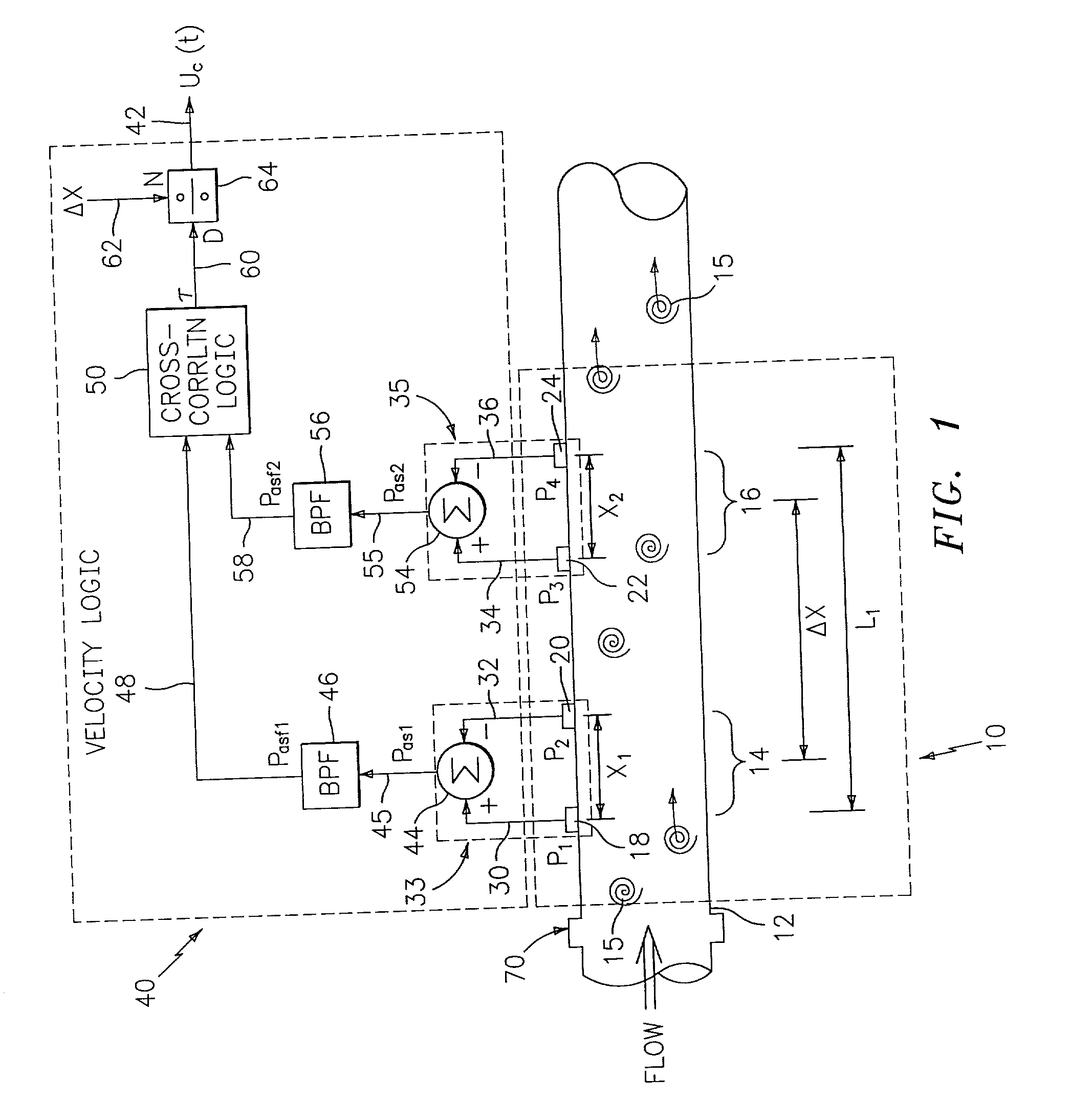Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1910 results about "Axial distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
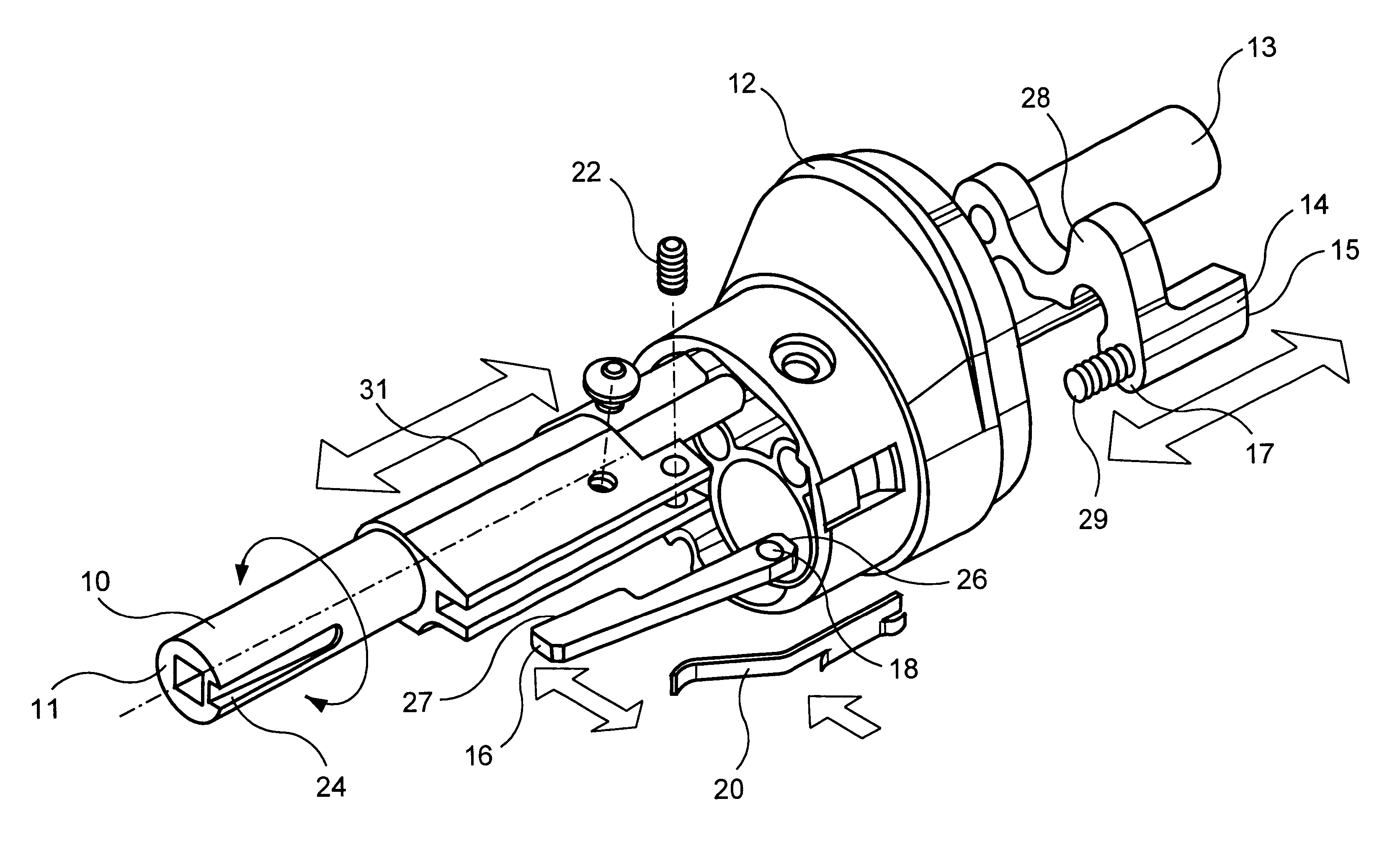
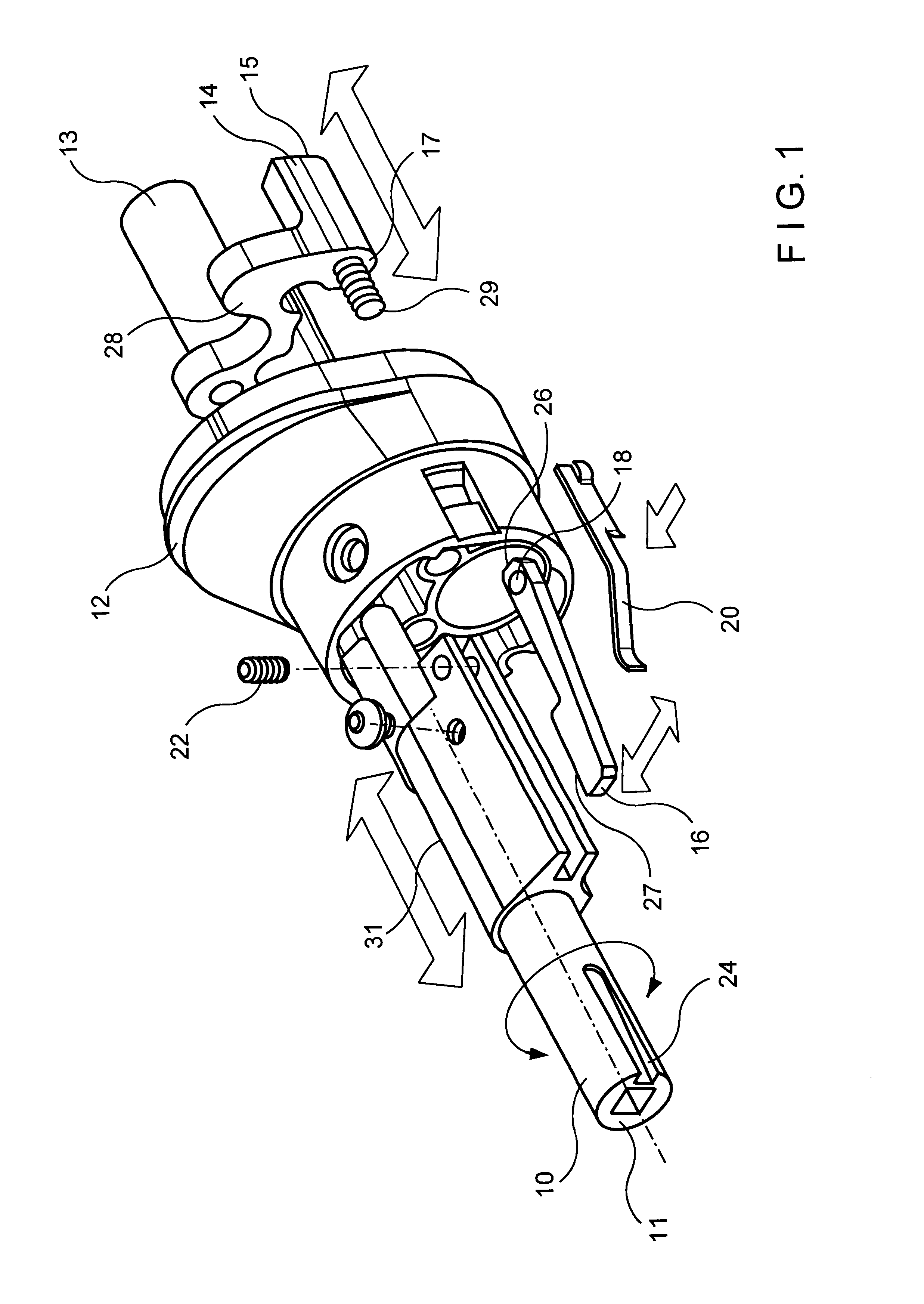
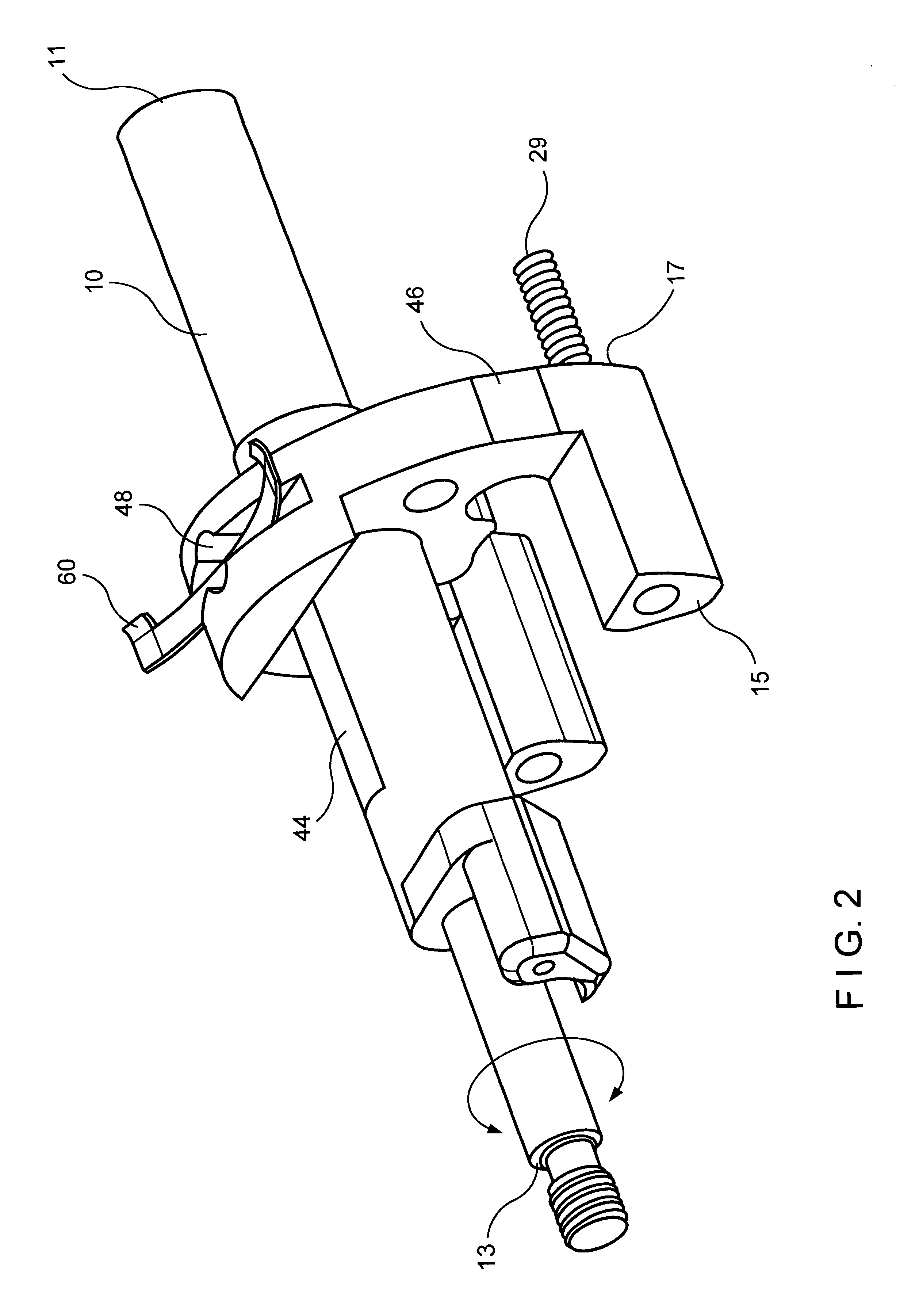
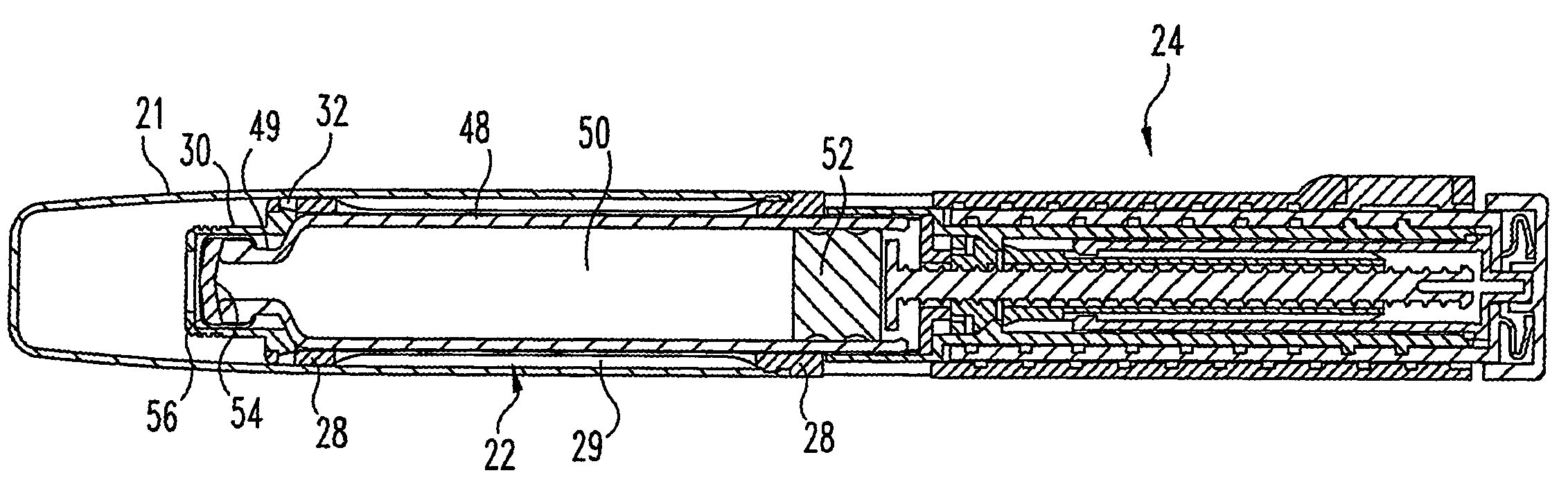
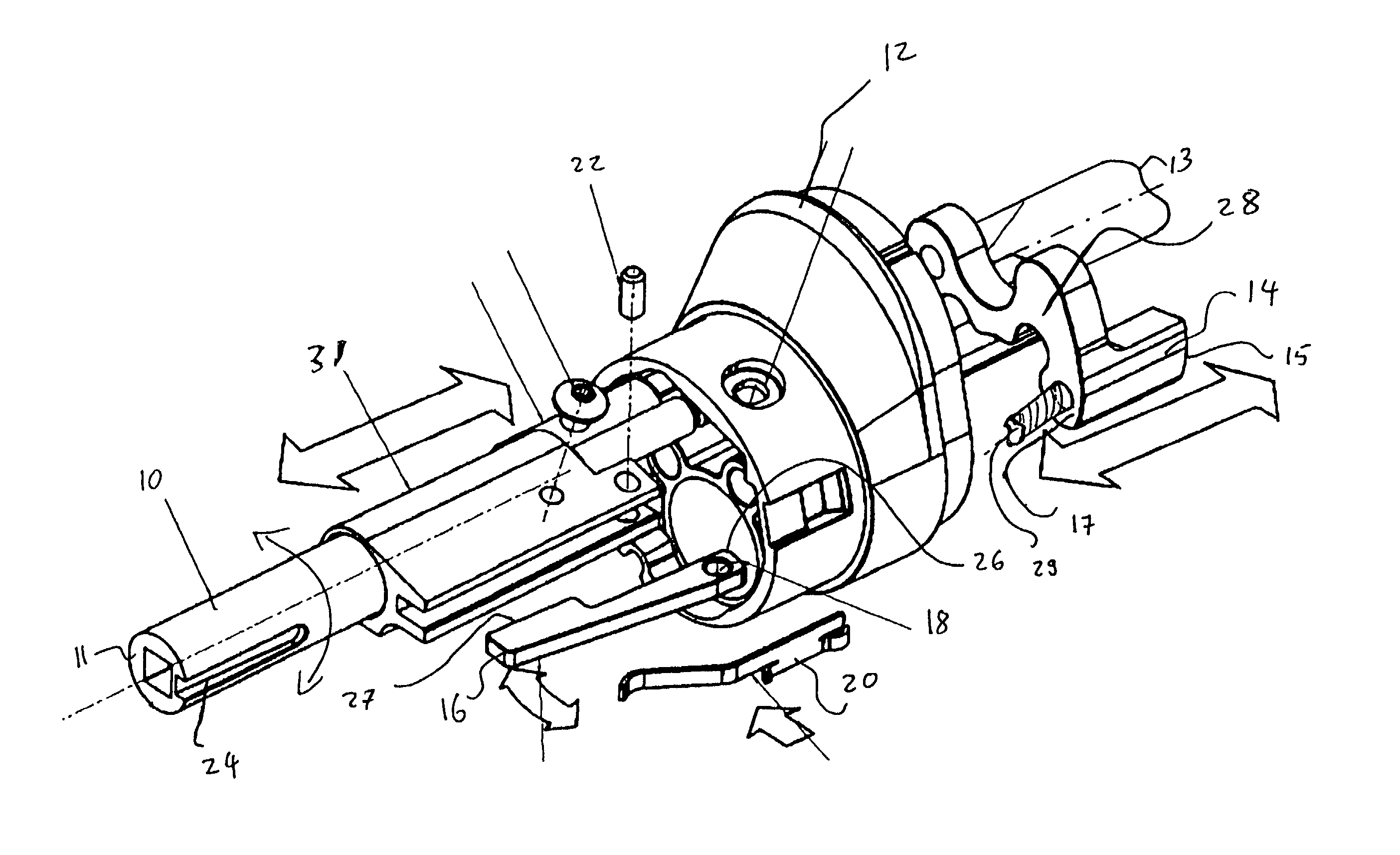
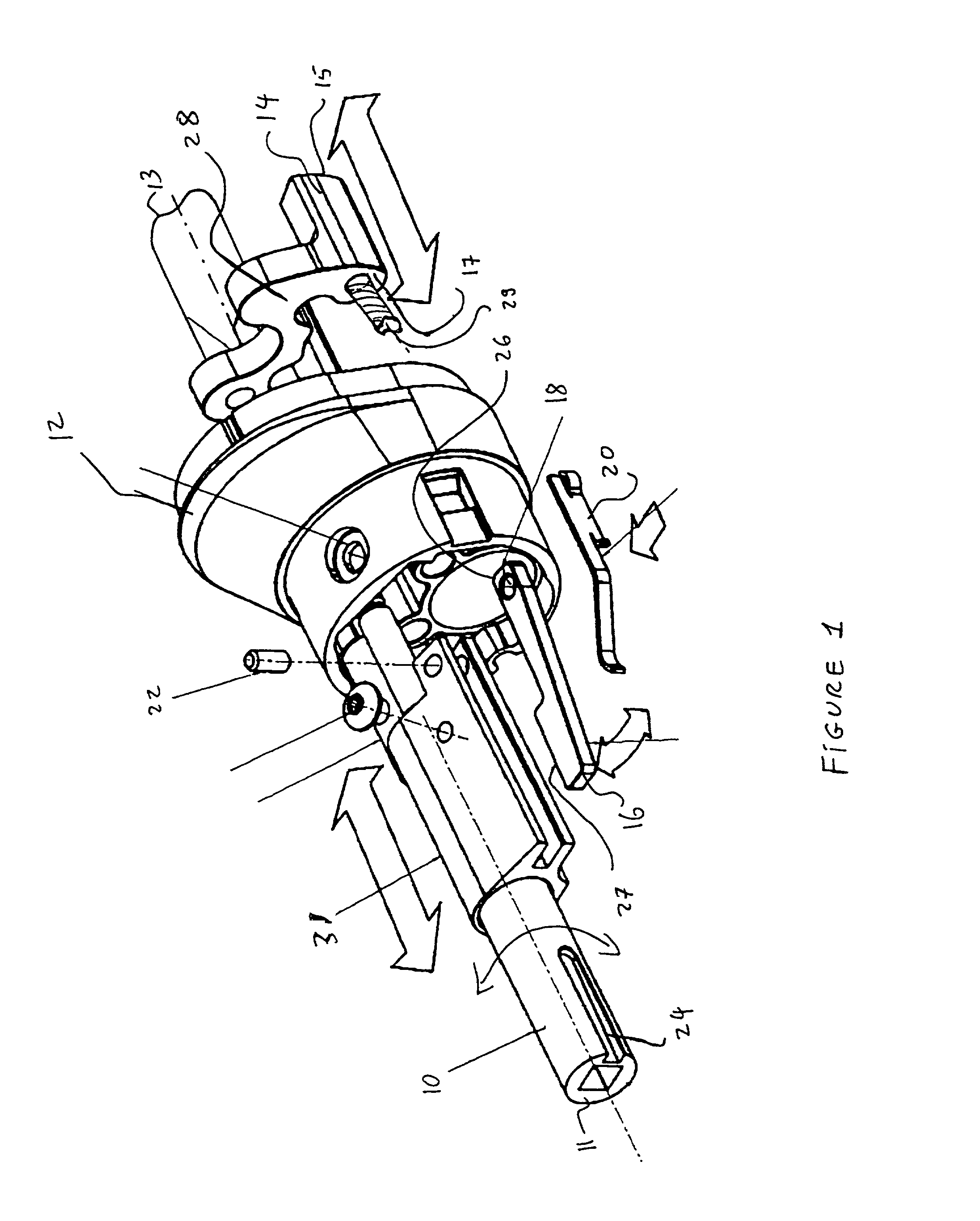
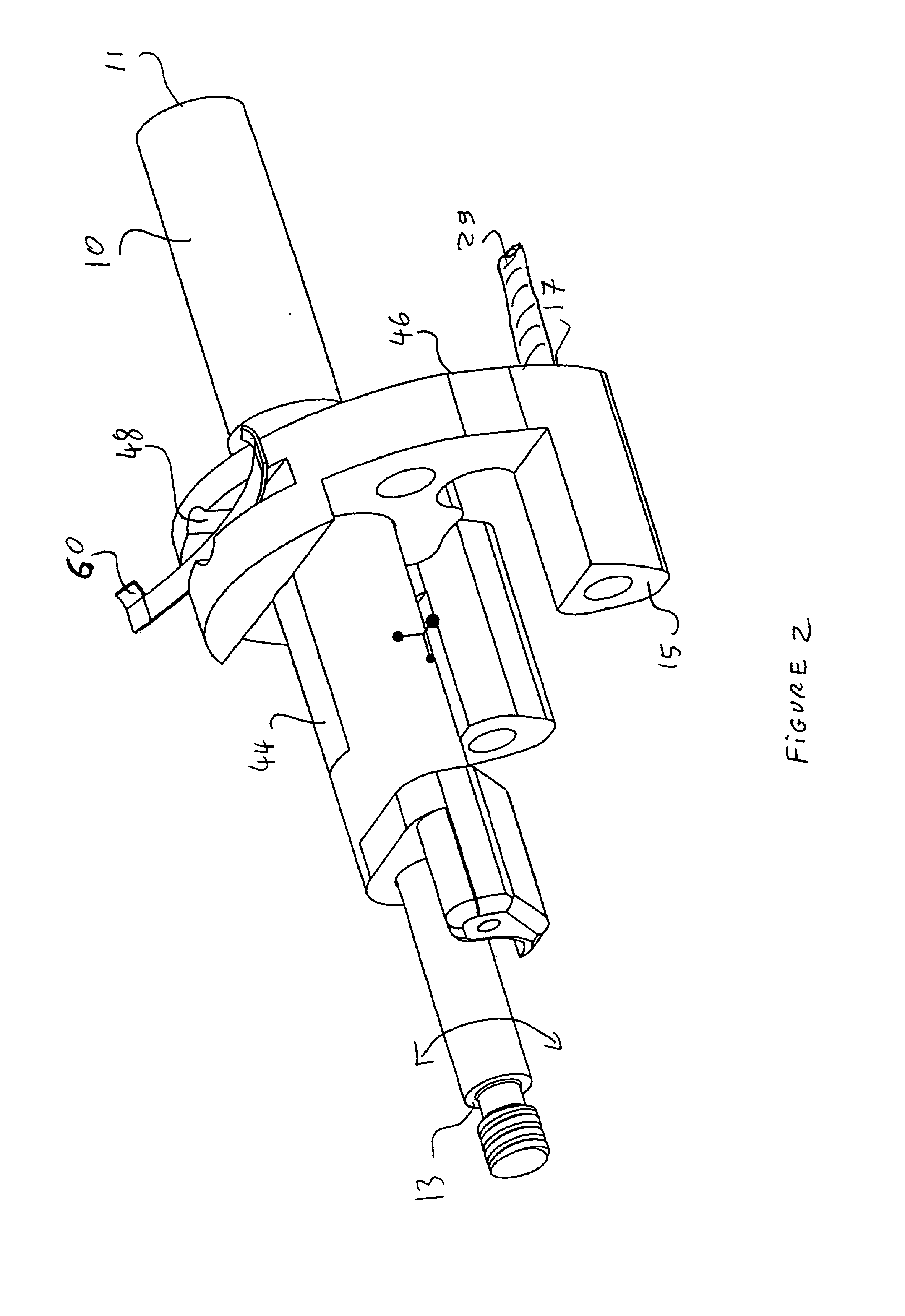
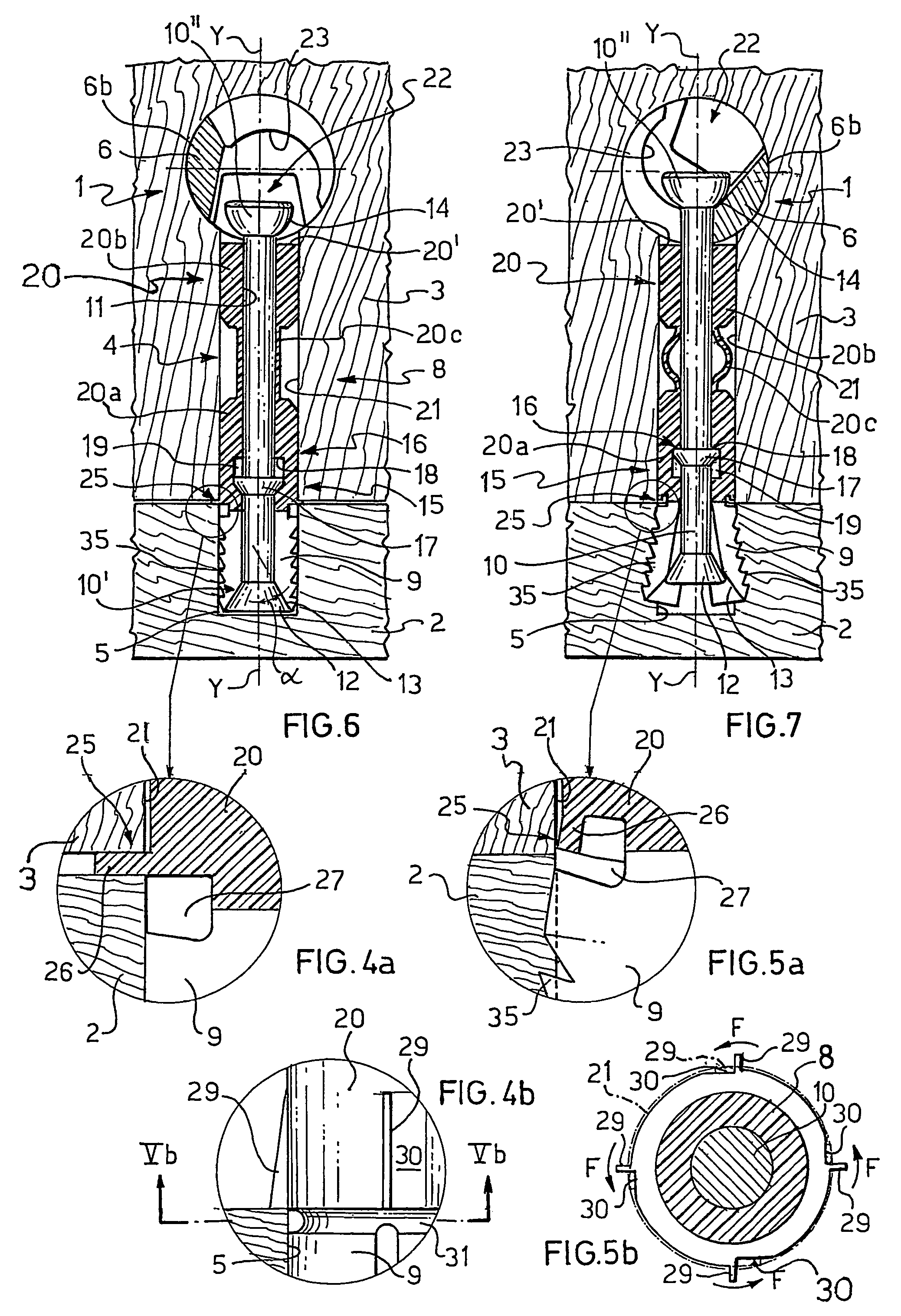
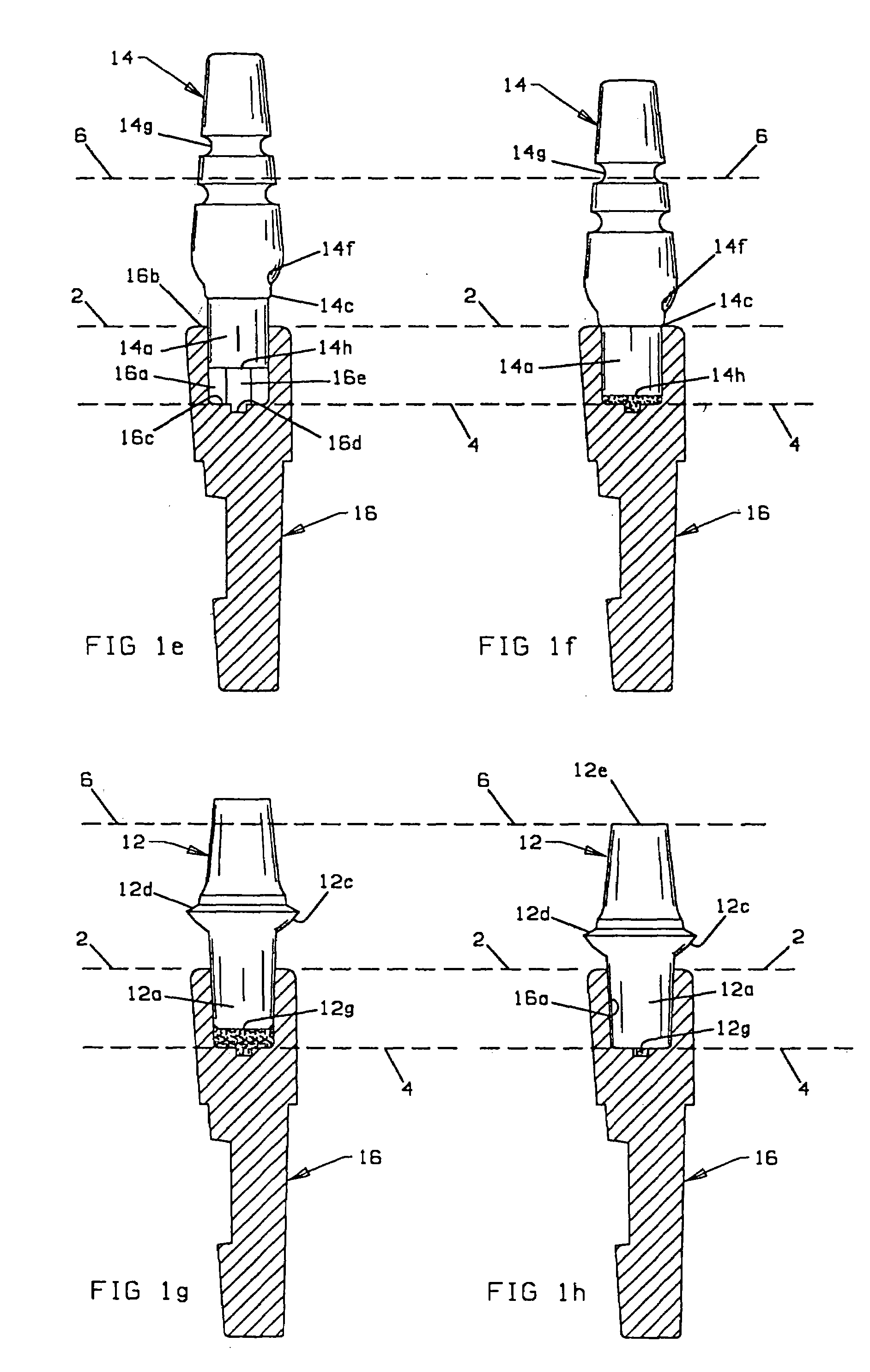
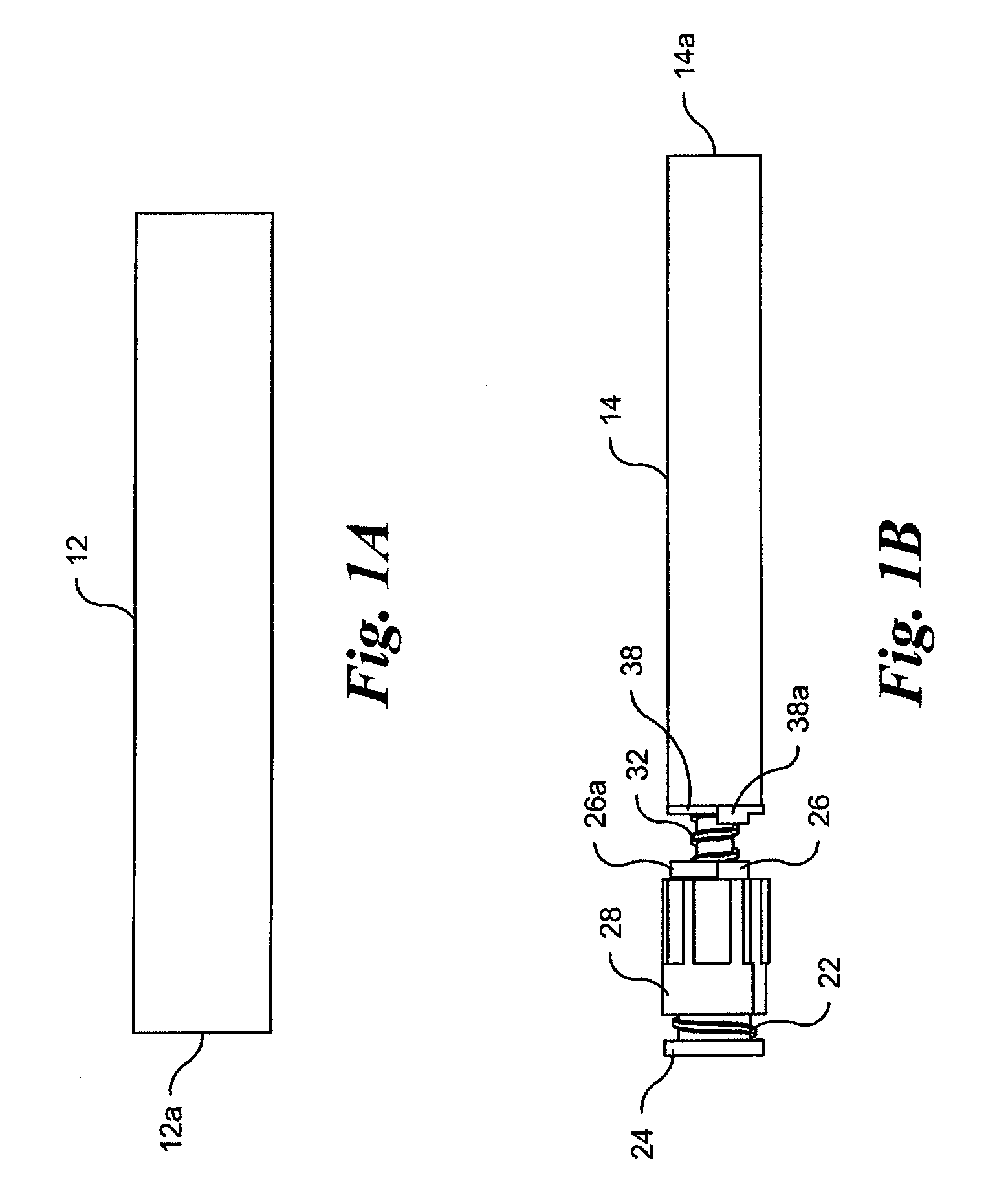
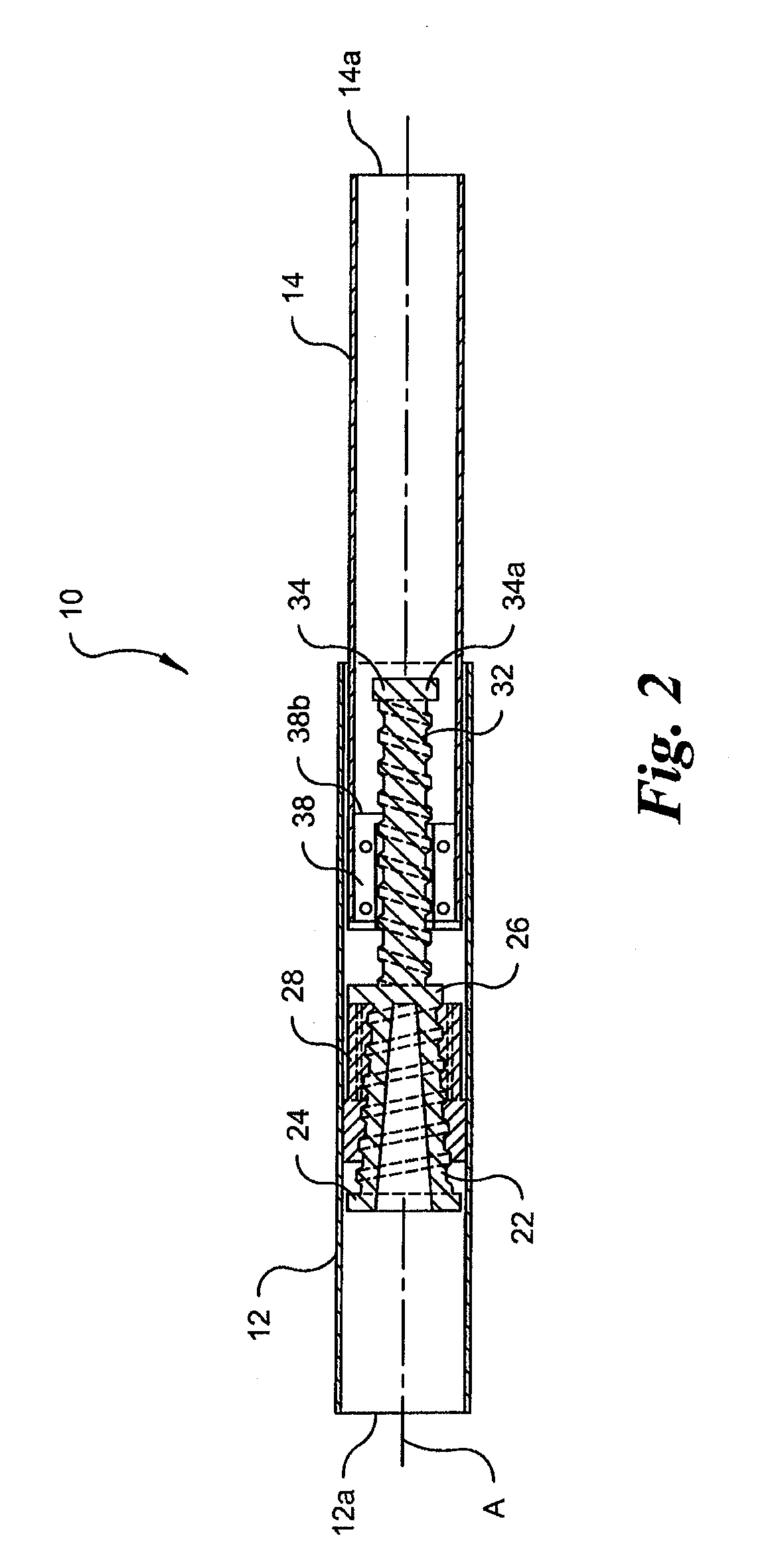
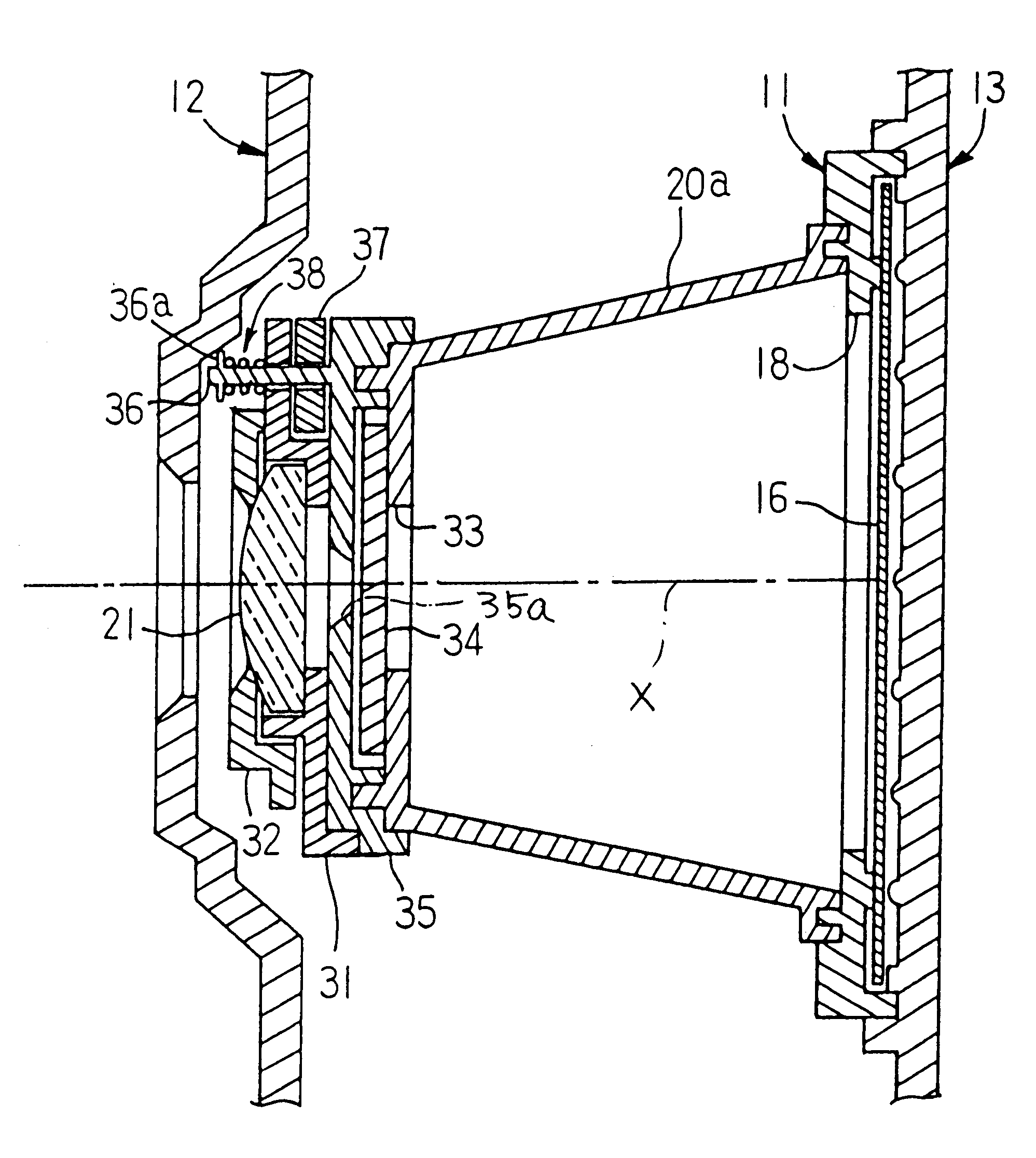
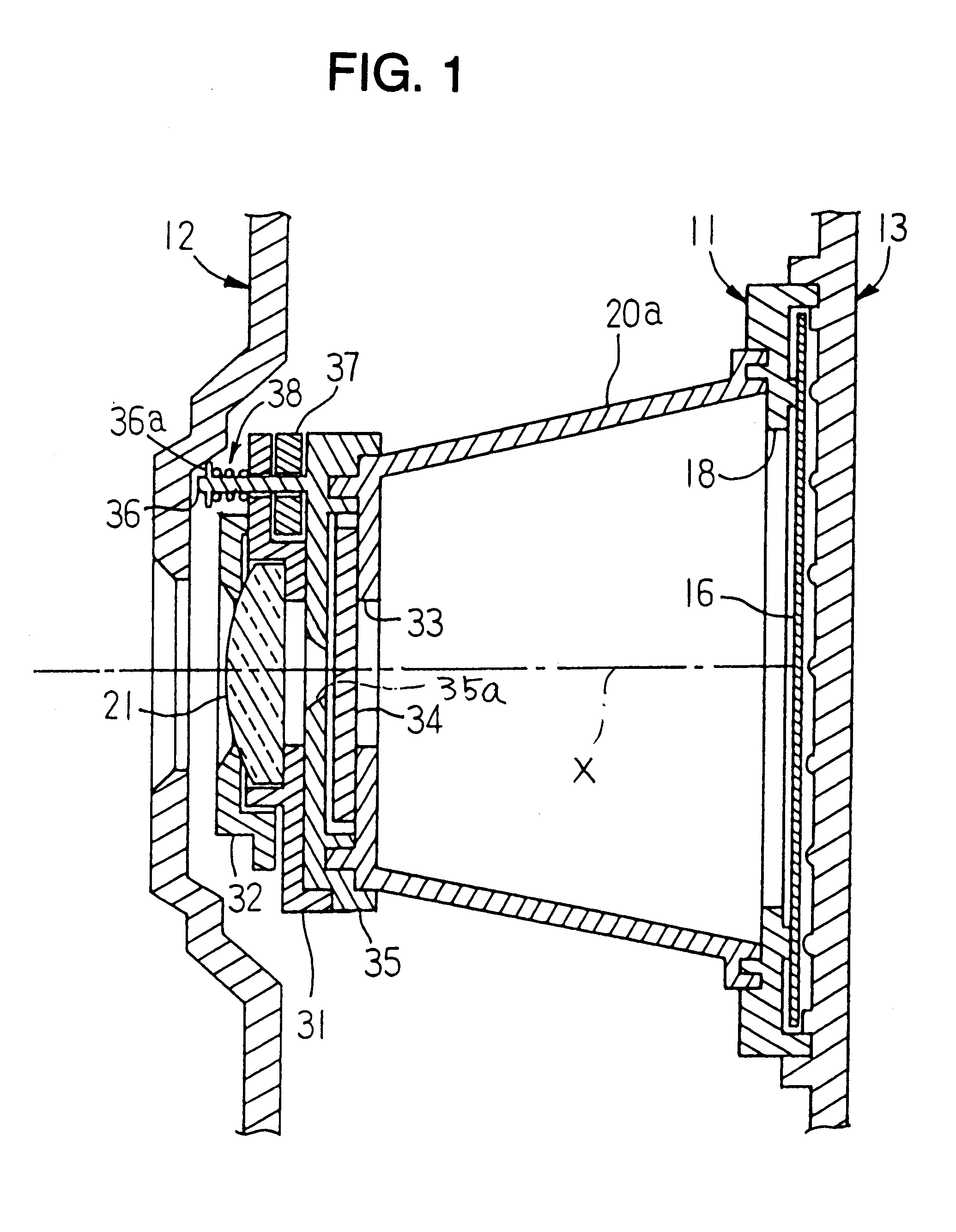
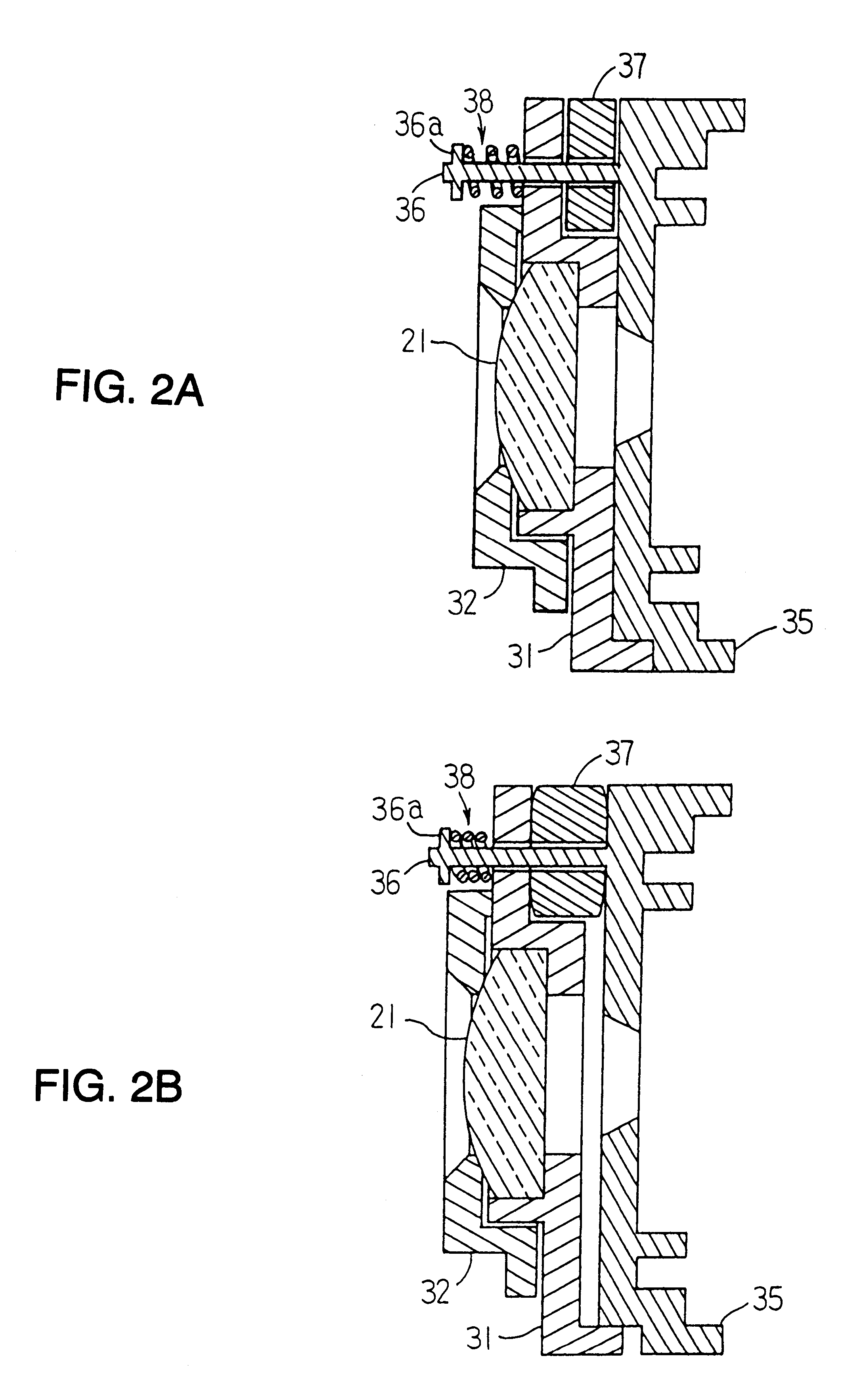
Safety lockout for actuator shaft
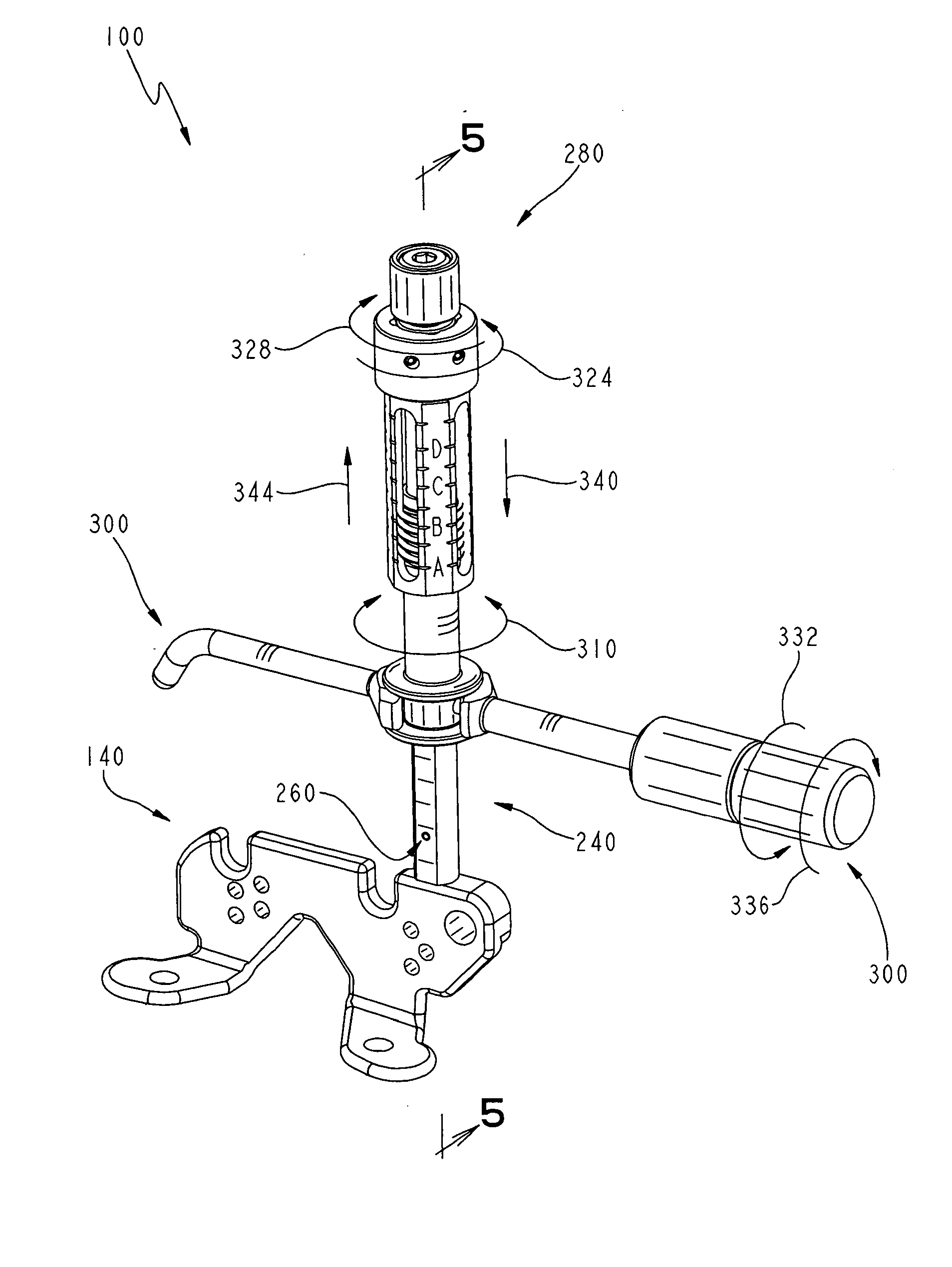
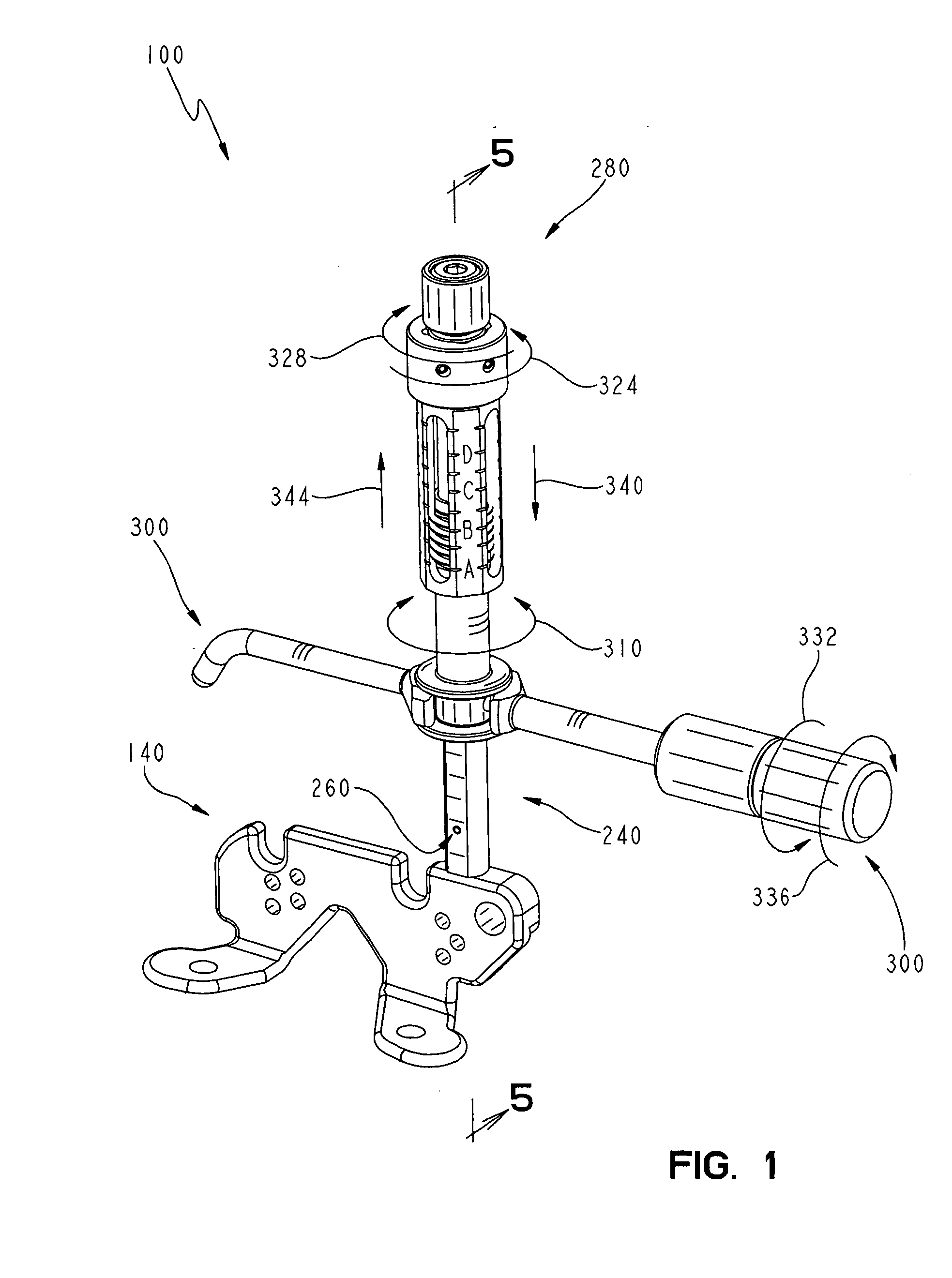
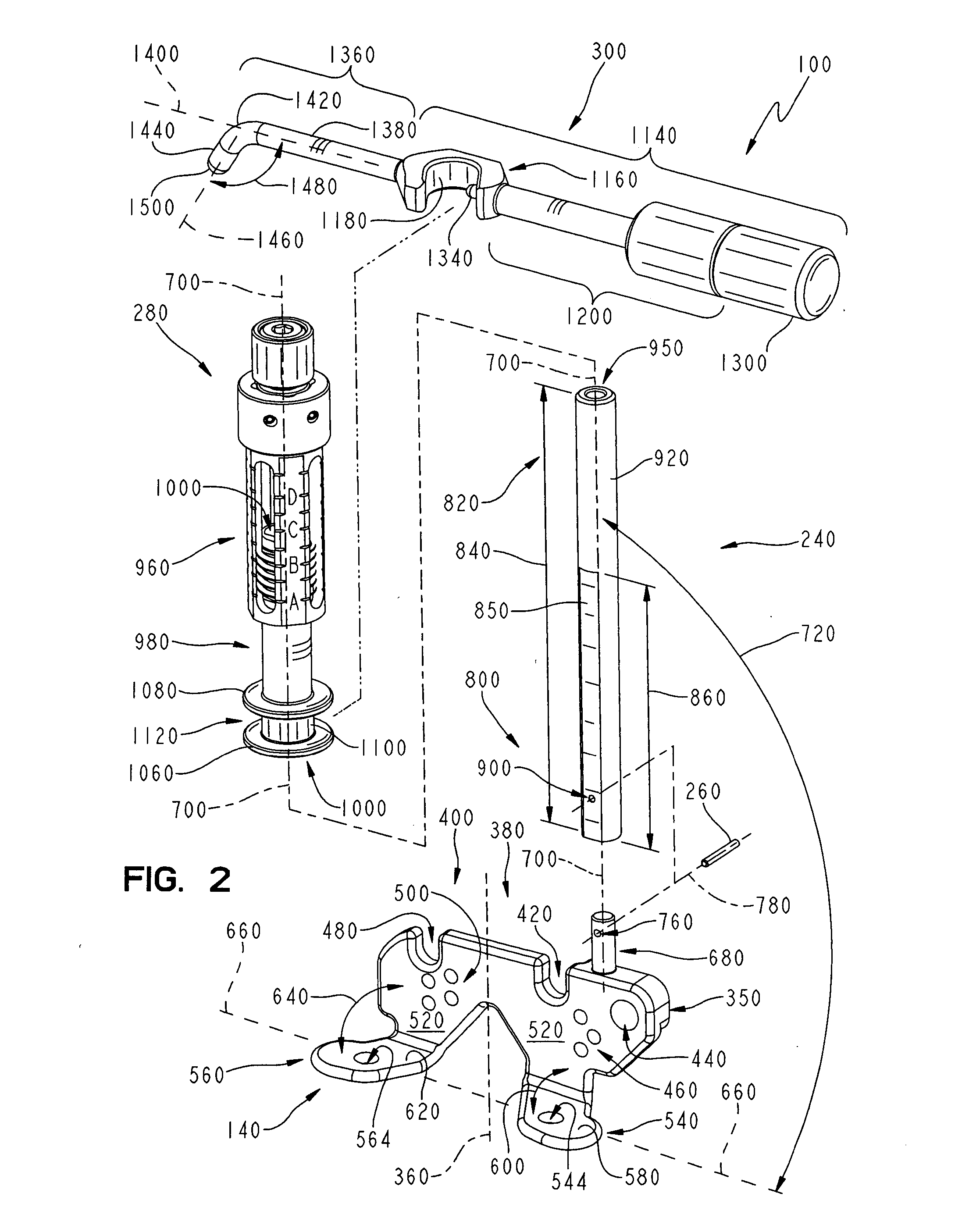
A safety lock-out to prevent rotation of a rotary actuator is described. When an axial distance between a first and a second portion of an actuated mechanism exceeds a selected distance, the lock-out prevents the rotation. The safety lock-out includes a shaft rotatably connected to the first portion and axially movable relative to the second portion. A locking member is adapted to lock the rotary actuator by placing a protrusion in a notch of the shaft, thus preventing rotation of the shaft. The device also includes a spring member urging the locking member in the locking position, and an unlocking member adapted to urge the locking member in the unlocked position when the selected distance is not exceeded.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Medication dispensing apparatus with triple screw threads for mechanical advantage
A medication dispensing apparatus that provides a mechanical advantage. During dose preparing, a nut rotating element (410) and a screw element (368) are in a first axial arrangement such that a screwing motion of the nut rotating element and screw element relative to the apparatus housing that moves the elements a first axial distance from a home position screws a nut (364) along a drive member threaded shaft (362) a second axial distance different than the first axial distance. During dose dispensing, the nut rotating element and the screw element are in a second axial arrangement, whereby a screwing motion of the screw element relative to the housing back toward the home position advances a plunger (366) in the distal direction to axially advance the nut and thereby the drive member and a fluid container piston to dispense medicine.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
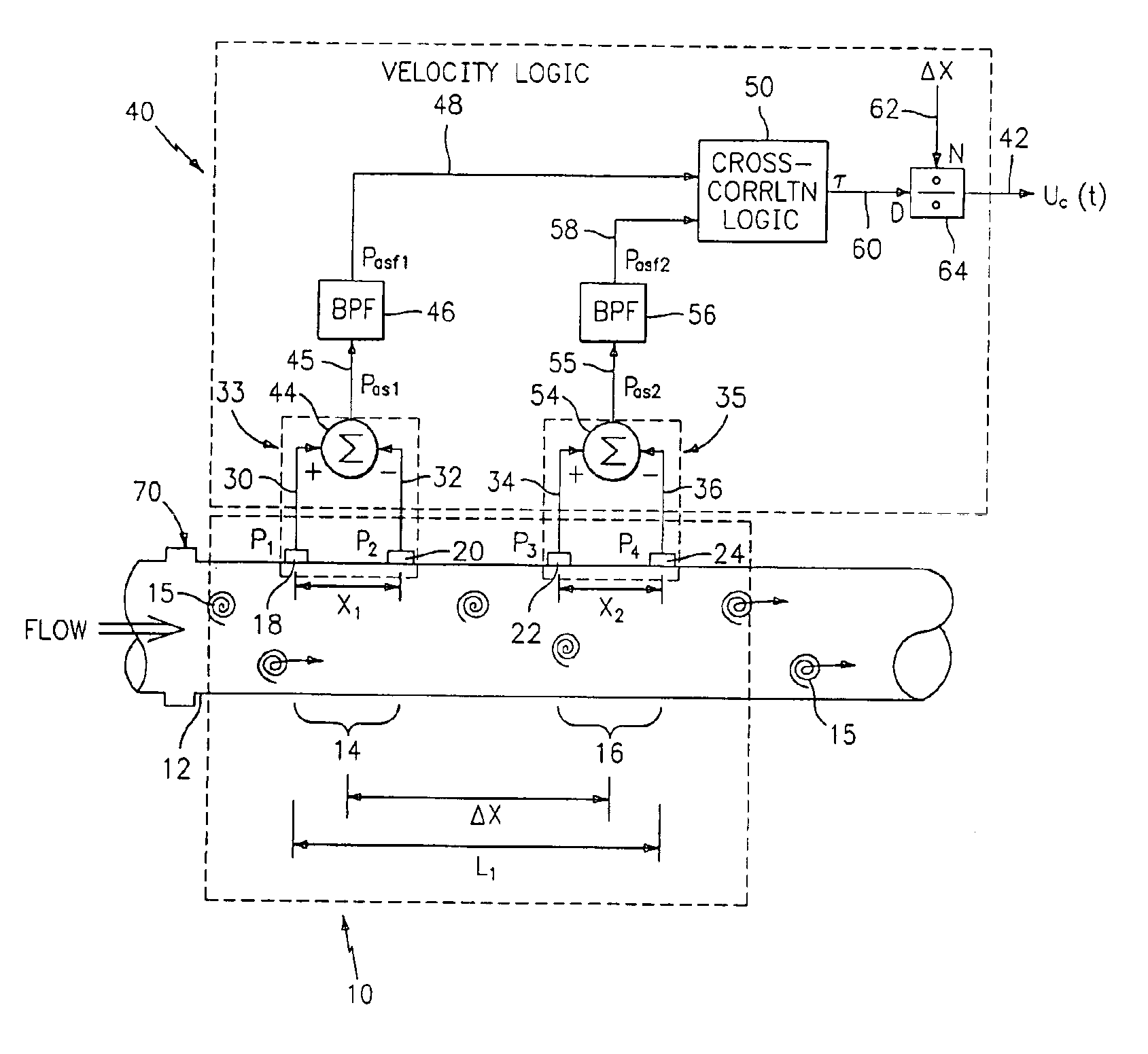
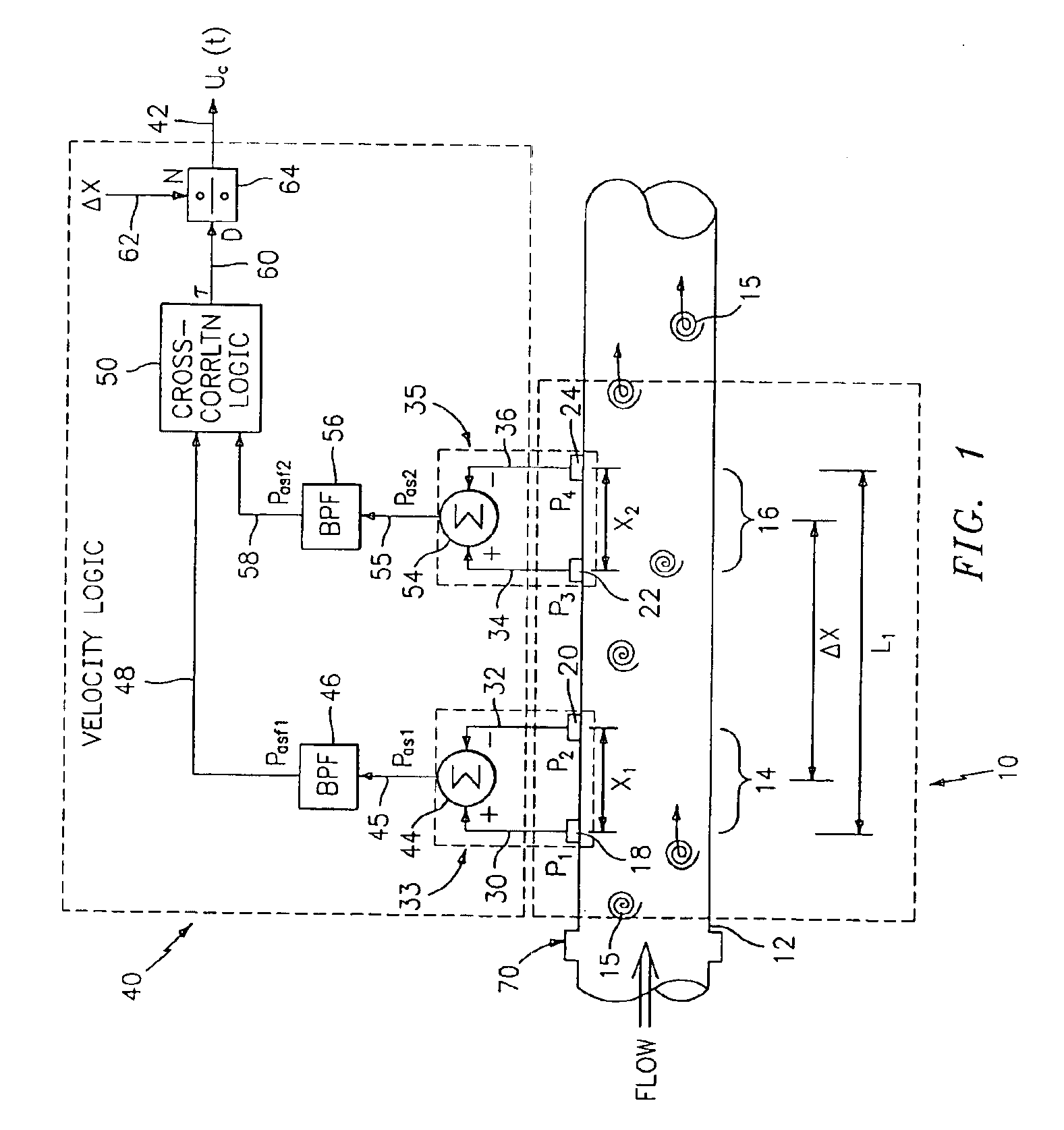
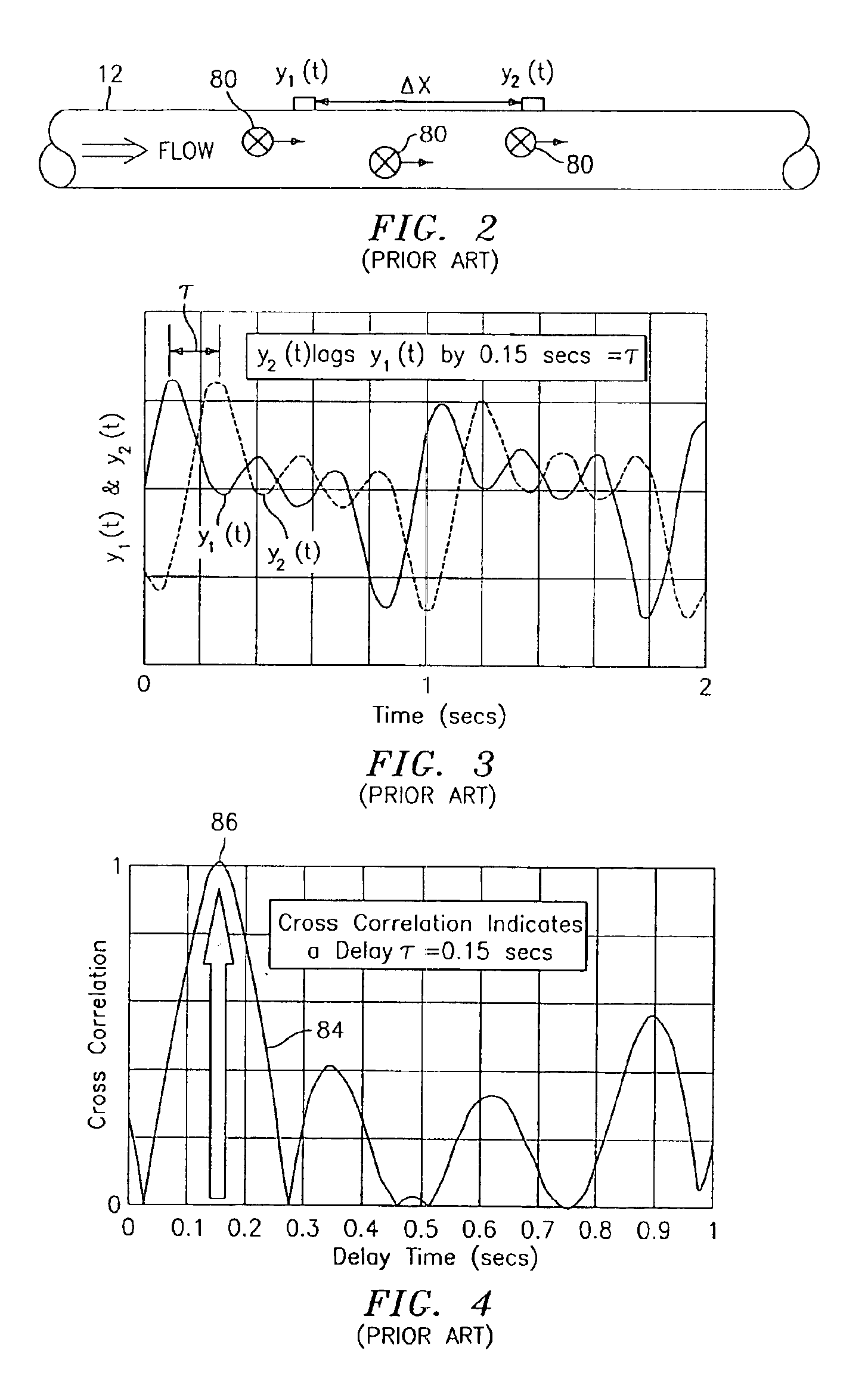
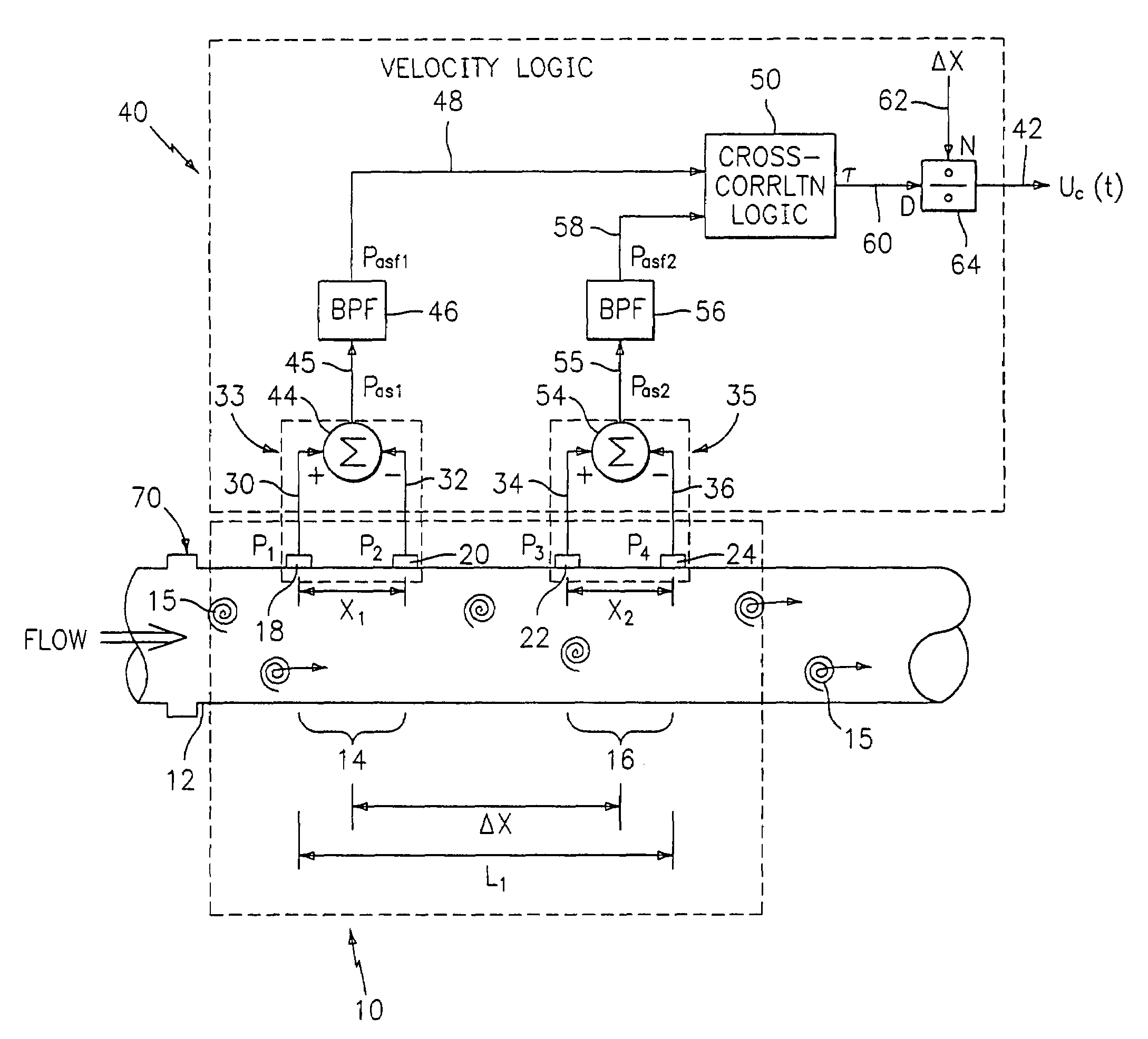
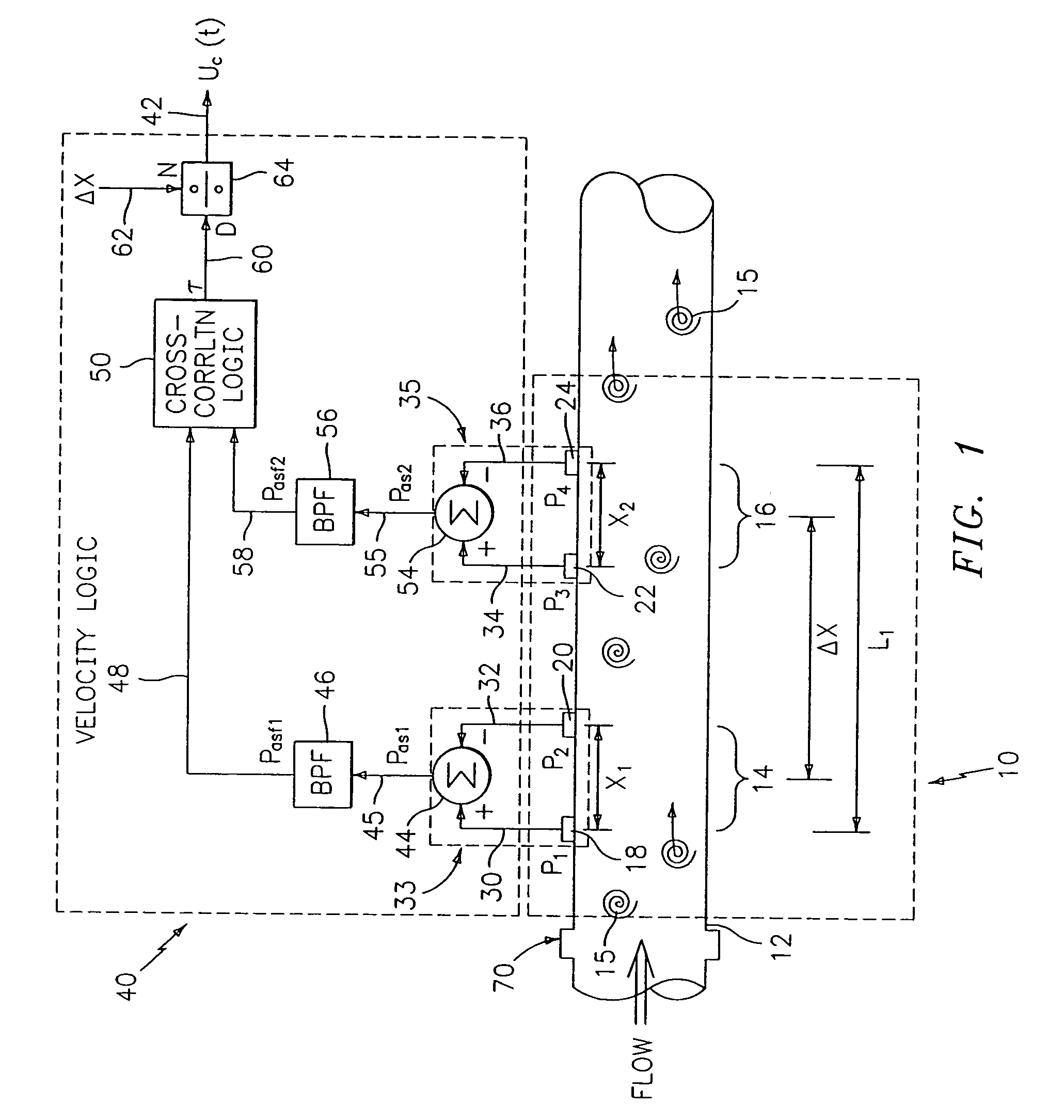
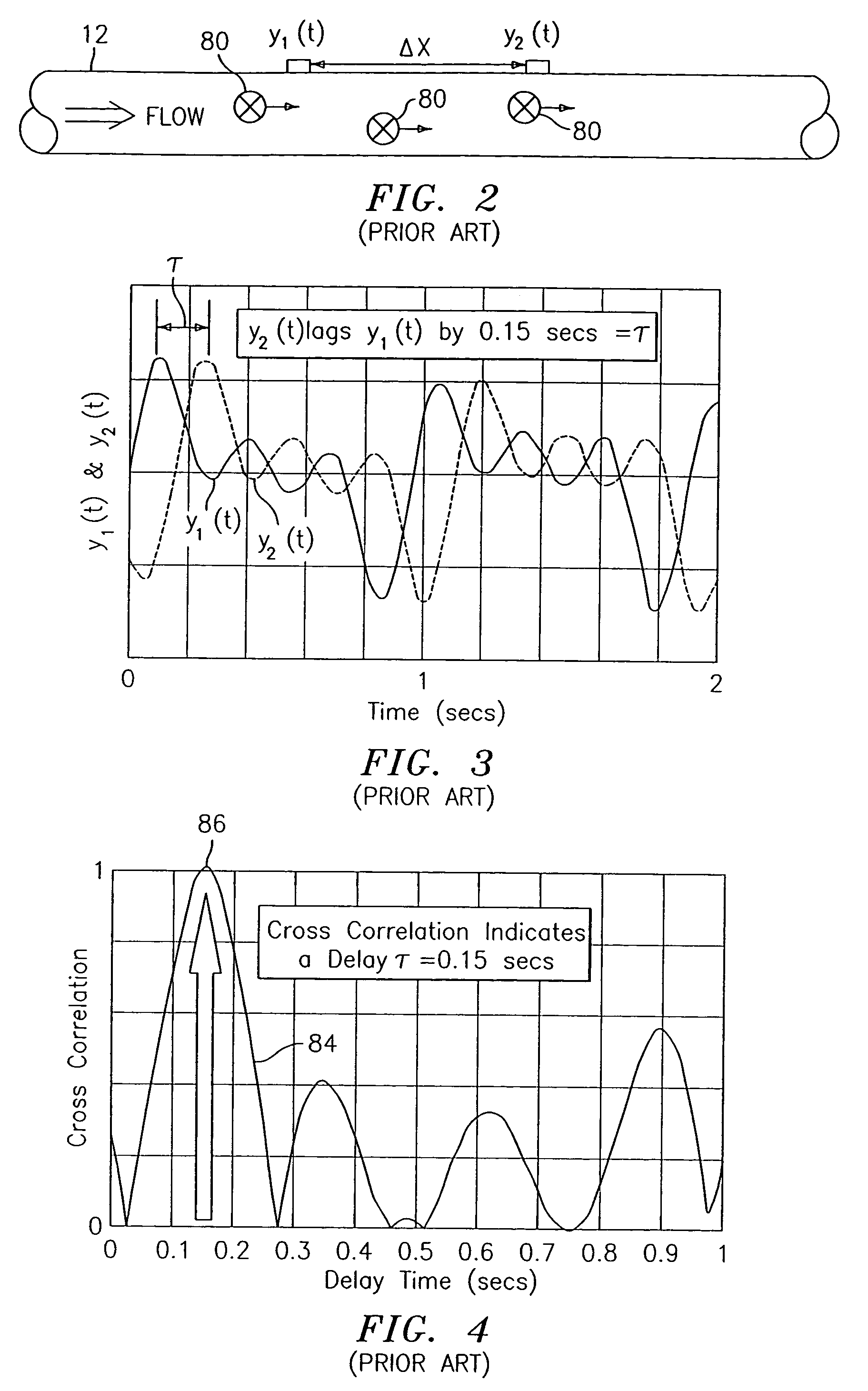
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
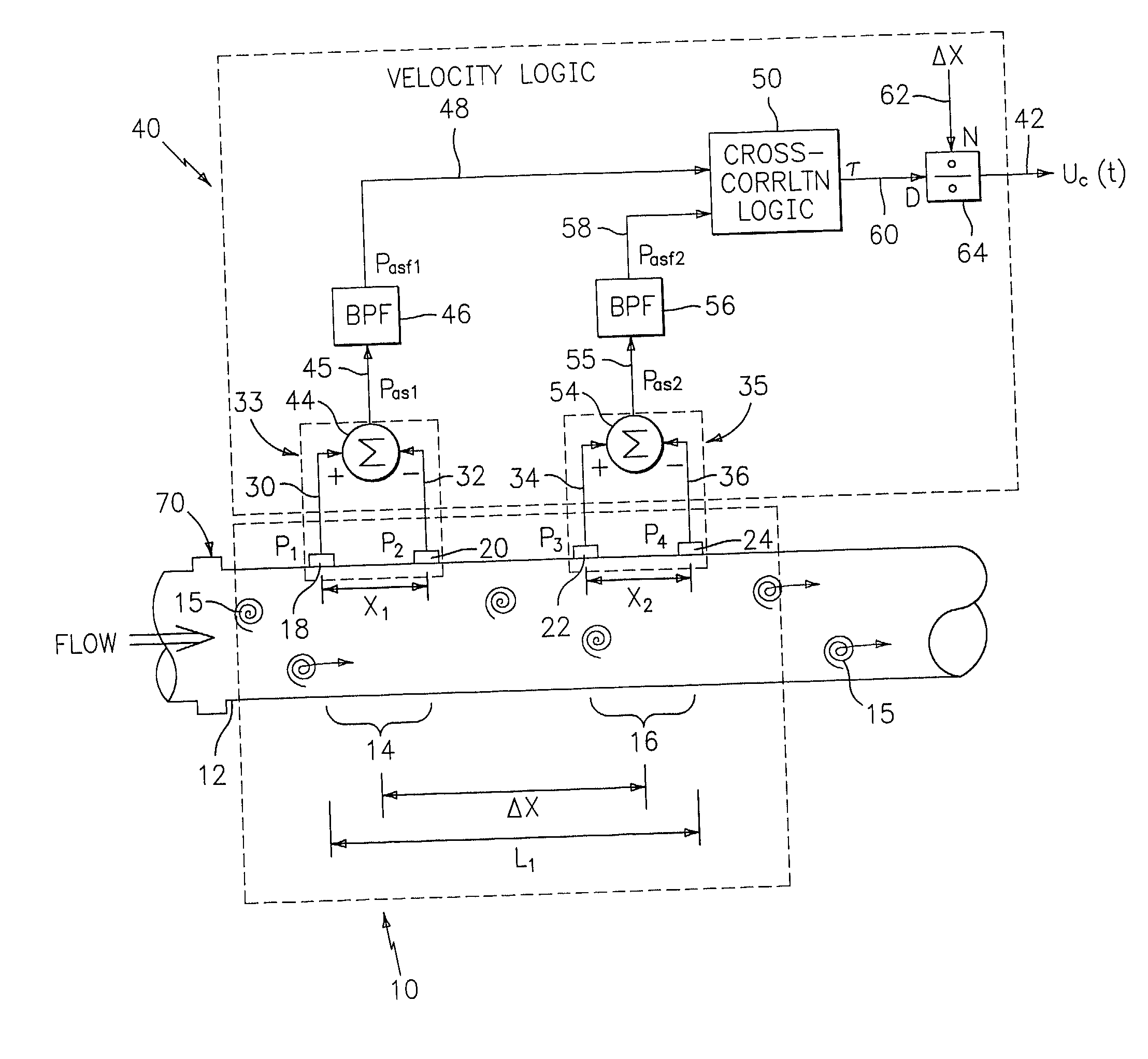
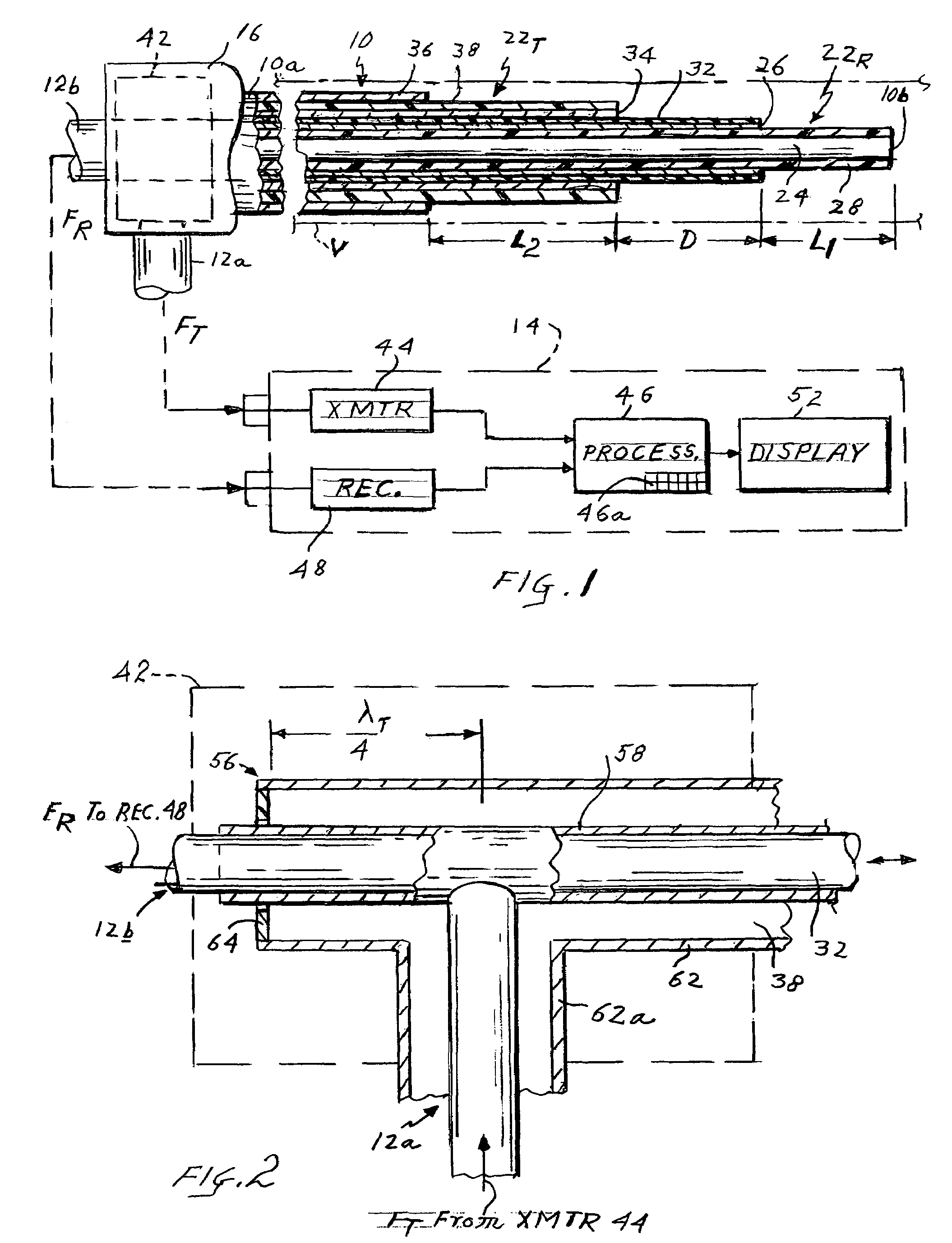
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance ΔX apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35 filters out acoustic pressure disturbances Pacoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances Pvortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals Pas1,Pas2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The Pvortical -dominated filtered signals Pasf1,Pasf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay τ between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance ΔX to obtain a convection velocity Uc(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Medication dispensing apparatus with triple screw threads for mechanical advantage
ActiveUS20060206057A1Easy plungingHigh mechanical advantageAmpoule syringesMedical devicesEngineeringAxial distance
A medication dispensing apparatus that provides a mechanical advantage. During dose preparing, a nut rotating element (410) and a screw element (368) are in a first axial arrangement such that a screwing motion of the nut rotating element and screw element relative to the apparatus housing that moves the elements a first axial distance from a home position screws a nut (364) along a drive member threaded shaft (362) a second axial distance different than the first axial distance. During dose dispensing, the nut rotating element and the screw element are in a second axial arrangement, whereby a screwing motion of the screw element relative to the housing back toward the home position advances a plunger (366) in the distal direction to axially advance the nut and thereby the drive member and a fluid container piston to dispense medicine.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance .DELTA.X apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X.sub.1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X.sub.2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35 filters out acoustic pressure disturbances P.sub.acoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances P.sub.vortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals P.sub.as1,P.sub.as2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The P.sub.vortical -dominated filtered signals P.sub.asf1,P.sub.asf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay .tau. between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance .DELTA.X to obtain a convection velocity U.sub.c(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
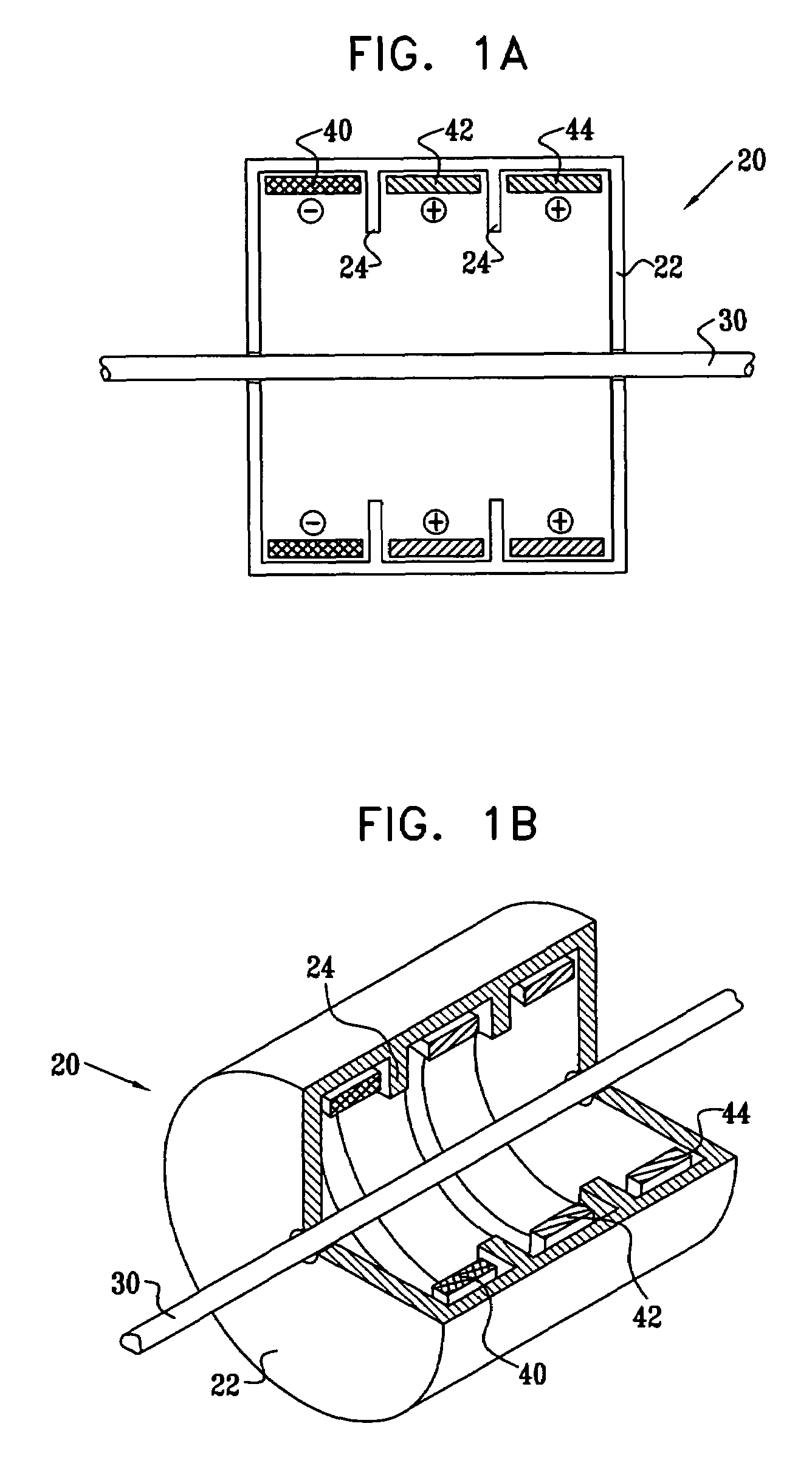
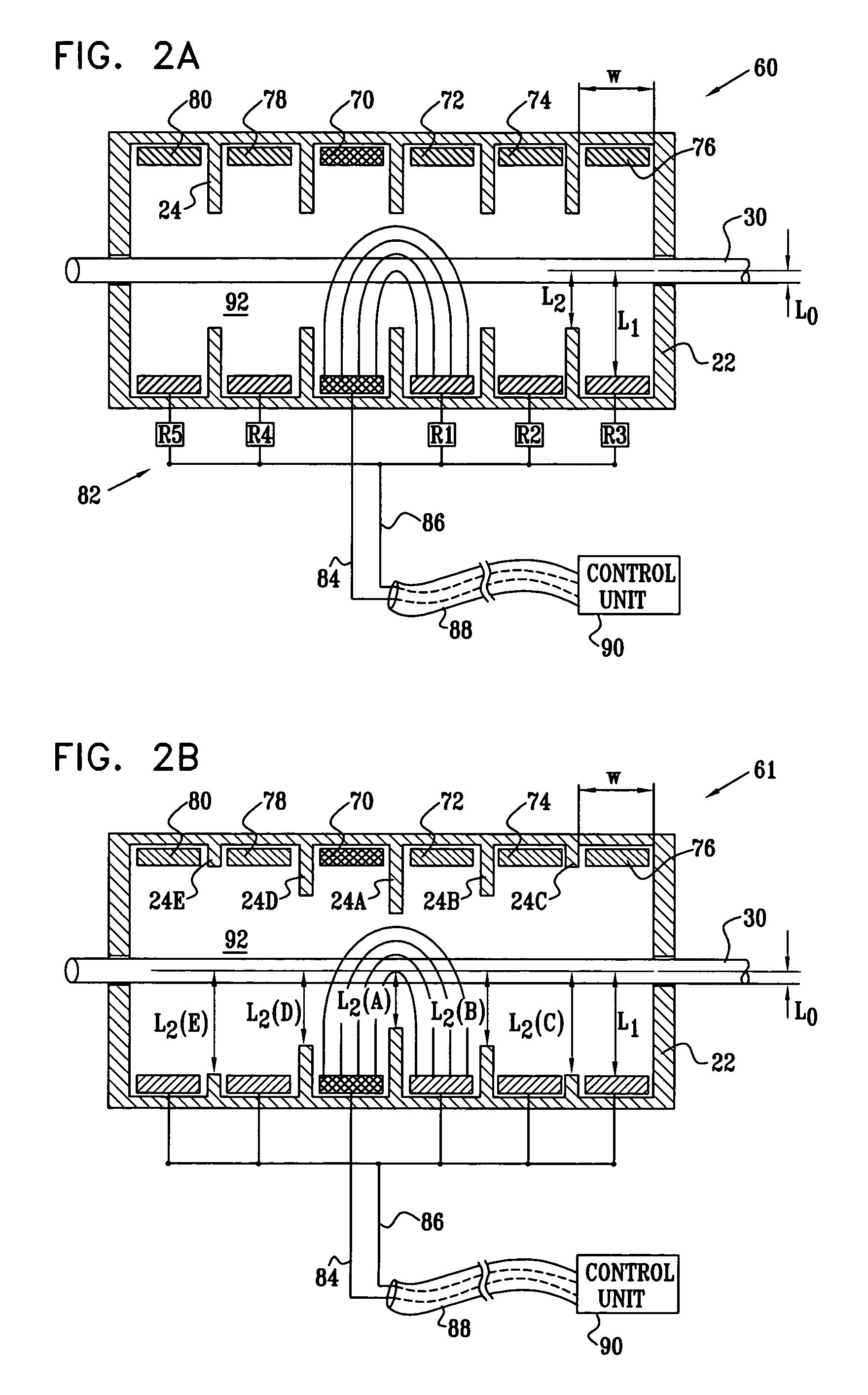
Construction of electrode assembly for nerve control
InactiveUS7561922B2Minimize cathode effectWeakening rangeSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesPower flowAxial distance
Apparatus is provided for applying current to a nerve, including a housing that is adapted to be placed in a vicinity of the nerve. First, second, and third electrodes are fixed to the housing at first, second, and third longitudinal sites of the housing, respectively. The first, second, and third electrodes do not come in direct physical contact with the nerve. The second site is between the first and third sites. The second electrode has an electrode surface axial length. The apparatus also includes first and second internal insulating elements, which are fixed to the housing between the first and second longitudinal sites, and between the second and third longitudinal sites, respectively. The first and second internal insulating elements are shaped so as to define, upon placement of the housing, a nerve axial distance between the first and second internal insulating elements that is less than the electrode surface axial length.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
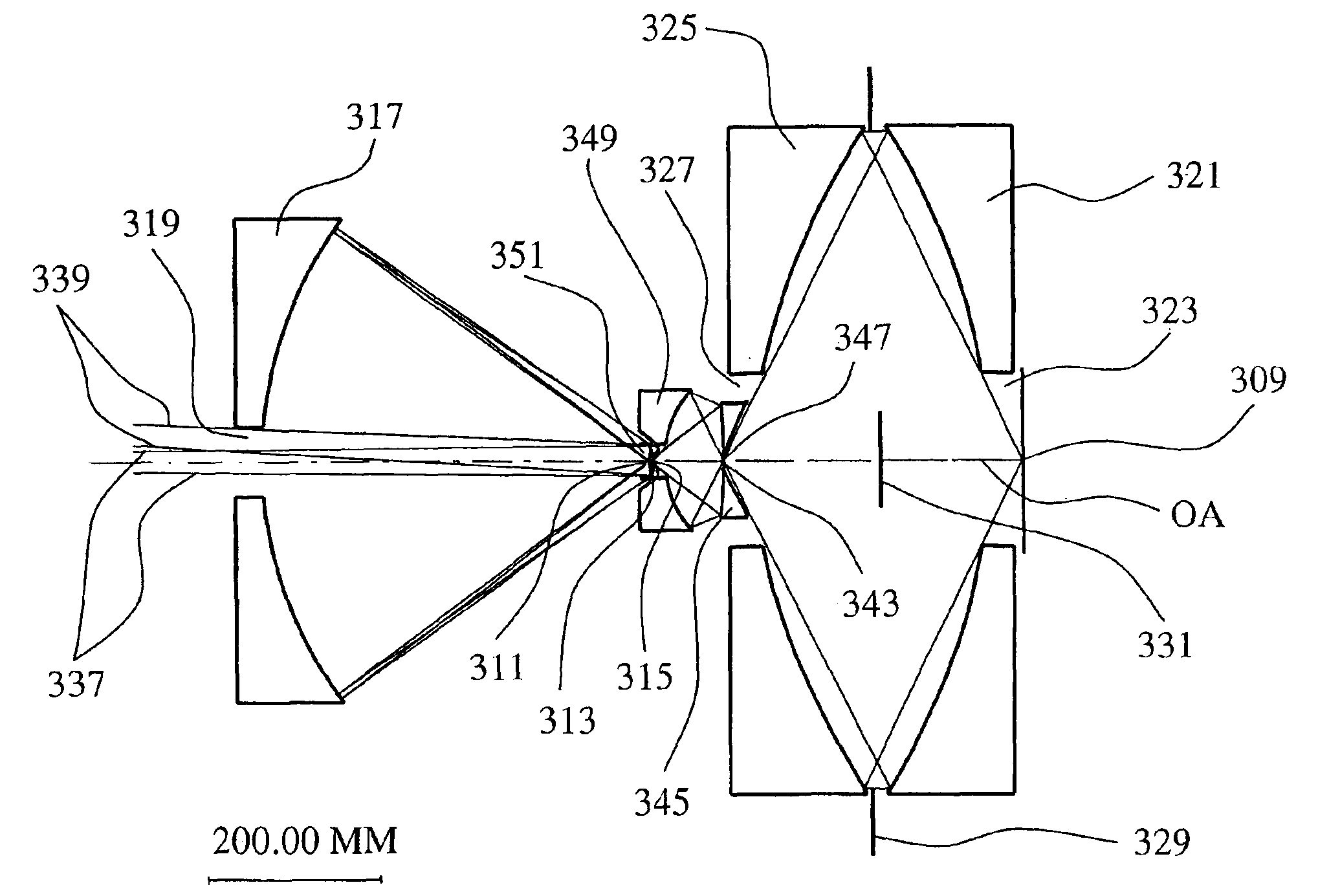
Objective with pupil obscuration
InactiveUS6894834B2Reduce occlusionAvoid excessive diameterMirrorsOptical filtersIntermediate imagePupil
An objective is configured with a first partial objective and a second partial objective. The first partial objective, which projects a first field plane onto an intermediate image, has a first, convex mirror and a second, concave mirror. The second partial objective, which projects the intermediate image onto a second field plane, has a third and a fourth mirror, both concave. All of the four mirrors have central mirror apertures. The axial distance between the first and second mirrors is in a ratio between 0.95 and 1.05 relative to the distance between the second mirror and the intermediate image. The axial distance ZM3-IM between the third mirror and the second field plane conforms to the relationship 0.03·DuM3+5.0 mm<ZM3-IM<0.25·DuM3tan(arcsin(NA)).NA represents the numerical aperture NA in the second field plane, and DuM3 represents the diameter of the third mirror. The objective furthermore has a Petzval radius with an absolute value larger than the distance between the first and second field planes.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Large diopter range real time sequential wavefront sensor
InactiveUS20120026466A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEliminate speckleOptical measurementsRefractometersWavefront sensorLight beam
Example embodiments of a large dynamic range sequential wavefront sensor for vision correction or assessment procedures are disclosed. An example embodiment optically relays a wavefront from an eye pupil or corneal plane to a wavefront sampling plane in such a manner that somewhere in the relaying process, the wavefront beam from the eye within a large eye diopter range is made to reside within a desired physical dimension over a certain axial distance range in a wavefront image space and / or a Fourier transform space. As a result, a wavefront beam shifting device can be disposed there to fully intercept and hence shift the whole beam to transversely shift the relayed wavefront.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
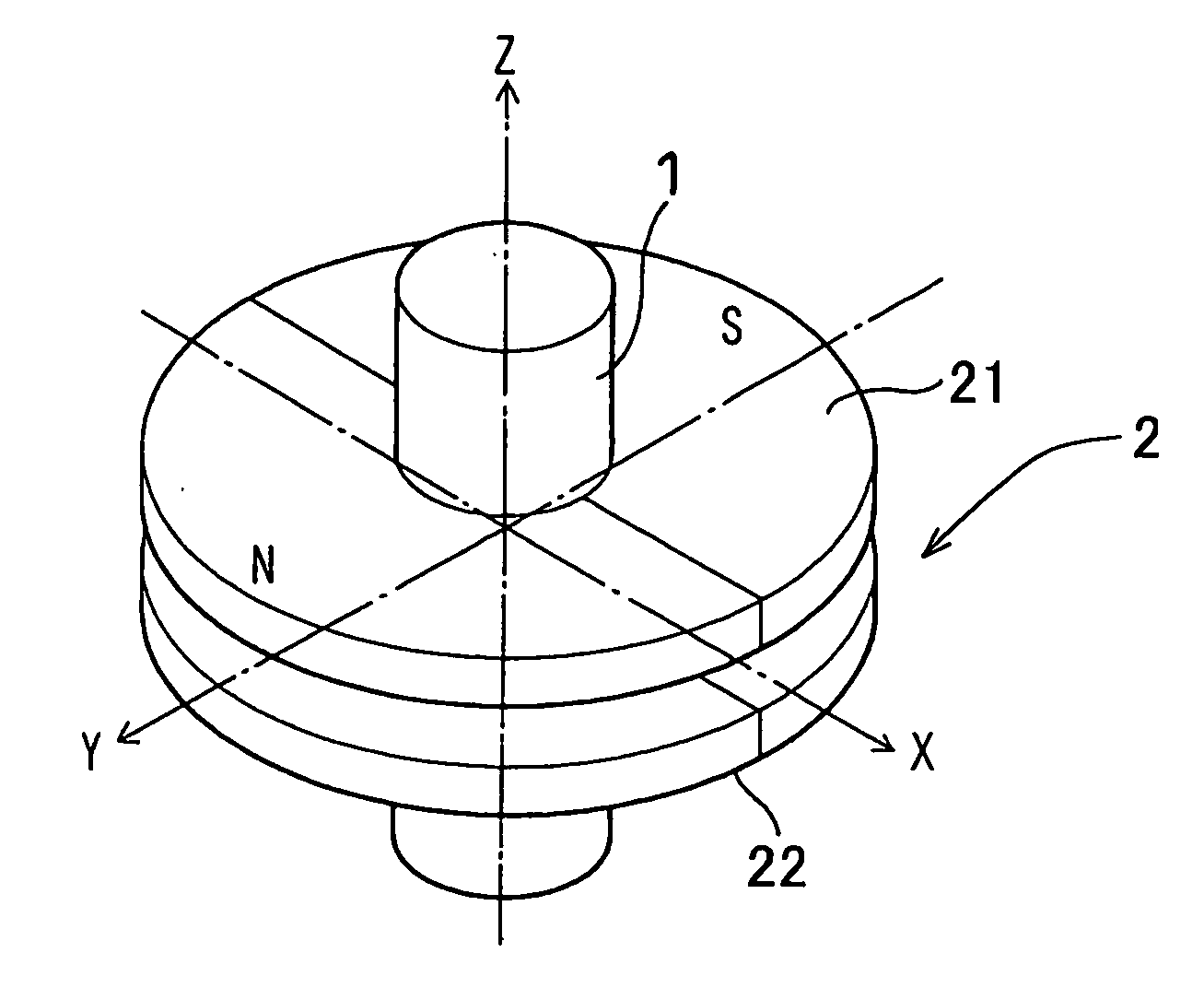
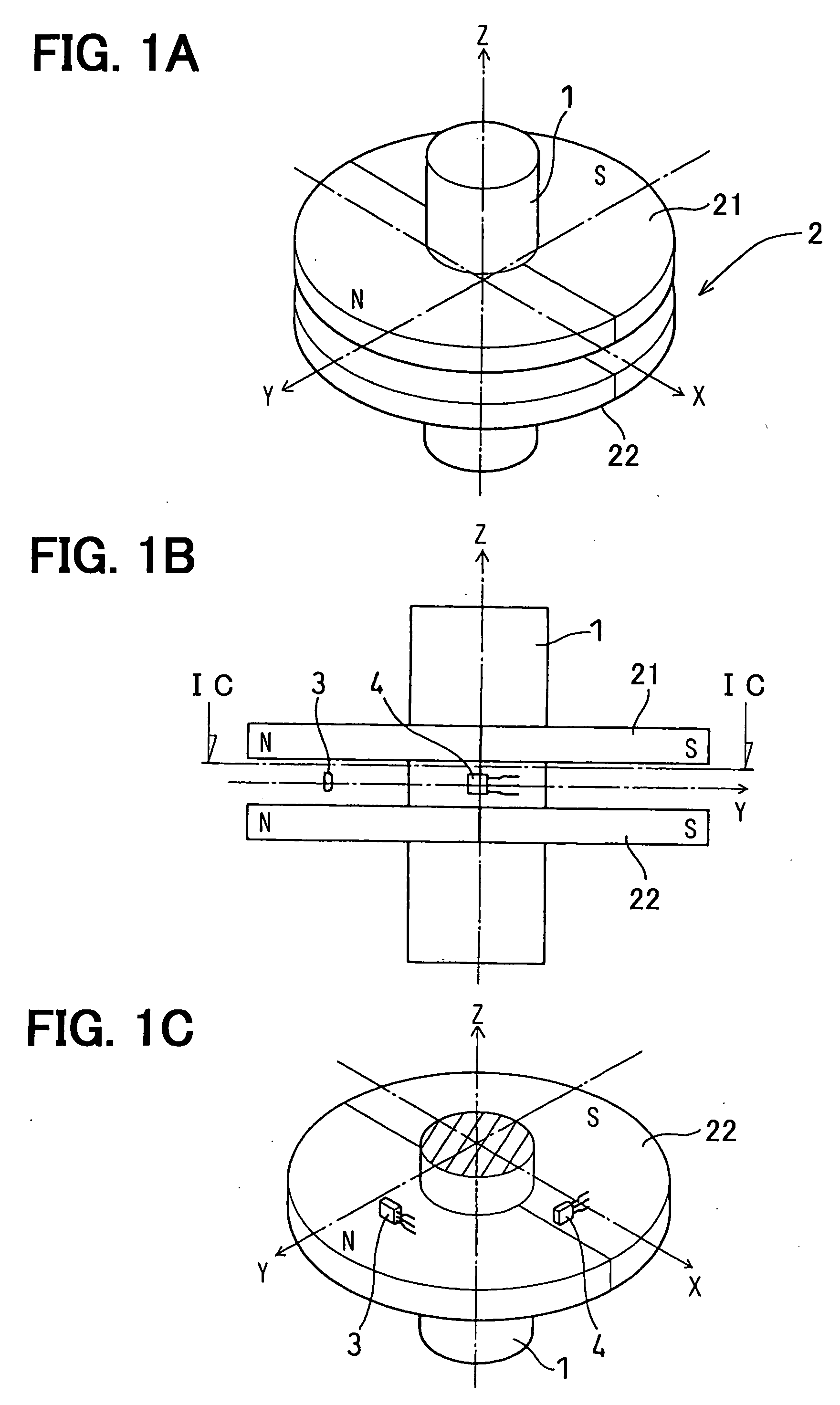
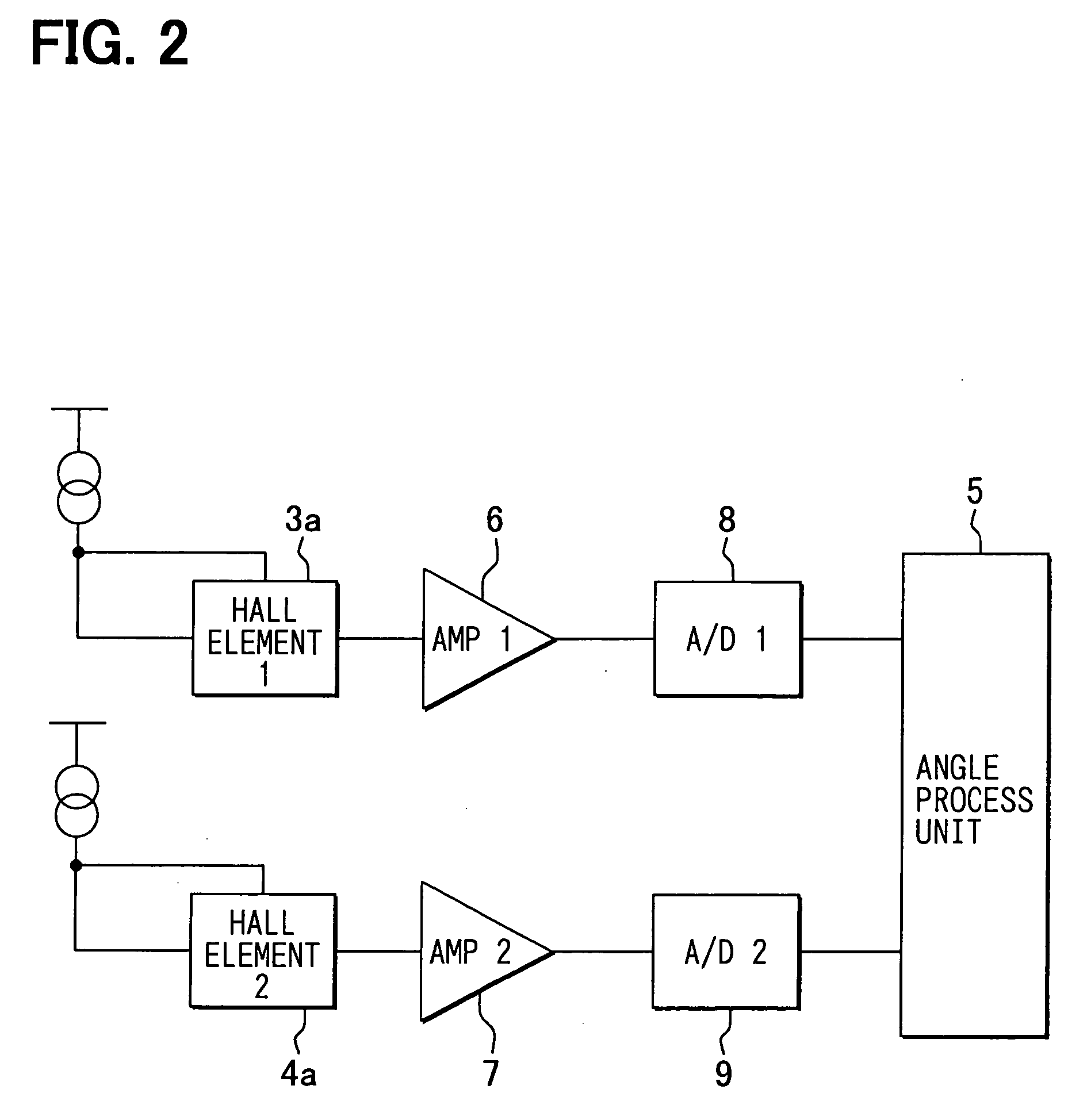
Rotation angle detecting device
InactiveUS20060028203A1Increase the rotation angleDetection errorUsing electrical meansConverting sensor outputMagnetic polesAxial distance
An improved rotation angle detecting device that detects a rotation angle of a first member relative to a second member is proposed. The rotation angle detecting device includes a magnet unit fixed to the first member and a pair of magnetic sensors fixed to the second member to provide output signals whose phase is different from each other at 90 degrees in angle. The magnet unit includes a pair of disk plates that has the same magnetic poles at the same circumferential positions and is disposed at a prescribed axial distance and a shaft that is made of magnetic material to support the disk plates at the center thereof. The magnetic unit provides a uniform magnetic field in a space around the shaft between the pair of disk plates, and a pair of magnetic sensors is disposed in the space.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
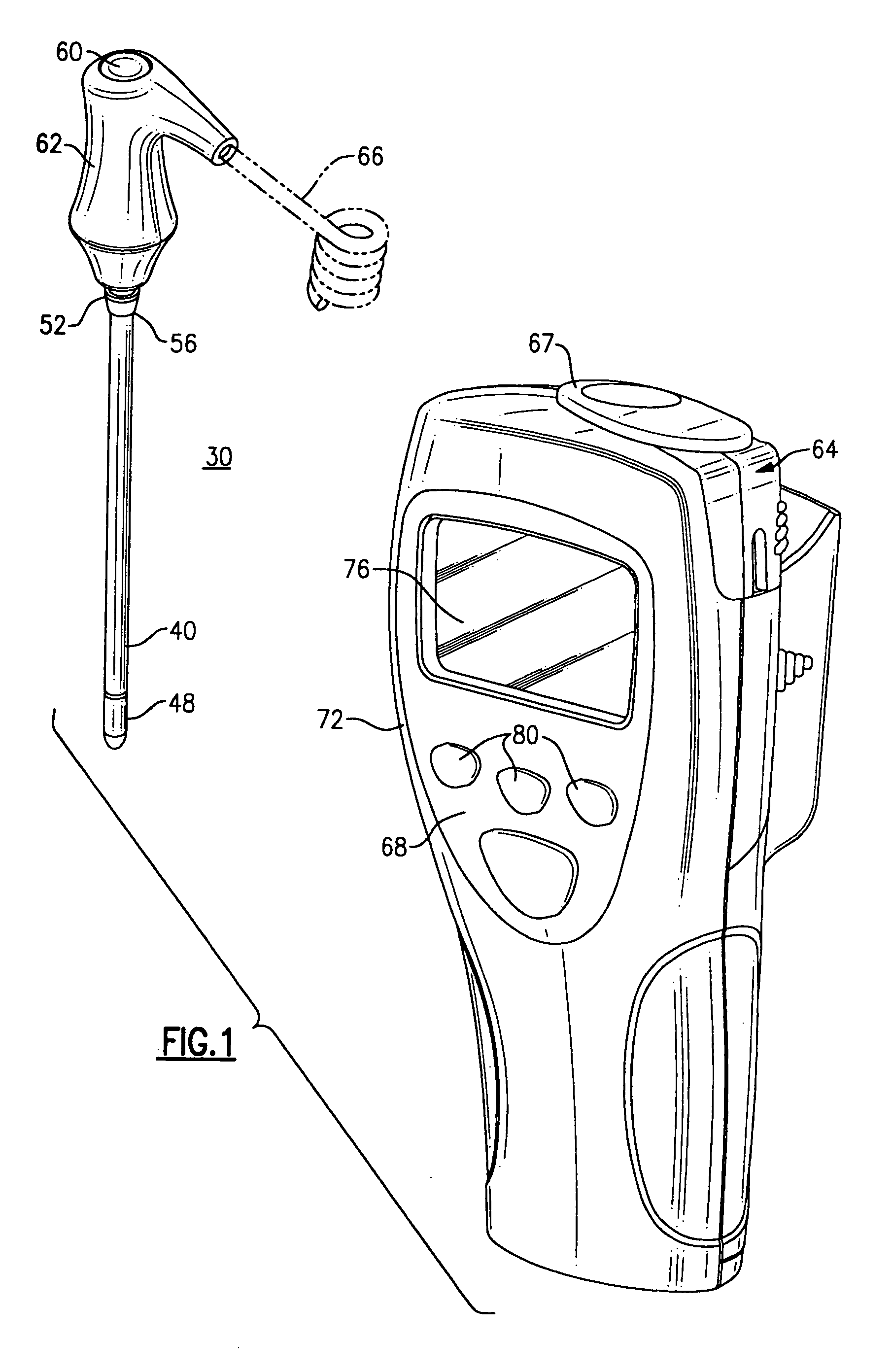
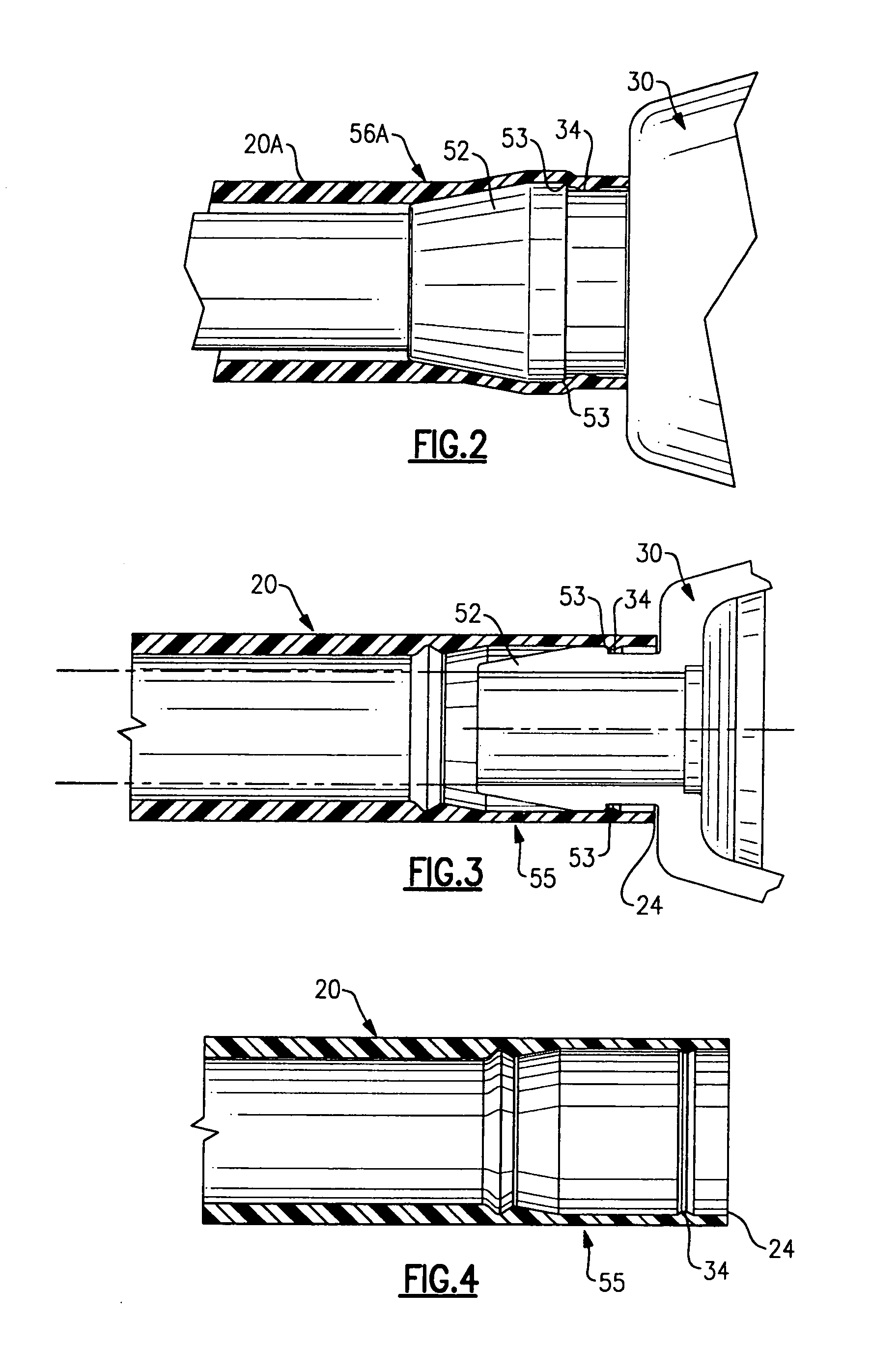
Probe cover for thermometry apparatus
InactiveUS7572056B2Reduce the risk of contaminationImprove versatilityThermometer detailsMedical devicesEngineeringAxial distance
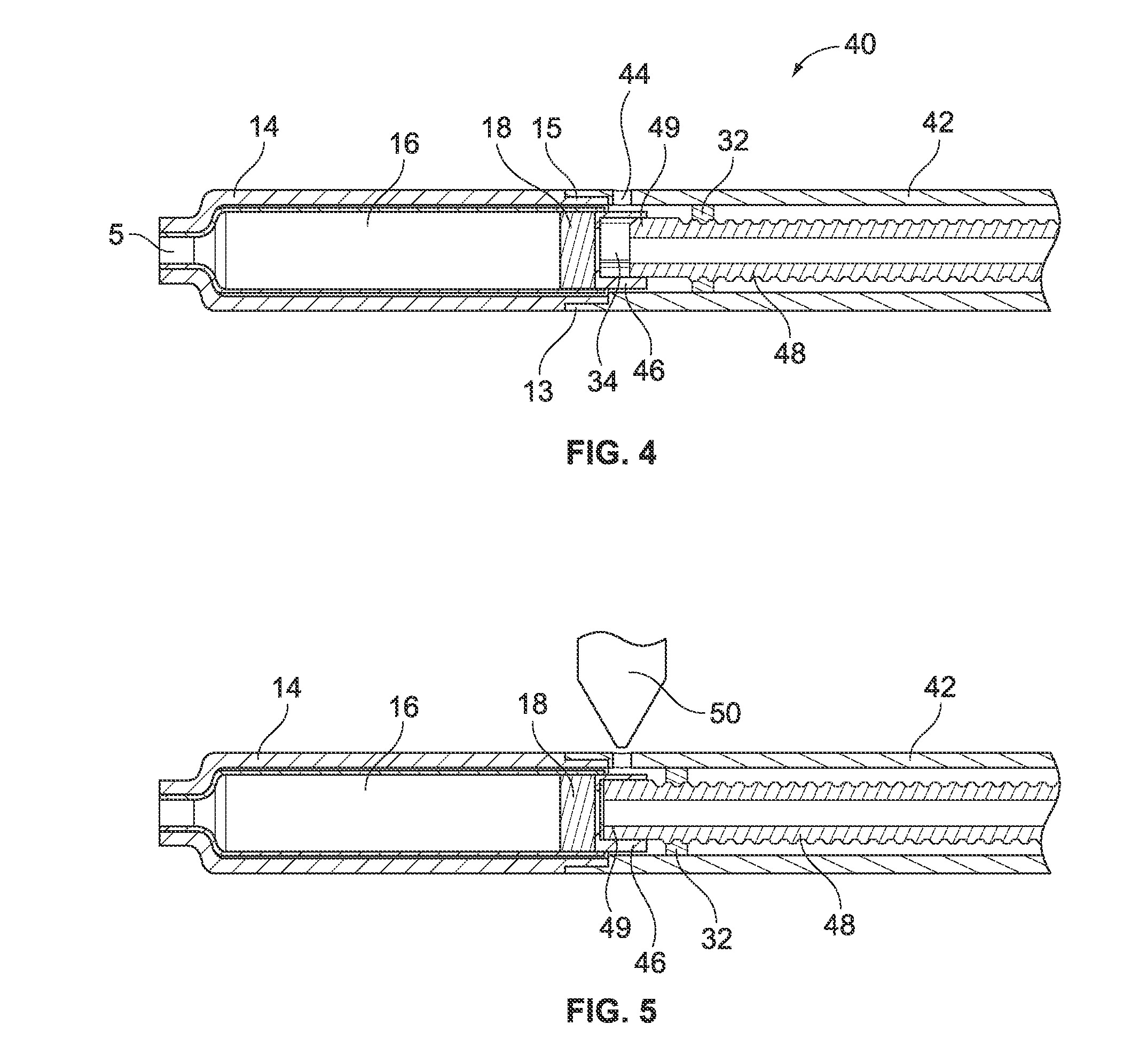
A disposable cover for an elongated probe of a portable thermometry apparatus includes an open proximal end and a distal tip sized to fit over at least an axial portion of the elongated probe. The cover includes a transitional wall thickness at its proximal end for fitting over a holding barb of said probe, the transitional wall thickness varying between a first wall thickness adjacent the proximal end and a second wall thickness that is substantially thinner than the first wall thickness at a distal axial distance relative to the proximal end. The second wall thickness defines a weakened wall portion which is ruptured when the cover has been ejected from said holding barb by an ejection mechanism of the thermometry apparatus. The cover can also include a thinned walled portion over at least a portion of the distal tip and can also include a feature that permits the user to detect when a cover has been attached to a probe.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Safety lockout for actuator shaft
A safety lock-out to prevent rotation of a rotary actuator is described. When an axial distance between a first and a second portion of an actuated mechanism exceeds a selected distance, the lock-out prevents the rotation. The safety lock-out includes a shaft rotatably connected to the first portion and axially movable relative to the second portion. A locking member is adapted to lock the rotary actuator by placing a protrusion in a notch of the shaft, thus preventing rotation of the shaft. The device also includes a spring member urging the locking member in the locking position, and an unlocking member adapted to urge the locking member in the unlocked position when the selected distance is not exceeded.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Construction of electrode assembly for nerve control
InactiveUS20060136024A1Minimize depolarization portionAvoid adversely decreasing magnitudeSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesAxial distanceBiomedical engineering
Apparatus is provided for applying current to a nerve, including a housing that is adapted to be placed in a vicinity of the nerve. First, second, and third electrodes are fixed to the housing at first, second, and third longitudinal sites of the housing, respectively. The first, second, and third electrodes do not come in direct physical contact with the nerve. The second site is between the first and third sites. The second electrode has an electrode surface axial length. The apparatus also includes first and second internal insulating elements, which are fixed to the housing between the first and second longitudinal sites, and between the second and third longitudinal sites, respectively. The first and second internal insulating elements are shaped so as to define, upon placement of the housing, a nerve axial distance between the first and second internal insulating elements that is less than the electrode surface axial length.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance ΔX apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35filters out acoustic pressure disturbances Pacoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances Pvortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals Pas1,Pas2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The Pvortical-dominated filtered signals Pasf1,Pasf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay τ between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance ΔX to obtain a convection velocity Uc(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Apparatus for measuring intravascular blood flow
ActiveUS7263398B2Reduce usageQuickly and accurately measure blood flow rateCatheterSensorsCoaxial cableNormal blood volume
Microwave apparatus for measuring the blood flow rate in a patient's blood vessel includes an intravascular catheter having proximal and distal ends and containing an inner coaxial cable forming a first antenna and an outer cable coaxial with the inner cable and forming a second antenna, the first antenna extending axially beyond the second antenna a selected distance. The apparatus also includes a control unit including a microwave transmitter, a microwave receiver and a processor controlling the transmitter and receiver. A diplexer is connected between the first and second antenna and the control unit to couple signals from the transmitter to the second antenna but not to the receiver and to couple signals from the first antenna to the receiver but not to the transmitter. The transmitter transmits microwave pulses to the first antenna which heat blood around that antenna. When the heated blood volume flows to the second antenna this is detected at the receiver which produces a detect signal. The processor measures the time interval between each pulse a subsequent detect signal and divides that time interval into the axial distance between the two antennas to compute the flow rate.
Owner:CORAL SAND BEACH LLC
Apparatus and method for sizing a distal femur
An apparatus for sizing a distal femur includes a base configured to concurrently abut a distal surface and a posterior surface of the distal femur, and further includes an axial distance scale. The scale includes a first sleeve axially fixedly coupled to the base and further includes a second sleeve spirally movably coupled to the first sleeve. A method for sizing a distal femur includes concurrently abutting a base against a distal surface and a posterior surface of the distal femur, and further includes measuring a distance relative to the base. The measuring step includes spirally moving a first sleeve relative to a second sleeve.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Miniature gas turbine combustion chamber
ActiveCN101818910AShorten the axial distanceImprove cooling effectContinuous combustion chamberCombustion chamberHigh energy
The invention discloses a miniature gas turbine combustion chamber, which has an annular structure and mainly comprises a flame tube, an outer casing, an inner casing, a swirler and a fuel oil supply system. The flame tube is formed by welding an outer flame tube, a head end wall and an inner flame tube; the rear end of the flame tube is connected with a rear flange of the casing of the combustion chamber through a screw; the rear end of the outer casing is connected with the rear flange of the casing through a bolt; and a front flange of the casing is connected with the front end of the casing through a bolt. An inlet of the combustion chamber is welded on the front flange of the casing; air radially enters the inlet of the combustion chamber; the front end of the inner casing is fixed in a hole of the inlet of the combustion chamber; the swirler is welded on the head end wall; the fuel oil supply system is fixed on an outer ring of the inlet of the combustion chamber; a main combustion hole, a mixing hole and an air film cooling hole are formed on the flame tube; and an air film slot tongue is welded on the lower part of the air film cooling hole for guiding cooling airflow. A high-energy DC igniter is inserted into the flame tube for realizing ignition starting of the totally annular combustion chamber; and gas is discharged out of the combustion chamber radially under the guiding of a slope of the outer flame tube and a vertical section of the outer flame tube. The miniature gas turbine combustion chamber is applied to a miniature gas turbine. Because the gas at the outlet directly impacts a centripetal turbine, the axial distance of the miniature gas turbine can be shortened, and the space is fully utilized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for measuring formation conductivities from within cased wellbores by combined measurement of casing current leakage and electromagnetic response
ActiveUS20060028208A1Easy to measureElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationElectromagnetic responseAxial distance
A method is disclosed for determining spatial distribution of resistivity of Earth formations surrounding a wellbore having a conductive pipe therein. The method includes measuring resistivity of the Earth formations using measurements of current leakage along the pipe at selected axial positions. Electromagnetic properties of the Earth formations are measured from within the pipe. The measurements of electromagnetic properties correspond to a larger axial distance and to a greater lateral distance than the measurements of resistivity from current leakage. The current leakage and electromagnetic measurements are jointly inverted to obtain a model of the spatial distribution.
Owner:KJT ENTPR
Device and method for detachably connecting abutting structural parts and tie member for use to form said device
InactiveUS7223045B2Reduced time and laborRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyRod connectionsAbutmentEngineering
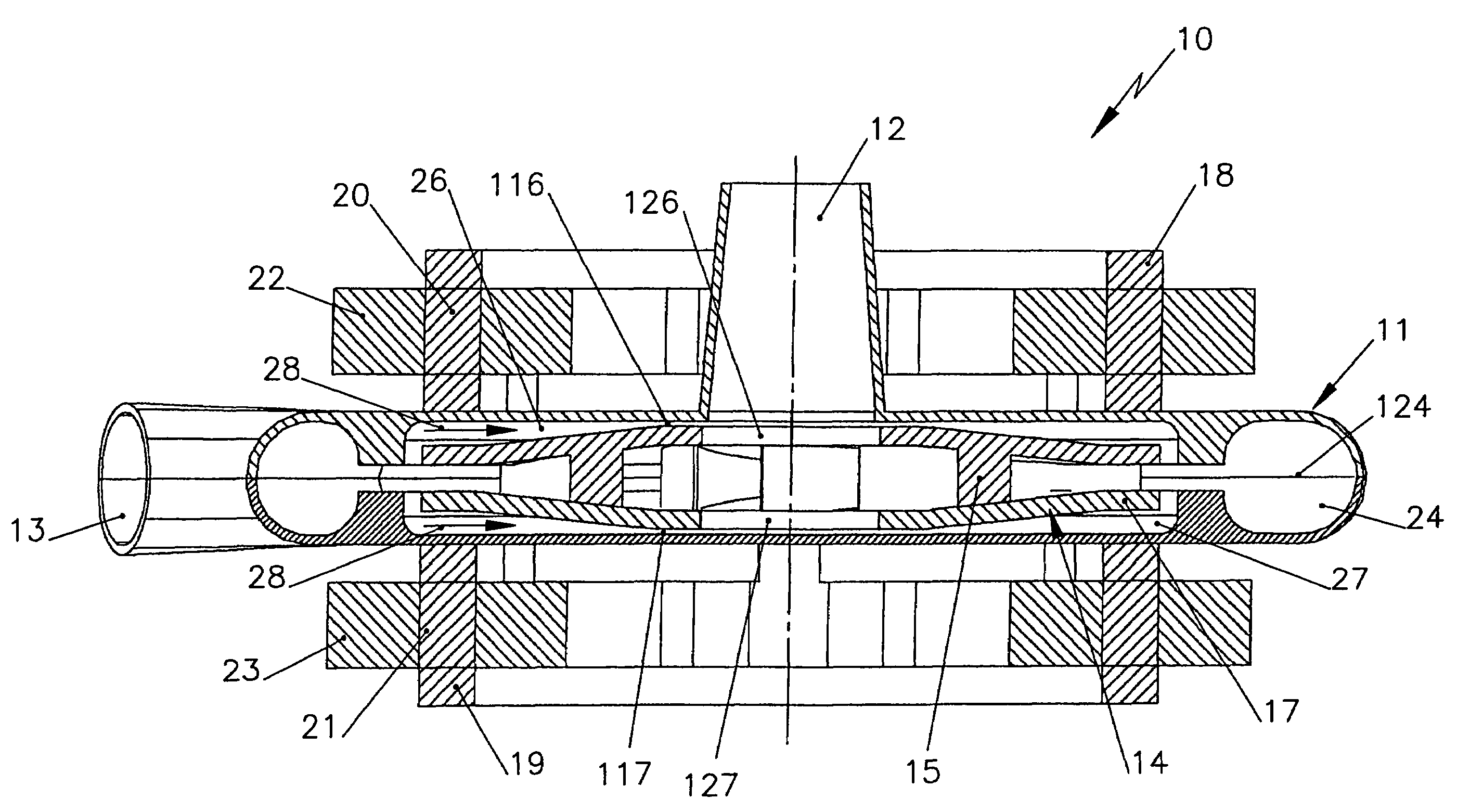
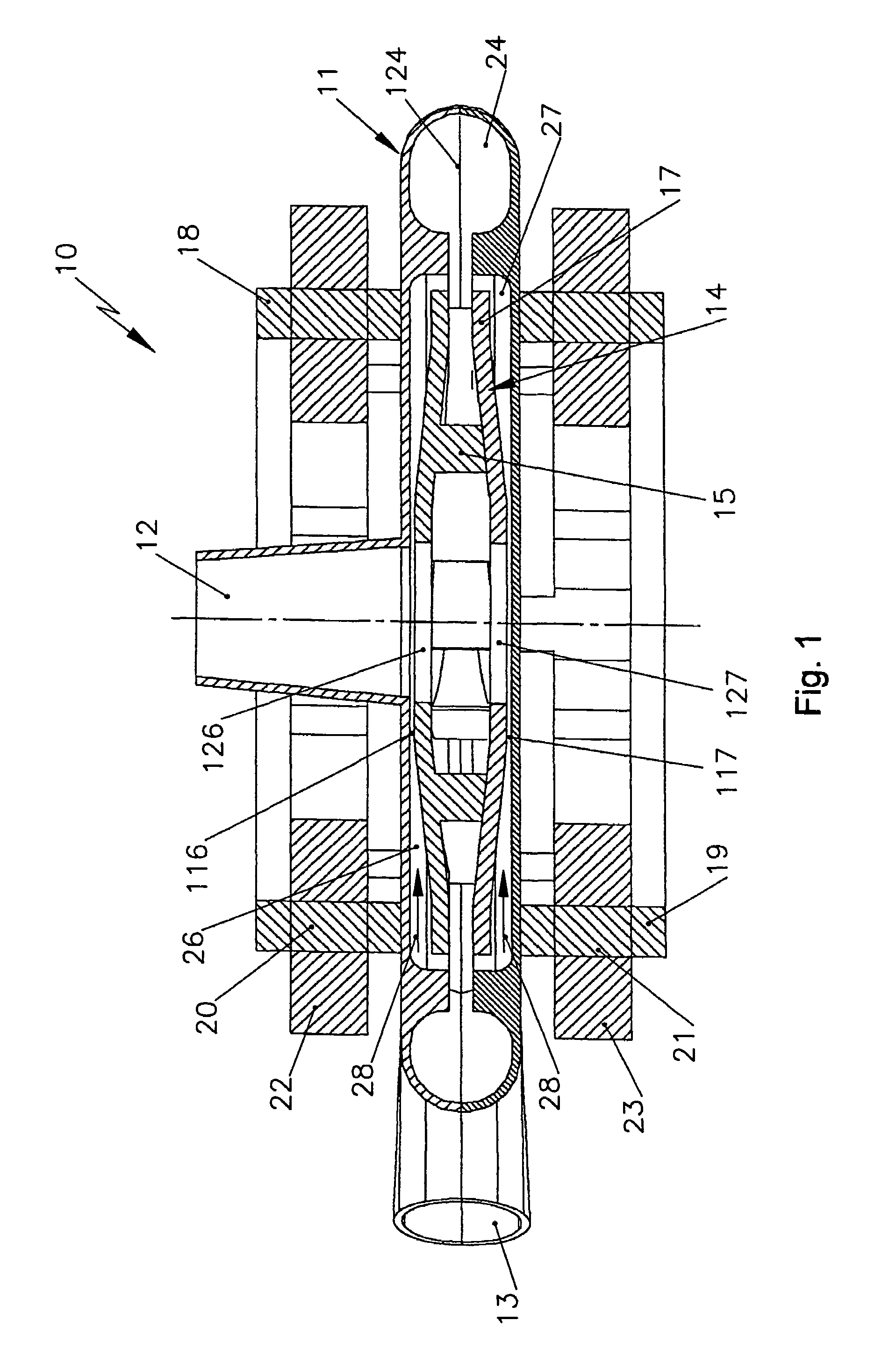
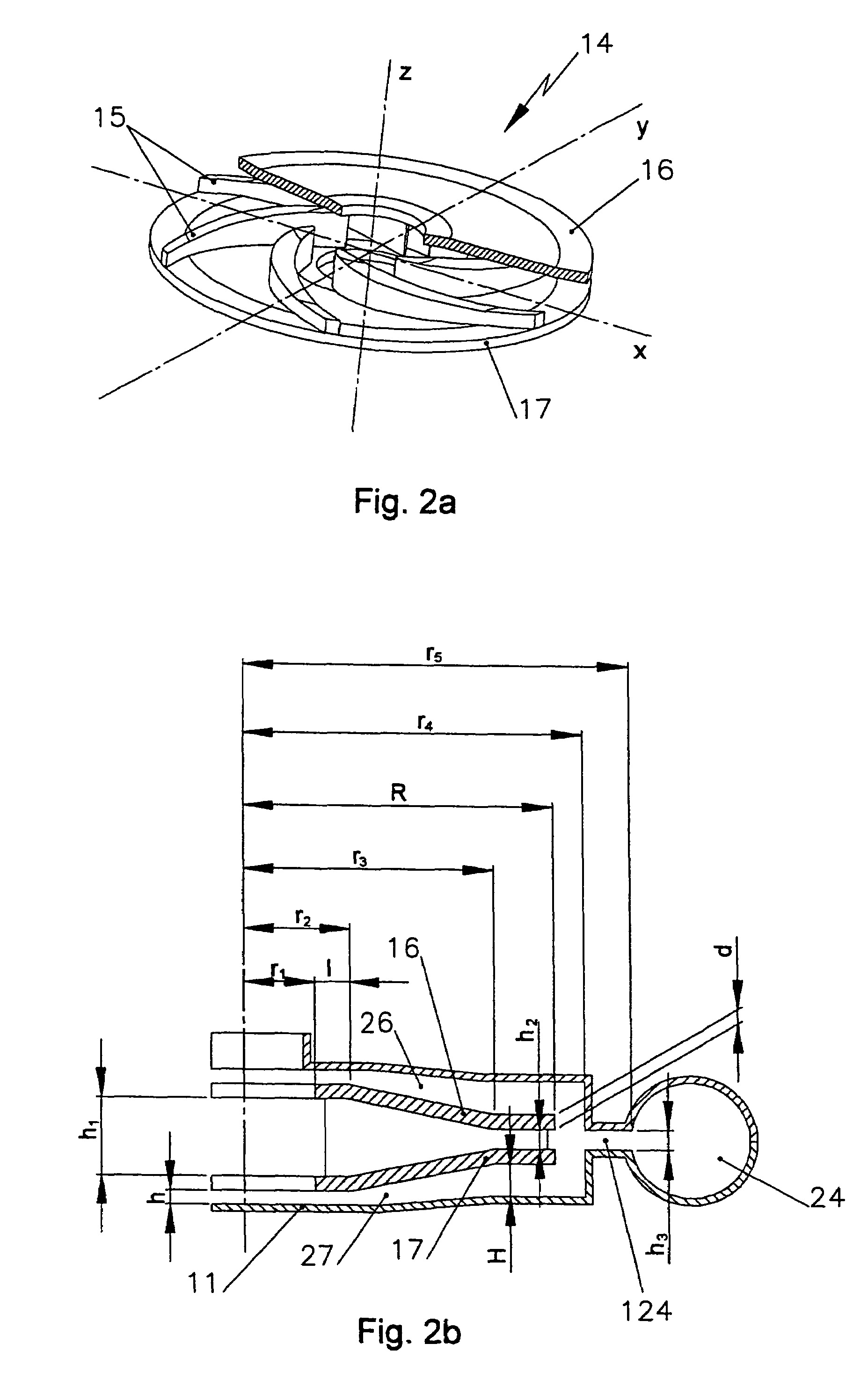
A device (1) for detachably connecting two abutting structural parts (2, 3) comprises a tie member (4), adapted to be at least partially inserted in a recess (5) formed in a first (2) of the structural parts (2, 3), and a locking element (6) operable to be disposed in a second (3) of the structural parts (2, 3) and to cooperate with an engagement surface (14, 45) of a rod member (10), slidably housed in a body (8) of the tie member (4), to pull the same towards the second structural part (3). The body (8) is provided with a first, expandable, portion (9) adapted to frictionally engage the recess (5) and with an engaging zone (13) cooperating with an expander region (12) of the rod member (10) operable to expand the first, expandable, portion (9) of the body (8) upon displacement of the rod member (10) relative to the same. The rod member (10) is provided with a traction portion (15) radially outwardly extending therefrom and adapted to cooperate with abutment means (16) radially formed in the body (8) of the tie member (4) at a predetermined axial distance from the engaging zone (13) to effect a substantially simultaneous displacement towards the second structural part (3) of the first, expandable, portion (9) of the body (8) of the tie member (4) and of the first structural part (2) in frictional engagement therewith.
Owner:TITUS D O O DEKANI
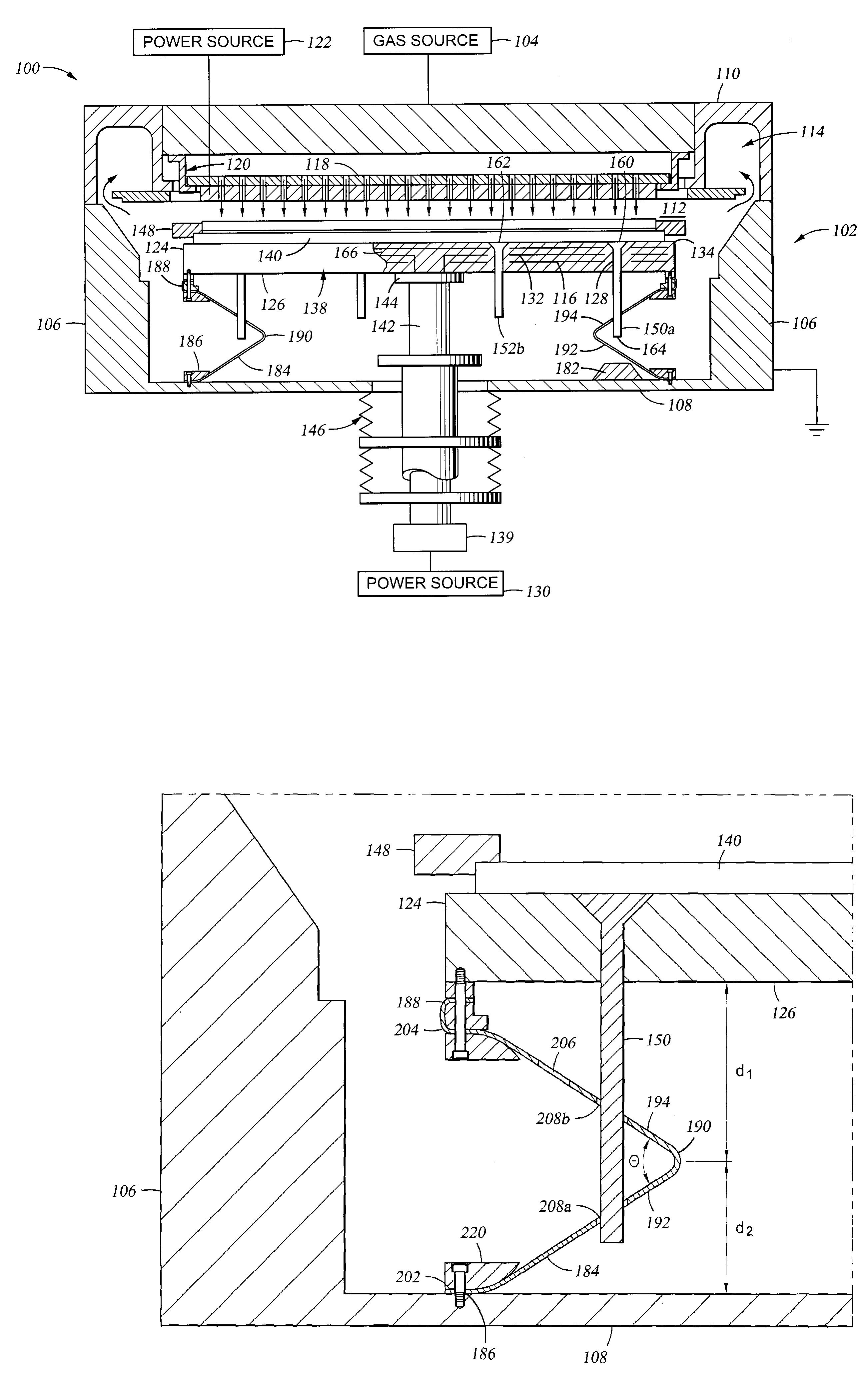
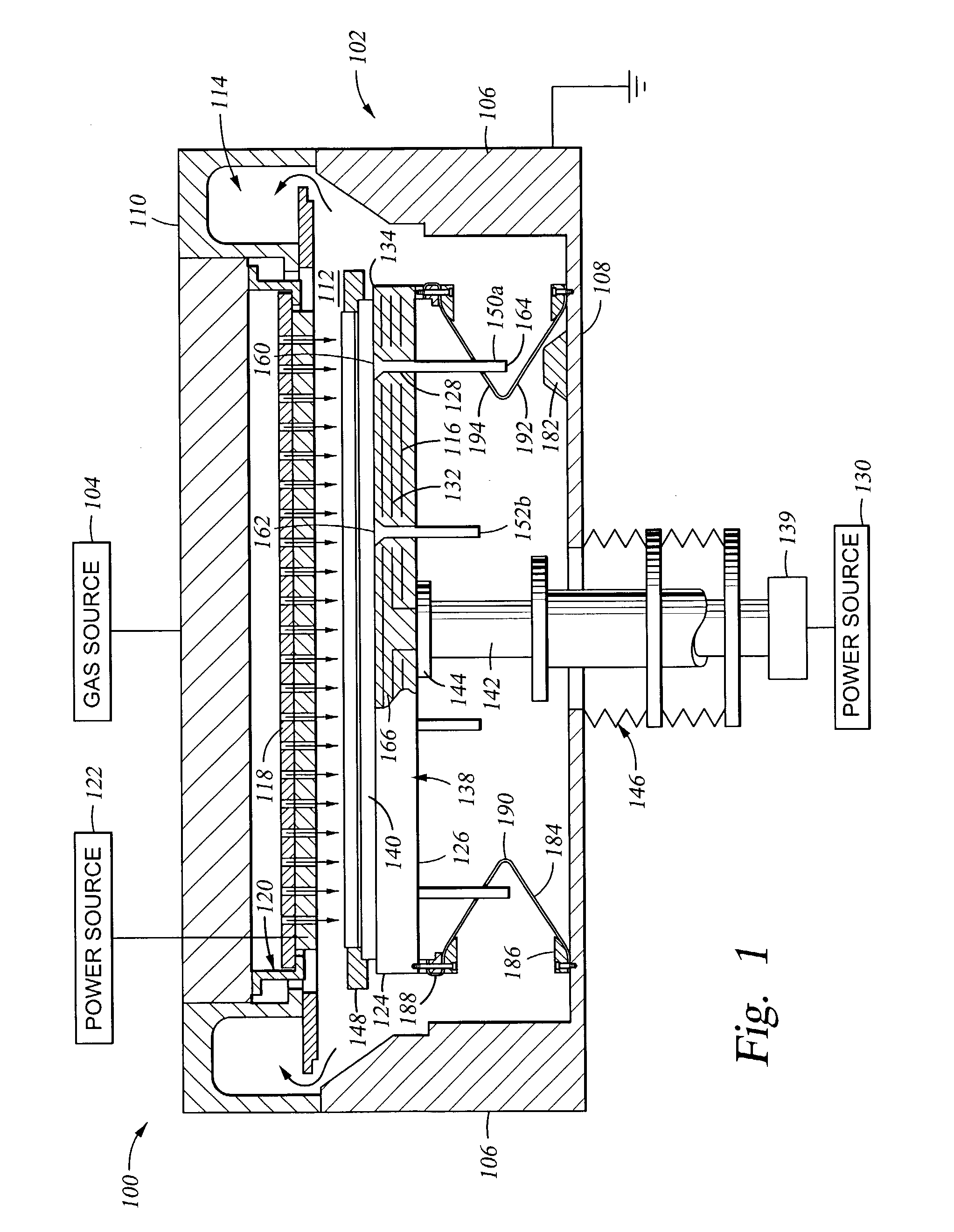
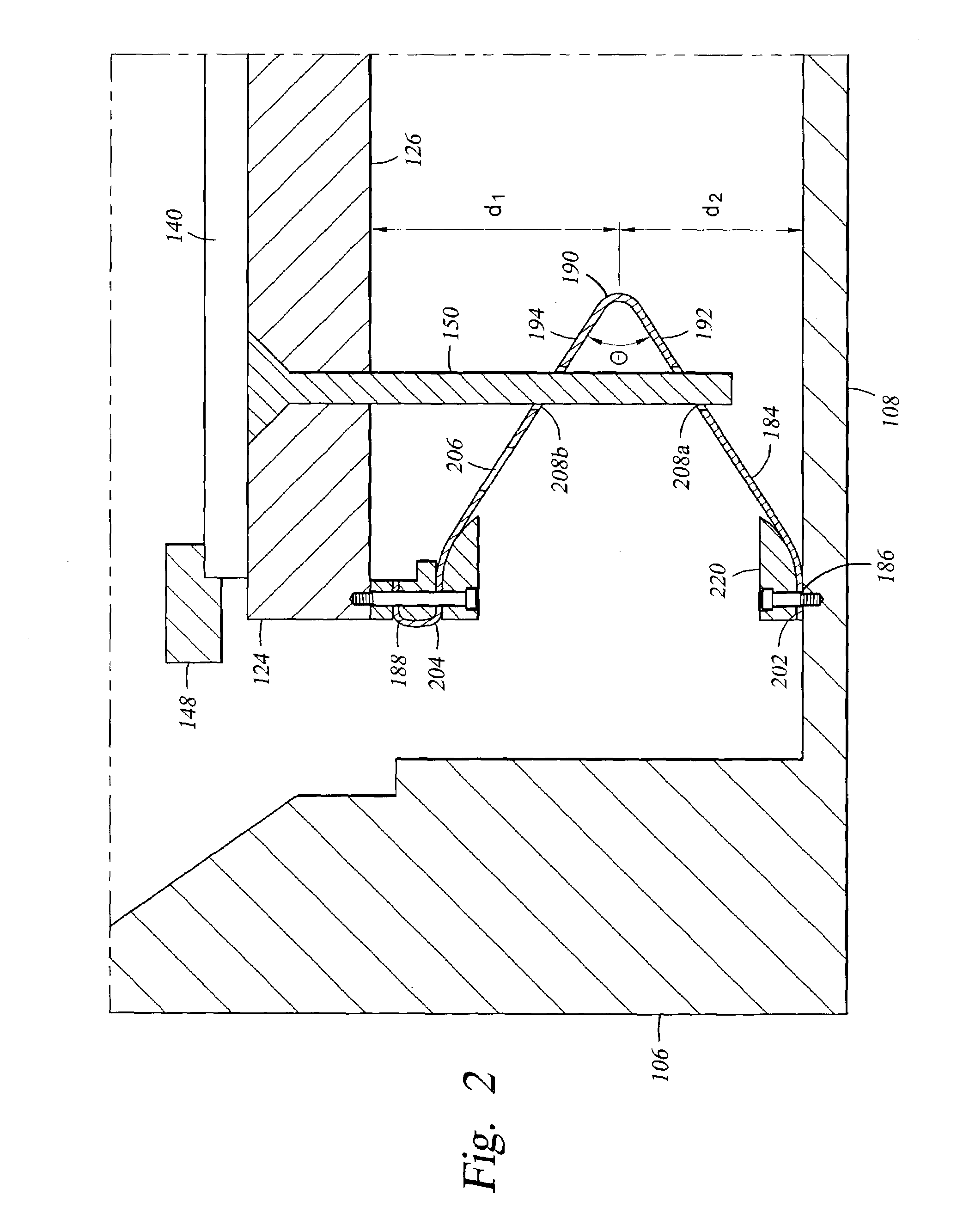
RF current return path for a large area substrate plasma reactor
InactiveUS7083702B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReturn currentEngineering
An apparatus for providing a return current path for RF current between a chamber wall and a substrate support is provided comprising a low impedance flexible curtain having a first end and a second end, the first end adapted to be electrically connected to the chamber wall and the second end adapted to be connected to the substrate support, wherein the curtain further comprises at least one fold in the curtain material, located an axial distance between the first end and the second end, and at least one perforation cut into the curtain proximate the second end.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
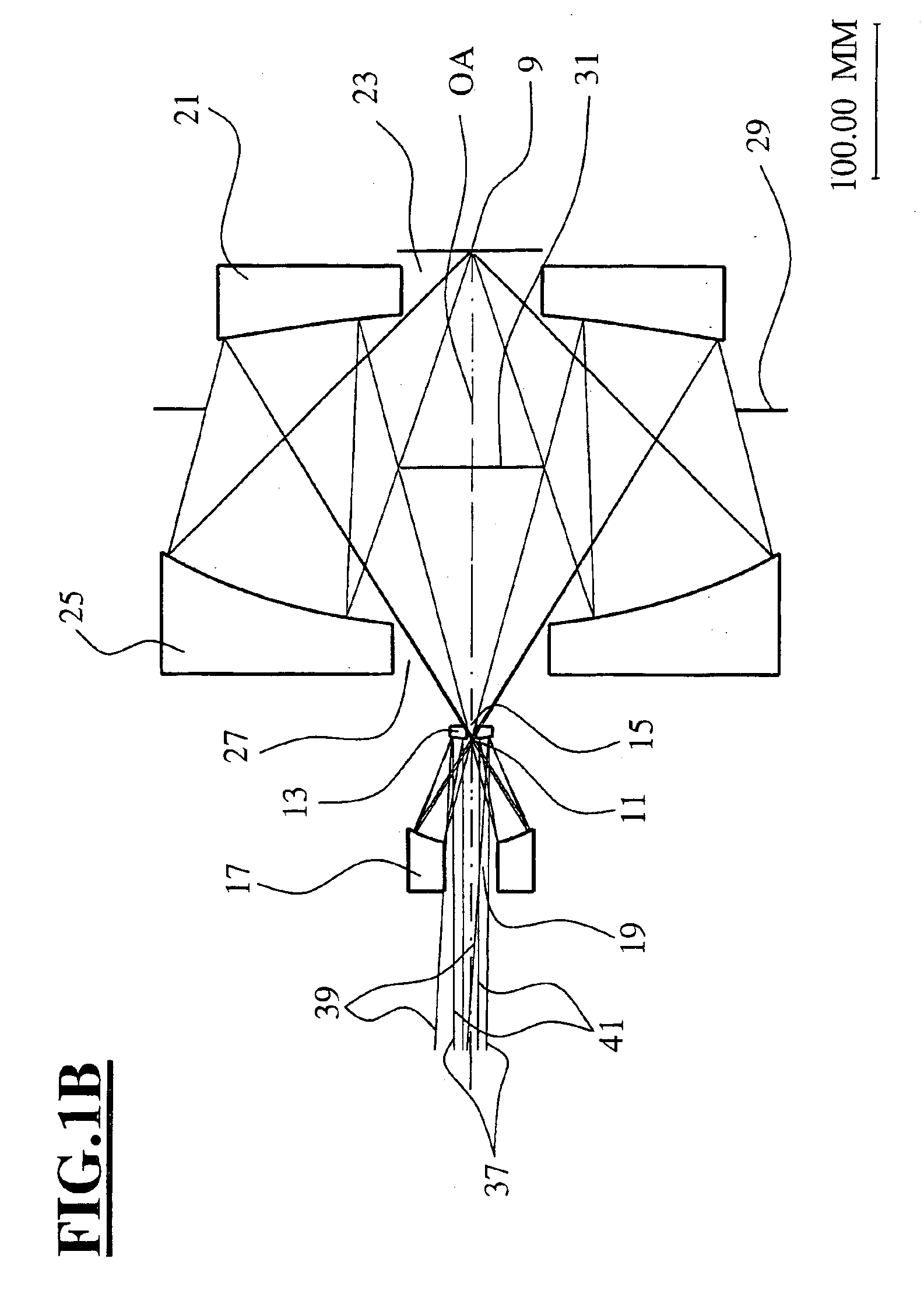
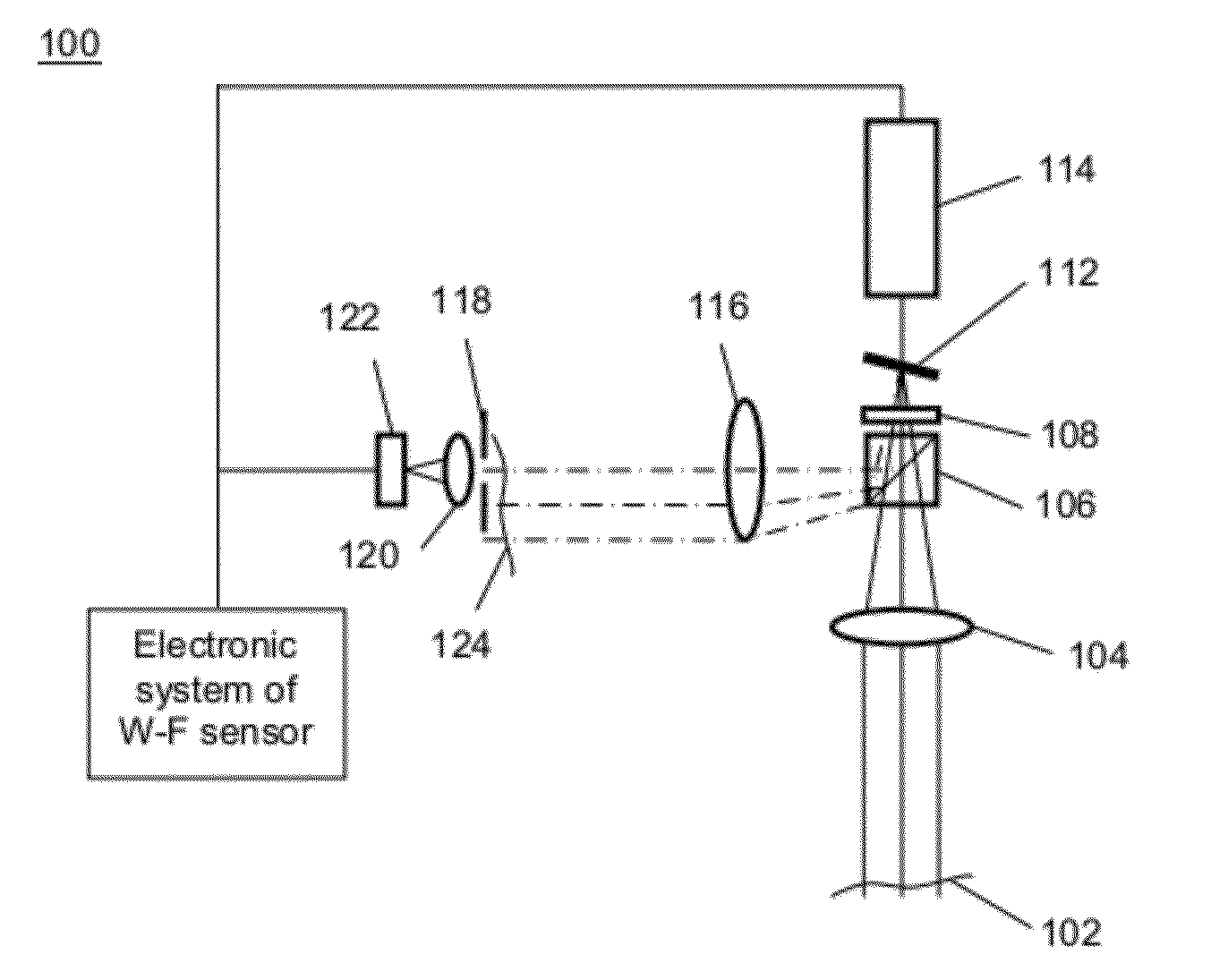
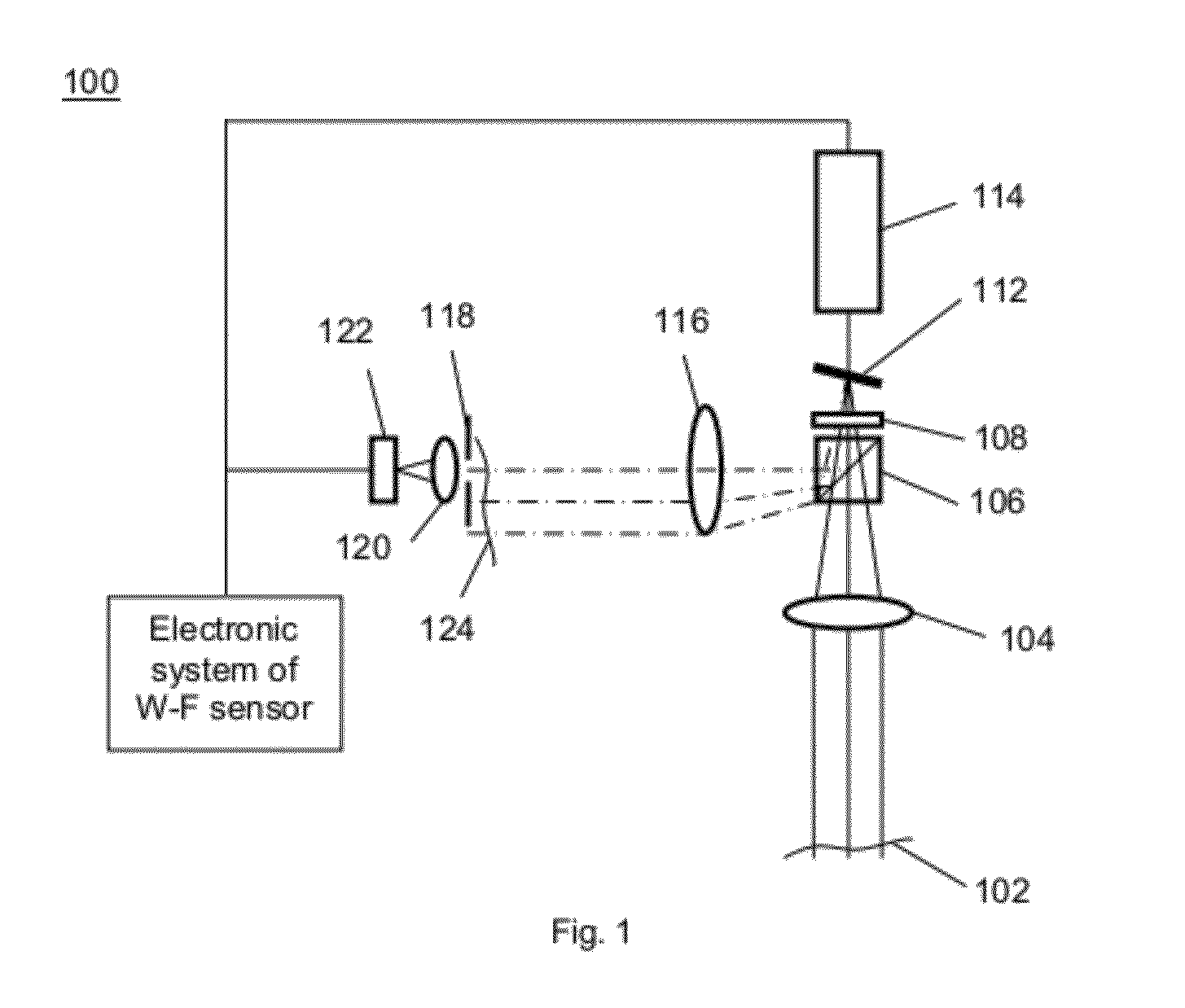
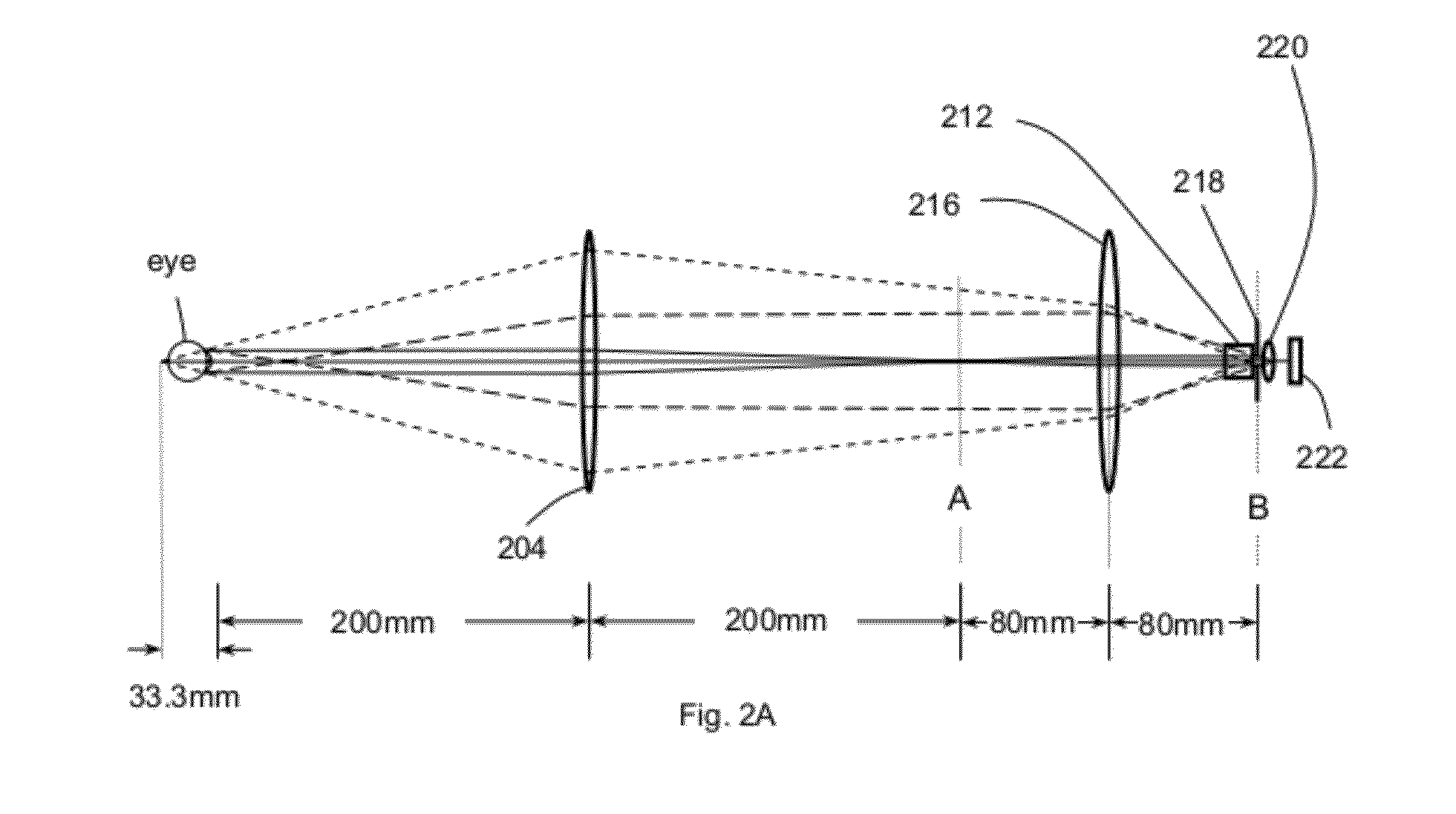
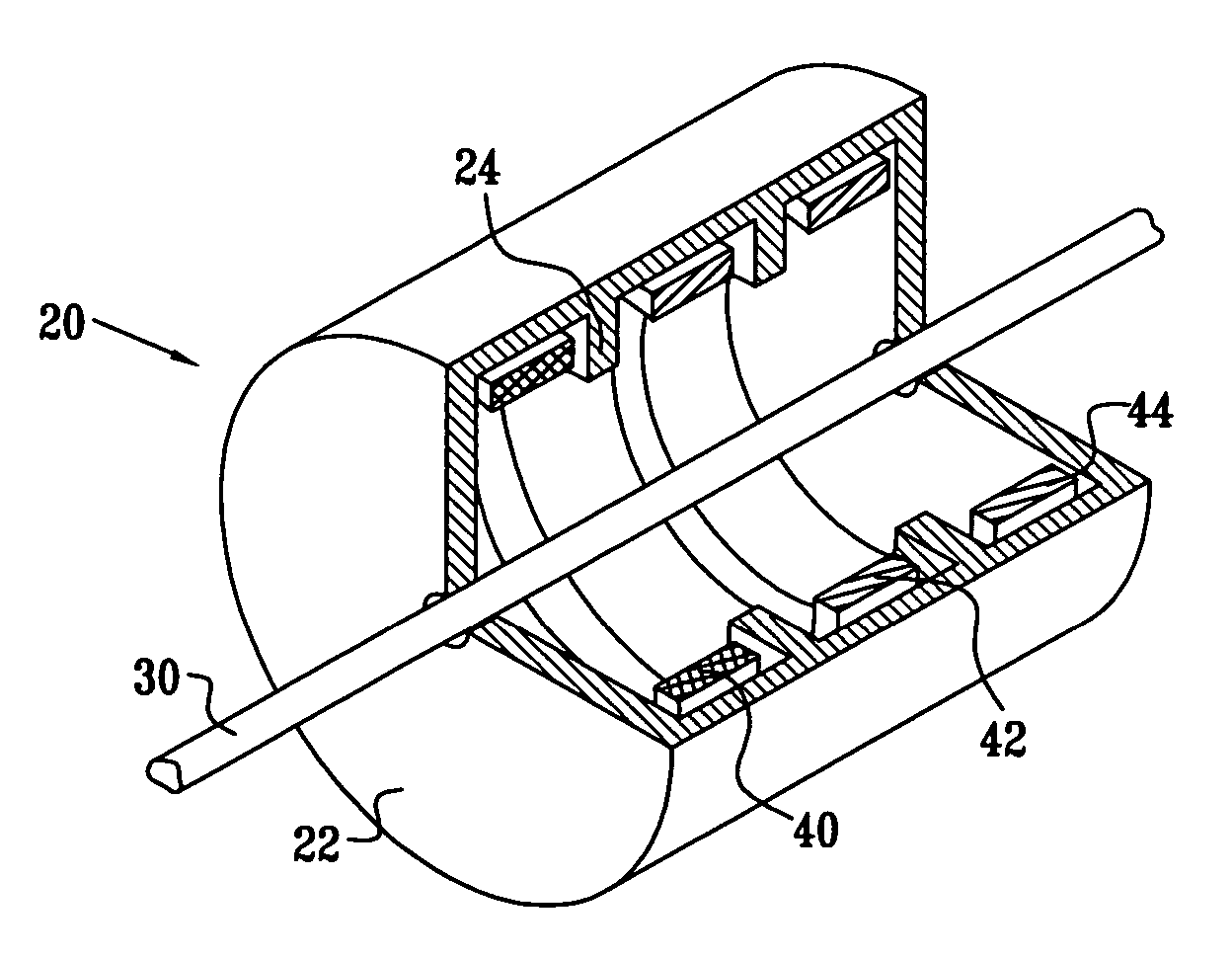
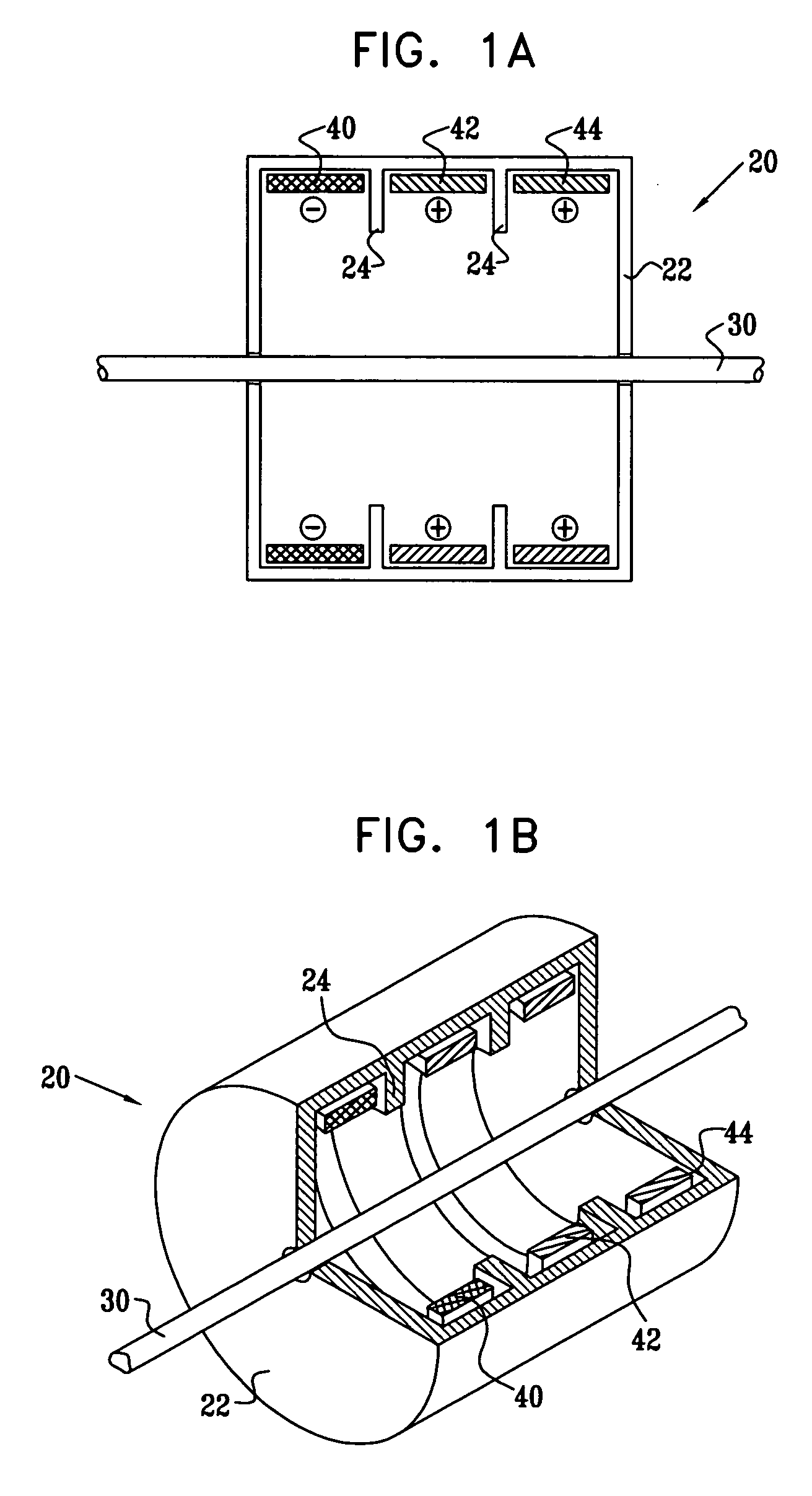
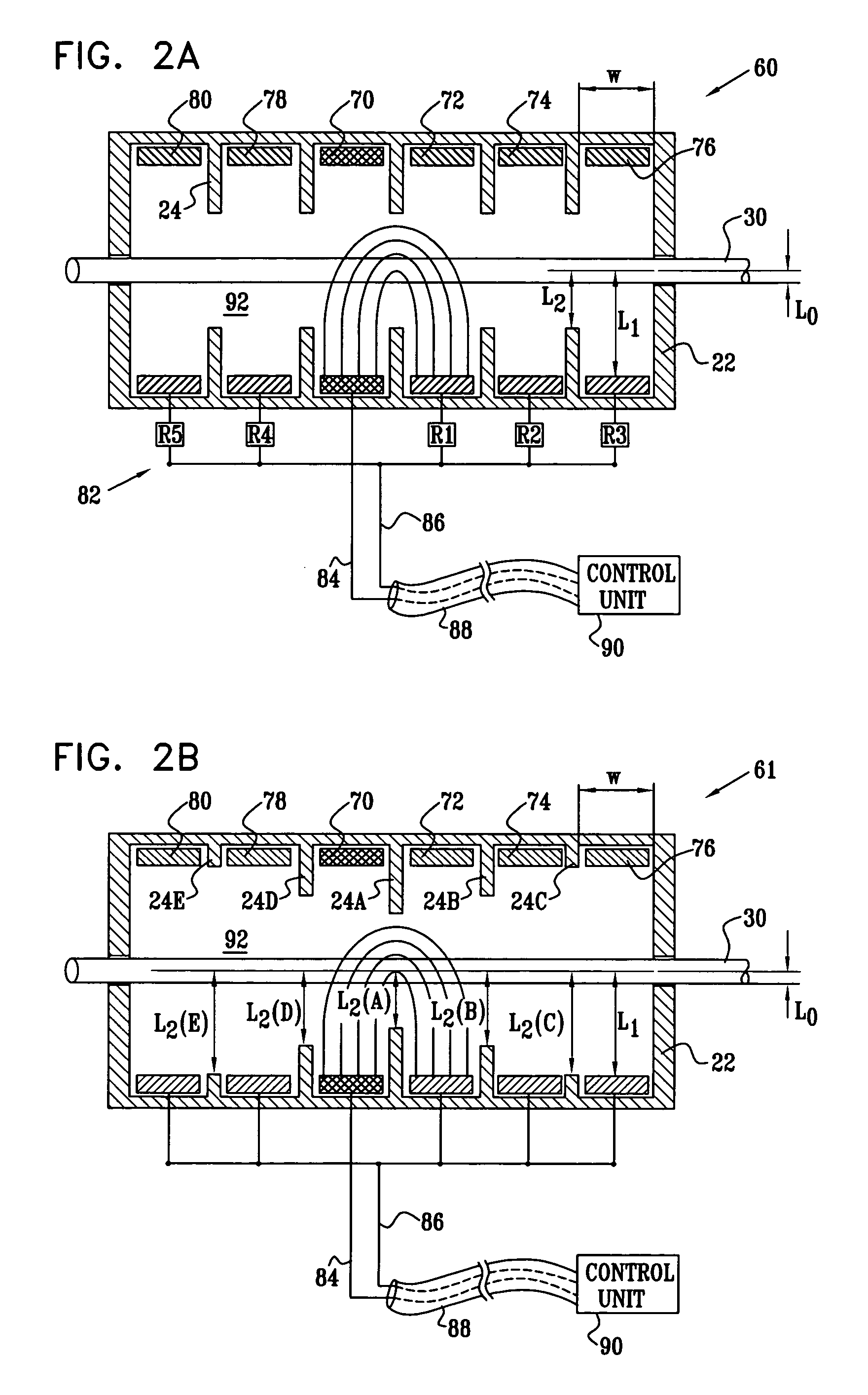
Devices and methods for measuring axial distances
Owner:WF SYST
Device and method for detachably connecting abutting structural parts and tie member for use to form said device
InactiveUS20050042027A1Shorten the timeReduce laborRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyRod connectionsEngineeringAbutment
A device (1) for detachably connecting two abutting structural parts (2, 3) comprises a tie member (4), adapted to be at least partially inserted in a recess (5) formed in a first (2) of the structural parts (2, 3), and a locking element (6) operable to be disposed in a second (3) of the structural parts (2, 3) and to cooperate with an engagement surface (14, 45) of a rod member (10), slidably housed in a body (8) of the tie member (4), to pull the same towards the second structural part (3). The body (8) is provided with a first, expandable, portion (9) adapted to frictionally engage the recess (5) and with an engaging zone (13) cooperating with an expander region (12) of the rod member (10) operable to expand the first, expandable, portion (9) of the body (8) upon displacement of the rod member (10) relative to the same. The rod member (10) is provided with a traction portion (15) radially outwardly extending therefrom and adapted to cooperate with abutment means (16) radially formed in the body (8) of the tie member (4) at a predetermined axial distance from the engaging zone (13) to effect a substantially simultaneous displacement towards the second structural part (3) of the first, expandable, portion (9) of the body (8) of the tie member (4) and of the first structural part (2) in frictional engagement therewith.
Owner:TITUS D O O DEKANI
Drug delivery device for delivery of a medicament
ActiveUS20100280461A1Eliminate gapsEliminating axial clearanceAmpoule syringesMedical devicesPharmaceutical drugAxial distance
Various embodiments of drug delivery devices and methods of assembling such devices are provided. In one embodiment, a drug delivery device for dispensing medicament comprises a medicament cartridge, wherein the cartridge comprises (i) a distal end, (ii) a proximal end that is opposite the distal end along a body axis of the cartridge, and (iii) a movable piston arranged substantially at the proximate end of the cartridge. The drug delivery device further comprises a piston rod having a distal end for axially moving the piston in the distal direction during dispensing of a set dose of medicament, wherein a relative axial distance between the distal end of the piston rod and a proximal face of the piston is set during assembly of the drug delivery system. The relative axial position between may be set such that the piston rod and the proximal face of the piston abut each other.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Centrifugal pump
InactiveUS7699588B2Improve efficiencyIncrease the projected areaPump componentsBlood pumpsEngineeringDrive motor
The invention relates to a centrifugal pump, especially for blood, comprising a pump rotor which is arranged in a rotational manner and without a bearing in a liquid-tight and gas-tight closed housing, except for at least one inlet opening and at least one outlet opening. The rotor is also the rotor of a drive motor. The rotor is symmetrical with respect to the centre plane thereof and comprises an upper and a lower covering. The rotor and / or the pump housing are formed in such a way that the axial distances between the upper and the lower coverings and the upper and lower housing walls are smaller in the radially inner region of the rotor than in the radially outer region. In the radially inner region of the rotor, each lateral rotor chamber comprises a flow-restrictor gap which, when in operation, influences back flows oriented in a radially inward manner in the lateral rotor chambers, such that during an axial deflection of the rotor above and below the rotor, various pressure distributions appear, enabling forces acting upon the predominant surface of the coverings to be produced, the forces bringing about an axial stabilisation of the rotor and acting, in the same manner, against tilting of the rotor inside the housing.
Owner:JOSTRA AG
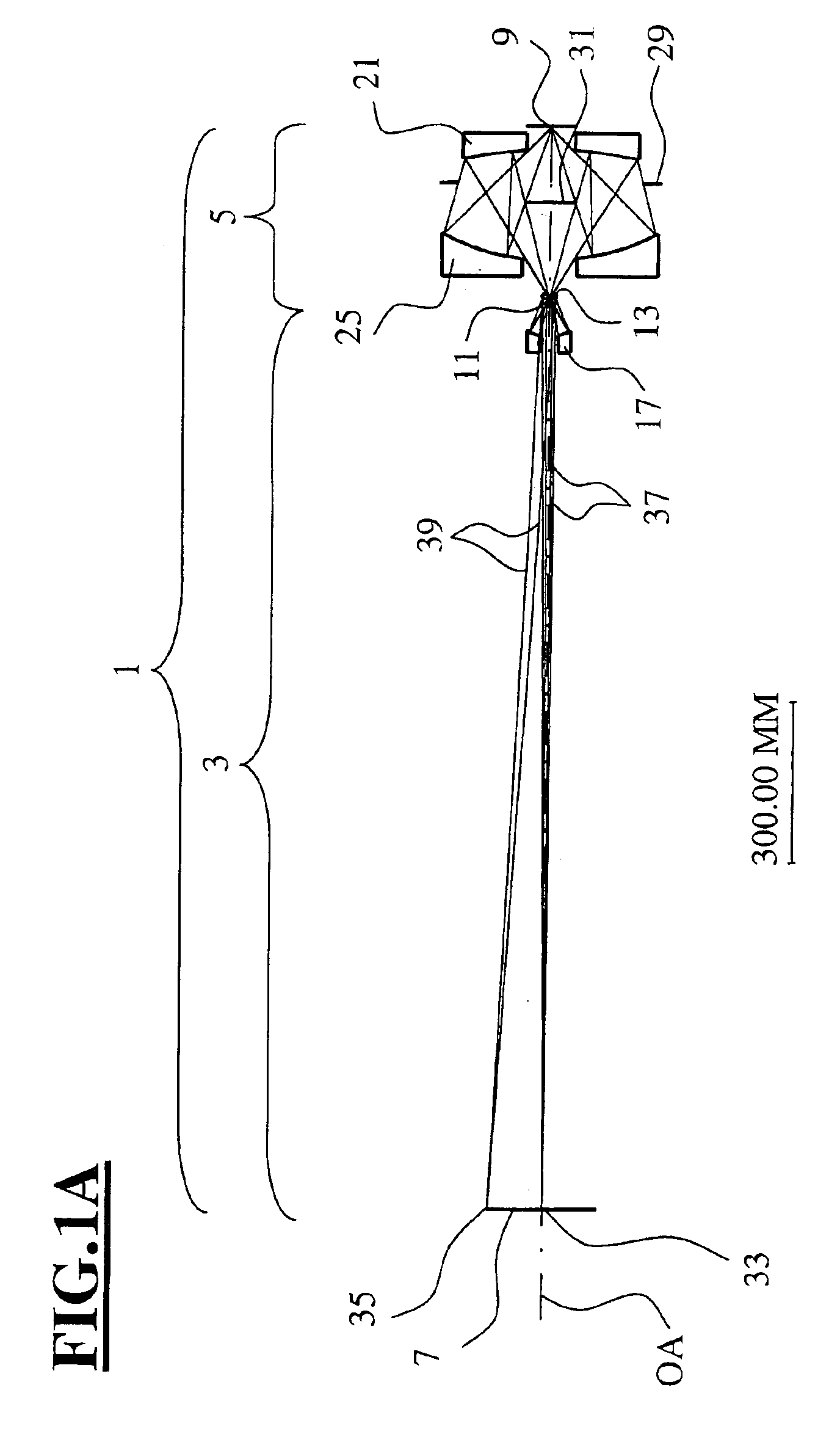
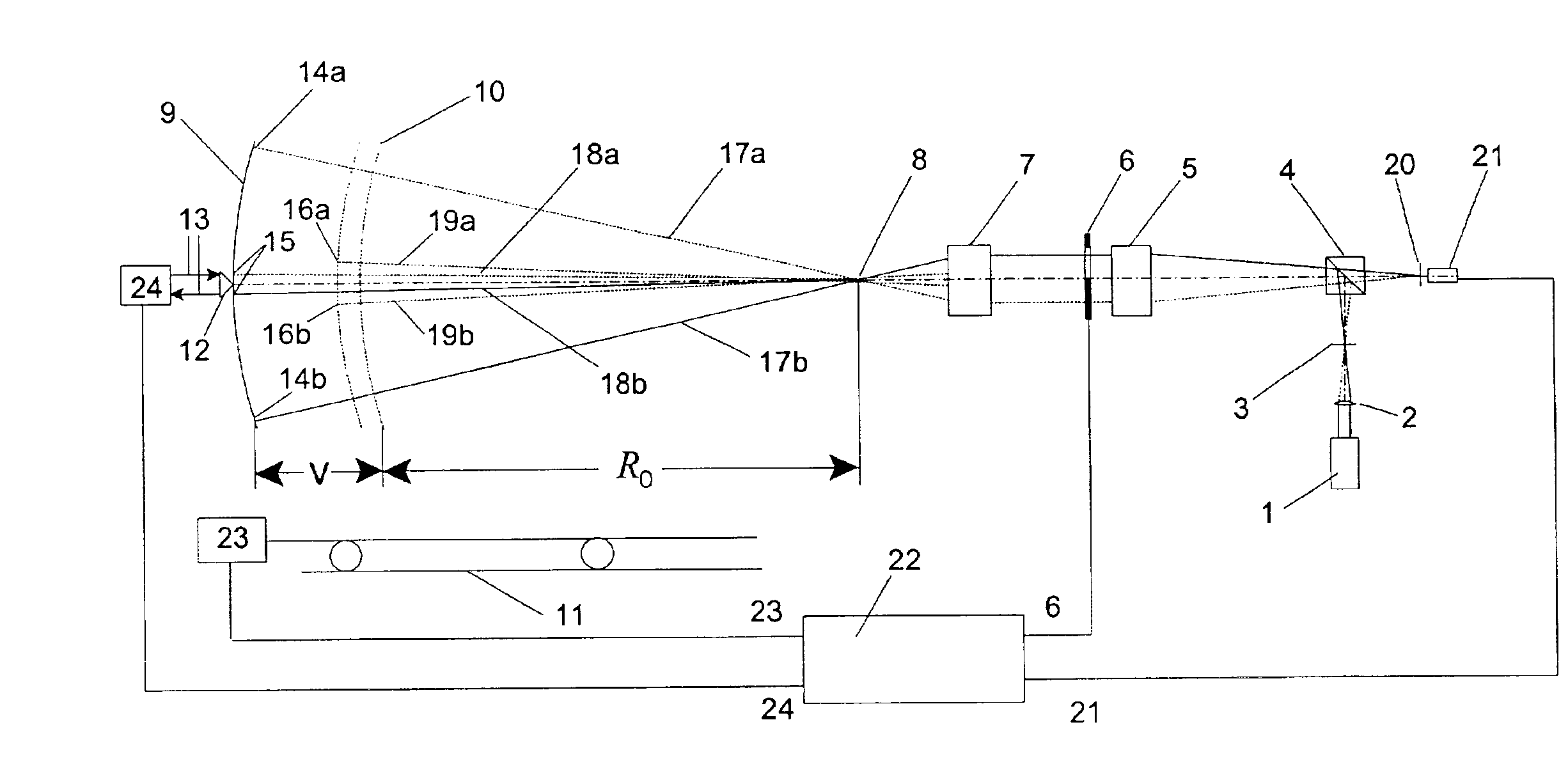
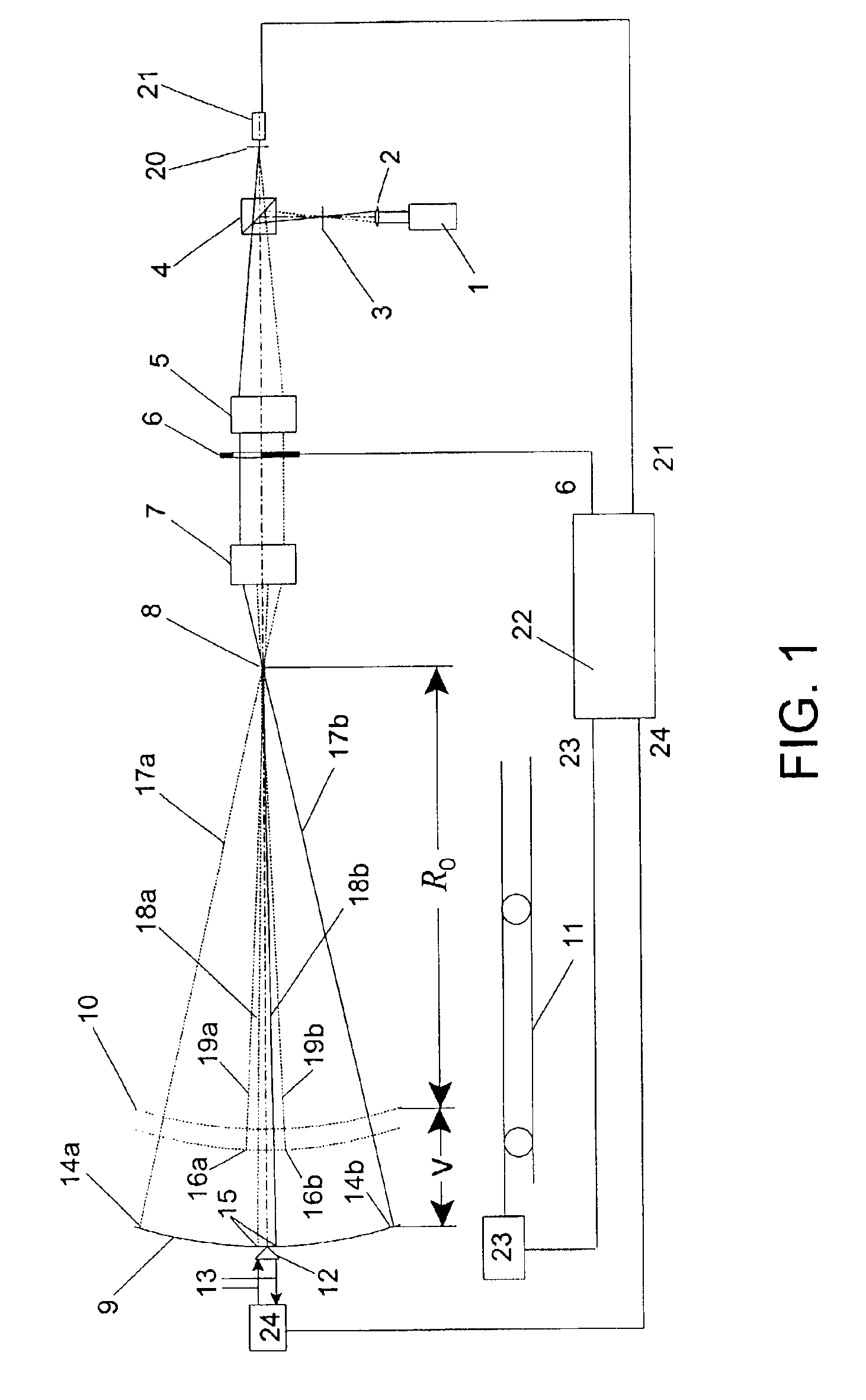
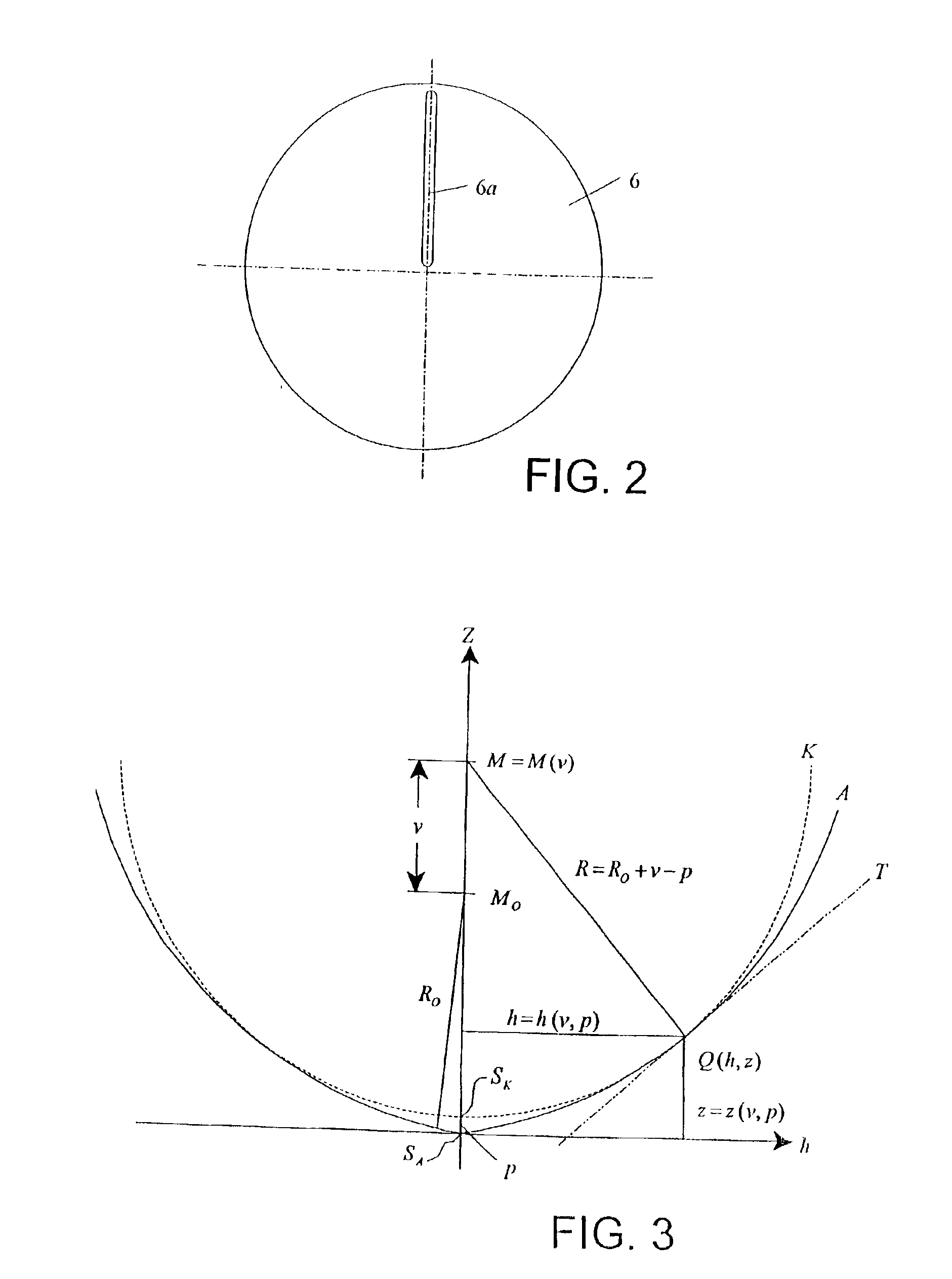
Scanning interferometer for aspheric surfaces and wavefronts
Interferometric scanning method(s) and apparatus for measuring rotationally and non-rotationally symmetric test optics either having aspherical surfaces or that produce aspherical wavefronts. A spherical or partial spherical wavefront is generated from a known origin along an optical axis. The test optic is aligned with respect the optical axis and selectively moved along it relative to the known origin so that the spherical wavefront intersects the test optic at the apex of the aspherical surface and at radial positions where the spherical wavefront and the aspheric surface intersect at points of common tangency. An axial distance, ν, and optical path length, p, are interferometrically measured as the test optic is axially scanned by the spherical wavefront where ν is the distance by which the test optic is moved with respect to the origin and p is the optical path length difference between the apex of an aspherical surface associated with the test optic and the apex of the circles of curvature that intersect the aspherical surface at the common points of tangency. Coordinates of the aspherical surface are calculated wherever the circles of curvature have intersected the aspherical surface and in correspondence with the interferometrically measured distances, ν and p. Afterwards, the shape of the aspheric surface is calculated. Where the test optic comprises a refracting optic a known spherical reflecting surface is provided upstream of the refracting optic for movement along the optical axis and a known wavefront is made to transit the refracting optic, reflects from the known spherical surface, again transits the refracting optic traveling towards the known origin after which the interferogram is formed. In another aspect of the invention, a spherical reference surface is provided to form a Fizeau that is used to generate phase information for measuring spheres, mild aspheres, and multiple mild aspheres.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
Tension rod mechanism with opposing threads
ActiveUS20120152872A1Increase axial distanceCurtain suspension devicesRod connectionsAxial distanceScrew thread
A tension rod mechanism for a tension rod having a first outer shaft with a second inner shaft slideable therein. A first collar receiveable in the first outer shaft of a tension rod for rotational movement therewith and slidable axial movement relative thereto threadingly engages a tapered first threaded shaft and is configured to apply a outwardly-directed radial force to the first outer shaft. A second collar fixedly receivable in the second inner shaft for movement therewith engages the second threaded shaft. A first rotation of the first outer shaft relative to the second inner shaft increases the outwardly-directed radial force applied by the first collar to the first outer shaft, and a second rotation in an opposite direction increases the axial distance between the first and second collars.
Owner:DECOLIN INC
Method and apparatus for replicating the position of intra-osseous implants and abutments relative to analogs thereof
InactiveUS7214062B2Improve the immunityRelieve and prevent buildDental implantsElectrical resistance and conductanceAbutment
The position of intra-osseous implants and abutments to analogs is enabled and enhanced by using the longitudinal axial locked position of a post (12a) of an implant (12) having a locking taper in a bore (10a) of an implant (10) having a generally matching locking taper as a reference to determine the position of a stop surface (14c) on impression posts, abutment analog posts and the like received in the bore of an implant and implant analog. In another embodiment the bore (16) of an implant analog (16) is provided with a shelf (16c) located at a position determined by the axial distance of the locked position of the abutment post to prevent over-seating. Controlled retentive resistance and stability of a post is provided by using flats formed in the bore of an implant analog and by forming rings on a post receivable in the bore of an implant or implant analog. One such ring (18c) is formed with an outer periphery sized and configured to allow bending of the outer peripheral portion in a direction opposite to the direction of insertion in a bore to provide greater retentive resistance than insertion resistance.
Owner:DEBBIE
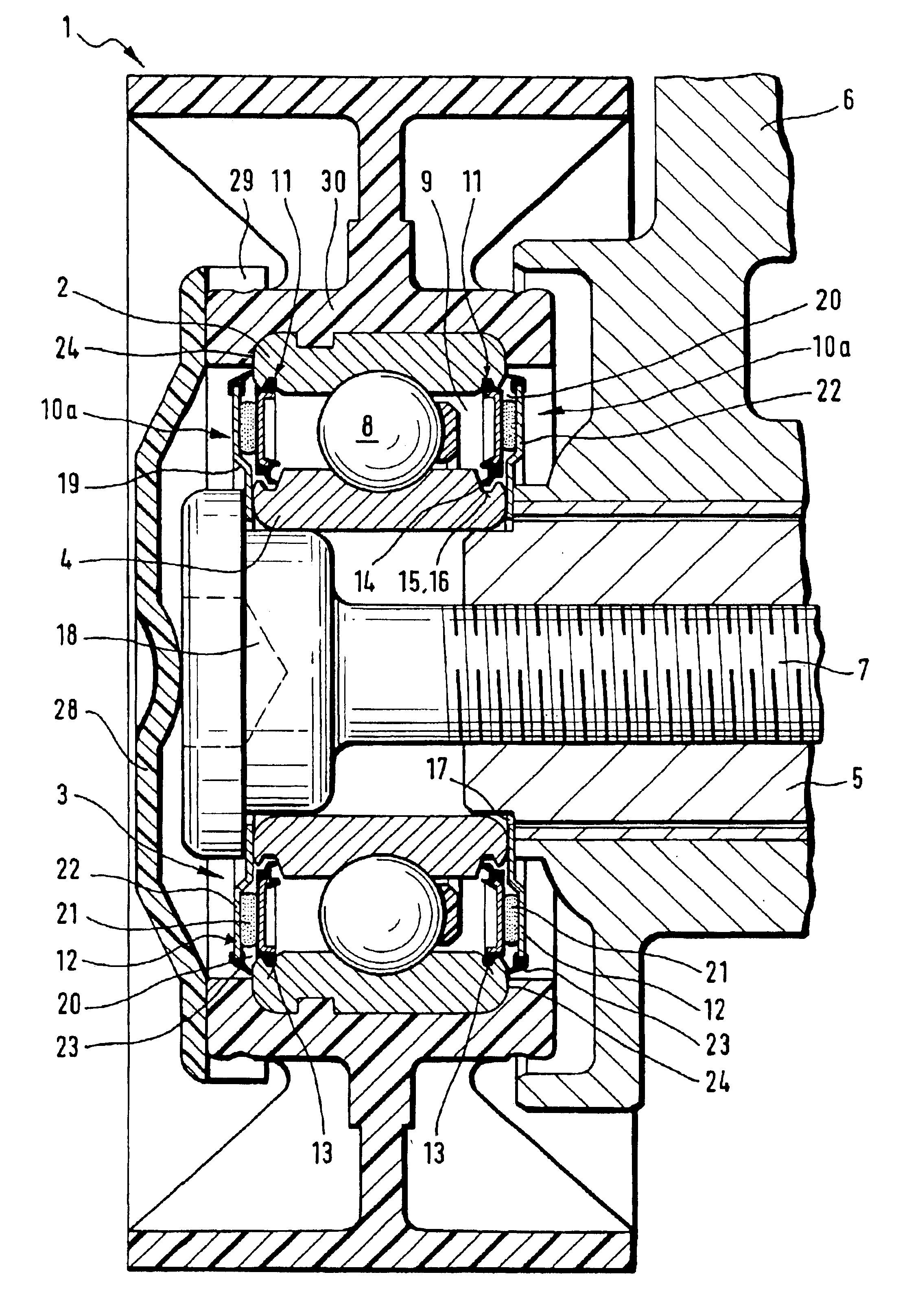
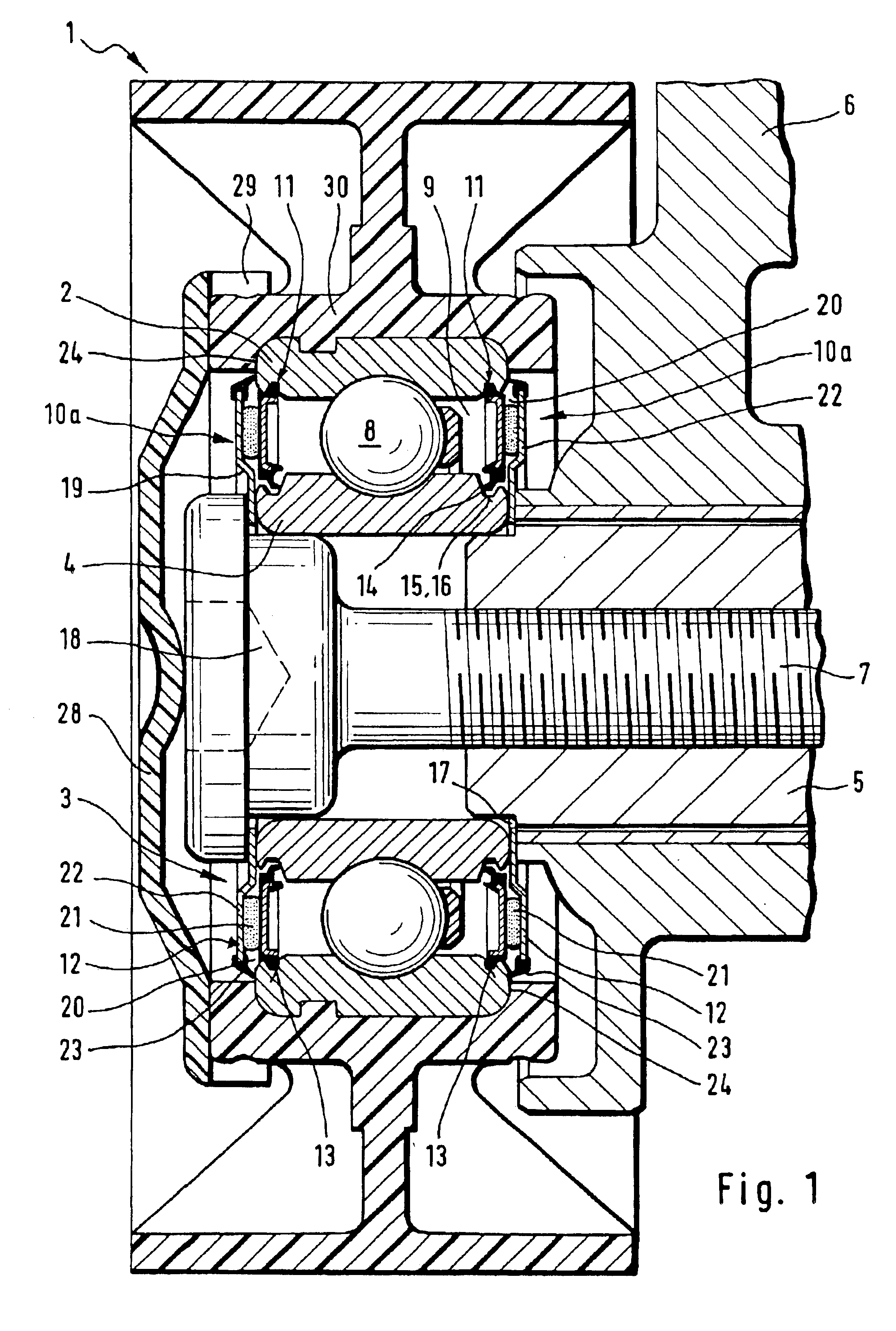
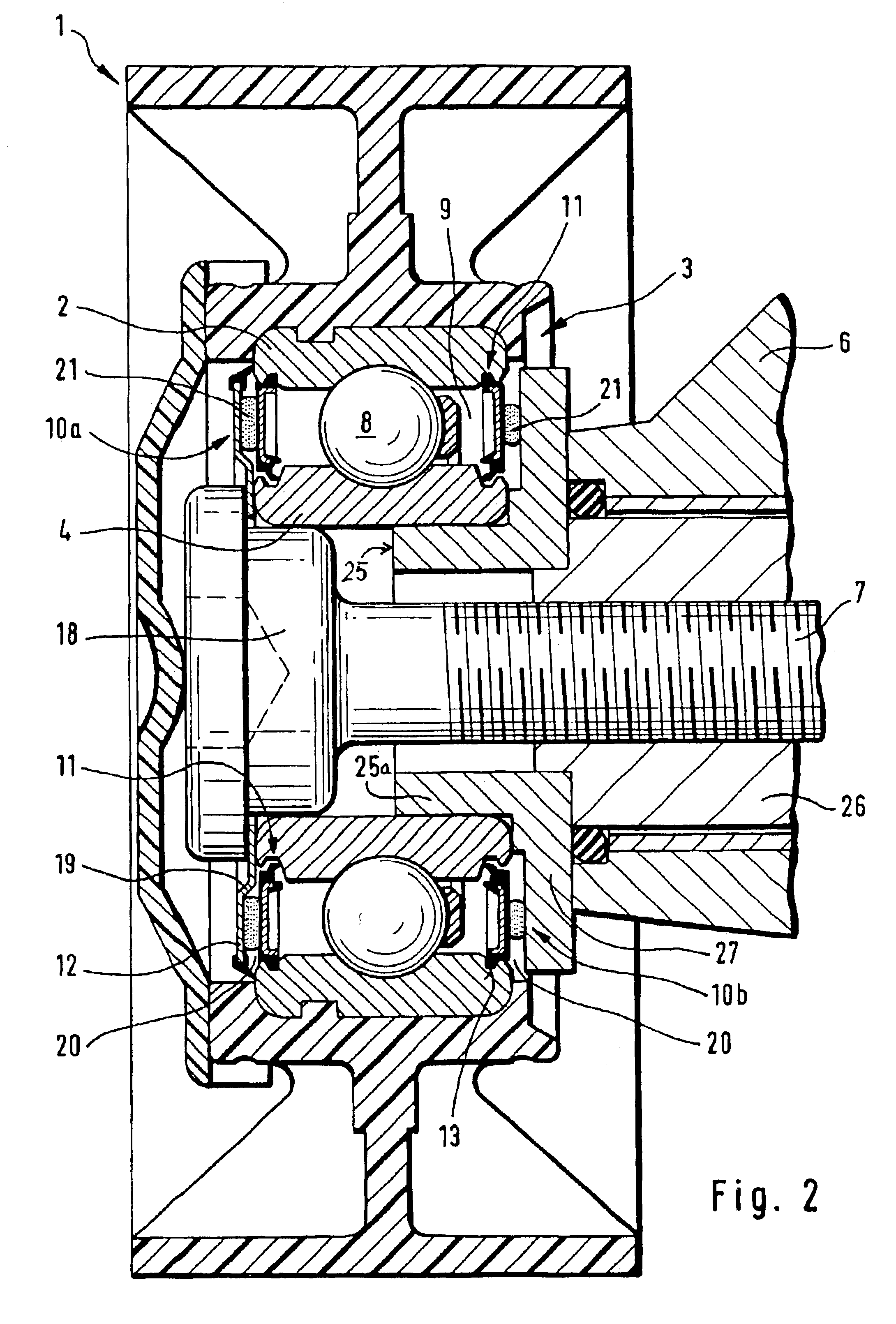
Sealing arrangement for a rolling-contact bearing
InactiveUS6854893B2Improve efficiencyAdded costEngine sealsGearingRolling-element bearingEngineering
A two-stage sealing arrangement for sealing an annular gap between an outer bearing ring and an inner bearing ring of a rolling-contact bearing, includes a first sealing element securely fixed to the outer bearing ring and having at least one sealing lip supported against the inner bearing ring. A second sealing element is disposed at an axial distance to the first sealing element, thereby defining a circular ring shaped sealing gap in a radial direction for accommodating, at least partially, a sealing material.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Tension rod mechanism with opposing threads
ActiveUS8827587B2Increase axial distanceCurtain suspension devicesRod connectionsEngineeringAxial distance
Owner:DECOLIN INC
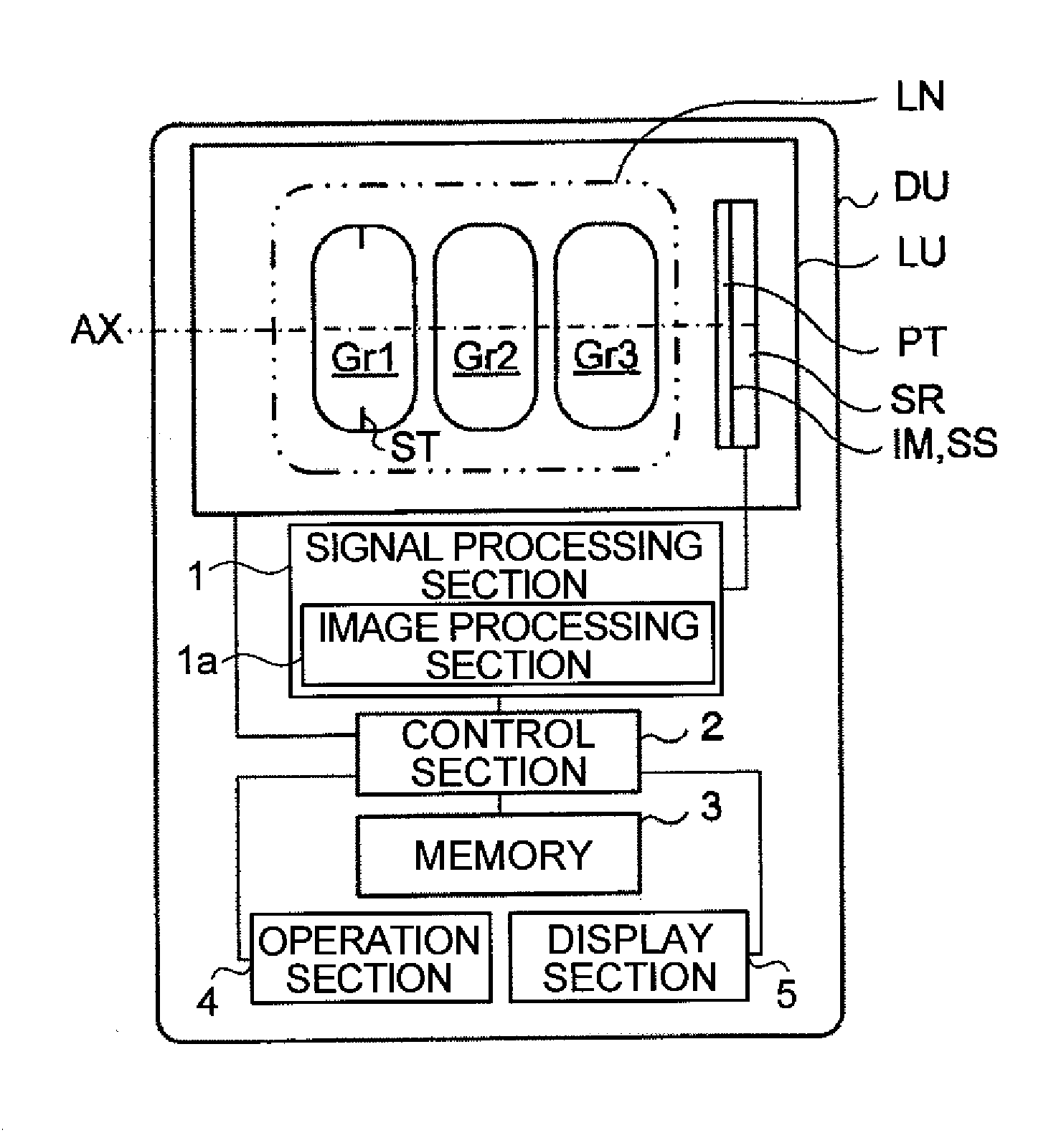
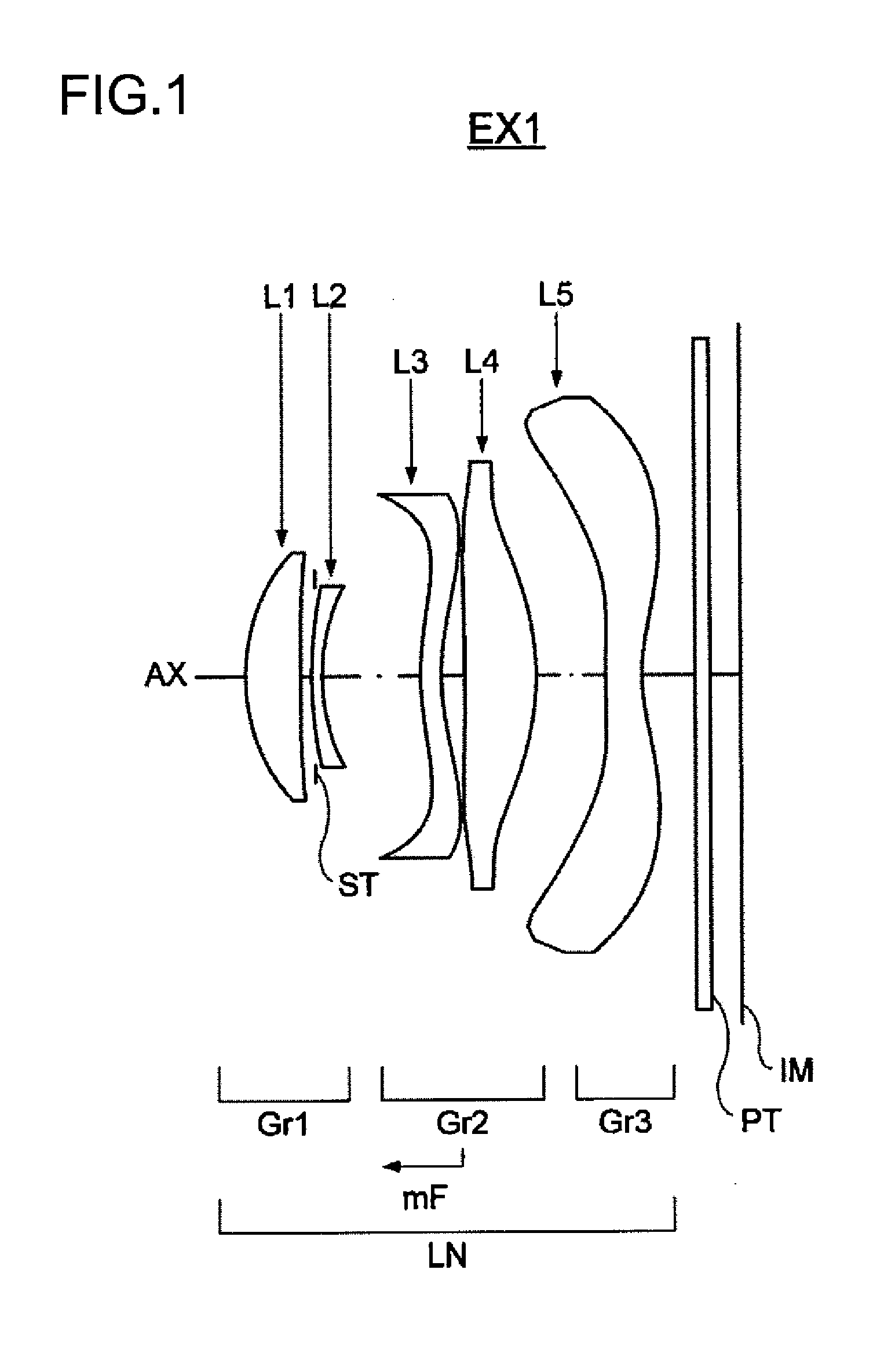
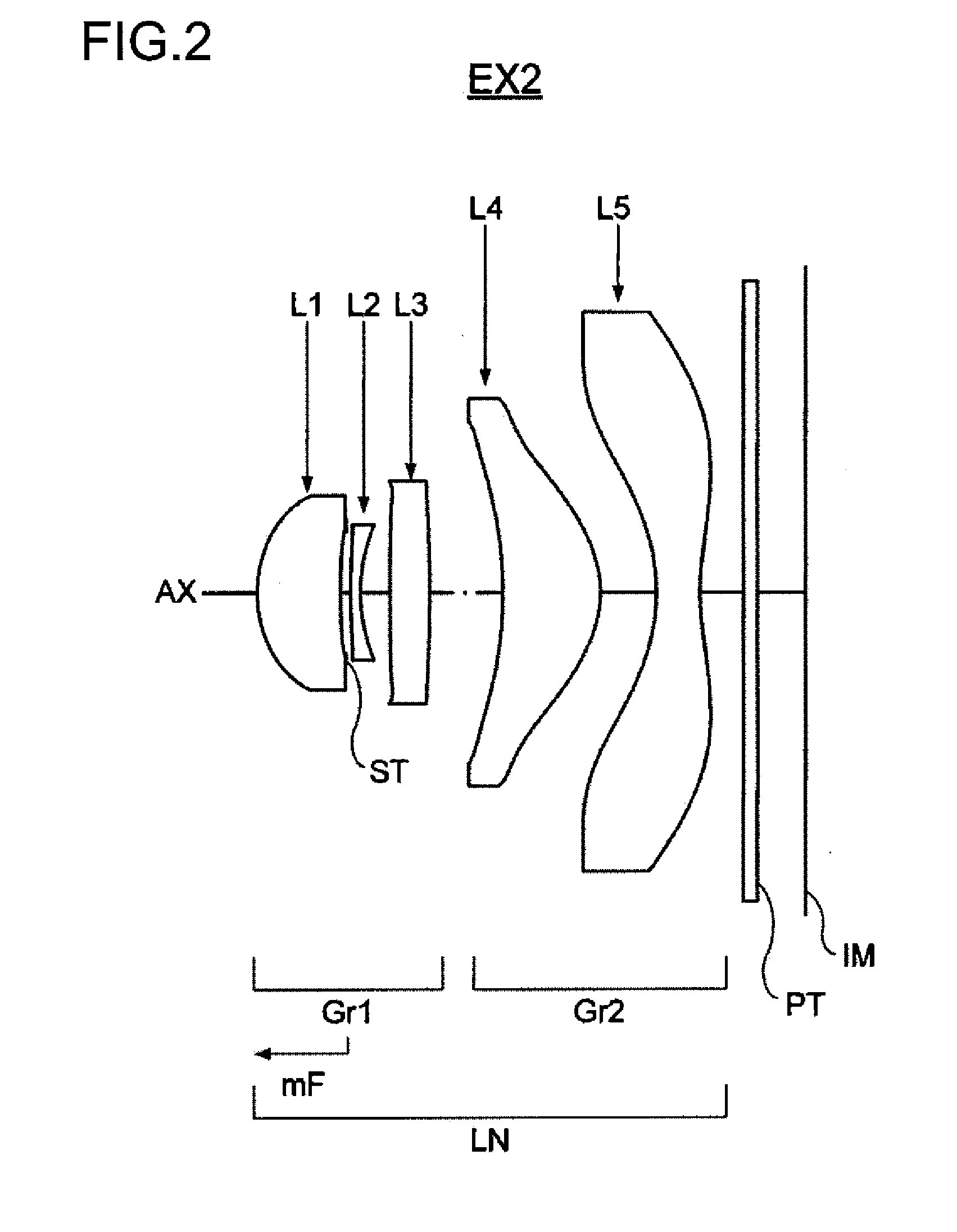
Imaging Lens, Imaging Optical Device, and Digital Equipment
ActiveUS20130016278A1Compactly add high-performance image input capabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOphthalmologyImaging lens
An imaging lens system has, from an object side, at least one positive lens element convex to the object side, a negative lens element, and at least one lens element having an aspherical surface. The positive and negative lens elements are arranged next to each other. The formulae 0.1<Ton / Dopn<7, 0.1<(Rona−Ronb) / (Rona+Ronb)<1.5, and 0.3<Y′ / TL<0.9 are fulfilled, where Ton represents the axial thickness of the most object-side negative lens element, Dopn represents the axial distance between the most object-side negative lens element and the positive lens element located to the object side of and next to that negative lens element, Rona represents the paraxial radius of curvature of the object-side surface of the most object-side negative lens element, Ronb represents the paraxial radius of curvature of the image-side surface of the most object-side negative lens element, Y′ represents the maximum image height, and TL represents the axial distance from the vertex of the most object-side lens surface to the image surface (in a case where a parallel-plane plate is included, the air equivalent length).
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Lens-fitted film unit with plastic taking lens
InactiveUS6188841B1Simple structureIncrease changeProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensFilm plane
A lens-fitted film unit is provided with a thermally expandable axial distance adjusting member which has a thermal expansion coefficient greater than plastic lens elements of a taking lens held by an axially movable lens holder and disposed between the lens holder and a stationary shutter cover and which expands or contracts in accordance with a change in ambient temperature to change an axial distance between the lens holder and a film plane so as thereby to shift a focal point of the taking lens in an axial direction to compensate a variation of the focal length of the taking lens due to a change in refractive power of the plastic lens element which is caused by axial expansion or axial contraction of the plastic lens element due to the change in ambient temperature.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com