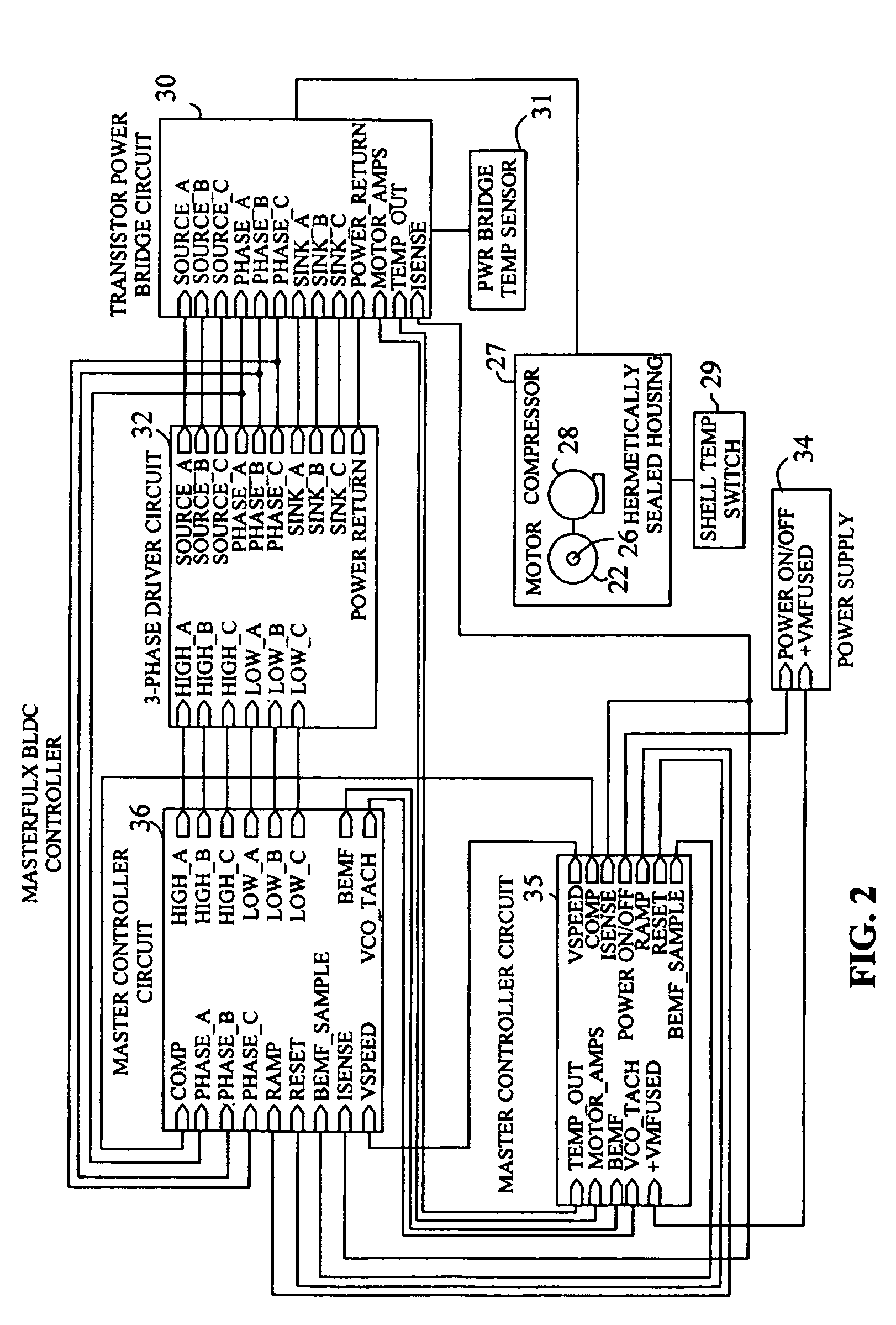
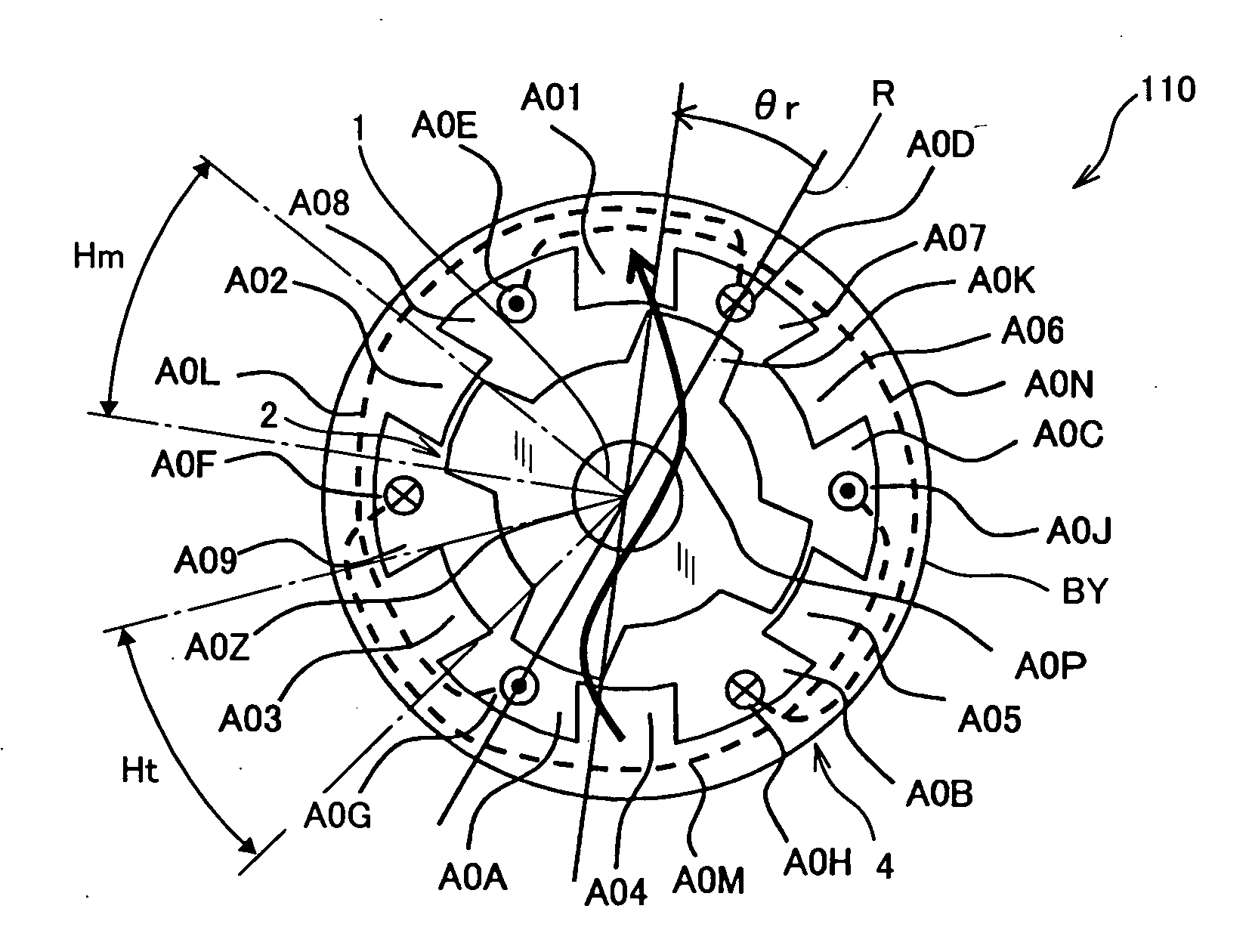
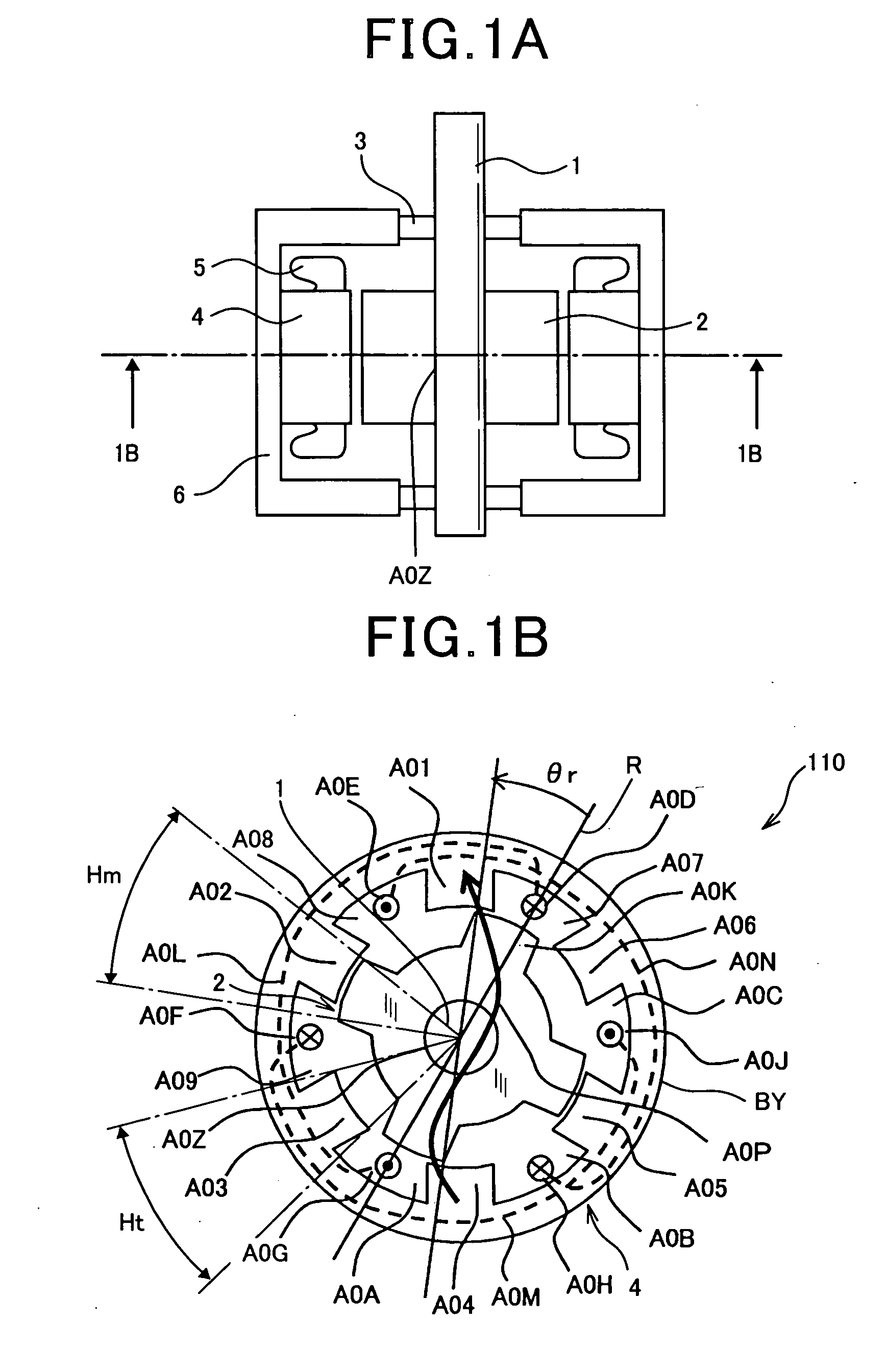
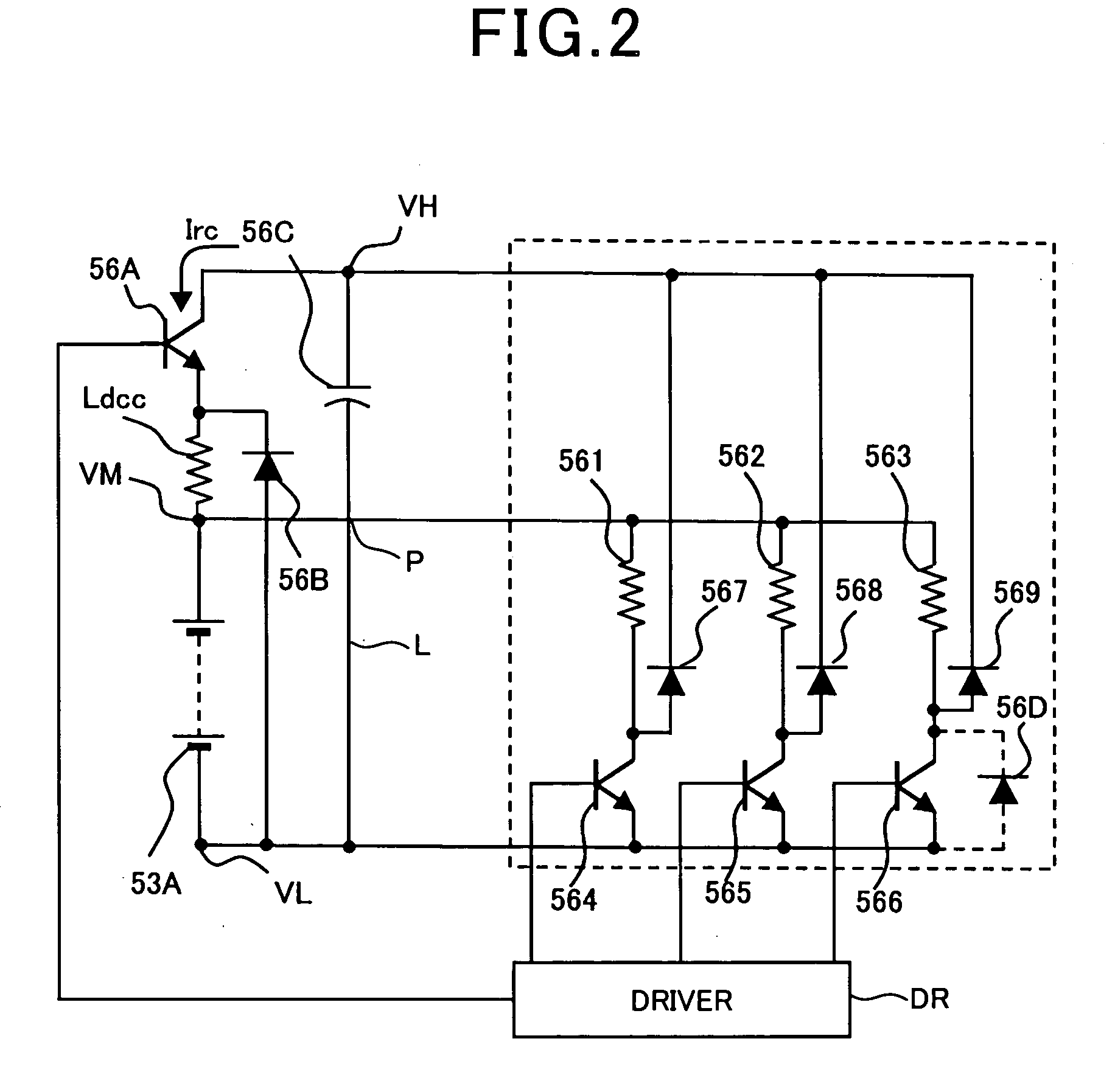
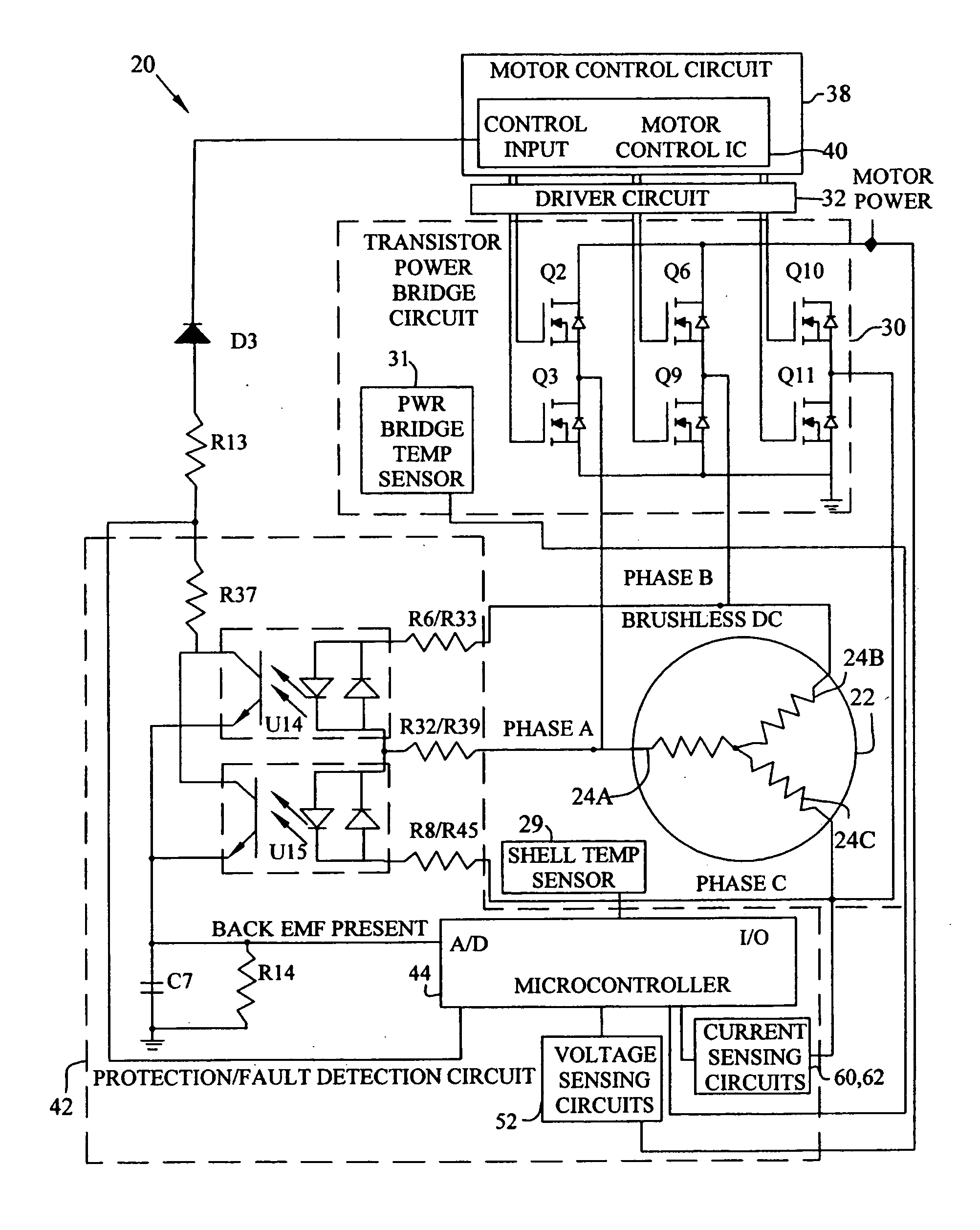
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5227results about "Synchronous motors starters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Motor having controllable torque
InactiveUS8125168B2Single-phase induction motor startersCommutation monitoringMotor controlElectric motor
A controllable motor includes a rotor. A first stator winding set is operable, upon being energized, to generate and apply a first torque to the rotor. A second stator winding set independent of the first stator winding set is operable, upon being energized, to generate and apply a second torque to the rotor. A motor control is coupled to the first and second stator winding sets. The motor control is operable to selectively energize one of the first or second stator winding sets to thereby generate and apply one of the first or second torques to the rotor, and simultaneously energize both the first and second stator winding sets to thereby generate and apply a third torque greater than the first or the second torque.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Motor drive circuit with short startup time
An H-bridge circuit is connected to a coil of the vibration motor that is to be driven. A comparator receives Hall signals indicating position information of a rotor of the vibration motor, and converts to an FG signal. A pulse width modulator generates a pulse-modulated pulse signal specifying energization time of the coil of the vibration motor. The pulse width modulator, in a first mode, after commencing start-up of the vibration motor, sets a duty ratio of the pulse signal to 100%, and after that, switches the duty ratio to a predetermined value in accordance with rotational frequency of the motor. In a second mode, the duty ratio of the pulse signal continues to be set to 100%. In a third mode, frequency and the duty ratio of the pulse signal are set based on a control signal of a pulse form inputted from outside. The control signal is used also in switching mode.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Method of driving DC motor and related circuit for avoiding reverse current
ActiveUS8183807B2Avoid it happening againMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlDriver circuitPower flow
Owner:ANPEC ELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Brushed motor position control based upon back current detection
InactiveUS20060261763A1Exact numberStop preciseElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersReverse currentEngineering
Owner:MASCO CORP
Apparatus and method for controlling hybrid motor
ActiveUS8228020B2Reduce capacityReduce electricity loadSingle-phase induction motor startersWindingsDriver circuitPower switching
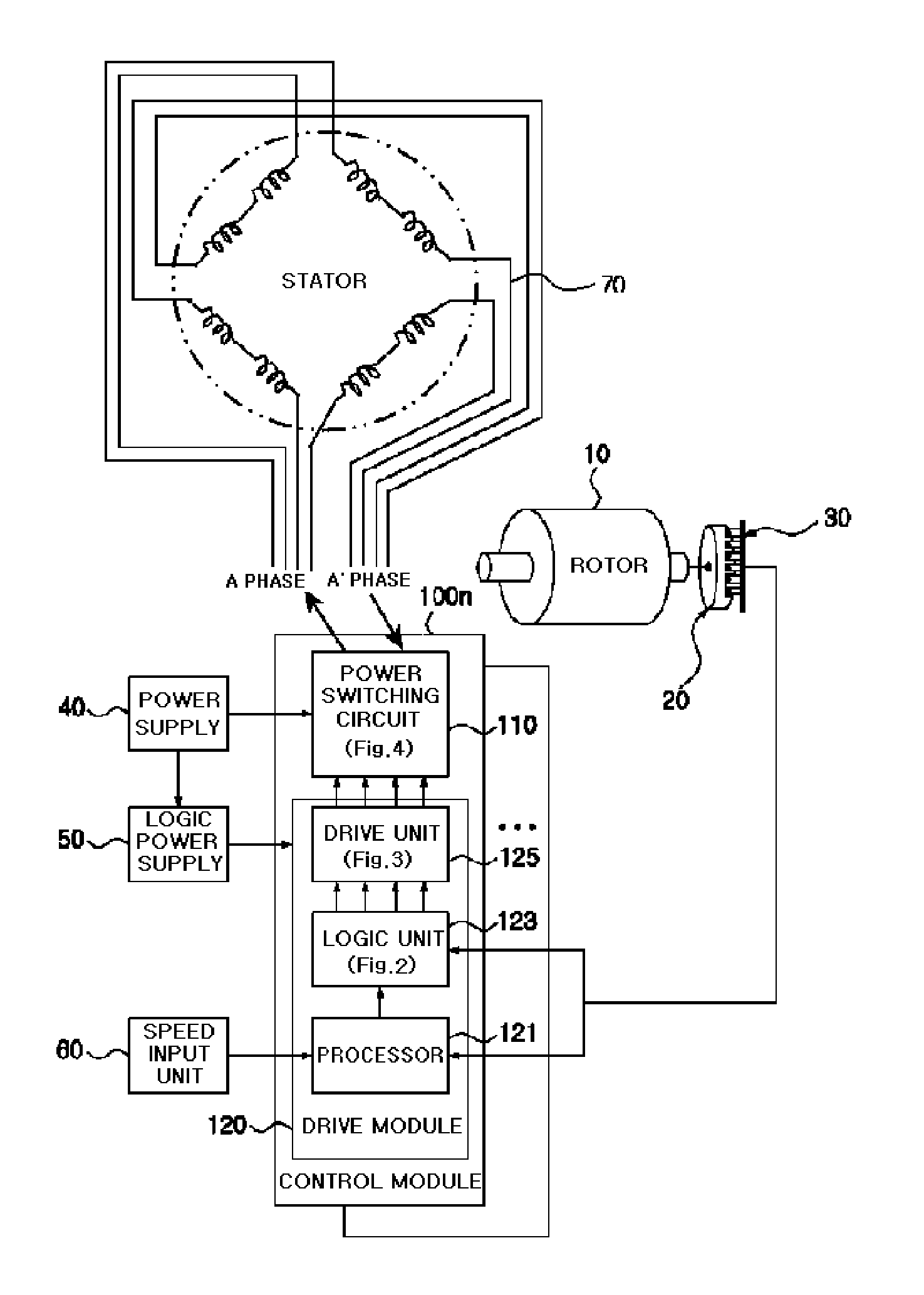
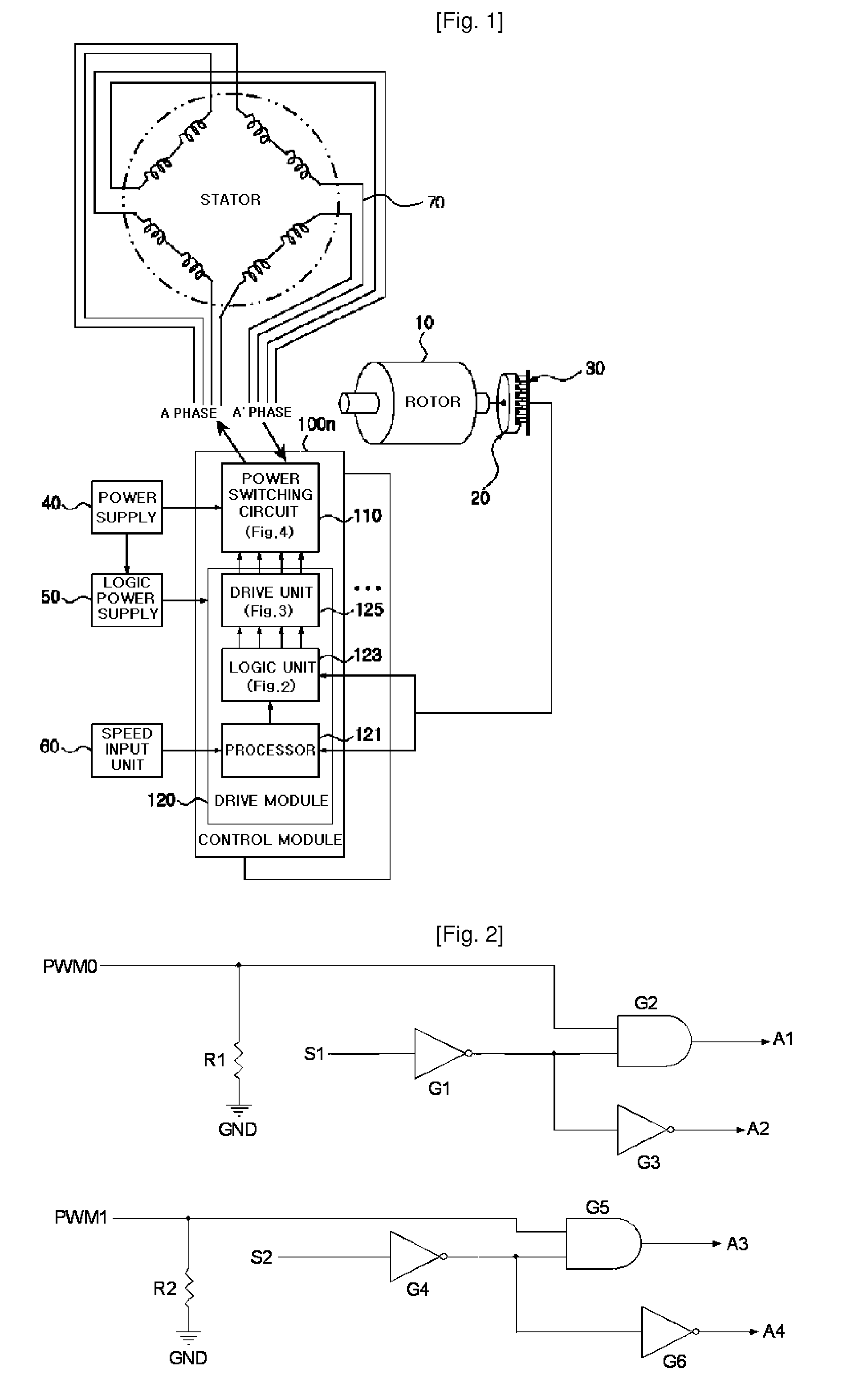
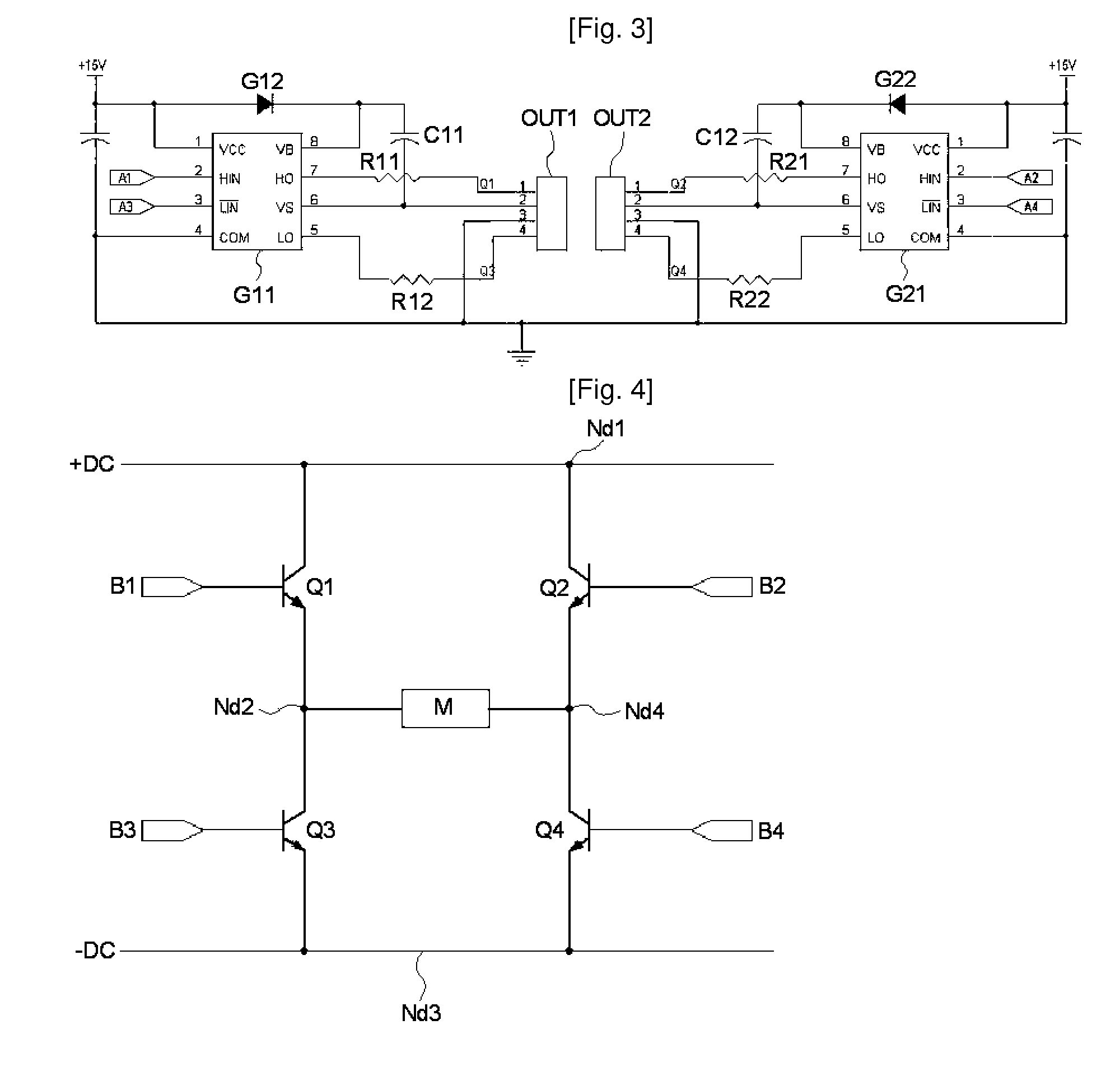
An apparatus and method for controlling a hybrid motor, The hybrid motor, uses a permanent magnet instead of a field coil for a rotor, winds a coil round a stator in a multi-phase independent parallel manner, fixes a rectifying type encoder to the rotor and connects a sensor to a driving circuit. The apparatus comprises: an encoder attached to a rotor in cooperation with a pole sensor a speed input unit for generating a speed instruction signal a power switching circuit to generate motor driving signals; a drive module receiving the speed instruction signal and the sensor signal and outputting the speed instruction signal synchronized with the sensor signal as a driving motor signal; a power supply for applying a DC voltage to the power switching circuit; A logic power supply for converting the DC voltage into a logic voltage, and applying logic voltage to the drive module. The motor has n phases, n power switching circuits and n drive modules.
Owner:NAMYANG NEXMO CO LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling electronically commutated motor operating characteristics
InactiveUS6895176B2Operation controlSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlBrushless motorsControl electronics
A permanent magnet DC brushless motor control assembly permits a user to select the permanent magnet DC brushless motor operating characteristics by selecting appropriate control circuits to interface with the motor. The assembly includes a permanent magnet DC brushless motor, a commutator electrically coupled to the motor, and at least one control module electrically coupled to the commutator, to control operating characteristics of the permanent magnet DC brushless motor.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
DC brushless motor drive circuit with speed variable-voltage
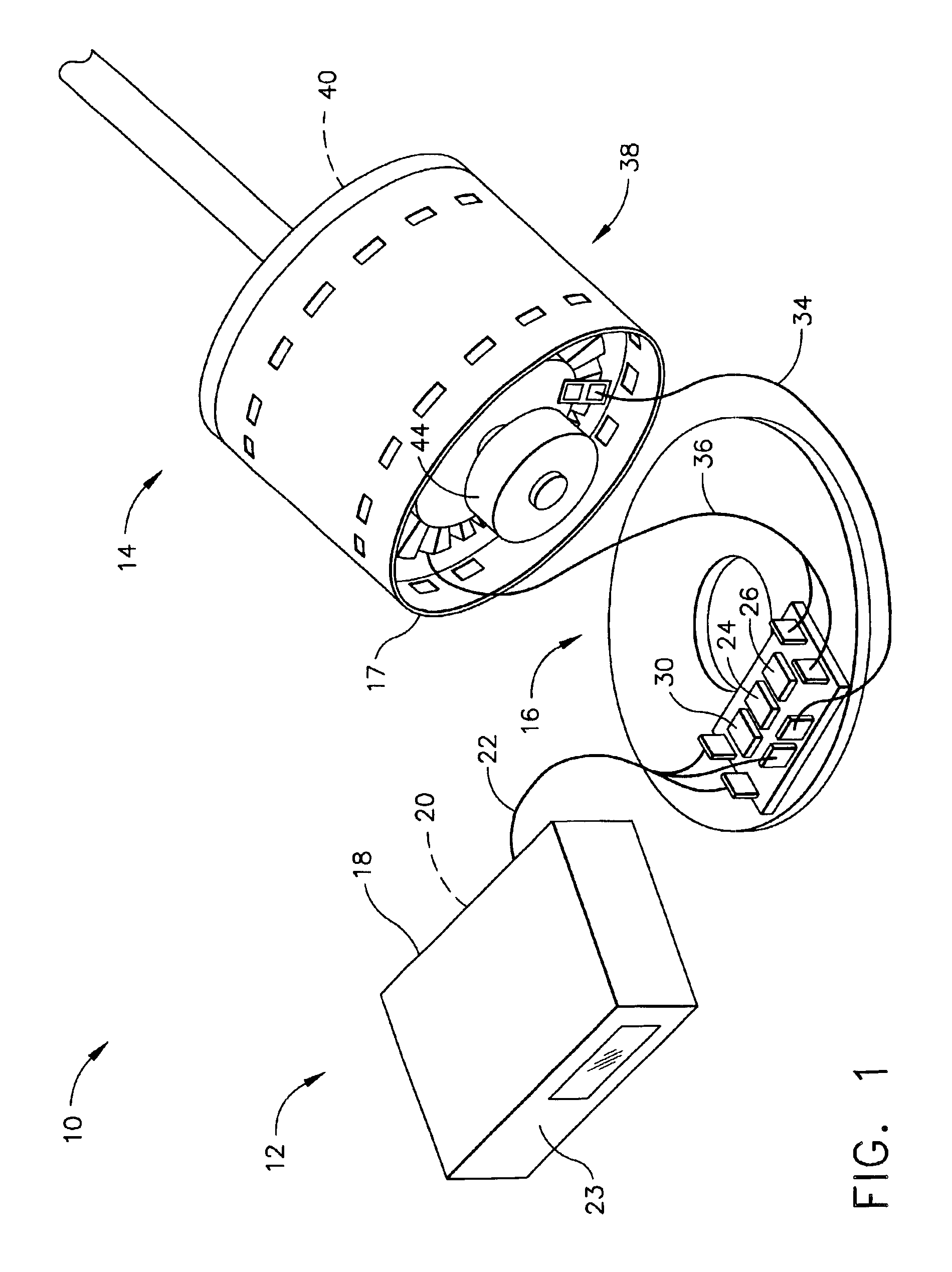
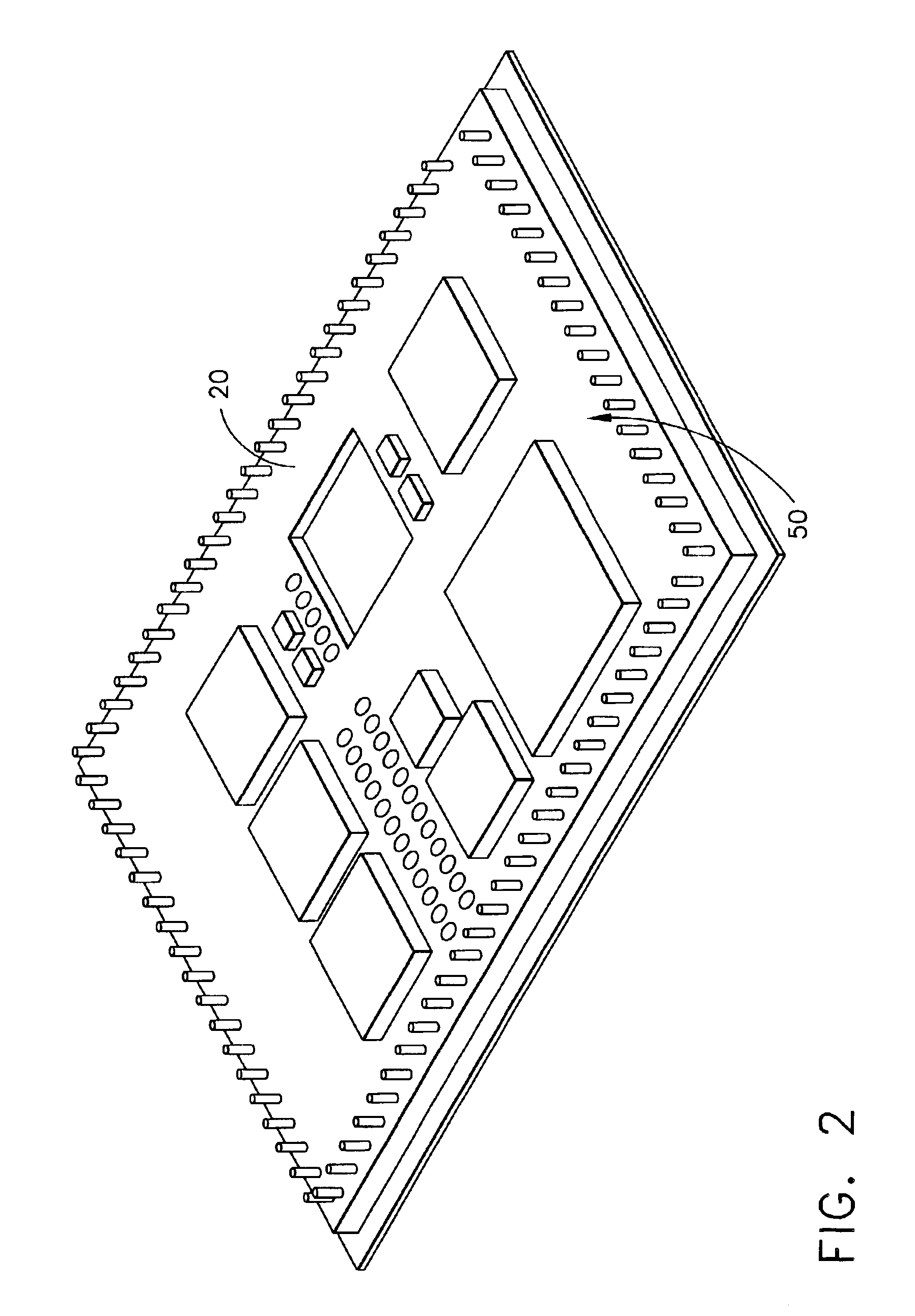
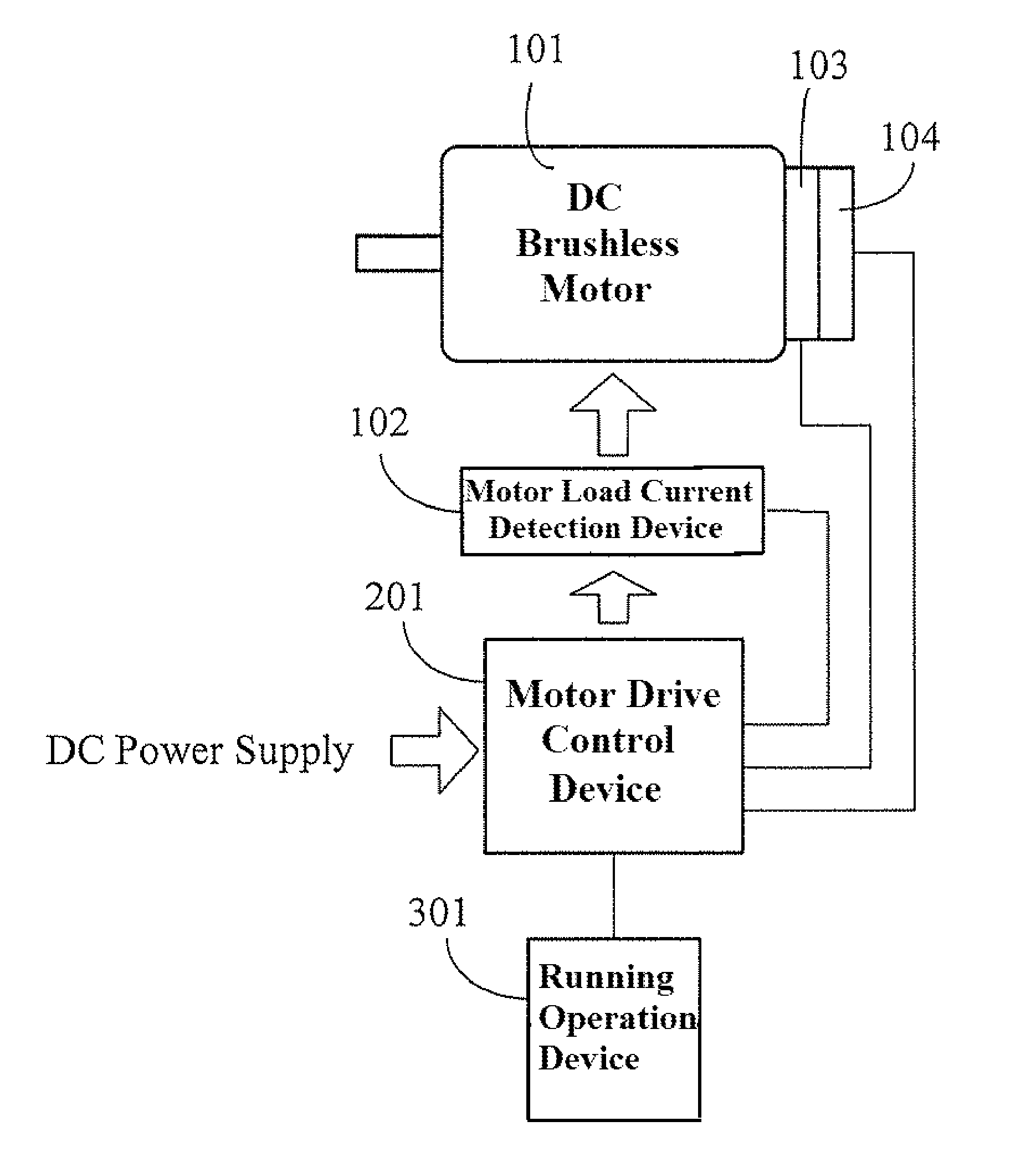
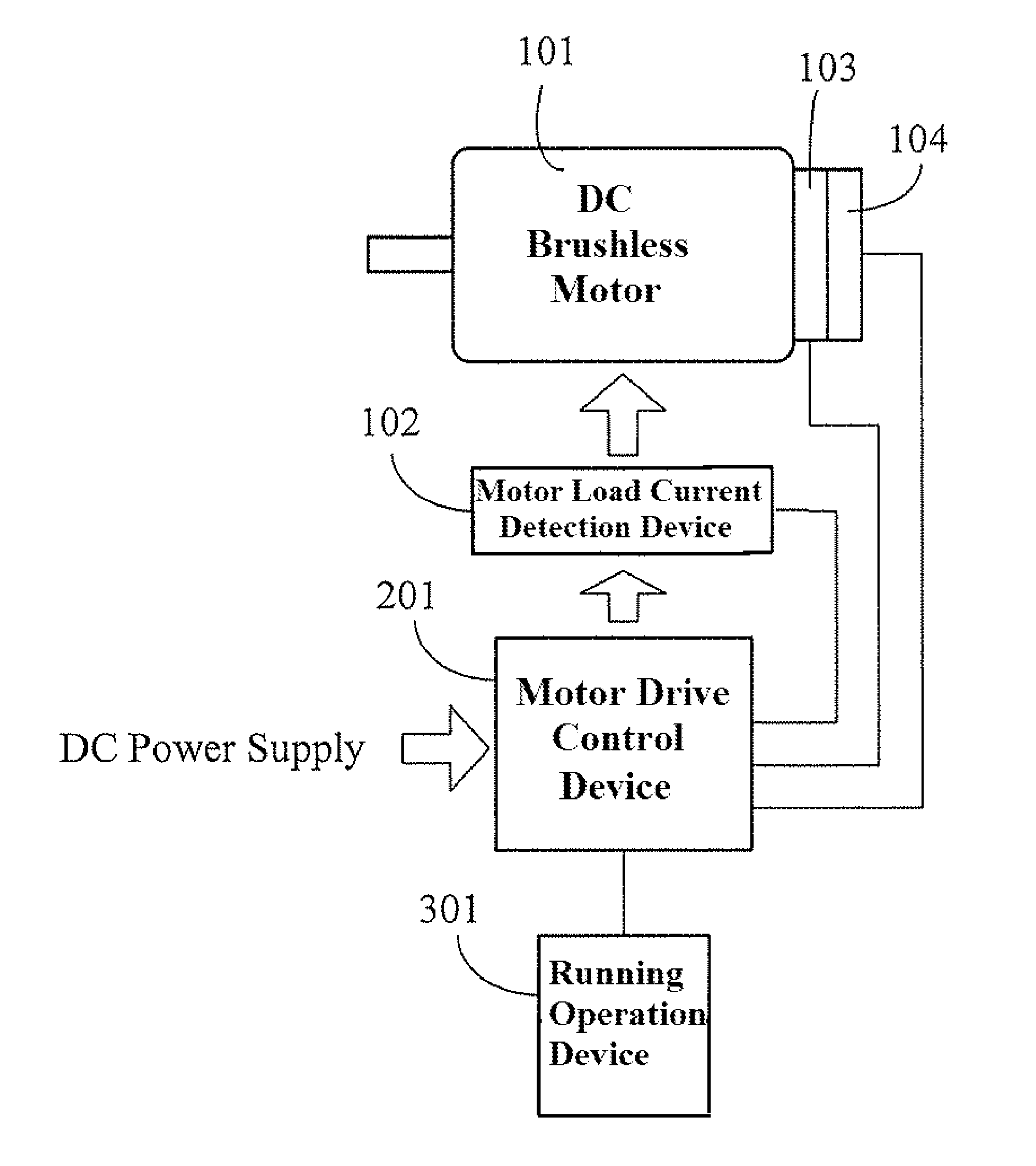
ActiveUS8288984B2Increase inputOvercome increased inductive impedanceTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersBrushless motorsMotor drive
For the present invention, under various running speeds statuses, the voltage supplied to the DC brushless motor is relatively increased or decreased on the basis of the internal setting of the motor drive control device according to the increased or decreased rotational output speed, so as to prevent the shortcoming of too much variation of the input impedance caused by the inductive reactance of the winding accordingly changed when the speed of the DC brushless motor is changed, specifically, to prevent the shortcoming of unable producing required torque resulting from the increased inductive reactance caused by increasing the rotational speed which makes the current value become too low when input by the original working voltage.
Owner:YANG TAI HER
Inverter device and air conditioner including the same
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Brushless DC motor control
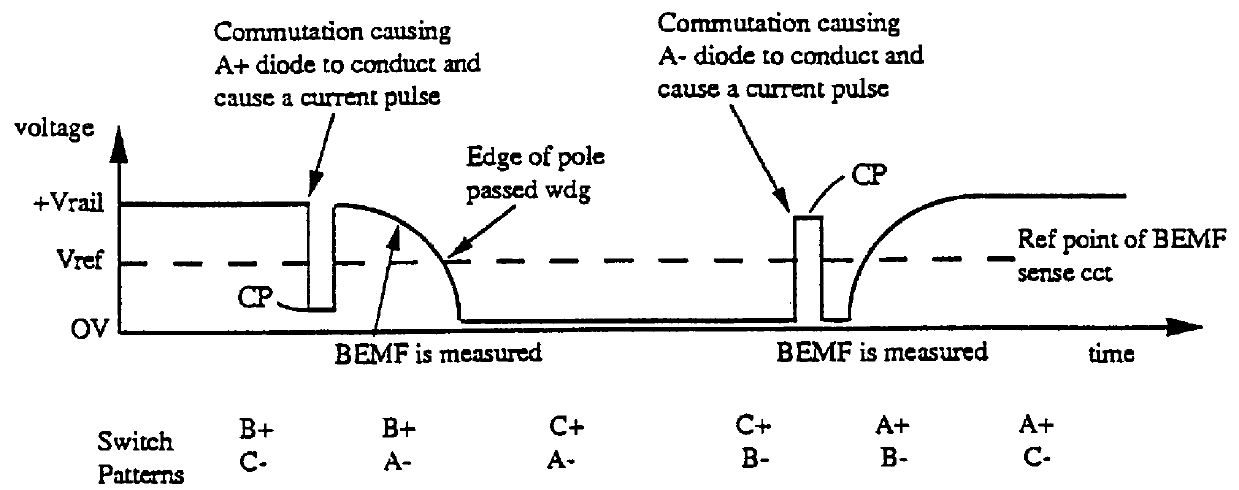
An electronically commutated brushless DC motor primarily for fractional horsepower applications of the type where at any instant one motor winding is unpowered and used to detect back EMF zero-crossings which information is used to initiate winding commutations. The duration of the pulse produced in this winding due to dissipation of stored energy by free-wheel diodes in parallel with the commutation devices after supply of current has been removed from this winding is used to provide a measure of motor current. This allows for simplified commutation device current limiting circuits and is available for control purposes which are a function of motor torque. There is also disclosed a method for maximizing useful power output by reducing the phase angle between the motor current and the back EMF. This is accomplished by introducing a delay in commutating the motor windings beyond the occurrence of each back EMF zero-crossing, with the delay being a function of the time between commutations.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
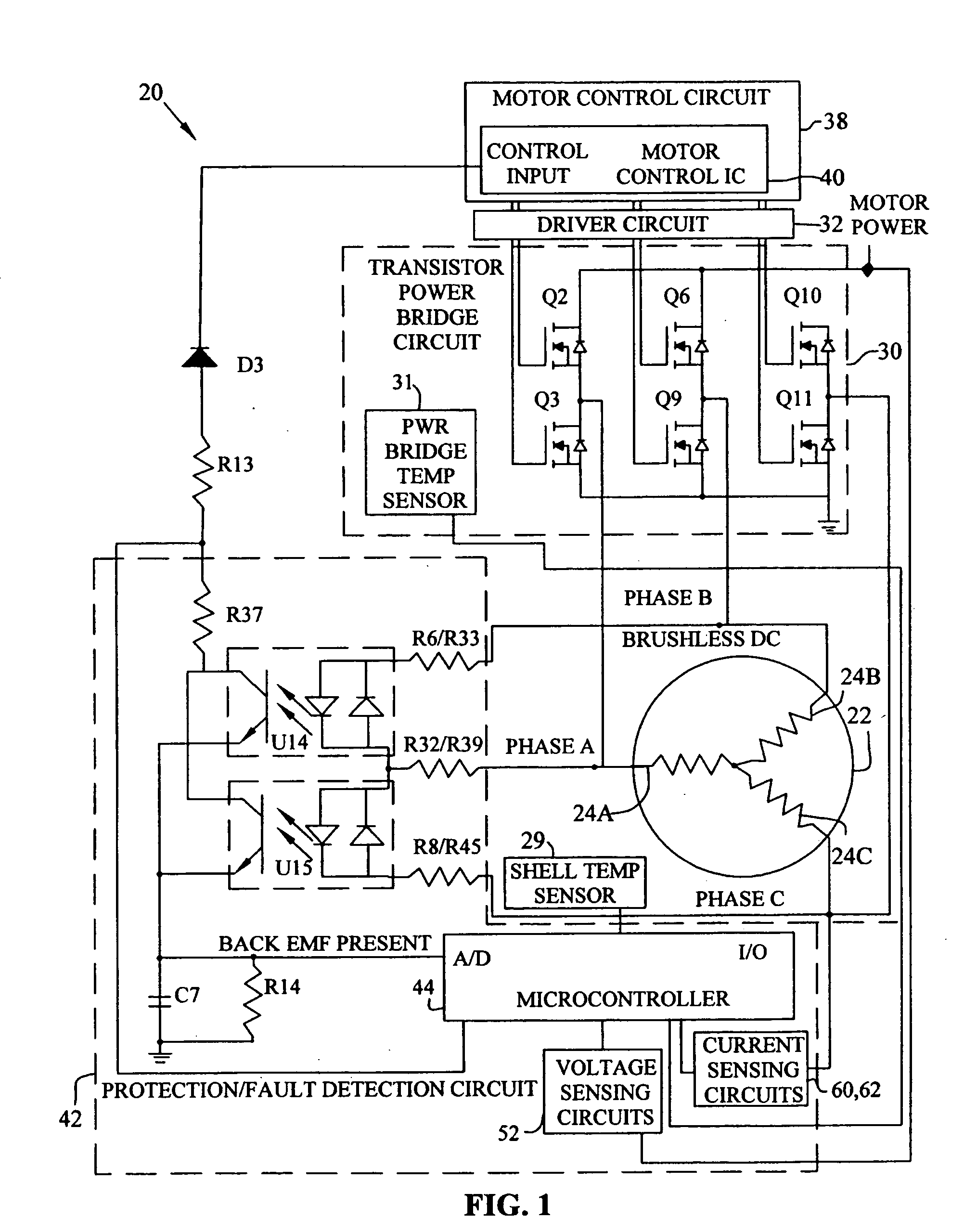
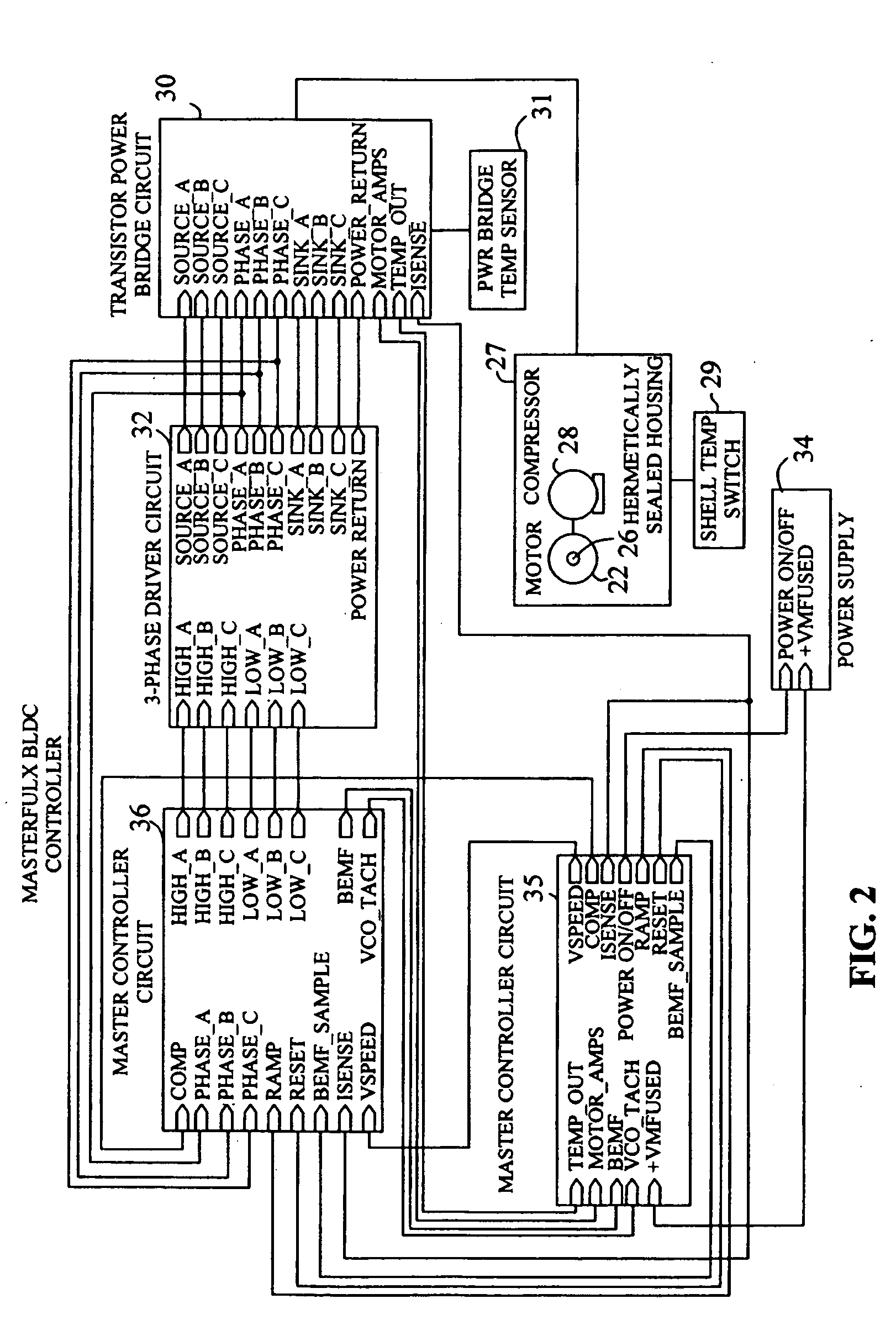
Brushless and sensorless DC motor control system with locked and stopped rotor detection
ActiveUS7042180B2Simple control methodEasily interfaceCommutation monitoringAC motor controlMotor speedDc motor control
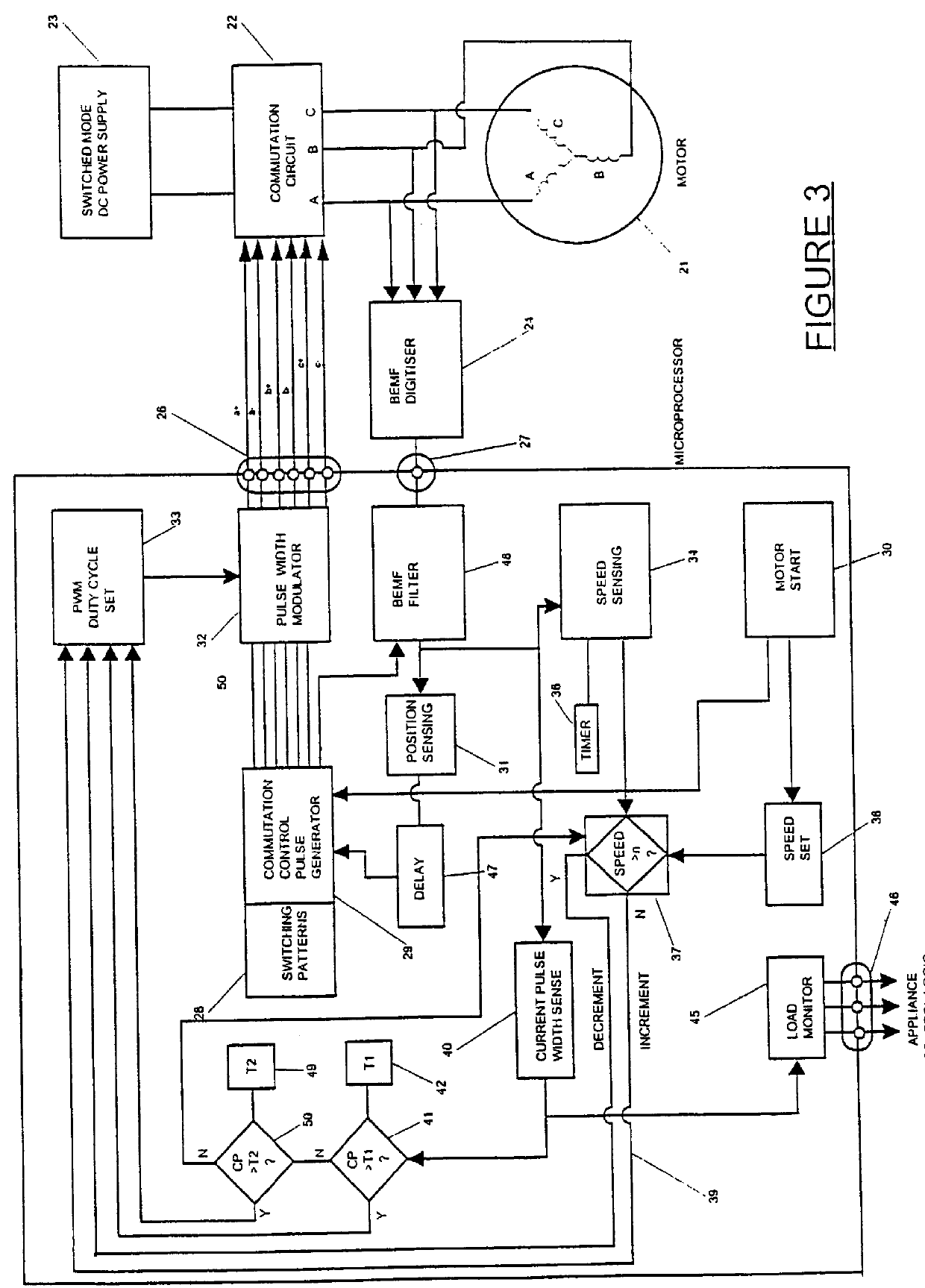
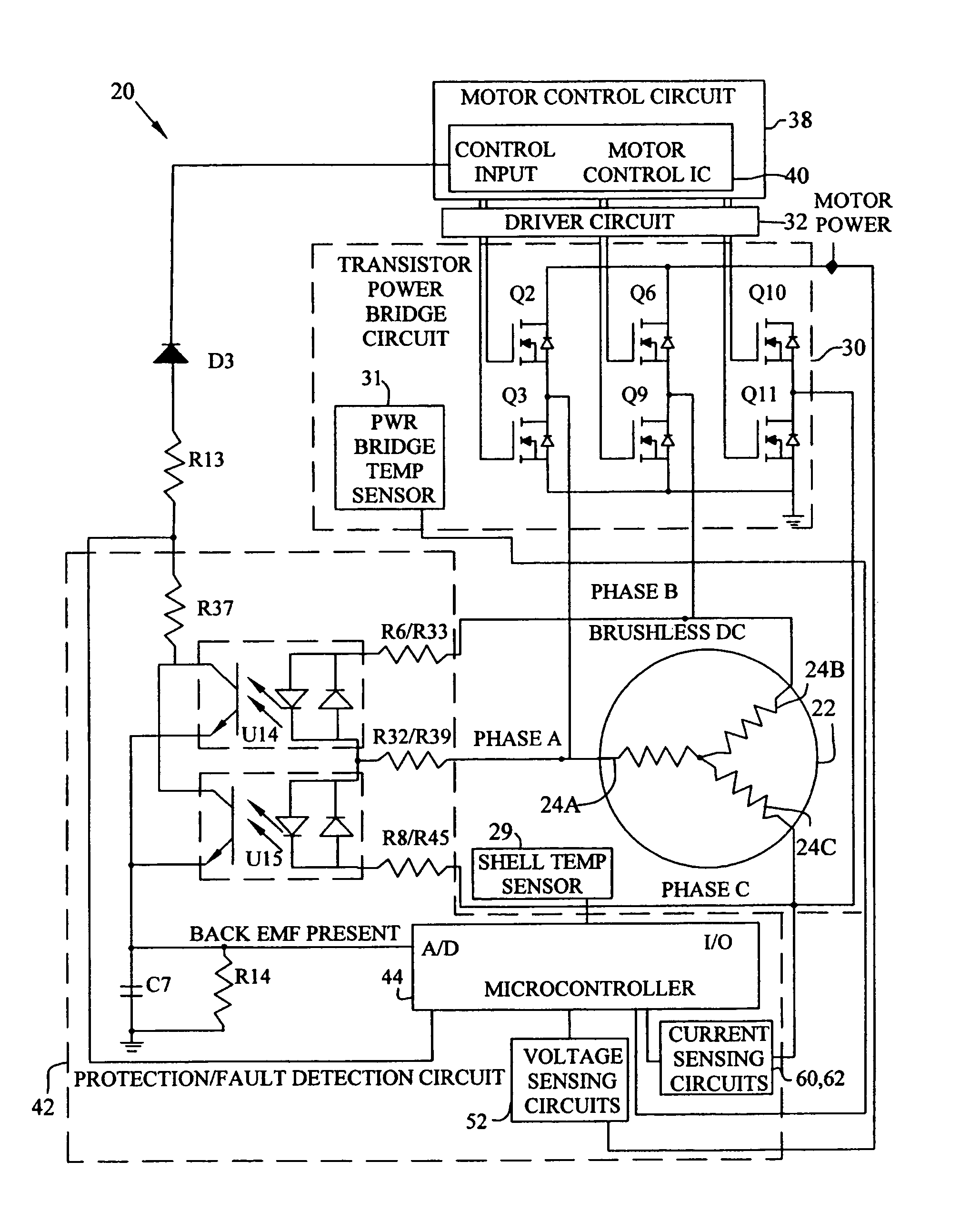
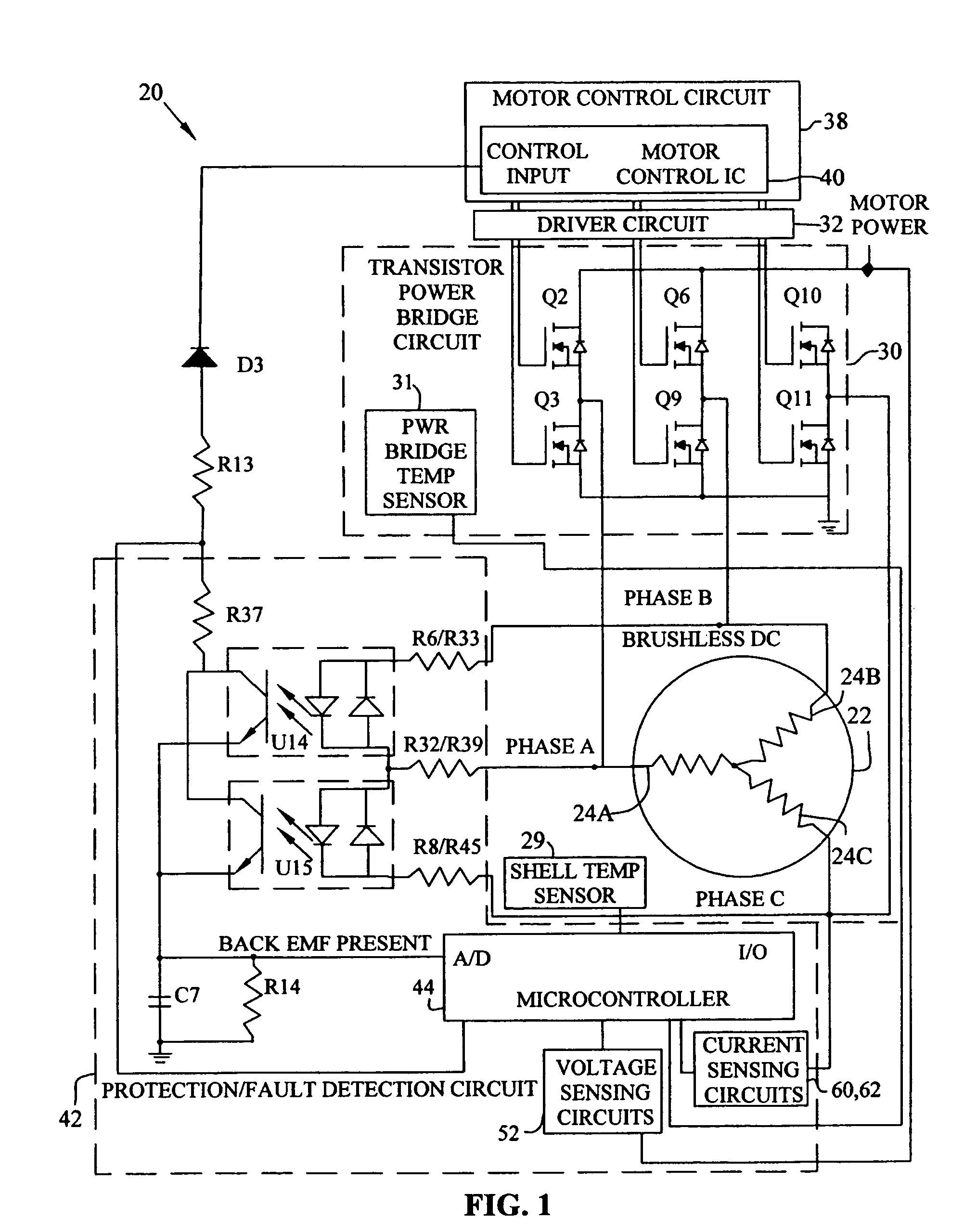
A motor control system for a brushless and sensorless DC motor for driving a compressor, pump or other application, includes a protection and fault detection circuit for detecting a locked rotor and a rotor which has stopped because of lost rotor phase lock. The motor control system also includes an off-the-shelf motor control integrated circuit having an input for disabling power outputs to the motor phase coils. The protection and fault detection circuit uses a back EMF sampling circuit coupled to the motor phase coils and momentarily disables power to the motor phase coils, via the motor control integrated circuit input, to determine if the motor rotor is rotating. The system also monitors supply voltage, supply current, temperature, and motor speed limits to detect faults and protect system components.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
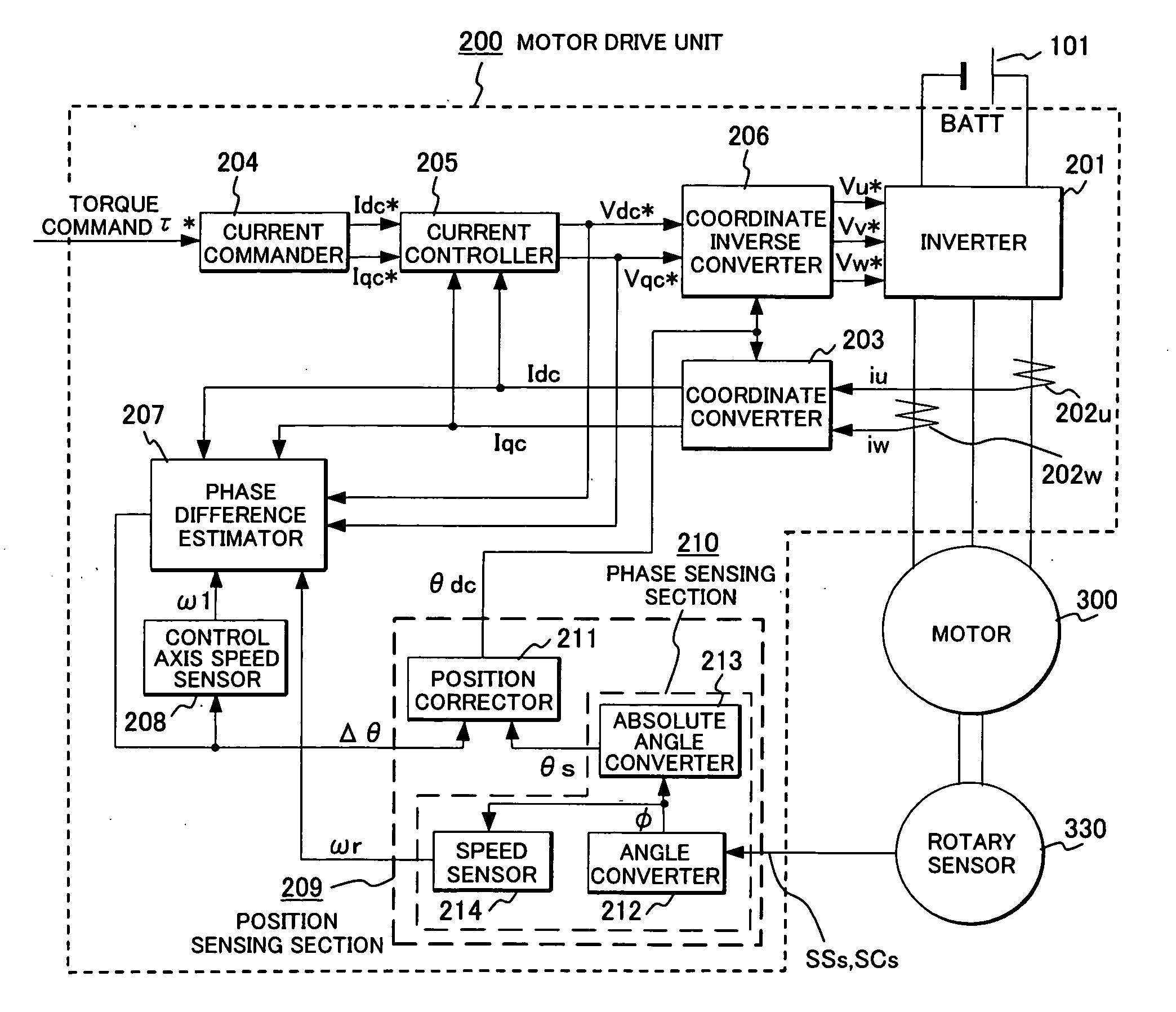
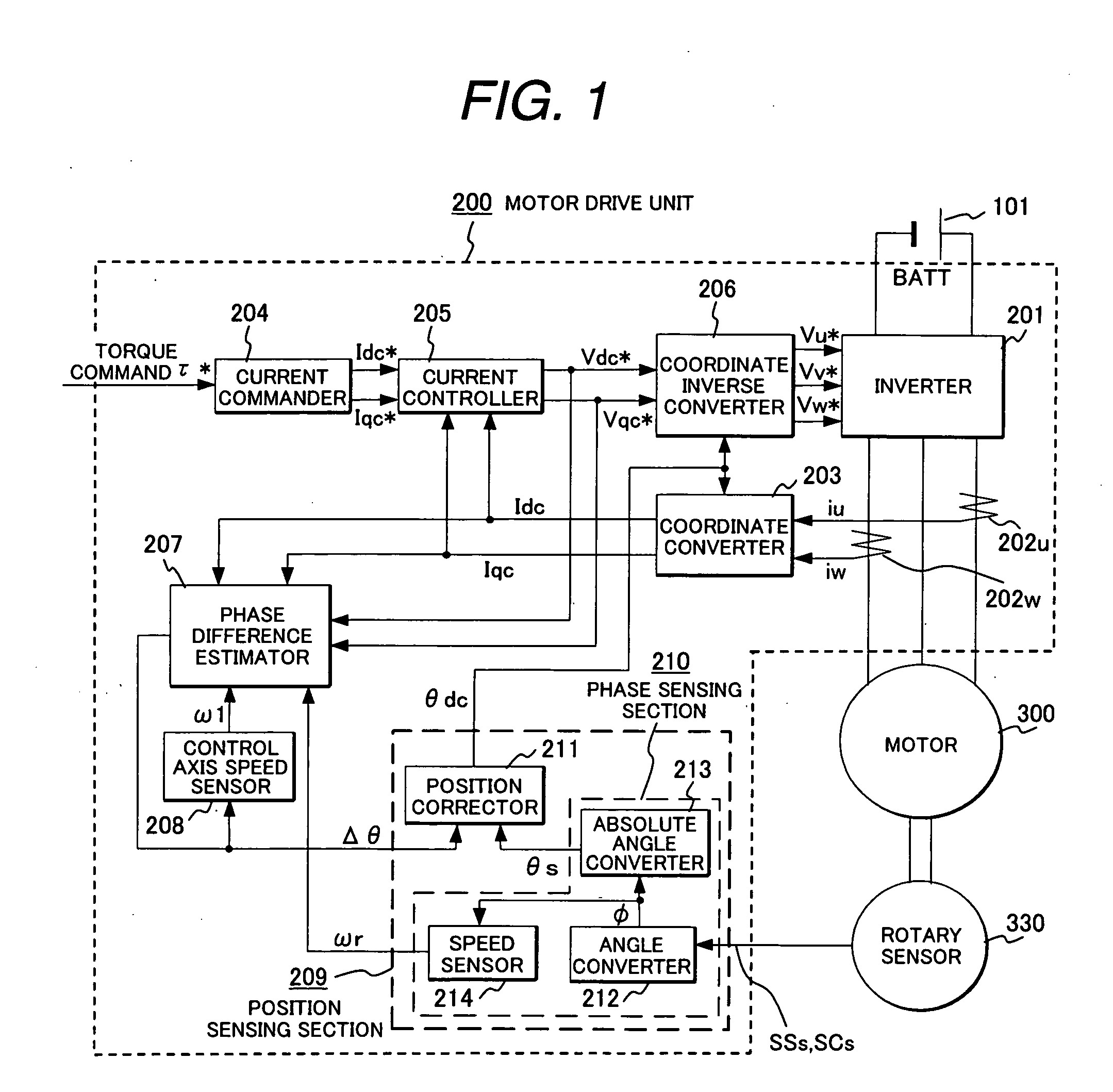
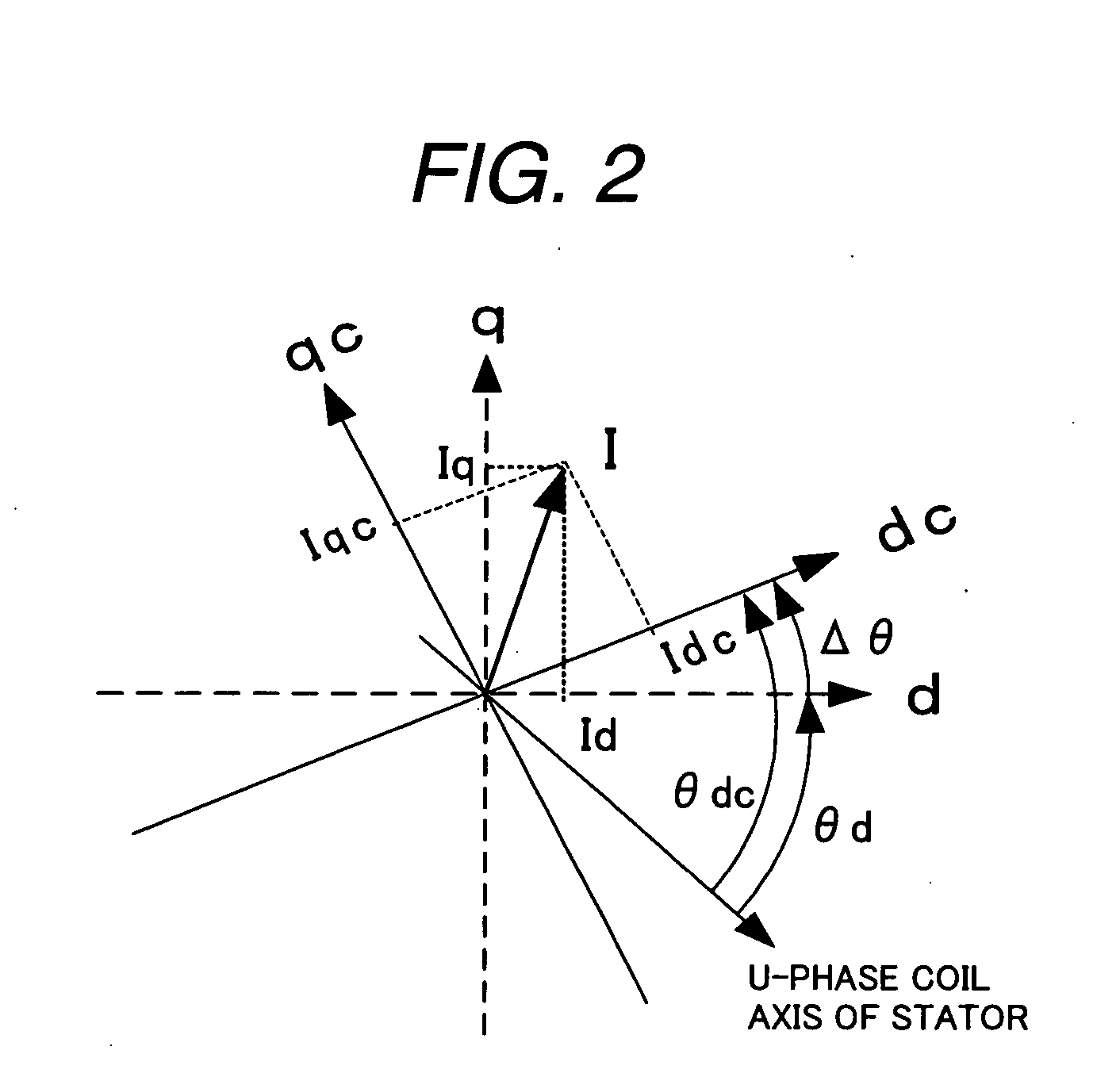
Synchronous motor drive unit and a driving method thereof
InactiveUS20060125439A1Efficient driveImprove maintainabilityAsynchronous induction motorsElectric energy vehiclesSynchronous motorPhase difference
A rotary sensor that outputs two analog signals, such as one sine wave and one cosine wave and has multiple periods within one period of the electrical angle of a motor is employed. The motor is energized at each position for a specified length of time upon its startup by using multiple electrical angles corresponding to the multiple candidate absolute angles obtained from the rotary sensor signal as the initial position of the motor, and the electrical angle at which the motor acceleration becomes maximum is determined as the absolute angle. While the motor drive is in operation, on the other hand, the phase difference Δθ between the phase of the motor at the counter electromotive voltage and the control phase is directly computed from the parameters of the motor, sensed current, voltage command and angle speed so as to correct the shifted position. A high-efficiency motor drive unit with improved maintainability of rotary sensor and improved accuracy of sensing the magnet pole position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor that accelerates and decelerates very quickly in a wide range of speed is realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Reluctance motor with improved stator structure
InactiveUS20100123426A1Reduce efficiency of motorHigh cost of controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlReluctance motorEngineering
Owner:DENSO CORP
Brushless and sensorless DC motor control system with locked and stopped rotor detection
ActiveUS20050029976A1Easy to modifyEasily interfaceCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlMotor speedDc motor control
A motor control system for a brushless and sensorless DC motor for driving a compressor, pump or other application, includes a protection and fault detection circuit for detecting a locked rotor and a rotor which has stopped because of lost rotor phase lock. The motor control system also includes an off-the-shelf motor control integrated circuit having an input for disabling power outputs to the motor phase coils. The protection and fault detection circuit uses a back EMF sampling circuit coupled to the motor phase coils and momentarily disables power to the motor phase coils, via the motor control integrated circuit input, to determine if the motor rotor is rotating. The system also monitors supply voltage, supply current, temperature, and motor speed limits to detect faults and protect system components.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
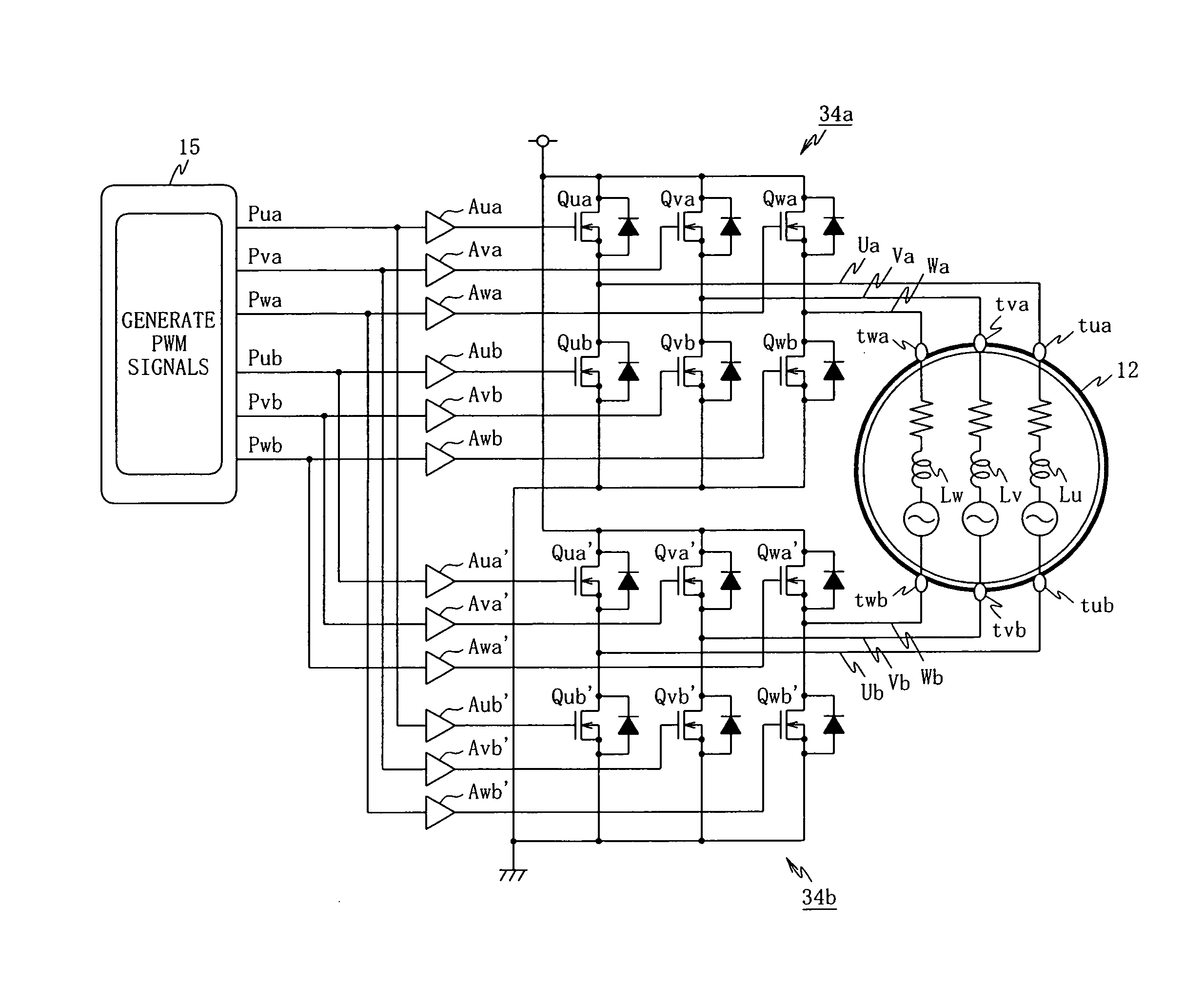
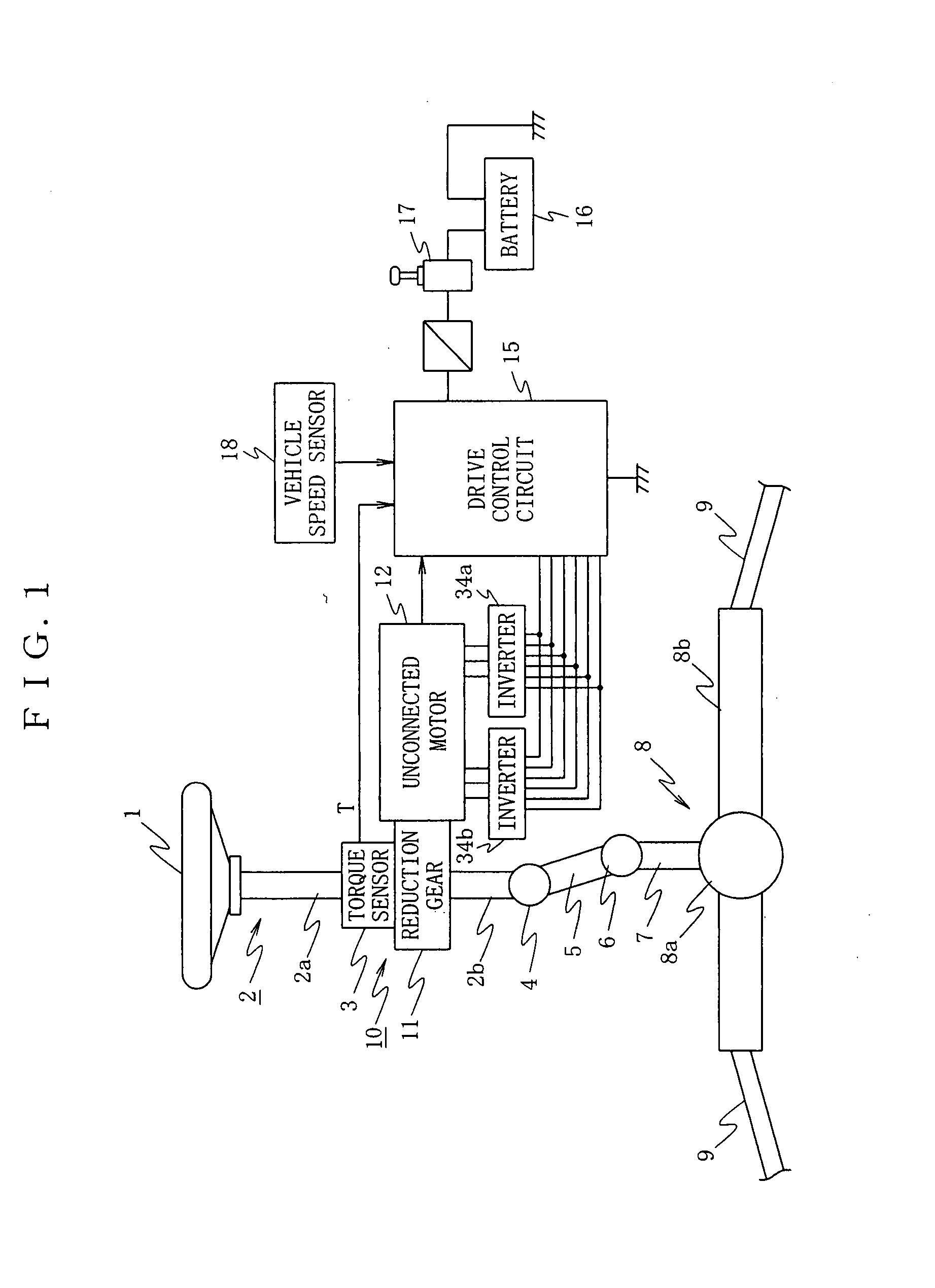
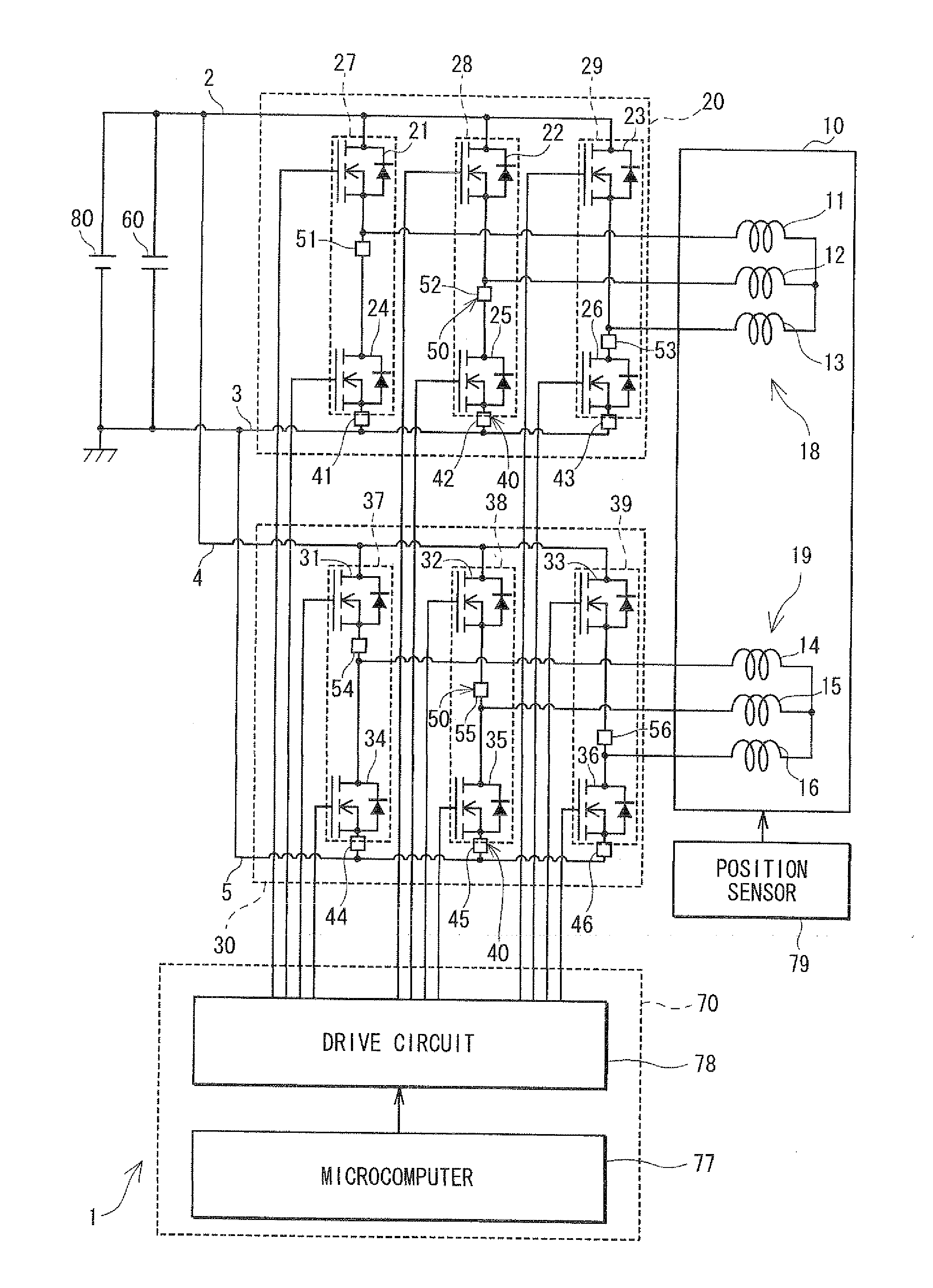
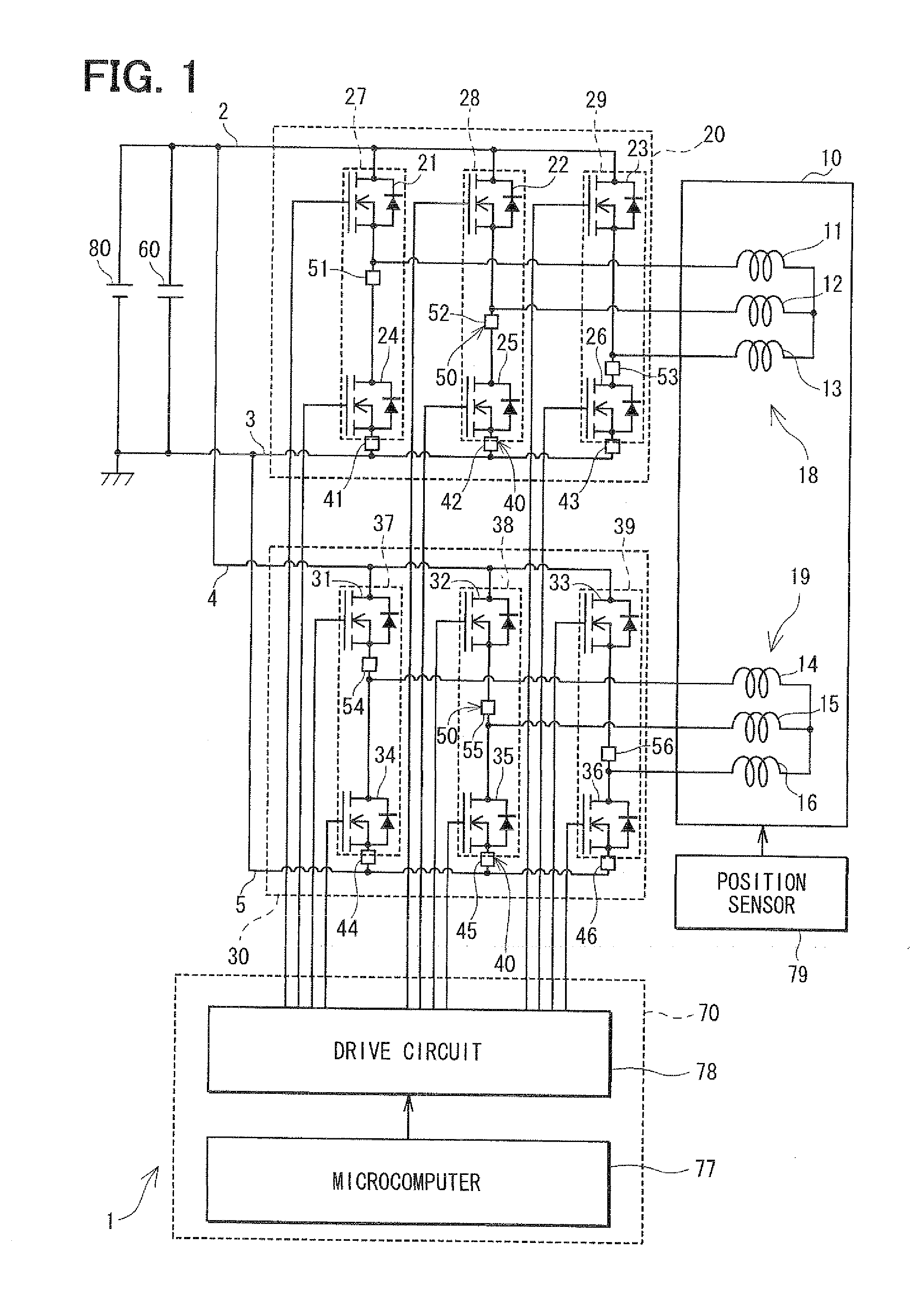
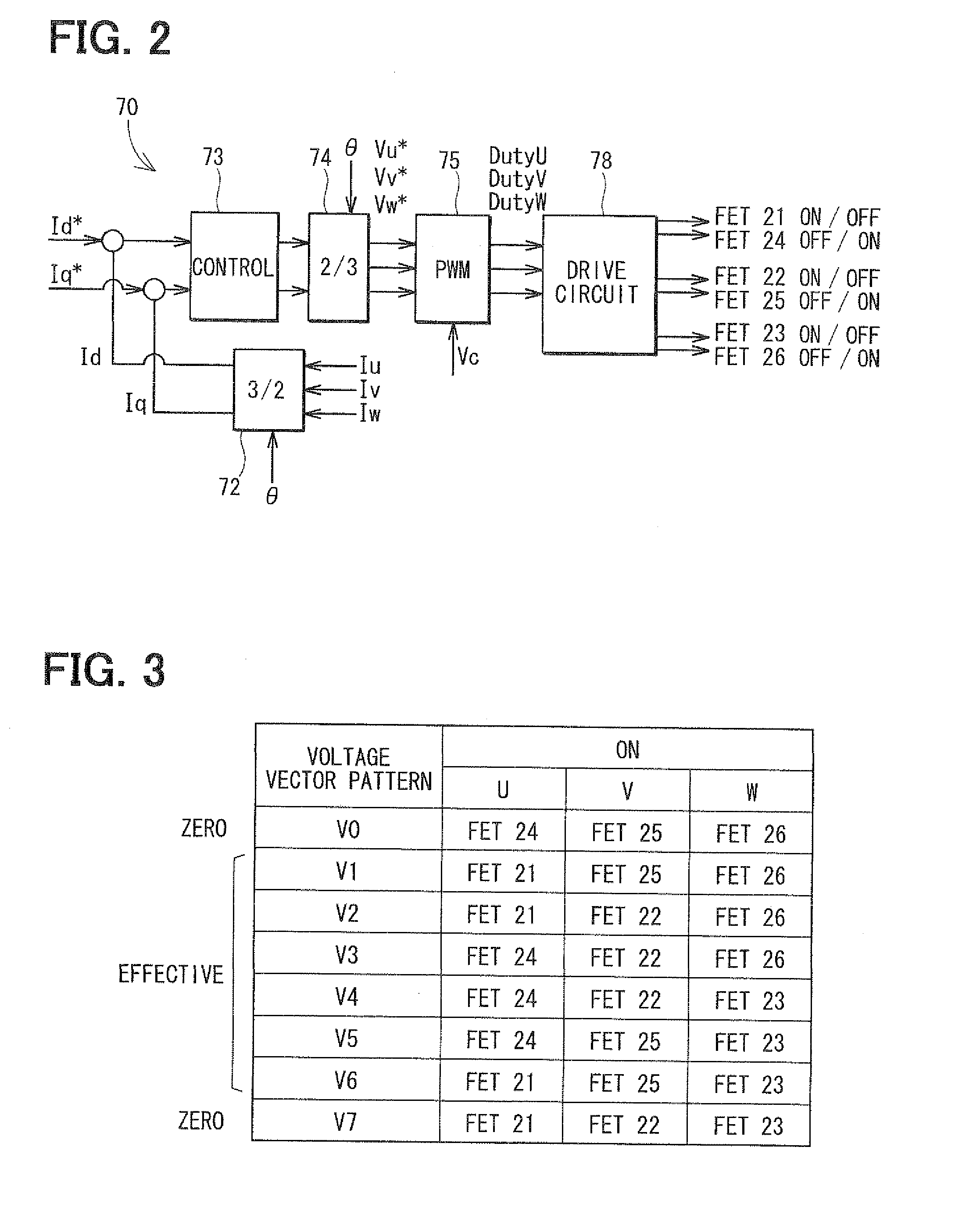
Unconnected Motor, Drive Control Device Thereof, And Electric Power Steering Device Using Drive Control Device Of Unconnected Motor
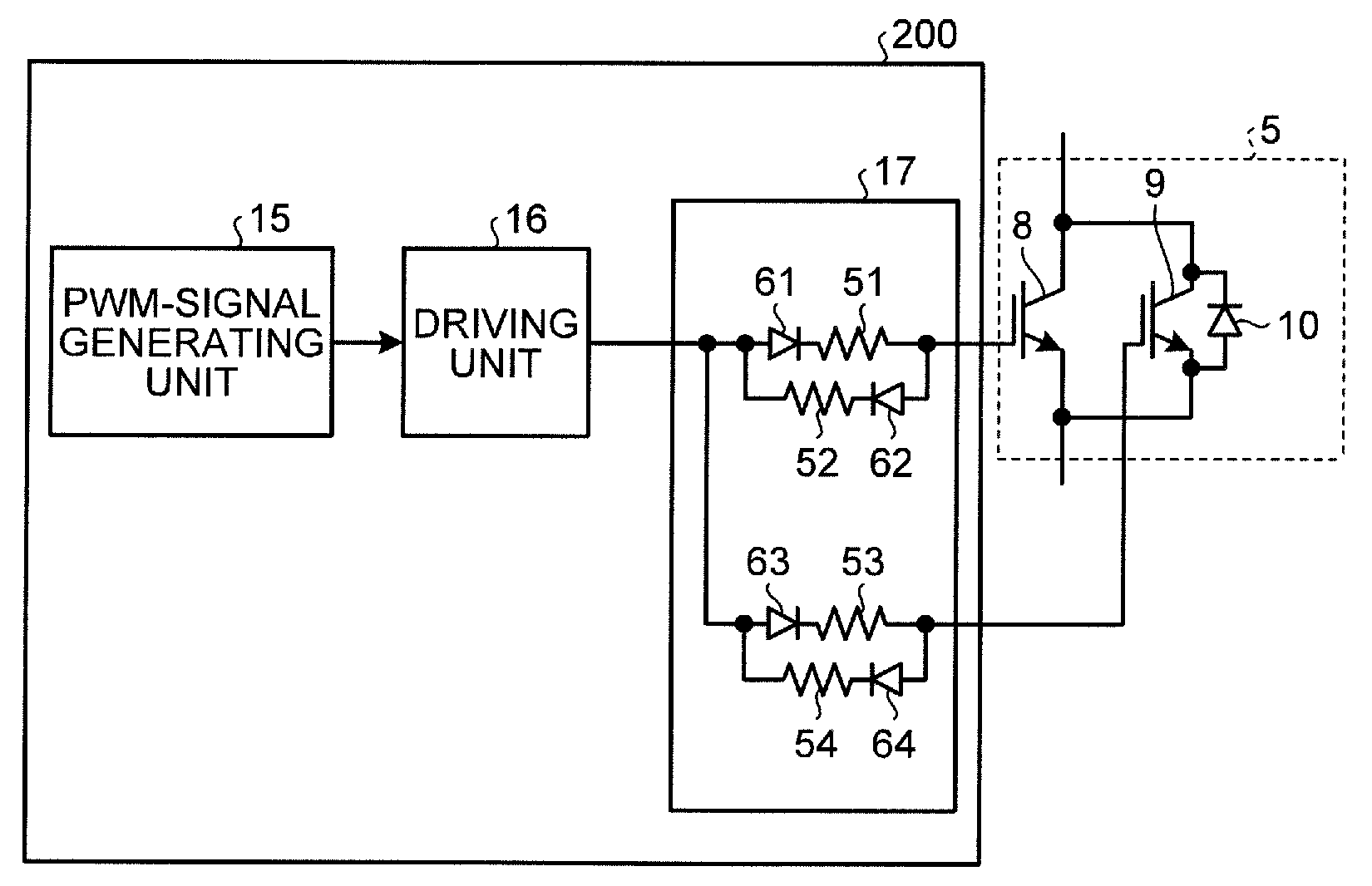
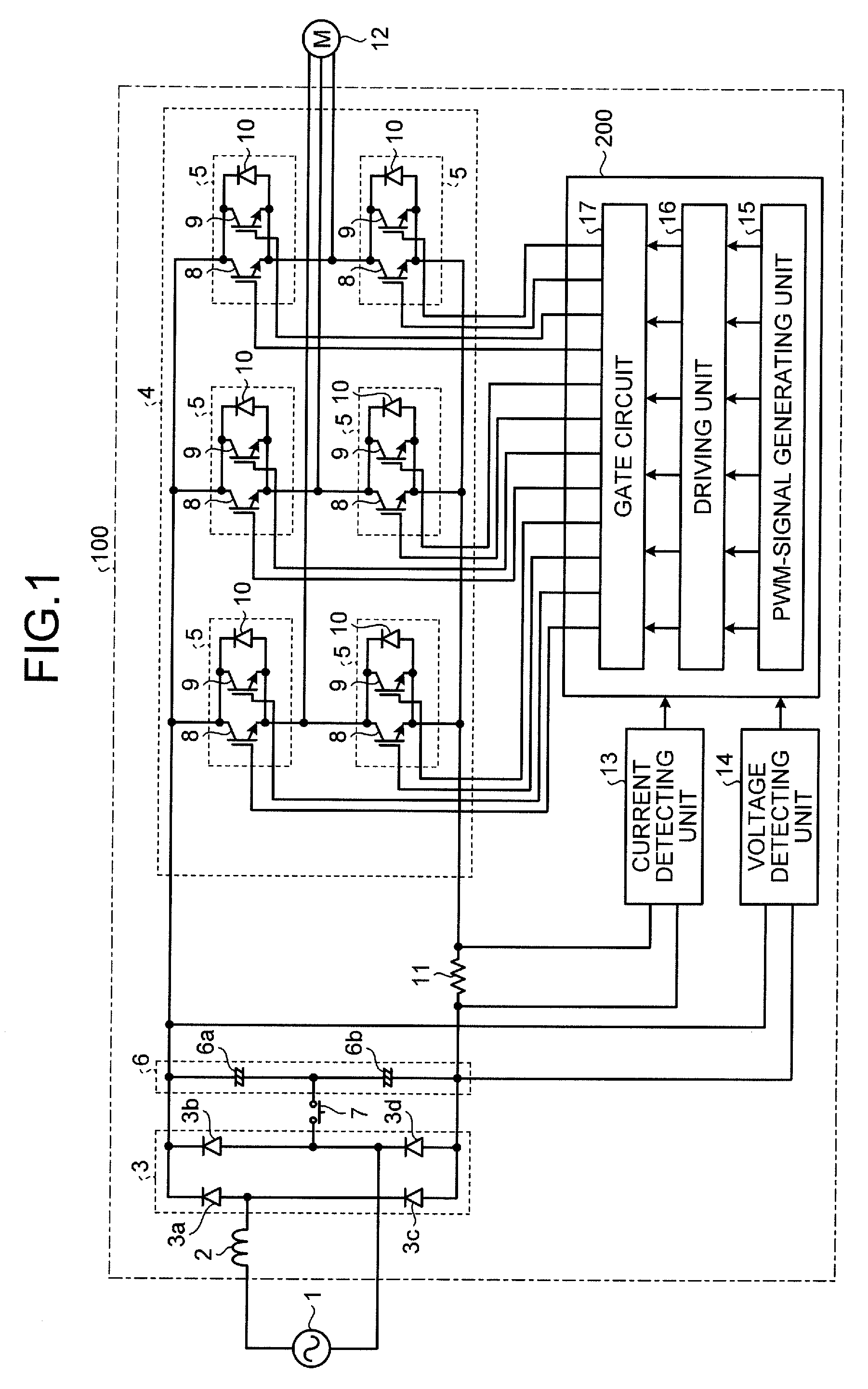
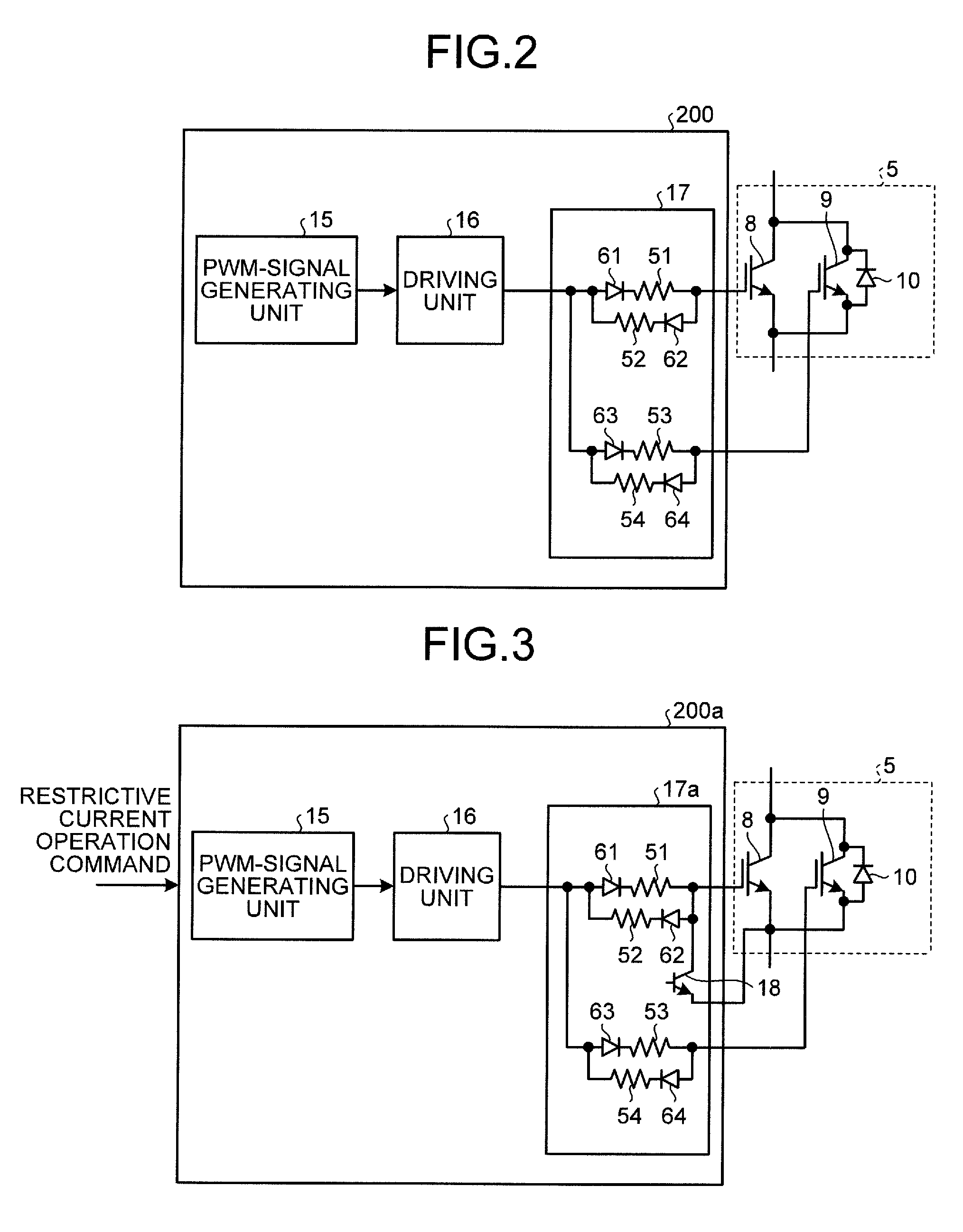
InactiveUS20080067960A1Constant gainIncreased current consumptionMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectric power steeringControl signal
A drive control device of an unconnected motor capable of resolving power shortage and increasing motor output without using a boost circuit, and an electric power steering device using the unconnected motor. The drive control device comprises an unconnected motor (12) having a rotor in which permanent magnets are allocated and a stator opposing the rotor, in which armature winding Lu to Lw of a plurality (N number) of phases are independently arranged, a pair of inverter circuits (34a, 34b) individually connected to both ends of each armature winding, and a drive control circuit (15) which drives the pair of inverter circuits (34a, 34b) with a predetermined number (e.g. 2N) of PWM drive control signals.
Owner:NSK LTD
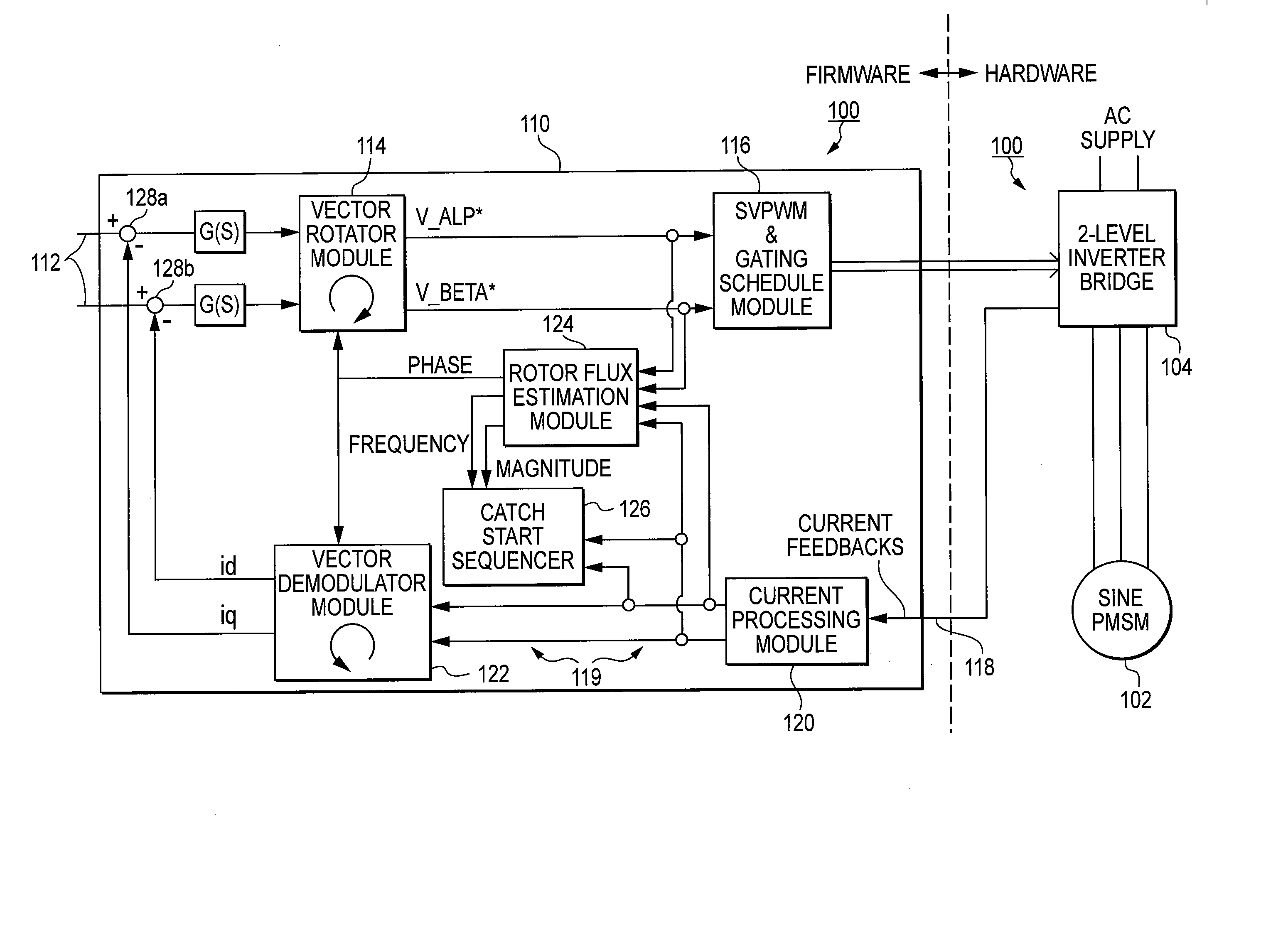
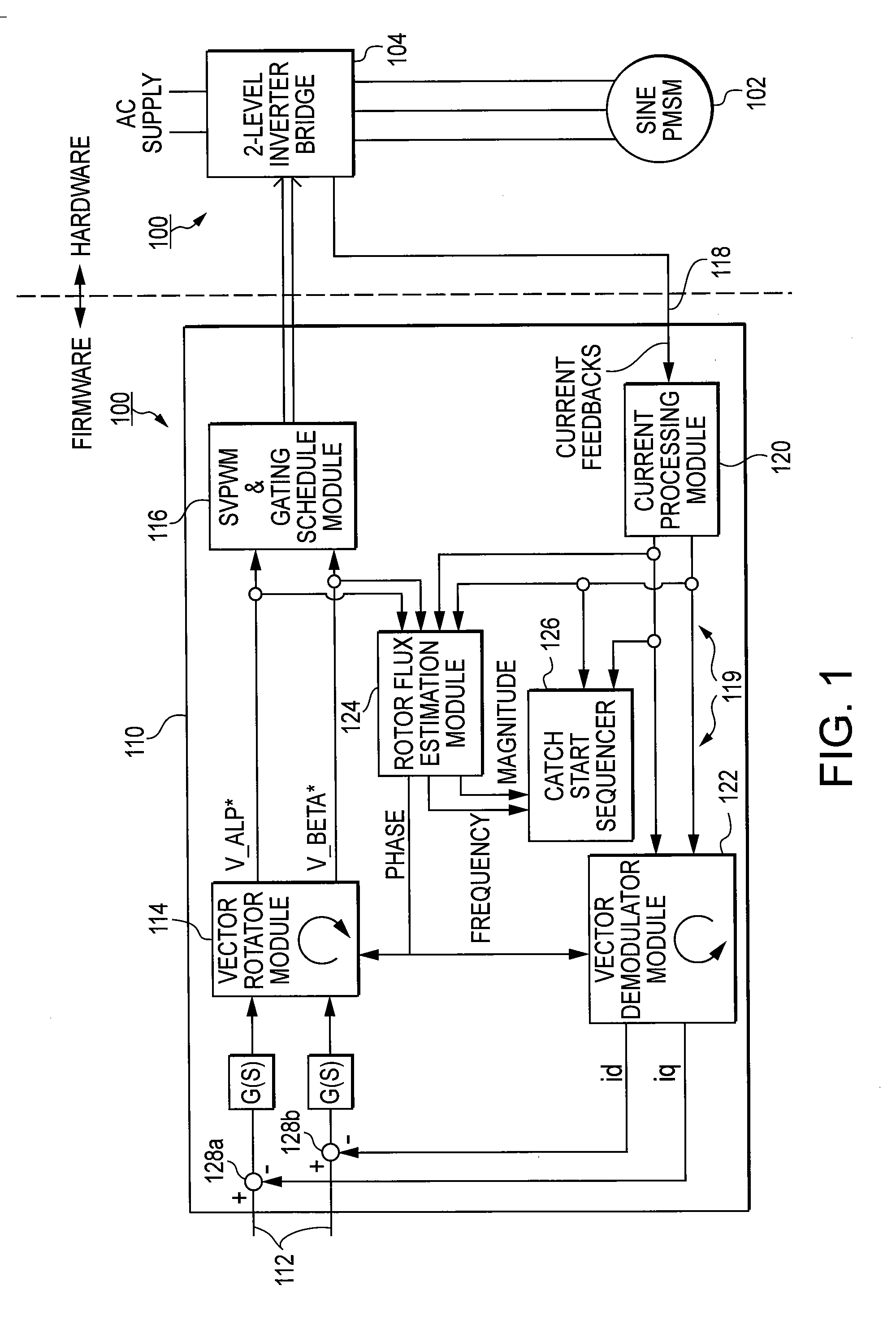
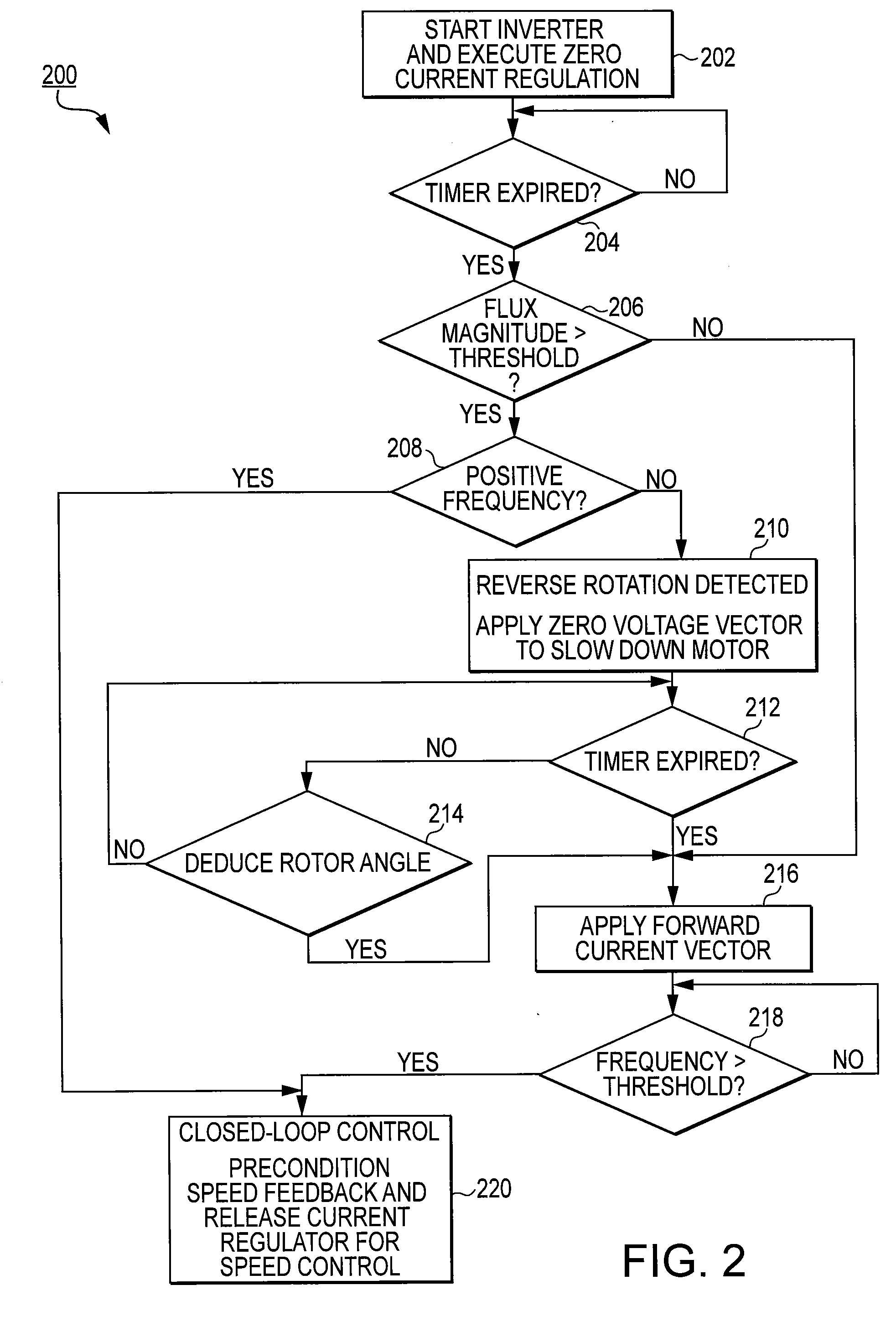
Method and system for starting a sensorless motor
ActiveUS20070001635A1Preventing over current shutdownHigh currentAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersMotor driveEngineering
A motor drive system for a sensorless motor includes a catch start sequencer that controls the motor drive system to robustly start the motor in the event the motor rotor is rotating in forward or reverse direction prior to activating the motor drive system. In particular, the catch start sequencer causes the motor drive system to initially find and track the rotor position, and then determines the speed and possibly the direction of rotation of the rotor. If the rotor is rotating in the reverse direction, the catch start sequencer controls the motor drive system to slow the speed of rotation and to then start the rotor rotating in the forward direction.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
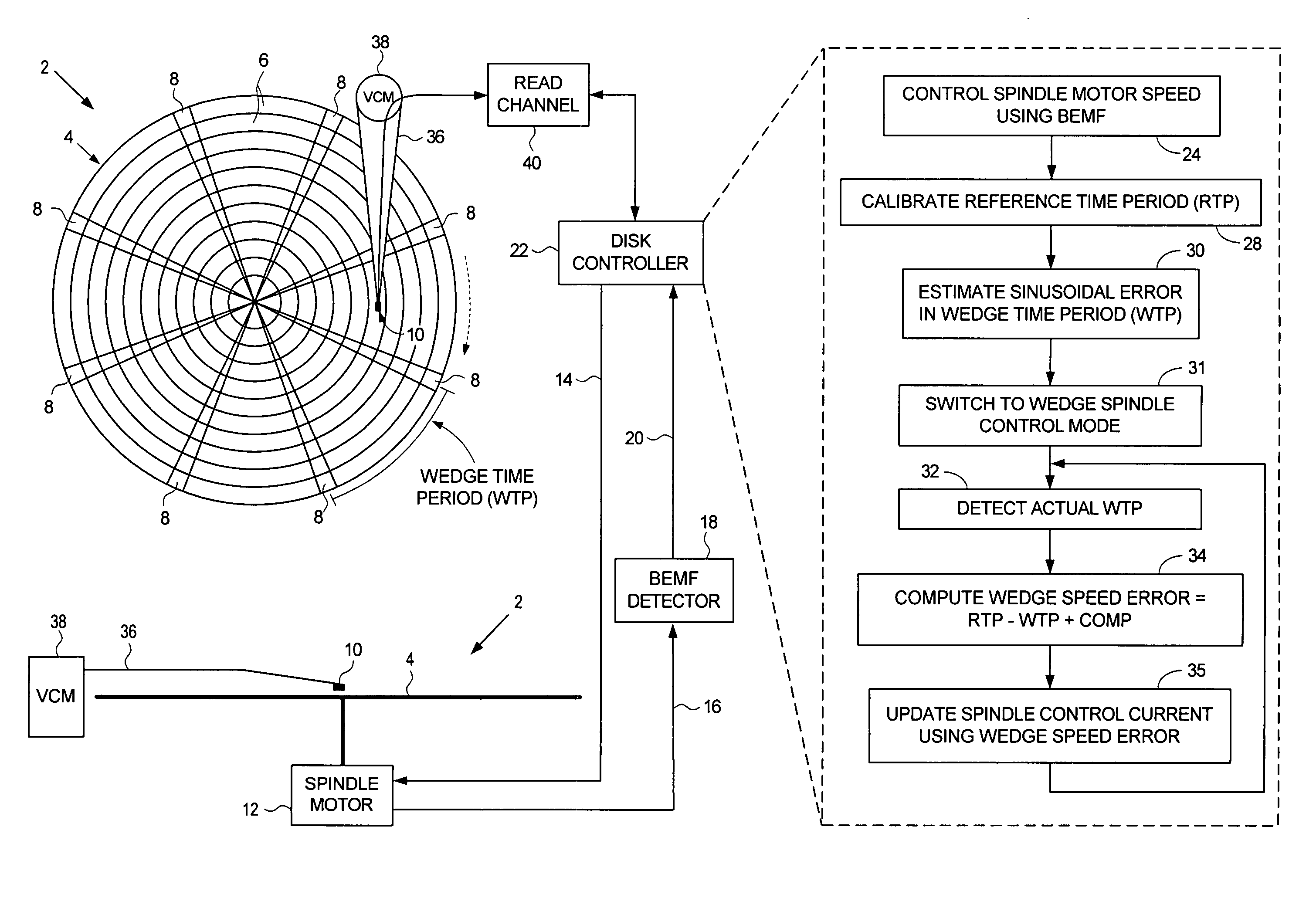
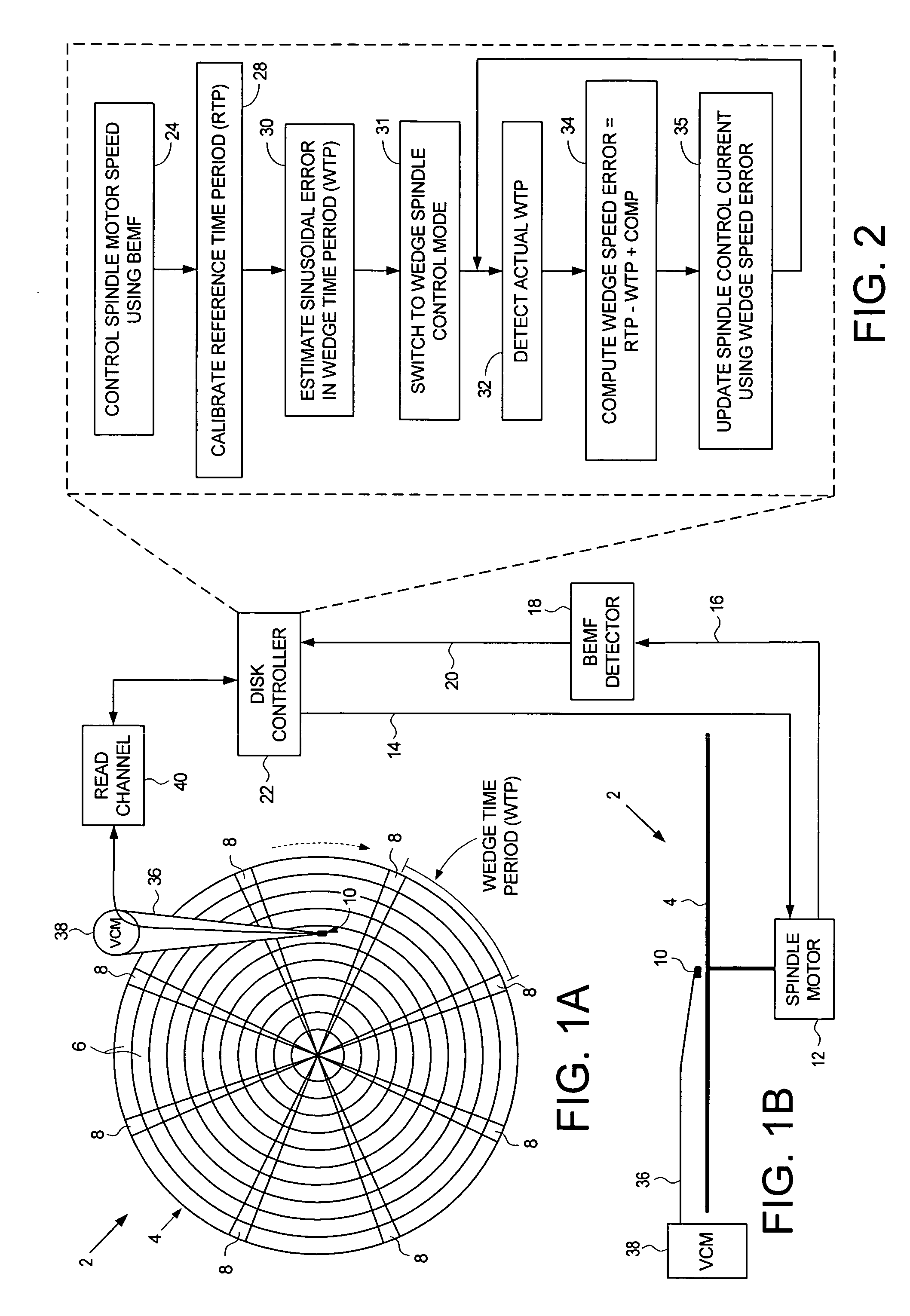
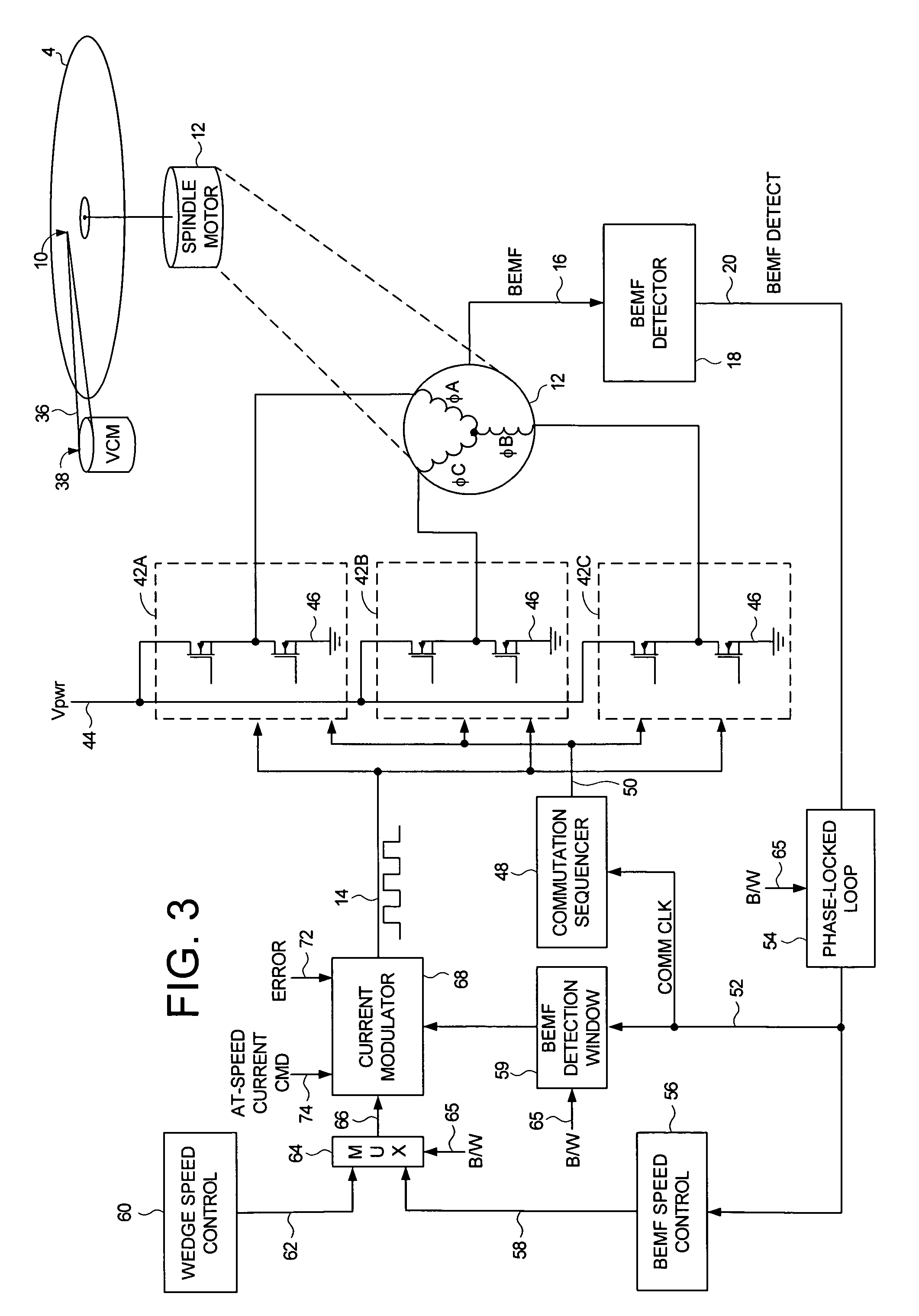
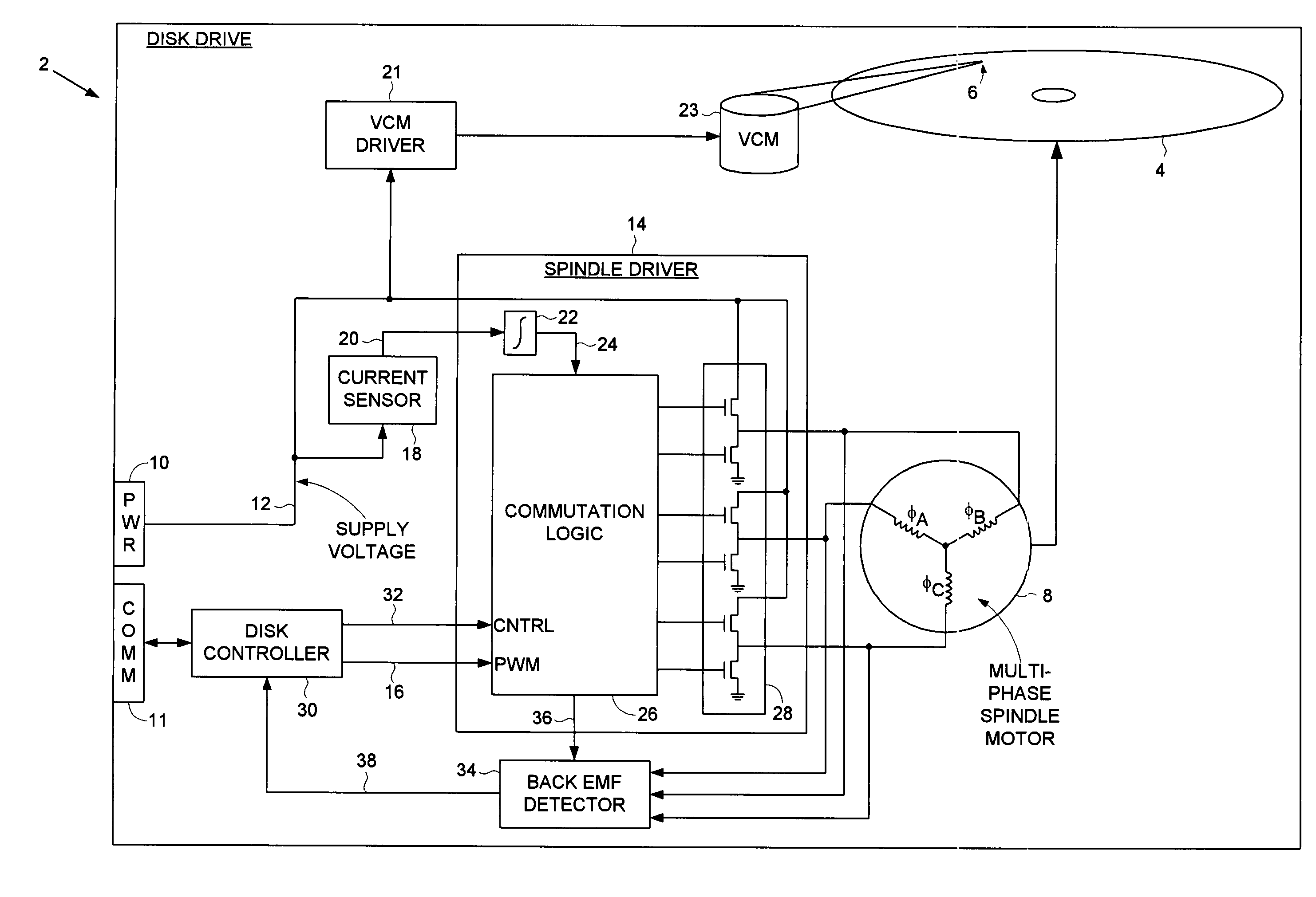
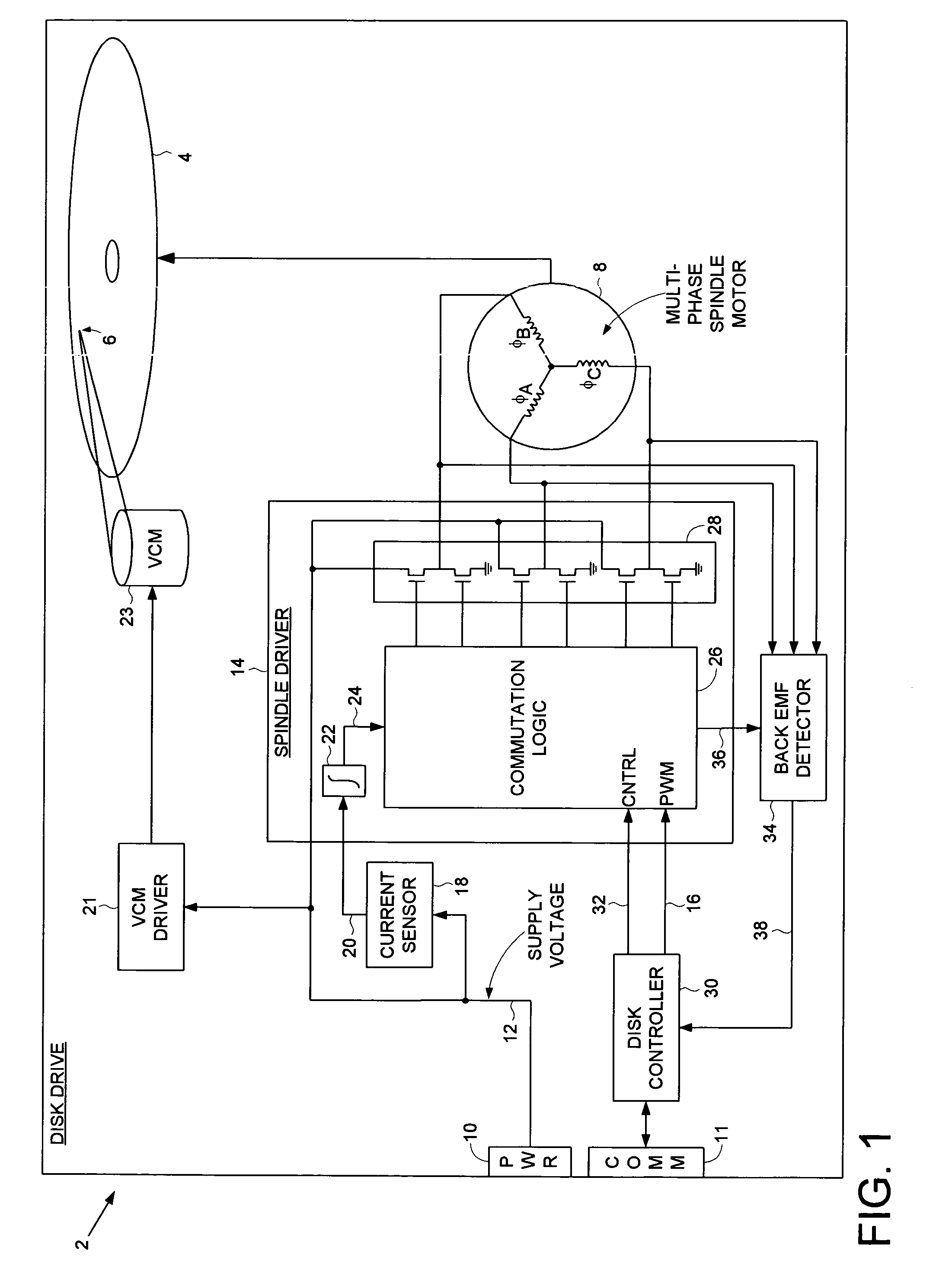
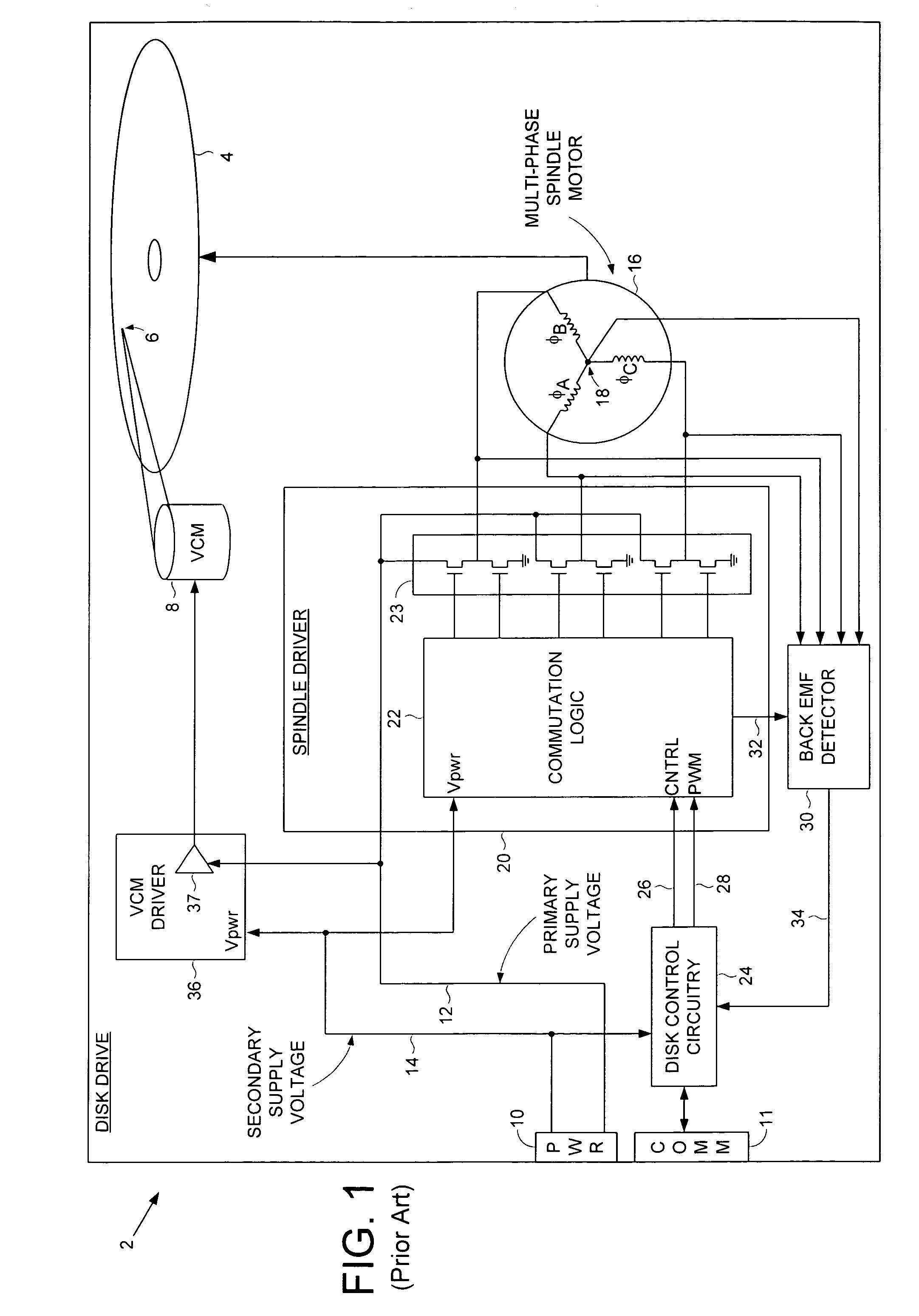
Disk drive employing wedge spindle speed control with eccentricity compensation
A disk drive is disclosed wherein a BEMF speed error is measured during a BEMF spindle speed control mode, and a spindle control current is updated in response to the BEMF speed error to drive the disk at an operating speed. A reference time period (RTP) is calibrated, and a sinusoidal error in a wedge time period (WTP) due to eccentricity in the disk rotating is estimated to generate an eccentricity compensation value. After switching to a wedge spindle speed control mode, an actual WTP is detected and a wedge speed error is generated in response to the RTP, the detected actual WTP, and the eccentricity compensation value. The disk is then maintained at the operating speed by updating the spindle control current in response to the wedge speed error.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System and method for controlling motor using parameter associated with magnetic flux
InactiveUS20080129243A1Reliably graspTorque ripple controlSynchronous motors startersDriving currentOperating point
A control method for a motor that rotates based on flux linkages to a winding member of the motor when the winding member is energized by a drive current is provided. The method includes storing magnetic-state information indicative of a relationship between each of a plurality of predetermined operating points of the drive current and a magnetic-state parameter associated with the flux linkages. The method includes obtaining at least one of command information associated with an operating state of the motor and detection information associated with the operating state of the motor. The method includes referencing the magnetic-state information with the use of the obtained at least one of the command information and detection information to obtain a value of the magnetic-state parameter based on a result of the reference. The method includes controlling an output of the motor based on the obtained value of the magnetic-state parameter.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Sensorless control method and apparatus for a motor drive system
InactiveUS20050007044A1Quick calculationAccurate predictionDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlKaiman filterControl power
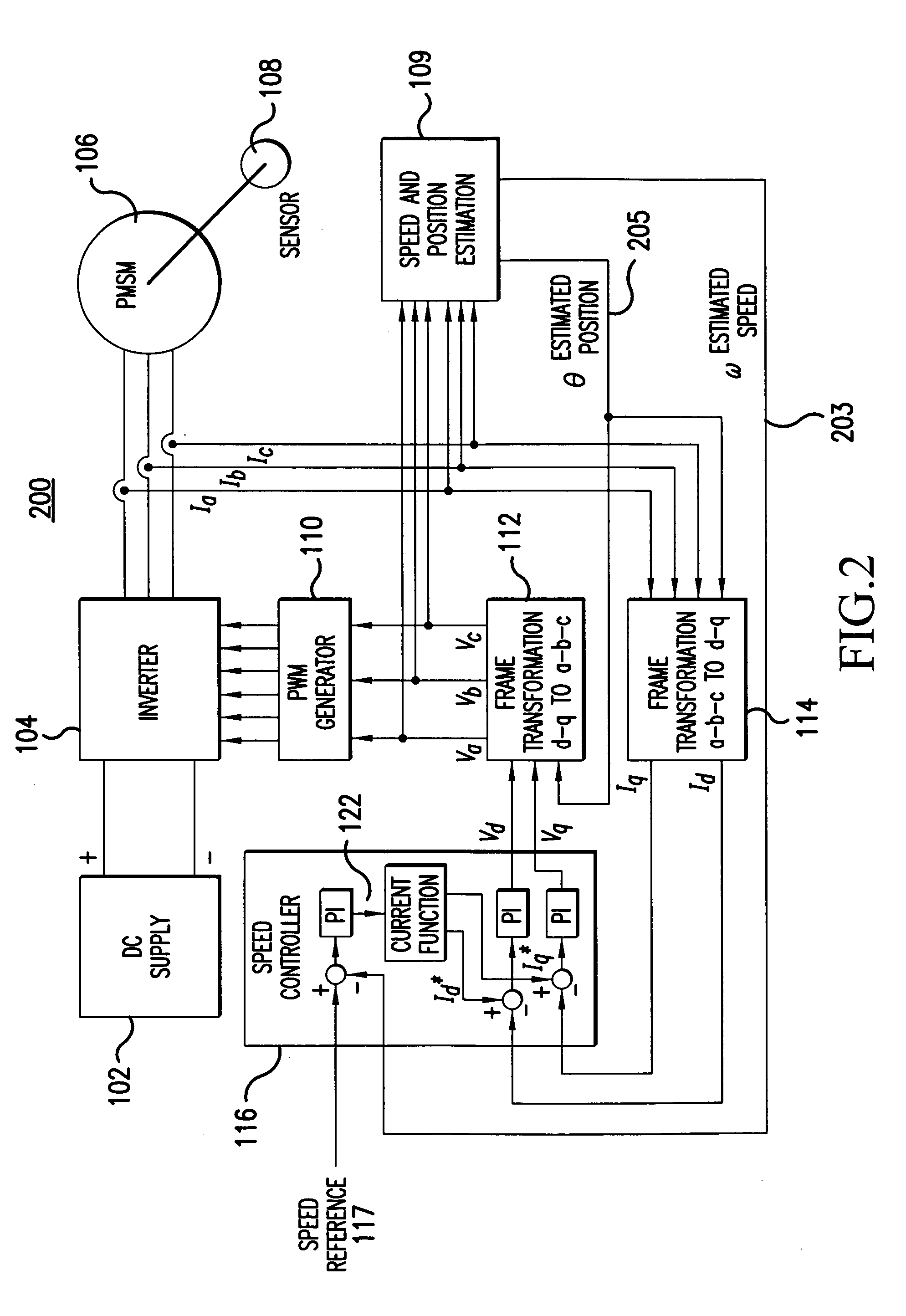
A method and apparatus provide a state observer control system 600 for a motor 106 that uses an extended Kalman filter 330 to predict initial rotor position and afterwards accurately predict rotor position and / or speed under variable types of loading conditions. A control system model 300 is generated that allows variable setting of an initial rotor position to generate estimated rotor position and speed as outputs. The control system model 300 includes an EKF (extended Kalman filter) estimator 330, speed controller 322, a current controller 324, and a variable load component 310. During operation, EKF estimator 330 estimates rotor speed 327 and position 333 based on reference voltages 402, 404 and currents 1325 generated by speed and current controllers 322, 324 and input from frame transformers 326, 328. Additionally, the reference currents and voltages 402, 404, 1325 are frame-transformed to be used as feedback signals 418, 346 in the system 600 and as drive signals to control power to be applied to a motor load 602.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Electric motor and motor control
InactiveUS8575873B2Reduce noiseHigh complexitySingle-phase induction motor startersTorque ripple controlElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
Various embodiments of an electric motor and electronic control for an electric motor are disclosed. An exemplary electric motor comprises a single-phase brushless permanent magnet electric motor. In exemplary embodiments, the electronic motor control is configured to commutate an electric motor at a frequency other than line frequency, perform pulse width modulation, and drive the electric motor with a drive waveform that approximates the counter-electromotive force of the motor.
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
Permanent magnetically excited electrical rotary drive
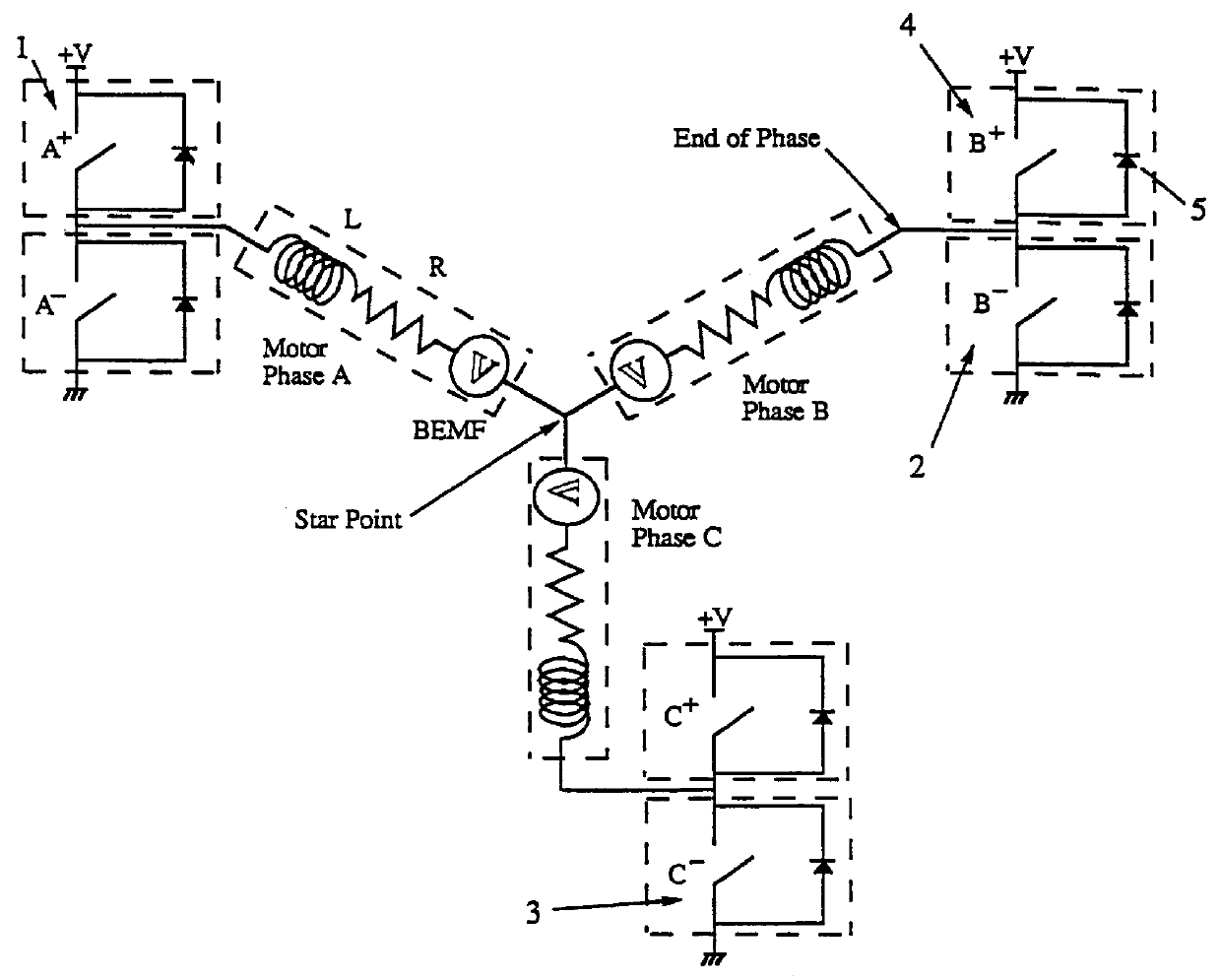
InactiveUS6278251B1Improve fault toleranceGuaranteed uptimeSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlPhase currentsElectricity
A permanent magnetically excited electrical rotary drive for a blood pump is proposed, comprising a permanent magnetic rotor and a stator, said stator comprising a drive winding having at least two loops for the production of a magnetic drive field which produces a torque on the rotor, with each loop belonging to a different electrical phase, furthermore comprising a setting device which supplies each loop in each case with a phase current or in each case with a phase voltage as a setting parameter, with the setting device comprising a separate power amplifier for each loop so that the setting parameter for each loop can be regulated independently of the setting parameter for the other loops.
Owner:THORATEC CORPORTION
Method and apparatus for controlling brushless DC motors in implantable medical devices
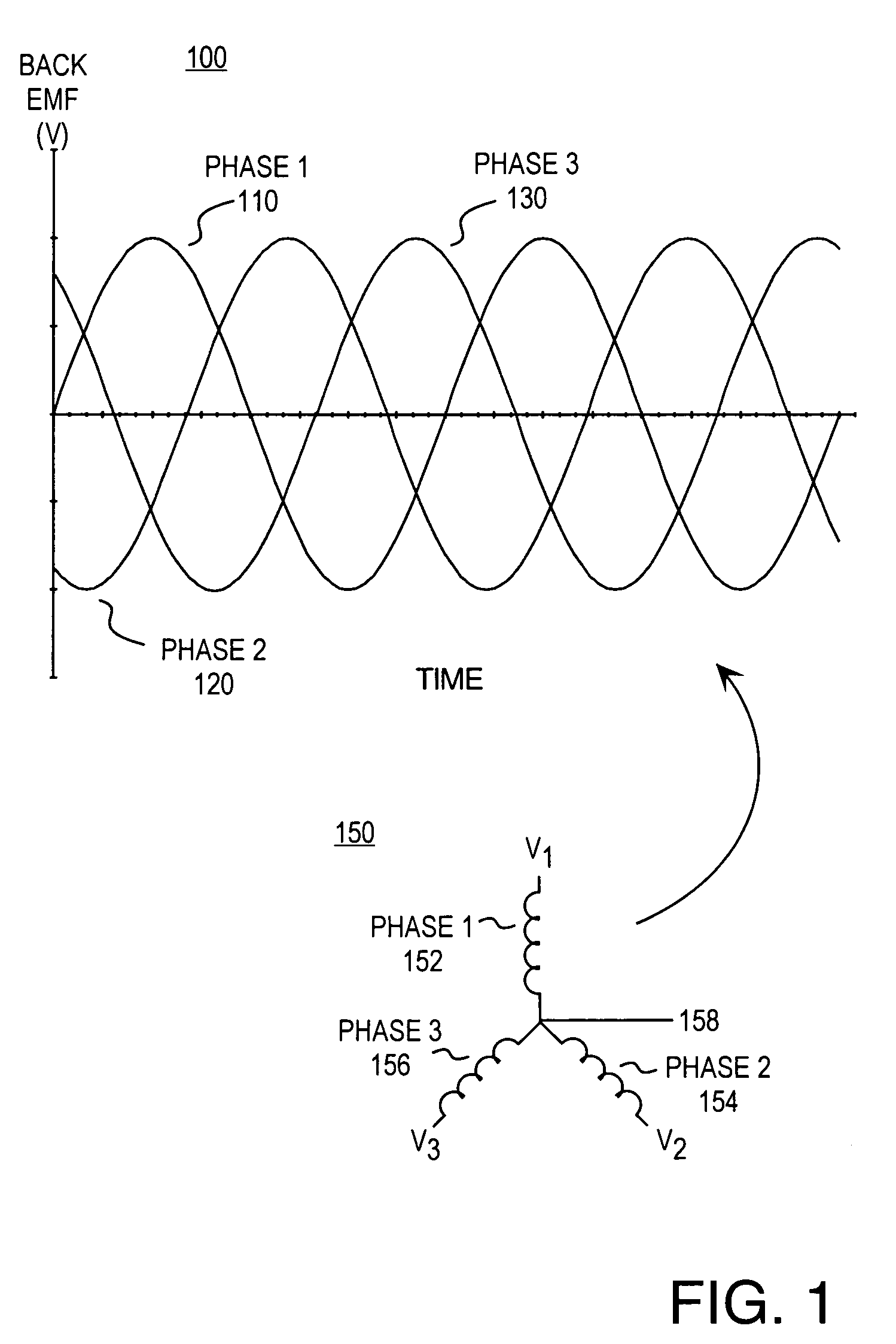
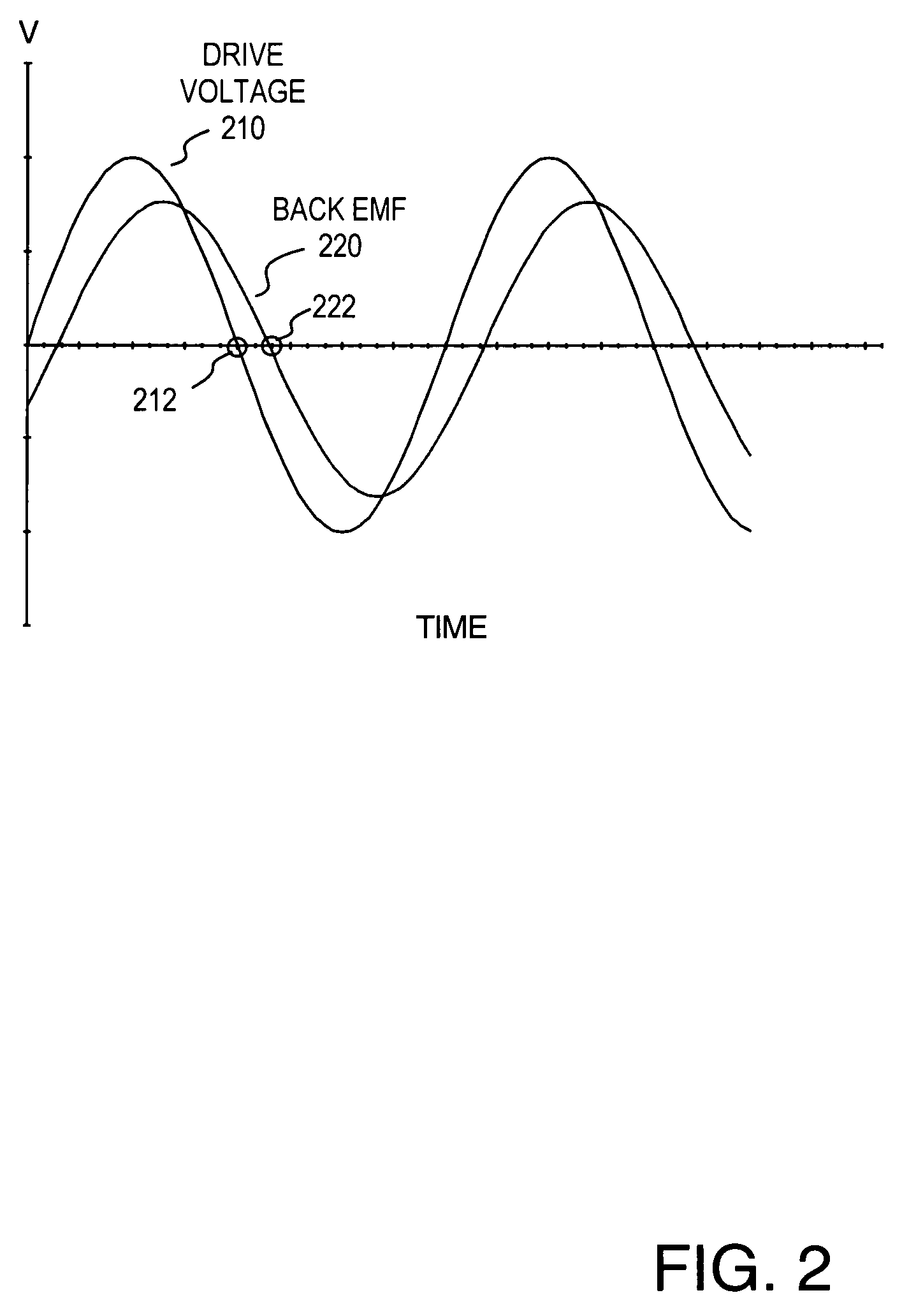
Methods and apparatus for controlling a polyphase motor in implantable medical device applications are provided. In one embodiment, the polyphase motor is a brushless DC motor. The back emf of a selected phase of the motor is sampled while a drive voltage of the selected phase is substantially zero. Various embodiments utilize sinusoidal or trapezoidal drive voltages. The sampled back emf provides an error signal indicative of the positional error of the rotor. In one embodiment, the sampled back emf is normalized with respect to a commanded angular velocity of the rotor to provide an error signal proportional only to the positional error of the motor rotor. The error signal is provided as feedback to control a frequency of the drive voltage. A speed control generates a speed control signal corresponding to a difference between a commanded angular velocity and an angular velocity inferred from the frequency of the drive voltage. The speed control signal is provided as feedback to control an amplitude of the drive voltage. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a brushless DC motor and a commutation control. The commutation control provides a commutation control signal for a selected phase of the motor in accordance with a sampled back electromotive force (emf) of that phase. The back emf of the phase is sampled only while the corresponding drive voltage for the selected phase is substantially zero, wherein a frequency of a drive voltage of the motor is varied in accordance with the commutation control signal.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
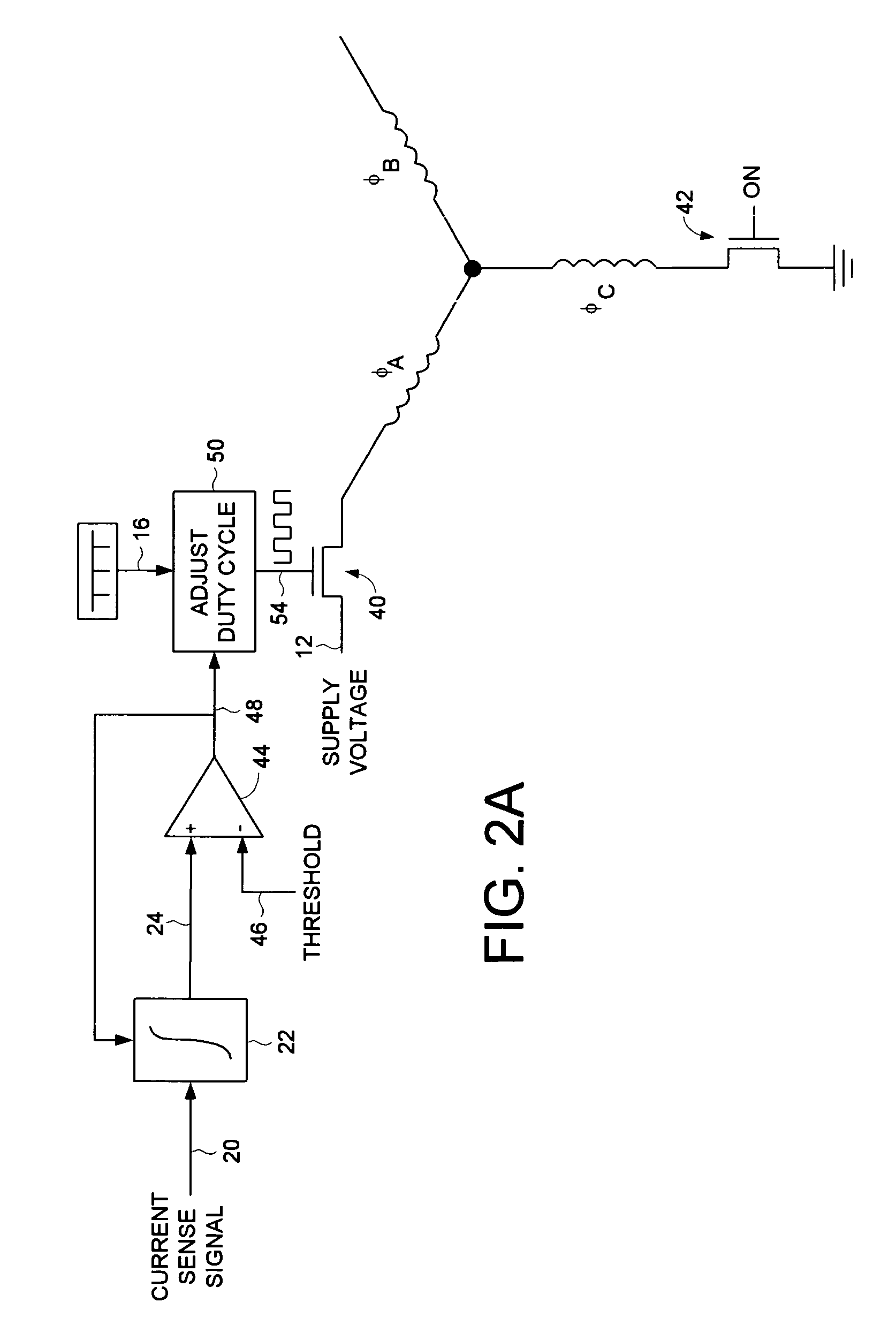
Decreasing spin up time in a disk drive by adjusting a duty cycle of a spindle motor PWM signal to maintain constant average input current
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a spindle motor for rotating a disk, wherein the current applied to the spindle motor is controlled by adjusting a duty cycle of a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal. A current sensor generates a current sense signal representing a current flowing from a supply voltage. The current sense signal is integrated to generate an integration signal. The integration signal is compared to a threshold, and the result of the comparison is used to adjust the duty cycle of the PWM signal. In this manner the disk drive draws essentially constant average input current from the supply voltage which decreases the spin up time of the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Modular multi-axis motion control and driving system and method thereof
InactiveUS20060100723A1Improve performanceReduced dimensionSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlMOSFETNetwork service
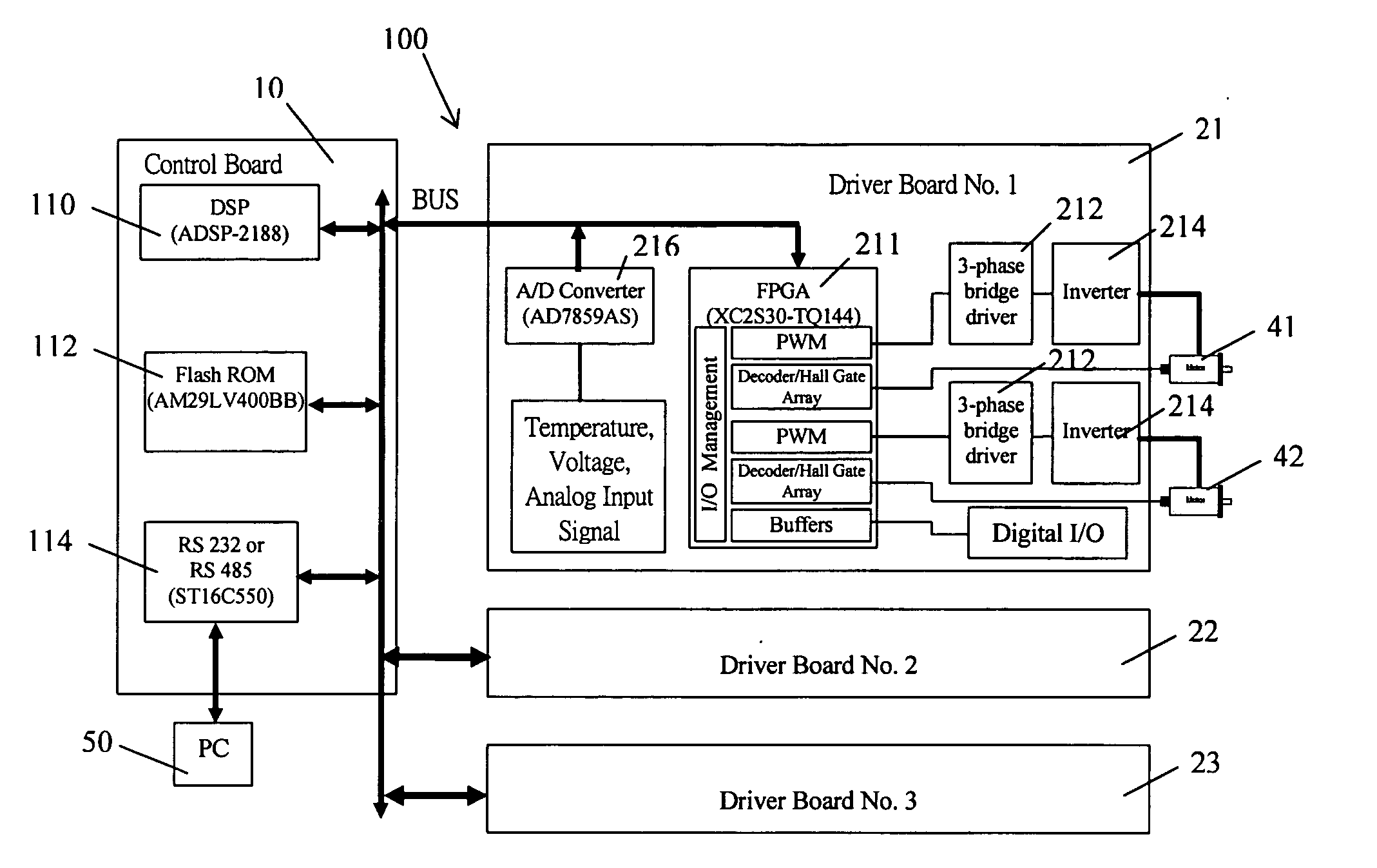
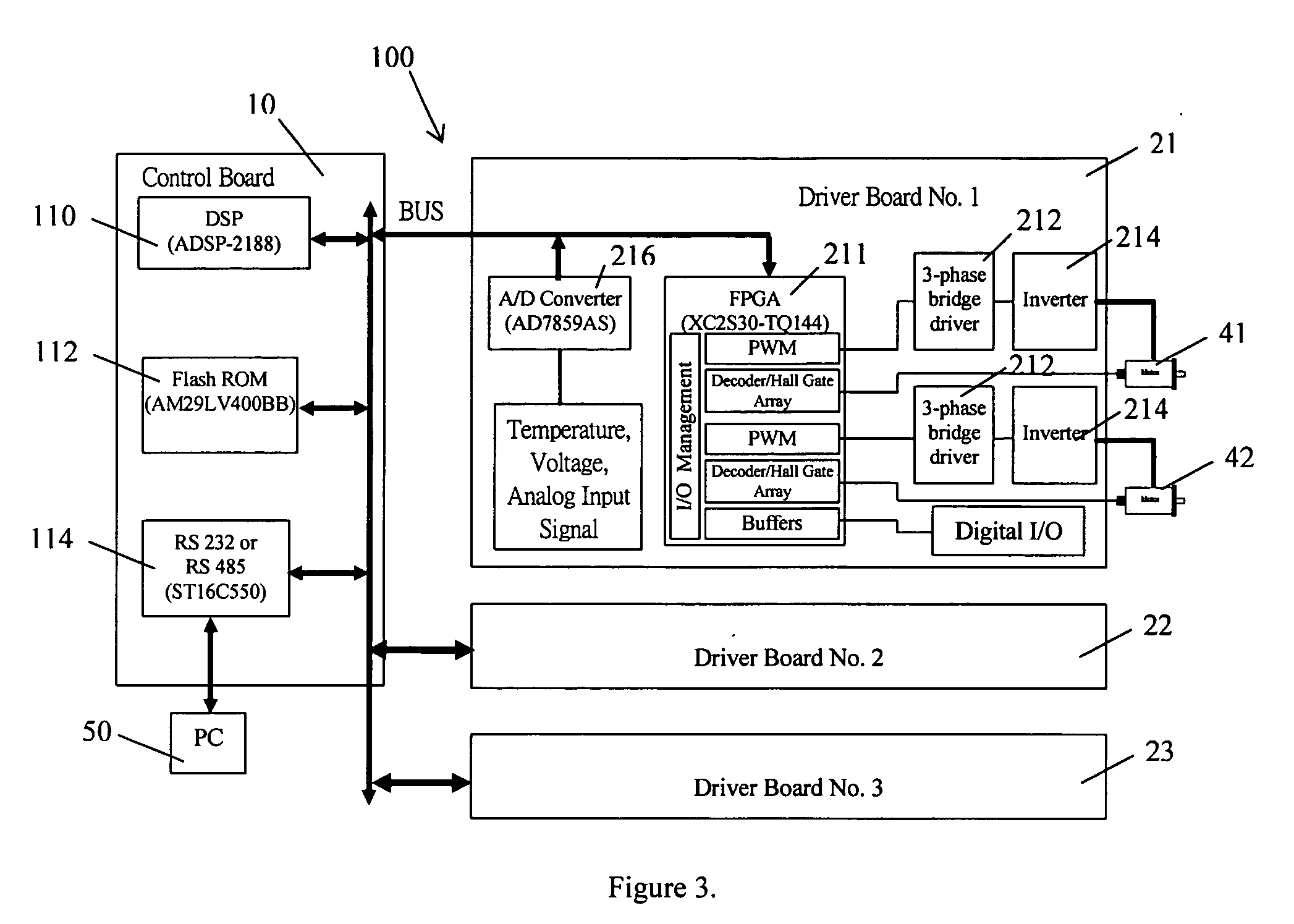
A modular multi-axis motion control and driving system is developed by using advanced Digital Signal Processor (DSP) and Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) technologies. A modular multi-axis motion control and driving system comprises: a control board comprising a DSP and Flash ROM connected to each other, for performing position control and current control of said system; a plurality of driver boards, connected to the control board through a bus, each of which comprise a FPGA device and a plurality of MOSFET power amplifier, for driving a plurality of servo motors; a computer, connected to said control board, for providing graphic user interface, through which motor setting, current and position loop tuning and diagnostic can be performed; Wherein, a control program, system parameters and FPGA configuration file are stored in said Flash ROM, when the system power is on, the DSP automatically executes an loader firmware to transfer the control program from said Flash ROM to the memory of DSP for execution, then the DSP reads the FPGA configuration file from the Flash ROM and configure the FPGA in the driver board, after that, the control program runs into a circulation loop to do system diagnose, network service and check command queue, while the current and position controls are implemented in an interrupt service.
Owner:DYNACITY TECH HK
Disk drive employing active braking using inductive sense
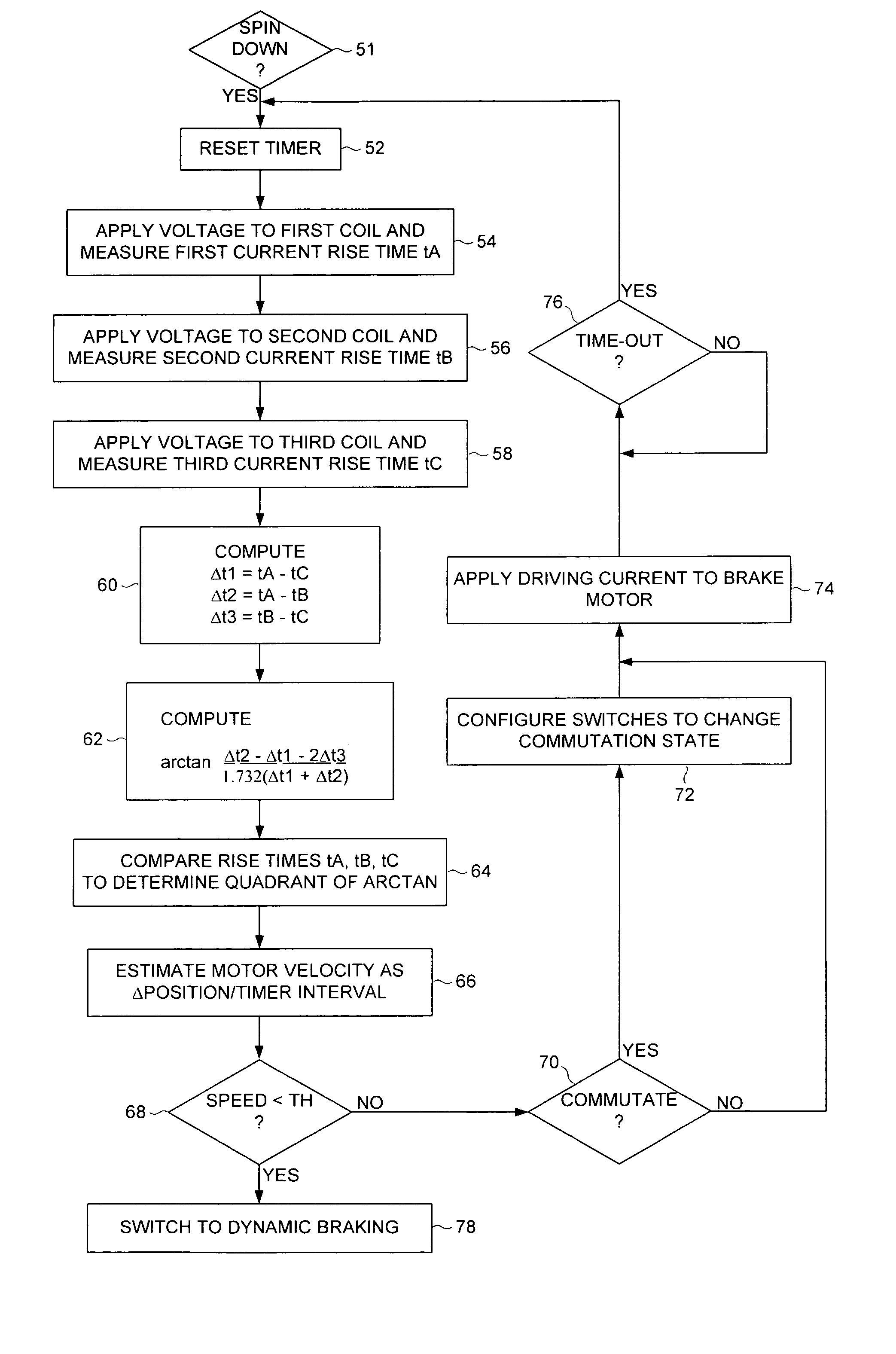
InactiveUS7158329B1Synchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlDriving currentControl circuit
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk, a head actuated over the disk, and a spindle motor for rotating the disk, the spindle motor comprising a plurality of windings. Disk control circuitry executes a spin-down operation of the spindle motor by estimating an angular position of the spindle motor by applying a voltage to at least one of the windings and evaluating a rise time of current flowing through the winding. The windings are commutated in response to the estimated angular position, and a driving current is applied to the windings to brake the spindle motor.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Power electronics device for controlling an electric machine
InactiveUS6326761B1Small space requirementCompact designElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectric machineEngineering
A power electronics device for controlling an electric machine including a power section arranged within a housing which can be closed via a cover element. The power section has a plurality of capacitors and a plurality of power semiconductors which are connected to a power bus bar. In addition, a control device is provided for controlling the power electronics device. The capacitors, power semiconductors, and control device are cooled via a cooling device which is formed as a profile having an essentially U-shaped cross section. The cooling device has two lateral limbs and a base region through which cooling ducts are arranged. A suitable cooling medium flows through the cooling ducts and the ends of the cooling ducts opposite the housing cover are closed by a covering element. The capacitors, the power semiconductors and the control device are connected to the cooling device such that thermal exchange occurs between these components and the cooling device.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
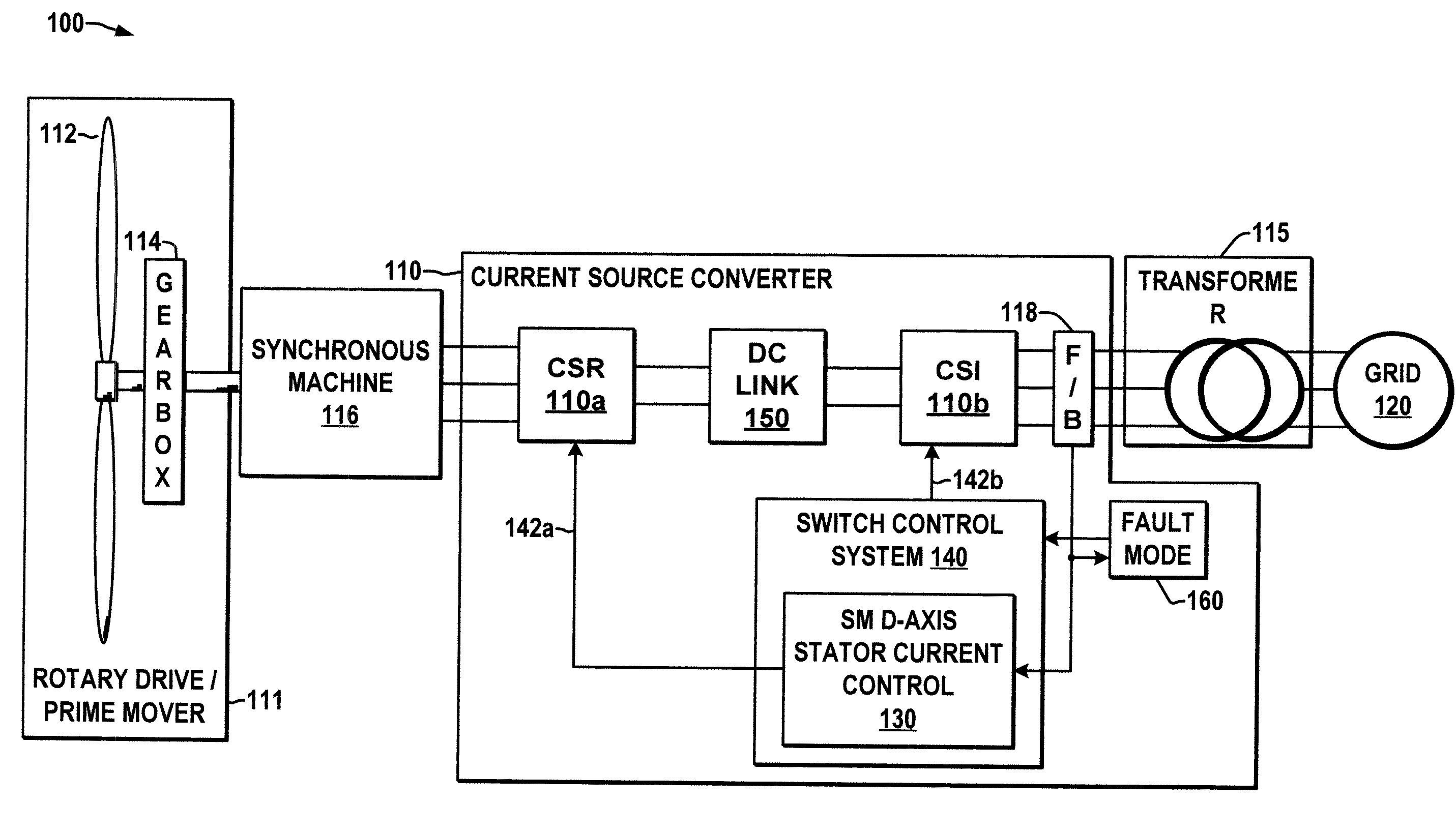
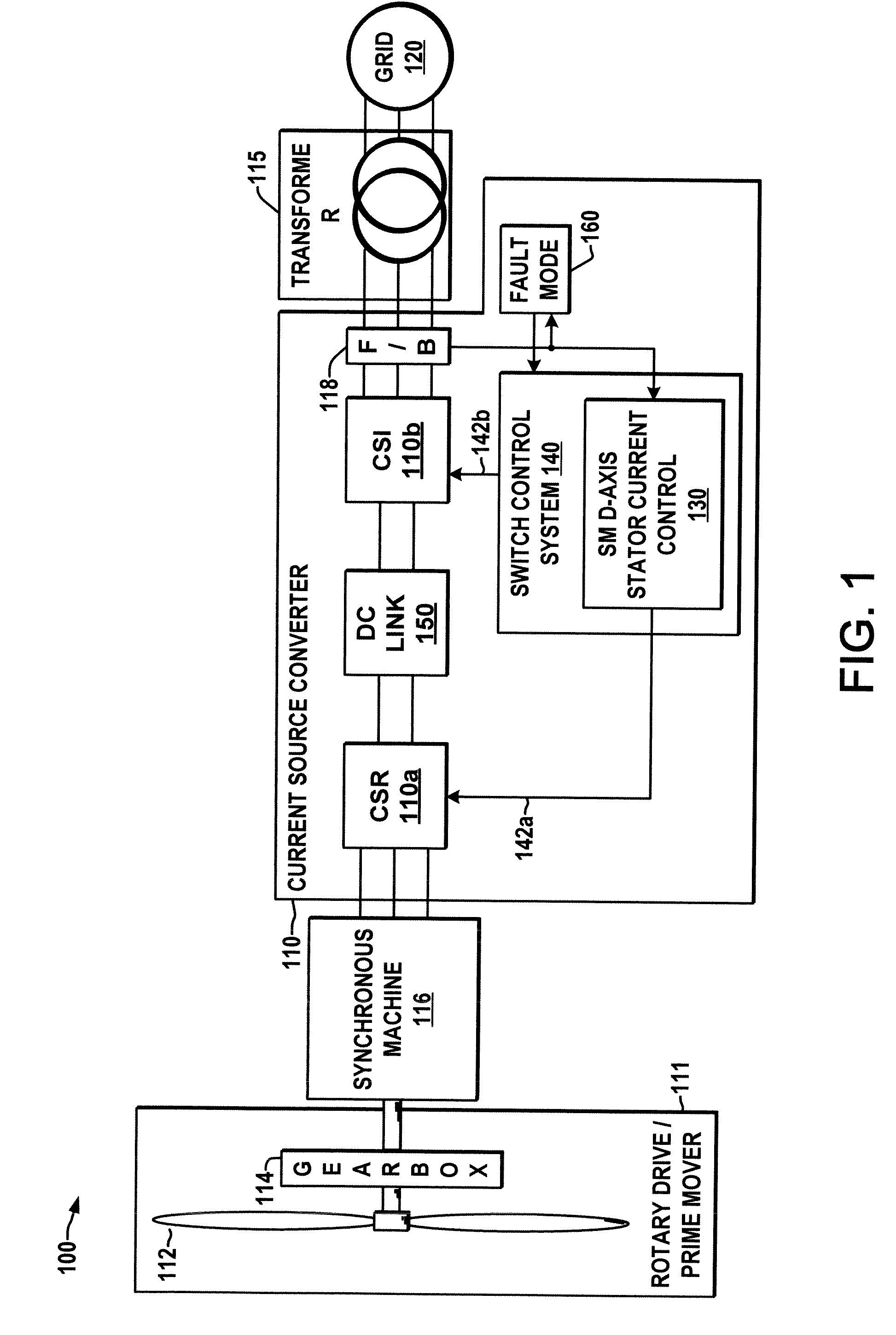
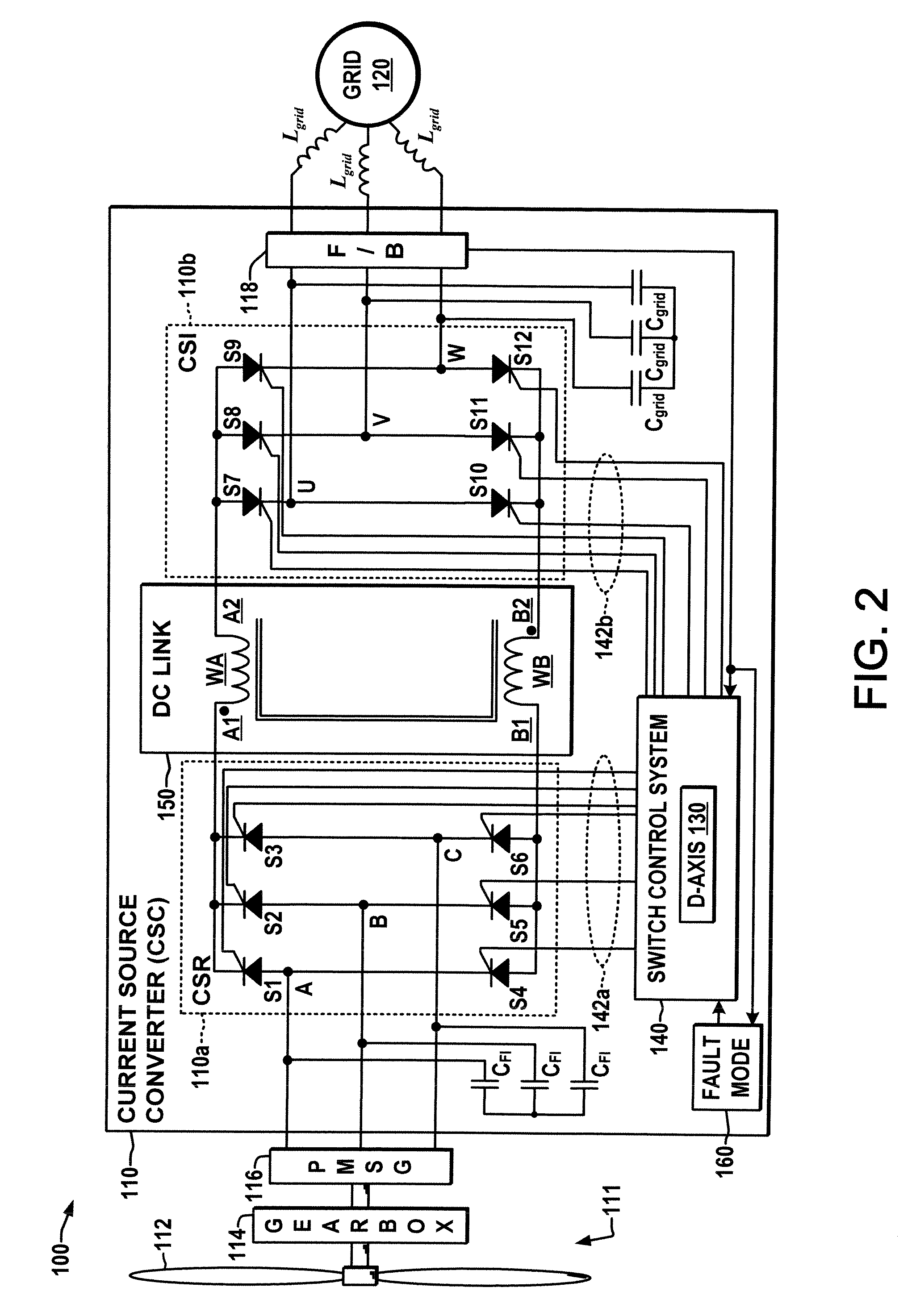
Current source converter-based wind energy system
ActiveUS20100025995A1Excess power being dissipatedAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersResistEngineering
Power conversion apparatus and methods are presented for providing electrical power to a grid or other load in which a synchronous machine is driven by a wind turbine or other prime mover to provide generator power to a switching type current source converter (CSC), with a current source rectifier (CSR) of the CSC being switched to provide d-axis control of the synchronous machine current based on grid power factor feedback, and with a current source inverter (CSI) of the CSC being switched to provide leading firing angle control and selective employment of dumping resists to dissipate excess generator energy in a fault mode when a grid voltage drops below a predetermined level.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Control apparatus for multi-phase rotary machine and electric power steering system
ActiveUS20110074333A1Smooth rideInhibition effectCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlBrake torqueElectric power steering
A control apparatus for a multi-phase rotary machine includes a control unit and a plurality of power supply systems including respective inverter units. When a short-circuiting failure occurs in one of the systems due to an ON-failure in any one of FETs in an inverter unit of the failure system, the control unit stops driving of the rotary machine by bringing all the FETs in the failure system into the OFF state. The control unit controls FETs of the non-failure system such that a brake torque generated in the failure system is cancelled or the influence of the brake torque exerted on the driving of the motor is reduced.
Owner:DENSO CORP
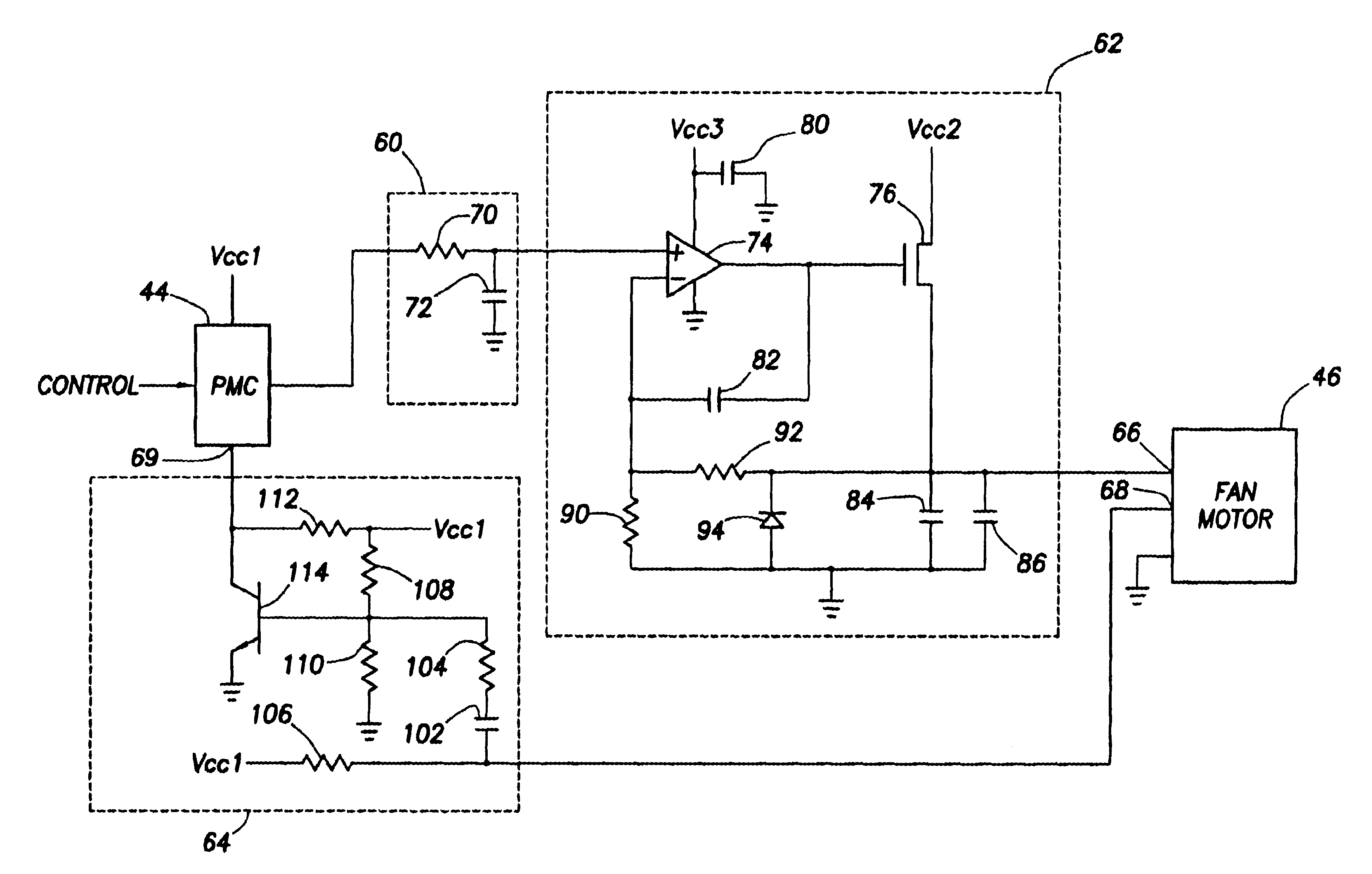
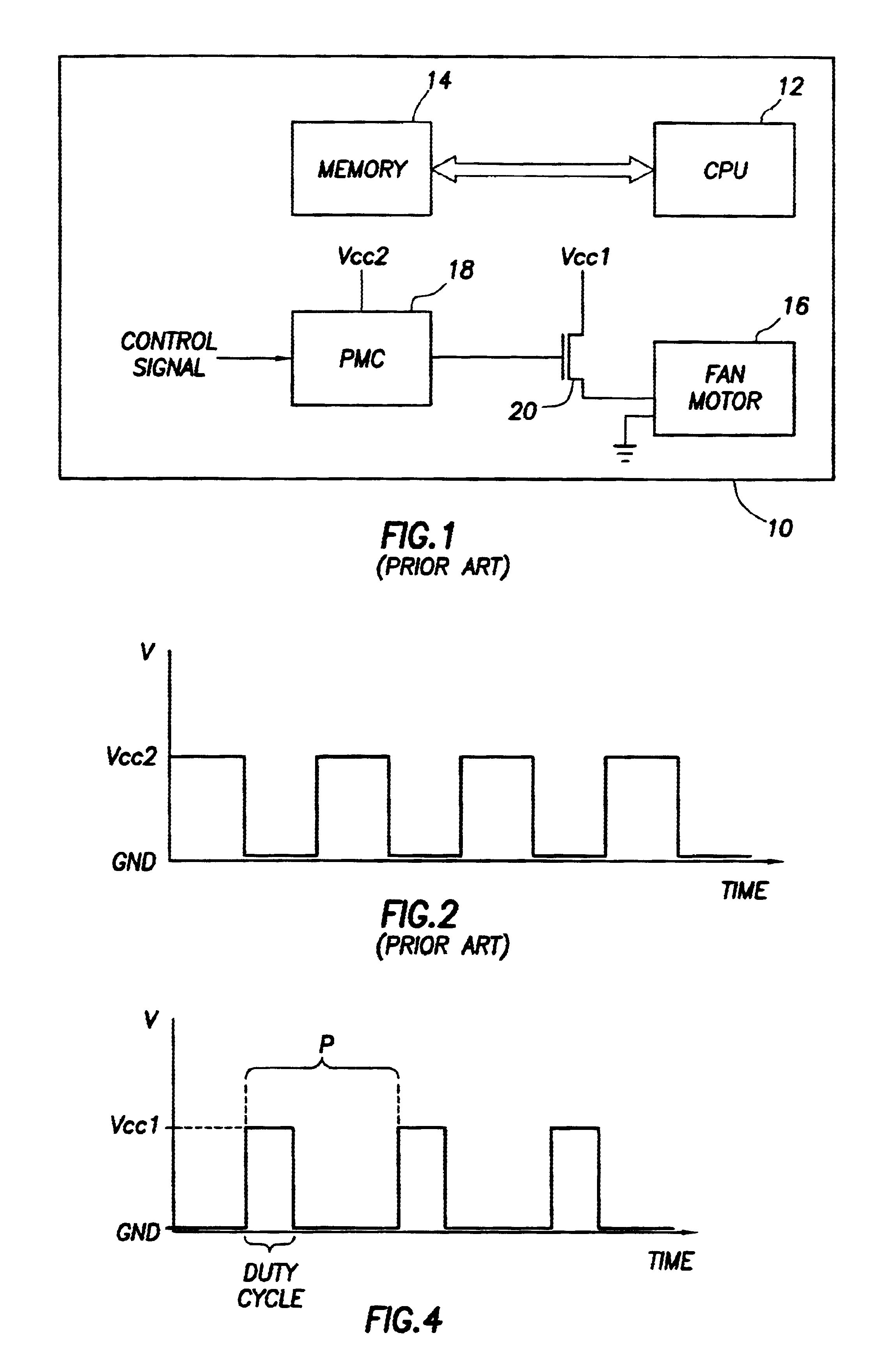
Fan speed controller with conditioned tachometer signal
The speed of a fan motor is controlled by varying a DC voltage to the fan motor. A series pass transistor is used to vary the DC voltage to the fan motor. A power management controller sets the fan motor speed by outputting pulses to a pulse-to-DC voltage converter that changes the pulses to a proportional DC control voltage for controlling the series pass transistor. A tachometer output amplifier circuit is used to remove DC components and amplify to useful logic levels a low level tachometer output signal from the fan motor. The amplified tachometer signal is used by the power management controller in controlling the rotational speed of the fan motor.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
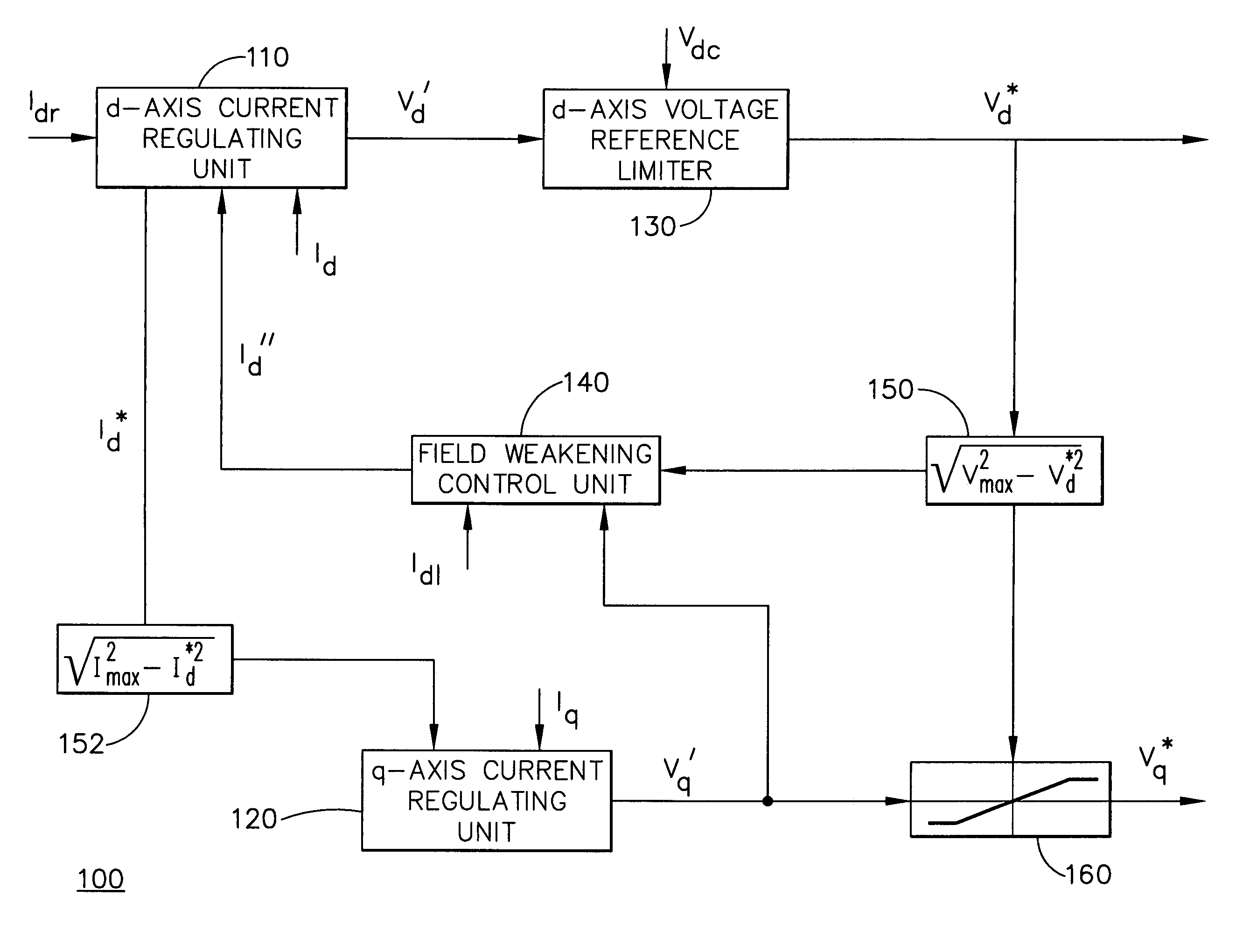
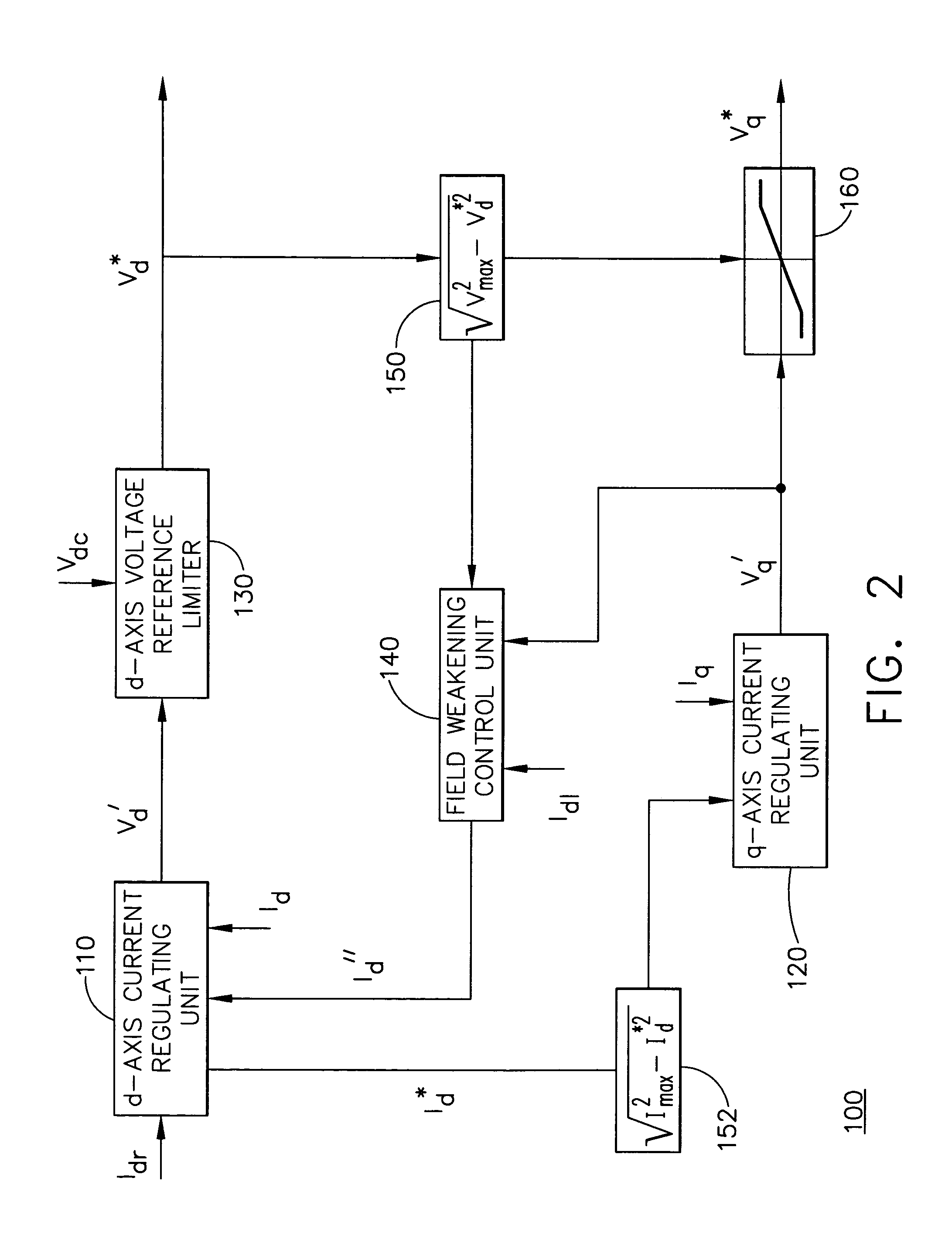
Method and apparatus for field weakening control in an AC motor drive system
InactiveUS6965212B1Reduce selection requirementsElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl signalExcitation current
A method and apparatus control a power converter (20) of an AC motor drive system (10). The method and apparatus: generate a field current regulating signal to control a field current component flowing from the power converter (20) to the AC motor (30), thereby achieving field current regulation; generate a torque current regulating signal to control a torque current component flowing from the power converter (20) to the AC motor (30), thereby achieving torque current regulation, the torque current regulation having lower priority than the field current regulation; and execute a close-loop field weakening control scheme, which generates a field weakening control command as a function of the difference between a torque current regulation voltage demand and voltage available for torque current regulation. The field current regulating signal is adjusted in accordance with the field weakening control signal to selectively reduce back EMF of the AC motor (30), thereby enabling the step of generating a toque current regulating signal to achieve a toque current component needed to drive the AC motor (30) at a desired speed despite a limitation on DC voltage available to the power converter (20).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
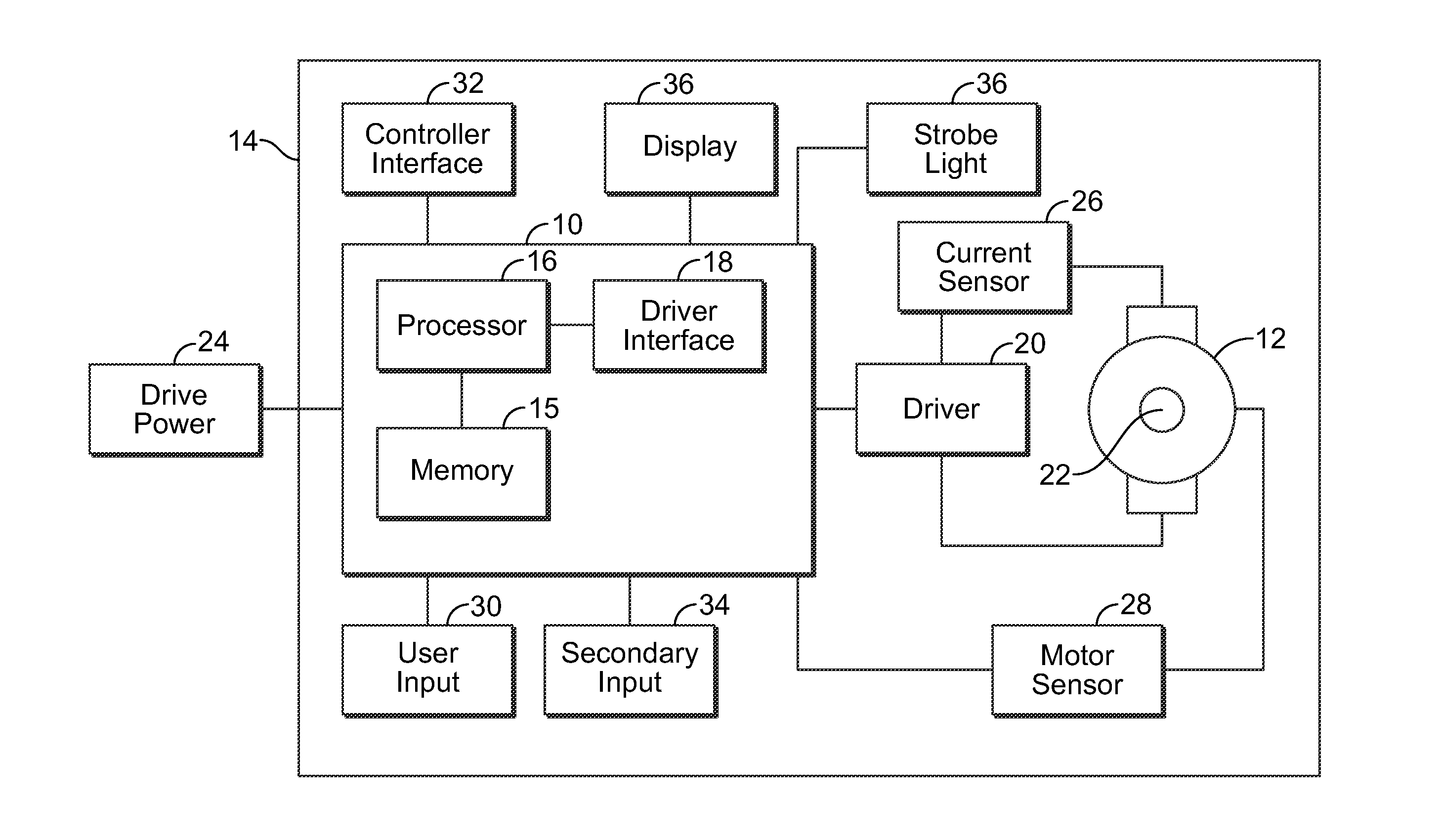
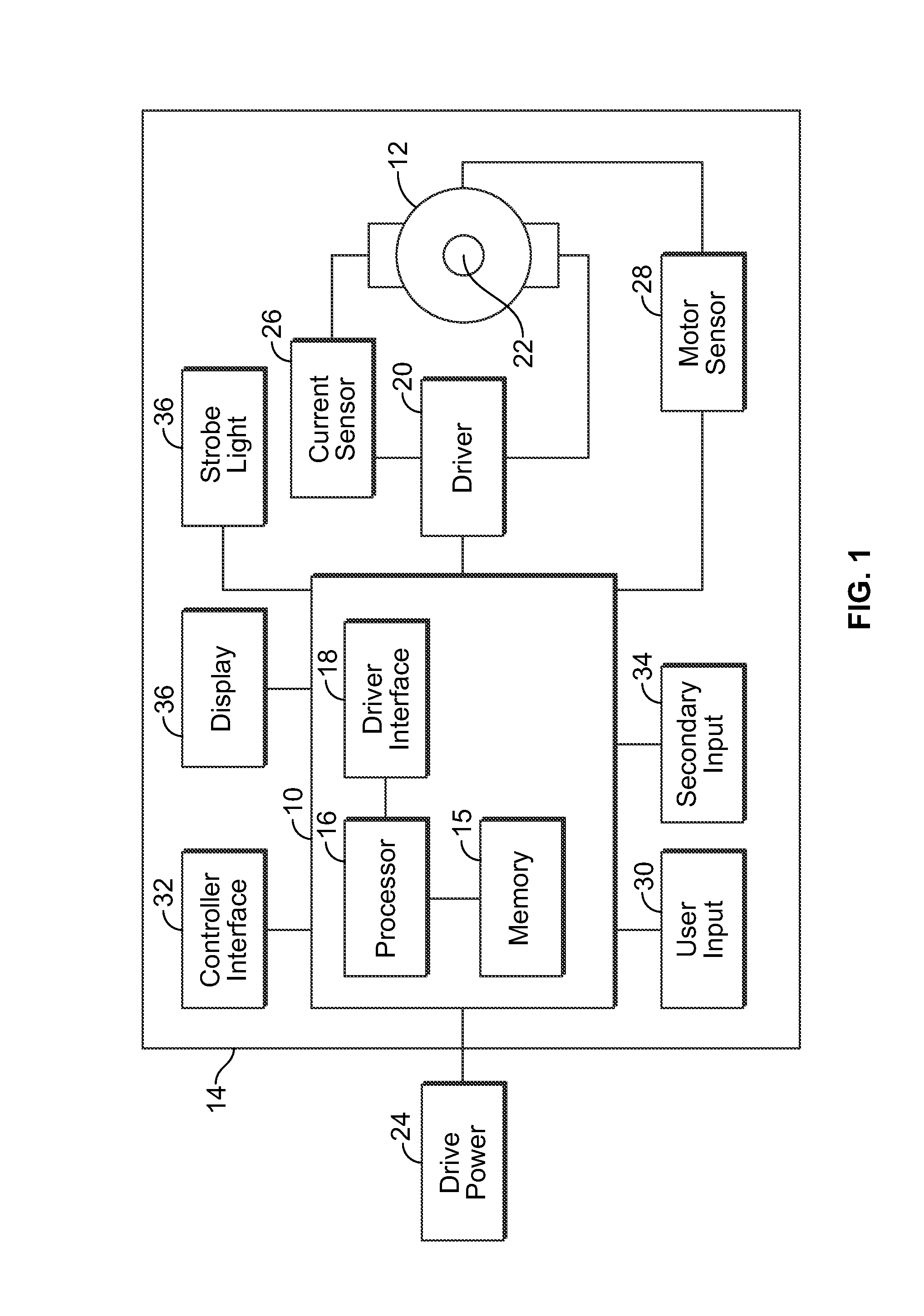
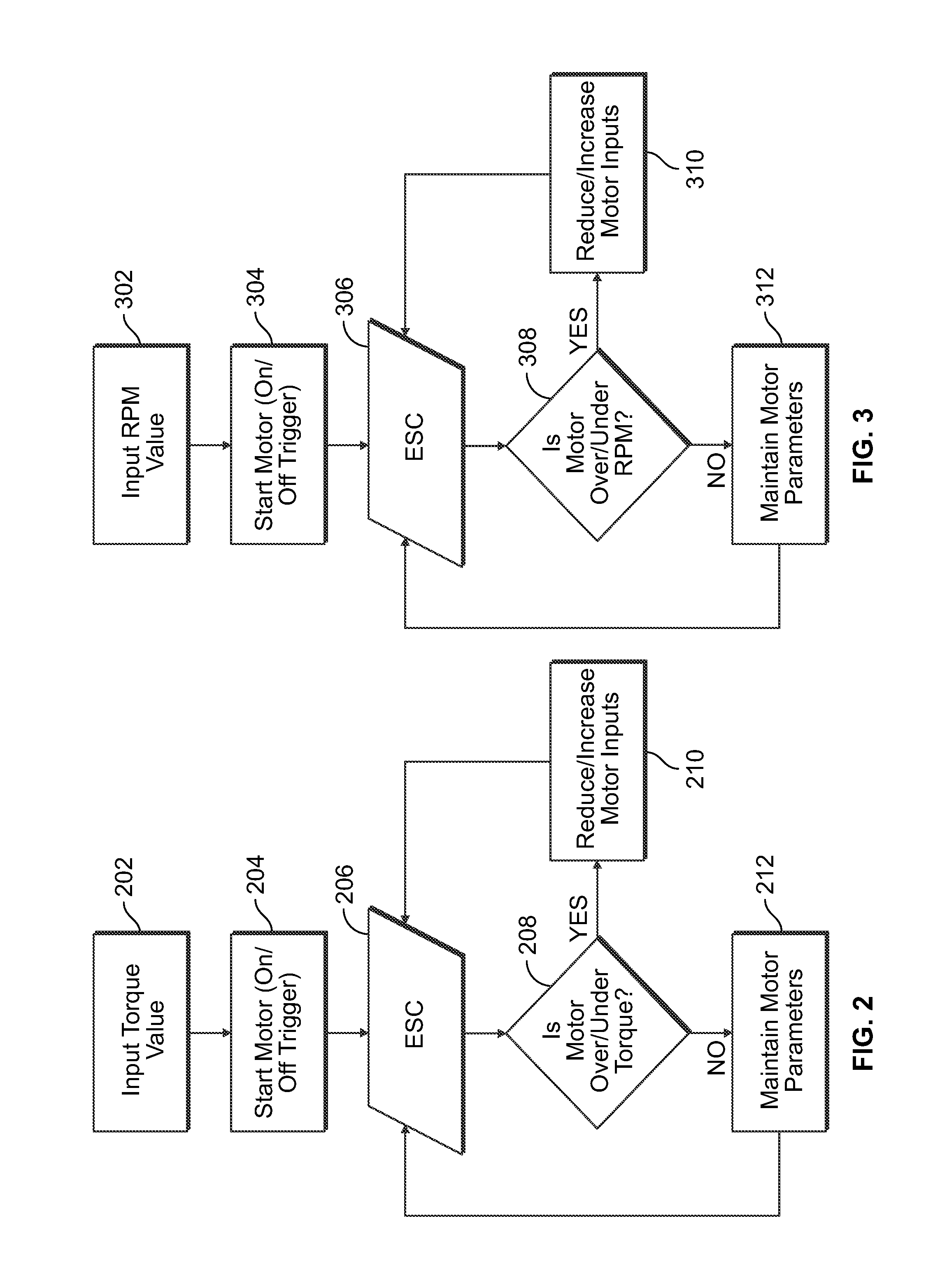
Programmable power tool with brushless DC motor
ActiveUS20130187587A1High performance featuresAccurate stopMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersEngineeringPower tool
A power tool that includes a brushless DC motor, one or more motor sensors, and a controller, such as, for example, an electronic speed control (ESC) circuit. The controller is adapted to provide instructions to control the operation of one or more parameters of the brushless DC motor. The controller is also adapted to receive feedback from one or more motor sensors that reflect whether the motor is attaining the one or more parameters. The controller may also be adapted to have a learning mode, in which feedback provided during use of the power tool is stored by the controller as a program so that the same operating parameters may be subsequently replicated by using the program to operate the tool. The controller may also use the feedback to adjust the operation of the motor so that the motor maintains one or more selected or programed operating parameters.
Owner:TRANSFORM SR BRANDS LLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com