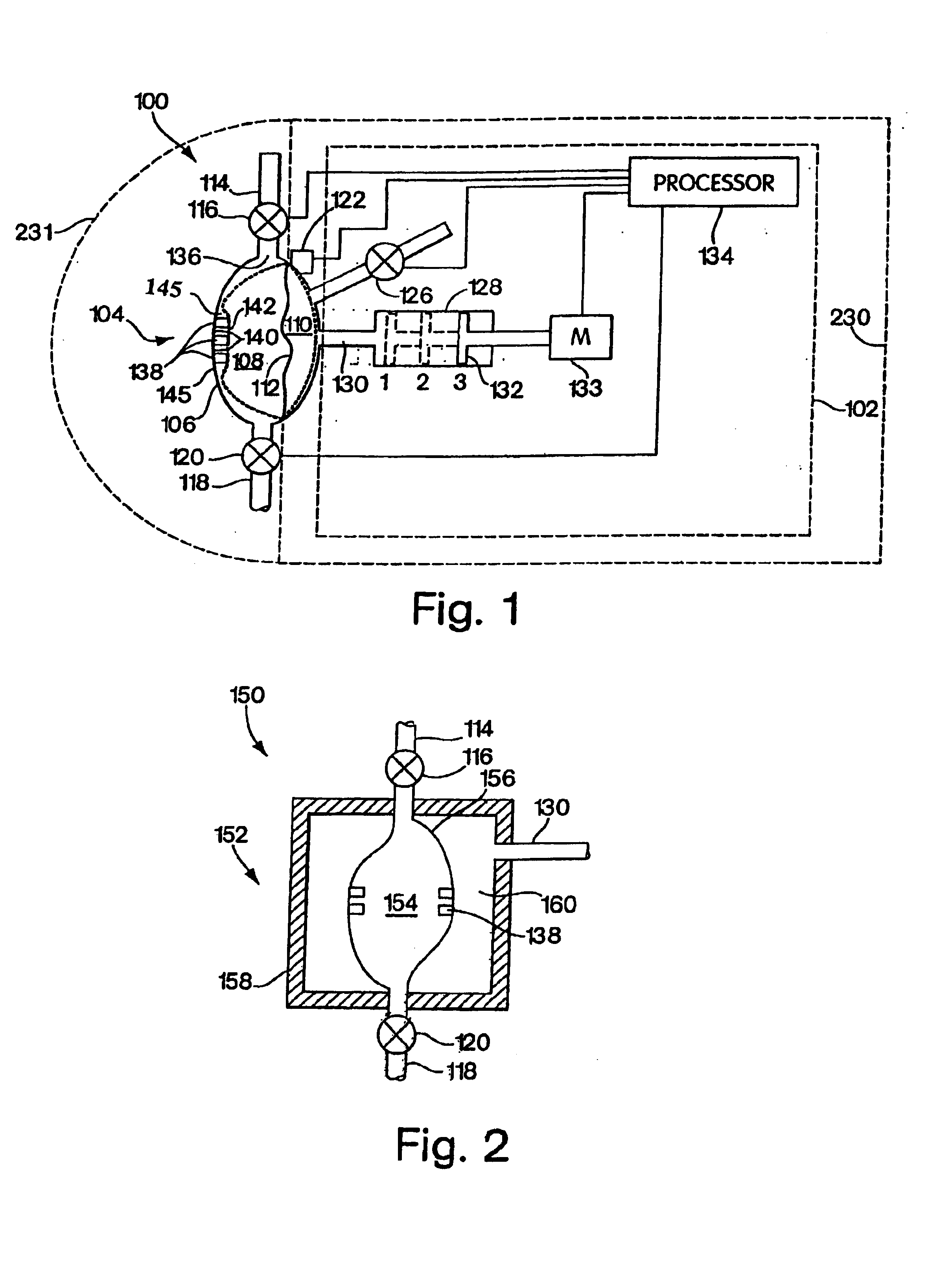
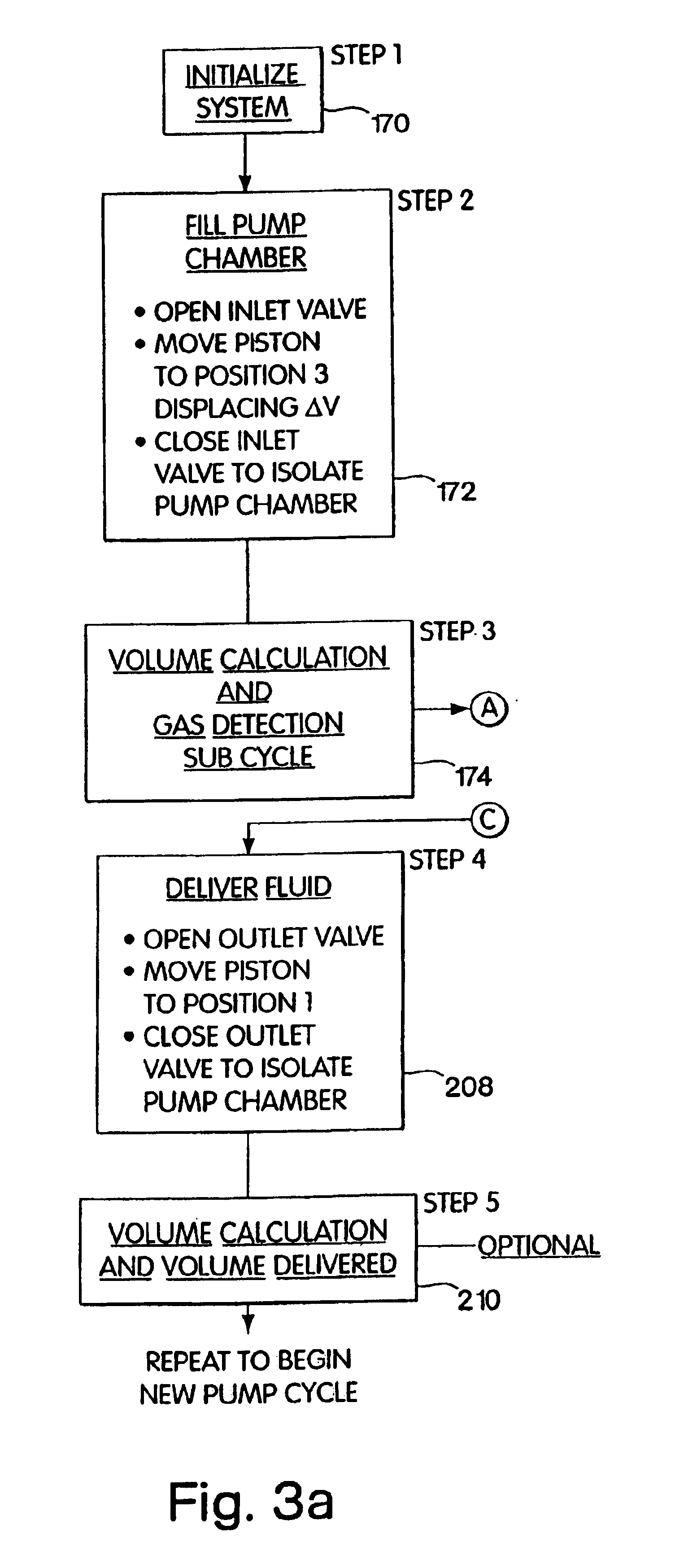
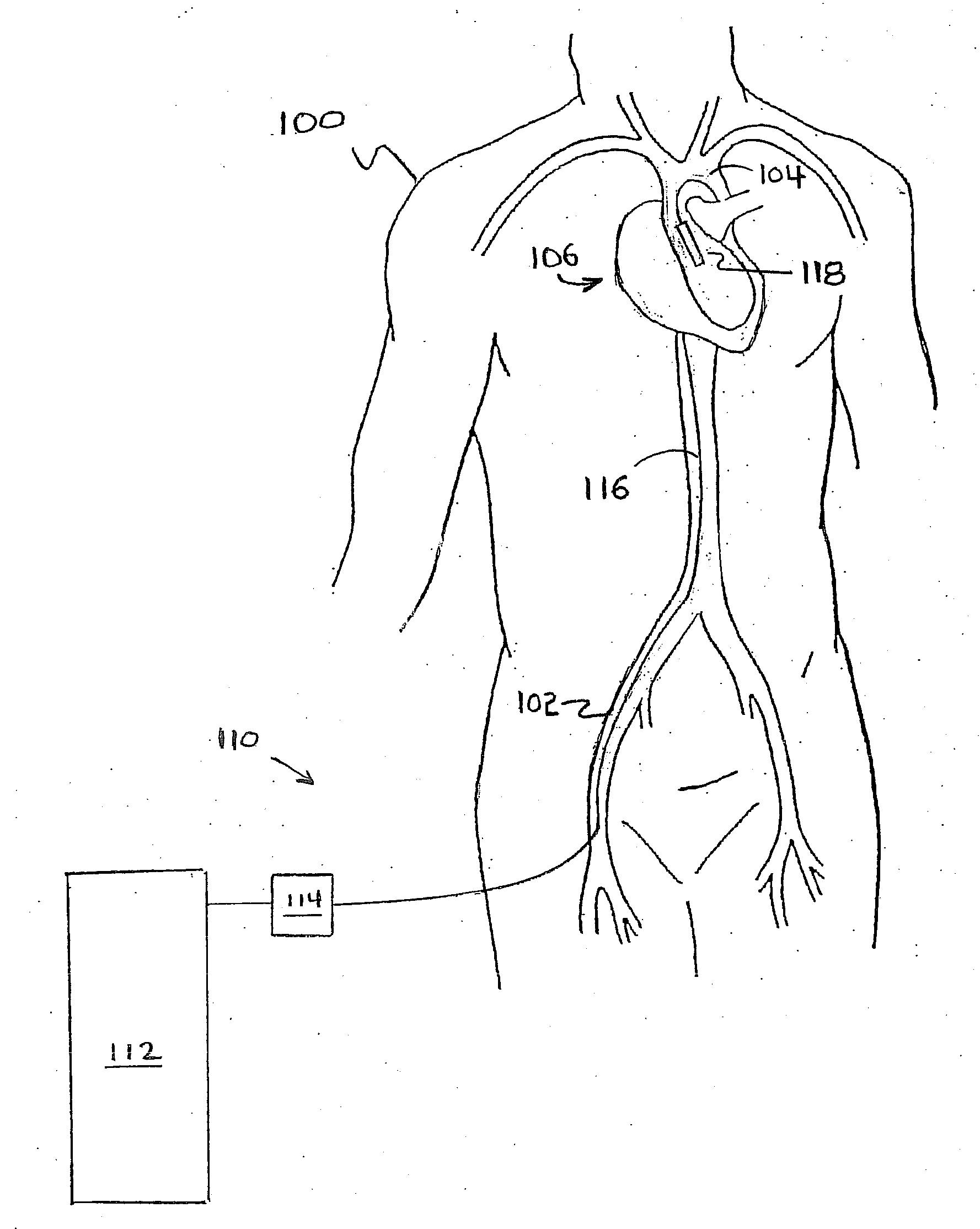
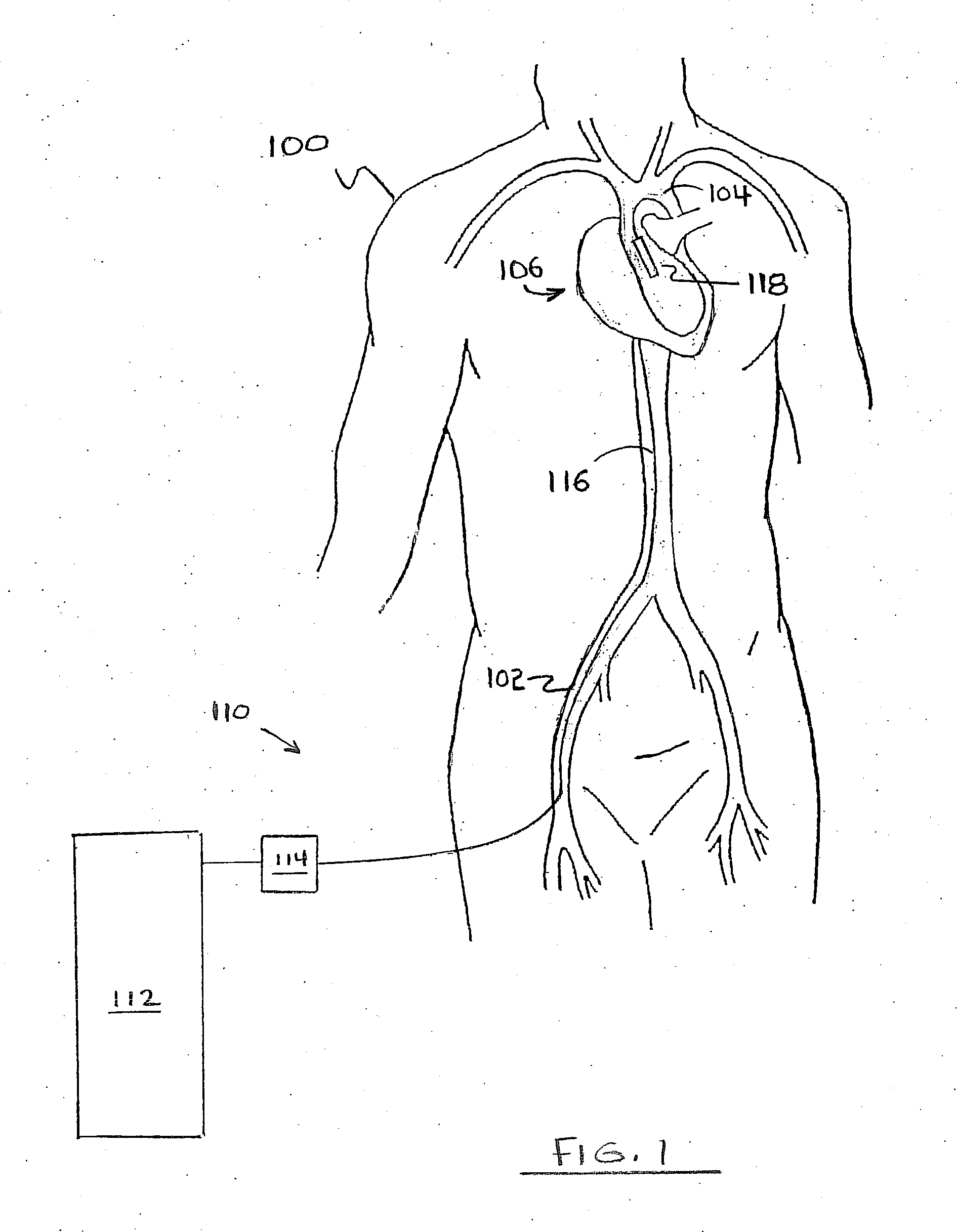
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1824results about "Blood pump" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
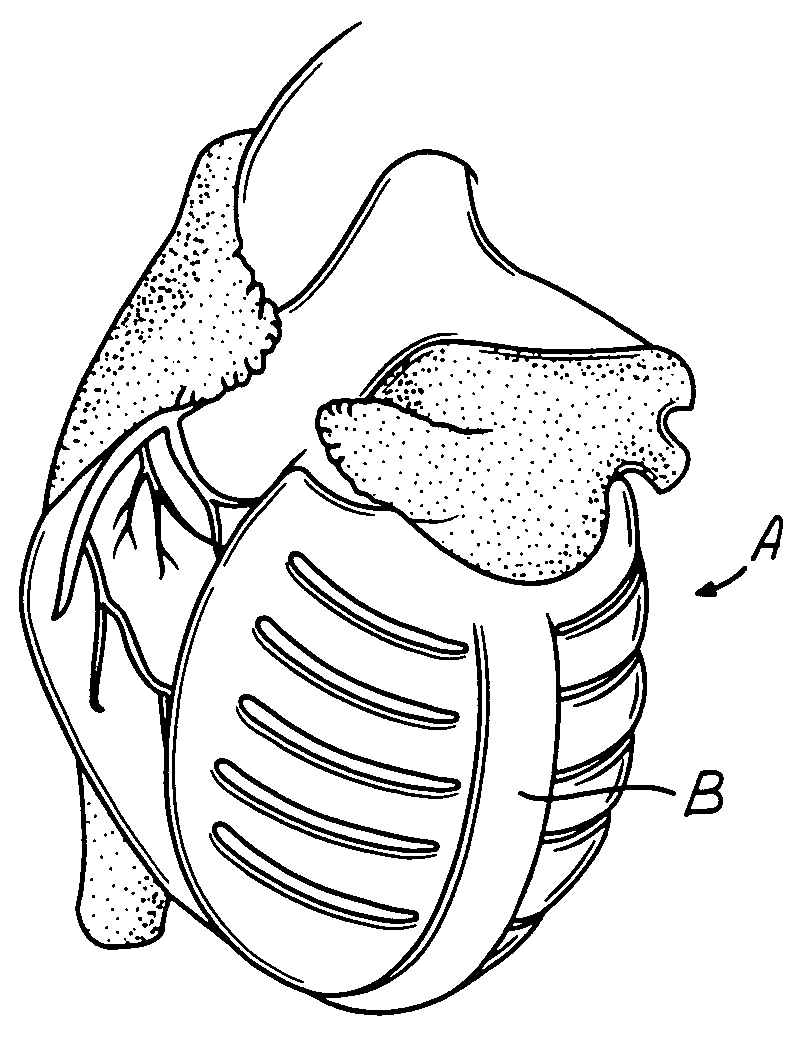
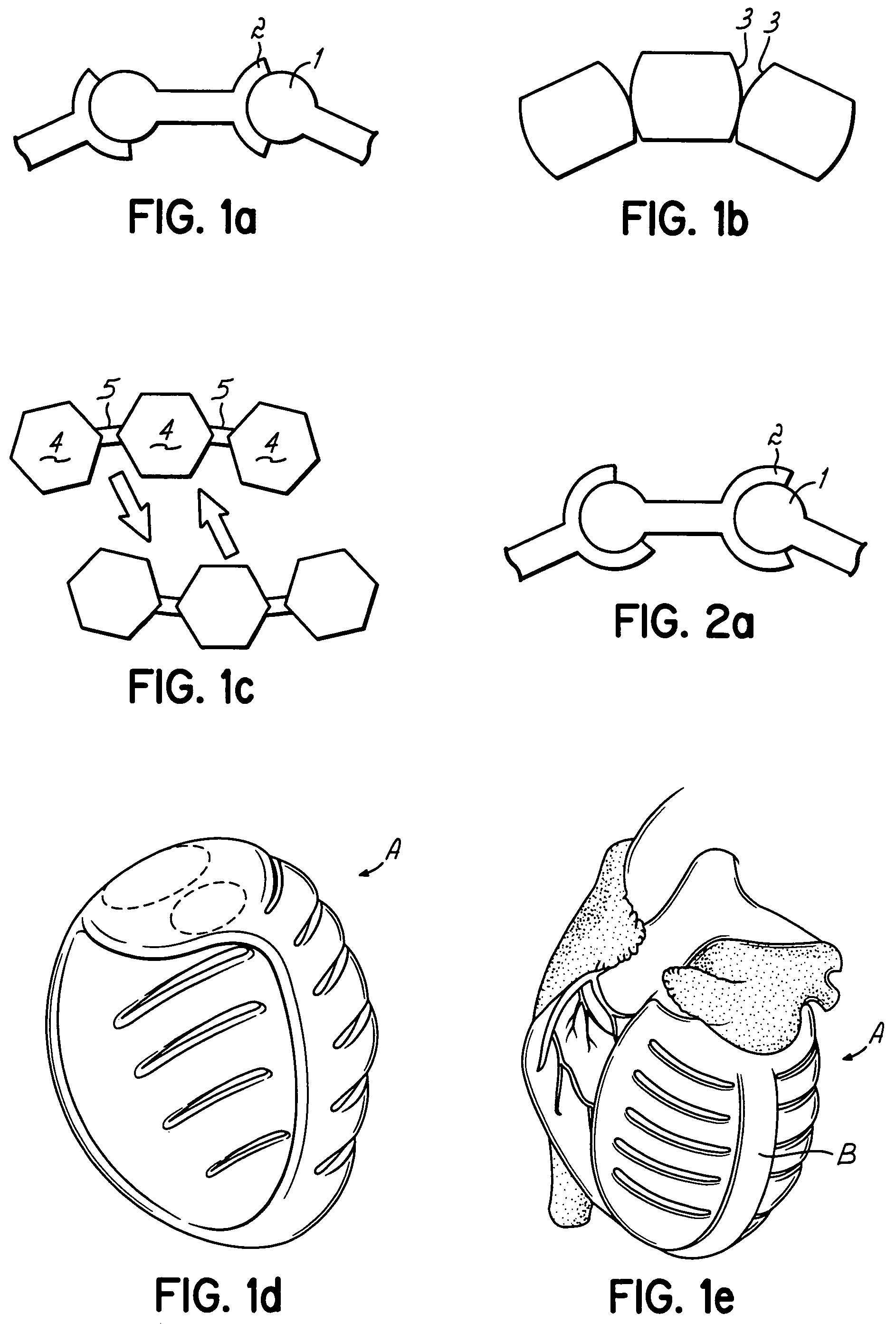
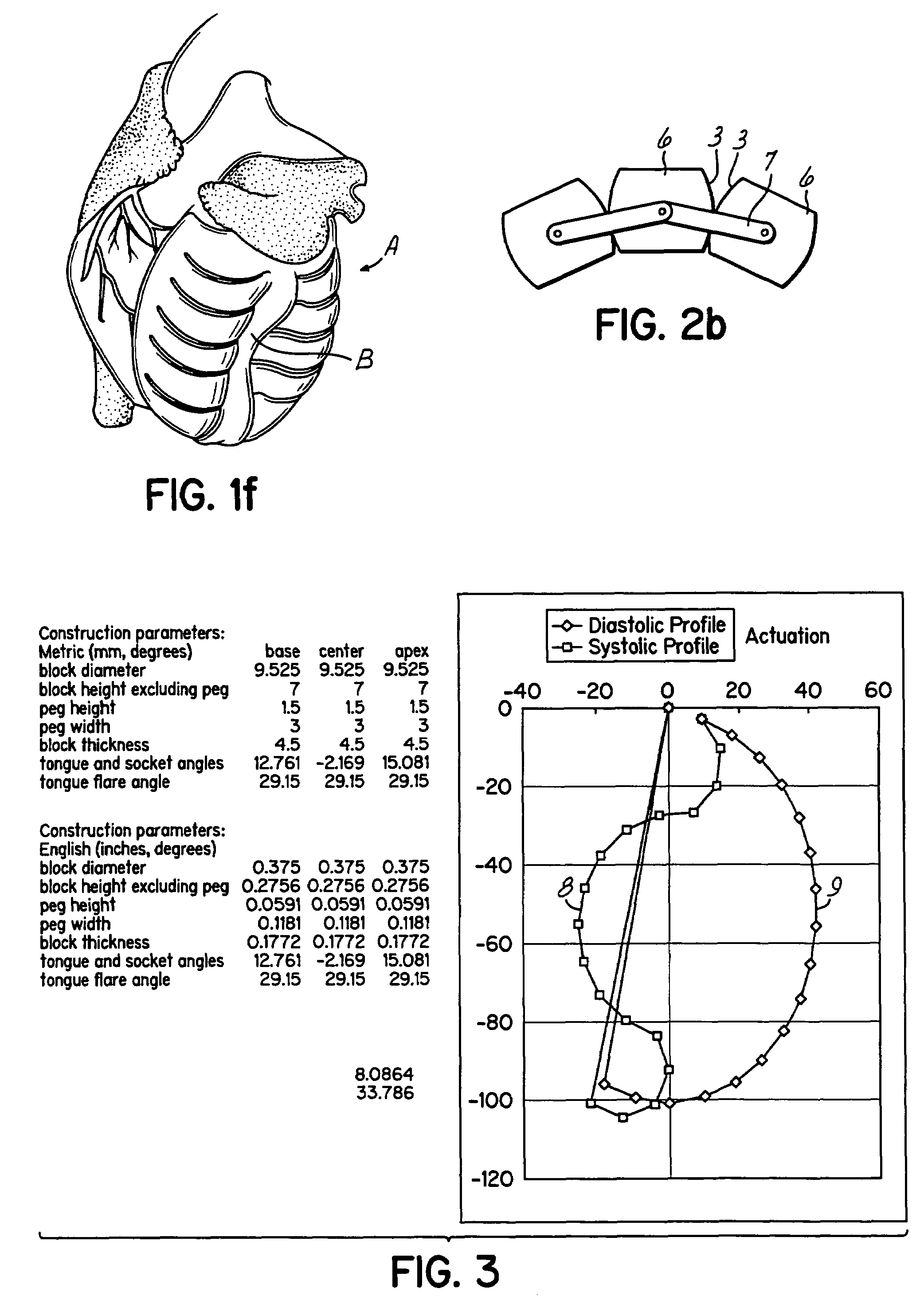
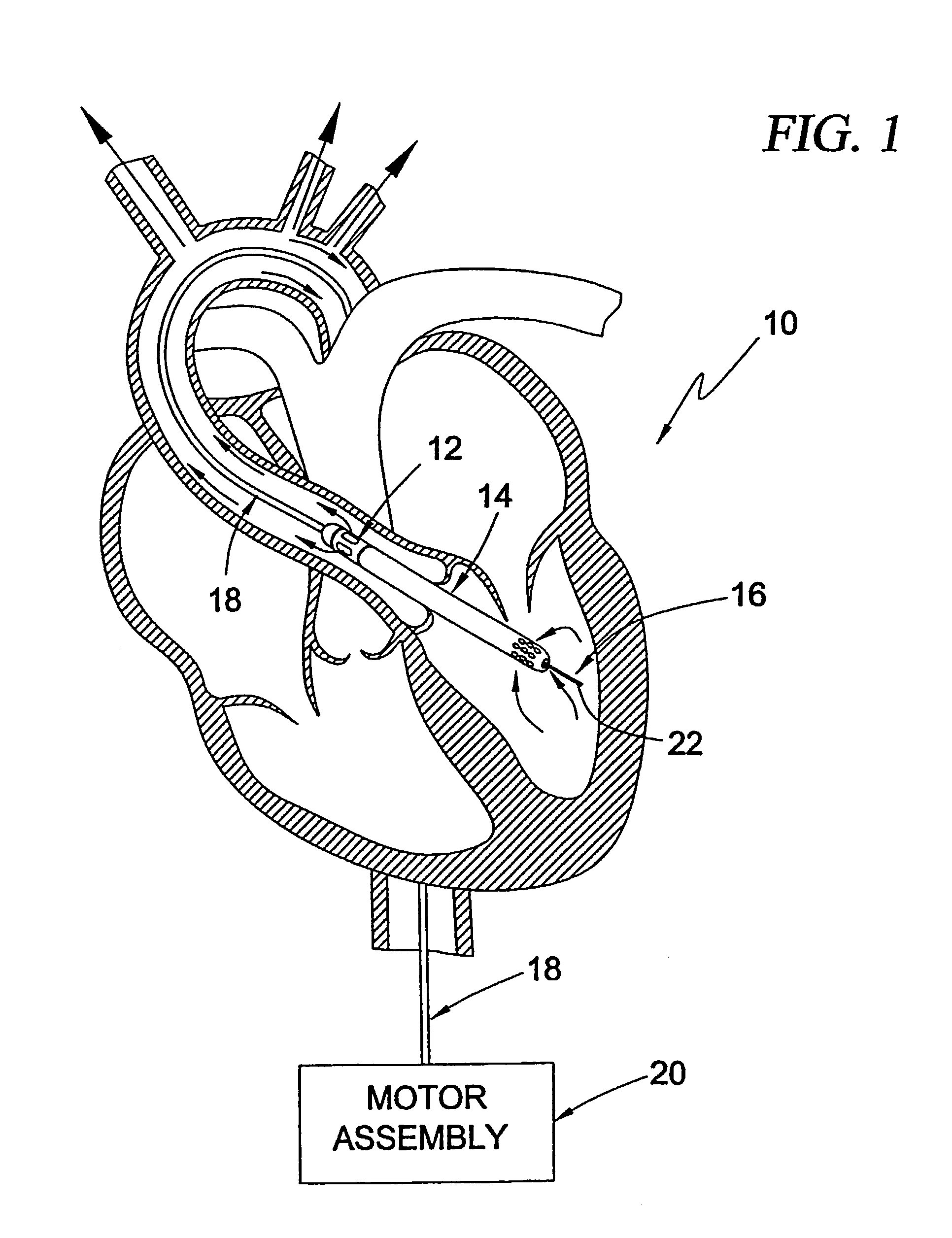
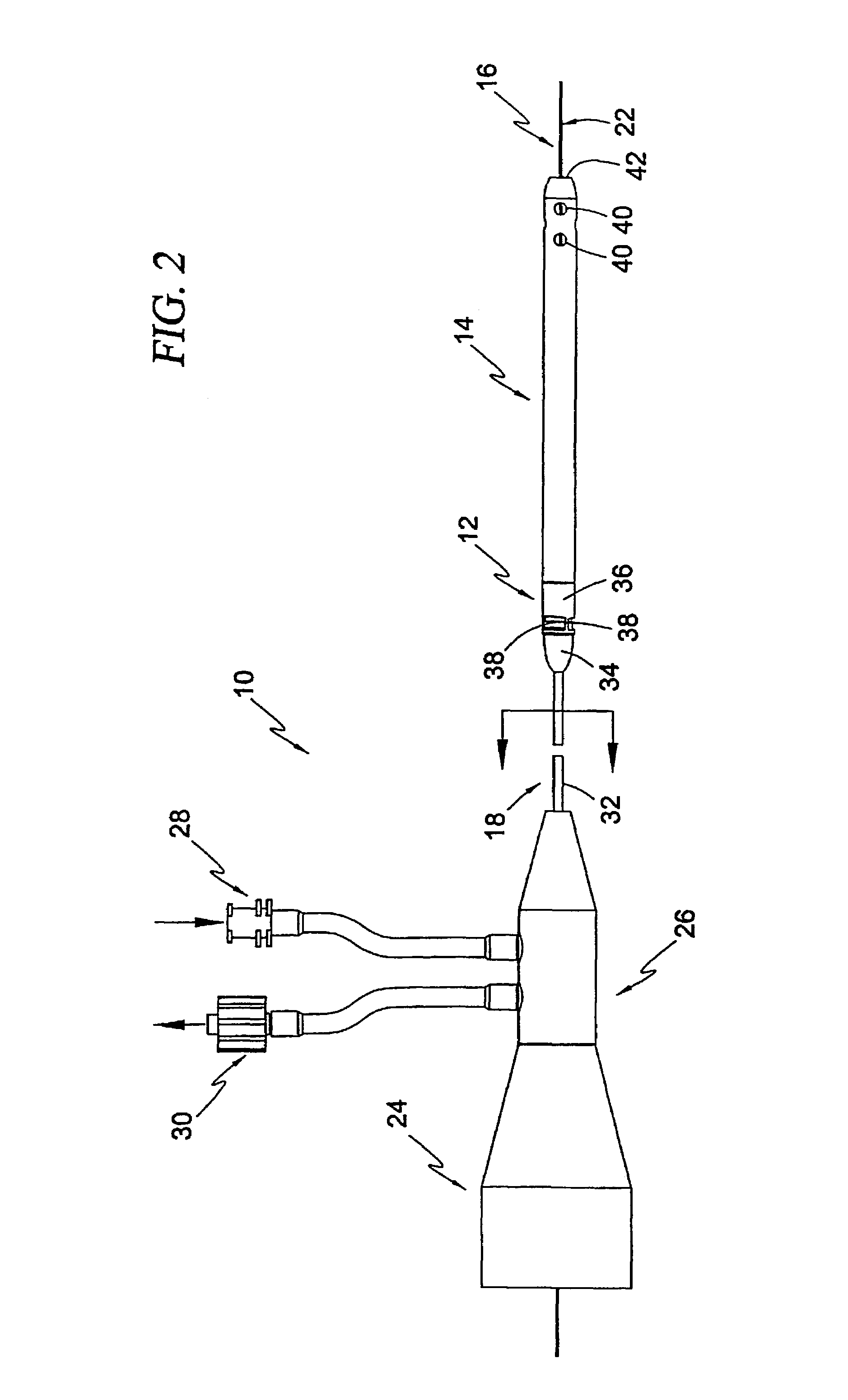
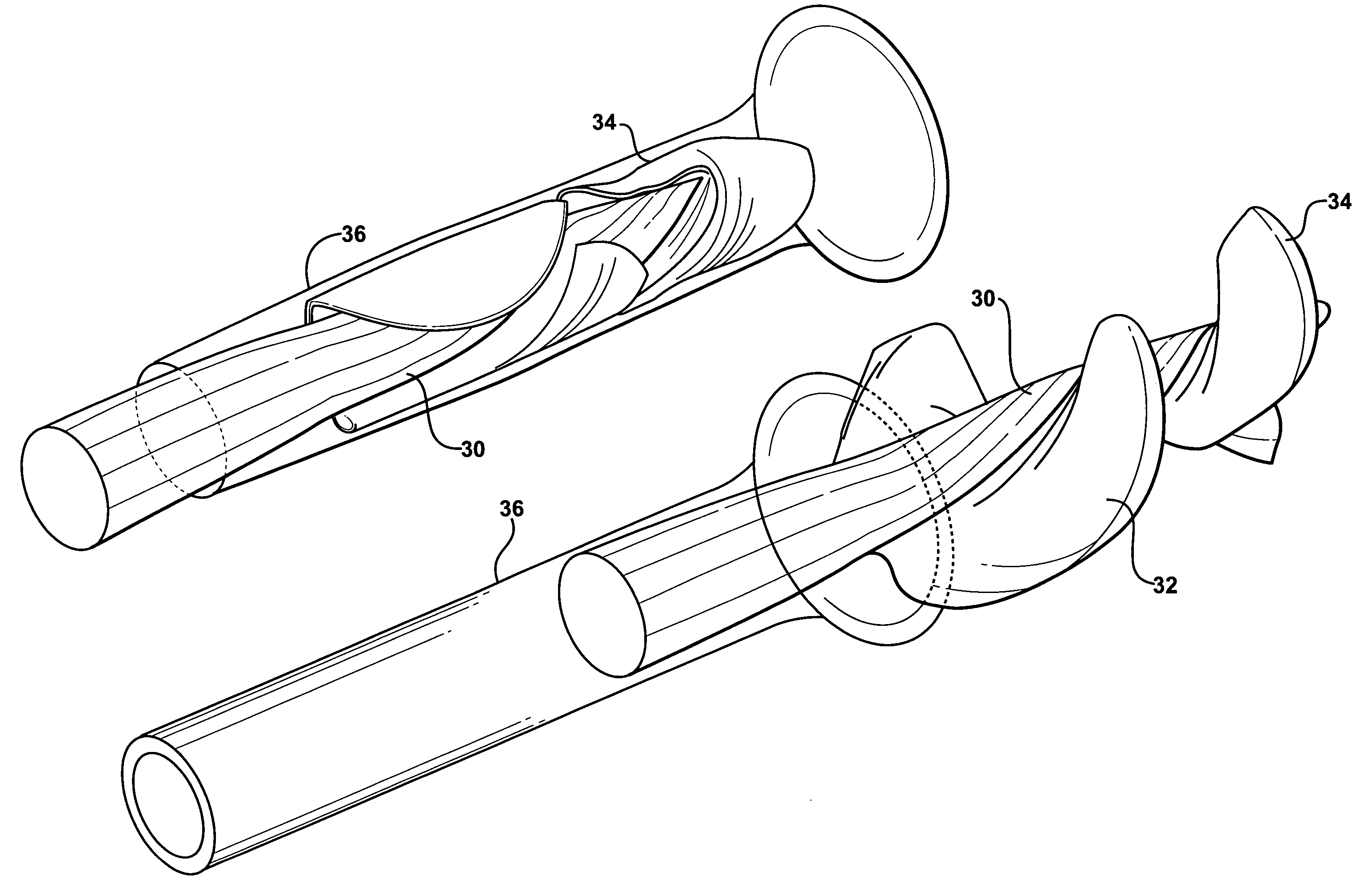
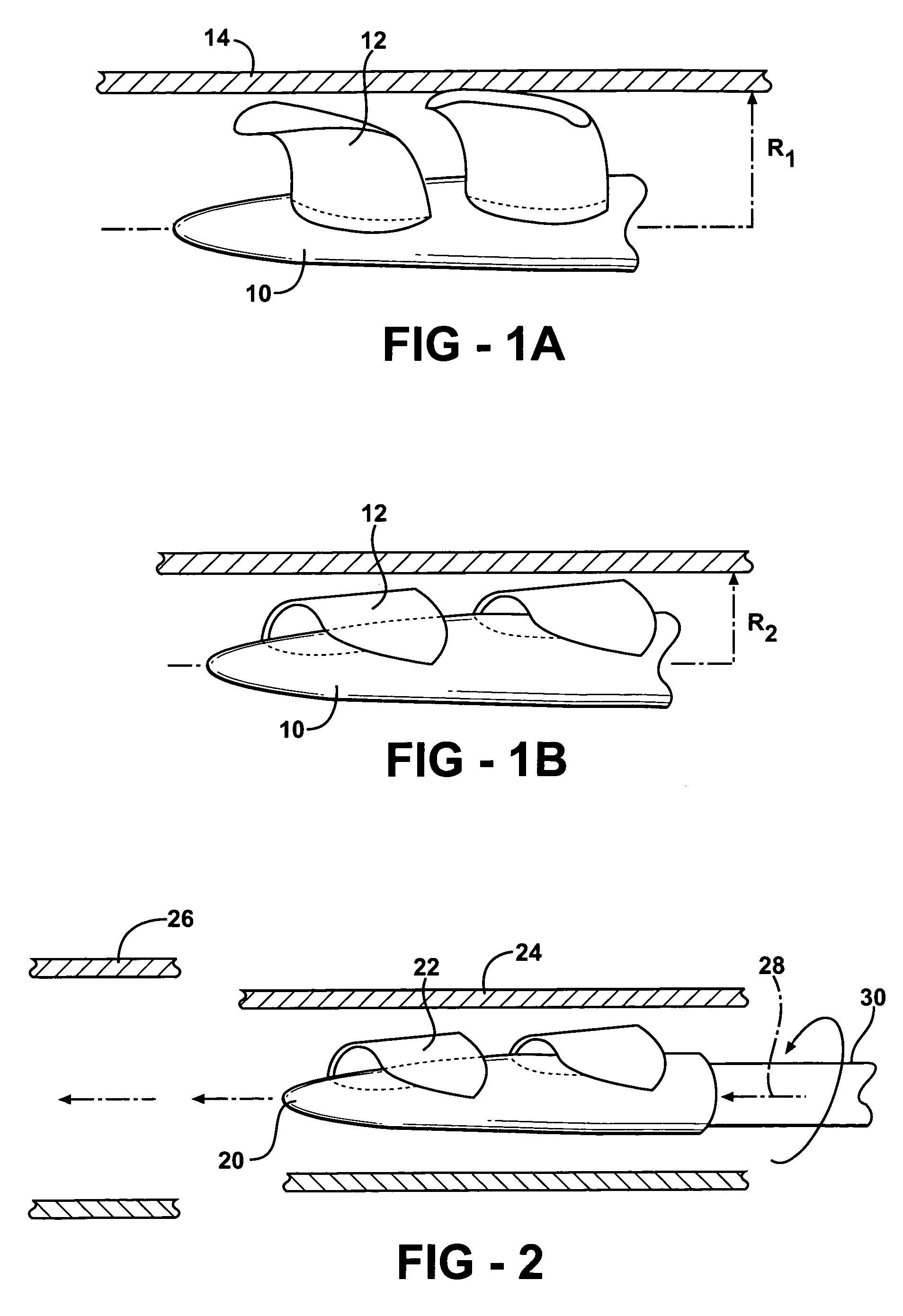
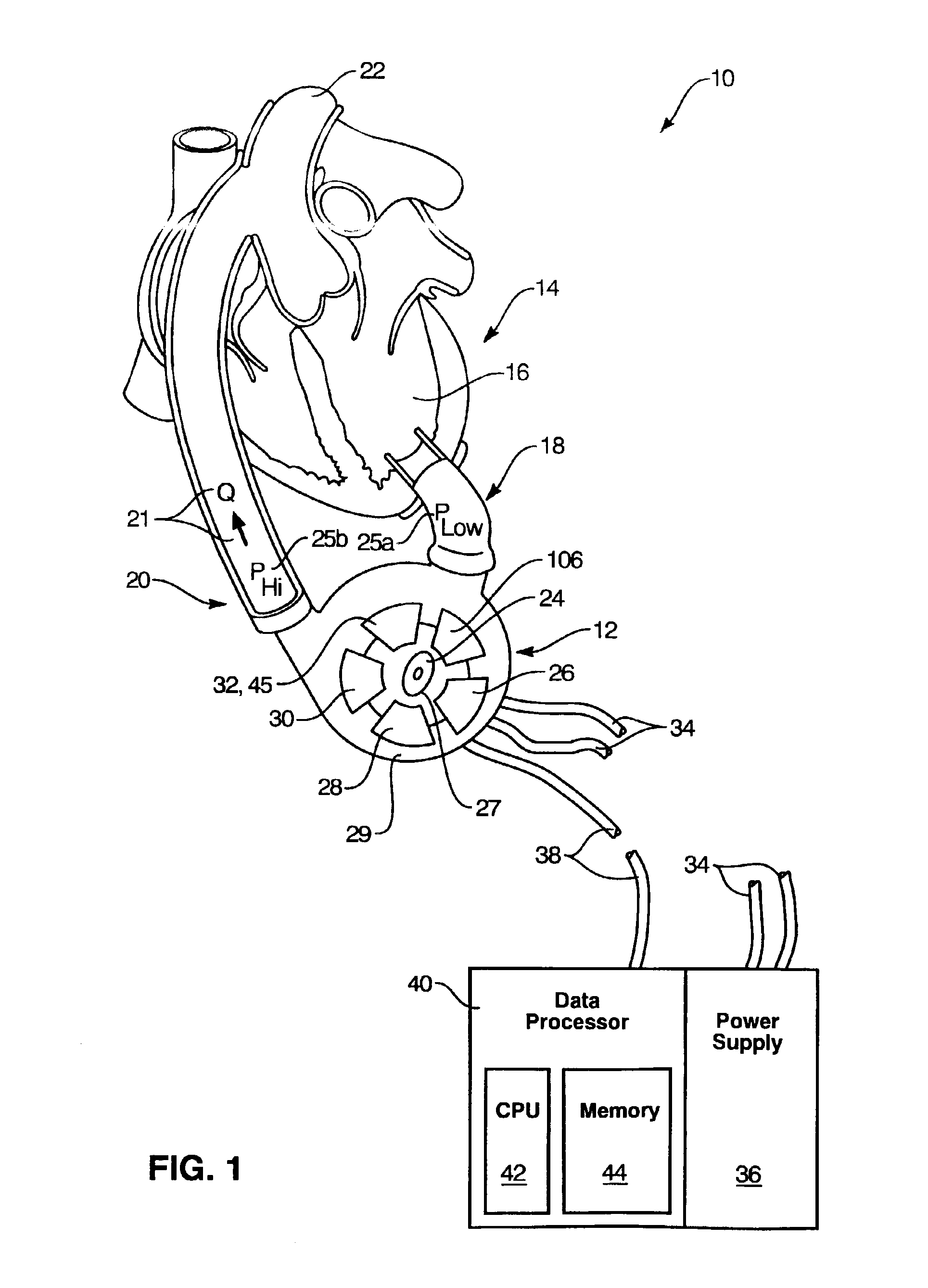
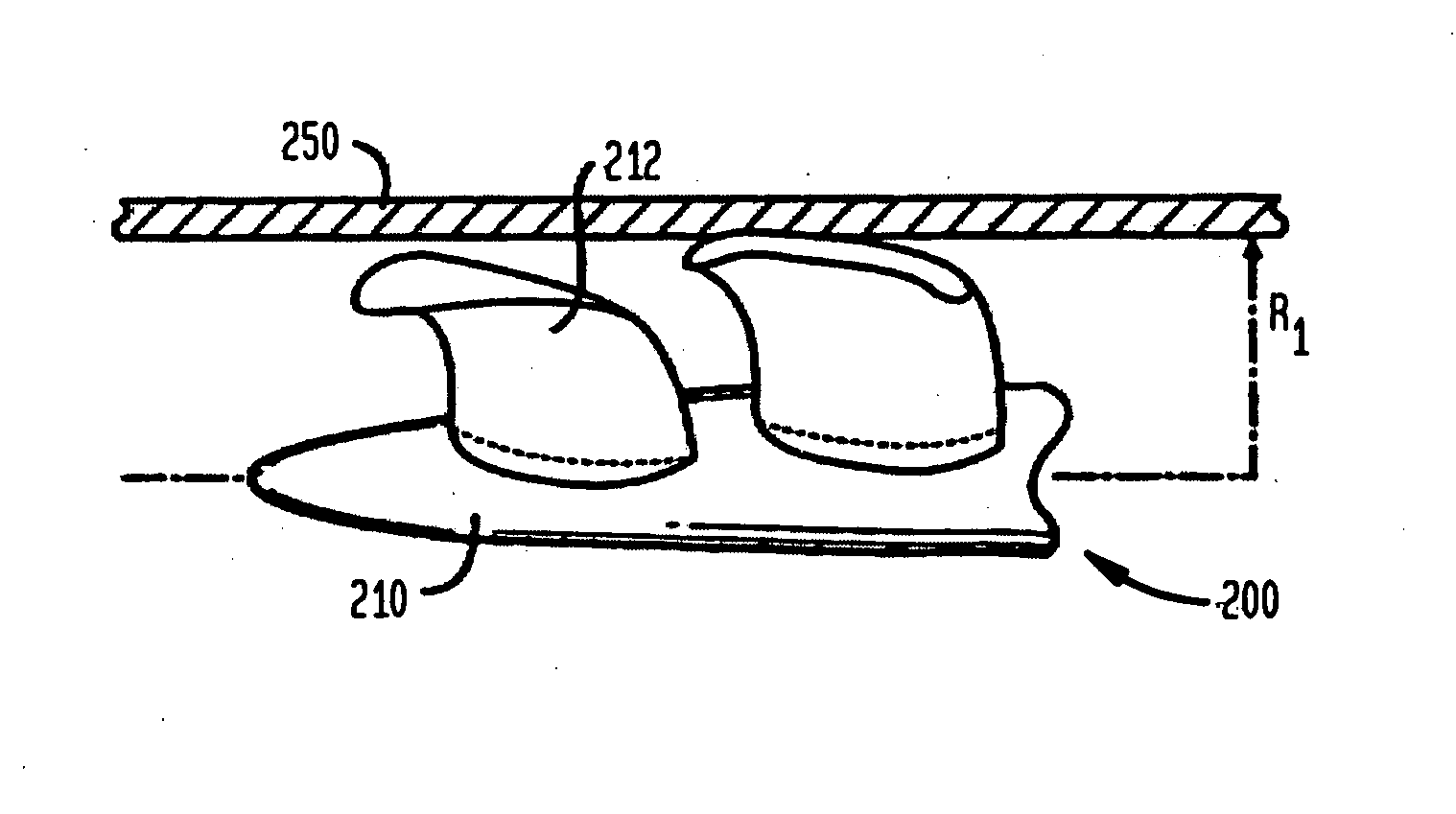
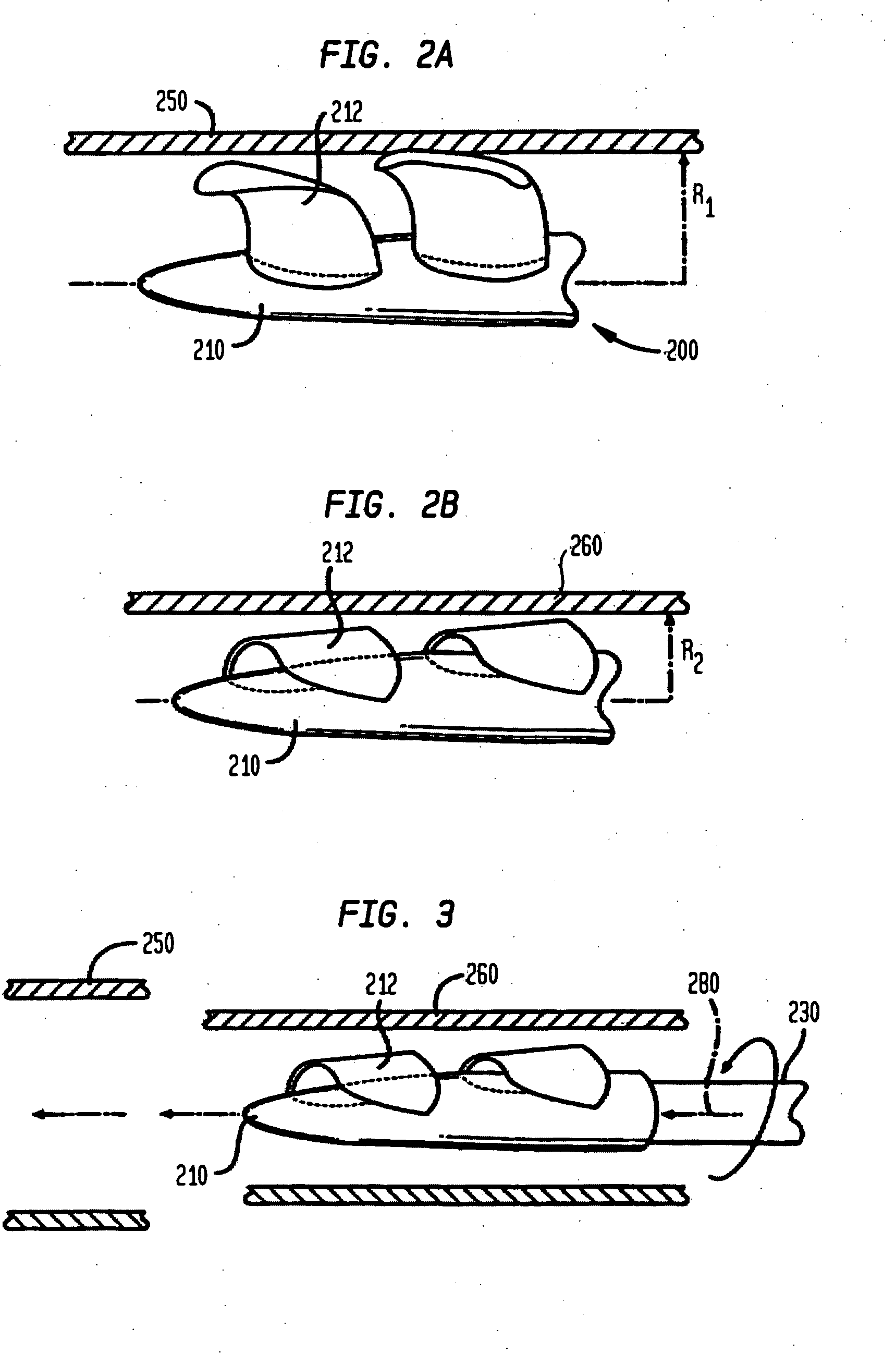
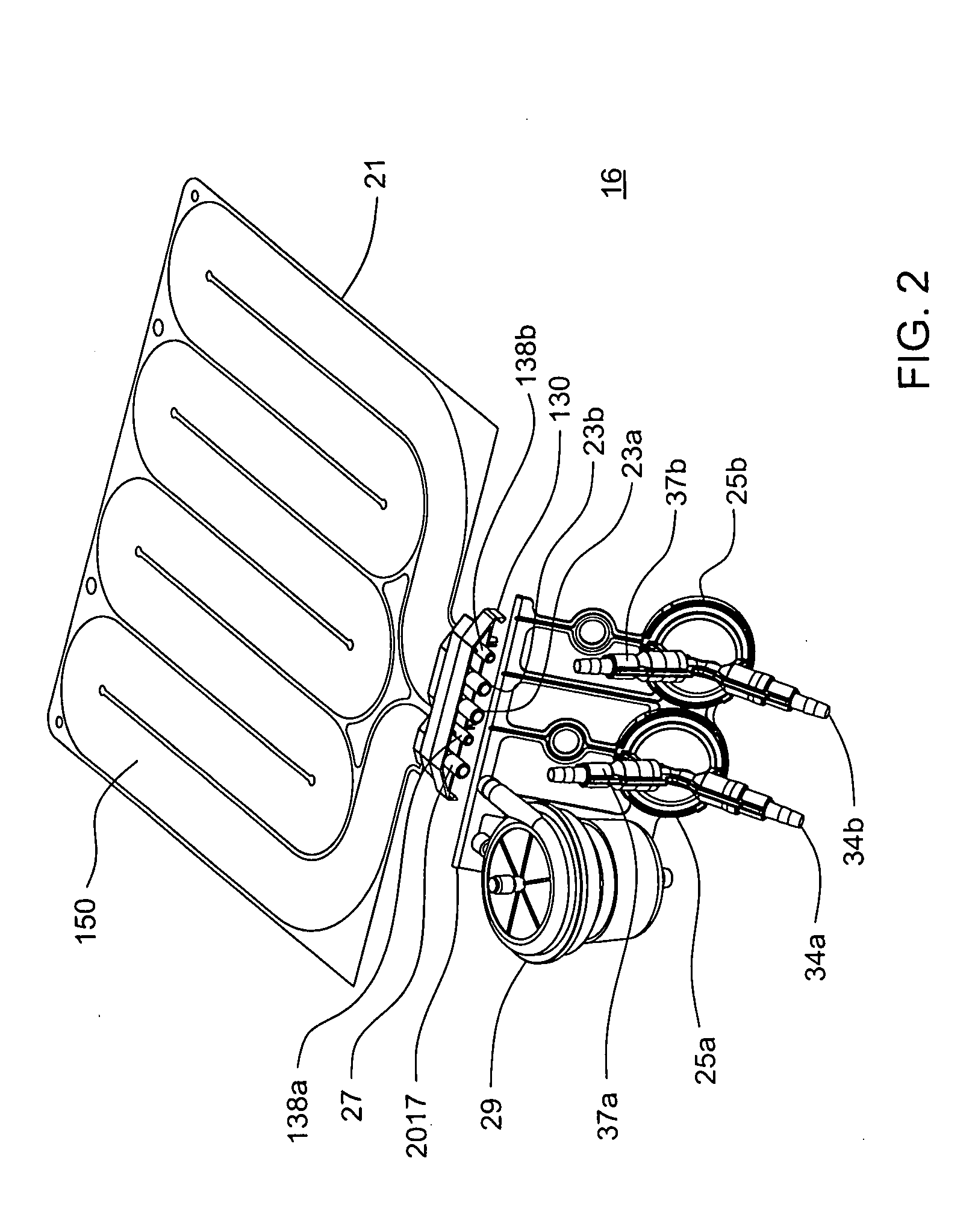
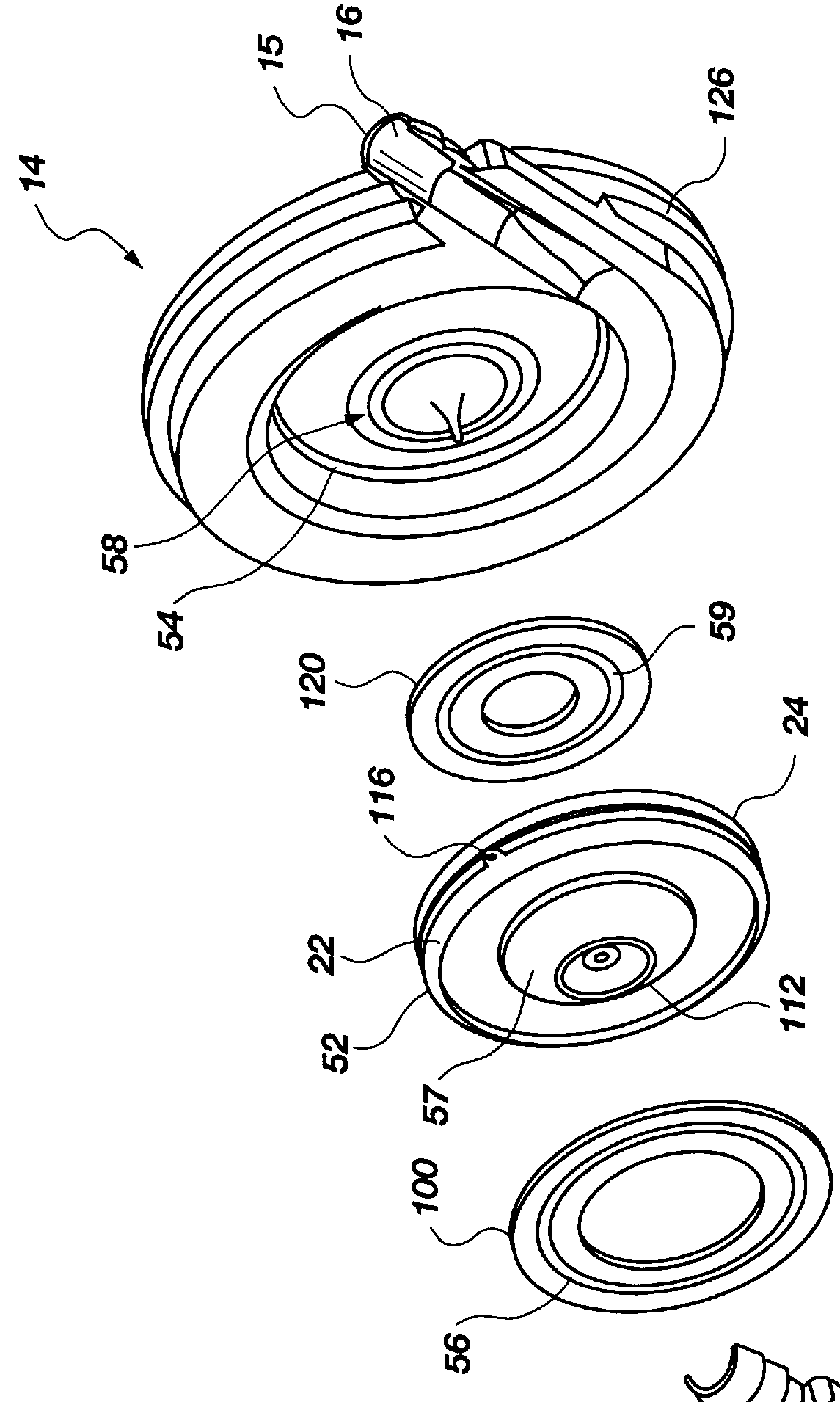
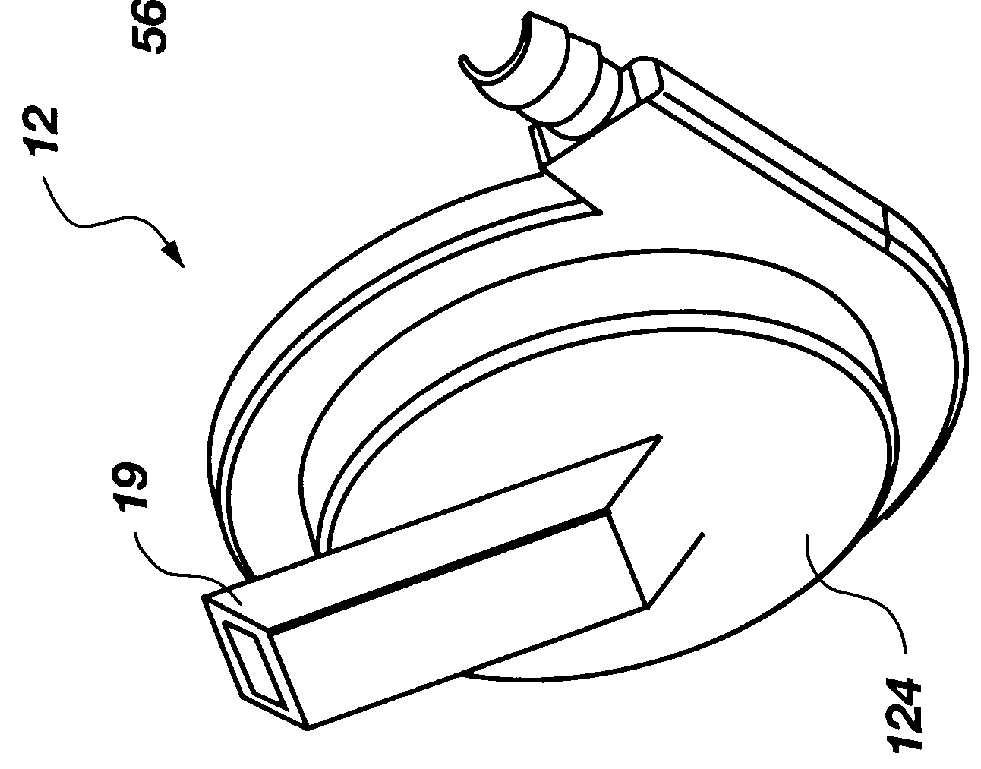
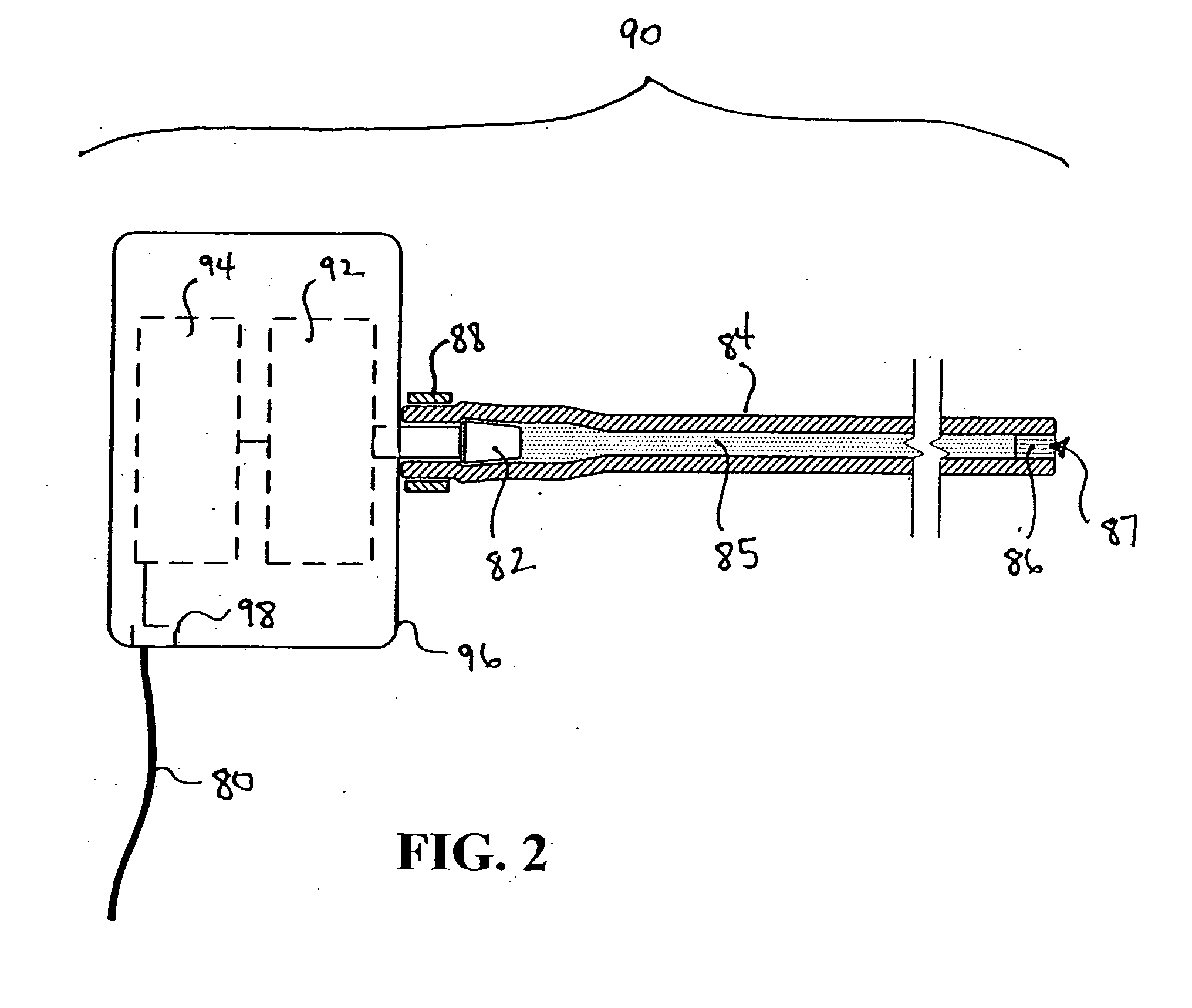
Actuation mechanisms for a heart actuation device
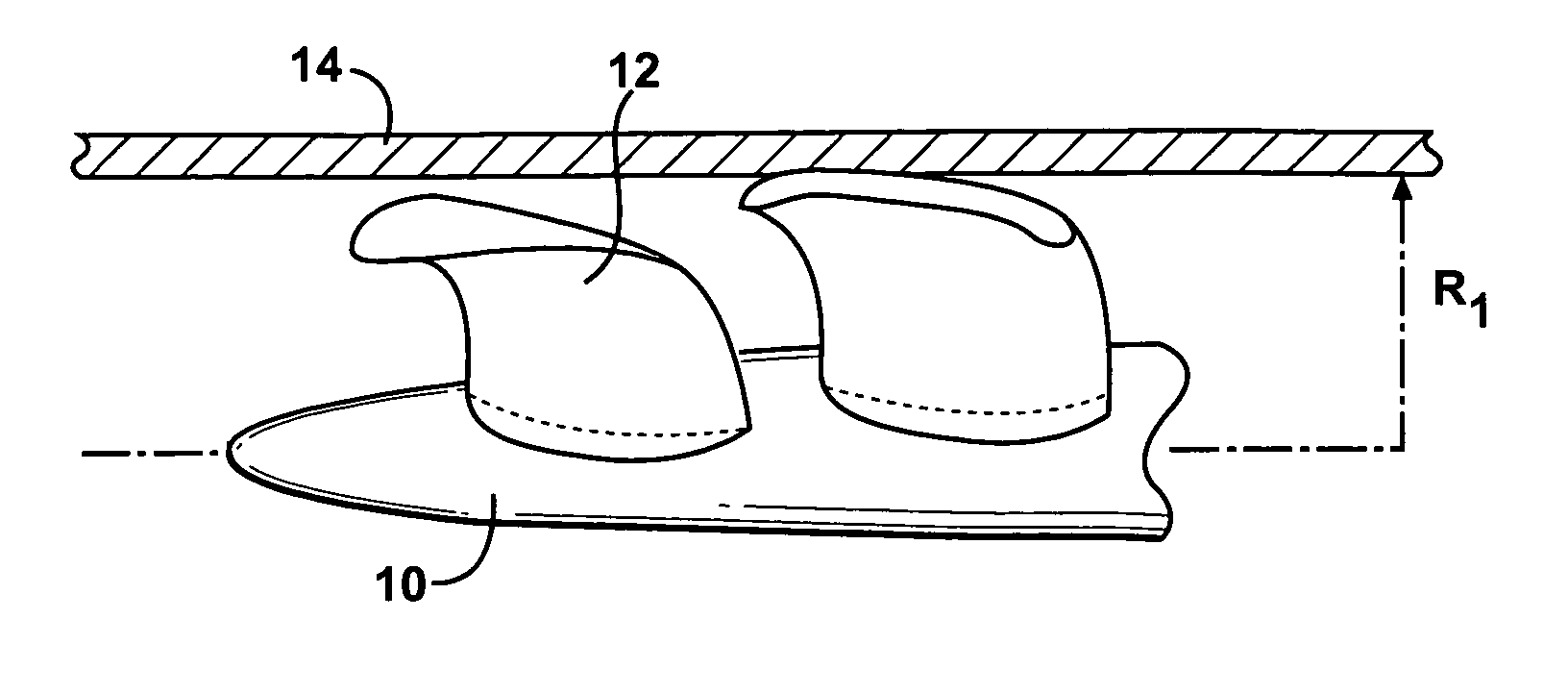
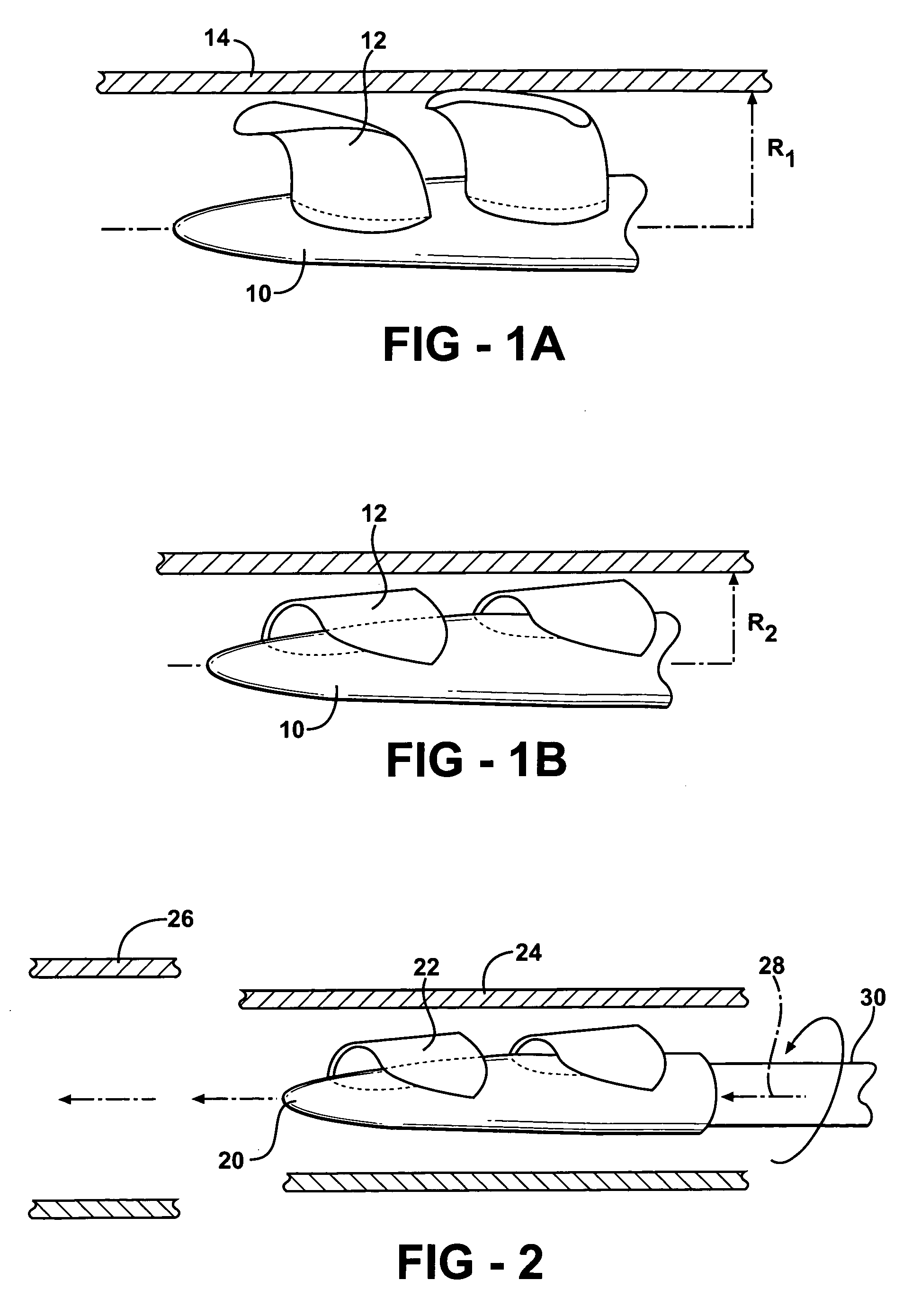
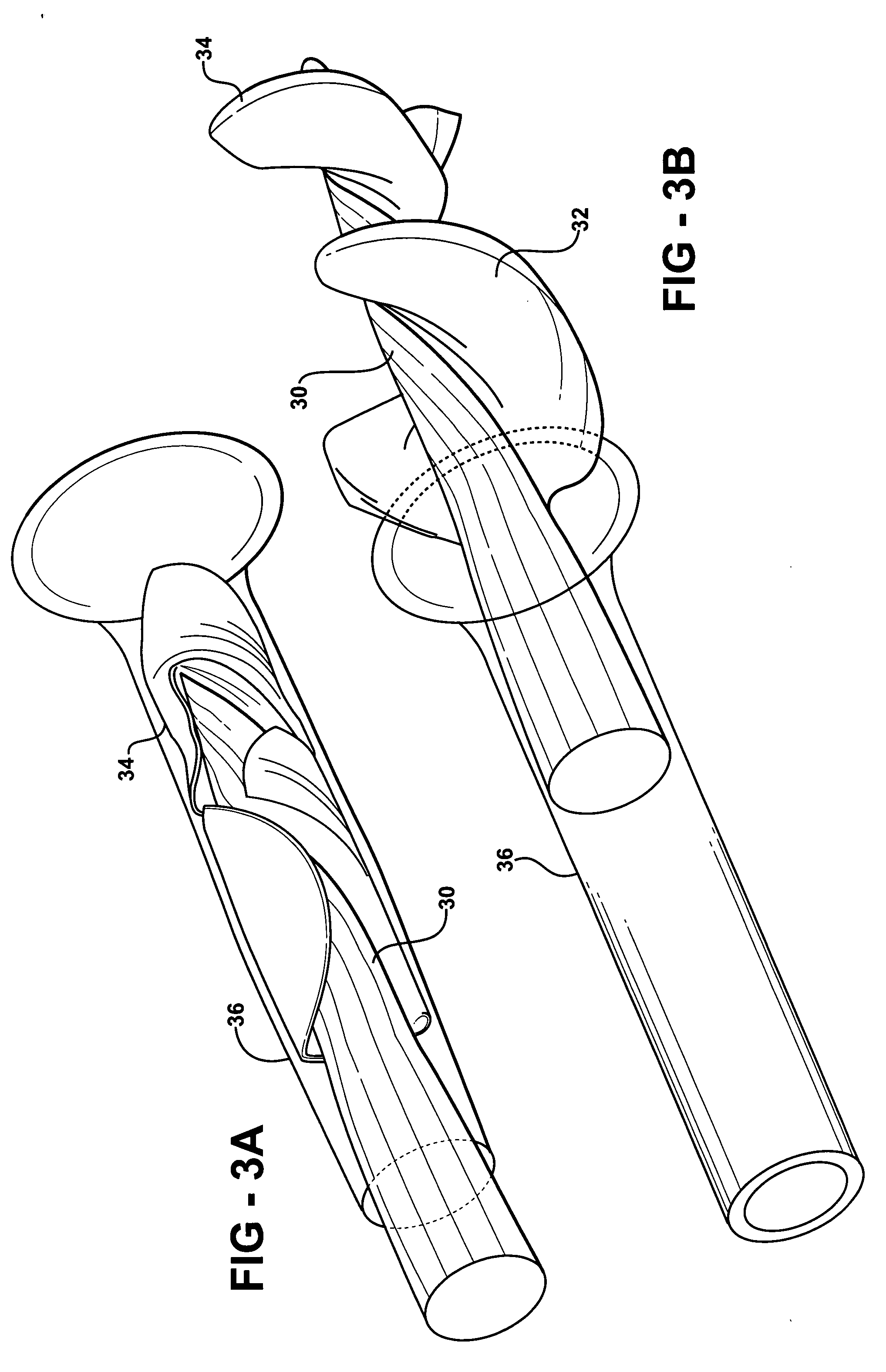
An actuation mechanism for assisting the operation of the natural heart has a varying shape for deforming the heart. In one embodiment, a plurality of links articulates with respect to each other for varying the shape of the actuation mechanism. The plurality of links is configured for being positioned proximate to an outer surface of the heart for deforming the heart by varying the shape of the actuation mechanism. In another embodiment, a jacket for coupling with an outer surface of the heart has a tether coupled to successive sections of the jacket. The tether is operable to be translated with respect to the jacket sections to vary the shape of the jacket for deforming the heart. In another embodiment, a plurality of concentric ring structures are coupled together to move with respect to each other in a concentric fashion. A movement mechanism coupled to the rings is operable to vary their positions with respect to each other to vary the overall shape for deforming the heart.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI +1
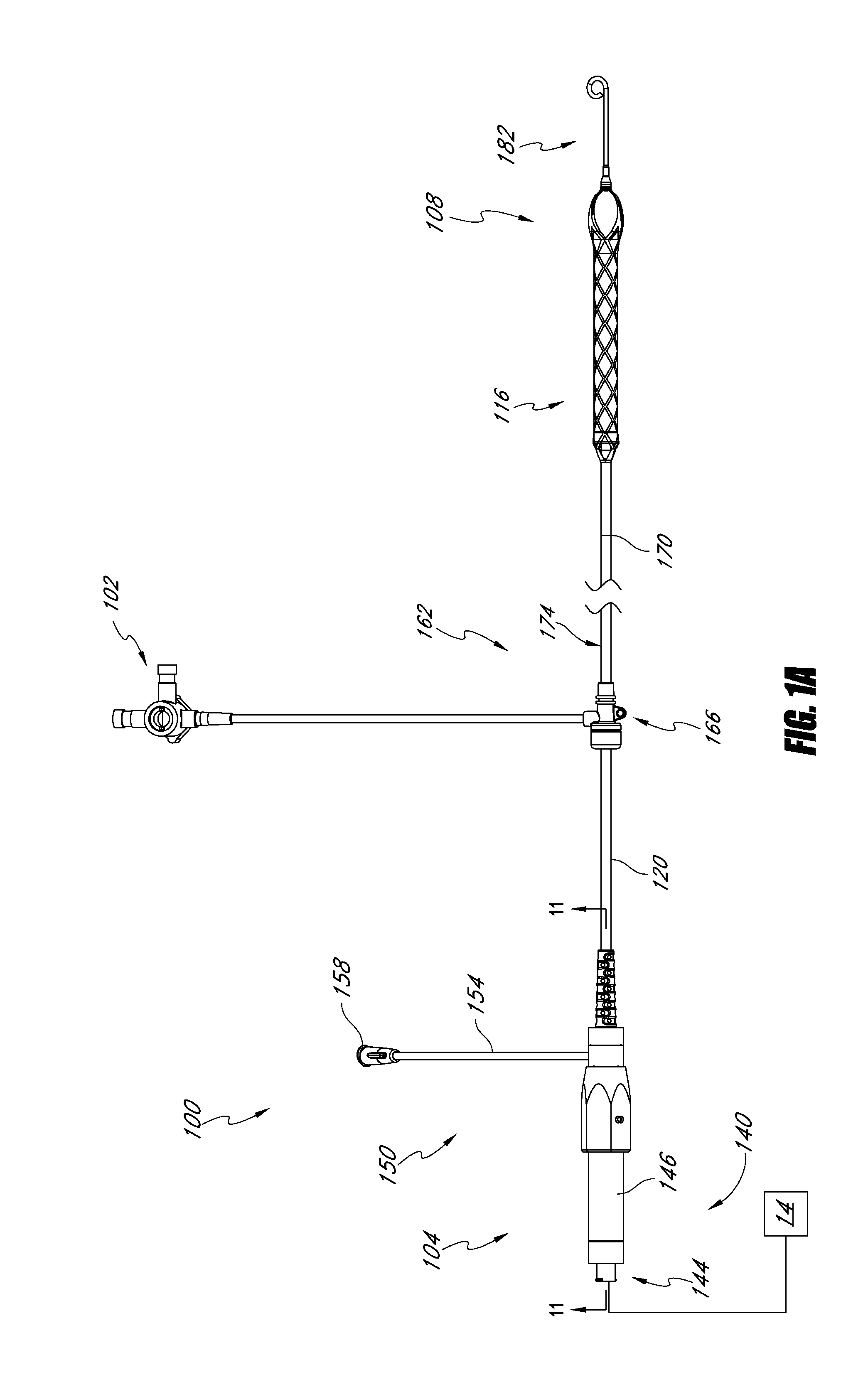
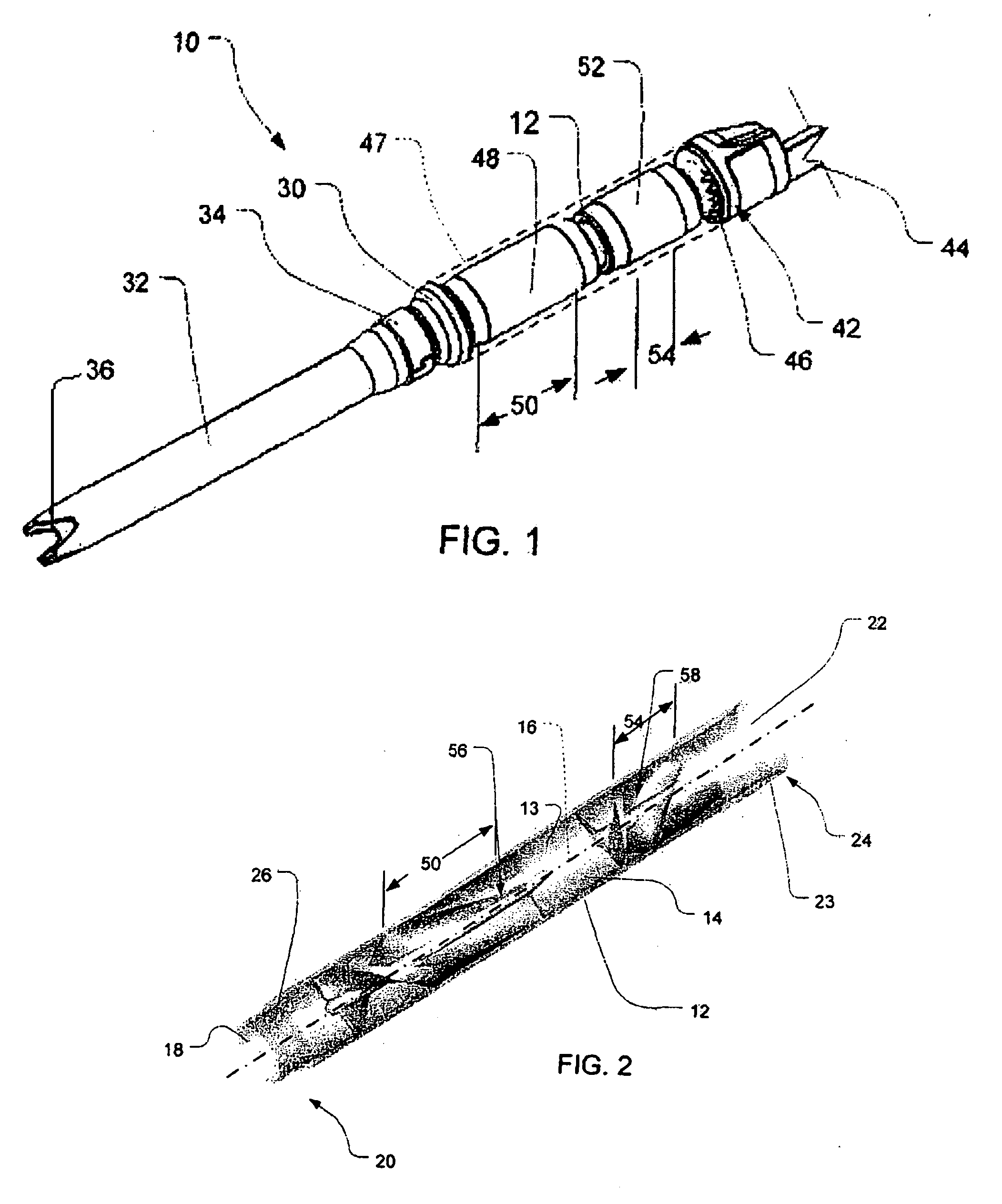
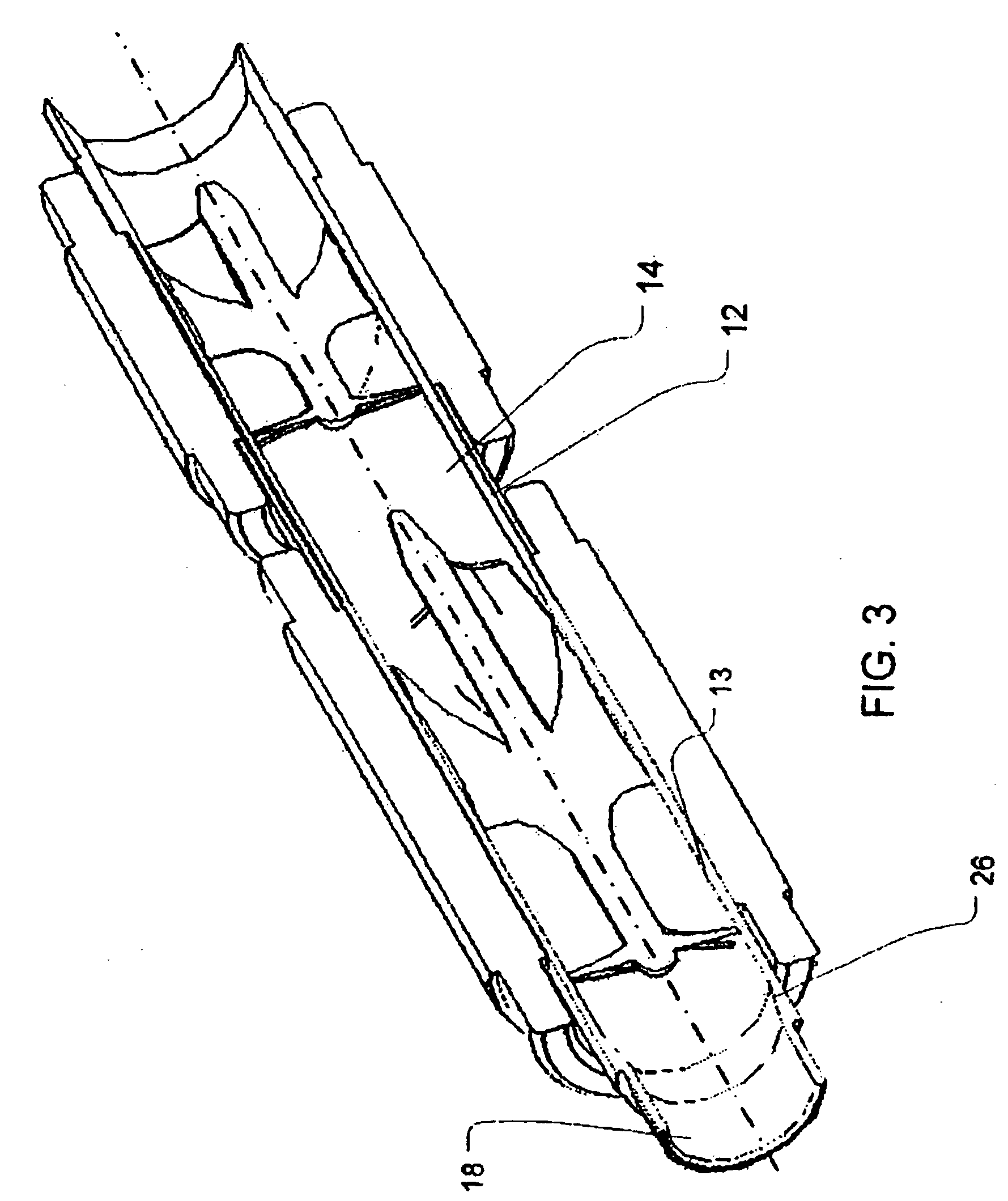
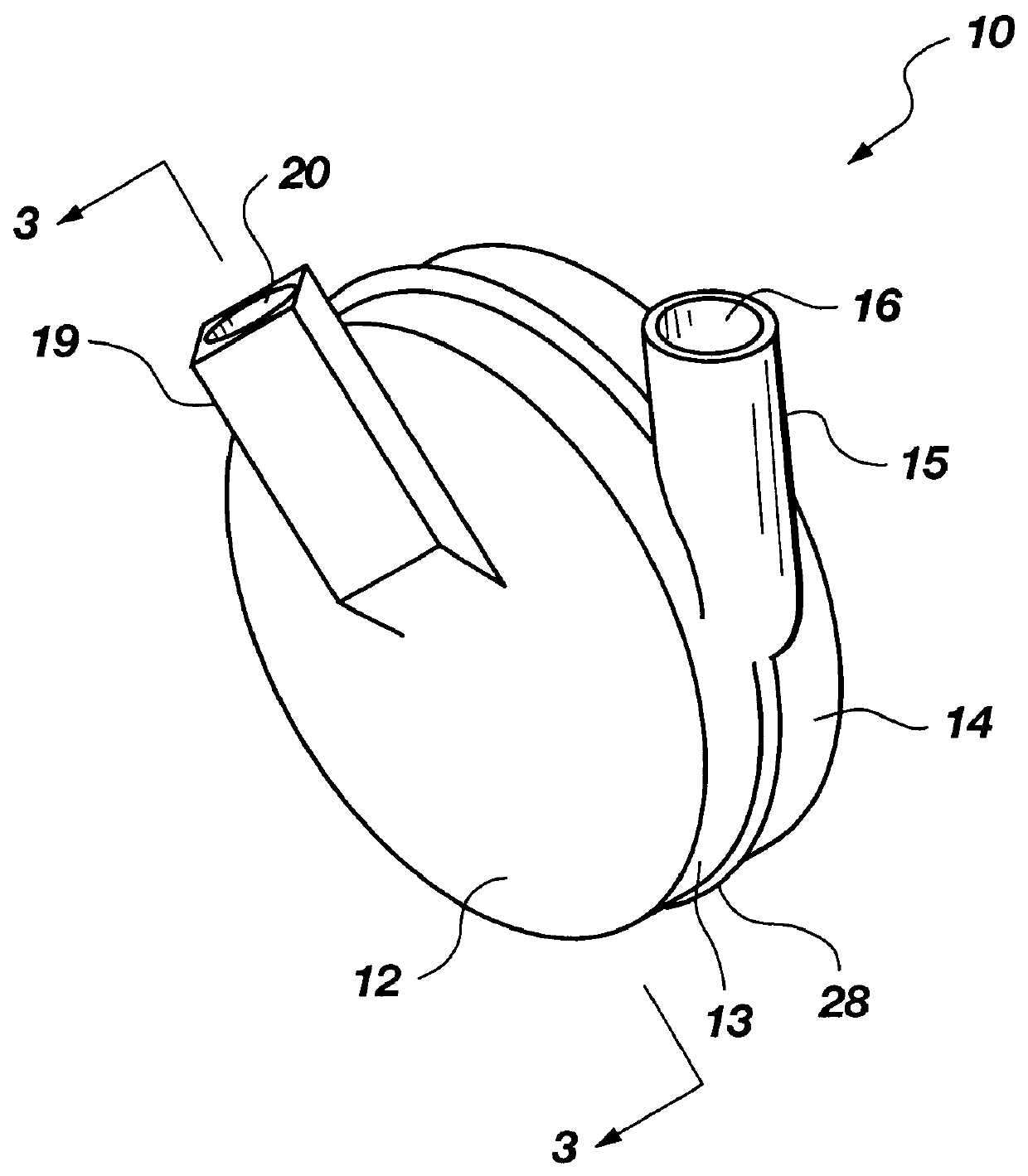
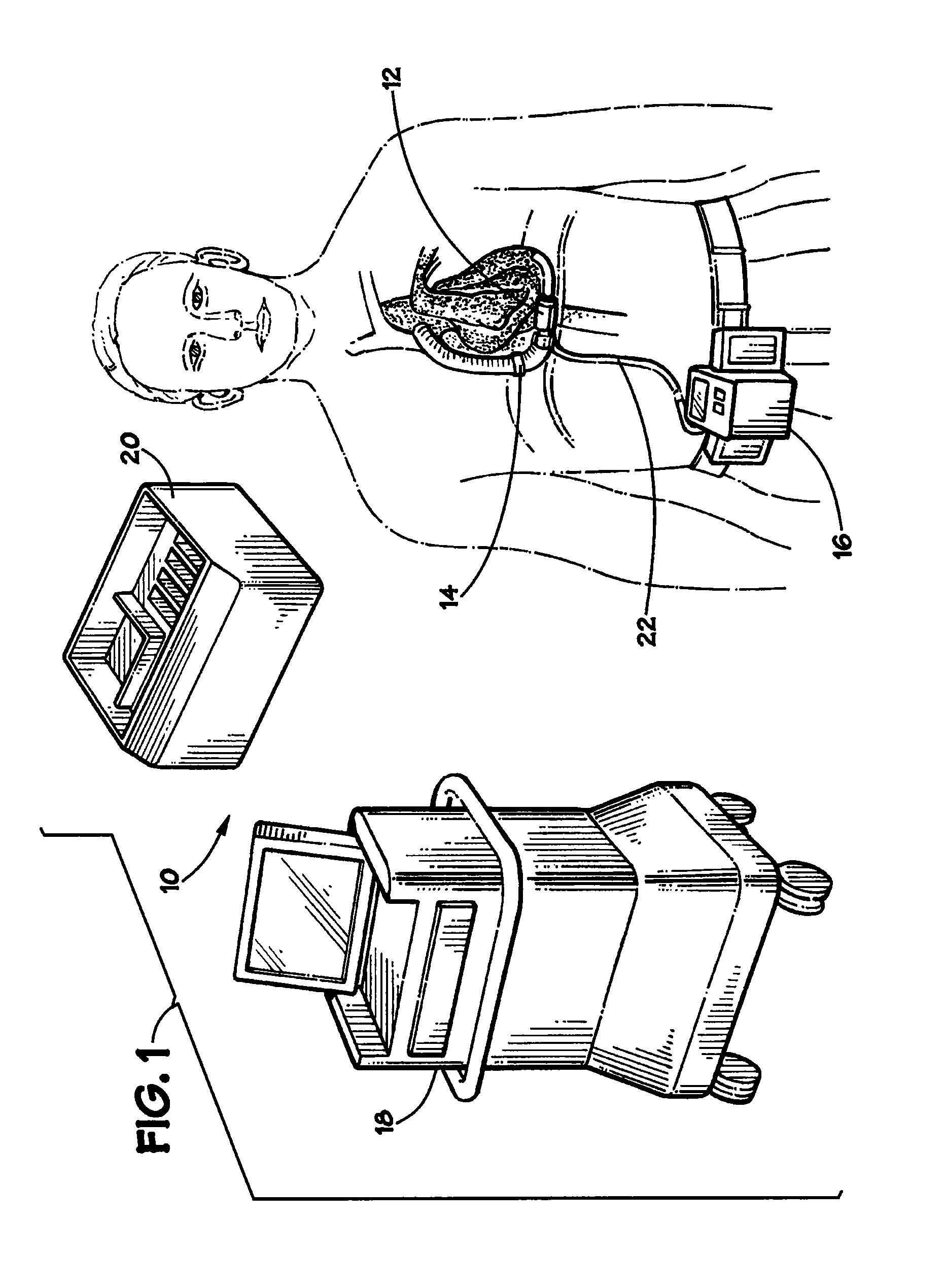
Guidable intravascular blood pump and related methods
InactiveUS7022100B1Integration of featureEliminate needGuide wiresControl devicesBlood pumpBlood vessel
An improved intravascular blood pump system (10) and related methods involving the broad inventive concept of equipping the intravascular blood pump (12) with guiding features such that the intravascular blood pump can be selectively positioned at a predetermined location within the circulatory system of a patient.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
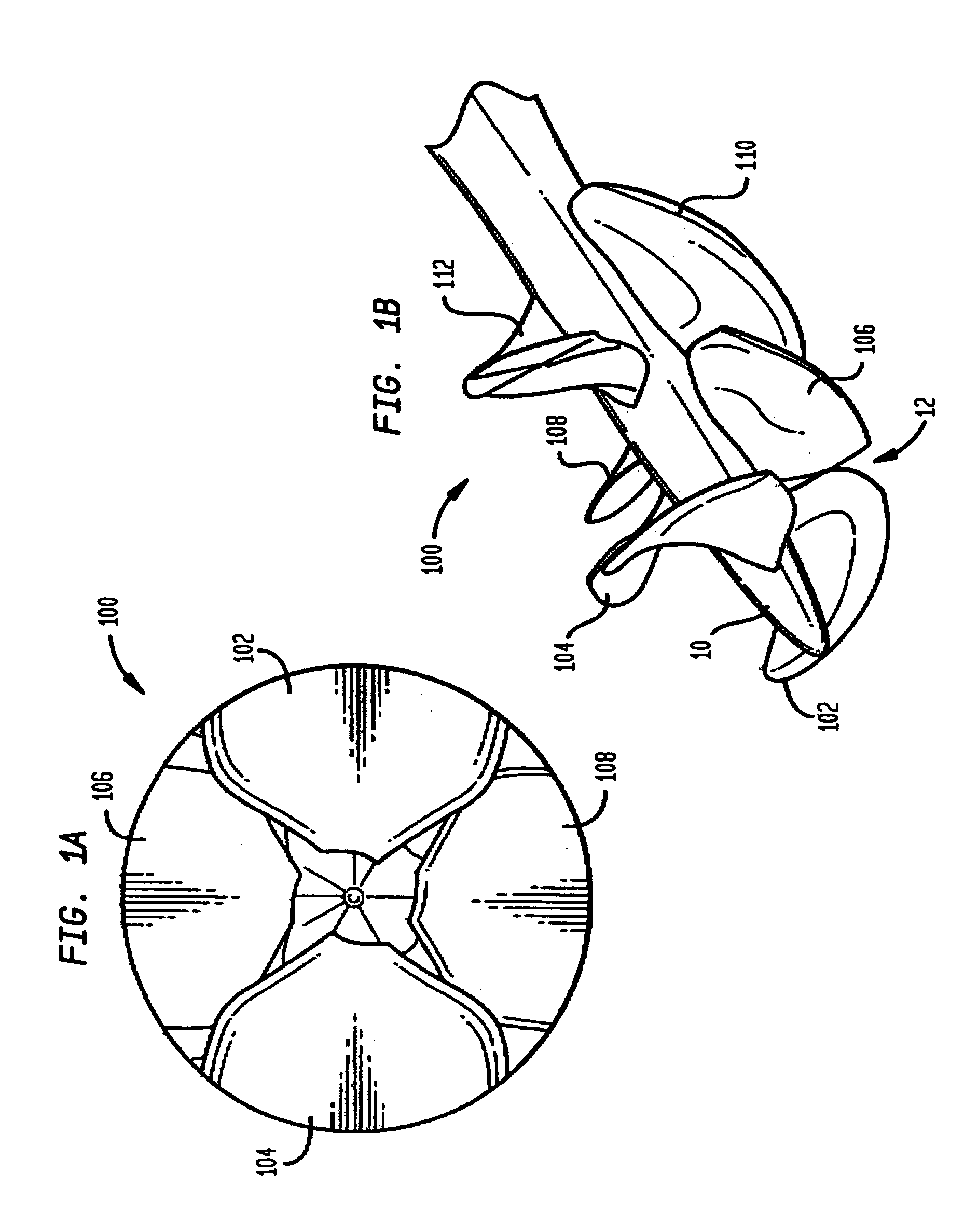
Expandable impeller pump
ActiveUS7393181B2Easy to compressReduced form requirementsPropellersEngine manufactureImpellerEngineering
An impeller according to an example of the present invention comprises a hub, and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub, and a stored configuration in which the impeller is radially compressed, for example by folding the blade towards the hub. The impeller may comprise a plurality of blades, arranged in blade rows, to facilitate radial compression of the blades. The outer edge of a blade may have a winglet, and the base of the blade may have an associated indentation to facilitate folding of the blade.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
Heart assist device with expandable impeller pump
An impeller includes a hub and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a stored configuration in which the blade is compressed so that its distal end moves towards the hub, and a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub. The impeller may be part of a pump for pumping fluids, such as pumping blood within a patient. A blood pump may include a cannula having a proximal portion with a fixed diameter, and a distal portion with an expandable diameter. The impeller may reside in the expandable portion of the cannula. The cannula may have a compressed diameter which allows it to be inserted percutaneously into a patient. Once at a desired location, the expandable portion of the cannula may be expanded and the impeller expanded to the deployed configuration. A flexible drive shaft may extend through the cannula for rotationally driving the impeller within the patient's body.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
Wireless energy transfer for implantable devices
ActiveUS20120032522A1Improves range tolerable offsetMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionEnergy transferPower cable
Described herein are improved configurations for a wireless power transfer. Described are methods and designs for implantable electronics and devices. Wireless energy transfer is utilized to eliminate cords and power cables puncturing the skin to power an implantable device. Repeater resonators are employed to improve the power transfer characteristics between the source and the device resonators.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
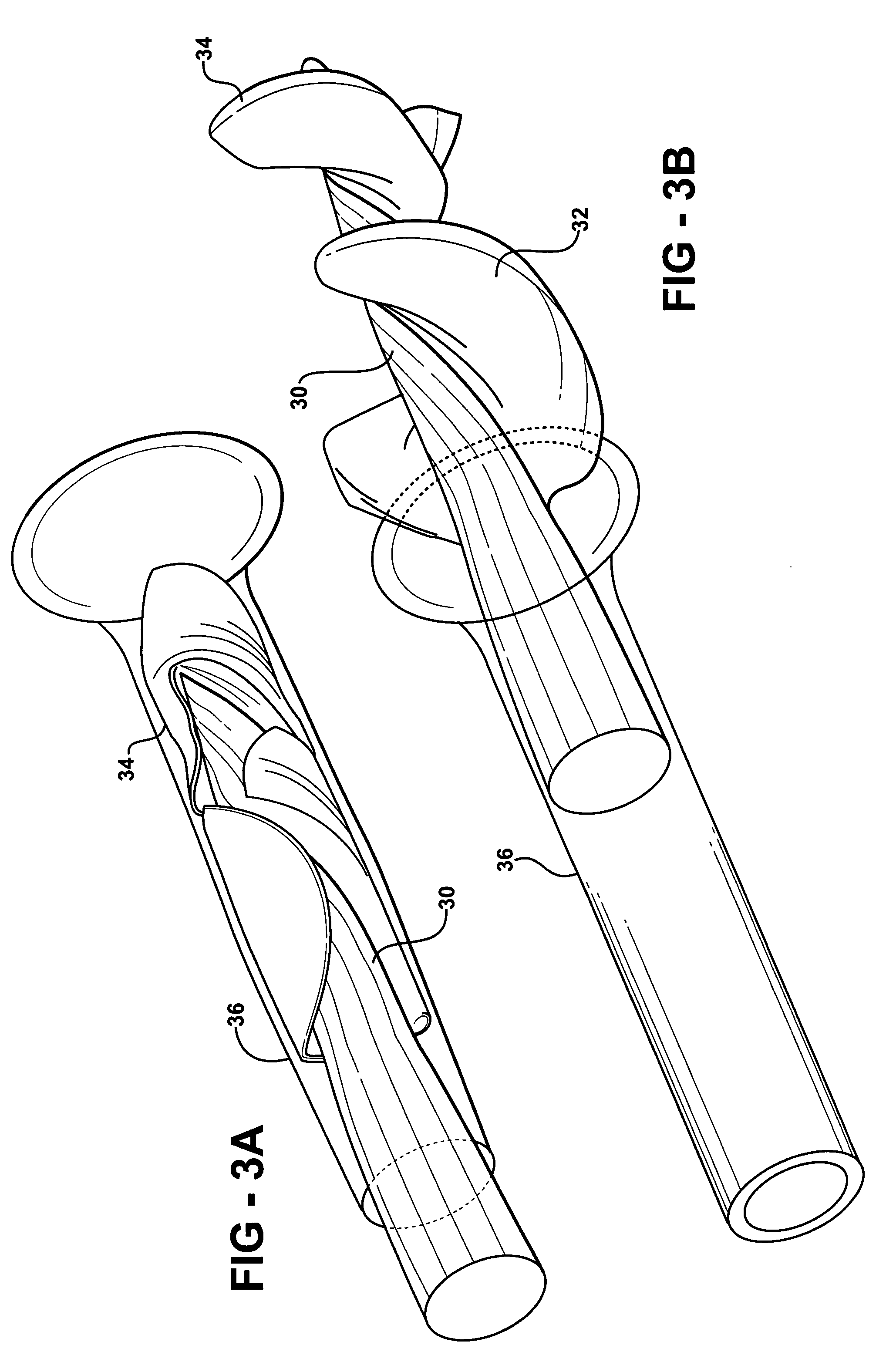
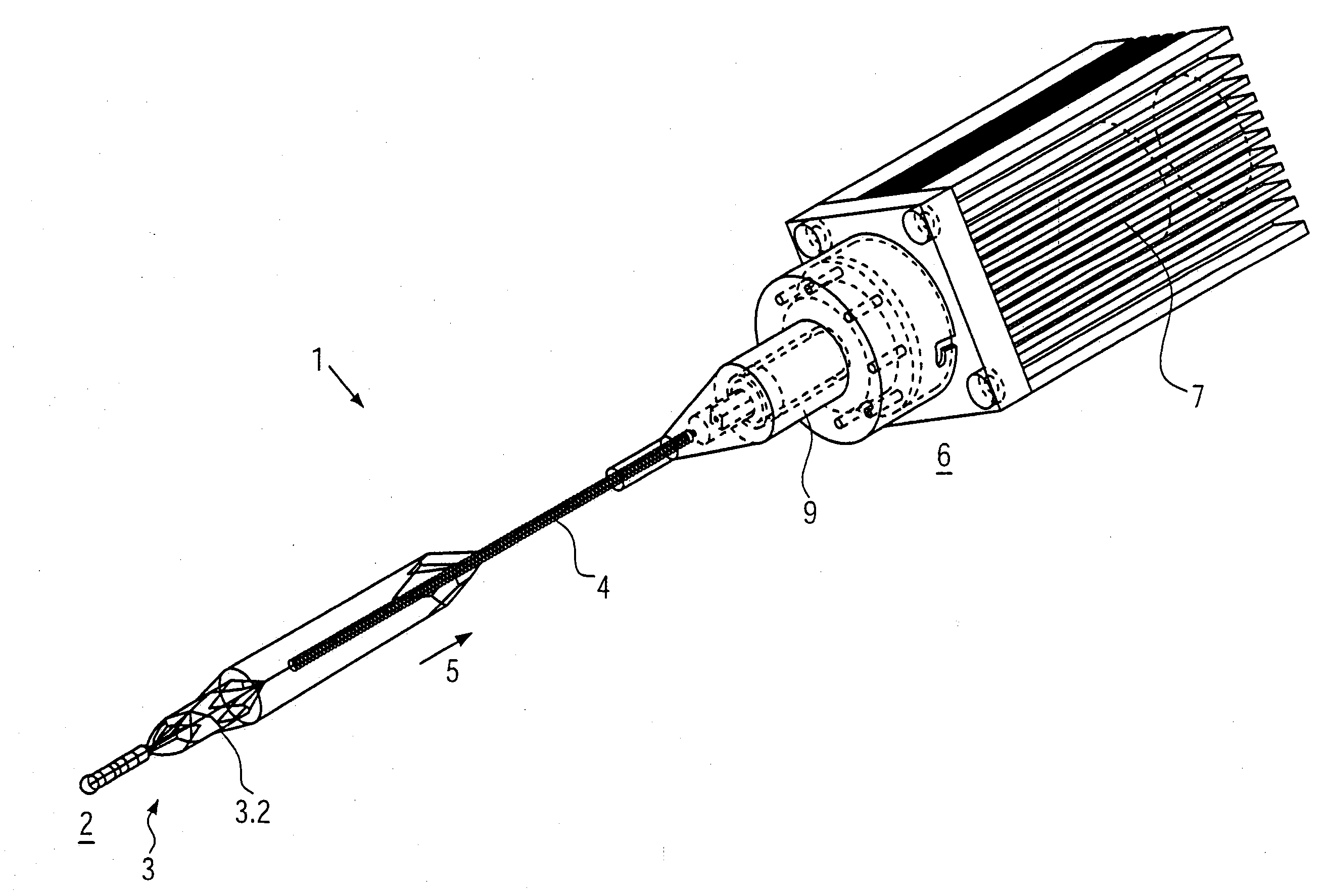
Catheter device
ActiveUS20090093764A1Impairing rotatabilityAccurate settingElectrotherapyCarpet cleanersDrive shaftClutch
The catheter device comprises a motor located at the proximal end of the catheter device and a drive shaft, extending from the proximal end section to the distal end section of the catheter device, for driving a rotating element located at the distal end of the catheter device. The catheter device also comprises a hose-like catheter body which encompasses the drive shaft and extends from the proximal end section to the distal end section of the catheter device. At the proximal end of the catheter device, the drive shaft is connected to a motor by a clutch. The clutch is a magnetic clutch with a proximal and a distal magnet unit. The proximal magnet unit is connected to the motor and the distal magnet unit to the drive shaft. The distal magnet unit is mounted fluid-tight in a clutch housing. The proximal end of the catheter body makes a fluid-tight connection with the clutch housing.
Owner:AIS AACHEN INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS
Catheter device
ActiveUS20090093796A1Maximum pump performanceImprove performancePump componentsSurgeryDrive shaftMechanical engineering
The catheter device comprises a drive shaft connected to a motor, and a rotor mounted on the drive shaft at the distal end section. The rotor has a frame structure which is formed by a screw-like boundary frame and rotor struts extending radially inwards from the boundary frame. The rotor struts are fastened to the drive shaft by their ends opposite the boundary frame. Between the boundary frame and the drive shaft extends an elastic covering. The frame structure is made of an elastic material such that, after forced compression, the rotor unfolds automatically.
Owner:AIS AACHEN INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS
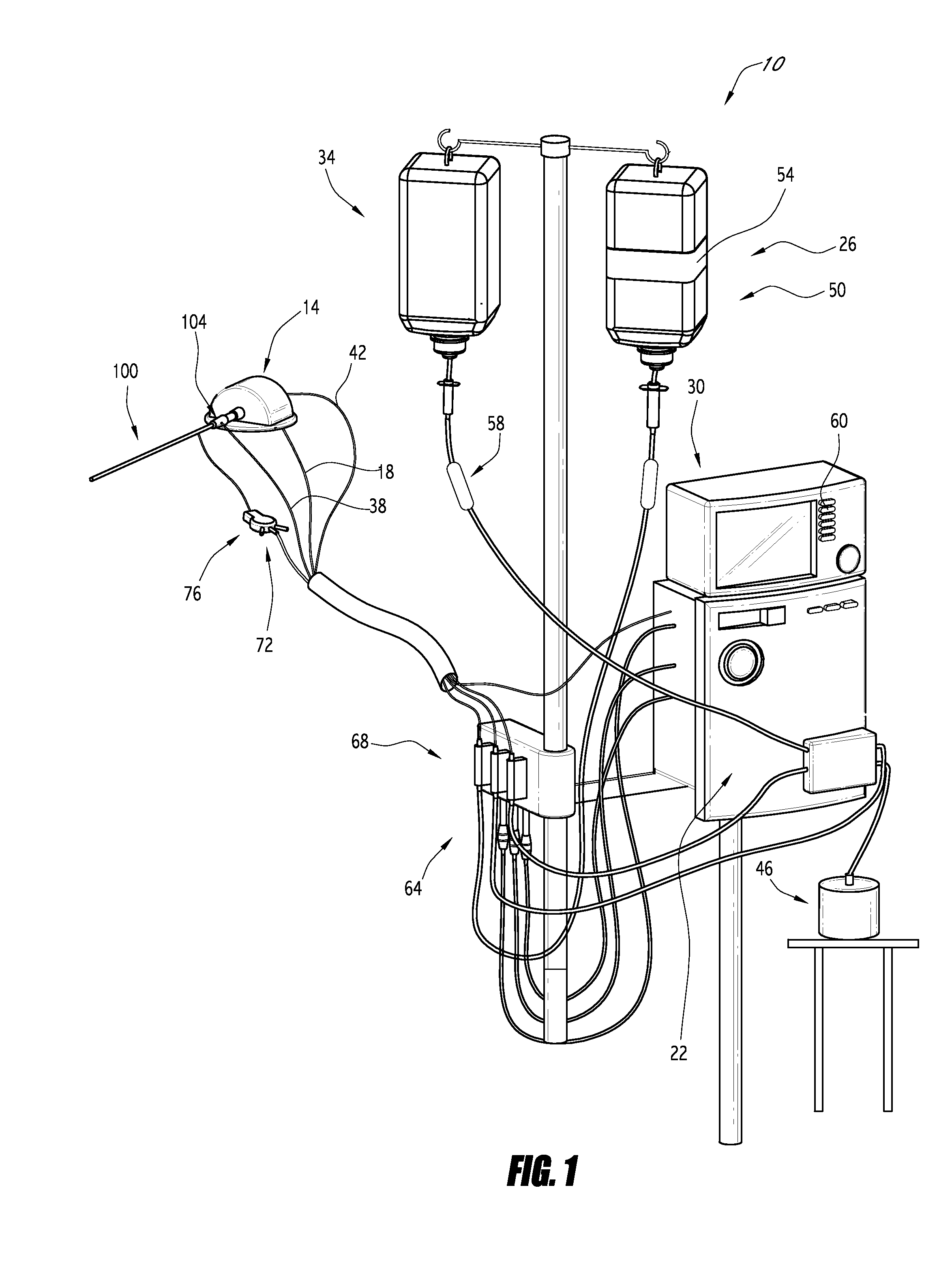
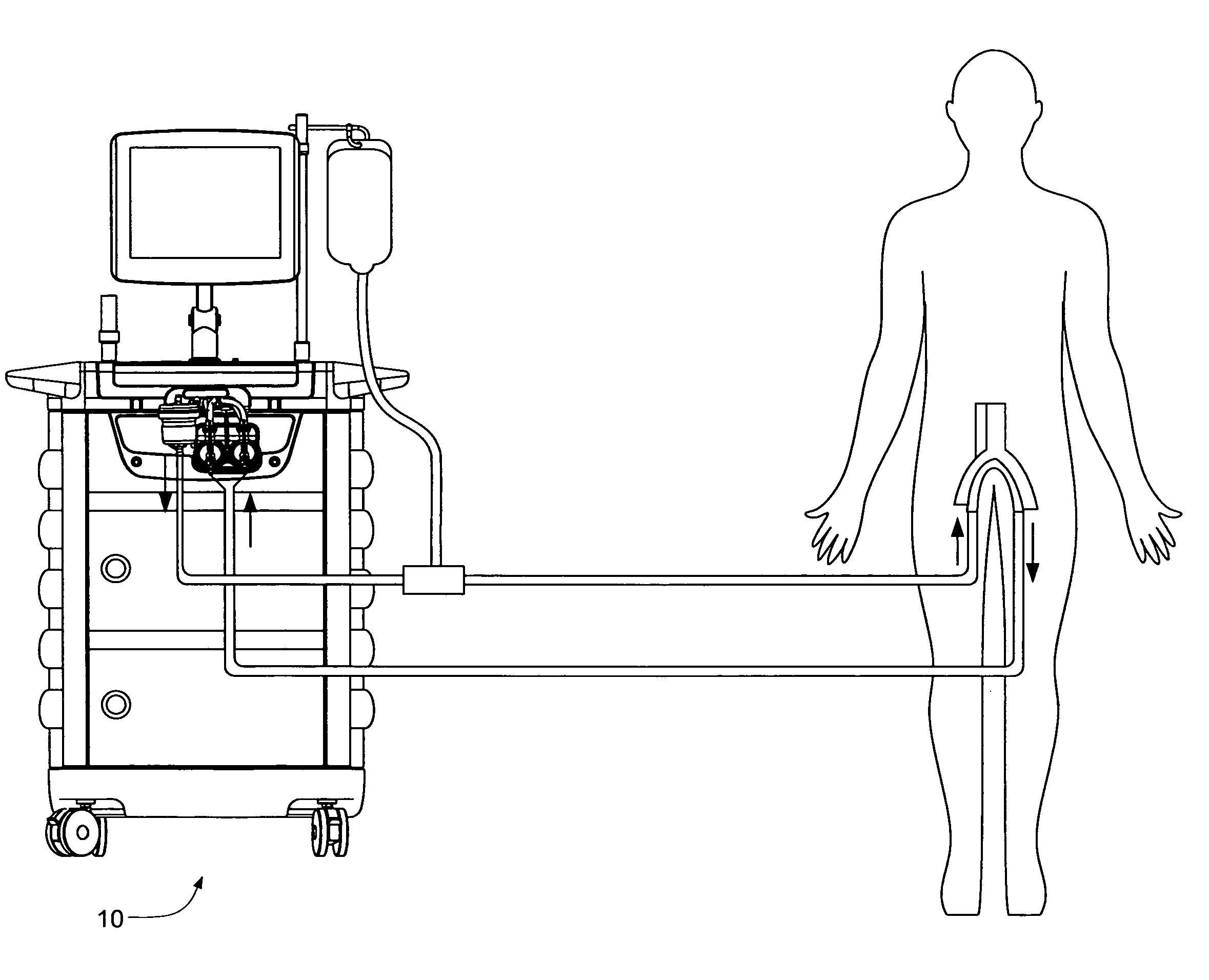
Methods, systems, and kits for the extracorporeal processing of blood
InactiveUS7004924B1Easy to detectOther blood circulation devicesControl devicesExtracorporeal circulationLine tubing
Methods, systems, and kits for extracorporeally circulating and processing blood are described. The systems include a pump, a processing unit, and blood drawn return lines for accessing a patient's vasculature. Blood flow through the return line is measured and pump speed controlled to maintain a desired blood flow rate. Alarm conditions can be initiated when expected pump performance differs from that needed to maintain the control point flow rate. By using a ultrasonic flow detector, gas bubbles in the blood flow can be detected.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL
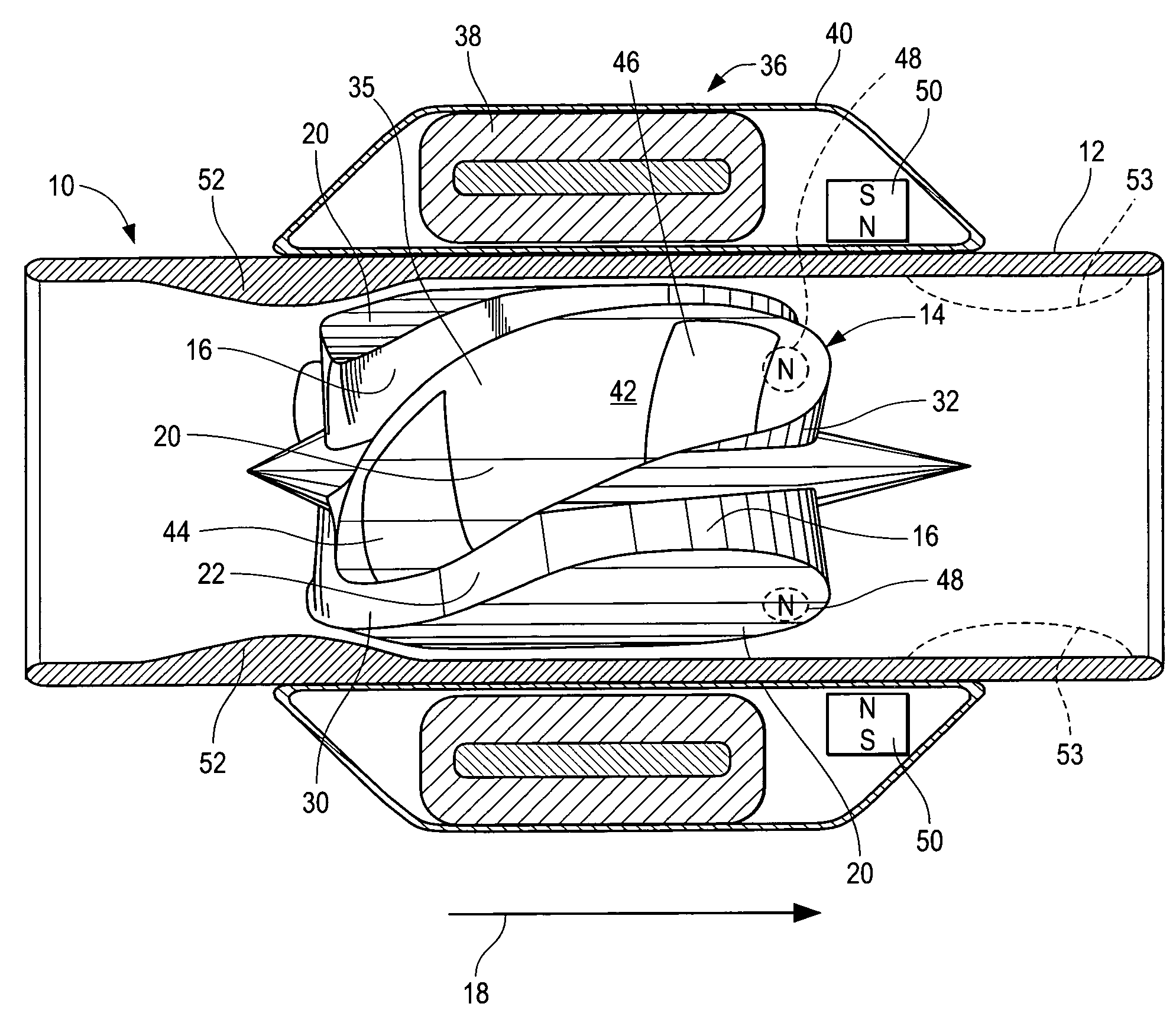
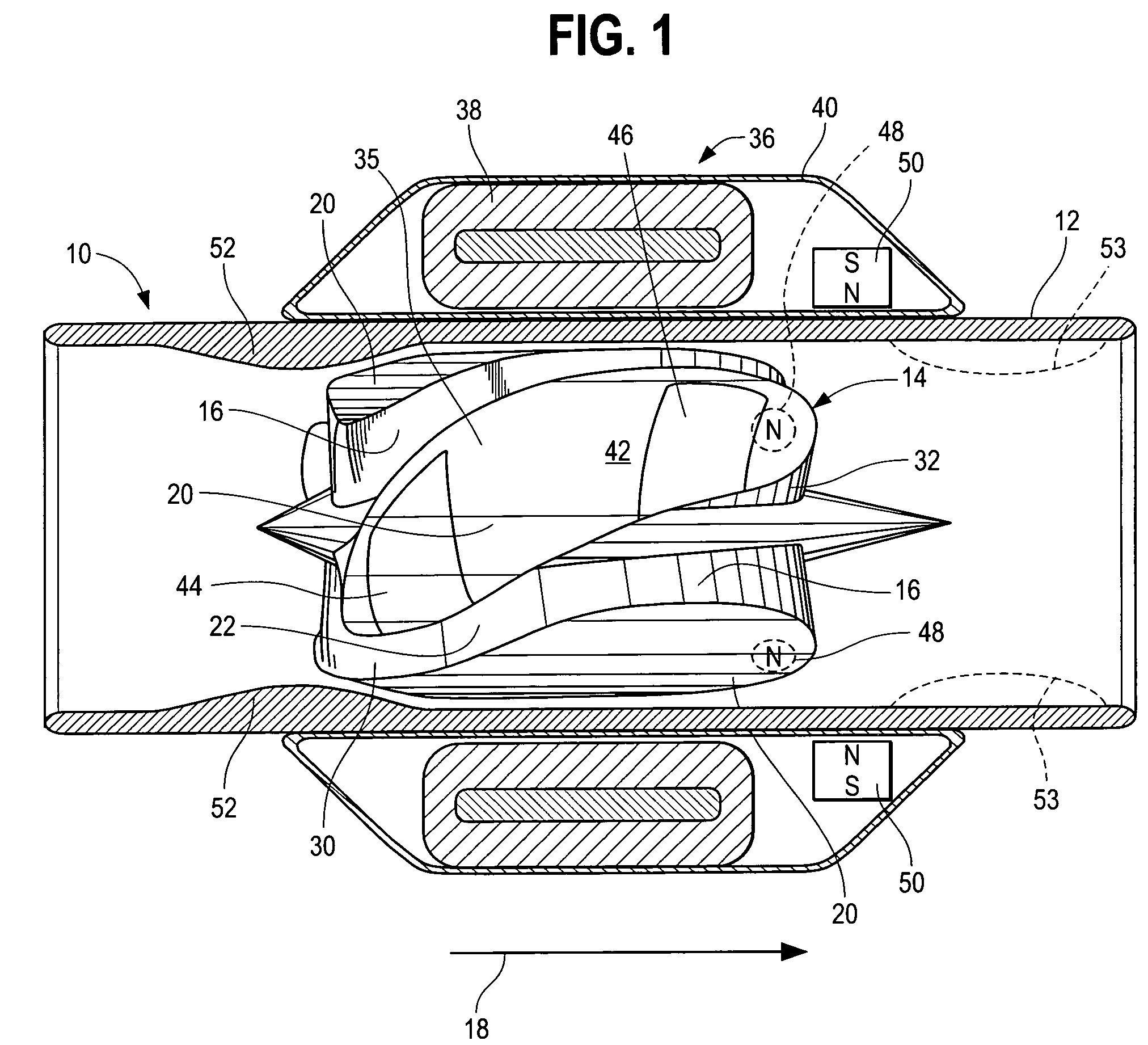
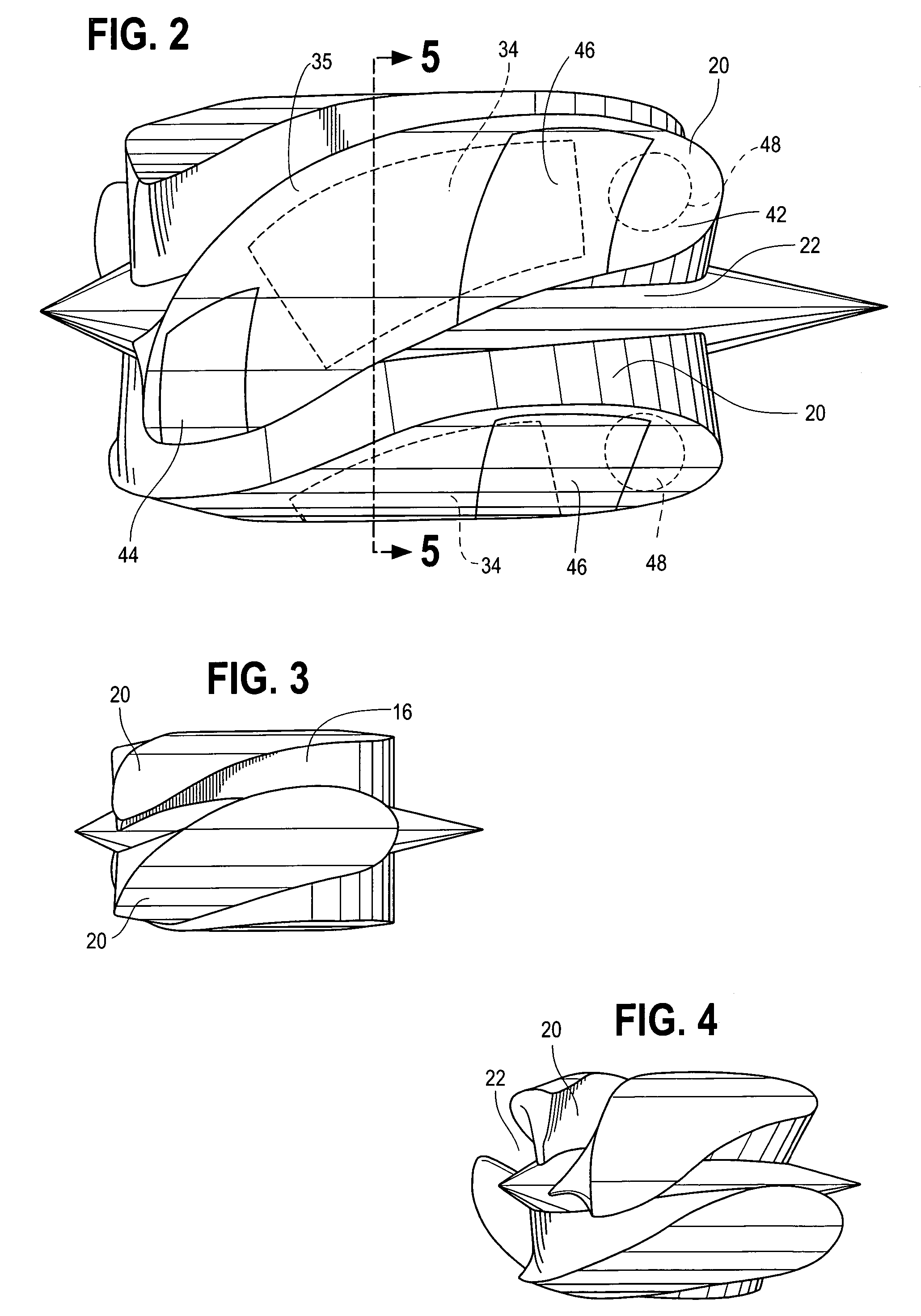
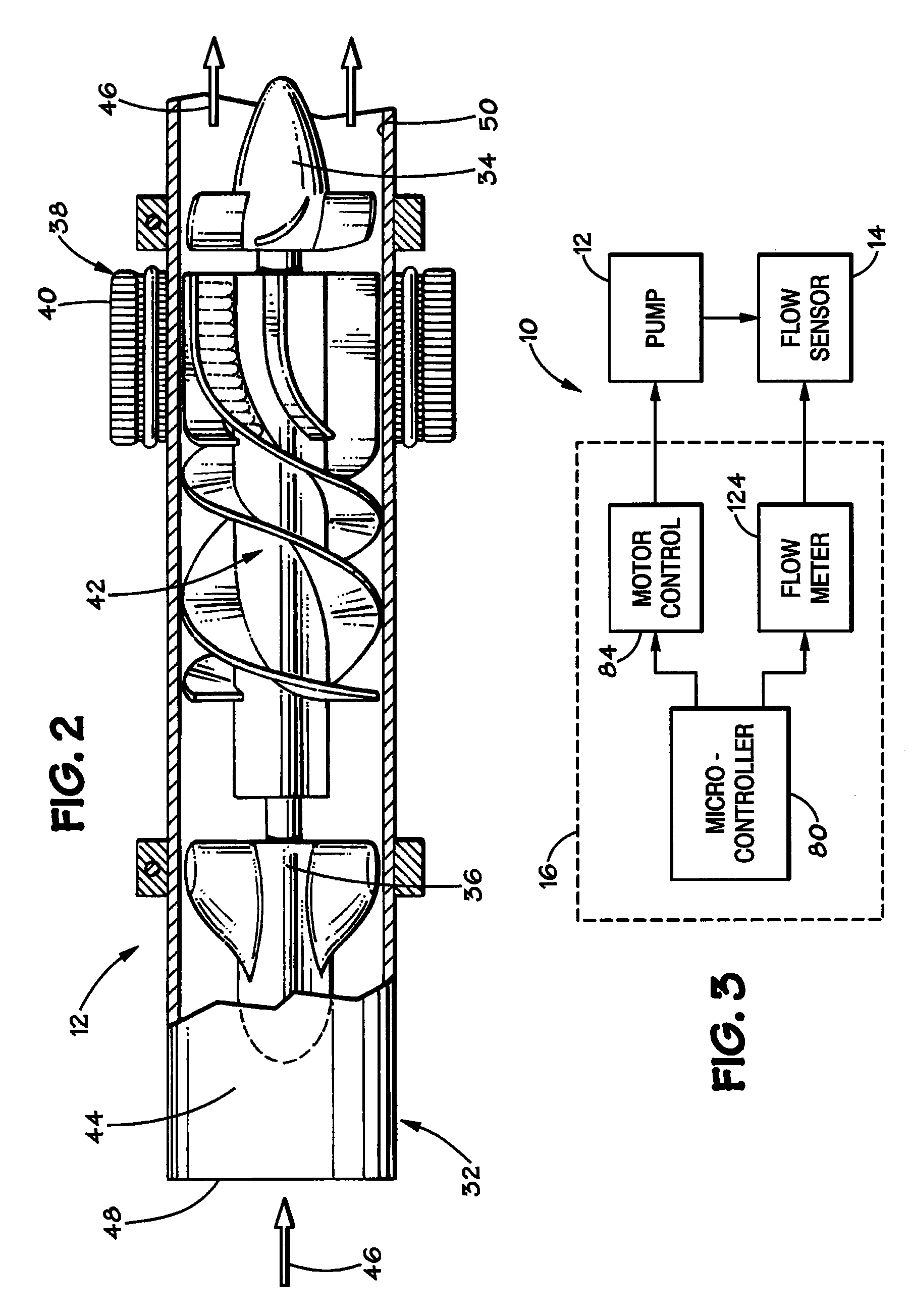
Wide blade, axial flow pump
ActiveUS7699586B2Increase the magnetic fluxReduce air gapControl devicesBlood pumpsAxial-flow pumpImpeller
A blood pump comprises a pump housing; a rotor positioned in the housing and comprising an impeller having a hydrodynamic surface for pumping blood; and a motor including a plurality of magnets carried by the impeller, plus a rotor stator, including an electrically conductive coil located adjacent to or within the housing. The impeller comprises radially outwardly extending, bladelike projections that define generally longitudinally extending spaces between the projections. The shape of the projections and the spaces therebetween tend to drive blood in the spaces in an axial direction as the impeller is rotated. The spaces collectively have a total width along most of their lengths at the radial periphery of the rotor, that is substantially equal to or less than the collective width of the projections along most of their lengths at the radial periphery. Thus, the bladelike projections are thicker, achieving significant advantages.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
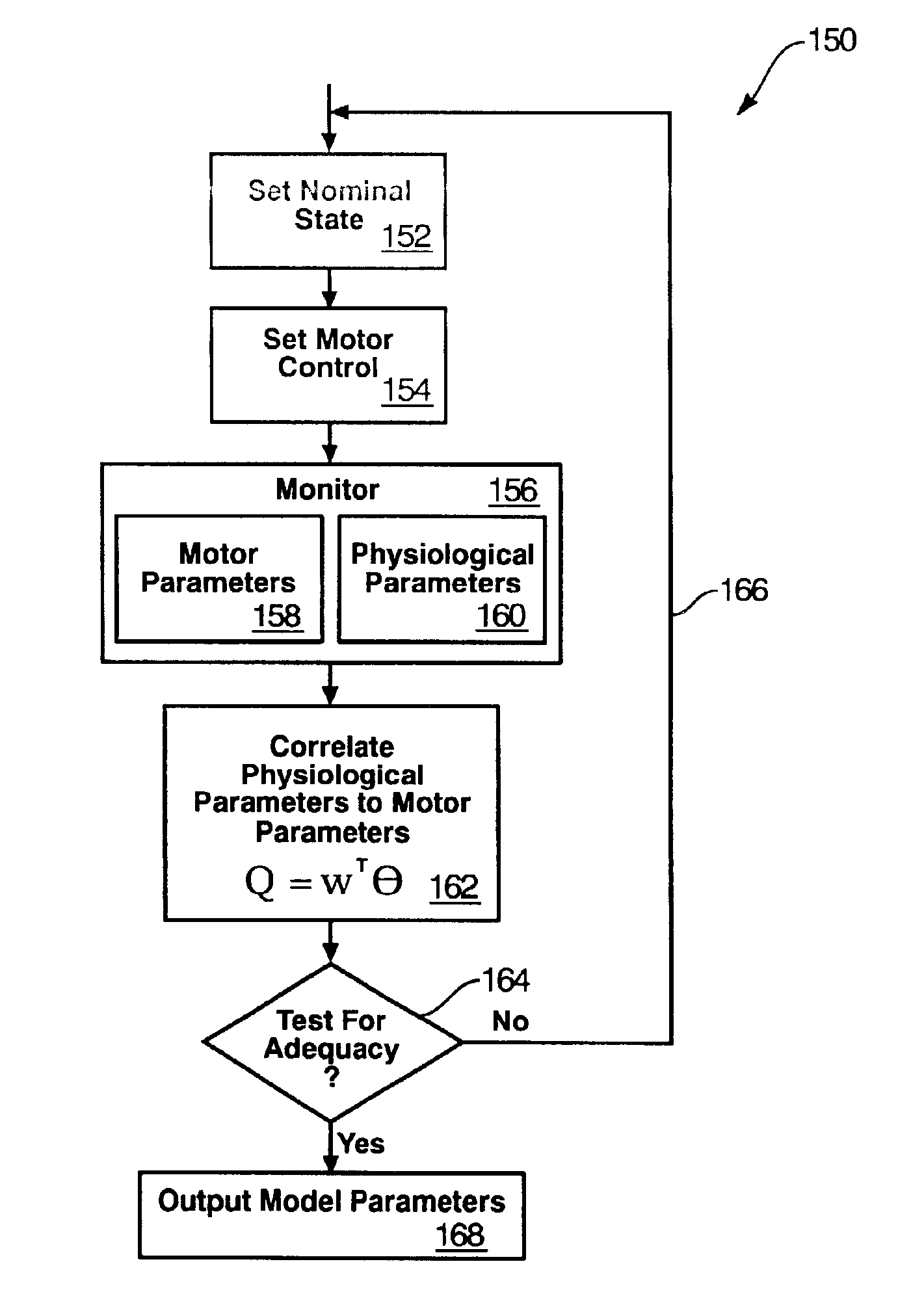
Rotary blood pump diagnostics and cardiac output controller
A method and apparatus for controlling a ventricular assist device are disclosed. The method includes the step of providing a ventricular assist device which can be defined in terms of operational parameters such as pump speed or current. Measuring at least one physiological parameter reflecting a physiological state corresponding to a patient. Correlating at least one physiological parameter measured from the patient to at least one operational parameter using an estimation method. Selecting a physiological state definable by desired values of the physiological parameters. Monitoring at least one operational parameter. Controlling input values of the operational parameter based on output from the monitoring step. The apparatus includes a pump driven by a motive drive and having an impeller. A sensor detects the value of an operational parameter of the pump. A processor provides a statistical correlation between patients physiological parameter and the operational parameter of the pump and adjusts the operational parameter to affect a predetermined optimal physiological state.
Owner:WORLD HEART
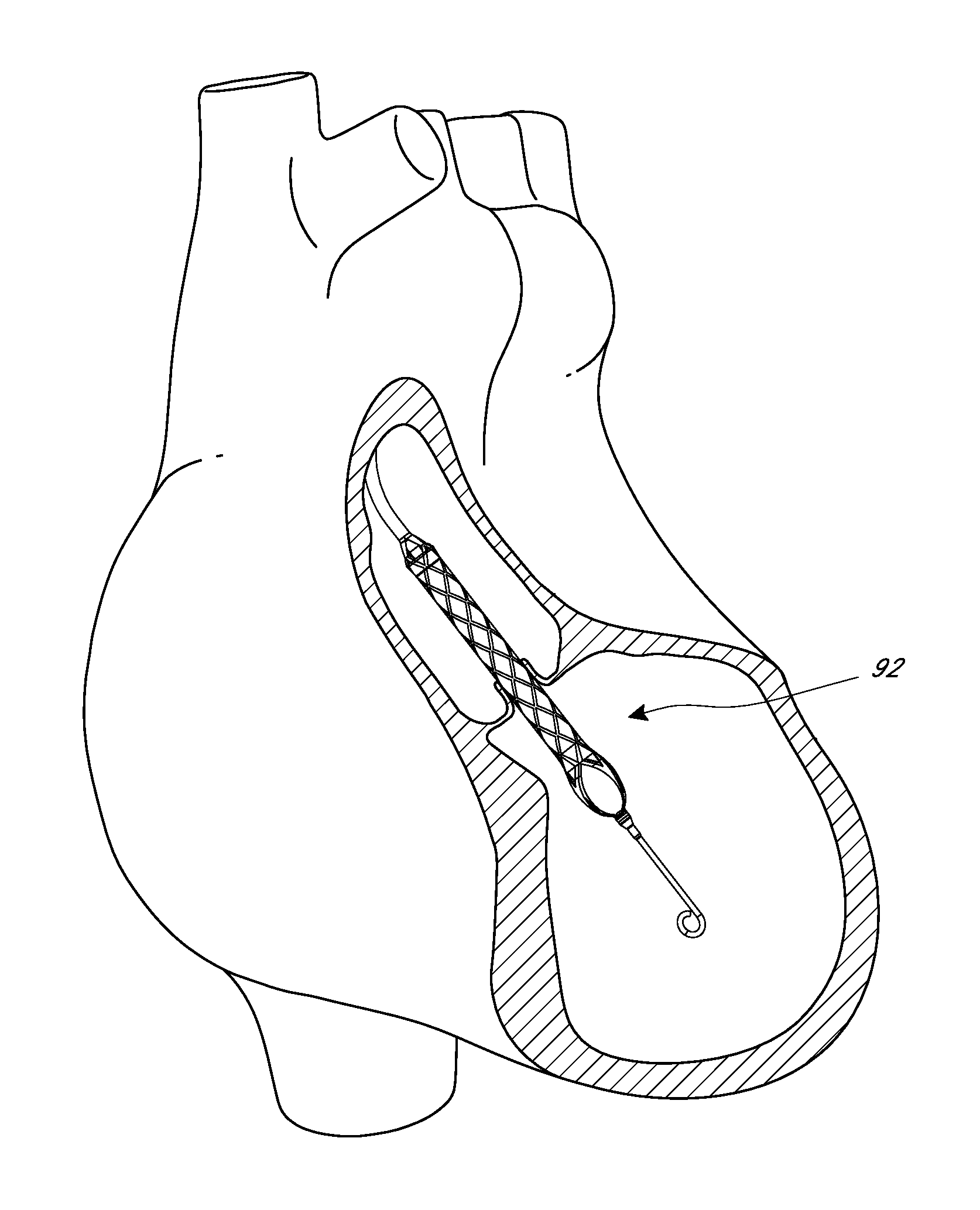
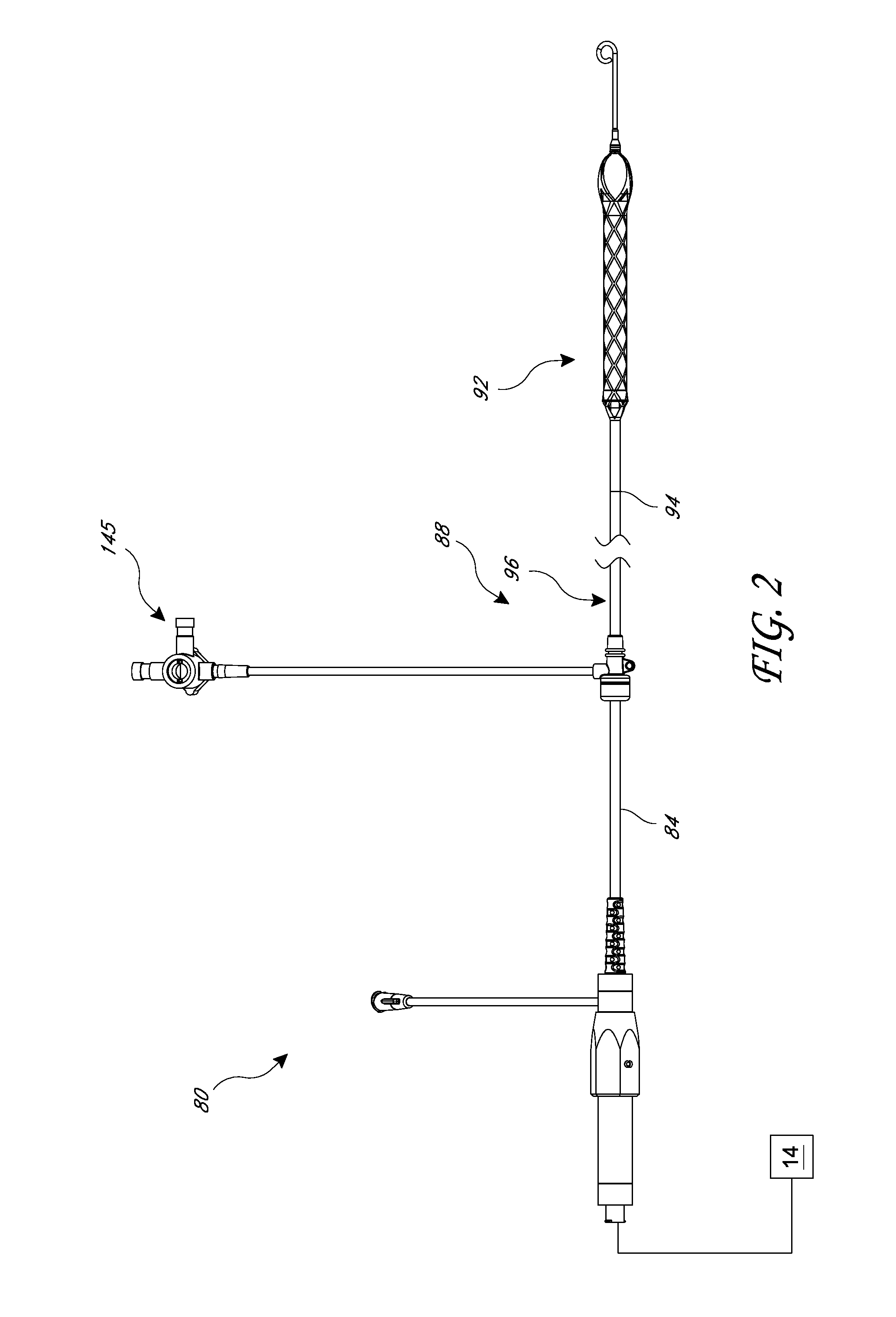
Percutaneous heart pump
Disclosed herein are heart pumps that can include a catheter body and an impeller coupled with a distal end of the catheter body. The impeller can include a tip that is resealable or that includes a resealable member. The heart pump can also include a diffuser disposed between the distal end of the catheter body and the impeller, wherein the diffuser includes a flow directing surface.
Owner:TUBEMASTER INC +2
Temporary blood circulation assist device
InactiveUS6981942B2Avoid lacerationsPrevent perforationBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesImpellerEngineering
An inflatable circulation assist device is disclosed consisting of an inflatable stator housing an impeller with inflatable blades of varying shapes and sizes. The invention is introduced into the patient percutaneously. The circulation assist device is a small pump packaged into a compact form that is attached to a long flexible driveshaft. The pump is inserted along a guidewire to a target location, and then the pump is inflated. The circulation assist device's exterior is designed to expand only so much as to closely fit whatever cardiovascular system element in which it is placed for operation. The vascular assist device can be expanded either by inflation with a fluid. The driveshaft, which connects to the circulation assist device's impeller and extends outside the patient's body, is rotated by an external motor. After the circulation assist device is no longer needed, it is collapsed into a compact form and removed from the patient percutaneously.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Heart assist device with expandable impeller pump
An impeller includes a hub and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a stored configuration in which the blade is compressed so that its distal end moves towards the hub, and a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub. The impeller may be part of a pump for pumping fluids, such as pumping blood within a patient. A blood pump may include a cannula having a proximal portion with a fixed diameter, and a distal portion with an expandable diameter. The impeller may reside in the expandable portion of the cannula. The cannula may have a compressed diameter which allows it to be inserted percutaneously into a patient. Once at a desired location, the expandable portion of the cannula may be expanded and the impeller expanded to the deployed configuration. A flexible drive shaft may extend through the cannula for rotationally driving the impeller within the patient's body.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
Pumping cartridge having an integrated filter and method for filtering a fluid with the cartridge
InactiveUS6905479B1Positive displacement pump componentsOther blood circulation devicesParticulatesEngineering
The present invention involves, in some embodiments, reusable pump drive systems, which are coupled to removable, and preferably disposable, pumping cartridges. The invention provides, in some embodiments, novel pumping cartridges for use in pumping systems. One such cartridge includes an integrated filter element therein for filtering fluids, for example fluids pumped to the body of a patient in a medical procedure. In some embodiments, the integrated filter is utilized as a blood clot removal filter and in other embodiments is used to remove particulates liquids infused to a patient. The filter element includes a filter with pores therein that are preferably sized to permit essentially unrestricted flow of individual human blood cells therethrough and to block or collect blood clots, cell clumps, particulates etc. with sizes substantially larger than the average size of a human blood cell.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
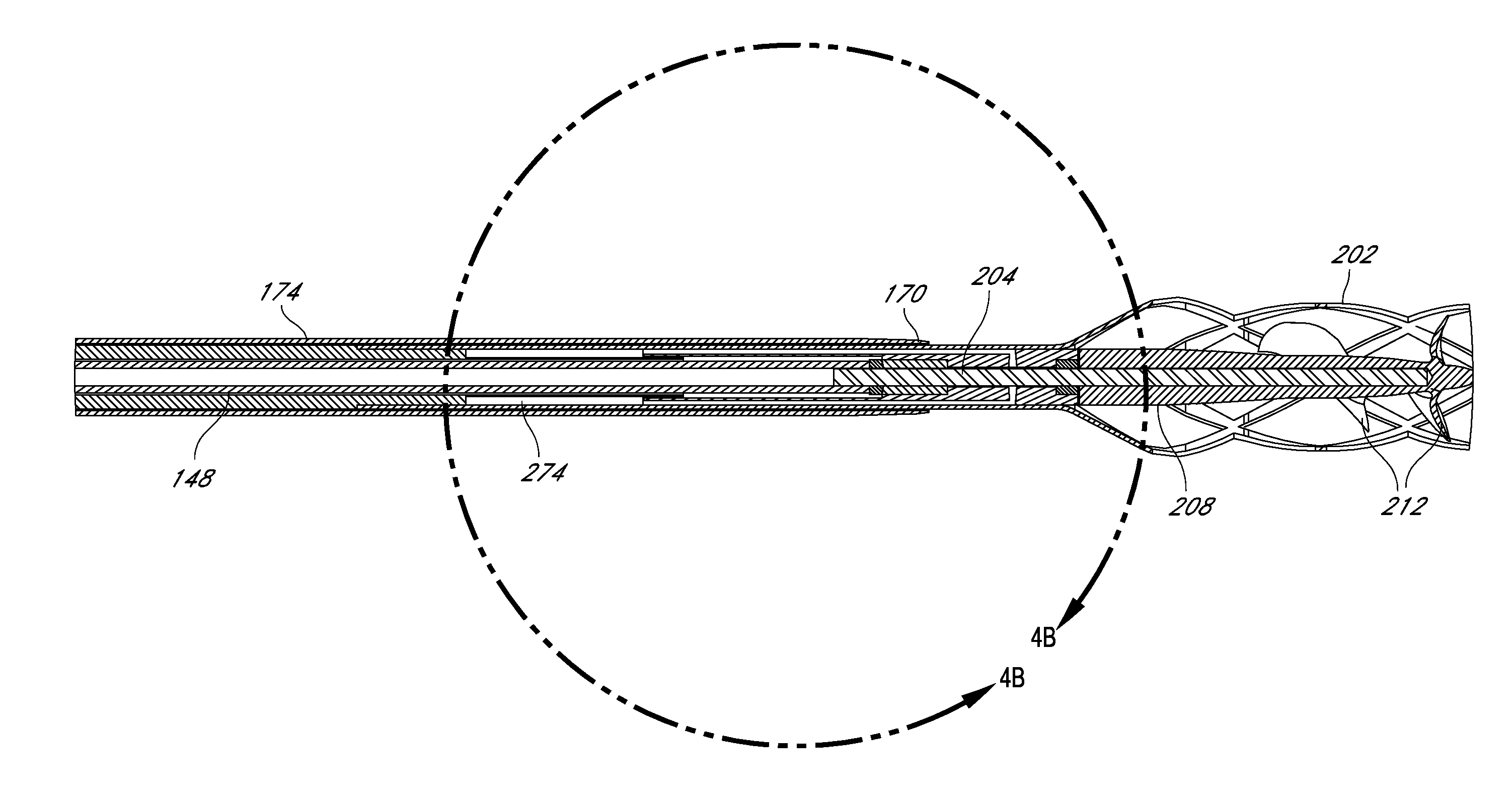
Method for Deployment of a Medical Device
InactiveUS20080132748A1Reduce bending loadMinimizing contact pressureControl devicesBlood pumpsAortic archMedical device
A method for deploying a cardiac-assist device is disclosed. In accordance with the illustrative embodiment, an introducing tube, such as a catheter, sheath, or the like is inserted into the vascular system and advanced beyond the aortic arch. The cardiac-assist device is then inserted into the tube, advanced through it, and deployed from its distal end. In some embodiments, the diameter of the cardiac-assist device expands when it deploys from the distal end of the tube.
Owner:MEDICAL VALUE PARTNERS
Implantable wireless power system
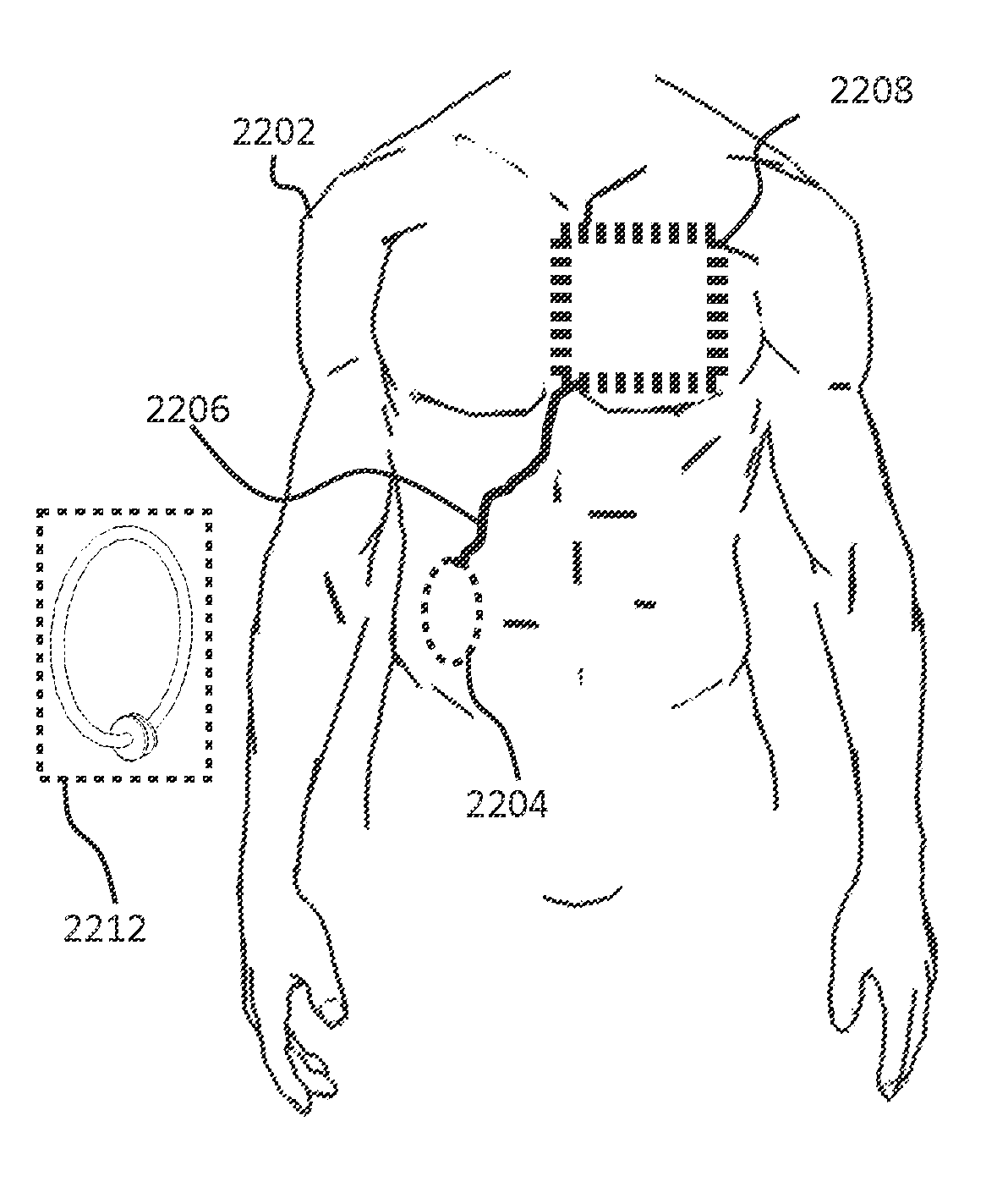
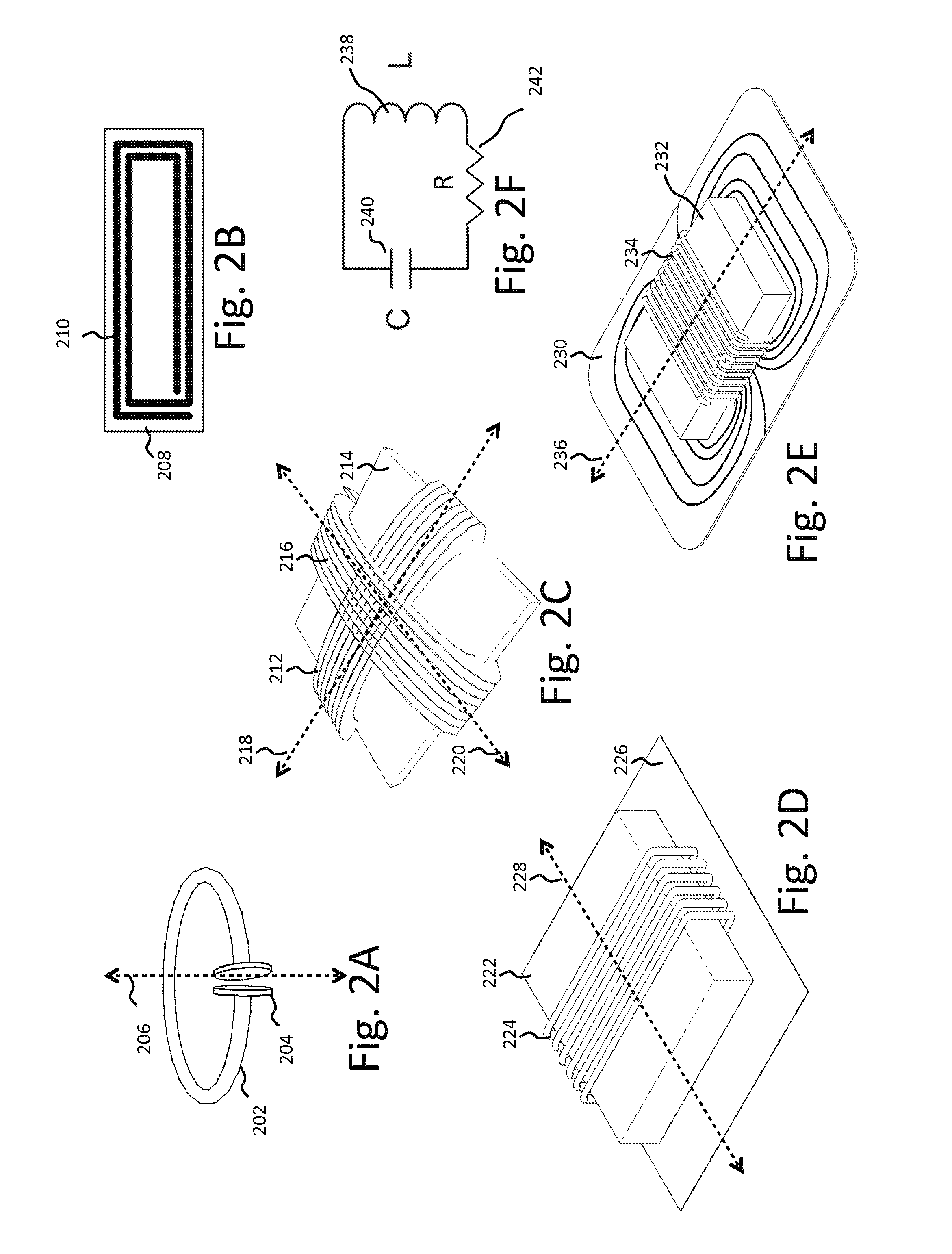
A wireless power system capable of transmitting power through the skin without percutaneous wires over distances ranging from a few inches to several feet includes an external transmitting coil assembly and a receiving coil assembly. The transmitting coil assembly includes an excitation coil and transmitting resonant coil which are inductively coupled to each other. The receiving coil assembly includes a receiving resonant coil and a power pick-up coil which are also inductively coupled to each other. A high frequency AC power input, such as radio frequency (RF), supplied to the excitation coil inductively causes the transmitting resonant coil to resonate resulting in a local time varying magnetic field. The transmitting and receiving resonant coils are constructed as to have closely matched or identical resonant frequencies so that the magnetic field produced by the transmitting resonant coil is able to cause the receiving resonant coil to resonate strongly also, even when the distance between the two resonant coils greatly exceeds the largest dimension of either coil. The receiving resonant coil then creates its own local time varying magnetic field which inductively produces a voltage in a power pick-up coil to provide power to an active implantable medical device or implantable rechargeable battery.
Owner:CORVION INC
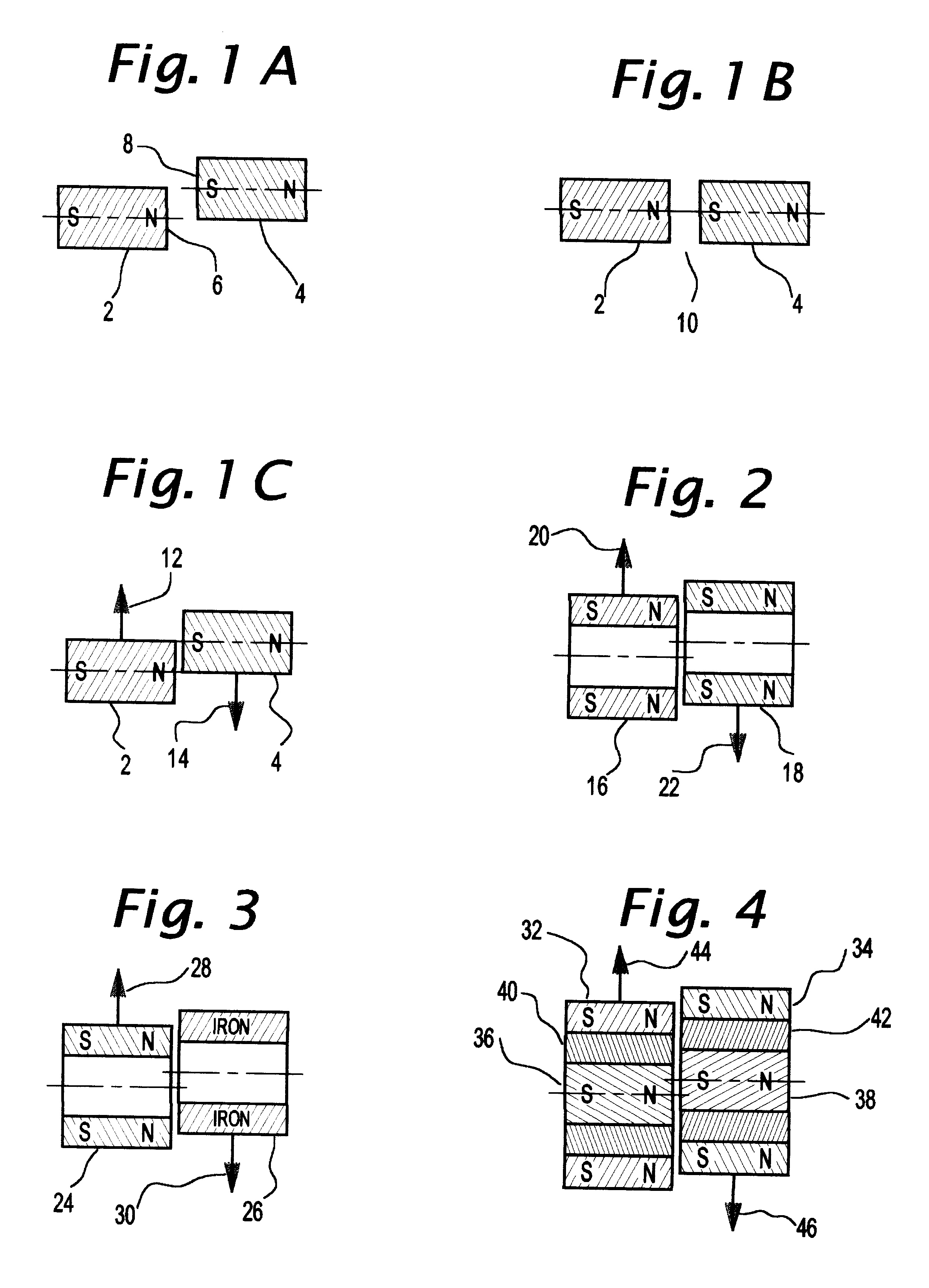
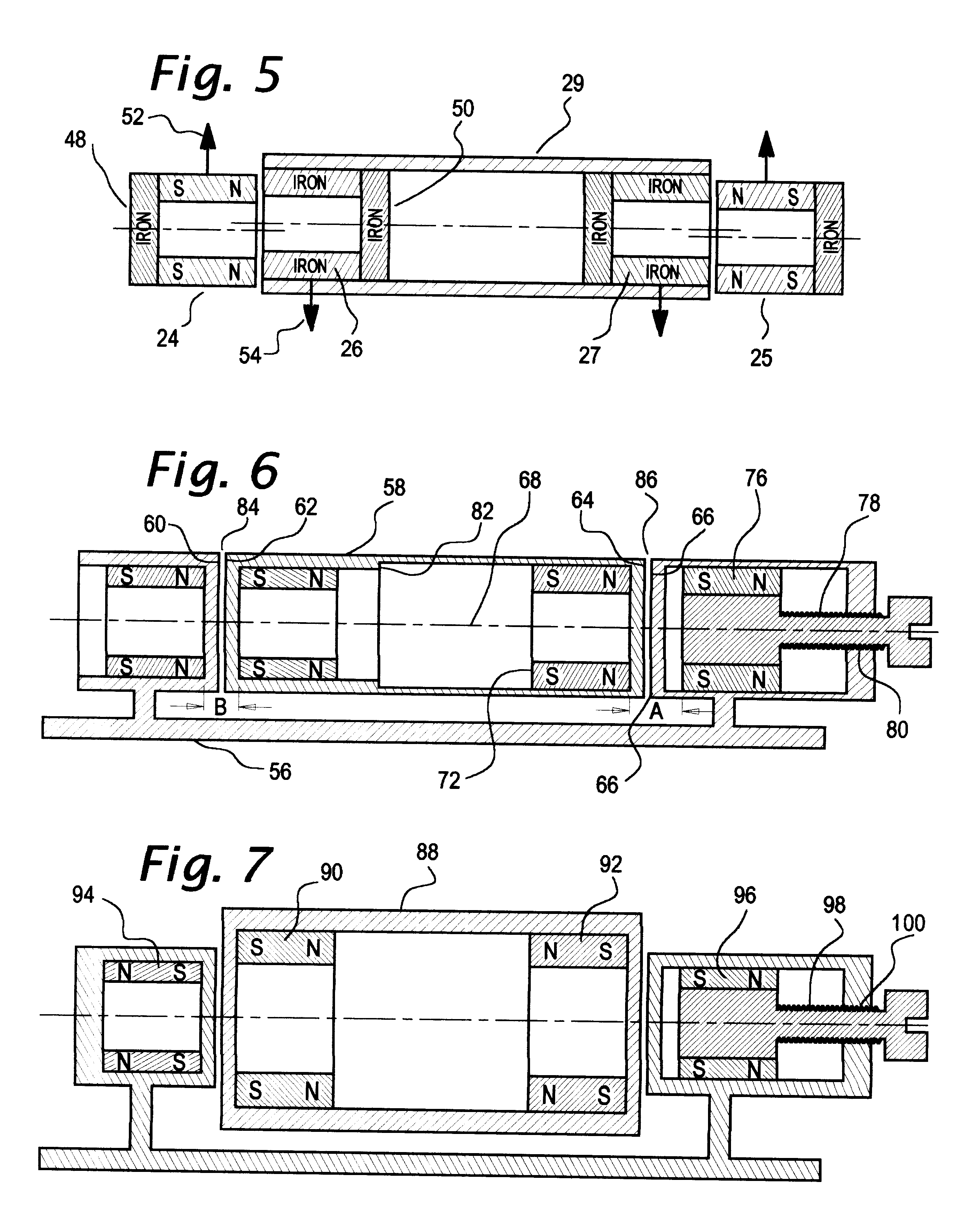
Axial force null position magnetic bearing and rotary blood pumps which use them
InactiveUS6227820B1Improve radial stiffnessSimple designPump componentsSurgeryAxial-flow pumpMagnetic tension force
A generally cylindrical rotor very closely confined between two rigid thrust bearing surfaces is radially suspended by an array of attracting or repelling magnets or by a combination of permanent magnets and ring shaped members composed of ferromagnetic material. The geometry permits very small spacing between magnetic components to achieve high radial stiffness. High magnetic axial forces exerted between the rotor and stationary component on one end of the rotor are counter-balanced by equal and opposite forces at the other end of the rotor. Precise positioning of the rotor in the location where the opposing axial magnetic forces counterballance each other yields a net magnetic axial force on the rotor of near zero, hence the reference to this as the null position. Wear resistant mechanical thrust bearings confine the rotor axially to maintain this position during rotatioin. Precisely balance the magnetic axial forces in the proper geometry with relation to the mechanical thrust bearings. Blood pumps utilizing this type of bearing are disclosed, including both axial flow pump and centrifugal flow pump configurations with high flow washing of the junction of the rotating and stationary parts to prevent thrombus accumulation.
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
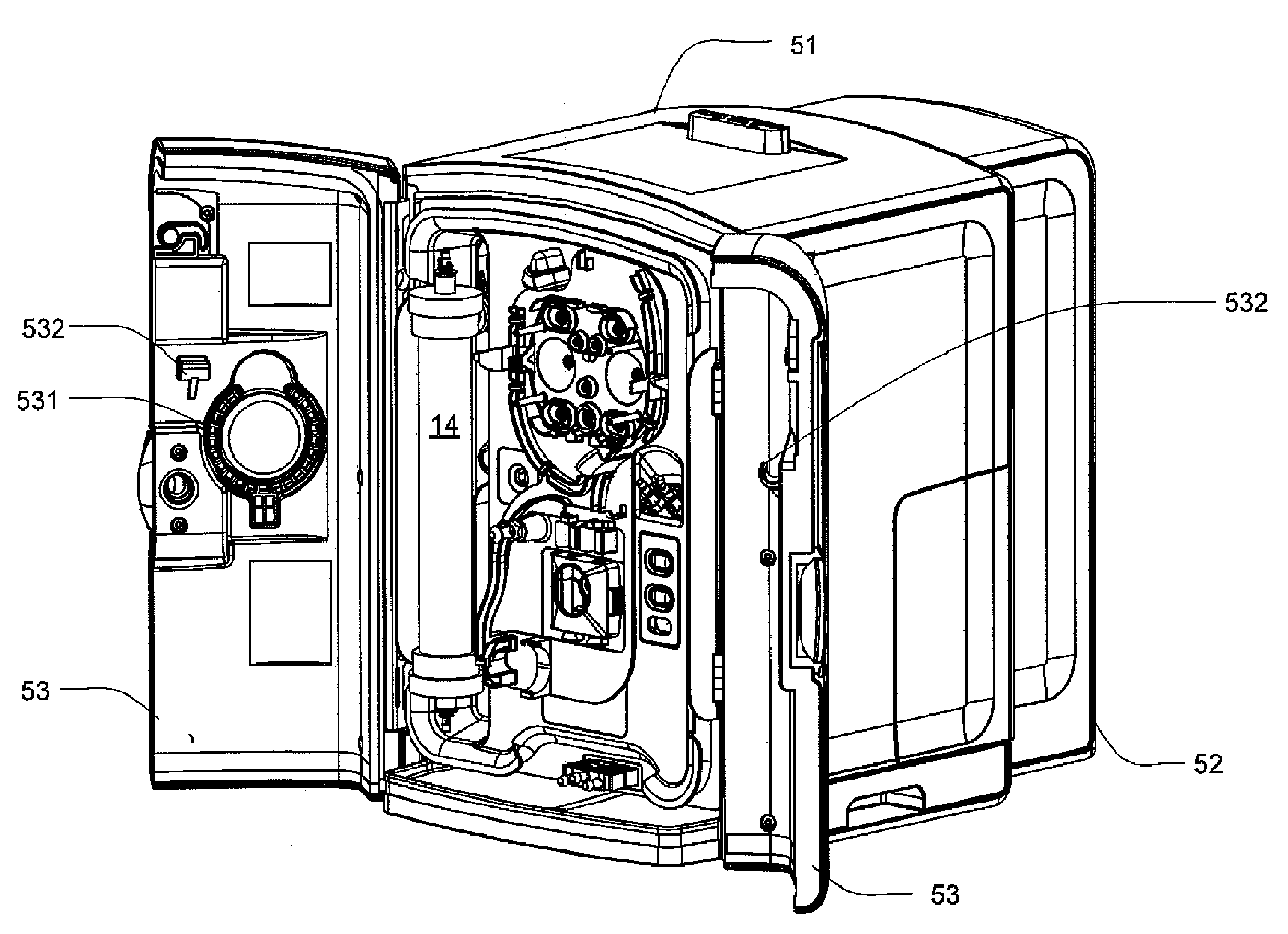
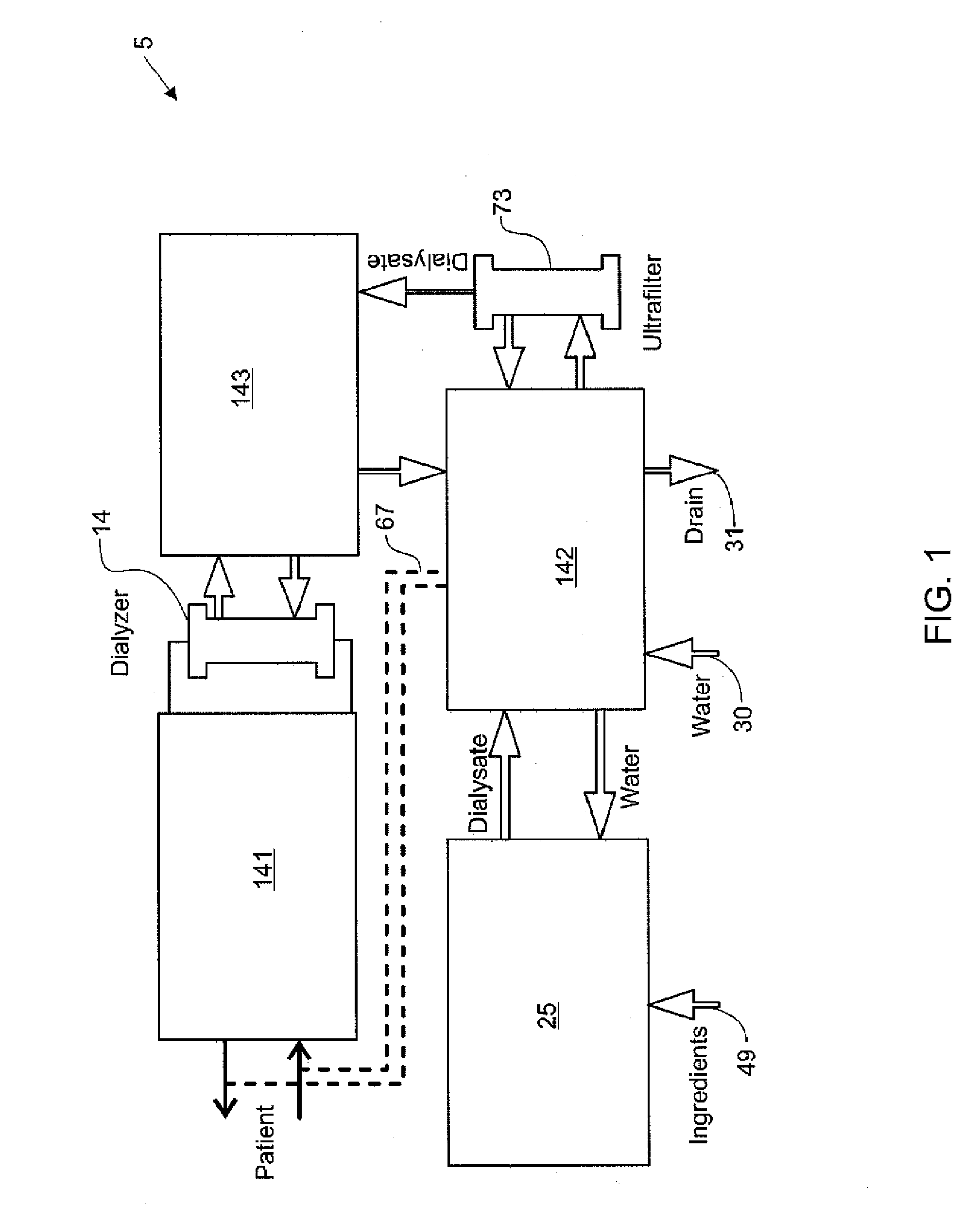
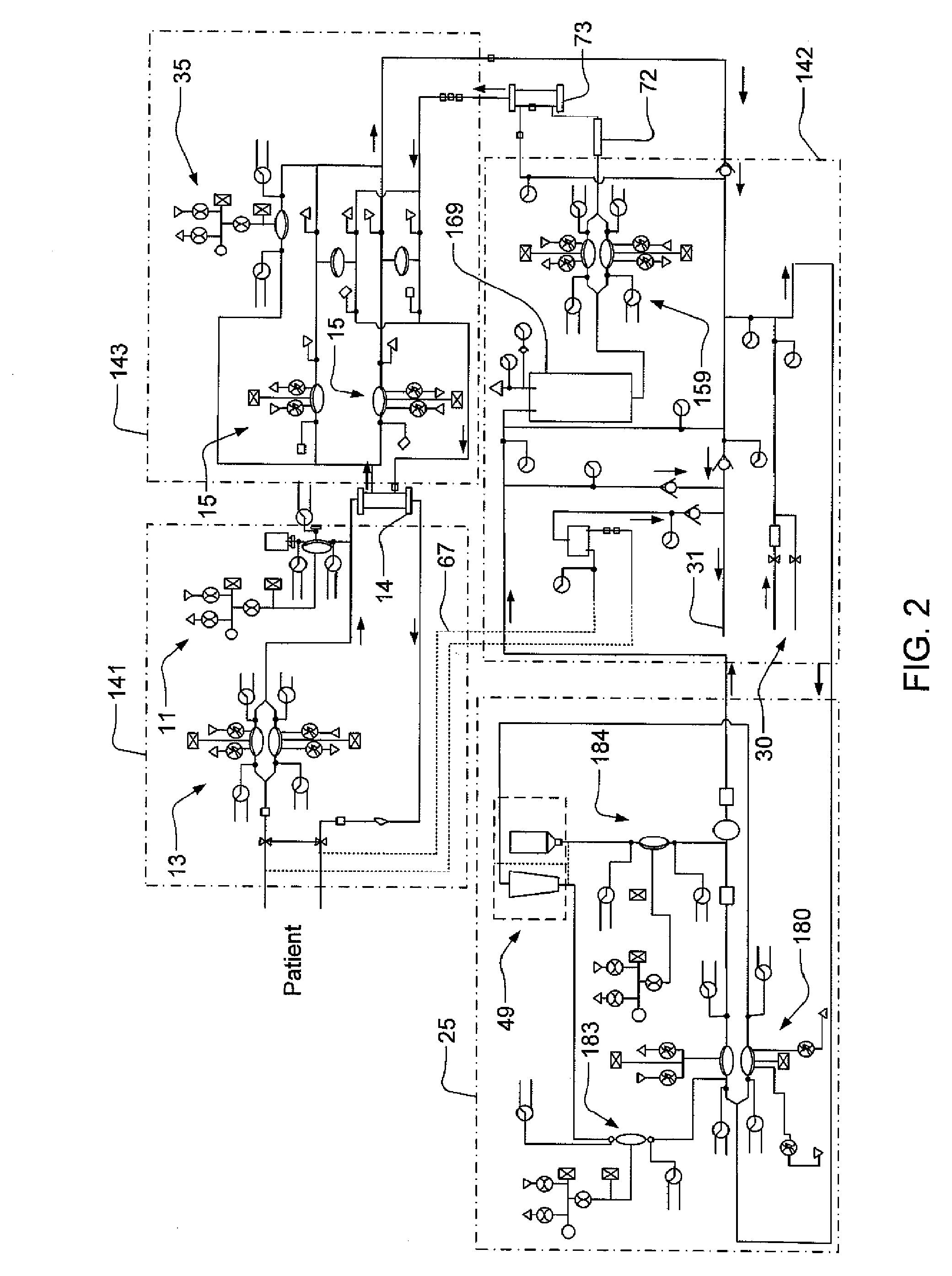
Modular assembly for a portable hemodialysis system
ActiveUS20090101549A1Easy to useOptimize locationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOther blood circulation devicesHaemodialysis machineModularity
A modular assembly for a portable hemodialysis system may include a dialysis unit, e.g., that contains suitable components for performing hemodialysis, such as a dialyzer, one or more pumps to circulate blood through the dialyzer, a source of dialysate, and one or more pumps to circulate the dialysate through the dialyzer, and a power unit having a housing that contains suitable components for providing operating power to the pumps of the dialysis unit. The power unit may be selectively connected to the dialysis unit and provide power (e.g., pneumatic power in the form of pressure and / or vacuum) to the dialysis unit for the pumps when connected to the dialysis unit, but may be incapable of providing power to the dialysis unit when disconnected from the dialysis unit. The dialysis unit and the power unit are sized and weighted to each be carried by hand by a human.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
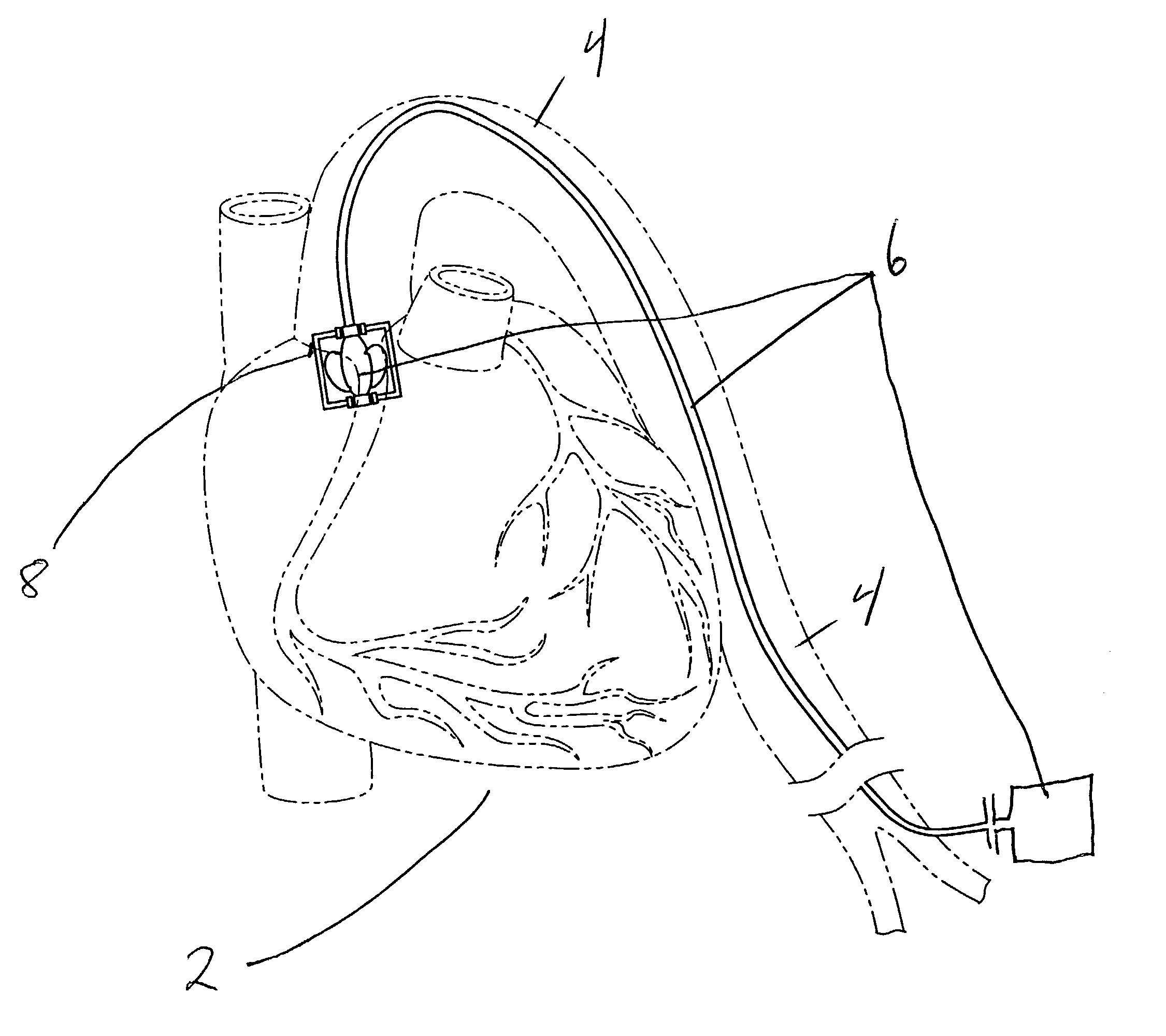
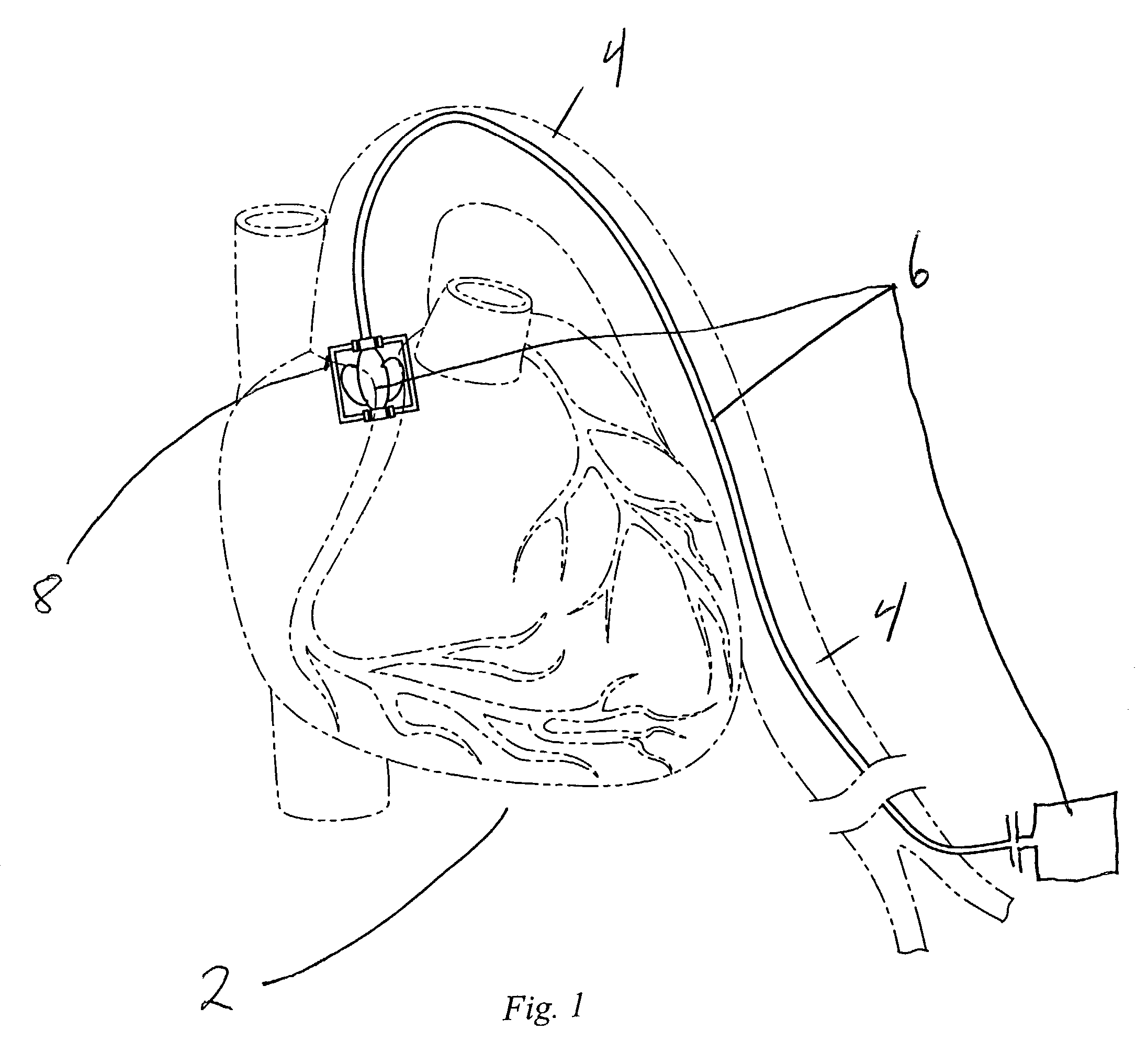
Single port cardiac support apparatus
A reverse flow pump comprising two concentric passageways and an interior compartment having cut out portions in communication with a pump passageway for the directional flow of fluid relative to the pump, and a rotor positioned within the interior compartment for reversing the directional flow of fluid through a region in communication with another pump passageway. A reverse flow pump and cannula system is further provided comprising an inner cannula adjoining a pump passageway, and an outer conduit adjoining another pump passageway for the reverse flow of fluid relative to the pump. A method of transporting fluid between body cavities is also provided comprising the steps of selecting a reverse flow pump and cannula system, forming an opening in a body passageway, positioning the outer conduit through the opening, inserting the inner cannula into the outer conduit so that the distal openings of the inner cannula and the outer conduit are positioned in separated portions of the body, connecting the inlet and the outlet passageways of the pump to the proximal ends of the inner cannula and the outer conduit, and activating the pump to transport fluid between the separated portions of the body.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Wireless energy transfer for implantable devices
ActiveUS20130320773A1Improves range tolerable offsetMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionEnergy transferPower cable
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Expandable impeller pump
An impeller according to an example of the present invention comprises a hub, and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub, and a stored configuration in which the impeller is radially compressed, for example by folding the blade towards the hub. The impeller may comprise a plurality of blades, arranged in blade rows, to facilitate radial compression of the blades. The outer edge of a blade may have a winglet, and the base of the blade may have an associated indentation to facilitate folding of the blade.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
Thermal and conductivity sensing systems, devices and methods
A sensing probe is described. The sensing probe includes a probe housing having a probe tip. A thermal sensor in the housing is also included. The thermal sensor has a sensing end and a connector end, where the sensing end is thermally coupled to the probe tip. Also included are at least two leads. The leads transfer electrical signals that are used to determine temperature and conductivity. Also included is a thermal well. The thermal well includes a hollow housing of a thermally conductive material. The housing has an outer surface and an inner surface. The inner surface is a predetermined shape so as to form a mating relationship with a sensing probe. The mating thermally couples the inner surface with a sensing probe. In some embodiments, the thermal well is located on a disposable portion and the sensing probe on a reusable portion.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
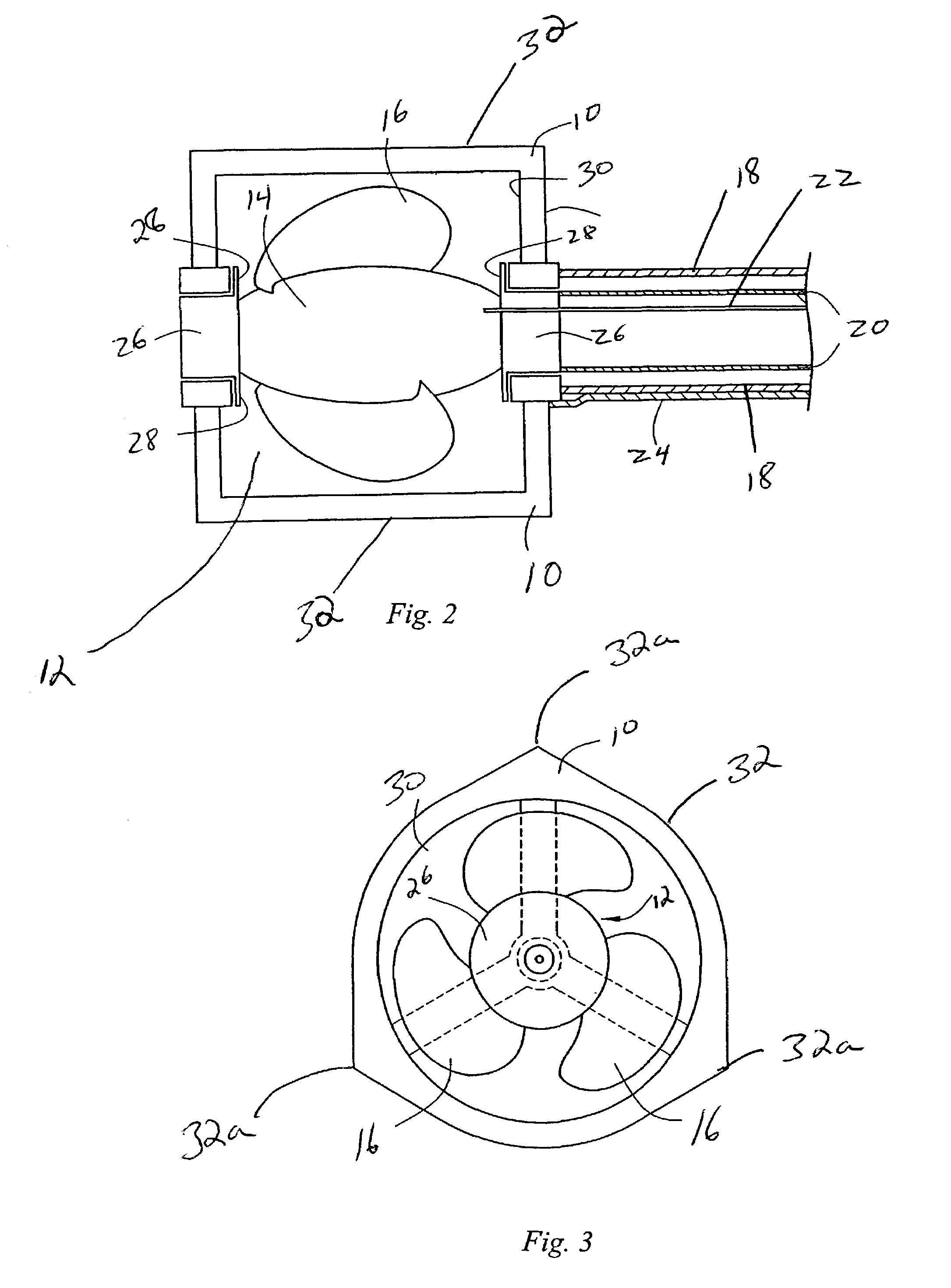
Fluid pumping systems, devices and methods
ActiveUS20080175719A1Reduces shear on the fluidReduce hemolysisThermometer detailsFlexible member pumpsHemolysisPeritoneal fluid
Embodiments of the present invention relate generally to certain types of reciprocating positive-displacement pumps (which may be referred to hereinafter as “pods,”“pump pods,” or “pod pumps”) used to pump fluids, such as a biological fluid (e.g., blood or peritoneal fluid), a therapeutic fluid (e.g., a medication solution), or a surfactant fluid. The pumps may be configured specifically to impart low shear forces and low turbulence on the fluid as the fluid is pumped from an inlet to an outlet. Such pumps may be particularly useful in pumping fluids that may be damaged by such shear forces (e.g., blood, and particularly heated blood, which is prone to hemolysis) or turbulence (e.g., surfactants or other fluids that may foam or otherwise be damaged or become unstable in the presence of turbulence).
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
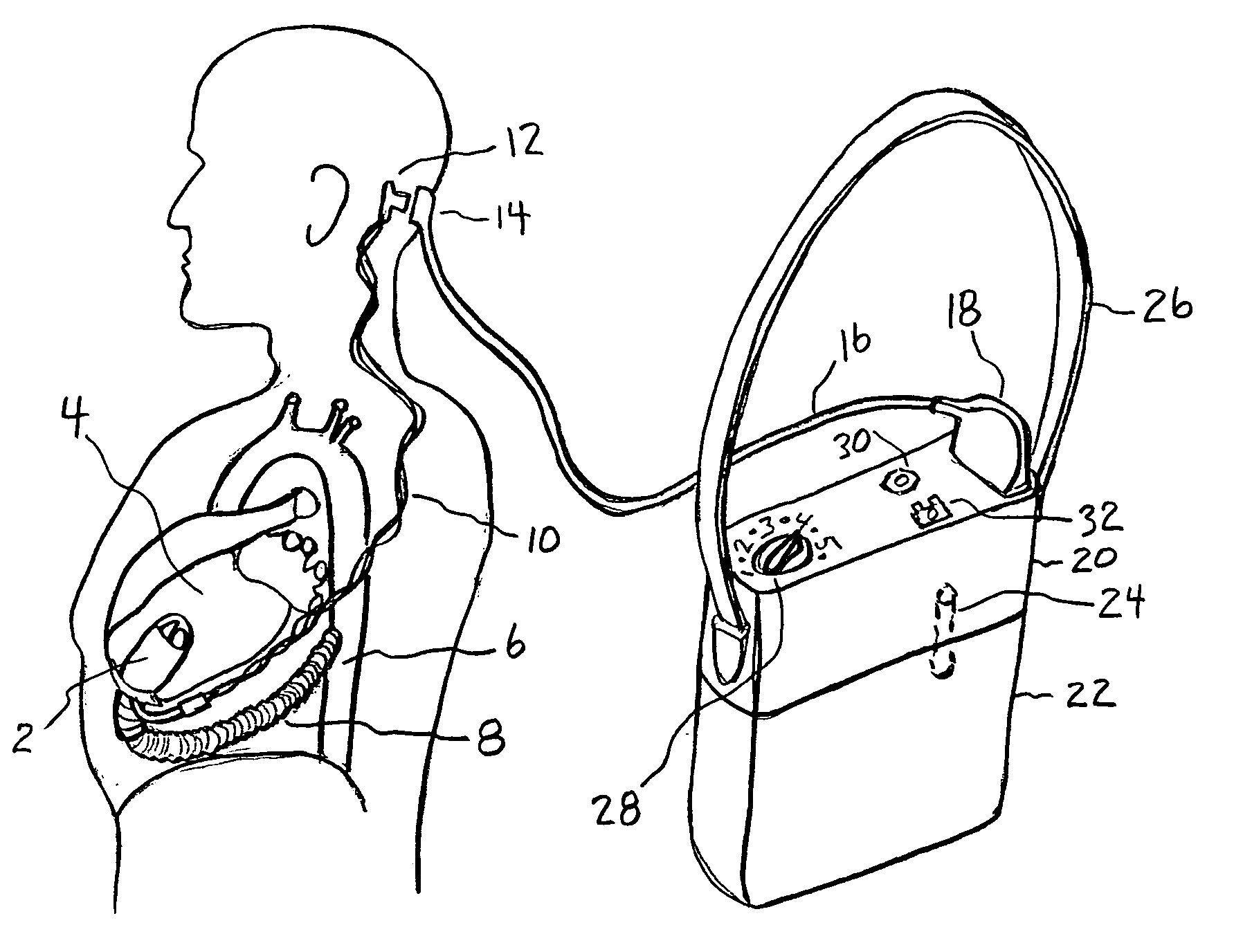
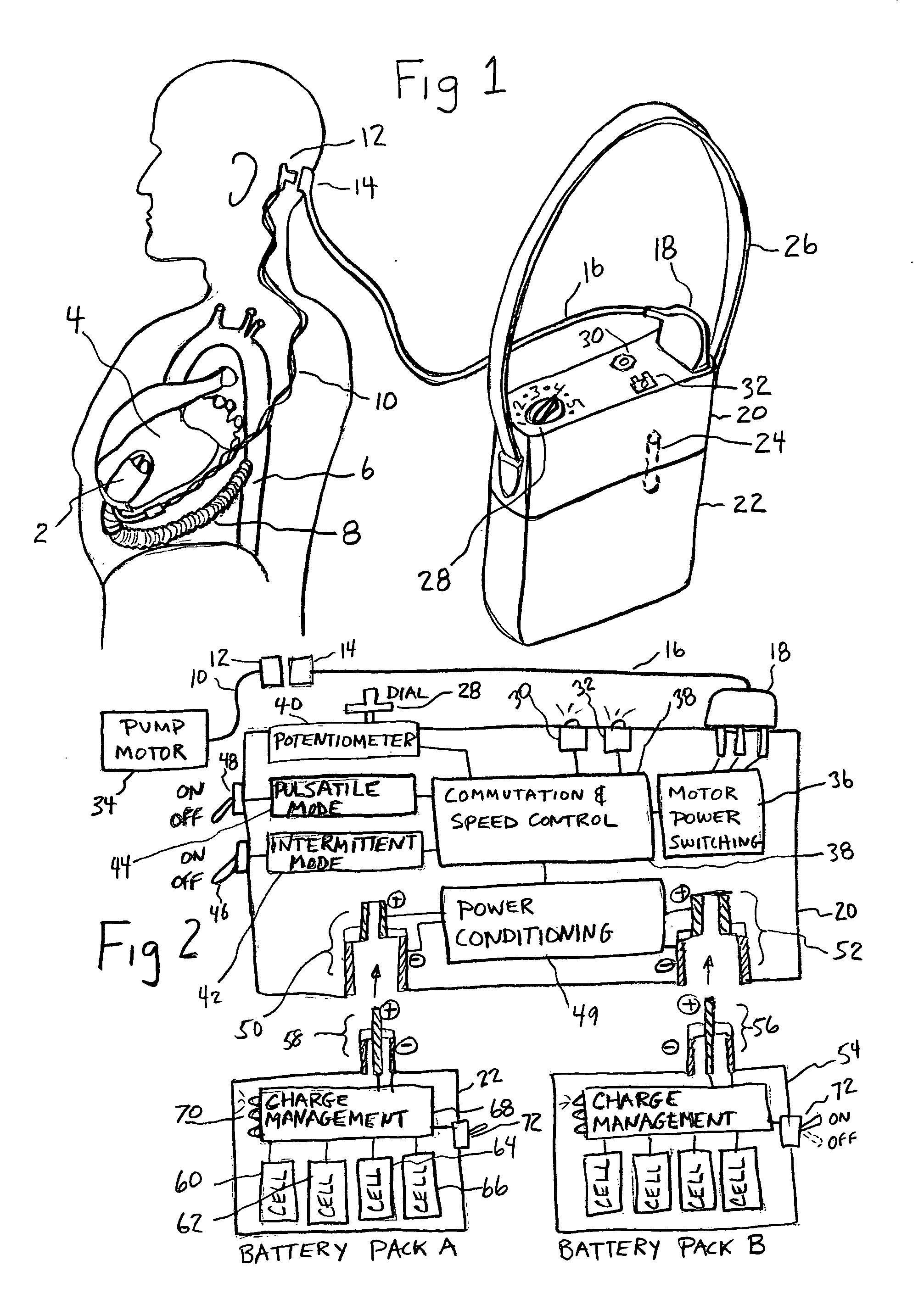
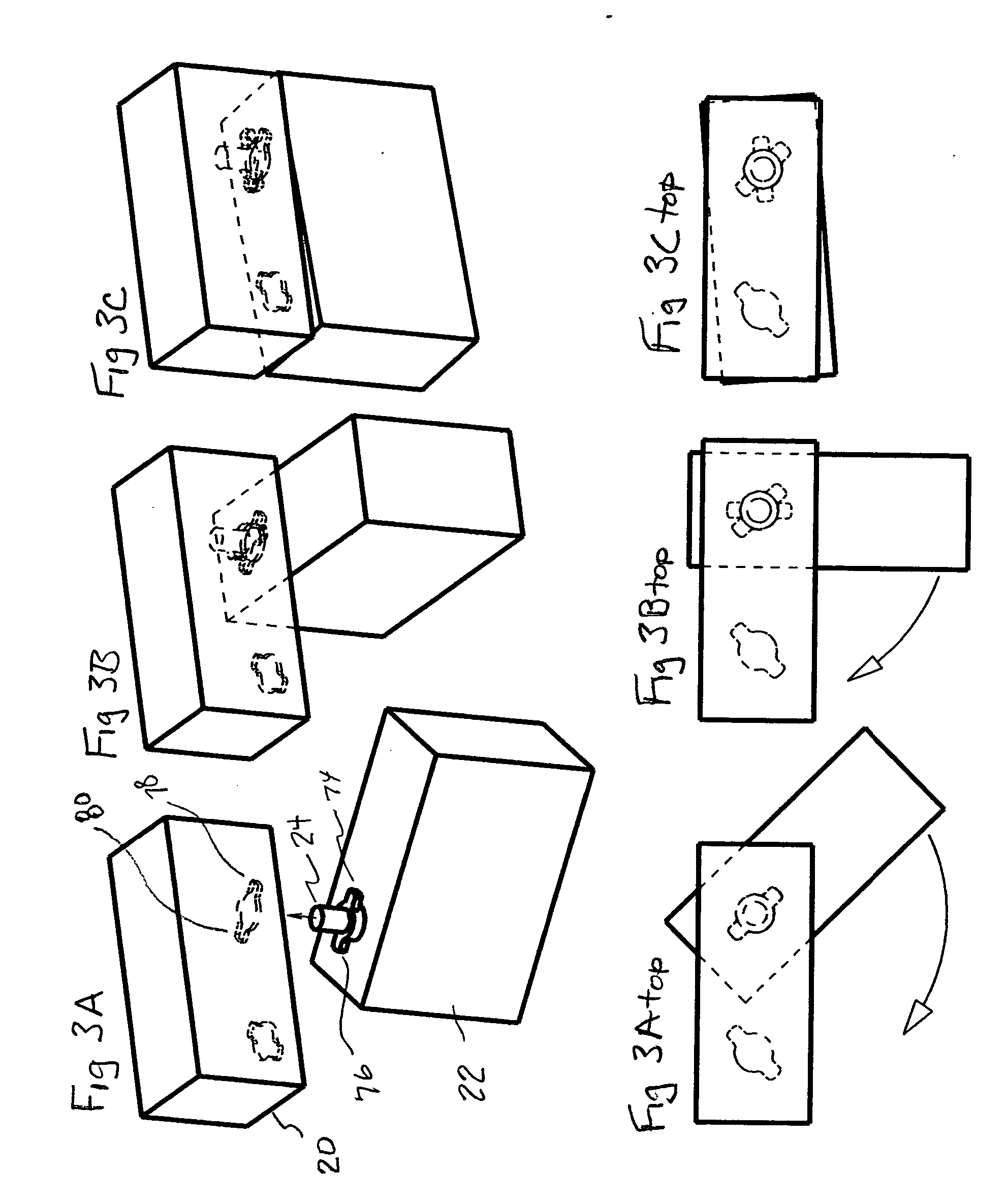
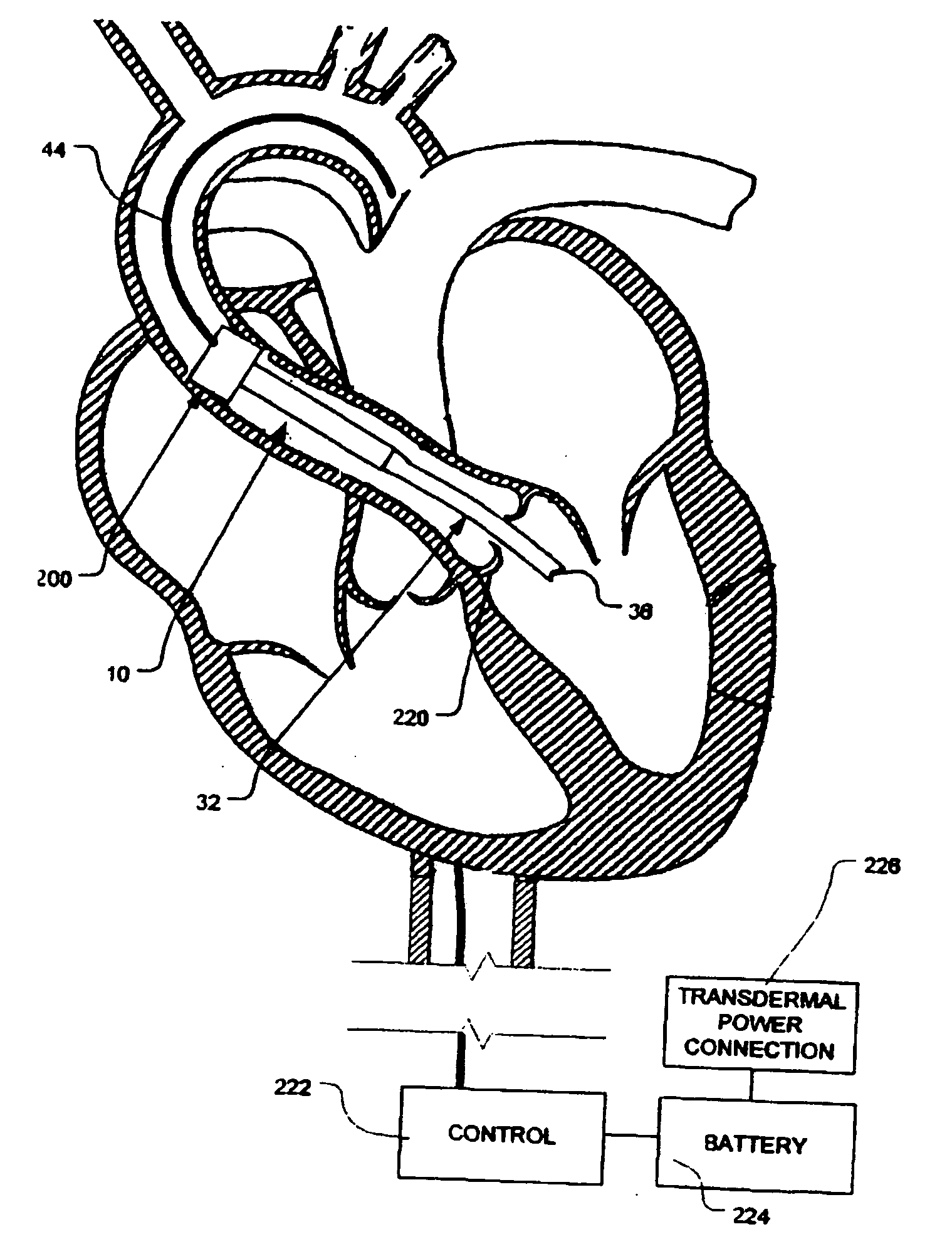
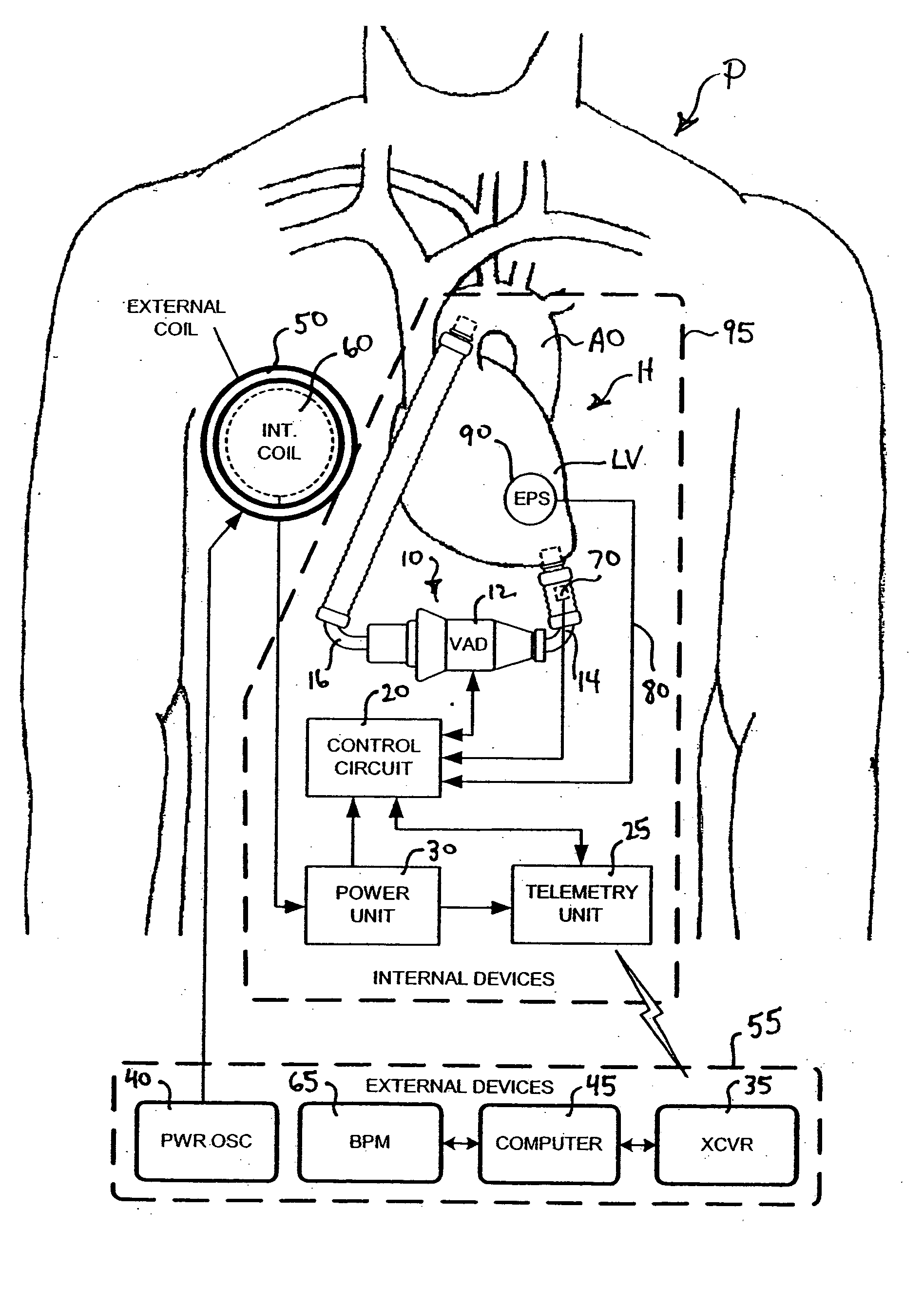
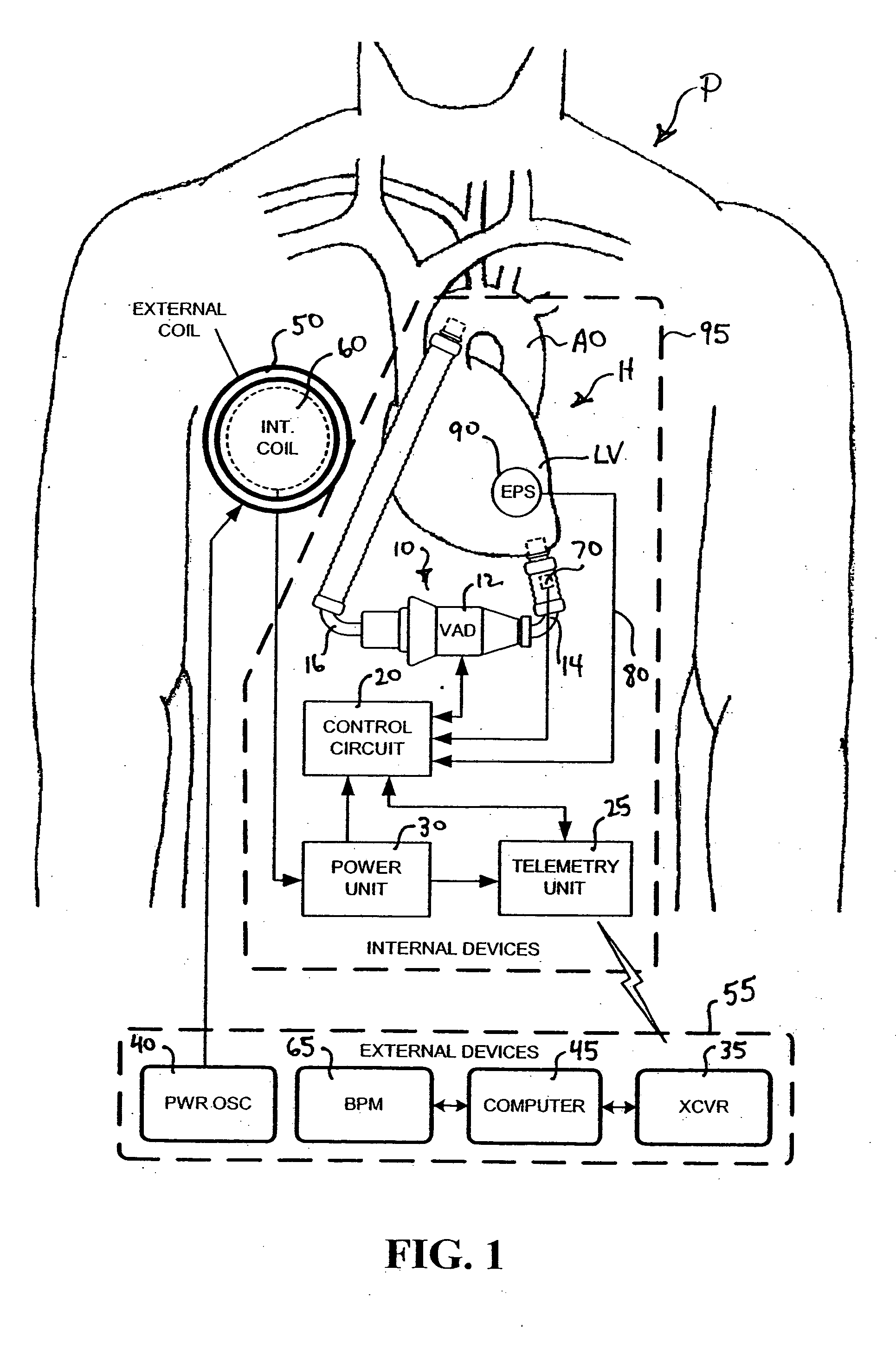
Artificial heart power and control system
InactiveUS20050071001A1Secure attachmentReduce trafficPrimary cell maintainance/servicingControl devicesControl theoryElectric cables
The present invention provides a human engineered power and control system for artificial hearts or assist devices configured for ease of use, ruggedness, and high reliability. Battery powered systems of the prior art have required multiple cables and connectors that are subject to failure due to damage or wear. In the present invention, direct connection of the batteries to the control system eliminates multiple cables and connectors used with previous designs. A novel method of connecting batteries to the control system and exchanging batteries without interruption of power is provided in a compact user friendly configuration. The control system may provide periodic reductions in assist device flow to permit the natural ventricle to eject blood through the natural outflow valve, open the valve leaflets to prevent them from adhering together, and achieve sufficient washout to prevent thrombosis. Using either software based control or software independent electronic circuitry, the flow pumped by the artificial heart is reduced for a long enough period of time to permit at least a few beats of the natural heart to generate sufficient pressure to open the outflow valve. In a control system embodiment in which the patient manually adjusts the pump speed to incremental settings for rest and exercise conditions, a pulsatile flow mode is disclosed which provides approximately the same flow at a given incremental setting as the pump produces when running in a constant speed mode at the same setting. As the patient learns which speed setting is best for daily activities, the patient may use the same setting with either a pulsatile or constant pump speed mode.
Owner:EDER JEFFREY
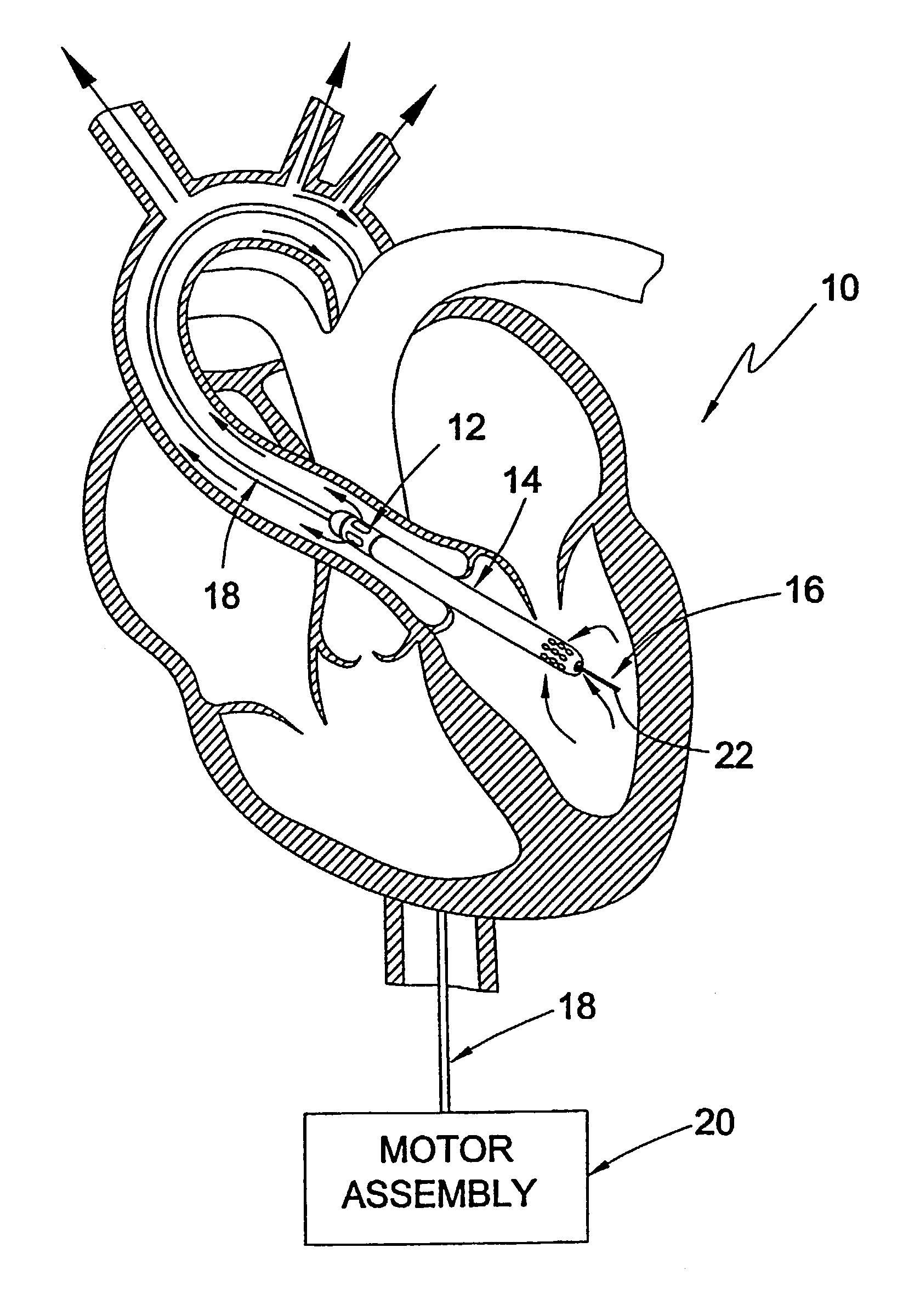
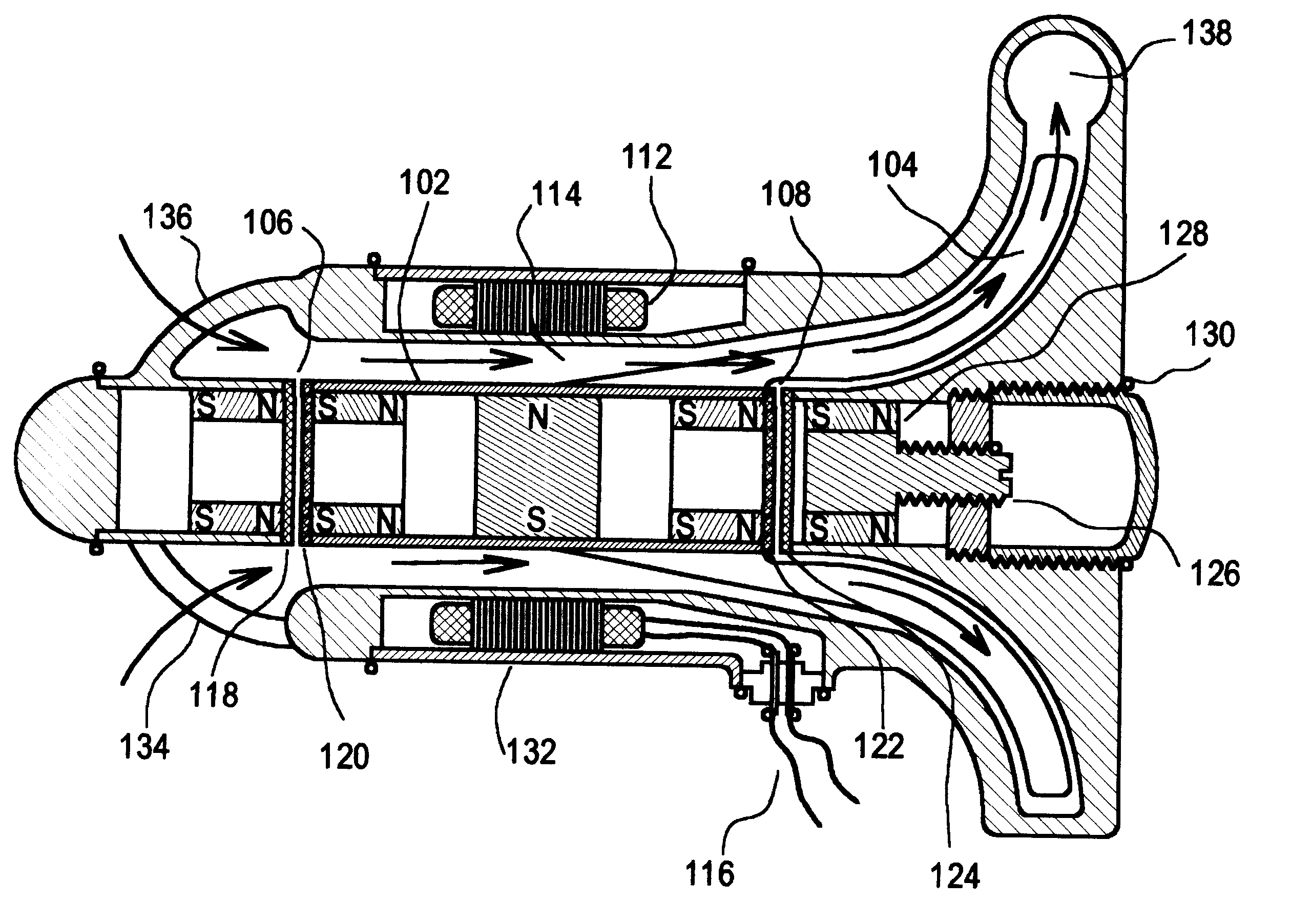
Intravascular ventricular assist device
One aspect of an intravascular ventricular assist device is an implantable blood pump where the pump includes a housing defining a bore having an axis, one or more rotors disposed within the bore, each rotor including a plurality of magnetic poles, and one or more stators surrounding the bore for providing a magnetic field within the bore to induce rotation of each of the one or more rotors. Another aspect of the invention includes methods of providing cardiac assistance to a mammalian subject as, for example, a human. Further aspects of the invention include rotor bodies having helical channels formed longitudinally along the length of the body of the rotor where each helical channel is formed between peripheral support surface areas facing radially outwardly and extending generally in circumferential directions around the rotational axis of the rotor.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Hybrid magnetically suspended and rotated centrifugal pumping apparatus and method
InactiveUS6074180AAvoid displacementEfficient startSpecific fluid pumpsPump componentsMotor speedRotary pump
An apparatus and method for a centrifugal fluid pump for pumping sensitive biological fluids, which includes (i) an integral impeller and rotor which is entirely supported by an integral combination of permanent magnets and electromagnetic bearings and rotated by an integral motor, (ii) a pump housing and arcuate passages for fluid flow and containment, (iii) a brushless driving motor embedded and integral with the pump housing, (iv) a power supply, and (v) specific electronic sensing of impeller position, velocity or acceleration using a self-sensing method and physiological control algorithm for motor speed and pump performance based upon input from the electromagnetic bearing currents and motor back emf-all fitly joined together to provide efficient, durable and low maintenance pump operation. A specially designed impeller and pump housing provide the mechanism for transport and delivery of fluid through the pump to a pump output port with reduced fluid turbulence.
Owner:WORLD HEART +2
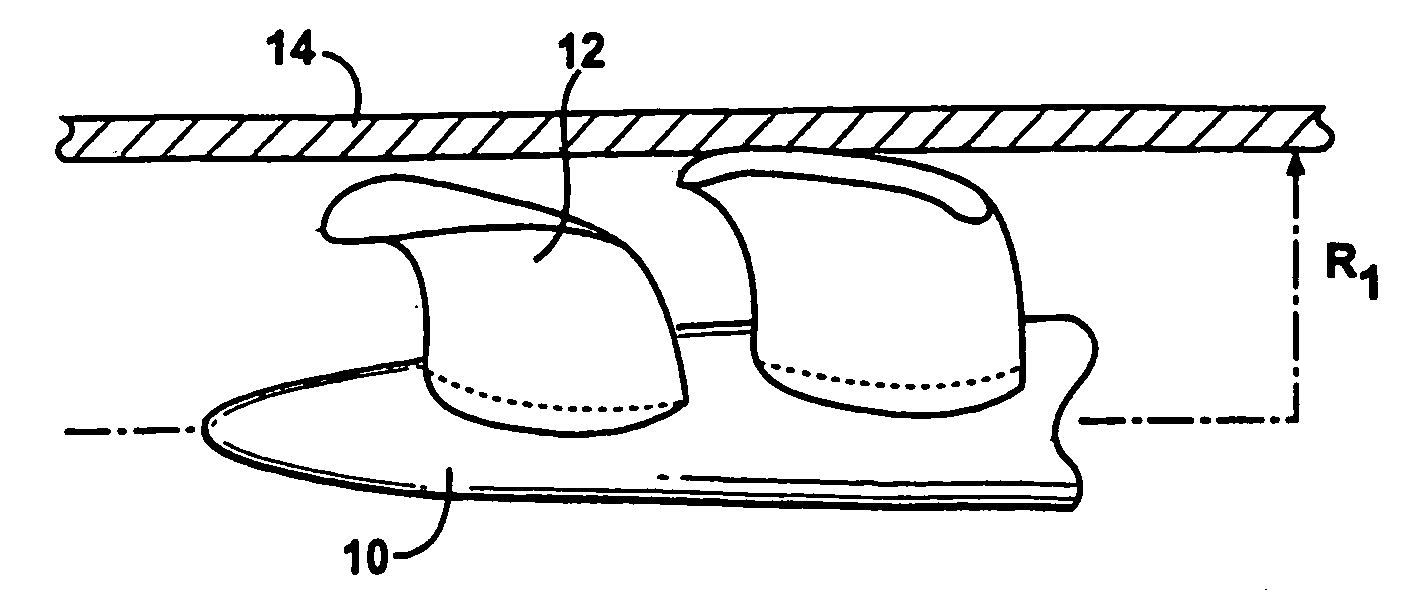
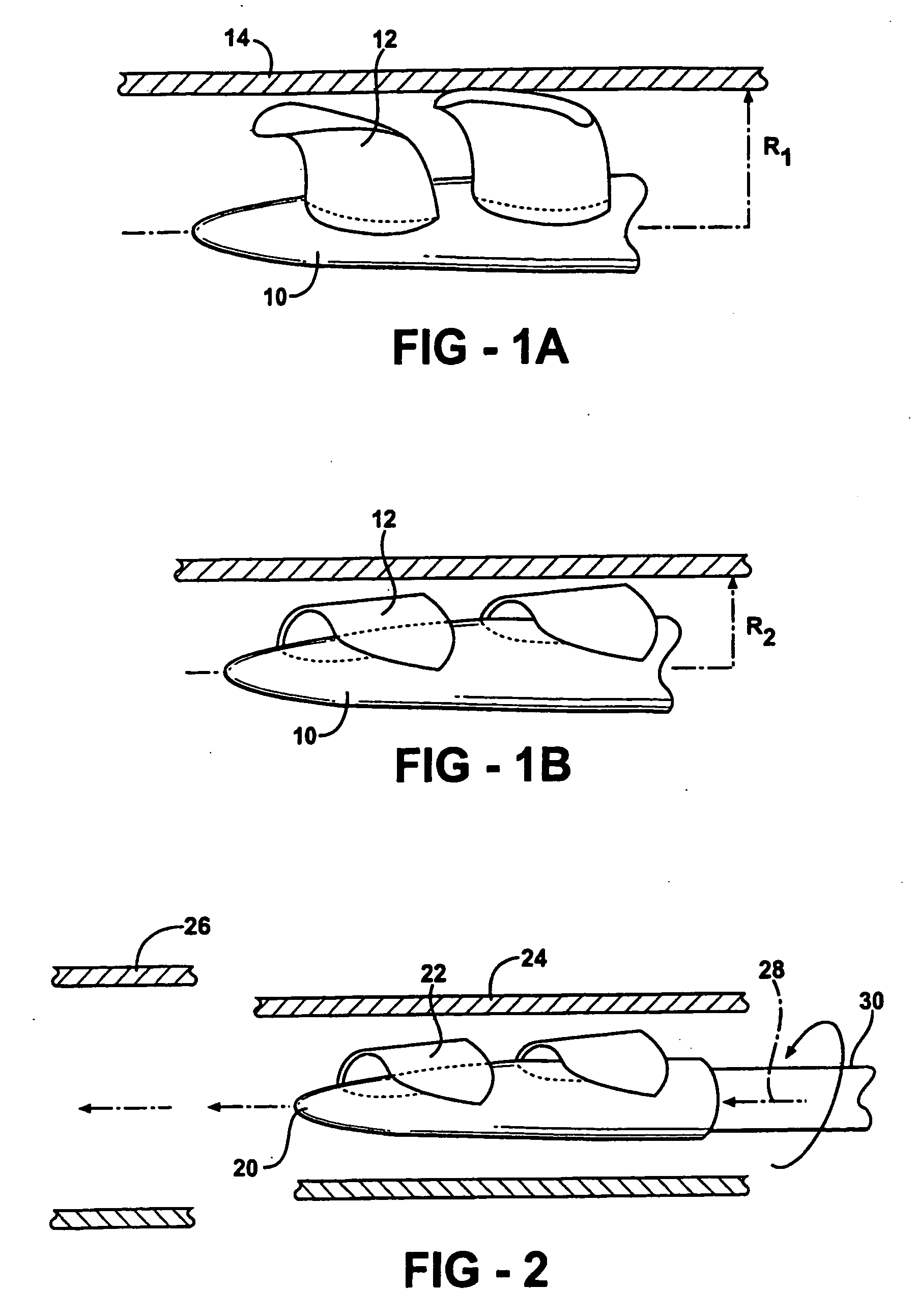
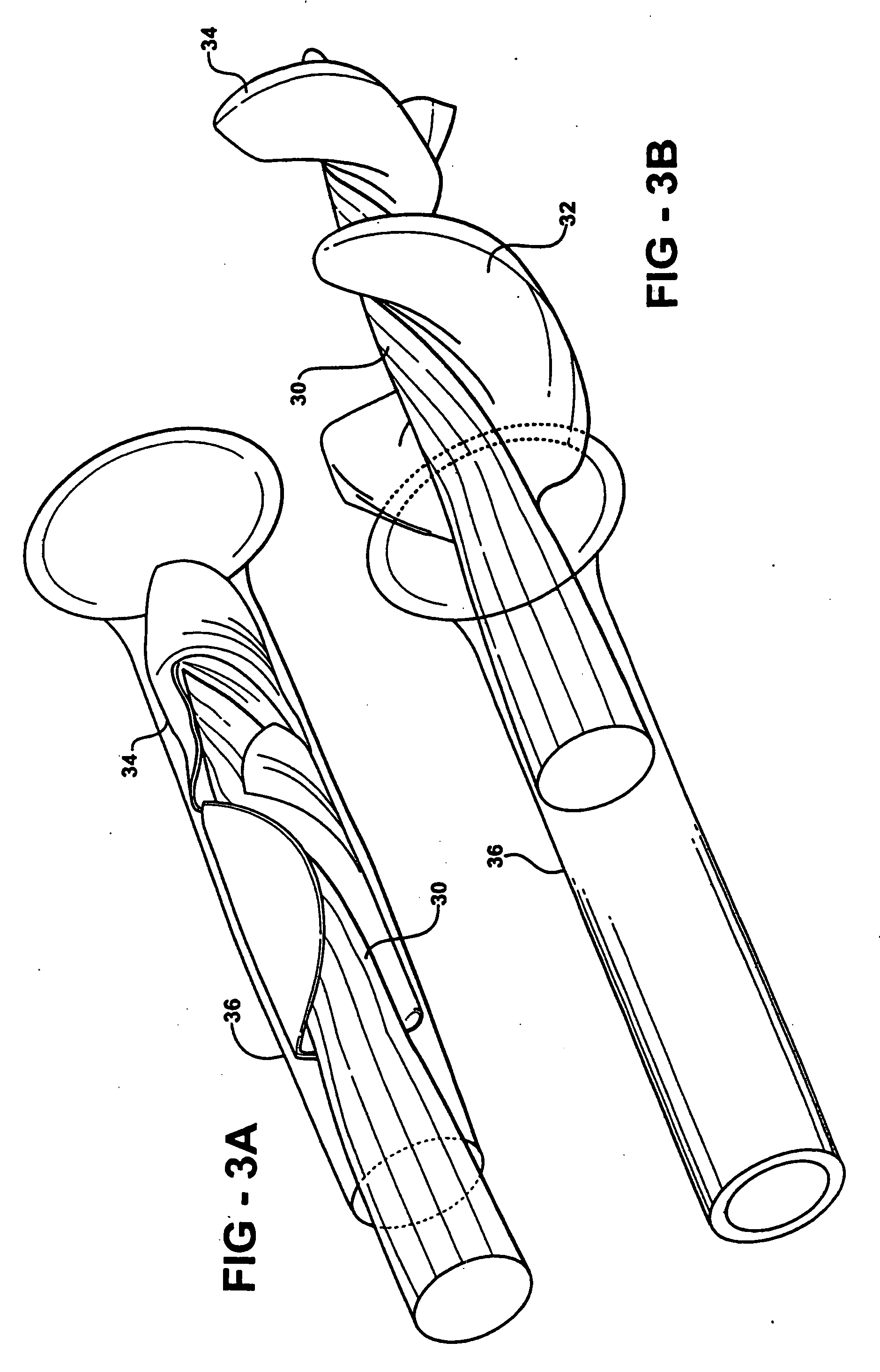
Feedback control of ventricular assist devices
InactiveUS20050107658A1Reliable and accurate pressure feedbackGood curative effectControl devicesBlood pumpsVentricular assistancePhysical therapy
Various devices, systems and methods for providing effective, long term and reliable use of pressure feedback in VADs. Exemplary embodiments are described which provide for direct LV pressure measurement, non-invasive calibration techniques to detect ventricular collapse and recalibrate the feedback mechanism, improved pressure sensor designs with reduced drift, and barometric pressure correction schemes. These devices and methods may be used alone or in combination with each other, and may also be combined with other feedback mechanisms.
Owner:TRANSOMA MEDICAL
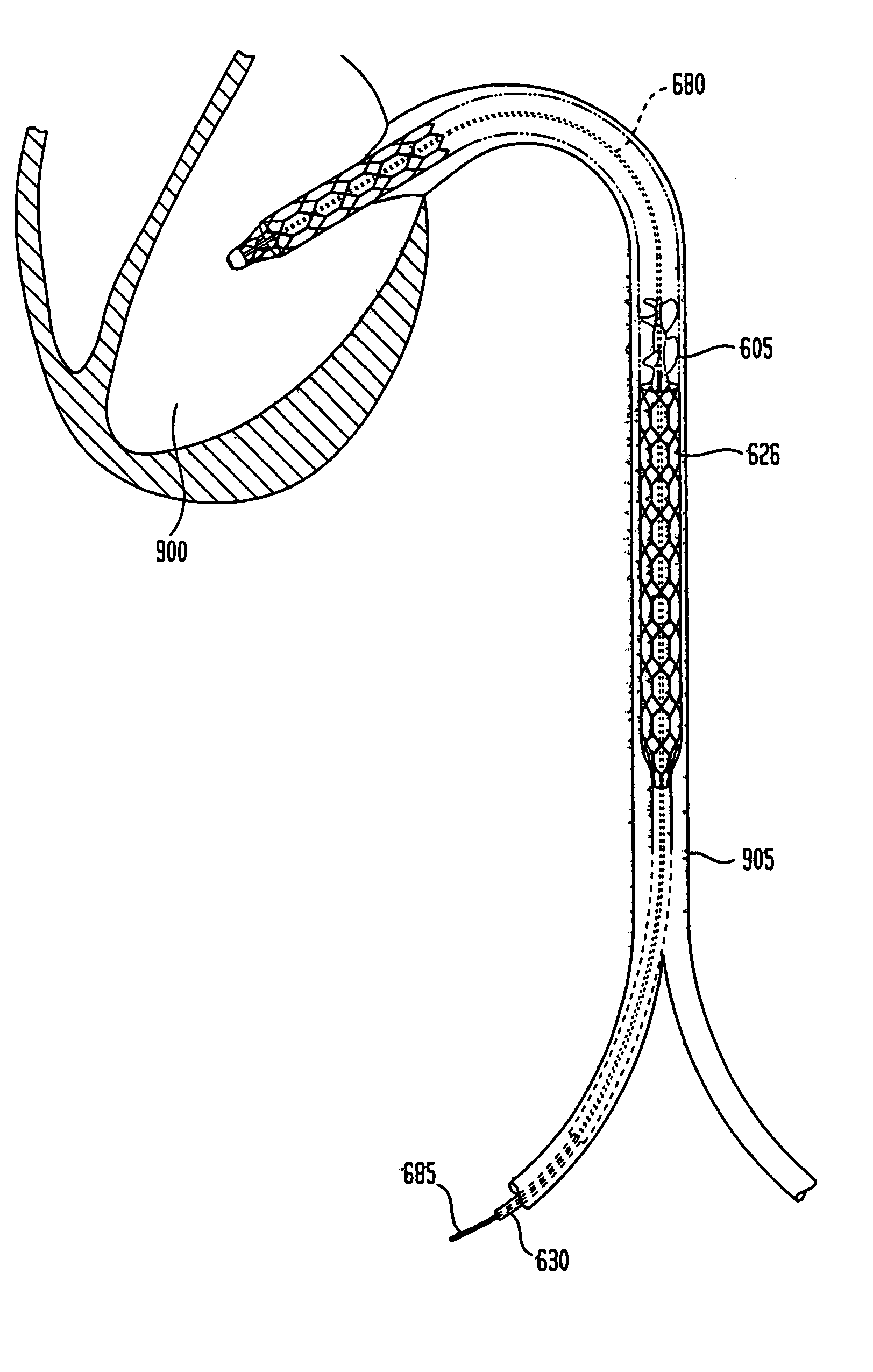
Sheath system for catheter pump
ActiveUS20130303969A1Firmly connectedLow resistance to deformationBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesDistal portionCatheter device
A catheter pump assembly is provided that includes an elongate polymeric catheter body, a cannula, and a tubular interface. The elongate polymeric catheter body has a proximal end and a distal end. The cannula has an expandable portion disposed distally of the elongate polymeric catheter body. The cannula can also have another tubular portion that is proximal to the distal portion. The tubular interface has an outer surface configured to be joined to the tubular portion of the cannula and an inner surface. The inner surface is disposed over the distal end of the elongate polymeric catheter body. The tubular interface has a plurality of transverse channels extending outward from the inner surface of the tubular interface. An outer surface of the elongate polymeric catheter body projects into the transverse channels to mechanically integrate the elongate polymeric catheter body with the tubular interface.
Owner:TC1 LLC
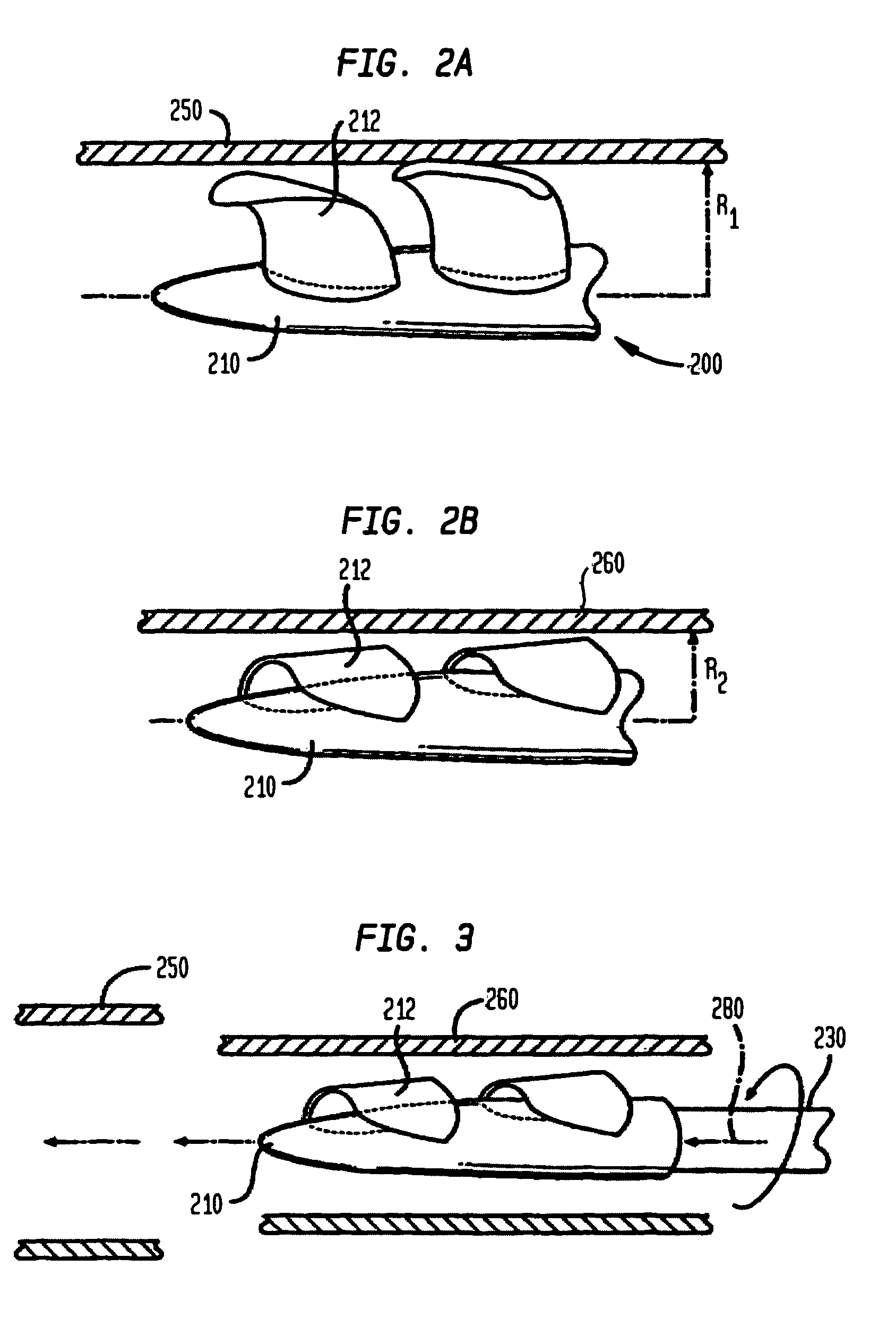
Expandable impeller pump
An impeller includes a hub, and a plurality of blades supported by the hub, the blades being arranged in at least two blade rows. The impeller has a deployed configuration in which the blades extend away from the hub, and a stored configuration in which at least one of the blades is radially compressed, for example by folding the blade towards the hub. The impeller may also have an operational configuration in which at least some of the blades are deformed from the deployed configuration upon rotation of the impeller when in the deployed configuration. The outer edge of one or more blades may have a winglet, and the base of the blades may have an associated indentation to facilitate folding of the blades.
Owner:TC1 LLC +2
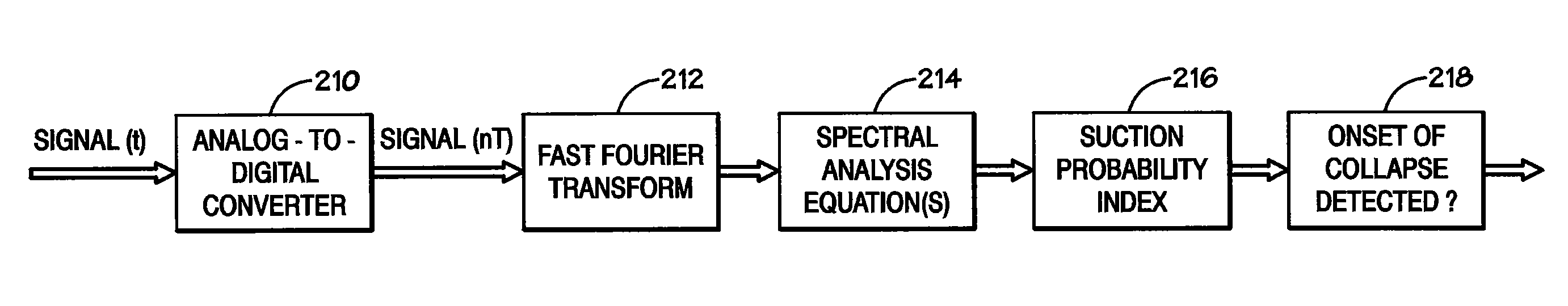
Method and system for detecting ventricular collapse
A pump system includes an implantable pump including a motor having a rotor and a stator. The stator includes a plurality of stator windings, and a motor controller is coupled to the motor to energize the windings so as cause the rotor to turn. A time-based system parameter of the pump is sampled and the system parameter is analyzed to calculate a suction probability index that provides an indication of the imminence of ventricle collapse.
Owner:RELIANTHEART
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com