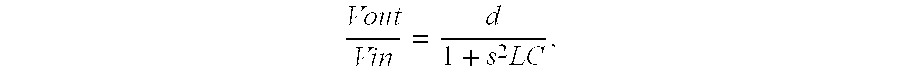Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1064 results about "Amplitude control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
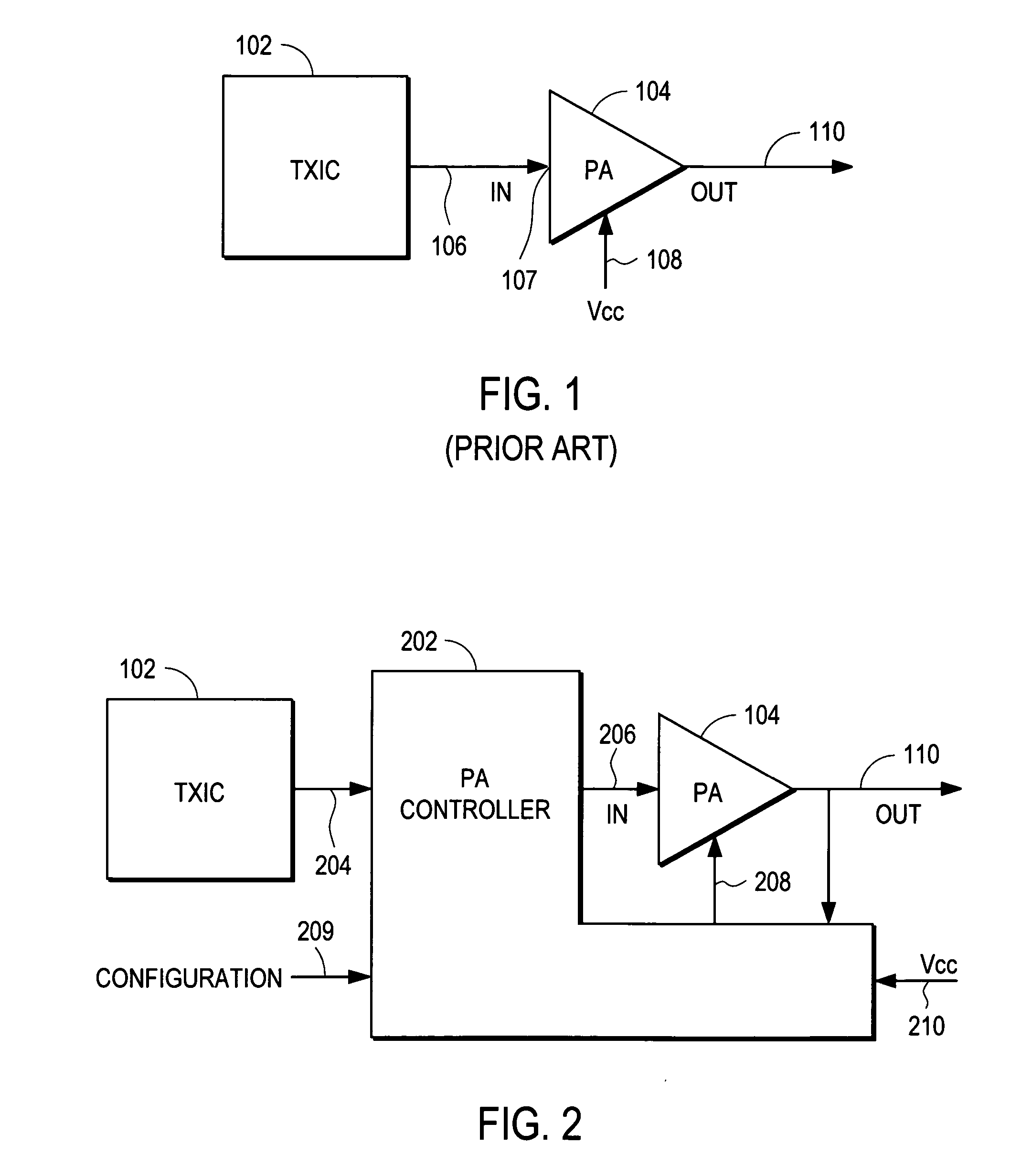
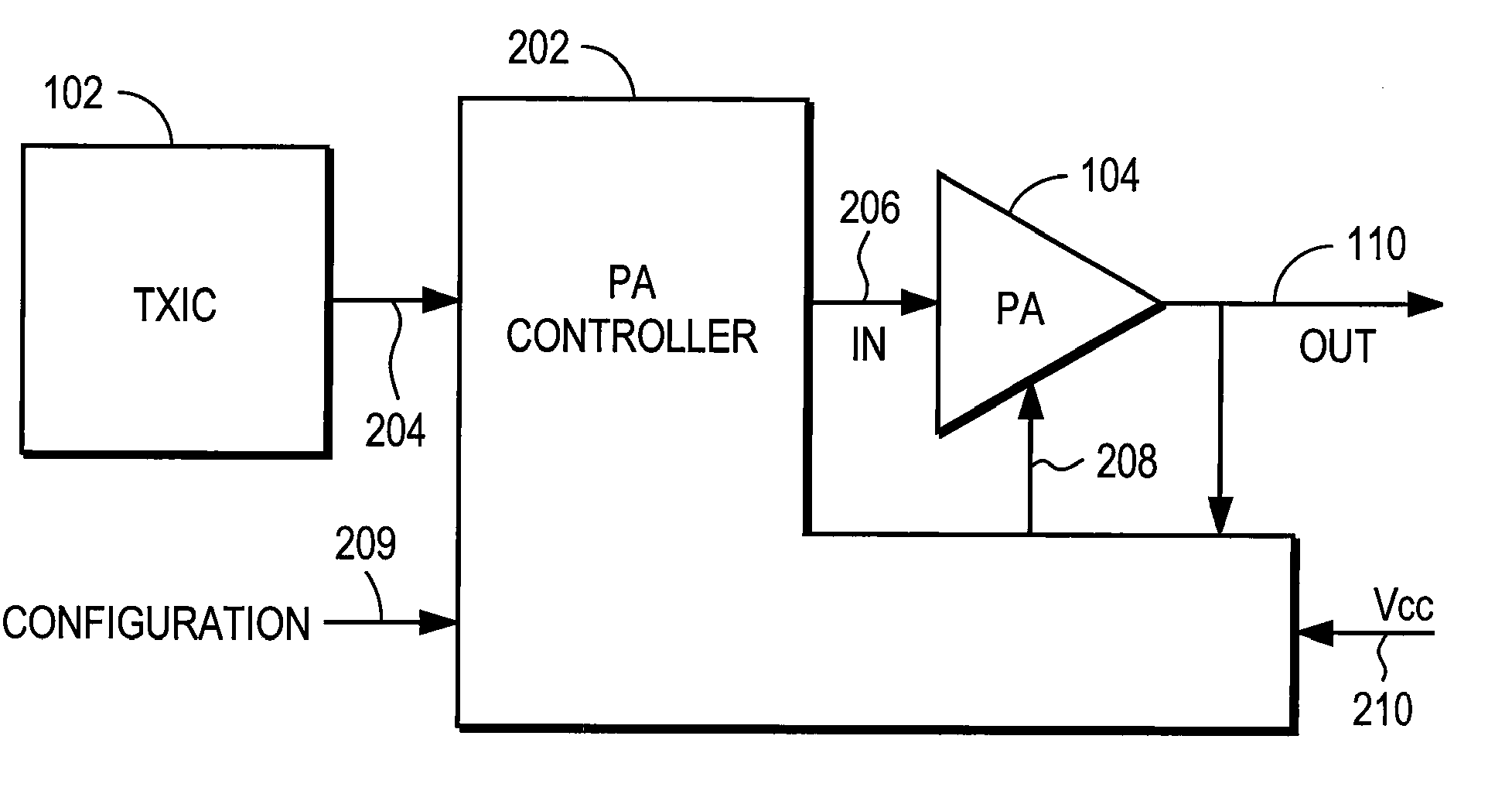
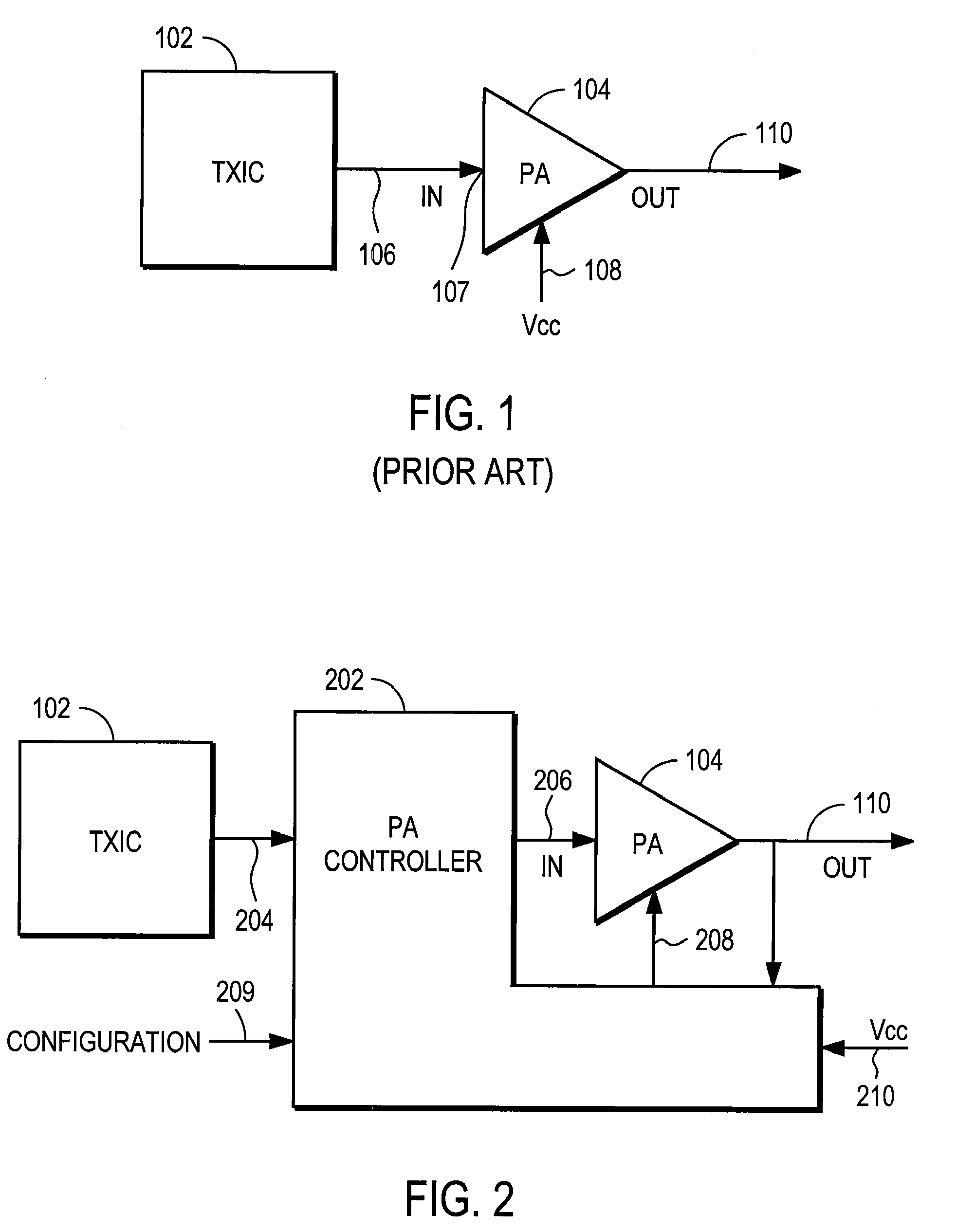
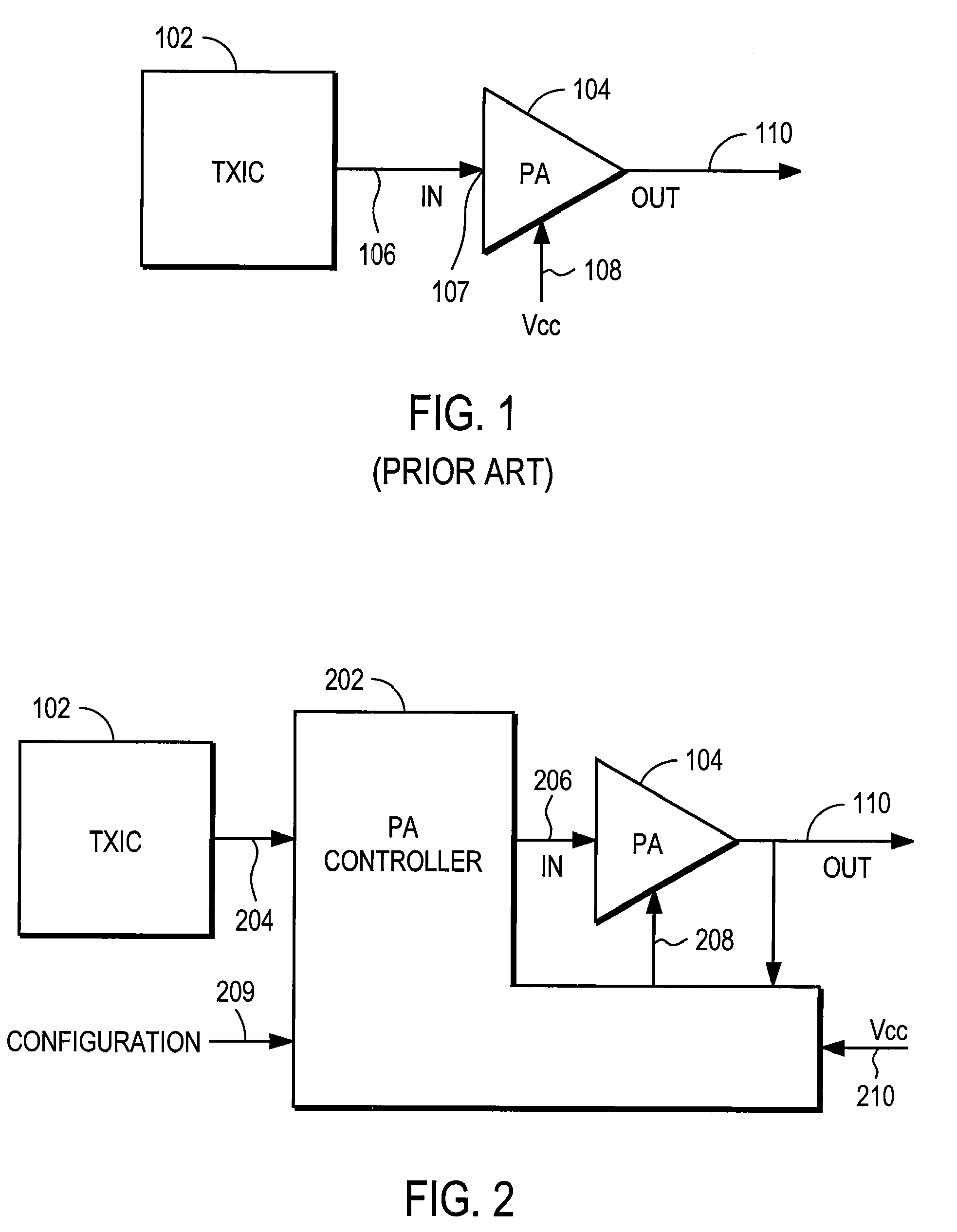
The Amplitude adjusting (also referred to as Amplitude control) enables the power control of electric loads, which are operated with AC voltage.
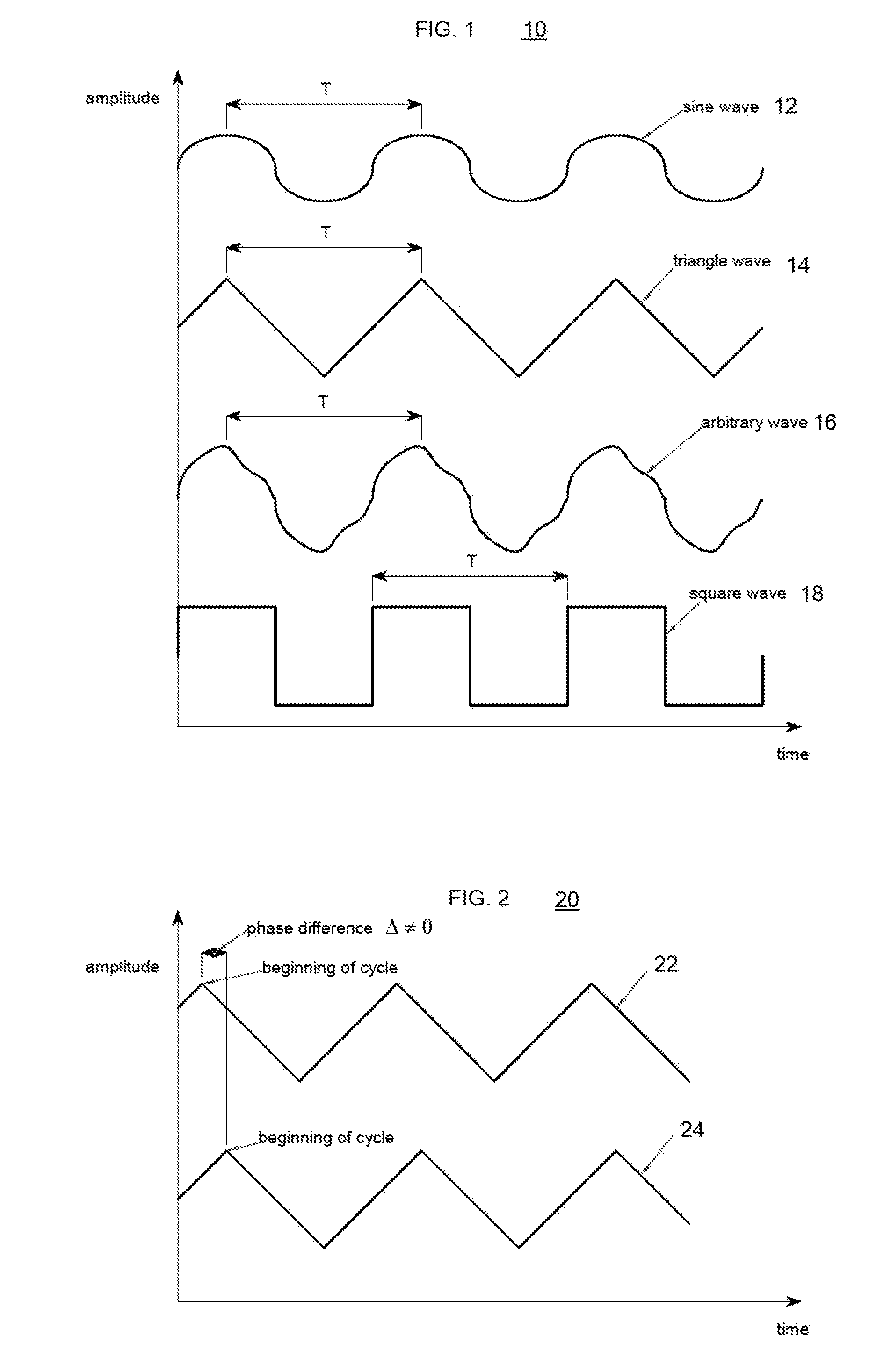
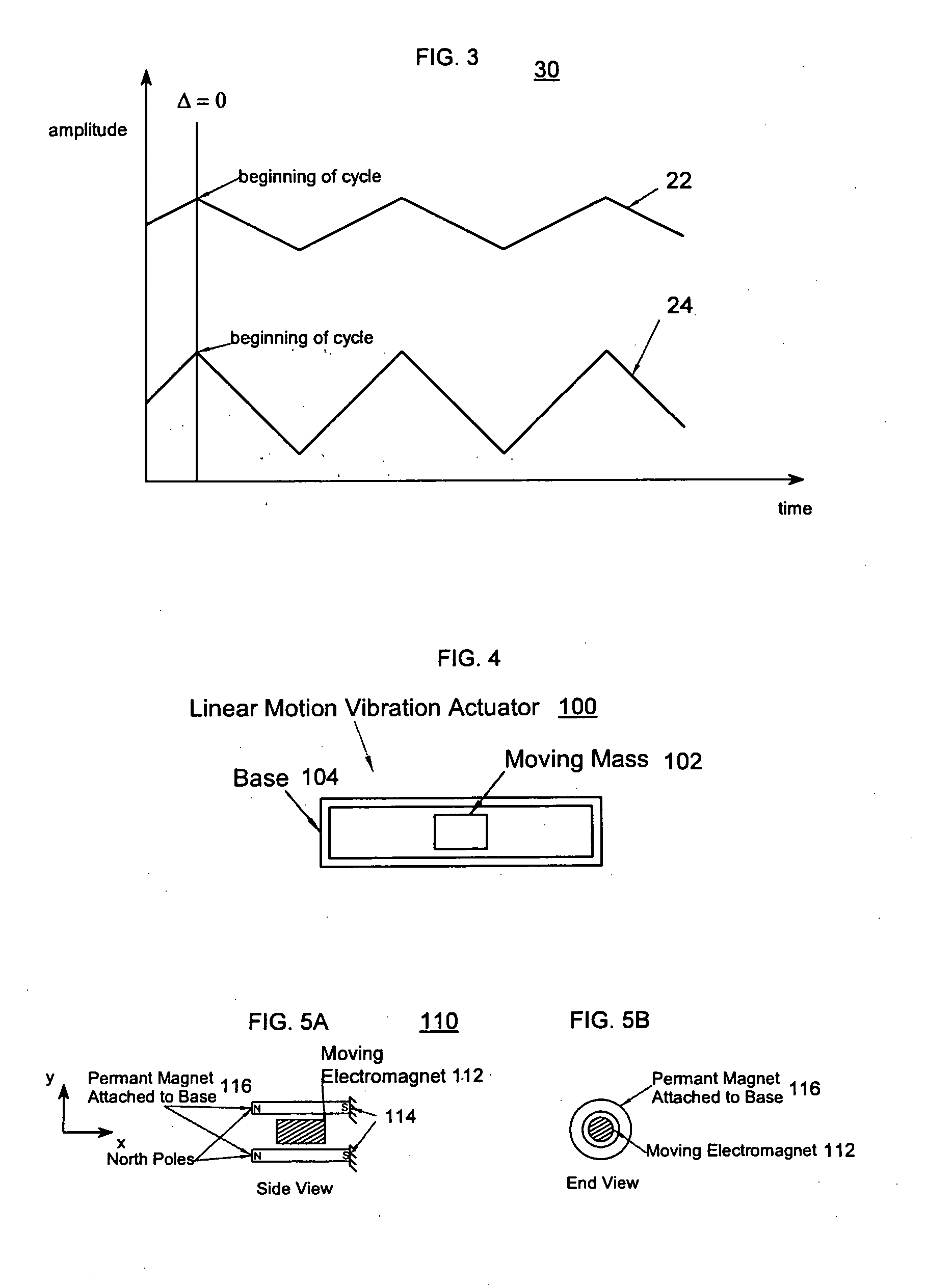
Synchronized vibration device for haptic feedback
ActiveUS20060290662A1DC motor speed/torque controlAc-dc conversion without reversalDriver circuitVibration control
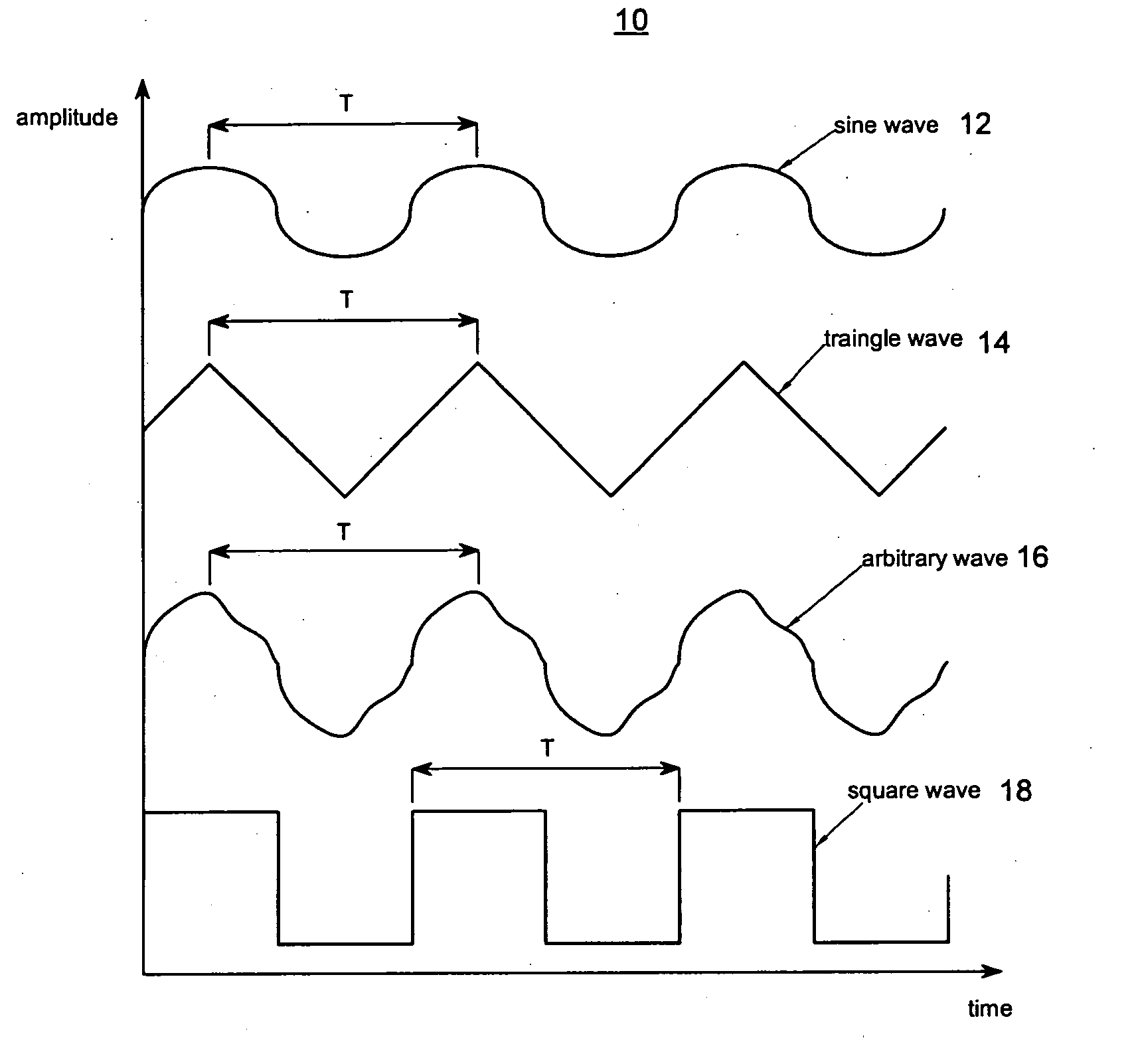
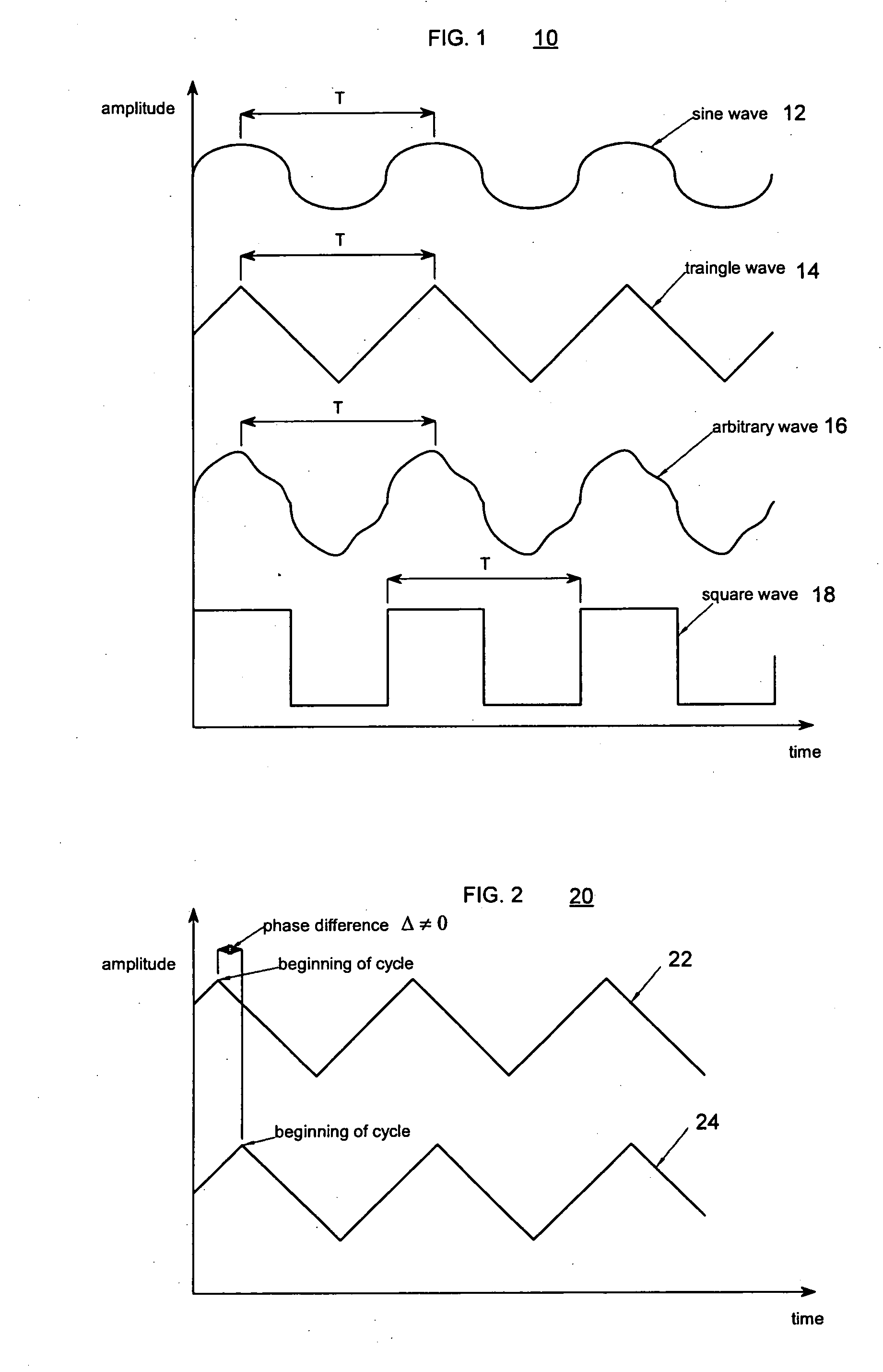
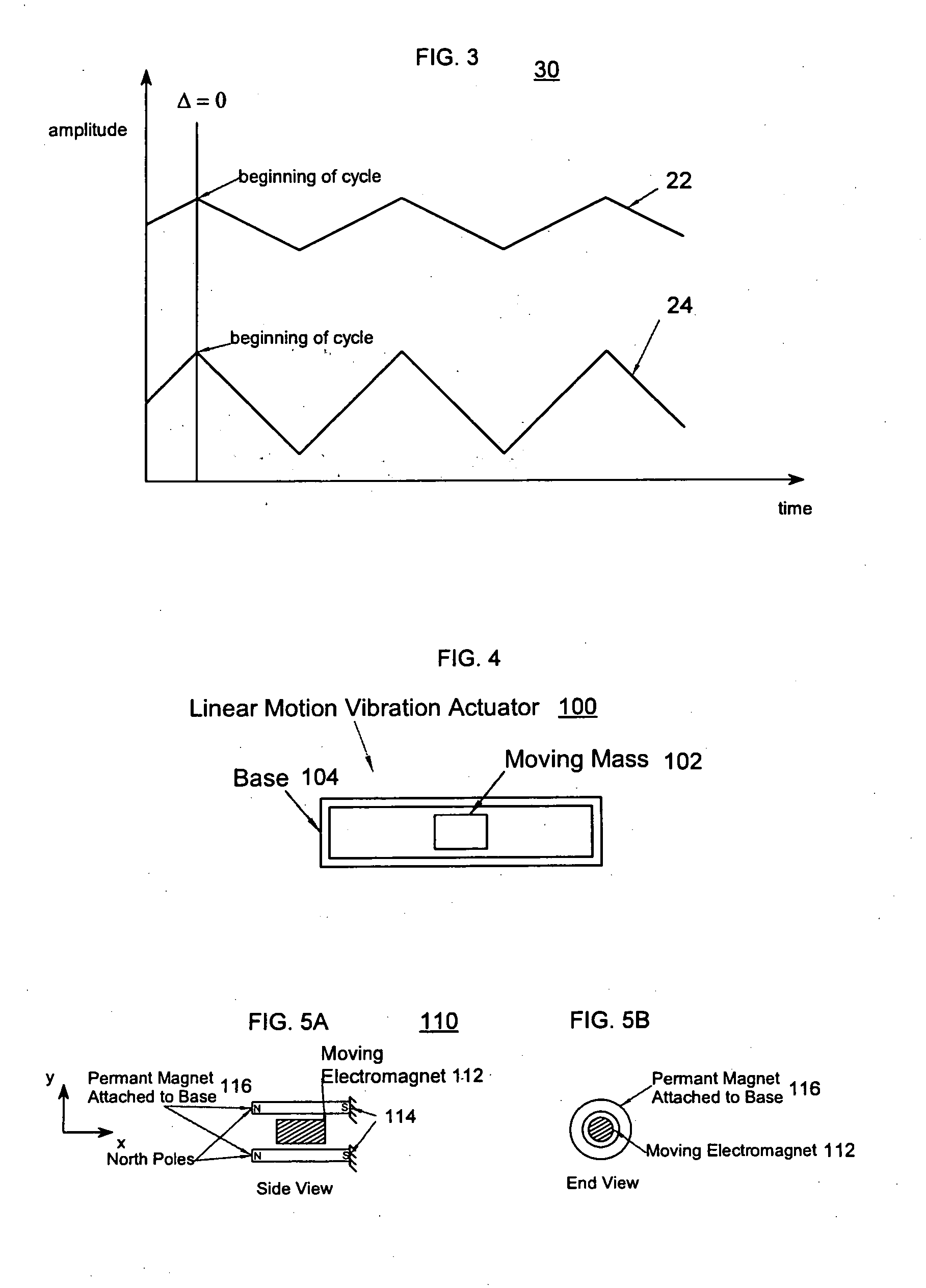
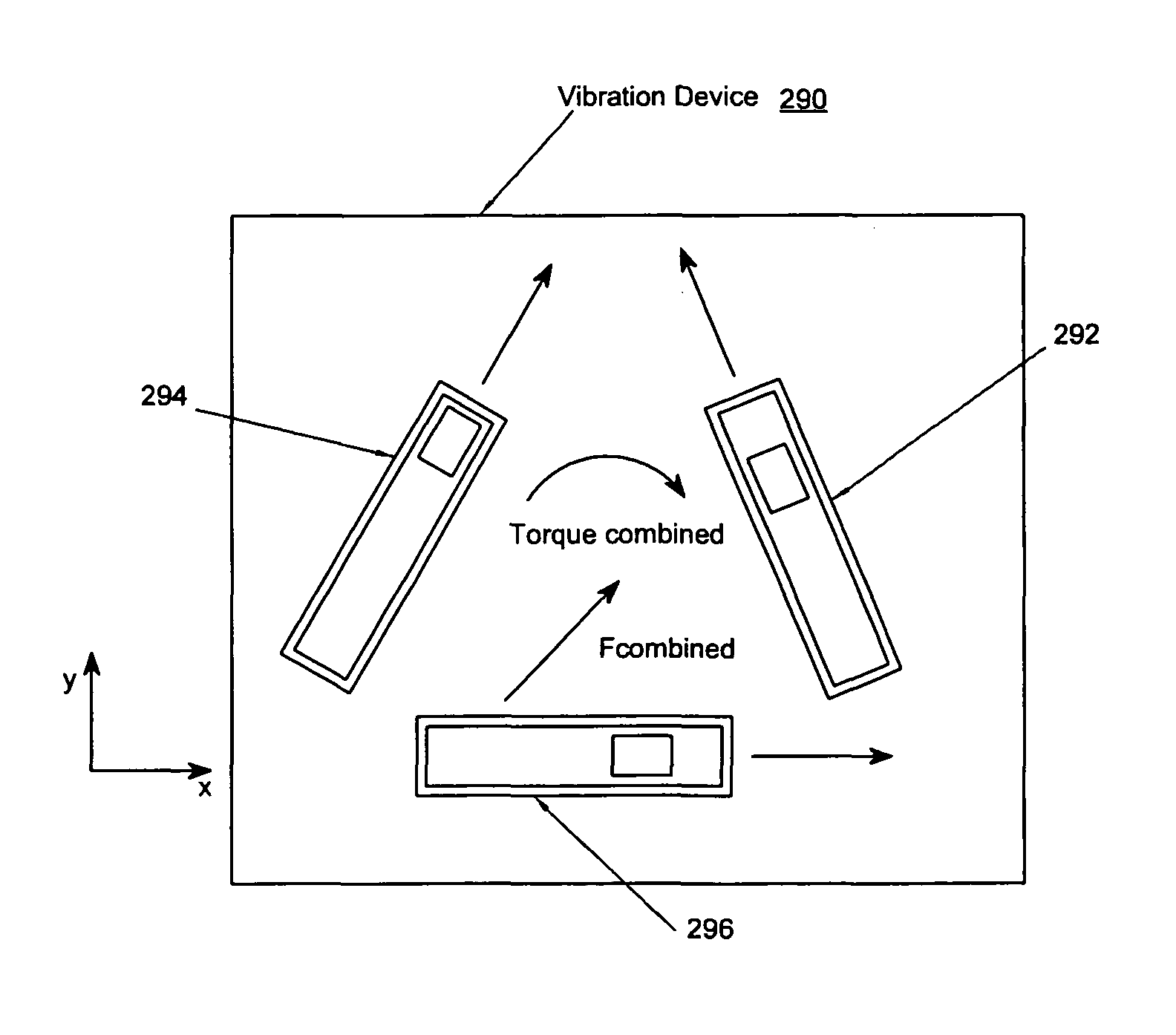
The present invention relates to synchronized vibration devices that can provide haptic feedback to a user. A wide variety of actuator types may be employed to provide synchronized vibration, including linear actuators, rotary actuators, rotating eccentric mass actuators, and rocking mass actuators. A controller may send signals to one or more driver circuits for directing operation of the actuators. The controller may provide direction and amplitude control, vibration control, and frequency control to direct the haptic experience. Parameters such as frequency, phase, amplitude, duration, and direction can be programmed or input as different patterns suitable for use in gaming, virtual reality and real-world situations.
Owner:COACTIVE DRIVE CORP
Synchronized vibration device for haptic feedback
ActiveUS7919945B2DC motor speed/torque controlAc-dc conversion without reversalDriver circuitVibration control
The present invention relates to synchronized vibration devices that can provide haptic feedback to a user. A wide variety of actuator types may be employed to provide synchronized vibration, including linear actuators, rotary actuators, rotating eccentric mass actuators, and rocking mass actuators. A controller may send signals to one or more driver circuits for directing operation of the actuators. The controller may provide direction and amplitude control, vibration control, and frequency control to direct the haptic experience. Parameters such as frequency, phase, amplitude, duration, and direction can be programmed or input as different patterns suitable for use in gaming, virtual reality and real-world situations.
Owner:COACTIVE DRIVE CORP
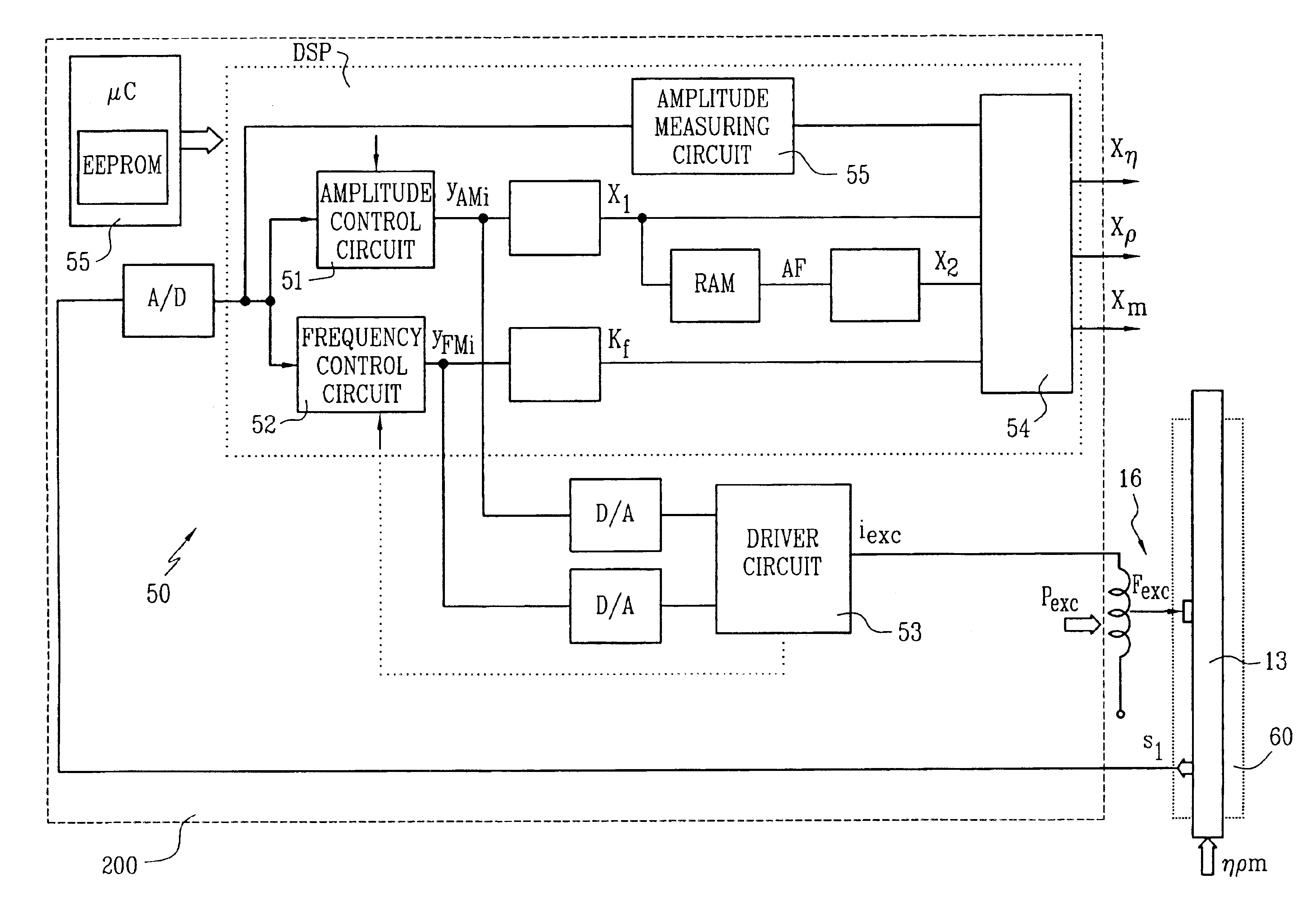
Viscometer
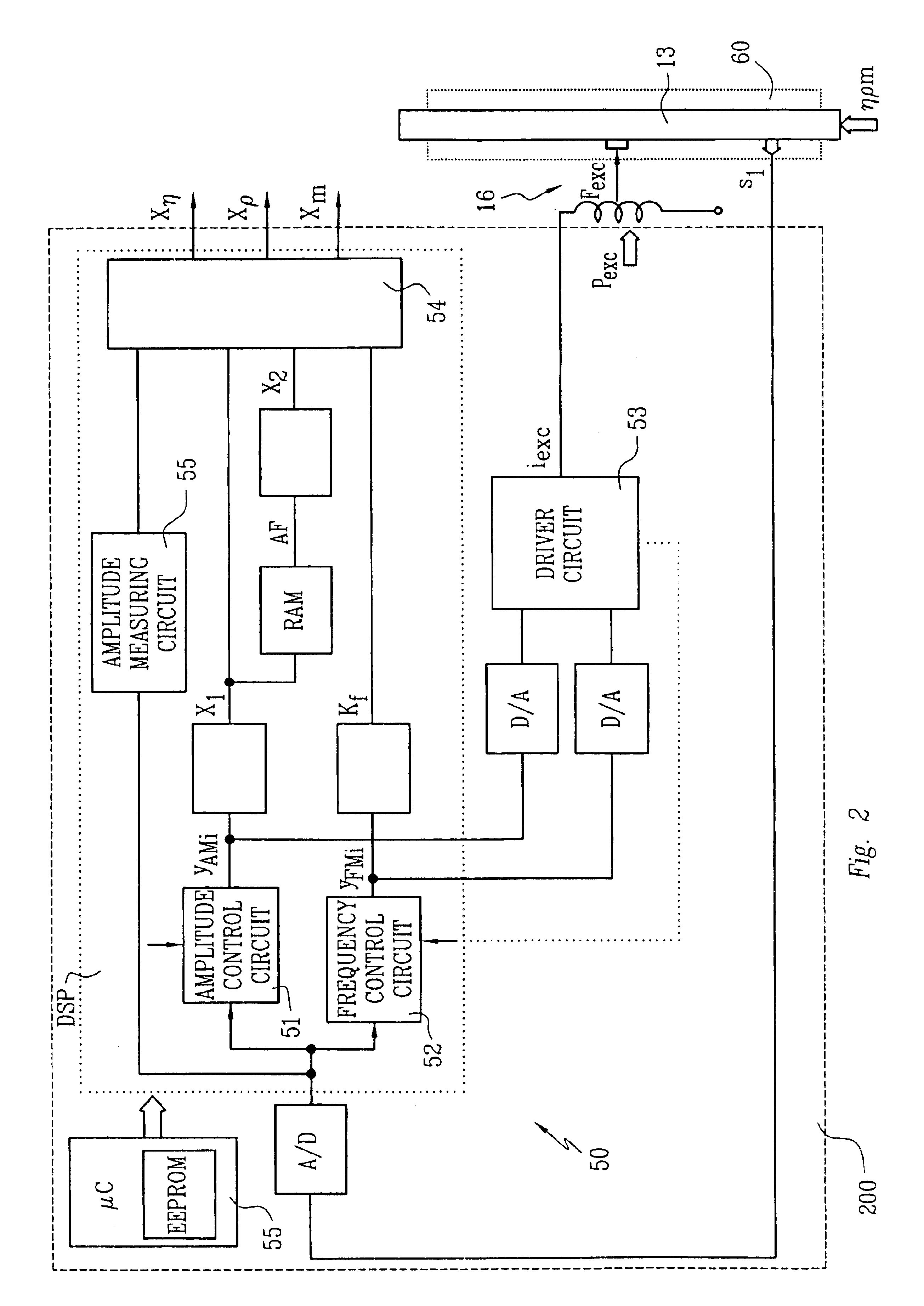
The viscometer provides a viscosity value (Xη) which represents the viscosity of a fluid flowing in a pipe connected thereto. It comprises a vibratory transducer with at least one flow tube for conducting the fluid, which communicates with the pipe. Driven by an excitation assembly, the flow tube is vibrated so that friction forces are produced in the fluid. The viscometer further includes meter electronics which feed an excitation current (iexc) into the excitation assembly. By means of the meter electronics, a first internal intermediate value (X1) is formed, which corresponds with the excitation current (iexc) and thus represents the friction forces acting in the fluid. According to the invention, a second internal intermediate value (X2), representing inhomogeneities in the fluid, is generated in the meter electronics, which then determine the viscosity value (Xη) using the two intermediate values (X1, X2). The first internal intermediate value (X1) is preferably normalized by means of an amplitude control signal (yAM) for the excitation current (iexc), the amplitude control signal corresponding with the vibrations of the flow tube. As a result, the viscosity value (Xη) provided by the viscometer is highly accurate and robust, particularly independently of the position of installation of the flow tube.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
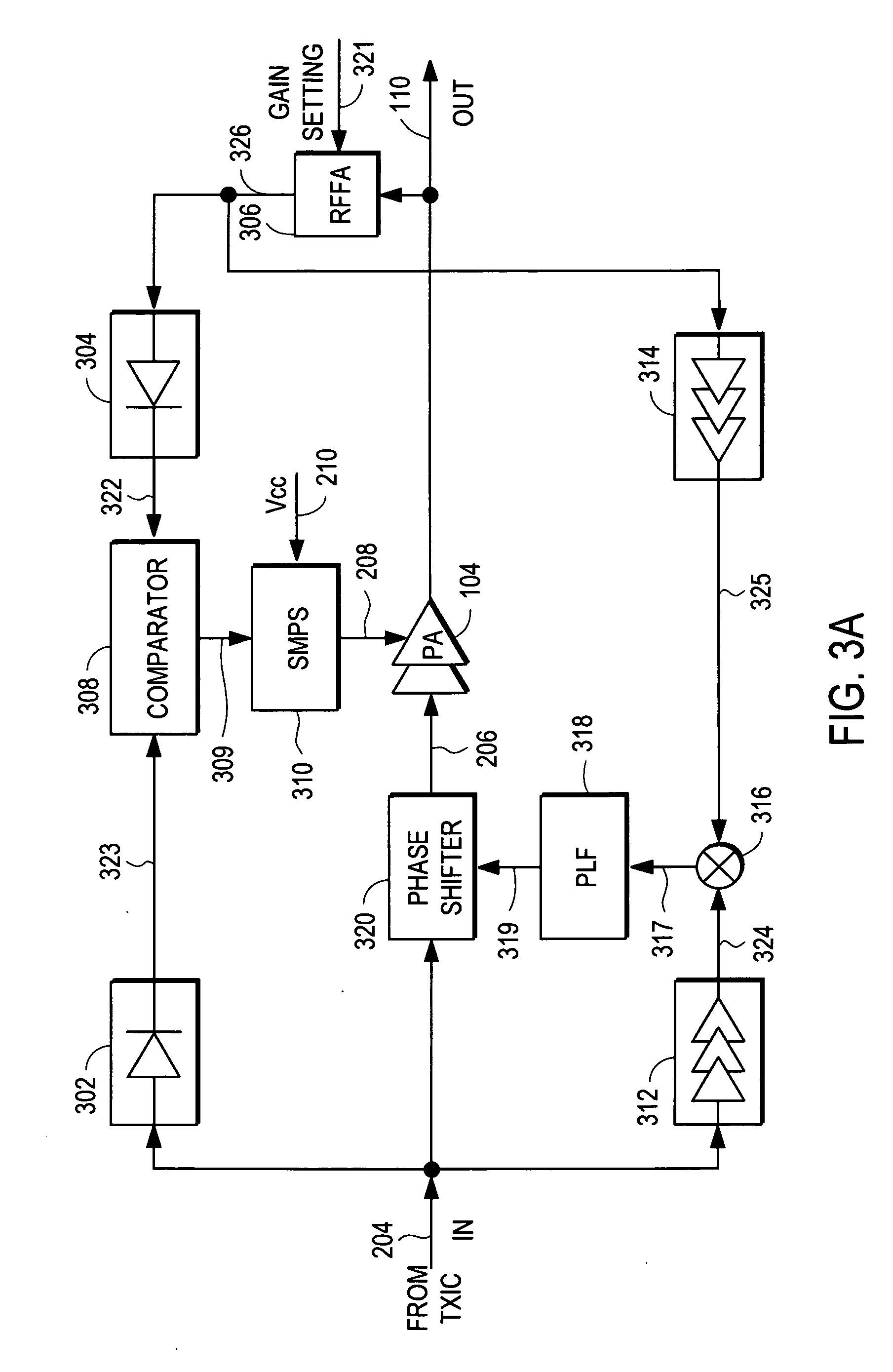
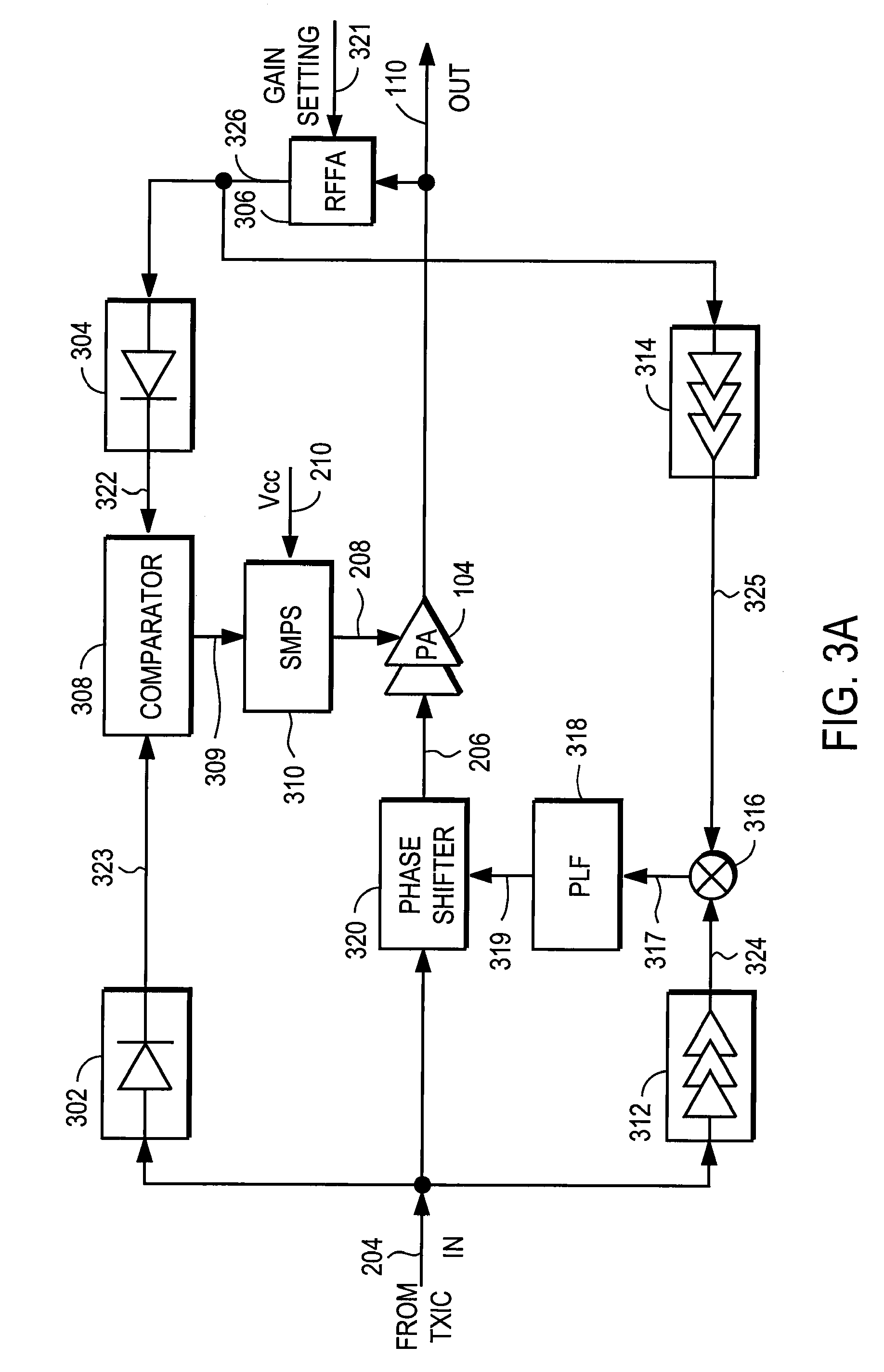
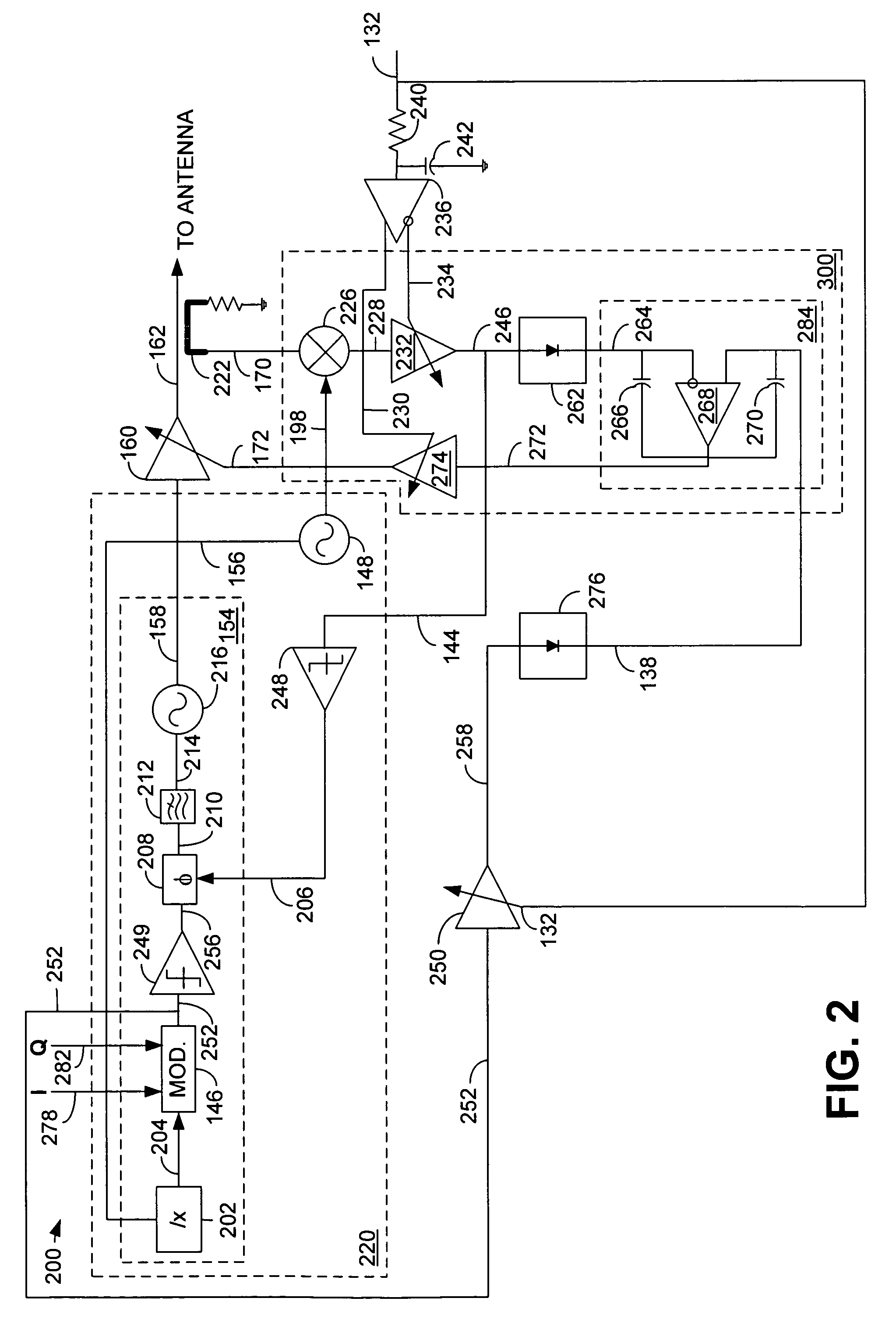
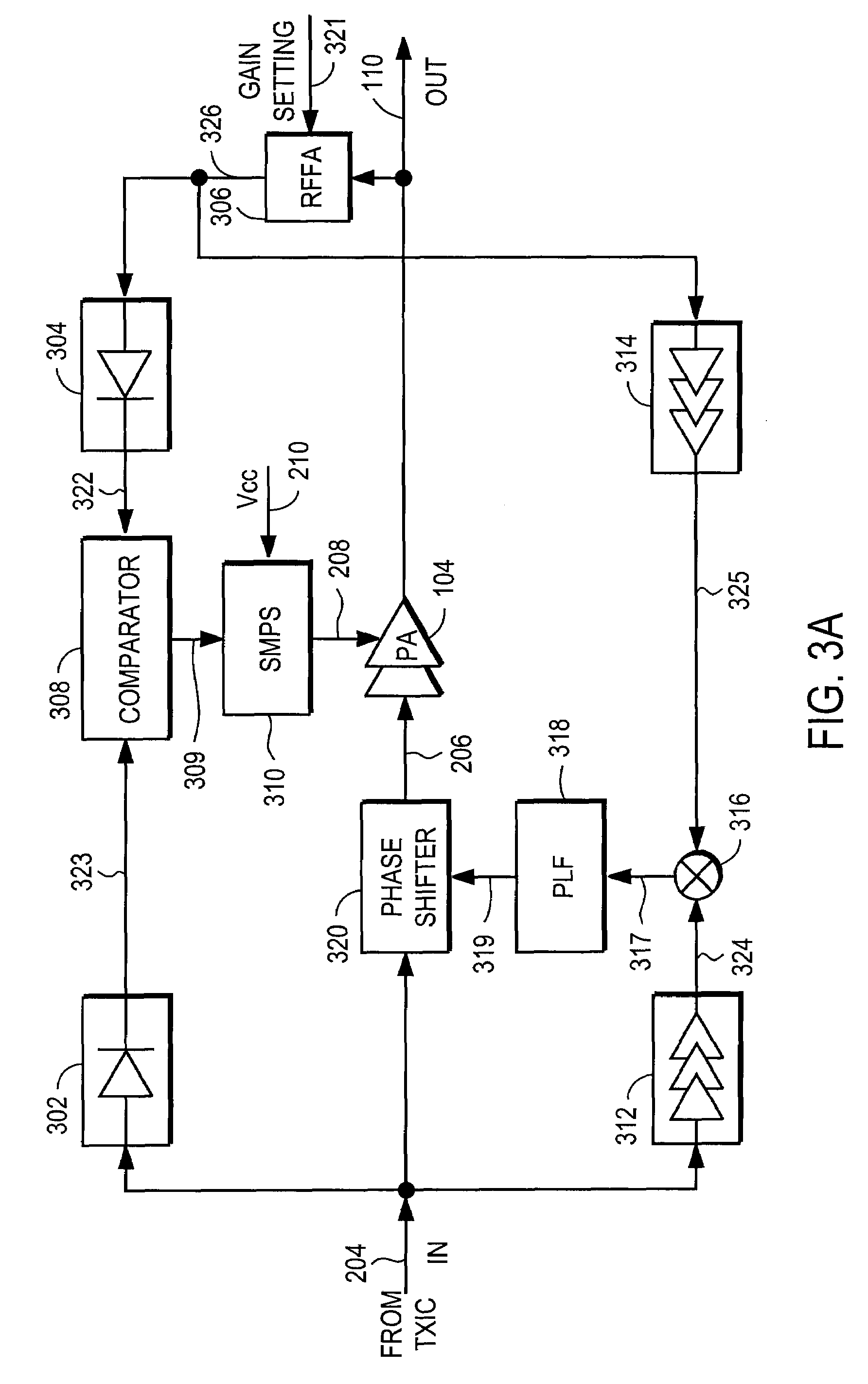
RF Power Amplifier Controller Circuit Including Calibrated Phase Control Loop
ActiveUS20070184794A1Reduce phase distortionNarrow bandwidthResonant long antennasPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierPhase difference
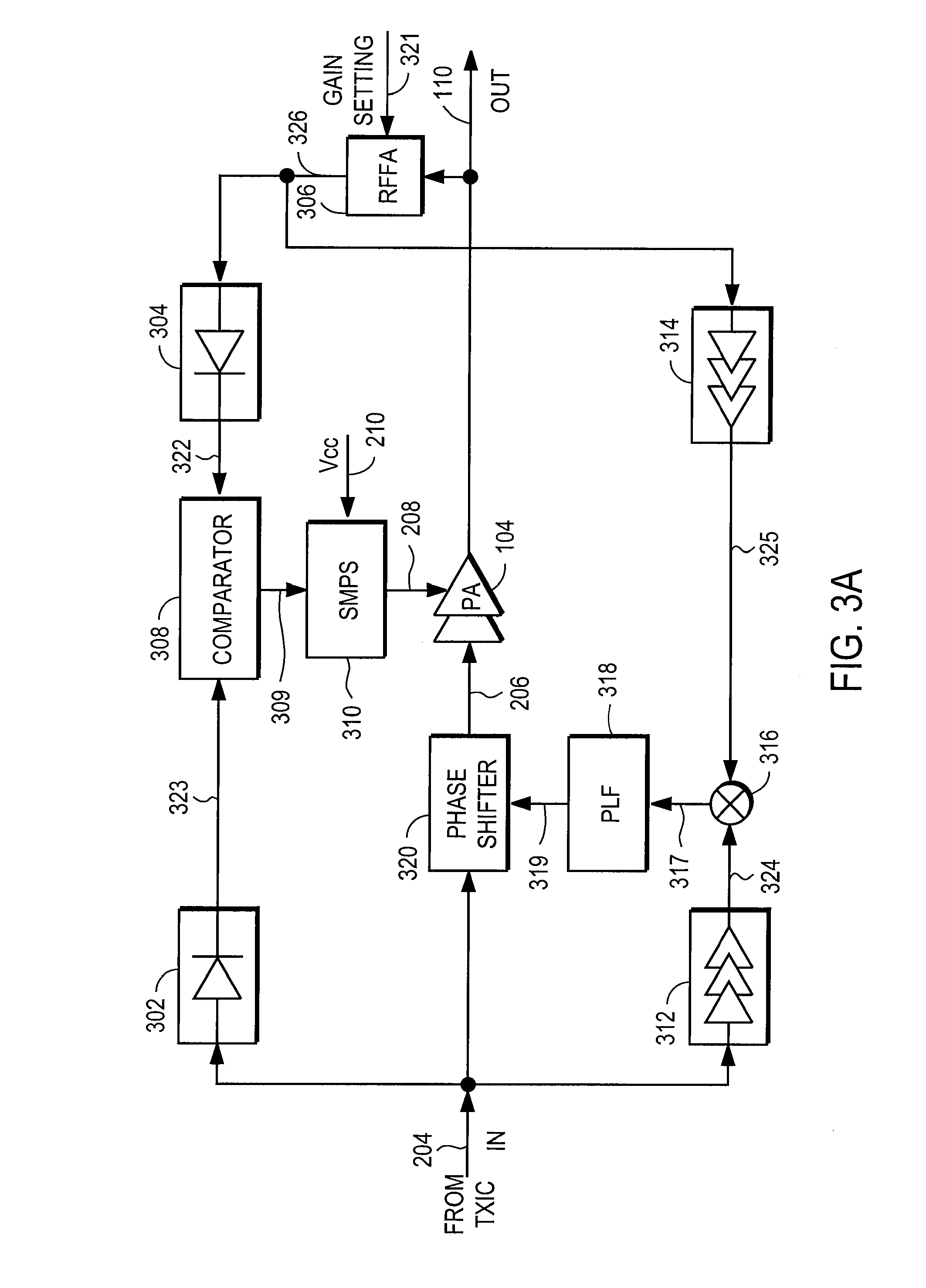
An RF power amplifier system comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal. The phase control loop may comprise one or more variable phase delays introducing a relative phase delay to allow the phase differences between the input and output signals of the PA circuit to be within a range compatible with a phase comparator generating the phase error signal, and a low frequency blocking module that removes the larger extent, lower frequency components of the phase error signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Method and system of controlling automotive equipment remotely
A apparatus and method for providing enhanced utilization of transponder devices and for creating control embodiments that are particularly suited for use dynamically generating or controlling audio from a remote location. Transponders units are configured with trace buffers, external dynamic inputs, response delays, and other mechanisms to enhance utility. By way of example, the transponders are incorporated within embodiments such as a steering wheel, skateboard, or sensor glove controlled musical instrument, or control system. Other embodiments include a mix-memory audio system and an audio amplitude control solution for automobiles.
Owner:RAST RODGER H
Microwave applicator with margin temperature sensing element
InactiveUS20080033422A1ElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingTissue heatingAmplitude control
A microwave applicator for applying microwave radiation to body tissue includes a temperature sensor positioned along the applicator to measure the temperature of body tissue at a margin of the tissue to be treated. By monitoring the temperature of the tissue at the margin of the tissue to be treated, the heating of the tissue can be better controlled to ensure that the tissue to be treated is heated to the required temperature while damage to surrounding normal tissue is minimized. Treatment can include positioning one or more applicators into body tissue and applying microwave radiation to the applicators. Phase and amplitude control of the microwave radiation can be used to produce a desired heating pattern. Optimization of the number and location of microwave applicators and the phase and amplitude of microwave energy applied thereto can be determined through pretreatment simulation.
Owner:BSD MEDICAL
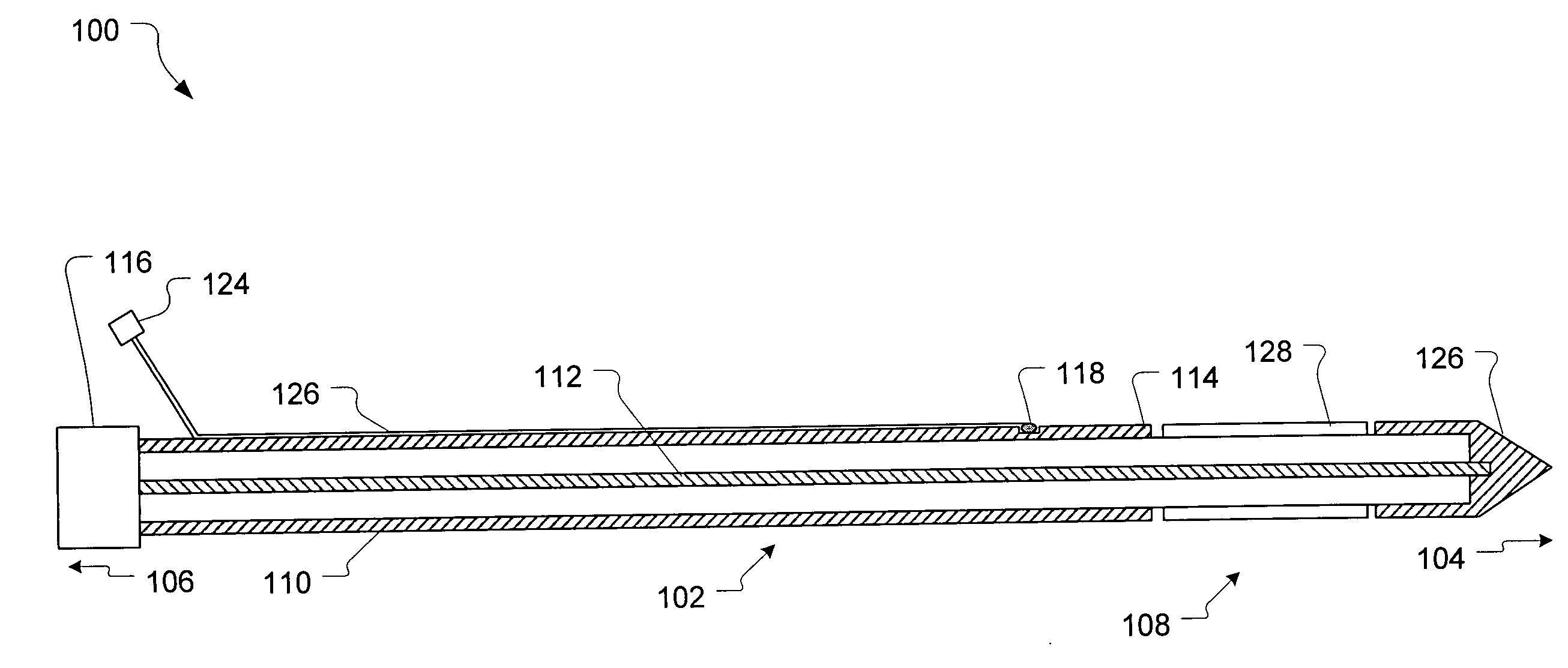
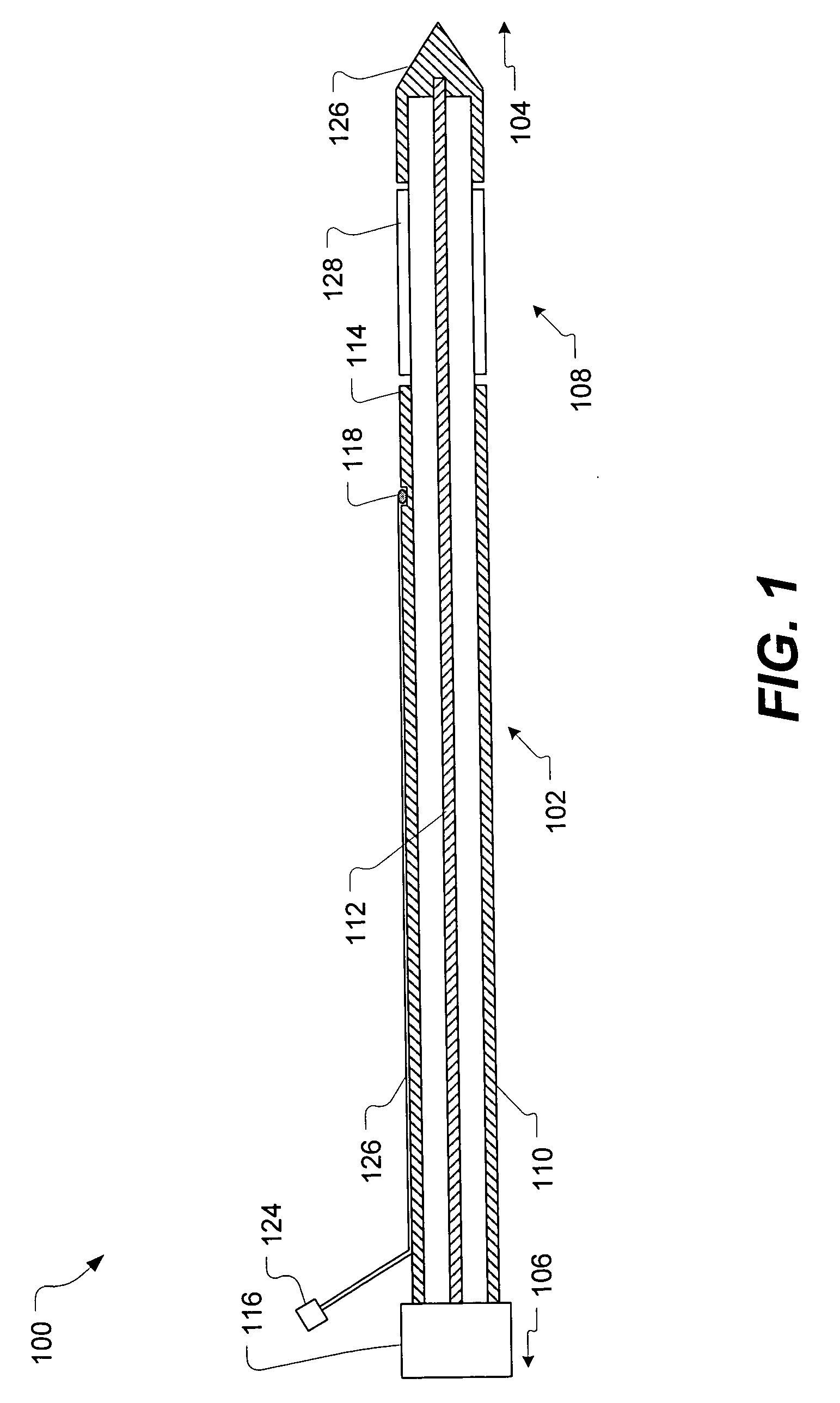
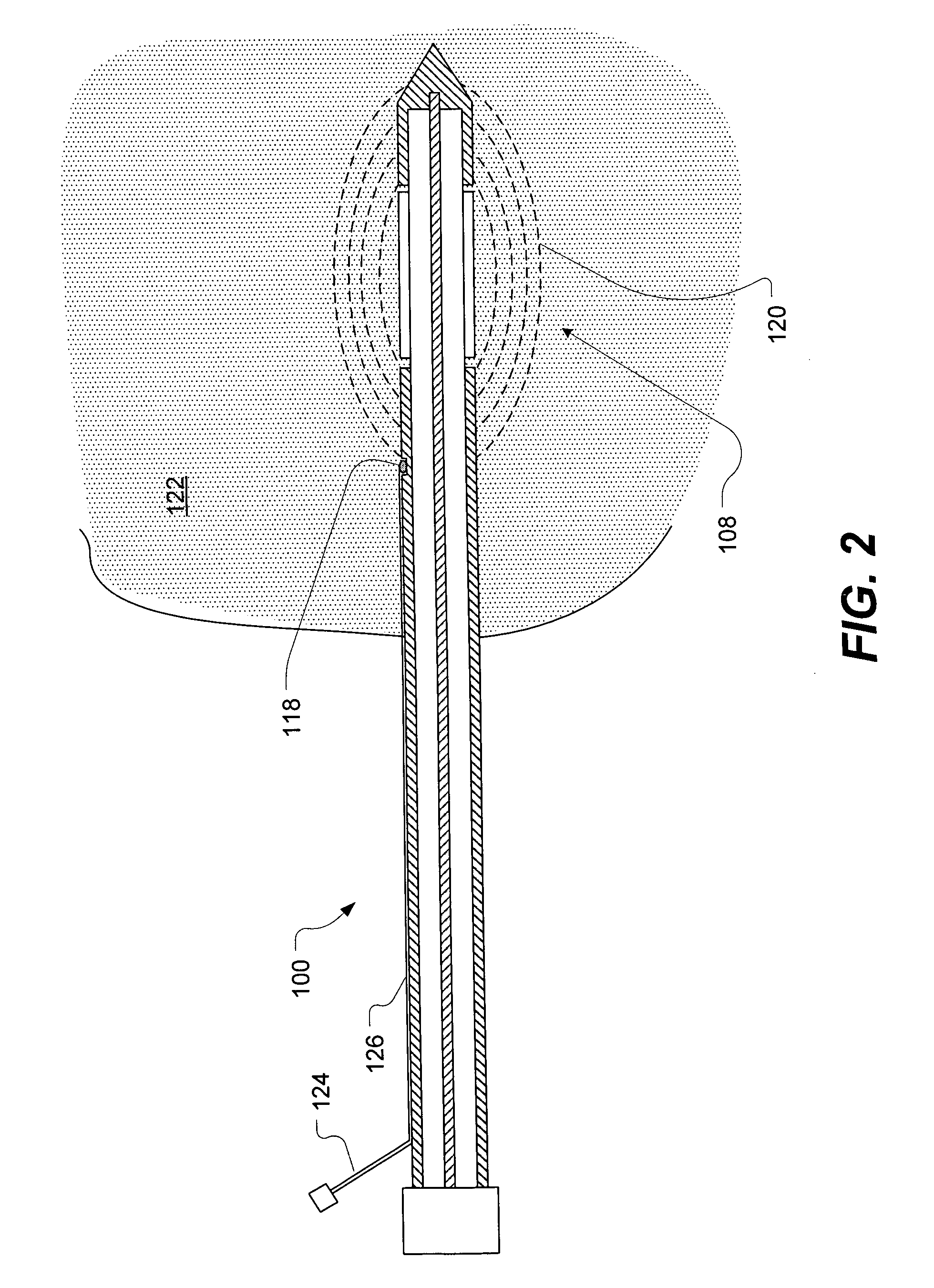
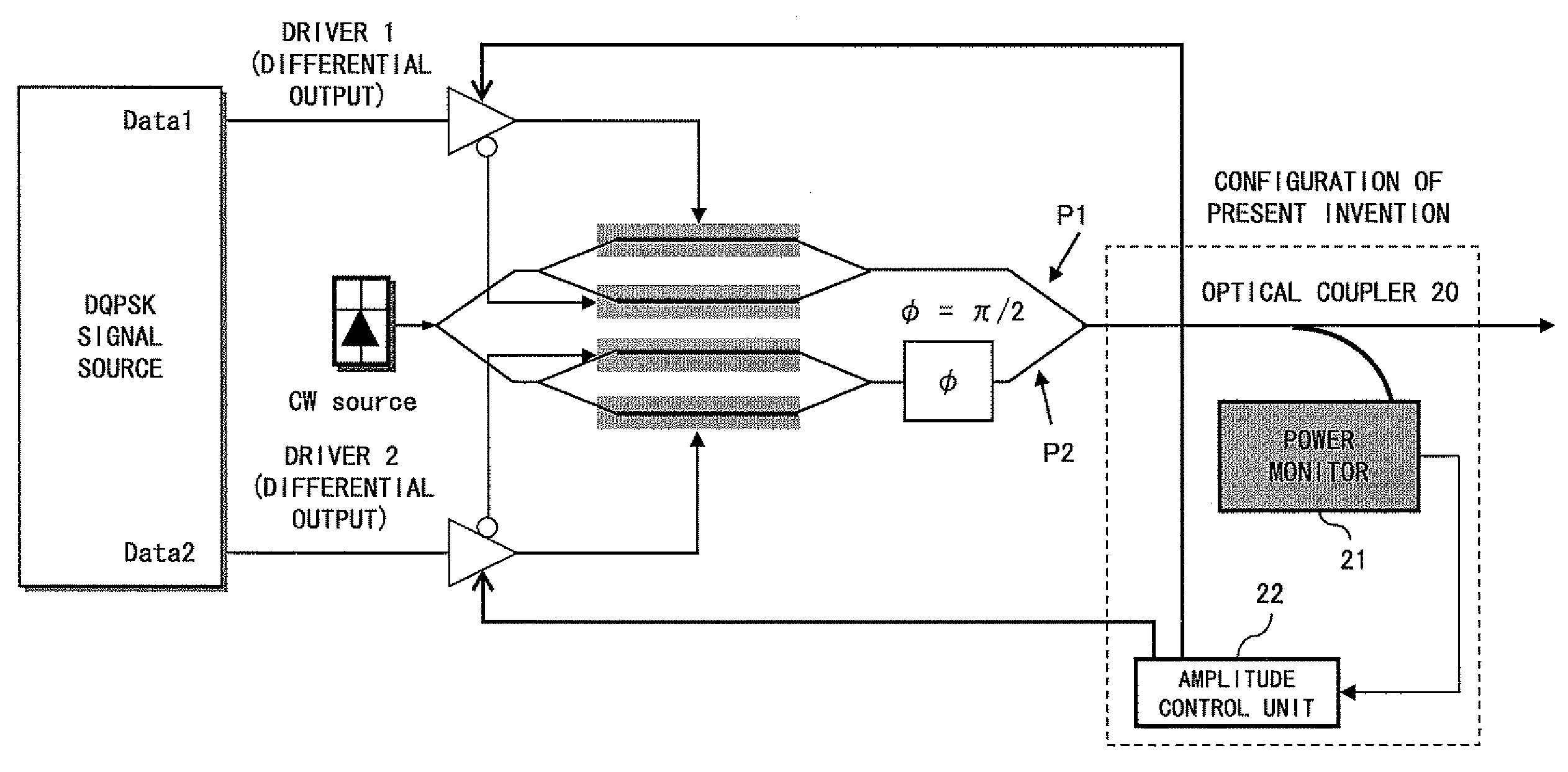
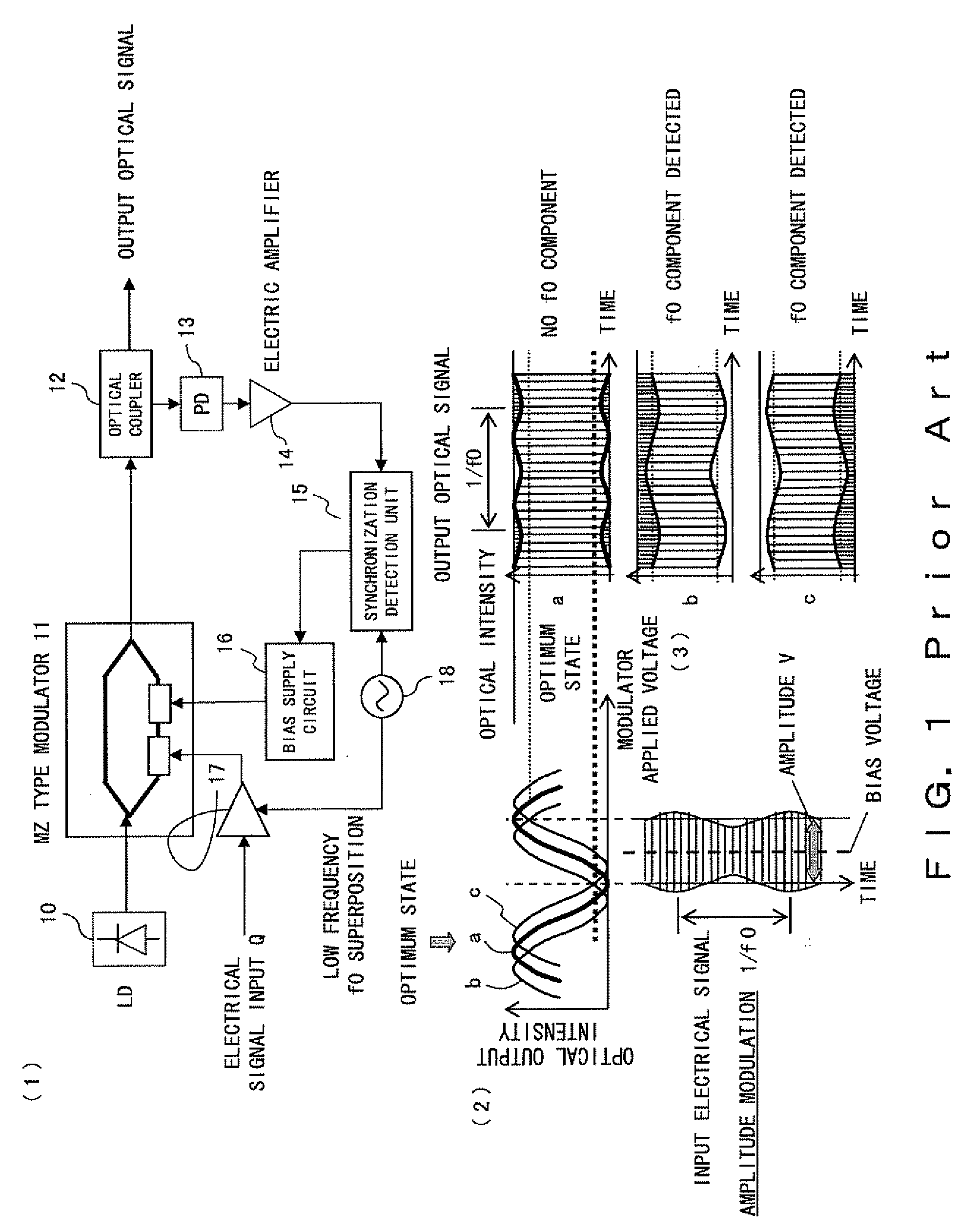
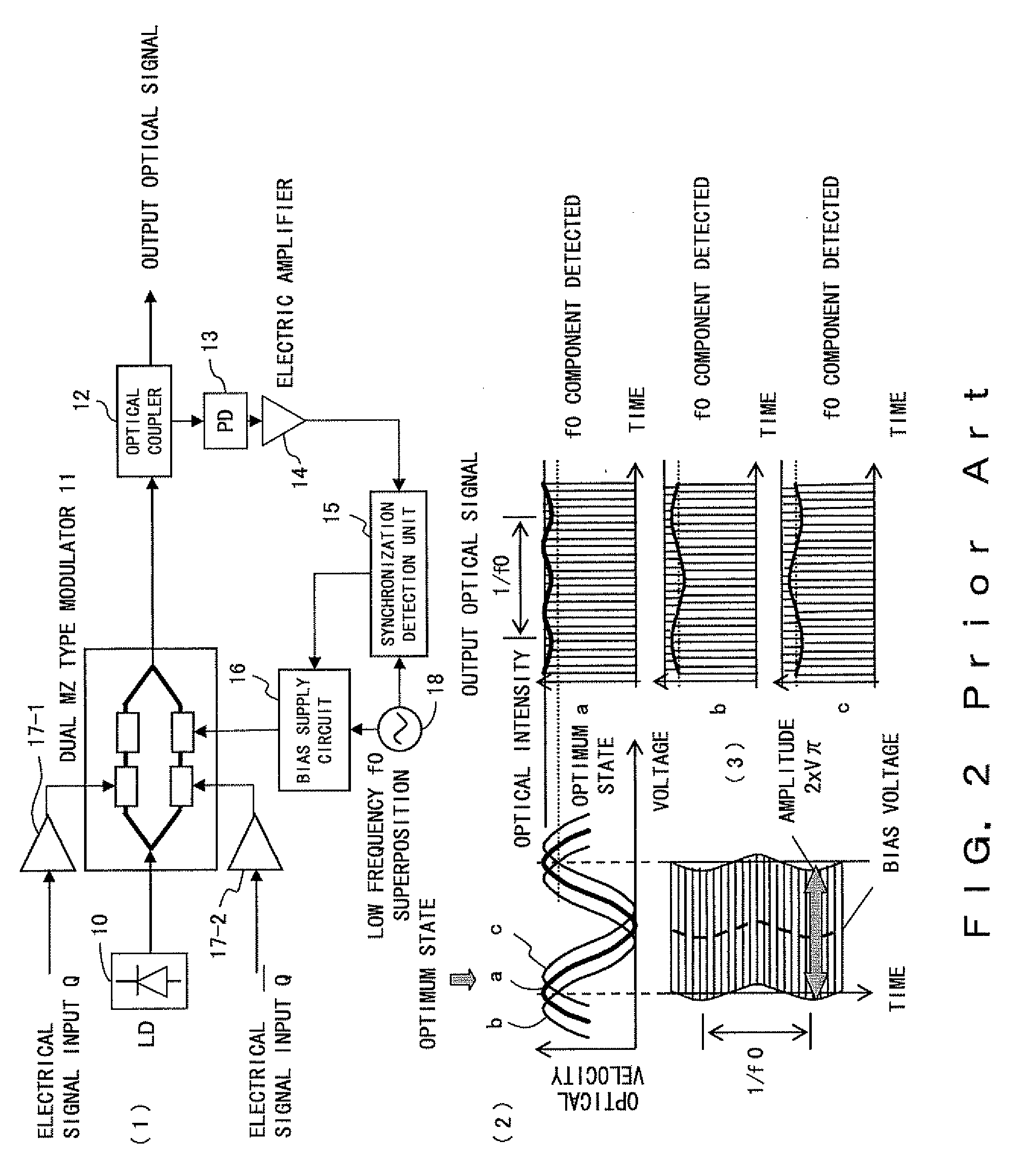
Optical transmitter
InactiveUS20080080872A1Avoid signal attenuationDegradation of the quality of a transmission signal can be suppressedPhase-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringAmplitude controlOptical coupler
A signal Data1 and Data2 are output from a DQPSK signal source. The output signal is input to the modulator drivers 1 and 2 of the differential output. A drive signal is applied from the drivers 1 and 2 to a modulator, and modulated light is output. An optical coupler 20 branches modulator output, and a power monitor 21 detects the power of the branched light. A detection result is transmitted to an amplitude control unit 22. The amplitude control unit 22 adjusts the amplitude of the drivers 1 and 2 such that the detection result of the power monitor 21 can be the maximum.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
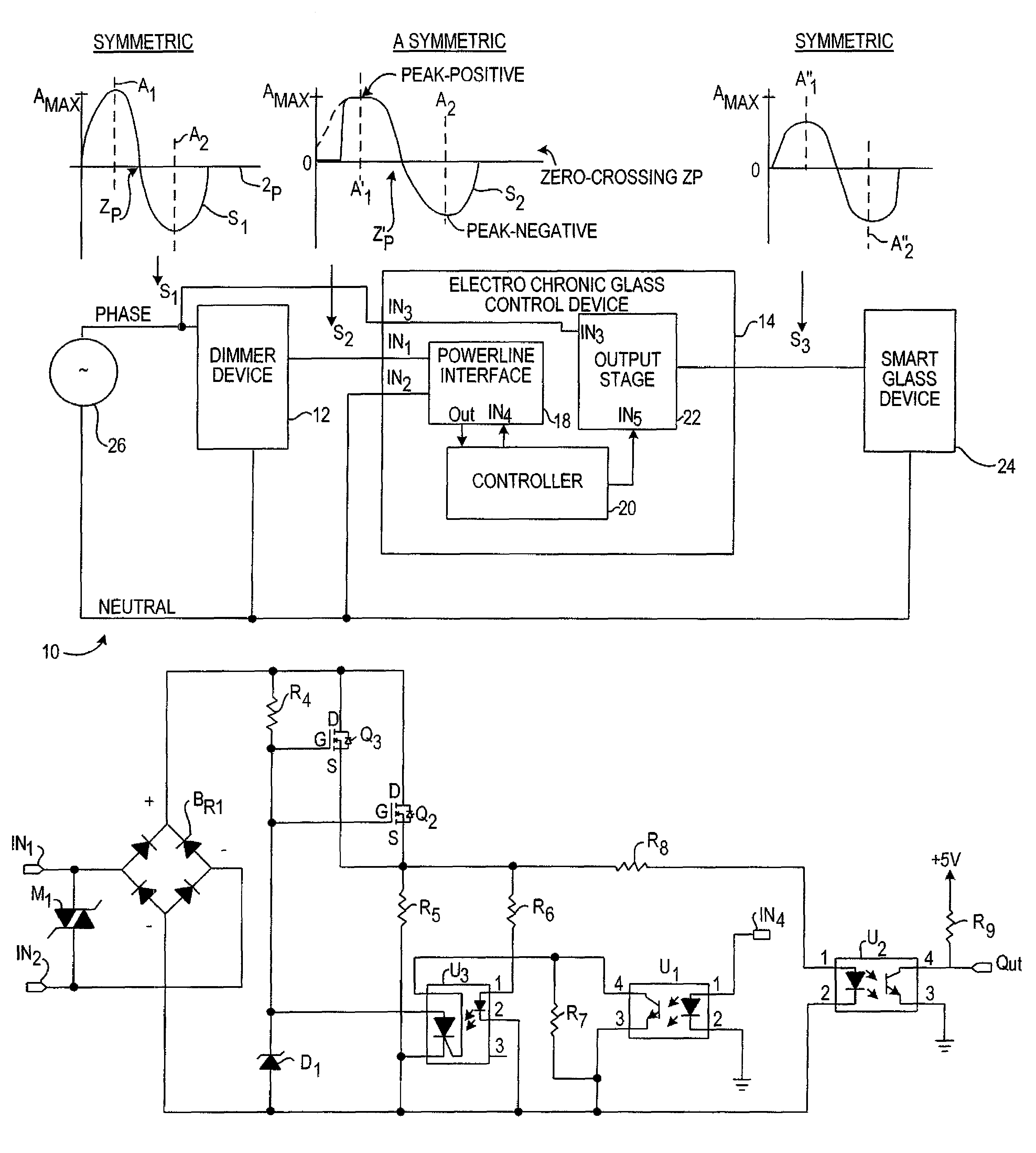
Electrochromic glass control device
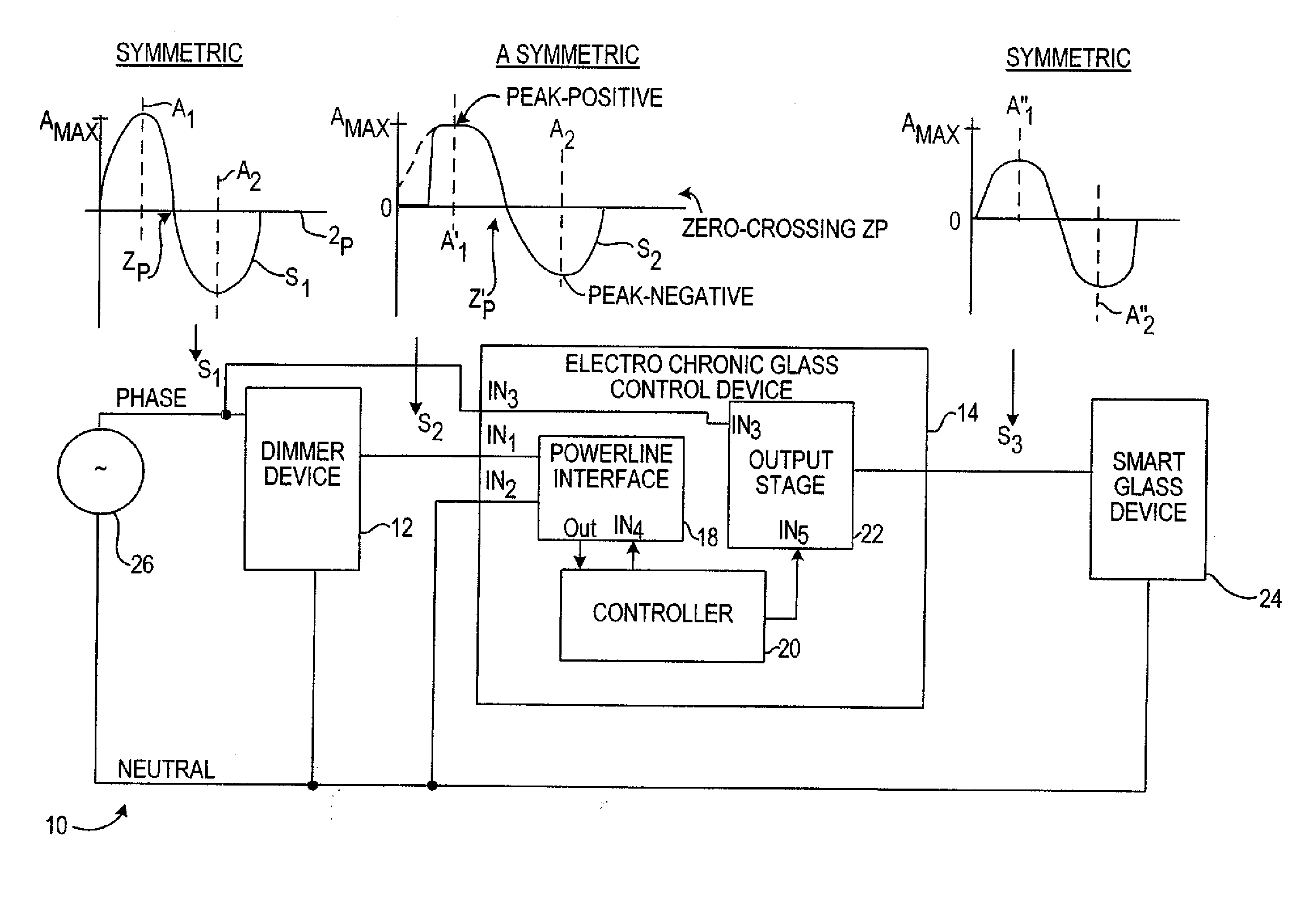
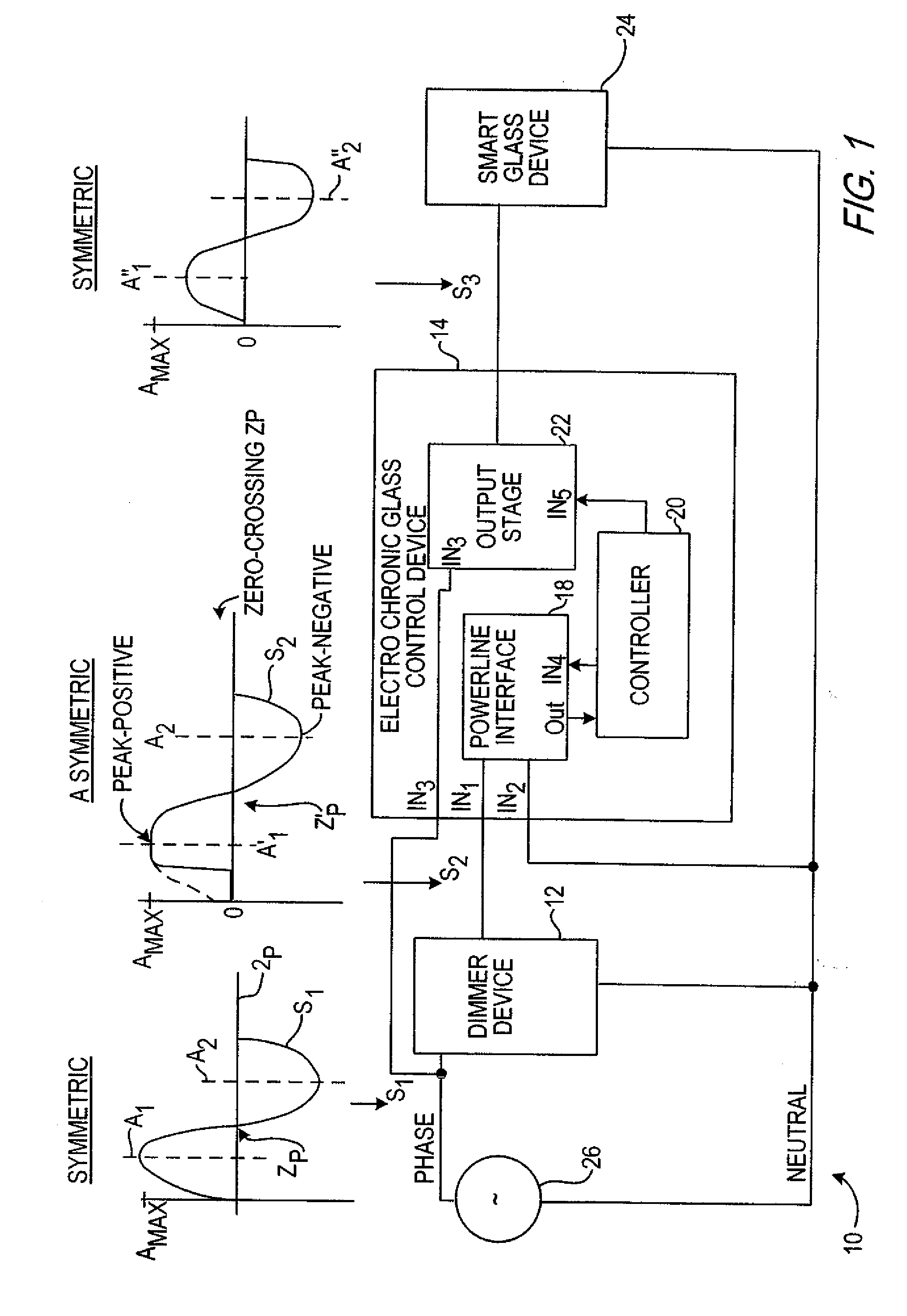
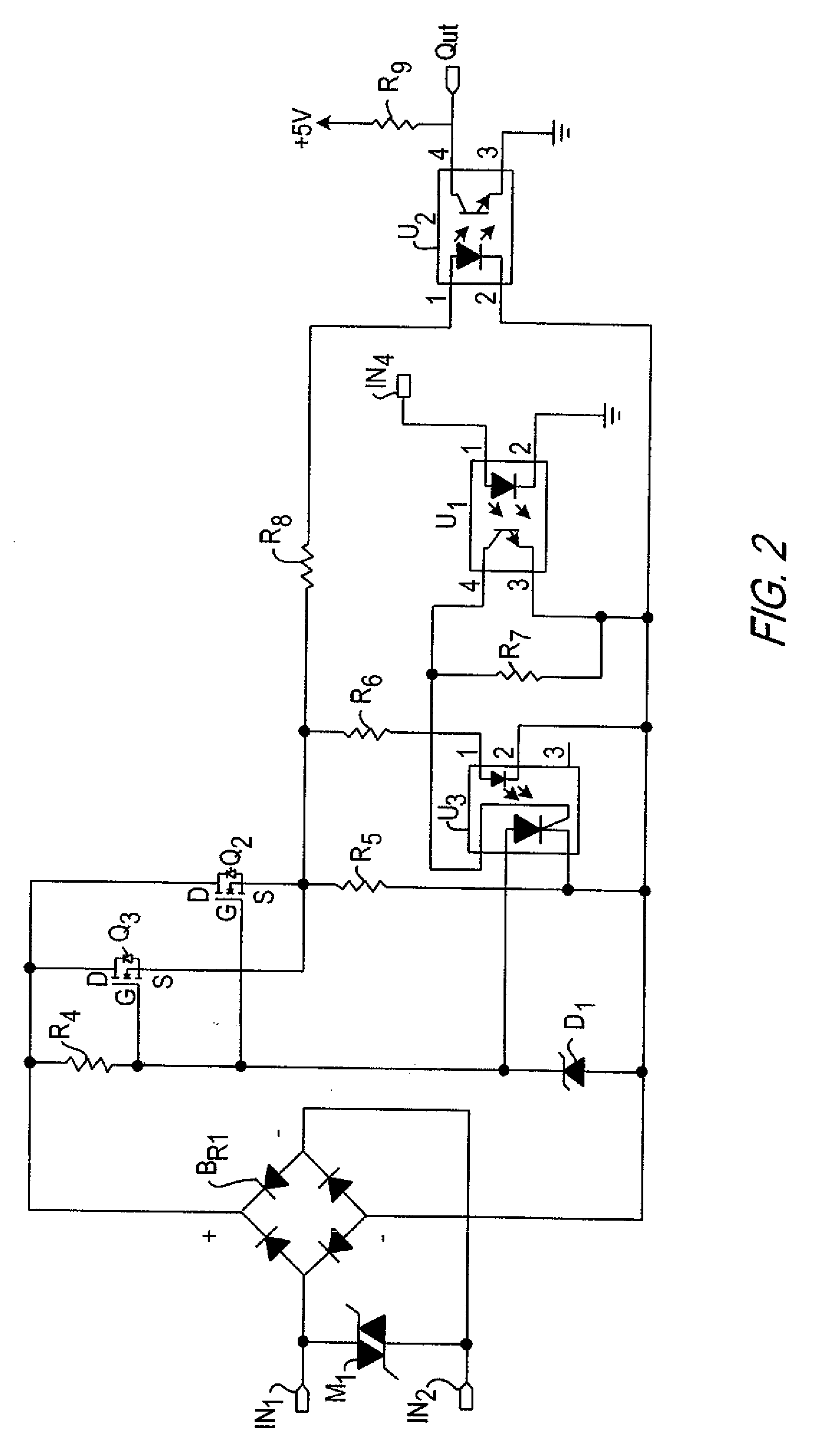
InactiveUS7375871B2Reduce heatReduce problemsStatic indicating devicesPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesControl signalAmplitude control
A light control system having a full range of dimming for smart-glass by providing an interface between an off-the-shelf dimmer and a electrochromic glass device is disclosed herein. The light control system or electrochromic glass control device acts as an interface that converts an asymmetric alternating current (AC) power signal from the dimmer device into a symmetric, amplitude controlled AC output signal for controlling the tint of the smart-glass device. The electrochromic glass control device includes a powerline interface circuit that receives the asymmetric AC power signal from the dimmer. A controller connects to the powerline interface circuit to generate a control signal responsive to the asymmetric AC power signal. Connecting between the dimmer and the controller, an output stage generates the symmetrical AC output signal responsive to the control signal to control the electrochromic glass device.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
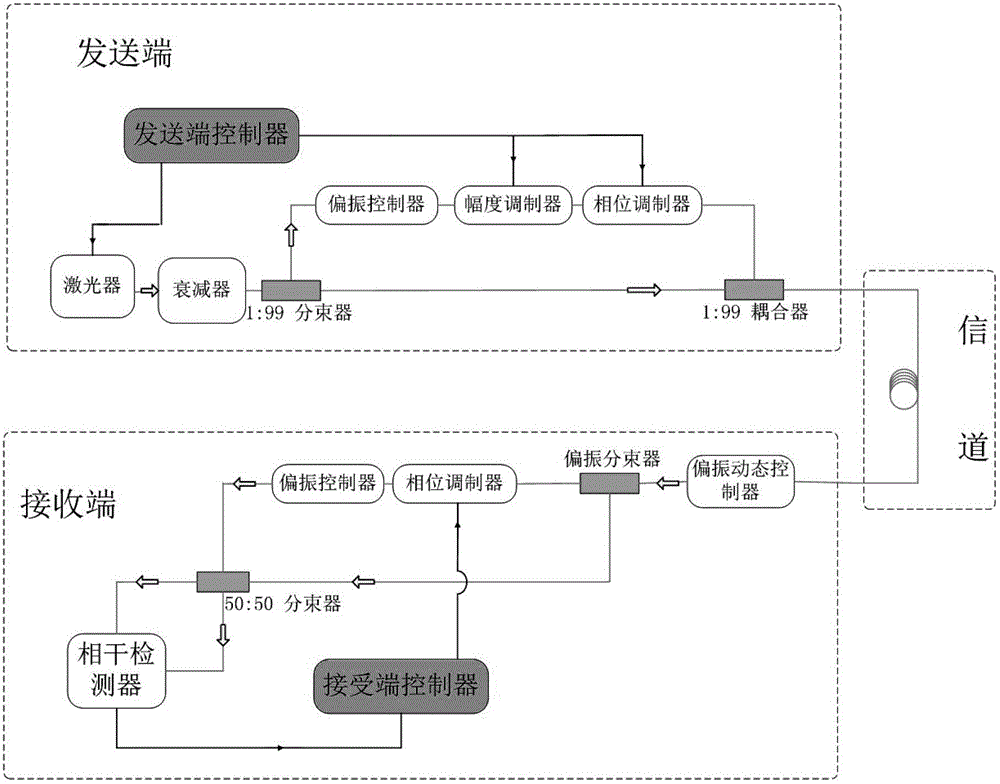
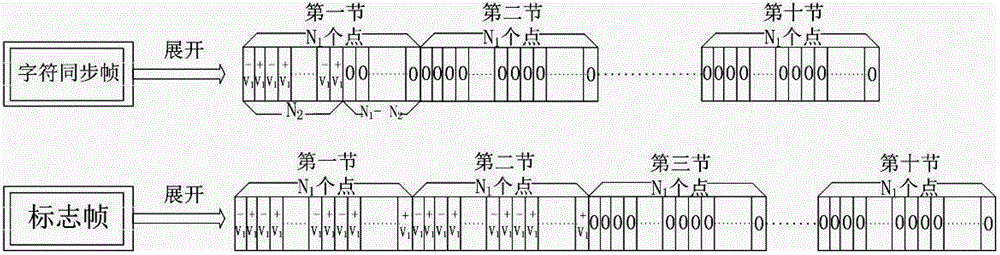
Continuous variable quantum key distribution system and synchronous realization method thereof
ActiveCN102724036AImprove bit error rateAvoid interferenceKey distribution for secure communicationMulti-frequency code systemsBeam splitterAmplitude control
The invention discloses a continuous variable quantum key distribution system and a synchronous realization method thereof. The continuous quantum key distribution system consists of a light path part and a circuit control part, wherein the light path part mainly consists of a laser, an attenuator, a beam splitter, a polarization controller, am amplitude controller, a phase controller and a coupler. A control part is a transmission end controller module and consists of a true random key generator, an analog voltage output and a trigger clock output. The synchronous method comprises a bit synchronizing step and a frame synchronizing step. The invention provides a completely novel synchronous realization scheme based on properties of continuous variable quantum in an optical fiber, the practical orientation of the continuous variable quantum key distribution system is promoted, and the interference that the continuous variable quantum on the synchronous realization in the optical communication process also can be effectively overcome.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAODA INTELLECTUAL PORPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD +1
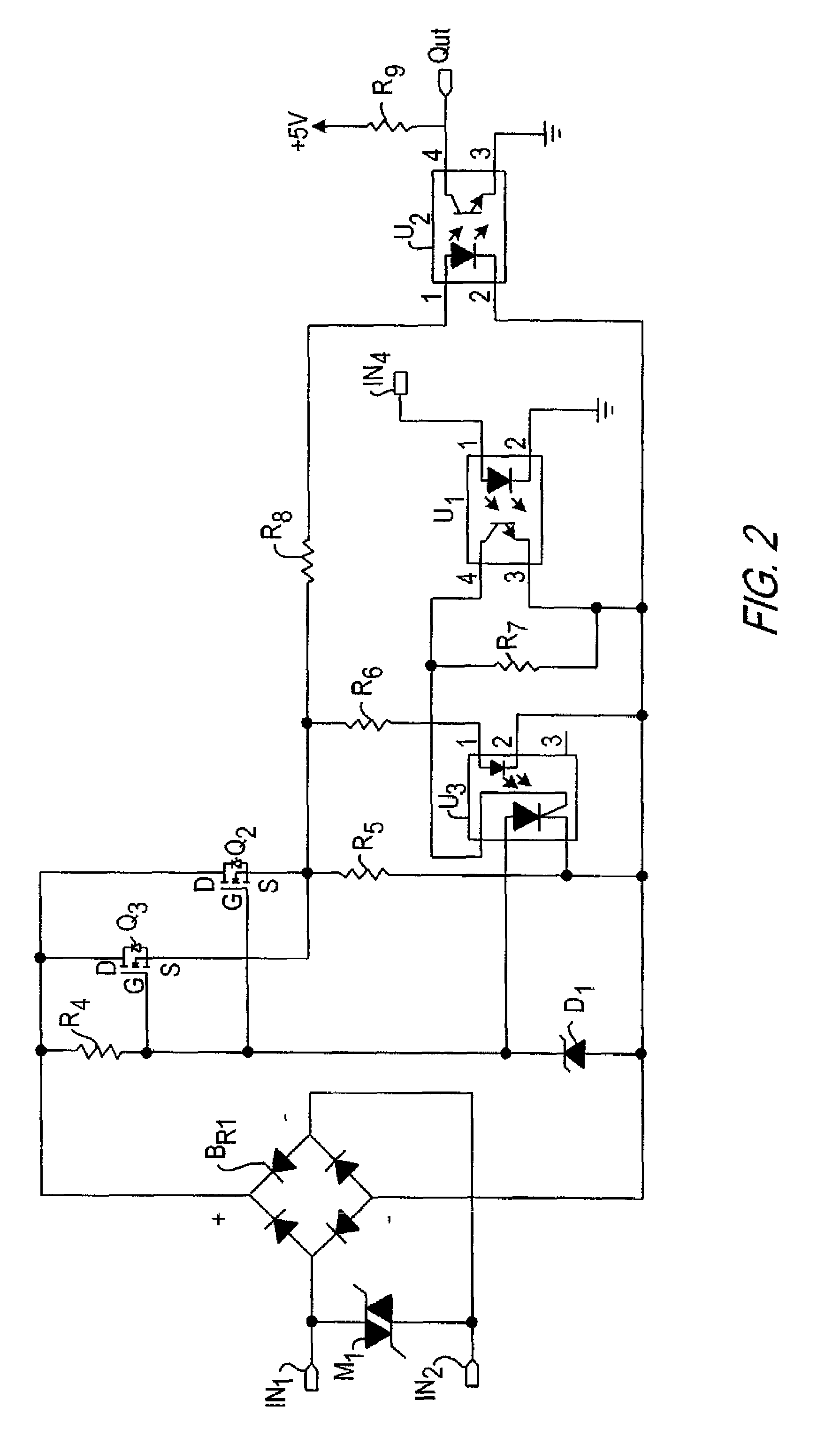
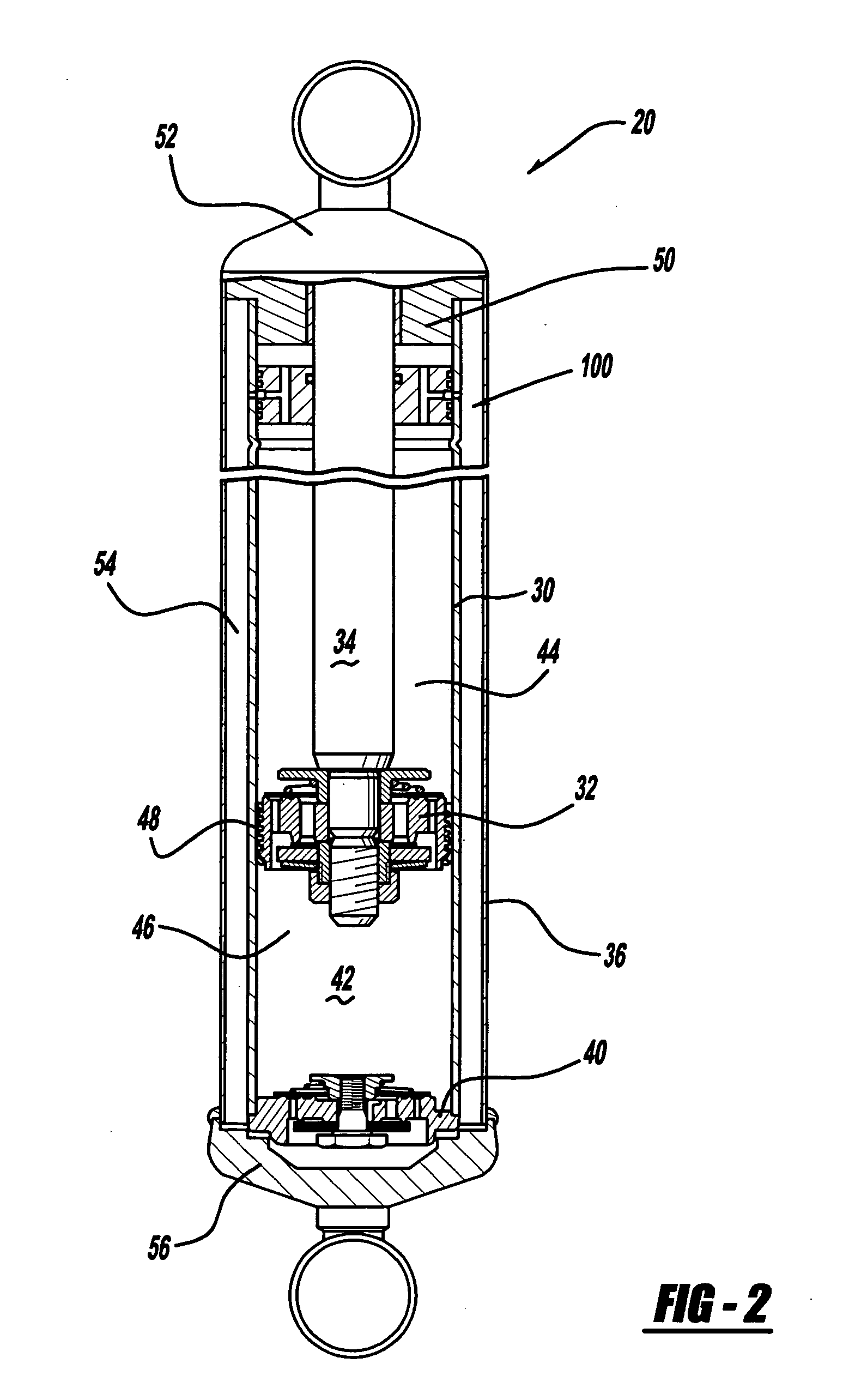
Amplitude controlled orifice valving
A dual tube shock absorber includes a spool valve located between the upper working chamber and the reserve chamber. The spool valve moves with the piston rod to open and close a flow path between the upper working chamber and the reserve chamber. This provides a low damping characteristic for small movements of the piston rod which changes to a high damping characteristic for larger movement of the piston rod.
Owner:TENNECO AUTOMOTIVE OPERATING CO INC
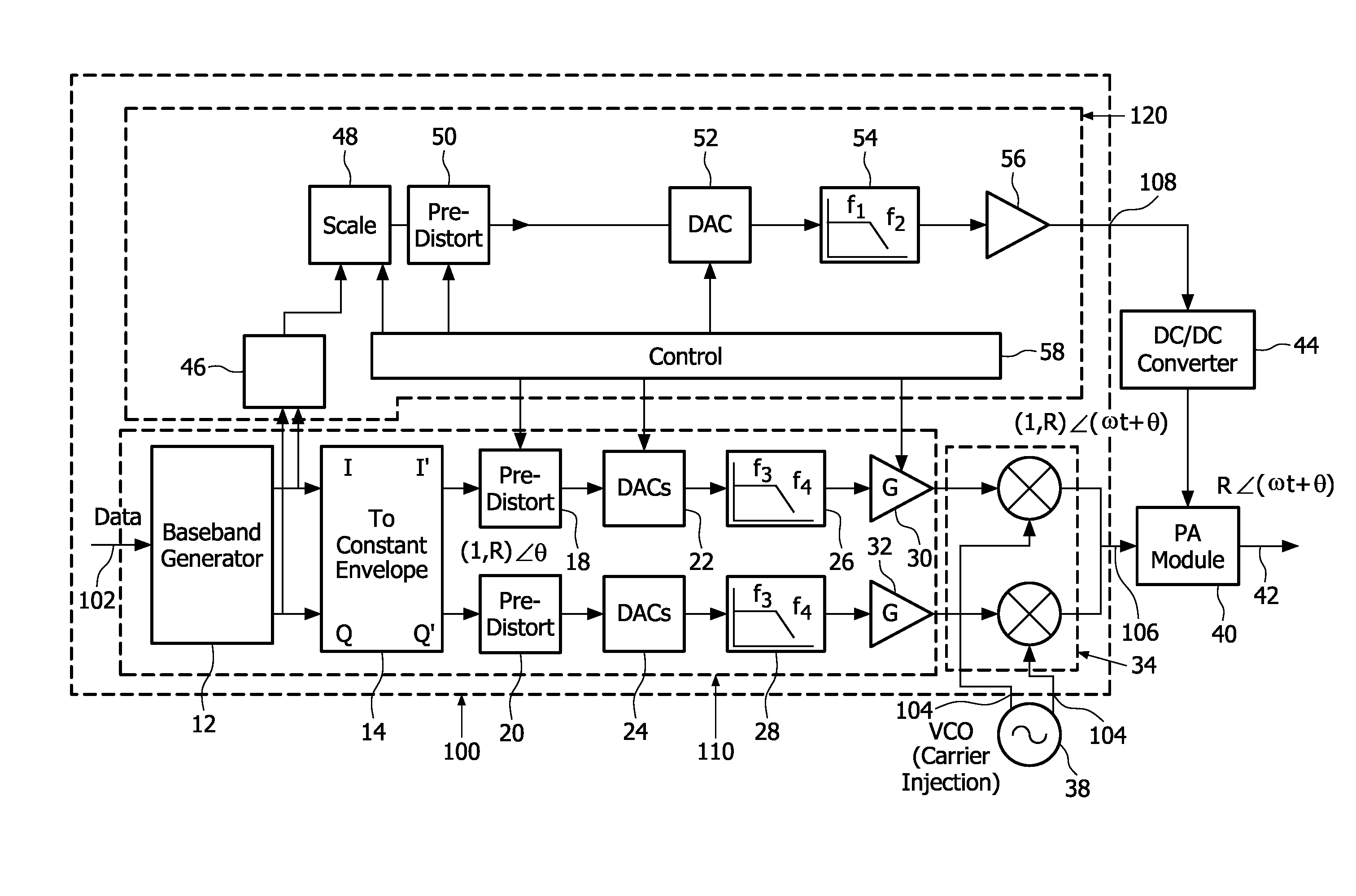
Multi-mode radio transmitters and a method of their operation
InactiveUS20100233977A1Improve power efficiencyConsume excessive powerResonant long antennasPower amplifiersReal signalAmplitude control
A multi-mode radio transmitter for use in mobile radio cellular standards, such as 2G, 2.5G and 3G, and a method of operating the transmitter in which an input signal is modulated independently of controlling the drive of a power amplifier (PA) module (40). The transmitter comprises circuitry (12, 60) for extracting the phase (θ) and amplitude (R) components from envelope information in the input signal. A modulator (110) uses the phase component (θ) to produce a constant-envelope signal comprising a phase modulated real signal at the transmitter frequency. This signal is multiplied in a multiplier (72) with either a fixed bias voltage (Vg1) to produce a constant envelope signal or a low level envelope tracking signal derived from an amplitude component (R) by a first amplitude control circuit (78) to produce a signal modulated exactly by the amplitude component. An output from the multiplier is applied to the PA module (40) having a control input (41). The PA module is controllable in a plurality of manners dependent on the characteristics and the required output power of the signal being transmitted. These manners include applying a predetermined fixed voltage to the control input or a less precise envelope tracking signal which is derived by a second amplitude control circuit (120) from the amplitude component (R).
Owner:NXP BV
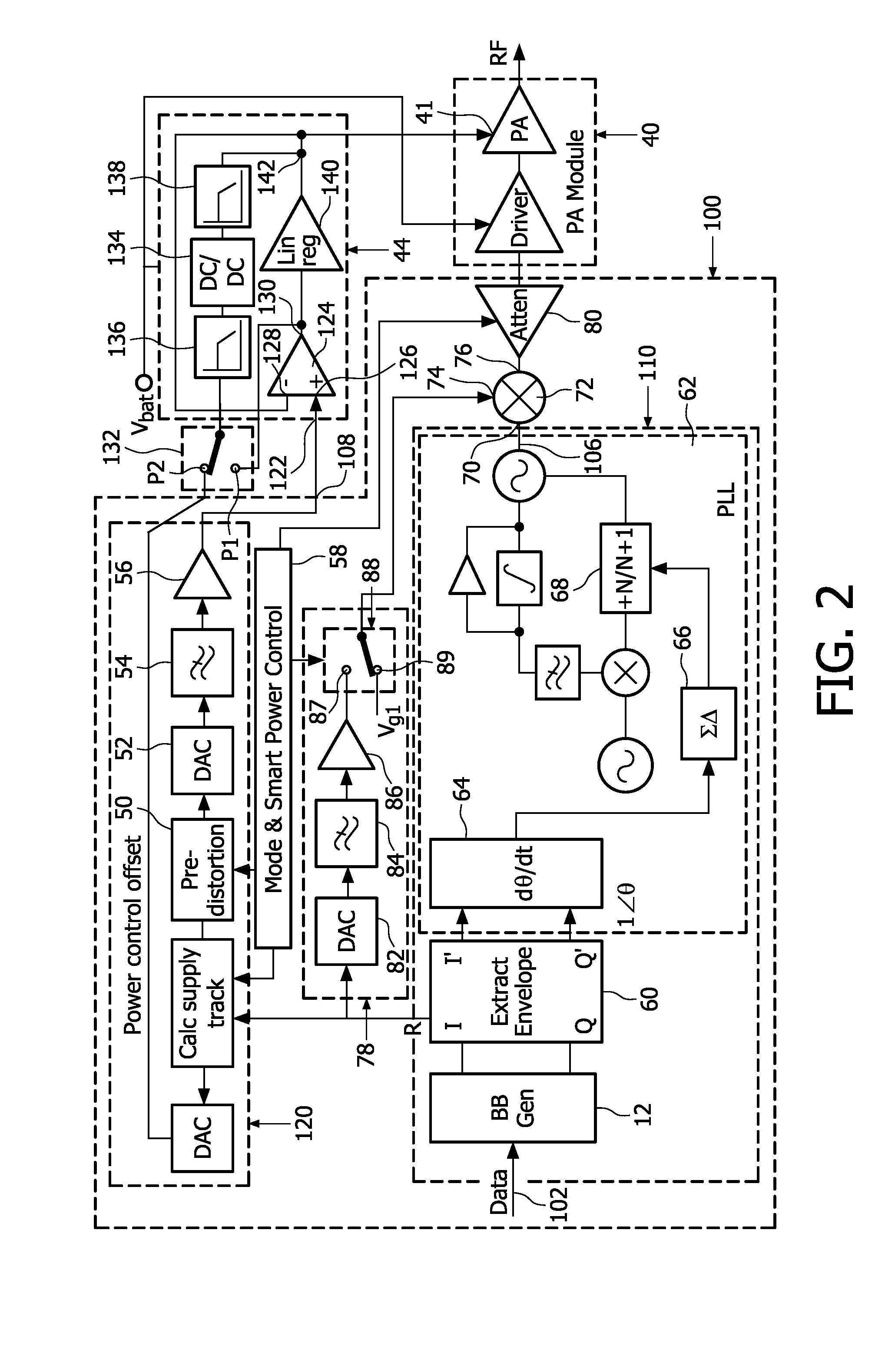
Amplifier compression controller circuit
ActiveUS20070184796A1Narrow bandwidthSacrificing efficiencyResonant long antennasAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The amplitude loop may include a variable gain amplifier adjusting the amplitude of the input signal. The amplitude loop can include a compression control block which may be configured either to adjust the gain in the variable gain amplifier or the voltage from the power supply based upon the operating level of the other, in addition to being based upon the amplitude correction signal, thus providing a way of maintaining the depth beyond the PA's compression point and allowing a control of the efficiency of the RF power amplifier.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Power amplifier controller circuit
ActiveUS20070184791A1Narrow bandwidthSacrificing efficiencyResonant long antennasPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierPhase distortion
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The amplitude correction signal may also be split into two or more signals with different frequency ranges and provided respectively to different types of power supplies with different efficiencies to generate the adjusted supply voltage to the power amplifier. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal to reduce phase distortion generated by the power amplifier.
Owner:QUANTANCE
RF Power Amplifier Controller Circuit With Compensation For Output Impedance Mismatch
ActiveUS20070184793A1Narrow bandwidthSacrificing efficiencyResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierPhase distortion
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The amplitude control loop may also compensate for impedance mismatch with the load by increasing the power delivered from the power amplifier to the load, or decrease the output power of the power amplifier upon detection of excessive power dissipation in the power amplifier. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal to reduce phase distortion generated by the power amplifier.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Amplitude- and frequency- or phase-modulated radio frequency signal generator and the transmitter incorporating same
An amplitude- and frequency- or phase-modulated radio frequency signal generator that is used for radio emission, generates a phase or frequency control signal and an amplitude control signal from a phase or frequency modulation signal and from an amplitude modulation signal respectively. The generator comprises a phase or frequency modulator and a variable-gain radio frequency power amplifier. The amplitude of the output signal is automatically controlled. In addition, adaptive pre-distortion is carried out in order to pre-distort the phase or frequency control signal in accordance with the amplitude modulation signal during a permanent operating phase. During a learning phase, a pre-distortion module is adapted from the amplitude modulation signal and from the amplitude control signal.
Owner:CASSIDIAN SAS
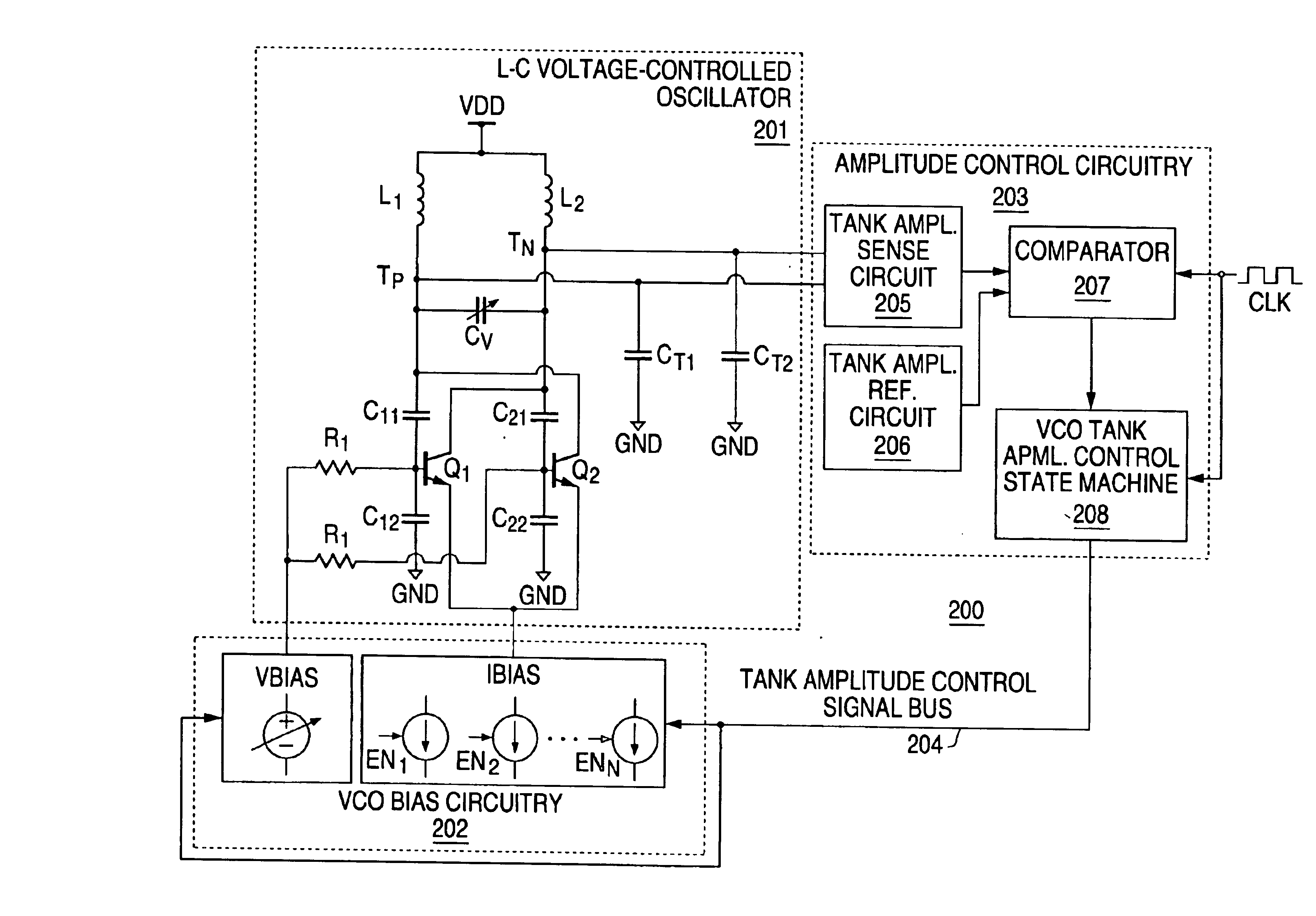
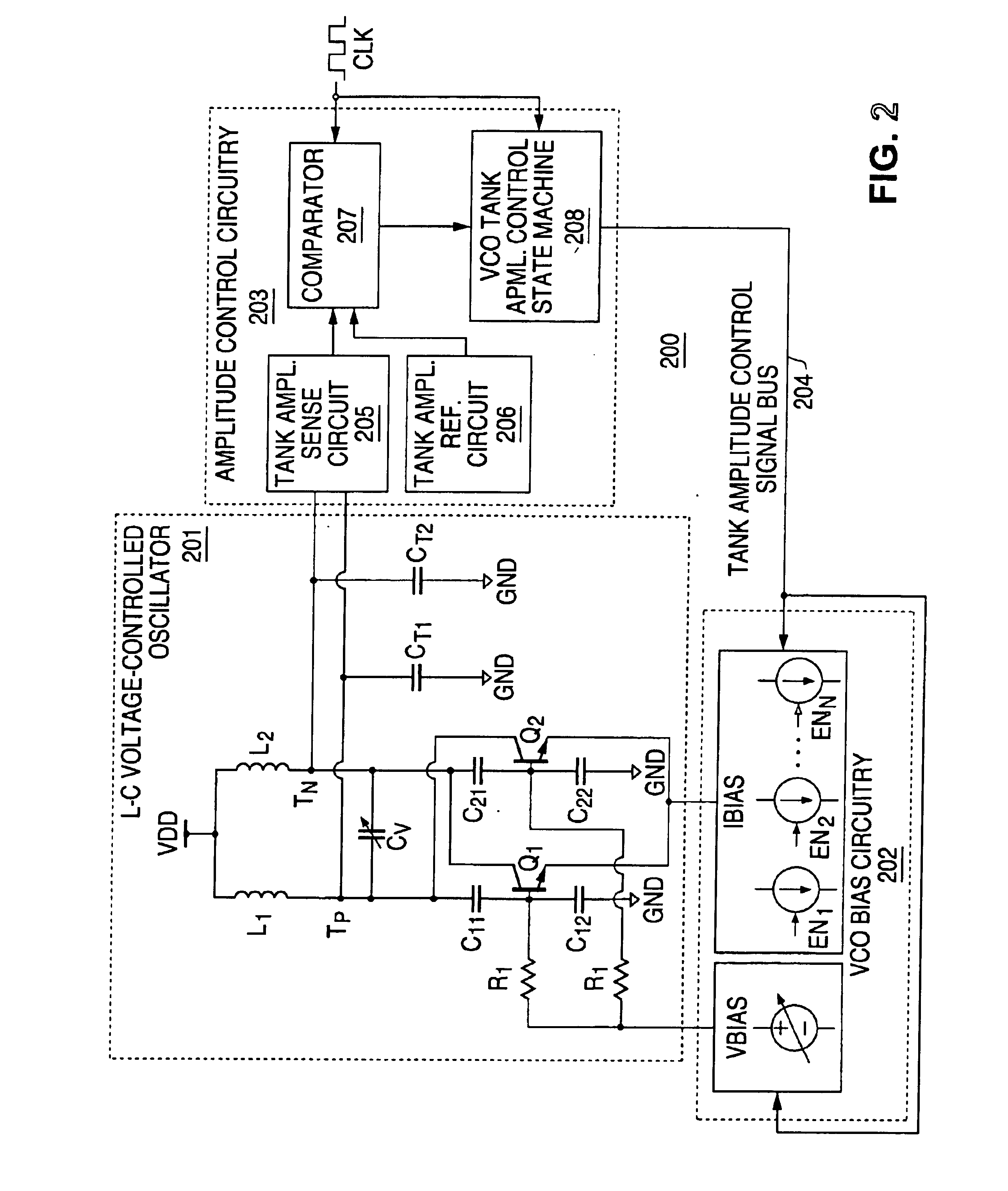
Discrete-time amplitude control of voltage-controlled oscillator
ActiveUS6909336B1Pulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Phase noise
Periodically, sensed amplitude for the output signal of a voltage-controlled oscillator is compared to a reference and biasing of the voltage-controlled oscillator is correspondingly set, thereby controlling amplitude of the voltage-controlled oscillator output signal. Process and temperature dependencies of the amplitude are eliminated while achieving low phase noise and large signal-to-noise ratio in the output signal, and consequently low phase noise.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
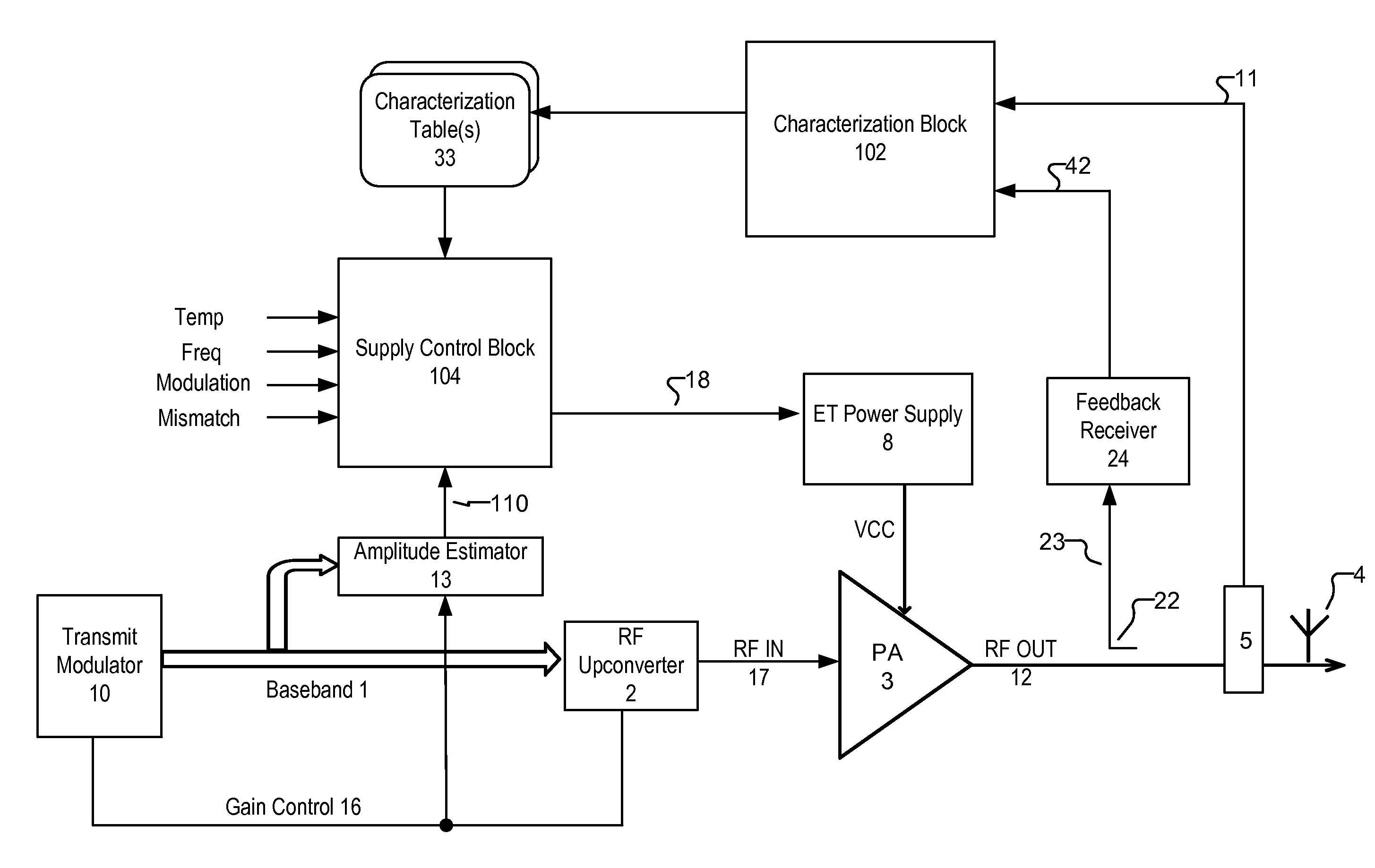
Envelope Tracking System with Internal Power Amplifier Characterization
ActiveUS20140266423A1Achieve correctionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierAmplitude control
An RF PA system that generates its own local characterization information. The RF PA system includes a PA to generate a RF output signal from a RF input signal, the PA powered by a supply voltage. A characterization block generates characterization information corresponding to a relationship between the supply voltage and performance (e.g., gain, power efficiency, distortion, receive band noise) of the RF PA system for a plurality of levels of one or more operating conditions (e.g., temperature, operating frequency, modulation format, antennae mismatch, etc.) of the RF PA system. An amplitude estimator block estimates an amplitude of the RF input signal. A supply control block generates a supply voltage control signal for controlling the supply voltage based on the characterization information and the amplitude of the RF input signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
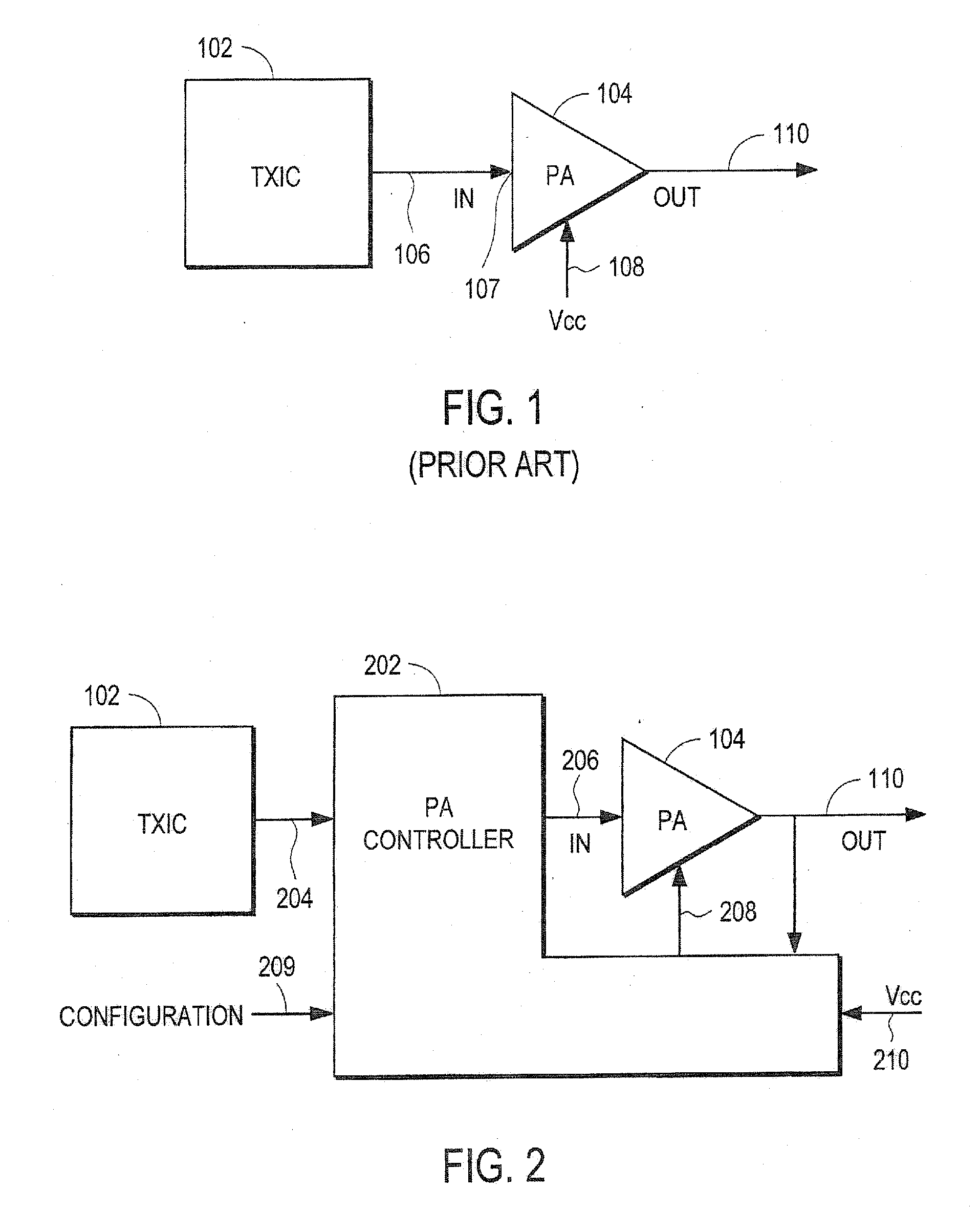
Communication semiconductor integrated circuit, a wireless communication apparatus, and a loop gain calibration method
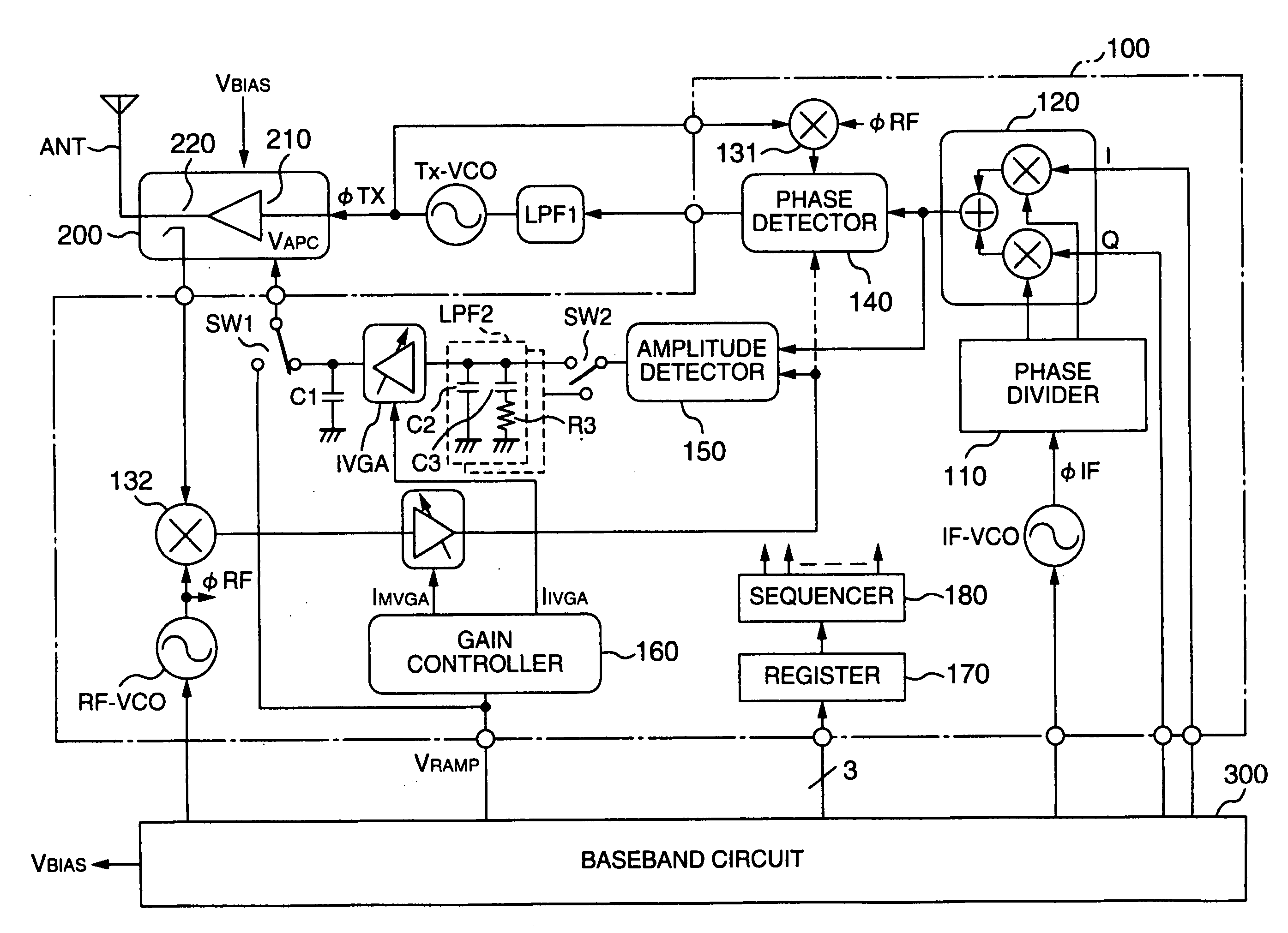
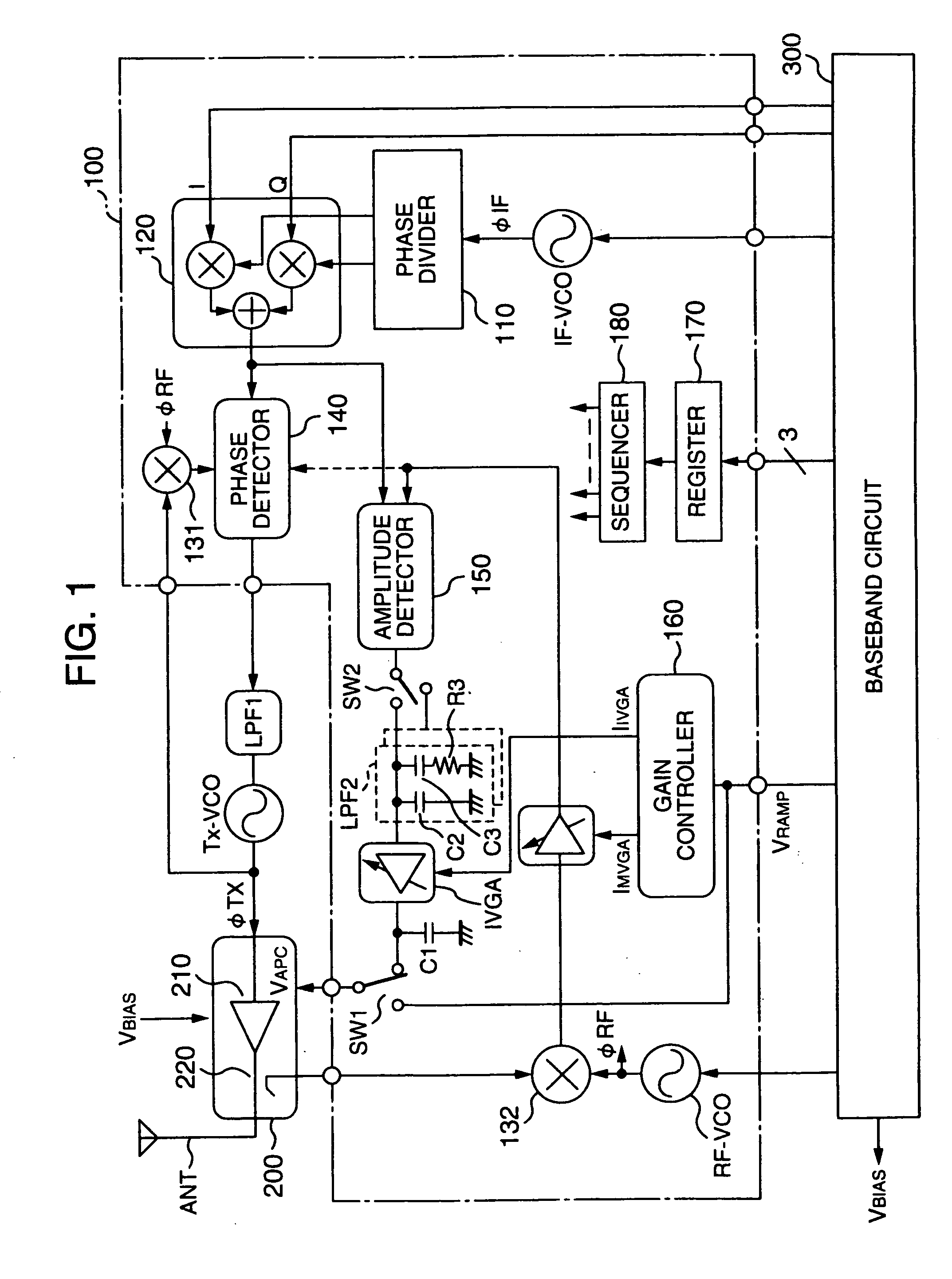
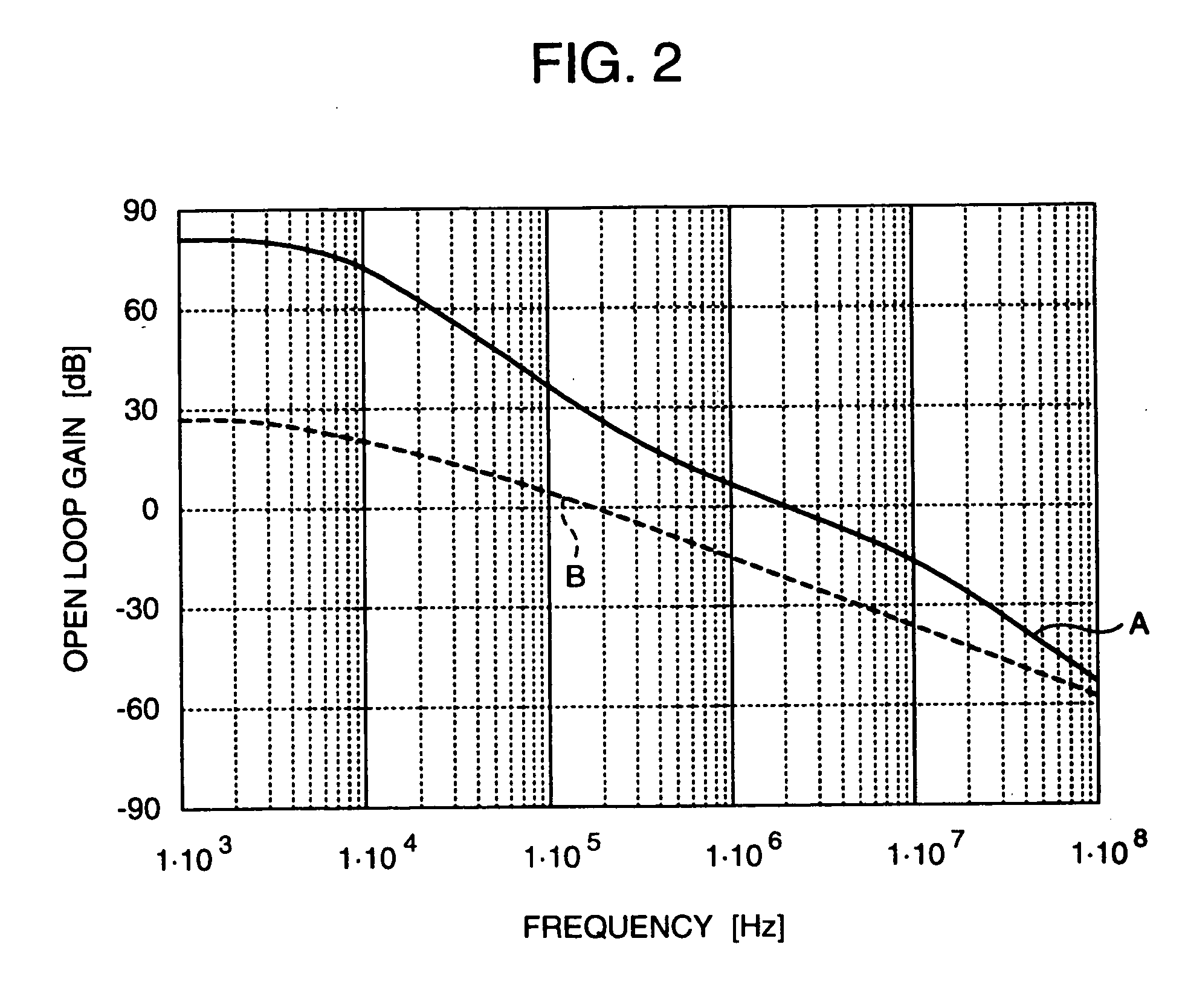
InactiveUS20060189285A1Reduced stabilityReduce a phase marginResonant long antennasGain controlControl signalAmplitude control
A polar-loop wireless communication apparatus includes, on a forward path between an amplitude detector and a power amplifier which constitute an amplitude control loop, a variable gain amplifier and a switch to change characteristics of a loop filter to output a frequency bandwidth of the amplitude control loop to an order less than an order for normal operation. The system is operated with the characteristics set to the lower order to measure outputs from the power amplifier to calibrate the output power of the power transmitter, and the register is operated with the characteristics set to the higher order to measure the open loop gain of the amplitude control. According to results of the calculation, data to correct gain characteristics of the variable gain amplifier with respect to an output control signal is stored in a nonvolatile memory of a baseband circuit.
Owner:TAKANO RYOICHI +4
Power amplifier
InactiveUS20050030104A1Highly efficiently controlled transmission powerContinuous levelAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierAmplitude control
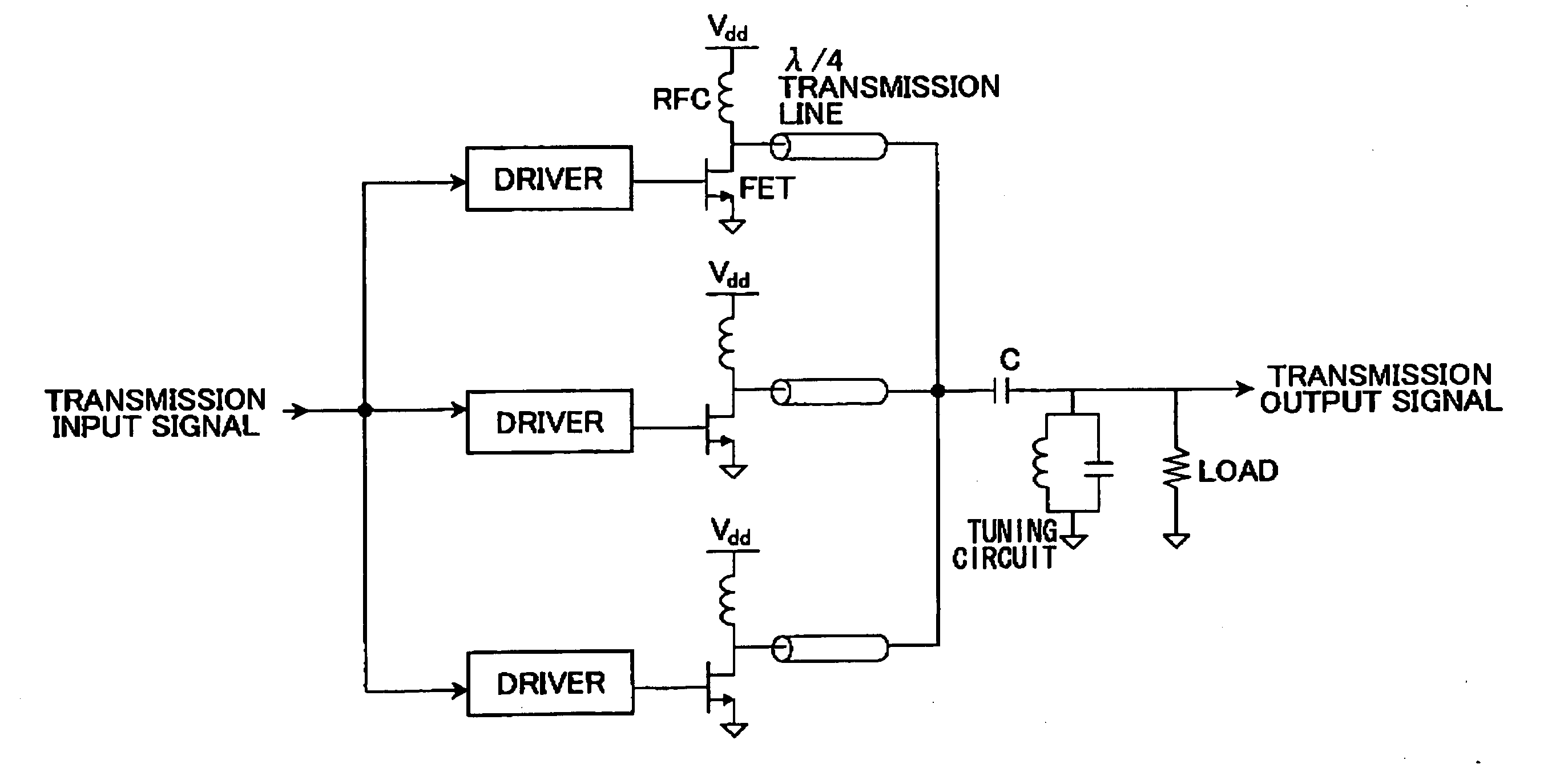
A power amplifier (1) for receiving and amplifying an input signal (10) and outputting an output signal (11) is disclosed. The power amplifier comprises: N power amplifying units (12) (N is an integer larger than 1) connected in parallel so as to output amplified signals in response to the input signal (10); an output combining unit (14) for combining the output signals from the N power amplifying units (12) and outputting a combined signal as the output signal (11) of the power amplifier; and an amplitude controlling unit (15) for selectively turning ON each of the N power amplifying units (12) based on an amplitude of the input signal (10). In the power amplifier, the amplitude controlling unit (15) may comprise N amplitude adjusters (113) connected in parallel for adjusting the amplitude of the input signal (110) of the power amplifier; and a controller (115) for selectively turning ON each of the N power amplifying units (112) and controlling the amplitude adjusters (113) so that an amplitude of the output signal (111) becomes a substantially continuous function with respect to the amplitude of the input signal (110). The power amplifier may further comprise a local oscillator (222) outputting an constant envelope signal, receiving a modulation signal (210) as the input signal of the power amplifier and outputting an amplified modulated signal (211) as the output signal of the power amplifier; wherein the N power amplifying units comprise N saturation amplifying units connected in parallel so as to amplify the constant envelope signal from the local oscillator; and the amplitude controlling unit comprises an amplifying controller (215) for selectively turning ON each of the N saturation amplifying units (212) based on an amplitude of the modulation signal (210).
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
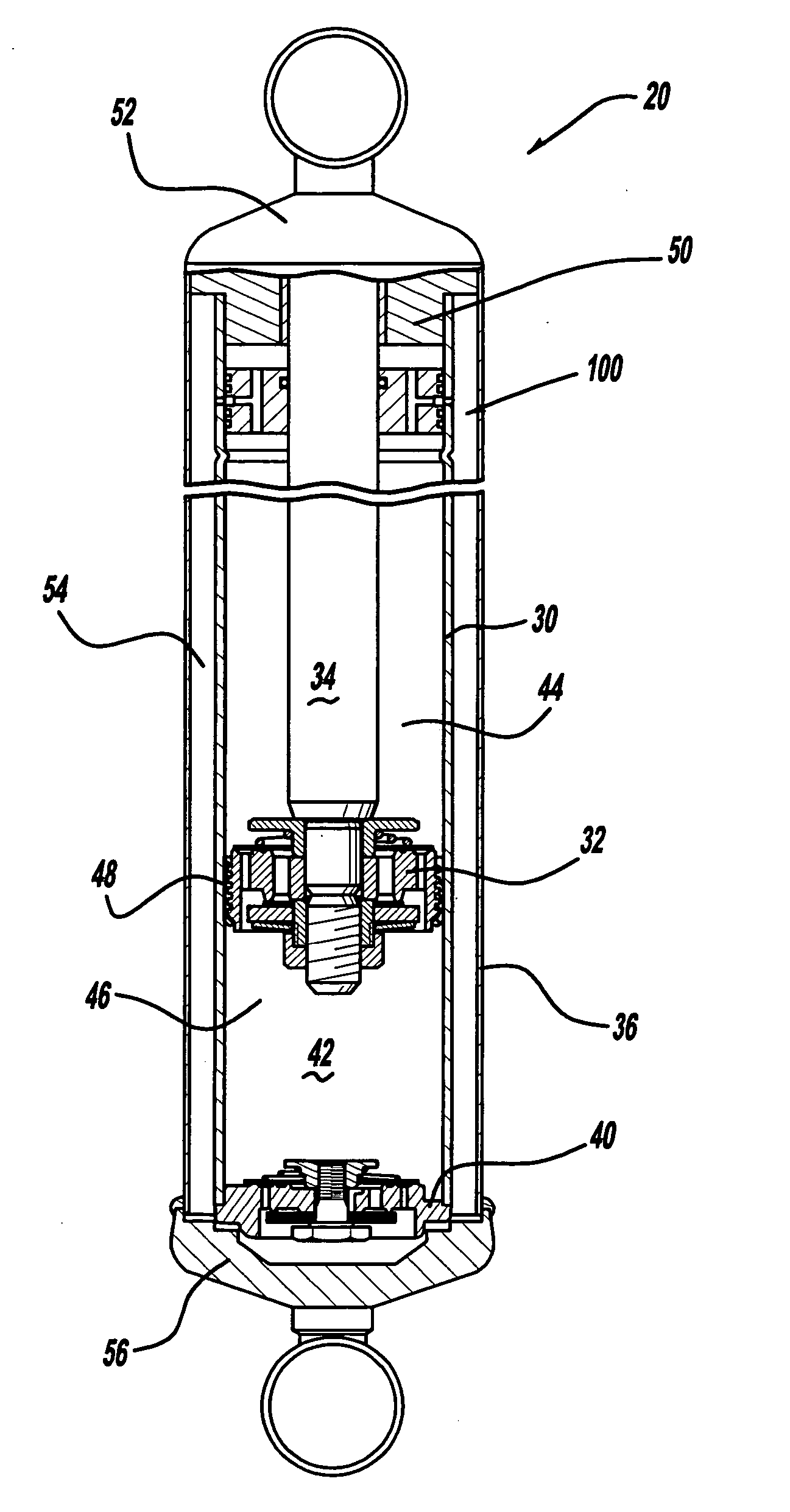
Linear oscillator
InactiveUS6873067B2Reduce vibrationLittle noiseMetal working apparatusPropulsion systemsResonanceReciprocating motion
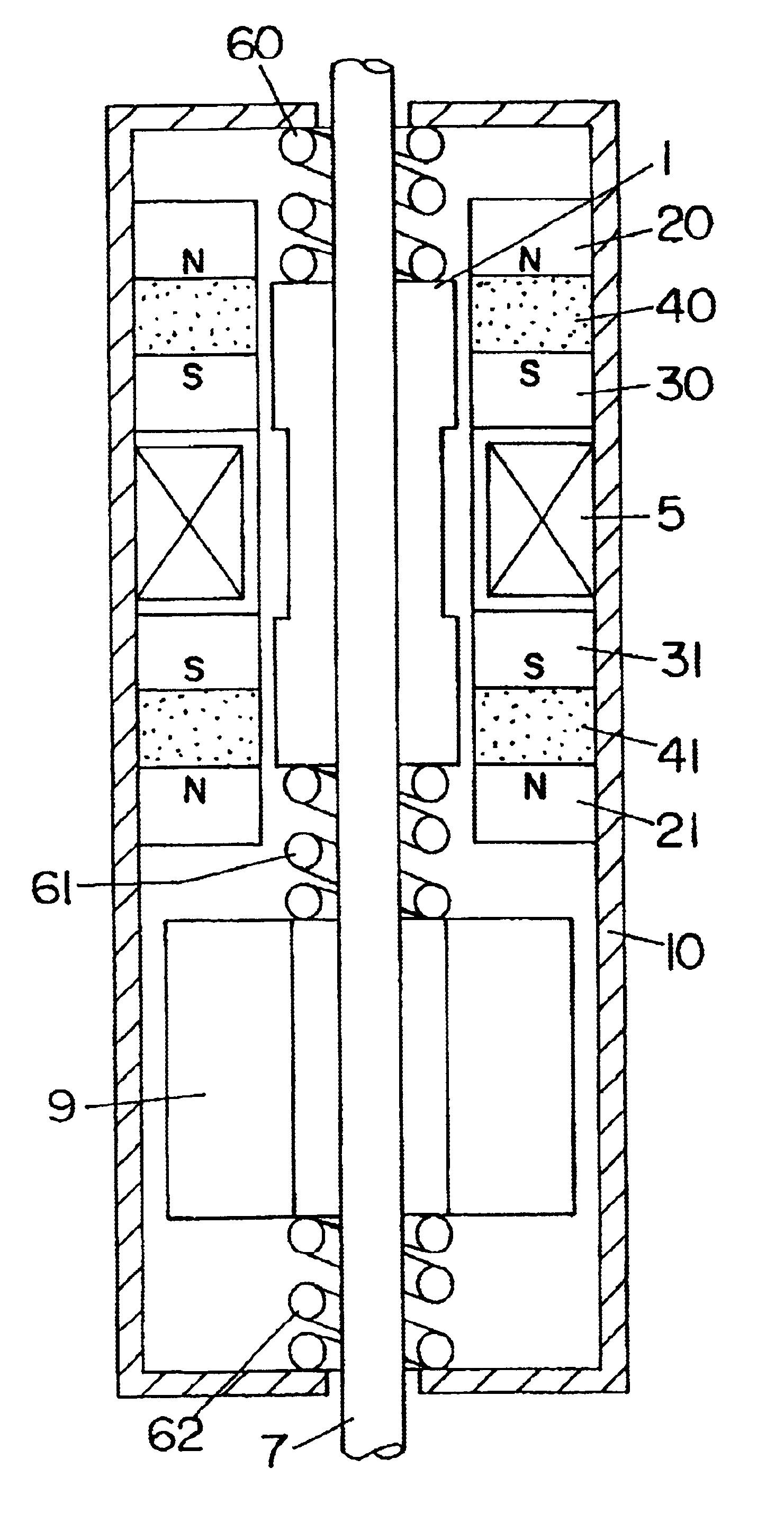
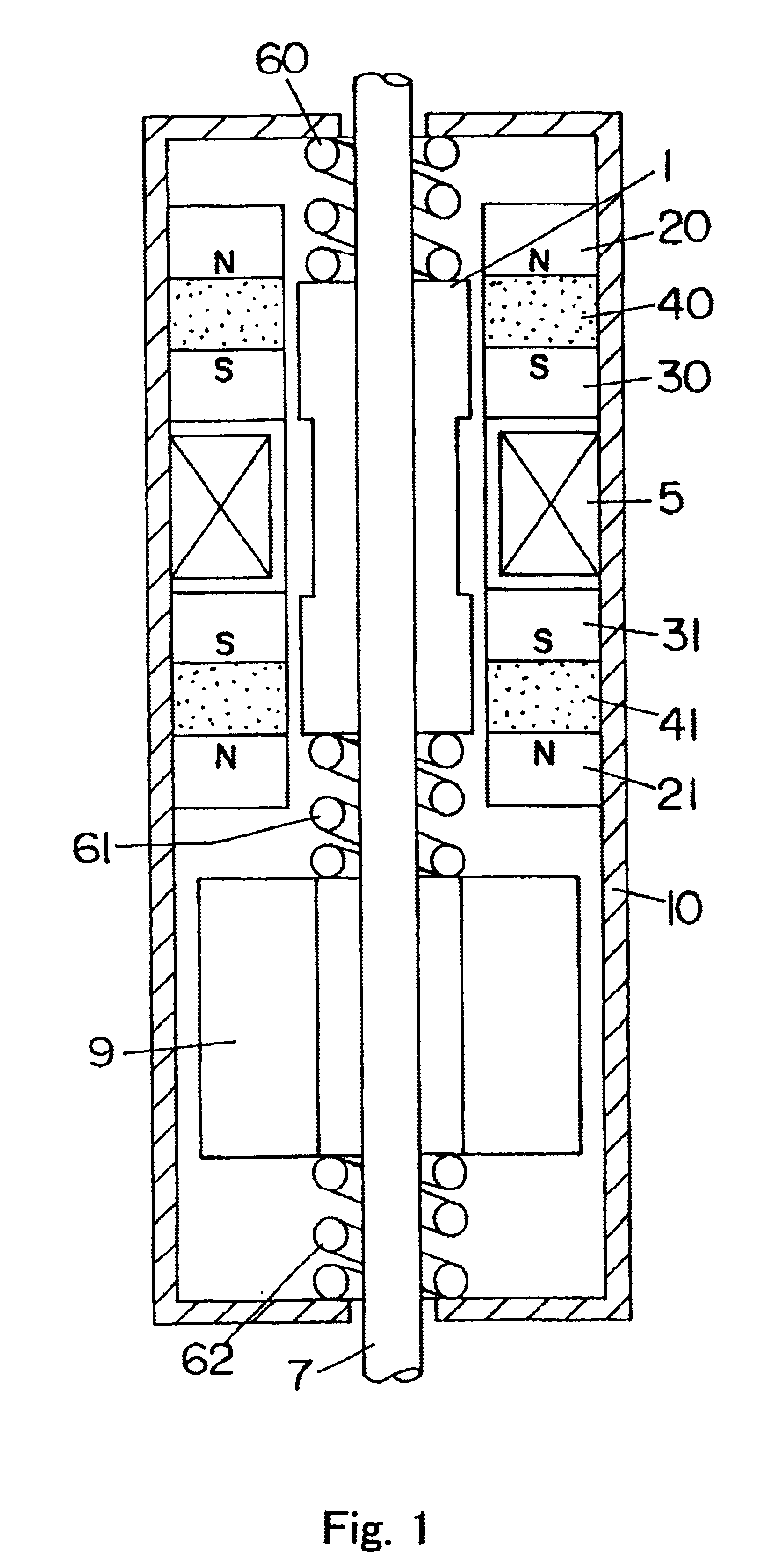
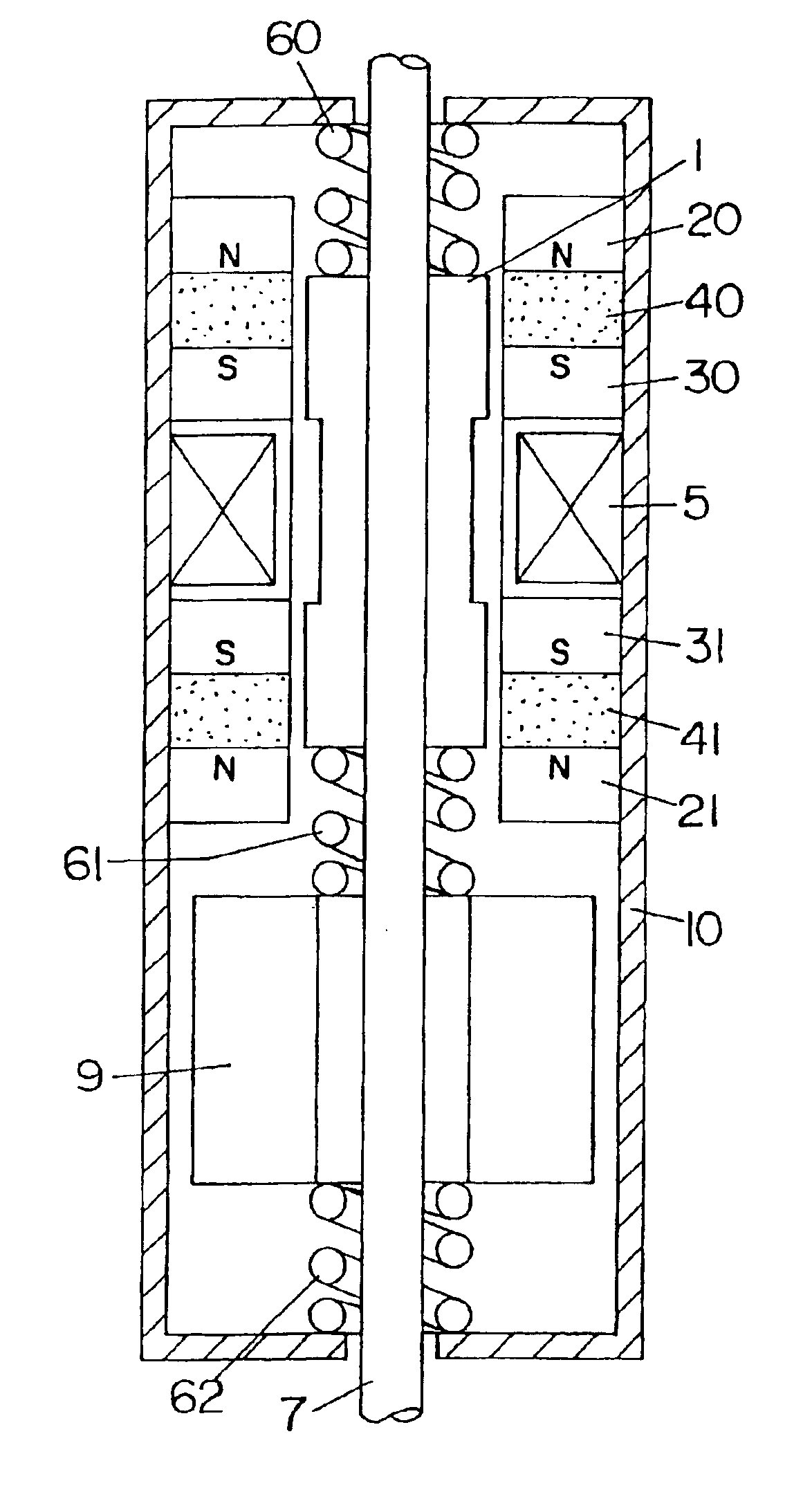
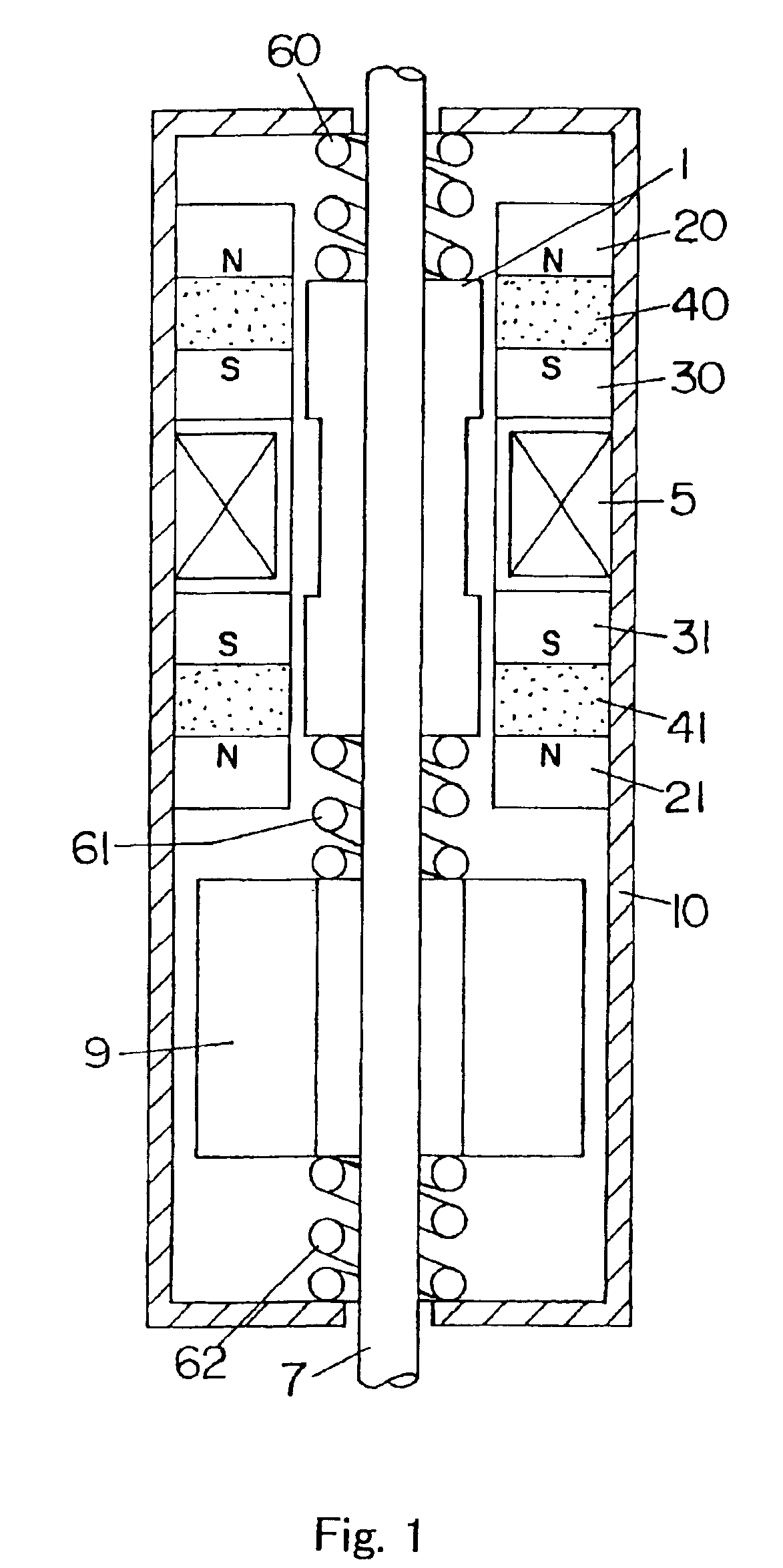
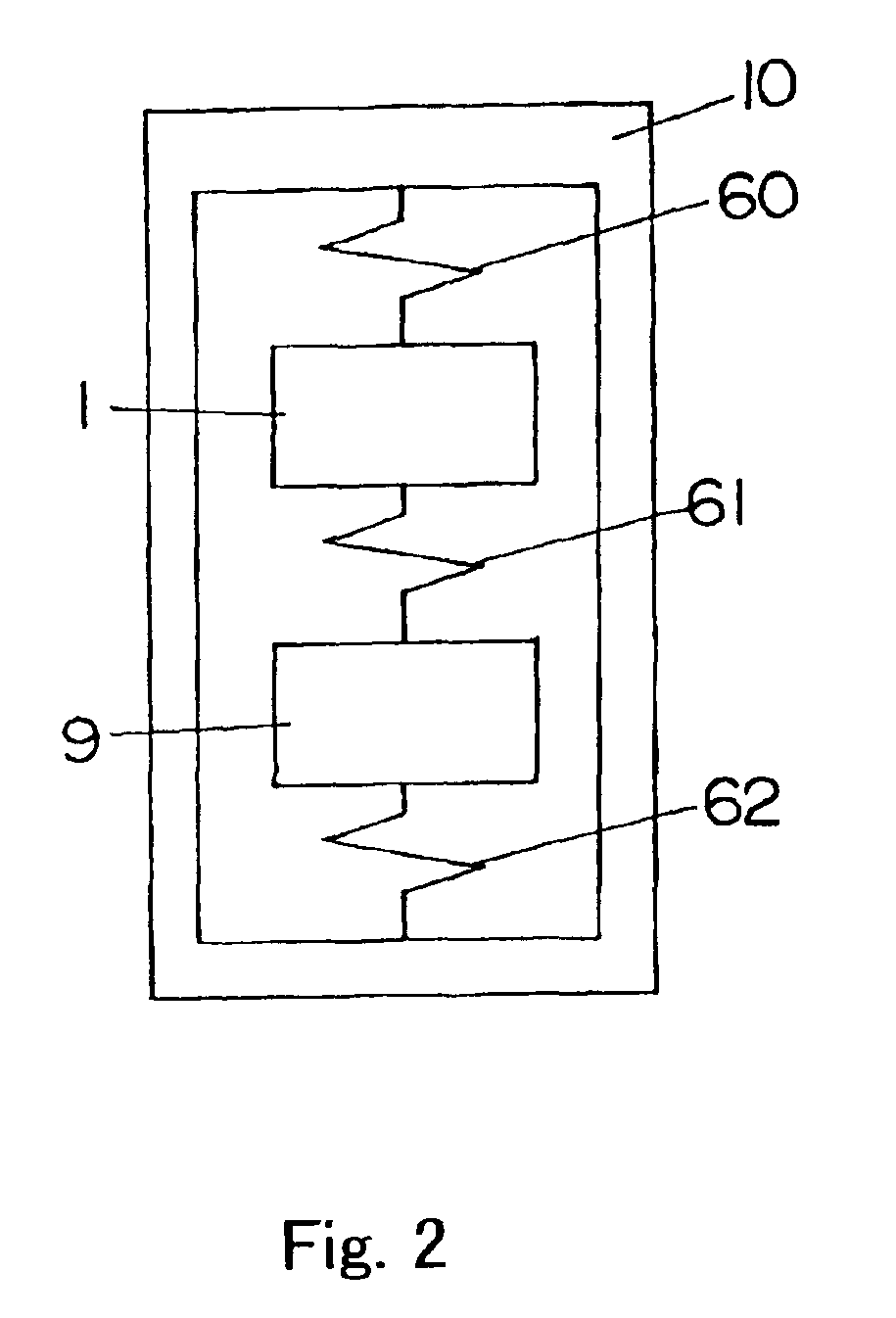
A linear oscillator includes a reciprocating moving part, a case to contain the moving part, and an amplitude control spindle moveably supported in the case. The moving part and the amplitude control spindle reciprocate at a frequency approximately equal to the resonance frequency of the linear oscillator.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Radio-frequency communication device
ActiveUS20090130981A1Exact strengthAccurate detectionWave based measurement systemsRadio transmissionAmplitude controlEngineering
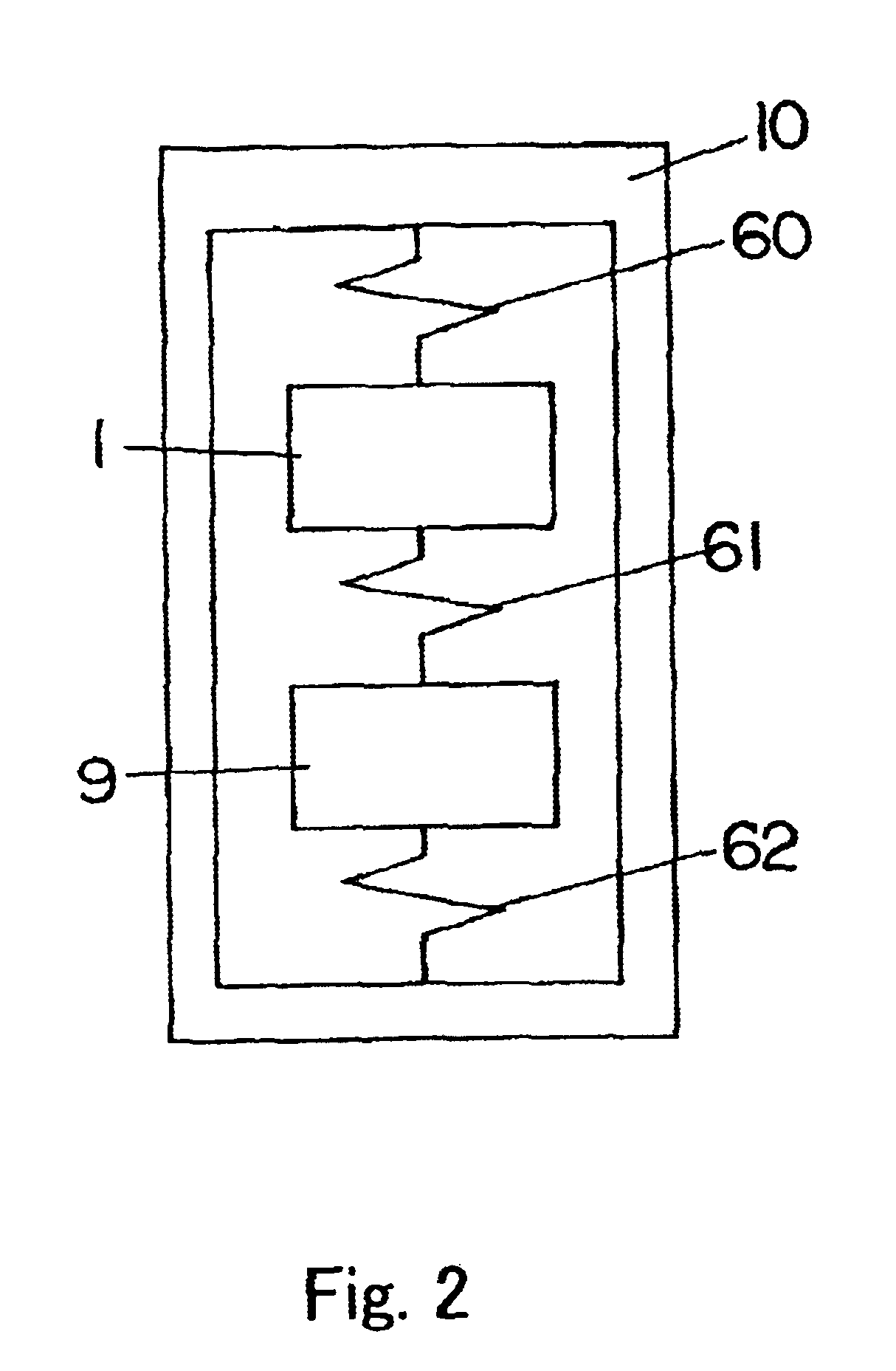
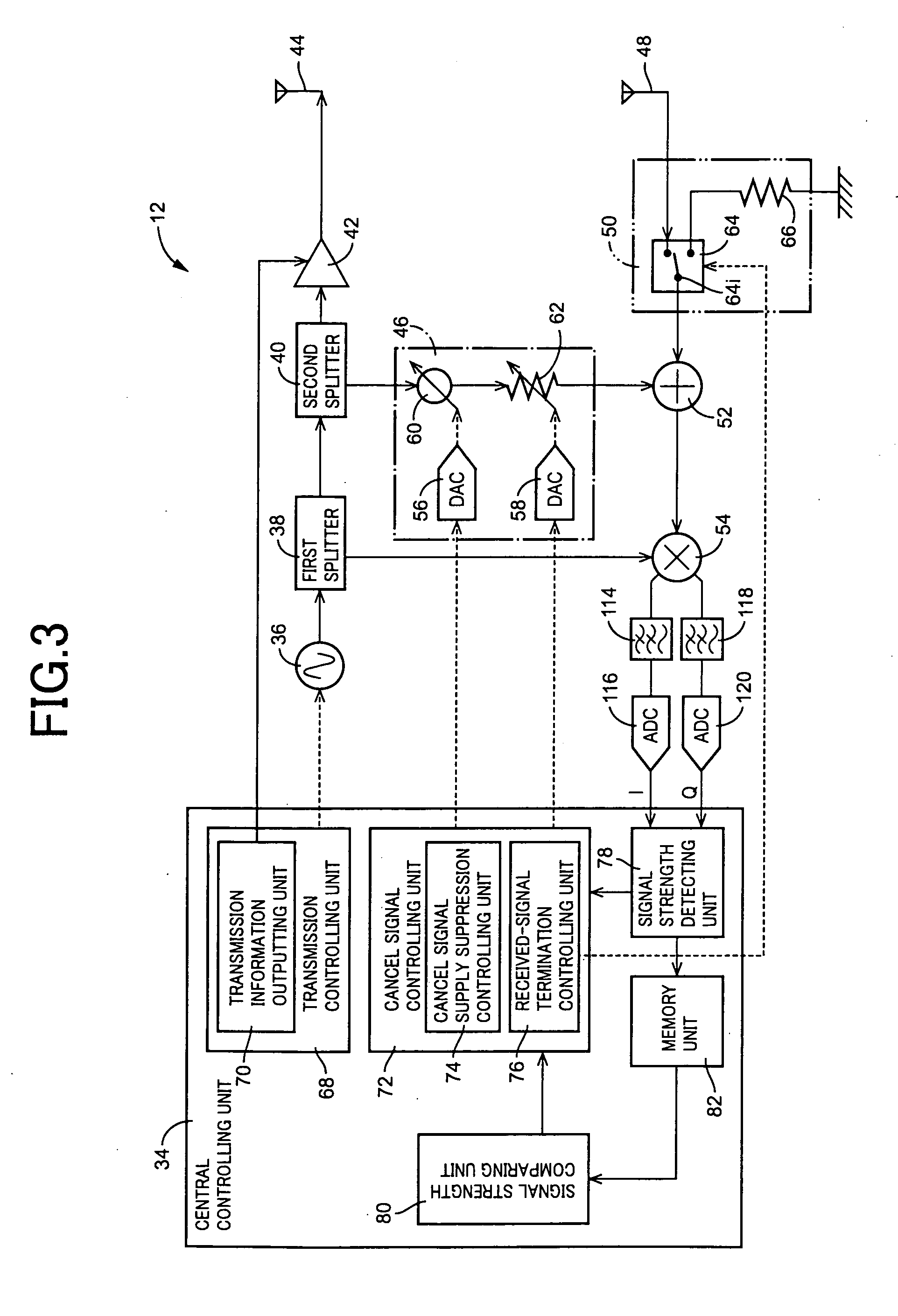
There is provided a radio-frequency communication device that can sufficiently eliminate a leakage signal from a transmission side included in a received signal. The communication device includes a cancel amplitude controlling unit 62 selectively suppressing supply of a cancel signal to a cancel signal synthesizing unit 52, a received-signal terminating unit 50 selectively terminating a received-signal input terminal 64i, a signal strength detecting unit 78 detecting a signal strength, a memory unit 82 storing a signal strength detected by the signal strength detecting unit 78, a signal strength comparing unit 80 comparing a plurality kinds of signal strengths read out from the memory unit 82, and a cancel signal controlling unit 72 controlling an amplitude and / or a phase of the cancel signal based on a result of the comparison by the signal strength comparing unit 80. Thus, suppressing the cancel signal by the cancel amplitude controlling unit 62 enables accurate detection of a strength of the received signal, as well as terminating the received signal by the received-signal terminating unit 50 enables accurate detection of a strength of the cancel signal.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
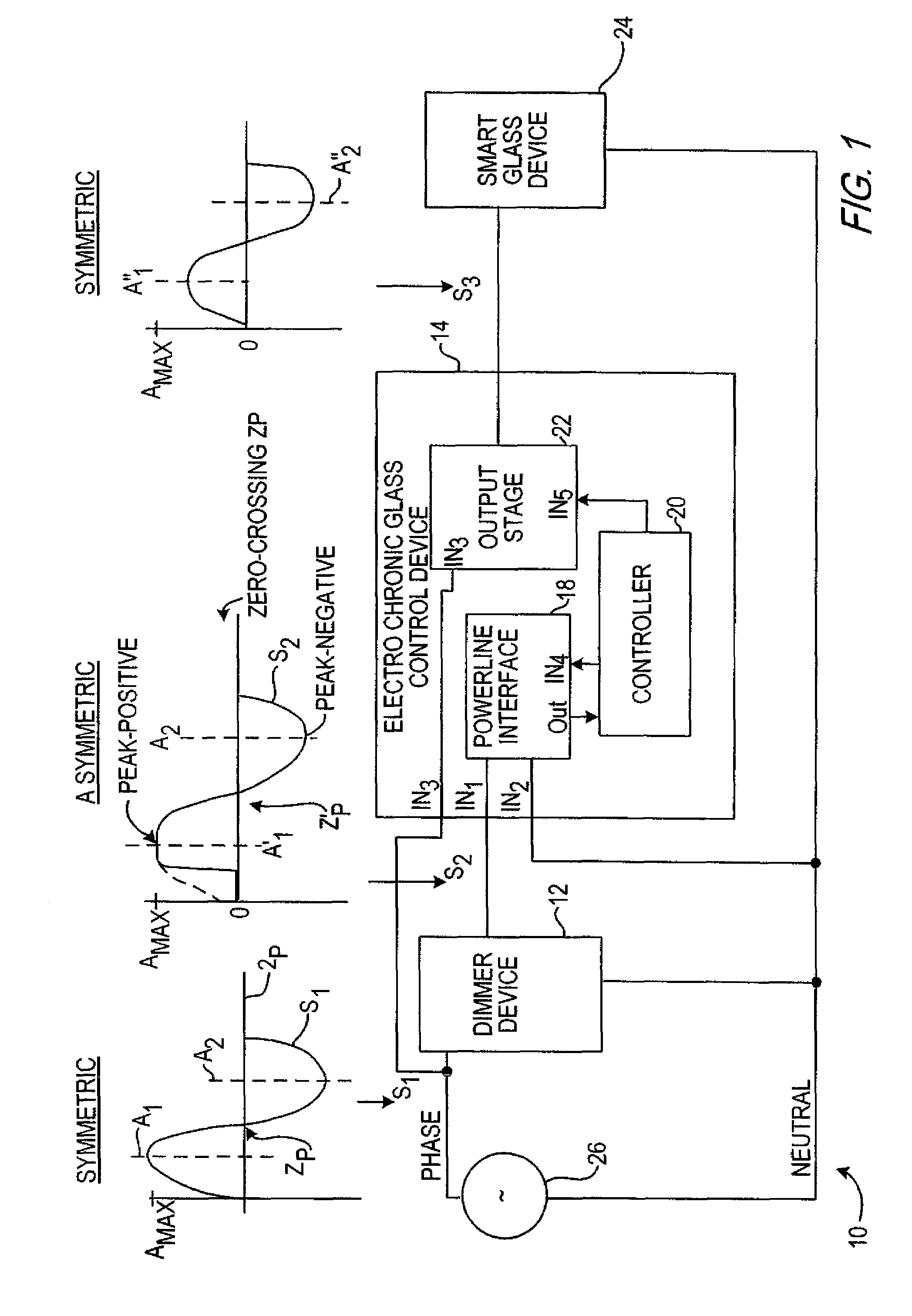
Electrochromic glass control device
InactiveUS20070097484A1Reduce heatReduce problemsStatic indicating devicesPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesElectric forceControl signal
A light control system having a full range of dimming for smart-glass by providing an interface between an off-the-shelf dimmer and a electrochromic glass device is disclosed herein. The light control system or electrochromic glass control device acts as an interface that converts an asymmetric alternating current (AC) power signal from the dimmer device into a symmetric, amplitude controlled AC output signal for controlling the tint of the smart-glass device. The electrochromic glass control device includes a powerline interface circuit that receives the asymmetric AC power signal from the dimmer. A controller connects to the powerline interface circuit to generate a control signal responsive to the asymmetric AC power signal. Connecting between the dimmer and the controller, an output stage generates the symmetrical AC output signal responsive to the control signal to control the electrochromic glass device.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Integrated tracking filters for direct conversion and low-IF single conversion broadband filters
ActiveUS7336939B2Radio transmissionTransmission noise suppressionAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A radio frequency (RF) tuner includes a programmable tracking filter bank receiving an RF input and outputting a filtered RF signal. A mixer stage receives the filtered RF signal and outputs a first quadrature component of the filtered RF signal and a second quadrature component of the filtered RF signal. Two variable gain amplifiers receive the first and second quadrature components and output amplitude-controlled I and Q components of the filtered RF signal. In one embodiment, the programmable tracking filter bank includes a plurality of tank circuits each connected to the RF input through an impedance. Each tank circuit include an inductor and a capacitor connected in parallel thereby forming an LC network, and a plurality of switched capacitors in parallel with the LC network and switched in and out of the tank circuit by programmable switches. In another embodiment, the programmable tracking filter bank includes a plurality of peaked low-pass circuits each connected to the RF input through an impedance. Each peaked low-pass circuit includes a capacitor connected to ground, and a plurality of switched capacitors in parallel with the capacitor and switched in and out of the peaked low-pass circuit by programmable switches.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
RF power amplifier controller circuit with compensation for output impedance mismatch
ActiveUS7761065B2Reduce phase distortionNarrow bandwidthResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersPhase distortionAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The amplitude control loop may also compensate for impedance mismatch with the load by increasing the power delivered from the power amplifier to the load, or decrease the output power of the power amplifier upon detection of excessive power dissipation in the power amplifier. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal to reduce phase distortion generated by the power amplifier.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Apparatus, system, and method for integrated phase shifting and amplitude control of phased array signals
ActiveUS20100013527A1Simplifies reduces costSimpler variable phase and amplitude shifterModulation transferencePulse automatic controlPhase shiftedAmplitude control
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for phase shifting and amplitude control. A two-phase local oscillator generates an in-phase sinusoidal signal of a fixed frequency and a quadrature sinusoidal signal of the fixed frequency having a ninety degree phase shift from the in-phase sinusoidal signal. A signal generator receives the in-phase sinusoidal signal and the quadrature sinusoidal signal and generates a controllable sinusoidal signal of the fixed frequency. The controllable sinusoidal signal has a variable amplitude and a shiftable phase. A mixer varies the amplitude and shifts the phase of an input signal by mixing the input signal with the controllable sinusoidal signal to generate an output signal. The input signal and the output signal carry phase and amplitude information required for phased array signal processing. Either a receiver or a transmitter may be implemented using the present invention.
Owner:OVZON LLC
Amplifier circuit
InactiveUS7068095B2Improve power supply rejection ratioNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierAmplitude control
The invention is directed to an amplifier circuit based on the principle of a class D amplifier. To avoid unwanted convolution effects and to improve the power supply rejection ratio, provision is made for the amplitude of the ramp signal used for pulse width modulation to track proportionally the supply voltage for the amplifier circuit. For this purpose, the ramp signal generator has an amplitude control input suitably connected to supply and reference potentials. This ensures a constant duty ratio which is independent of the supply voltage. The present circuit may be used, for example, as a DC / DC converter or as an audio amplifier.
Owner:INTEL MOBILE COMM GMBH
Linear oscillator
InactiveUS6958553B2Reduce vibrationLittle noiseMechanical energy handlingMetal working apparatusResonanceReciprocating motion
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
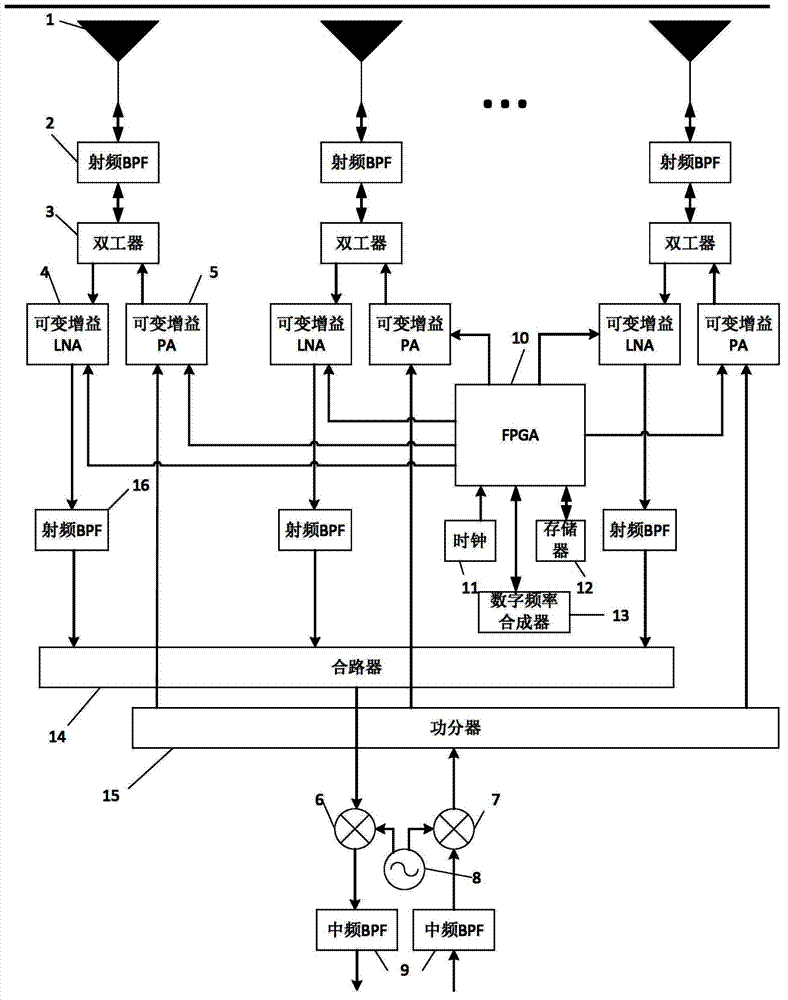
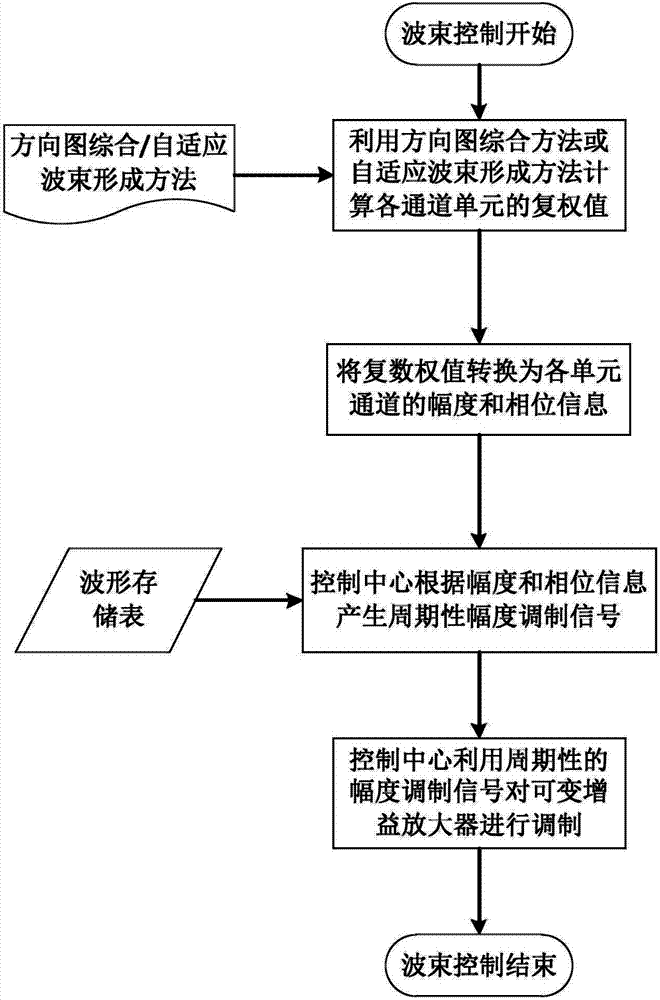
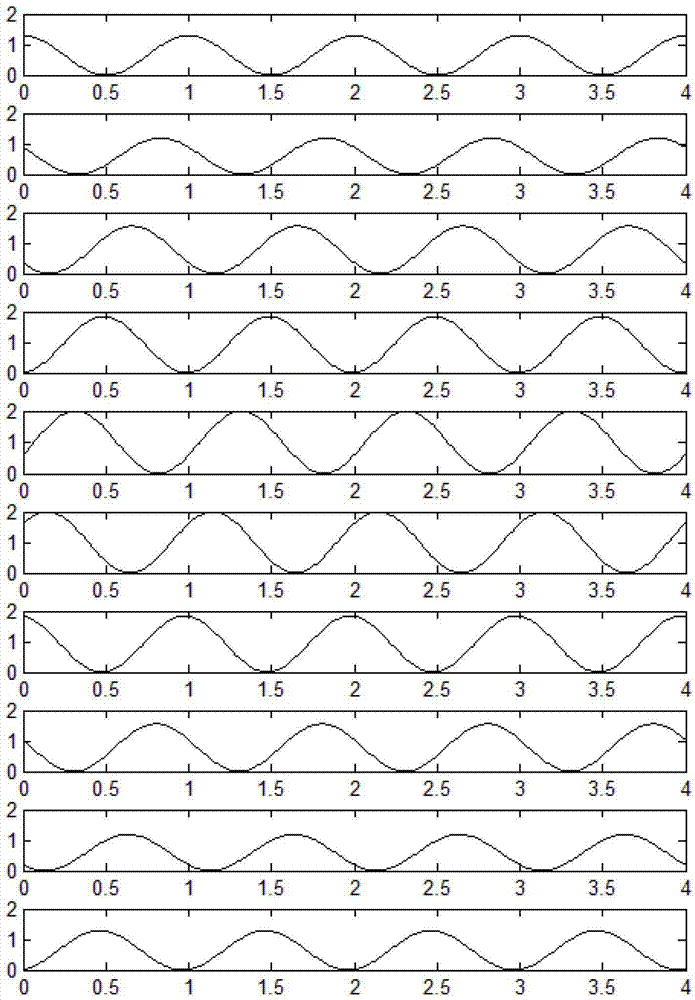
Periodic amplitude control-based phased-array antenna system and wave beam control method
The invention discloses a periodic amplitude control-based phased-array antenna system. The periodic amplitude control-based phased-array antenna system comprises a plurality of phased-array antenna unit passages, a combiner, a power divider, a frequency converter unit and a medium frequency band pass filter unit, wherein each phased-array antenna unit passage comprises an antenna, a first radio frequency band pass filter, a duplexer, a variable gain amplifier unit, a second radio frequency band pass filter and an amplifier control unit; and the amplifier control unit periodically controls the gain of the variable gain amplifier unit. The invention also discloses a wave beam control method of the periodic amplitude control-based phased-array antenna system. By periodically controlling the amplitude of a transmitted / received radio frequency signal, combined control over the amplitude and the phase of the phased-array antenna system is realized, and directional diagram synthesis and adaptive wave beam formation of a phased-array antenna array can be realized without using a phase shift device; and the periodic amplitude control-based phased-array antenna system can be widely applied to systems requiring flexible wave beam control such as phased-array radar and electronic countermeasure.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Polar loop radio frequency (RF) transmitter having increased dynamic range amplitude control
ActiveUS7787570B2Power managementAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsControl systemPower control system
A closed loop power control system for a radio frequency (RF) transmitter comprises a first variable gain element located in a power control loop and configured to receive a power level signal and an inverse representation of a power control signal, a second variable gain element located in the power control loop and configured to receive an error signal and the power control signal, and a third variable gain element configured to receive an amplitude modulated (AM) signal and the power control signal, the third variable gain element having a gain characteristic configured to operate to reduce the gain applied to the AM signal when the power control signal falls below a minimum predetermined value, and to provide the AM signal as a reference signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
RF Power Amplifier Controller Circuit
ActiveUS20070184792A1Reduce phase distortionNarrow bandwidthResonant long antennasSupply voltage varying controlPhase distortionAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal to reduce phase distortion generated by the power amplifier. The amplitude control loop and the phase control loop may also adjust the gain and / or phase of the power amplifier, respectively.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com