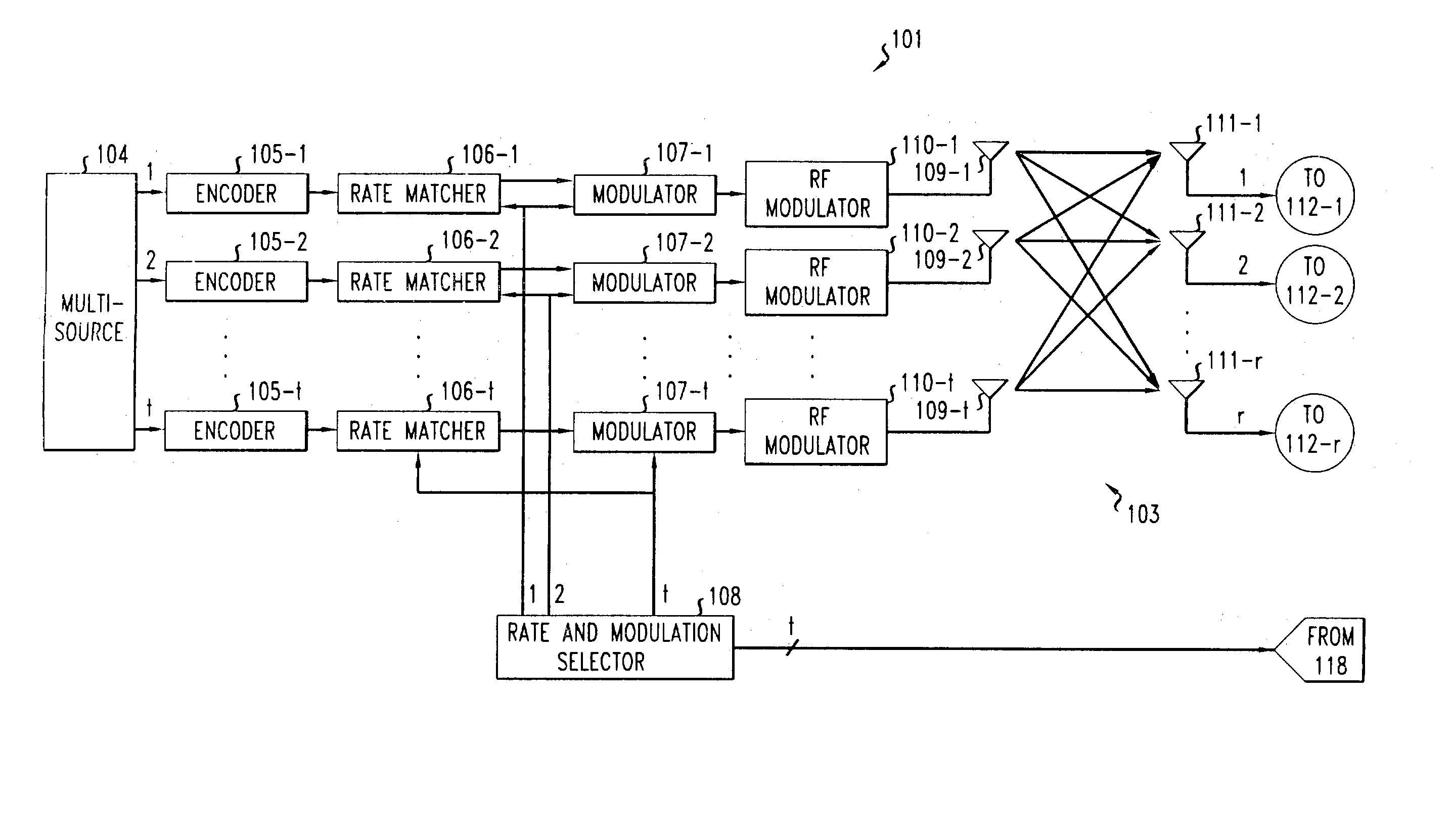
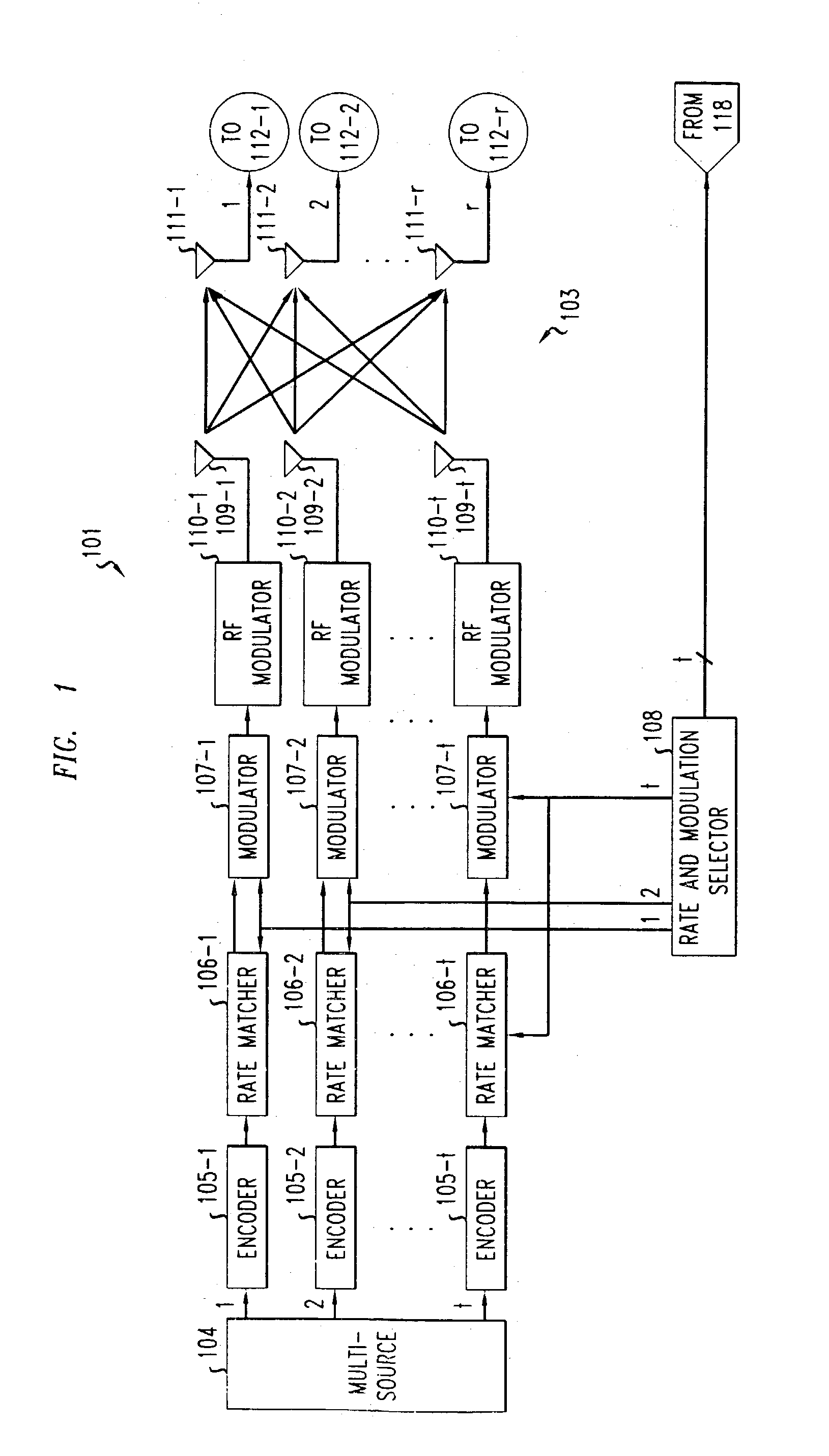
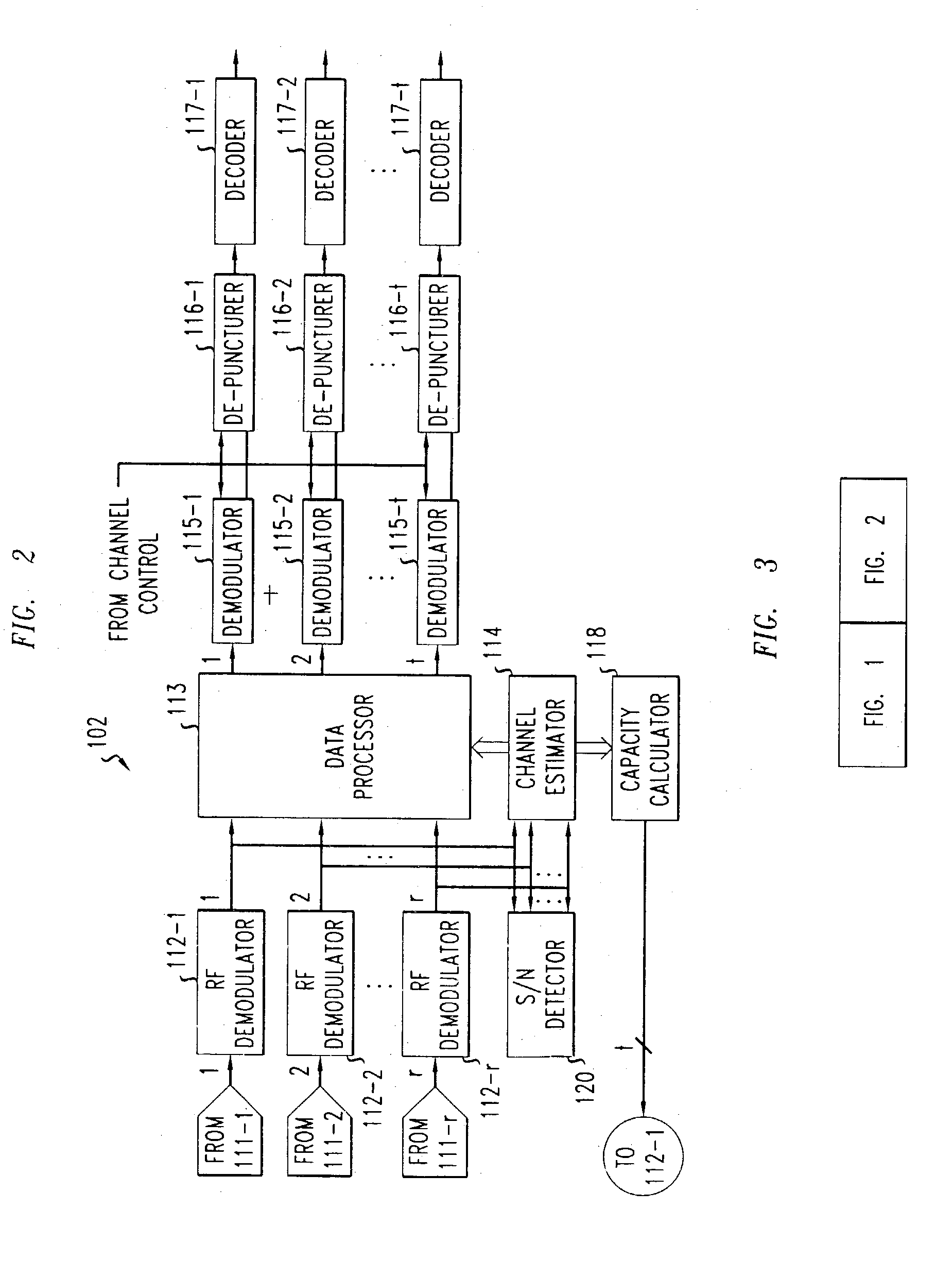
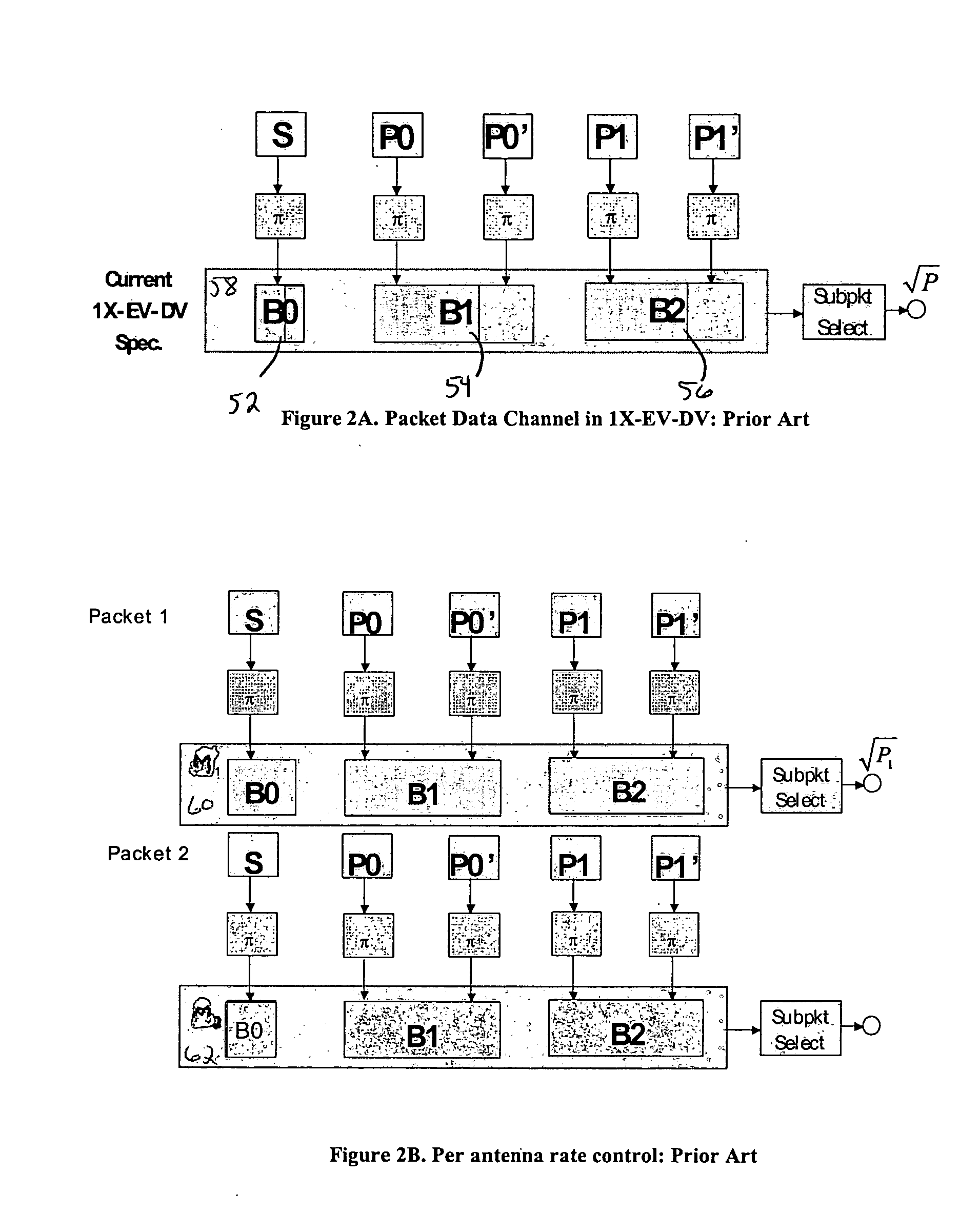
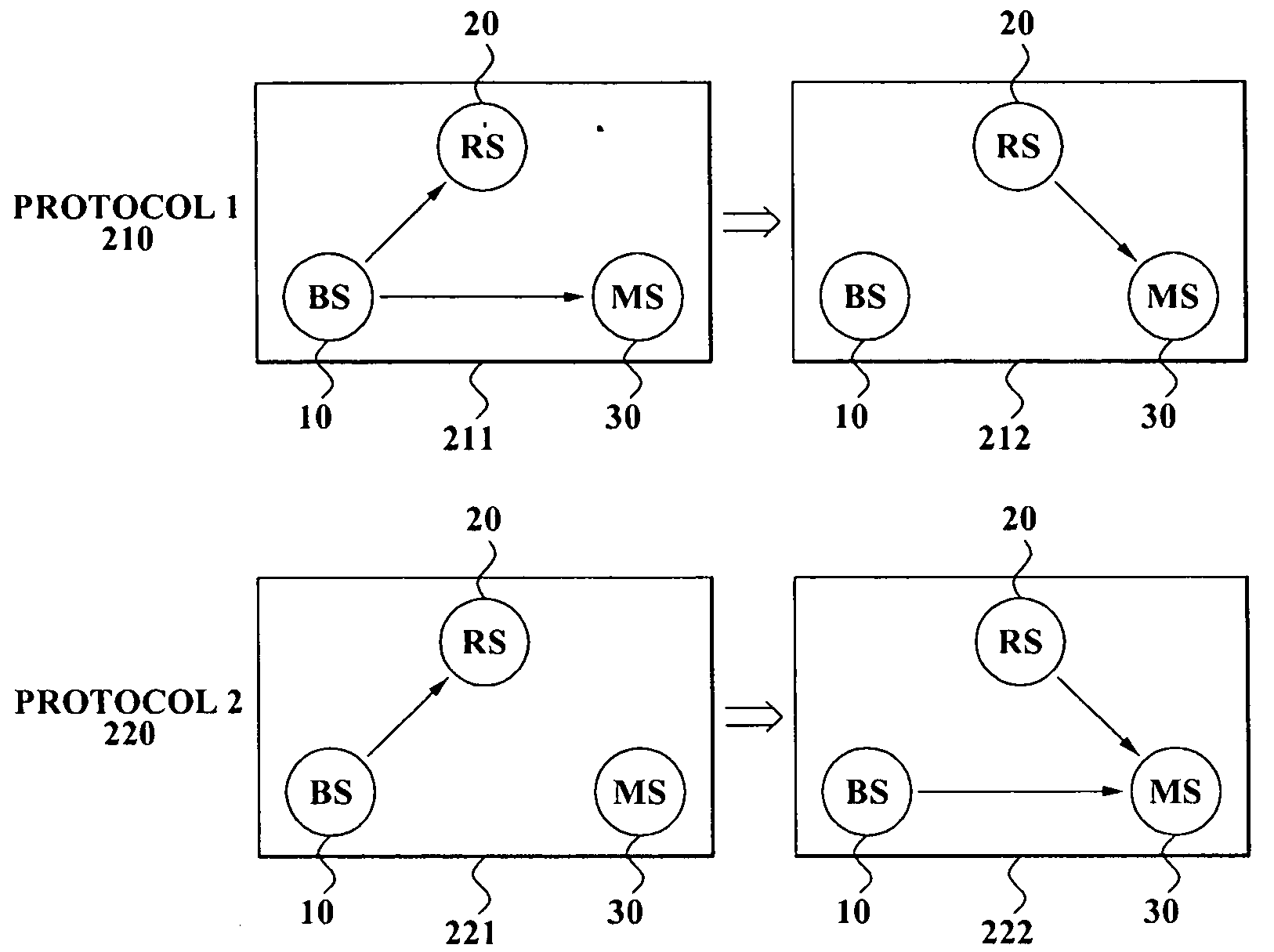
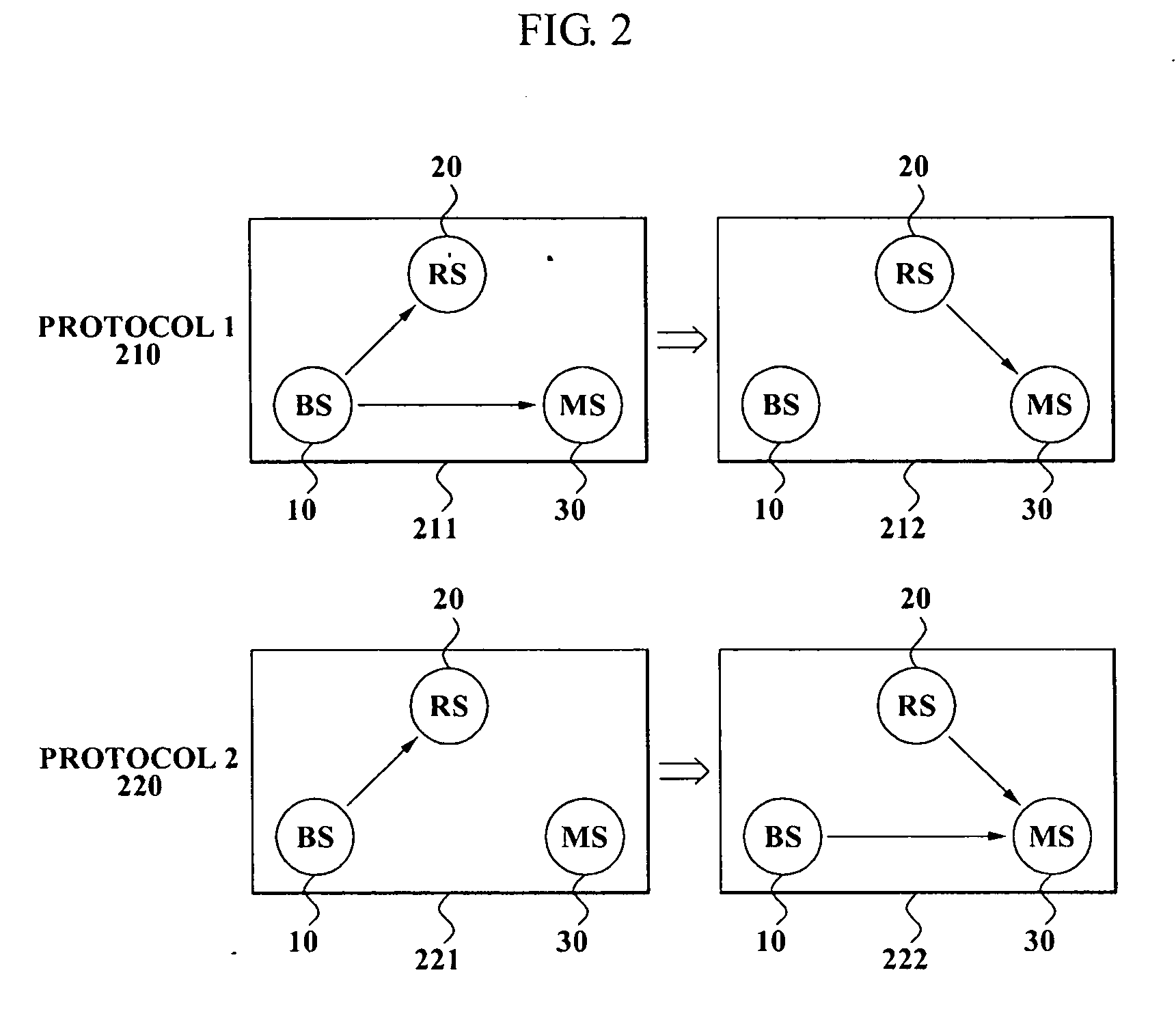
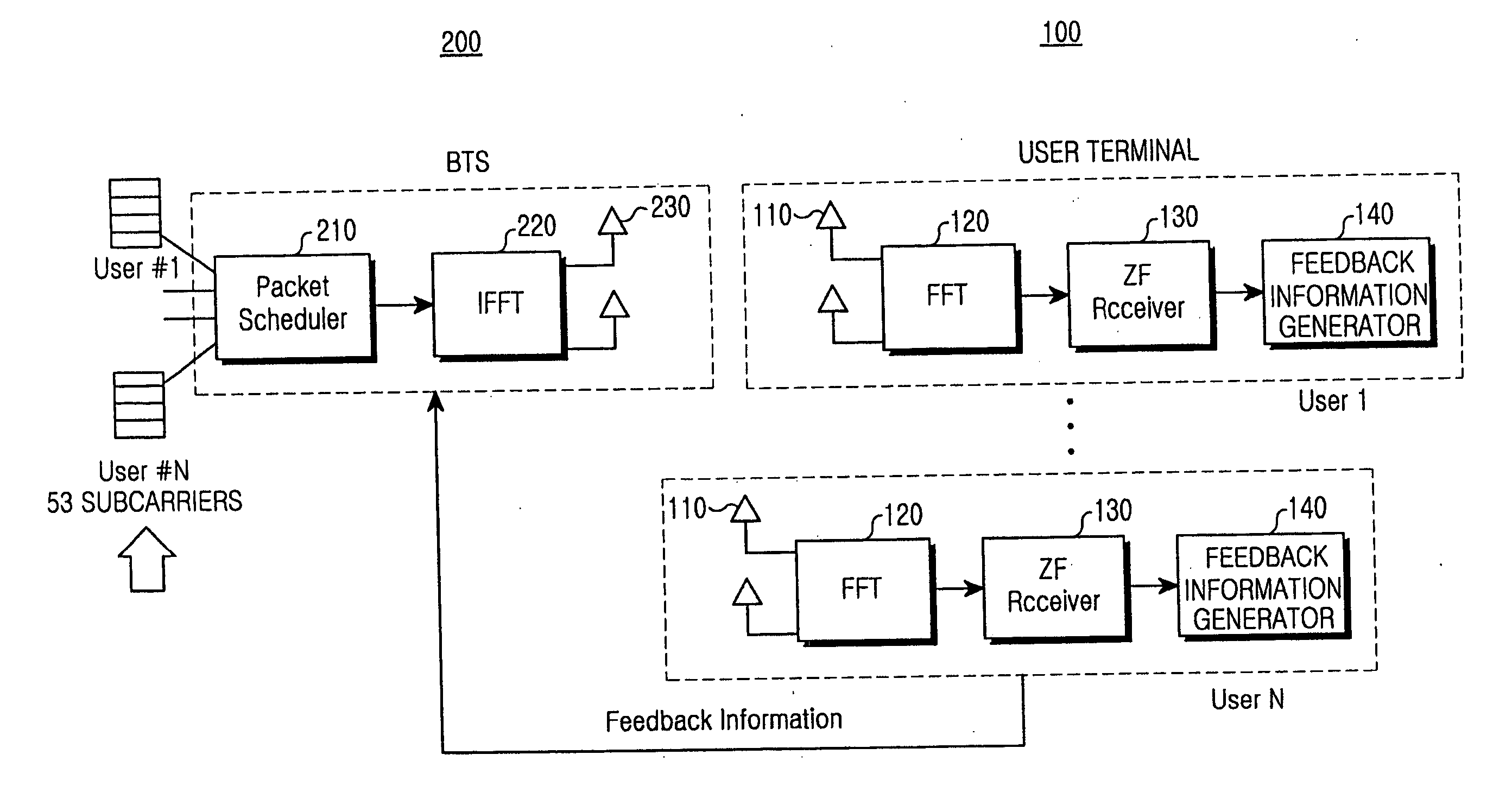
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1466 results about "Channel capacity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Channel capacity, in electrical engineering, computer science, and information theory, is the tight upper bound on the rate at which information can be reliably transmitted over a communication channel.
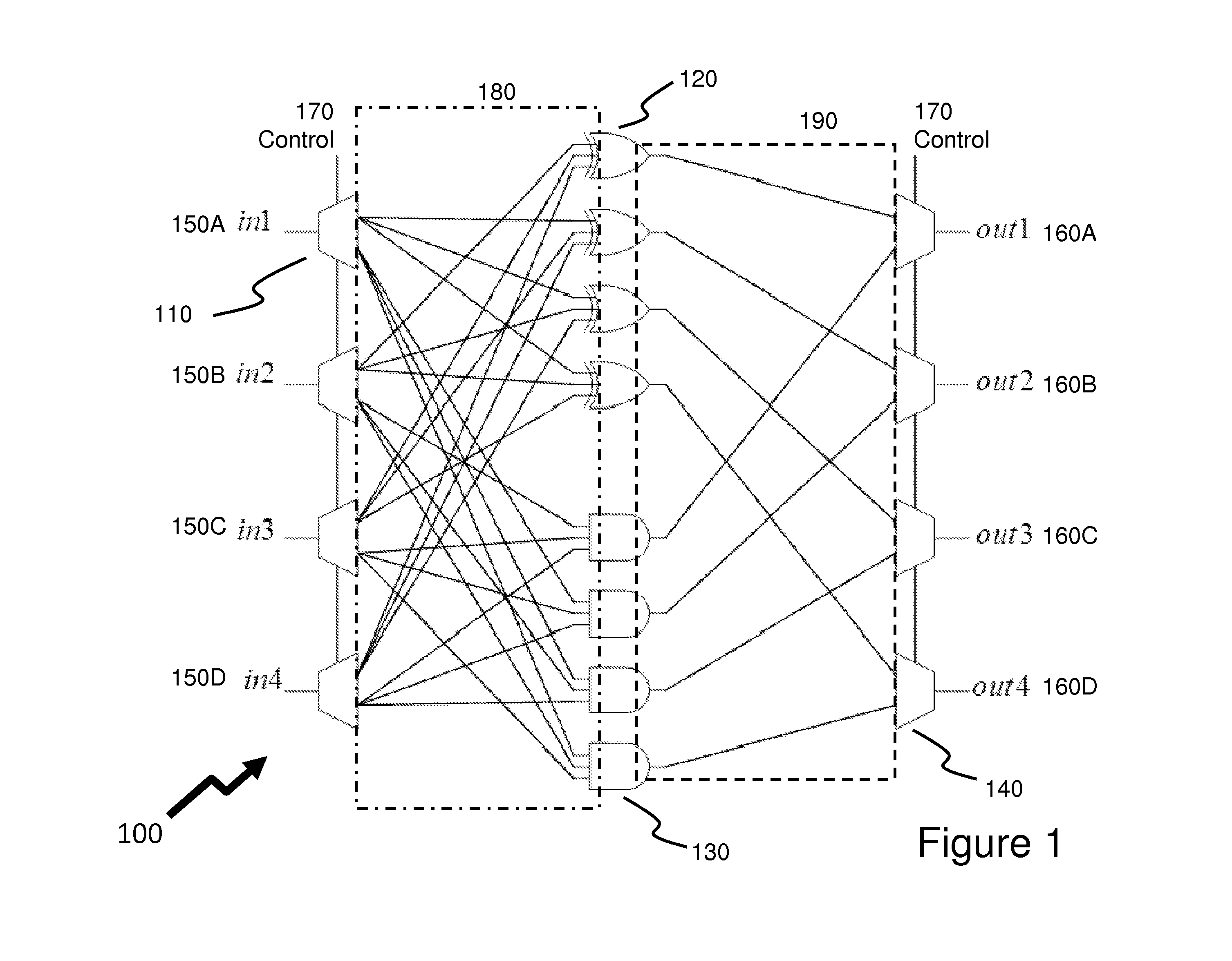
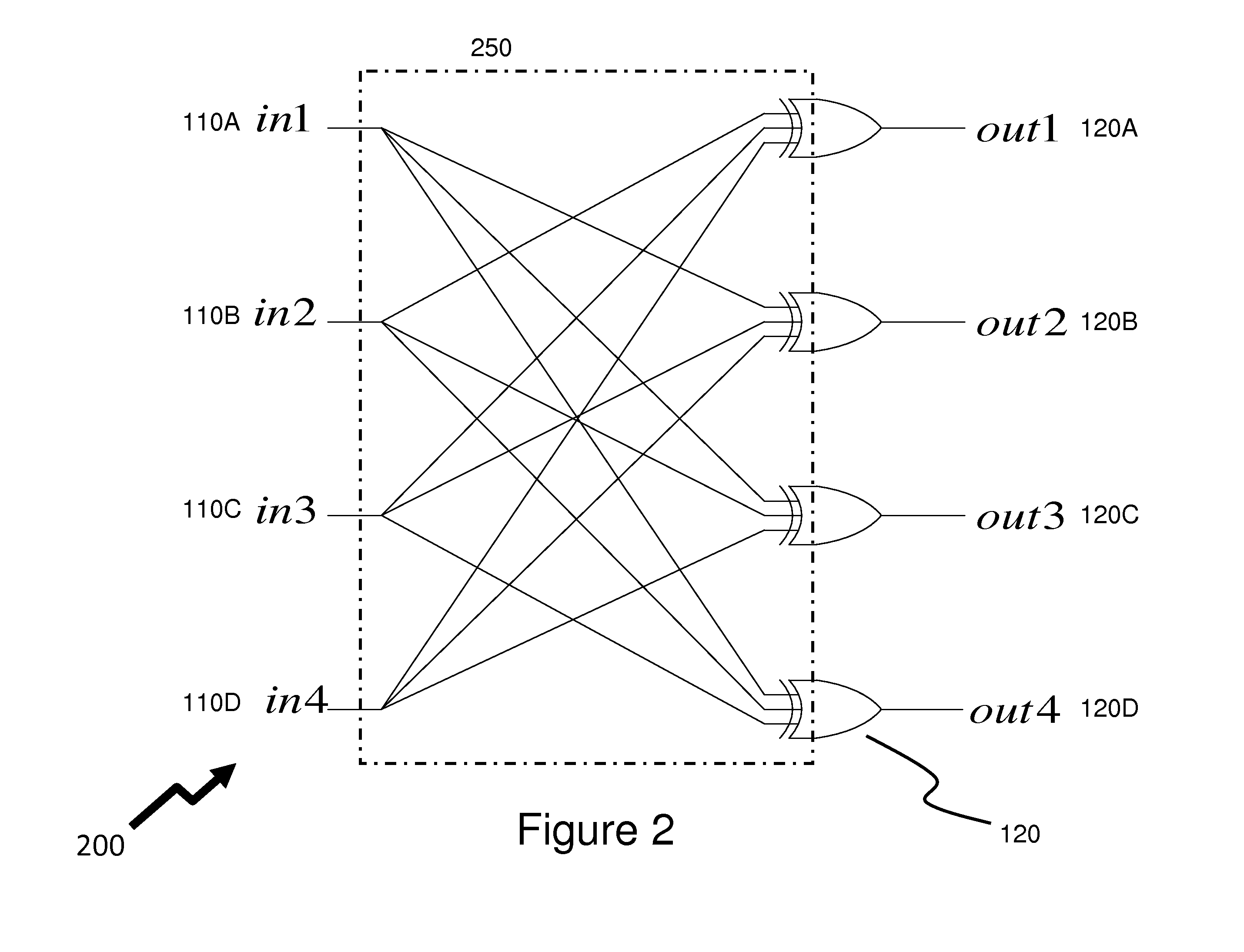
Channel equalization system and method
InactiveUS6904110B2Increase high performance and data rate capacityLow costMultiple-port networksChannel dividing arrangementsFiberEngineering
A system and method for delivering increases speed, security, and intelligence to wireline and wireless systems. The present invention increases channel capacity by using a parallel or multi-channel structure in such wireless and wireline at the edge or the core of. This new architecture of the present invention uses parallel bitstreams in a flexible way and distributed switching / routing technique, is not only to avoid the potential bottlenet of centralized switches, but also to increase speed with intelligence that is seamlessly integrating into the Fiber Optic Backbone such as WDM and SONET of the MAN / WAN network with a Real-time guarantees, different types of traffic (such as Stringent synchronous, isochronous, and asynchronous data messages) with different demands, and privacy & security of multi access and integrated services environment.
Owner:B C LEOW
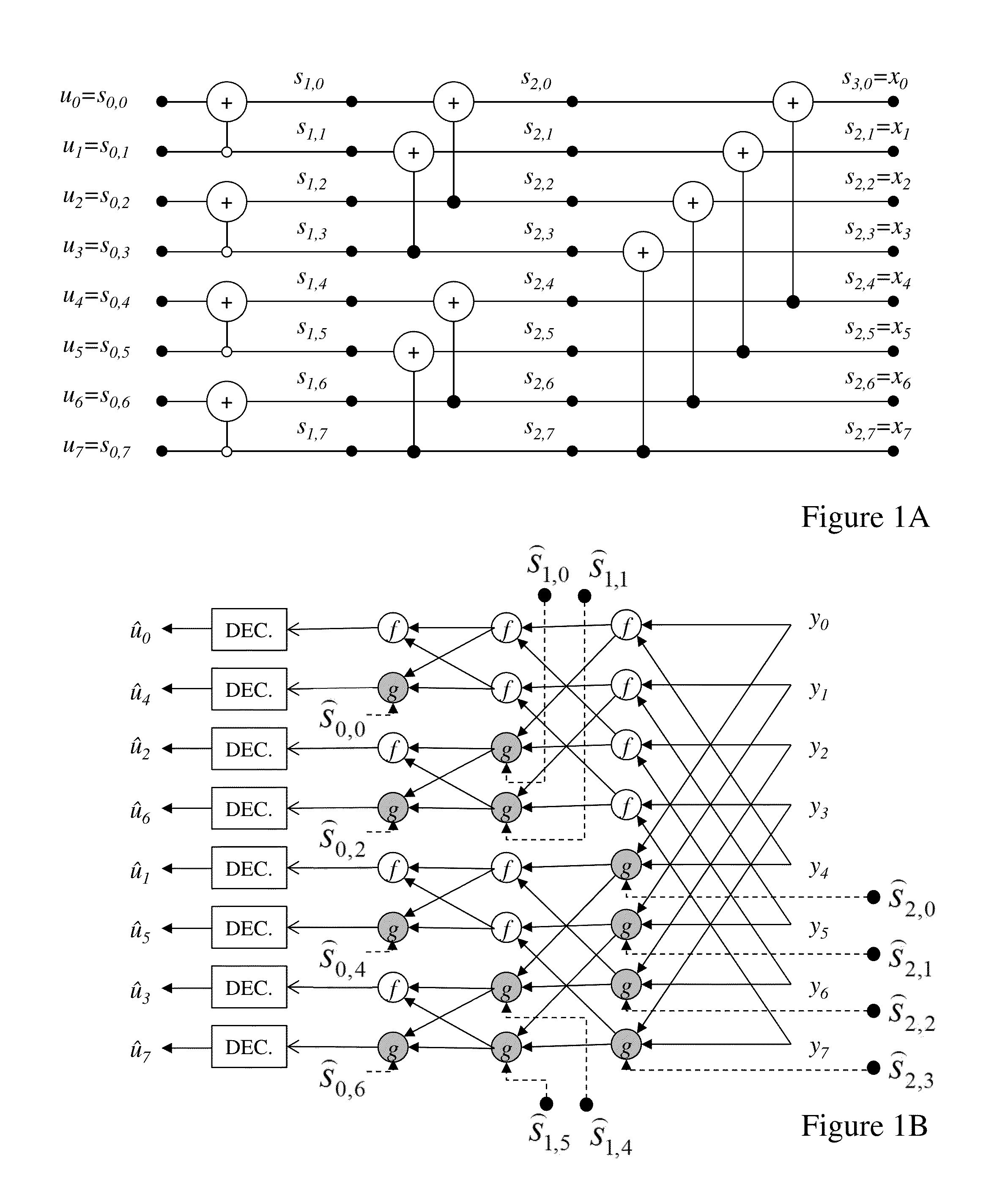
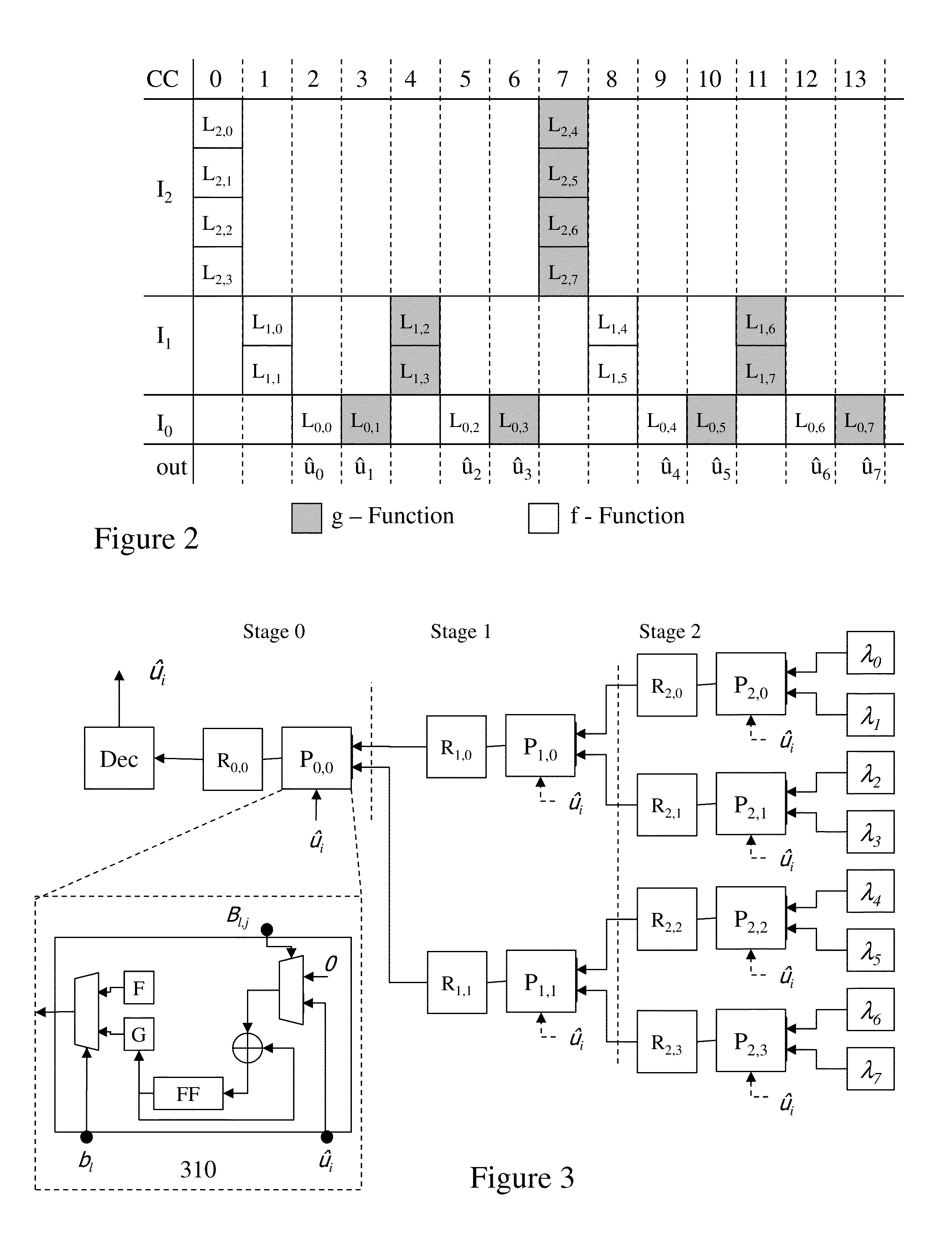
Methods and Systems for Decoding Polar Codes
ActiveUS20130117344A1Improve performanceMitigate such drawbackCode conversionError correction/detection using linear codesProcessing elementHardware implementations
Coding within noisy communications channels is essential but a theoretical maximum rate defines the rate at which information can be reliably transmitted on this noisy channel. Capacity-achieving codes with an explicit construction eluded researchers until polar codes were proposed. However, whilst asymptotically reaching channel capacity these require increasing code lengths, and hence increasingly complex hardware implementations. It would be beneficial to address architectures and decoding processes to reduce polar code decoder complexity both in terms of the number of processing elements required, but also the number of memory elements and the number of steps required to decode a codeword. Beneficially architectures and design methodologies established by the inventors address such issues whilst reducing overall complexity as well as providing methodologies for adjusting decoder design based upon requirements including, but not limited to, cost (e.g. through die area) and speed (e.g. through latency, number of cycles, number of elements etc).
Owner:THE ROYAL INSTITUTION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF TECH MCGILL UNIV +1
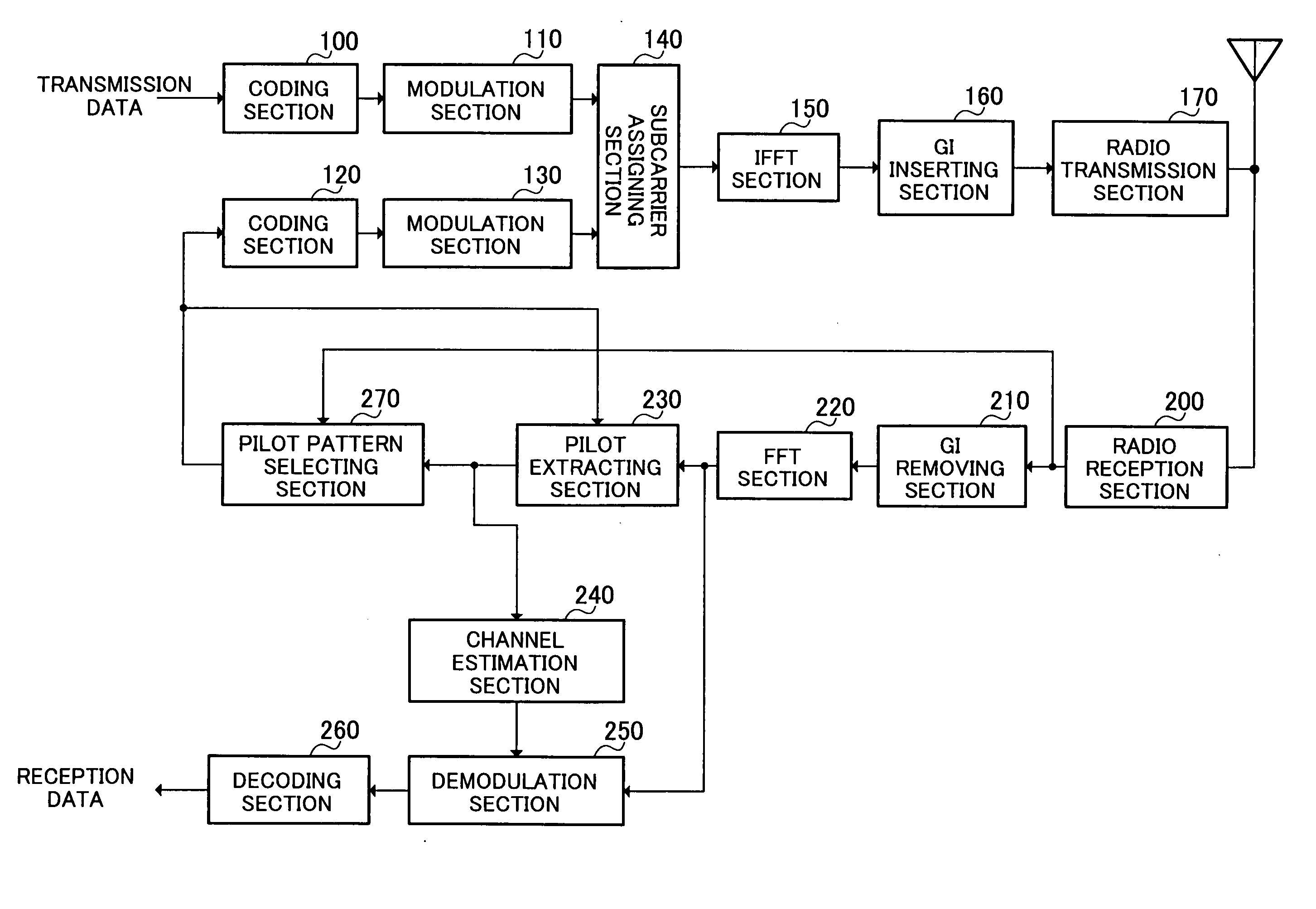
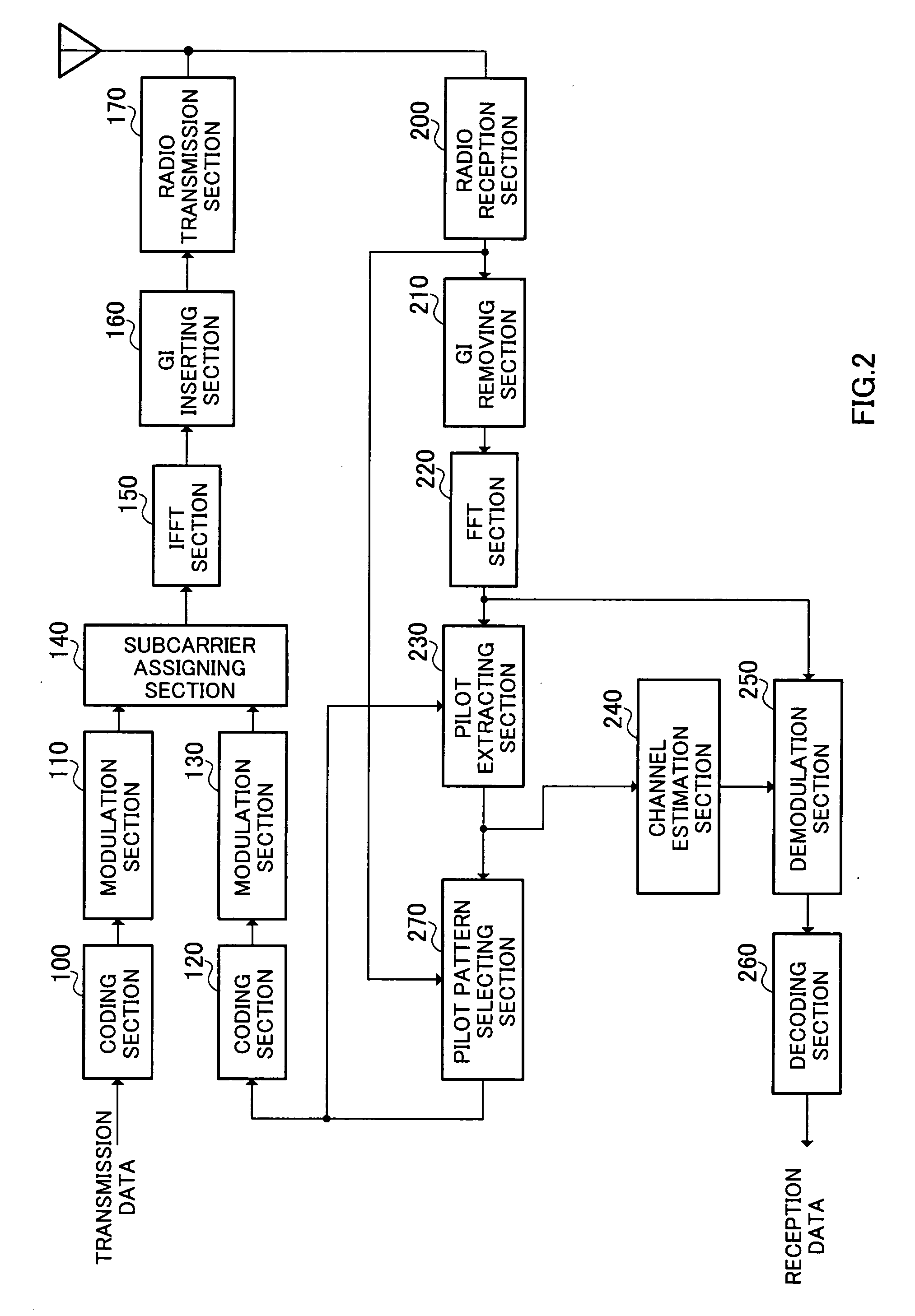
Radio communication apparatus and pilot symbol transmission method
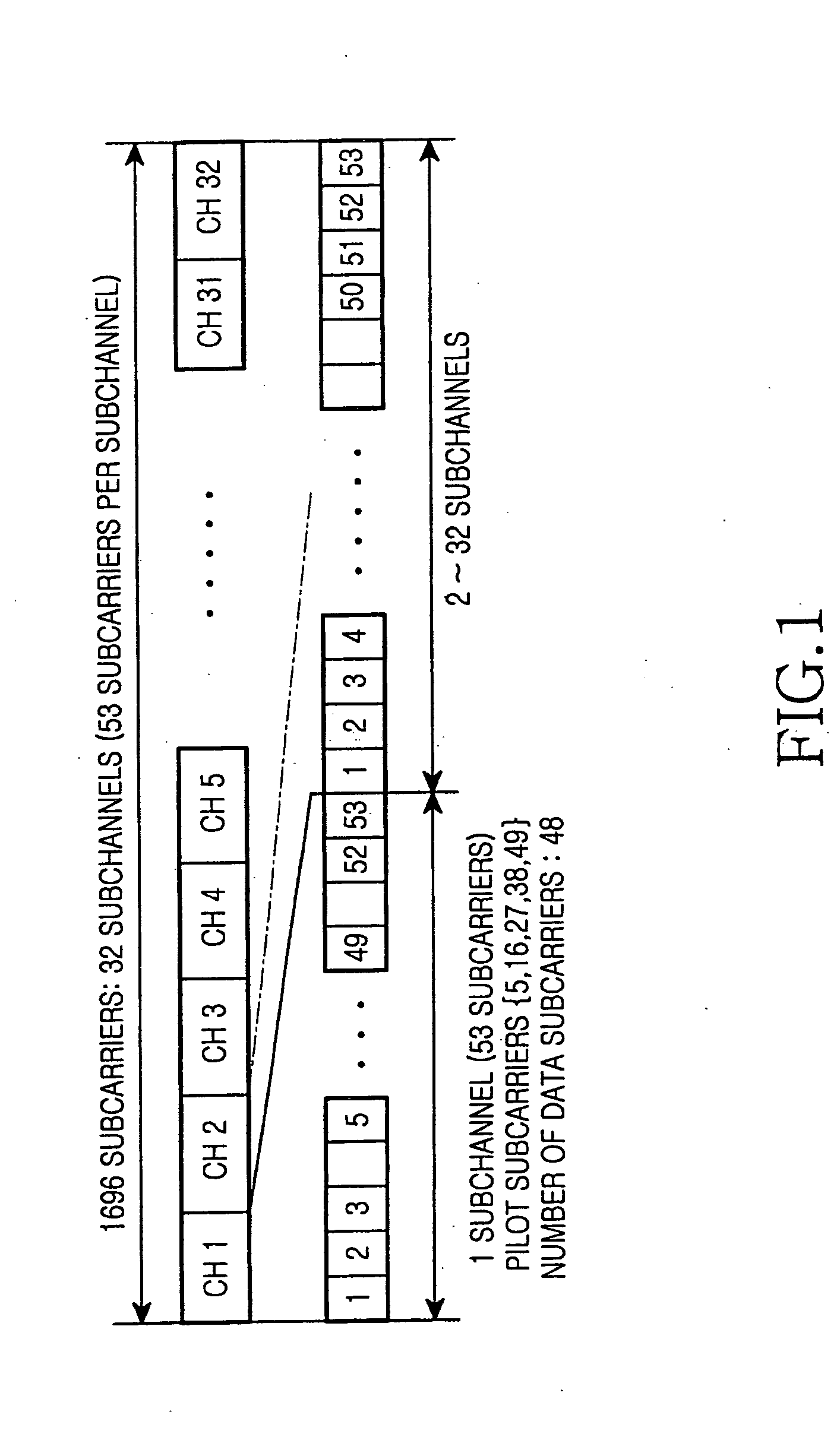
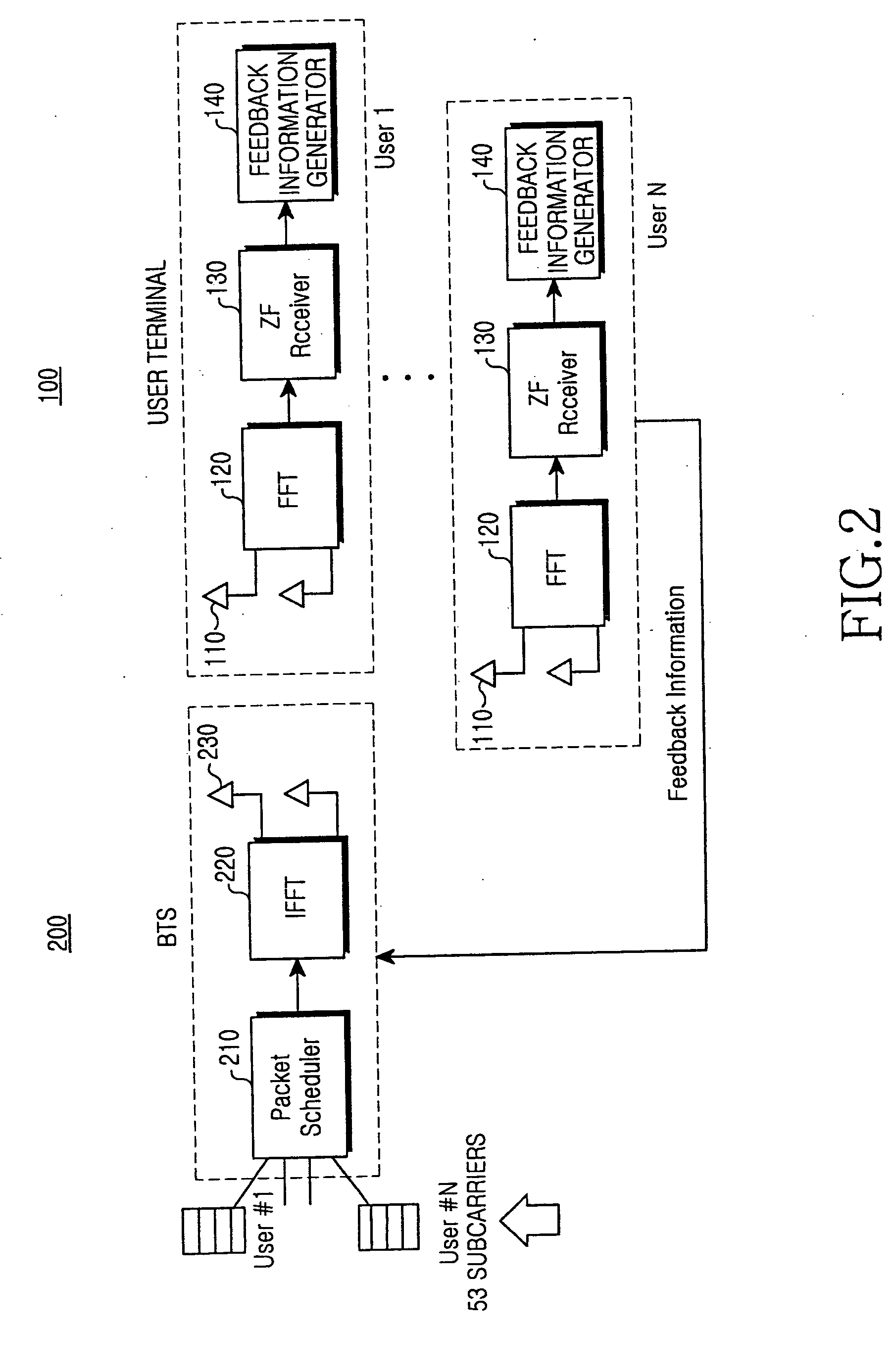
ActiveUS20060172704A1Channel capacity can be to minimumGuaranteed normal transmissionTransmission path divisionRadio transmissionEngineeringMobile station
A radio communication apparatus is disclosed that enables the influence of the feedback information on the channel capacity to be kept to the minimum without reducing the transmission efficiency of information by transmission of pilot symbol. In the apparatus, a delay dispersion measuring section (272) generates a delay profile using the received signal, and measures delay dispersion indicative of dispersion of delayed versions. A moving speed estimating section (274) estimates moving speed of a mobile station apparatus that transmits a pilot symbol based on the variation in reception power of the pilot symbol. An other-cell interference measuring section (276) measures other-cell interference caused by signals transmitted in cells except the cell to which the apparatus belongs. Corresponding to the delay dispersion, moving speed and other-cell interference, a pilot pattern information generating section (278) selects a pilot pattern such that placement of pilot symbol is optimal in a frame, and generates the pilot pattern information.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
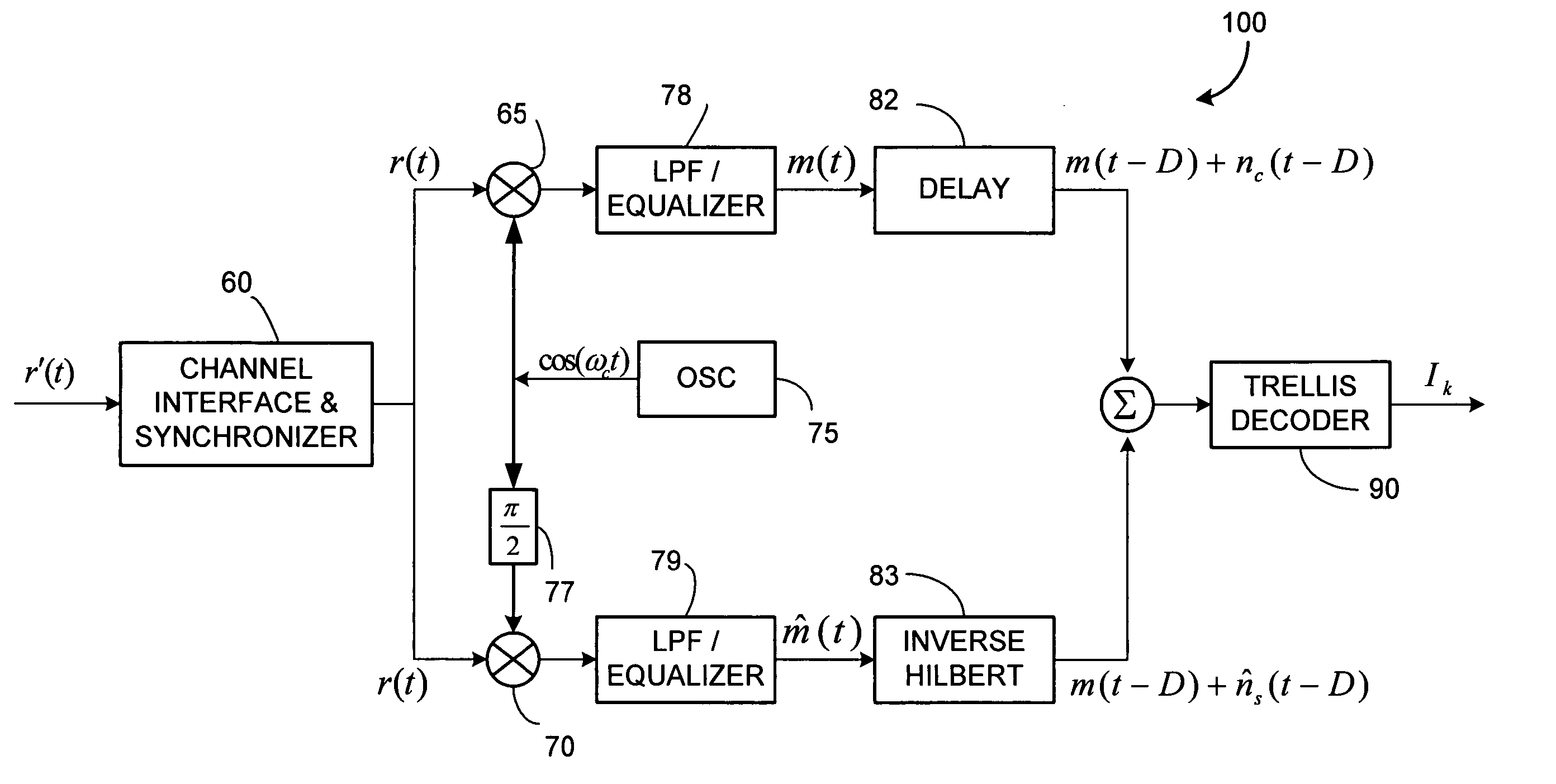
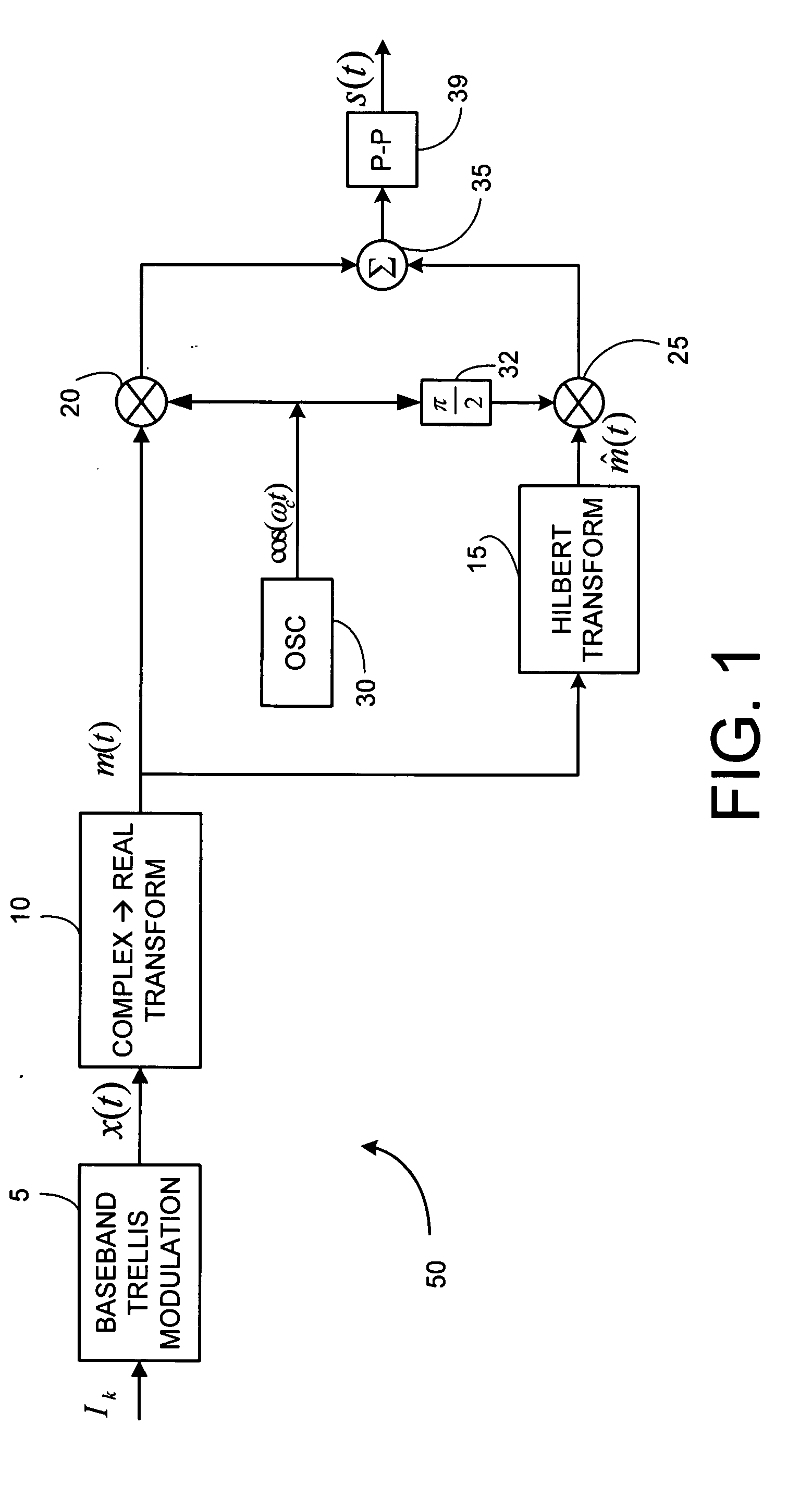
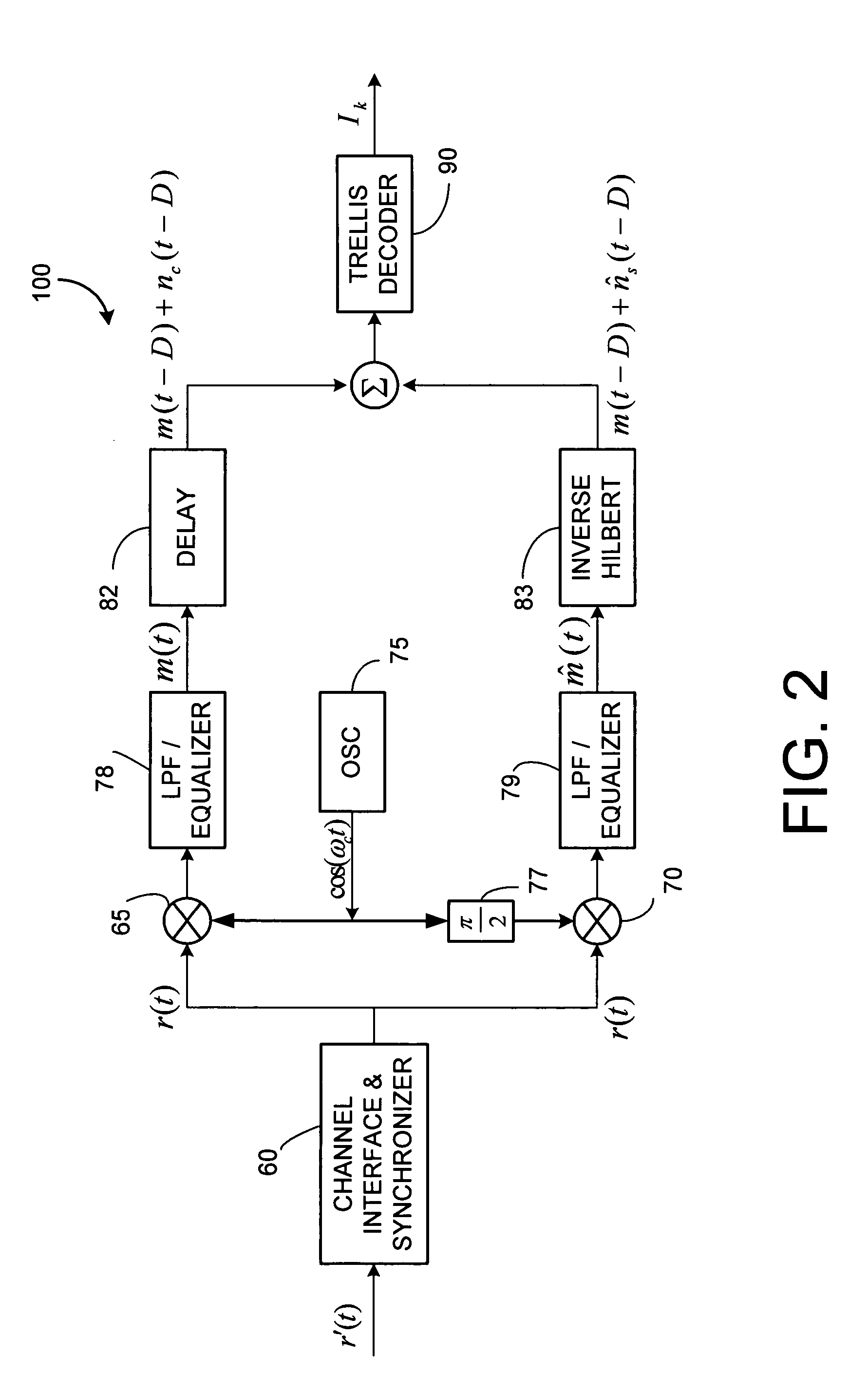
Single sideband and quadrature multiplexed continuous phase modulation
InactiveUS20070092018A1Error preventionSecret communicationCommunications systemFrequency-division multiplexing
A class of bandwidth reduction techniques are used develop a broad class of modulation types collectively called SSB-FM. These signals can be used to construct communication systems that provide bandwidth-normalized performance gains of 10 dB or more when compared to popular prior art modulation methods. An aspect of the invention involves mapping trellis paths in a complex signal space onto corresponding real-valued trellis signals with desirable spectral properties. The invention can be used map continuous phase modulated (CPM) signals onto simpler amplitude-modulated trellis signals having double the channel capacity of prior art CPM signals. Multi-amplitude signaling and frequency division multiplexing may also be incorporated to further accommodate more information per symbol.
Owner:TRELLIS PHASE COMM LP
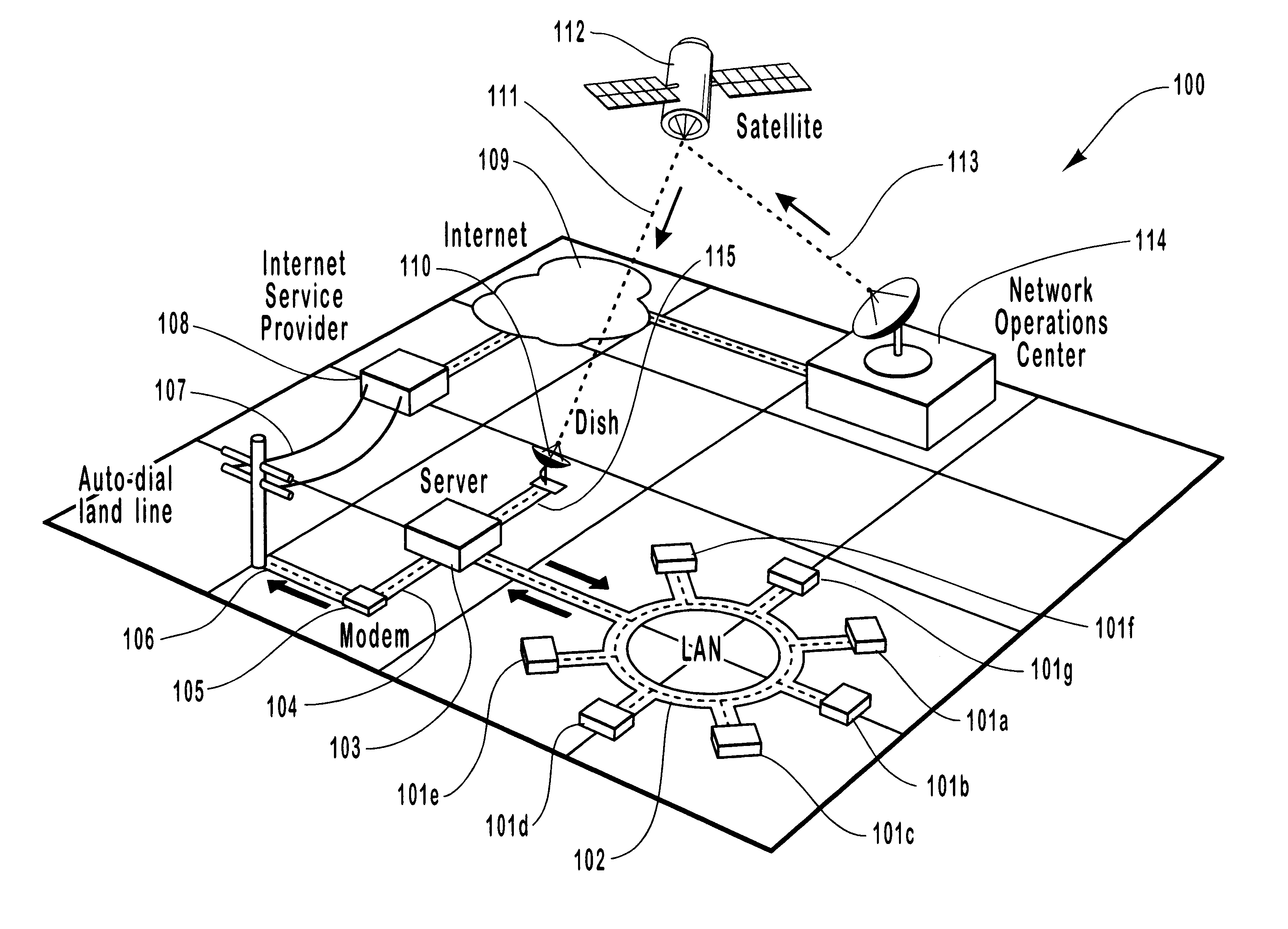
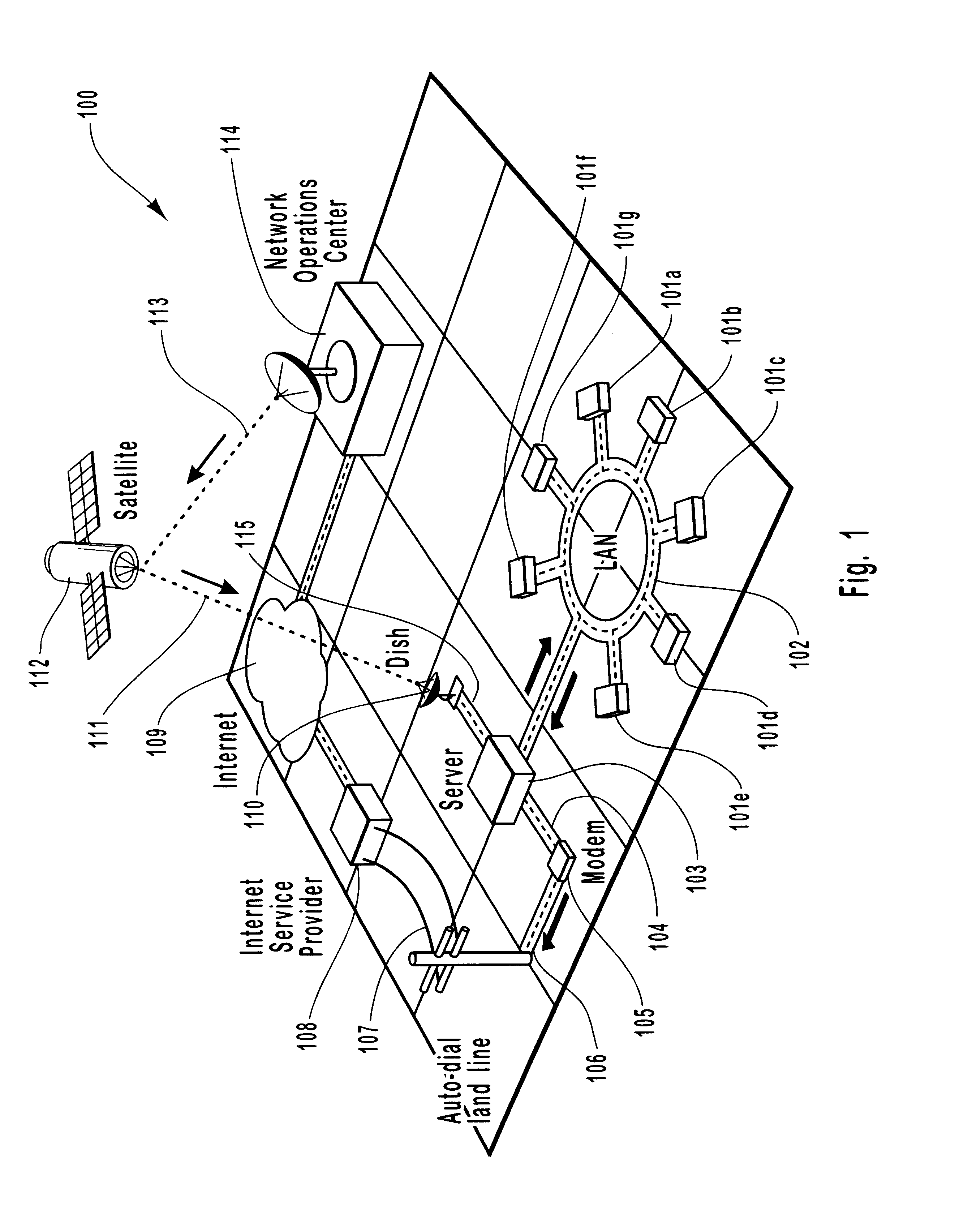
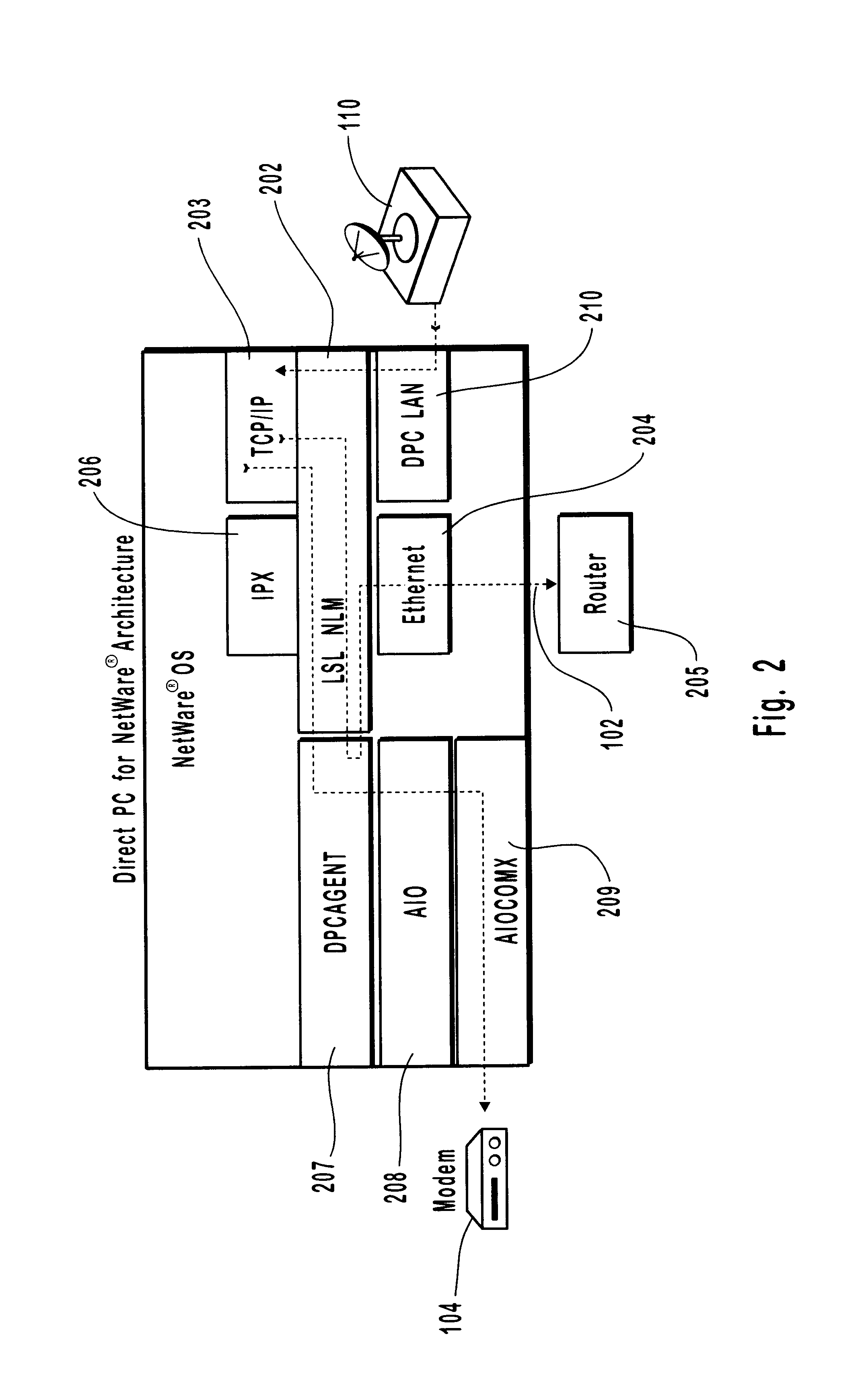
Method and system for asymmetric satellite communications for local area networks
InactiveUS6205473B1Efficient communicationIncrease speedError preventionTransmission systemsNon symmetricLow speed
A method and system for providing high-speed, satellite-based information delivery is described. Improved communication channel efficiency is accomplished by employing an asymmetric data flow. The high bandwidth channel capacity of digital satellite systems is used for the download of large volumes of data. While relatively low speed communication channels are used for upstream data requests. The use of separate channels for upstream data and downloaded data provides an increased efficiency of use for typical internet and other electronic information service subscribers. A typical user in such systems generally makes relatively short information requests. These requests are then followed by large amounts of information being transferred to the user's computer in response to the request. The volume of data being downloaded often causes a capacity overload of typically used land lines. This invention solves this problem, without becoming prohibitively expensive, by employing digital satellite dish receivers to receive the high volume of downloaded data and using the relatively low speed communication channels low volume upstream requests. Moreover, this invention is designed to interface with all common communication devices as well as being designed to operate on and with all common computing platforms.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
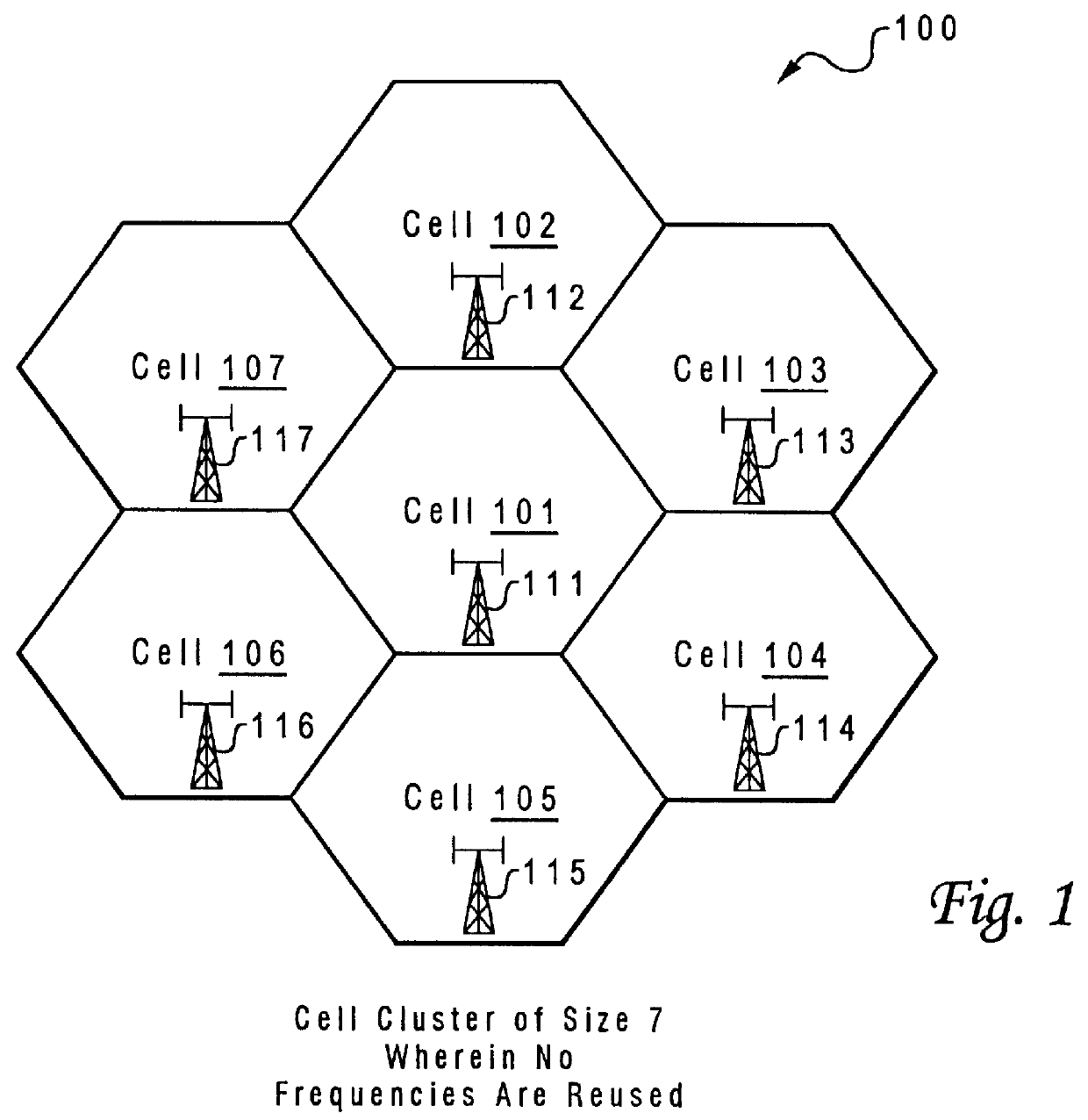
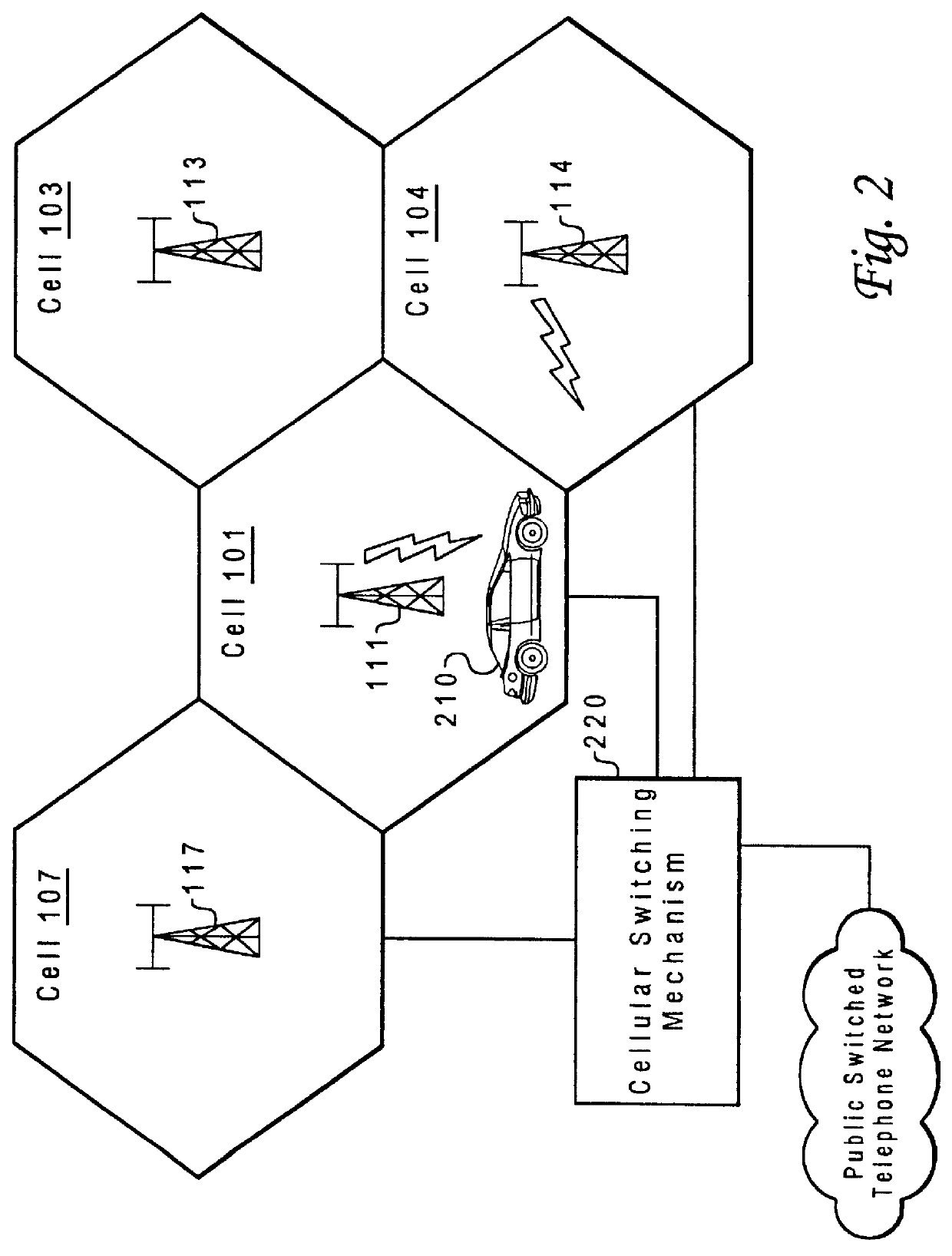
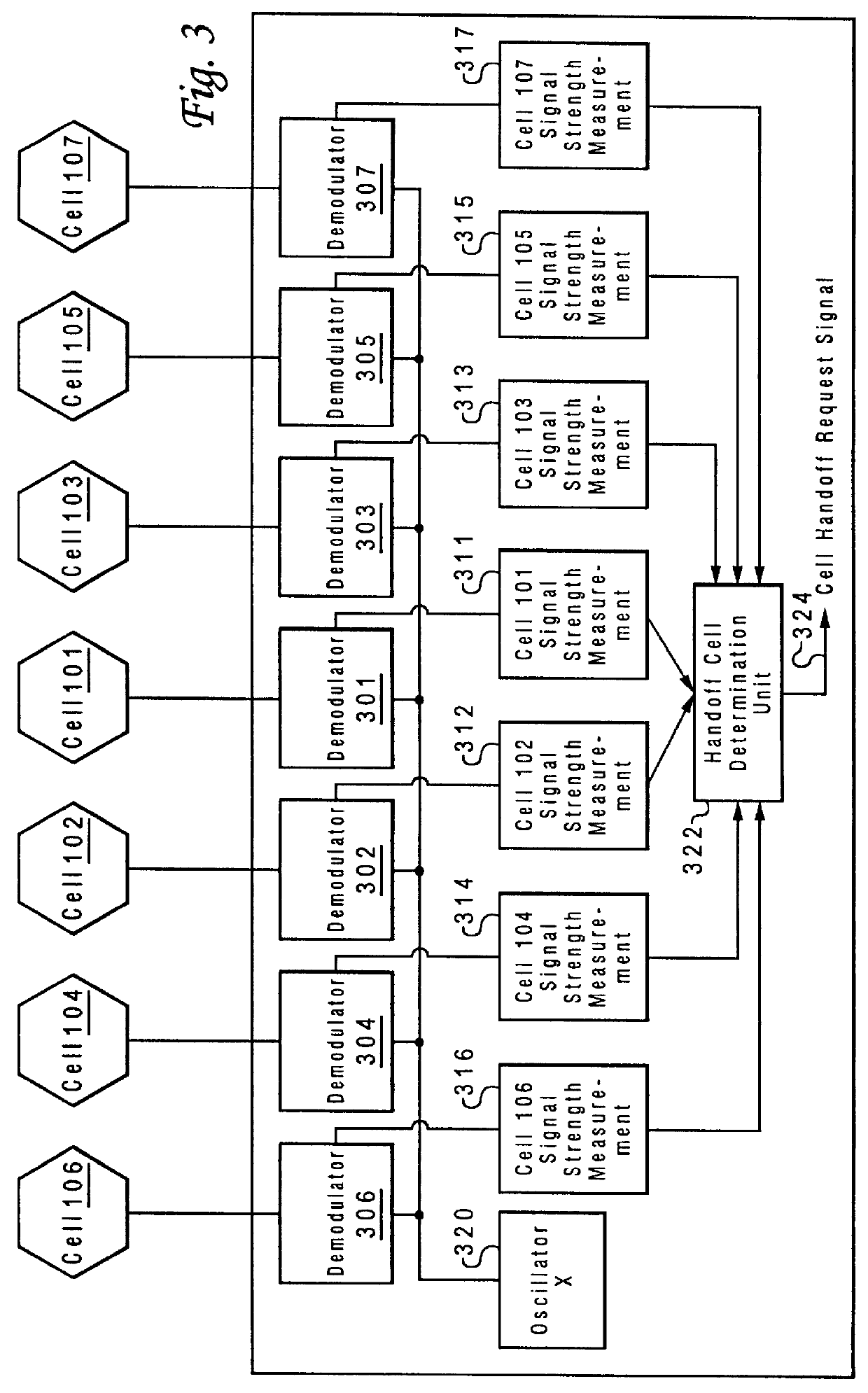
Method and system for assuring near uniform capacity and quality of channels in cells of wireless communications systems having cellular architectures
InactiveUS6011970AMaximized cellular concept of frequency reuseReduce power outputRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringCellular architectureSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method and system for use with wireless communication systems having a cellular architecture with at least a first and a second cell. The method and system provided ensure near uniform capacity and quality of channels within the second cell via the following steps. The noise signal power in unused data channels within the second cell is monitored. When a request for channel access is received, a determination is made whether the request for channel access is either a request for handoff from the first cell into the second cell, or not. In the event that the request is not a request for handoff, a determination is made whether idle channels exist to satisfy the request for channel access. In the event of a determination either that the request for channel access is a request for handoff, or both that the request is not a request for handoff and that idle channels exist to satisfy the request, a measured received signal power of a mobile unit subscriber unit making the request is determined. One of the unused channels in the second cell is then preferentially assigned to the mobile subscriber unit where such preference in assigning is to assign a channel, provided that a signal to noise ratio calculated upon the monitored received signal power and the monitored noise signal power of the preferentially assigned noisy channel meets or exceeds a required signal to noise ratio.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
MIMO communications
ActiveUS20050085195A1Increase capacity ratioIncrease channel capacitySpatial transmit diversityError preventionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Communications system
The present invention allows a wireless communication system, such as a base station, to select N antennas from an associated group of M antennas for transmitting multiple streams of data to a given user. Based on the channel conditions between the M antennas of the wireless communication system and the multiple antennas at the receiver, the N antennas to use for transmission are selected to enhance channel capacity, signal-to-noise ratios, or a combination thereof. The channel conditions are measured at the receiver, and may be sent back to the wireless communication system for processing or may be processed at the receiver, wherein instructions are transmitted back to the wireless communication system to control antenna selection.
Owner:APPLE INC
MIMO communications
ActiveUS7120395B2Increase capacityRaise the ratioSpatial transmit diversityError preventionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Communications system
The present invention allows a wireless communication system, such as a base station, to select N antennas from an associated group of M antennas for transmitting multiple streams of data to a given user. Based on the channel conditions between the M antennas of the wireless communication system and the multiple antennas at the receiver, the N antennas to use for transmission are selected to enhance channel capacity, signal-to-noise ratios, or a combination thereof. The channel conditions are measured at the receiver, and may be sent back to the wireless communication system for processing or may be processed at the receiver, wherein instructions are transmitted back to the wireless communication system to control antenna selection.
Owner:APPLE INC
Systems and methods for autonomously determining network capacity and load balancing amongst multiple network cells
A networked computing system including multiple network base stations, user equipment, a network resource controller (NRC), and a data communications network facilitating communications amongst all devices of the networked computing system. The NRC determines a current radio channel available capacity based on a user load associated with regional user equipment, and then forecasts a maximum radio channel capacity based on the current radio channel available capacity. The NRC may be a network base station and it may determine a number of additional user equipment it can support as a component of the forecast maximum radio channel capacity. The NRC / base station may be further configured to determine a handover threshold utilizing the forecast maximum radio channel capacity, and when the NRC base station's number of users exceeds the handover threshold, one or more user equipment may be handed over to a second network base station with better service capacity.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
MIMO communication system and method capable of adaptive user scheduling
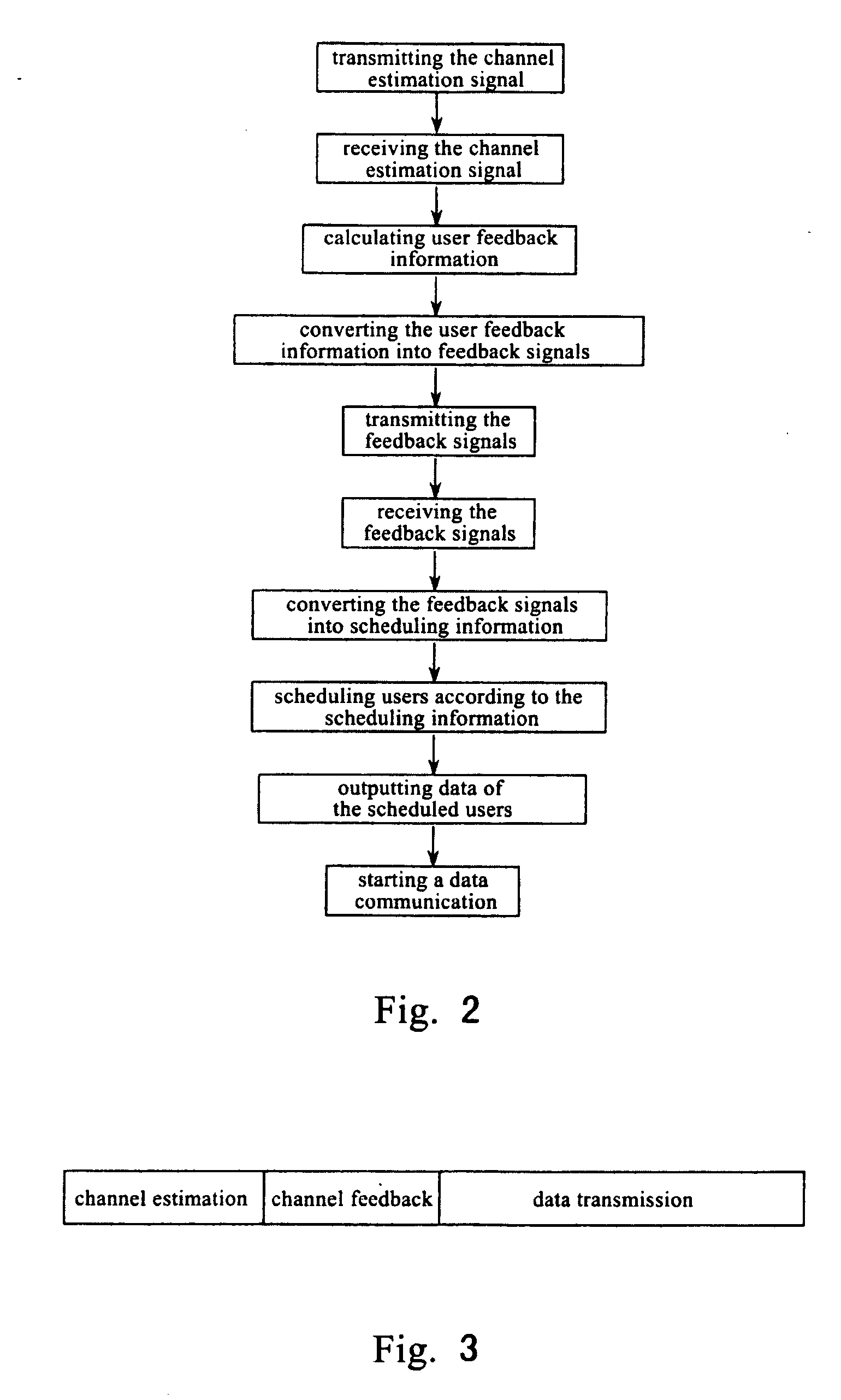
InactiveUS20060146755A1Simplify complexityStability of the communicationPolarisation/directional diversityMultiplex communicationData streamSelf adaptive
A MIMO communication system capable of adaptive user scheduling. The MIMO communication system comprises a transmitting terminal, which sends data frames containing at least channel estimation signal and user data, and at least one receiving terminal, which recovers the user data and generates corresponding feedback information. The feedback information comprises an optimal transmitting antenna set dedicated to the receiving terminal, the achievable channel capacity by each antenna within the antenna set, and the degradation factors caused by each of other unselected antennas to each of the selected antennas. Depending on the feedback information, the transmitting terminal generates scheduling information based on which the adaptive user scheduling is conducted. The scheduling information comprises the scheduled users, number of data streams supported by each scheduled user, and the corresponding transmitting antenna for each of the data streams. The MIMO system can achieve the optimal channel capacity through adaptive user scheduling.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Methods for efficient bandwidth scaling of compressed video data
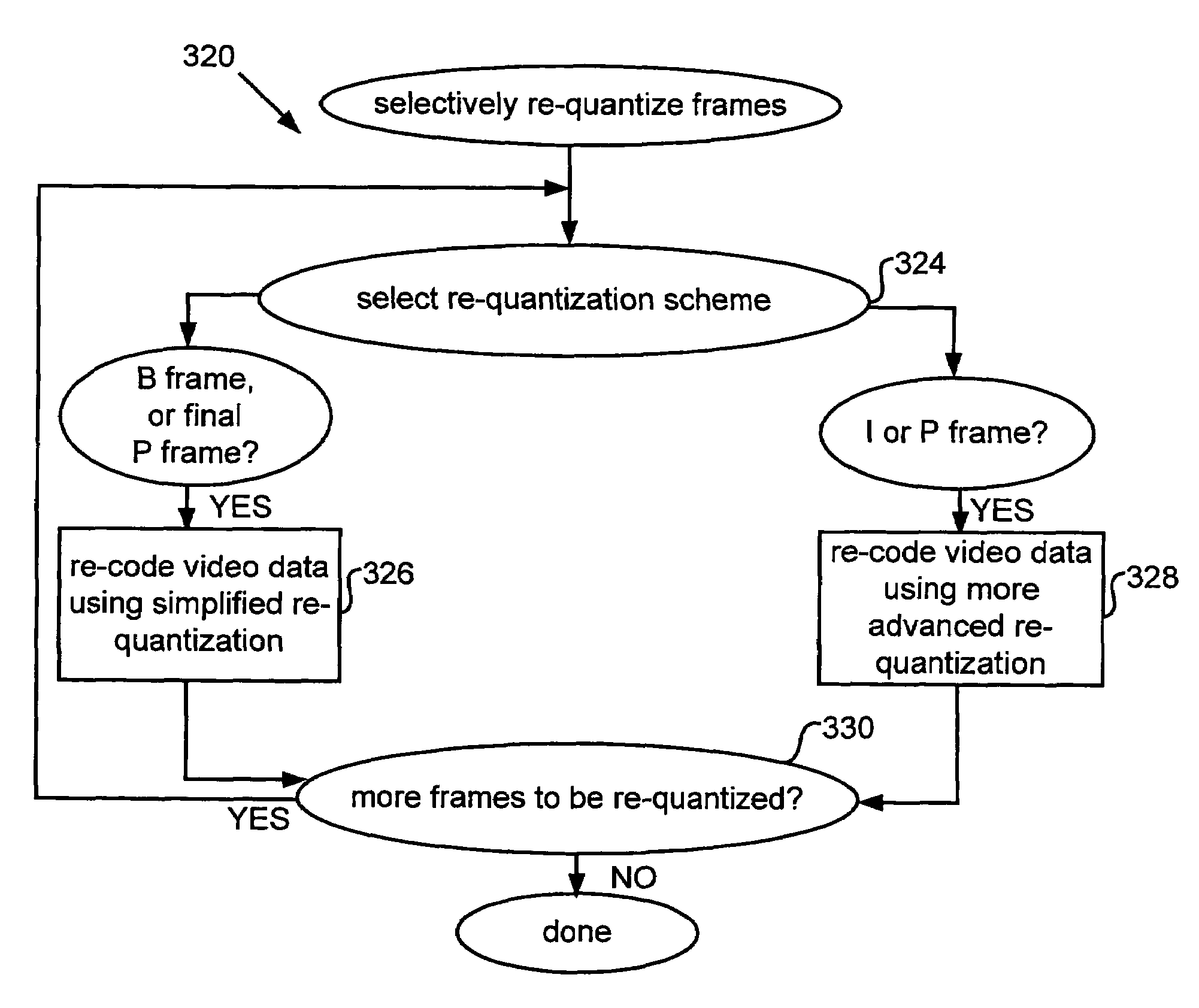
InactiveUS7477688B1Effective bandwidthGuaranteed data transmission efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData integrityParallel computing
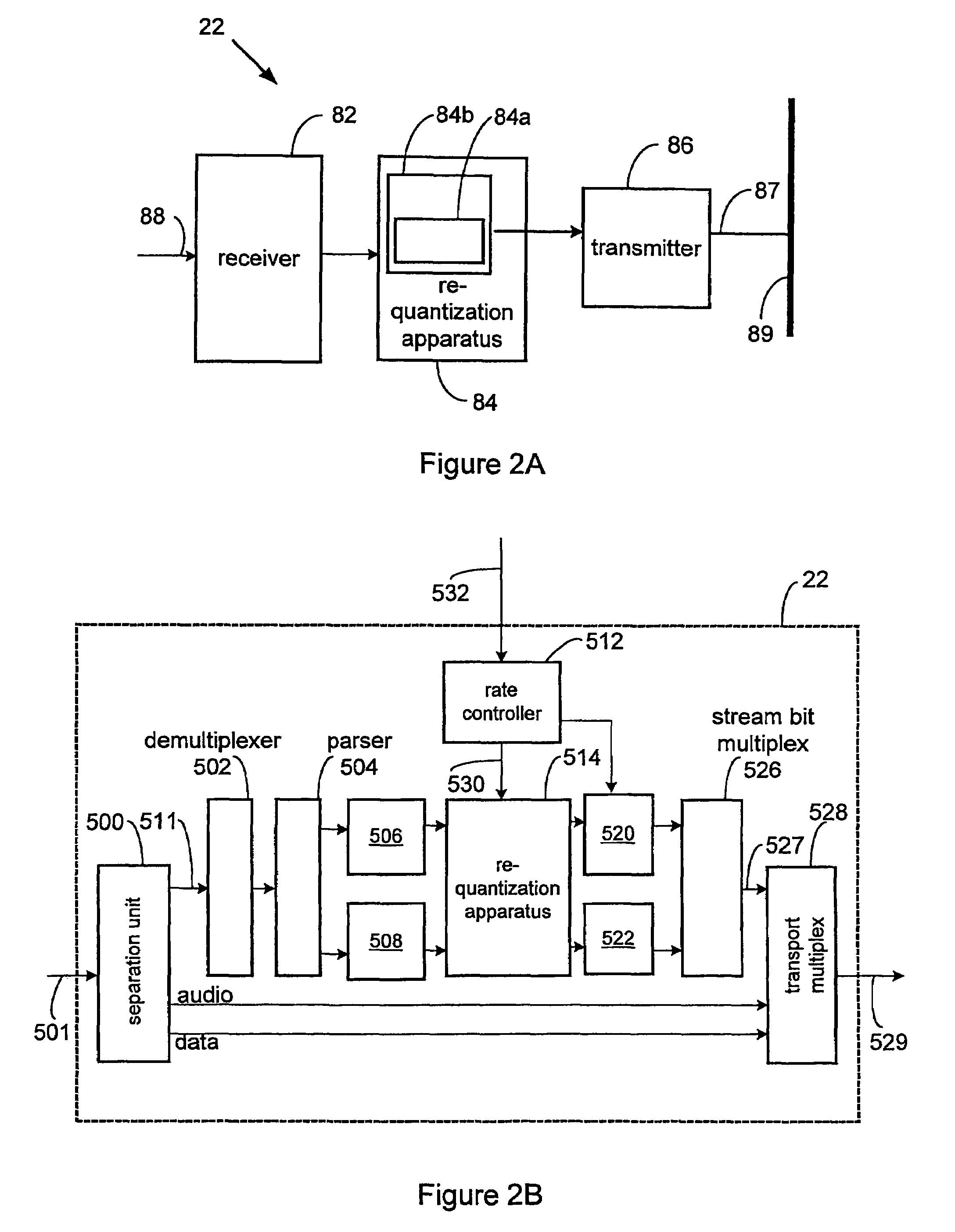
The present invention relates to systems and methods for efficient bit rate alteration of a bitstream to match an available channel capacity. The efficient bit rate alteration includes selective re-quantization of the compressed bitstream. Selective re-quantization according to the present invention applies multiple re-quantization schemes to different portions of a bitstream. In one embodiment, the multiple re-quantization schemes each have a different computational load. By selectively choosing which type of re-quantization is performed on each portion, efficient bandwidth scaling and data transmission may be achieved both when computational capacity is limited and when video data integrity is important.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Heterogeneous channel capacities in an interconnect
InactiveUS20140098683A1Different widthError preventionTransmission systemsComputer architectureChannel width
Systems and methods involving construction of a system interconnect in which different channels have different widths in numbers of bits. Example processes to construct such a heterogeneous channel NoC interconnect are disclosed herein, wherein the channel width may be determined based upon the provided specification of bandwidth and latency between various components of the system.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method of determining the capacity of each transmitter antenna in a multiple input/multiple output (MIMO) wireless system
InactiveUS7154960B2Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityChannel state informationData stream
The per antenna capacity of each of the transmitter antennas in a MIMO system are individually determined from measurable information at the receiver end. Specifically, the channel capacity for each individual transmitter antenna is calculated at the receiver end as a function of measurable channel coefficients (also known as channel state information), the measurable average signal-to-noise ratio, and the number of transmitter antennas. Once the per antenna capacity of each transmitter antenna is individually determined at the receiver end, the maximum transmission rate for each data stream transmitted by each transmitter antenna is determined from that individual capacity either at the receiver end and fed back to the transmitter end, or is determined at the transmitter end from the individual transmitter antenna capacities that are fed back by the receiver end to the transmitter end. A modulation scheme that supports each maximum transmission rate is then determined based on some defined criteria.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
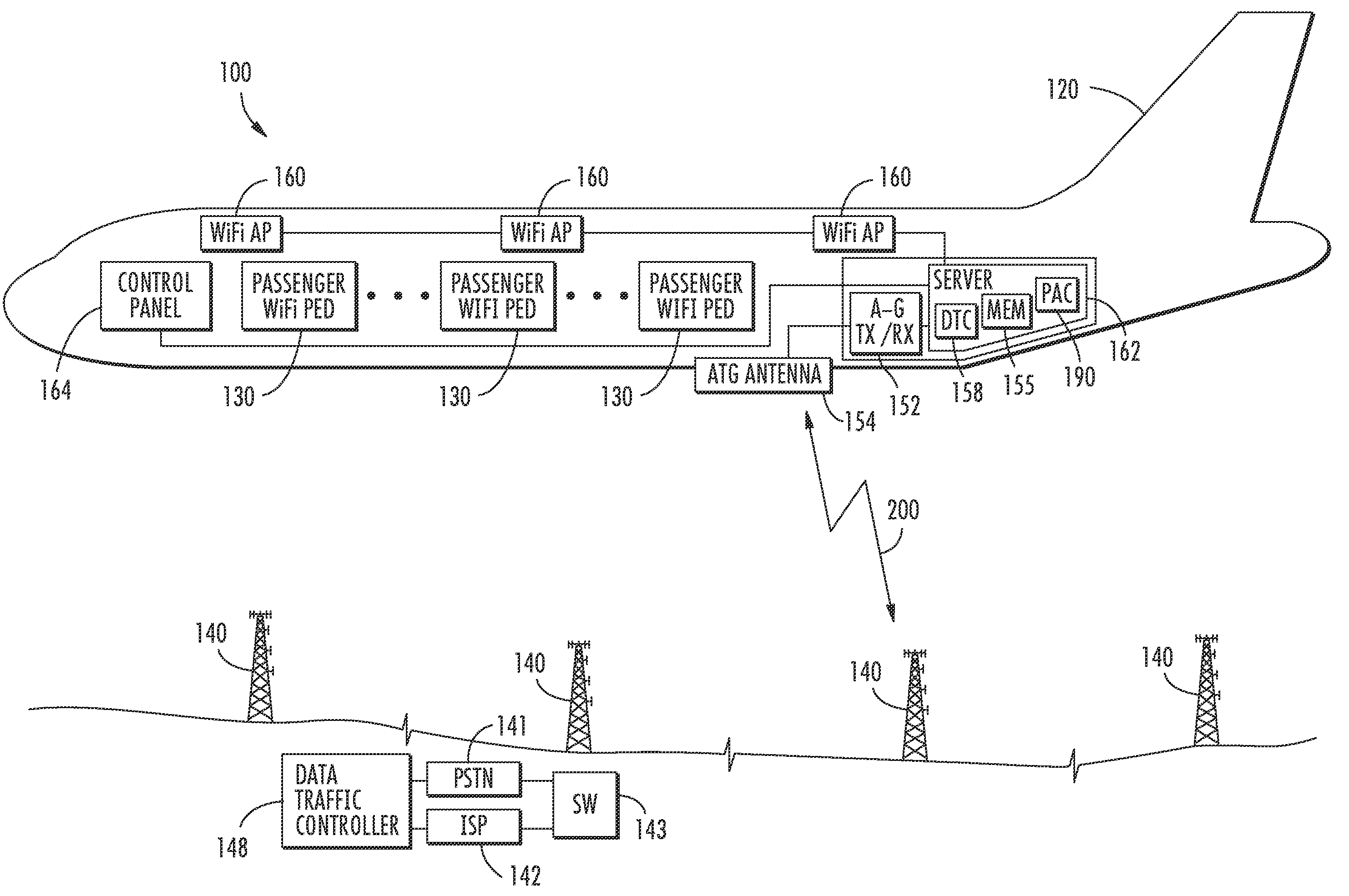
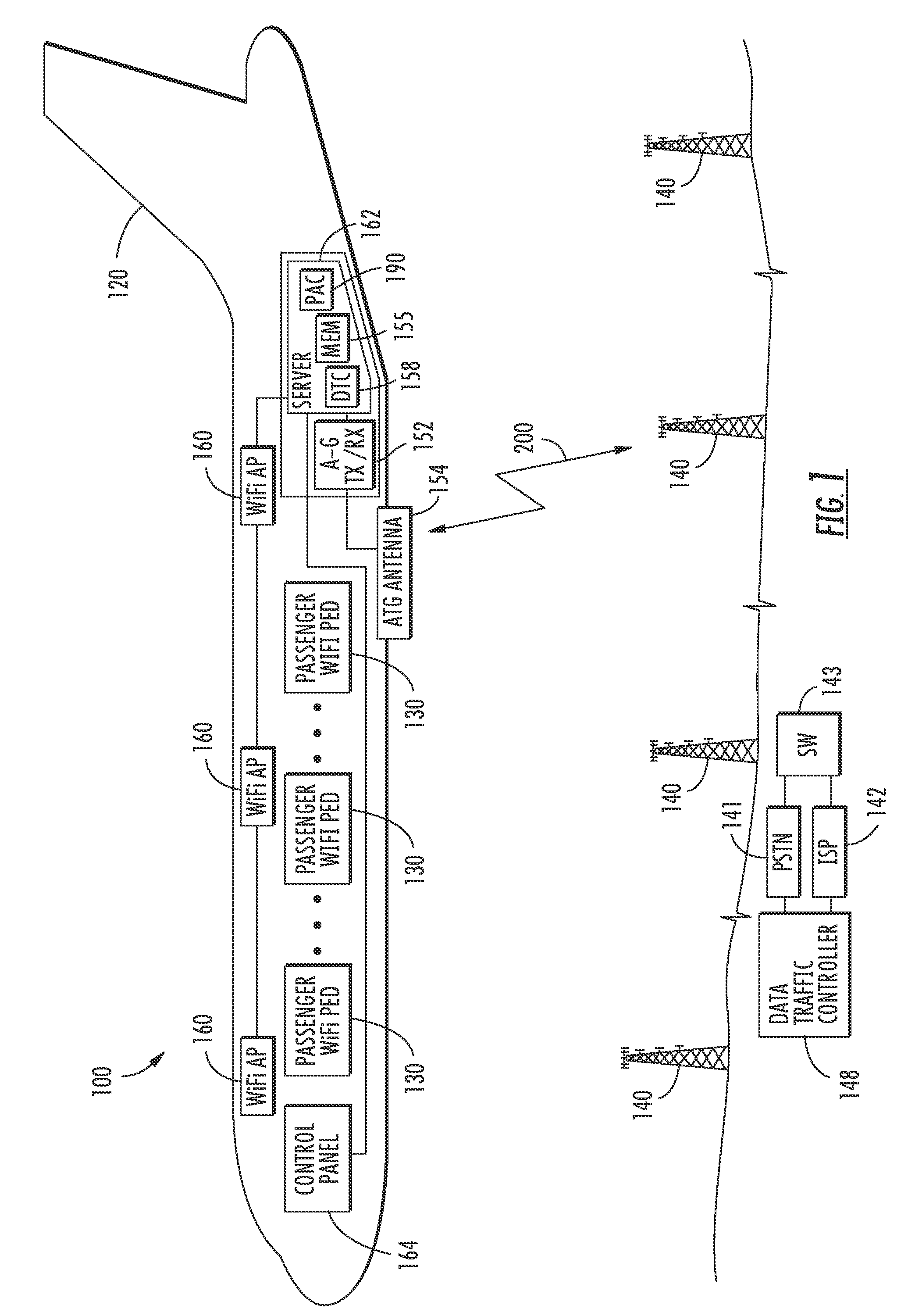
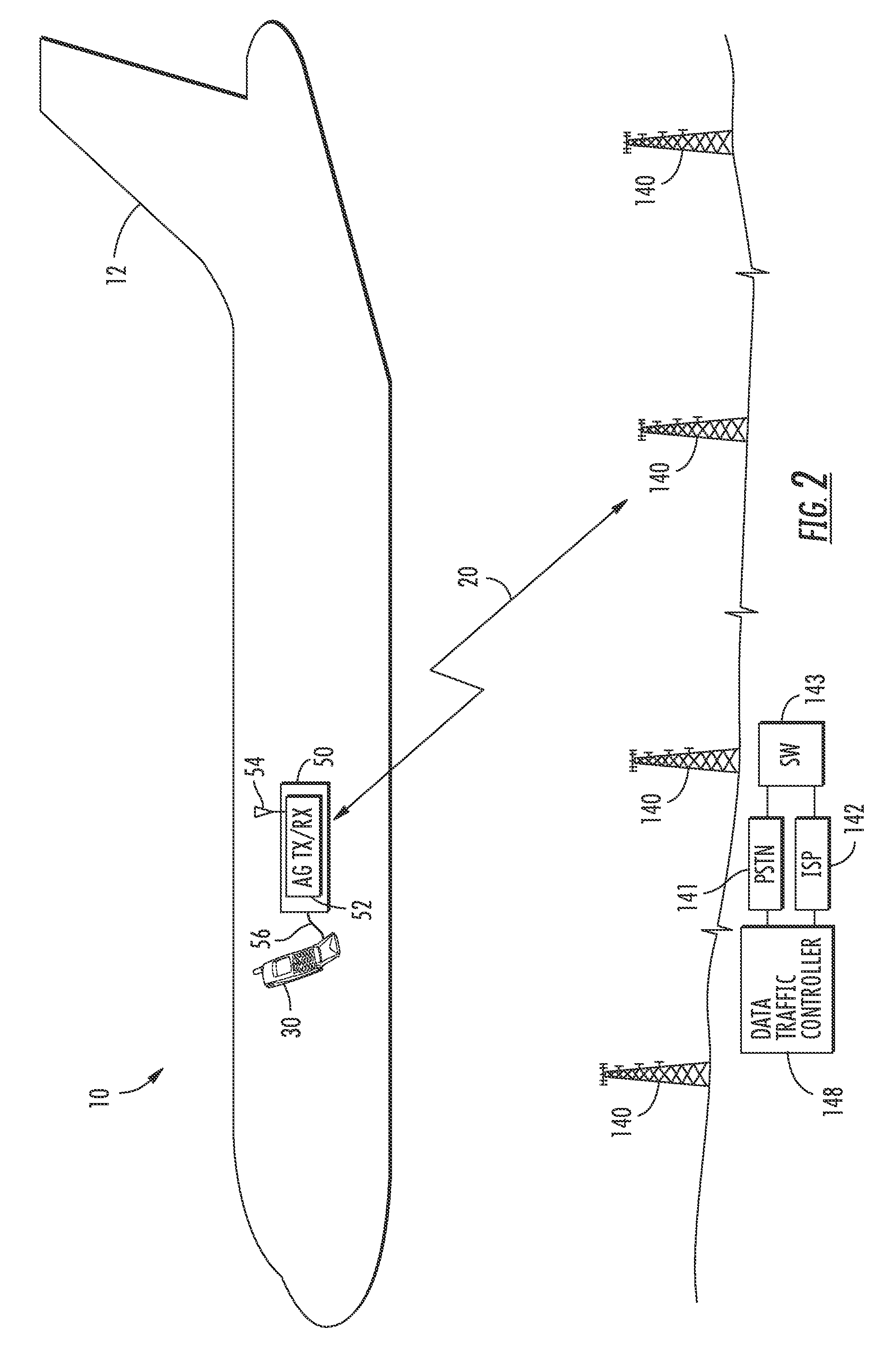
Aircraft communications system selectively allocating data communications channel capacity and associated methods
ActiveUS20080240029A1Limit communication of dataNetwork topologiesActive radio relay systemsCommunications systemTransceiver
A communications system for an aircraft carrying personnel having personal electronic devices (PEDs) for wireless data communications outside the aircraft includes a ground-based communications network, and an access point in the aircraft for providing a WLAN for data communications with the PEDs. An air-to-ground transceiver in the aircraft cooperates with the access point for data communications with the ground-based communications network. At least one data traffic controller selectively allocates data communications channel capacity between the PEDs and the ground-based communications network.
Owner:LIVETV
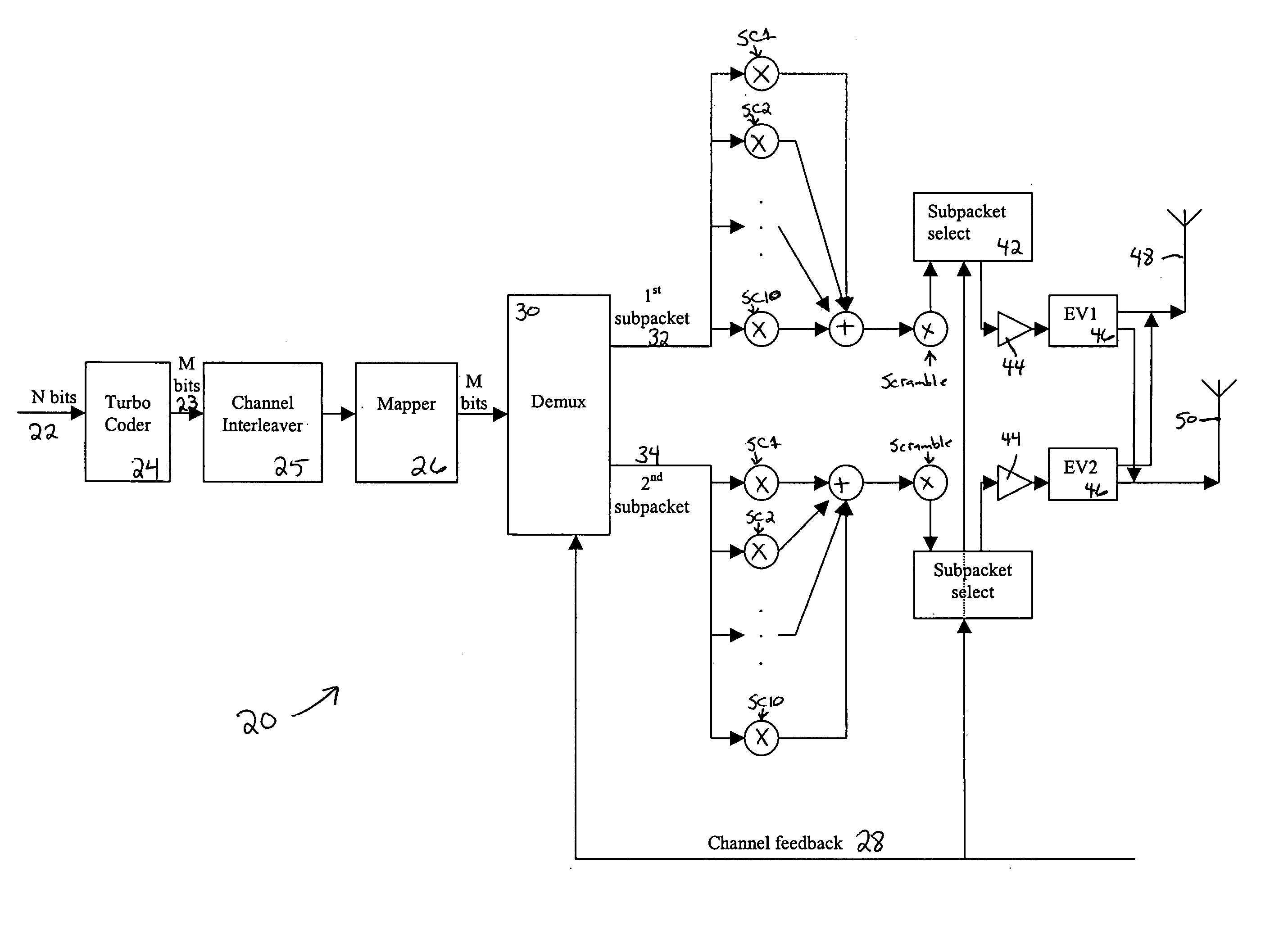
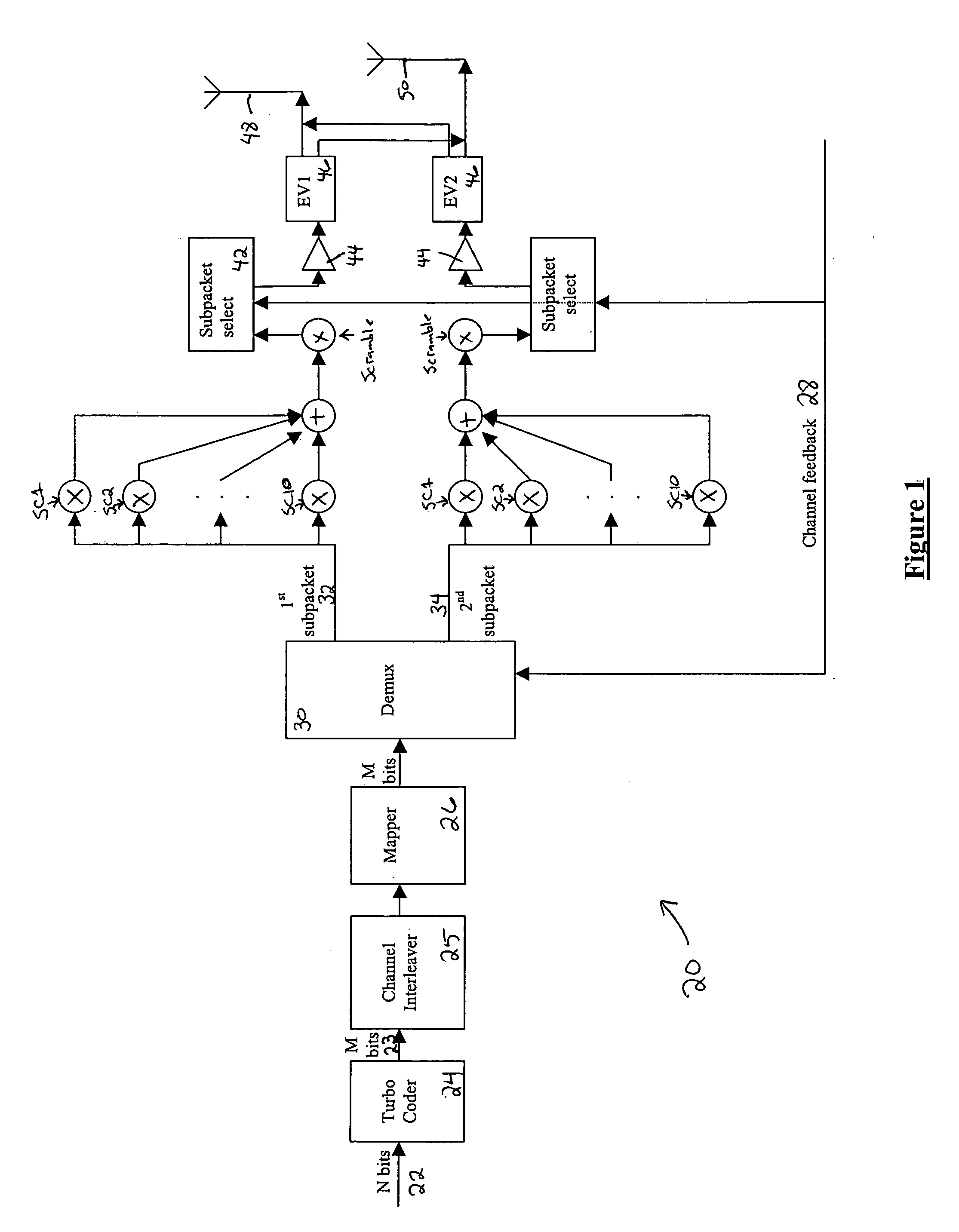
Flexible rate split method for MIMO transmission
InactiveUS20050111376A1Wide diversityReduce error rateSpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsMimo transmissionSelection system
A method for transmitting a packet of N input bits includes encoding all of the N bits as a single entity, such as with an interleaver of length N within a turbo coder, outputting M encoded bits, channel interleaving the M bits, splitting the M encoded bits into a parallel first and second portion, and transmitting them over separate channels to achieve spatial diversity. The size of the first and second portion is determined based on a closed feedback loop that provides some knowledge of the channel, preferably a measure of channel capacity. The feedback loop may also provide channel knowledge to a subpacket selector associated with each transmit antenna, which determines an appropriate rate for that channel and selects subpackets to fill a transmission packet for that channel. The subpacket selectors choose a subpacket of systematic bits and fill the remaining transmission packet size with subpackets of parity bits. Eigenvectors may be employed to transmit each transmission packet over more than one channel with a power disparity between the channels. A transmitter according to the present invention is also described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Promotion server using video on demand channel
InactiveUS7237250B2Increase incomeAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast information monitoringBroadcast channelsRadio channel
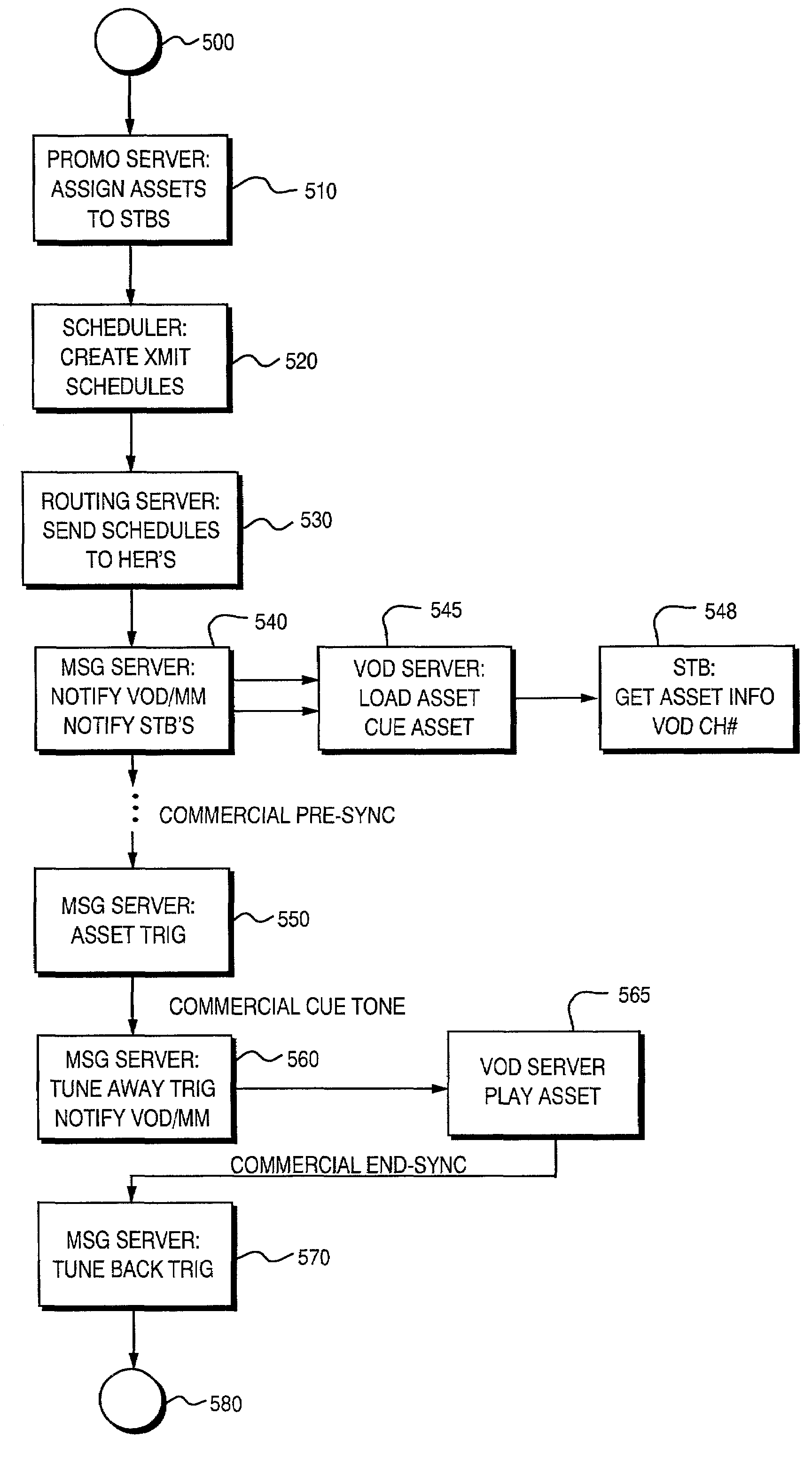
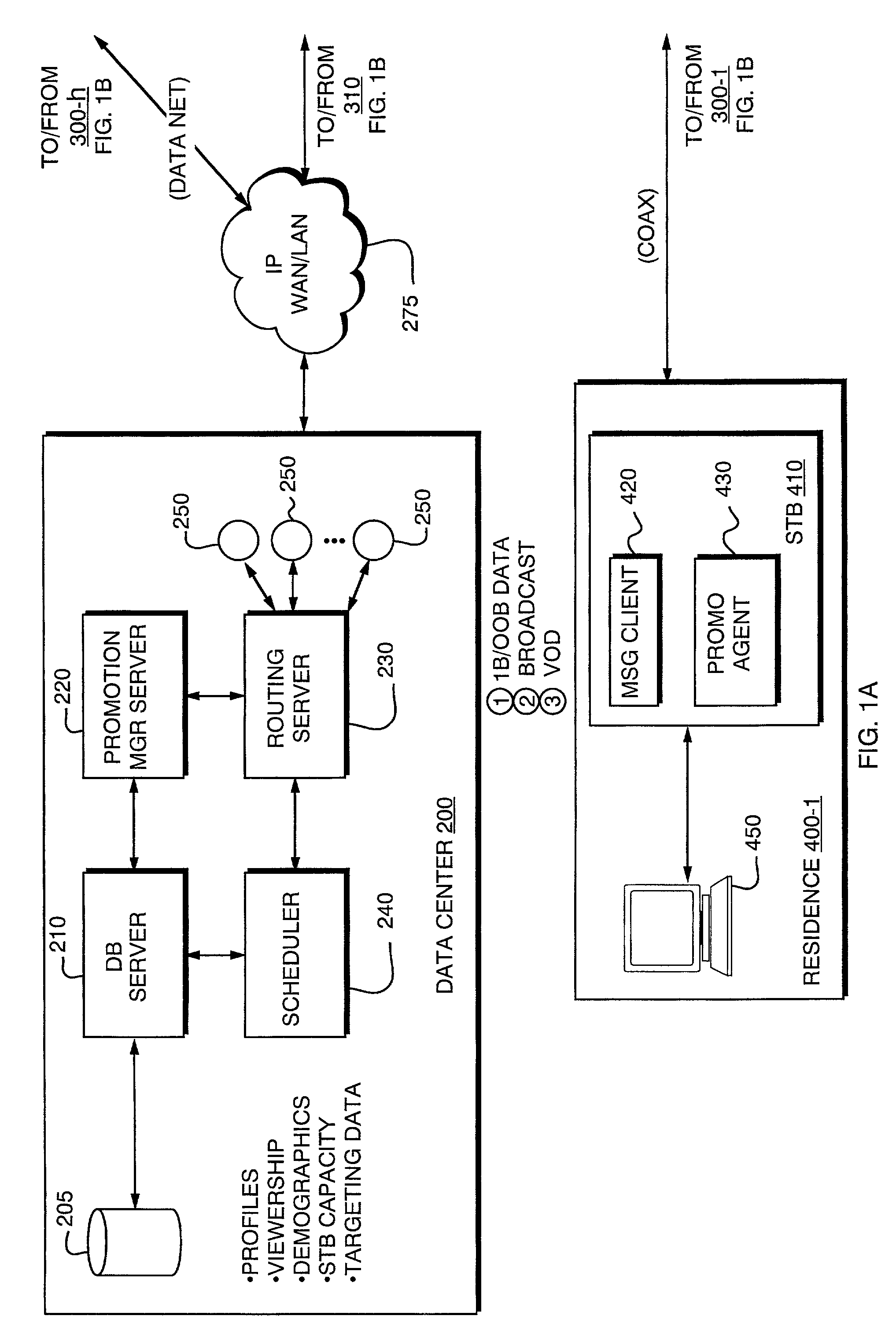
Idle Video-On-Demand (VOD) channel capacity is used to deliver promotional content to selected set-top boxes (STBs) in a cable television network. Commercial segment cues are used to instruct a set-top box to switch away from a broadcast program to the VOD channel during a commercial segment, and then switch back again to the original broadcast program at the end of the segment.More particularly, a promotion server determines an asset to be distributed such as a targeted promotion item (e.g., a commercial), and a list of STBs that are to receive it. The promotion server causes the video promotion content to be stored in VOD servers located at the head ends. A scheduler process then delivers schedule messages to head end message servers which identify each promotion asset, and an STB which is to receive it. The head end message server notifies its associated VOD server which then cues the asset by loading the asset, starting the asset, but pausing it. Prior to the occurrence of a commercial slot in a broadcast program, an asset trigger is inserted into the broadcast stream at the head end. This asset trigger contains general information concerning the asset to be sent, and an idle VOD channel number. The STB receives the asset trigger and readies itself to tune to the VOD channel when cued for at the beginning of a commercial segment, but does not yet tune to the VOD channel. Upon detection of a commercial cue tone in the broadcast channel, the head end message server sends a tune away trigger to the STB, and also instructs the VOD server to start playing the cued promotion. When the STB receives a tune away trigger, it switches from the broadcast channel being played to the selected idle VOD channel, and the promotion is viewed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Frequency and power distributing method based on NOMA (non-orthogonal multiple access) system
ActiveCN104640220AImprove practicalityImprove energy efficiency utilizationHigh level techniquesWireless communicationChannel capacityAssignment methods
The invention relates to a frequency and power distributing method based on an NOMA (non-orthogonal multiple access) system. The frequency and power distributing method comprises the following steps: confirming a user set for sending information to a cell by a base station and obtaining CSI (channel state information) of the user set at a base station end; distributing each sub channel to a user with the best CSI condition, and regarding the user as a strong user; based on this, combining the strong user with other users in sequence, calculating a maximum channel capacity value of each pair of sets, selecting one pair of set with maximum channel capacity value, and regarding another user in the set as a weak user; distributing two users which are respectively the strong user and the weaker user on each sub channel, wherein the set comprising the strong user is a strong user set Omega A, and the set comprising the weak user is a weak user set Omega B; performing optimal power distribution on the strong user and the weak user on each sub channel respectively. The method can meet large-scale user transmission needs in the future, and increases access probability of the user, so that the spectrum efficiency of the system is improved.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
Methods and systems for communication with beamforming antennas
ActiveUS20170127295A1Increase network capacityHigh data rateAssess restrictionRadio transmissionTelecommunicationsAdaptive routing
Owner:DE INVENSHN SAJENS FAND UAN ELELSI
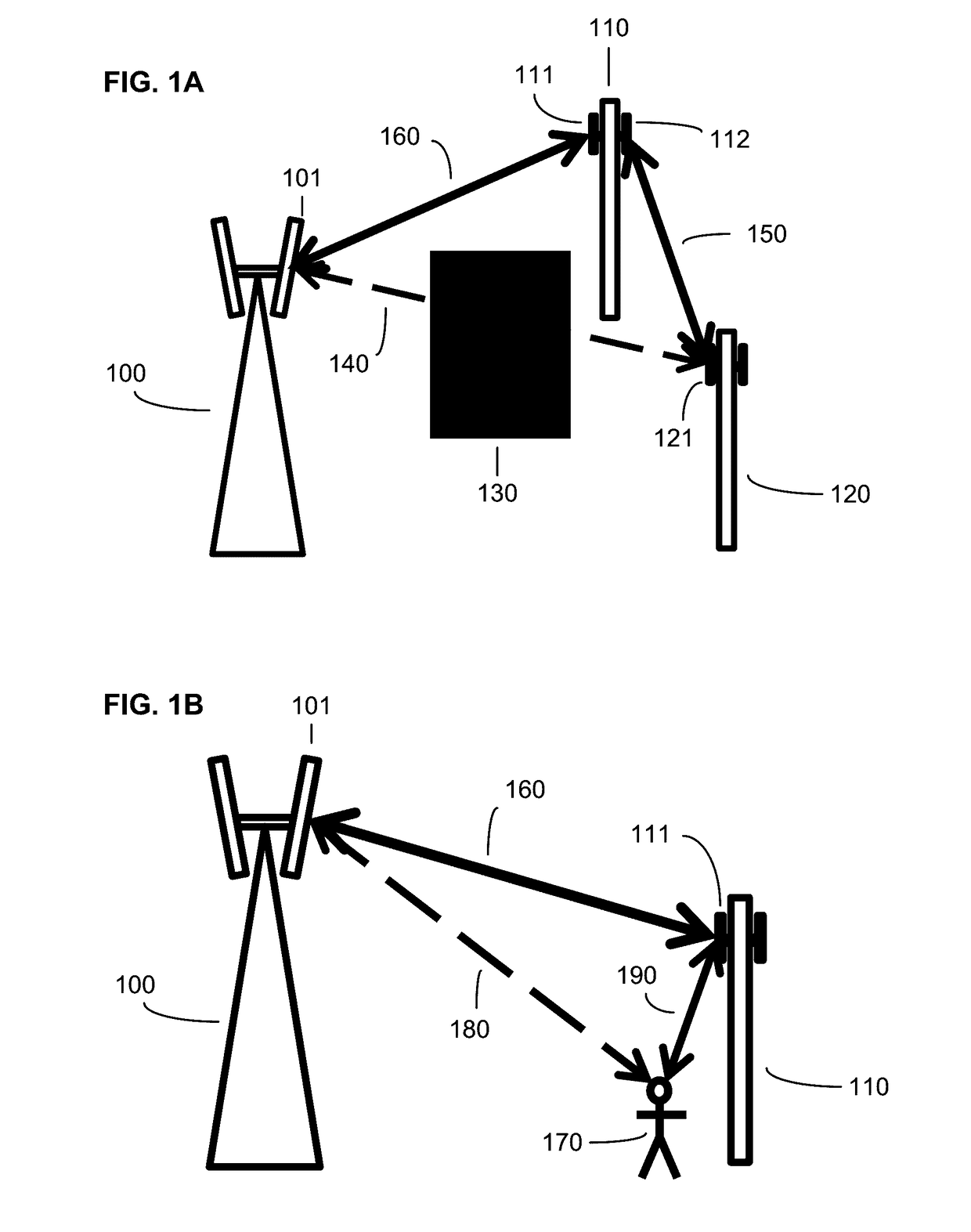
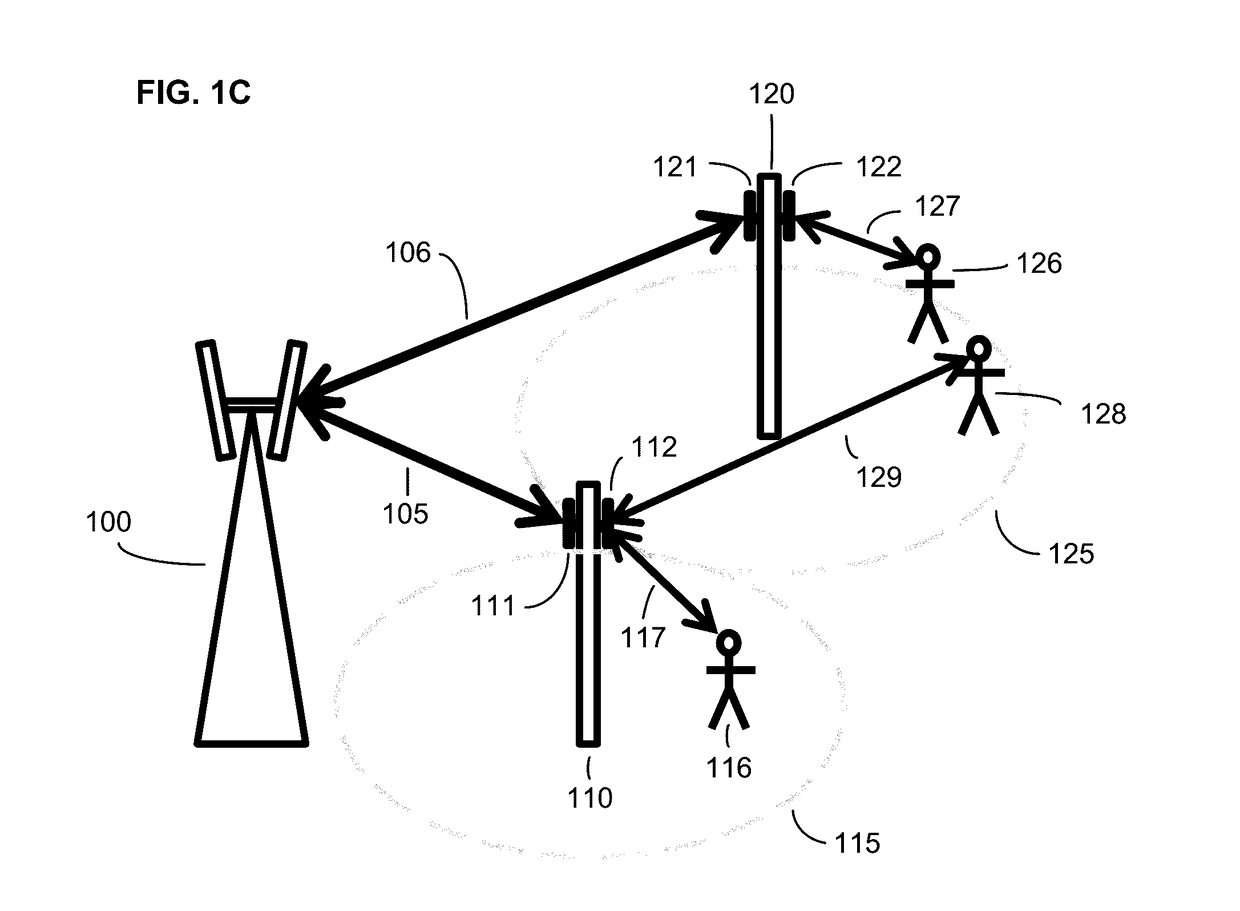
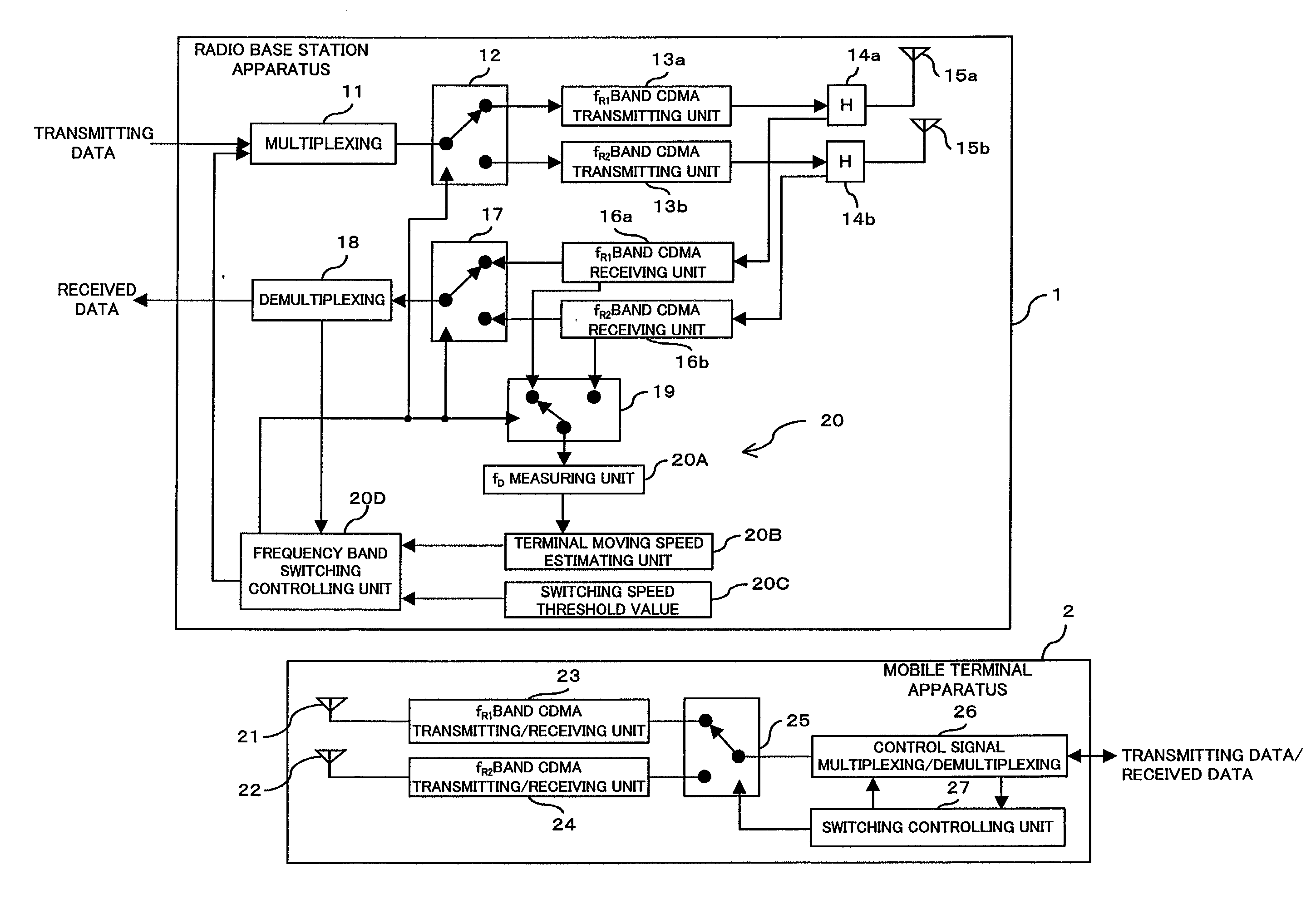
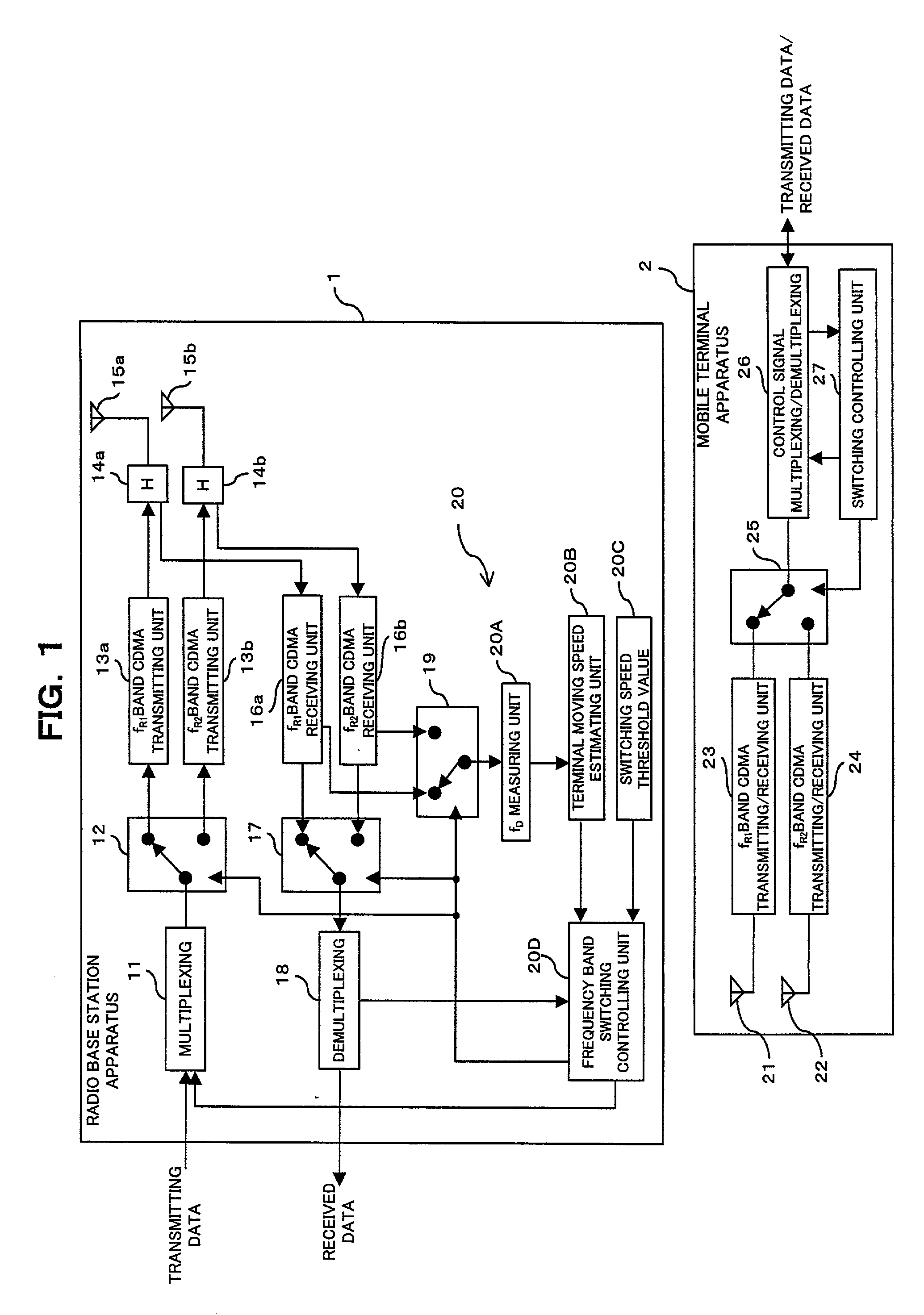
Mobile communication system, and a radio base station, a radio apparatus and a mobile terminal
InactiveUS20030064729A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionLow speedLow frequency band
A mobile communication system comprises a detecting unit to detect information concerning a moving speed of a mobile terminal, and a selection controlling unit to select a use frequency in a higher frequency band when the speed information detected by the detecting unit is a higher speed, while selecting the use frequency in a lower frequency band when the detected information is a lower speed, and assigning it to the mobile terminal. In a mobile communication system in which a relationship between a terminal moving speed (Doppler frequency) and transmission quality degradation is non-monotonous, the communication quality can be improved and the channel capacity can be increased.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
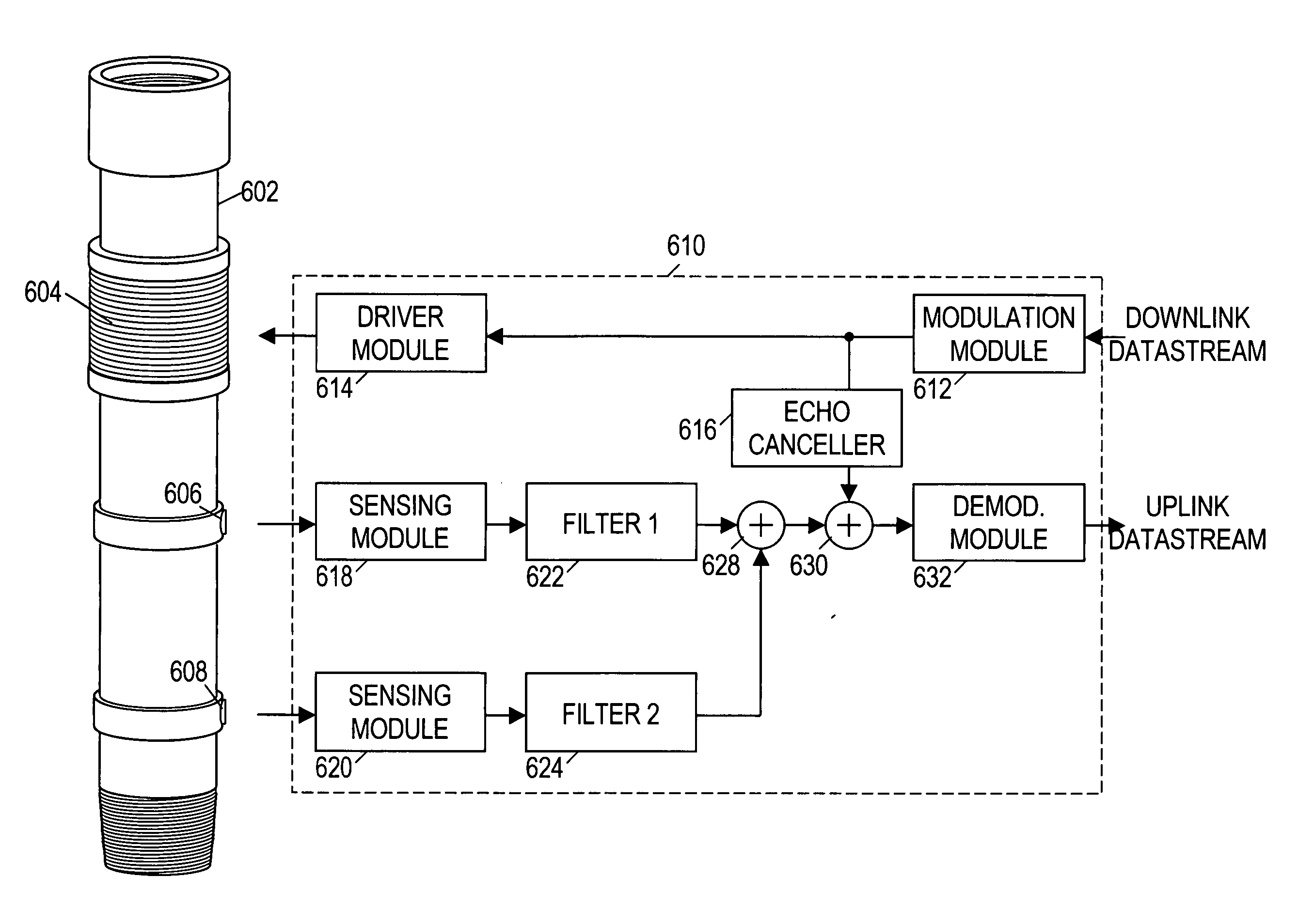
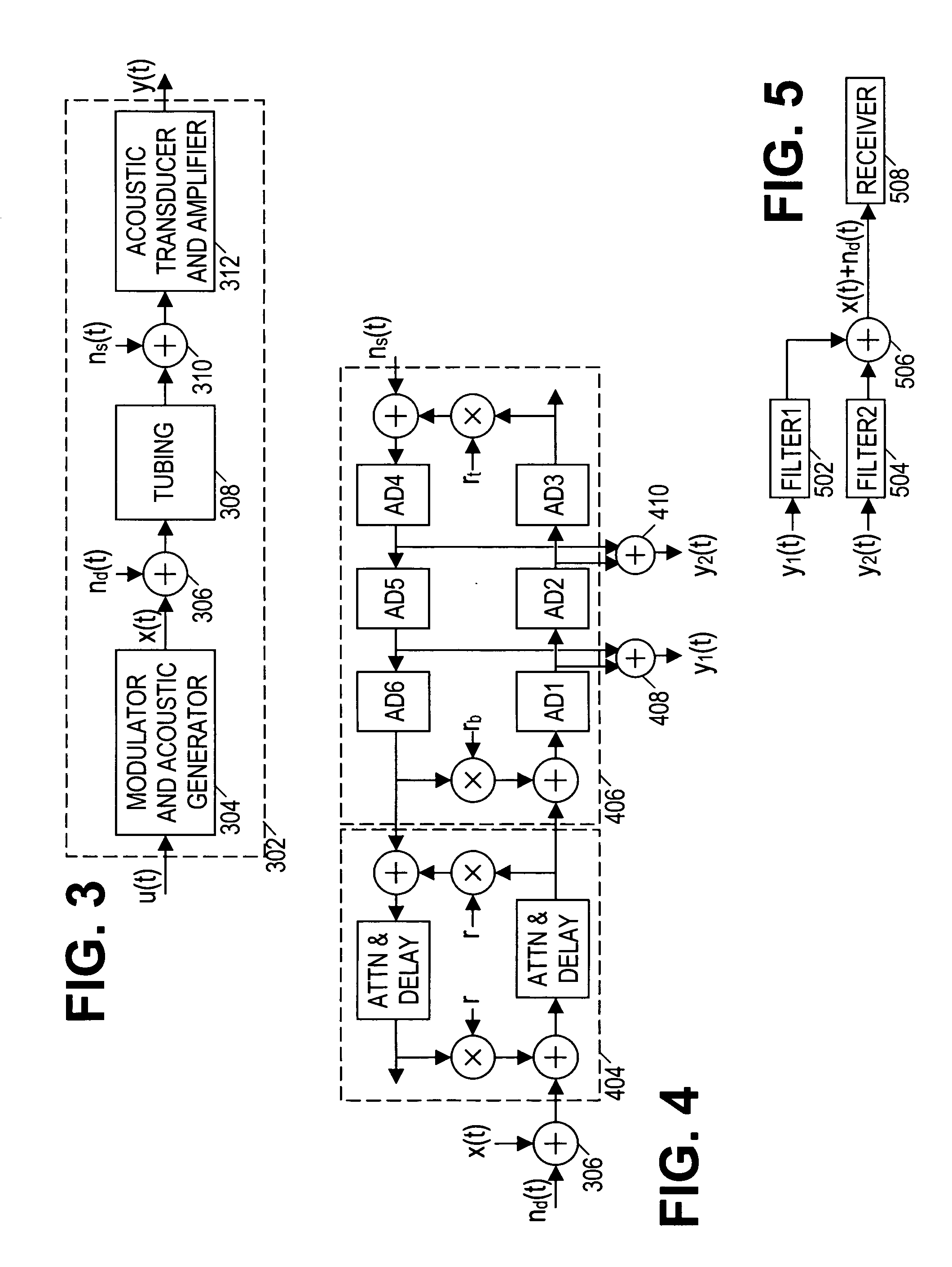
Directional acoustic telemetry receiver
ActiveUS20050024232A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioIncrease channel capacitySurveyNon-electrical signal transmission systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Computer module
Acoustic telemetry devices and methods that provide directional detection. In one embodiment, a disclosed acoustic telemetry device comprises at least two acoustic sensors and an electronics module. A first of the acoustic sensors detects a communication signal that propagates along a tubing string in a first direction. A second of the acoustic sensors is configured to detect the communication signal before the first acoustic sensor. The electronics module combines the detection signals from the acoustic sensors to obtain a combined signal that substantially excludes signals propagating in a direction opposite to the communication signal. Such signal suppression may significantly enhance the communication signal's signal-to-noise ratio, thereby increasing channel capacity. The acoustic telemetry device may be configured to support logging while drilling and / or full-duplex communication.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method of controlling data transmission in a wireless relay system, and the relay system implementing the method
ActiveUS20080045212A1Increase battery capacityImprove throughputFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementControl dataTransfer mode
A data transmission method in a wireless relay system, and a method of selecting an optimal transmission mode based on a channel capacity of an individual link that is measured by a mobile station. The data transmission method includes: transmitting a first ratio of first partial data of the data from a base station to a mobile station; transmitting a second ratio of second partial data of the data from the base station to a first relay station; and forwarding the second partial data from the first relay station to the mobile station, wherein the first ratio or the second ratio is determined based on any one of a channel capacity of a first link between the base station and the mobile station, and a channel capacity of a second link between the first relay station and the mobile station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for scheduling downlink channels in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access system and a system using the same
ActiveUS20050265223A1Reduce the amount requiredTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationCommunications systemCapacity value
A downlink channel scheduling method and apparatus for obtaining optimal system performance in a downlink of a wireless communication system using an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) scheme are provided. Terminals compute a plurality of channel capacities and search for a channel with a maximum capacity. The terminals send, to a base station (BS), feedback information including a channel number and a capacity value of the channel with the maximum capacity. The BS performs a first channel allocation process for allocating a channel with an optimal capacity to each terminal on the basis of the feedback information. The BS performs a second channel allocation process for allocating an adjacent channel to a corresponding terminal using the window bit when the terminal is not allocated a channel in the first channel allocation process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for time slotted code division multiple access communication in a wireless communication environment
InactiveUS7061898B2Increase the number ofAvoid the needTelephonic communicationConnection managementCode division multiple accessTime alignment
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for improved memory reliability, availability and serviceability
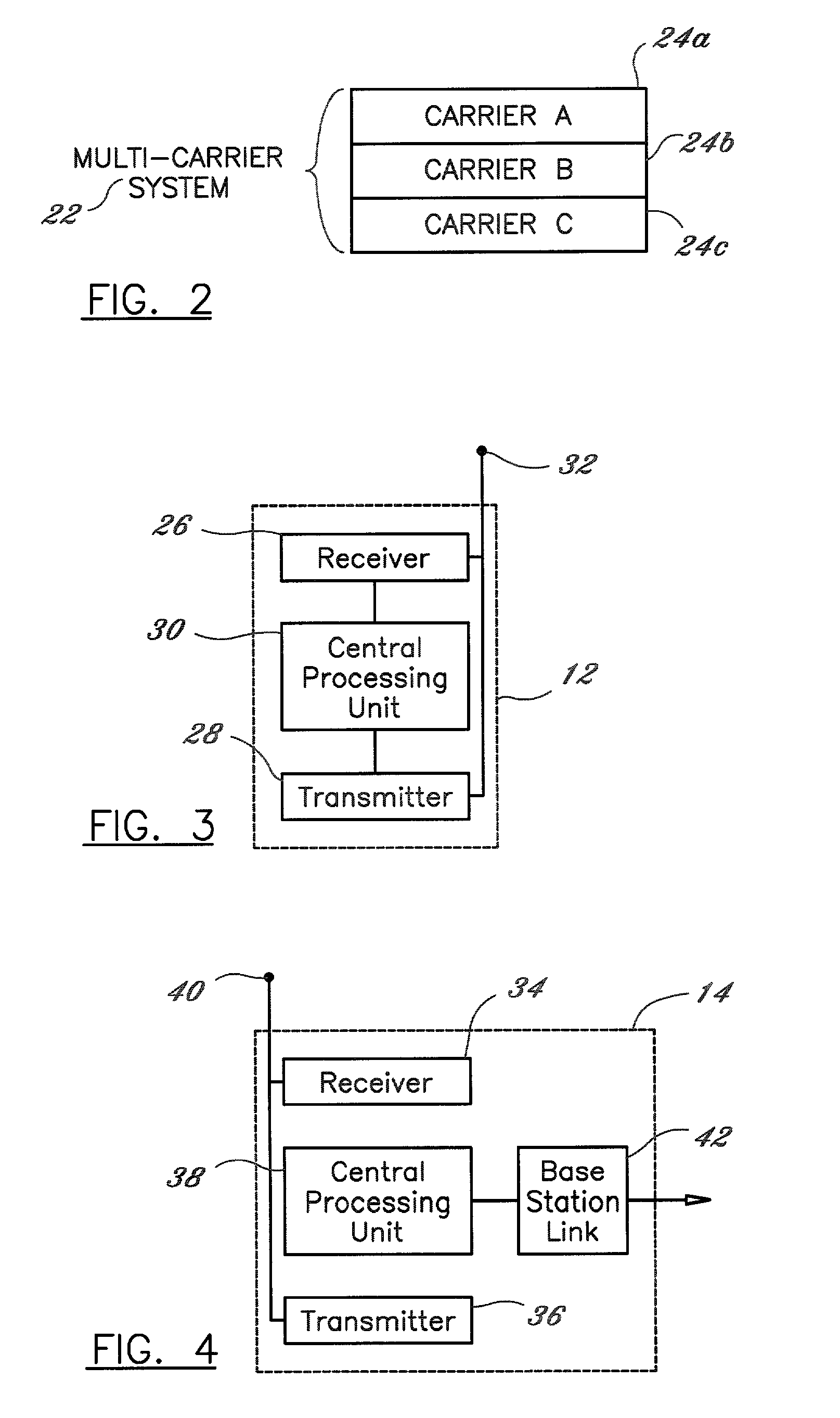
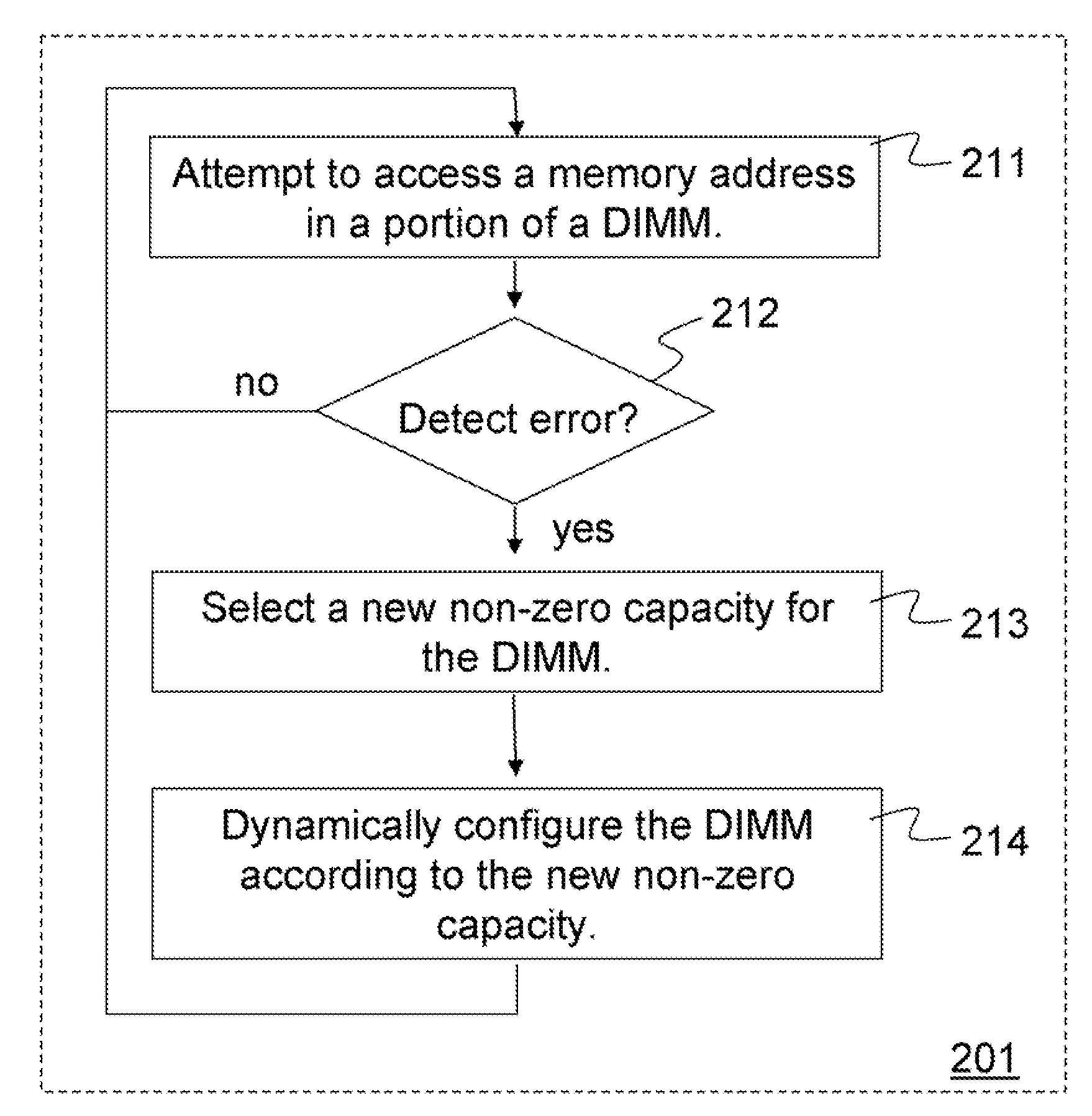
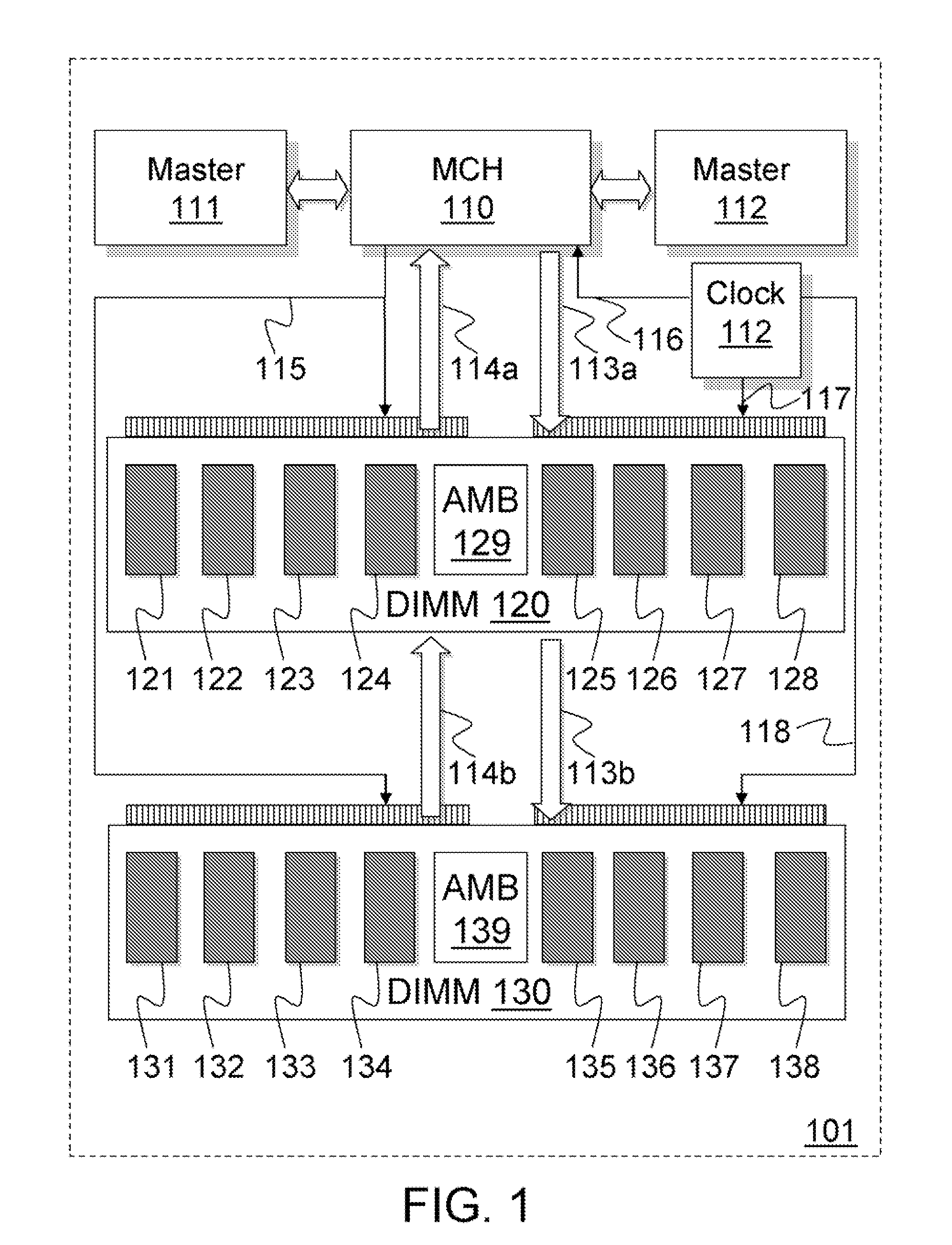
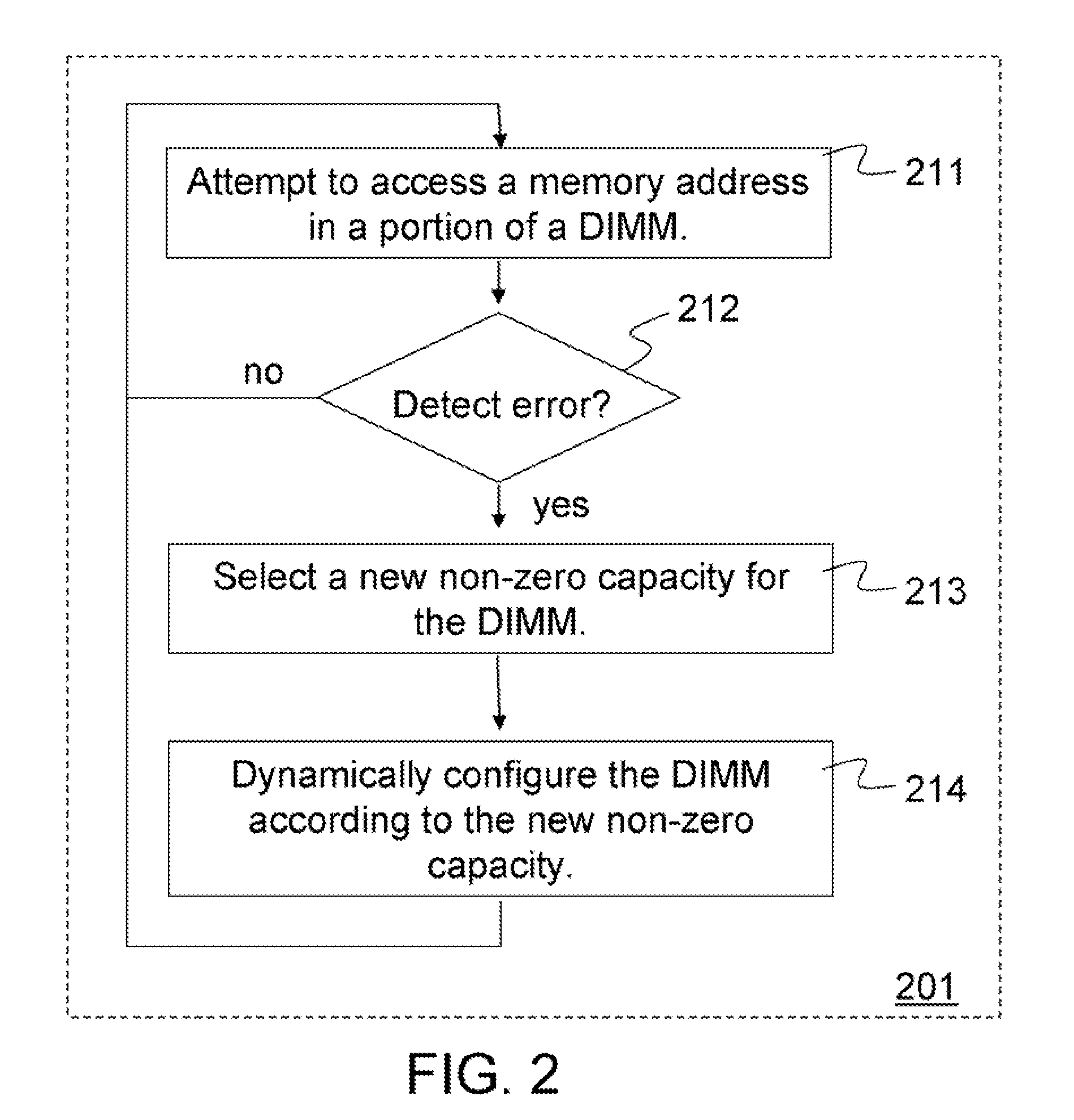
Methods and apparatus dynamically reconfigure storage or channel capacities in a memory system. A fully-buffered dual in-line memory module (DIMM) is configured for a particular storage capacity and a particular channel capacity. An error may be detected at a memory address in some portion of the DIMM. To resolve the problem, the storage capacity or the channel capacity may be reduced and the DIMM may be dynamically reconfigured according to the reduced capacity. For one embodiment the DIMM may be reconfigured by mapping the portion of the DIMM containing the error as unavailable and taking that portion off-line without taking the entire DIMM off-line. For another embodiment the DIMM may be reconfigured by throttling the DIMM at a reduced frequency. The portion of the DIMM containing the error may be retested at the reduced frequency. If no errors are detected, the DIMM may be made available at the reduced frequency.
Owner:INTEL CORP
MIMO communication system having deterministic channels and method
InactiveUS20090296846A1Large communication capacityNone is problem freeMultiplex communicationDiversity/multi-antenna systemsFormation matrixChannel capacity
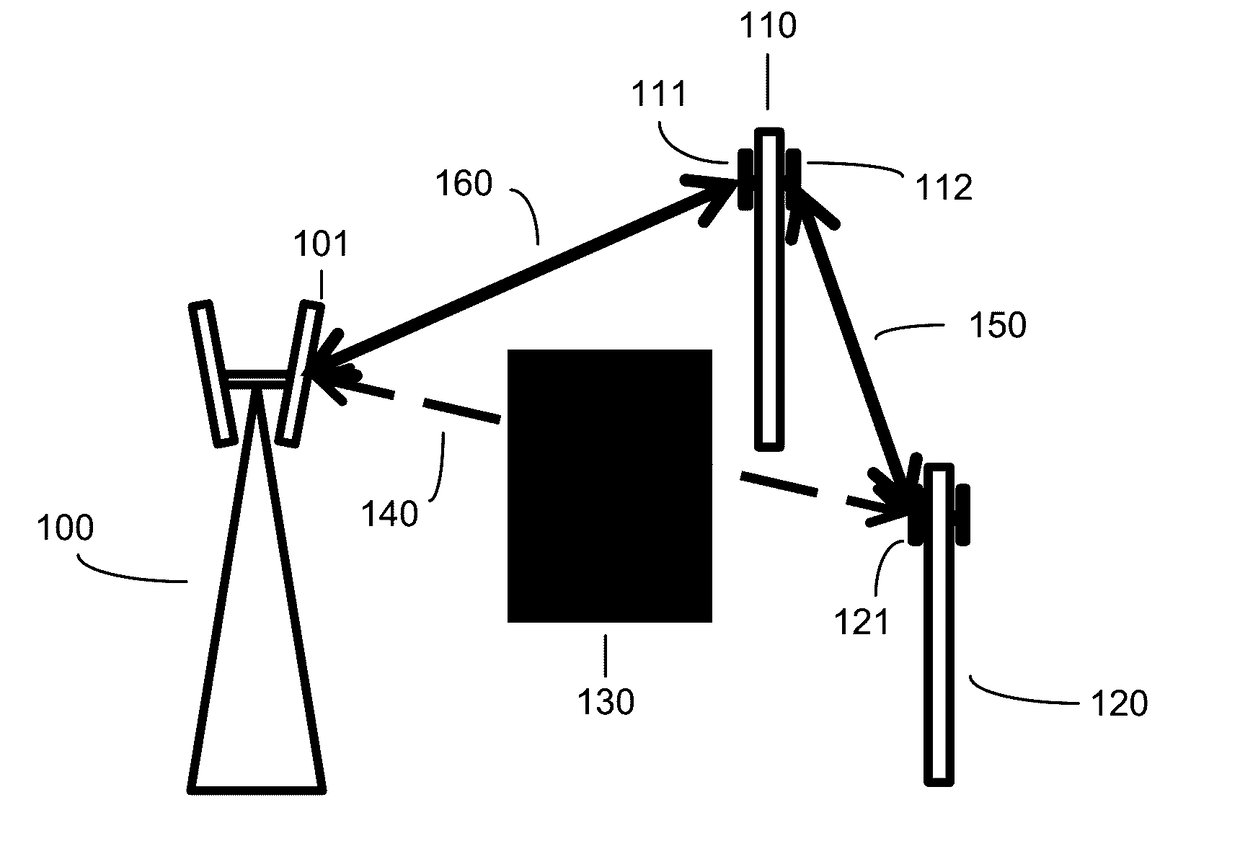
A MIMO communication system having deterministic channels wherein MIMO is applied to line-of-sight channels having a fixed geometrical positional relationship so as to increase the channel capacity. A line-of-sight MIMO communication system having a plurality of channels includes a channel matrix calculation processing section on a transmission or reception side or both of the transmission and reception sides. The channel matrix calculation processing section updates an orthogonal channel formation matrix in accordance with a fluctuation of a transmission antenna position or reception antenna position or a fluctuation of the channels.
Owner:NEC CORP
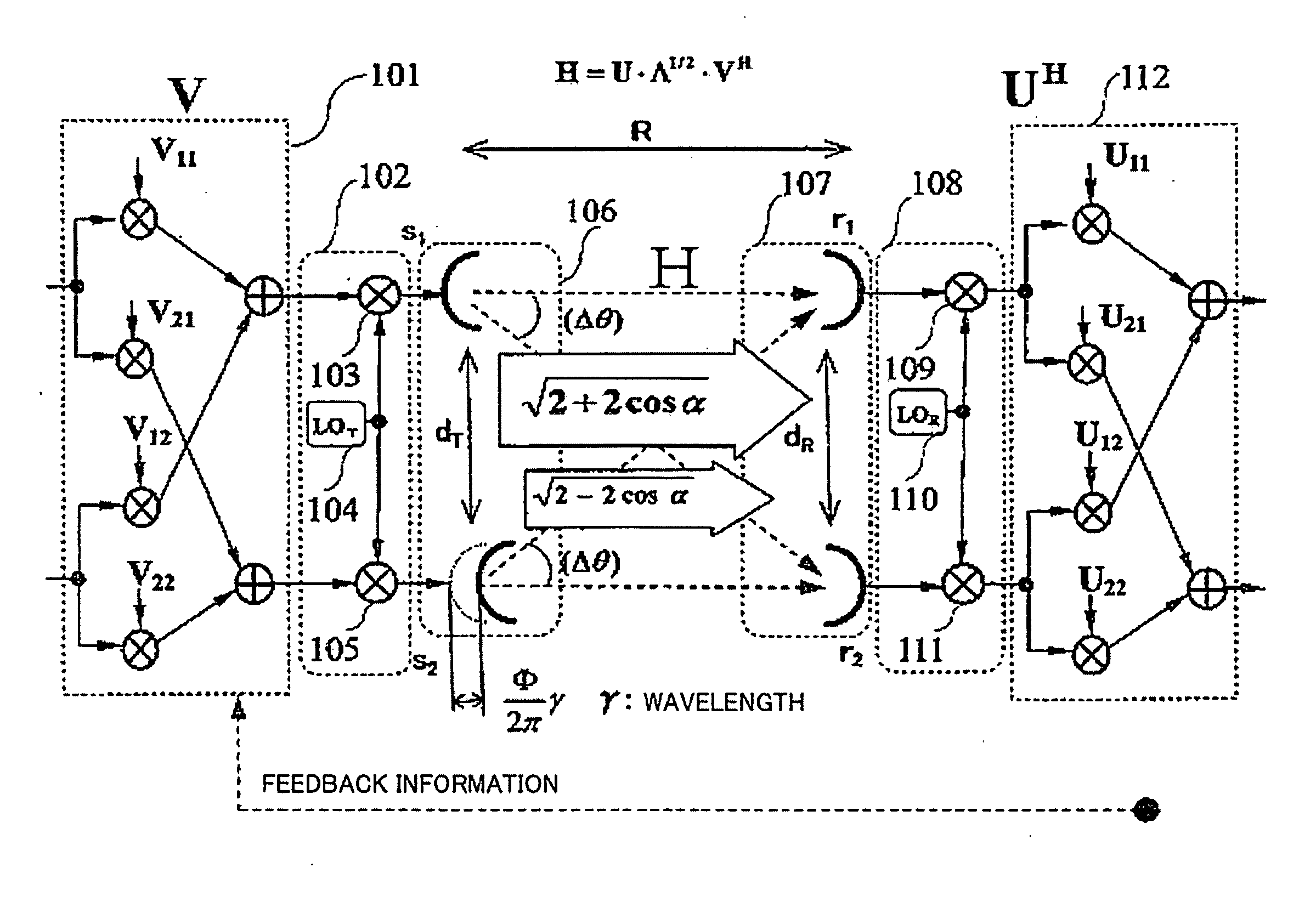
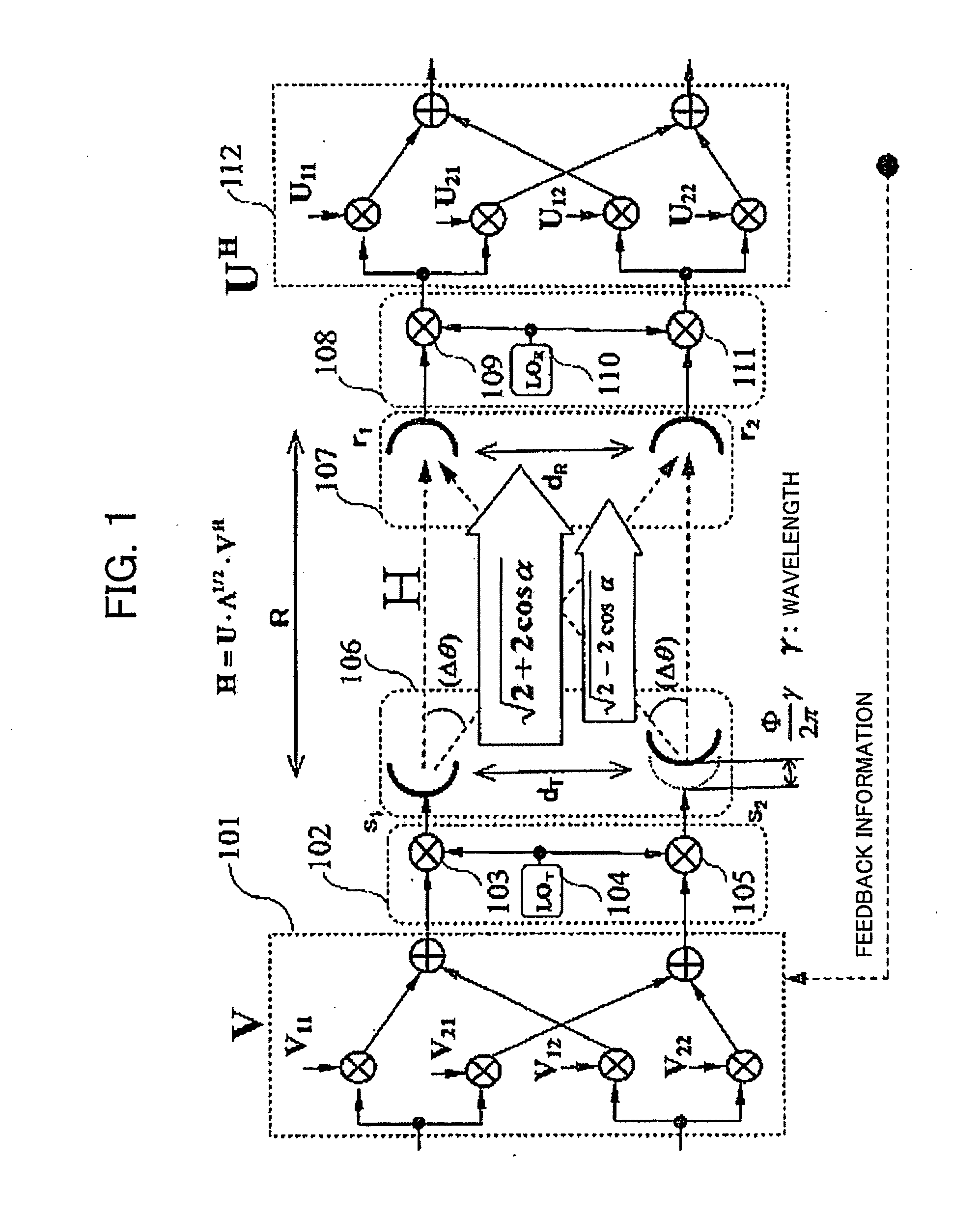
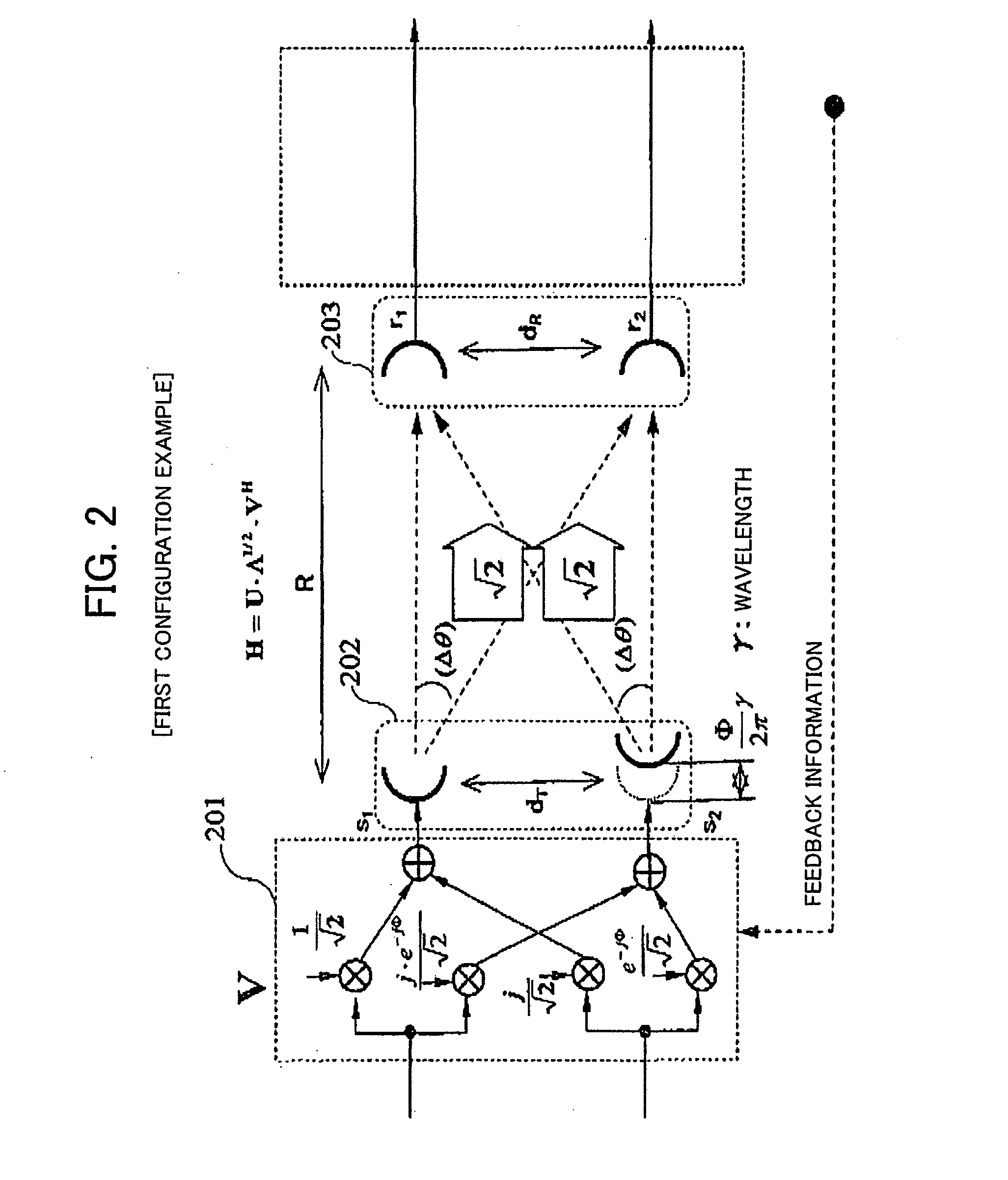
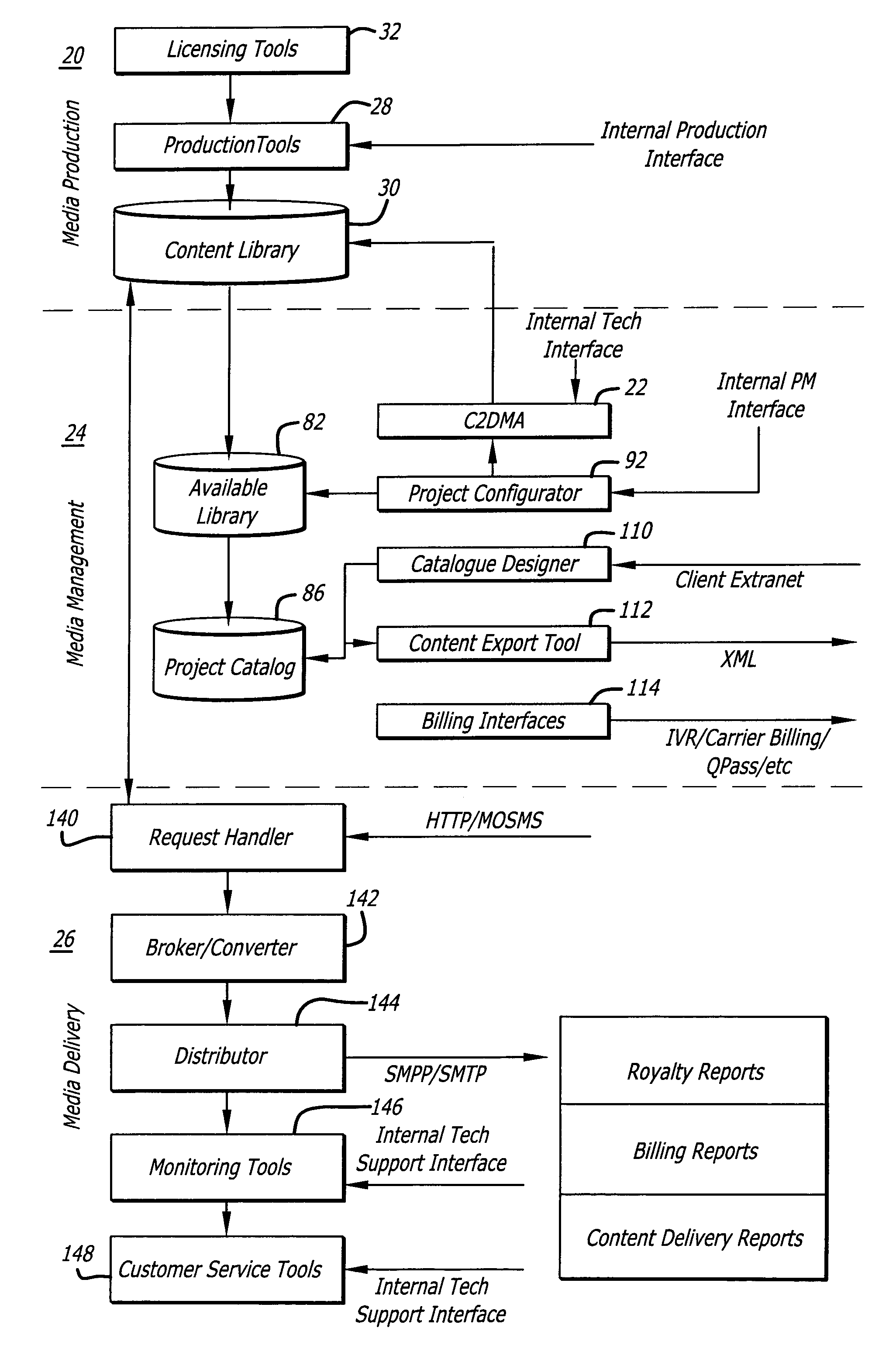
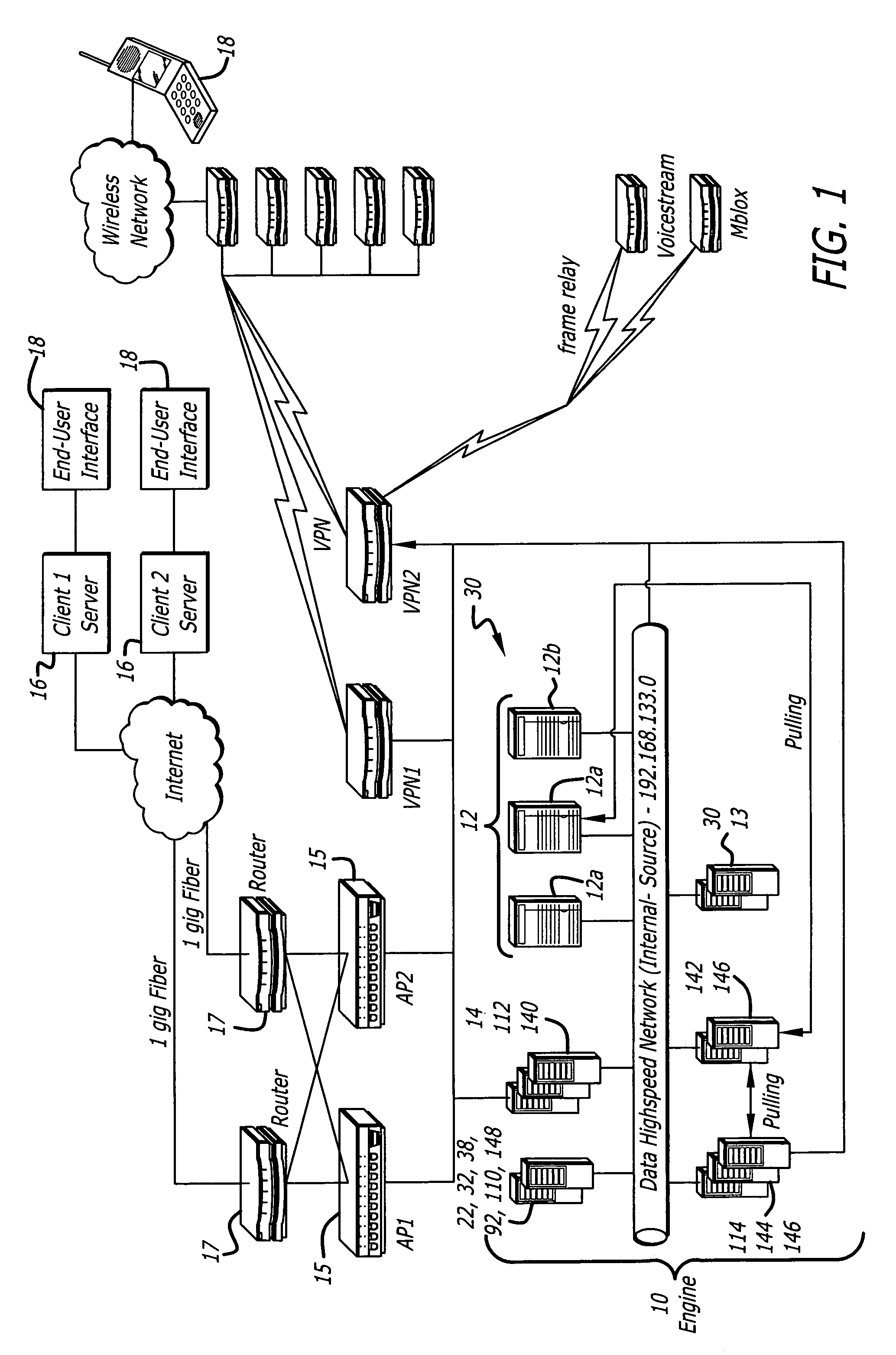
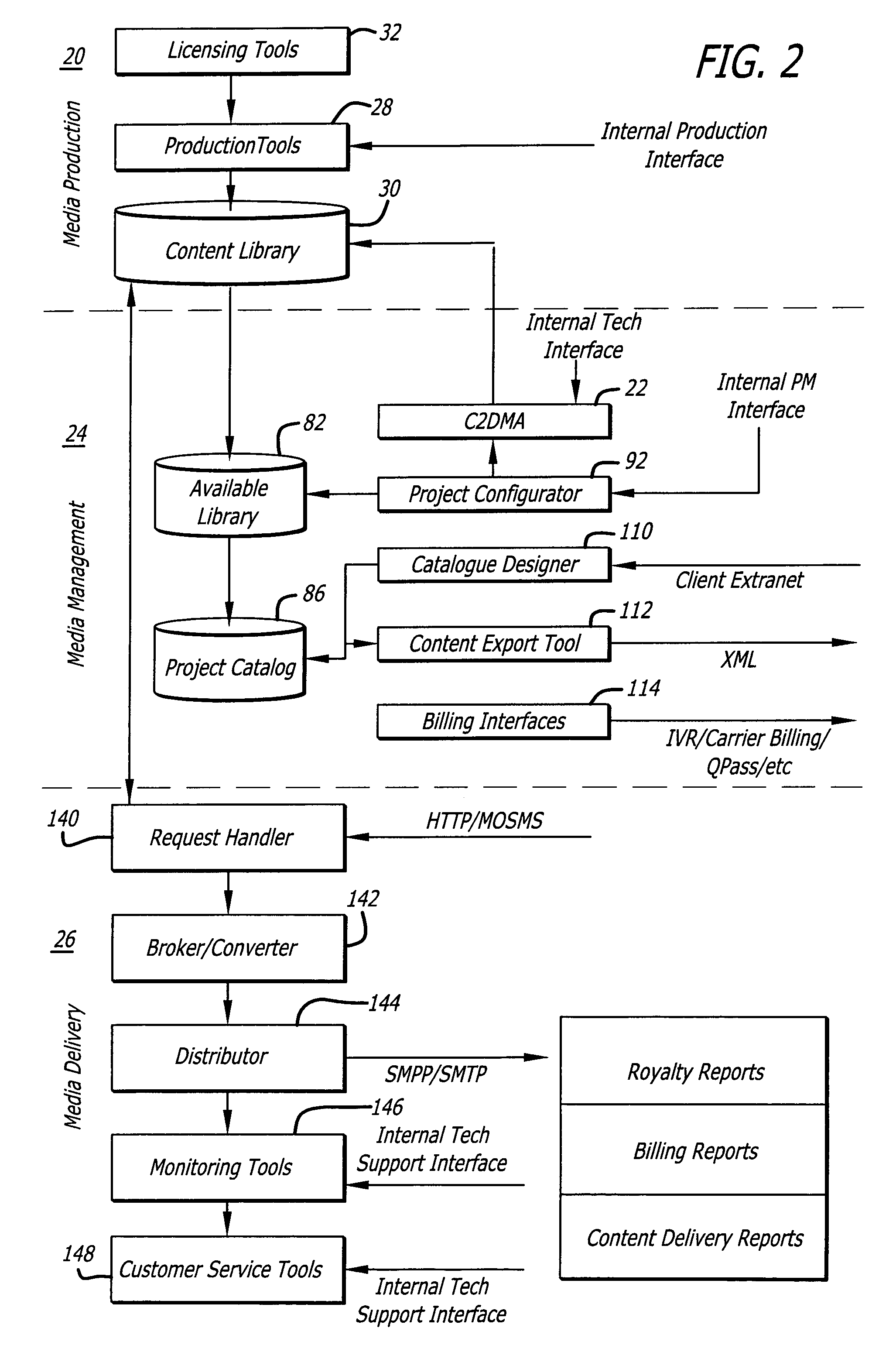
System for supporting production, management and delivery of media content for wireless devices
InactiveUS7461067B2Rule out the possibilityData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalMedia typeVia device
In a system for providing media content to a communication device, a device capabilities determination is made by a rules engine that compares content attributes with constraints on those attributes for a device. Metadata describing the content is derived and entered into a database. As the specifications of different devices are entered into the system, corresponding constraints are associated with the devices that tell the engine the valid range of values for the content attributes. The engine creates an available content library for each class of devices by excluding all instances of content that have attributes outside the range of values prescribed in the constraints. A similar rule set determines whether the content can be distributed through a particular delivery channel, based on the distribution channel capacity to support a media type. The subset of content that passes both the device capabilities tests and the distribution capability tests is viable for delivery to a device over a particular distribution channel.
Owner:VOLTARI OPERATING
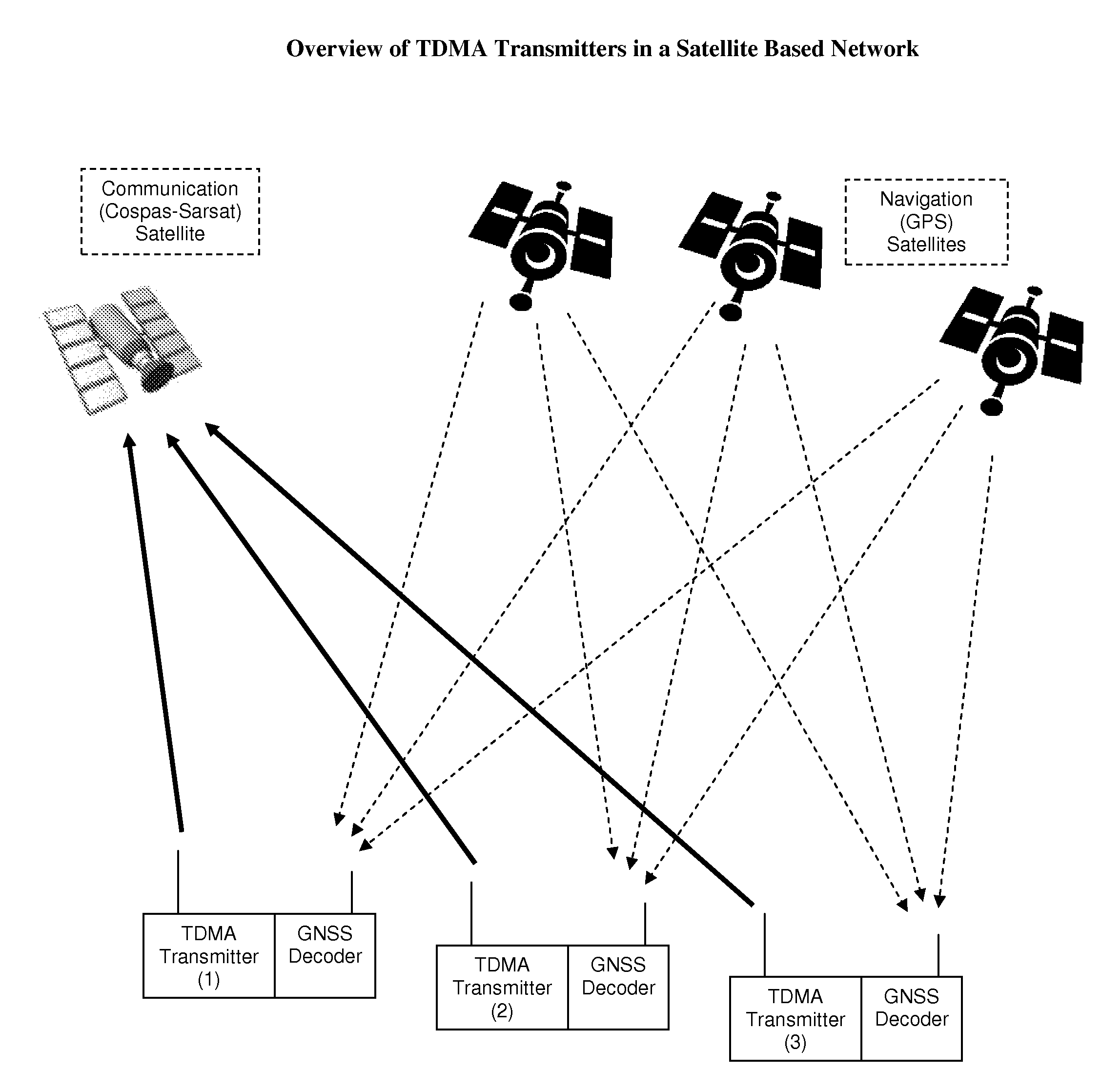
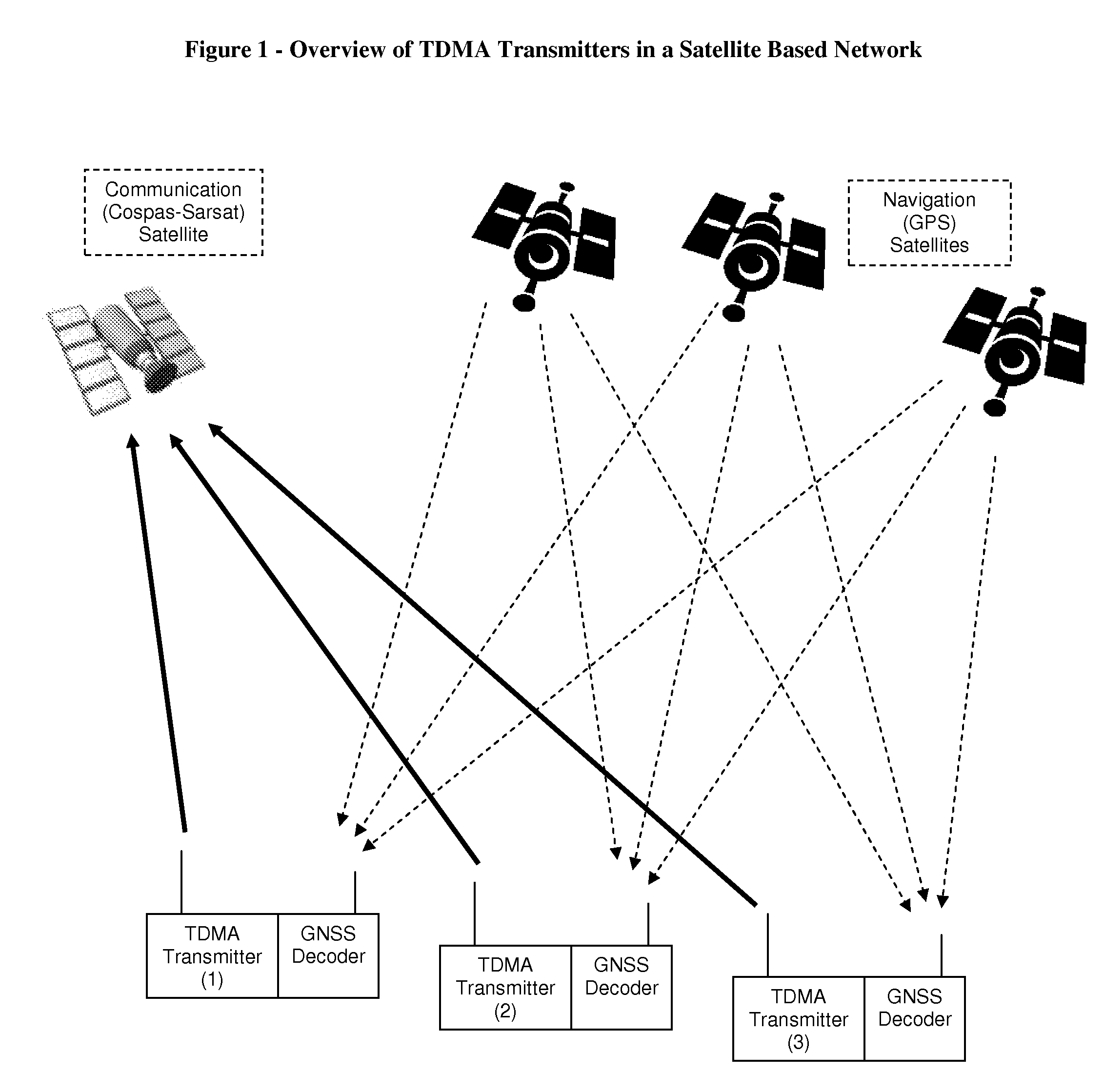
Increasing channel capacity of TDMA transmitters in satellite based networks
InactiveUS7440427B1Decrease transmission collision rateIncrease channel capacityTime-division multiplexLoop networksGeolocationEngineering
The present invention discloses a method for increasing the channel capacity of a communications network, comprising a plurality of one-way TDMA transmitters sharing said channel, and at least one compatible receiver, by reducing transmission collisions among said transmitters. This is achieved by coupling a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) decoder, such as a GPS receiver, to each transmitter, and limiting transmissions to discrete time slots, determined by timing signals provided by said GNSS. Further, this basic set of time slots is divided into several sub sets, and each transmitter selects a sub set of time slots according to its geographic location, in order to enable reusing time slots in spaced apart areas, as frequencies are reused in cellular networks. Then, each transmitter selects its own transmission time slot, from said sub set, in a way that statistically minimizes collisions among nearby transmitters. The present invention does not intend to ensure collision-free communications, yet is projected to reduce the transmission collision rate among simplex in nature transmitters, which have no means to detect other transmissions, or discover if a transmission was successful. One embodiment of this invention is related to distress radio beacons in satellite based Search and Rescue (SAR) systems, such as Cospas-Sarsat.
Owner:MOBIT TELECOM
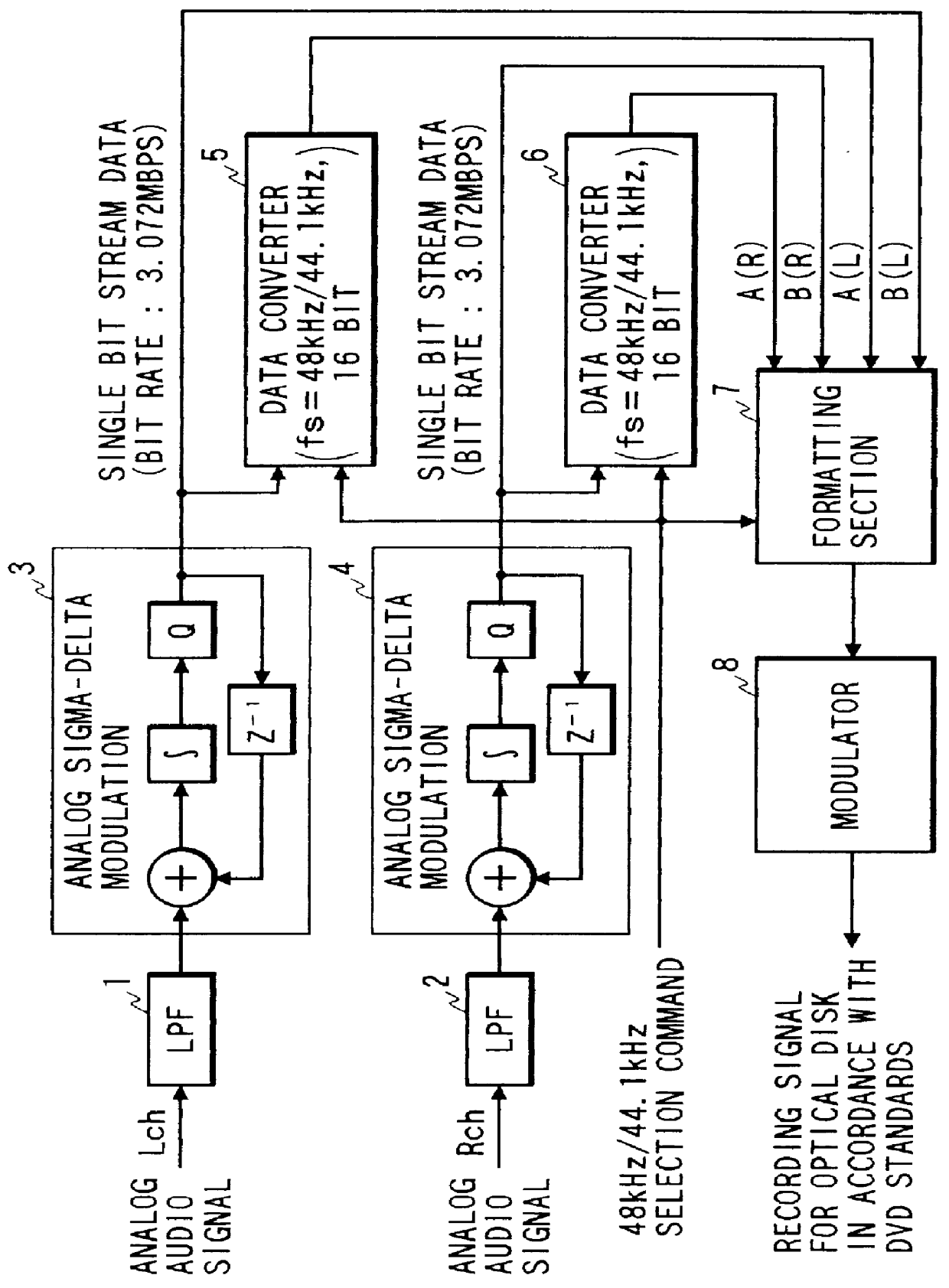
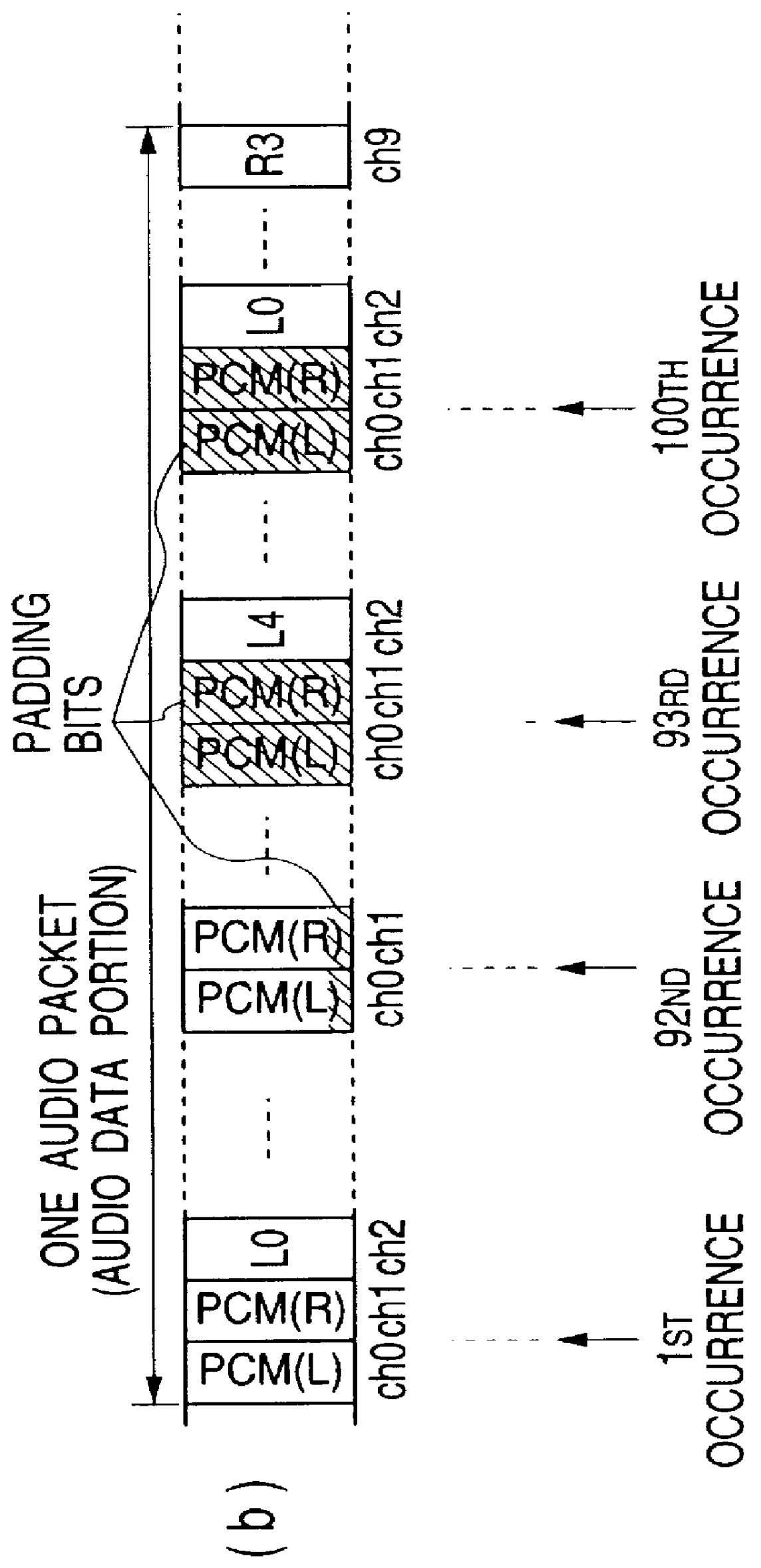
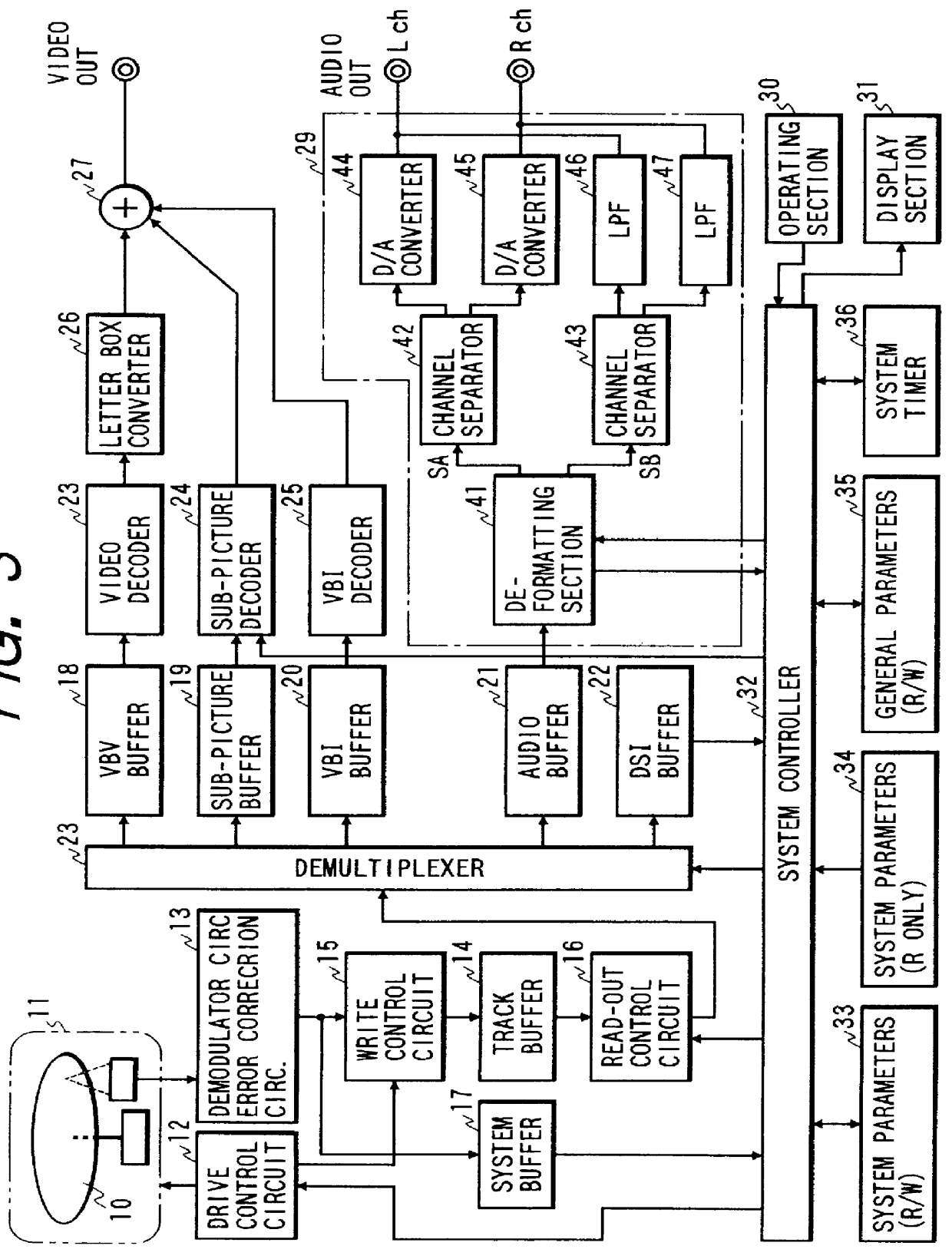
DVD-compatible optical recording disk conveying audio signals encoded both as PCM data and as single bit stream data generated by sigma-delta modulation, and encoder apparatus and decoder apparatus for same
An optical recording disk has audio signals recorded as data encoded in accordance with DVD specifications, both as PCM data and as single bit stream data that are generated by sigma-delta modulation, thereby providing both the improved audio reproduction capability of single bit stream data and also compatibility with existing types of DVD playback apparatus. Data are recorded using proposed new DVD stream modes, having 10 data channels, 48 kHz PCM sampling frequency and 16 or 20 bits / sample, with the ratio (2:8) of data channel capacities allocated to the PCM data and single bit stream data being made identical to the ratio of the respective bit rates at which the PCM data and single bit stream data are generated.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Method and system for decoding
ActiveUS20120054576A1Improve performanceIncreased complexityCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesValue setCommunication link
Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) codes offer error correction at rates approaching the link channel capacity and reliable and efficient information transfer over bandwidth or return-channel constrained links with data-corrupting noise present. They also offer performance approaching channel capacity exponentially fast in terms of the code length, linear processing complexity, and parallelism that scales with code length. They also offer challenges relating to decoding complexity and error floors limiting achievable bit-error rates. Accordingly encoders with reduced complexity, reduced power consumption and improved performance are disclosed with various improvements including simplifying communications linking multiple processing nodes by passing messages where pulse widths are modulated with the corresponding message magnitude, delaying a check operation in dependence upon variable node states, running the decoder multiple times with different random number generator seeds for a constant channel value set, and employing a second decoder with a randomizing component when the attempt with the first decoder fails.
Owner:POLAR TECH
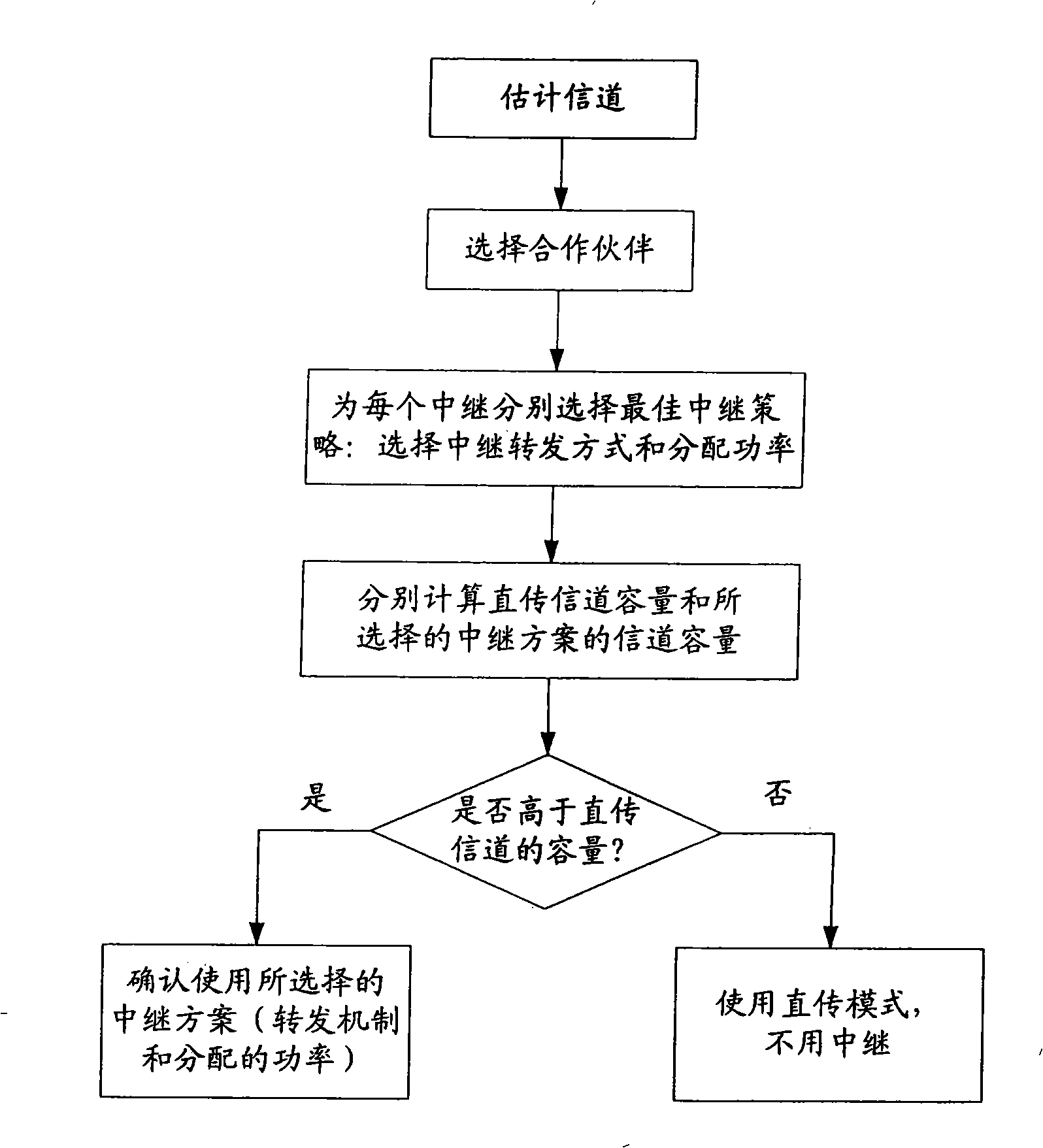
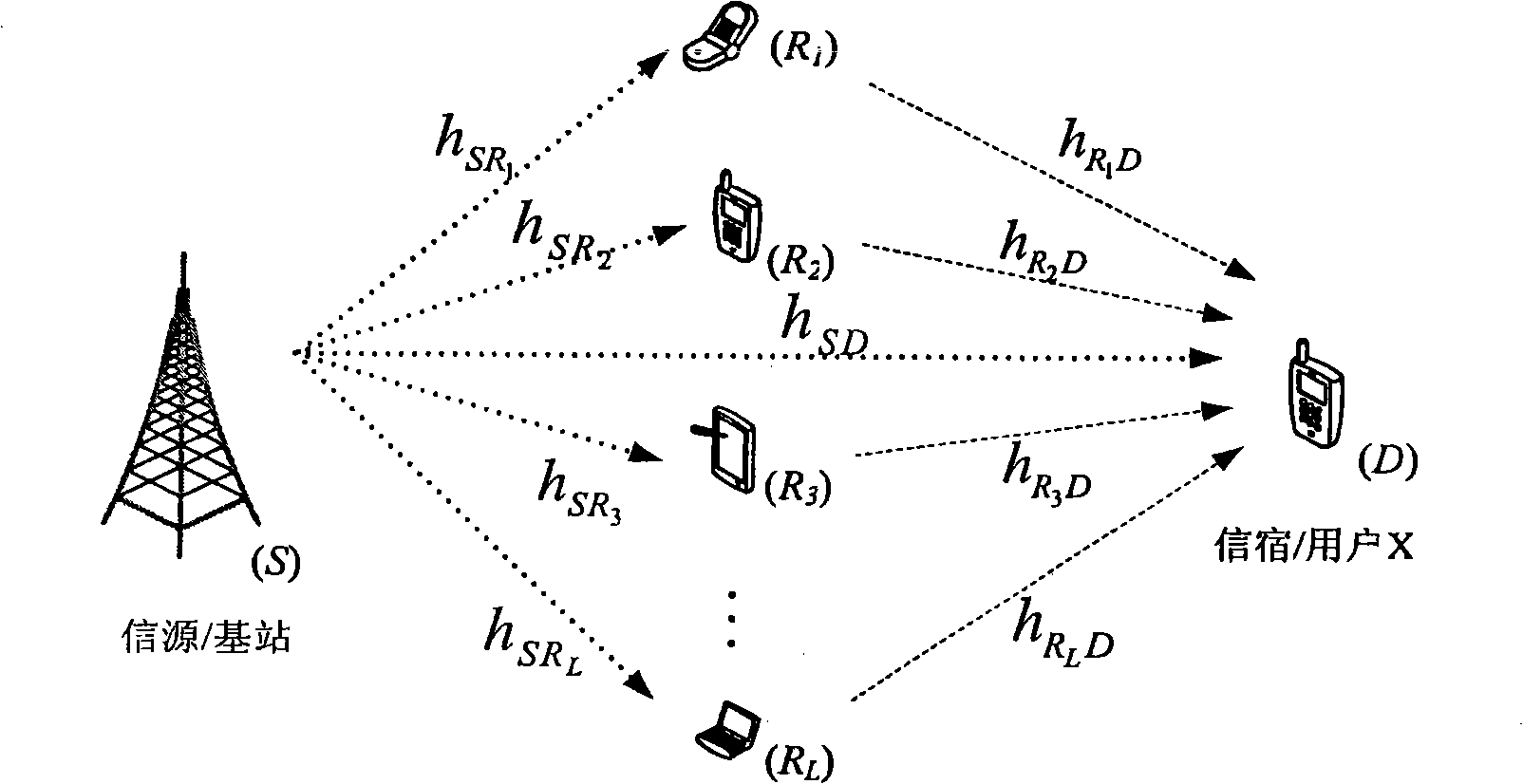
Method for self-adaption selection of relay strategy for multi-relay collaboration communication
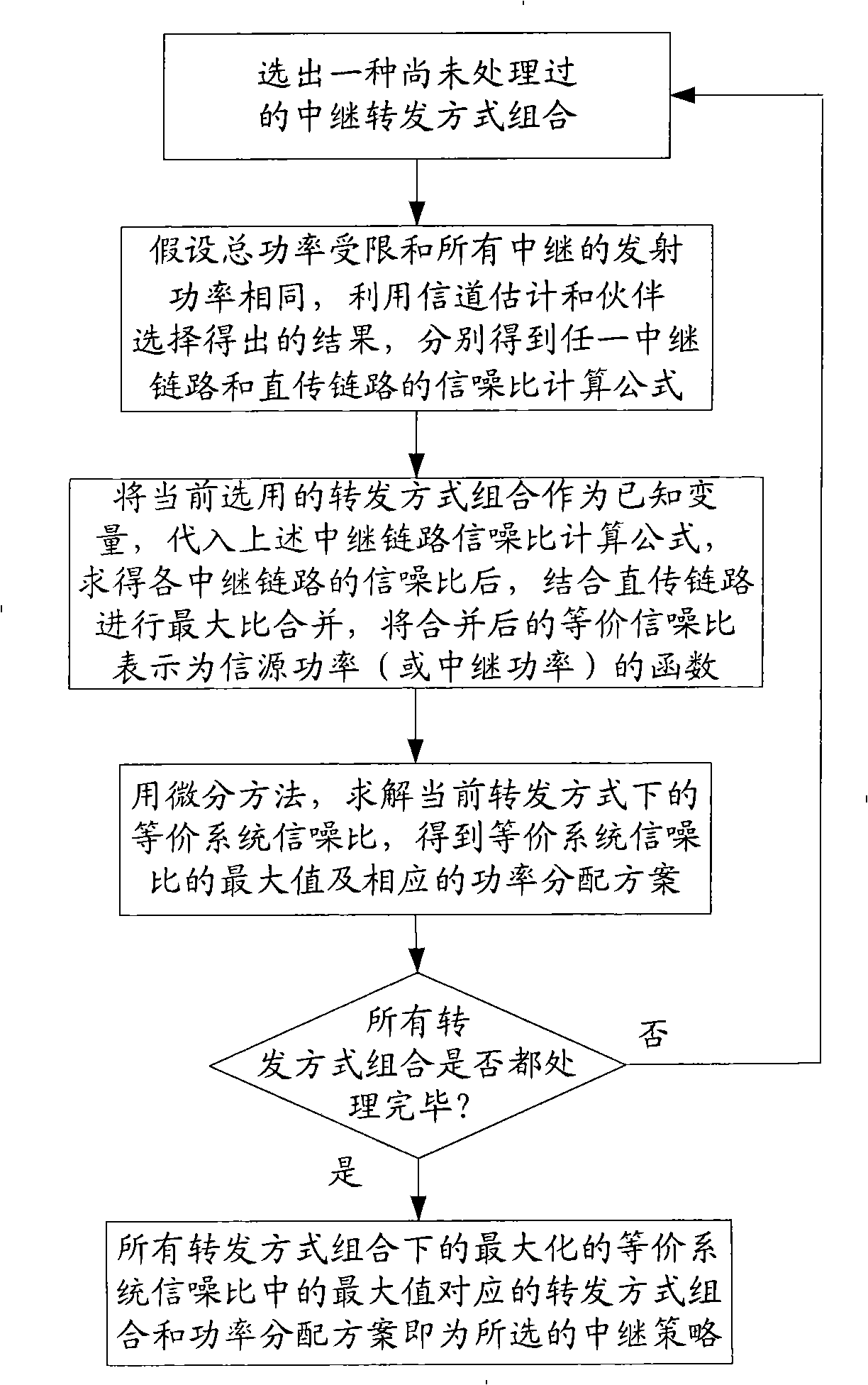
InactiveCN101282199AImprove transmission performanceBaseband system detailsTransmission control/equalisingCurrent channelTransmission channel
A self-adapting method which is used for a relay strategy of a multiple-relay cooperative communication respectively selects an appropriate retransmission mode and distributes a corresponding transmission power for each relay code according to the state of current real-time channel. Or a direct transmission mode is decided to be selected in order to realize the maximization of the channel capacity of the system and provide a high-efficiency communication under the state of reliability. The method mainly comprises the following operation procedures: (1) estimating the channel, (2) selecting a cooperative partner, (3) choosing an optimum relay strategy for each rely with the result of channel estimation and partner selection, (4) respectively calculating the capacity of the direct transmission channel and the capacity of the channel of the selected relay plan according to the formula of channel capacity, and (5) taking the plan with larger capacity of the equivalent channel as a final selection result. The method determines whether the relay is used according to the current channel state, and selects an optimum retransmission strategy for each relay under the precondition that the reliability and availability of the communication are considered and reasonably distribute power between the signal source and each relay.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com