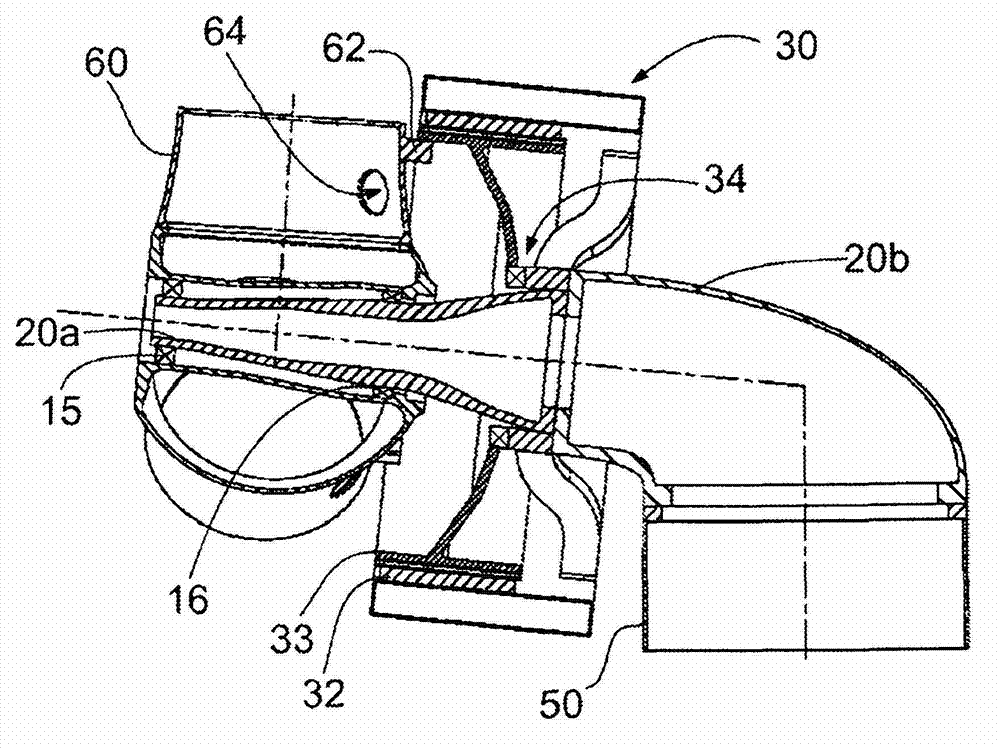
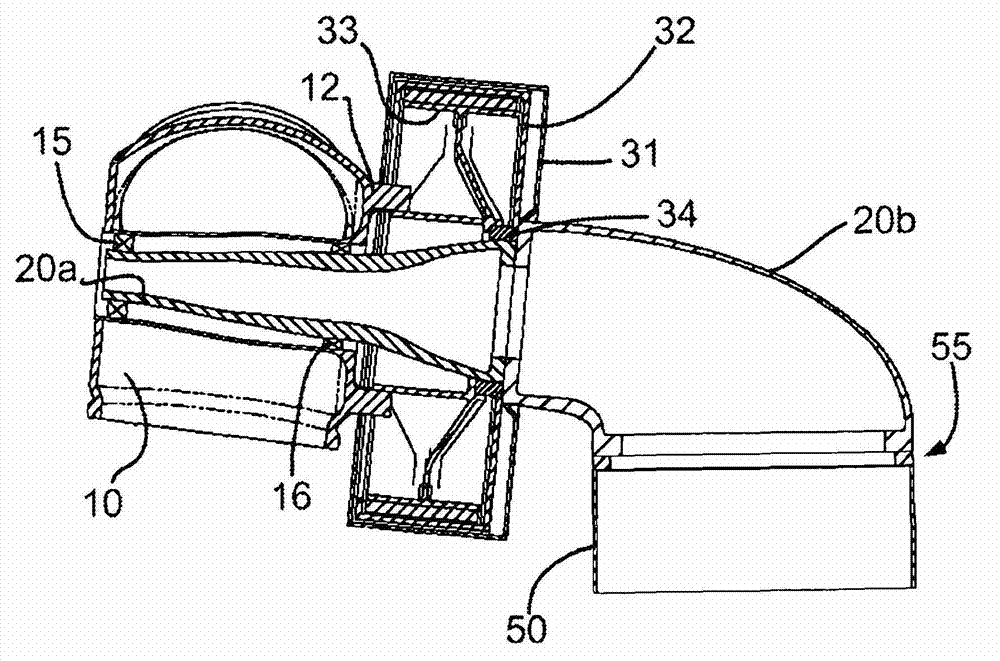
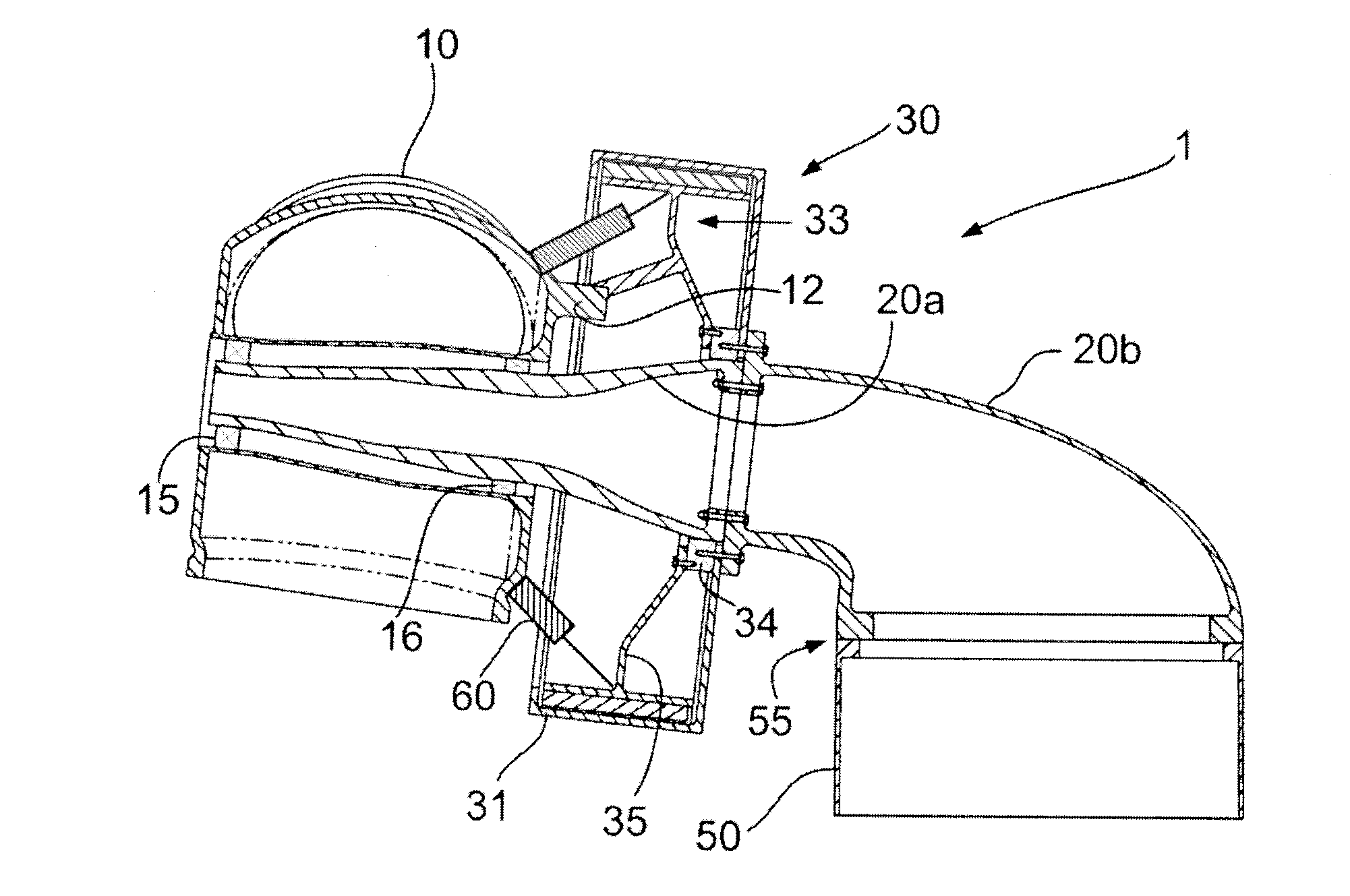
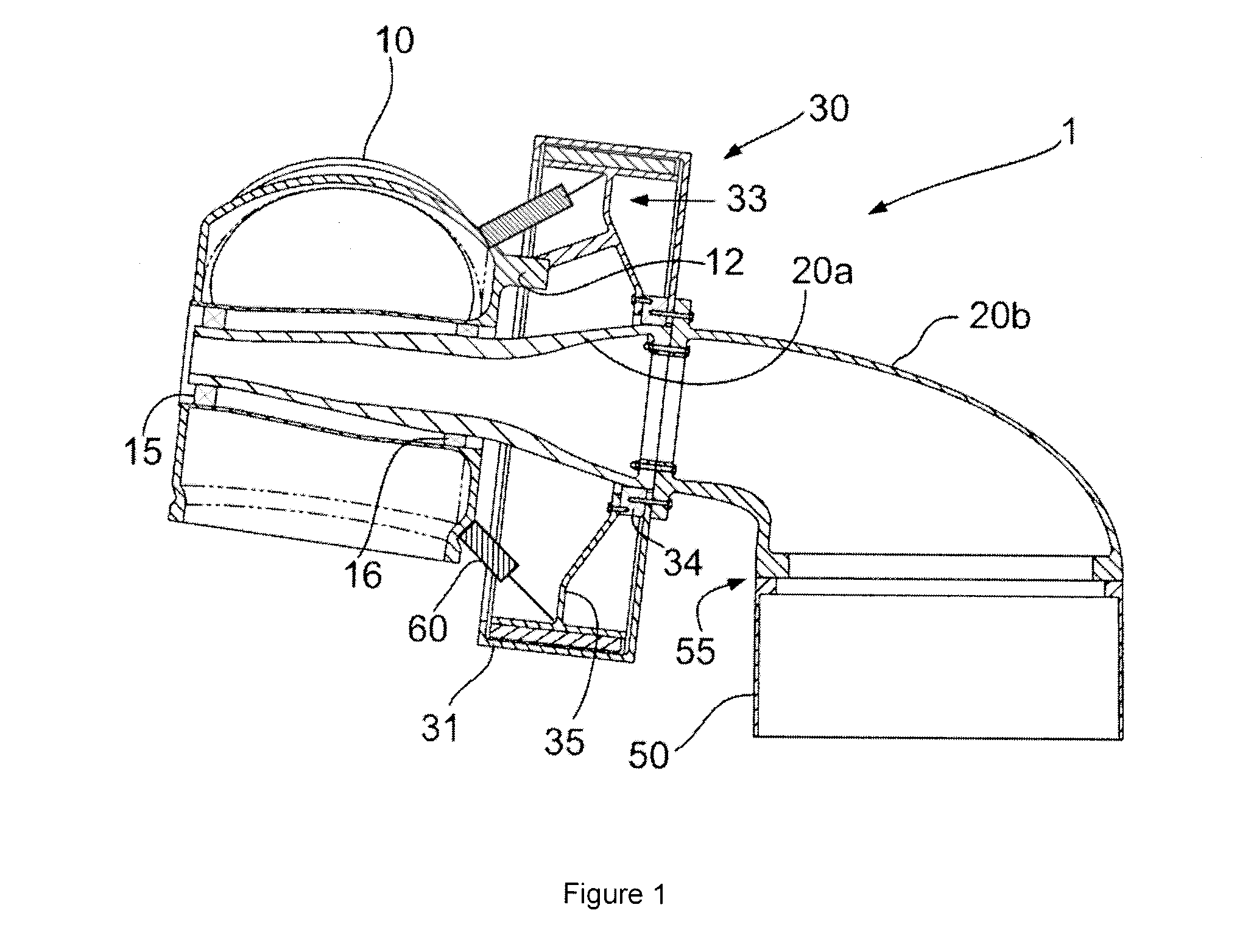
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
81results about How to "Reduce bending load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
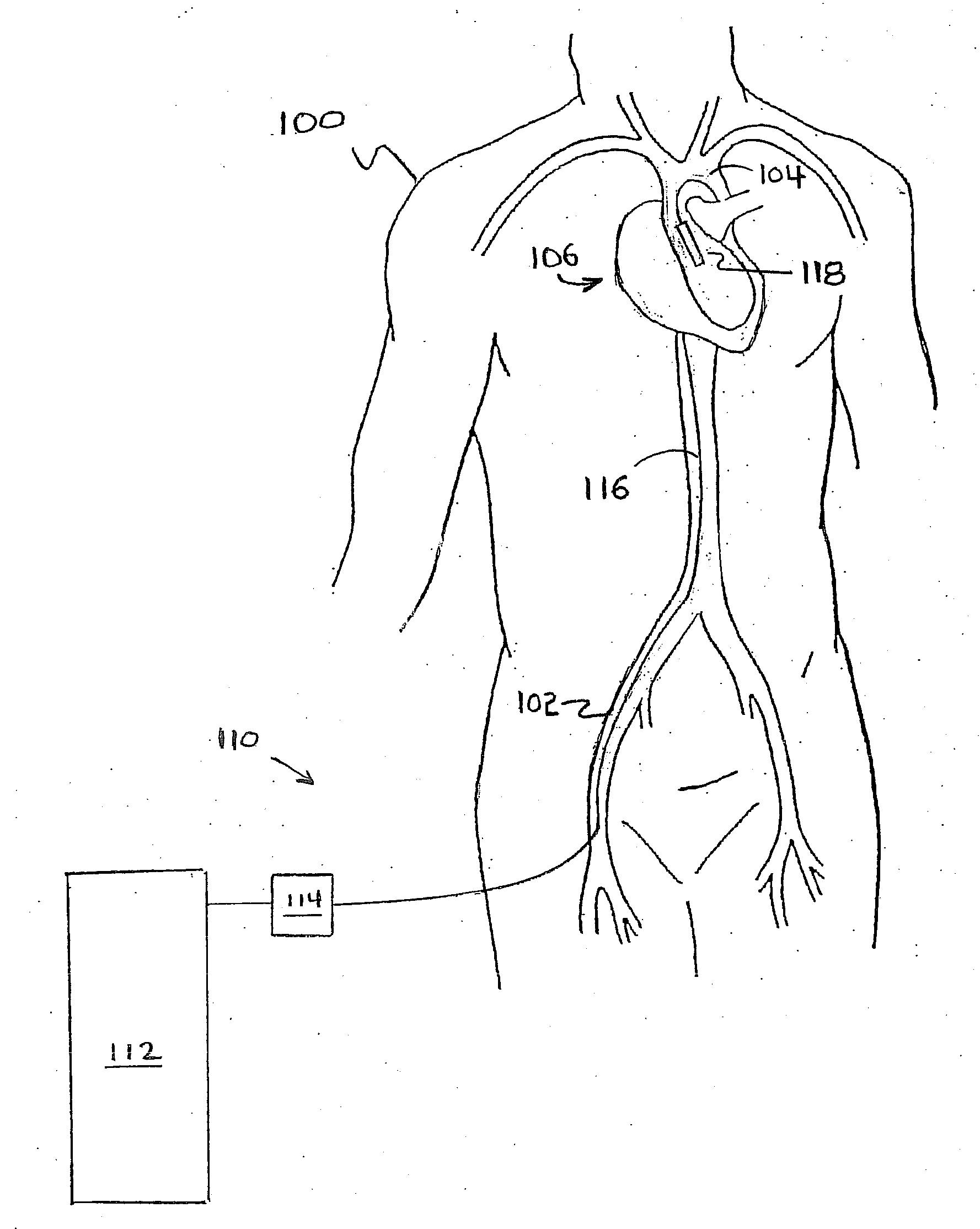
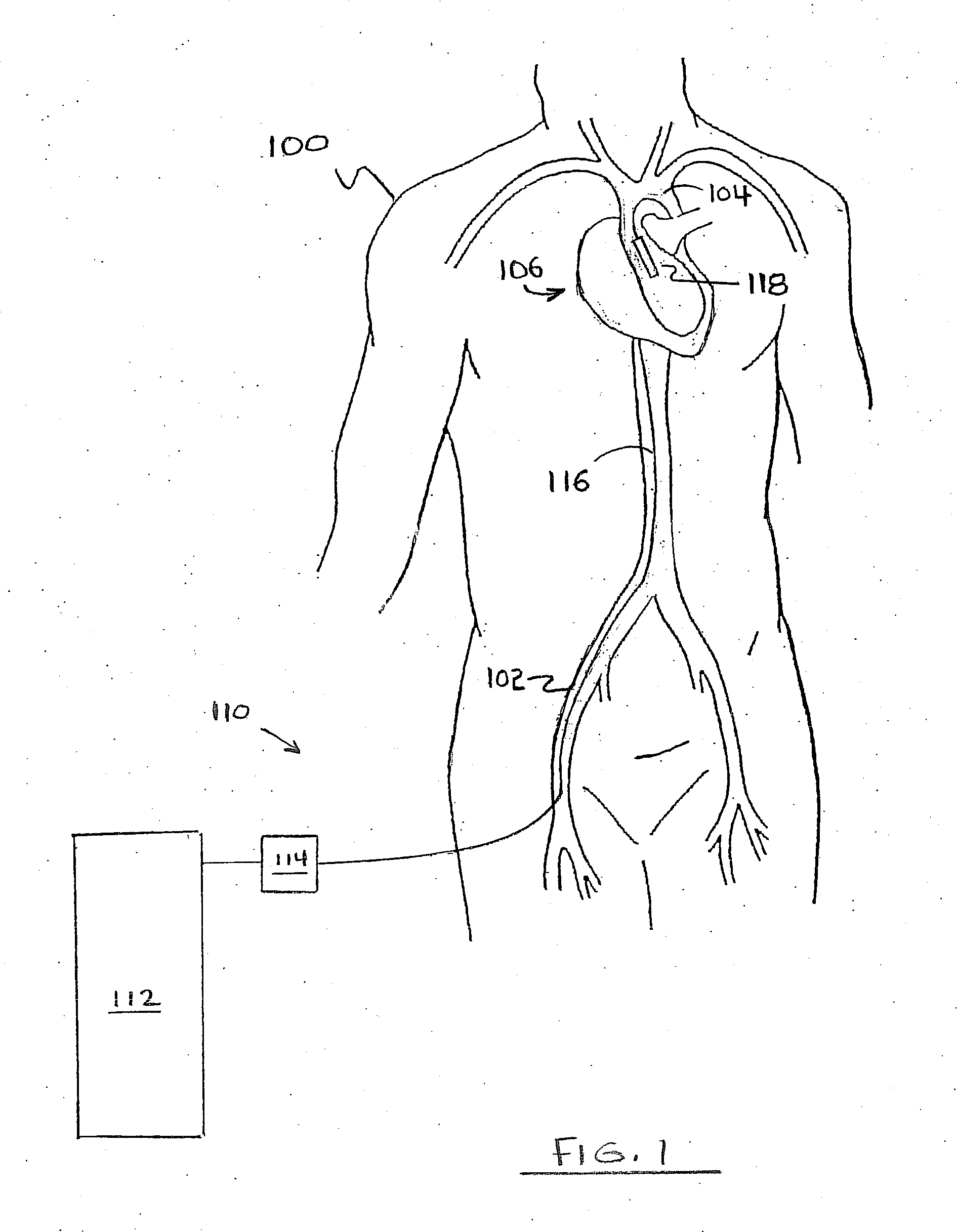
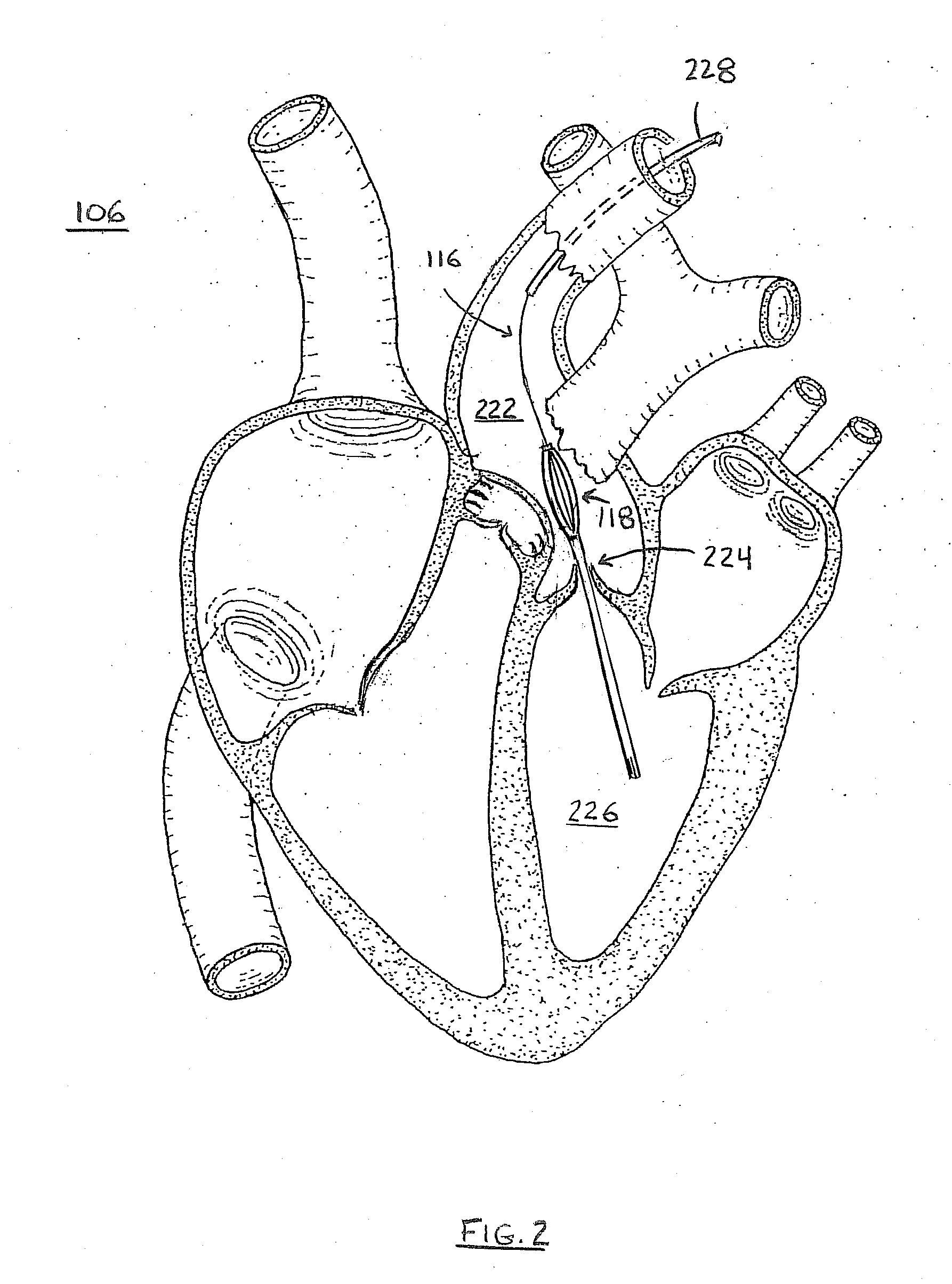
Method for Deployment of a Medical Device
InactiveUS20080132748A1Reduce bending loadMinimizing contact pressureControl devicesBlood pumpsAortic archMedical device
A method for deploying a cardiac-assist device is disclosed. In accordance with the illustrative embodiment, an introducing tube, such as a catheter, sheath, or the like is inserted into the vascular system and advanced beyond the aortic arch. The cardiac-assist device is then inserted into the tube, advanced through it, and deployed from its distal end. In some embodiments, the diameter of the cardiac-assist device expands when it deploys from the distal end of the tube.
Owner:MEDICAL VALUE PARTNERS
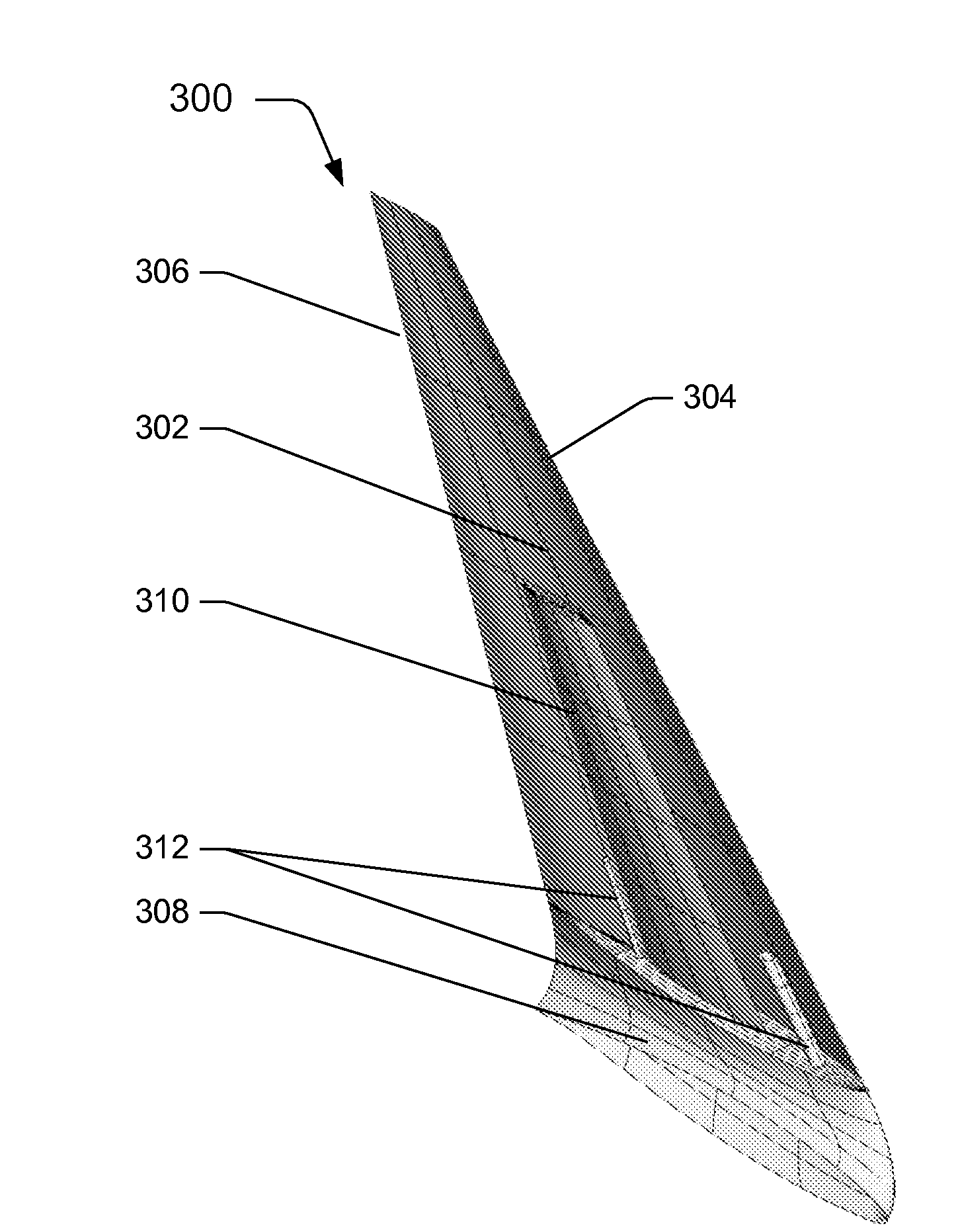
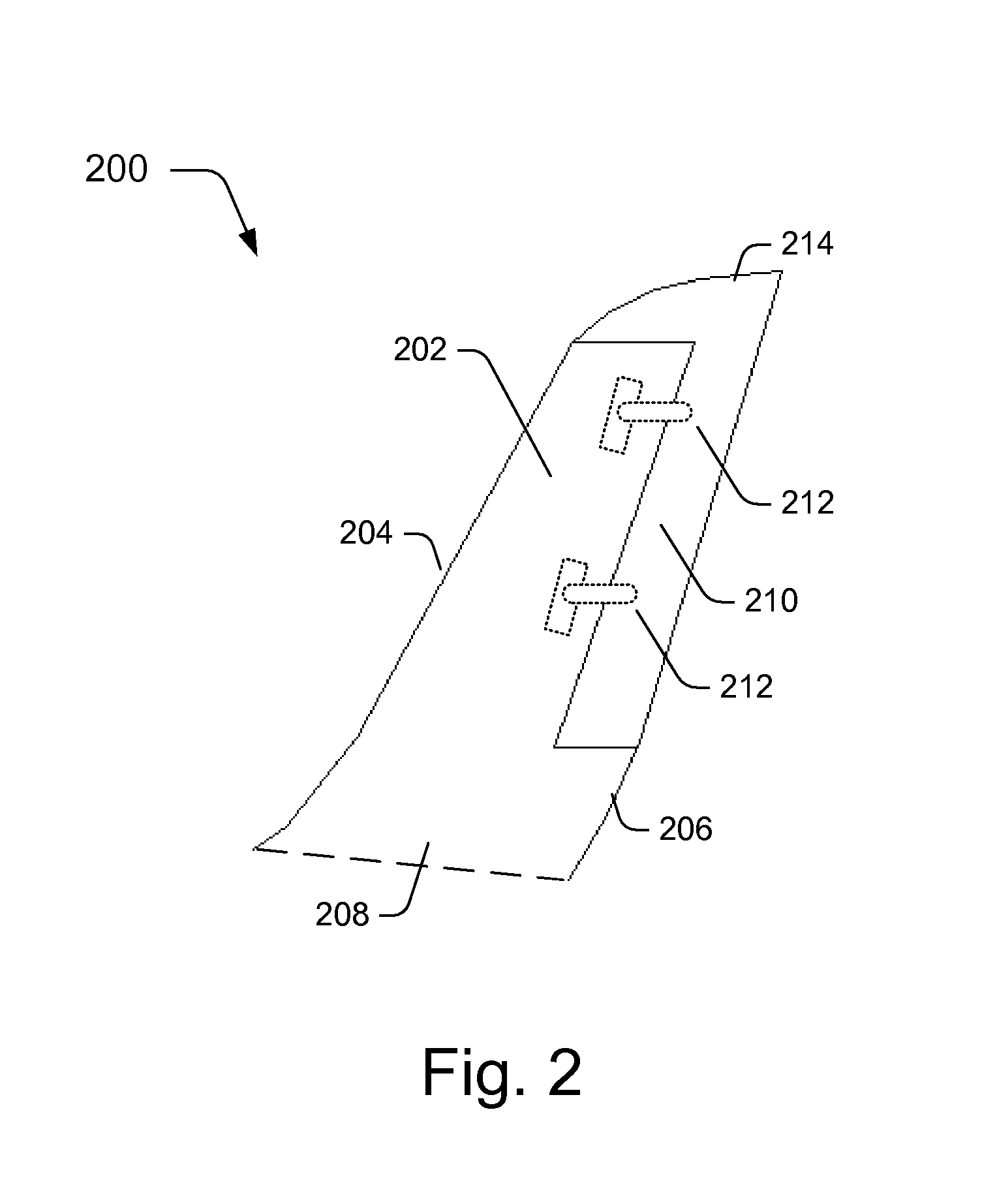
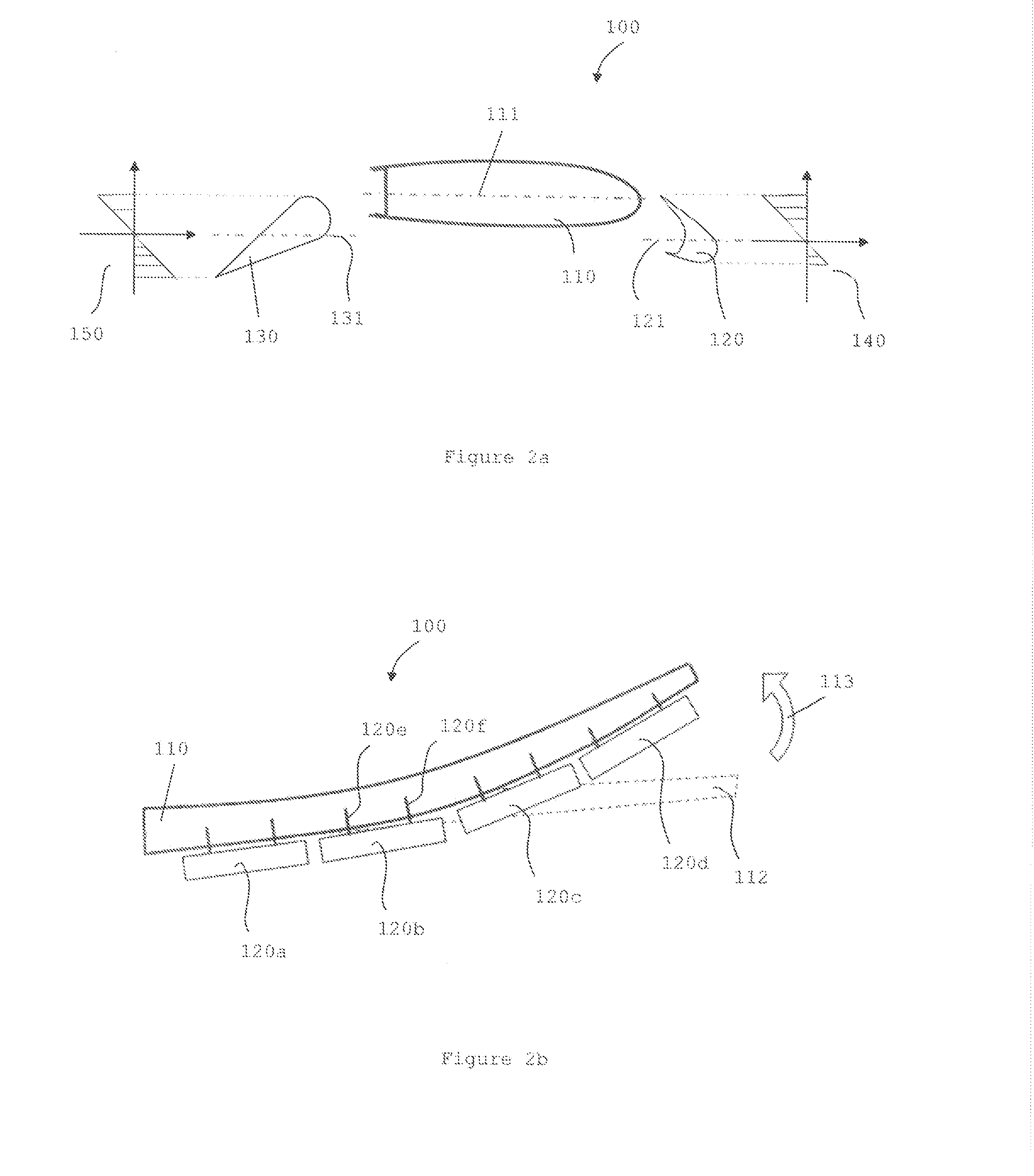
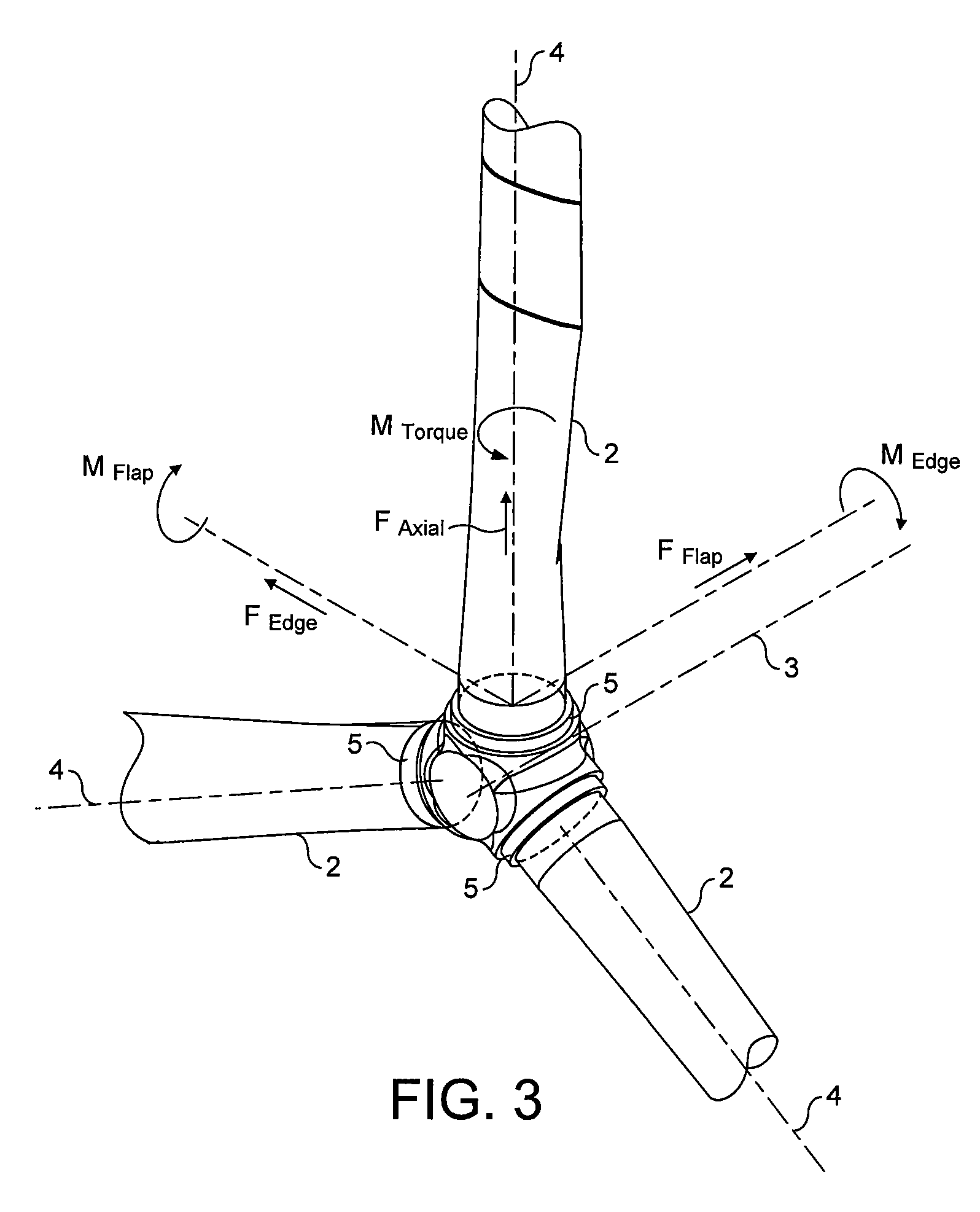
Controllable winglets
InactiveUS20080308683A1Wing bending loadMaximizing airborne wingspanInfluencers by generating vorticesWingsShape-memory alloyVariable geometry
Systems and methods for providing variable geometry winglets to an aircraft are disclosed. In one embodiment, a winglet includes a base portion configured to attach to a wing. The winglet further includes a body portion. In turn, the body portion includes at least one of a deflectable control surface, a shape memory alloy (SMA) bending plate, and a SMA torque tube. The base portion is configured to attach to the wing such that the body portion projects at an upward angle from the wing.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Controllable winglets
InactiveUS7744038B2Reduce the total wingspan of an aircraftFuel efficiencyInfluencers by generating vorticesWingsShape-memory alloyVariable geometry
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Compressor blade root for engine blades of aircraft engines
InactiveUS20050084379A1Taking up and transferring high forceEasy to usePropellersPump componentsMicro structureMetallic enclosure
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE DEUT LTD & CO KG
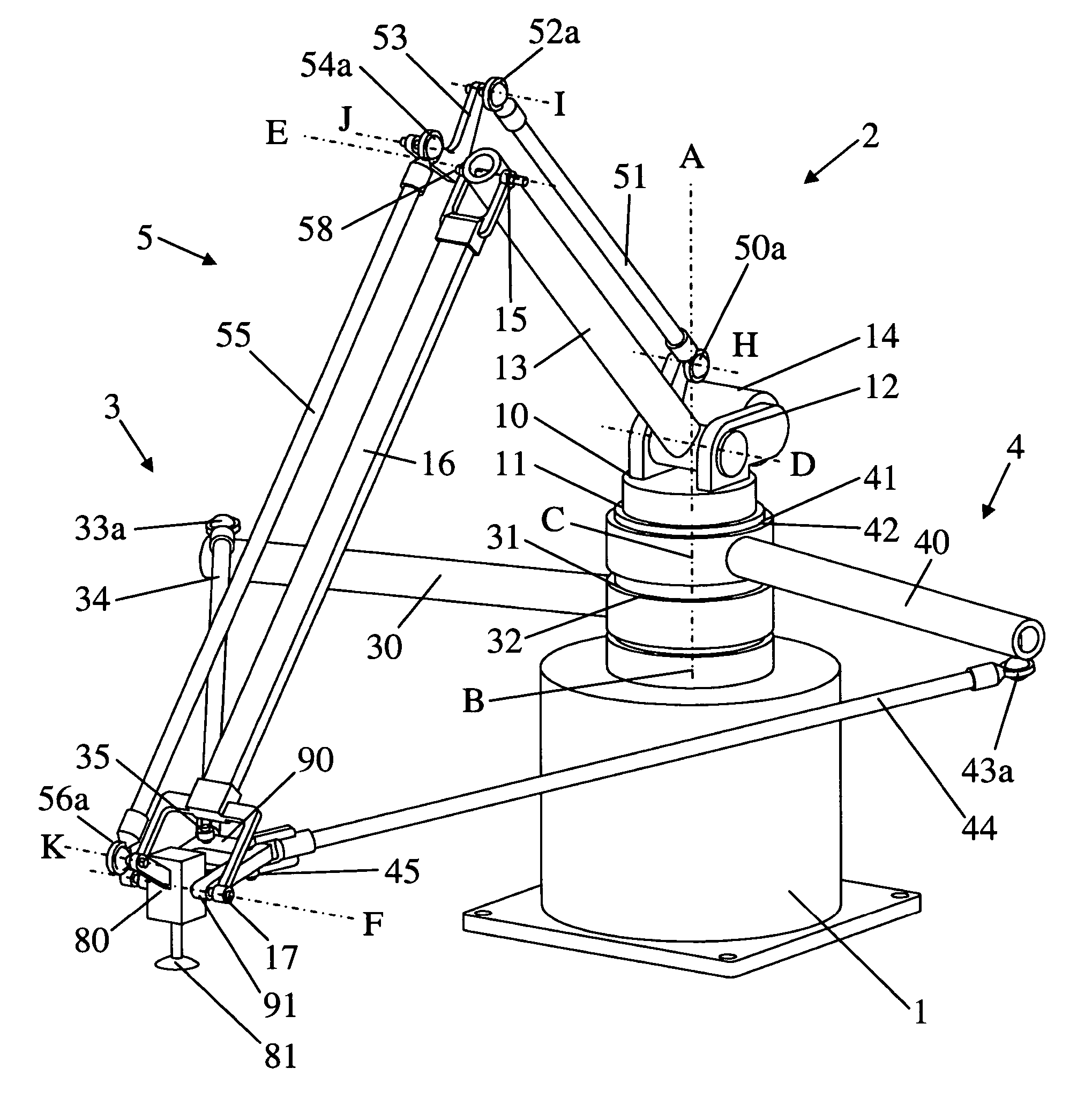
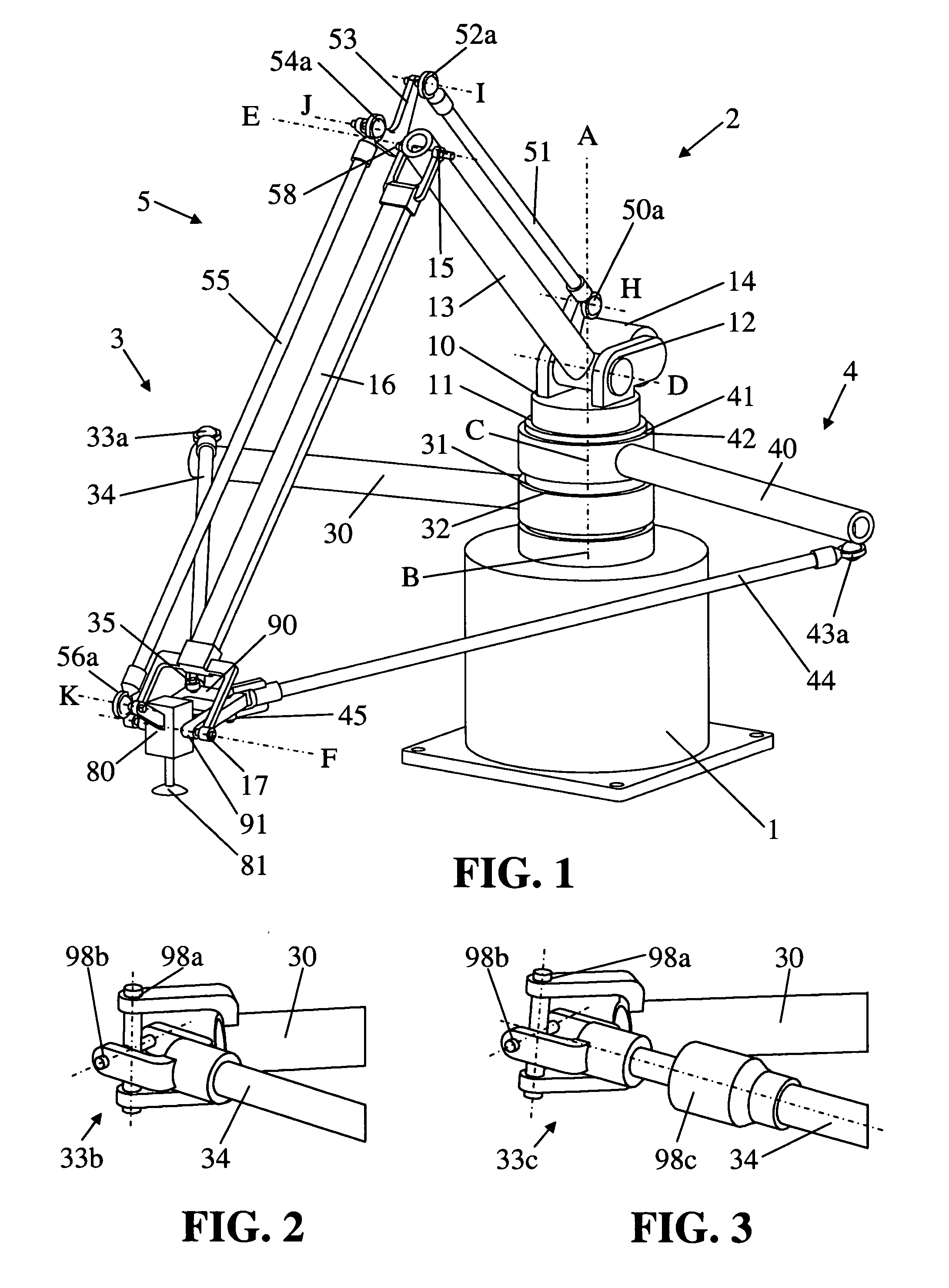
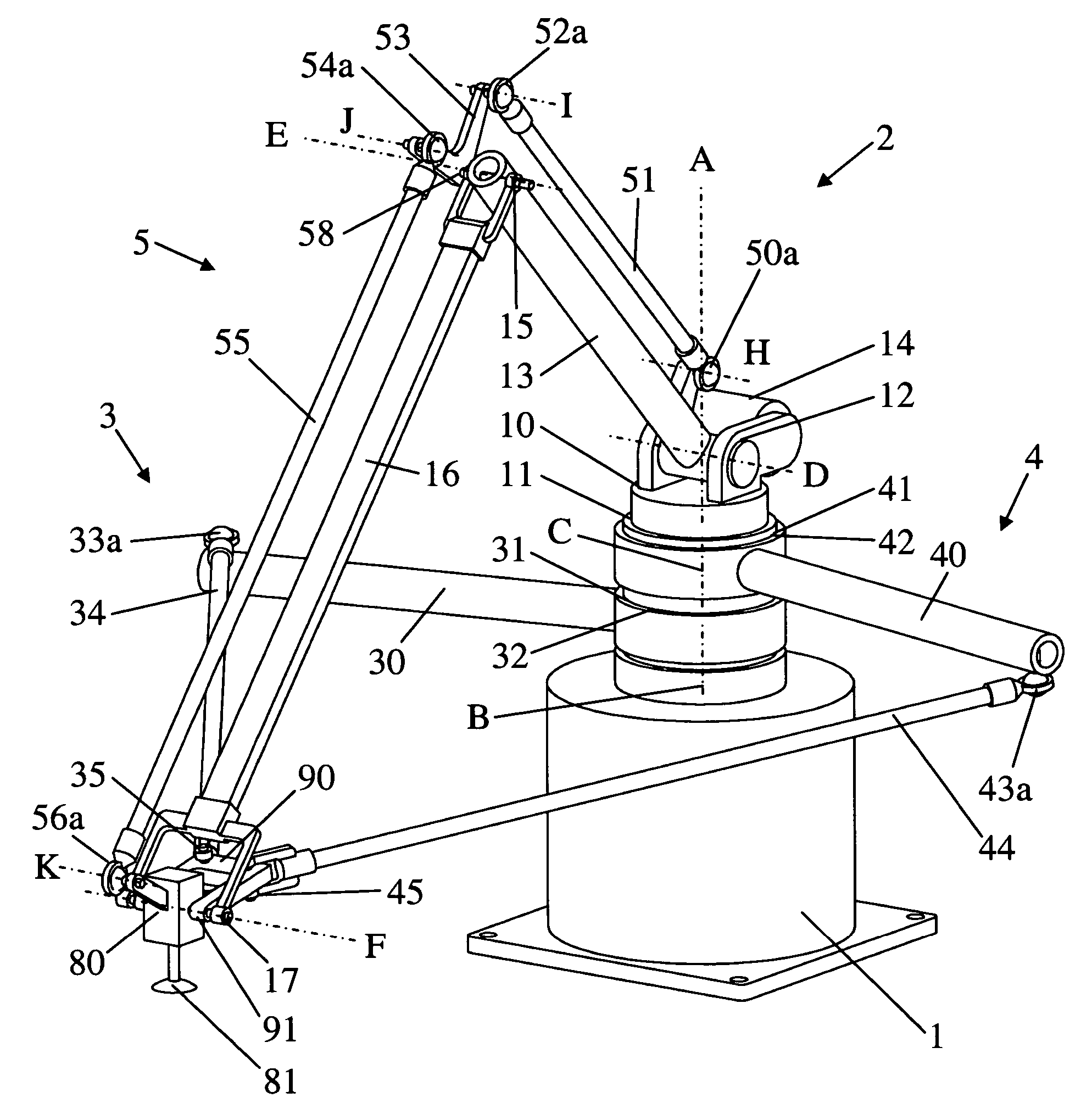
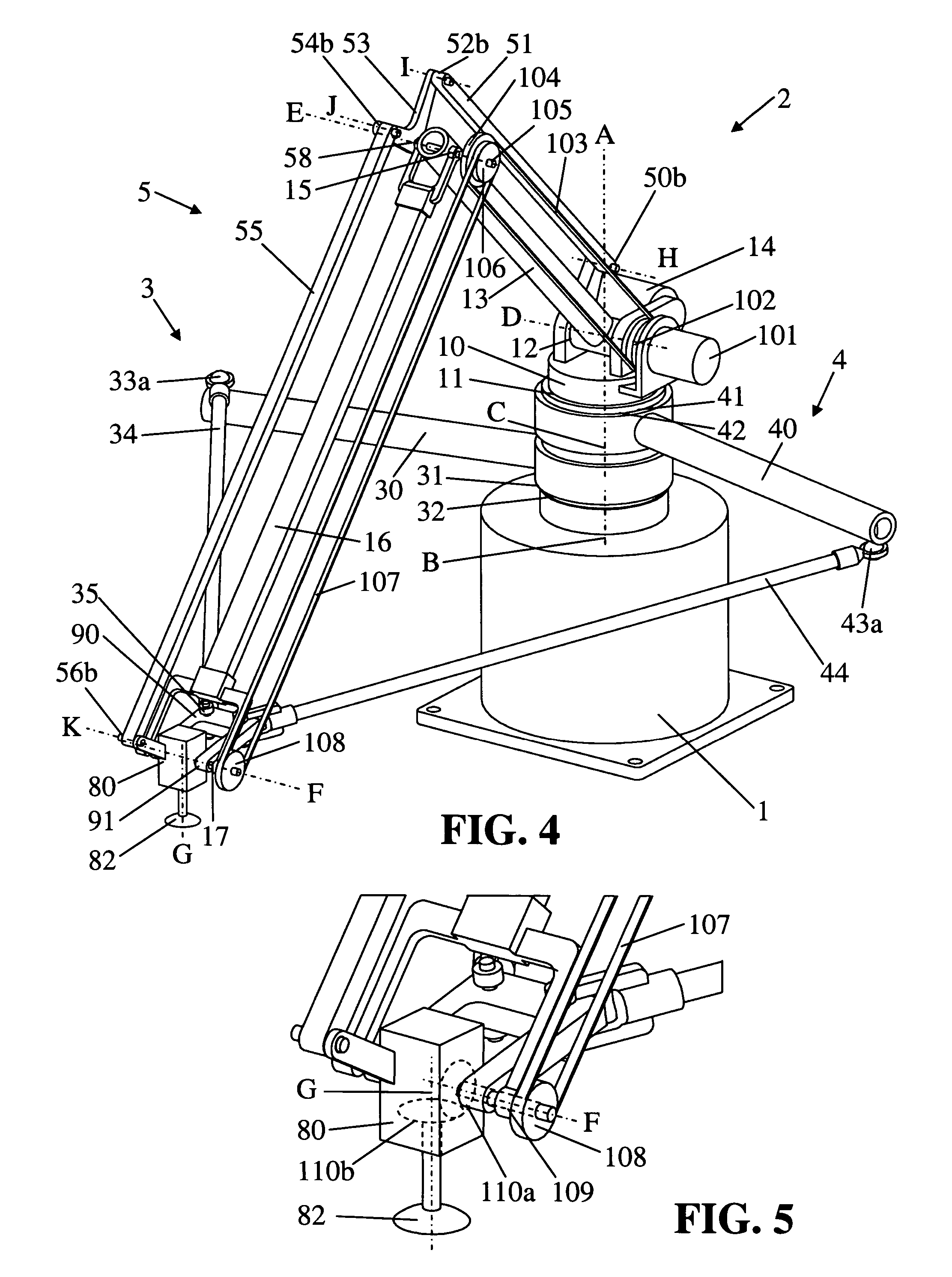
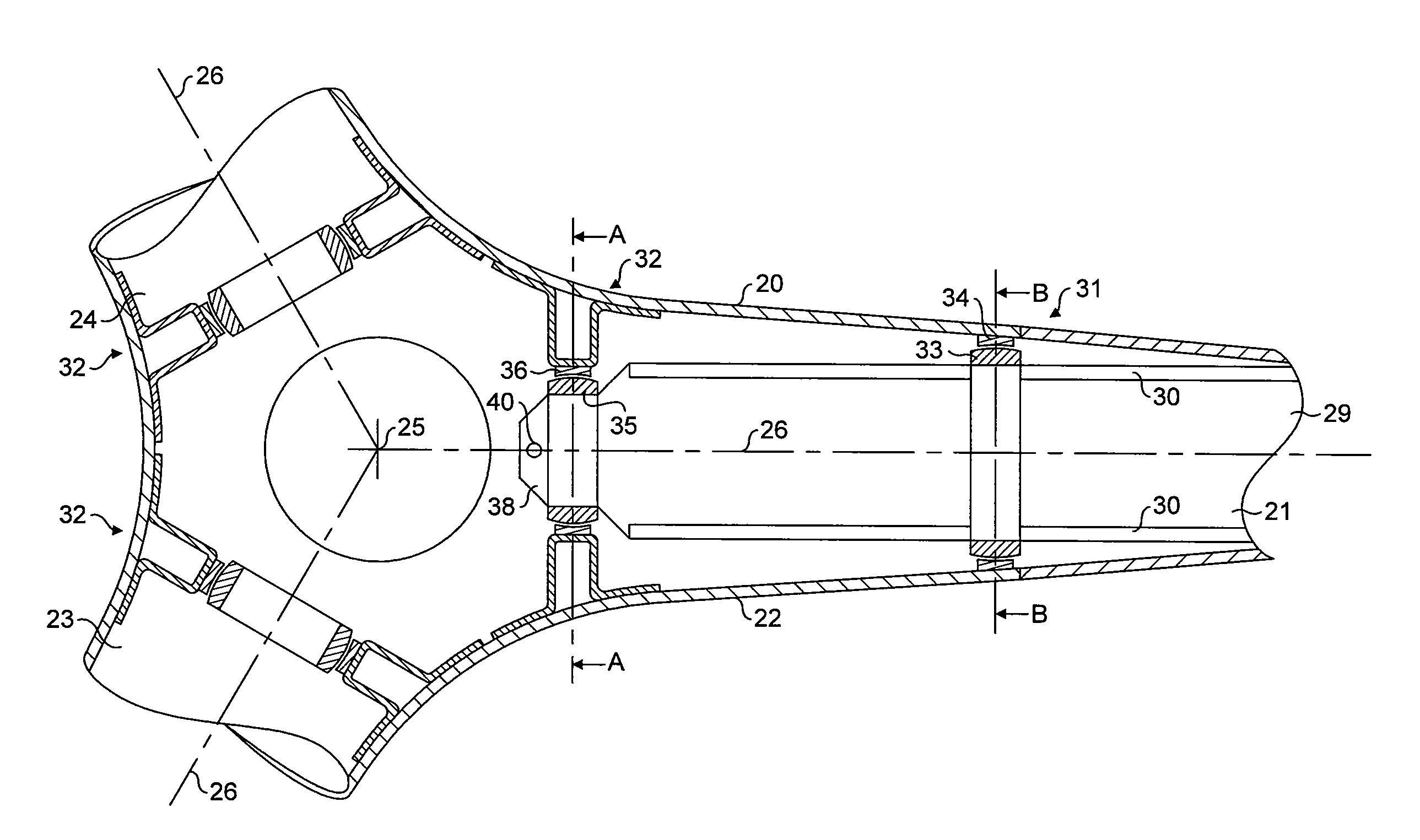
Parallel robot
ActiveUS20060245894A1Large workspace-to-footprint ratioSimple designProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusThree degrees of freedomParallel kinematics
A parallel robot or parallel kinematics mechanism is provided for uses such as robotics or machining. The mechanism comprises a fixed base, a main arm, and a first and second support arm to position and orient an object in a cylindrical space with at least three degrees of freedom and retained inclination. The main arm includes an end component for supporting the object and linkage means to retain the inclination of the end component with respect to the base for all positions and orientations of the end component. The mechanism advantageously provides a large cylindrical workspace and a small footprint and is capable of moving an object at high accelerations and speeds. The mechanism can be equipped with an additional motor to orient an object, thereby providing the mobility of a SCARA robot. Alternatively, it can be equipped with passive transmission means that allow for an object to be displaced in parallel to itself.
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA +1
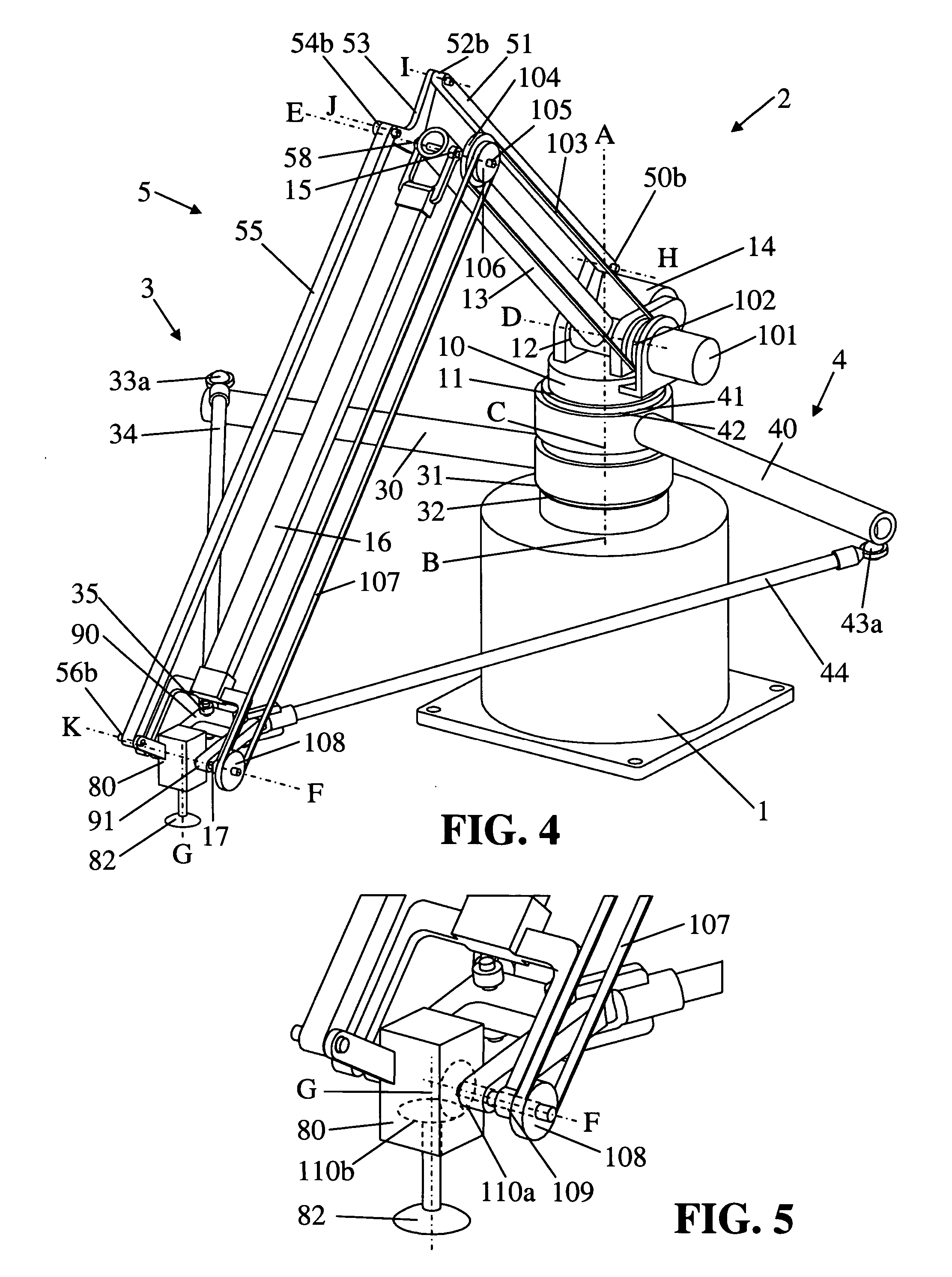
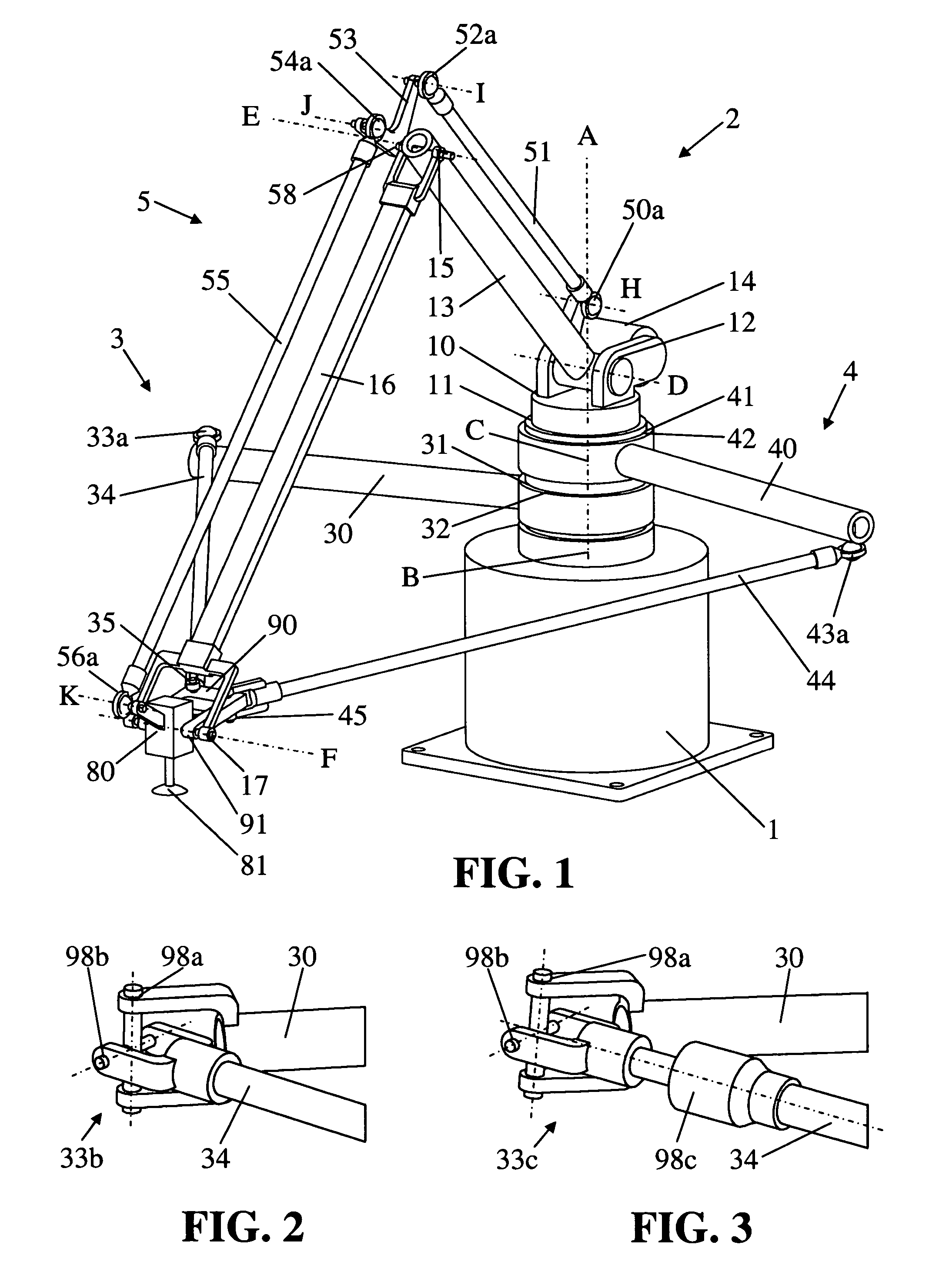
Parallel robot
ActiveUS7331750B2Large workspace-to-footprint ratioSimple designProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusRoboticsThree degrees of freedom
A parallel robot or parallel kinematics mechanism is provided for uses such as robotics or machining. The mechanism comprises a fixed base, a main arm, and a first and second support arm to position and orient an object in a cylindrical space with at least three degrees of freedom and retained inclination. The main arm includes an end component for supporting the object and linkage means to retain the inclination of the end component with respect to the base for all positions and orientations of the end component. The mechanism advantageously provides a large cylindrical workspace and a small footprint and is capable of moving an object at high accelerations and speeds. The mechanism can be equipped with an additional motor to orient an object, thereby providing the mobility of a SCARA robot. Alternatively, it can be equipped with passive transmission means that allow for an object to be displaced in parallel to itself.
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA +1
Blade control system
A wind turbine system for blade control which employs means for adjusting the pitch and yaw of the blades rotating about an axis and the resulting speed of the blades powering a wind turbine. The control system selectively resists movement of said blades to a different incline position based on a comparison of the measured rotational speed with a target speed value, the target speed value being determined based on an energy output level for said turbine. The control system includes at least one adjustable hydraulic actuator for movement of said blades to a different incline position.
Owner:DEERING KENNETH JAMES
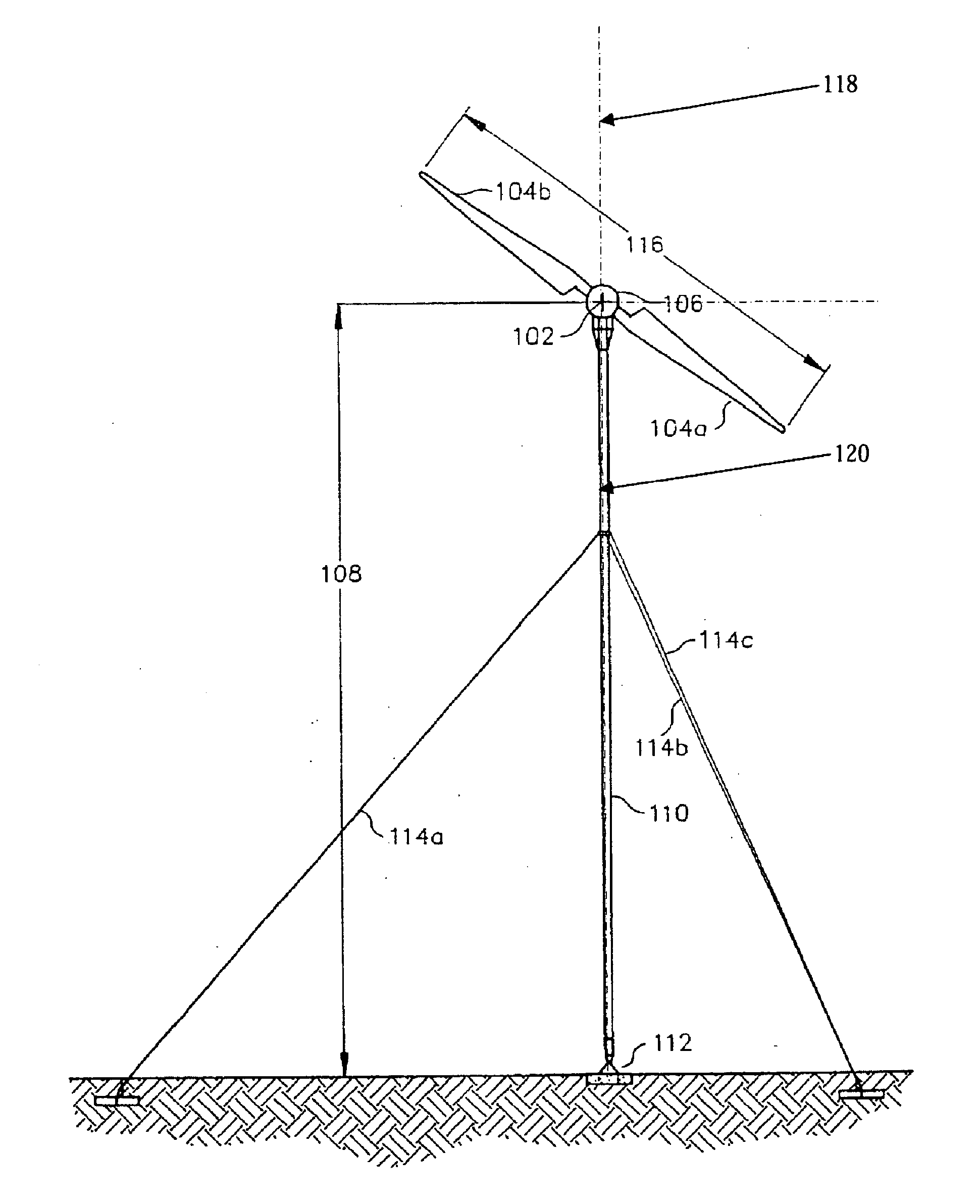
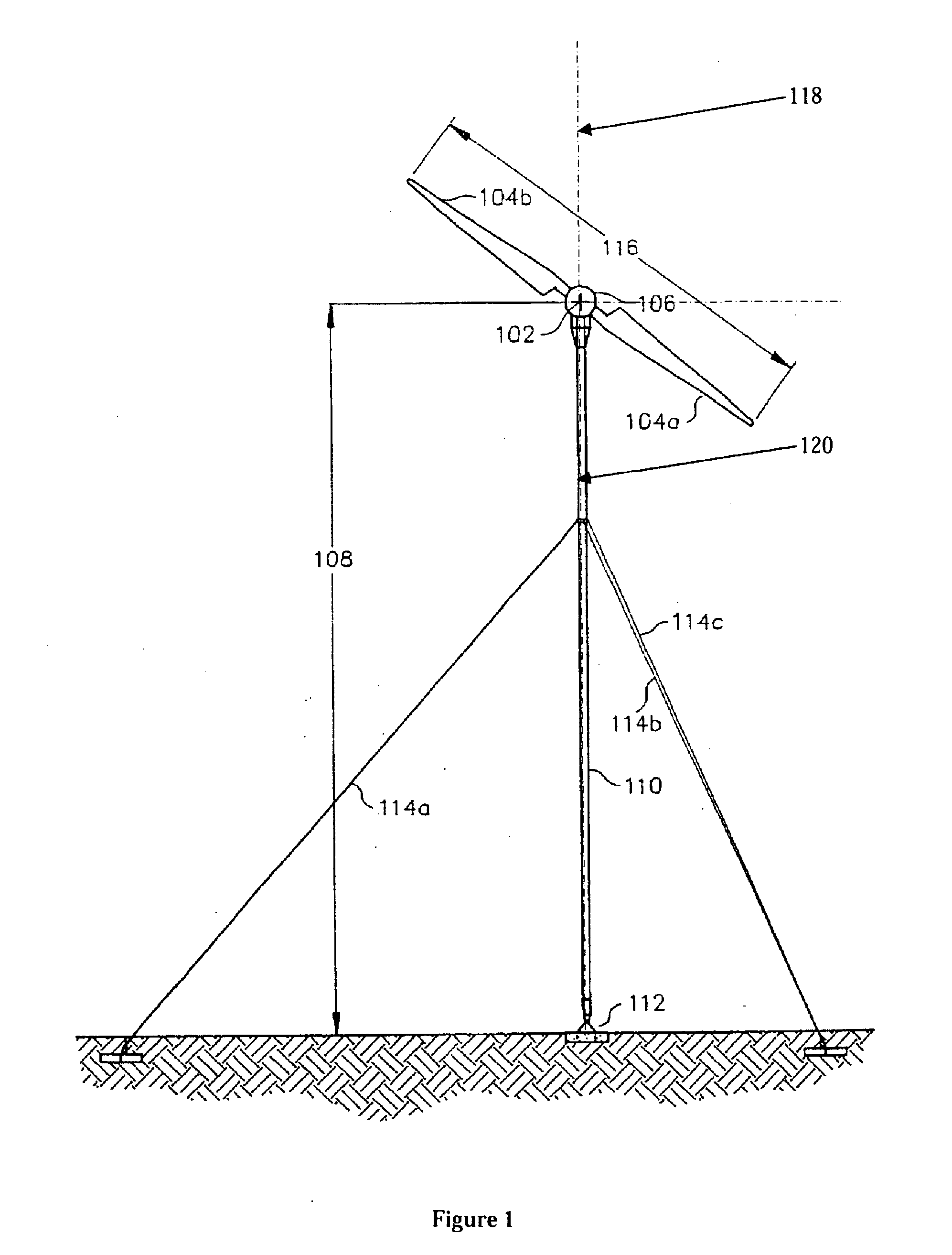
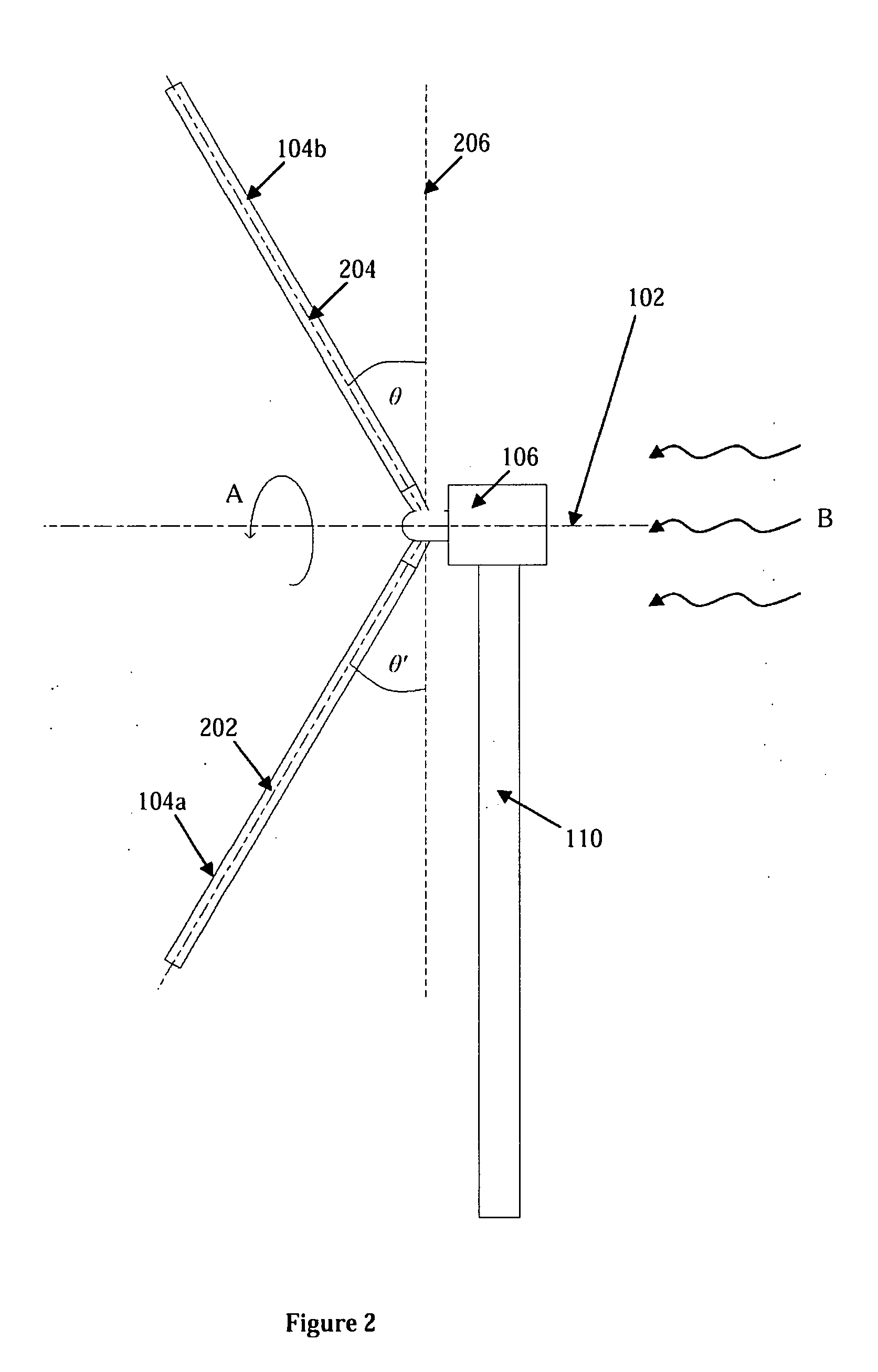
Wind turbine rotor
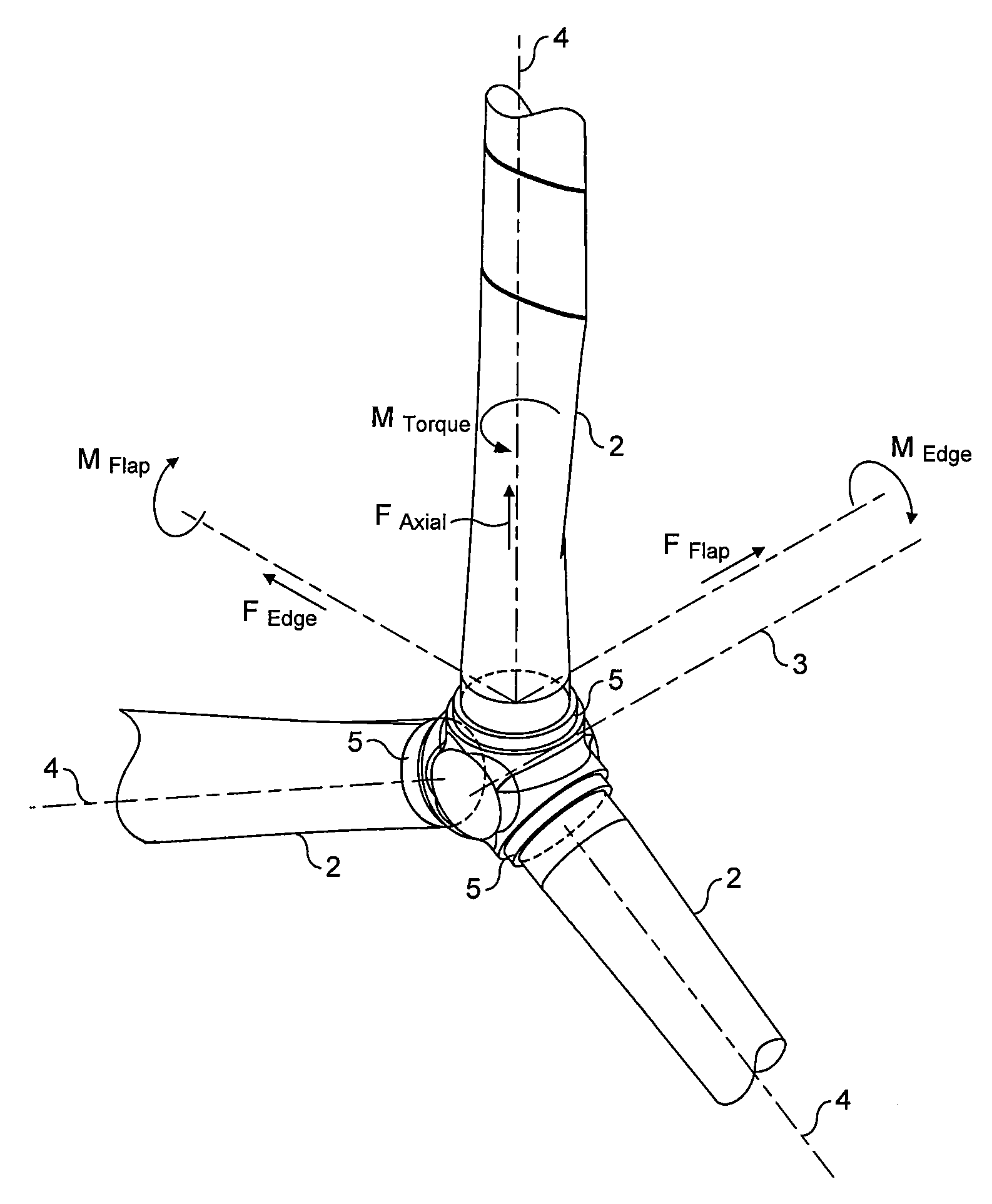
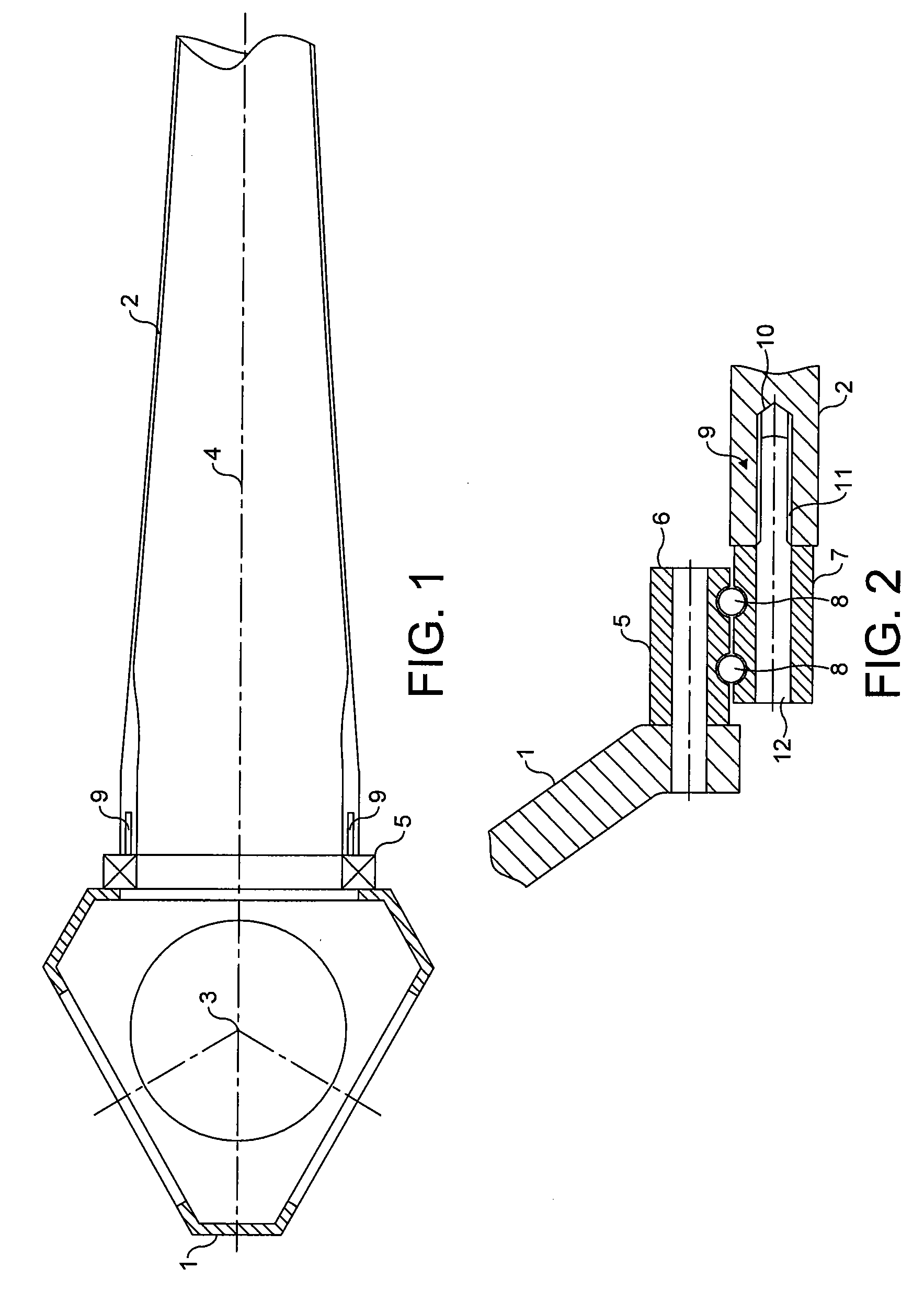
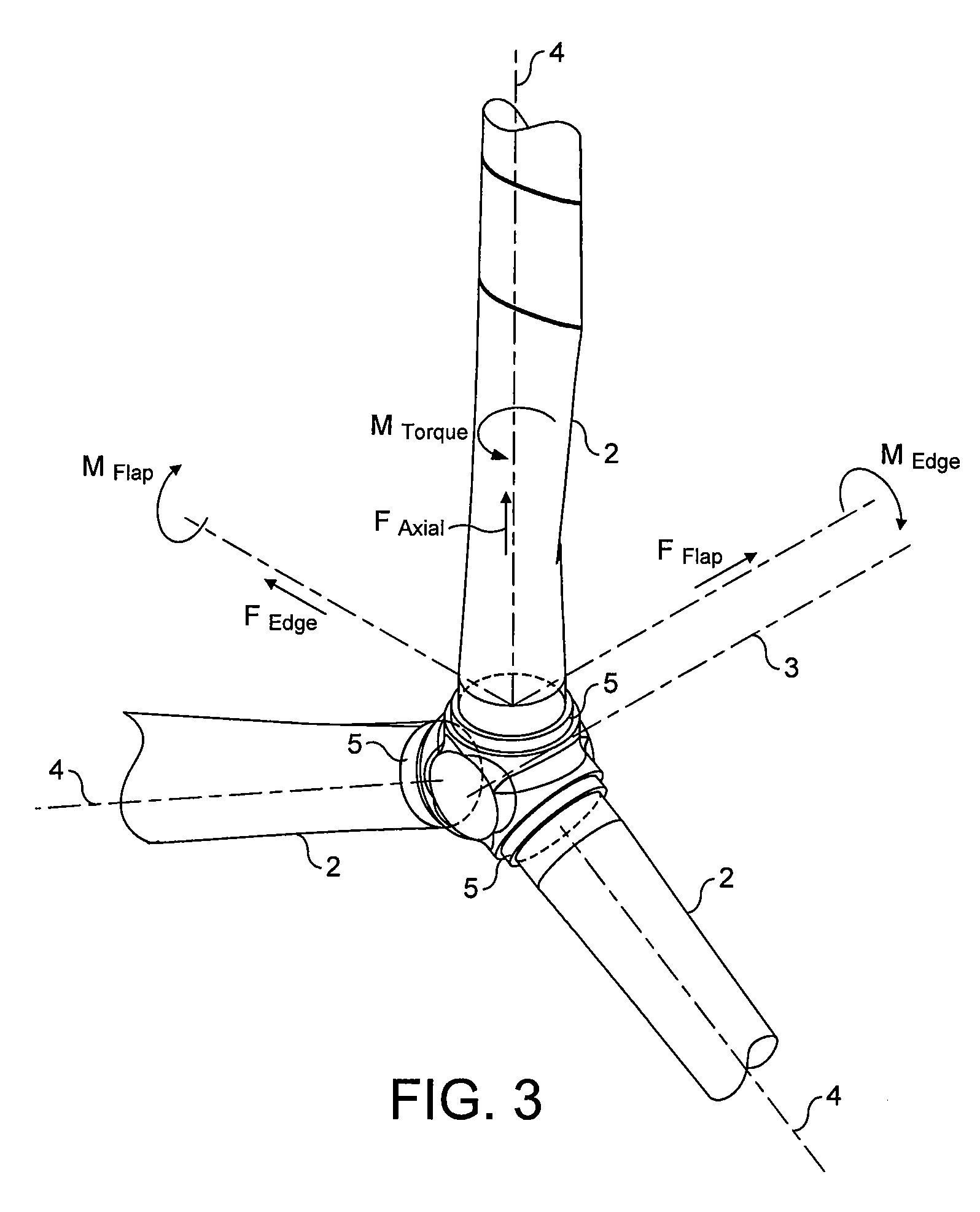
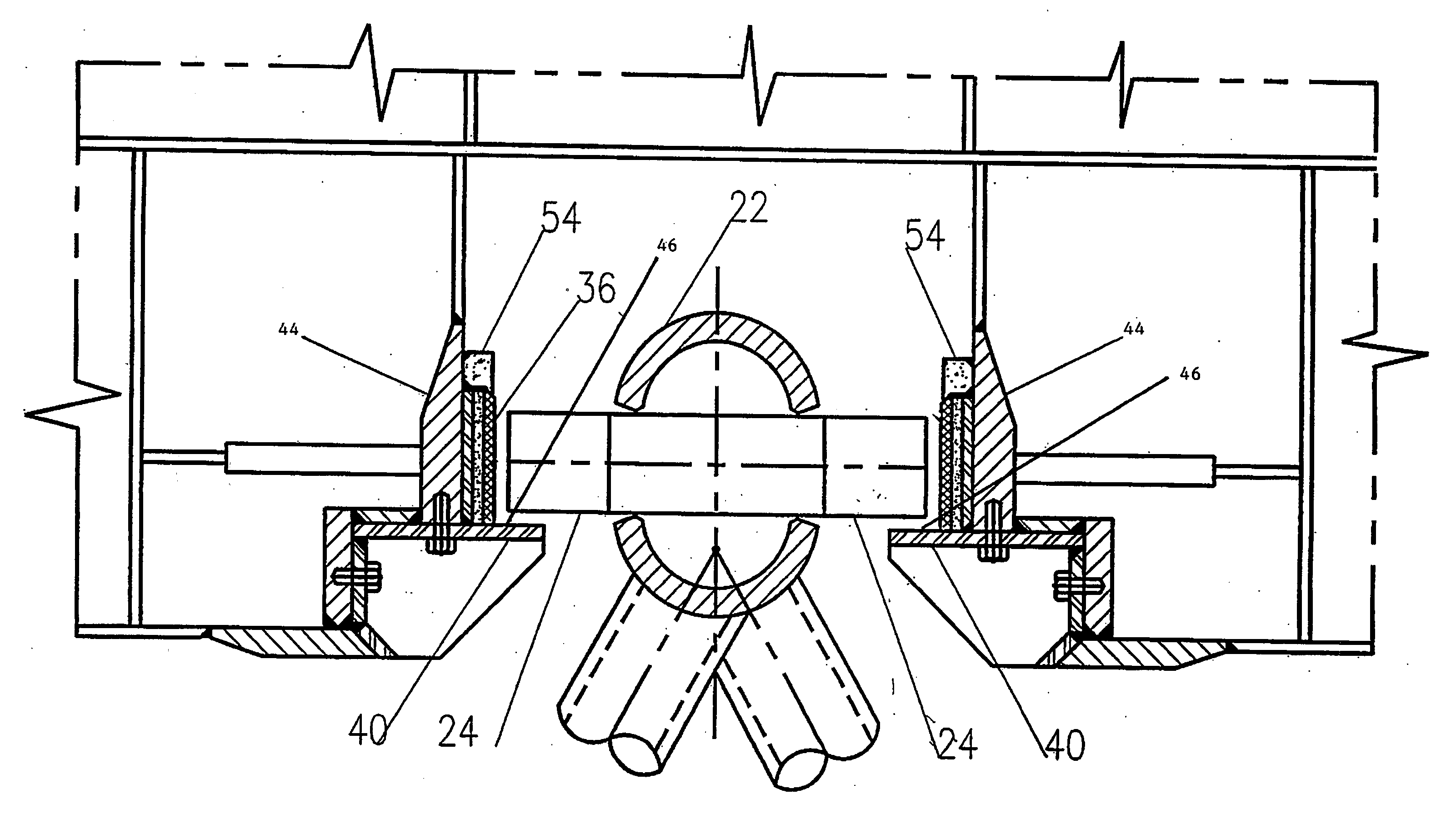
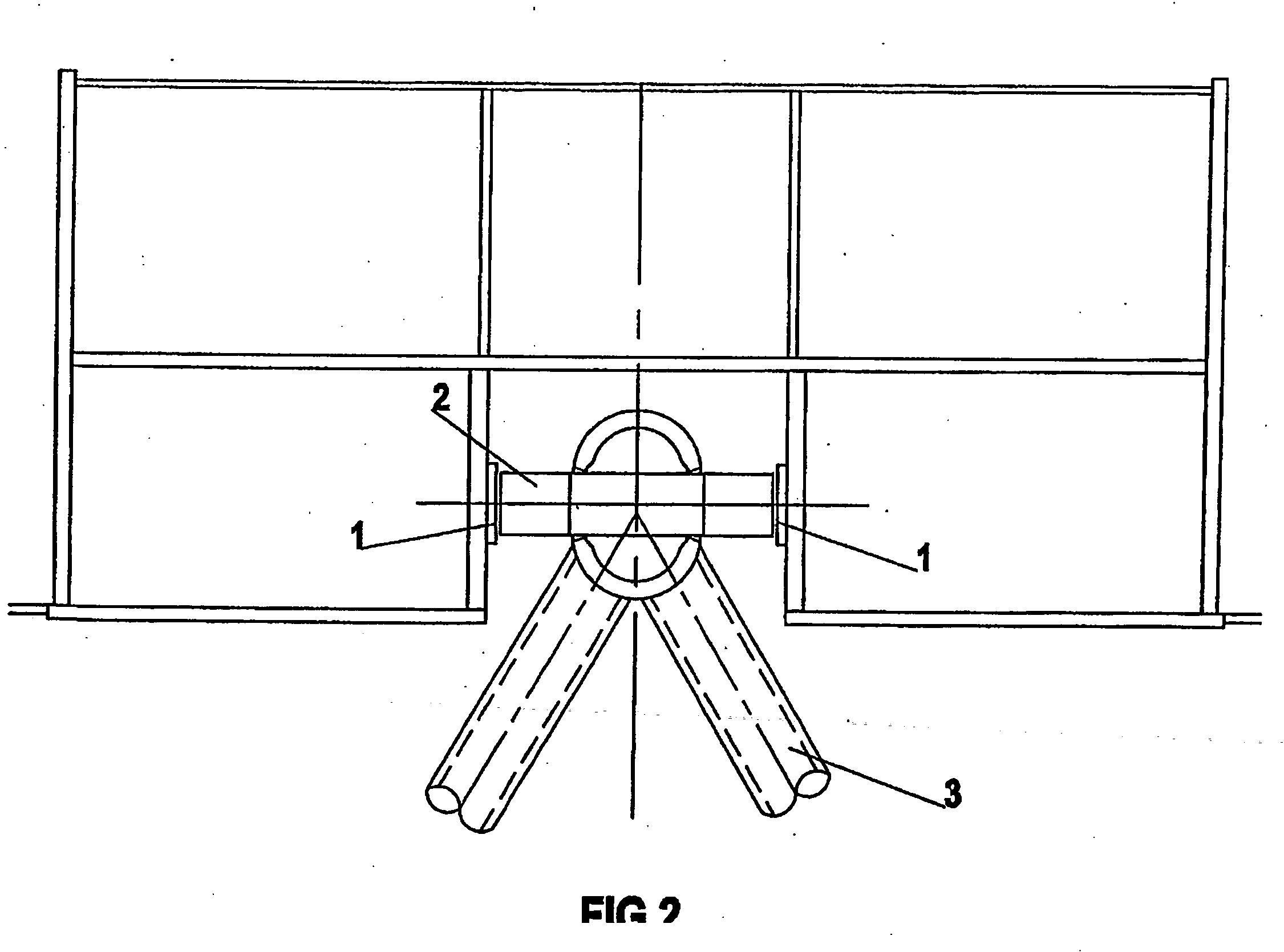
A wind turbine rotor comprising a hub and a plurality of blades. The hub comprises a plurality of sites, each having a pair of spaced apart annular bearings for receiving a respective wind turbine blade. Each blade has a spar extending along a substantial portion of the length of the blade and protrudes from the proximal end of the blade. The spar protrudes into and is rotatably received within the respective spaced apart bearings and is fixed to the hub.
Owner:BLADE DYNAMICS LTD
Morphing segmented wind turbine and related method
ActiveUS20130064663A1Prevent speedingHigh average lift coefficientPropellersWind motor controlMorphingWind speed
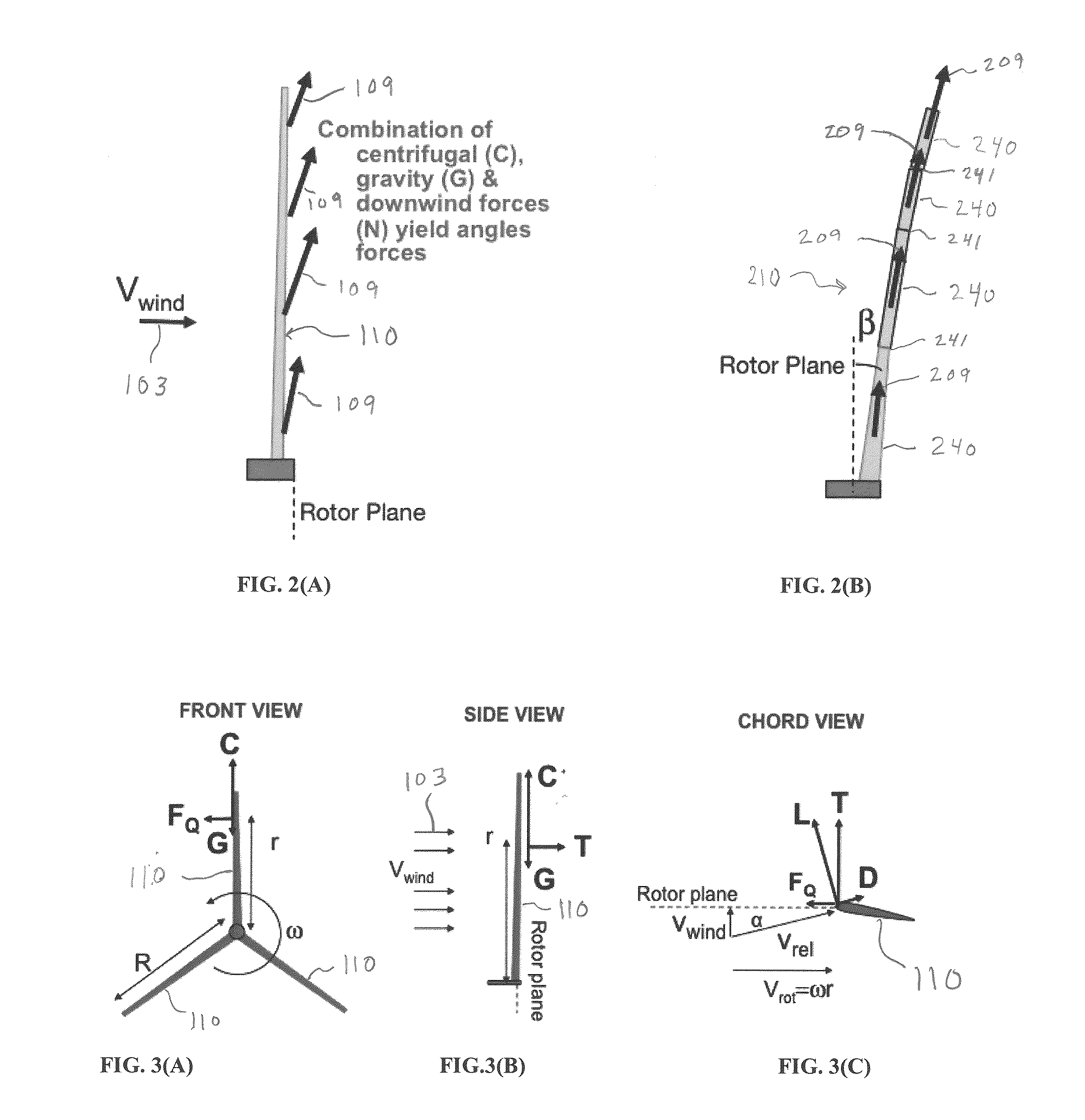
A downwind morphing rotor that exhibits bending loads that will be reduced by aligning the rotor blades with the composite forces. This reduces the net loads on the blades which therefore allow for a reduced blade mass for a given maximum stress. Also provided is a pre-aligned configuration rotor whereby the rotor geometry and orientation does not change with wind speed, and instead is fixed at a constant downwind deflection consistent with alignment at or near the rated wind speed conditions. Also provided is a twist morphing rotor where the airfoil-shapes around the spars twist relative to the wind due to aerodynamic forces so as to unload the rotors when there is a gust. This can help reduce unsteady stresses on the blade and therefore may allow for reduced blade mass and cost. The twist morphing rotor may be combined with either downwind morphing rotor or pre-alignment rotor.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
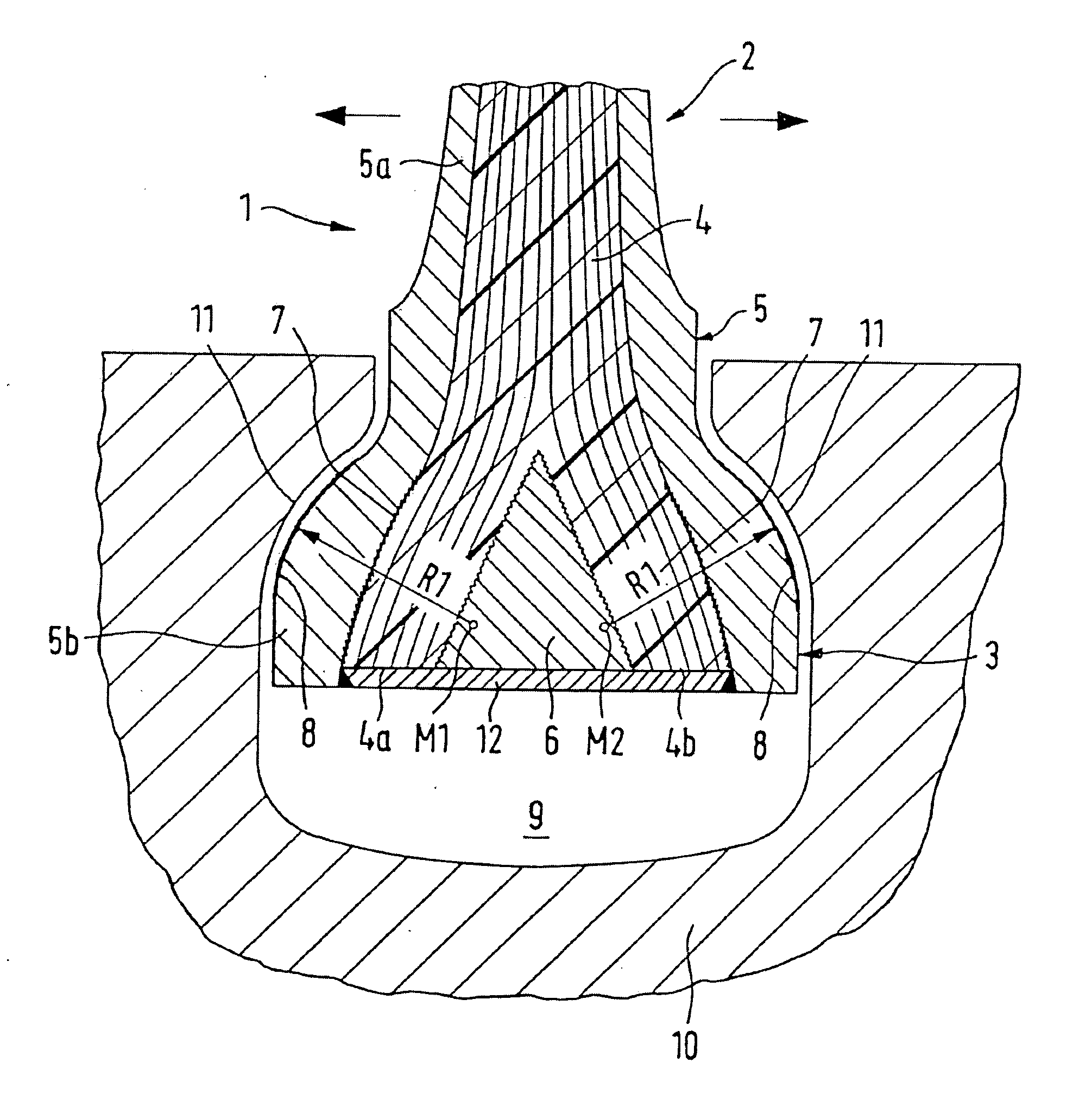
Variable compression ratio device for internal combustion engine
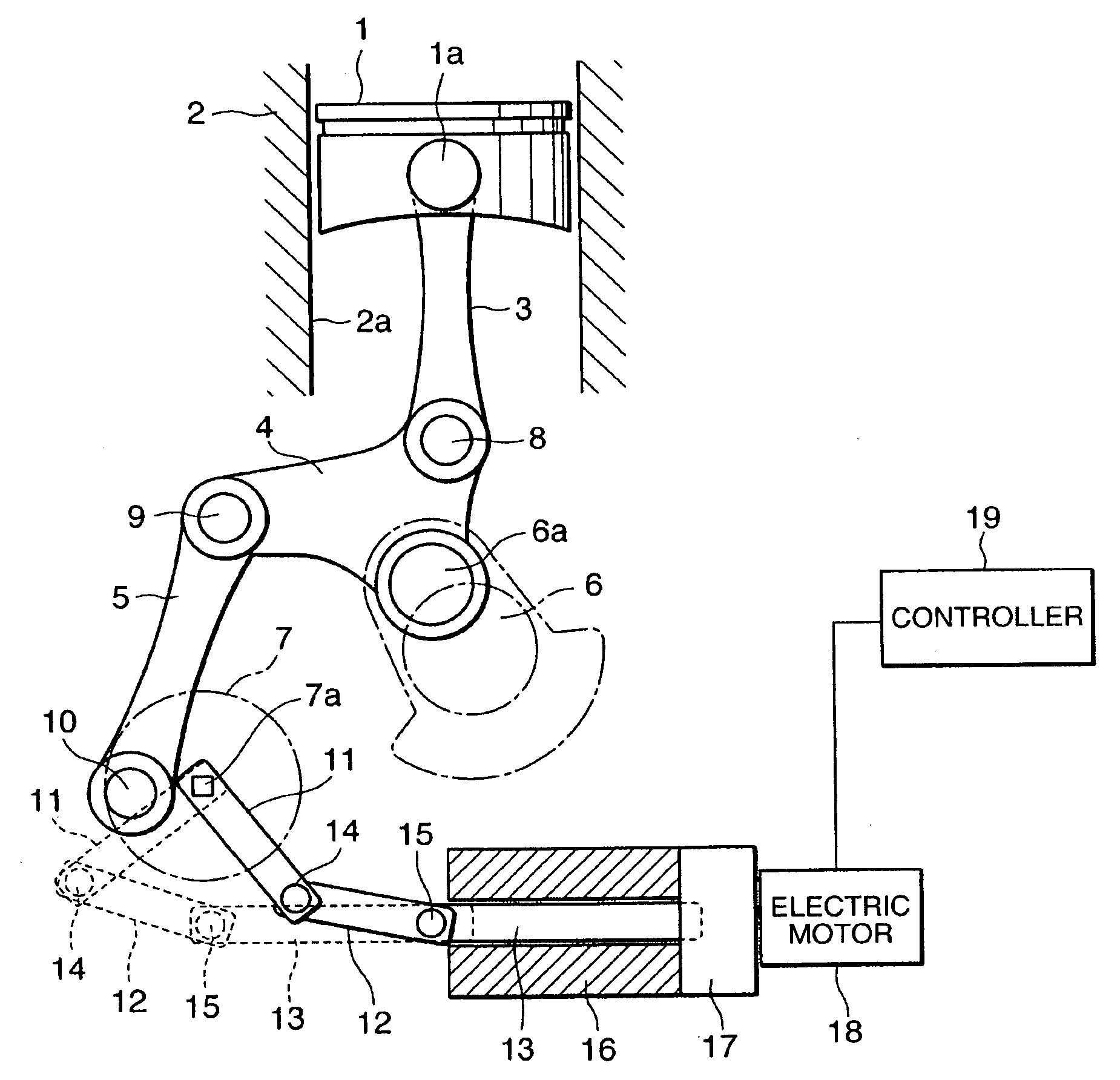
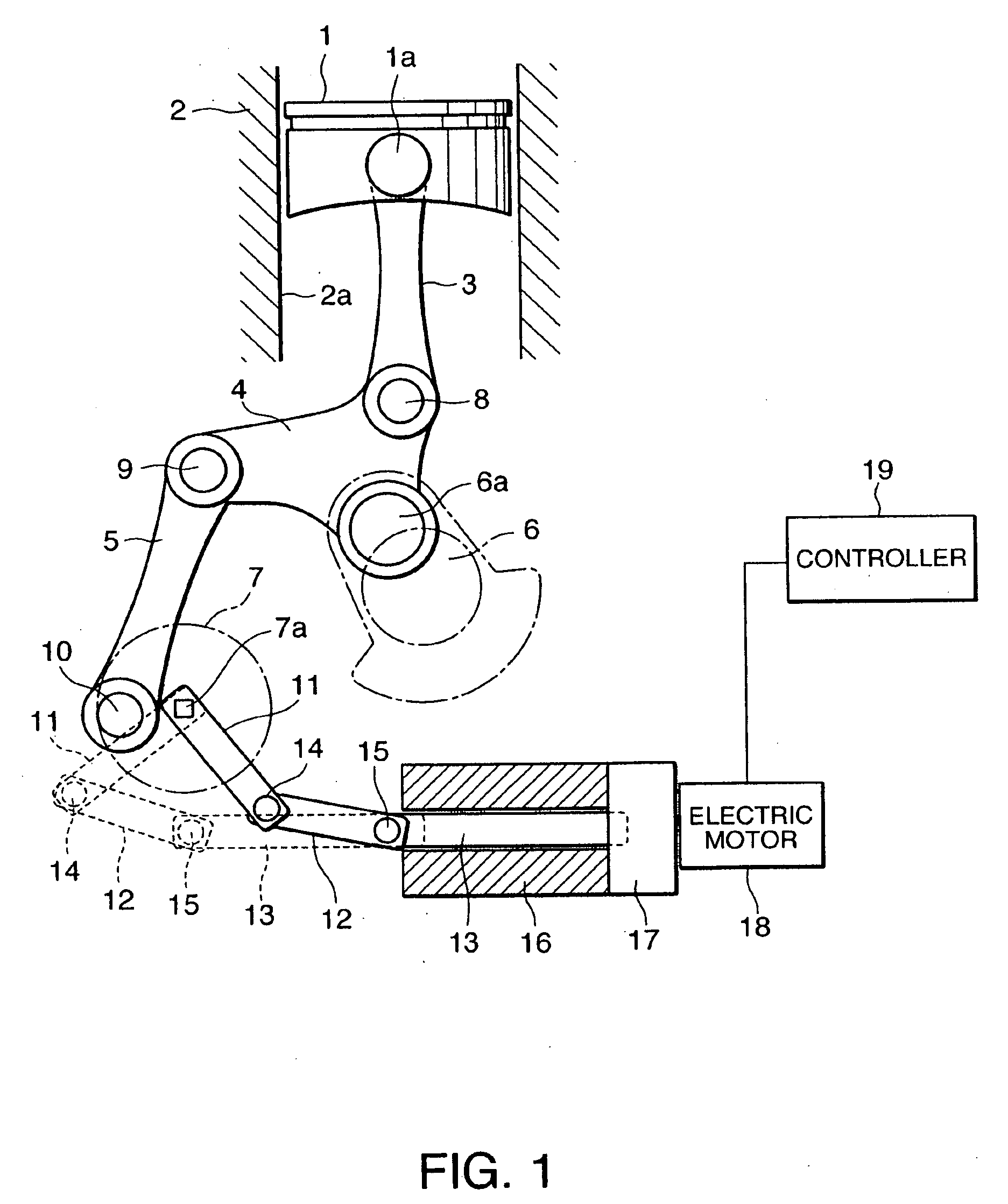
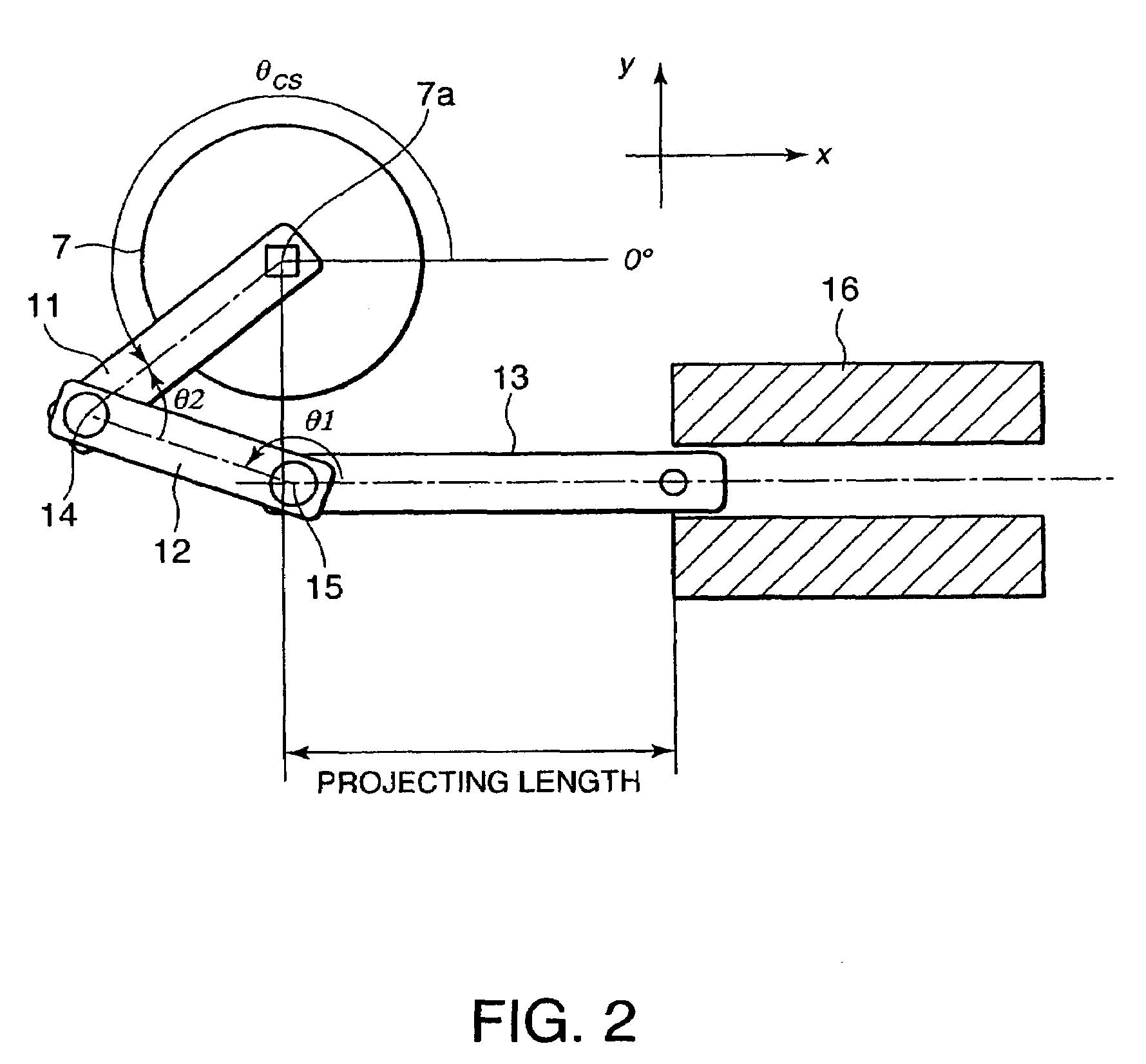
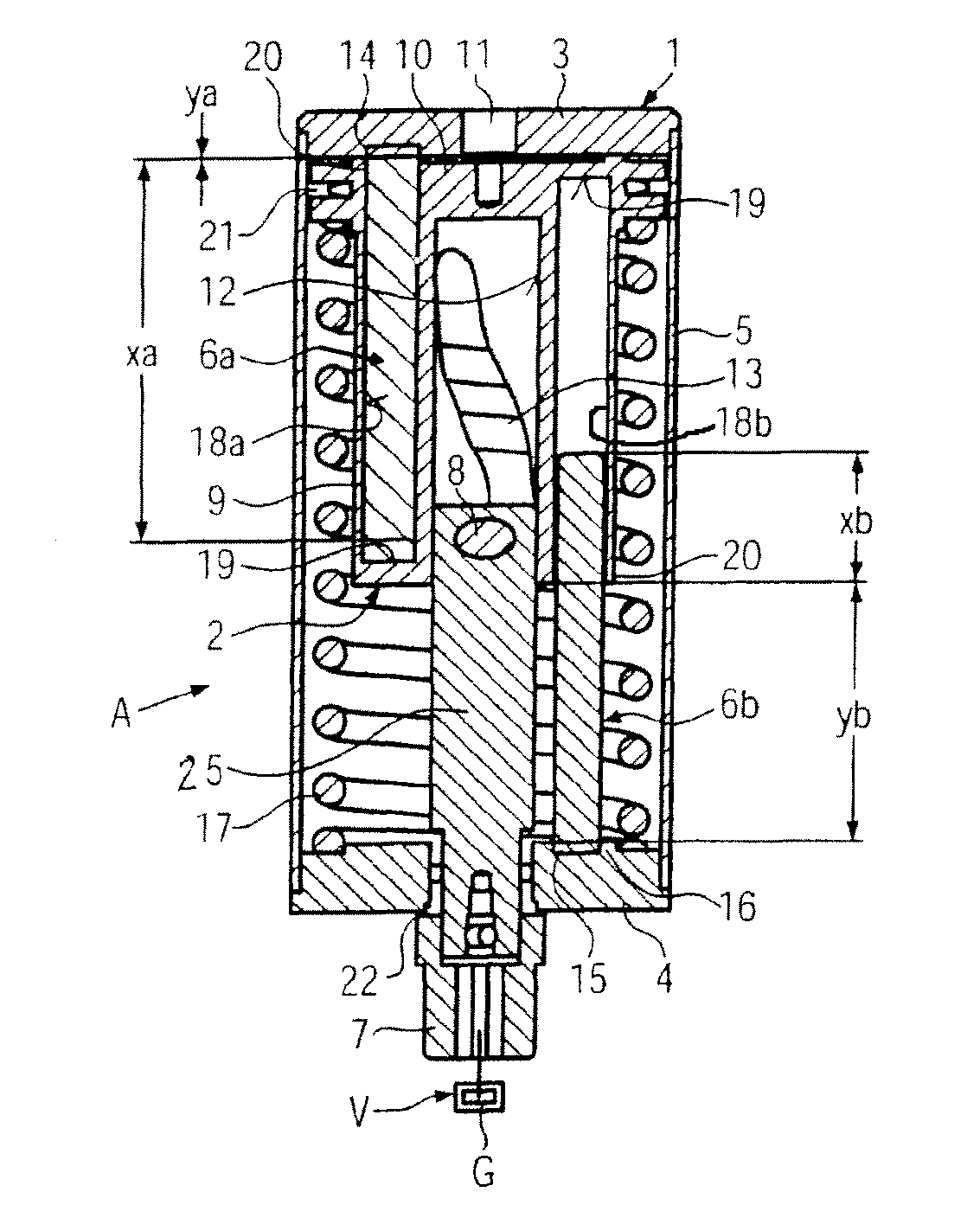
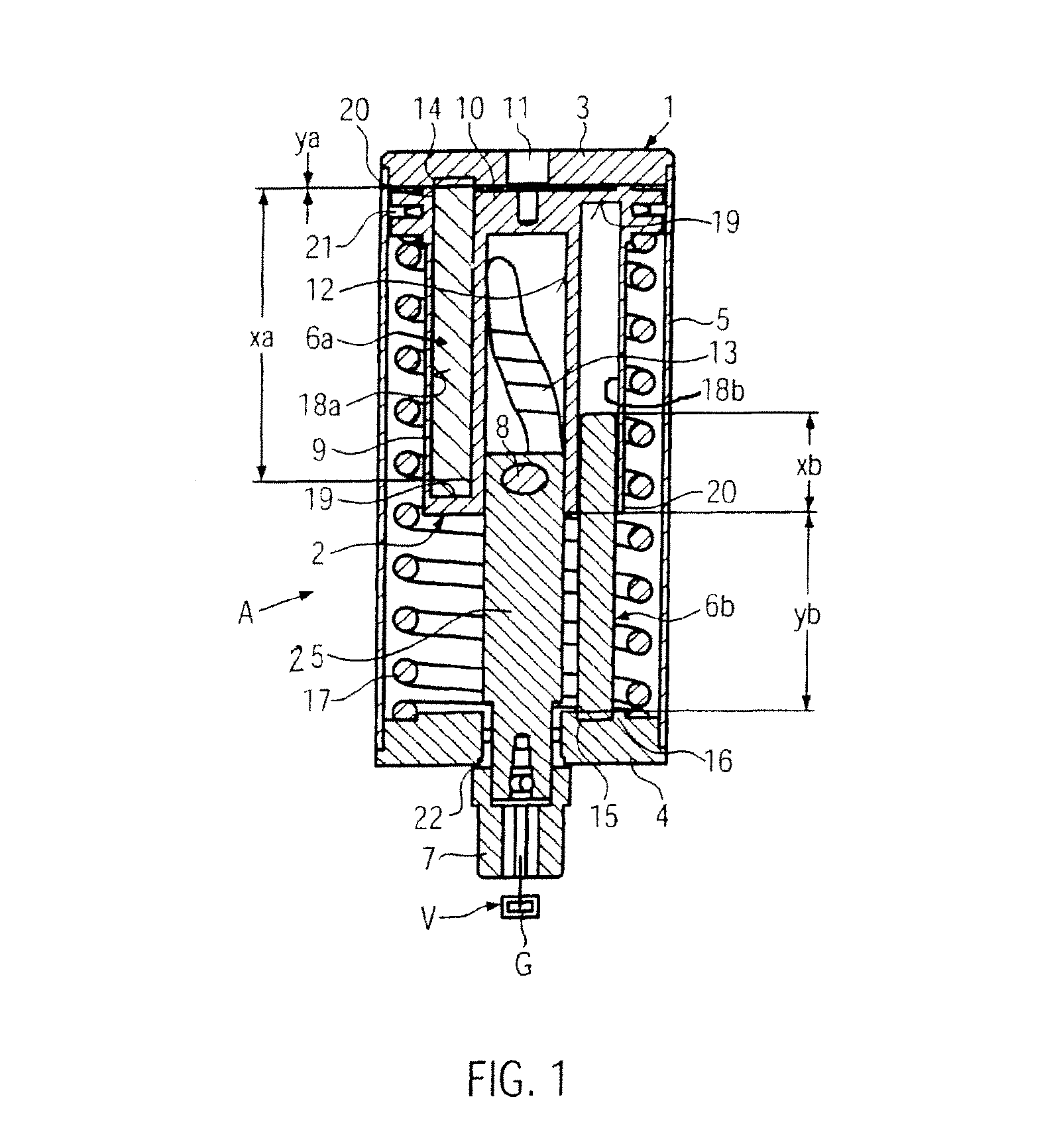
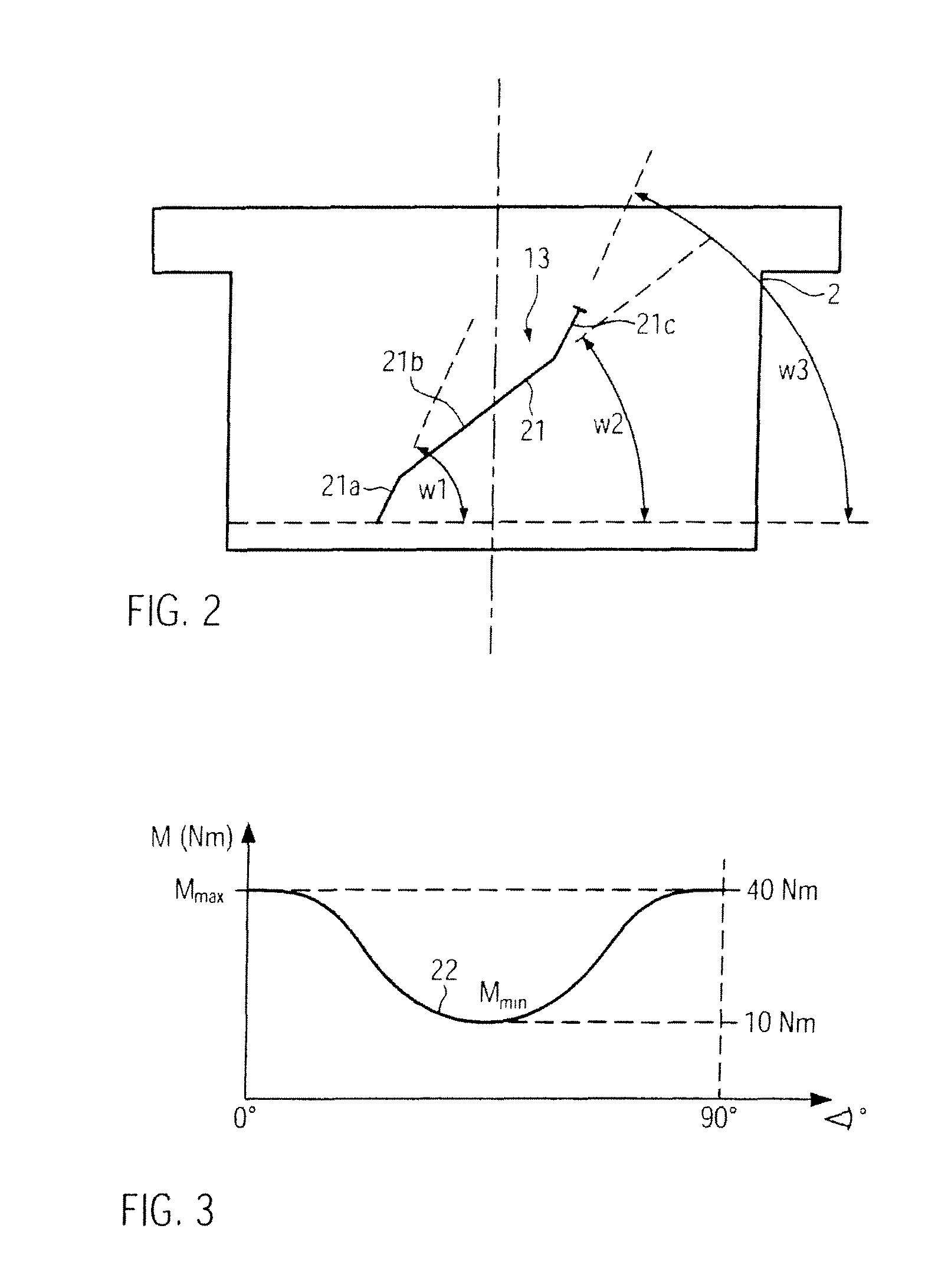
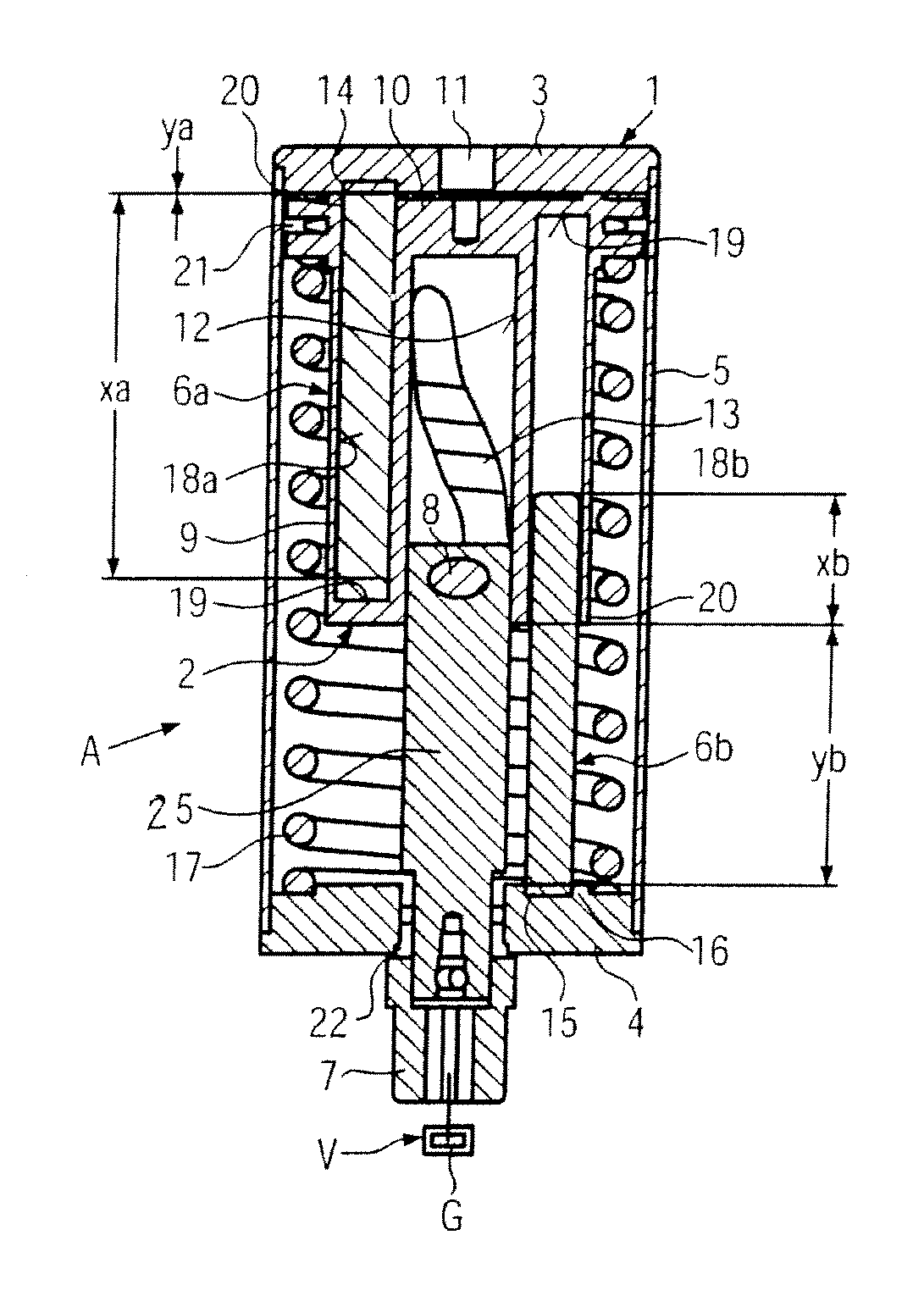
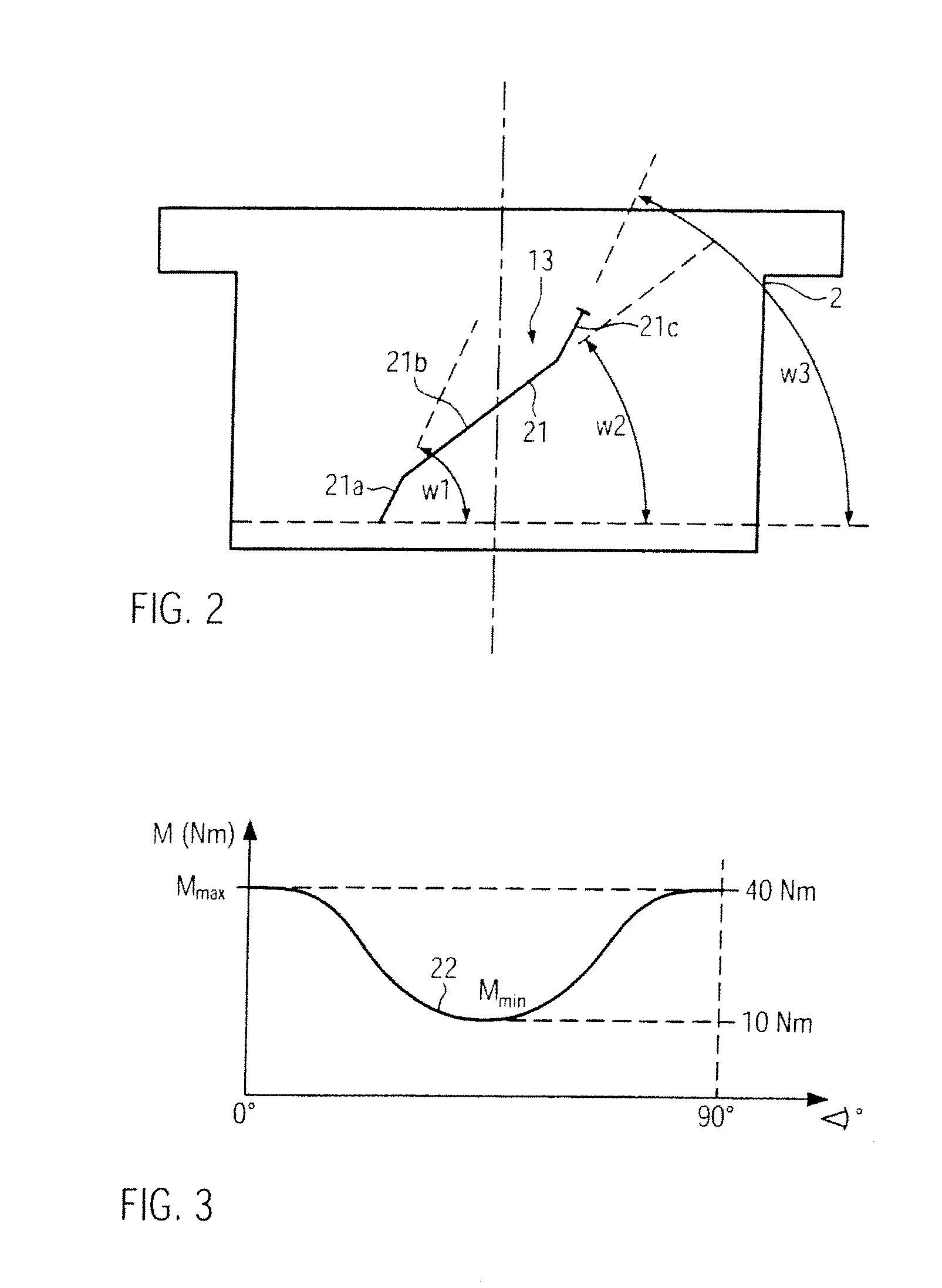
ActiveUS20090038588A1Reduce bending stressReduce stiffnessEngine controllersMachines/enginesControllabilityLinear actuator
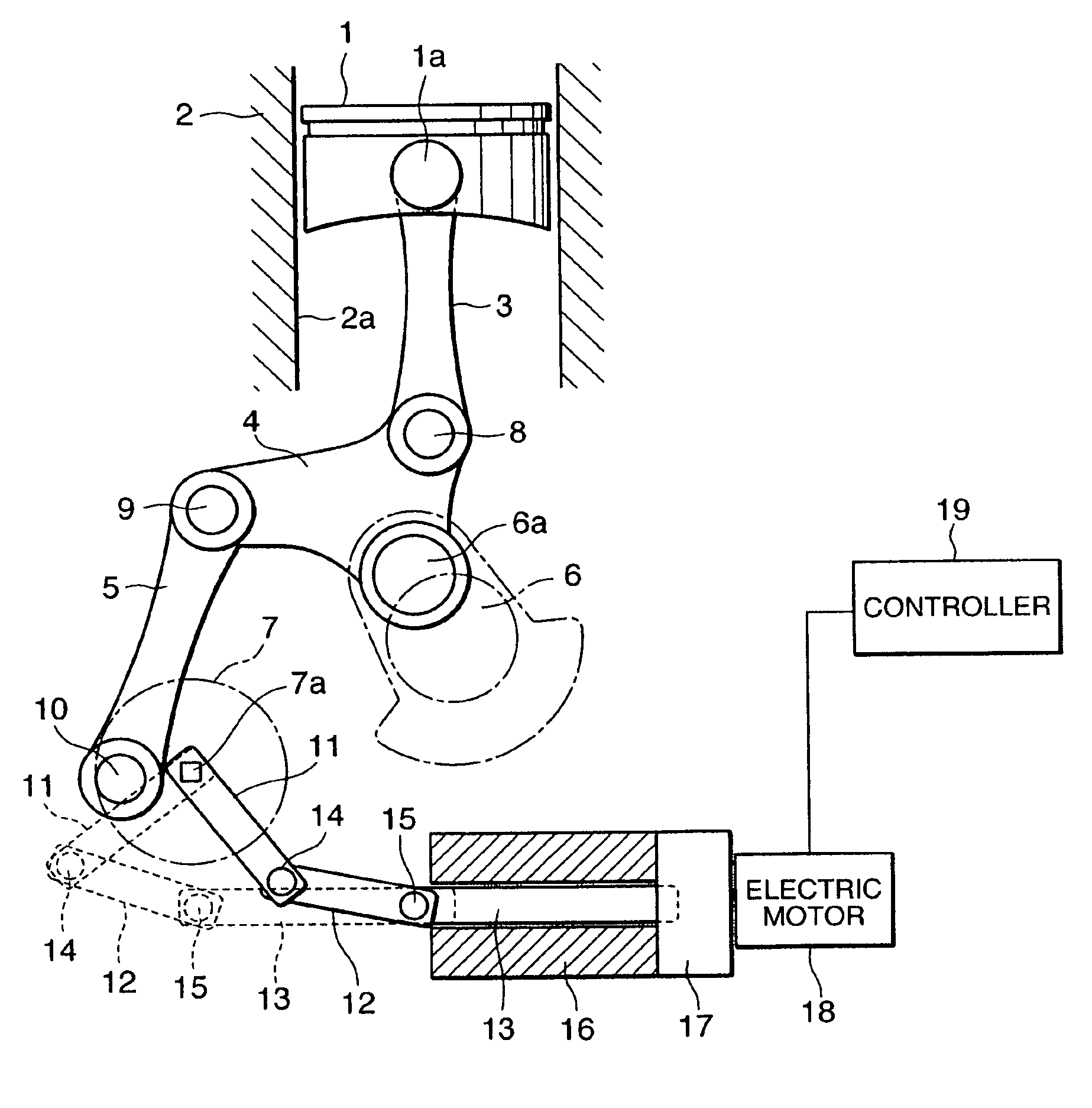
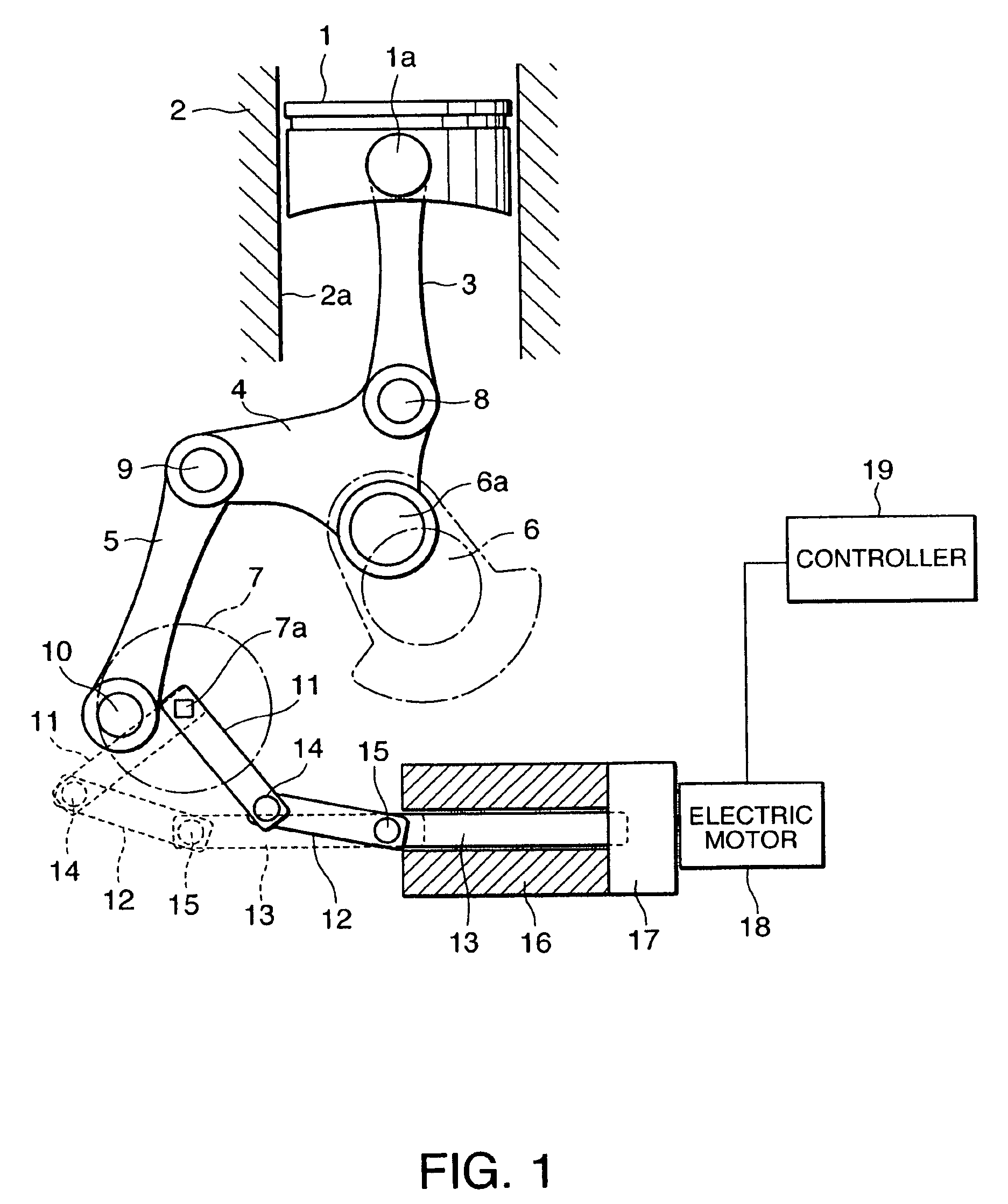
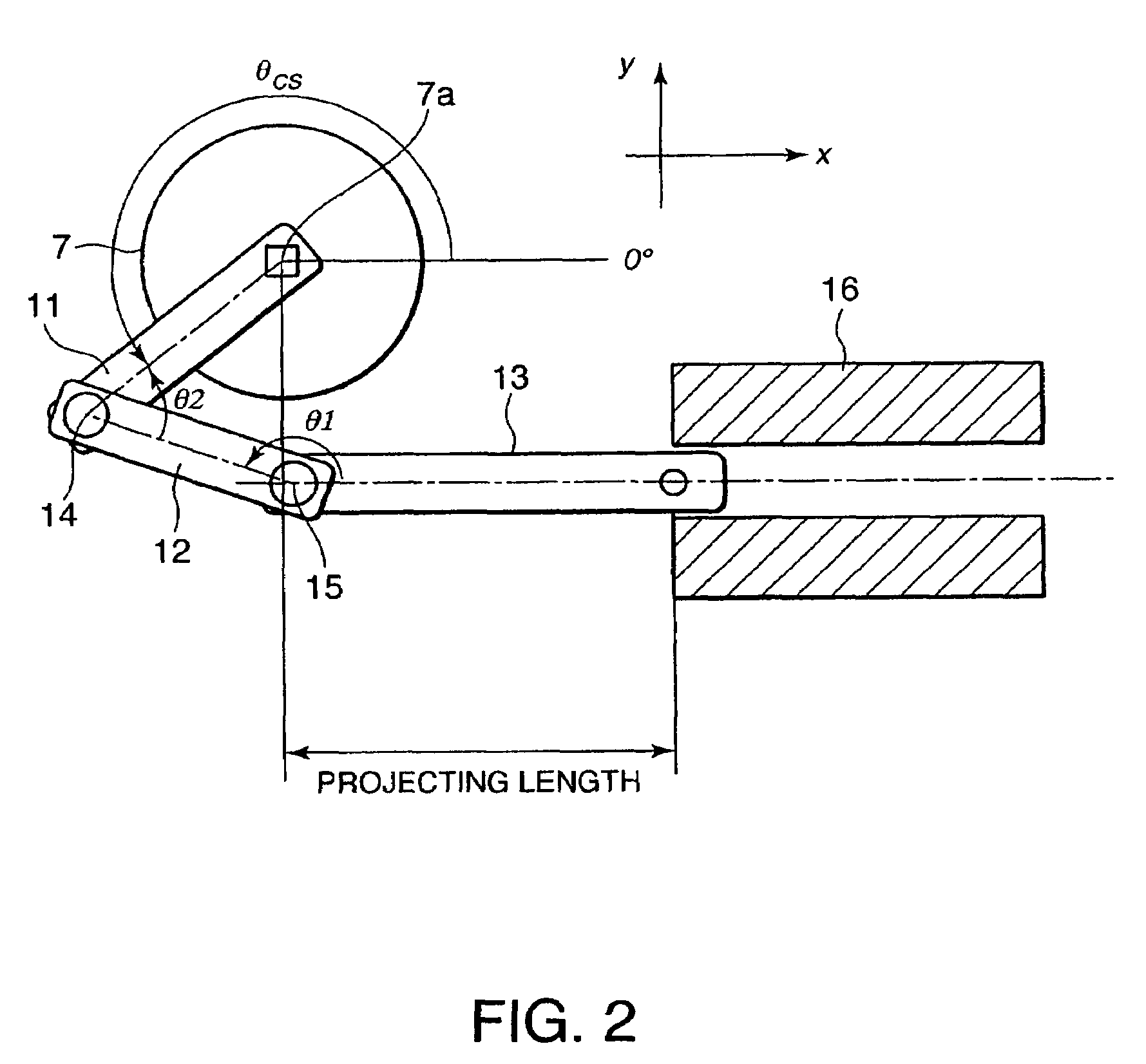
A variable compression ratio device for an internal combustion engine comprises a control shaft (7) that varies a compression ratio of the internal combustion engine in accordance with a rotational displacement, and a linear actuator (13, 16, 17, 18). A connecting link (12) connects a first point (14) offset from a rotation axis (7a) of the control shaft (7) to an actuator rod (13) of the linear actuator (13, 16, 17, 18). Thus, a bending load acting on the actuator rod (13) is reduced, and controllability of the compression ratio is improved.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
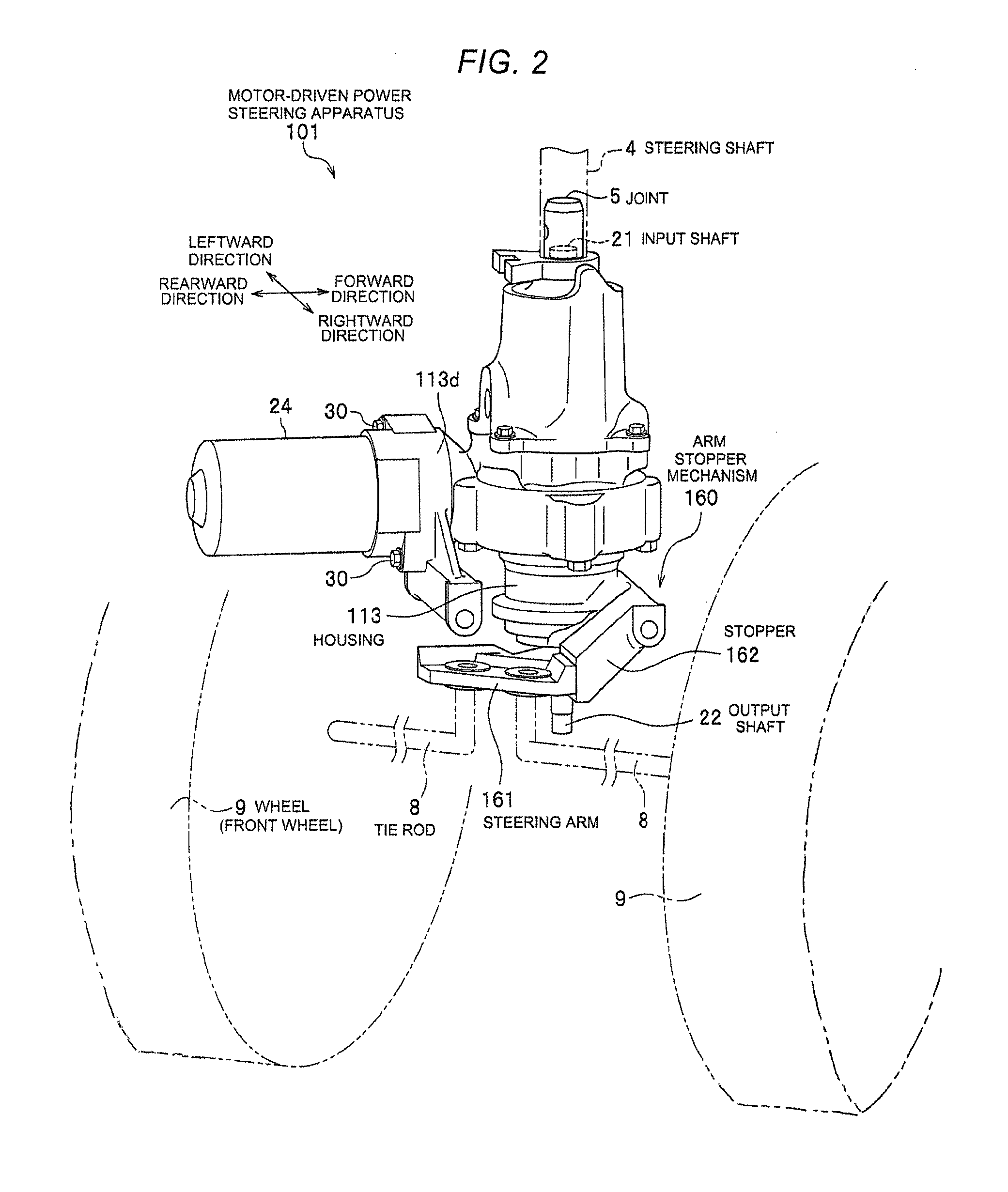
Steering apparatus
ActiveUS9193384B1Reduce bending loadAvoid it happening againCyclesSteering linkagesAngular degreesEngineering
A steering apparatus includes: an output shaft that outputs a steering force to wheels of a vehicle; a steering arm which turns about the output shaft, and to which two tie rods, to which the wheels are respectively connected, are attached; a stopper which is provided in a vicinity of the output shaft, and restricts an angle of the turning of the steering arm; a worm wheel that is fixed to the output shaft; a worm that is driven by a motor, and meshes with the worm wheel; a bearing that rotatably support the worm; a housing that holds the bearing; and a worm damper that is provided at an axial inner side or an axial outer side of the bearing in an axial direction of the worm, and is elastically deformable so as to move the worm in the axial direction, as defined herein.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Wind Turbine Blades and Wind Turbine
ActiveCN102269117AReduce lossesReduce intensityEngine fuctionsMachines/enginesElectricityTurbine blade
The invention provides a paddle of a wind power generating set. The paddle comprises a paddle root section (6), a paddle tip section (5) and a connection piece which connects the paddle root section (6) and the paddle tip section (5) and has an intensity less than those of the paddle root section (6) and the paddle tip section (5); when the paddle of the wind power generating set is blown by strong winds, such as typhoon and the like, and loads exceed the bearing capability of the connection piece, the connection piece fractures, thus the paddle tip section falls off; and due to the falling of the paddle tip section, the diameter of the paddle of the whole wind power generating set and the rotor swept area are decreased, and further bending loads applied to a tower frame and a foundation by the whole paddle are decreased. The tower frame and the foundation are stored in the strong wind environment such as typhoon and the like by the paddle of the wind power generating set, and the loss of the whole wind power generating set is reduced. The invention also provides the wind power generating set.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WINDEY
Fan failure braking device of aero-engine
ActiveCN103775212AReduce bending loadAvoid severe deformationGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsAviationFan blade
A fan failure braking device of an aero-engine comprises a fan shaft, a fan blade, a bearing support piece and a bearing component, wherein a rotor brake disc is arranged on the fan shaft; the fan blade is mounted on the fan shaft; one end of the bearing support piece is mounted on an aero-engine casing, the bearing support piece is provided with a stator brake disc which circumferentially surrounds the rotor brake disc and is radially spaced from the rotor brake disc; one end of the bearing component is coupled with the other end of the fan shaft, and connected with the bearing support piece by a predetermined bending moment; when the fan blade fractures, the fan shaft deflects outwards, so that when the mutation bending moment between the bearing component and the bearing support piece exceeds the predetermined bending moment, the bearing component and the bearing support piece are disconnected, and thus the rotor brake disc and the stator brake disc are jointed. when the fan blade fails and fractures, rub-impact occurs between the rotor brake disc and the stator brake disc, limits the radial displacement of bending of the fan shaft and reduces the rotational speed of the fan shaft and the FBO (Fan Blade Out) load.
Owner:AECC COMML AIRCRAFT ENGINE CO LTD
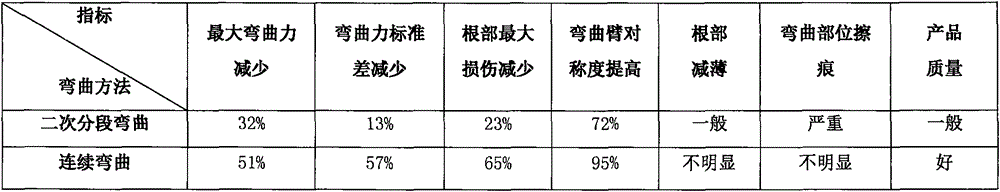
Accurate continuous bending method of U-shaped large forging
InactiveCN106825153AAvoid damageReduce bending loadShaping toolsMetal-working feeding devicesEngineeringBack pressure
The invention discloses an accurate continuous bending method of a U-shaped large forging. The method is realized through an arc-shaped inlet female mold, a male mold matched with the female mold, and a back pressure mold with a bent guiding plate. The method comprises the following steps: heating a forging blank to perform preforging; performing back pressure trimming; performing residual heat accurate positioning; enabling the bent guiding plate to drive the bent part of the forging to move and be bent along the arc-shaped track of a female mold inlet, and the like. The method has the advantages that the surface of the bent part is high in quality and small in damage, and the symmetry of the forging is high.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
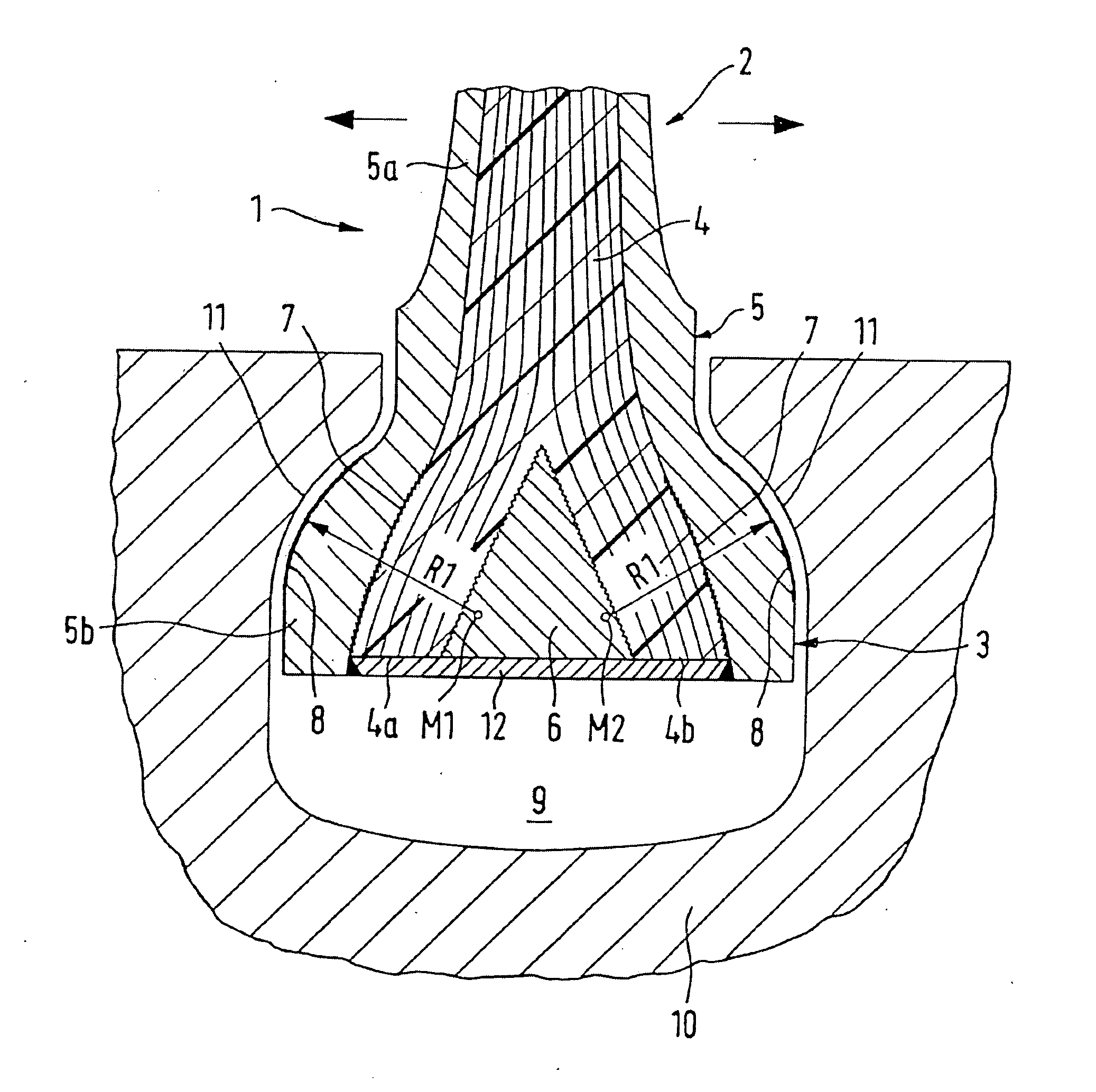
Variable compression ratio device for internal combustion engine
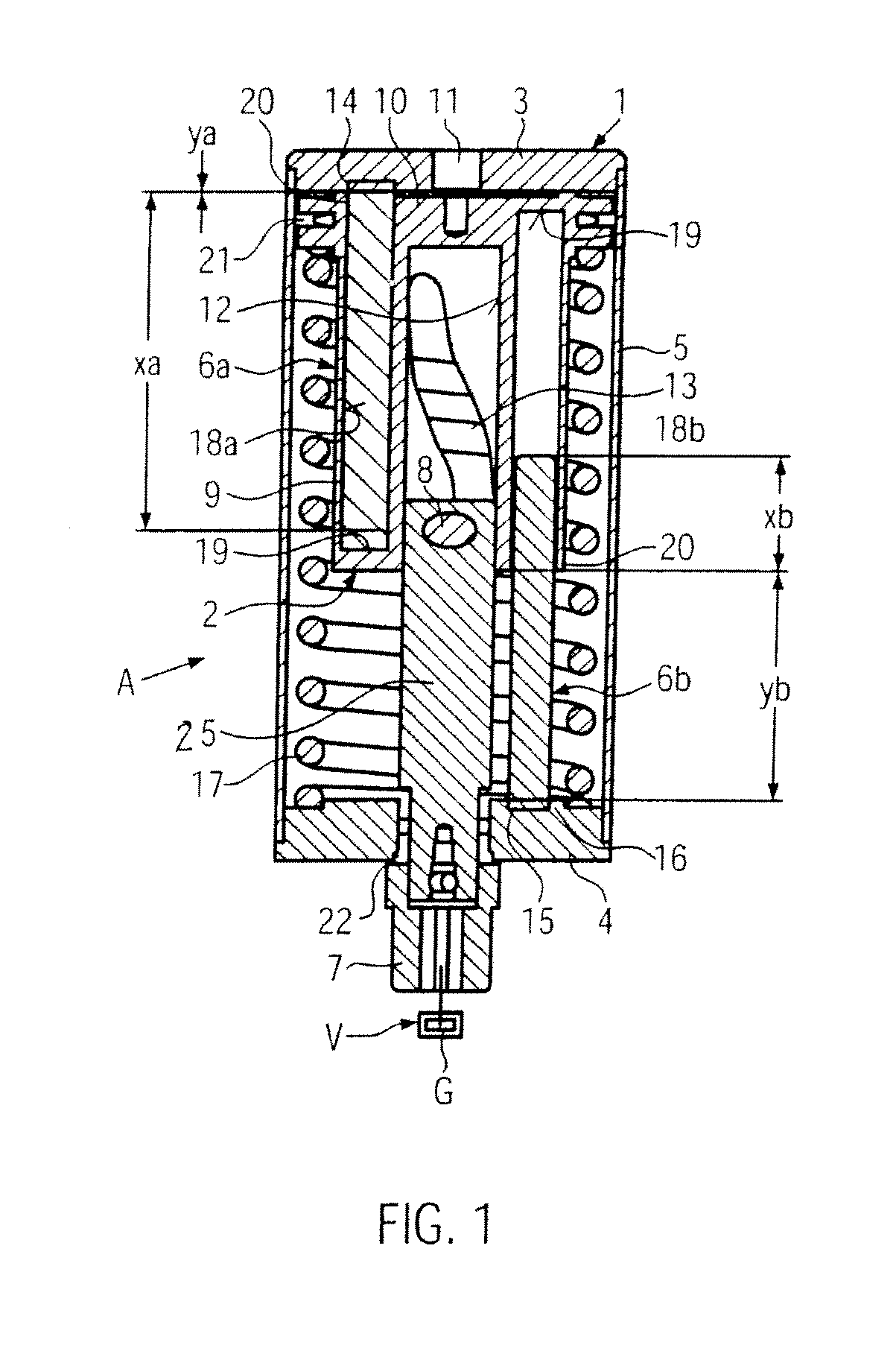
ActiveUS8397683B2Reduce bending stressReduce stiffnessEngine controllersMachines/enginesExternal combustion engineLinear actuator
A variable compression ratio device for an internal combustion engine comprises a control shaft (7) that varies a compression ratio of the internal combustion engine in accordance with a rotational displacement, and a linear actuator (13, 16, 17, 18). A connecting link (12) connects a first point (14) offset from a rotation axis (7a) of the control shaft (7) to an actuator rod (13) of the linear actuator (13, 16, 17, 18). Thus, a bending load acting on the actuator rod (13) is reduced, and controllability of the compression ratio is improved.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Wind turbine
ActiveCN103026061AReduce hardnessImprove flexibilityEngine fuctionsWind motor combinationsCouplingTurbine
Wind turbine comprising a rotor and a generator, said rotor comprising a rotor hub and one or more rotor blades and said generator comprising a generator stator and a generator rotor, wherein the hub is rotatably mounted on a frame, the generator rotor comprises a carrying structure carrying magnetic or electromagnetic elements, one or more circumferentially arranged substantially axial protrusions are attached to said rotor, wherein said axial protrusions extend into the generator rotor carrying structure, and one or more flexible couplings are arranged between one or more of said axial protrusions and said carrying structure.
Owner:GE RENEWABLE TECH WIND BV
Direct drive wind turbine and method for controlling an air gap
A direct drive wind turbine comprising a rotor and a generator, the rotor comprising a hub and a plurality of blades and being rotatably mounted on a frame, and the generator comprising a generator rotor and a generator stator, further comprising one or more dampers arranged between the rotor and the generator rotor and extending at least partially in an axial direction.
Owner:GE RENEWABLE TECH WIND BV
Torque coupler
ActiveUS9470290B2Reduced axial leverageReduce bending loadRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingCouplingEngineering
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
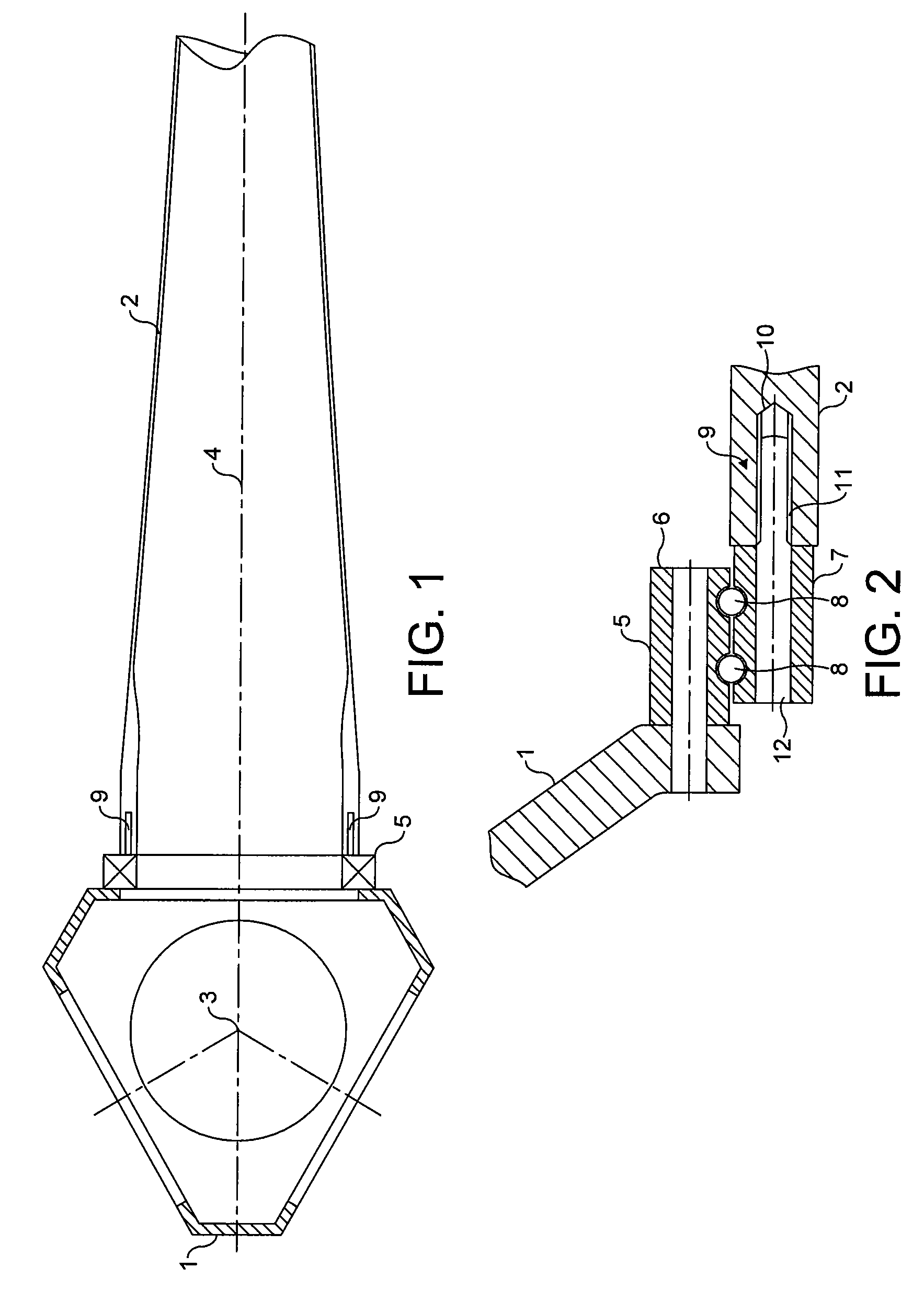
Interactive leg guide for offshore self-elevating unit
InactiveUS20060056920A1Reduce bending loadReduce stiffnessArtificial islandsProtective foundationLongitudinal planeEngineering
A leg guide for use in a leg of a jack up unit adapted to provide sliding guidance of the leg during vertical movement of the leg. The leg guide has a first portion contacting an edge of a leg chord and a second portion contacting a face of the leg chord along a longitudinal plane opposite the contact plane of the first portion. The edge contacting guide has a deflecting guide unit, which uses a compressible member sandwiched between two rigid plates. As the leg moves, the teeth of the leg chord contact the edge guide unit, with the compressible member absorbing compressible loads acting on the leg chord. The second portion provides for a face plate mounted transversely to the edge contacting guide for reducing the build-up of horizontal moment acting on the leg chord during the vertical movement of the leg and for reducing bending moments acting on the leg.
Owner:OFFSHORE TECH DEVMENT PTE
Electromechanical automatic leveling rotating base
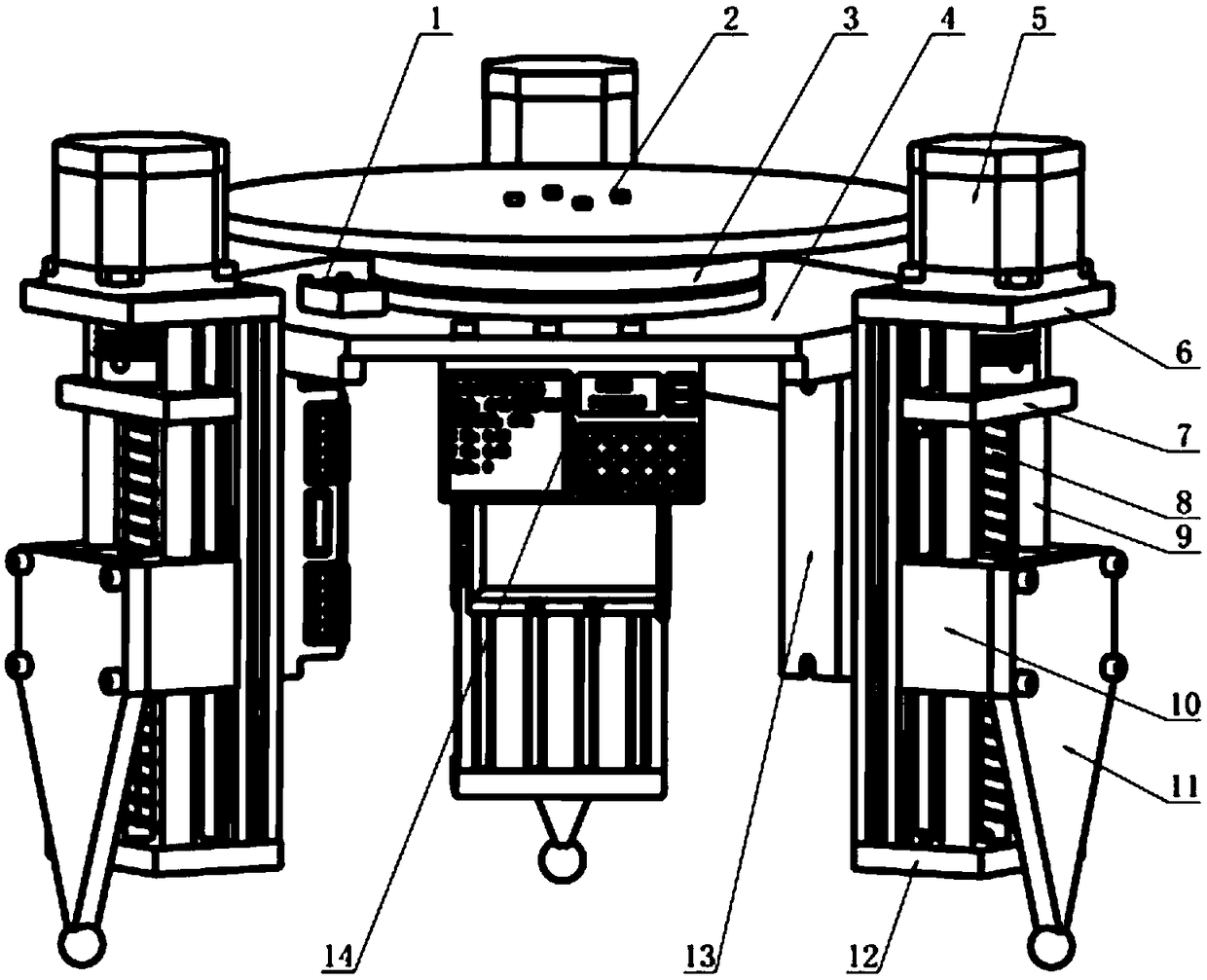
ActiveCN109084149AExtended service lifeReduce bending loadProgramme controlComputer controlOptical axisMiniaturization
The invention discloses an electromechanical automatic leveling rotating base. The electromechanical automatic leveling rotating base comprises an upper end flat plate, a connecting plate, a rotatingmechanism, a horizontal sensor, a control display unit, a first motor driver, three second motor drivers and three sets of leveling supporting mechanisms; the rotating mechanism comprises a first stepping motor, a shaft connecting block and a thrust bearing; each leveling supporting mechanism comprises a supporting frame, a second stepping motor, a lead screw, a sliding table, an upper end connecting piece, a middle connecting piece, a lower end connecting piece, a supporting foot, and two optical shafts; and the control display unit comprises a central processor, a display screen, a key arrayand a receiver. The electromechanical automatic leveling rotating base utilizes the principle of chase-type leveling, the central processor detects level degree data of the horizontal sensor in realtime to control rising and falling of the three supporting feet, and thus leveling is achieved; meanwhile, the central processor further detects an input instruction of the key array and a receiver instruction, and responds to the instructions; and the electromechanical automatic leveling rotating base has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, miniaturization and automation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aerodynamic device
ActiveUS20150259061A1Reduces in-plane bending stiffnessLow bending stiffnessWeight reductionWing adjustmentsLeading edgeTrailing edge
The invention provides an aerodynamic device configured for being mounted to an aerodynamic structure of an aircraft, the aerodynamic device having a spanwise length, a chordwise width, a leading edge section along a leading edge of the device, for being mounted to the aerodynamic structure of the aircraft, and a trailing edge section along a trailing edge of the device, for providing a required aerodynamic profile, wherein a first chordwise extending segment of the trailing edge section is moveable in a spanwise direction with respect to the leading edge section or with respect to a second chordwise extending segment of the trailing edge section.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
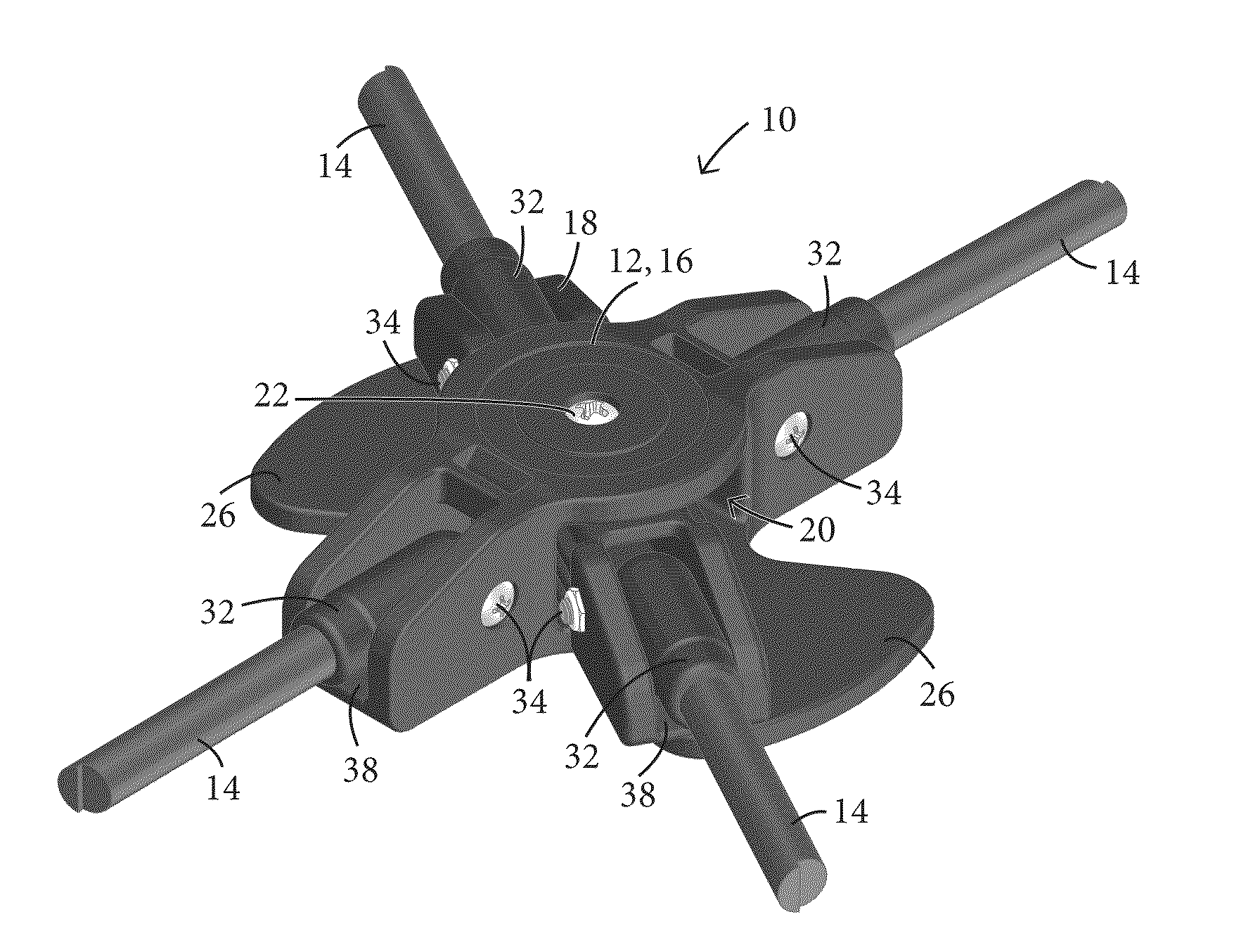
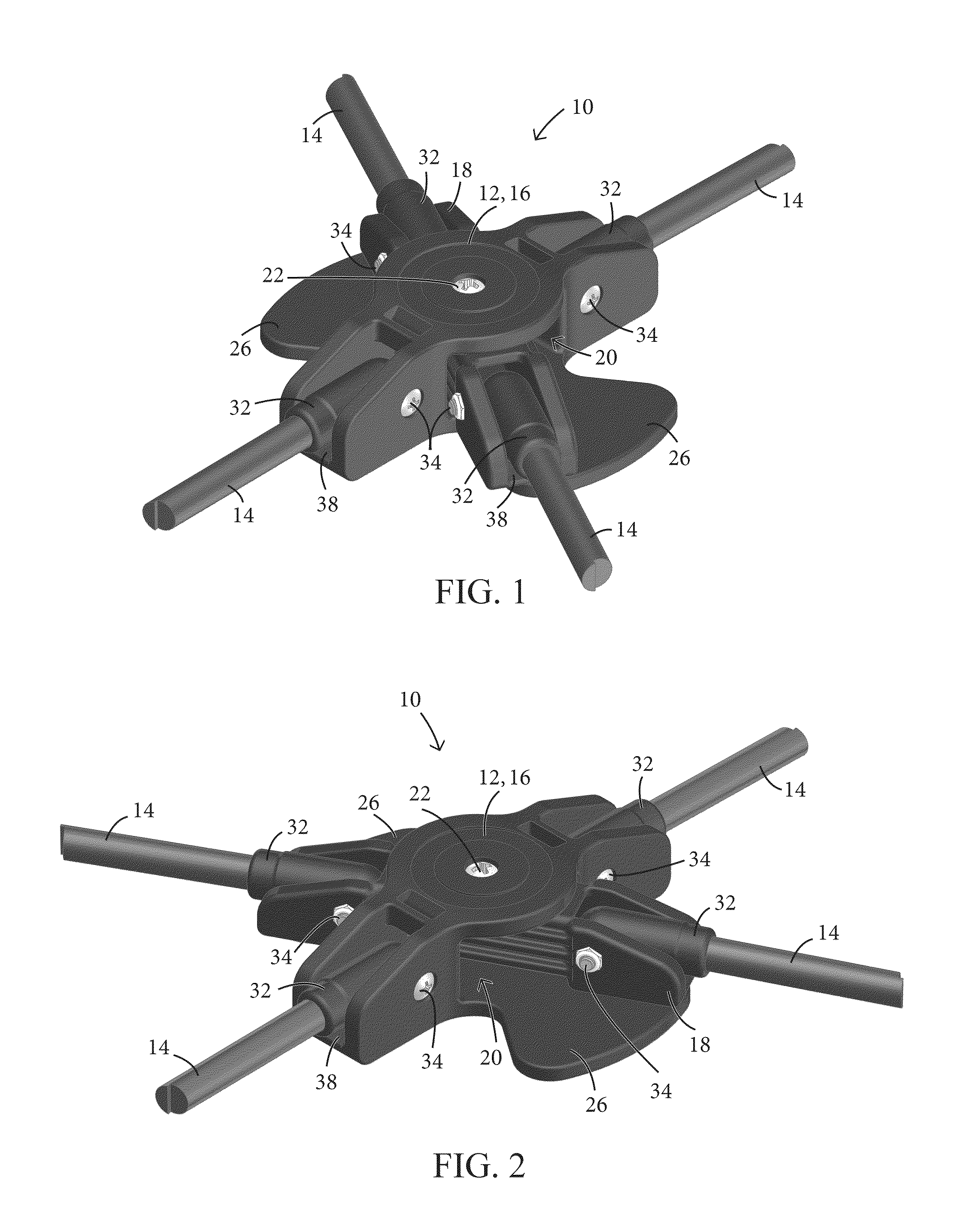
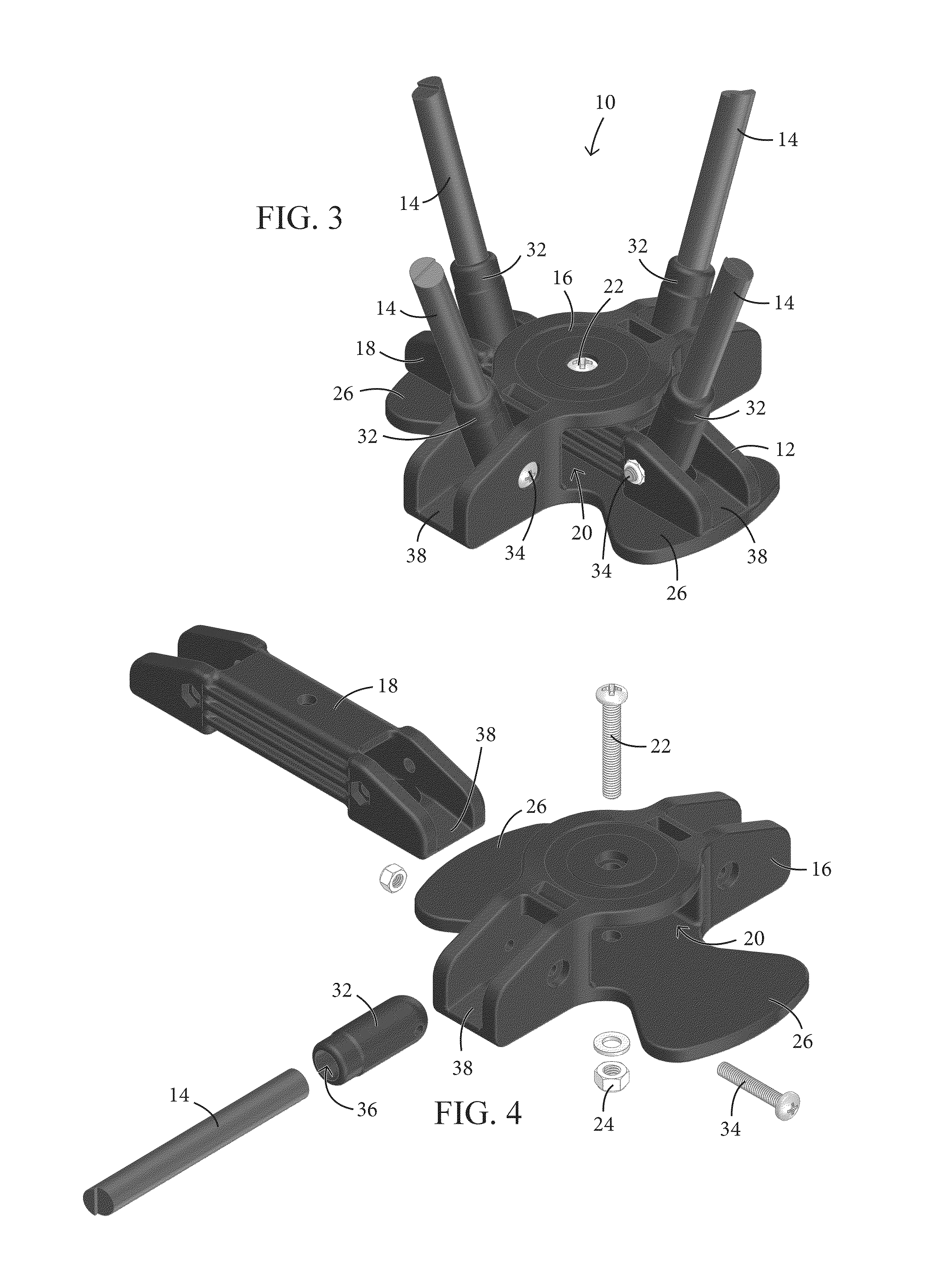
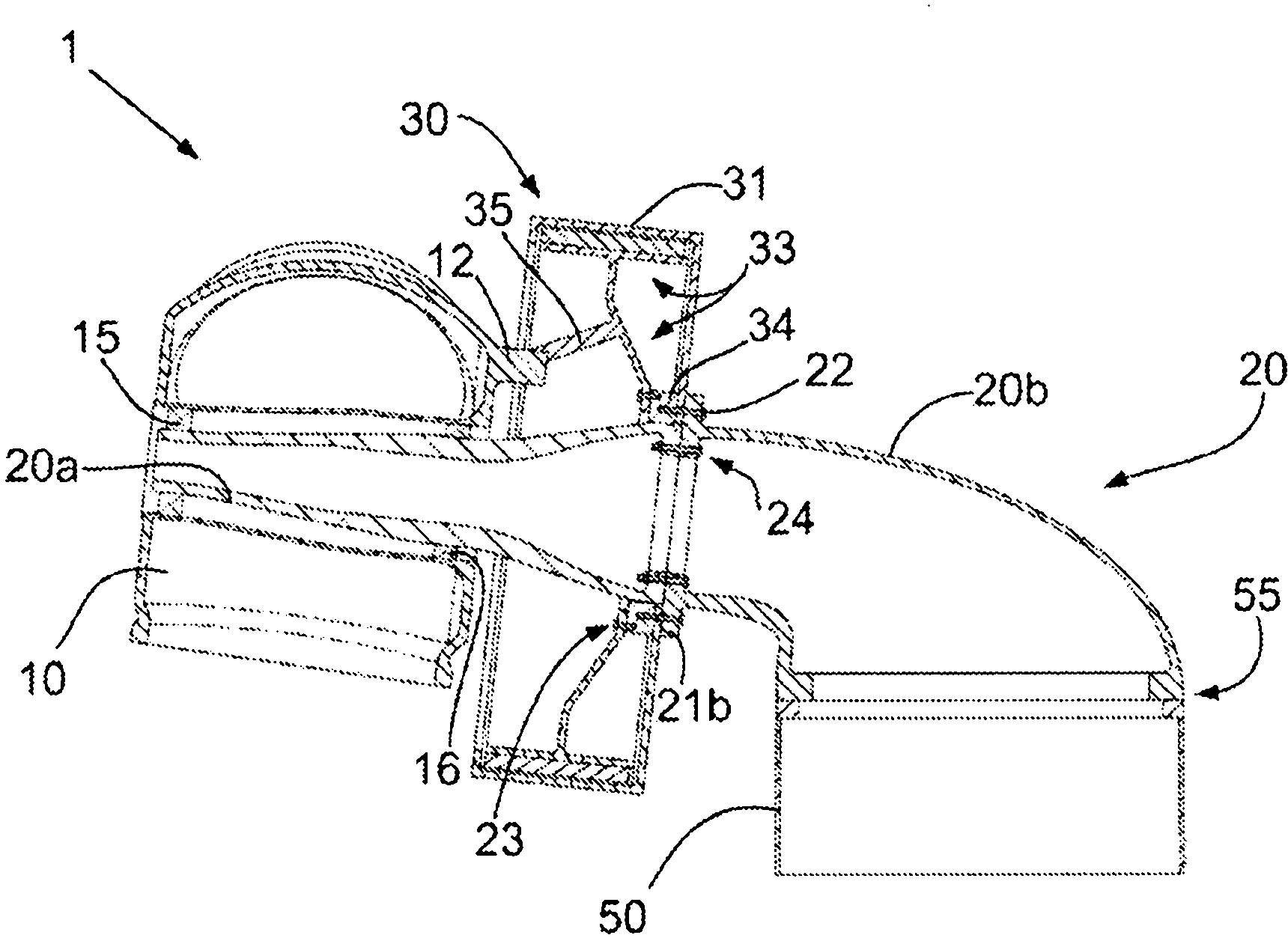
Articulating Pole Hub for a Collapsible Shelter and Method of Forming a Collapsible Shelter
ActiveUS20140182643A1Efficiently transfer loadConvenient to accommodateTents/canopiesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A pole hub for a collapsible shelter, such as a tent, canopy, or sun-shade is configured and adapted to connect at least two pairs of poles to each other in manner such that the pairs of poles are able to pivot relative to each other about an axis, while each pair of poles remains generally rigid.
Owner:WESTFIELD OUTDOORS
Actuator for a closing element of a valve
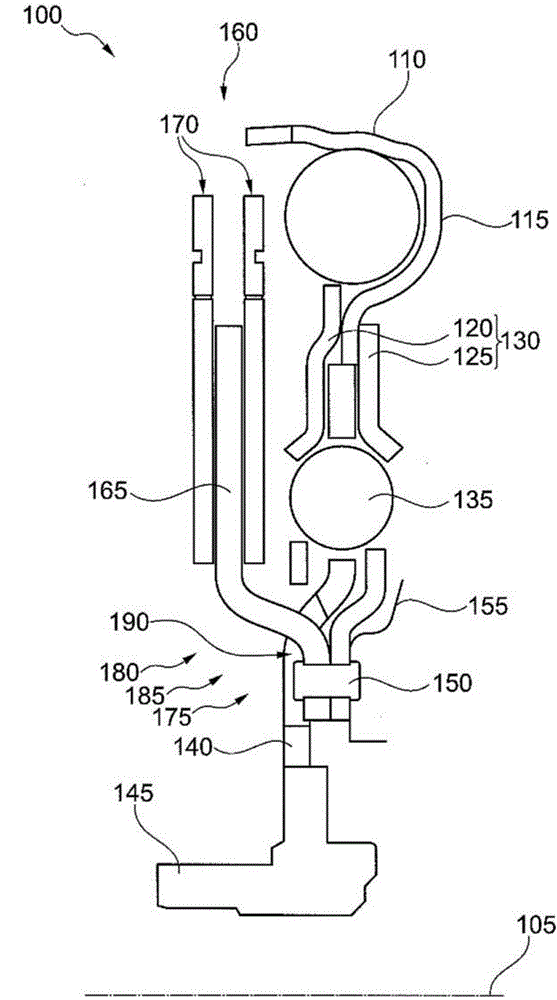
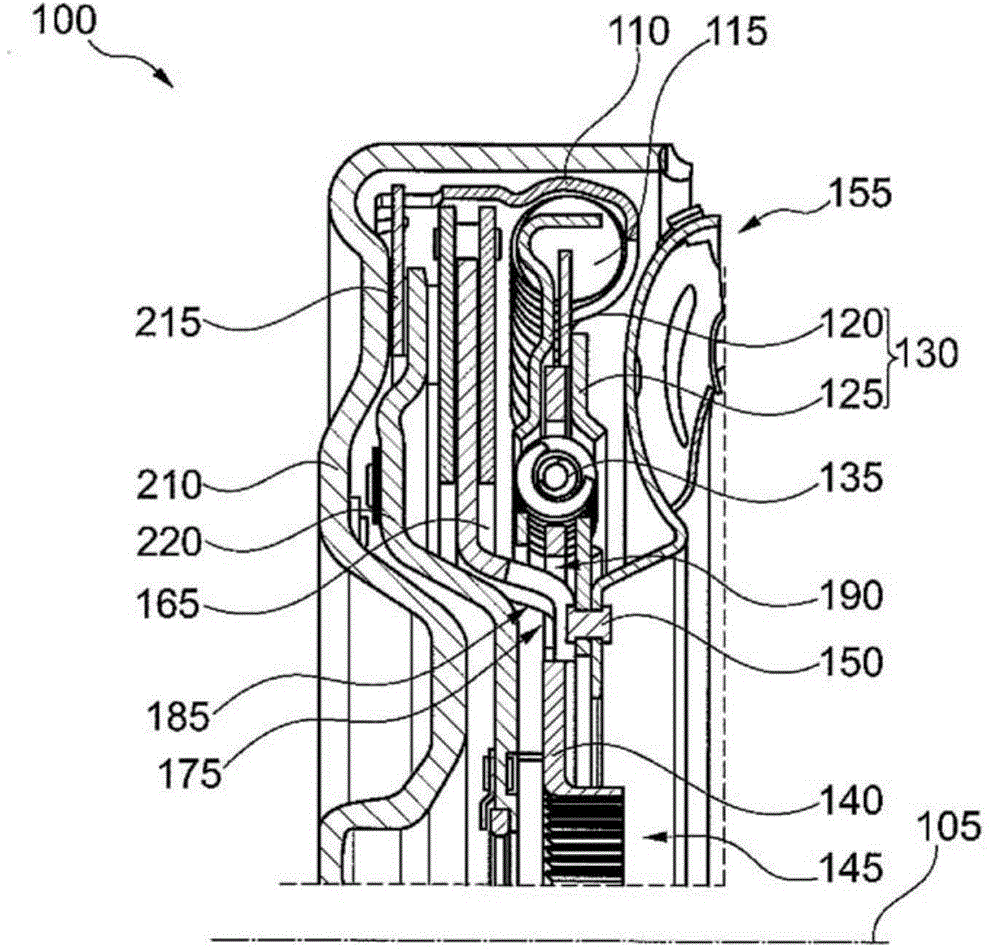
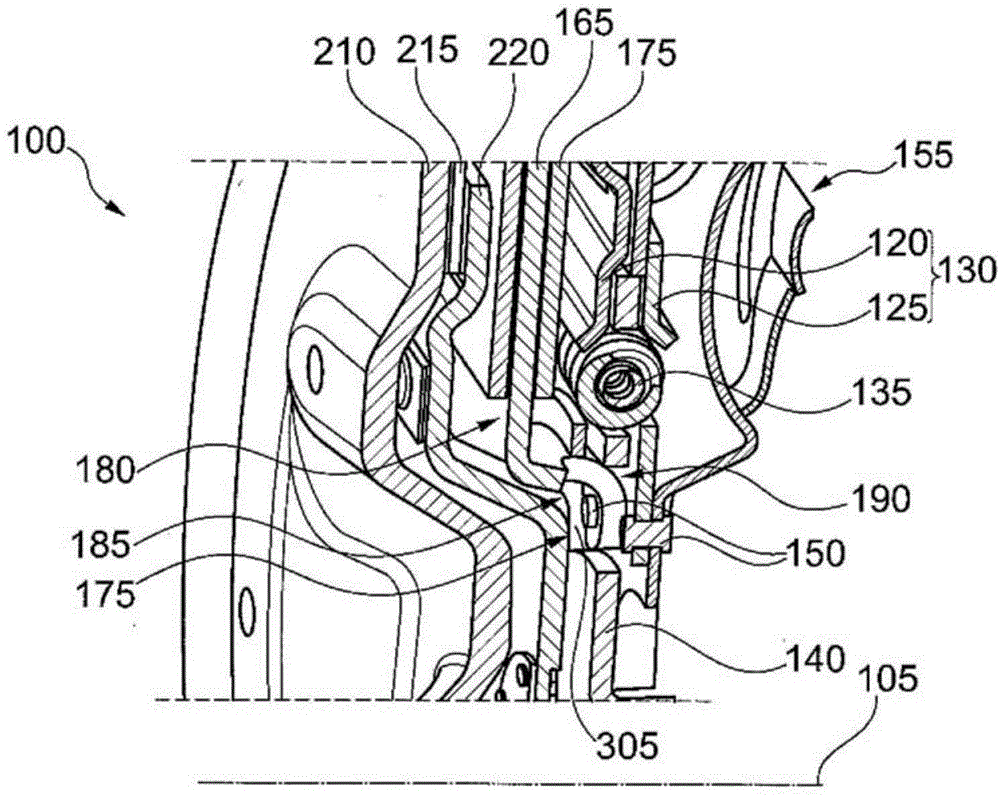
ActiveUS8667887B2Reduces bending load and bending stressReduce wearOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGearingTransverse axisReciprocating motion
An actuator for a rotary function element, having a housing with at least one pressure means supply and being closed at both sides by a cover, in which housing a piston is guided to reciprocate in a sealing manner, the piston containing diametrically opposed, convolution-like connecting links for a transverse axis of an actuator shaft rotatably mounted in one cover, and having two guide rods firmly anchored in the housing only at one end and engaging into guides in the piston, with the one guide rod anchored in one cover, whereas the other guide rod is anchored in the other cover, and the two guides end blind in the piston in opposite directions.
Owner:KRONES AG
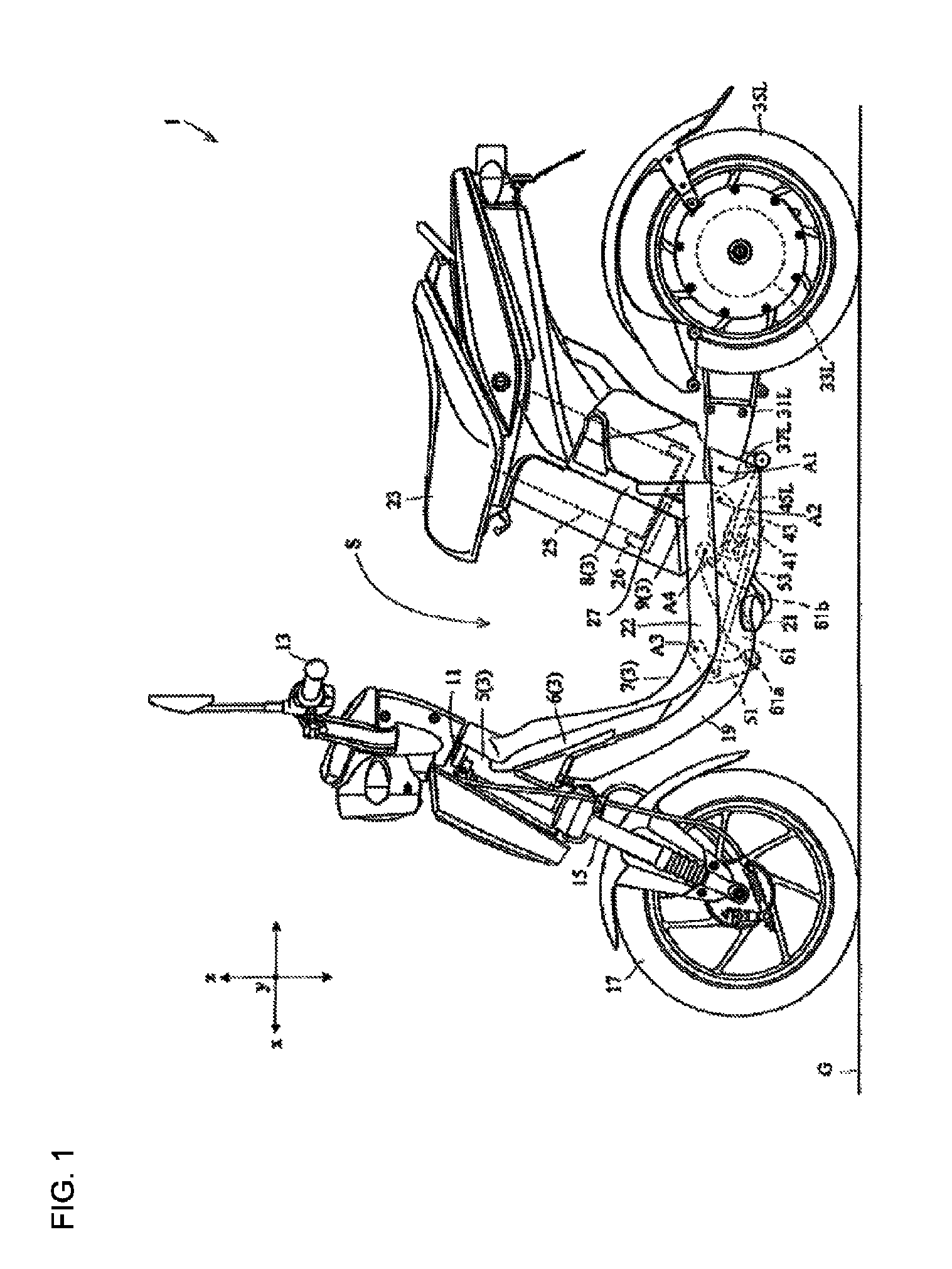
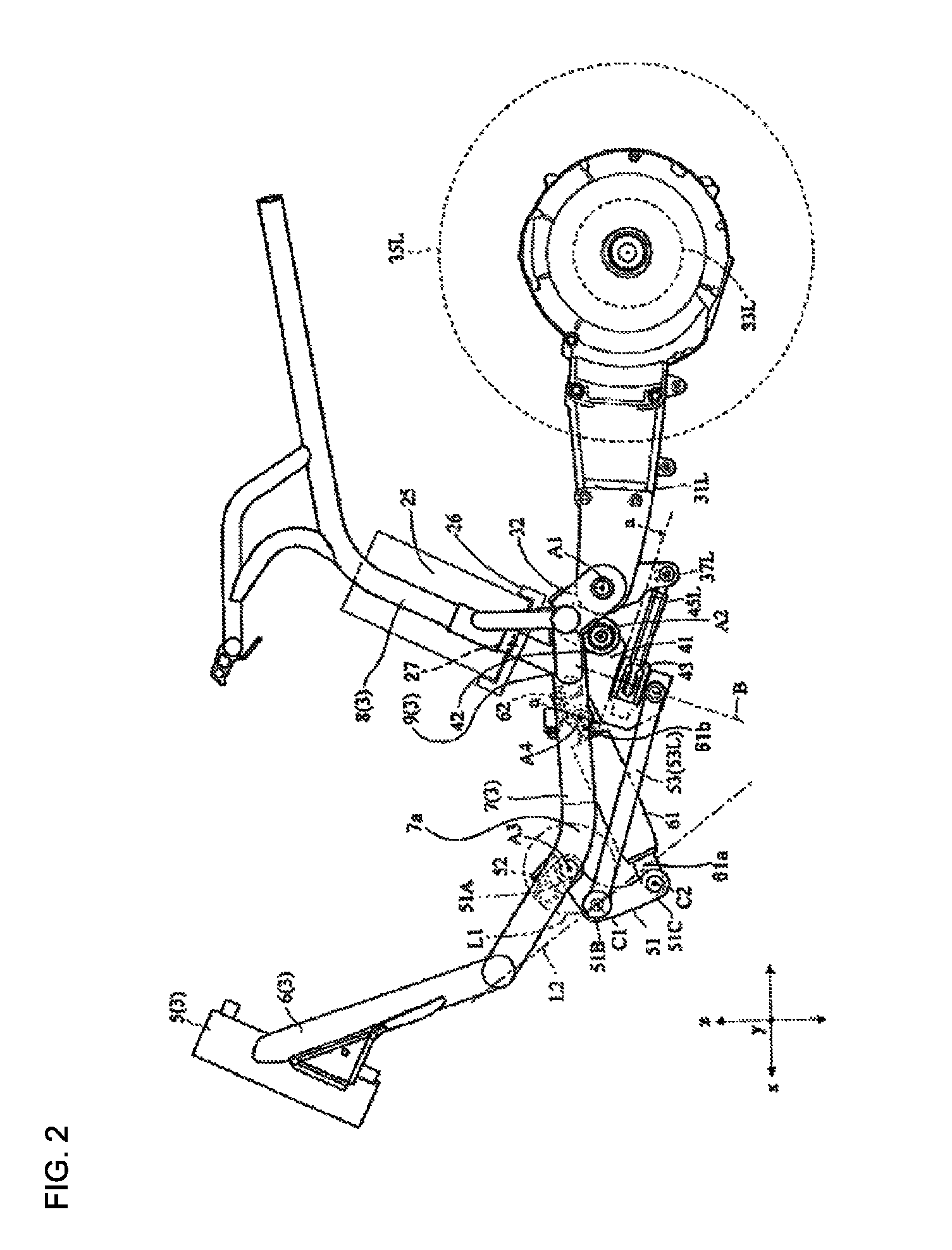
Two-rear-wheel electric vehicle
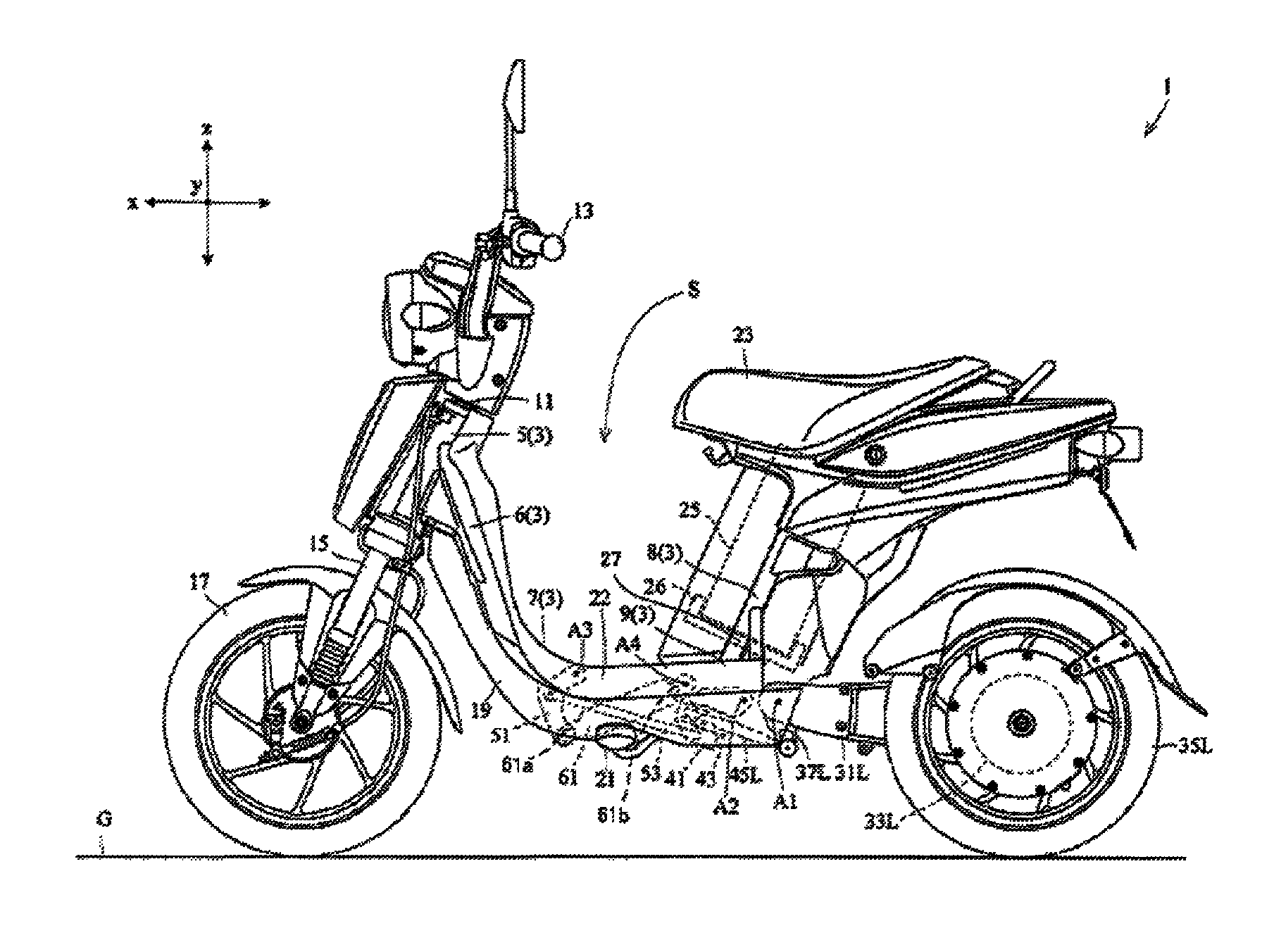
InactiveUS8915323B2Reduce weightLarge capacityUnderstructuresInterconnection systemsEngineeringElectric vehicle
A two-rear-wheel electric vehicle configured to lean its vehicle body frame when turning includes a vehicle body frame, a pair of right and left rear arms, a battery, and a shock absorber. The vehicle body frame includes a head pipe, a front inclined portion, a bottom portion, and a rear inclined portion. The front inclined portion extends obliquely downward and rearward from the head pipe. The bottom portion includes a front support portion that supports a front end portion of the shock absorber. The bottom portion extends rearward in a front-back direction of the vehicle from a rear end portion of the front inclined portion. The rear inclined portion includes a battery support portion, and extends obliquely upward and rearward from a rear end portion of the bottom portion. A swing shaft is positioned rearward of the front support portion and below the battery support portion.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Wind turbine rotor
A wind turbine rotor comprising a hub and a plurality of blades. The hub comprises a plurality of sites, each having a pair of spaced apart annular bearings for receiving a respective wind turbine blade. Each blade has a spar extending along a substantial portion of the length of the blade and protrudes from the proximal end of the blade. The spar protrudes into and is rotatably received within the respective spaced apart bearings and is fixed to the hub.
Owner:BLADE DYNAMICS LTD
Drive belt for transmitting drive movement, and method for producing drive belt
InactiveCN103228947AReduce dosageAvoid damageV-beltsDriving beltsCarbon fibersUltimate tensile strength
Owner:ARNTZ BET GMBH & CO KG
Wind turbine
ActiveCN102985690AEasy to manufactureReduce bending loadWind motor controlEngine fuctionsWind forceRotational axis
Wind turbine comprising a rotor, a generator and a tower, said rotor comprising a rotor hub and one or more rotor blades and said generator comprising a generator stator and a generator rotor, wherein the rotor hub is rotatably mounted on a frame and the generator and tower are arranged on the same of the rotor, and the generator stator is attached to said frame substantially in a plane perpendicular to the rotor's rotational axis, and wherein the generator rotor is rotatably mounted on a part of the generator stator.
Owner:GE RENEWABLE TECH WIND BV
Actuator
ActiveUS20110220819A1Easy to manufactureReduces bending load and bending stressOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid-pressure actuatorsTransverse axisReciprocating motion
An actuator for a rotary function element, having a housing with at least one pressure means supply and being closed at both sides by a cover, in which housing a piston is guided to reciprocate in a sealing manner, the piston containing diametrically opposed, convolution-like connecting links for a transverse axis of an actuator shaft rotatably mounted in one cover, and having two guide rods Firmly anchored in the housing only at one end and engaging into guides in the piston, with the one guide rod anchored in one cover, whereas the other guide rod is anchored in the other cover, and the two guides end blind in the piston in opposite directions.
Owner:KRONES AG
Torque coupler
ActiveCN104620019AReduce bending loadReduce loadRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingRotational axisCentrifugal force
A torque coupler comprises an input side and an output side, which are rotatably disposed about a rotational axis, further an intermediate disk for coupling to the input side, an output flange for coupling to the output side, a spring damper for coupling the intermediate disk to the output flange and a centrifugal-force pendulum having a pendulum flange and a pendulum mass. The pendulum flange extends between a first region, in which the pendulum flange is fastened to the intermediate disk, and a second region, in which the pendulum mass is mounted on the pendulum flange. The output flange has a cutout section through which a portion of the pendulum flange connecting the two regions runs.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Fastening mechanism of a fuel cell stack
InactiveCN1614797AImprove sealing characteristicsRaise unrestrictedFuel cells groupingCell component detailsFuel cellsMechanical engineering
A fuel cell fixing mechanism, comprising: a pair of end plates, which are respectively installed at both ends of the fuel cell stack to support the fuel cell stack; and a plurality of fixing belts extending in the stacking direction of the fuel cell stack, used for The end plates are pressed by a predetermined pressure. This securing mechanism creates uniform pressure on the separator and improves the sealing of the fuel cell stack.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com