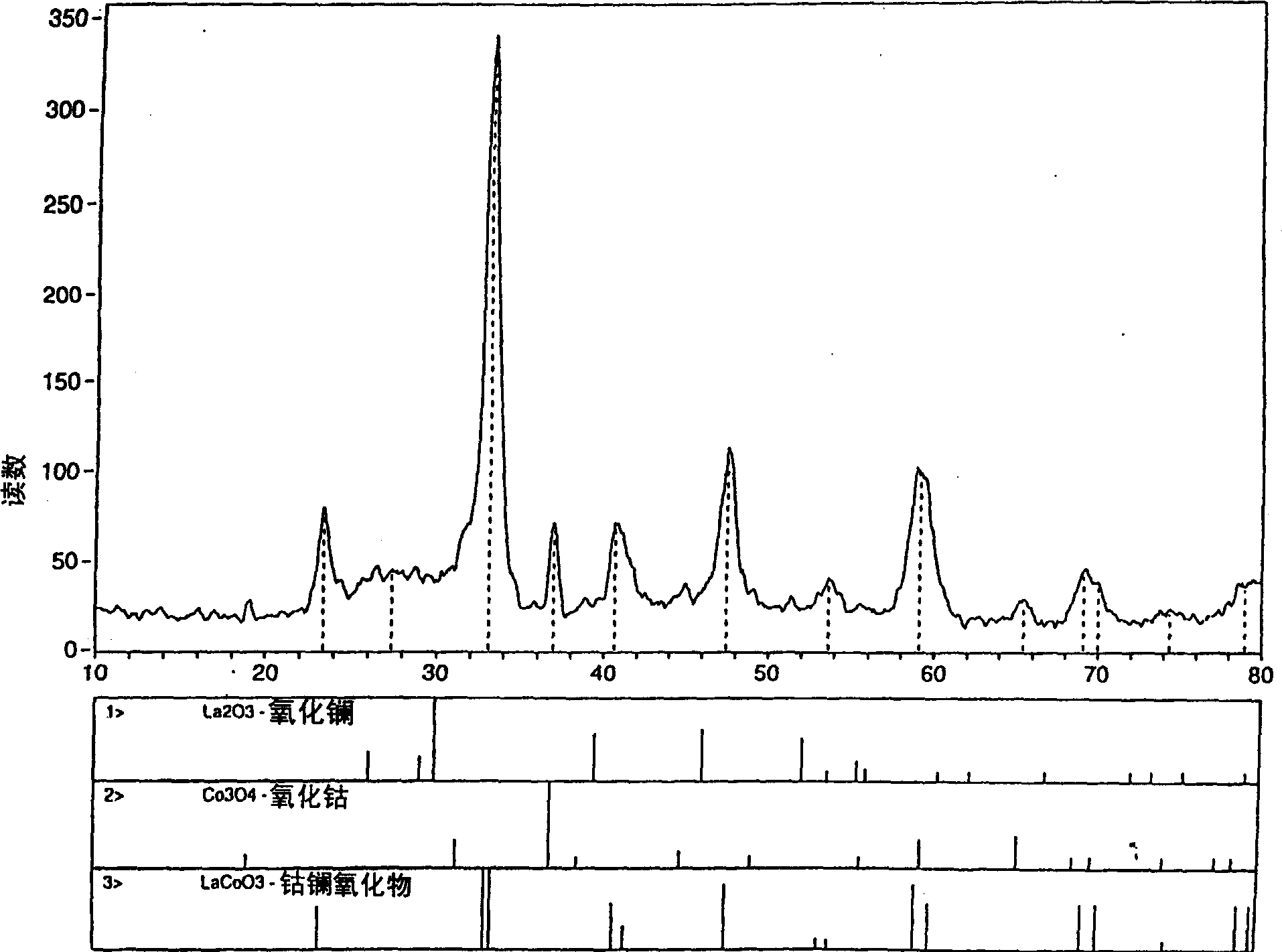
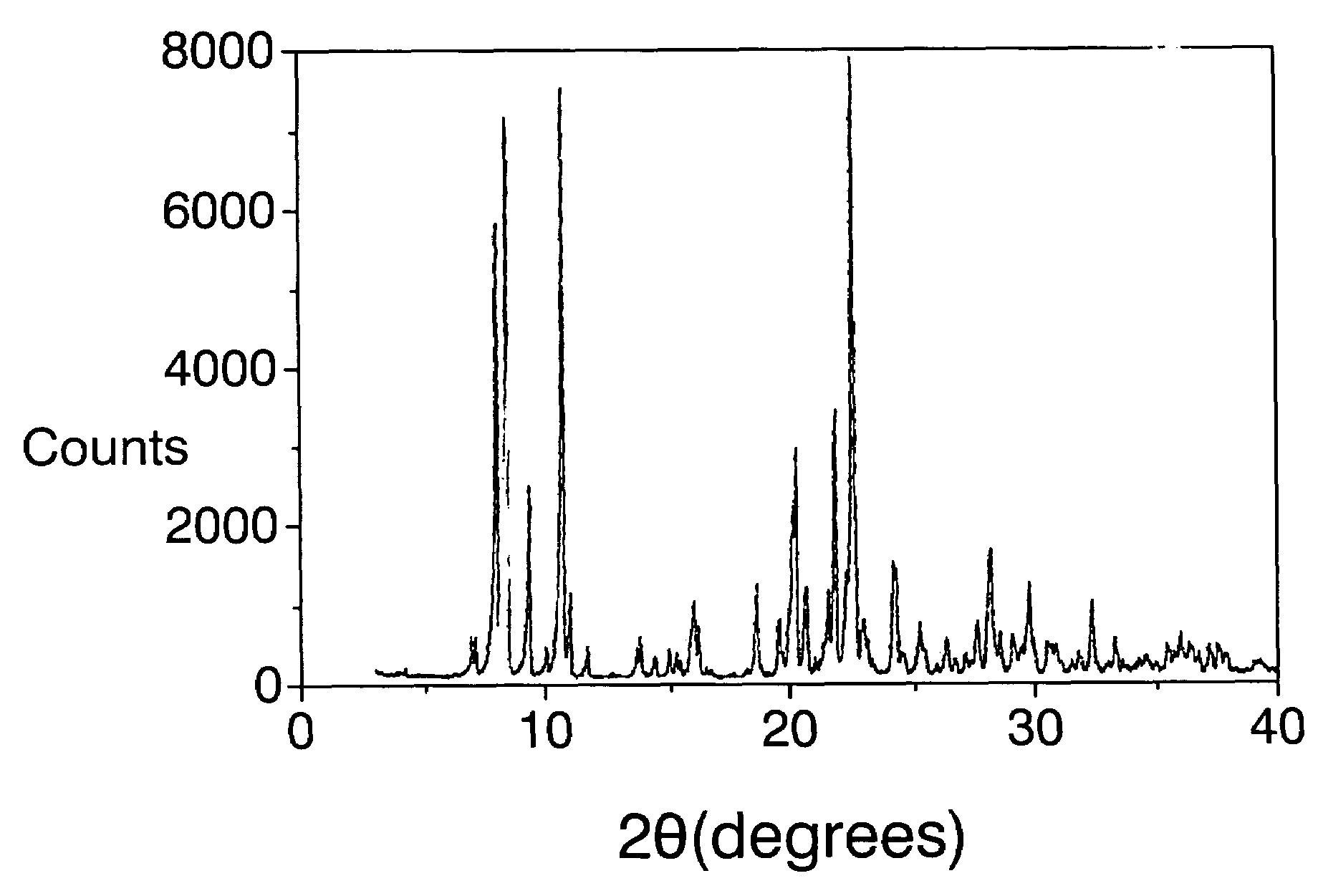
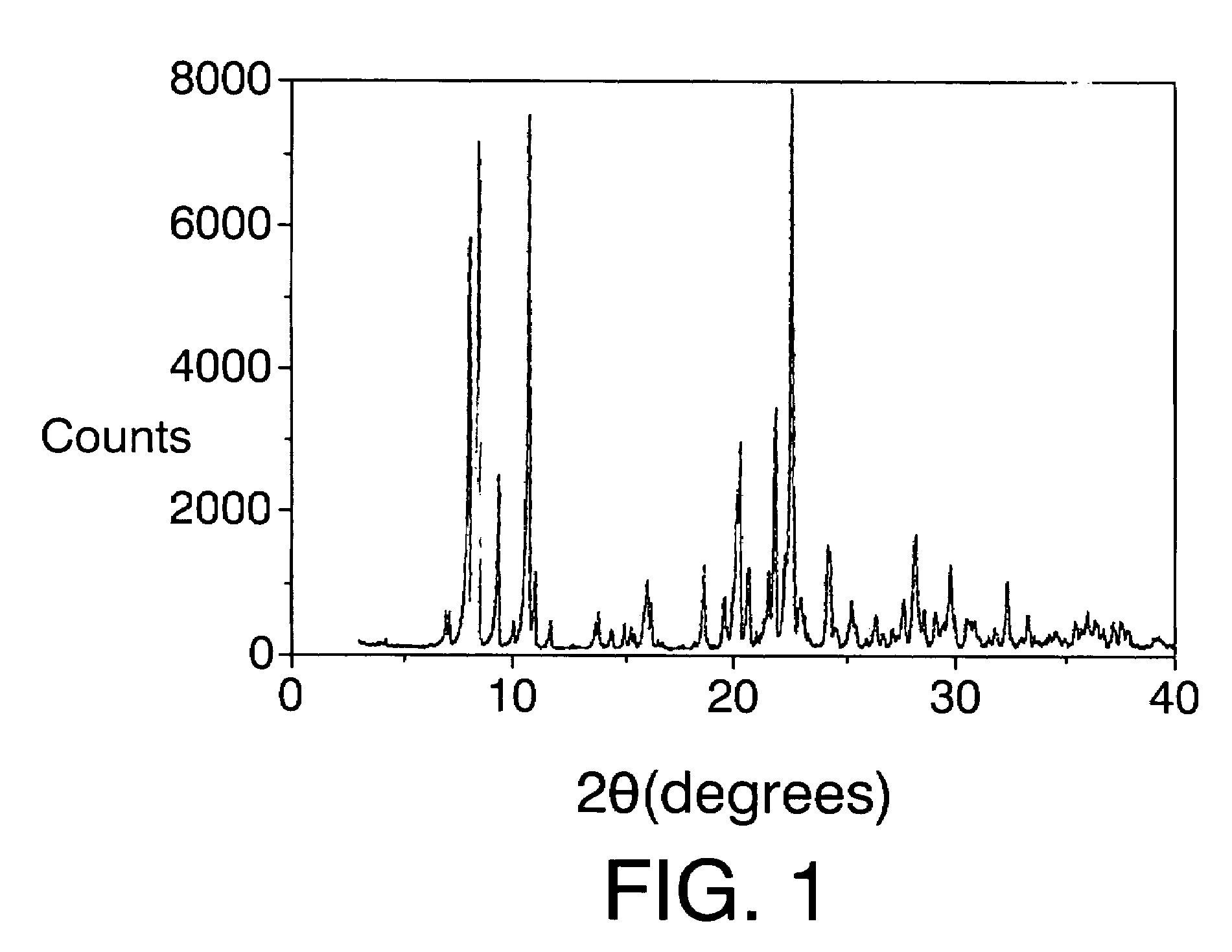
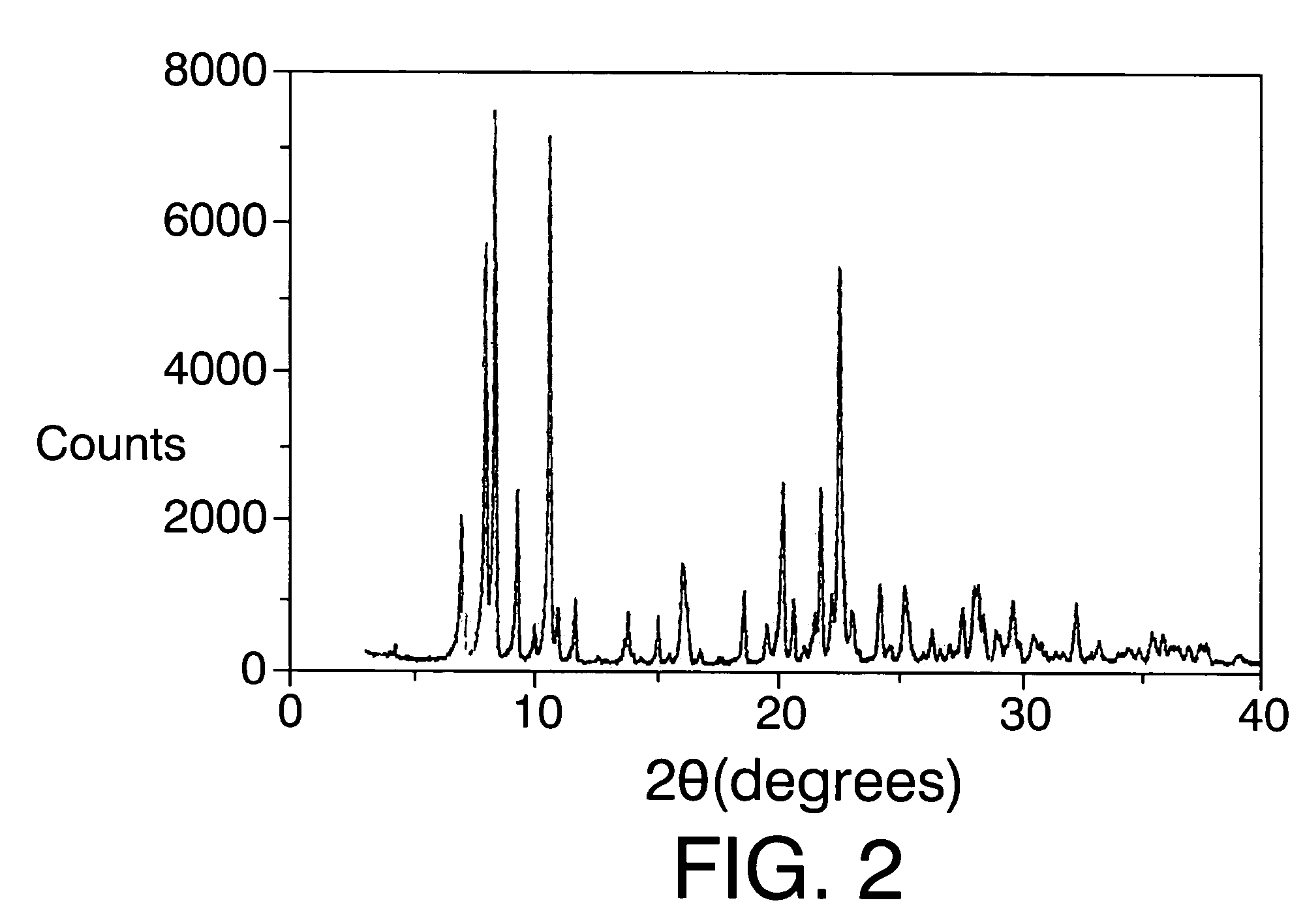
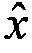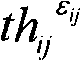Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
741 results about "Empirical formula" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
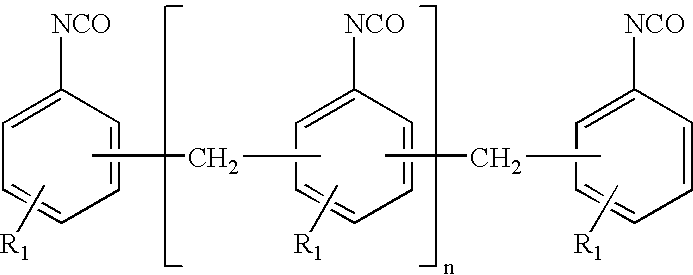
In chemistry, the empirical formula of a chemical compound is the simplest positive integer ratio of atoms present in a compound. A simple example of this concept is that the empirical formula of sulfur monoxide, or SO, would simply be SO, as is the empirical formula of disulfur dioxide, S₂O₂. This means that sulfur monoxide and disulfur dioxide, both compounds of sulfur and oxygen, will have the same empirical formula. However, their molecular formulas, which express the number of atoms in each molecule of a chemical compound, may not be the same.
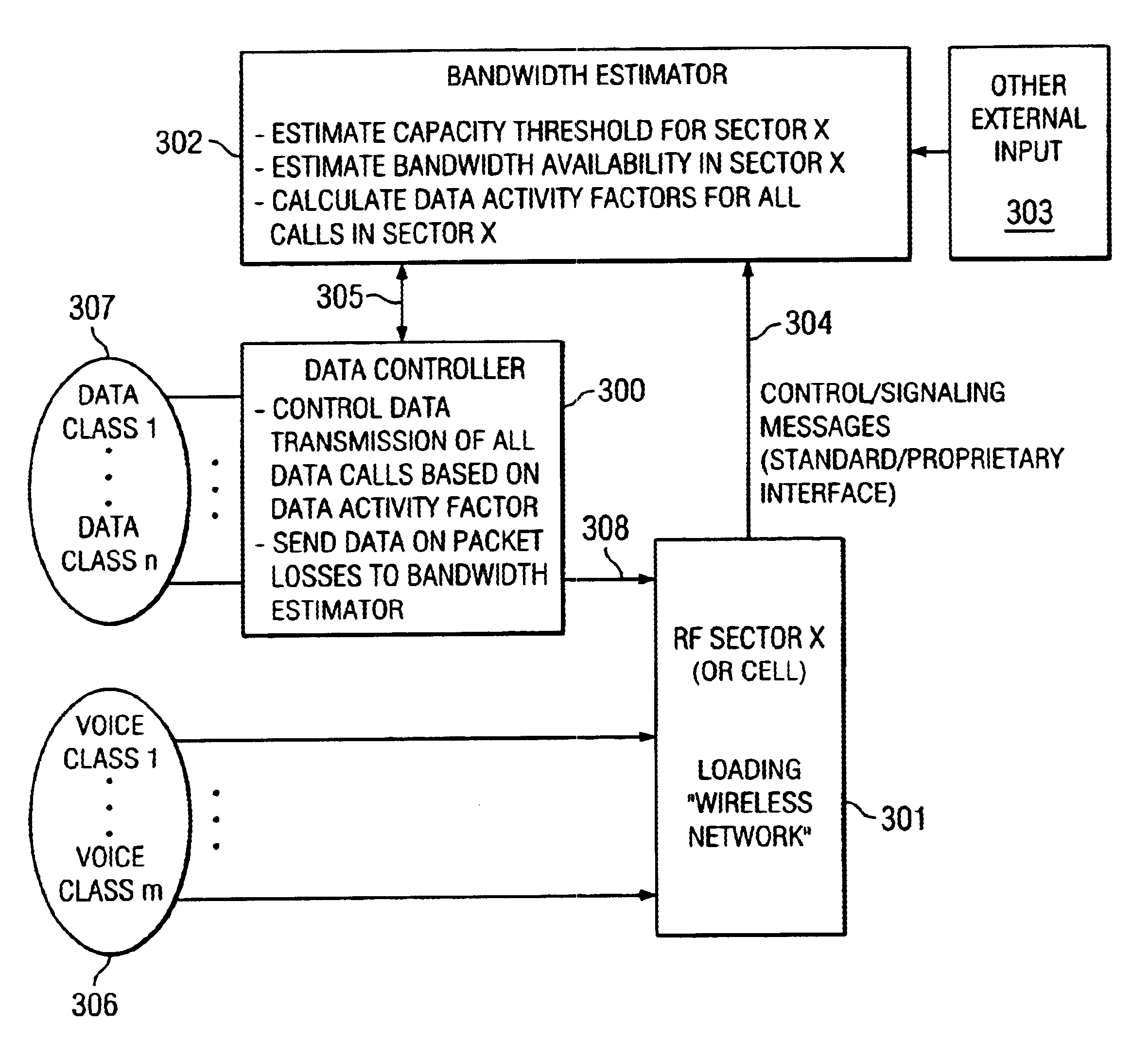
Method and apparatus for class based transmission control of data connections based on real-time external feedback estimates obtained using messaging from a wireless network
InactiveUS6697378B1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexData connectionWireless mesh network
A system of wireless network with capabilities of transporting data packets, wherein the data transmission activity of each data connection is determined using the localized air interface capacity threshold and available bandwidth estimates obtained via the messages sent by the wireless network (FIG. 3). The system provides a unique and efficient way of providing control over data packet transmissions over a wireless network. The localized wireless network capacity threshold and available bandwidth estimates are obtained via use of empirical formulae and are improved upon via the use of messaging obtained from the wireless network by the Bandwidth Estimator (302) (FIG. 5 and 6). The data transmission activity factors of all data connections are determined by the Bandwidth Estimator using the localized capacity threshold and available bandwidth estimates, along with the priority / class of traffic of specific data calls (FIG. 7). The data transmission activity factors are implemented using the transmission window size update and local queuing by the Data Controller (300) (FIG. 8). Various implementations and interconnectivities of the Bandwidth Estimator and Data Controller functions are outlined (FIGS. 9-13).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Lithium-ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20080008933A1Safer chemistry characteristicLow cathode costPrimary cell to battery groupingElectrode carriers/collectorsManganateManganese
In one embodiment, an active cathode material comprises a mixture that includes: at least one of a lithium cobaltate and a lithium nickelate; and at least one of a manganate spinel represented by an empirical formula of Li(1+x1)(Mn1−y1A′y1)2−x1Oz1 and an olivine compound represented by an empirical formula of Li(1−x2)A″x2MPO4. In another embodiment, an active cathode material comprises a mixture that includes: a lithium nickelate selected from the group consisting of LiCoO2-coated LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2, and Li(Ni1 / 3Co1 / 3Mn1 / 3)O2; and a manganate spinel represented by an empirical formula of Li(1+x7)Mn2−y7Oz7. A lithium-ion battery and a battery pack each independently employ a cathode that includes an active cathode material as described above. A method of forming a lithium-ion battery includes the steps of forming an active cathode material as described above; forming a cathode electrode with the active cathode material; and forming an anode electrode in electrical contact with the cathode via an electrolyte. A system comprises a portable electronic device and a battery pack or lithium-ion battery as described above.
Owner:BOSTON POWER INC
Gradient cathode material for lithium rechargeable batteries
InactiveUS6921609B2Increase capacityImproved cyclabilityAluminium compoundsAlkaline accumulatorsManganesePotassium
A composition suitable for use as a cathode material of a lithium battery includes a core material having an empirical formula LixM′zNi1−yM″yO2. “x” is equal to or greater than about 0.1 and equal to or less than about 1.3. “y” is greater than about 0.0 and equal to or less than about 0.5. “z” is greater than about 0.0 and equal to or less than about 0.2. M′ is at least one member of the group consisting of sodium, potassium, nickel, calcium, magnesium and strontium. M″ is at least one member of the group consisting of cobalt, iron, manganese, chromium, vanadium, titanium, magnesium, silicon, boron, aluminum and gallium. A coating on the core has a greater ratio of cobalt to nickel than the core. The coating and, optionally, the core can be a material having an empirical formula Lix1Ax2Ni1−y1−z1Coy1Bz1Oa. “x1” is greater than about 0.1 a equal to or less than about 1.3. “x2,”“y1” and “z1” each is greater than about 0.0 and equal to or less than about 0.2. “a” is greater than 1.5 and less than about 2.1. “A” is at least one element selected from the group consisting of barium, magnesium, calcium and strontium. “B” is at least one element selected from the group consisting of boron, aluminum, gallium, manganese, titanium, vanadium and zirconium.
Owner:TIAX LLC
Radiation curable ink compositions suitable for ink-jet printing
InactiveUS20040163570A1Improve stabilityImprove compatibilityPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsHydrogenSilsesquioxane
A radiation curable ink composition comprising at least one initiator and at least one polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) represented by the following empirical formula [R(SiO1.5)]n wherein n=4,6,8,10,12,14,16 and larger and each R is independently hydrogen, an inorganic group, an alkyl group, an alkylene group, an aryl group, an arylene group, or non-heterocyclic group-containing organo-functional derivatives of alkyl, alkylene, aryl or arylene groups; and a process for obtaining a colourless, monochrome or multicolour ink jet image comprising the steps of jetting one or more streams of ink droplets having the above-mentioned composition onto an ink-jet ink receiver material, and subjecting the obtained image to radiation curing.
Owner:AGFA NV
Electrochemical systems comprising mxenes and max phase compositions and methods of using the same
Disclosed herein are electrochemical cells comprising electrodes prepared from layered materials comprising a substantially two-dimensional ordered array of cells having an empirical formula of Mn+1Xn, where M comprises a transition metal selected from the group consisting of a Group IIIB metal, a Group IVB metal, a Group VB metal, a Group VIB metal, and any combination thereof, X is CxNy wherein x+y=n, and n is equal to 1, 2, or 3. Also disclosed herein are batteries comprising the electrochemical cells and methods for electrochemically preparing MXene compositions with the use of the electrochemical cells.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
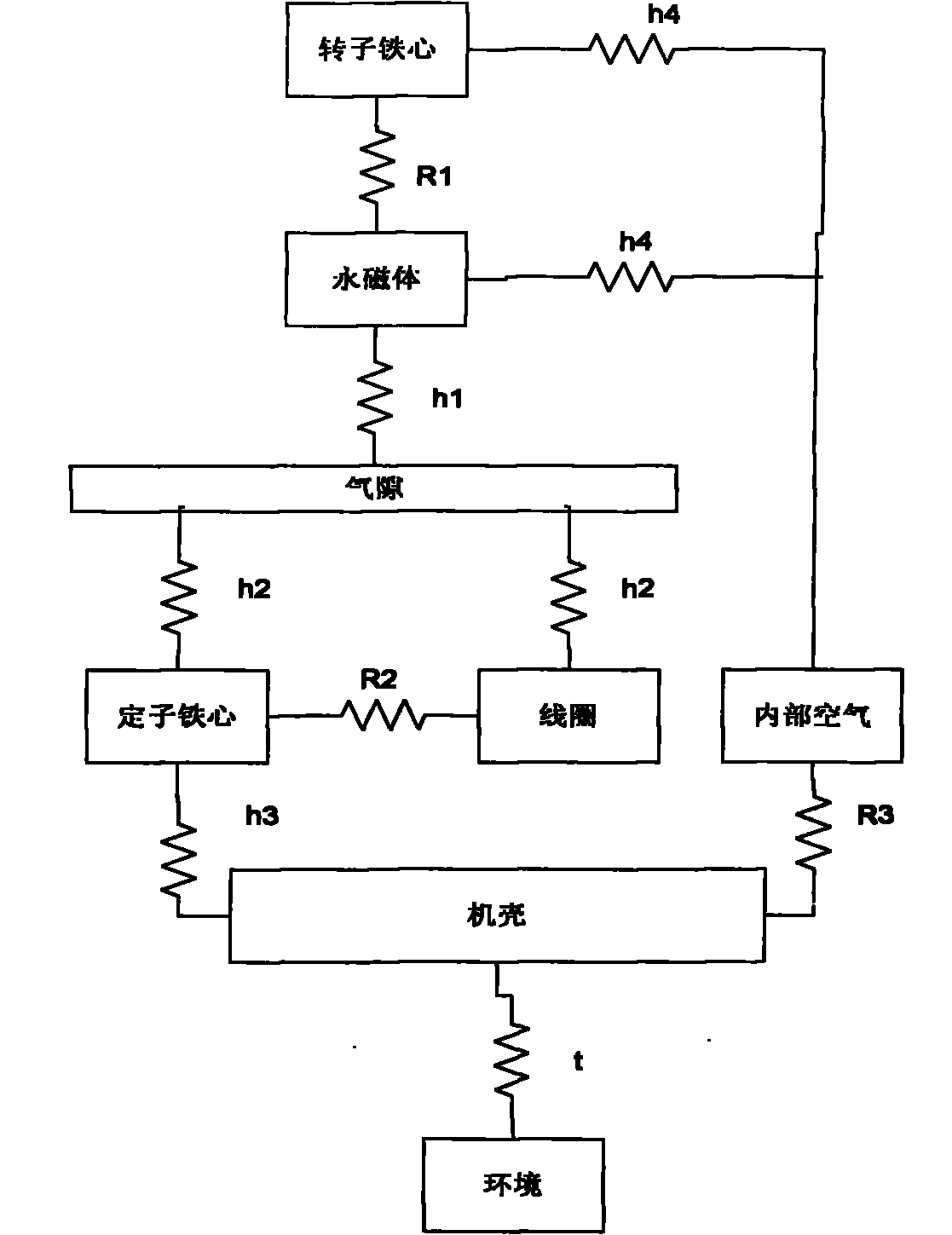
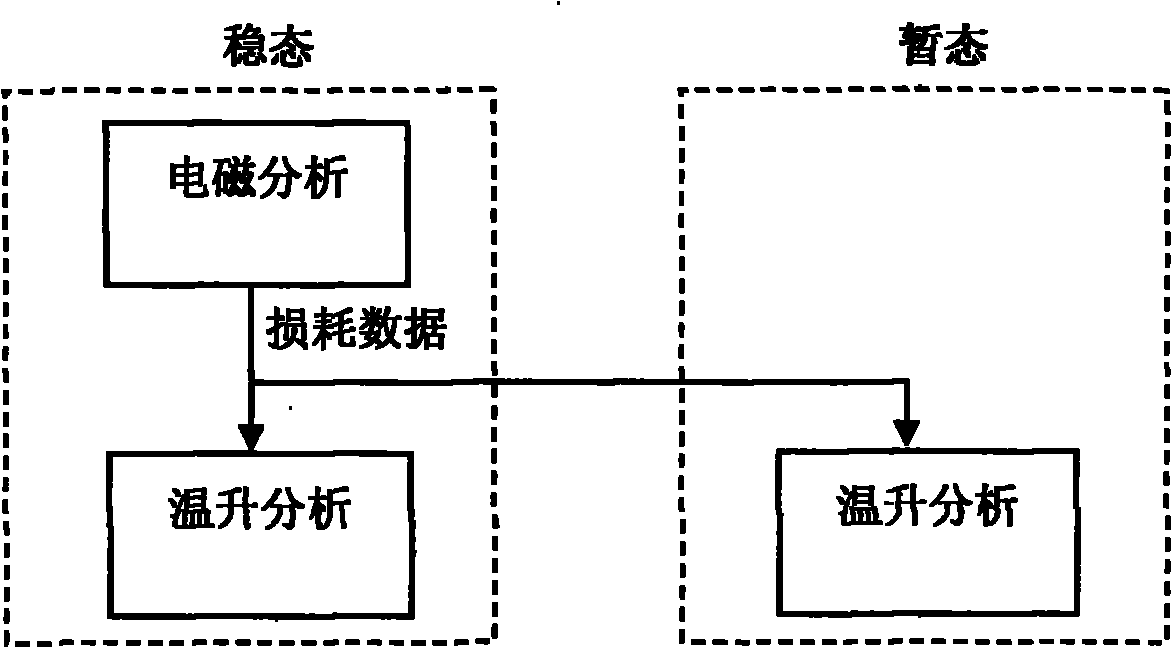
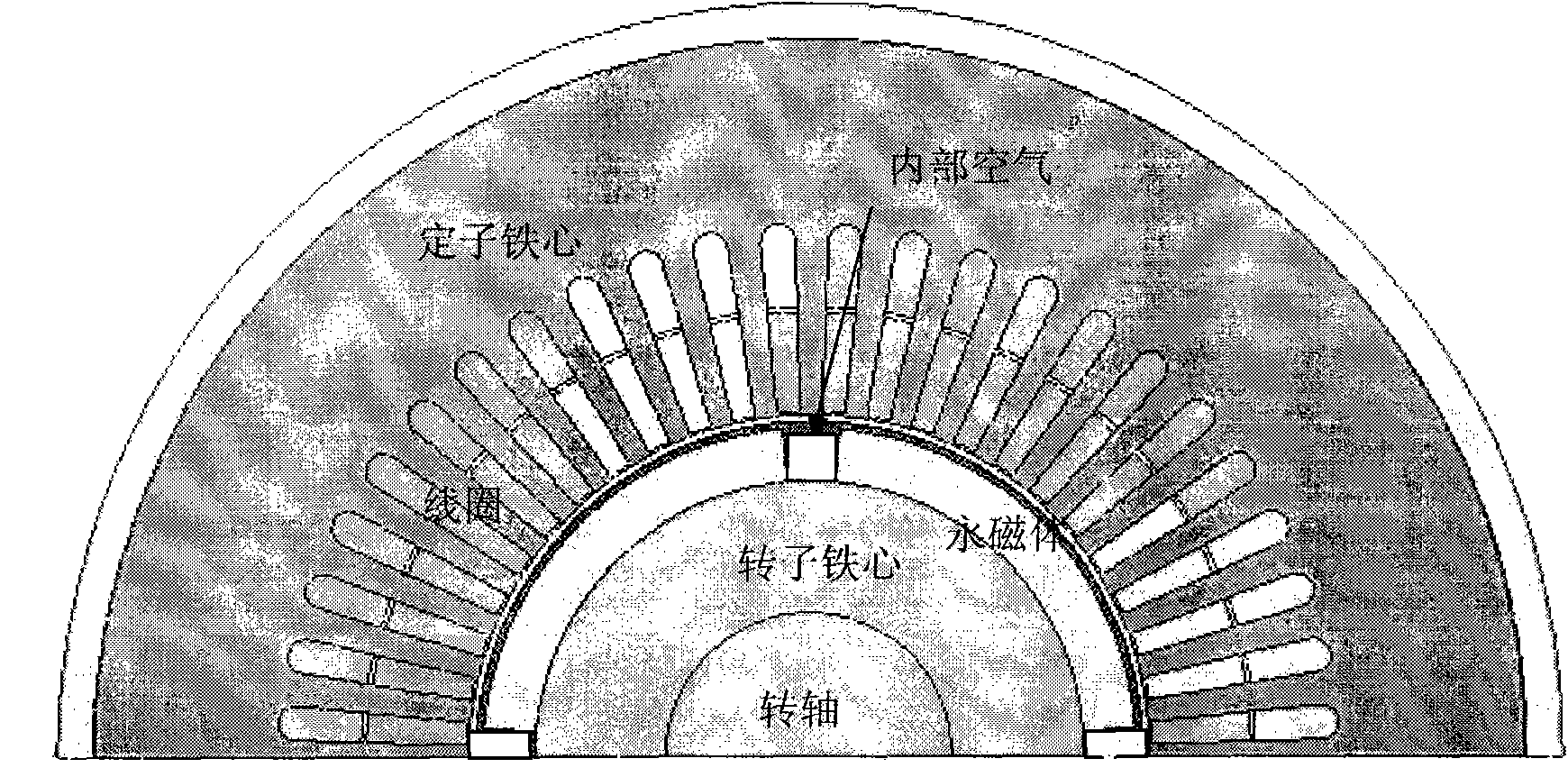
Temperature rise analytical method for predicting temperature of permanent magnet in permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN101769797AAccurate predictionAvoid difficulties such as air gap temperature measurementThermometerDynamo-electric machine testingModel selectionPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention relates to a temperature rise analytical method for predicting temperature of a permanent magnet in a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), belonging to the application electrical engineering design field; the method is characterized in that: distributed heat source of a motor is analyzed by a filed-circuit compact coupling method, comprising eddy current loss in the permanent magnet, iron loss in an iron core and copper loss in armature; on the consideration of precision requirements, the coupling analysis of a magnetic field and a temperature filed can be realized by single-way coupling mode. A thermal model of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is built based on a mixing method of a novel equivalent heat network and a finite element, heat parameters are rationally selected by adopting a combining mode of experimental measurement and empirical formula, the heat transferring coefficient and cooling condition of the motor are described completely, a stator and a rotor can be systematically combined by adopting air gap joints in the heat network, the stator and rotor unified temperature rise model is formed, the difficulty of measuring air gap temperature is avoided, material parameters are adopted at the practical working temperature, so as to lead the analysis to be rational; the accurate and optical method for predicting the temperature of the permanent magnet is realized by special correction processing in experimental links; in addition, the design method is used to give suggestions for model selection of the permanent magnet material in the motor.
Owner:李虎
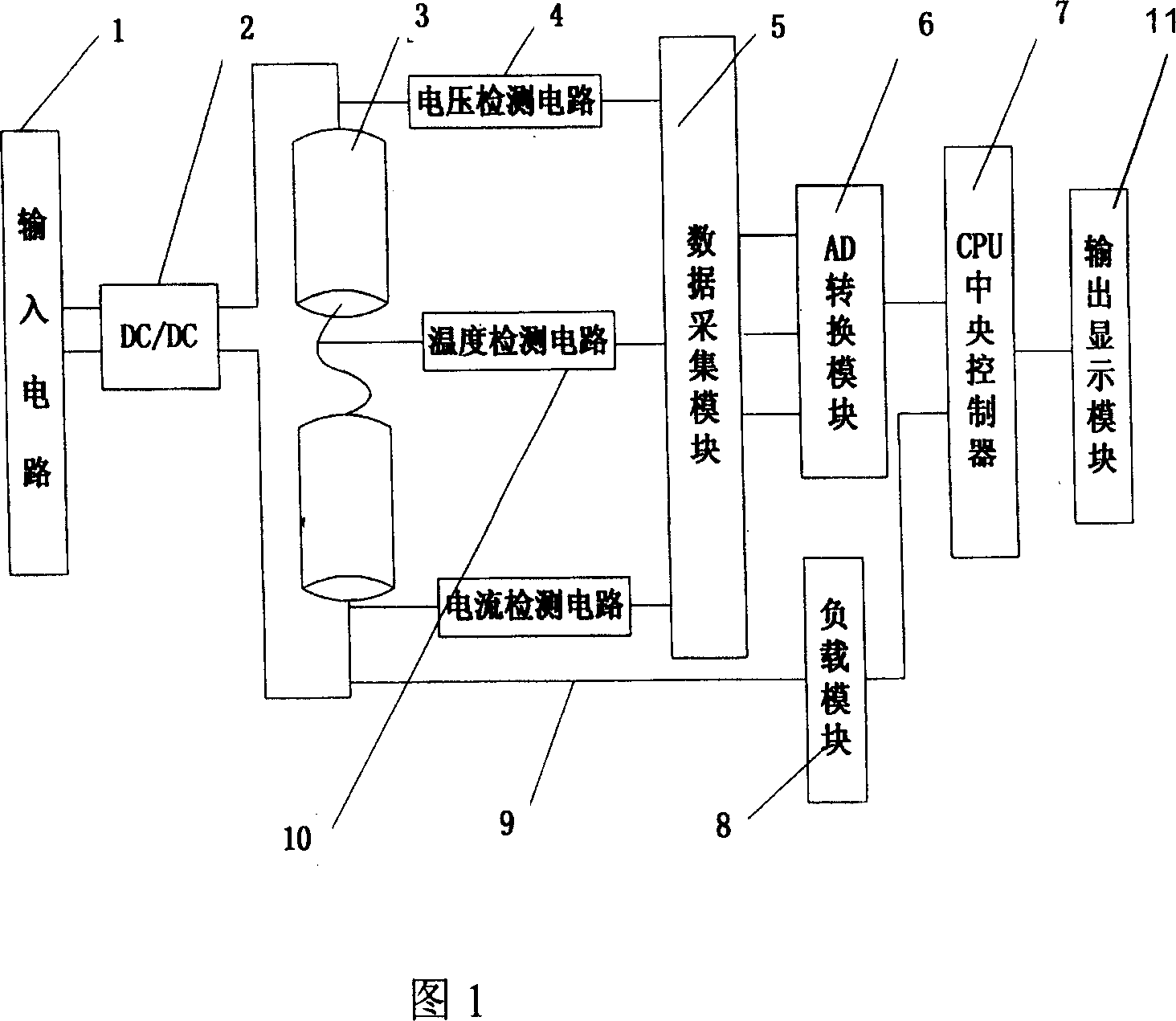
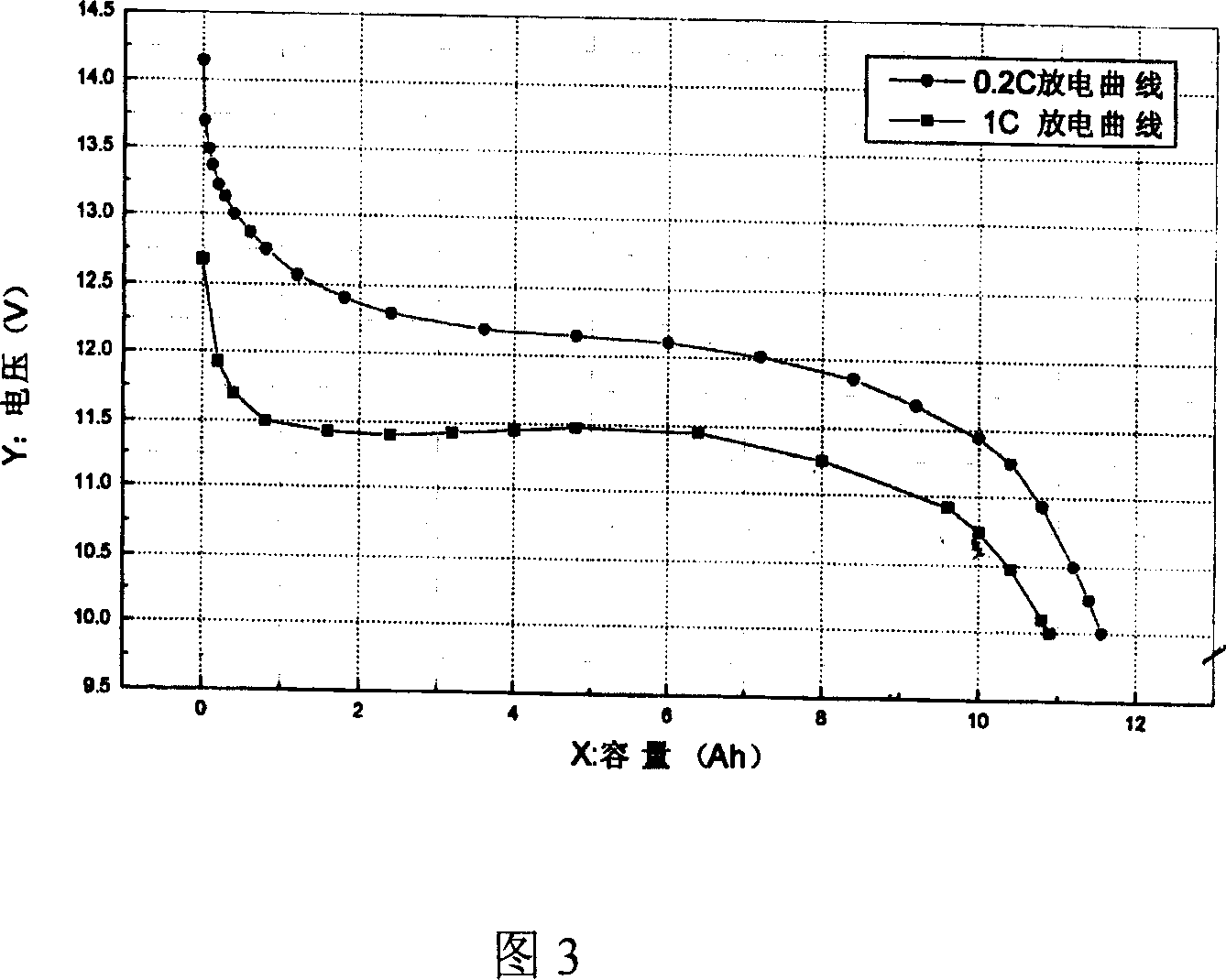
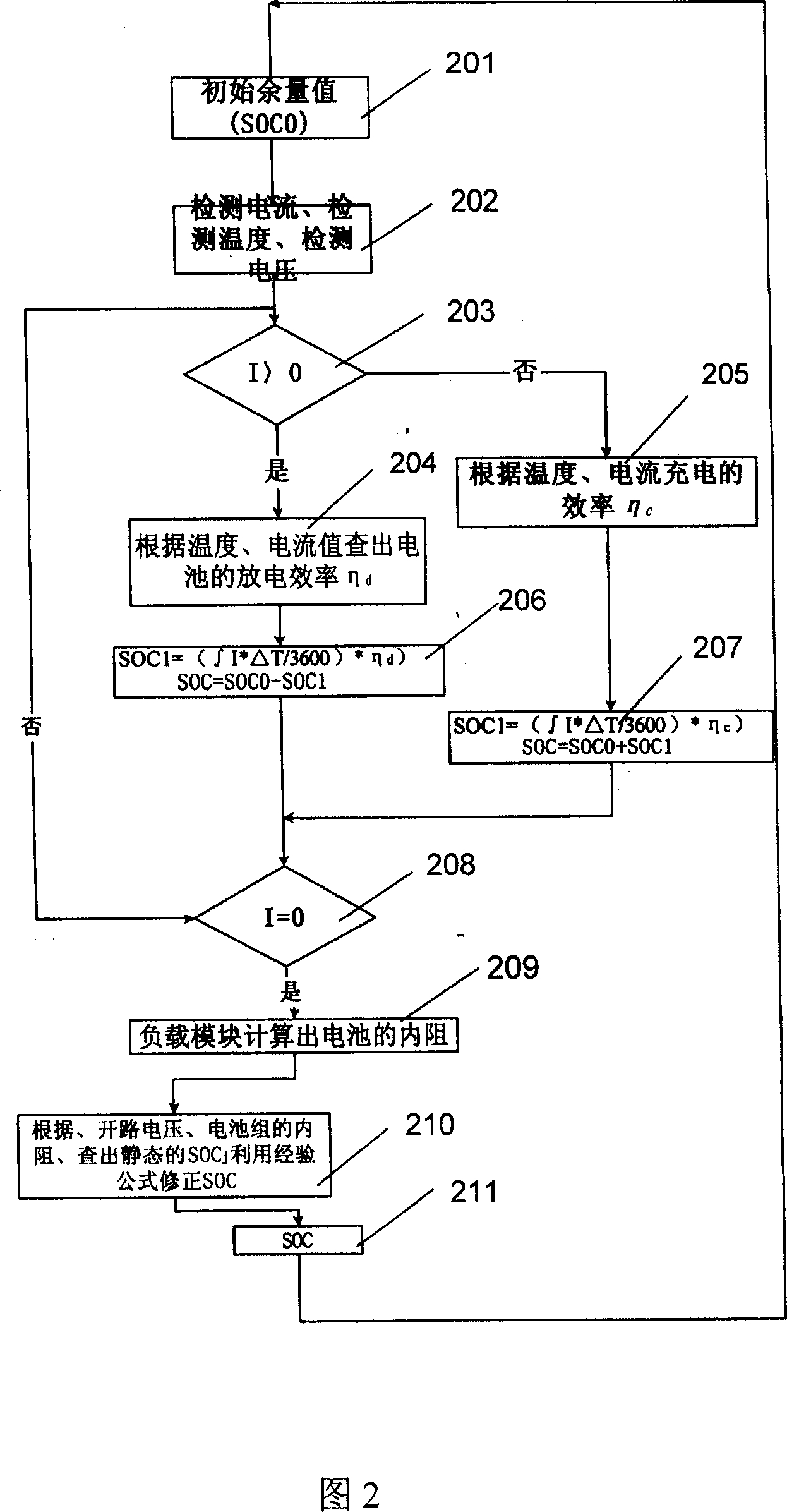
Detecting device and method for mixed power automobile battery remainder
InactiveCN1945345AExtended service lifeImprove accuracyElectric devicesElectrical testingElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical battery
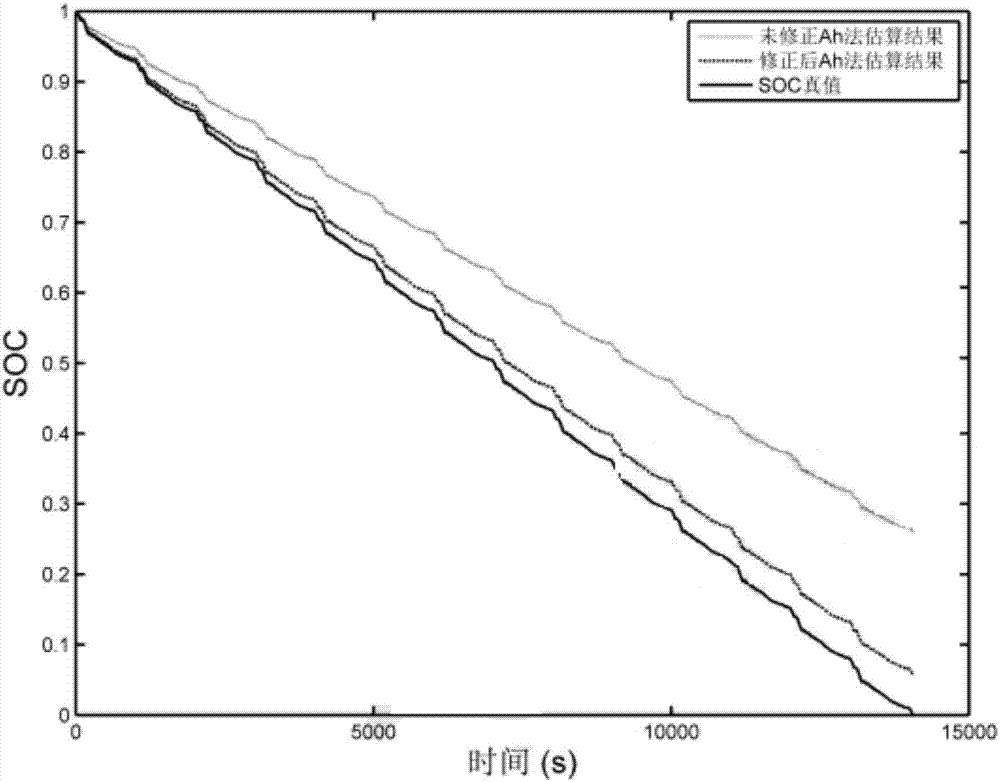
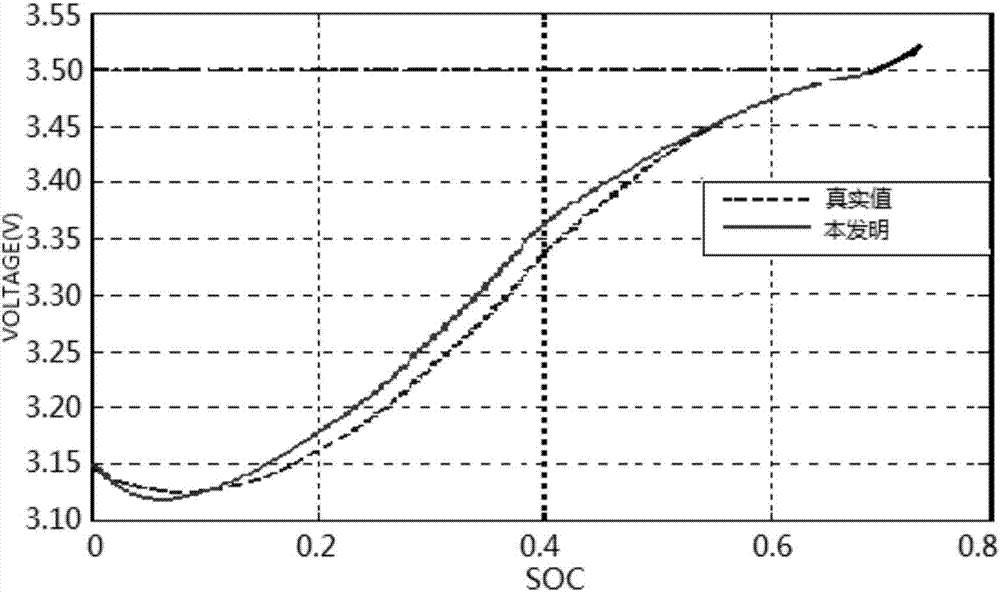
The present invention discloses device and method of detecting the battery remainder in mixed power automobile. Between the CPU and the battery, one load module is set for calculating the resistance value of the battery according to its voltage and current. The CPU calculates the capacity of the battery via integrating the current to the time and corrects the capacity by means of the voltage the voltage detecting circuit detects, the temperature the temperature detecting circuit detects, the resistance the load module calculates, and the empirical formula. The present invention has raised accuracy, and is favorable to reasonable utilization of battery and long service life of battery.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
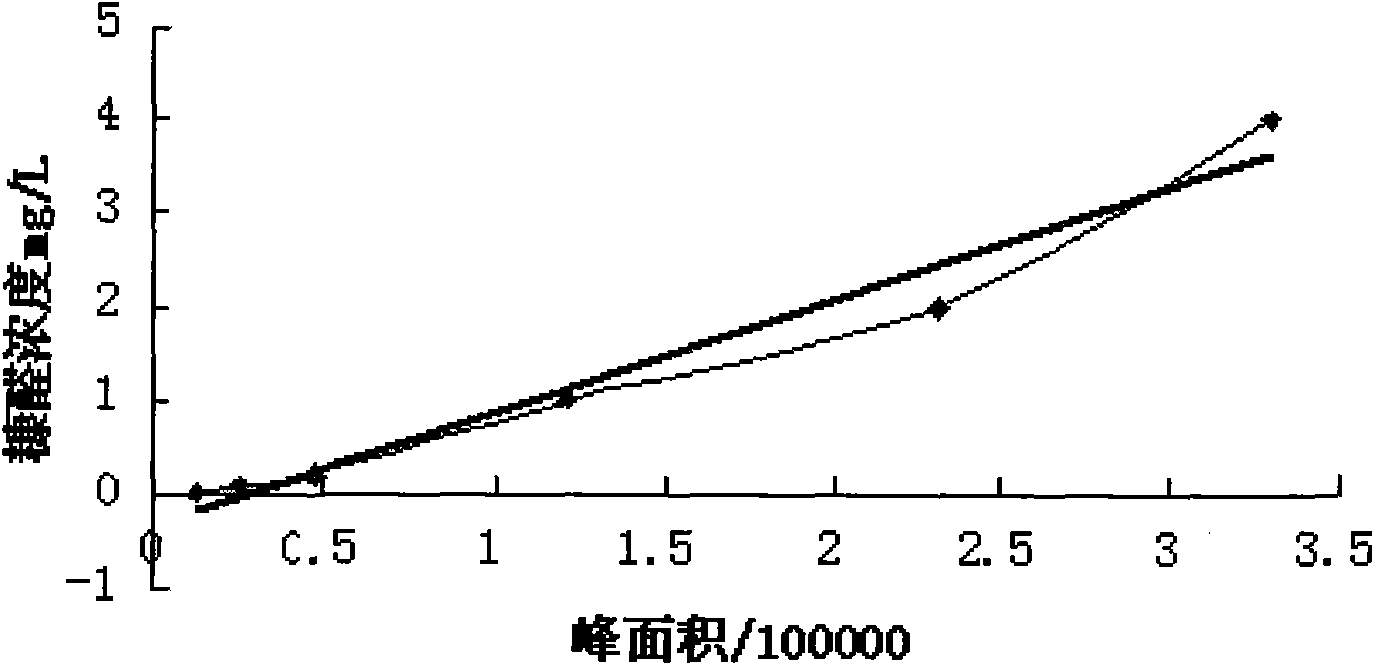
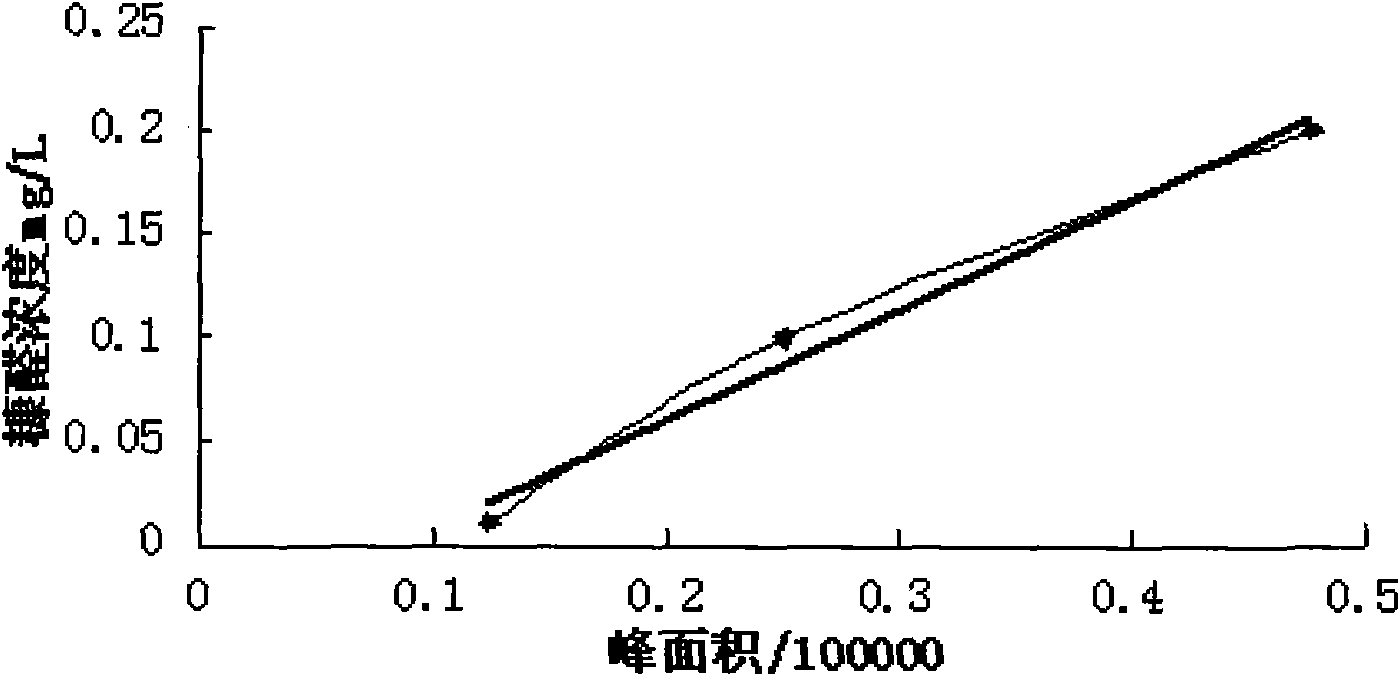
Judging method of solid insulating and aging degrees of transformer
InactiveCN101887094AEasy to operateNo power outageWeighing by removing componentComponent separationTransformerElectric network
The invention relates to a judging method of the solid insulating and aging degrees of a transformer, which sequentially comprises the following steps of: 1. preparing a gradient concentration standard solution of a furfural solution, carrying out liquid chromatographic detection, and making a standard curve I; 2. taking insulating paper samples in an actual electric network transformer, carrying out the liquid chromatographic detection, and obtaining the furfural concentration in each sample according to the standard curve I; 3. respectively measuring the water content H thereof by adopting the insulating paper samples in the step 2, computing the dry paper concentration C, additionally sampling, measuring the specific viscosity thereof, and computing the polymerization degree of the insulating paper samples according to a Martin empirical formula; 4. making a standard curve II by using the polymerization degree of insulating paper as an abscissa and using the logarithm of the furfural concentration as an ordinate; and 5. measuring the furfural concentration for an unknown sample, obtaining the polymerization degree of the insulating paper according to the standard curve II in the step 4, and judging the solid insulating and aging degrees of the transformer according to an IEC60450 standard. The method only needs to extract proper oil samples, has simple operation, does not need power failure, and is a quite practical method.
Owner:JIYUAN POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER
Instantaneous ultrasonic measurement of bladder volume
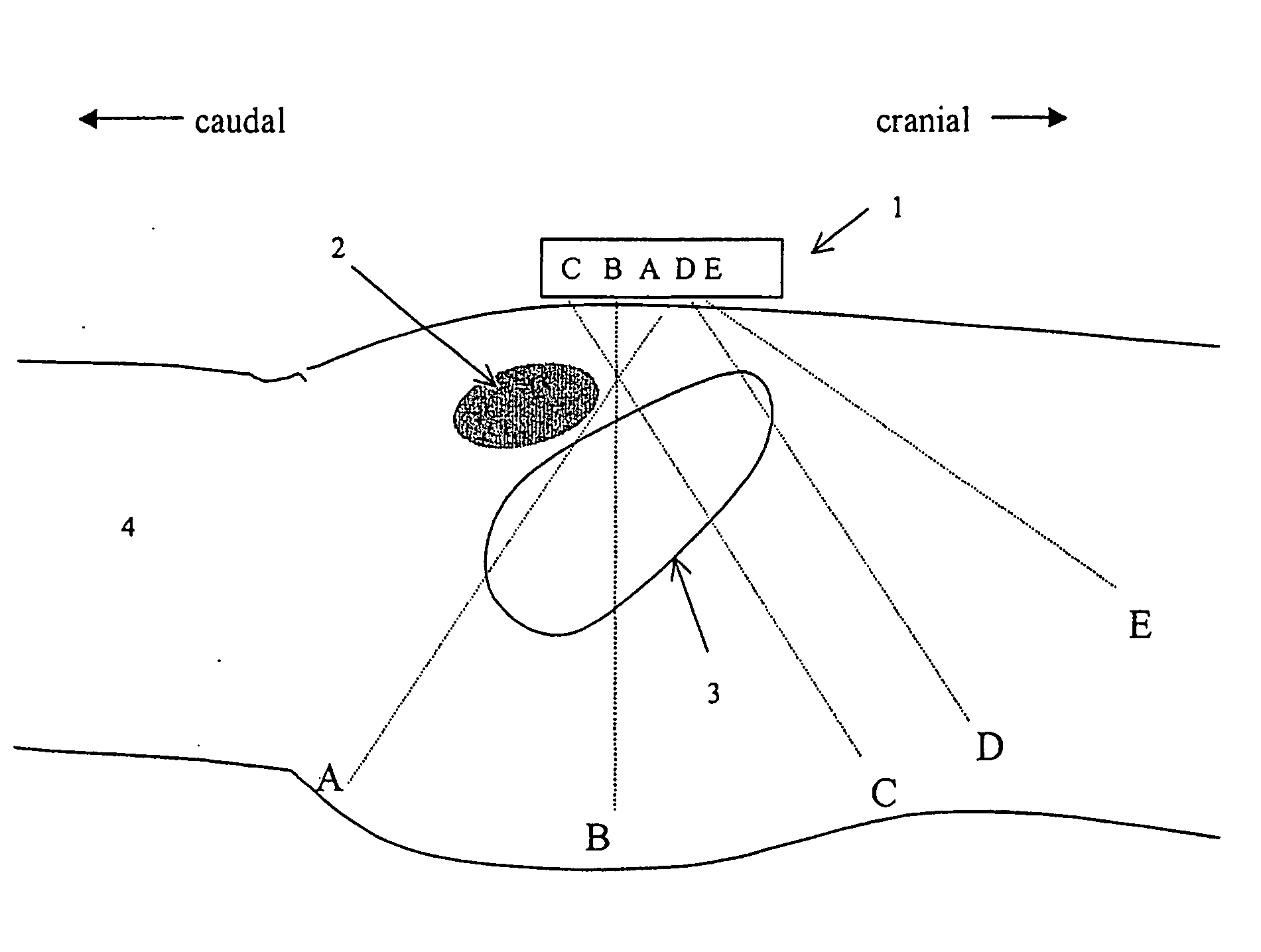
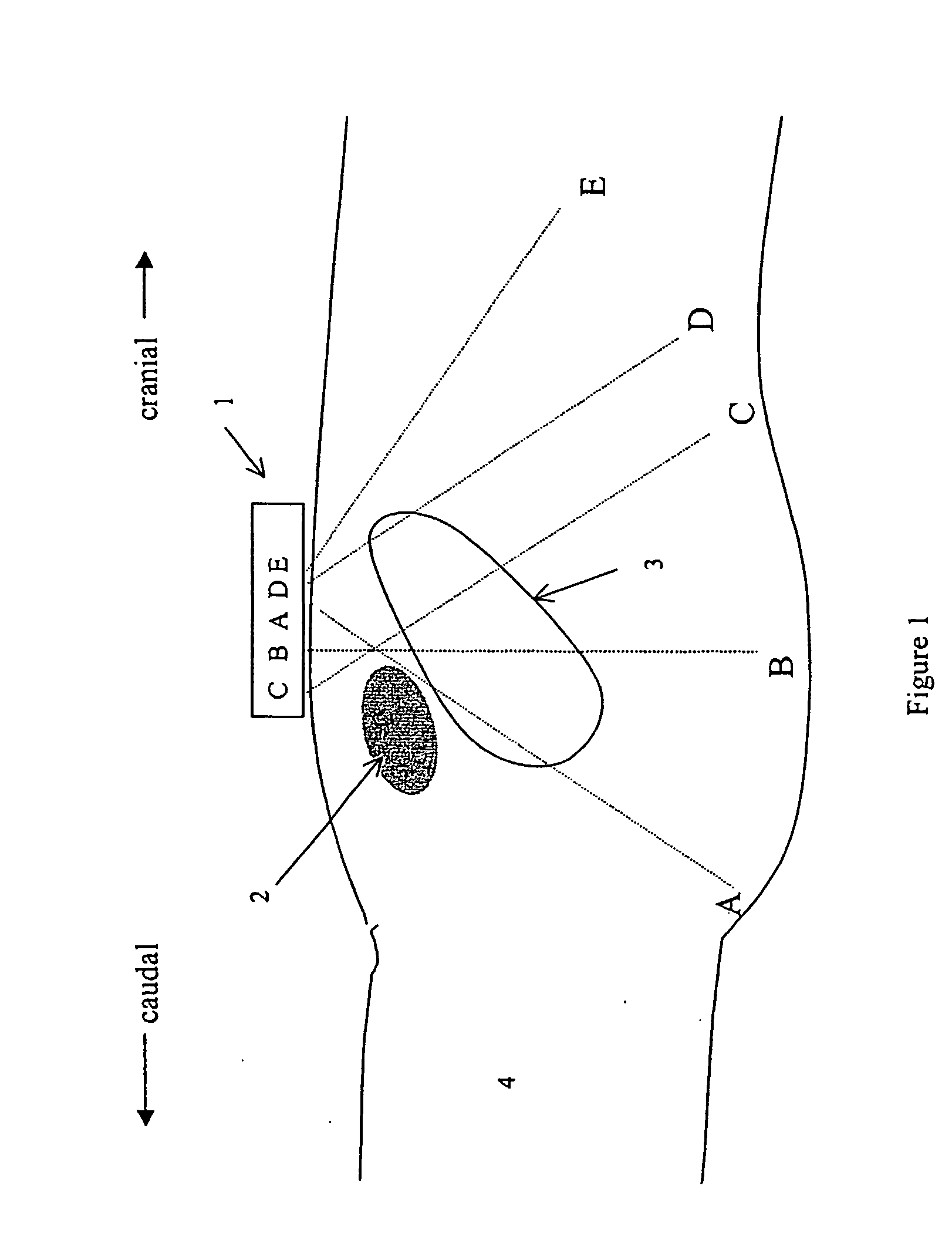
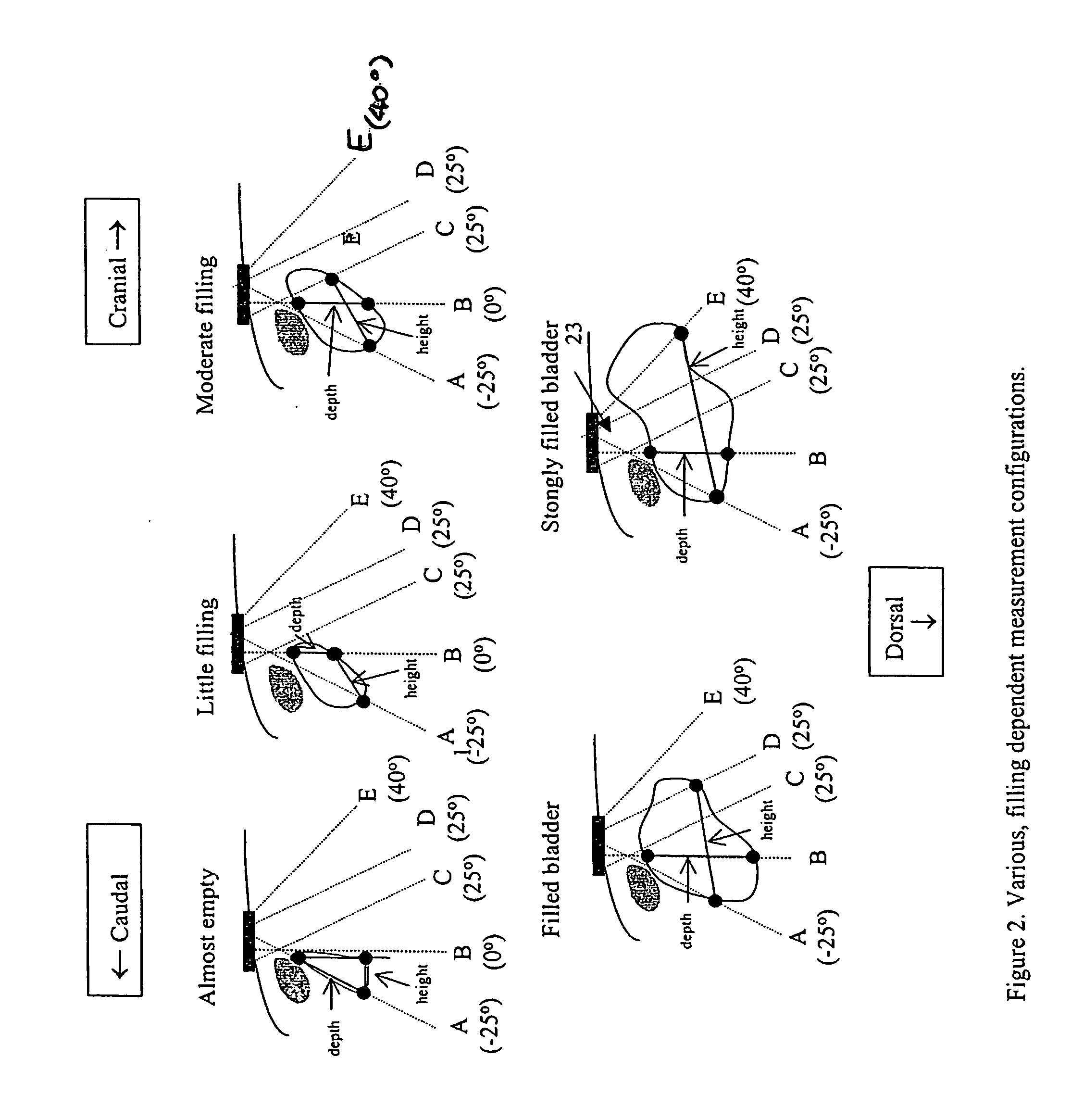
An apparatus and methods to quantify the volume of urine in a human bladder with a limited number of acoustic beams is disclosed. In a first version the apparatus is composed of a transducers assembly that transmits a plurality of narrow ultrasound beams in different directions towards the bladder and receives the returning ultrasound signals; a receiver detector for processing the returned signals; an analog-to-digital converter; a memory to store the digitized data and a volume display allowing to define the optimal position of the transducer assembly. The apparatus also includes a signal processing software that automatically determines the bladder Depth D and Height H and computes the volume of urine using an empirical formula corrected by specific, empirically measured, filling dependant correction factors. In a second version a single wide angle ultrasound beam transducer transmitting ultrasound signals at fundamental frequency is used to quantify the urine volume. Return signals originating from a depth beyond the usual position of the posterior wall depth of a filled bladder are analyzed for presence of higher harmonic signals which in turn are related to presence or absence of urine. Both methods or a combination thereof can be used us a simple warning device for presence of residual urine after voiding or indicate the presence of a critical bladder urine filling level.
Owner:VERATHON
Method for in-situ detection of aerosol particle concentration and detector thereof
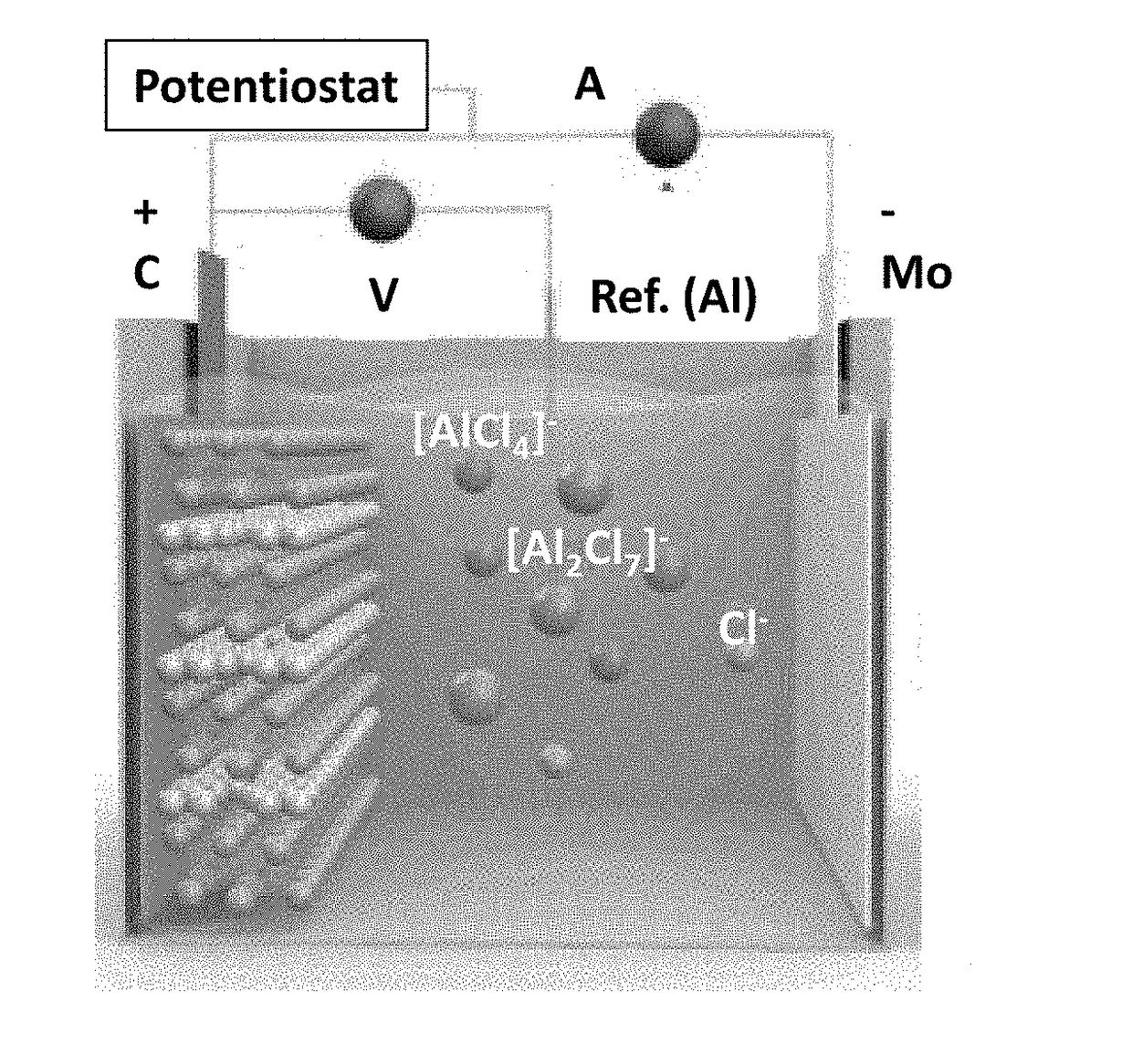
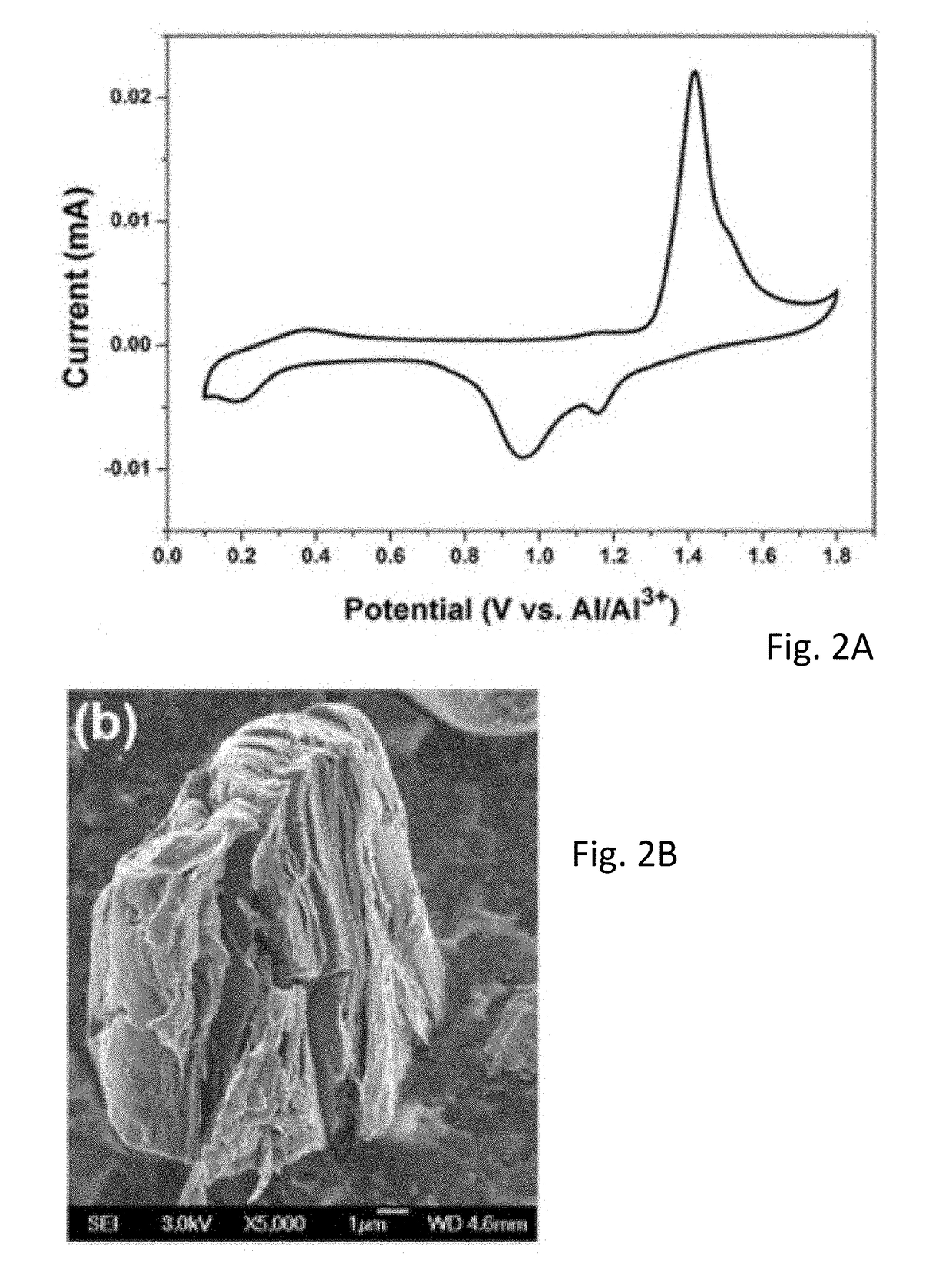
InactiveCN1837778ARapid and Sensitive DetectionIncreased sensitivityParticle suspension analysisMaterial resistanceHigh pressureEmpirical formula
This invention relates to a method for in-situ detection of aerosol particle concentration and detector thereof. <0}Wherein, putting the pipe-shaped probe with a positive / negative high voltage electrode metal wire for forming at least one corona field into the airflow with aerosol particle; forcing the gas flow the firmer field to let partial aerosol particles bring negative charge; in the corona field, depositing the charged particles on the positive electrode; detecting the current or voltage variation of the circuit connected with the positive electrode; comparing the detection data with standard or conventional result for scaling and the corresponding relation curve or empirical formula; finally, getting the particle concentration. This invention has wide application.
Owner:天津青碧科技有限公司
Lithium-Ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20090181296A1Safer chemistry characteristicMinimize the numberPrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureManganateSpinel
A lithium-ion battery includes a cathode that includes an active cathode material. The active cathode material includes a cathode mixture that includes a lithium cobaltate and a manganate spinel a manganate spinel represented by an empirical formula of Li(1+x1)(Mn1−y1A′y2)2−x2Oz1 or Li(1+x1)Mn2Oz1. The lithium cobaltate and the manganate spinel are in a weight ratio of lithium cobaltate:manganate spinel between about 0.9:0.1 to about 0.6:0.4. A lithium-ion battery pack employs a cathode that includes an active cathode material as described above. A method of forming a lithium-ion battery includes the steps of forming an active cathode material as described above; forming a cathode electrode with the active cathode material; and forming an anode electrode in electrical contact with the cathode via an electrolyte.
Owner:BOSTON POWER INC
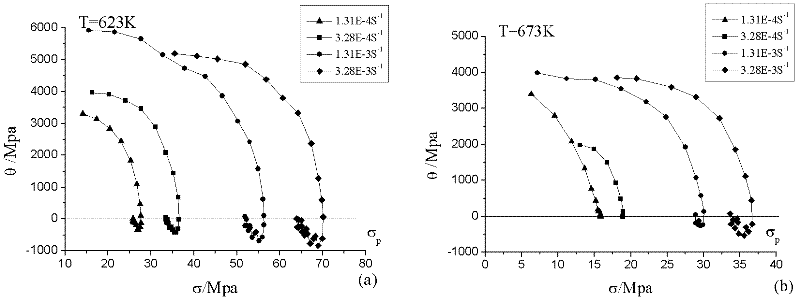
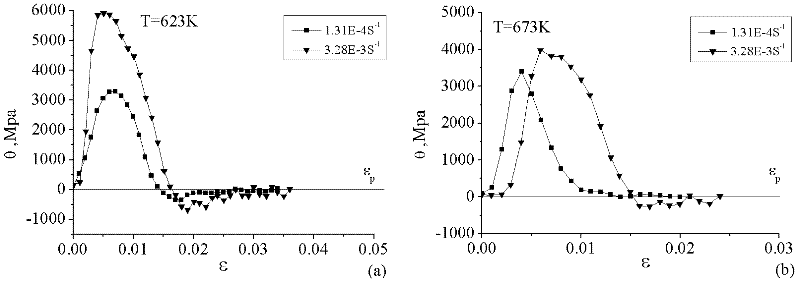
Method for establishing aluminium alloy dynamic recrystallization model by using true stress-true strain curve
InactiveCN102519801AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMathematical modelStress–strain curve
The invention discloses a method for establishing an aluminium alloy dynamic recrystallization model by using a true stress-true strain curve, belonging to the field of analyzing of material microstructures. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a hardening rate of a material by adopting the true stress-true strain curve obtained through a high-temperature tensile test, determining peak value strain, peak value stress and steady-state stress under different conditions by analyzing the change of the hardening rate, and establishing a peak value strain and critical strain mathematical model and a dynamic recrystallization volume fraction according to an empirical formula. The method disclosed by the invention overcomes the disadvantages of being lagging, time-consuming, incomplete and imprecise by using a metallographic method to research the recrystallization behaviour of the material. After being combined with finite element software, the method is capable of quantitatively analyzing the change condition of the dynamic recrystallization volume fraction of aluminium alloy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Cathode material for lithium rechargeable batteries
InactiveUS6855461B2Increase capacityImproved cyclabilityAluminium compoundsActive material electrodesManganeseOxygen
A crystal which can be employed as the active material of a lithium-based battery has an empirical formula of Lix1A2Ni1-y-zCoyBzOa, wherein “x1” is greater than about 0.1 and equal to or less than about 1.3, “x2,”“y” and “z” each is greater than about 0.0 and equal to or less than about 0.2, “a” is greater than about 1.5 and less than about 2.1, “A” is at least one element selected from the group consisting of barium, magnesium, calcium and strontium and “B” is at least one element selected from the group consisting of boron, aluminum, gallium, manganese, titanium, vanadium and zirconium. A method includes combining lithium, nickel, cobalt and at least one element “A” selected from the group consisting of barium, magnesium, calcium and strontium, has at least one element “B” selected from the group consisting of boron, aluminum, gallium, manganese, titanium, vanadium and zirconium, in the presence of oxygen, wherein the combined components have the relative ratio of Lix1:Ax2:Ni1-y-z:Coy:Bz, wherein “x1,”“x2,”“y” and “z” have the values given for the empirical formula shown above.
Owner:TIAX LLC
Magnesium Aluminum Titanate Crystal Structure and Method for Producing Same
InactiveUS20070224110A1Increase resistanceSmall coefficient of thermal expansionTitanium oxides/hydroxidesThermal expansionEmpirical formula
To provide an aluminum magnesium titanate crystal structure which can be used stably in variable high temperatures, because of its excellent heat resistance, thermal shock resistance, high thermal decomposition resistance and high mechanical property, and a process for its production. An aluminum magnesium titanate crystal structure, which is a solid solution wherein at least some of Al atoms in the surface layer of aluminum magnesium titanate crystal represented by the empirical formula MgxAl2(1−x)Ti(1+x)O5 (wherein 0.1≦x<1) are substituted with Si atoms, and which has a thermal expansion coefficient of from −6×10−6 (1 / K) to 6×10−6 (1 / K) in a range of from 50 is to 800° C. at a temperature raising rate of 20° C. / min, and a remaining ratio of aluminum magnesium titanate of at least 50%, when held in an atmosphere of 1,100° C. for 300 hours.
Owner:OHCERA CO LTD
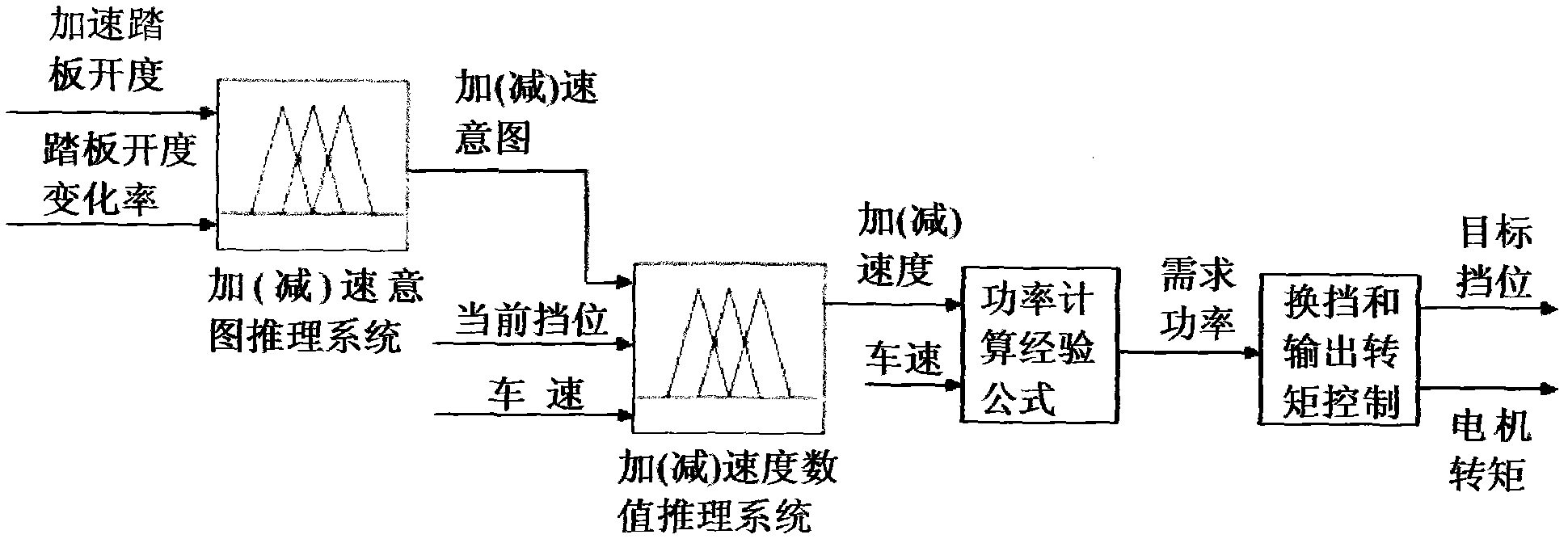
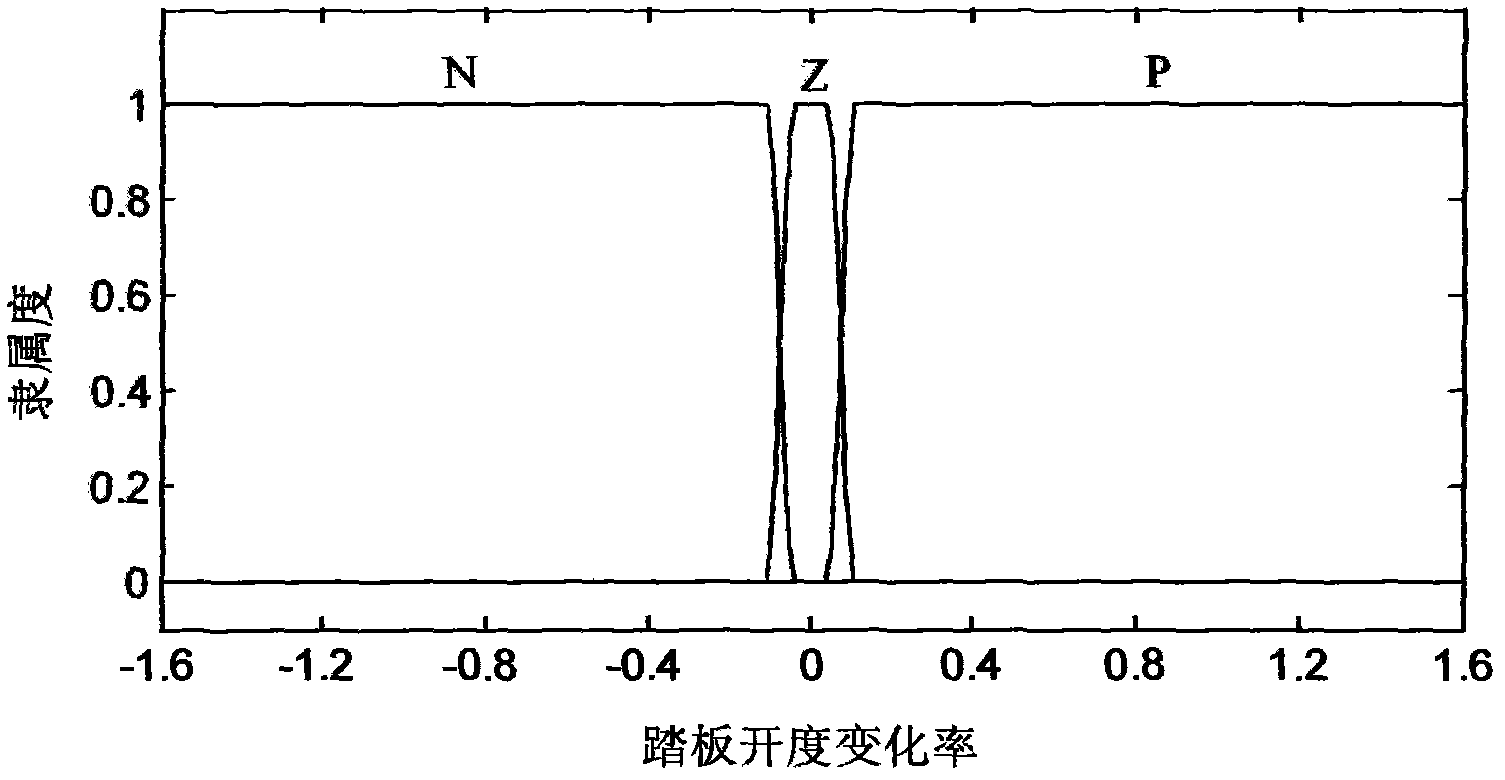
Control method of transmission gear and motor torque of electric vehicle
InactiveCN102275527AGuaranteed power demandReduce lossSpeed controllerElectric energy managementElectric vehicleControl theory
A method for controlling the transmission gear and motor torque of an electric vehicle. The method utilizes fuzzy control theory to identify the driver's expected acceleration (deceleration) speed during acceleration and coasting according to the opening of the accelerator pedal, the rate of change of the opening of the accelerator pedal, the current gear and the change of the vehicle speed. According to the empirical formula, the required power at the output end of the motor is calculated. Based on the efficiency graph of the motor, the current gear and the required power, the target gear of the transmission and the output torque of the motor are determined with the goal of maximizing the working efficiency of the motor under the premise of meeting the vehicle power demand. Under the premise of ensuring the power demand of the vehicle, the method can make the motor work in the theoretical highest efficiency zone and reduce the electric energy loss of the whole vehicle.
Owner:杨伟斌
Thermal network modeling method applied to electric spindle steady temperature field
ActiveCN102867088AA Method for Accurate Thermal Boundary Condition DescriptionAccurate calculationAerodynamics improvementSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelPhysical model
The invention discloses a thermal network modeling method applied to an electric spindle steady temperature field. The method comprises the following steps of (1) building an electric spindle axisymmetric two-dimensional model; (2) building an equivalent thermal network of an axis; (3) calculating the overall heating value of a bearing and a motor, and distributing the heat to heating nodes; (4) according to heat transfer theory empirical formulas under different radiation conditions, calculating a convective heat transfer coefficient for heat exchange between a boundary node and fluid; (5) equalizing heat transfer between the nodes into ideal geometric heat transfer, obtaining conduction heat resistance of each part and boundary thermal-convection resistance, and building a heat transfer physical model; and (6) building a mathematical model and selecting a solution algorithm. A thermal network method is applied to a high-speed main shaft system with two heat sources, i.e. the bearing and the motor, and a complex convective heat exchange boundary, so that the difficulty in solving the characteristic temperature of each part of a complex assembling body of the main shaft is reduced. Compared with the method of solving a heat transfer differential equation, the thermal network modeling method is a quick and accurate steady temperature field calculation method.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Process for synthesizing metal oxides and metal oxide having perovskite or perovskite-like crystal structure
InactiveCN1315920ALarge specific surface areaSimple methodNanotechOxide/hydroxide preparationHigh densityLattice defects
Perovskite-type structure compounds having the general empirical formula ABO3 are prepared by a process comprising subjecting a mixture of starting powders formulated to contain the components represented by A and B in the formula to a high energy milling sufficient to induce chemical reaction of the components and thereby synthesize a mechanically-alloyed powder comprising the perovskite in the form of nanostructural particles. The process according to the present invention is simple, efficient, not expensive and does not require any heating step for producing a perovskite that may easily show a very high specific surface area. Another advantage is that the perovskite obtained according to the present invention also has a high density of lattice defects thereby showing a higher catalytic activity, a characteristic which is highly desirable in their eventual application as catalysts and electronic conductors.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
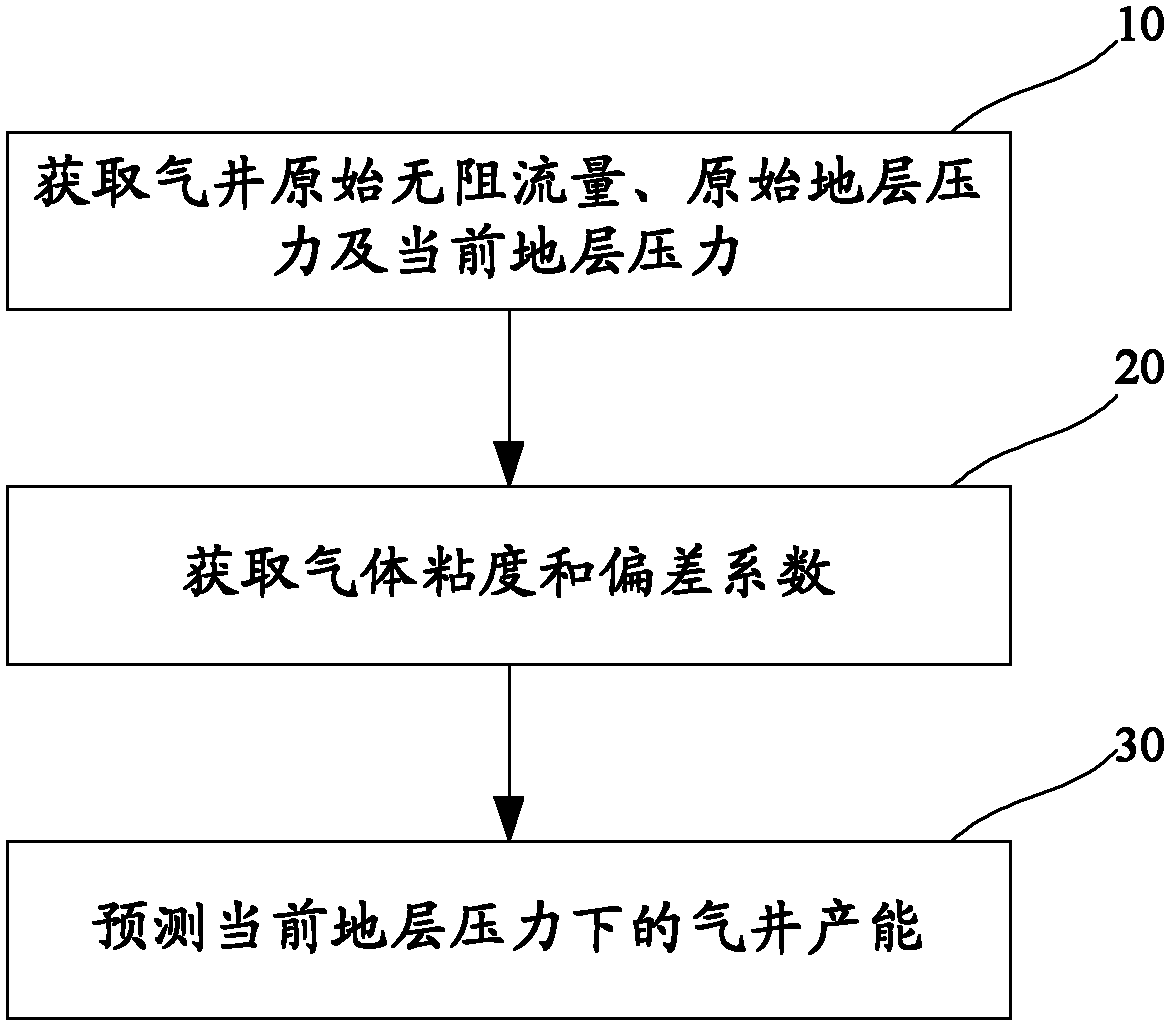
Dynamic gas well productivity forecasting method
ActiveCN102509179AThe evaluation result is accurateEvaluation results are reliableForecastingDynamic methodPredictive methods
The invention discloses a dynamic gas well productivity forecasting method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the initial open-flow potential qAOFi, initial formation pressure pi and current formation pressure pm of the gas well; obtaining the gas viscosity mu g and the deviation factor z; and forecasting the gas well productivity under the current formation pressure according to the obtained parameters. Starting with the theoretical formula of the gas well yield, the dynamic method for forecasting productivity in the gas well production process is provided in combination with the relevant empirical formulas on the premise of certain assumptions. The method has the following beneficial effects: the influence caused by formation pressure variation in the conventional productivity evaluation methods is eliminated; the evaluation results are more accurate and reliable; and application proves that the method is applicable, simple and convenient, repeated well testing is not needed, lots of manpower and money can be saved and the method has greater practical value and economic value.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Catalyst for producing unsaturated nitrile
InactiveUS6479691B1High selectivityGood physical propertiesCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationAtomic groupCerium
A catalyst composition represented by the following empirical formula which is useful in production of unsaturated nitrites by ammoxidation:wherein F represents at least one element selected from the group consisting of zirconium, lanthanum and cerium, G represents at least one element selected from the group consisting of magnesium, cobalt, manganese and zinc, H represents at least one element selected from the group consisting of vanadium, niobium, tantalum and tungsten, x represents at least one element selected from the group consisting of phosphorus, boron, and tellurium, Y represents at least one element selected from the group consisting of lithium, sodium, rubidium and cesium, the suffixes a-k, x and y represent a ratio of atoms or atomic groups, and a=0.1-3, b=0.3-15, c=0-20, d=3-8, e=0.2-2, f=0.05-1, e / f>1, g=0-5, h=0-3, k=0.1-1, x=0-3, y=0-1, i is the number of oxygen produced by bonding of the above respective components, and j=0-100.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Cross-scale high-precision dynamic crop growth monitoring and yield assessment method based on high-resolution remote sensing data and a crop model
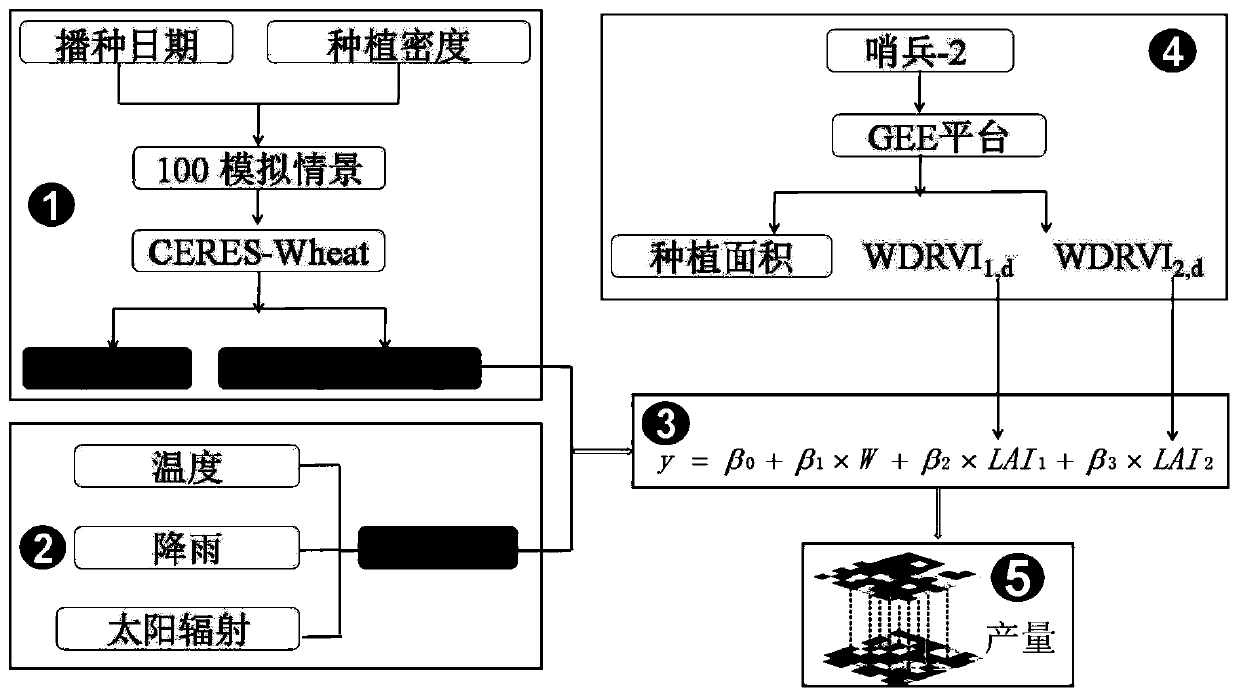
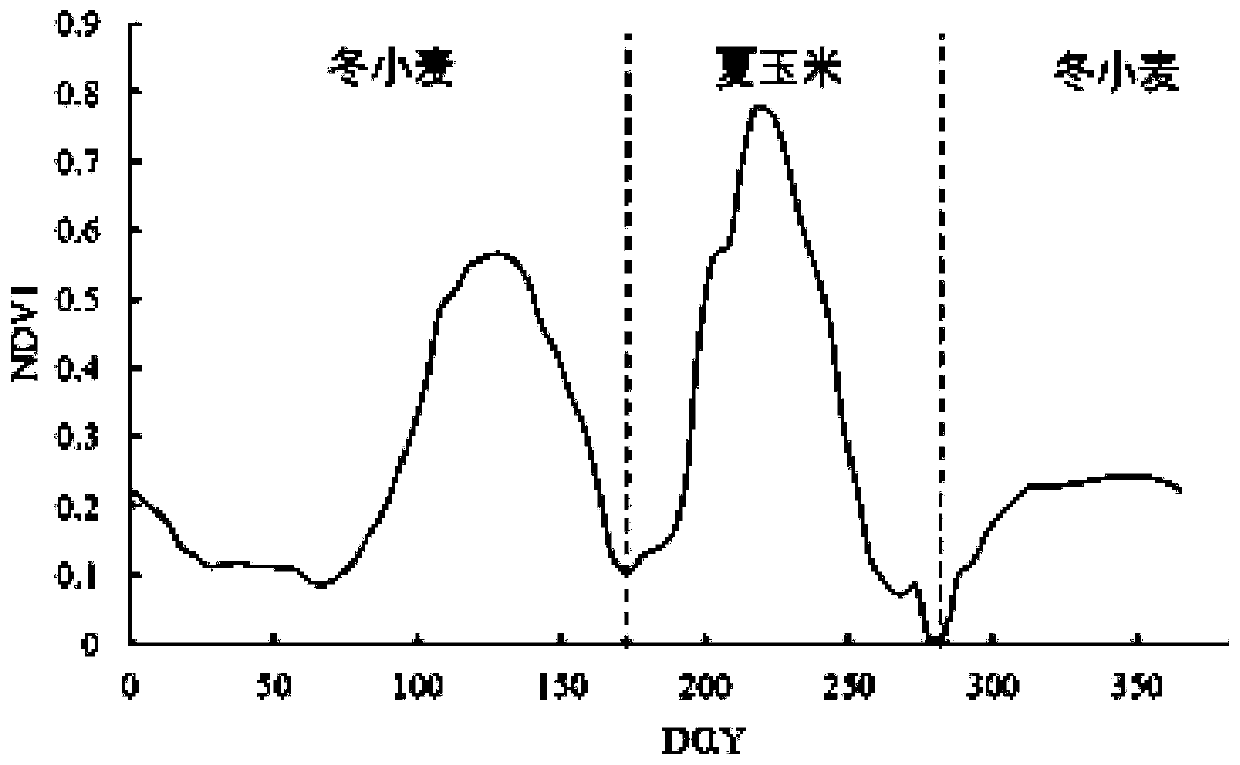
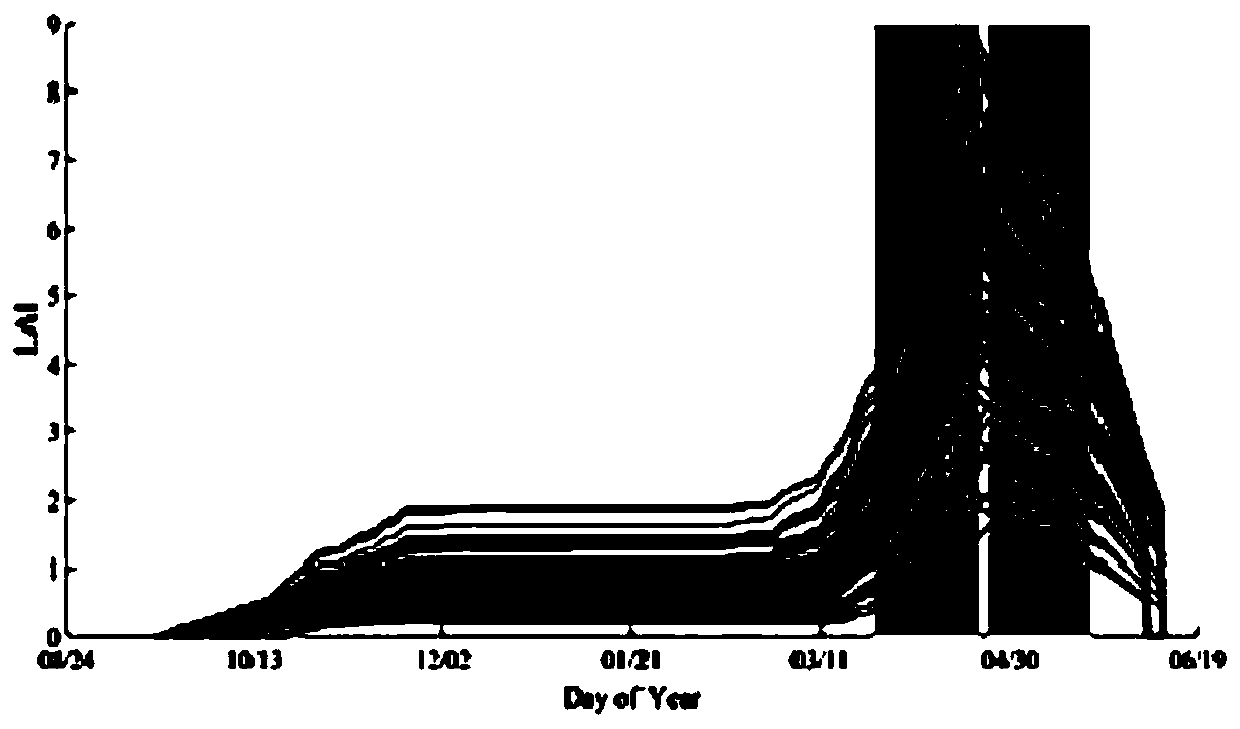
ActiveCN109829234AEasy to operateStrong space application abilityData processing applicationsComplex mathematical operationsNODALVegetation
The invention discloses a cross-scale high-precision dynamic crop growth monitoring and yield assessment method based on high-resolution satellite remote sensing data and a crop model. The method comprises the steps of achieving localization of the model is achieved; performing spatial matching on the remote sensing data and the ground data by using a GEE platform; designing a plurality of simulation scenes; dividing the growth period of the crops into a front time window and a rear time window by taking the green returning period as a node, and calculating various meteorological factors in the whole growth period; constructing a regression equation, and establishing a regression equation of each day in all growth periods; Extracting the maximum values of the satellite remote sensing observation vegetation indexes of two time windows before and after each year and corresponding dates thereof pixel by pixel, and converting the extracted maximum values of the vegetation indexes into independent variables LAI of a regression equation through an empirical formula; And taking the observation dates of the two time windows before and after extraction as references, carrying out pixel-by-pixel calculation by utilizing a regression equation corresponding to the combination date, and obtaining the crop simulation yield after operation on all pixels is completed.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Control system for lithium ion battery of electric car
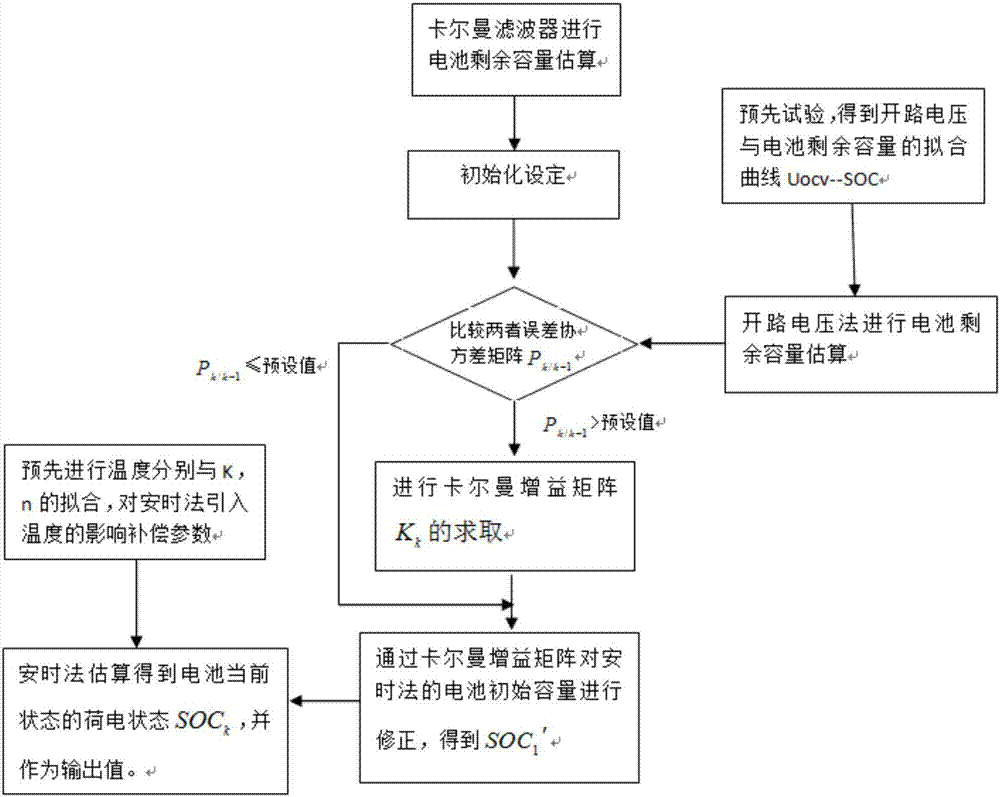
ActiveCN107037366AReduce estimation errorReduce mistakesElectrical testingMathematical modelSafety control
Owner:JIANGSU FUWEI ENERGY CO LTD
State monitoring device of complex electromechanical system for flow industry and method
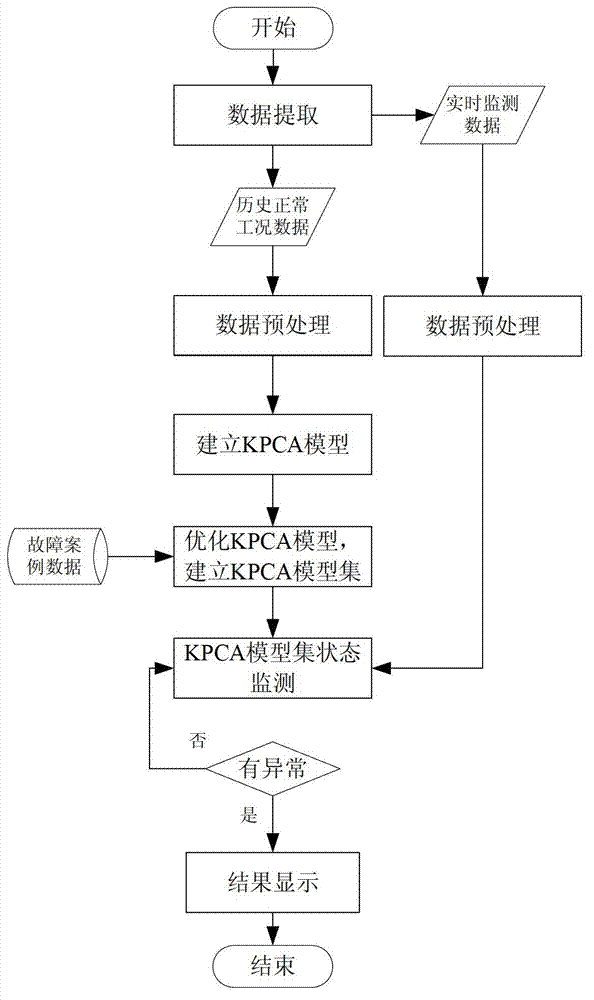
ActiveCN102736546AEasy fault detectionTimely and accurate monitoringProgramme controlComputer controlKernel principal component analysisIndustrial systems
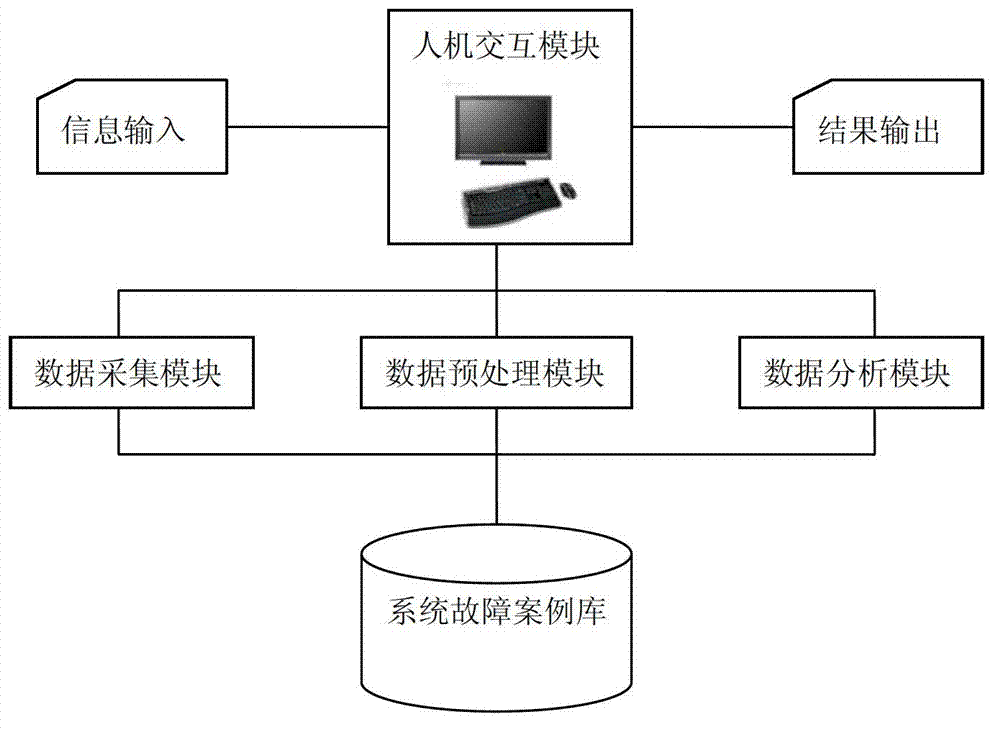
The invention relates to a state monitoring device of a complex electromechanical system for a flow industry and a method. The device comprises a man-machine interaction module, a data collecting module, a data preprocessing module, a data analyzing module and a failure case library. According to the device and the method provided by the invention, whether the system fails or is in abnormal states or not can be monitored and early warming for tripping accidents or other accidents of the flow industry system can be made. Meanwhile, a KPCA (Kernel Principal Component Analysis) method with double parameter optimization is used to overcome the deficiency that parameters are selected by empirical formula in conventional KPCA methods, thereby improving the state monitoring ability. Furthermore, the failure case database is adequately used in the historical production process so that failures of the system can be monitored more immediately and accurately.
Owner:HANGZHOU HOLLYSYS AUTOMATION
Electric blower
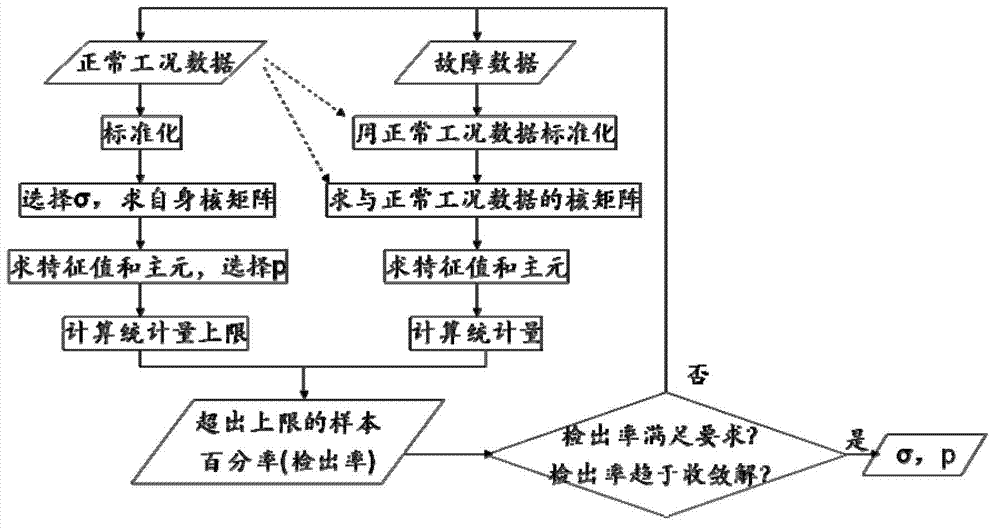
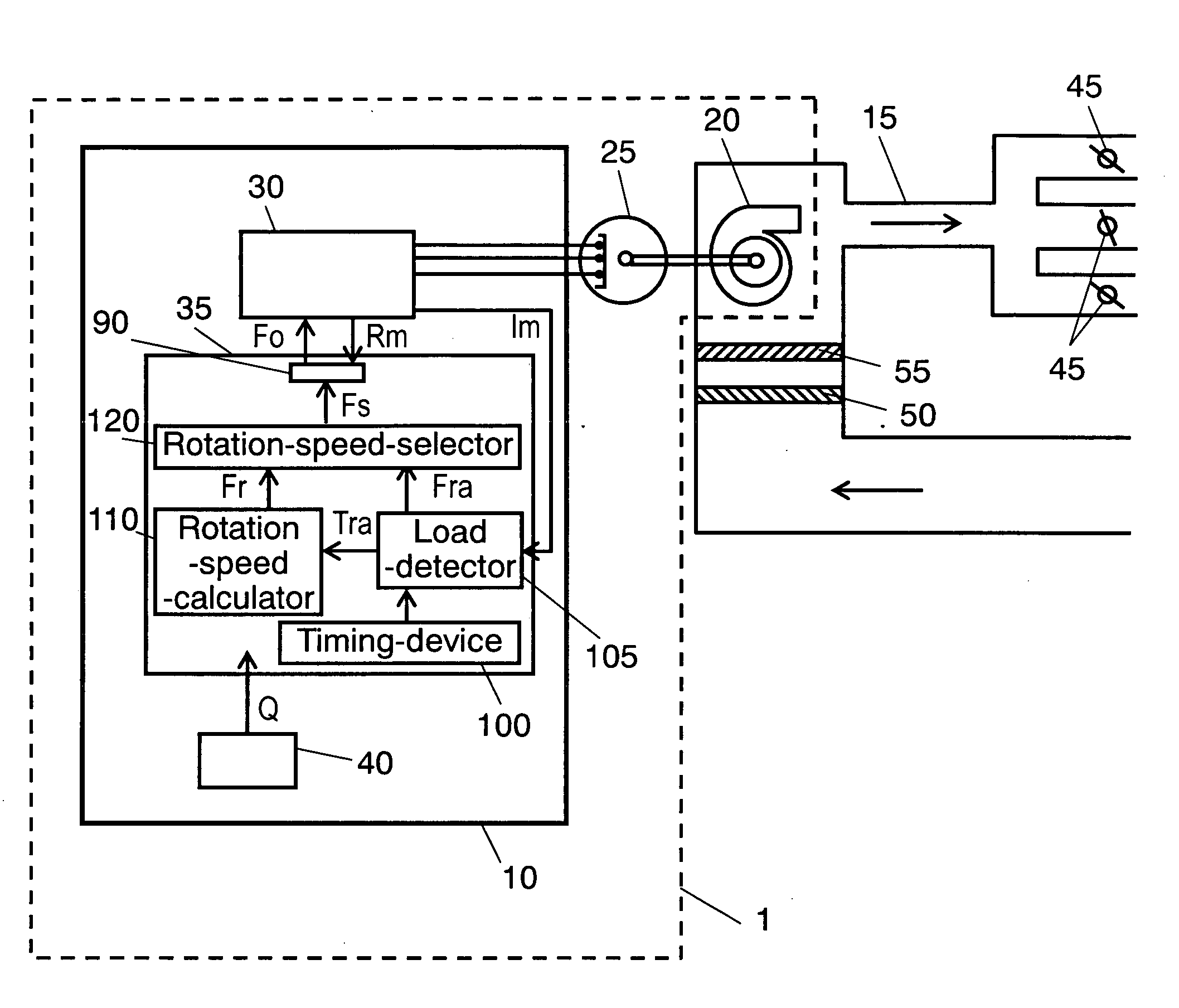
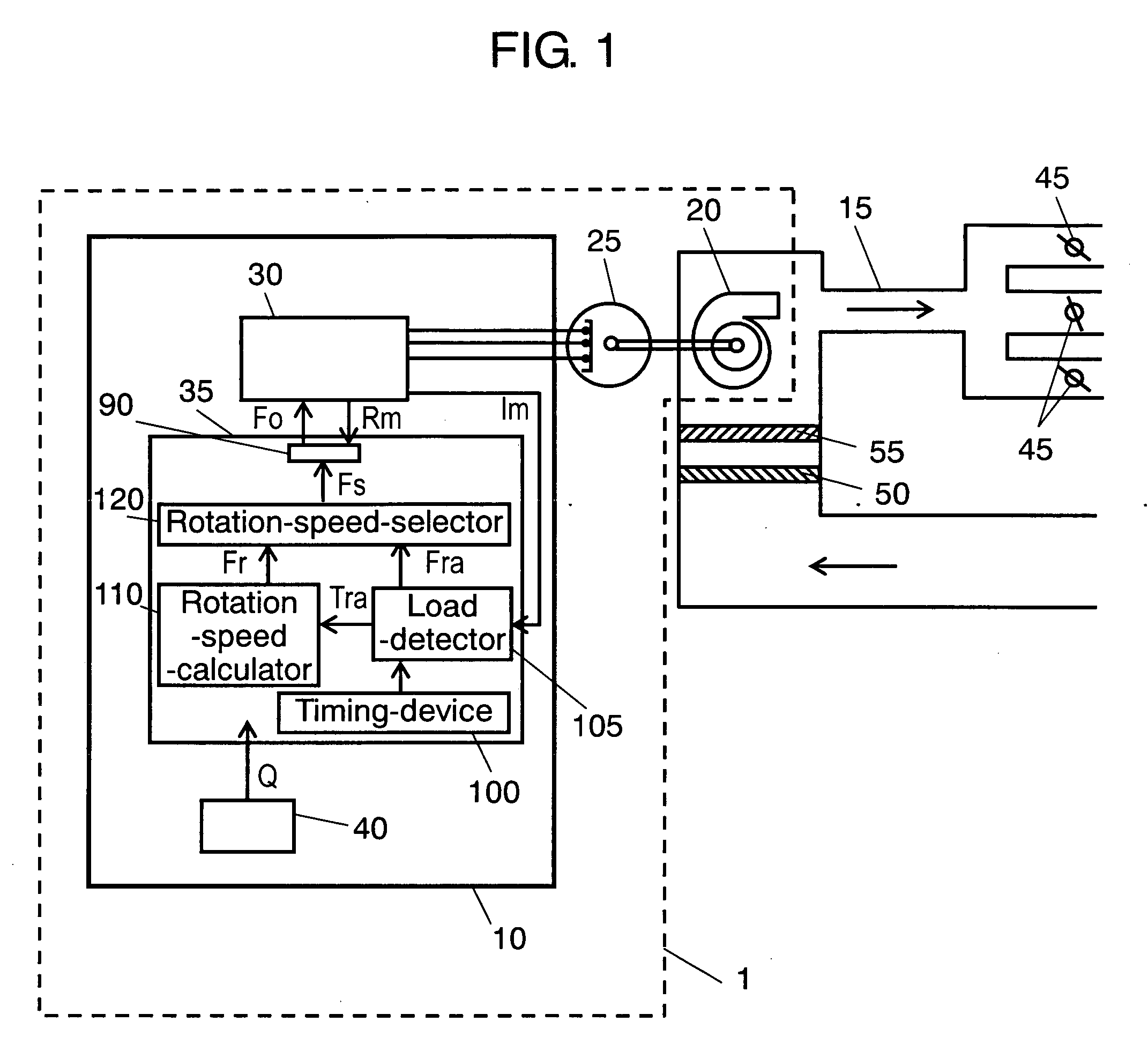
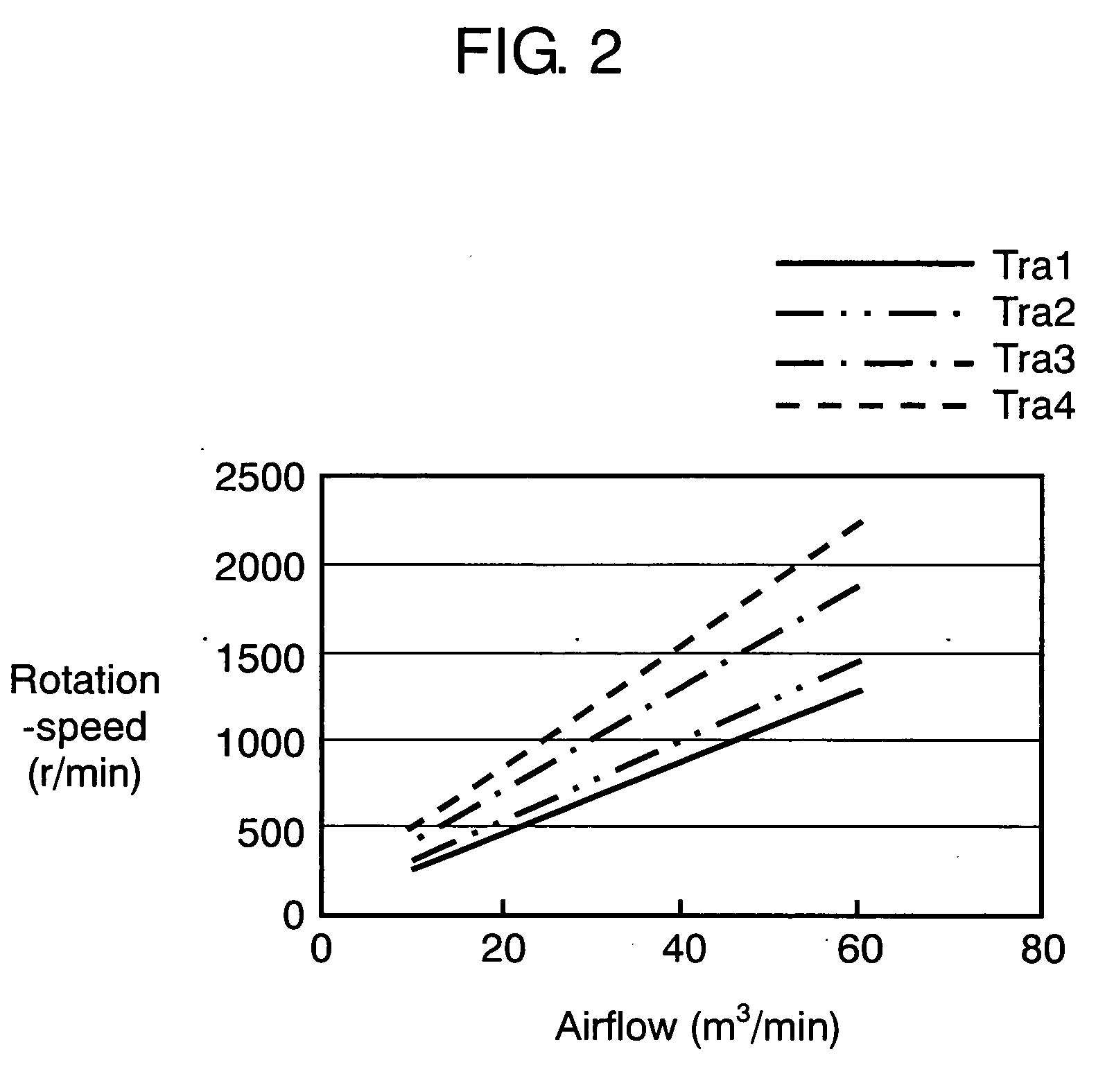
InactiveUS20060099084A1Guaranteed uptimeDischarging the amount of target airflowSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringEmpirical formula
The present invention provides an electric blower that performs: measuring an amount of airflow against a fan rotation speed of the blower with a load magnitude detected previously; determining an empirical formula to calculate a fan rotation speed to discharge an amount of target airflow in response to the magnitude of a load of the blower according to the data obtained from the above measurement repeated a plurality of times varying the magnitude of the load on the blower; operating, firstly in practice, the blower to detect the magnitude of the load of the blower, then to calculate the fan rotation speed to discharge the amount of target airflow using the empirical formula; and then changing the blower operation to the fan rotation speed given by the calculation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Microporous crystalline zeolite material (zeolite ITQ-22), synthesis method thereof and use of same as a catalyst
InactiveUS7449169B2Eliminate occlusionIncrease contentOxygen-containing compound preparationAluminium compoundsSynthesis methodsOxidation state
The present invention refers to a microporous crystalline material of zeolitic nature (ITQ-22) which, in the calcined state, has the empirical formula x(M1 / nX02):yYO2:zR:wH20whereinM is H+ or at least one inorganic cation of charge +n;X is at least one chemical element of oxidation state +3, preferably selected from the group consisting of Al, Ga, B, Fe and Cr;Y is at least one chemical element with oxidation state +4 other than Si and Ge, preferably selected from the group consisting of Ti, Sn and V;x has a value less than 0.2, preferably less than 0.1 and can take the value zero,y has a value less than 0.1, preferably less than 0.05 and can take the value zero,z has a value less than 0.8, preferably between 0.005 and 0.5 and can take the value zero,with a characteristic X-ray diffraction pattern, to the method of preparation and to the use of the material in separation and transformation processes of organic compounds.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
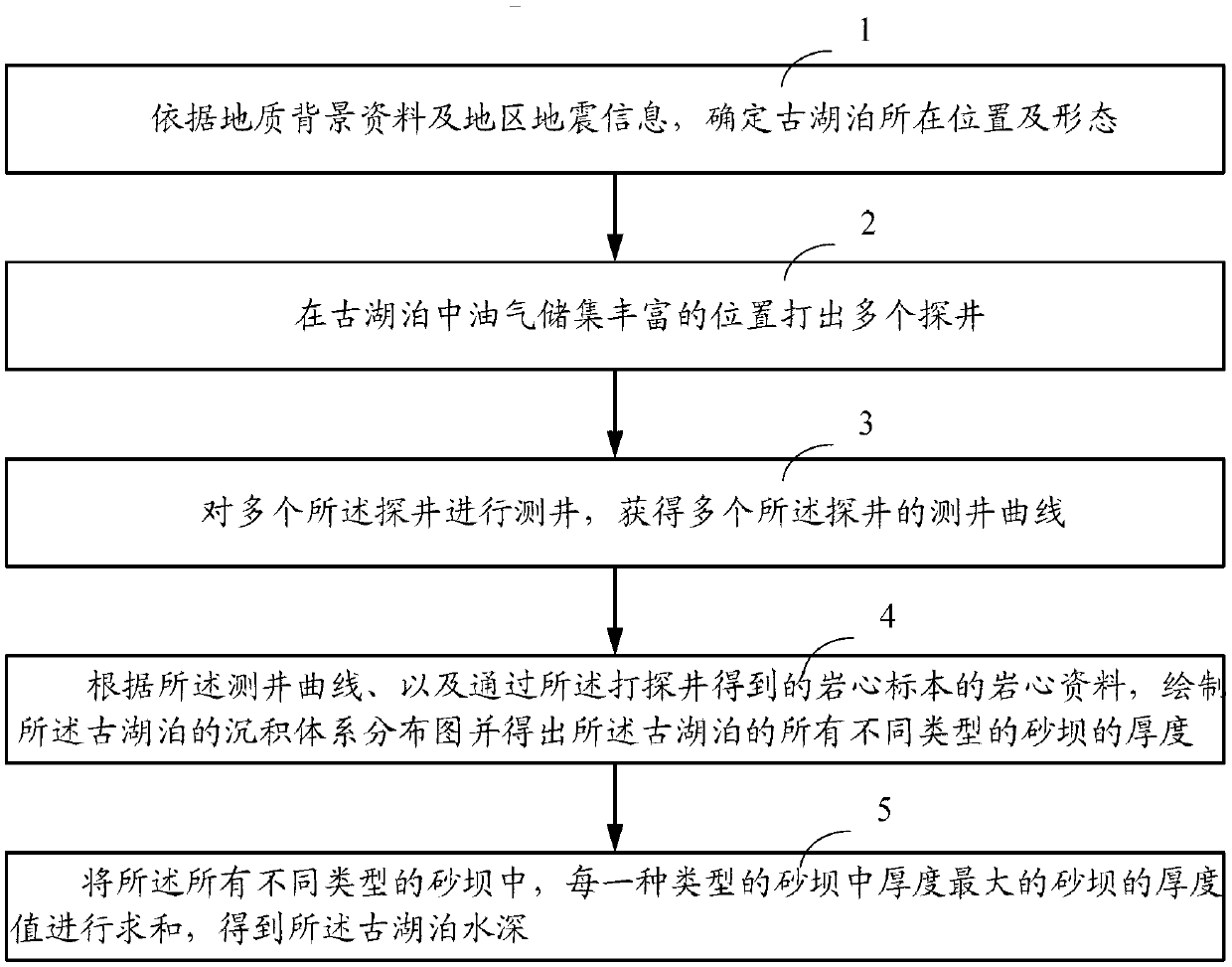
Ancient lake depth measuring method
InactiveCN103345001ASolve computationally complex problemsAvoid choosing random questionsGeological measurementsRock coreWell logging
The invention relates to the field of mining, in particular to an ancient lake depth measuring method. The method includes the steps of (1) confirming the position and the shape of an ancient lake according to geological background information and regional earthquake information, (2) drilling a plurality of exploratory wells in the position where oil reservoir is rich in the ancient lake, (3) detecting the exploratory wells, and obtaining well logging curves of the exploratory wells, (4) drawing a sedimentary system distribution map of the ancient lake according to the well logging curves and rock core information of rock core specimens obtained from the drilled exploratory wells, and obtaining the thicknesses of sandbanks of different types in the ancient lake, and (5) summing the thickness values of the sandbanks with the maximum thickness in all types of the sandbanks, and obtaining the depth of the ancient lake. According to the method, in measuring of the depth of the ancient lake, the number of transported sediments does not need to be calculated, procedures are few, calculation is simple, the problem that the calculation is complex by means of a ripple mark empirical formula method is solved, and the problem that randomness of parameter selection in the ripple mark empirical formula method is large is avoided.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
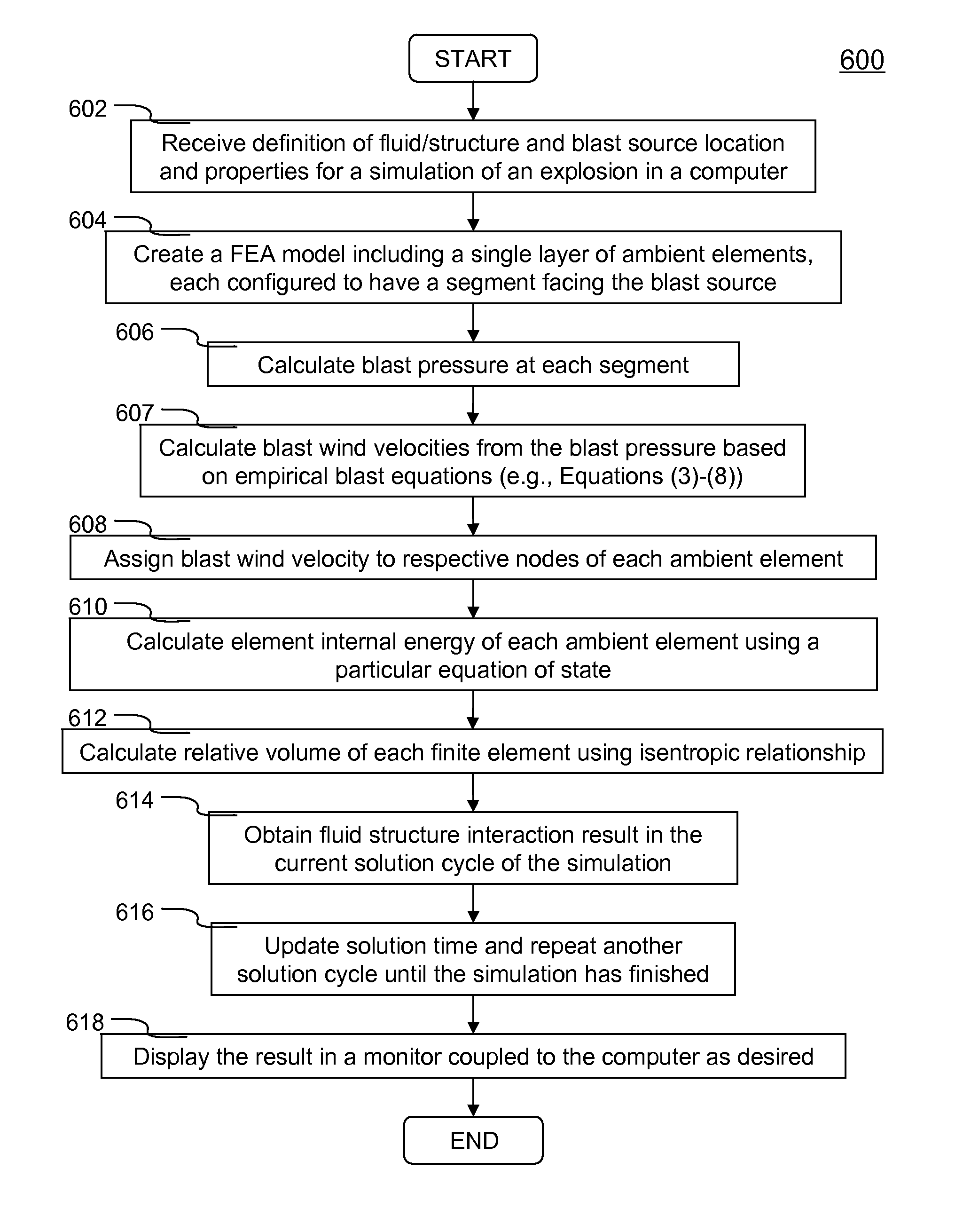
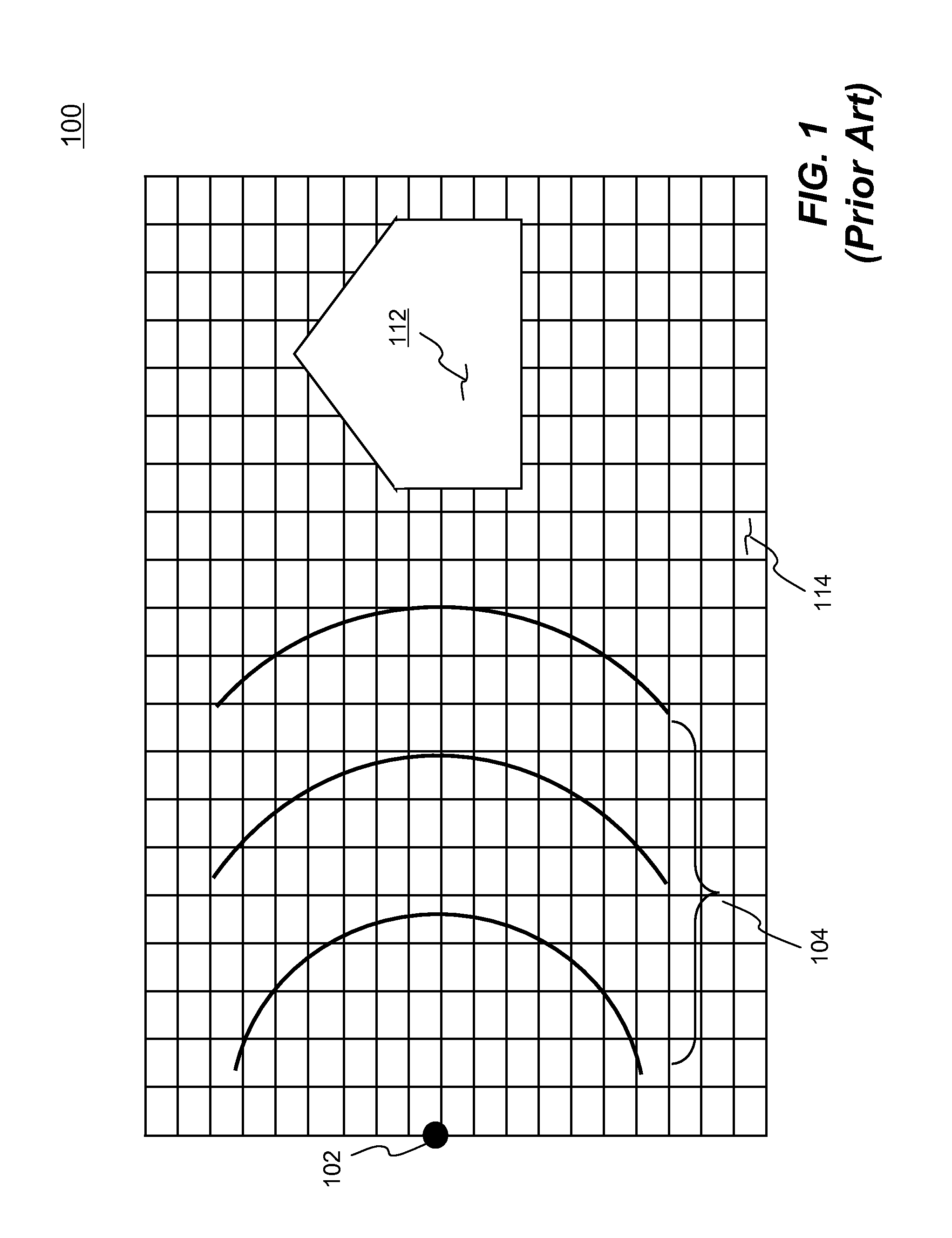
Explosion Simulation in Finite Element Analysis
ActiveUS20100256957A1Reduce computing timeImprove userComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationProduction rateElement analysis
Systems and methods of simulating an explosion in time-marching finite element analysis are disclosed in the present invention. According to one aspect, a method is configured for increasing user (e.g., engineer or scientist) productivity by reducing computation time of simulating fluid-structure interaction due to an explosion. The method comprises a creation of a finite element analysis model that includes structure, surrounding fluid, a blast source of the explosion and a single layer of ambient elements each having a segment representing a boundary of the fluid facing the blast source. Each ambient element is associated with a particular finite element representing the fluid at the boundary. The ambient elements are configured to be situated between the blast source and the structure such that the simulation can be carried on a set of boundary conditions specified thereon. The boundary conditions comprise a set of nodal velocities that are determined from the empirical formula (e.g., Friedlander equation).
Owner:ANSYS
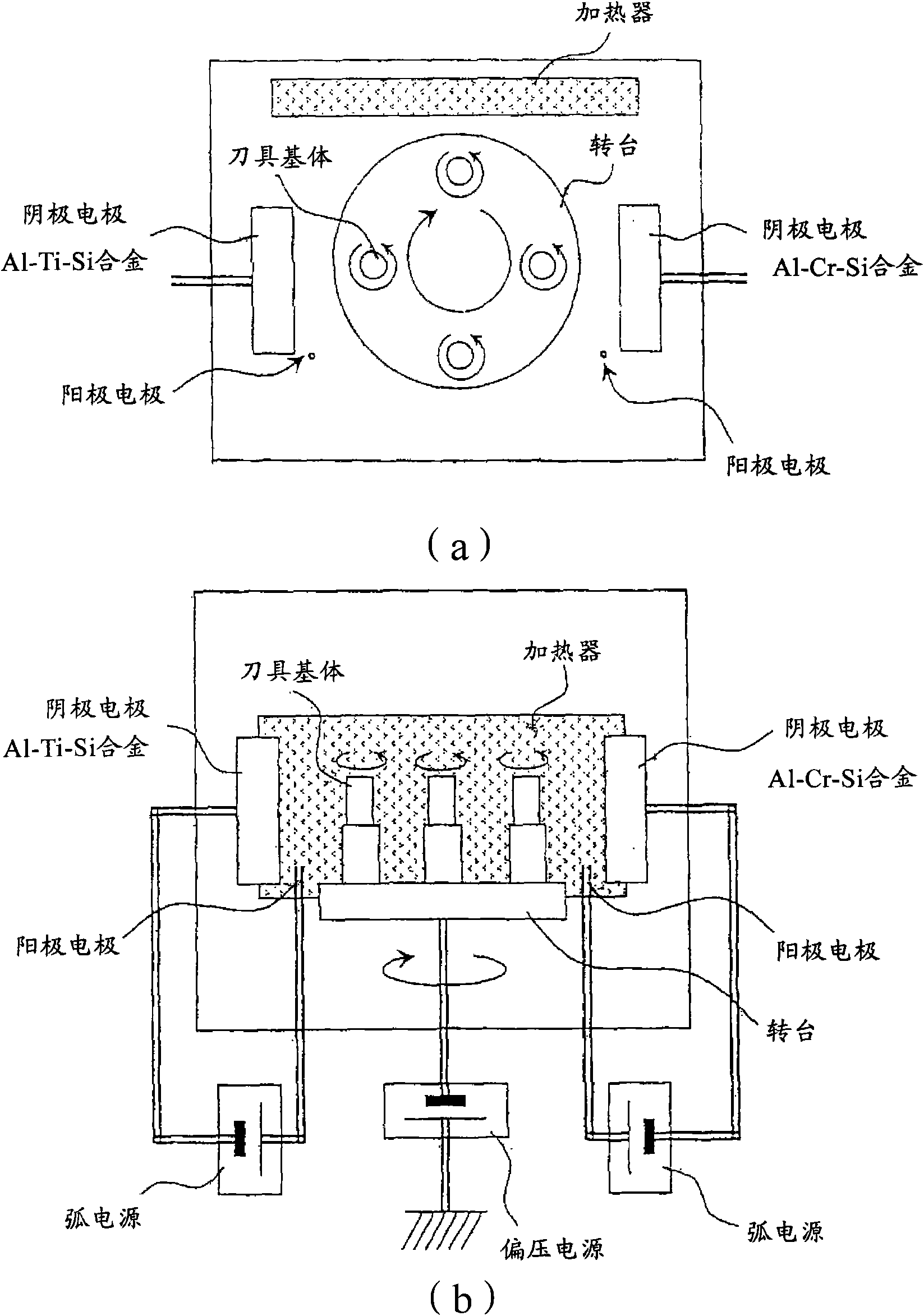
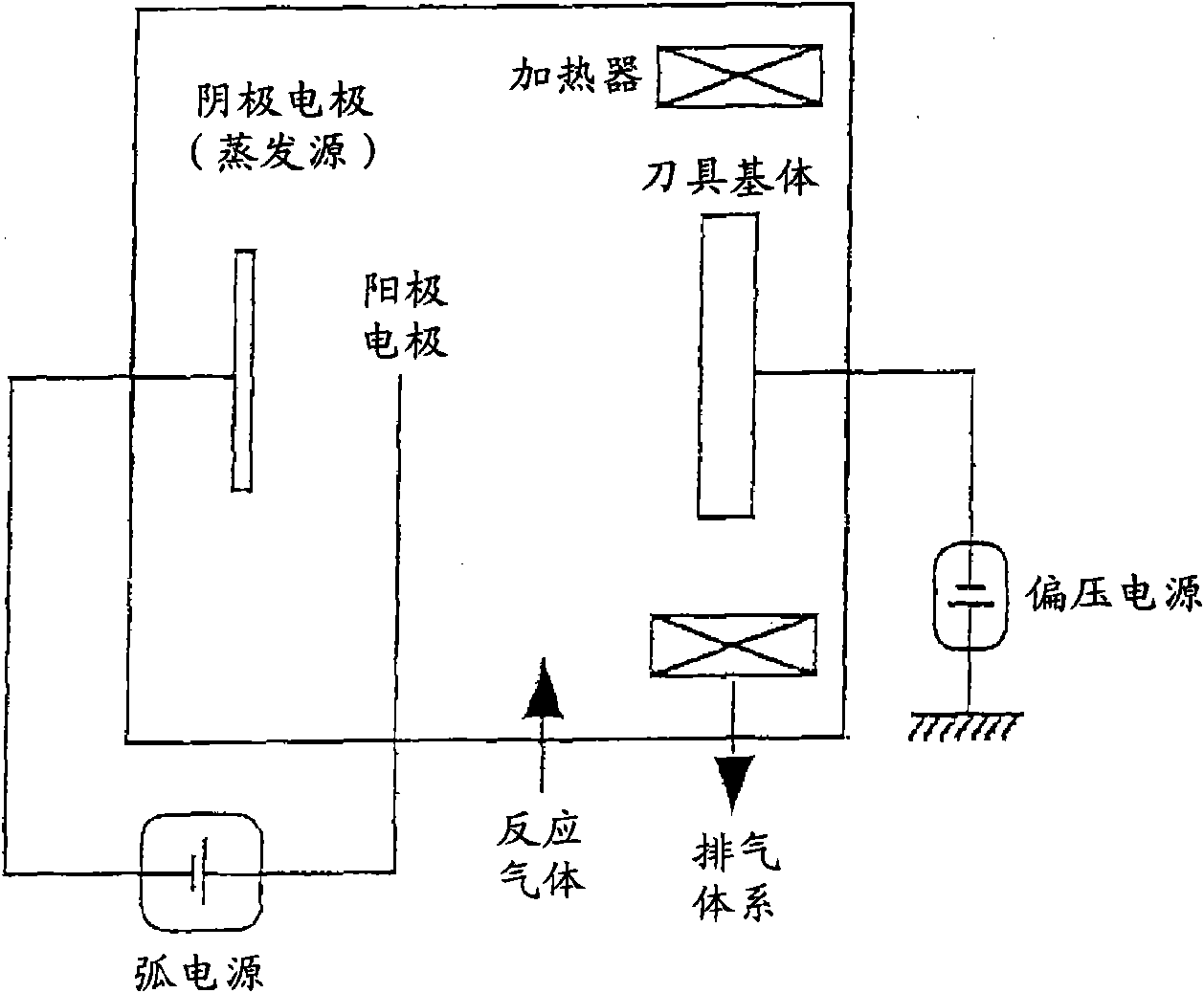
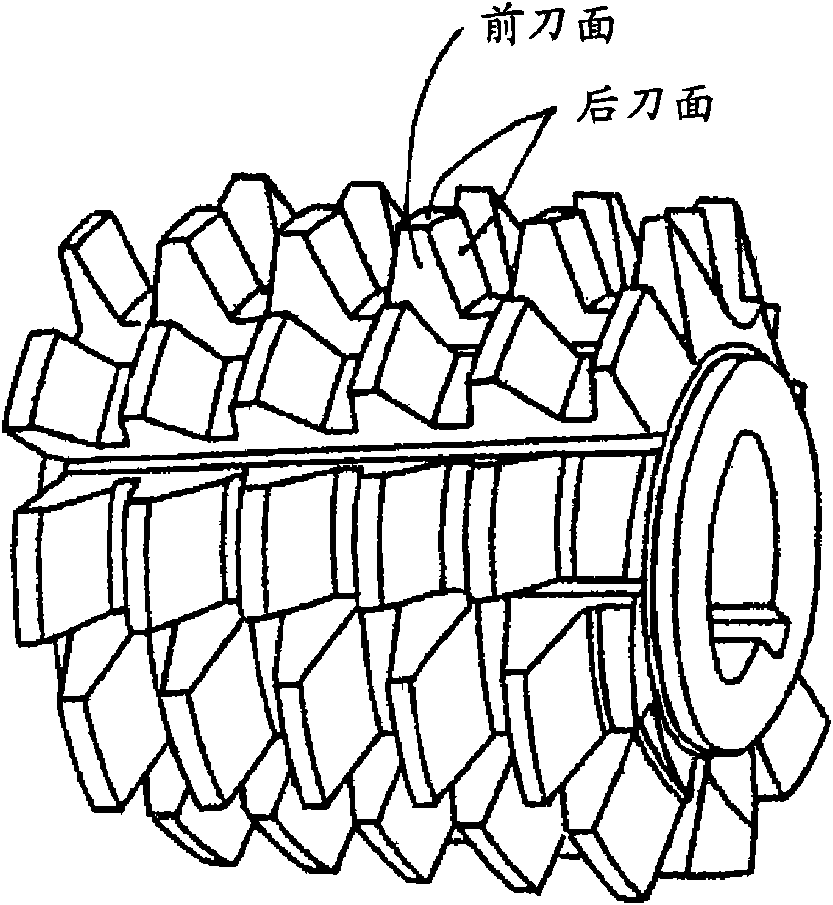
Surface-coated cutting tool
ActiveCN101678467AExcellent high temperature hardnessExcellent high temperature toughnessMilling cuttersVacuum evaporation coatingThin layerCemented carbide
A surface-coated cutting tool which has excellent chipping resistance and wearing resistance in high-speed cutting processing such as high-speed gear cutting processing, high-speed milling processing,and high-speed drilling processing. The surface-coated cutting tool comprises a tool base, e.g., a cemented carbide base, cermet base, or high-speed tool steel base, and at least a hard coating layerformed on a surface of the tool base and having a multilayer structure composed of a thin layer (A) and a thin layer (B) alternating therewith. The thin layer (A) is constituted of an (Al,Cr,Si)N layer satisfying the empirical formula ¢AlXCrYSiZ!N (wherein 0.2 <= X <= 0.45, 0.4 <= Y <= 0.75, 0.01 <=Z <= 0.2, and X+Y+Z=1 in terms of atomic ratio), and the thin layer (B) is constituted of an (Al,Ti,Si)N layer satisfying the empirical formula ¢AlUTiVSiW!N (wherein 0.05 <= U <= 0.75, 0.15 <= V <= 0.94, 0.01 <= W <= 0.1, and U+V+W=1 in terms of atomic ratio).
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Particle swarm optimization method for air combat decision
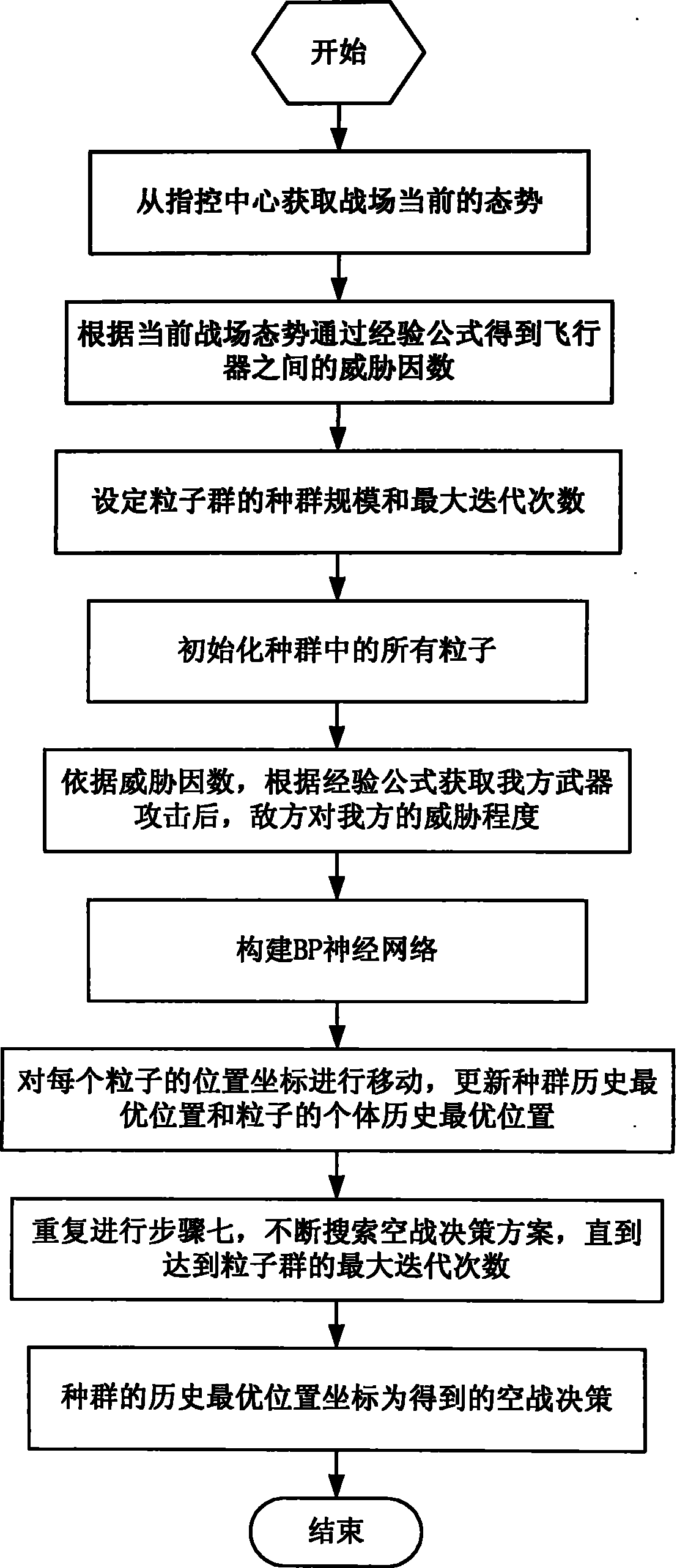
InactiveCN101908097AGood air combat decisionsAddress inherent shortcomingsBiological neural network modelsSpecial data processing applicationsDecision schemeEmpirical formula
The invention discloses a particle swarm optimization method for an air combat decision, comprising the following steps of: firstly, acquiring the current situation of a battlefield from a command control center; secondly, acquiring a threat factor among aircrafts according to the current situation of the battlefield; thirdly, setting the particle swarm scale and the maximum iterations of the particle swarm; fourthly, initializing all particles of the particle swarm; fifthly, acquiring the threat degree of an enemy party on a first party after weapon attacks of the first part according to an empirical formula; sixthly, constructing a BP (Back Propagation) neural network; seventhly, updating the historical optimal position of the particle swarm and the individual historical optimal position of the particles; eighthly, continuously searching an air combat decision scheme until the maximum iterations of the particle swarm are achieved; and ninthly, determining the historical optimal position coordinate of the particle swarm as the obtained air combat decision. By processing the input and the output of the BP neural network, the decision method can move in a set solution space and has favorable search capability on the optimal solution.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Material for thermal barrier coating
InactiveCN100376505CHigh thermal expansionLow thermal conductivityMolten spray coatingEfficient propulsion technologiesDivalent metalOperating temperature range
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Pot-type insulator lifetime assessment method based on artificial accelerated aging test
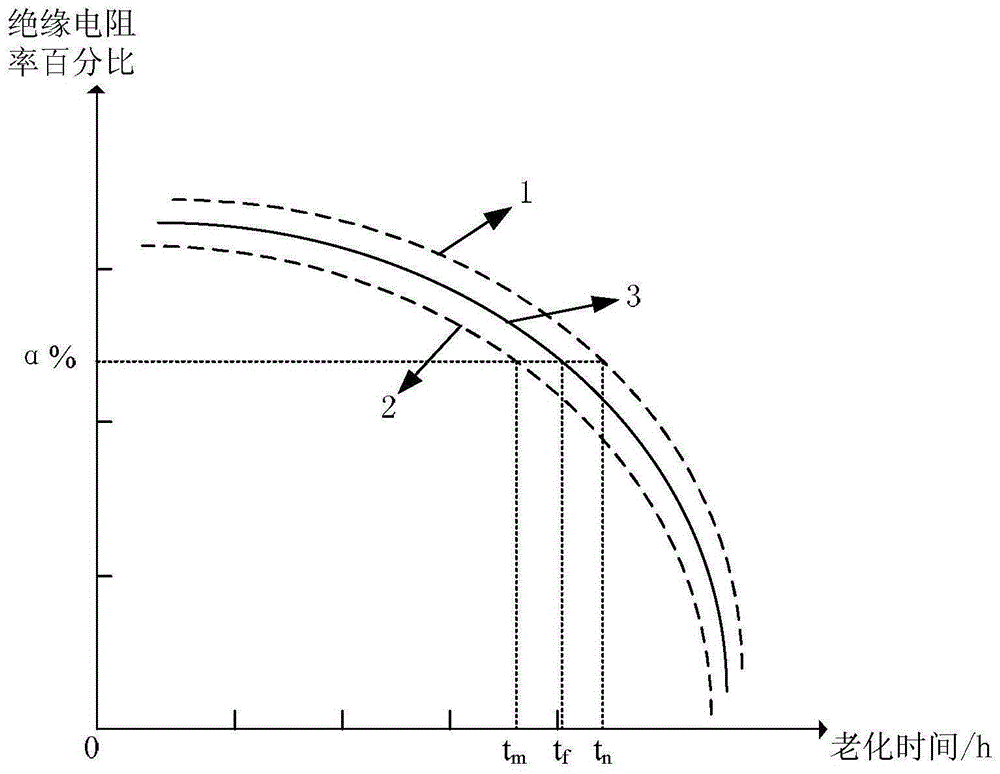
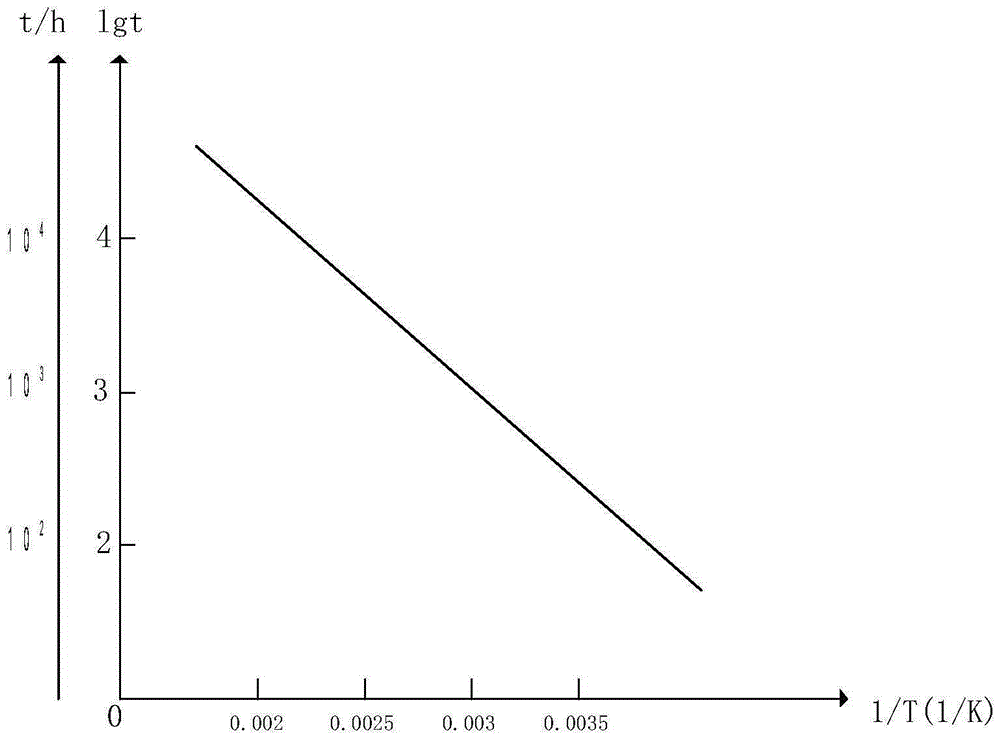
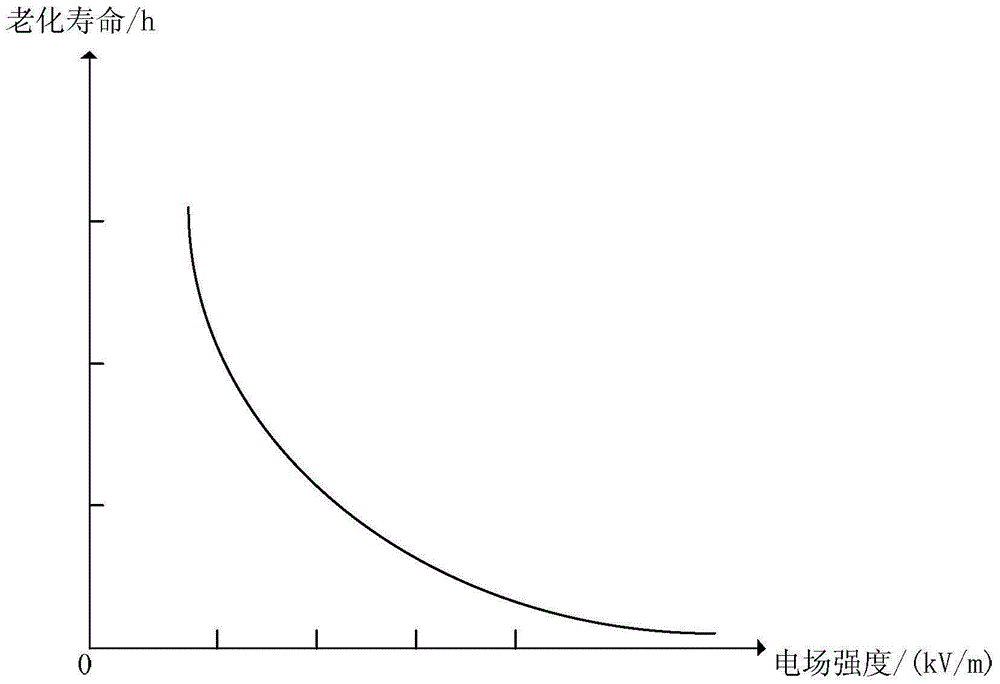
The invention provides a pot-type insulator lifetime assessment method based on an artificial accelerated aging test. According to the characterizes of sealing, high temperature and long-time bearing on high voltage of a pot-type insulator, an artificial accelerated aging test platform with electric heating comprehensive factors is designed by means of a multiple-factor laboratory, and characteristic quantities of multiple epoxy resin samples under different degrees of aging are measured. On this basis, analyzing is conducted on test data, by means of an existing empirical formula, a curve-fitting technique and a Weibull probability distribution method are adopted, internal relations among all aging factors, the electrical test quantity and the aging life are researched, relationship is established between the test data of epoxy resin materials and the aging assessment of the pot-type insulator, and the pot-type insulator lifetime assessment method is provided.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGXI POWER GRID CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com