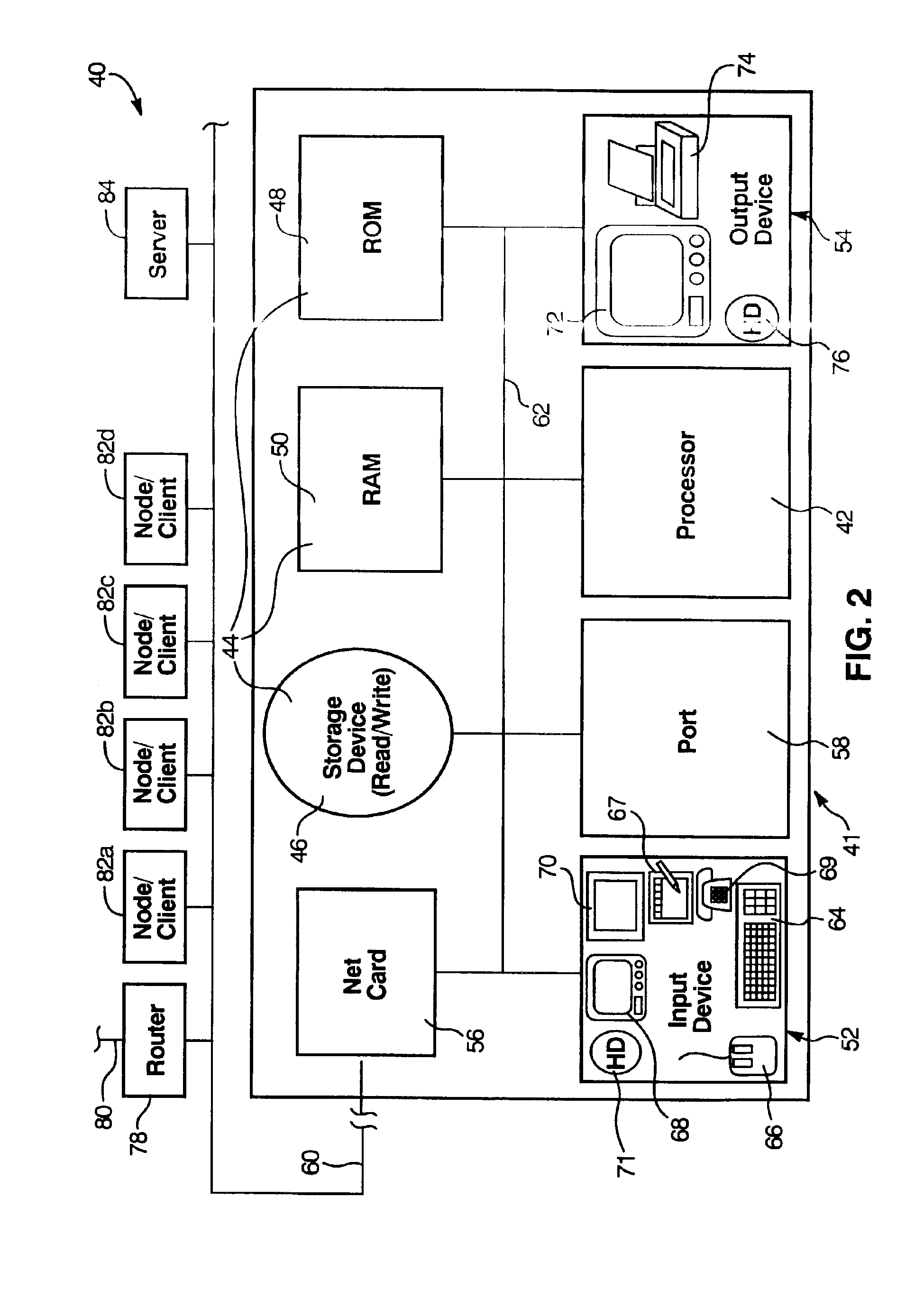
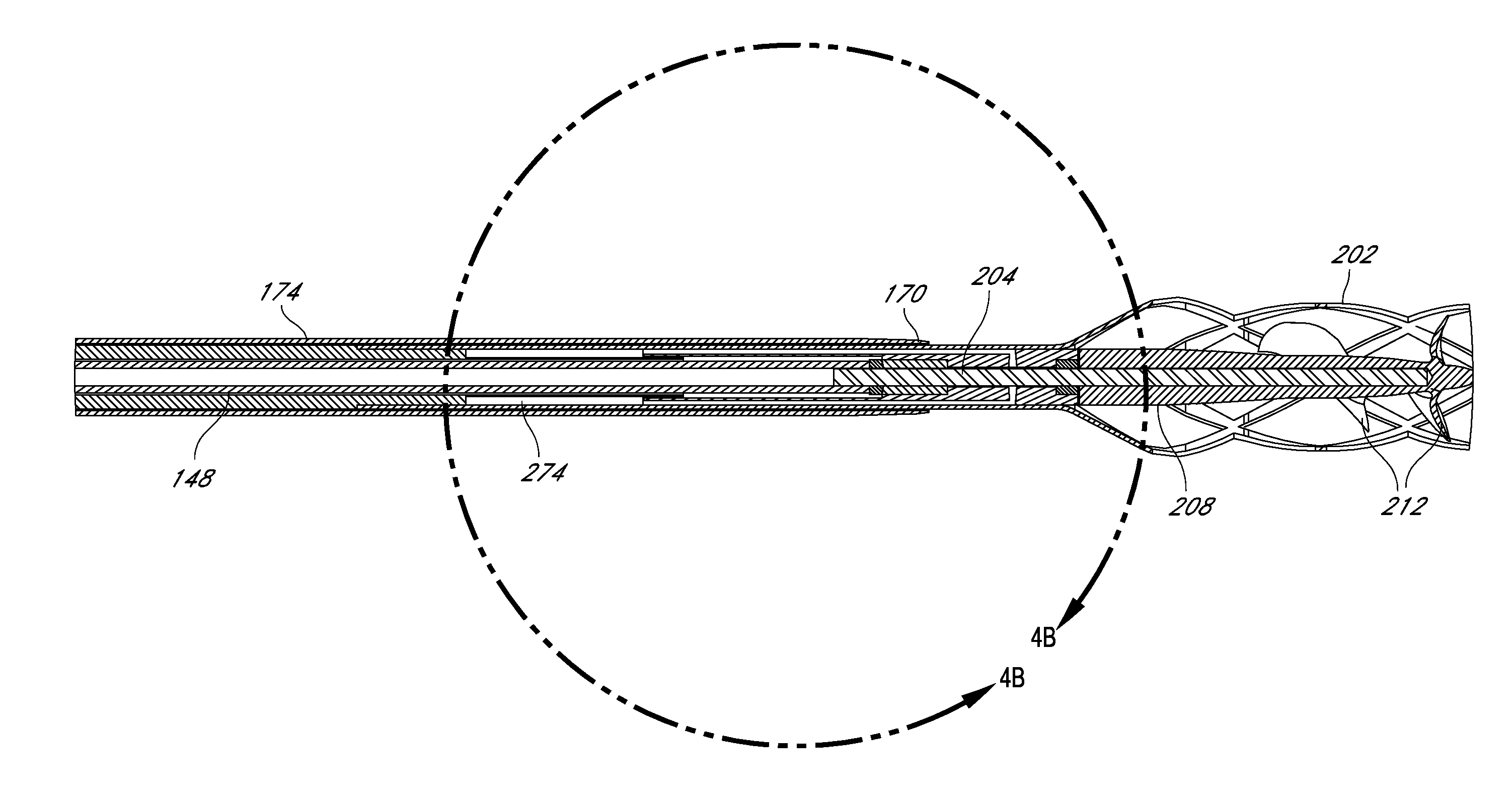
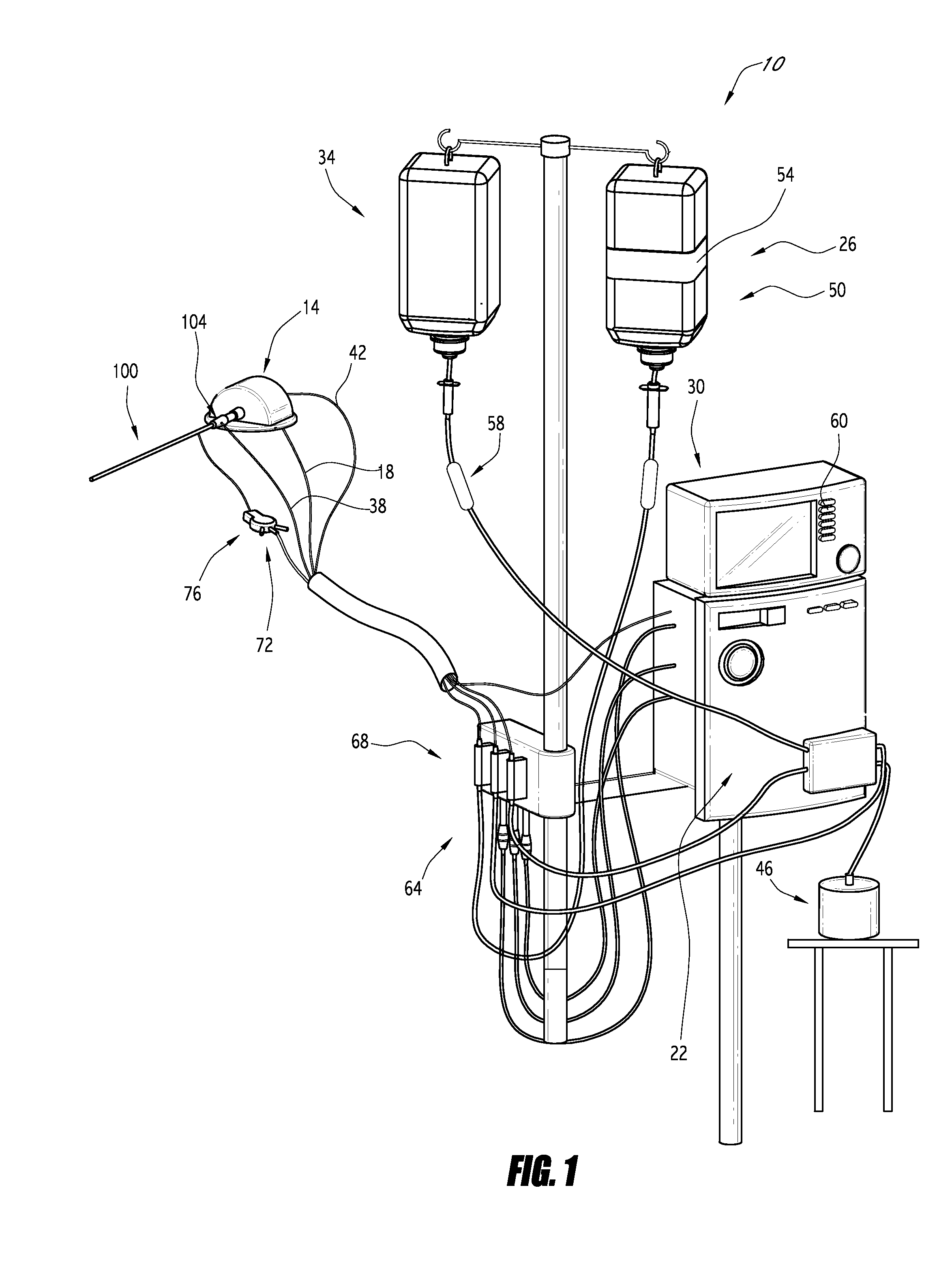
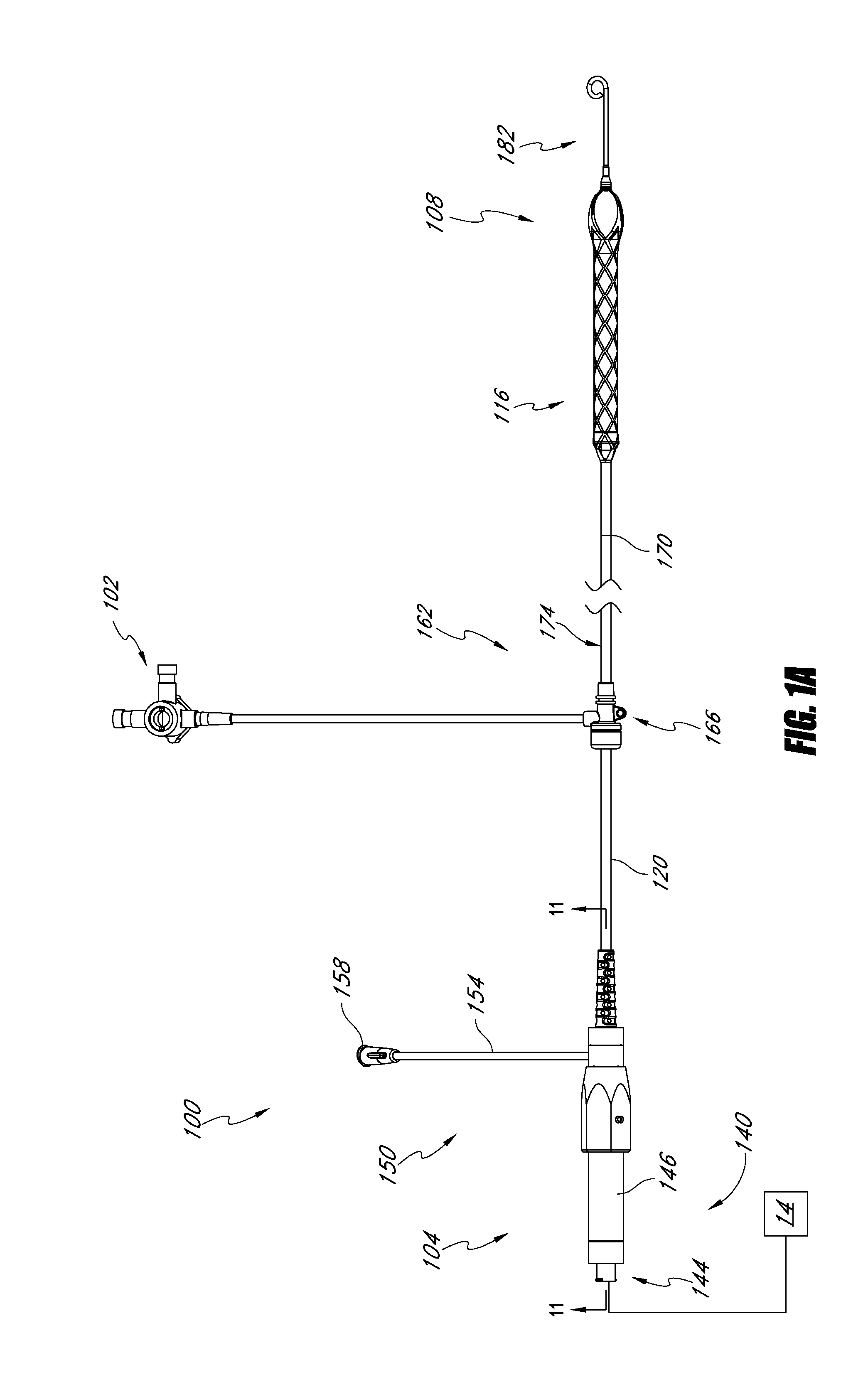
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2126results about "Blood pumps" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
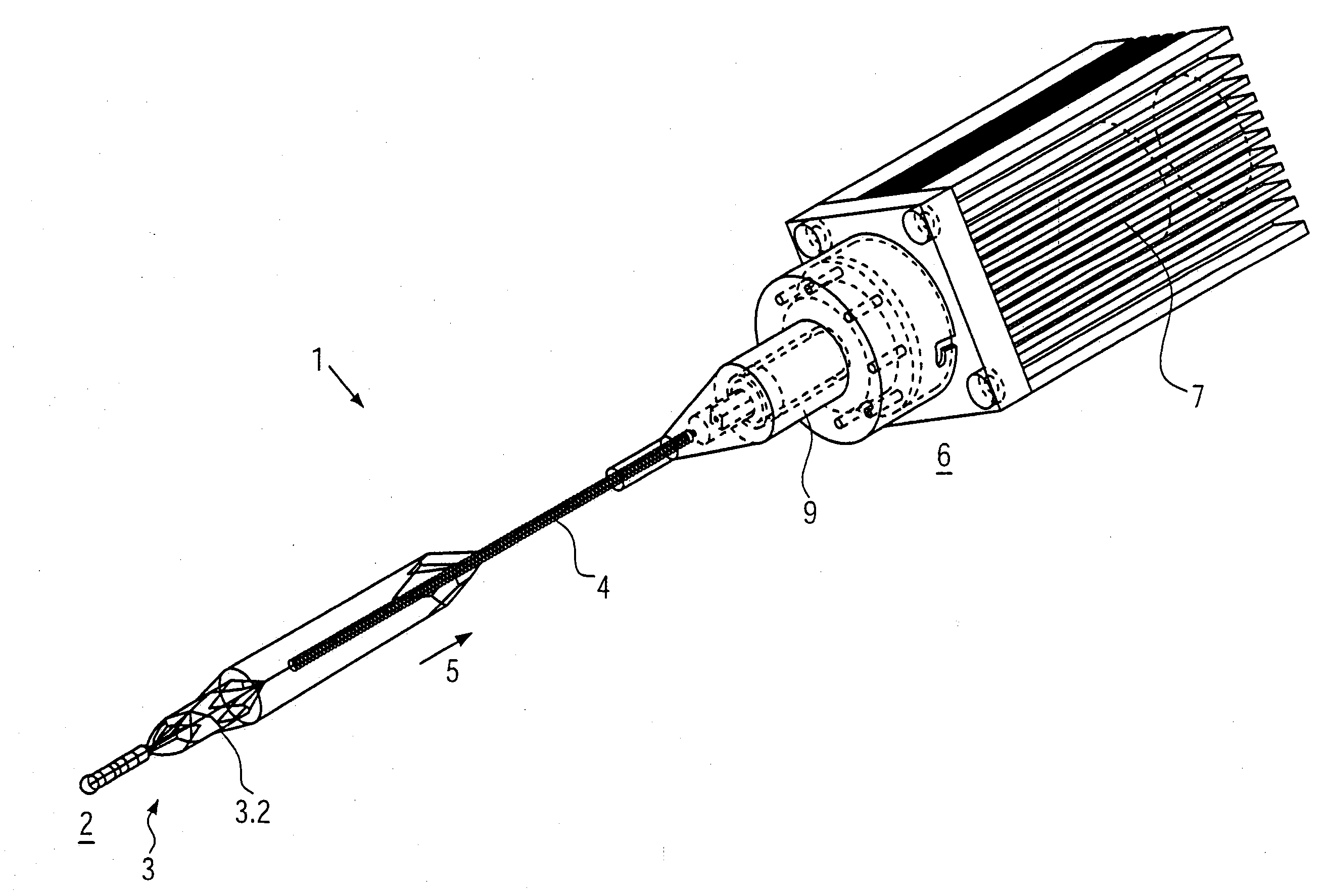
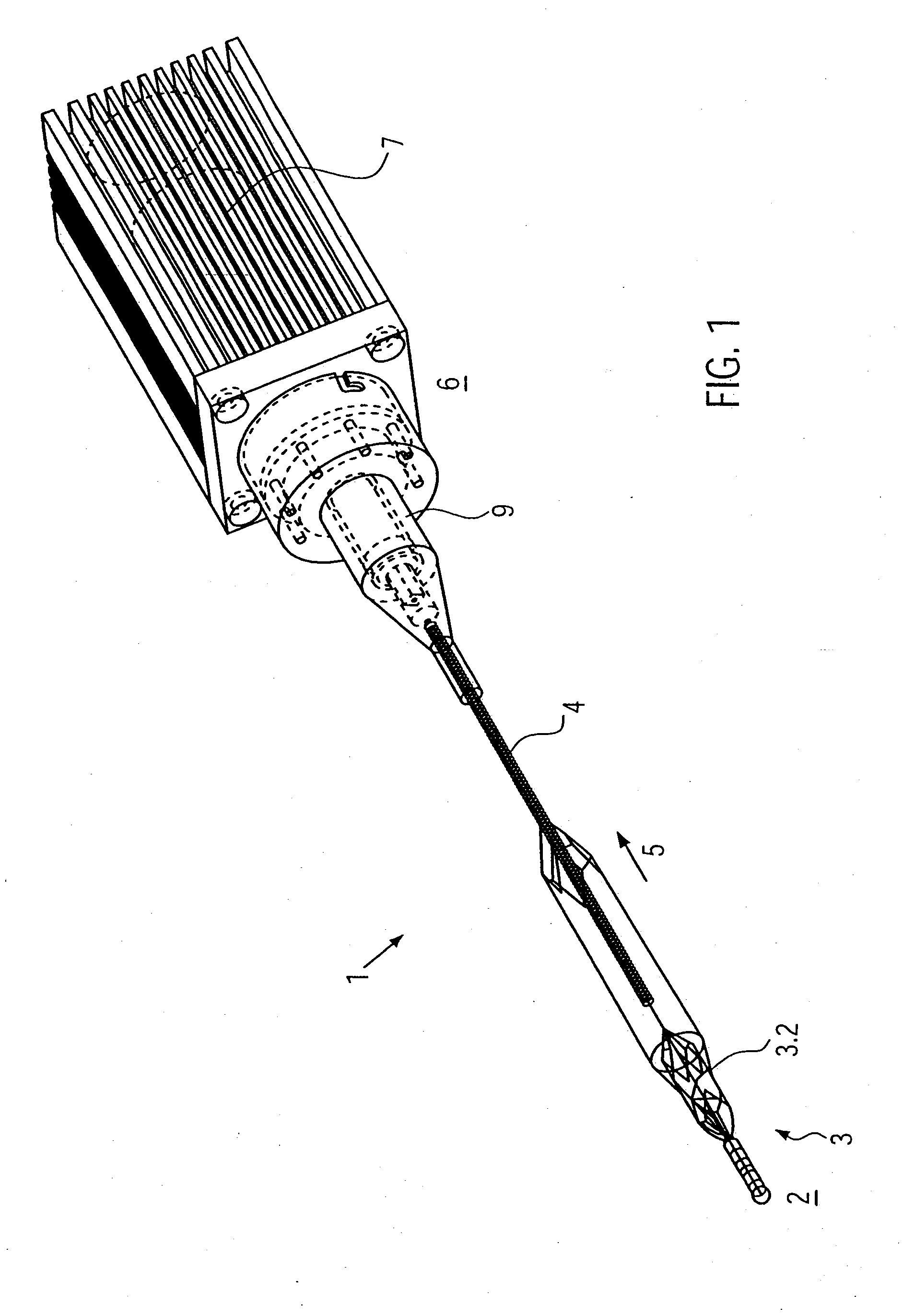
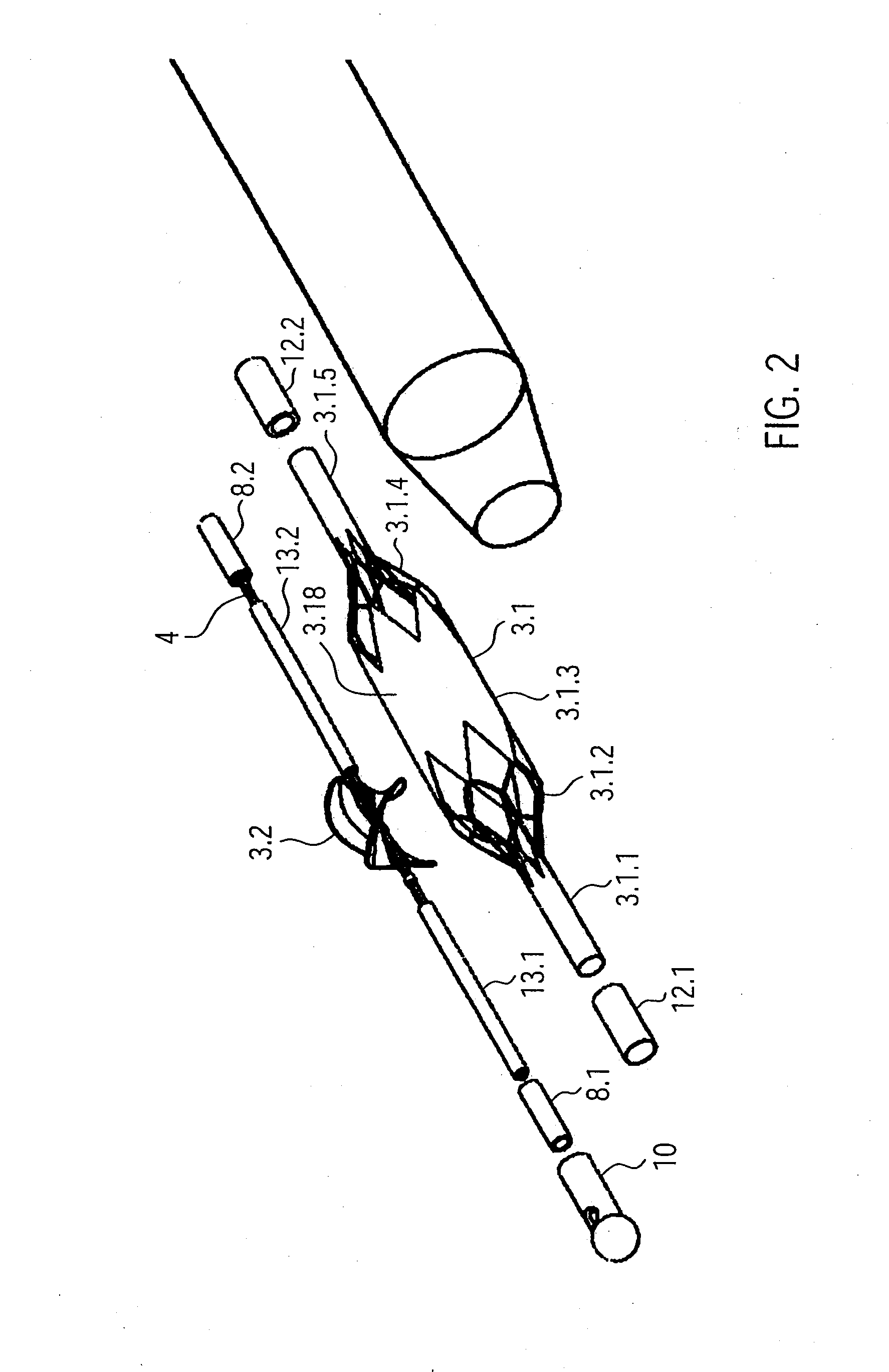
High convection home hemodialysis/hemofiltration and sorbent system
InactiveUS20050131332A1Easily set up sterile blood therapy systemImprove efficiencySemi-permeable membranesHaemofiltrationPositive pressureSorbent
A system, method and apparatus for performing a renal replacement therapy is provided. In one embodiment, two small high flux dialyzers are connected in series. A restriction is placed between the two dialyzers in the dialysate flow path. The restriction is variable and adjustable in one preferred embodiment. The restriction builds a positive pressure in the venous dialyzer, causing a high degree of intentional backfiltration. That backfiltration causes a significant flow of dialysate through the high flux venous membrane directly into the patient's blood. That backfiltered solution is subsequently ultrafiltered from the patient from the arterial dialyzer. The diffusion of dialysate into the venous filter and removal of dialysate from the arterial dialyzer causes a convective transport of toxins from the patient. Additionally, the dialysate that does not diffuse directly into the patient but instead flows across the membranes of both dialyzers provides a diffusive clearance of waste products.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +1
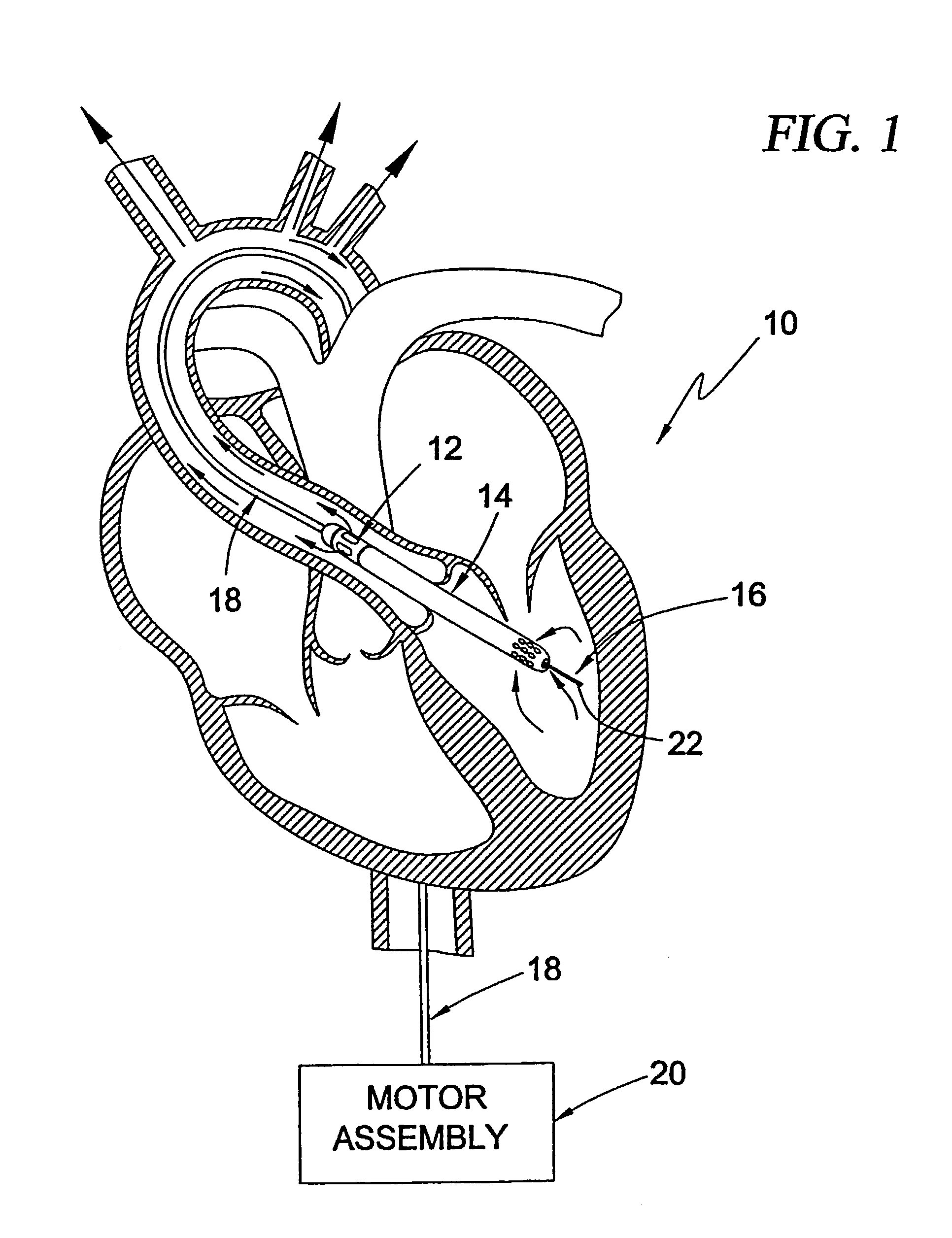
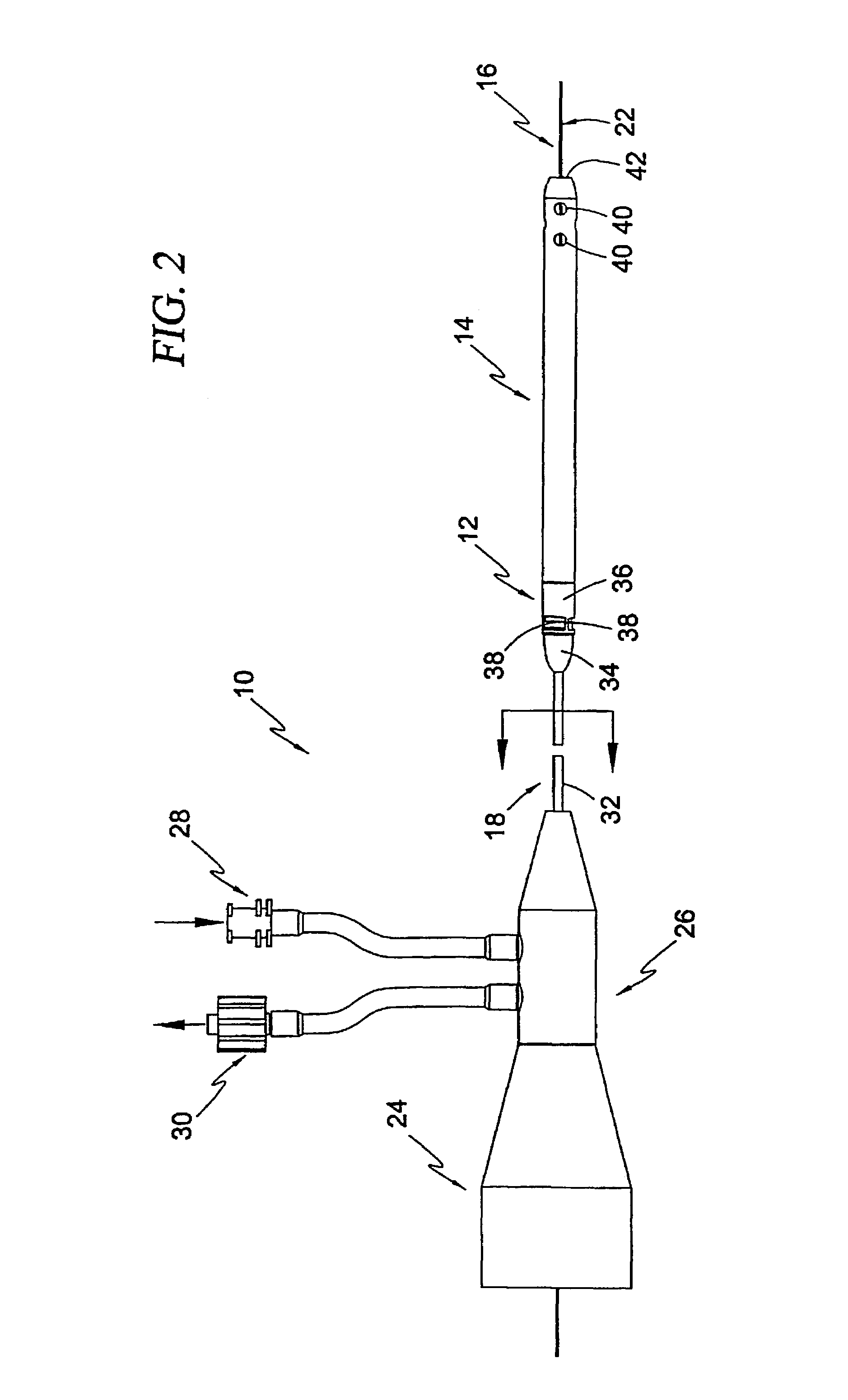
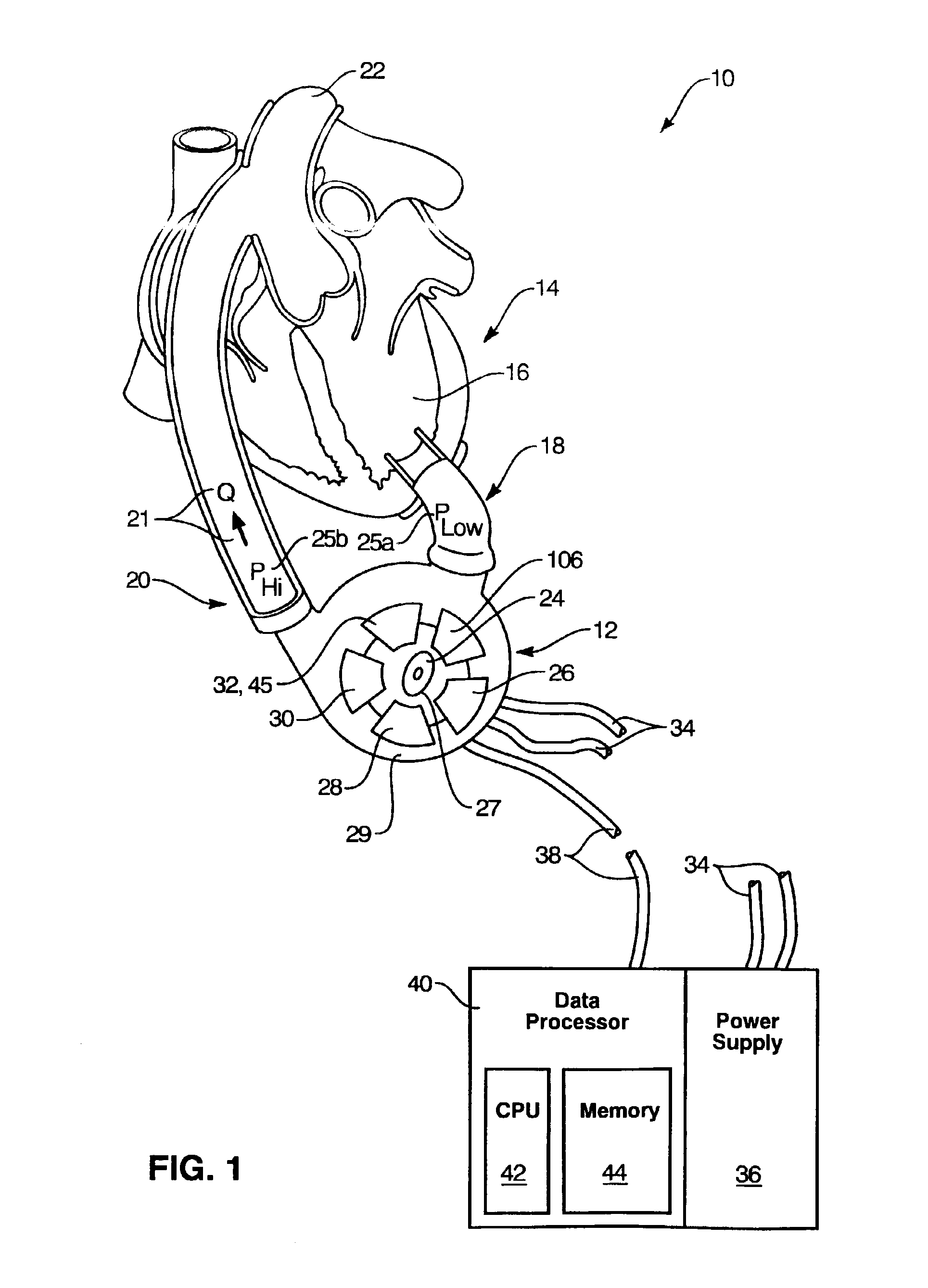
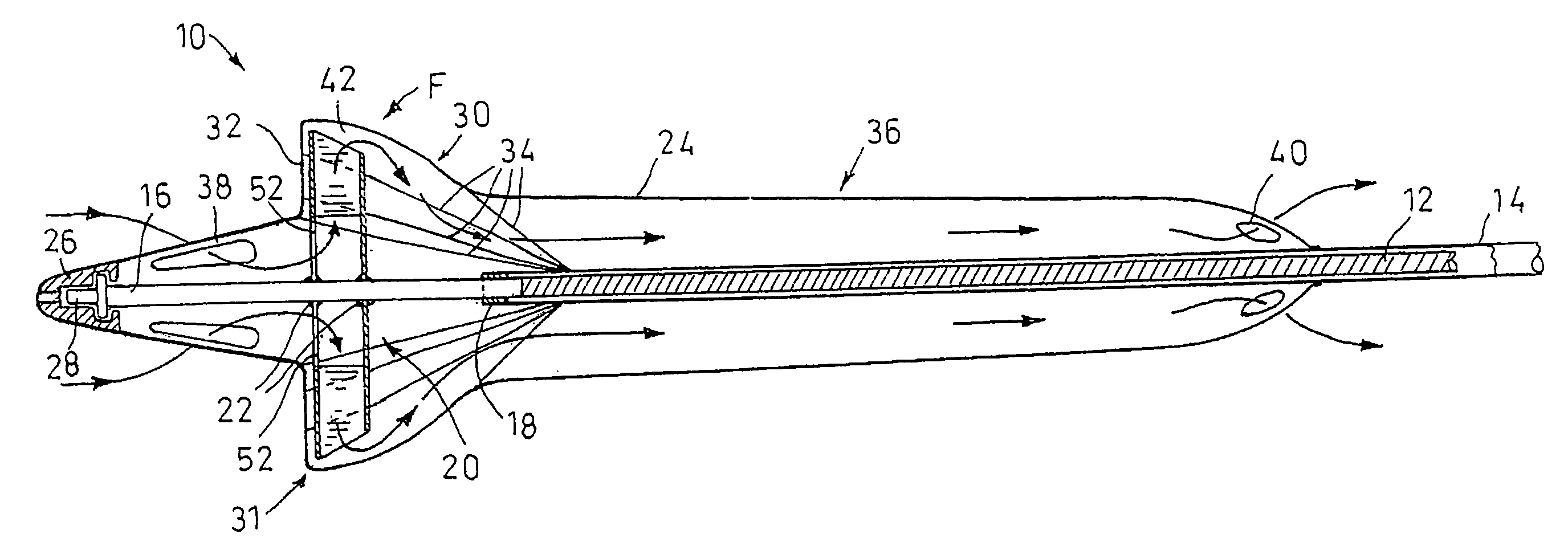
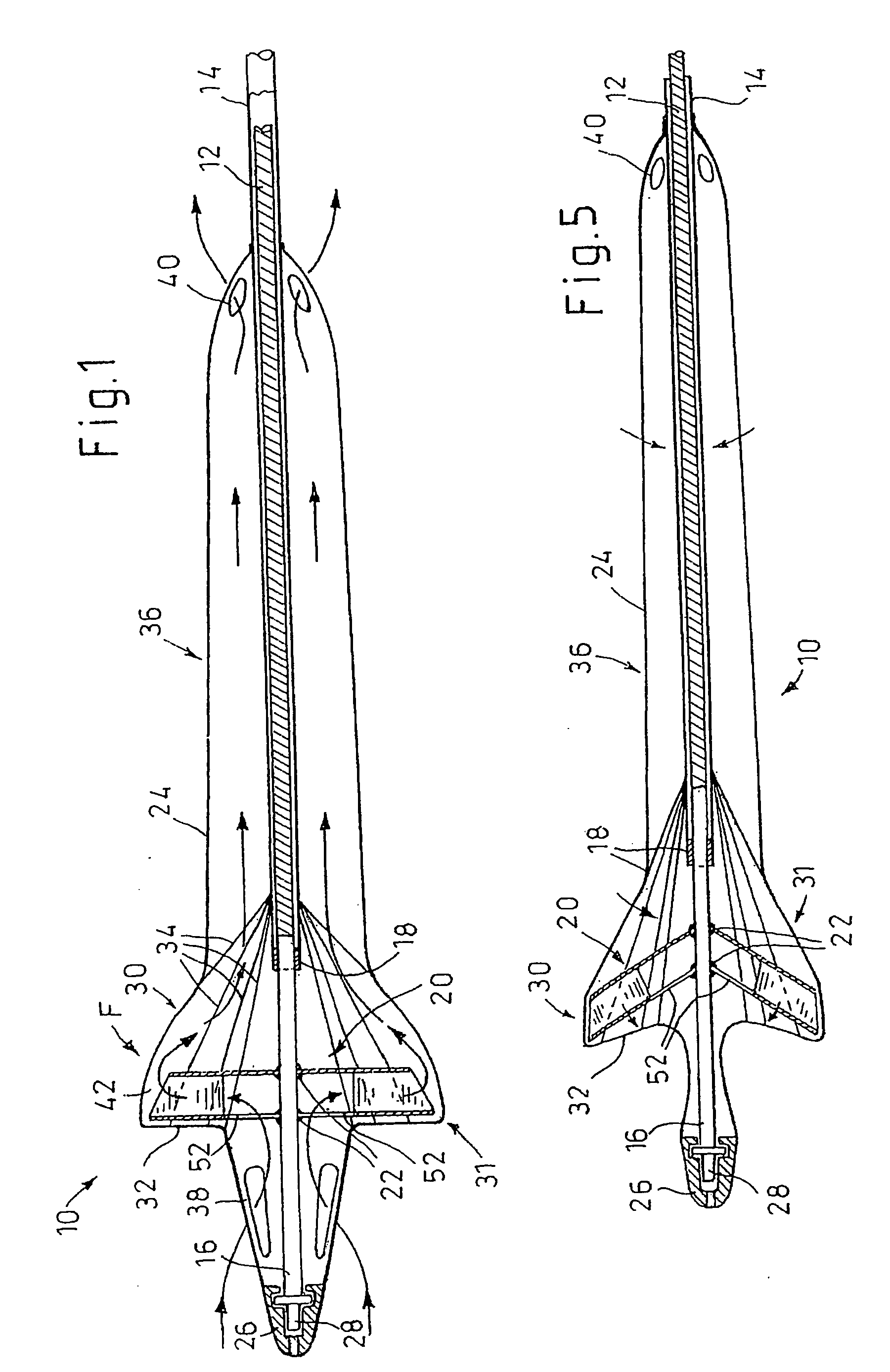
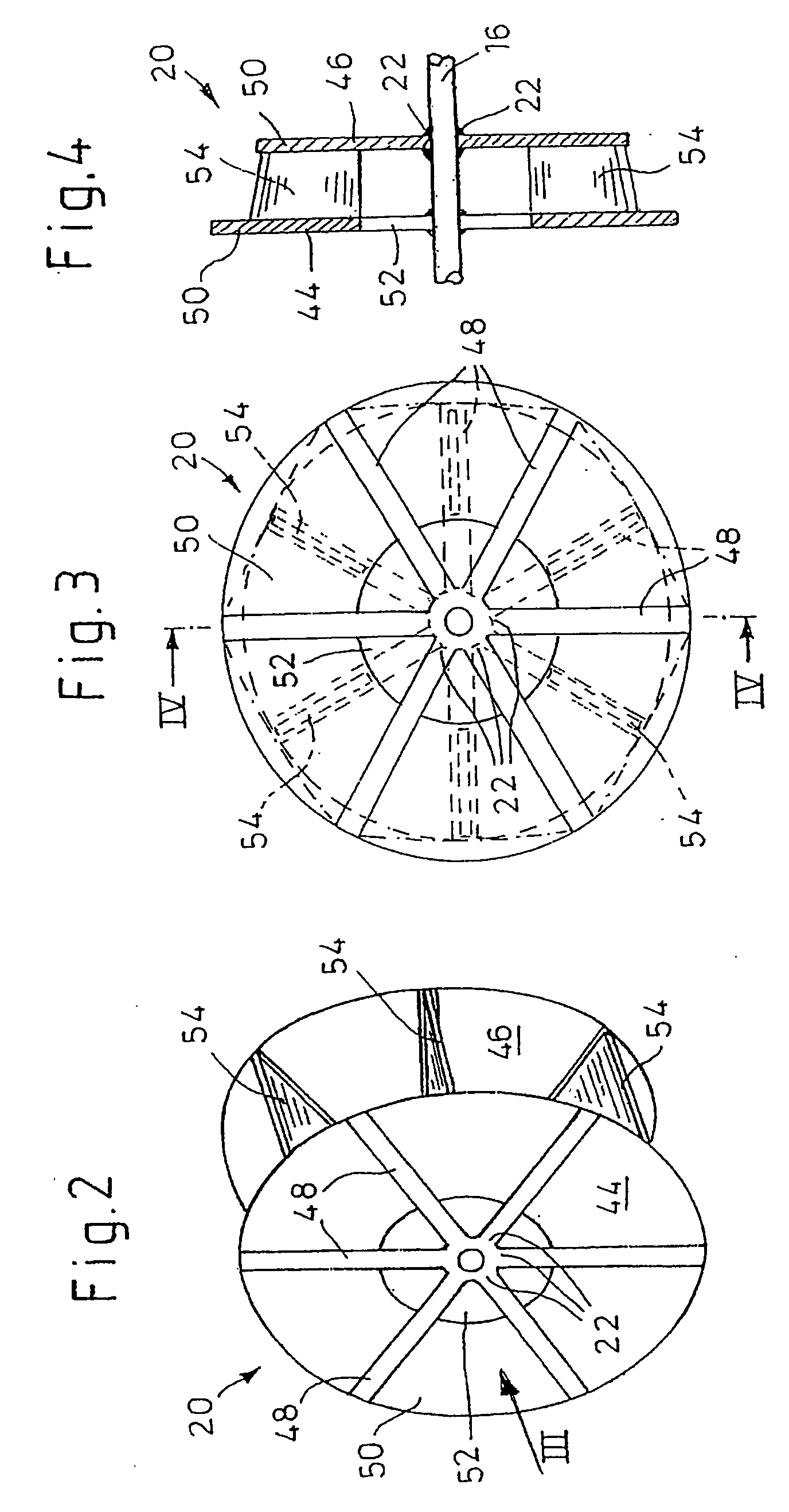
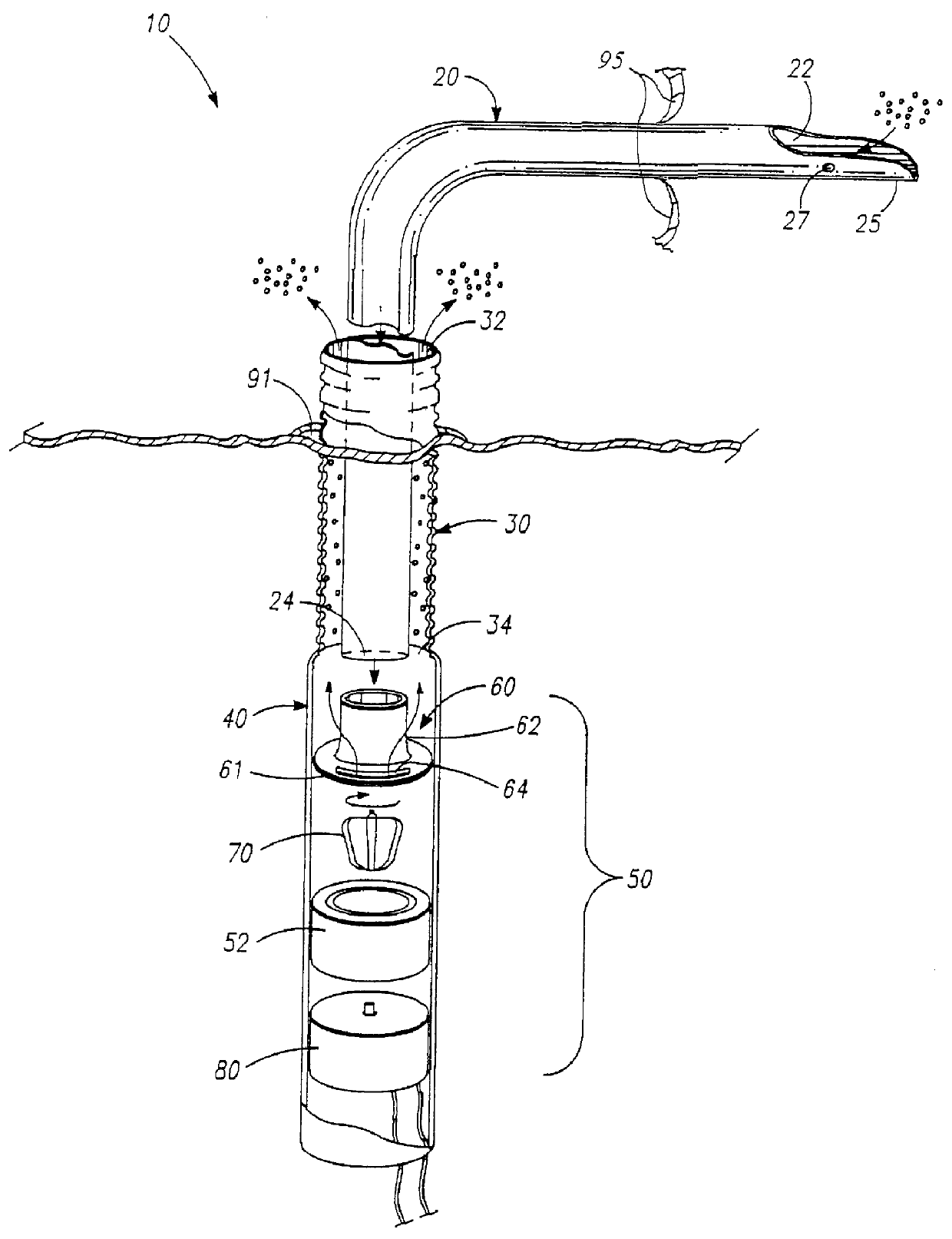
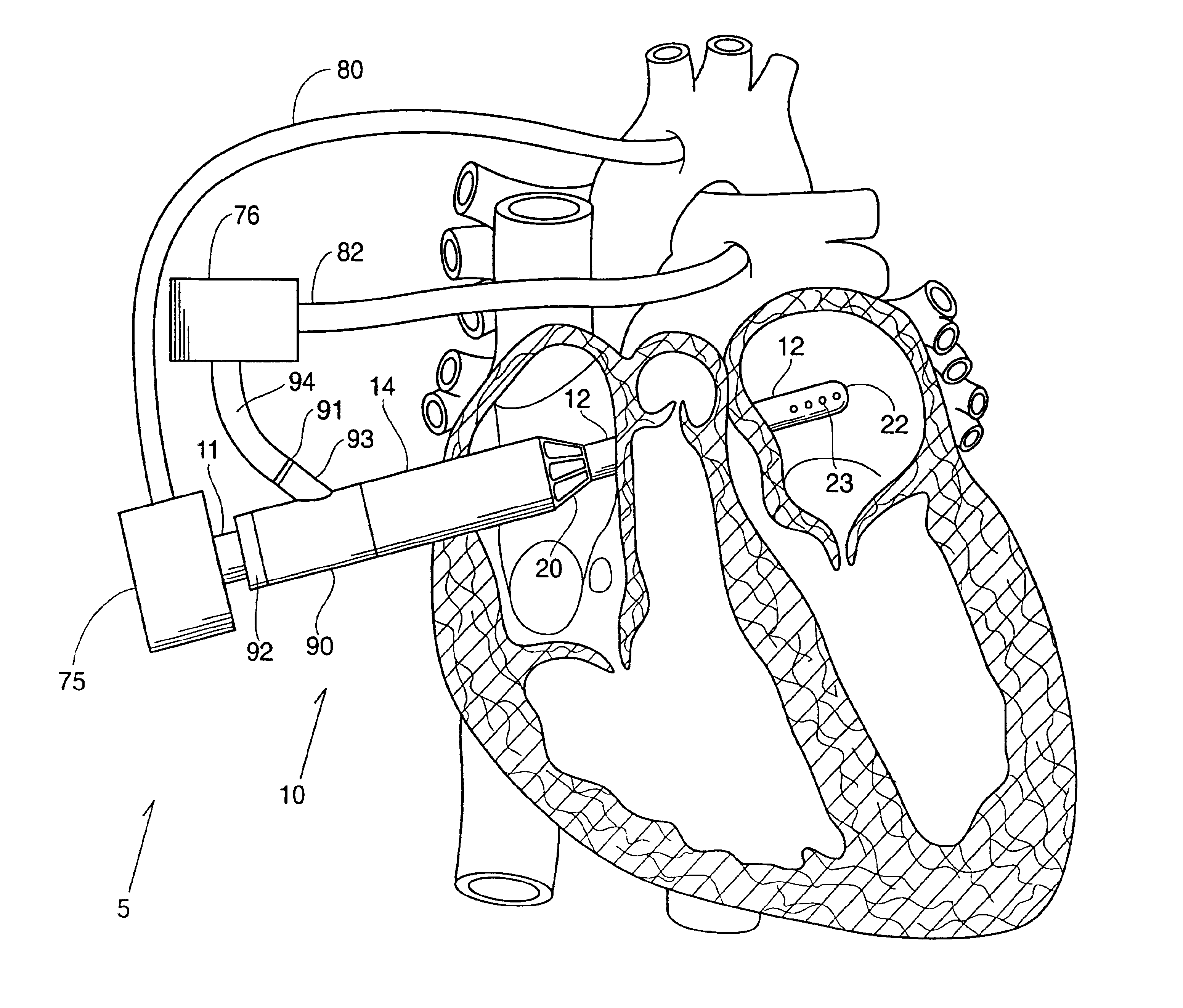
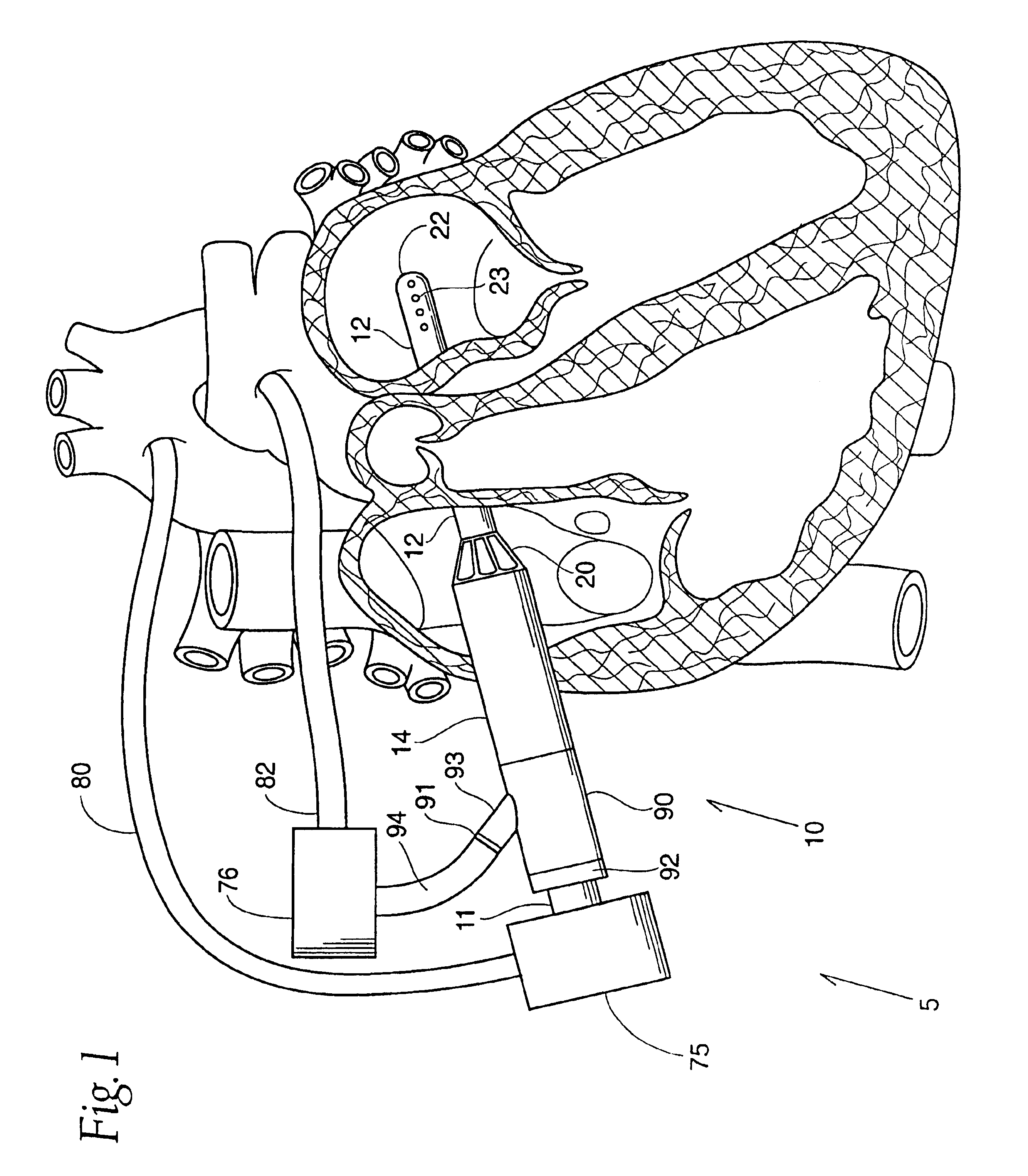
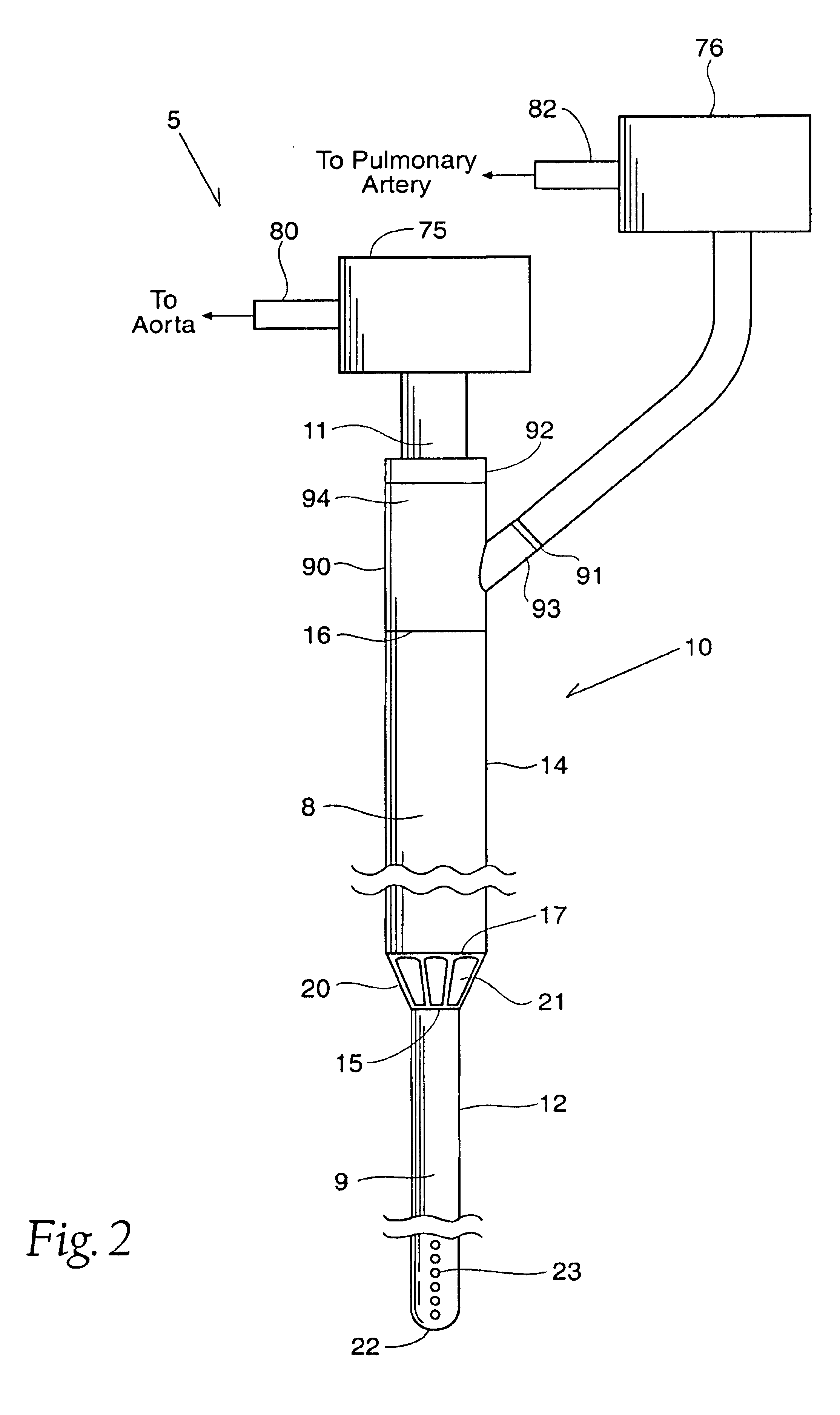
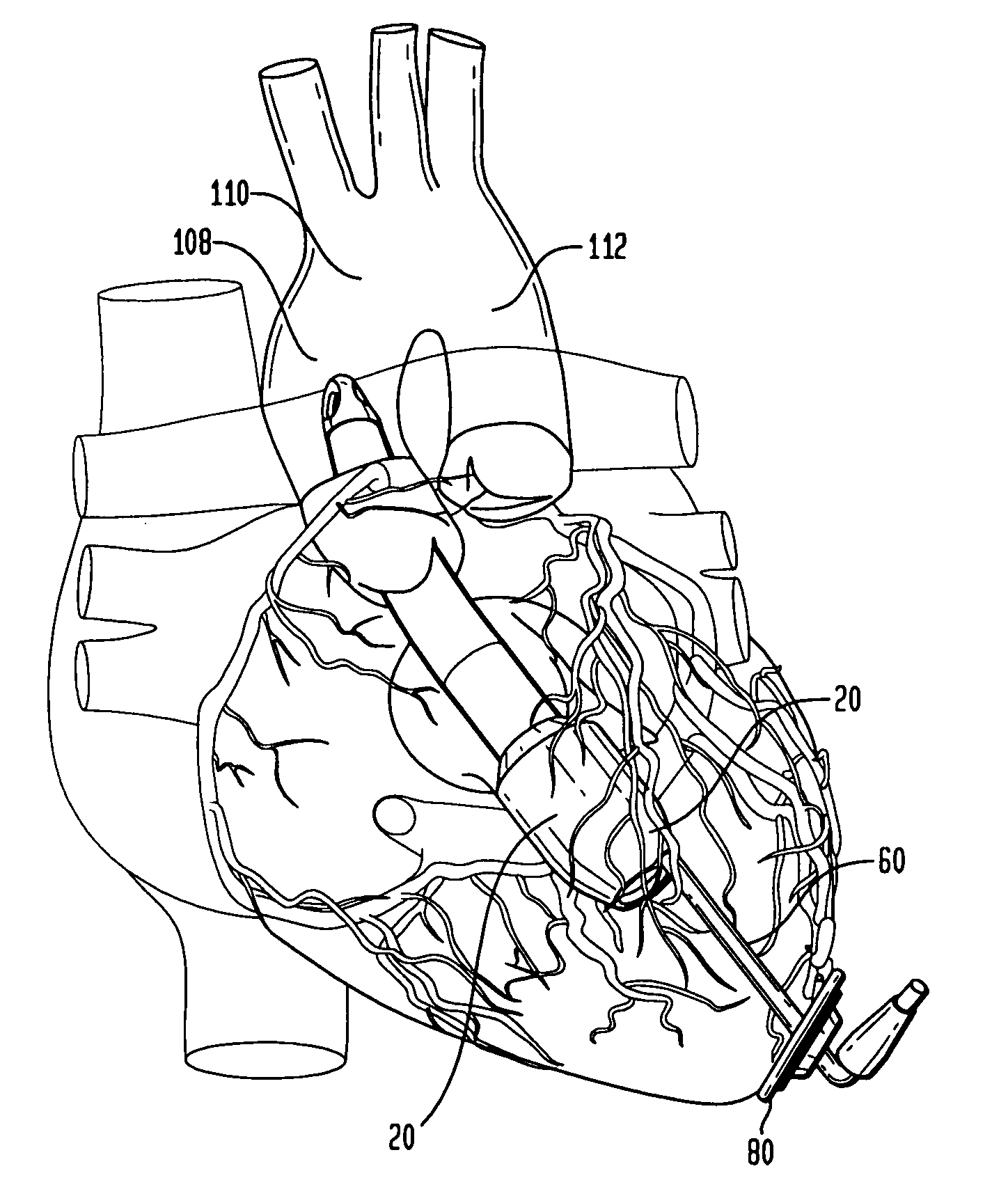
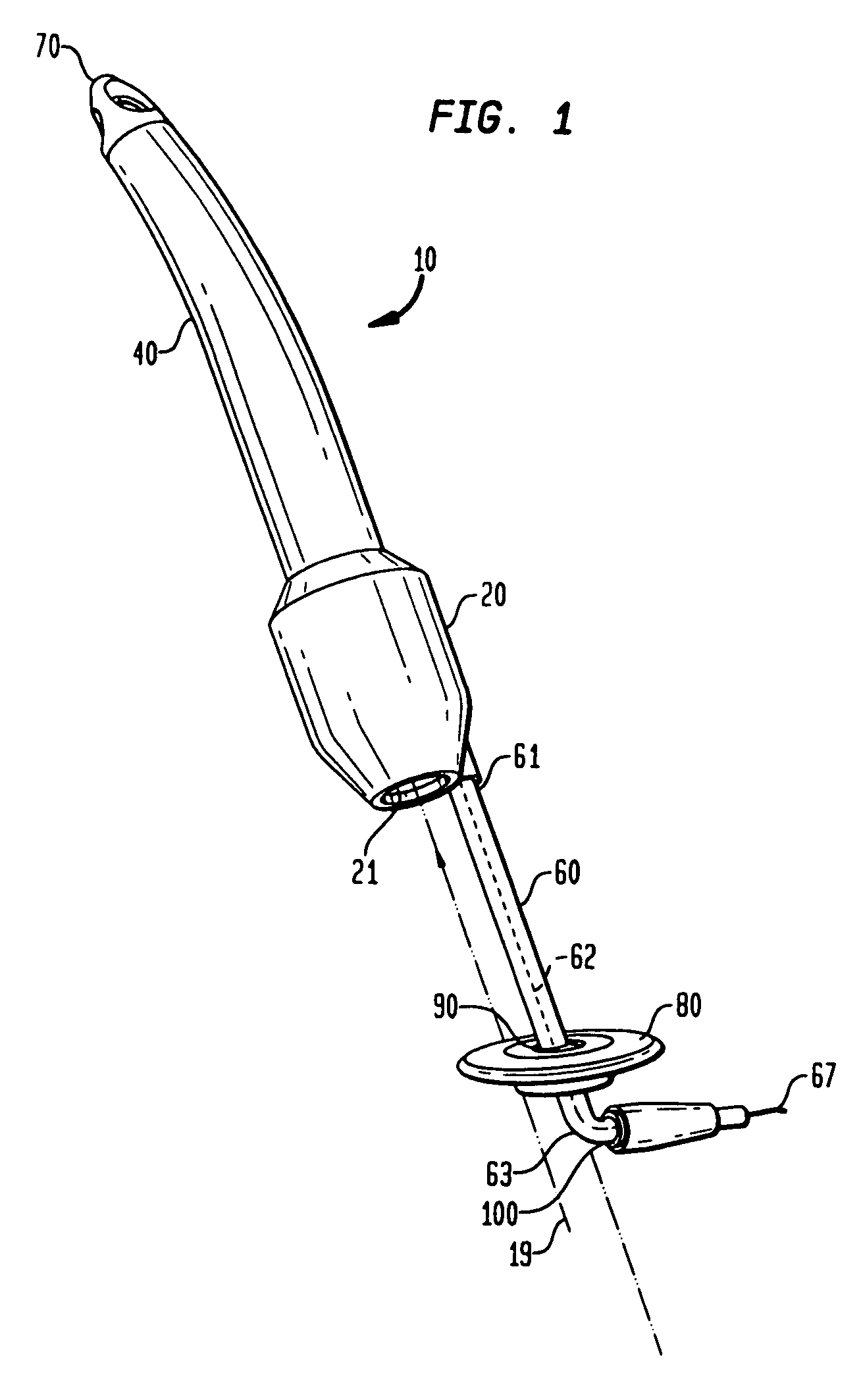
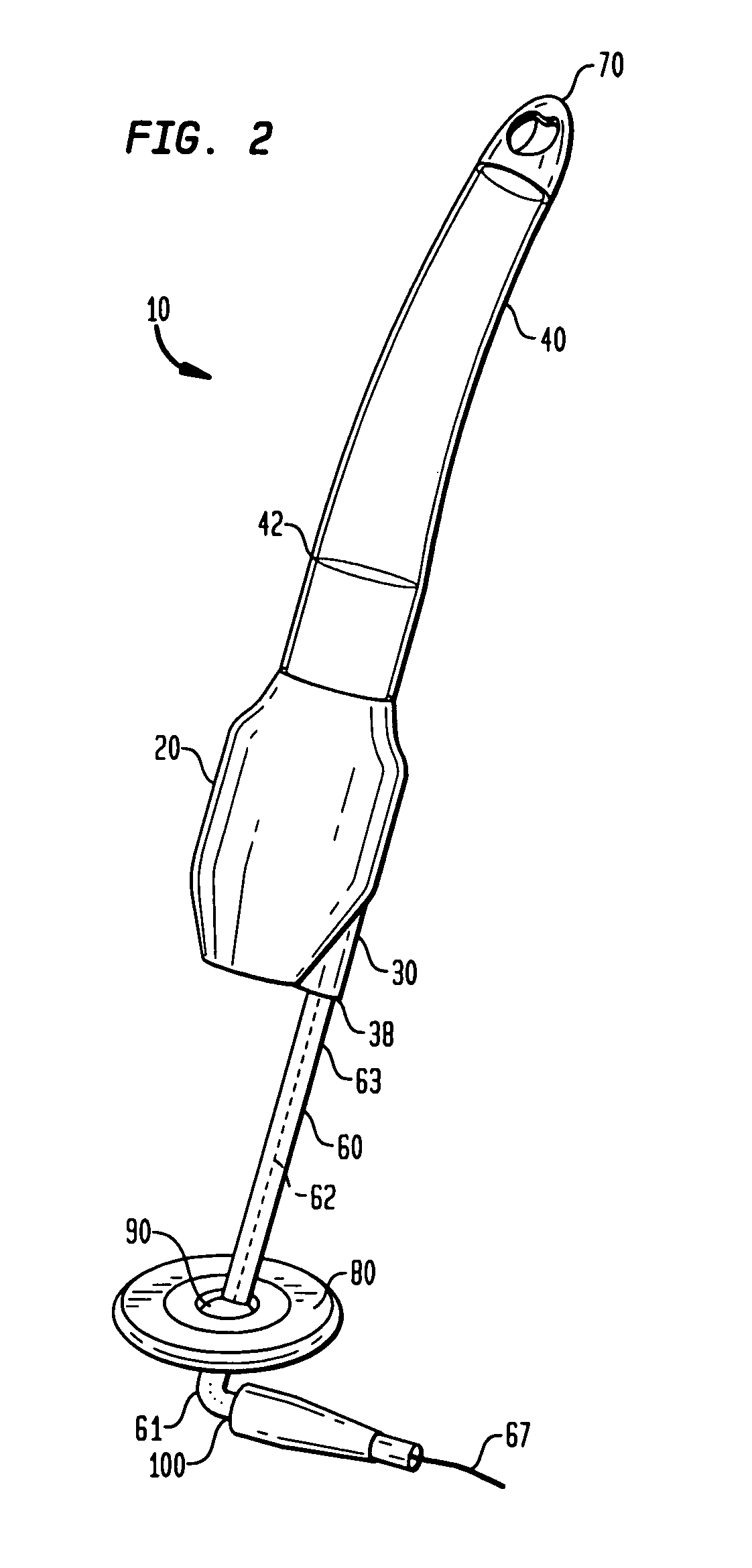
Guidable intravascular blood pump and related methods
InactiveUS7022100B1Integration of featureEliminate needGuide wiresControl devicesBlood pumpBlood vessel
An improved intravascular blood pump system (10) and related methods involving the broad inventive concept of equipping the intravascular blood pump (12) with guiding features such that the intravascular blood pump can be selectively positioned at a predetermined location within the circulatory system of a patient.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Expandable impeller pump
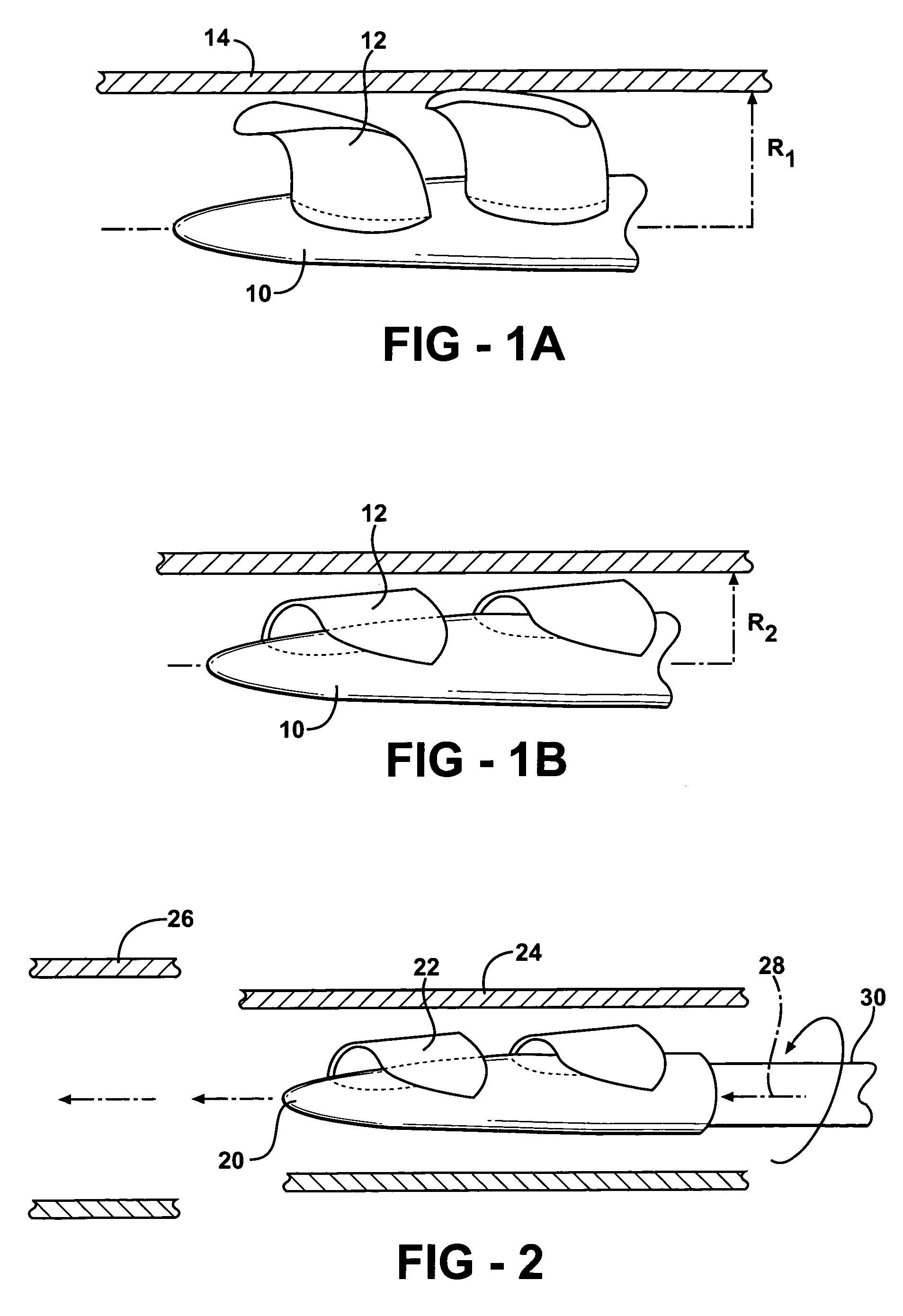
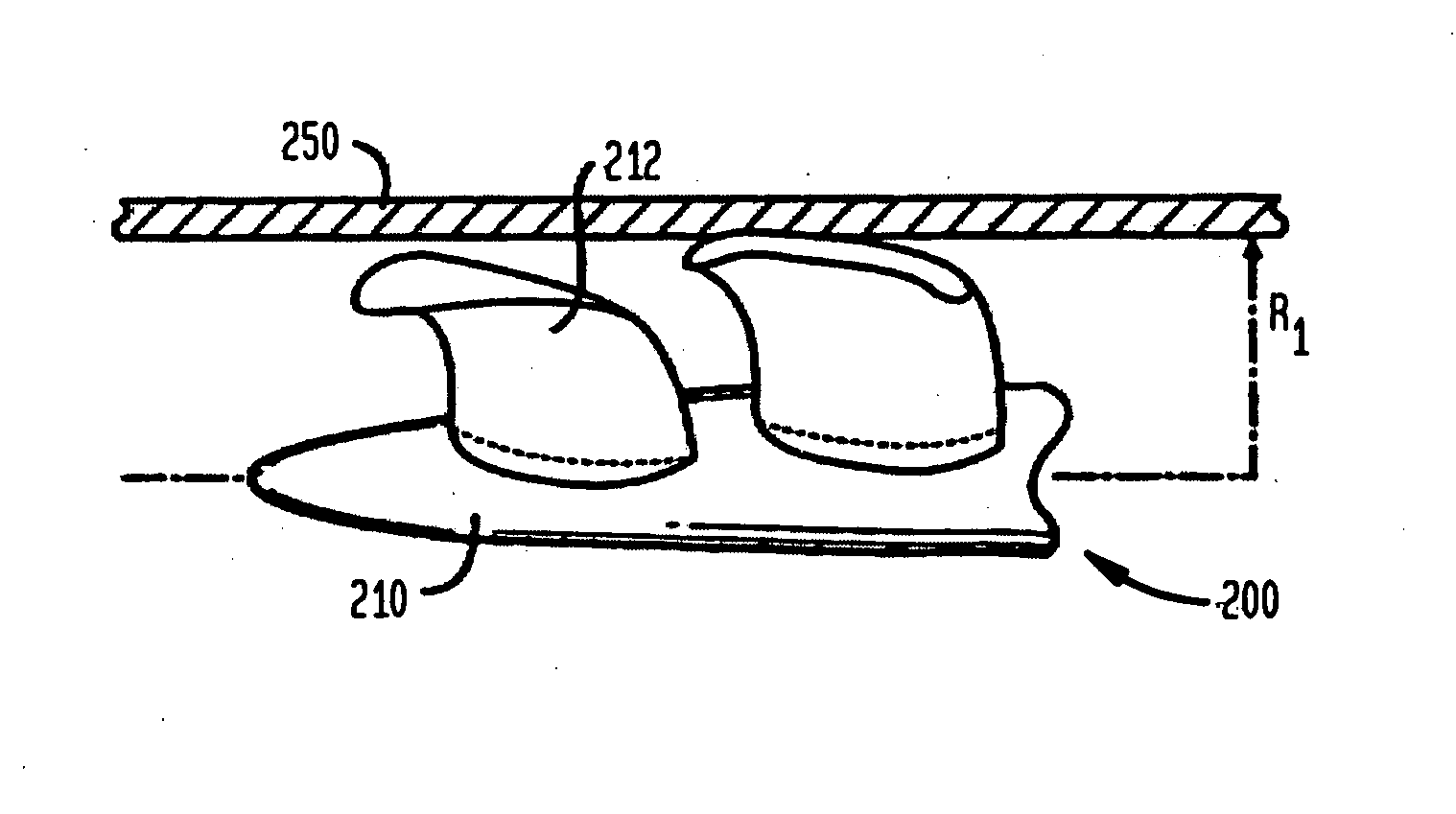
ActiveUS7393181B2Easy to compressReduced form requirementsPropellersEngine manufactureImpellerEngineering
An impeller according to an example of the present invention comprises a hub, and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub, and a stored configuration in which the impeller is radially compressed, for example by folding the blade towards the hub. The impeller may comprise a plurality of blades, arranged in blade rows, to facilitate radial compression of the blades. The outer edge of a blade may have a winglet, and the base of the blade may have an associated indentation to facilitate folding of the blade.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
Heart assist device with expandable impeller pump
An impeller includes a hub and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a stored configuration in which the blade is compressed so that its distal end moves towards the hub, and a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub. The impeller may be part of a pump for pumping fluids, such as pumping blood within a patient. A blood pump may include a cannula having a proximal portion with a fixed diameter, and a distal portion with an expandable diameter. The impeller may reside in the expandable portion of the cannula. The cannula may have a compressed diameter which allows it to be inserted percutaneously into a patient. Once at a desired location, the expandable portion of the cannula may be expanded and the impeller expanded to the deployed configuration. A flexible drive shaft may extend through the cannula for rotationally driving the impeller within the patient's body.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
Catheter device
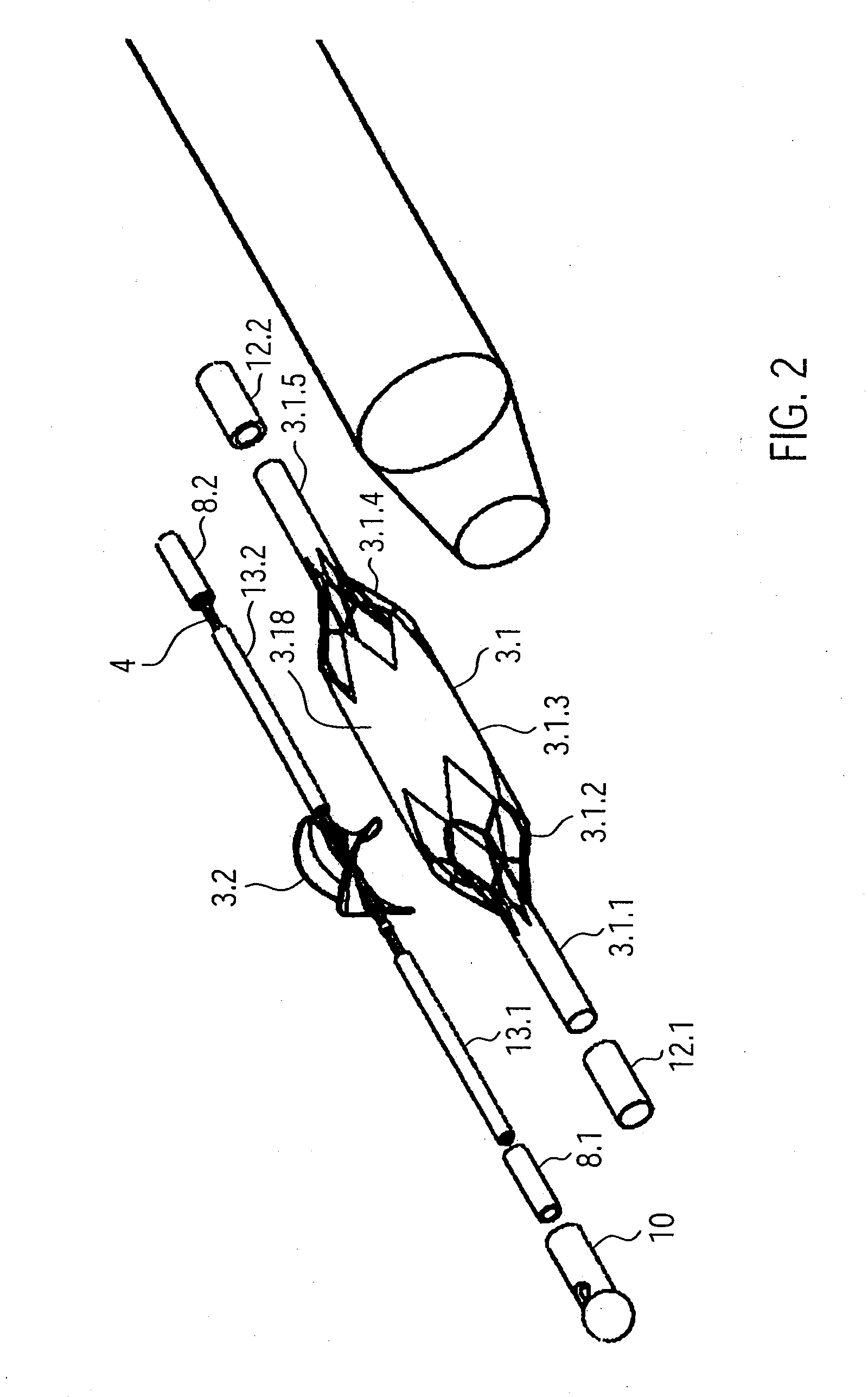
ActiveUS20090093764A1Impairing rotatabilityAccurate settingElectrotherapyCarpet cleanersDrive shaftClutch
The catheter device comprises a motor located at the proximal end of the catheter device and a drive shaft, extending from the proximal end section to the distal end section of the catheter device, for driving a rotating element located at the distal end of the catheter device. The catheter device also comprises a hose-like catheter body which encompasses the drive shaft and extends from the proximal end section to the distal end section of the catheter device. At the proximal end of the catheter device, the drive shaft is connected to a motor by a clutch. The clutch is a magnetic clutch with a proximal and a distal magnet unit. The proximal magnet unit is connected to the motor and the distal magnet unit to the drive shaft. The distal magnet unit is mounted fluid-tight in a clutch housing. The proximal end of the catheter body makes a fluid-tight connection with the clutch housing.
Owner:AIS AACHEN INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS
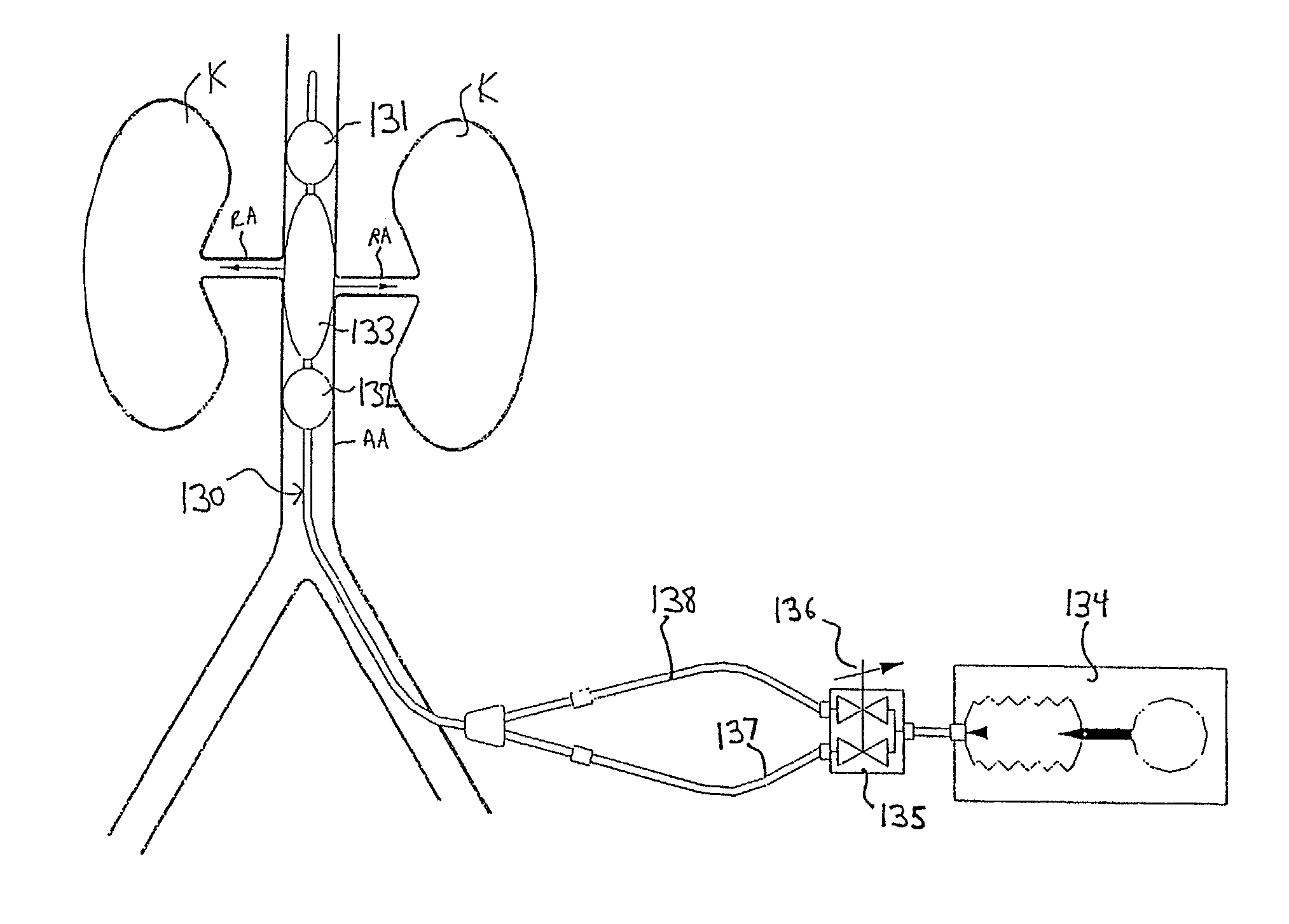
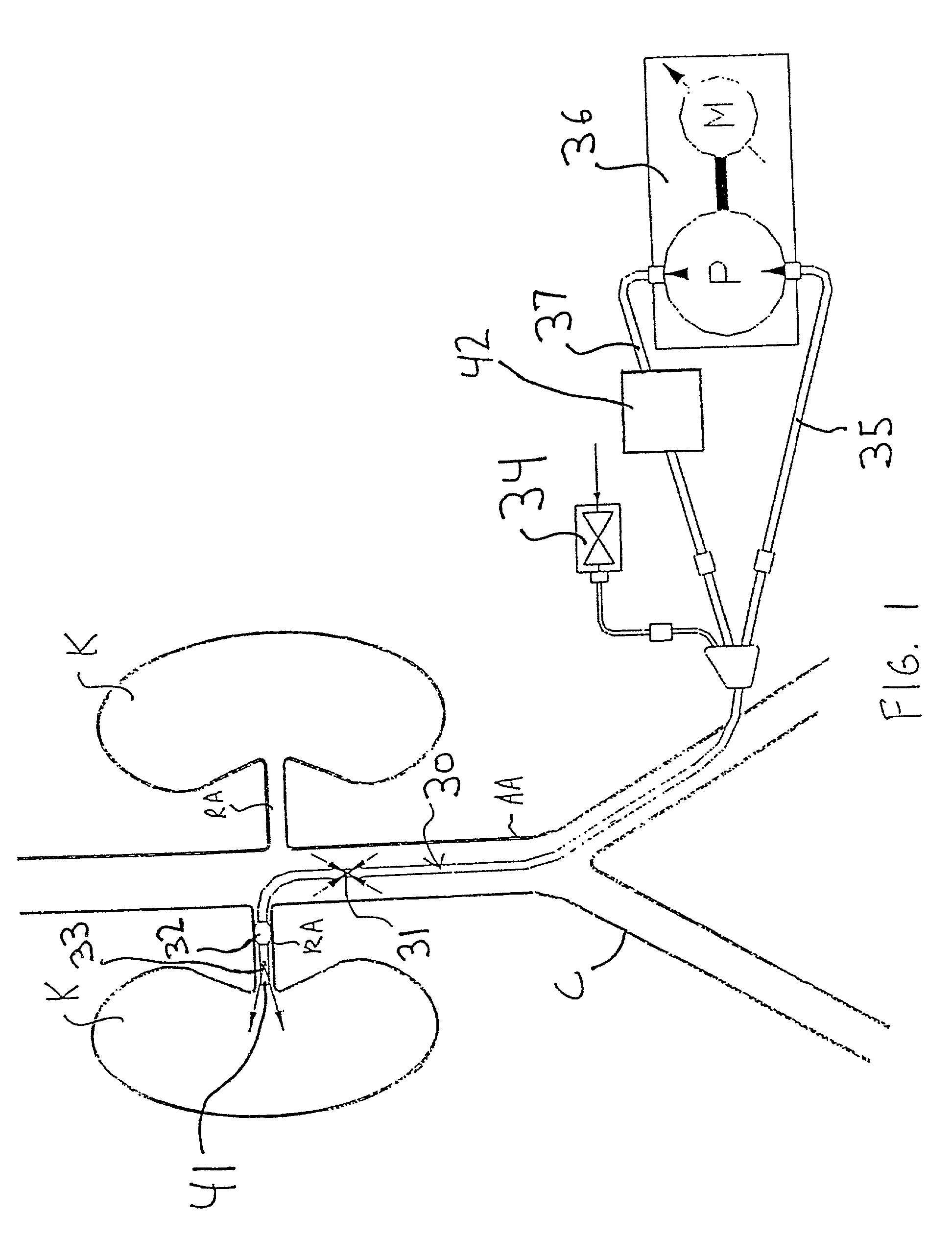
Apparatus and methods for treating congestive heart disease
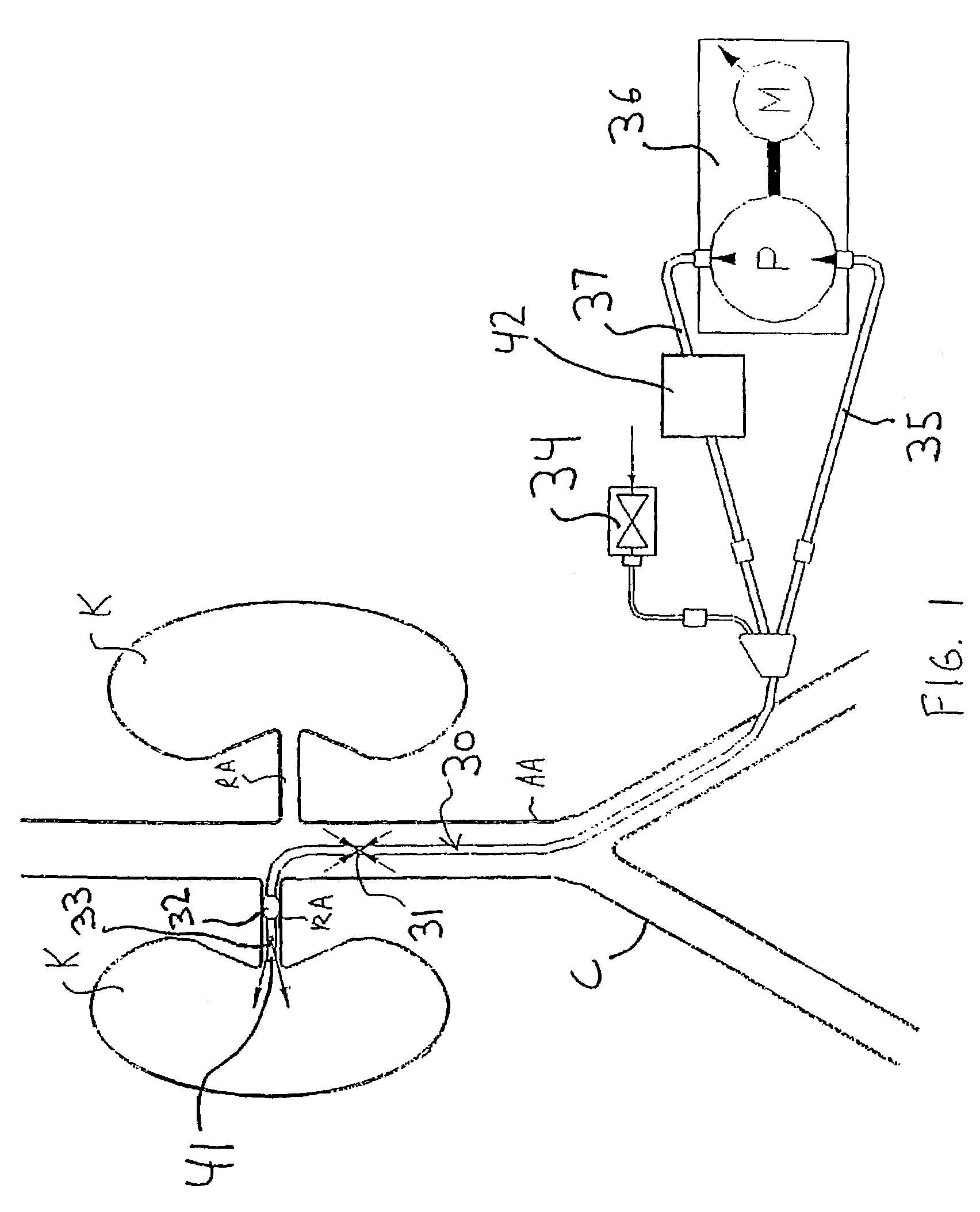
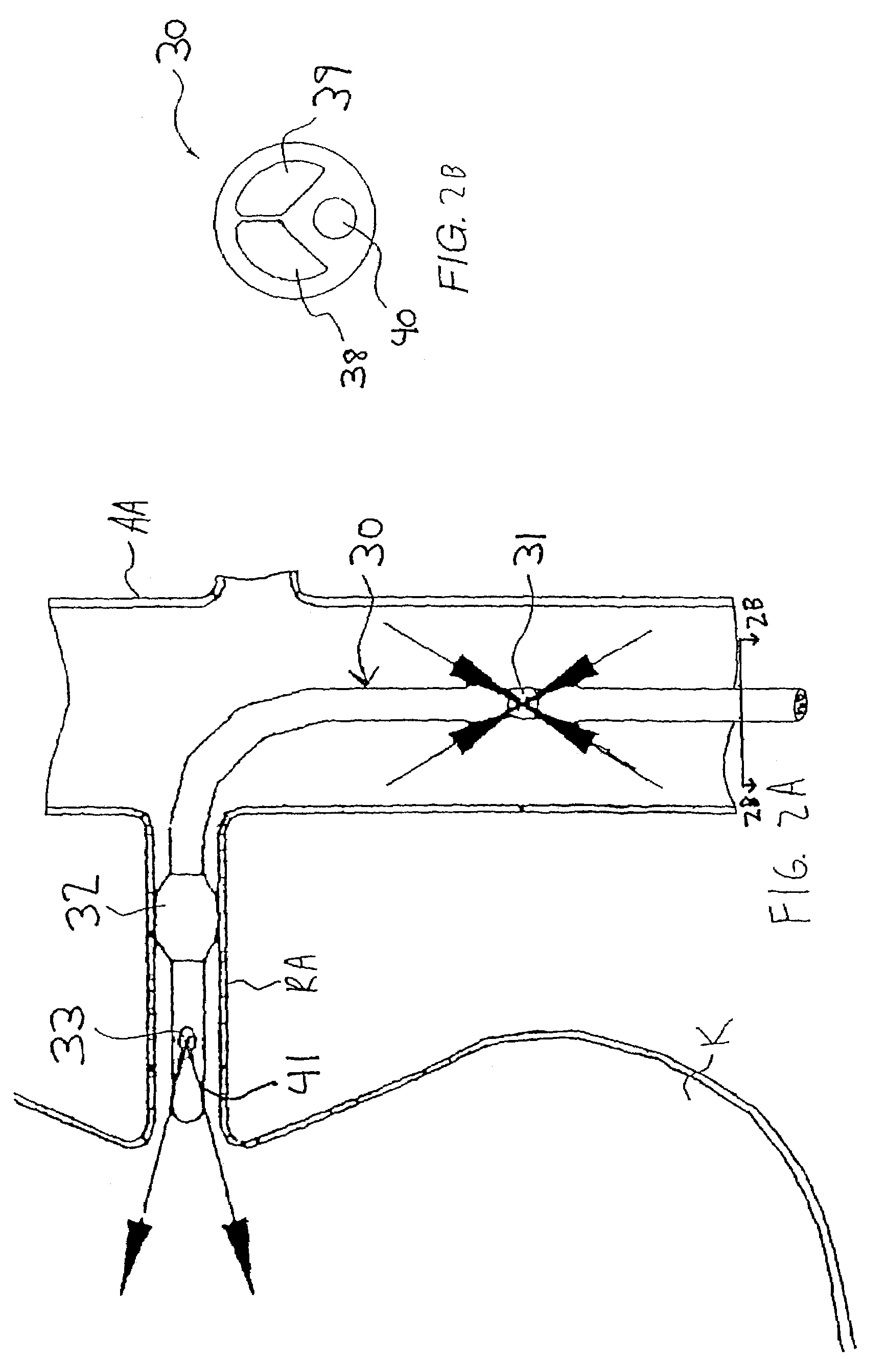
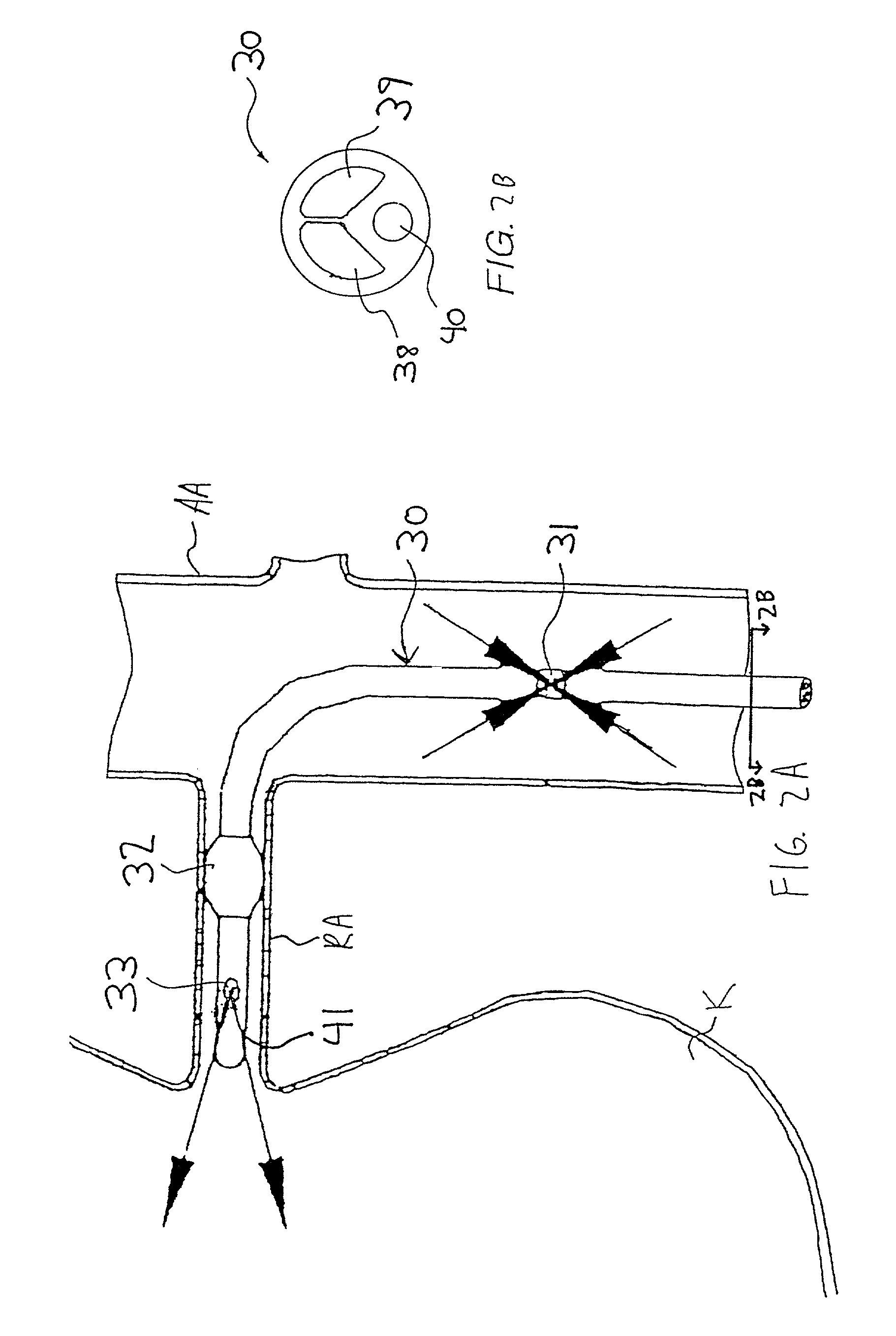
InactiveUS7335192B2Increase blood flowImprove kidney functionBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesInsertion stentPeri-aortic
Methods and apparatus are provided for treating congestive heart by actively or passively enhancing perfusion to the renal arteries. A first embodiment comprises a specially configured balloon catheter and extracorporeal pump, wherein the pump operates in a “once-through” fashion or alternating volume displacement mode. In another embodiment the catheter includes a pair of balloons to isolate a region of the aorta, and a third balloon that directs flow into the renal arteries. In still further embodiments, a stent or cuff having a constricted region is deployed in or around the aorta, respectively, to create a backpressure upstream of the stent or cuff. Methods of enhancing renal perfusion also are provided.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Catheter device
ActiveUS20090093796A1Maximum pump performanceImprove performancePump componentsSurgeryDrive shaftMechanical engineering
The catheter device comprises a drive shaft connected to a motor, and a rotor mounted on the drive shaft at the distal end section. The rotor has a frame structure which is formed by a screw-like boundary frame and rotor struts extending radially inwards from the boundary frame. The rotor struts are fastened to the drive shaft by their ends opposite the boundary frame. Between the boundary frame and the drive shaft extends an elastic covering. The frame structure is made of an elastic material such that, after forced compression, the rotor unfolds automatically.
Owner:AIS AACHEN INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS
Methods, systems, and kits for the extracorporeal processing of blood
InactiveUS7004924B1Easy to detectOther blood circulation devicesControl devicesExtracorporeal circulationLine tubing
Methods, systems, and kits for extracorporeally circulating and processing blood are described. The systems include a pump, a processing unit, and blood drawn return lines for accessing a patient's vasculature. Blood flow through the return line is measured and pump speed controlled to maintain a desired blood flow rate. Alarm conditions can be initiated when expected pump performance differs from that needed to maintain the control point flow rate. By using a ultrasonic flow detector, gas bubbles in the blood flow can be detected.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL
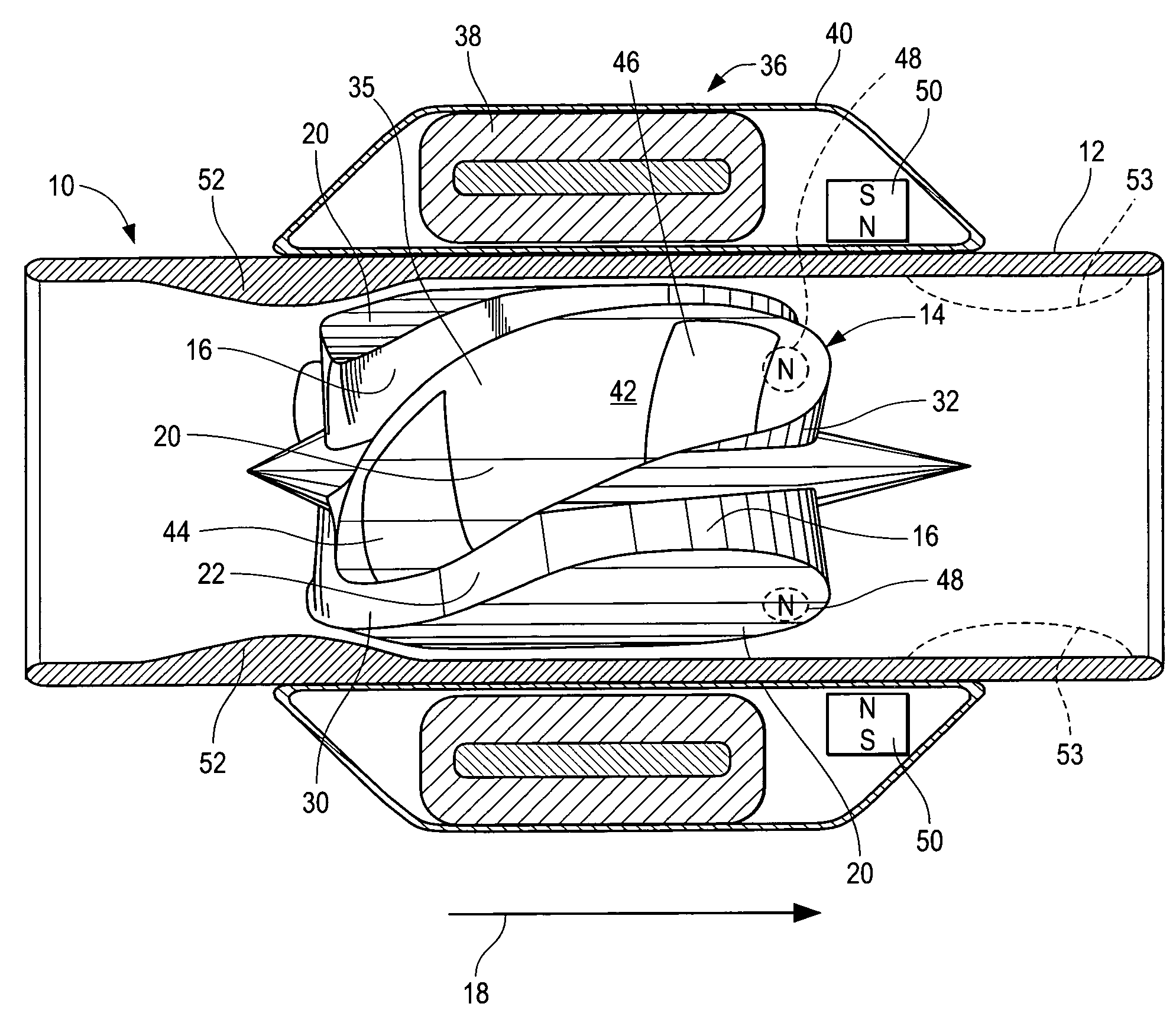
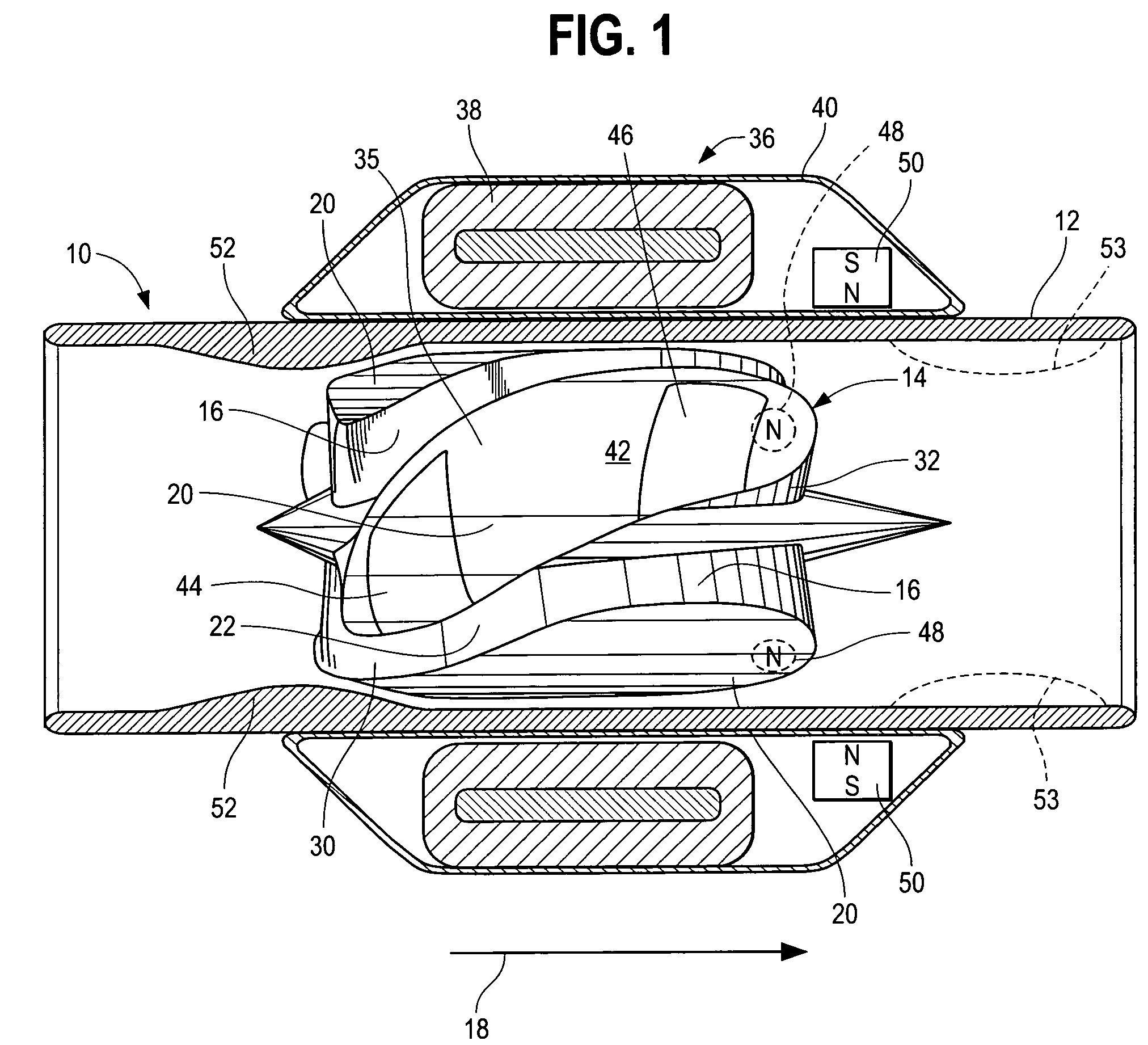
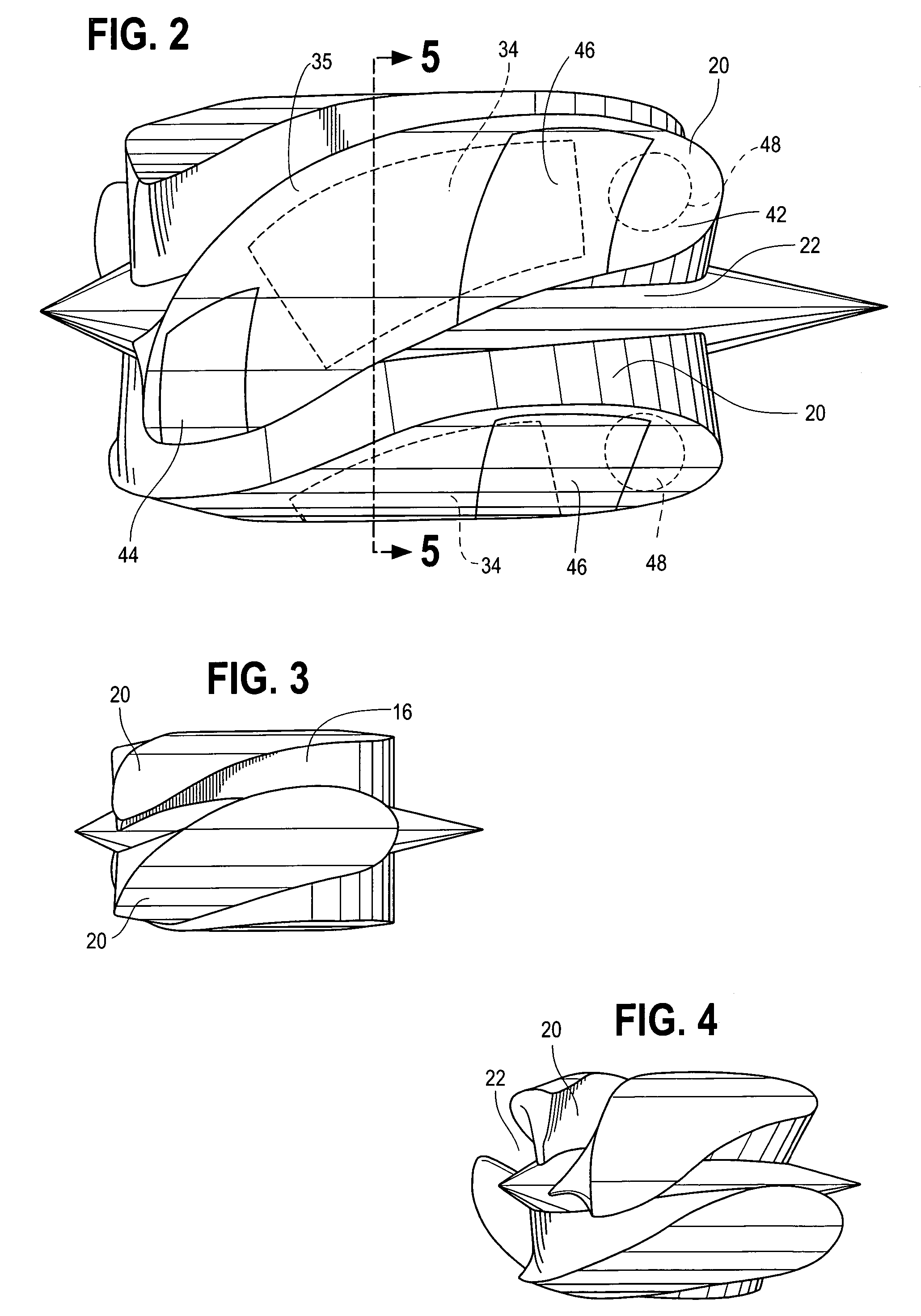
Wide blade, axial flow pump
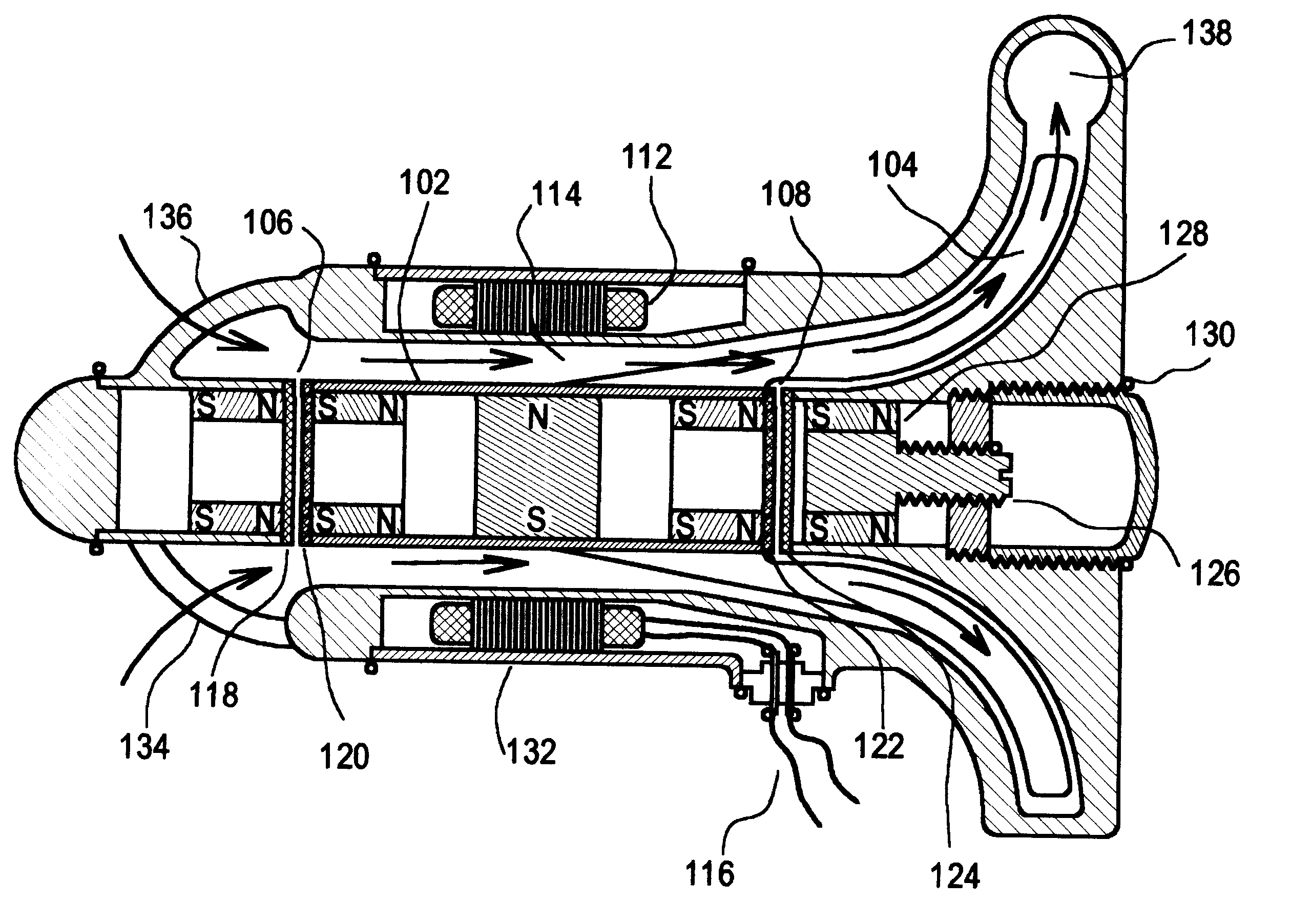
ActiveUS7699586B2Increase the magnetic fluxReduce air gapControl devicesBlood pumpsAxial-flow pumpImpeller
A blood pump comprises a pump housing; a rotor positioned in the housing and comprising an impeller having a hydrodynamic surface for pumping blood; and a motor including a plurality of magnets carried by the impeller, plus a rotor stator, including an electrically conductive coil located adjacent to or within the housing. The impeller comprises radially outwardly extending, bladelike projections that define generally longitudinally extending spaces between the projections. The shape of the projections and the spaces therebetween tend to drive blood in the spaces in an axial direction as the impeller is rotated. The spaces collectively have a total width along most of their lengths at the radial periphery of the rotor, that is substantially equal to or less than the collective width of the projections along most of their lengths at the radial periphery. Thus, the bladelike projections are thicker, achieving significant advantages.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Blood pump with expandable cannula
ActiveUS20110004046A1Minimizing potential poolingPromote crashBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesImpellerDistal portion
A blood pump includes an impeller having a plurality of foldable blades and a cannula having a proximal portion with a fixed diameter, and a distal portion with an expandable diameter. The impeller can reside in the expandable portion of the cannula. The cannula has a collapsed condition for percutaneous delivery to a desired location within the body, and an expanded condition in which the impeller can rotate to pump blood. A flexible drive shaft can extend through the cannula for rotationally driving the impeller within the patient's body.
Owner:TC1 LLC +1
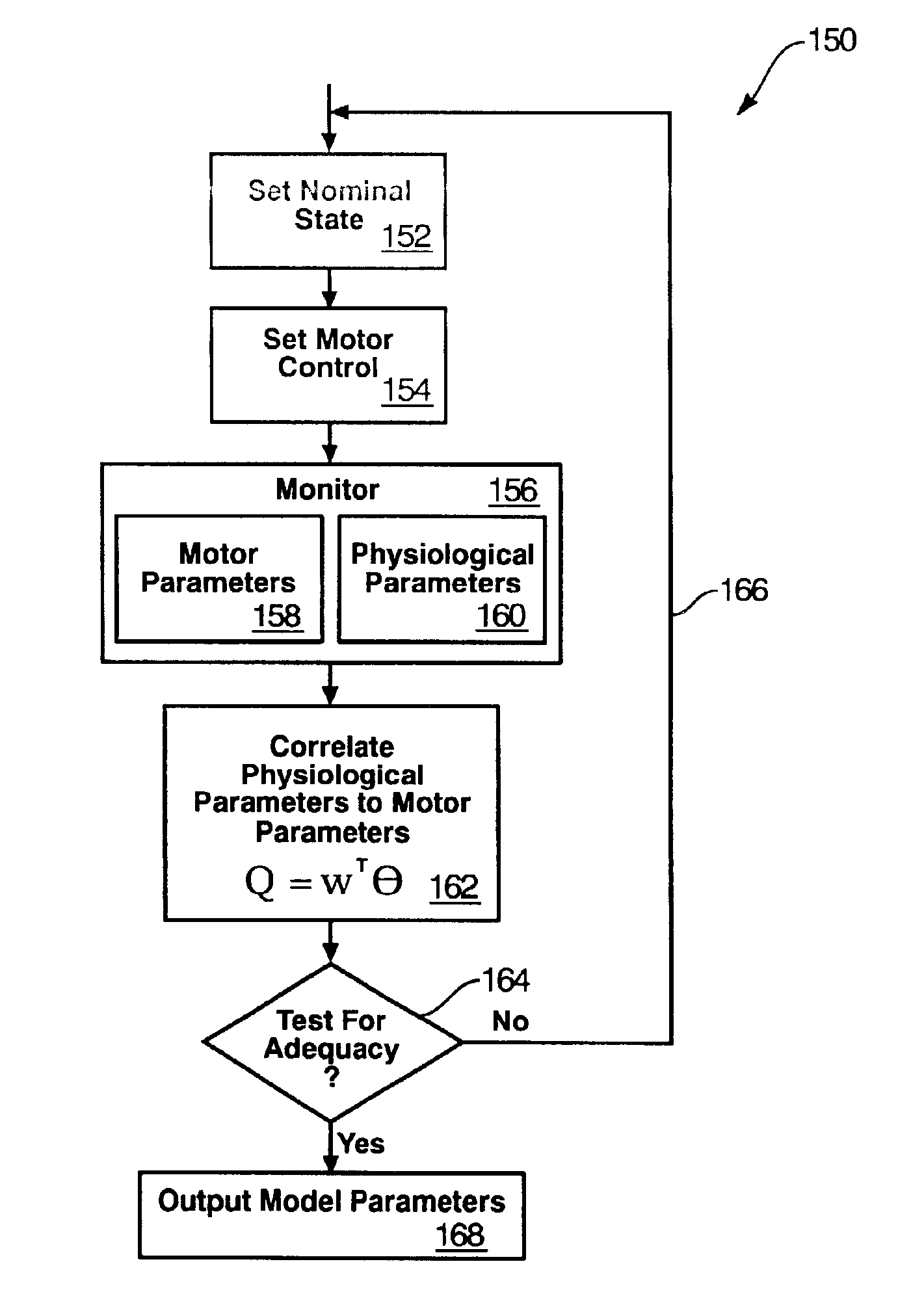
Rotary blood pump diagnostics and cardiac output controller
A method and apparatus for controlling a ventricular assist device are disclosed. The method includes the step of providing a ventricular assist device which can be defined in terms of operational parameters such as pump speed or current. Measuring at least one physiological parameter reflecting a physiological state corresponding to a patient. Correlating at least one physiological parameter measured from the patient to at least one operational parameter using an estimation method. Selecting a physiological state definable by desired values of the physiological parameters. Monitoring at least one operational parameter. Controlling input values of the operational parameter based on output from the monitoring step. The apparatus includes a pump driven by a motive drive and having an impeller. A sensor detects the value of an operational parameter of the pump. A processor provides a statistical correlation between patients physiological parameter and the operational parameter of the pump and adjusts the operational parameter to affect a predetermined optimal physiological state.
Owner:WORLD HEART
Percutaneous heart pump
Disclosed herein are heart pumps that can include a catheter body and an impeller coupled with a distal end of the catheter body. The impeller can include a tip that is resealable or that includes a resealable member. The heart pump can also include a diffuser disposed between the distal end of the catheter body and the impeller, wherein the diffuser includes a flow directing surface.
Owner:TUBEMASTER INC +2
Temporary blood circulation assist device
InactiveUS6981942B2Avoid lacerationsPrevent perforationBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesImpellerEngineering
An inflatable circulation assist device is disclosed consisting of an inflatable stator housing an impeller with inflatable blades of varying shapes and sizes. The invention is introduced into the patient percutaneously. The circulation assist device is a small pump packaged into a compact form that is attached to a long flexible driveshaft. The pump is inserted along a guidewire to a target location, and then the pump is inflated. The circulation assist device's exterior is designed to expand only so much as to closely fit whatever cardiovascular system element in which it is placed for operation. The vascular assist device can be expanded either by inflation with a fluid. The driveshaft, which connects to the circulation assist device's impeller and extends outside the patient's body, is rotated by an external motor. After the circulation assist device is no longer needed, it is collapsed into a compact form and removed from the patient percutaneously.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Heart assist device with expandable impeller pump
An impeller includes a hub and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a stored configuration in which the blade is compressed so that its distal end moves towards the hub, and a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub. The impeller may be part of a pump for pumping fluids, such as pumping blood within a patient. A blood pump may include a cannula having a proximal portion with a fixed diameter, and a distal portion with an expandable diameter. The impeller may reside in the expandable portion of the cannula. The cannula may have a compressed diameter which allows it to be inserted percutaneously into a patient. Once at a desired location, the expandable portion of the cannula may be expanded and the impeller expanded to the deployed configuration. A flexible drive shaft may extend through the cannula for rotationally driving the impeller within the patient's body.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
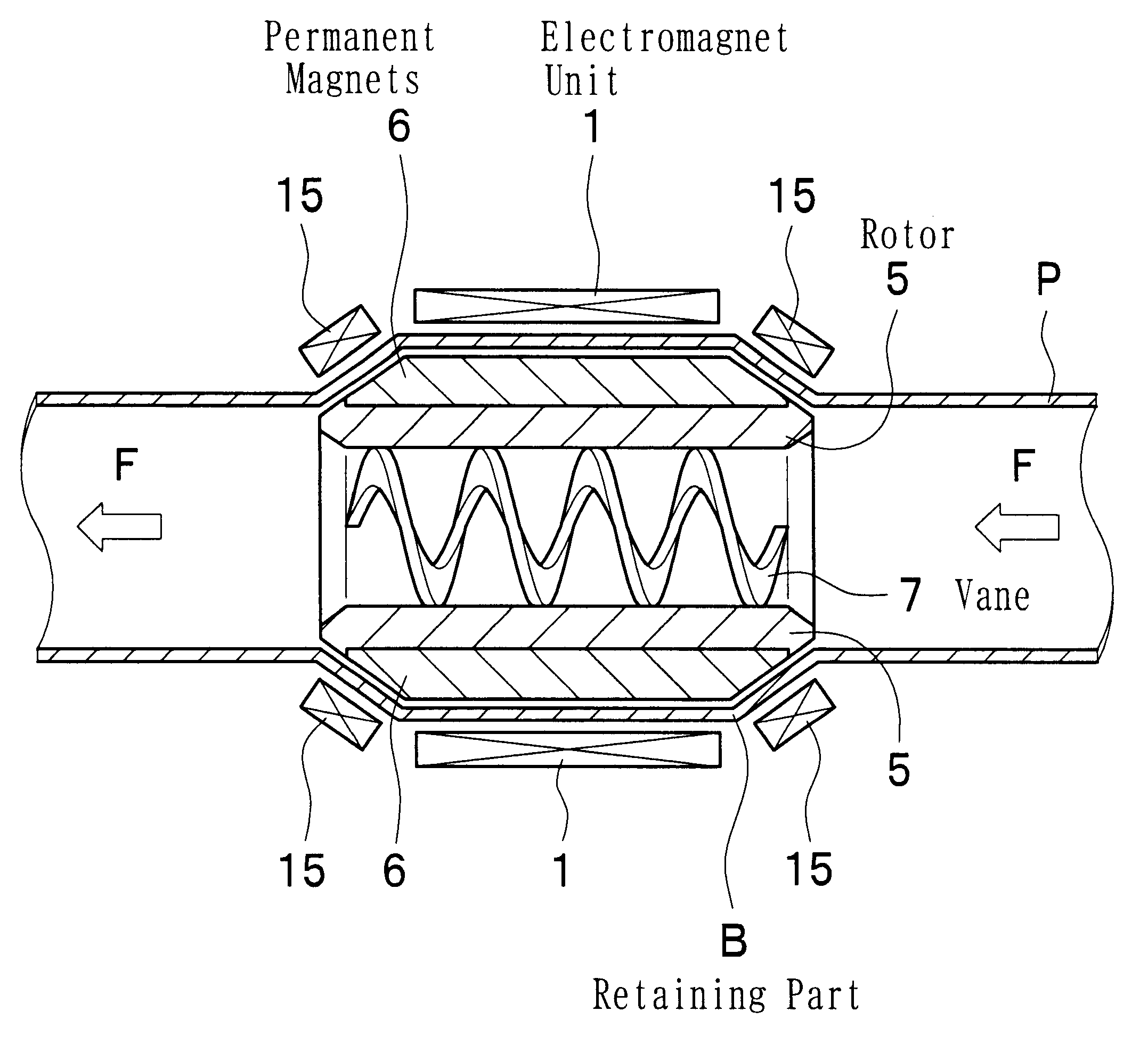
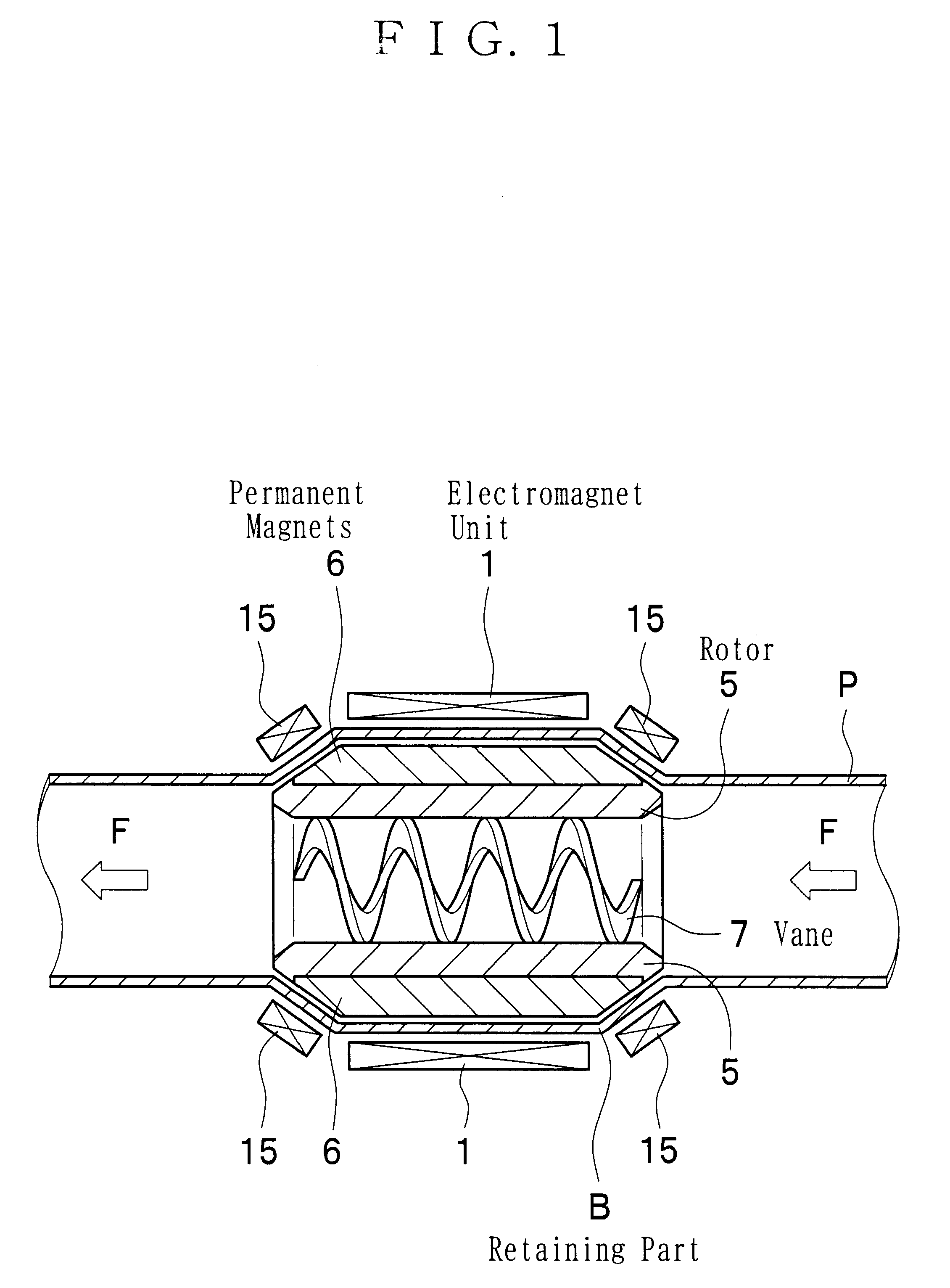
Magnetically driven axial-flow pump
A magnetically driven, axial flow pump comprises an electromagnetic unit arranged about the periphery of a pipe. A cylindrical rotor is accommodated within the pipe and is equipped with permanent magnets mounted on the periphery. A spiral, hollow vane is formed on an inner surface of the rotor by either casting or by cutting, such as with a NC machine, thus precluding the occurrence of gaps between the rotor and the vane. The lack of gaps within the pump makes the pump suitable for use as a blood pump.
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Method for Deployment of a Medical Device
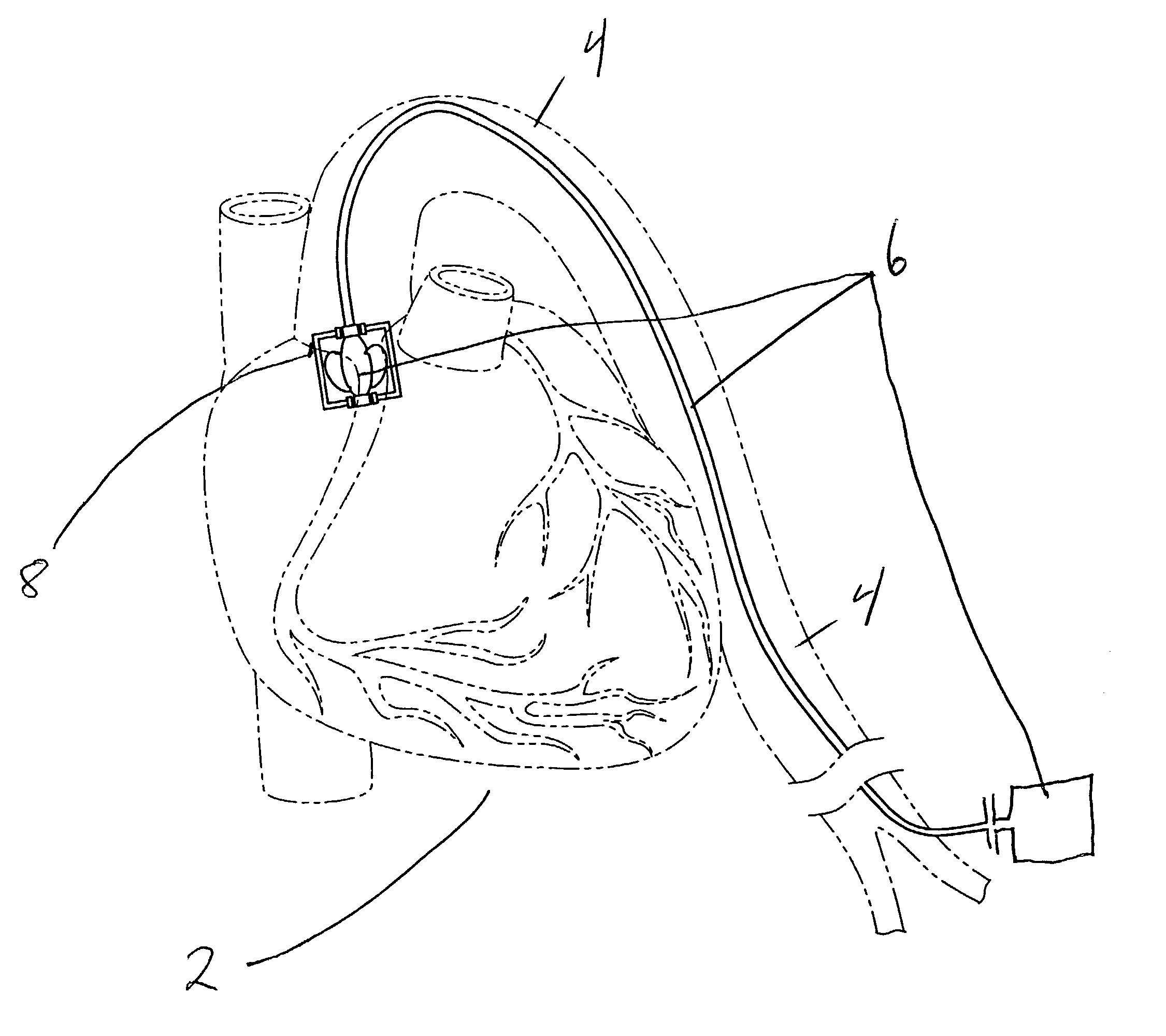
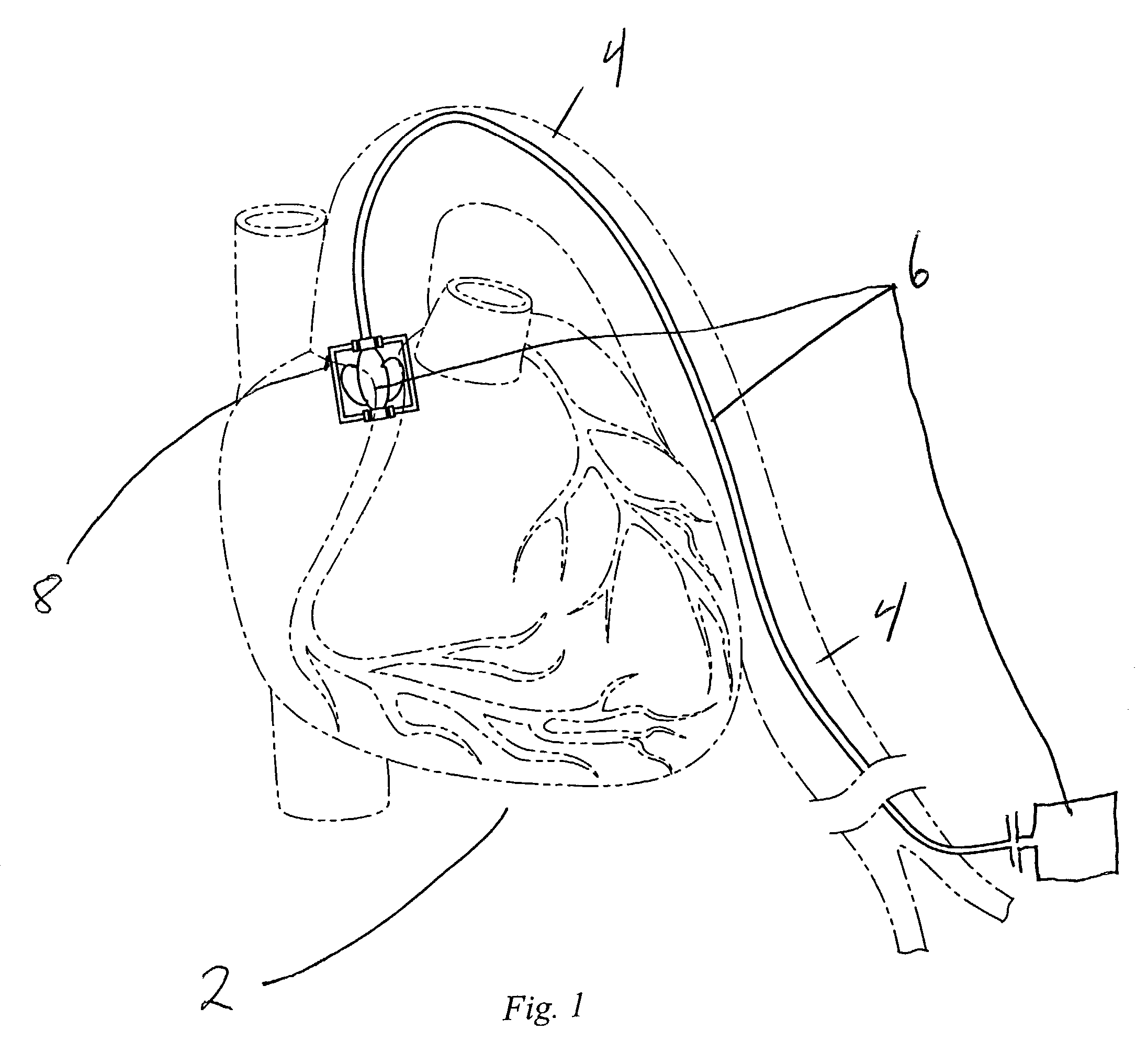
InactiveUS20080132748A1Reduce bending loadMinimizing contact pressureControl devicesBlood pumpsAortic archMedical device
A method for deploying a cardiac-assist device is disclosed. In accordance with the illustrative embodiment, an introducing tube, such as a catheter, sheath, or the like is inserted into the vascular system and advanced beyond the aortic arch. The cardiac-assist device is then inserted into the tube, advanced through it, and deployed from its distal end. In some embodiments, the diameter of the cardiac-assist device expands when it deploys from the distal end of the tube.
Owner:MEDICAL VALUE PARTNERS
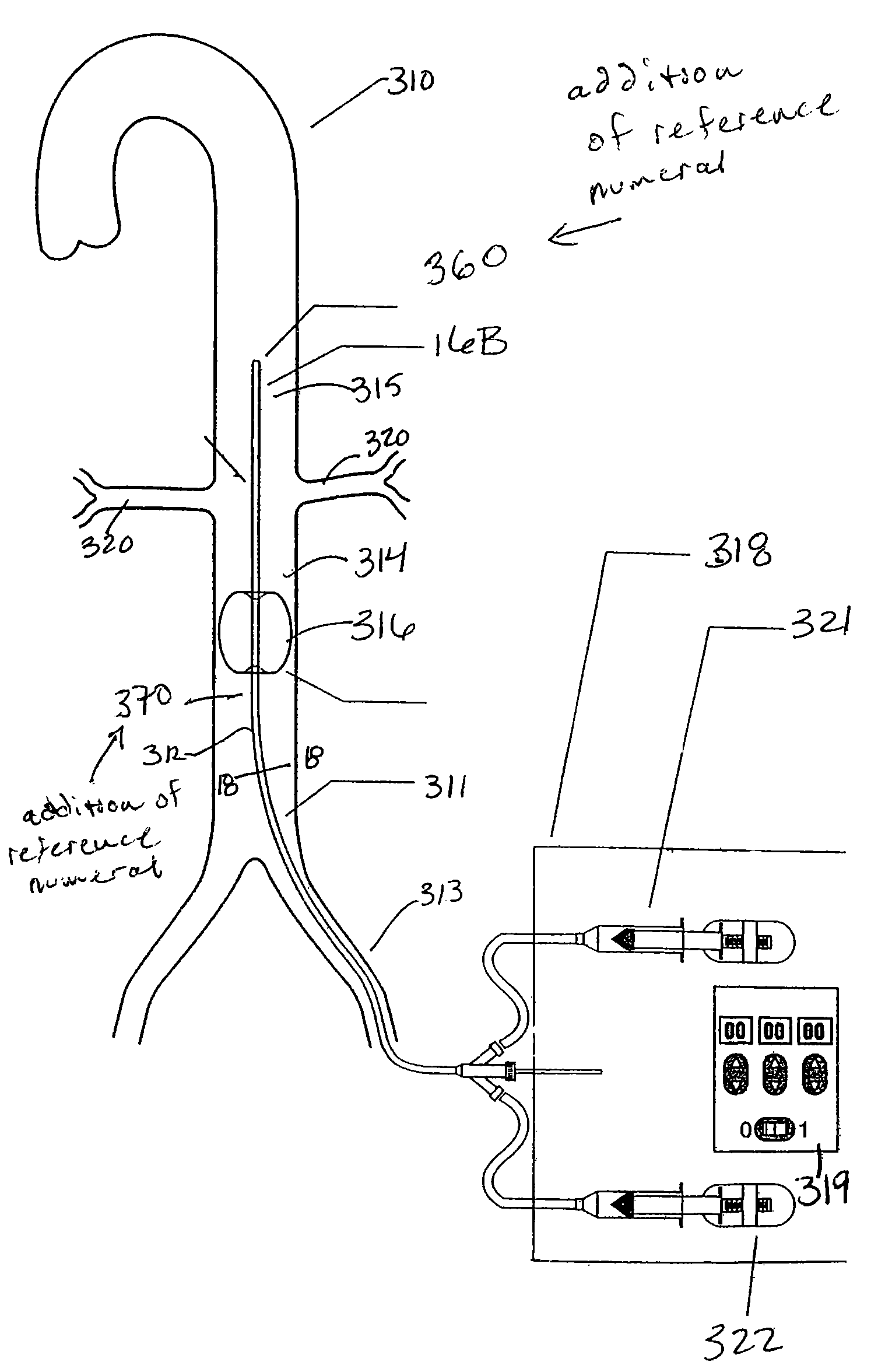
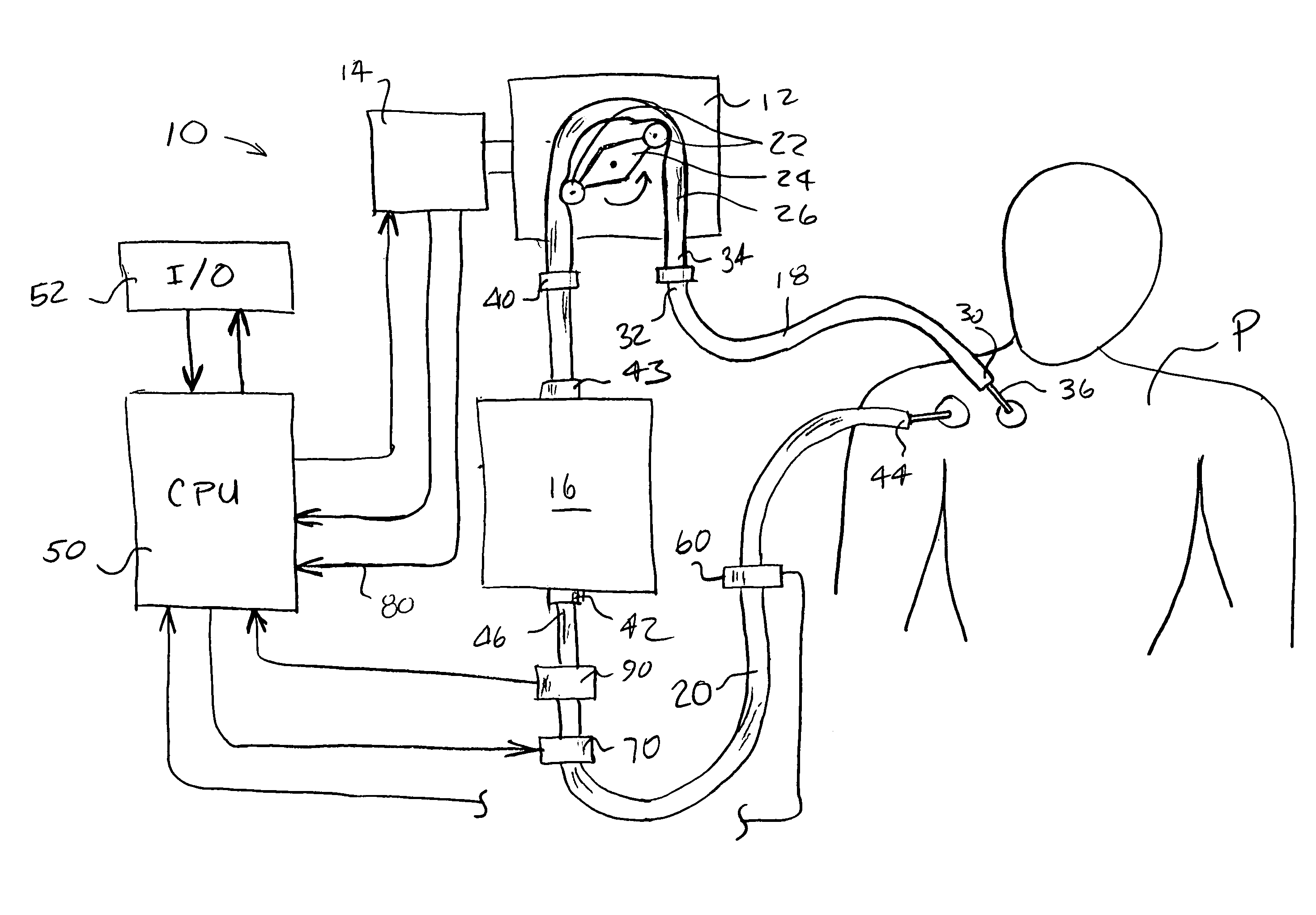
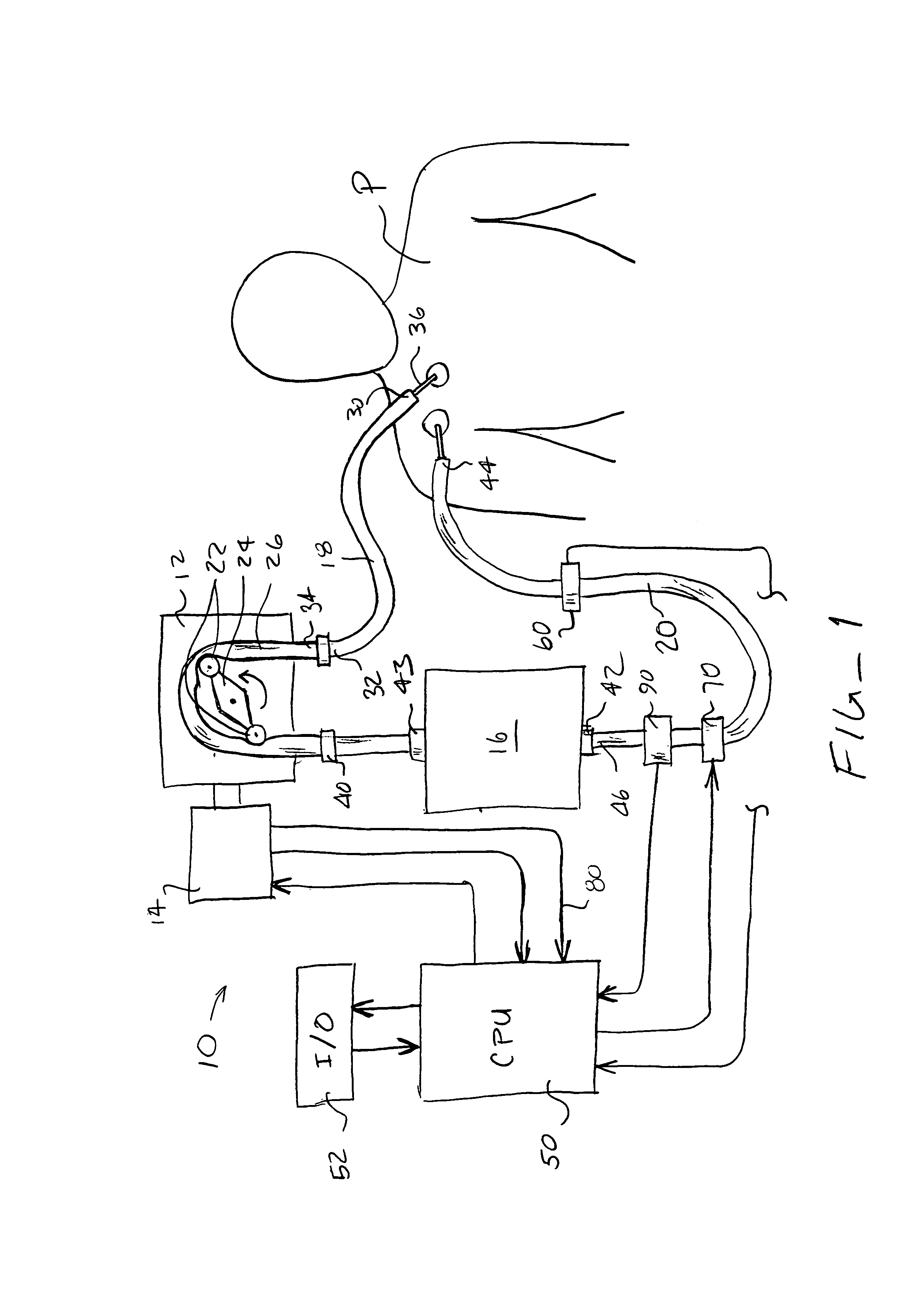
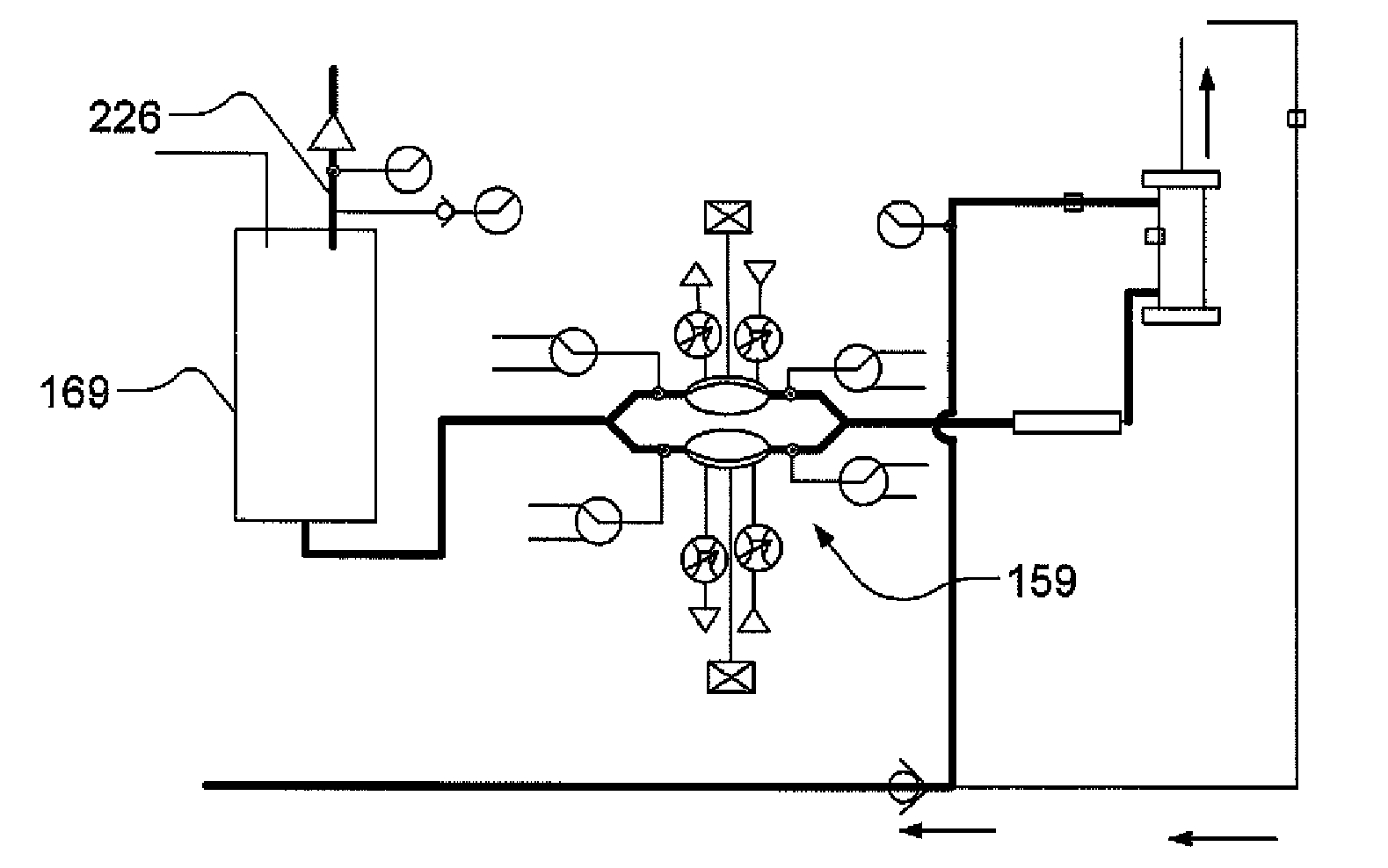
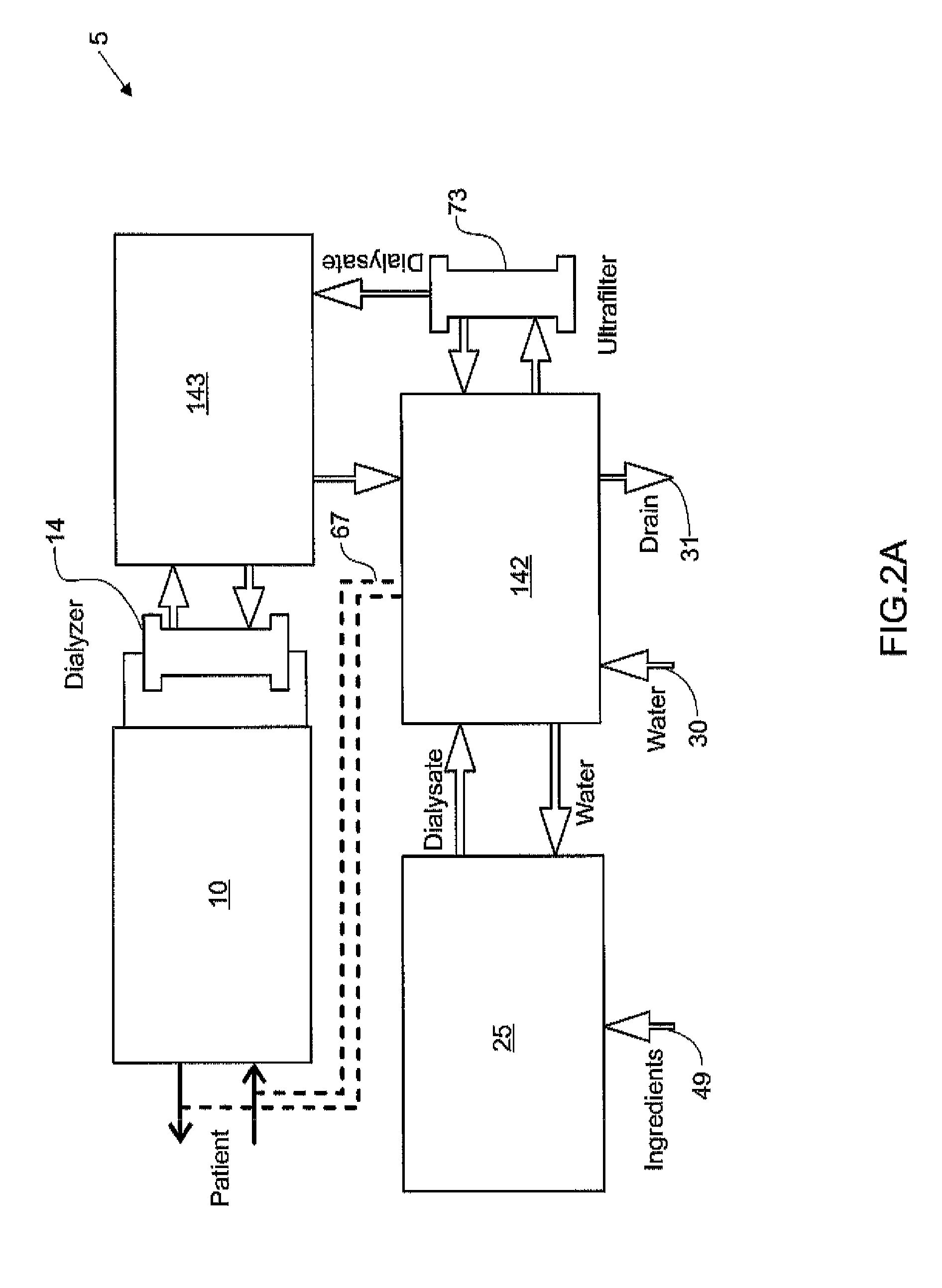
Hemodialysis systems and methods
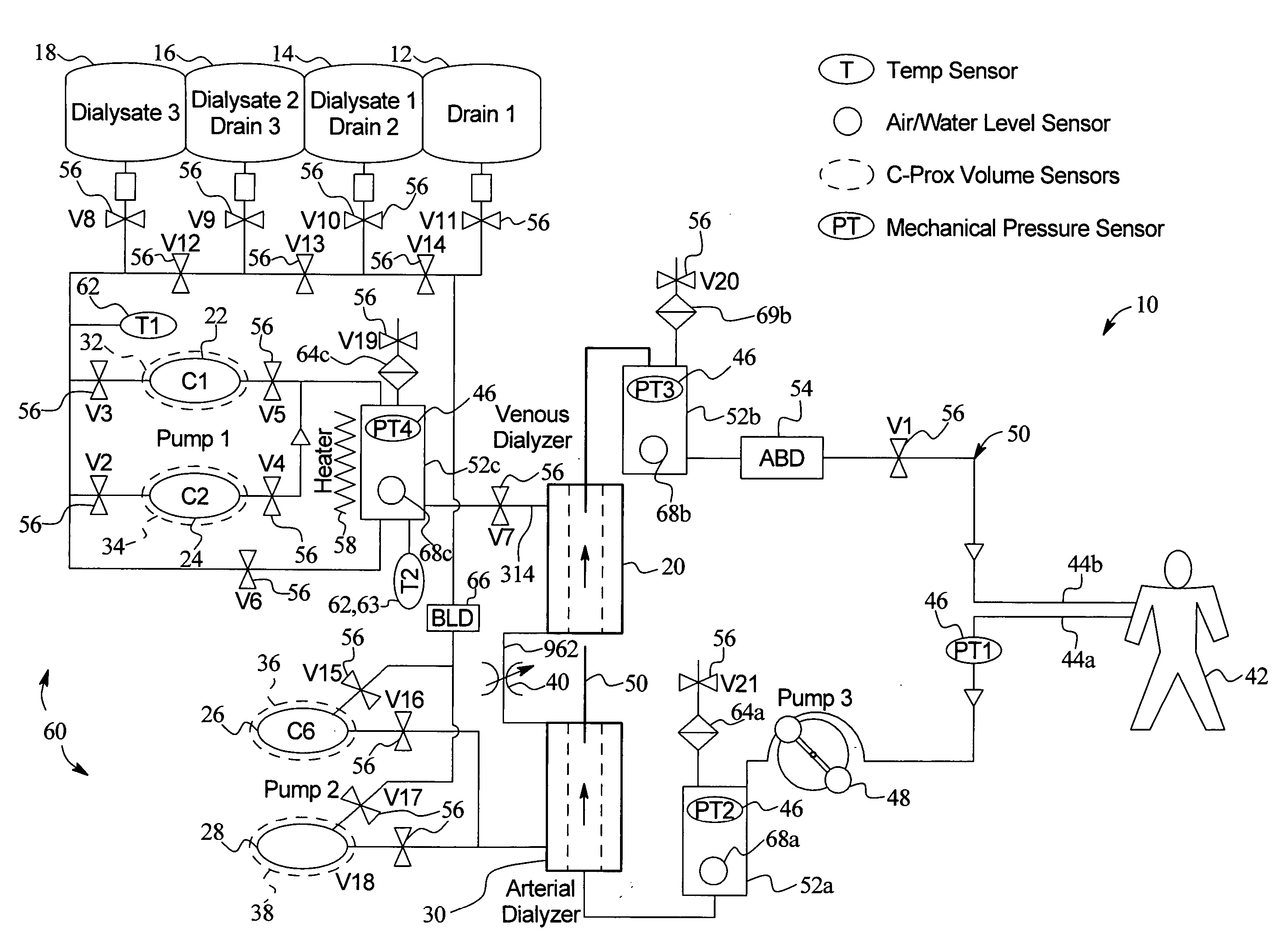
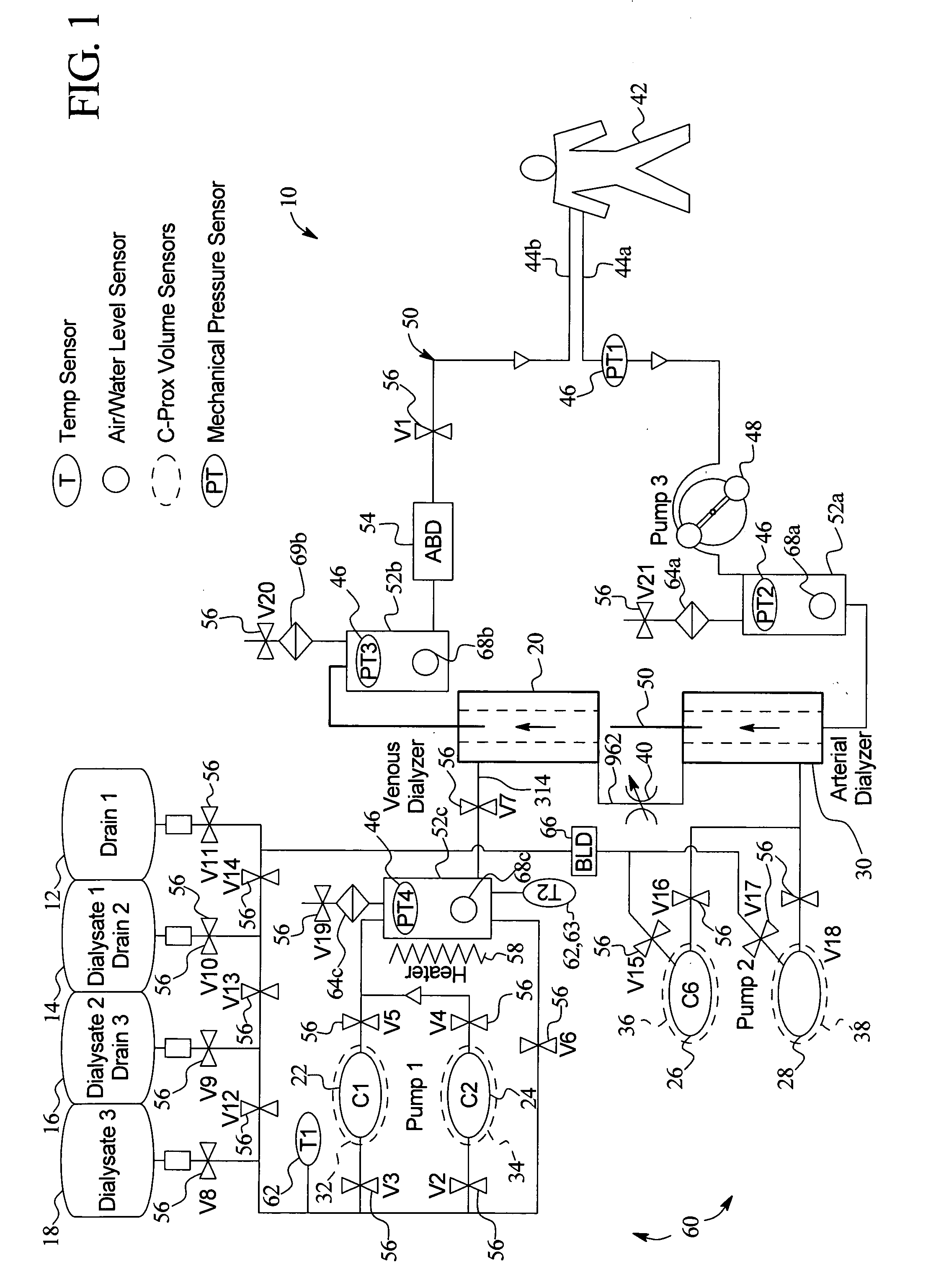
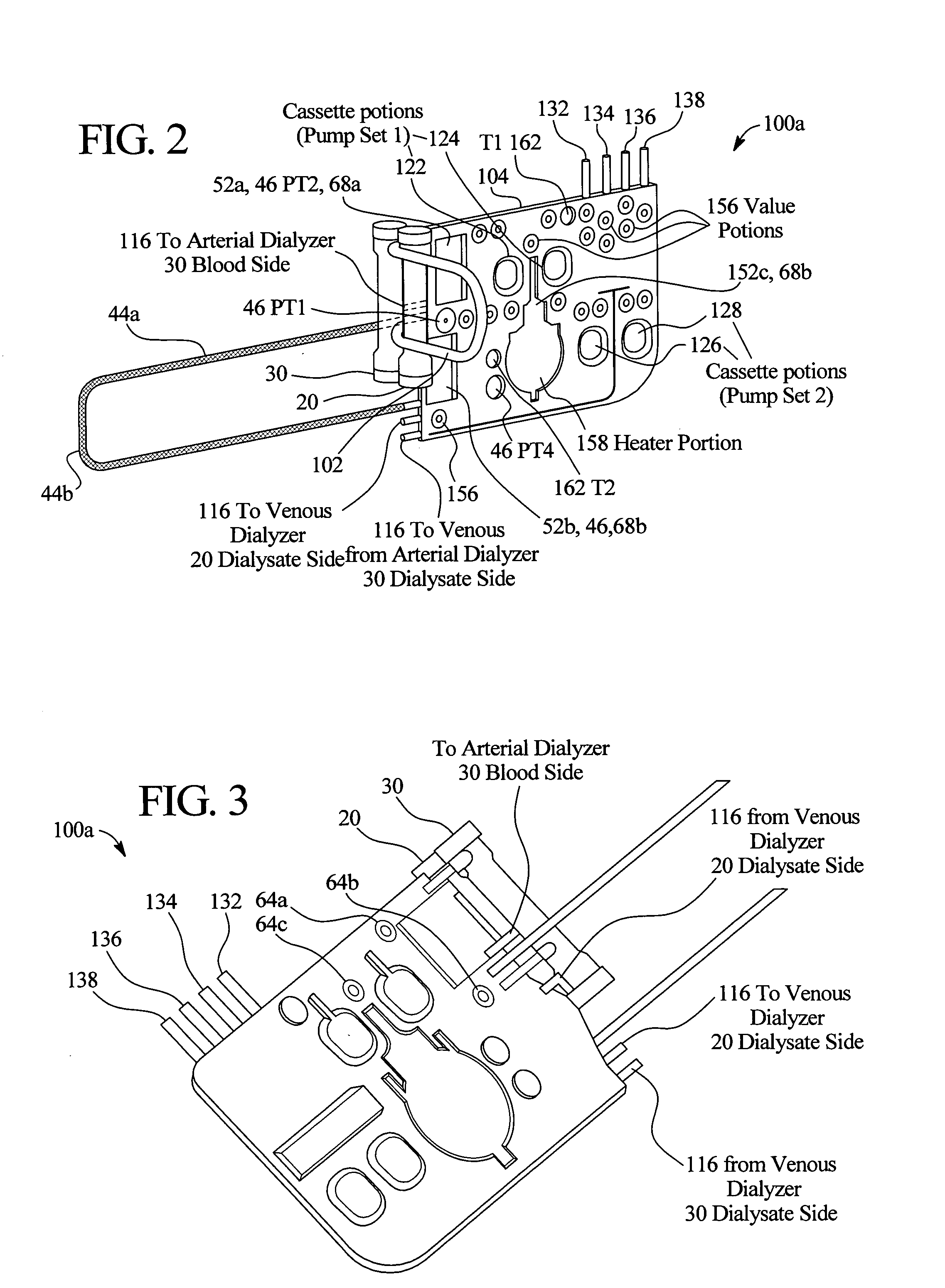
The present invention generally relates to hemodialysis and similar dialysis systems, including a variety of systems and methods that would make hemodialysis more efficient, easier, and / or more affordable. One aspect of the invention is generally directed to new fluid circuits for fluid flow. In one set of embodiments, a hemodialysis system may include a blood flow path and a dialysate flow path, where the dialysate flow path includes one or more of a balancing circuit, a mixing circuit, and / or a directing circuit. Preparation of dialysate by the preparation circuit, in some instances, may be decoupled from patient dialysis. In some cases, the circuits are defined, at least partially, within one or more cassettes, optionally interconnected with conduits, pumps, or the like. In one embodiment, the fluid circuit and / or the various fluid flow paths may be at least partially isolated, spatially and / or thermally, from electrical components of the hemodialysis system. In some cases, a gas supply may be provided in fluid communication with the dialysate flow path and / or the dialyzer that, when activated, is able to urge dialysate to pass through the dialyzer and urge blood in the blood flow path back to the patient. Such a system may be useful, for example, in certain emergency situations (e.g., a power failure) where it is desirable to return as much blood to the patient as possible. The hemodialysis system may also include, in another aspect of the invention, one or more fluid handling devices, such as pumps, valves, mixers, or the like, which can be actuated using a control fluid, such as air. In some cases, the control fluid may be delivered to the fluid handling devices using an external pump or other device, which may be detachable in certain instances. In one embodiment, one or more of the fluid handling devices may be generally rigid (e.g., having a spheroid shape), optionally with a diaphragm contained within the device, dividing it into first and second compartments.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
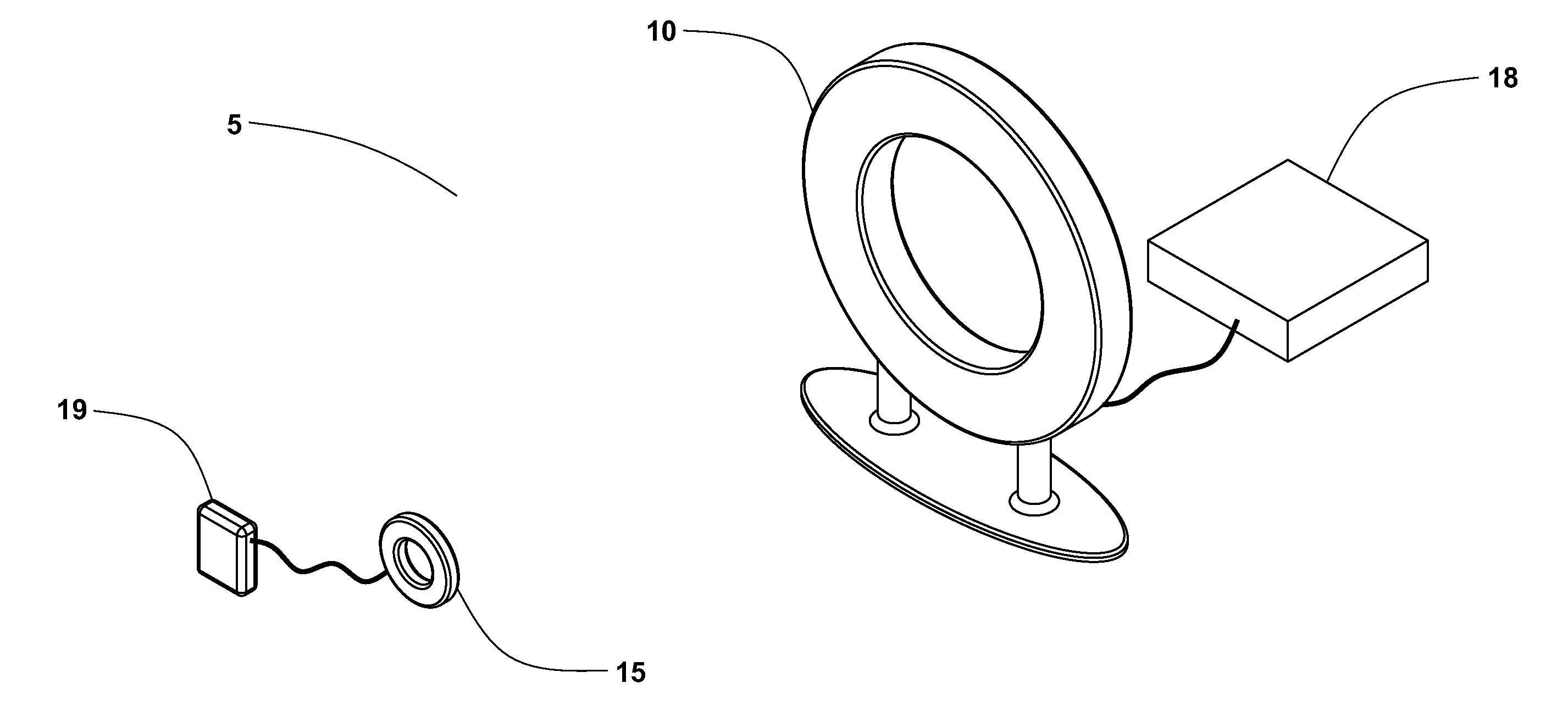
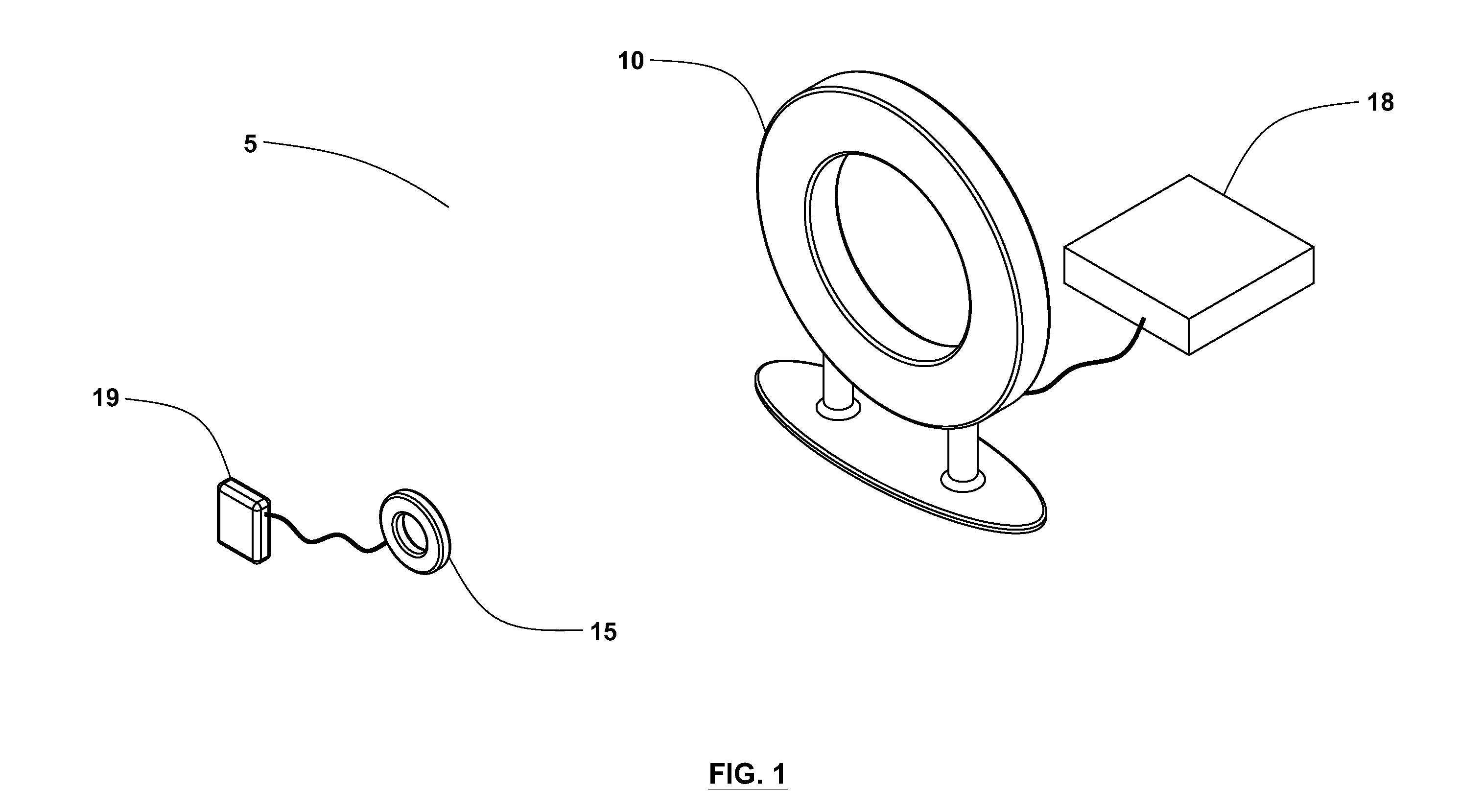
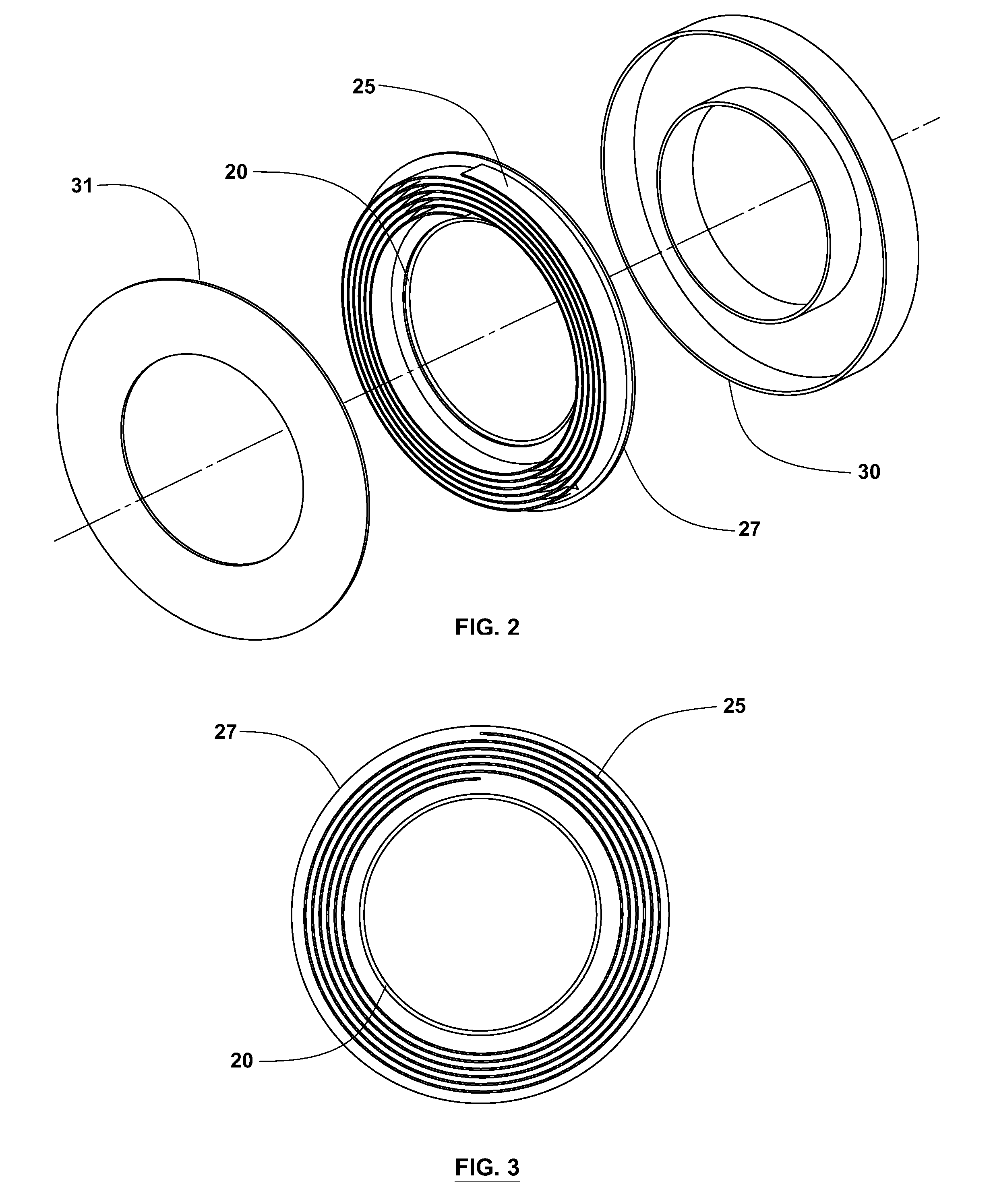
Implantable wireless power system
A wireless power system capable of transmitting power through the skin without percutaneous wires over distances ranging from a few inches to several feet includes an external transmitting coil assembly and a receiving coil assembly. The transmitting coil assembly includes an excitation coil and transmitting resonant coil which are inductively coupled to each other. The receiving coil assembly includes a receiving resonant coil and a power pick-up coil which are also inductively coupled to each other. A high frequency AC power input, such as radio frequency (RF), supplied to the excitation coil inductively causes the transmitting resonant coil to resonate resulting in a local time varying magnetic field. The transmitting and receiving resonant coils are constructed as to have closely matched or identical resonant frequencies so that the magnetic field produced by the transmitting resonant coil is able to cause the receiving resonant coil to resonate strongly also, even when the distance between the two resonant coils greatly exceeds the largest dimension of either coil. The receiving resonant coil then creates its own local time varying magnetic field which inductively produces a voltage in a power pick-up coil to provide power to an active implantable medical device or implantable rechargeable battery.
Owner:CORVION INC
Apparatus and methods for treating congestive heart disease
InactiveUS7766892B2Improve kidney functionIncrease blood flowBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesInsertion stentPeri-aortic
Methods and apparatus are provided for treating congestive heart by actively or passively enhancing perfusion to the renal arteries. A first embodiment comprises a specially configured balloon catheter and extracorporeal pump, wherein the pump operates in a “once-through” fashion or alternating volume displacement mode. In another embodiment the catheter includes a pair of balloons to isolate a region of the aorta, and a third balloon that directs flow into the renal arteries. In still further embodiments, a stent or cuff having a constricted region is deployed in or around the aorta, respectively, to create a backpressure upstream of the stent or cuff. Methods of enhancing renal perfusion also are provided.
Owner:LIBRA MEDICAL SYST
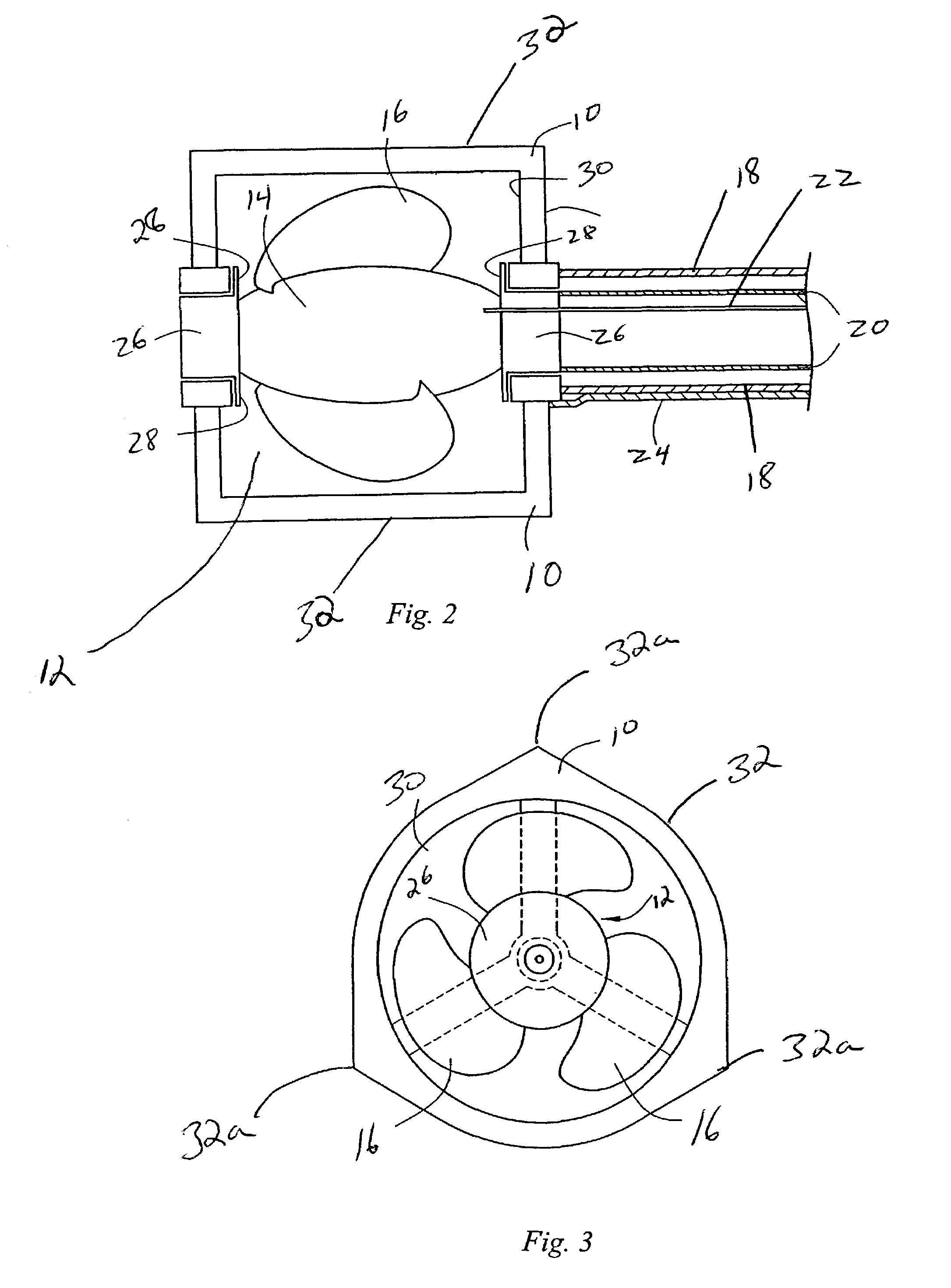
Axial force null position magnetic bearing and rotary blood pumps which use them
InactiveUS6227820B1Improve radial stiffnessSimple designPump componentsSurgeryAxial-flow pumpMagnetic tension force
A generally cylindrical rotor very closely confined between two rigid thrust bearing surfaces is radially suspended by an array of attracting or repelling magnets or by a combination of permanent magnets and ring shaped members composed of ferromagnetic material. The geometry permits very small spacing between magnetic components to achieve high radial stiffness. High magnetic axial forces exerted between the rotor and stationary component on one end of the rotor are counter-balanced by equal and opposite forces at the other end of the rotor. Precise positioning of the rotor in the location where the opposing axial magnetic forces counterballance each other yields a net magnetic axial force on the rotor of near zero, hence the reference to this as the null position. Wear resistant mechanical thrust bearings confine the rotor axially to maintain this position during rotatioin. Precisely balance the magnetic axial forces in the proper geometry with relation to the mechanical thrust bearings. Blood pumps utilizing this type of bearing are disclosed, including both axial flow pump and centrifugal flow pump configurations with high flow washing of the junction of the rotating and stationary parts to prevent thrombus accumulation.
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
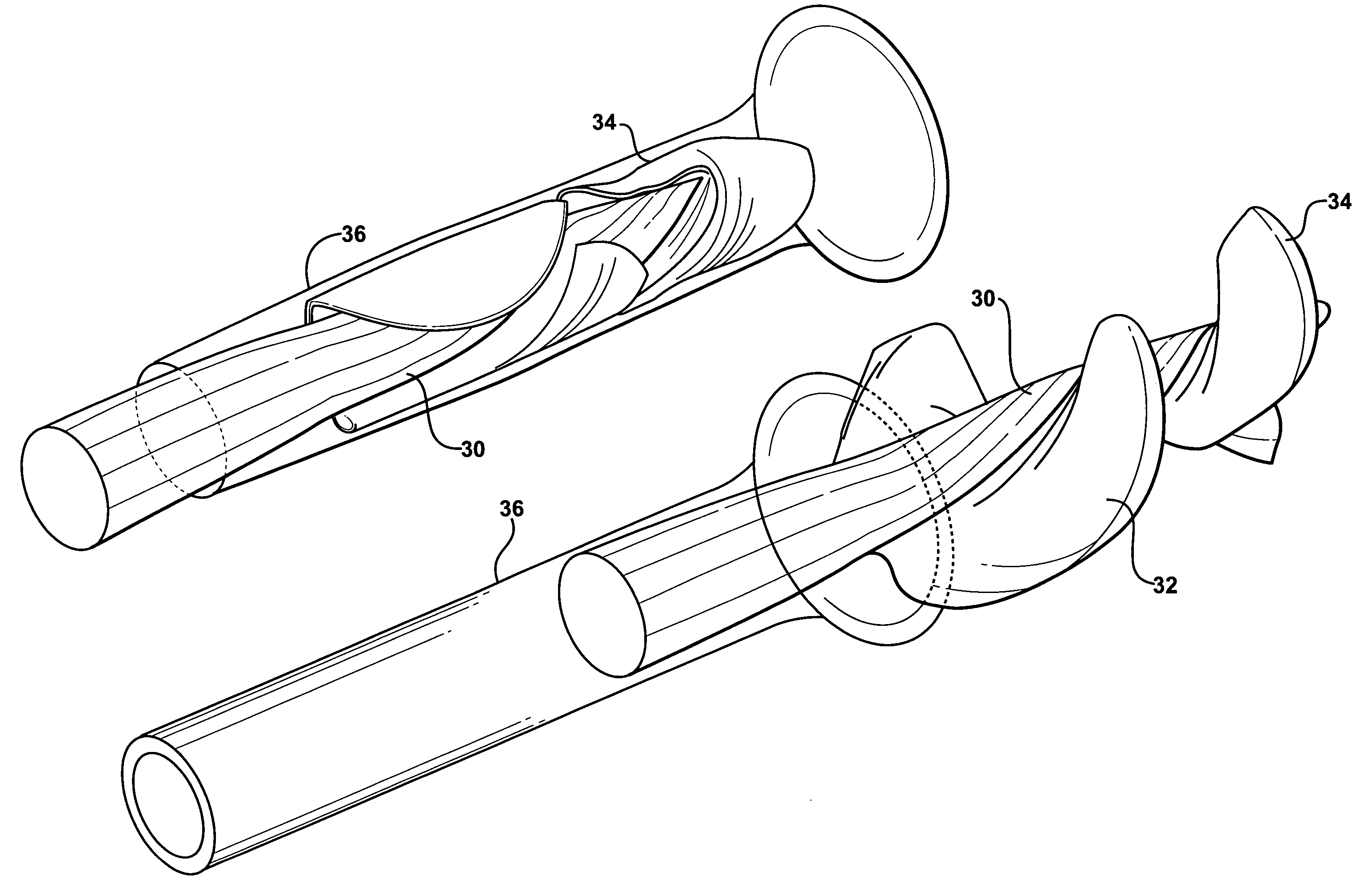
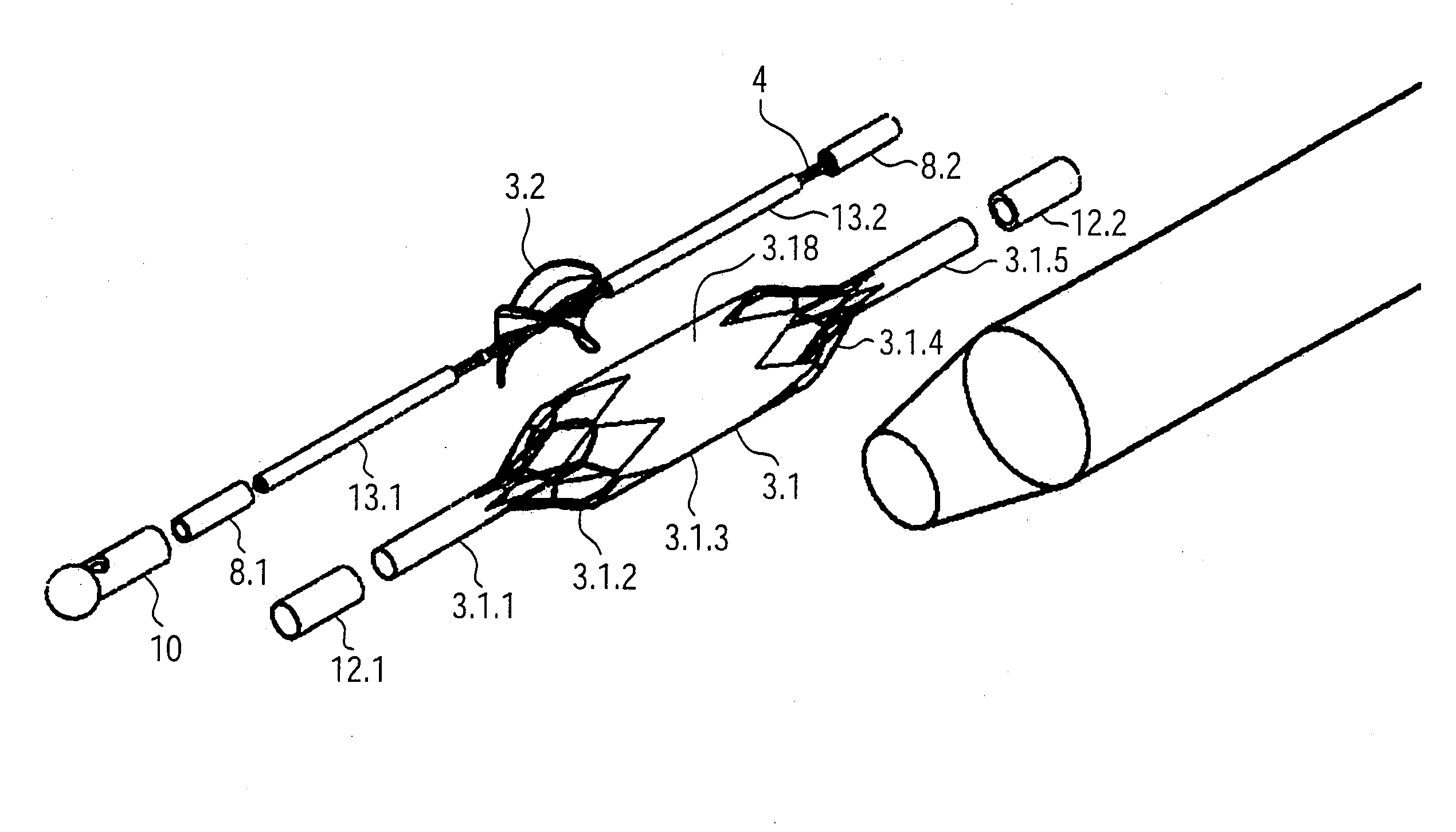
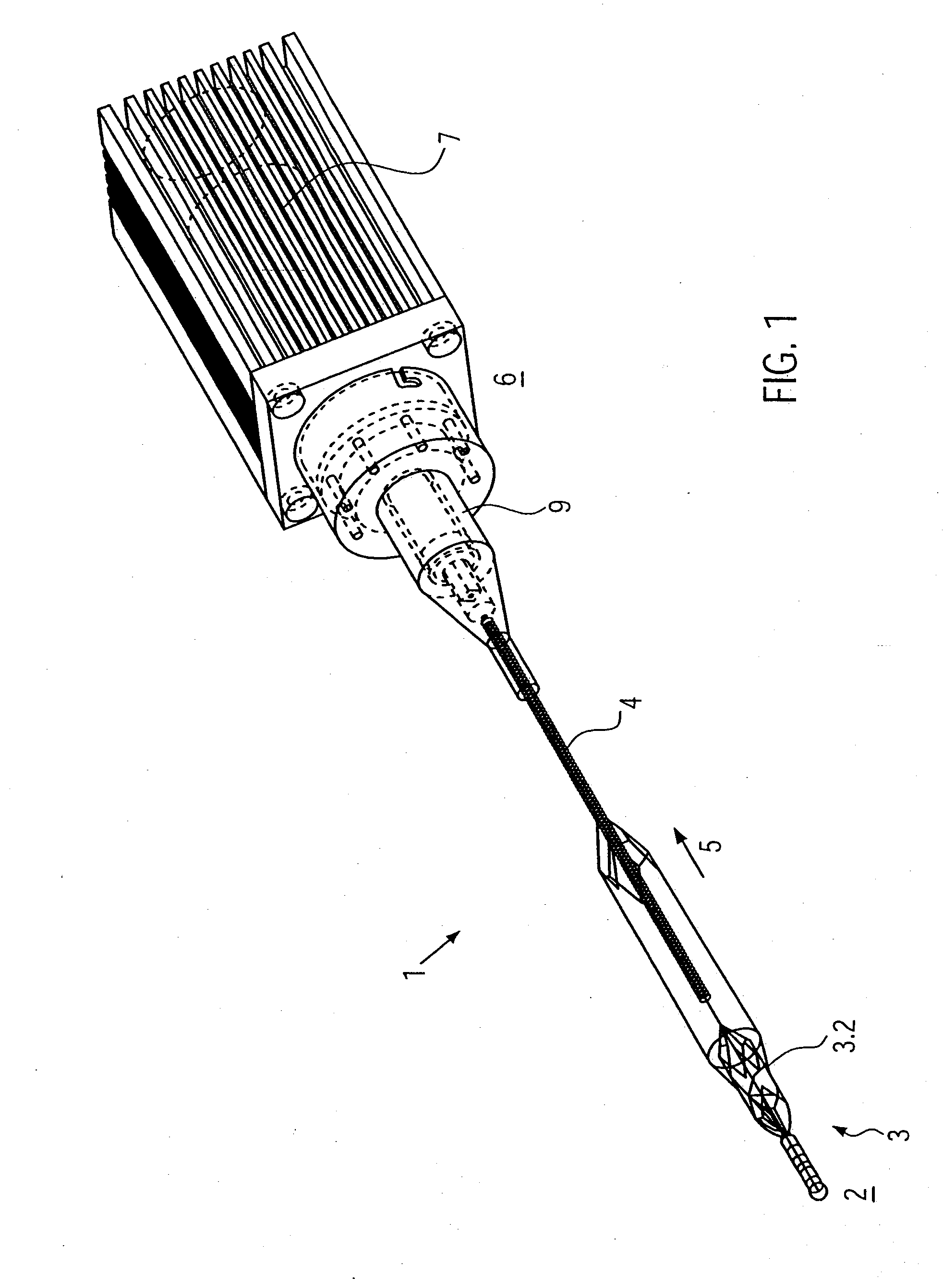
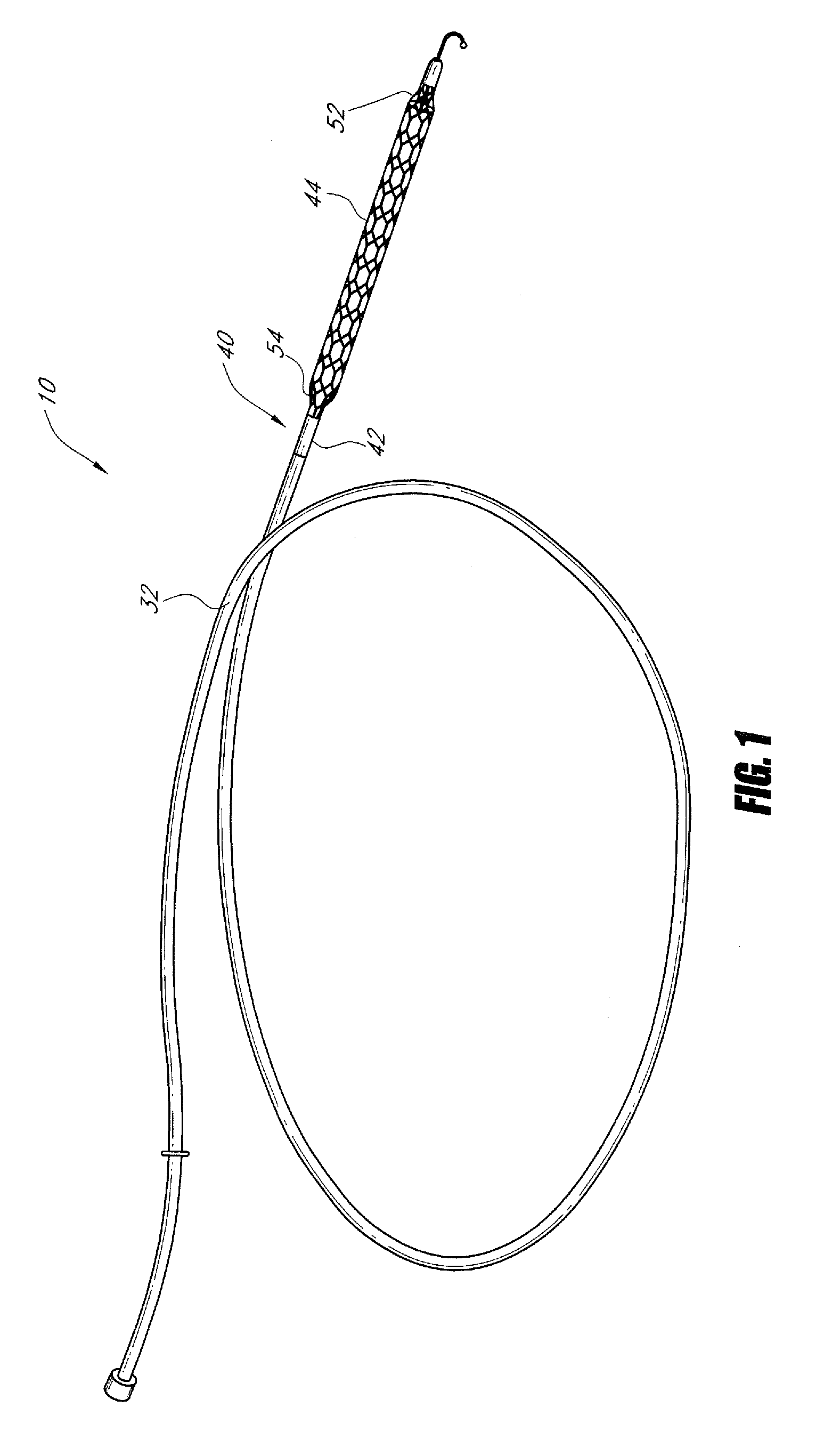
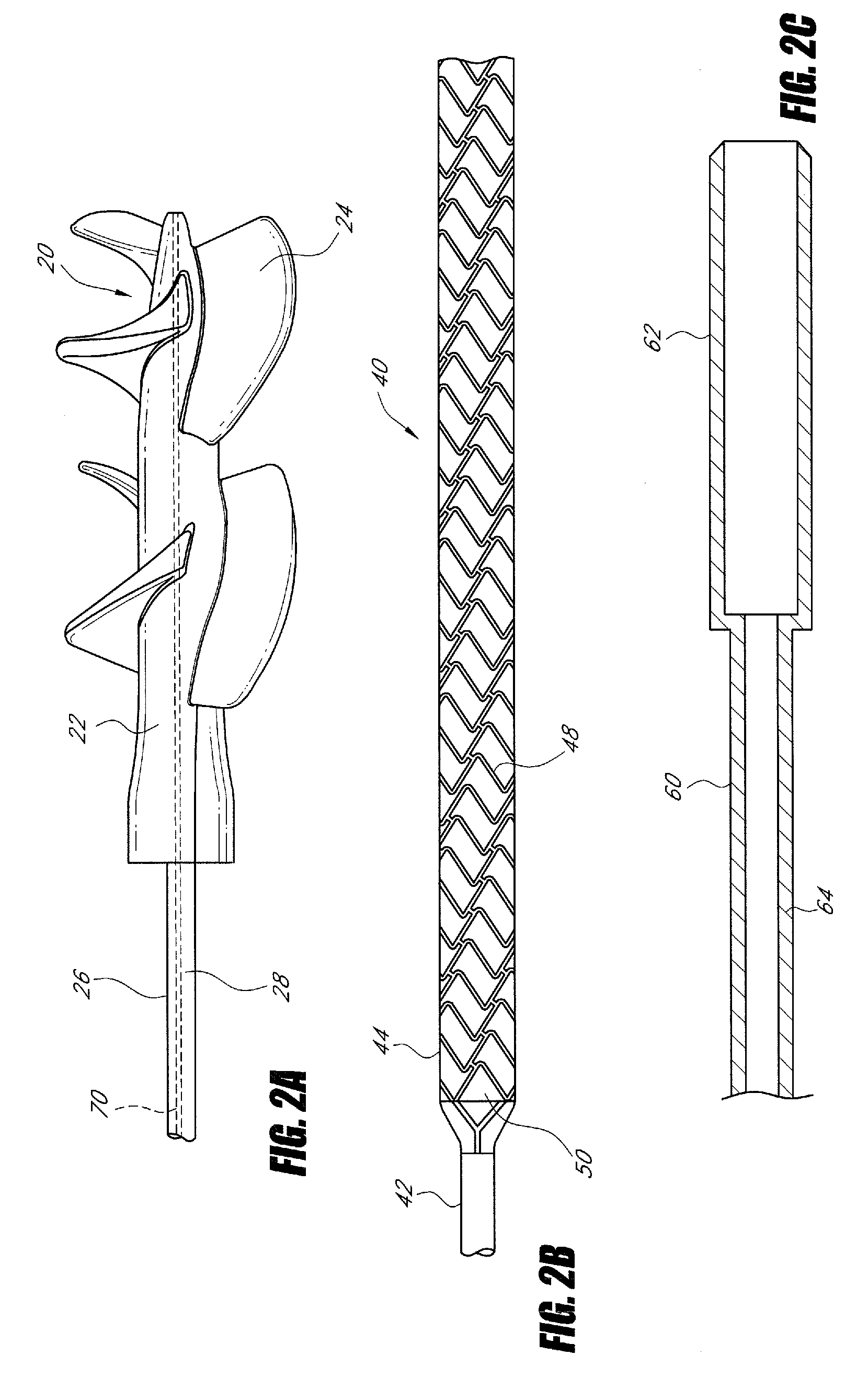
Foldable Intravascularly Inserted Blood Pump
ActiveUS20080103591A1Simple configurationReduced susceptibility to failureBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesRelative displacementImpeller
A foldable intravascularly insertable blood pump comprises a rotatable impeller provided with vanes, a flexible shaft extending through a catheter and adapted to drive said impeller, and an envelope enclosing said impeller. For simplifying the technical setup of the blood pump and enhancing its robustness, the impeller comprises radially delivering vanes. The envelope comprises an annular bulge in the region of the impeller, wherein between the radially outer ends of the vanes and the envelope an annular deflection channel is defined. The impeller and the envelope are adapted to be folded by relative displacement of the shaft and the catheter.
Owner:ABIOMED EURO
Single port cardiac support apparatus
A reverse flow pump comprising two concentric passageways and an interior compartment having cut out portions in communication with a pump passageway for the directional flow of fluid relative to the pump, and a rotor positioned within the interior compartment for reversing the directional flow of fluid through a region in communication with another pump passageway. A reverse flow pump and cannula system is further provided comprising an inner cannula adjoining a pump passageway, and an outer conduit adjoining another pump passageway for the reverse flow of fluid relative to the pump. A method of transporting fluid between body cavities is also provided comprising the steps of selecting a reverse flow pump and cannula system, forming an opening in a body passageway, positioning the outer conduit through the opening, inserting the inner cannula into the outer conduit so that the distal openings of the inner cannula and the outer conduit are positioned in separated portions of the body, connecting the inlet and the outlet passageways of the pump to the proximal ends of the inner cannula and the outer conduit, and activating the pump to transport fluid between the separated portions of the body.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
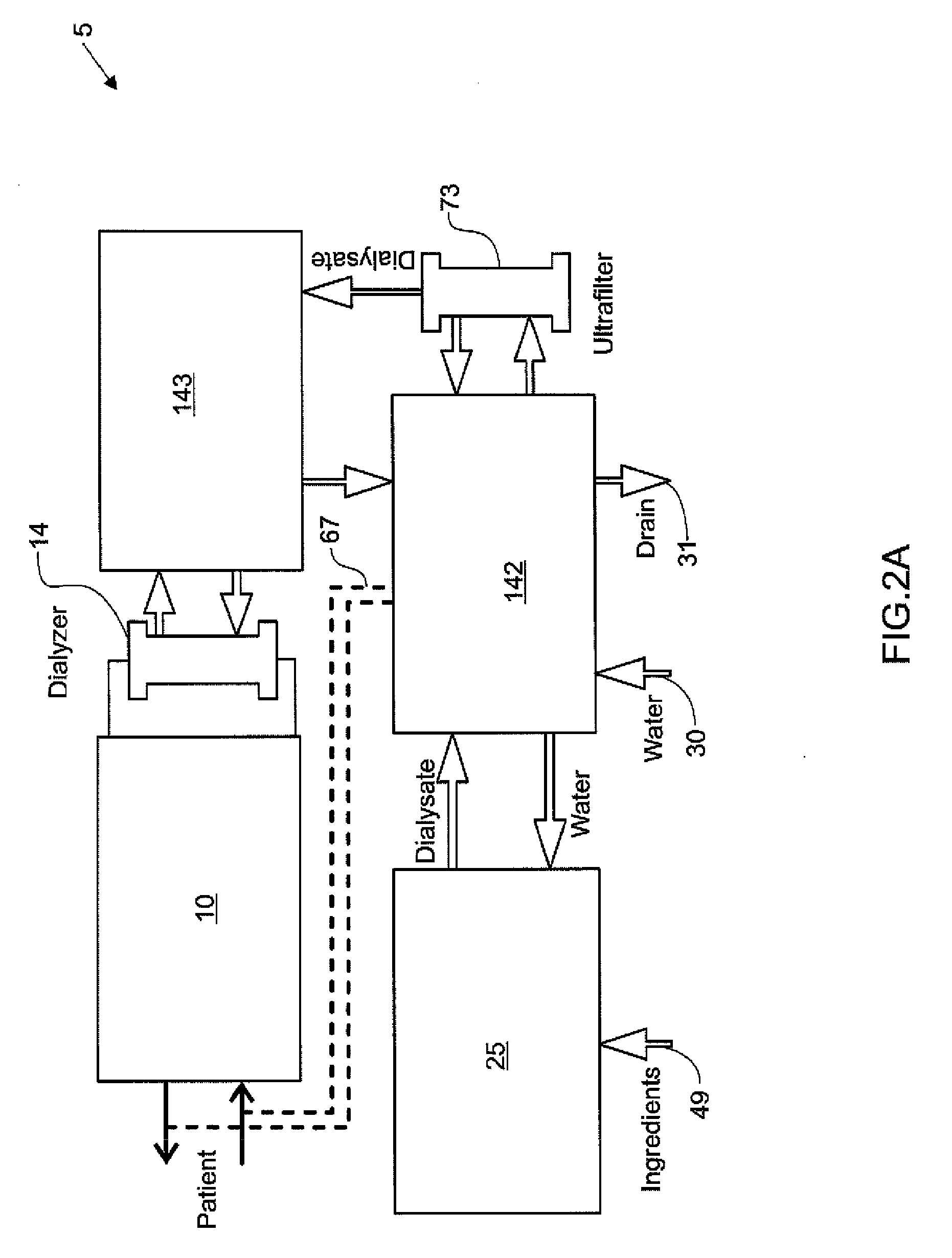
Hemodialysis systems and methods
The present invention generally relates to hemodialysis and similar dialysis systems, including a variety of systems and methods that would make hemodialysis more efficient, easier, and / or more affordable. One aspect of the invention is generally directed to new fluid circuits for fluid flow. In one set of embodiments, a hemodialysis system may include a blood flow path and a dialysate flow path, where the dialysate flow path includes one or more of a balancing circuit, a mixing circuit, and / or a directing circuit. Preparation of dialysate by the preparation circuit, in some instances, may be decoupled from patient dialysis. In some cases, the circuits are defined, at least partially, within one or more cassettes, optionally interconnected with conduits, pumps, or the like. In one embodiment, the fluid circuit and / or the various fluid flow paths may be at least partially isolated, spatially and / or thermally, from electrical components of the hemodialysis system. In some cases, a gas supply may be provided in fluid communication with the dialysate flow path and / or the dialyzer that, when activated, is able to urge dialysate to pass through the dialyzer and urge blood in the blood flow path back to the patient. Such a system may be useful, for example, in certain emergency situations (e.g., a power failure) where it is desirable to return as much blood to the patient as possible. The hemodialysis system may also include, in another aspect of the invention, one or more fluid handling devices, such as pumps, valves, mixers, or the like, which can be actuated using a control fluid, such as air. In some cases, the control fluid may be delivered to the fluid handling devices using an external pump or other device, which may be detachable in certain instances. In one embodiment, one or more of the fluid handling devices may be generally rigid (e.g., having a spheroid shape), optionally with a diaphragm contained within the device, dividing it into first and second compartments.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Impeller housing for percutaneous heart pump
Disclosed herein are heart pumps that include a catheter assembly and that can be applied percutaneously. Some embodiments include a locking device that prevents components of the catheter assembly from being separated when in use. The catheter assembly can include an expandable tip. In some embodiments, the catheter assembly includes a housing having a wall structure, a portion of which can have a bulbuous shape or can be deformable. In other embodiments, the housing can be configured to reduce fluttering or deflection of the housing and / or to maintain a gap between the housing and an impeller blade disposed therein.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
Left and right side heart support
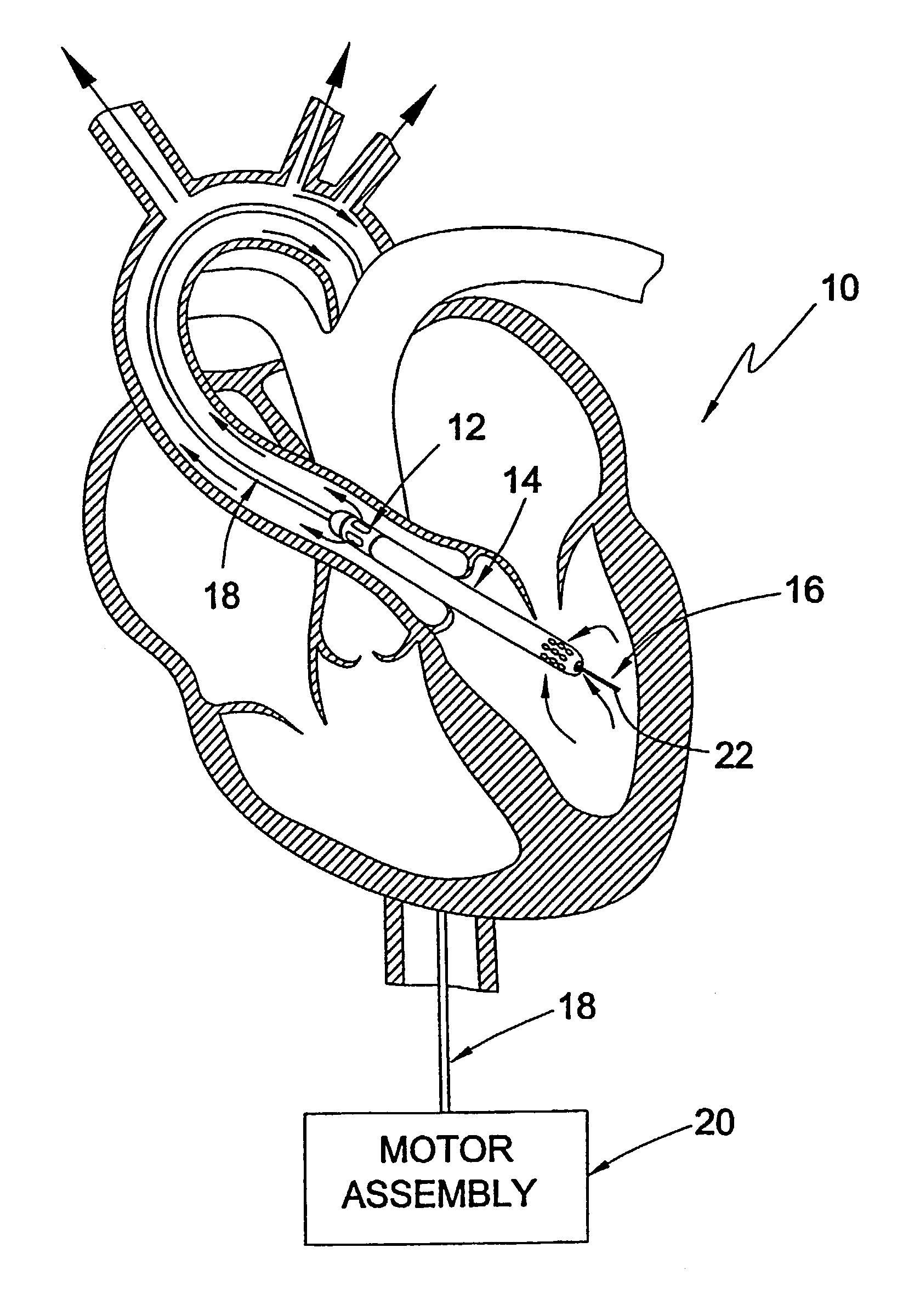
InactiveUS6926662B1Lower the volumeReduce the amount requiredOther blood circulation devicesBlood pumpsOuter CannulaRight atrium
A cannulation system for cardiac support uses an inner cannula disposed within an outer cannula. The outer cannula includes a fluid inlet for placement within the right atrium of a heart. The inner cannula includes a fluid inlet extending through the fluid inlet of the outer cannula and the atrial septum for placement within at least one of the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. The cannulation system also employs a pumping assembly coupled to the inner and outer cannulas to withdraw blood from the right atrium for delivery to the pulmonary artery to provide right heart support, or to withdraw blood from at least one of the left atrium and left ventricle for delivery into the aorta to provide left heart support, or both.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Expandable impeller pump
An impeller according to an example of the present invention comprises a hub, and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub, and a stored configuration in which the impeller is radially compressed, for example by folding the blade towards the hub. The impeller may comprise a plurality of blades, arranged in blade rows, to facilitate radial compression of the blades. The outer edge of a blade may have a winglet, and the base of the blade may have an associated indentation to facilitate folding of the blade.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
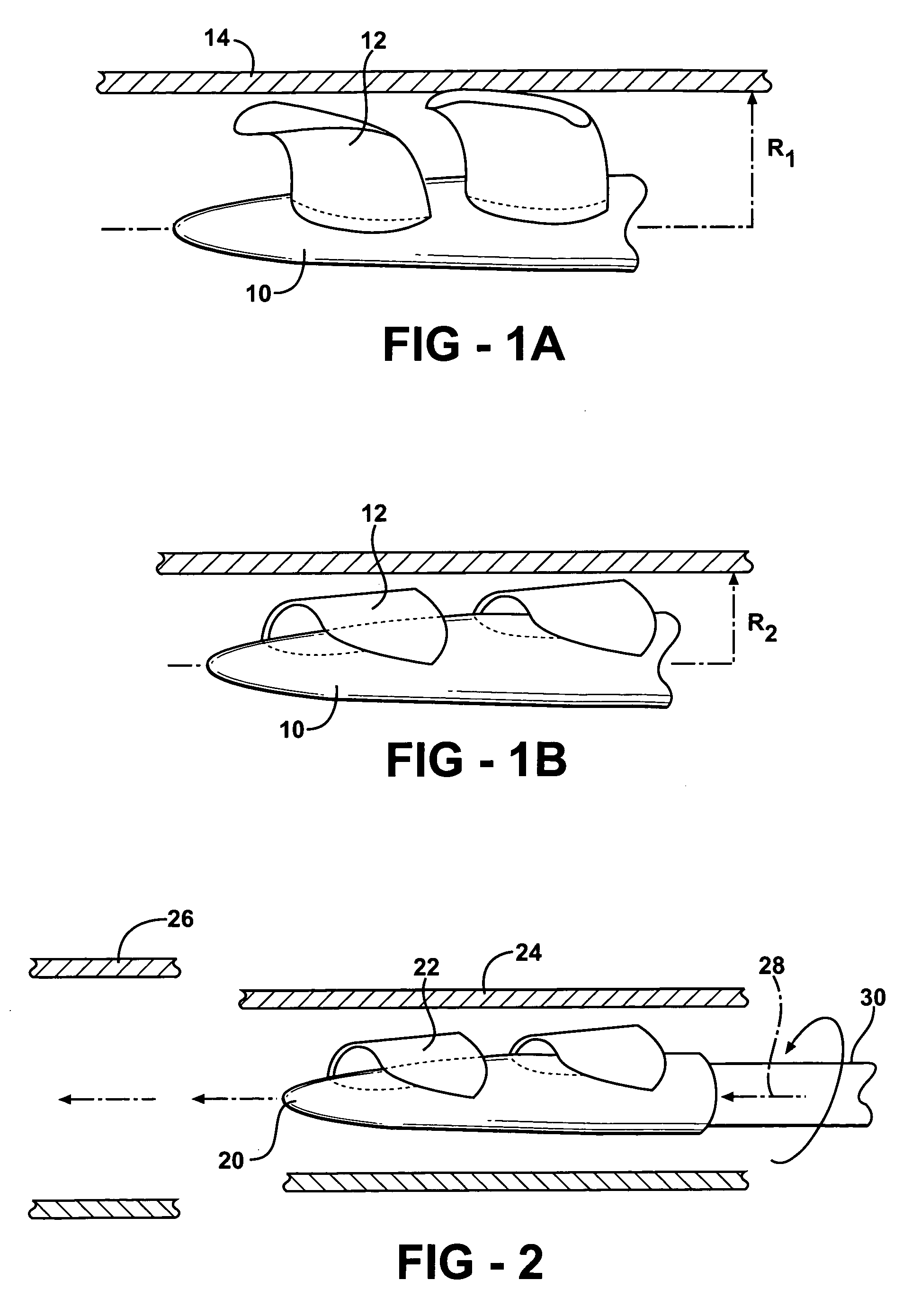
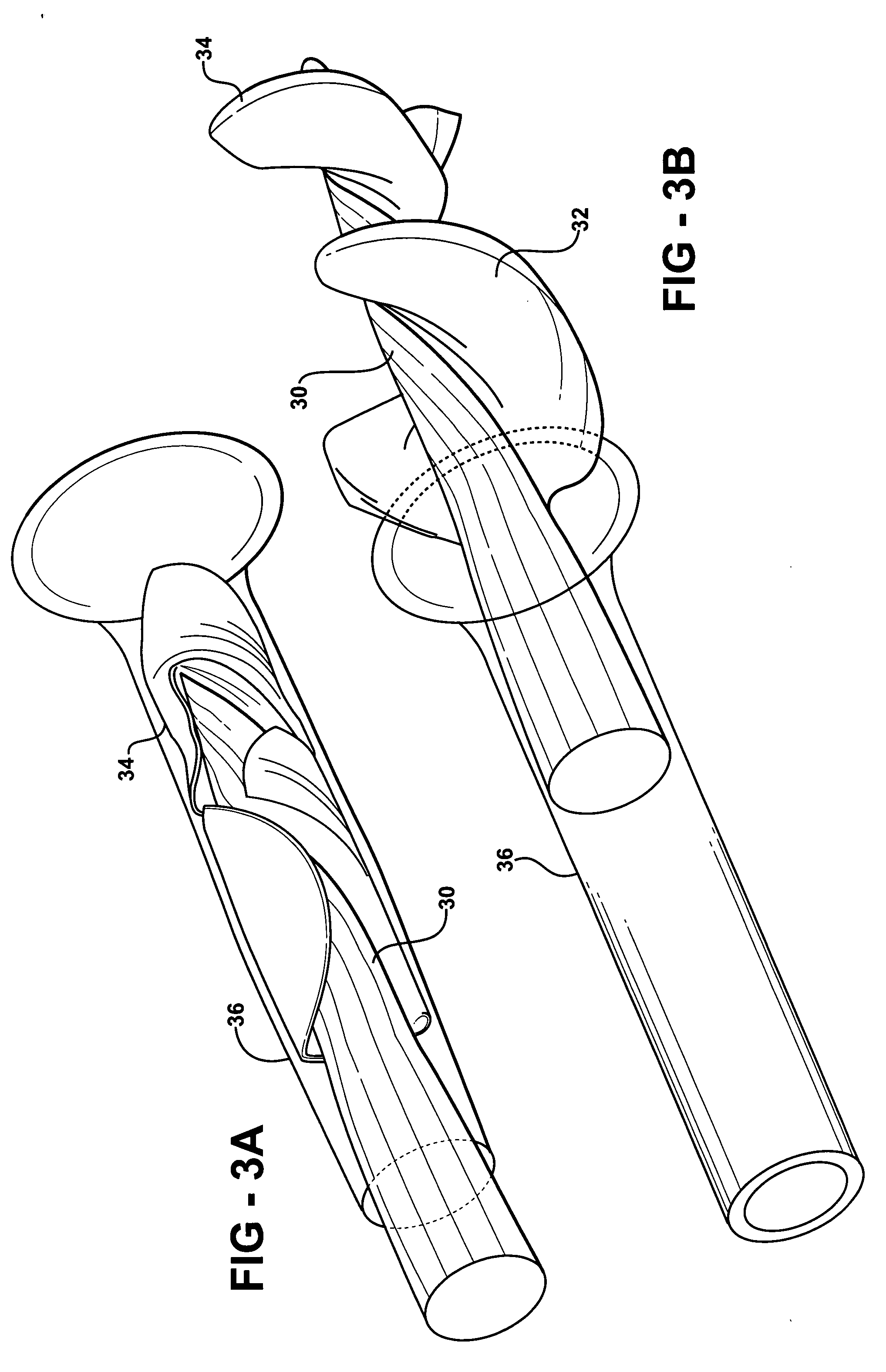
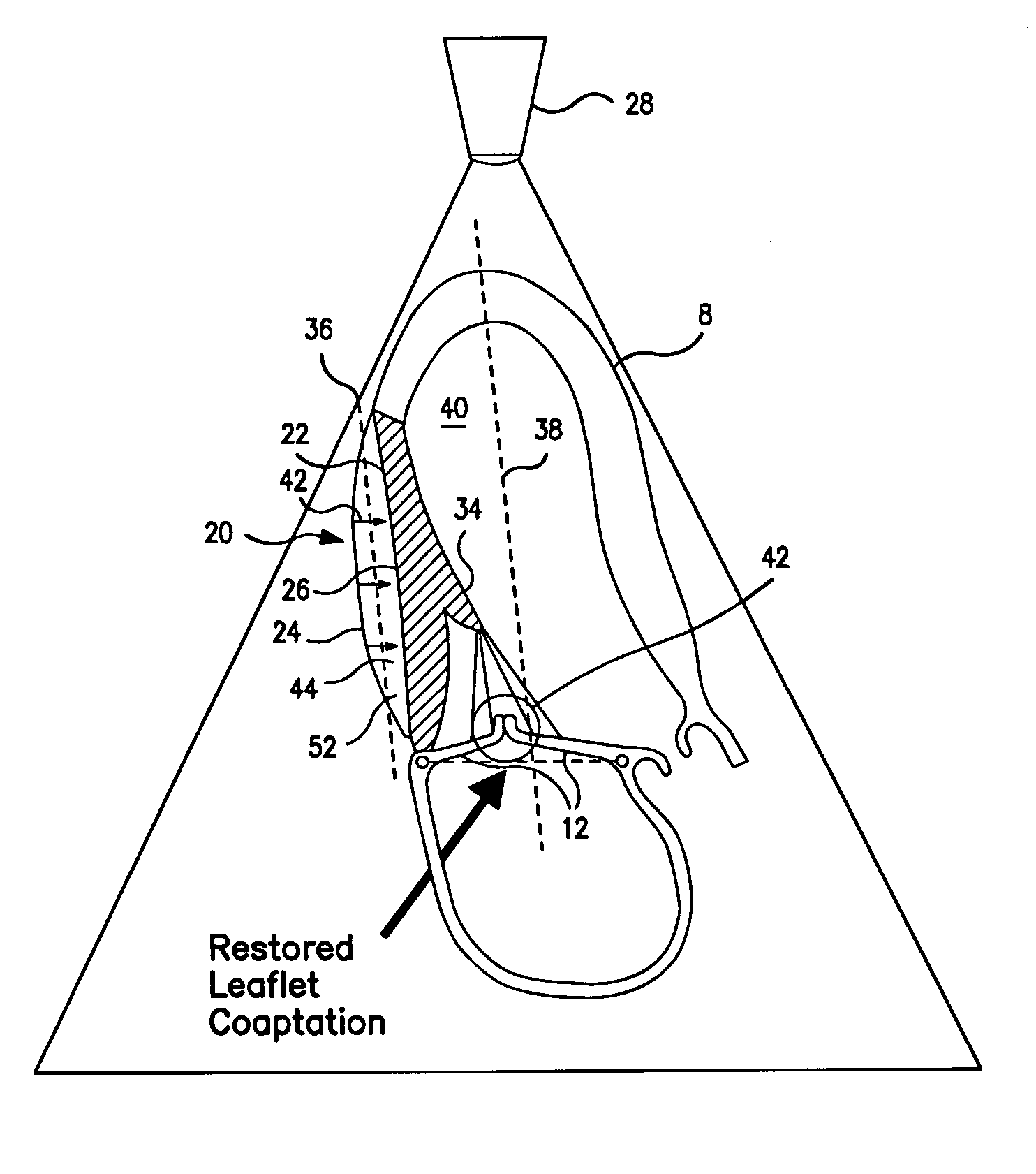
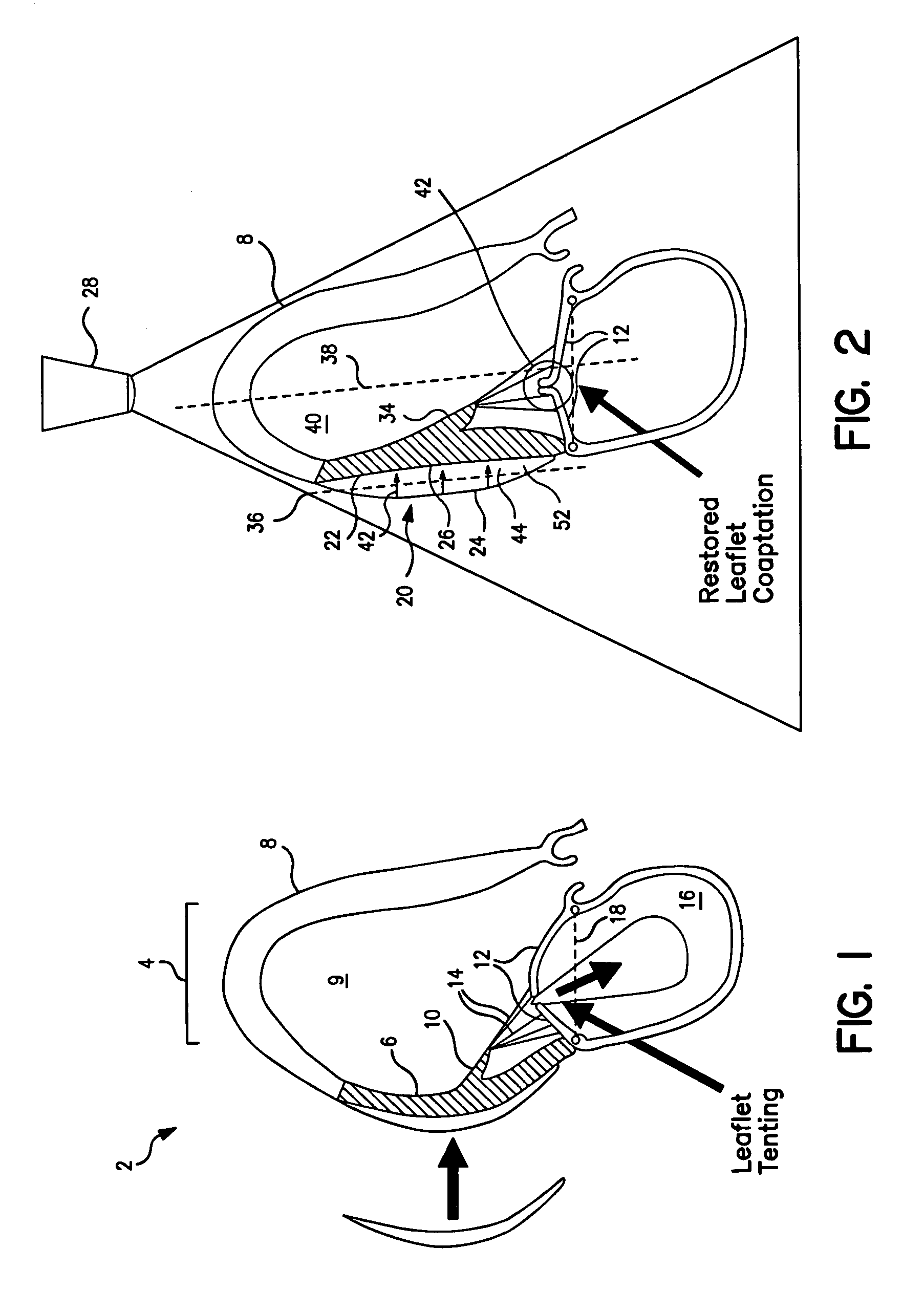
Systems for and methods of atrioventricular valve regurgitation and reversing ventricular remodeling
InactiveUS20060129025A1Improve leaflet coaptationKeep the pressureAdditive manufacturing apparatusAnnuloplasty ringsLeft Ventricle RemodelingAtrioventricular valves
Methods of and devices for restoring the normal geometry of a heart, including but not limited to the structures supporting the atrioventricular valves. The techniques and devices described herein operate on the principle of displacement, both active and passive, to reverse cardiac remodeling and limit ischemic atrioventricular valve regurgitation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Chronic performance control system for rotodynamic blood pumps
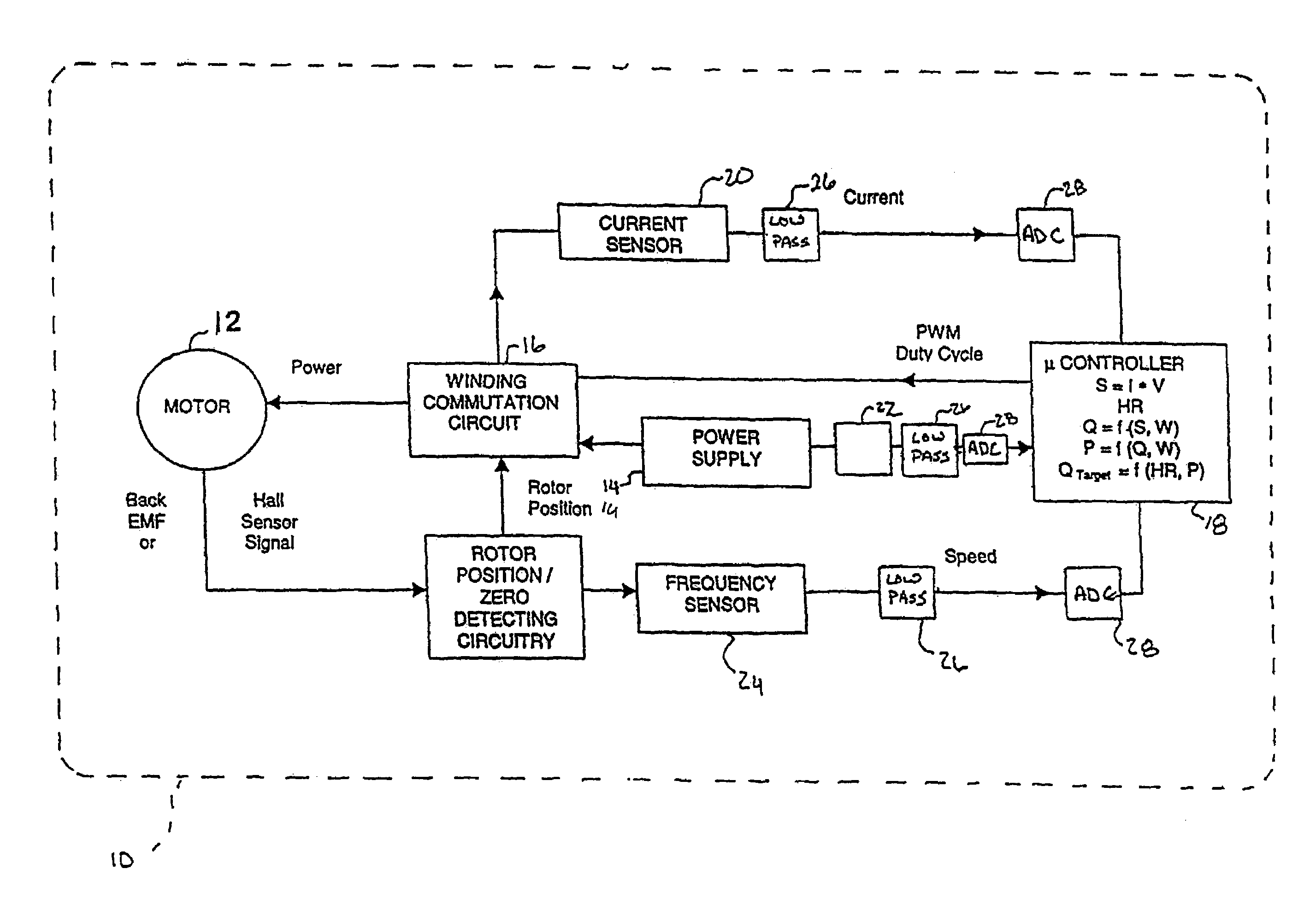
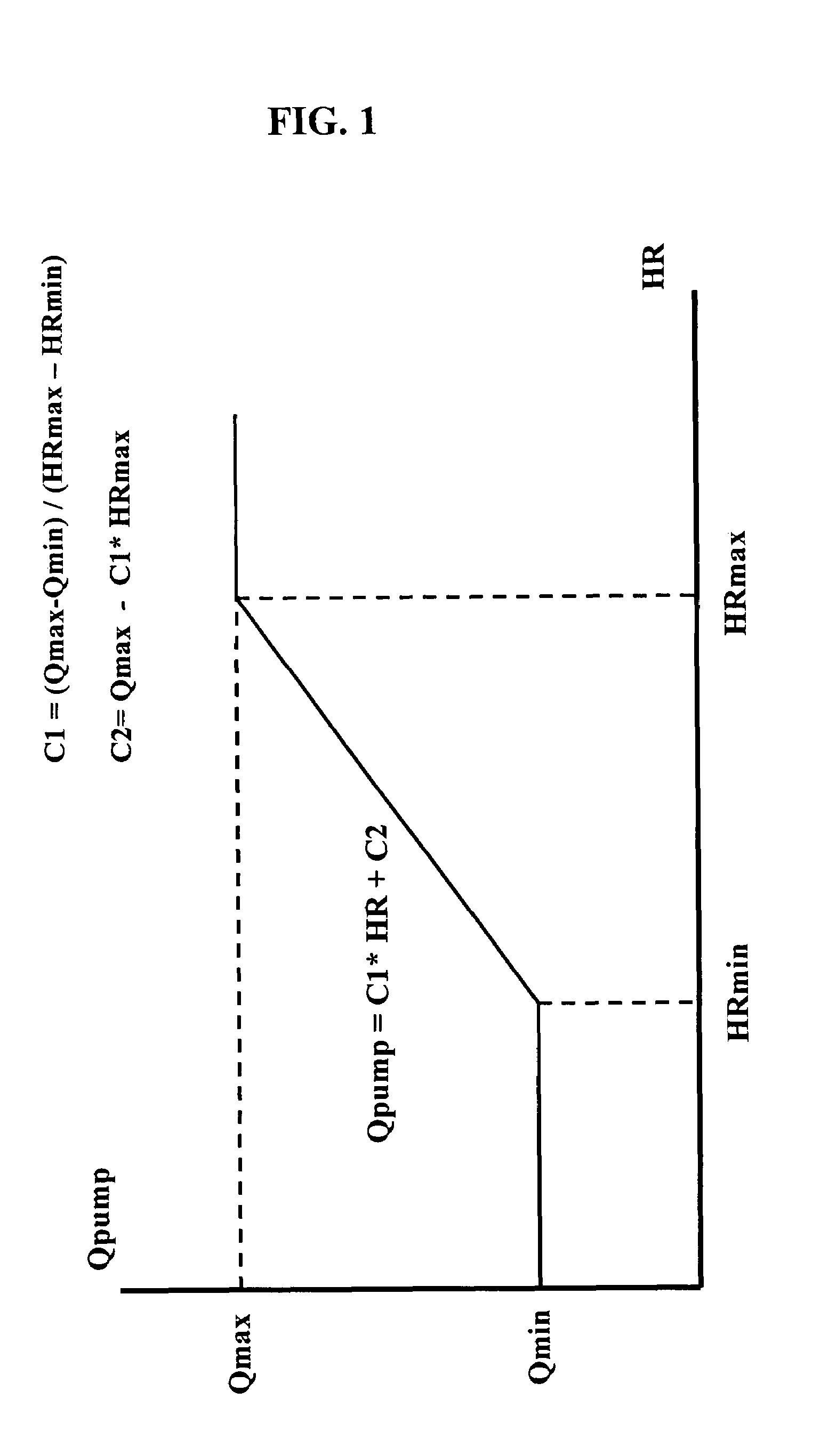
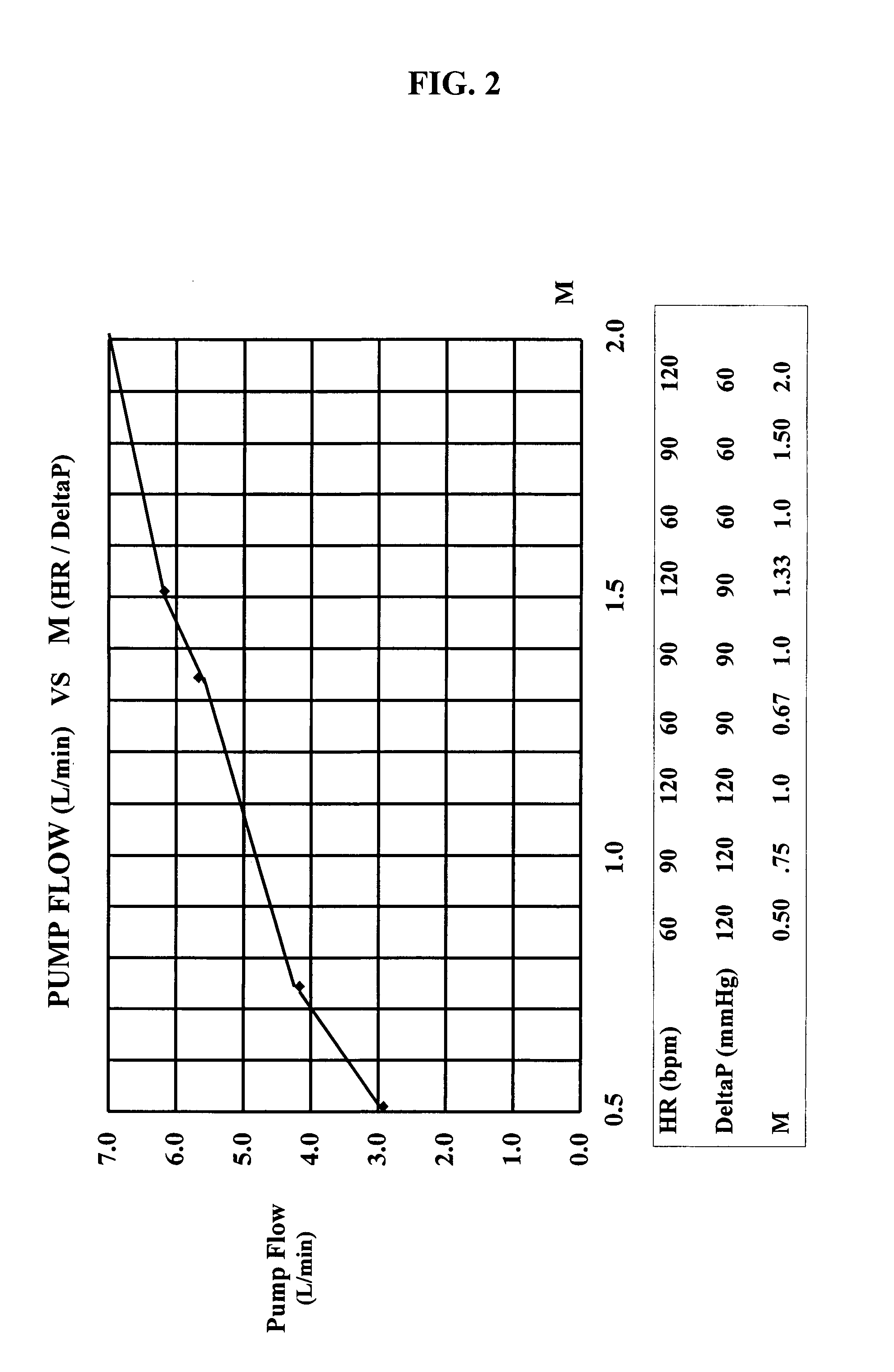
InactiveUS7645225B2Simple control circuitIncrease control flexibilityDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlMicrocontrollerMotor speed
In a left ventricular assist device (LVAD) a rotodynamic blood pump (10) is powered by a brushless DC motor (12). A power supply (14) supplies power to the motor (12). Three feedback channels, one for each of voltage, current, and motor speed lead to a microcontroller or microprocessor (18). The three feedback waveforms are analyzed, and from these waveforms, motor input power, patient heart rate, current pump flow rate, and systemic pressure are determined. The microprocessor (18) then calculates a desired flow rate proportional to the patient heart rate. The microprocessor communicates a new power output to a commutation circuit (16), which regulates power to the motor (12). The pump (10) also includes safety checks that are prioritized over desired pump flow. These include prevention of ventricular suction, low pulsatility, minimum and maximum pump speed, minimum speed-relative pump flow, minimum absolute pump flow, minimum and maximum motor input power.
Owner:MEDVEDEV ALEXANDER +2
Ventricular assist device for intraventricular placement
A ventricular assist device includes a pump such as an axial flow pump, an outflow cannula connected to the outlet of the pump, and an anchor element. The anchor element is physically connected to the pump, as by an elongate element. The pump is implanted within the left ventricle with the outflow cannula projecting through the aortic valve but desirably terminating short of the aortic arch. The anchor element is fixed to the wall of the heart near the apex of the heart so that the anchor element holds the pump and outflow cannula in position.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
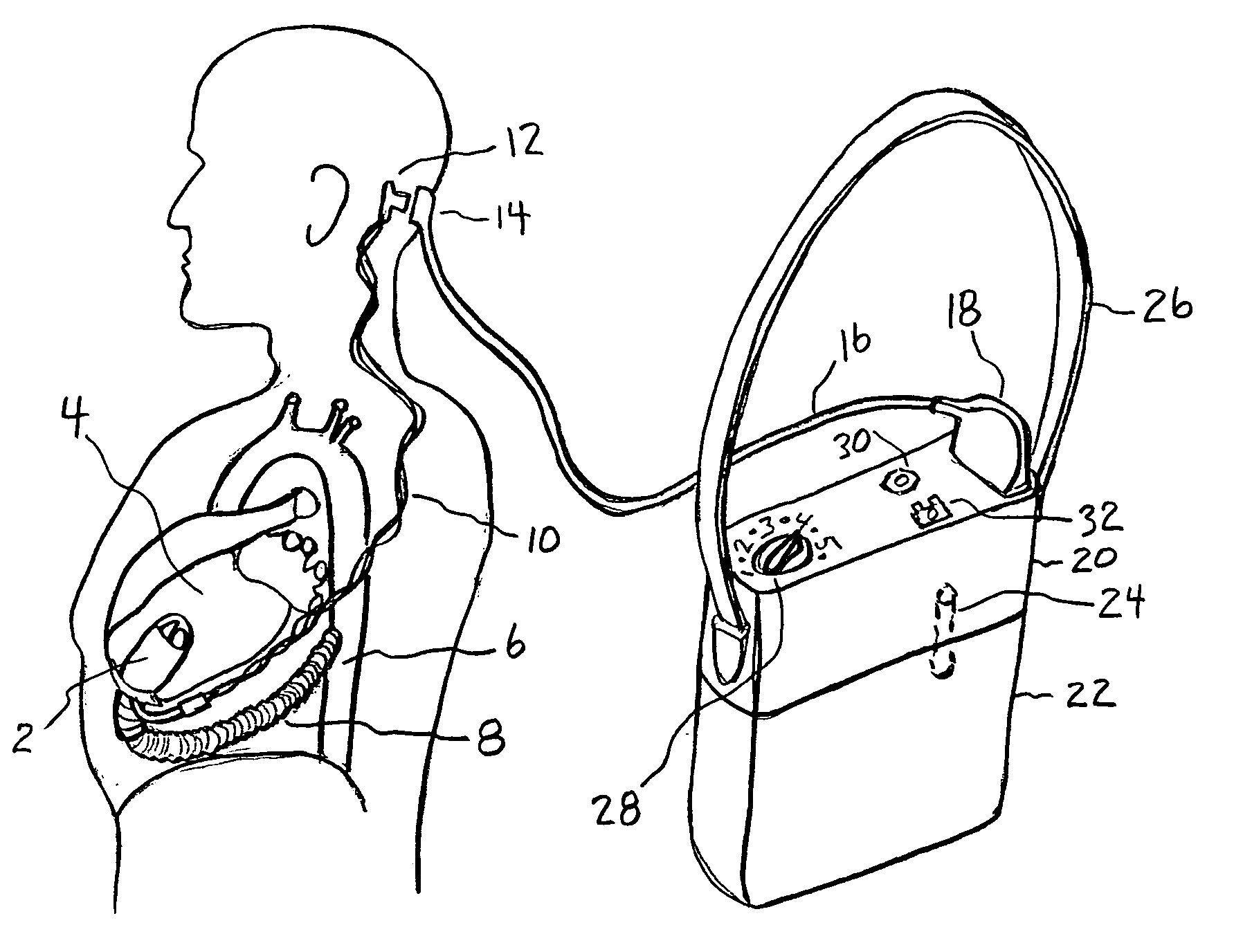
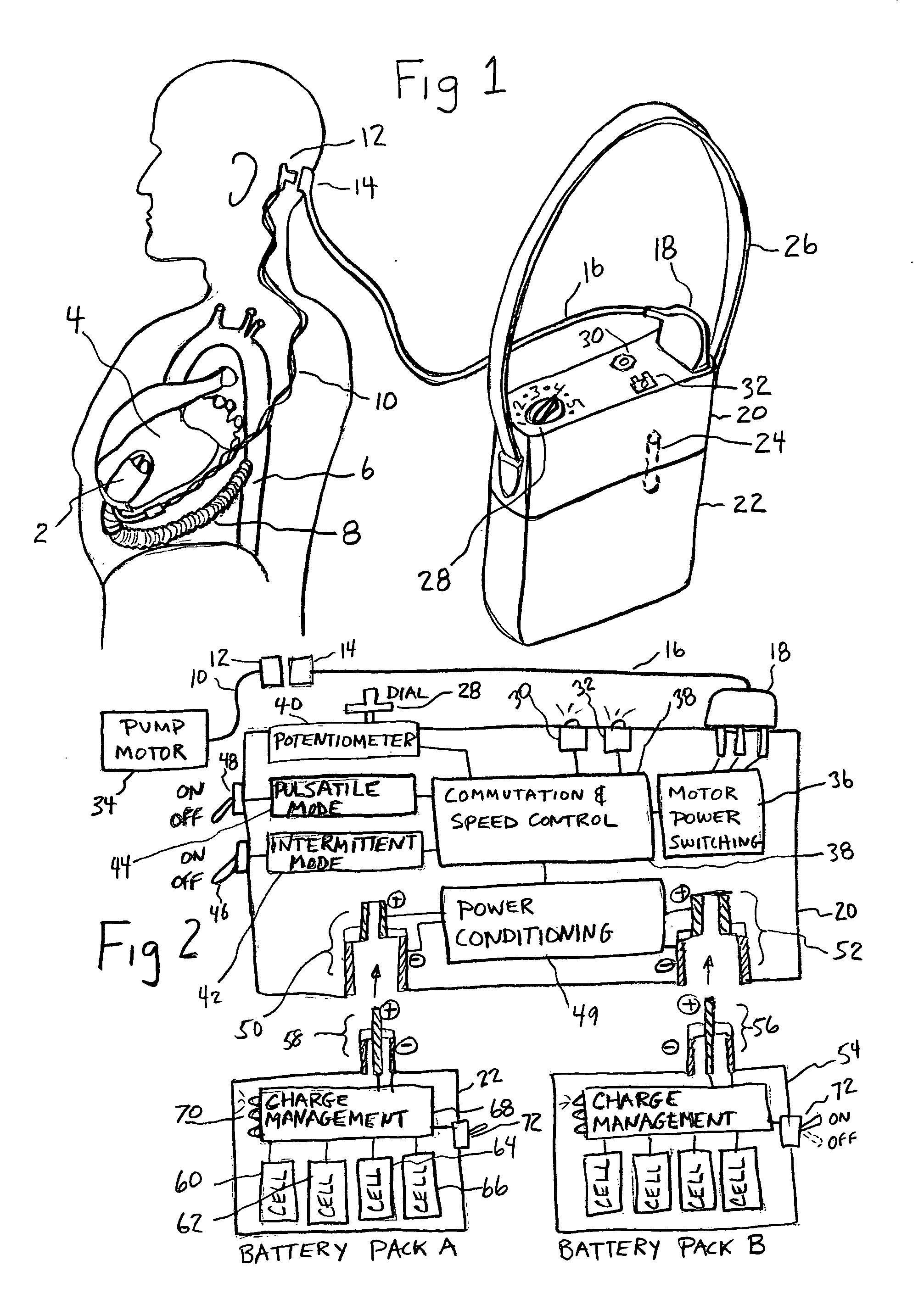
Artificial heart power and control system
InactiveUS20050071001A1Secure attachmentReduce trafficPrimary cell maintainance/servicingControl devicesControl theoryElectric cables
The present invention provides a human engineered power and control system for artificial hearts or assist devices configured for ease of use, ruggedness, and high reliability. Battery powered systems of the prior art have required multiple cables and connectors that are subject to failure due to damage or wear. In the present invention, direct connection of the batteries to the control system eliminates multiple cables and connectors used with previous designs. A novel method of connecting batteries to the control system and exchanging batteries without interruption of power is provided in a compact user friendly configuration. The control system may provide periodic reductions in assist device flow to permit the natural ventricle to eject blood through the natural outflow valve, open the valve leaflets to prevent them from adhering together, and achieve sufficient washout to prevent thrombosis. Using either software based control or software independent electronic circuitry, the flow pumped by the artificial heart is reduced for a long enough period of time to permit at least a few beats of the natural heart to generate sufficient pressure to open the outflow valve. In a control system embodiment in which the patient manually adjusts the pump speed to incremental settings for rest and exercise conditions, a pulsatile flow mode is disclosed which provides approximately the same flow at a given incremental setting as the pump produces when running in a constant speed mode at the same setting. As the patient learns which speed setting is best for daily activities, the patient may use the same setting with either a pulsatile or constant pump speed mode.
Owner:EDER JEFFREY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com