWithout performanceFuel and primary cellsAlkaline accumulatorsElectrochemical cellBattery cell
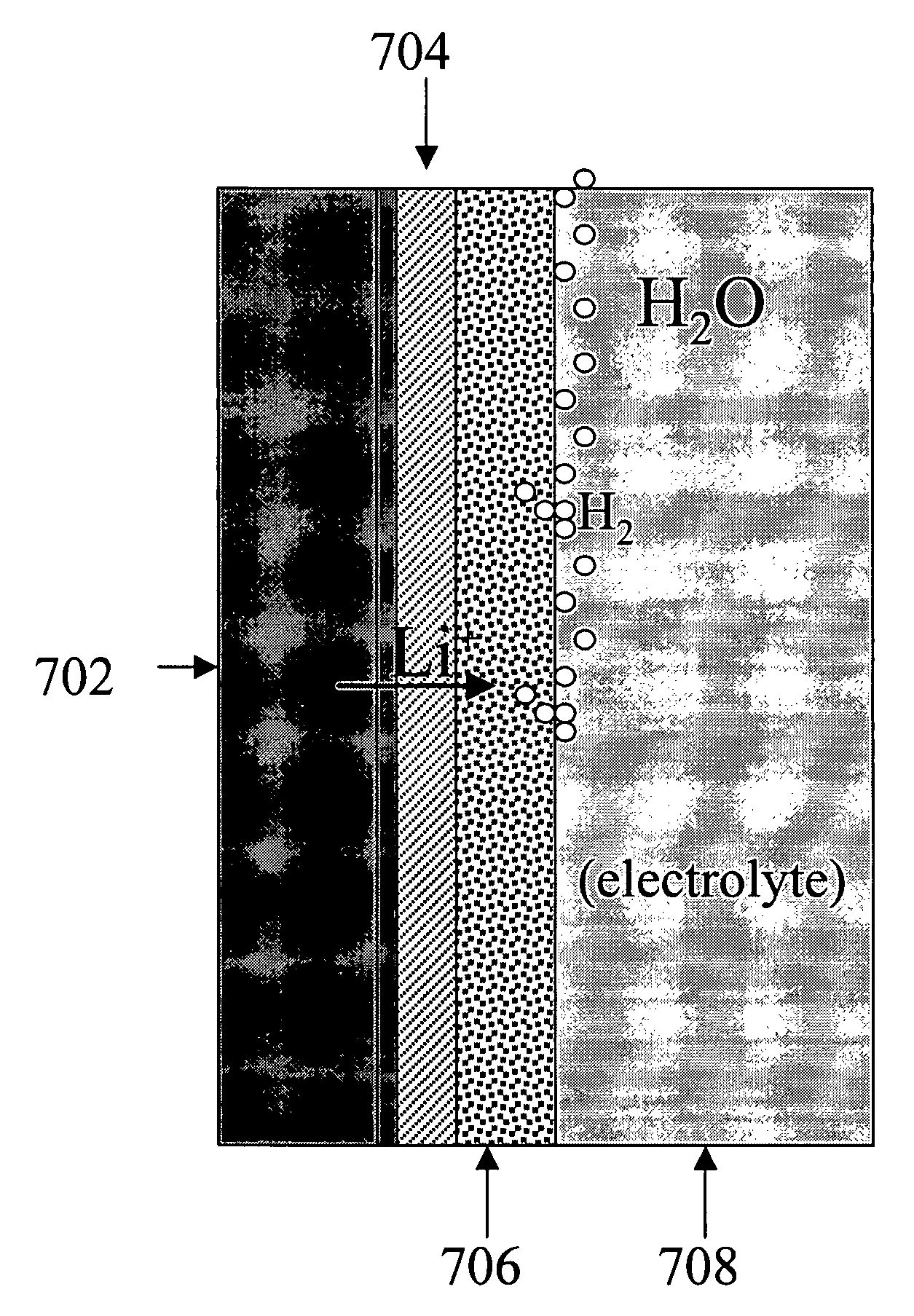
Alkali (or other active) metal battery and other electrochemical cells incorporating active metal anodes together with aqueous cathode / electrolyte systems. The battery cells have a highly ionically conductive protective membrane adjacent to the alkali metal anode that effectively isolates (de-couples) the alkali metal electrode from solvent, electrolyte processing and / or cathode environments, and at the same time allows ion transport in and out of these environments. Isolation of the anode from other components of a battery cell or other electrochemical cell in this way allows the use of virtually any solvent, electrolyte and / or cathode material in conjunction with the anode. Also, optimization of electrolytes or cathode-side solvent systems may be done without impacting anode stability or performance. In particular, Li / water, Li / air and Li / metal hydride cells, components, configurations and fabrication techniques are provided.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Method and apparatus for crystal growth using a membrane-assisted semi-closed reactor
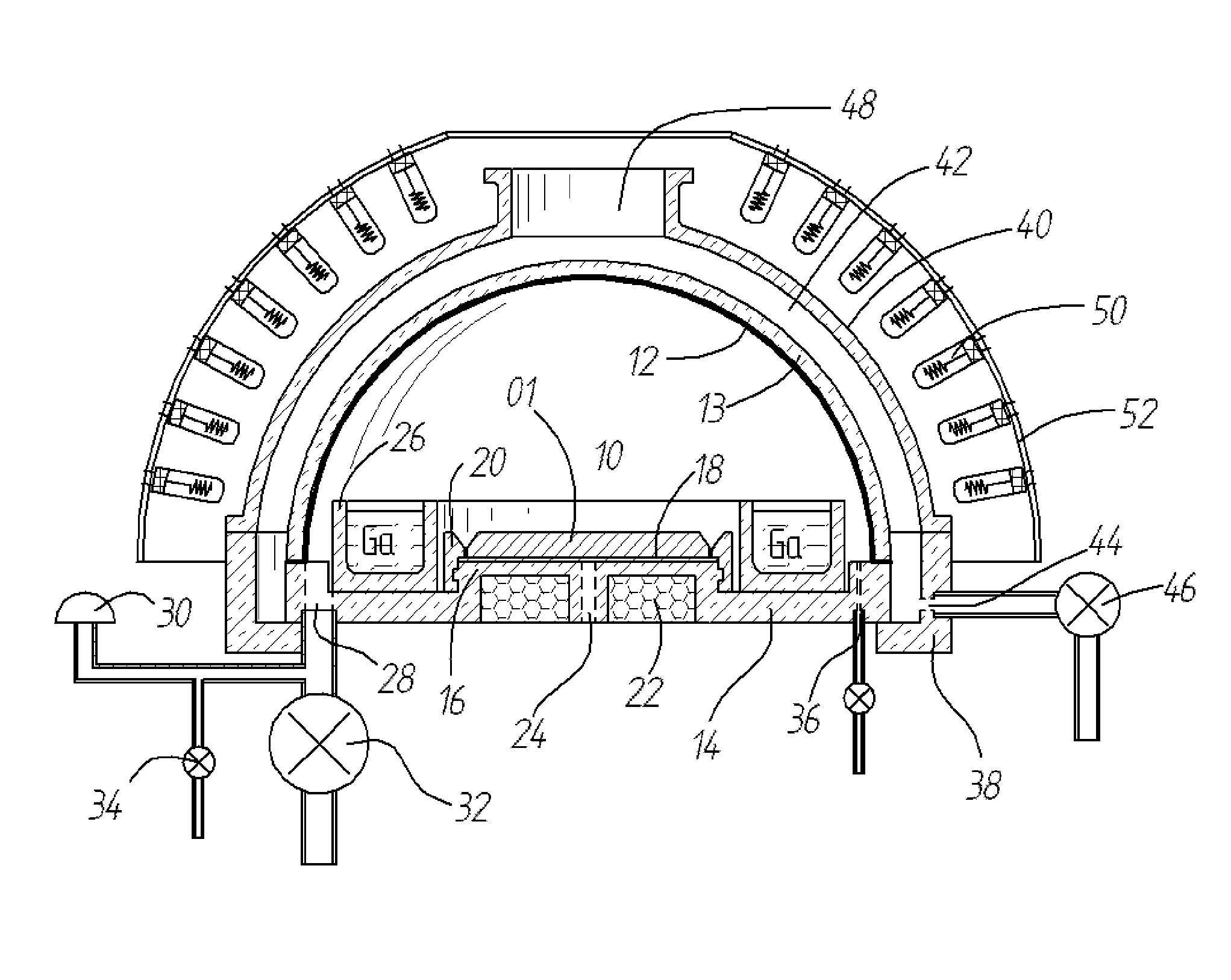
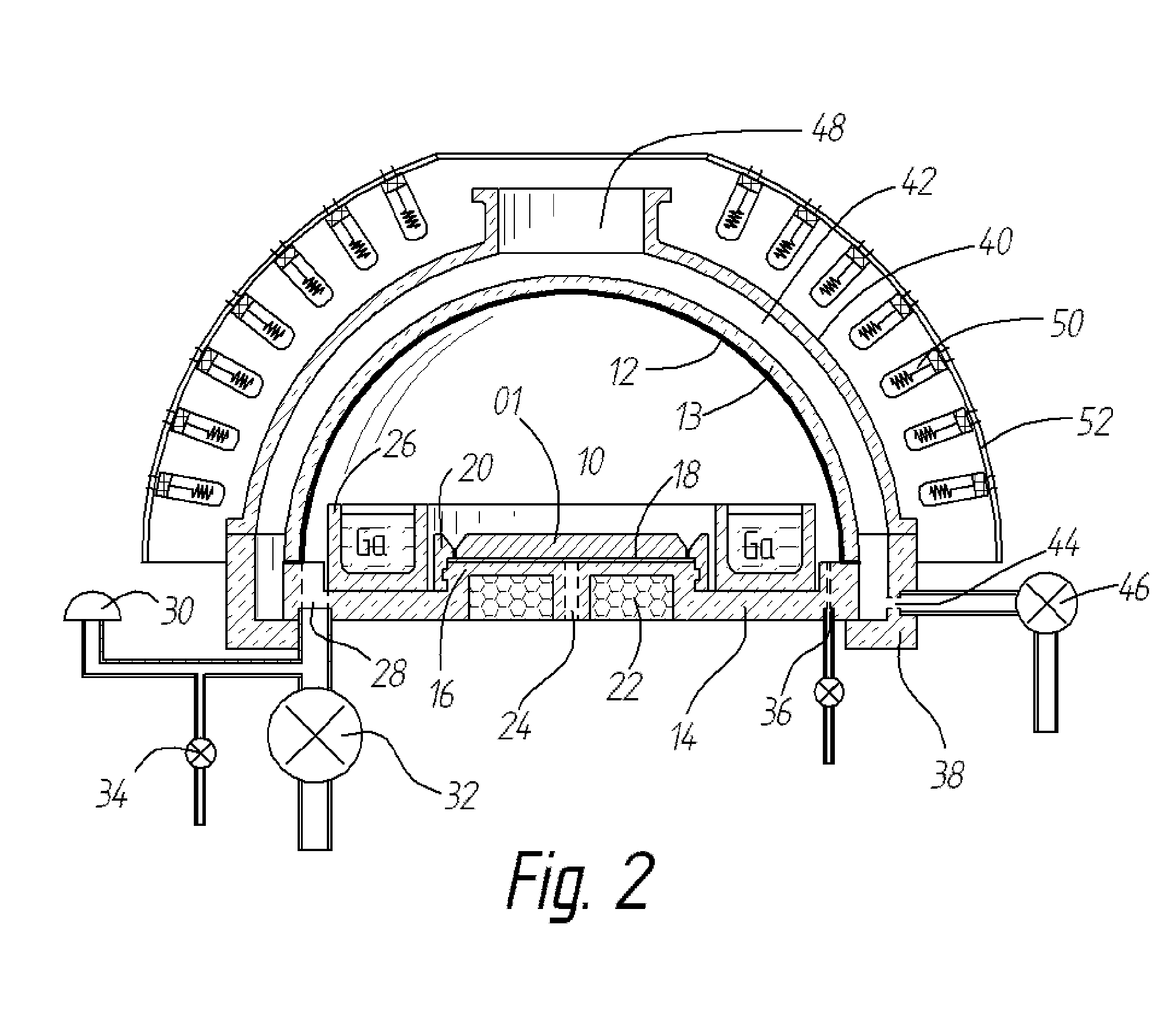
InactiveUS20120291696A1Polycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesTemperature controlVapor phase
A method and apparatus for depositing III-V material is provided. The apparatus includes a reactor partially enclosed by a selectively permeable membrane 12. A means is provided for generating source vapors, such as a vapor-phase halide of a group III element (IUPAC group 13) within the reactor volume 10, and an additional means is also provided for introducing a vapor-phase hydride of a group V element (IUPAC group 15) into the volume 10. The reaction of the group III halide and the group V hydride on a temperature-controlled substrate 18 within the reactor volume 10 produces crystalline III-V material and hydrogen gas. The hydrogen is preferentially removed from the reactor through the selectively permeable membrane 12, thus avoiding pressure buildup and reaction imbalance. Other gases within the reactor are unable to pass through the selectively permeable membrane.
Owner:CLARKE ANDREW PETER
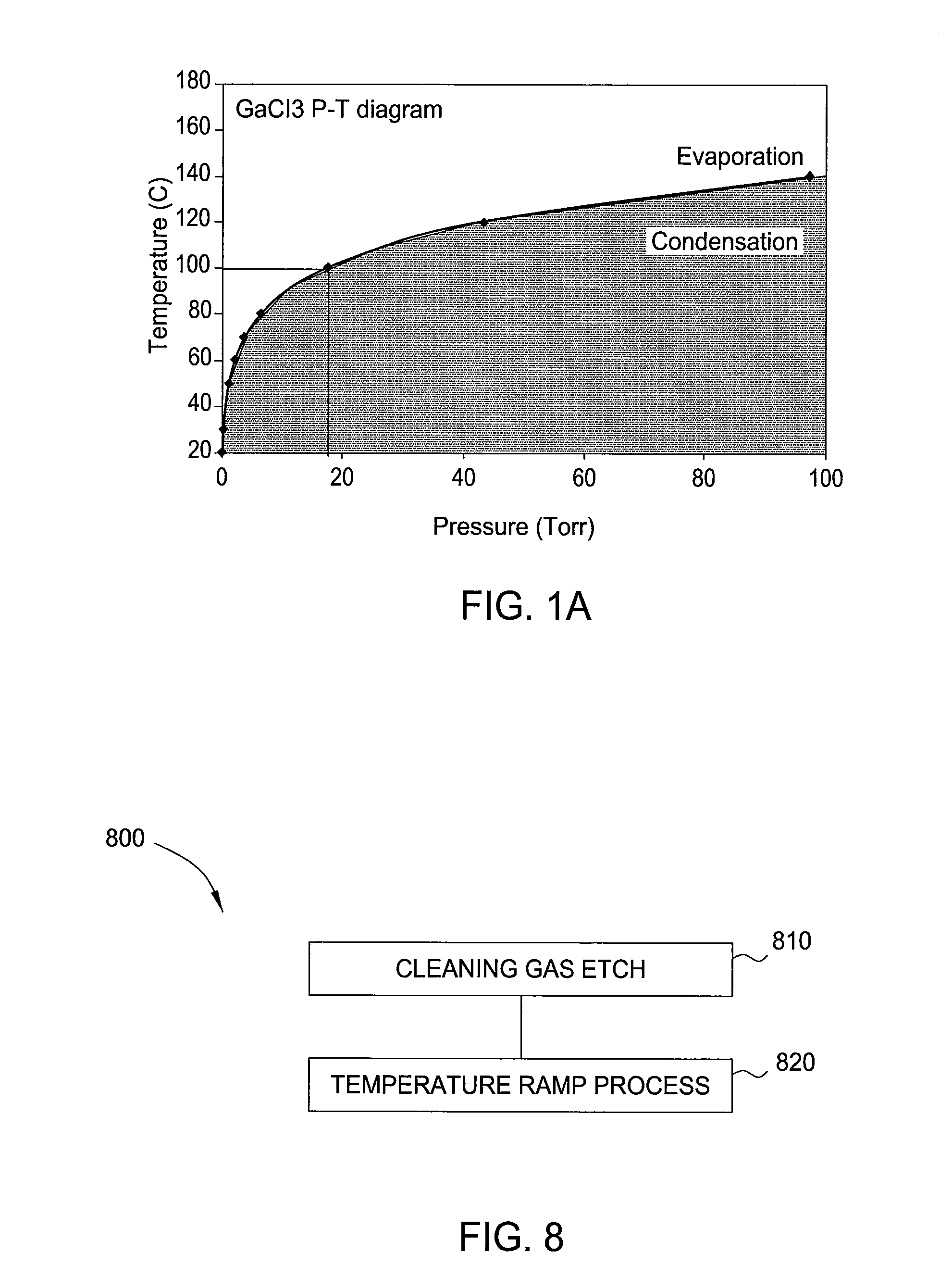
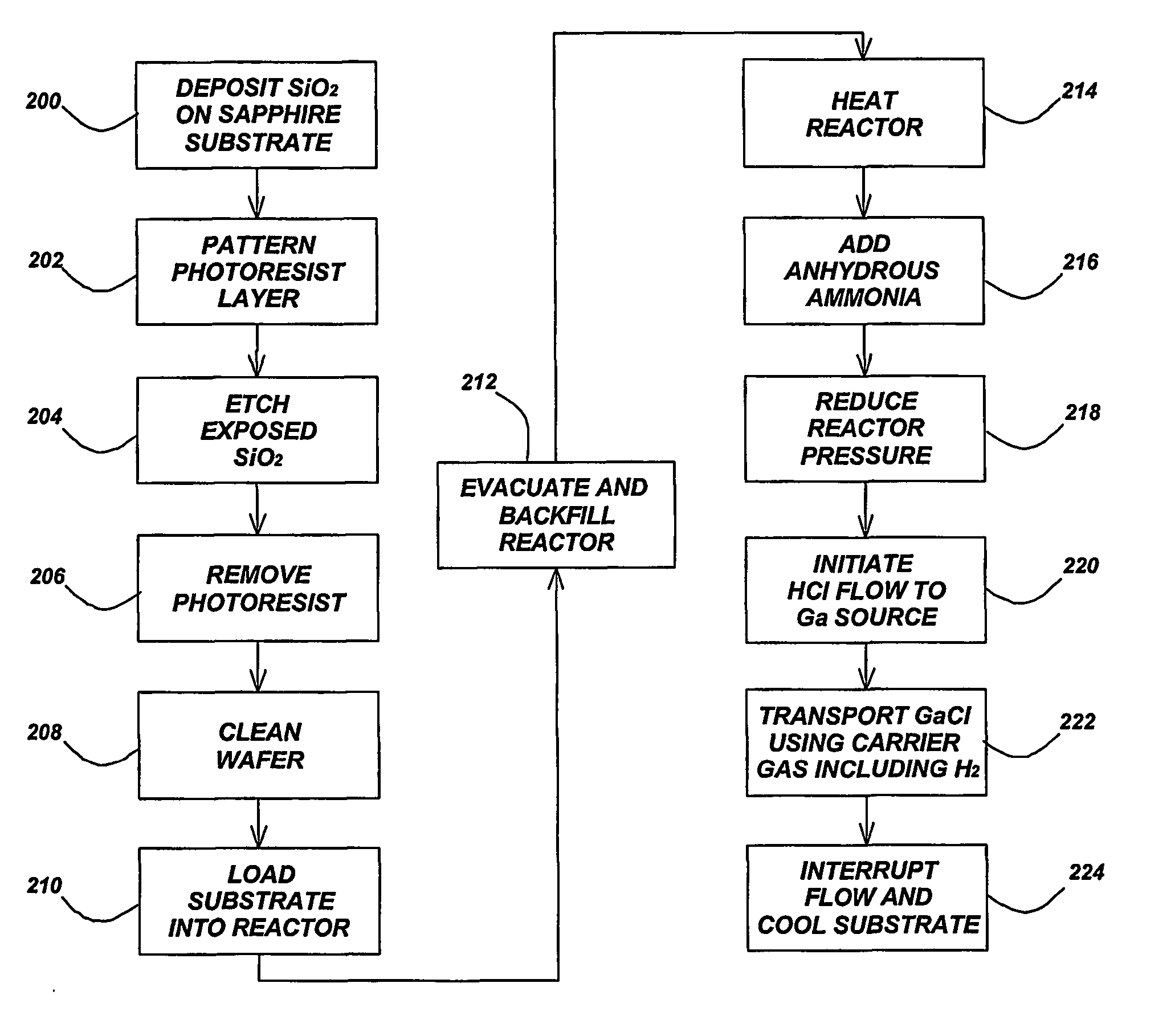
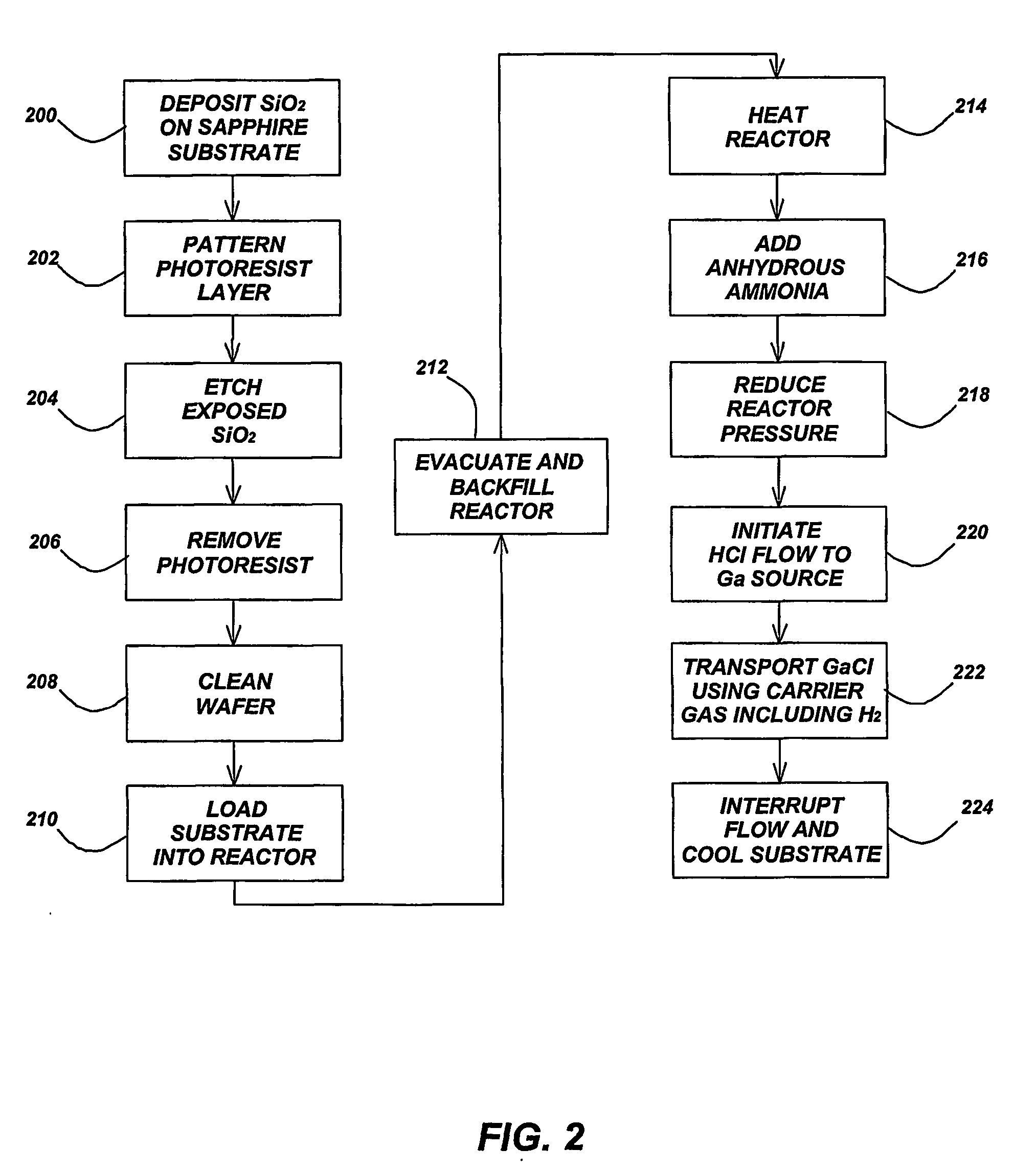
Growth of reduced dislocation density non-polar gallium nitride by hydride vapor phase epitaxy
InactiveUS20060128124A1Reduce threading dislocation densityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium nitrideVapor phase
Lateral epitaxial overgrowth (LEO) of non-polar a-plane gallium nitride (GaN) films by hydride vapor phase epitaxy (HVPE) results in significantly reduced defect density.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Low oxygen refractory metal powder for powder metallurgy
InactiveUS6261337B1Electrolytic capacitorsTransportation and packagingMetallic hydrogenOxygen content
One step process for producing formed Ta / Nb powder metallurgy products using Ta and / or Nb hydride powders with an oxygen content greater than a target level, e.g., 300 ppm, heating the metal hydride in the presence of another metal having a higher affinity for oxygen, removing the other metal and any reaction byproducts, to form a metal powder with an oxygen content less than the target level and forming a metallurgical product from said oxygen reduced Ta / Nb powder with an oxygen content less than the target level.
Owner:H C STARCK INC
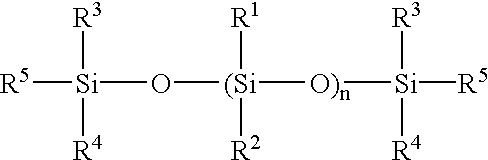
Low temperature, fast curing silicone compositions
InactiveUS6573328B2Low curing temperatureImproves of curedLayered productsSolid-state devicesPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
Heat-curable silicone compositions employing a reactive silicone, a silicone hydride crosslinker and a catalyst system which includes a rhodium-based catalyst, a stabilizing system are disclosed. A combination of rhodium and platinum-based catalysts are employed as well. The compositions are low temperature curing and are capable of providing low coefficient of thermal expansion compositions. A stabilizer system which includes in combination a peroxide and an acetylenic compound is also disclosed.
Owner:HENKEL LOCTITE CORP
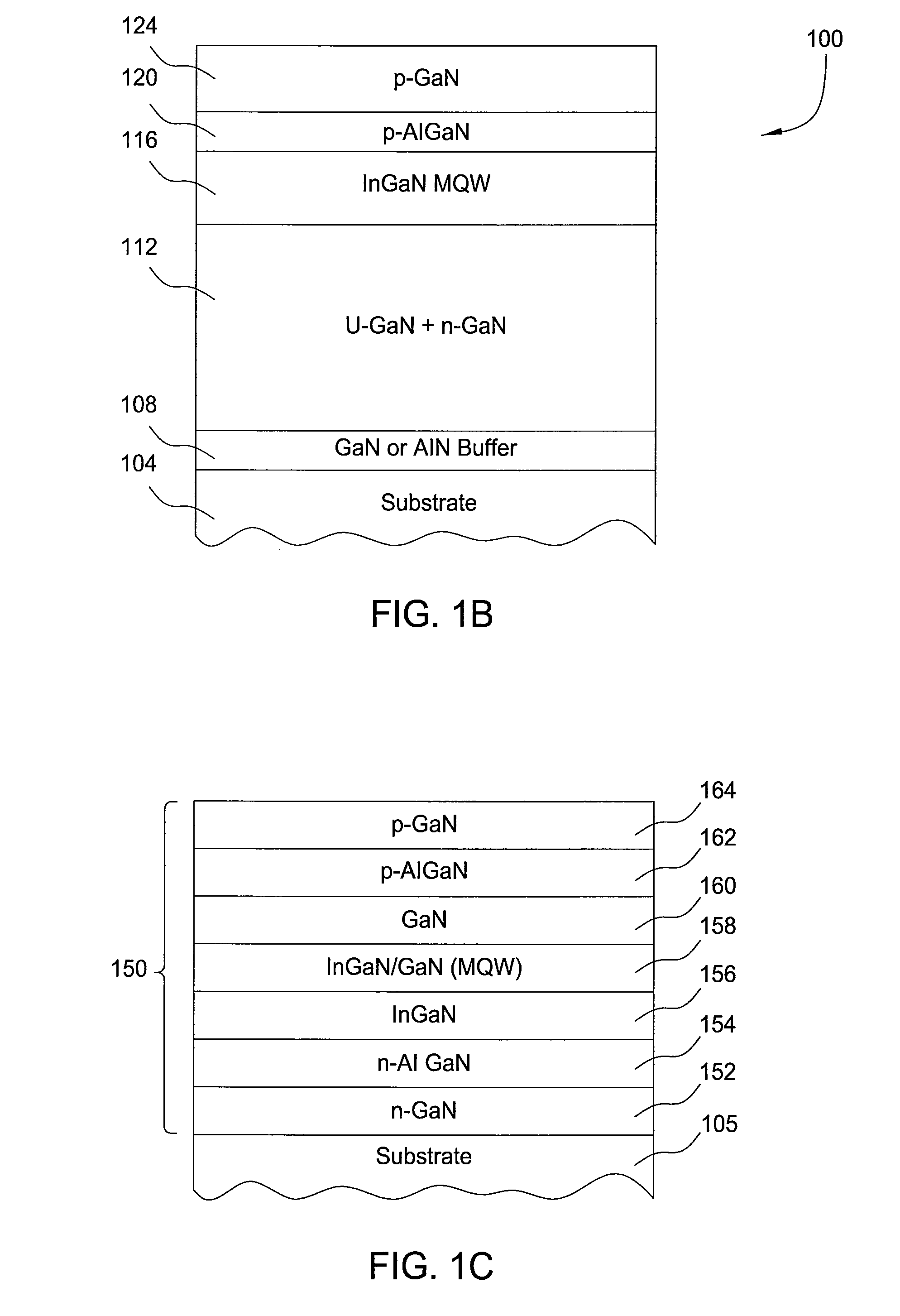
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110269266A1Easy to understandSuppress variation in electrical characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesResistEngineering
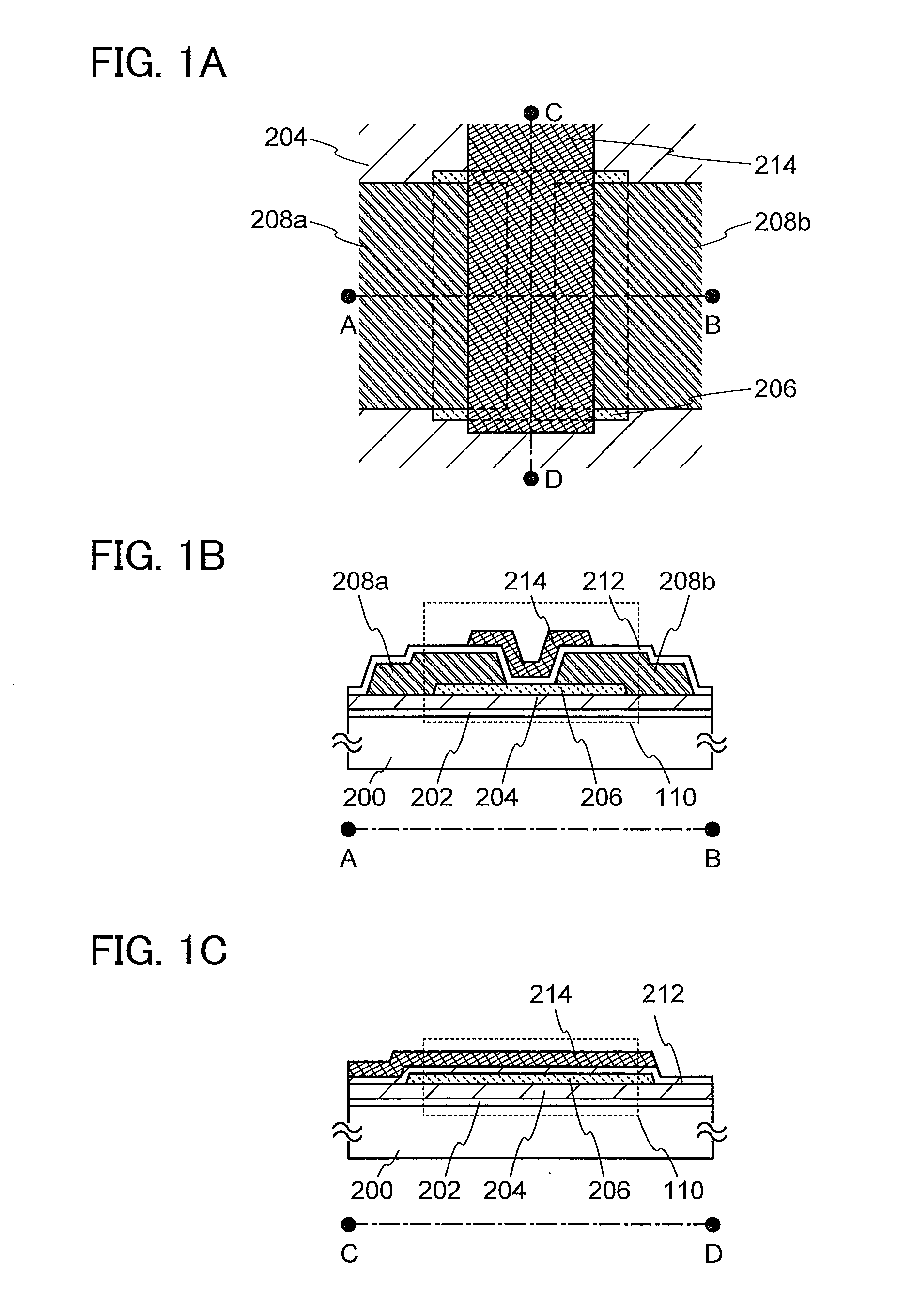
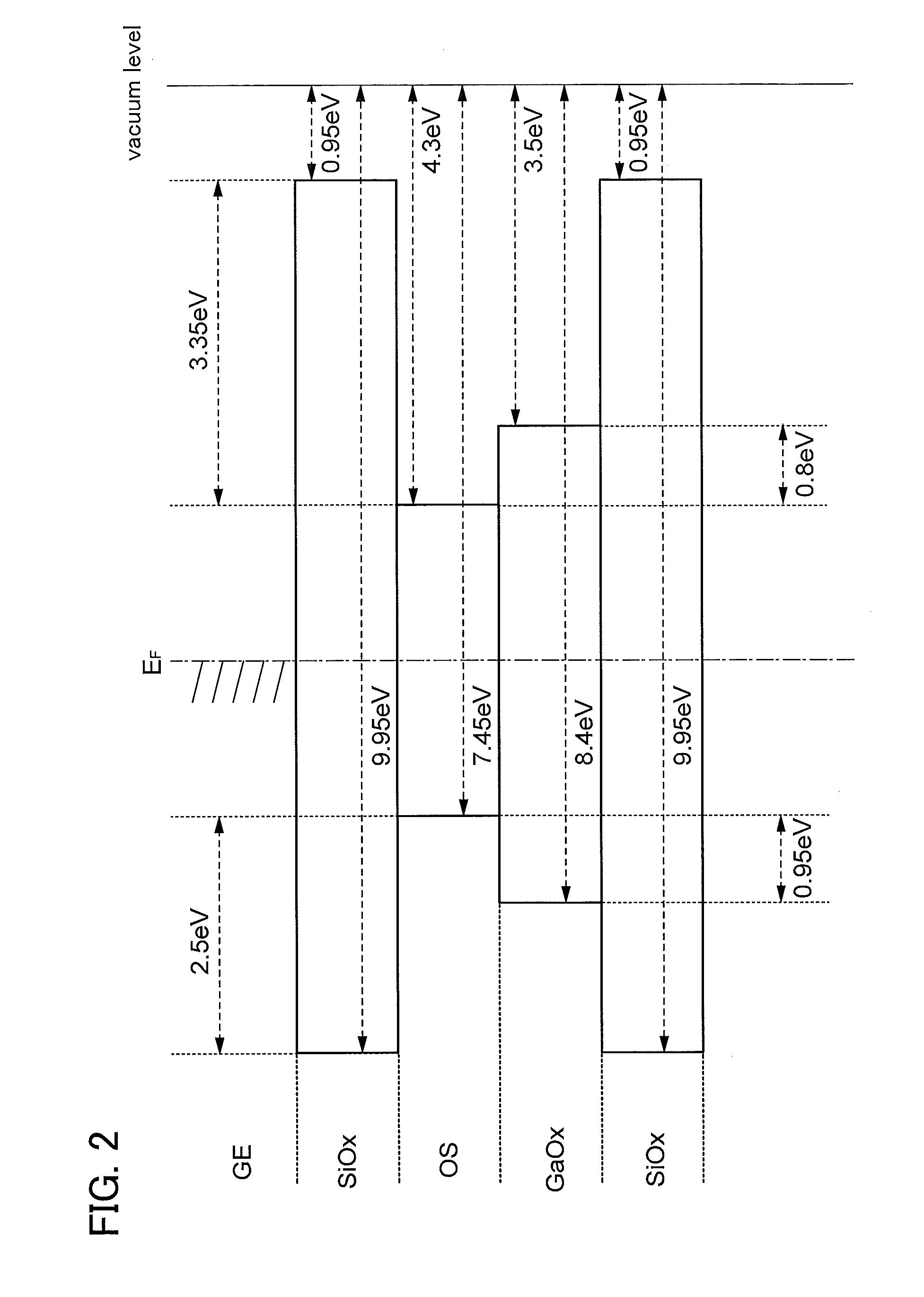
A semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor with stable electric characteristics and high reliability is provided. An island-shaped oxide semiconductor layer is formed by using a resist mask, the resist mask is removed, oxygen is introduced (added) to the oxide semiconductor layer, and heat treatment is performed. The removal of the resist mask, introduction of the oxygen, and heat treatment are performed successively without exposure to the air. Through the oxygen introduction and heat treatment, impurities such as hydrogen, moisture, a hydroxyl group, or hydride are intentionally removed from the oxide semiconductor layer, whereby the oxide semiconductor layer is highly purified. Chlorine may be introduced to an insulating layer over which the oxide semiconductor layer is formed before formation of the oxide semiconductor layer. By introducing chlorine, hydrogen in the insulating layer can be fixed, thereby preventing diffusion of hydrogen from the insulating layer into the oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Active metal/aqueous electrochemical cells and systems
InactiveUS7666233B2Degree of flexibilityWithout performanceFuel and primary cellsElectrode manufacturing processesManufacturing technologyElectrochemical cell
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110240992A1Improve reliabilityExcellent electrical propertiesTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesOxygenActive layer
A transistor is provided in which the bottom surface portion of an oxide semiconductor film is provided with a metal oxide film containing a constituent similar to that of the oxide semiconductor film, and an insulating film containing a different constituent from the metal oxide film and the oxide semiconductor film is formed in contact with a surface of the metal oxide film, which is opposite to the surface in contact with the oxide semiconductor film In addition, the oxide semiconductor film used for the active layer of the transistor is an oxide semiconductor film highly purified to be electrically i-type (intrinsic) through heat treatment in which impurities such as hydrogen, moisture, hydroxyl, and hydride are removed from the oxide semiconductor and oxygen which is one of main component materials of the oxide semiconductor is supplied and is also reduced in a step of removing impurities.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
System for hydrogen generation
InactiveUS7083657B2Liquid degasificationPhysical/chemical process catalystsAqueous solutionWater pipe
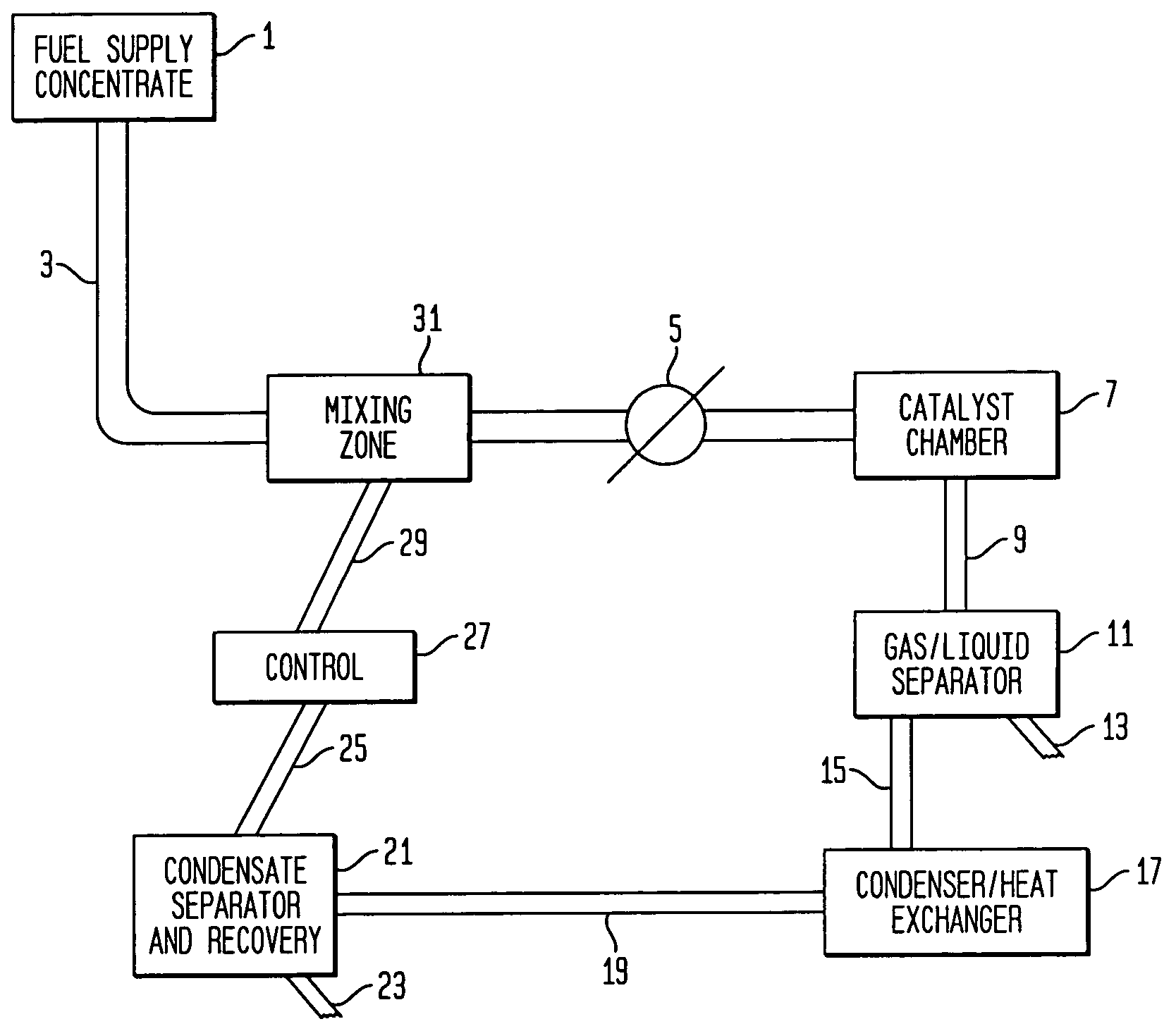
The present invention relates to an improvement in a system for the generation of hydrogen by contacting an aqueous solution of a metal hydride salt with a hydrogen generation catalyst. In particular, the present invention relates to the incorporation within the system of a recycle line of water condensed from the fluid product to the feed line to be contacted with the catalyst. the internal recycle line permits the use of a more concentrated solution of metal hydride as it is diluted by the recycle line prior to contact with the catalyst.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com