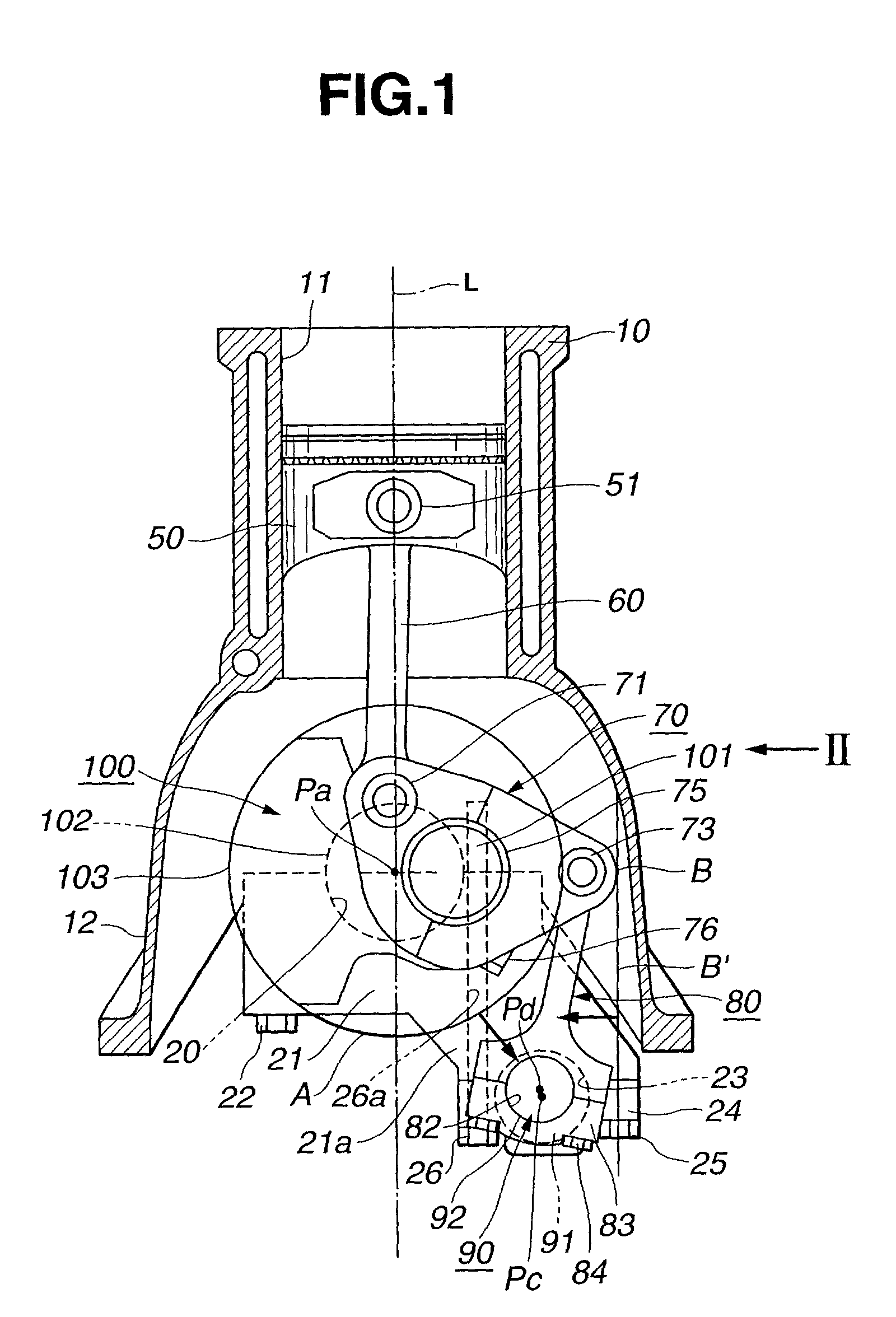
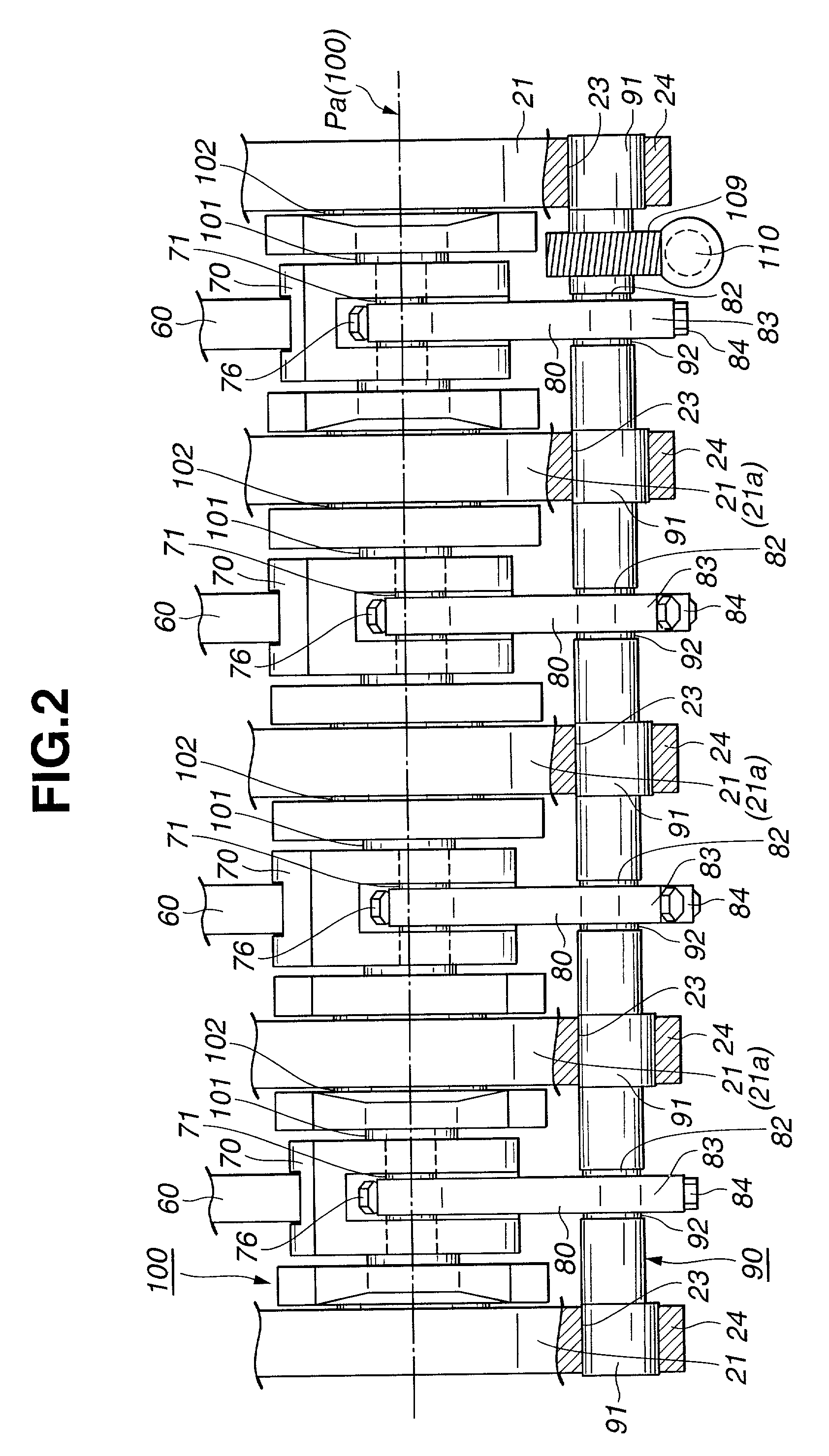
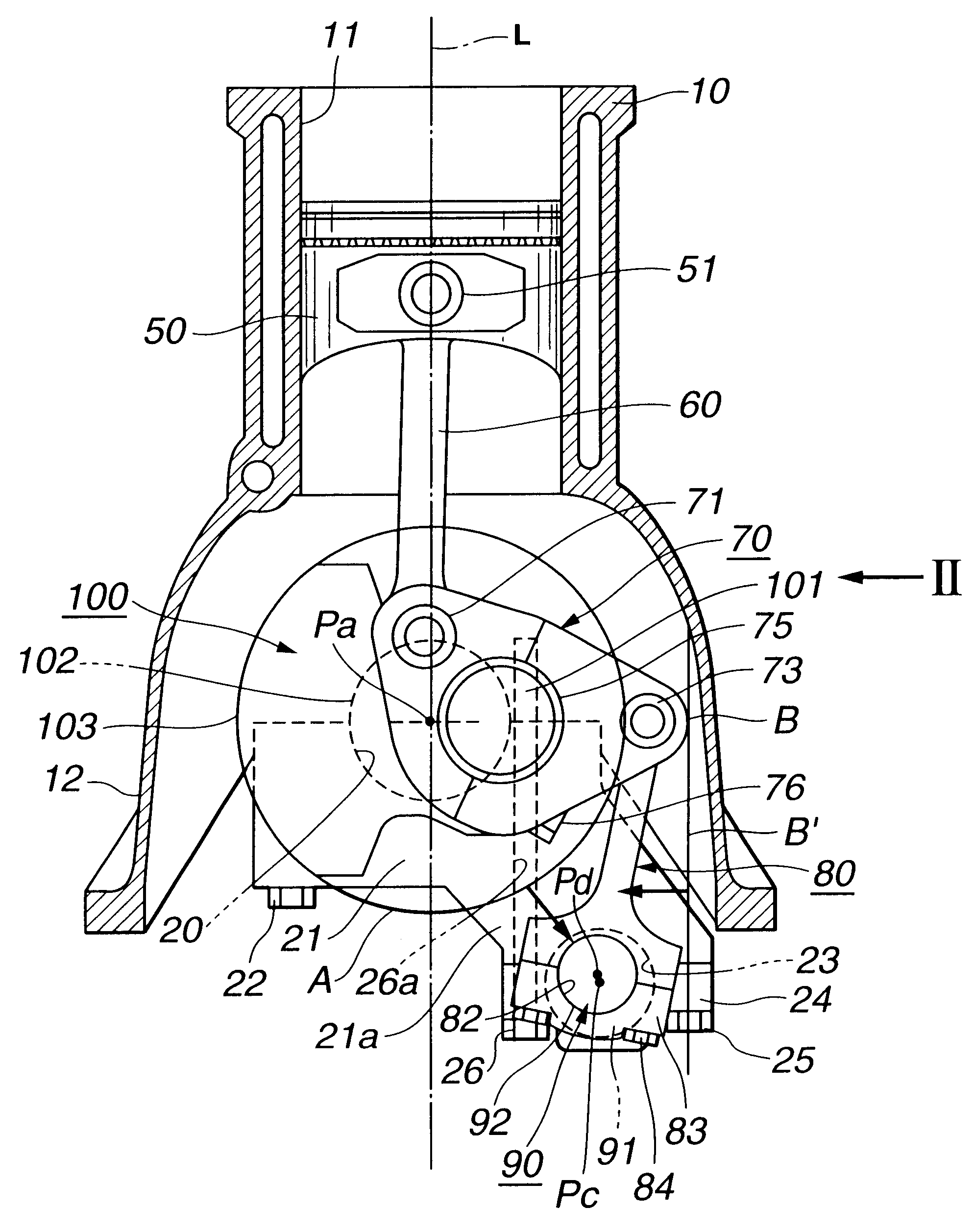
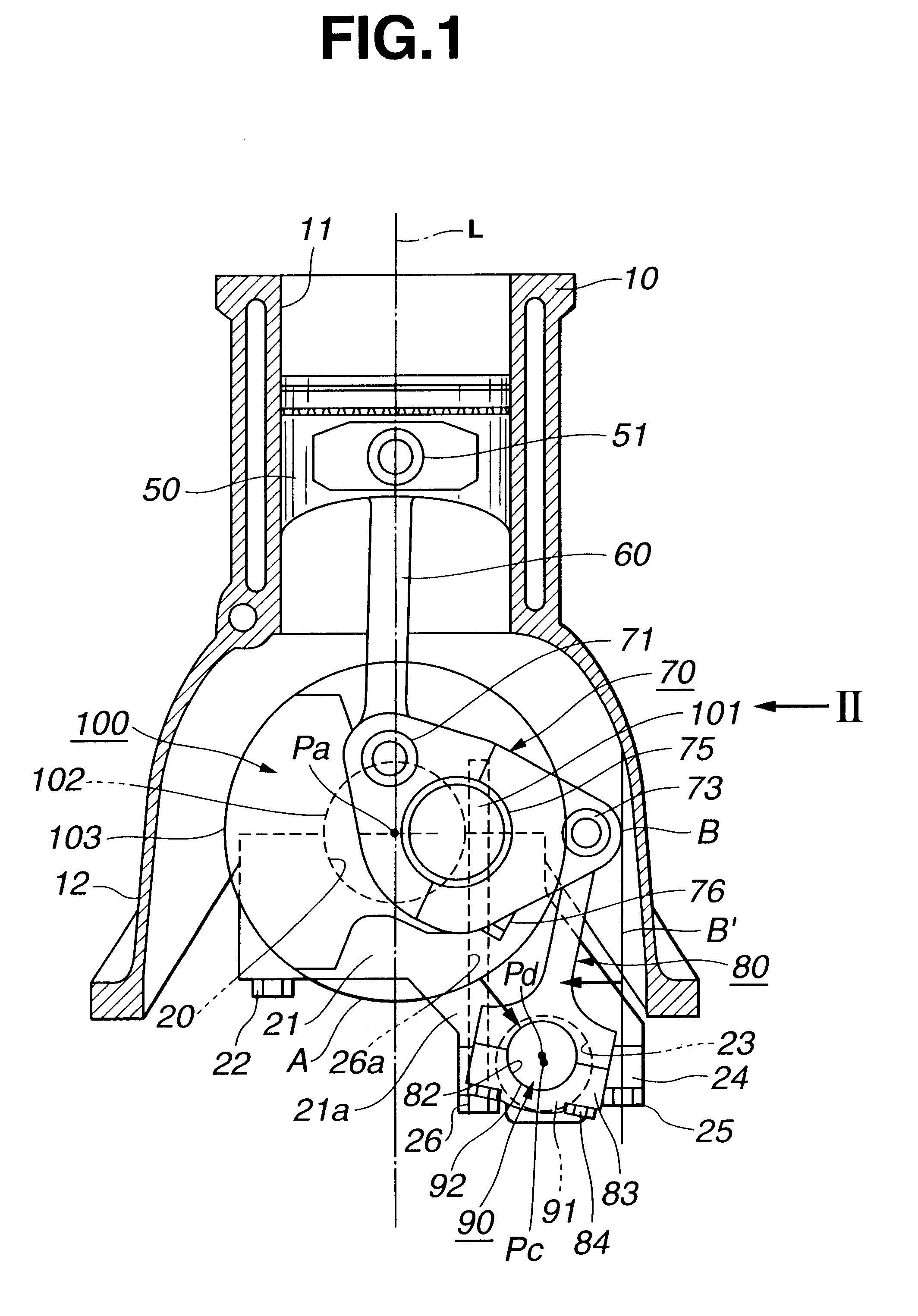
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
890 results about "Variable compression ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
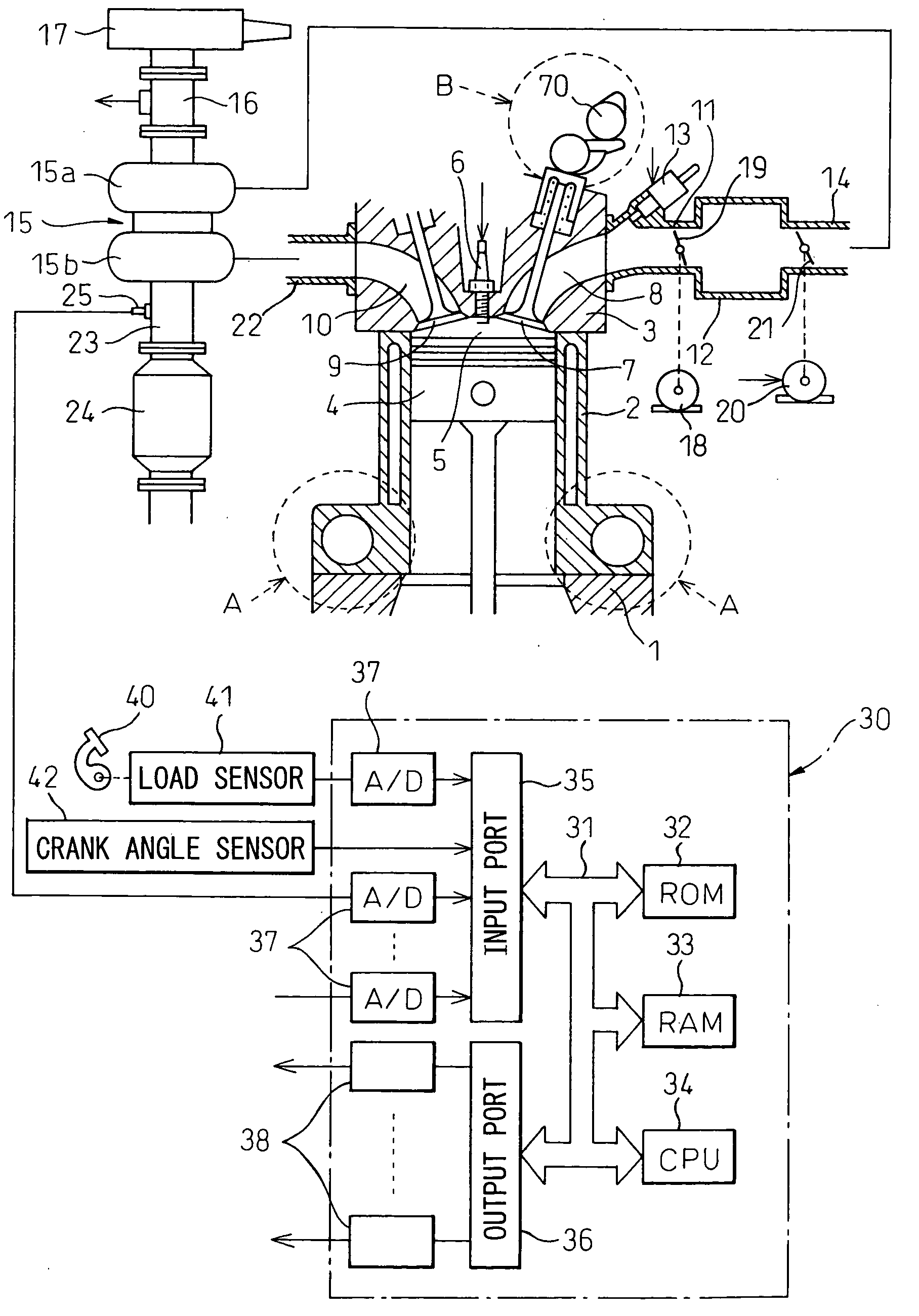
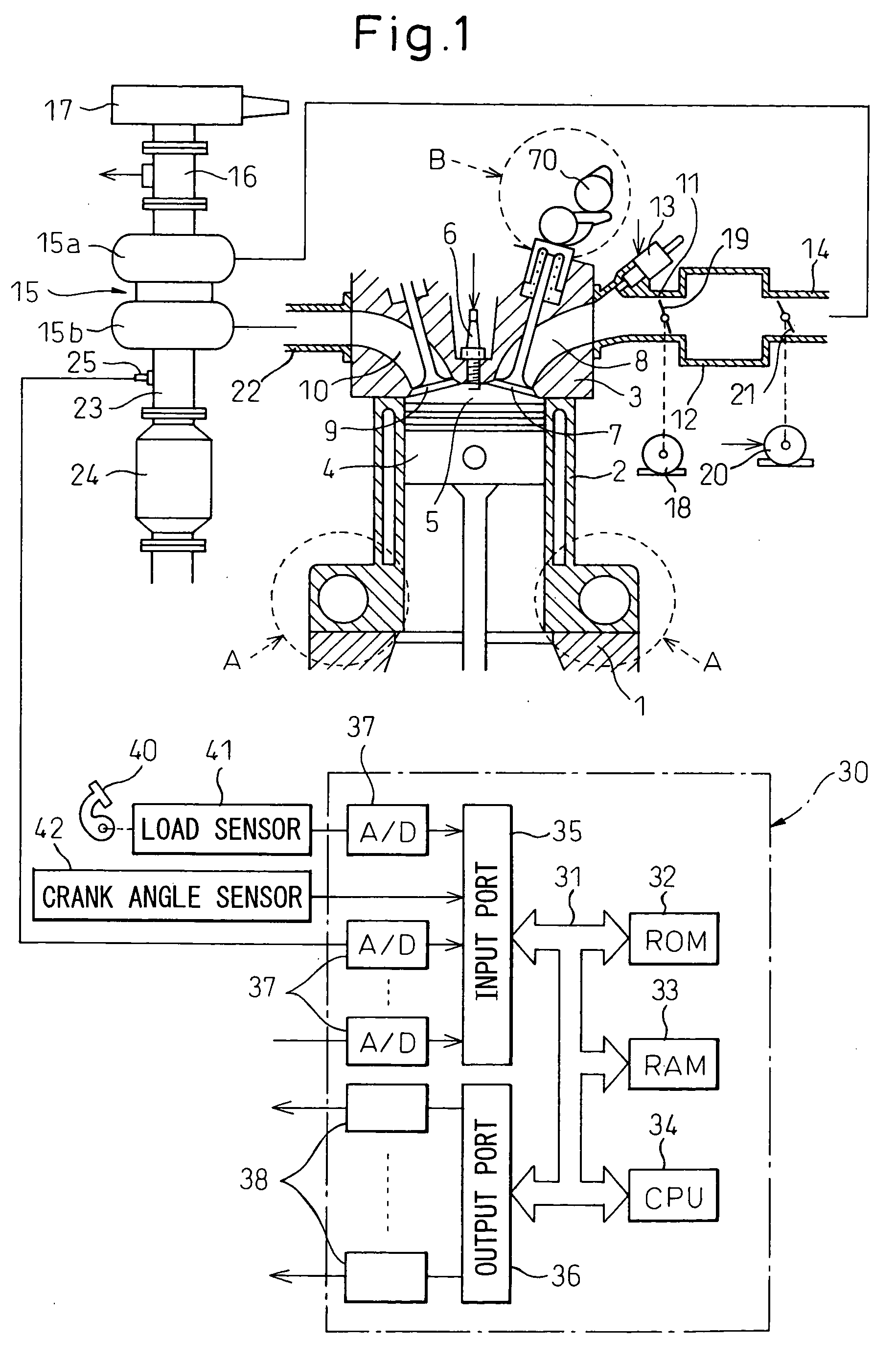
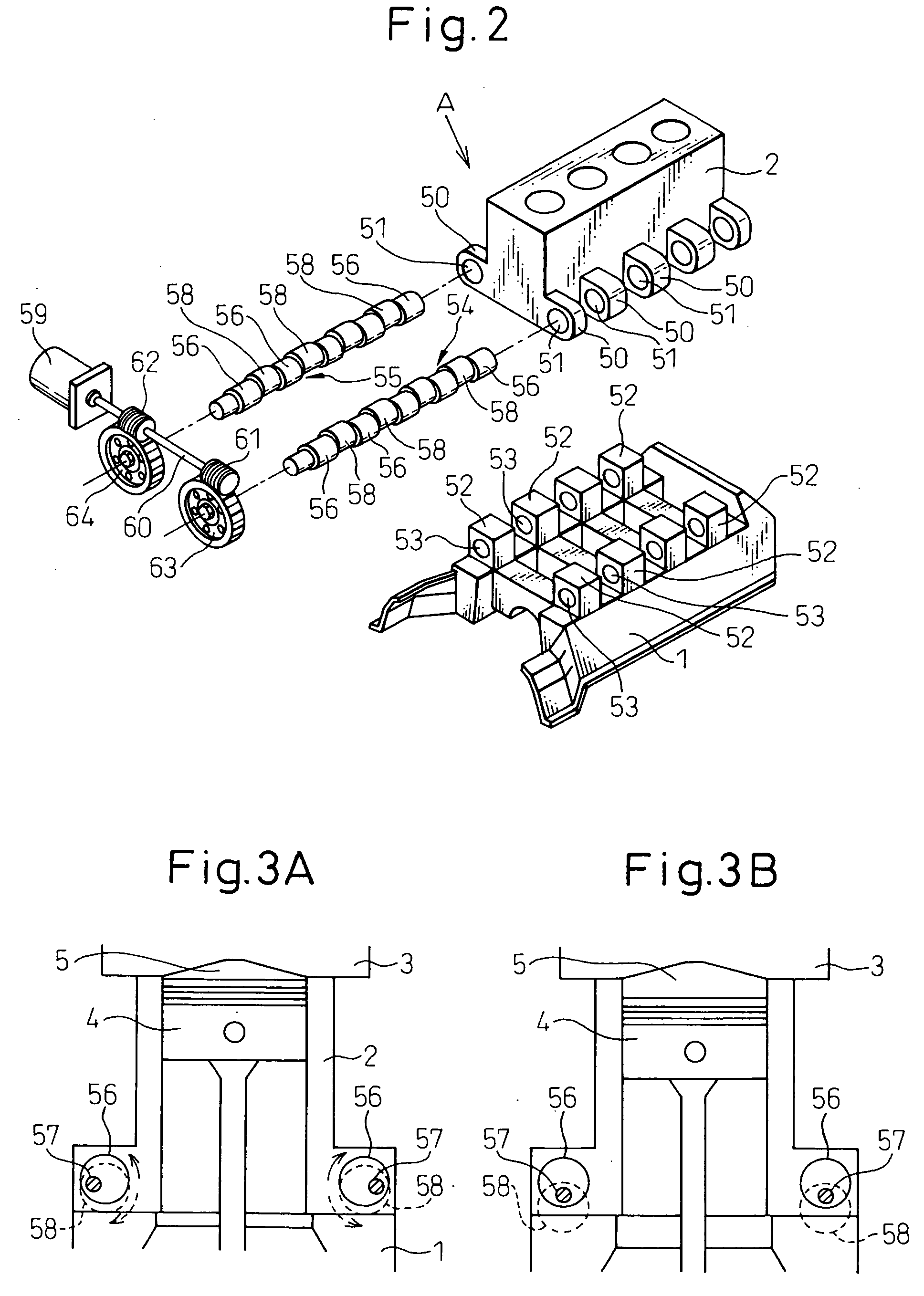
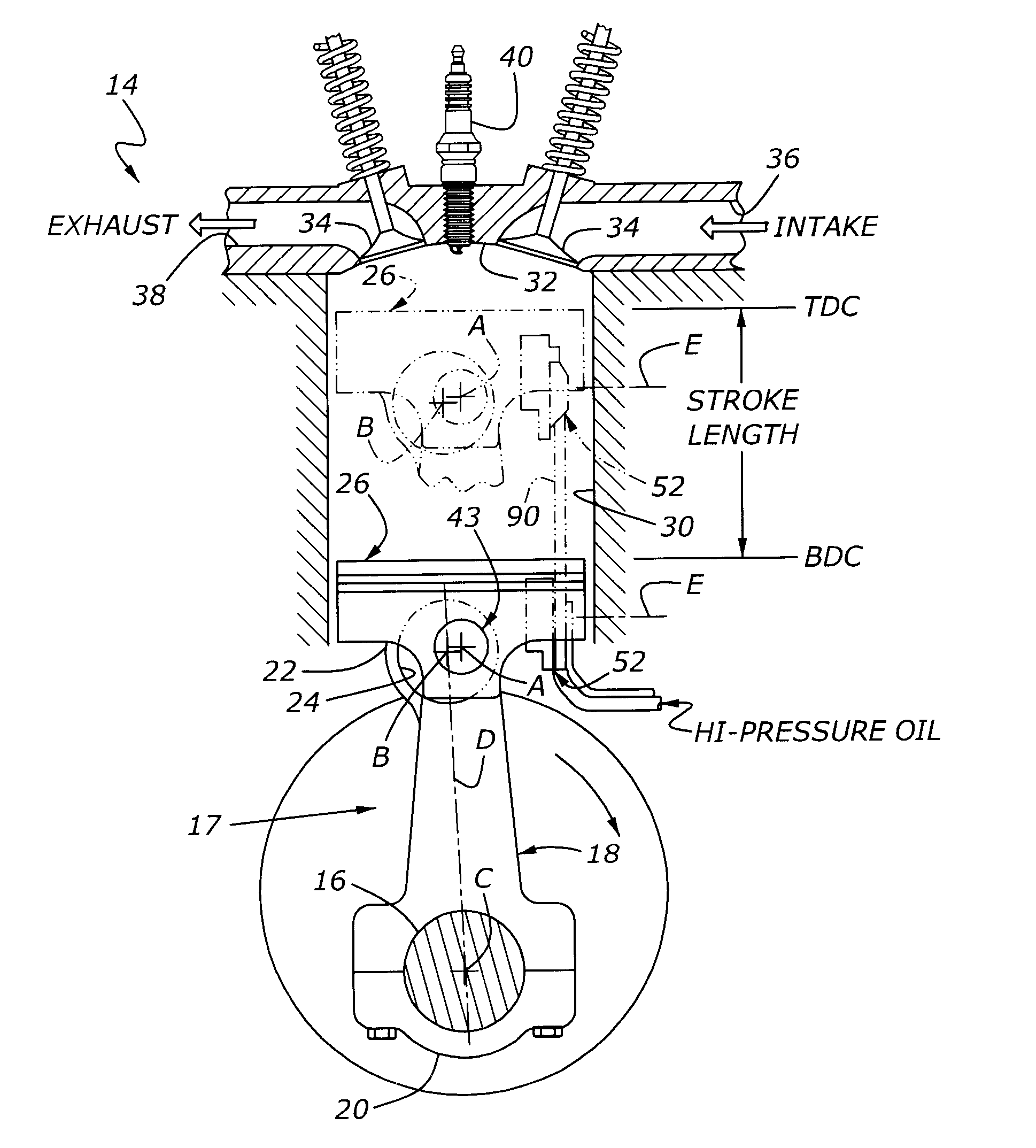
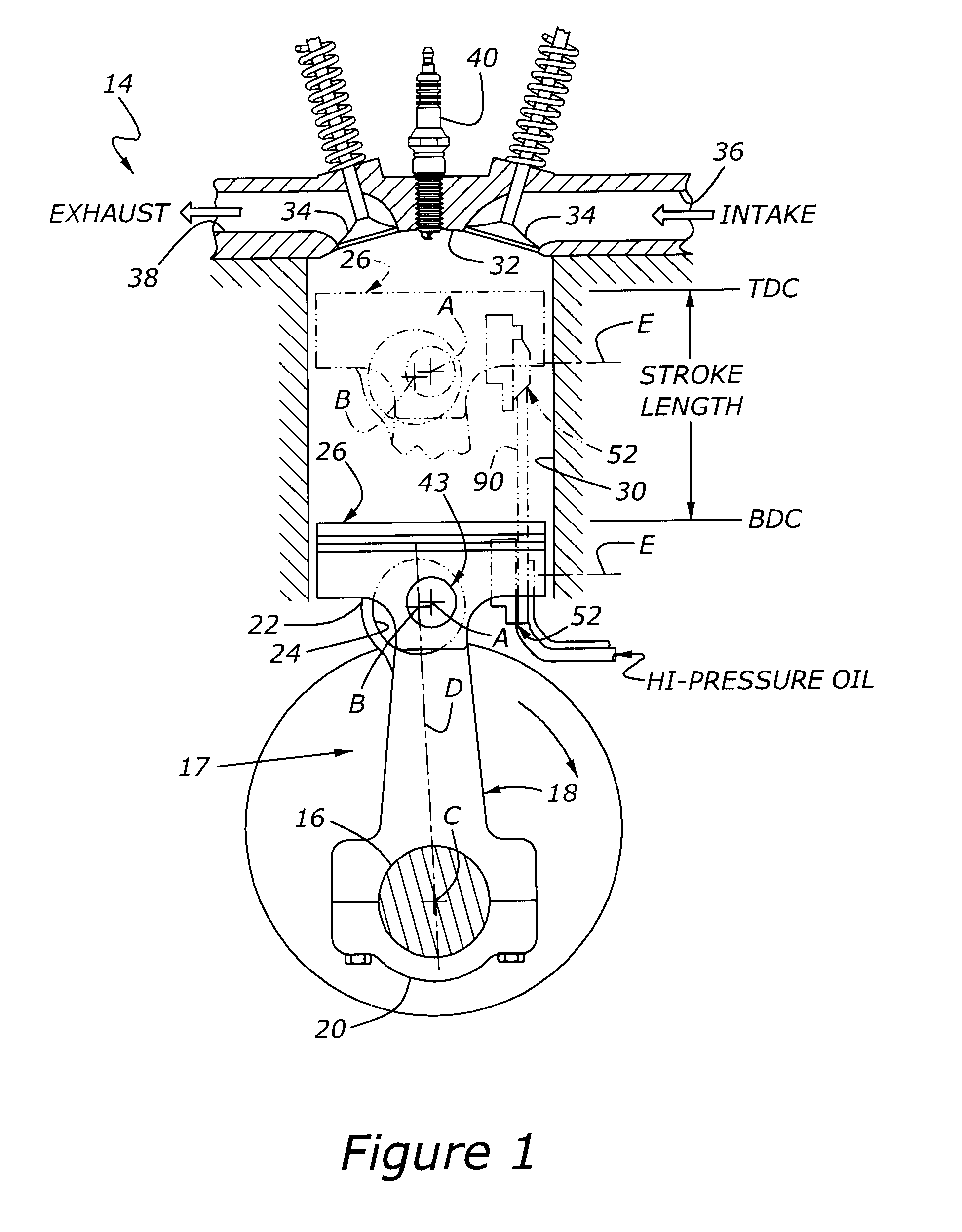
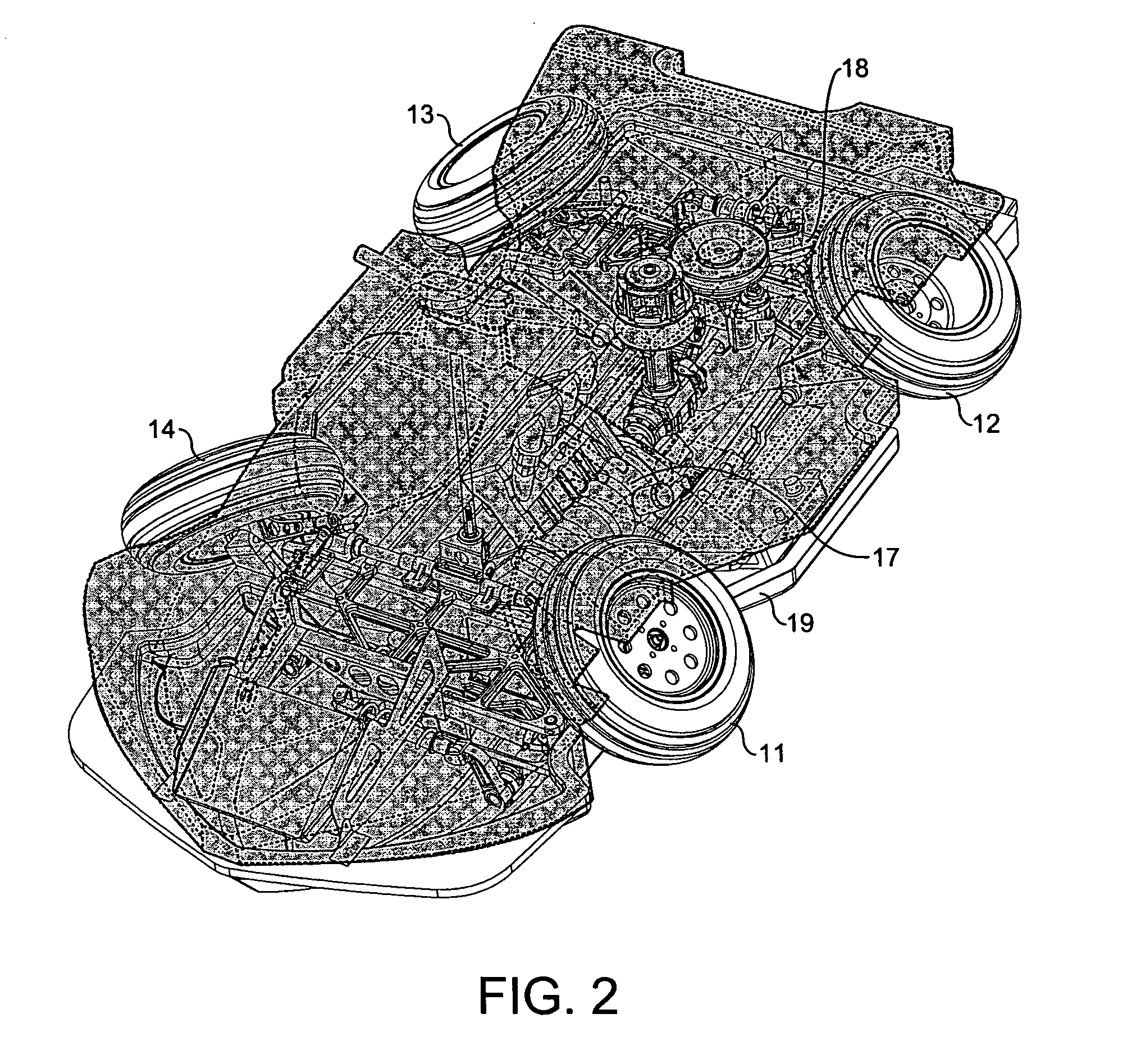
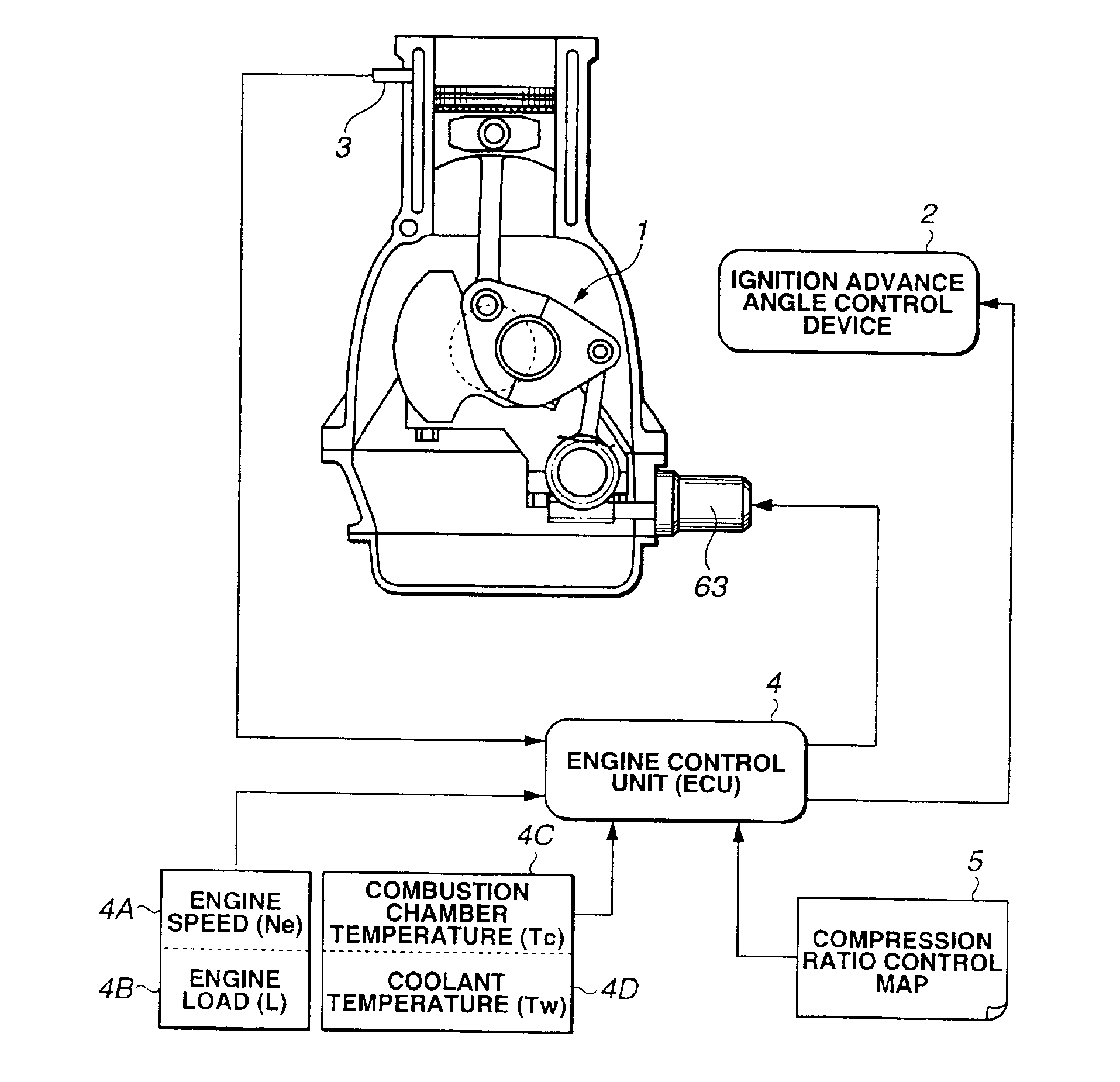
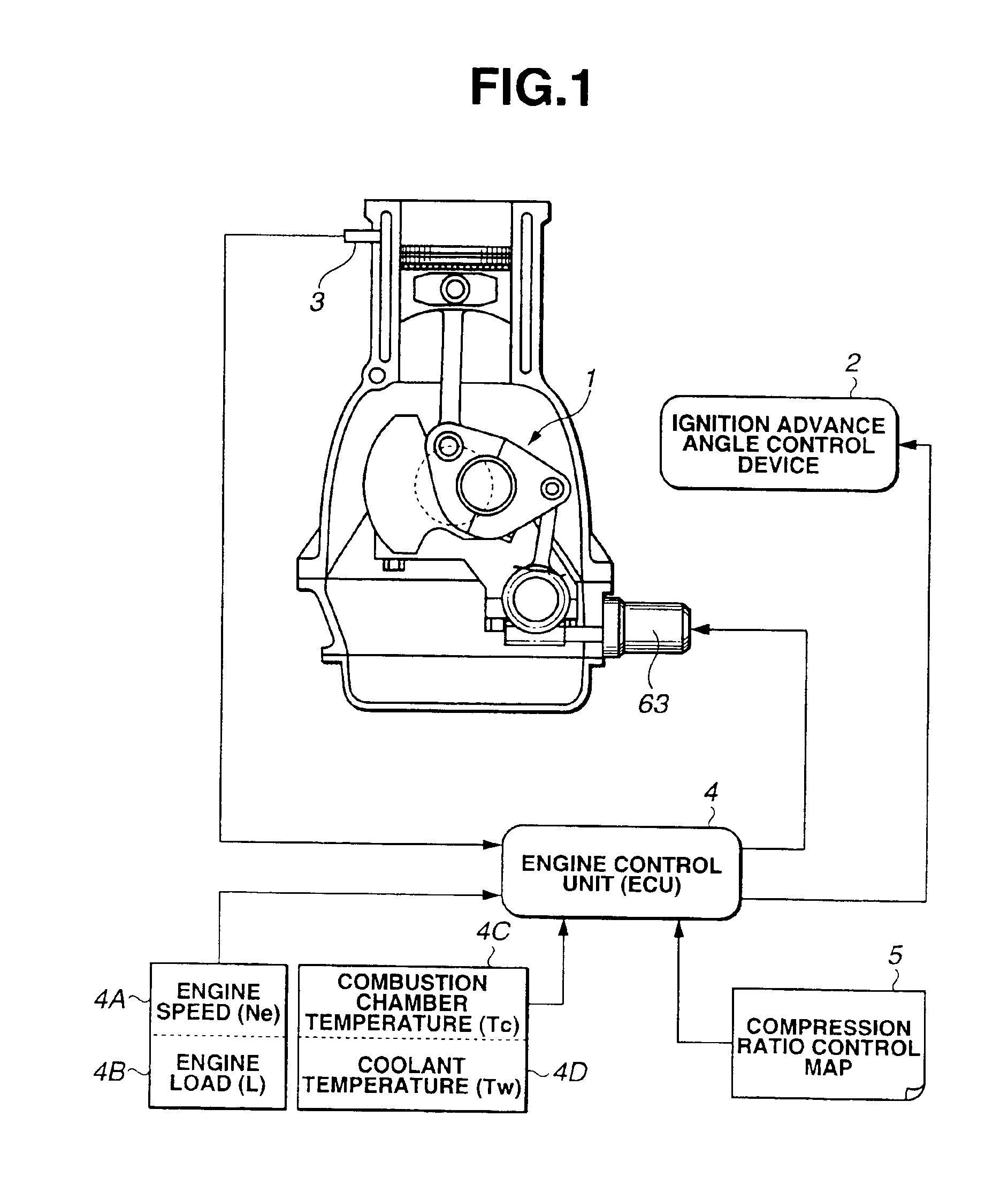
Variable compression ratio is a technology to adjust the compression ratio of an internal combustion engine while the engine is in operation. This is done to increase fuel efficiency while under varying loads. Variable compression engines allow the volume above the piston at top dead centre to be changed. Higher loads require lower ratios to increase power, while lower loads need higher ratios to increase efficiency, i.e. to lower fuel consumption. For automotive use this needs to be done as the engine is running in response to the load and driving demands. The 2019 Infiniti QX 50 is the first commercially available car that uses a variable compression ratio engine.
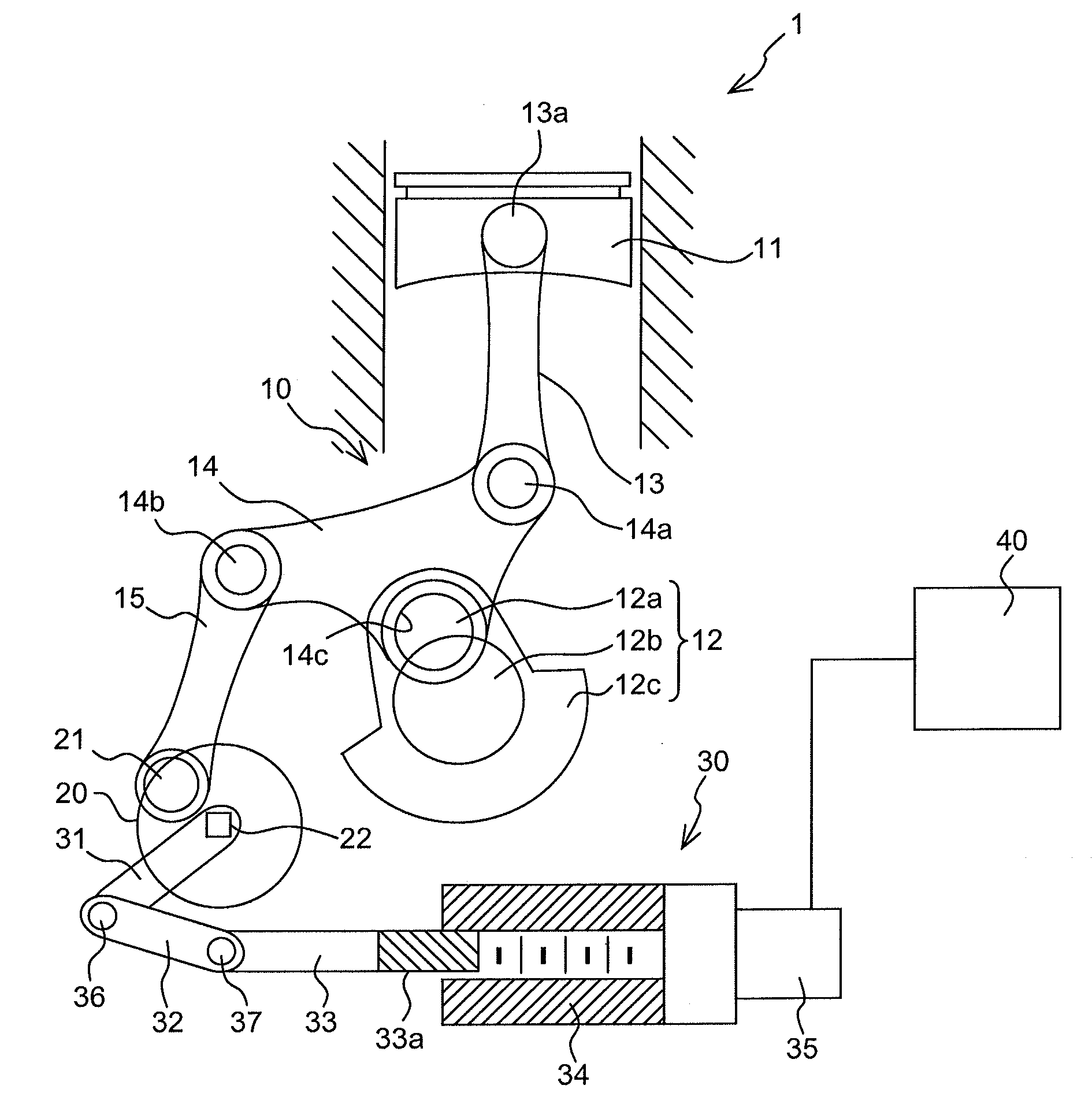
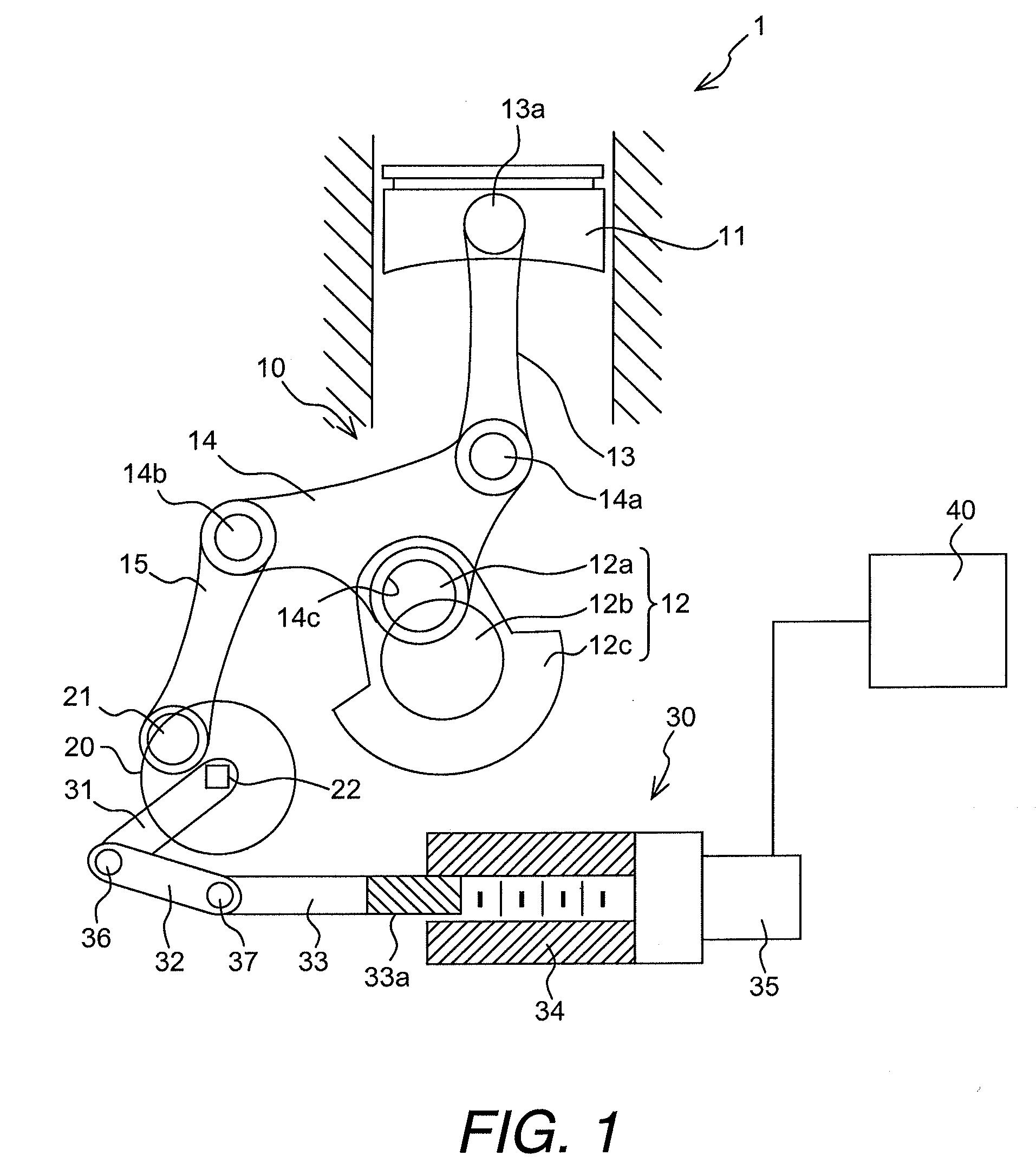
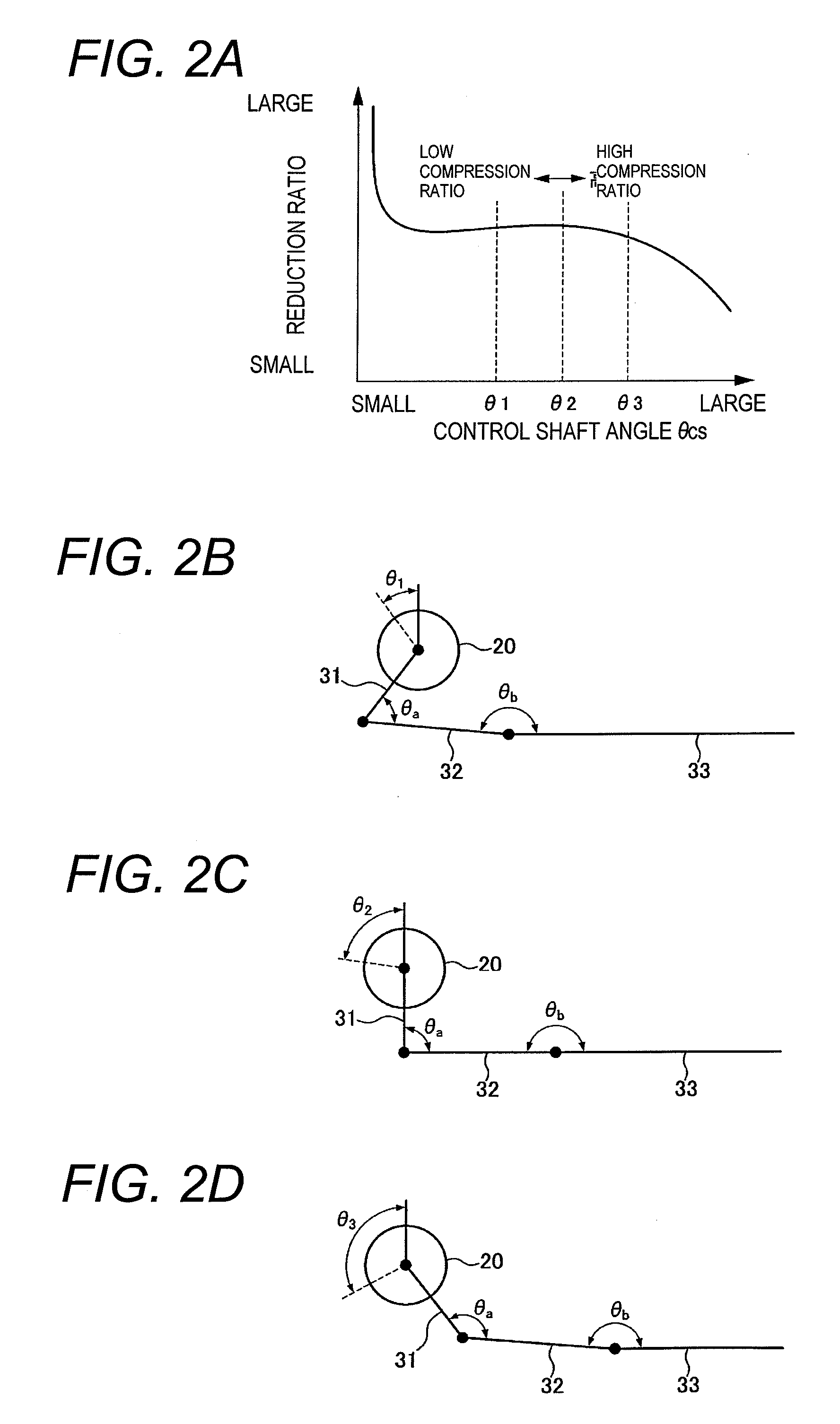
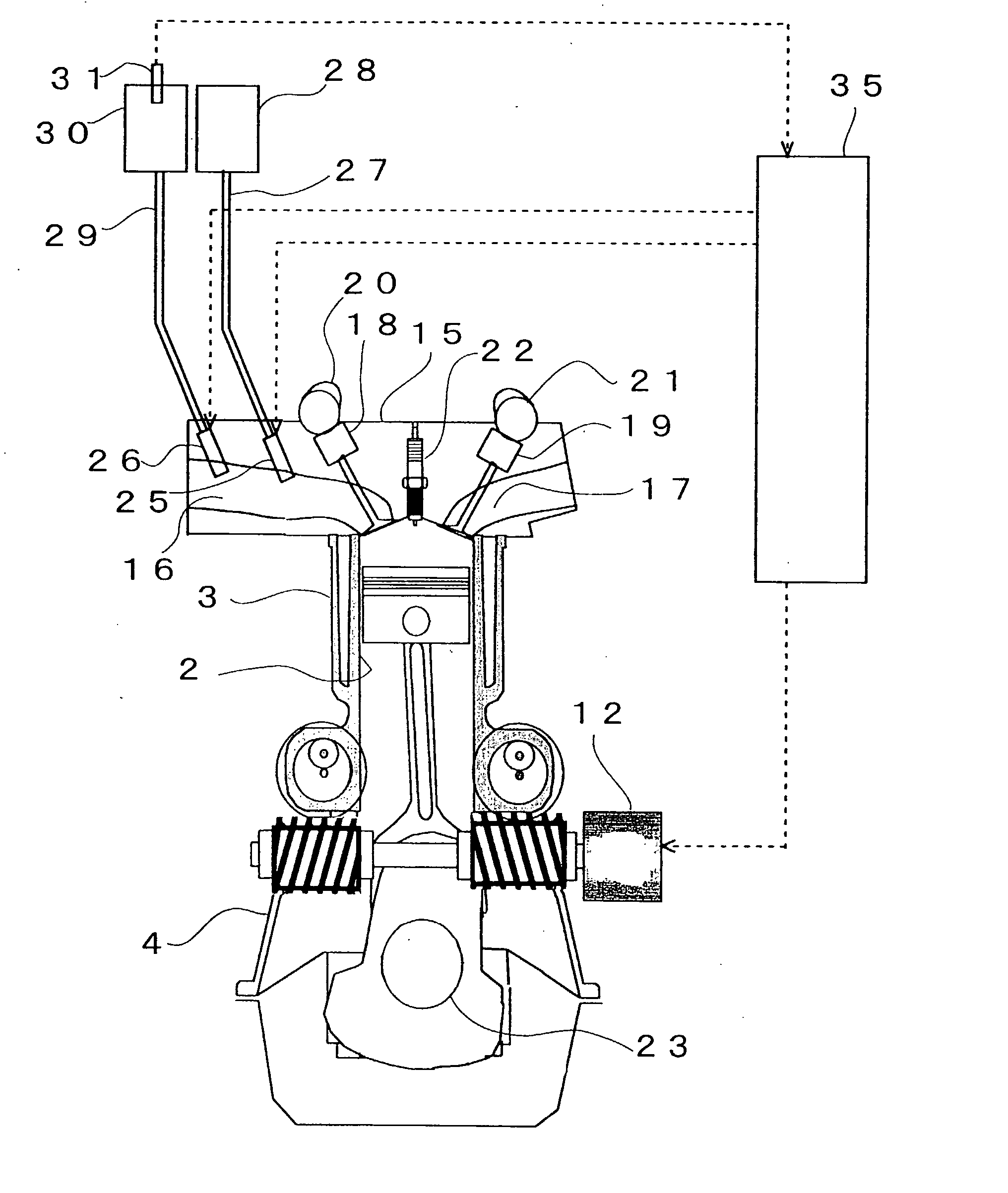
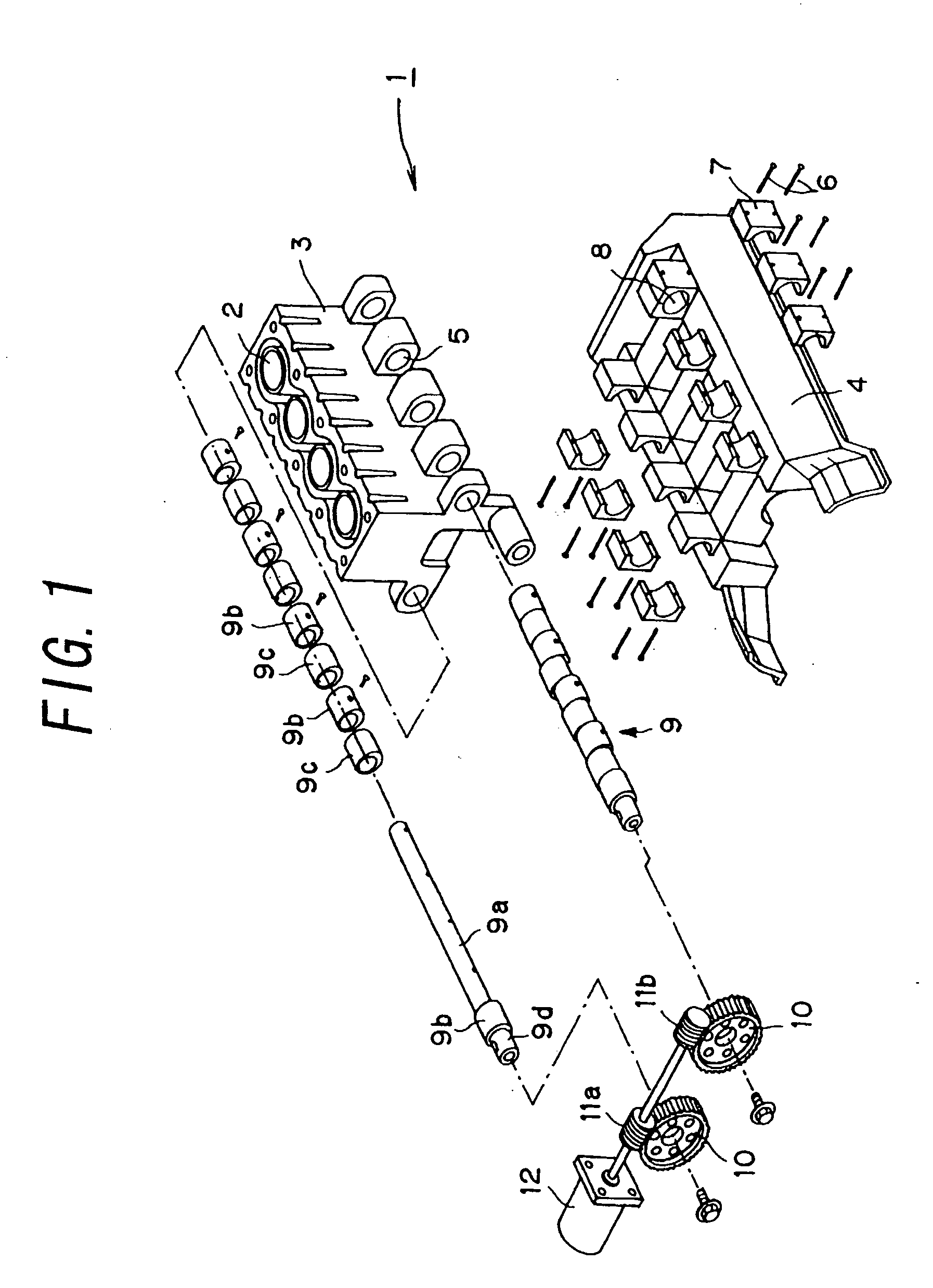
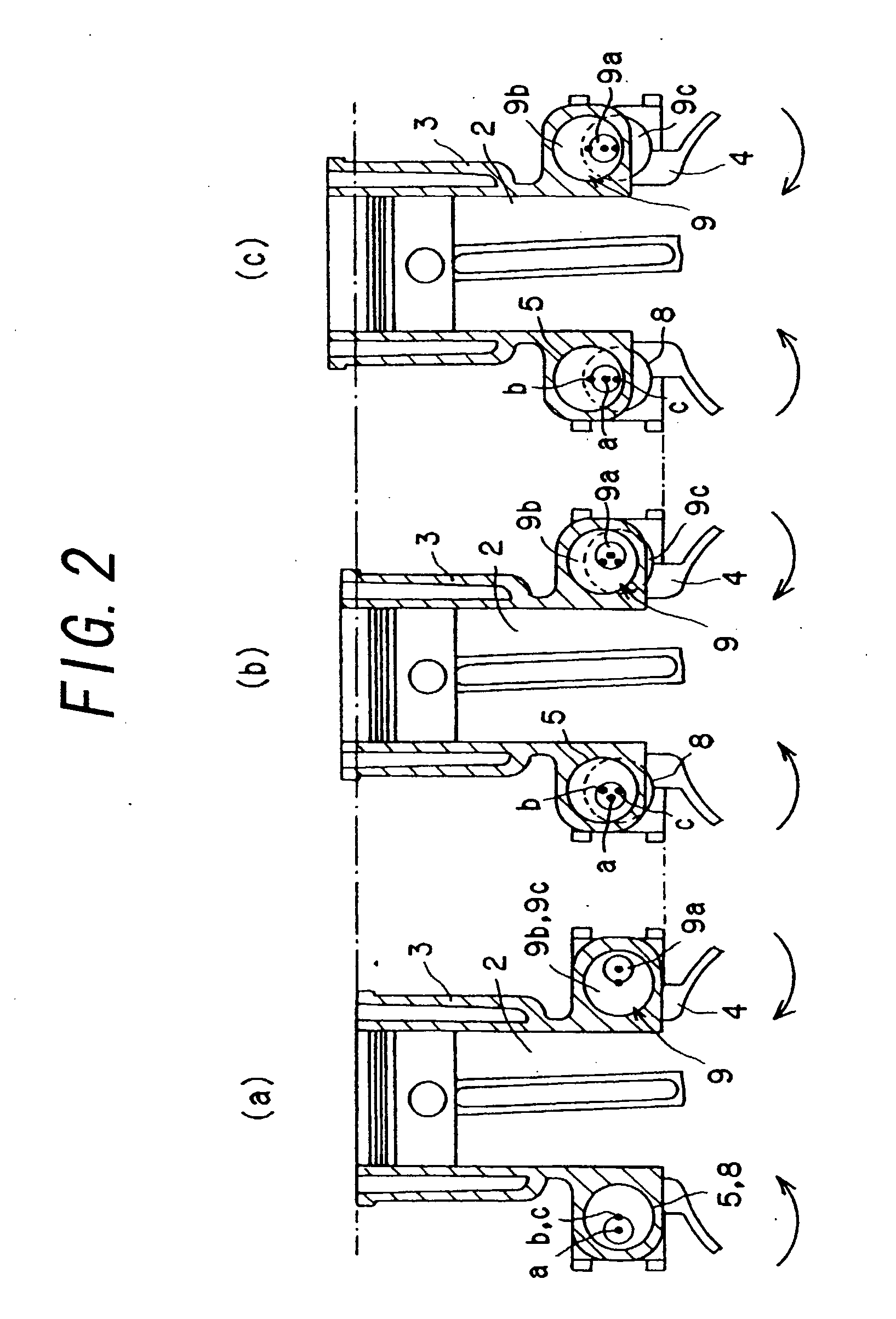
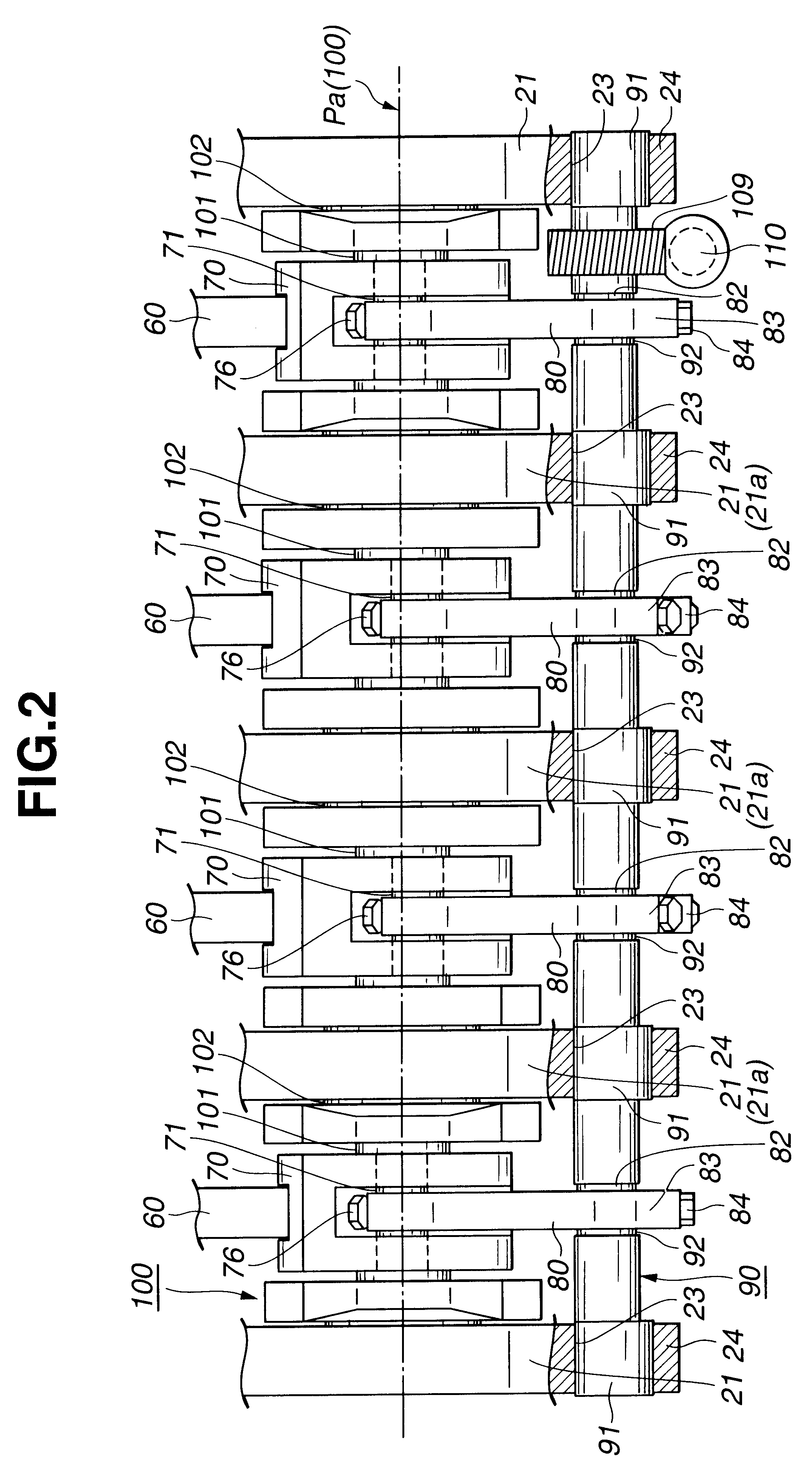
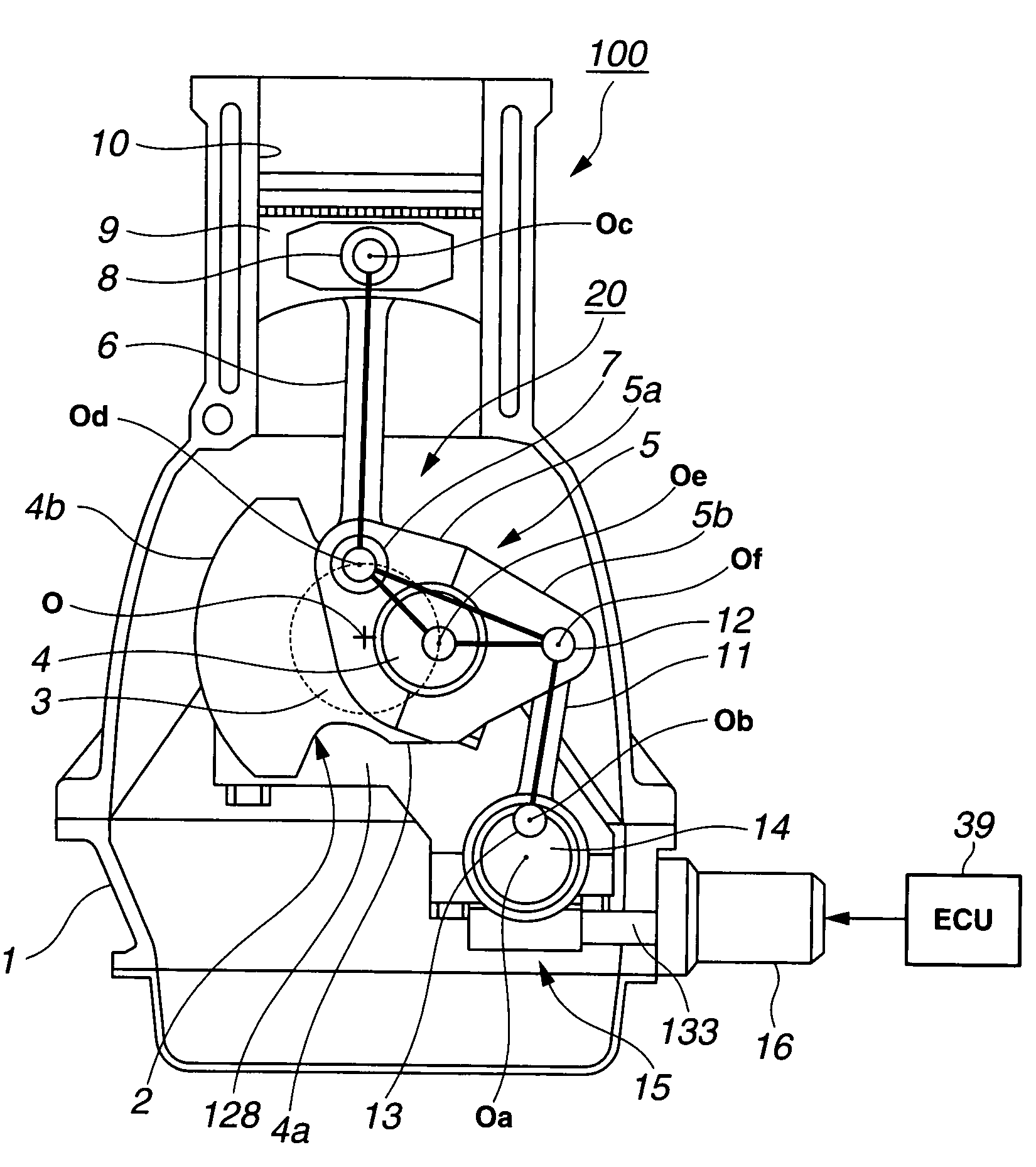
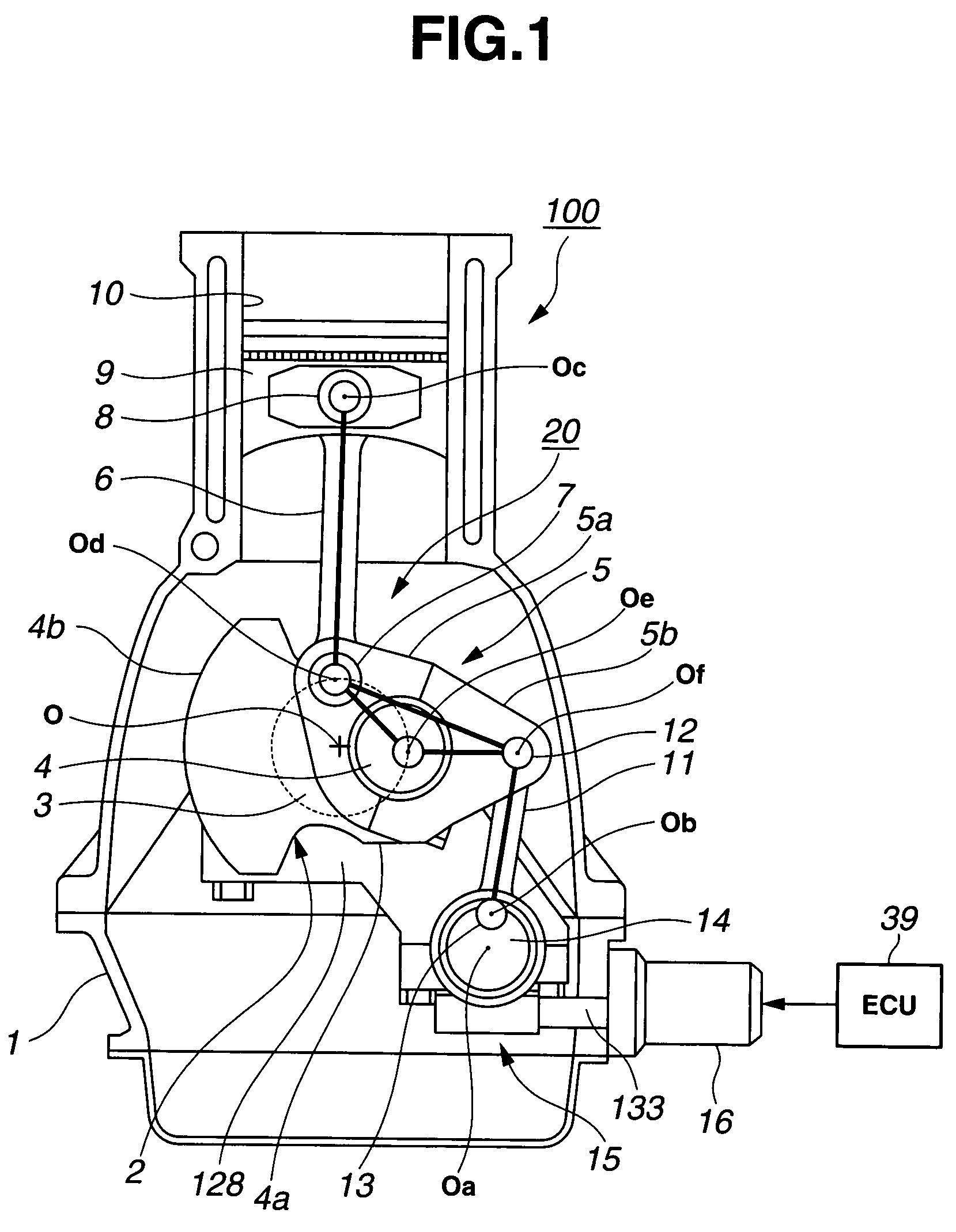
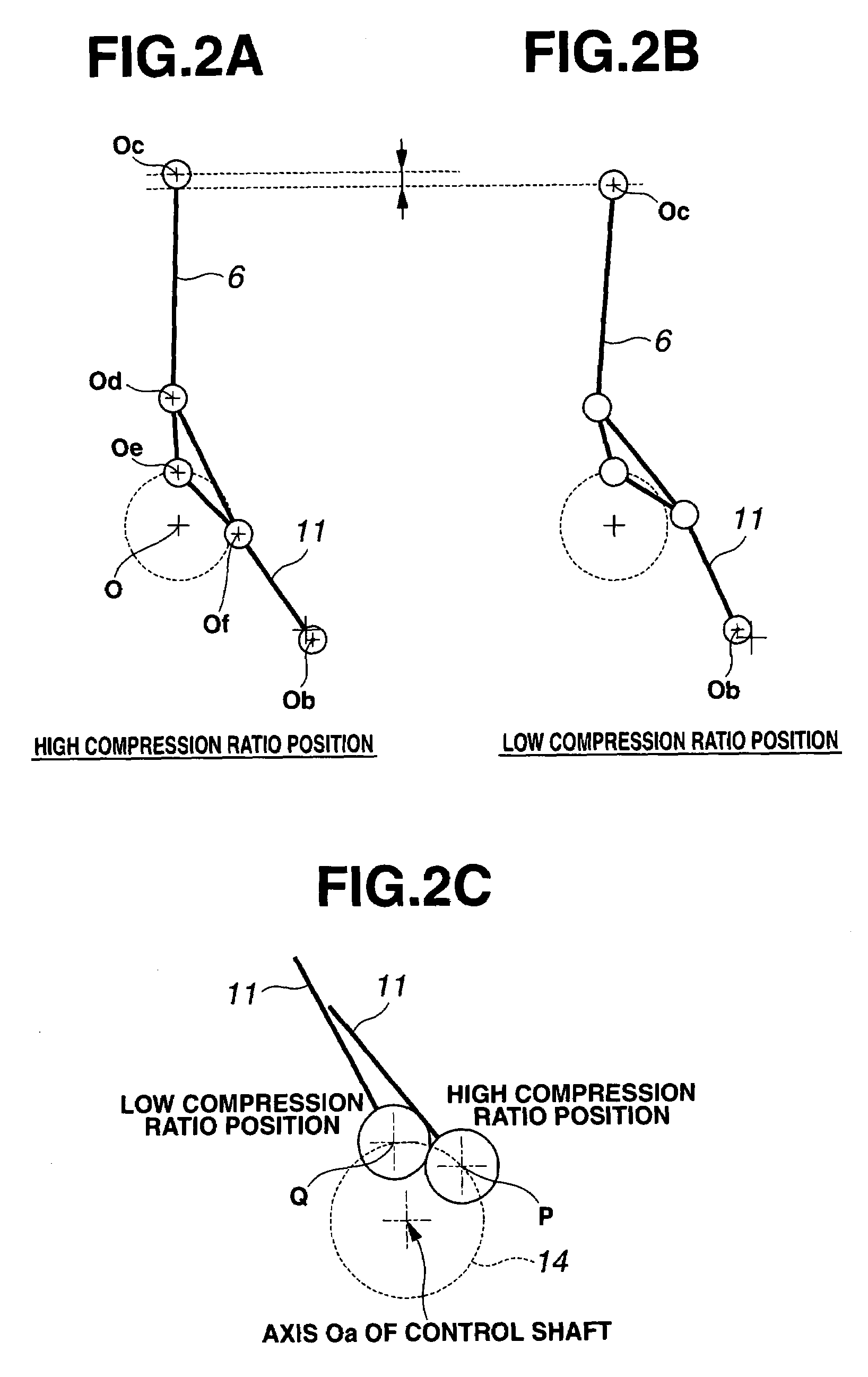
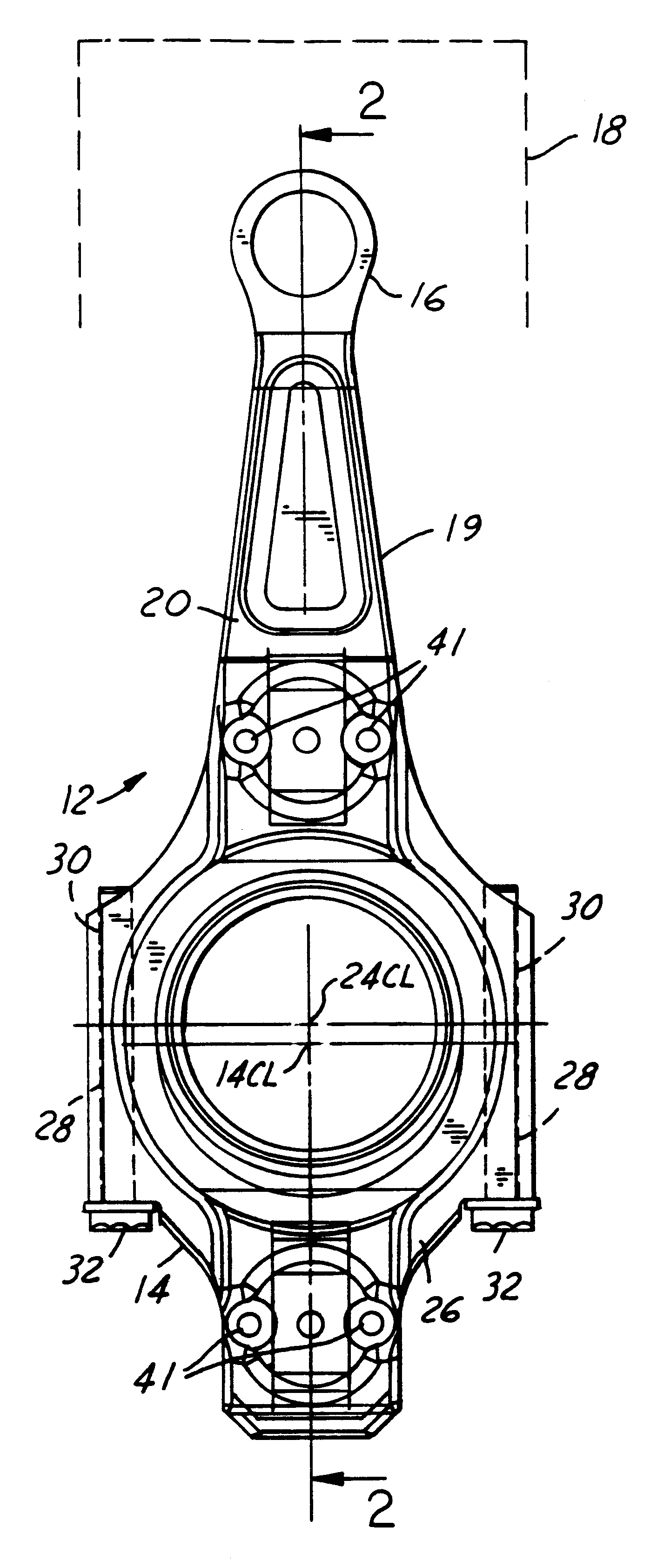
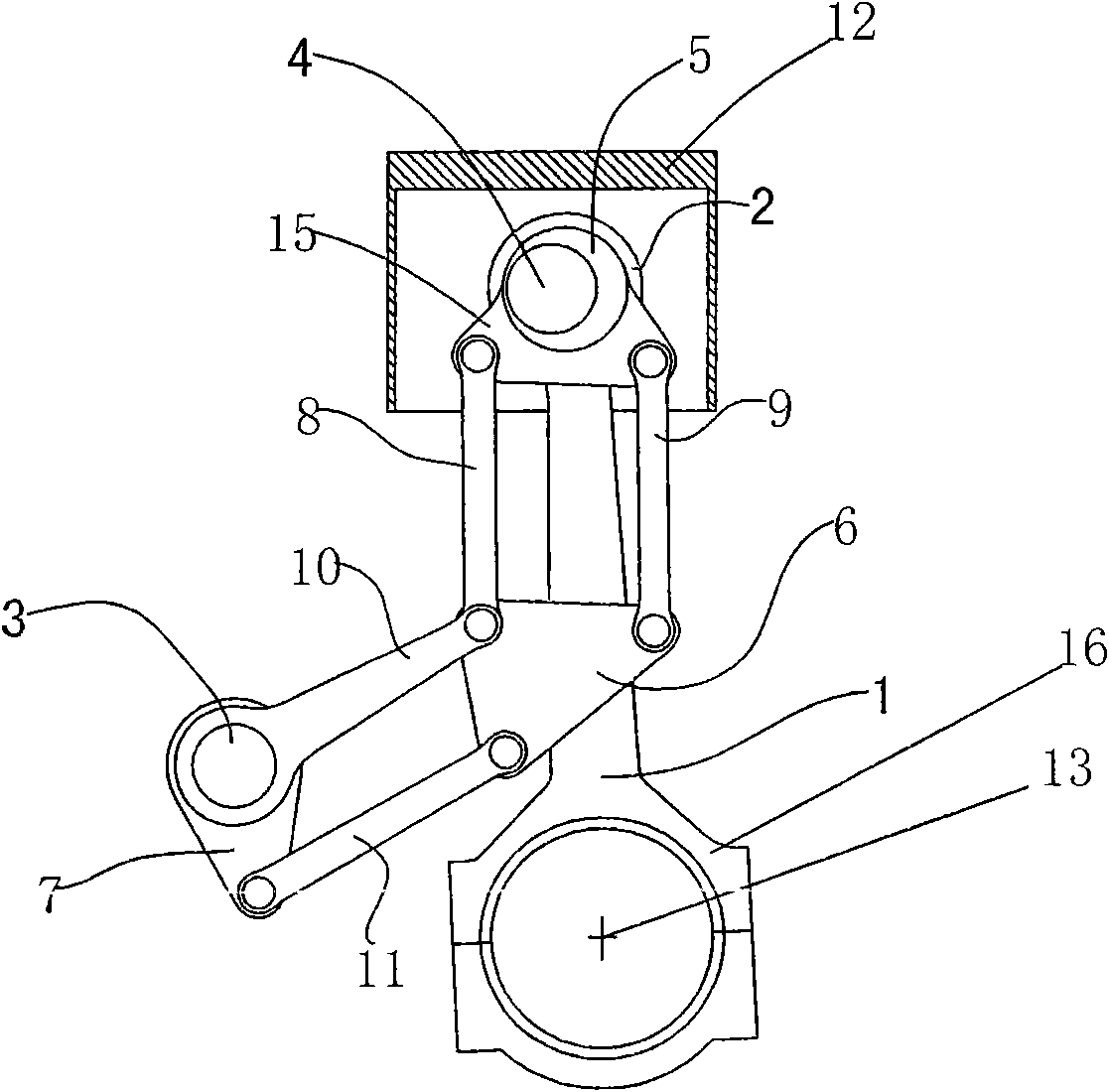
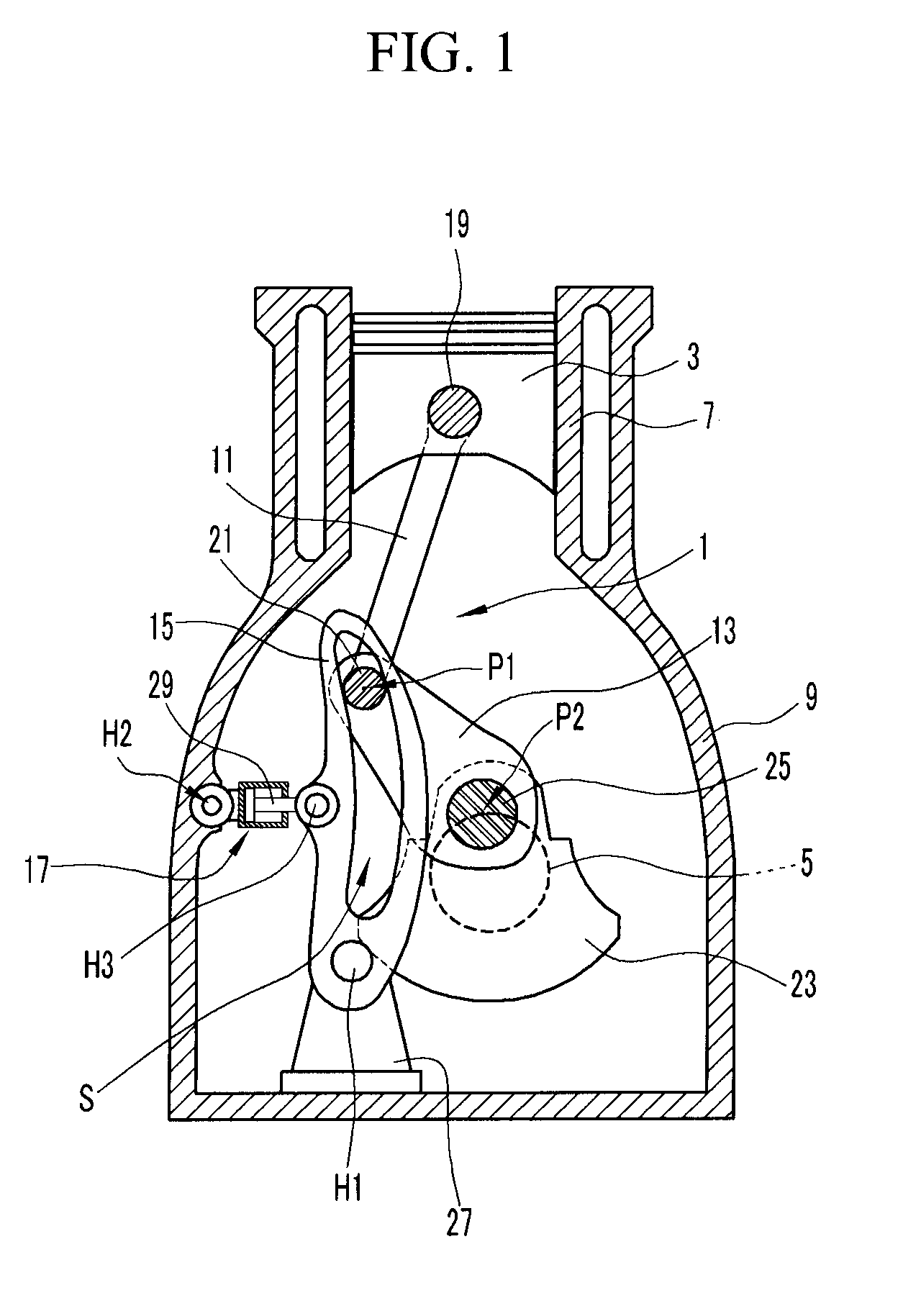
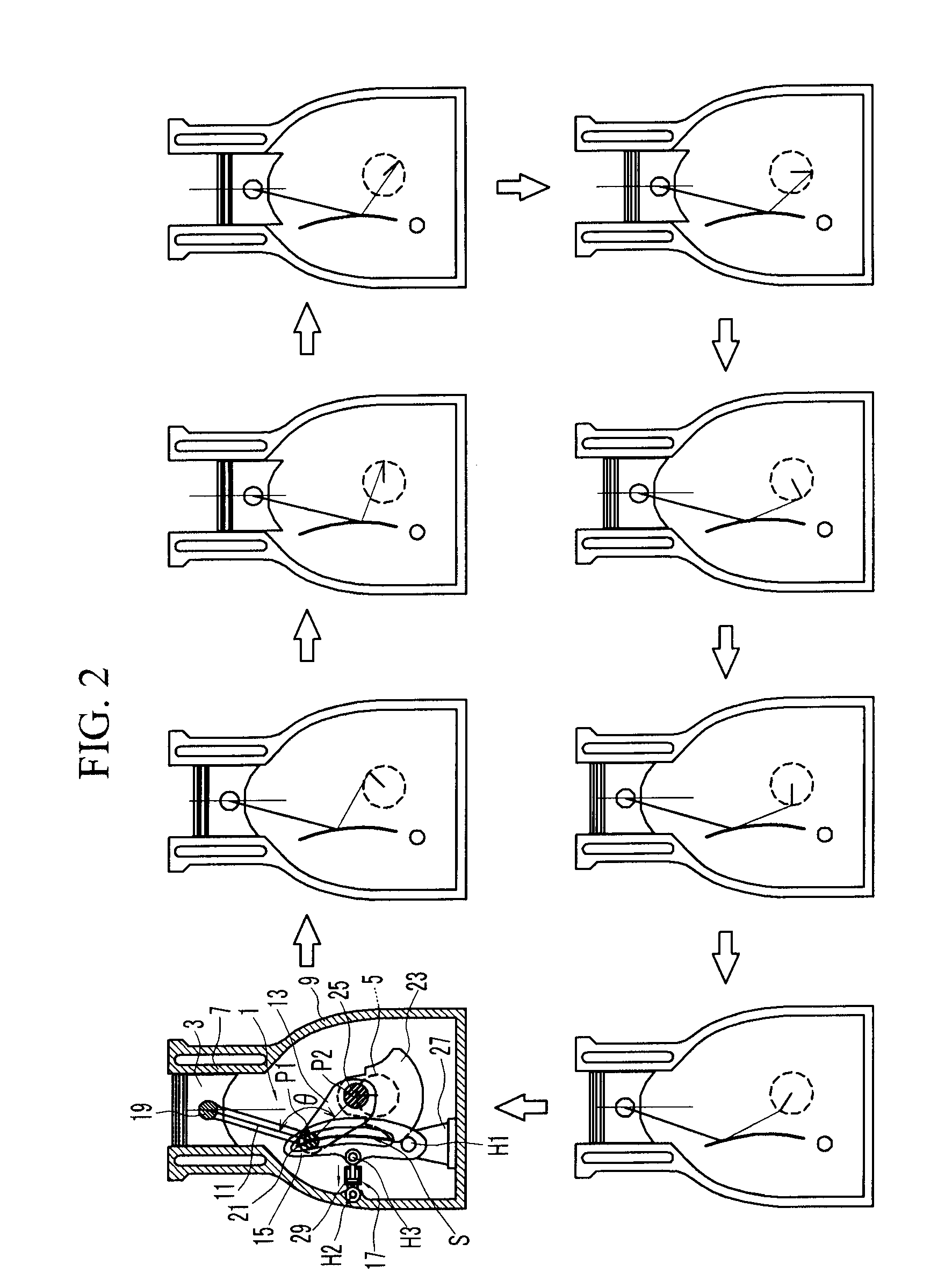
Multi-link variable compression ratio engine
ActiveUS20090107454A1Frequently knockedInhibitionConnecting rodsMachines/enginesTop dead centerReduction ratio
A multi-link variable compression ratio engine is provided with a crankshaft, a piston, a control shaft, a linkage, a motor and a reduction mechanism. The crankshaft moves the piston within an engine cylinder. The control shaft has an eccentric axle eccentric relative to its center-axis. The linkage operatively connects the piston to the crankshaft and the crankshaft to the eccentric axle of the control shaft. The motor rotates the control shaft so a top-dead-center position of the piston changes to vary compression ratios by changing the positions of the eccentric axle and the linkage. The reduction mechanism couples the motor to the control shaft to transmit a reduced rotation of the motor to the control shaft so a reduction ratio of a rotation angle of the motor to a rotation angle of the control shaft is less at high-compression ratios than at intermediate compression ratios.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
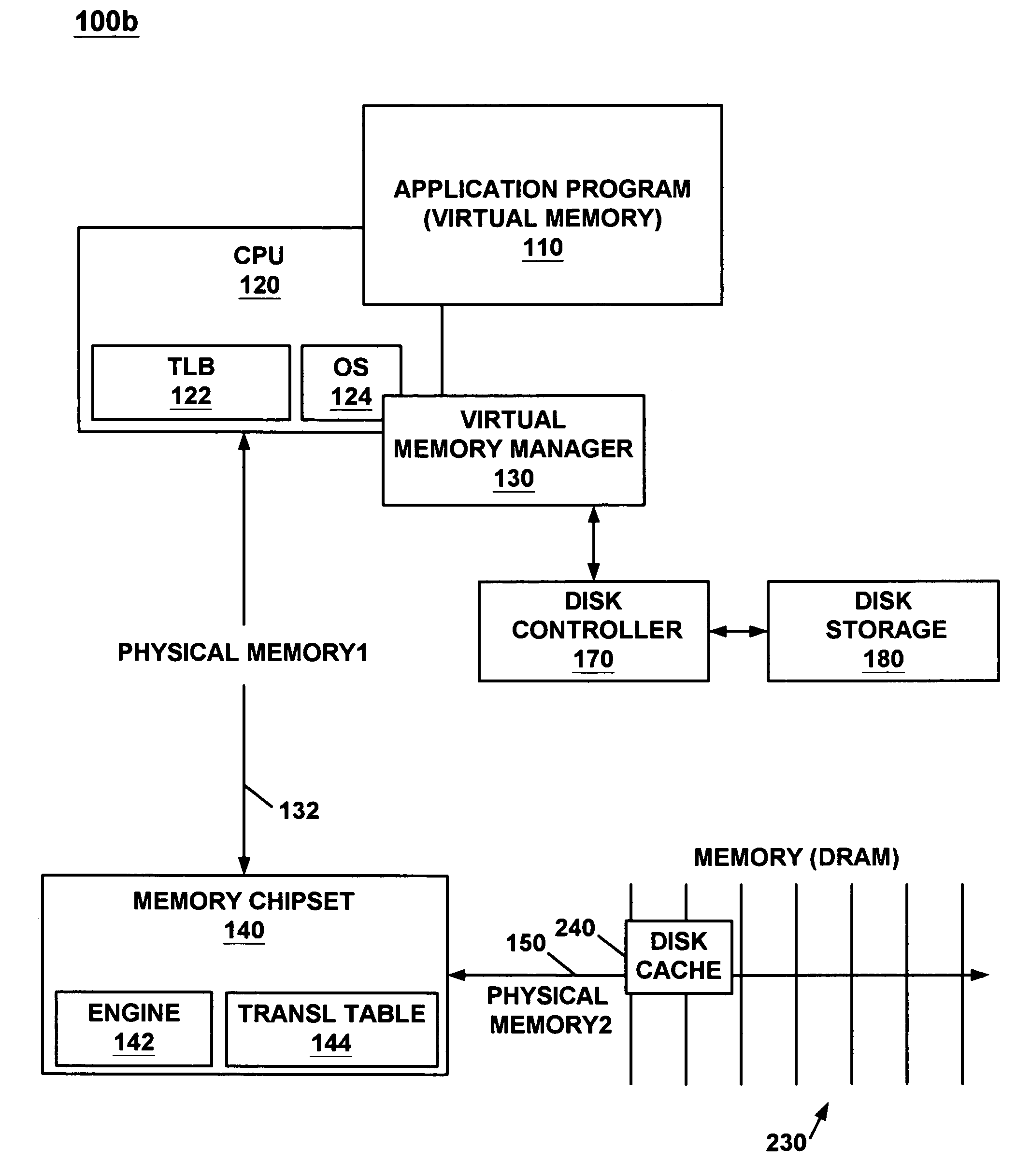
Method and system for transparent compressed memory paging in a computer system
ActiveUS6968424B1Improve system performanceReduce duplicate memory pageMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTData compressionOperational system
A method and system for implementing transparent compressed memory paging within a computer system. Data compression is performed in memory to increase resources available to the computer system and to reduce disk accesses. The compression is performed transparently to the operating system which requires no special software interfaces to make use of the reclaimed memory. In a first embodiment, data compression is performed in hardware to reclaim memory. This reclaimed memory is not made available to the operating system but is rather used as a hardware controlled disk cache to increase system performance. In this embodiment, a novel method is employed to reduce duplicate memory pages in the disk cache and the operating system memory. In another embodiment, the reclaimed memory is made available in a transparent way to the operating system. Variable compression ratios can lead to varying physical memory space available for the operating system. Therefore, if actual memory space becomes near exhausted, a process is automatically triggered that exclusively allocates blocks of physical memory to a driver thereby removing them from operating system usage. In the second embodiment, a special cache table is used for uncompressed physical memory pages.
Owner:NVIDLA CORP +1
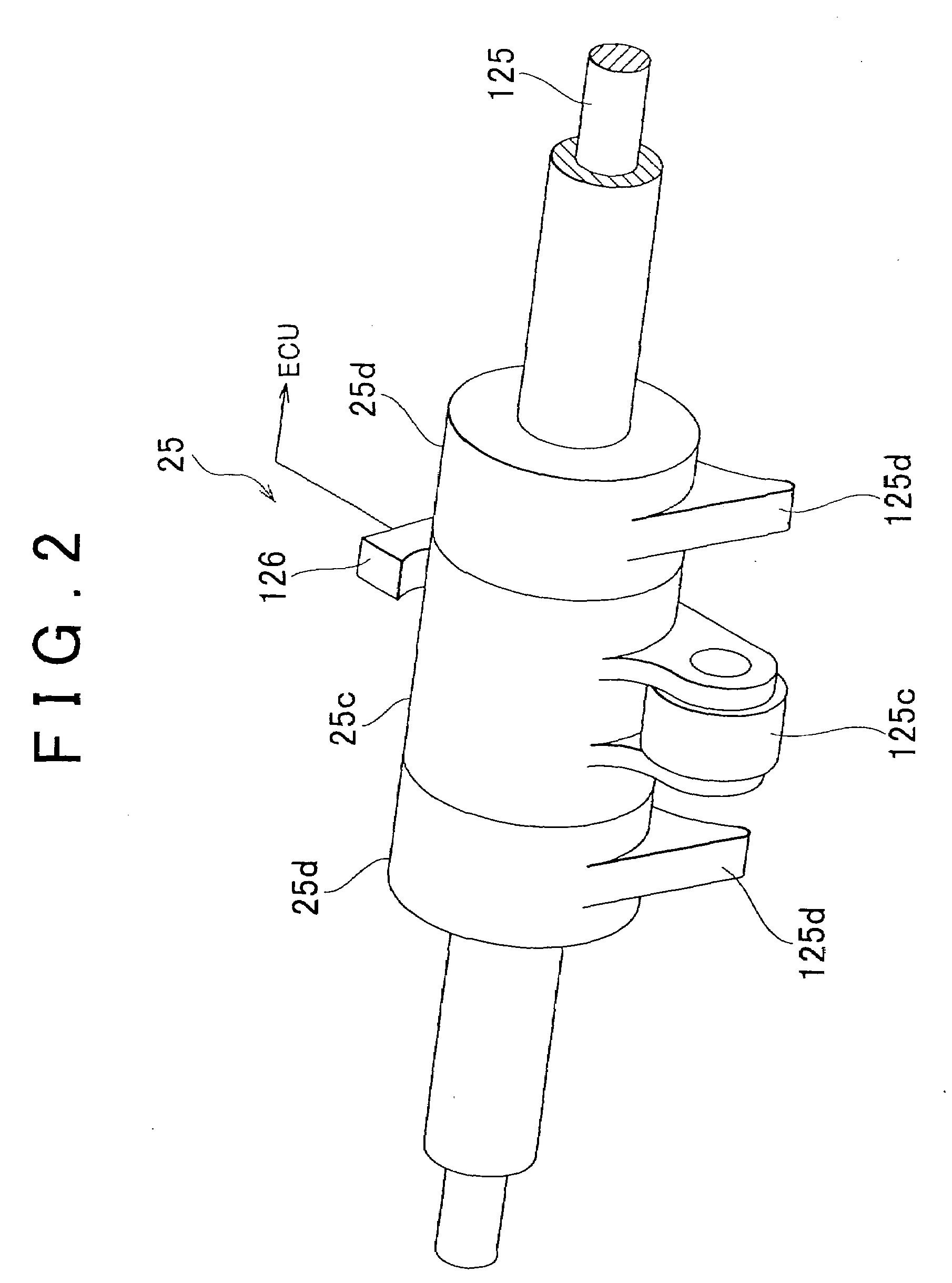
Variable compression ratio system
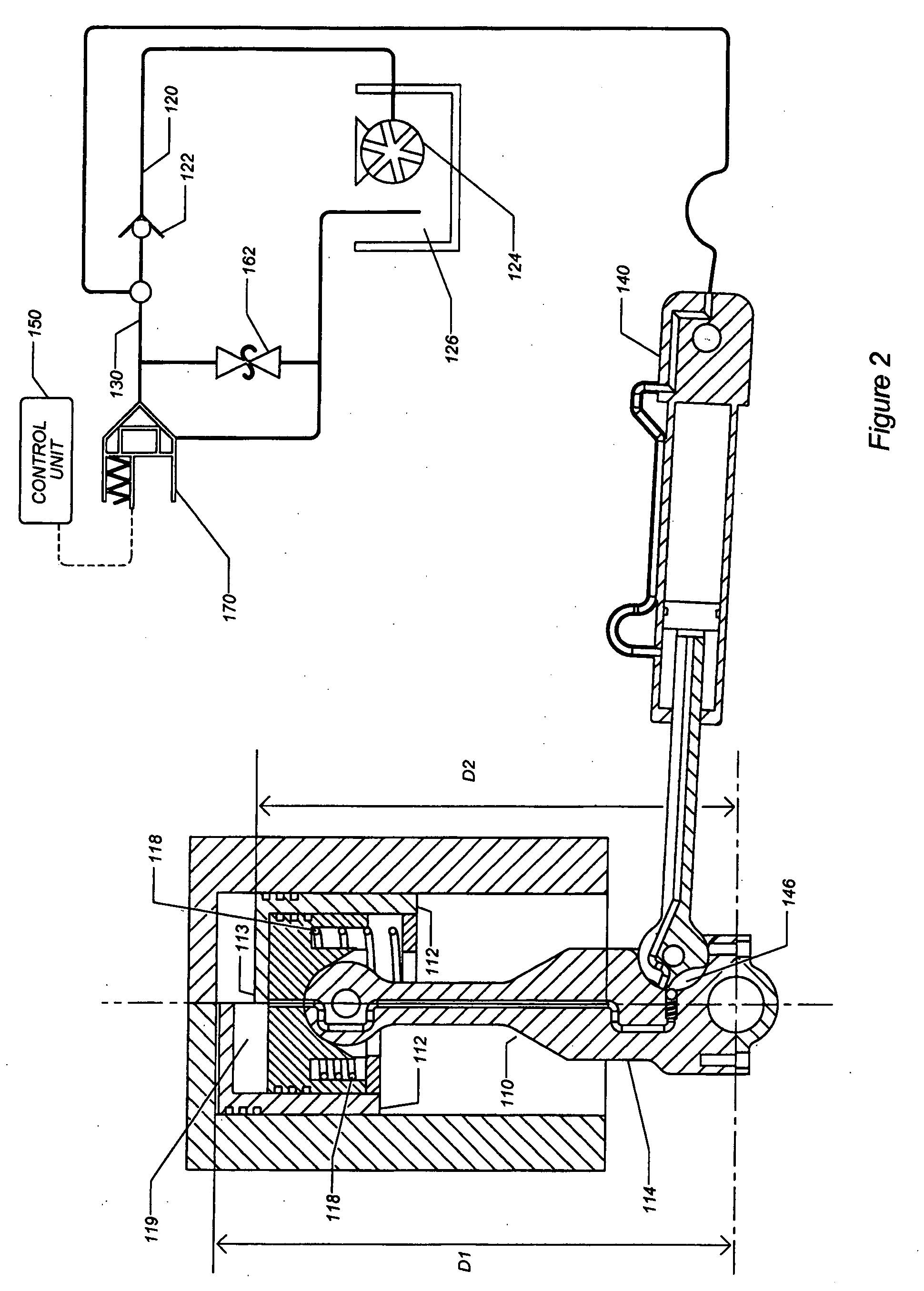
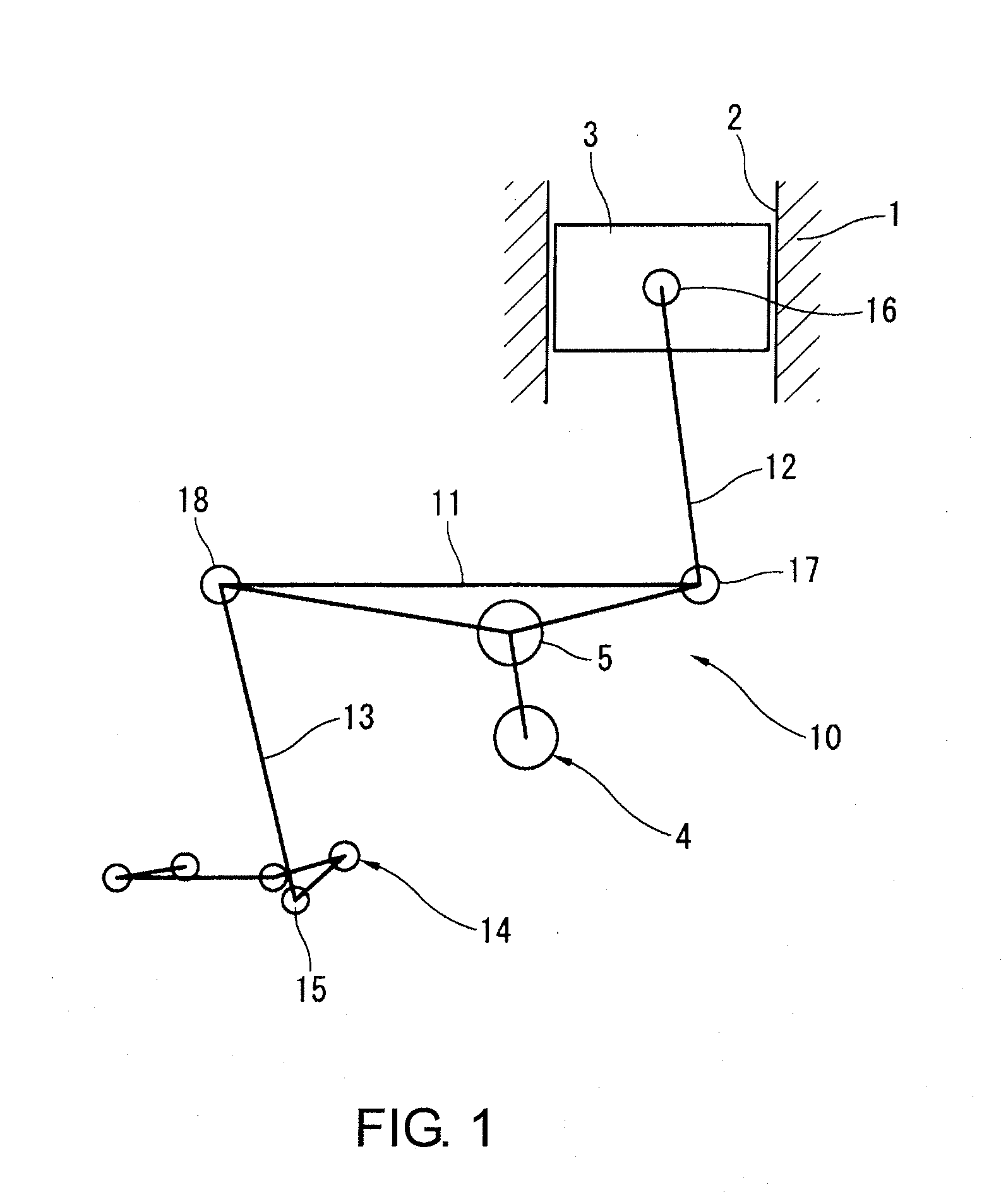
A variable compression ratio system for use in a reciprocating-piston engine. The system allows the compression ratio in a combustion cylinder of the engine to be varied by varying the distance from a combustion chamber facing surface of a piston to the center of pivotal connection of a connecting rod to a crankshaft. The distance is varied responsive to the supply and withdrawal of pressurized hydraulic fluid. The hydraulic fluid is supplied and discharged by a slave pump pivotally connected to the connecting rod at a first end and pivotally connected to a stationary point at a second end. The slave pump supplies and withdraws hydraulic fluid responsive to the rotation of the crankshaft and a hydraulic backpressure controlled using a pressure control valve.
Owner:TONAND BRAKES
Self-adaption compression ratio variable engine
An engine with variable compression ratios that is simple, reliable and cheap is provided. The compression ratio is at maximum at idling, and is at minimum at the max. valve position, and can be changed automatically and continuously under any valve position, so that the compression ratio of the engine will approach to the max. allowable value for detonation, so the engine is of very high efficiency and substantially complete combustion, very low emission of waste gas, and is a target pursued by the automobile industry at present in the world. The principle of the invention is, a link rod of variable lengths is used, and the length of the link rod is depending upon the pressure of the combustible mixture gas before ignition combustion; when the pressure is approaching and exceeding the detonation pressure, the link rod will shorten automatically, the compression ratio will drop, so that the pressure will not increase any more, and detonation is avoided. The key tech in the invention is that the link rod uses a plunger type hydraulic cylinder, the oil in which is supplied and closed by the neck connected by the link rod on the crankshaft, so that the length of the link rod is variable in the compression period, and not variable during the ignition and work period.
Owner:陈晨
Variable Compression Ratio Internal Combustion Engine
InactiveUS20080022982A1Improve engine performanceImprove combustion efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionFuel injection
The invention is directed to a variable compression ratio internal combustion engine in which the compression ratio of the engine can be varied and multiple types of fuels having different combustion velocities are used. The invention provides a technology for achieving excellent engine performance for respective types of fuels. In the variable compression ratio internal combustion engine in which the compression ratio can be varied and multiple types of fuels having different combustion velocities are injected through multiple fuel injection valves, maps from which a target compression ratio of the internal combustion engine is read out are switched in accordance with the fuel used, thereby suppressing knocking or other disadvantages.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Return flow scavenging type hydraulic free piston diesel engine
InactiveCN102705076AOmit the crankshaftReduce intermediate conversion linksInternal combustion piston enginesFree piston enginesHydraulic motorHydraulic pump
The invention discloses a return flow scavenging type hydraulic free piston diesel engine, which comprises a single-cylinder two-stroke diesel engine without a crankshaft connecting rod and a valve distribution mechanism, and a hydraulic system provided with a linear hydraulic pump and a hydraulic motor, wherein a piston in the single-cylinder two-stroke diesel engine is connected with a plunger in the hydraulic system, and a space in the linear hydraulic pump in the hydraulic system is divided into a high-pressure cavity and a low-pressure cavity; the piston in the single-cylinder two-stroke diesel engine can drive the linear hydraulic pump to output high-pressure oil in an expansion travel, and the high-pressure oil is output to the hydraulic motor from a pipe joint C; the piston is pushed back to an upper dead center from a lower dead center by the low-pressure oil end, so that a compression travel of the piston is completed. According to the invention, a crankshaft in the conventional internal combustion engine is omitted, and a middle conversion step of power output is reduced, so that the heat efficiency is about 5% higher than that of the conventional internal combustion engine, the diesel engine can be operated at a variable compression ratio, the best heat efficiency of a full operation work condition is ensured, and the fuel economy is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Flexible fuel engine with alterable compression ratio and control method thereof
InactiveCN101131126AValve arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion systemVariable valve timing
The present invention discloses one kind of engine with changeable compression ratio and changeable fuel and its control method. The engine includes one combustion system, one fuel pressure regulating system, one liquid fuel providing system, one gas fuel providing system, one changeable gas valve timing mechanism, one electronic control unit and one sensor module. According to the acquired signal, the electronic control unit determines the current fuel type, regulates the compression ratio, combustion controlling strategy and gas distribution phase of the engine and regulates the pressure of the fuel injector, so as to fit the fuel. The engine of the present invention can burn gas fuel, liquid fuel and mixed fuel, and has compression ratio adjustable in 8-18 and high dynamic performance and economic performance in burning different types of fuel.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
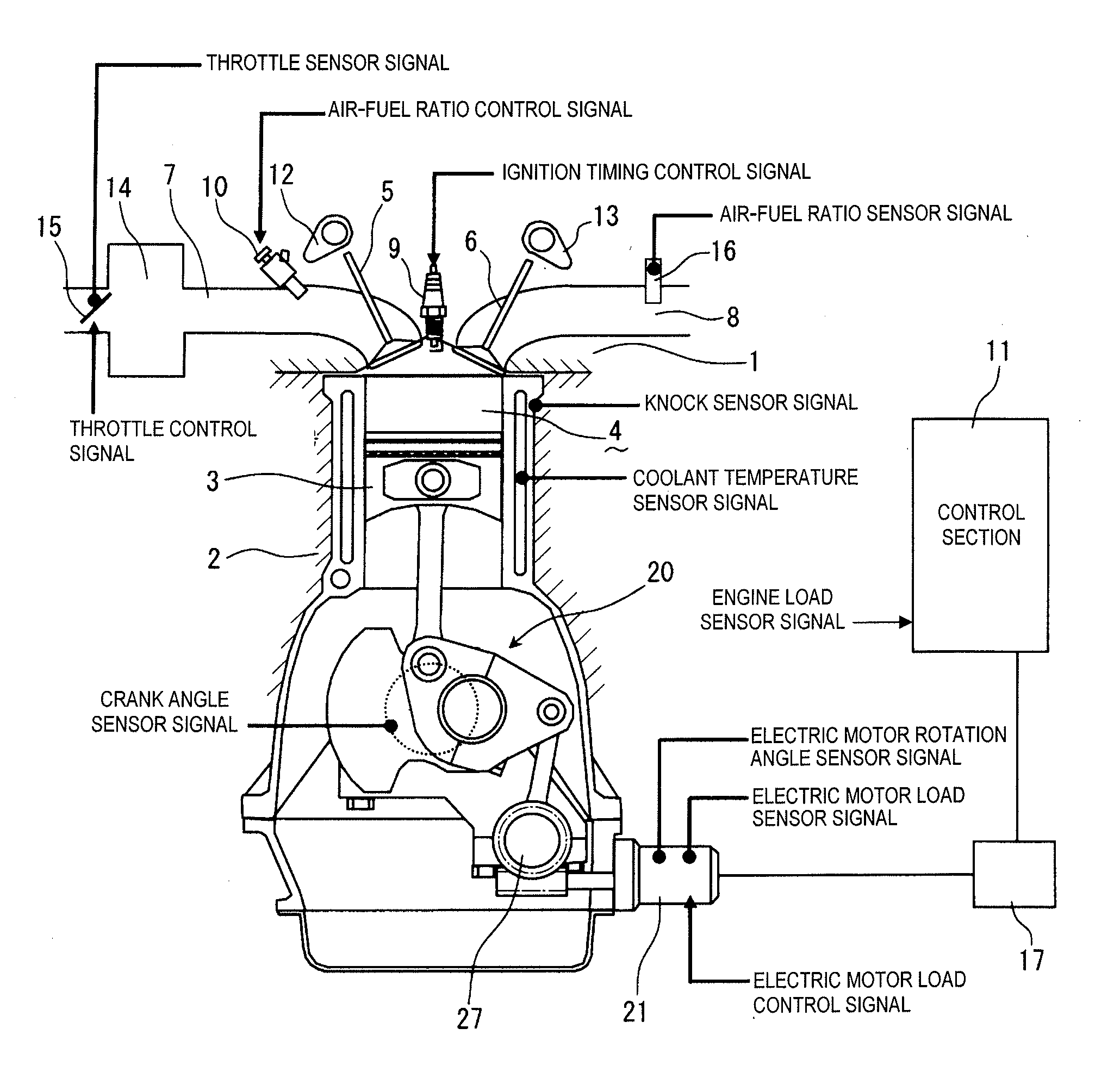
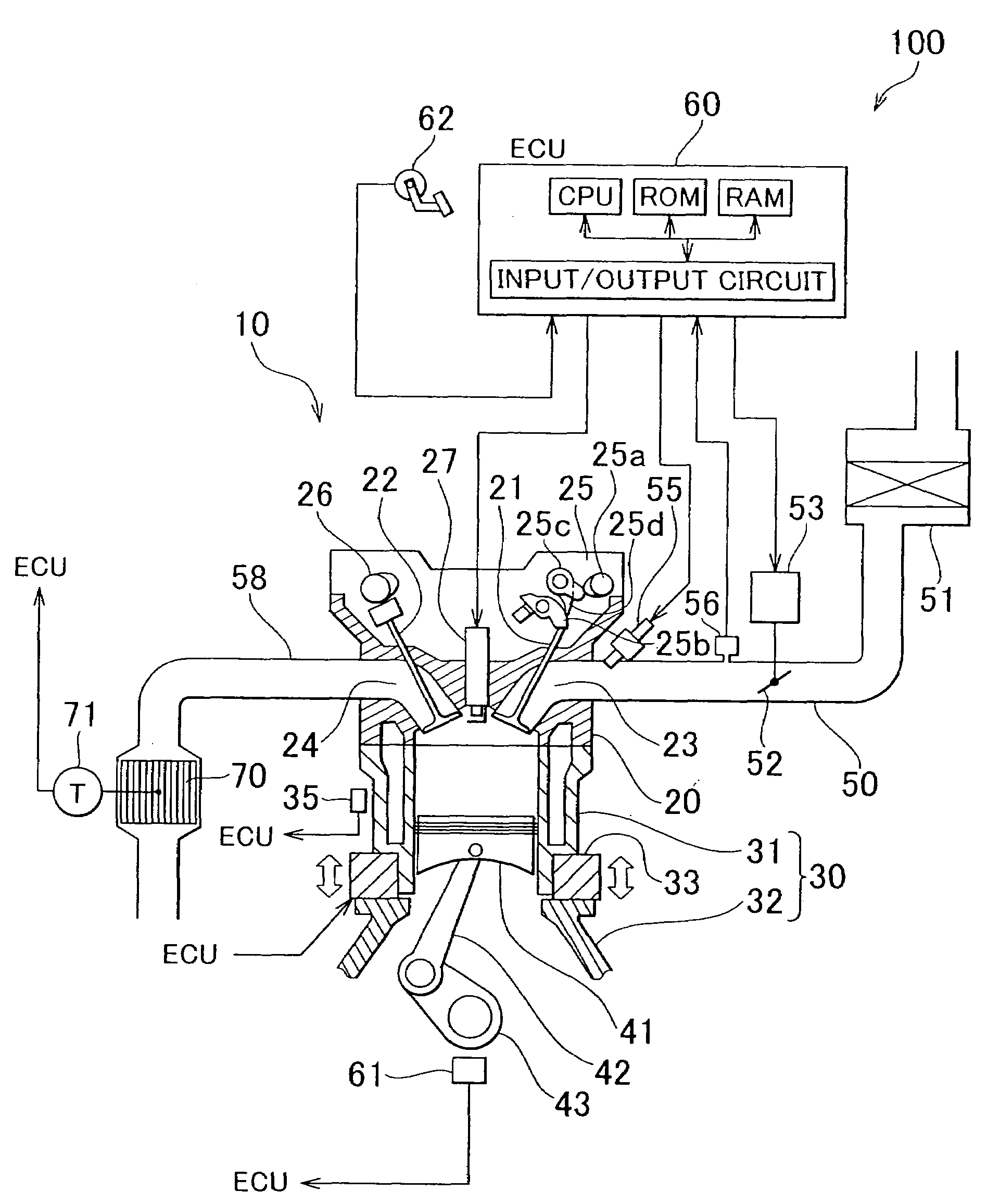
Method of Controlling a Mechanical Compression Ratio, a Closing Timing of an Intake Valve and Air Stream
A spark ignition type internal combustion engine comprises a variable compression ratio mechanism able to change a mechanical compression ratio, a variable valve timing mechanism able to control a closing timing of an intake valve, and an air flow control valve controlling an air flow in a cylinder and able to control the amount of intake air fed into a combustion chamber. The mechanical compression ratio is made maximum so as to obtain the maximum expansion ratio at the time of engine low load operation and the actual compression ratio at the time of engine low load operation is made an actual compression ratio substantially the same as that at the time of engine medium and high load operation. When the engine load is in an extremely low load region, the air flow control valve is used to control an amount of intake air fed into the combustion chamber. Due to this, a high heat efficiency can be realized even in a region where the amount of intake air is difficult to control by changing the closing timing of the intake valve.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
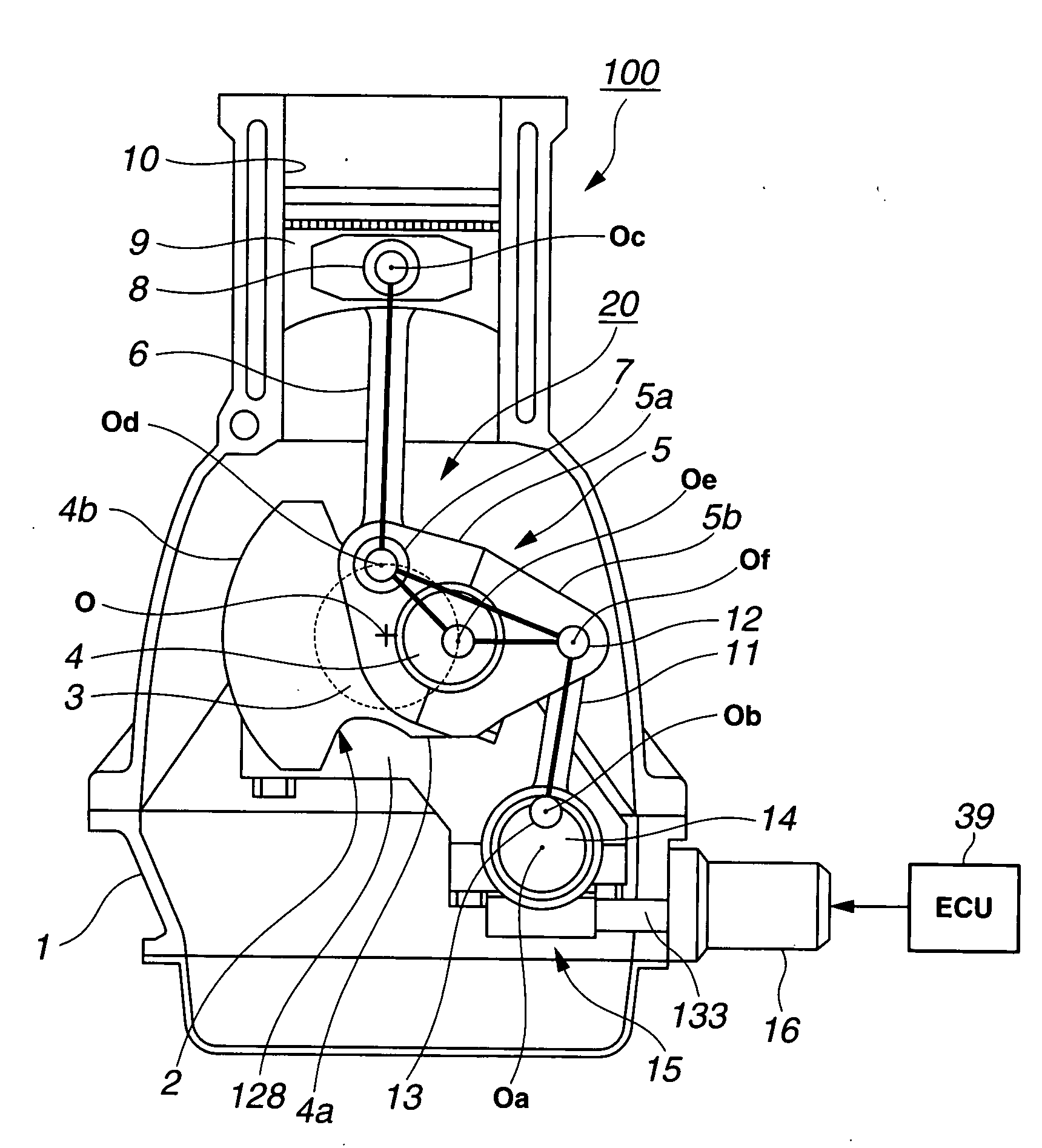
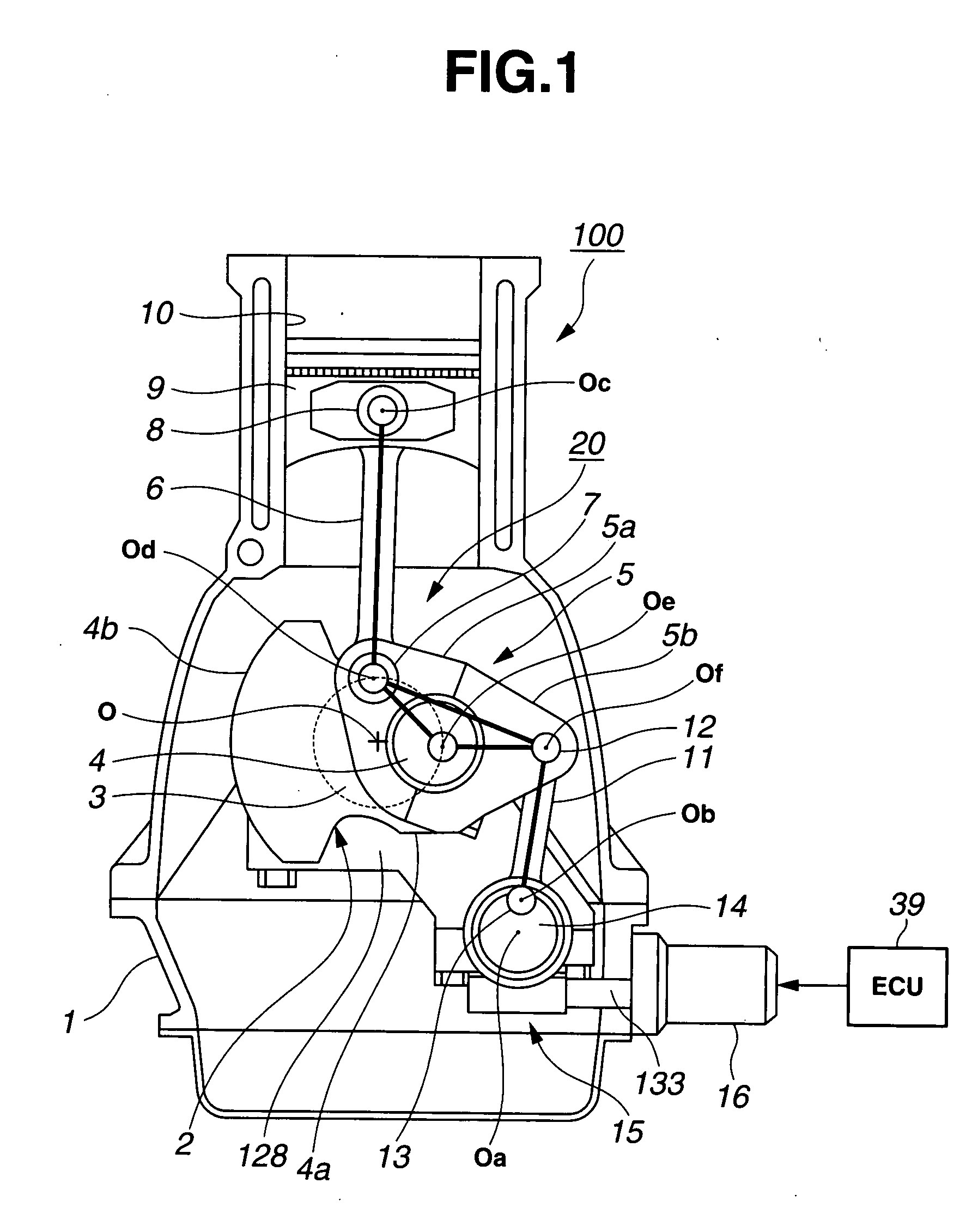
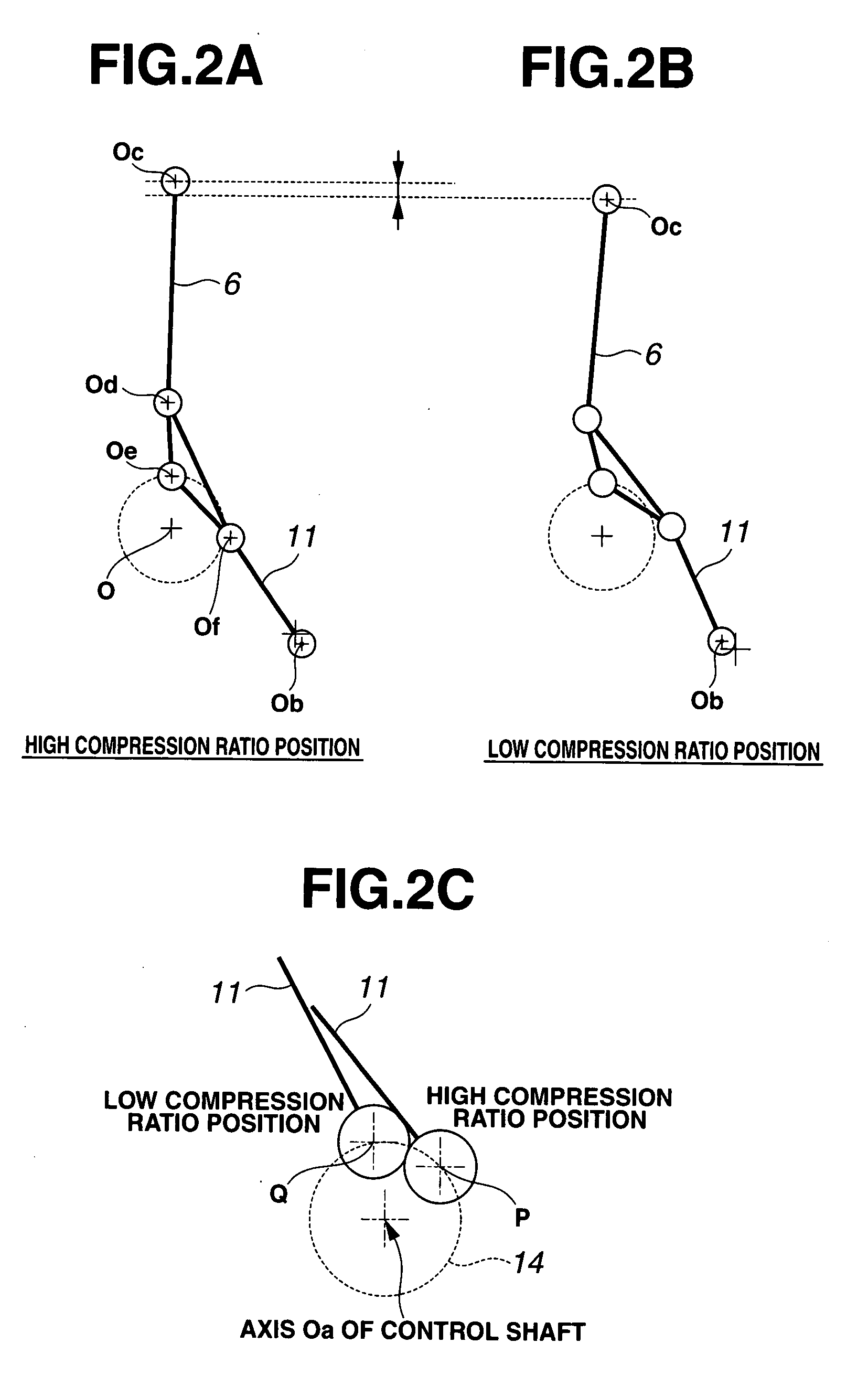
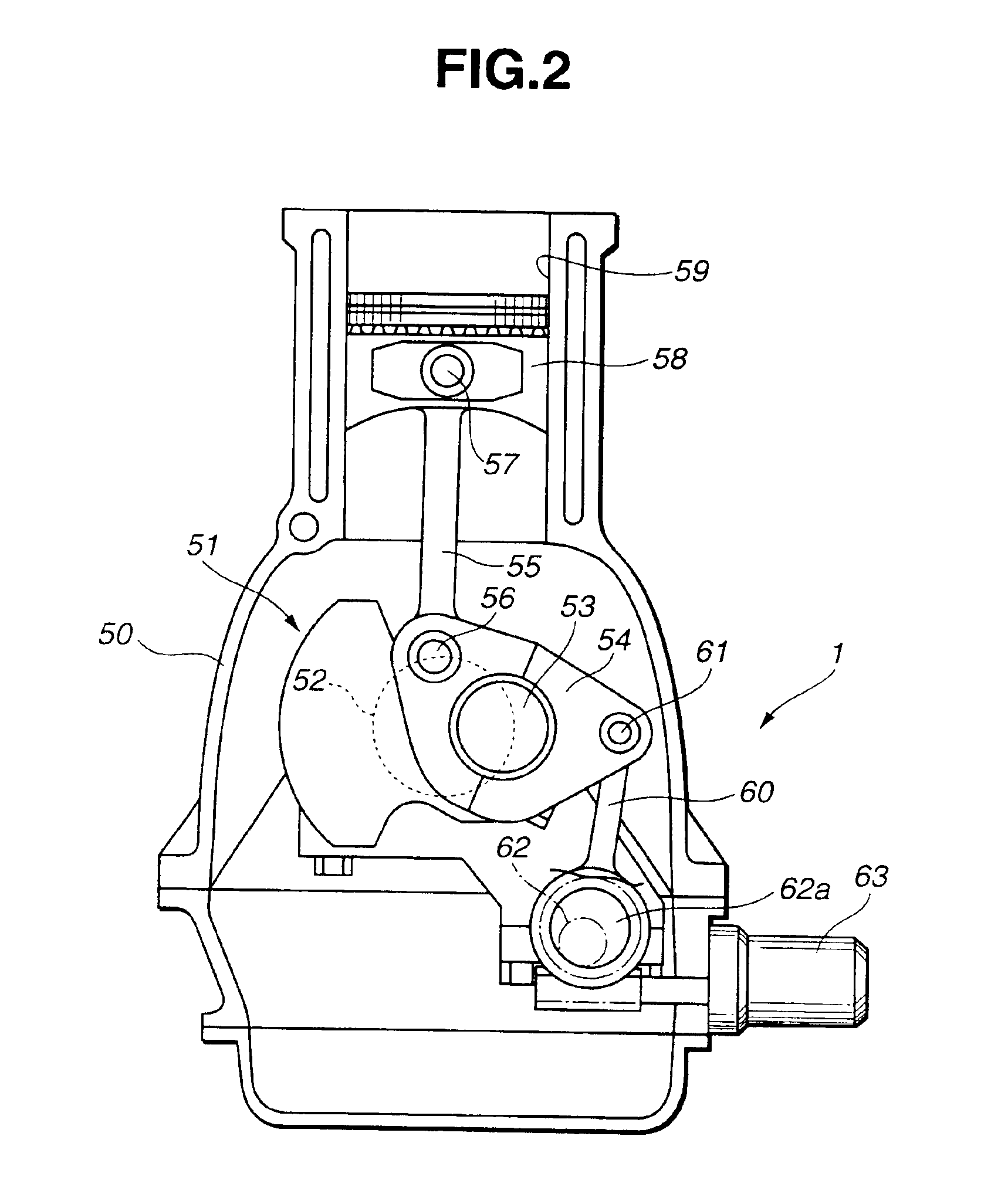
Internal combustion engine with variable compression ratio mechanism
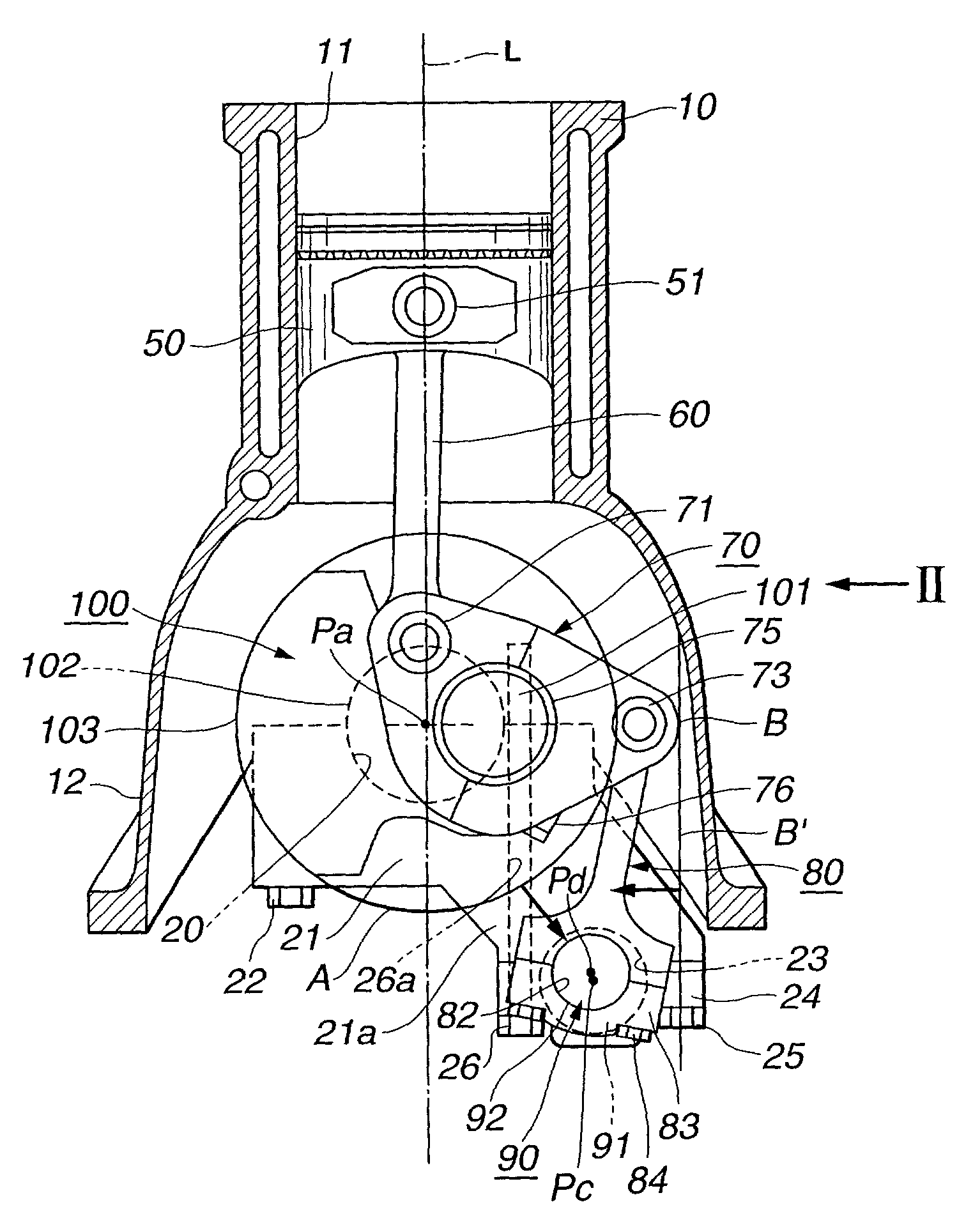
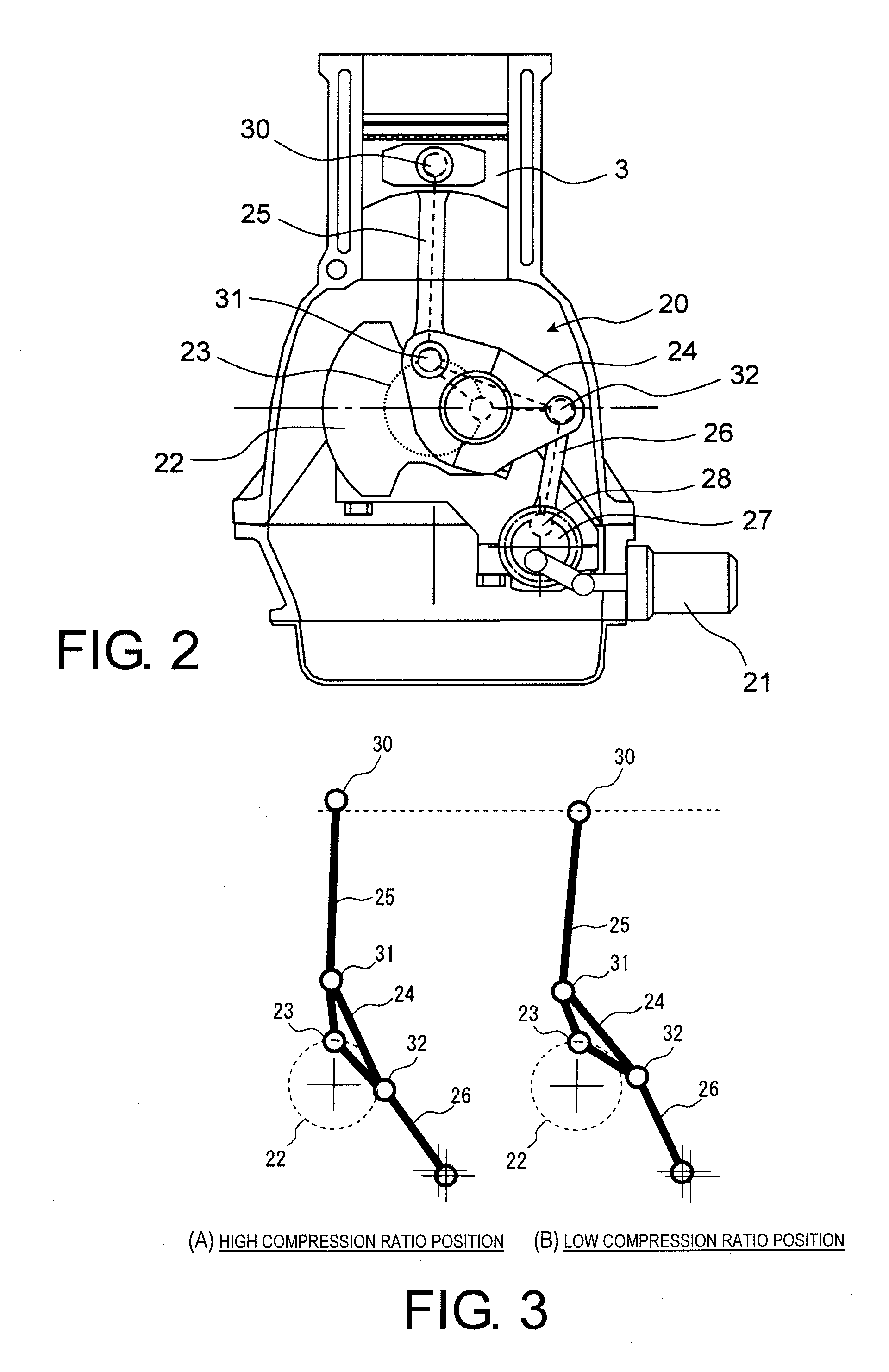
An internal combustion engine is constructed to include a variable compression ratio mechanism. The mechanism has the following structure. An upper link has one end pivotally connected to a piston pin of a piston of the engine. A lower link is pivotally disposed on a crank pin of a crankshaft of the engine and has one part pivotally connected to the other end of the upper link. A control shaft extends substantially in parallel with the crankshaft. A control link has an end pivotally connected to the other part of the lower link. The other end of the control link is connected to the control shaft through an eccentric bearing structure, so that rotation of the control shaft about its axis induces a pivoting of the lower link about the crank pin varying the stroke of the piston.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Internal combustion engine with variable compression ratio mechanism
An internal combustion engine is constructed to include a variable compression ratio mechanism. The mechanism has the following structure. An upper link has one end pivotally connected to a piston pin of a piston of the engine. A lower link is pivotally disposed on a crank pin of a crankshaft of the engine and has one part pivotally connected to the other end of the upper link. A control shaft extends substantially in parallel with the crankshaft. A control link has an end pivotally connected to the other part of the lower link. The other end of the control link is connected to the control shaft through an eccentric bearing structure, so that rotation of the control shaft about its axis induces a pivoting of the lower link about the crank pin varying the stroke of the piston.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Variable compression ratio engine control apparatus
InactiveUS20130055990A1Improve fuel efficiencyAlleviate and suppress deceleration torqueElectrical controlMachines/enginesCombustionFuel injection
A variable compression ratio engine control apparatus includes a fuel injection device, a variable compression ratio device, a target compression ratio setting section and a compression ratio controlling section. The fuel injection device injects fuel into an engine for combustion. The variable compression ratio device varies an engine compression ratio of the engine. The target compression ratio setting section sets a target compression ratio. The compression ratio controlling section controls the engine compression ratio toward the target compression ratio. The target compression ratio setting section sets the target compression ratio based on an engine rotational speed, during a fuel cut operating state in which fuel injection by the fuel injection device is stopped.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7669559B2Improve thermal efficiencyReducing a cooling lossInternal combustion piston enginesOutput powerCombustion chamberTop dead center
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
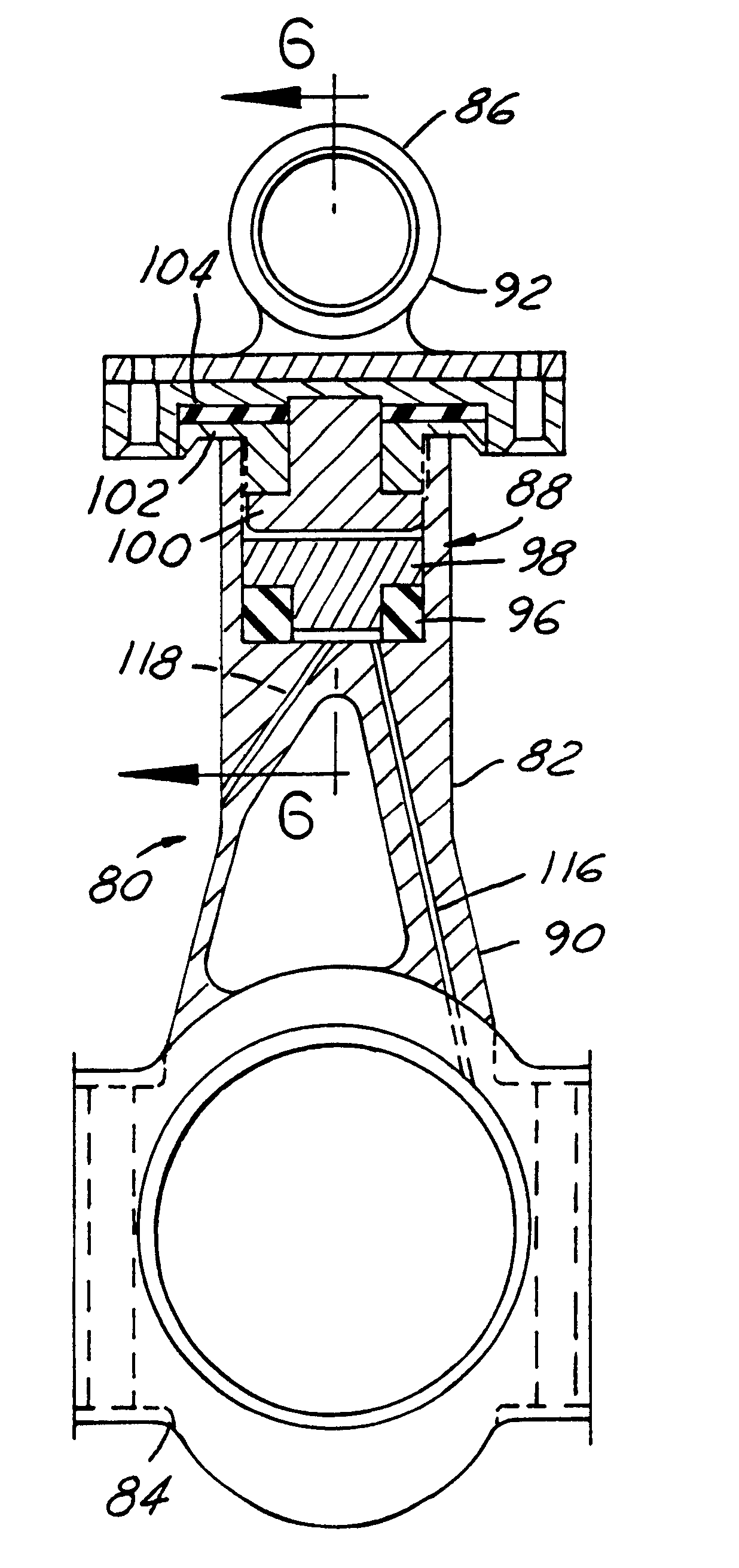
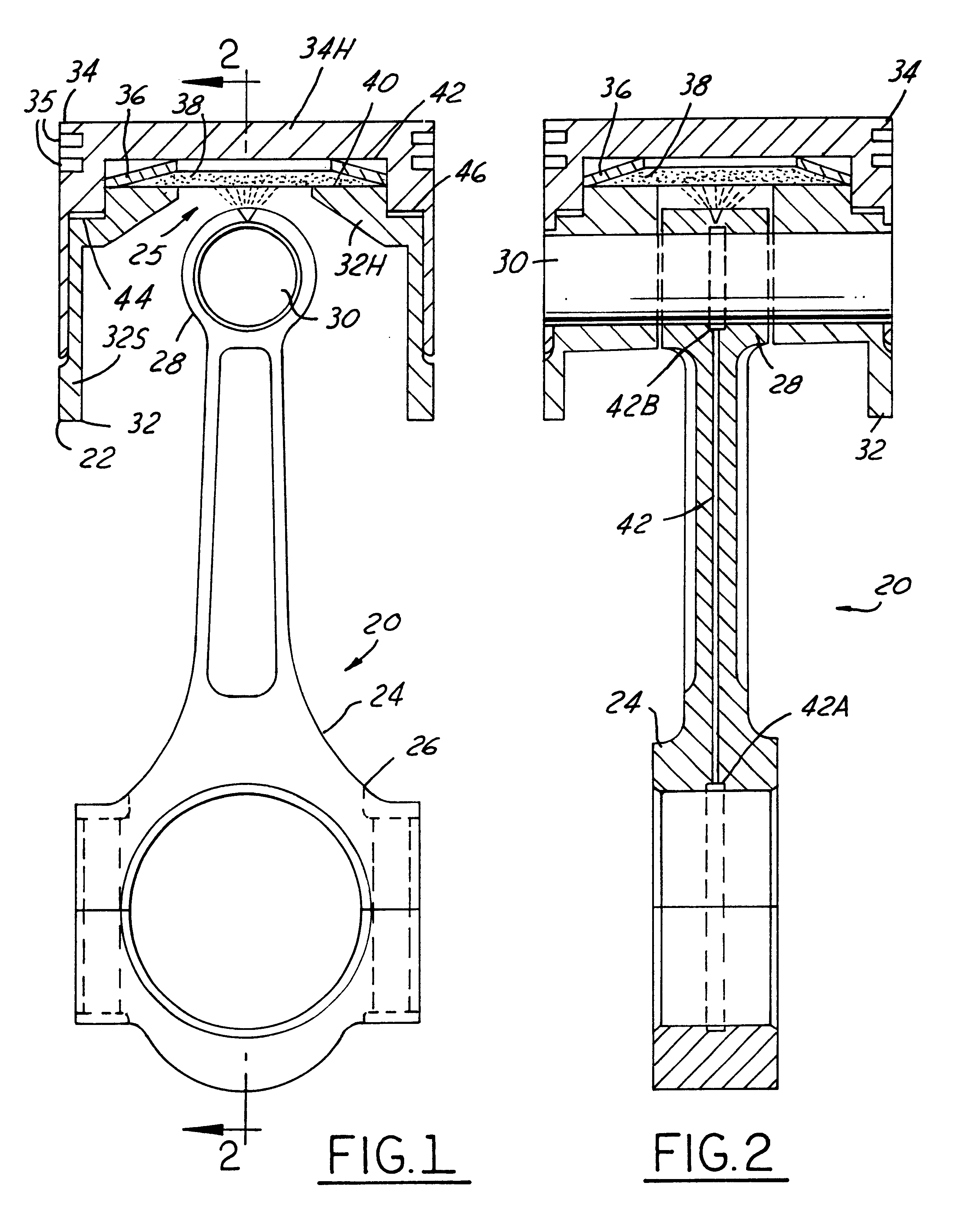
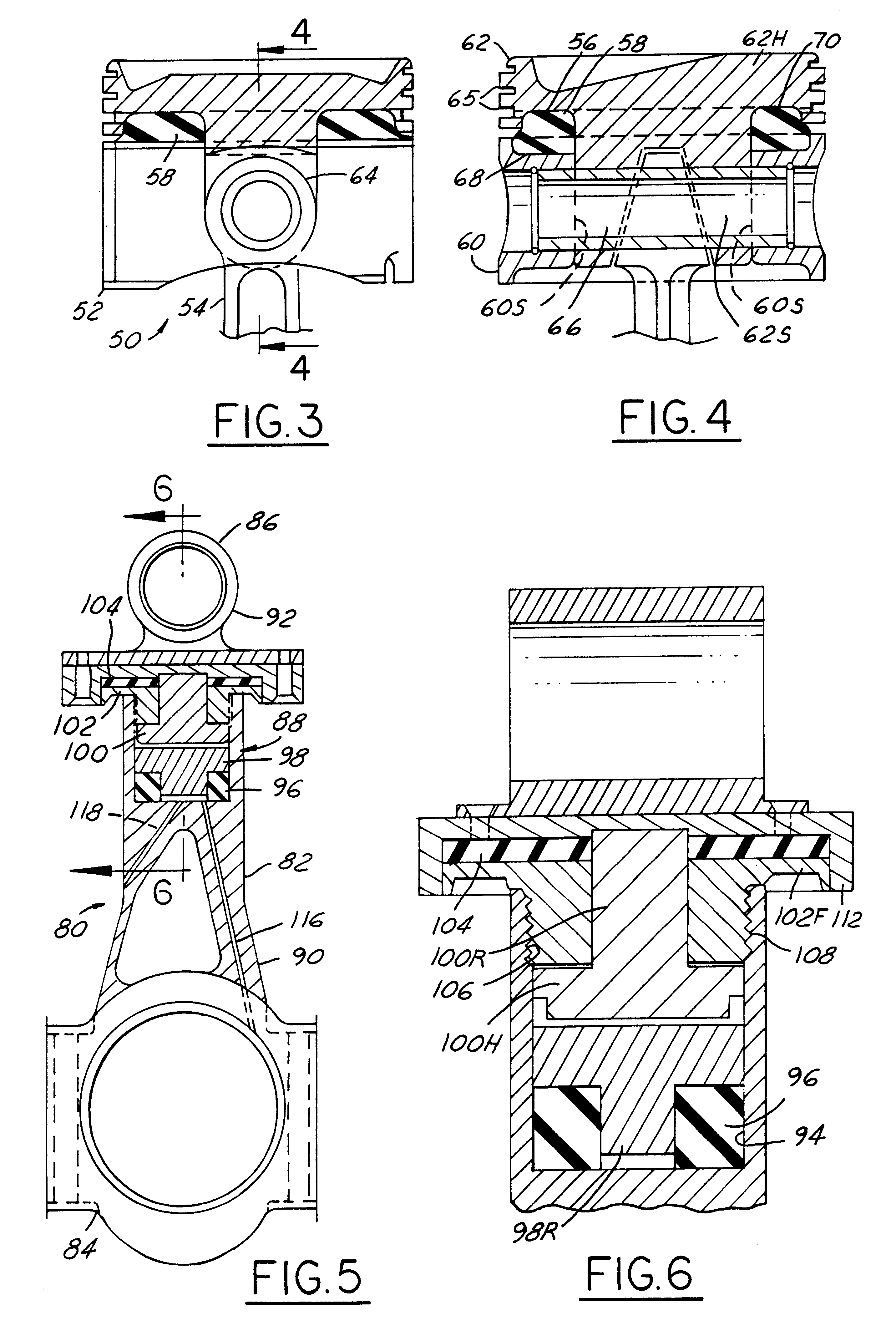
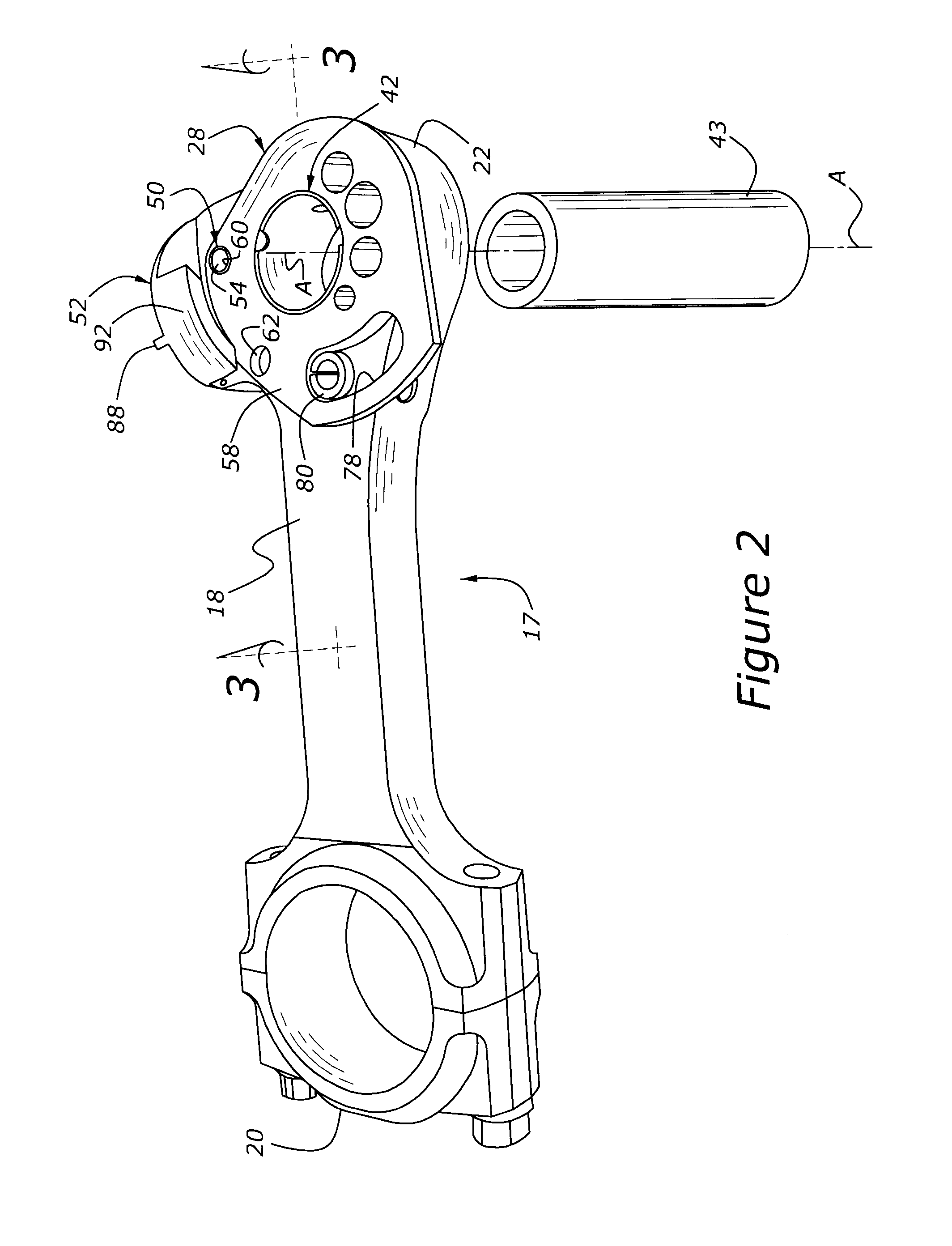
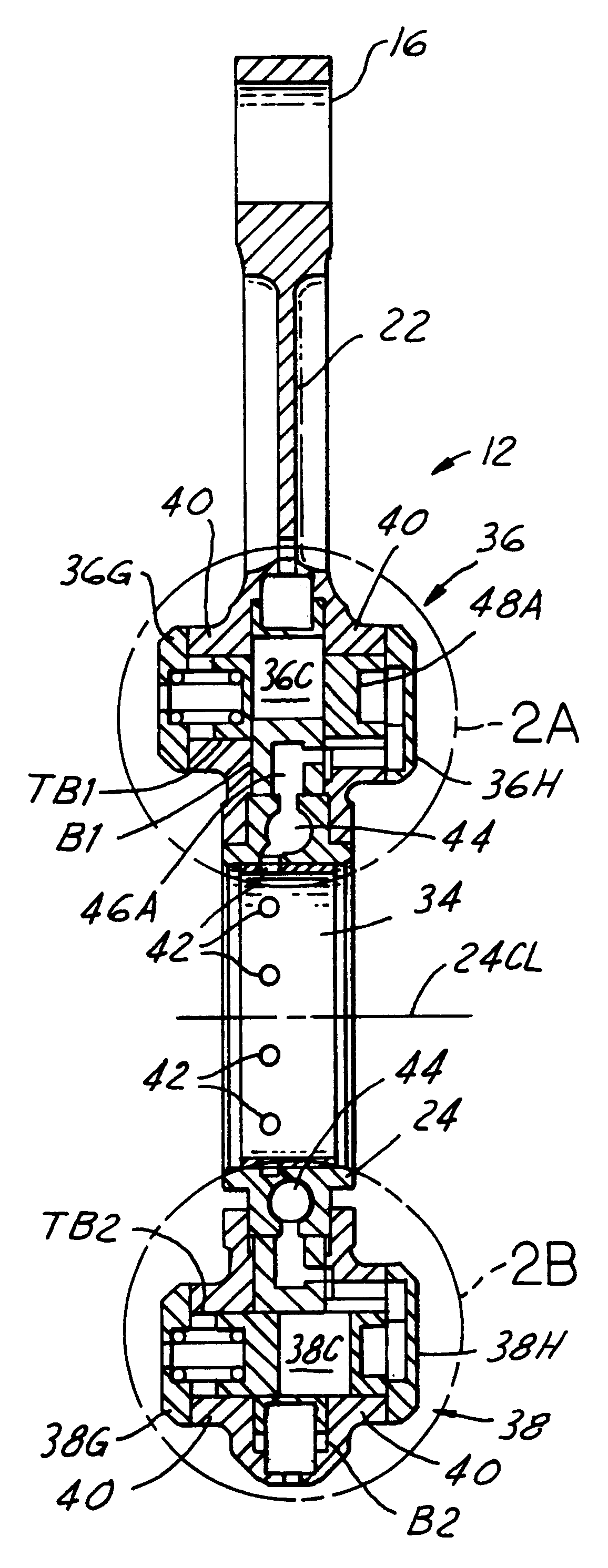
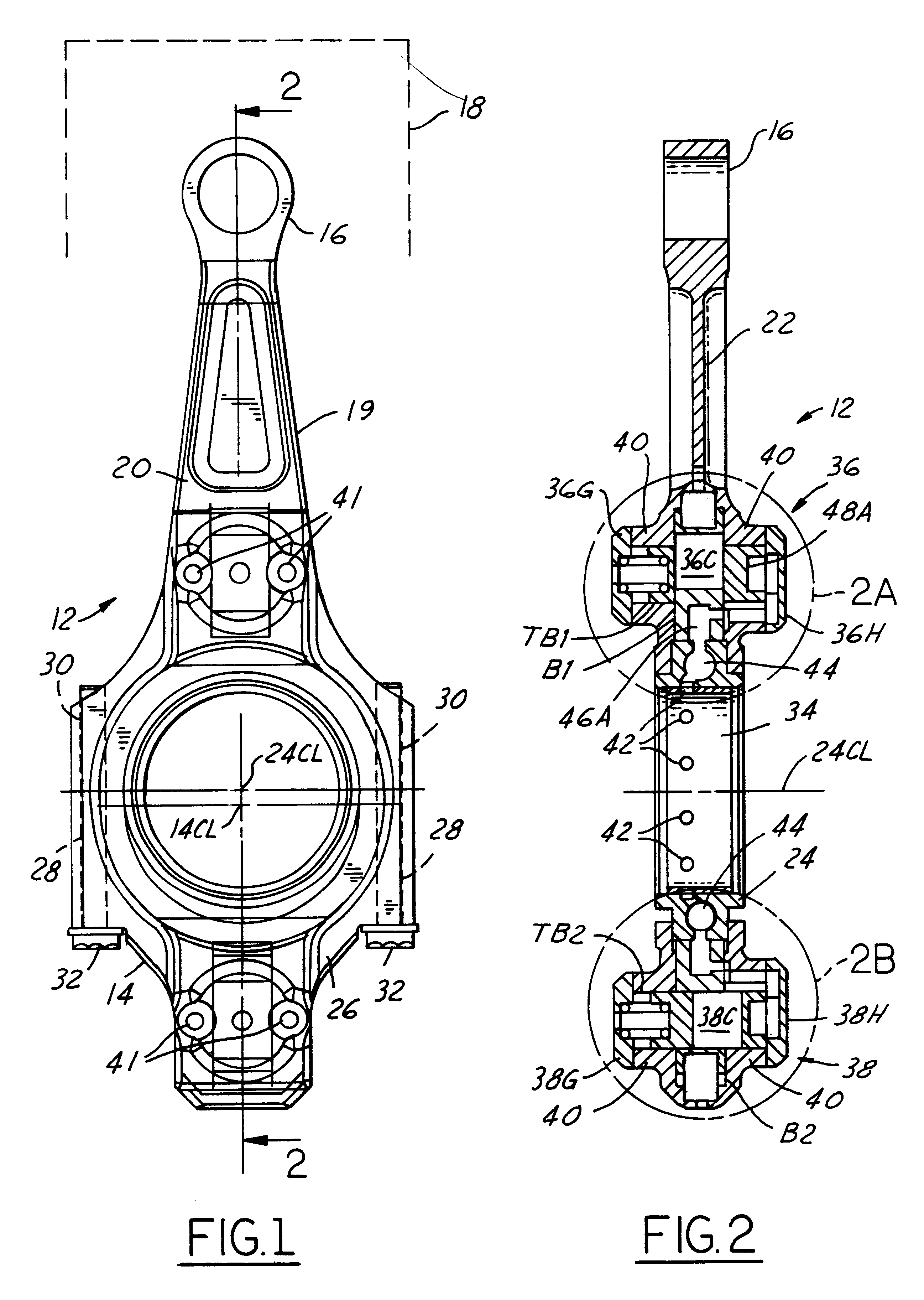
Variable compression ratio pistons and connecting rods
Various embodiments (20; 50; 50; 120) of variable length piston and connecting rod assemblies for imparting a variable compression ratio to an internal combustion engine. The embodiments incorporate novel arrangements of relatively movable parts (32, 34; 60, 62; 84, 86; 124, 126) related by various elastomeric elements (38; 58; 96, 104; 136) and oil passages (42; 116, 118; 140, 142) to change compression ratios.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Internal combustion engine with variable compression ratio and valve characteristics
ActiveUS7278383B2Improve economyImprove efficiencyValve arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesControl theoryVariable compression ratio
When controlling the valve characteristics of an intake valve and changing the compression ratio, an upper variation limit compression ratio, which is the upper limit of the variation of compression ratio, is determined according to the actual valve characteristics of the intake valve characteristics control. The upper variation limit compression ratio is set to a valve at which the intake valve does not collide with the piston. When a target compression ratio corresponding to the operation state of the engine is larger than the upper variation limit compression ratio, the compression ratio is set to the upper variation limit compression ratio that is smaller than the target compression ratio. Thus, collision between the intake valve and the piston can be prevented while allowing the compression ratio to be increased up to the maximum compression ratio of the range where the collision does not occur.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Engine with variable compression ratio
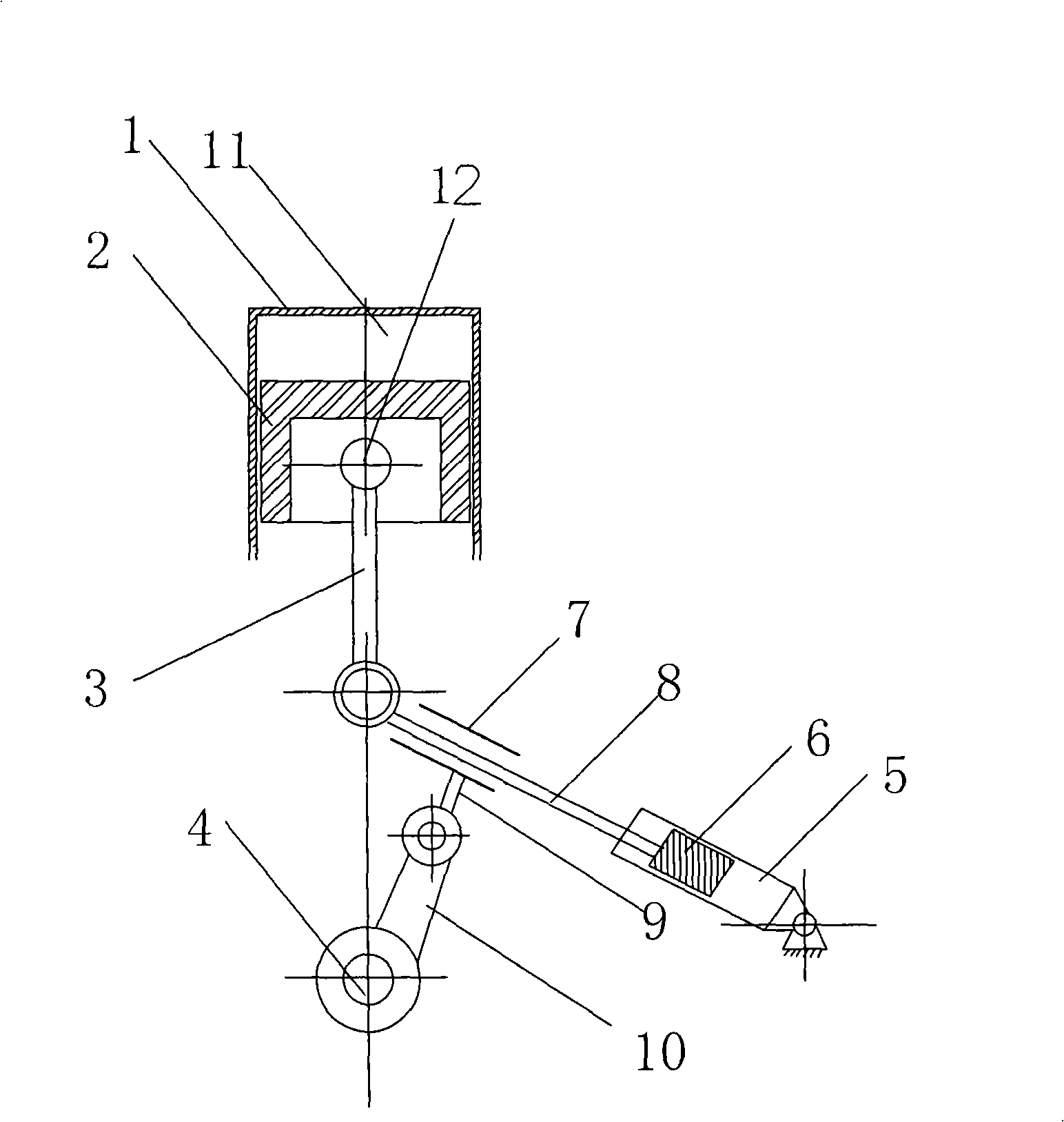
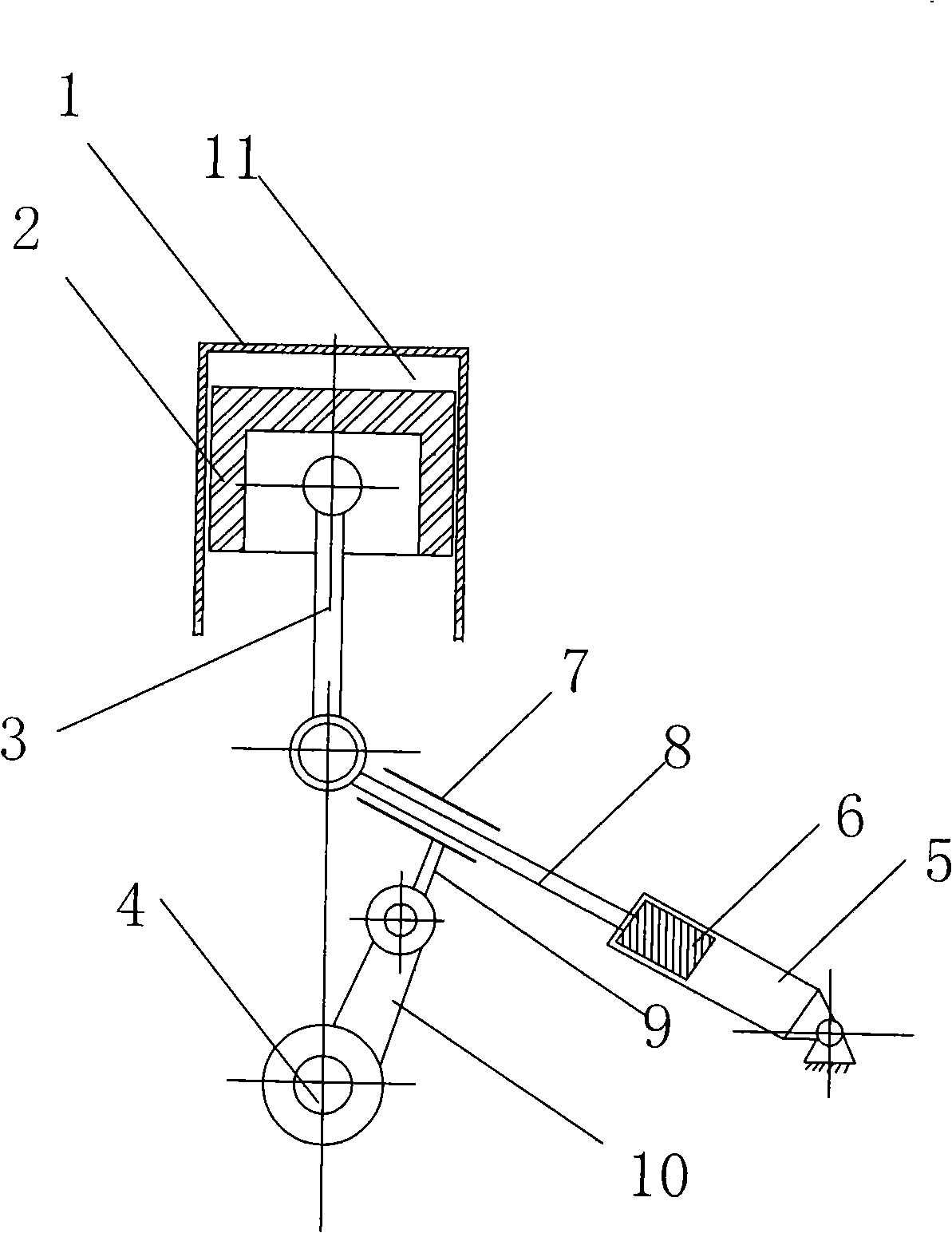
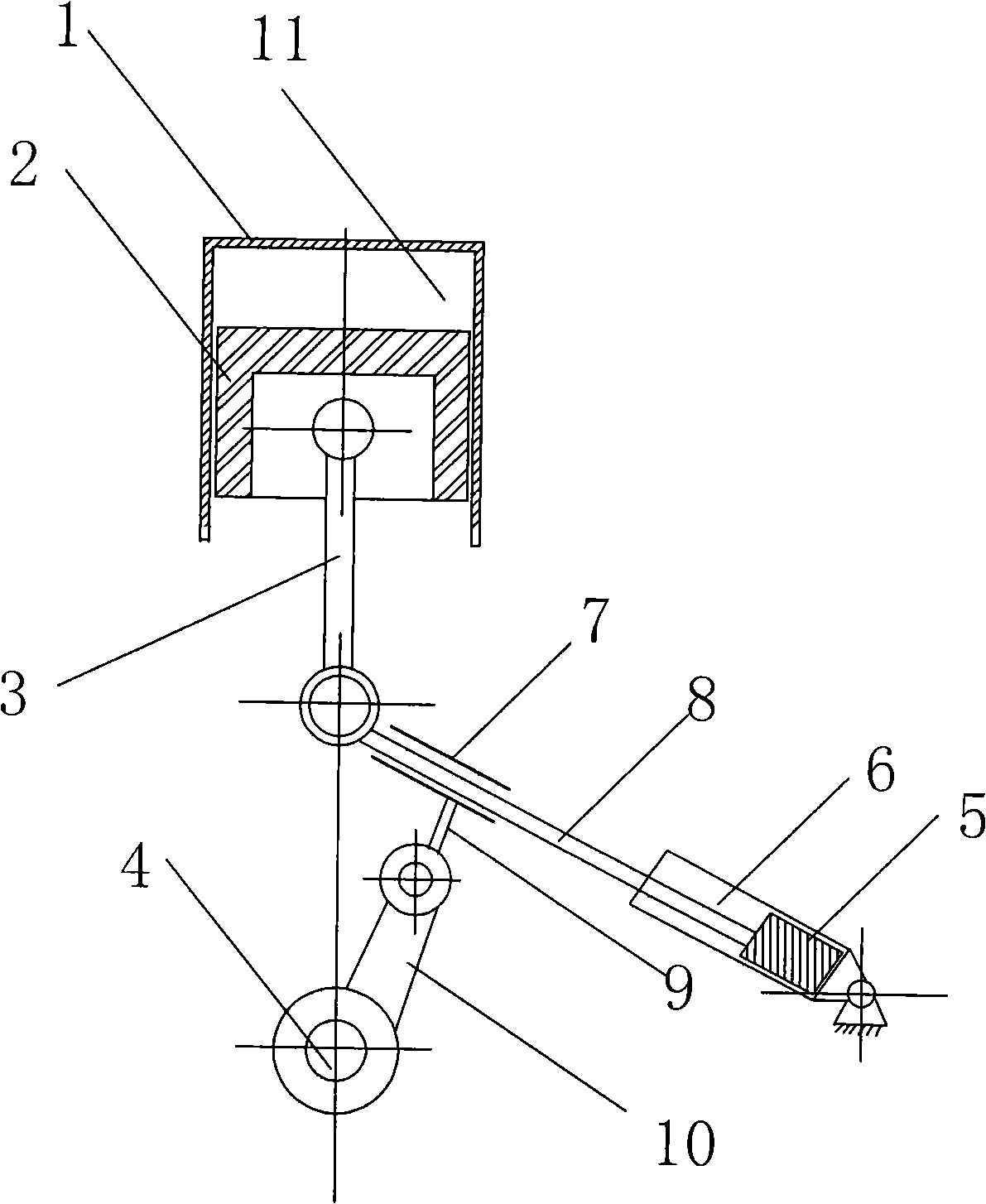
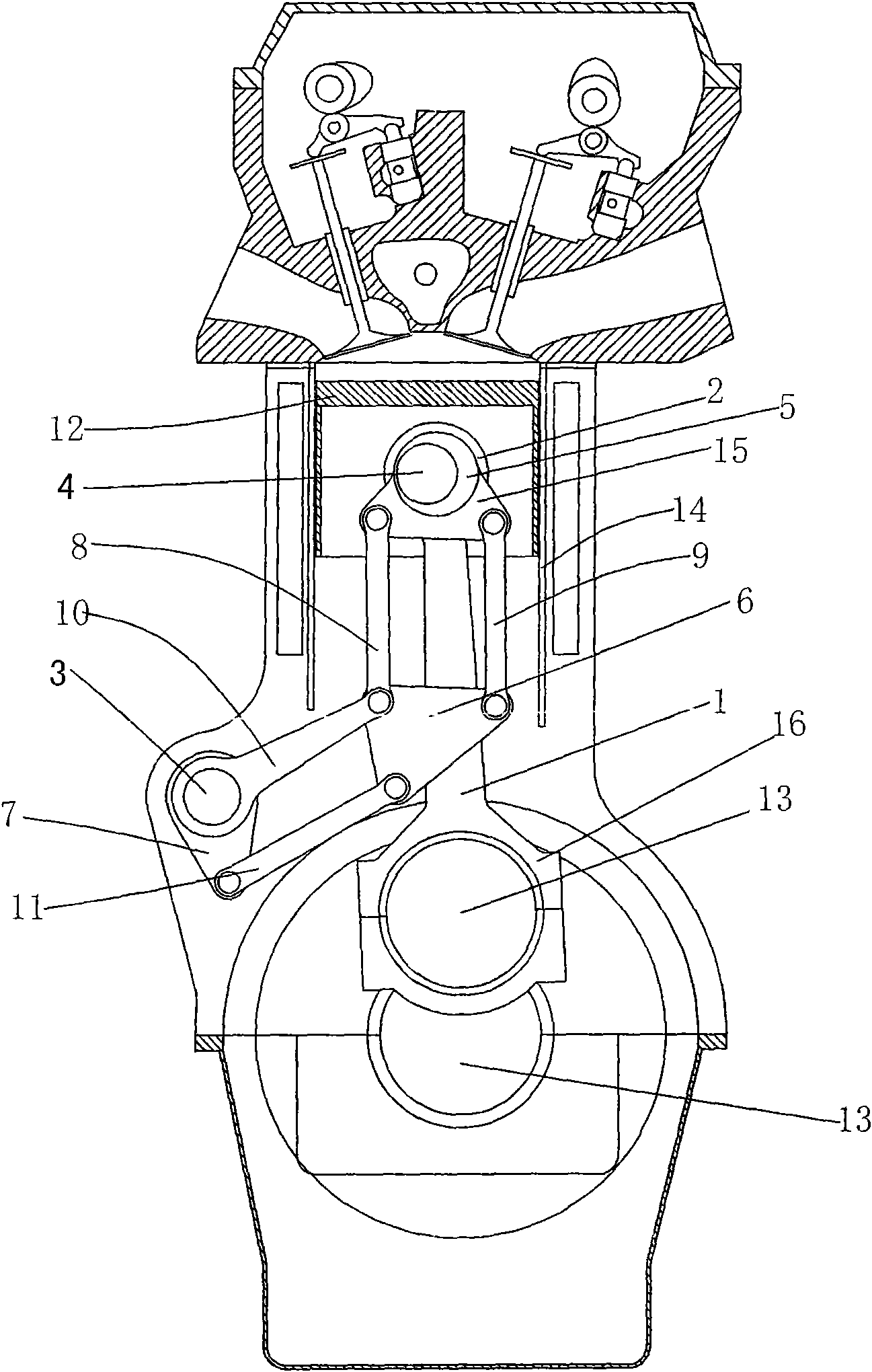
InactiveCN101403342AChange volumeChange the compression ratioEngine controllersMachines/enginesEffective lengthHydraulic pump
The invention discloses a variable compression ratio engine, including a cylinder body (1) internally provided with a cylinder, a piston (2), a connecting rod (3) and a crankshaft (4), wherein, the piston (2) is arranged in the cylinder, the connecting rod (3) is linked with the crankshaft (4) and the piston (2), the cylinder body (1) is also provided with a mechanism which can change the effective length of the connecting rod (3), and two ends of the mechanism are respectively linked with the connecting rod (3) and the crankshaft (4). The mechanism which can change the effective length of the connecting rod is a retractable hydraulic lever mechanism and controlled by a hydraulic pump controlled by ECU and a triple valve. The variable compression ratio engine has the following advantages that the compression ratio can be continuously changed and the change is controllable; the structure is simple; the control strategy is relatively simple; and the dynamic property and the fuel economy of the engine can be effectively improved.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Variable compression ratio internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20130306035A1Reduce vibrationVibrations of the first control shaft can be suppressedEngine controllersMachines/enginesActuatorInternal combustion engine
A variable compression ratio internal combustion engine includes a variable compression ratio mechanism, an actuator and a linking mechanism. The actuator is varies and maintains a rotational position of the first control shaft. The linking mechanism includes a second control shaft and a lever. The second control shaft is selectively turned by the actuator. The lever links the second control shaft to the first control shaft such that transference of vibration of the first control shaft to the second control shaft is suppressed. The first control shaft is pivotally linked to a first end of the lever by a first linking pin. The second control shaft is pivotally linked to a second end of the lever by a second linking pin.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Variable compression ratio engine with lost motion coupling
InactiveUS20090107467A1Effective compression ratioEffectively alter compression ratioRotary bearingsConnecting rodsCouplingFlange
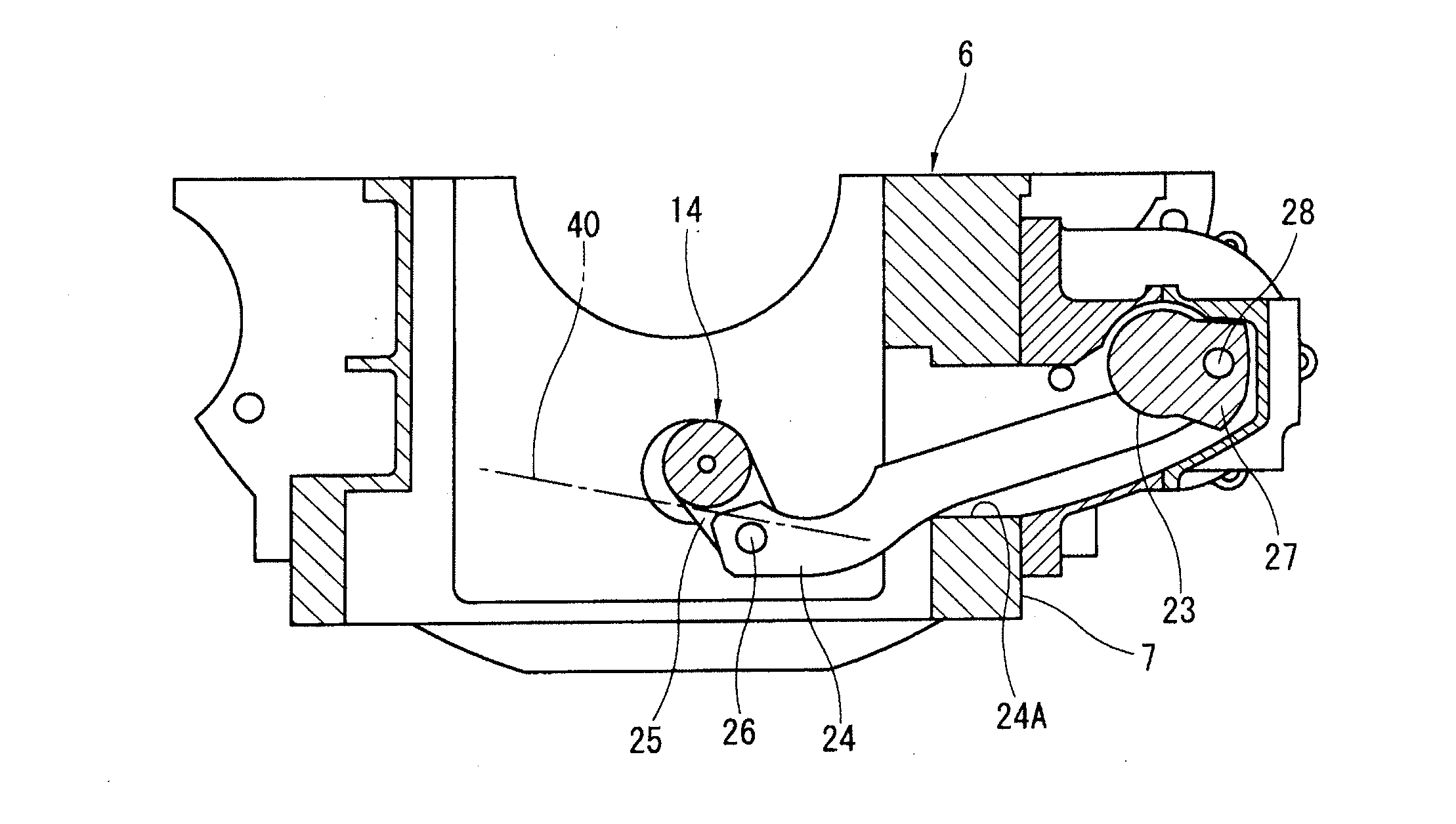
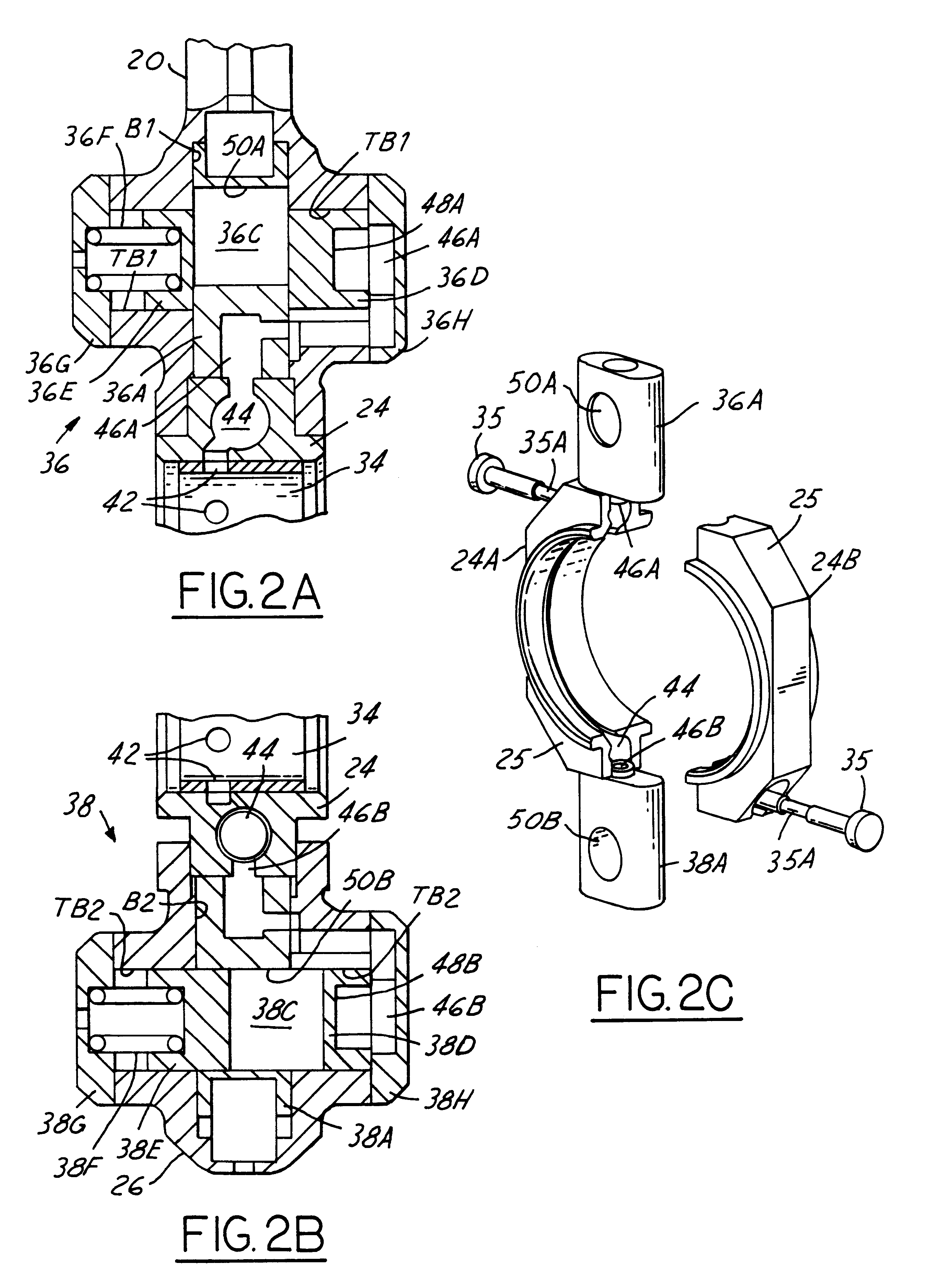
A variable compression ratio piston (26) and connecting rod (18) assembly for an internal combustion engine (14) includes an eccentric bushing (28) that carries a piston pin bushing (42) and contains a journaled portion (48) held in the rod bore (24) of the connecting rod (18). The eccentric bushing (28) can be selectively rotated between either of two angle adjusted positions to effect a change in the height of the piston (26) relative to the connecting rod (18), and thus change the compression ratio of the assembly. A latch (50) mechanism is actuated by oil jets (90, 91) external to the connecting rod (18). The latch (50) includes bolts (54, 56) with tapered tips that seat in oblong holes (60, 62) in a flange plate (58) to reduce destructive lash. A resilient stop post (80) bears the brunt of stresses associated with stopping the flange plate (58) during switching events to protect the latching bolts (54, 56).
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Amphibious vehicle
ActiveUS7207851B1Transmission limitIncrease motivationAmphibious vehiclesPropulsion power plantsRolling resistanceCompressed natural gas
Amphibious vehicle needs less power on land than on water. A control system is provided to limit power and / or speed on land, using: restriction of flow of fuel, air, or exhaust gases; heated intake air; exhaust gas recirculation; declutching of a supercharger; bypassing of a turbocharger; a variable throttle stop, dual throttles, or a switchable throttle damper; cylinder or intake valve deactivation; a dual length intake manifold; dual mode ignition or engine mapping; dual fuel—gasoline on water, compressed natural gas on road; variable compression ratios or valve timing; a clutch designed to slip; automatic brake application; or aerodynamic brakes. The suspension may tilt the vehicle to increase aerodynamic resistance. The road transmission may be geared to limit maximum speed. High rolling resistance tires or twin engines may be used. A sensor on retractable suspension may indicate whether the vehicle is on land or on water.
Owner:GIBBS TECH
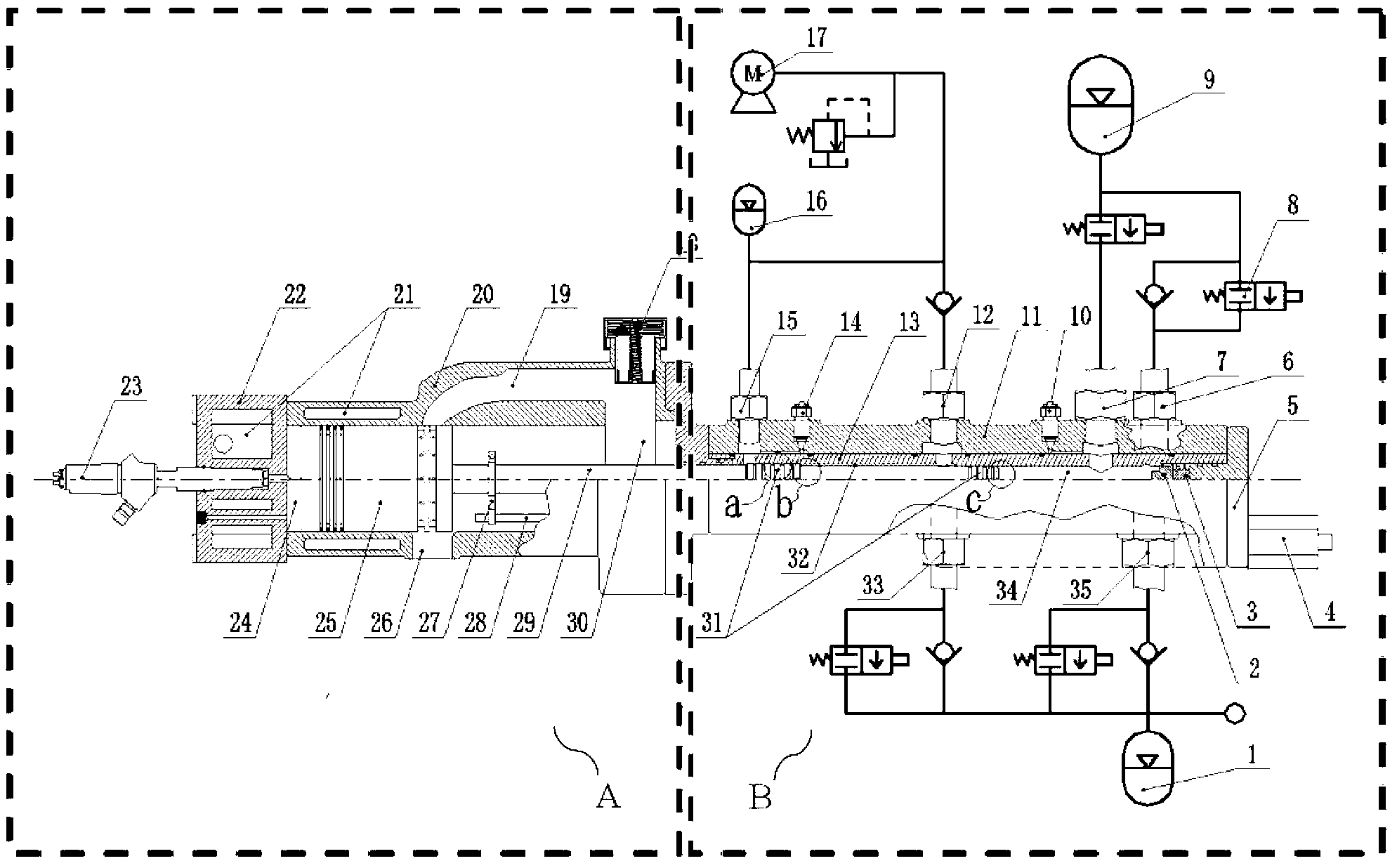
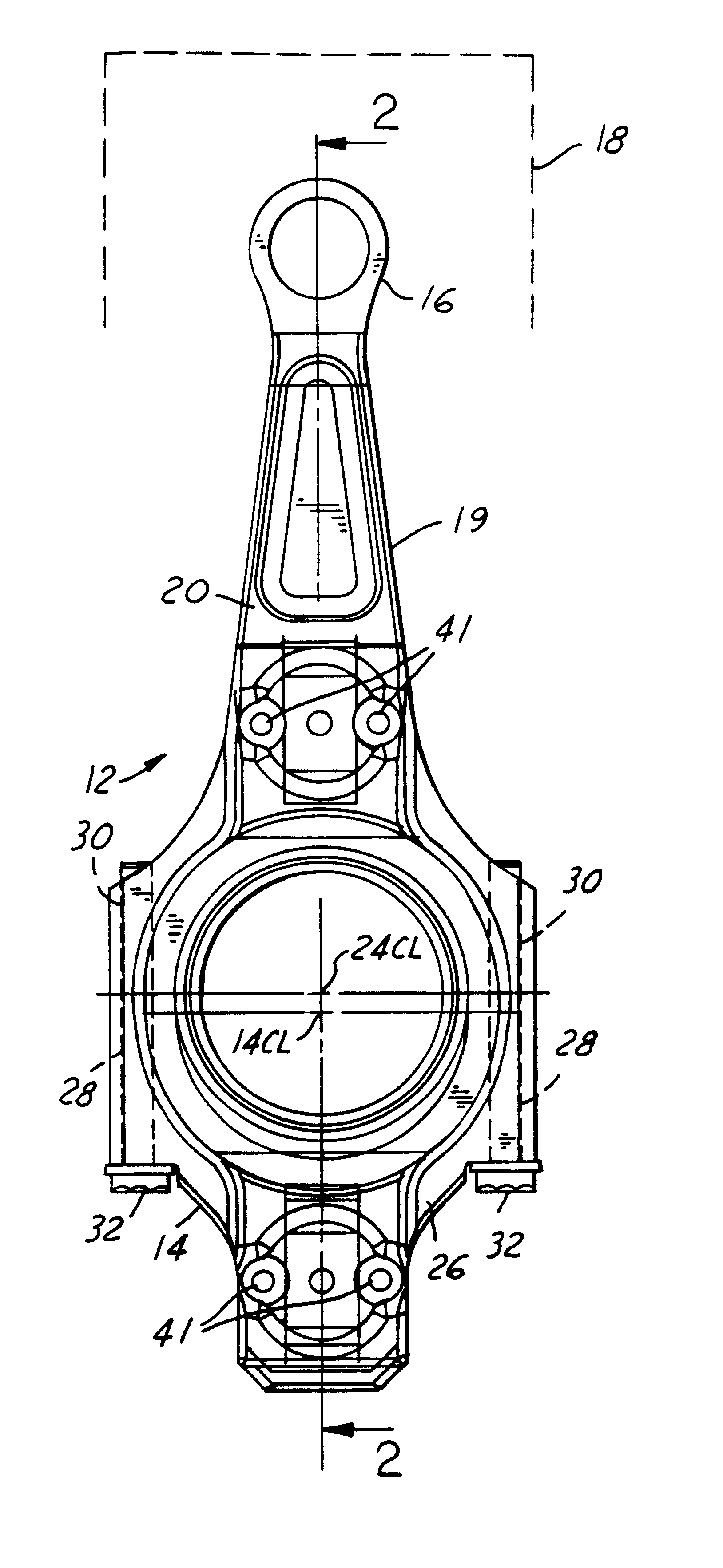
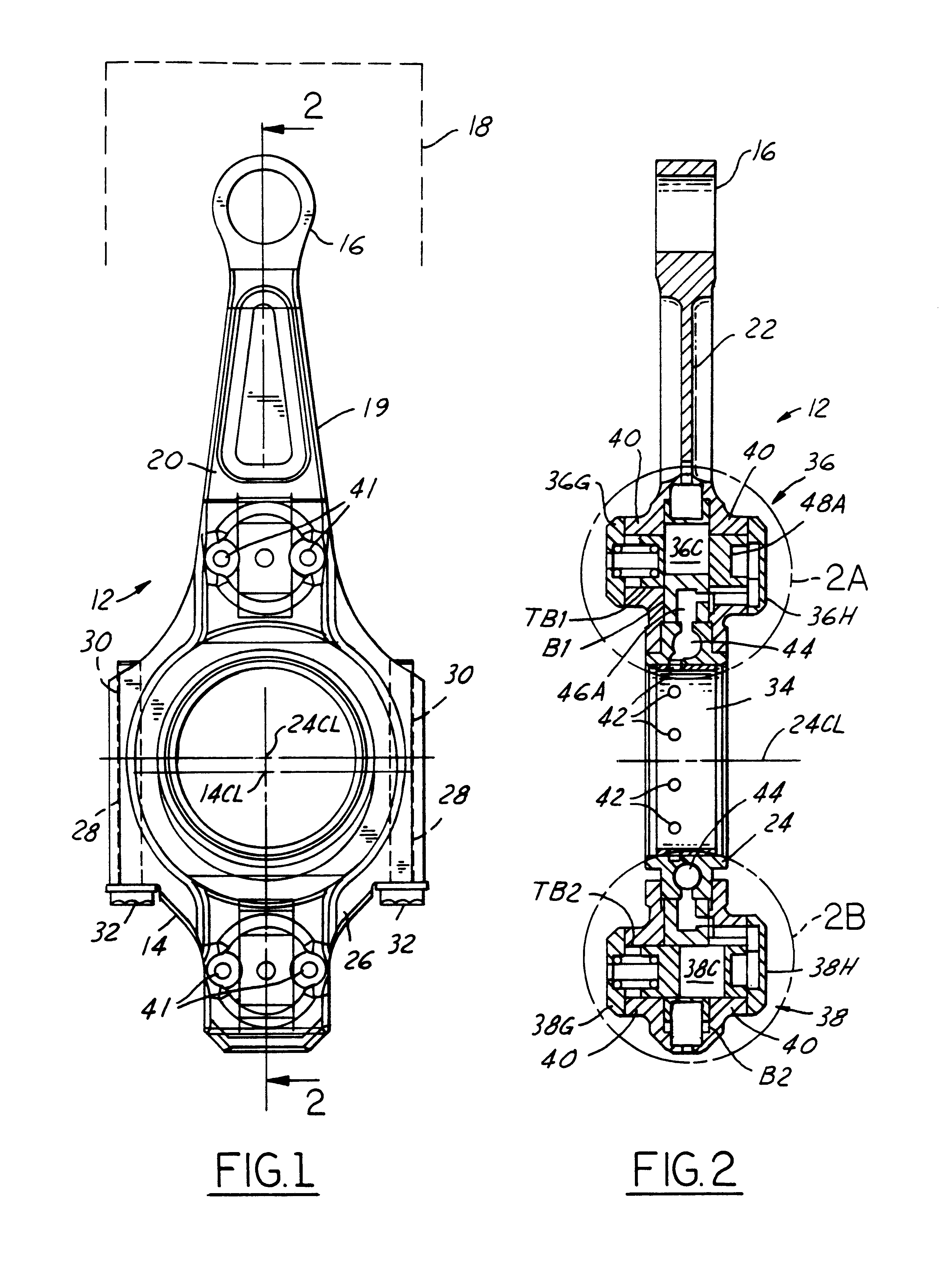
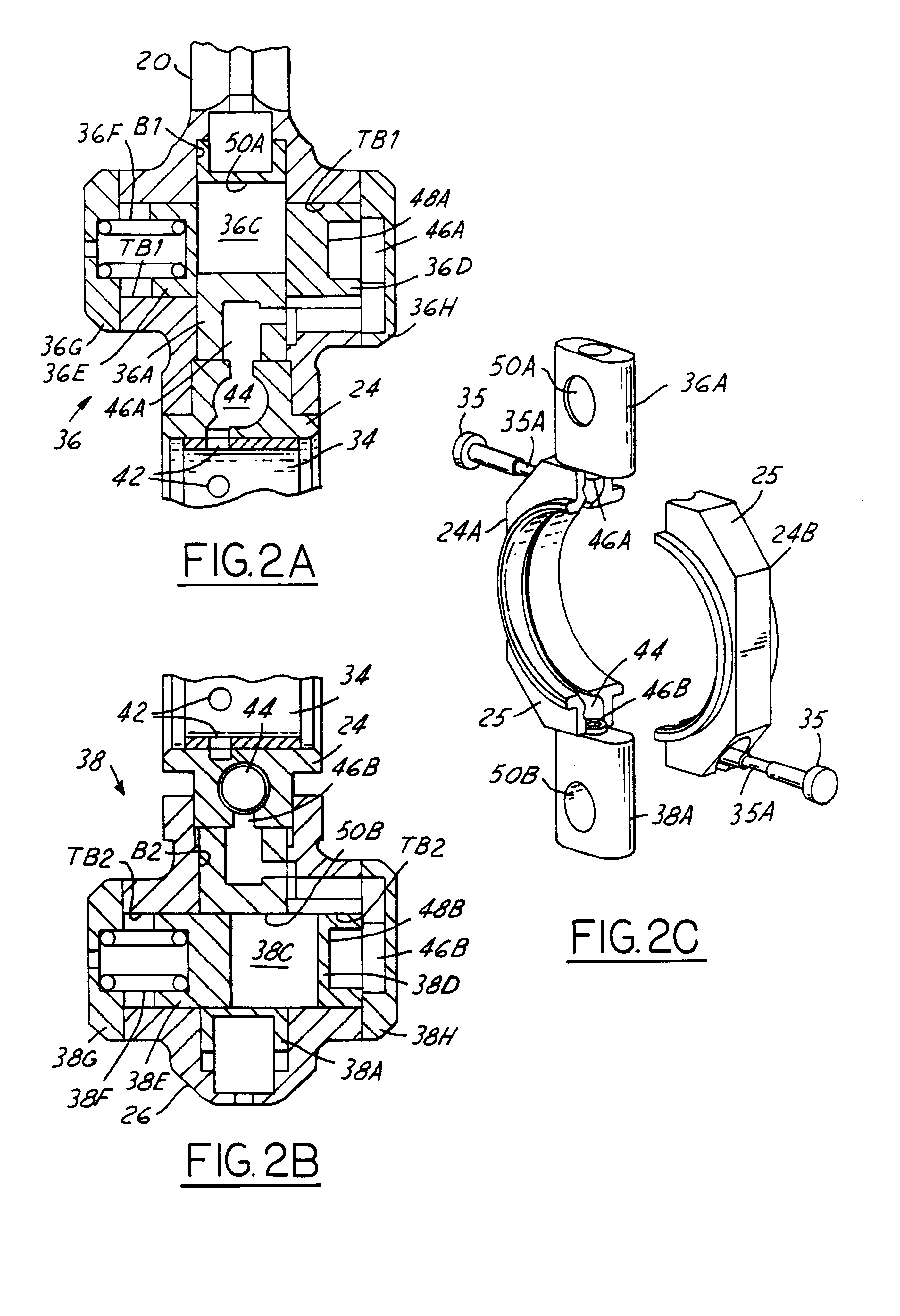
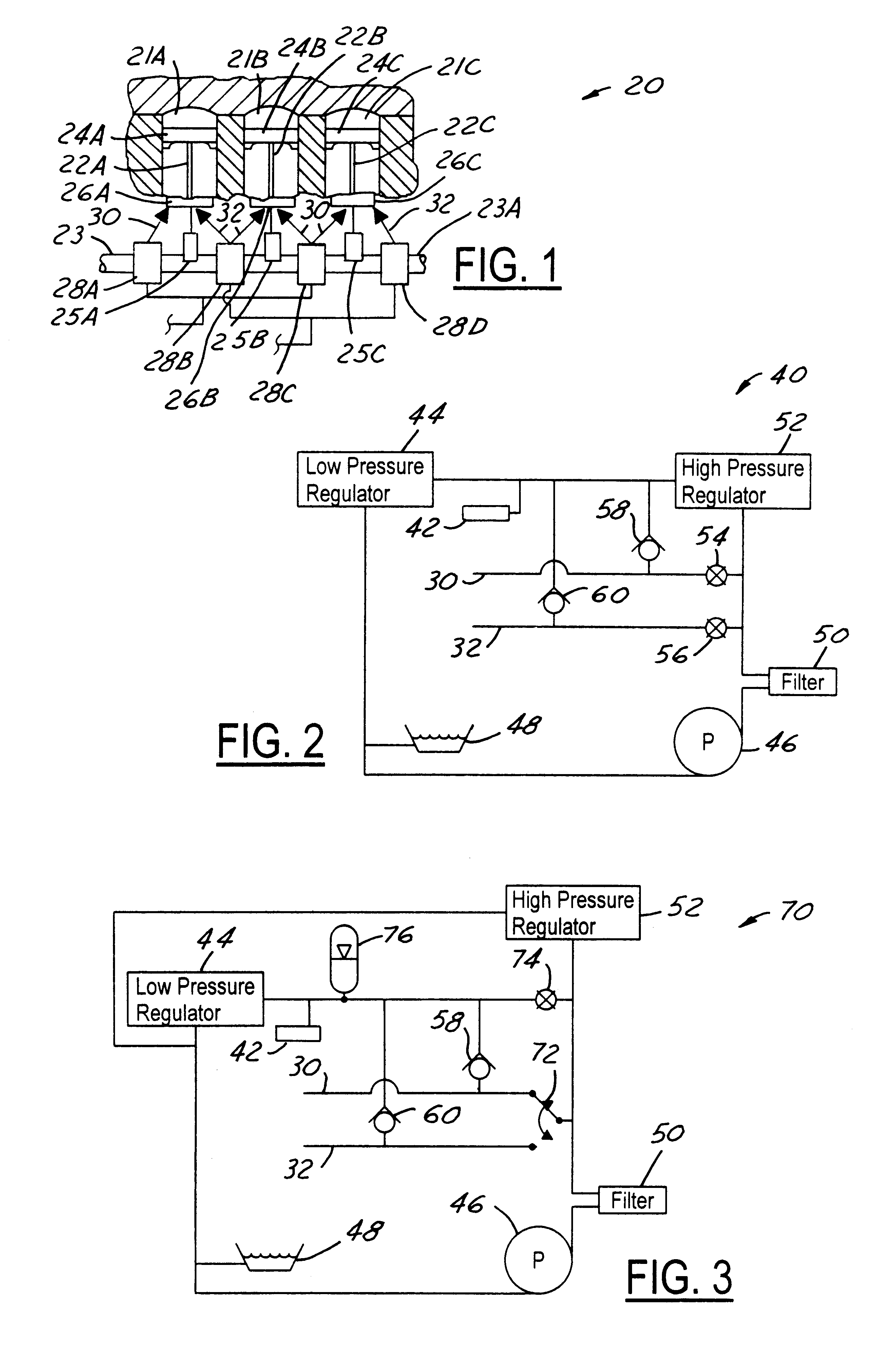
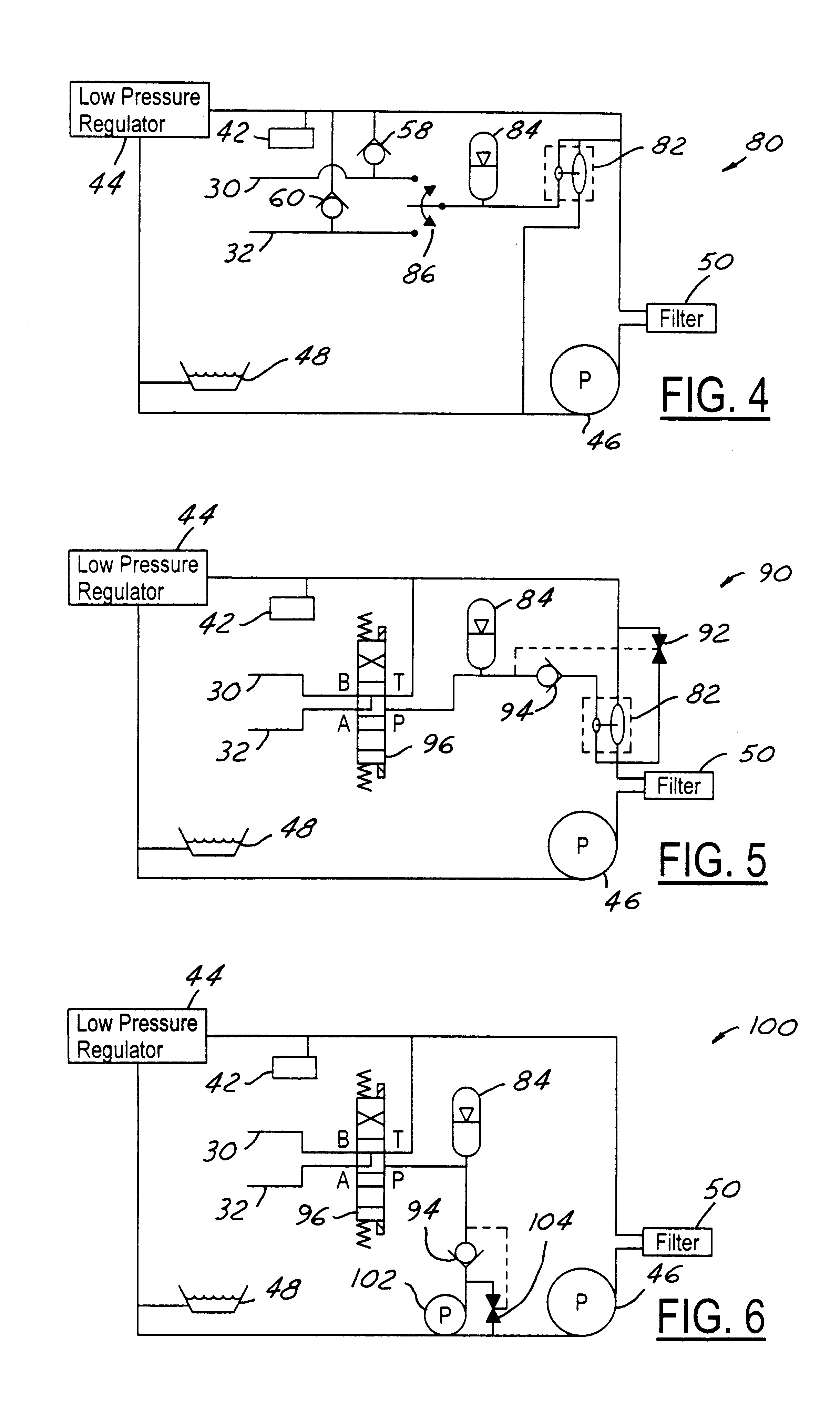
Variable compression ratio connecting rod locking mechanism I
A variable length connecting rod (12) has a first locking mechanism (36) for releasably locking connecting rod parts in a first effective length setting (FIG. 3) for the rod, and a second locking mechanism (38) for releasably locking the connecting rod parts in a second effective length setting (FIG. 2) to change the compression ratio for an engine cylinder. When a length change is to be made, hydraulic fluid unlocks a locked one of the locking mechanisms, allowing inertial force to effect the length change during an engine cycle. At completion of a length change, the other locking mechanism automatically unlocks.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
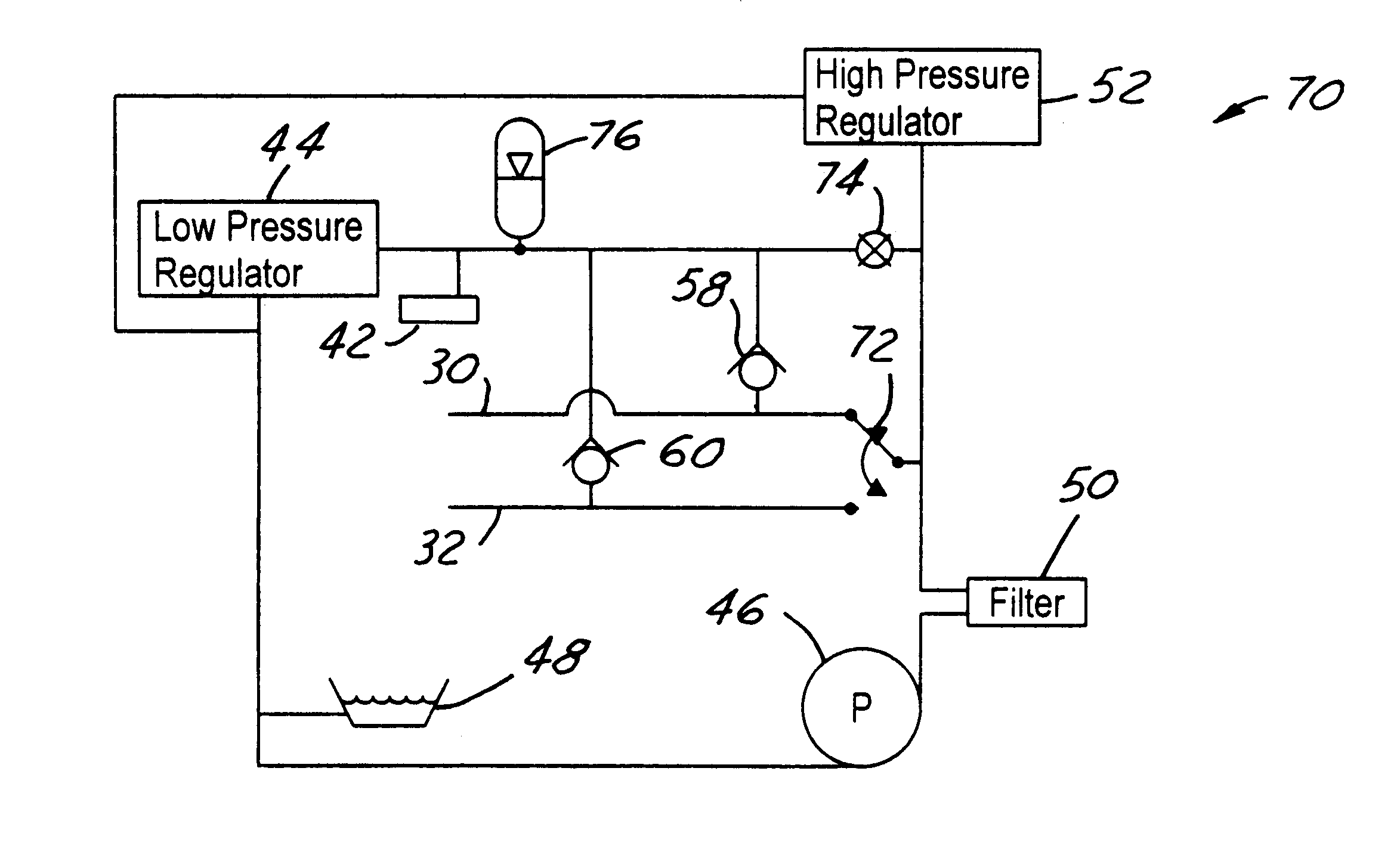
Hydraulic circuit having accumulator for unlocking variable compression ratio connecting rod locking mechanisms-II
A variable length connecting rod (12) has a first locking mechanism (36) for releasably locking connecting rod parts in a first effective length setting (FIG. 7) for the rod, and a second locking mechanism (38) for releasably locking the connecting rod parts in a second effective length setting to change the compression ratio for an engine cylinder. When a length change is to be made, hydraulic fluid unlocks a locked one of the locking mechanisms, allowing inertial force to effect the length change during an engine cycle. At completion of a length change, the other locking mechanism automatically unlocks.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20080087255A1Improve thermal efficiencyAvoid knockingInternal combustion piston enginesOutput powerFree-piston engineTop dead center
In a reciprocating piston engine employing a variable compression ratio mechanism configured to be linked to a reciprocating piston for variably adjusting a geometrical compression ratio by varying at least a top dead center position of the piston responsively to a controlled variable, a controller is configured to control the variable compression ratio mechanism depending on an engine operating condition. A part of a wall surface of a combustion chamber is formed of a non-metallic material having a higher heat-insulating and heat-reserving property as compared to a base structural material of each of the combustion chamber and the piston.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Hydraulic circuit for unlocking variable compression ratio connecting rod locking mechanisms
A variable length connecting rod (12) has a first locking mechanism (36) for releasably locking connecting rod parts in a first effective length setting (FIG. 7) for the rod, and a second locking mechanism (38) for releasably locking the connecting rod parts in a second effective length setting to change the compression ratio for an engine cylinder. When a length change is to be made, hydraulic fluid unlocks a locked one of the locking mechanisms, allowing inertial force to effect the length change during an engine cycle. At completion of a length change, the other locking mechanism automatically unlocks.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Variable compression ratio device of automobile engine
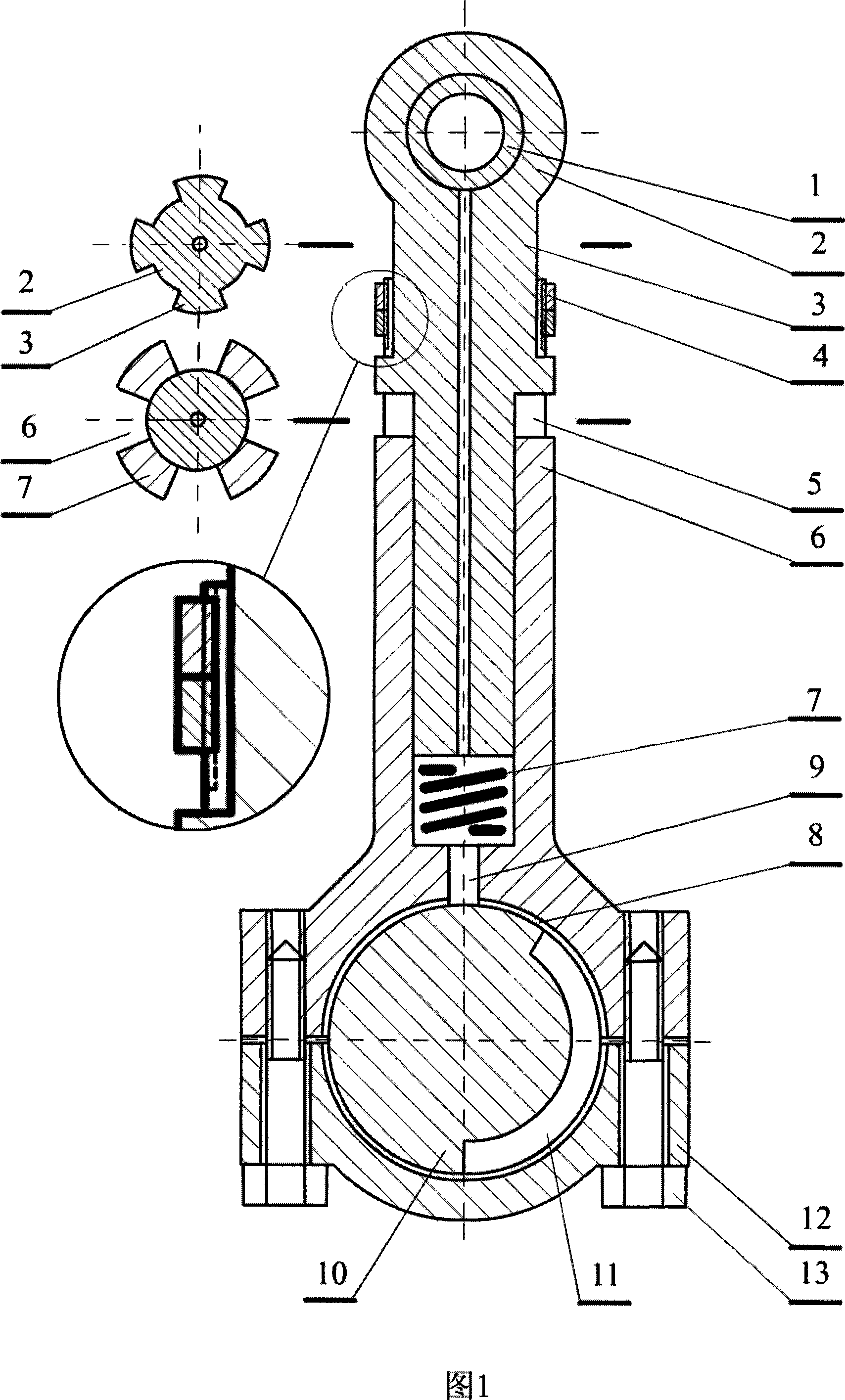
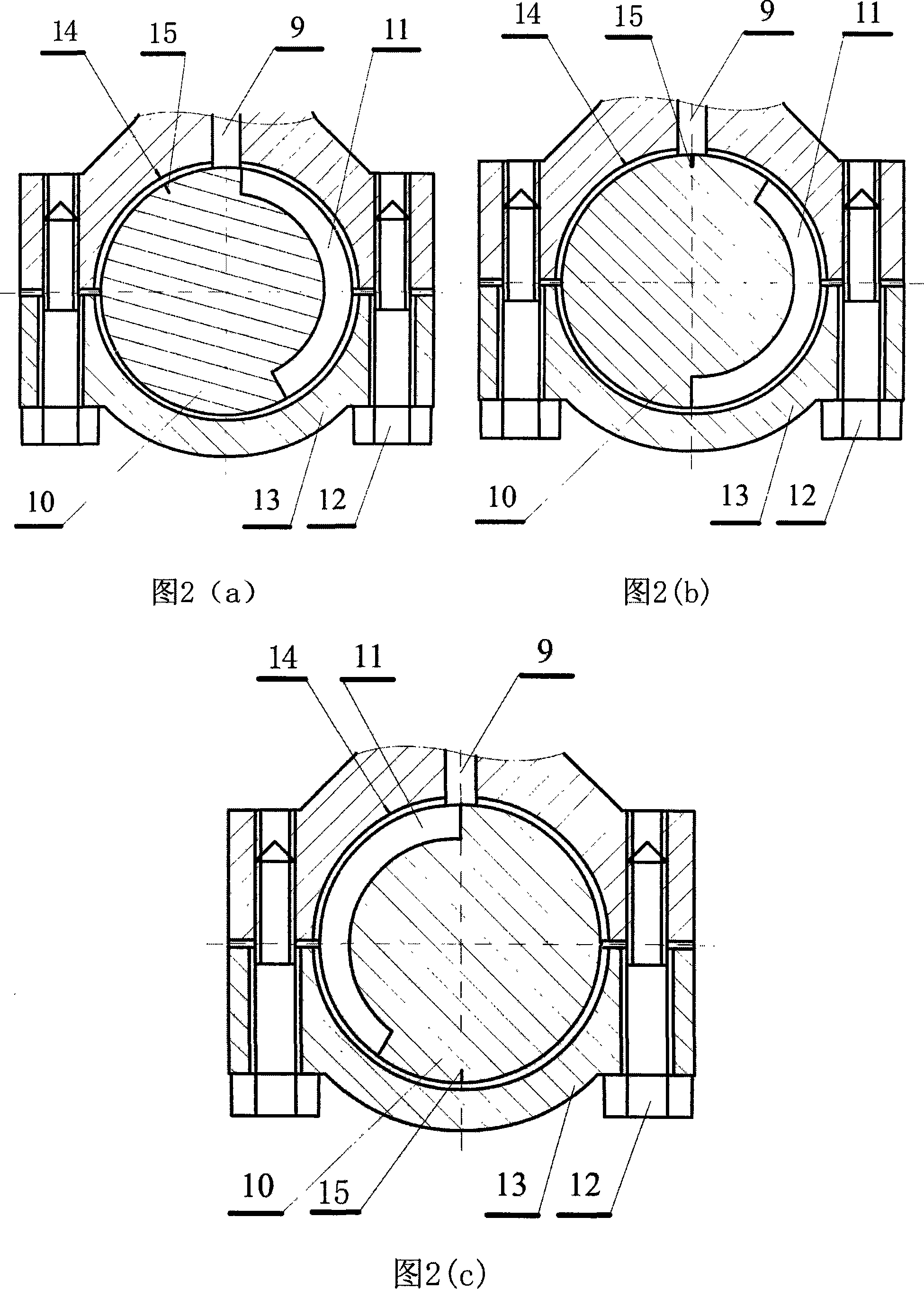
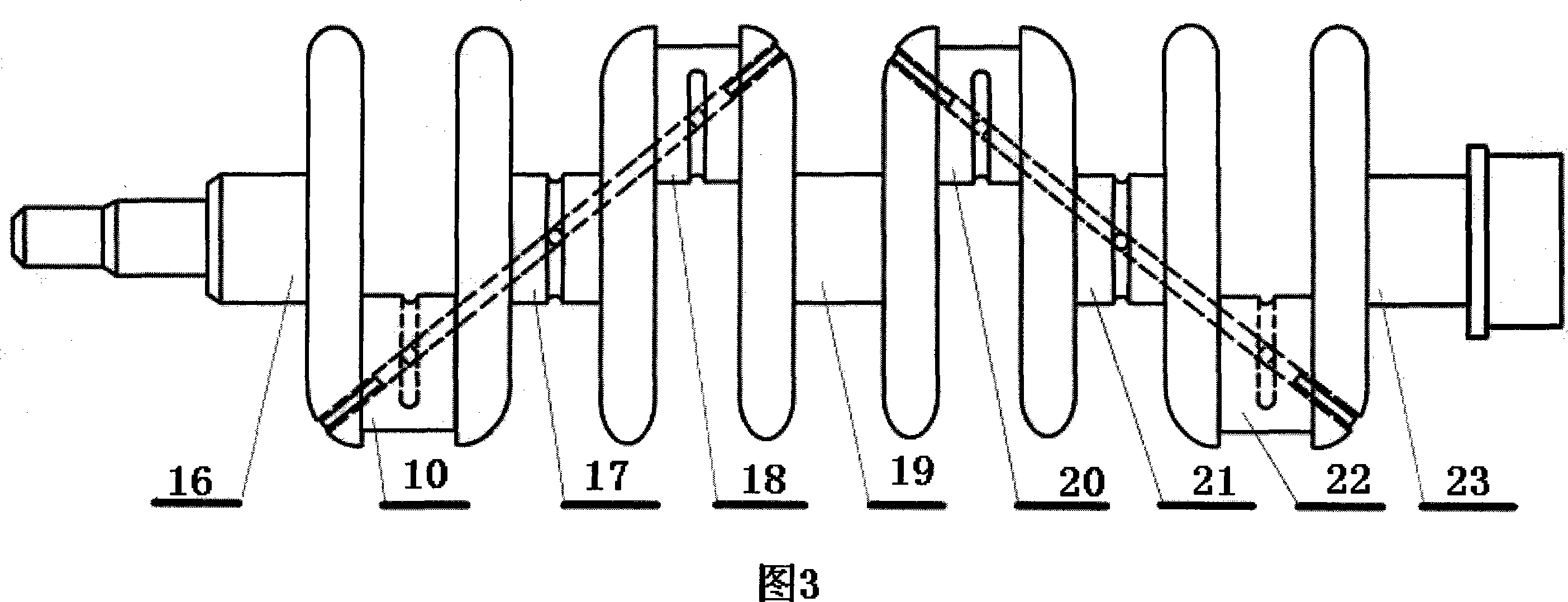
InactiveCN101560917ADynamic balance does not affectSimple structureEngine controllersMachines/enginesCrankcaseControl theory
The invention discloses a variable compression ratio device of an automobile engine, comprising a crank shaft, a main connecting rod, a piston, an eccentric sleeve, a hinge bar transmission mechanism and a regulating shaft; a small end of the main connecting rod is connected with the piston by a piston pin, and a large end thereof is connected with the crank shaft; the eccentric sleeve is arranged between the small end of the main connecting rod and the piston pin, a connecting rod neck and the large end of the main connecting rod, or a main journal of the crank shaft and a main bearing saddle bore of a crank shaft case; the hinge bar transmission mechanism is used for the transmission between the regulating shaft and the eccentric sleeve. The hinge bar transmission mechanism controls the rotation of the eccentric sleeve, and can change the position of a dead point on the piston so as to change the compression ratio of the engine; furthermore, the hinge bar transmission mechanism is formed by two parallelogrammic hinged four-bar linkage mechanisms, so that the variable compression ratio device has the advantages of simple structure, easy fabrication, convenient control, reliable use, durability and low cost.
Owner:张志强
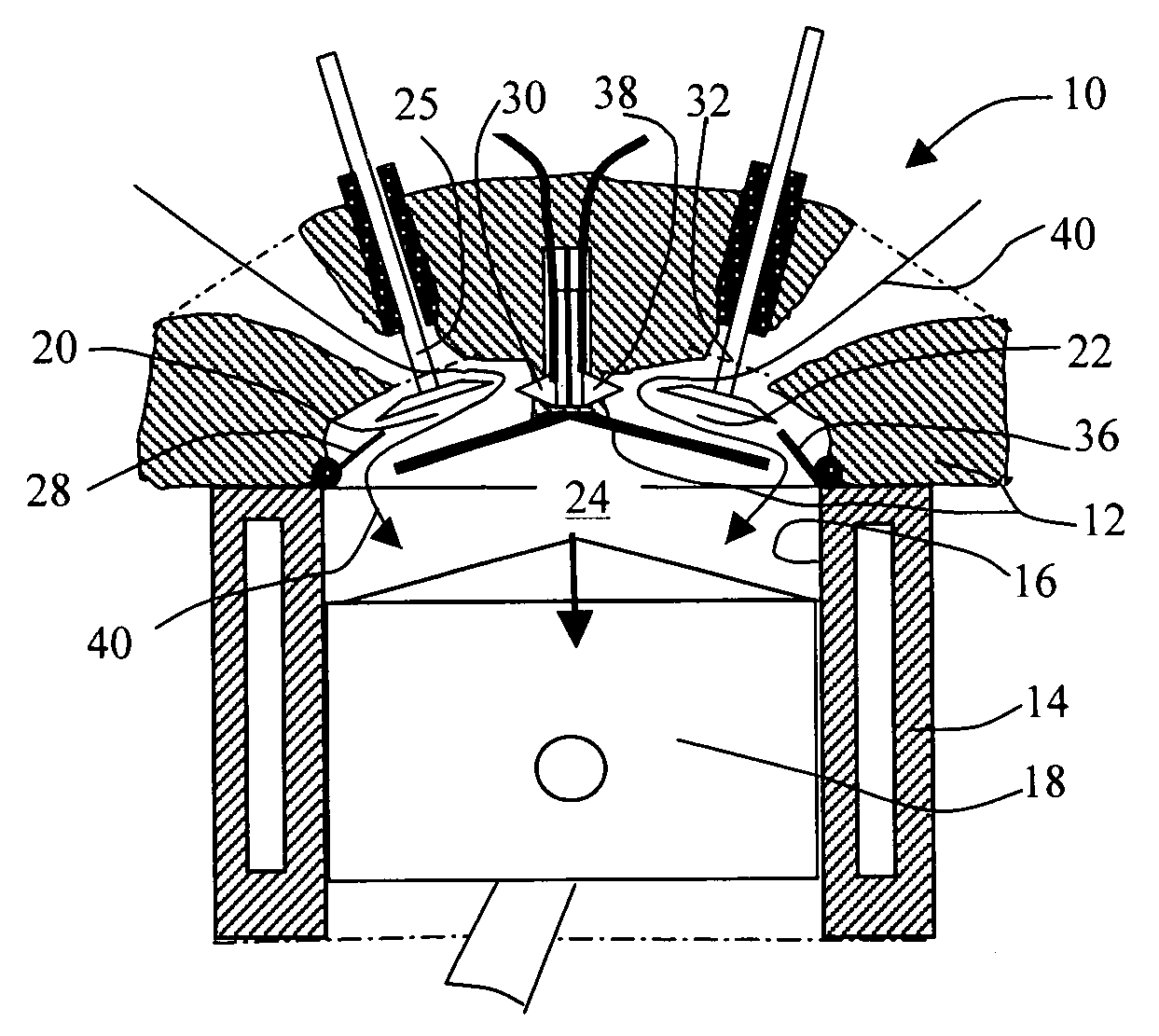
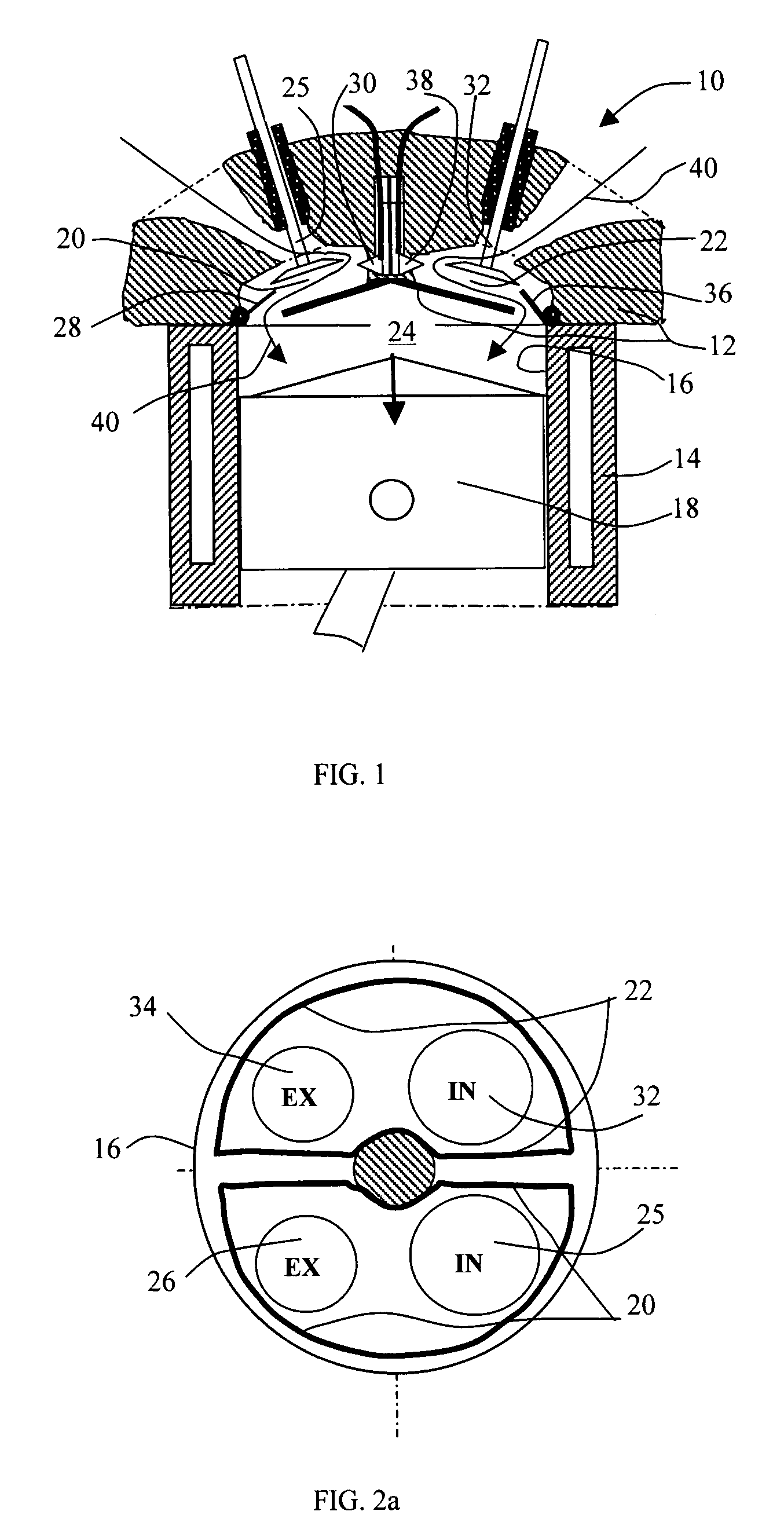
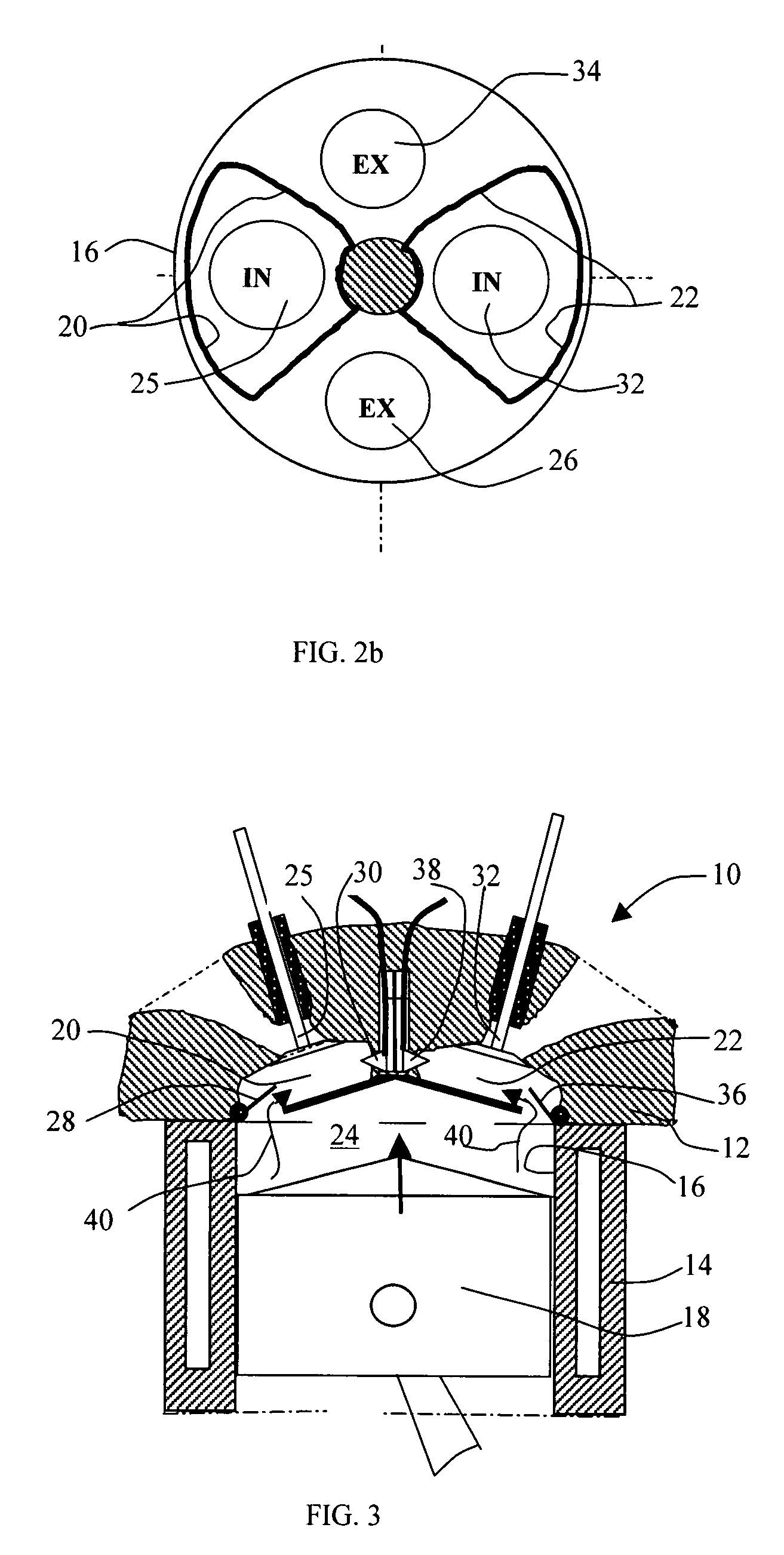
Cao cycles of internal combustion engine with increased expansion ratio, constant-volume combustion, variable compression ratio, and cold start mechanism
InactiveUS7624709B2Internal combustion piston enginesOutput powerAlternative fuelsExternal combustion engine
This invention provides an internal combustion engine that has a substantially increased expansion ratio, a variable compression ratio, and subsequently a significantly improved thermal efficiency. This improvement in thermal efficiency is attained without involving a complex mechanical structure or an enlarged engine size. The engine comprises at least a piston and cylinder assembly including a piston reciprocatingly mounted within the cylinder space, and at least two combustion chambers associated with said cylinder, each said combustion chamber having a port leading to said cylinder space and a combustion-chamber valve, said valve opens and closes said port to establish or block the communication between said combustion chamber and cylinder space, wherein said internal combustion engine is adapted to operate on preferred cycles in accordance with load conditions to substantially increase the engine's expansion ratio or provide a variable compression ratio mechanism under part load conditions. For an engine having two combustion chambers associated with each cylinder, the expansion ratio or compression ratio may be nearly doubled. Additionally, a cold start mechanism particularly for an engine operating on alternative fuels, such as ethanol or methanol, and engine valves that are operationally suitable for the engine cycles in accordance with the present invention are disclosed.
Owner:CAO YIDING
Variable compression ratio internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20100163002A1Reduce noiseCasingsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExternal combustion engineCrankcase
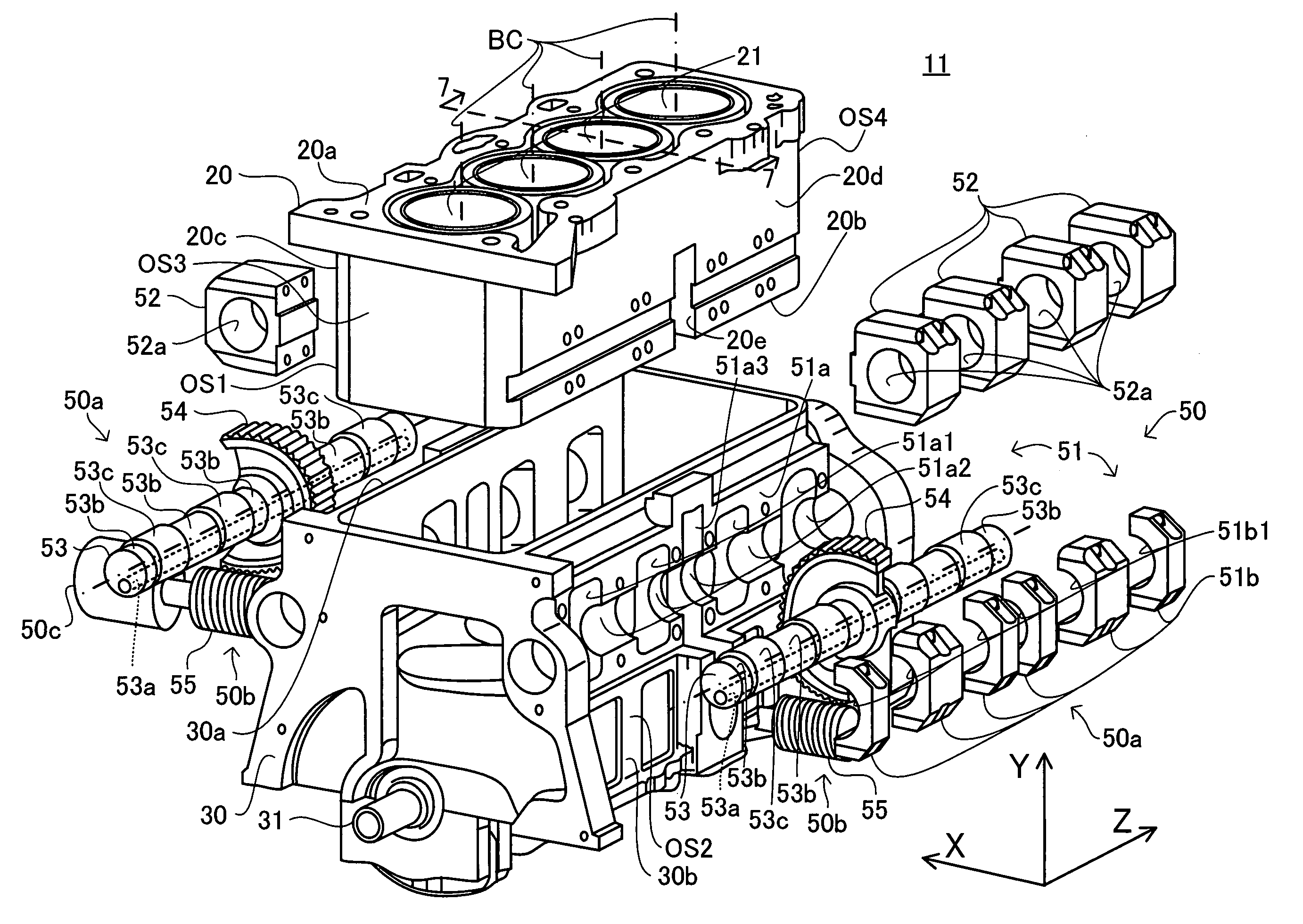
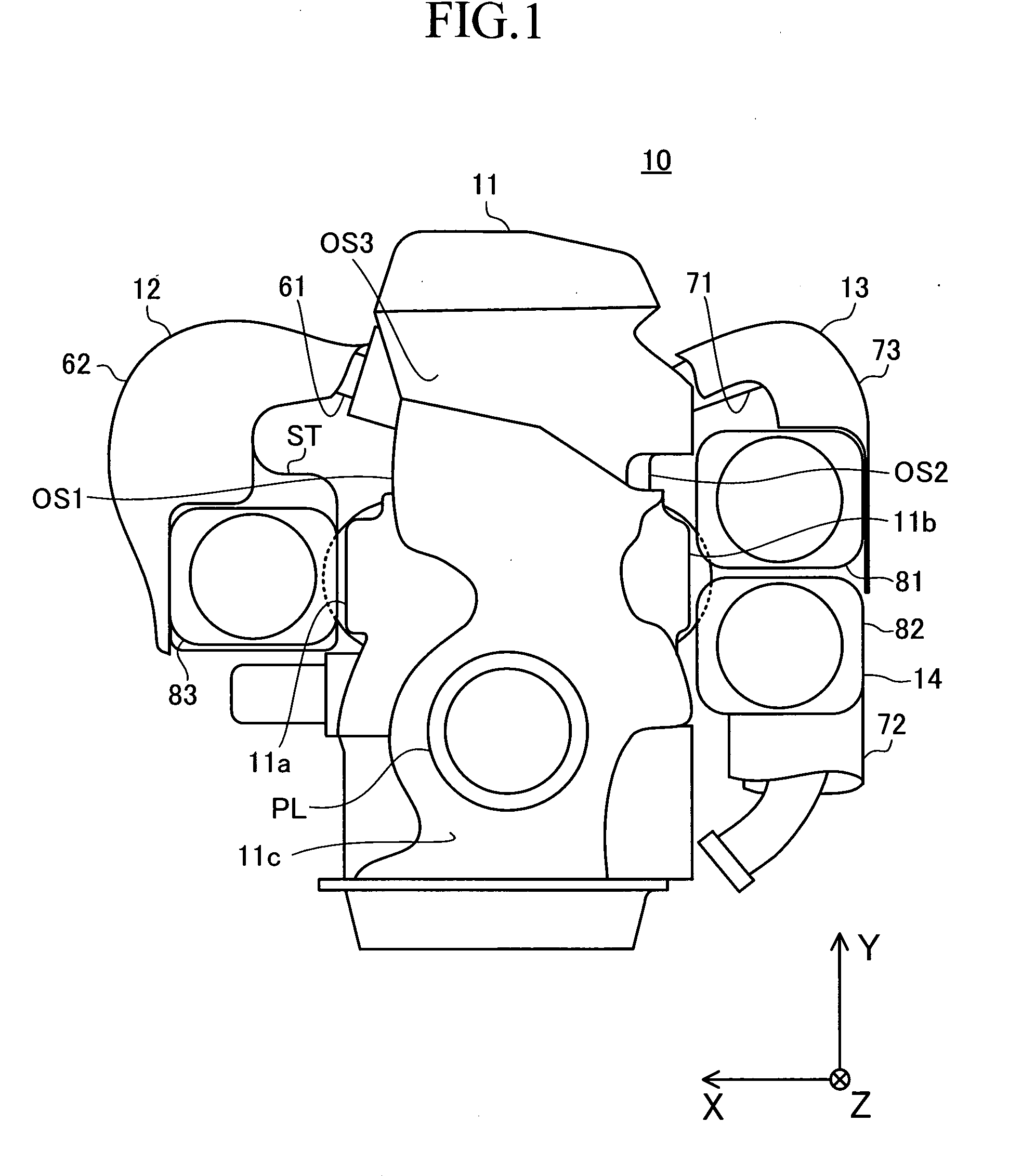
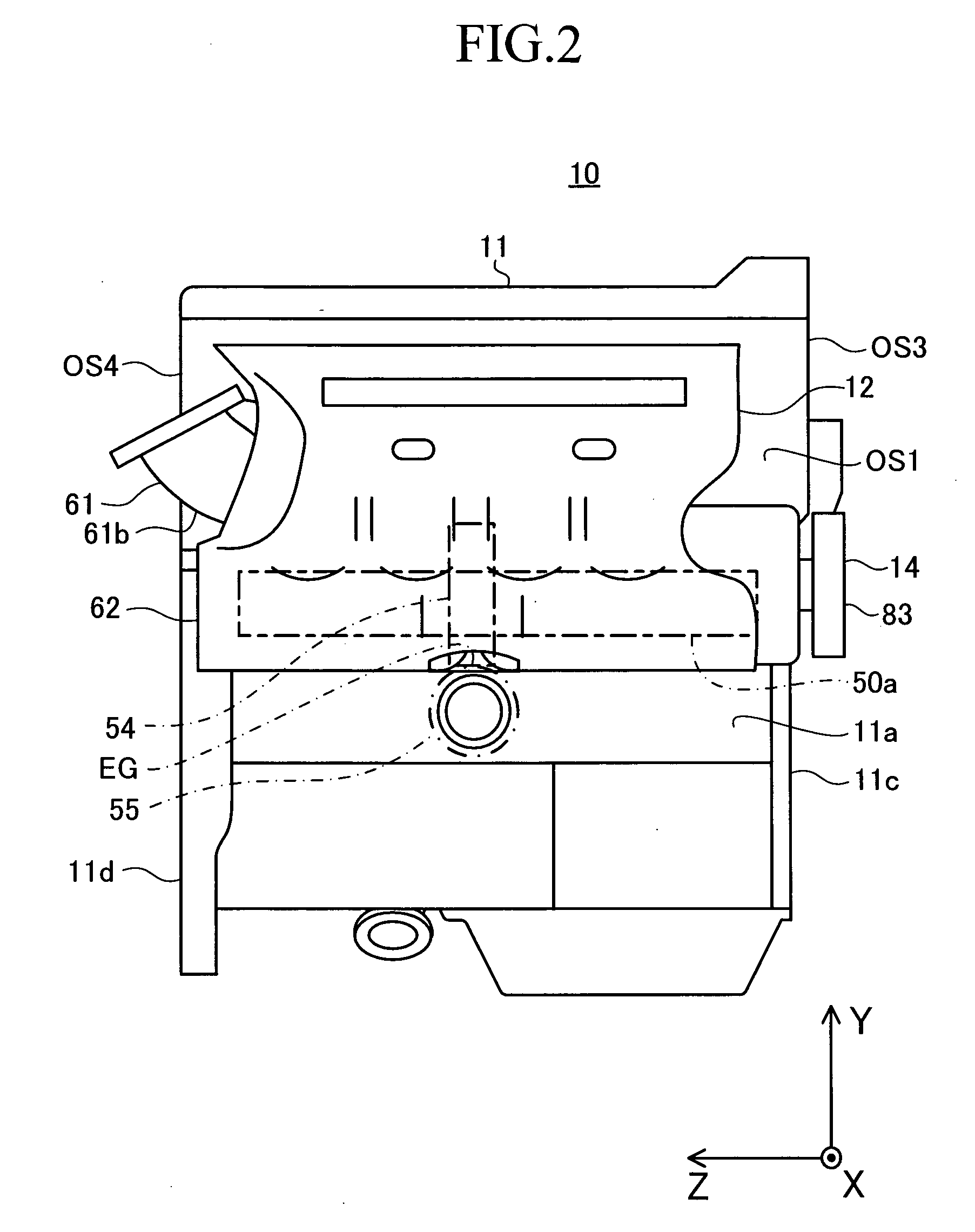
An internal combustion engine 10 comprises a device having a mechanism that moves a cylinder block relative to a crankcase, a worm wheel (wheel) 54 fixed to the mechanism, and a worm 55 meshed with the wheel. The device is disposed at the position in the vicinity of an disposed-face OS1 and within the OS3 disposed-face when the disposed-face is viewed from the front. The internal combustion engine drives the worm for rotatably driving the wheel to drive the mechanism. The internal combustion engine has a noise shielding members 61, 62, and 83 arranged so as to cover a meshing portion EG where the wheel and the worm are meshed with each other, when the disposed-face is viewed from the front. The noise generated at the meshing portion is attenuated by the noise shielding member, and propagated to the outside of the internal combustion engine. Consequently, the noise heard at the outside is reduced.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Variable Compression Ratio Apparatus
InactiveUS20100132671A1Improve fuel efficiencyImprove output efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A variable compression ratio apparatus for varying a compression ratio, may include a connecting rod that is connected to a piston to take a combustion force; a pin link, one end of which is eccentrically connected to a crankshaft and the other end of which is pivotally connected to the connecting rod to form a connection portion therebetween; a slot link including a control slot to receive and guide the connection portion along the control slot; and a driving unit coupled to the slot link and configured to move the control slot to control a position of the connection portion.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Device for removing engine vibration and engine whose stroke characteriscts are variable
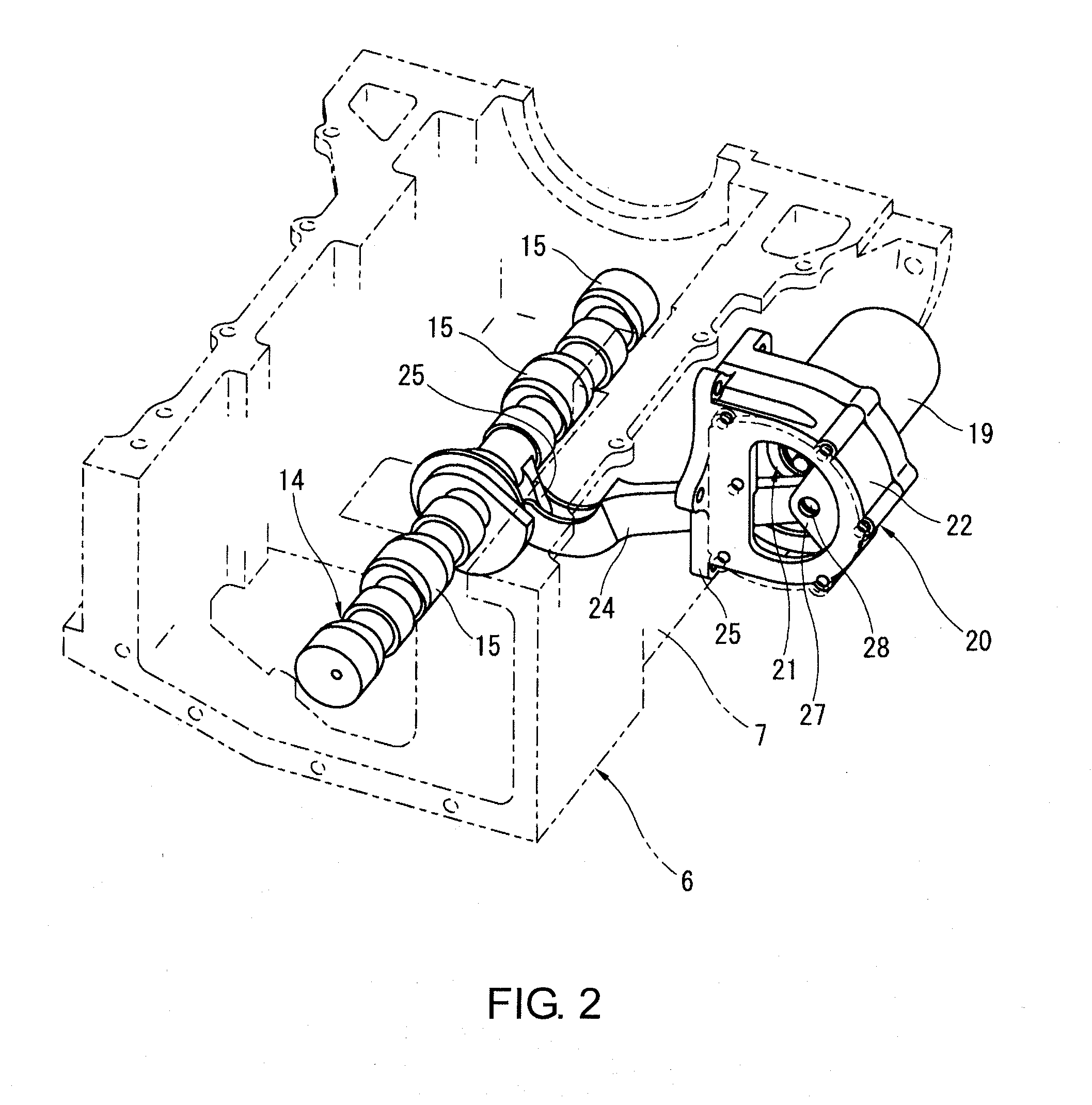
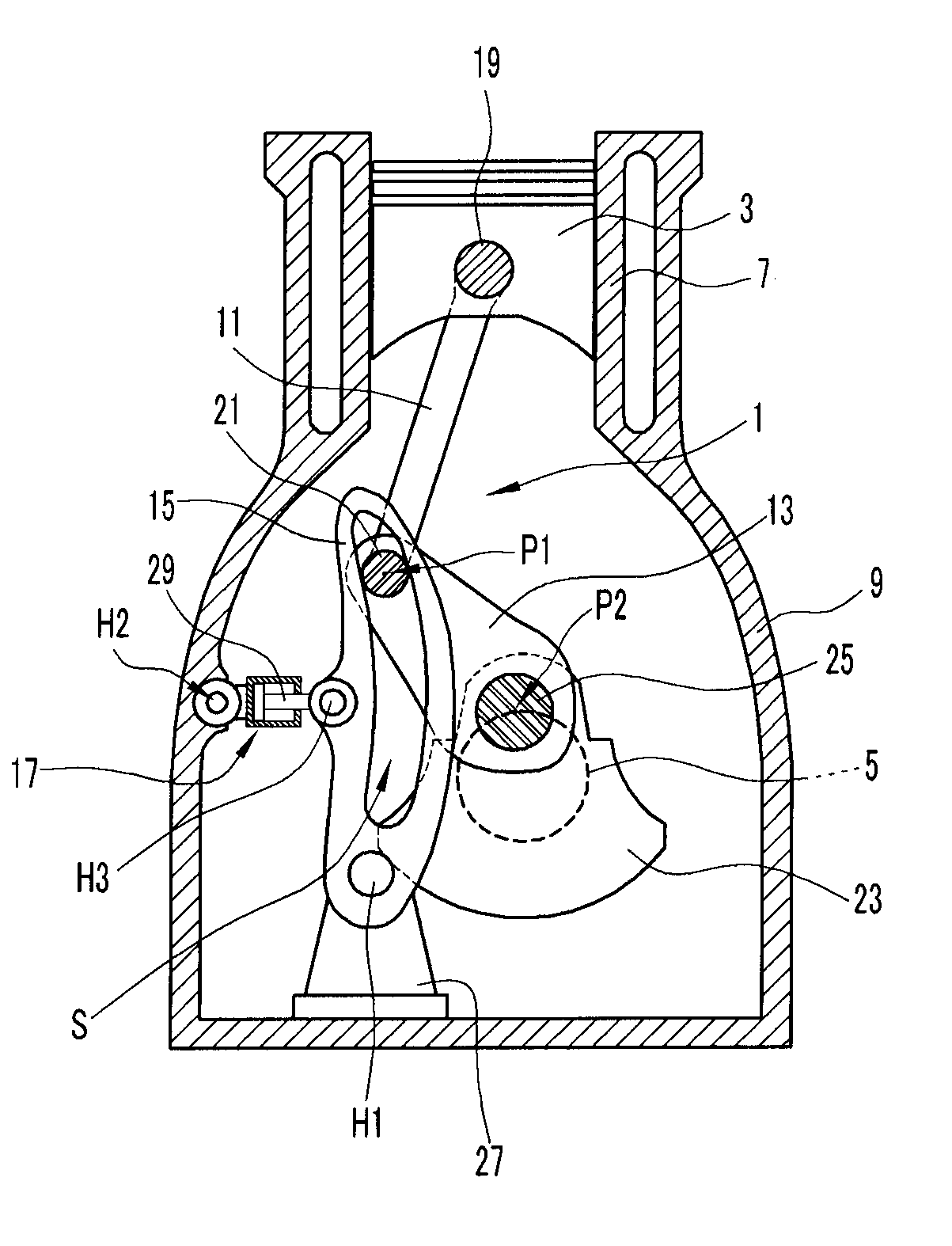
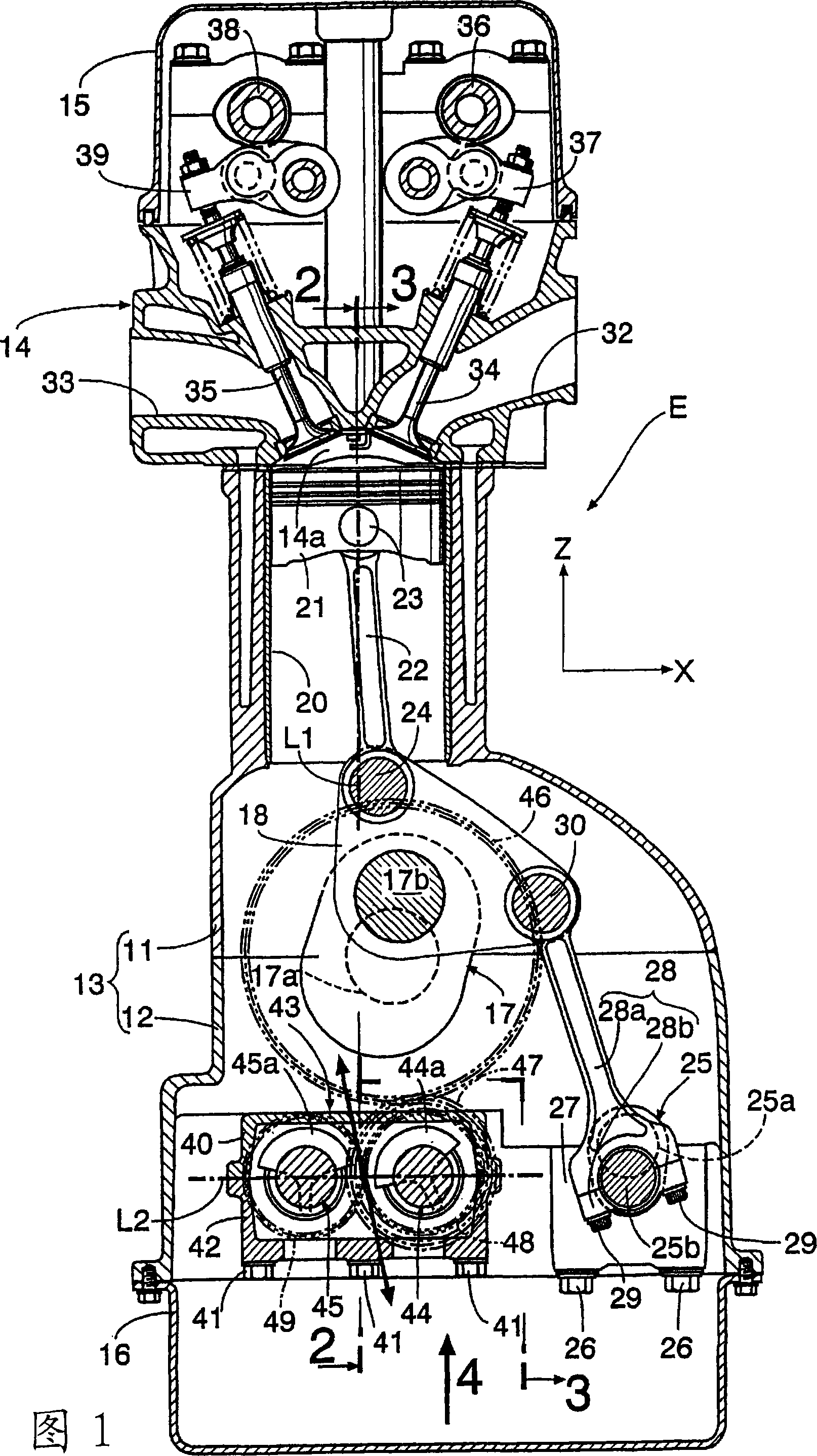
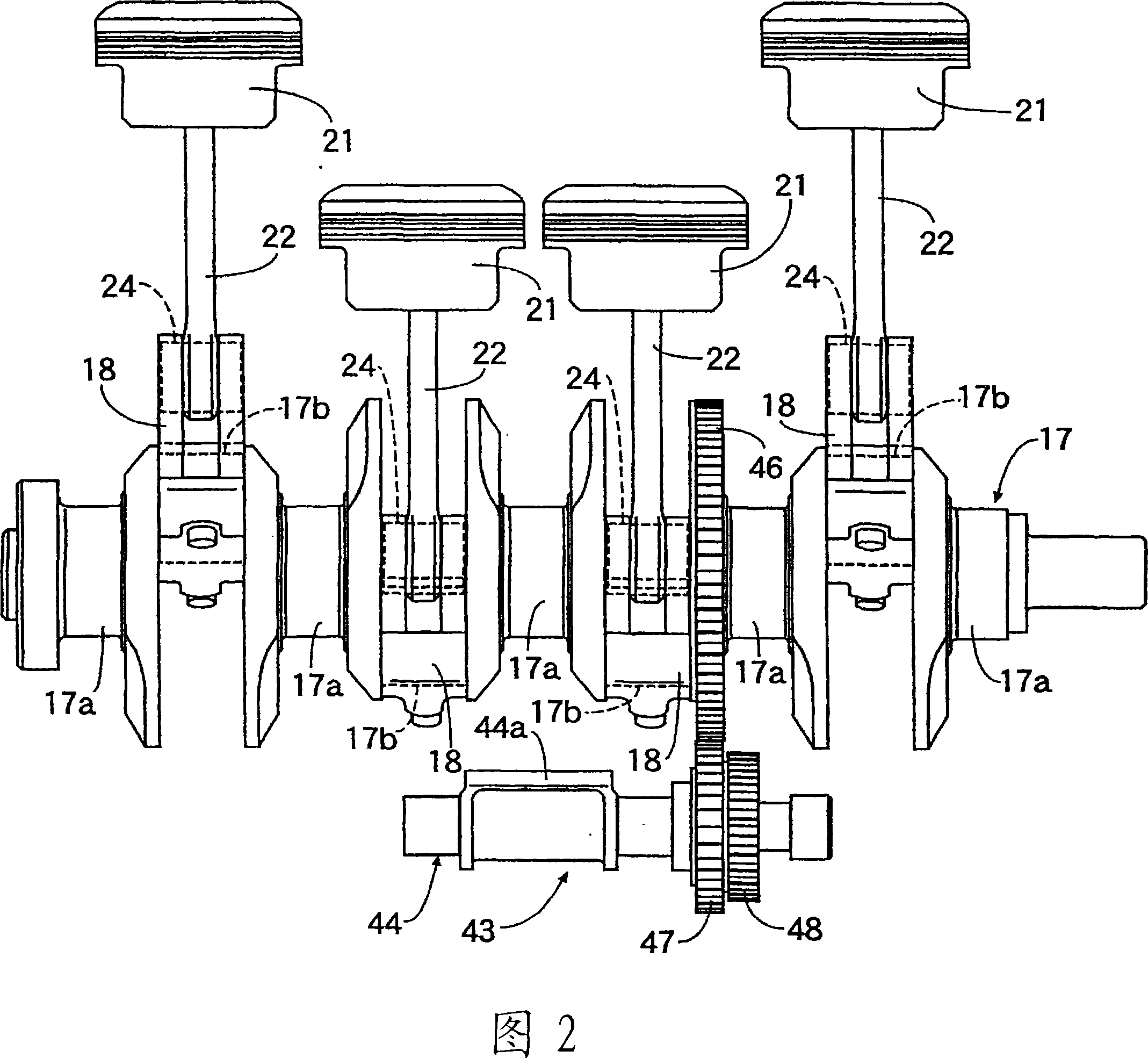
InactiveCN101052822AEliminate vibrationInertia force compensationMachines/enginesEngineeringBalance shaft
A device for removing engine vibration, capable of effectively removing secondary vibration cause by reciprocation of a piston (21) of a multilink-type variable compression ratio engine (E). The secondary vibration can be removed even if the direction of the secondary vibration is inclined relative to the cylinder axis (L1), and the removal is made by inclining the direction (see the arrow direction) of vibration exciting force, produced by a secondary balancer device (43), so that it matches the direction of the secondary vibration. The secondary balancer device (43) is constructed by having balancer weights (44a, 45a) respectively supported by a pair of balancer shafts (44, 45) rotating in the directions opposite from each other. Displacing the phases of the balancer weights (44a, 45b) enables the direction of the produced vibration exciting force to be inclined so that it matches the direction of the secondary vibration of the engine (E).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Oiling systems and methods for changing lengths of variable compression ratio connecting rods
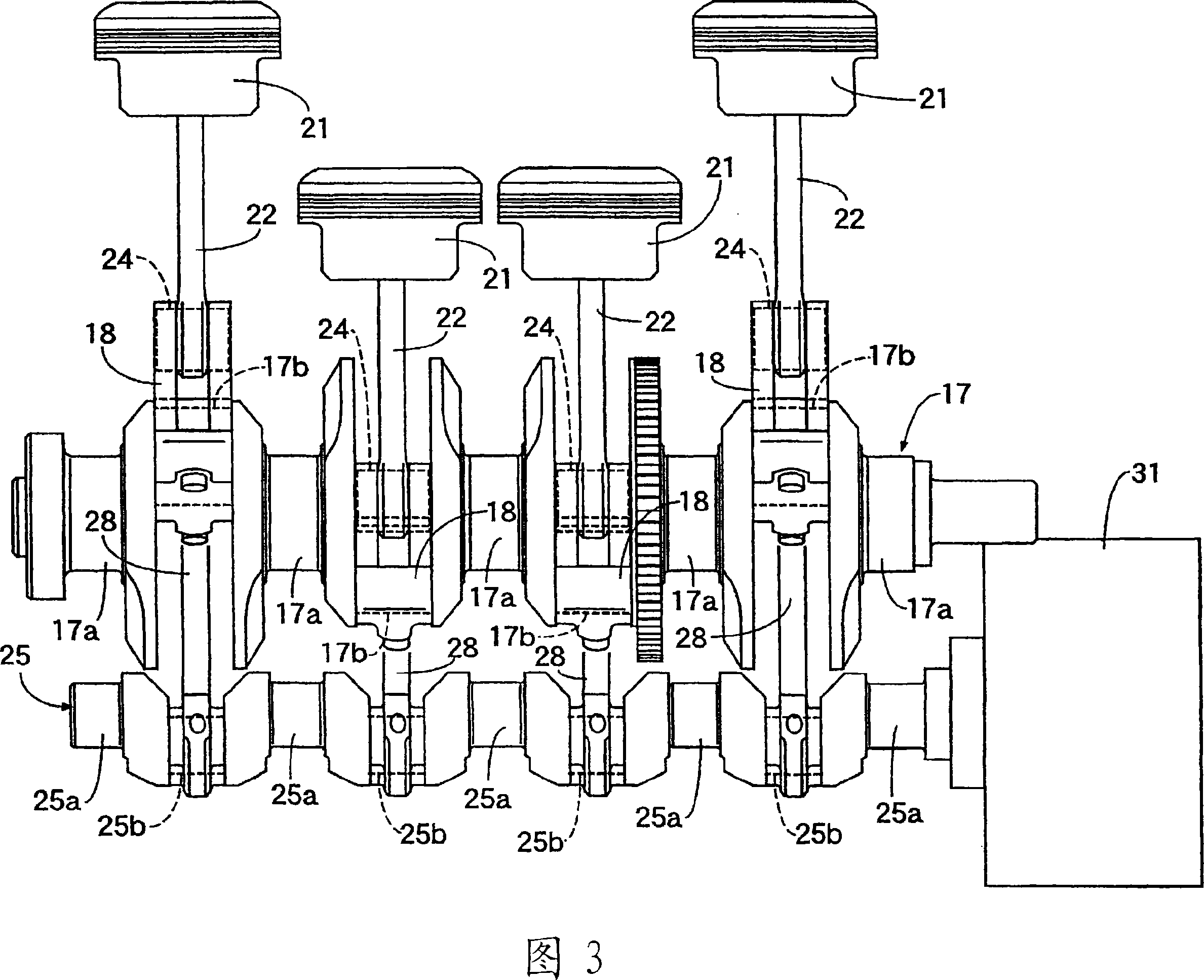
An engine 20 has an oiling system including a pump (46) that delivers oil under nominal engine lubrication pressure to lubricate moving surfaces of the engine mechanism (42). The system also has first and second control passages (30, 32) to effect engine compression ratio change by operating connecting rod length change mechanisms (26A, 26B, 26C). Selectively operated hydraulic control devices cause pressure in the first passage to be greater than pressure in the second passage to effect an increase in engine compression ratio and pressure in the second passage to be greater than pressure in the first passage to effect a decrease in engine compression ratio. Multiple embodiments of the invention are disclosed.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Compression ratio controlling apparatus and method for spark-ignited internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6915766B2Avoid uneven performanceAvoid it happening againElectrical controlMachines/enginesTransient stateLow load
In a compression ratio controlling apparatus and method for a spark-ignited internal combustion engine, the variable compression ratio mechanism is controlled by a compression controlling section on the basis of a detected engine speed and engine load in such a manner that the compression ratio is varied toward a target high compression ratio when the engine load falls in a predetermined low load region and toward a target low compression ratio when the engine load falls in a predetermined high load region and a predetermined delay is provided in a variation in the compression ratio toward one of the target high and low compression ratios in accordance with at least one of an engine driving history immediately before a transient state of a change in the engine load occurs and a wall temperature of a combustion chamber of the engine immediately before the transient state thereof occurs.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
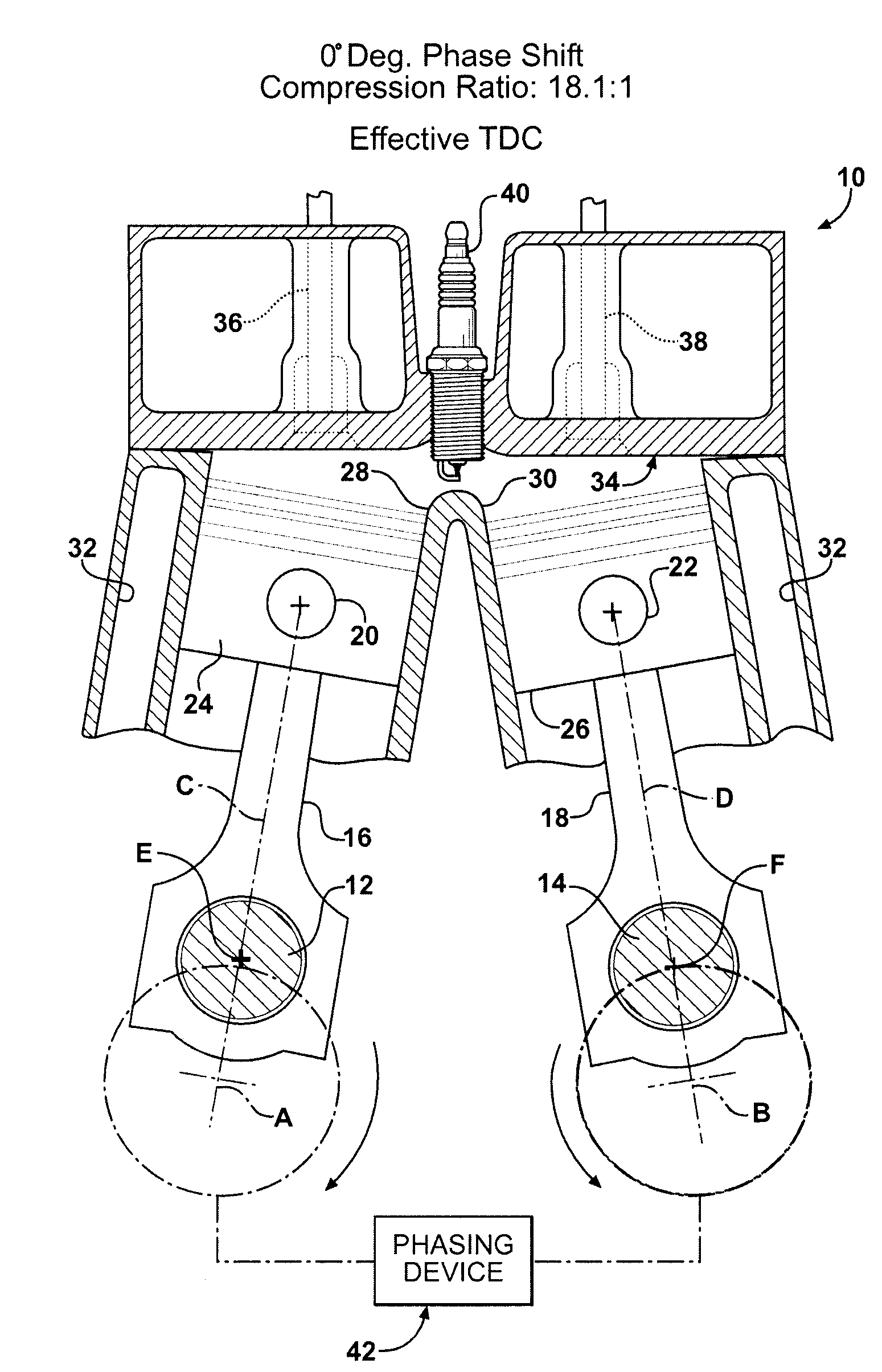
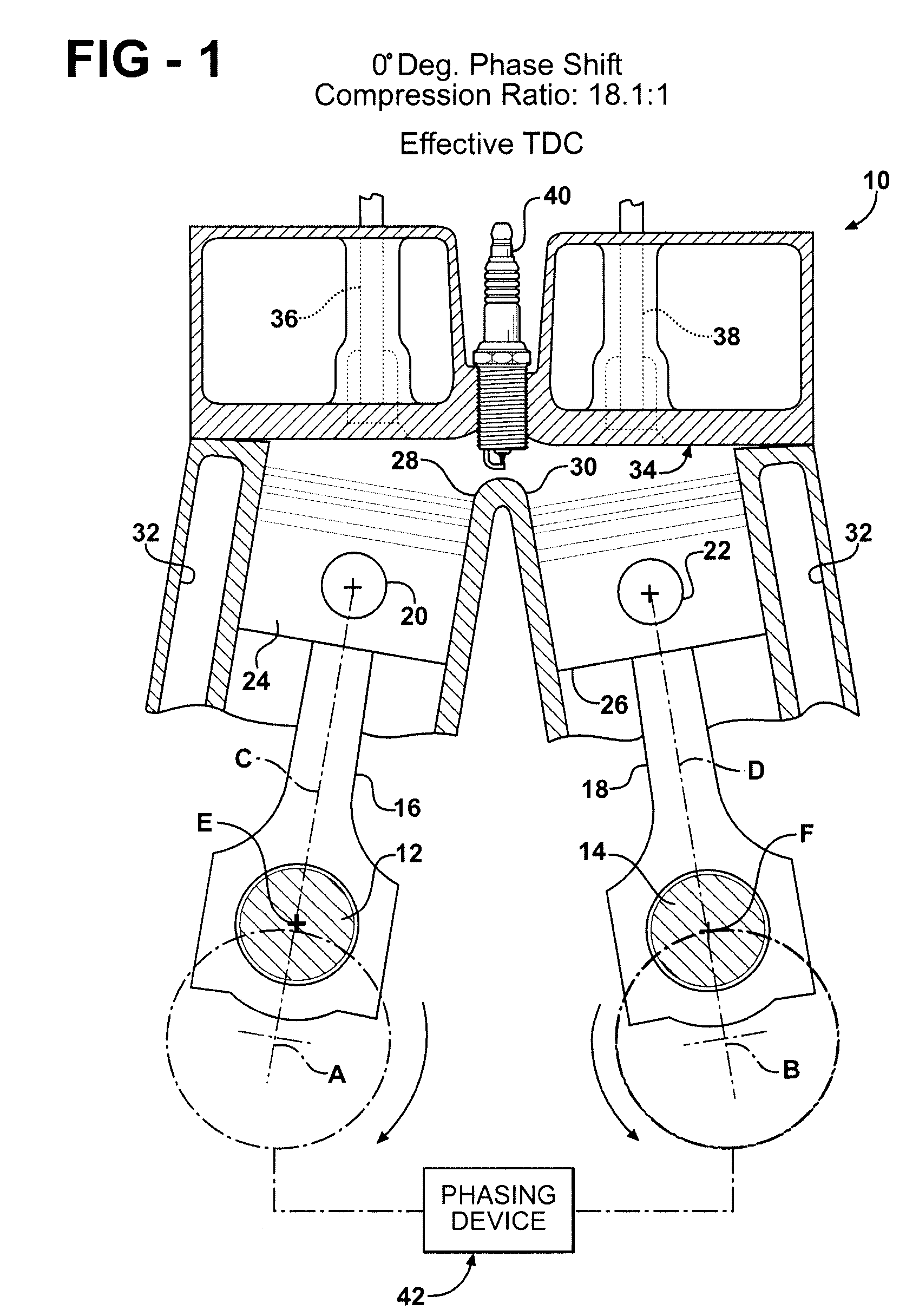
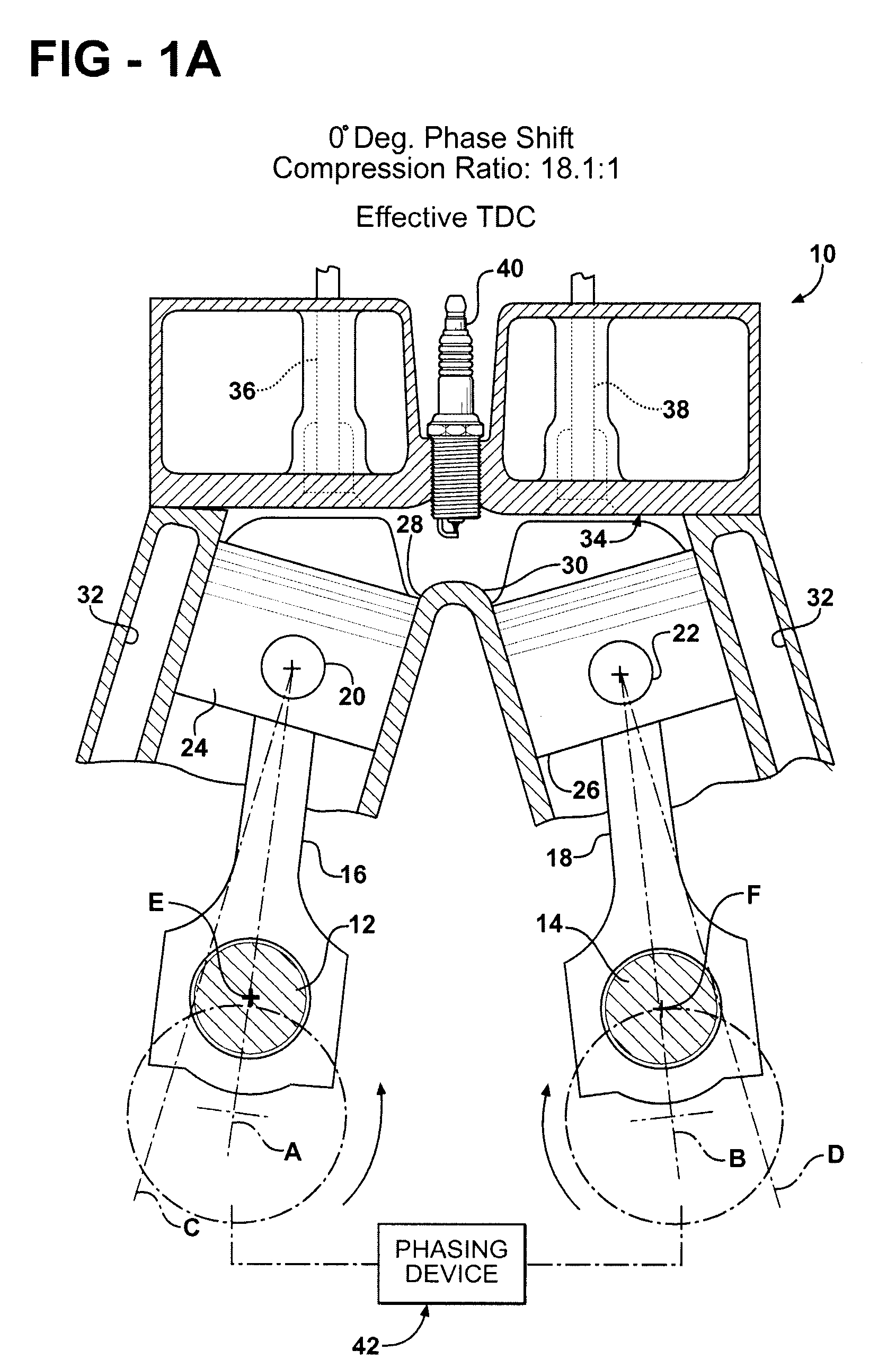
Variable compression ratio dual crankshaft engine
ActiveUS7584724B2Change the compression ratioEnhanced couplingInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersExhaust valveCombustion chamber
A synchronized, dual crankshaft engine (10) uses a phase-shifting device (42) to alter the angular position of one crankshaft (12) relative to the other crankshaft (14) for dynamically varying the engine's developed compression ratio. Each crankshaft (12, 14) drives a respective connecting rod (16, 18) which, in turn, reciprocates a piston (24, 26) in a cylinder (28, 30). The center lines (C, D) of each cylinder (28, 30) are skewed relative to each other so that the pistons (24, 26) converge toward a common combustion chamber formed under a common cylinder head (34). Movable exhaust valves (36) are located above the piston (24) whose phase shifted orientation is retarded or lagging dead center conditions, whereas movable intake valves (38) are located above the piston (26) that is leading or advanced in its phase displacement relative to dead center conditions.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com