Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1295 results about "Rotary actuator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A rotary actuator is an actuator that produces a rotary motion or torque. The simplest actuator is purely mechanical, where linear motion in one direction gives rise to rotation. The most common actuators though are electrically powered. Other actuators may be powered by pneumatic or hydraulic power, or may use energy stored internally through springs.
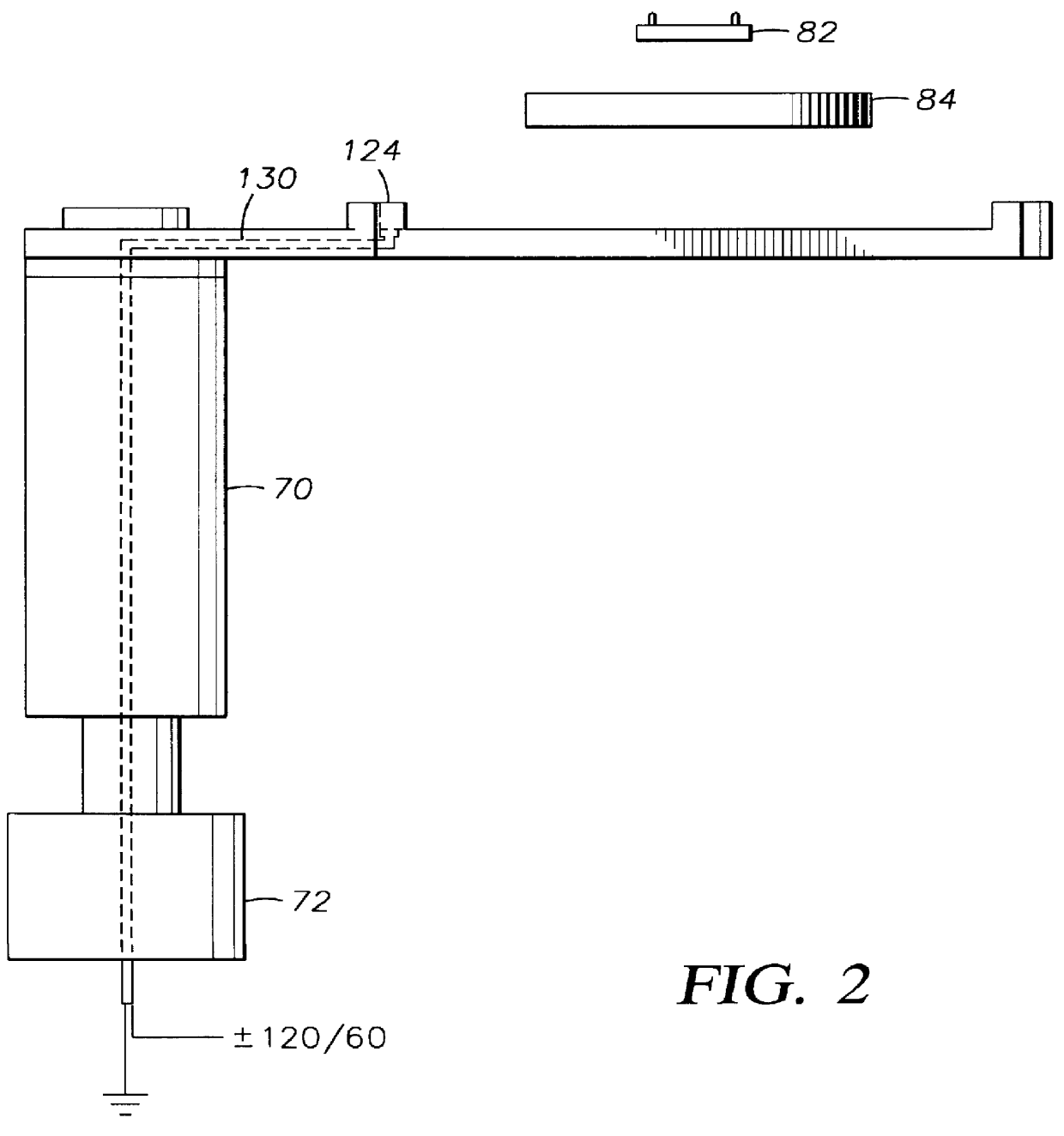
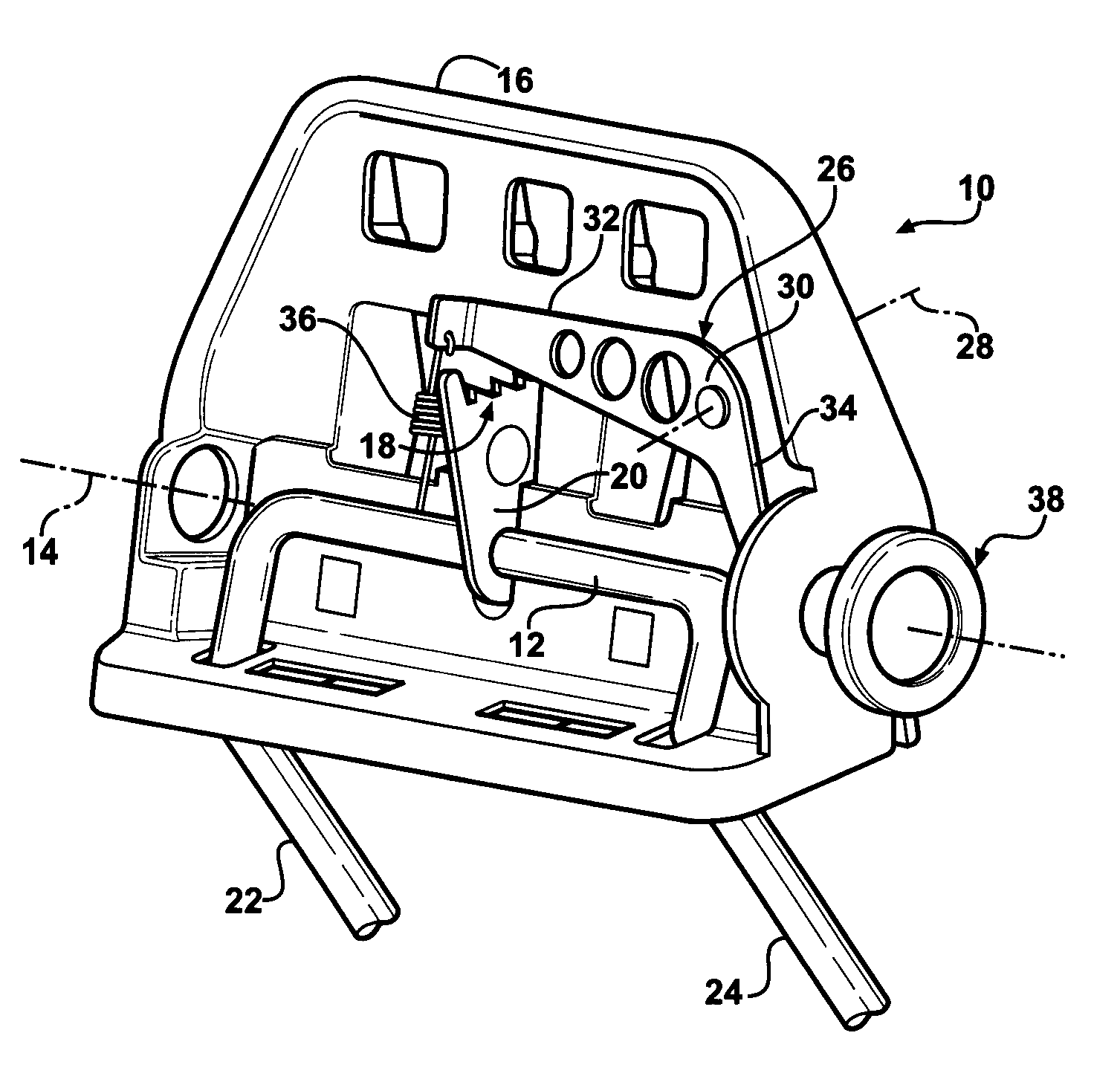
Safety lockout for actuator shaft
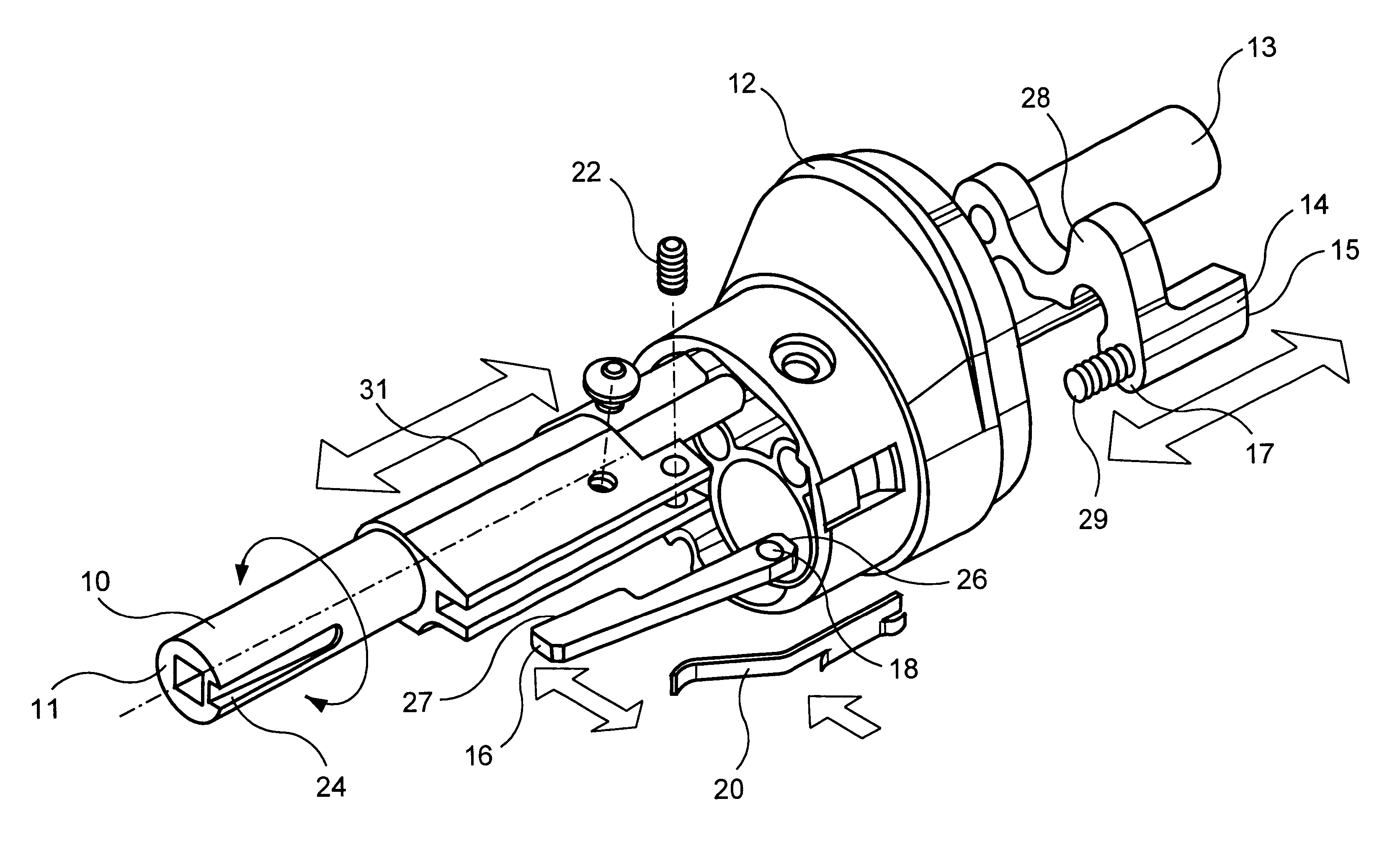
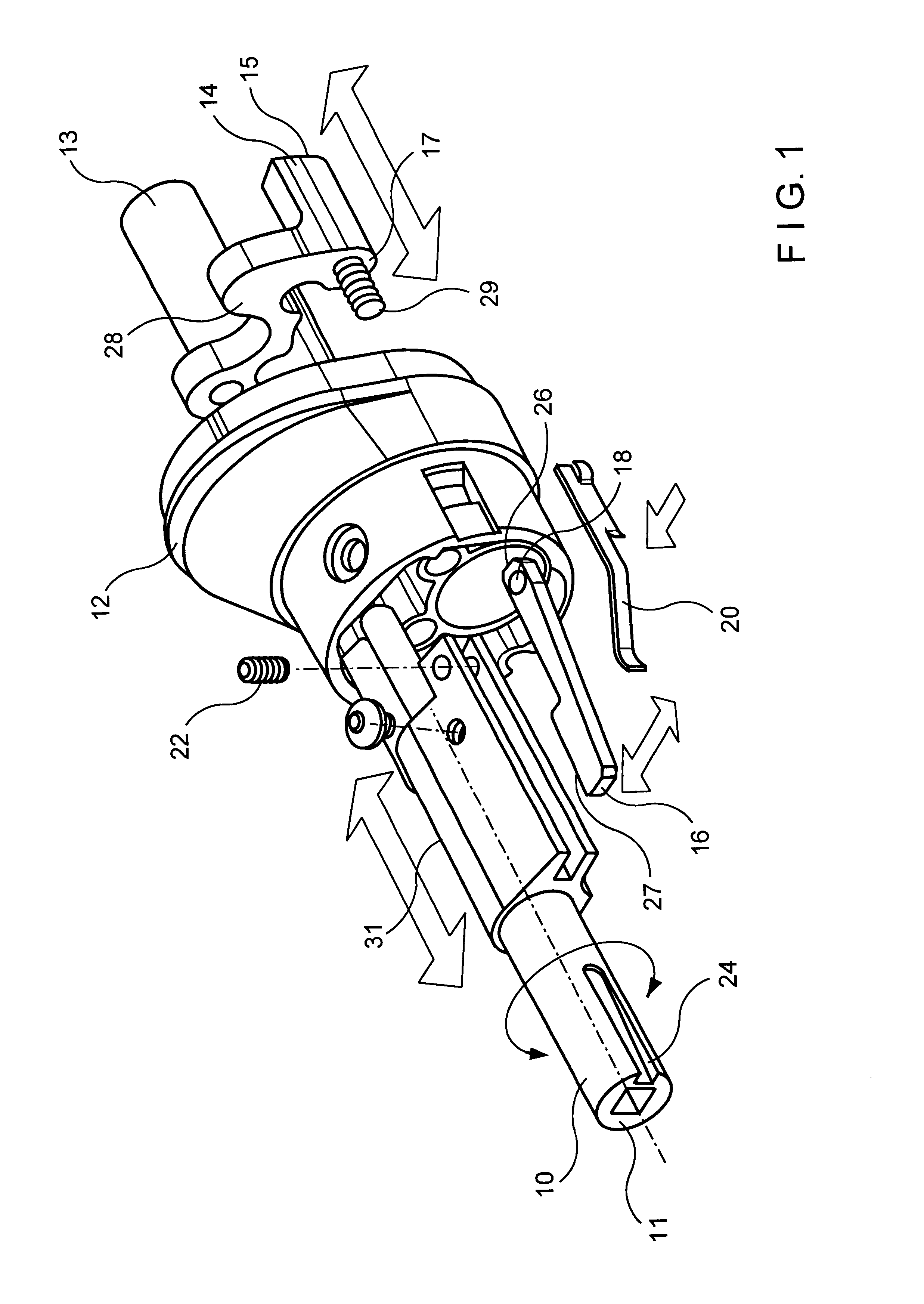
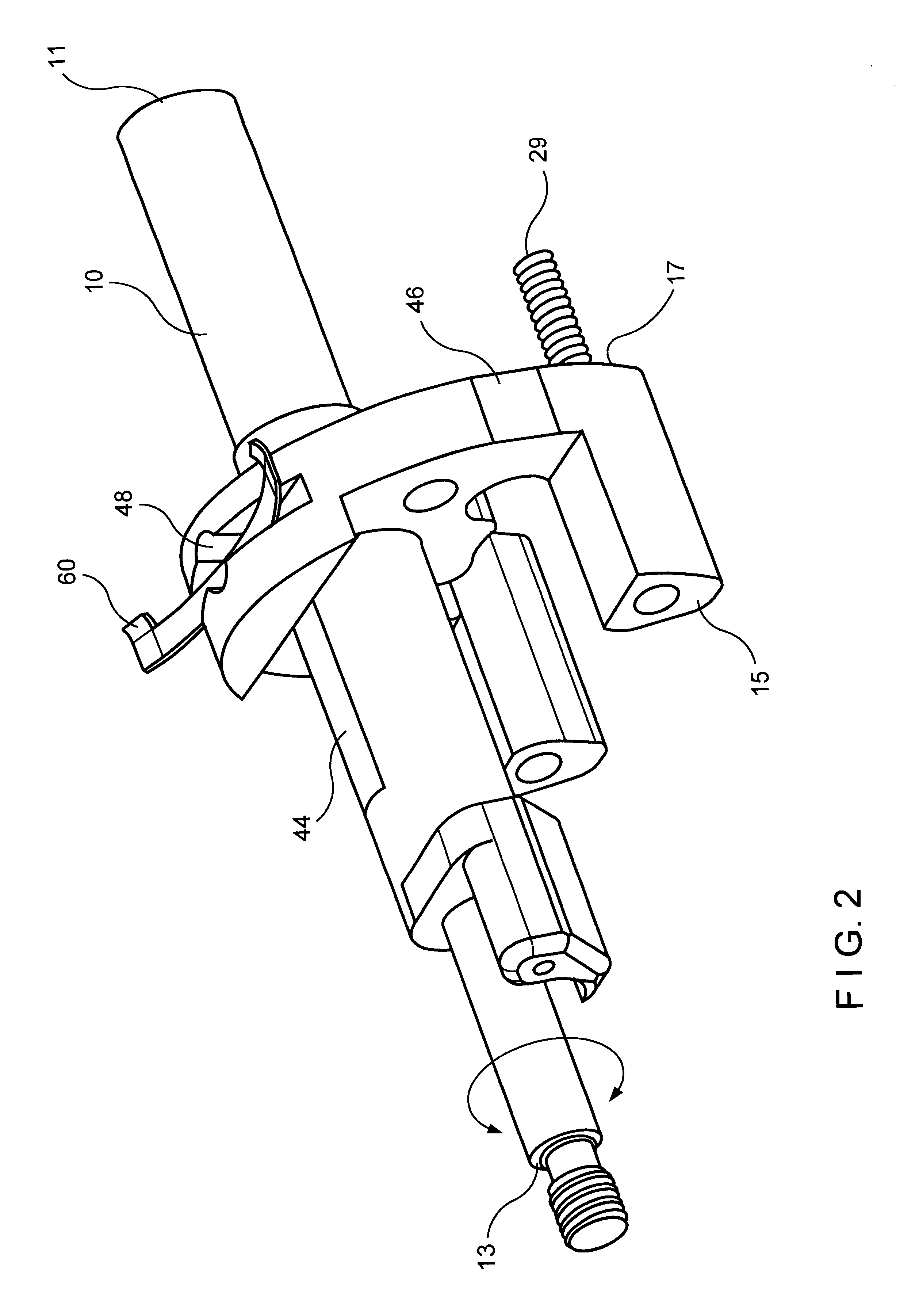
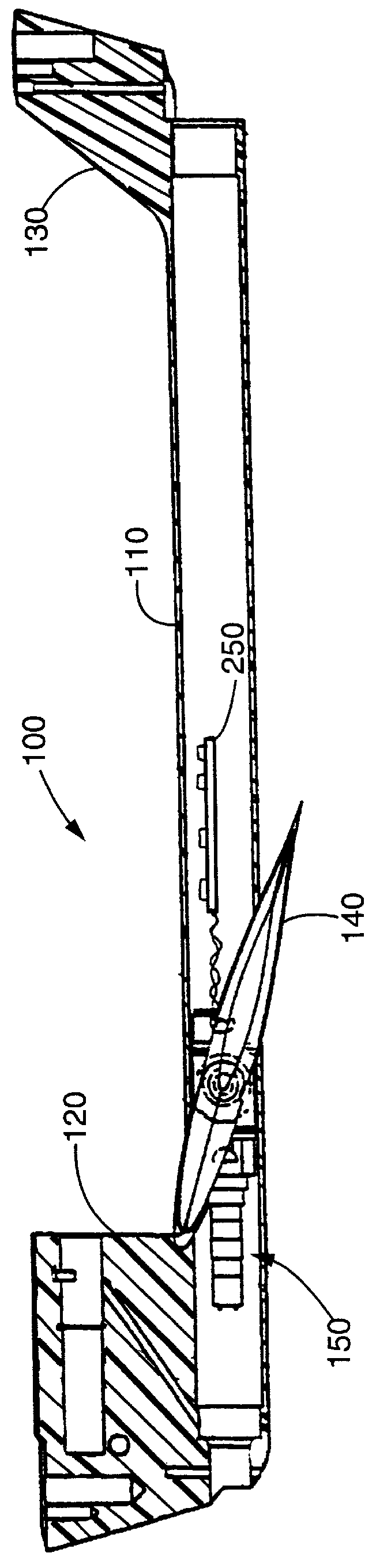
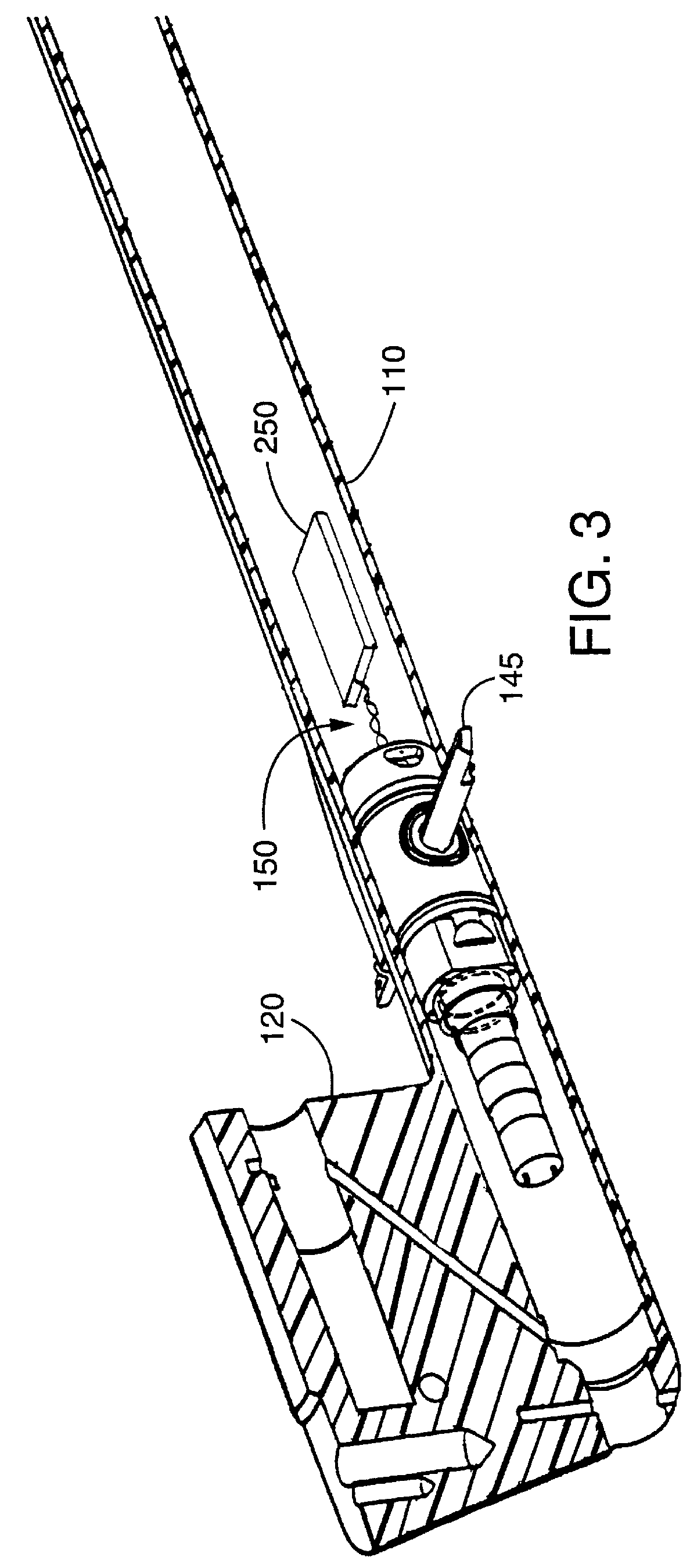
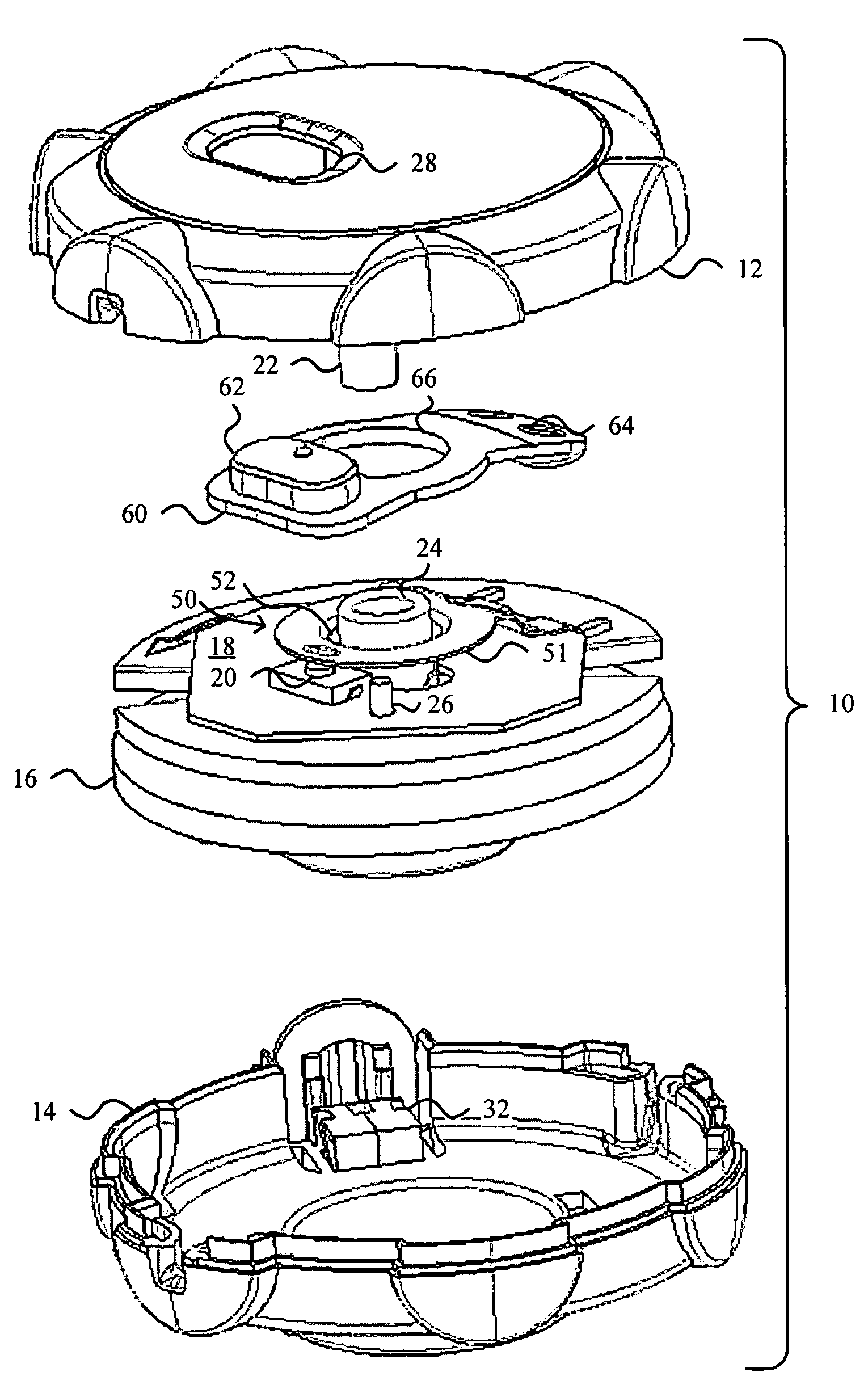
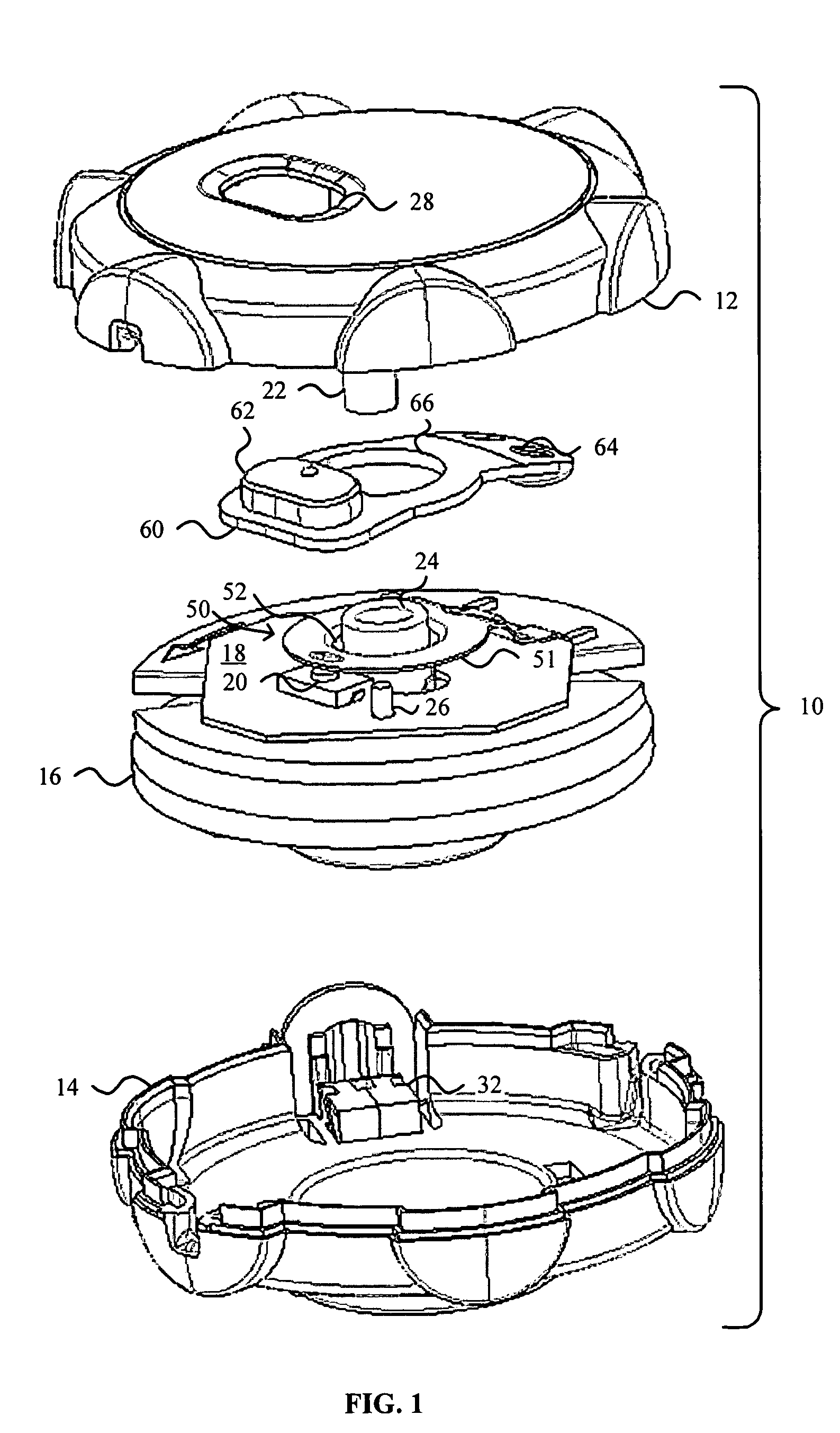
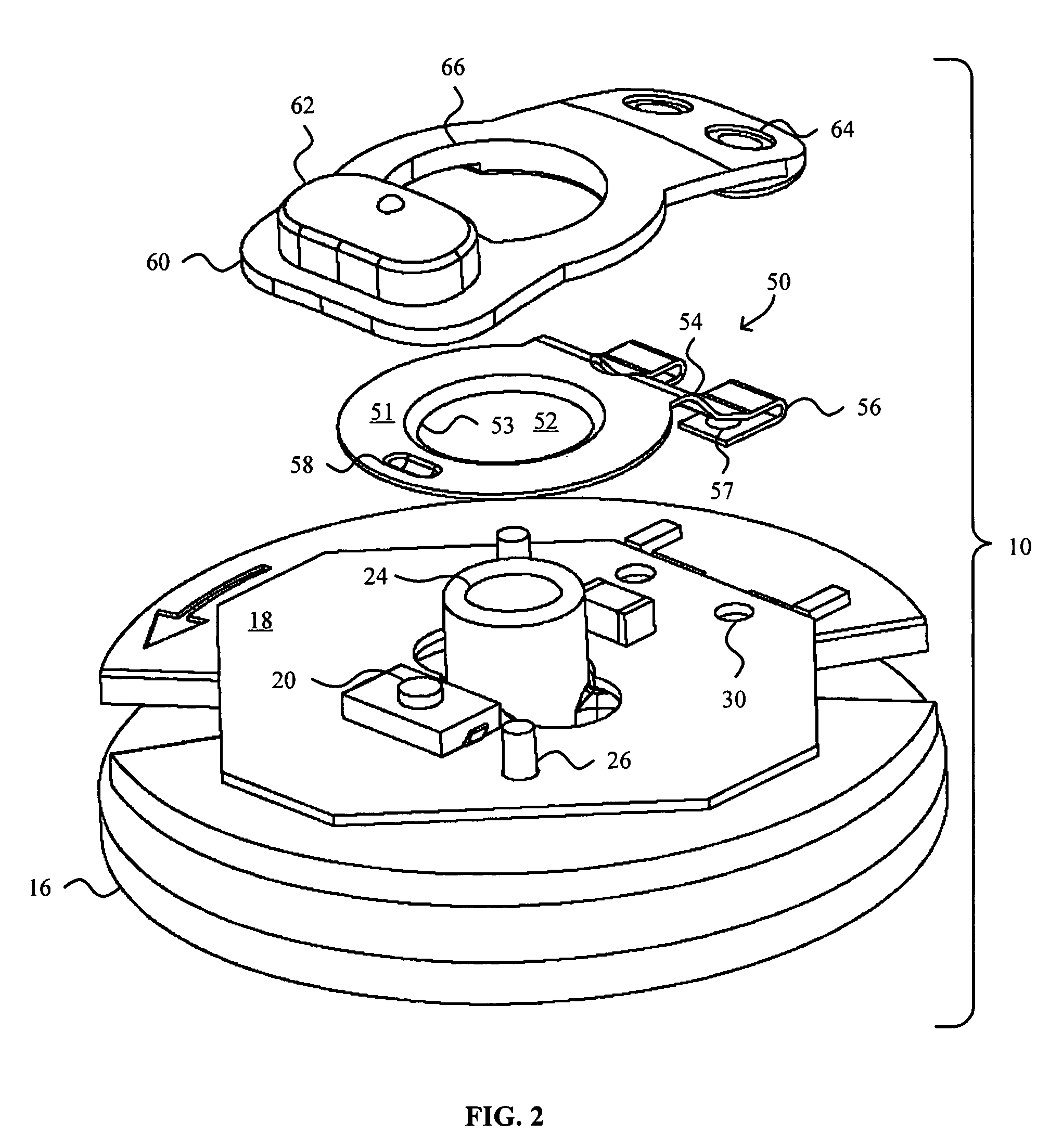
A safety lock-out to prevent rotation of a rotary actuator is described. When an axial distance between a first and a second portion of an actuated mechanism exceeds a selected distance, the lock-out prevents the rotation. The safety lock-out includes a shaft rotatably connected to the first portion and axially movable relative to the second portion. A locking member is adapted to lock the rotary actuator by placing a protrusion in a notch of the shaft, thus preventing rotation of the shaft. The device also includes a spring member urging the locking member in the locking position, and an unlocking member adapted to urge the locking member in the unlocked position when the selected distance is not exceeded.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method For Feeding Staples In a Low Profile Surgical Stapler
A method for feeding a fastener including the step of providing a device having a housing, at least one fastener within the housing, wherein the fastener is disposed within the housing in a first plane, an elongated actuator disposed within the housing, the actuator comprising a shaft substantially parallel to a longitudinal axis of the housing and rigidly spaced from the fastener in a second plane the actuator comprising at least one radially extending advancer disposed along a length thereof. The method further includes the step of rotating the actuator so to engage the fastener, and longitudinally moving the actuator to advance the fastener.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
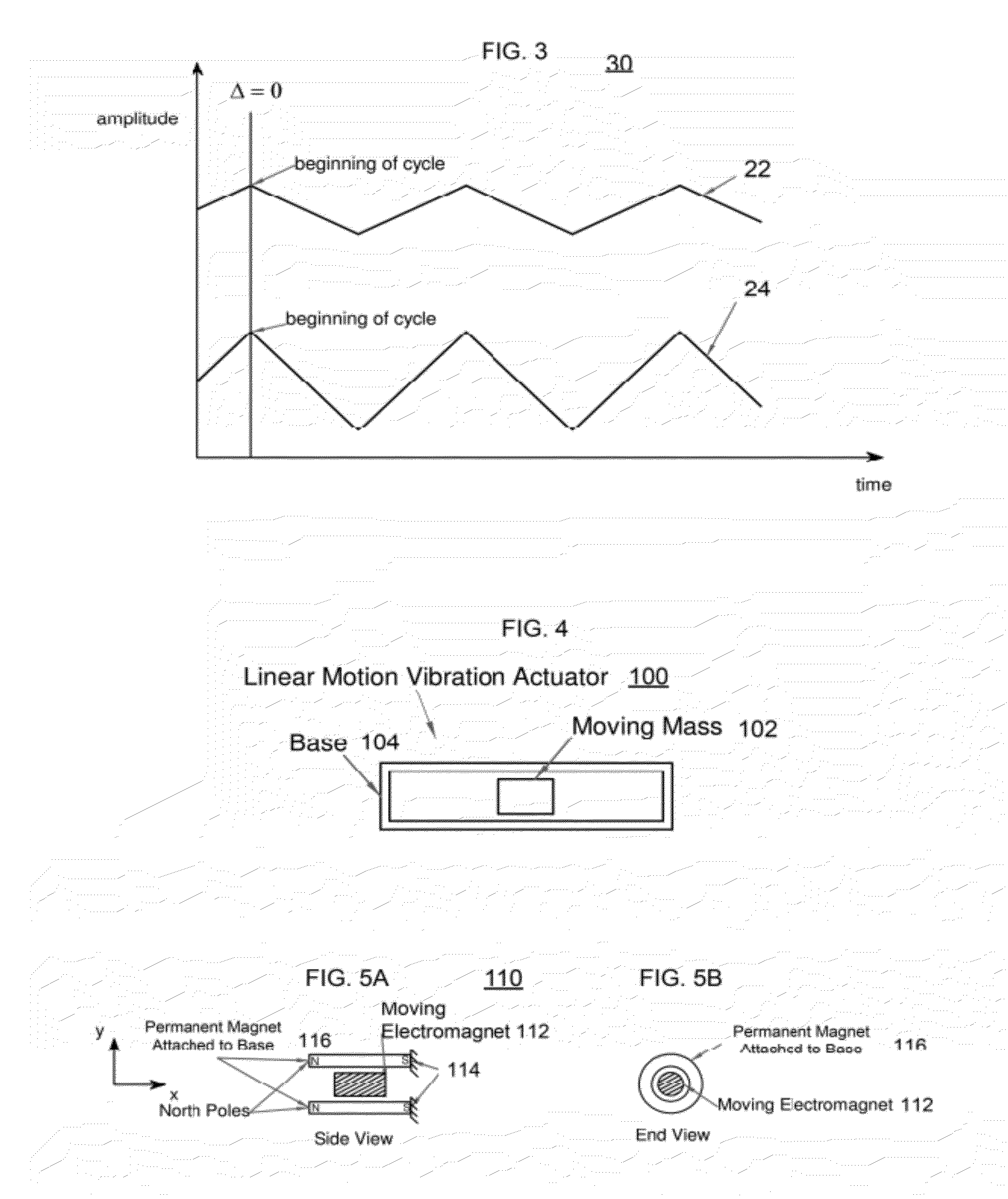
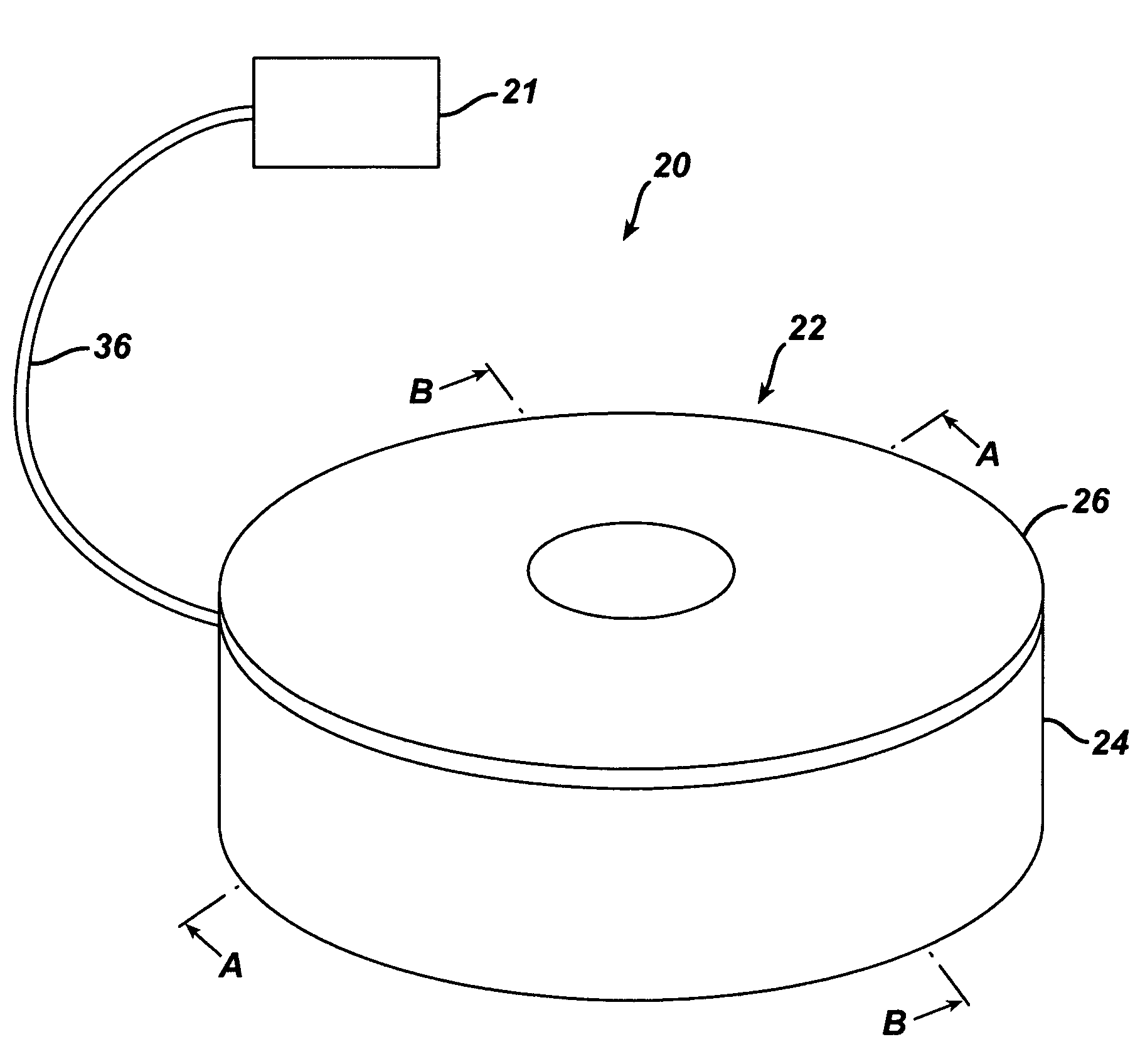
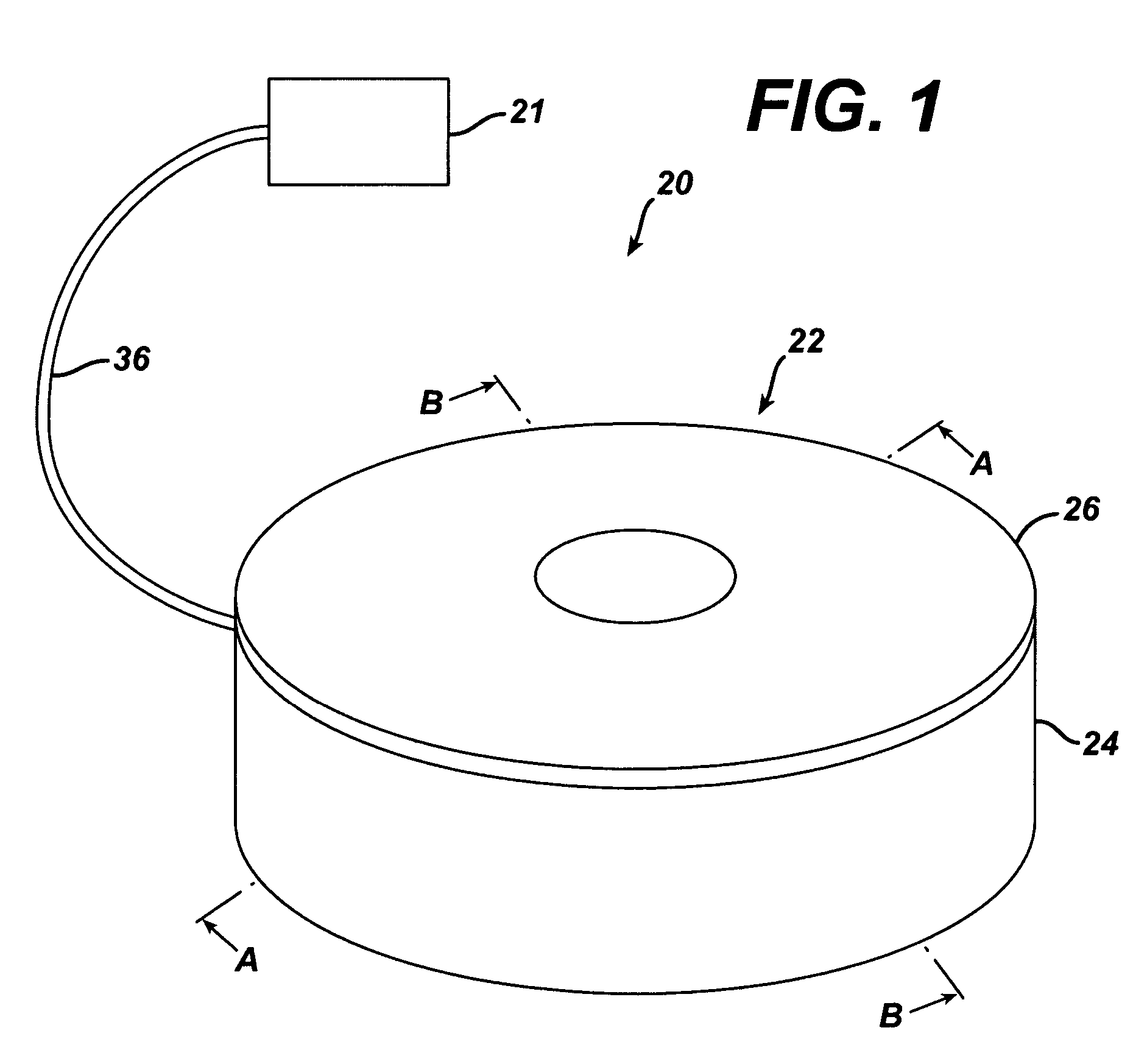
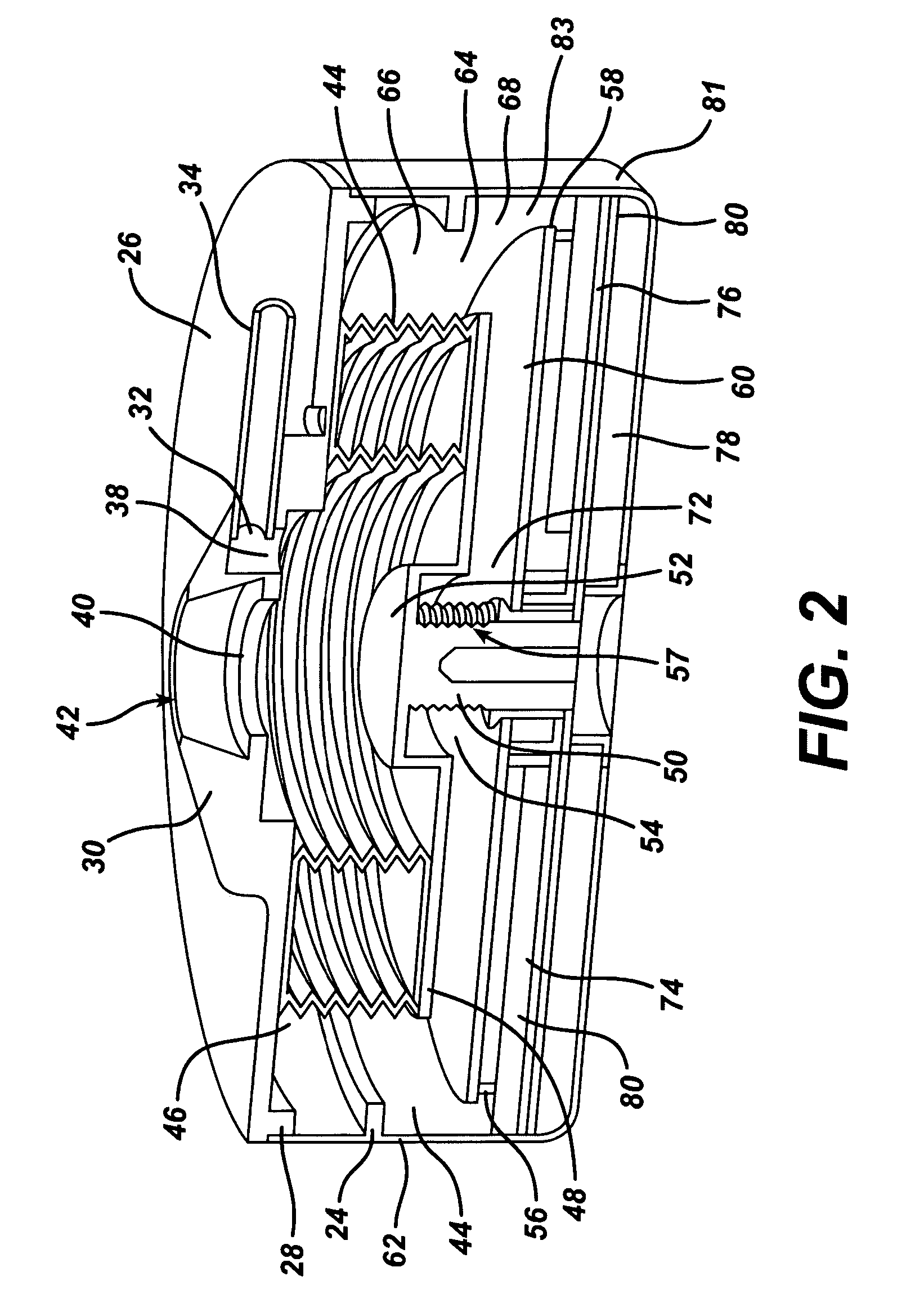
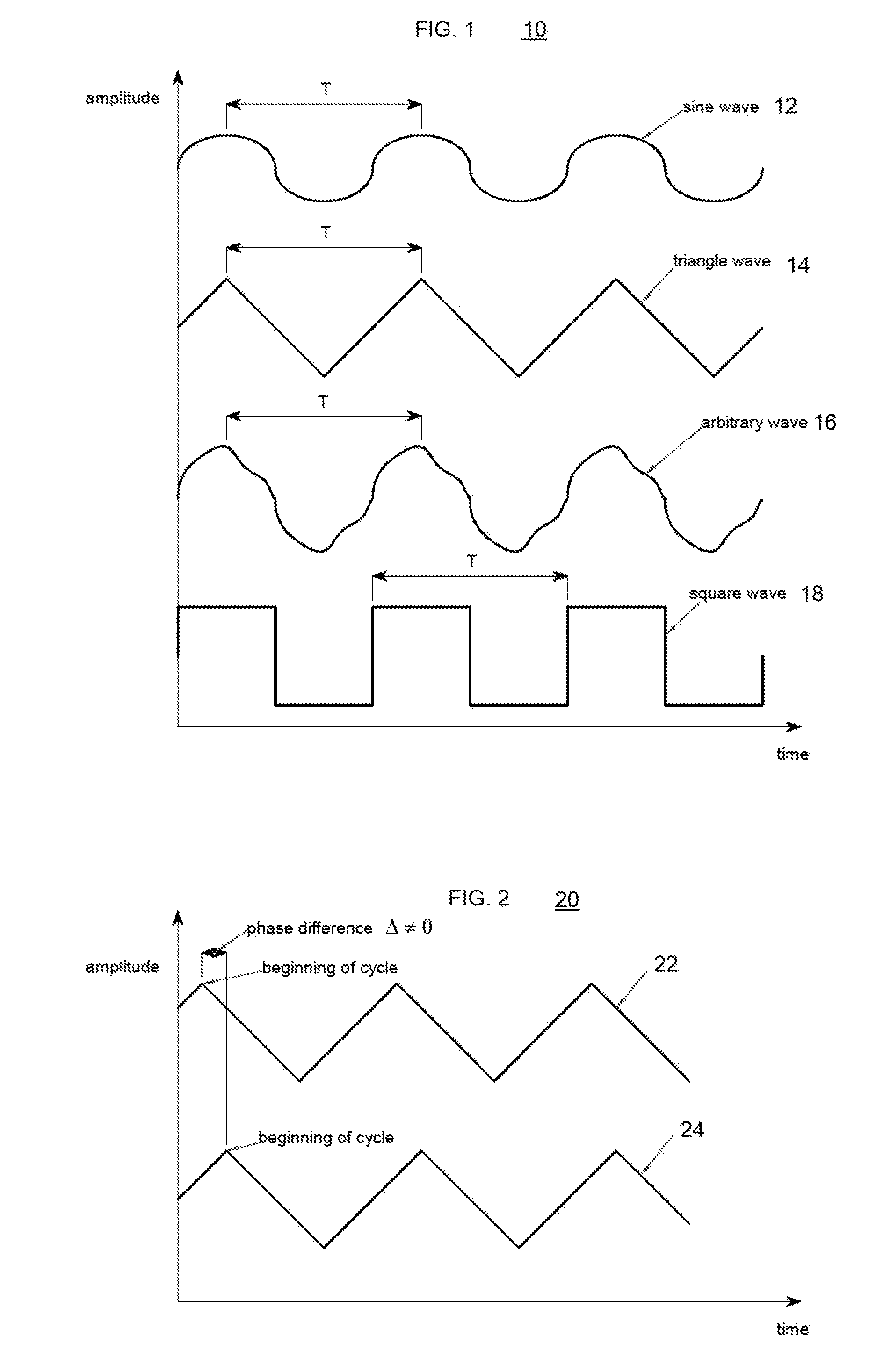
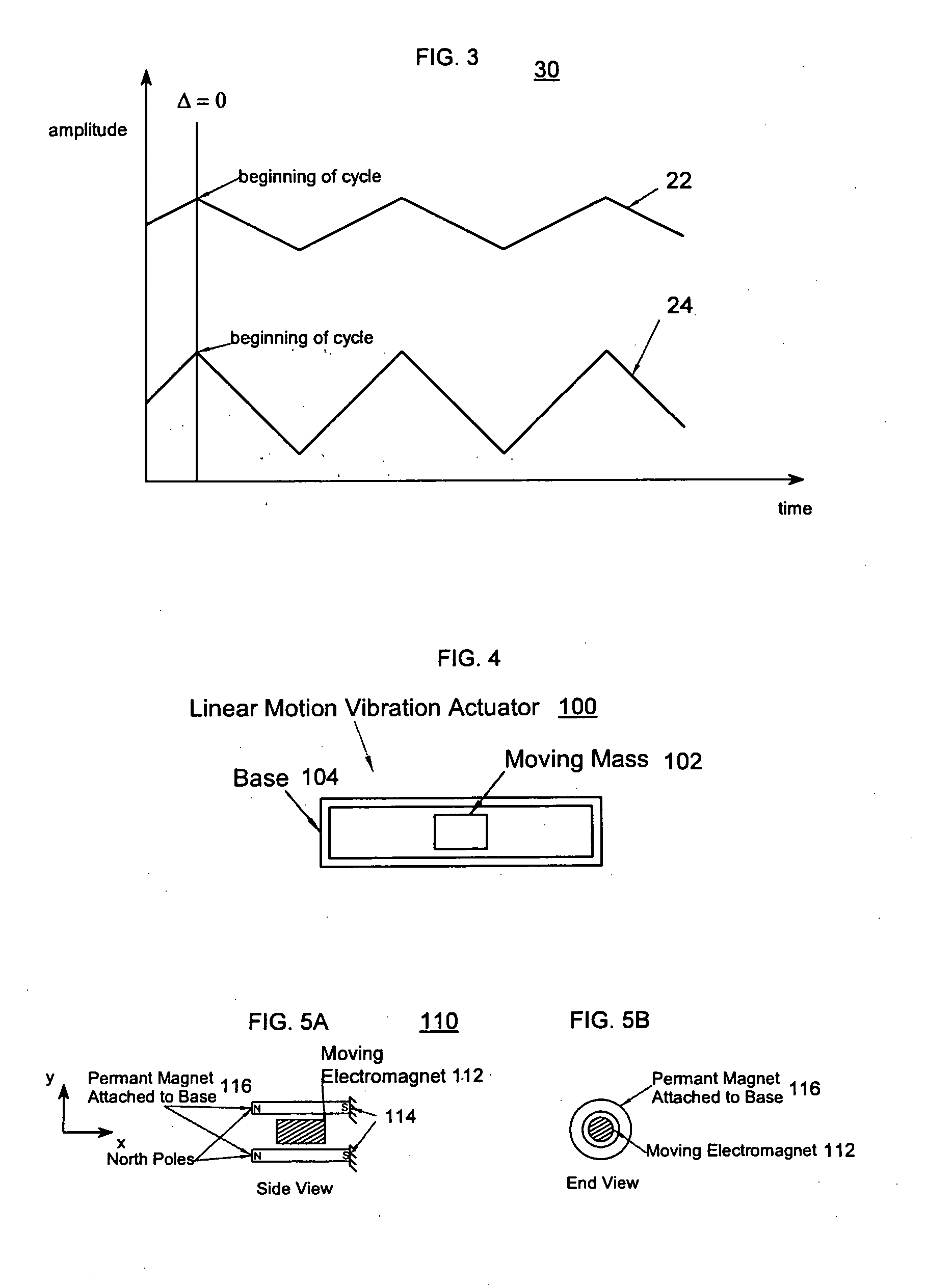
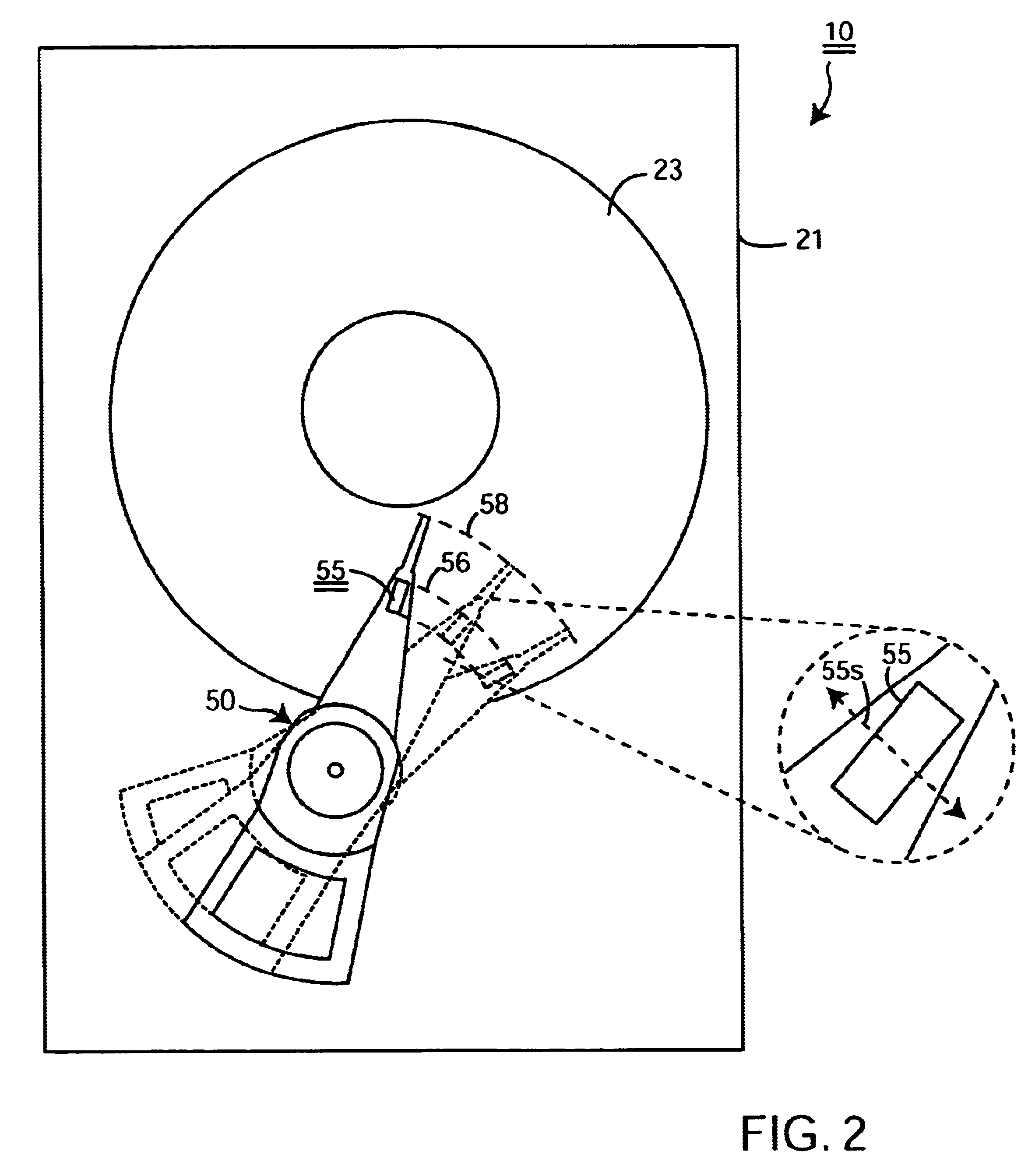
Synchronized vibration device for haptic feedback
ActiveUS20060290662A1DC motor speed/torque controlAc-dc conversion without reversalDriver circuitVibration control
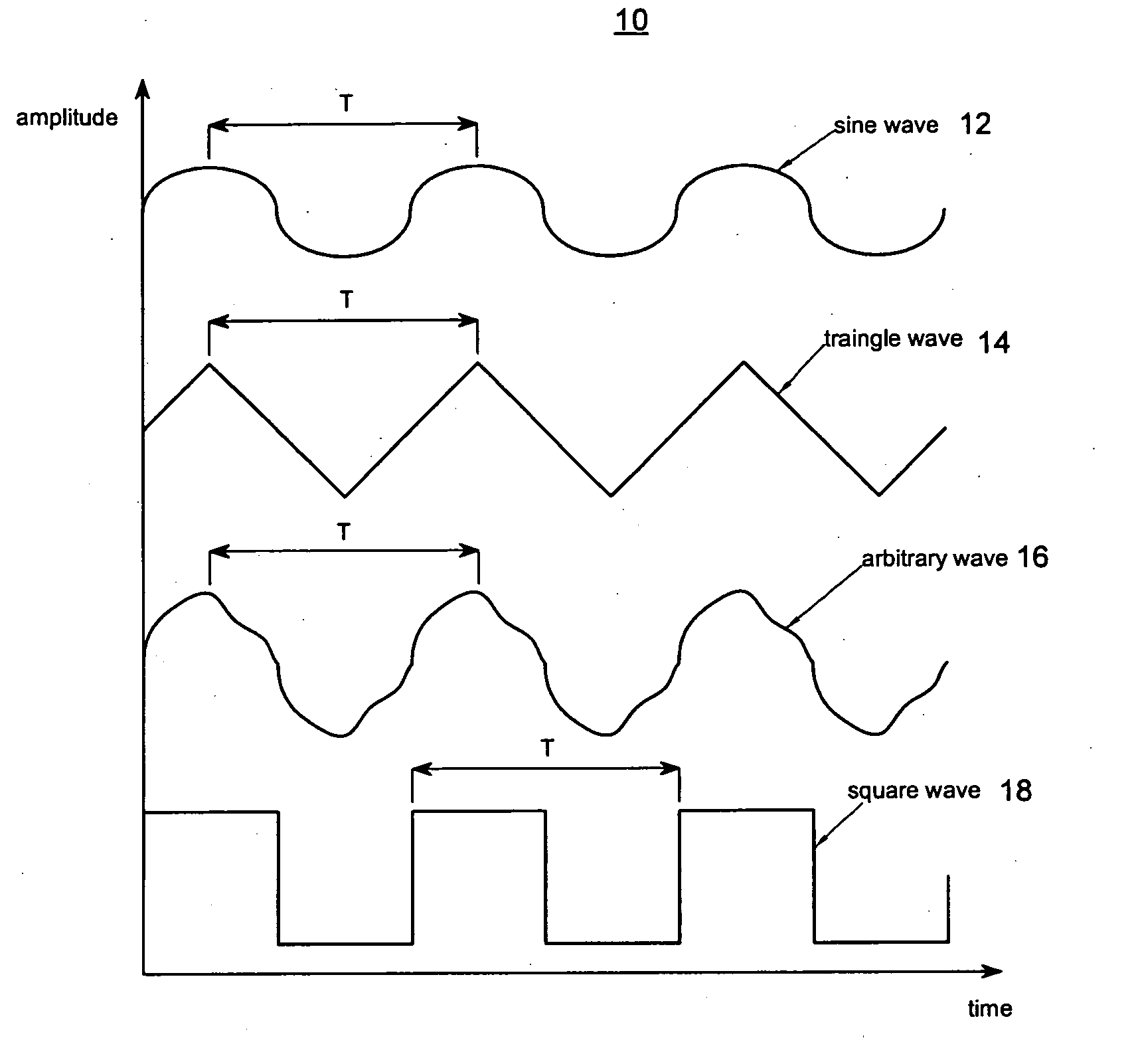
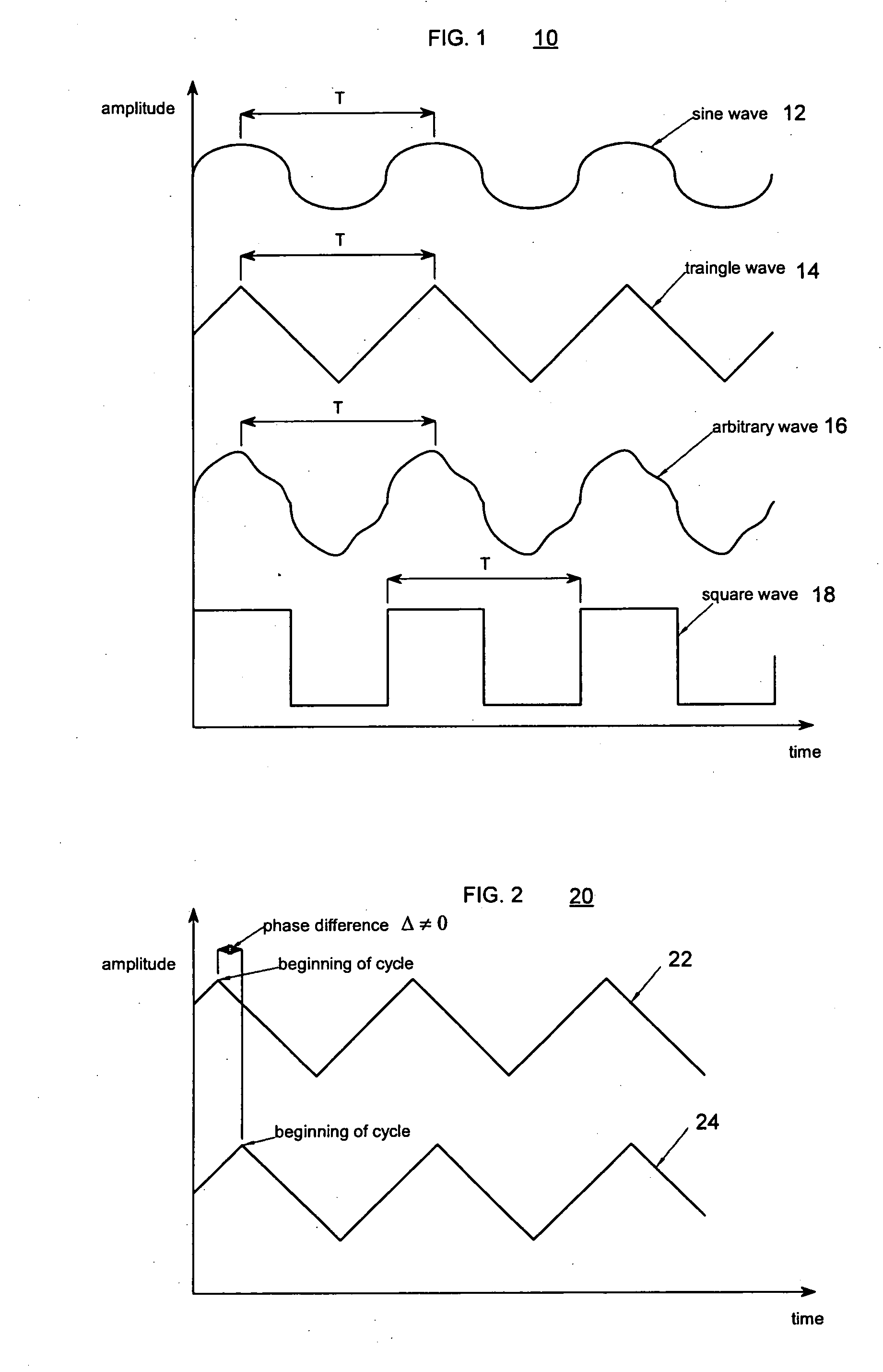
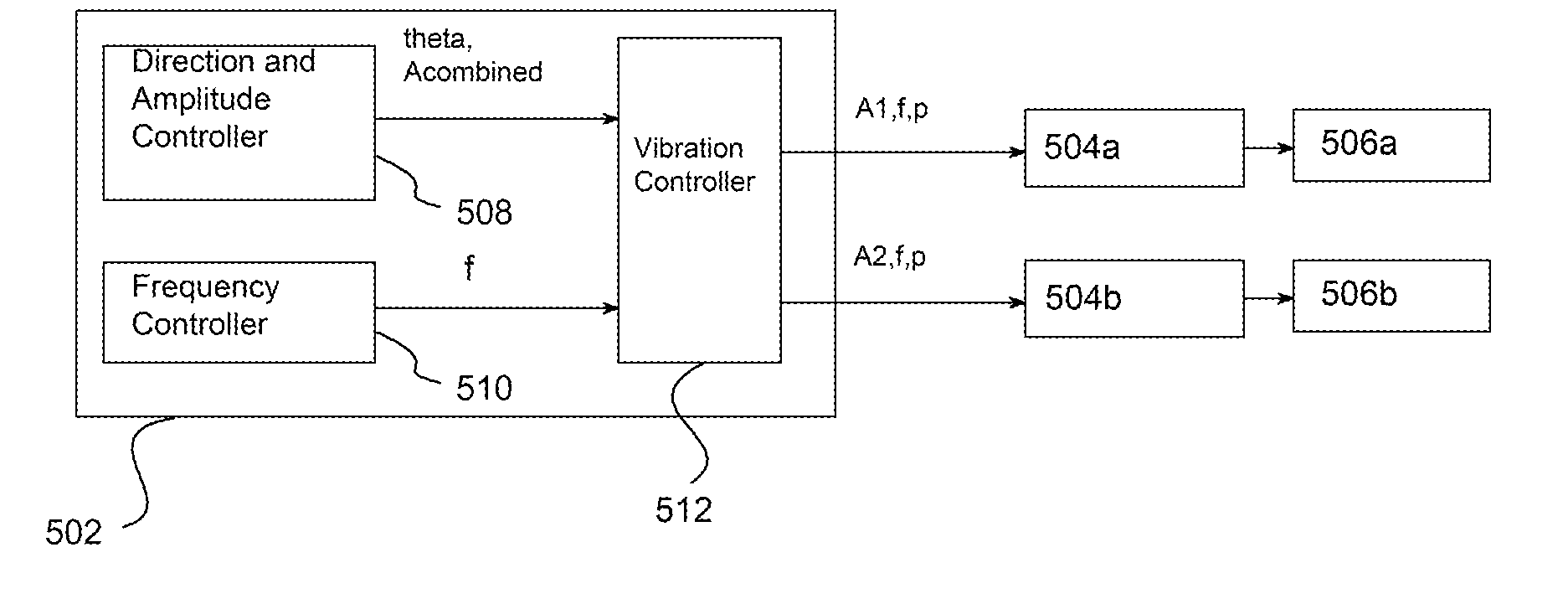
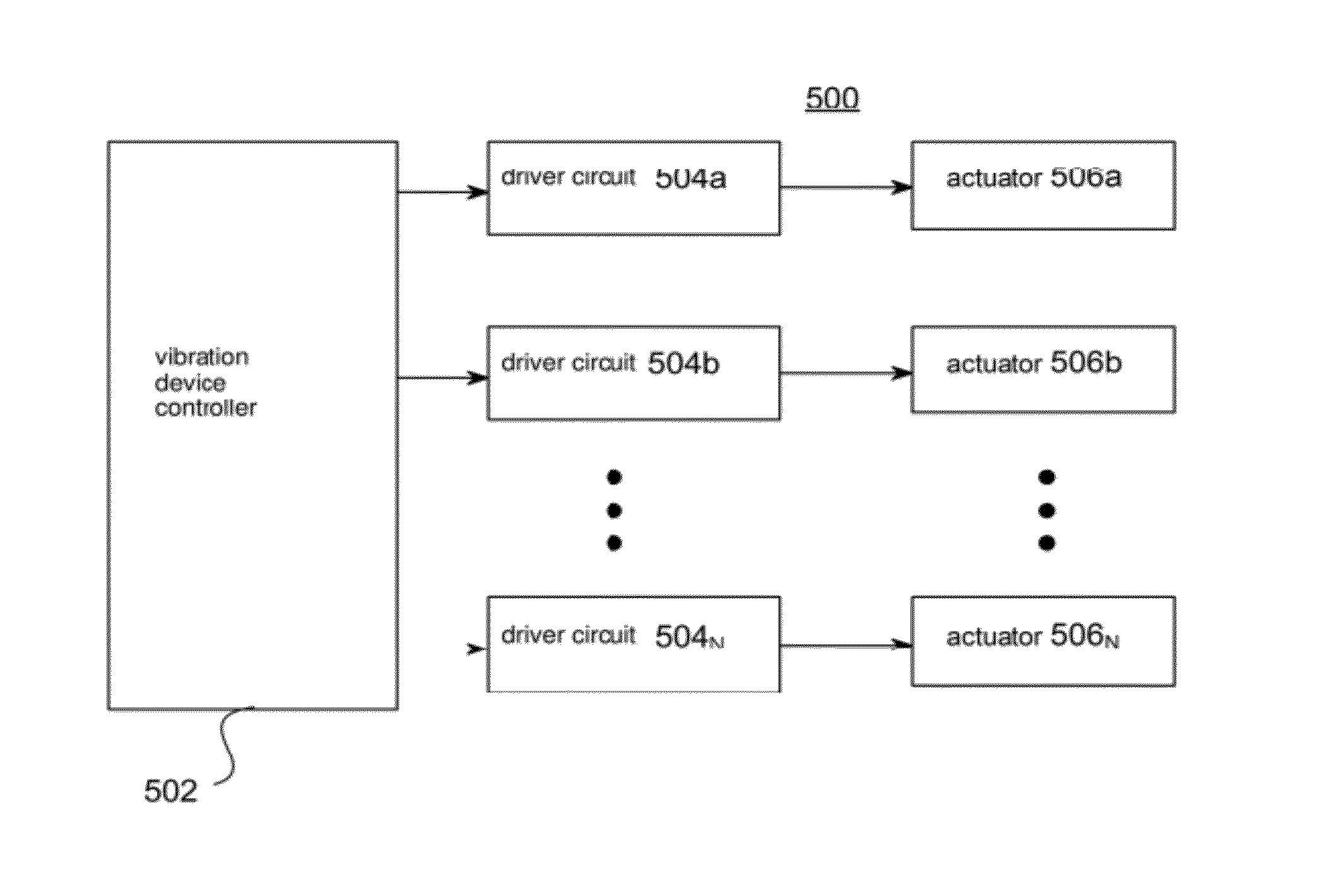
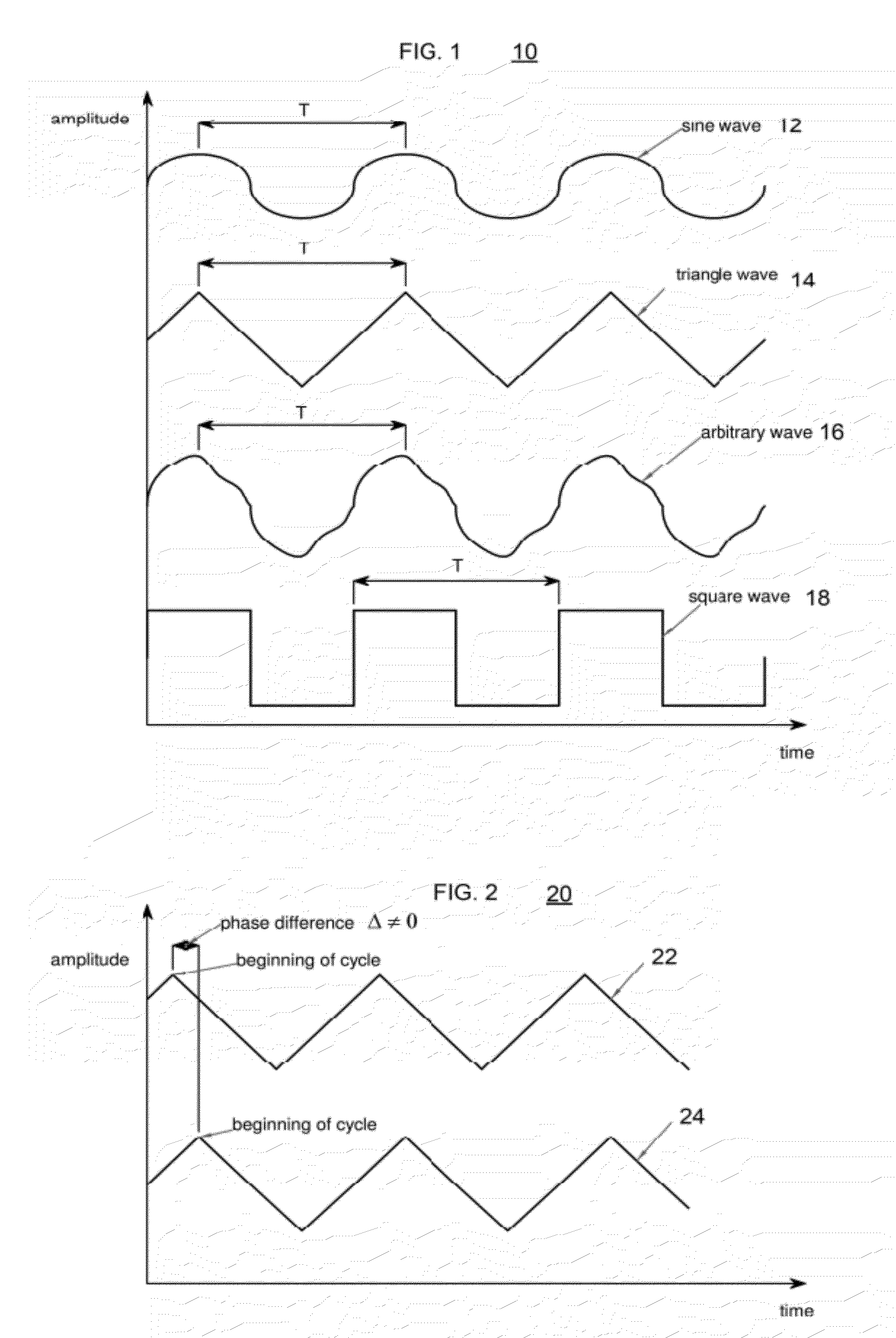
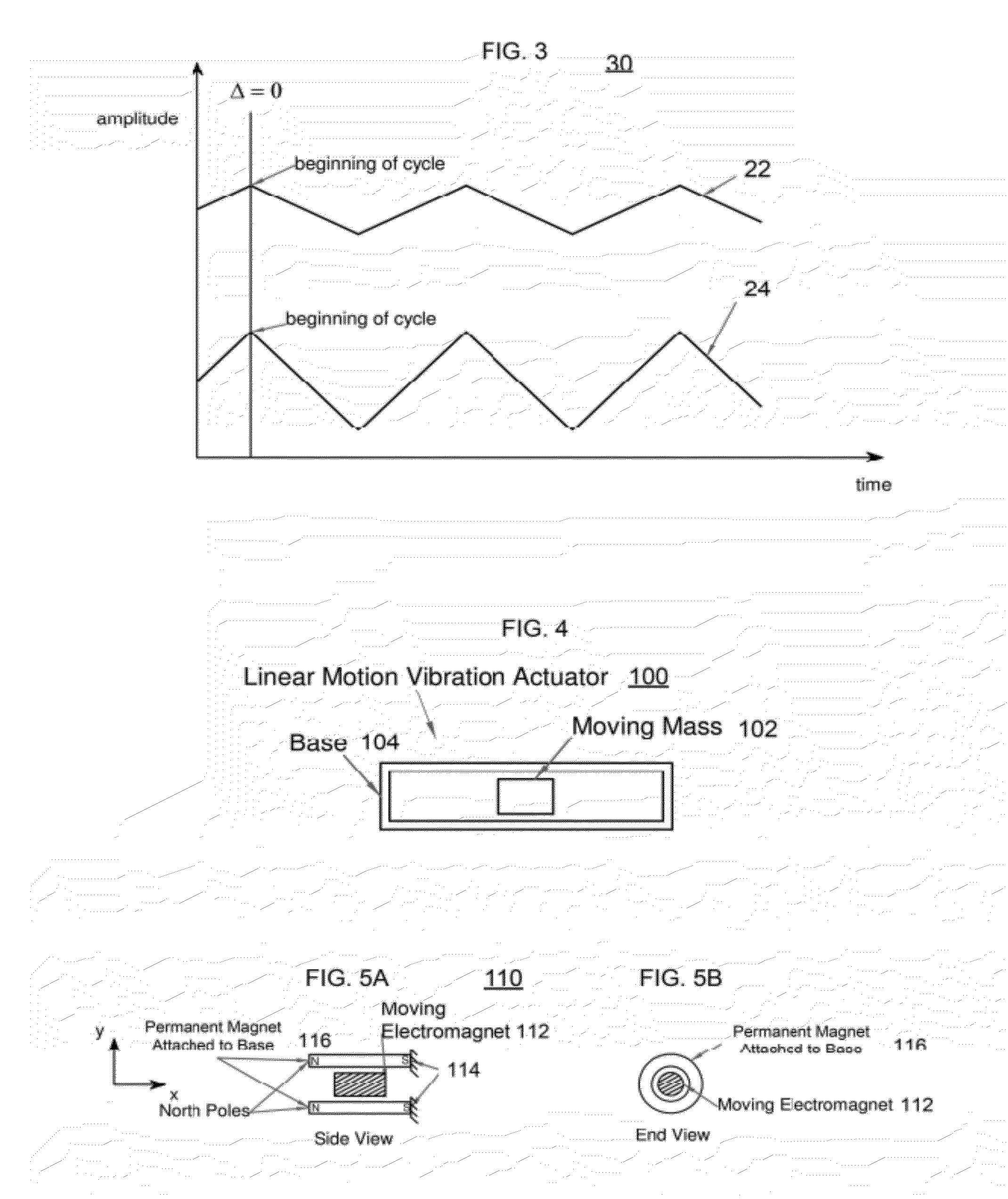
The present invention relates to synchronized vibration devices that can provide haptic feedback to a user. A wide variety of actuator types may be employed to provide synchronized vibration, including linear actuators, rotary actuators, rotating eccentric mass actuators, and rocking mass actuators. A controller may send signals to one or more driver circuits for directing operation of the actuators. The controller may provide direction and amplitude control, vibration control, and frequency control to direct the haptic experience. Parameters such as frequency, phase, amplitude, duration, and direction can be programmed or input as different patterns suitable for use in gaming, virtual reality and real-world situations.
Owner:COACTIVE DRIVE CORP
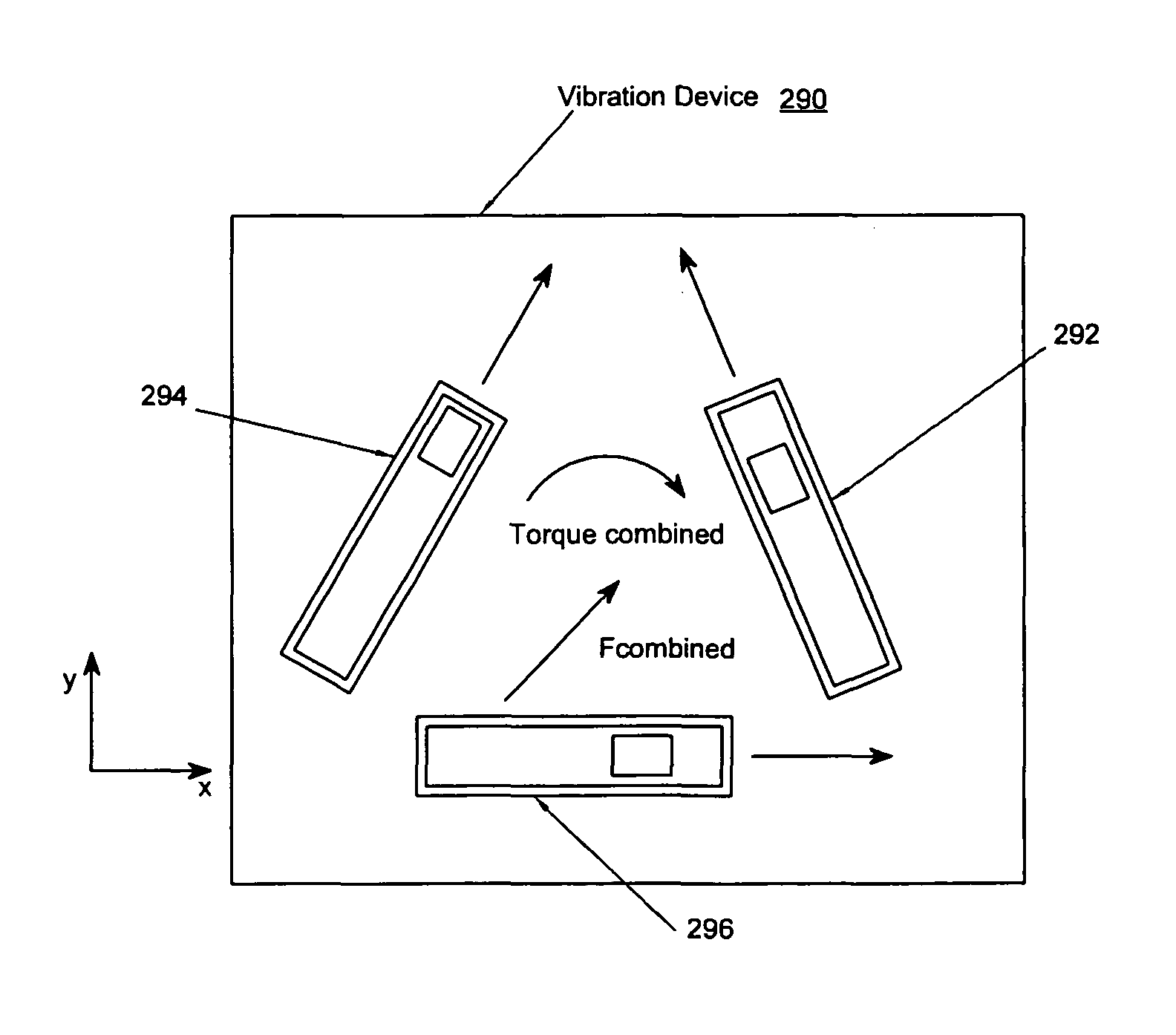
Asymmetric and general vibration waveforms from multiple synchronized vibration actuators
InactiveUS20120232780A1Low costImprove responsivenessDC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDriver circuitPeak value
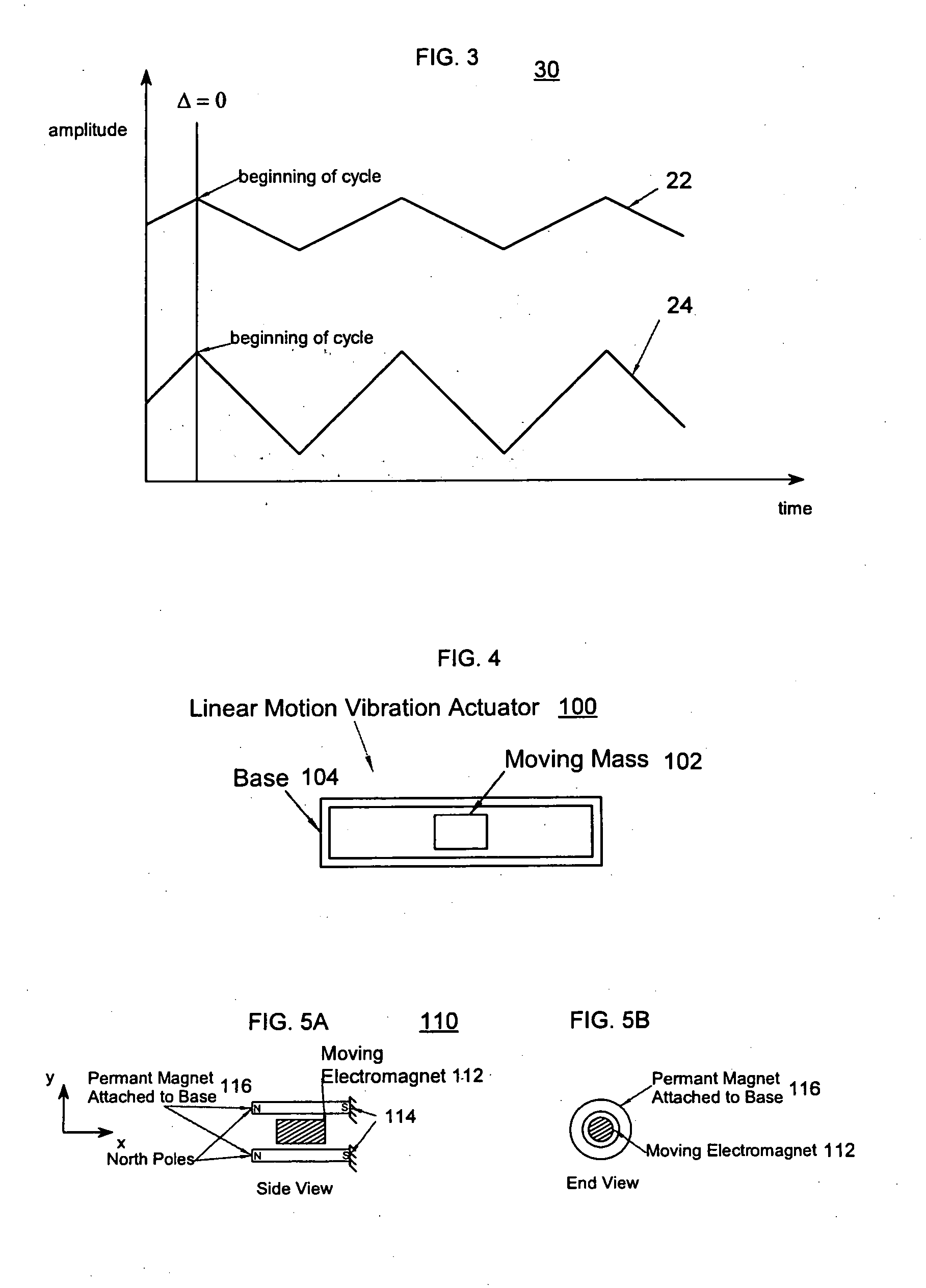
The disclosure relates to General Synchronized Vibration devices that provide haptic feedback to a user and improve the performance of existing vibratory devices. Different actuator types may be employed to provide synchronized vibration, including linear rotary actuators, rotating eccentric mass actuators including interleaved rotating mass actuators, and rocking mass actuators. A controller sends signals to one or more driver circuits to provide adjustment of vibration magnitude, frequency, and direction of the actuators. The system may apply forces onto an object, and a sensor measures a feature(s) of the object. This information is provided to a vibration device controller, which can then modify the vibration waveform to improve overall system performance. Fourier synthesis can be used to approximate arbitrarily shaped waveforms by controlling the phase and frequency of vibration actuators. These waveforms can include asymmetry where the peak force in one direction is higher than the peak force in another direction.
Owner:COACTIVE DRIVE CORP
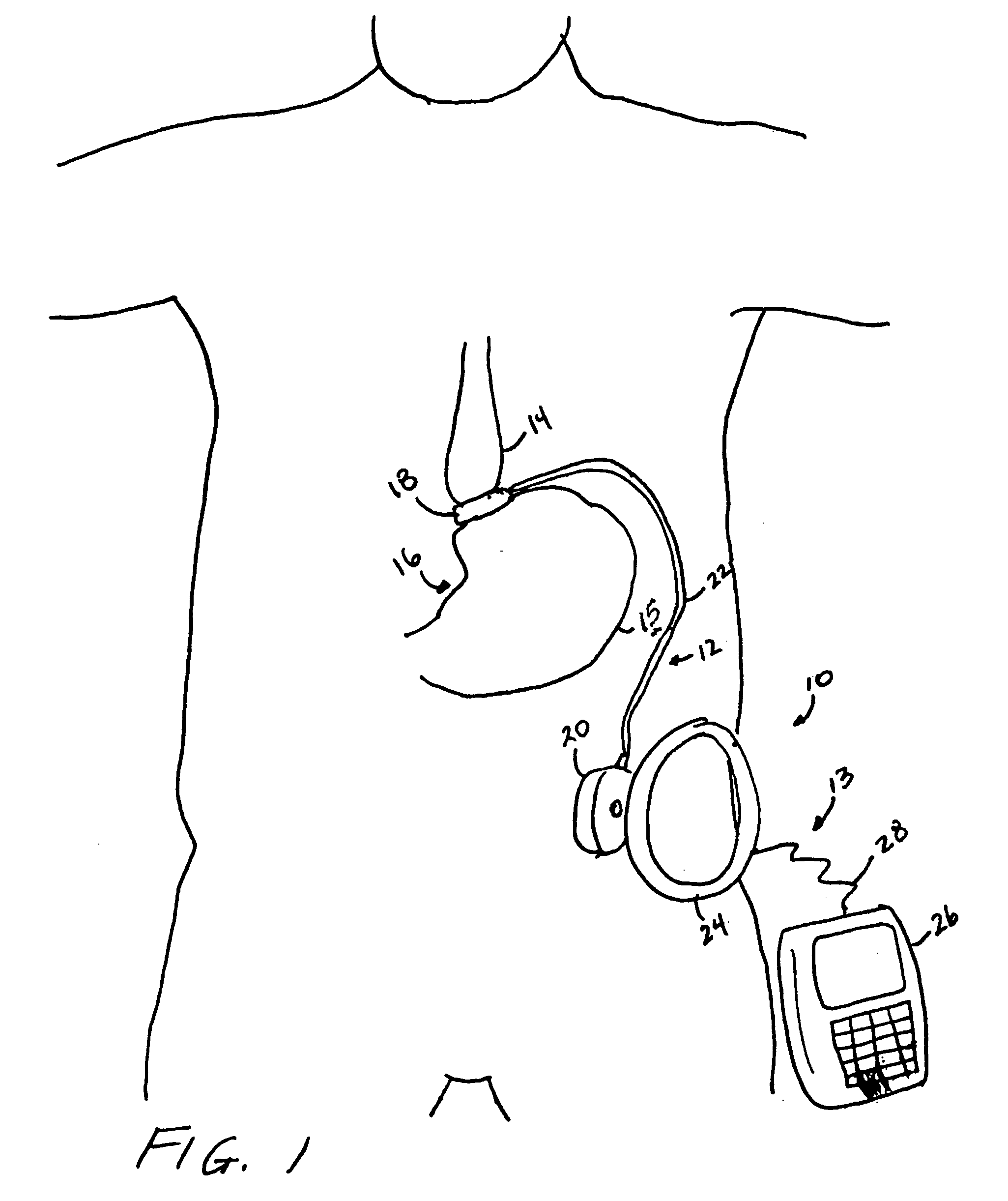
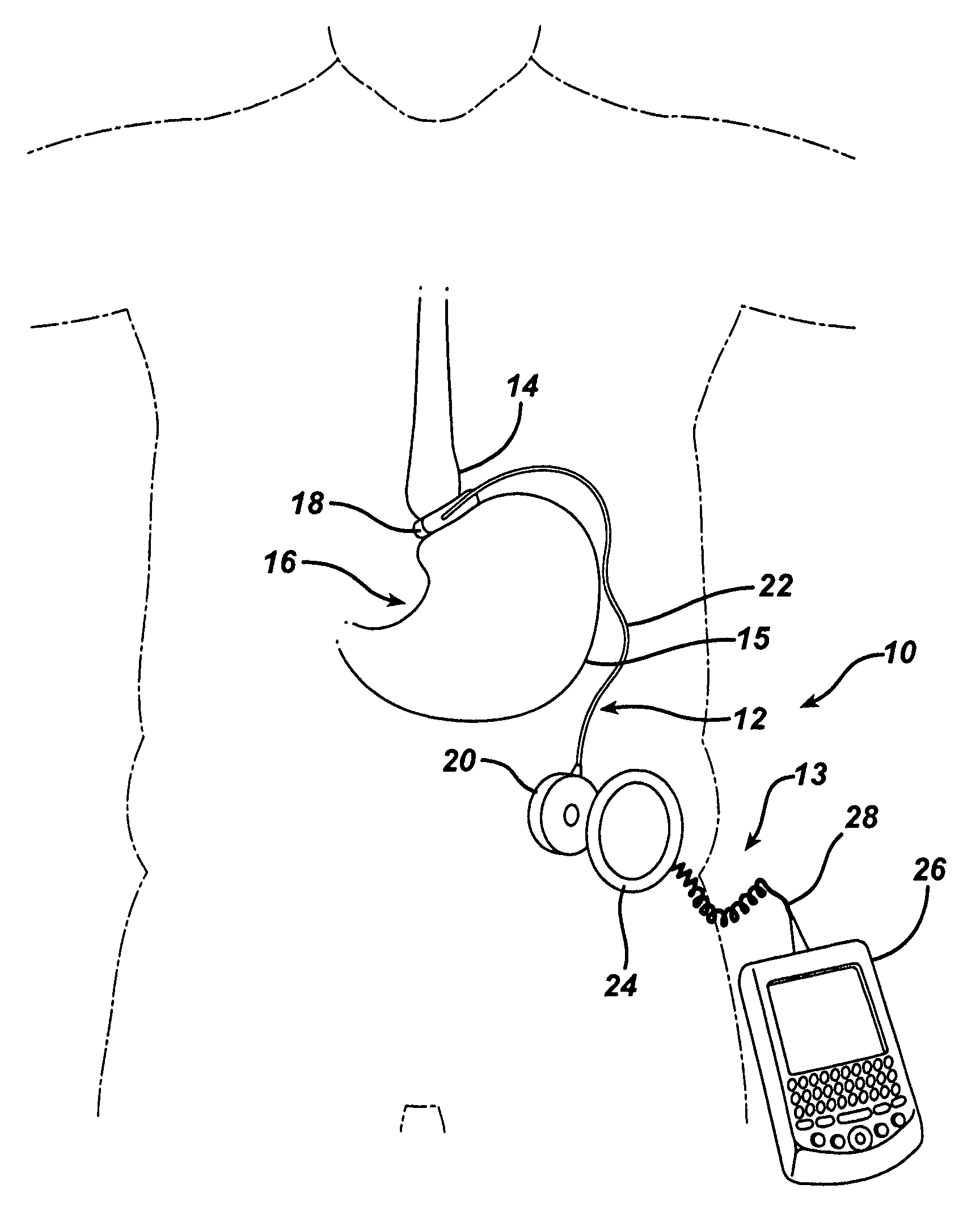
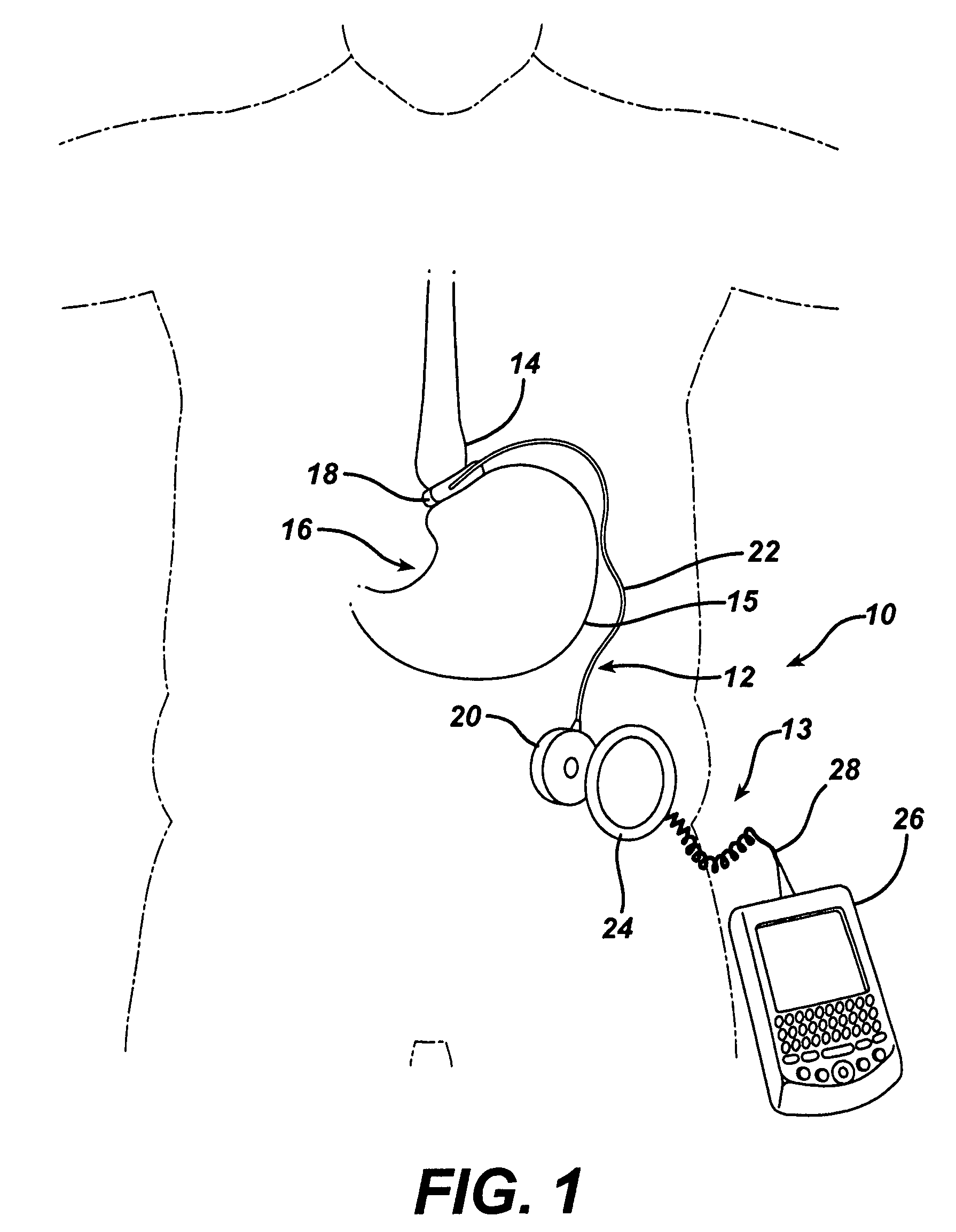
Piezo electrically driven bellows infuser for hydraulically controlling an adjustable gastric band
A remotely controlled gastric band system that is practically immune to external magnetic fields, such as from a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine, incorporates a bi-directional pump and fluid reservoir to adjust fluid volume in a gastric band. A piezoelectrically driven (e.g., rotary actuator, linear actuator) selectively compresses and expands a metal bellows hermetically sealed within a biocompatible and nonferromagnetic case such as titanium.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
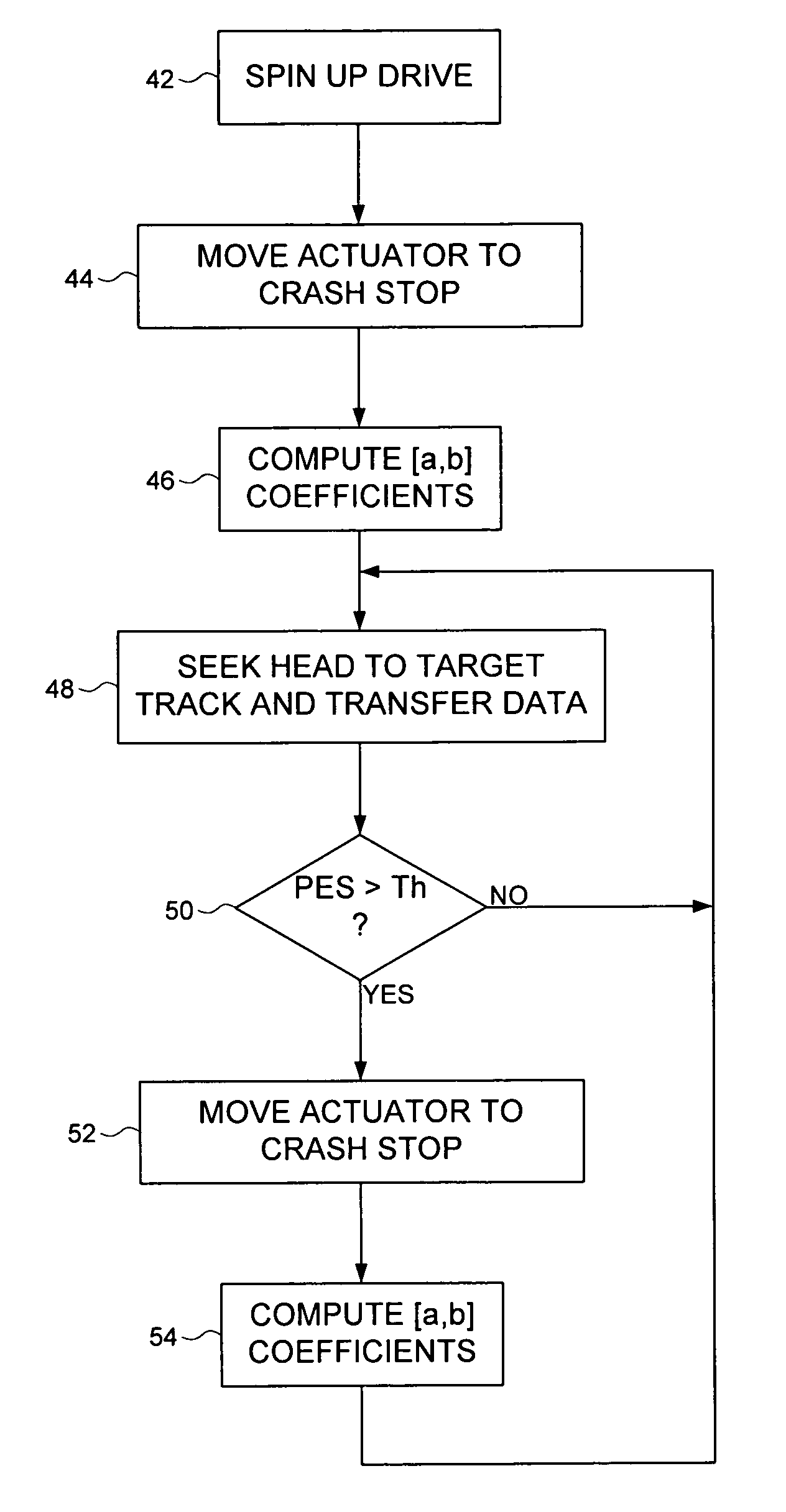
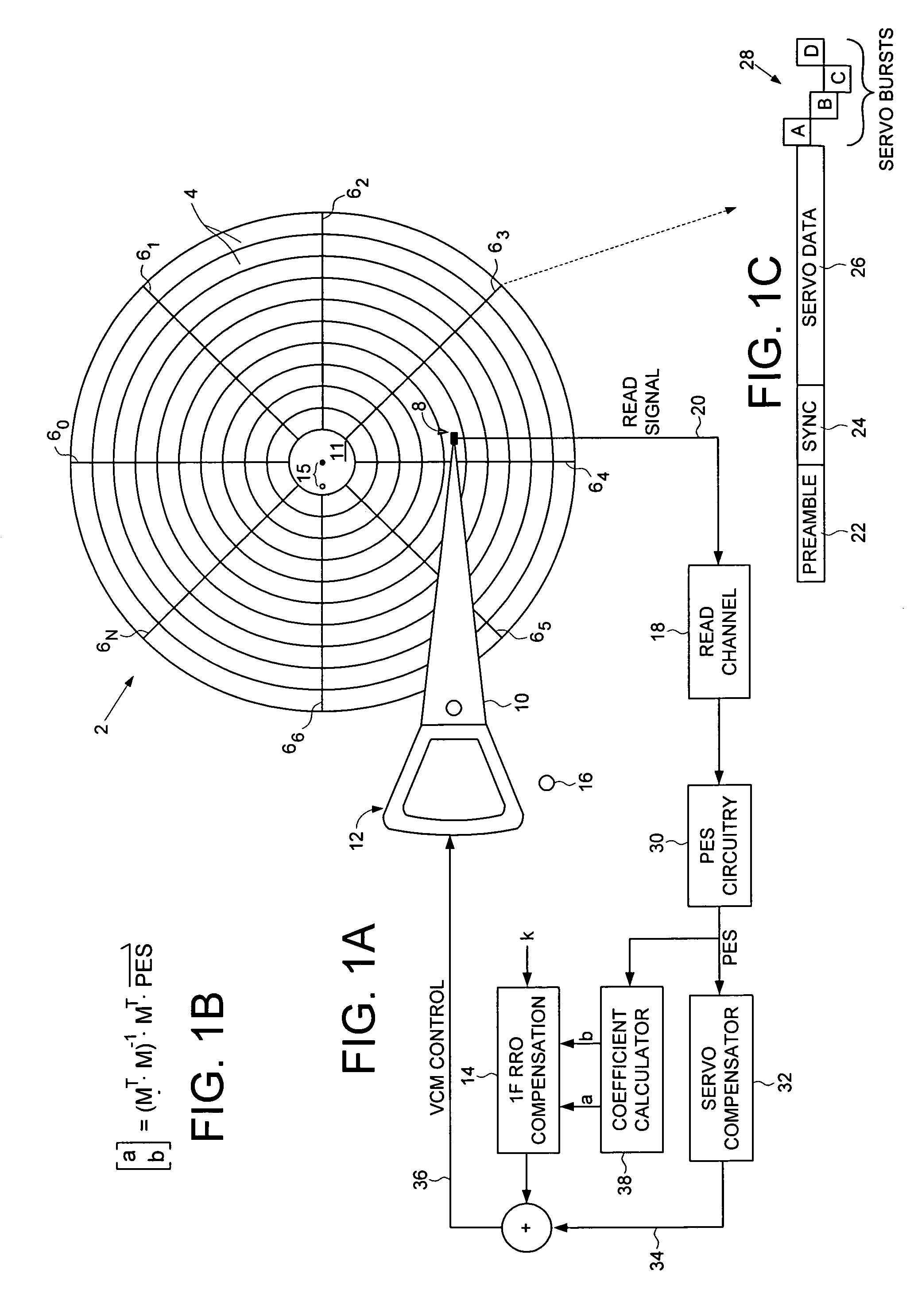
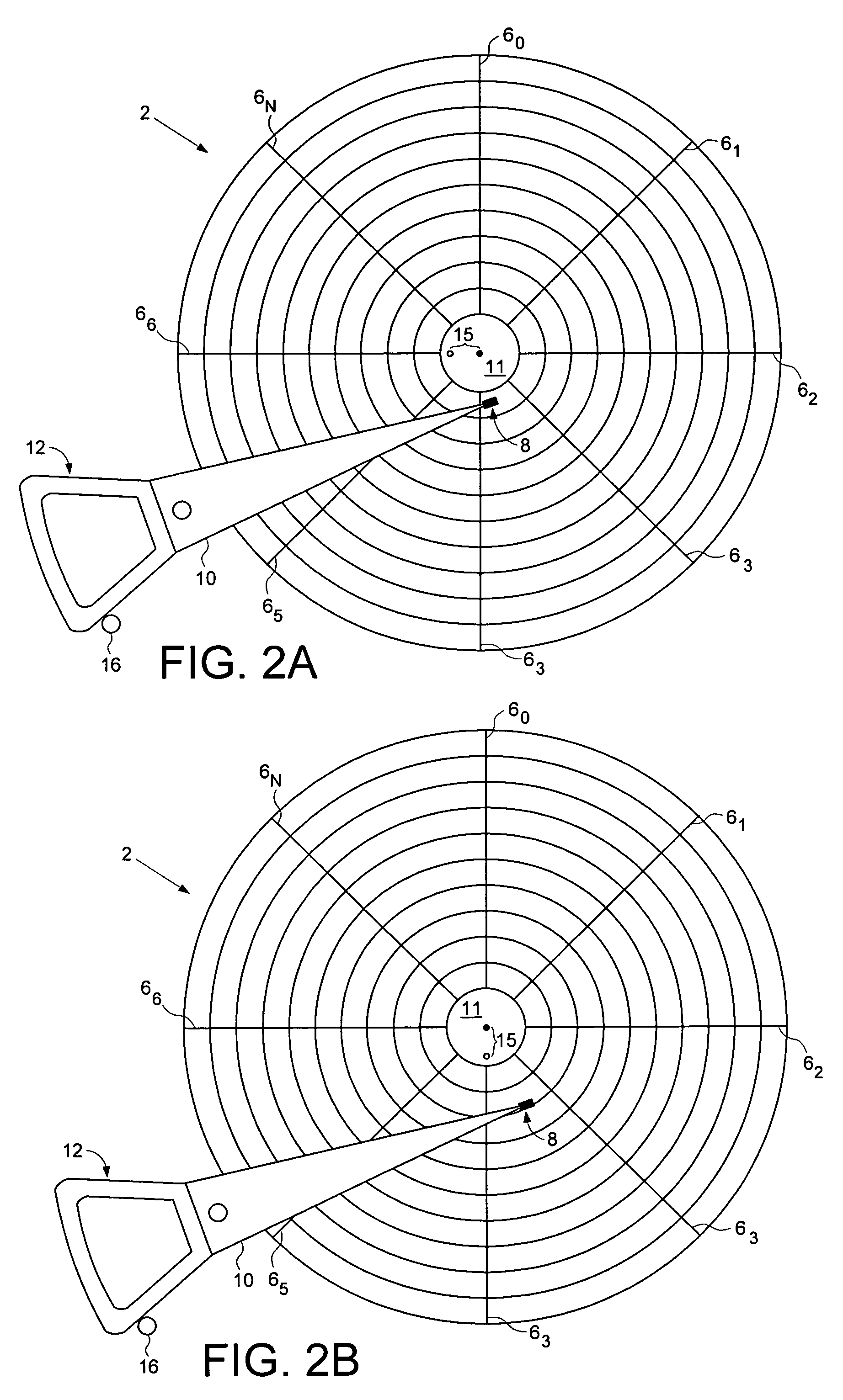
Disk drive computing repeatable run out while actuator arm is pressed against crash stop
InactiveUS7265933B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksControl theoryRotary actuator
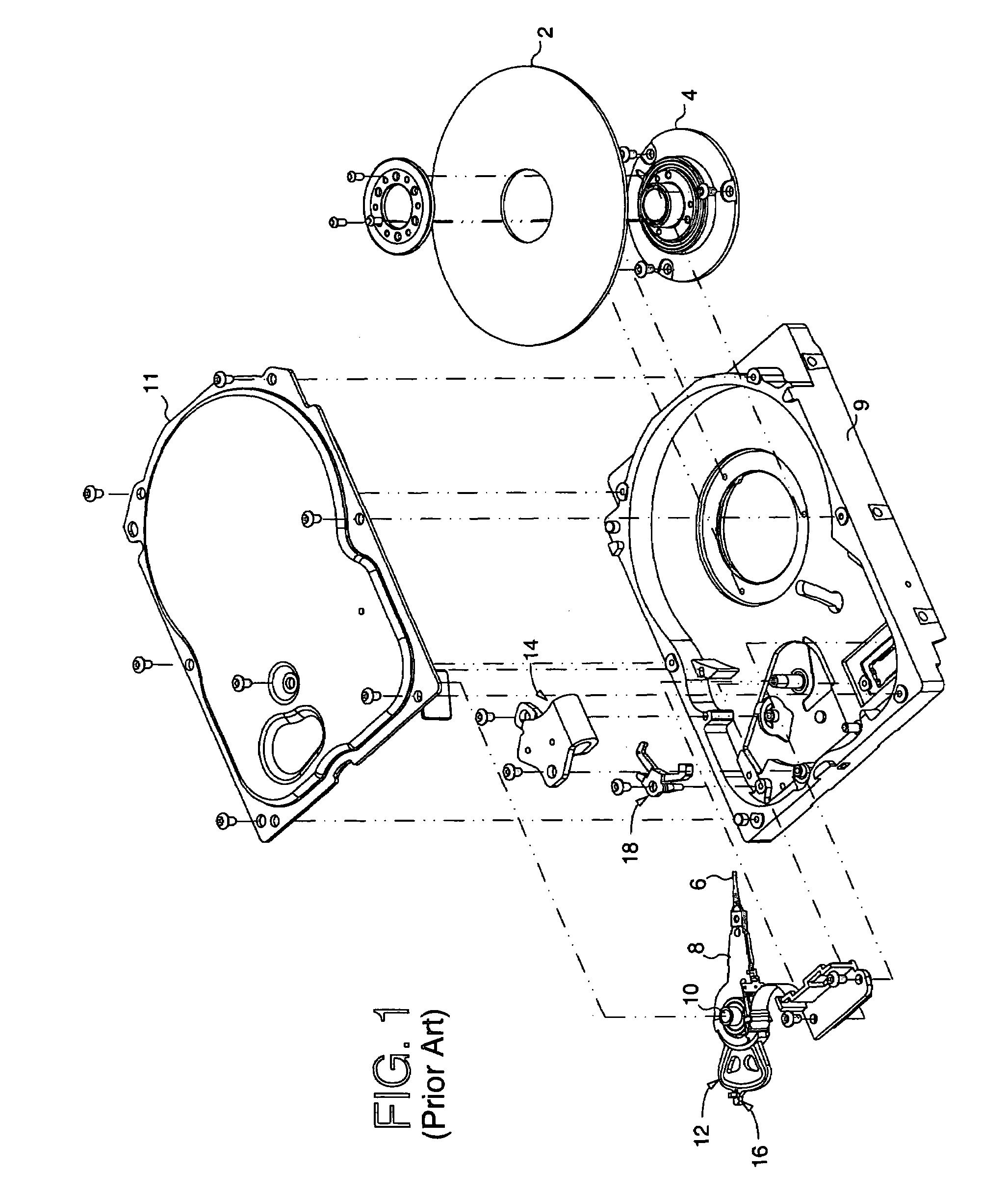
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a voice coil motor (VCM) for rotating an actuator arm about a pivot in order to actuate a head over a disk. The disk is rotated by a spindle motor, and a feed-forward compensation value is computed that compensate for a non-centric alignment of the disk with respect to the spindle motor. During a calibration mode, the VCM is controlled to press the actuator arm against a crash stop, and the feed-forward compensation value is computed in response to a position error signal (PES). The PES is generated in response to embedded servo sectors recorded on the disk, wherein each embedded servo sector comprises a track address for coarse alignment and servo bursts for fine alignment.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Piezo electrically driven bellows infuser for hydraulically controlling an adjustable gastric band
A remotely controlled gastric band system that is practically immune to external magnetic fields, such as from a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine, incorporates a bi-directional pump and fluid reservoir to adjust fluid volume in a gastric band. A piezoelectrically driven (e.g., rotary actuator, linear actuator) selectively compresses and expands a metal bellows hermetically sealed within a biocompatible and nonferromagnetic case such as titanium.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Metal bellows position feedback for hydraulic control of an adjustable gastric band
InactiveUS7481763B2Avoid the needNon-surgical orthopedic devicesObesity treatmentClosed loopEngineering
A remotely controlled gastric band system that is practically immune to external magnetic fields, such as from a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine, incorporates a bi-directional pump and fluid reservoir to adjust fluid volume for hydraulic control of a gastric band. A piezoelectric driver (e.g., rotary actuator, linear actuator) selectively compresses and expands a metal bellows hermetically sealed within a biocompatible and nonferromagnetic enclosure or case such as titanium. Directly sensing a position of the metal bellows yields an accurate reading of volume contained therein, allowing for closed-loop control of the gastric band.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Synchronized vibration device for haptic feedback
ActiveUS7919945B2DC motor speed/torque controlAc-dc conversion without reversalDriver circuitVibration control
The present invention relates to synchronized vibration devices that can provide haptic feedback to a user. A wide variety of actuator types may be employed to provide synchronized vibration, including linear actuators, rotary actuators, rotating eccentric mass actuators, and rocking mass actuators. A controller may send signals to one or more driver circuits for directing operation of the actuators. The controller may provide direction and amplitude control, vibration control, and frequency control to direct the haptic experience. Parameters such as frequency, phase, amplitude, duration, and direction can be programmed or input as different patterns suitable for use in gaming, virtual reality and real-world situations.
Owner:COACTIVE DRIVE CORP
Vibrotactile haptic feedback devices
InactiveUS7561142B2Easy to useInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsCouplingRemote control
Method and apparatus for controlling magnitude and frequency of vibrotactile sensations for haptic feedback devices. A haptic feedback device, such as a gamepad controller, mouse, remote control, etc., includes a housing, an actuator coupled to the housing, and a mass. In some embodiments, the mass can be oscillated by the actuator and a coupling between the actuator and the mass or between the mass and the housing has a variable compliance. Varying the compliance allows vibrotactile sensations having different magnitudes for a given drive signal to be output. In other embodiments, the actuator is a rotary actuator and the mass is an eccentric mass rotatable by the actuator about an axis of rotation. The eccentric mass has an eccentricity that can be varied relative to the axis of rotation while the mass is rotating. Varying the eccentricity allows vibrotactile sensations having different magnitudes for a given drive signal.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Metal bellows position feedback for hydraulic control of an adjustable gastric band
InactiveUS20050267500A1Precise motion controlAvoid the needNon-surgical orthopedic devicesObesity treatmentClosed loopEngineering
A remotely controlled gastric band system that is practically immune to external magnetic fields, such as from a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine, incorporates a bi-directional pump and fluid reservoir to adjust fluid volume for hydraulic control of a gastric band. A piezoelectric driver (e.g., rotary actuator, linear actuator) selectively compresses and expands a metal bellows hermetically sealed within a biocompatible and nonferromagnetic enclosure or case such as titanium. Directly sensing a position of the metal bellows yields an accurate reading of volume contained therein, allowing for closed-loop control of the gastric band.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
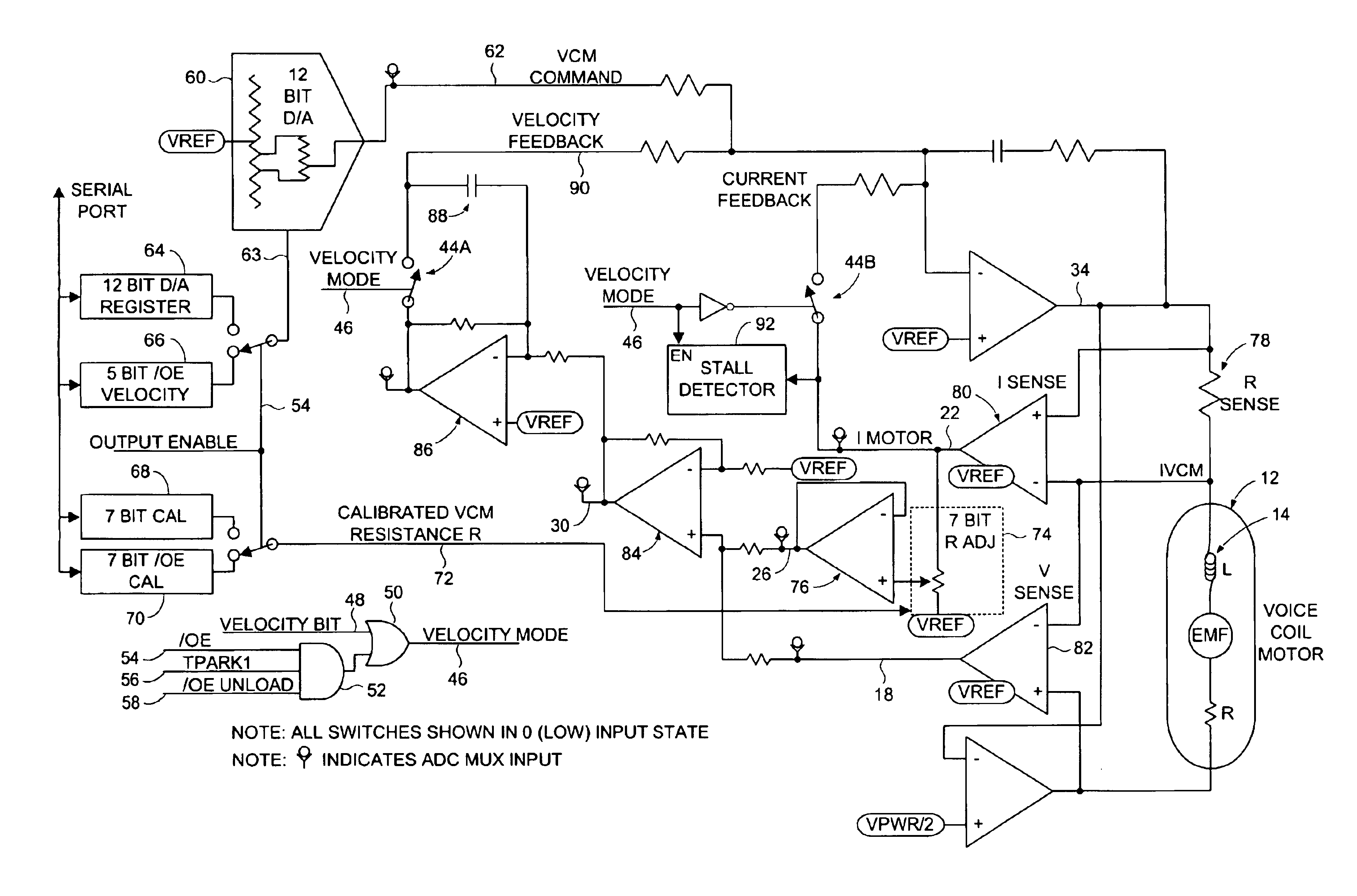
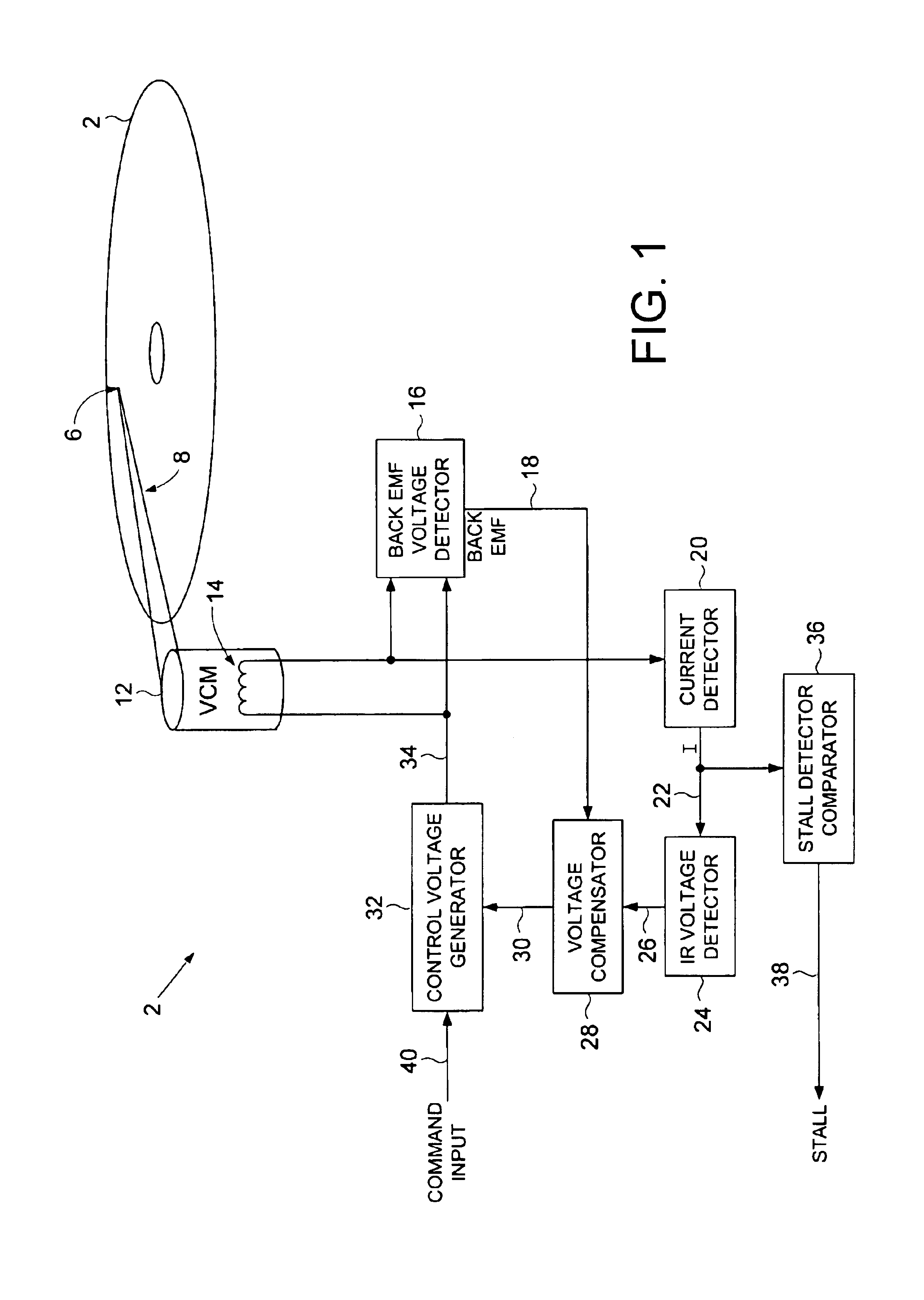
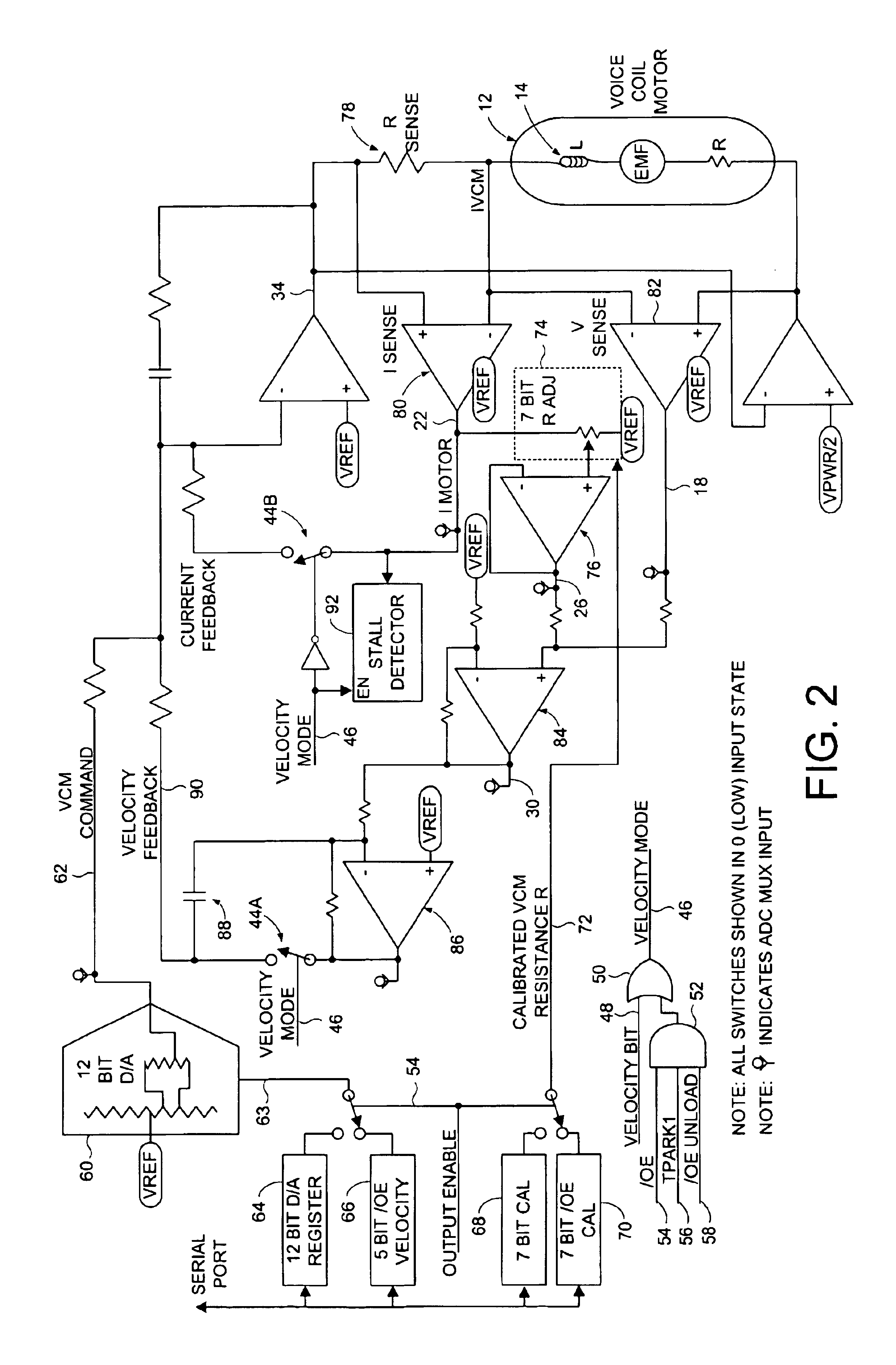
Disk drive comprising VCM stall detector for velocity control of an actuator arm
InactiveUS6867944B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageVoltage generatorElectric machine
The present invention may be regarded as a disk drive comprising a disk, a head, an actuator arm for actuating the head radially over the disk, and a voice coil motor (VCM) for rotating the actuator arm about a pivot, the VCM comprising a coil comprising a VCM resistance R. A back EMF voltage detector measures a back EMF voltage across the coil, and a current detector detects a current I flowing through the coil. An IR voltage detector, responsive to the current I detected by the current detector, detects an IR voltage proportional to the current I times the VCM resistance R. A voltage compensator substantially cancels the IR voltage from the measured back EMF voltage to generate a compensated back EMF voltage. A control voltage generator, responsive the compensated back EMF voltage, generates a control voltage applied to the coil to generate the current I flowing through the coil. A stall detector compares the current I detected by the current detector to a threshold, wherein a VCM stall condition is detected if the current I exceeds the threshold for a predetermined interval.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Disk drive comprising an optical sensor for vibration mode compensation
InactiveUS7365932B1Large componentUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionFilamentary/web record carriersControl signalControl theory
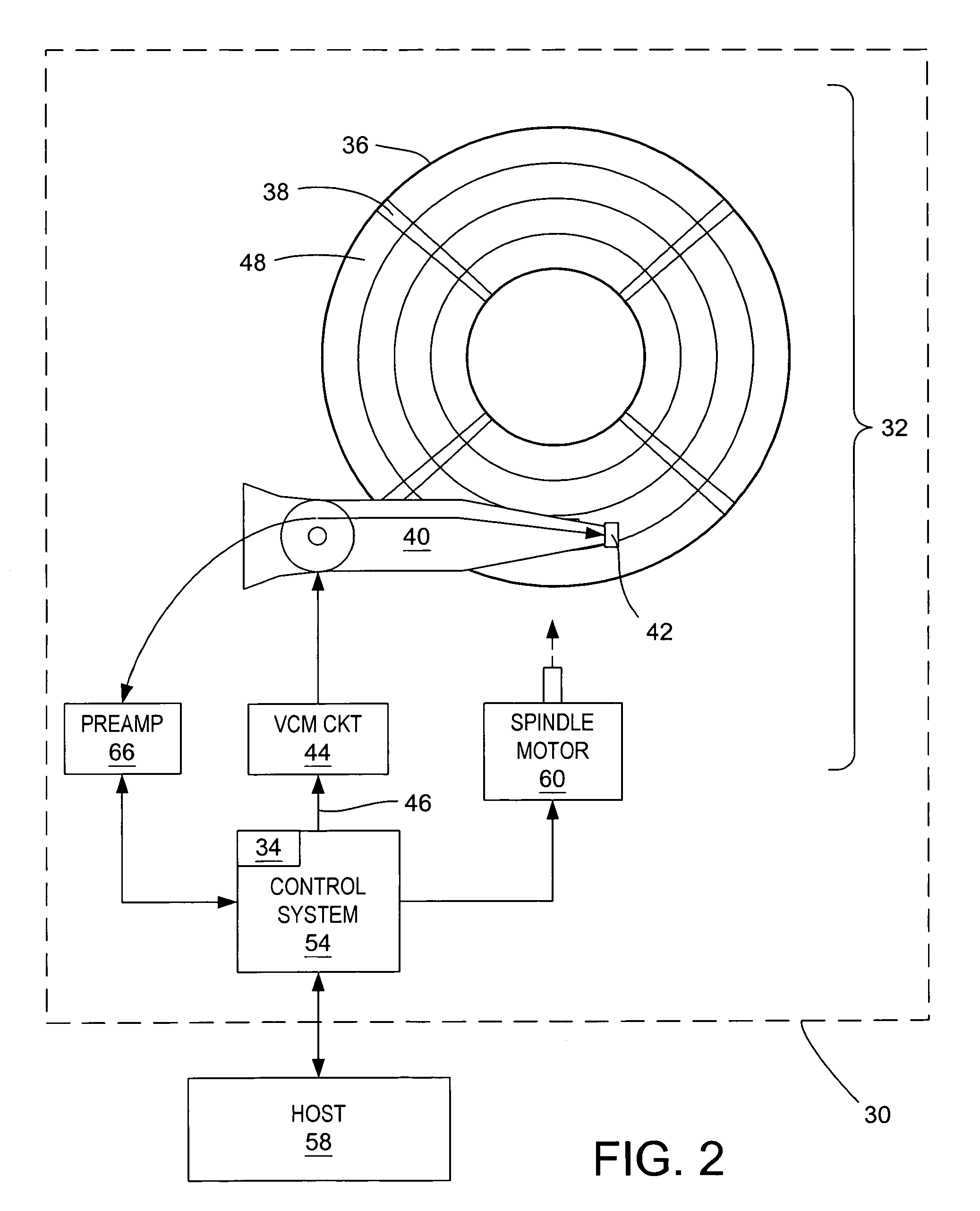
A disk drive is disclosed comprising an actuator arm, a head attached to a distal end of the actuator arm, a voice coil motor for rotating the actuator arm about a pivot, and an optical sensor operable to generate a first position signal representing a position of the actuator arm with respect to the disk, wherein the first position signal is substantially unaffected by a vibration mode of the actuator arm. Servo sectors recorded on the disk are processed to generate a second position signal representing a position of the head with respect to the disk, wherein the second position signal comprises a significant component due to the vibration mode of the actuator arm. A control signal is applied to the voice coil motor in response to the first and second position signals.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Disk drive adjusting predictive caching based on temperature of voice coil motor
InactiveUS7450334B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDriving/moving recording headsRotary actuatorComputer science
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for determining repeatable runout cancellation values in a magnetic disk drive using filtering
InactiveUS6975480B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksControl theoryRotary actuator
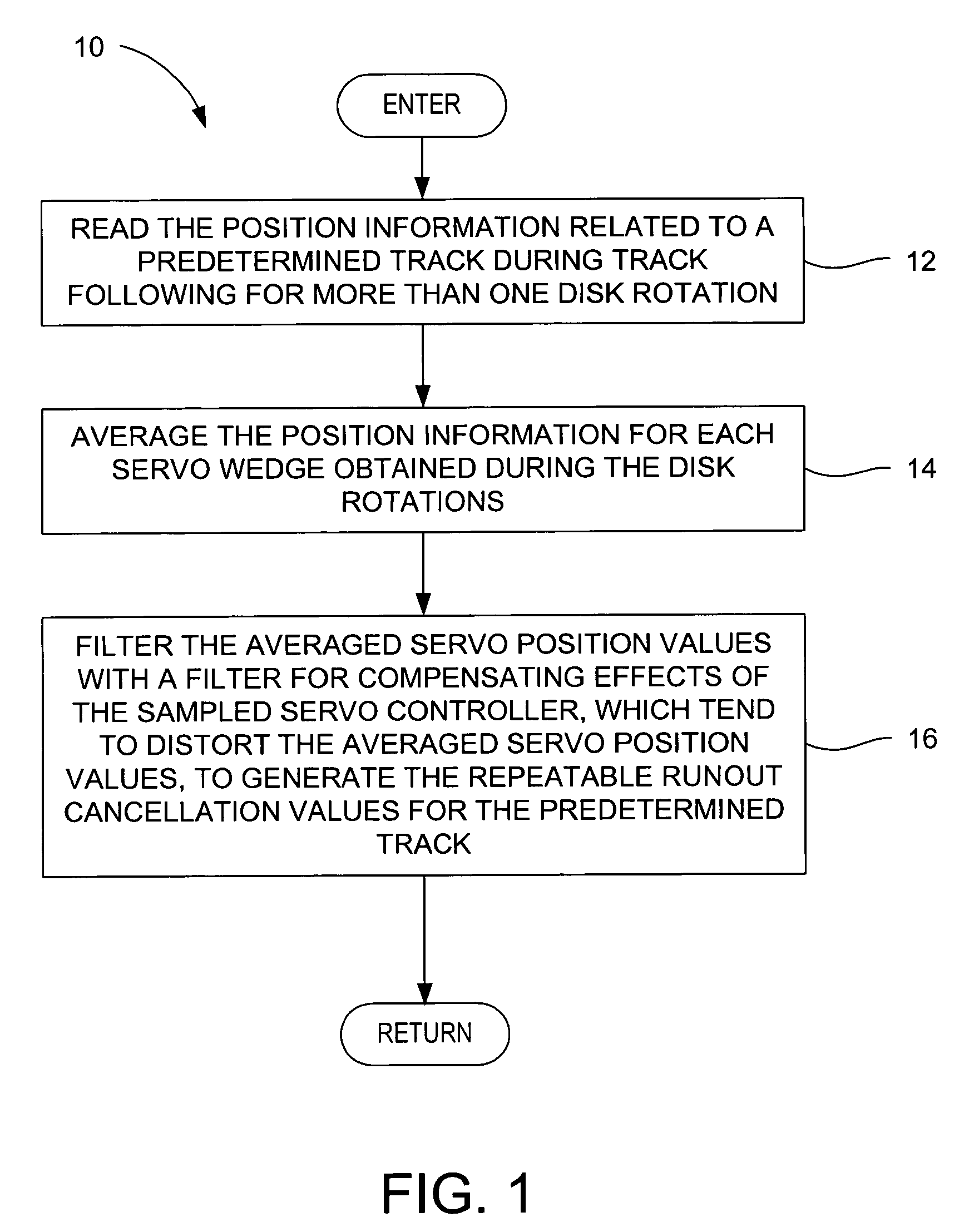
A method is disclosed for determining repeatable runout (RRO) cancellation values in a disk drive having a head disk assembly (HDA) and a sampled servo controller. The HDA includes a disk having distributed position information in servo wedges, a rotary actuator carrying a head that periodically reads the position information, and a voice coil motor circuit that responds to a control effort signal. The servo controller periodically adjusts the control effort signal during a track-following operation. In the method, the position information related to a predetermined track is read during track following for more than one disk rotation. The position information is averaged for each servo wedge obtained during the disk rotations. The averaged servo position values are filtered with a filter for compensating effects of the sampled servo controller, which tend to distort the averaged servo position values, to generate the RRO cancellation values for the predetermined track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
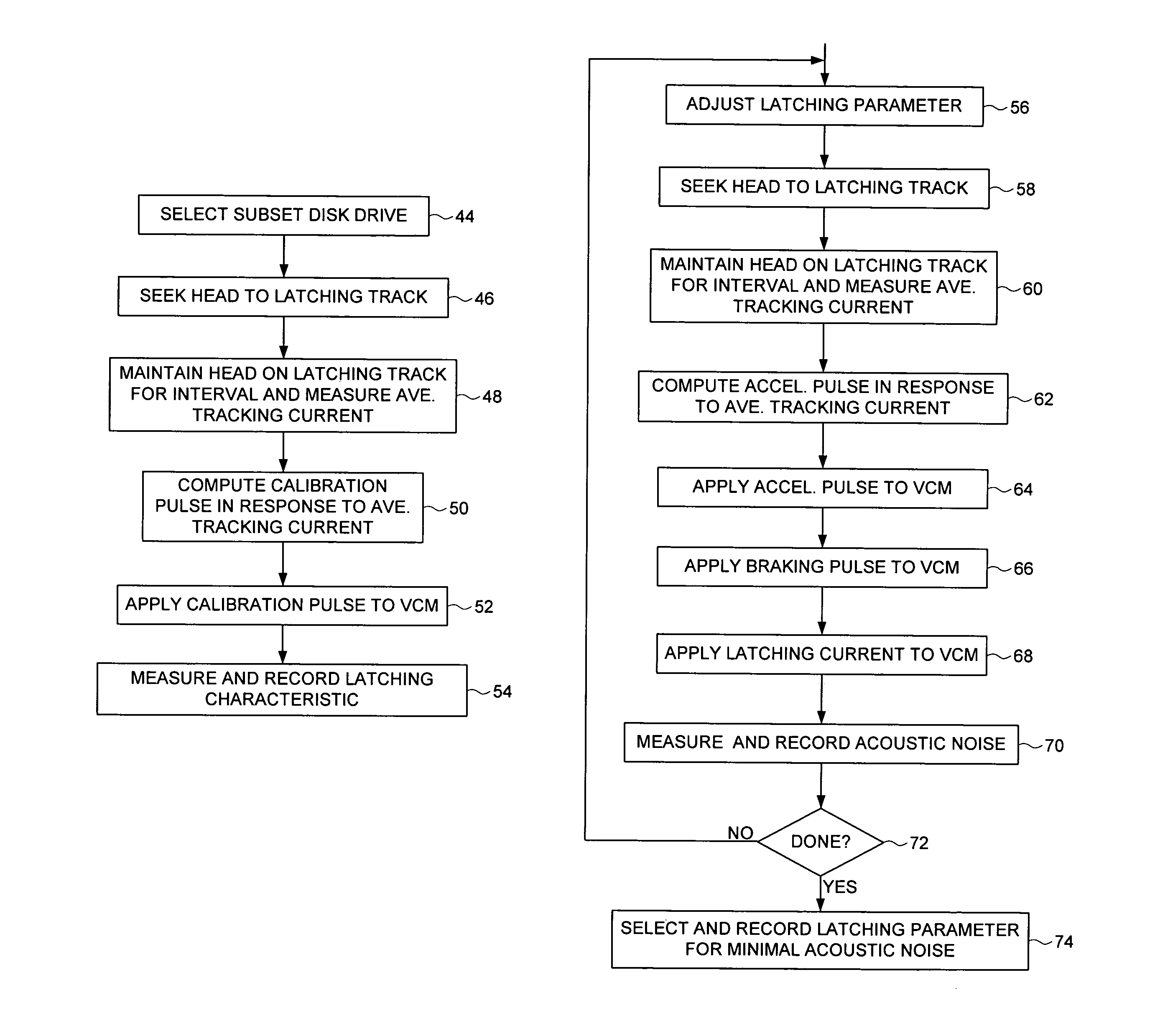
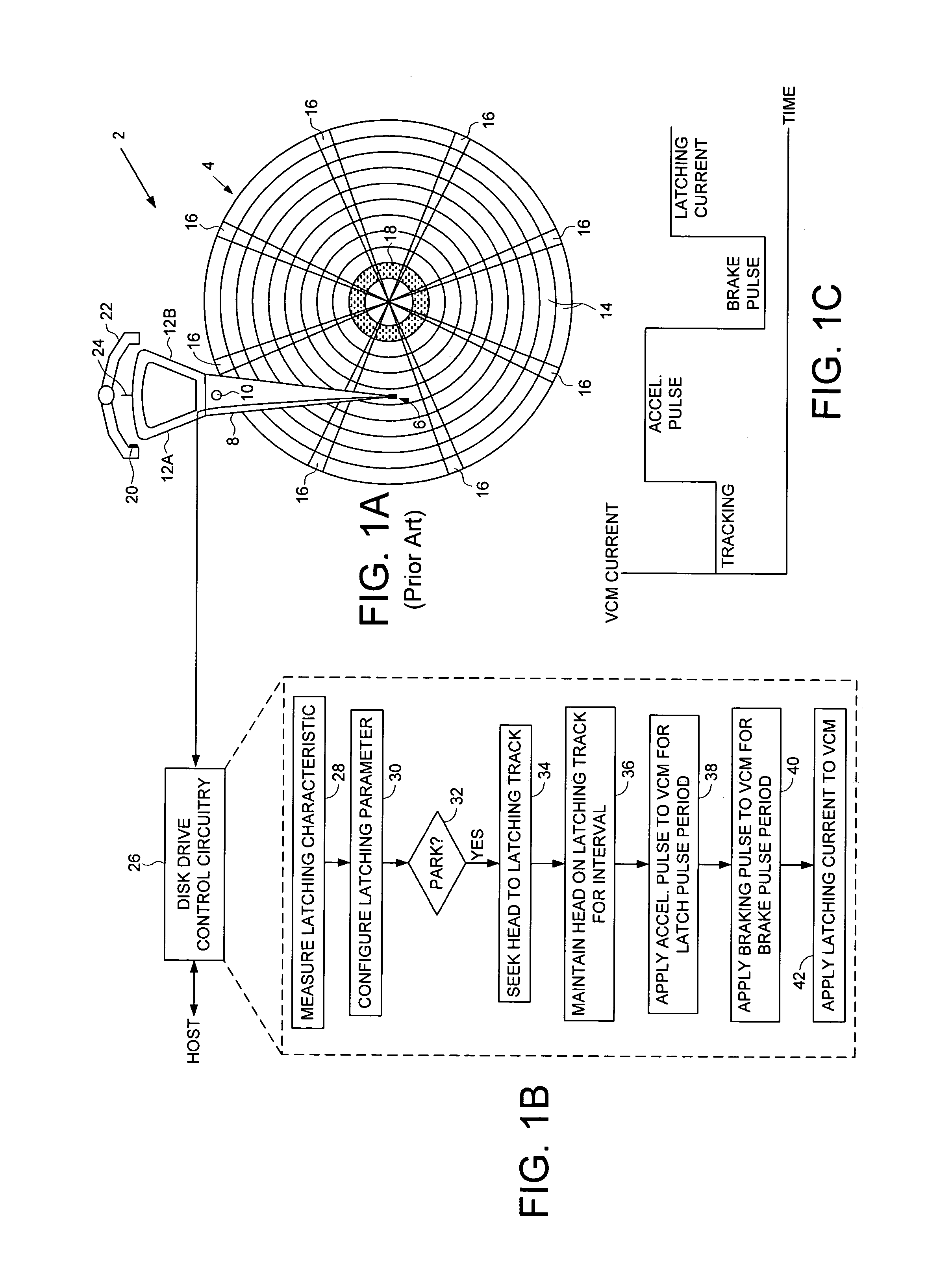
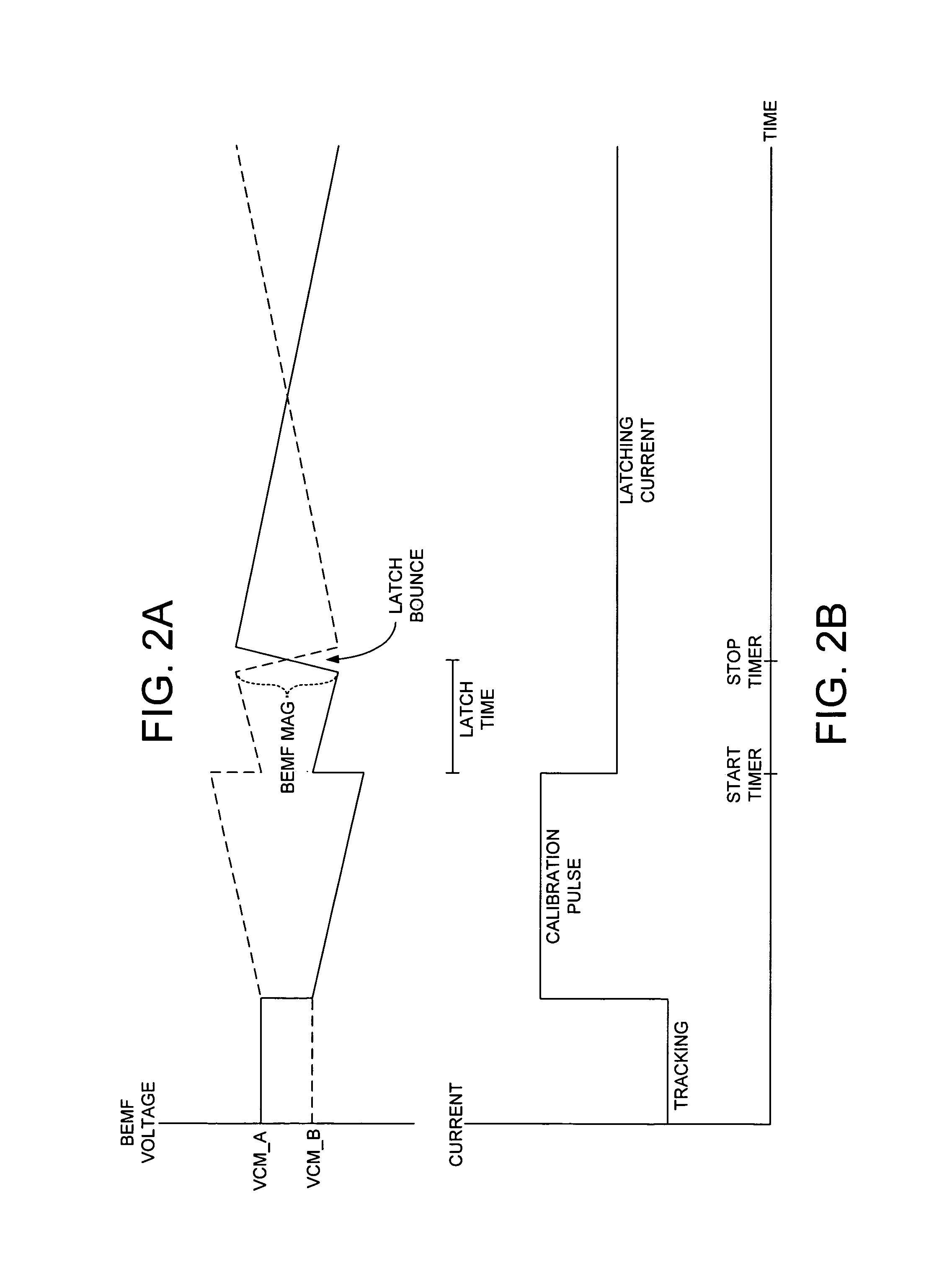
Disk drive employing a calibrated brake pulse to reduce acoustic noise when latching an actuator arm
InactiveUS7224546B1Reduce noiseMinimize acoustic noiseDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageEngineeringControl theory
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk and a voice coil motor (VCM) for rotating an actuator arm about a pivot in order to actuate a head over the disk. During a park operation, a latching characteristic associated with latching the actuator arm is measured and used to configure a latching parameter that reduces acoustic noise. The latching parameter is used to latch the actuator arm by seeking the head to a latching track, maintaining the head over the latching track for a predetermined interval, applying an acceleration pulse to the VCM for an acceleration pulse period, applying a braking pulse to the VCM for a brake pulse period, and applying a latching current to the VCM.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
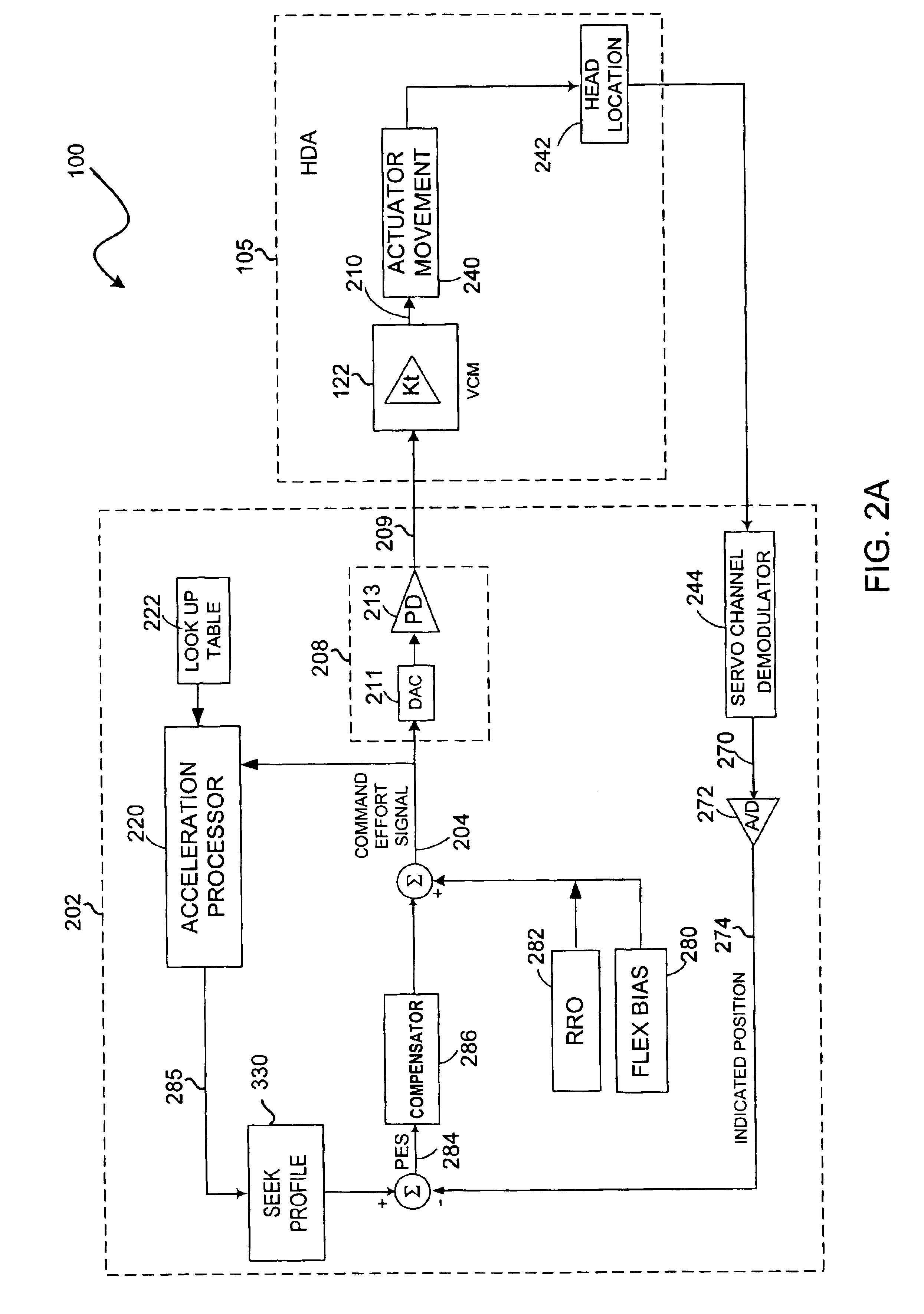
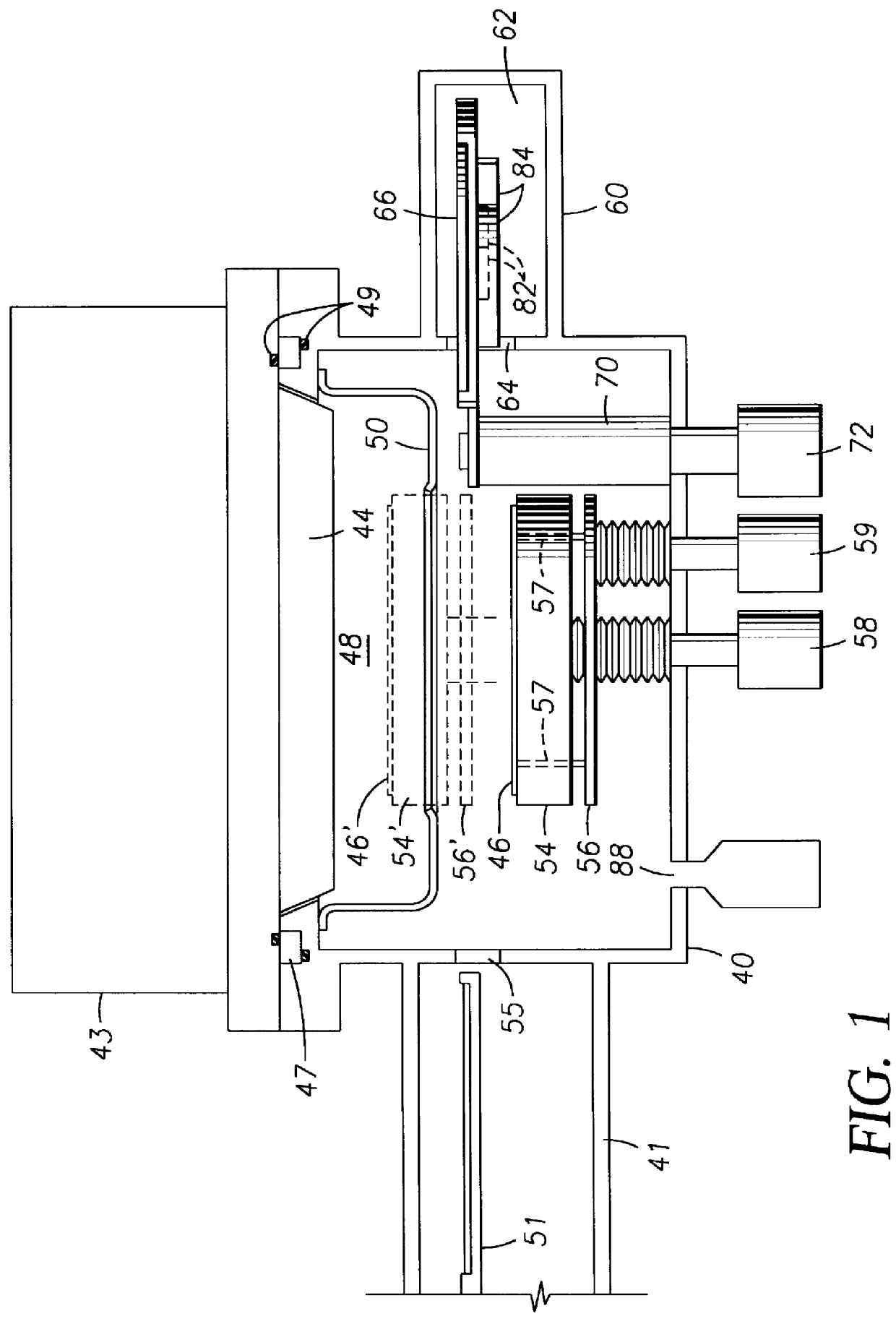
Performance of a rotary actuator in a disk drive
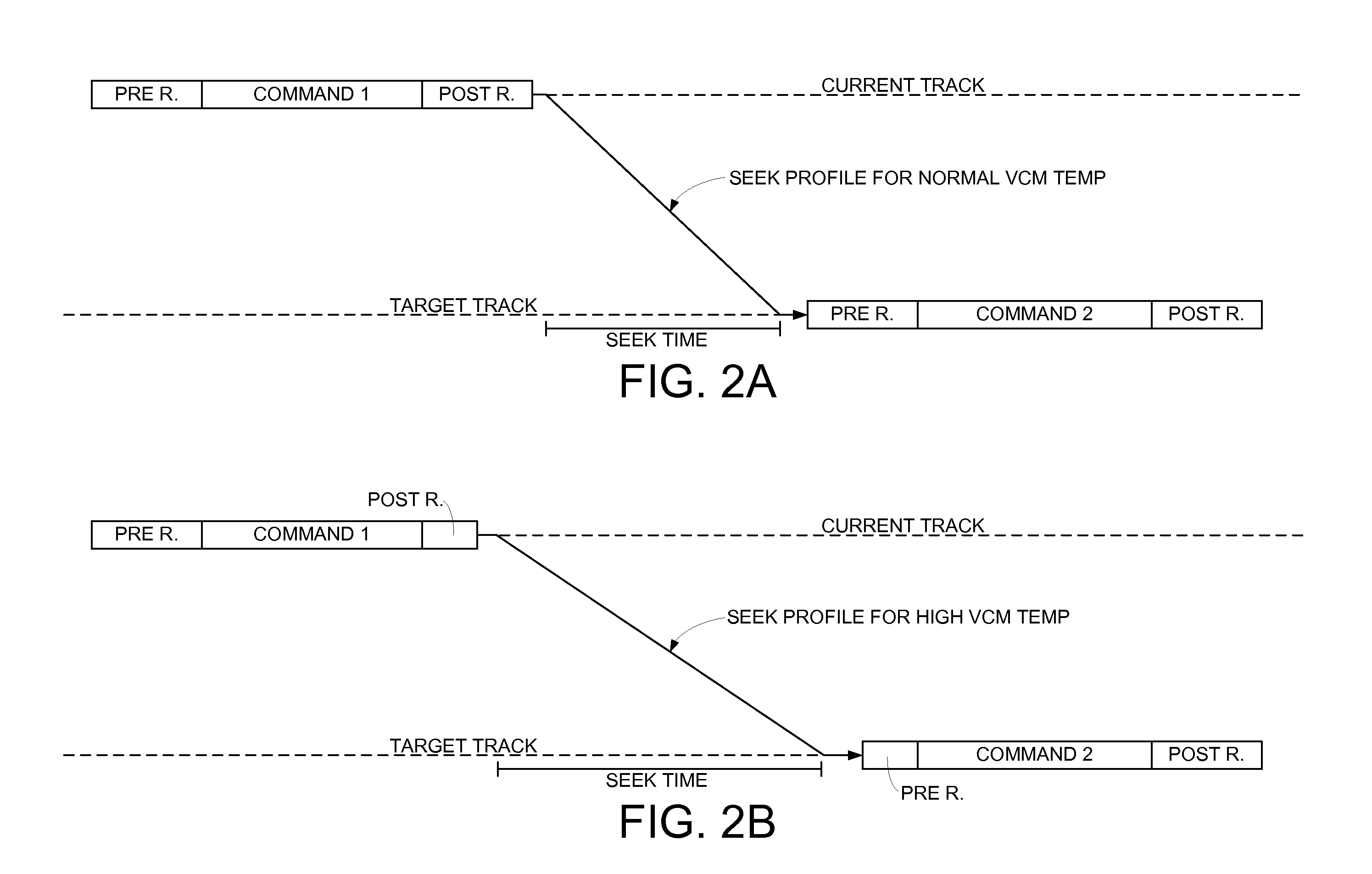
ActiveUS6903897B1Improve performanceTemperatue controlRecord information storageDriver circuitRotary actuator
A method for improving the performance of a rotary actuator in a disk drive, the rotary actuator comprises a voice coil motor (VCM) characterized by a torque parameter, the disk drive comprises a servo control system having a motor driver circuit for receiving a series of command effort signals (CEFs) transmitted based on a first seek profile, and for providing an operating current to VCM based on the CEFs for causing a movement of the actuator from a first radial location to a target radial location. The method includes recording the transmitted CEFs, and while actuator is moving: adjusting each recorded CEF to account for a disk drive influence on actuator movement; storing adjusted CEFs; monitoring velocity of moving actuator; calculating an acceleration value corresponding to moving actuator from the stored CEFs and monitored velocity; and adjusting the acceleration value to account for a radial torque parameter variation.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
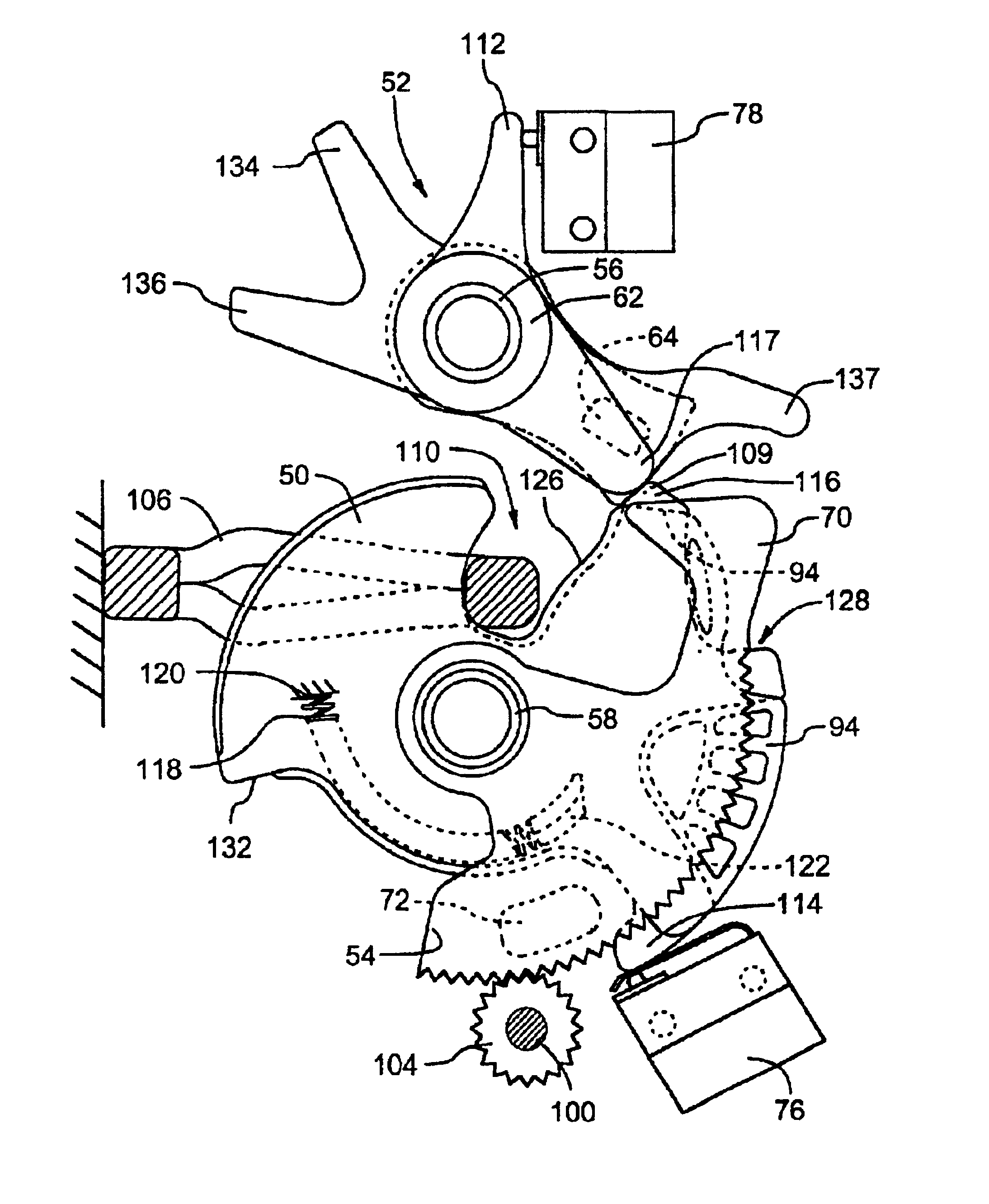
Power door latch assembly
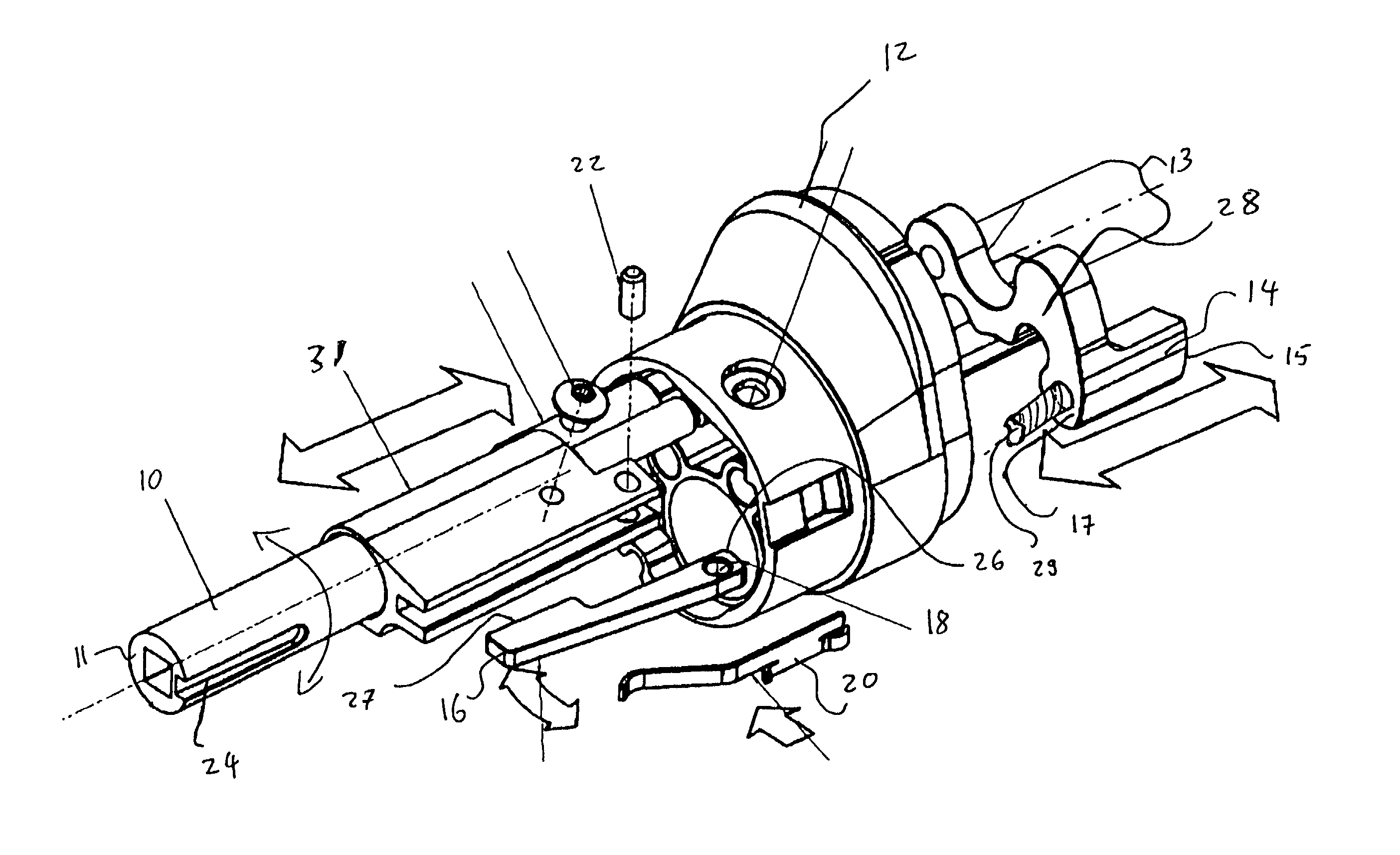
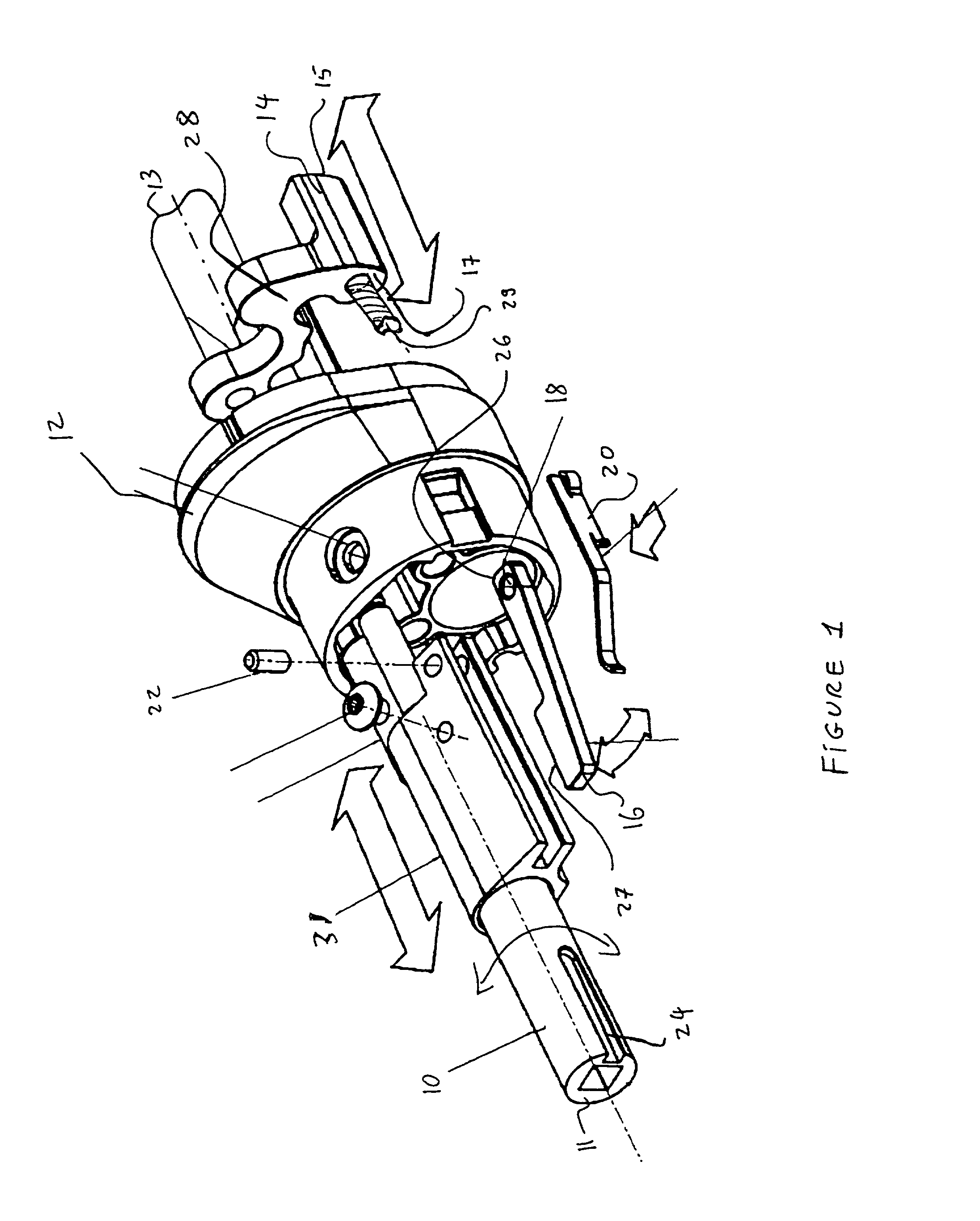
A power door latch assembly consists of a ratchet (50) for engaging a door striker, a pawl (52), a rotary actuator (54) for rotating the ratchet (50) towards the closed position and for disengaging the pawl (52) and a drive actuator (96) for driving the rotary actuator (54). The drive actuator (96) includes a prime mover (98) an output member (104) in engagement with the rotary actuator (54), and releasable coupling (102) coupled between the prime mover (98) and the output member (104) for selectively transferring torque between the prime mover (98) and the rotary actuator (54). A drive controller (108) is coupled to the releasable coupling (102) and is configured for disengaging the prime mover (98) from the rotary actuator (54) when the ratchet (50) is disposed in either the open or closed positions.
Owner:ATOMA INT CORP
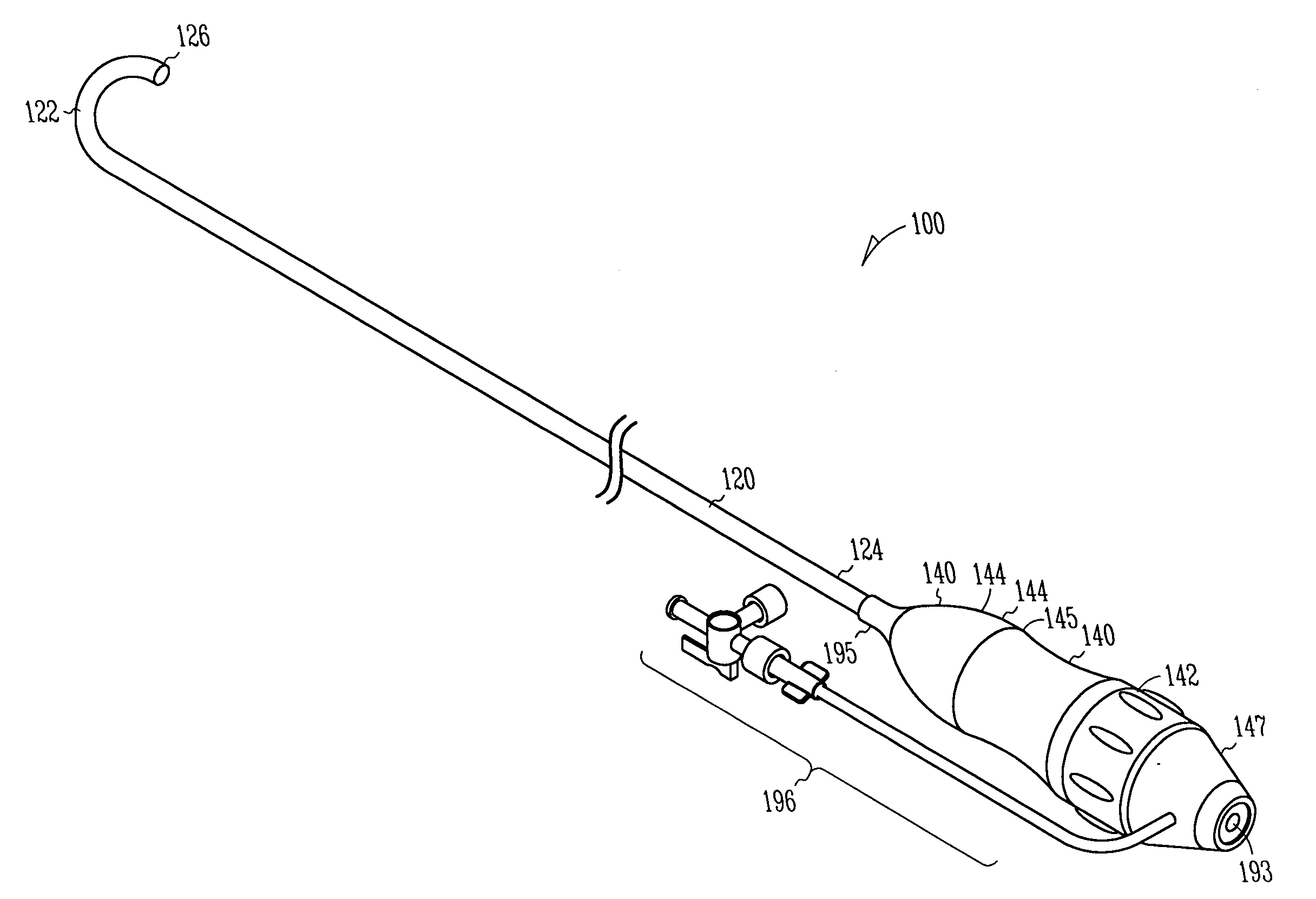
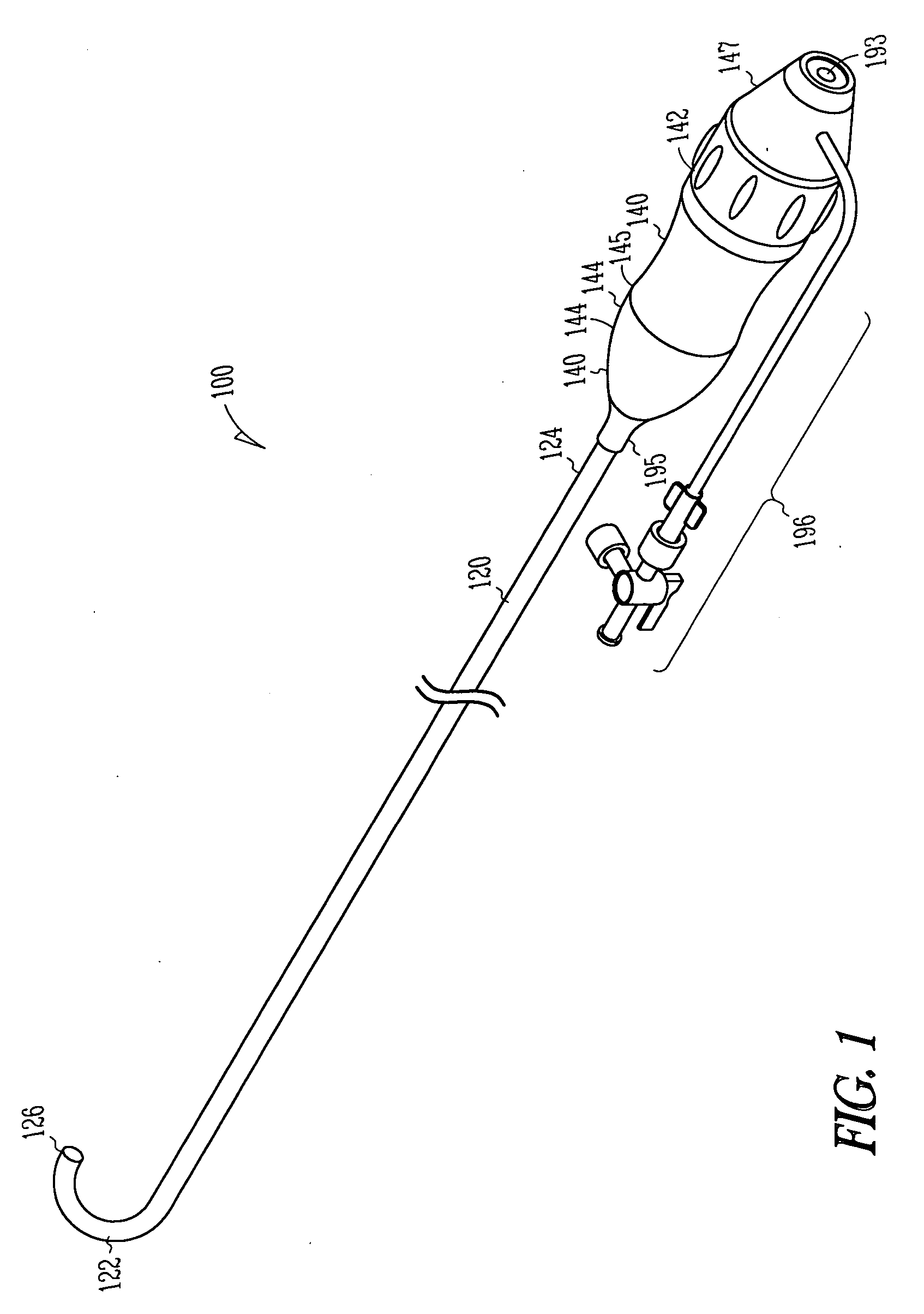
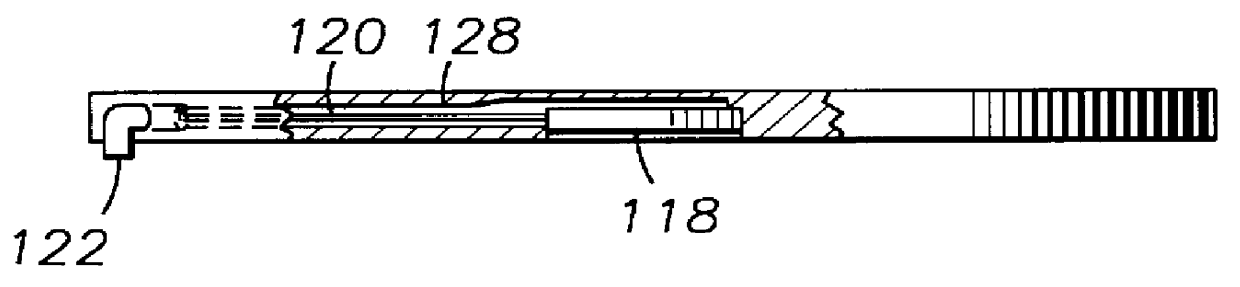
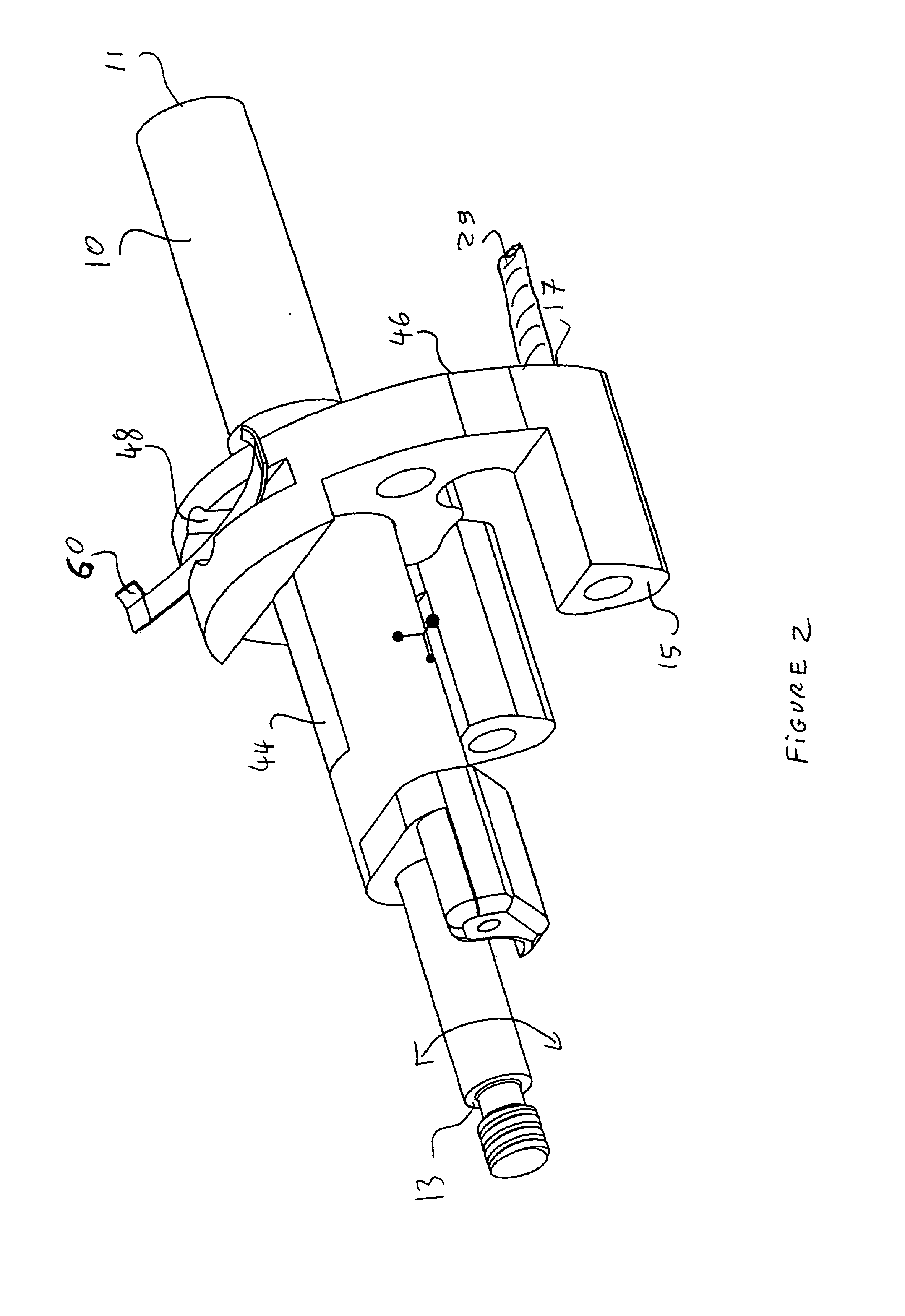
Deflectable sheath handle assembly and method therefor
A deflectable catheter assembly includes a deflectable body manipulatable by a rotating actuator of a housing assembly. The housing assembly includes a sliding member having a threaded portion including a first threaded portion having a first pitch and a second threaded portion having a second pitch, where the first pitch is different than the second pitch.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
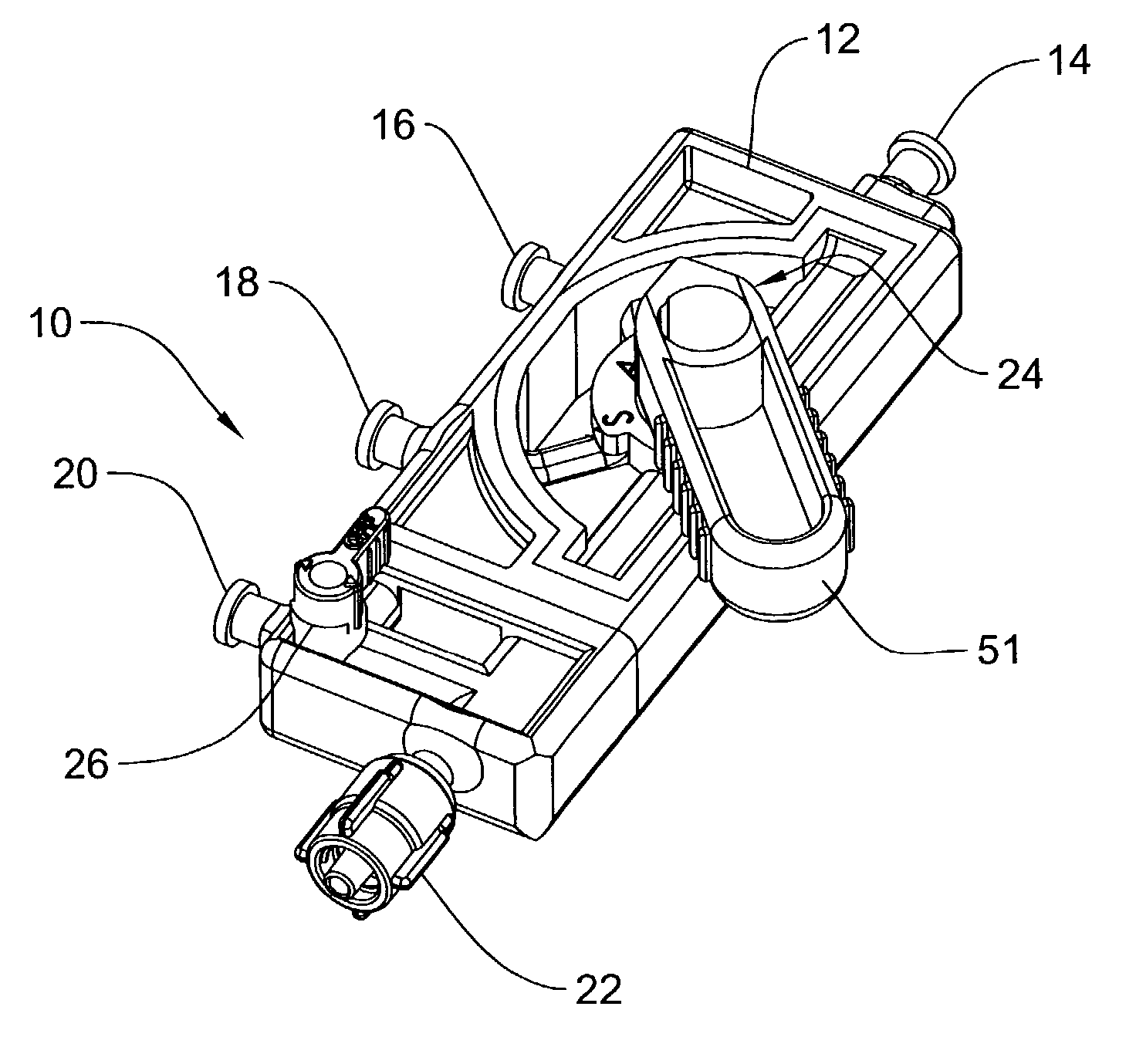
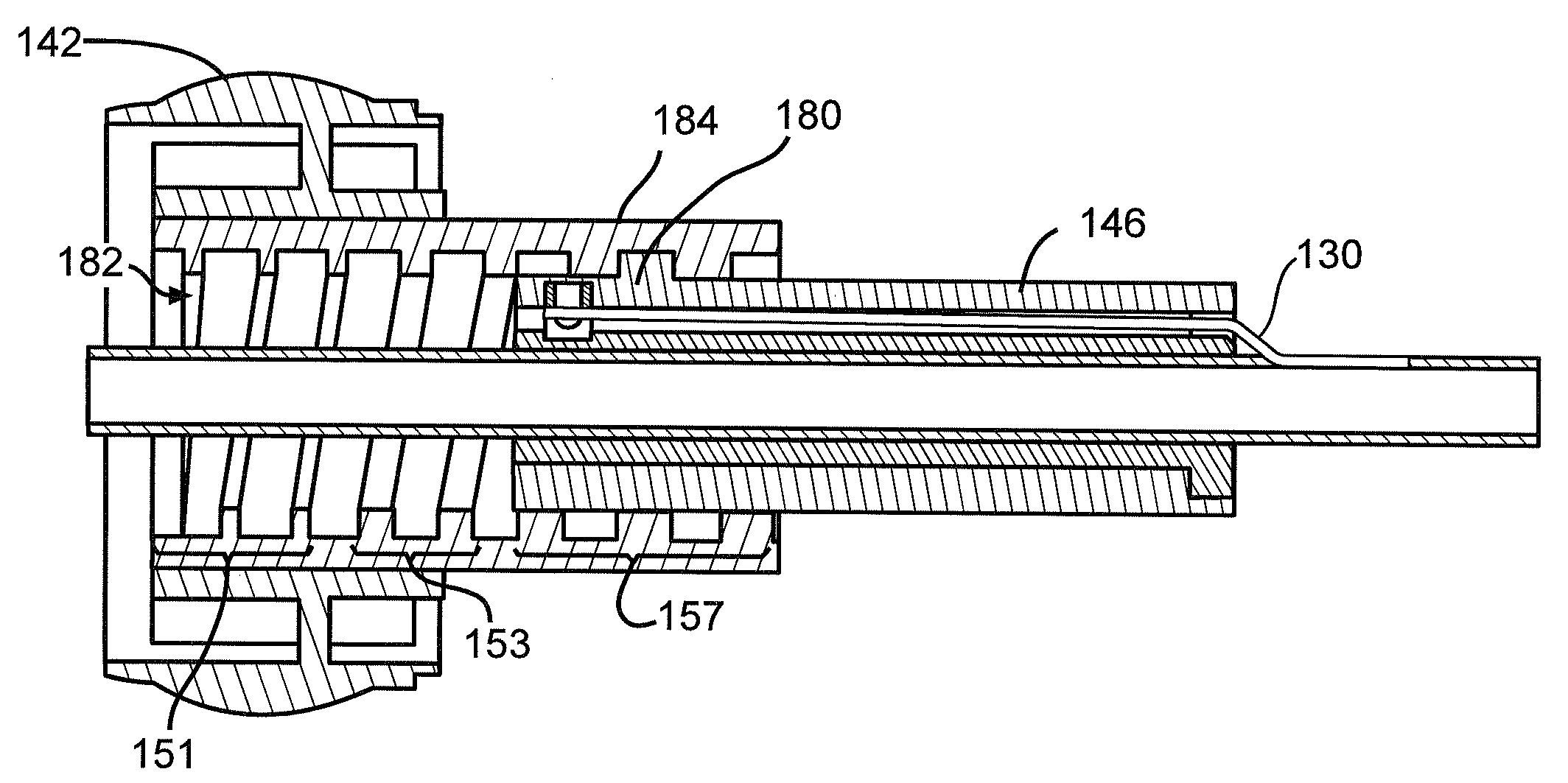
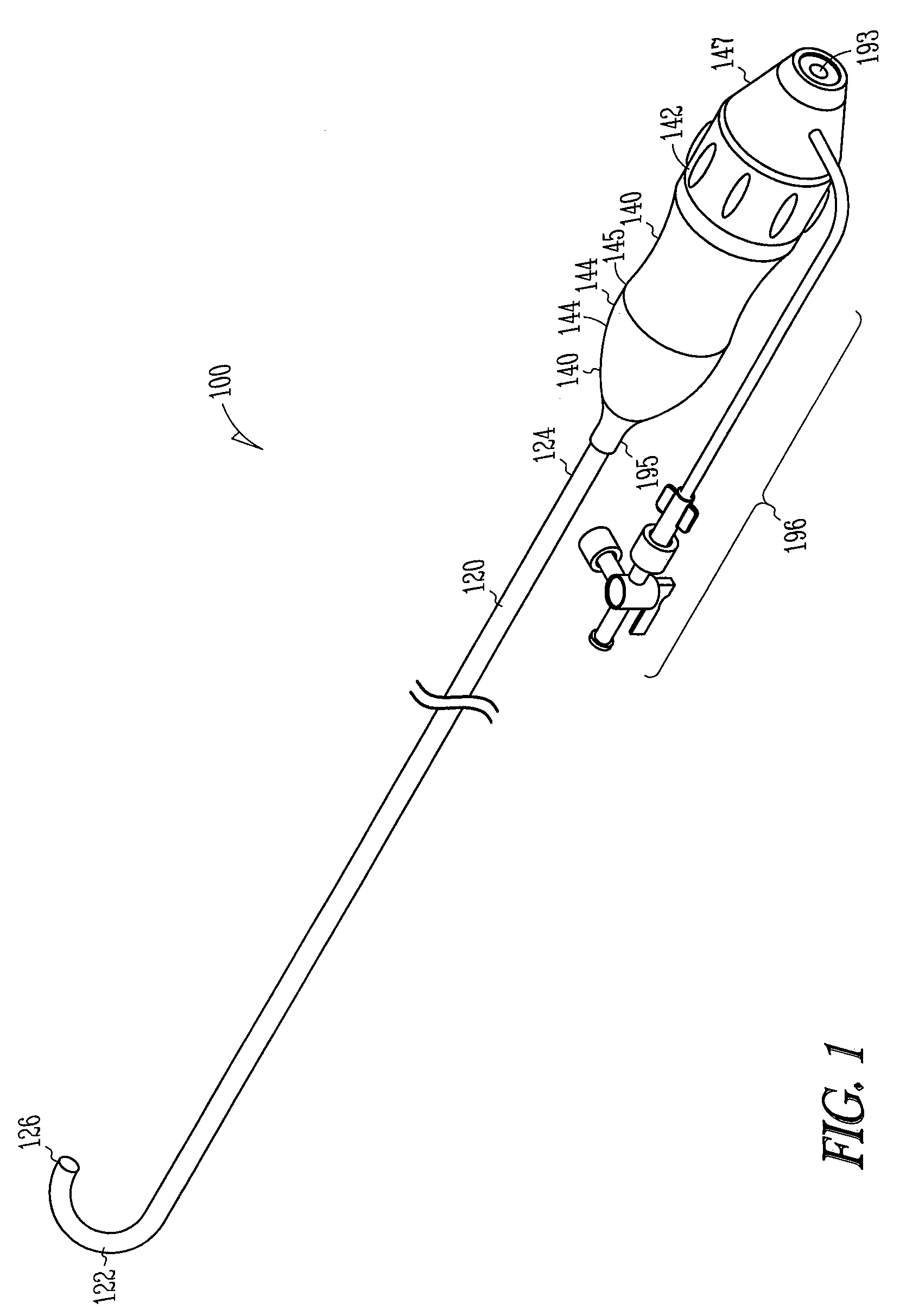
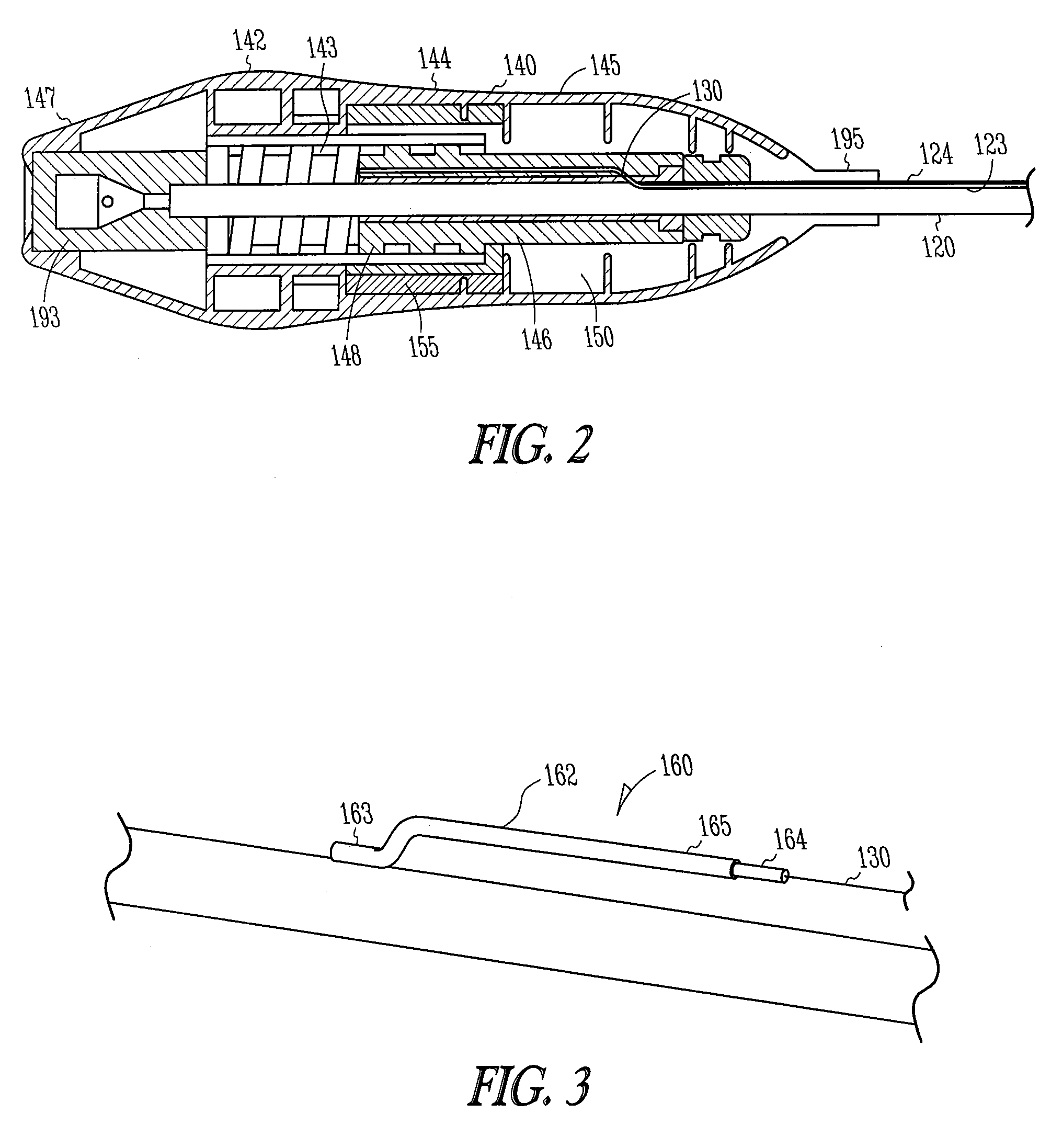
Manifold system for a medical device
InactiveUS7172572B2Prevent backflowMultiple way valvesIntravenous devicesRotary actuatorMedical device
A number of devices are illustrated for providing a manifold that can simply and selectively couple a number of different therapeutic and diagnostic elements to a catheter or other medical device. Some examples include devices having sliding actuators, rotary actuators, button actuators, or combinations thereof, for easily changing the valve scheme and fluid pathways within a manifold.
Owner:MEDLINE INDUSTRIES
In situ cleaning of the surface inside a vacuum processing chamber
InactiveUS6098637AQuick cleanDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingUltravioletRotary actuator
The invention provides generally a method and an apparatus for in situ cleaning of a surface in a semiconductor substrate processing chamber which operates quickly and reduces the downtime for chamber cleaning. The apparatus comprises an ultraviolet (UV) radiation plate moveable between a cleaning position and a storage position and at least one UV radiation source disposed on the UV radiation plate. Preferably, the apparatus includes a reflector disposed adjacent the UV radiation source to focus emitted UV radiation and a rotary actuator pivotally attached to a transport arm to move the UV radiation plate between the cleaning position and the storage position. The method comprises: providing a UV radiation plate having at least one UV radiation source disposed thereon, moving the UV radiation plate into a cleaning position, introducing a cleaning gas into the processing chamber and exposing the surface to UV radiation.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Disk drive having separate motion sensors for base and actuator
InactiveUS6674600B1Good tracking effectReducing off-track errorDisposition/mounting of recording headsDriving/moving recording headsAccelerometerRotary actuator
A disk drive that includes a base, a magnetic disk, a rotary actuator that carries a head for reading and writing data from the disk in a track-following mode under the control of a servo control system, and at least two sensors--one fixed sensor rigidly coupled to the overall disk drive and one mobile sensor mounted to the rotating actuator--for differentially detecting accelerations of the rotary actuator relative to the overall disk drive and its disk. The disk drive detects and actively compensates for accelerations imparted to a balanced actuator that has an effective imbalance. The fixed sensor is preferably mounted to a PCBA that is secured to the base. The mobile sensor is preferably mounted to an actuator arm of the rotary actuator, as far outboard as possible, and so as to align with the fixed sensor as the rotary actuator swings through its range of travel. The preferred sensors are linear accelerometers.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Asymmetric and general vibration waveforms from multiple synchronized vibration actuators
InactiveUS8981682B2Low costImprove responsivenessEmergency protective circuit arrangementsNavigation instrumentsDriver circuitEngineering
The disclosure relates to General Synchronized Vibration devices that provide haptic feedback to a user and improve the performance of existing vibratory devices. Different actuator types may be employed to provide synchronized vibration, including linear rotary actuators, rotating eccentric mass actuators including interleaved rotating mass actuators, and rocking mass actuators. A controller sends signals to one or more driver circuits to provide adjustment of vibration magnitude, frequency, and direction of the actuators. The system may apply forces onto an object, and a sensor measures a feature(s) of the object. This information is provided to a vibration device controller, which can then modify the vibration waveform to improve overall system performance. Fourier synthesis can be used to approximate arbitrarily shaped waveforms by controlling the phase and frequency of vibration actuators. These waveforms can include asymmetry where the peak force in one direction is higher than the peak force in another direction.
Owner:COACTIVE DRIVE CORP
Articulating headrest assembly
InactiveUS20070164593A1Reduce complexityReduce manufacturing costVehicle seatsOperating chairsHorizontal axisEngineering
A headrest assembly that is rotatable to various positions includes a support defining a horizontal axis. A shell is rotatably mounted to the support. Notches are disposed on the support, and each notch is associated with one of the positions. A lever is mounted to the shell and has a locking portion rotatable about the pivot axis and partially disposed in one of the notches to prevent movement of the shell. An actuator is mounted to the shell and rotates the locking portion of the lever about a pivot axis in a direction transverse to the horizontal axis. The actuator moves the locking portion out of one of the notches to allow the shell to rotate about the horizontal axis. Furthermore, the actuator moves the locking portion into one of the notches to prevent the shell from rotating about the horizontal axis.
Owner:WINDSOR MACHINE & STAMPING
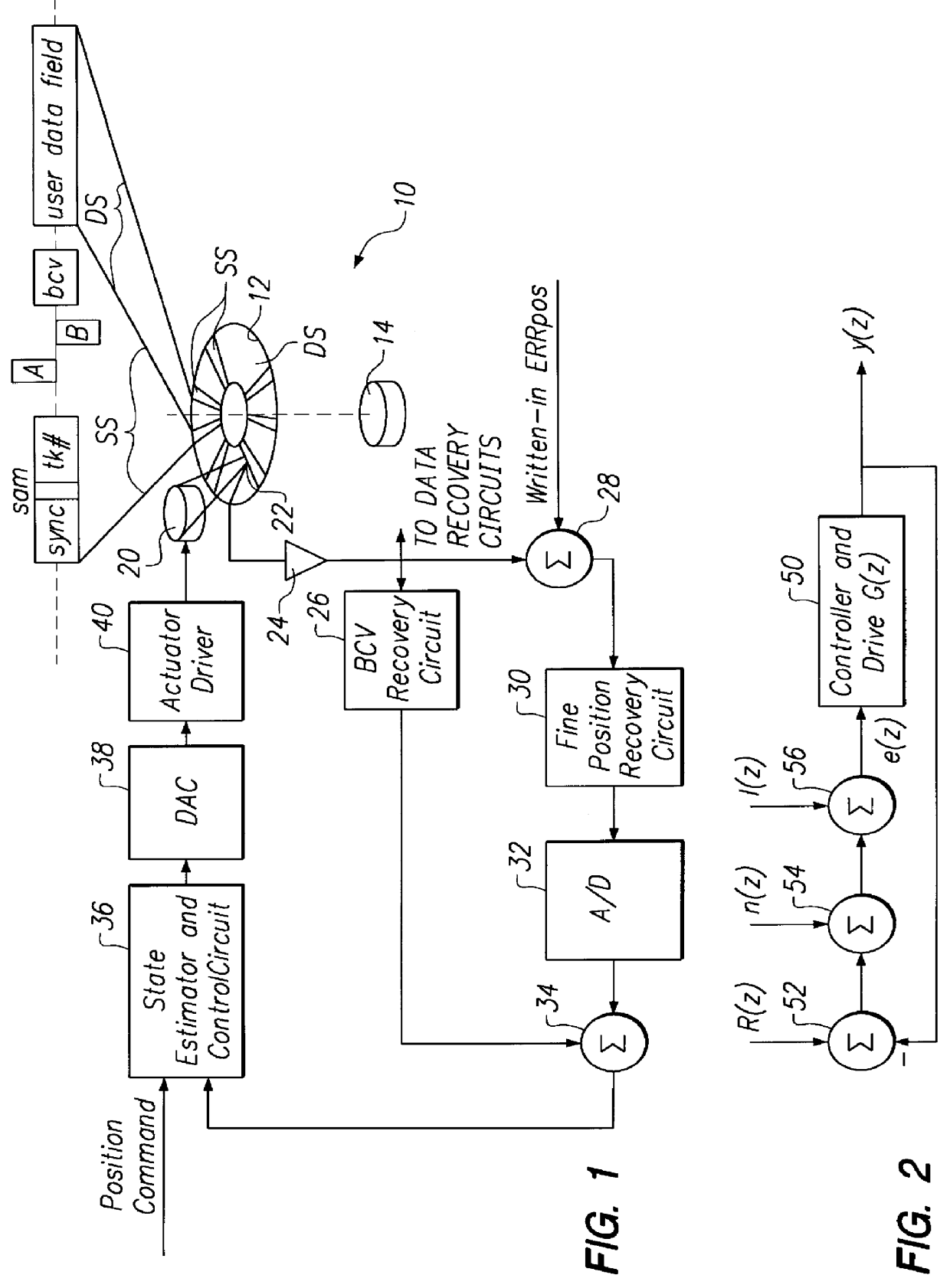
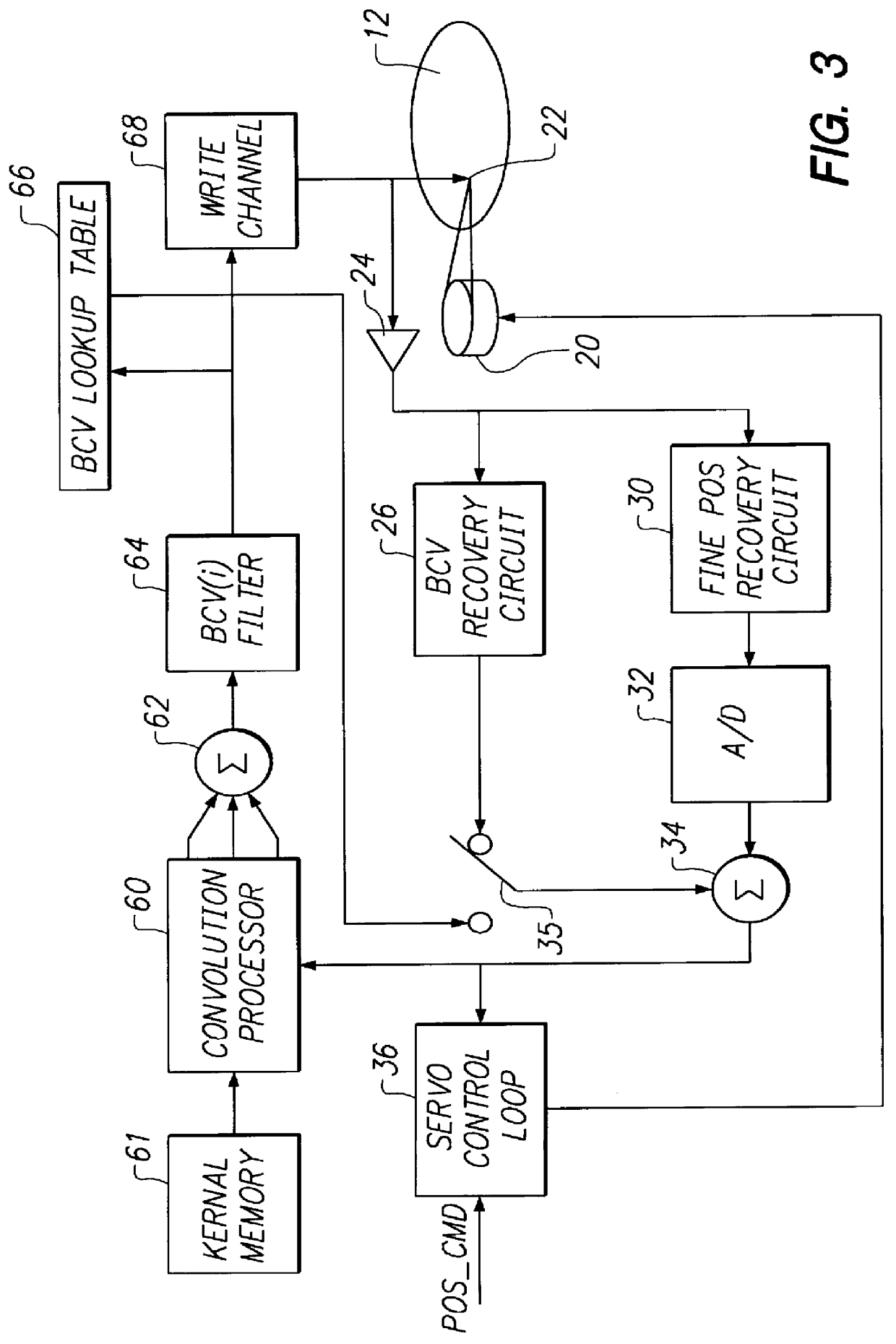
In-drive correction of servo pattern errors
InactiveUS6061200AImprove RRO correction valueTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveClosed loop
Embedded servo sectors within a data track of a hard disk drive including a rotating data storage disk and a closed loop rotary actuator structure for positioning a data transducer head relative to the data track are written by a method including the steps of positioning the rotary actuator structure relative to the data track with a laser-interferometer-based servo writer and writing a pattern of circumferentially sequential, radially offset fine position bursts within each servo sector with the data transducer head, this step including writing-in undetermined position errors within each pattern being written, moving the disk drive to a self scan environment away from the servo writer, operating the rotary actuator structure in closed loop for following the data track by reference to the servo burst pattern, extracting the undetermined position error from each pattern thereby to iteratively determine written-in position errors, generating burst correction values from the determined written-in position errors, and writing the burst correction values to the data track for later use by the closed loop rotary actuator structure during following of the data track to remove the written-in position errors.
Owner:MATSUSHITA KOTOBUKI ELECTRONICS IND LTD
Depth control device for an underwater cable
InactiveUS6016286AImprove impact resistanceEasy to assembleTowing/pushing equipmentLiquid surface applicatorsDrive shaftControl theory
A depth control device for an underwater cable includes a rotary actuator having a rotating output shaft connected to a swash plate. Rotation of the swash plate by the actuator causes a rocker arm to pivot about an axis transverse to the axis of the output shaft. The rocker arm is drivingly connected to a drive shaft for rotating wings about their pitch axes. The pitch axes of the wings can be perpendicular to and intersecting the axis of the actuator output shaft, enabling the depth control device to be extremely compact.
Owner:DIGICOURSE
Safety lockout for actuator shaft
A safety lock-out to prevent rotation of a rotary actuator is described. When an axial distance between a first and a second portion of an actuated mechanism exceeds a selected distance, the lock-out prevents the rotation. The safety lock-out includes a shaft rotatably connected to the first portion and axially movable relative to the second portion. A locking member is adapted to lock the rotary actuator by placing a protrusion in a notch of the shaft, thus preventing rotation of the shaft. The device also includes a spring member urging the locking member in the locking position, and an unlocking member adapted to urge the locking member in the unlocked position when the selected distance is not exceeded.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Deflectable sheath handle assembly and method therefor
ActiveUS7615044B2Solve the quick positioningSmall sizeMedical devicesCatheterRotary actuatorCatheter device
A deflectable catheter assembly includes a deflectable body manipulatable by a rotating actuator of a housing assembly. The housing assembly includes a sliding member having a threaded portion including a first threaded portion having a first pitch and a second threaded portion having a second pitch, where the first pitch is different than the second pitch.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Cable winding device with clocked keycap and revolving electrical switch
InactiveUS7017721B1Easy to optimizeIncrease contactCathode-ray tube indicatorsArrangements using take-up reel/drumElectricityElectrical control
Mechanisms for providing electrical controls on a rotating assembly such as a cable winding device are disclosed. The cable winding device generally includes an electronic control actuator such as a keycap attached to a housing and providing an actuating pad actuatable via an opening provided in the housing, the housing containing a spool, a circuit component including an electronic control such as a switch actuatable via the actuating pad, and a rotational actuator interface such as a skid pad located over the electronic control to interface between the actuator pad and the electronic control at all rotational orientations of the switch relative to the actuating pad and / or even while the spool is rotating. The circuit component and the skid pad are configured to rotate with the spool relative to the housing. The switch is disposed off of an axis of rotation and may be, for example, an answer / end, on / off, mute, volume, play / stop, rewind / fast forward, and / or enter / accept control. The cable winding apparatus may be incorporated in a headset system.
Owner:PLANTRONCS
Disk drive rotary actuator assembly having a constrained layer damper attached to a flat actuator coil
InactiveUS6937444B1Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageSnubberCantilever
A head stack assembly for a disk drive includes a rotary actuator assembly. The rotary actuator assembly includes an actuator body having a bore defining a pivot axis, an actuator arm cantilevered from the actuator body, and a coil portion cantilevered from the actuator body in a direction opposite from the actuator arm. The coil portion includes a coil support, a flat coil supported by the coil support, the flat coil including a coil surface generally perpendicular to the pivot axis, and a constrained layer damper attached to the coil surface. The constrained layer damper includes a stiffening layer having a coil-facing planar surface generally perpendicular to the pivot axis and an adhesive layer positioned between the coil-facing planar surface and the coil surface.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com