Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
454results about "Single phase motor control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
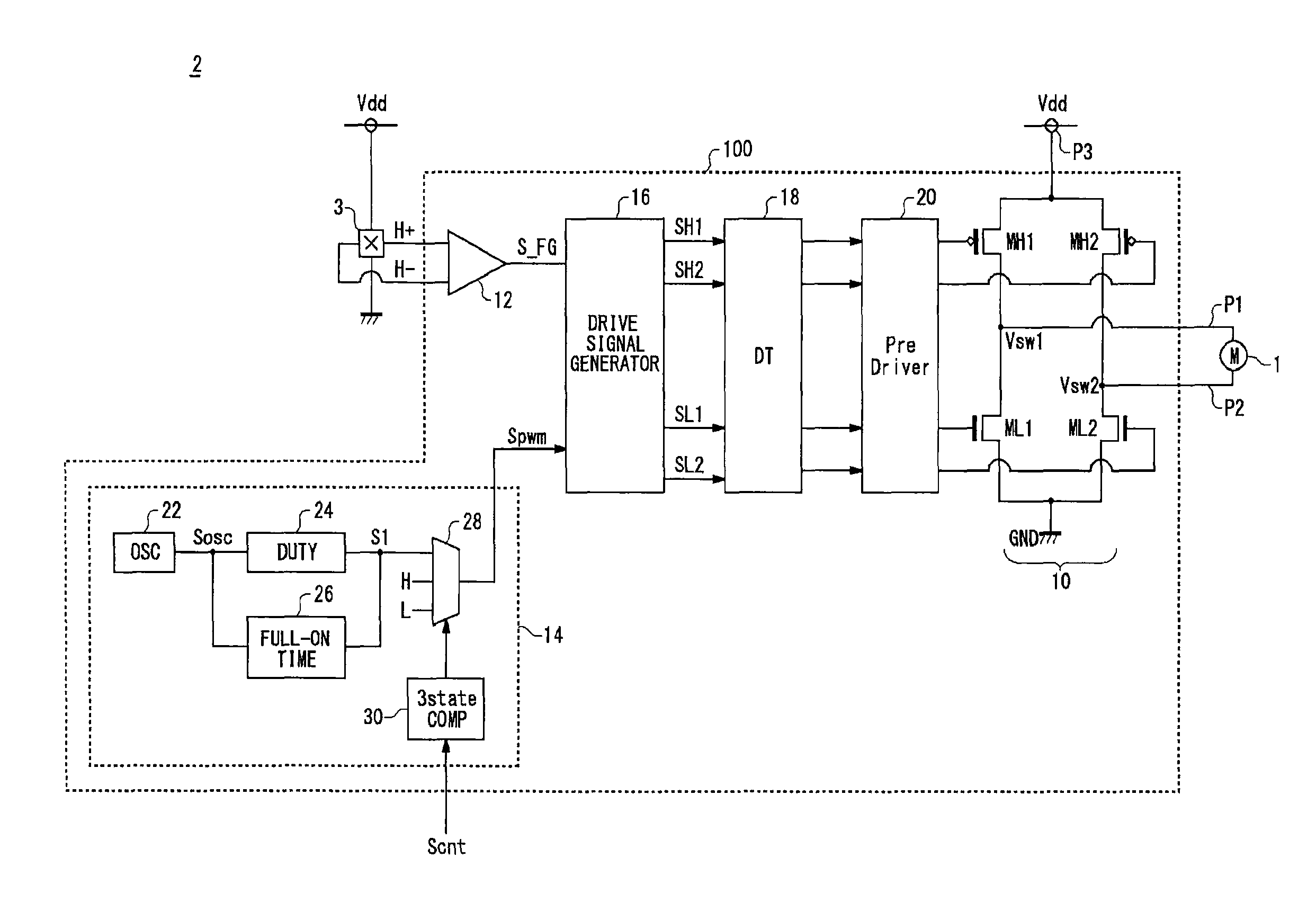
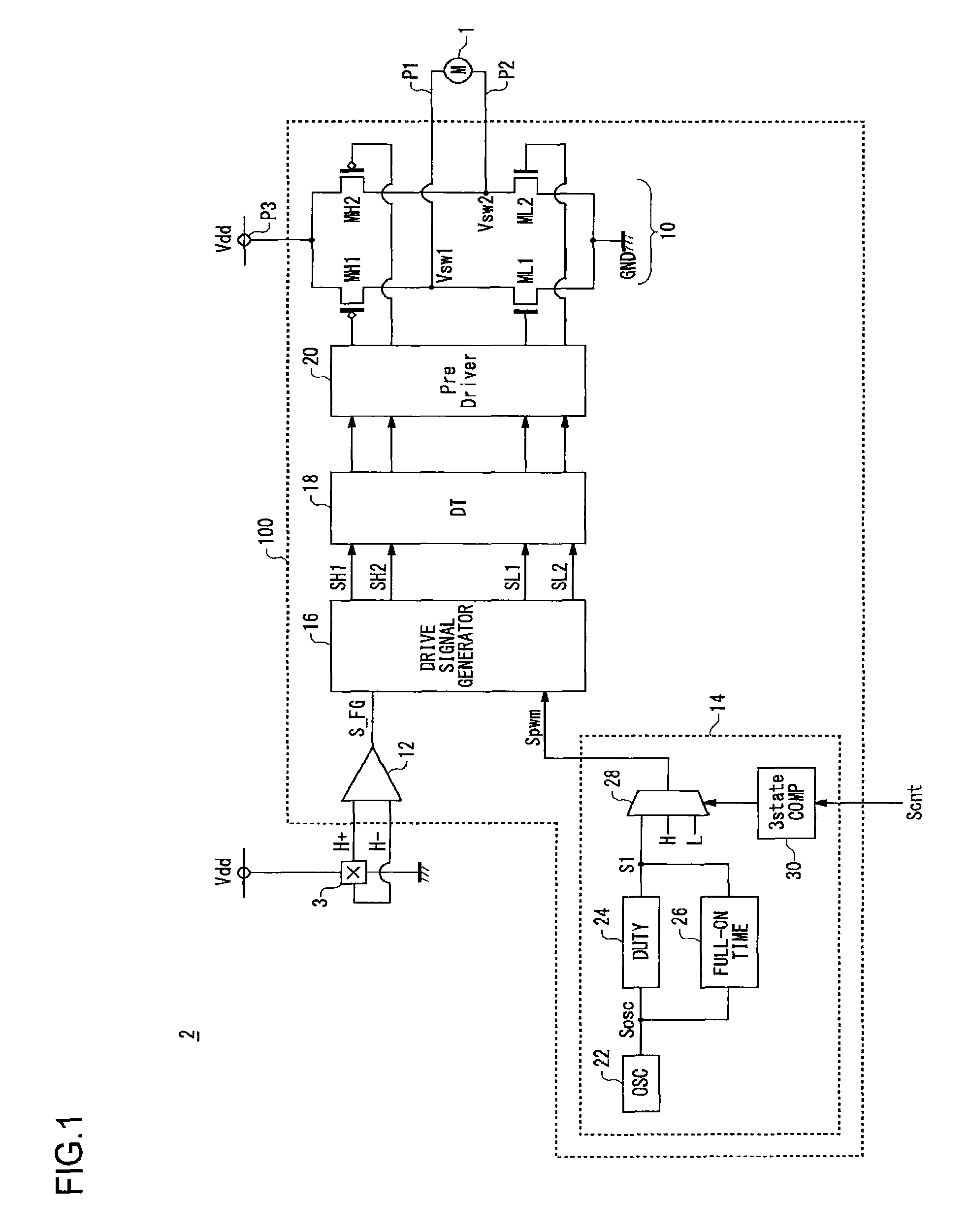
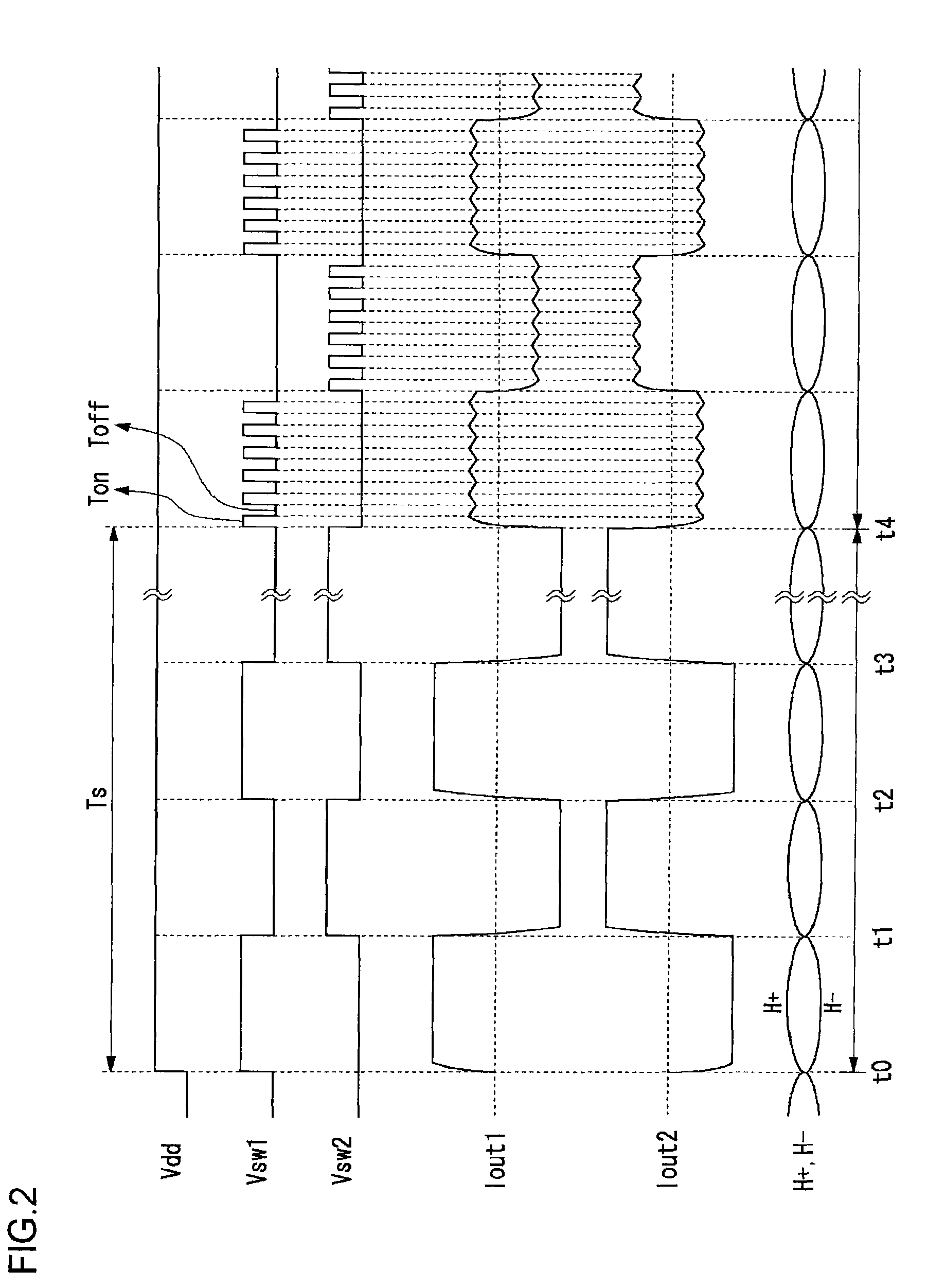
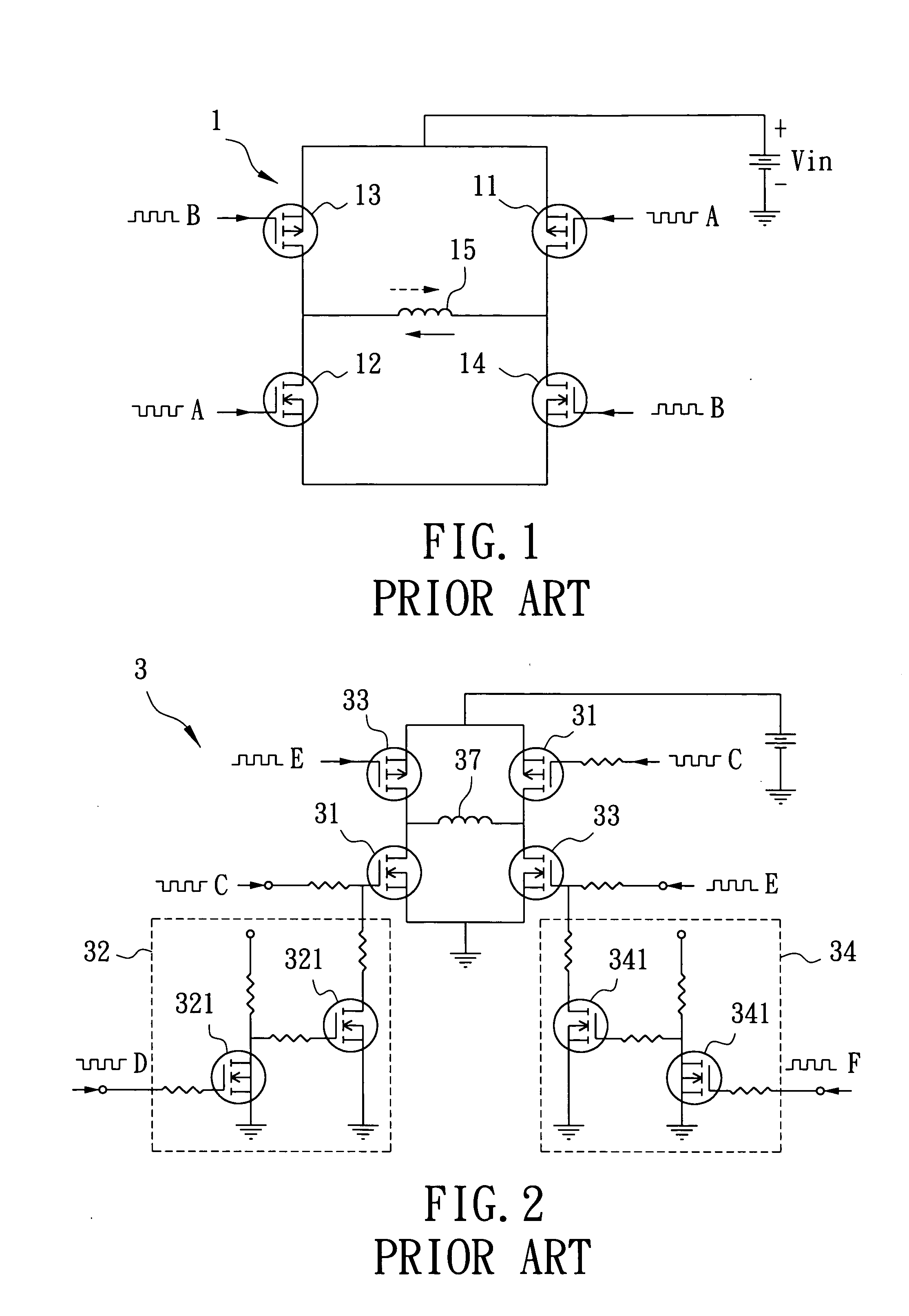
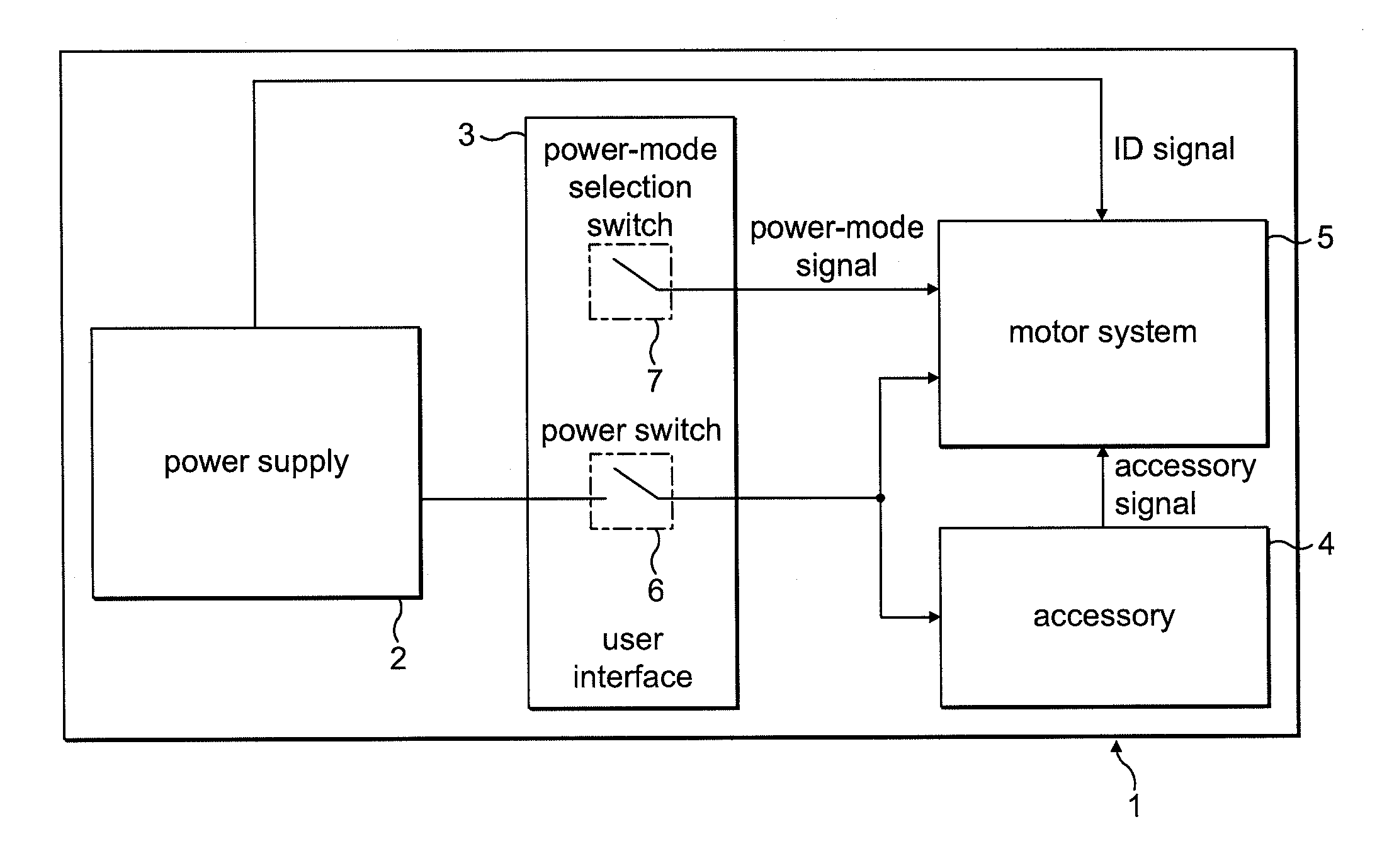
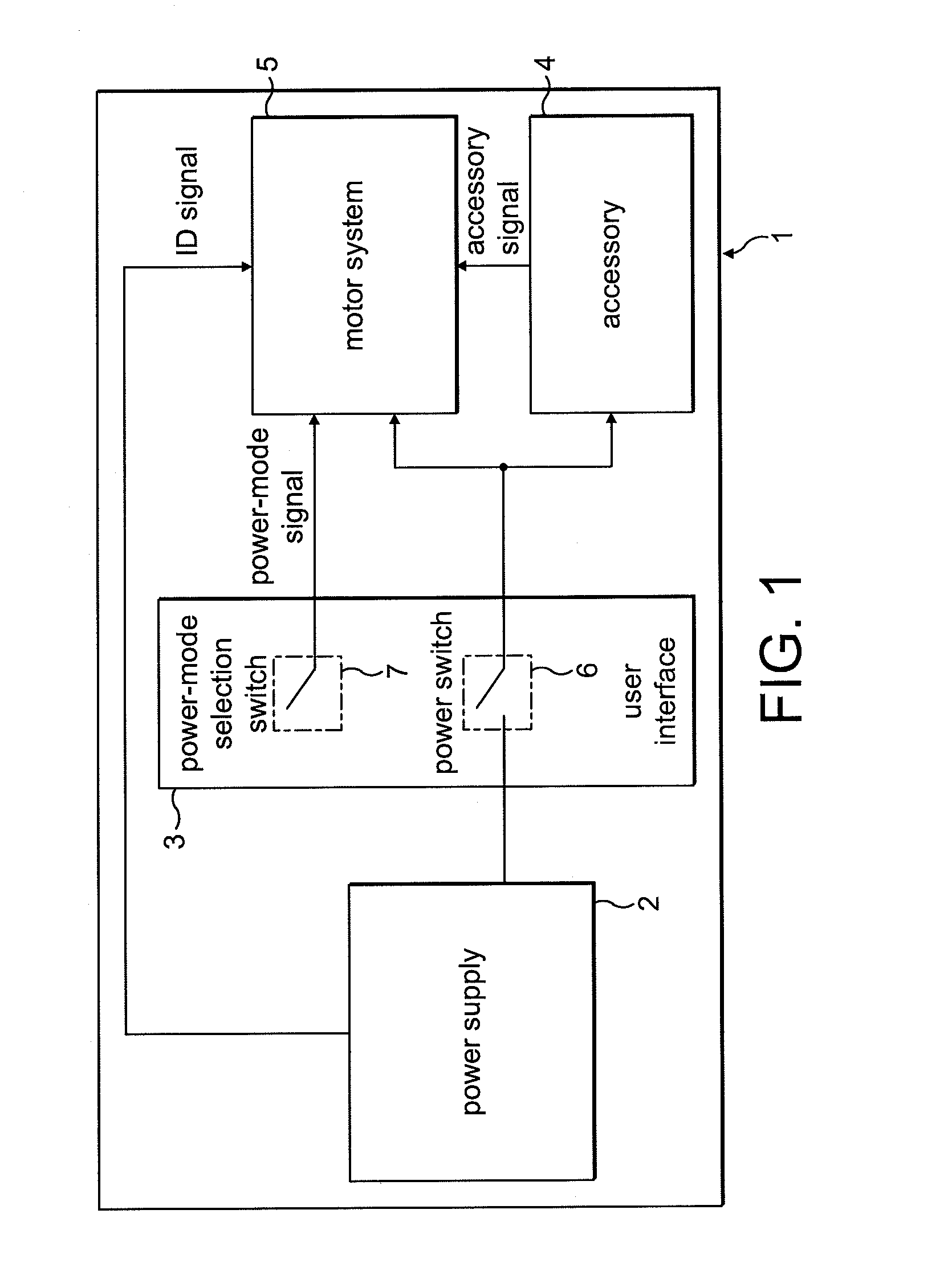
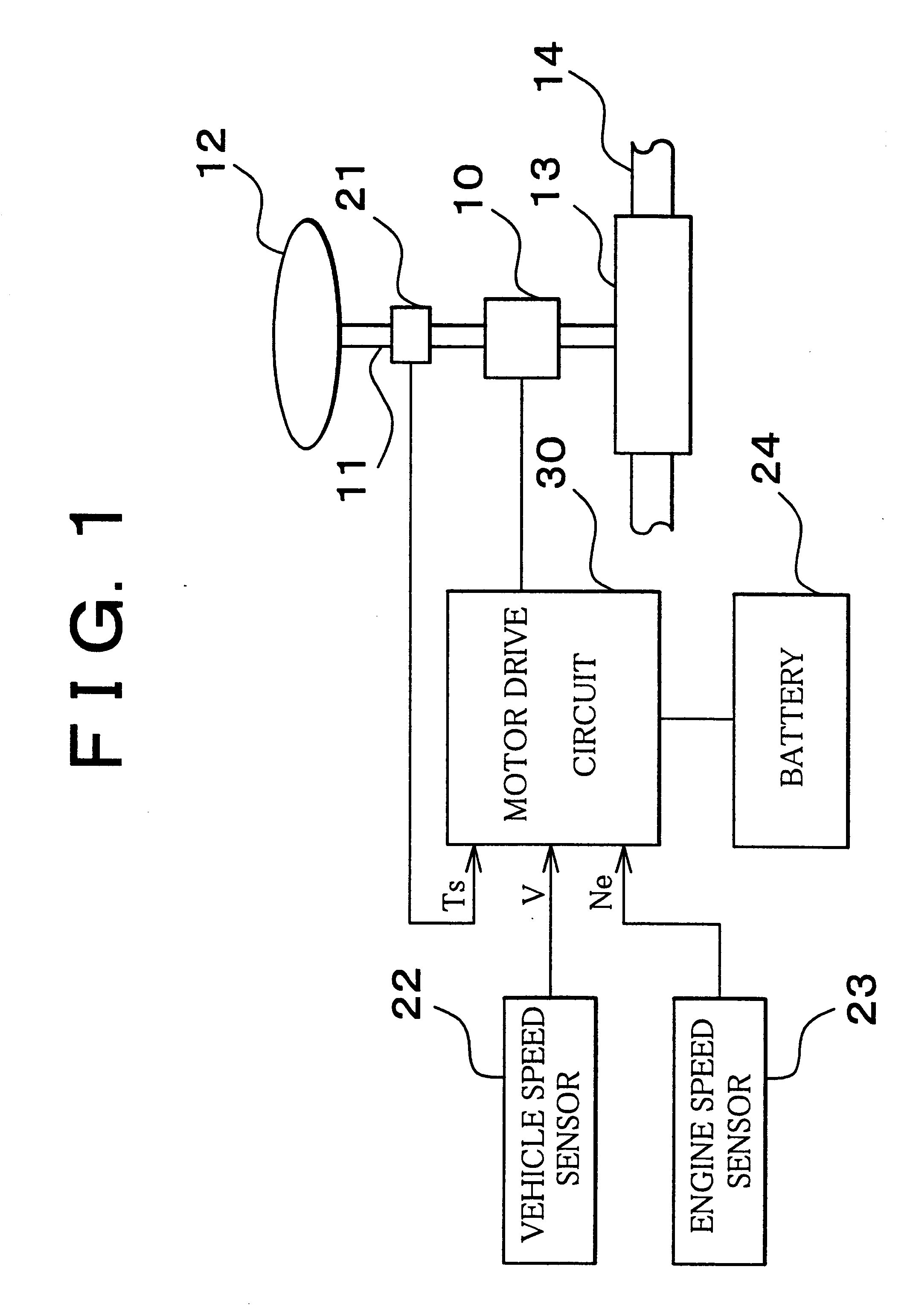
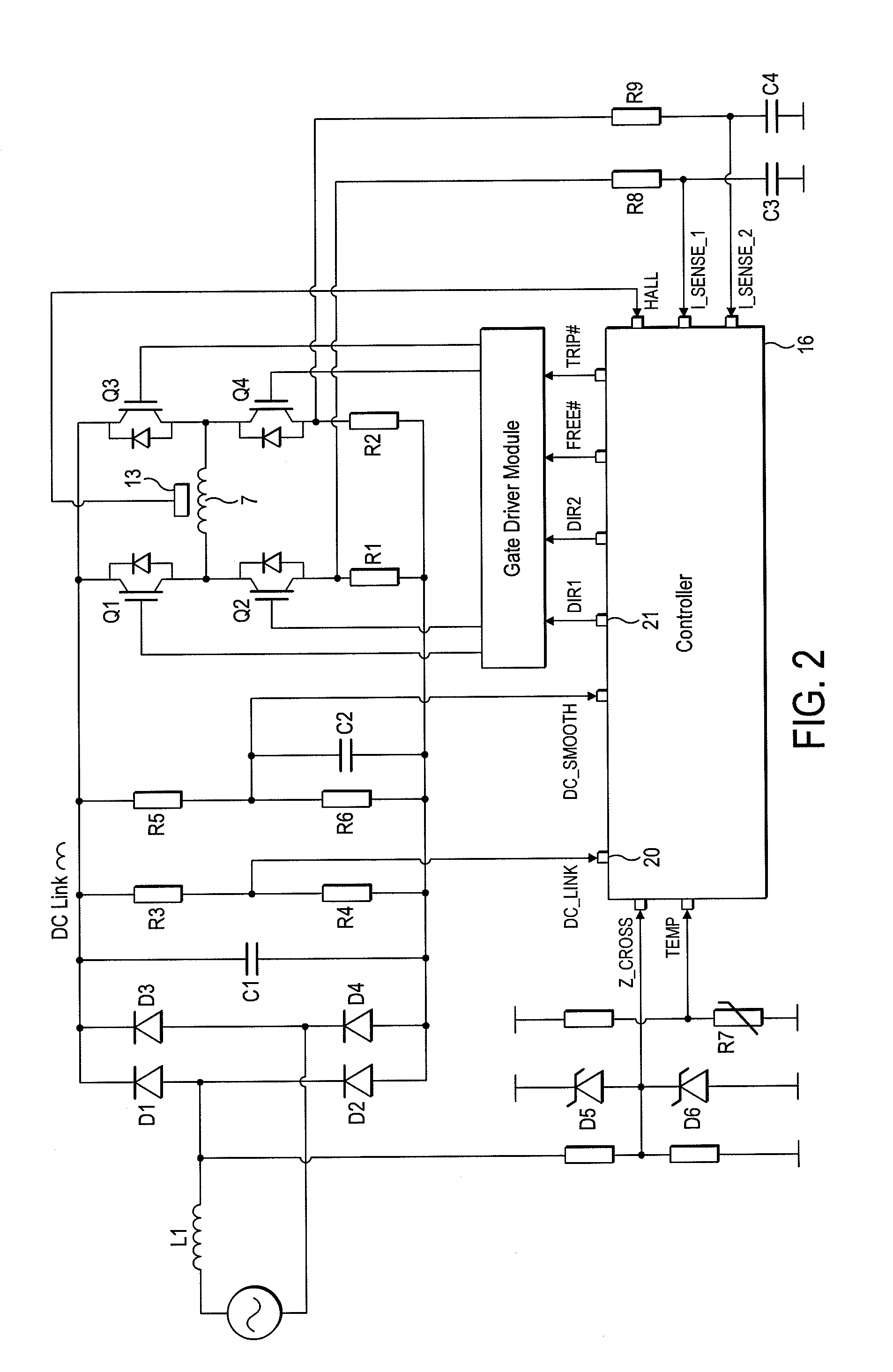
Motor drive circuit with short startup time
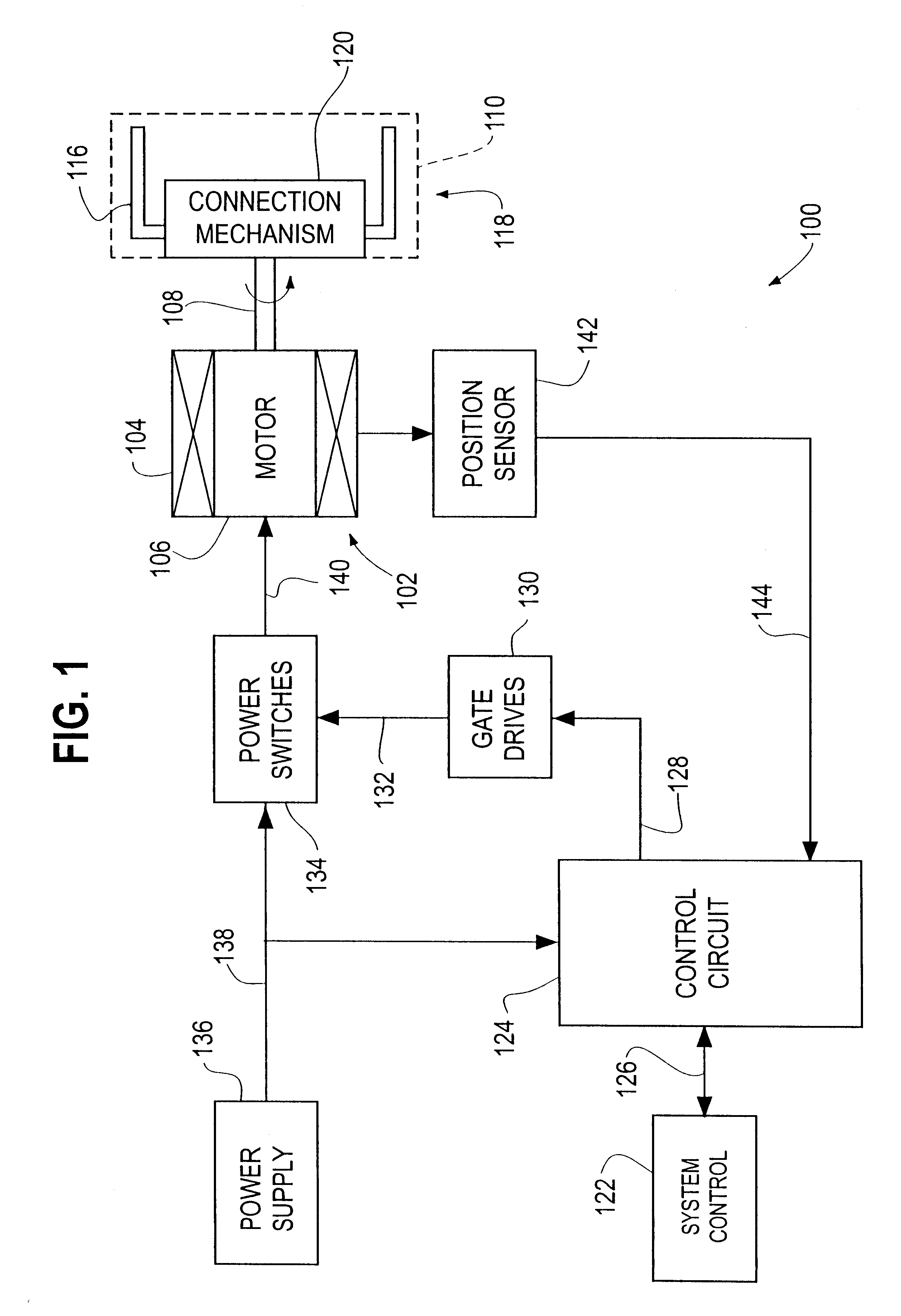
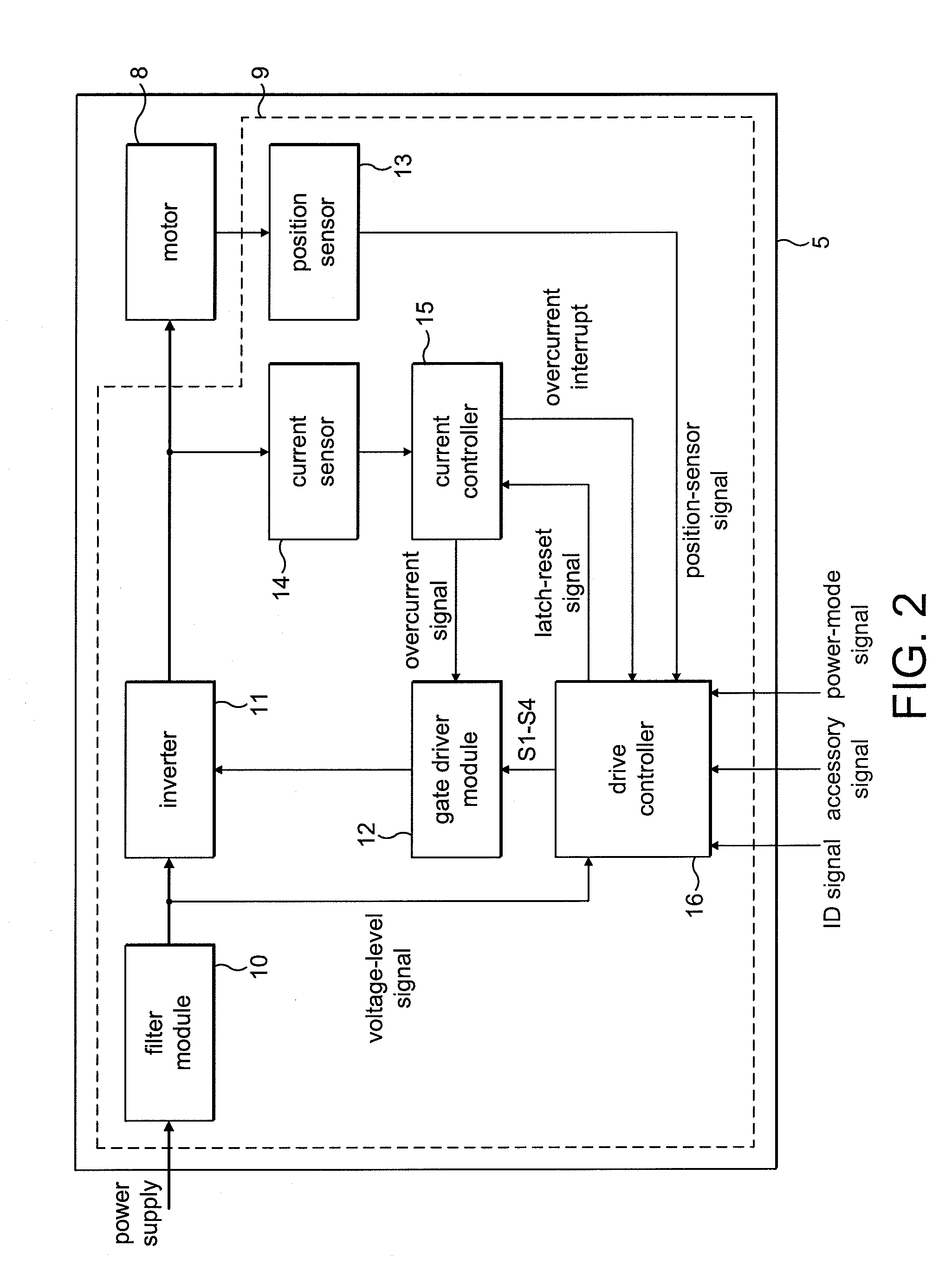
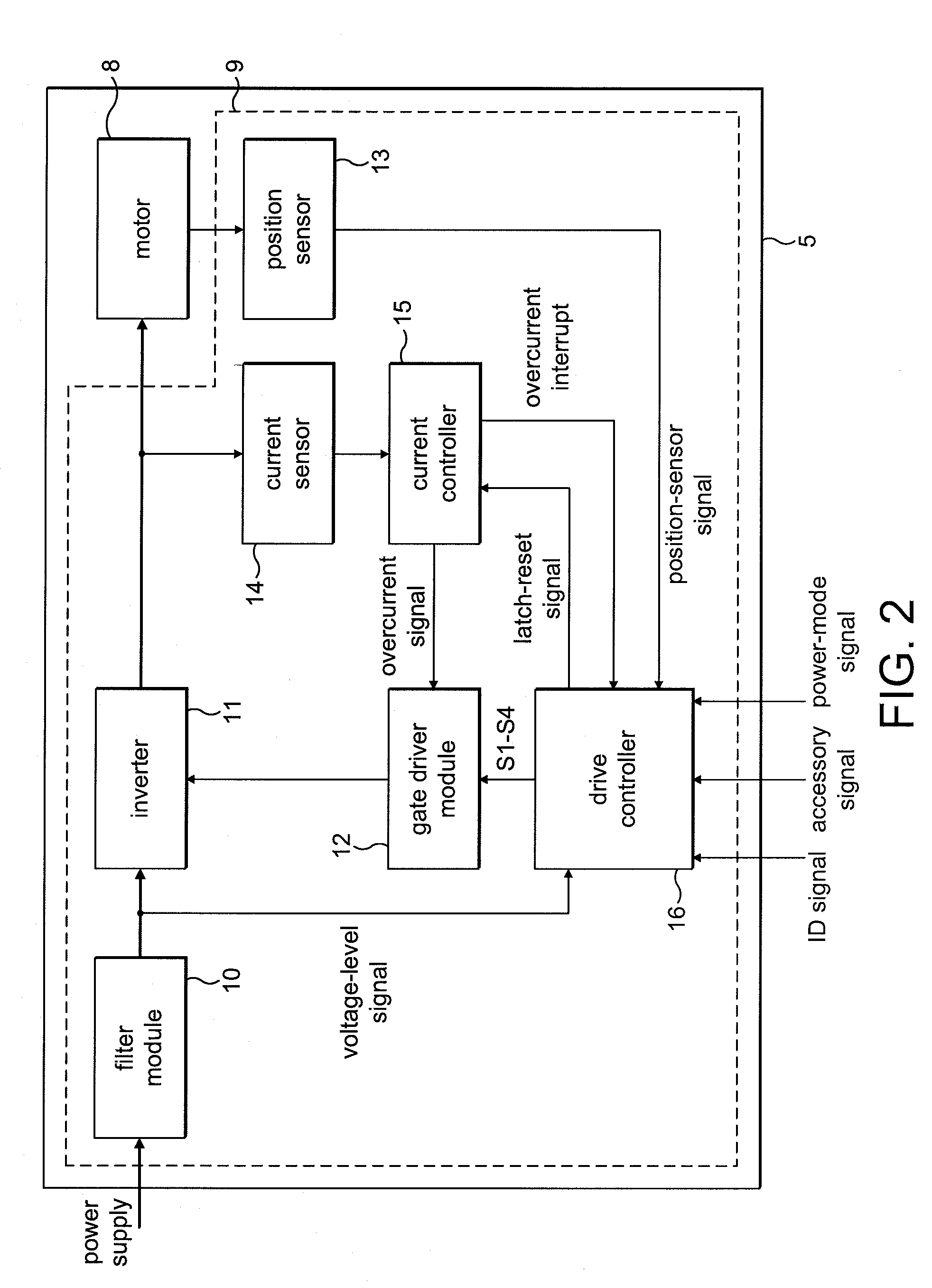
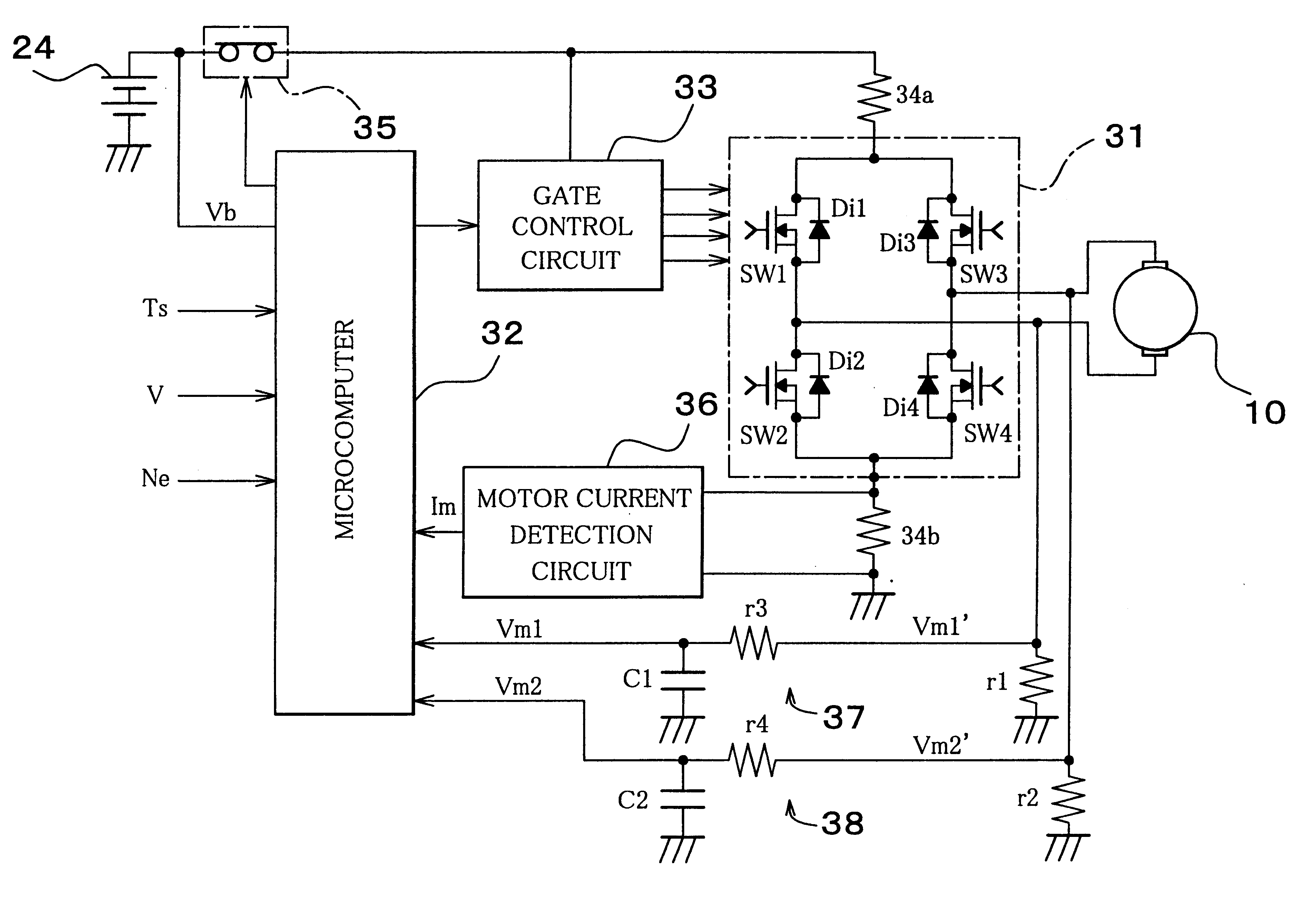
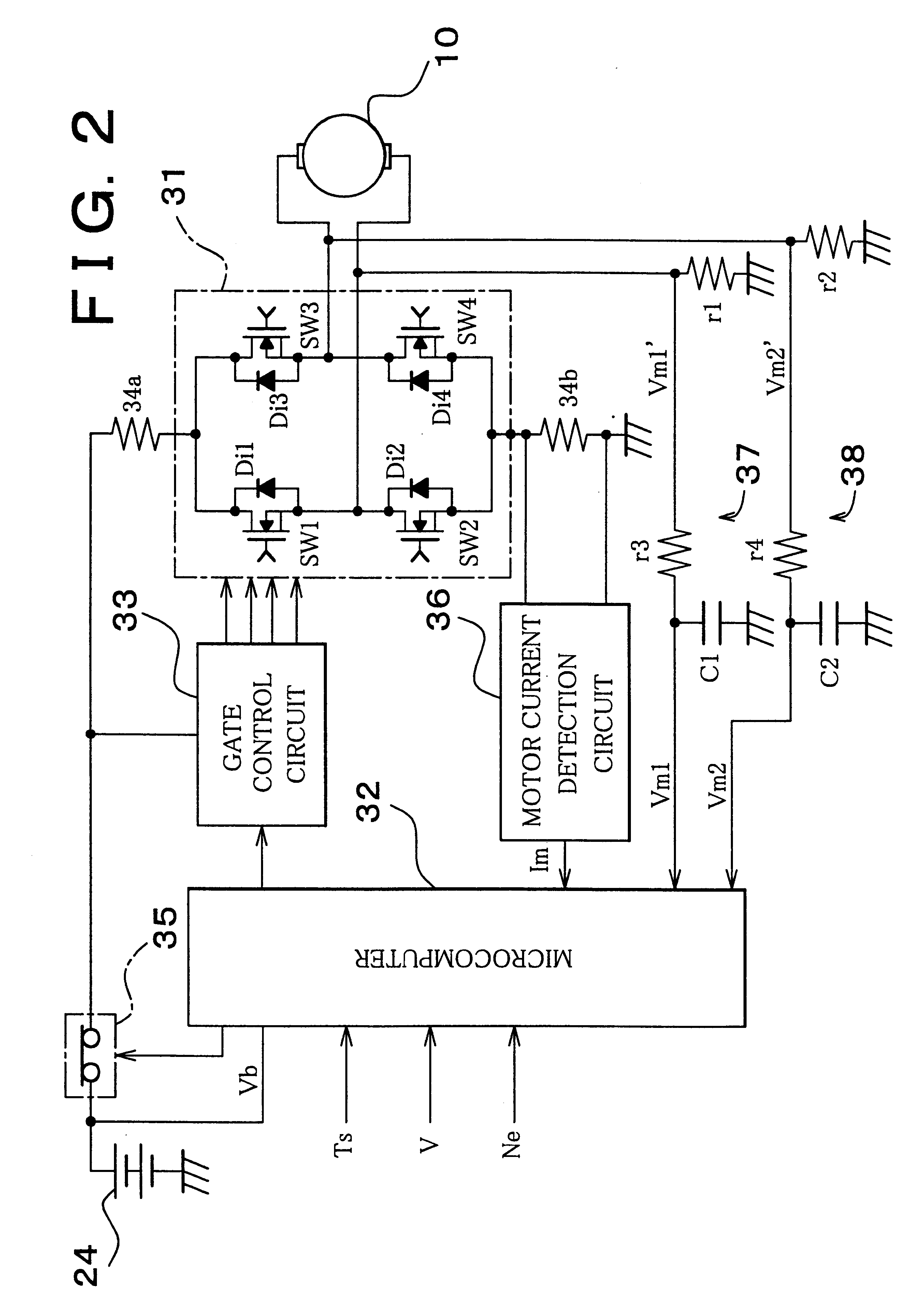
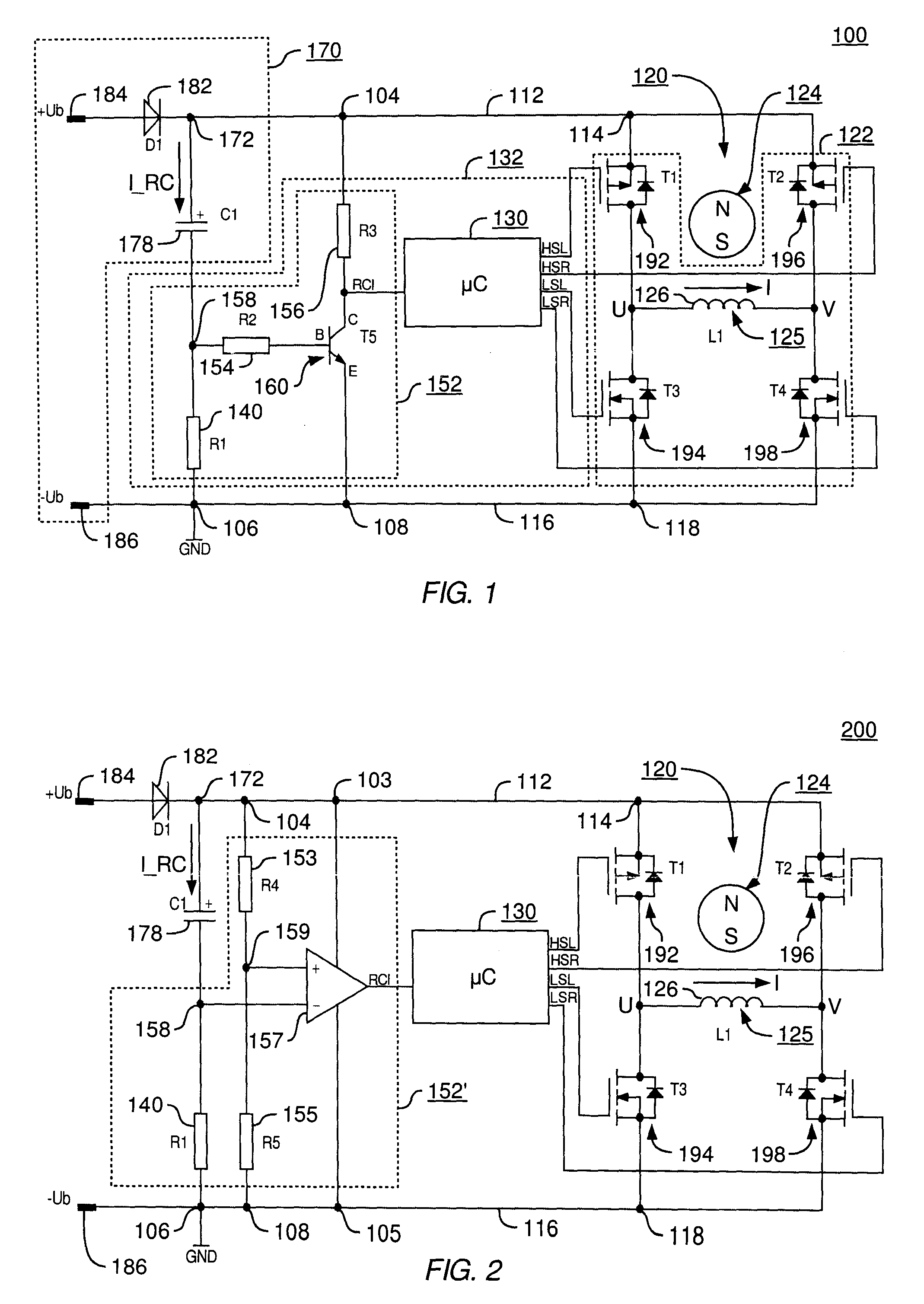
An H-bridge circuit is connected to a coil of the vibration motor that is to be driven. A comparator receives Hall signals indicating position information of a rotor of the vibration motor, and converts to an FG signal. A pulse width modulator generates a pulse-modulated pulse signal specifying energization time of the coil of the vibration motor. The pulse width modulator, in a first mode, after commencing start-up of the vibration motor, sets a duty ratio of the pulse signal to 100%, and after that, switches the duty ratio to a predetermined value in accordance with rotational frequency of the motor. In a second mode, the duty ratio of the pulse signal continues to be set to 100%. In a third mode, frequency and the duty ratio of the pulse signal are set based on a control signal of a pulse form inputted from outside. The control signal is used also in switching mode.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
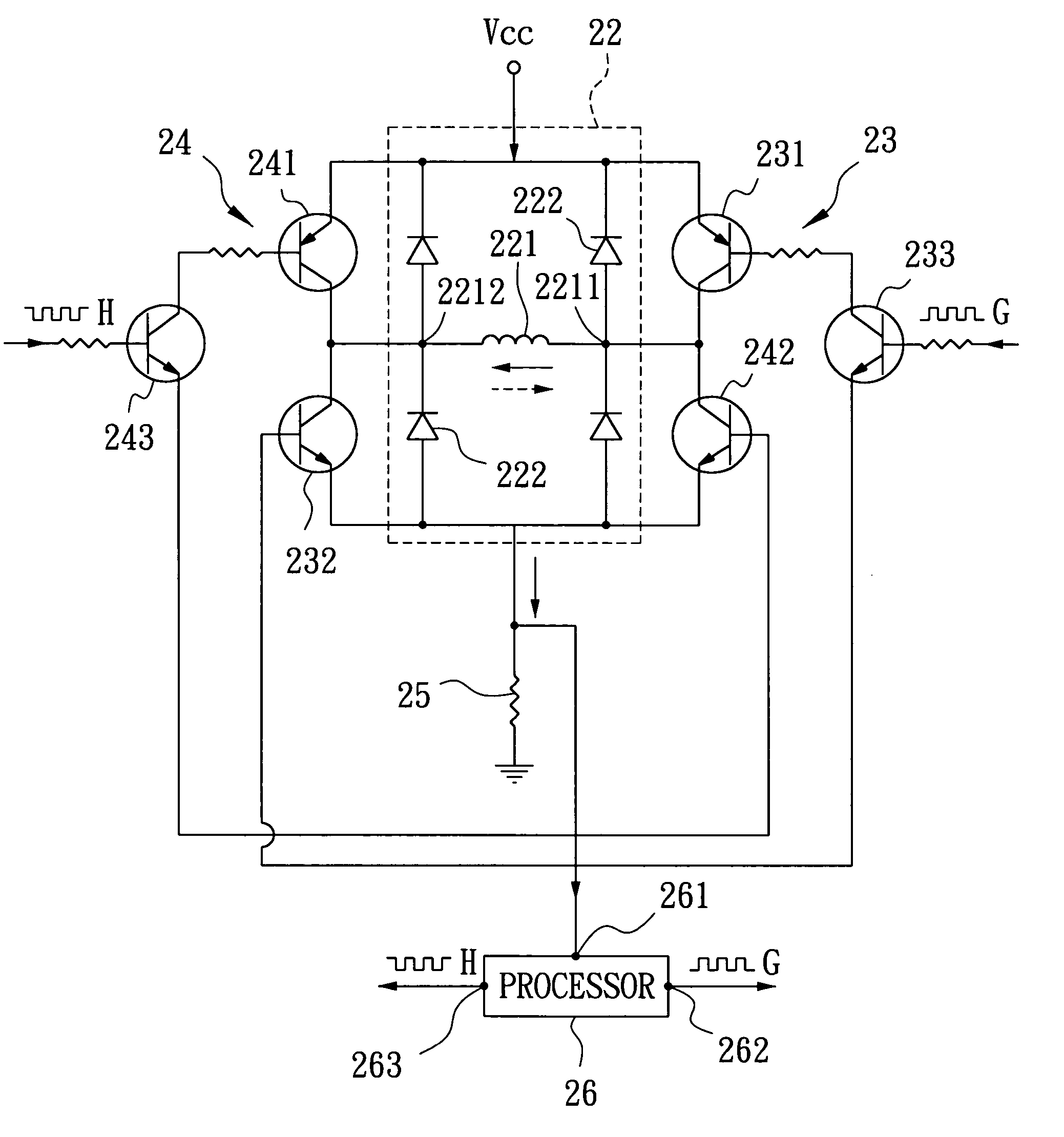
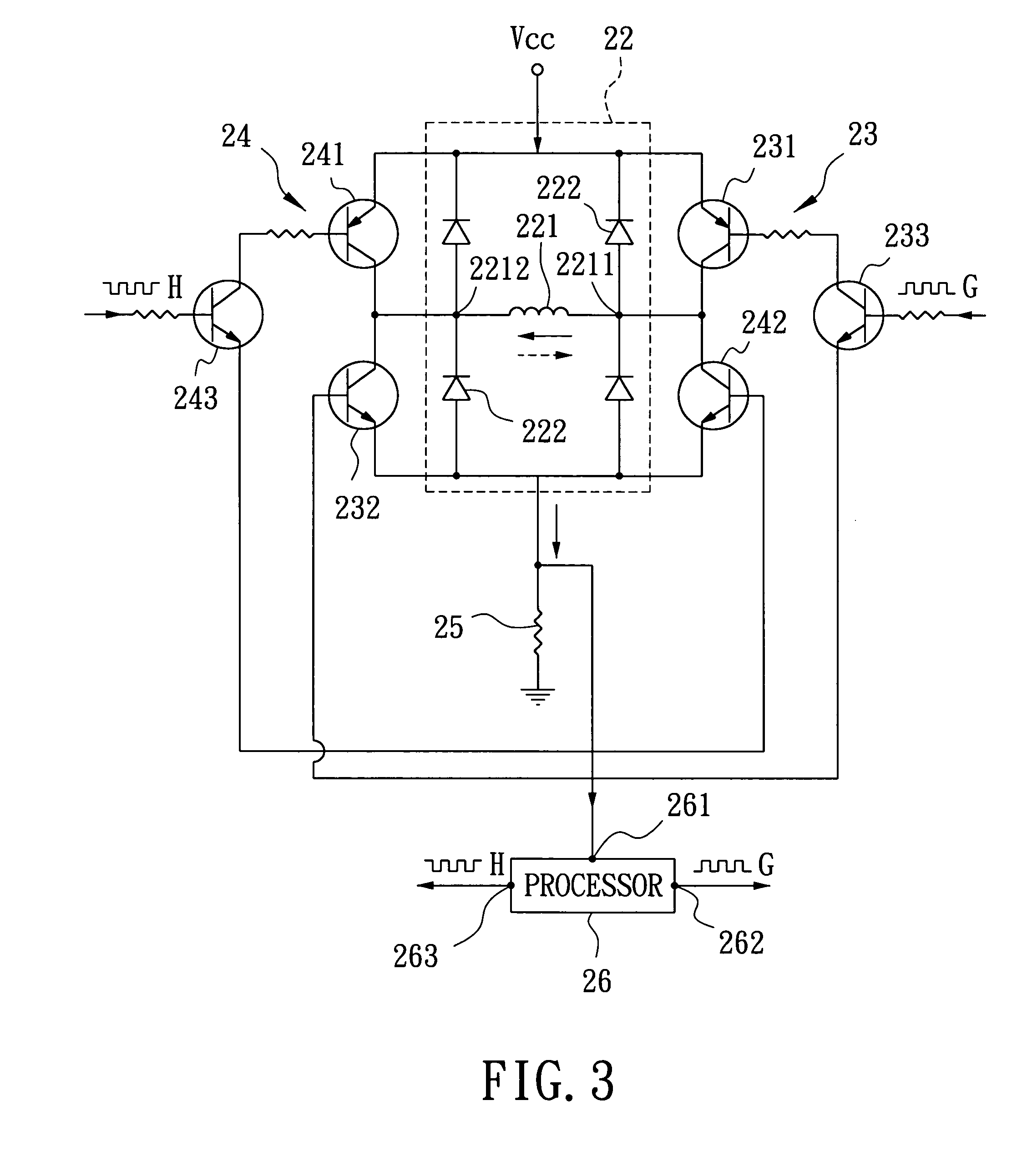
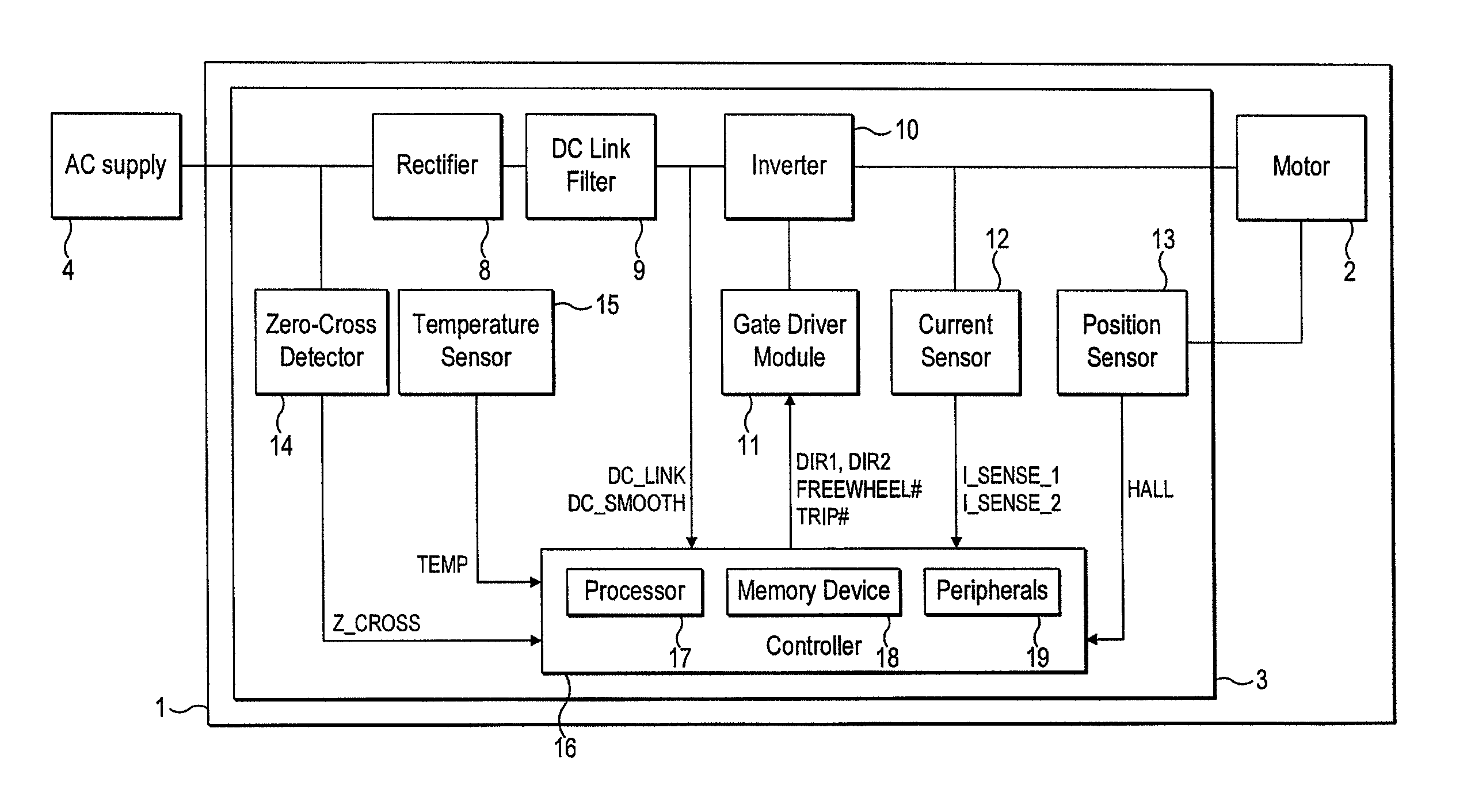
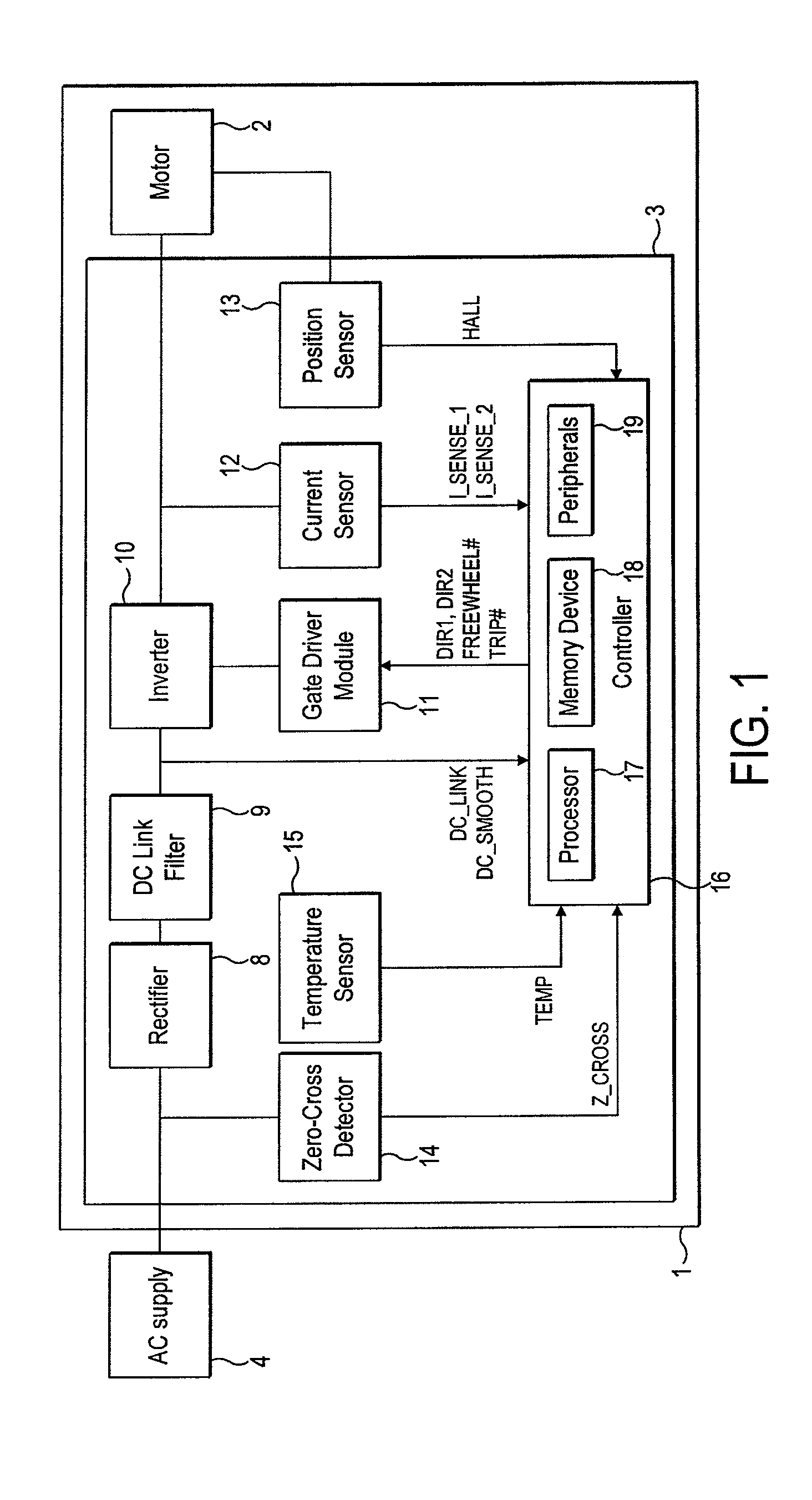
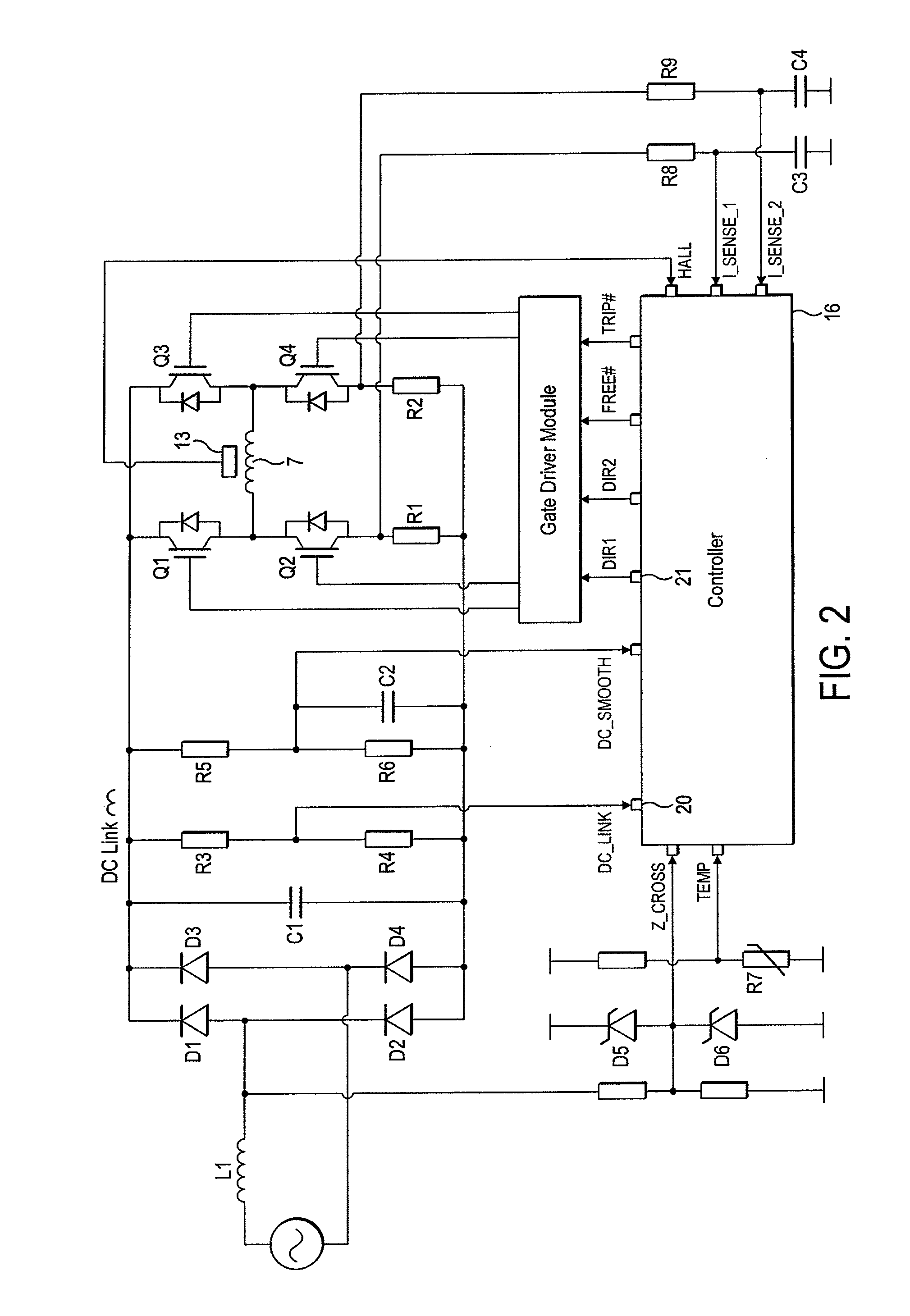
Motor controller
InactiveUS20070152612A1Accurate speed regulationAccurately control conduction and non-conduction of transistorsSingle motor speed/torque controlDynamo-electric converter controlElectricityVoltage drop
A motor controller includes a power source unit providing a direct current output, a drive unit including a drive coil, first and second transistor units, a voltage drop component, and a processor. The transistor units are coupled to the power source unit and the drive unit, and enable electricity to flow through the drive coil in a first direction when the first and the second transistor units are in conducting and non-conducting states respectively, and in an opposite second direction when the first and the second transistor units are in non-conducting and conducting states respectively. The voltage drop component has a first end coupled to the drive unit and a grounded second end. The processor is coupled to a junction of the drive unit and the voltage drop component, and provides first and second pulse-width-modulated signals to the first and second transistor units, respectively.
Owner:YEN SUN TECH CORP
Electric motor and motor control
InactiveUS8575873B2Reduce noiseHigh complexitySingle-phase induction motor startersTorque ripple controlElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
Various embodiments of an electric motor and electronic control for an electric motor are disclosed. An exemplary electric motor comprises a single-phase brushless permanent magnet electric motor. In exemplary embodiments, the electronic motor control is configured to commutate an electric motor at a frequency other than line frequency, perform pulse width modulation, and drive the electric motor with a drive waveform that approximates the counter-electromotive force of the motor.
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
Current controller for an electric machine
ActiveUS20100253250A1Easy to assembleReduce control system costsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionElectric machineEngineering
A current controller for an electric machine that includes an input, an output, a threshold generator and a comparator. The threshold generator stores a scaling factor and includes a PWM module that operates on a reference voltage to generate a threshold voltage. The duty cycle of the PWM module is then defined by the scaling factor. The comparator compares a voltage at the input against the threshold voltage and causes an overcurrent signal to be generated at the output when the voltage at the input exceeds the threshold voltage.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
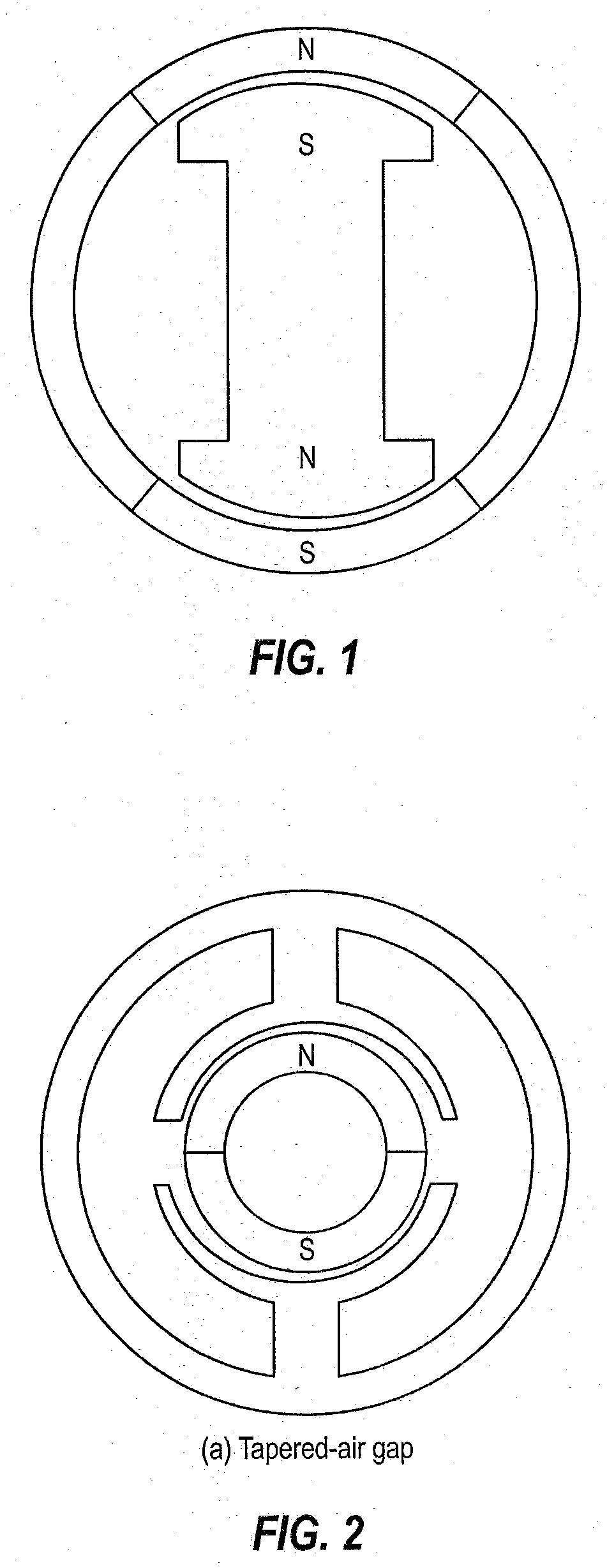
Single phase motor with positive torque parking positions
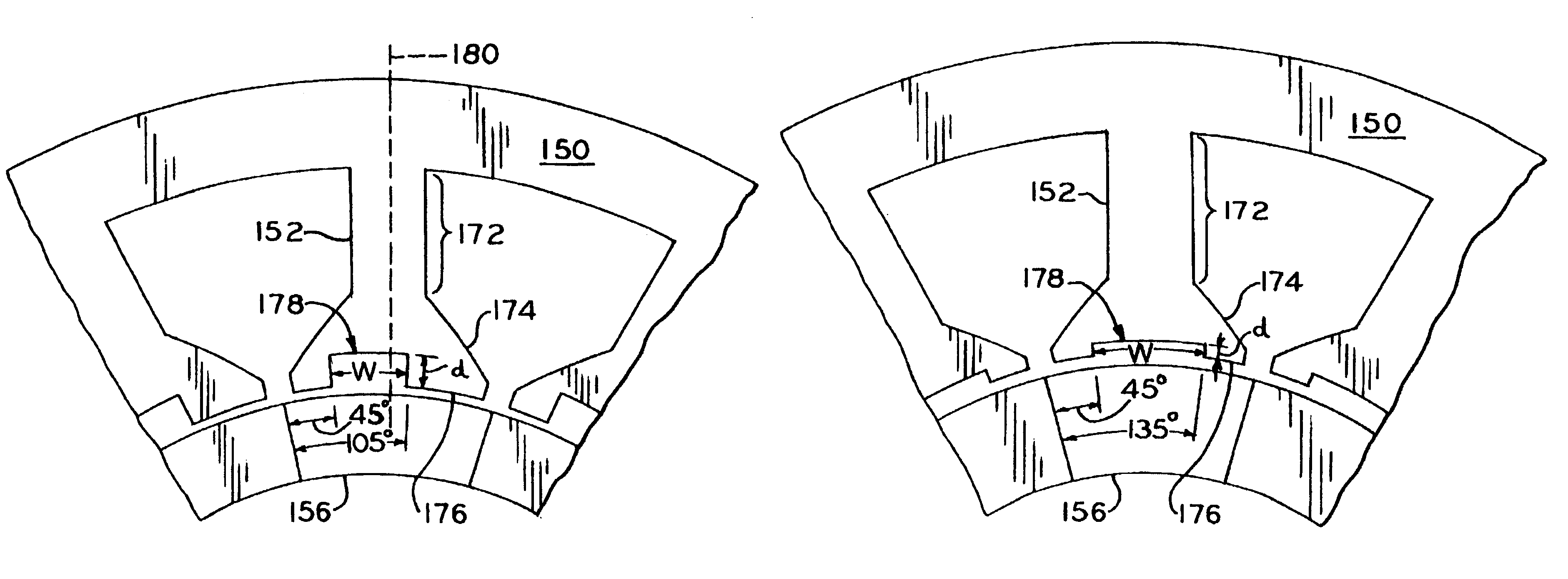
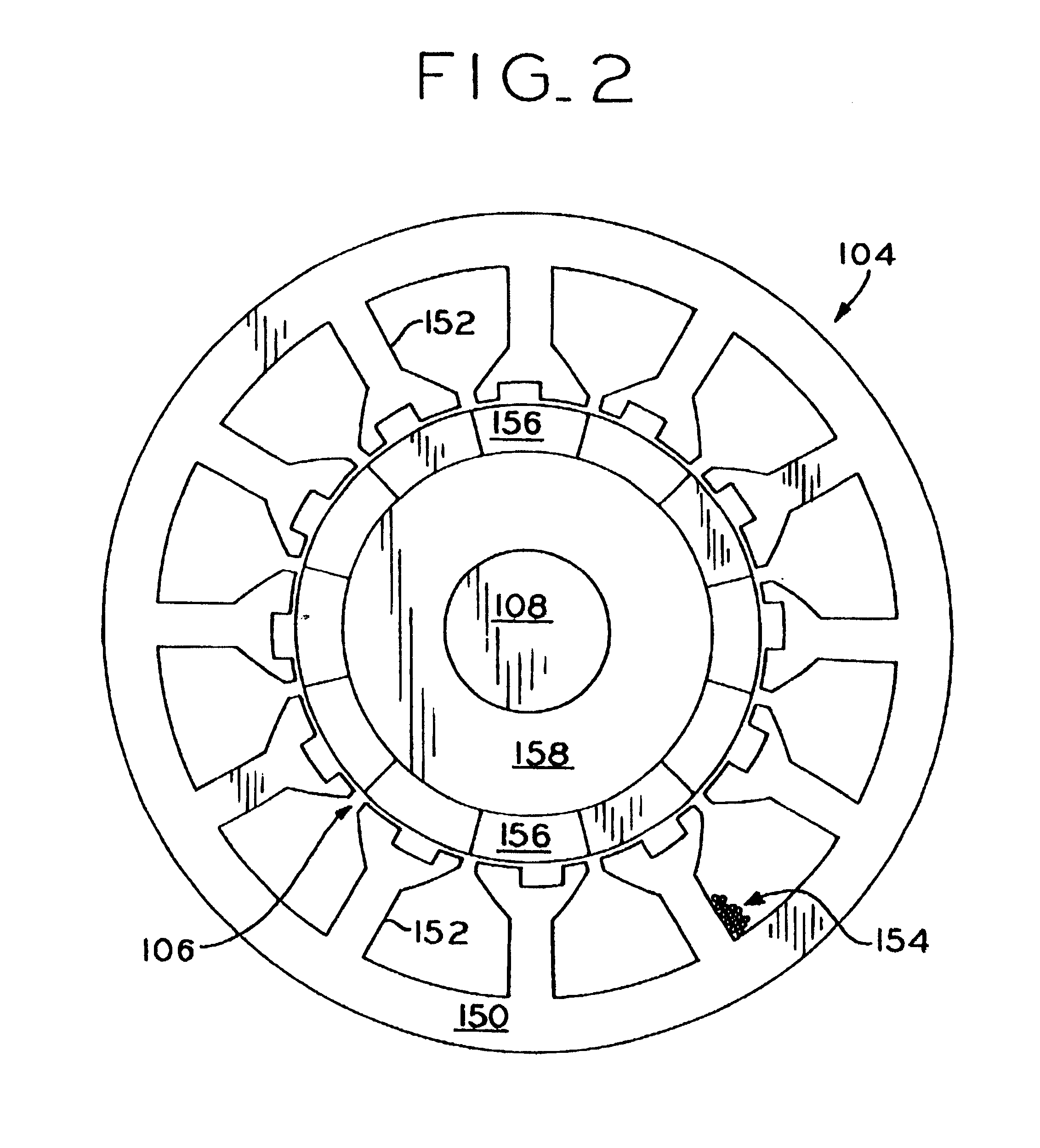
A motor with positive torque parking positions. The motor includes a rotor which is rotatable about an axis of rotation and a stator in magnetic coupling relation with the rotor. The stator includes a plurality of teeth each having a radially extending shaft and an axially extending face. The faces of the stator teeth define an aperture for receiving the rotor and the faces of the stator teeth and the rotor define a air gap therebetween. Each stator tooth has a notch in its face that is approximately at least as wide as the shaft of the stator tooth so that the stator has a magnetic configuration relative to the rotor for parking the rotor in a rest position corresponding to a positive torque starting position. The motor also includes a winding on the shafts of the stator teeth and a control circuit for controlling current in the winding whereby an electromagnetic field is produced for rotating the rotor at a desired speed or torque during the operation of the motor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS20100253264A1Increase powerLess torqueTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersFreewheelControl system
A method of controlling an electric machine that includes sequentially exciting and freewheeling a winding of the electric machine. The winding is excited in advance of zero-crossings of back emf in the winding by an advance angle, and the winding is freewheeled over a freewheel angle. The method then includes varying the advance angle and the freewheel angle in response to changes in the speed of the electric machine. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS20100253265A1Good control over powerConvenient power controlSynchronous motors startersVacuum cleaner apparatusFreewheelElectric machine
A method of controlling an electric machine that includes sequentially exciting and freewheeling a winding of the electric machine. The winding is excited in advance of zero-crossings of back emf in the winding by an advance angle, and the winding is freewheeled over a freewheel angle. The method then includes varying the advance angle and the freewheel angle in response to changes in the voltage used to excite the winding. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
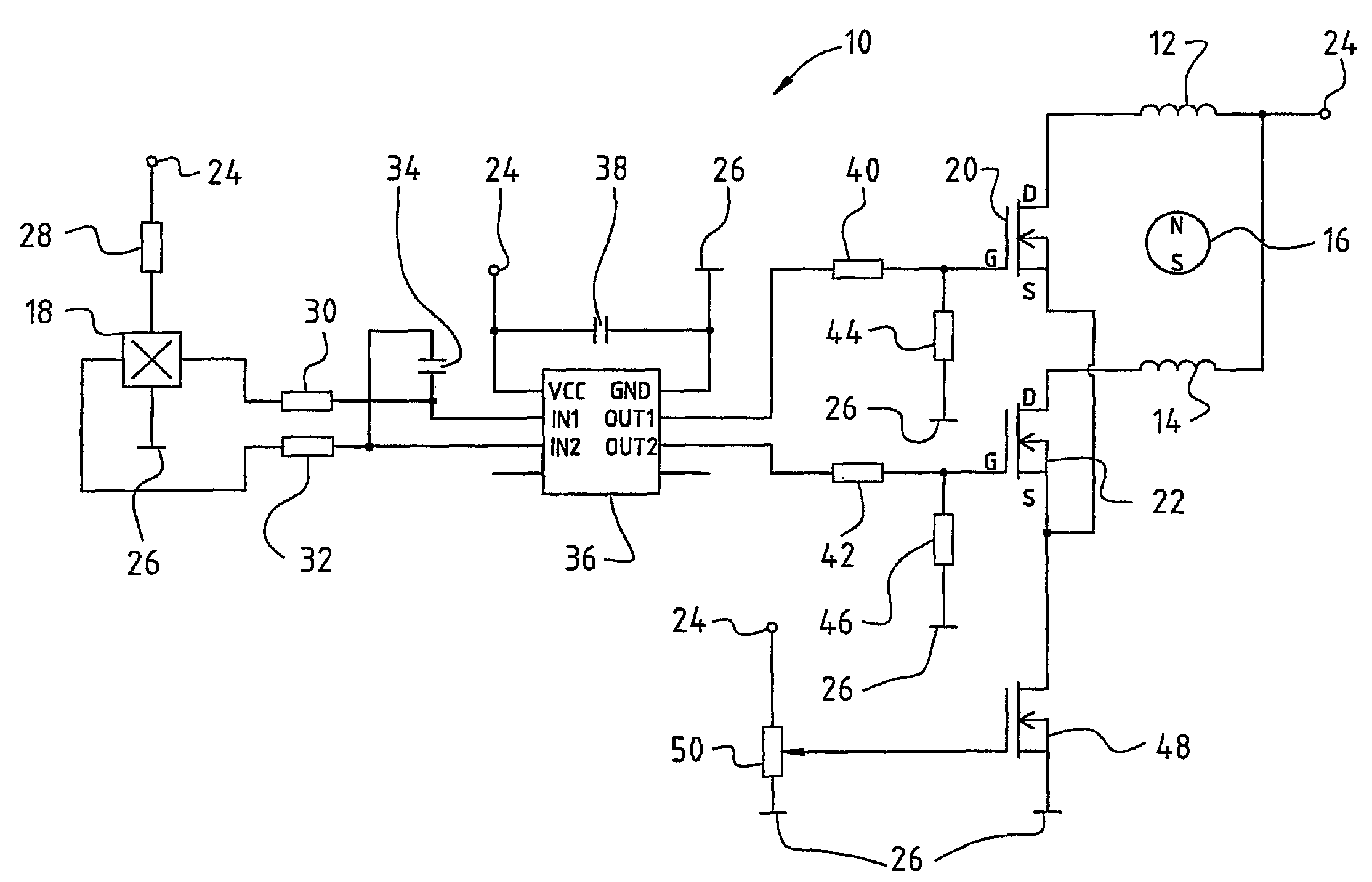
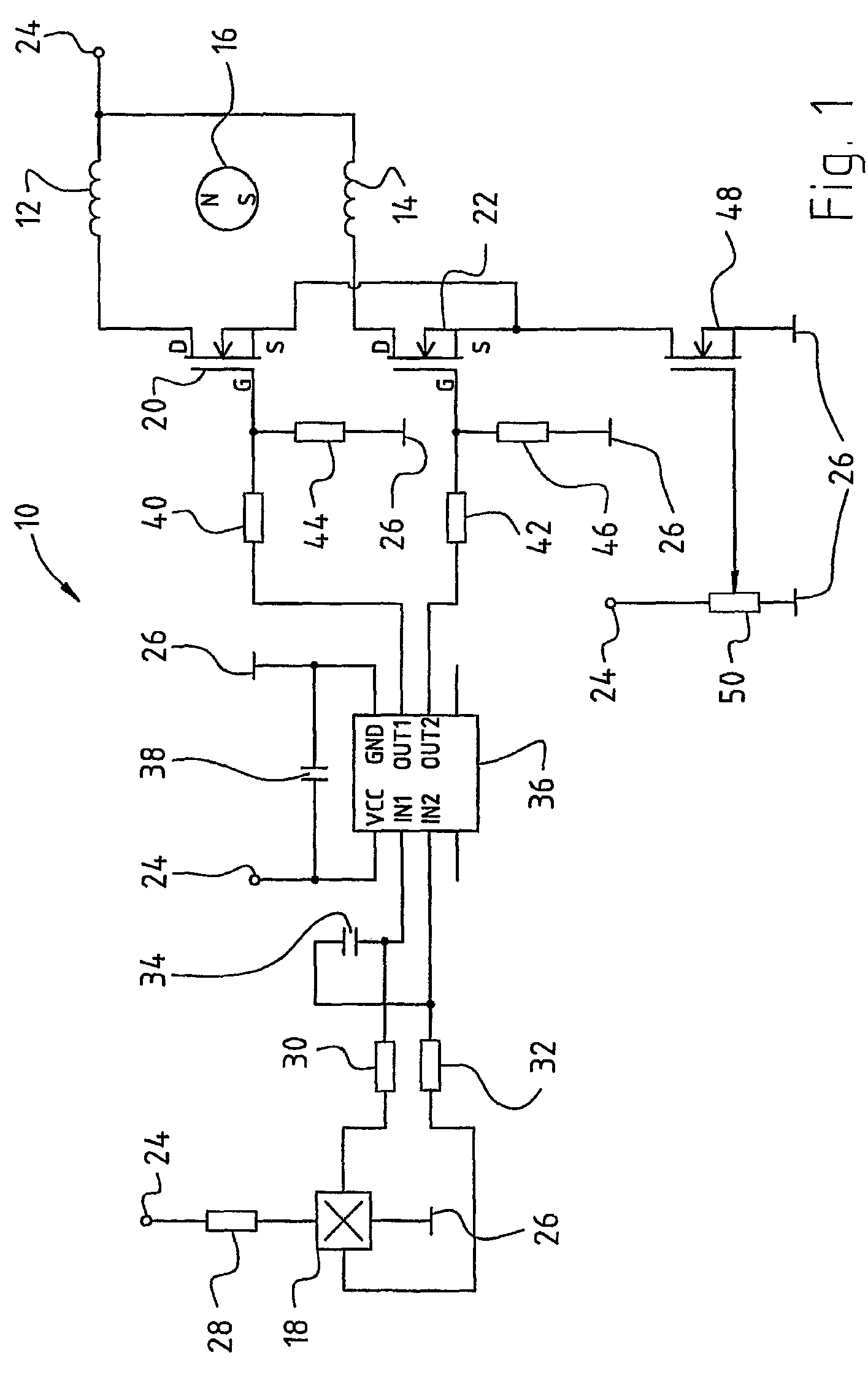
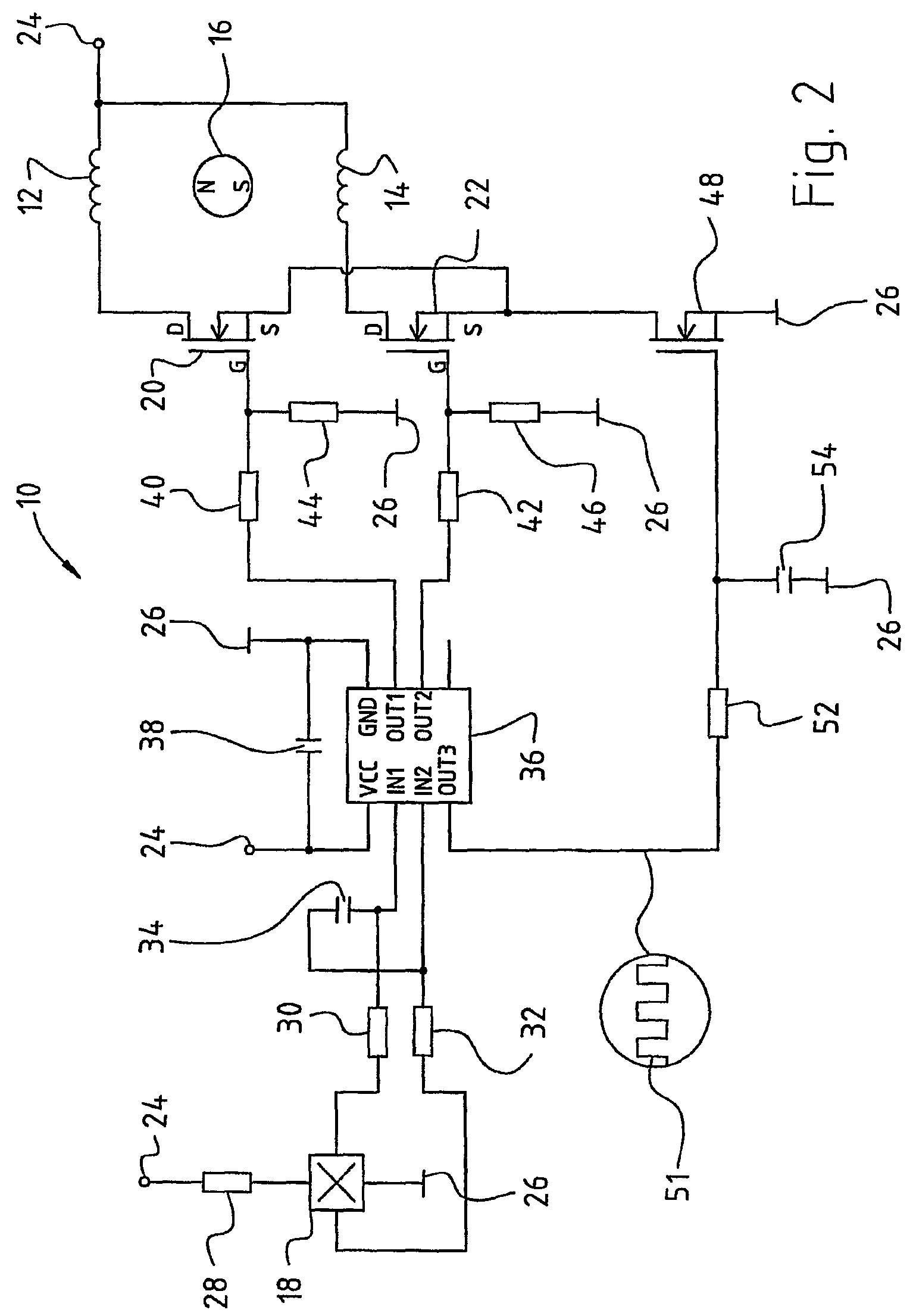
Method for limiting the current in an electric motor, and a motor for carrying out one such method
InactiveUS6906484B1Interruption in deliveryReduce power lossDC motor speed/torque controlSingle motor speed/torque controlFull bridgeEngineering
A method of limiting current in a DC motor acts on a full bridge circuit (137) through which the stator winding arrangement (102) of that motor is supplied with current. Upon response of the current limiter, energy supply to the stator winding arrangement (102) from the DC power network is interrupted. The stator winding arrangement is then operated substantially in short circuit via semiconductor switches of the full bridge circuit, and the decaying current flowing in that context serves substantially to continue driving the motor. When that current has reached a lower value, energy supply from the DC power network to the motor is once again activated. The effective value of the current flowing to the motor is preferably reduced when the current limiter responds. The time period during which that current flows, in the form of current blocks, is then increased in compensatory fashion.
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
Control of a permanent-magnet motor
ActiveUS20100251511A1Less torqueEfficient processSynchronous motors startersMultiple motor speed/torque controlControl systemPermanent magnet motor
A method of controlling a permanent-magnet motor that includes sequentially exciting and freewheeling a winding of the motor. The method includes varying the angle over which the winding is freewheeled in response to changes in speed of the motor. Additionally, a control system for a permanent-magnet motor, and a product incorporating the control system and motor.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
High-speed electric system
ActiveUS20100251509A1Improve efficiencyConstant output powerSynchronous motors startersMultiple motor speed/torque controlElectric machineControl system
An electric system that includes a single-phase permanent-magnet electric machine and a control system for driving the electric machine under load at speeds in excess of 60 krpm. Additionally, a product that includes the electric system.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
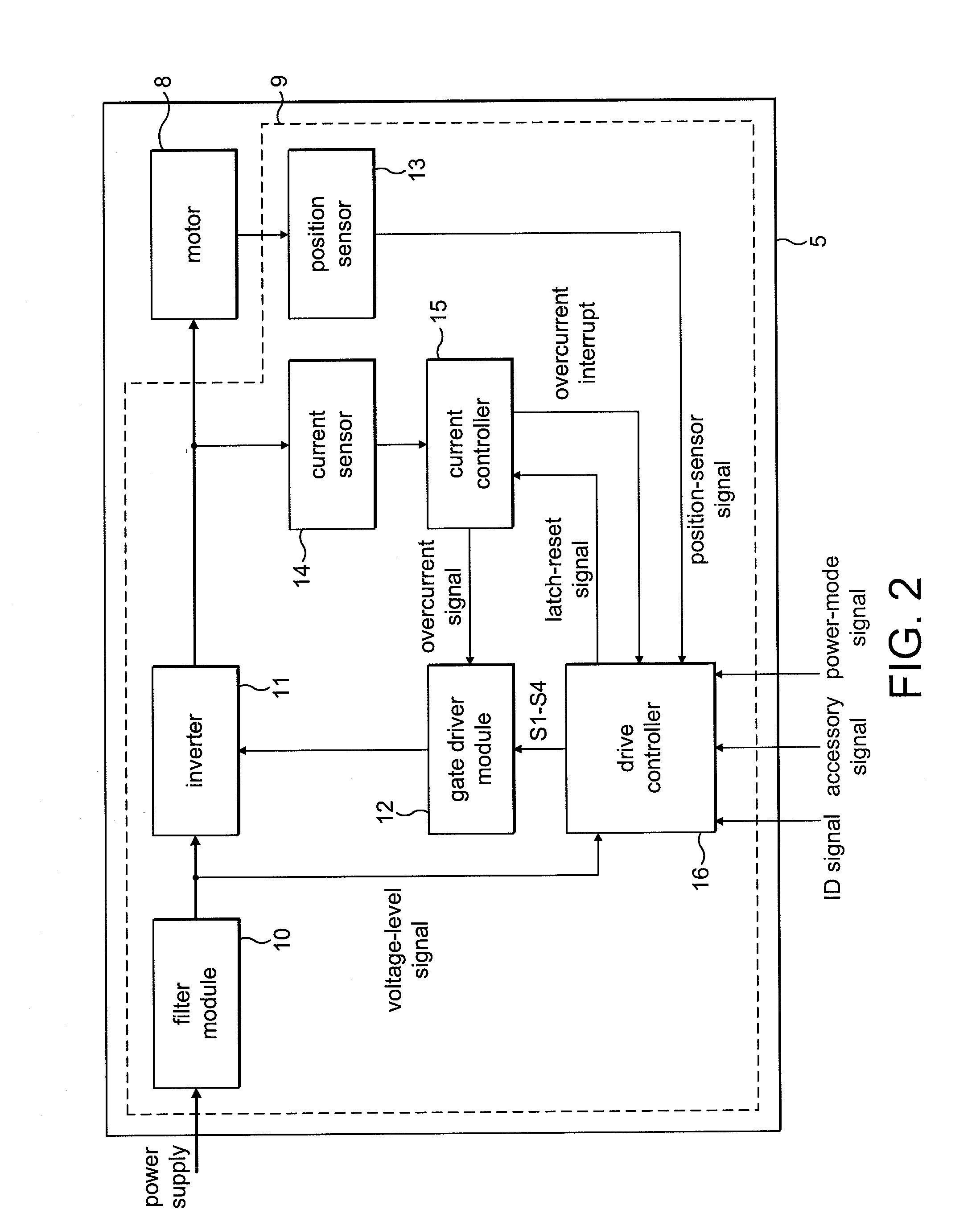
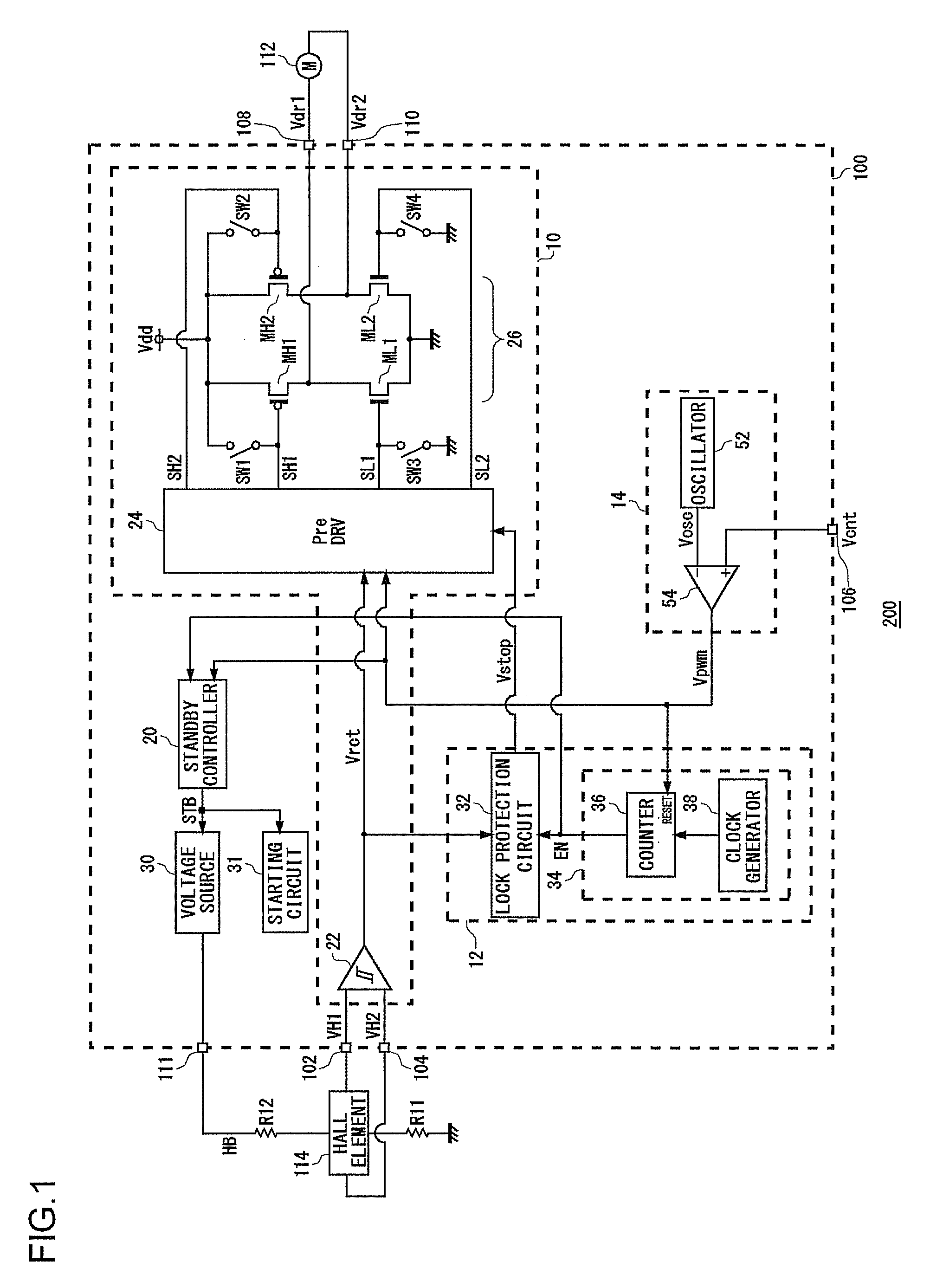
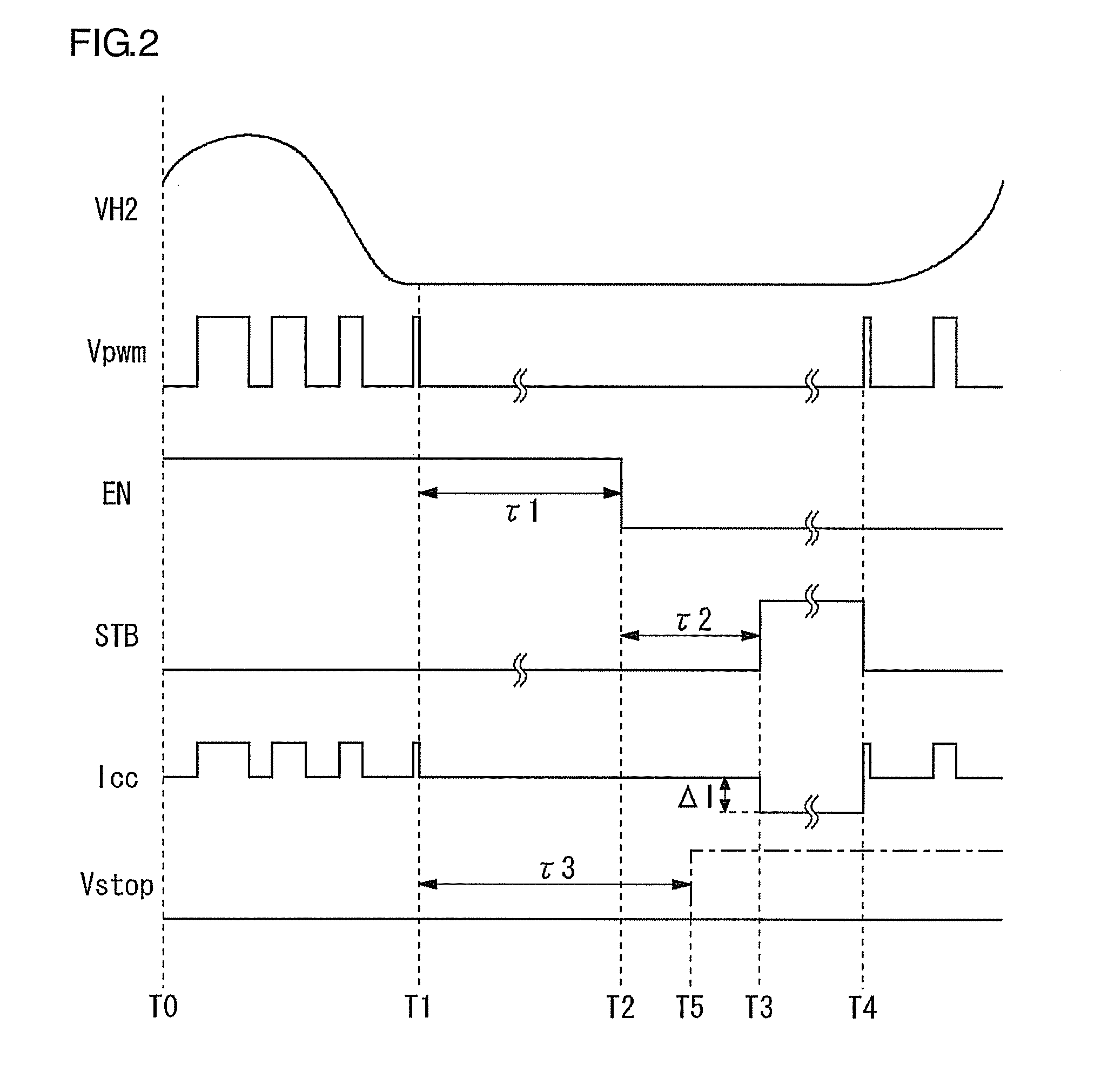
Motor drive device with lock protection function
ActiveUS20080315808A1SpeedReduce power consumptionCommutation monitoringSynchronous motors startersStart timeMotor drive
A cooling system is provided with a motor drive device, a fan motor, and a Hall element. The motor drive device includes a lock protection circuit and a lock controller. When a control signal instructing rotation of the fan motor that is to be driven instructs stoppage of the motor for a predetermined time-period or longer, the lock controller has the lock protection circuit inactive. At an occasion when the control signal has continued to instruct stoppage of the fan motor for a first time-period or longer, a standby controller starts time measurement, and after a further predetermined second time-period has elapsed, makes at least a part of the motor drive device transition to a standby mode.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
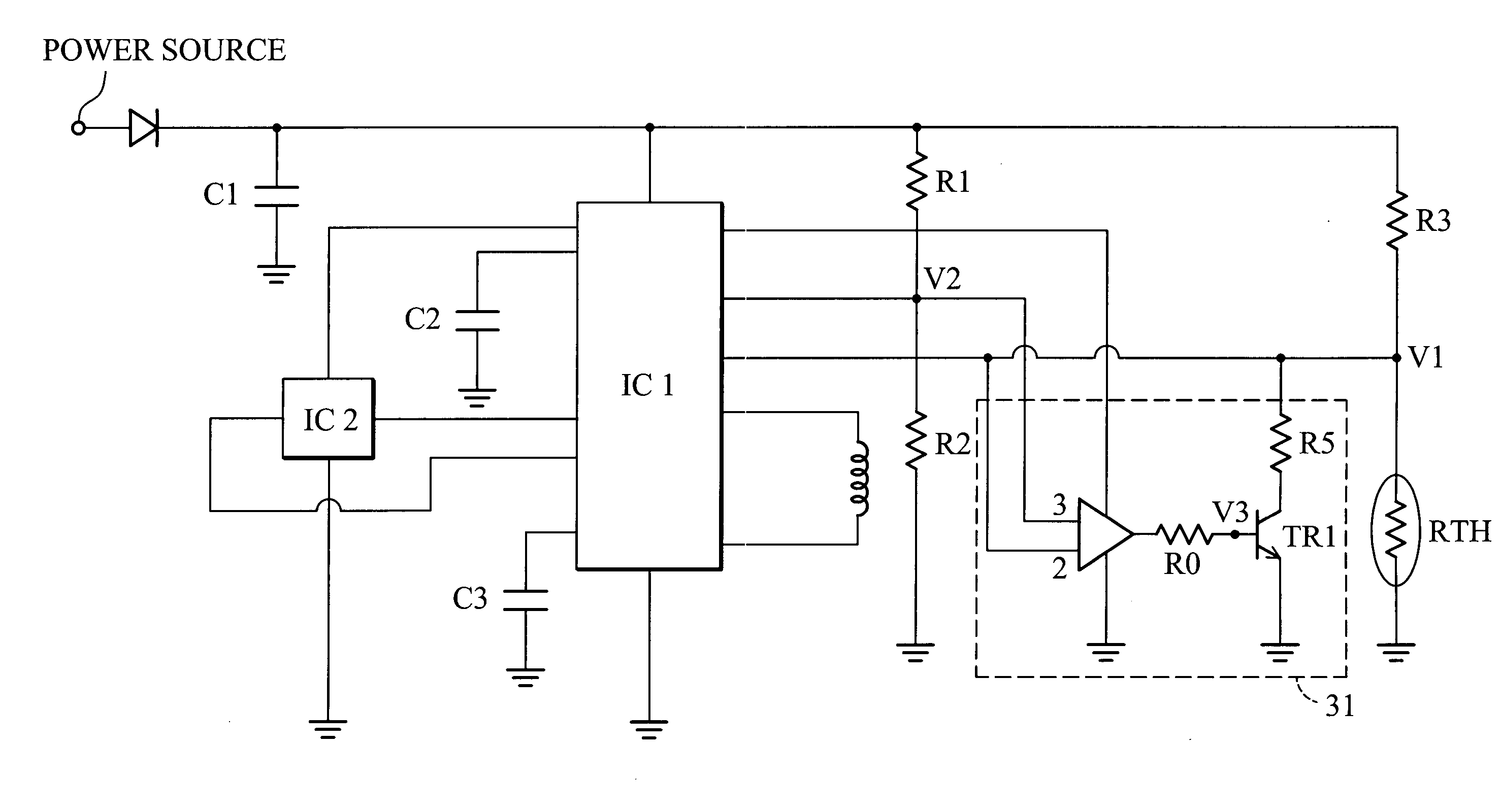
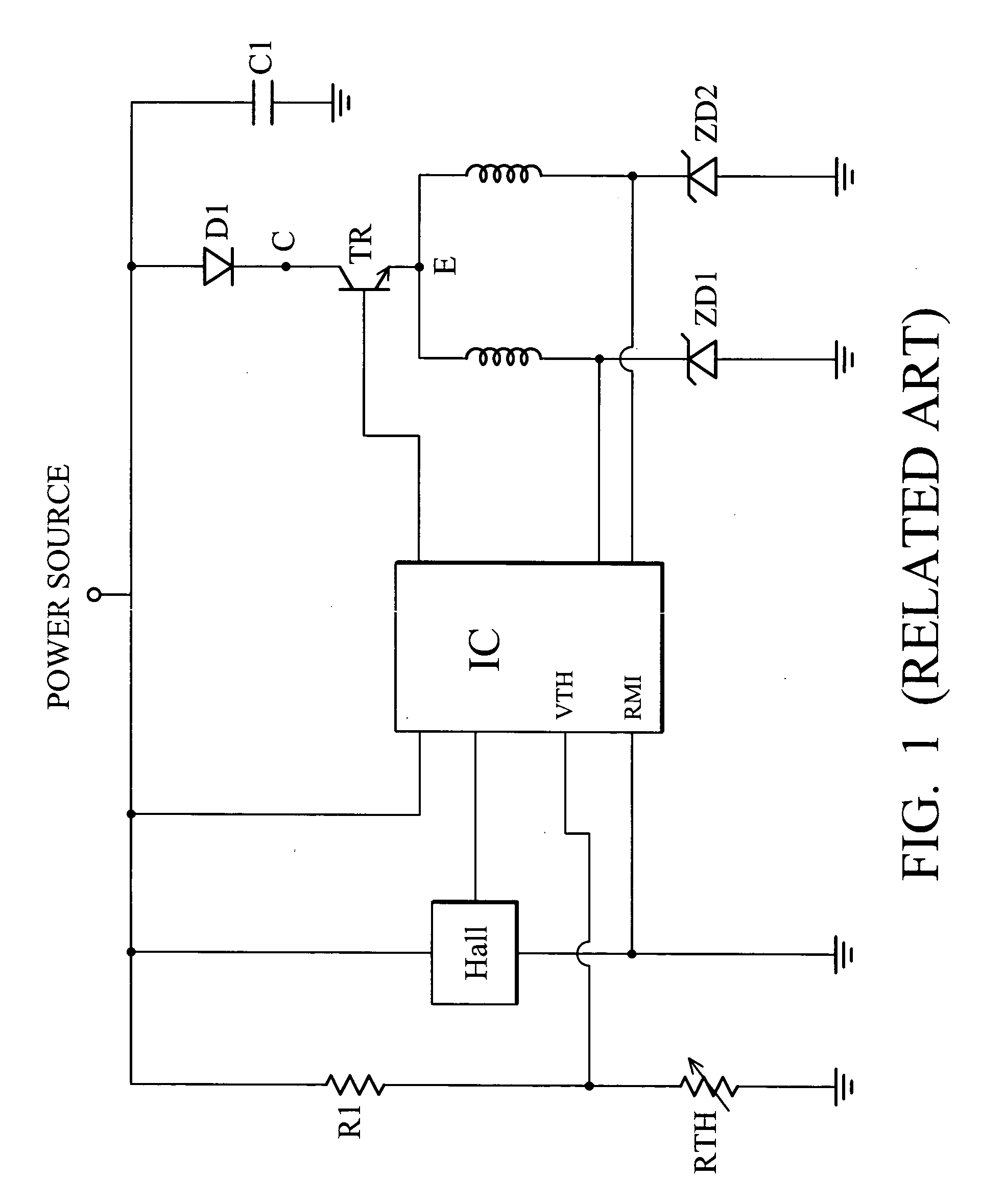
Motor speed control device
InactiveUS20050047762A1Easy to controlLower temperature rangeSingle motor speed/torque controlField or armature current controlMotor speedDriven element
A motor speed control device. The motor speed control device applied to a direct current (DC) fan includes a driving element constituted by a driving IC and Hall IC, a thermal sensor and a control element electrically connected between the driving element and the thermal sensor. The present invention utilizes a thermal sensor and a simple control element to effectively and stably control the variable speed of the fan within different temperature ranges.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Control of a brushless motor
ActiveUS8643319B2Reduce peak magnetic flux densityEfficient and small motorSingle-phase induction motor startersAc-dc conversion without reversalBrushless motorsMotor speed
A method of controlling a brushless motor that includes rectifying an alternating voltage to provide a rectified voltage, and exciting a winding of the motor with the rectified voltage. The winding is excited in advance of predetermined rotor positions by an advance period and is excited for a conduction period over each electrical half-cycle of the motor. The length the advance period and / or the conduction period is defined by a waveform that varies periodically with time. The method then includes adjusting the phase of the waveform relative to the alternating voltage in response to a change in one of motor speed and RMS value of the alternating voltage. Additionally, a control system that implements the method, and a motor system that incorporates the control system.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Motor drive unit and method of detecting malfunction of motor drive unit
A DC motor is connected to diagonal positions of a bridge circuit having of four sides including switching elements and reflux diodes. At least one of two terminals is connected to a power line, and at least the other terminal is grounded. By performing pulse width modulation control of the switching elements, operation of the DC motor is controlled. When the DC motor is in operation, the sum of the terminal voltages of the DC motor is equal to the power voltage. When the DC motor is out of operation, the sum of the voltages is set to a predetermined voltage. If the sum of the voltages has deviated from the power voltage or the predetermined voltage by at least a predetermined value, the occurrence of a malfunction is judged.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS20100253263A1Convenient power controlDecreasing freewheel angleMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersFreewheelFree rotation
A method of controlling an electric machine that includes sequentially exciting and freewheeling a winding of the electric machine. The winding is excited by an excitation voltage and is freewheeled over a freewheel angle. The method then includes varying the freewheel angle in response to changes in the excitation voltage. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
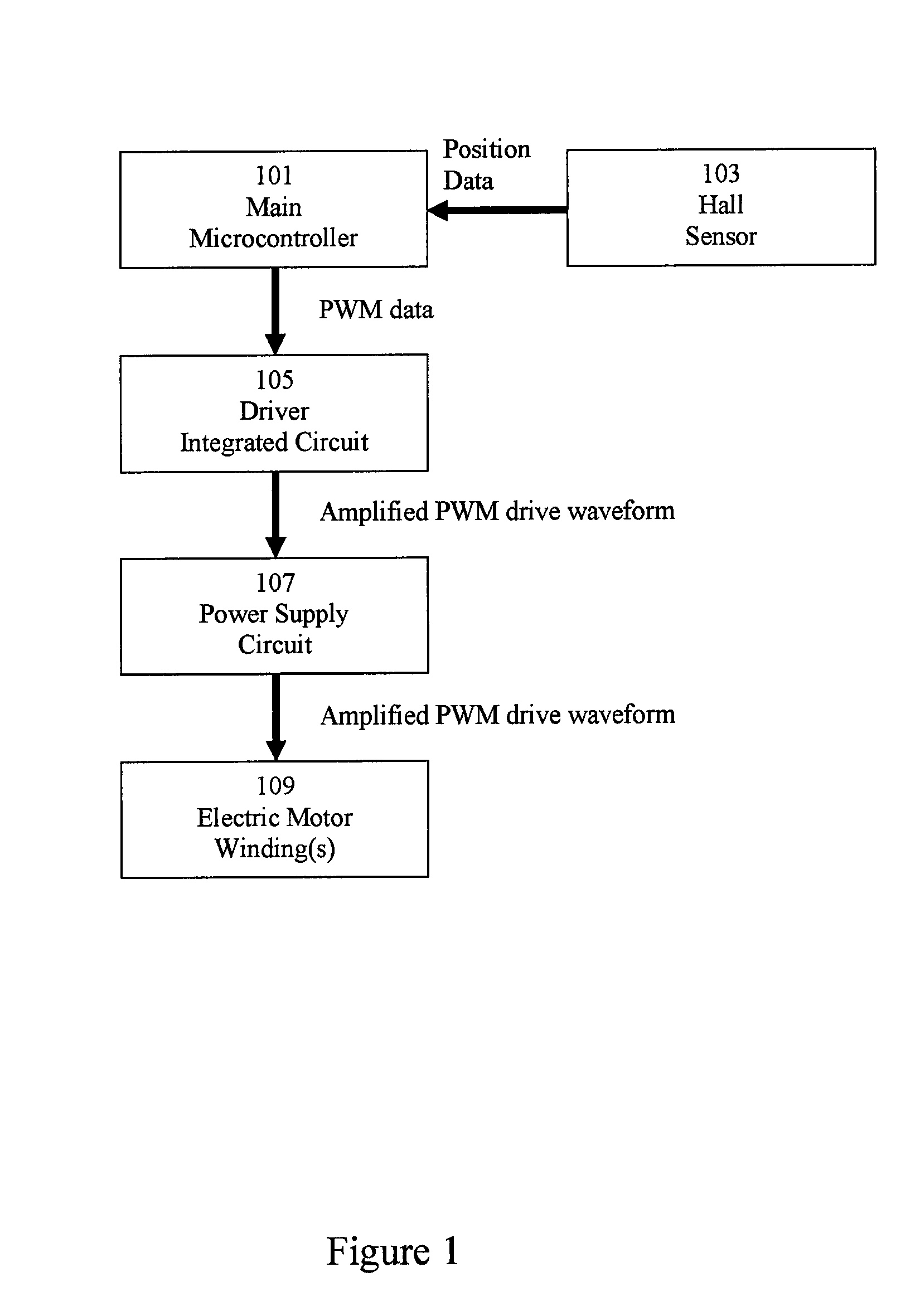
Control system for an electric machine
ActiveUS20100253262A1Improve performanceNarrow speed rangeMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectric machineControl system
A control system for an electric machine, the control system including a position sensor and a drive controller. The drive controller generates one or more control signals for exciting a winding of the electric machine in response to edges of a signal output by the position sensor. The times at which the control signals are generated by the drive controller are corrected by a position-sensor offset that is fixed over an operating speed range of the electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Method & arrangement for sensorless operation of an electronically commutated motor
InactiveUS20070241705A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlConductor CoilCapacitor
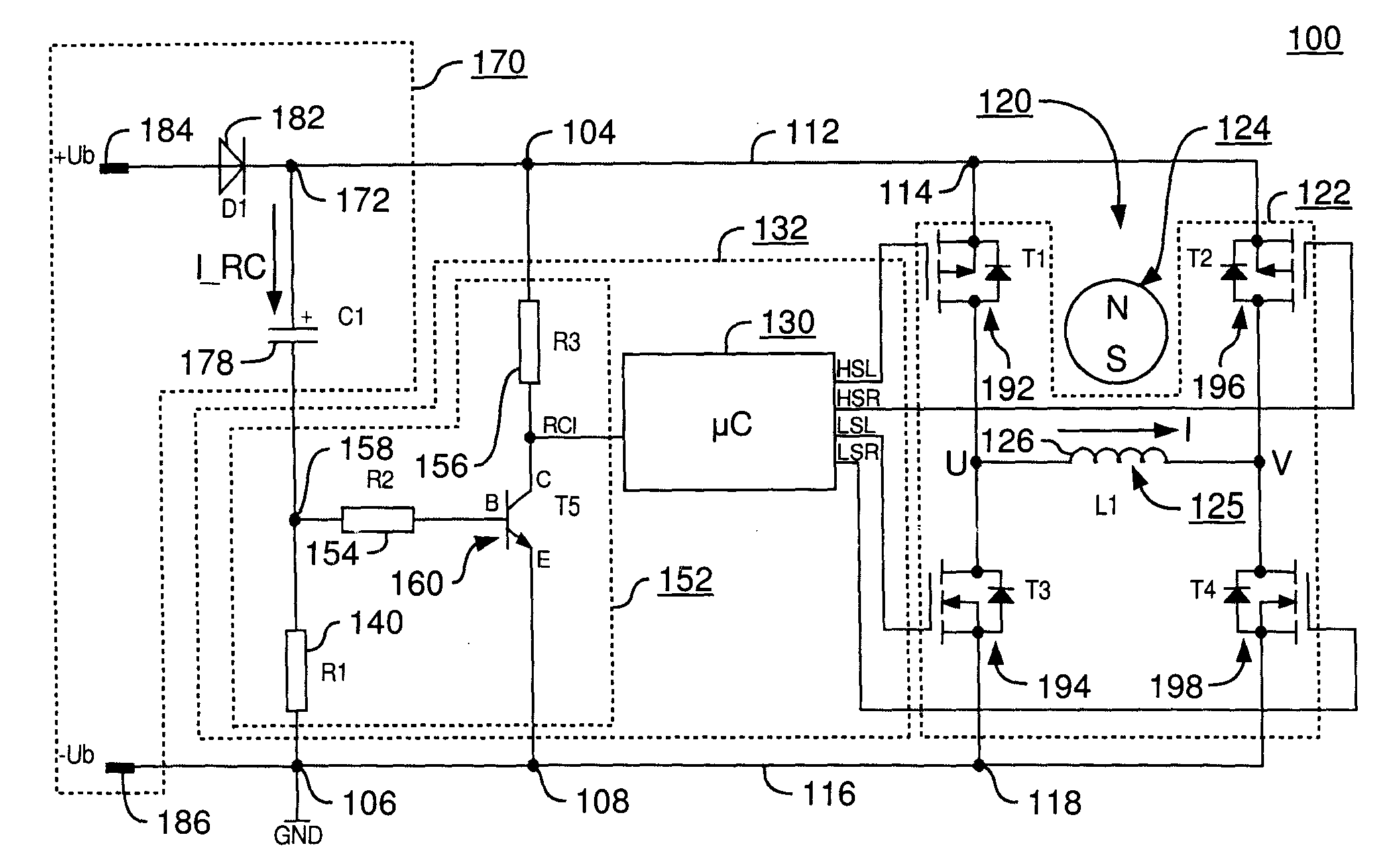
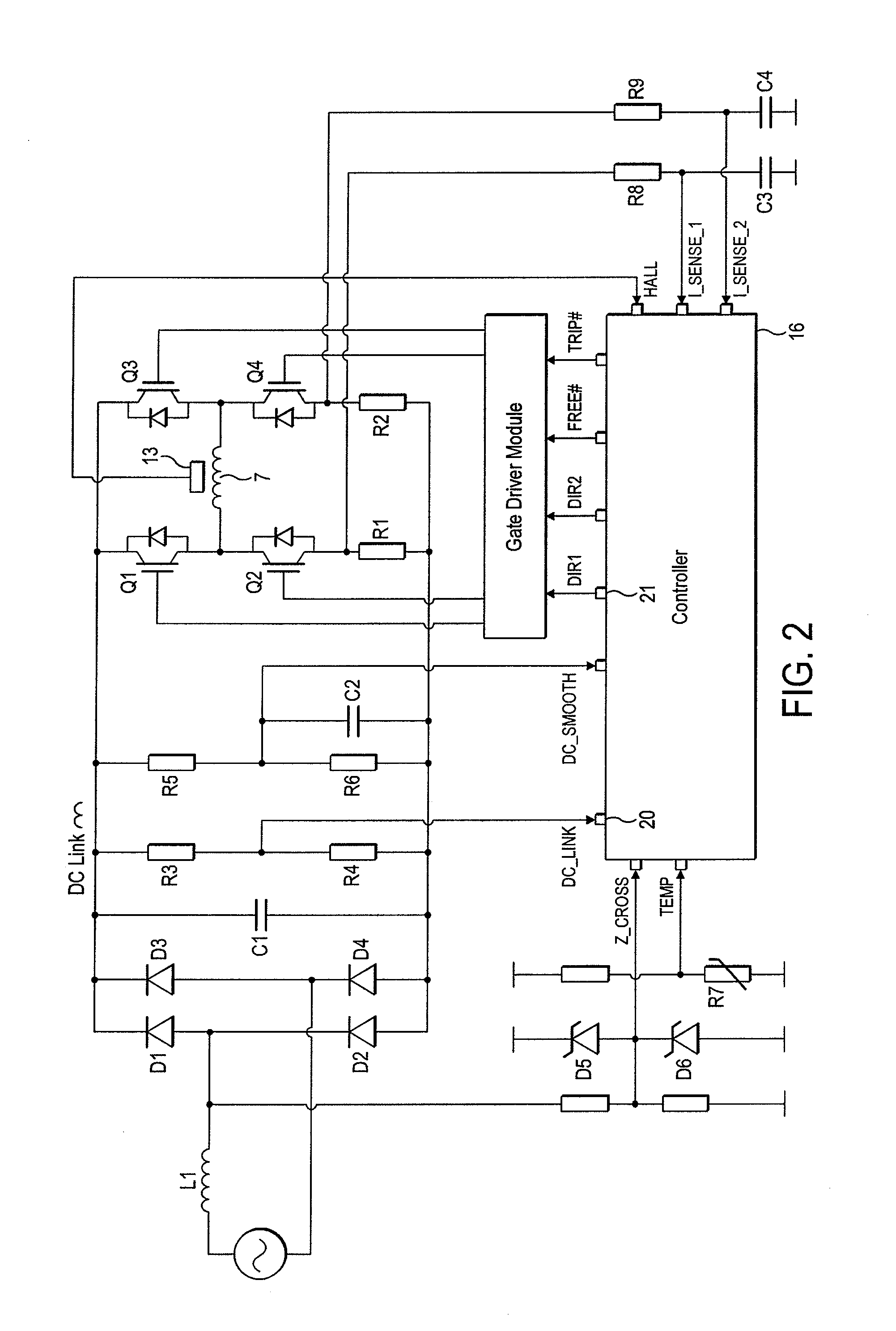
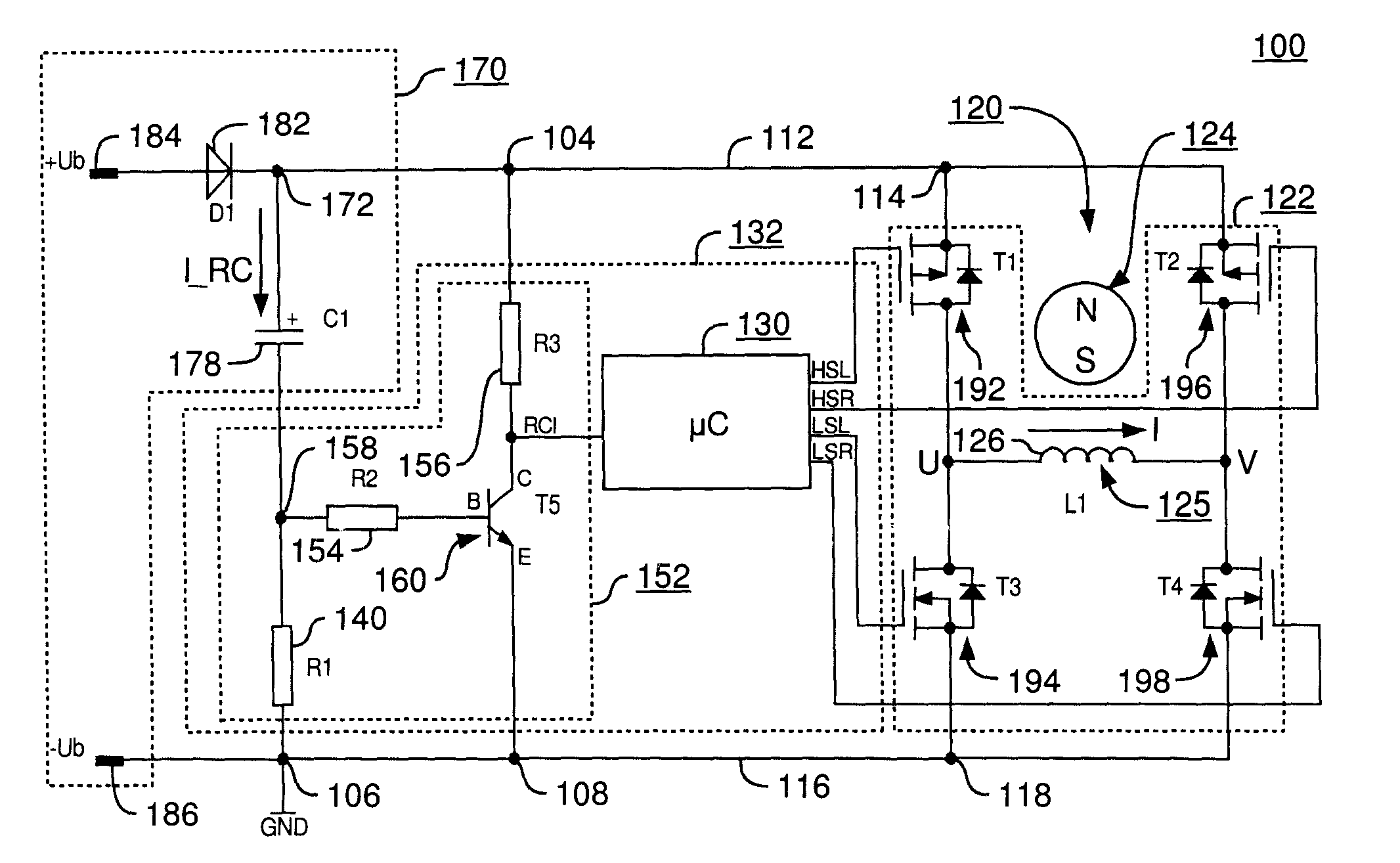
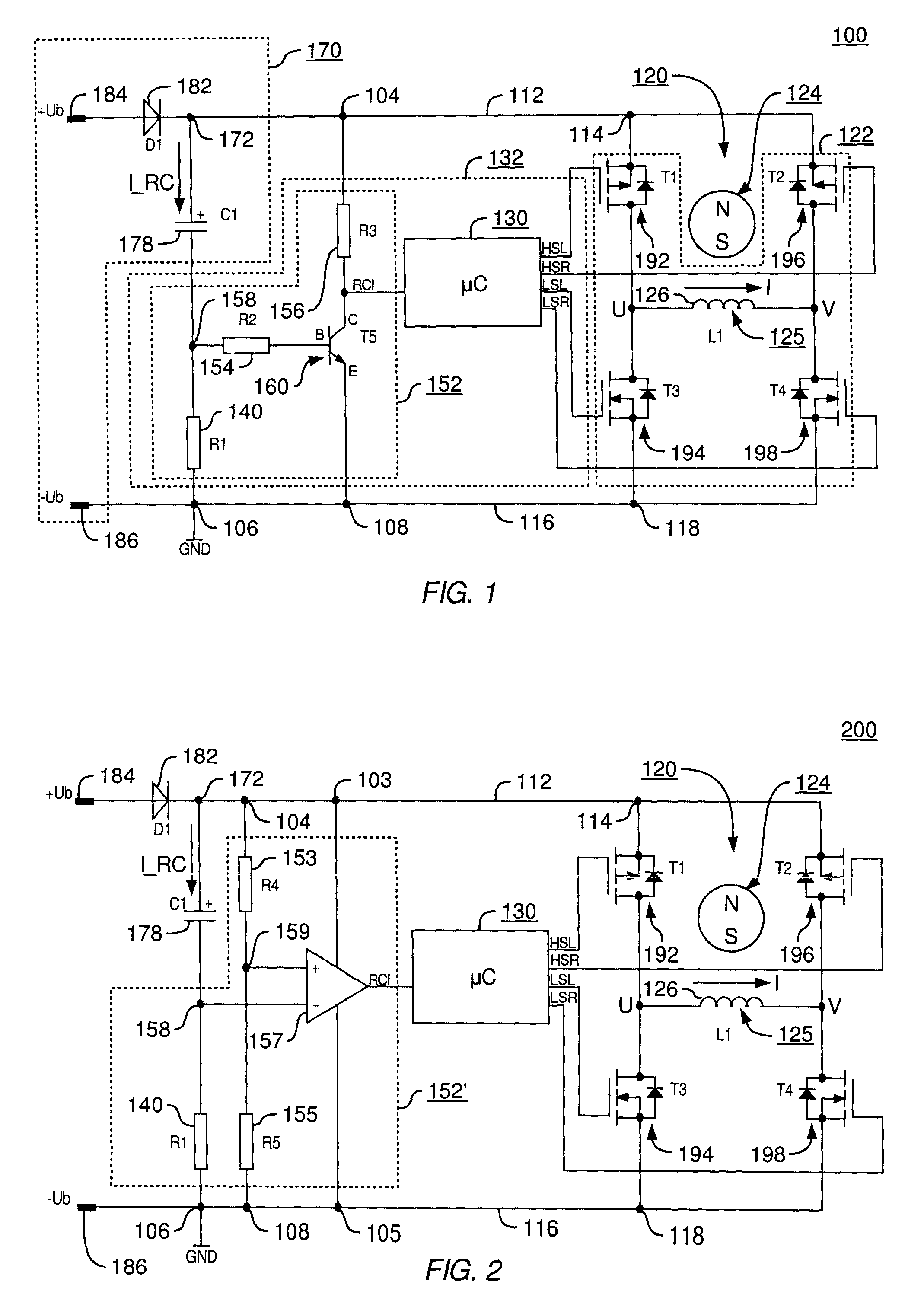
An improved electric motor has a rotor (124), a stator (125) having at least one phase winding strand (126), an output stage (122) for influencing the current flow in said phase winding strand, a DC link circuit (170) for supplying the output stage (122) with current, including a link circuit capacitor (178), and a control unit (132) having an arrangement (152) for sensing a value characterizing the current recharge into the link circuit capacitor (178), which control unit (132) is configured to specify commutation instants as a function of the sensed value, and to perform commutation operations in the power stage (122) at the commutation instants thus specified. Avoiding a need for prolonged “currentless intervals” permits achieving higher efficiency and power output, particularly in a motor having less than three winding phases.
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
Control of a brushless permanent-magnet motor
ActiveUS20110254488A1Constant powerImprove power factorMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectricityControl system
A method of controlling a brushless permanent-magnet motor that includes rectifying an alternating voltage to provide a rectified voltage having a ripple of at least 50%, and exciting a winding of the motor with the rectified voltage. The winding is excited in advance of zero-crossings of back EMF by an advance period and is excited for a conduction period over each electrical half-cycle of the motor. The advance period and / or the conduction period are then adjusted in response to changes in the speed of the motor and / or the RMS value of the alternating voltage so as to maintain constant average power. Additionally, a control system that implements the method, and a motor system that incorporates the control system.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Method and arrangement for sensorless operation of an electronically commutated motor
InactiveUS7902776B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersConductor CoilCapacitor
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
Constant-power electric system
ActiveUS20100251510A1Easy to controlKeep for a long timeSynchronous motors startersSingle motor speed/torque controlConstant powerControl system
An electric system that includes a single-phase permanent-magnet electric machine and a control system for driving the electric machine. The control system sequentially excites and freewheels a winding of the electric machine so as maintain substantially constant power over an operating speed range spanning at least 10 krpm and / or an excitation voltage range extending between a minimum voltage and a maximum voltage, the minimum voltage being less than 80% of the maximum voltage. Additionally, a product comprising the electric system.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for driving a DC motor
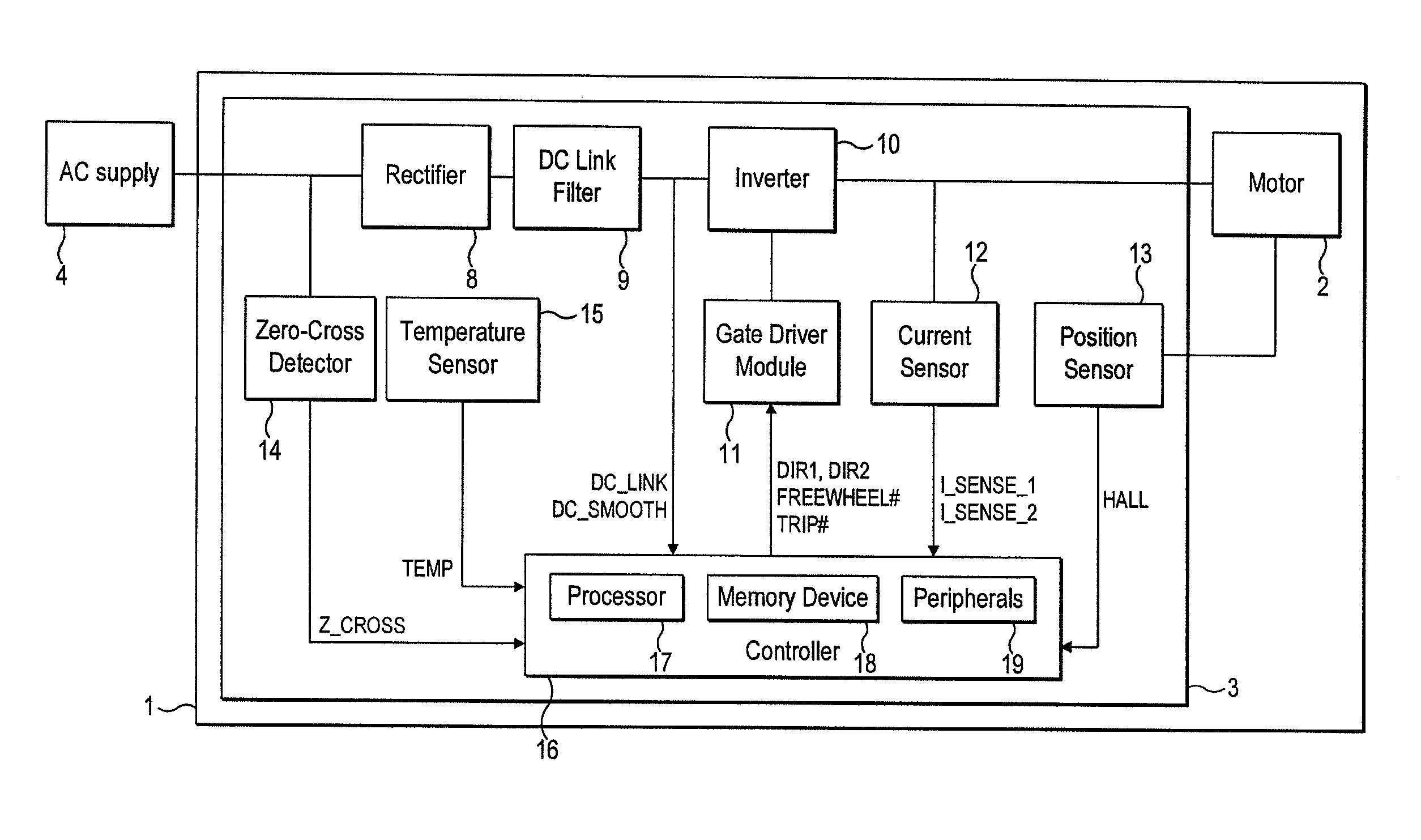
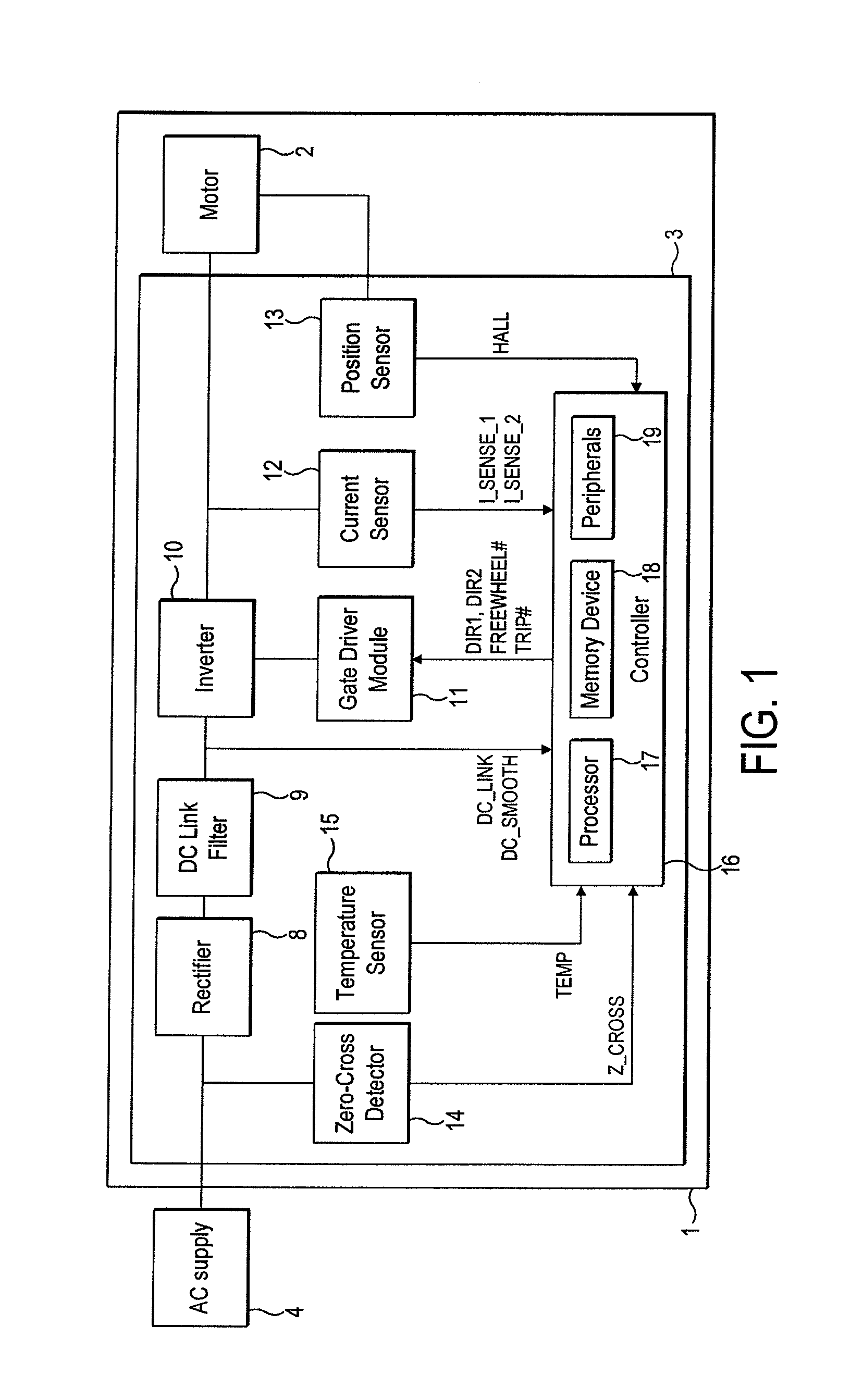
ActiveUS20080197794A1Synchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlControl signalEngineering
A circuit for determining a direction of rotation of an electric motor, the motor having asymmetry and / or eccentricity in a profile of back electromotive force as a function of angular position of a rotor with respect to a stator, the circuit receiving a signal representing the BEMF, and use the corresponding asymmetry and / or eccentricity in the signal to derive the direction of rotation. The signal representing the back emf can be generated by a control circuit. The control circuit can have a feedback loop regulator to generate a control signal (TL or TR) to control a current drive circuit (11,12) to control an amplitude of current (iw) in the windings, the feedback loop regulator being arranged to compare the amplitude of the current (iw) in the windings with a reference value (iset), and use the control signal to provide the signal representing the back electromotive force.
Owner:AMI SEMICON BELGIUM
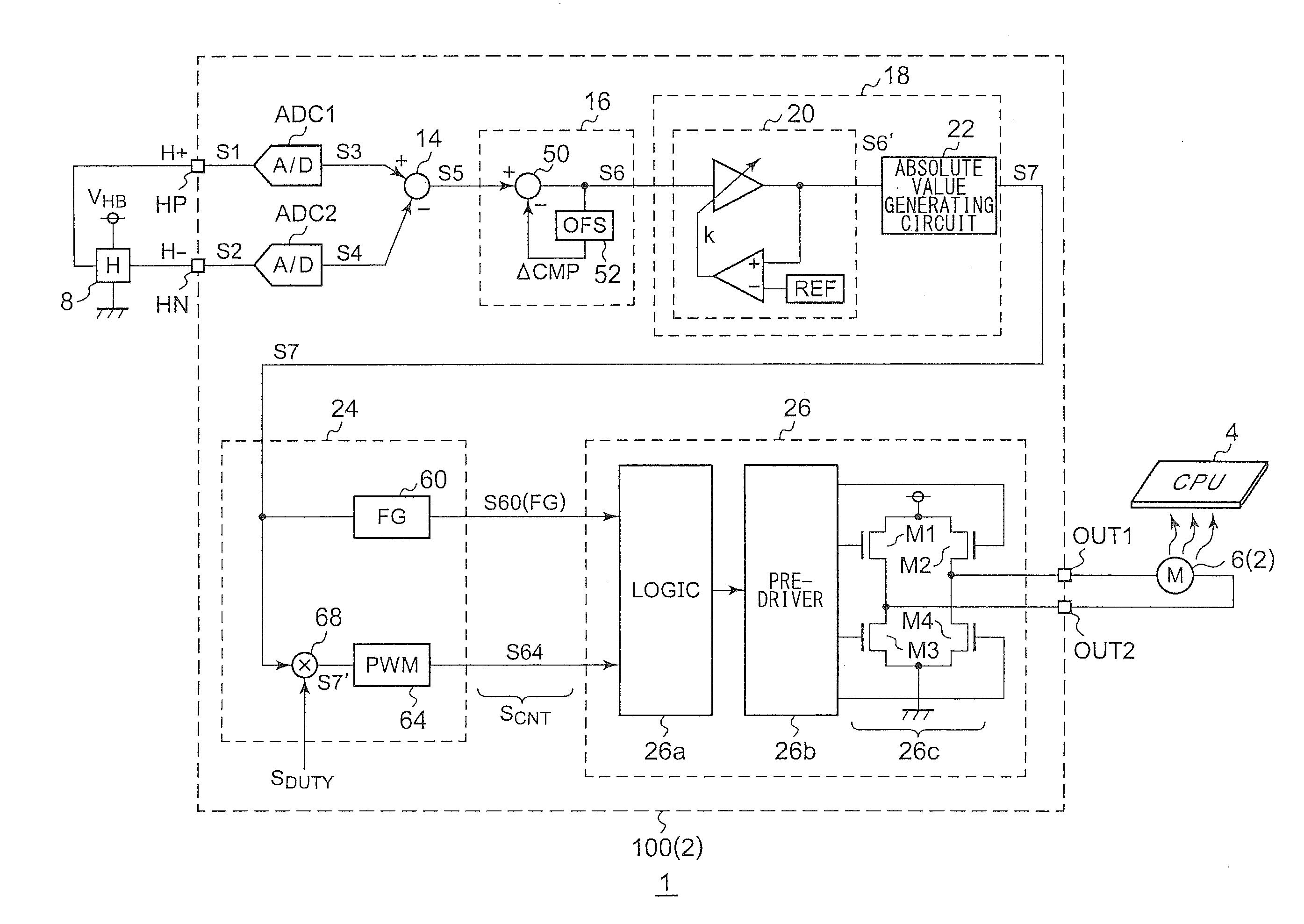
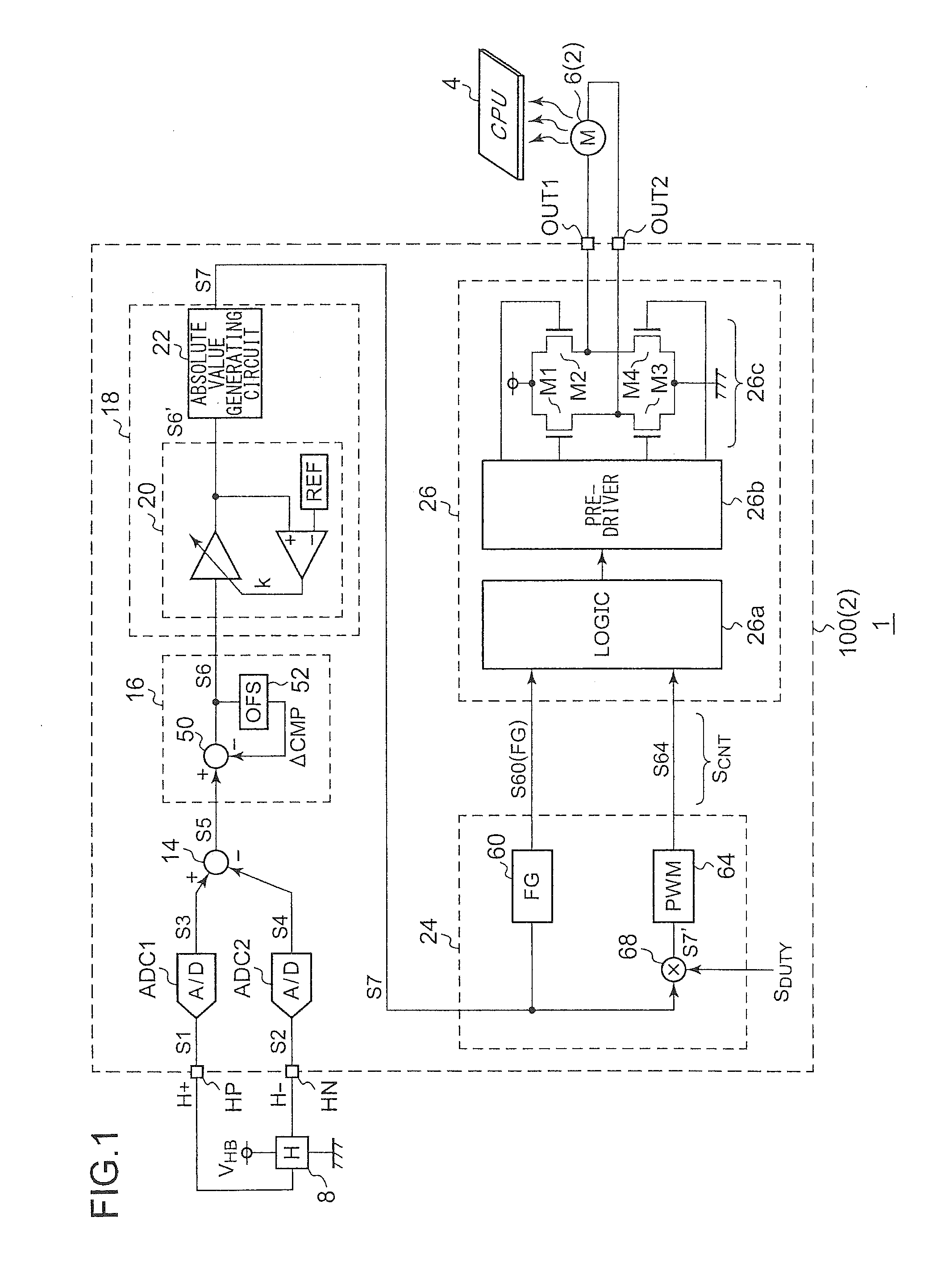
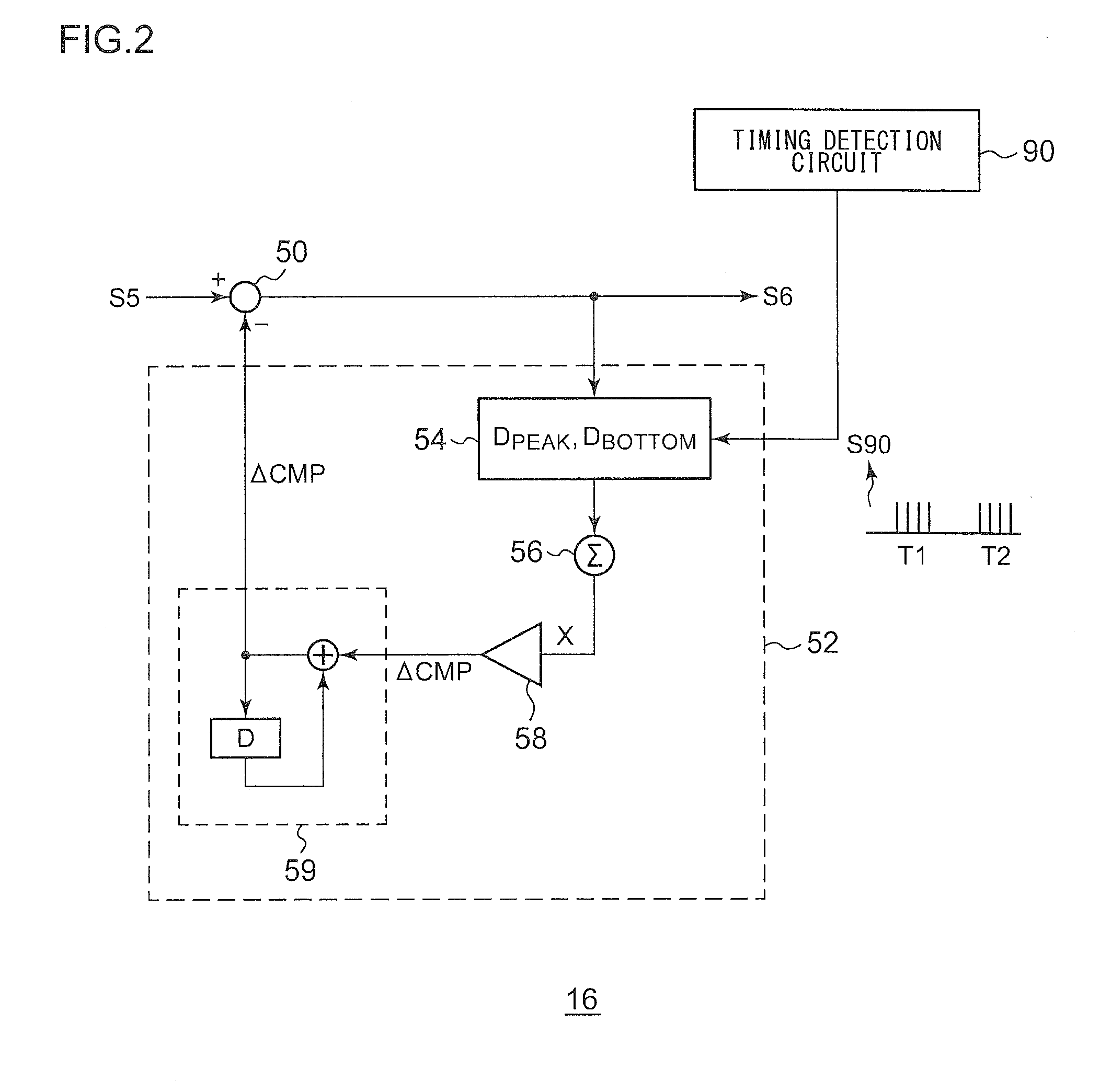
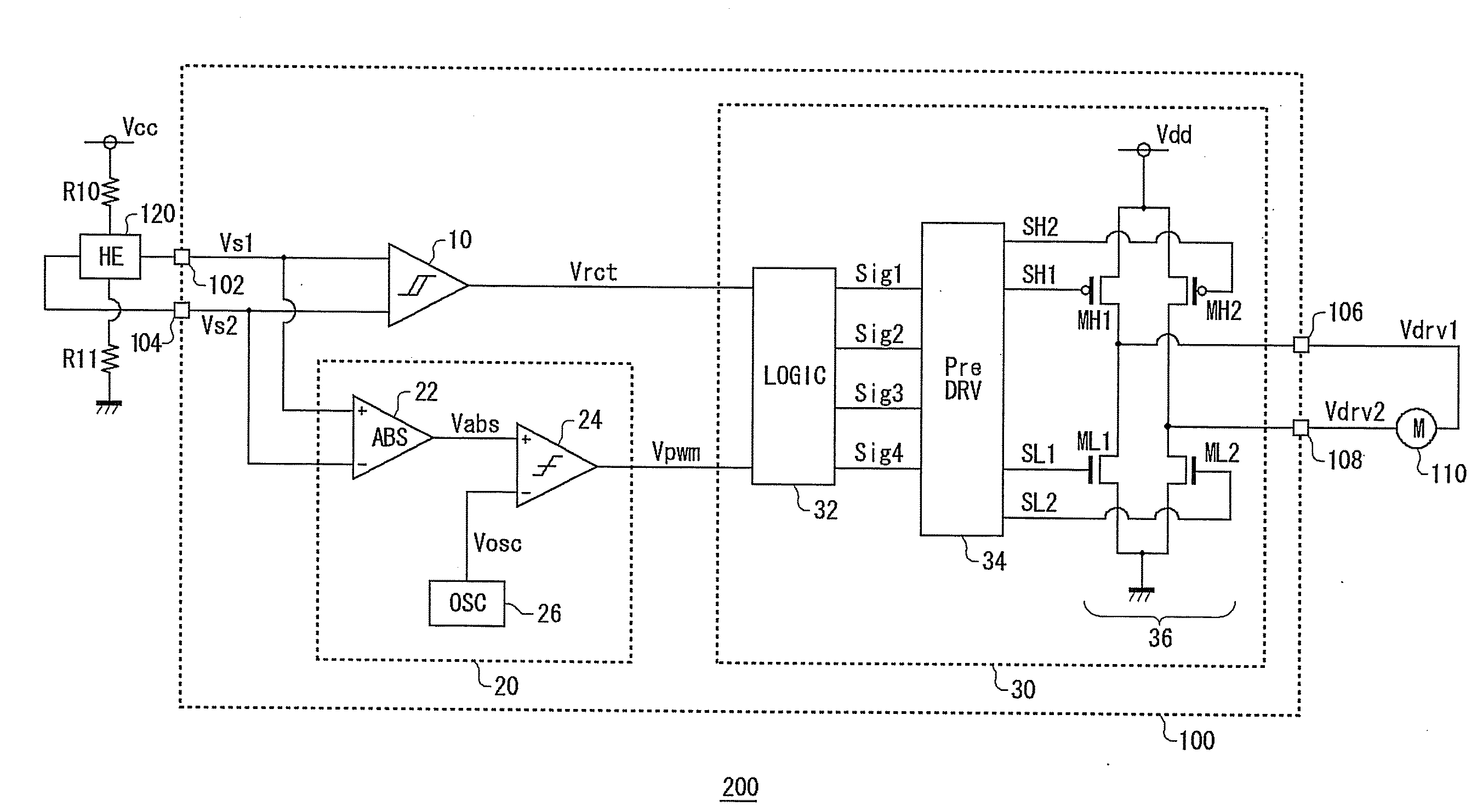
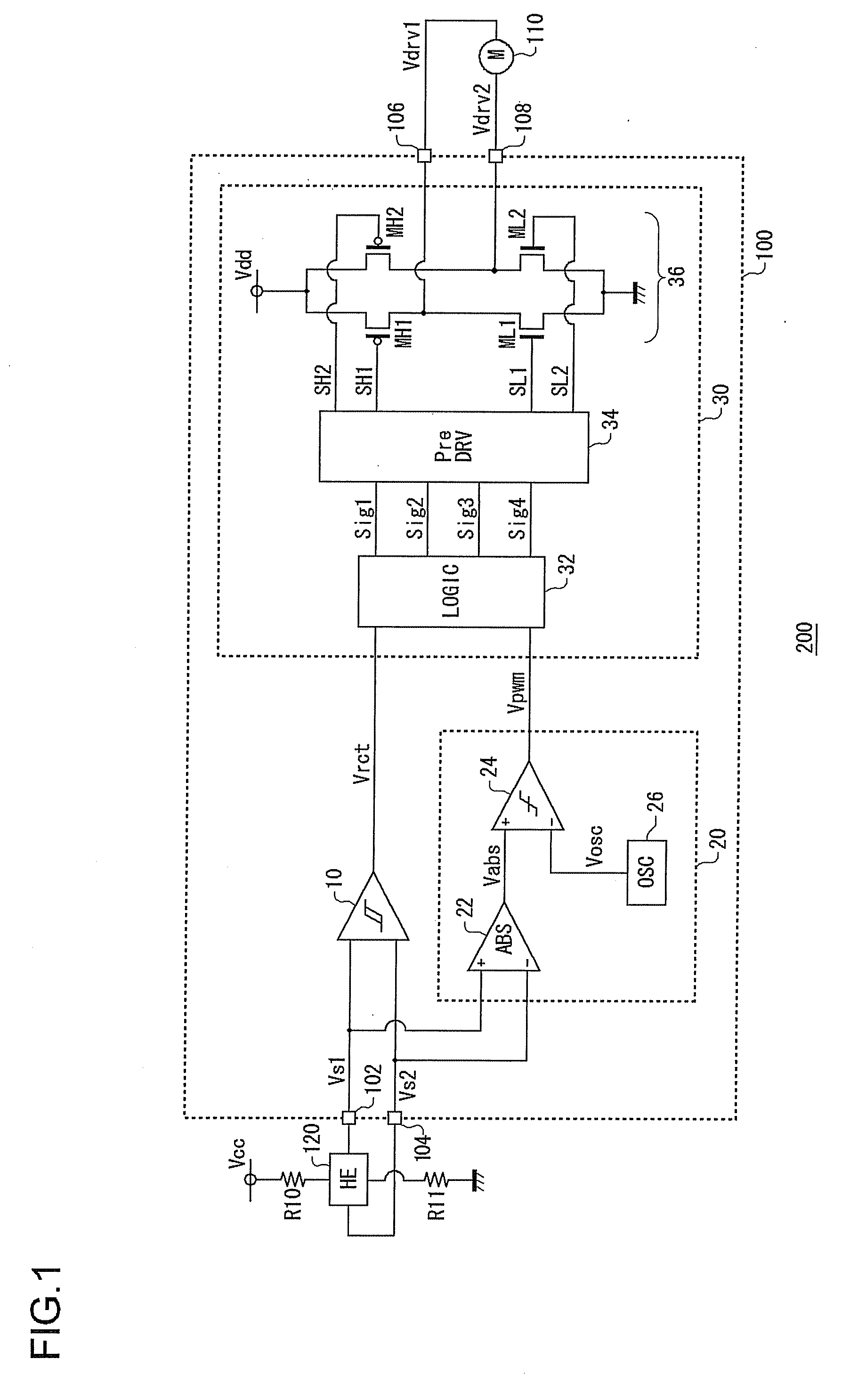
Motor driving circuit
ActiveUS20110279072A1Appropriately drivenMotor/generator/converter stoppersCommutation monitoringMotor driveControl signal
First and second A / D converters perform analog / digital conversion of first and second signals of a Hall signal so as to generate third and fourth signals as digital signals. A differential conversion circuit generates a fifth signal as a single-ended signal that corresponds to the difference between the third and fourth signals. An offset correction circuit corrects offset of the fifth signal so as to generate a sixth signal. An amplitude control circuit stabilizes the amplitude of the sixth signal to a predetermined target value, and generates its absolute value, thus generating a seventh signal. A control signal generating unit generates a control signal upon the seventh signal. A driver circuit drives a motor according to the control signal.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Control of an electrical machine
ActiveUS20120081064A1Relieve pressureImprove electricity efficiencyMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectric machineControl system
A method of controlling an electrical machine that includes exciting a phase winding with a supply voltage, and freewheeling the phase winding when current in the phase winding exceeds a threshold. The threshold is then adjusted in response to changes in the supply voltage and / or the speed of the electrical machine. Additionally, a control system that implements the method and an electrical machine comprising the control system are described.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
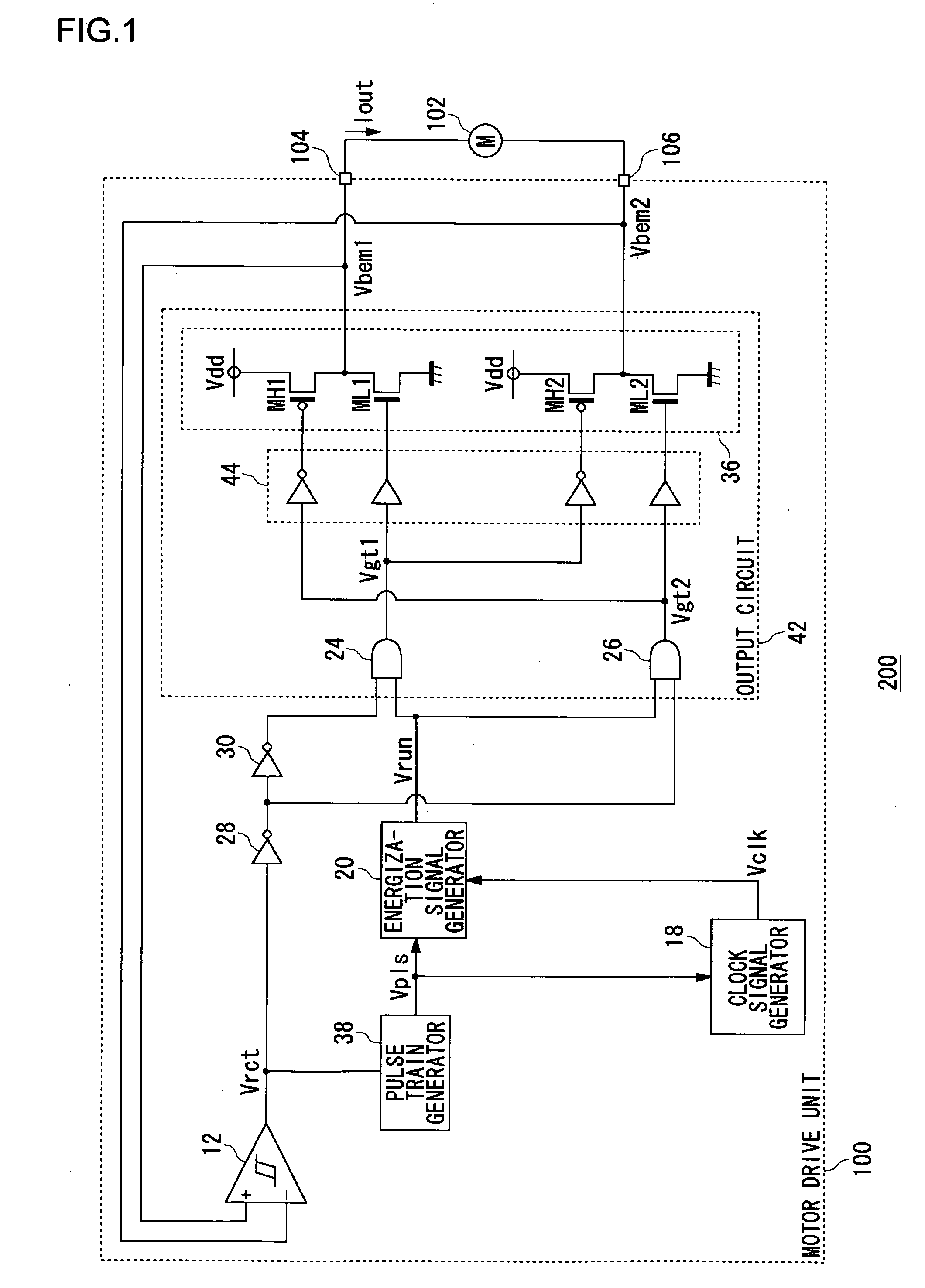
Motor drive unit
InactiveUS20070092232A1Reduce circuit areaSimple configurationDC motor speed/torque controlSingle motor speed/torque controlSignal generatorMotor Drive Unit
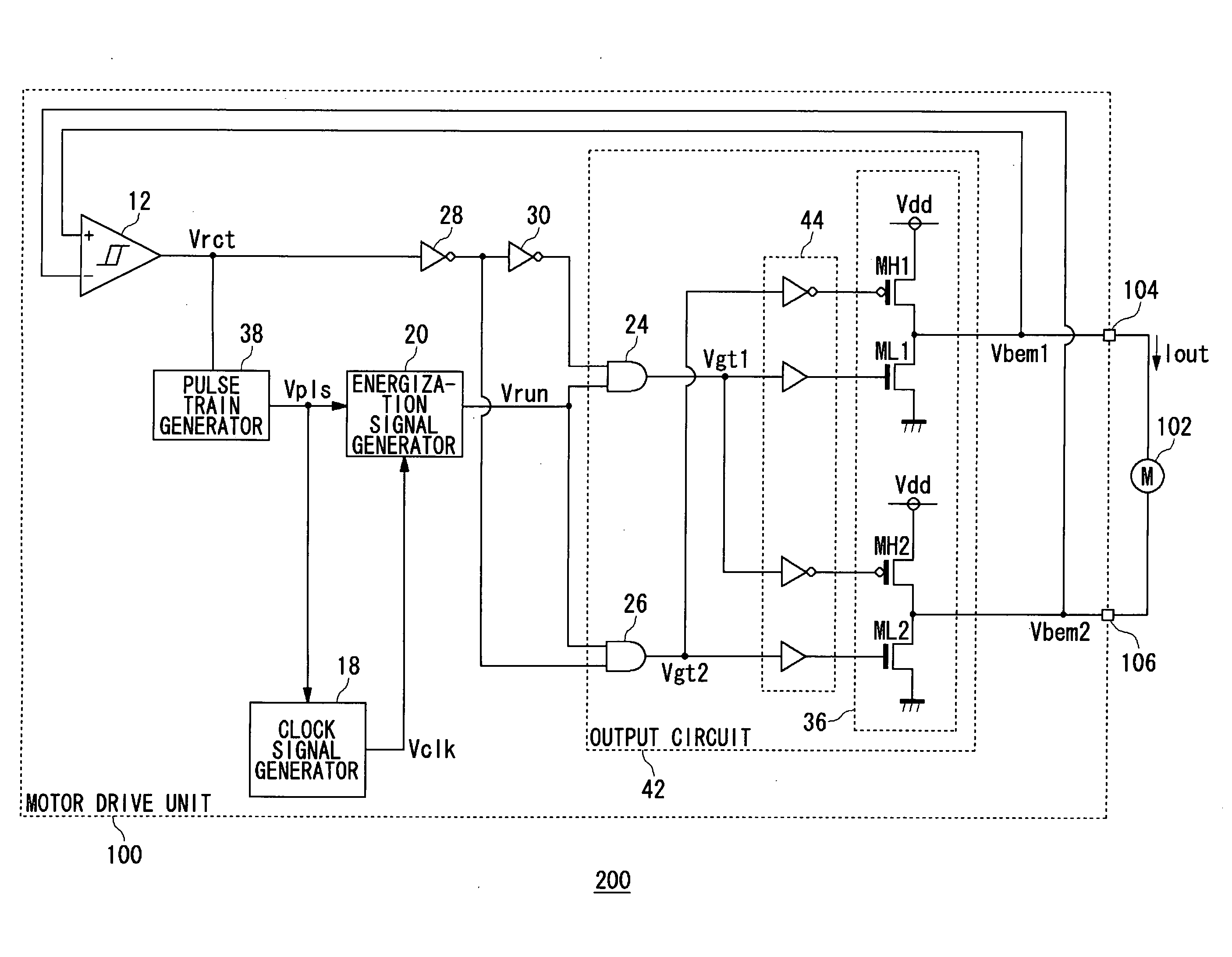
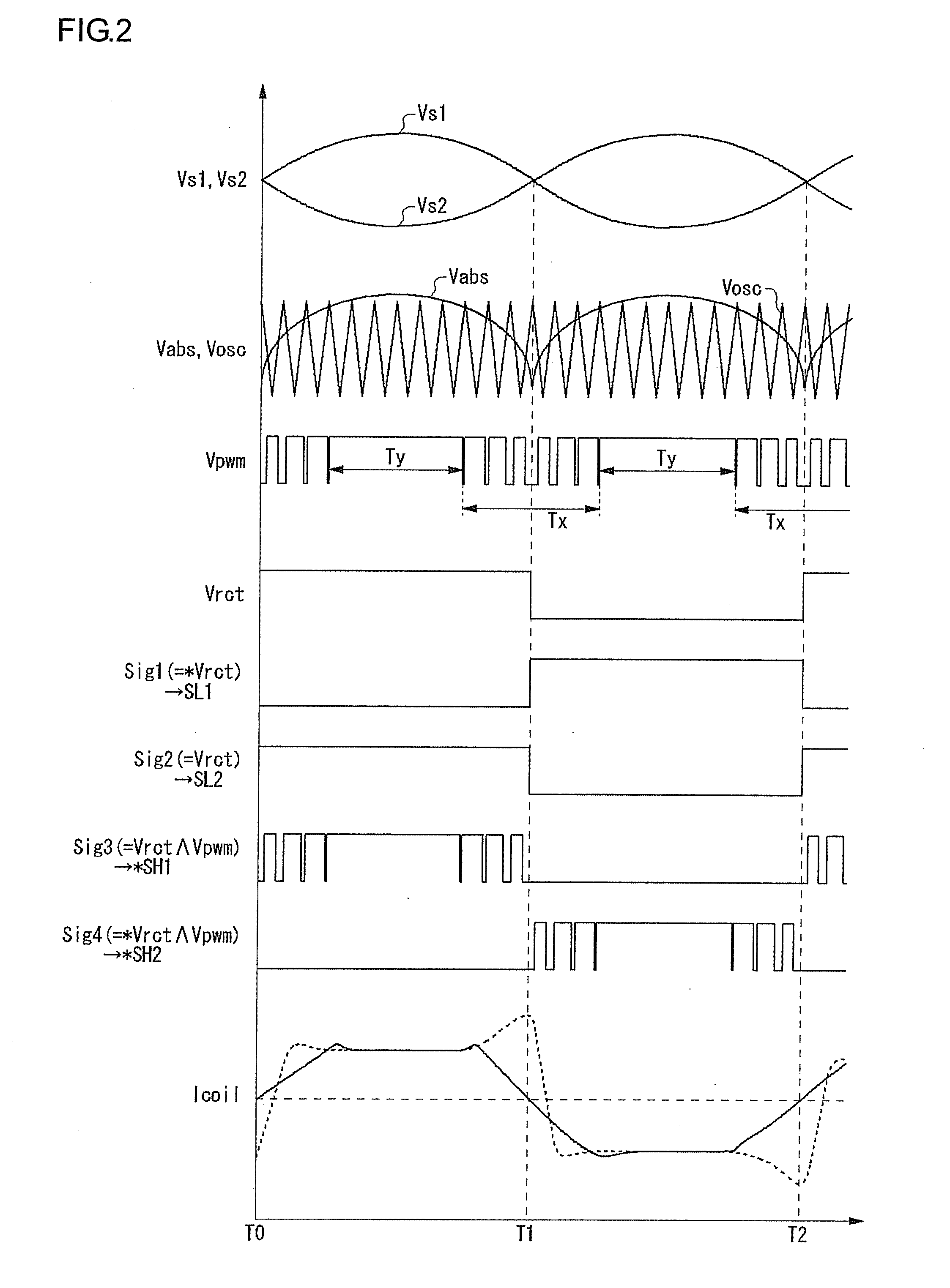
A motor drive unit (100) includes a pulse train generator 38, a clock signal generator (18), and an energization signal generator (20). The pulse train generator (38) creates a pulse each time an edge of a square wave signal (Vrct) is detected, and generates a pulse train (Vpls). The clock signal generator (18) generates a clock signal (Vclk) having a frequency N times a frequency of the pulse train (Vpls). The energization signal generator (20) generates an energization signal having a level that designates energization for a coil of a motor (102), for a time period in which the clock signal (Vclk) is counted M times, and, after that, having a level that indicates non-energization for the coil, for a time period in which the clock signal (Vclk) is counted (N−M) times.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Control of a brushless motor
ActiveUS20110254489A1Simplifies control of motorCheap and simpleMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersBrushless motorsMotor speed
A method of controlling a brushless motor that includes exciting a winding of the motor until current in the winding exceeds a threshold, and then continuing to excite the winding for an overrun period. The length of the overrun period is adjusted in response to a change in one of time, motor speed and excitation voltage. Additionally, a control system that implements the method, and a motor system that incorporates the control system.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Electric Motor and Motor Control
InactiveUS20120032629A1Less audible noiseIncrease costSingle-phase induction motor startersTorque ripple controlWave shapeMotor control
Various embodiments of an electric motor and electronic control for an electric motor are disclosed. An exemplary electric motor comprises a single-phase brushless permanent magnet electric motor. In exemplary embodiments, the electronic motor control is configured to commutate an electric motor at a frequency other than line frequency, perform pulse width modulation, and drive the electric motor with a drive waveform that approximates the counter-electromotive force of the motor.
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
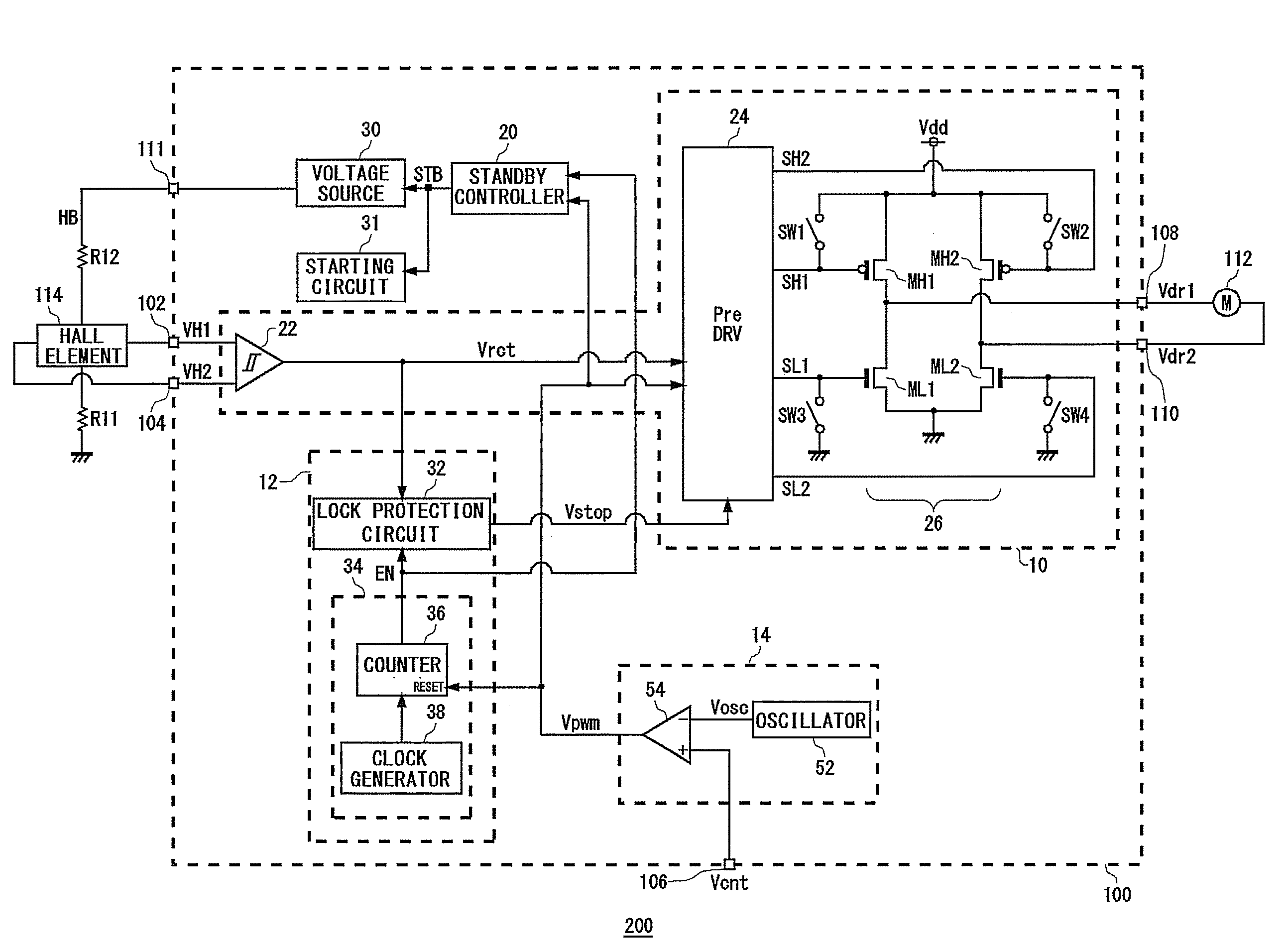
Motor drive device, method, and cooling device using the same
ActiveUS20090153084A1Reduce circuit areaReduce noiseSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlMotor driveHall element
In the motor drive apparatus, a Hall element outputs a first sinusoidal signal and a second sinusoidal signal, of mutually opposite phases, in accordance with rotor position. A hysteresis comparator compares the first sinusoidal signal and the second sinusoidal signal outputted from the Hall element, and outputs a rectangular wave signal. A pulse width modulation signal generation circuit detects timing at which phase switches, based on the first sinusoidal signal and the second sinusoidal signal outputted from the Hall element, and outputs a pulse width modulation signal in which duty ratio gradually changes, in a predetermined time-period in which the phase switches. A drive circuit combines the rectangular wave signal and the pulse width modulation signal by a logical operation, and drives the fan motor.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Motor drive device and cooling device using the same
InactiveUS20090096402A1Improve linearityReduce impactAC motor controlDigital data processing detailsMotor driveLogical operations
A drive circuit of a fan motor is provided. In an embodiment of the drive circuit, a first PWM comparator compares a temperature detection voltage with a cyclic voltage, and outputs a first PWM signal. A second PWM comparator compares a minimum frequency setting voltage indicating a minimum frequency of the fan motor, with the cyclic voltage, and outputs a second PWM signal. The drive circuit combines the first PWM signal and the second PWM signal by a logical operation, to drive the fan motor. The drive circuit includes a first logic gate which generates a logical sum of the first PWM signal and the second PWM signal, and a second logic gate which generates a logical product of the first PWM signal and an inverted signal of the second PWM signal. The drive circuit switches drive mode based on the first logic gate and the second logic gate.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Electronically commutated motor and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS7586276B2Reduce noiseTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectric machineControl theory
Owner:ELEKTROSIL SYST DER ELEKTRONIK
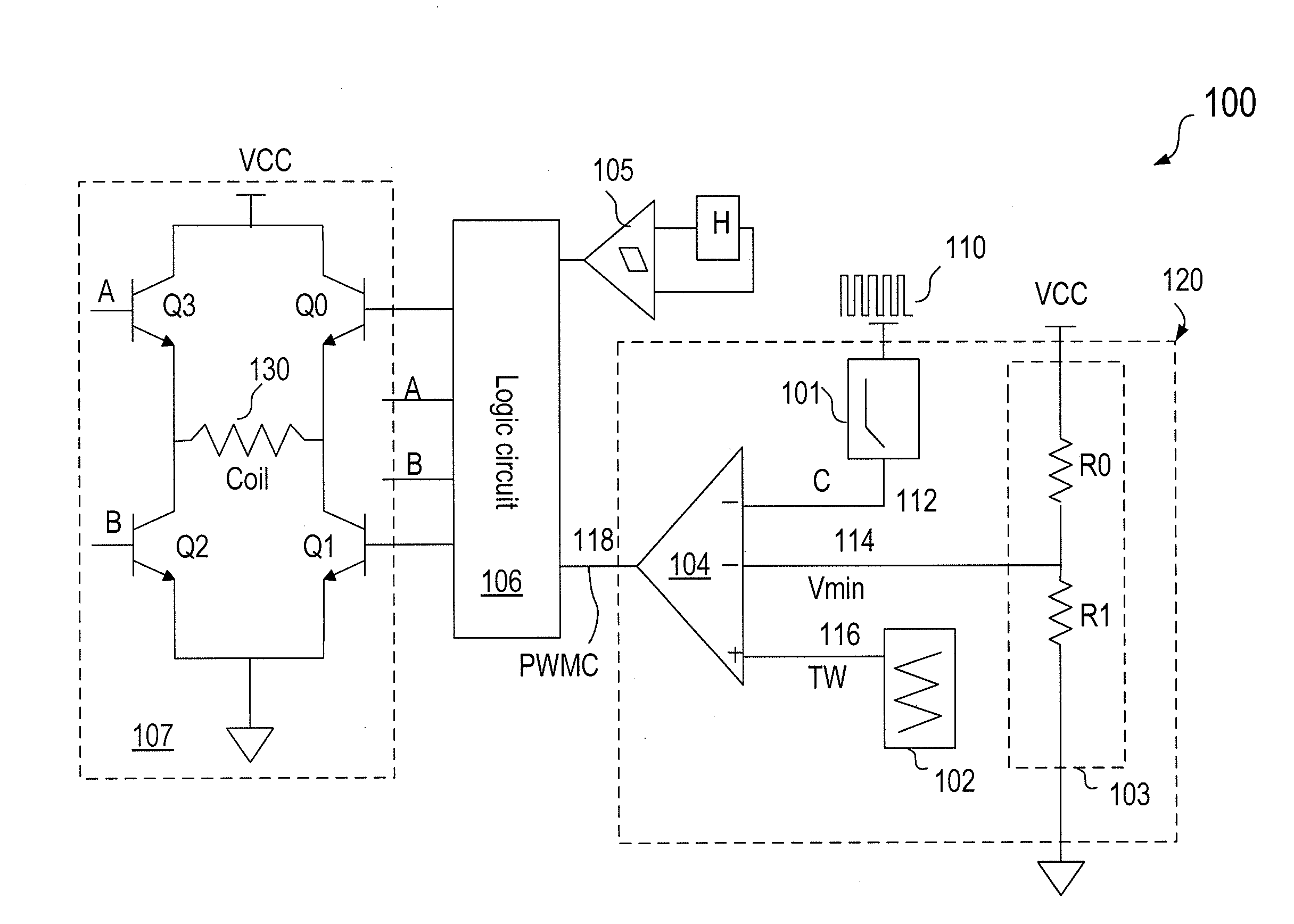
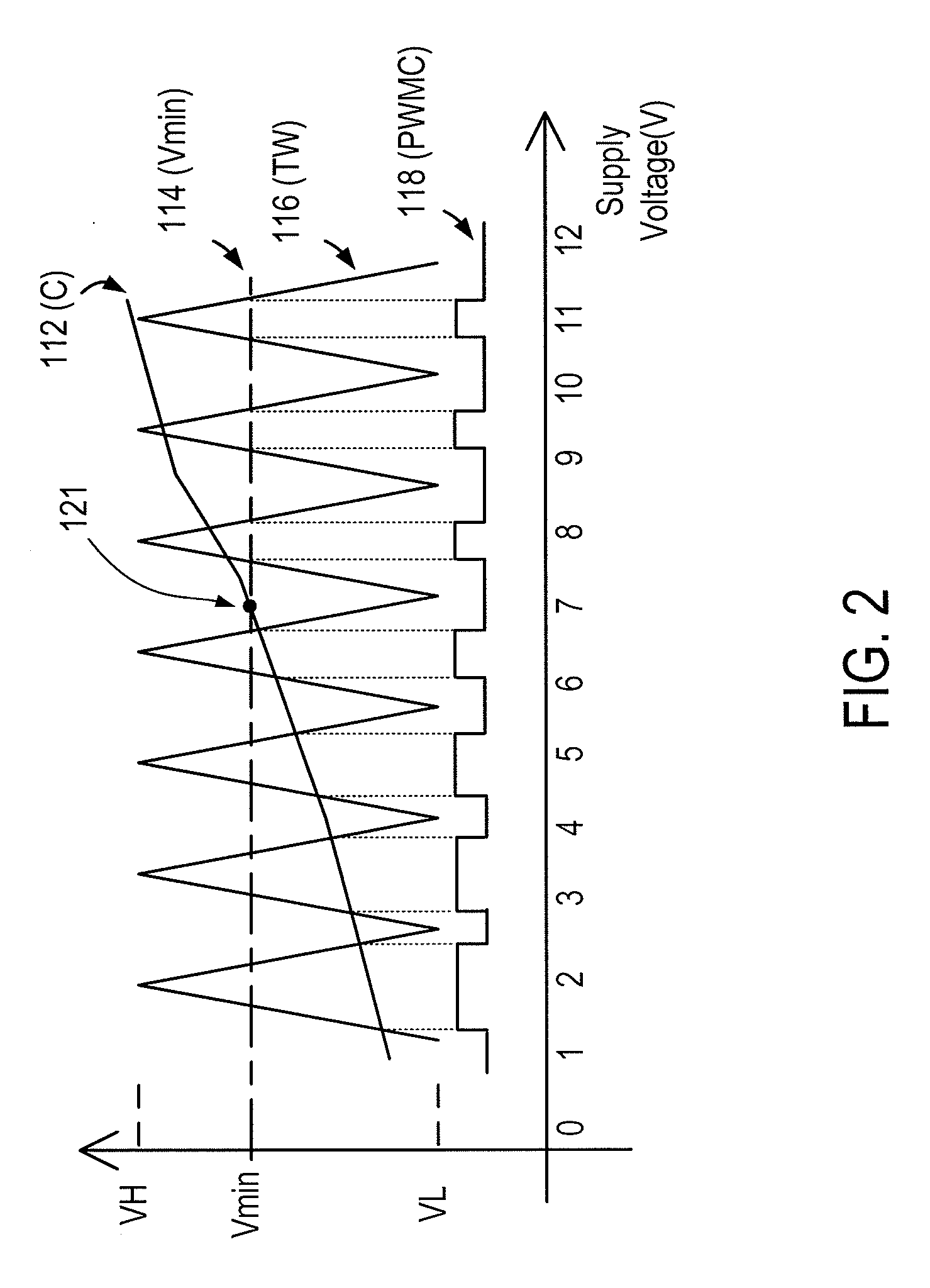
Pulsed width modulated control method and apparatus
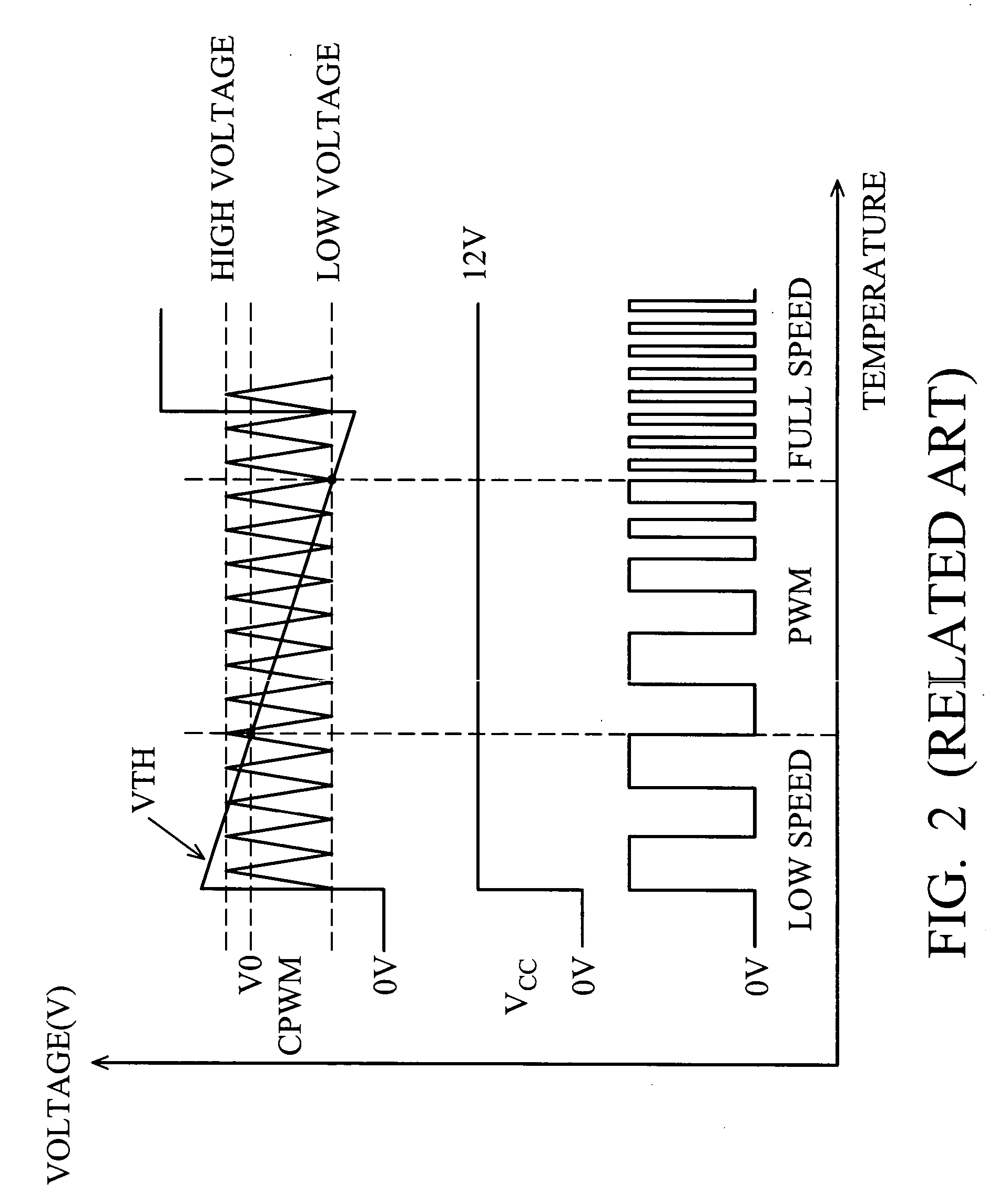
A pulse width modulated (PWM) controller has an input terminal for receiving a pulsed input signal having a first duty cycle, a power supply terminal for receiving a power supply voltage. a minimum duty cycle reference voltage signal, and a control circuit for providing a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) output signal having a second duty cycle related to the first duty cycle of the pulsed input signal. The PWM output control signal having a minimum duty cycle that is adjustable in response to a change in the power supply voltage. In an embodiment, the second duty cycle and the first duty cycle are correlated in a substantially linear relationship. In an embodiment, the PWM control circuit also has a triangle wave generation circuit for generating a triangle wave signal configured to oscillate between an upper limit voltage and a lower limit voltage, which are adjustable in response to a change in the power supply voltage.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
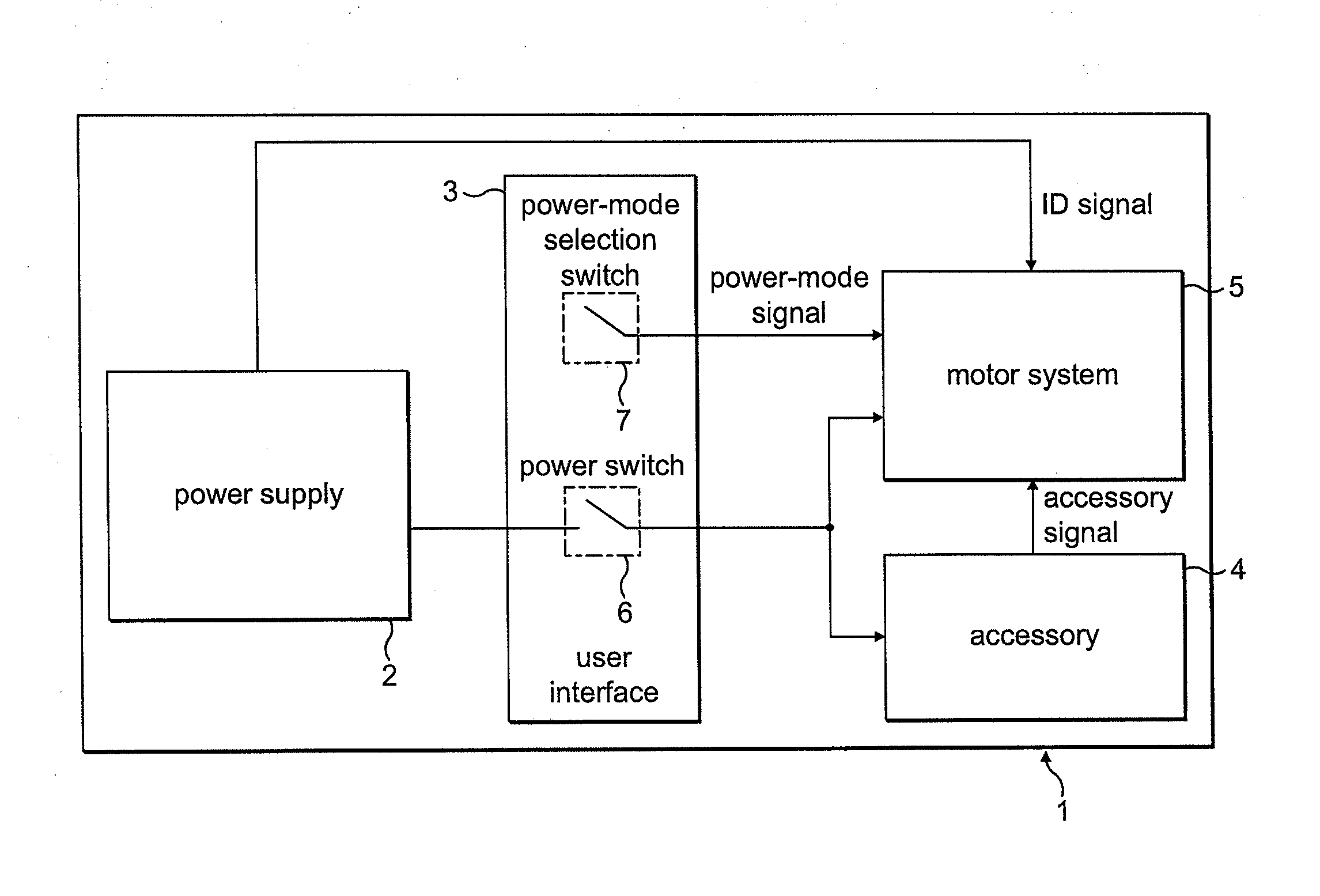
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com