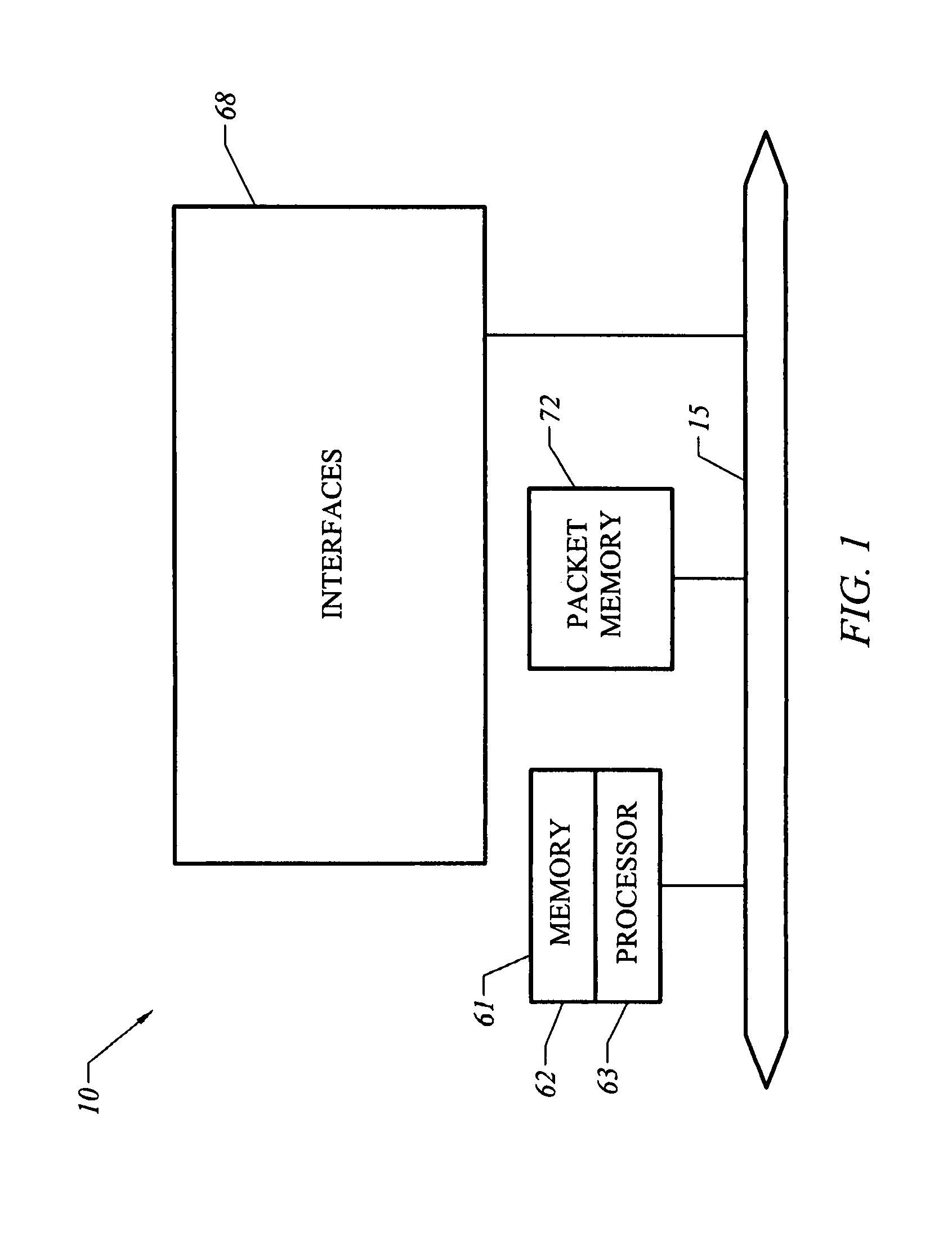
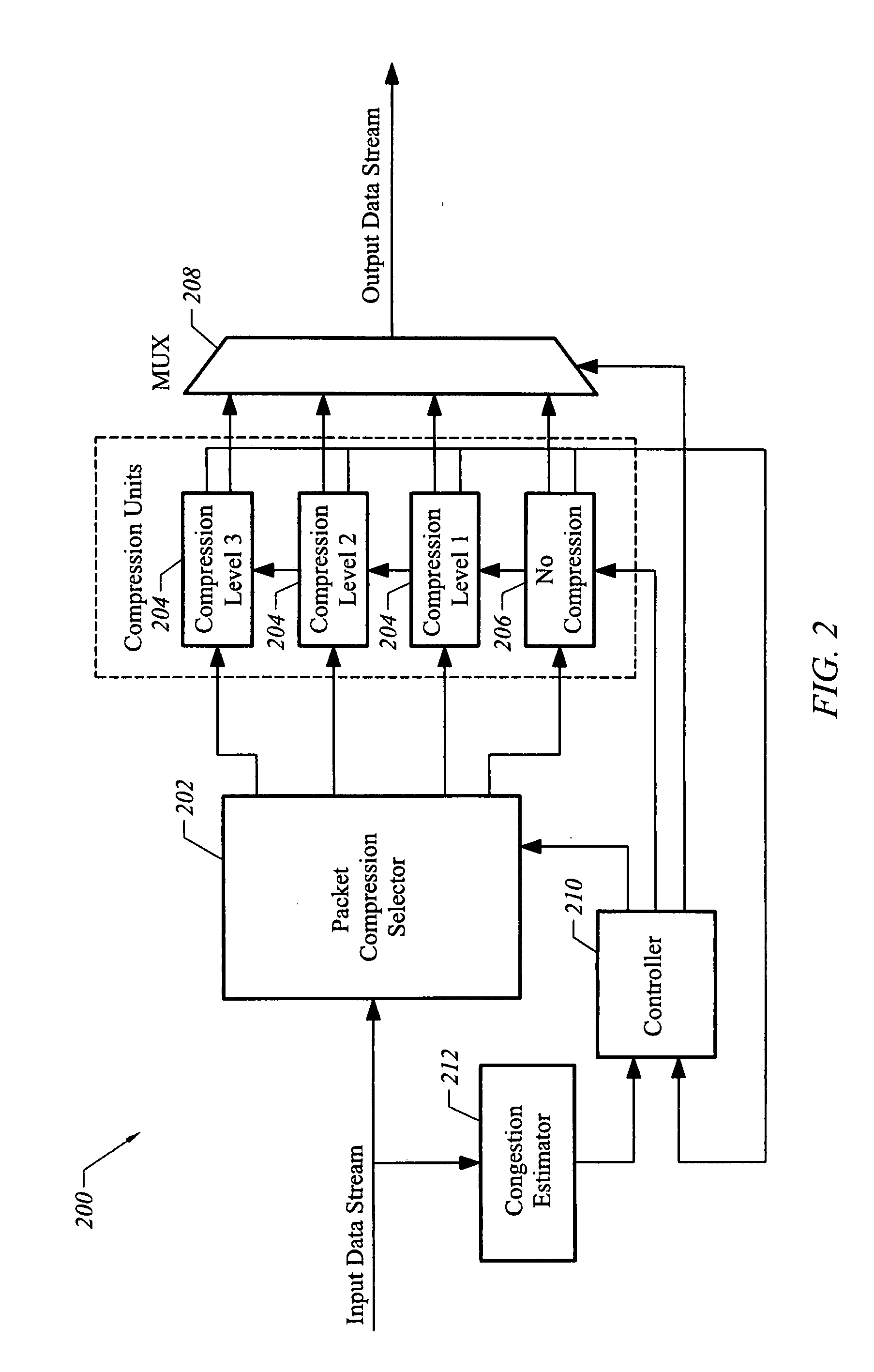
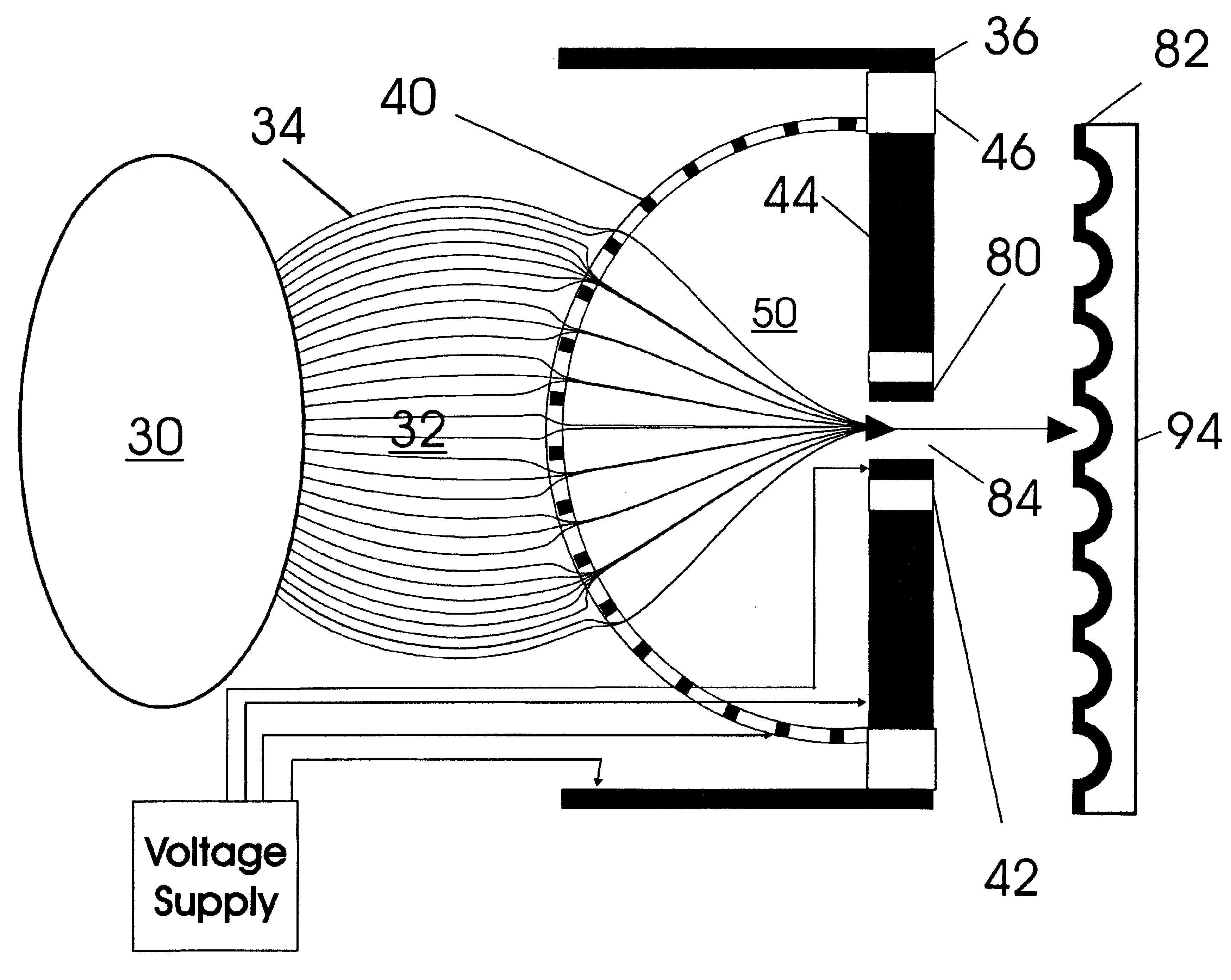
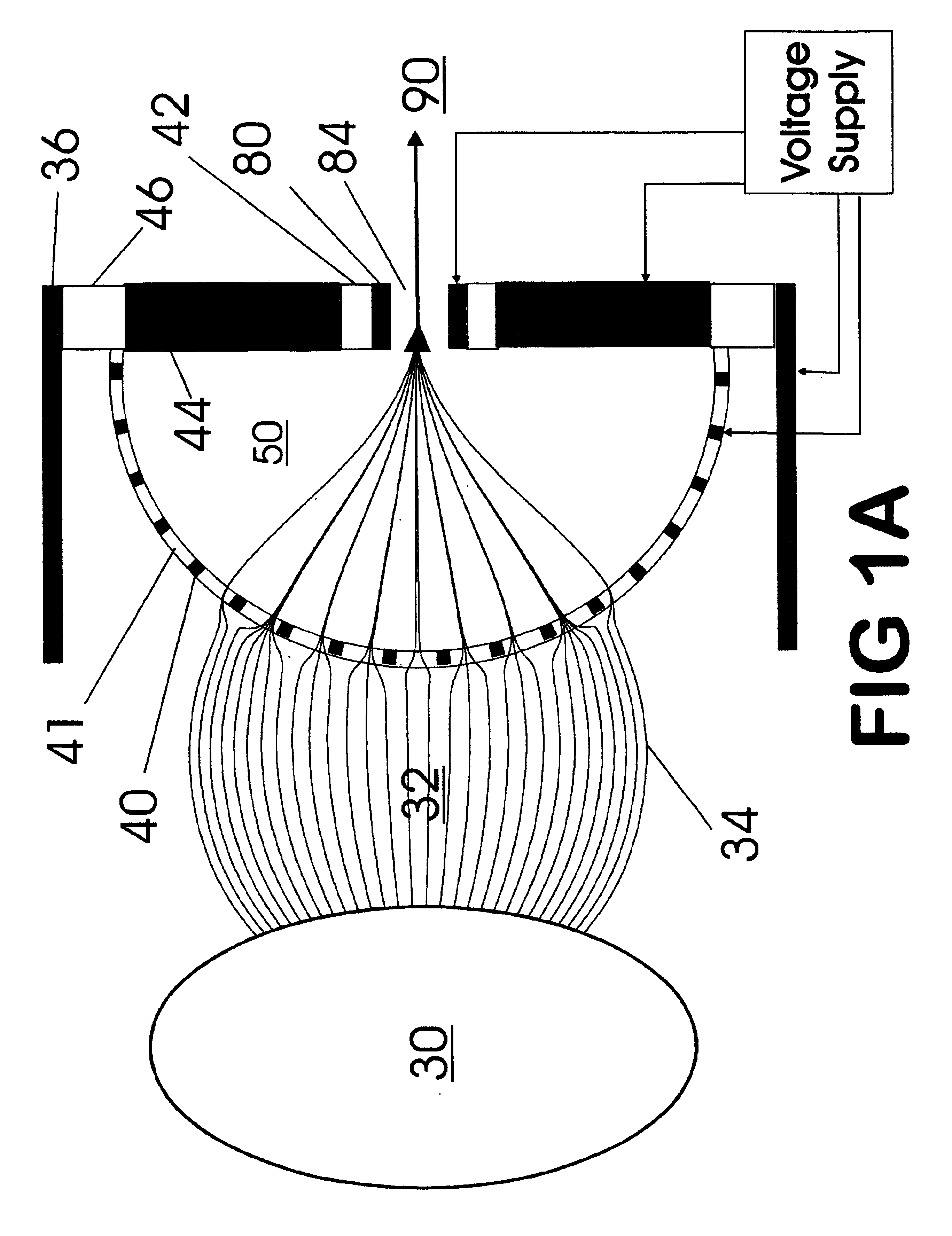
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4781 results about "Compression ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
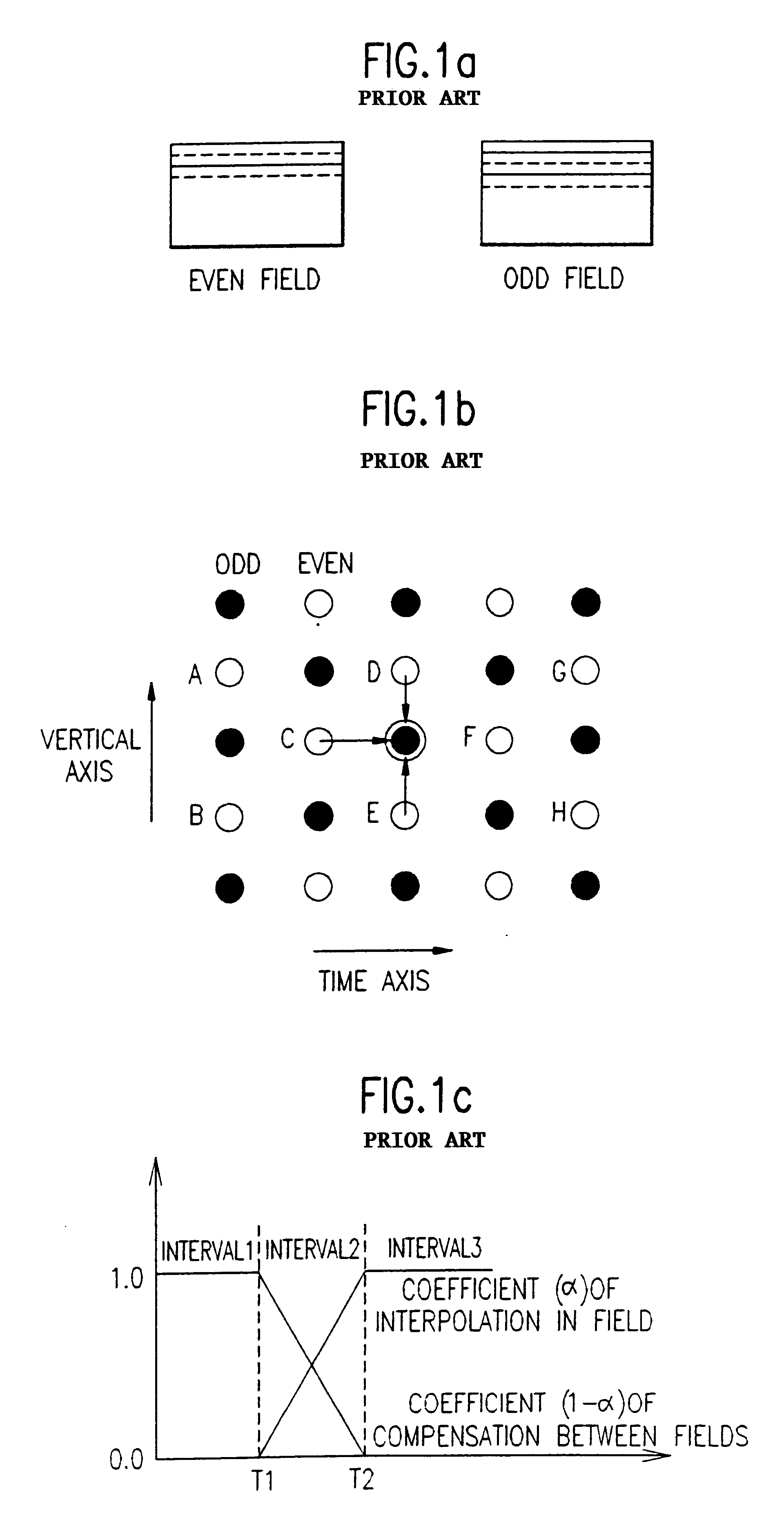
In a combustion engine, the static compression ratio is calculated based on the relative volumes of the combustion chamber and the cylinder. It is a fundamental specification for combustion engines. The dynamic compression ratio is a more advanced calculation which also takes into account gasses entering and exiting the cylinder during the compression phase.
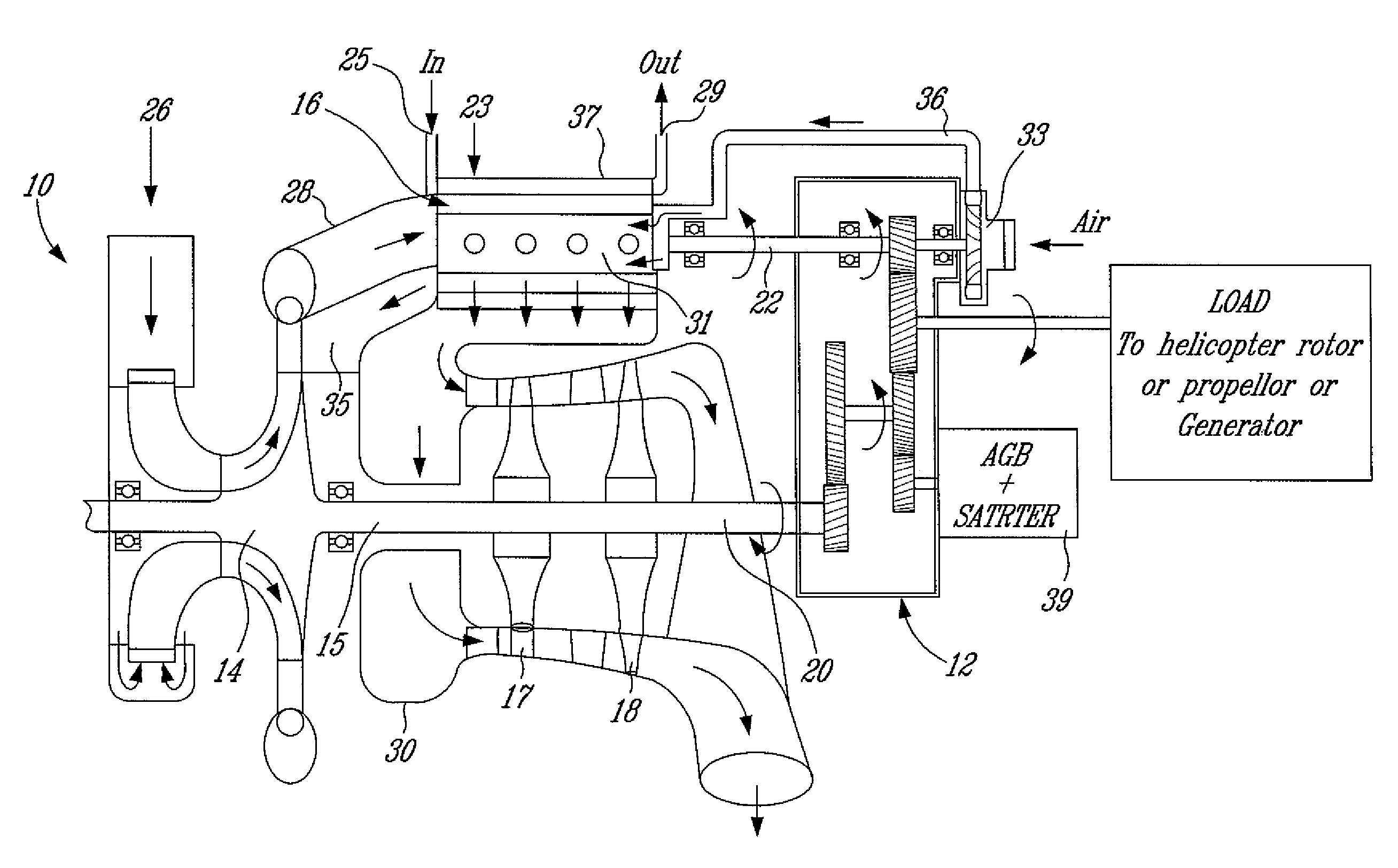
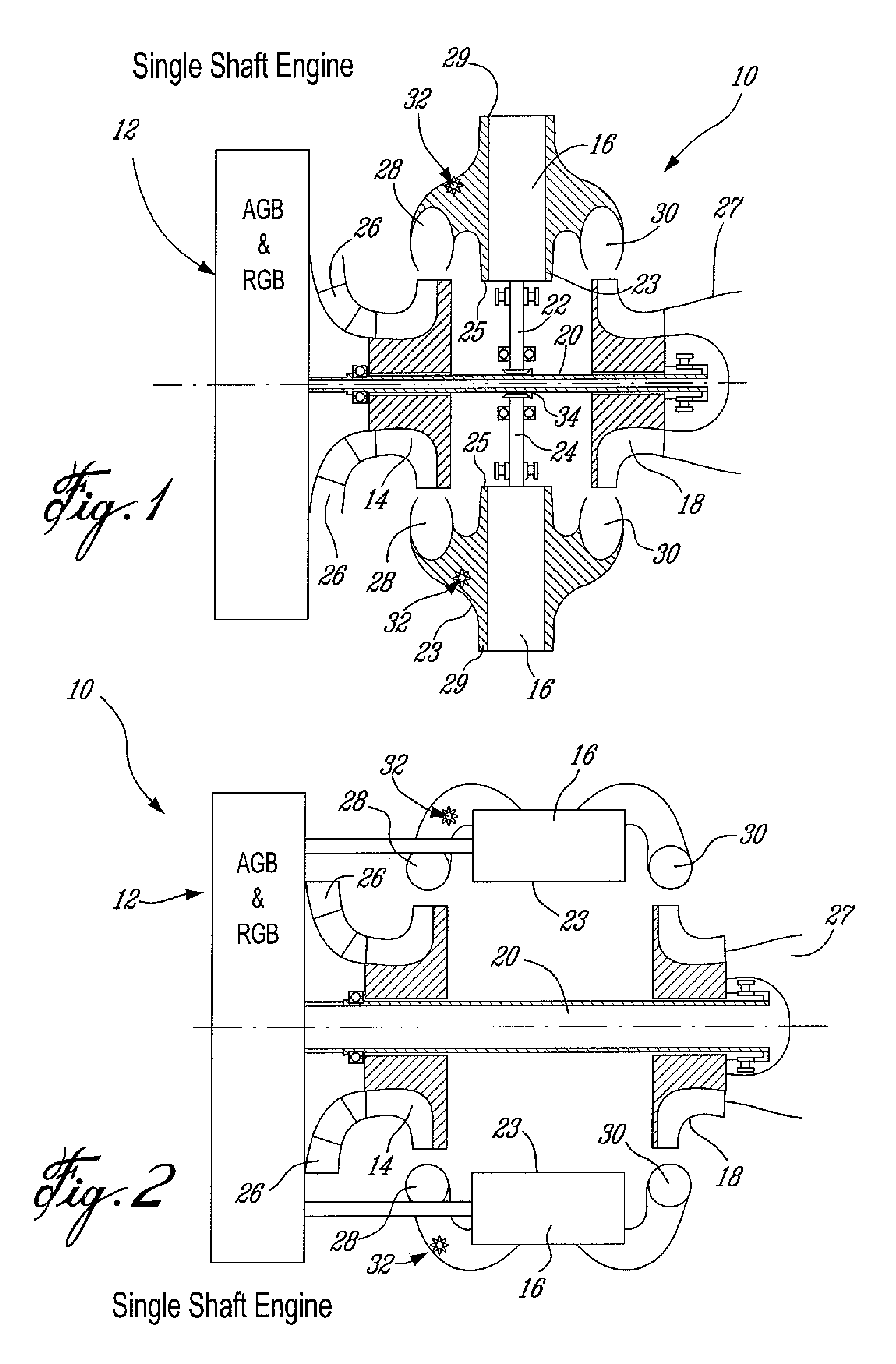
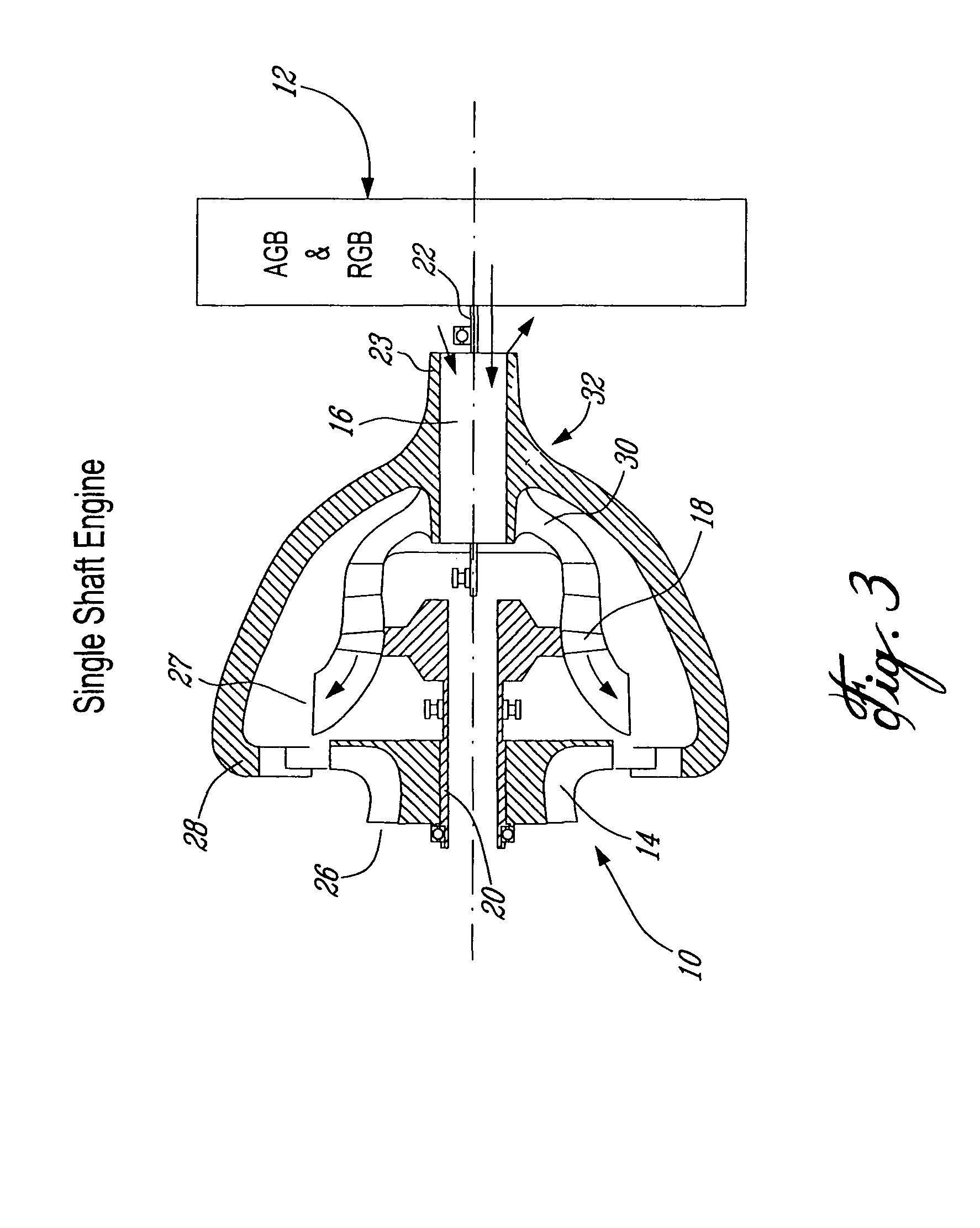
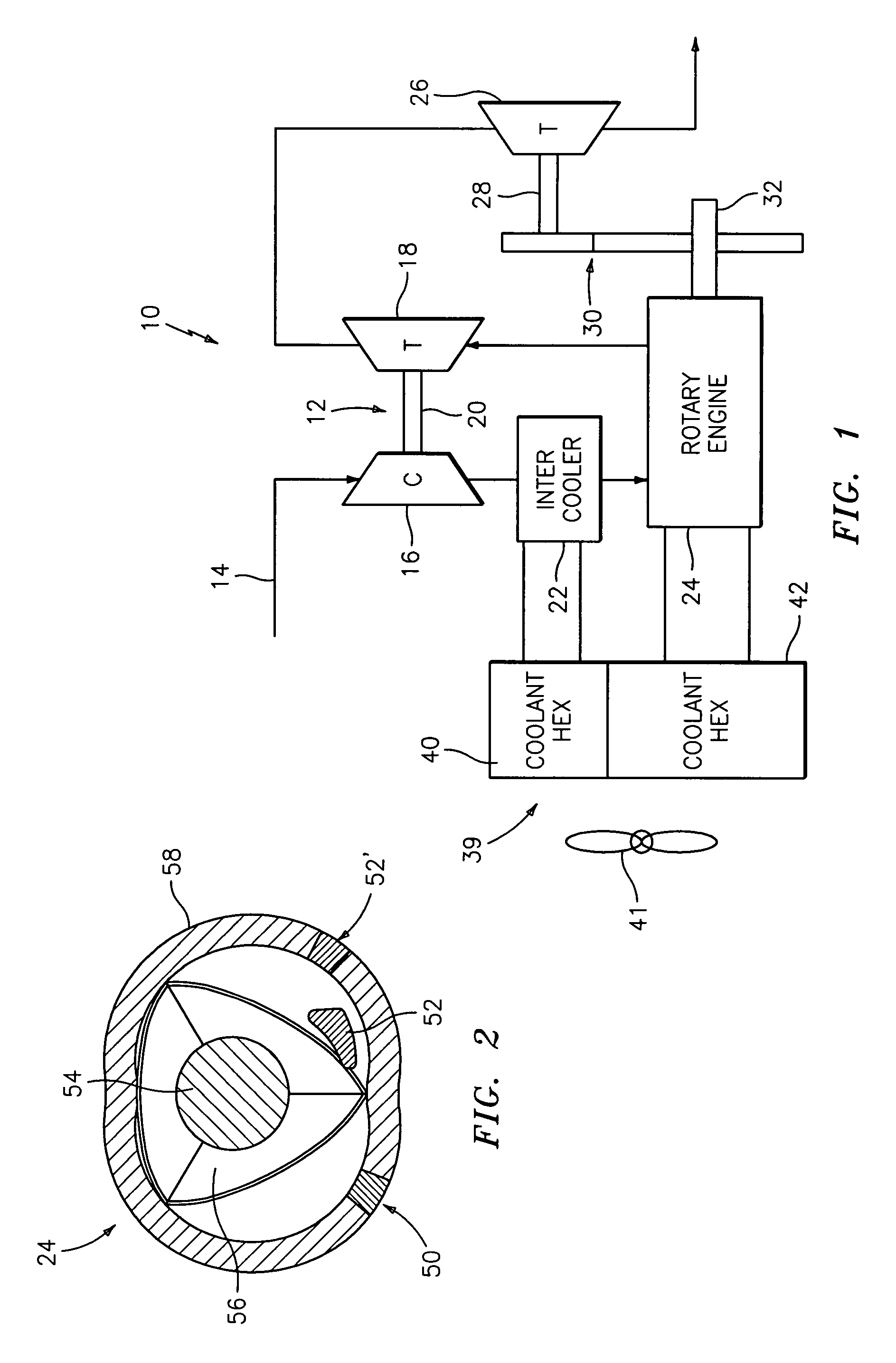
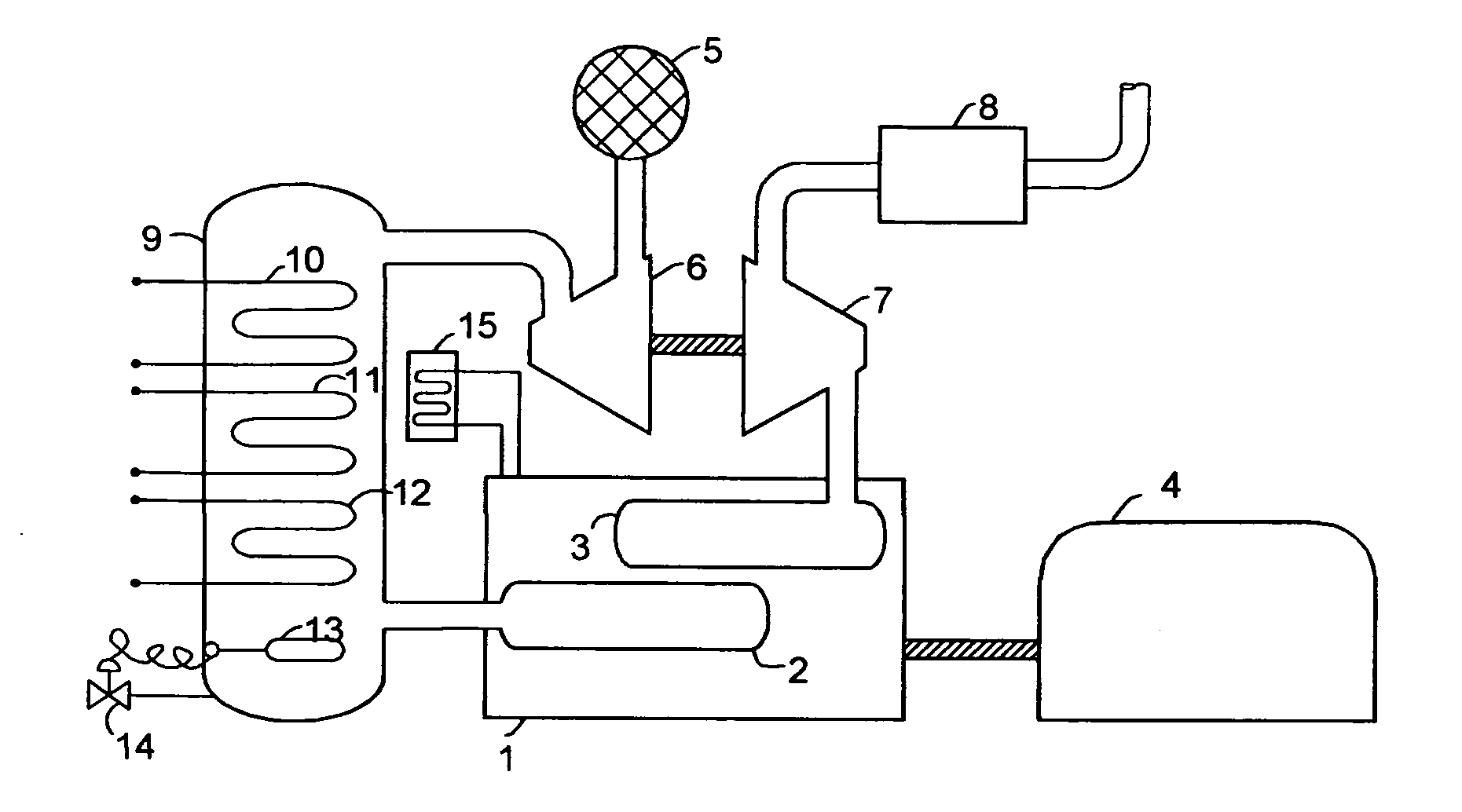
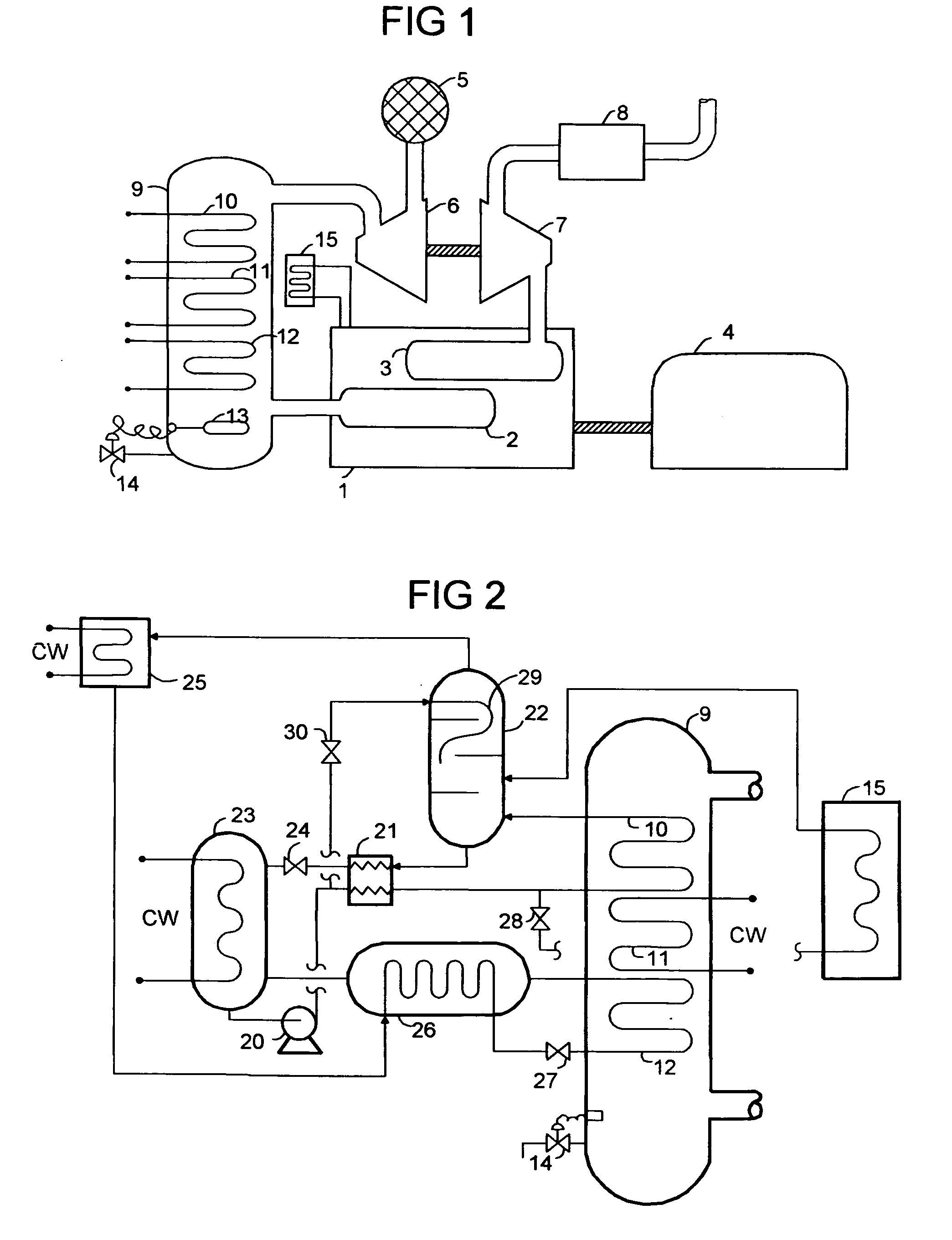
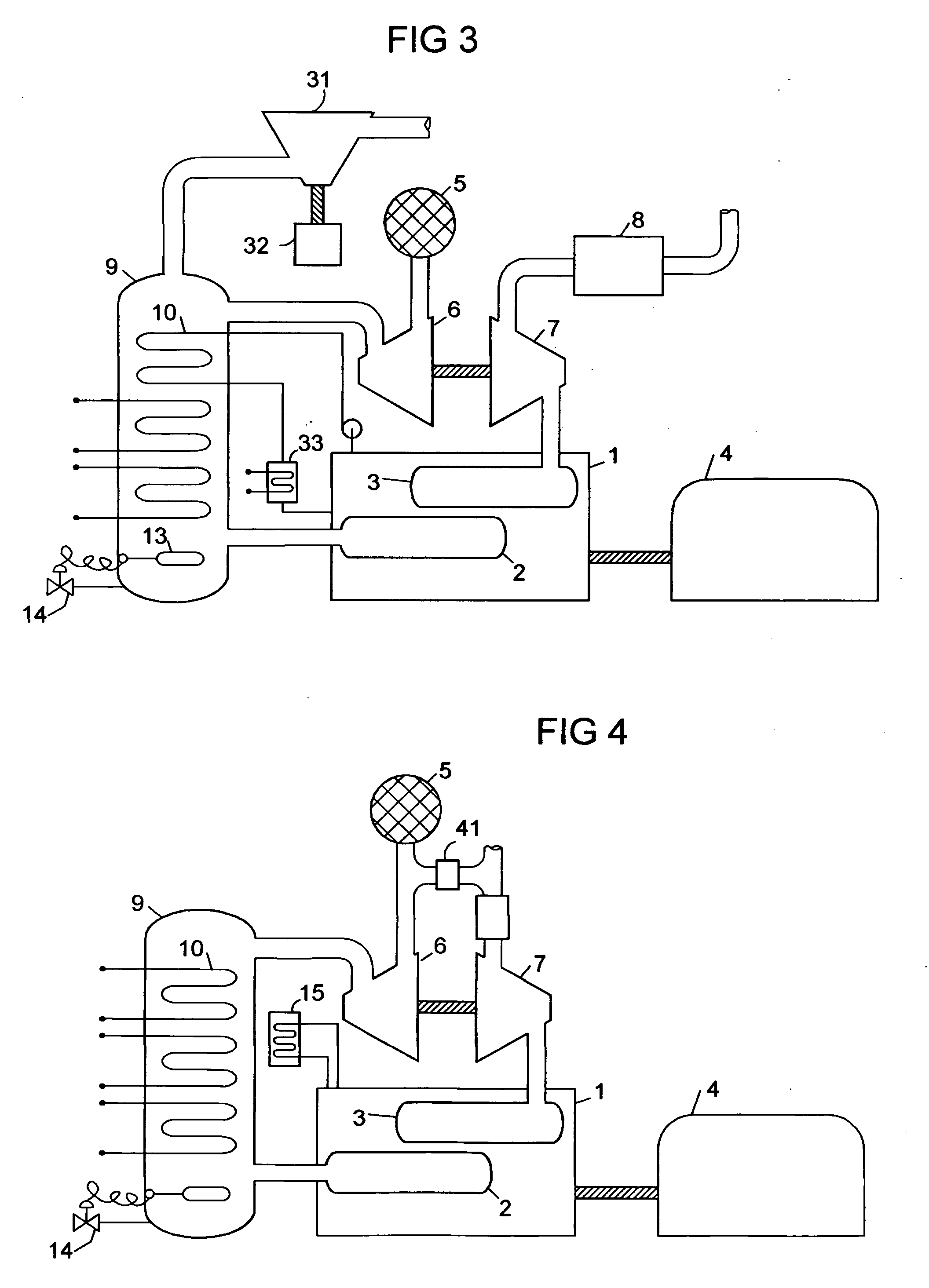
Low volumetric compression ratio integrated turbo-compound rotary engine
ActiveUS7775044B2Reduce the compression ratioImprove thermal efficiencyGas turbine plantsEfficient propulsion technologiesAir cycleRotary engine
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
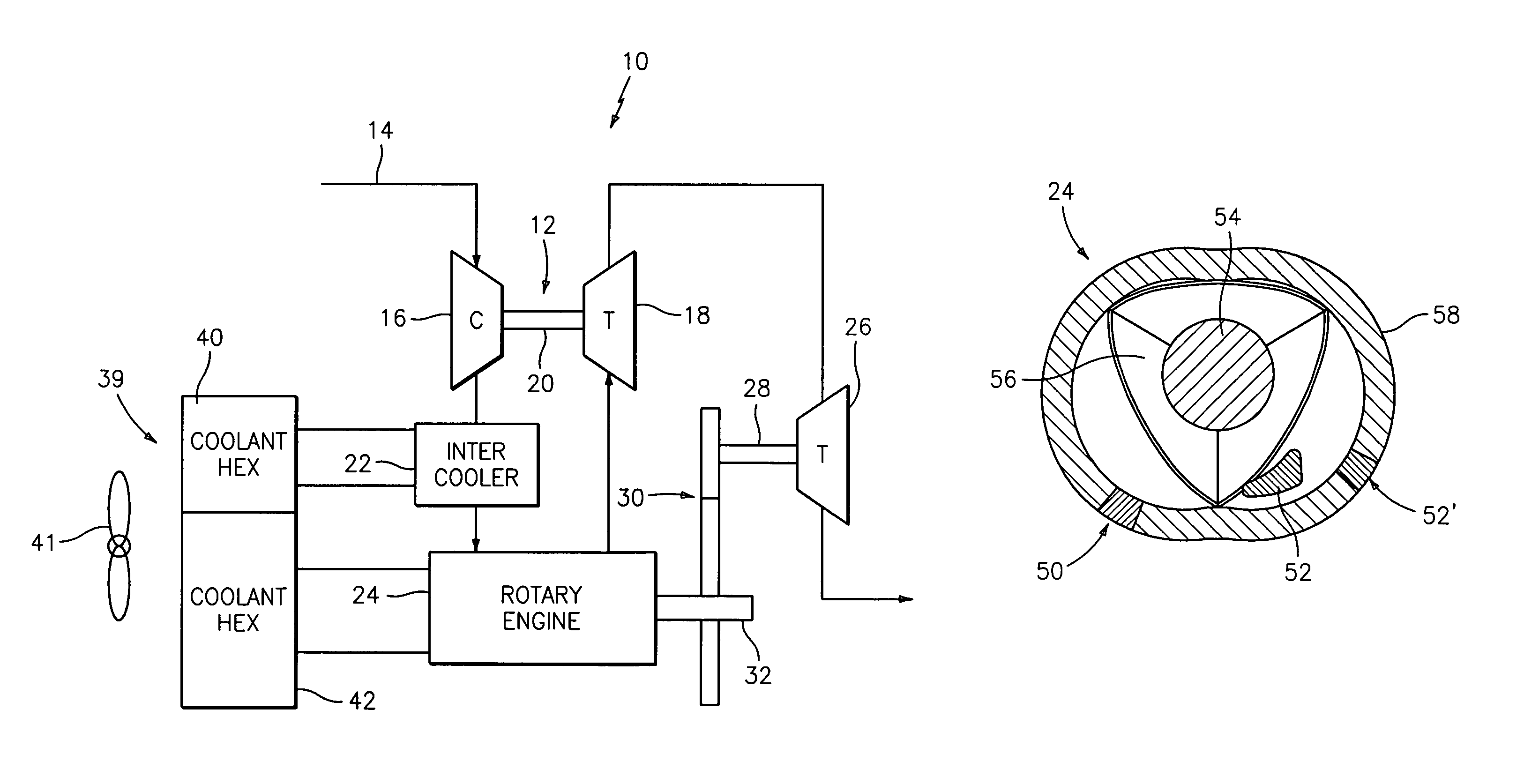
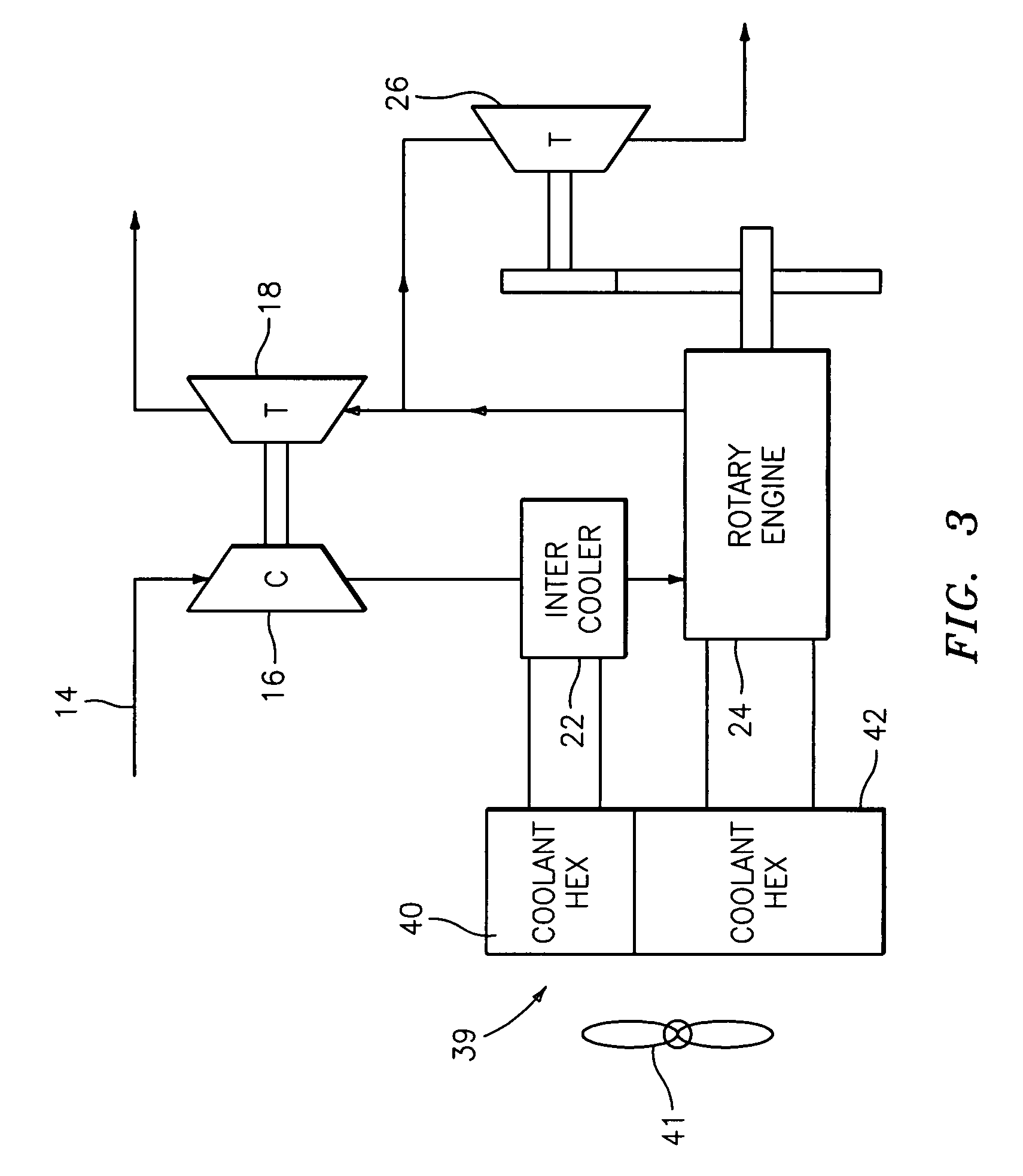
Compound cycle rotary engine
ActiveUS7753036B2High power to weightReduce fuel consumptionInternal combustion piston enginesCombination enginesRotary engineIntercooler
A compound cycle engine system has a rotary engine, which rotary engine generates exhaust gas. The system further has a compressor for increasing the pressure of inlet air to be supplied to the engine to a pressure in the range of from 3.0 to 5.0 atmospheres and an intercooler for providing the inlet air to the engine at a temperature in the range of from 150 to 250 degrees Fahrenheit. The system further has one or more turbines for extracting energy from the exhaust gas. The Miller Cycle is implemented in the rotary engine, enabling the compression ratio to be lower than the expansion ratio, allowing the overall cycle to be optimized for lowest weight and specific fuel consumption.
Owner:RTX CORP
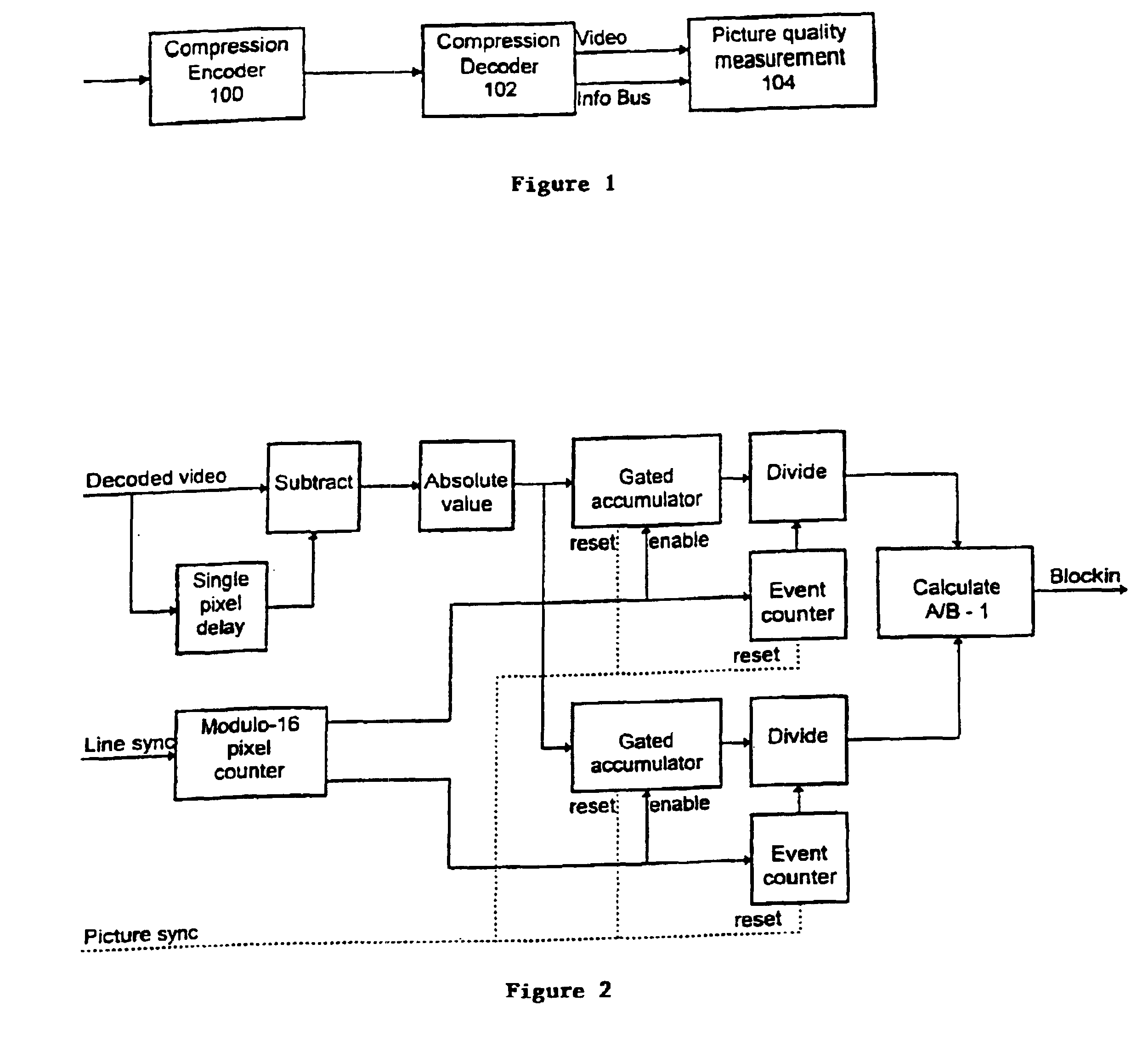
Method and apparatus for blocking effect reduction
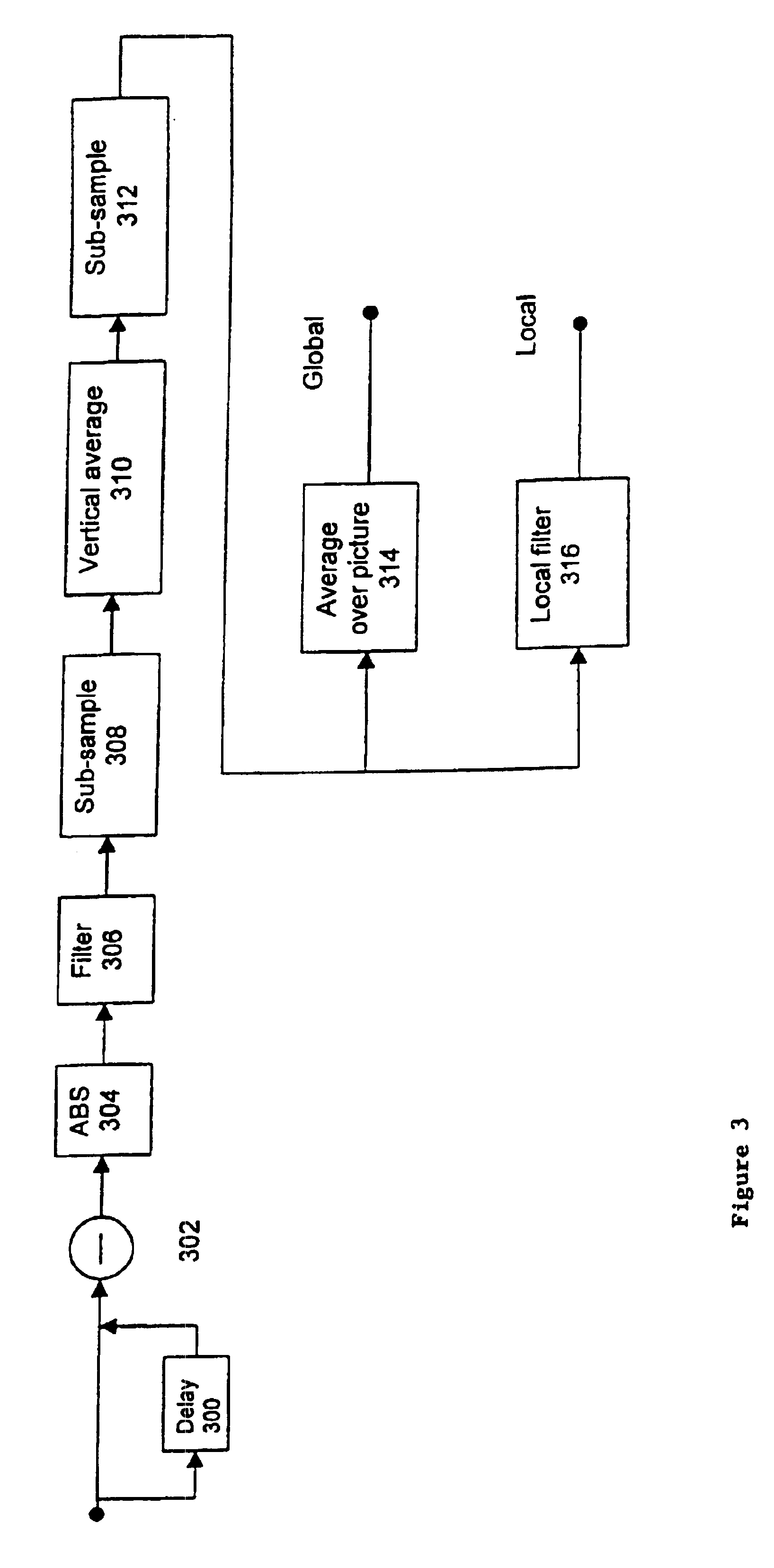
InactiveUS6898321B1Improve subjective qualityImage enhancementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Source material
By utilizing parameters derivable from a compressed bit-stream, measures are obtained of the subjective quality of a decoded picture, without the necessity for reference to source material. A blockiness measure is derived both locally and globally and used to control a de-blocking filter. An estimate of signal-to-noise ratio is derived from quantization values.
Owner:AMBERFIN
Method and device for image and video transmission over low-bandwidth and high-latency transmission channels
InactiveUS20070183493A1Increase the compression ratioLow priorityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVideo transmissionEncoding algorithm
The present invention provides a method for transmission of a images and / or video over bandwidth limited transmission channels having varying available bandwidth, which method comprises the use of a classification algorithm for decomposing the images and / or video to be transmitted into multiple spatial areas, each area having a specific image type; detecting the image type of each of those areas separately selecting for each of those areas an image and / or video encoding algorithm having a compression ratio. The classification algorithm prioritizes each of the areas, the classification algorithm increasing the compression ratio of the image and / or video encoding algorithm dedicated to spatial areas having lower priority in case of decreasing bandwidth.
Owner:BARCO NV
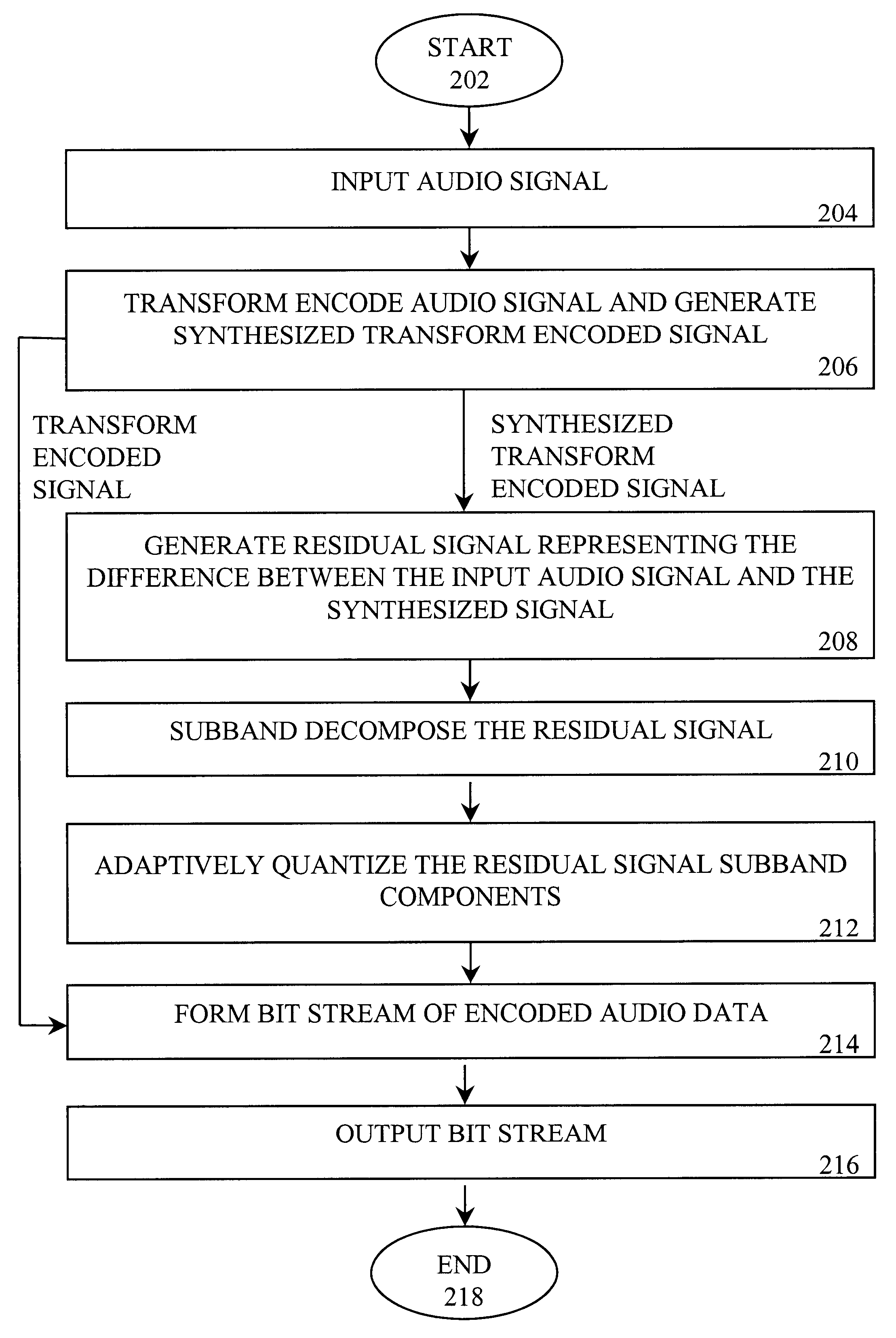
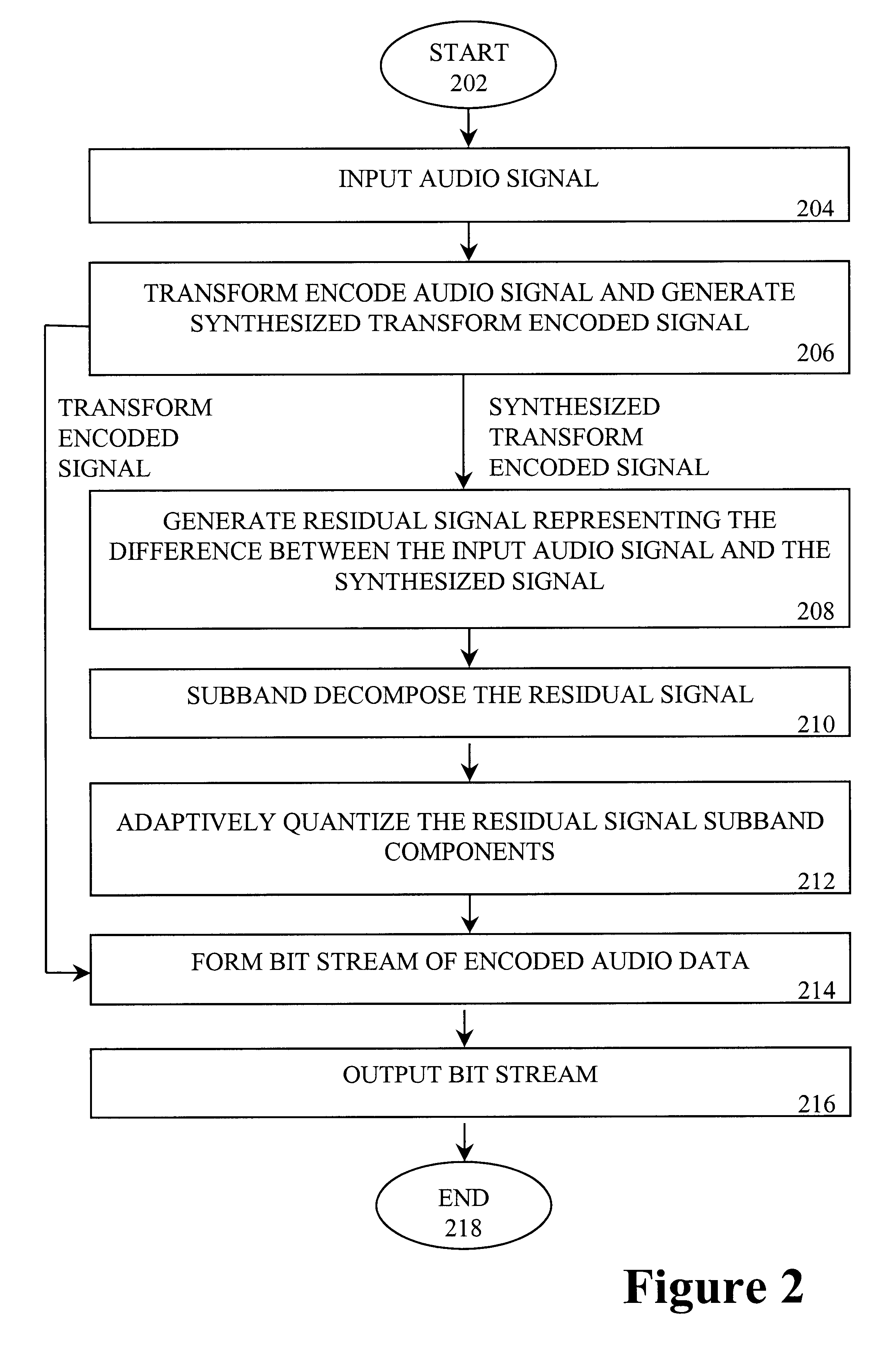
Audio compression and decompression employing subband decomposition of residual signal and distortion reduction
A method and apparatus to achieve relatively high quality audio data compression / decompression, while achieving relatively low bit rates (e.g., high compression ratios). According to one aspect of the invention, a residual signal is subband decomposed and adaptively quantized and encoded to capture frequency information that may provide higher quality compression and decompression relative to transform encoding techniques. According to a second aspect of the invention, an input audio signal is compared to an encoded signal based on the input audio signal to detect and reduce, as necessary, distortion in the encoded signal or portions thereof.
Owner:XVD TECH HLDG LTD IRELAND
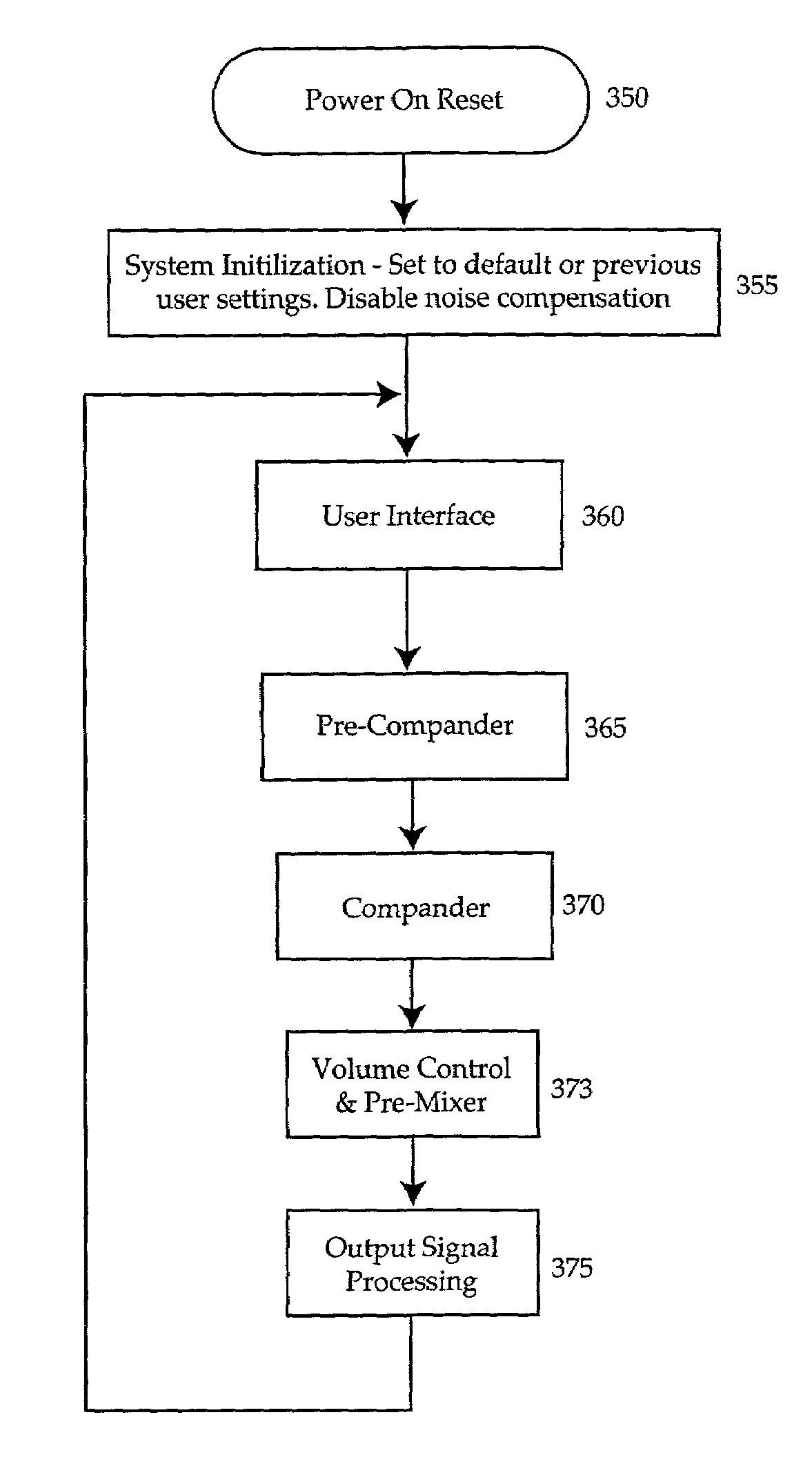
System output control method and apparatus
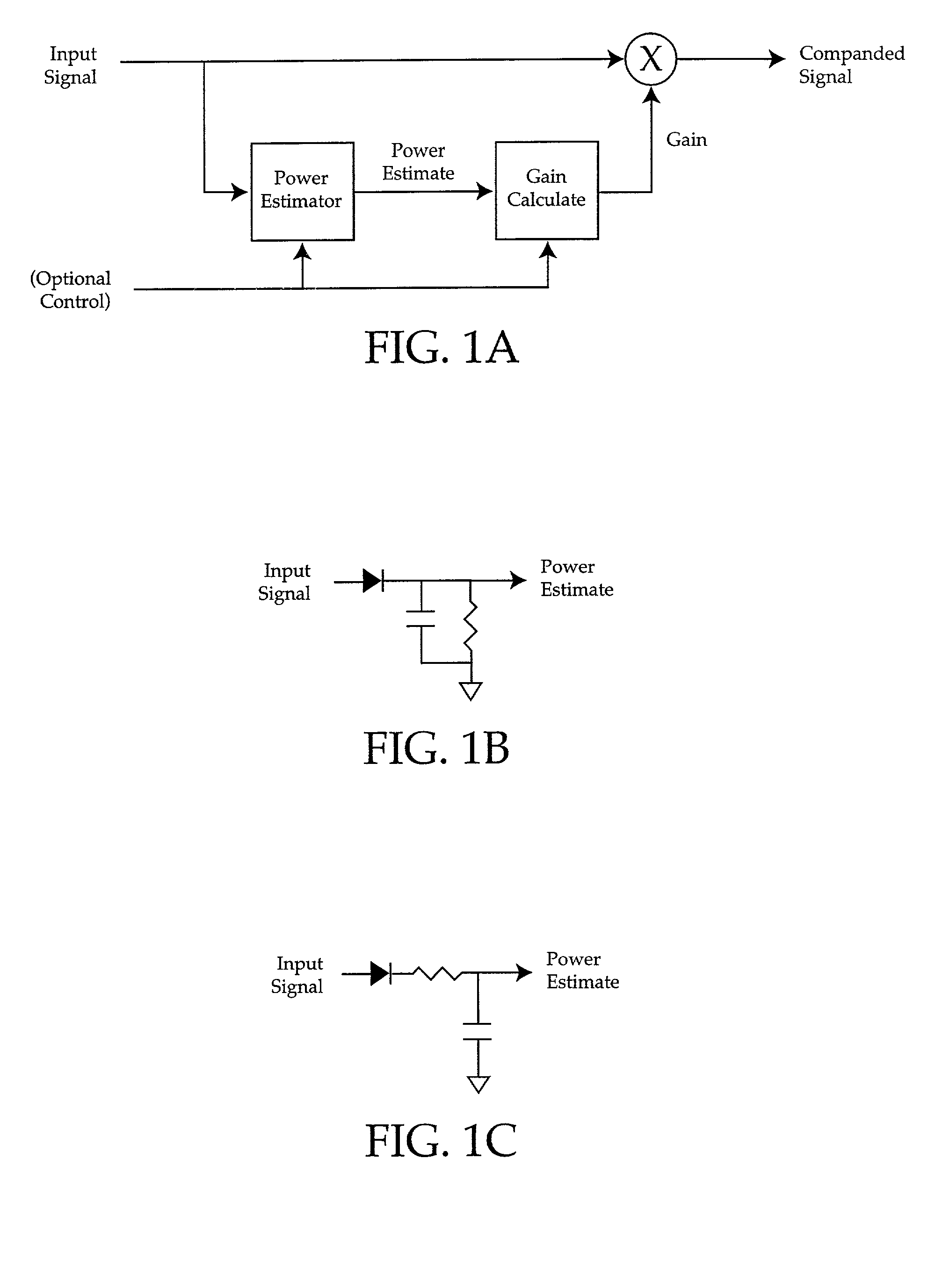
ActiveUS7027981B2Maximum flexibilityImplemented cost-effectivelyVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesGain controlControl systemCompression ratio
Output control system and method includes calculating gain for an input signal, detecting a predetermined condition, and modifying the gain calculation in accordance with one or more kneepoints to provide a varying output signal. A companding ratio is then established in accordance with the kneepoints. System gain is then adjusted, and the companding ratio may be further adjusted by adjusting one of the kneepoints relative to another.
Owner:BIZJAK KARL M
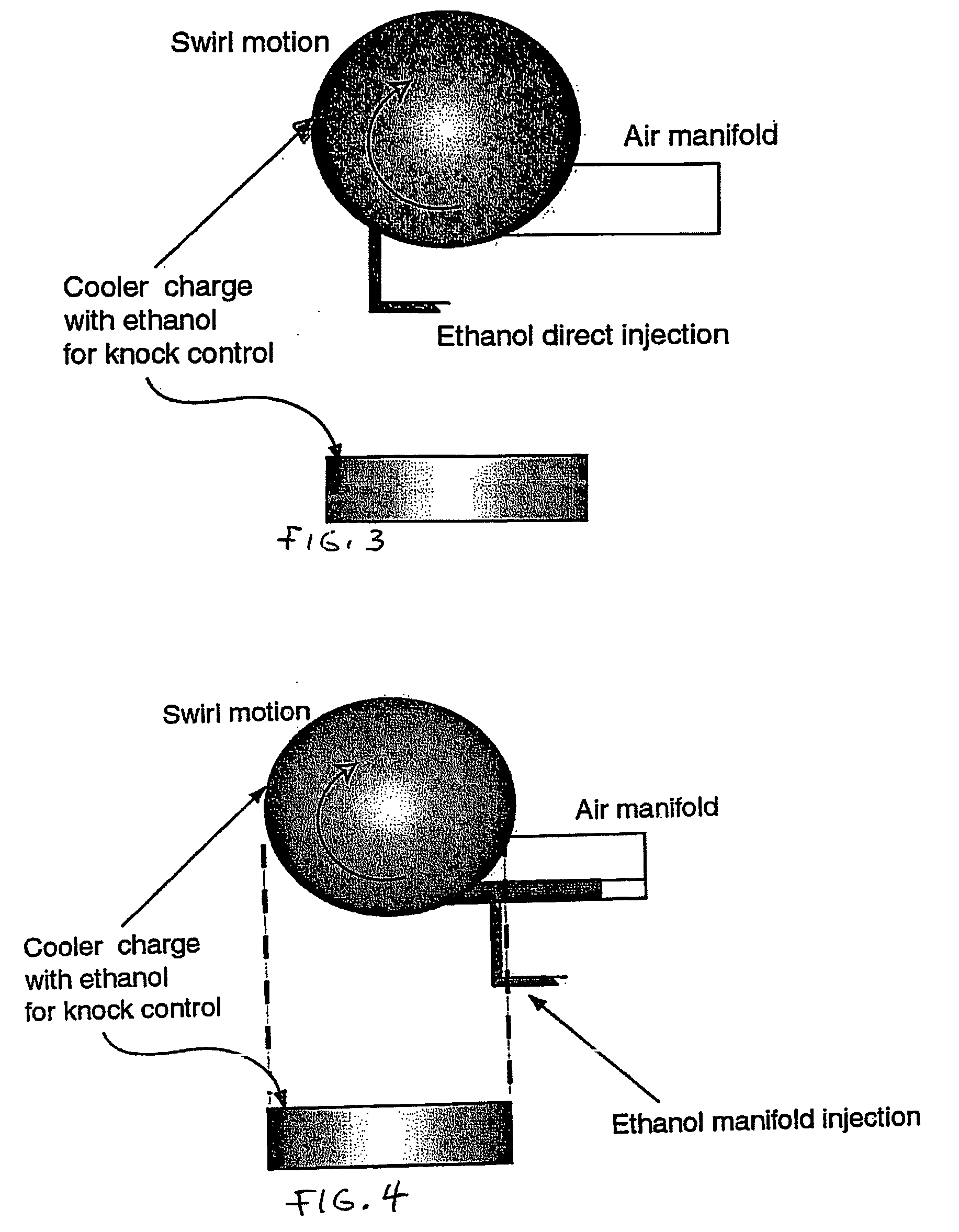
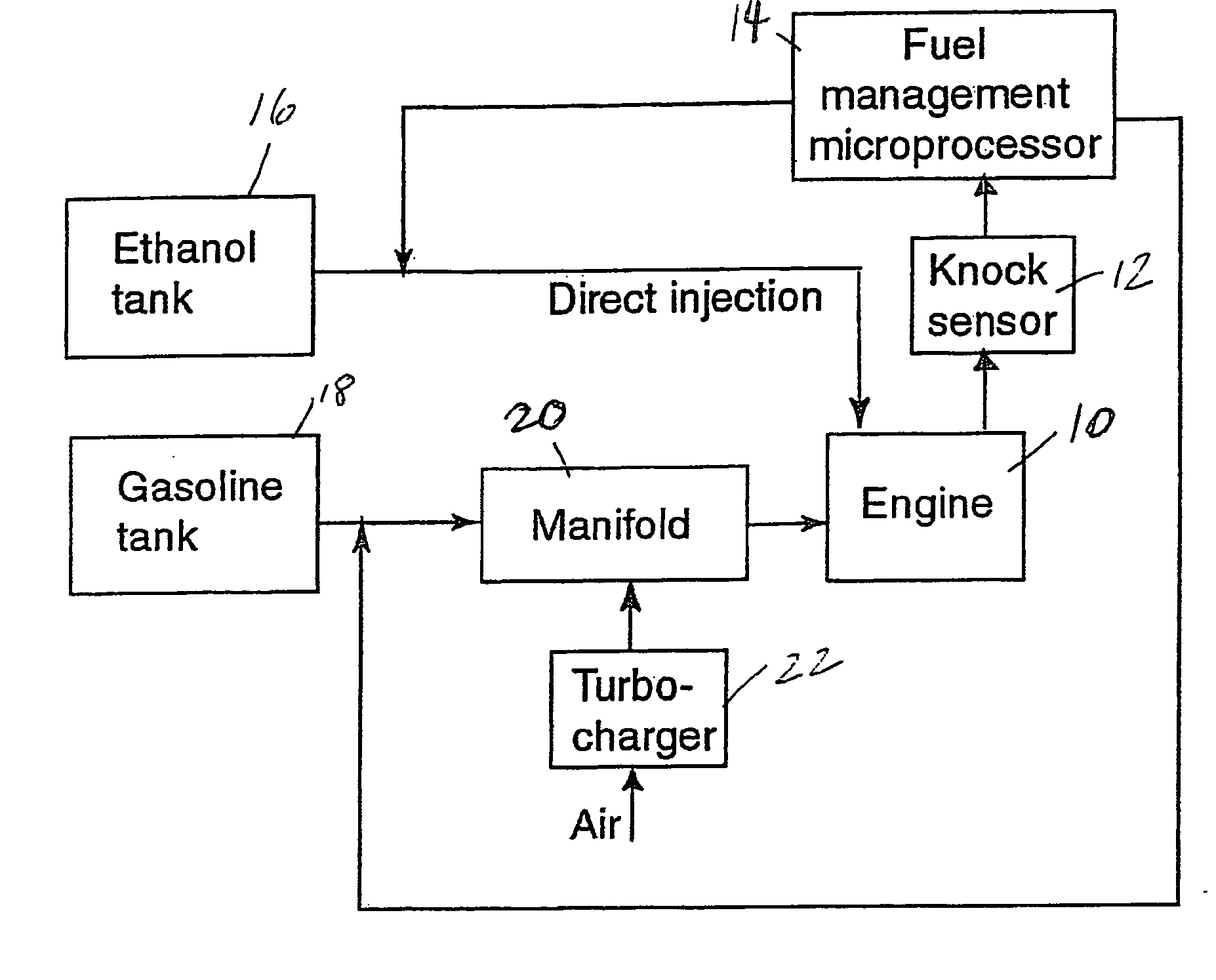
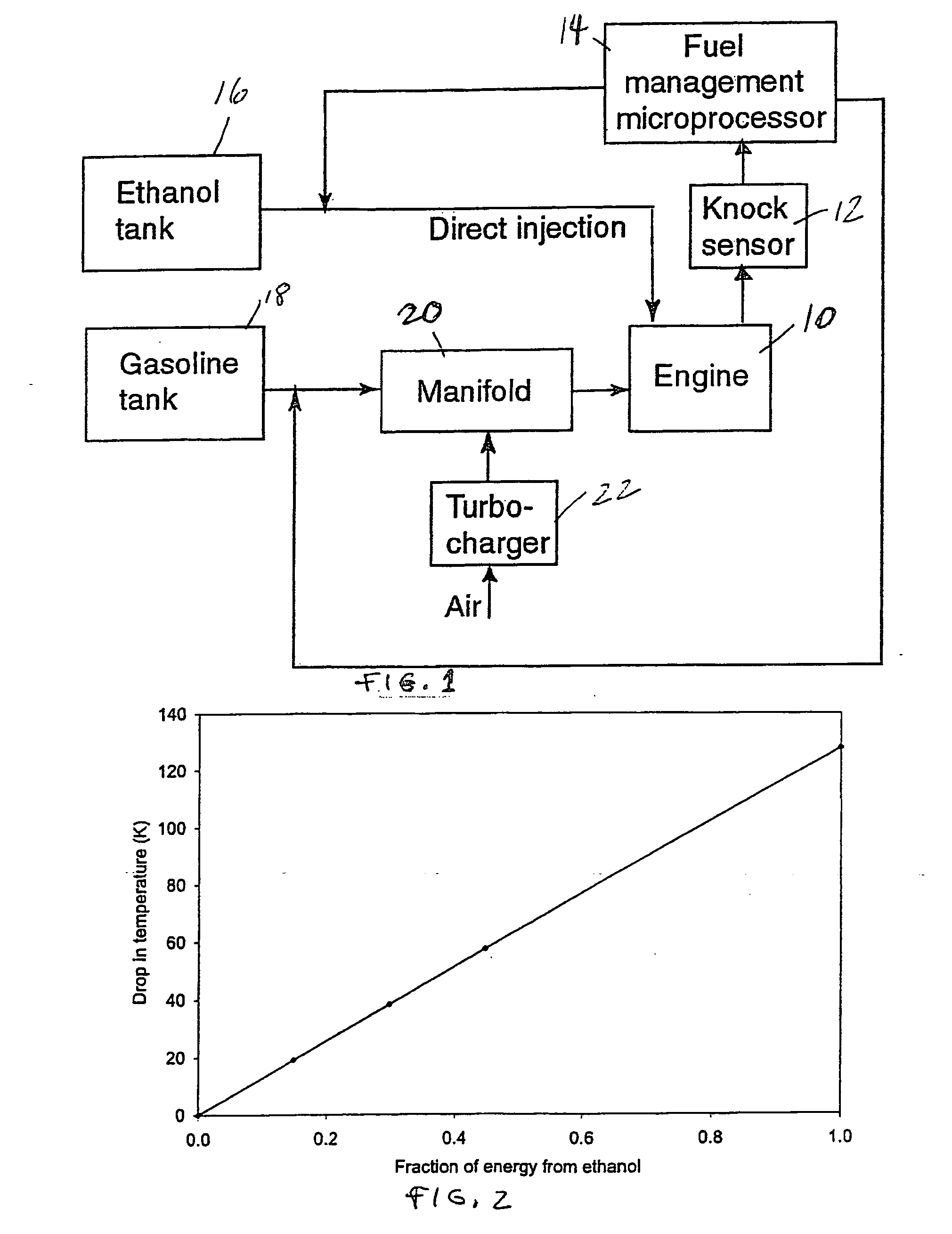
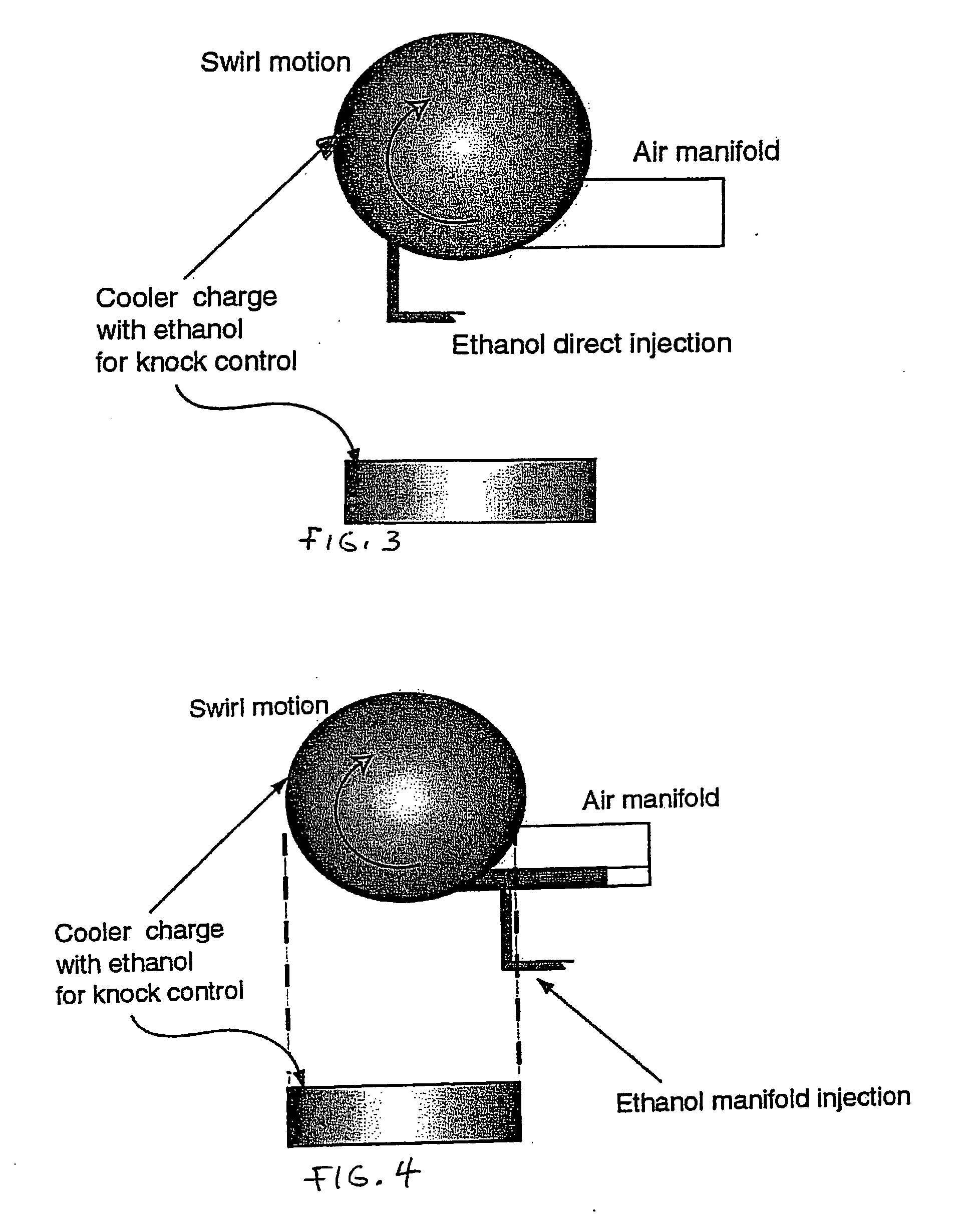
Fuel management system for variable ethanol octane enhancehment of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102145A1Increase heatMeet cutting requirementsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEthanol InjectionEngineering
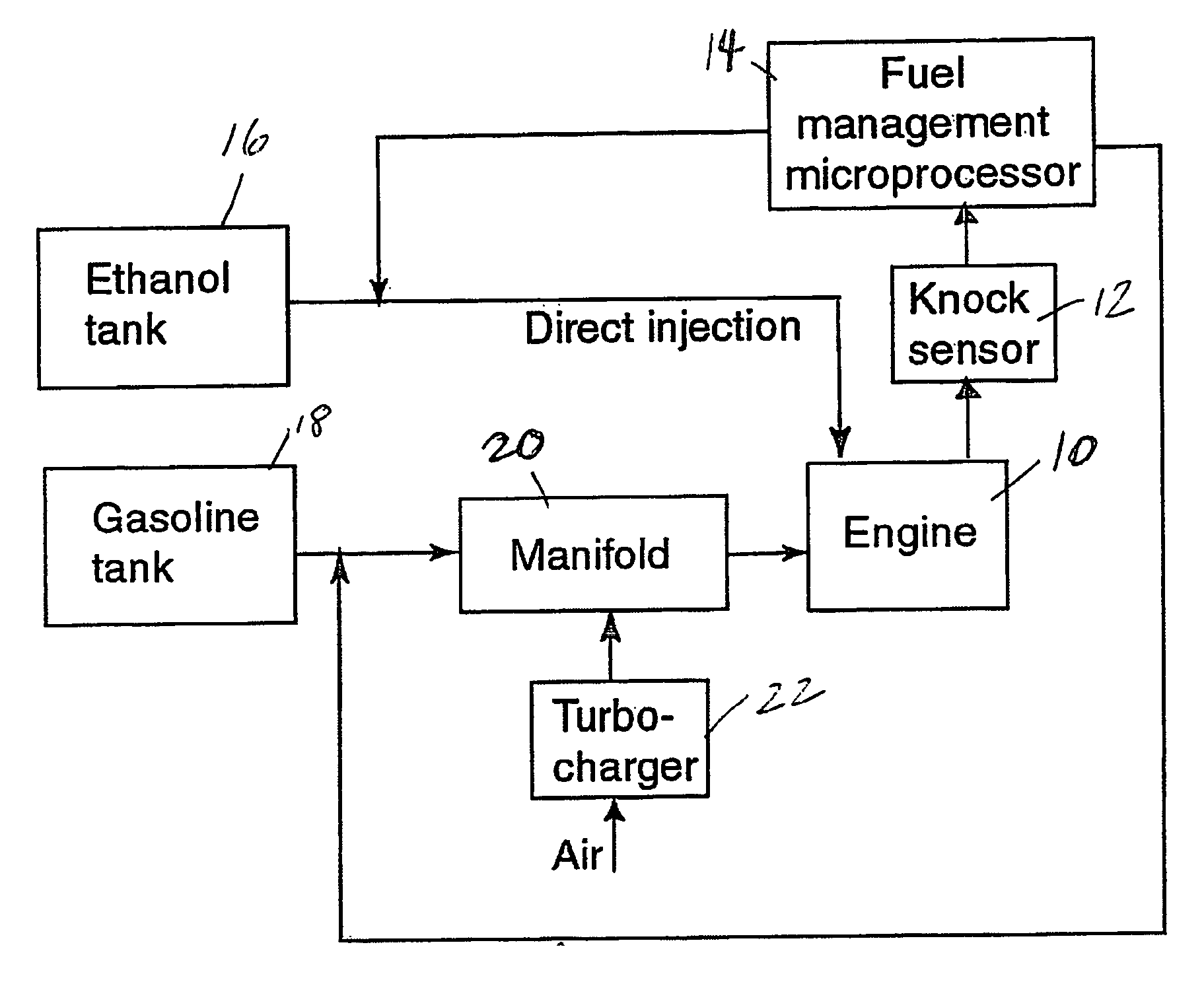
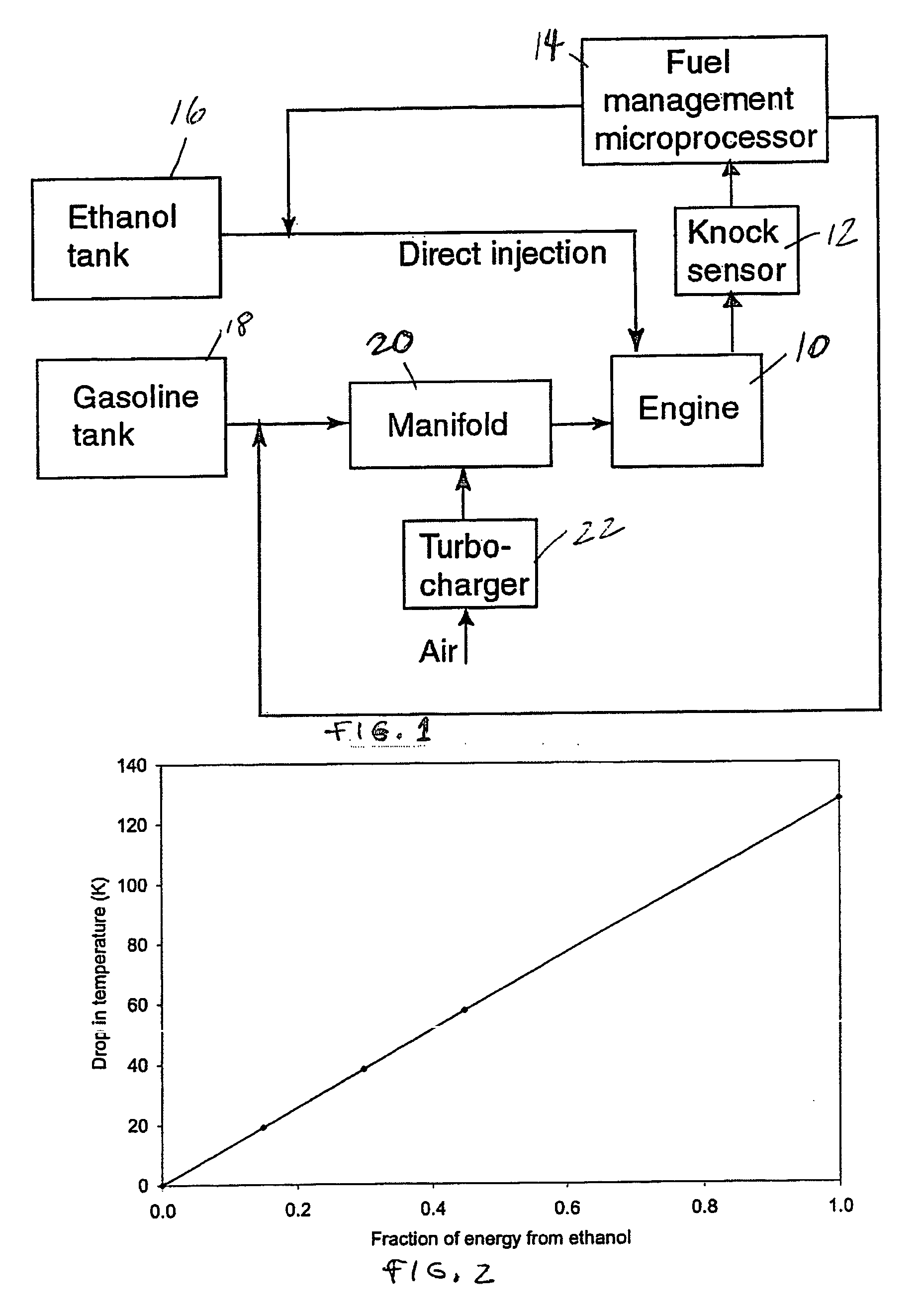
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Fuel management system for variable anti-knock agent octane enhancement of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102146A1Increase heatReduces octane requirementElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEthanol InjectionEngineering
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Adaptive memory compression
InactiveUS20050071579A1Increasing data blockMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingTerm memory
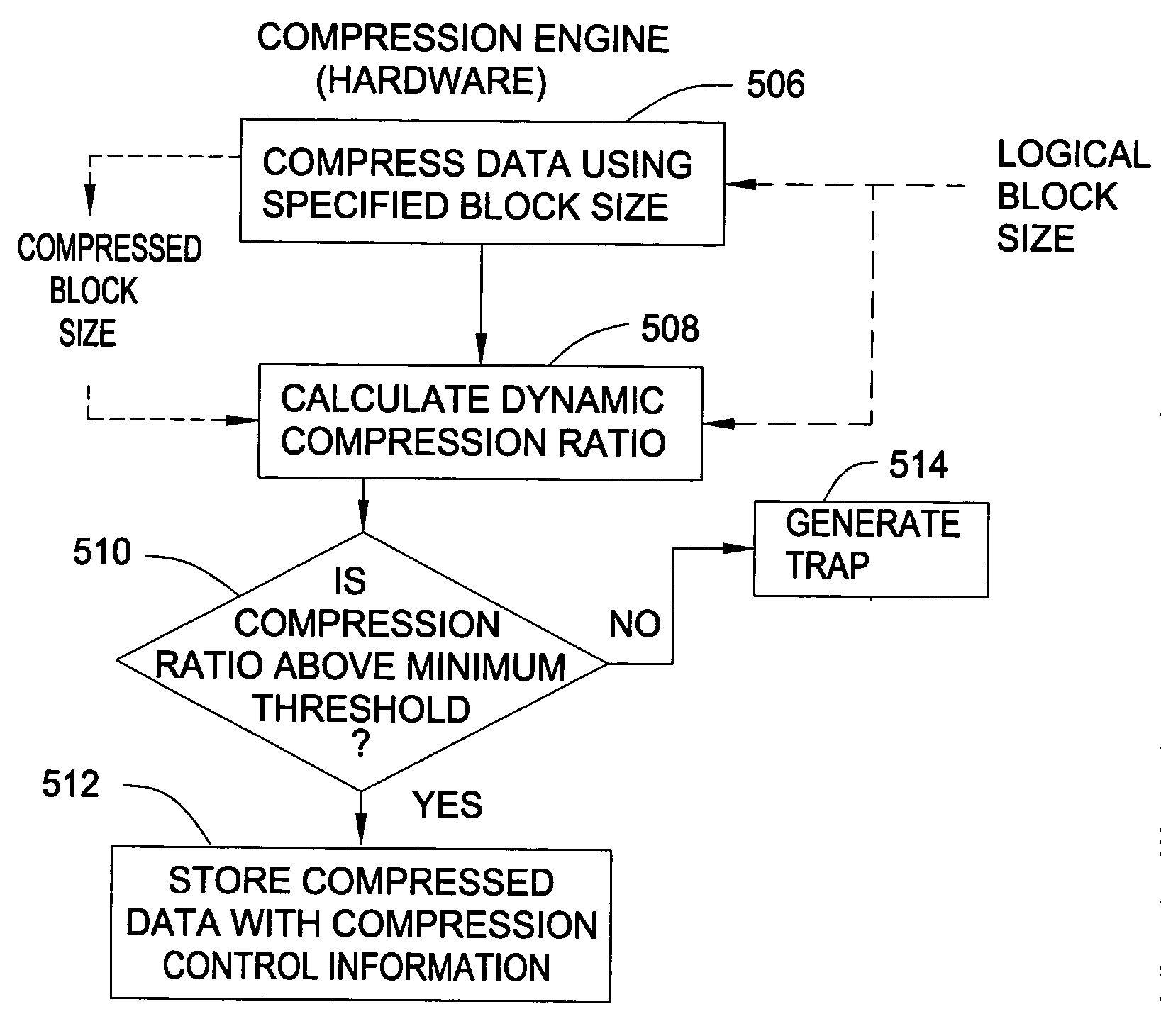
Compressed memory systems and methods that reduce problems of memory overflow and data loss. A compression engine compresses blocks of data for storage in a compressed memory. A compression monitor monitors the achieved compression ratio and provides a software trap when the achieved compression ratio falls below a minimum. After the trap is provided software monitors the fill state of the compressed memory. If the compressed memory is approaching full, the software changes the block size to improve the compression ratio.
Owner:IBM CORP
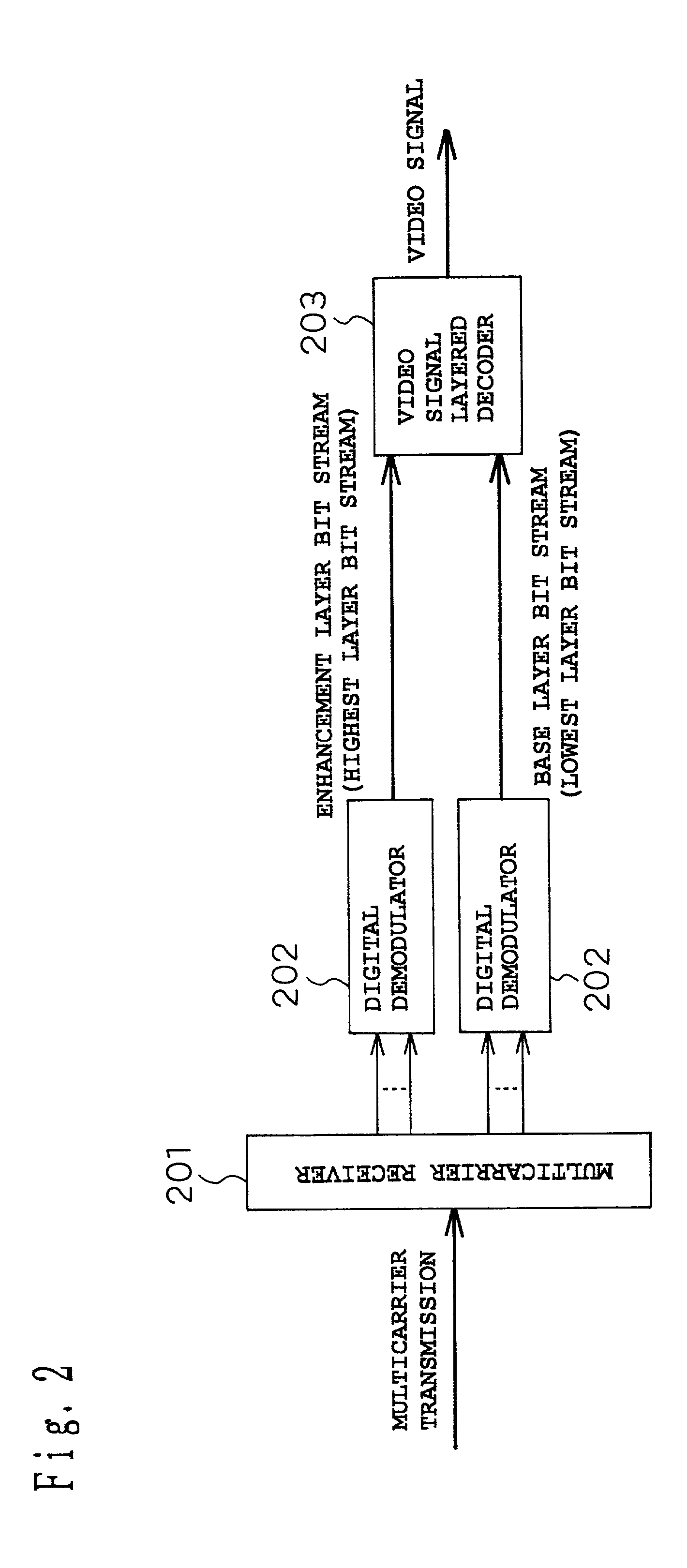
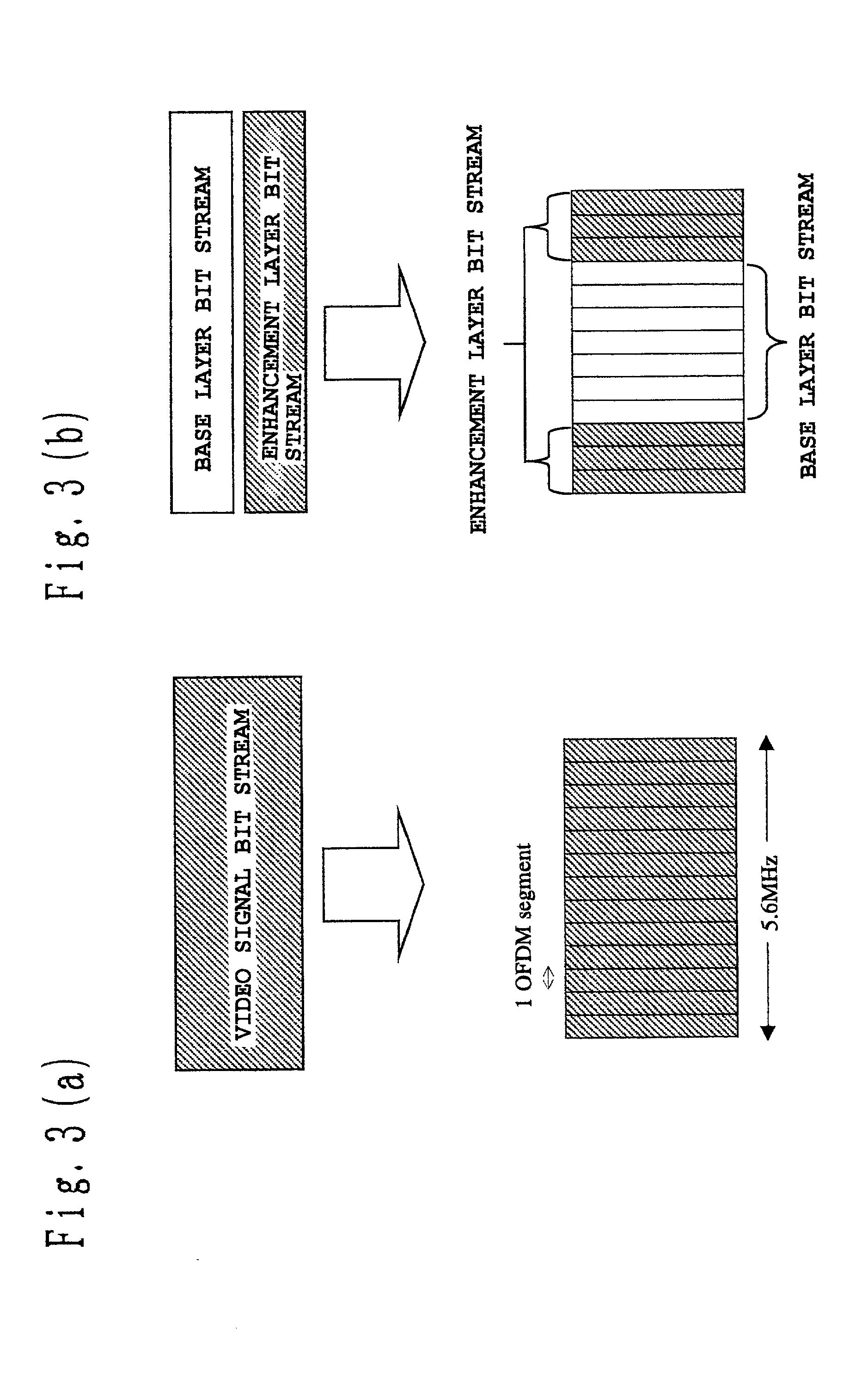
Signal encoding transmission apparatus, signal decoding receiving apparatus, and program recording medium
InactiveUS20010012322A1Digital video signal modificationMulti-frequency code systemsComputer hardwareCarrier signal
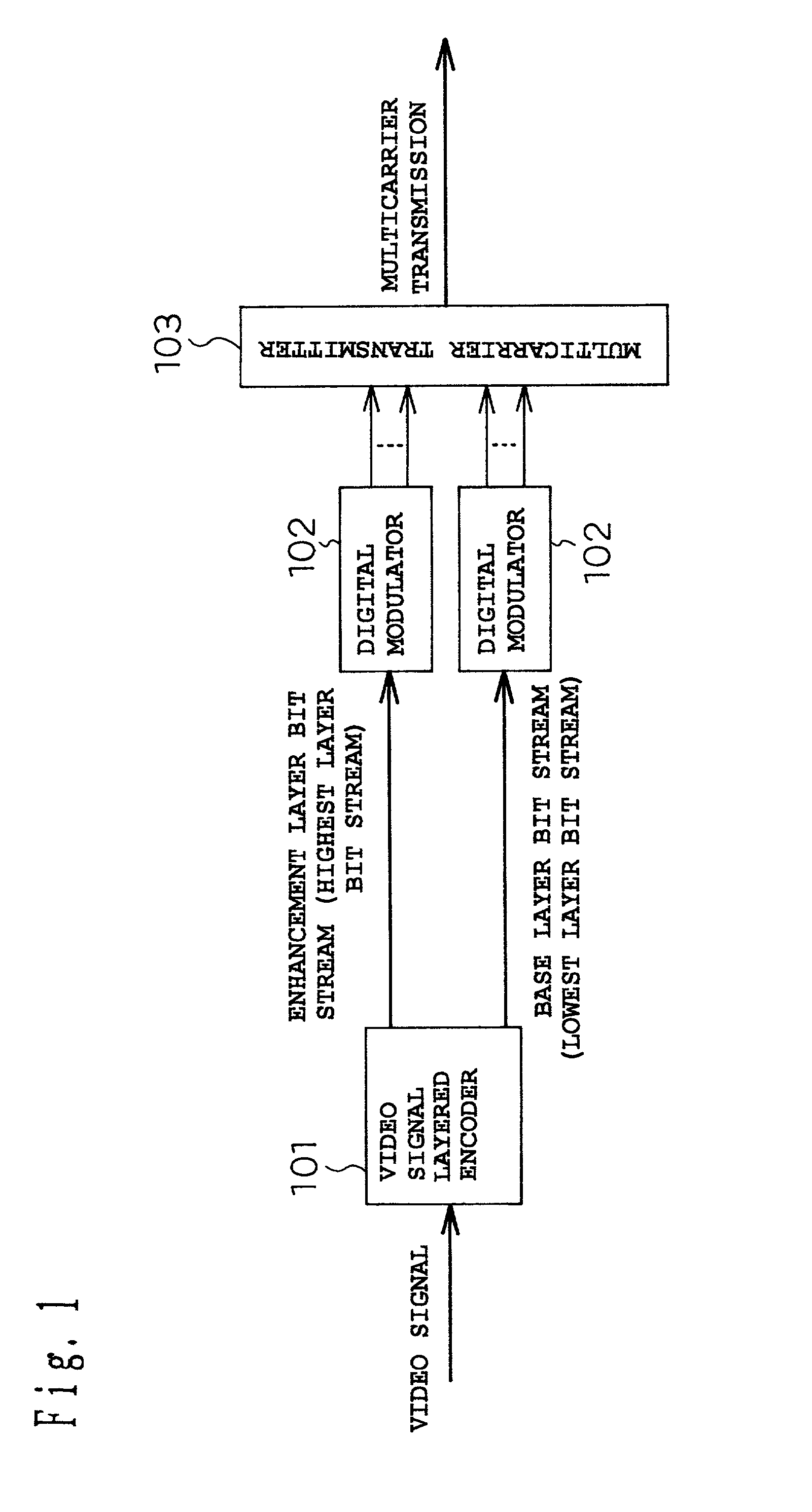
A signal encoding transmission apparatus has layered encoding means of structuring a transmission signal in a plurality of layers in a hierarchy, and of outputting a plurality of compressed bit streams generated by encoding the respective layered signals; and modulating / transmitting means of (1) modulating each of the output compressed bit streams by a modulation method determined for each layer, and / or (2) transmitting the compressed bit streams by using carriers determined for each layer.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
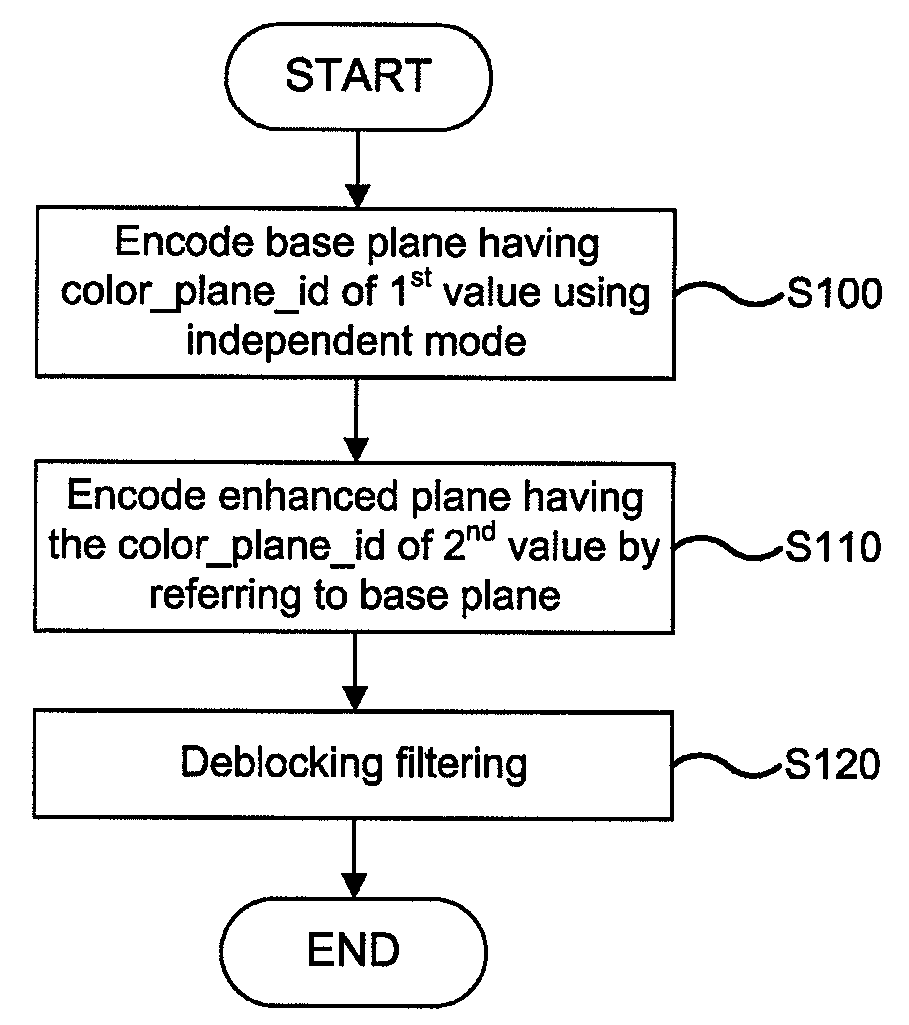
Method for Coding RGB Color Space Signal
InactiveUS20080298694A1Reduce redundancyIncrease the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionYcbcr color space
A method for coding an RGB color space signal is disclosed. In accordance with the method, a base plane is encoded using an independent mode, and an enhanced plane is encoded by referring to the base plane without converting the RGB color space signal into YCbCr color space signal to reduce a redundancy between RGB planes and improve a compression ratio of an image.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRONICS TECH INST
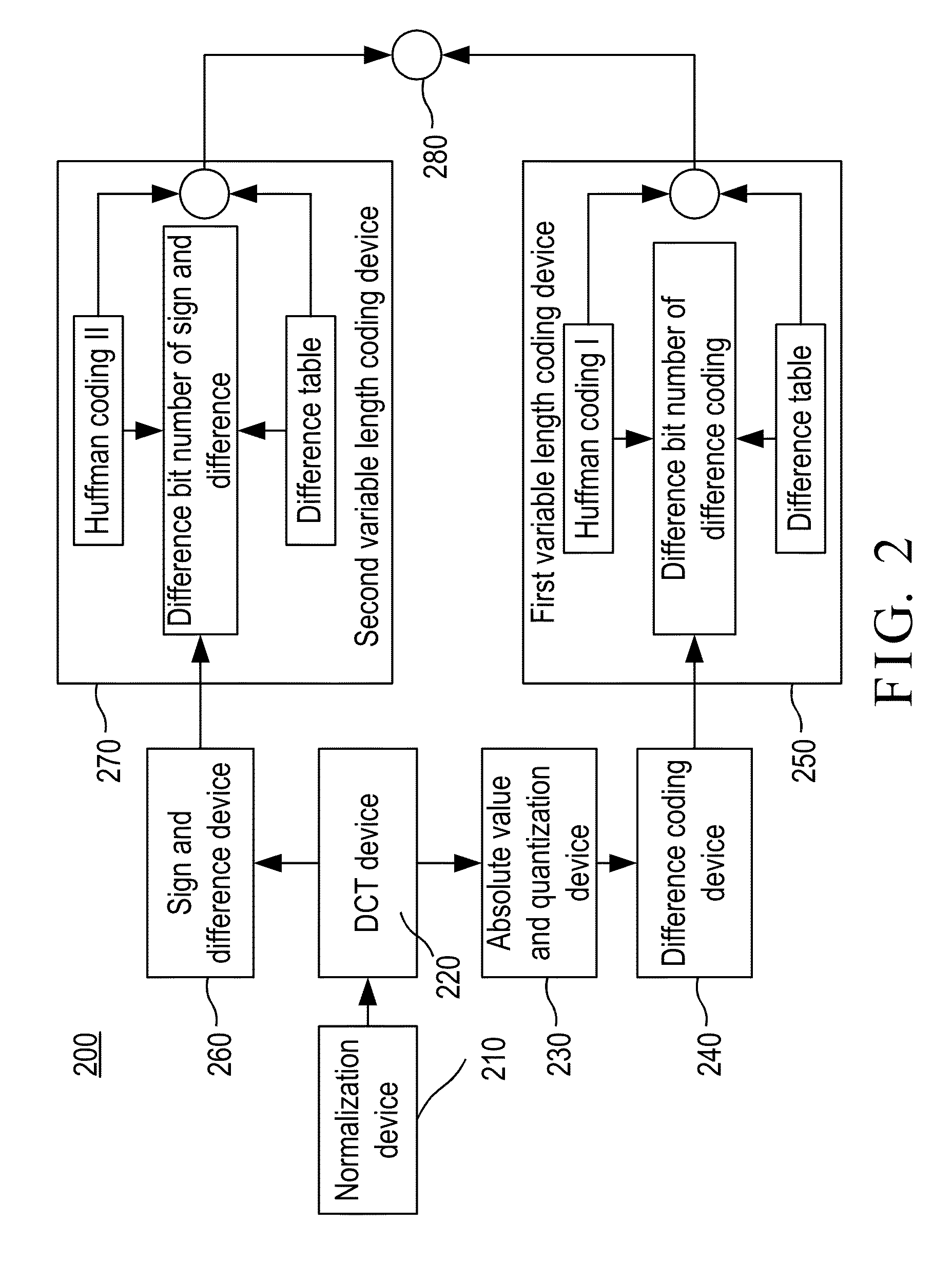
Electrocardiogram signal compression and de-compression system
InactiveUS20130243105A1Improve quality scoreLow distortion rateCode conversionComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionEcg signalFrequency spectrum
The invention provides an electrocardiogram signal compression and de-compression system. The invention uses the sign characteristics of the coefficients of the discrete cosine transform type IV and the characteristics of quantization of spectrum to perform the differential pulse code modulation of the spectrum for preserving the high frequency characteristics of the spectrum of the discrete Fourier transform. The invention also uses the Huffman coding to increase the compression ratio. Different from the conventional compression technology, the invention uses the fact that the quantization values of the spectrum in the high frequency are almost the same to increase the compression ratio and preserve the characteristics of high frequency components of the spectrum.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
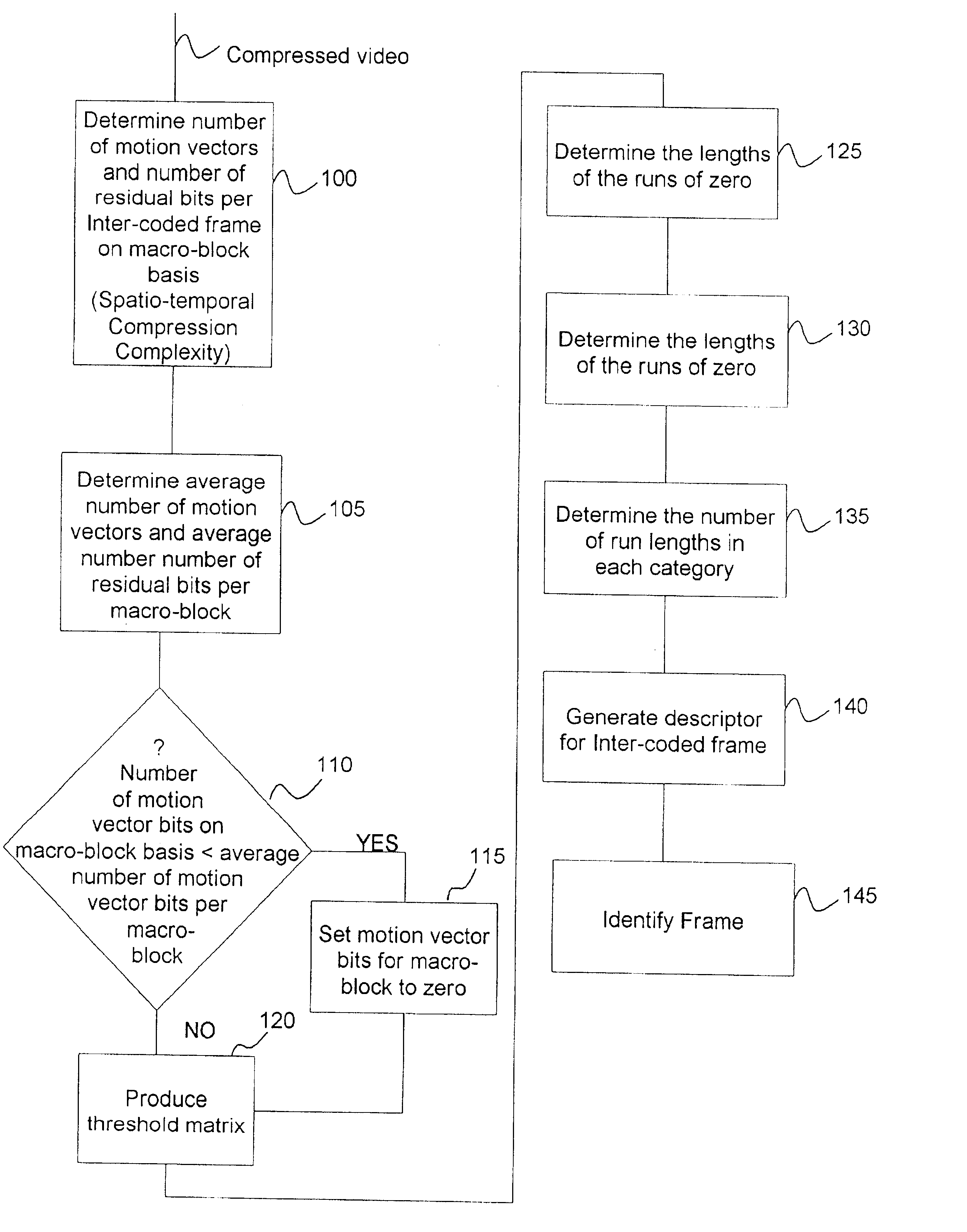
Methods of feature extraction of video sequences
InactiveUS6618507B1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionVideo sequence
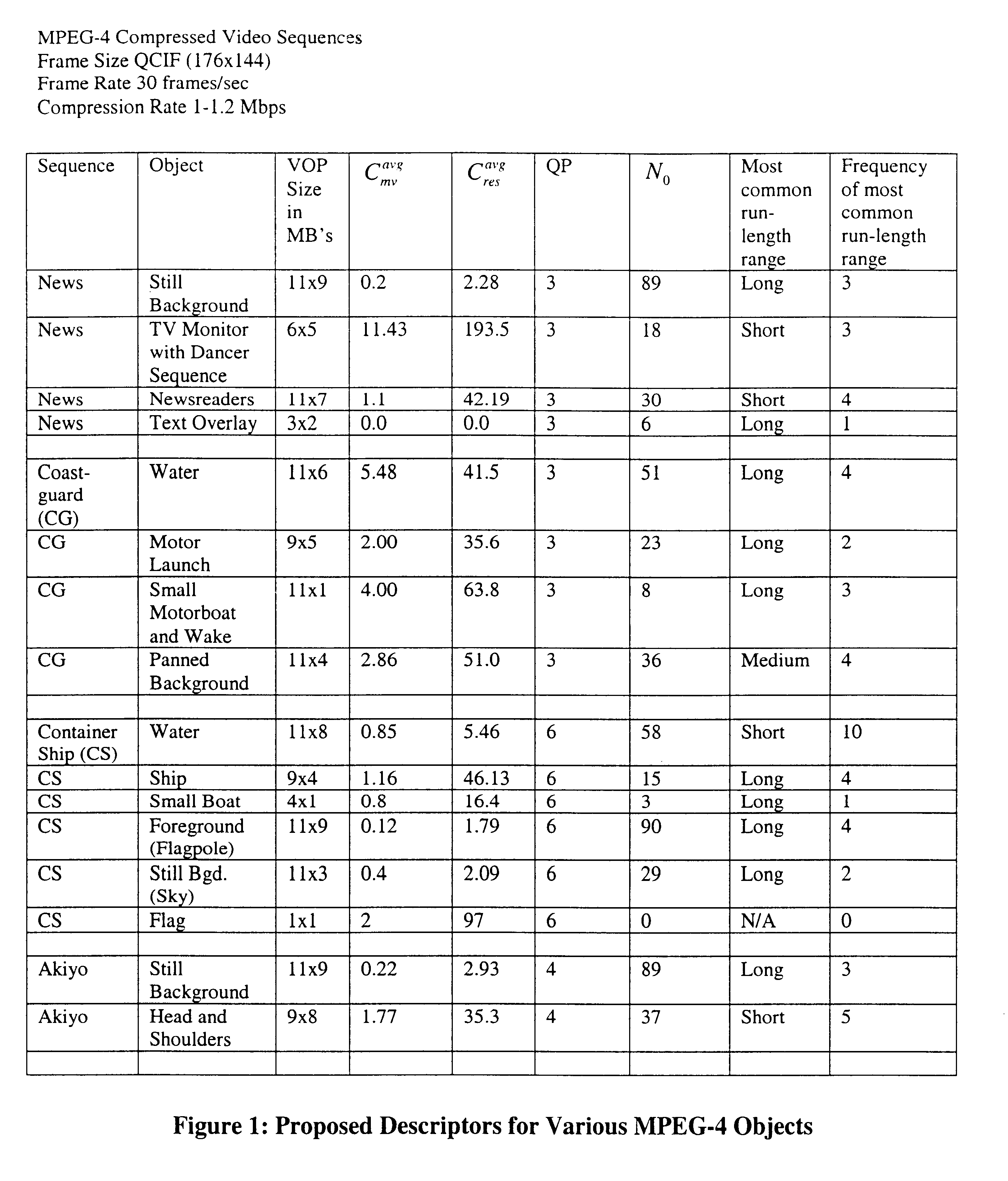
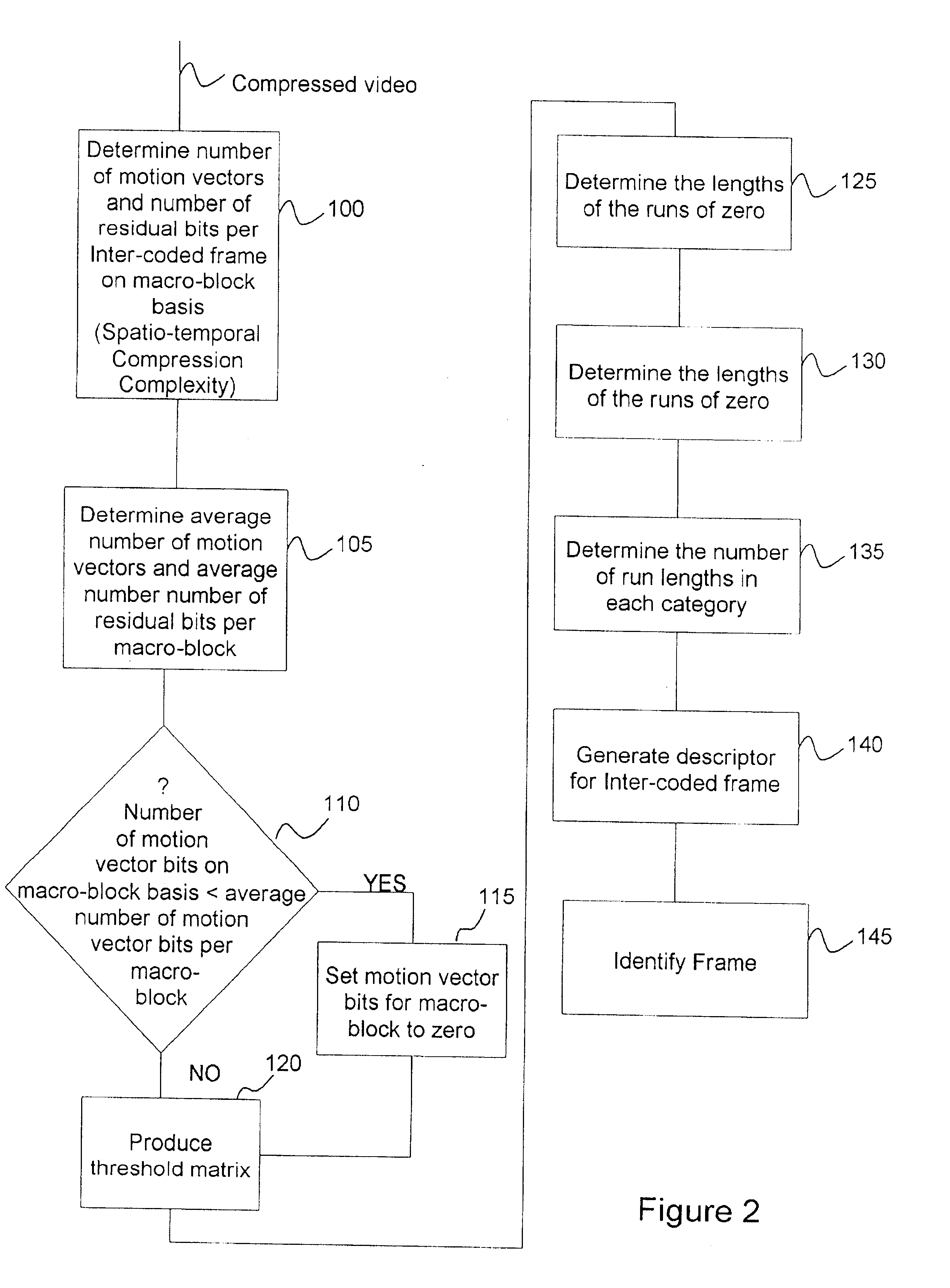
This invention relates to methods of feature extraction from MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 compressed video sequences. The spatio-temporal compression complexity of video sequences is evaluated for feature extraction by inspecting the compressed bitstream and the complexity is used as a descriptor of the spatio-temporal characteristics of the video sequence. The spatio-temporal compression complexity measure is used as a matching criterion and can also be used for absolute indexing. Feature extraction can be accomplished in conjunction with scene change detection techniques and the combination has reasonable accuracy and the advantage of high simplicity since it is based on entropy decoding of signals in compressed form and does not require computationally expensive inverse Discrete Cosine Transformation (DCT).
Owner:MICRO COMPACT CAR AG +1
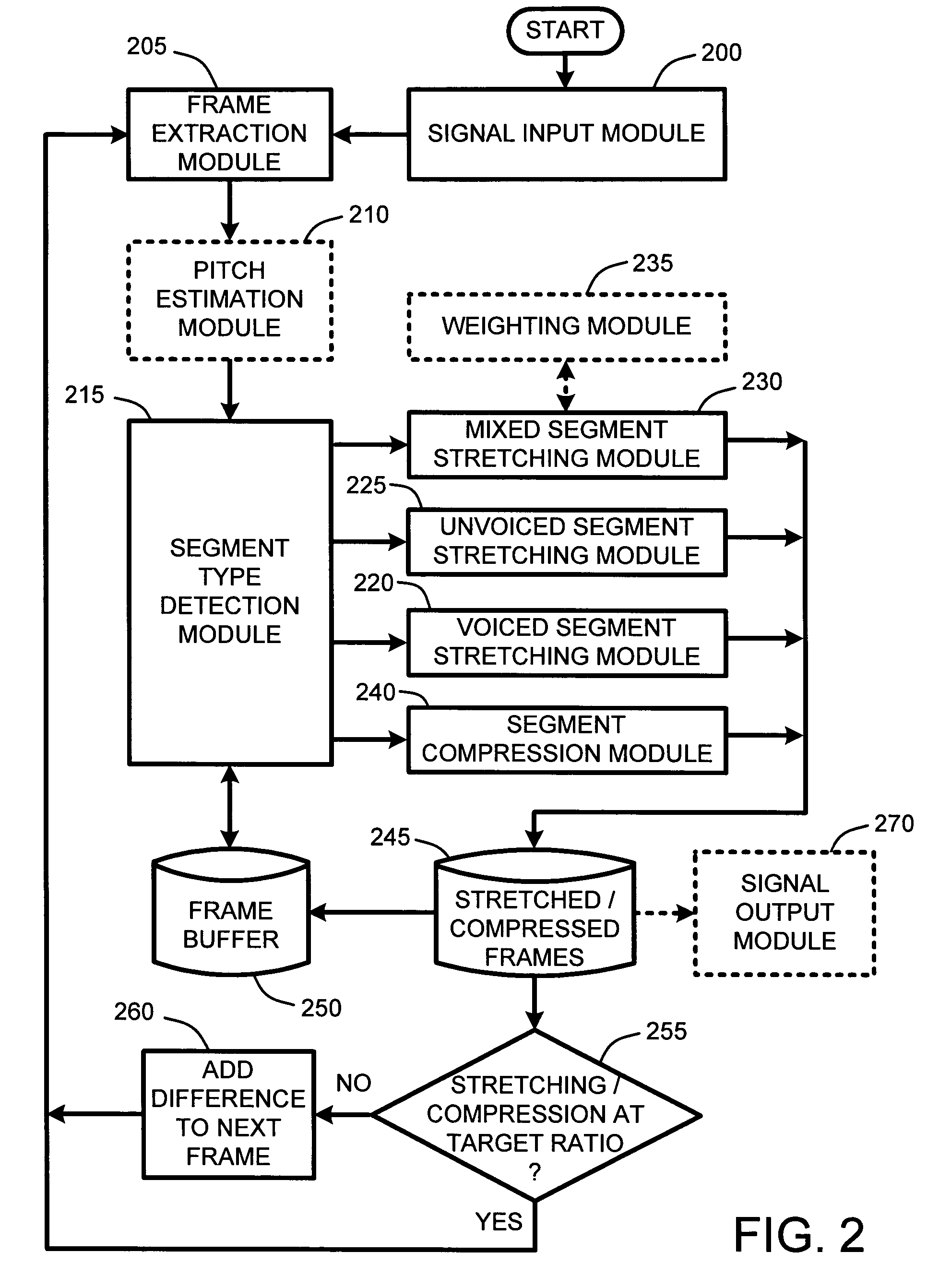
System and method for providing high-quality stretching and compression of a digital audio signal
InactiveUS7337108B2Quality improvementImprove intelligibilitySpeech analysisCode conversionCompression methodSelf adaptive
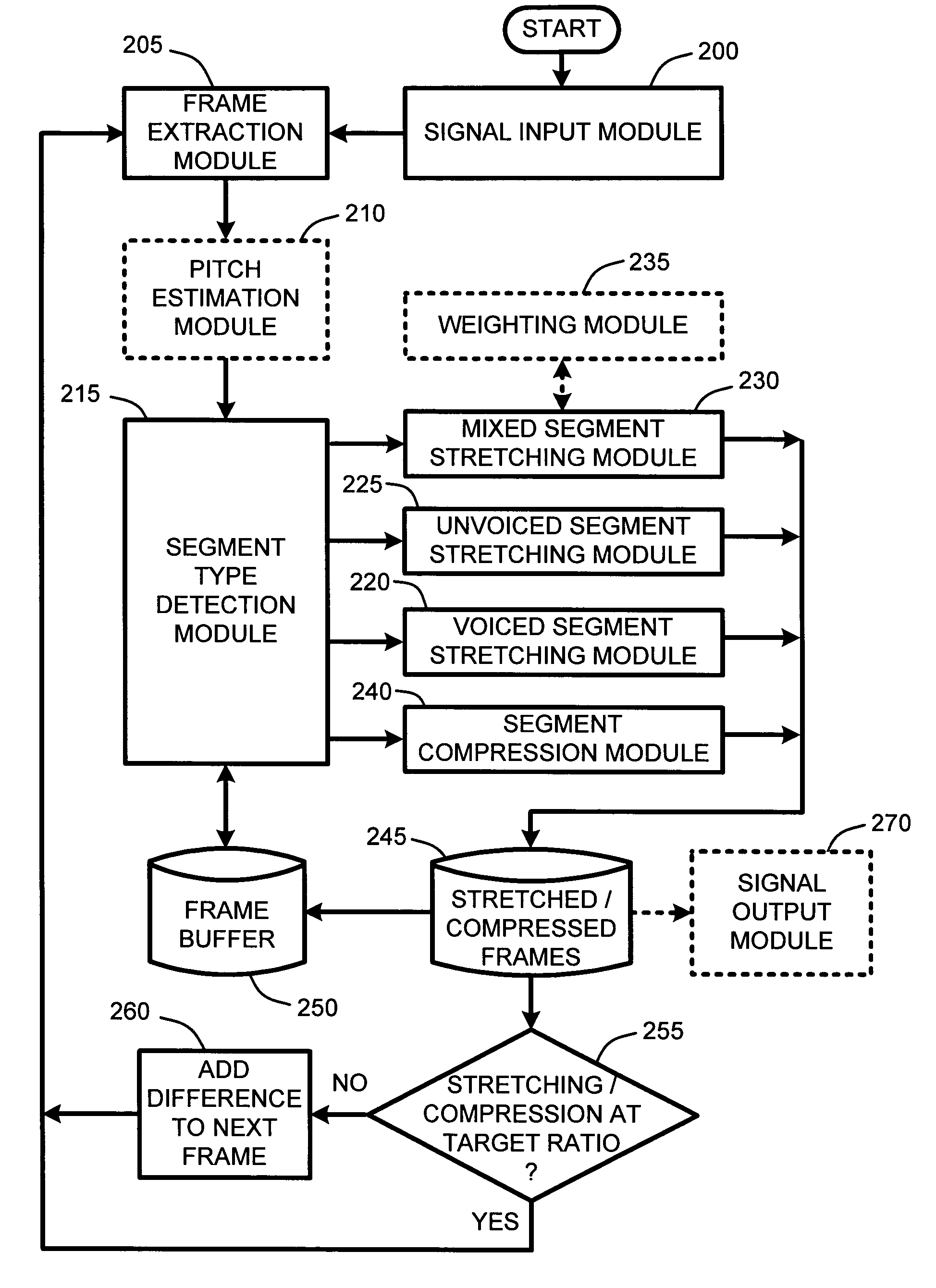
An adaptive “temporal audio scaler” is provided for automatically stretching and compressing frames of audio signals received across a packet-based network. Prior to stretching or compressing segments of a current frame, the temporal audio scaler first computes a pitch period for each frame for sizing signal templates used for matching operations in stretching and compressing segments. Further, the temporal audio scaler also determines the type or types of segments comprising each frame. These segment types include “voiced” segments, “unvoiced” segments, and “mixed” segments which include both voiced and unvoiced portions. The stretching or compression methods applied to segments of each frame are then dependent upon the type of segments comprising each frame. Further, the amount of stretching and compression applied to particular segments is automatically variable for minimizing signal artifacts while still ensuring that an overall target stretching or compression ratio is maintained for each frame.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
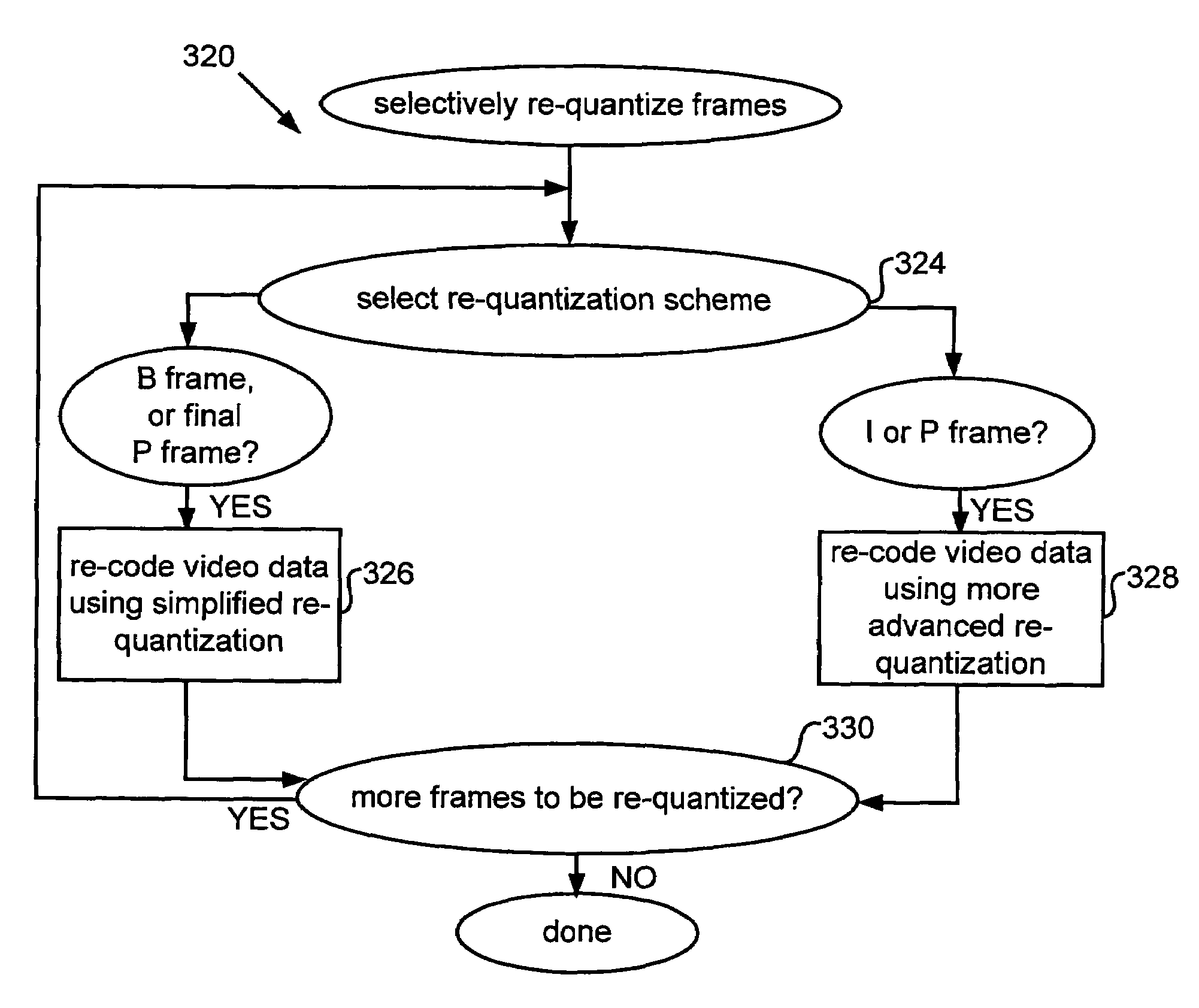
Methods for efficient bandwidth scaling of compressed video data
InactiveUS7477688B1Effective bandwidthGuaranteed data transmission efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData integrityParallel computing
The present invention relates to systems and methods for efficient bit rate alteration of a bitstream to match an available channel capacity. The efficient bit rate alteration includes selective re-quantization of the compressed bitstream. Selective re-quantization according to the present invention applies multiple re-quantization schemes to different portions of a bitstream. In one embodiment, the multiple re-quantization schemes each have a different computational load. By selectively choosing which type of re-quantization is performed on each portion, efficient bandwidth scaling and data transmission may be achieved both when computational capacity is limited and when video data integrity is important.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
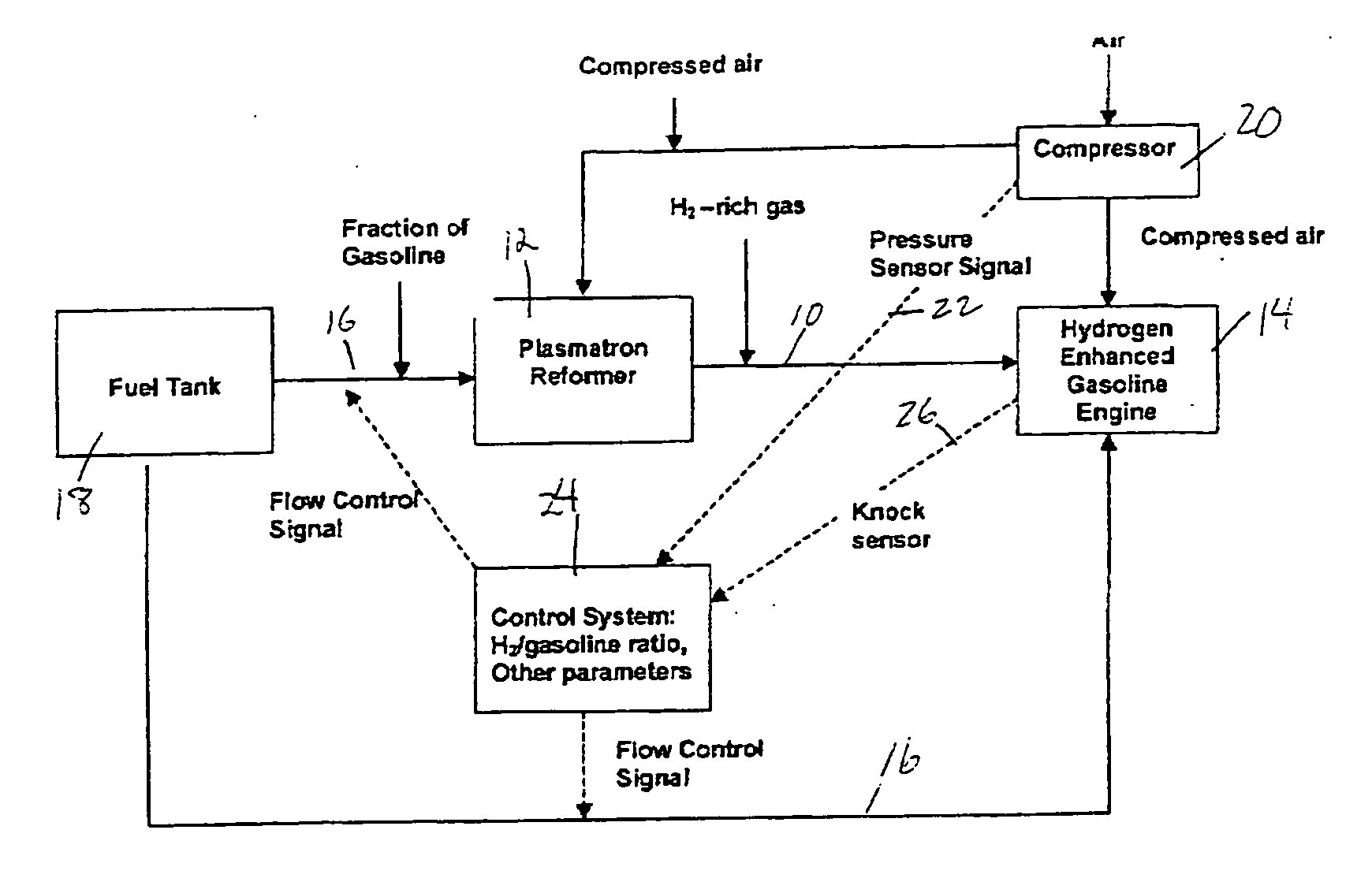
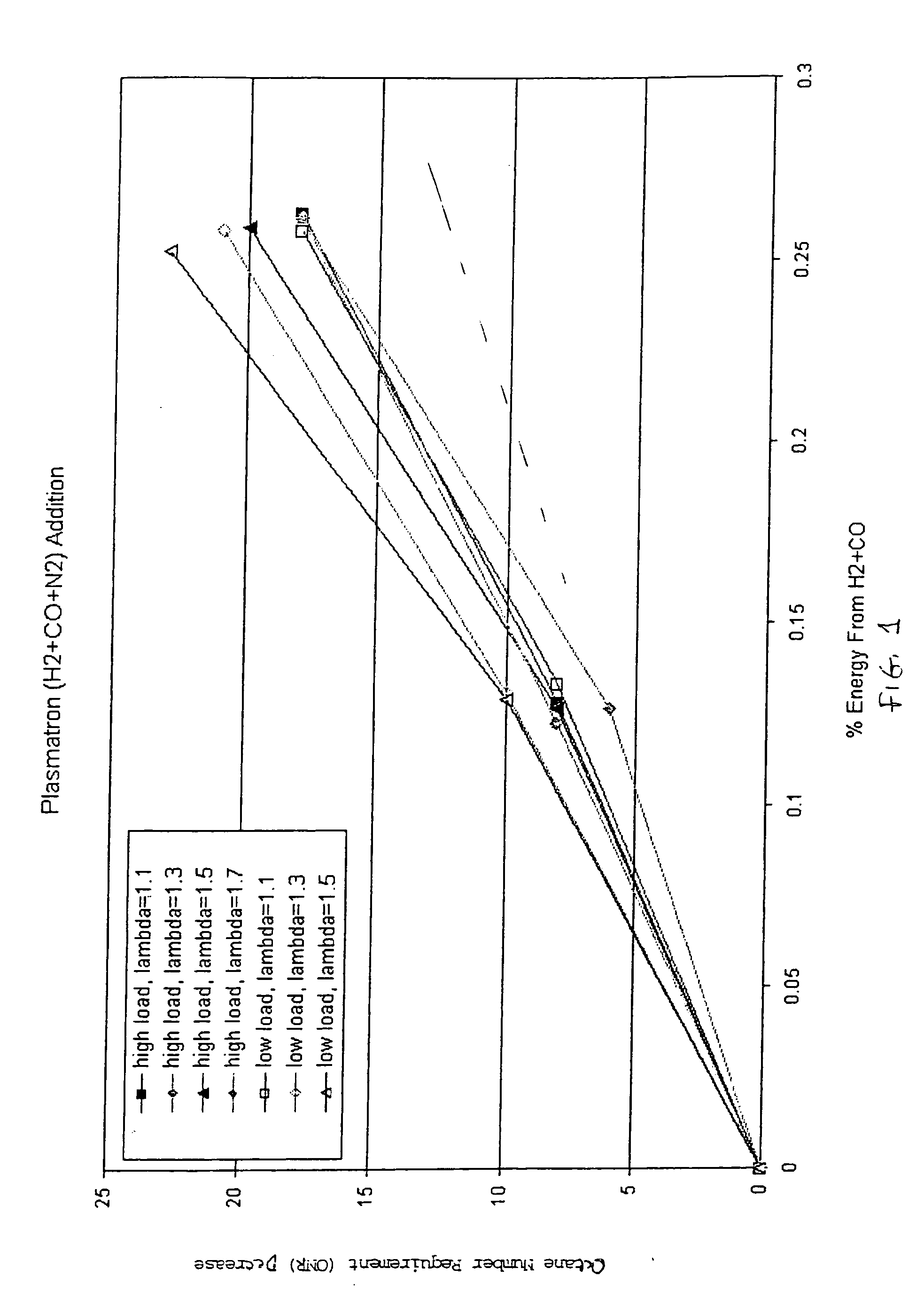
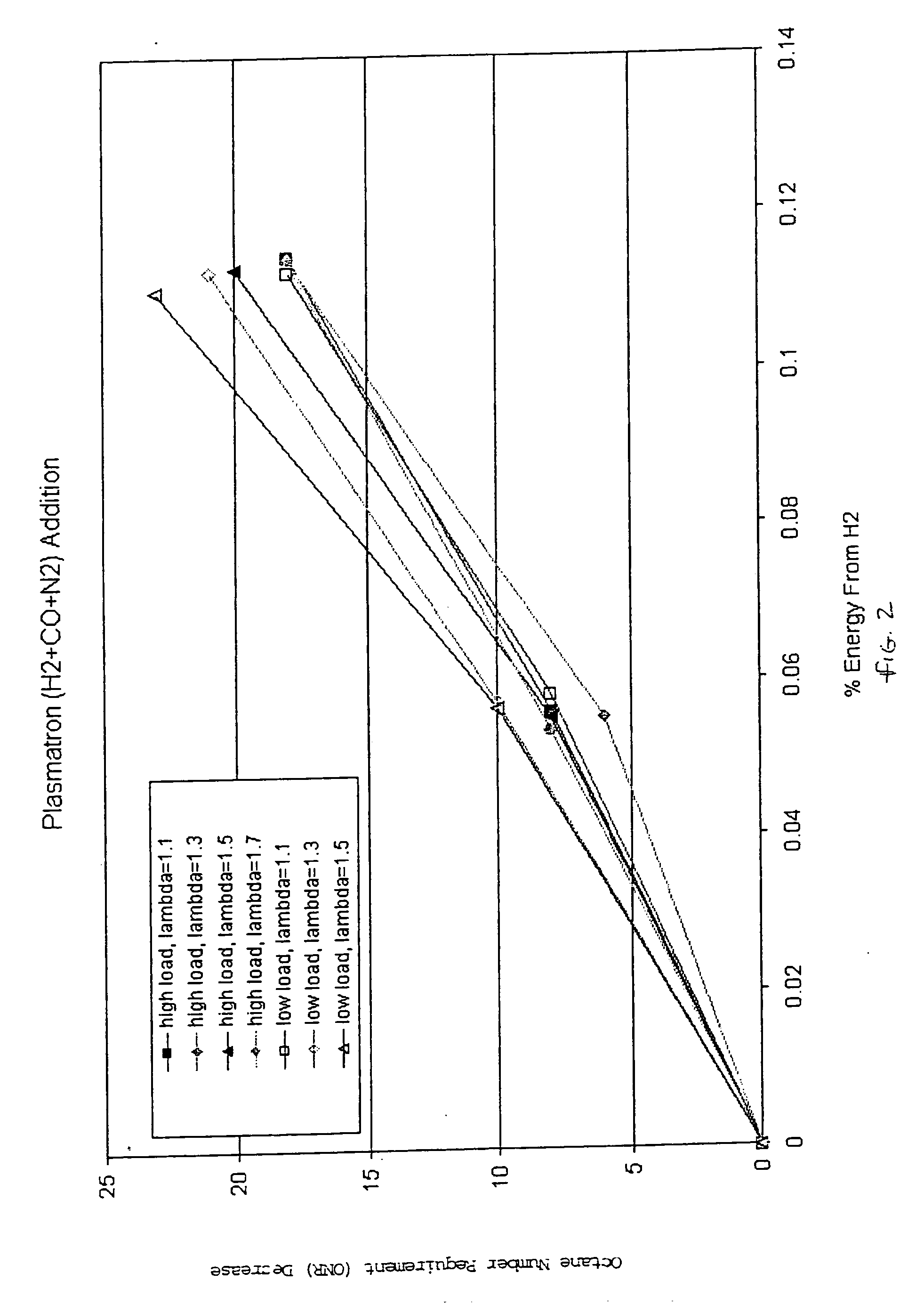
Hydrogen and carbon monoxide enhanced knock resistance in spark ignition gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060075991A1Good anti-knock performanceGreater spark retardElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHydrogenCombustion
A method for reducing required octane number and a spark ignition gasoline engine system with hydrogen-enhanced knock resistance. The method for reducing required octane number of gasoline needed to prevent knock includes the addition of hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas containing carbon monoxide to gasoline. Octane number can be improved by 5 or more for a hydrogen energy fraction of 10%. The spark ignition gasoline engine system includes a spark ignition gasoline engine and a source of gasoline and hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas. Apparatus is provided to supply the gasoline and the hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas to the engine at a varying hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas to gasoline ratio selected both to prevent knock and to ensure a desired level of combustion stability throughout a full range of engine operation. The engine system may be normally aspirated or boosted; the compression ratio may be high such as greater than 11 or below 11, and EGR may be added. The hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas to gasoline ratio may be controlled as a function of boost pressure, torque, engine speed, or air / fuel mixture ratio.
Owner:HEYWOOD JOHN B +4
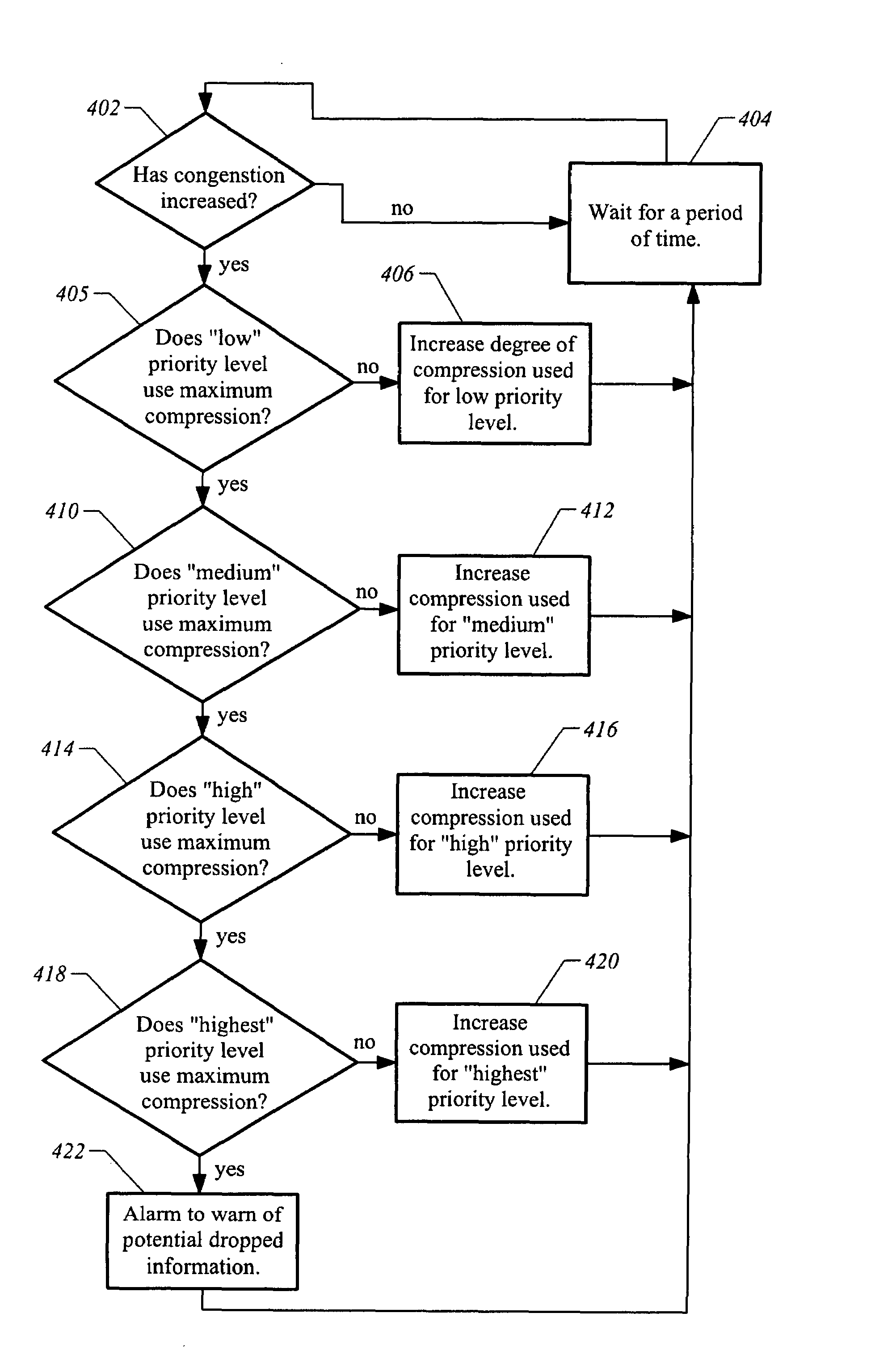
Communication system with priority data compression
InactiveUS7319667B1Great compression related delaySignificant portionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData compressionCommunications system
A data compression system that dynamically adapts the degree of compression used in response to the priority of the data to be compressed is provided by virtue of one embodiment of the present invention. In one embodiment, only low priority data is compressed while high priority data is passed through to the network in uncompressed form. Also, the compression ratio can be varied depending on the priority of the data to allocate a larger portion of available bandwidth to higher priority traffic while imposing greater compression related delay on lower priority traffic.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus and method for focusing ions and charged particles at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS6744041B2Samples introduction/extractionIsotope separationInductively coupled plasmaElectrospray
Improvements have been made for collection and focusing of ions generated from atmospheric pressure sources such as electrospray, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization, inductively coupled plasma, discharge, photoionization and atmospheric pressure matrix assisted laser desorption ionization. A high transmission electro-optical surface is placed between the source regions and the focusing regions to optimize the field geometries and strengths in each respective region. Compression ratios of greater than 5000 are capable of transferring virtually all ions from large volume dispersive ion regions into ion beam cross-sections of less than 1 mm. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric pressure ionization sources.
Owner:SHEEHAN EDWARD W +1
Enhanced data converters using compression and decompression
InactiveUS7088276B1Less bandwidthLess storageElectric signal transmission systemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital interfaceA d converter
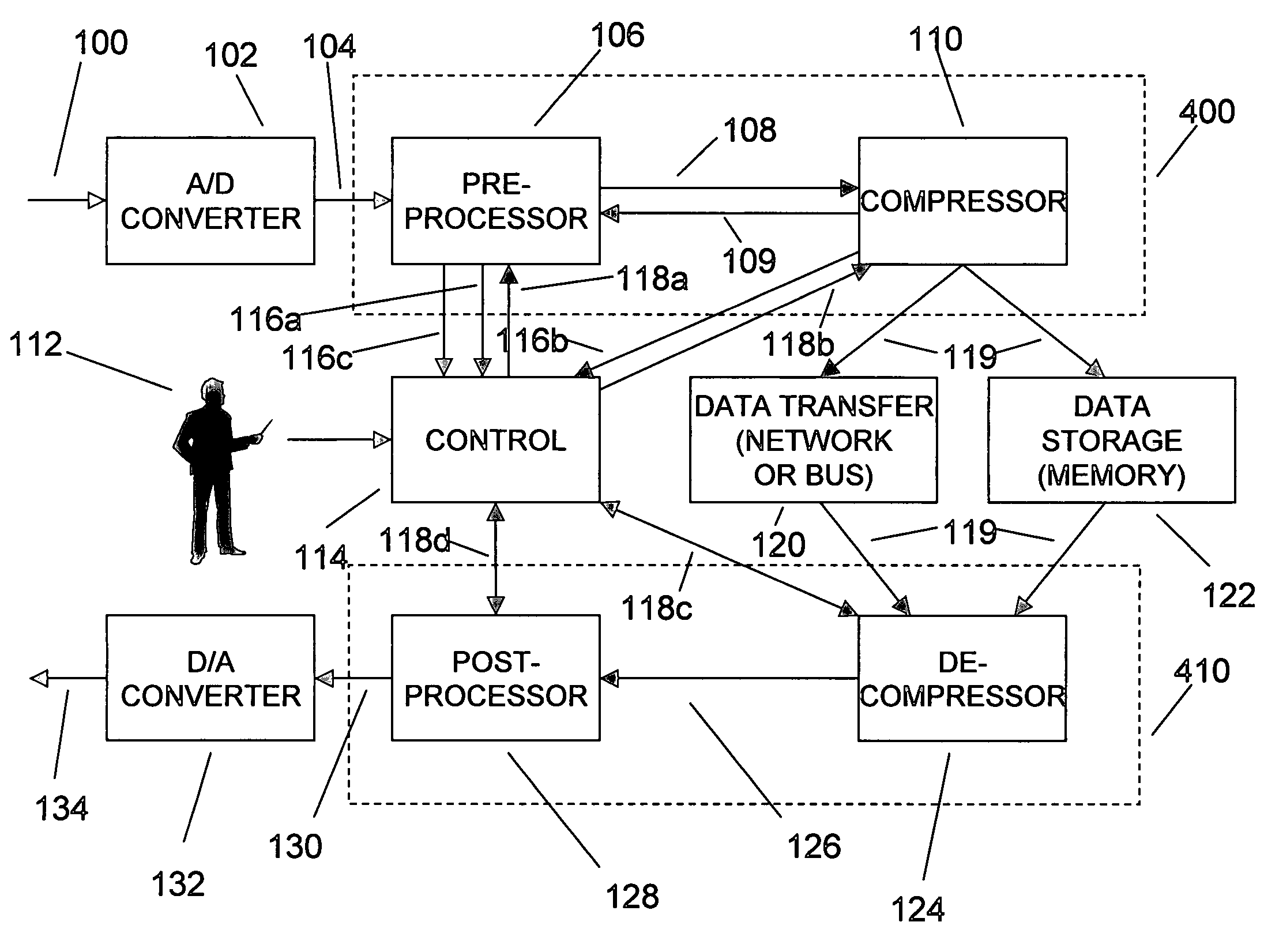
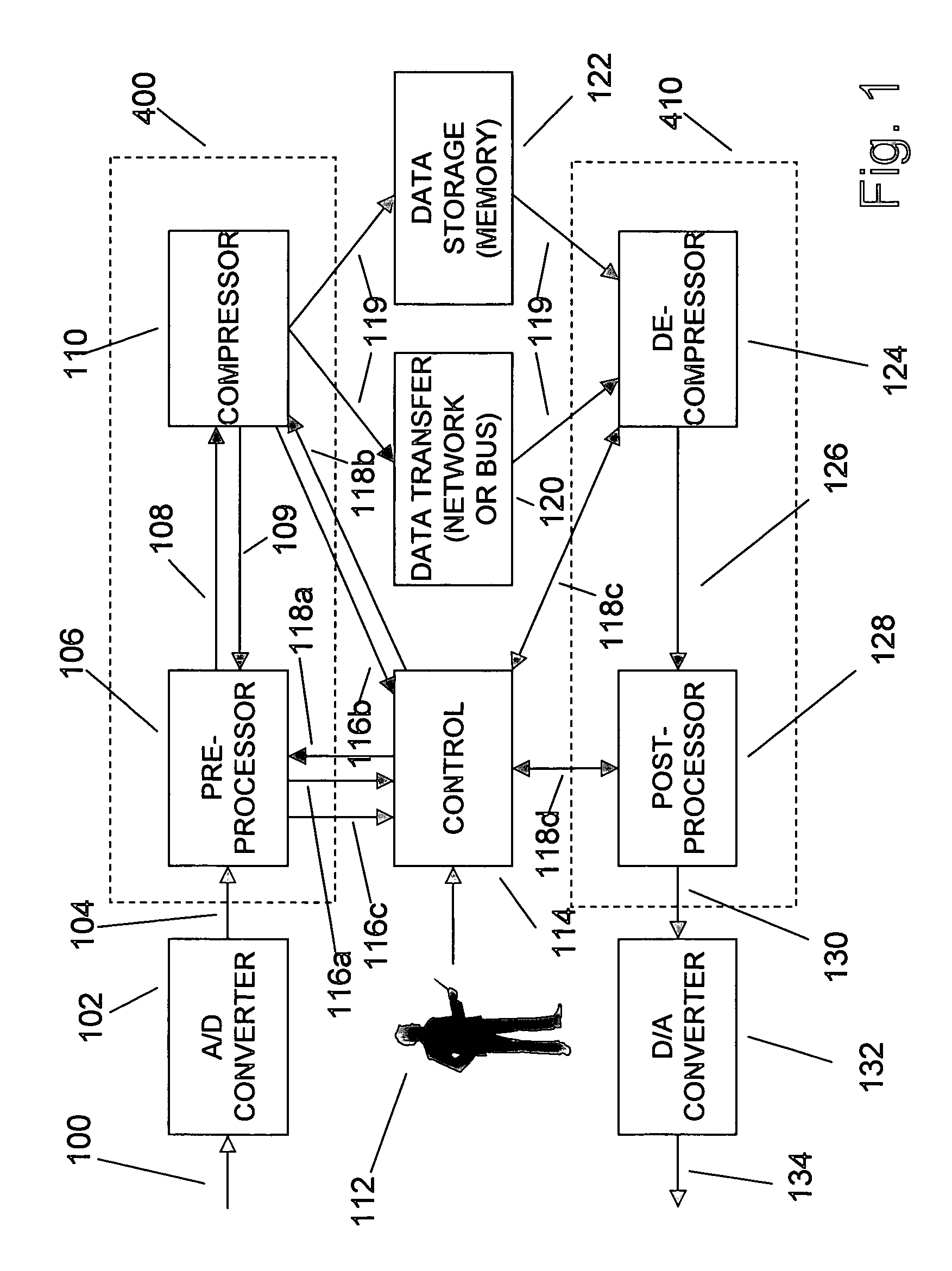
An enhancement that reduces the digital interface rate of analog-to-digital (A / D) and digital-to-analog (D / A) converters through the use of compression and decompression is described. The present invention improves A / D converters by compressing the sampled version of the A / D converter's analog input signal in real time, thereby significantly decreasing the required bit rate of the A / D converter's digital interface. Similarly, the present invention improves D / A converters by decreasing the required bit rate of the D / A converter's digital interface. D / A converters enhanced by the present invention include a decompressor that decompresses the D / A converter's compressed digital input in real time, prior to conversion to an analog output signal. The present invention's simplicity and its ability to be implemented using multiple compression and decompression elements allow its use in A / D and D / A converters with arbitrarily high sampling rates. By selecting a desired compression ratio during lossy compression, users of the present invention can precisely control the bit rate of the A / D and D / A converter's digital interface. Users of the present invention can dynamically choose the desired balance between the quality and the bit rate of A / D and D / A converters by adjusting various compression and decompression control parameters.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Apparatus for converting picture format in digital TV and method of the same
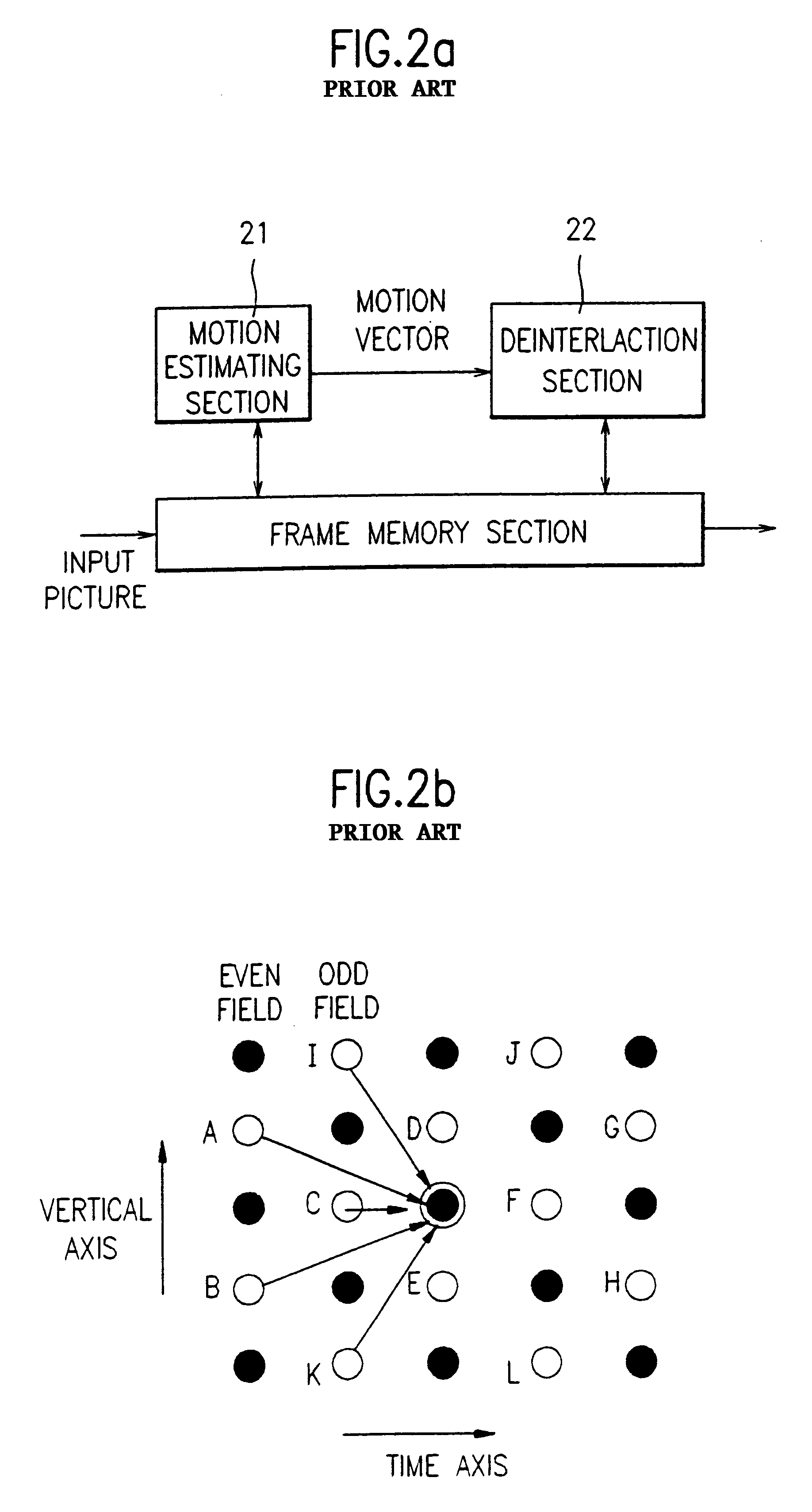
InactiveUS6268886B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesFeature extractionInterlaced video
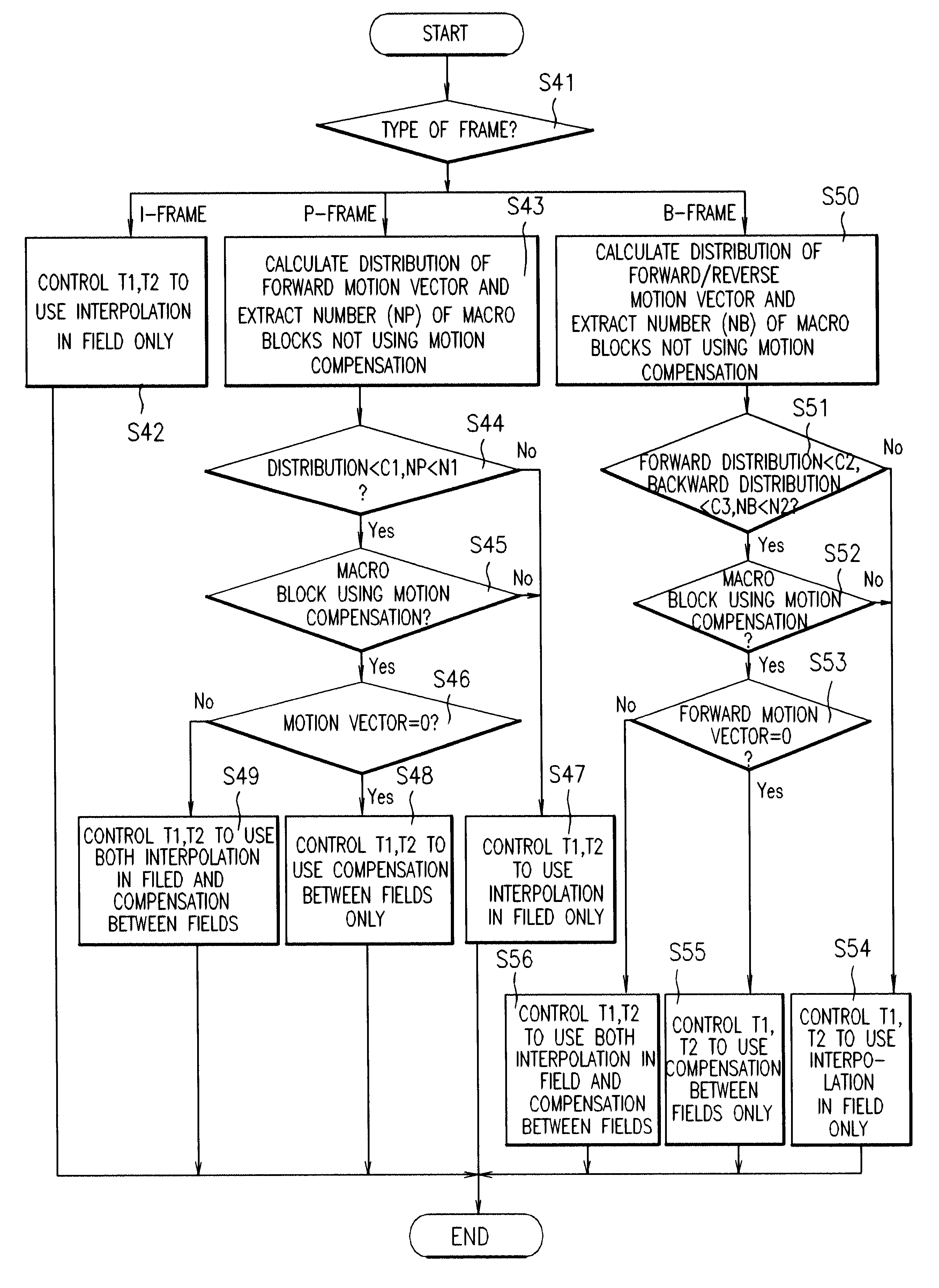
An apparatus and method for converting a picture format in a digital TV is disclosed including a picture characteristic extracting section analyzing a compressed bit stream of every input picture scanned in an interlaced scanning pattern to analyze the characteristic of each picture; an interpolation determining section determining an interpolation operation processing in an adaptable manner using information each extracted from every given pictures at the picture characteristic extracting section; and an operation performing section performing the related operation according to the interpolation operation processing determined by the interpolation determining section to perform an interpolation.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Wireless terminal dynamically programmable proxies
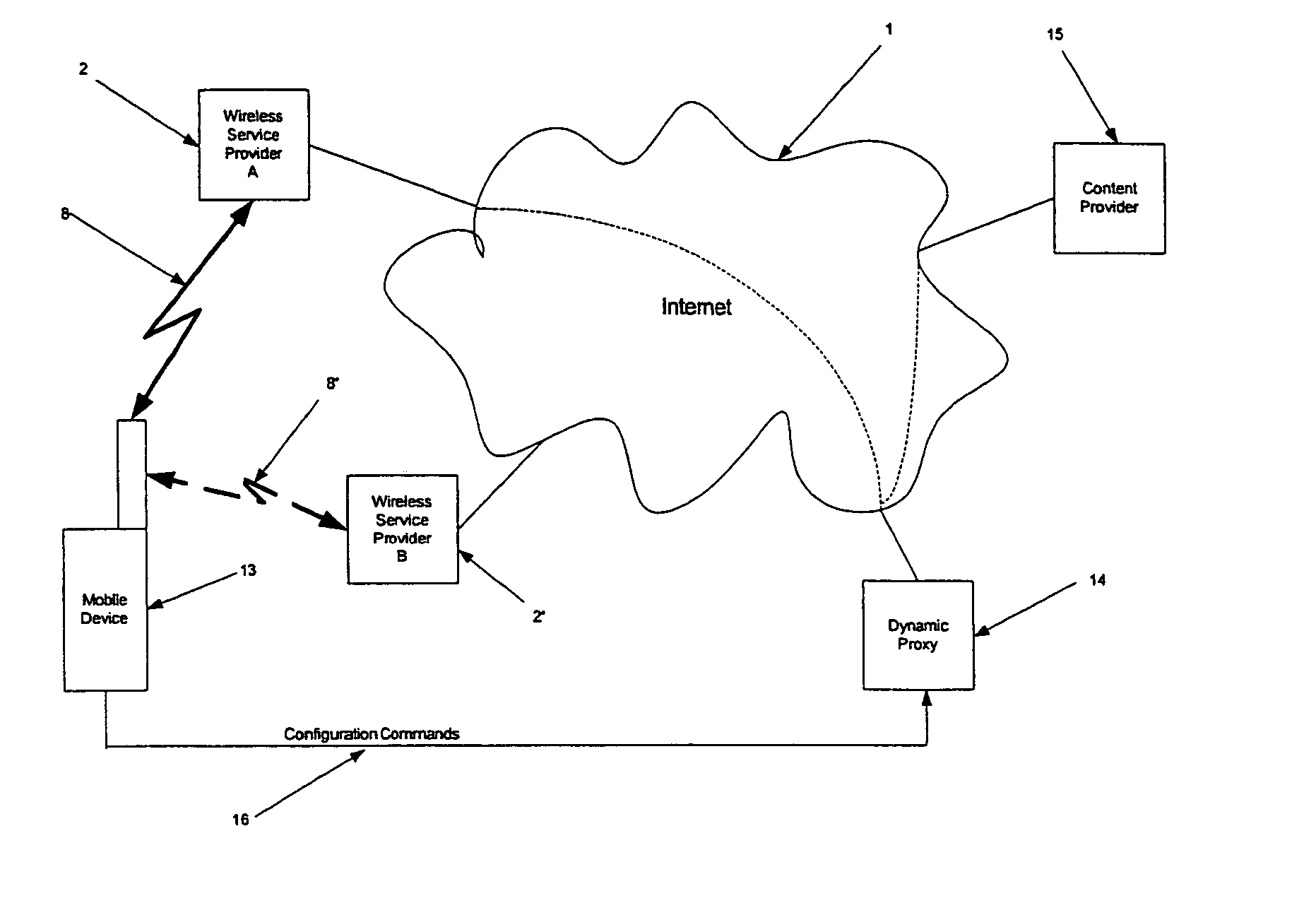
InactiveUS20060013235A1Web contentImprove file transfer timeInformation formatData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionTranscoding
The present invention relates to scheduling, compression and transcoding of data content for mobile terminals with limited resources. The present invention provides a method of transferring information or content to or from a terminal dependent on a number of parameters associated with the terminal. Such parameters might include its battery level, processing resource status and memory resource status, and the nature of its connection(s) to the network(s) (network performance). Thus for example a terminal with plenty of processor resources but a single narrowband wireless link may implement a high compression ratio in order to improve the file transfer time to the terminal, even if this requires a high de-compression processing overhead. Such a set-up may be changed during a connection session, for example if the battery runs low necessitating reduced processing. In preferred embodiments this method of transferring content is implemented using a programmable or dynamically adaptable proxy device which adjusts the transcoding and / or compression, as well as its scheduling or rate and timing of transfer of the transcoded / compressed information to and from the terminal over one or more network connections.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
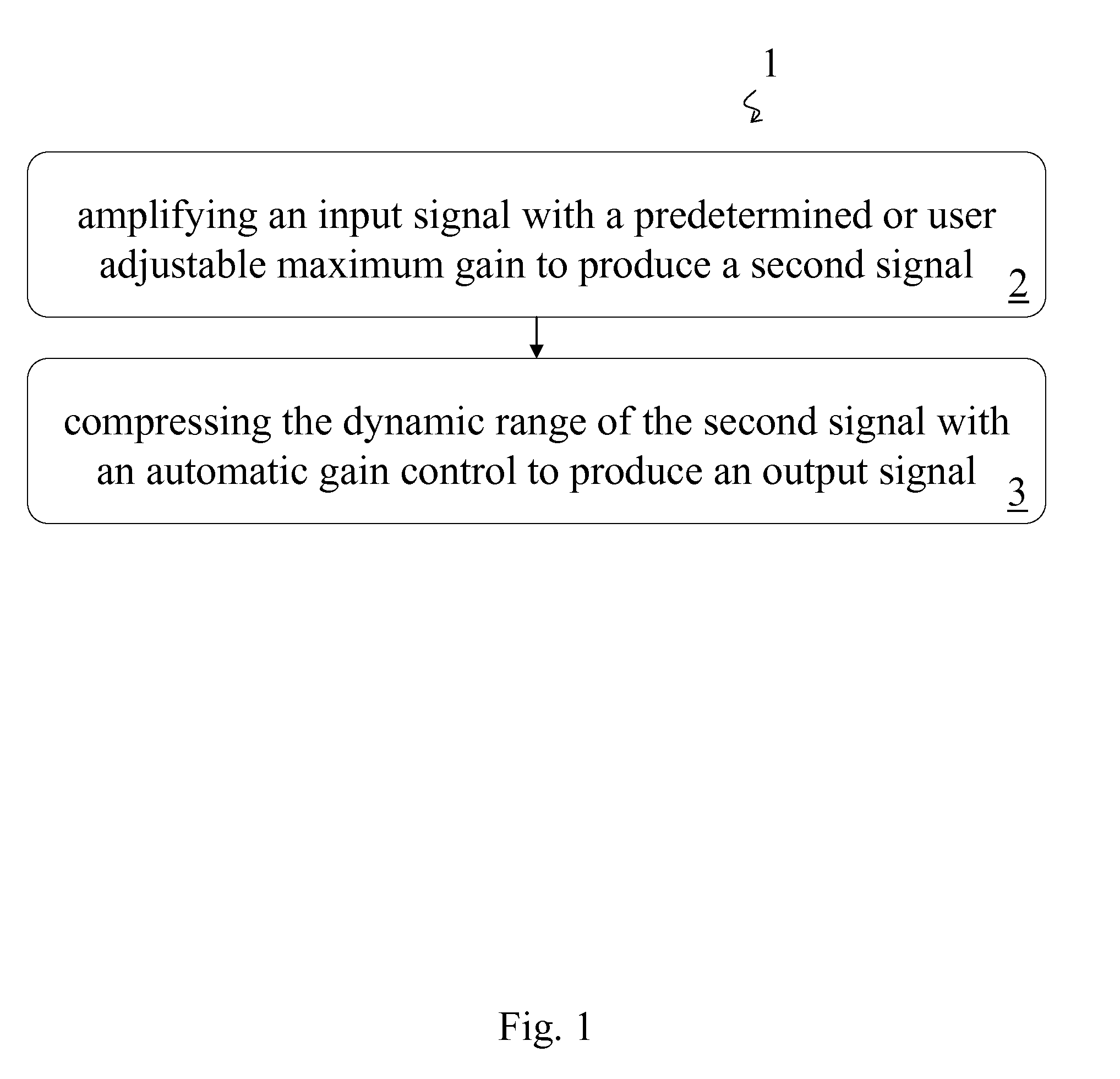
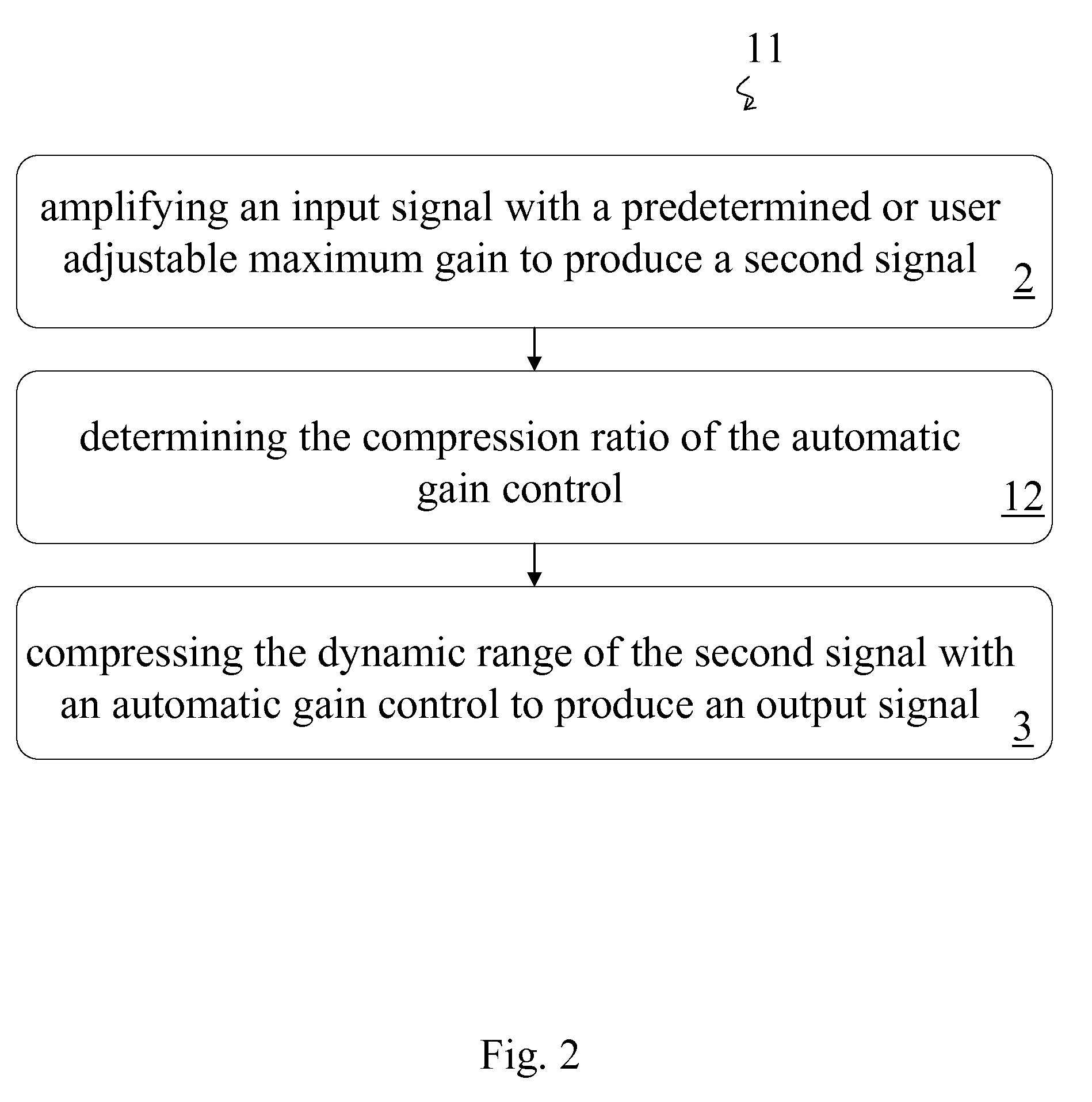
Amplifier and Method of Amplification
InactiveUS20080069385A1Cancel noiseVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersFrequency response correctionAudio power amplifierEngineering
A method of amplification includes amplifying an input signal with a predetermined or user adjustable maximum gain to produce a second signal and compressing the dynamic range of the second signal with an automatic gain control to produce an output signal. The compression ratio of the automatic gain control is greater than one for output signals below a predetermined threshold output signal level and is essentially one for output signals above the predetermined threshold output signal level. The compression ratio may be predetermined or the method may include determining the compression ratio of the automatic gain control. The compression ratio may be determined according to the amplitude of the output signal or according to an input-output curve. The input-output curve my be predetermined and may be selected according to the auditory needs of a listener. Preferably the input-output curve is determined according to the predetermined or user adjustable maximum gain.
Owner:REVITRONIX
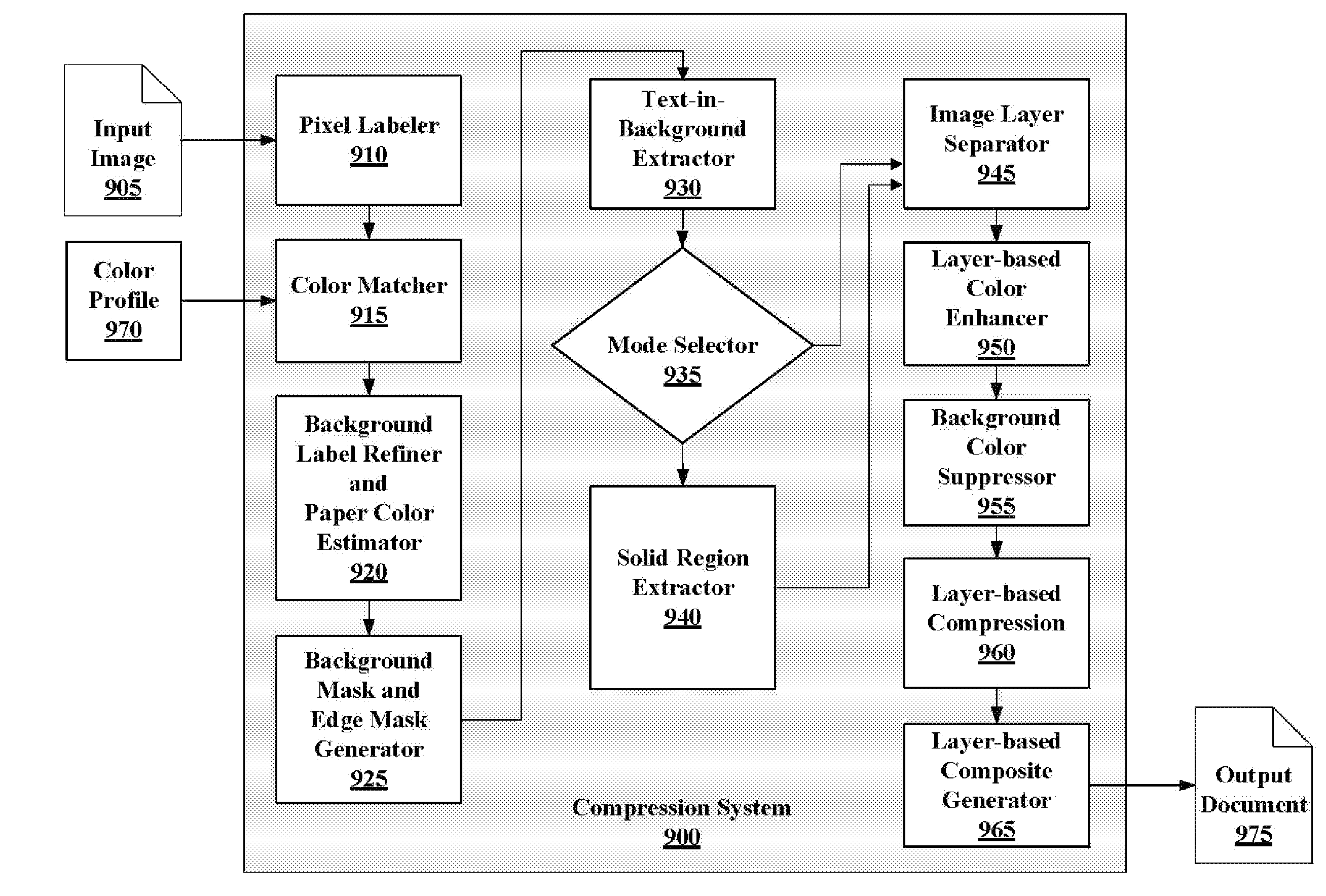
Systems and Methods for Generating Background and Foreground Images for Document Compression
InactiveUS20070189615A1Increase the compression ratioMaintain image qualityCharacter recognitionPictoral communicationImaging processingImaging analysis
Disclosed are embodiments of systems and methods to generate background and foreground images for a document, which enables high-quality and high-ratio document compression. In embodiments, high-accuracy layer processing enables text enhancement, paper color removal, and many other advanced image analysis and processing. Embodiments of the systems support several operation modes and its many parameters, such as layer compression ratios, image segmentation, and modulized image processing, may be adjusted to generate optimal compressed files for different purposes.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Tree-structure-based grade tree aggregation-divided video image compression method
InactiveCN1581977ASolve the amount of image dataSolve lengthImage codingTelevision systemsCompression methodVideo image
The method includes steps: first at encoding end, obtaining distribution of image energy on time and frequency domain through discrete wavelet transform; based on correlation between wavelet coefficient, wavelet coefficient in each order is divided according to tree structure; SPIHT encoding is carried out for wavelet coefficient of each tree; encoding result is deposited on encoding end momentarily; finally, results of encoding each tree are synthesized as a code stream in use for storing or transferring. The invention realizes video compression in high compression ratio and low degree of distortion by using less memory space, particular suitable to dedicated system realized through hardware.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Compression store free-space management
InactiveUS7024512B1Avoid system abendsAvoid operating inefficienciesMemory architecture accessing/allocationData processing applicationsParallel computingImproved method
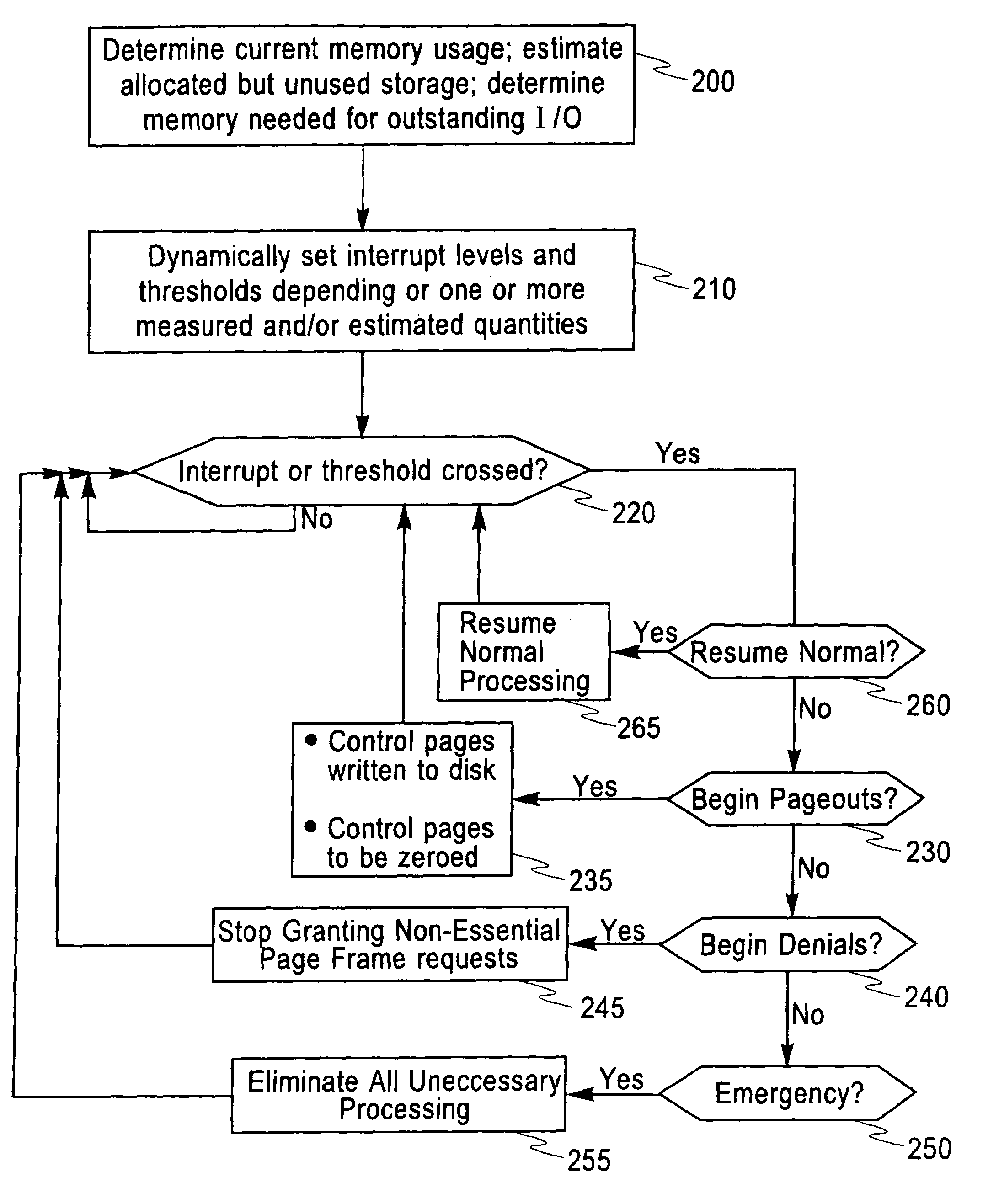
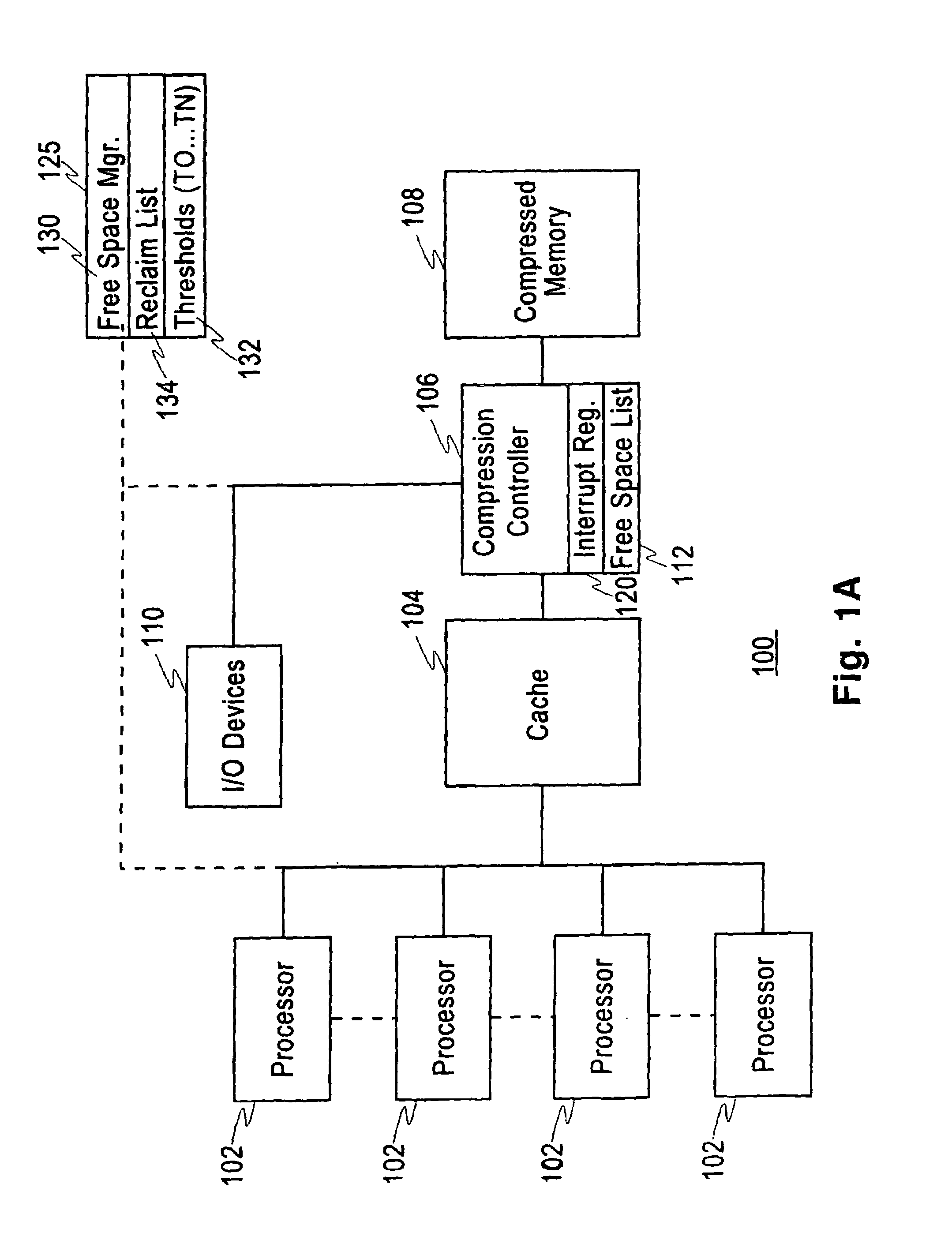
An improved method, system, and a computer program storage device (e.g., including software embodied on a magnetic, electrical, optical, or other storage device) for management of compressed main memory allocation and utilization which can avoid system abends or inefficient operation that would otherwise result. One feature reduces (and ultimately eliminates) all unessential processing as the amount of available storage decreases to a point low enough to threaten a system abend. In another example, the amount of current memory usage is determined as well as one or more of: an estimate of an amount of allocated but unused memory; a determination of the amount of memory required for outstanding I / O requests. The compressed memory is managed as a function of the current memory usage and one or more of the other measured or estimated quantities. The compressed memory can be managed by maintaining a set of dynamic thresholds; estimating the amount of storage that can easily be freed (used but available) and the amount of storage that is committed (allocated but unused). The estimate of committed storage can include: the current storage utilization; and an estimate of storage committed to new pages (based on the number of new pages granted), the times at which this was done, the estimated compression ratio, and estimates of residency times in the cache.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for optimized combustion in an internal combustion engine utilizing homogeneous charge compression ignition and variable valve actuation
InactiveUS20060144356A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHomogeneous charge compression ignitionExhaust valve
A valvetrain system mechanization for an internal combustion engine using compression ignition, including homogeneous charge compression ignition, having two intake and one or more exhaust valves per cylinder. The valves are operated by dual overhead camshafts having two-step cams. The intake and exhaust camshafts are provided with phasers for varying the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves. A two-step roller finger follower is disposed for each valve between the cam lobes and the valve stem. The two sets of intake and exhaust valves are controlled by separate oil control valves. Swirl of gases may be introduced by mismatching the lifts of the valves. The valve opening times, closing times, lifts, fuel injection, compression ratio, and exhaust gas recirculation may be varied to optimize combustion conditions for a range of engine operating modes.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
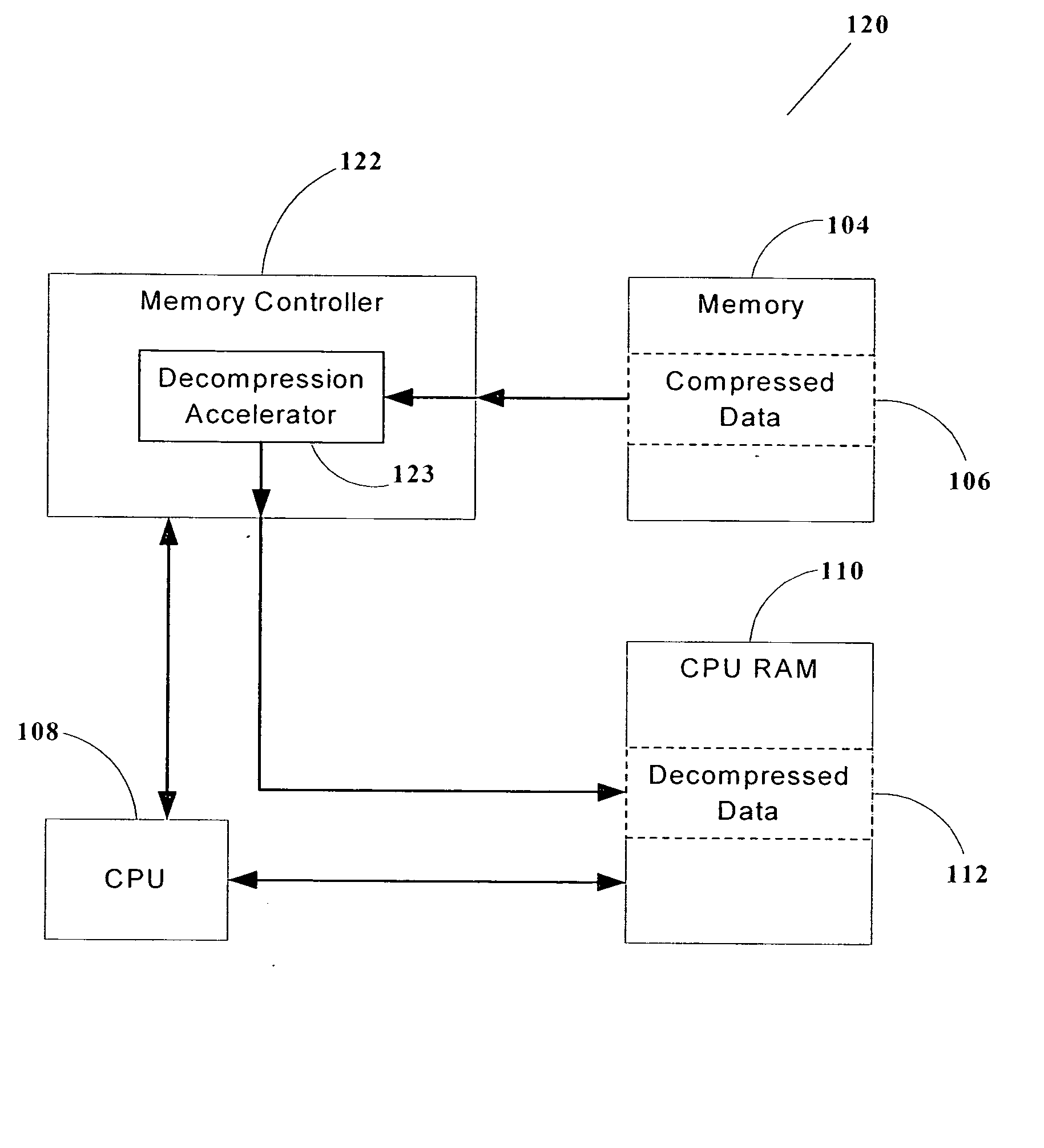
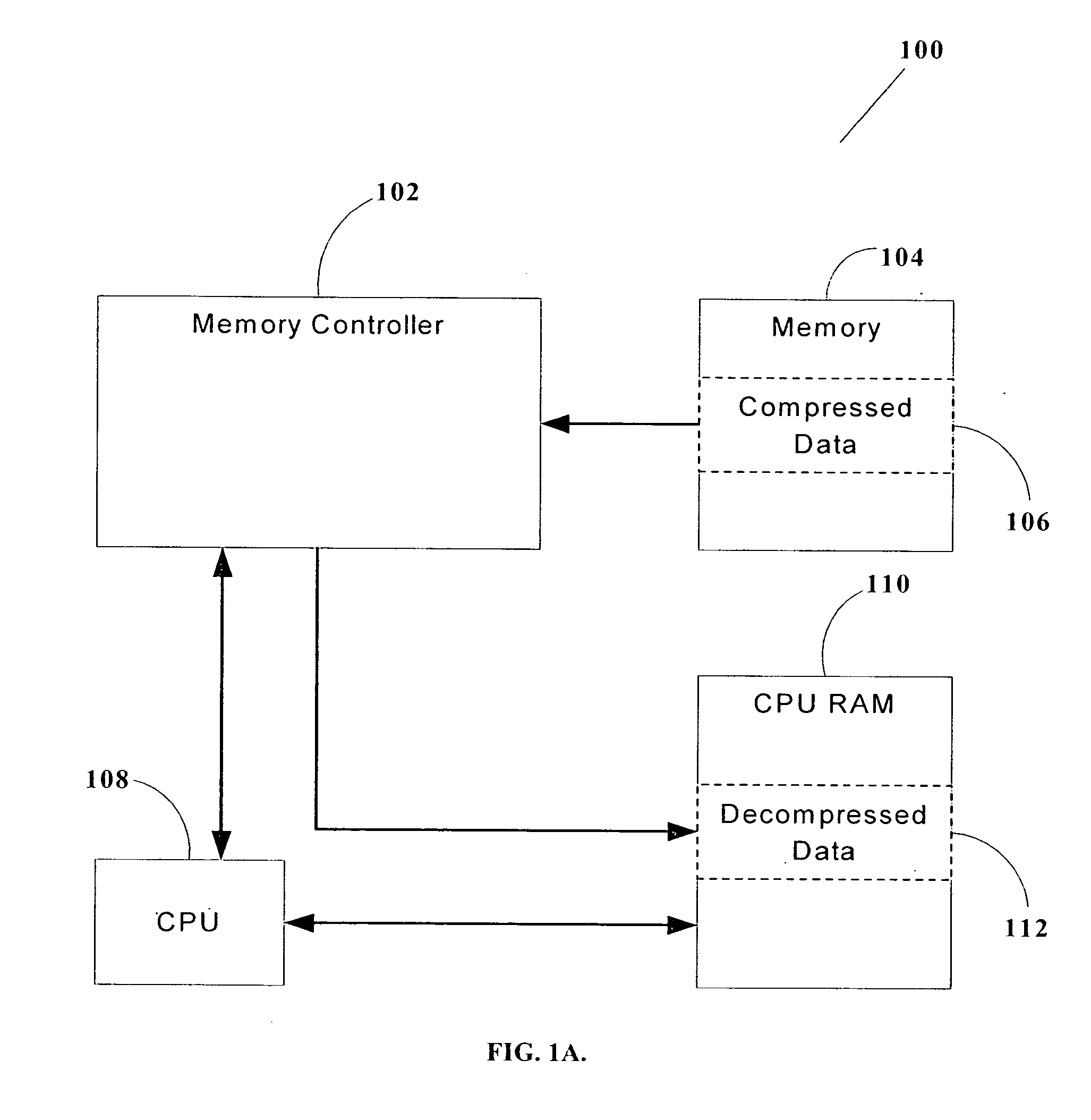
Decompression accelerator for flash memory
ActiveUS20050104753A1Improve performanceEffectively decompressedCode conversionMemory systemsHuffman decodingData compression ratio
A hardware accelerator for improving the decompression performance when decompressing data in Lempel-Ziv-Huffman compressed data format. The use of a Huffman encoding second stage in the popular and widely-used Lempel-Ziv-Huffman standard improves the compression ratio but complicates the decompression, because the Huffman encoding is applied selectively only to certain parts of the Lempel-Ziv tokens, and thus Huffman decoding must also be applied selectively during decompression. The present invention features a variable-length token decoder which is able to selectively decode the Huffman-encoded portions of the compressed data, and therefore enables high-performance decompression for compressed data having a very good compression ratio. Such an accelerator is well-suited for use in data processors which are to be loaded with pre-compressed data and software applications, particularly those employing flash memory.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
Charge air chiller
InactiveUS20090031999A1Maximum increase in energy efficiencyIncrease boost pressureInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelTurbochargerInlet valve
A system for chilling the pressurized charge air to a reciprocating engine is disclosed wherein the chilling is provided by a thermally activated refrigeration cycle powered by waste heat from the engine system. This reduces the required compression power, and also retards knock, making higher compression ratios possible. The chilling system is designed to minimize the amount of chilling required, and also to enable use of compression heat to power the chiller. The disclosed improvement also accommodates exhaust gas recirculation, plus providing activation heat from the exhaust gas, plus Miller cycle timing of the intake valves. Referring to FIG. 1, the charge air from turbocharger 5 is cooled in three stages: heat recovery stage 10; ambient-cooled stage 11; and chilling stage 12. Condensed moisture is removed from the charge air by valve 14 before the charge is supplied to inlet manifold 2.
Owner:ERICKSON DONALD CHARLES
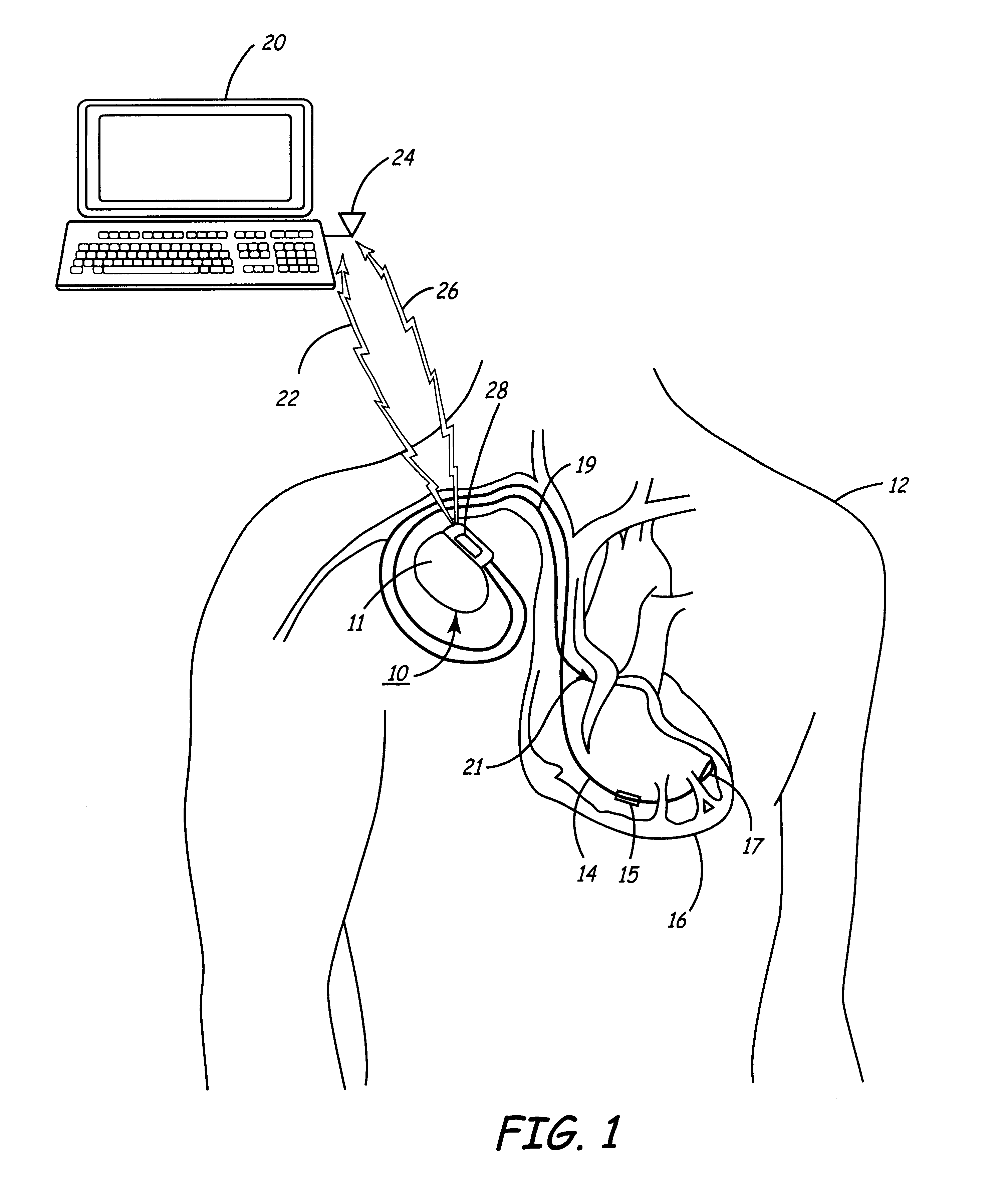
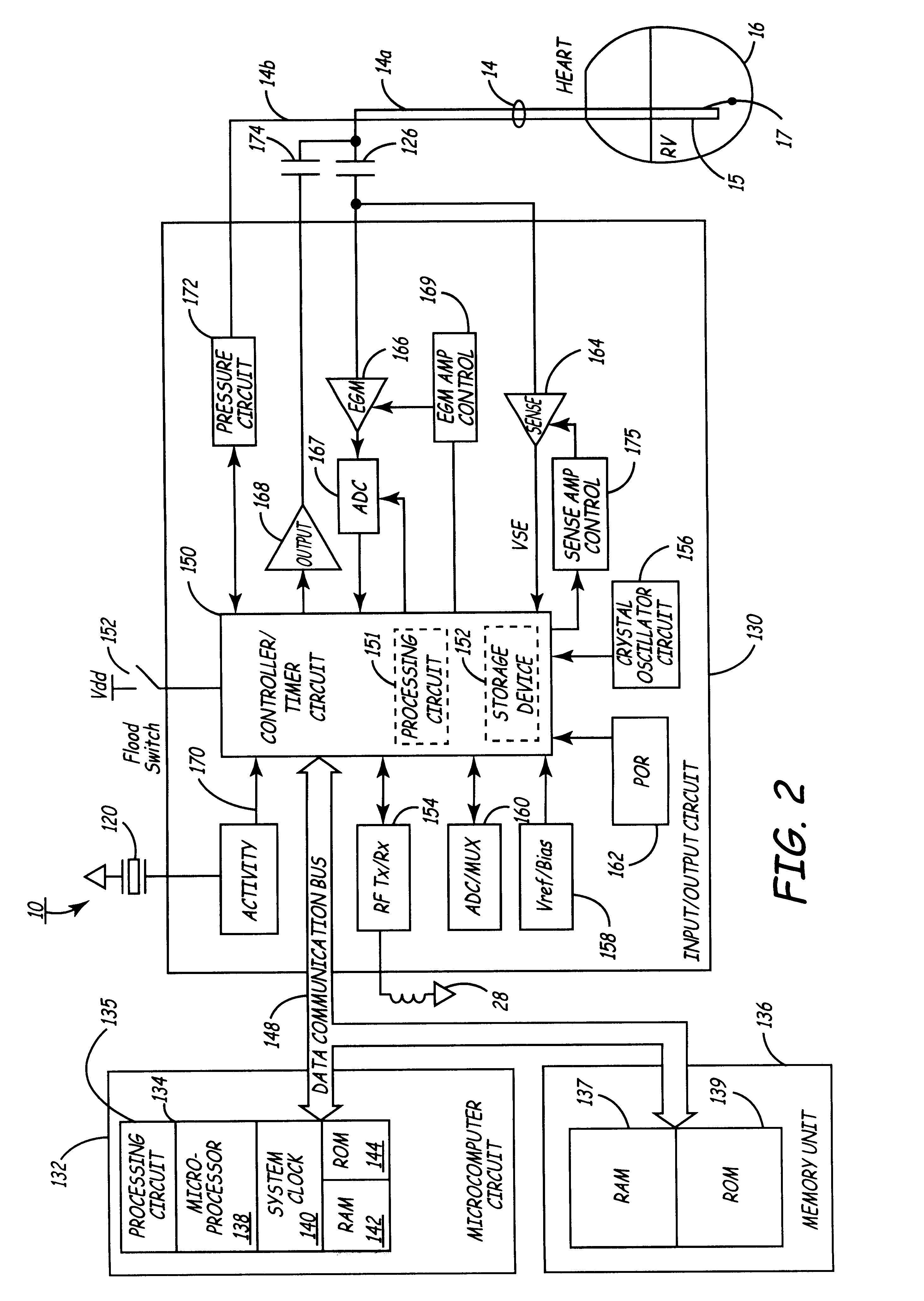
Method and apparatus for data compression of heart signals
InactiveUS6599242B1Easy to compressReliable choiceElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyData compressionElectrical polarity
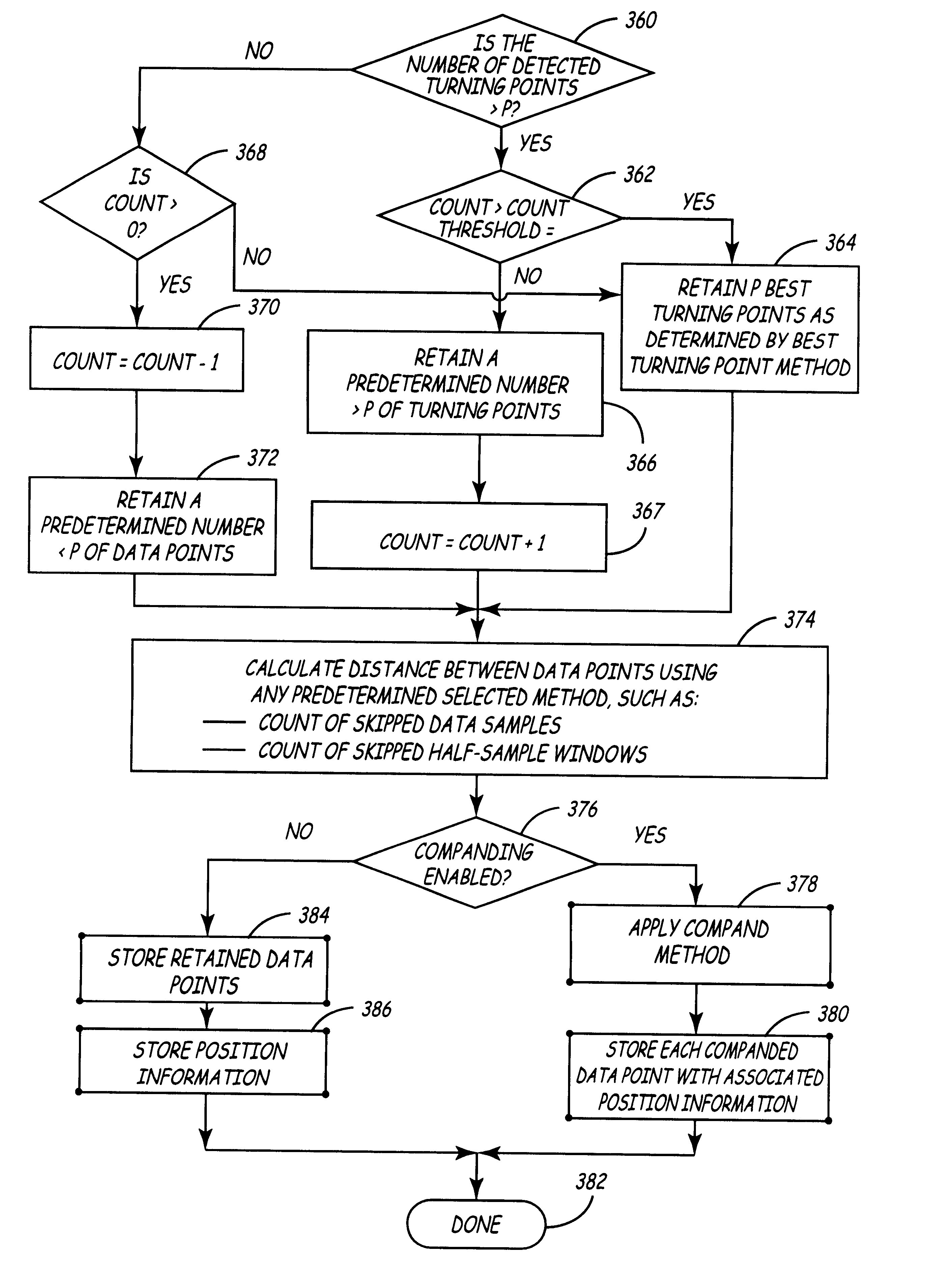
An improved turning point system and method for performing data compression is disclosed. The system improves the conventional turning point compression method by selecting a predetermined number of the "best" turning points in the sample window including data samples X0 and XN. From this sample-window, ones of the data samples X1 through X(N-1) will be identified as turning points using a selected one of a disclosed set of turning point detection methods. In one embodiment, a turning point is identified by determining that the slopes in the lines interconnecting adjacent data points have different polarities. In an alternative embodiment, a data sample XM is considered a turning point if the slope of the line between the data samples XM and X(M+1) has a different polarity as compared to the slope of the last waveform segment that was encountered that did not have a slope of zero. According to one mechanism, amplitude thresholding is used to detect whether an identified turning point is likely the result of noise such that the turning point status of the data sample should be disregarded. After data samples are identified as turning points, ones of the identified turning points are identified as the "best" turning points to be selected for retention. The best turning points may be identified by determining which waveform segment included within a sample window has the largest change of amplitude. An alternative embodiment detects which of the turning points has the greatest signal amplitude compared to a reference value. Yet another embodiment selects as the best turning point that point having an amplitude that differs the most from the amplitude of the first data sample in the sample window. Still other embodiments retain the turning point having an amplitude which is more positive, or alternatively, more negative, than the other data samples. According to one aspect of the invention, the compression ratio varies based on the frequency of the input waveform. In another embodiment, position data is retained to indicate the relative position of retained data samples as compared to the position of other retained data samples. This position data may be calculated at a frequency that is less than the frequency of the sampled data.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
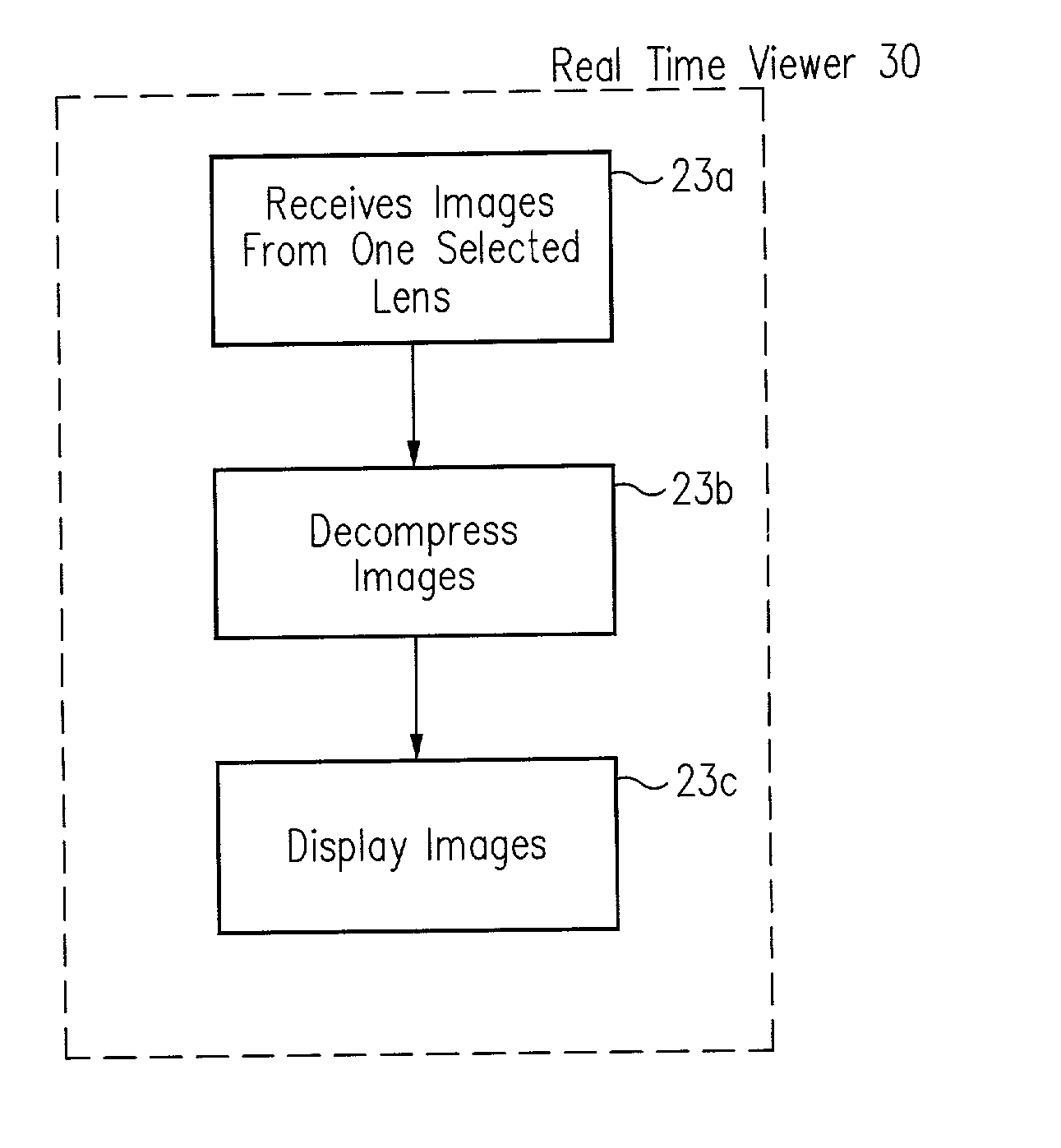
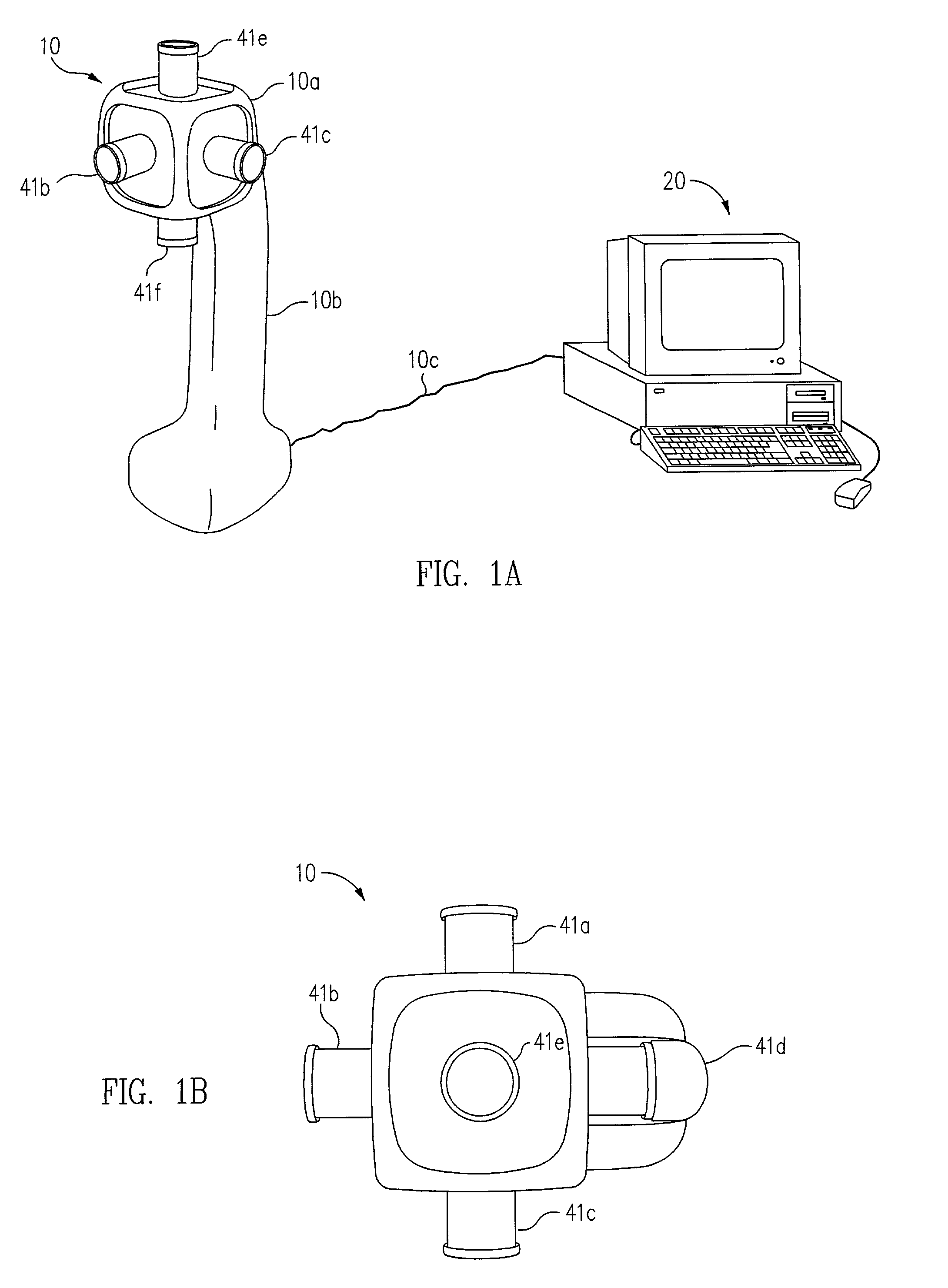
System for digitally capturing and recording panoramic movies
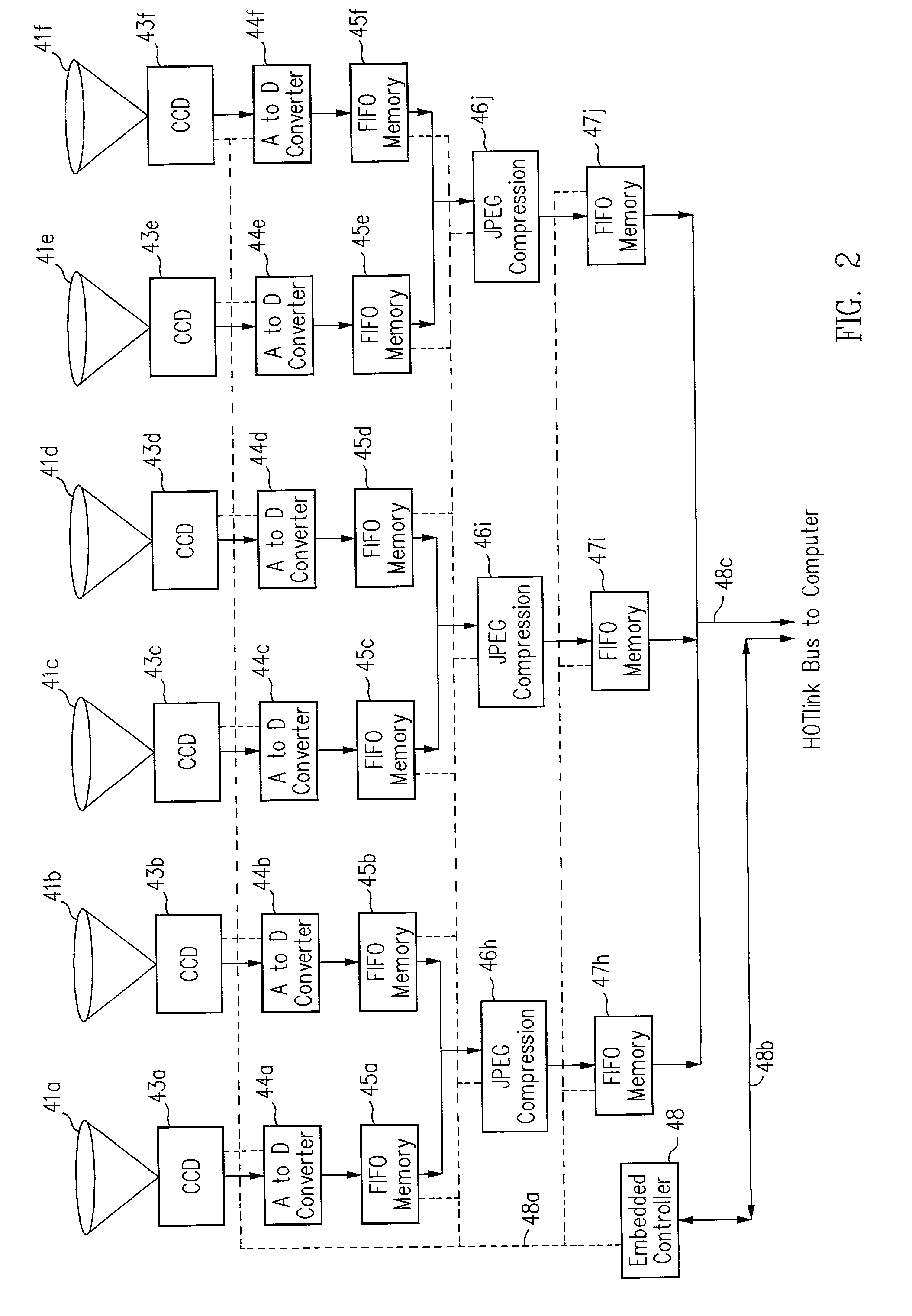
InactiveUS20020046218A1Flexible and convenient controlEffective apertureTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingCamera lensData compression
The present invention provides a very flexible, digital system for capturing and storing panoramic images using progressive scan (that is, non interlaced) technology. The system includes a digital image input device and an associated control computer. Since the image capture device is digital it can be easily and flexibly controlled by software in the control computer. The image input device has six lenses positioned on the six faces of a cube. While the image input system can have other lens configurations, the use of six lenses in a cubic configuration is optimal for a system that is used to capture a spherical panorama. The six lenses simultaneously focuses different images on six CCDs (Charge Coupled Devices). The image input device also includes an embedded controller, and data compression circuitry. The embedded controller controls the exposure time of the CCDs (i.e. the effective aperture and effective shutter speed) and reads image data from the CCDs. The image data read from the CCDs is compressed, multiplexed, and sent to the control computer. The control computer stores the images in frames, each of which have one image from each of the six lenses. Each frame includes six images that were simultaneously recorded and any associated information, such as audio tracks, textual information, or environmental information such as GPS (Global Position System) data or artificial horizon data. The control computer includes a user interface which allows a user to specify control information such as frame rate, compression ratio, gain, etc. The control computer sends control information to the embedded controller which in turn controls the CCDs and the compression circuitry. The images can be sent from the control computer to a real time viewer so that a user can determine if the correct images are being captured. The images stored at the control computer are later seamed into panoramas and made into panoramic movies.
Owner:GILBERT SCOTT +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com