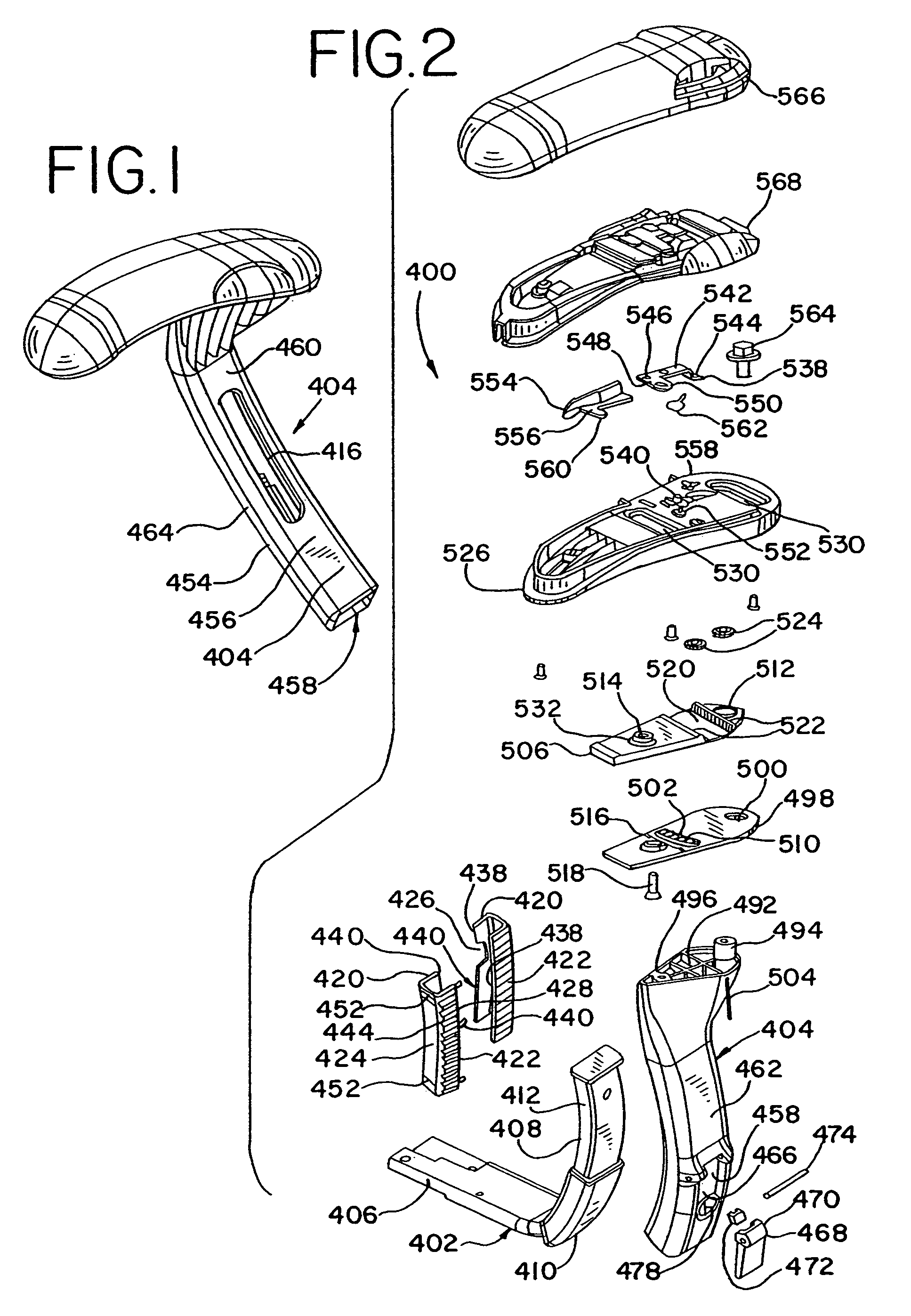
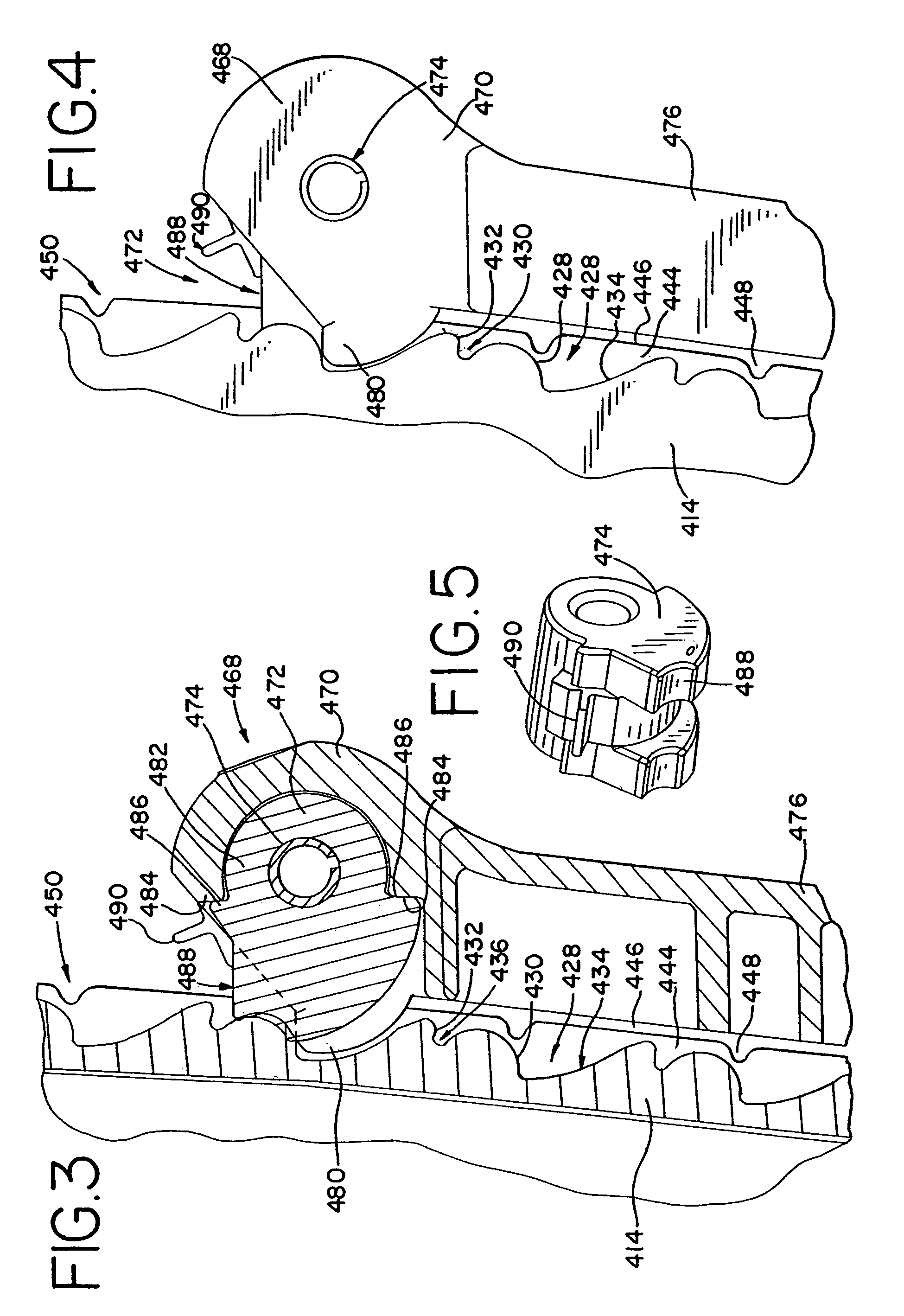
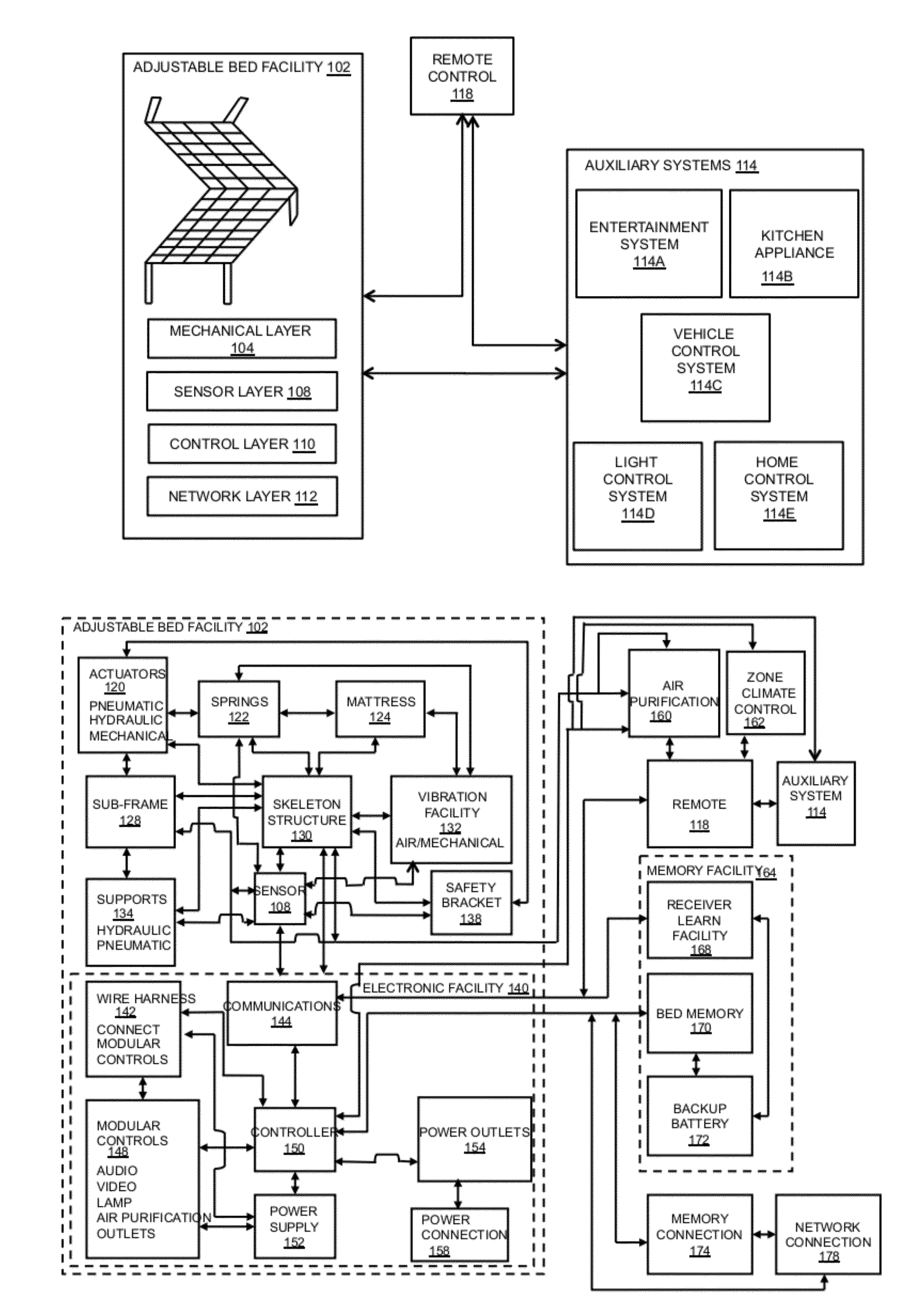
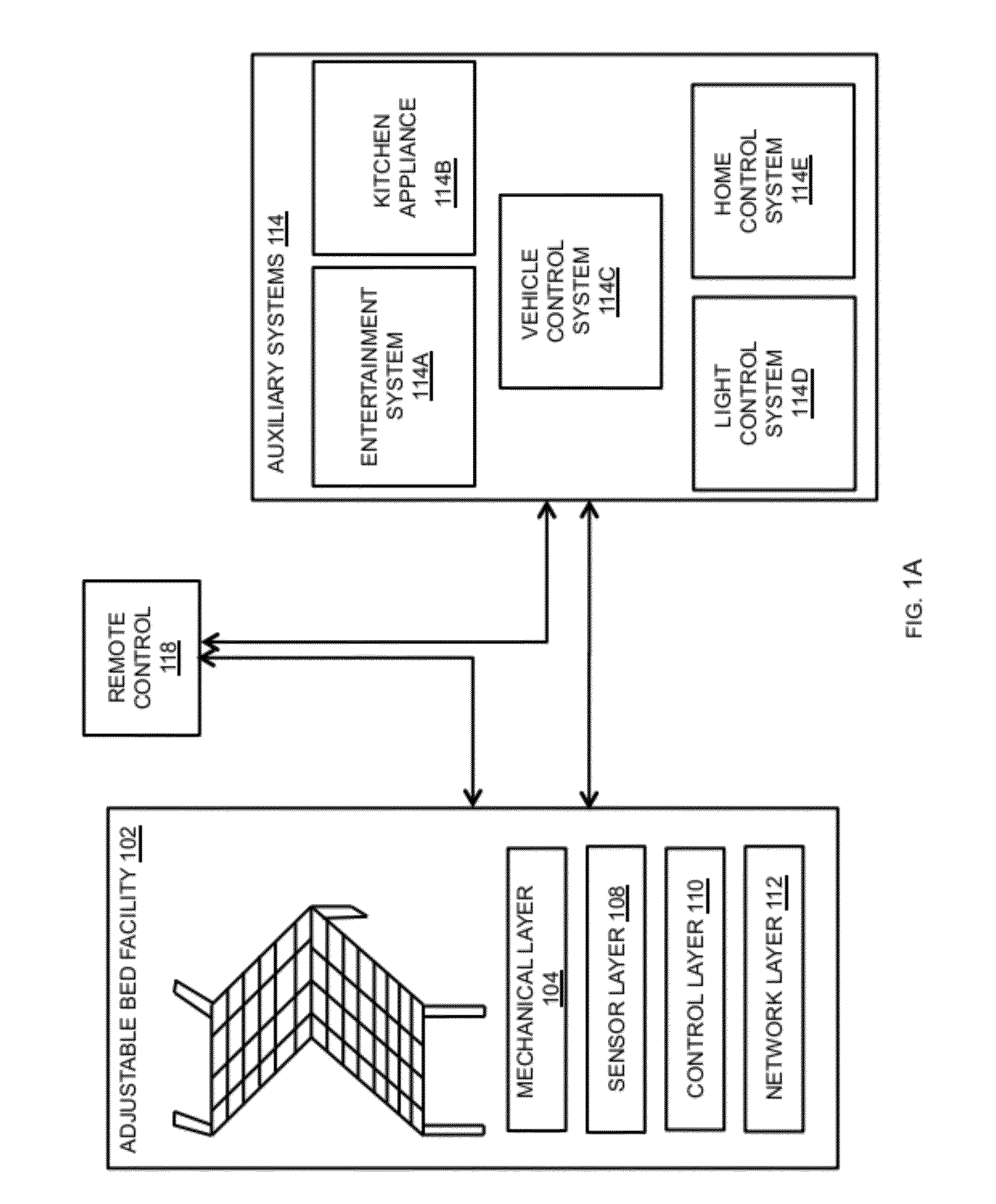
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4609results about "Operating chairs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
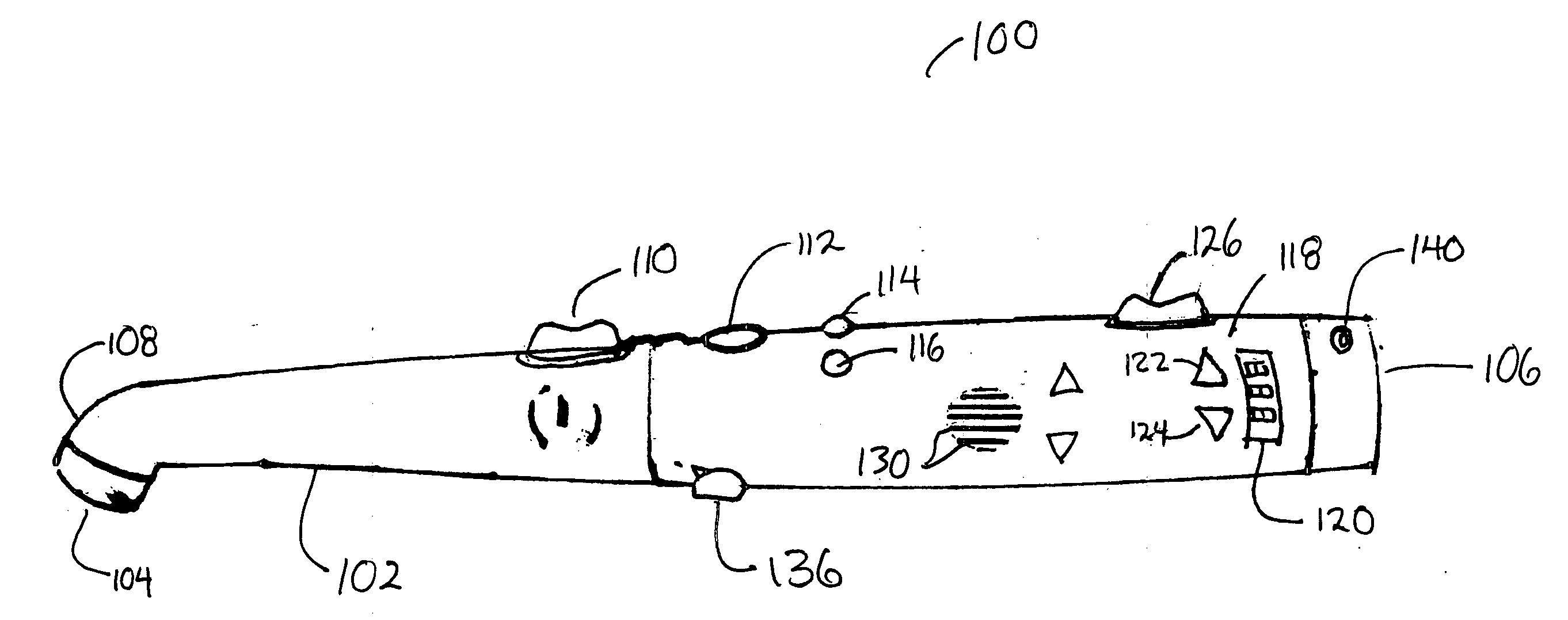
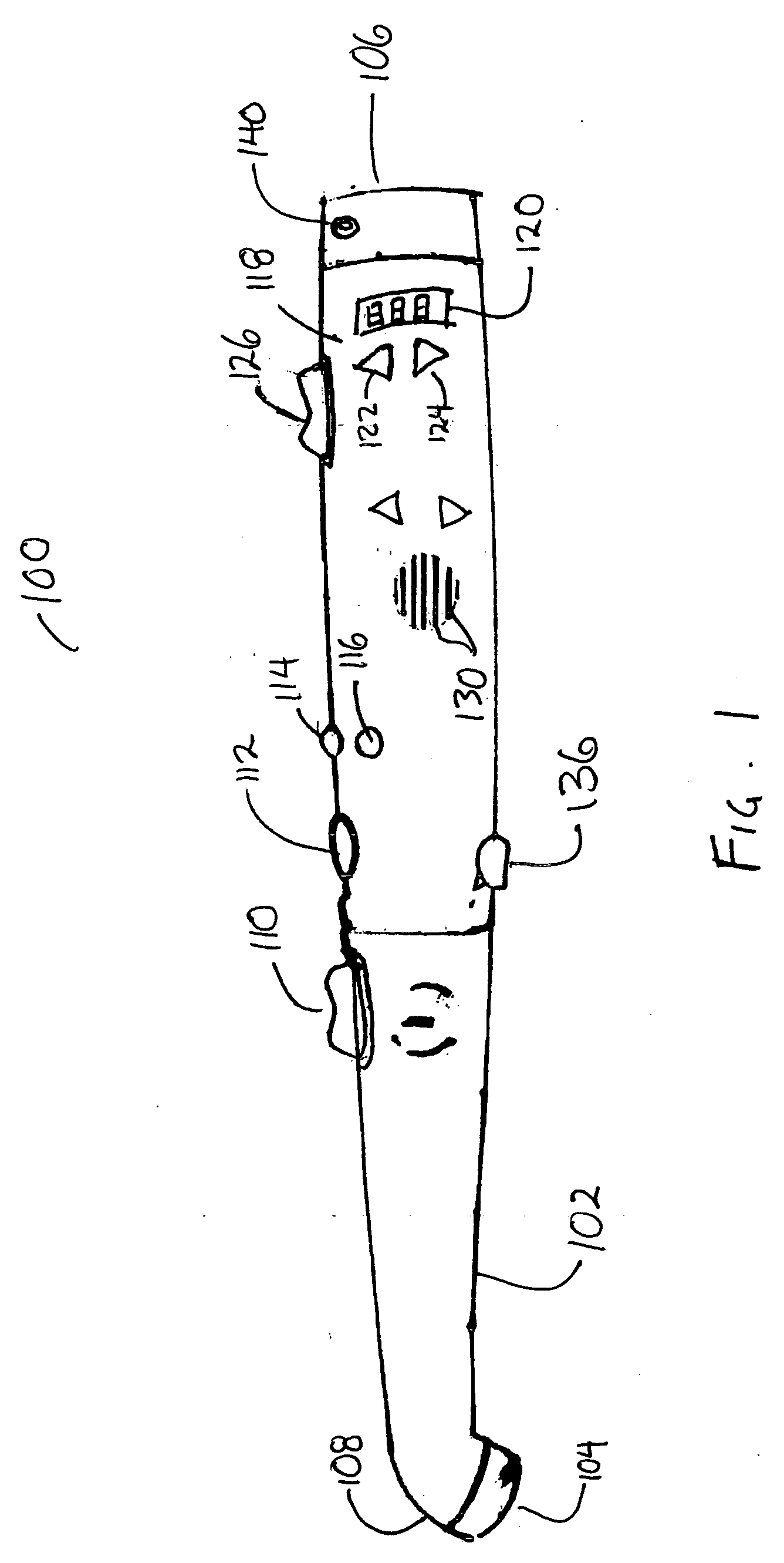
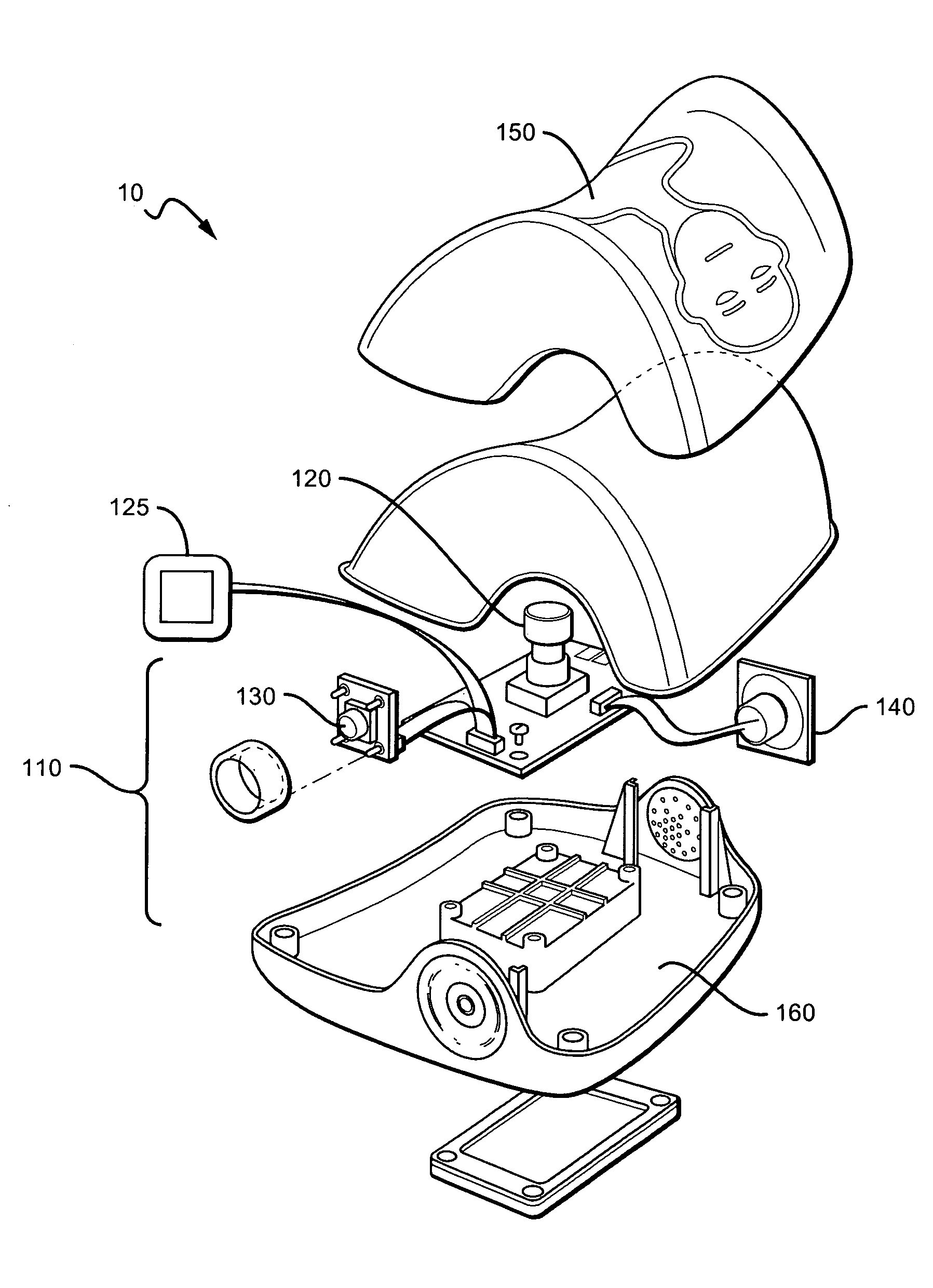
Voice alert in dentistry
InactiveUS20060008787A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracyCosmetic preparationsTime indicationSpeech soundComputer science
Owner:DISCUS DENTAL LLC
CPR system with feed back instruction
CPR systems that provide guidance to a CPR provider are presented. Contemplated CPR systems include sensors that collect a victim's biometric data during CPR. The data is processed by an electronic assembly which provides feedback to the CPR provider. The electronic assembly can be packaged within a cranio-cervical extension device having language independent instructions encoded on a surface of the device.
Owner:CPAIR
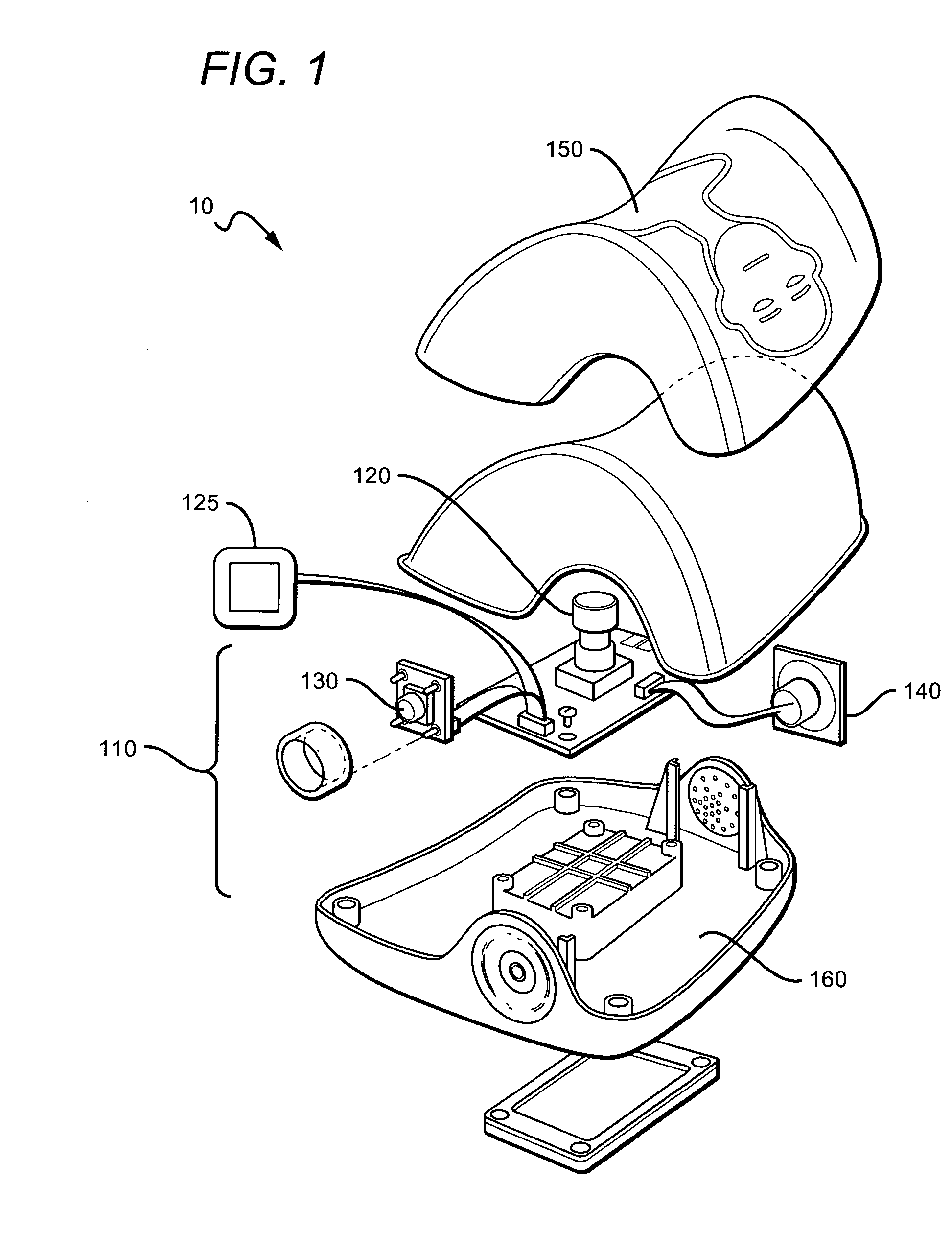
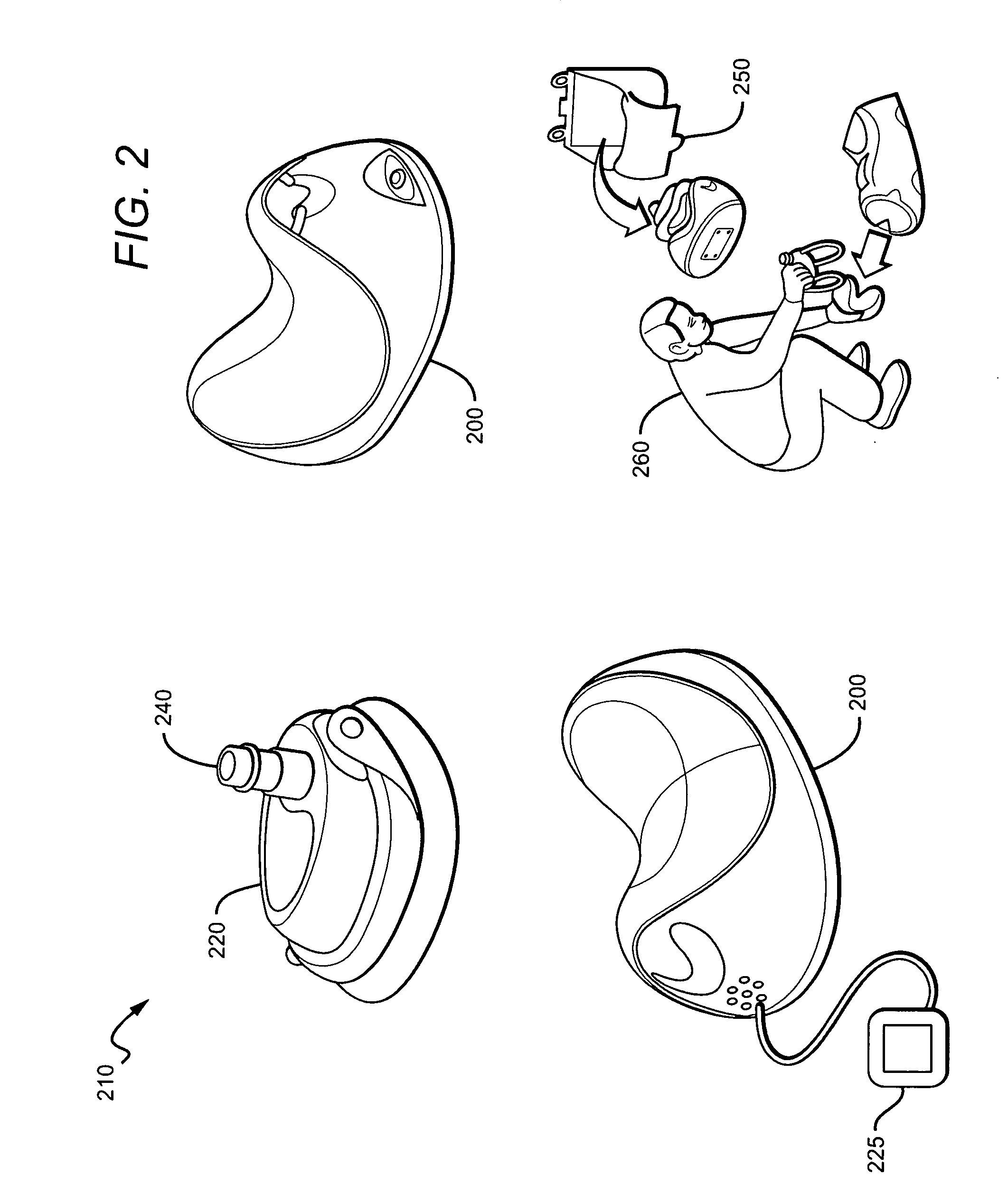
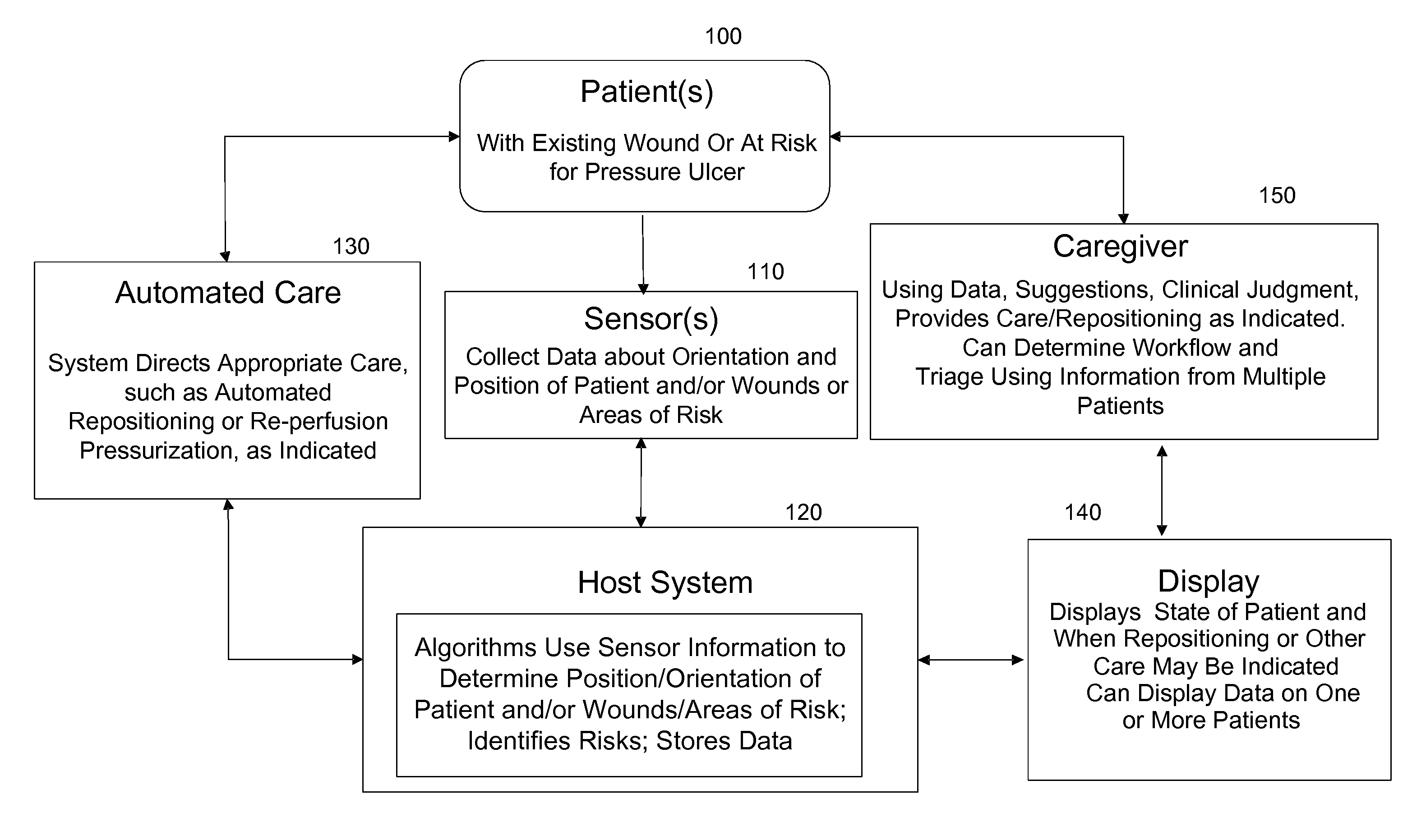
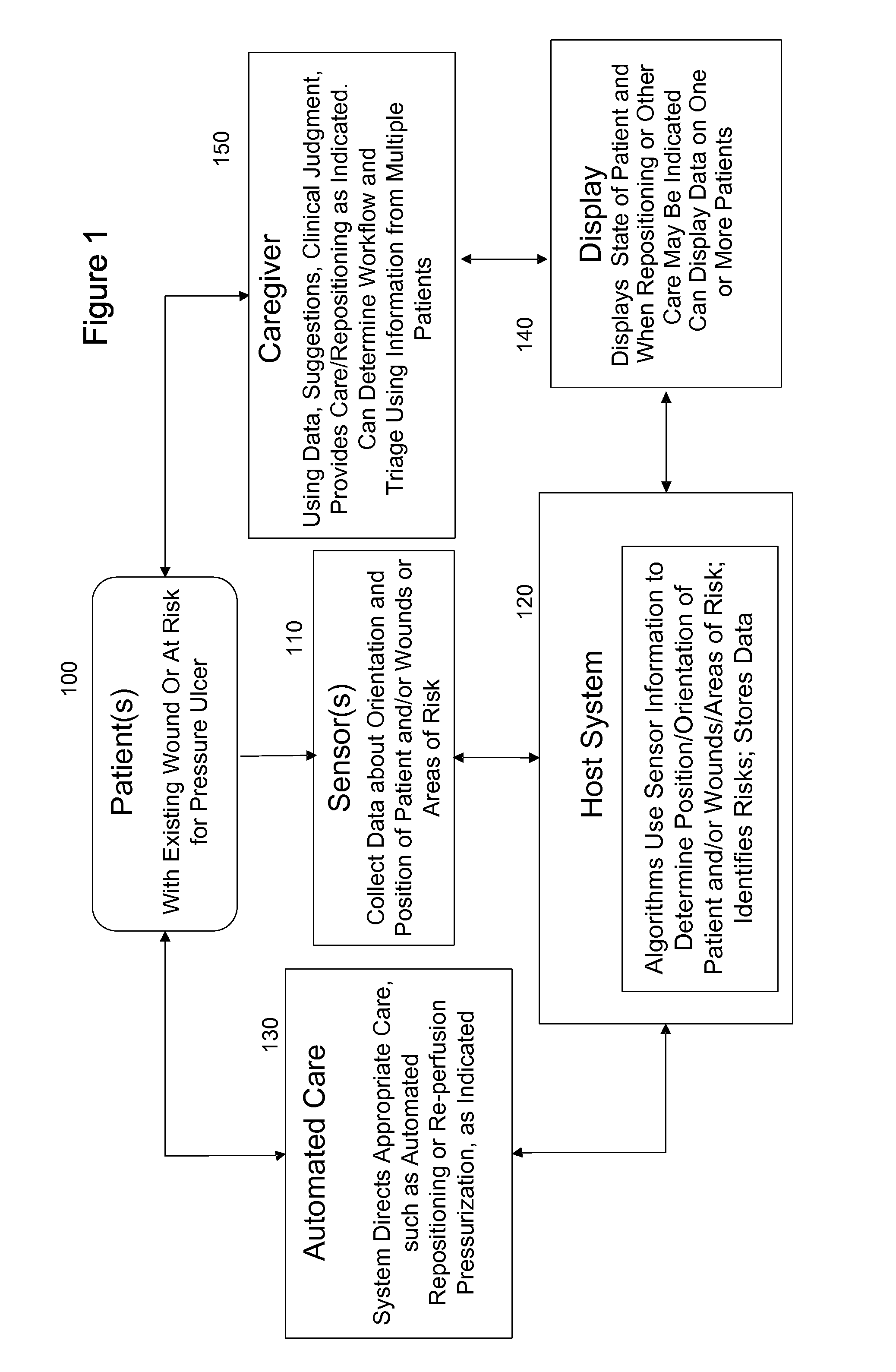
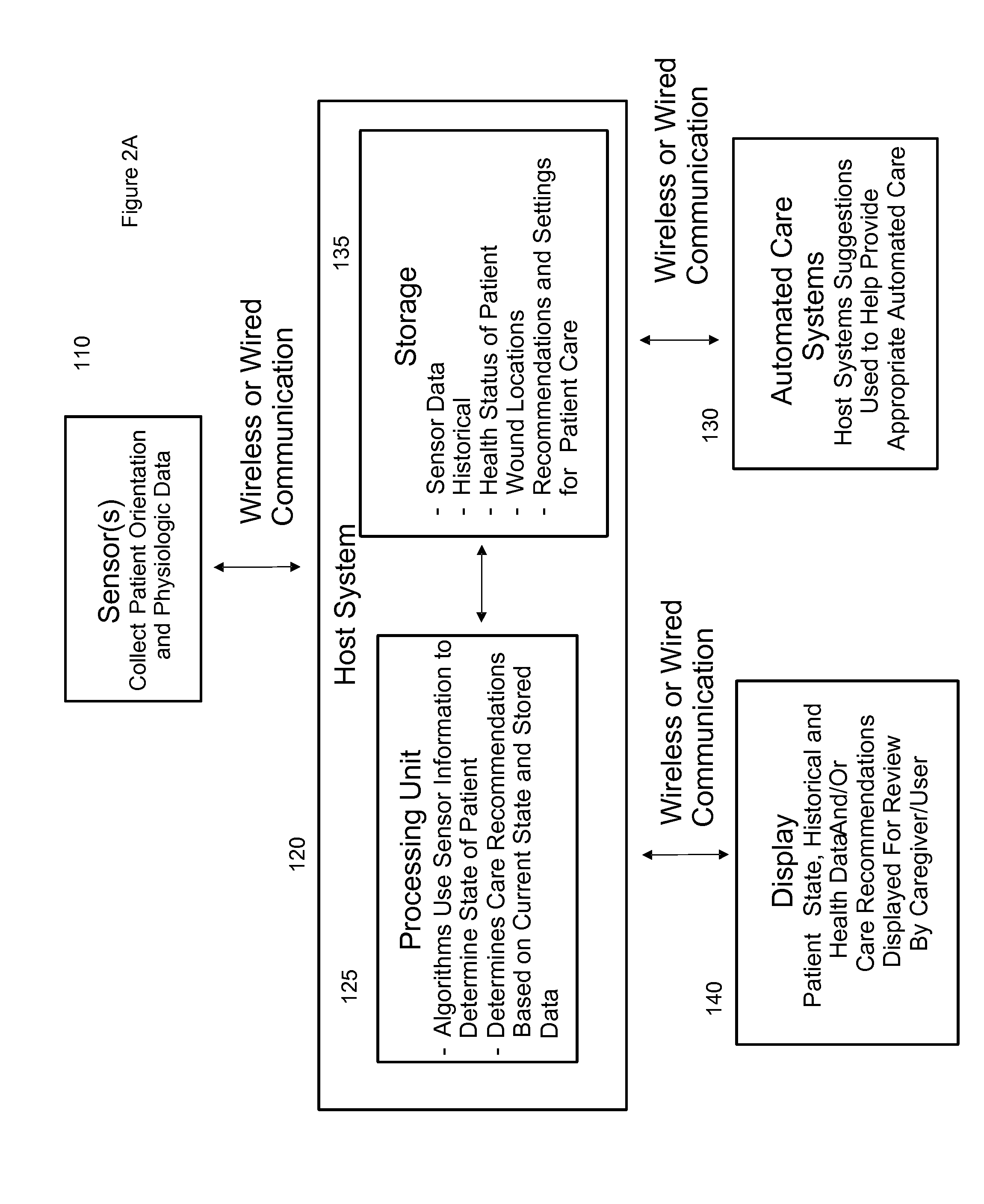
Systems, devices and methods for preventing, detecting and treating pressure-induced ischemia, pressure ulcers, and other conditions
ActiveUS20110263950A1Minimize and eliminate physical contactPromote blood circulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOperating chairsAccelerometerPatient characteristics
A system for monitoring medical conditions including pressure ulcers, pressure-induced ischemia and related medical conditions comprises at least one sensor adapted to detect one or more patient characteristic including at least position, orientation, temperature, acceleration, moisture, resistance, stress, heart rate, respiration rate, and blood oxygenation, a host for processing the data received from the sensors together with historical patient data to develop an assessment of patient condition and suggested course of treatment. In some embodiments, the system can further include a support surface having one or more sensors incorporated therein either in addition to sensors affixed to the patient or as an alternative thereof. The support surface is, in some embodiments, capable of responding to commands from the host for assisting in implementing a course of action for patient treatment. The sensor can include bi-axial or tri-axial accelerometers, as well as resistive, inductive, capactive, magnetic and other sensing devices, depending on whether the sensor is located on the patient or the support surface, and for what purpose.
Owner:LEAF HEALTHCARE
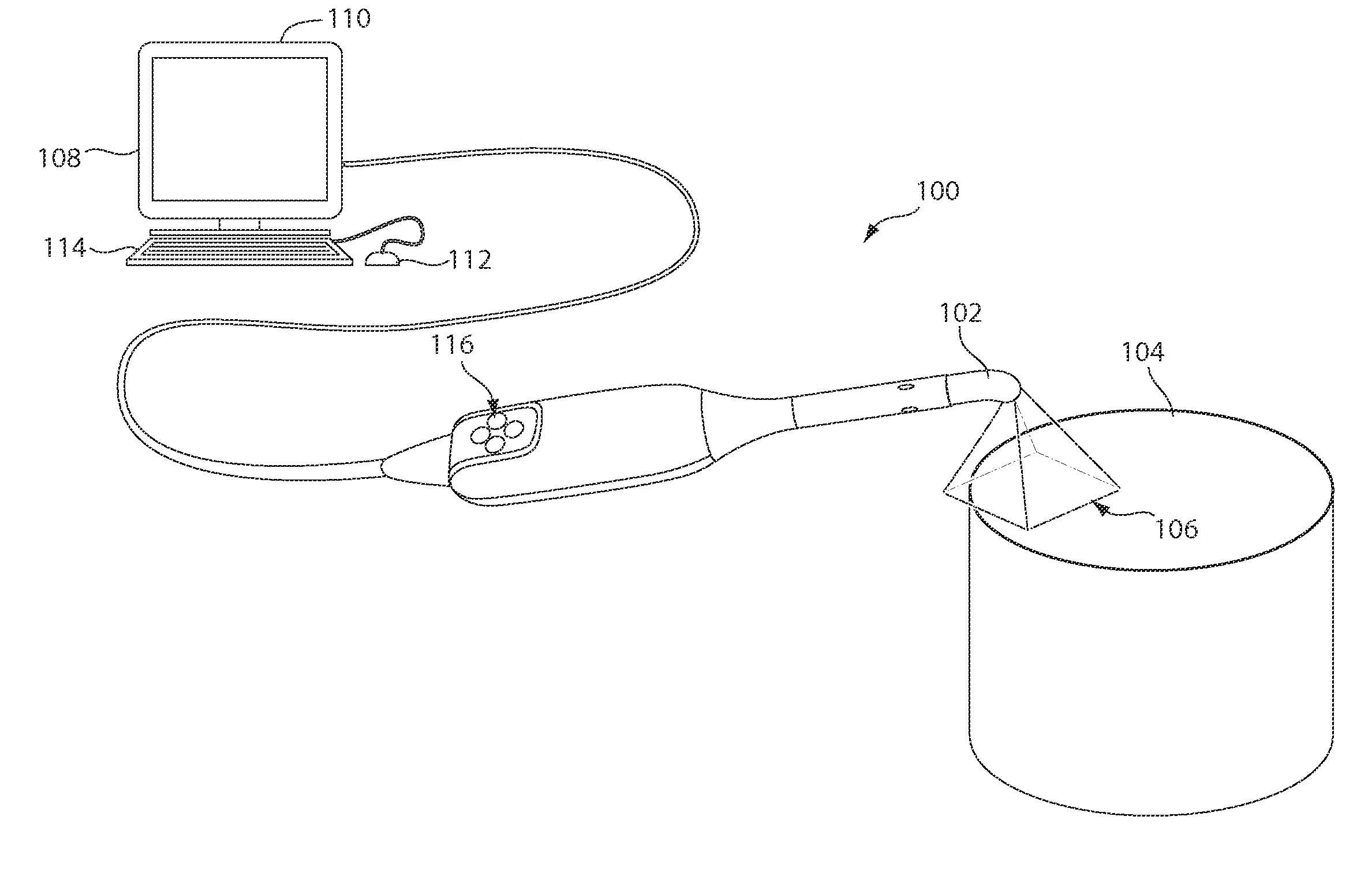
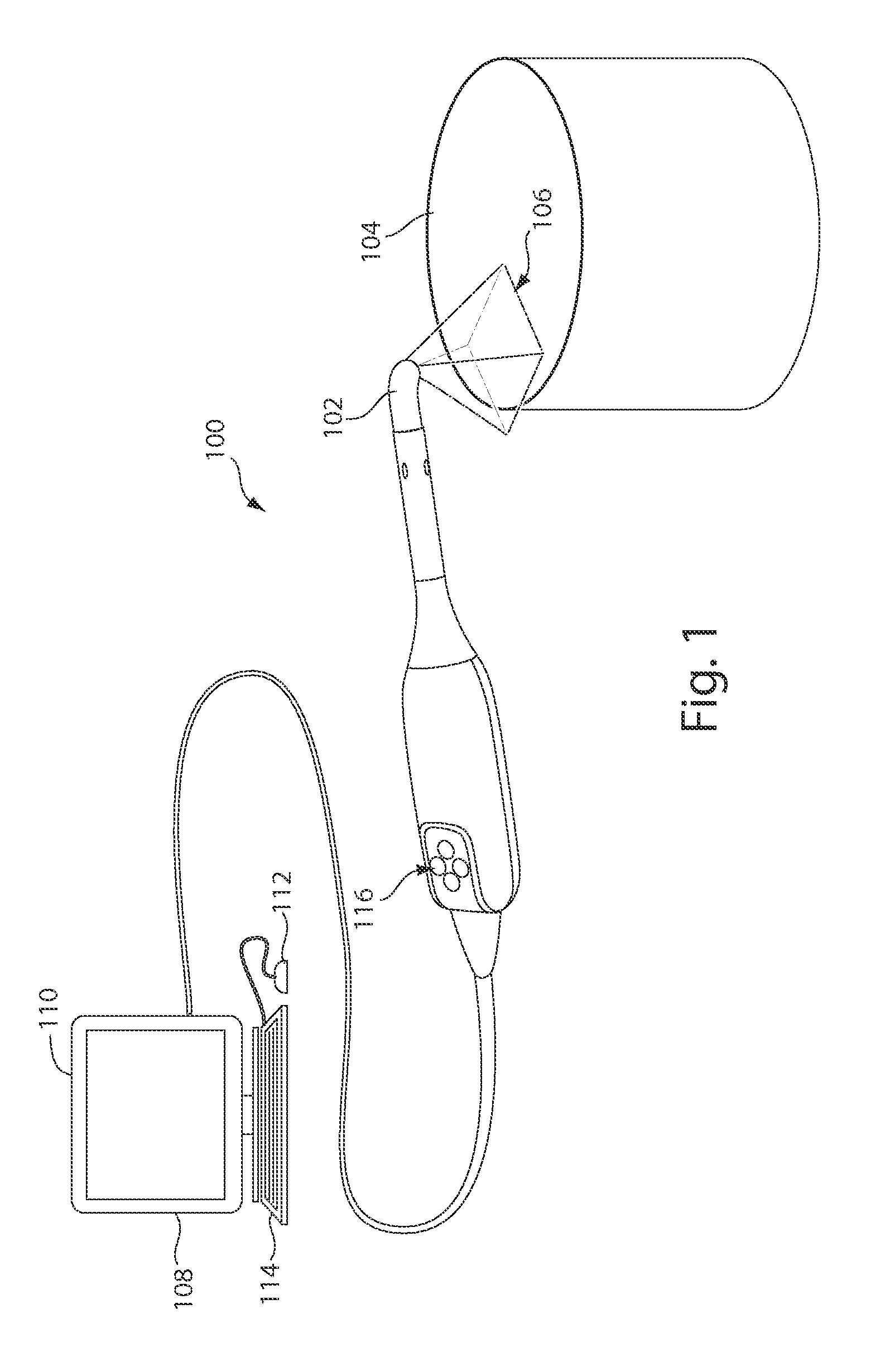
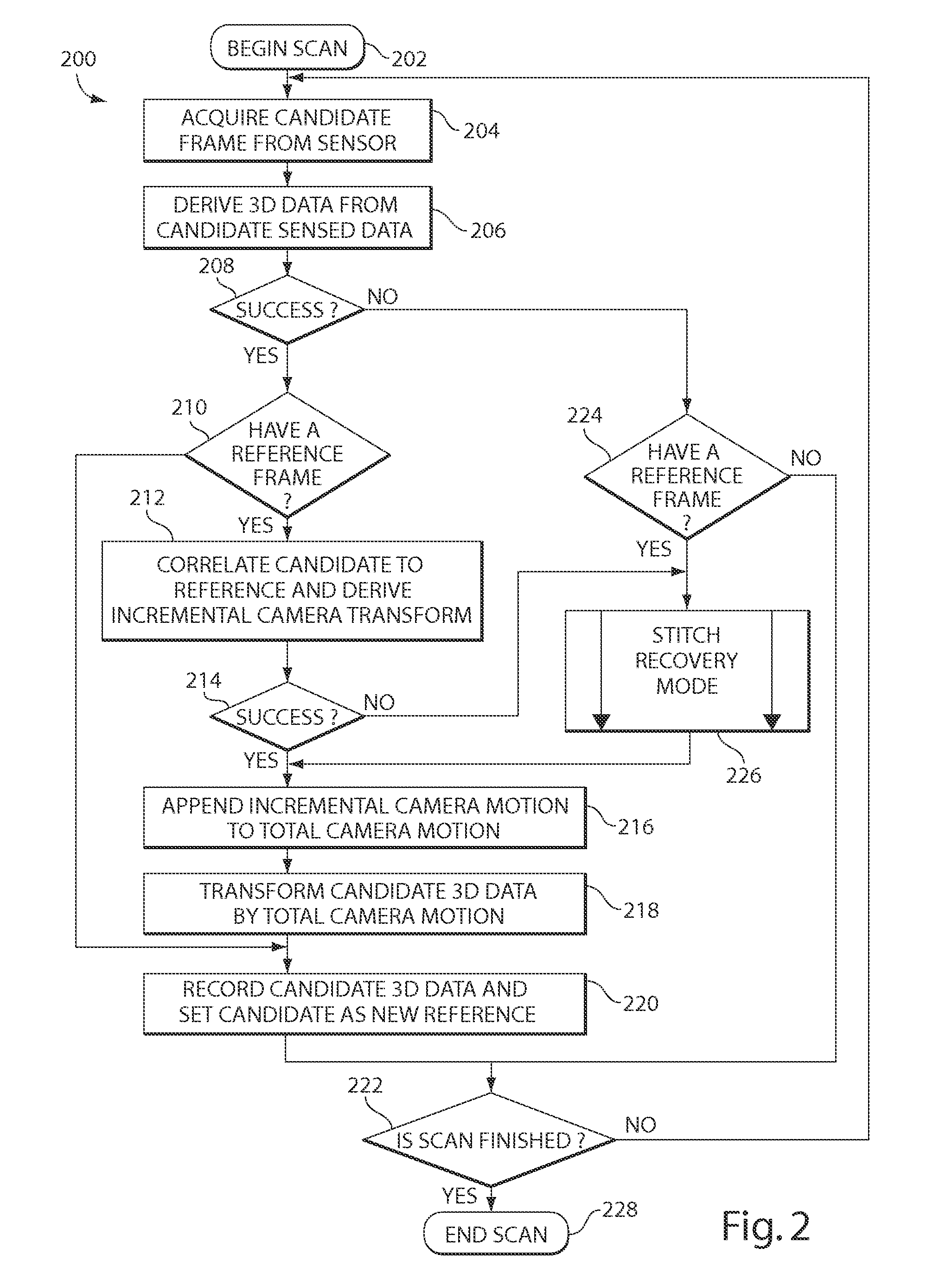
Three-dimensional scan recovery
A scanning system that acquires three-dimensional images as an incremental series of fitted three-dimensional data sets is improved by testing for successful incremental fits in real time and providing a variety of visual user cues and process modifications depending upon the relationship of newly acquired data to previously acquired data. The system may be used to aid in error-free completion of three-dimensional scans. The methods and systems described herein may also usefully be employed to scan complex surfaces including occluded or obstructed surfaces by maintaining a continuous three-dimensional scan across separated subsections of the surface. In one useful dentistry application, a full three-dimensional surface scan may be obtained for two dental arches in occlusion.
Owner:MEDIT CORP
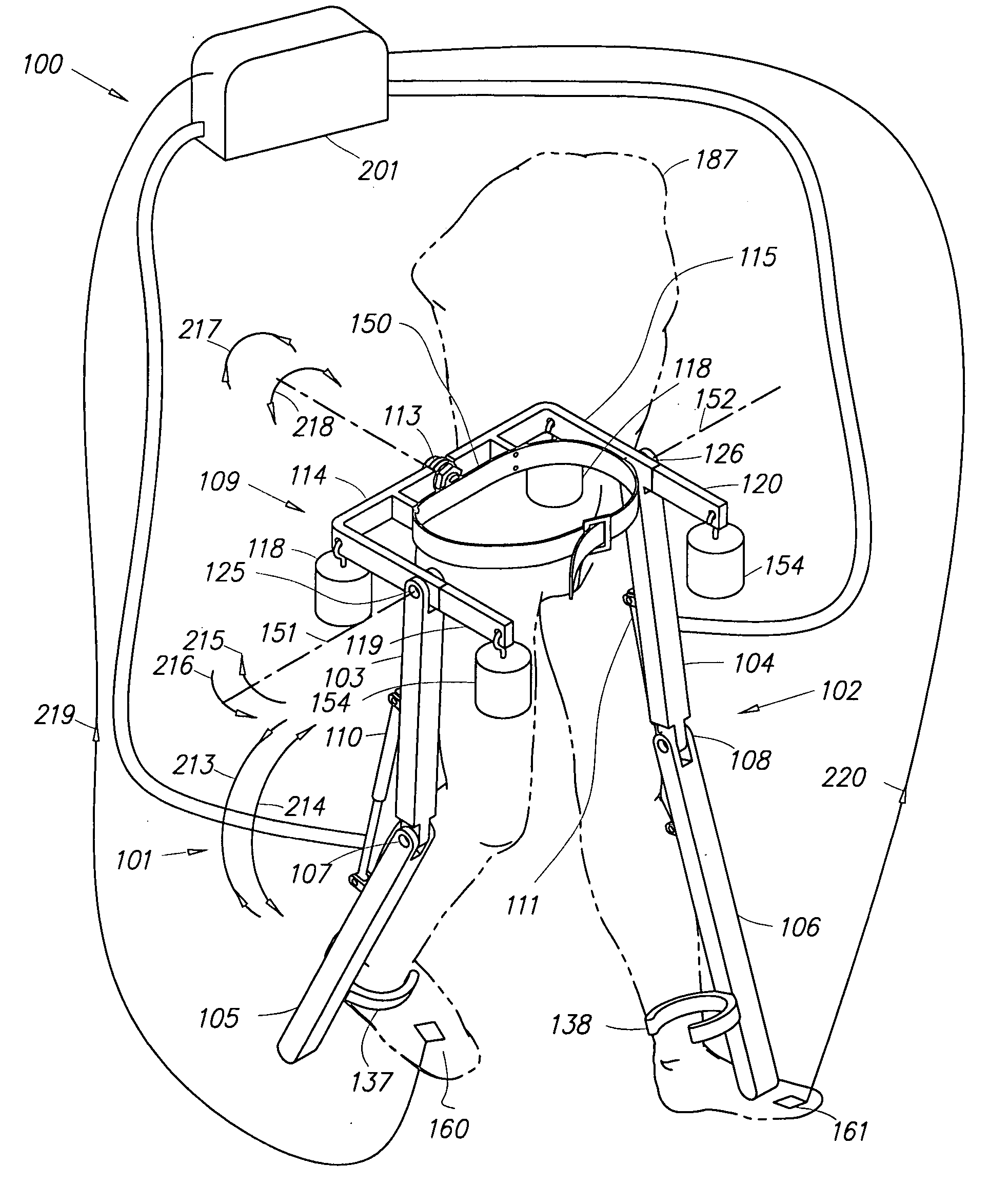
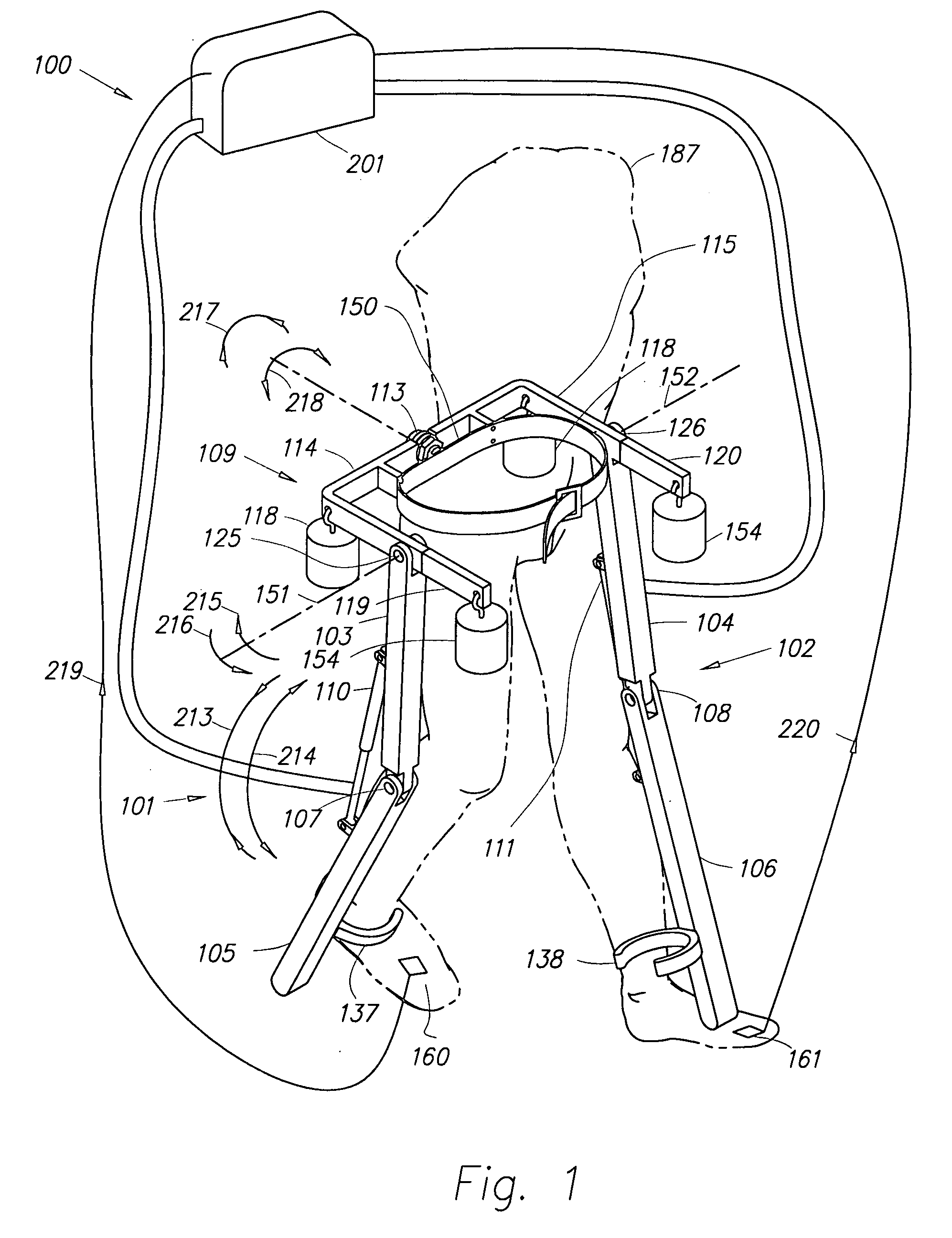
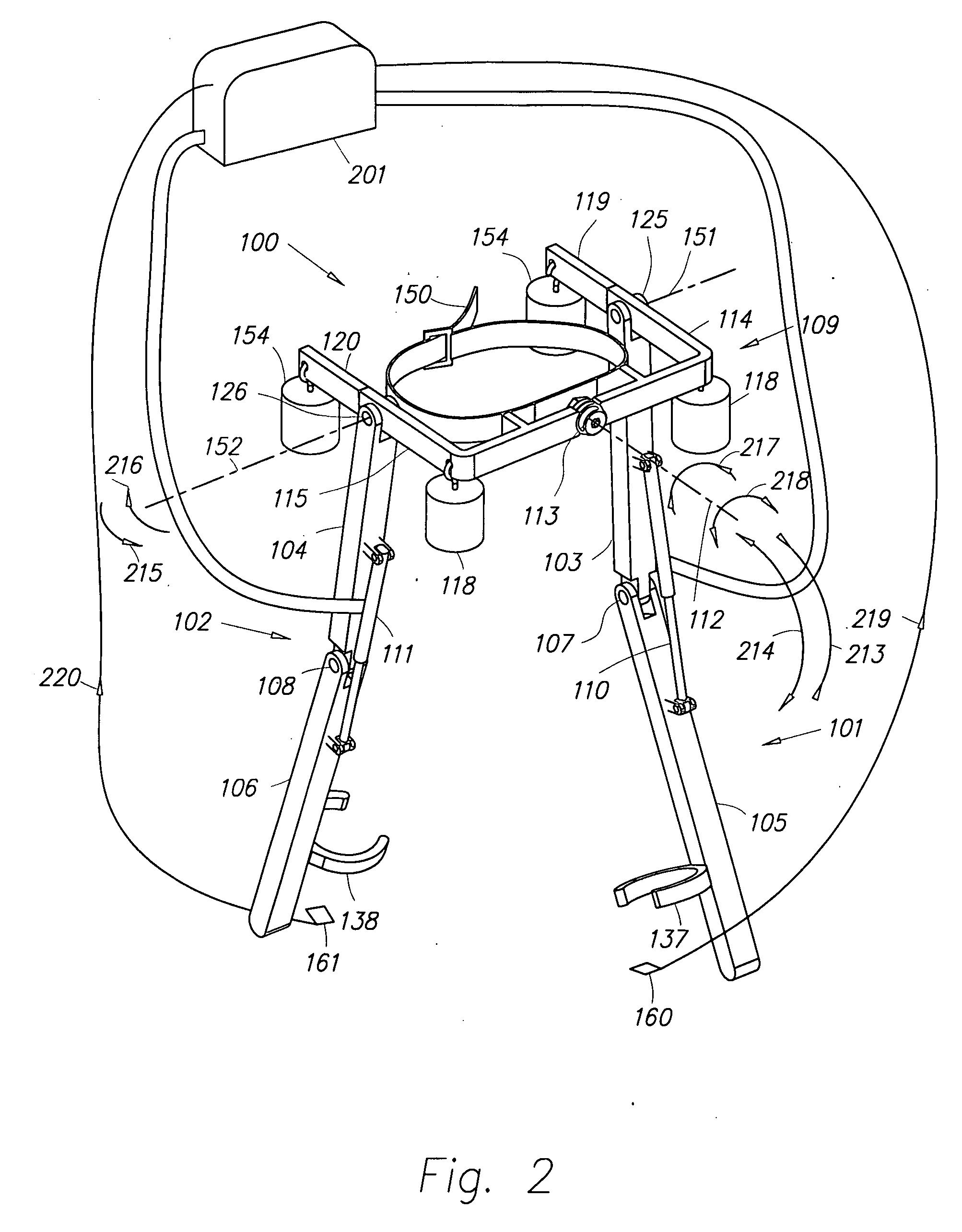
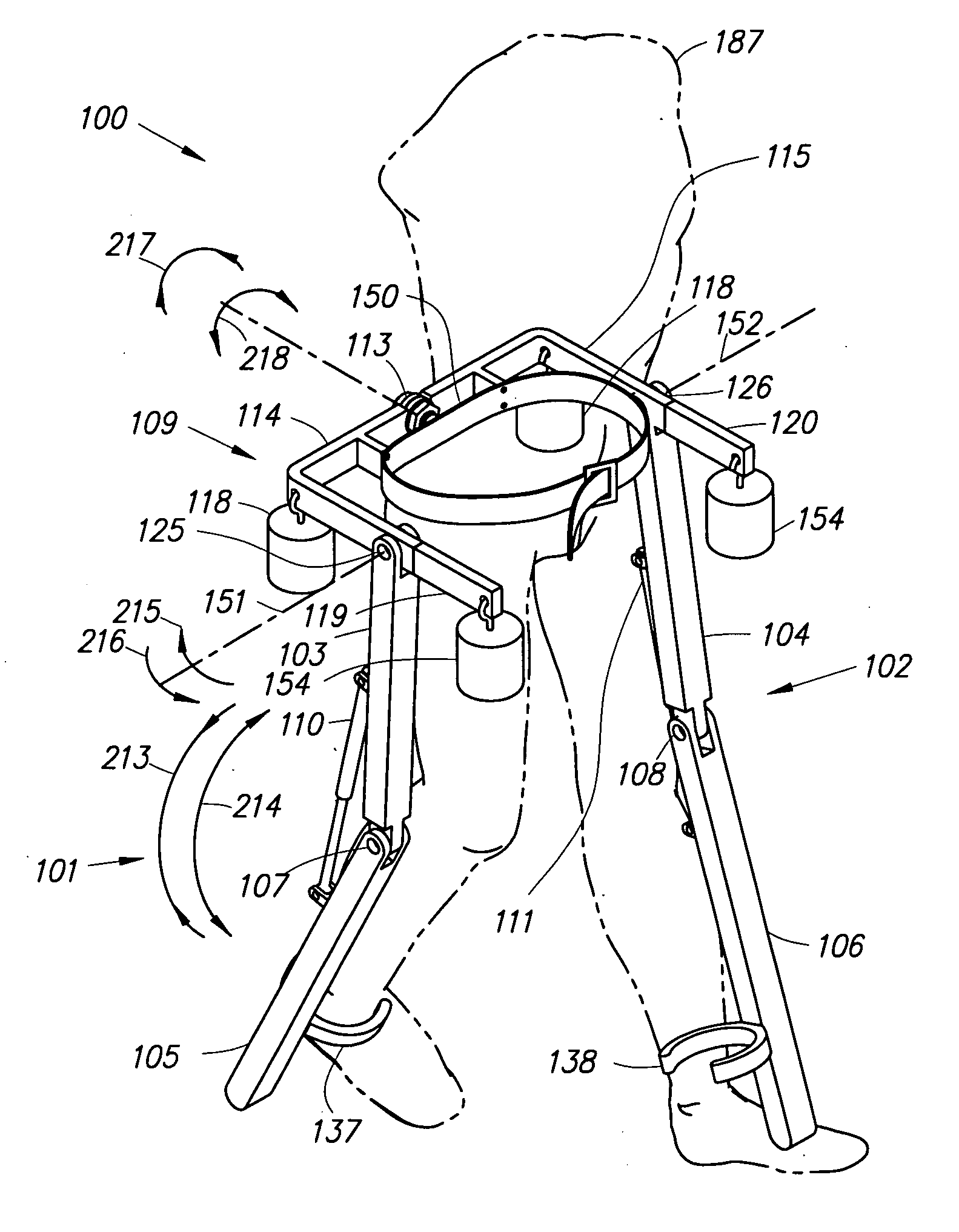
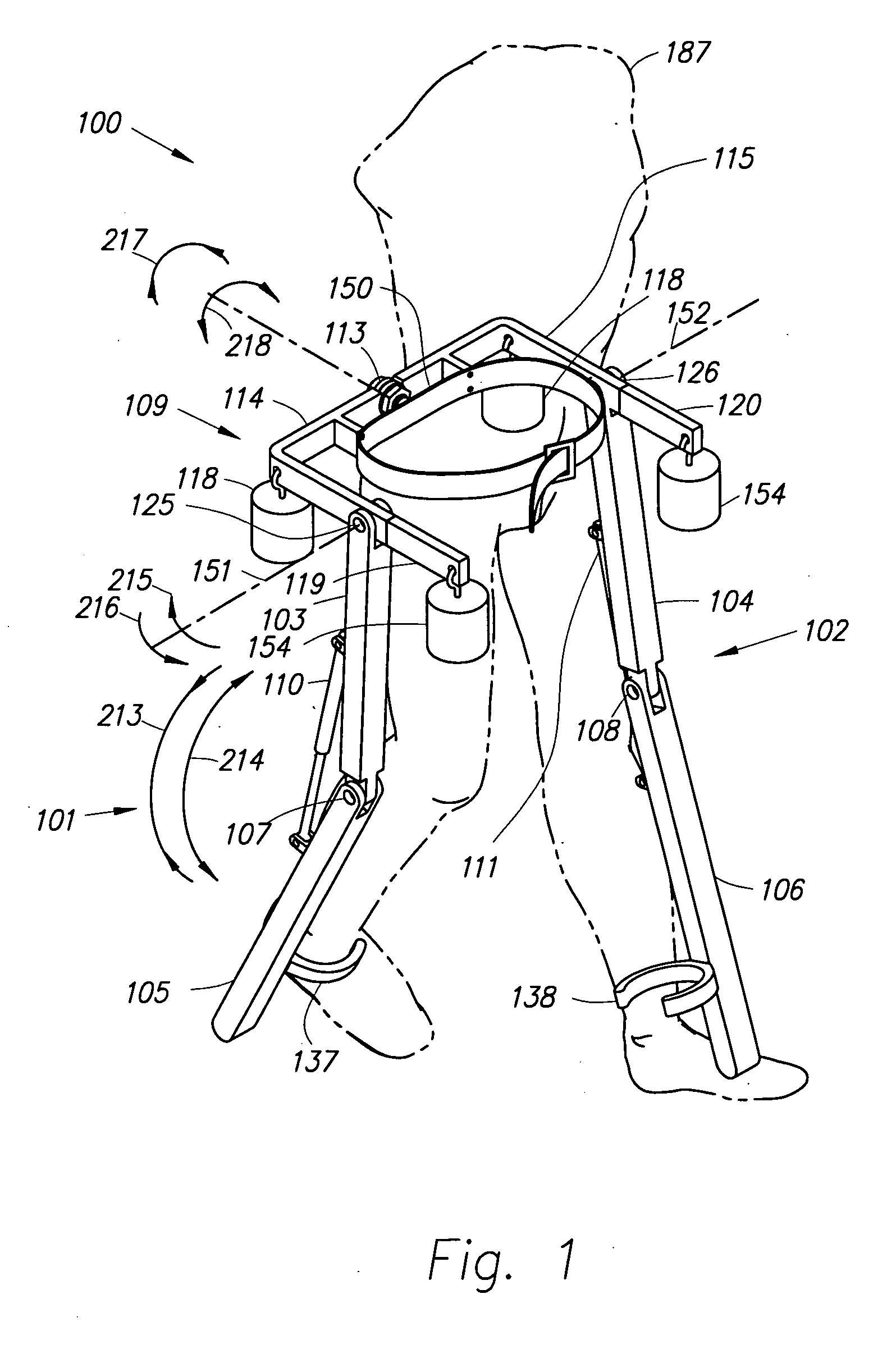
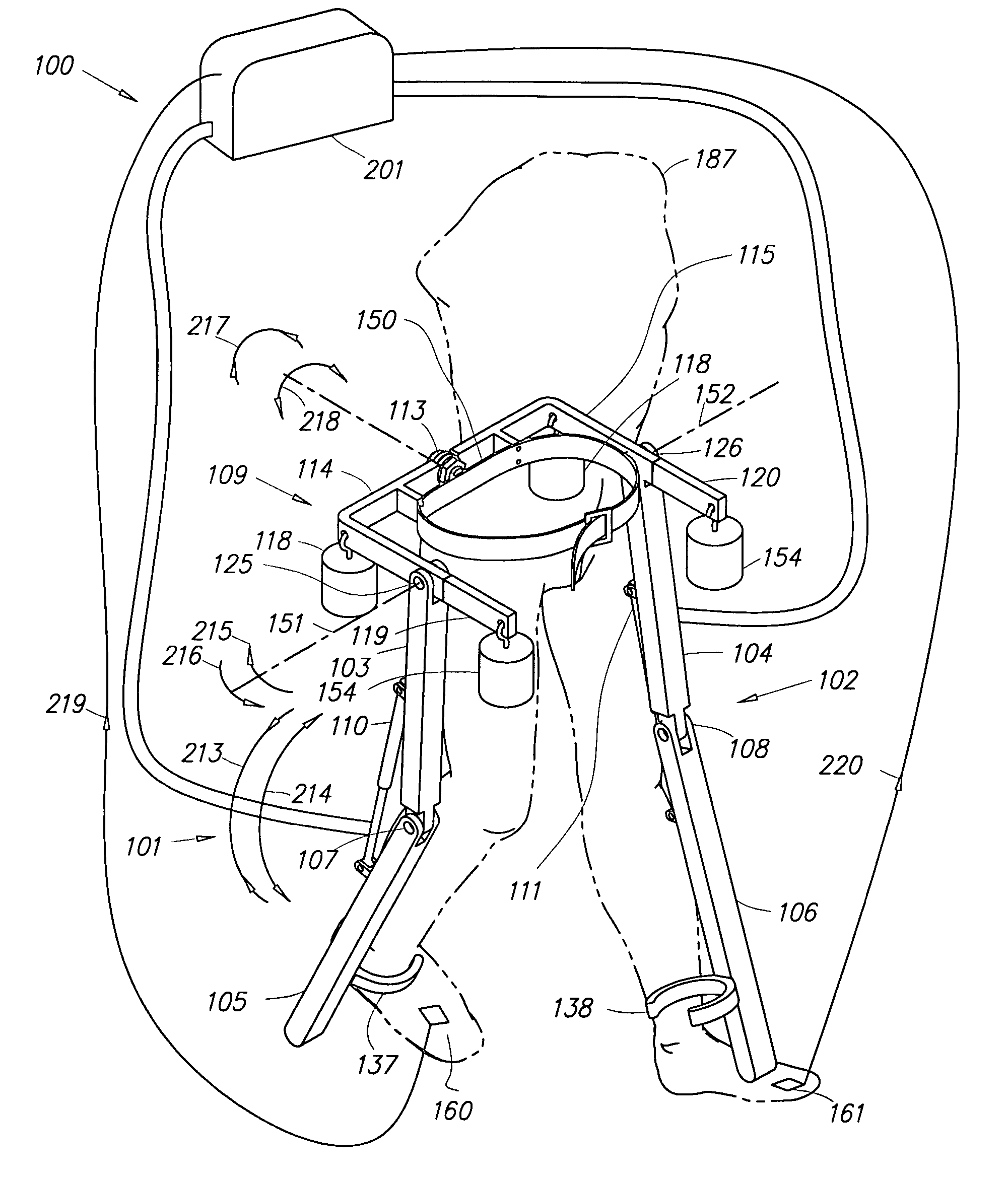
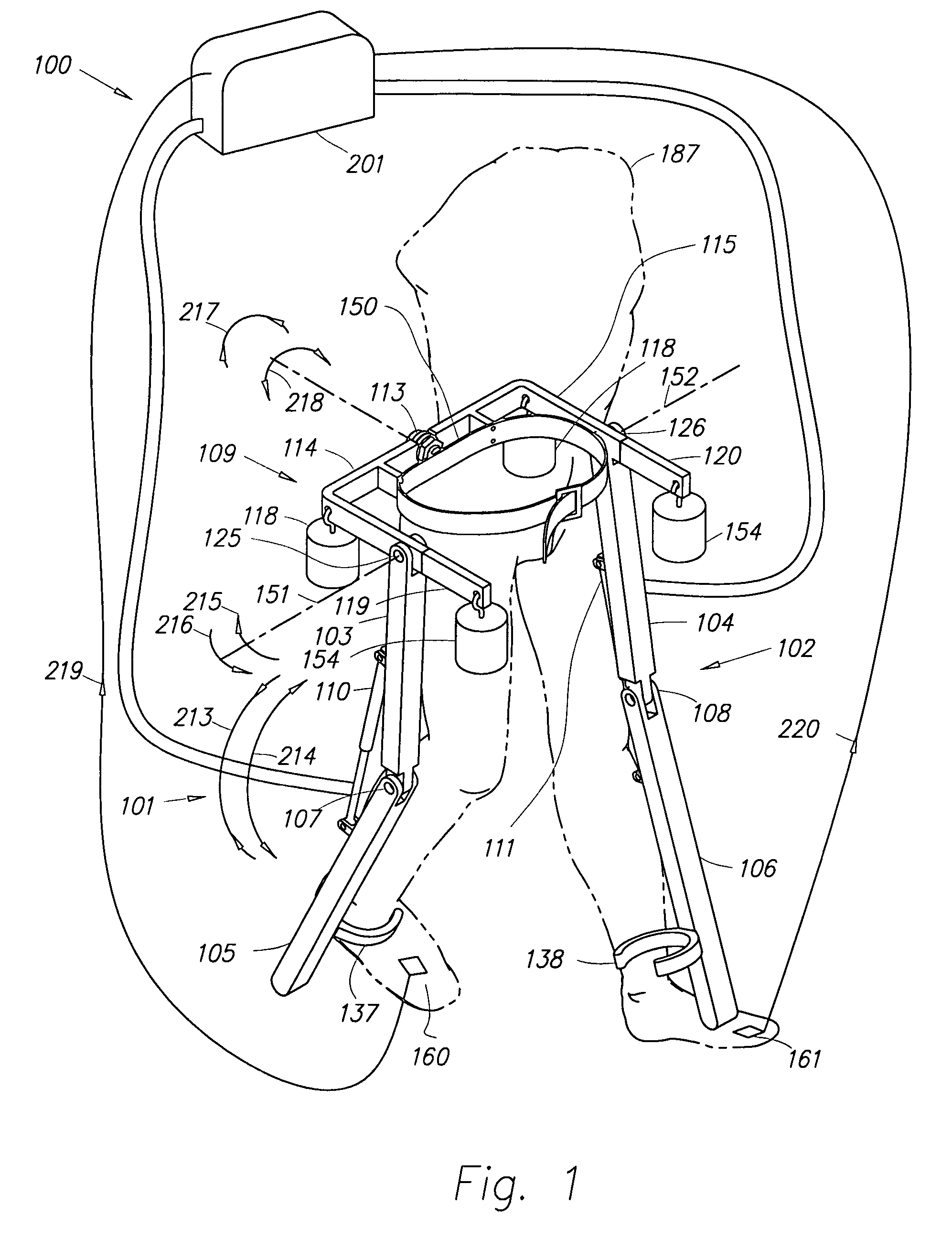
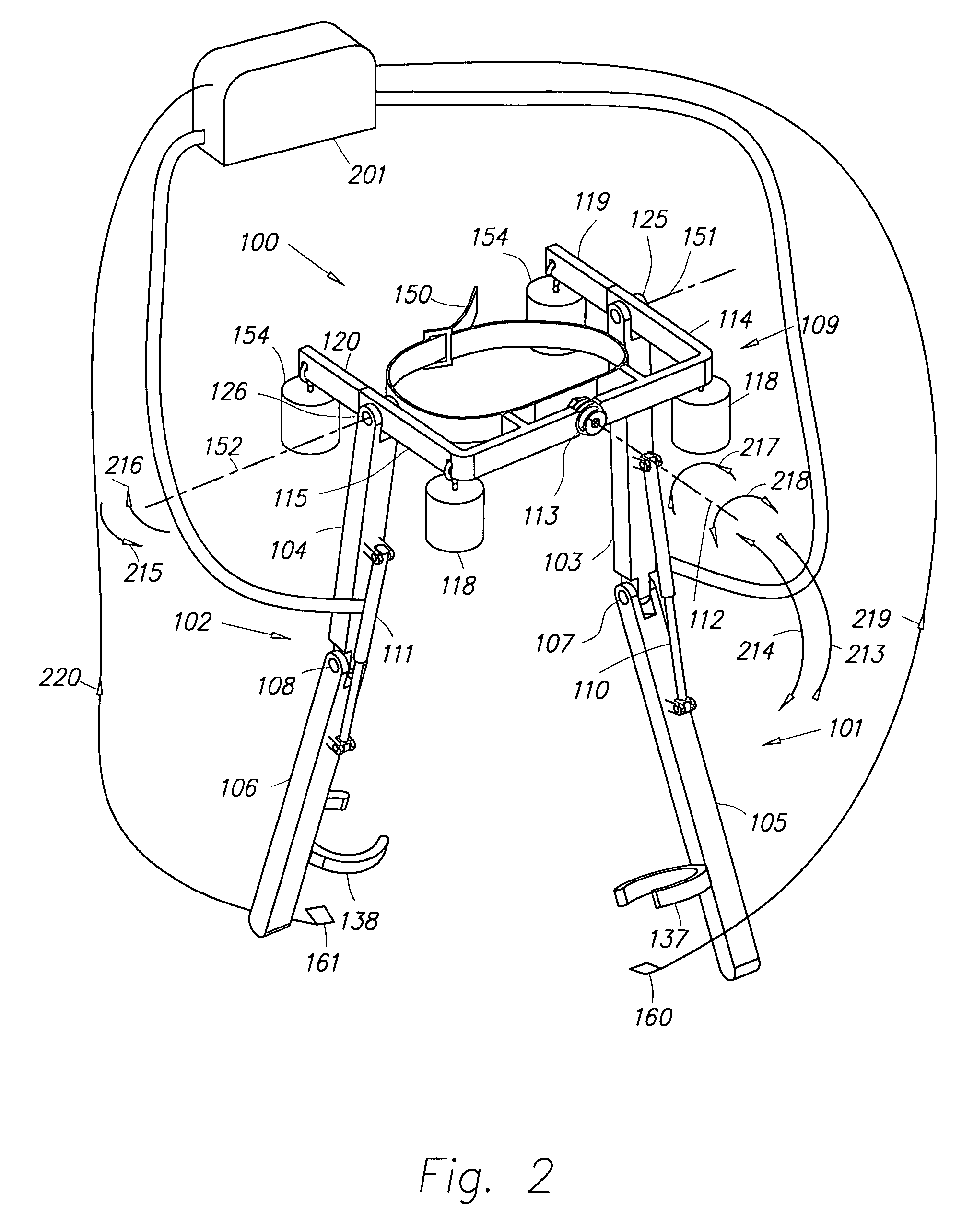
Semi-powered lower extremity exoskeleton
ActiveUS20070056592A1Drag minimizationProgramme-controlled manipulatorOperating chairsKnee JointEngineering
The lower extremity exoskeleton comprises two leg supports connectable to person's lower limbs and configured to rest on the ground during their stance phase. Each leg support comprises a thigh link and a shank link; a knee joint configured to allow flexion and extension between the shank link and the thigh link. The lower extremity exoskeleton further comprises an exoskeleton trunk connectable to the person'supper body. The exoskeleton trunk is connectable to the thigh links of the leg supports allowing for the flexion and extension between the leg supports and the exoskeleton trunk. Two torque generators are coupled to each of the knee joints. A power unit, capable of providing power, is coupled to the torque generators. In operation when a leg support is in a stance phase and climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit injects power into the respective torque generator thereby extending the respective knee angle. When a leg support is in stance phase and not climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to resist flexion of the respective knee joint. When a leg support is in a swing phase, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to minimize its resistance to knee flexion and extension.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
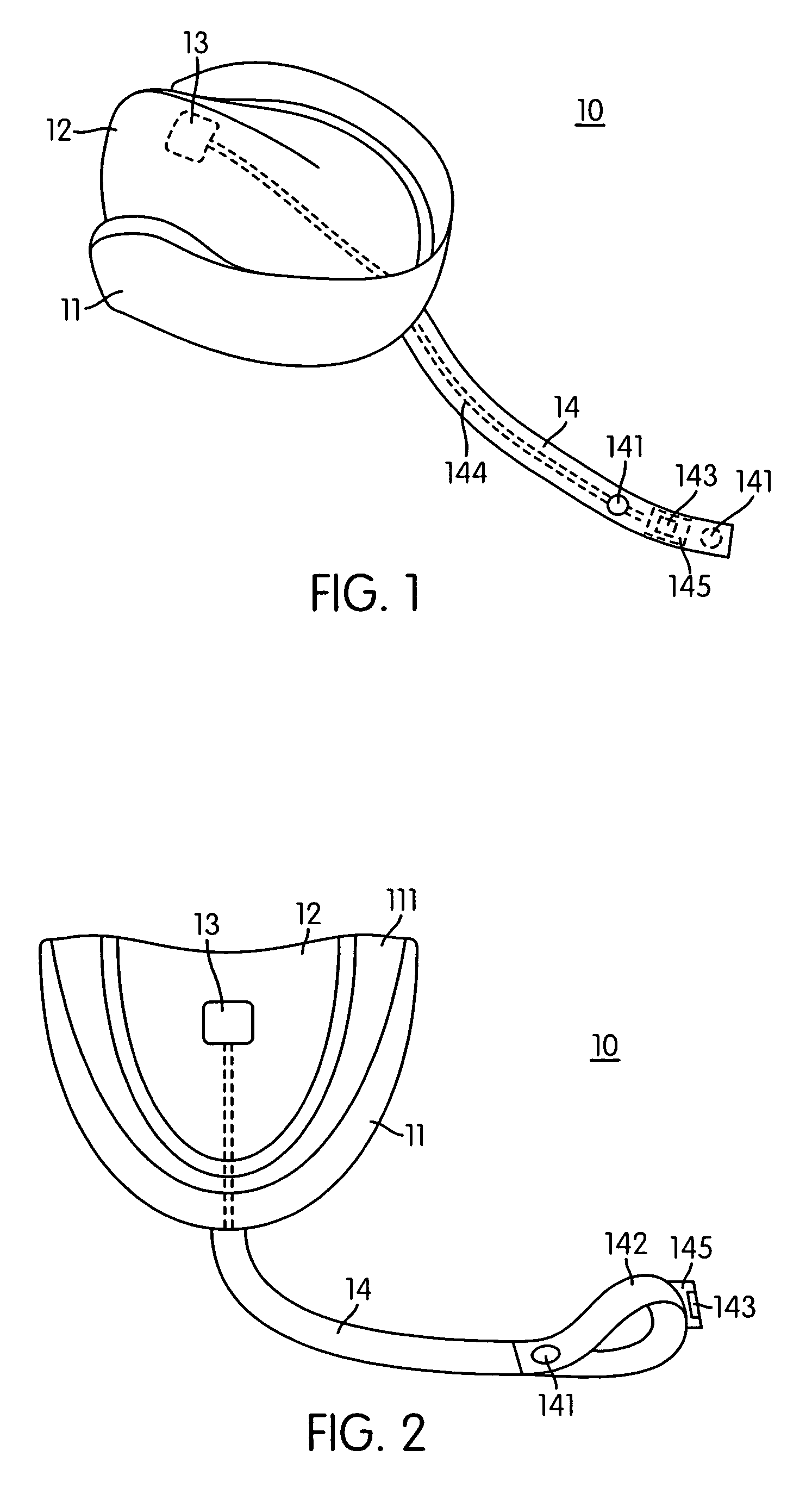
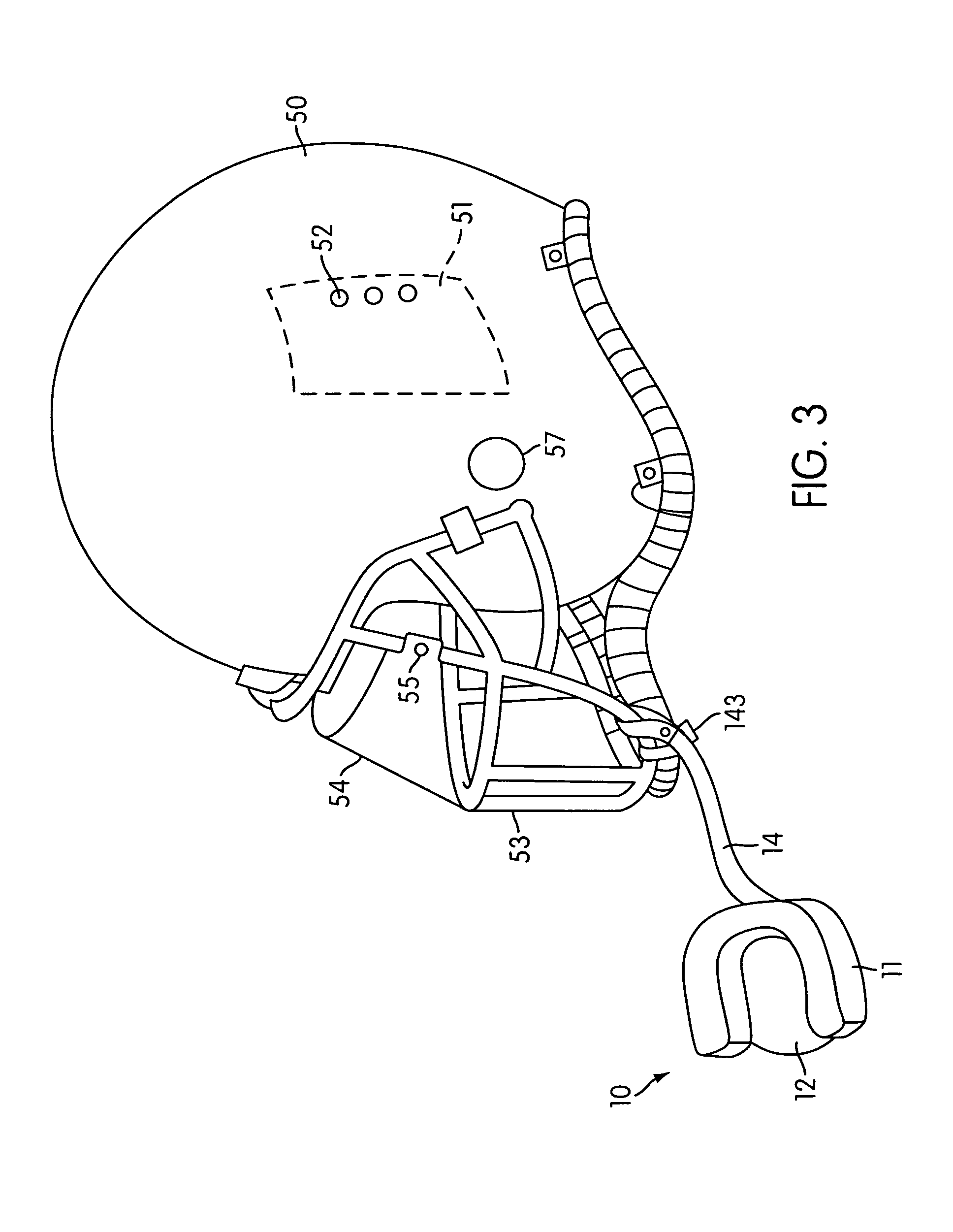
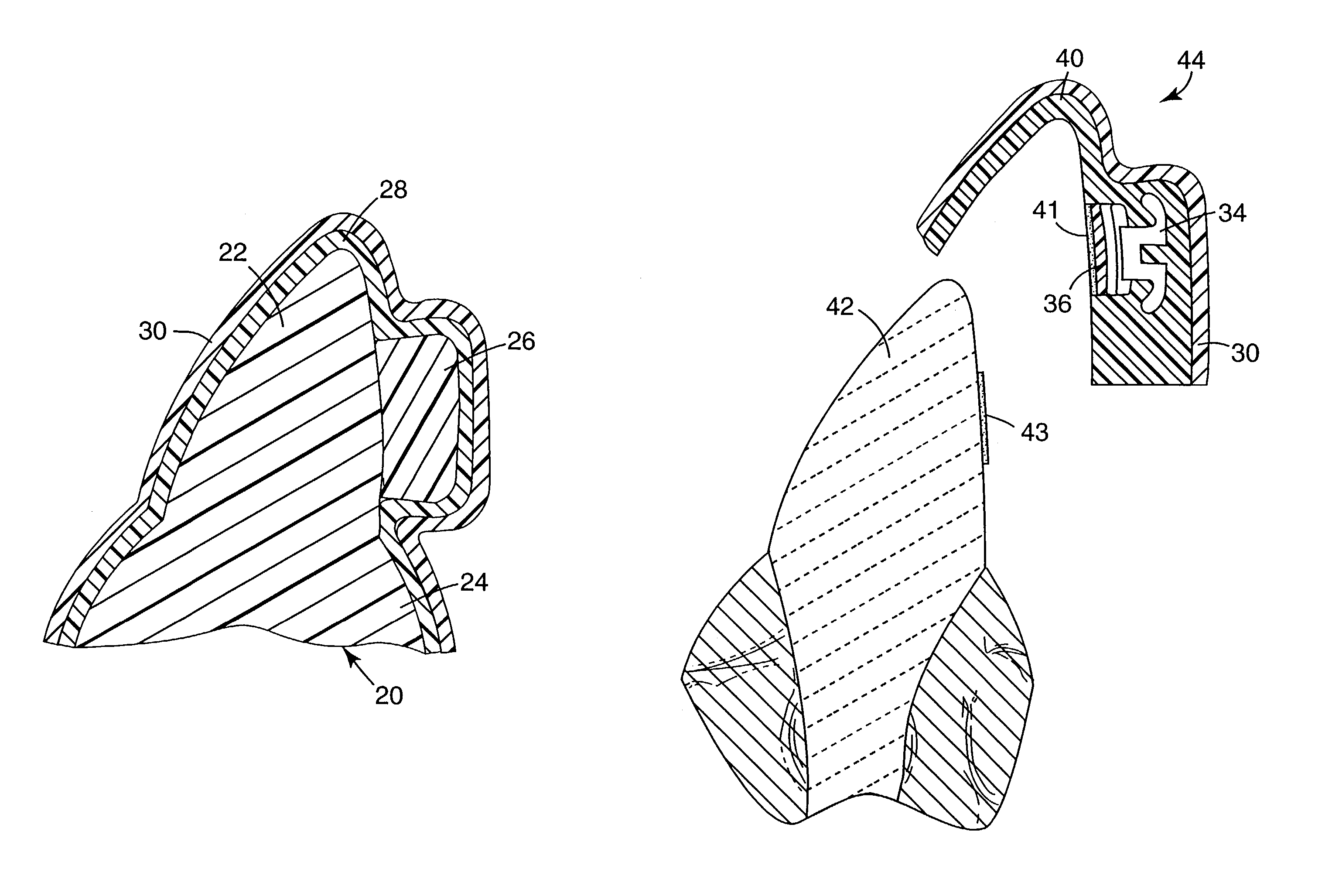
Athletic mouthpiece capable of sensing linear and rotational forces and protective headgear for use with the same
ActiveUS6941952B1Accurate measurementAccurate detectionEar treatmentOperating chairsEngineeringUpper teeth
A mouthpiece assembly for use in detecting impact forces on the neck and head of a user is disclosed. The mouthpiece assembly includes sensors which determine linear and rotational impact forces on the user. The mouthpiece assembly includes a mouth guard having a channel sized to receive the upper teeth therein. A raised dome portion extends from the mouth guard and is adapted to be positioned adjacent the roof of the mouth. The sensors are located in the raised dome portion and the mouth guard or in other locations of the mouthpiece if mouthpiece sensors are required. An indicator is provided to provide a visual and / or audible indication when the magnitude of an impact exceeds a threshold value.
Owner:BRAINLINC LLC
Lower extremity exoskeleton
A lower extremity exoskeleton, configurable to be coupled to a person, comprises two leg supports configurable to be coupled to the person's lower limbs and configured to rest on the ground during their stance phases. Each leg support comprises a thigh link, a shank link, and two knee joints. Each knee joint is configured to allow flexion and extension between the respective shank link and the respective thigh link. The lower extremity exoskeleton also comprises an exoskeleton trunk configurable to be coupled to the person's upper body. The exoskeleton trunk is rotatably connectable to the thigh links of the leg supports allowing for the flexion and extension between the leg supports and the exoskeleton trunk. In this exemplary embodiment, the energy required for flexion and extension movement between the shank link and the respective thigh link of a leg support over a cyclic knee motion is provided by the person.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Coupling system
There is elucidated a device (10) comprising first and second magnetic cores (30, 40; 30a, 30b, 30c, 40a, 40b, 40c) forming a magnetic circuit. The circuit includes a first set of electrical windings (300, 310) for magnetically coupling a first electrical signal through the device (10) via a first magnetic path (350) in the circuit. The circuit includes a second set of electrical windings (400, 410) for magnetically coupling a second electrical signal through the device (10) via a second magnetic path (450) in the circuit. The paths (350, 450) are partially spatially intersecting. The sets of windings (300, 310, 400, 410) are configured so that: (a) the first set of windings (300, 310) is sensitive to magnetic flux in the first magnetic path (350), and insensitive to magnetic flux in the second magnetic path (450); and (b) the second set of windings (400, 410) is sensitive to magnetic flux in the second magnetic path (450), and insensitive to magnetic flux in the first magnetic path (350). The first and second cores (30, 40; 30a, 30b, 30c, 40a, 40b, 40c) enable relative motion (50) there between whilst coupling the signals through the circuit. The device (10) is beneficially employed in a medical system (800).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
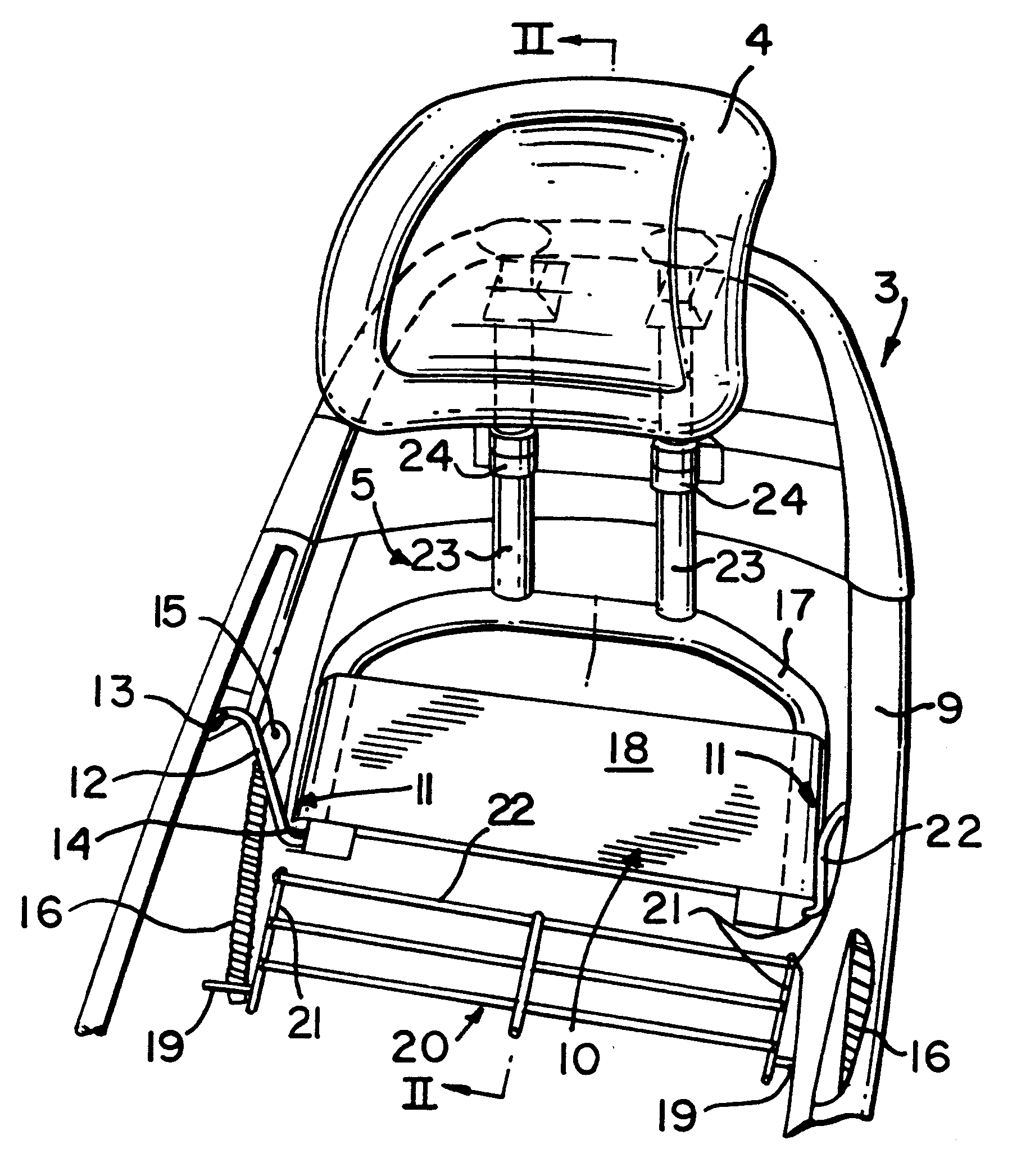
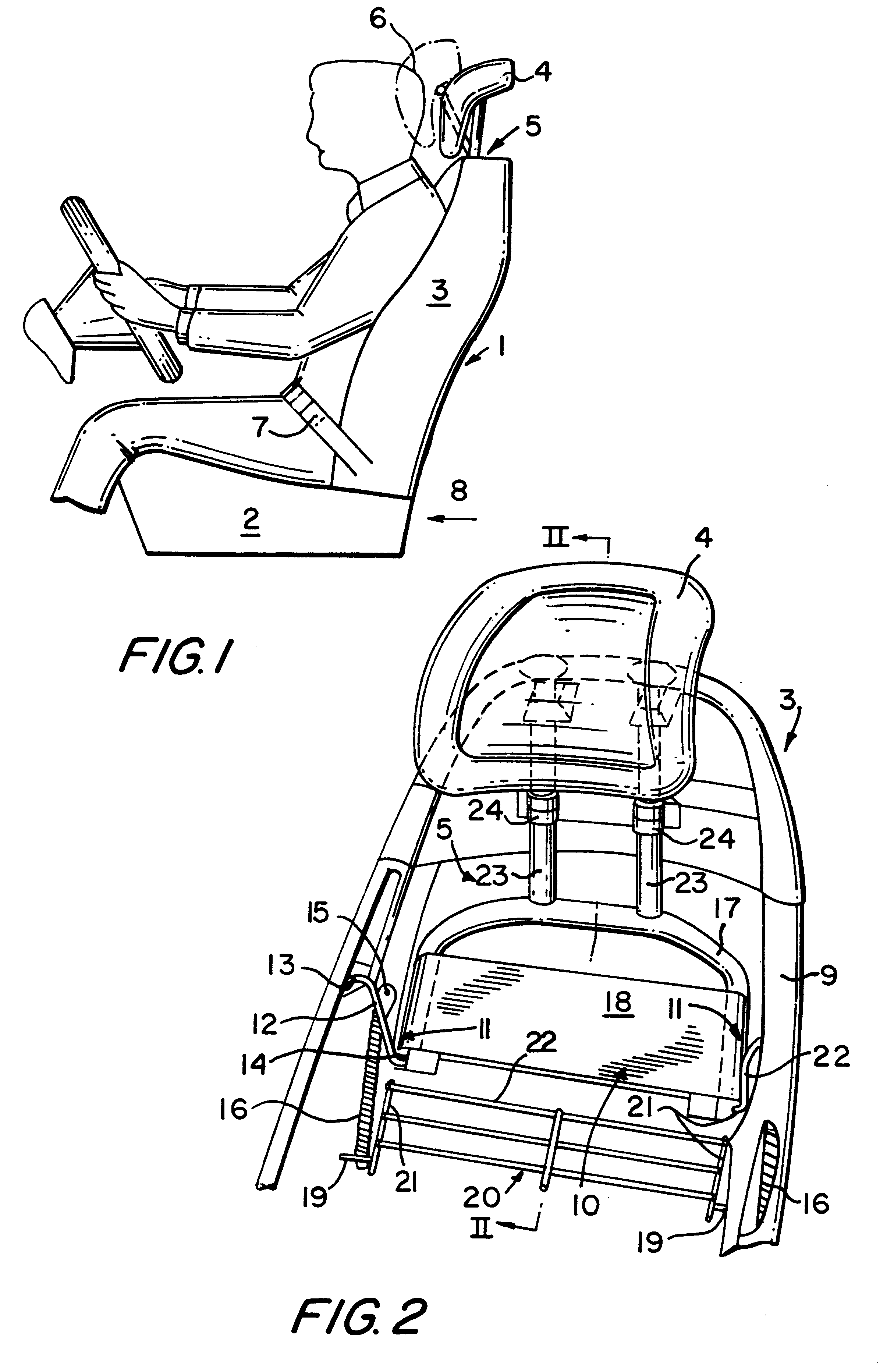
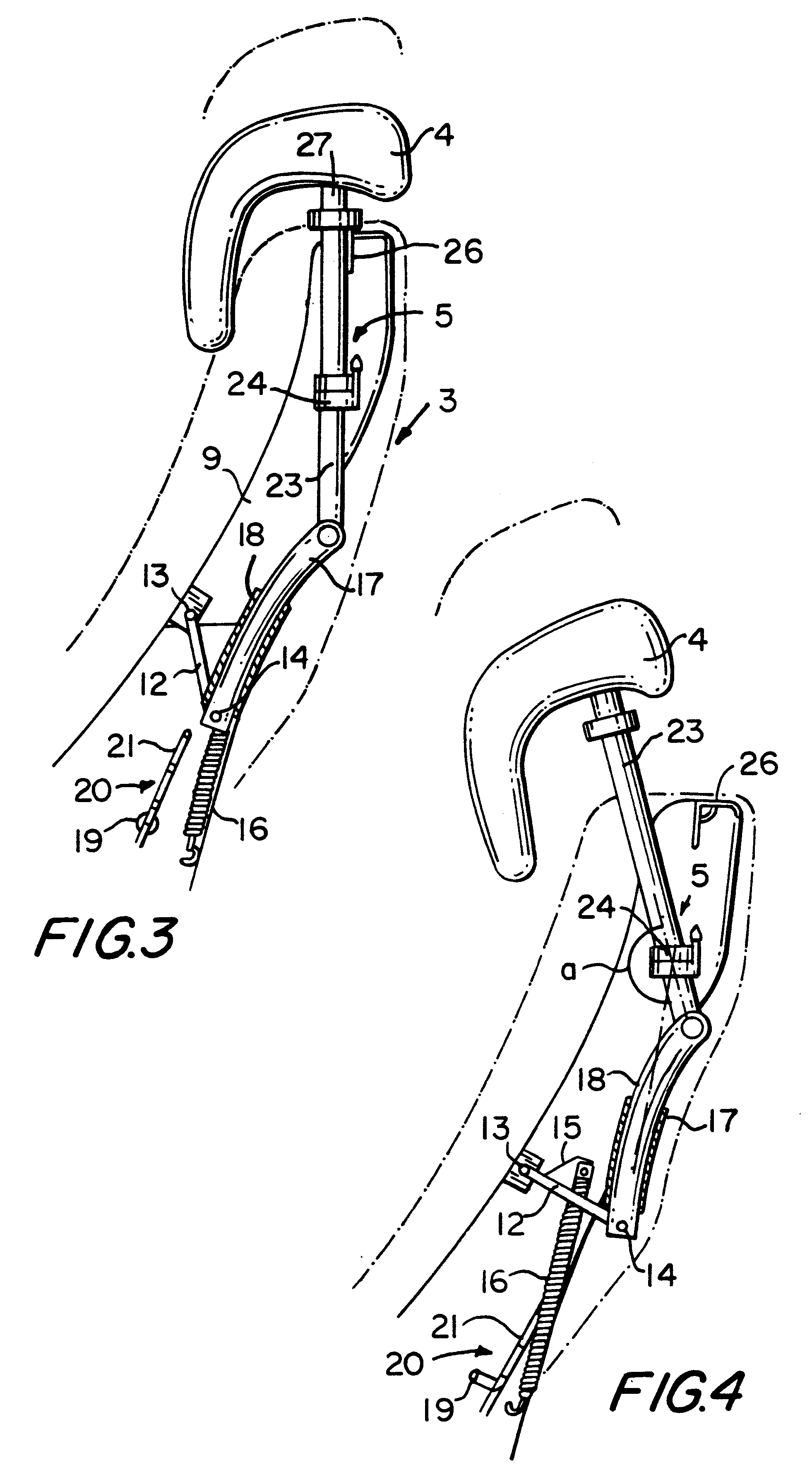
Vehicle seat provided with a headrest
Owner:BAIC HONG KONG INVESTMENT CORP
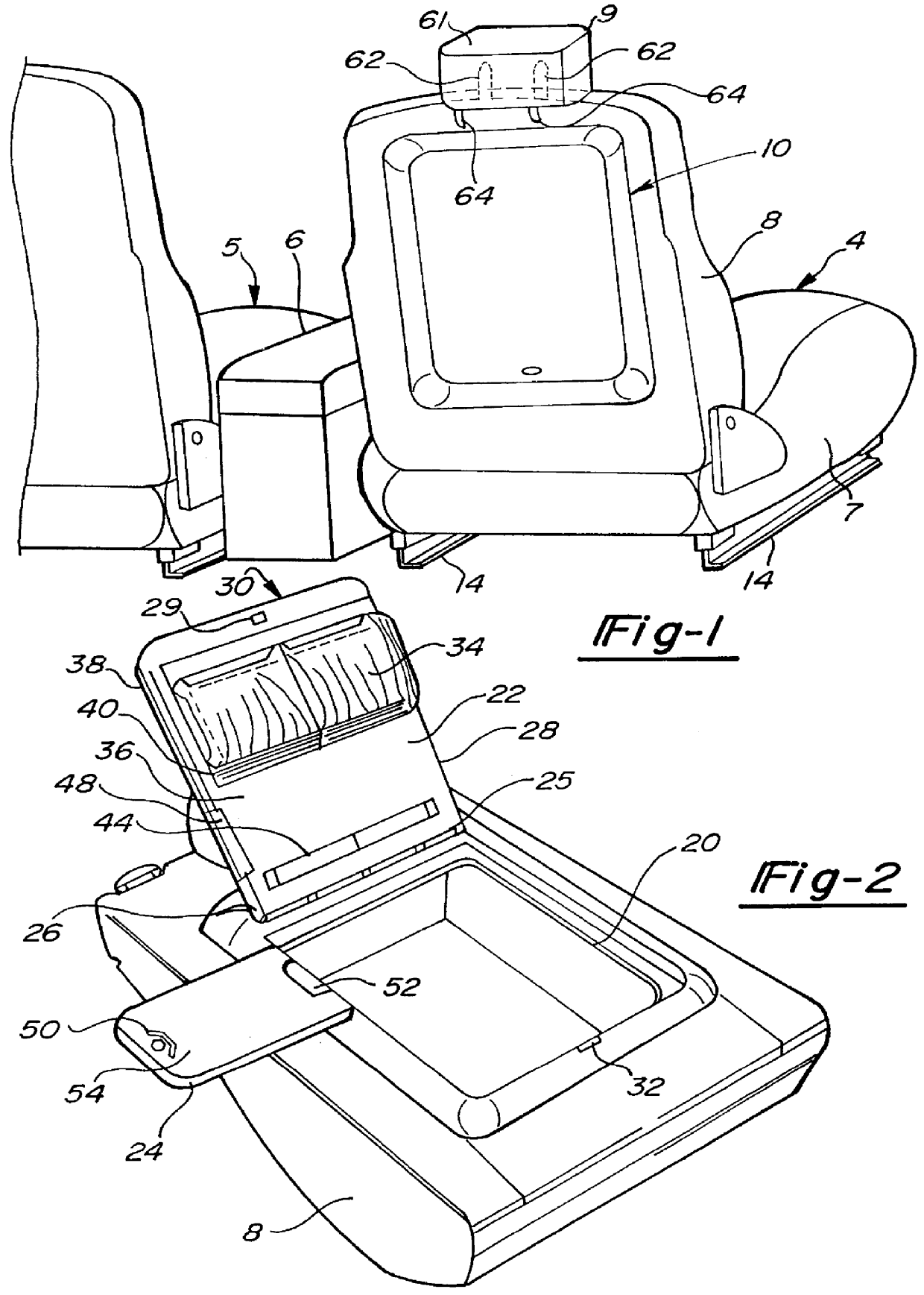
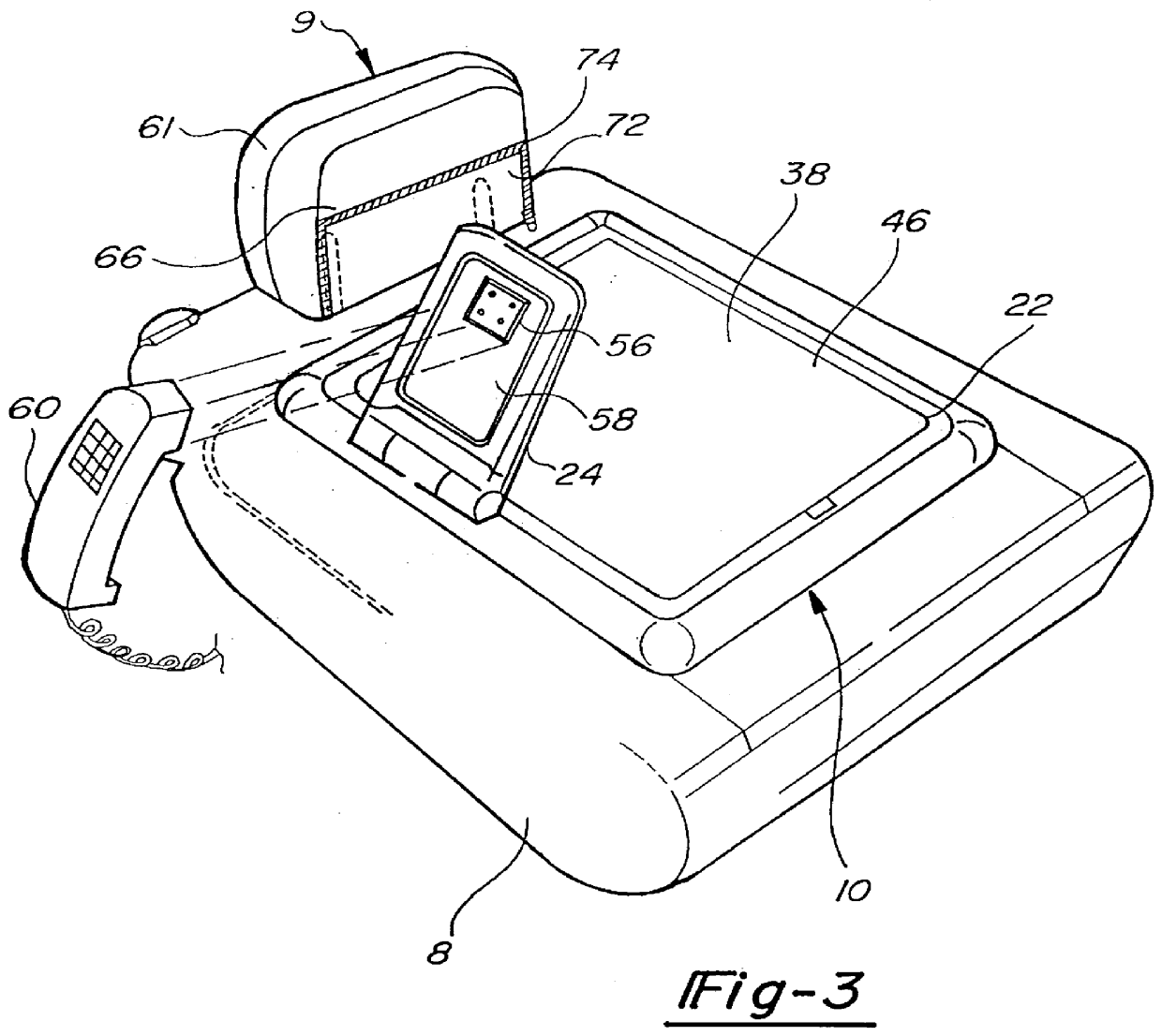
Seat back mounted fold down auto office
A seat back mounted fold down auto office having a bin portion mounted to the seat back of a vehicle seat assembly on the rear side thereof including a recessed storage area therein. A cover is provided for the recessed storage area and is rotatable upon a hinge to move the cover from a closed position to an open position to access the recessed storage area. Additional features include a fold out support panel that can rotate out from the storage bin toward a user after which the storage bin can be closed while the support panel extends from the storage bin. The support panel can be used to attach a notepad or and / or cellular telephone. In addition, the cover can be equipped with a light to illuminate the storage area in the bin.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TECH CO
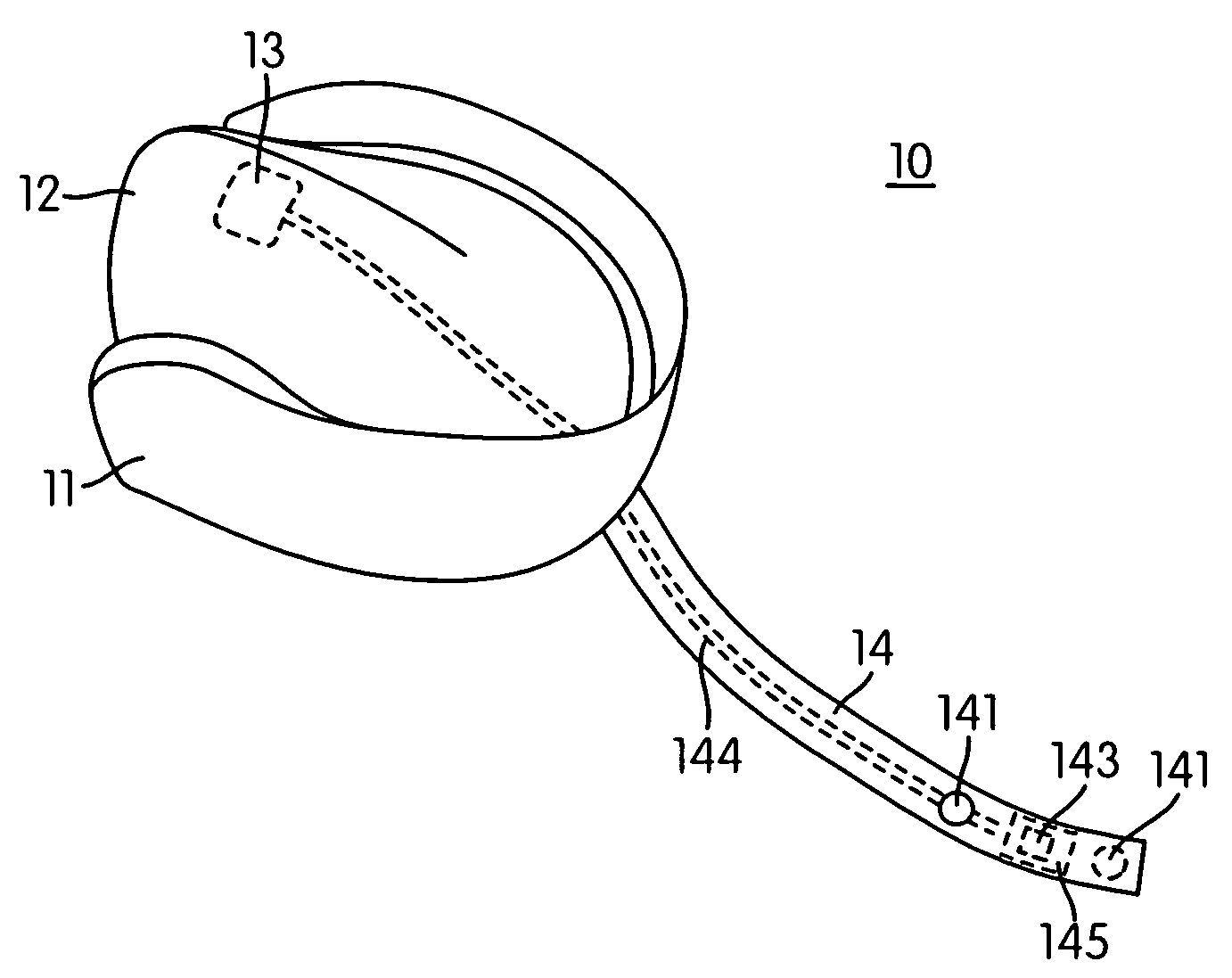
Limb encircling therapeutic compression device
ActiveUS20050192524A1Short and useMinimal numberChemical protectionHeat protectionCompression deviceEngineering
A therapeutic compression garment made of flexible, foldable, light weight Velcro-type loop fabric having a central region for wrapping partially around a body part and a plurality of bands integrally connected to the central region and extending outwardly in opposite directions from both sides of the central region to cross each other and encompass the body part.
Owner:MEDI MFG INC
Method and apparatus for indirect bonding of orthodontic appliances
ActiveUS7020963B2Broaden applicationEasy to disengageBracketsAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngineeringAnodic bonding
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
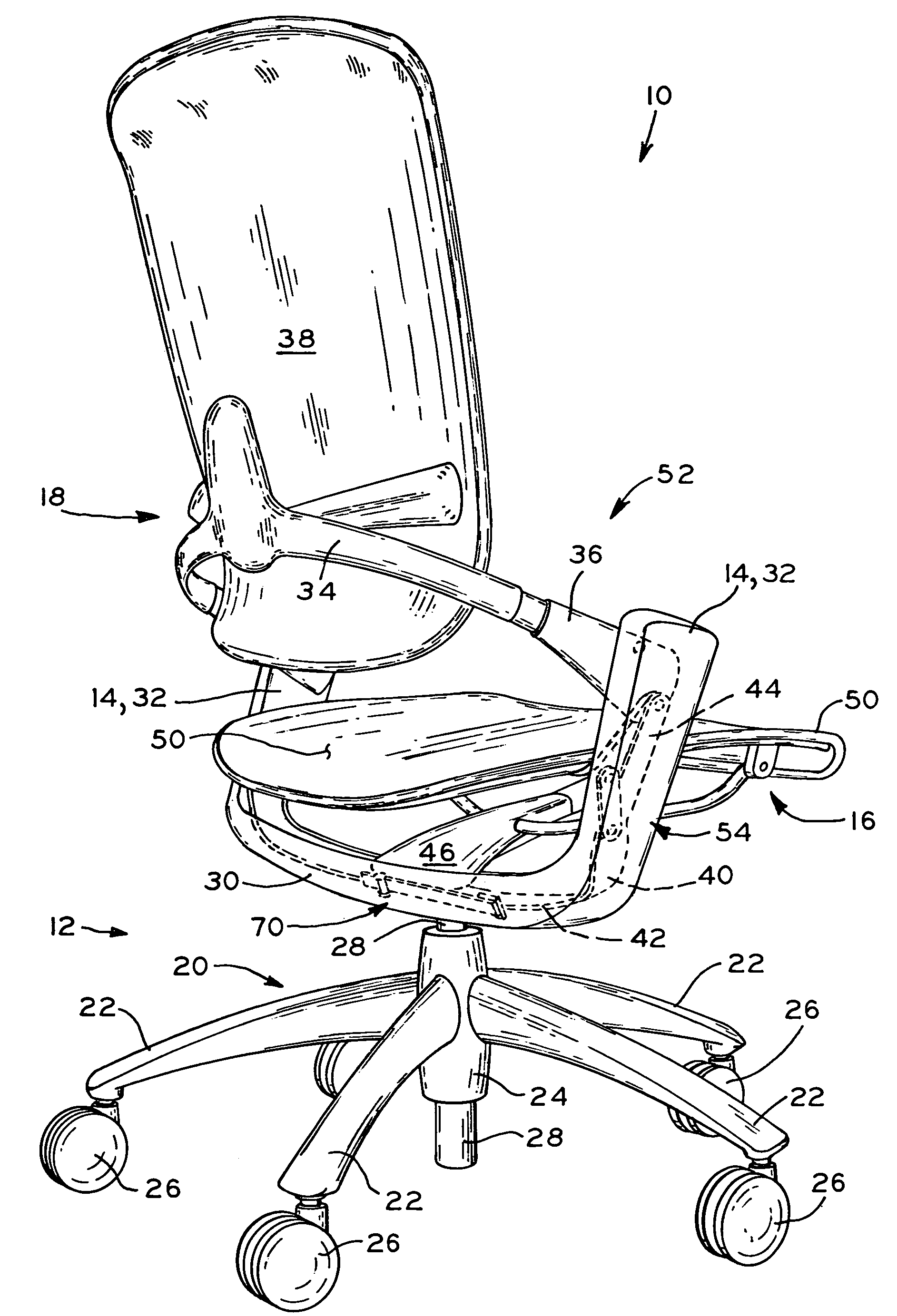
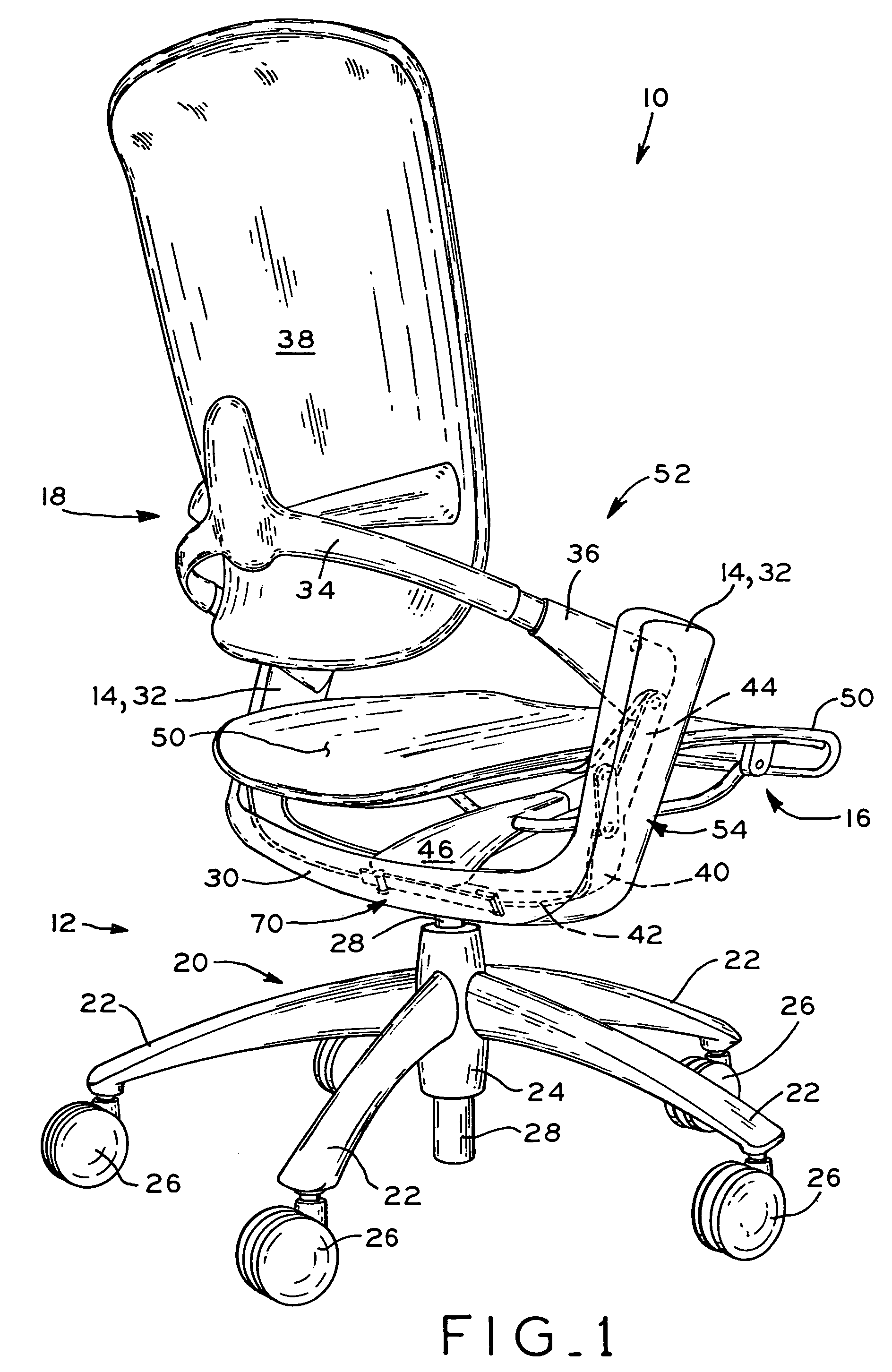
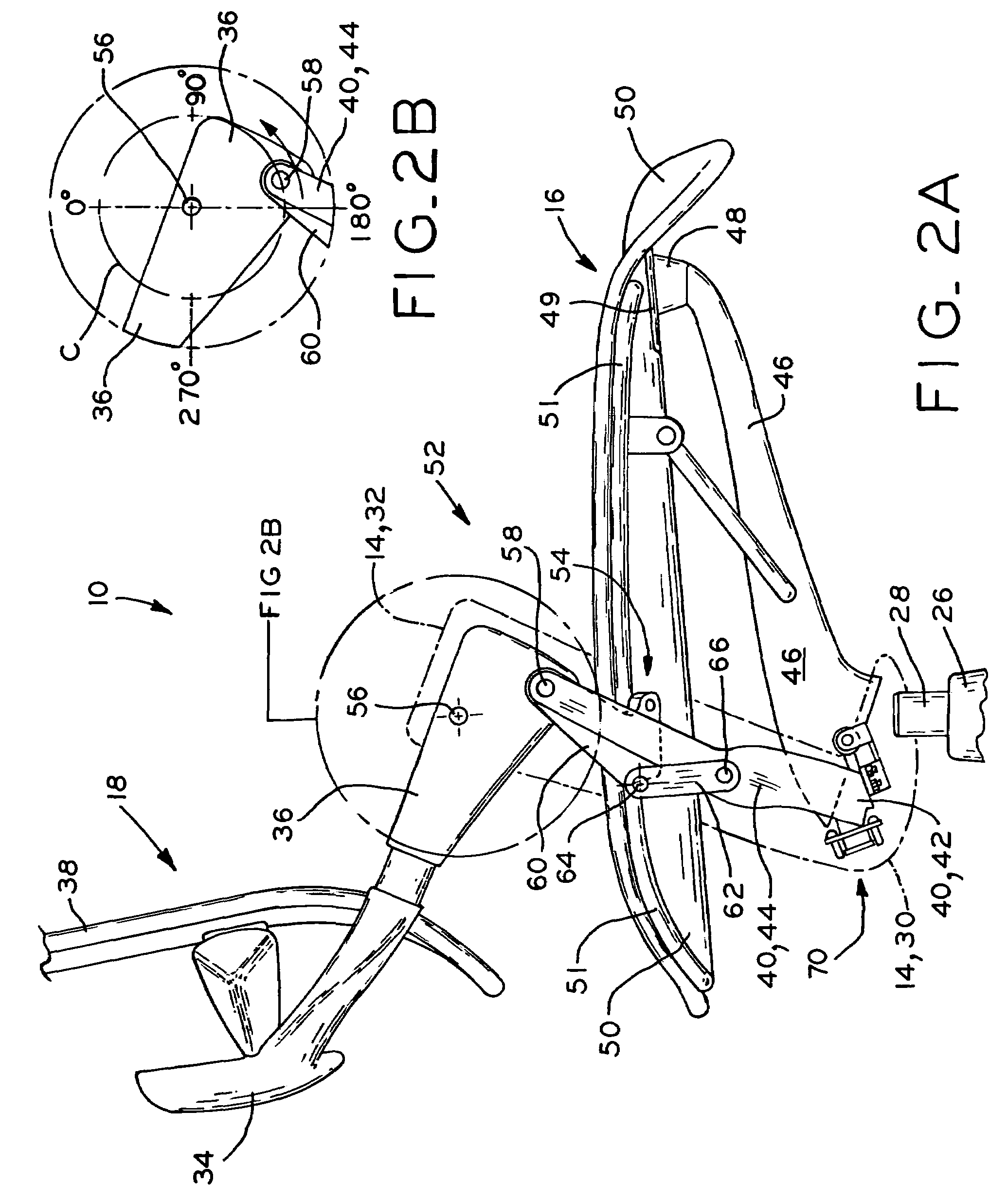
Support member for a seating structure
InactiveUS7419222B2Improved control mechanismEasy to adjustOffice stoolsOperating chairsMechanical engineering
Owner:MILLERKNOLL INC
System and method for mitigating snoring in an adjustable bed
InactiveUS20120138067A1Highly integratedEasy to useOperating chairsVibration massageEngineeringActuator
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for mitigating snoring in an adjustable bed. The systems and methods may include monitoring a sensor for a first reading indicative of a snoring user, activating an actuator to move the adjustable bed into an anti-snore position, monitoring the adjustable bed to confirm that it achieves the anti-snore position, monitoring the sensor for a second reading indicative of a non-snoring user, and after failing to receive the second reading, activating the actuator to move the adjustable bed into a second anti-snore position.
Owner:RAWLS MEEHAN MARTIN B
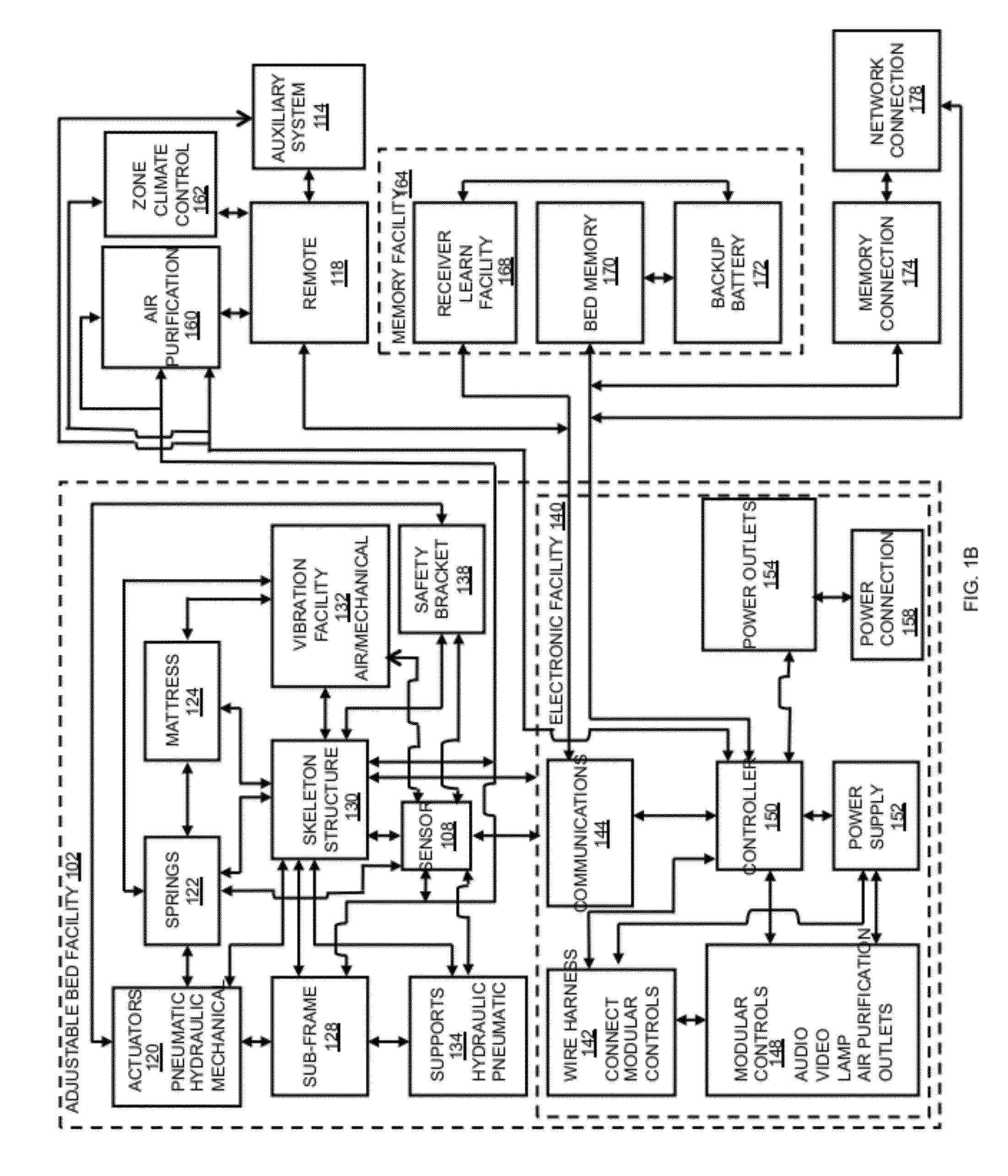
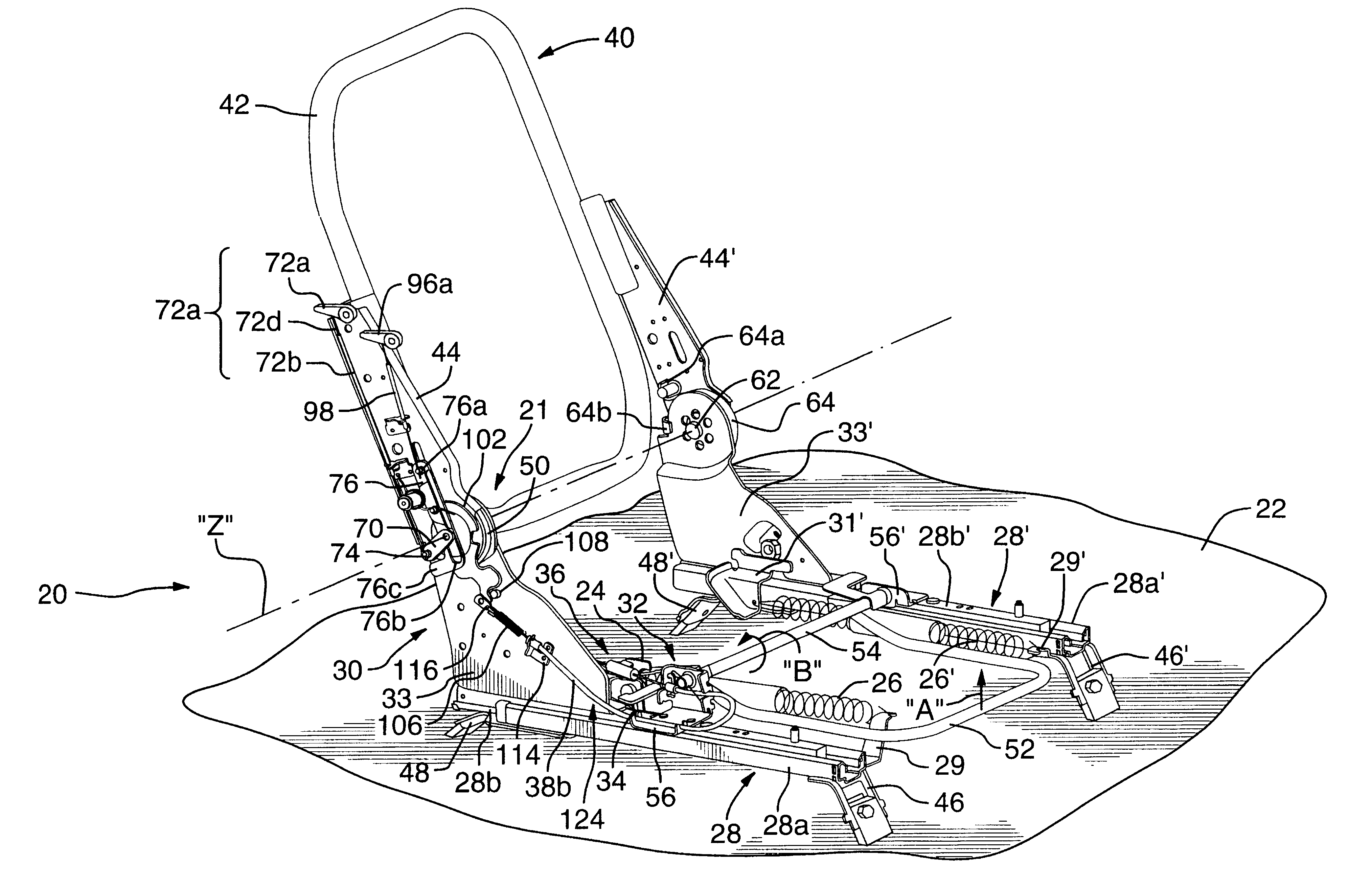
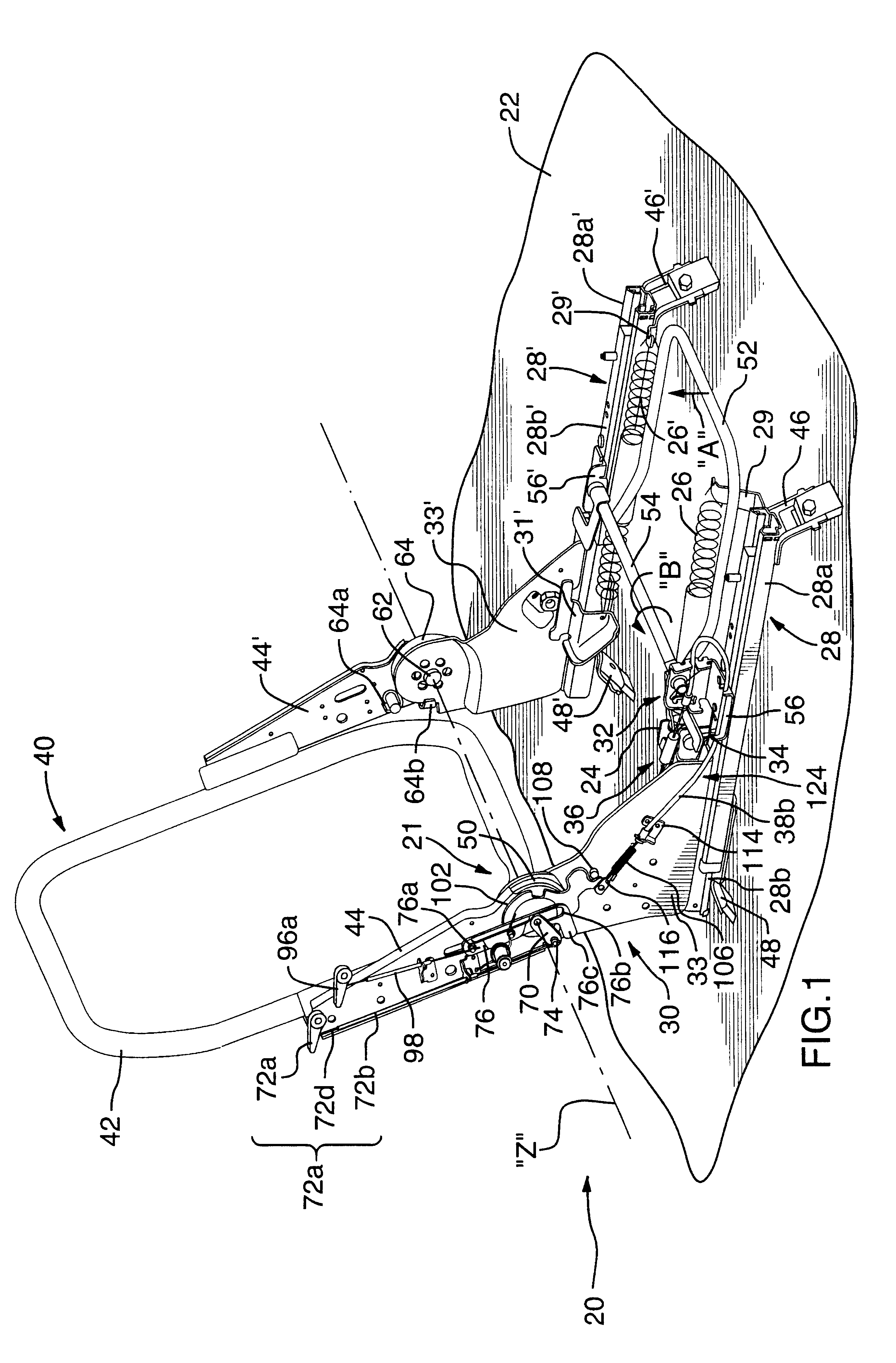
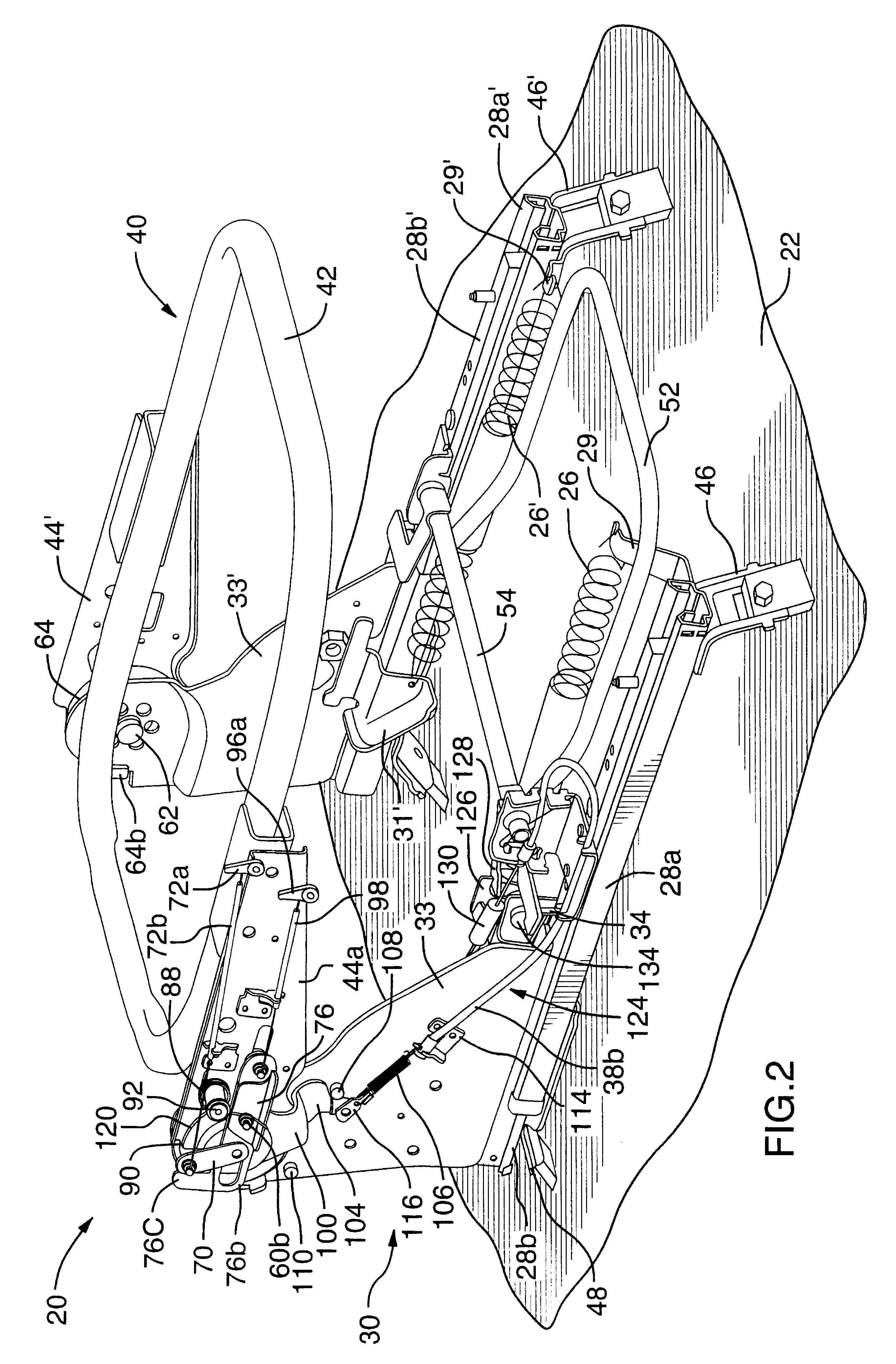
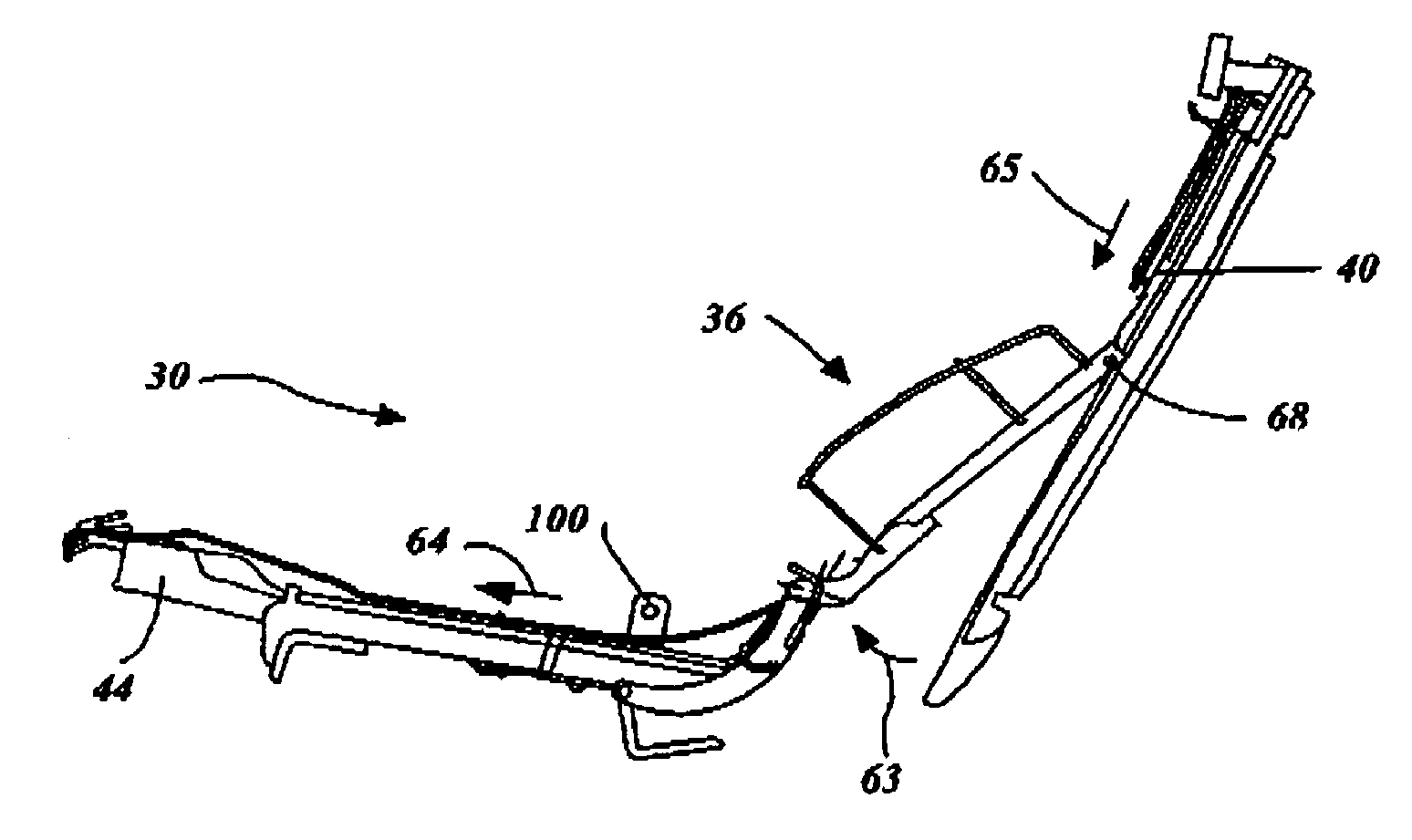
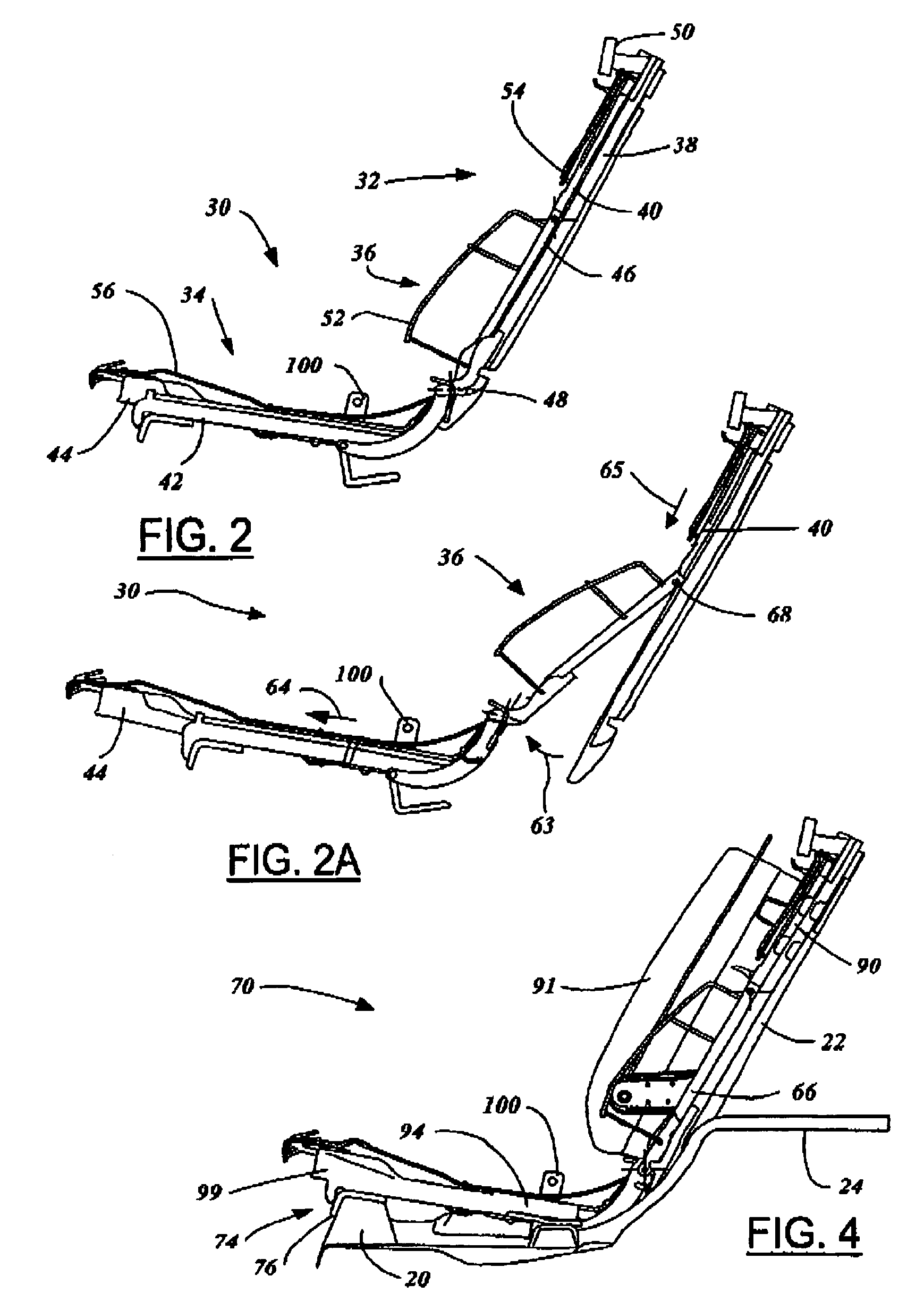
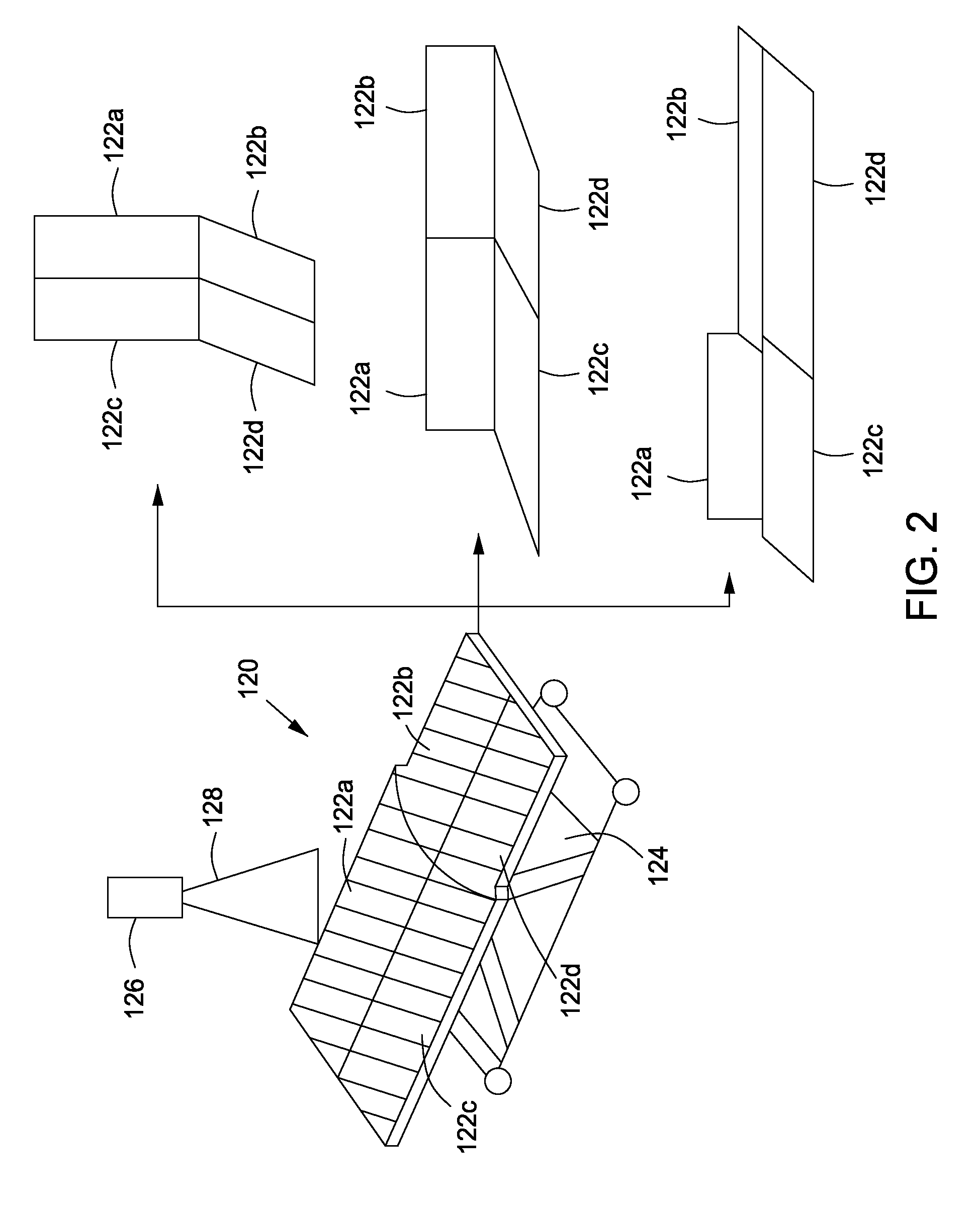
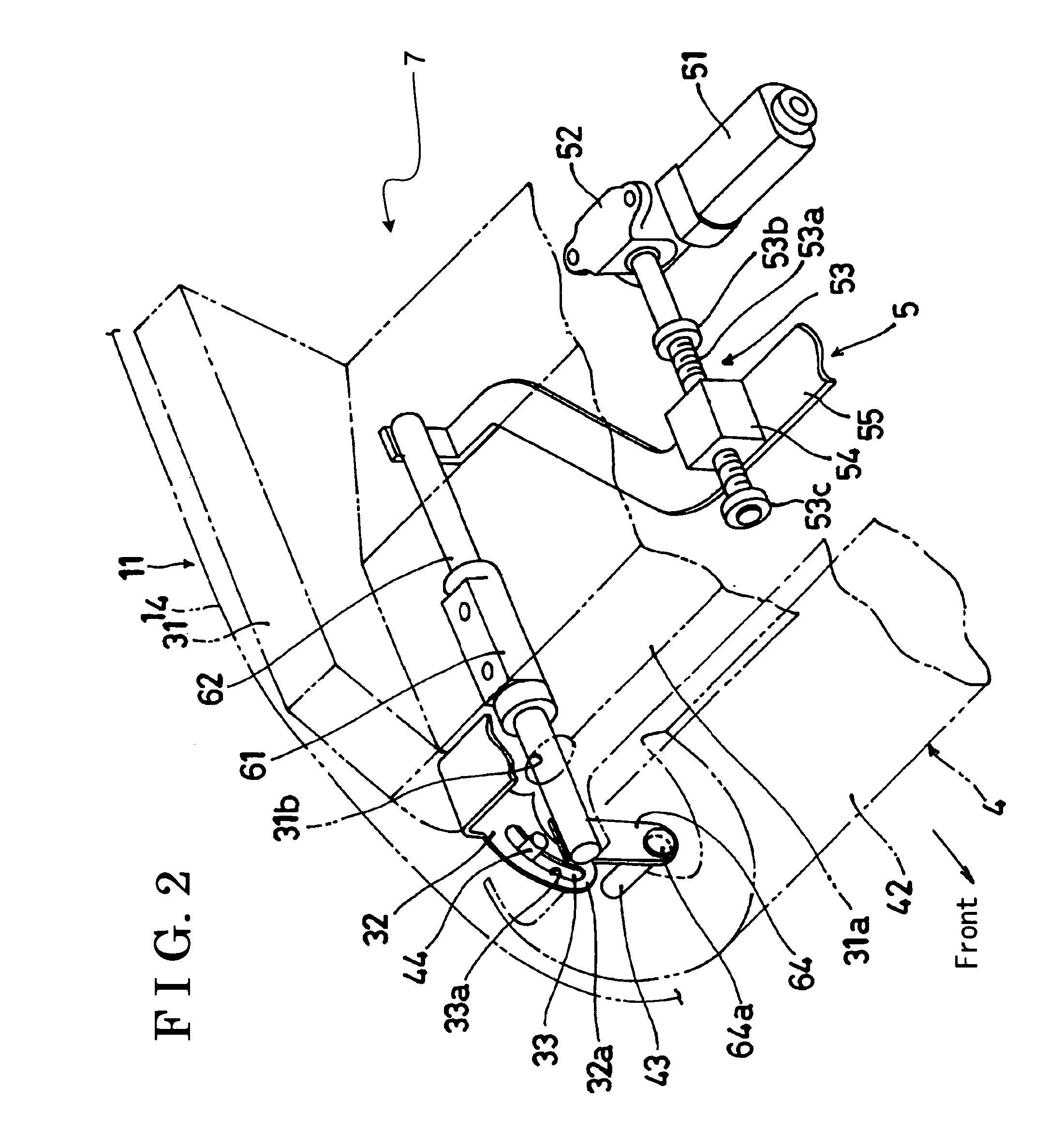
Rotary recliner control mechanism for multifunction vehicle seat applications
A rotary recliner control mechanism for use in a vehicle seat assembly, which vehicle seat assembly has a seat back member (44). A cam pin (94) is mounted on the link means (76) for driving engagement with the camming shoulder (112), upon forward pivotal movement of the seat back member (44) to cause the rotation of the interlock plate member (100) against the second biasing means (106), when the link member (76) is in the first link position. The cam pin (94) is also mounted on the linkmeans (76) for clearing motion of the camming shoulder (112) when the link member (76) is in the second link position. A connection means (124) is interconnected between the interlock plate (100) member and the track lock releasing means (36) for unlocking the track lock means when the interlock plate member (100) is rotated, under the driving contact of the cam pin (94).
Owner:BERTRAND FAURE COMPONENTS
Limb encircling therapeutic compression device
ActiveUS7329232B2Minimal numberEfficient use ofChemical protectionHeat protectionCompression deviceEngineering
A therapeutic compression garment made of flexible, foldable, light weight Velcro-type loop fabric having a central region for wrapping partially around a body part and a plurality of bands integrally connected to the central region and extending outwardly in opposite directions from both sides of the central region to cross each other and encompass the body part.
Owner:MEDI MFG INC
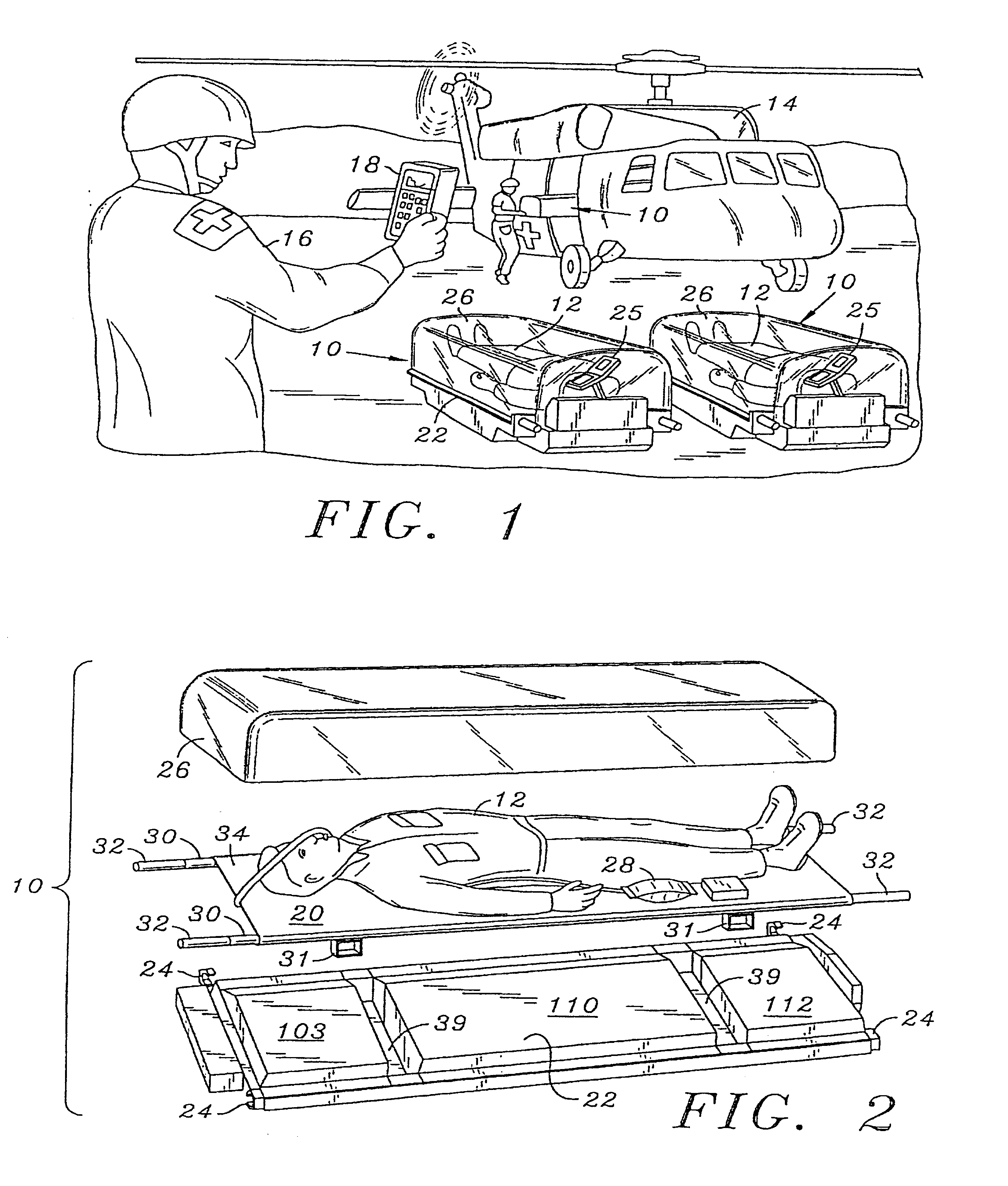
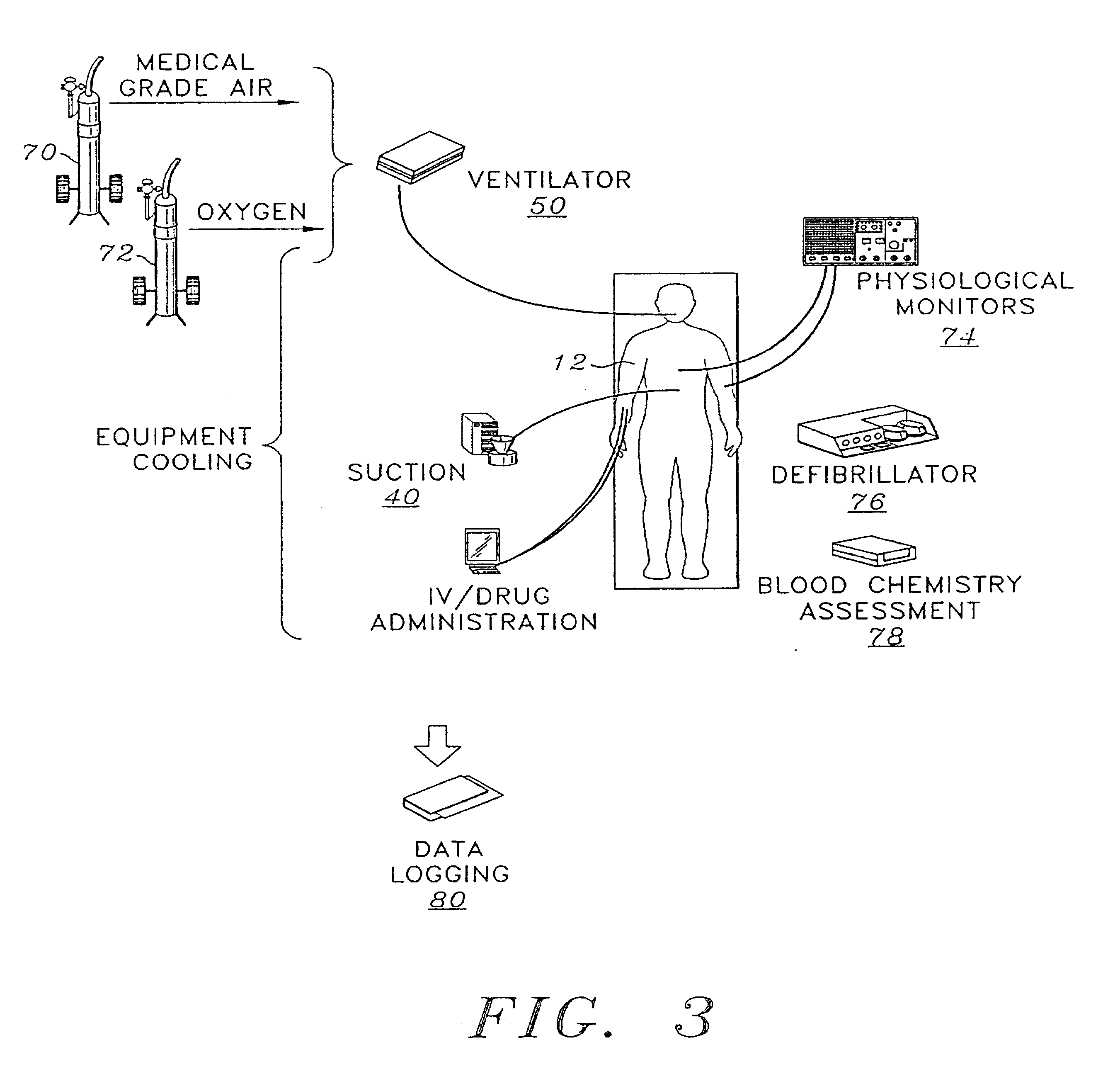
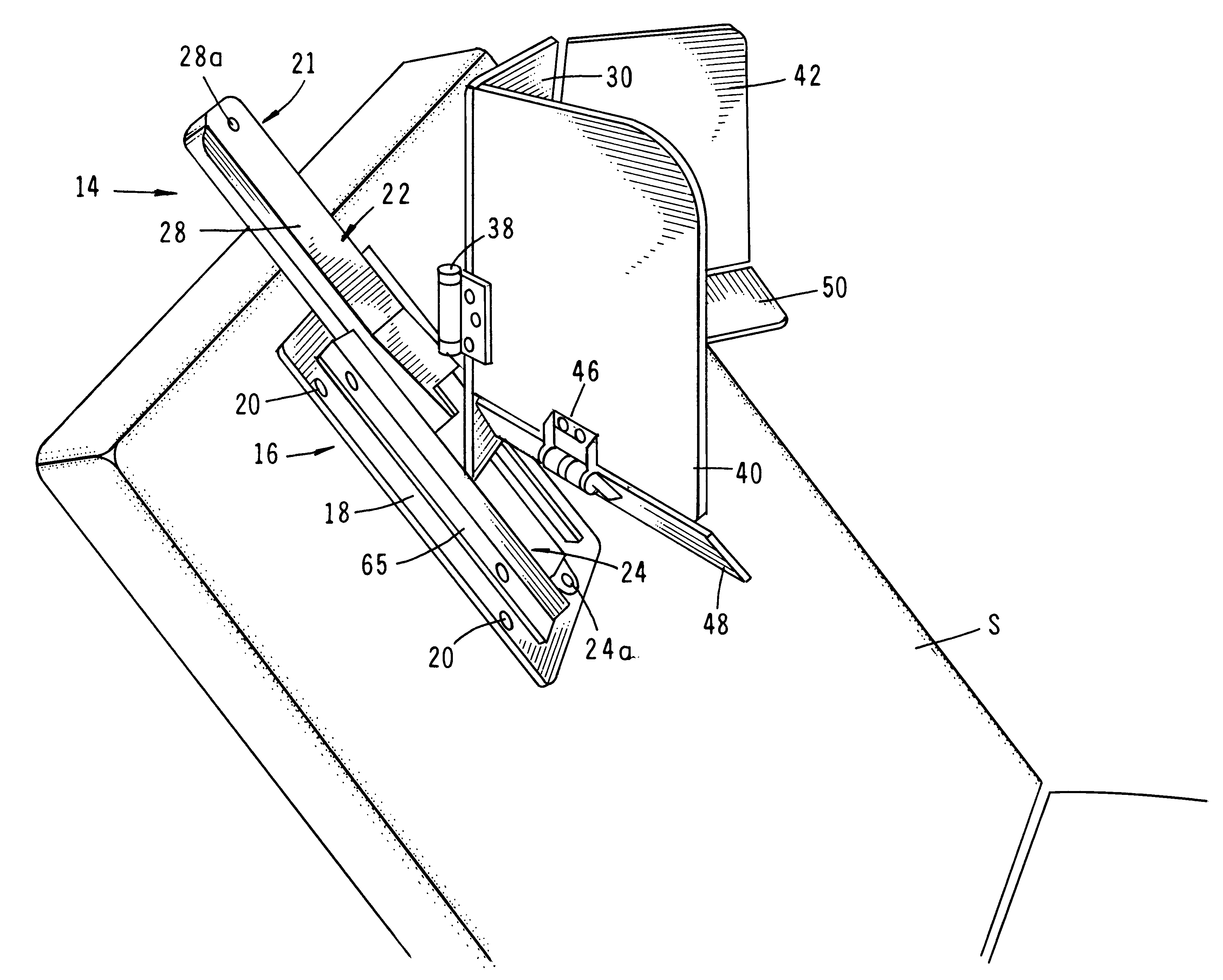
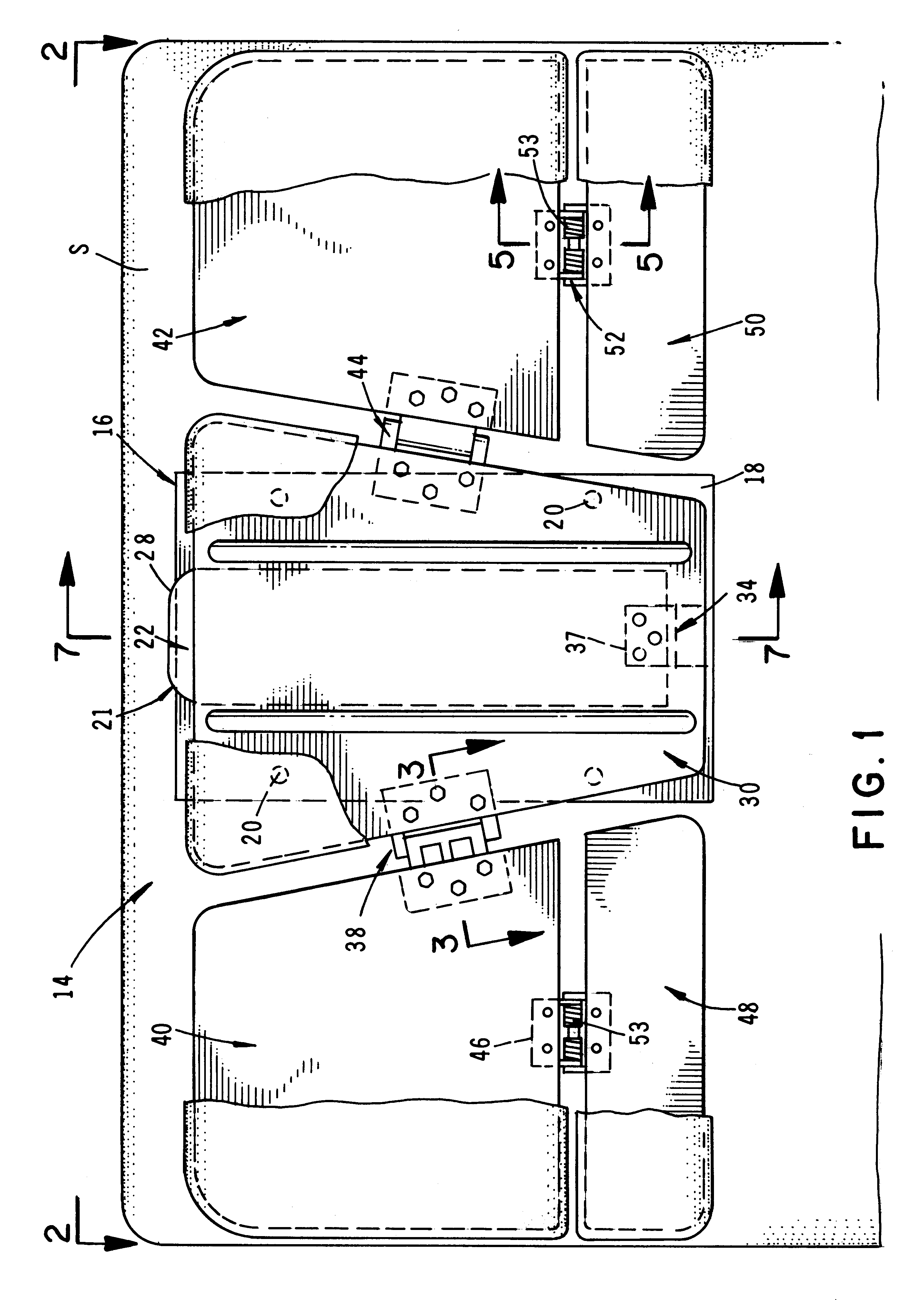
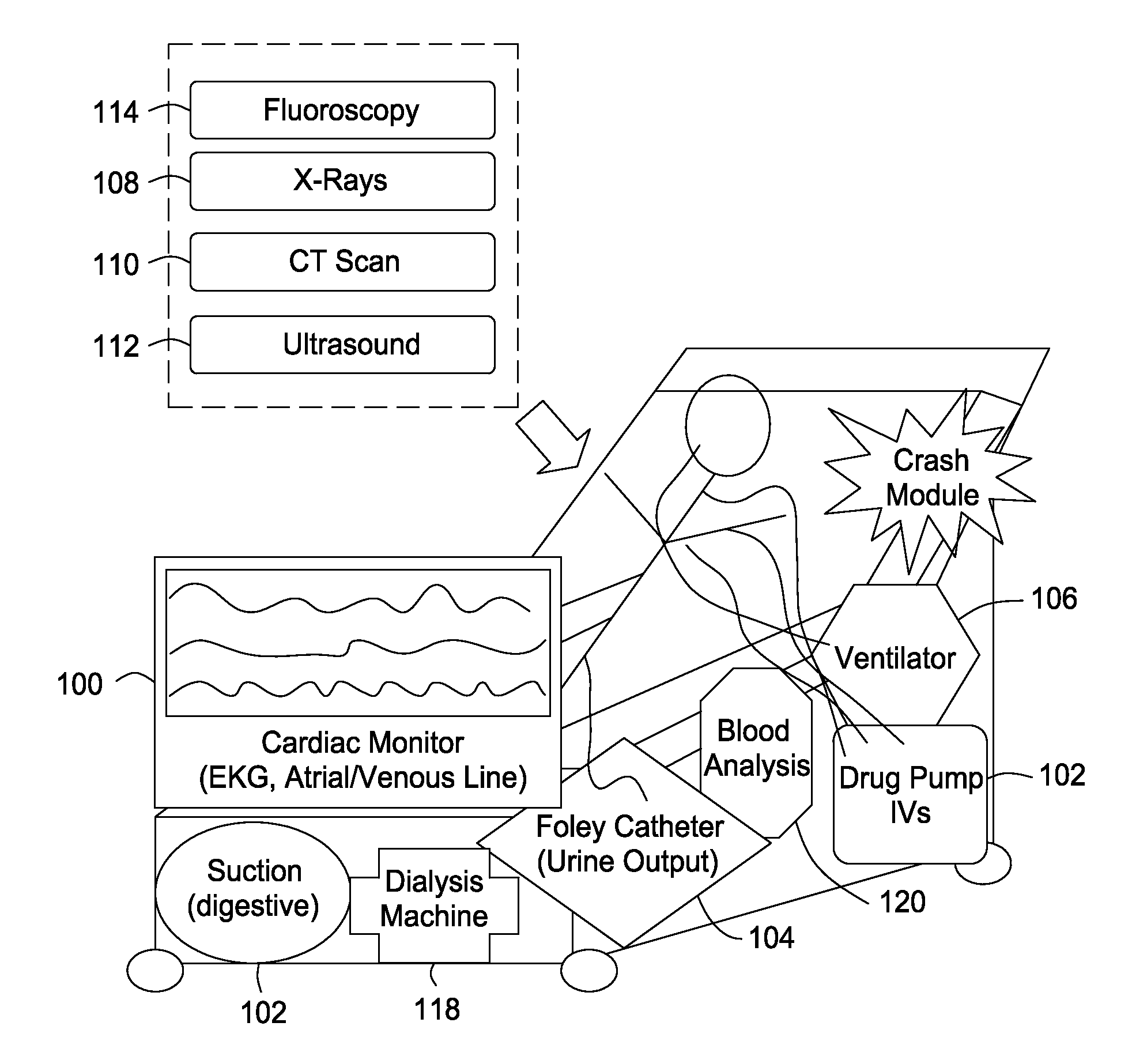
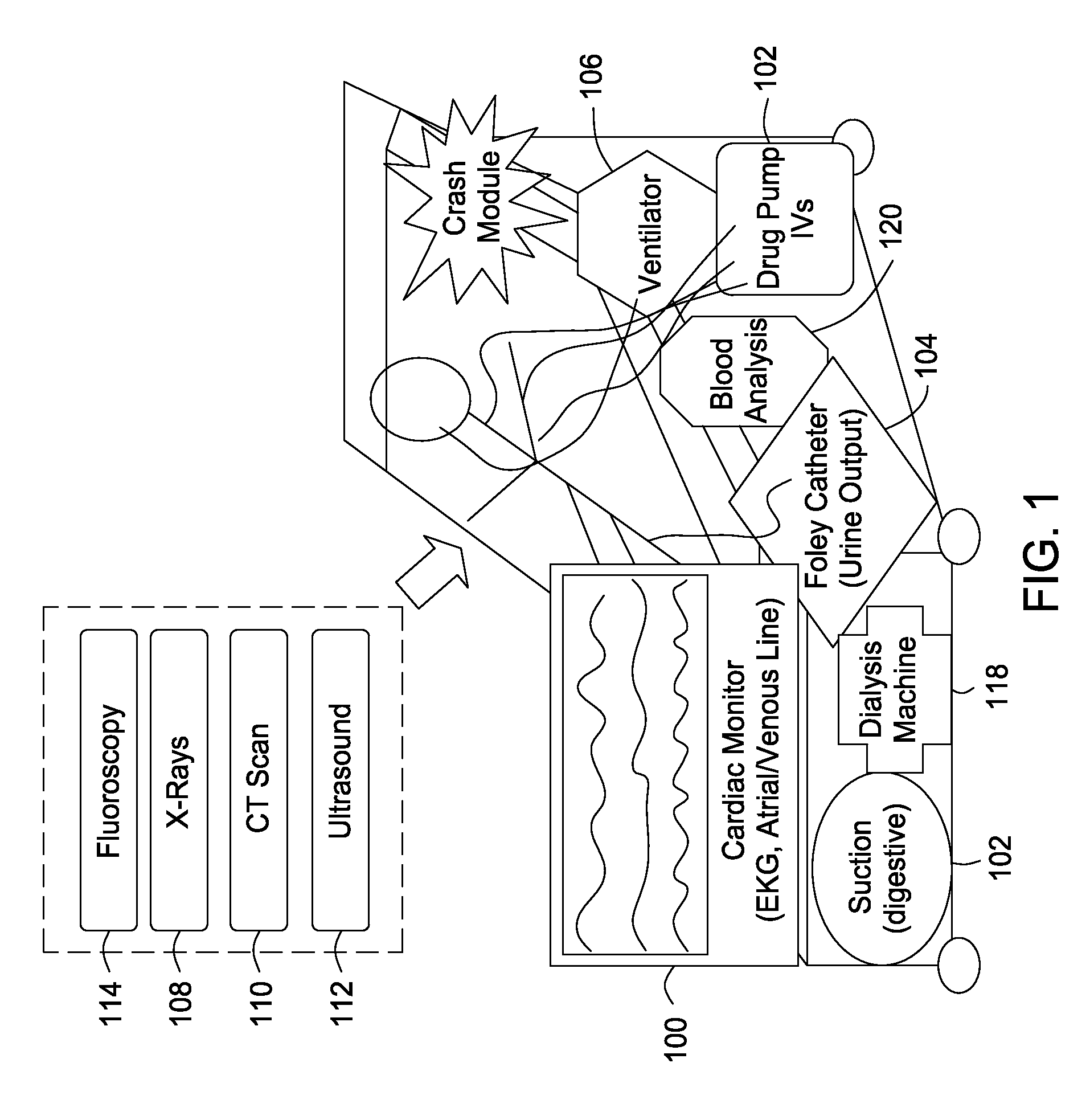
Self contained transportable life support system
A self-contained transportable life support system for resuscitation, stabilization, and transport of a patient has an environmentally controlled housing for receiving and supporting a patient and a plurality of medical devices disposed within the housing. A control circuit attached to the housing has at least a portion thereof extending to an external surface of the housing for regulating operation of the medical devices and environmental conditions of within the housing in response to monitored life support conditions of the patient.
Owner:INTEGRATED MEDICAL SYST
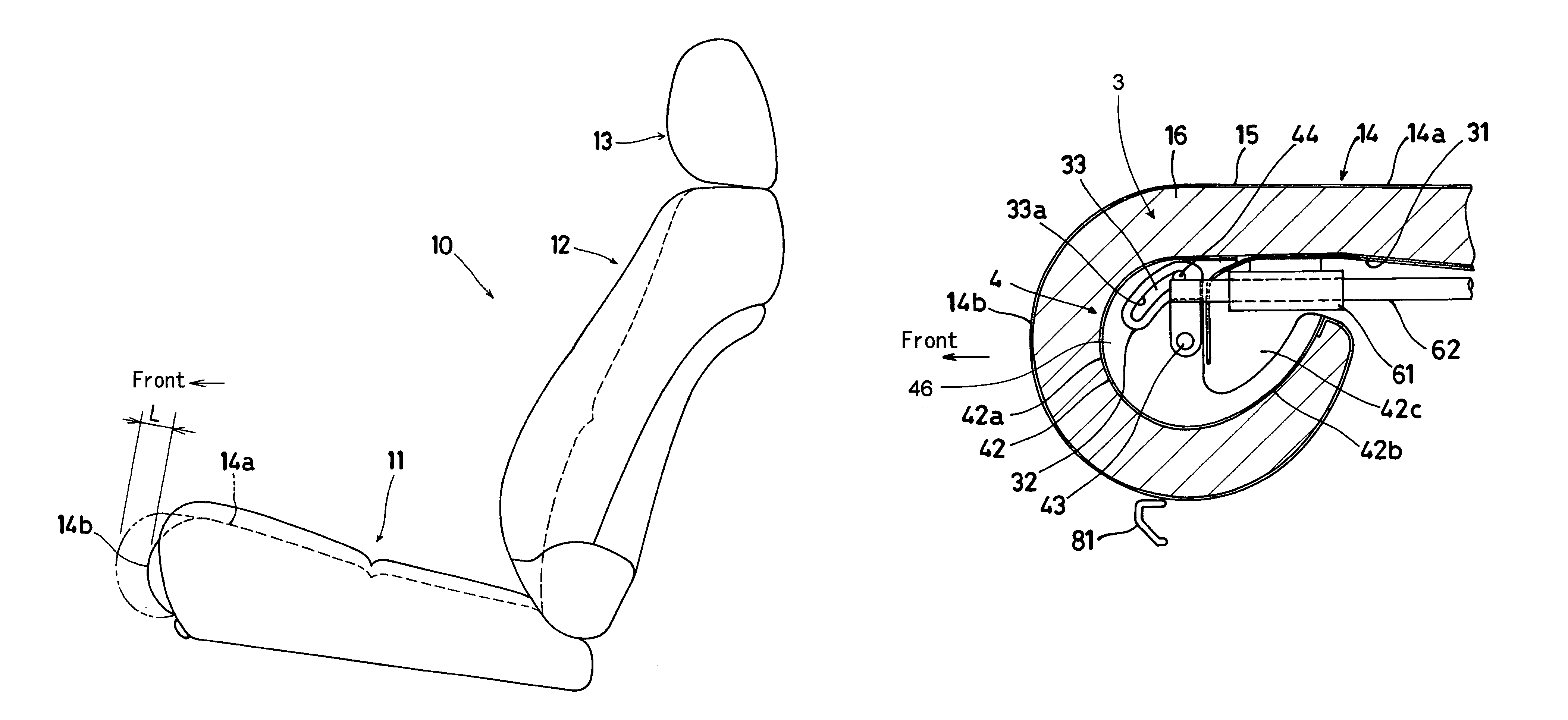
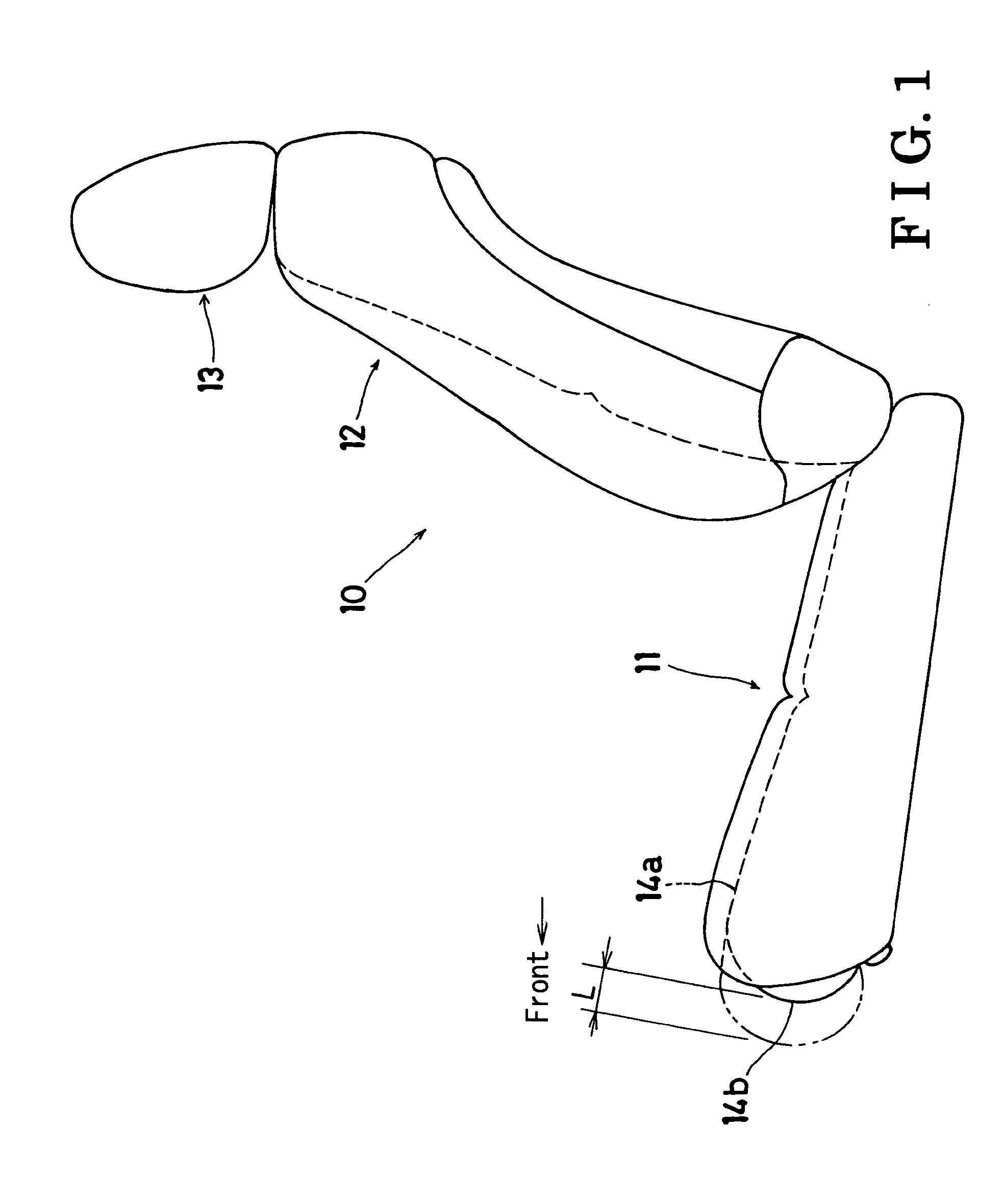
Seat headrest
InactiveUS6250716B1Easy height adjustmentReliable lockingVehicle seatsOperating chairsChinCombined use
An adjustable headrest that provides both support and comfort to the user and one that can be used in connection with furniture including household and office furniture and also in connection with various types of passenger vehicles. The headrest includes slide means for permitting easy height adjustment of the headrest and also includes locking means for securely locking the headrest in a desired elevated position. Further, the headrest includes easily adjustable, wing-like, side-support members that are pivotally connected to a centrally located, vertically adjustable head support member by means of constant torque hinges and also includes easily adjustable chin support members that are pivotally connected to the side support members by means of constant torque hinges.
Owner:CLOUGH ROBERT
Dual metal gate process: metals and their silicides
InactiveUS6475908B1High and work functionImprove work functionOperating chairsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideCMOS
Methods for forming dual-metal gate CMOS transistors are described. An NMOS and a PMOS active area of a semiconductor substrate are separated by isolation regions. A metal layer is deposited over a gate dielectric layer in each active area. Silicon ions are implanted into the metal layer in one active area to form an implanted metal layer which is silicided to form a metal silicide layer. Thereafter, the metal layer and the metal silicide layer are patterned to form a metal gate in one active area and a metal silicide gate in the other active area wherein the active area having the gate with the higher work function is the PMOS active area. Alternatively, both gates may be metal silicide gates wherein the silicon concentrations of the two gates differ. Alternatively, a dummy gate may be formed in each of the active areas and covered with a dielectric layer. The dielectric layer is planarized thereby exposing the dummy gates. The dummy gates are removed leaving gate openings to the semiconductor substrate. A metal layer is deposited over a gate dielectric layer within the gate openings to form metal gates. One or both of the gates are silicon implanted and silicided. The PMOS gate has the higher work function.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Slouch rear seat system
Owner:LEAR CORP
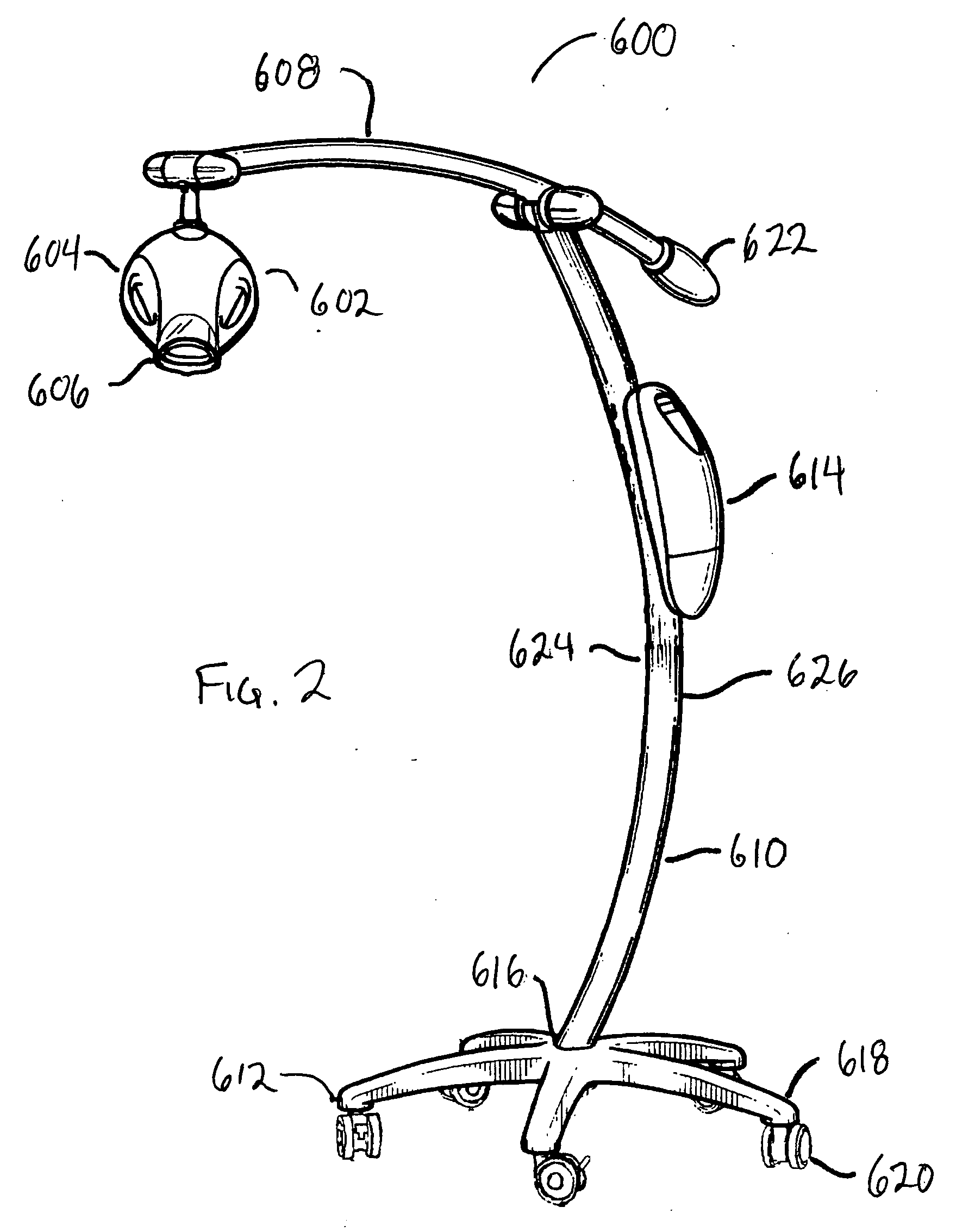
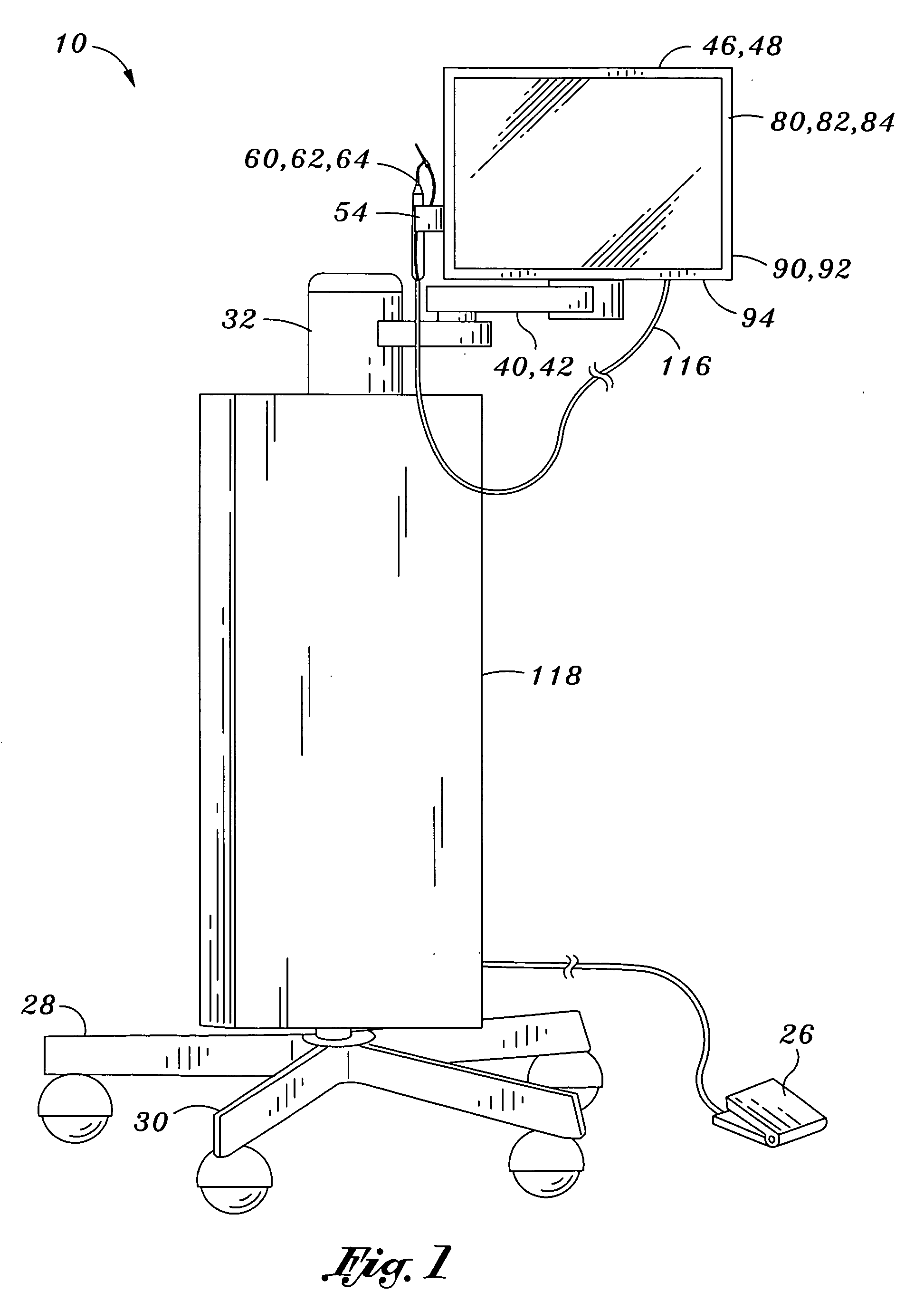
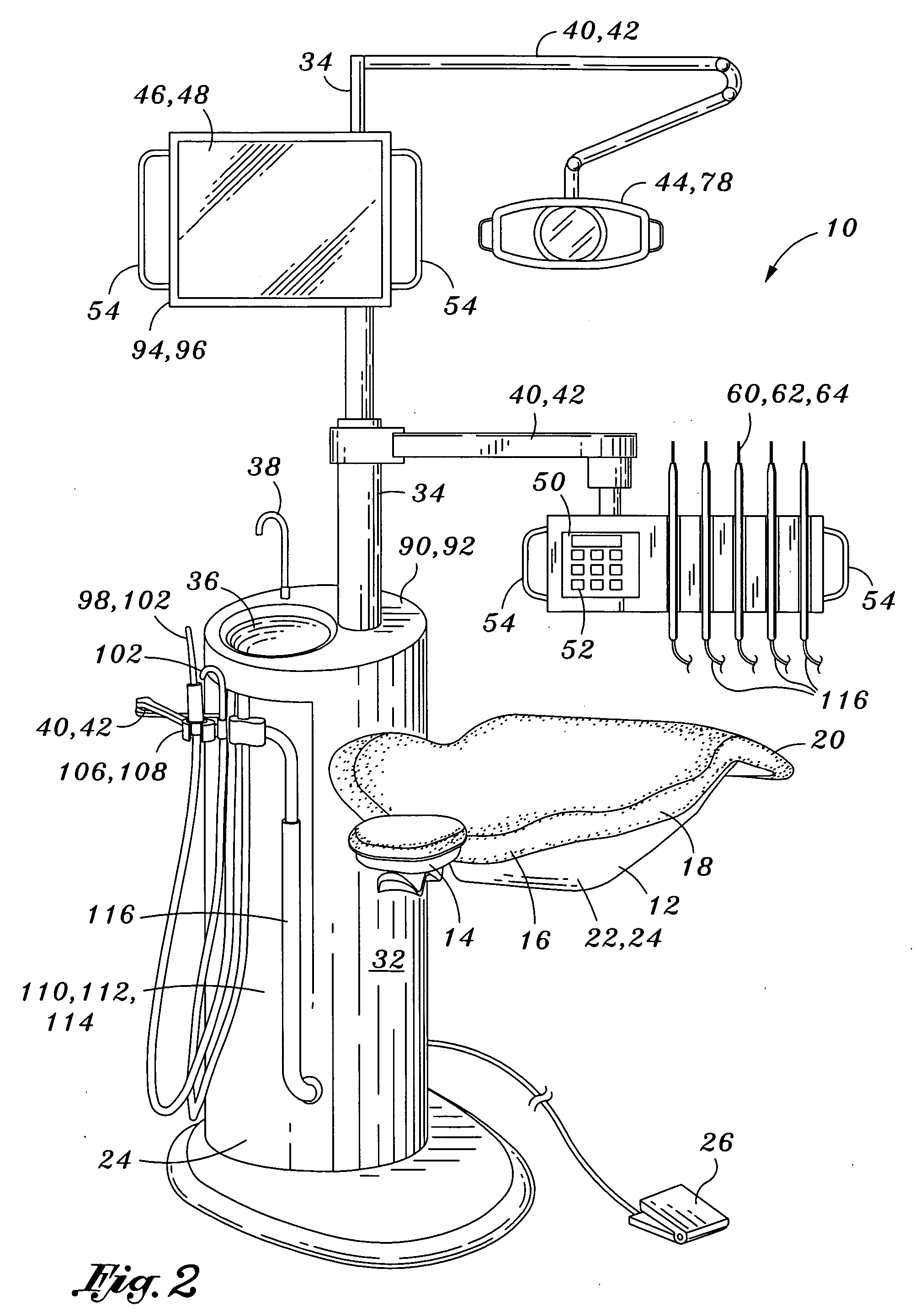
Dental imaging system and method of use
InactiveUS20060046226A1Easy to controlHigh resolutionOperating chairsDental chairsDisplay deviceEngineering
Provided is a dental imaging system comprising a support frame, an imaging device and a display device. The support frame may include an upright portion mounted upon a base portion which may be portably or stationarily mounted. The imaging device is integrally mounted to the support frame as is the display device. The display device is conductively connected to the imaging device and is preferably configured to display images produced by the imaging device. The dental imaging system is adapted for endoscopic viewing of subgingival anatomy in a unitary structure to minimize space limitations of dental facilities.
Owner:DENTALVIEW
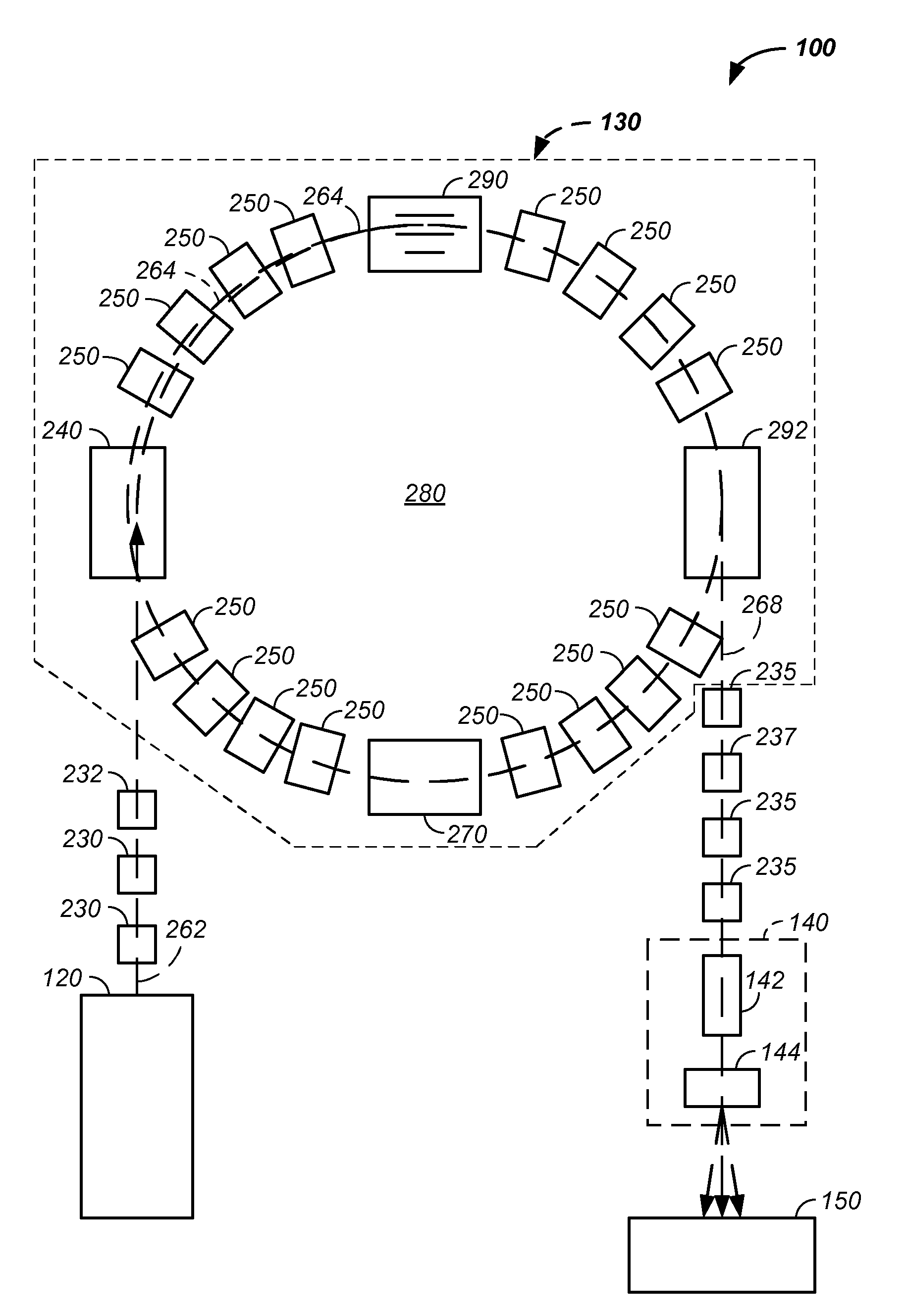
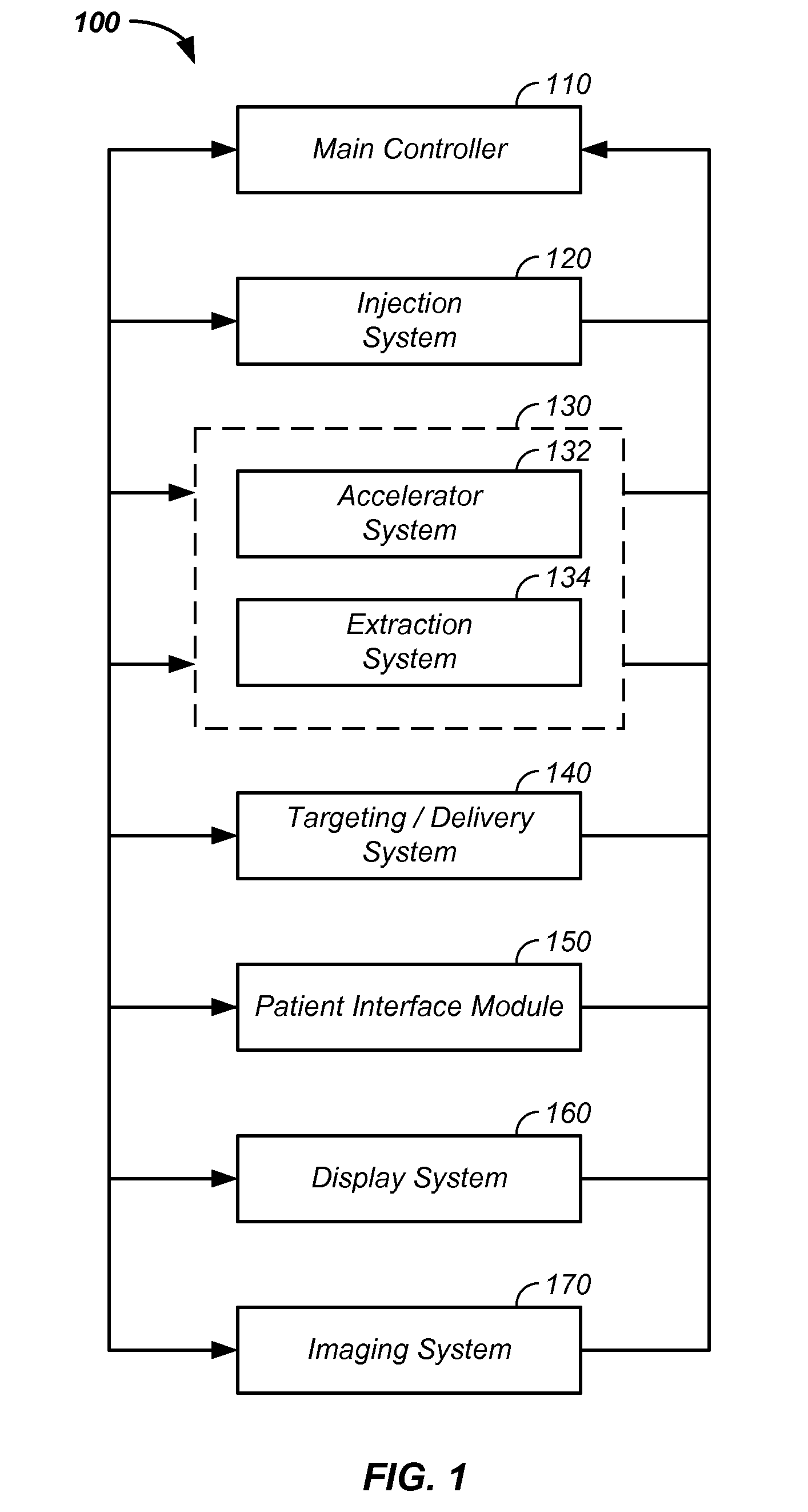
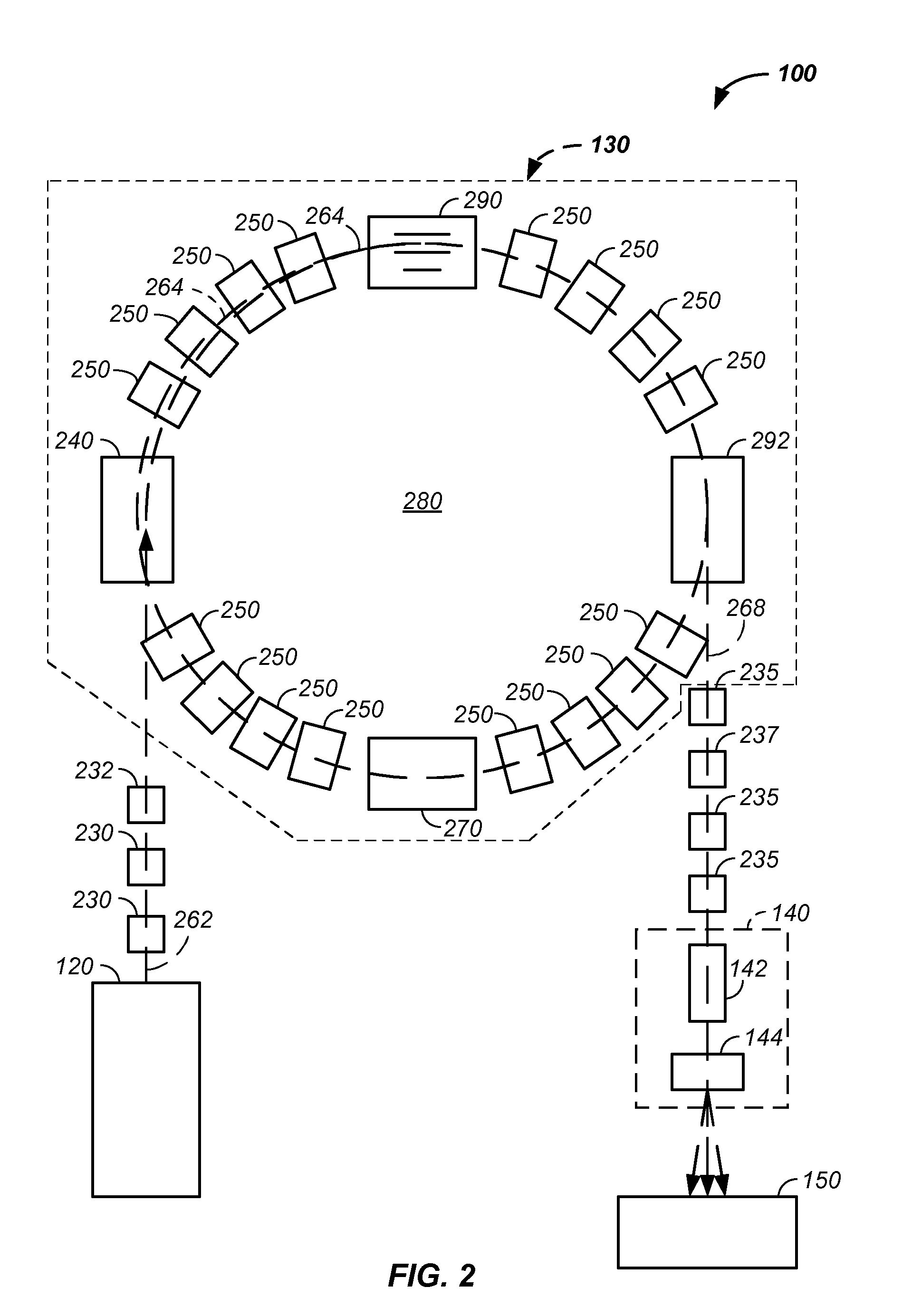
Charged particle cancer therapy and patient positioning method and apparatus
The invention comprises a laying, semi-vertical, or seated patient positioning, alignment, and / or control method and apparatus used in conjunction with multi-axis charged particle or proton beam radiation therapy of cancerous tumors. Patient positioning constraints are used to maintain the patient in a treatment position, including one or more of: a seat support, a back support, a head support, an arm support, a knee support, and a foot support. One or more of the positioning constraints are movable and / or under computer control for rapid positioning and / or immobilization of the patient. The system optionally uses an X-ray beam that lies in substantially the same path as a proton beam path of a particle beam cancer therapy system. The generated image is usable for: fine tuning body alignment relative to the proton beam path, to control the proton beam path to accurately and precisely target the tumor, and / or in system verification and validation.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
Chair ride mechanism with tension assembly
Owner:KIMBALL INTERNATIONAL
Semi-powered lower extremity exoskeleton
The lower extremity exoskeleton comprises two leg supports connectable to person's lower limbs and configured to rest on the ground during their stance phase. Each leg support comprises a thigh link and a shank link; a knee joint configured to allow flexion and extension between the shank link and the thigh link. The lower extremity exoskeleton further comprises an exoskeleton trunk connectable to the person'supper body. The exoskeleton trunk is connectable to the thigh links of the leg supports allowing for the flexion and extension between the leg supports and the exoskeleton trunk. Two torque generators are coupled to each of the knee joints. A power unit, capable of providing power, is coupled to the torque generators. In operation when a leg support is in a stance phase and climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit injects power into the respective torque generator thereby extending the respective knee angle. When a leg support is in stance phase and not climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to resist flexion of the respective knee joint. When a leg support is in a swing phase, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to minimize its resistance to knee flexion and extension.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Integrated patient bed system
InactiveUS20090275808A1Easy to monitorImprove treatmentRadiation diagnosis data transmissionMedical imagingTherapeutic DevicesComputer science
The present invention includes an integrated system and methods for patient treatment, the system includes a hospital bed; a plurality of patient diagnostic and treatment devices connected to a network, wherein each of the devices can communicate to a network and exchange information with the network about the care of a patient; and a processor accessible adjacent to the bed and connected to the network to integrate information obtained from the devices through the network with one or more additional sources of information databases, wherein the processor can communicate to one or more patient treatment devices either directly or via the network and the processor directs the one or more patient treatment devices to change the treatment of the patient.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Seating area adjuster
A seating area adjuster for a seat of a vehicle includes a seating member having a seating surface, a support portion supporting the seating member, an adjustment mechanism connected with the seating member and supported by the support portion to be movable in an adjustment direction in which a length of the seating surface is adjusted and rotatable about a shaft extending perpendicular to the adjustment direction and to an up and down direction of the adjustment mechanism, a movement mechanism moving the adjustment mechanism in the adjustment direction relative to the support portion, and a rotation control mechanism controlling the adjustment mechanism to a predetermined rotational position corresponding an amount of a movement of the adjustment mechanism in the adjustment direction.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Reclining computer chair apparatus
InactiveUS6056363AReduce fatigueReduce strainOperating chairsRocking chairsComputer terminalEngineering
An apparatus which will largely prevent irritated ligaments, and sore necks and backs arising from spending long hours at a computer terminal by allowing the user to position themselves in multiple comfortable positions is disclosed. The apparatus for use with a monitor and keyboard comprises: a base; a carriage slidably mounted on the base; a seat member having rear, and front side portions, said seat member carried on the carriage; a back member having a lower side portion pivoted to the rear portion of the seat member; a leg member having an upper side portion pivoted to the front side portion of the seat member; an arm member carried by the carriage, said arm member having a front end portion adapted to carry the keyboard; a monitor arm carried by the carriage; and motorized threaded screws used to move the carriage on the base, and move the back and leg members relative to the carriage.
Owner:MADDOX LEE W
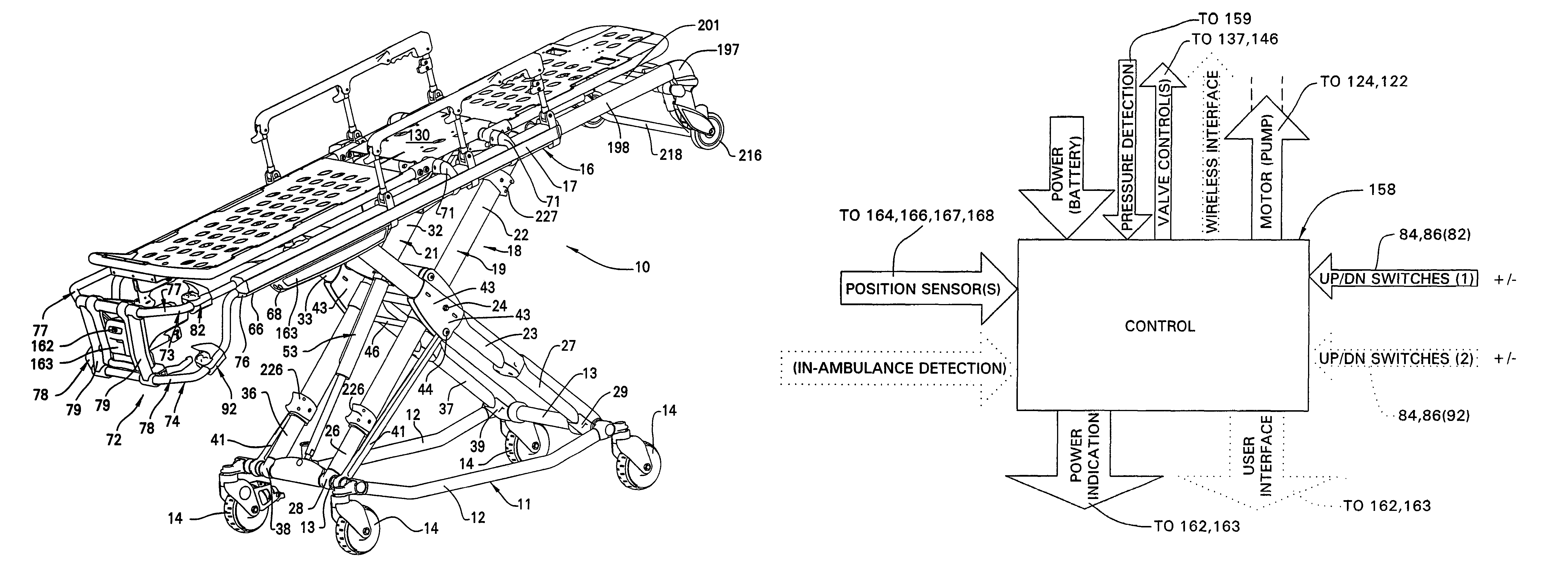
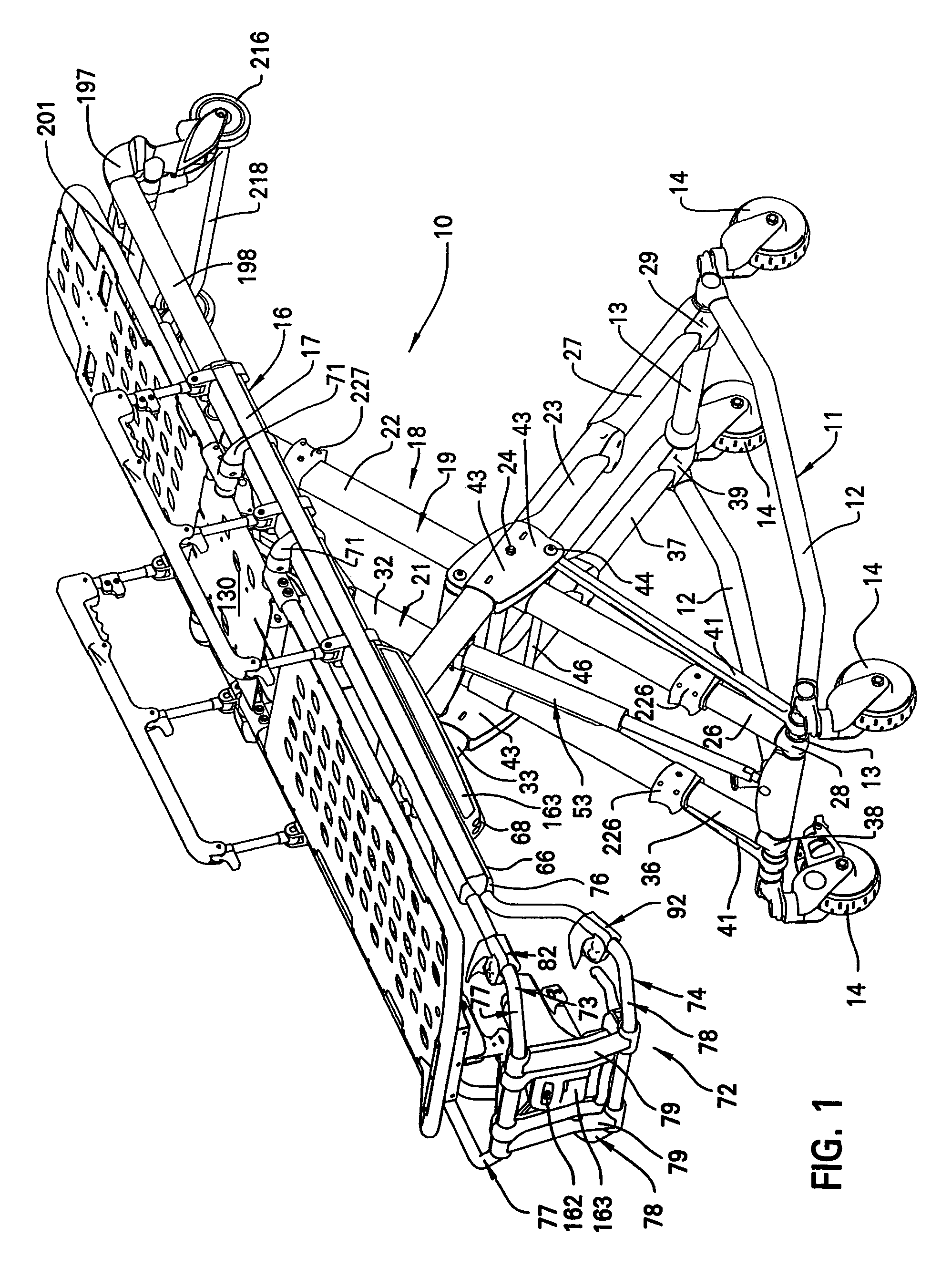
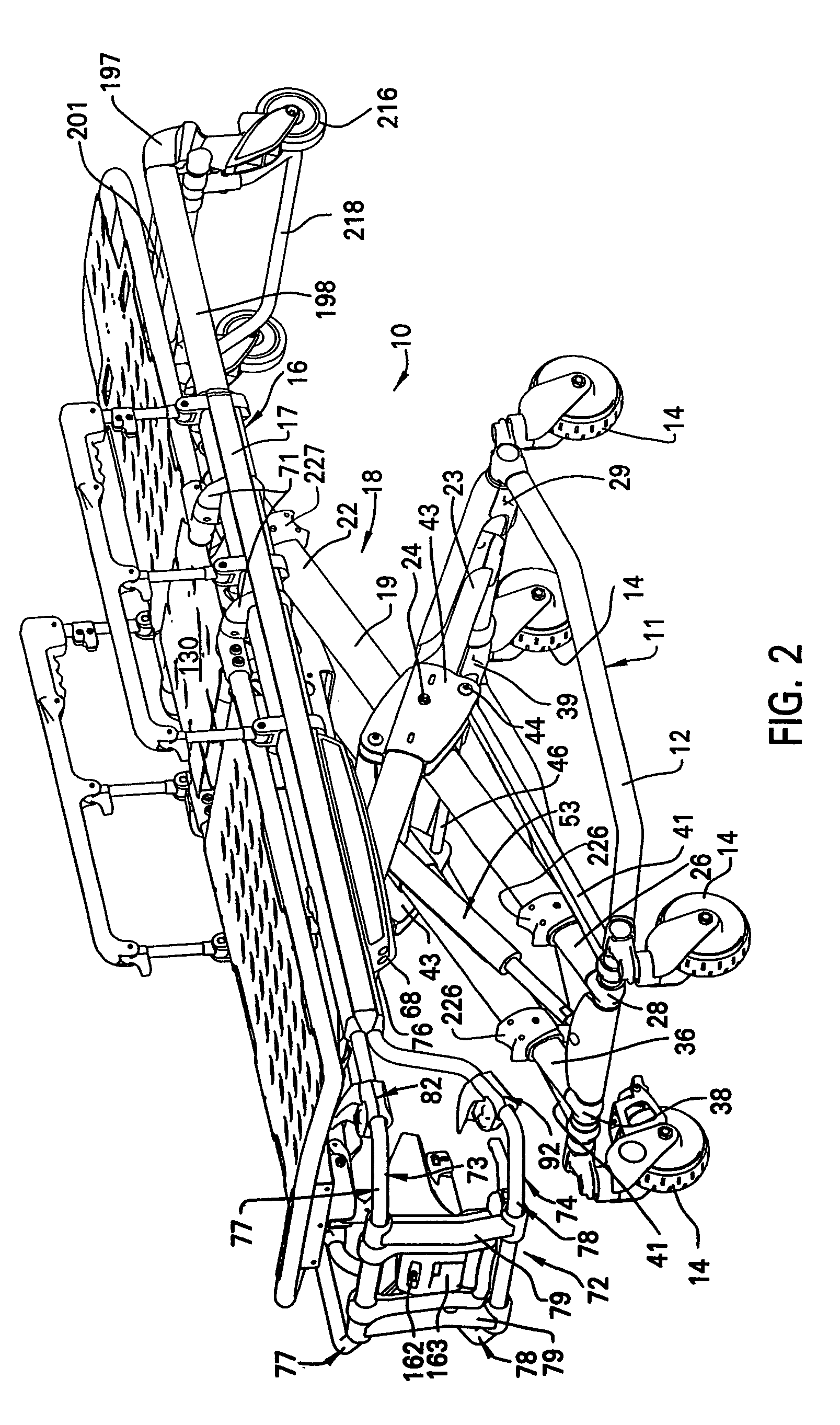
Ambulance cot and hydraulic elevating mechanism therefor
An ambulance cot is disclosed and the ambulance cot having a base frame configured for support on a surface, a litter frame configured for supporting thereon a patient and an elevating mechanism interconnecting the base frame and the litter frame and configured to interconnect the litter frame and the base frame in order to facilitate movement of the base frame and the litter frame toward and away from each other. A control mechanism is provided on the cot which is configured to facilitate the movement of the base frame and the litter frame toward each other and at differing speeds predicated on at least one of whether the base frame is supported on the surface and the litter frame is supported by an external support separate from the elevating mechanism.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
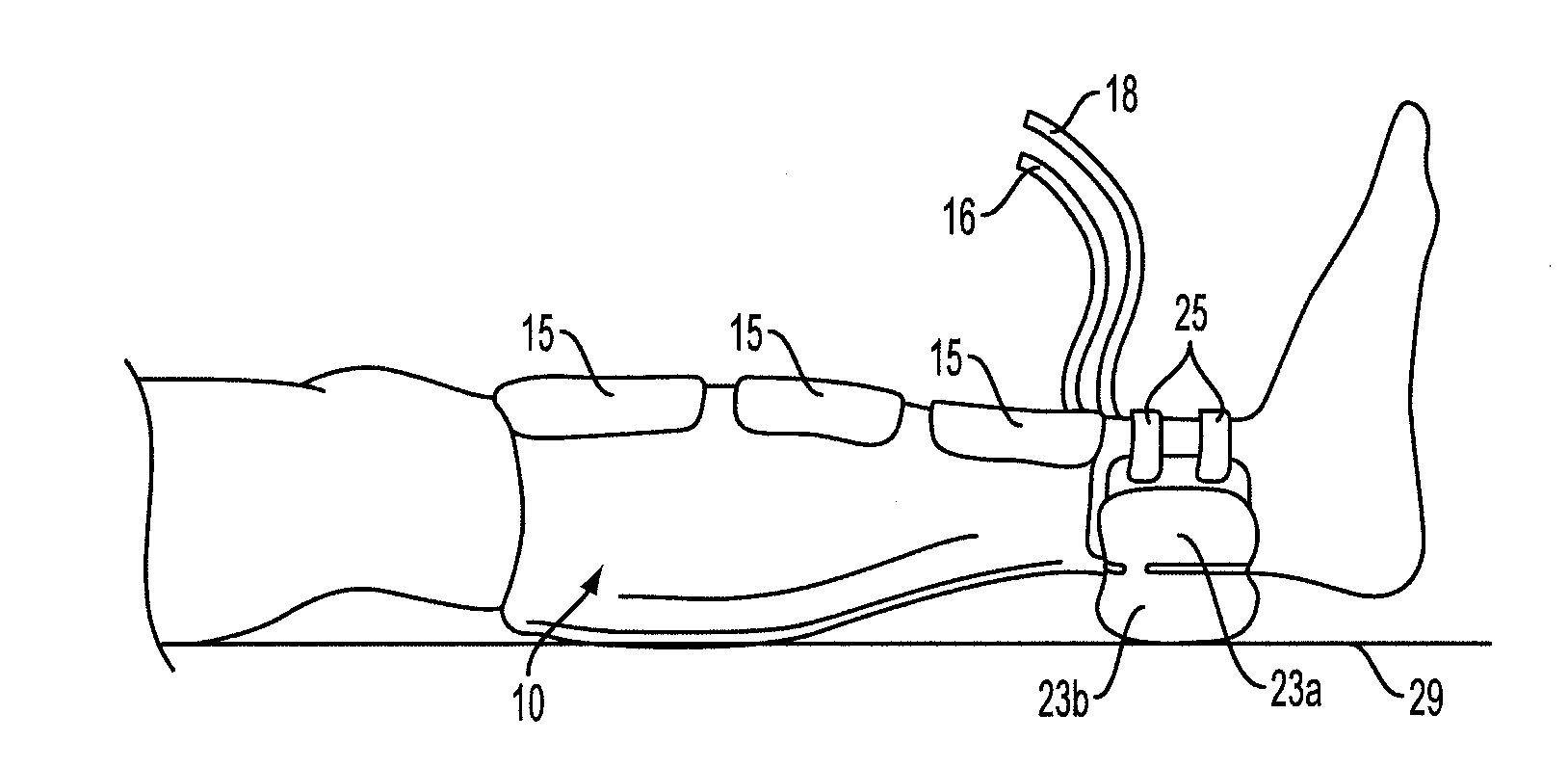
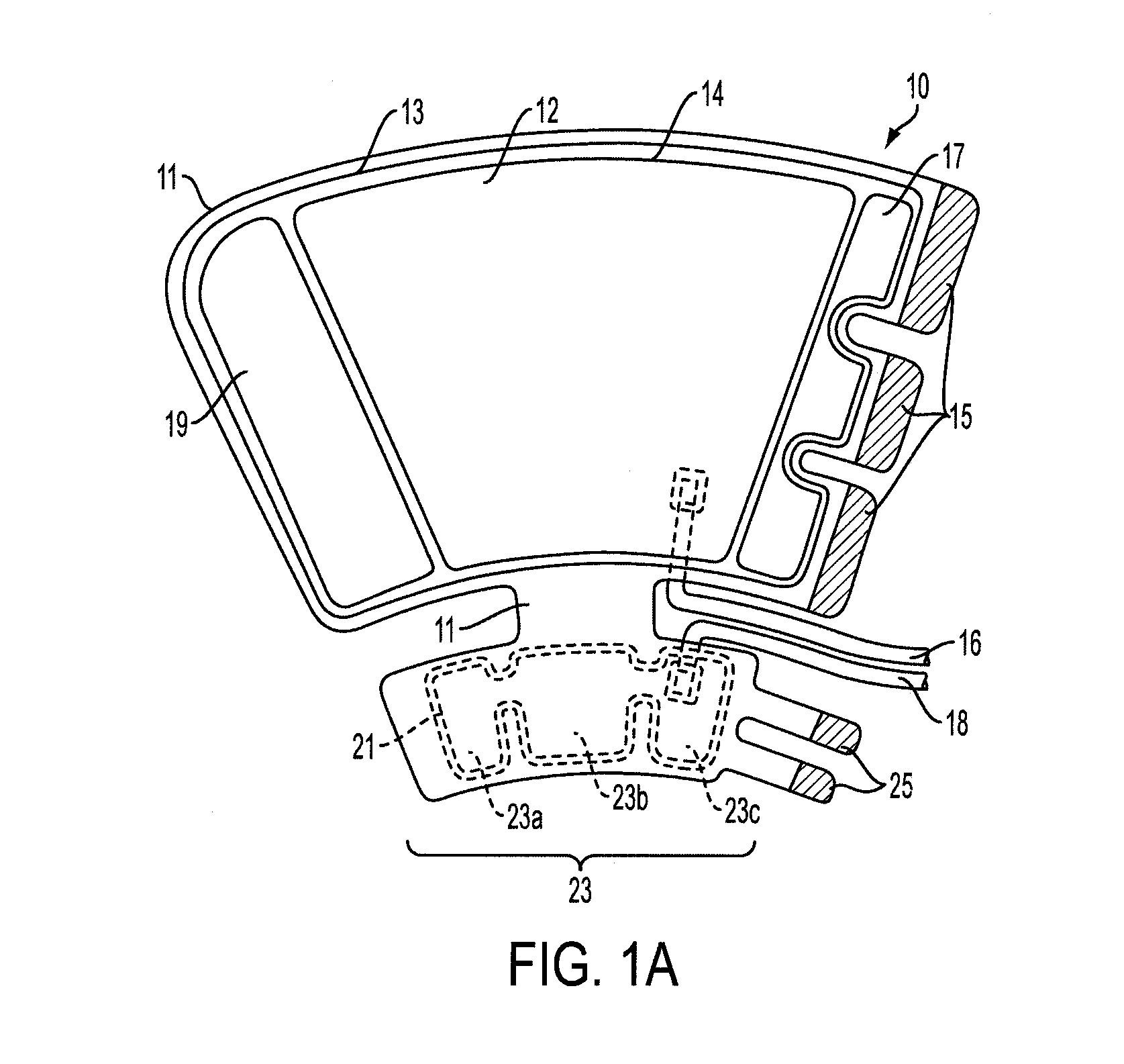
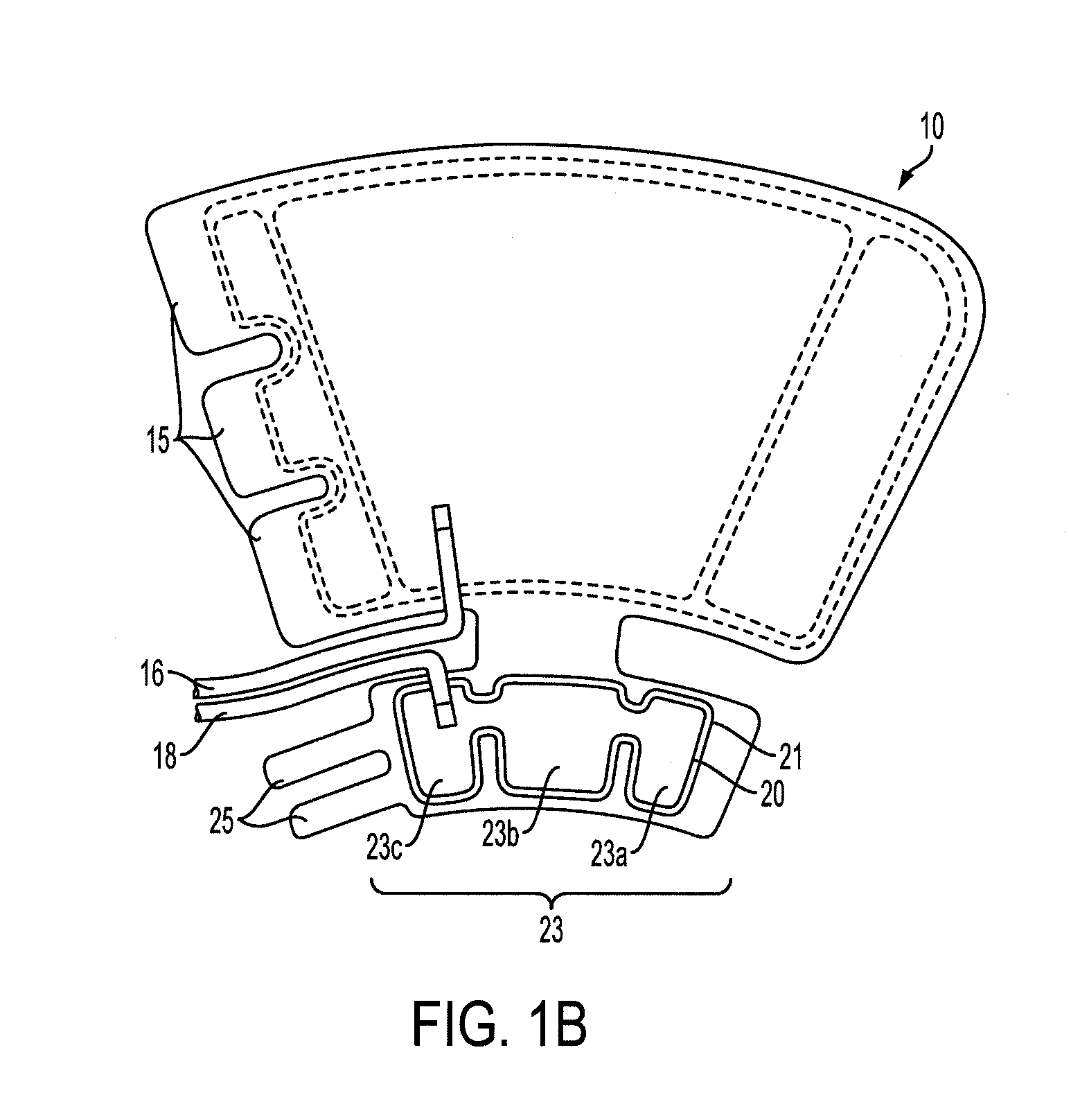
Compression garments with heel elevation
A compression garment includes a backing member with a proximal end portion and opposed distal end portion. The backing member is configured to be disposed about at least a portion of a lower leg between calf and heel and has an inner surface to be disposed facing the lower leg, and an opposite outer surface. The garment further includes at least one compression bladder disposed within the backing member configured to compress at least a portion of the lower leg to augment venous return flow in the lower leg, an elevation member operatively coupled to the backing member and configured to elevate the heel from an underlying support surface and at least one support member disposed along a portion of the elevation member and along a portion of the backing member to retain the elevation member in a desired position with respect to the backing member to elevate the heel.
Owner:SUN SCI
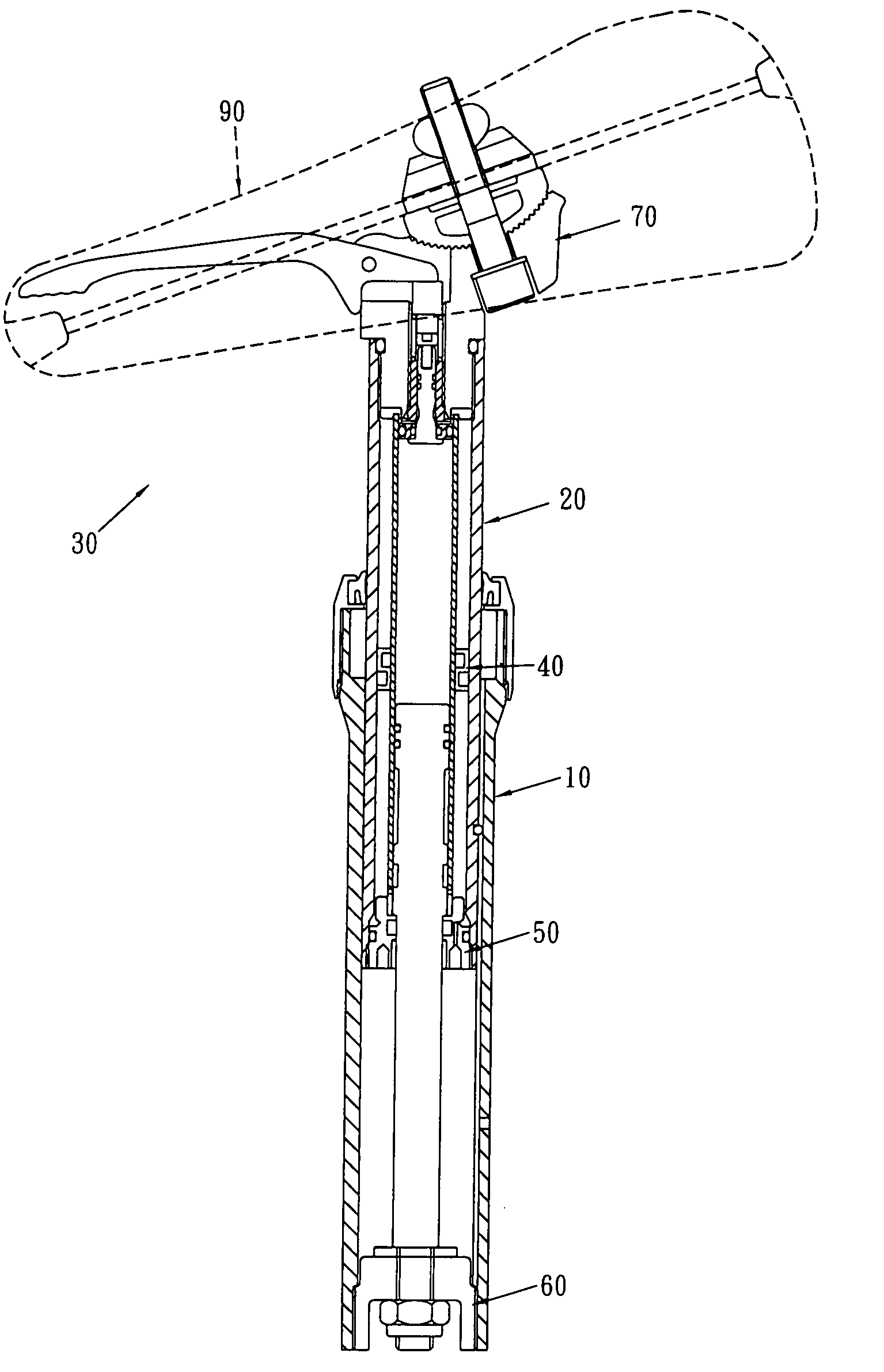
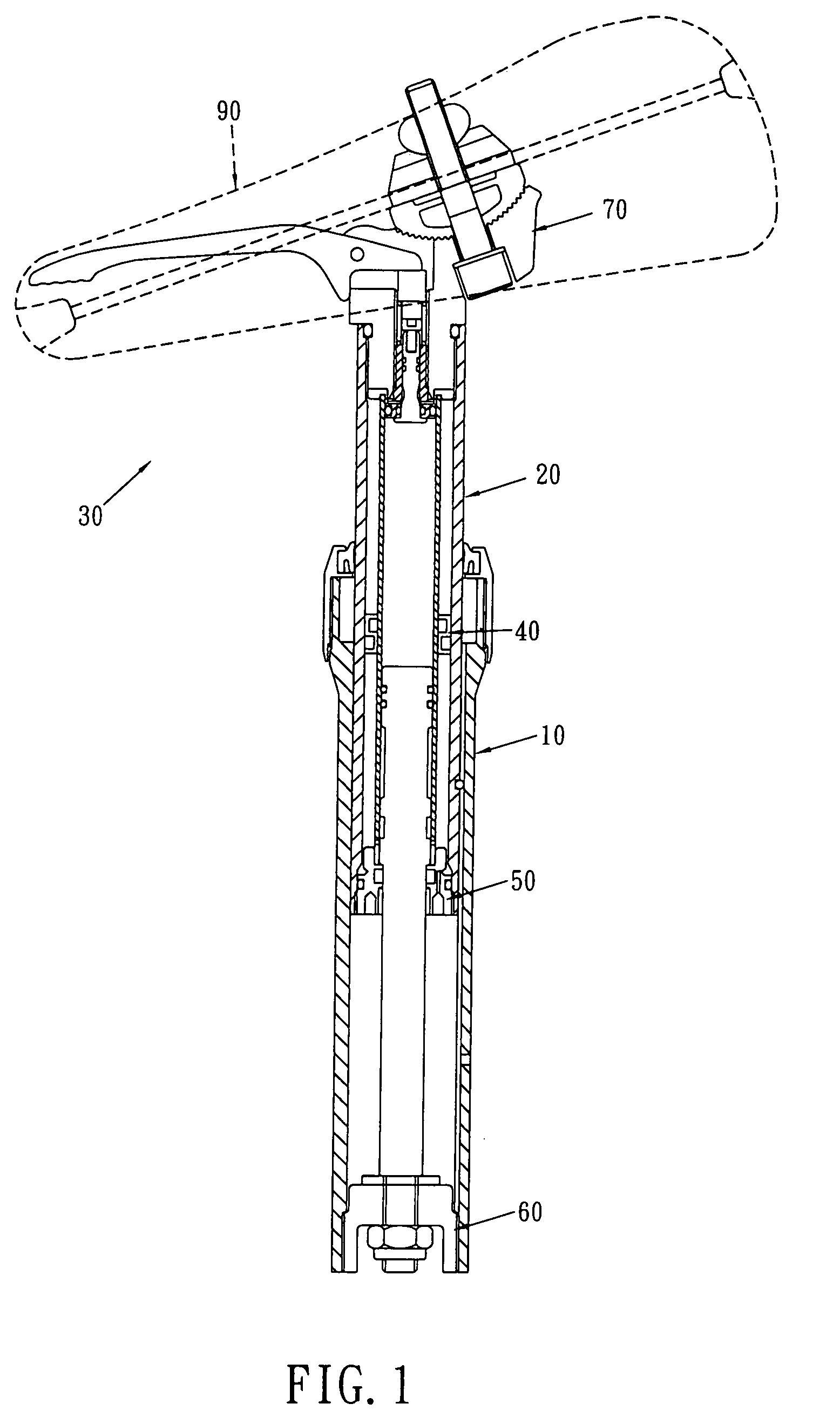
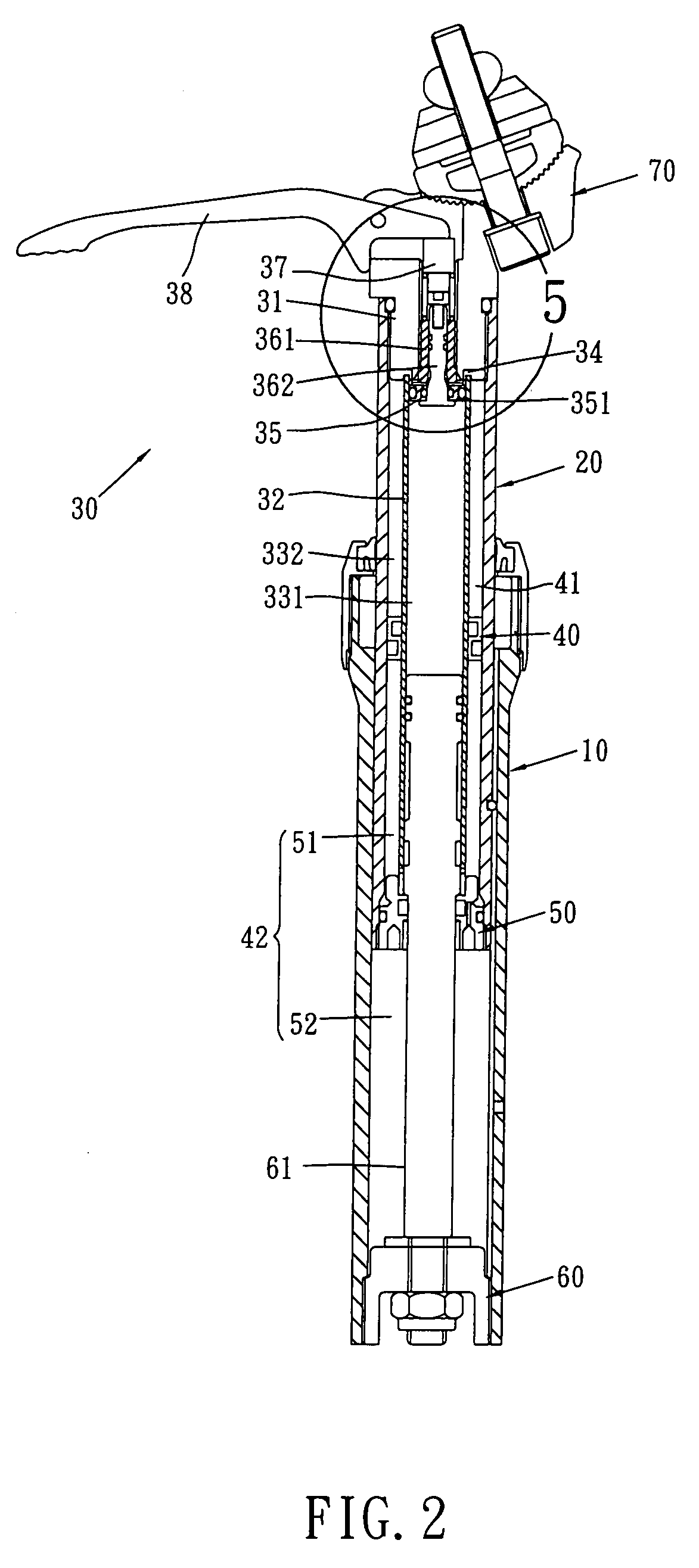
Adjustable bicycle seat assembly
An adjustable bicycle seat assembly includes an adjusting unit which includes a top end member connected to the seat post and an adjusting tube is connected to a lower end of the top end member. An inner space is defined in the adjusting tube and an outer space is defined between the adjusting tube and the seat post. A path is defined between the adjusting tube and the top end member so as to communicate with the inner space and the outer space. An axle is movably received in the path and removably seals the path. An anti-rotation device is located between the seat post and the seat tube so as to prevent the seat post from rotating relative to the seat tube.
Owner:HUMBOLDT STATE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com