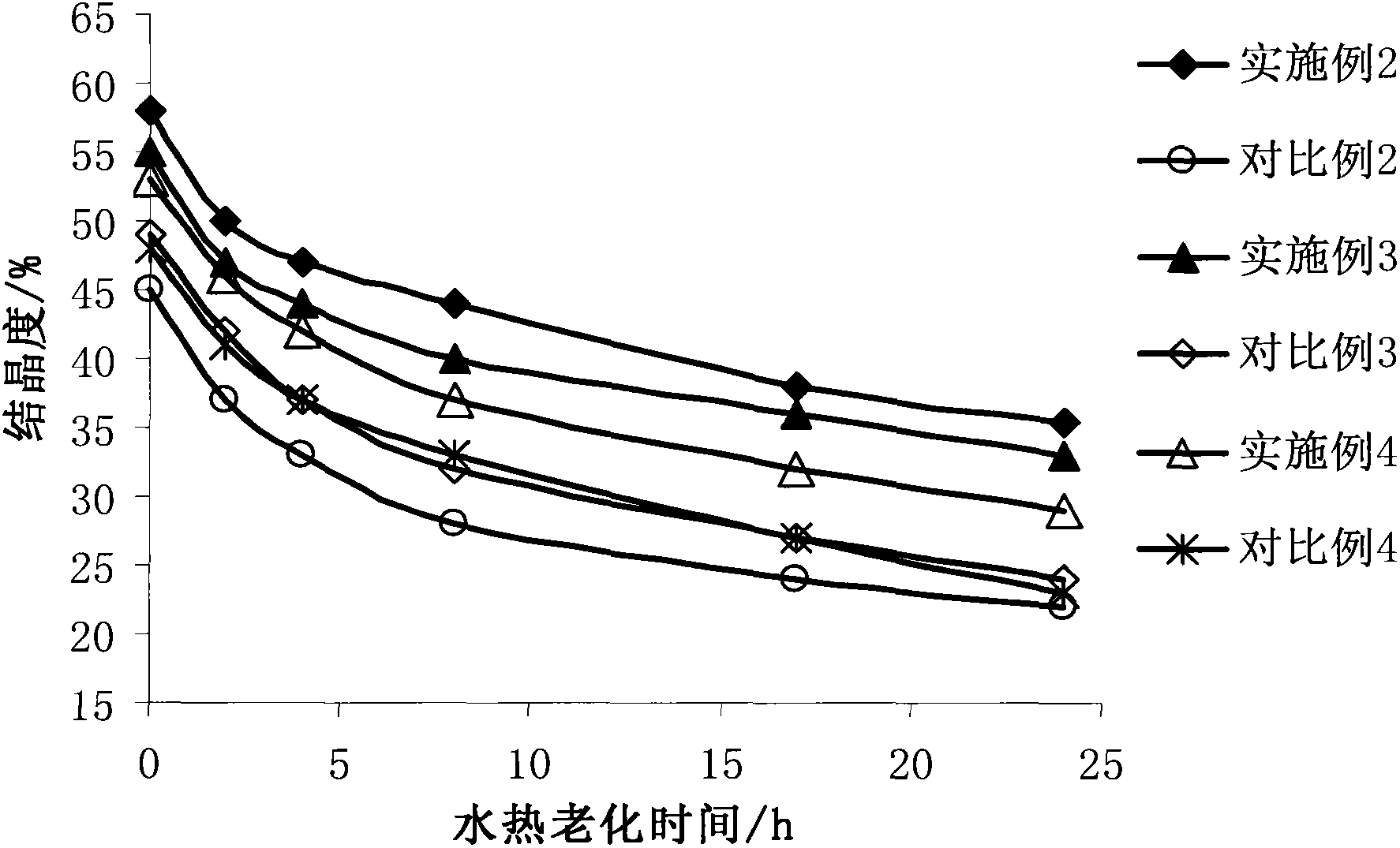
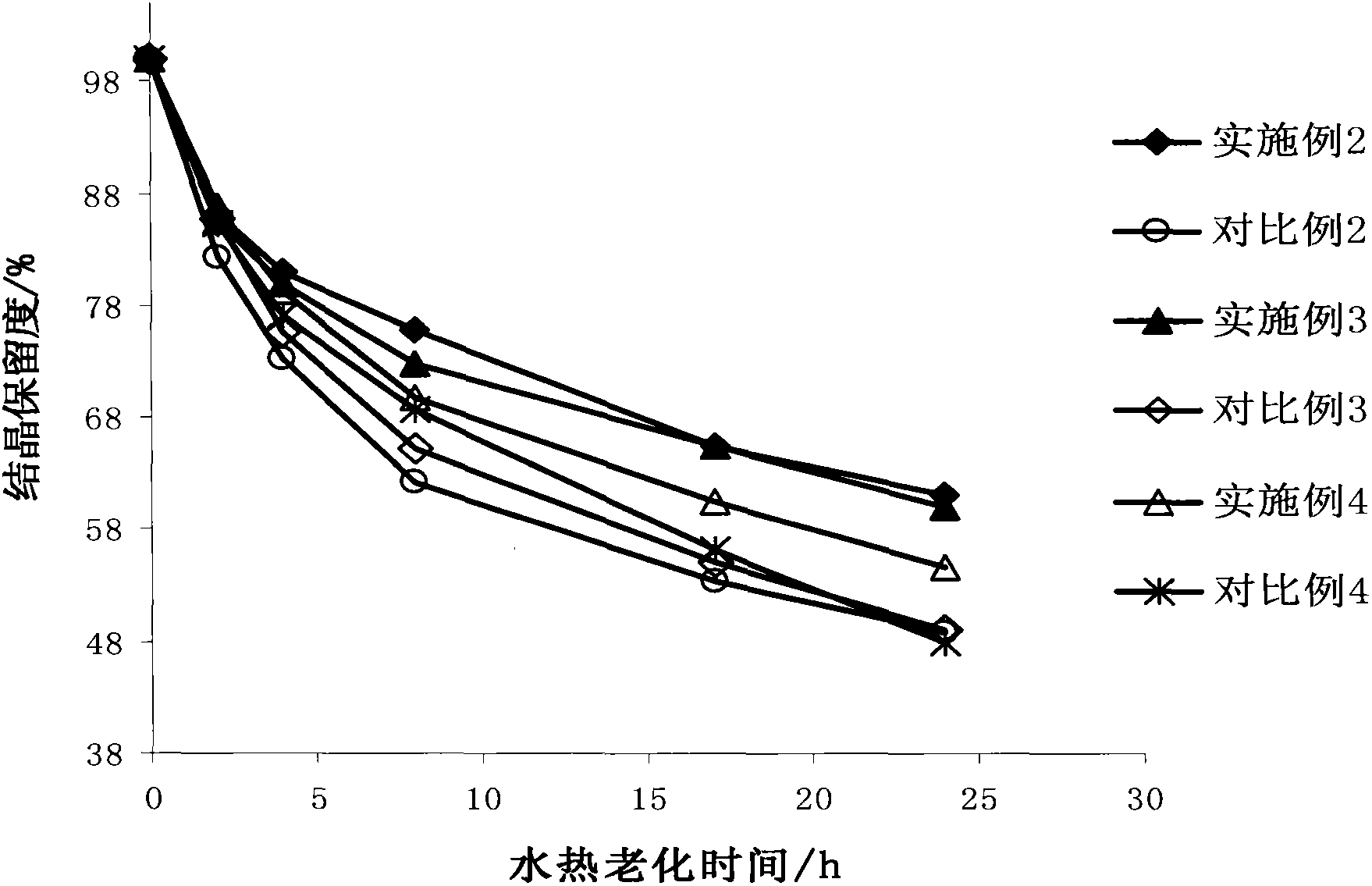
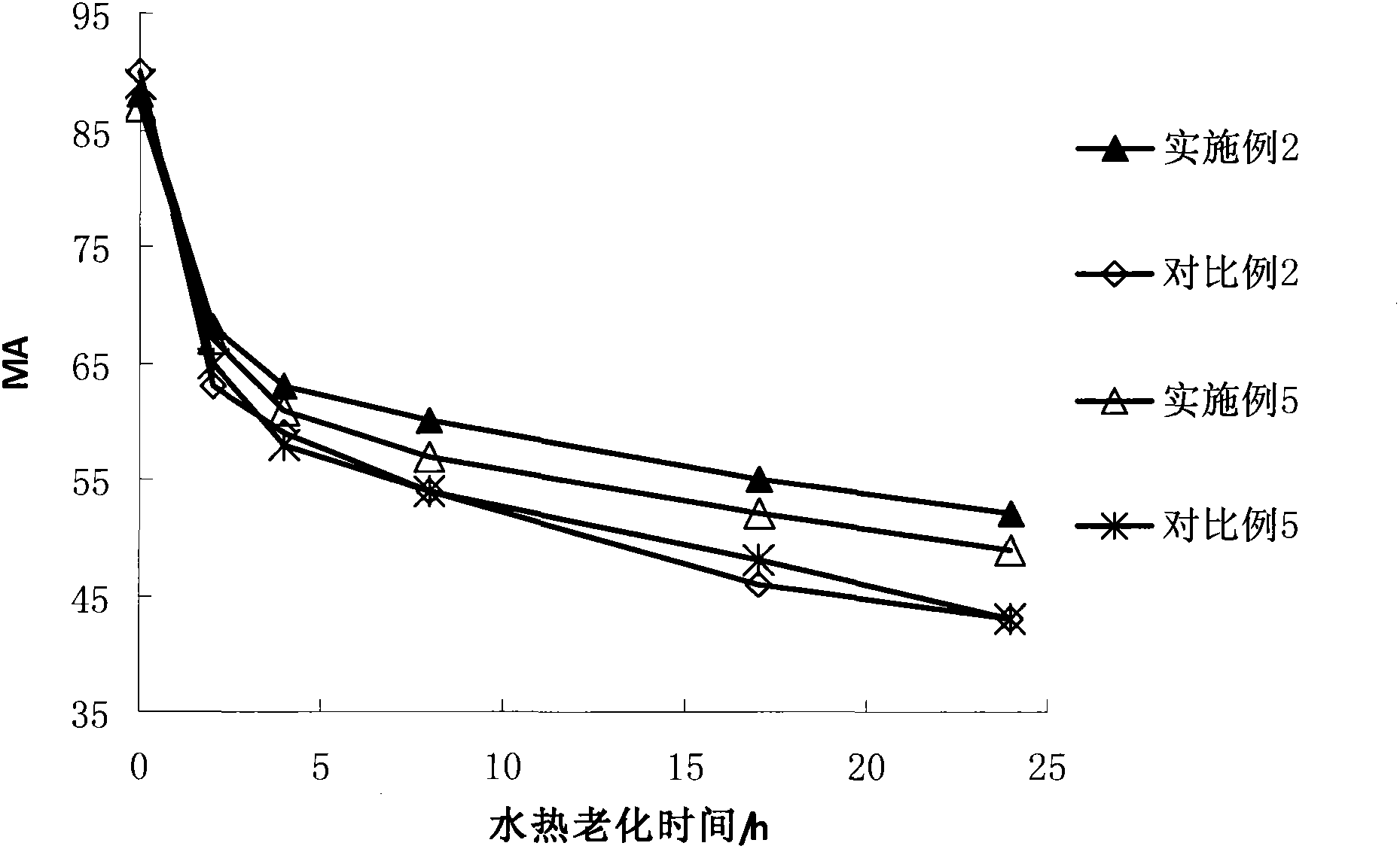
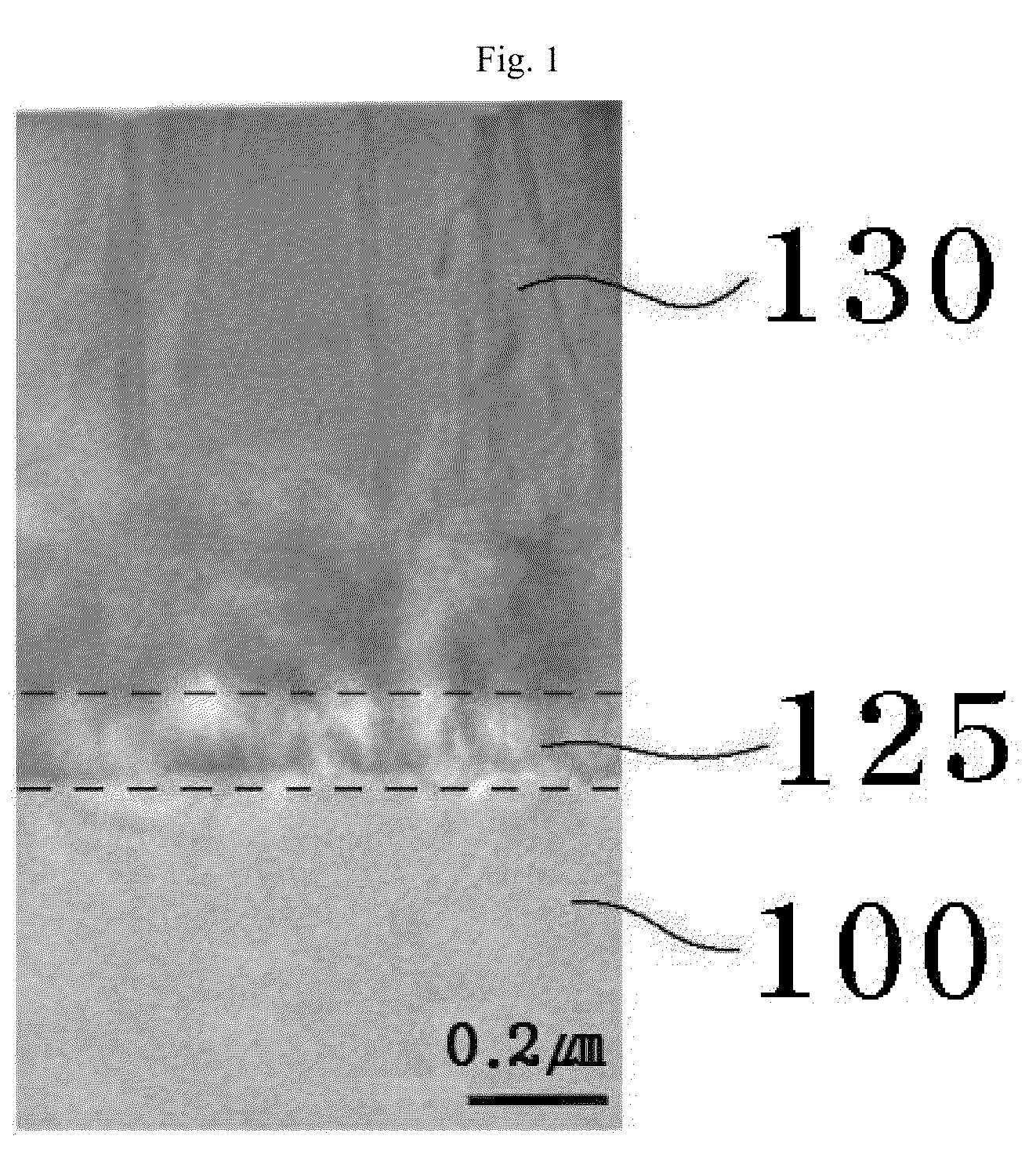
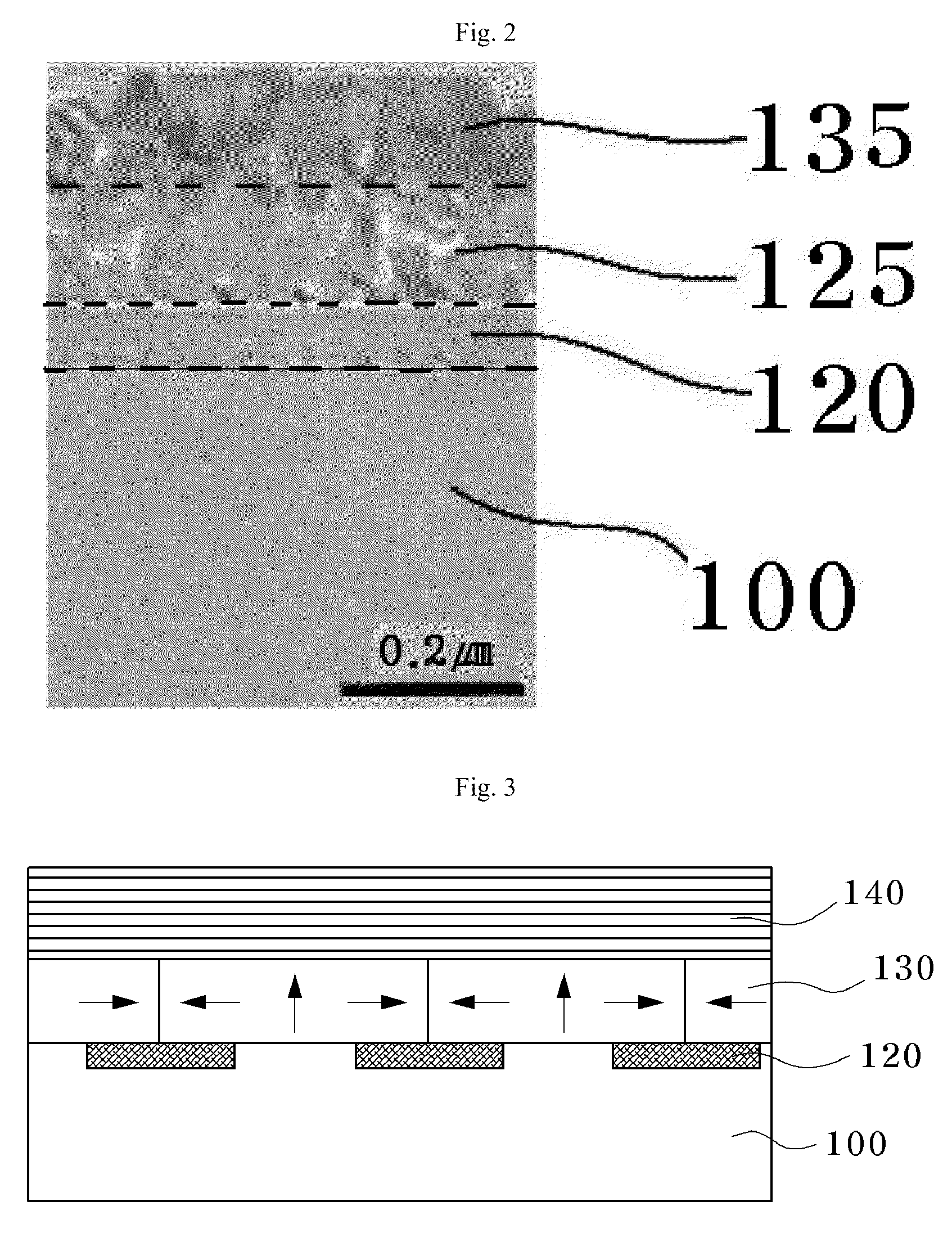
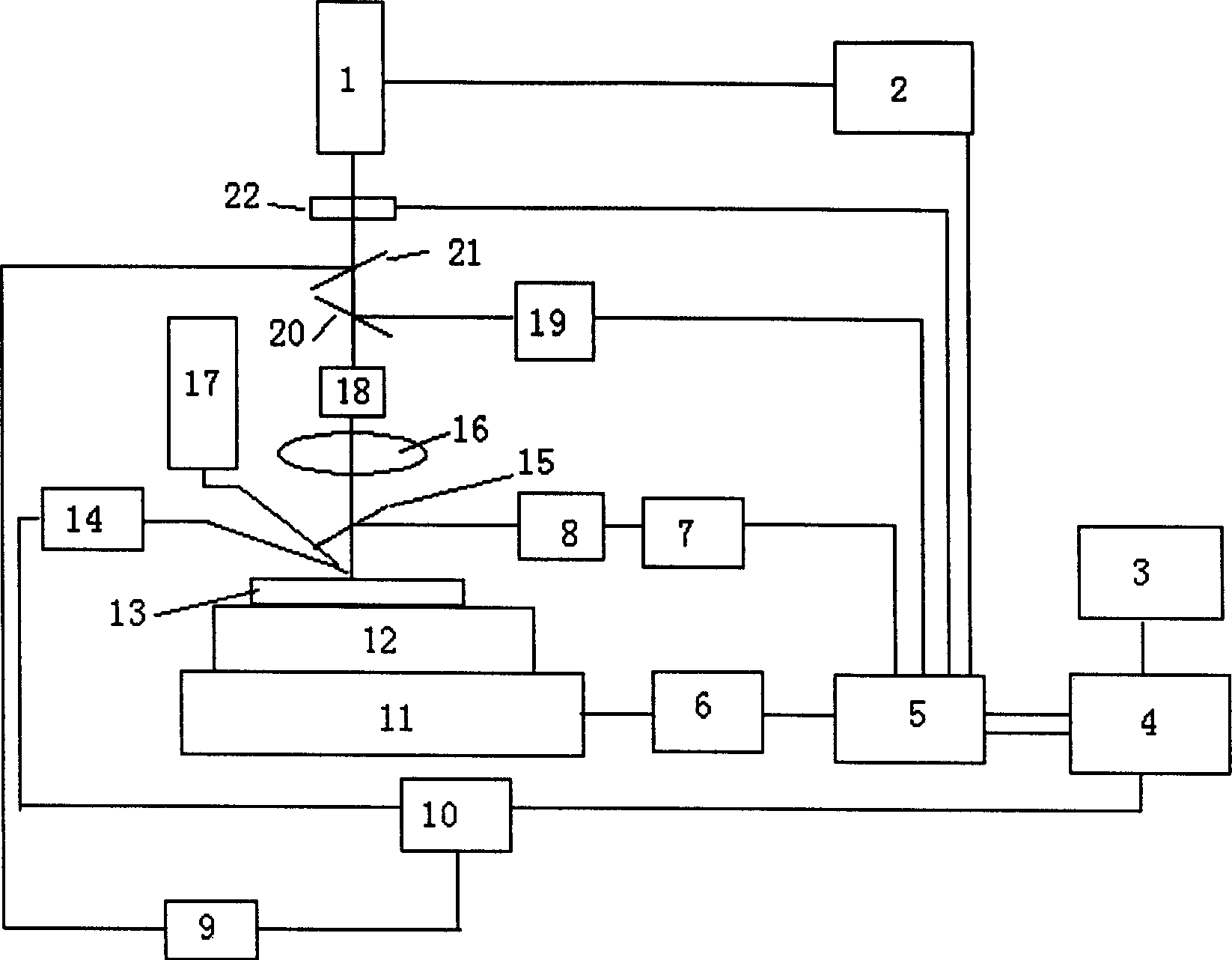
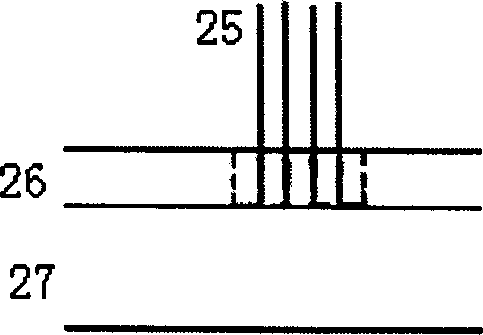
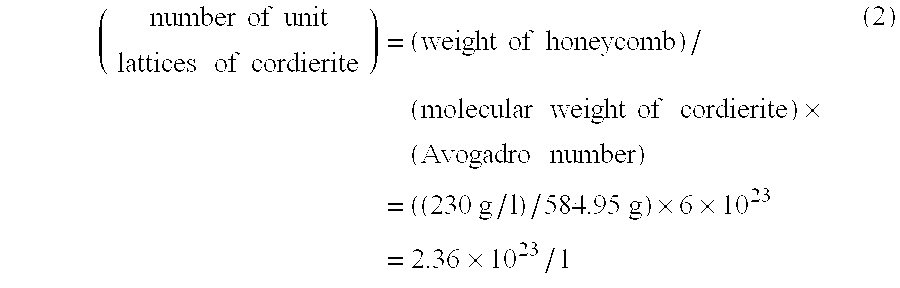Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
388 results about "Lattice defects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
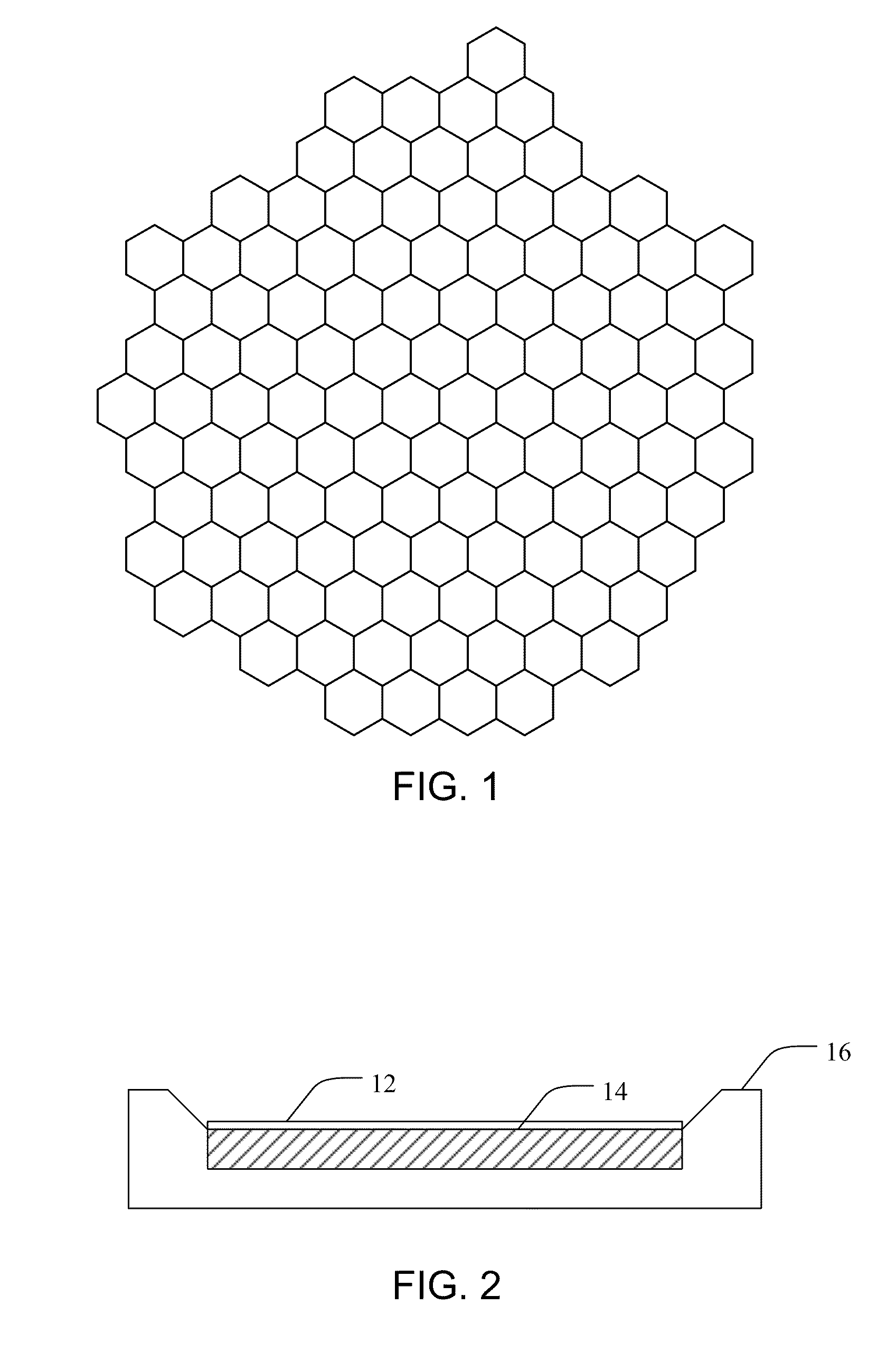
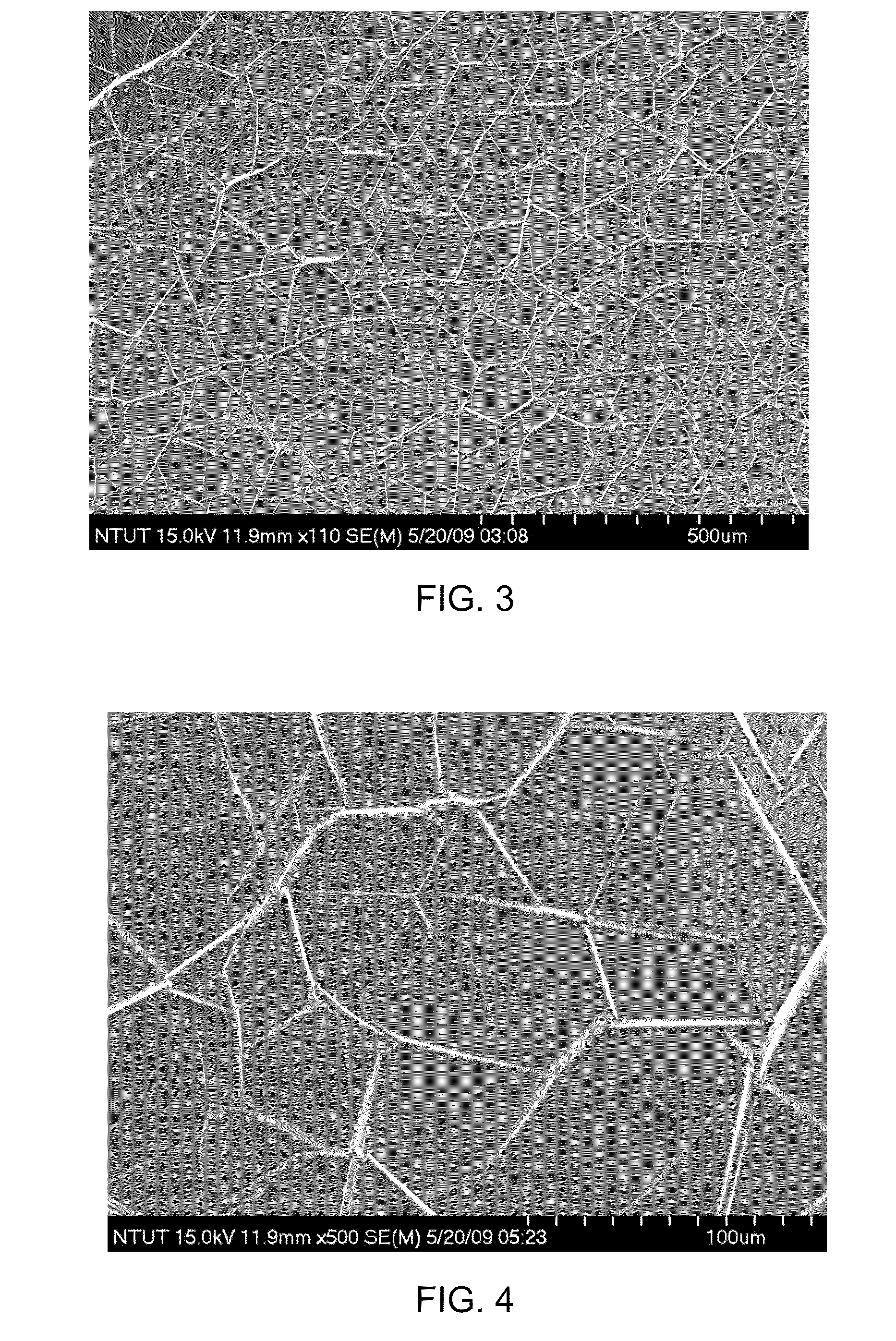
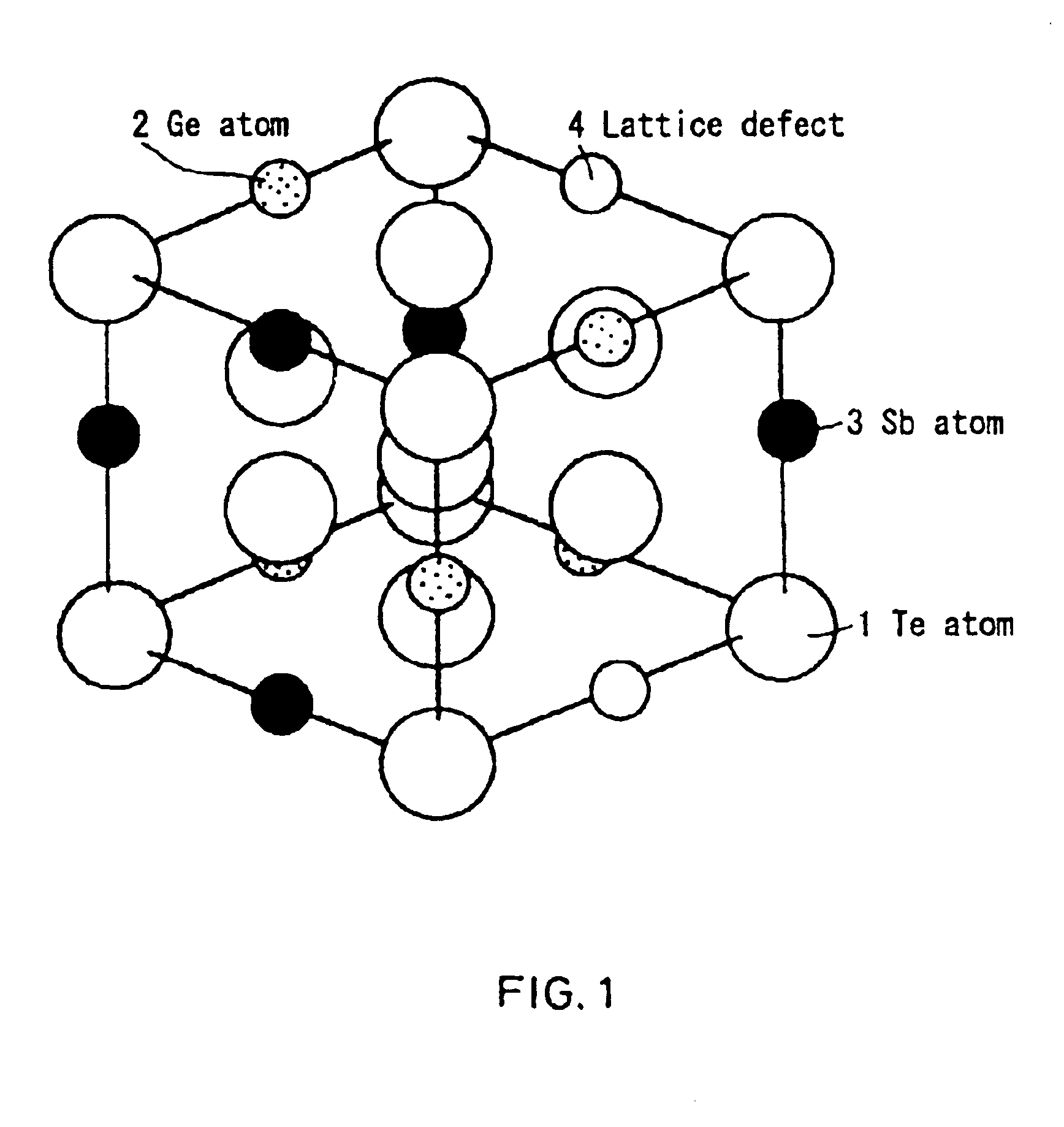
Lattice defects can be classified according to their dimensionality as zero-, one- or two-dimensional defects. Point defects are zero-dimensional: an atom isn't where it is supposed to be according to the ideal description that we have, or it is the wrong type of atom.
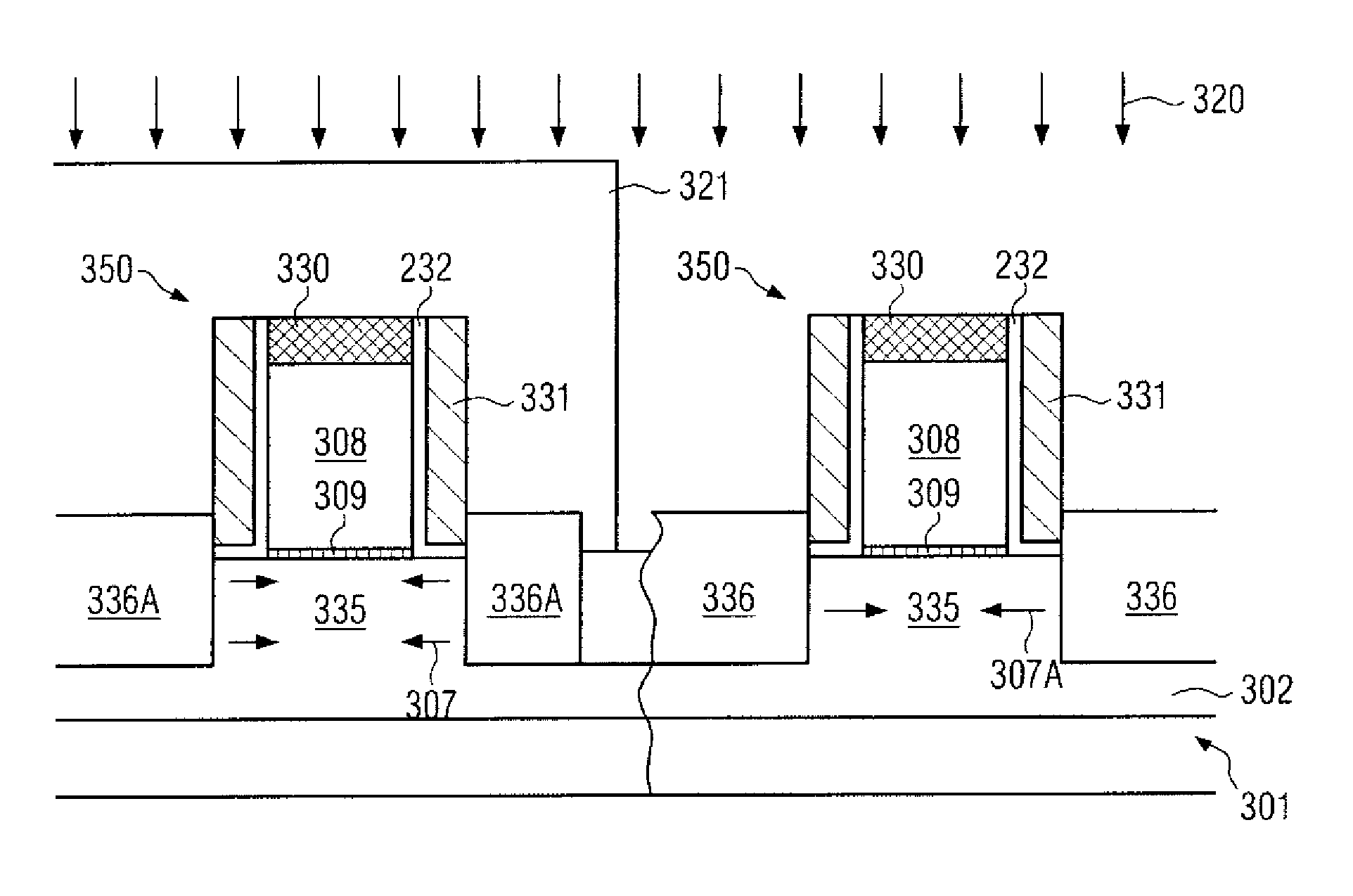
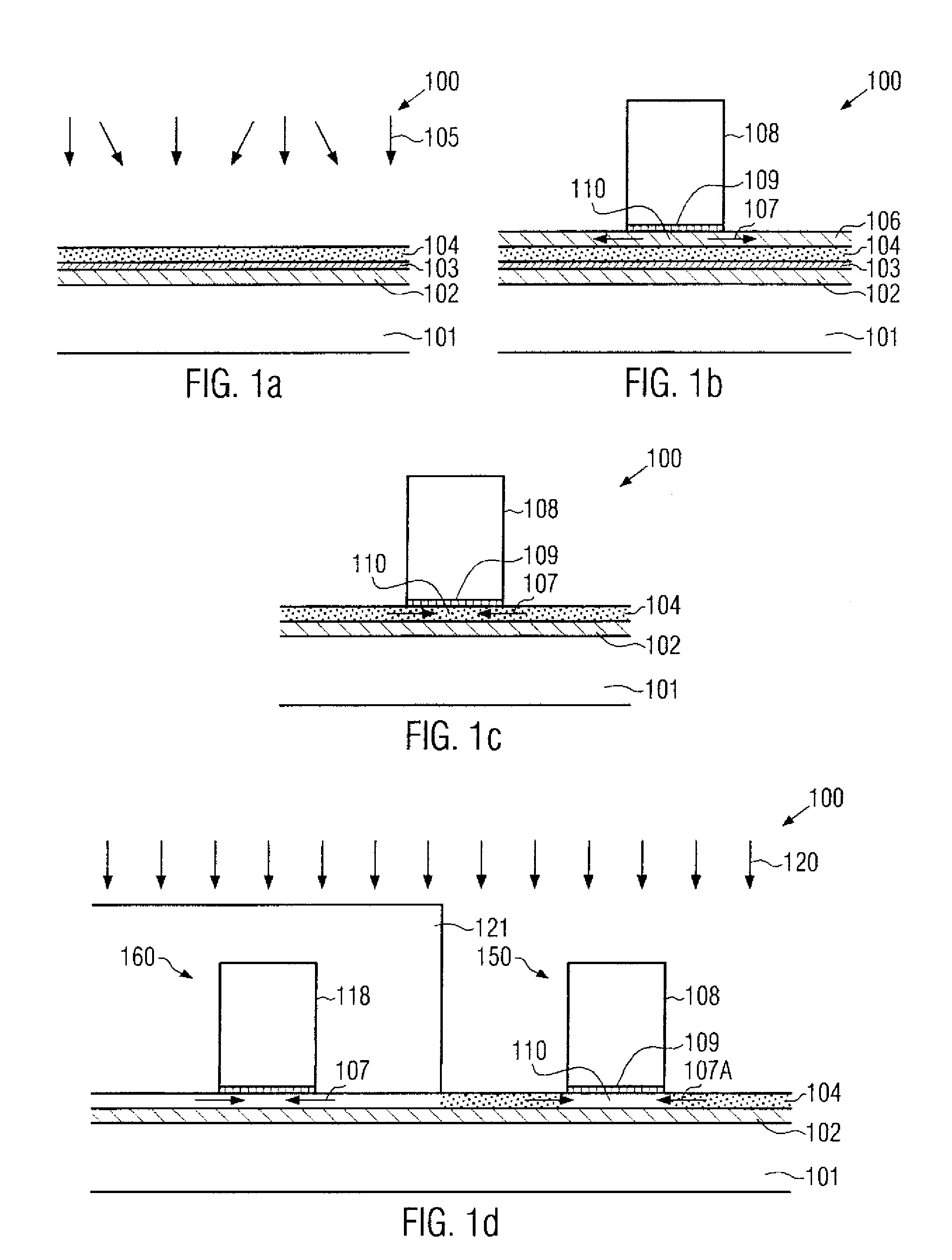
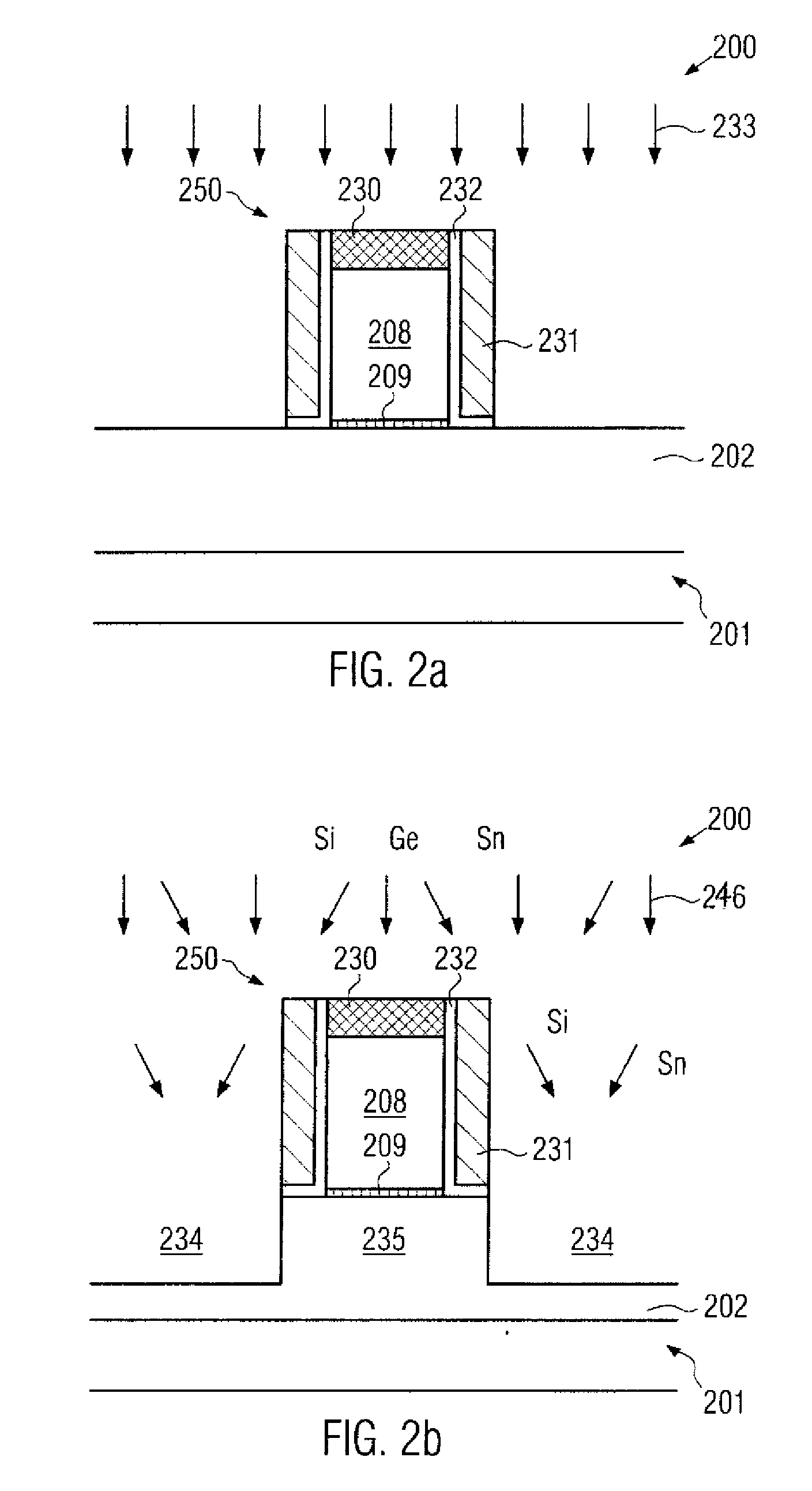
Technique for strain engineering in si-based transistors by using embedded semiconductor layers including atoms with high covalent radius
By incorporating an atomic species of increased covalent radius, which may at least partially substitute germanium, a highly efficient strain mechanism may be provided, in which the risk of stress relief due to germanium conglomeration and lattice defects may be reduced. The atomic species of increased radius, such as tin, may be readily incorporated by epitaxial growth techniques on the basis of tin hydride.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Graphene and Hexagonal Boron Nitride Planes and Associated Methods
Graphene layers made of primarily sp2 bonded atoms and associated methods are disclosed. In one aspect, for example, a method of forming a graphite film can include heating a solid substrate under vacuum to a solubilizing temperature that is less than a melting point of the solid substrate, solubilizing carbon atoms from a graphite source into the heated solid substrate, and cooling the heated solid substrate at a rate sufficient to form a graphite film from the solubilized carbon atoms on at least one surface of the solid substrate. The graphite film is formed to be substantially free of lattice defects.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
Ceramic support capable of supporting a catalyst, a catalyst-ceramic body and processes for producing same
InactiveUS20070173403A1Easy to cleanExhibits its performance more effectivelyMembranesSemi-permeable membranesLattice defectsOxygen vacancy
A ceramic support capable of supporting a catalyst comprising a ceramic body having fine pores with a diameter or width up to 1000 times the ion diameter of a catalyst component to be supported on the surface of the ceramic body, the number of the fine pores being not less than 1×1011 pores per liter, is produced by introducing oxygen vacancies or lattice defects in the cordierite crystal lattice or by applying a thermal shock to form fine cracks.
Owner:NIPPON SOKEN +1
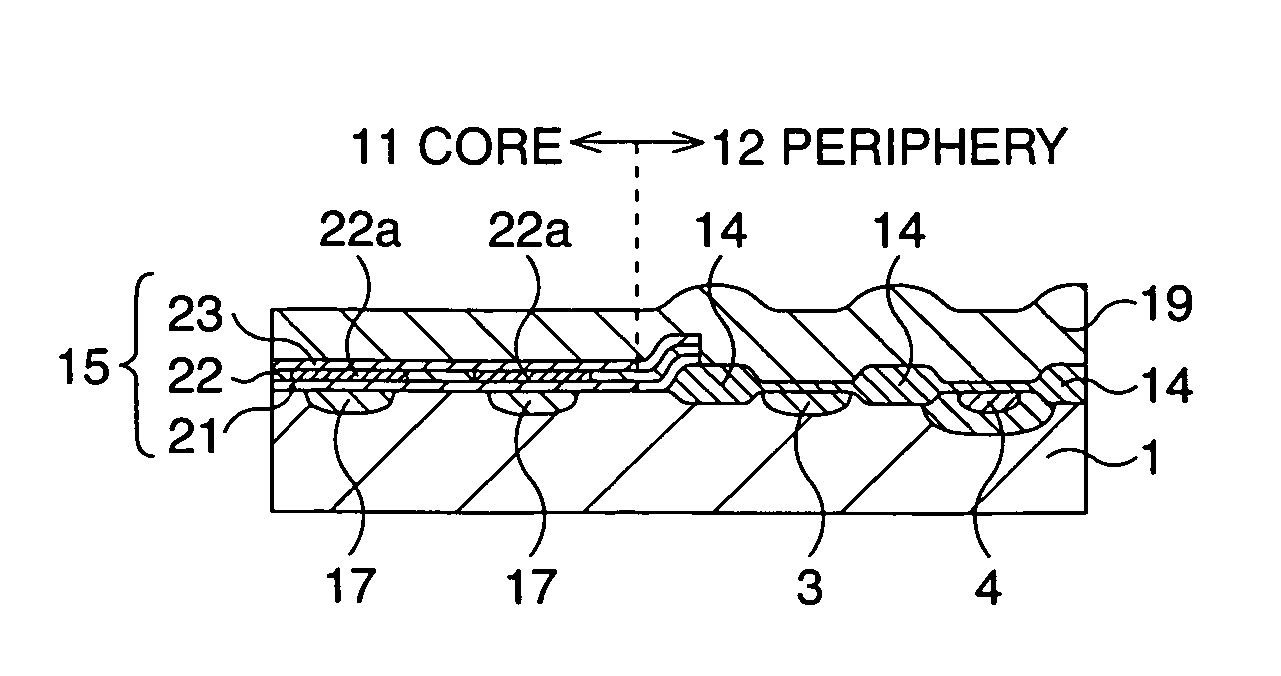
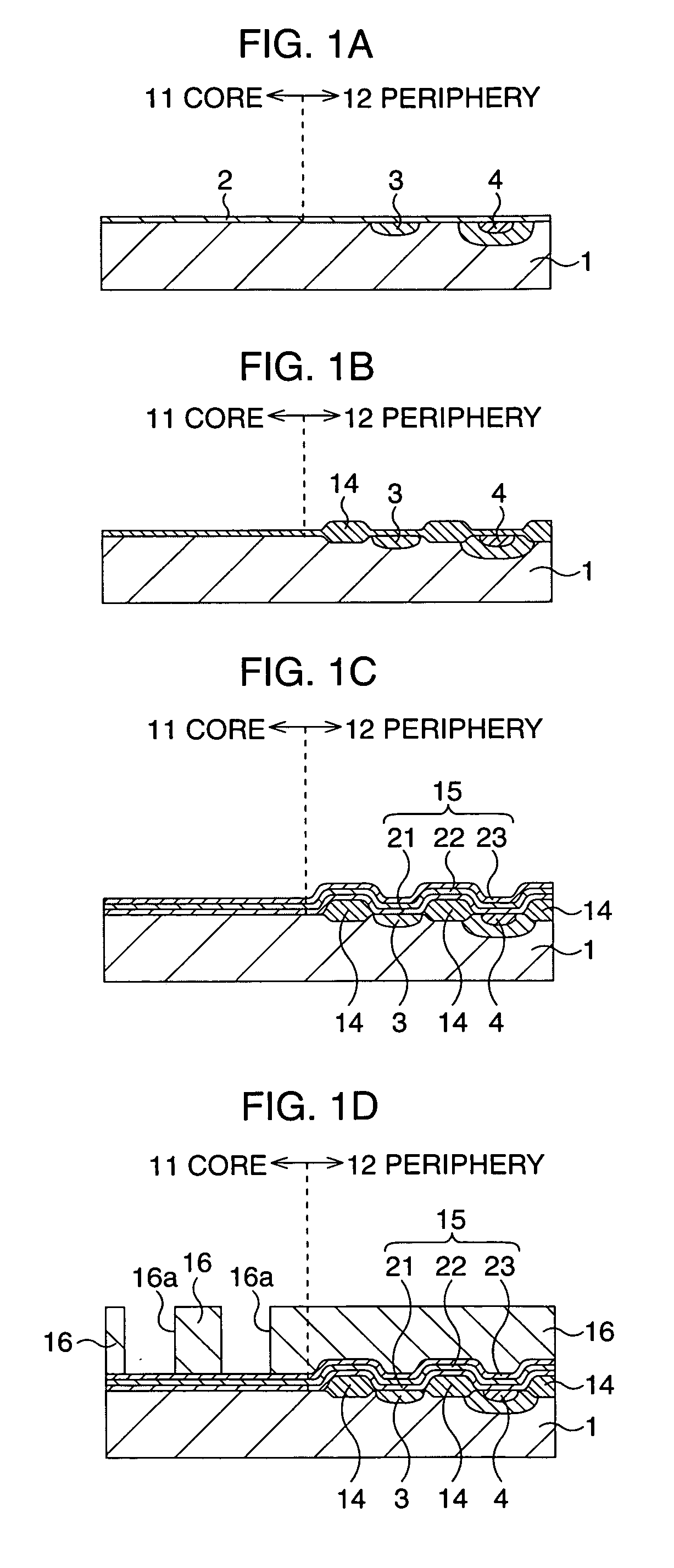
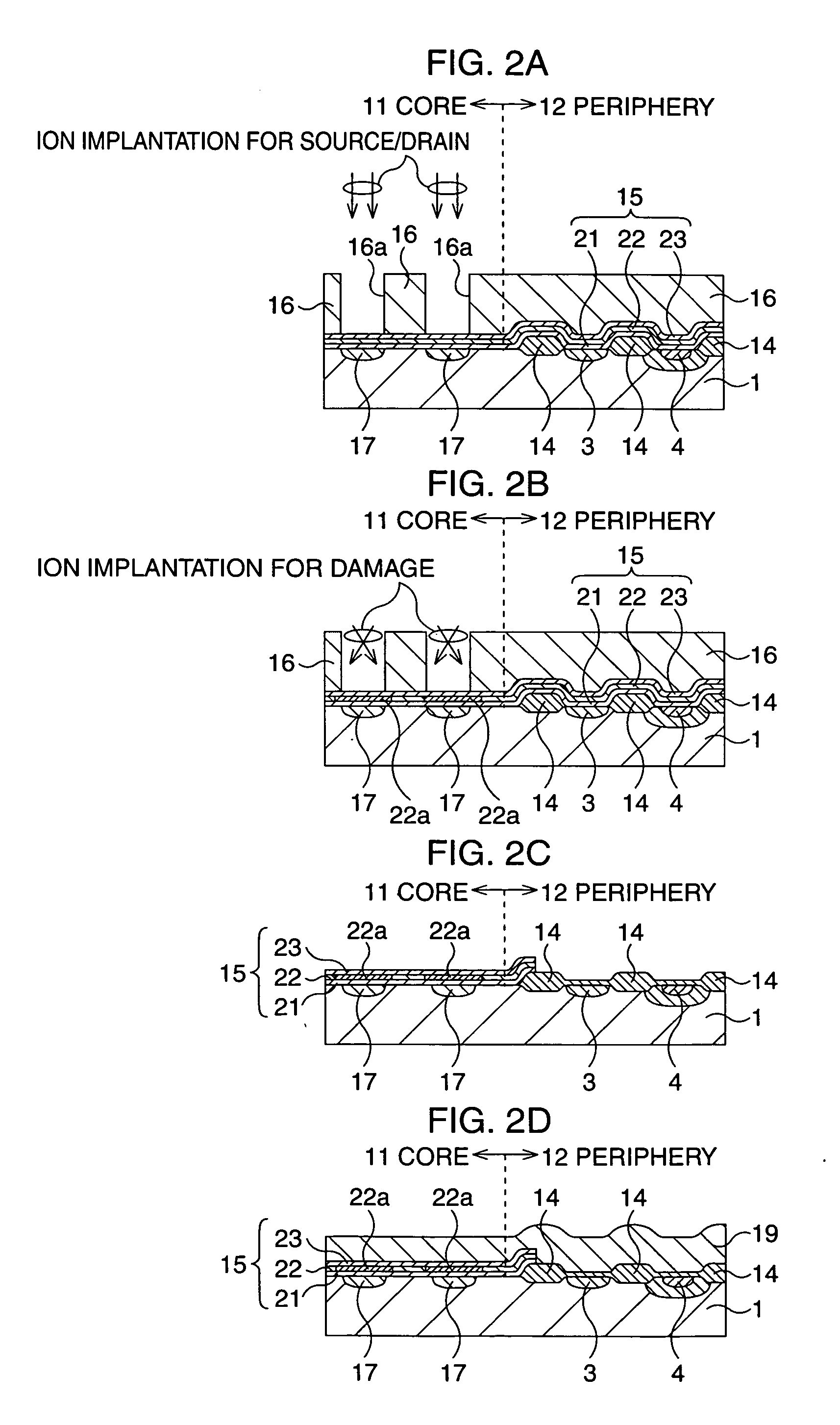
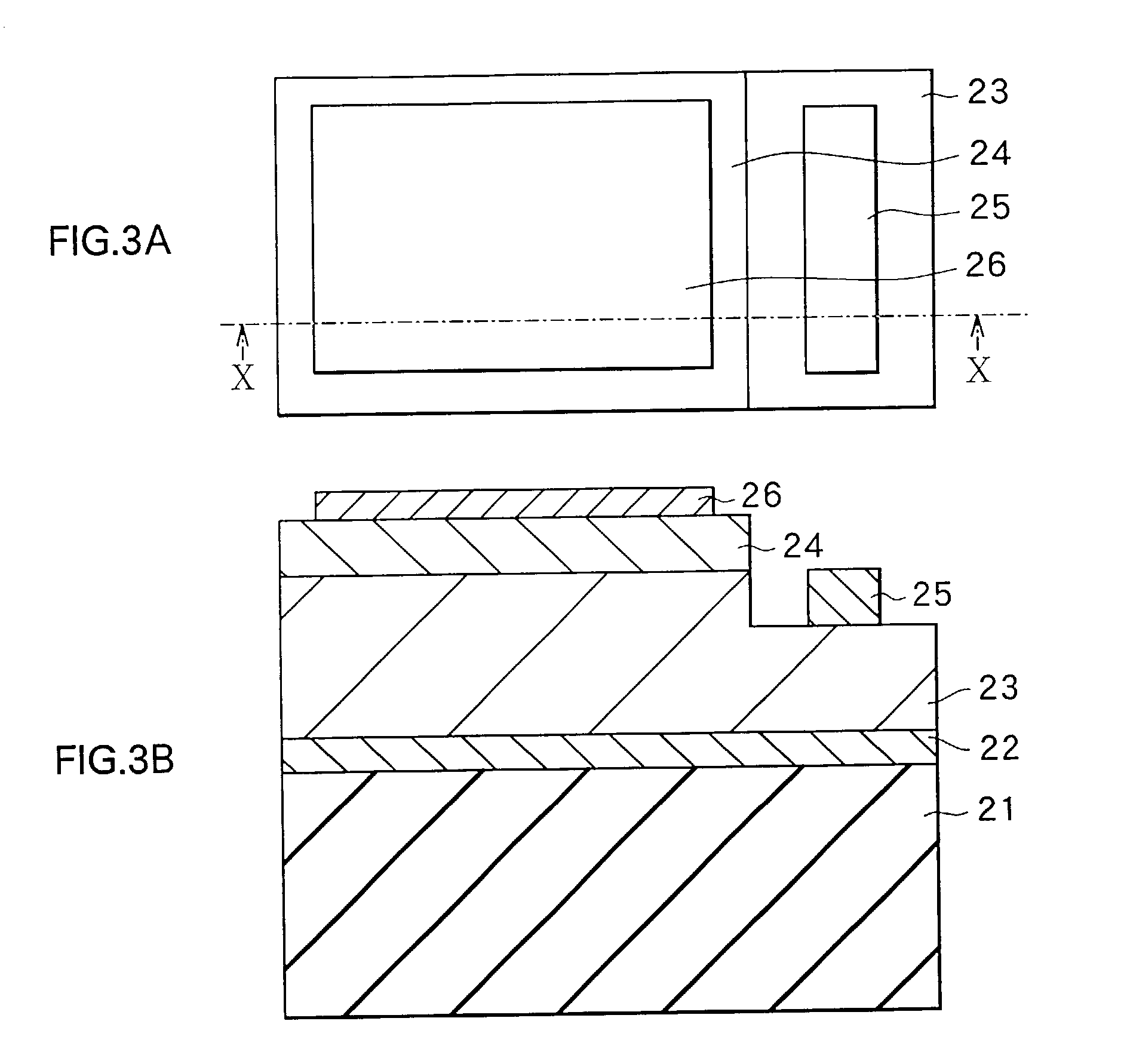
Semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
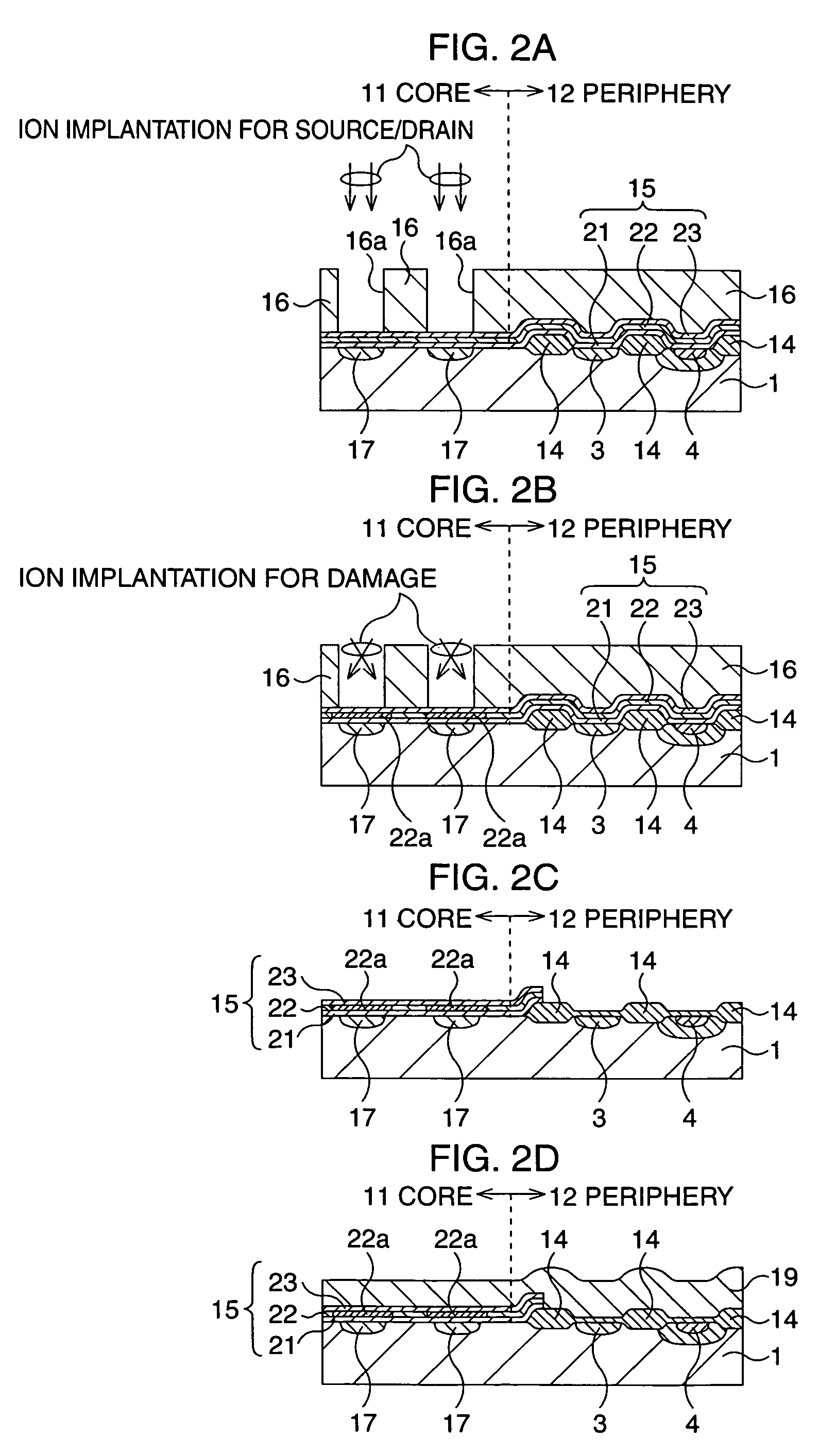
After an ONO film in which a silicon nitride film (22) formed by a plasma nitriding method using a plasma processor having a radial line slot antenna is sandwiched by silicon oxide films (21), (23), a bit line diffusion layer (17) is formed in a memory cell array region (11) by an ion implantation as a resist pattern (16) taken as a mask, then lattice defects are given to the silicon nitride film (22) by a further ion implantation. Accordingly, a highly reliable semiconductor memory device can be realized, in which a high quality nitride film is formed in a low temperature condition, in addition, the nitride film can be used as a charge trap film having a charge capture function sufficiently adaptable for a miniaturization and a high integration which are recent demands.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
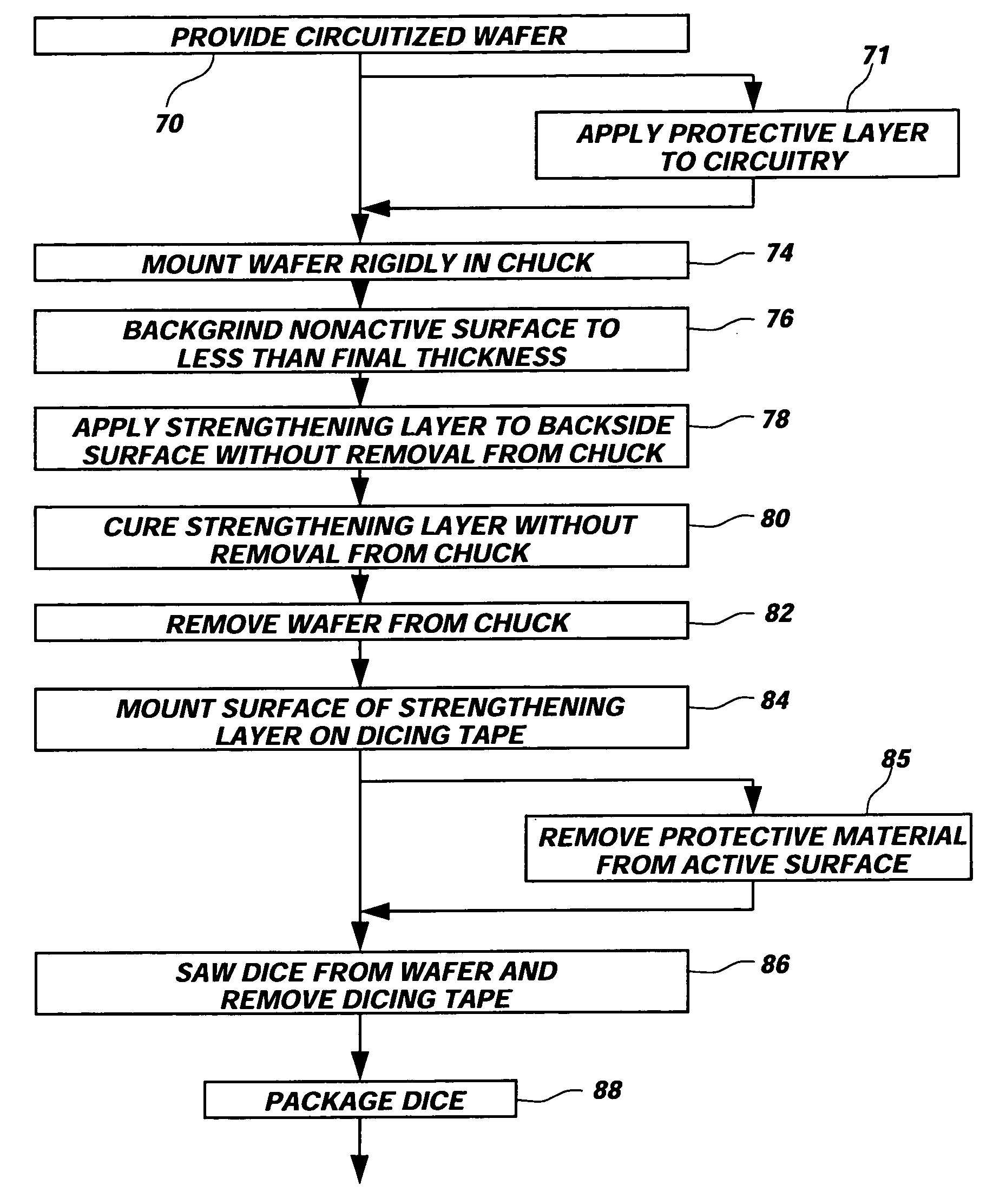
Process for strengthening semiconductor substrates following thinning
ActiveUS20050085008A1Improve adhesionProvide ionic barrierDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface layerLattice defects
A semiconductor wafer having a high degree of thinness and exhibiting an enhanced strength state. A layer of tenacious reinforcement material is disposed over a back side of the wafer while in a rough state from backgrinding, without prior, conventional polishing or plasma etching of the back side. The thin layer or film of reinforcement material fills grooves, fractures and scratches in the back side of the wafer, enhance the rigidity of the wafer and provide a planar, smooth, back side surface layer. The reinforcement material counteracts internal stresses of the wafer tending to warp, crack and propagate lattice defects in the wafer. The reinforcement material may also be configured to act as a die attach adhesive, may provide an ionic barrier, and may remain as part of the packaging for semiconductor dice singulated from the wafer.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
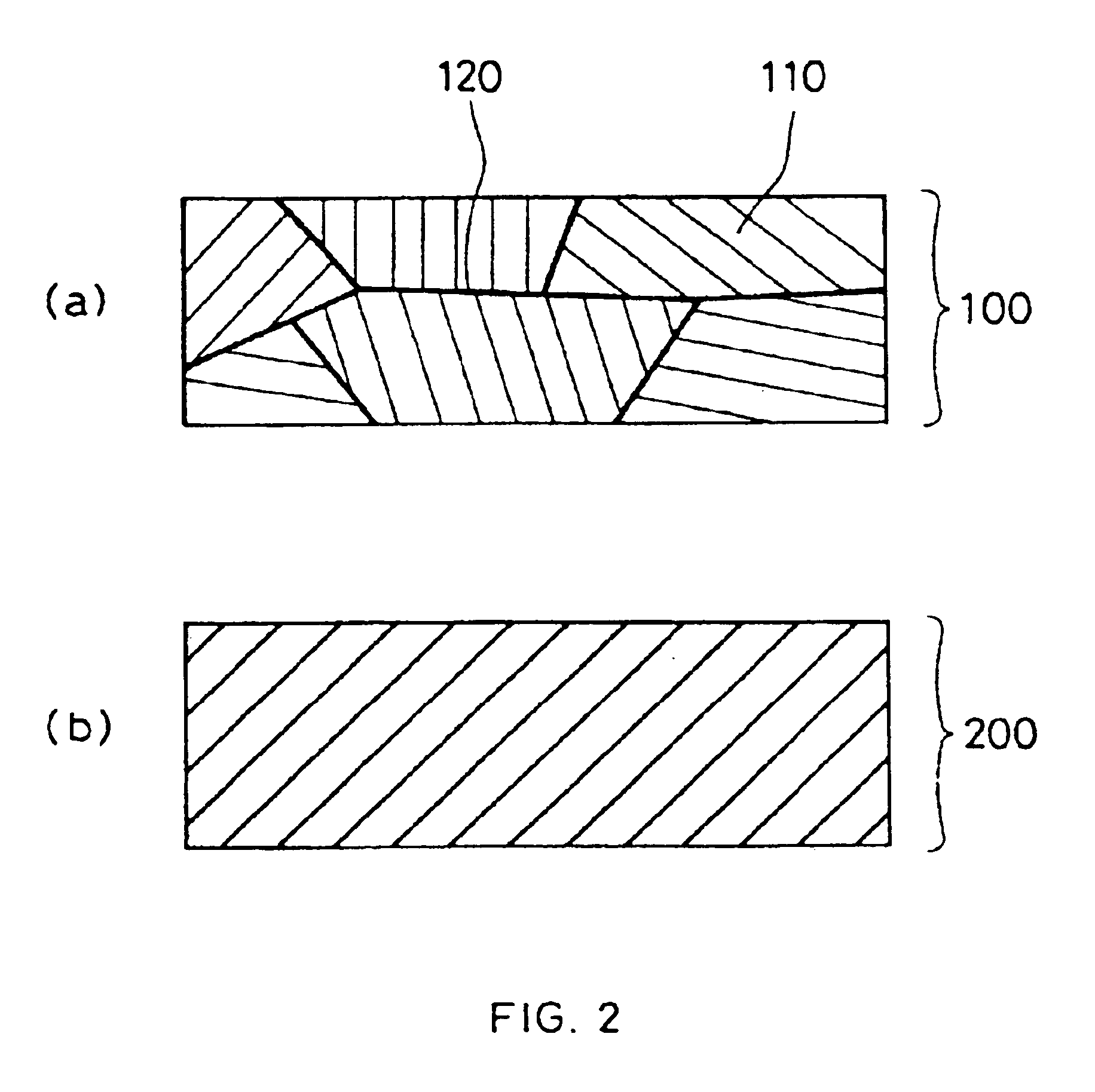
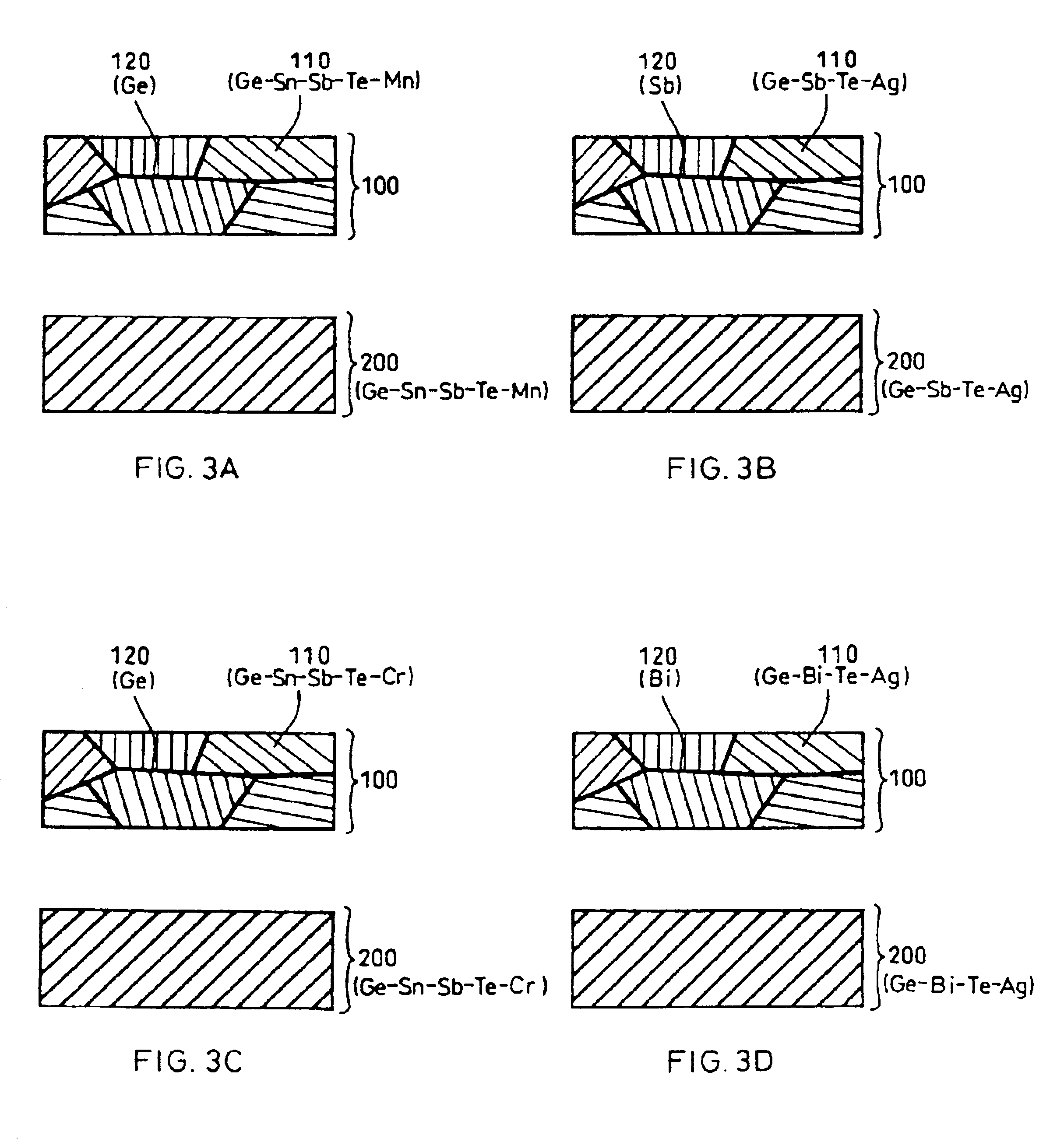
Information recording medium and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6858277B1Increased repetitionLess influenceRecording by optical meansLayered productsElectricityLattice defects
An information recording medium having such a recording material layer on a substrate where reversible phase change between electrically or optically detectable states can be caused by electric energy or electromagnetic energy. The recording material forming the recording layer is either a material having a crystal structure including lattice defects in one phase of the reversible phase change or a material having a complex phase composed of a crystal portion including a lattice defect in one phase of the reversible phase change and an amorphous portion. Both portions contain a common element. A part of the lattice defects are filled with an element other than the element constituting the crystal structure. The recording medium having a recording thin film exhibits little variation of the recording and reproduction characteristics even after repetition of recording and reproduction, excellent weatherability, strong resistance against composition variation, and easily controllable characteristics.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Stacking fault and twin blocking barrier for integrating III-V on Si
InactiveUS20080032478A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice defectsStacking fault
A stacking fault and twin blocking barrier for forming a III-V device layer on a silicon substrate and the method of manufacture is described. Embodiments of the present invention enable III-V InSb device layers with defect densities below 1×108 cm−2 to be formed on silicon substrates. In an embodiment of the present invention, a buffer layer is positioned between a III-V device layer and a silicon substrate to glide dislocations. In an embodiment of the present invention, GaSb buffer layer is selected on the basis of lattice constant, band gap, and melting point to prevent many lattice defects from propagating out of the buffer into the III-V device layer. In a specific embodiment, a III-V InSb device layer is formed directly on the GaSb buffer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100207097A1Increase resistanceImprove extraction efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh resistanceLattice defects
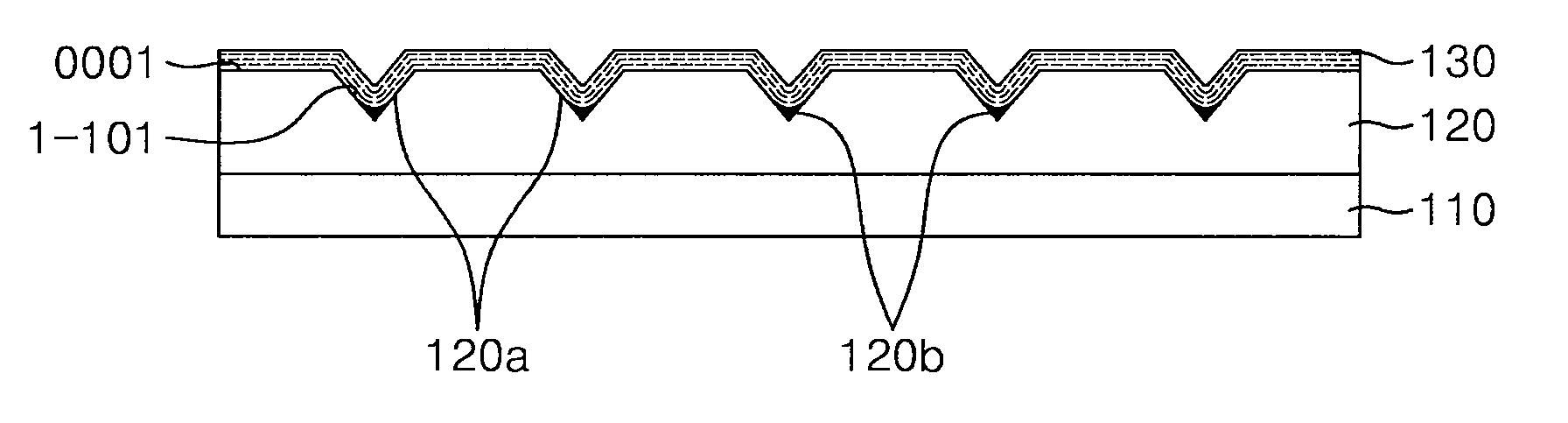
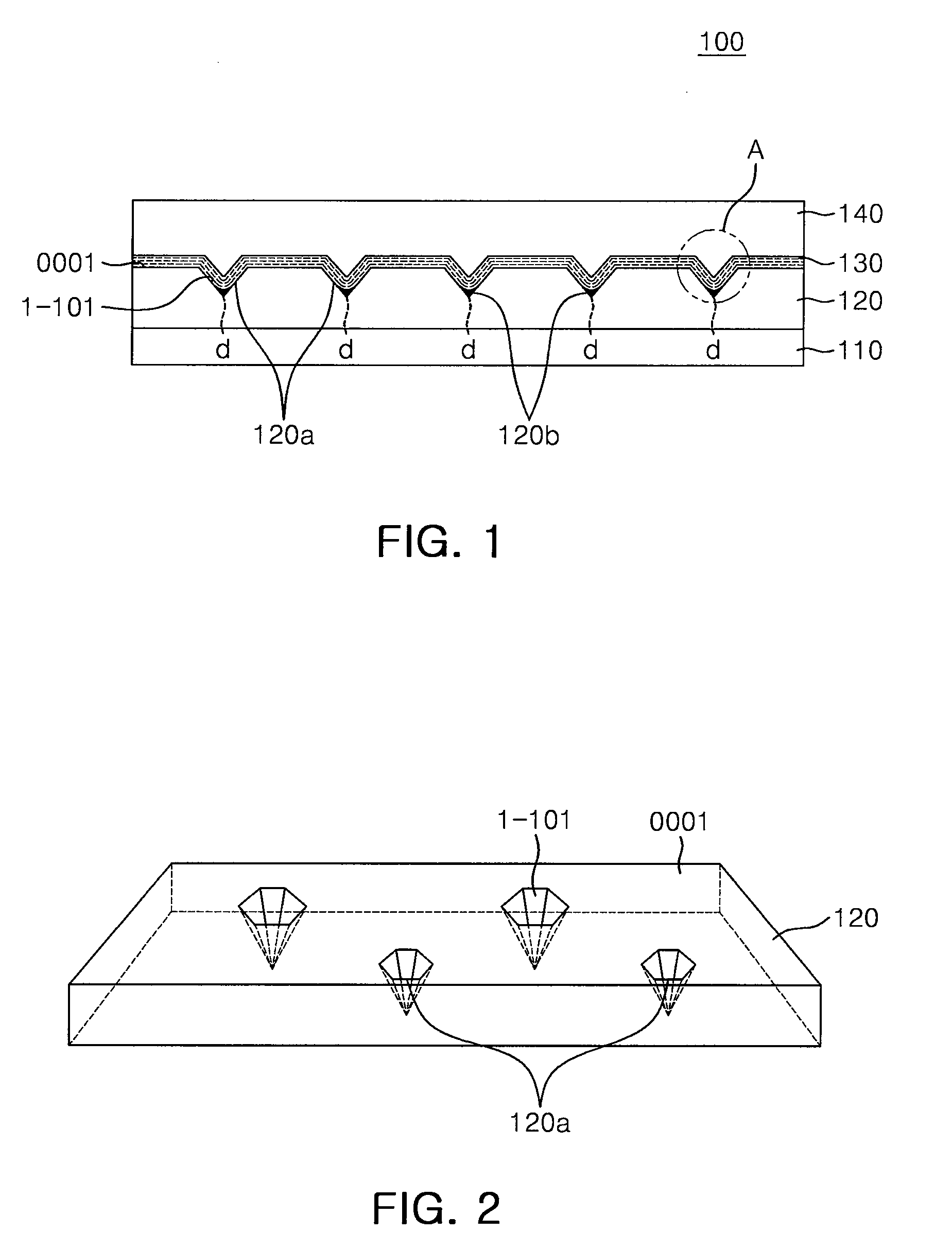
A nitride semiconductor light emitting device includes a substrate, a first conductivity type nitride semiconductor layer disposed on the substrate and including a plurality of V-pits placed in a top surface thereof, a silicon compound formed in the vertex region of each of the V-pits, an active layer disposed on the first conductivity type nitride semiconductor layer and including depressions conforming to the shape of the plurality of V-pits, and a second conductivity type nitride semiconductor layer disposed on the active layer. The nitride semiconductor light emitting device, when receiving static electricity achieves high resistance to electrostatic discharge (ESD) since current is concentrated in the V-pits and the silicon compound placed on dislocations caused by lattice defects.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device including schottky barrier diode and method of manufacturing the same
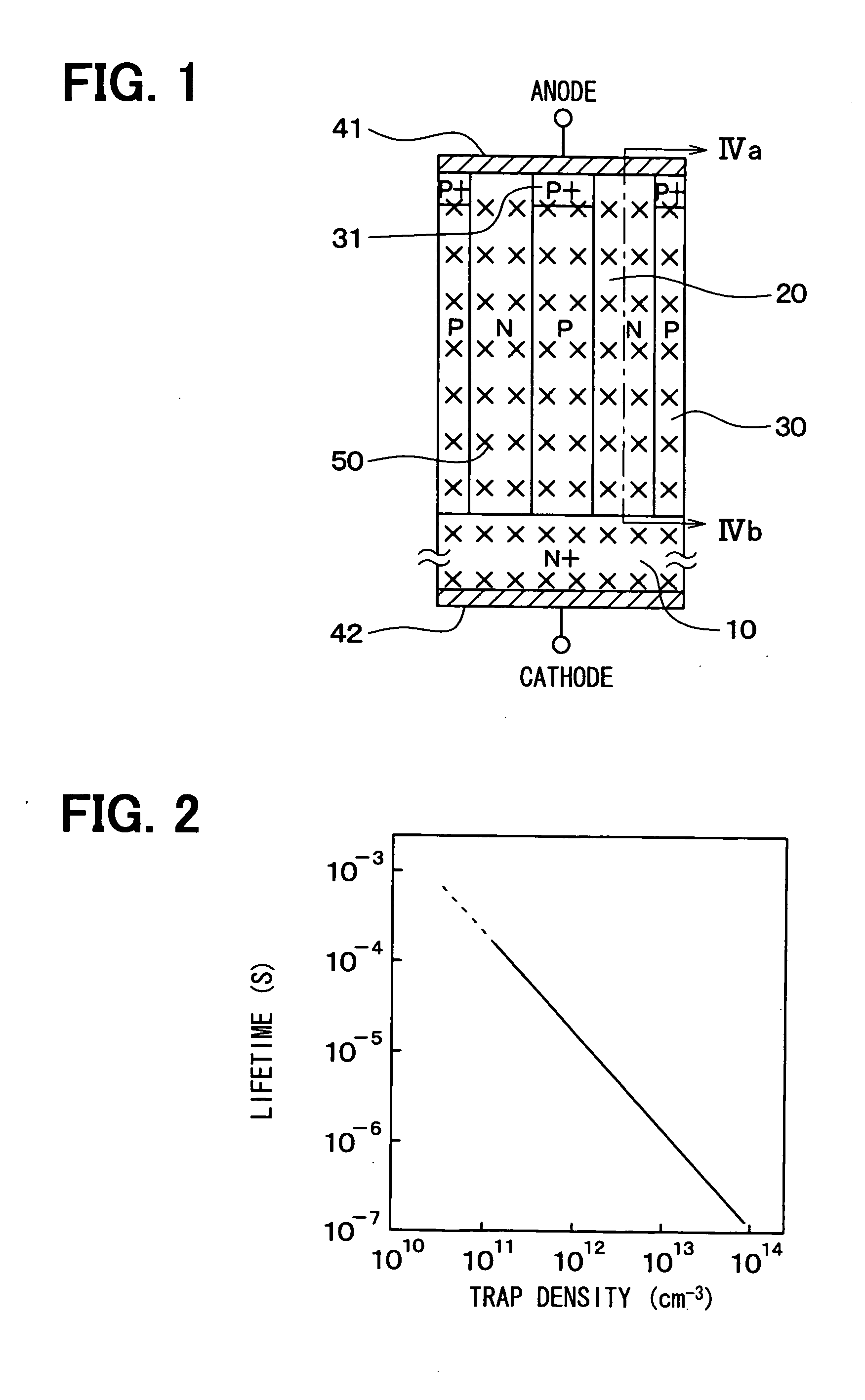
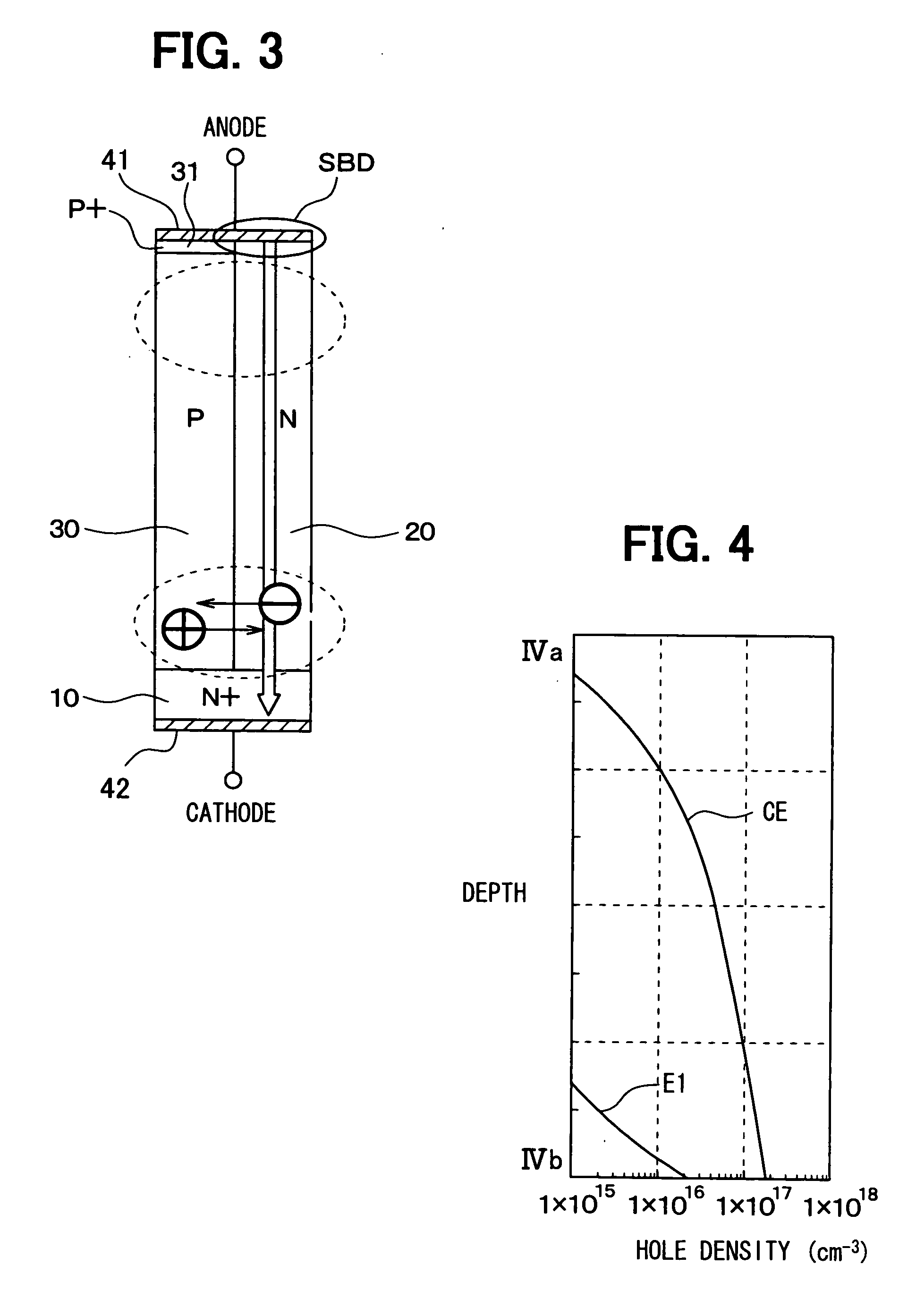
InactiveUS20080246096A1High voltage resistanceResistance of currentTransistorSolid-state devicesSchottky barrierLattice defects
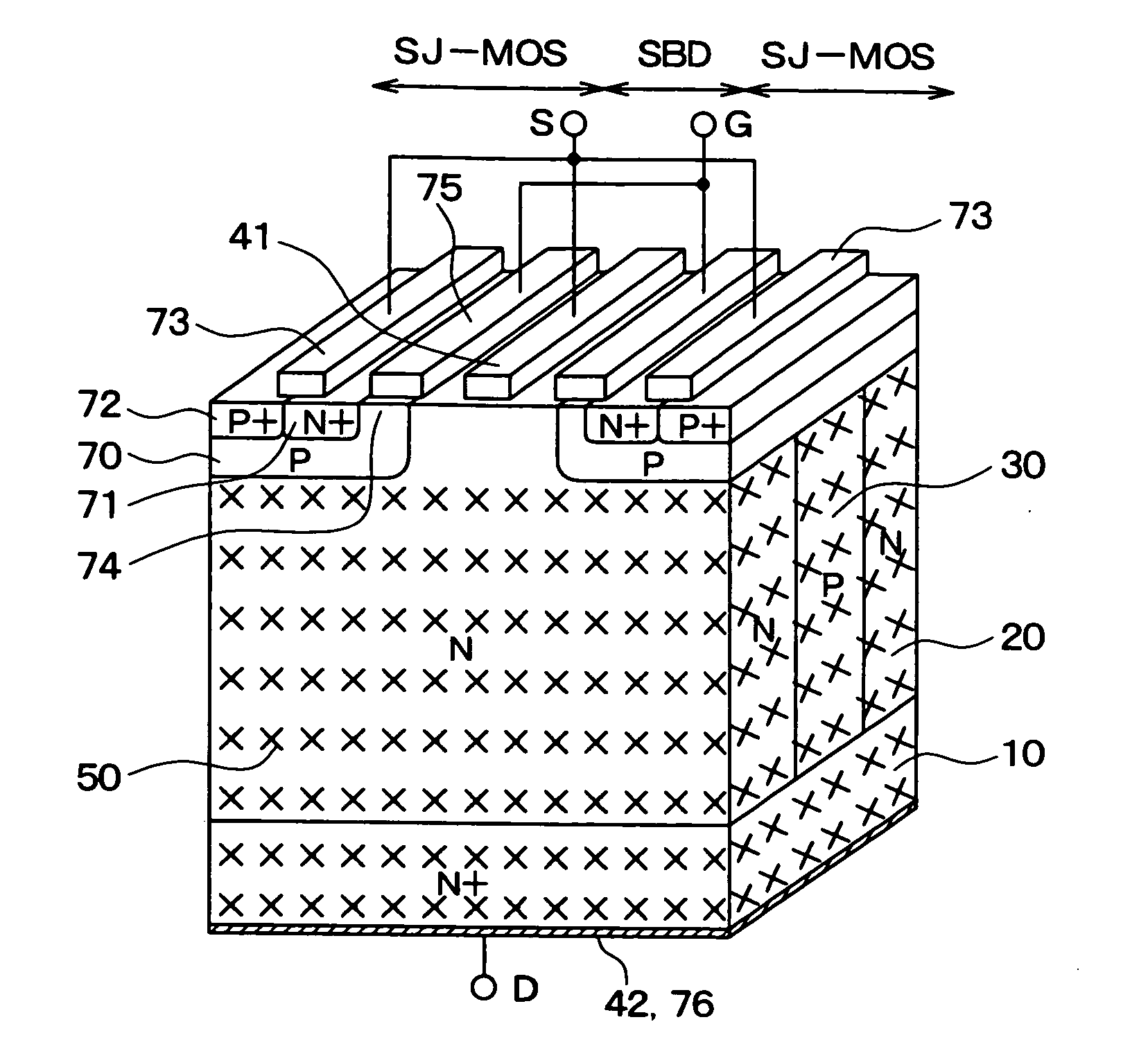
A semiconductor device includes a substrate, a plurality of first columns having a first conductivity type, a plurality of second columns having a second conductivity type, a first electrode, and a second electrode. The first columns and the second columns are alternately arranged on the substrate to provide a super junction structure. The first electrode is disposed on the super junction structure, forms schottky junctions with the first columns, and forms ohmic junctions with the second columns. The second electrode is disposed on the substrate on an opposite side of the super junction structure. At least a part of the substrate and the super junction structure has lattice defects to provide a lifetime control region at which a lifetime of a minority carrier is controlled to be short.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Group III nitride compound semiconductor thin film and deposition method thereof, and semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20030039866A1Uniform film qualitySimple methodLaser detailsVacuum evaporation coatingLattice defectsDislocation
A Group III nitride compound semiconductor thin film which can be deposited on any given substrate to have uniform film quality and excellent crystalline, and a deposition method thereof. A semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof. A poly-crystalline Group III nitride compound thin film is deposited on a substrate by sputtering at a deposition rate of 15 to 200 nm / hour using a Group III nitride compound target in a plazma atmosphere of gas comprising 10 mole % or more nitrogen. Then, the poly-crystalline Group III nitride compound semiconductor thin film deposited on the substrate is irradiated with an excimer pulsed laser with an energy density of about 200 mJ / cm2, in an atmosphere of gas with an oxygen content of 2 mole % or less. Thereby, lattice defects such as grain boundaries or dislocations which occur in the thin film are removed.
Owner:MITAMURA SATOSHI
Thermal-oxidizing-aging resisting polypropylene composite
ActiveCN102604209AImprove interface bonding performancePrevent free diffusionLattice defectsAntioxidant
The invention discloses a thermal-oxidizing-aging resisting polypropylene composite. The thermal-oxidizing-aging resisting polypropylene composite comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 30%-85% of polypropylene, 0-10% of flexibilizer, 2%-10% of compatilizer, 10%-40% of filling agent, 0.1%-0.5% of nucleating agent, 1%-10% of load type functional agent and 0.2%-1.0% of processing agent. Due to the nucleating agent, the polypropylene spherocrystal is refined, the crystallization is uniform and regular and the degree of crystallinity is increased, so that the lattice defect of a substrate is avoided effectively, and the oxygen is prevented from dispersing to the inner part from the surface of the composite freely; due to the compatilizer, the interface bonding force of the polypropylene and the filling agent is improved, so that two phase interfaces are combined tightly, the and the oxygen is prevented from dispersing to the inner part from the surface of the composite freely, and the thermal-oxidizing-aging resistance is improved; and the load type functional agent solves the problem of dispersibility and solvent resistance of an antioxidant and a light stabilizer. The thermal-oxidizing-aging resisting polypropylene composite has a simple preparation method, is high in thermal-oxidizing-aging resisting efficiency and is widely applied to the field of household appliances such as electric cookers, microwave ovens, washing machines, dish-washing machines and the like.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +2
Process for synthesizing metal oxides and metal oxide having perovskite or perovskite-like crystal structure
InactiveCN1315920ALarge specific surface areaSimple methodNanotechOxide/hydroxide preparationHigh densityLattice defects
Perovskite-type structure compounds having the general empirical formula ABO3 are prepared by a process comprising subjecting a mixture of starting powders formulated to contain the components represented by A and B in the formula to a high energy milling sufficient to induce chemical reaction of the components and thereby synthesize a mechanically-alloyed powder comprising the perovskite in the form of nanostructural particles. The process according to the present invention is simple, efficient, not expensive and does not require any heating step for producing a perovskite that may easily show a very high specific surface area. Another advantage is that the perovskite obtained according to the present invention also has a high density of lattice defects thereby showing a higher catalytic activity, a characteristic which is highly desirable in their eventual application as catalysts and electronic conductors.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Modified Y-type molecular sieve and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103073024AReduce yieldIncrease profitCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveLattice defects
The invention discloses a modified Y-type molecular sieve which is characterized in that a cell constant is 2.420-2.440nm. According to weight percentages, the molecular sieve comprises 0.05-6% of P, 0.03-10% of RE2O3, and less than 22% of alumina. A specific hydroxyl nest concentration is smaller than 0.35mmol / g. In a formula, M200 DEG C, M500 DEG C and M800 DEG C t respectively represent weight loss percentages of the sample measured at 200 DEG C, 500 DEG C and 800 DEG C. C is sample crystallinity degree. The molecular sieve provided by the invention has low lattice defect, and can be used in a catalytic cracking catalyst as an active component. With the molecular sieve, long-period stable activity can be maintained, coke yield can be effectively controlled, and heavy oil utilization rate can be improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Nitride Semiconductor Structure and Method of Making Same
ActiveUS20110068347A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice defectsCombined use
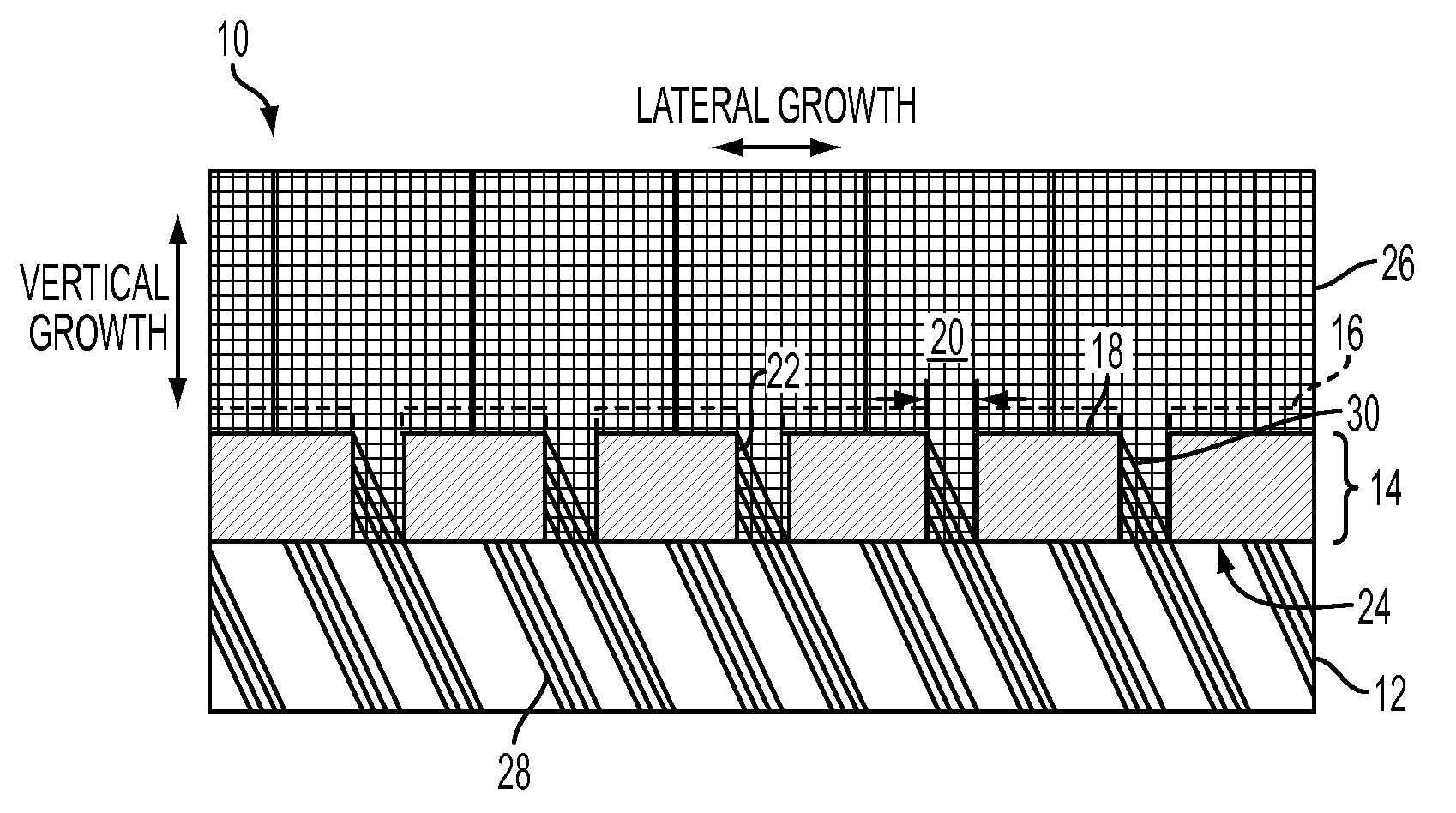
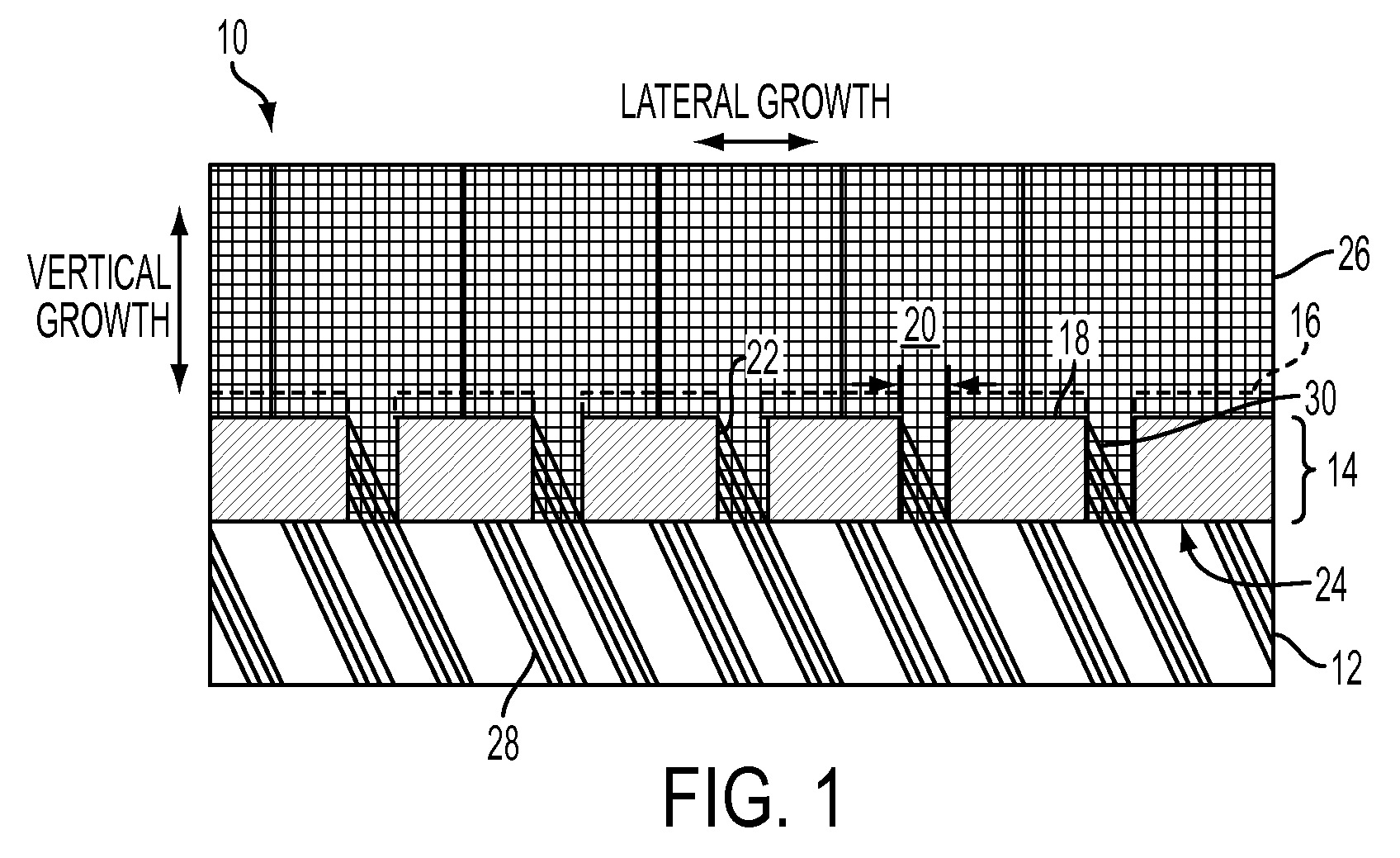
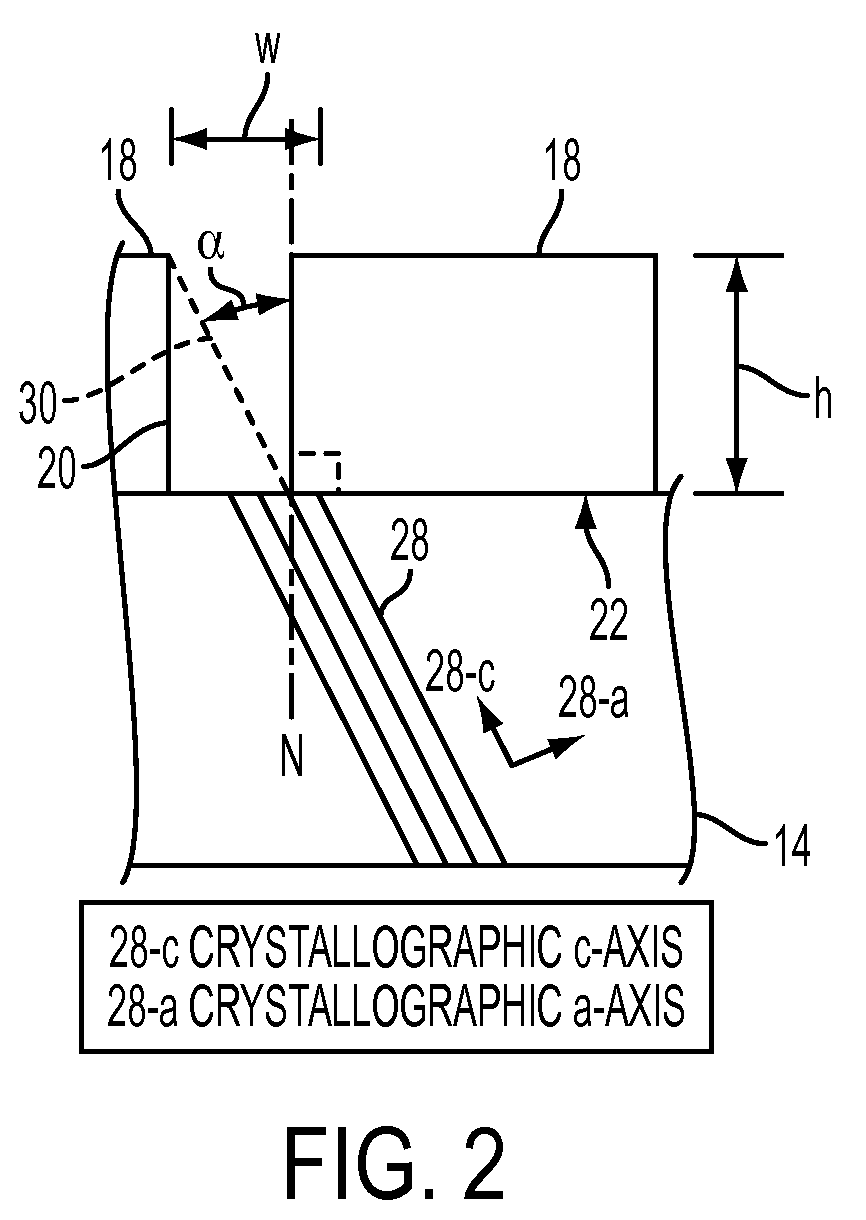
A structure method for producing same provides suppressed lattice defects when epitaxially forming nitride layers over non-c-plane oriented layers, such as a semi-polar oriented template layer or substrate. A patterned mask with “window” openings, or trenches formed in the substrate with appropriate vertical dimensions, such as the product of the window width times the cotangent of the angle between the surface normal and the c-axis direction, provides significant blocking of all diagonally running defects during growth. In addition, inclined posts of appropriate height and spacing provide a blocking barrier to vertically running defects is created. When used in conjunction with the aforementioned aspects of mask windows or trenches, the post structure provides significant blocking of both vertically and diagonally running defects during growth.
Owner:XEROX CORP
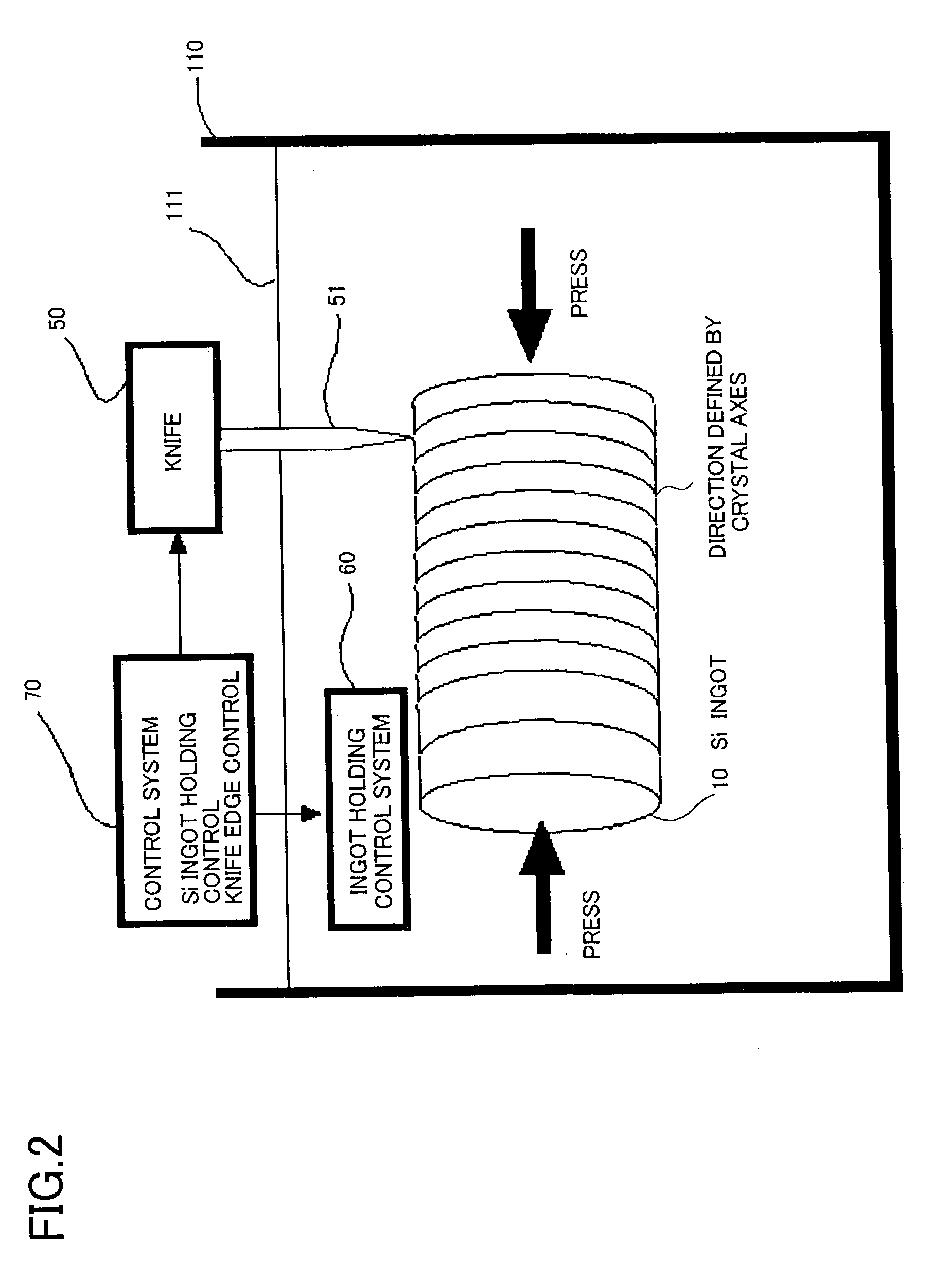
Cutting method and apparatus for ingot, wafer, and manufacturing method of solar cell
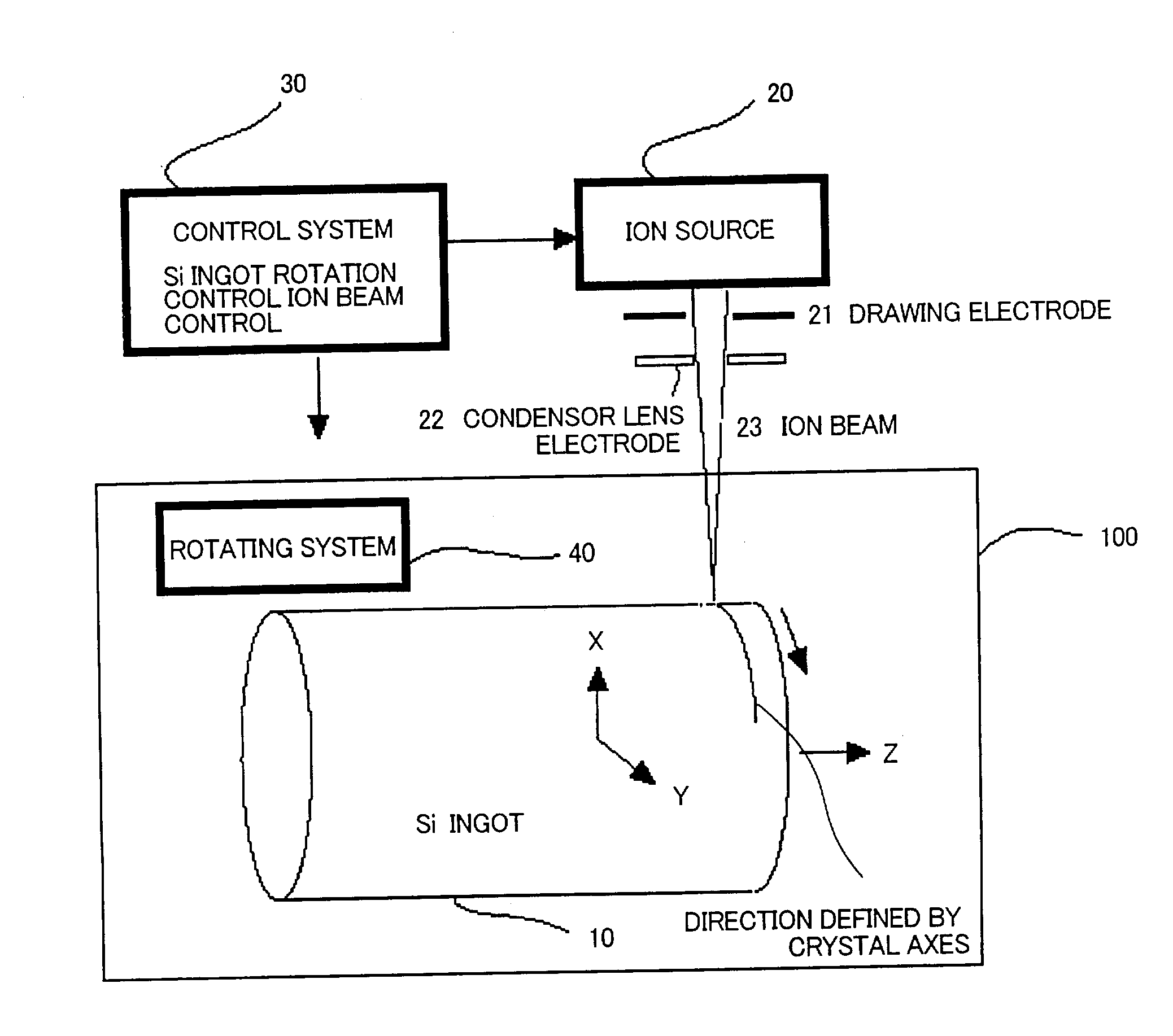
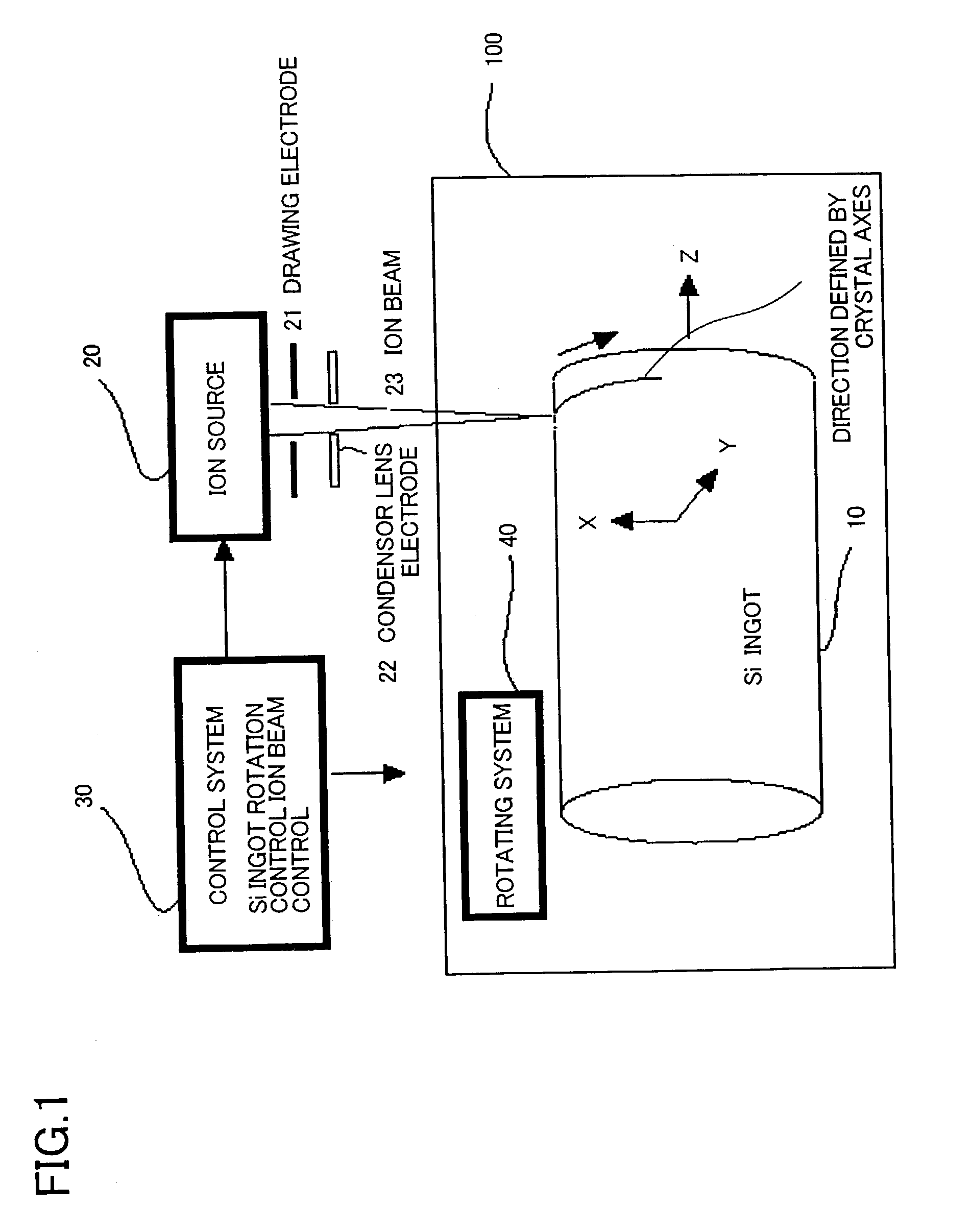
InactiveUS20040055634A1Shorten the timeProduce more and thinPolycrystalline material growthFinal product manufactureLattice defectsIon beam
Cutting method of ingot into wafers along cleavage plane. Onto surface of single crystal ingot 10 is implanted ion beam 23 to generate lattice defects in a direction defined by the crystal axes that corresponds to the cleavage plane. Cleavage is generated by applying a shock by a knife edge to the position of the lattice having a cutting face as a cleavage plane. Production time of waters is reduced with a more numbers of sliced wafers from one ingot.
Owner:Y Y L
Method for forming SOI substrate
InactiveUS6881650B2Low lattice defectsHigh carrier mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLattice defectsSoi substrate
A method for forming SOI substrates including a SOI layer containing germanium and a strained silicon layer disposed on the SOI layer, comprises forming a relaxed silicon-germanium layer on a first silicon substrate using an epitaxial growth method, and forming a porous silicon-germanium layer thereon. A silicon-germanium epitaxial layer is formed on the porous silicon-germanium layer, an oxide layer is formed on a second silicon substrate, the second silicon substrate is bonded where the oxide layer is formed to the first silicon substrate where the silicon-germanium epitaxial layer is formed. Layers are removed to expose the silicon-germanium epitaxial layer and a strained silicon epitaxial layer is formed thereon. The porous silicon-germanium layer prevents lattice defects of the relaxed silicon-germanium layer from transferring to the silicon-germanium epitaxial layer. Therefore, it is possible to form the silicon-germanium layer and the strained silicon layer of the SOI layer without defects.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
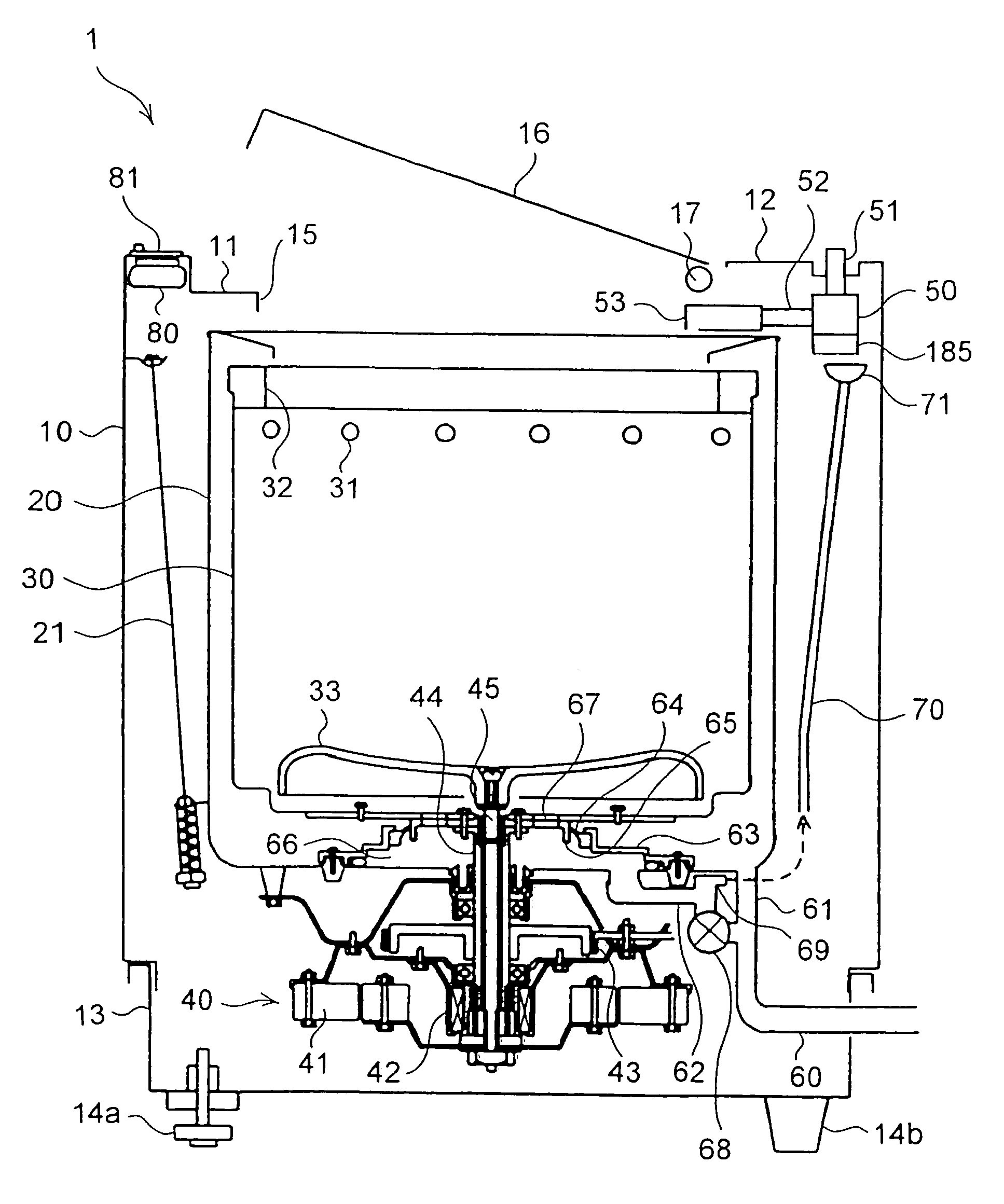
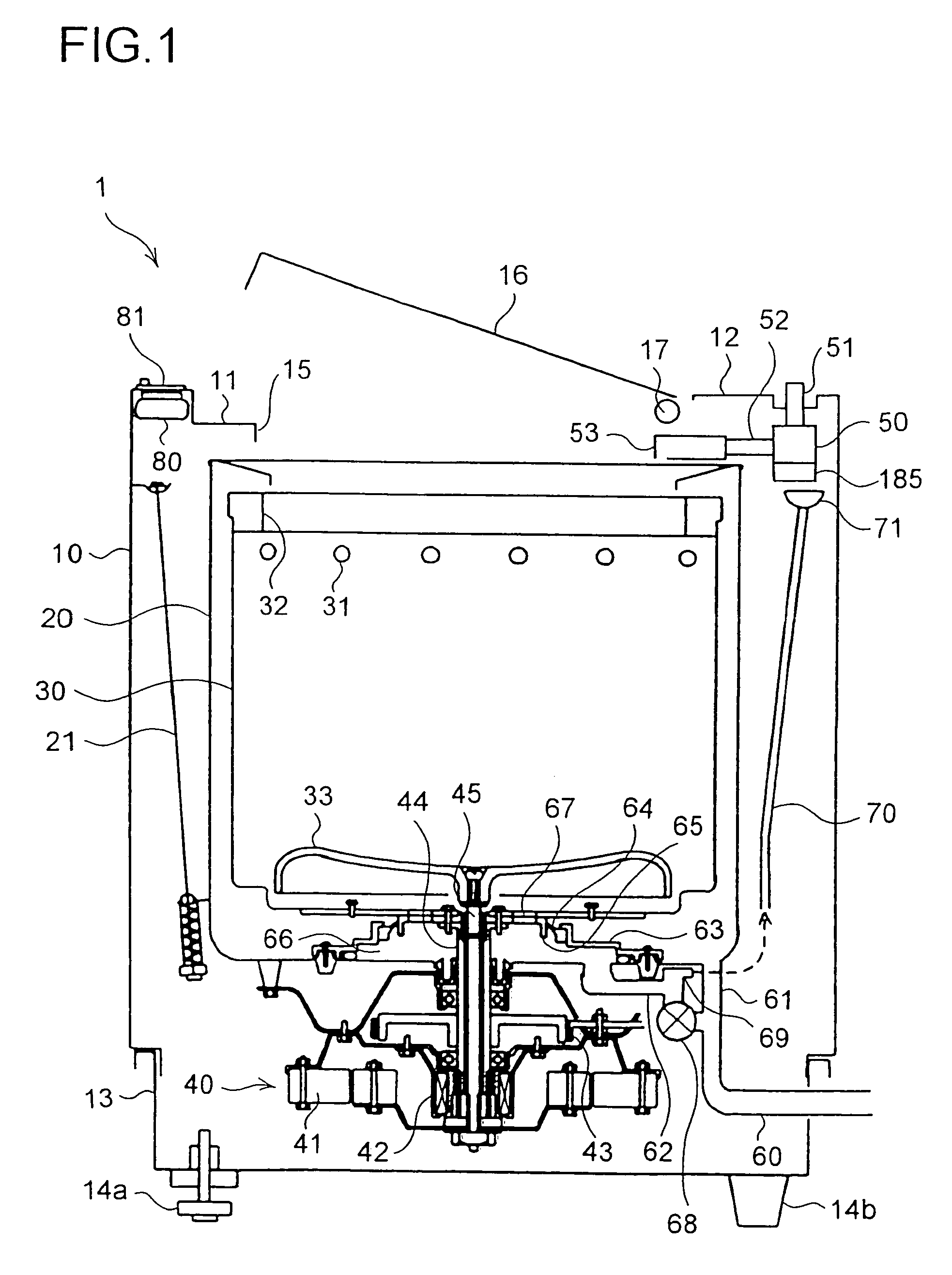
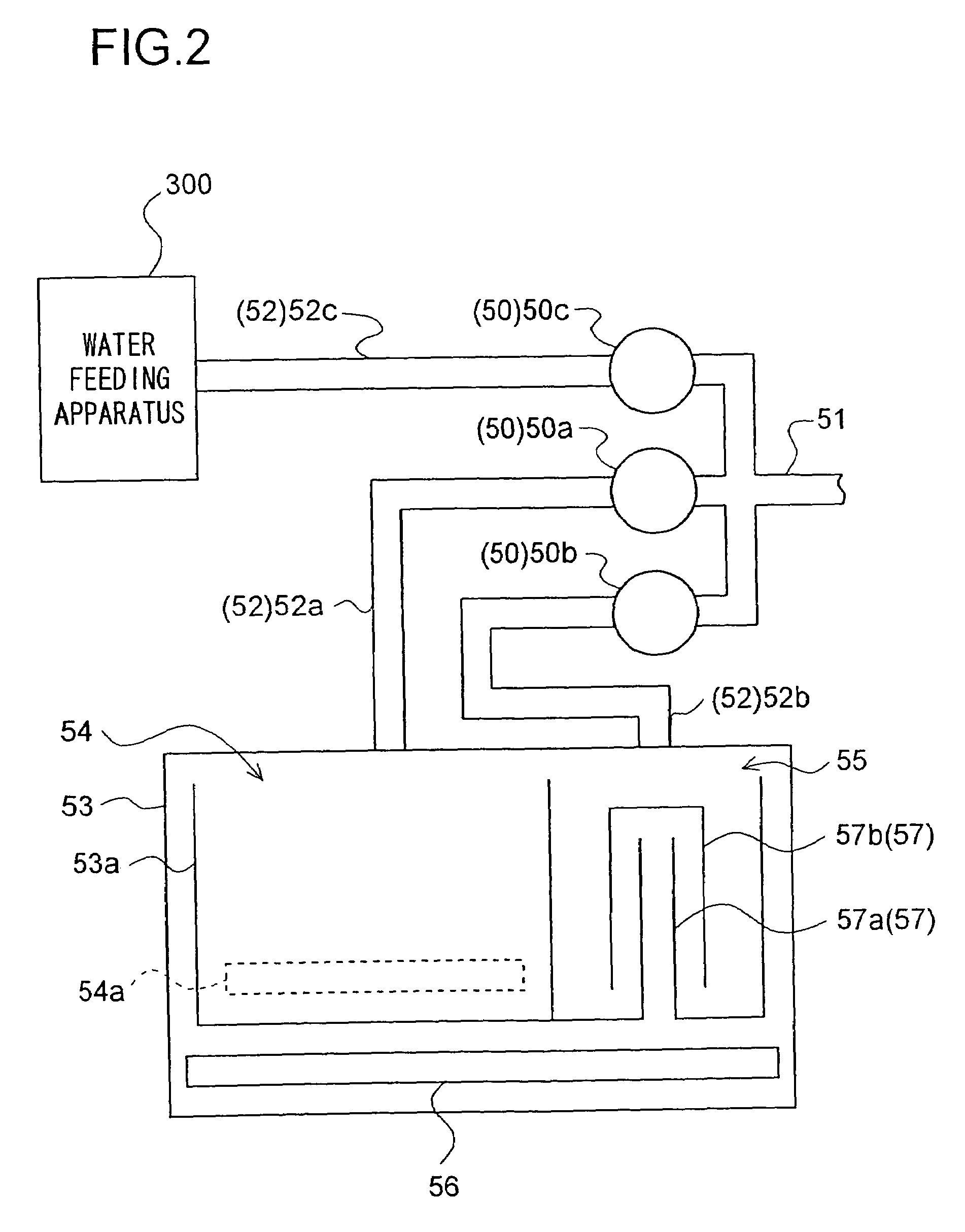
Water supply device, water supply method, and washing machine having water supply device
InactiveUS7624601B2Effect is exertedBiocideWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsLattice defectsEngineering
A water feeding apparatus (300) has an ion eluter (100) and a shower emitter (200). The shower emitter (200) receives water via a coupling pipe (250) from the ion eluter (100), and sprays the water, in the form of a shower, onto laundry. Liquid droplets in the form of a shower are small and easy to dry, and thus produce crystals having smaller particles (with large surface areas), having more lattice defects, and easier to dissolve. With these crystals attached to the laundry, when the crystals make contact with moisture next time, the silver ion in the liquid droplets easily dissolves. Even when the laundry is made of water-repellent or hydrophobic cloth, the solution dries up on the surface of the cloth before water is repelled. Thus, even this type of laundry can benefit from the antimicrobial effect of the silver ion.
Owner:SHARP KK
Manufacturing method for GaN epitaxy or substrate
InactiveCN103682016AStress reliefReduce or prevent defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice defectsOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for GaN epitaxy or substrate. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: 1), a buffer layer grows on a silicon substrate; 2), photoresisting coating and exposing are performed, and defined graphs are formed on the buffer layer; 3), a photoresist is used as a mask to etch the buffer layer and the silicon substrate, so as to enable a plurality of holes to be formed inside the silicon substrate; 4), the photoresist is removed; 5), thermal oxidation is performed on the inner surfaces of the holes inside the silicon substrate so as to enable the inner surfaces to be covered with monox; 6), the GaN epitaxy grows. The method can effectively relieve GaN stress, and prevents GaN cracking and GaN lattice defects.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Synthetic method of nano aluminum-rich beta-zeolite
ActiveCN101353168AReduce moisture contentReduce lattice defectsCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesLattice defectsCrystallinity
A method for synthesizing nano aluminum-rich beta-zeolite comprises the steps as follows: (1) an alumino silica gel which is formed by mixing an aluminum source and acid is evenly mixed with aluminum source particles, dried and crushed into alumino silica gel particles, wherein, the mol ratio of the aluminum source to the silicon source is 0.05-0.2; and (2) a template agent is added to the alumino silica gel particles obtained in the step (1) and evenly mixed to produce a reaction mixture which is crystallized at the temperature of 80-190 DEG C for 1-6 days, therefore a product is obtained through recovery. The mol ratios of the feeding ingredients of the reaction mixture are as follows: the mol ratio of the template agent to the silicon source equals 0.1-1.0, and that of water to the silicon source equals 2-12. The template agent is a mixture of a tetraethylammonium compound and a fluoride, or tetraethylammonium fluoride dihydrate. The method provided by the invention is characterized by high yield of a single kettle and low moisture of the synthesis system. The beta-zeolite synthesized by the method provided by the invention has high relative crystallinity, few lattice defects and good thermal stability, and the ratio between the silicon and aluminum of the synthesized beta-zeolite is 5-20, which is up to the nano crystal grain dimension.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Manufacture method of silicon epitaxial slice for fast recovery diode
ActiveCN104319235ANo lattice defectsImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice defectsMicrometer
The invention relates to a manufacture method of a silicon epitaxial slice for a fast recovery diode. The manufacture method of the silicon epitaxial slice for the fast recovery diode improves the thickness of an epitaxial slice and uniformity of electrical resistivity parameters and reduces occurrence rate of crystal defects by optimizing an existing technology and restraining self doping effects, and thereby meets use requirements of fast recovery diode devices, and greatly improves reliability and finished product rate of the fast recovery diode devices. Thickness non-uniformity of the silicon epitaxial slice prepared through the manufacture method of the silicon epitaxial slice for the fast recovery diode is less than 1%. Electrical resistivity non-uniformity of the silicon epitaxial slice is less than 2%. No lattice defect exists in the silicon epitaxial slice. The thickness of a transition area is less than 4 micrometers. Parameters of the silicon epitaxial slice prepared through the manufacture method of the silicon epitaxial slice for the fast recovery diode fully meets requirements of the fast recovery diode devices for silicon epitaxial materials. The silicon epitaxial slice prepared through the manufacture method of the silicon epitaxial slice for the fast recovery diode obtains general consent of users at present, and greatly propels improvement of performance of the domestic fast recovery diode devices.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 46 RES INST +1
Gallium nitride base LED chip and preparation method thereof
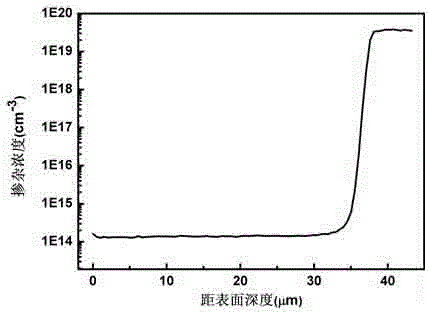
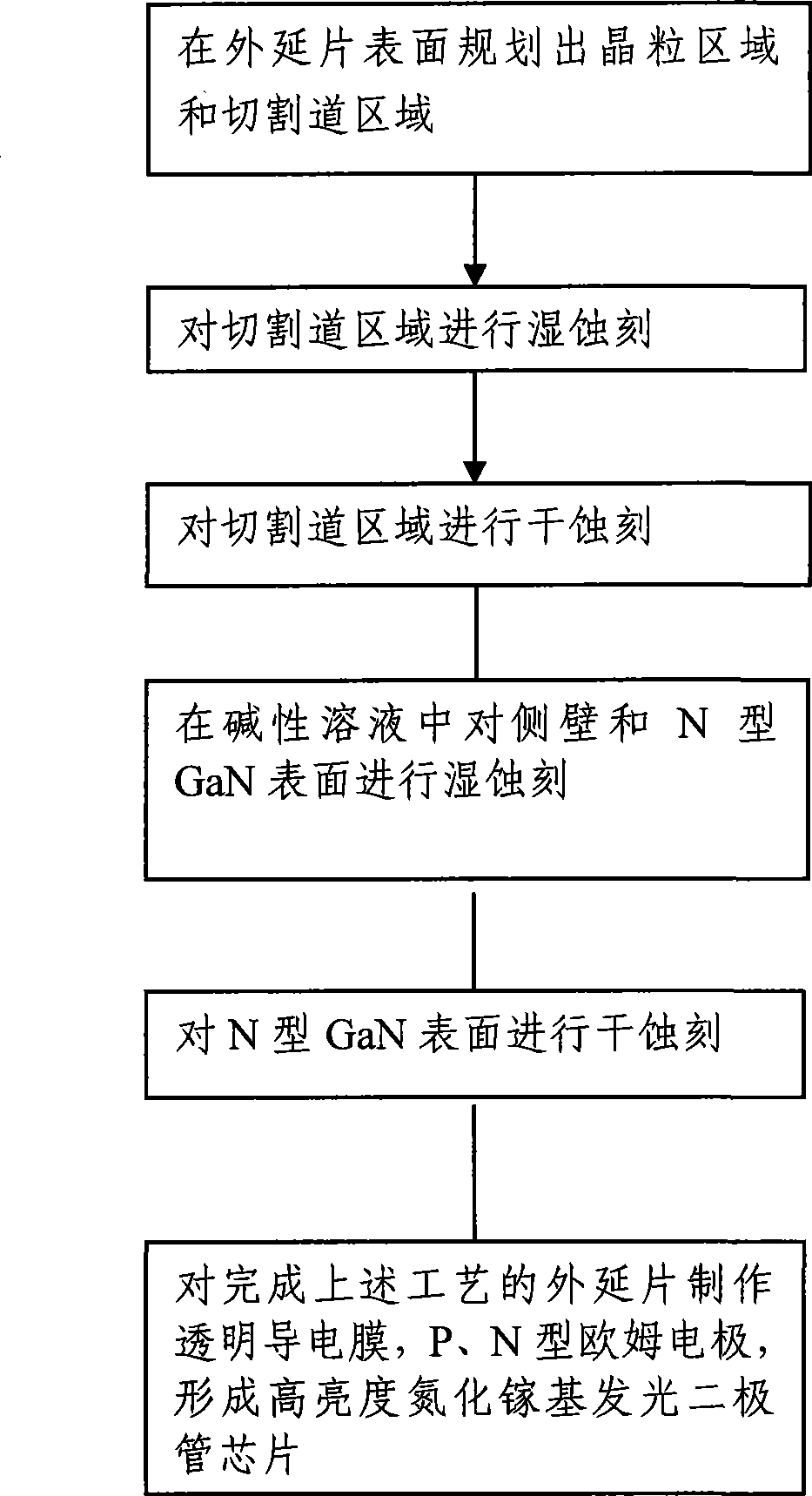
InactiveCN101436630AReduce reflectionImprove external luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesLattice defectsGallium nitride
The invention relates to a gallium nitride based light-emitting diode chip and a method for manufacturing the same. The method comprises the following steps: planning a crystal grain area and a cutting path area on the surface of an epitaxial slice; removing a protective mask of the cutting path area and then removing an undeveloped photoresist; performing dry etching on the cutting path area to expose N-type gallium nitride and form a side wall, wherein the distance between the surface of the N-type gallium nitride and the surface of a substrate of the epitaxial slice is between 1 and 1.5mu m; performing wet etching on the side wall and the surface of the N-type gallium nitride in an alkaline solution so as to form a roughened side wall of the N-type gallium nitride and a roughened surface of the N-type gallium nitride; and performing dry etching on the surface of the N-type gallium nitride, making use of the lattice defect formed in the process of epitaxy to form a nanometer columnar structure on the surface of the N-type gallium nitride, and finally manufacturing the chip. The chip can improve the external luminous efficiency of the gallium nitride based light-emitting diode chip.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INVENLUX TECH
Nano titanium dioxide (TiO2) for flue gas denitration catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102198397ASmall grainUniform grainDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCooking & bakingLattice defects
The invention provides a special nano titanium dioxide (TiO2) for a high-performance denitration catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The nano-TiO2 comprises the following components in mass percentage: 80-95% of TiO2 and 5-20% of SiO2; and the nano-TiO2 is prepared by a precipitation method, and precipitated precursors comprise TiOSO4 solution and silica sol. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving metatitanic acid used as raw material with concentrated sulfuric acid to obtain titanyl sulfate solution; precipitating titanyl sulfate and the silica sol by the precipitation method to obtain metatitanic acid slurry; and washing the metatitanic acid slurry with de-ionized water, drying and baking to finally obtain the special nano-scale TiO2 for the denitration catalyst. The preparation method has the following advantages: (1) the TiO2 obtained by the precipitation method has the characteristics of small and uniform crystal particles, large specific surface area and more surface lattice defects so that the TiO2 and active components of the catalyst such as vanadium and tungsten interact strongly so as to improve properties of the catalyst; and (2) the cheap silica sol is utilized as an additive, which improves surface acidity and specific surface area of the nano-TiO2 and causes no toxic or harmful substances after the silica sol is baked.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photodiode array, method of manufacturing the same, and detecting device
ActiveUS20100044677A1Improve production efficiencyImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLattice defectsPhotodiode
A photodiode array includes a p-side electrode provided on each p-type region formed by selective diffusion and an n-side electrode connected to a non-growth part of an InP substrate and extends to the top surface side of an epitaxial multilayer. A wall surface of an edge at the non-growth part side of the epitaxial multilayer is a smooth surface. A lattice defect density in a portion of the edge of the epitaxial multilayer is higher than a lattice defect density in the inside of the epitaxial multilayer. Furthermore, the non-growth part of the InP substrate to which the n-side electrode is connected has a flat surface continuous from the inside of the InP substrate.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
TiO2/BiVO4 photo-anode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104988533AEfficient separationEfficient decompositionElectrodesNano structuringLattice defects
The invention discloses a TiO2 / BiVO4 photo-anode material which comprises a substrate, a TiO2 nano-rod array perpendicularly grown on the surface of the substrate, and a BiVO4 nano-particle layer deposited on the surface of the TiO2 nano-rod array. Through adoption of the TiO2 / BiVO4 photo-anode material, the water photoelectrolysis property is improved; compared with other water photoelectrolysis materials, the TiO2 / BiVO4 photo-anode material effectively overcomes the lattice defect of an interface layer, reduces the composition of photo-generated electrons and hole pairs, improves the own stability, expands the absorption spectrum range of visible light, promotes the effective separation of the photo-generated electrons and the hole pairs, realizes the synchronous reaction of hydrogen production and oxygen production, ensures that the ratio of the hydrogen yield to the oxygen yield is close to 2: 1, and is a relatively ideal water photoelectrolysis material. Moreover, the invention further discloses a preparation method of the TiO2 / BiVO4 photo-anode material. The preparation method has the characteristics that the nano-structure control is easy to realize technically, the prepared binary nano-rod array is excellent in crystallization property, and the interface quality is relatively high.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Lithium-manganese-aluminum oxygen anode material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102683667AReduce solubilityIncrease the amount of participationCell electrodesLithiumLattice defects
The invention provides a lithium-manganese-aluminum oxygen anode material, which has the atomic ratio of LiaMn2-x-yAlxMyO4; the concentration of A1 is in a gradient distribution presenting gradually risen from the inner part of the lithium-manganese-aluminum oxygen anode material to the surface; the concentration of Mn is in a gradient distribution presenting gradually decreased from the inner part of the lithium-manganese-aluminum oxygen anode to the surface. The invention further provides a preparation method of lithium-manganese-aluminum oxygen anode material. By adding solution or turbid liquid of aluminum source compound in the precipitation process, the aluminum element replaces the position of a manganese element in the formed lithium-manganese-aluminum material, so that the spinel structure of the lithium-manganese-aluminum material is stabilized, the forming of the lattice defect is avoided and the well high-temperature circulating performance of the lithium-manganese-aluminum material is guaranteed, the dissolution of manganese in the electrolyte is reduced and the high-temperature circulating performance of the lithium-manganese-aluminum oxygen anode material is further improved.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
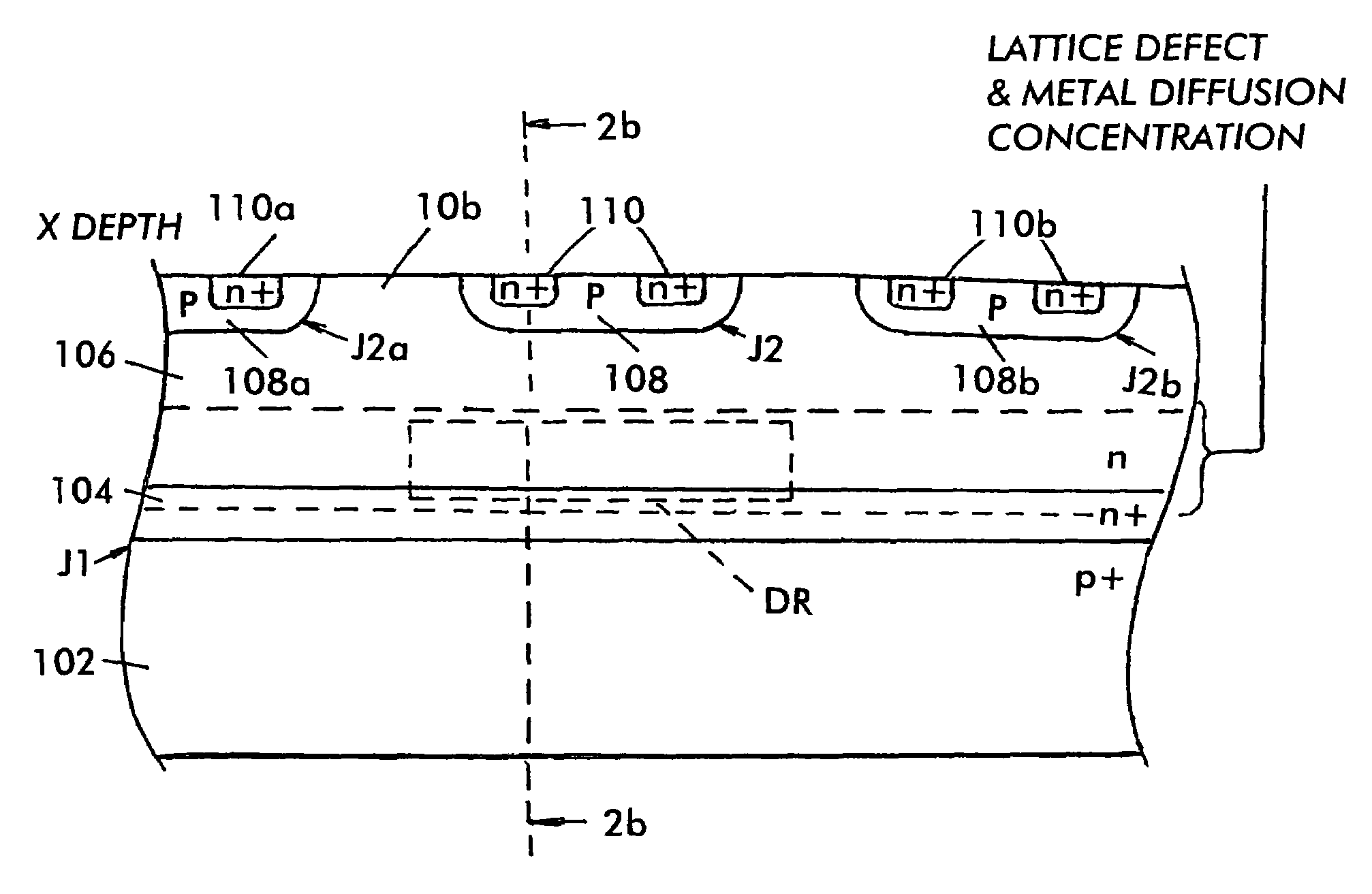
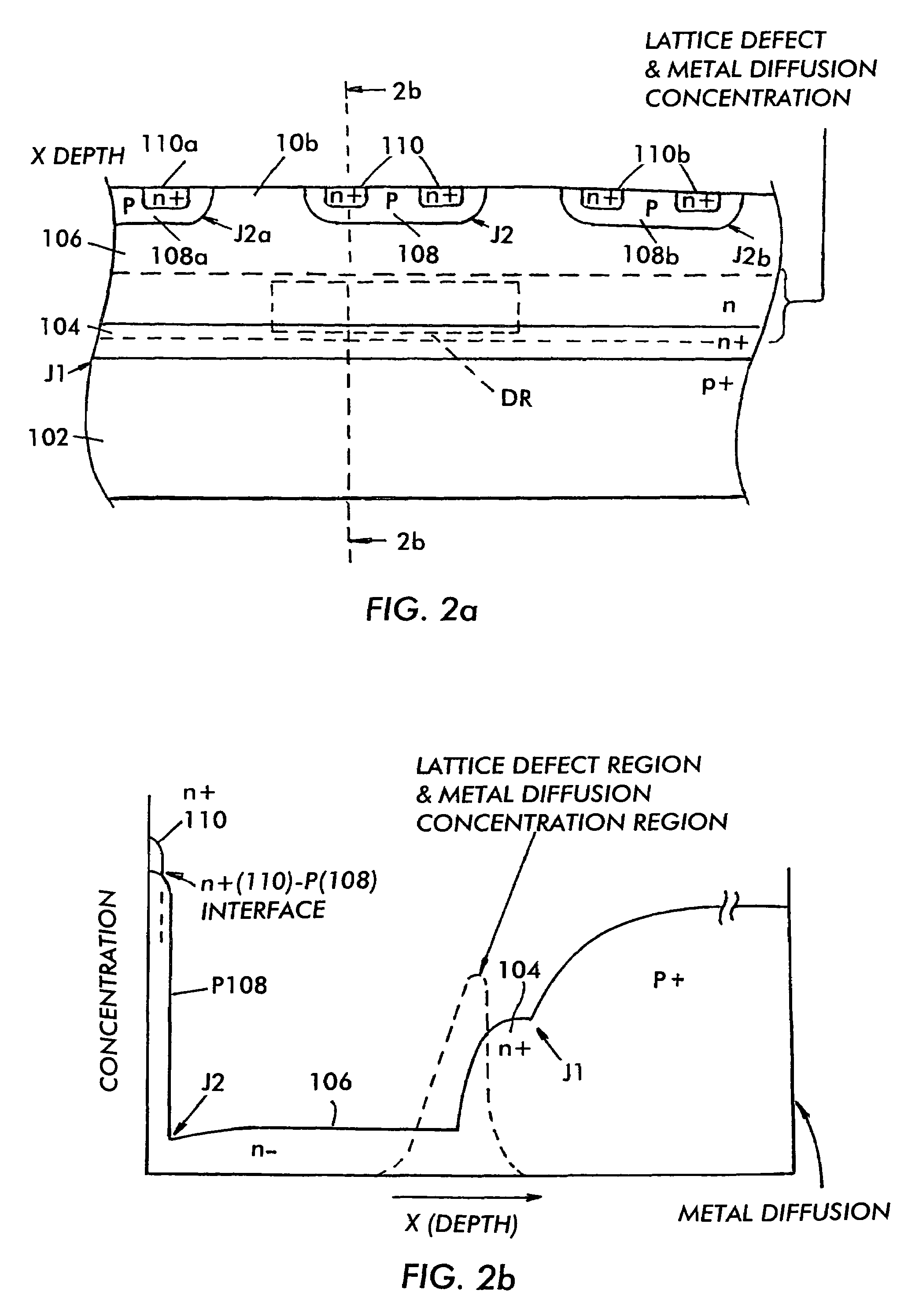
Process to create buried heavy metal at selected depth
InactiveUS7485920B2Reduced carrier lifetimeReduce disadvantagesTransistorThyristorLattice defectsParticle beam
Semiconductor devices having recombination centers comprised of well-positioned heavy metals. At least one lattice defect region within the semiconductor device is first created using particle beam implantation. Use of particle beam implantation positions the lattice defect region(s) with high accuracy in the semiconductor device. A heavy metal implantation treatment of the device is applied. The lattice defects created by the particle beam implantation act as gettering sites for the heavy metal implantation. Thus, after the creation of lattice defects and heavy metal diffusion, the heavy metal atoms are concentrated in the well-positioned lattice defect region(s).
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
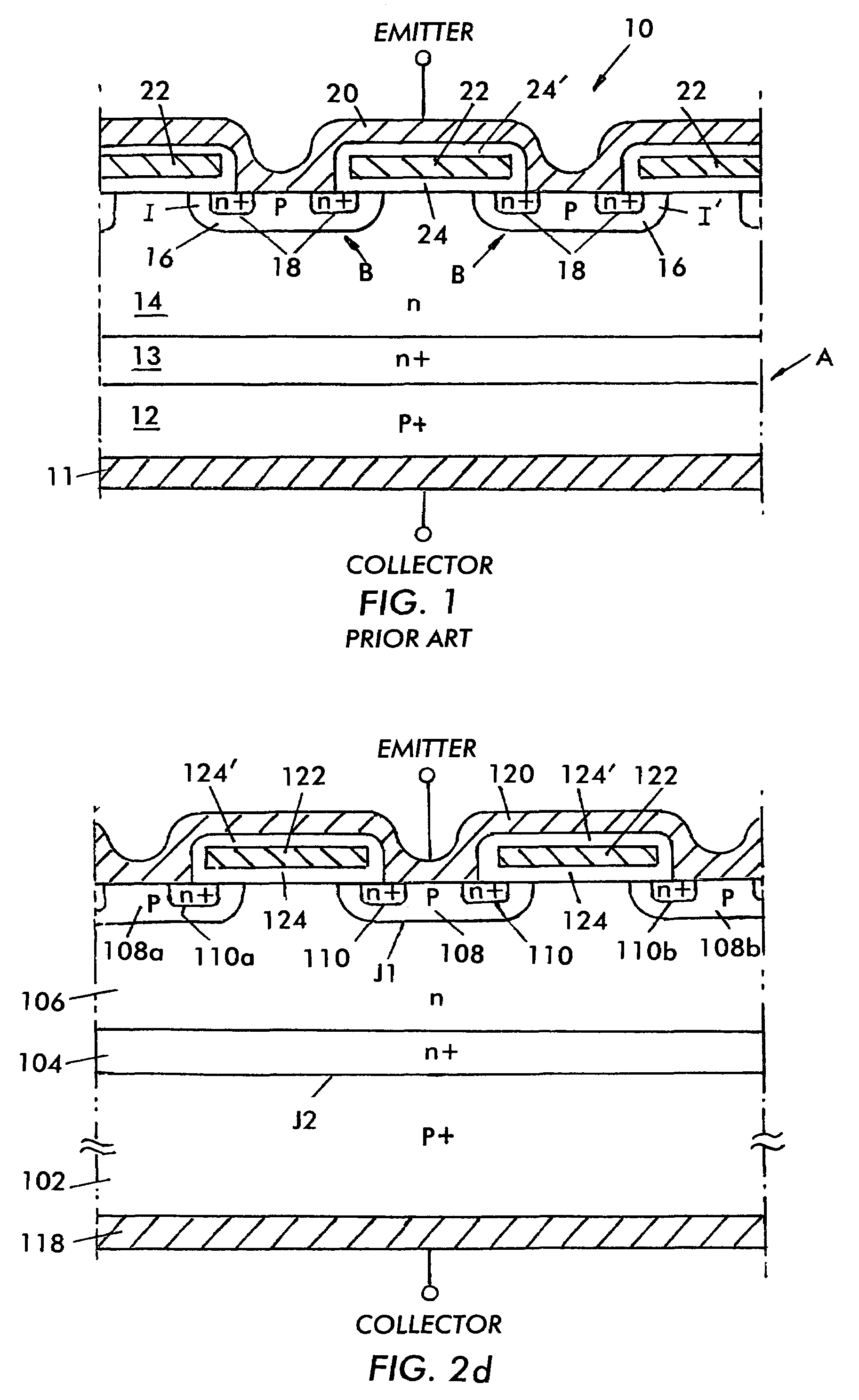
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080079119A1Optimal carrier lifetimeMinimize changesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice defectsDevice material
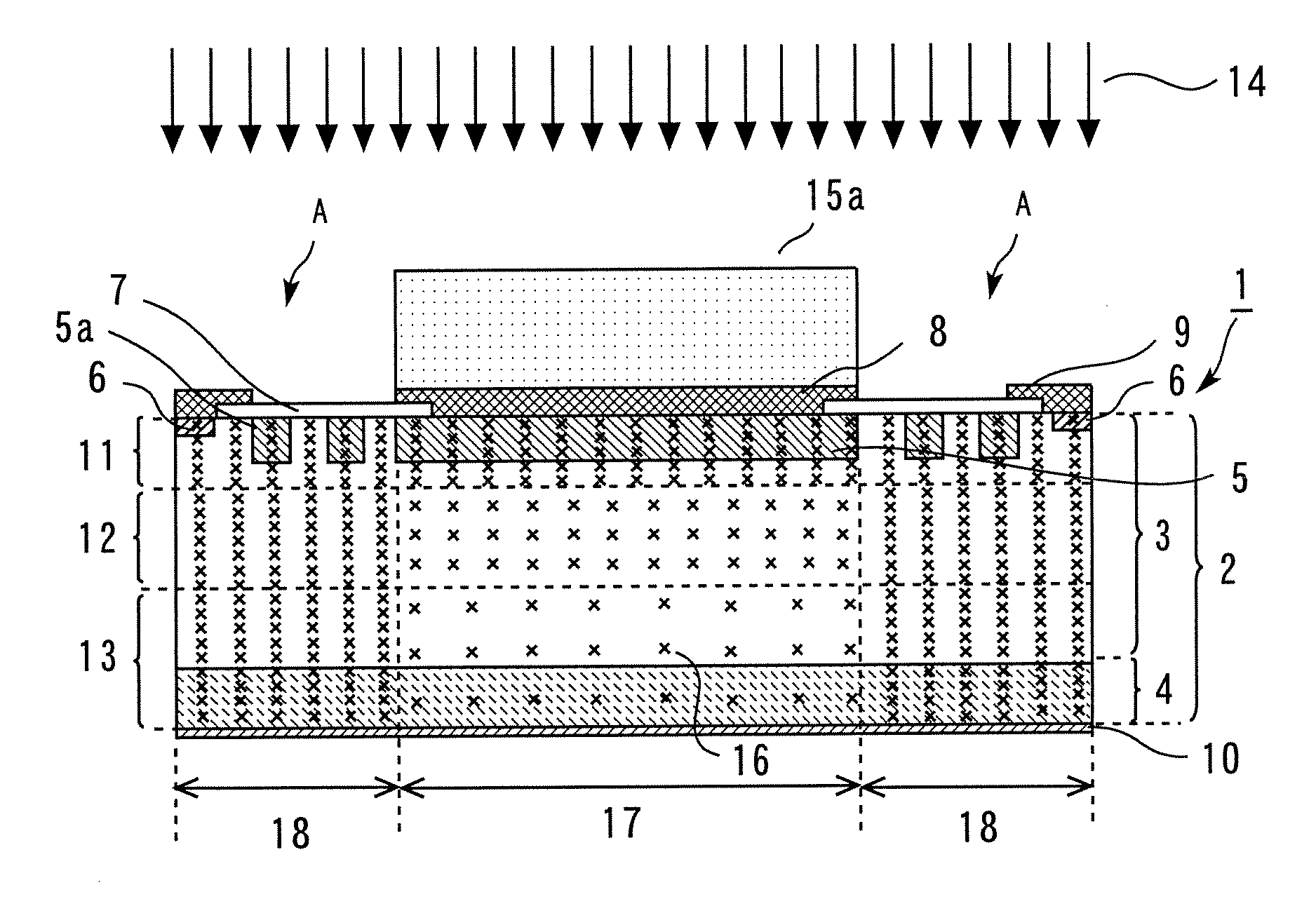
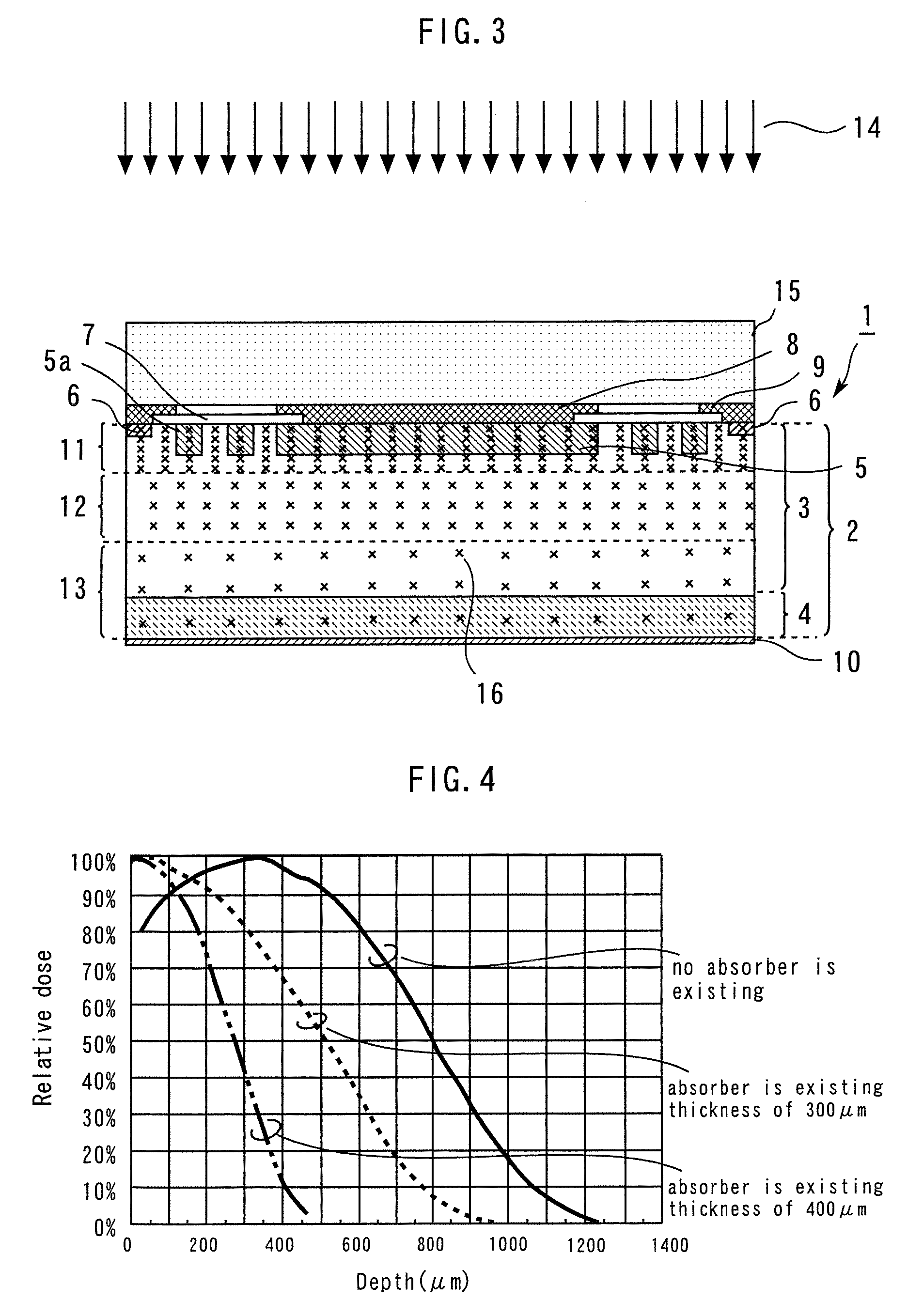
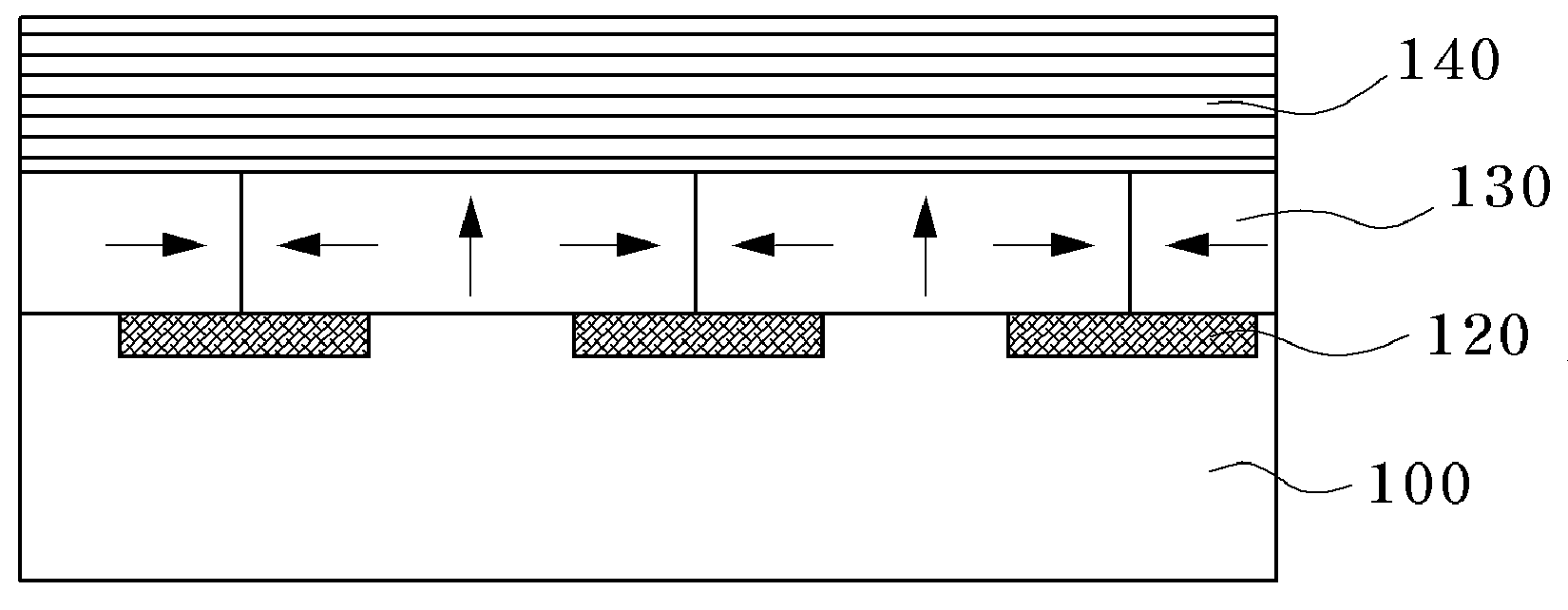
A p-n junction is formed at the interface of a low-concentration n-type impurity layer 3 and a p-type diffusion region 5 in the vicinity of the upper major surface of an n-type semiconductor substrate 2 of a semiconductor device 1. A mask 15 composed of an absorber is placed on the upper major surface of the semiconductor device 1, and electron beams are radiated. Thereafter, heat treatment is conducted. As a result, the peak of the crystal lattice defect densities is present in the vicinity of the upper major surface of the n-type semiconductor substrate 2, and the crystal lattice defect densities are decreasingly distributed toward the lower major surface. Thereby, a semiconductor device that can minimize the variation of the breakdown voltage characteristics of the p-n junction of the diode, and can control the optimum carrier lifetime can be obtained.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method of forming nitride semiconductor and electronic device comprising the same
InactiveUS20100065865A1Good effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersLattice defectsLateral overgrowth
A method of forming a nitride semiconductor through ion implantation and an electronic device including the same are disclosed. In the method, an ion implantation region composed of a line / space pattern is formed on a substrate at an ion implantation dose of more than 1E17 ions / cm2 to 5E18 ions / cm2 or less and an ion implantation energy of 30˜50 keV, and a metal nitride thin film is grown on the substrate by epitaxial lateral overgrowth, thereby decreasing lattice defects in the metal nitride thin film. Thus, the electronic device has improved efficiency.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Method and apparatus for measuring far-ultraviolet laser scratch of interface jointing strength
InactiveCN1405554ARealization of ablation processingThe mechanism of laser action is obviousUsing mechanical meansColor/spectral properties measurementsLattice defectsMathematical model
This invention relates to laser test and material performance test in which a continuously loading pulse avaser beam loads to the film surface of a subject directly via an incident laser beam optical path system to form lattice defect and plasma after optical decomposing, and valence photochange to realize erosion process to the subject or even break ibnding keys among moleculars or crystals to some materials by photons directly to break-off the film materials. At the same time, feeding system makes the subject to do feed movement, laser beam forms steadily deepened mars on the film surface until breaks down the film-matrix interface then the said laser beam energy energy is processed by a certain mathematical modeles to express the binding strength of the film-matrix interface.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com