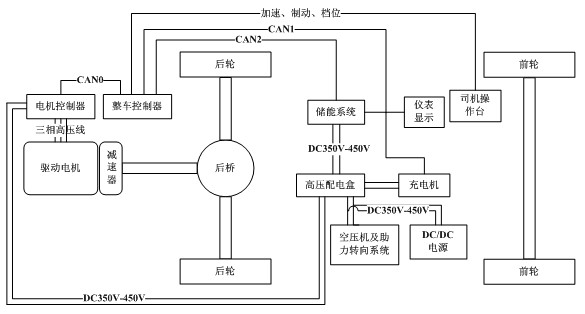
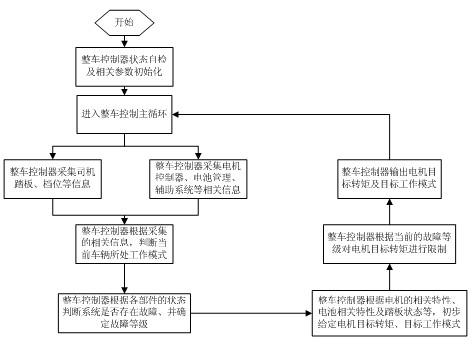
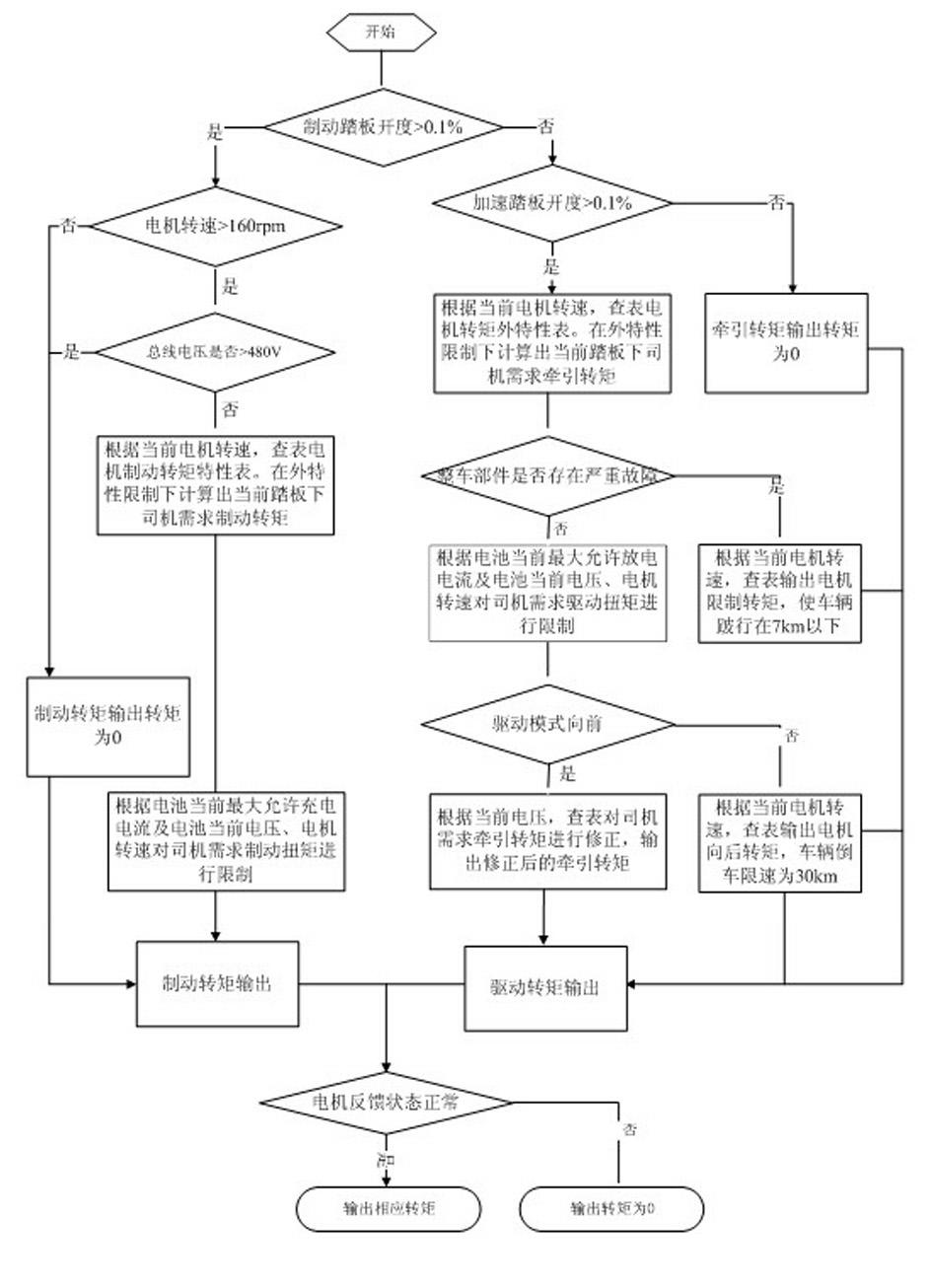
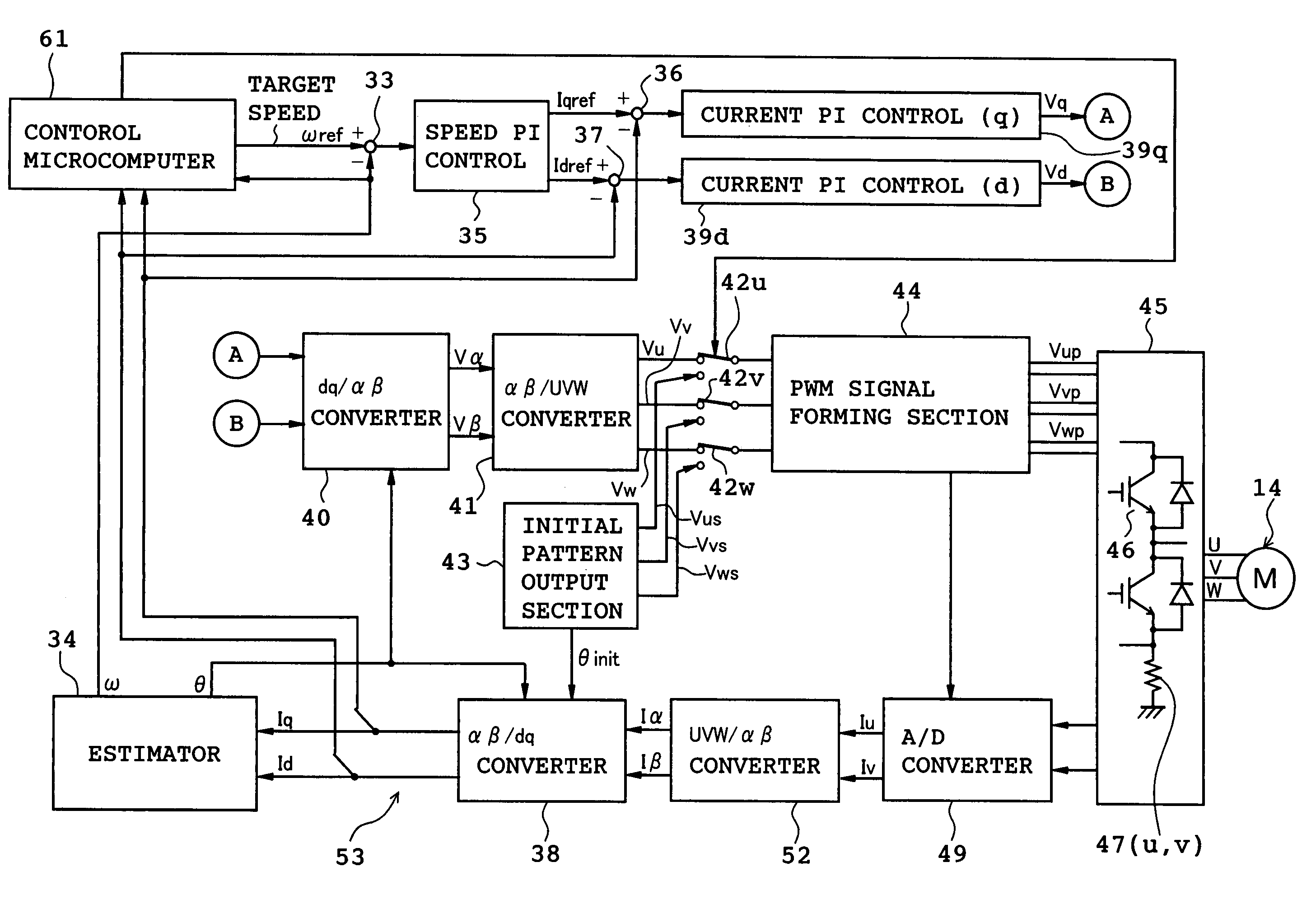
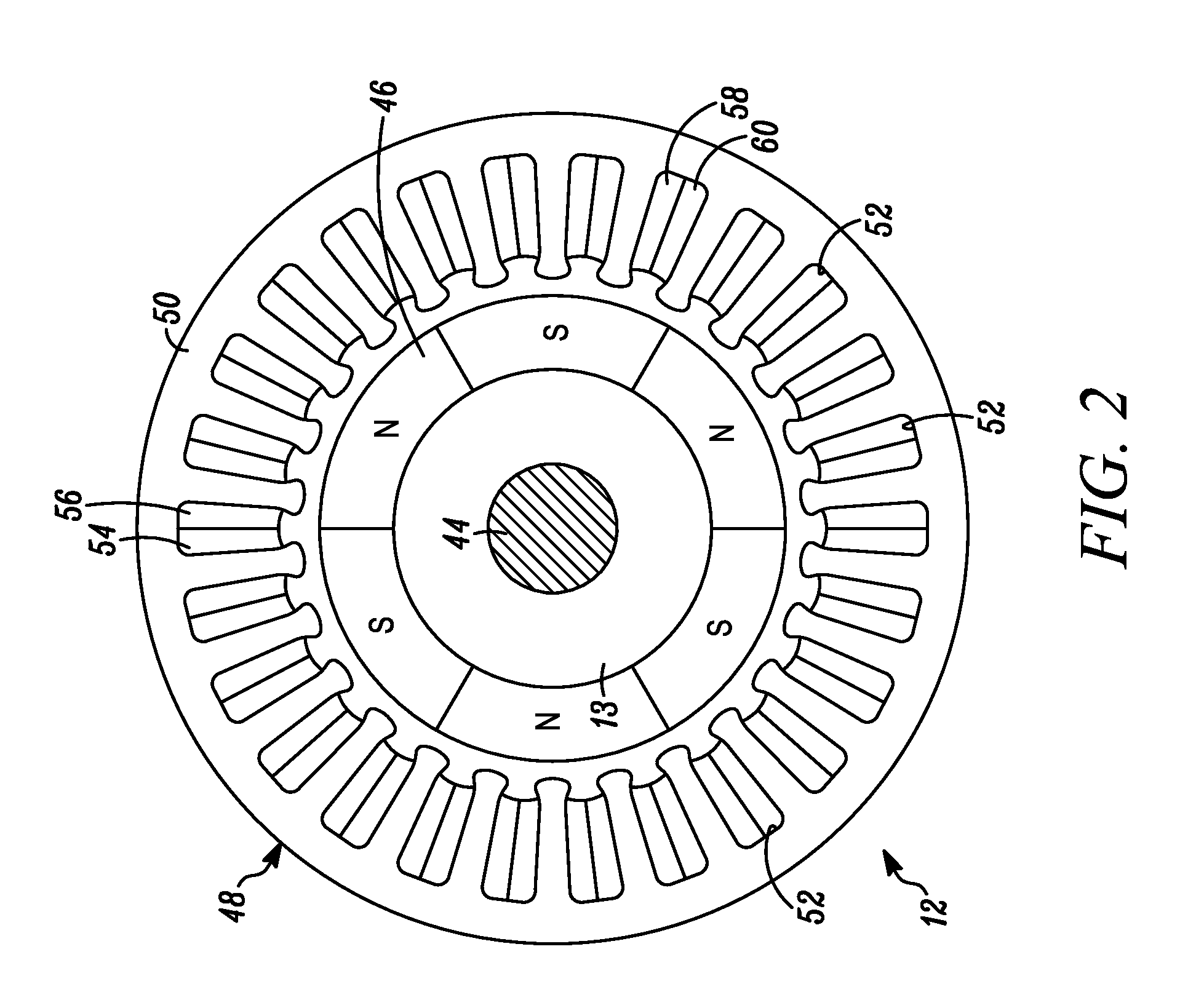
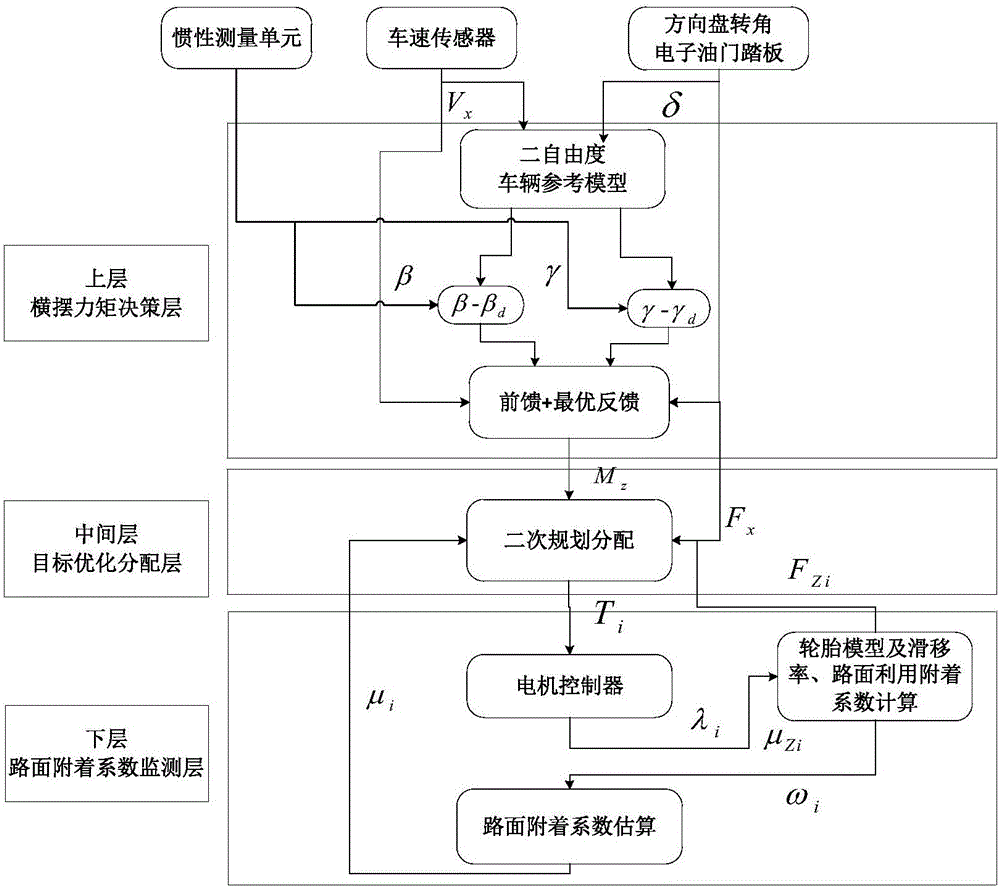
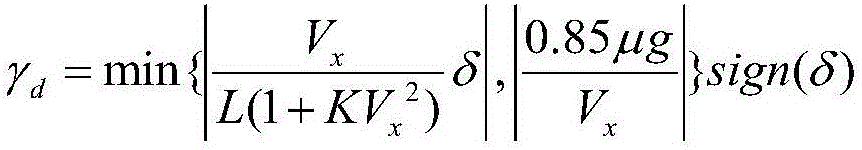Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3272 results about "Motor torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A torque motor is a specialized form of electric motor which can operate indefinitely while stalled, that is, with the rotor blocked from turning, without incurring damage. In this mode of operation, the motor will apply a steady torque to the load (hence the name). A torque motor that cannot perform a complete rotation is known...
Apparatus for controlling a fastener driving tool, with user-adjustable torque limiting control
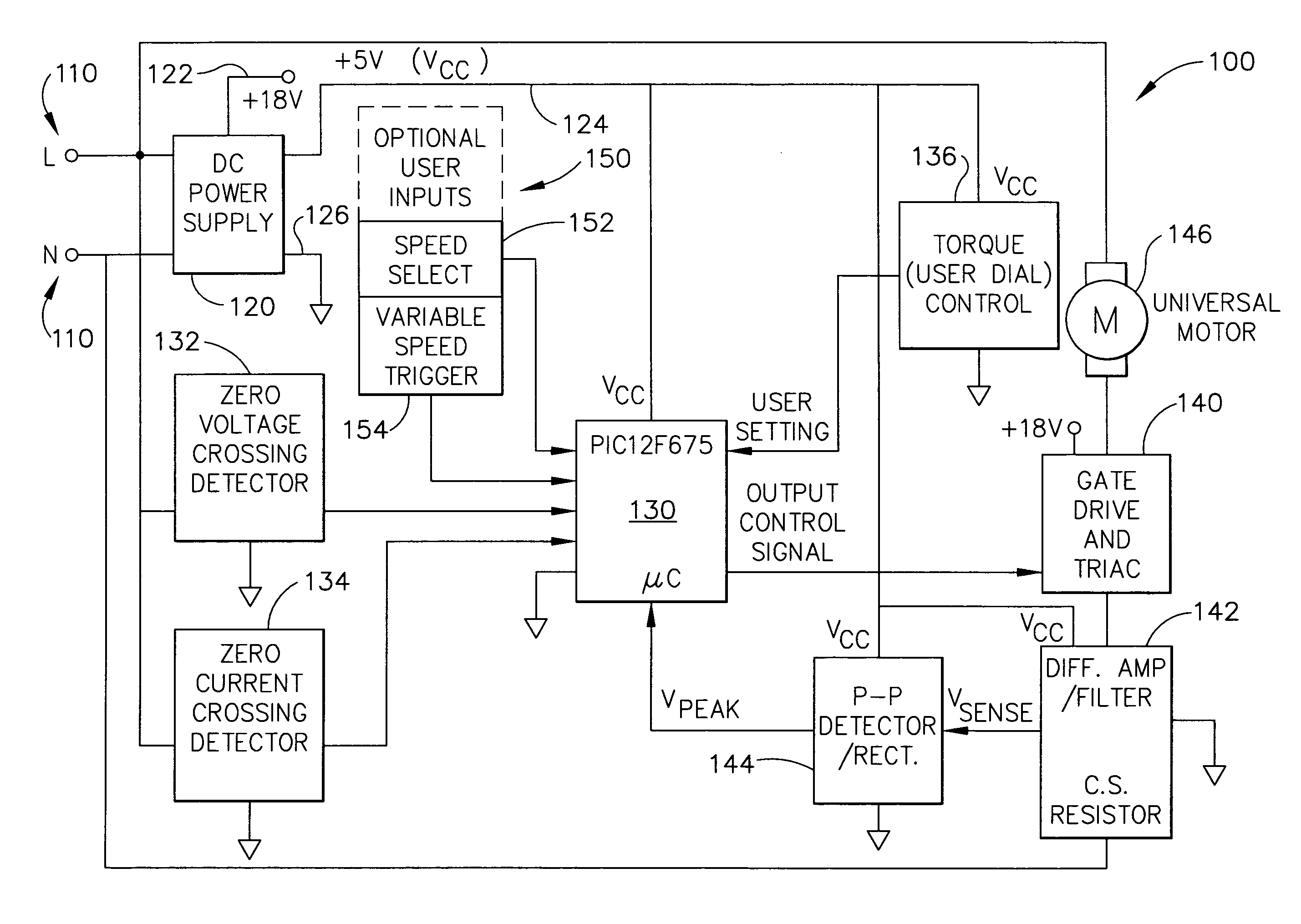
An improved hand-held fastener driving tool is provided with an adjustable torque limiting control. The tool is portable, and is electrically powered using either a battery pack or a power cord as a power source. The tool drives collated fasteners (e.g., screws) into solid objects. The motor current is measured to determine the amount of torque being applied to a screw by the motor and mechanical drive components. As the screw bottoms out, the motor torque increases to a point where it exceeds the user-adjusted torque limiting control. The motor is automatically turned off at that point, thereby preventing the screw from being stripped.
Owner:KYOCERA SENCO IND TOOLS INC
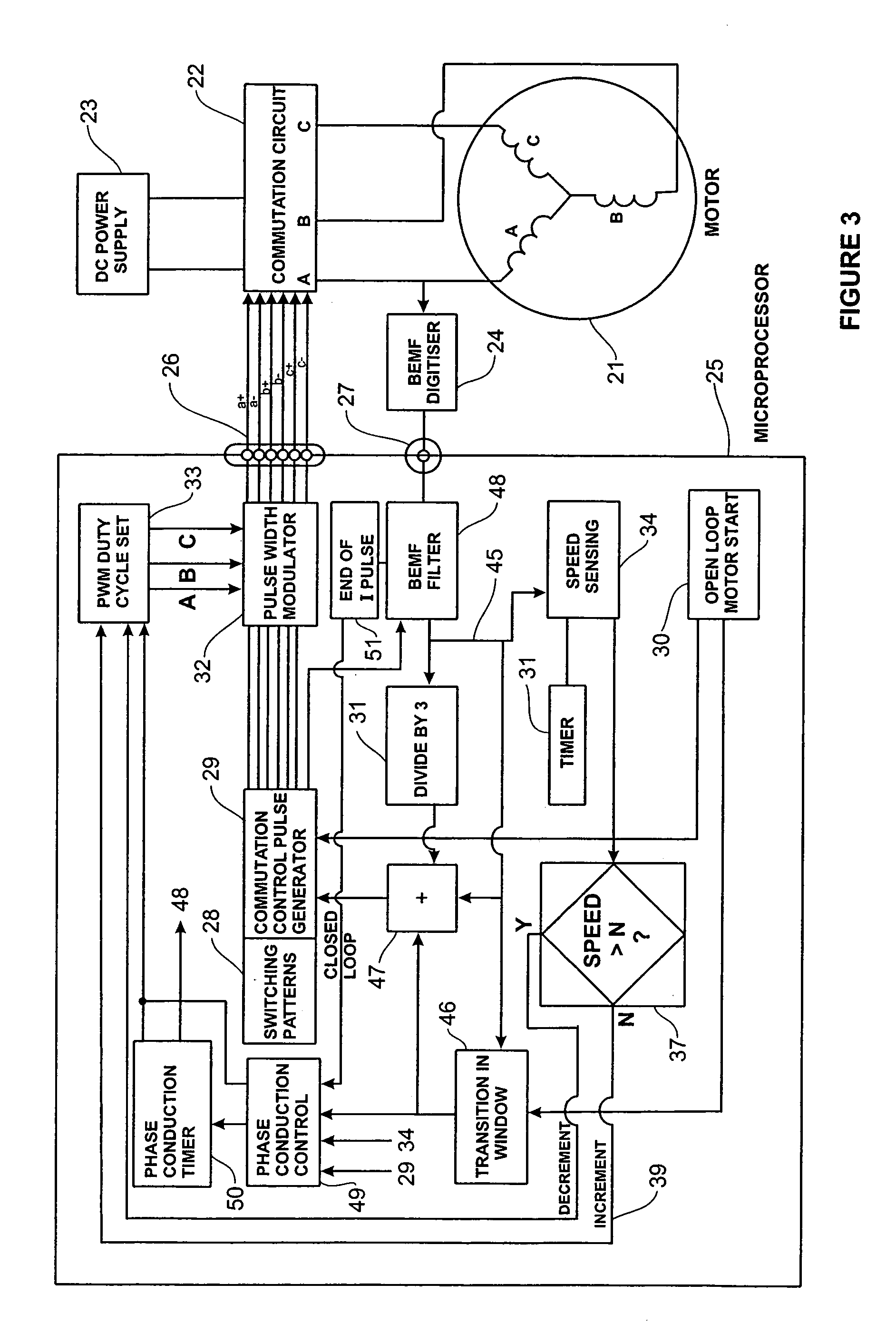
Brushless DC motor control
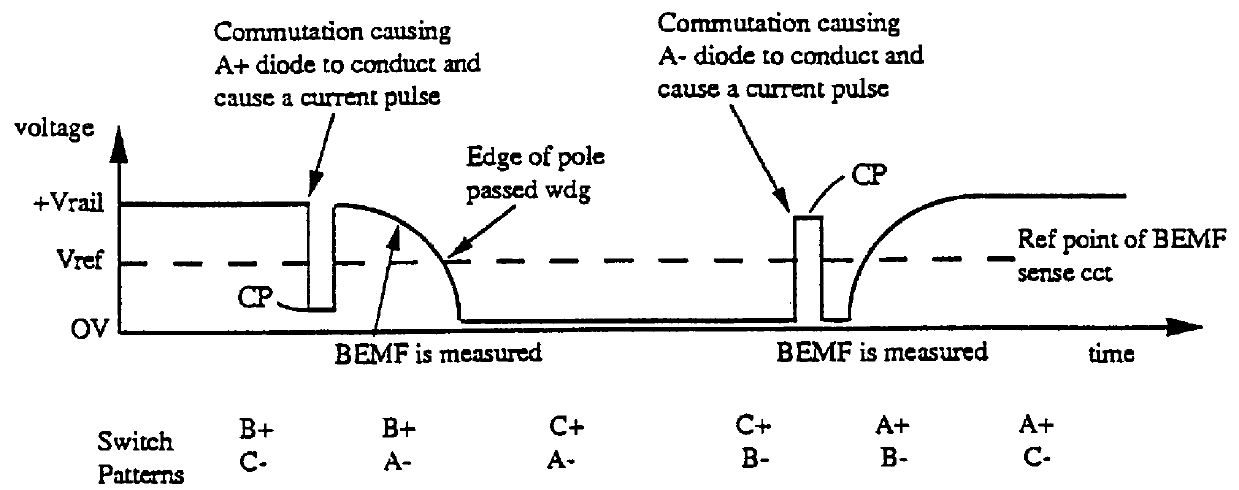
An electronically commutated brushless DC motor primarily for fractional horsepower applications of the type where at any instant one motor winding is unpowered and used to detect back EMF zero-crossings which information is used to initiate winding commutations. The duration of the pulse produced in this winding due to dissipation of stored energy by free-wheel diodes in parallel with the commutation devices after supply of current has been removed from this winding is used to provide a measure of motor current. This allows for simplified commutation device current limiting circuits and is available for control purposes which are a function of motor torque. There is also disclosed a method for maximizing useful power output by reducing the phase angle between the motor current and the back EMF. This is accomplished by introducing a delay in commutating the motor windings beyond the occurrence of each back EMF zero-crossing, with the delay being a function of the time between commutations.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
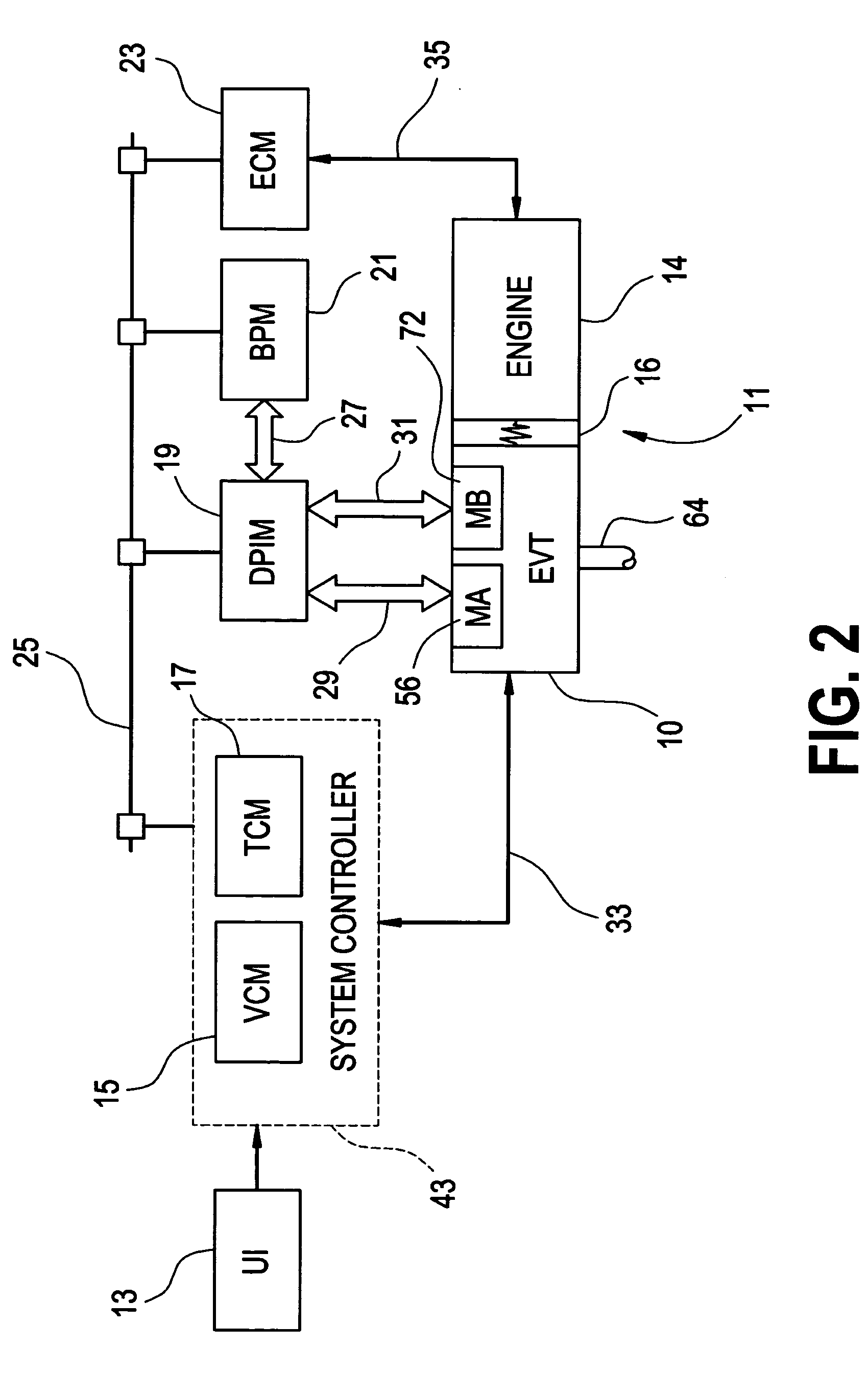
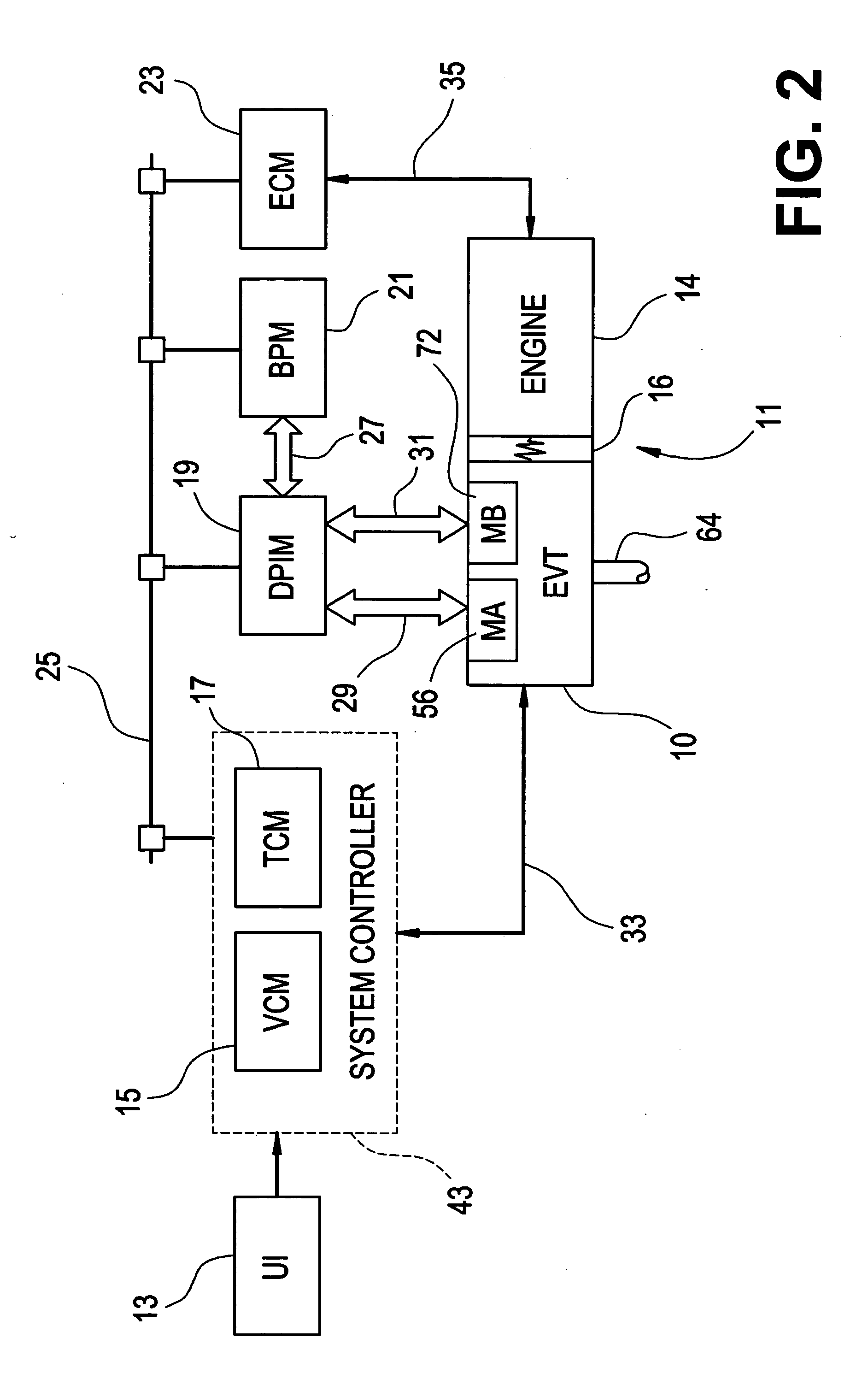
Method of providing electric motor torque reserve in a hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20050255964A1Improve control robustnessImproved shift qualityHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsDrivetrainBattery electric vehicle
A method of operating a vehicle powertrain system comprising an electric motor and transmission where the electric motor is operably and selectively coupled to the transmission and adapted to provide an output torque contribution thereto, and the electric motor has a predetermined maximum motor output torque and a predetermined minimum motor output torque which are used to determine a range of permissible control points for at least one transmission control parameter. The method includes establishing a motor torque reserve by performing at least one of decreasing the predetermined maximum motor output torque to a maximum reserved motor output torque and increasing the minimum motor output torque to a minimum reserved motor output torque, wherein the maximum reserved motor output torque and the minimum reserved motor output torque are used in place of the predetermined maximum motor output torque and the predetermined minimum motor output torque, respectively, to determine the range of permissible control points for the at least one transmission control parameter. The motor torque reserve may include a static motor torque reserve, a dynamic motor torque reserve, or a combination of both static and dynamic torque reserves. The dynamic torque reserve may include a predictive dynamic reserve, a reactive dynamic reserve, or a combination of a predictive reserve and a reactive reserve or reserves.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
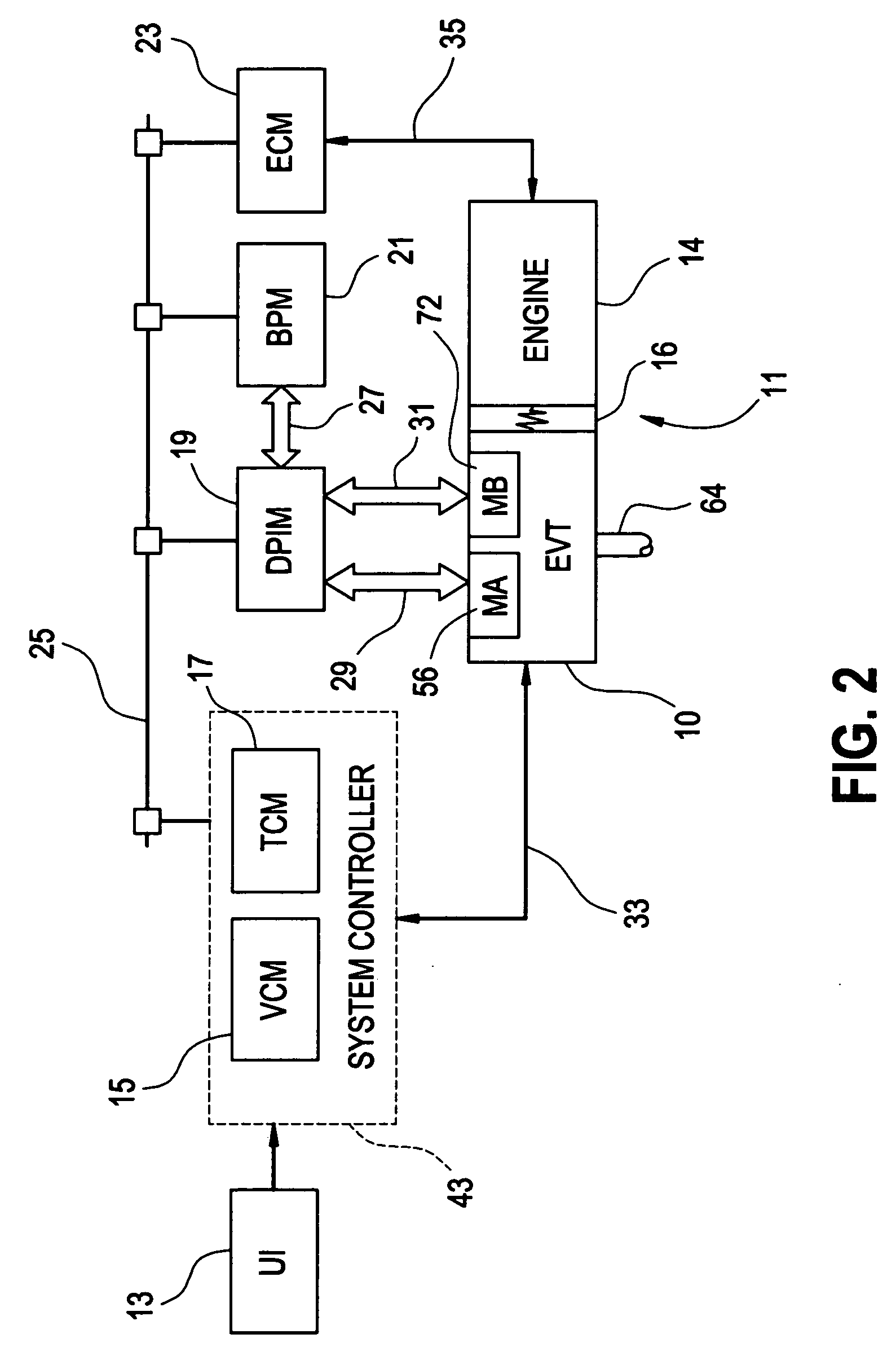
Robotic surgical system with joint motion controller adapted to reduce instrument tip vibrations
ActiveUS7689320B2Reduce vibrationWithout jeopardizing control system stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesControl systemJoints movement
A robotic surgical system has a robot arm holding an instrument for performing a surgical procedure, and a control system for controlling movement of the arm and its instrument according to user manipulation of a master manipulator. The control system includes a filter in its forward path to attenuate master input commands that may cause instrument tip vibrations, and an inverse filter in a feedback path to the master manipulator configured so as to compensate for delay introduced by the forward path filter. To enhance control, master command and slave joint observers are also inserted in the control system to estimate slave joint position, velocity and acceleration commands using received slave joint position commands and torque feedbacks, and estimate actual slave joint positions, velocities and accelerations using sensed slave joint positions and commanded slave joint motor torques.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Method for active engine stop of a hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20050255968A1Increased durabilityImprove smoothnessHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlElectric machineResonance
A method for providing an active engine stop of the engine of a hybrid electric vehicle. The method utilizes the electric machine to oppose the and rapidly stop the rotation of the engine at a controlled rate. The method includes the calculation of an input speed reduction trajectory using the engine speed when the active engine stop request is made and a predetermined speed reduction interval. The predetermined speed reduction interval is preferably less than a time from the active stop request to the shutoff command to the electric machine. The method provides rapid deceleration of the engine, particularly through the powertrain resonance speed, thereby reducing the amount of vibration energy dissipated through the powertrain and vehicle chassis. The method also removes the electric machine torques from the engine prior to achieving zero engine speed in order to avoid imparting a negative engine speed or counter-rotation of the engine. The method preferably comprises a complementary series of software control functions that allow the vehicle to actively stop the engine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for automatic traction control in a hybrid electric vehicle
InactiveUS20050256629A1Improve system performanceHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsElectric machineIn vehicle
A method for providing traction control in vehicle powertrain systems is particularly adapted for traction control in a powertrain system of a hybrid electric vehicle comprising an internal combustion engine, an electric machine and a transmission that is operatively coupled to the electric machine and the engine and adapted to provide a transmission torque output in response to a transmission torque input received as a torque output from either or both of the engine and the electric machine. The method is adapted to utilize conventional traction control and engine control hardware, software and communication standards to implement traction control. In one embodiment of the invention, a conventional traction controller is used to detect a wheel spin condition and provide a plurality of first output torque command messages in response thereto. The plurality of first output torque command messages are used to obtain a torque reduction which is applied to a reference output torque to obtain a corresponding plurality of traction control output torque commands for the powertrain system during the wheel spin condition. A rate limit may also be applied to control the rate of change between successive ones of the traction control output torque commands in order to reduce the possibility of extension of the wheel spin condition, or recurrence of another wheel spin condition. Each traction control output torque command may be used to determine an associated traction control engine torque output command and traction control electric machine torque output command.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
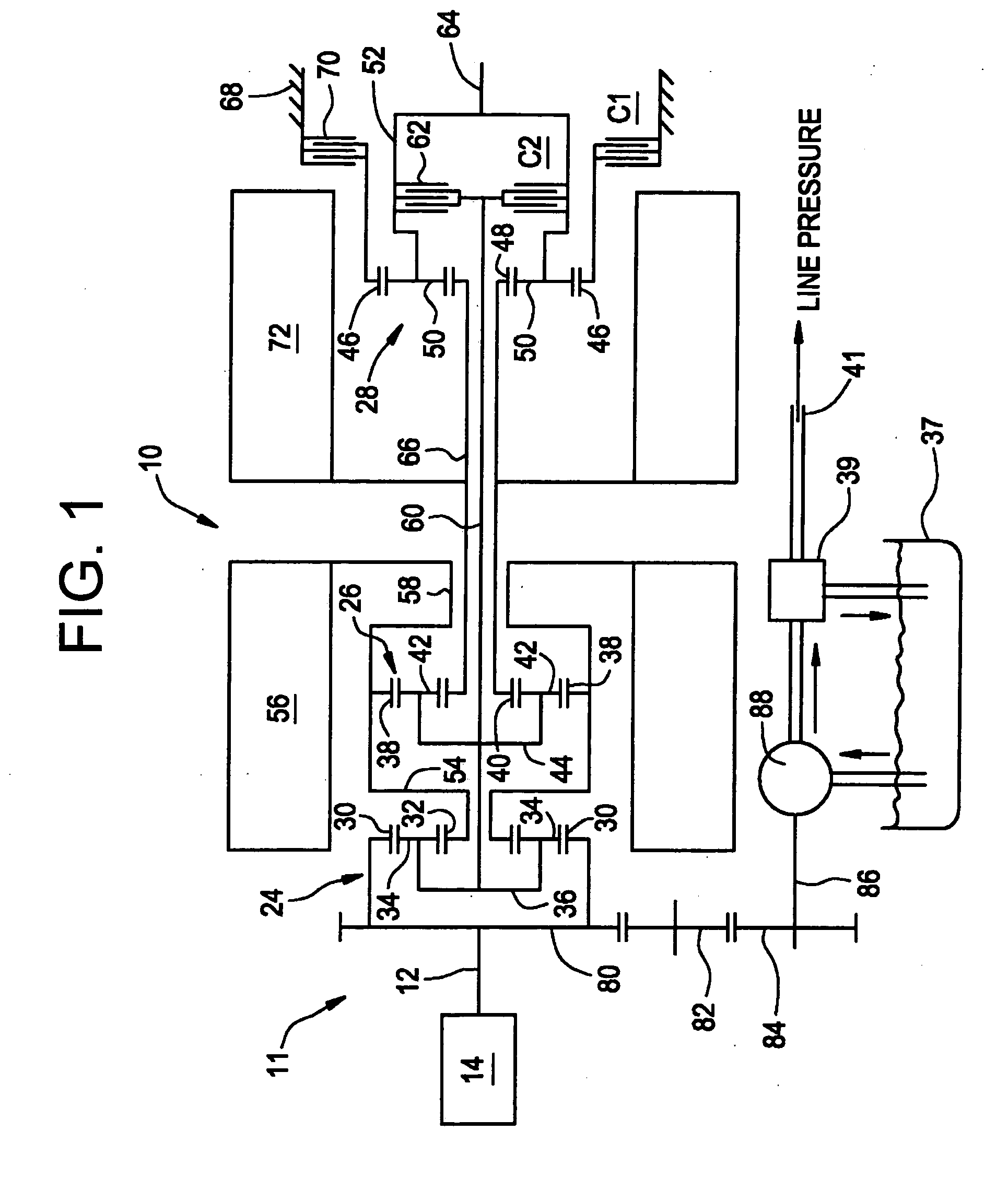
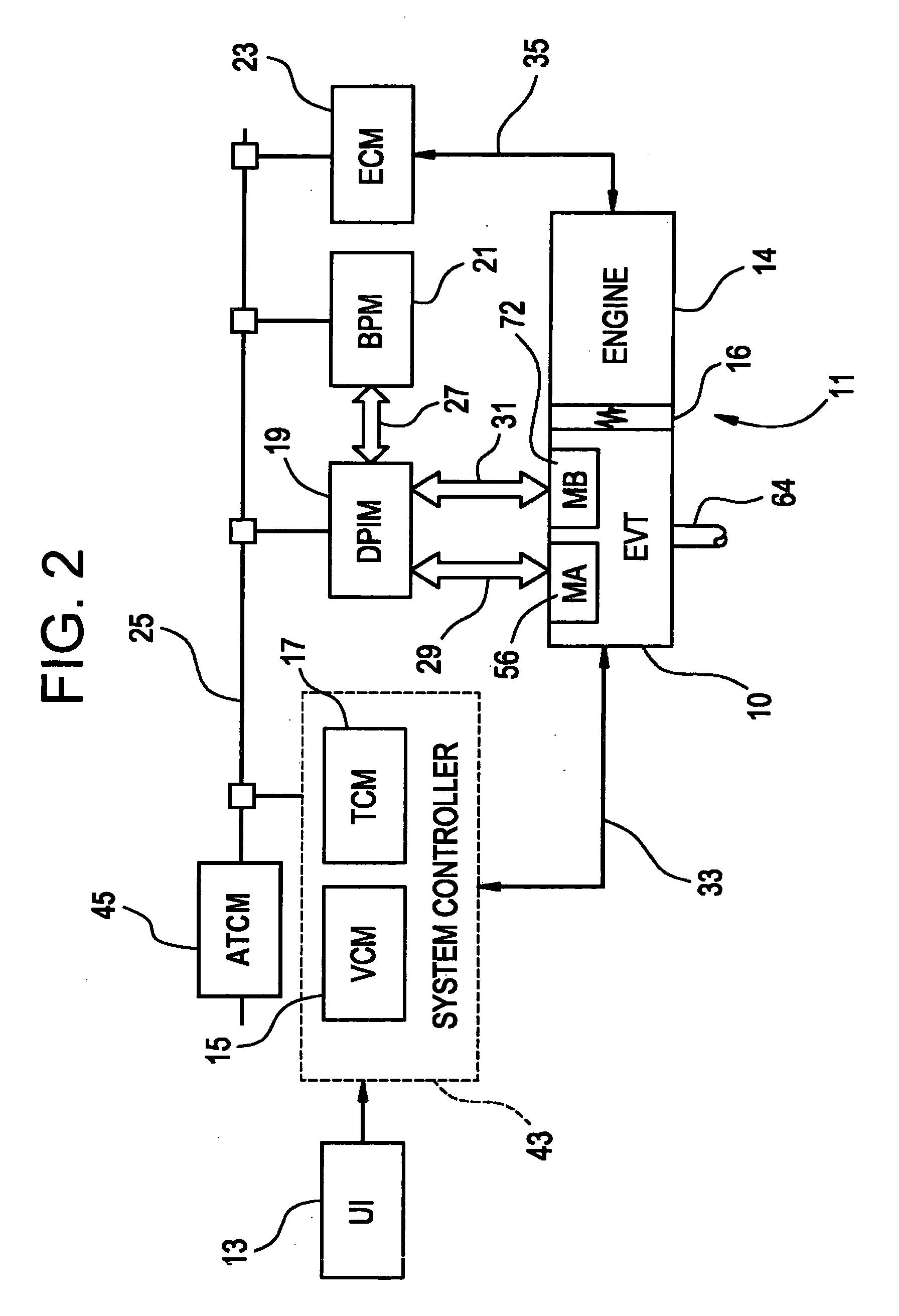
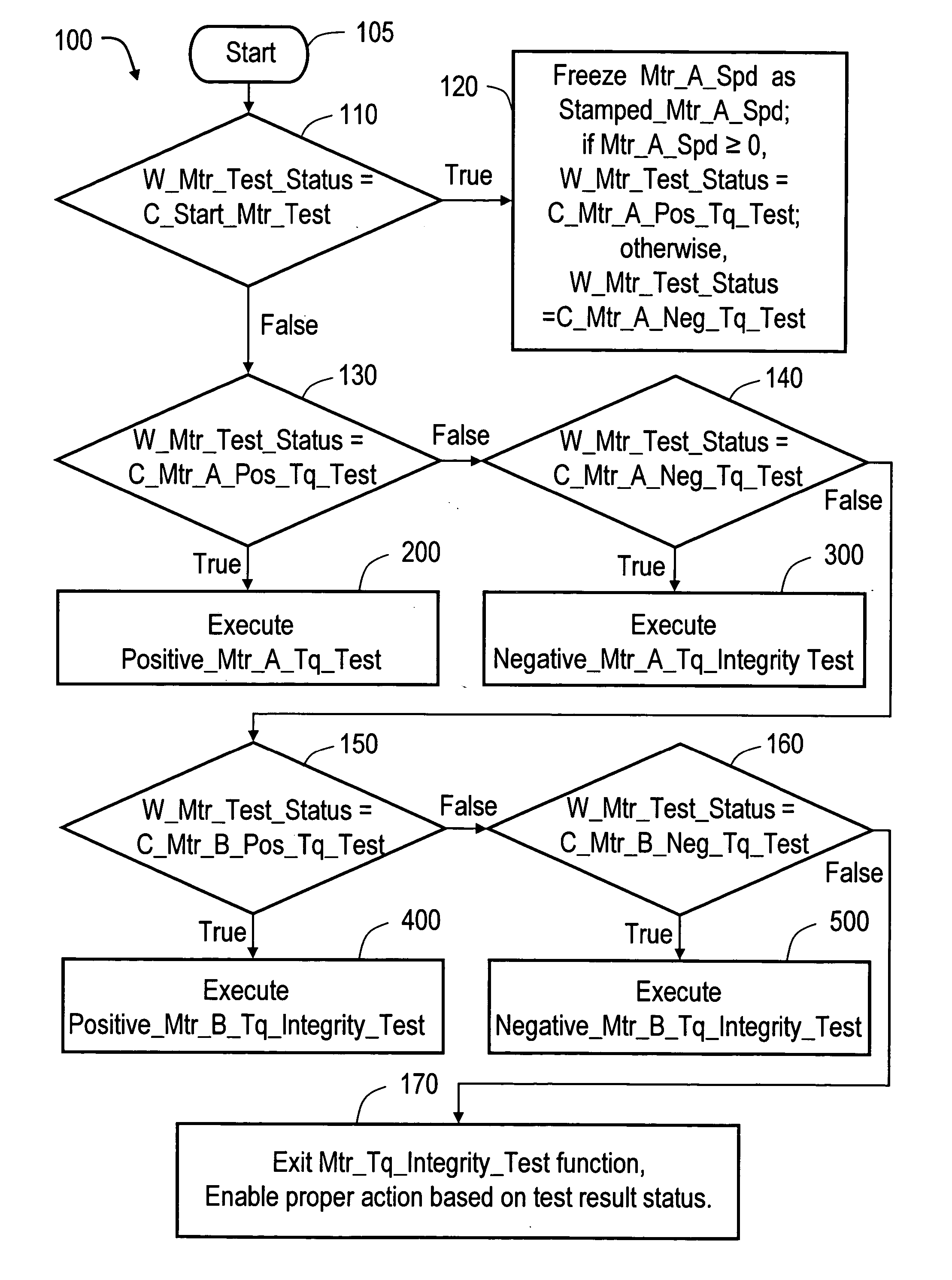
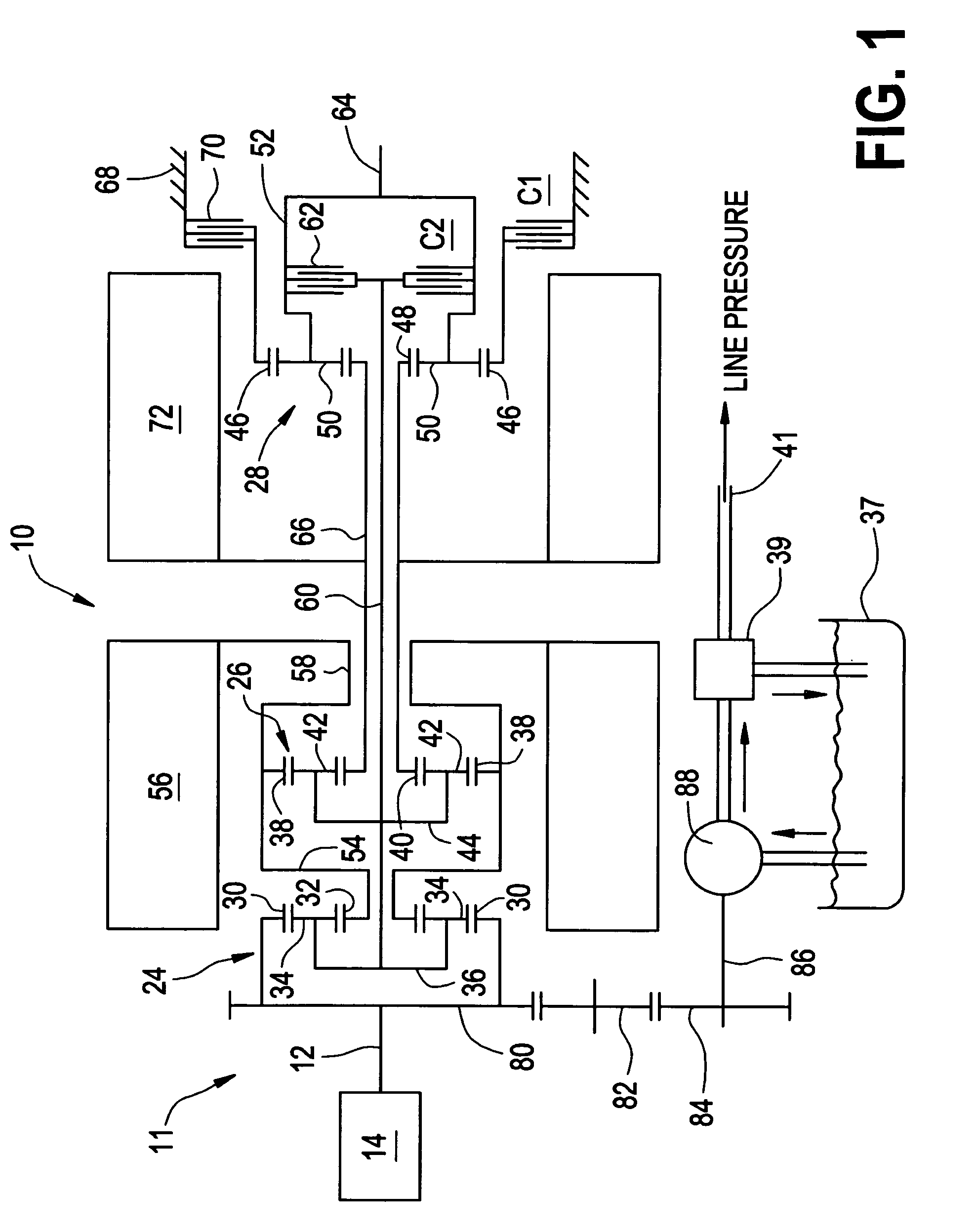
Method of testing motor torque integrity in a hybrid electric vehicle
InactiveUS20050256618A1DC motor speed/torque controlDigital data processing detailsMotor speedEngineering
A method of testing an electric motor that is adapted to provide a desired electric motor output torque to a vehicle powertrain system comprising an engine and the electric motor which are operatively and selectively coupled to a transmission. The method includes the steps of determining an initial motor speed of the electric motor, determining a motor torque command as a function of the initial motor speed, applying the motor torque command to the electric motor to produce an output torque from the electric motor, measuring a resultant motor speed of the electric motor and establishing a motor status as a function of the resultant motor speed. The method may be implemented as a computer control and diagnostic algorithm.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Diagnostic method for a torque control of an electrically variable transmission
ActiveUS20050252283A1Impaired speed controlImpaired torque controlVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesLoop controlLow speed
A condition of impaired speed and torque control of a parallel electrically variable transmission due to factors beyond nominal modeling and estimation errors is diagnosed under low speed operation. The transmission includes at least one electric machine and a motor torque controller for regulating the transmission input speed and output torque. The motor torque controller includes an open-loop control path based on predetermined torques and accelerations and a closed loop control path based on input speed error. The presence of a larger than expected closed-loop correction magnitude, combined with low output speed and one or more other conditions is used to diagnose a condition of potential torque error, in which case the transmission control is altered to prevent unwanted operation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Vehicle Range Finder
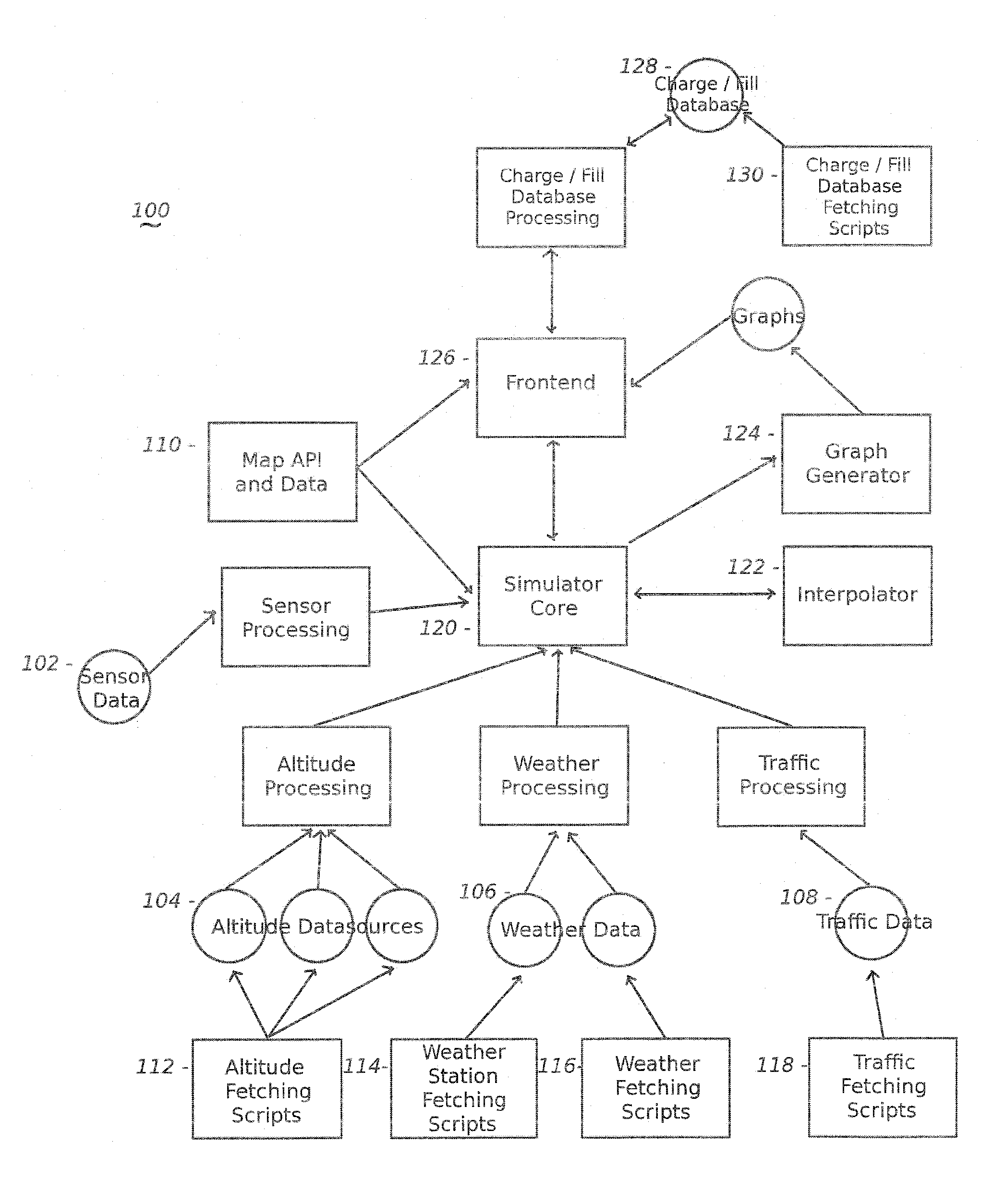
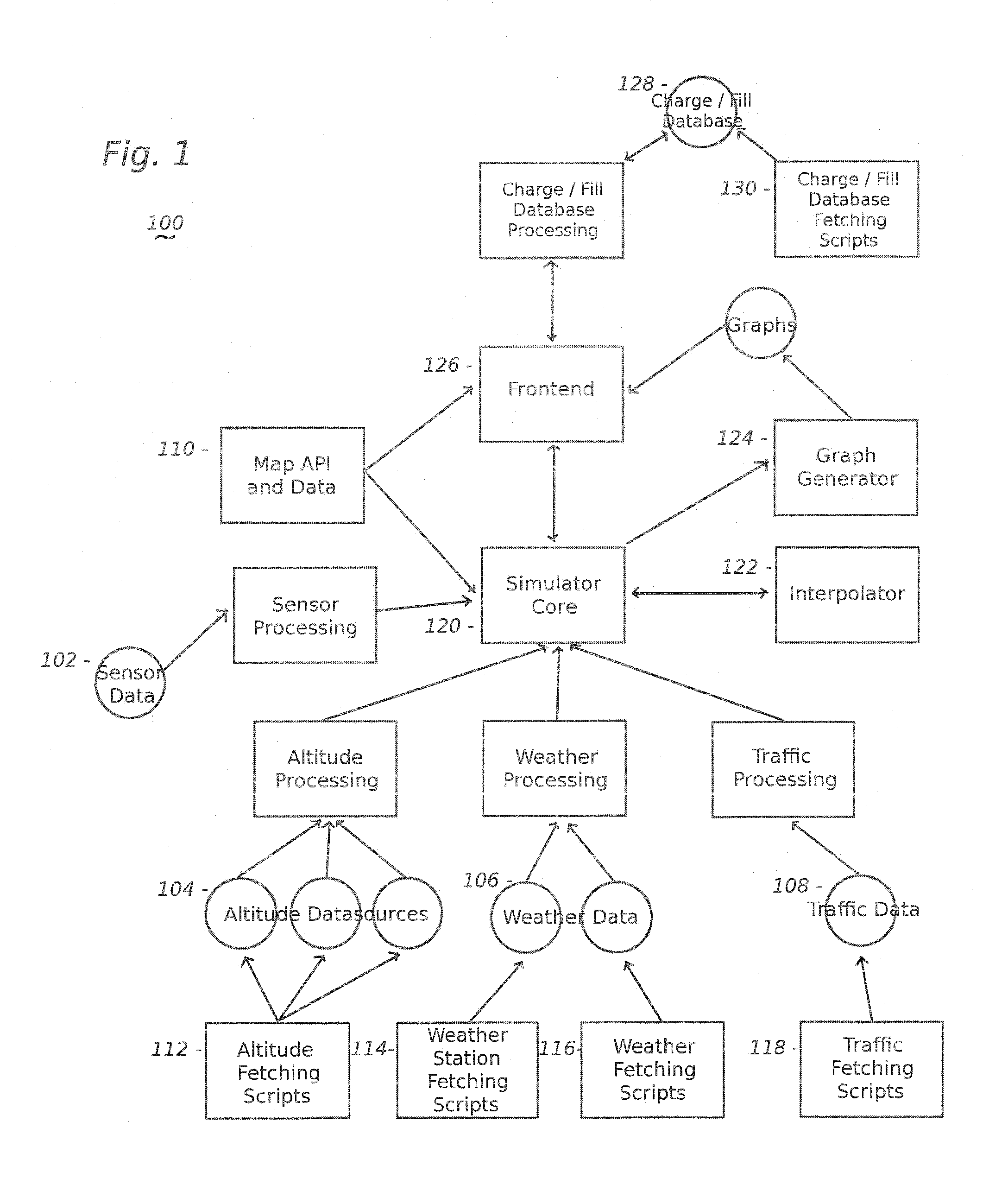
The present invention includes, among other embodiments, a system embedded in a vehicle including several inputs. The inputs may include one hard coded data, data from sensors on the vehicle, data from external sensors, user coded data, data received from remote databases, data received from broadcast data steams or data that has been accumulated during use of the vehicle. The inputs provide information regarding vehicle speed, motor rpm, motor torque, battery voltage, battery current, and battery charge level, etc. The embedded system also includes a processor unit that receives information from the plurality of inputs and calculates at least an expected vehicle range. The results of any calculations completed by the processing unit is supplied as an output to a display unit, which then displays the information to the user.
Owner:CELADON APPL
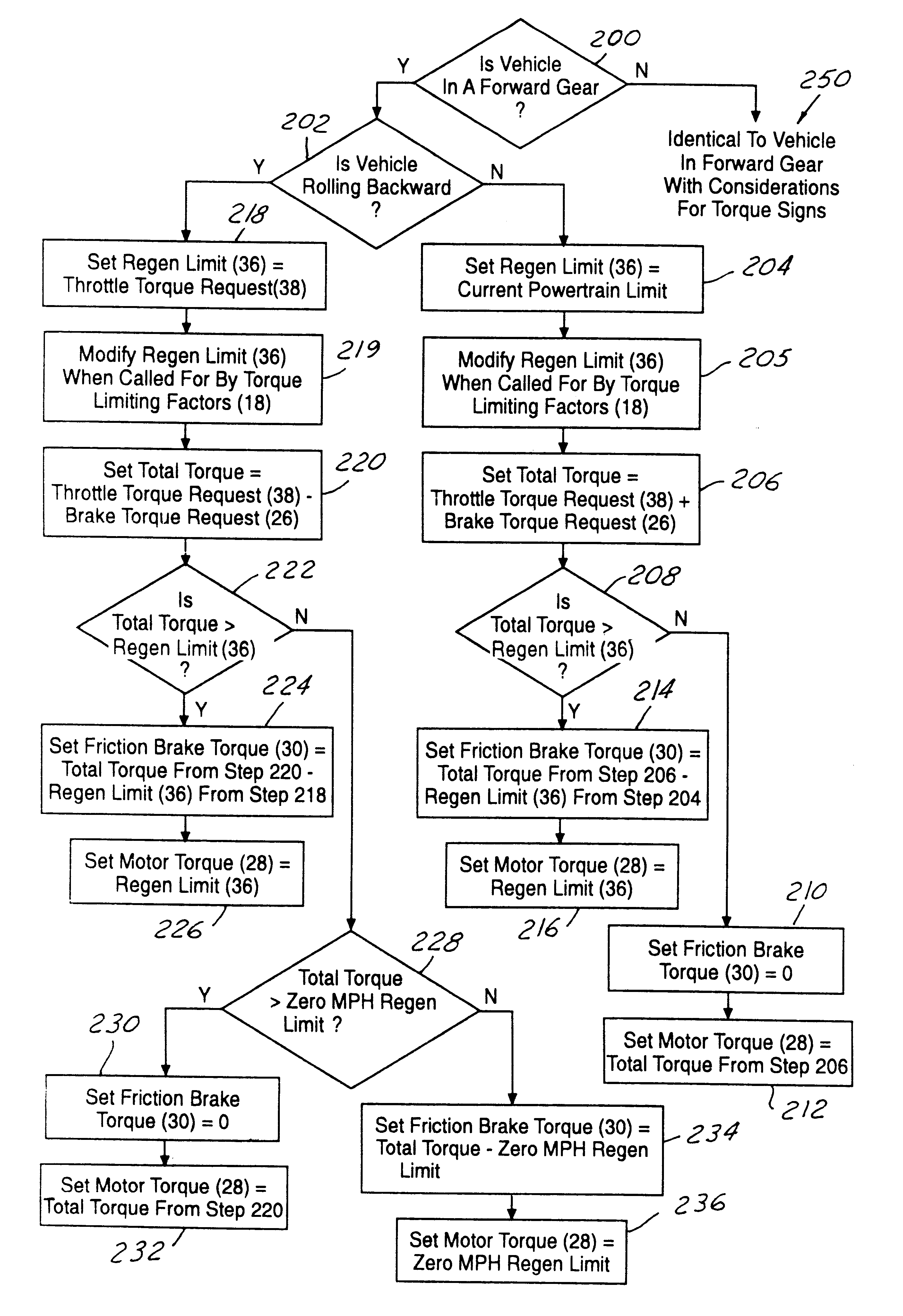
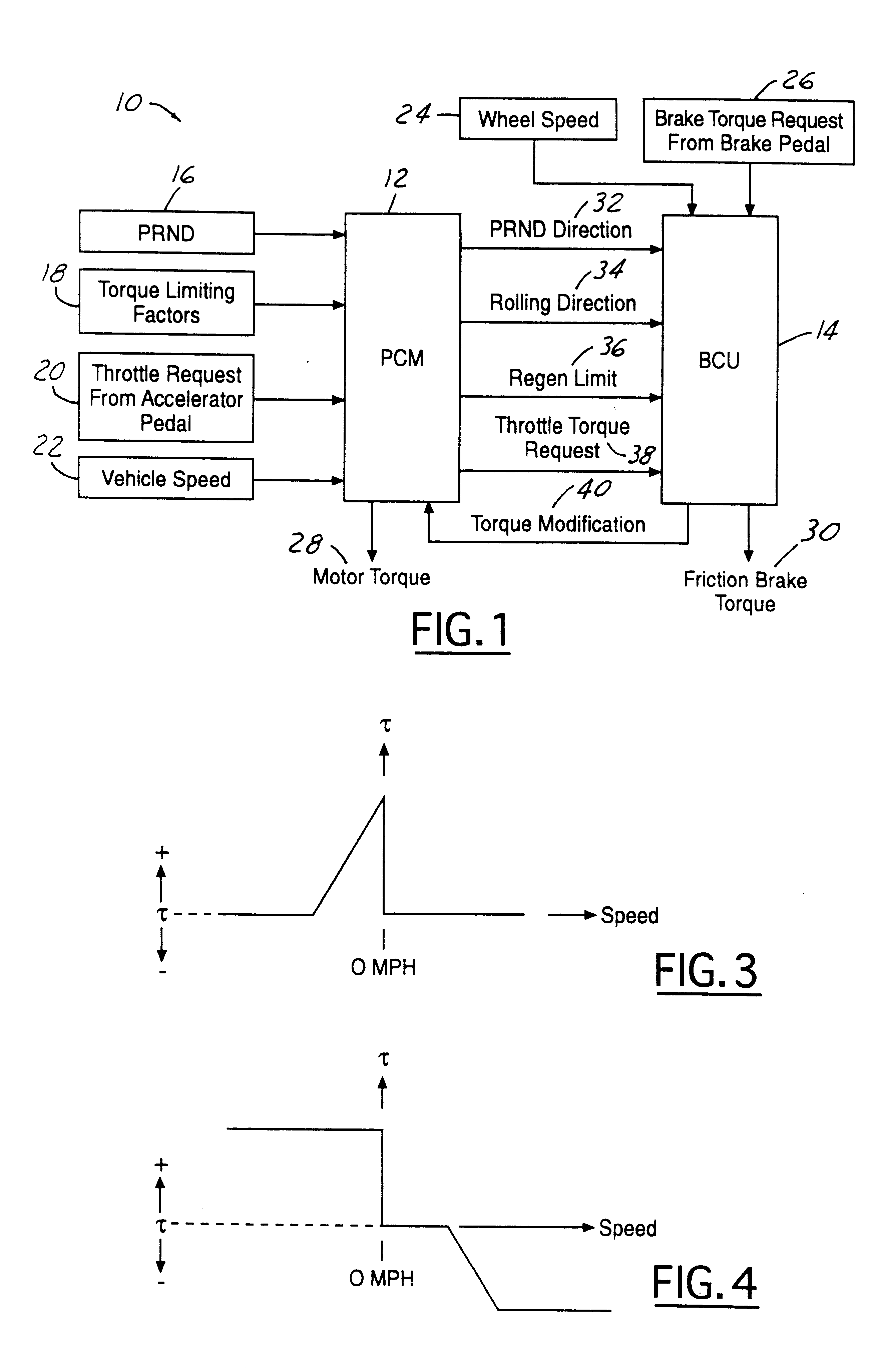
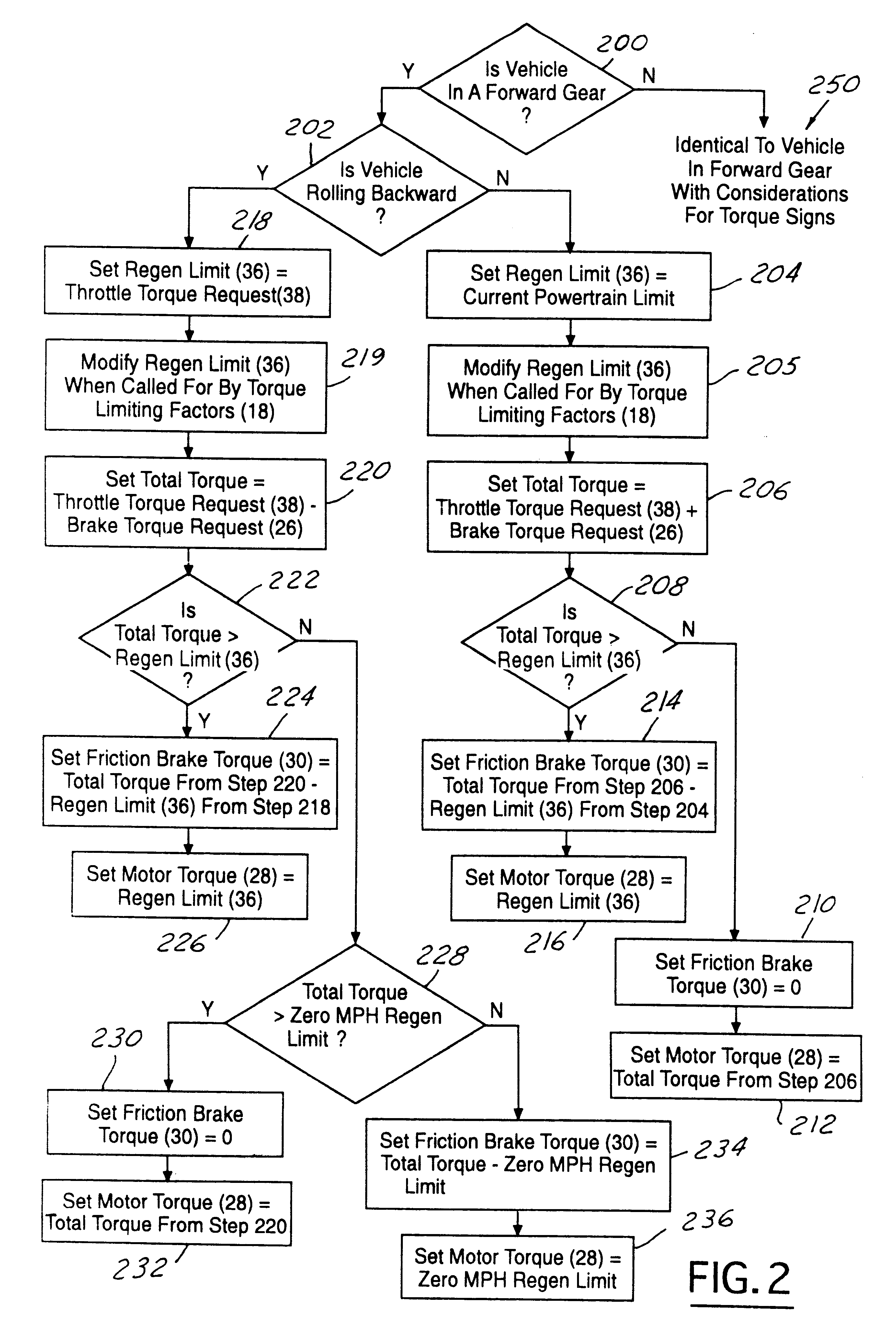
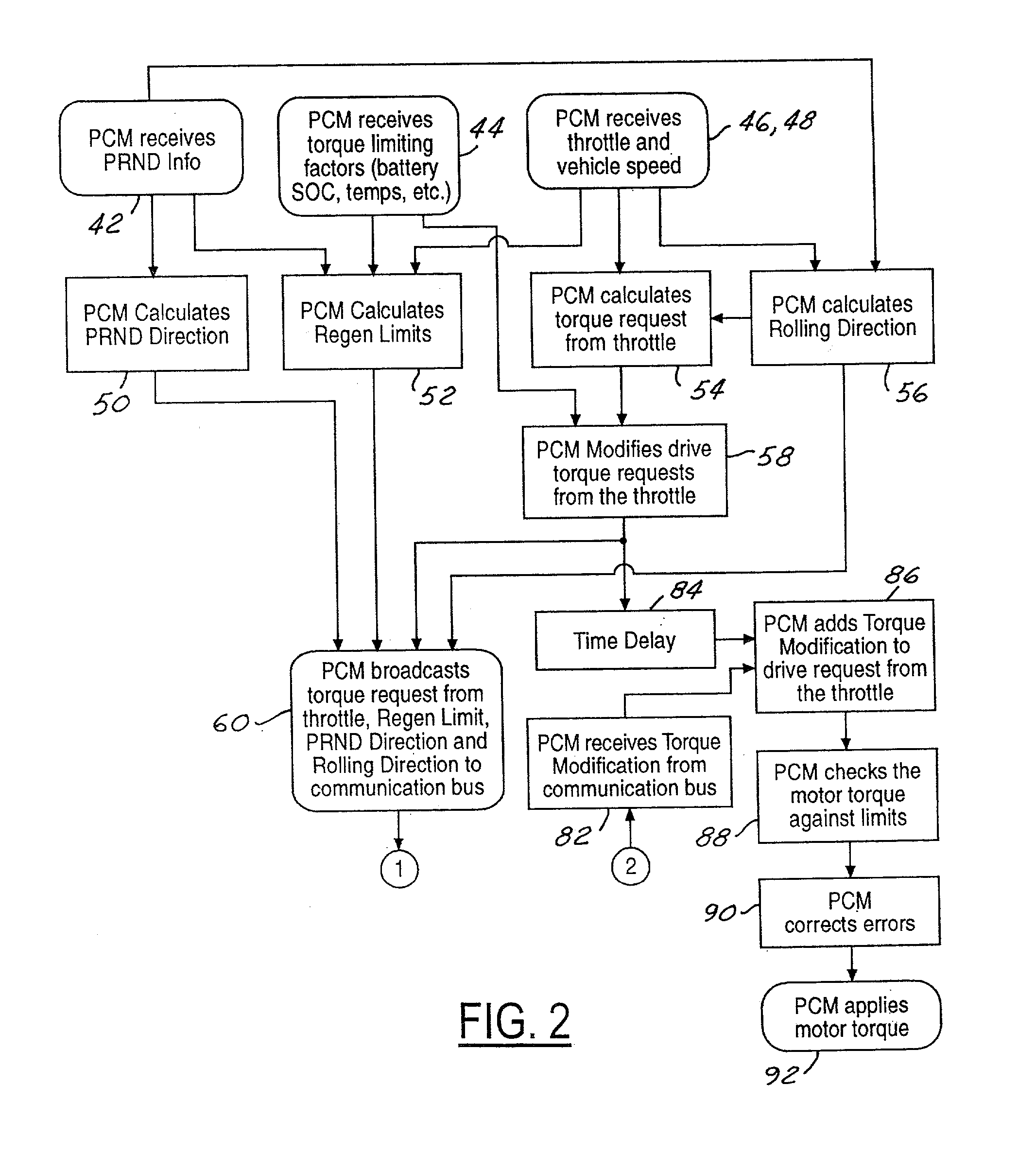
Torque control strategy for management of rollback in a wheeled vehicle whose powertrain includes a rotary electric machine
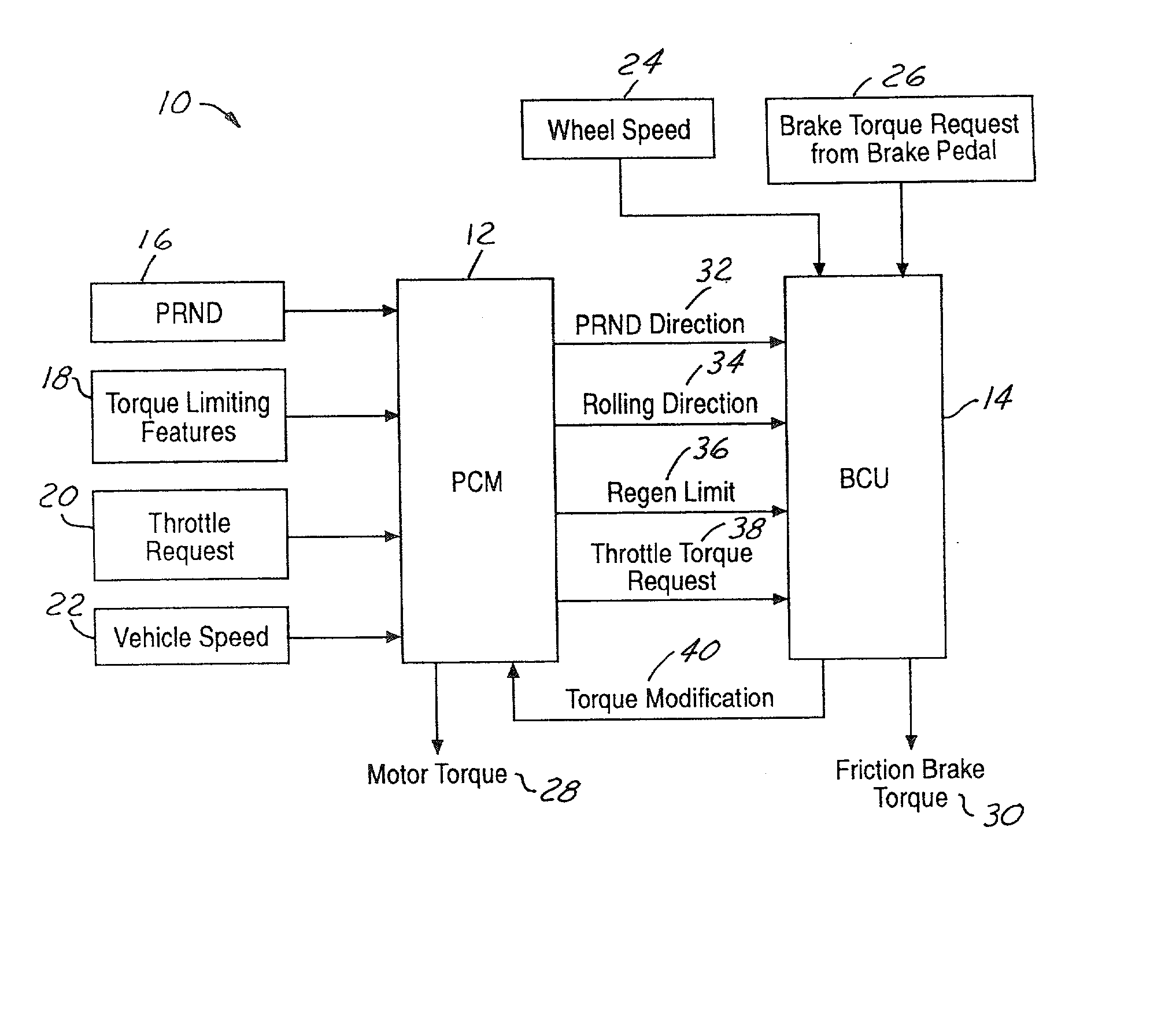
Requested brake torque and requested throttle torque are assigned opposite algebraic signs in both rollback and non-rollback states. In the non-rollback state, requested motor torque development includes a process step (206) in which requested brake torque and requested throttle torque are algebraically summed. In the rollback state, requested motor torque development includes a process step (218) in which requested throttle torque is substituted for the regeneration torque limit. In the rollback state, the difference between the requested throttle torque and the requested brake torque is compared with a zero vehicle speed regeneration torque limit (228) when the result of comparing the difference between requested throttle torque and the requested brake torque with the regeneration torque limit (222) discloses that the latter difference does not exceed the regeneration torque limit. The result is used to determine respective amounts of motor torque and friction brake torque (230, 232, 234, 236).
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
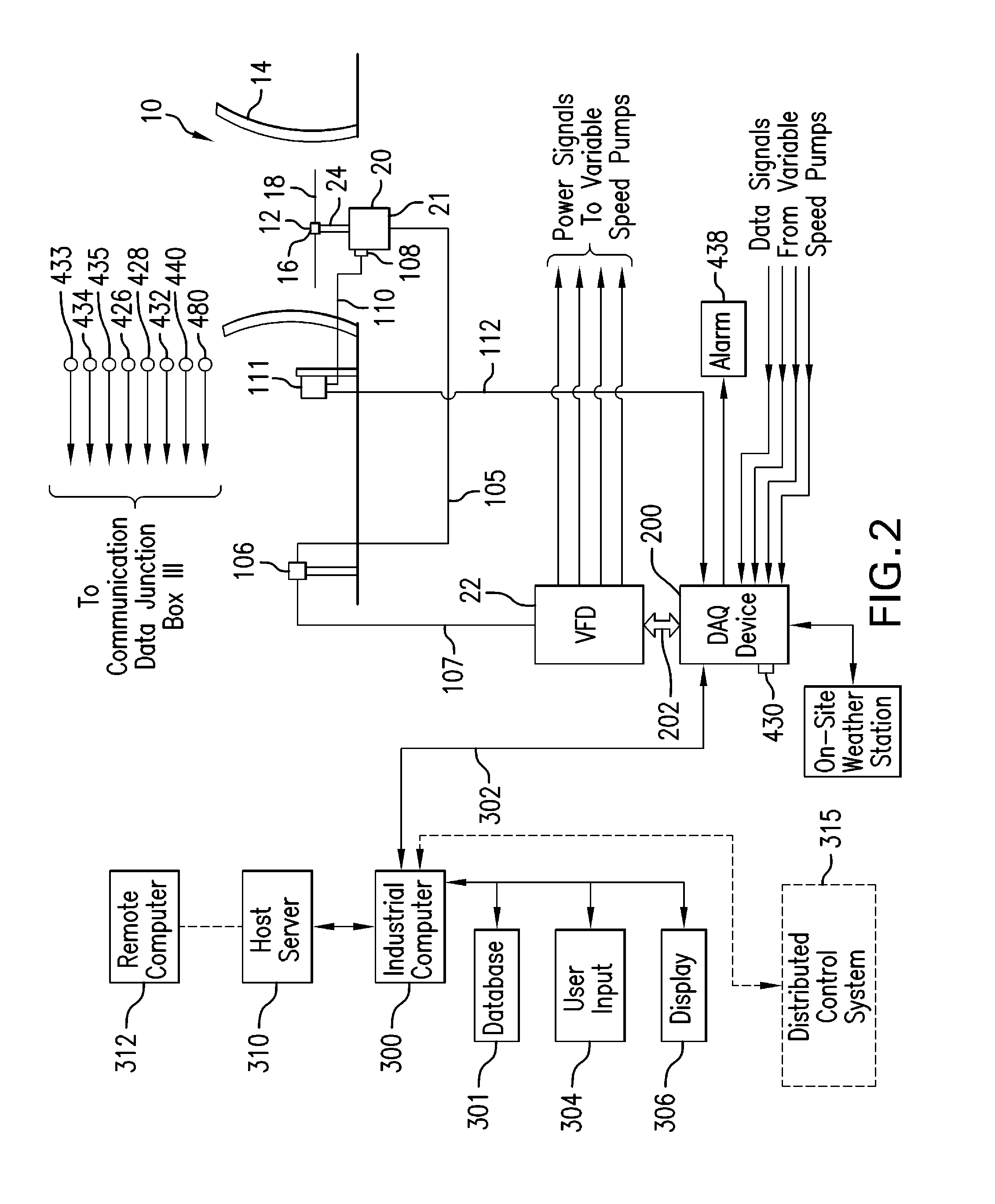
Direct drive fan system with variable process control
ActiveUS20140244051A1System smoothReduce vibrationTransportation and packagingEngine fuctionsCooling towerHigh torque
The present invention is directed to a direct-drive fan system and a variable process control system for efficiently managing the operation of fans in a cooling system such a as wet-cooling tower or air-cooled heat exchanger (ACHE), HVAC systems, mechanical towers or chiller systems. The present invention is based on the integration of key features and characteristics such as tower thermal performance, fan speed and airflow, motor torque, fan pitch, fan speed, fan aerodynamic properties, and pump flow. The variable process control system processes feedback signals from multiple locations in order control a high torque, variable speed, permanent magnet motor to drive the fan. Such feedback signals represent certain operating conditions including motor temperature, basin temperature, vibrations, and pump flow rates. Other data processed by the variable process control system in order to control the motor include turbine back pressure set-point, condenser temperature set-point and plant part-load setting. The variable process control system processes this data and the aforesaid feedback signals to optimize the operation of the cooling system in order to prevent disruption of the industrial process and prevent equipment (turbine) failure or trip. The variable process control system alerts the operators for the need to conduct maintenance actions to remedy deficient operating conditions such as condenser fouling. The variable process control system increases cooling for cracking crude and also adjusts the motor RPM, and hence the fan RPM, accordingly during plant part-load conditions in order to save energy.
Owner:PRIME DATUM
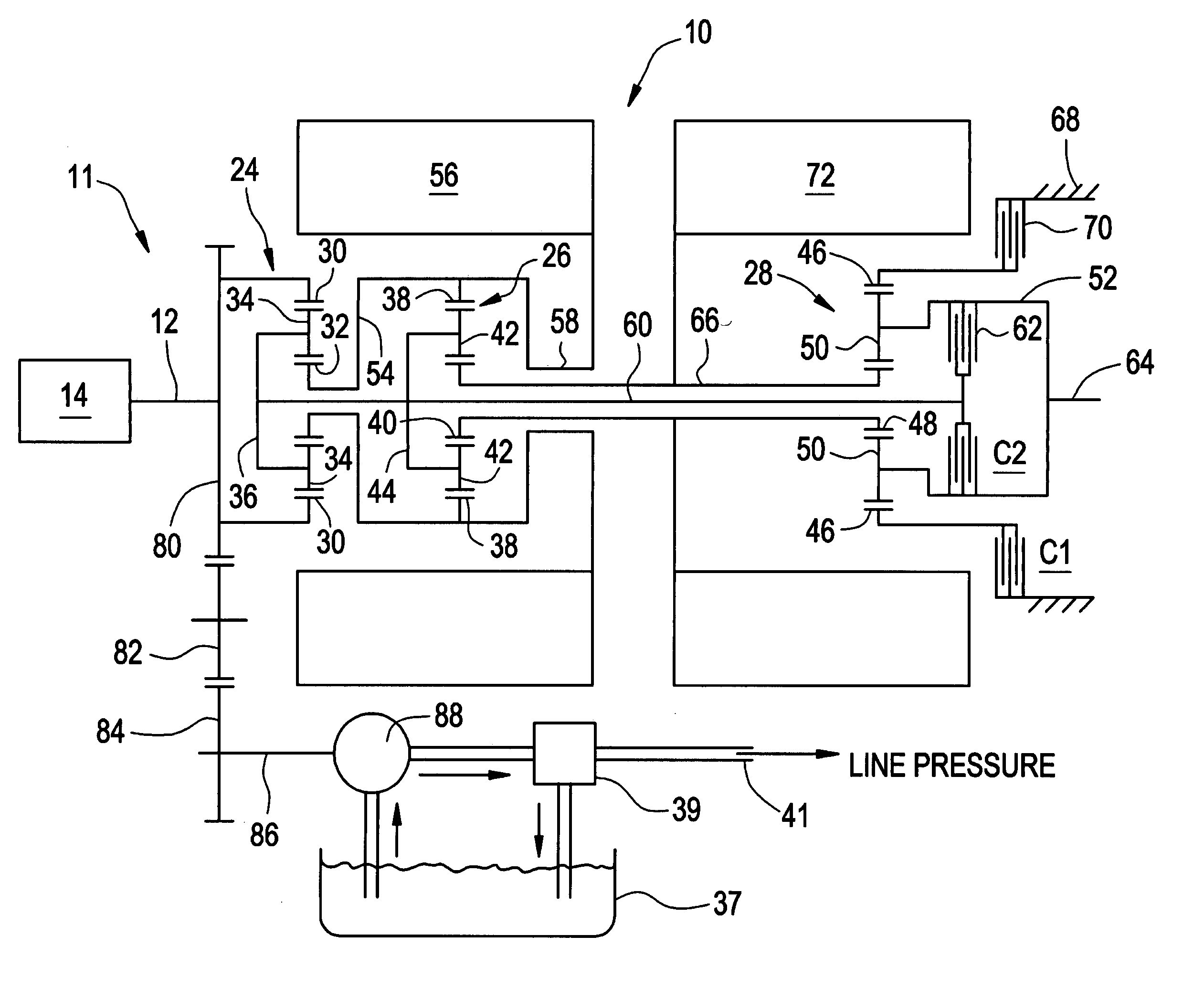
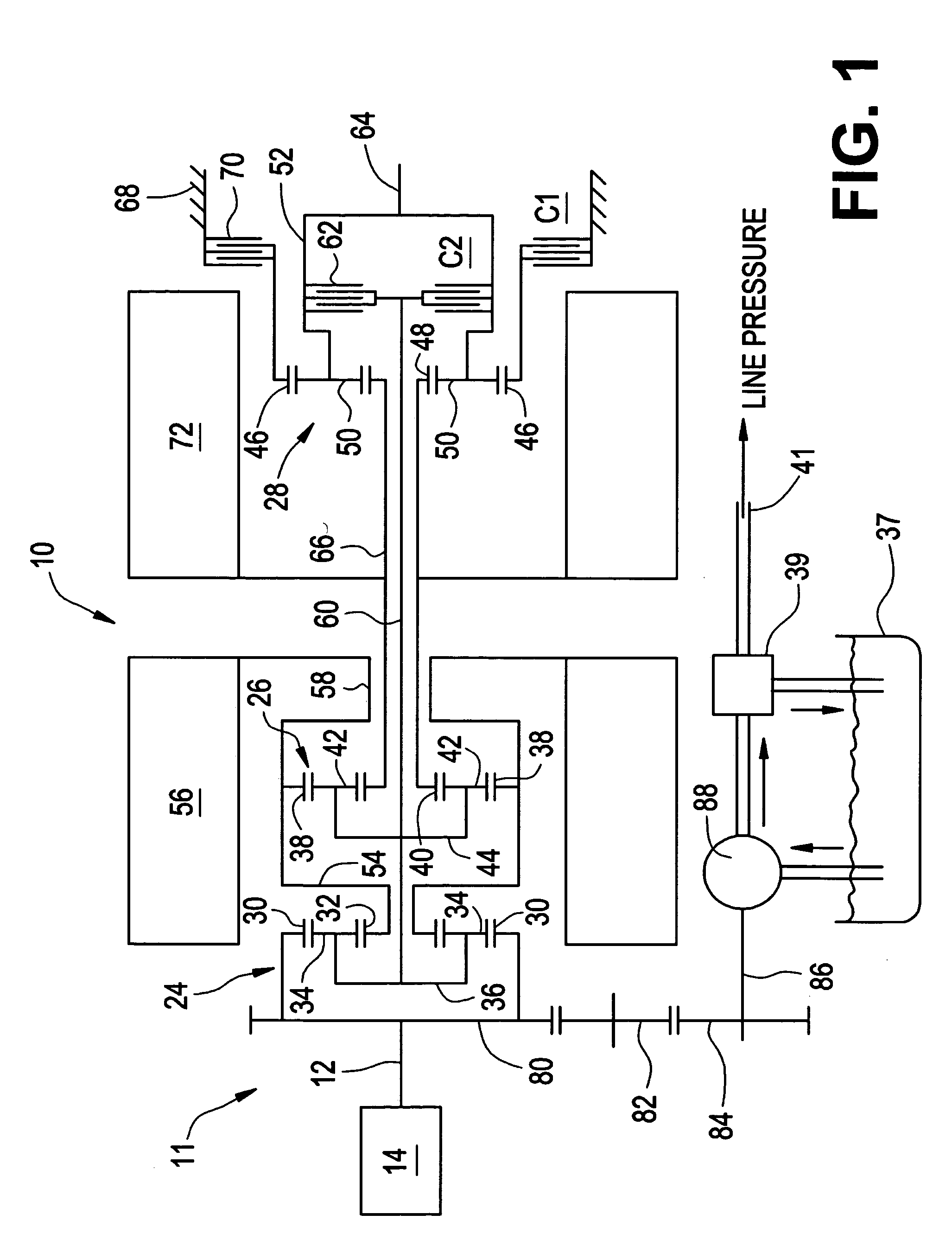
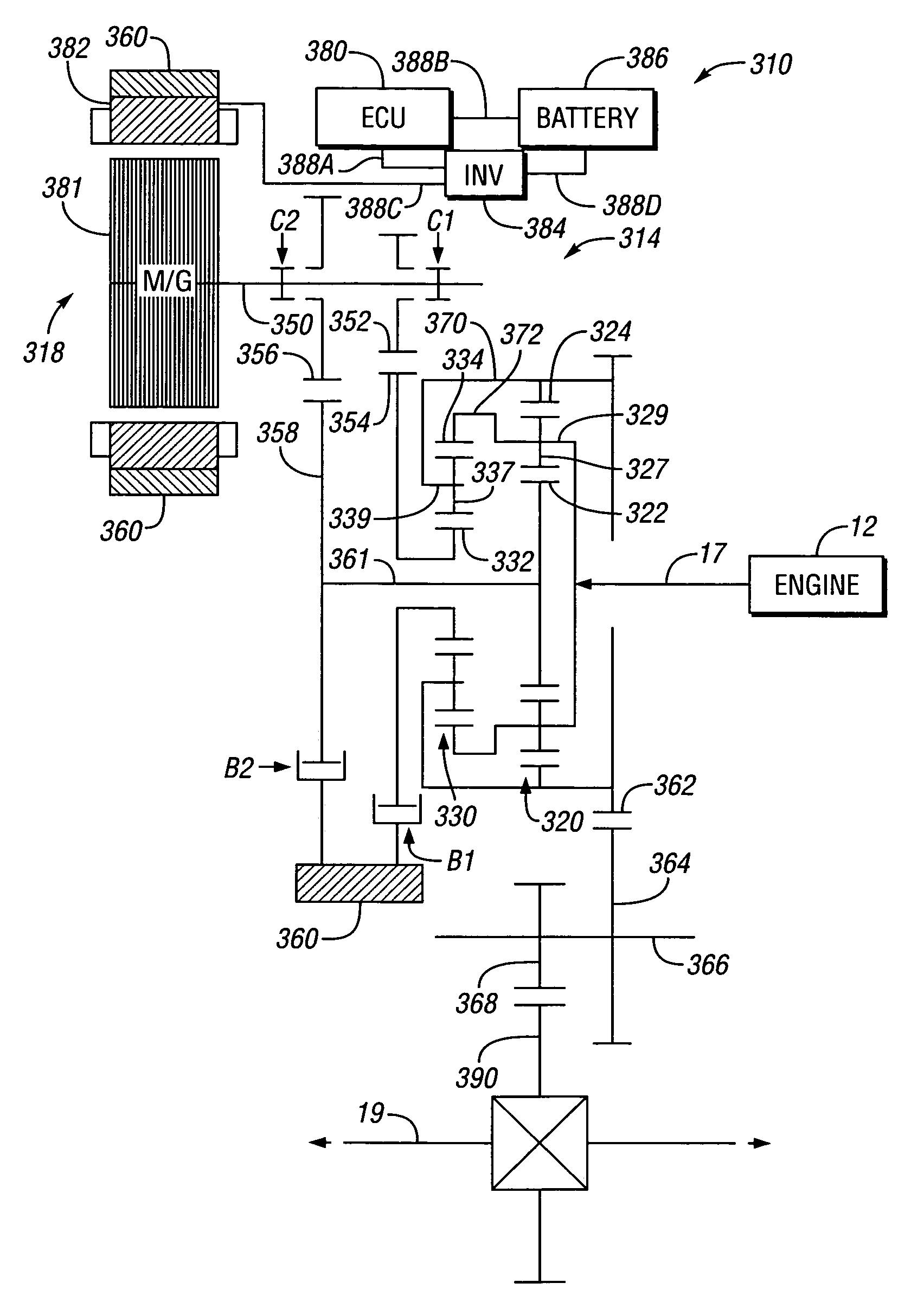
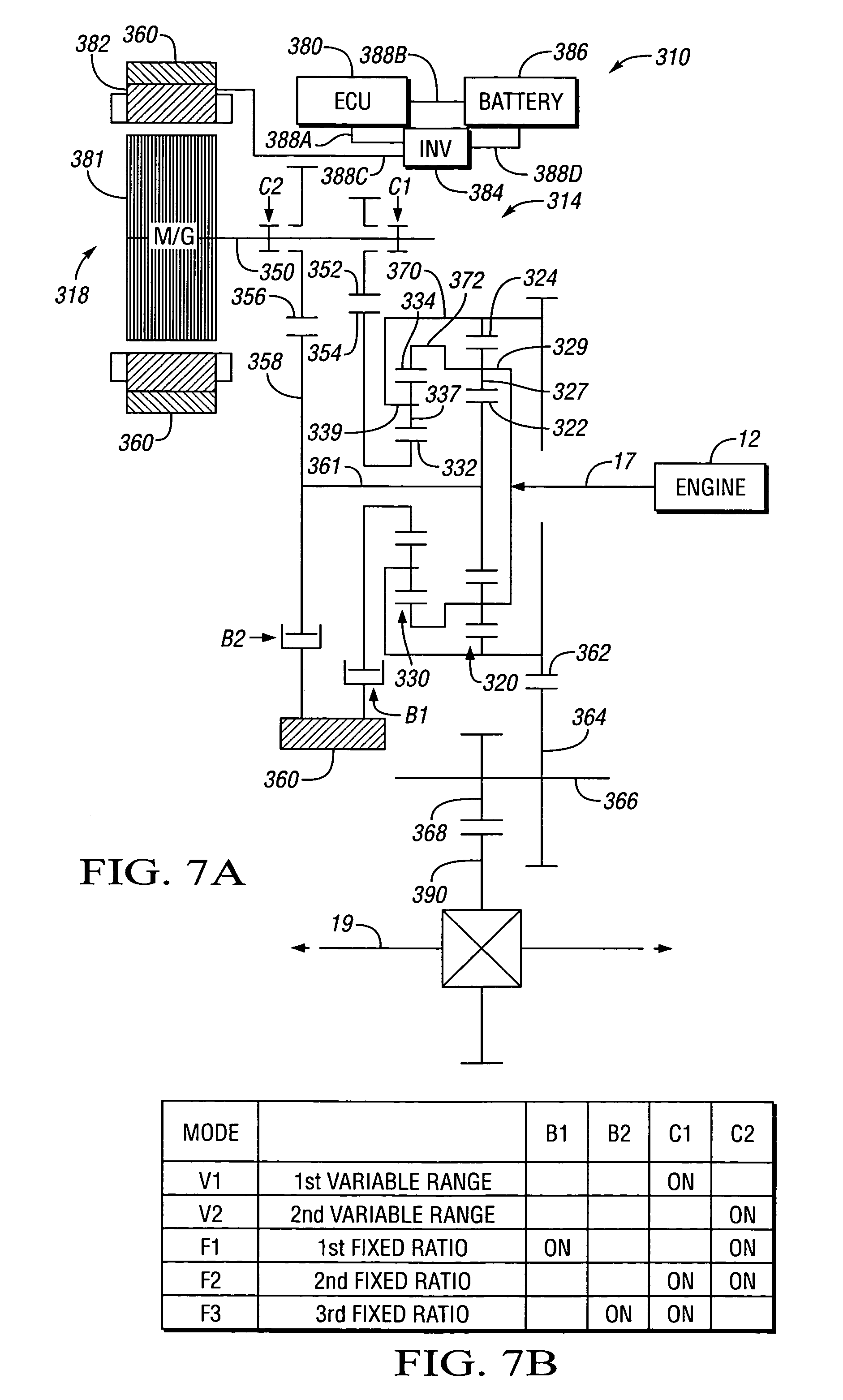
Hybrid electro-mechanical transmission with single motor/generator and method of control
InactiveUS7256510B2Low costEmission reductionElectric propulsion mountingToothed gearingsBattery chargeElectrical battery
An electro-mechanical transmission is provided having only a single motor / generator, at least one differential gear set and two torque-transmitting mechanisms. A first of the torque-transmitting mechanisms is selectively engageable to establish a first continuously variable operating mode and a second of the torque-transmitting mechanisms selectively engageable to establish a second continuously variable operating mode and a synchronous shift between the two operating modes is achievable. A method of control is provided in which vehicle operating characteristics are analyzed to identify a target operating state in terms of operating mode and ratio based on the available motor torque and motor power and on maximizing energy efficiency. The transmission is controlled to approach this operating mode as closely as possible and the diverge away from the optimum torque operating with zero net battery use as the battery charge of the battery connected with the motor / generator accumulates or depletes.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
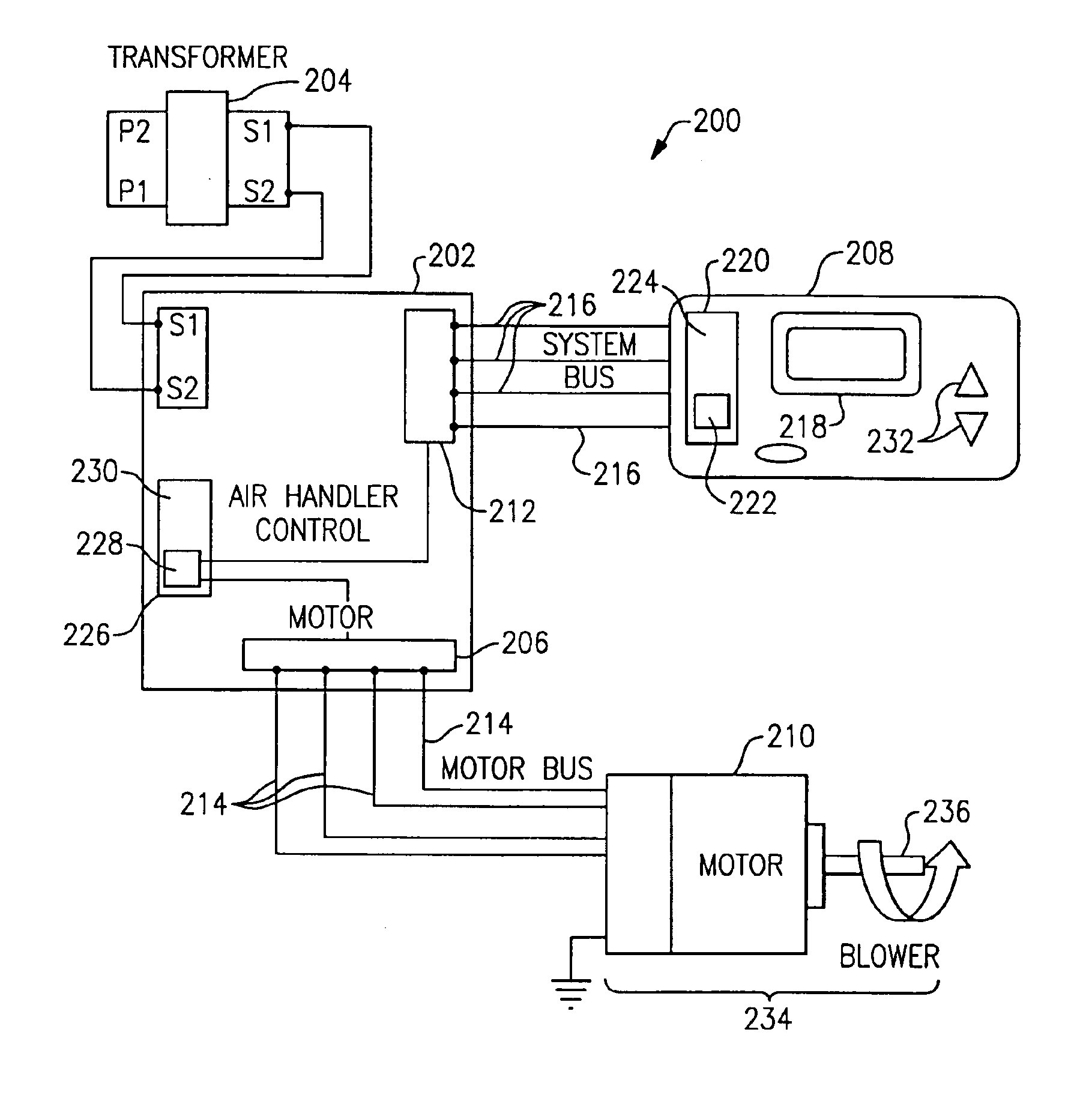
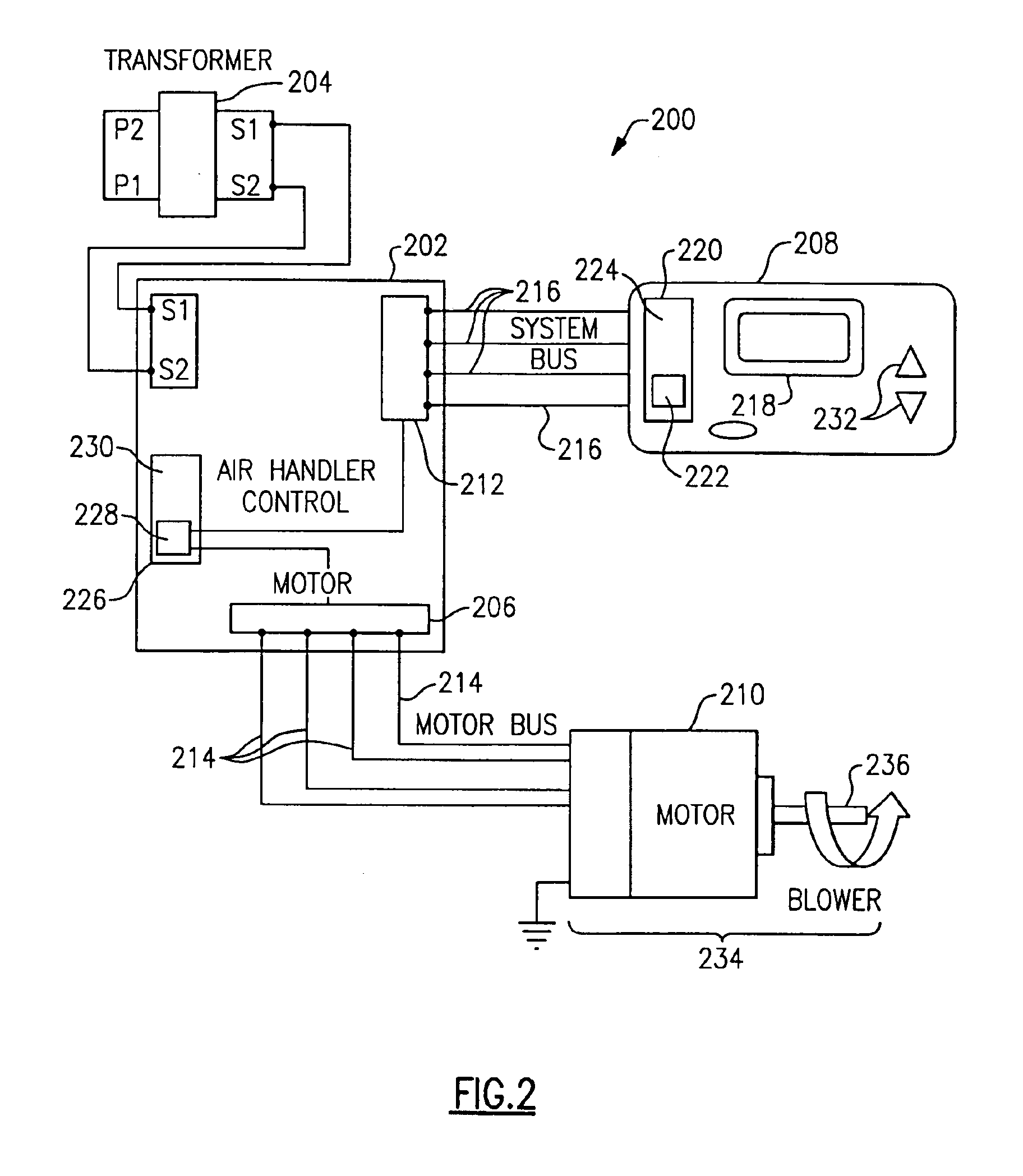
Method of determining static pressure in a ducted air delivery system using a variable speed blower motor
ActiveUS6994620B2Effective calculationDucting arrangementsMechanical apparatusMotor torqueMotor system
Systems and methods of determining static air pressure in an HVAC system are provided. Static air pressure is mathematically determined as a function of system parameters, such as blower speed, blower diameter, system volume airflow rate, and / or blower motor torque. The determined static pressure can be used during HVAC installation and during HVAC monitoring and maintenance.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
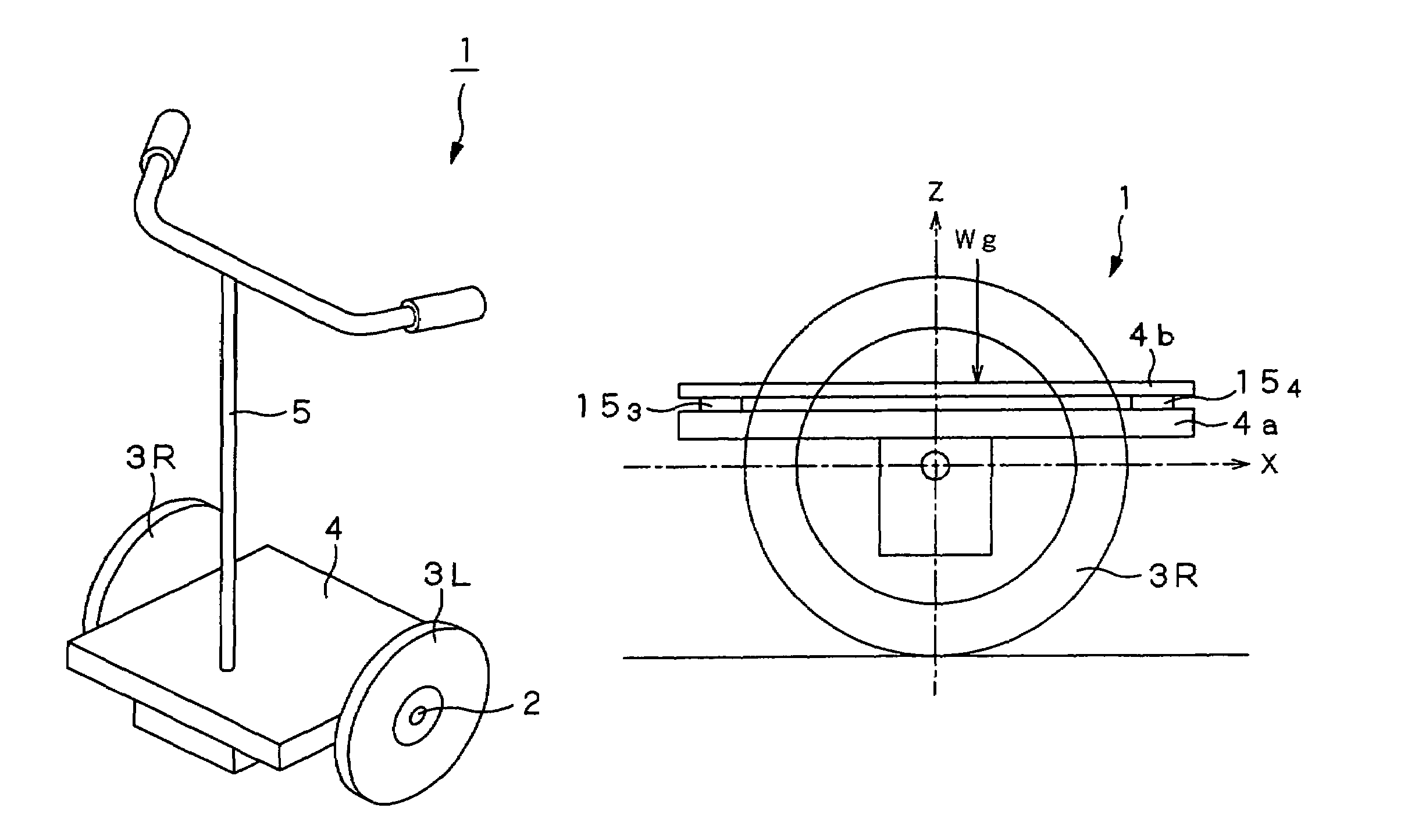
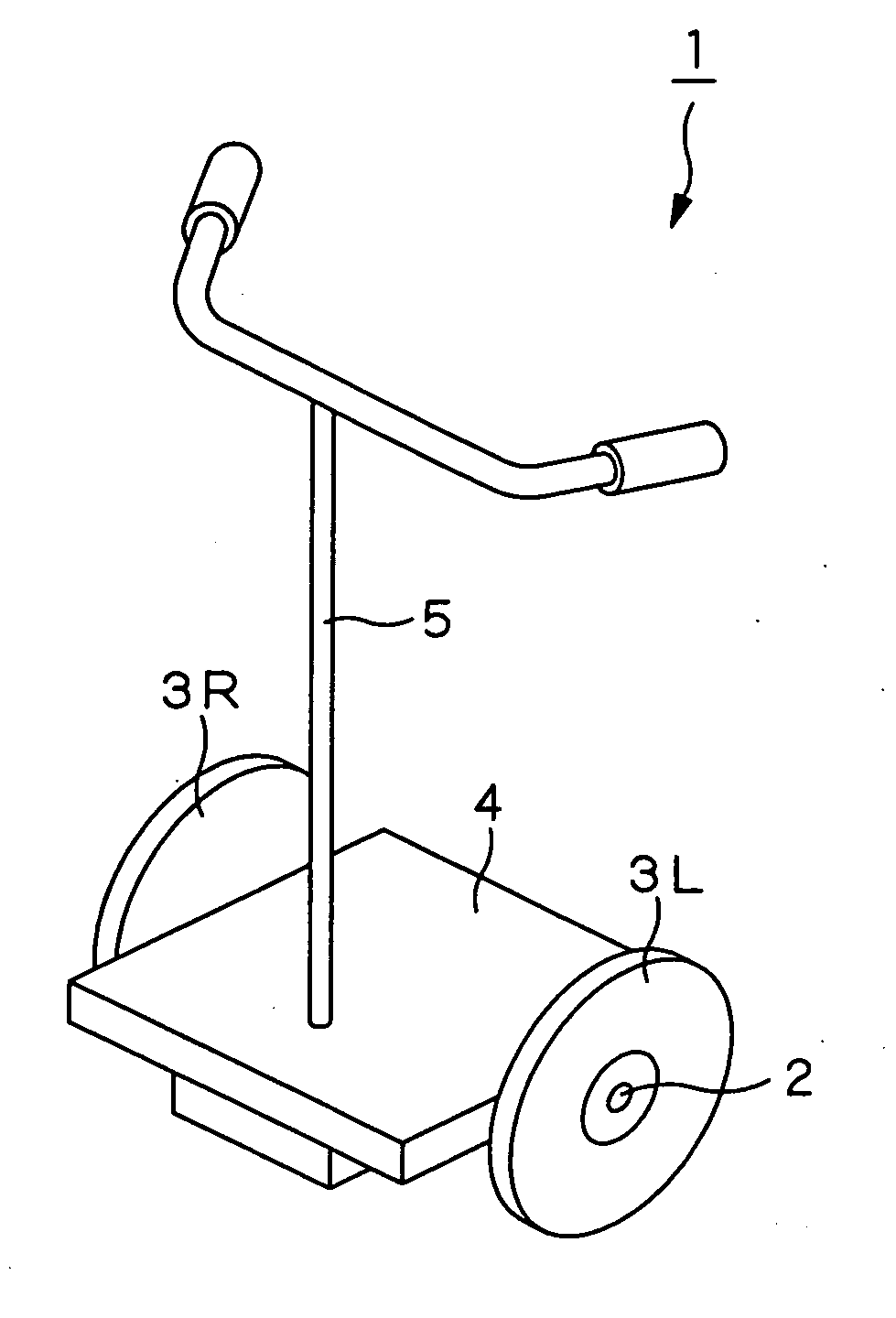
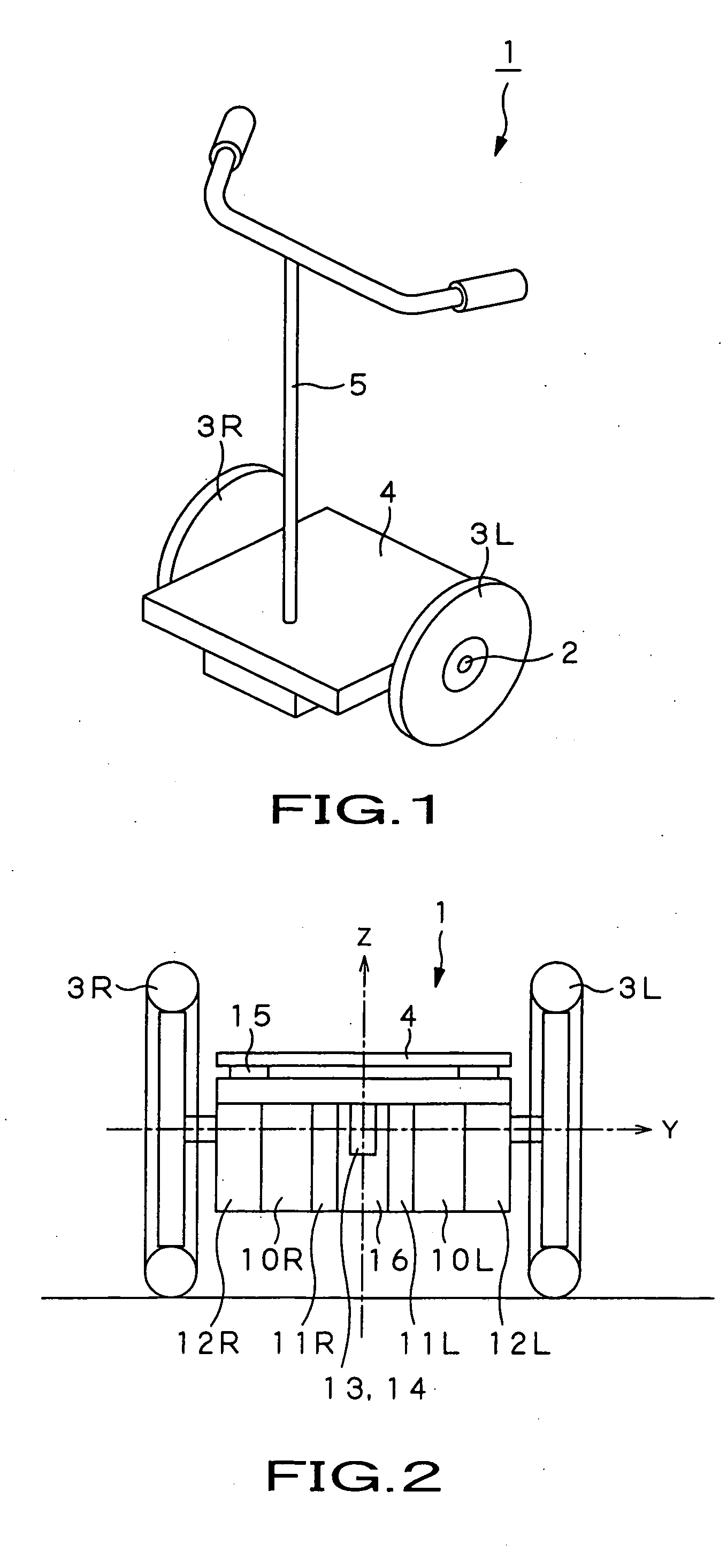
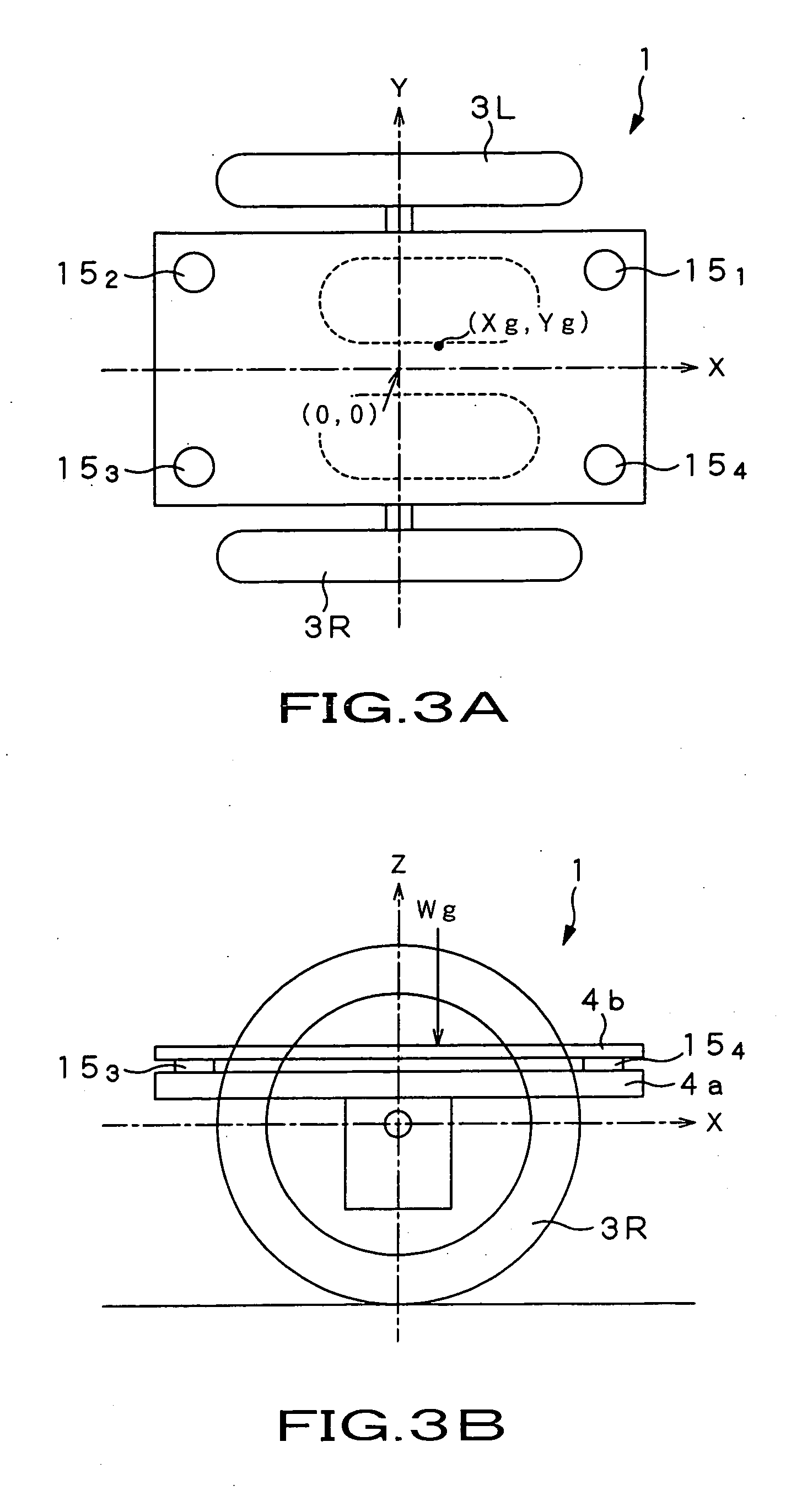
Coaxial motorcycle
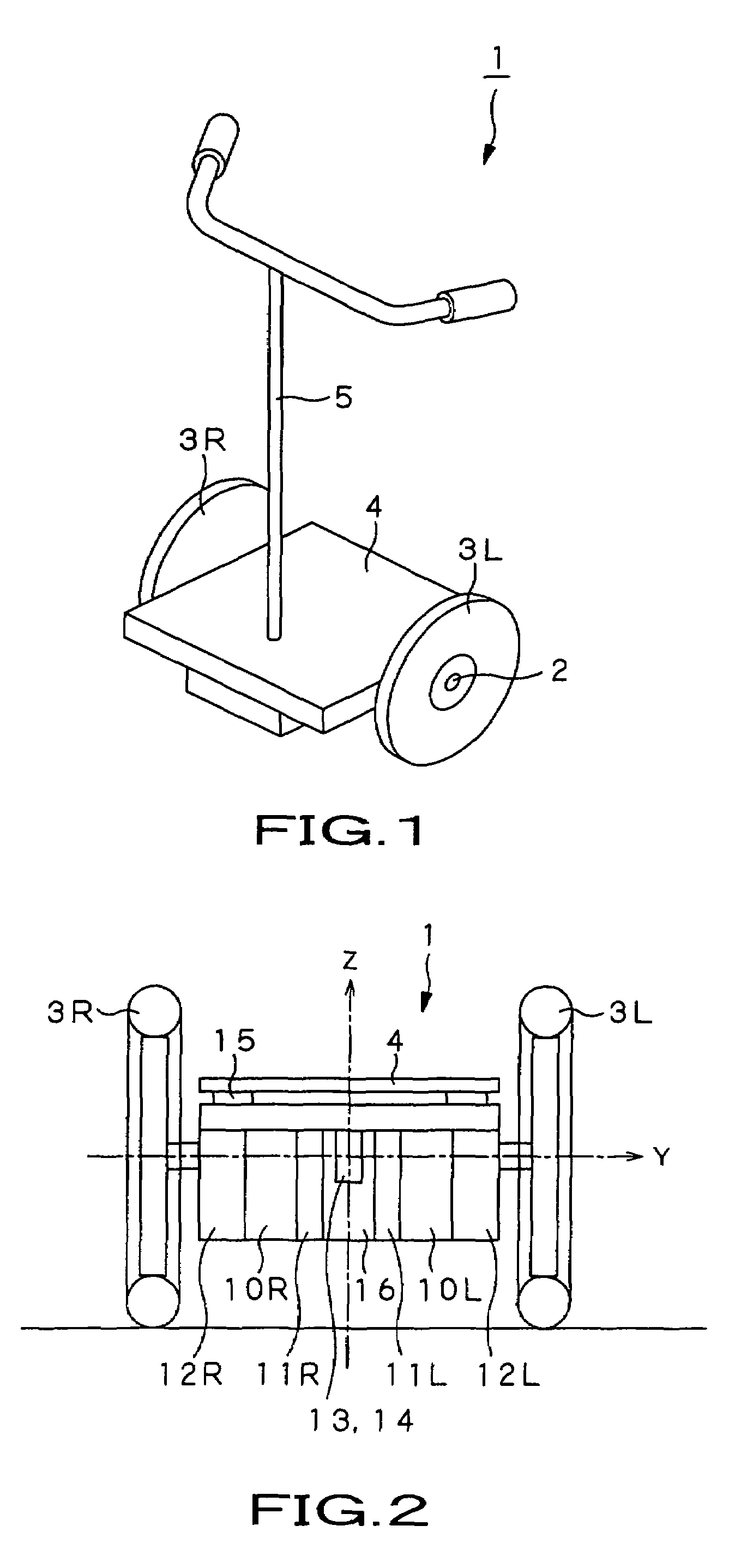
InactiveUS7703568B2Stable changeStably compatibly realizeUnicyclesElectric energy managementGyroscopeDifferentiator
In a coaxial two-wheeled vehicle, an attitude controller (84) calculates motor torque Tgyr for maintaining a base so that it has a target angle from deviation between base angle command θref serving as attitude command and current base angle θ0 calculated by using a gyro sensor (13) and an acceleration sensor (14). On the other hand, at a position proportional controller (86R), a differentiator (88R) and a velocity proportional controller (89R), there is performed PD control with respect to deviation between rotation position command Prefr of a motor rotor (92R) for right wheel and current rotation position θr of a motor rotor (92R). A current control amplifier (91R) generates motor current on the basis of added value of motor torque which is the control result and estimated load torque T1 calculated by using pressure sensors to drive the motor rotor (92R).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
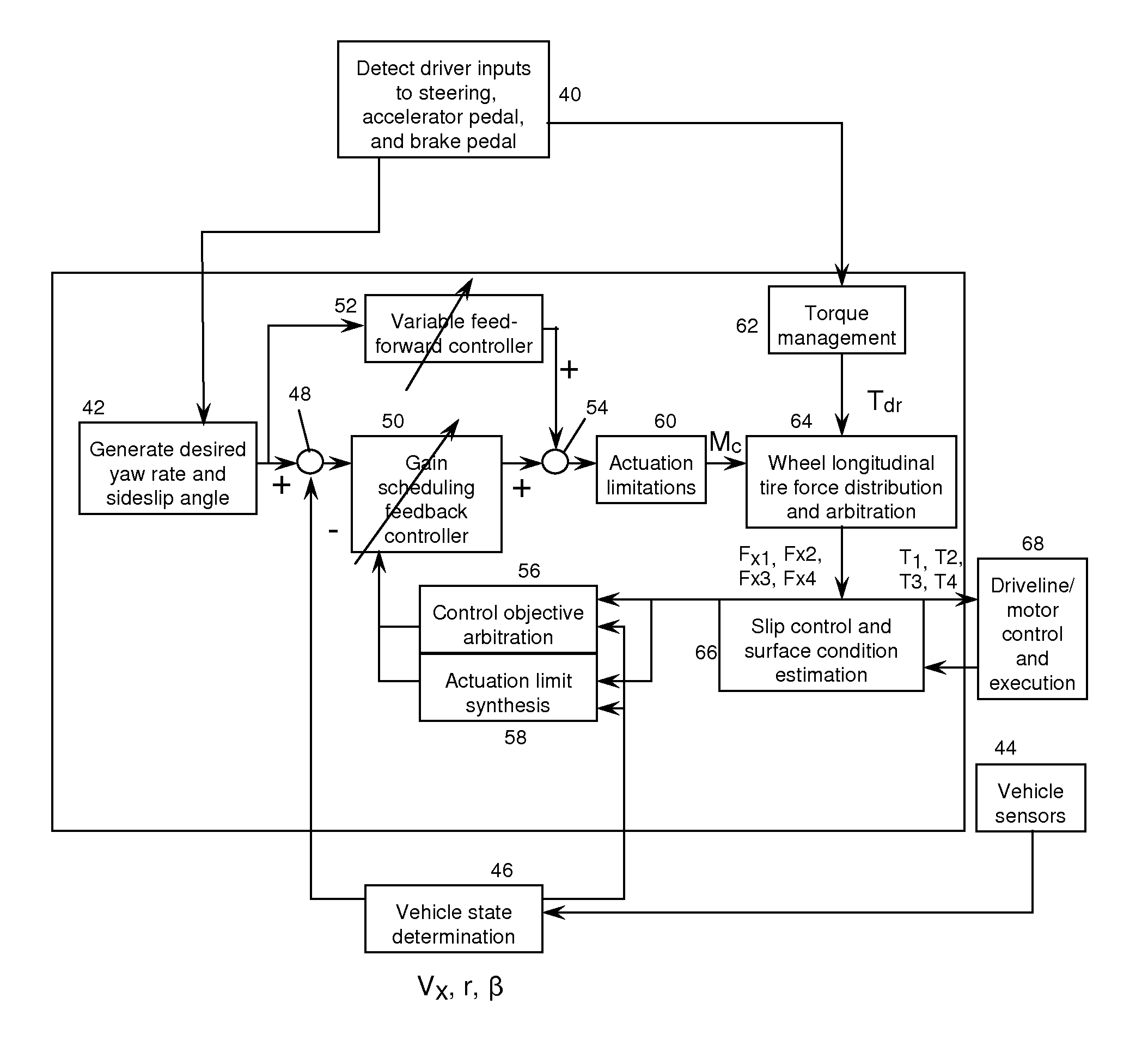
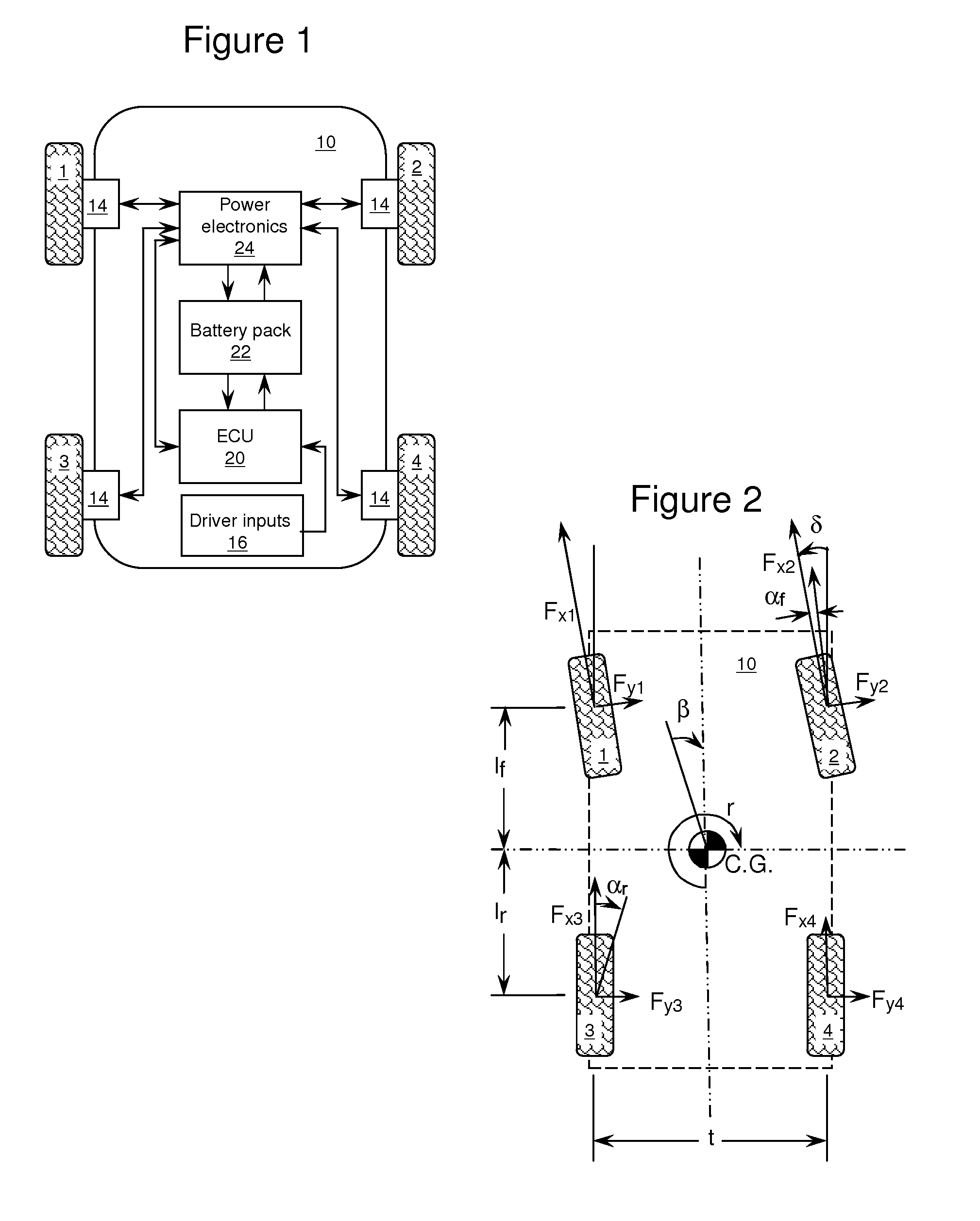
Vehicle steerability and stability control via independent wheel torque control
ActiveUS20110307129A1Overcome instabilityQuick and accurate responseDigital data processing detailsMotor depositionElectric vehicleControl theory
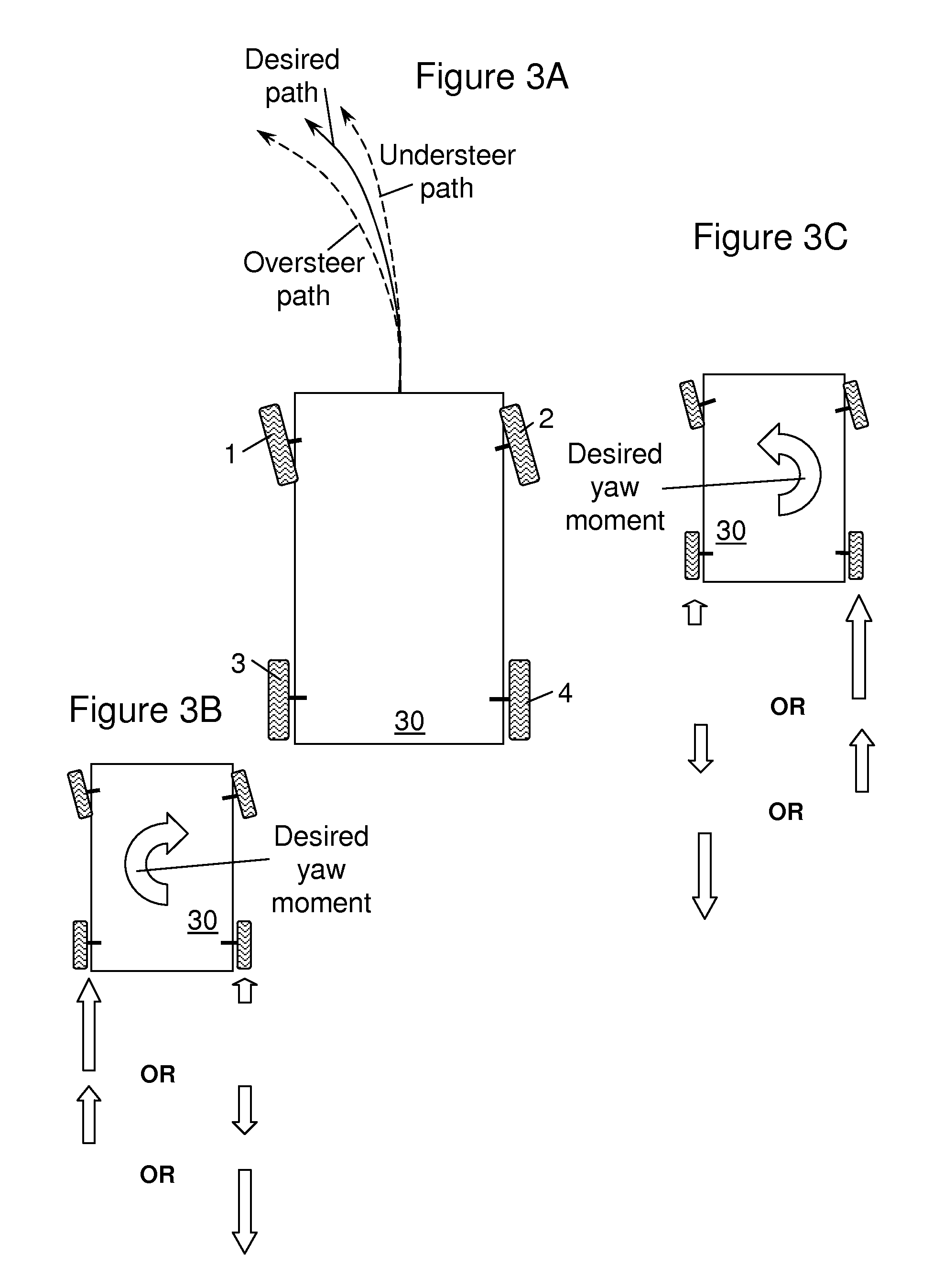
An independent wheel torque control algorithm is disclosed for controlling motor torques applied to individual electric motors coupled to vehicle wheels in an electric vehicle. In a first range of vehicle states, vehicle steerability is favored so that the operator of the vehicle suffers little or no longitudinal propulsion loss while steering is enhanced. In a second range of vehicle states, vehicle stability is favored. According to embodiments of the disclosure, a desired yaw moment is computed and then may be reduced in magnitude due to system limitations, electrical or friction limits, which prevents the desired yaw moment from being fully realized.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control apparatus for hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20050038576A1Accurate balanceMarketability deterioratesDigital data processing detailsPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsElectrical batteryDrive motor
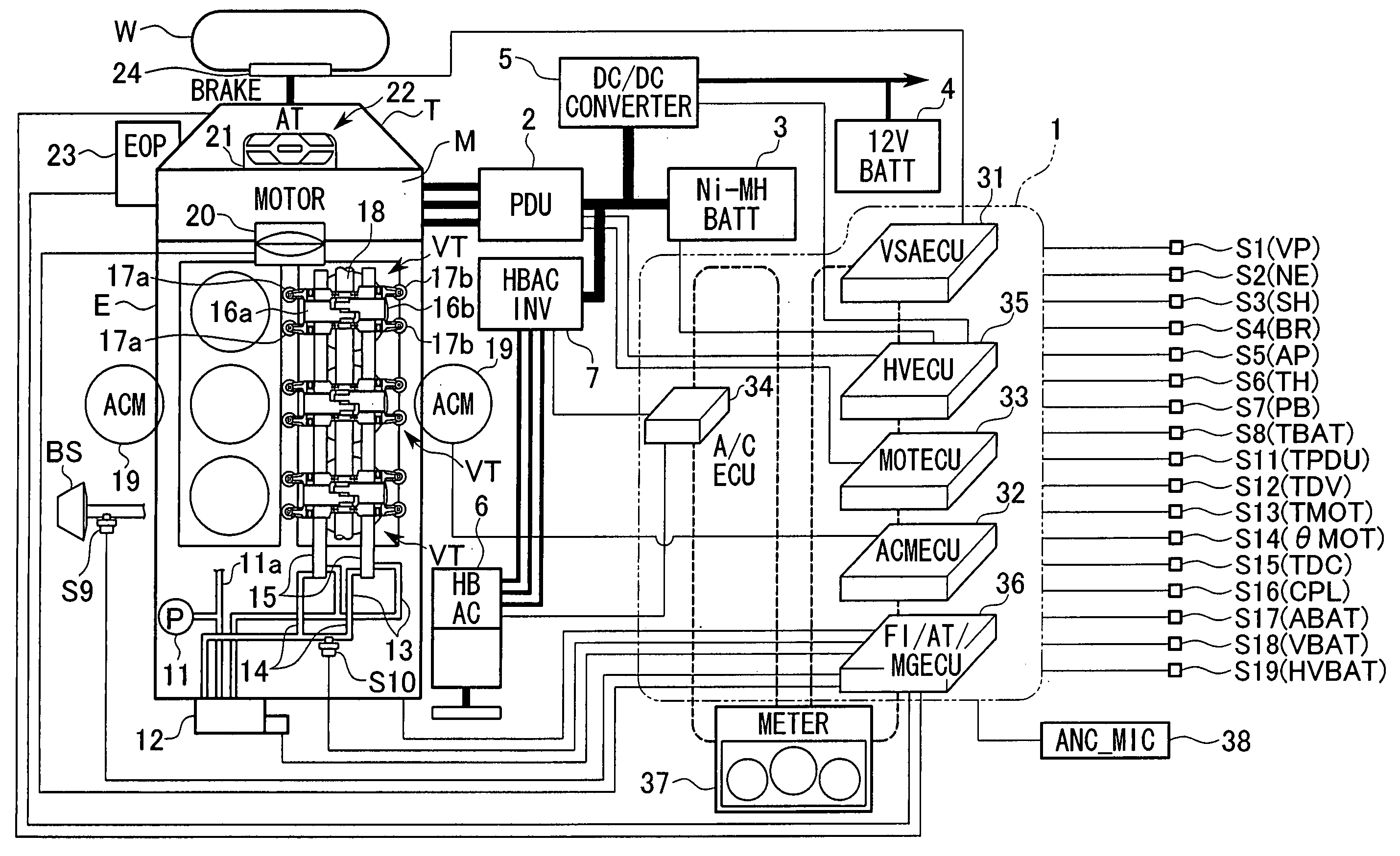
In a control apparatus for a hybrid vehicle which is able to travel under the driving force from at least one of an internal-combustion engine E and a drive motor connected to the internal-combustion engine, when an FI / AT / MGECU and a MOTECU execute motor damping which generates a torque for suppressing the torque vibration of the internal-combustion engine, in the motor M, the MOTECU corrects a motor torque calculating battery terminal current value obtained by multiplying an input-output current ABAT of the battery, by an offset value corresponding to the motor damping, and executes zero power control based on the corrected motor torque calculating battery current value. As a result, the input and output power of the power storage unit are accurately balanced and overcharge or overdischarge of the battery based on the input-output current ABAT of the battery including errors due to the damping control or the motor torque calculating battery current value, is avoided.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
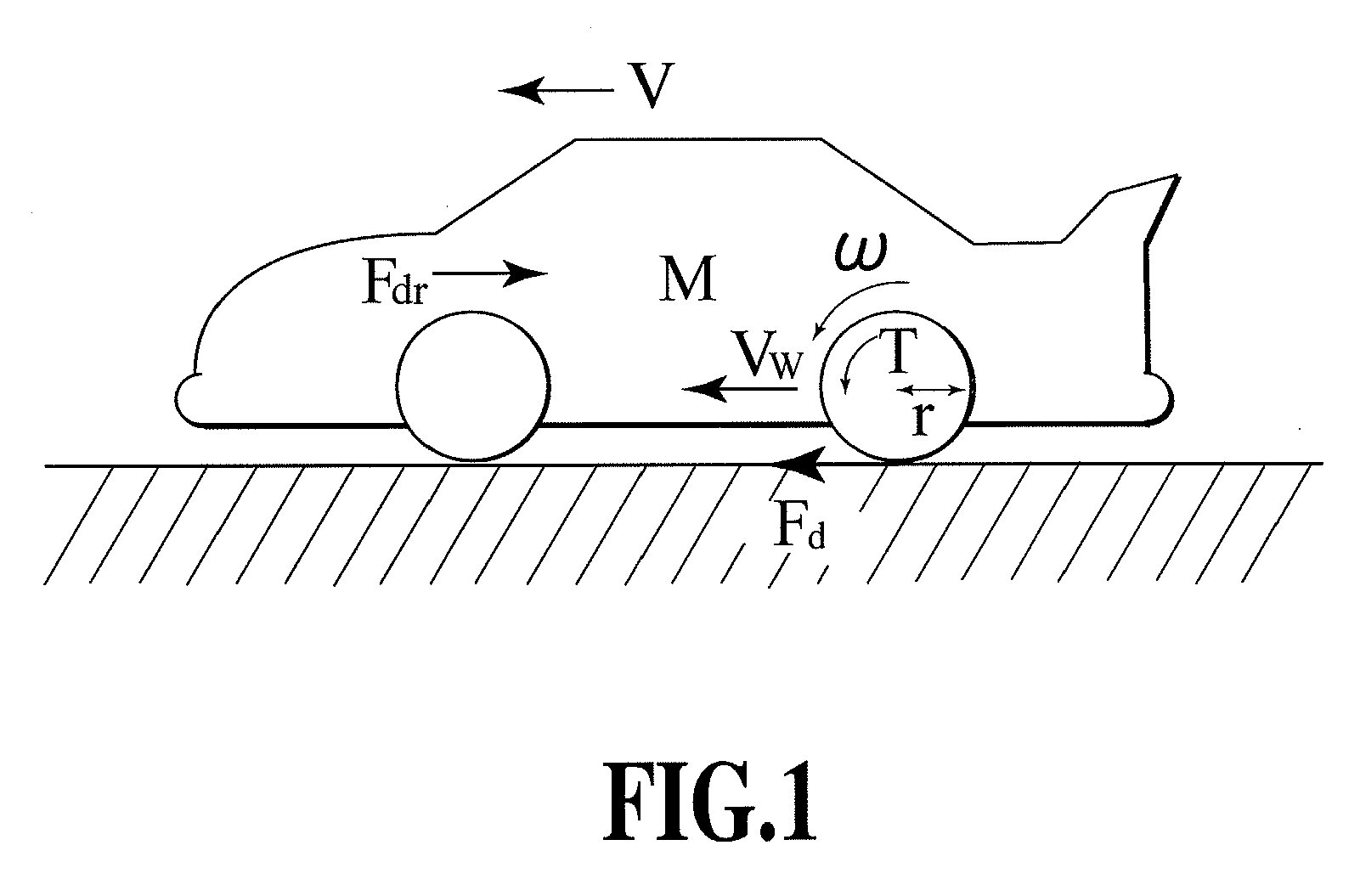
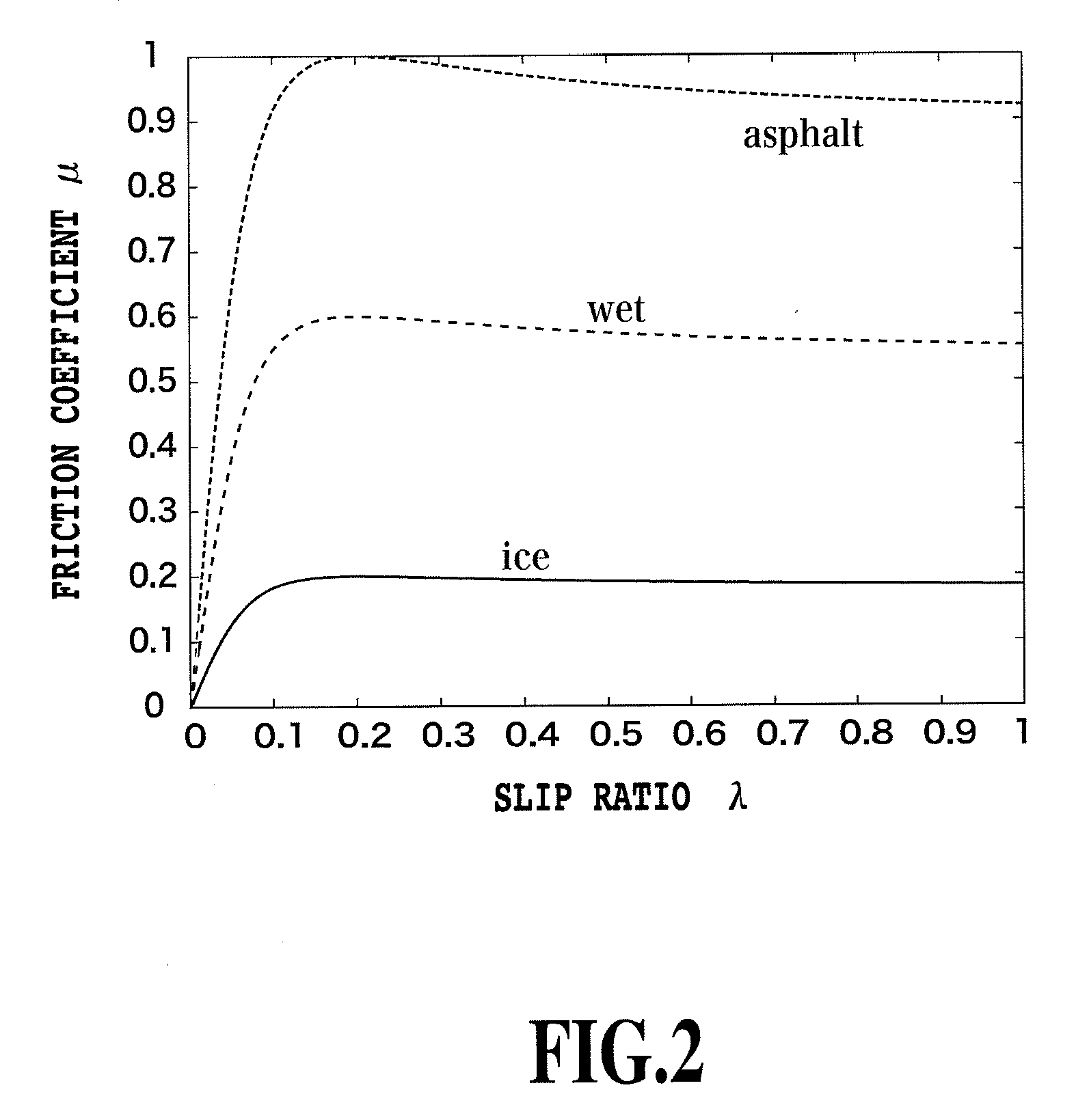
Slip ratio estimating device and slip ratio control device
InactiveUS20090210128A1Accurate estimateQuick implementationSpeed controllerElectric motor controlMeasuring instrumentRotation velocity
The present invention provides a slip rate estimating device measuring a slip ratio without the need for a body speed and a slip ratio control device using the slip ratio estimating device. A motor torque measured by a torque measuring instrument is input to each of a vehicle model (601) and an SRE (602) that performs calculations including time differentiation of the slip ratio. The vehicle model (601) derives a wheel rotation speed, a wheel rotation acceleration, and a body speed. The vehicle model (601) outputs the wheel rotation speed and the wheel rotation acceleration to the SRE (602). The SRE (602) outputs the slip ratio based on the motor torque, the wheel rotation speed, and the wheel rotation acceleration.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA NAT UNIV
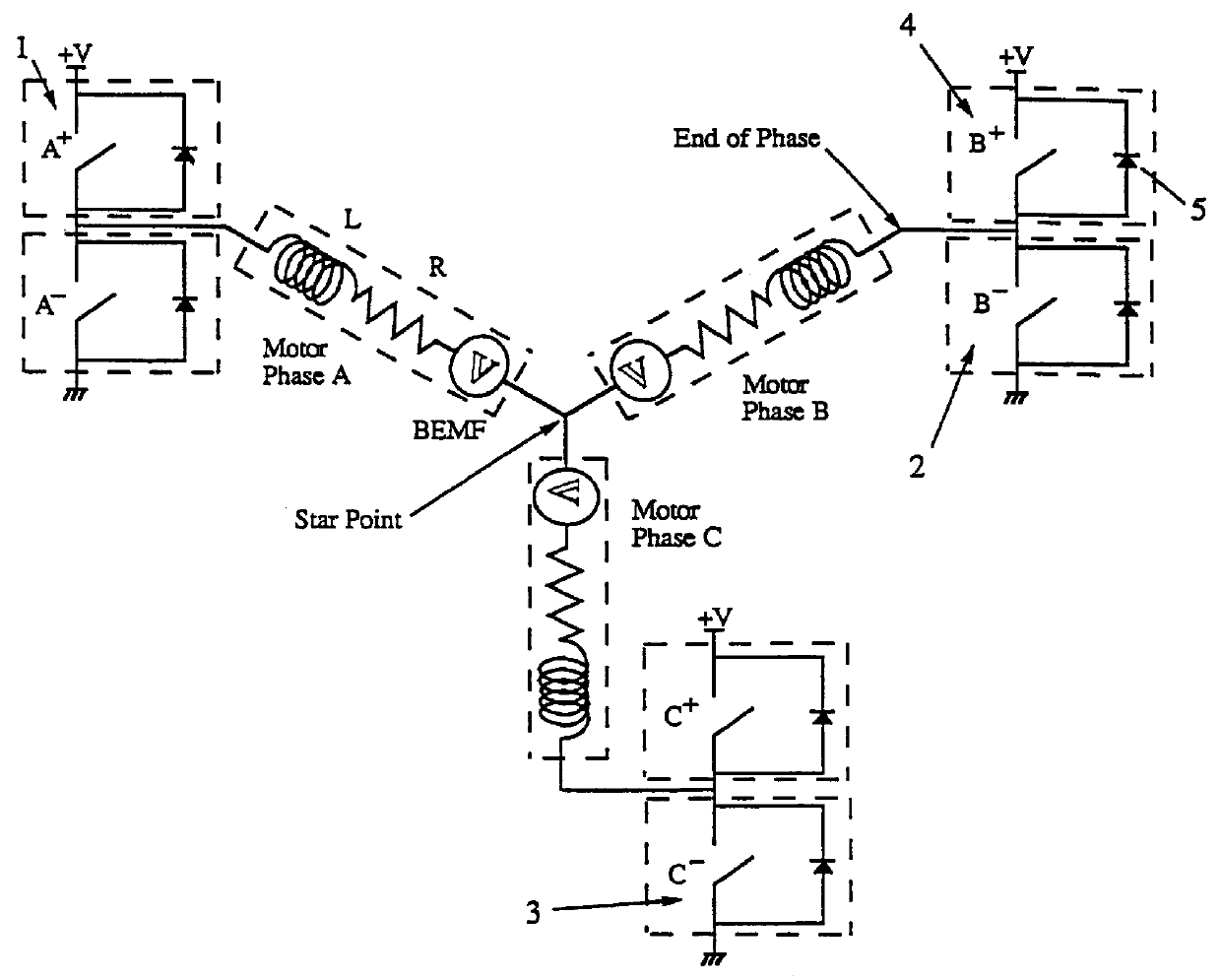
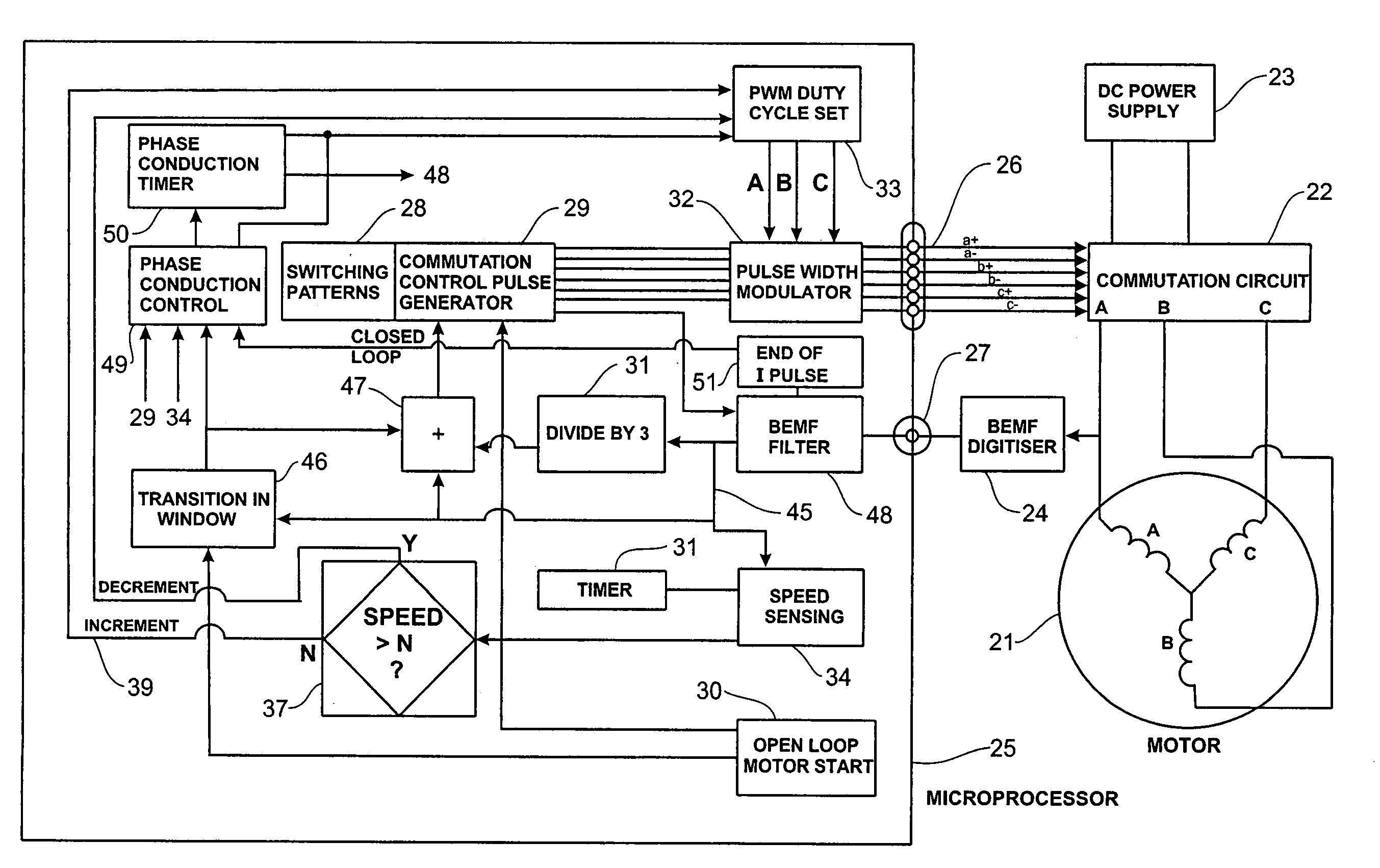
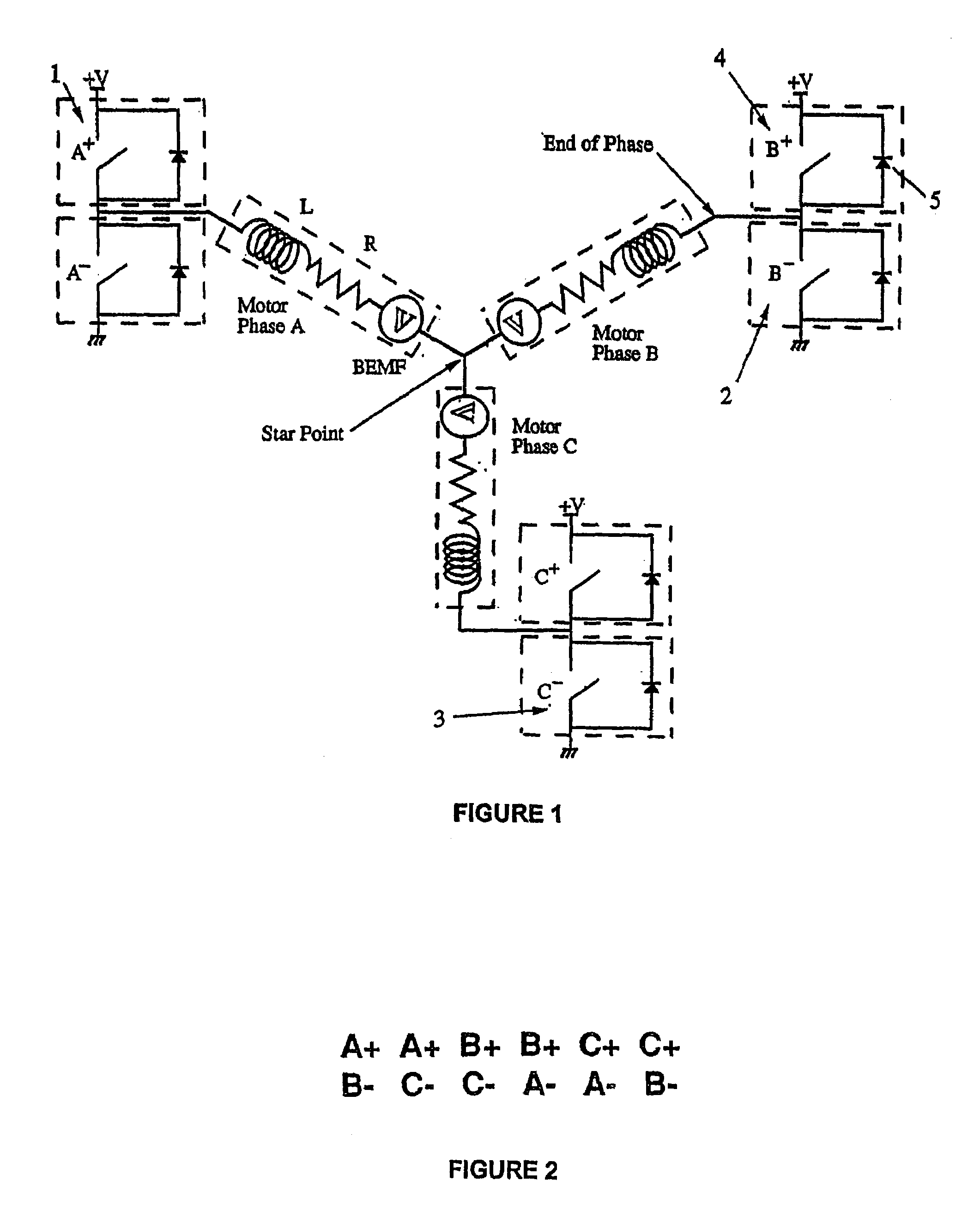
Low noise back EMF sensing brushless DC motor
InactiveUS7141949B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersLow noiseEngineering
A low noise electronic three phase bridge controlled brushless DC motor suitable for whiteware appliance pumps and other appliance applications. Back EMF zero crossing sensing is used to determine rotor position and thus stator winding commutation times. Motor torque and speed are controlled by pulse width modulating the operation of that bridge switching device which has just been switched from an OFF state to an ON state on each new commutation. All three stator windings have current flowing in each winding commutation to improve motor current waveform and thereby reduce motor noise, but the current in one winding is always terminated before the end of the commutation period to allow the back EMF in that winding to be sensed to zero crossing.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
Torque distribution control method for electric-wheel automobile hub motor torque distribution system
InactiveCN104175902AImproved directional stabilityImprove steering performanceSpeed controllerElectric energy managementLow speedDistribution system
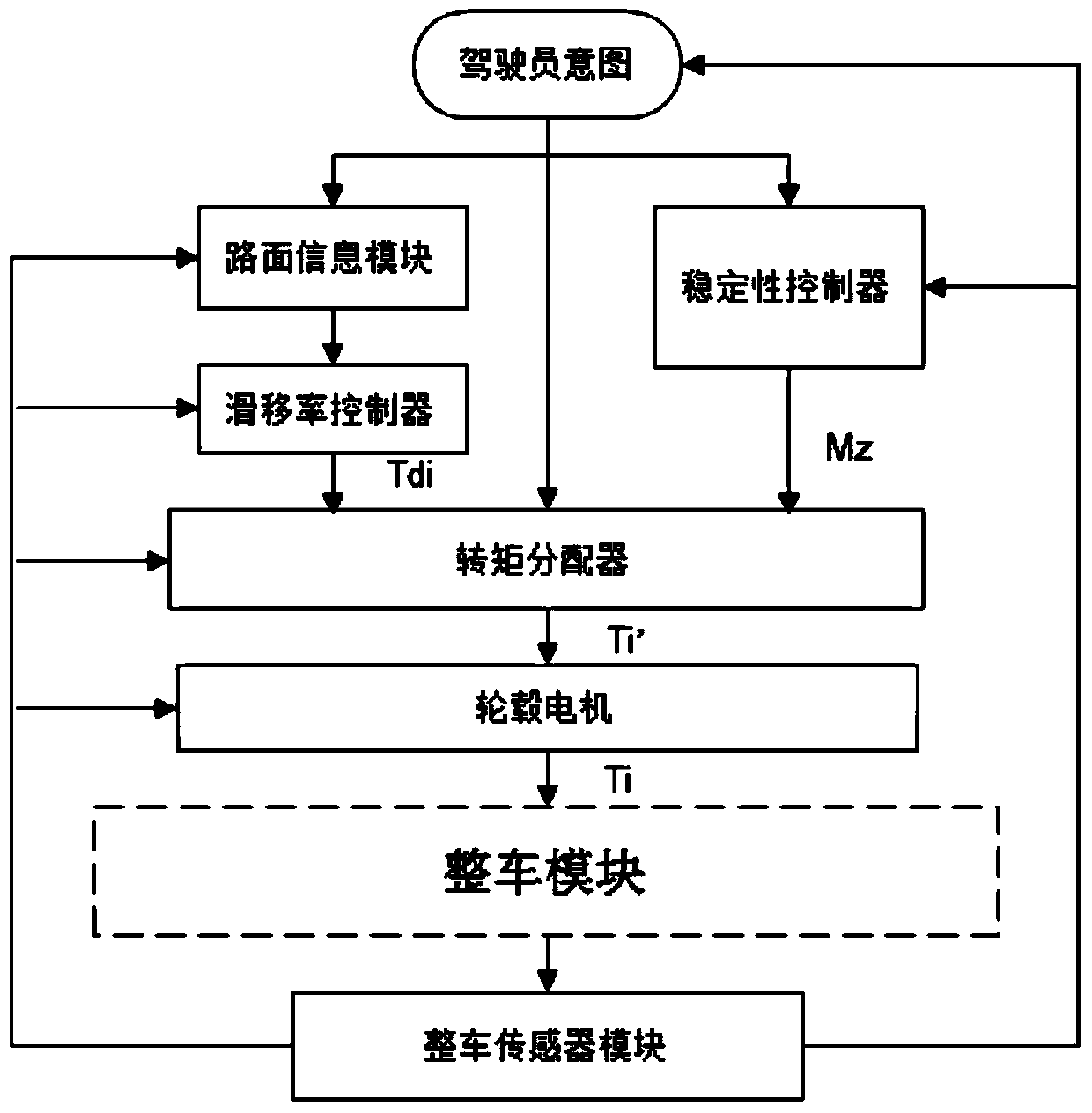
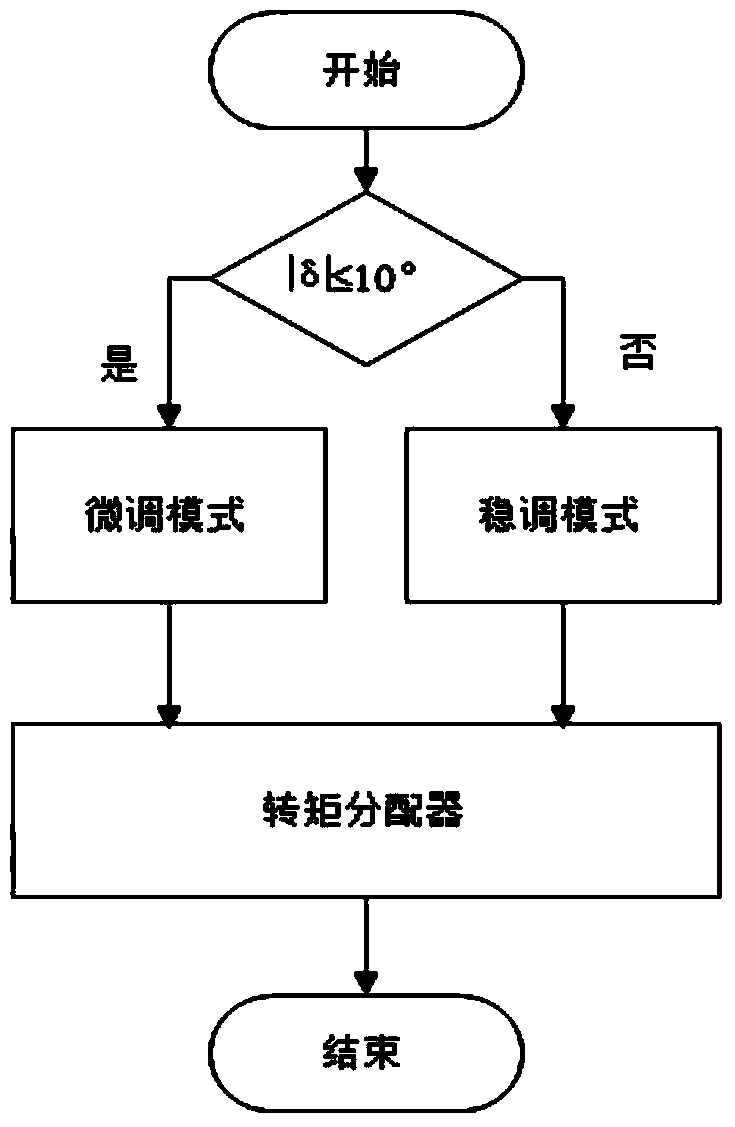
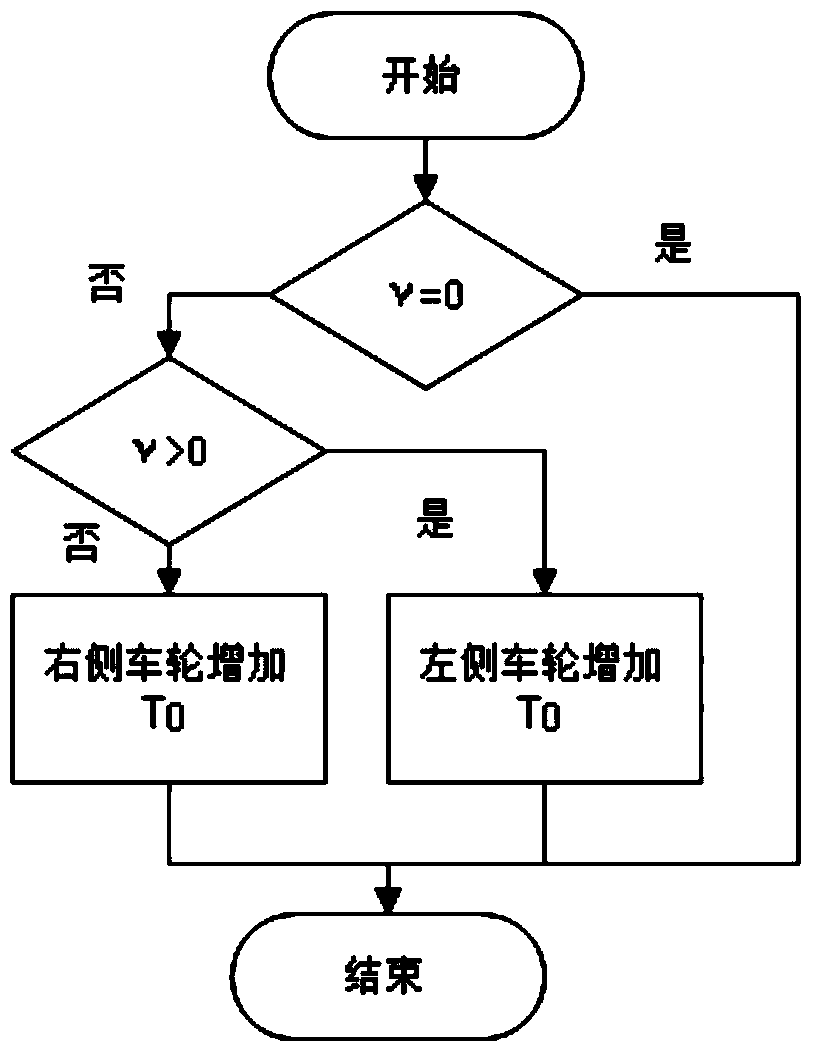
The invention discloses a torque distribution control method for an electric-wheel automobile hub motor torque distribution system, and belongs to the field of an electric-wheel automobile. The electric-wheel automobile hub motor torque distribution system comprises parts as follows: a driver intention module, a hub motor, a stability controller, a torque distributor, a slip rate controller, a whole automobile module, a pavement information module and a whole automobile sensor module, wherein the stability controller comprises a fine adjustment mode and a stable adjustment mode, and the torque distributor divides whole automobile movement into a dynamic mode, an economical mode and a stable mode. According to the torque distribution control method, a plurality of controlled variables such as the slip rate, attachment coefficient, yaw velocity, side slip angle, hub motor rotating speed and the like are combined to control the automobile, so that stability and dynamic performance of the automobile at the low speed or high speed are guaranteed; and the automobile torque is distributed, so that automobile drive capacity, motor utilization efficiency and whole automobile stability when the automobile is driven normally or has a slipping phenomenon are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Coaxial motorcycle
InactiveUS20060231313A1Stably compatibly realizeStable changeSpeed controllerElectric devicesGyroscopeDifferentiator
In a coaxial two-wheeled vehicle, an attitude controller (84) calculates motor torque Tgyr for maintaining a base so that it has a target angle from deviation between base angle command θref serving as attitude command and current base angle θ0 calculated by using a gyro sensor (13) and an acceleration sensor (14). On the other hand, at a position proportional controller (86R), a differentiator (88R) and a velocity proportional controller (89R), there is performed PD control with respect to deviation between rotation position command Prefr of a motor rotor (92R) for right wheel and current rotation position θr of a motor rotor (92R). A current control amplifier (91R) generates motor current on the basis of added value of motor torque which is the control result and estimated load torque T1 calculated by using pressure sensors to drive the motor rotor (92R).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
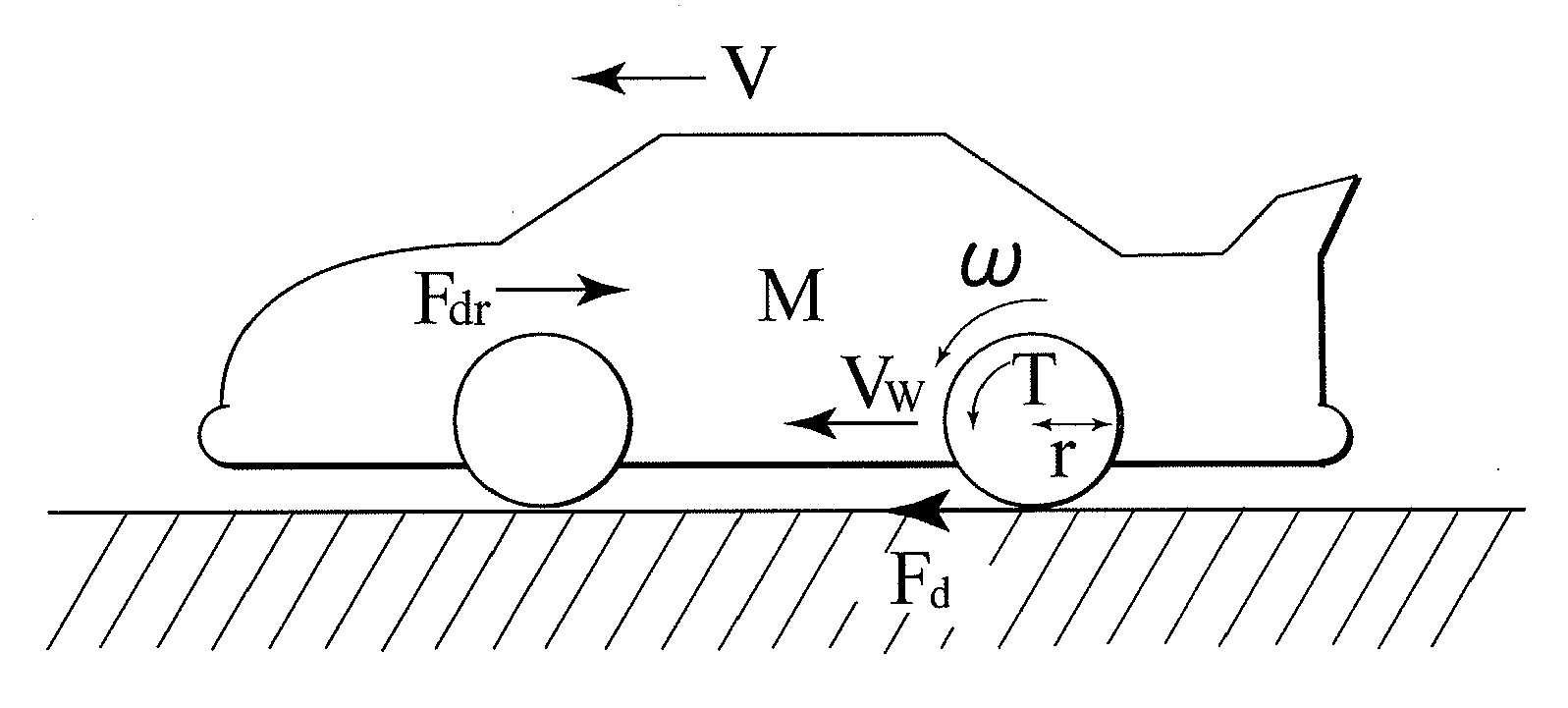
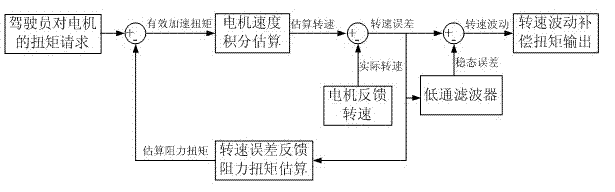
Model-based anti-shake control method for motor-driven vehicle
The invention discloses a model-based anti-shake control method for a motor-driven vehicle, which comprises the following steps of: obtaining a motor torque request, performing integral estimation on the rotating speed of a motor, performing negative feedback estimation on a rotating speed error and resistance torque, and performing low-pass filtering. The problem that an electrically-driven vehicle shakes because the motor shakes is solved. The motor torque request is subjected to torque compensation by a model-based rotating speed feedback control method in a closed loop control mode, so that the problem that the vehicle shakes and vibrates under specific working conditions is solved, and the driving comfort of the vehicle is improved; the problem that the vehicle shakes when a vehicle speed exceeds a vehicle speed interval corresponding to the resonant frequency of a power system under the working conditions of starting and accelerating, low-speed rapid accelerating and low-speed rapid decelerating is solved; and a way for solving the problem that the vehicle shakes on the premise of not sacrificing the power performance and braking performance of the vehicle is provided.
Owner:澳特卡新能源科技(上海)有限公司
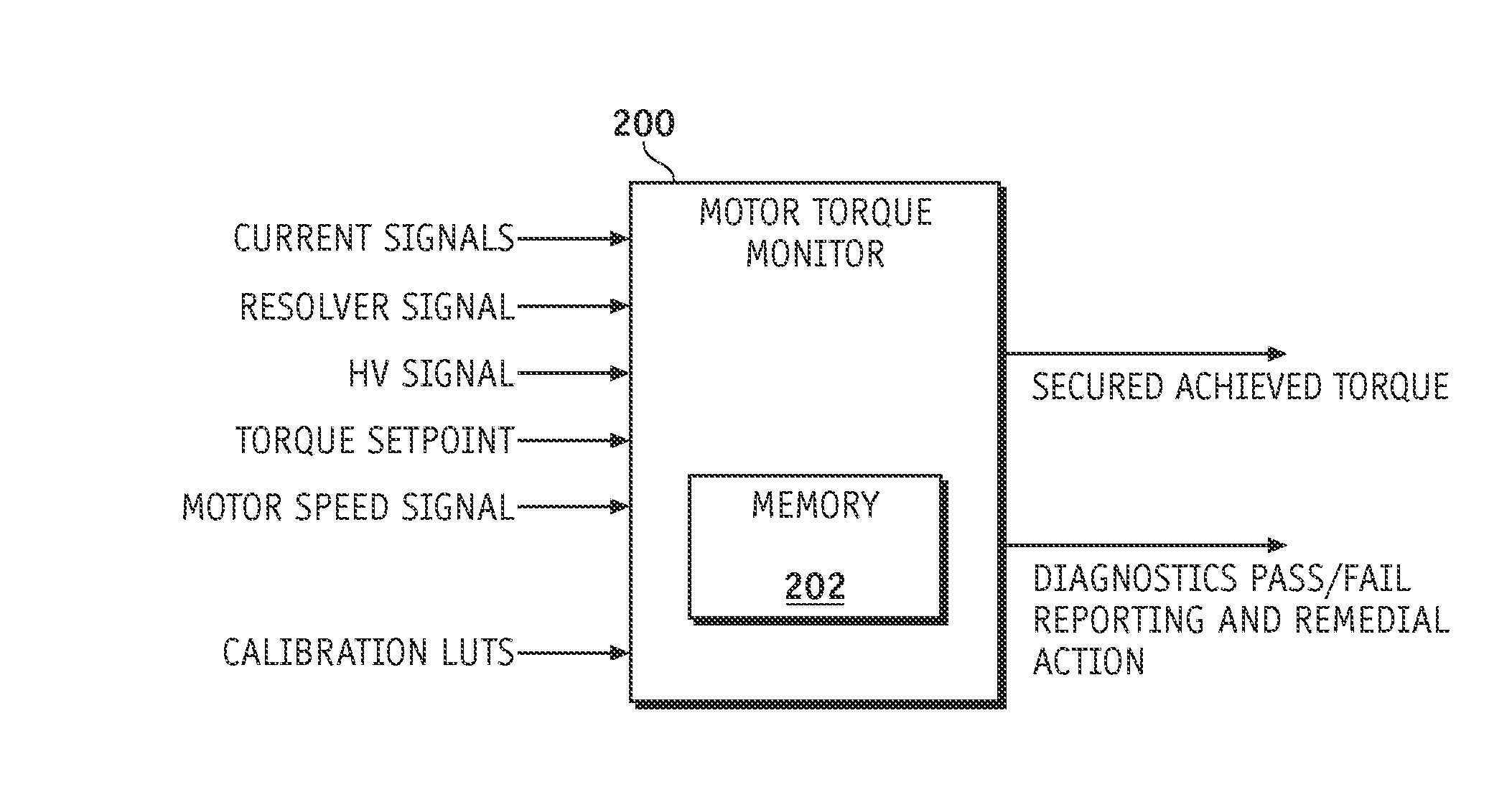
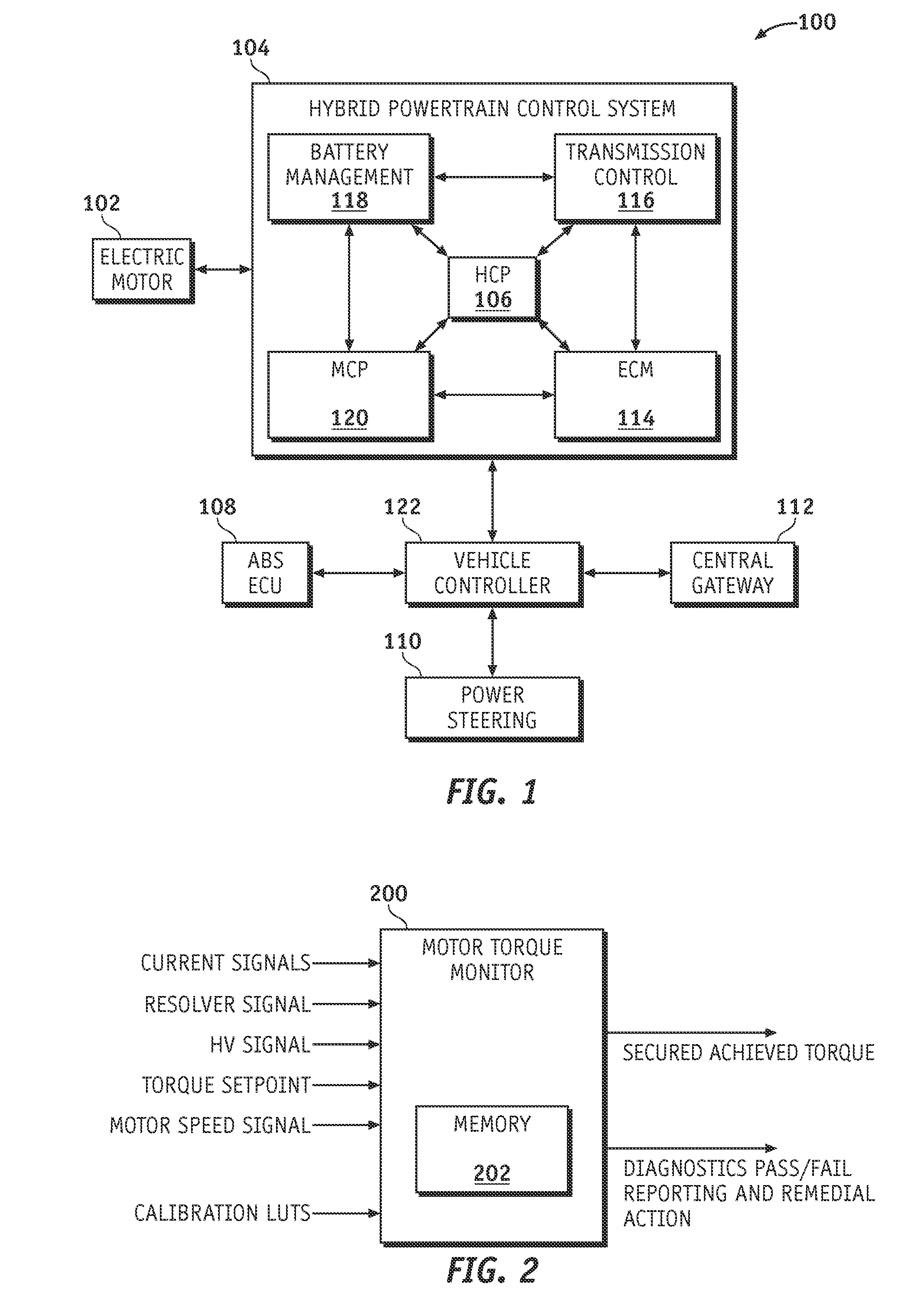
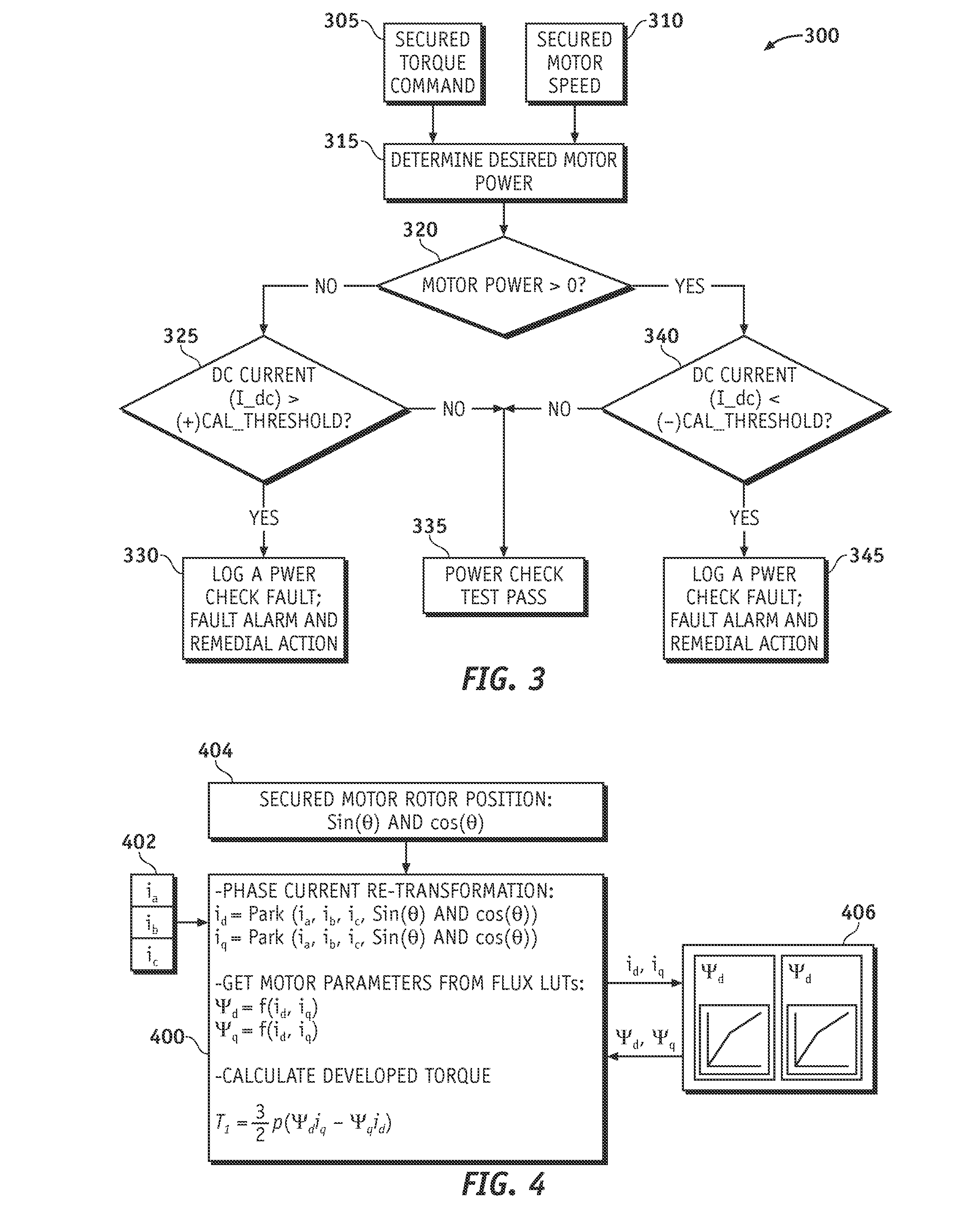
Method and apparatus for electric motor torque monitoring
Methods and apparatus are provided for monitoring an achieved motor torque produced by an electric motor. The method includes determining the achieved motor torque based on a rotor position of the electric motor and a phase current of the electric motor when the motor speed is not greater than a first pre-determined threshold, determining the achieved motor torque based on a loss-compensated power supplied to the electric motor when the motor speed is greater than the first pre-determined threshold, comparing the achieved motor torque with the torque command, and indicating a fault when the achieved motor torque is not within a pre-determined margin of the torque command.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Control method utilizing motor to start engine for double-clutch type hybrid electric vehicle
InactiveCN102490718AIncrease or decrease torqueReduce torqueHybrid vehiclesMotor speedHydraulic cylinder
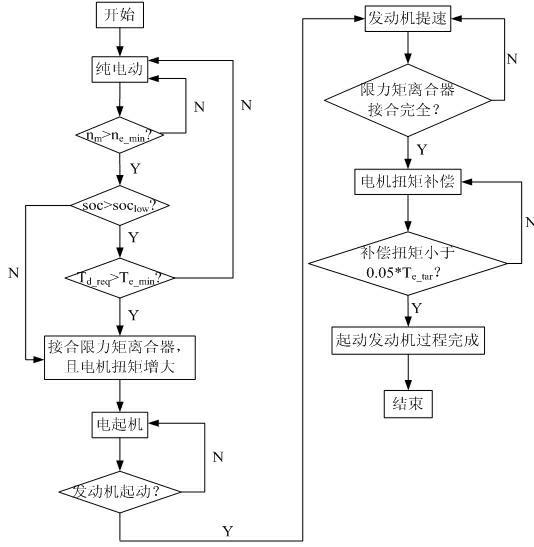
The invention enables a novel single-motor and double-clutch type hybrid electric vehicle to be a study object and provides a control method of the process of utilizing a motor to start an engine during vehicle running. First a structure and a working mode of the hybrid electric vehicle are analyzed, a system dynamics model is established, a working range of the hybrid electric vehicle is divided, corresponding torque management strategies are formulated; then in the practical application process, whether the conditions for utilizing the motor to start the engine are achieved is judged by calculating demand torque, value of state of charge (SOC) of a battery, a rotating speed of the motor; and when the conditions for utilizing the motor to start the engine are achieved, model switch is performed, a moment-limiting clutch jointing instruction is sent out, and the processing of utilizing the motor to start the engine is achieved by controlling oil pressure of a moment-limiting clutch hydraulic cylinder and utilizing the formulated torque coordination-control strategies to perform coordination control of motor torque, engine torque and transmission torque of a moment-limiting clutch. By utilizing the advantage that the motor responds fast and timely increasing or reducing the motor torque according to the control strategies, the control method provides the demand torque for starting the engine during the vehicle running or compensates the insufficiency of the engine torque, reduces impact degree in the switching process and improves ride comfort of the hybrid electric vehicle.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Torque control strategy for management of regenerative braking of a wheeled vehicle whose powertrain includes a rotary electric machine
InactiveUS20020116101A1Analogue computers for trafficBraking action transmissionBrake torqueRegenerative brake
A torque control strategy control for management of regenerative braking in a motor vehicle. A first processor (12) processes throttle request data (20) and torque modification data (40) from a second processor (14) to develop motor torque request data (28) for controlling rotary electric machine torque. The second processor processes brake request data (26), the throttle request data, and operating data from the at least one operating data source to develop friction brake torque data (30) for controlling friction brake torque applied to the vehicle and the torque modification data for the first processor. The two processors interact such that as long as the operating data from the at least one operating data source does not require that regenerative braking torque be limited, the torque modification data supplied to the first processor from the second processor equates to the brake torque request data, and the friction brake torque data does not cause the friction brakes to be applied, and when the operating data from the at least one operating data source calls for some limiting of the regenerative braking torque, the amount of limiting is subtracted from the torque modification data and the friction brake torque data equates to that amount of limiting for causing the friction brakes to be applied in that amount.
Owner:HASHIBA HITOSHI +5
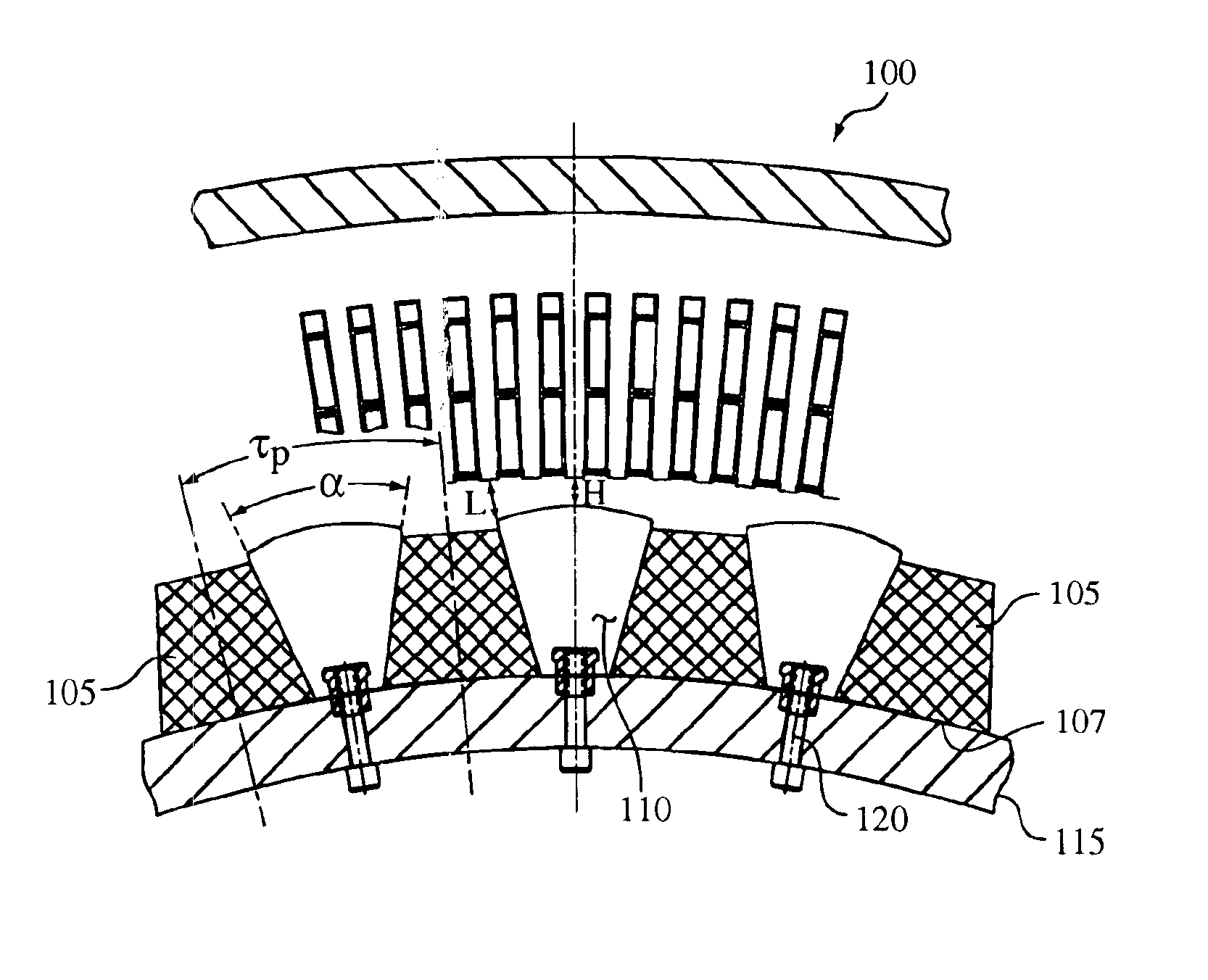
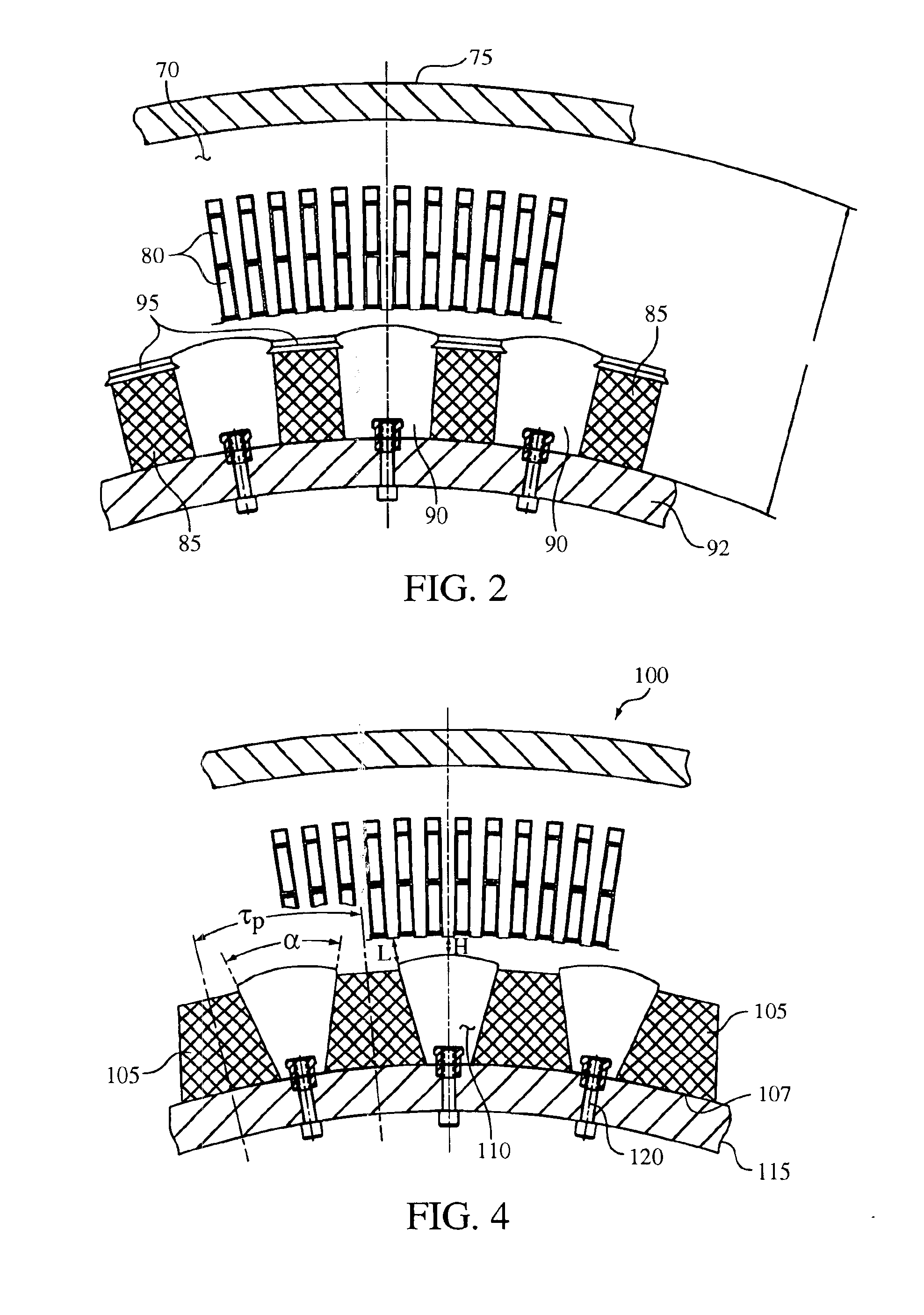
Trapezoidal shaped magnet flux intensifier motor pole arrangement for improved motor torque density
InactiveUS6879075B2Increase torqueImprove power characteristicsSynchronous generatorsWindingsPermanent magnet synchronous machineElectric machine
A permanent magnet synchronous machine with improved torque and power characteristics. A circumferential-oriented rotor assembly is provided with alternating permanent magnets and magnetic pole pieces. In order to reduce the amount of leakage flux in the rotor and increase the effective length of the permanent magnet, a trapezoidal or otherwise tapered permanent magnet structure is used. By alternating trapezoidal permanent magnet, and magnetic pole pieces, a higher intensity magnetic field is created in the air gap utilizing the same radial space in the motor without altering the weight or volume of the motor compared to conventional machines.
Owner:CURTISS WRIGHT ELECTRO MECHANICAL
Method for setting target torque of motor applicable to pure electric vehicle
The invention discloses a method for setting target torque of a motor applicable to a pure electric vehicle. The method is characterized in that: a general controller serves as a control core of the pure electric vehicle and is a main executor of a general control strategy. The method comprises the following steps that: the general controller judges a driving intention of a driver by acquiring driver signals of an accelerator pedal, a brake pedal, a gear switch and the like, confirms a traction or brake mode, performs information interaction with a motor controller and a battery management system, calculates target traction or brake torque, executes a corresponding general control strategy and outputs corresponding torque information and directional signals of the motor; and a related control instruction is transmitted to the motor controller, and the motor controller controls the motor to work under drive or brake working conditions according to the control instruction, so that energy distribution of the pure electric vehicle from an energy storage system to a motor driving system is effectively controlled, and the energy storage system, the motor driving system and the like are correspondingly protected.
Owner:HUNAN CSR TIMES ELECTRIC VEHICLE
Drum washing machine
ActiveUS7478547B2Increase rotation speedPrecise positioningOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusMotor speedBrushless motors
A drum washing machine including a cylindrical drum, a DC brushless motor directly connected to the drum, a current detector detecting current flowing through the motor, a torque control vector-controlling the motor on the basis of the current detected by the current detector so that motor torque becomes optimum at least in a wash or dehydration operation, and a laundry weight estimator accelerating the motor with a maximum output torque developed when determining that motor speed is between a first speed at which laundry is assumed to start falling from an uppermost part of inner periphery of the drum when motor speed is reduced from a high speed side and a second speed at which laundry is assumed to start sticking to an uppermost part of the inner periphery of the drum, estimating laundry weight according to a q-axis current value in the vector control during an accelerating period.
Owner:TOSHIBA LIFESTYLE PROD & SERVICES CORP
Motor having controllable torque
InactiveUS20090128084A1Increase in sizeSingle-phase induction motor startersCommutation monitoringEngineeringControl theory
A controllable motor includes a rotor. A first stator winding set is operable, upon being energized, to generate and apply a first torque to the rotor. A second stator winding set independent of the first stator winding set is operable, upon being energized, to generate and apply a second torque to the rotor. A motor control is coupled to the first and second stator winding sets. The motor control is operable to selectively energize one of the first or second stator winding sets to thereby generate and apply one of the first or second torques to the rotor, and simultaneously energize both the first and second stator winding sets to thereby generate and apply a third torque greater than the first or the second torque.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Hierarchical system used for four-wheel-hub motor-driven electric automobile, and control method
InactiveCN106585425AImprove stabilityImprove maneuverabilitySpeed controllerElectric devicesRoad surfaceEngineering
The invention discloses a hierarchical system used for a four-wheel-hub motor-driven electric automobile, and a control method. First of all, yaw moment is calculated as a yaw moment decision-making layer according to a vehicle speed sensor, a steering wheel rotary angle transmitter, an electronic throttle sensor and an inertia measurement unit; then according to automobile longitudinal force constraints, yaw moment constraints, a maximum adhesion force which can be provided by a pavement and restrictions of motor maximum output moment, target torque of each wheel hub motor is calculated as a target optimization analysis layer; and finally, degrees of similarity to six standard pavements are obtained by inputting two parameters, i.e., an adhesion coefficient and a wheel slip rate into a pavement adhesion coefficient estimation fuzzy controller by means of a current pavement, and an adhesion coefficient estimated value of the current pavement is obtained as a pavement adhesion coefficient monitoring layer after weighted averaging is performed. According to the invention, whole-vehicle stability is taken as a control target, motor torque is reasonably distributed according to operation working conditions, and the controllability, the stability and the economic property of vehicles are improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Hybrid electric vehicle
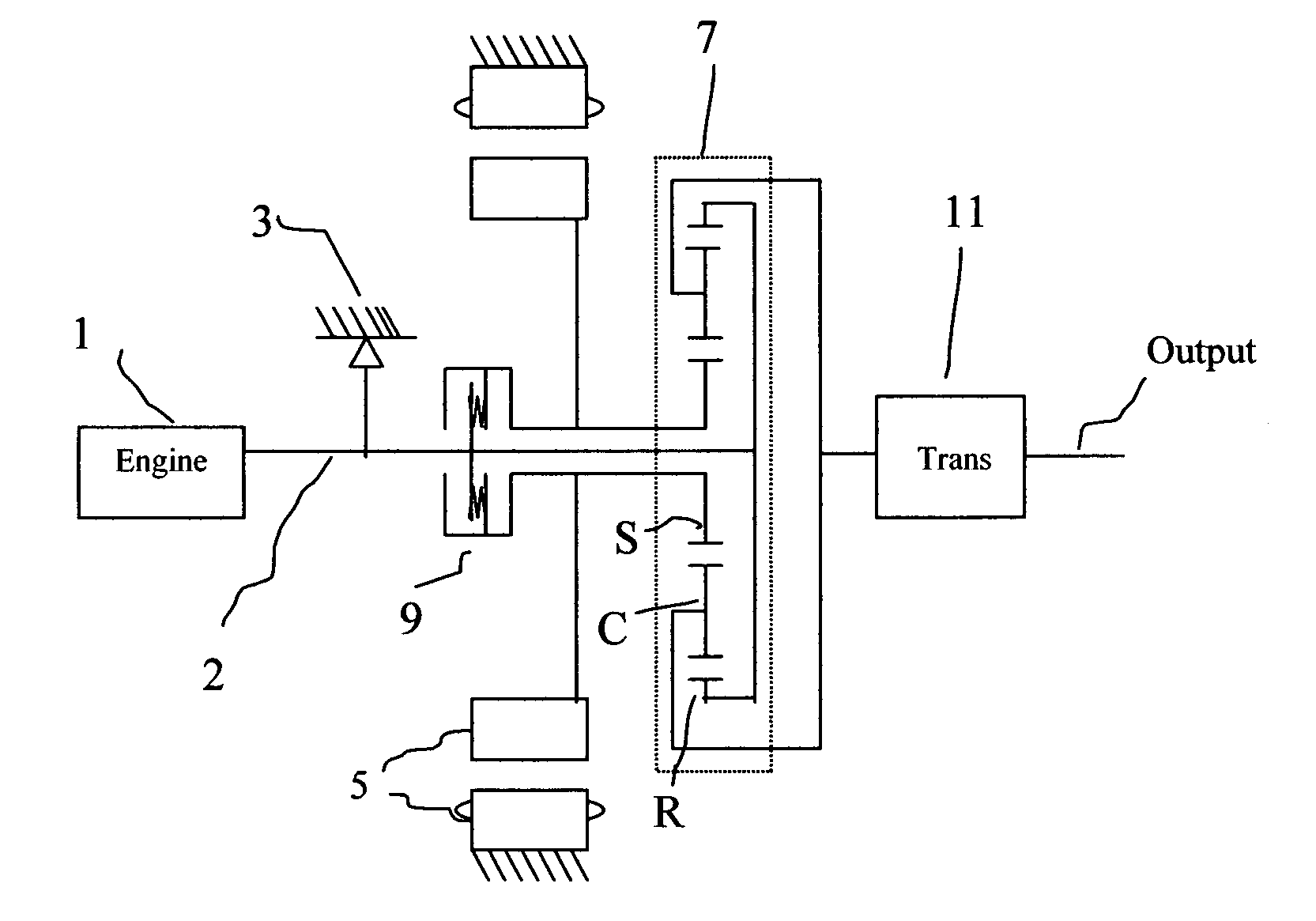
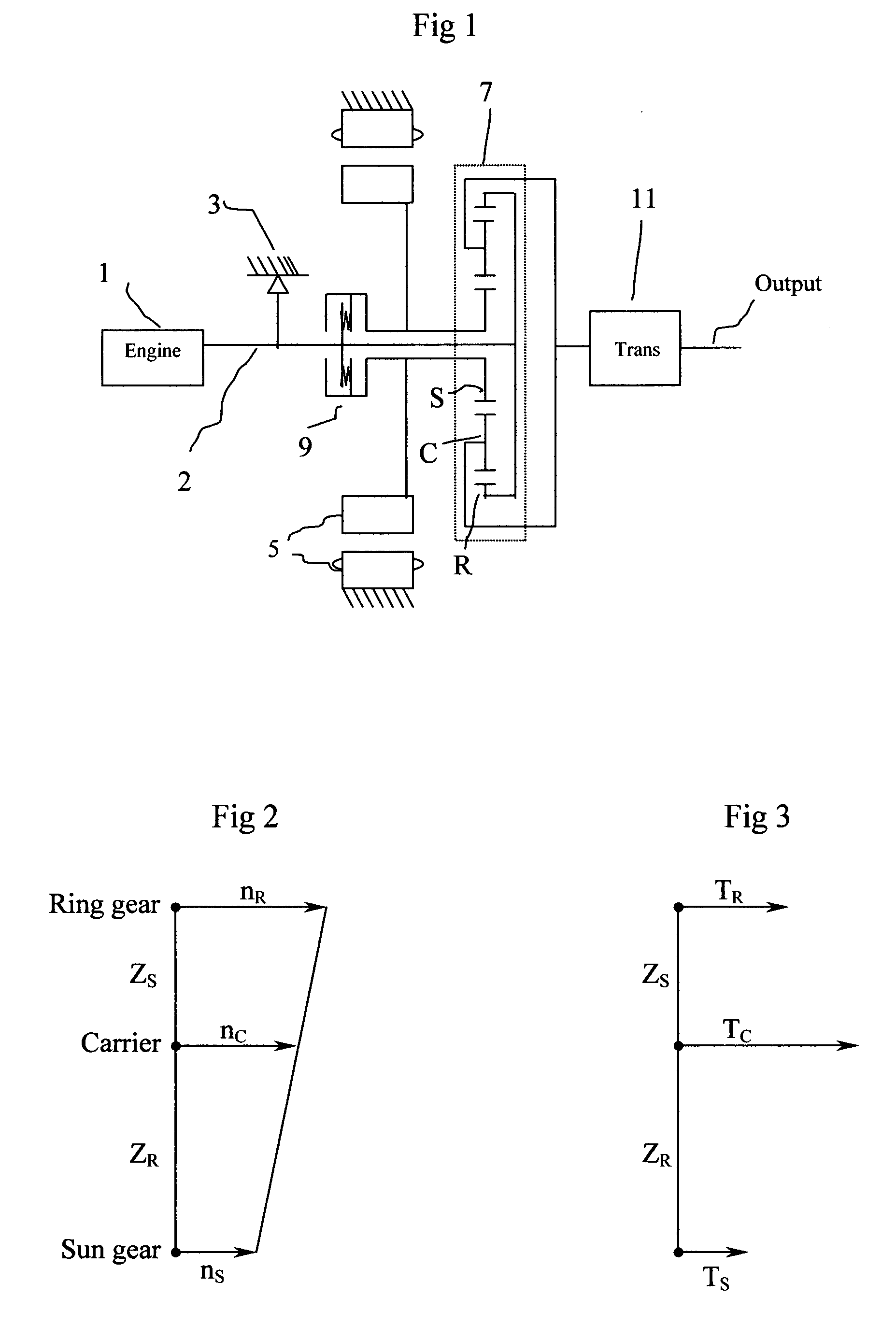
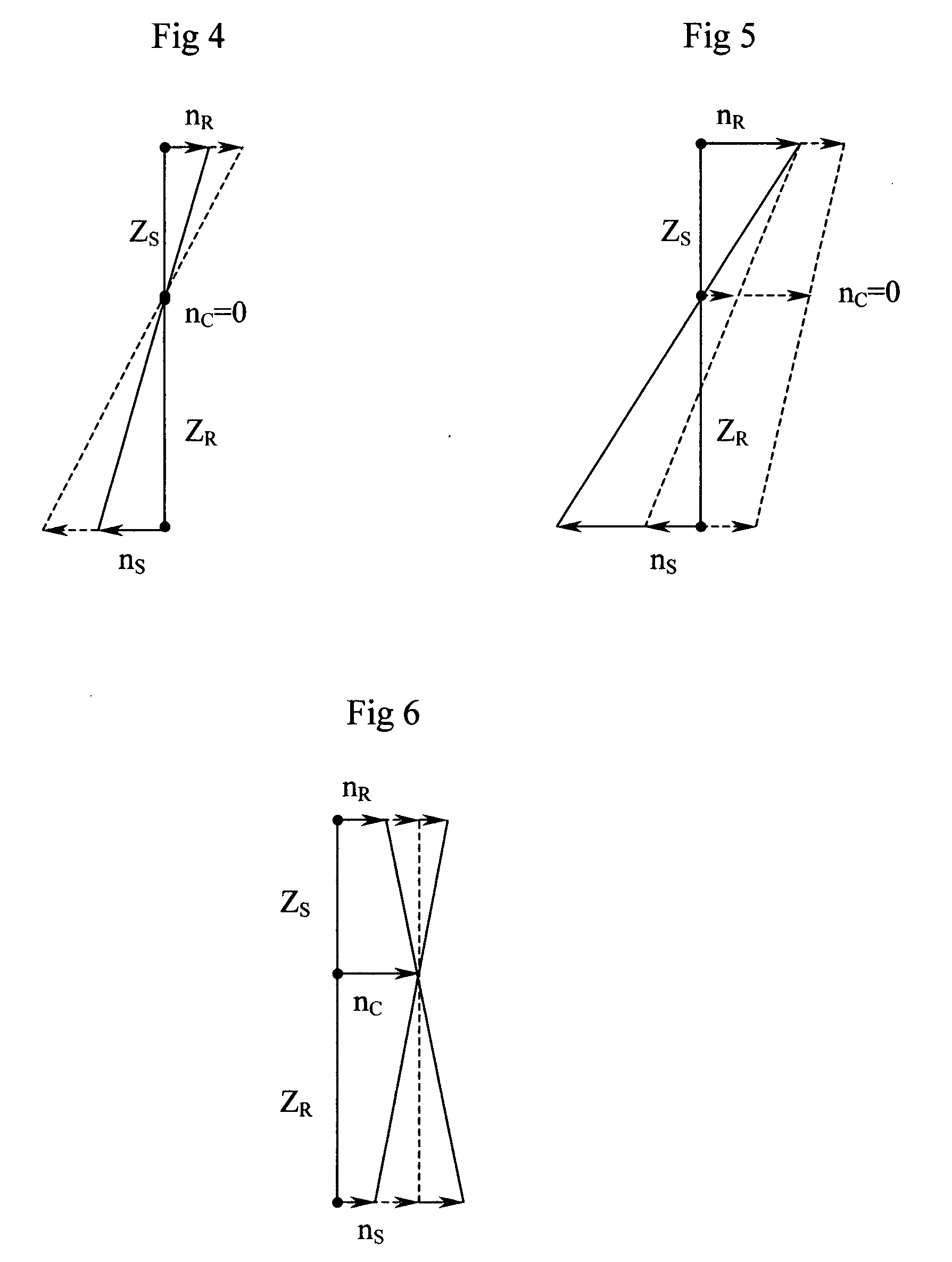
InactiveUS20090071733A1Torque is limitedSmooth startGas pressure propulsion mountingPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingGear wheelEngineering
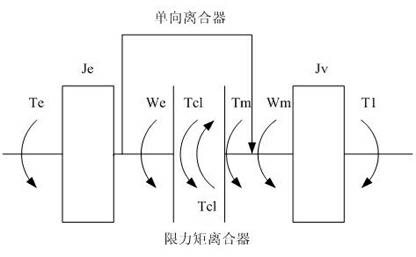
A full hybrid electric vehicle comprises a heat engine, a one-way-clutch connected to the engine shaft, an electric motor, a planetary gear unit, a clutch with limited torque, and a transmission. The planetary gear unit includes at least a sun gear (an input element), a ring gear (an input element) and a pinion carrier (an output element). The torque-limited clutch seats between two of the planetary gear elements. The engine is connected to and applies torque on one of the input elements. The electric motor is connected to and applies torque on the other input element. While the vehicle is running, the engine can be started smoothly by engaging the torque-limited clutch and controlling the motor torque, and a shock on the vehicle similar to a rough shift can be avoided.
Owner:DUAN ZHIHUI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com