Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1065 results about "Channel width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Channel width. [′chan·əl ‚width] (geology) The distance across a stream or channel as measured from bank to bank near bankful stage. (nuclear physics) The part of the total energy width of a nuclear energy level that corresponds to a particular mode of decay.
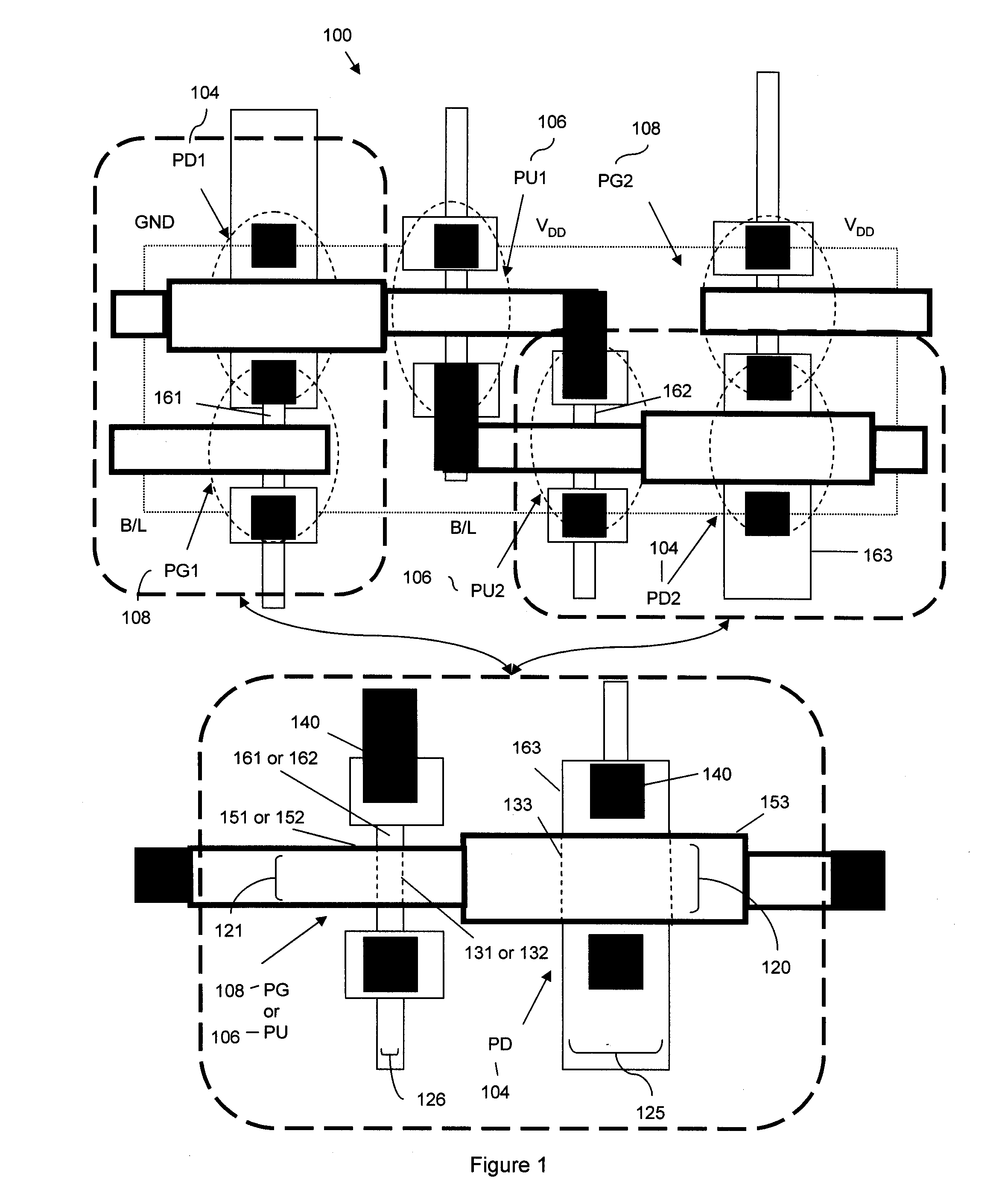
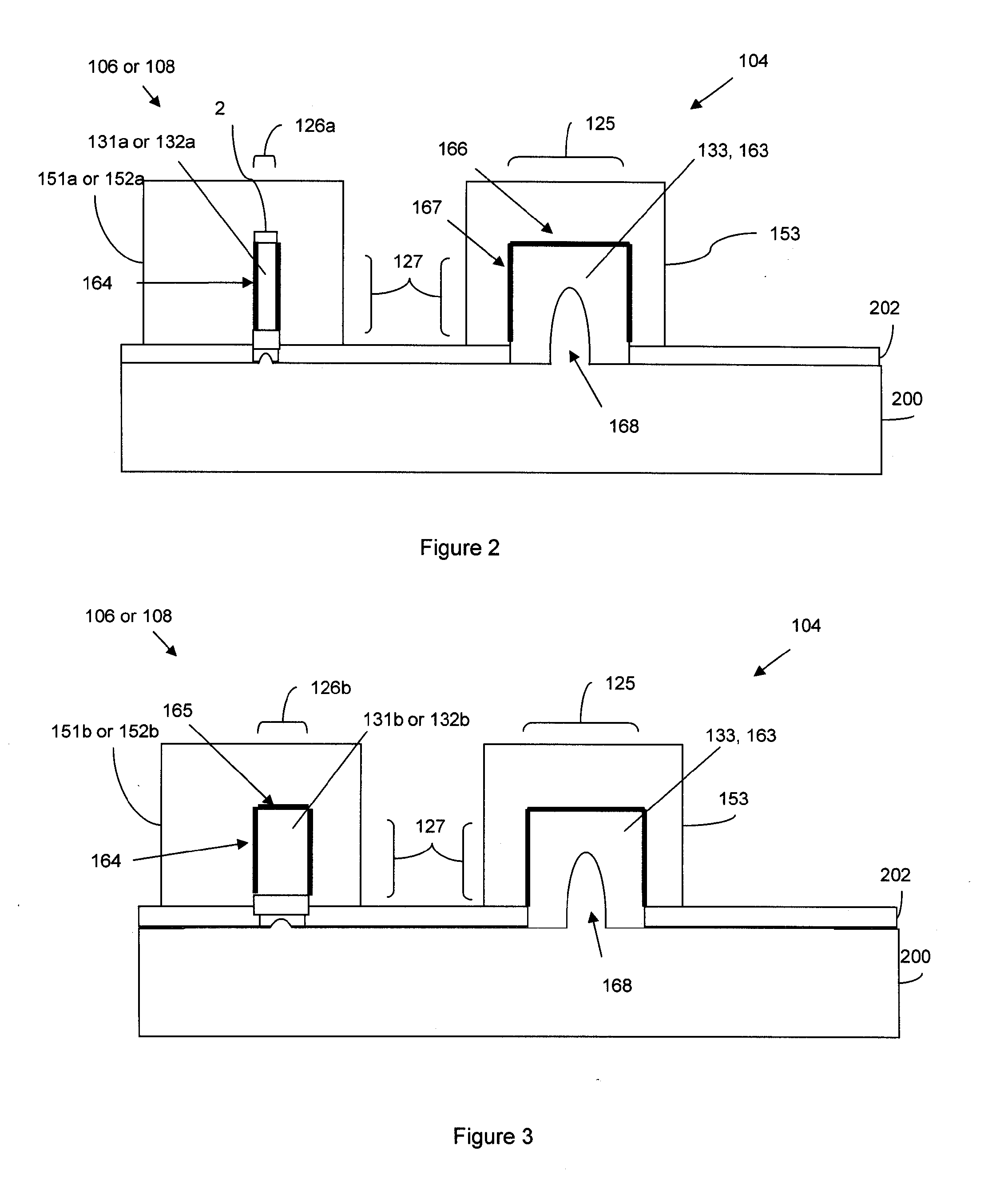
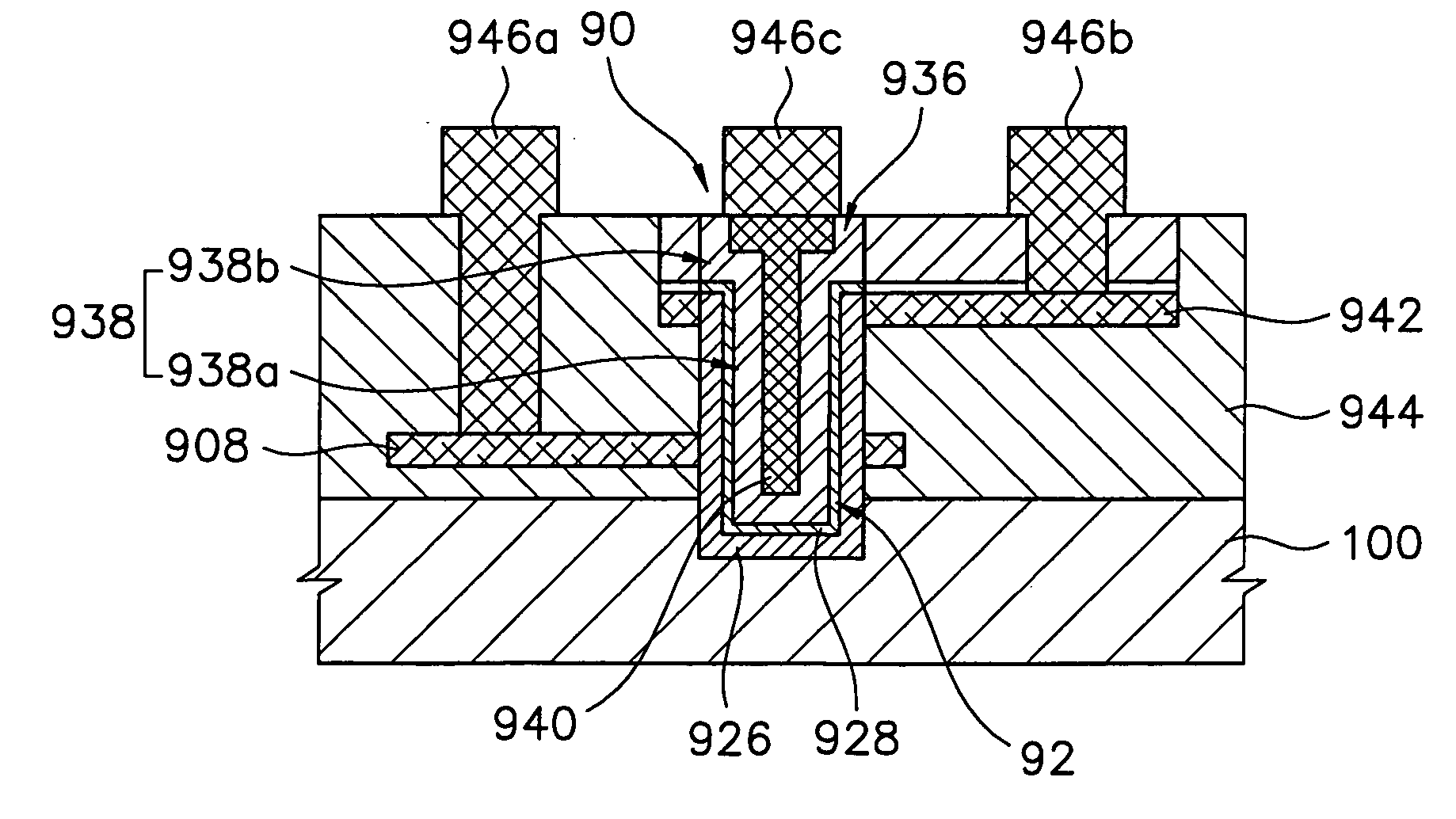
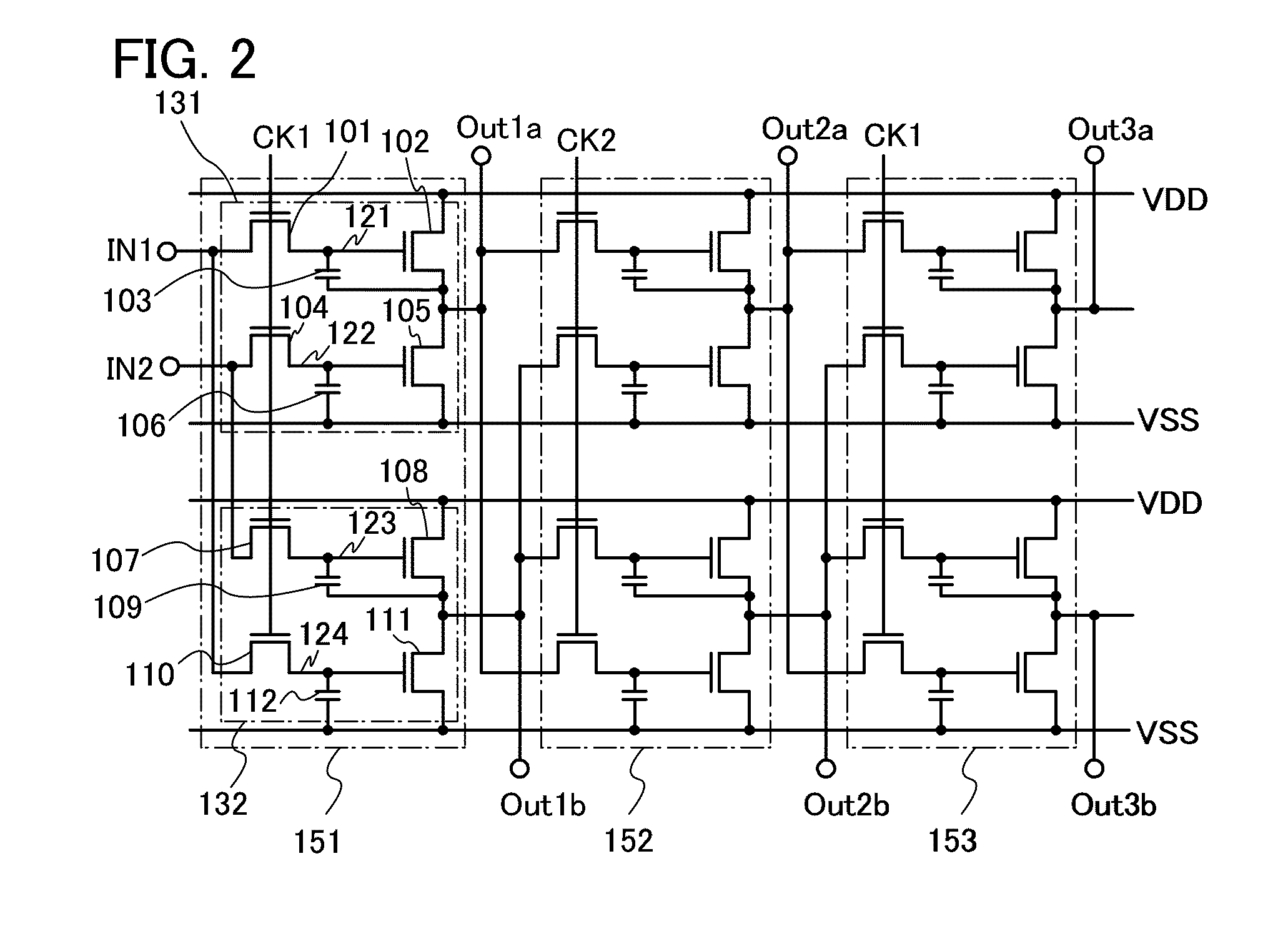
SRAM and logic transistors with variable height multi-gate transistor architecture
Multi-gate transistors having different channel widths formed on non-planar semiconductor bodies have different sidewall heights and method of manufacturing the same. In an embodiment, a multi-gate SRAM transistor is formed on a non-planar semiconductor body having a greater sidewall height than a non-planar semiconductor body utilized for a multi-gate logic transistor to improve performance of SRAM and logic transistors formed on the same substrate. In another embodiment, to reduce cell area, a first SRAM transistor is formed on a non-planar semiconductor body having a greater sidewall height than a non-planar semiconductor body utilized for a second multi-gate SRAM transistor.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Single-electron floating-gate MOS memory
A Single Electron MOS Memory (SEMM), in which one bit of information is represented by storing only one electron, has been demonstrated at room temperature. The SEMM is a floating gate Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) transistor in silicon with a channel width (about 10 nanometers) which is smaller than the Debye screening length of a single electron stored on the floating gate, and a nanoscale polysilicon dot (about 7 nanometers by 7 nanometers by 2 nanometers) as the floating gate which is positioned between the channel and the control gate. An electron stored on the floating gate can screen the entire channel from the potential on the control gate, and lead to: (i) a discrete shift in the threshold voltage; (ii) a staircase relation between the charging voltage and the shift; and (iii) a self-limiting charging process. The structure and fabrication of the SEMM is well adapted to the manufacture of ultra large-scale integrated circuits.
Owner:MINNESOTA RGT UNIV OF A CORP OF MN
Thin film transistor including low resistance conductive thin films and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7576394B2Decrease distance DHighly integratedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChannel widthSemiconductor
A thin film transistor includes a substrate, and a pair of source / drain electrodes (i.e., a source electrode and a drain electrode) formed on the substrate and defining a gap therebetween. A pair of low resistance conductive thin films are provided such that each coats at least a part of one of the source / drain electrodes. The low resistance conductive thin films define a gap therebetween. An oxide semiconductor thin film layer is continuously formed on upper surfaces of the pair of low resistance conductive thin films and extends along the gap defined between the low resistance conductive thin films so as to function as a channel. Side surfaces of the oxide semiconductor thin film layer and corresponding side surfaces of the low resistance conductive thin films coincide with each other in a channel width direction of the channel.
Owner:KOICHI IND PROMOTION CENT +1
Electro-optical device and electronic device
InactiveUS20040065902A1Simple structureTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide an EL display device having a high operation performance and reliability. The switching TFT 201 formed within a pixel has a multi-gate structure, which is a structure which imposes an importance on reduction of OFF current value. Further, the current control TFT 202 has a channel width wider than that of the switching TFT to make a structure appropriate for flowing electric current. Morever, the LDD region 33 of the current control TFT 202 is formed so as to overlap a portion of the gate electrode 35 to make a structure which imposes importance on prevention of hot carrier injection and reduction of OFF current value.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Multi-height FinFETS
InactiveUS6909147B2Raise the ratioReduce yieldTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorChannel width
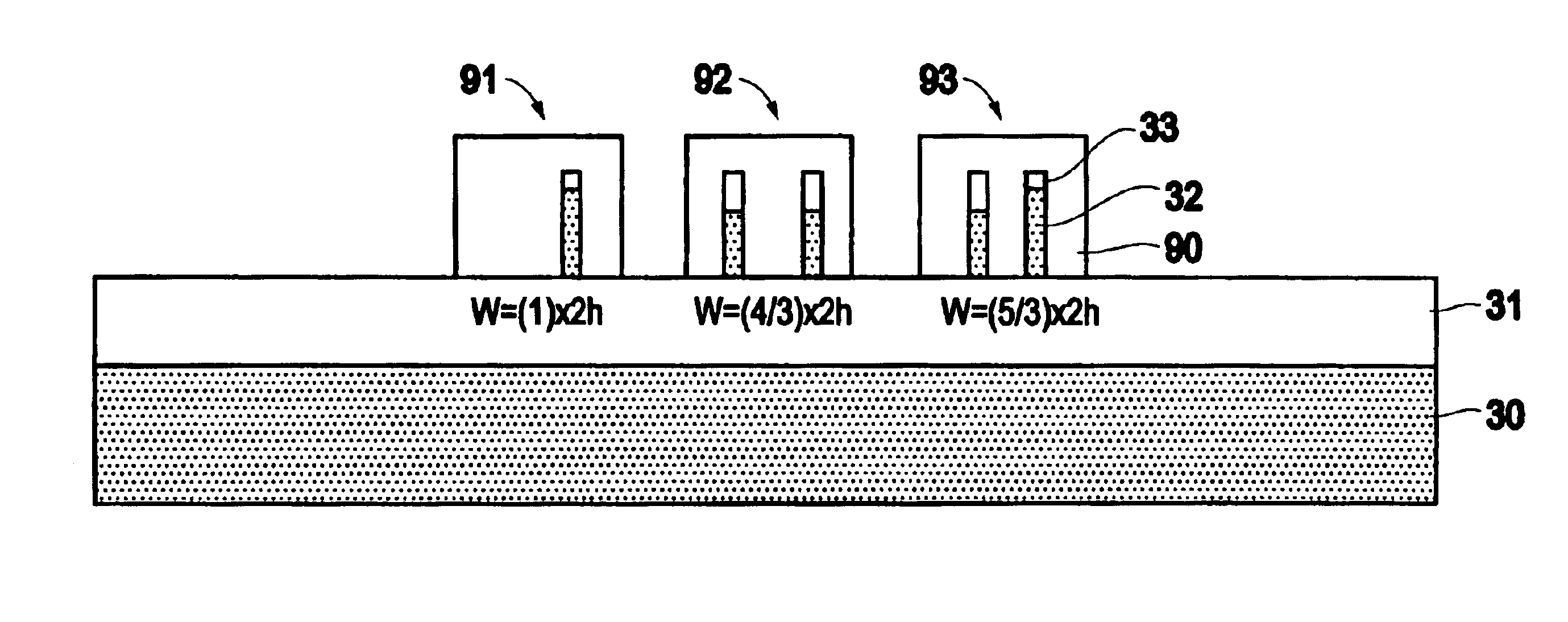
The present invention provides a FinFET device that has a first fin and a second fin. Each fin has a channel region and source and drain regions that extend from the channel region. The fins have different heights. The invention has a gate conductor positioned adjacent the fins. The gate conductor runs perpendicular to the fins and crosses the channel region of each of the first fin and second fin. The fins are parallel to one another. The ratio of the height of the first fin to the height of the second fin comprises a ratio of one to 2 / 3. The ratio is used to tune the performance of the transistor and determines the total channel width of the transistor.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
SRAM cell
InactiveUS20070108528A1Increase effective widthImprove carrying capacityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriving currentEngineering
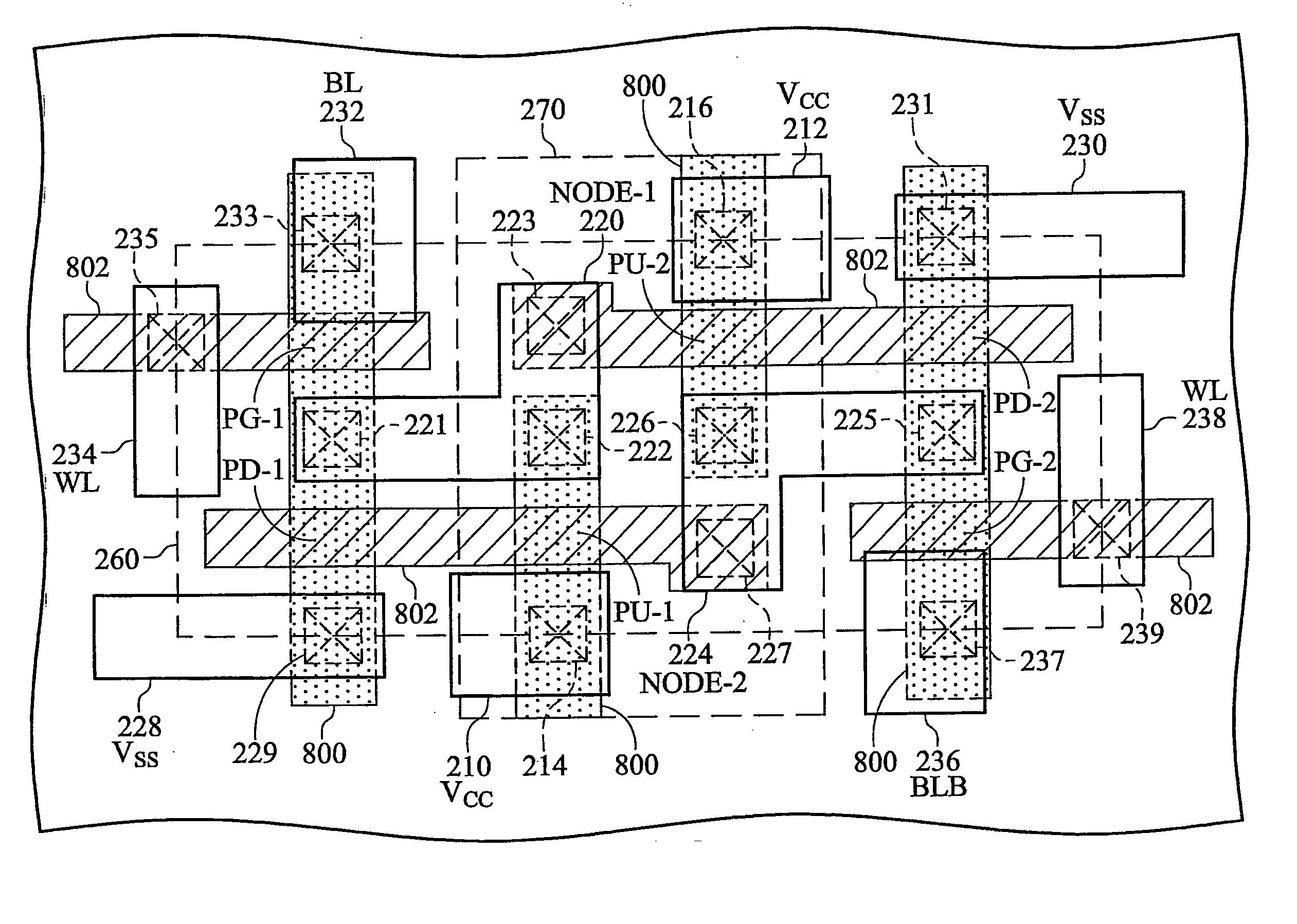
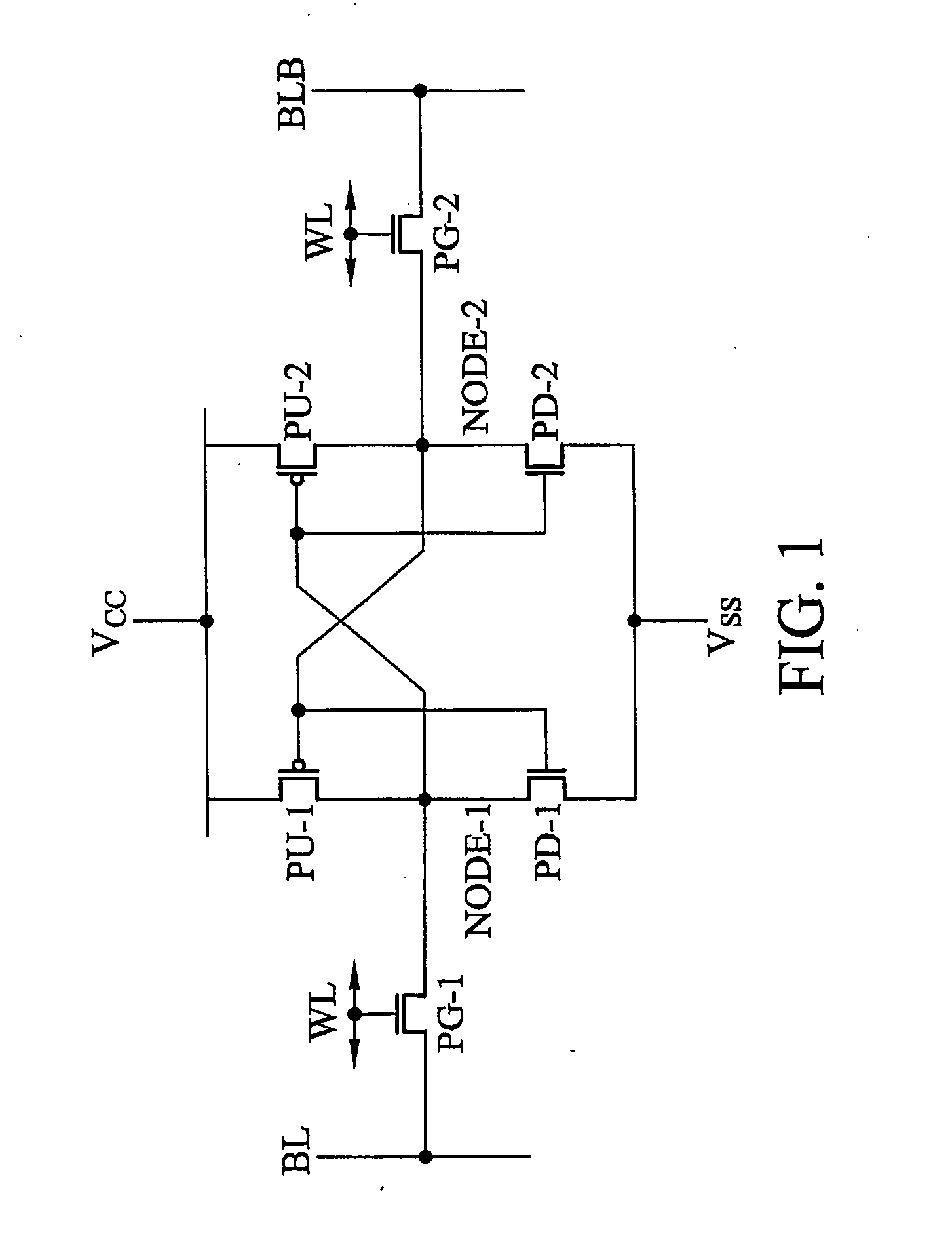
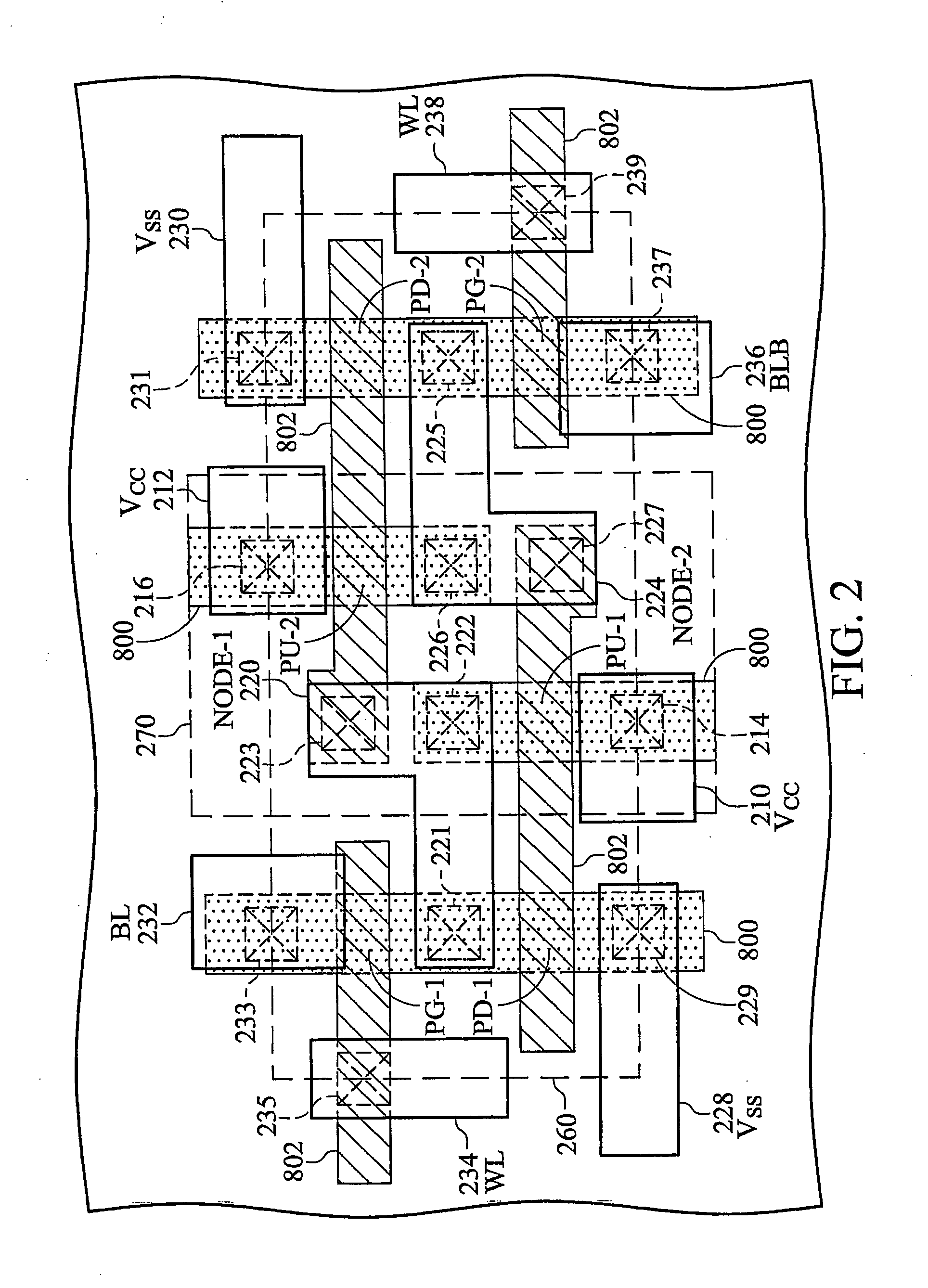
Disclosed is an SRAM cell on an SOI, bulk or HOT wafer with two pass-gate n-FETs, two pull-up p-FETs and two pull-down n-FETs and the associated methods of making the SRAM cell. The pass-gate FETs and pull-down FETs are non-planar fully depleted finFETs or trigate FETs. The pull-down FETs comprise non-planar partially depleted three-gated FETs having a greater channel width and a greater gate length and, thus, a greater drive current relative to the pass-gate and pull-up FETs. Additionally, for optimal electron mobility and hole mobility, respectively, the channels of the n-FETs and p-FETs can comprise semiconductors with different crystalline orientations.
Owner:IBM CORP
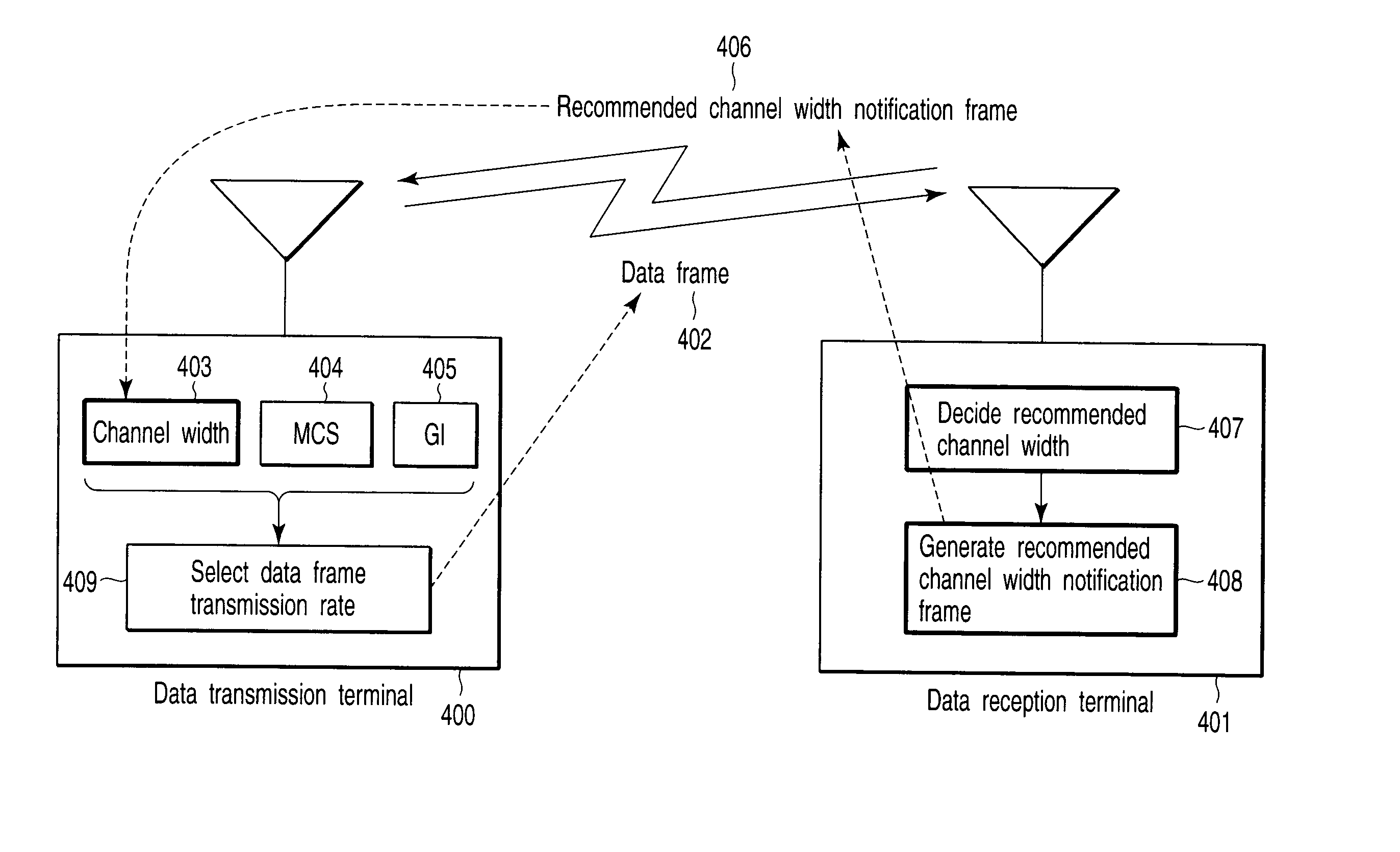
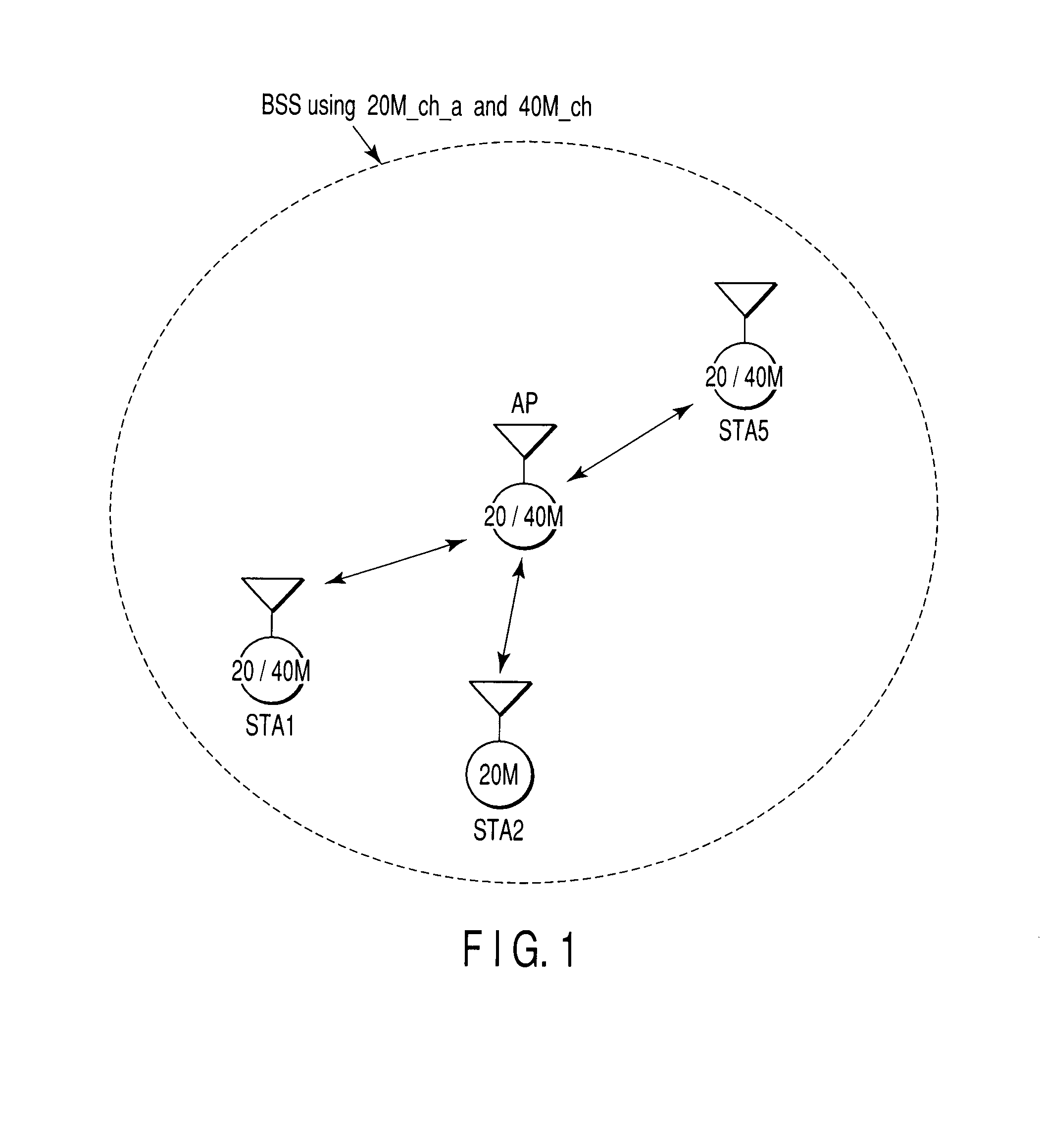
Radio communication apparatus and radio communication method
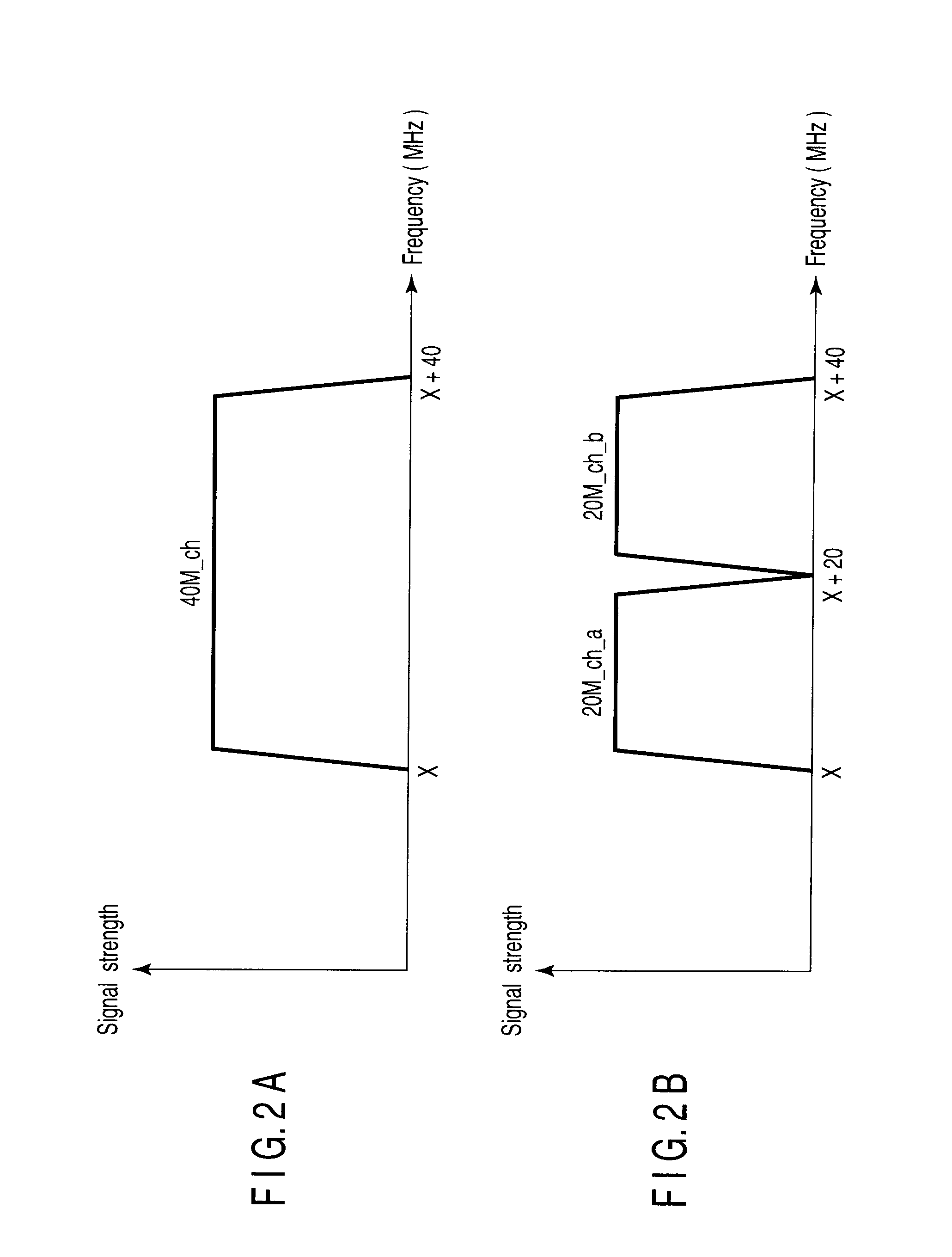
A radio communication apparatus that performs first radio communication using a first channel among two first channels each having a first channel width, and second radio communication using a second channel having a second channel width that is wider than the first channel width and also having a channel width overlapping with the two first channels. The apparatus includes an interference detection device which detects that interference occurs in the first channel among the two first channels, and a frame generation unit which generates a notification frame that recommends the use of only the first channel width. An instruction unit instructs the frame generation unit to generate the notification frame when the occurrence of interference is detected by the interference detection device. A frame transmission unit transmits the notification frame generated from the frame generation unit in response to the instruction from the instruction unit.
Owner:PALMIRA WIRELESS AG
Memory cell structure
An SRAM device includes an SRAM cell in a deep NWELL region in a substrate. PWELL regions in the SRAM cell occupy less than about 65% of the cell area of the SRAM cell. A ratio of a longer side of a cell area of the SRAM cell to a shorter side of the SRAM cell is larger than about 1.8. A total area of the active regions in the plurality of NMOS transistors in the SRAM cell occupies less than about 25% of the SRAM cell area. A ratio of the channel width of a pull up transistor in the SRAM cell to the channel width of a pull down transistor in the SRAM cell is greater than about 0.8. The SRAM cell further includes a boron free inter-layer-dielectric layer, an inter-metal-dielectric layer with dielectric constant less than about 3, and a polyimide layer with a thickness of less than about 20 microns.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20050068477A1Improve image qualityStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayParasitic capacitance
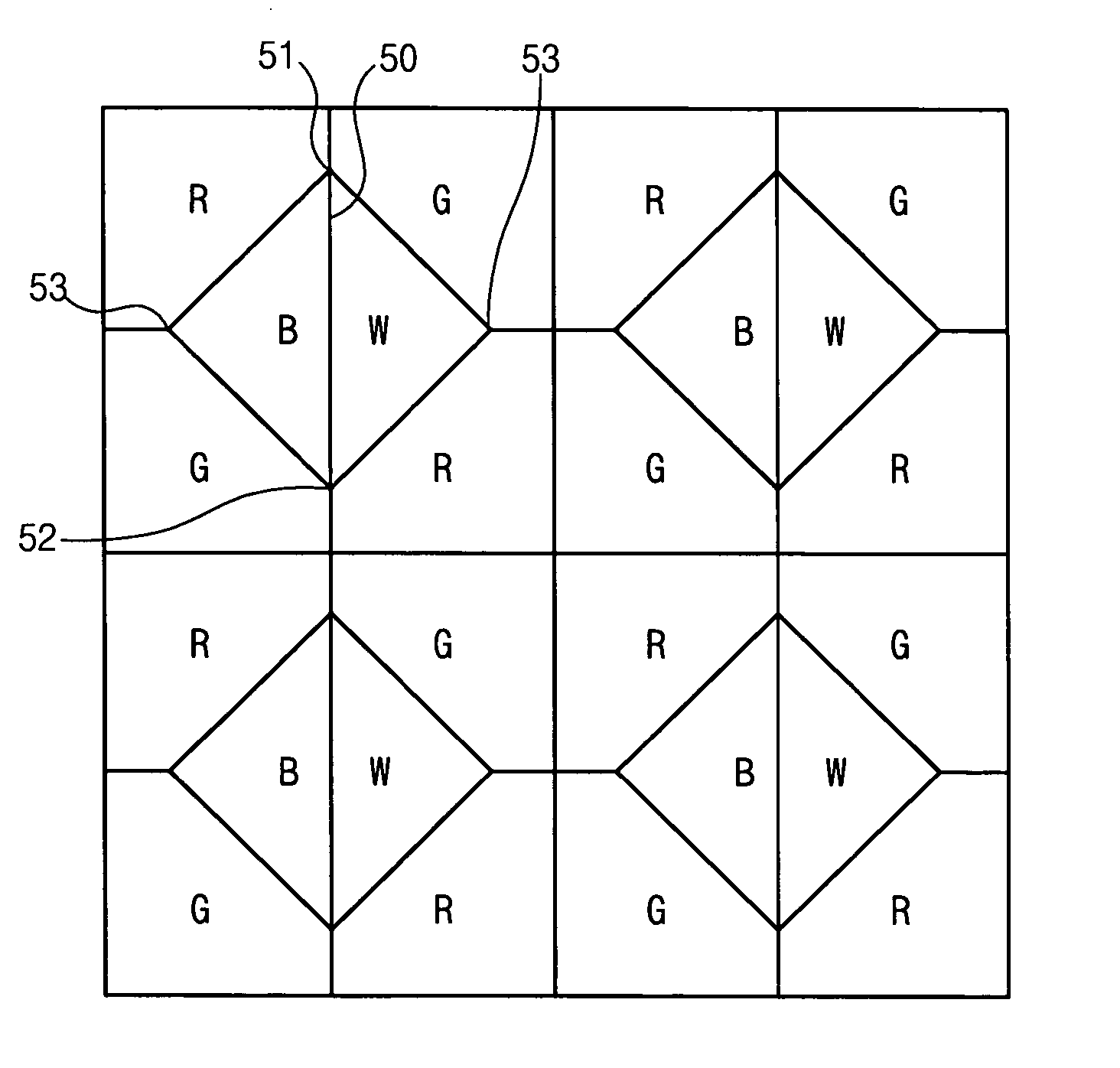
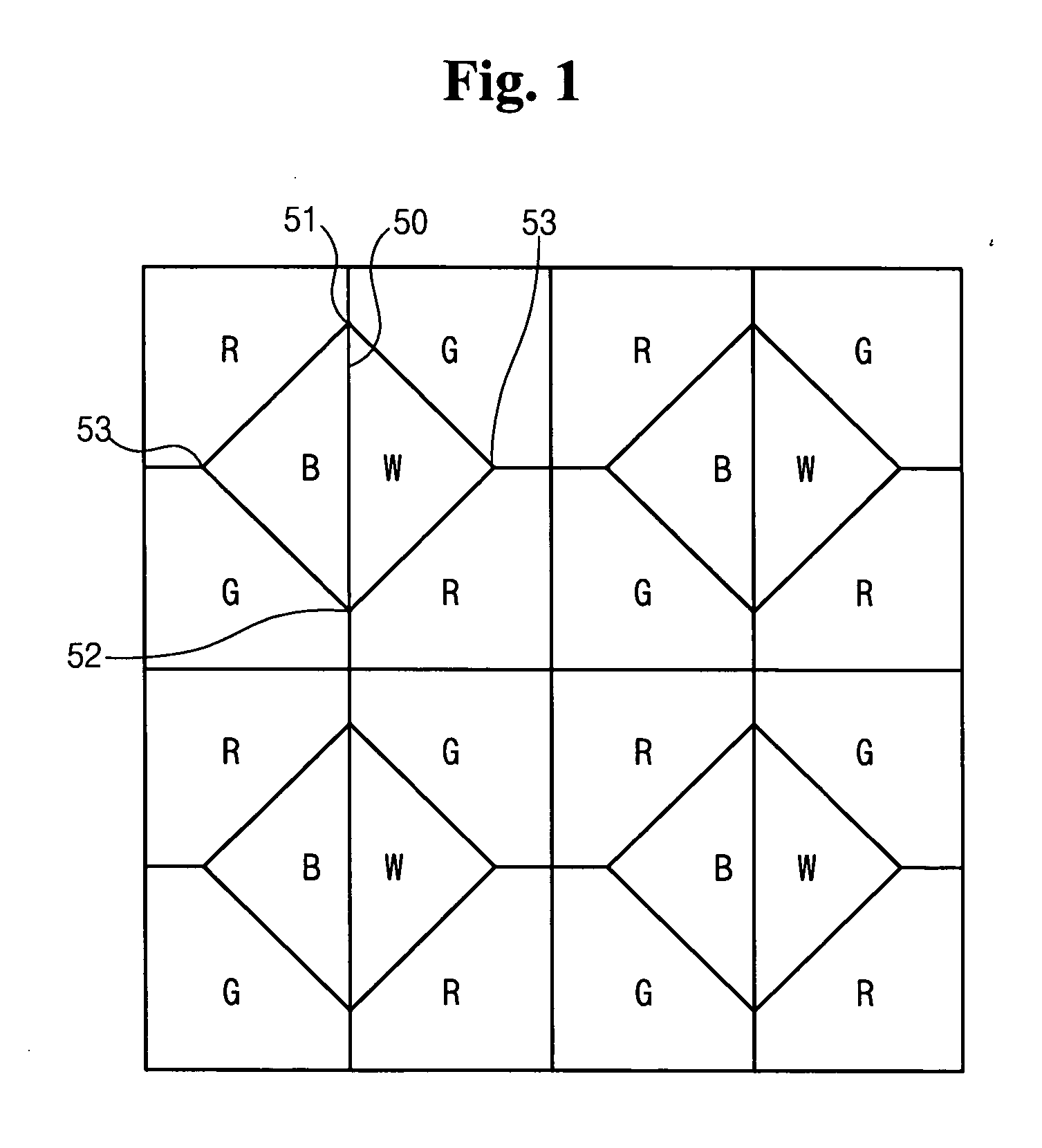
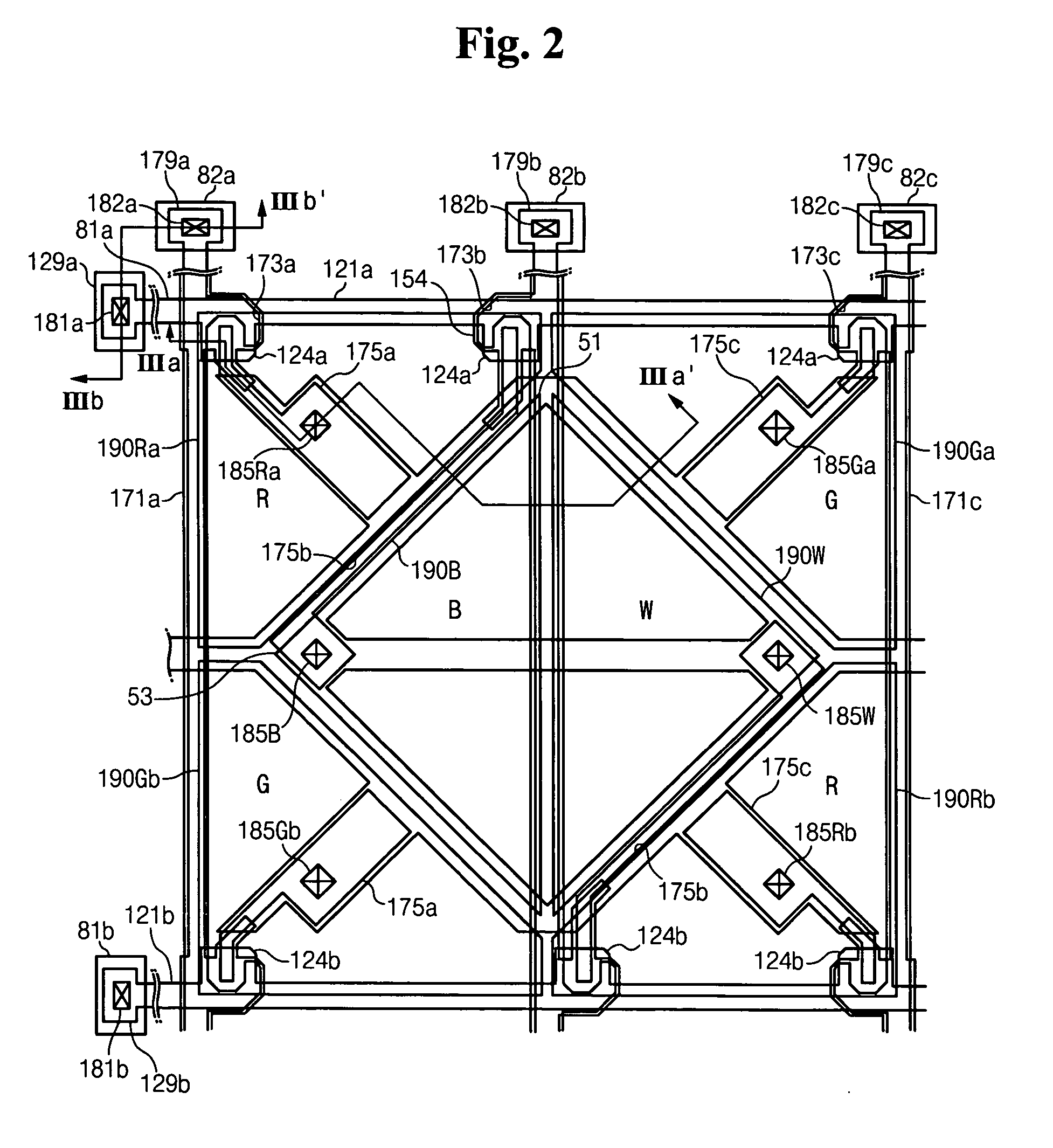
A liquid crystal display comprising an insulating substrate; a plurality of gate lines formed on the insulating substrate; a plurality of data lines formed on the insulating substrate and crossing the gate lines; a plurality of switching elements connected to the gate lines and data lines; and a plurality of pixel electrodes connected to the switching element, and wherein dots each having a red, green, blue, and white pixels are successively arranged, the ratios the liquid crystal capacitance, the storage capacitance, the parasitic capacitance, and ratio of channel width and length (W / L) of the switching elements between the red and green pixels and the blue and white pixels are same is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Metal-Gate High-K Reference Structure
Disclosed are embodiments of an integrated circuit structure that incorporates at least two field effect transistors (FETs) that have the same conductivity type and essentially identical semiconductor bodies (i.e., the same semiconductor material and, thereby the same conduction and valence band energies, the same source, drain, and channel dopant profiles, the same channel widths and lengths, etc.). However, due to different gate structures with different effective work functions, at least one of which is between the conduction and valence band energies of the semiconductor bodies, these FETs have selectively different threshold voltages, which are independent of process variables. Furthermore, through the use of different high-k dielectric materials and / or metal gate conductor materials, the embodiments allow threshold voltage differences of less than 700 mV to be achieved so that the integrated circuit structure can function at power supply voltages below 1.0V. Also disclosed are method embodiments for forming the integrated circuit structure.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
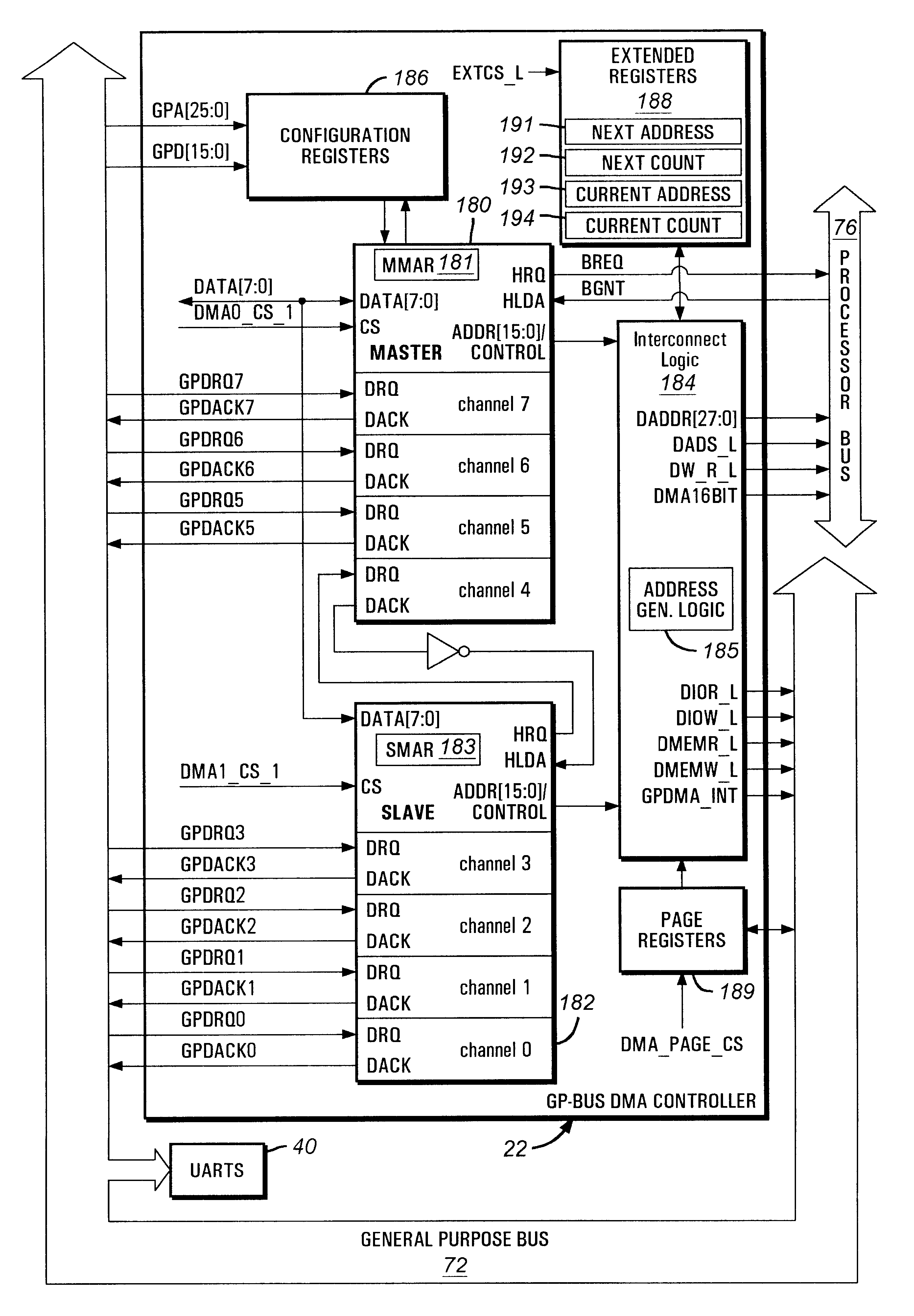
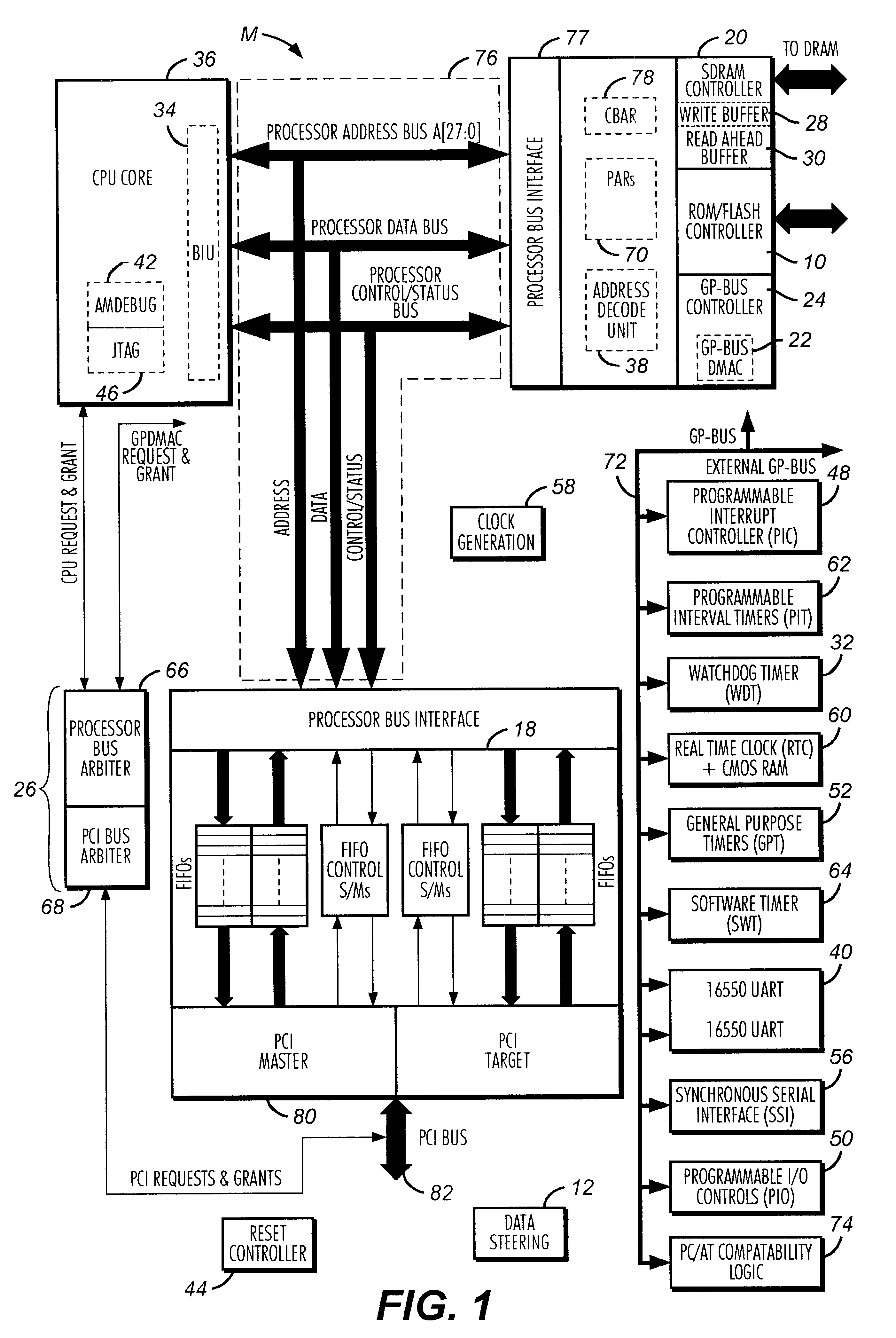
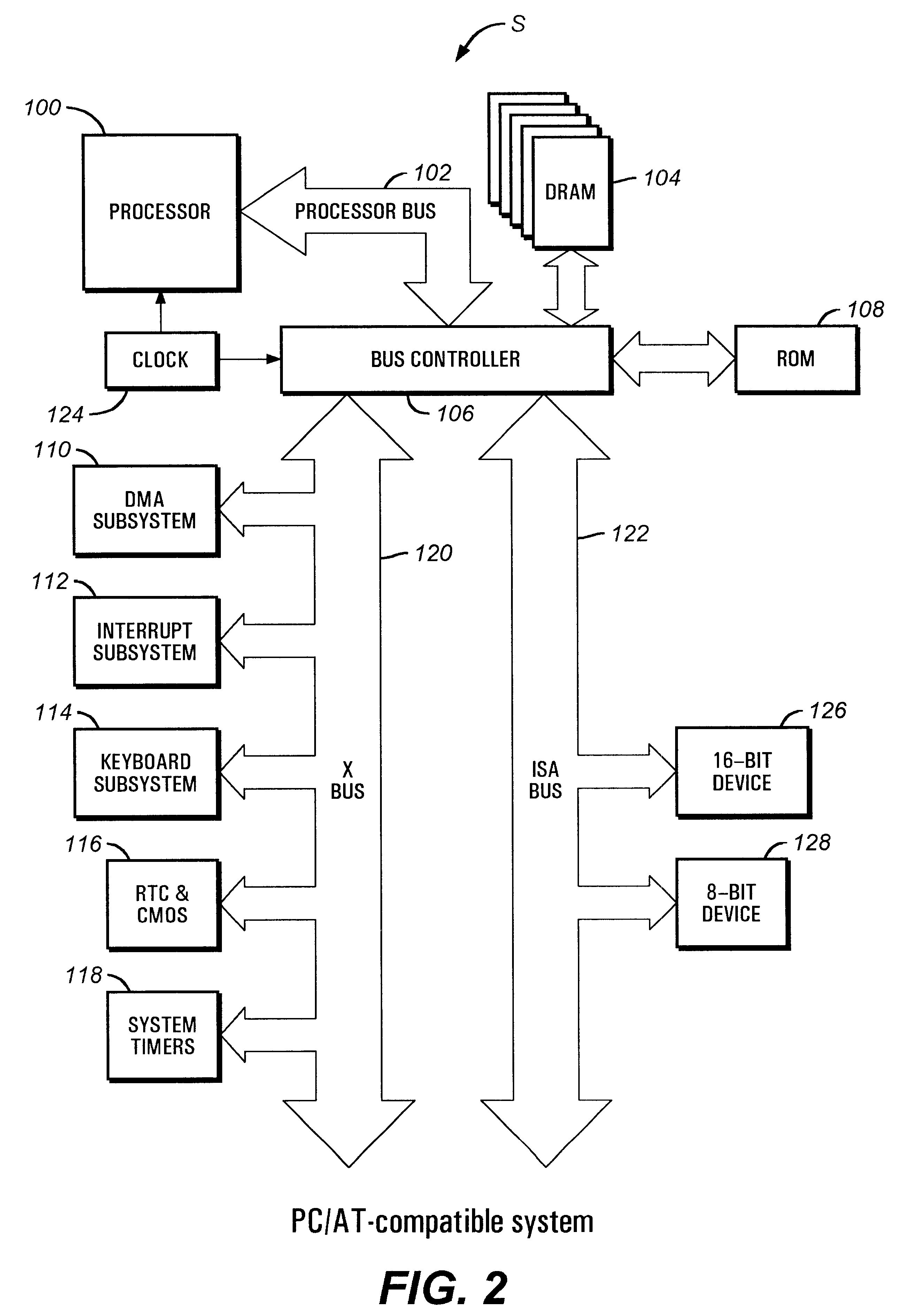
Direct memory access controller with channel width configurability support
A direct memory access (DMA) controller provides seven DMA channels configurable for a PC / AT compatible mode or an enhanced mode. In an enhanced mode of the DMA controller, three DMA master channels on a master DMA controller and a DMA channel on a slave DMA controller are individually configurable to be either 8-bit or 16-bit DMA channels. In addition, in the enhanced mode, a memory address can increment or decrement across a memory page boundary. The DMA controller includes a transfer count register selectively configured for 16-bit operation or 24-bit operation. The DMA controller also includes address generation logic selectively configured for 24-bit operation or 28-bit operation. In the PC / AT compatible mode, the DMA controller supports three 16-bit channels and four 8-bit channels. The DMA controller thus provides DMA channel width configurability.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Manufacturing method of thin film transistor including low resistance conductive thin films
InactiveUS20090269881A1Decrease distance DHighly integratedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesChannel widthSemiconductor
A manufacturing method of a thin film transistor includes forming a pair of source / drain electrodes on a substrate, such that the source / drain electrodes define a gap therebetween; forming low resistance conductive thin films, which define a gap therebetween, on the source / drain electrodes; and forming an oxide semiconductor thin film layer on upper surface of the low resistance conductive thin films and in the gap defined between the low resistance conductive thin films so that the oxide semiconductor thin film layer functions as a channel. The low resistance conductive thin films and the oxide semiconductor thin film layer are etched so that side surfaces of the resistance conductive thin films and corresponding side surfaces of the oxide semiconductor thin film layer coincide with each other in a channel width direction of the channel. A gate electrode is mounted over the oxide semiconductor thin film layer.
Owner:KOICHI IND PROMOTION CENT +1
Particle separation and concentration system
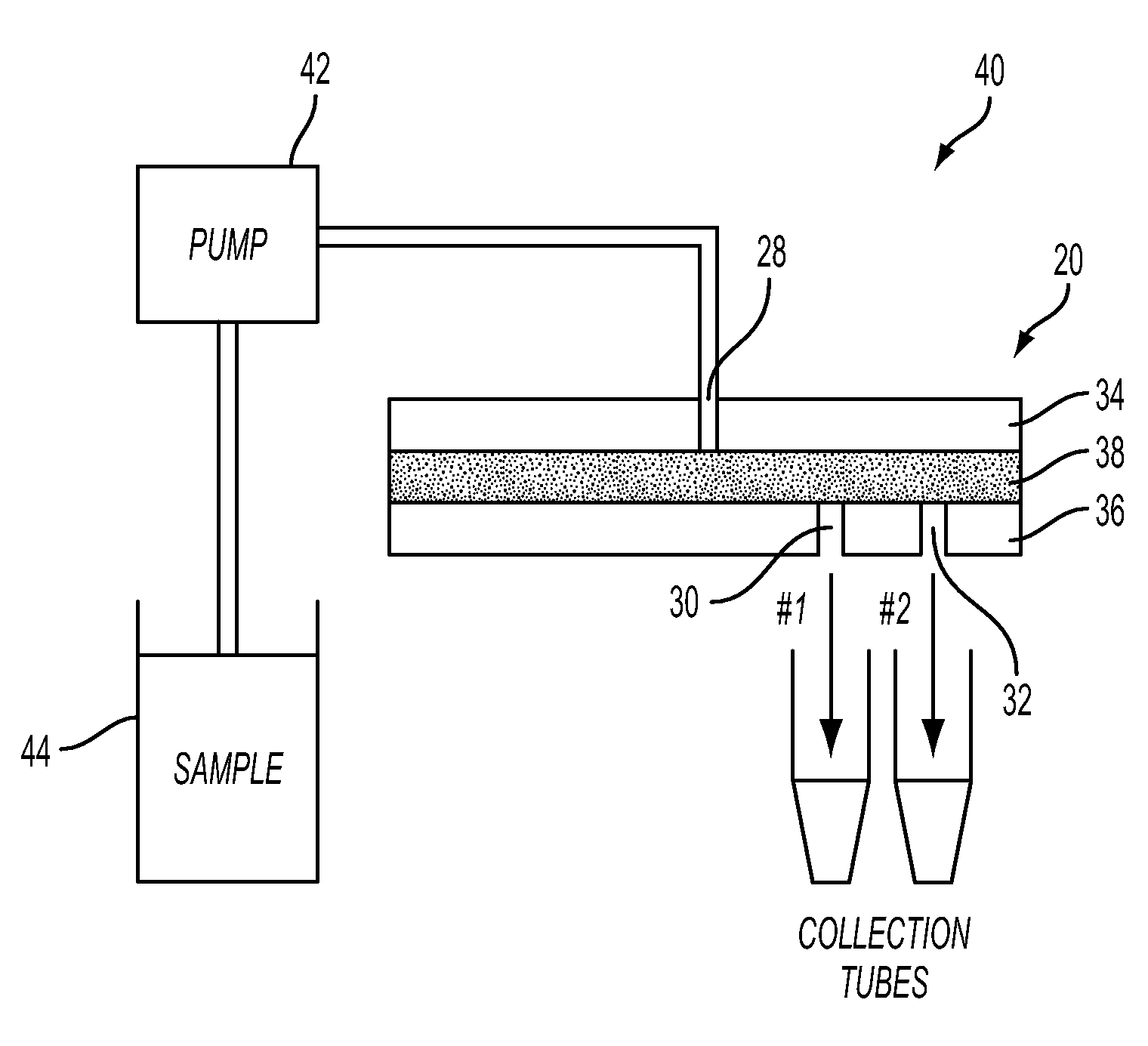
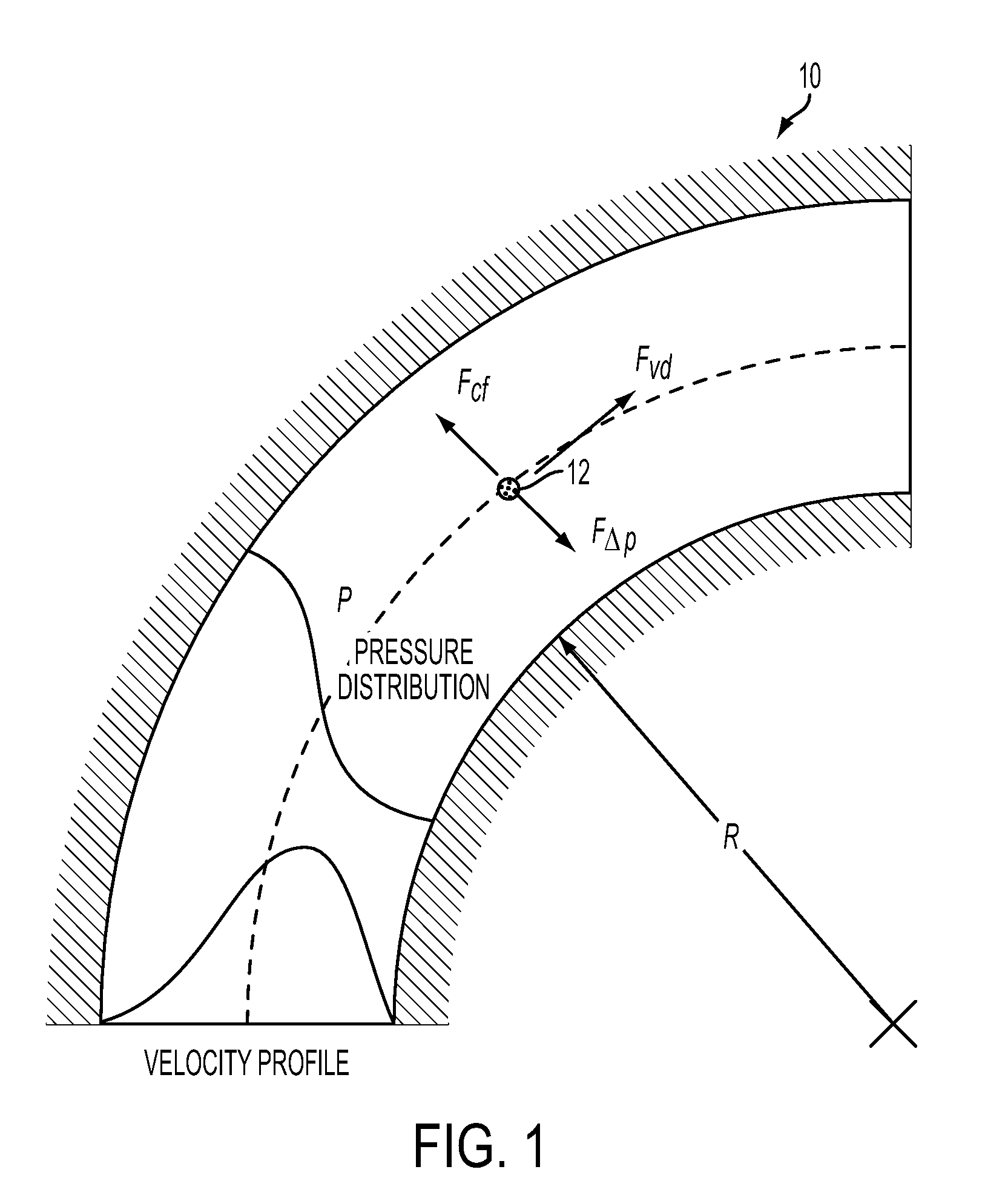
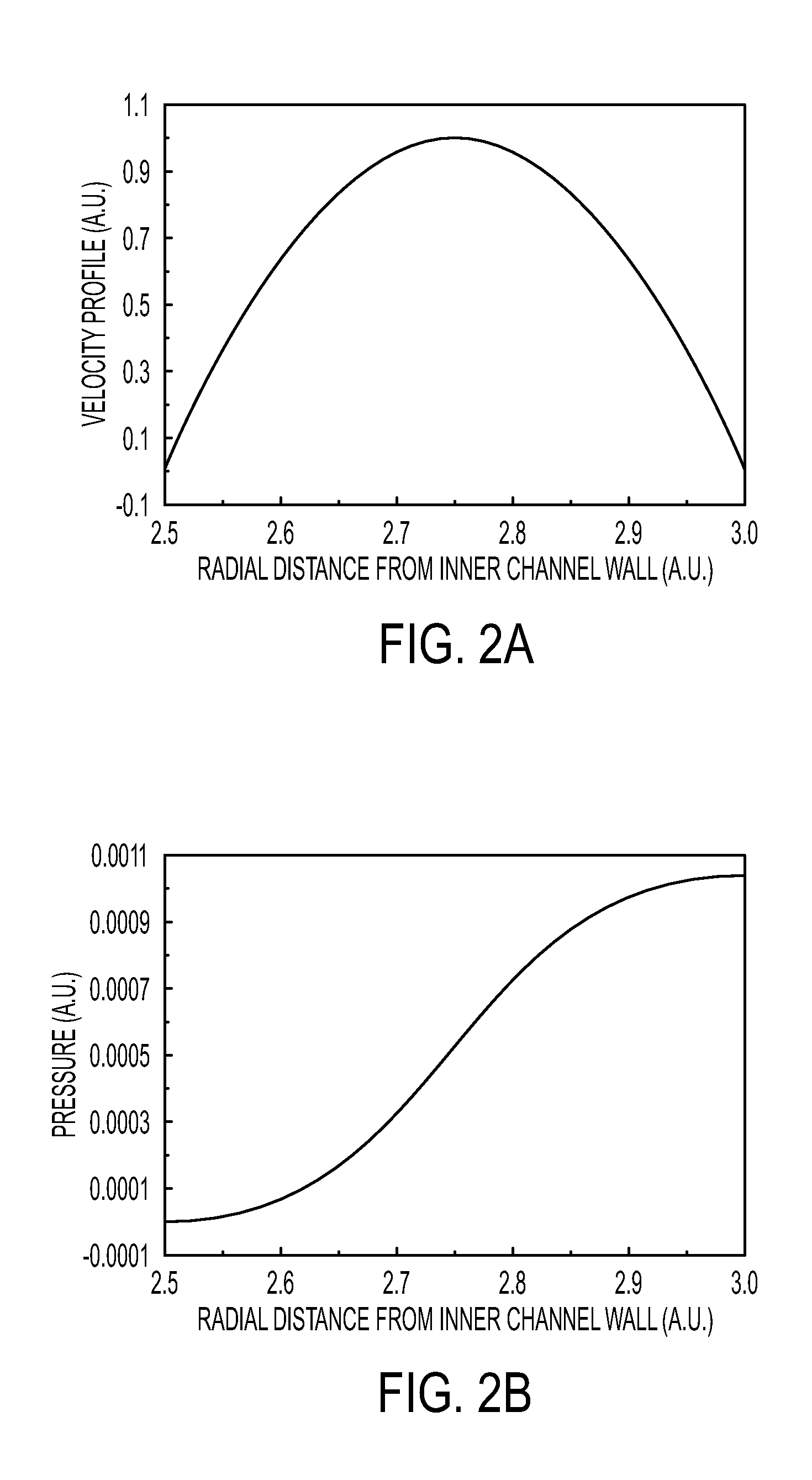
This invention is based on size and mass separation of suspended particles, including biological matter, which are made to flow in a spiral channel. On the spiral sections, the inward directed transverse pressure field from fluid shear competes with the outward directed centrifugal force to allow for separation of particles. At high velocity, centrifugal force dominates and particles move outward. At low velocities, transverse pressure dominates and the particles move inward. The magnitudes of the two opposing forces depend on flow velocity, particle size, radius of curvature of the spiral section, channel dimensions, and viscosity of the fluid. At the end of the spiral channel, a parallel array of outlets collects separated particles. For any particle size, the required channel dimension is determined by estimating the transit time to reach the side-wall. This time is a function of flow velocity, channel width, viscosity, and radius of curvature. Larger particles may reach the channel wall earlier than the smaller particles which need more time to reach the side wall. Thus a spiral channel may be envisioned by placing multiple outlets along the channel. This technique is inherently scalable over a large size range from sub-millimeter down to 1 μm.
Owner:XEROX CORP
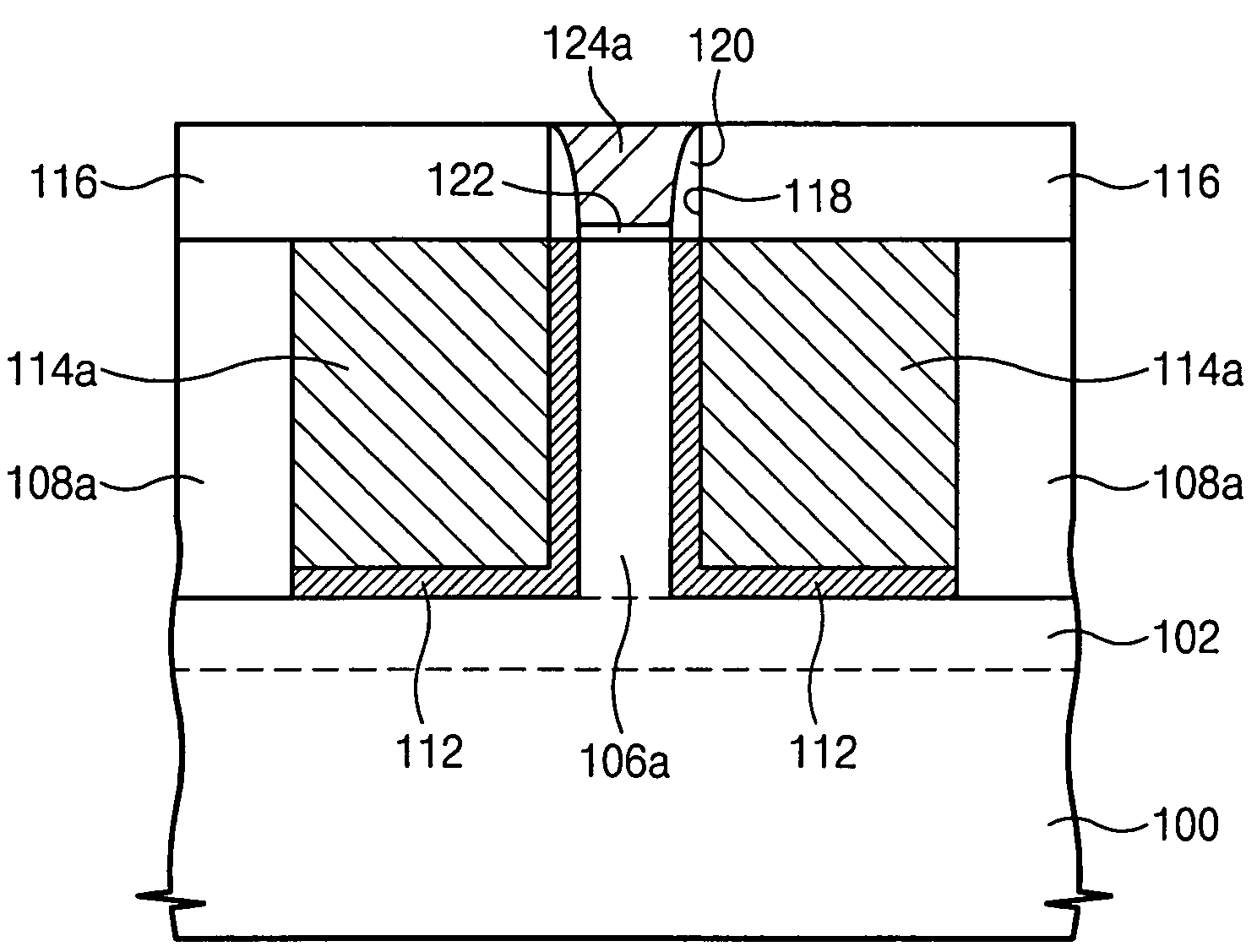
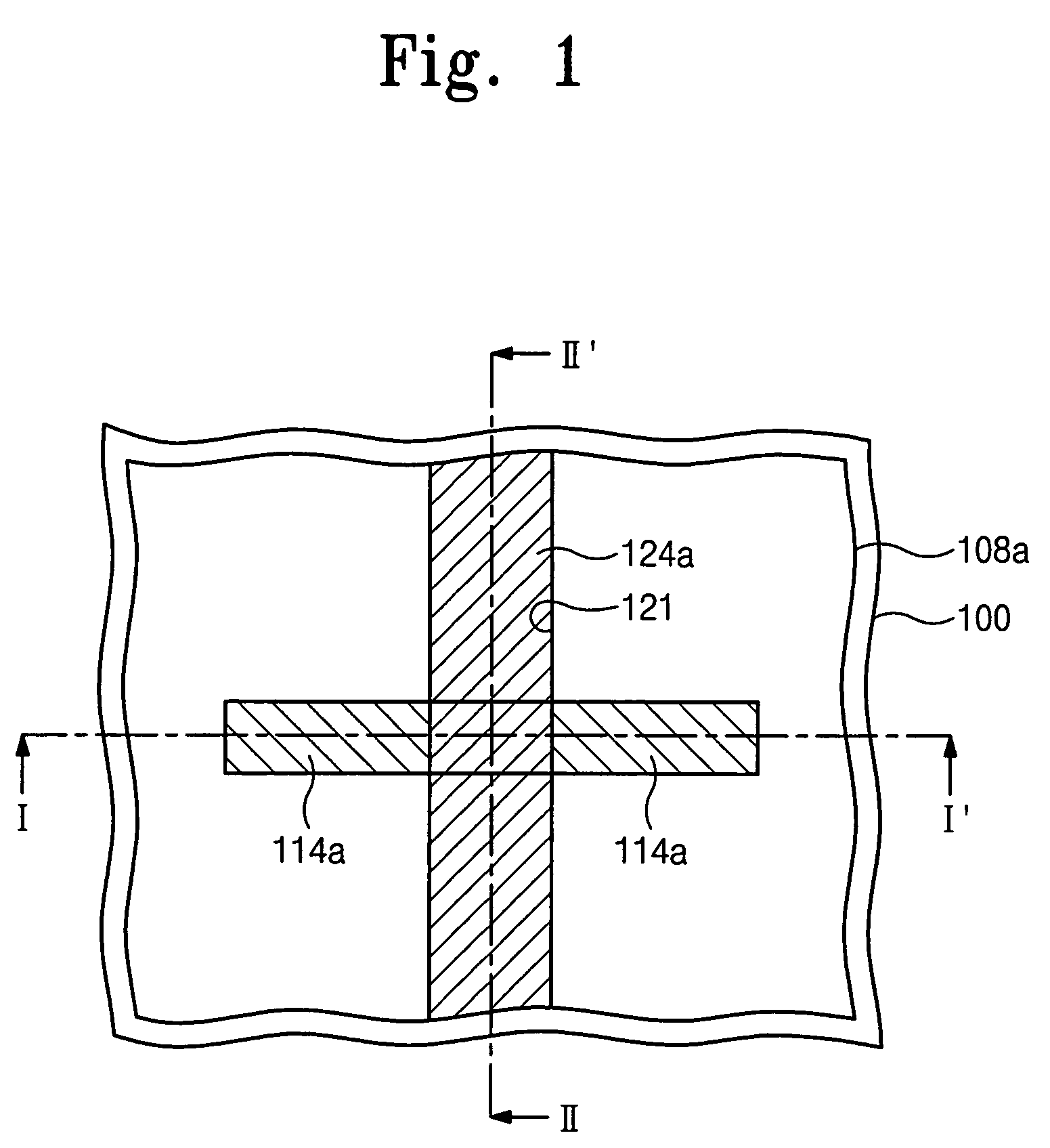
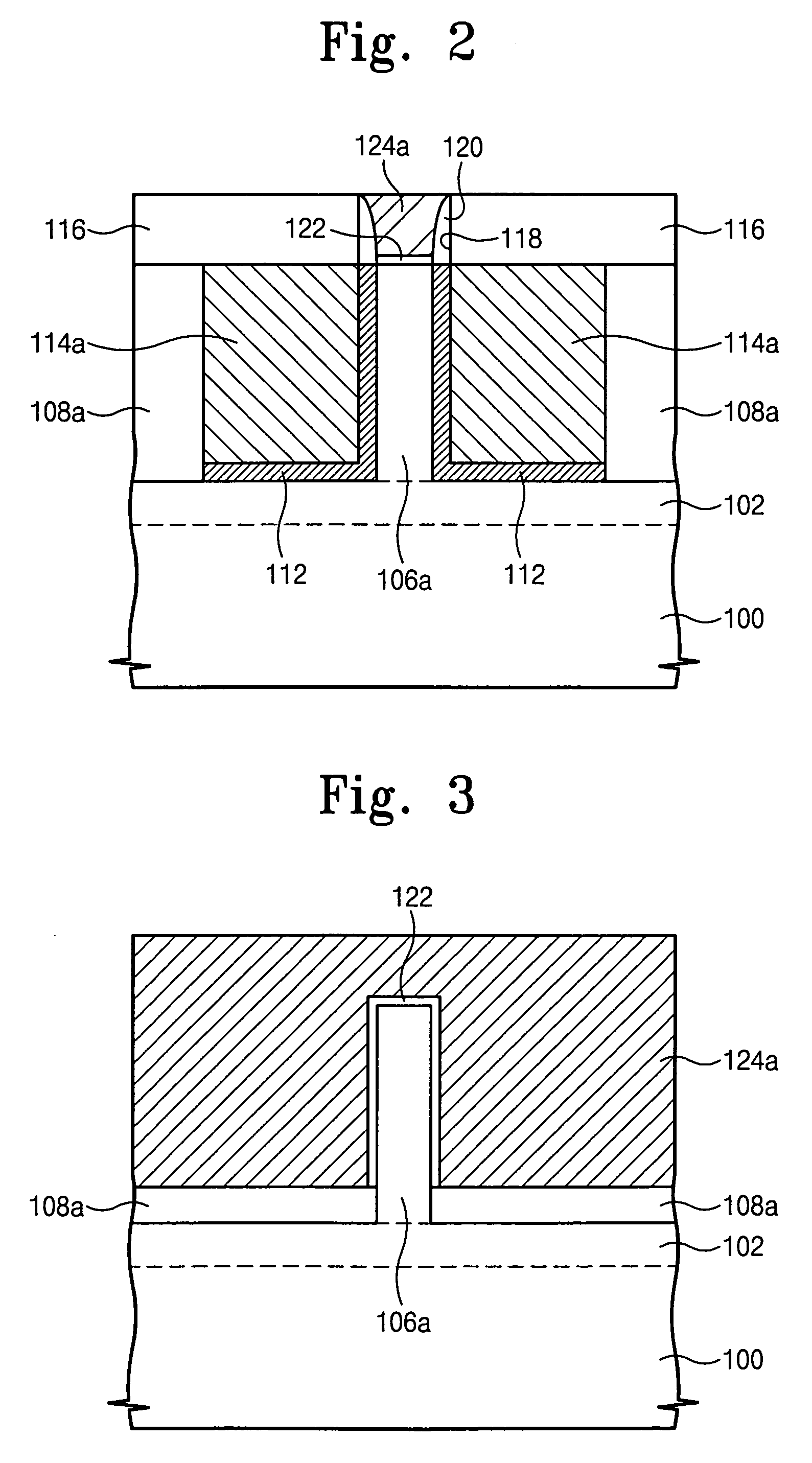
Semiconductor transistors having reduced channel widths and methods of fabricating same
ActiveUS20070238253A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialChannel width
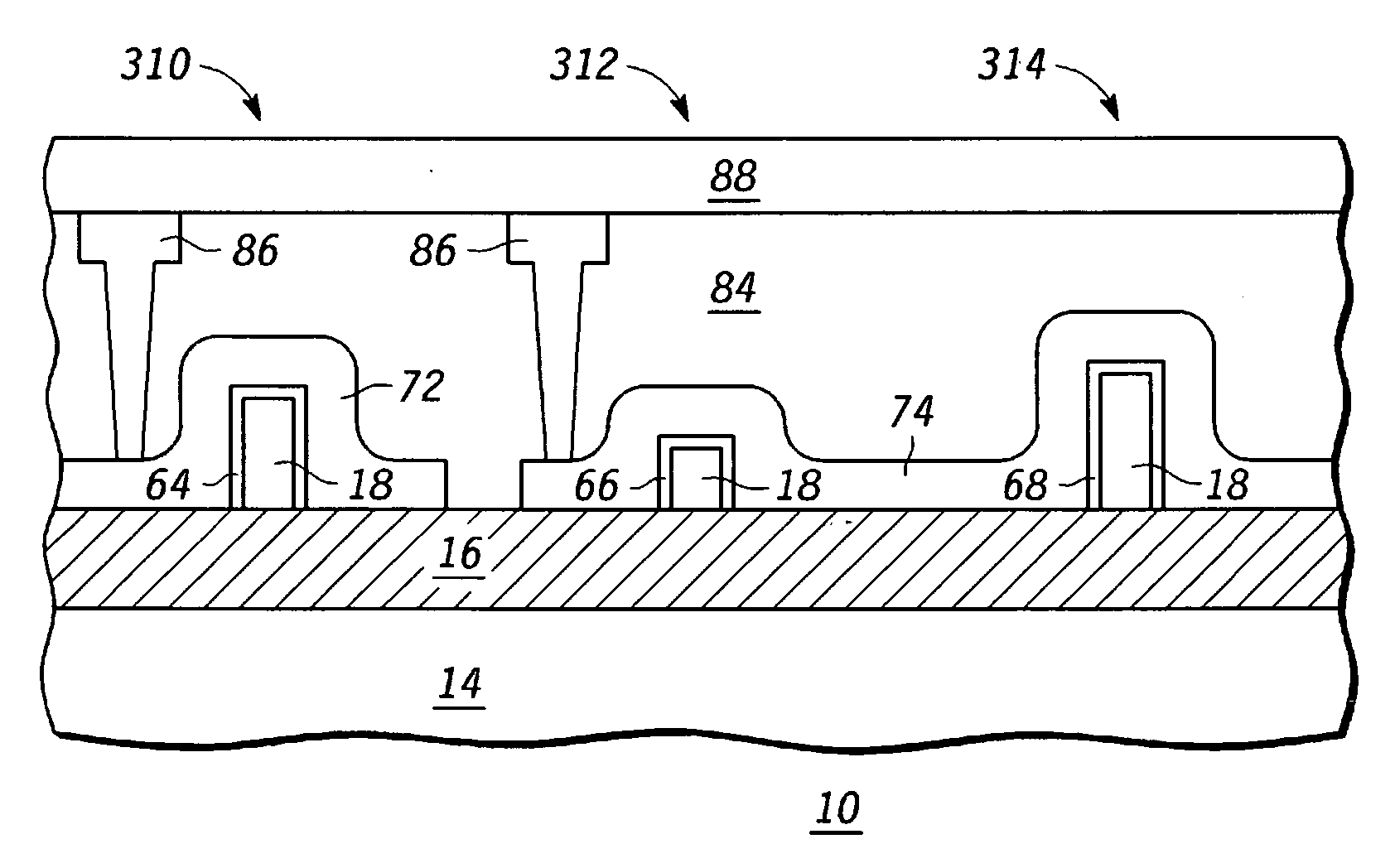
A method of forming a channel in a semiconductor device including forming an opening in a masking layer to expose a portion of an underlying semiconductor layer through the opening is provided. The method further includes disposing a screening layer and implanting a first type of ions in the portion of the underlying semiconductor layer through the screening layer and through the opening in the masking layer. A second type of ions are implanted in the portion of the underlying semiconductor layer through the screening layer and through the opening in the masking layer at an oblique ion implantation angle wherein a lateral spread of second type ions is greater than a lateral spread of first type ions. Semiconductor devices fabricated in accordance to above said method is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Heterogeneous channel capacities in an interconnect
InactiveUS20140098683A1Different widthError preventionTransmission systemsComputer architectureChannel width
Systems and methods involving construction of a system interconnect in which different channels have different widths in numbers of bits. Example processes to construct such a heterogeneous channel NoC interconnect are disclosed herein, wherein the channel width may be determined based upon the provided specification of bandwidth and latency between various components of the system.
Owner:INTEL CORP
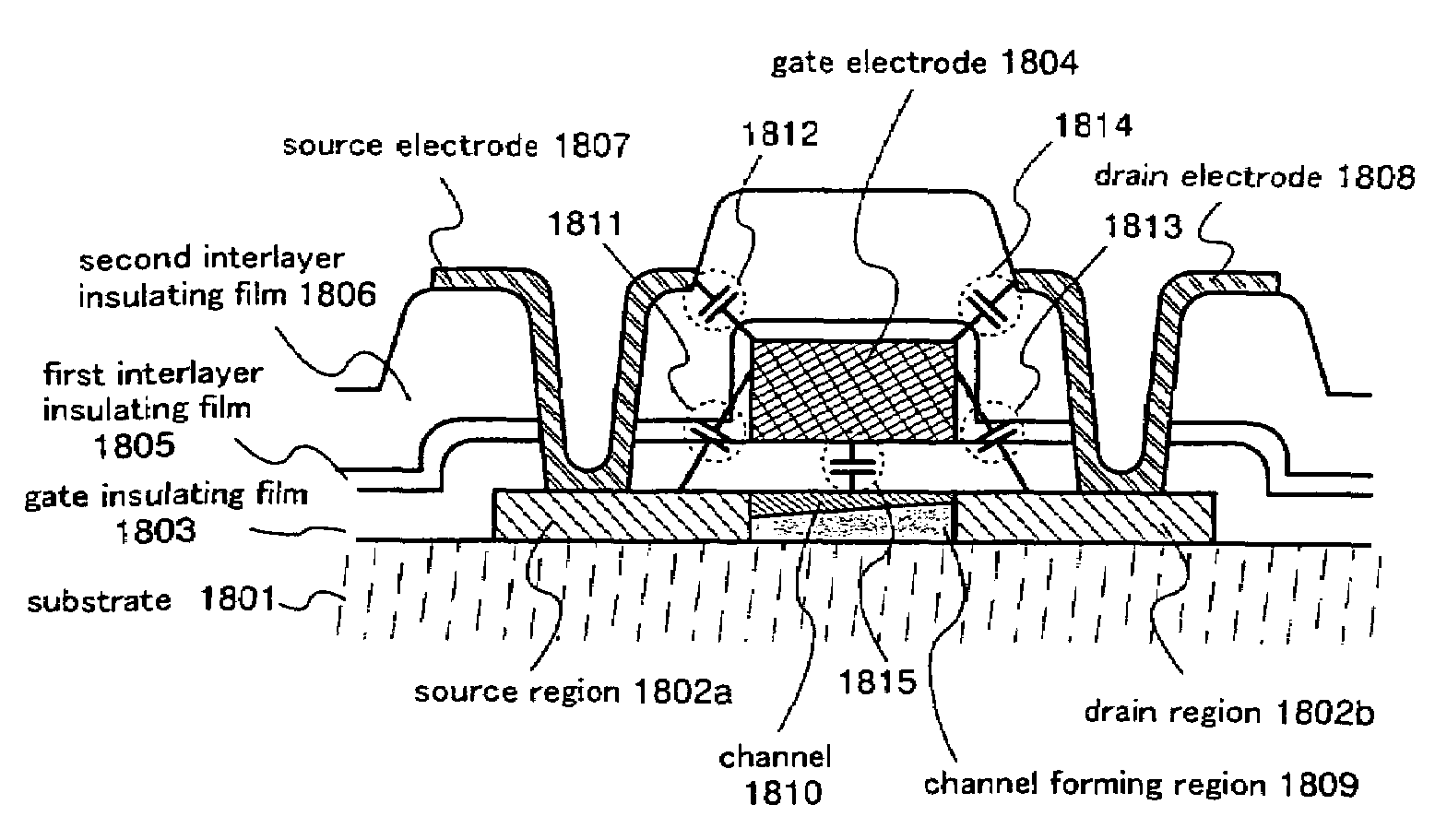
Insulated gate semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
Dot-pattern-like impurity regions are artificially and locally formed in a channel forming region. The impurity regions restrain the expansion of a drain side depletion layer toward the channel forming region to prevent the short channel effect. The impurity regions allow a channel width W to be substantially fined, and the resultant narrow channel effect releases the lowering of a threshold value voltage which is caused by the short channel effect.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
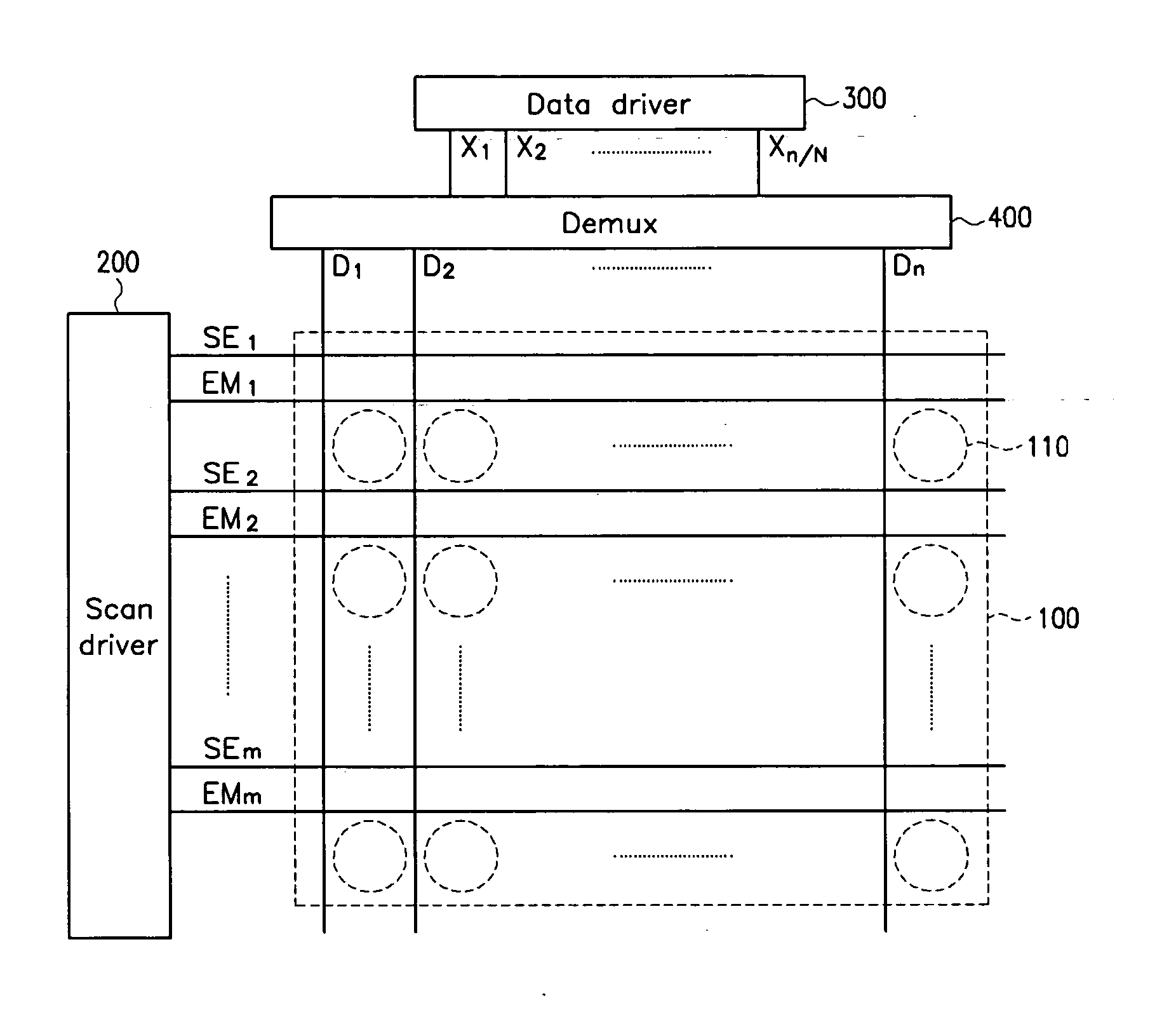
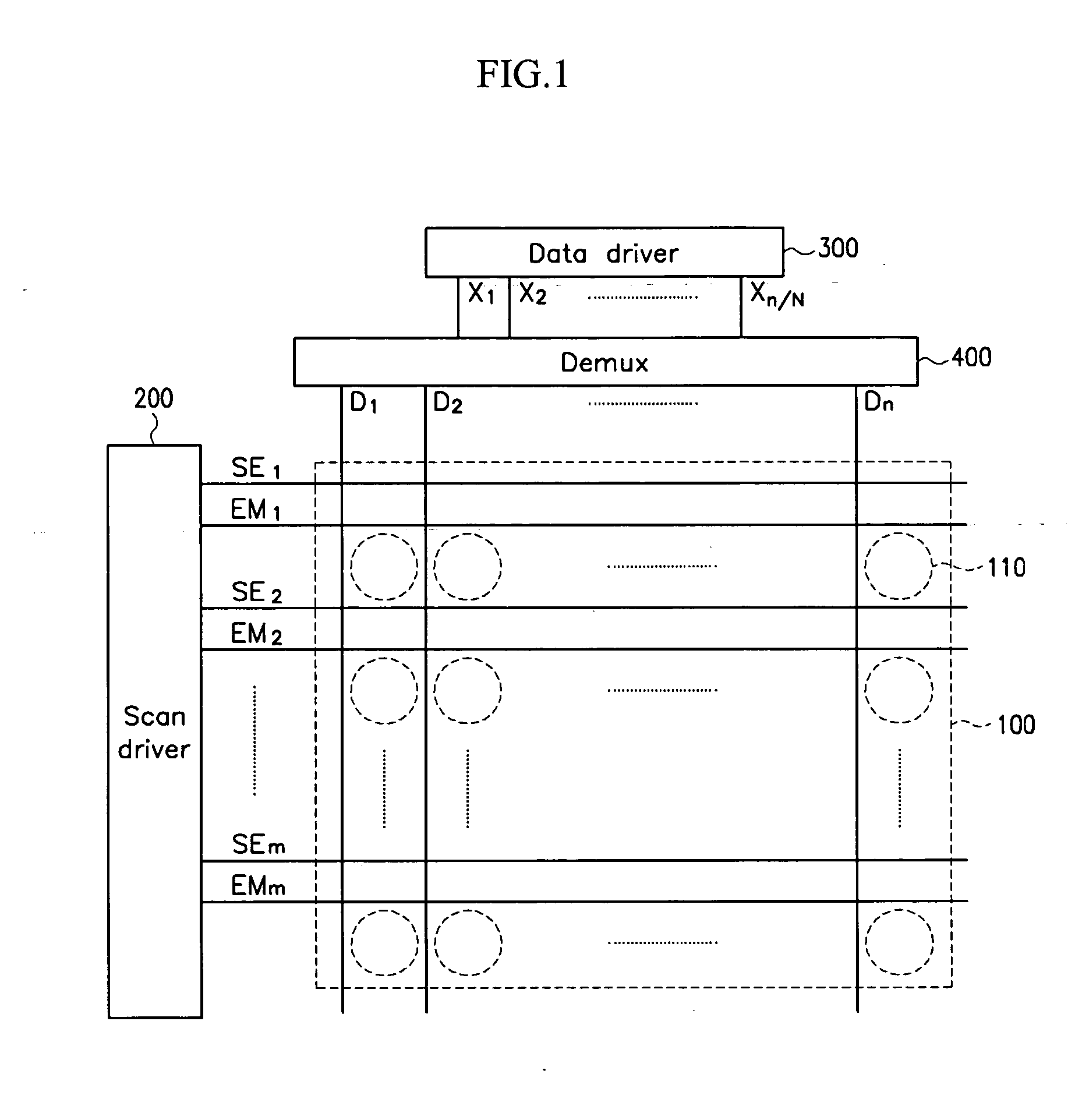
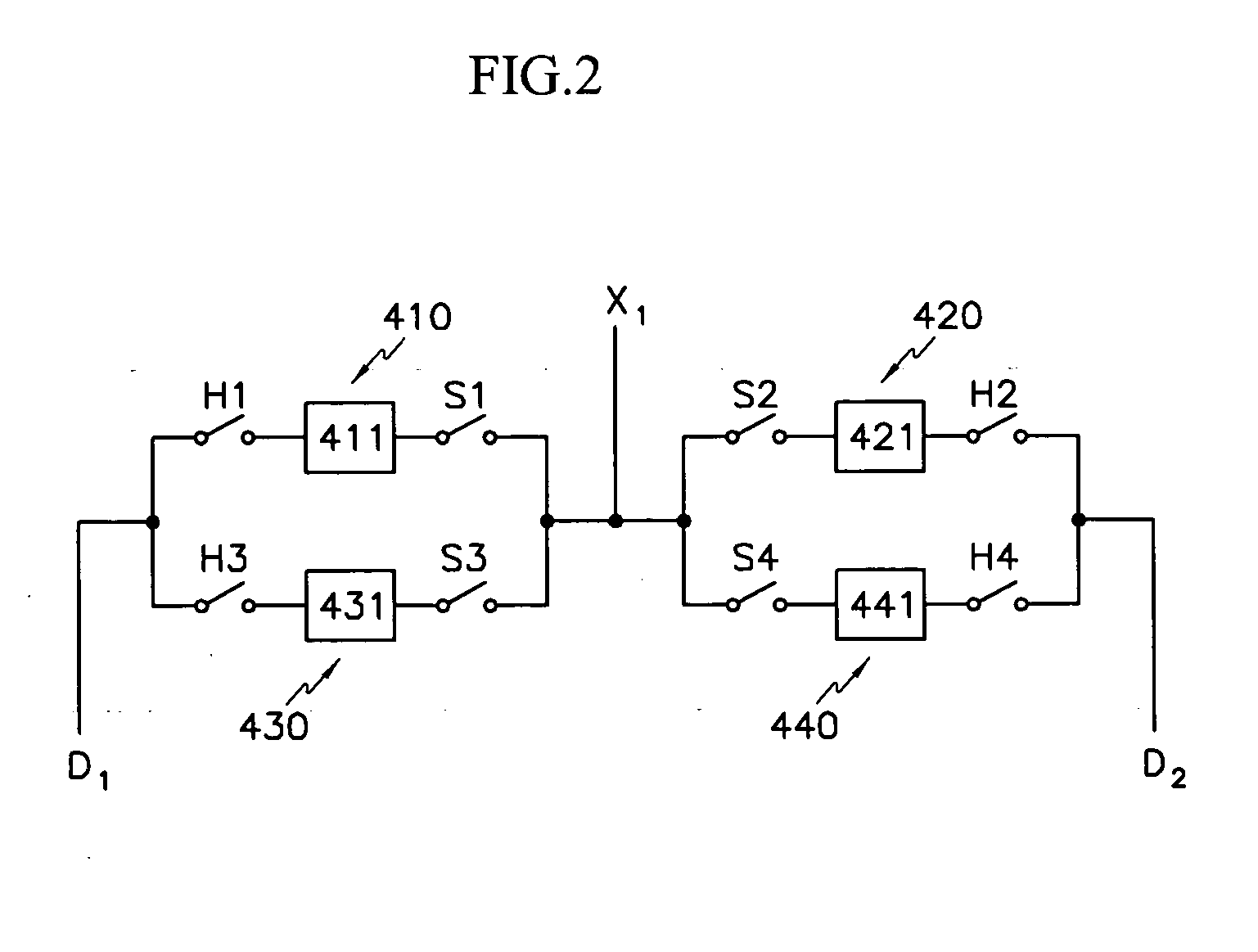
Demultiplexing device and display device using the same
In a display device, a demultiplexer is used to transmit a data current to a data line. The demultiplexer includes a plurality of sample / hold circuits for sampling the time-divided and sequentially input current and holding them to the data line. A plurality of data lines coupled to the demultiplexer are coupled to pixels of the same color, and hence, currents with different levels are transmitted to pixels of different colors. A sample / hold circuit for transmitting a higher level current uses a driving transistor having a larger ratio of a channel width and a channel length.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Granular channel width for power optimization
ActiveUS20120023473A1Improve performancePower optimizationDetecting faulty computer hardwarePower supply for data processingComputational sciencePower optimization
A storage medium recording a cell library having one or more cells that may be readable by a computer and may be used by the computer to design an integrated circuit. The one or more cells may have a physical dimension parameter and a channel width parameter. The physical dimension parameter may be a footprint of the one or more cells. The channel width parameter may have a minimum driver size and a maximum driver size. The channel width parameter may define a range within which a tool varies the channel width between the maximum driver size and the minimum driver size during a design flow of the integrated circuit based upon one or more power criteria without changing the footprint.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Solid-state imaging device and camera
InactiveUS20090140304A1Electric fieldReduce generationTransistorTelevision system detailsPhotoelectric conversionEngineering
Disclosed is a solid-state imaging device which includes a plurality of pixels in an arrangement, each of the pixels including a photoelectric conversion element, pixel transistors including a transfer transistor, and a floating diffusion region, in which the channel width of transfer gate of the transfer transistor is formed to be larger on a side of the floating diffusion region than on a side of the photoelectric conversion element.
Owner:SONY CORP
Process for forming an electronic device including a fin-type structure
ActiveUS20070161171A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
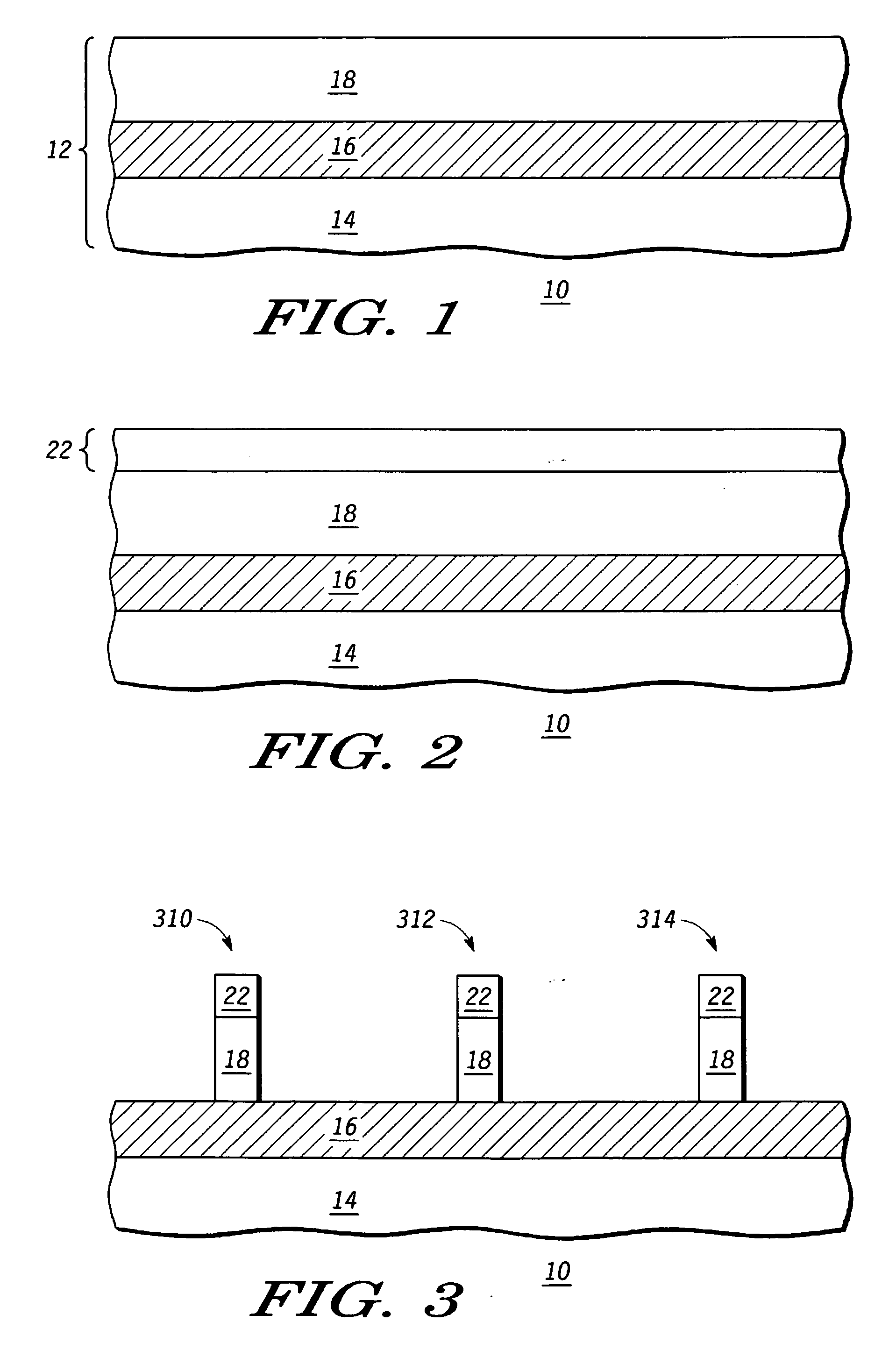
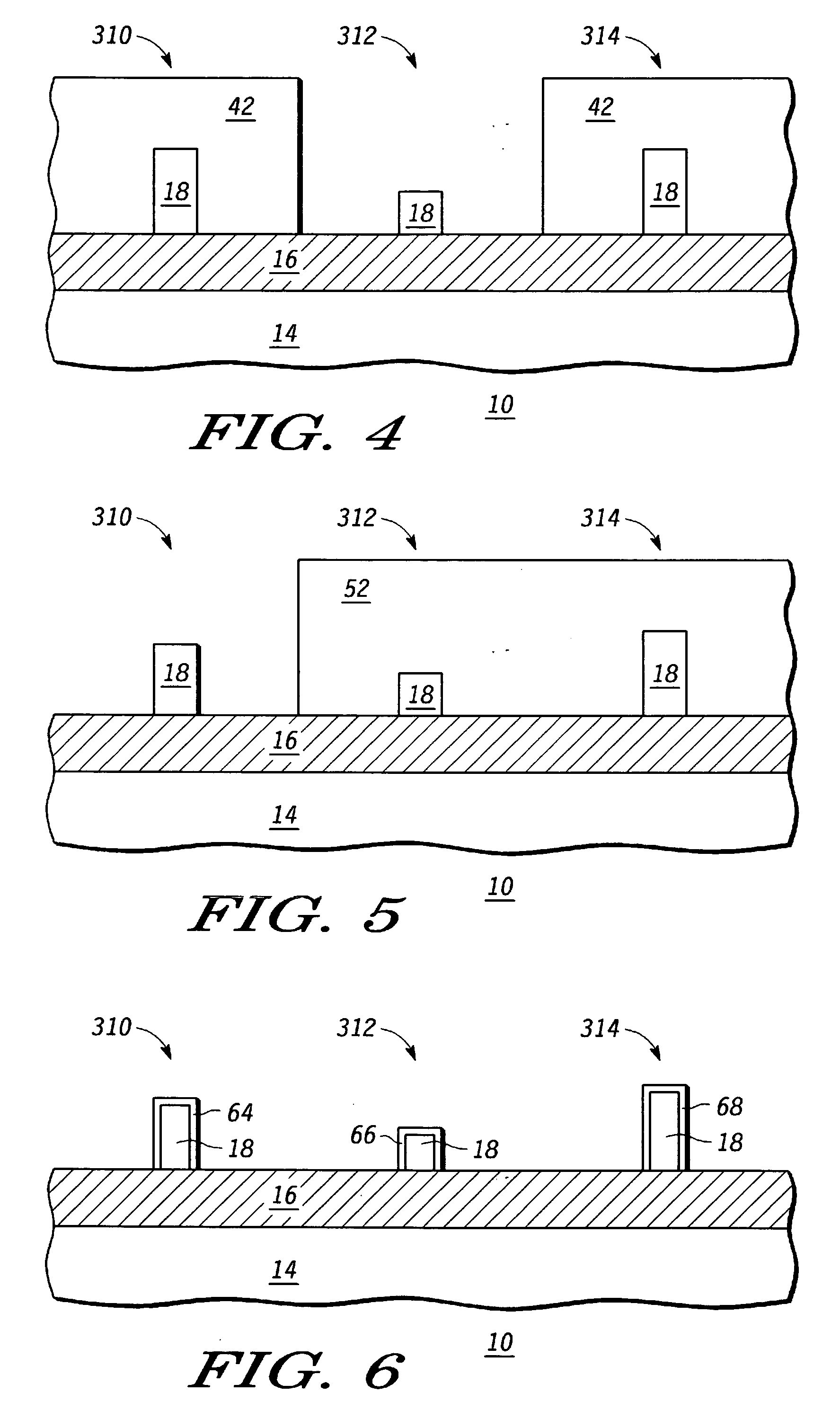
A process for forming an electronic device can include forming a semiconductor fin of a first height for a fin-type structure and removing a portion of the semiconductor fin such that the semiconductor fin is shortened to a second height. In accordance with specific embodiment a second semiconductor fin can be formed, each of the first and the second semiconductor fins having a different height representing a channel width. In accordance with another specific embodiment a second and a third semiconductor fin can be formed, each of the first, the second and the third semiconductor fins having a different height representing a channel width.
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
Semiconductor device gate structure and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20050184348A1Effective preventionEffectively preventTransistorSolid-state devicesInsulation layerDevice material
A MOS transistor includes a gate structure extending forrom a semiconductor substrate in a vertical direction is disclosed. The gate structure includes a gate electrode extending from the substrate in a vertical direction, and a gate insulation layer enclosing the gate electrode. A channel pattern encloses the gate insulation layer, and a first conductive pattern extends from a lower portion of the channel pattern in a first direction verticalperpendicular to the channel pattern and in parallel with the substrate. A second conductive pattern extends from an upper portion of the channel pattern in a second direction verticalperpendicular to the channel pattern and in parallel with the substrate. Accordingly, the channel length of the MOS transistor is determined by a distance between the first and second conductive patterns, and a channel width of the MOS transistor is determined by a diameter of the gate structure. Short channel and narrow width effects are sufficiently prevented in a MOS transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140340608A1Excellent electrical propertiesIncrease productionSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsDevice materialChannel width
A semiconductor device which includes an oxide semiconductor and in which formation of a parasitic channel due to a gate BT stress is suppressed is provided. Further, a semiconductor device including a transistor having excellent electrical characteristics is provided. The semiconductor device includes a transistor having a dual-gate structure in which an oxide semiconductor film is provided between a first gate electrode and a second gate electrode; gate insulating films are provided between the oxide semiconductor film and the first gate electrode and between the oxide semiconductor film and the second gate electrode; and in the channel width direction of the transistor, the first or second gate electrode faces a side surface of the oxide semiconductor film with the gate insulating film between the oxide semiconductor film and the first or second gate electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Logic circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110090184A1Reduce leakage currentTotal current dropSolid-state devicesElectronic switchingMicrometerChannel width
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor devices having field effect transistors
A semiconductor device having a field effect transistor and a method of fabricating the same. In-situ doped epitaxial patterns are respectively formed at both sidewalls of a protruded channel pattern from a substrate by performing an in-situ doped epitaxial growth process. The in-situ doped epitaxial pattern has a conformal impurity concentration throughout. Accordingly, source / drain regions with a conformal impurity concentration are connected throughout a channel width of a channel region including both sidewalls of a protruded channel pattern. As a result, it is possible to maximize a driving current of the filed effect transistor, and an on-off characteristic can be highly stabilized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
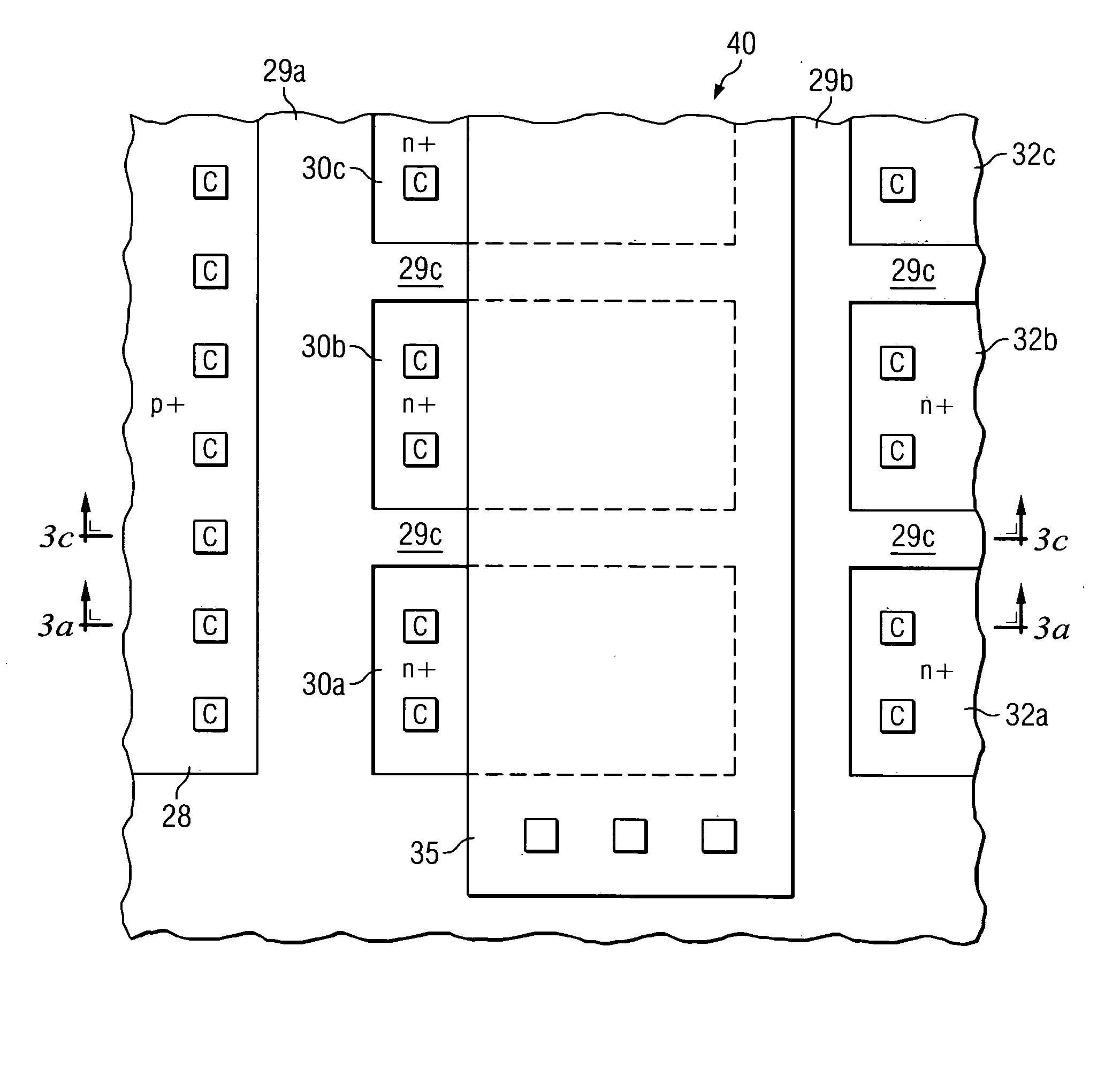
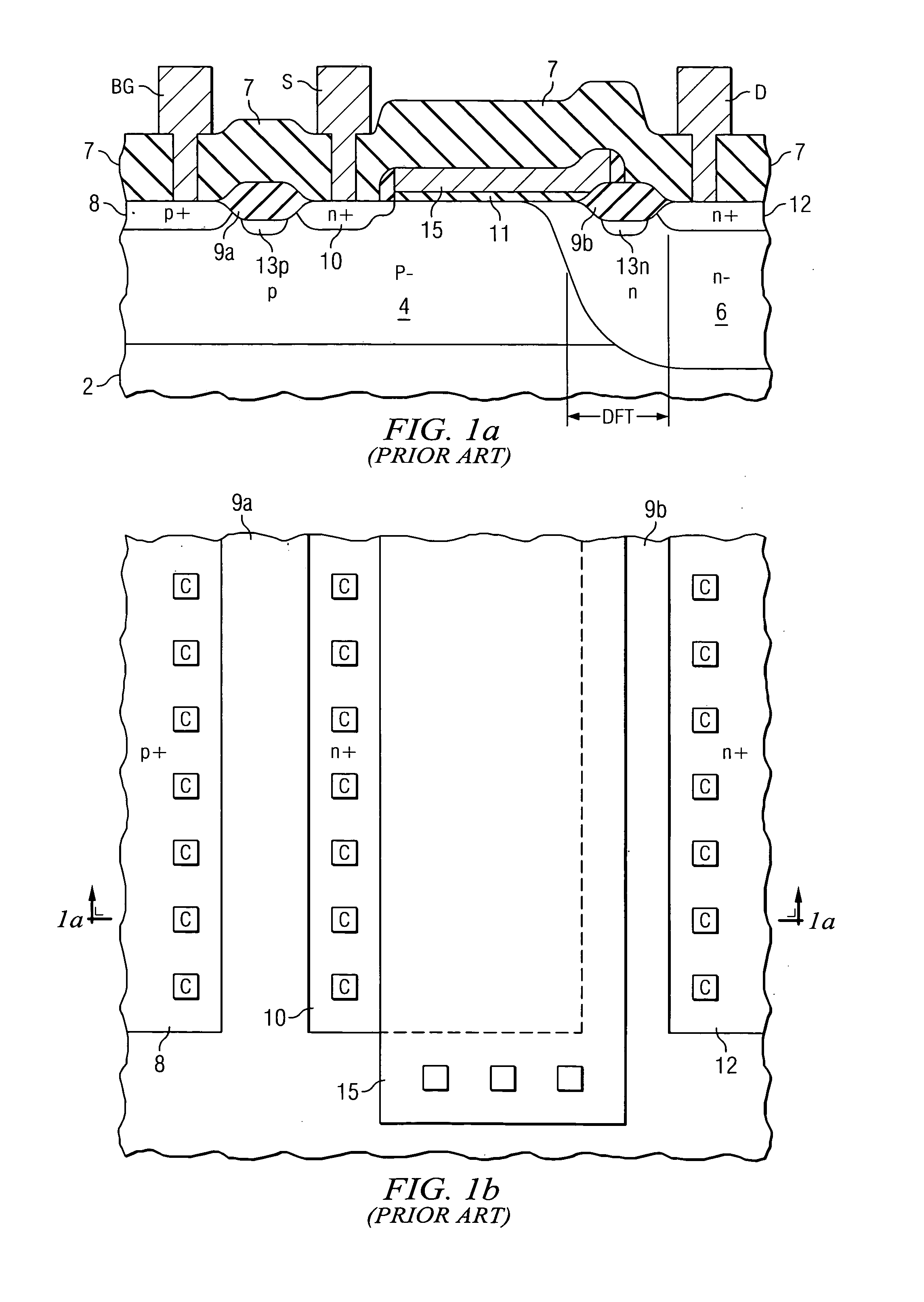
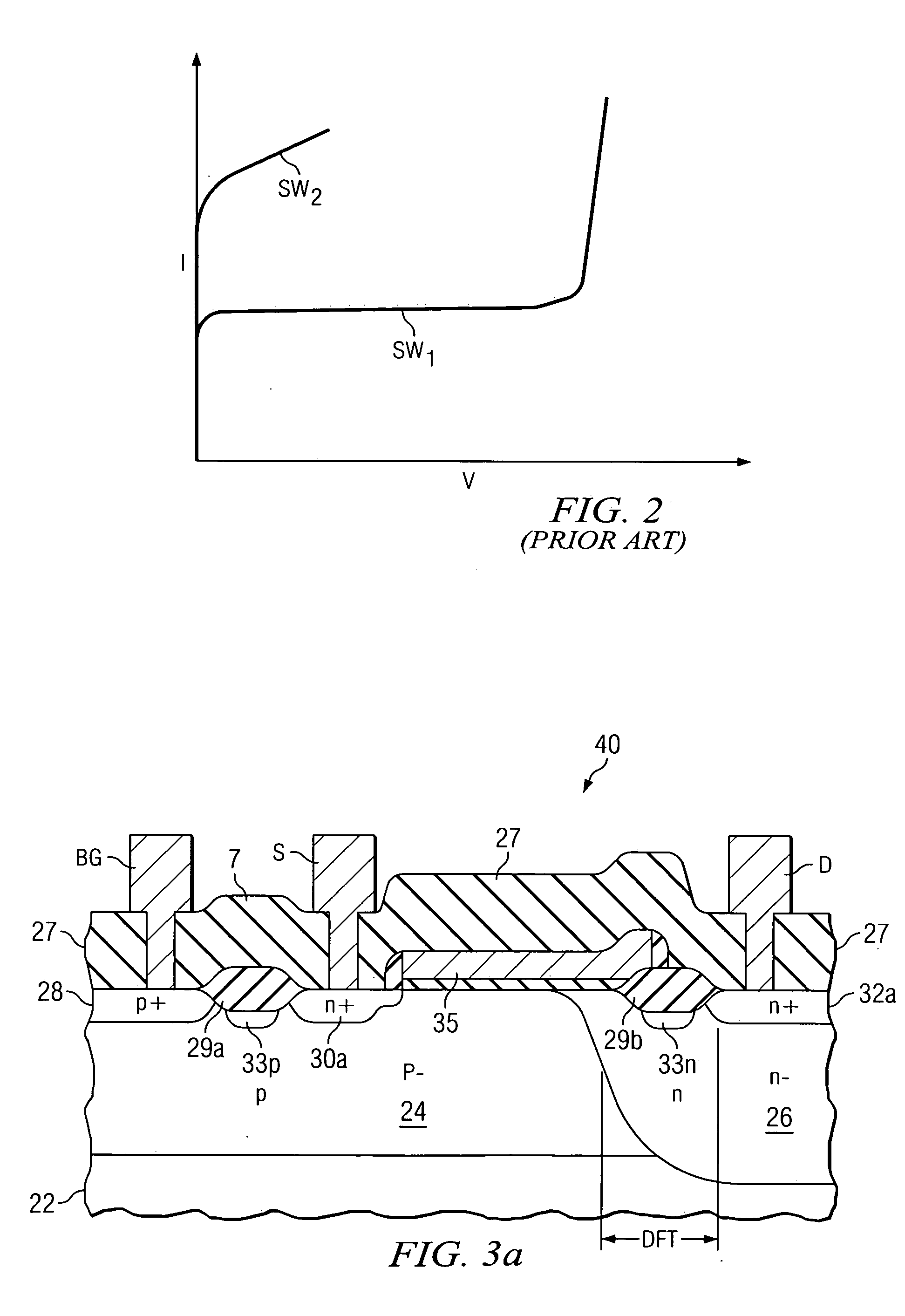
Drain extended MOS transistor with improved breakdown robustness
ActiveUS20050110081A1High currentLocalized damageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChannel widthSemiconductor
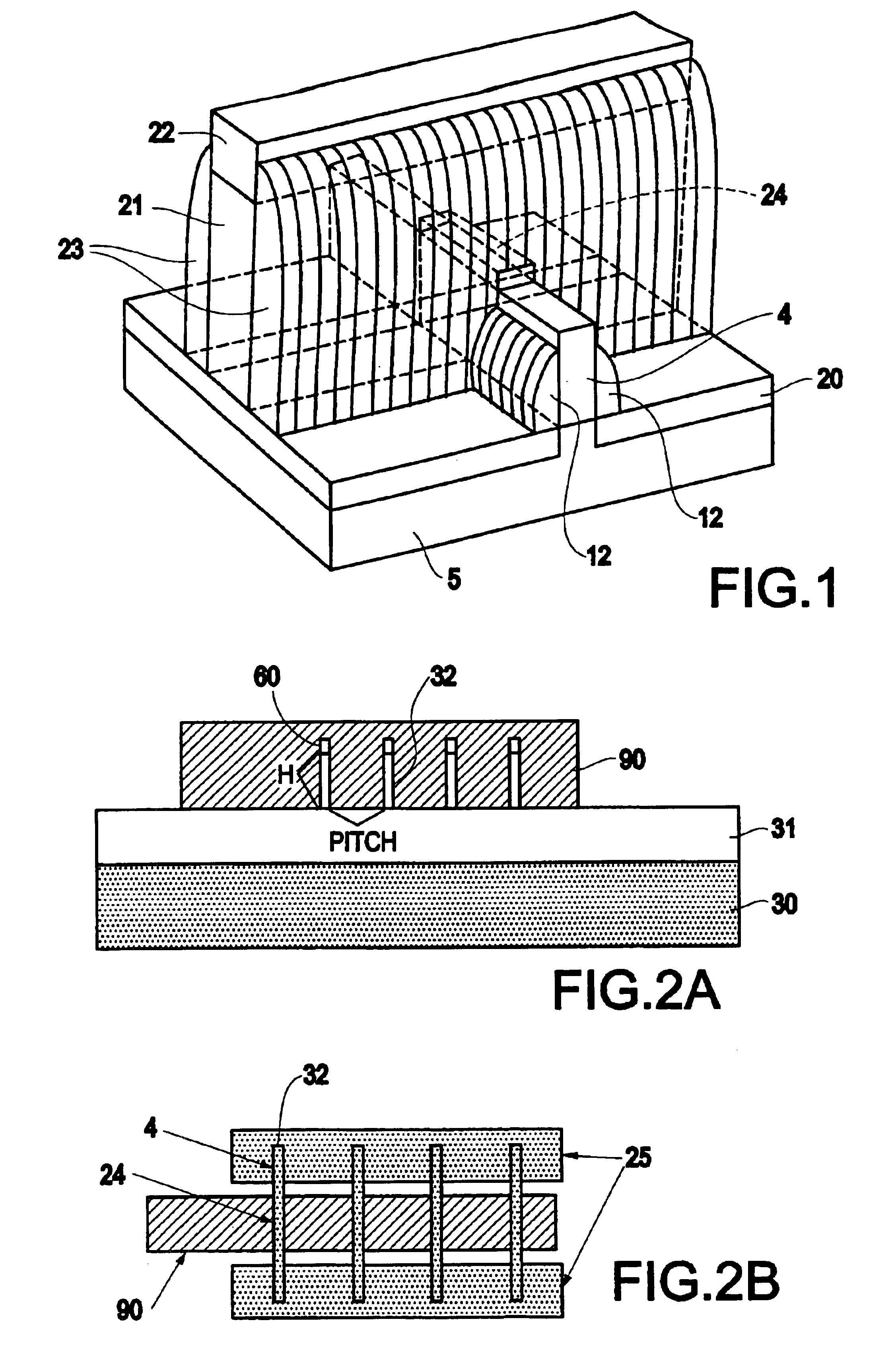
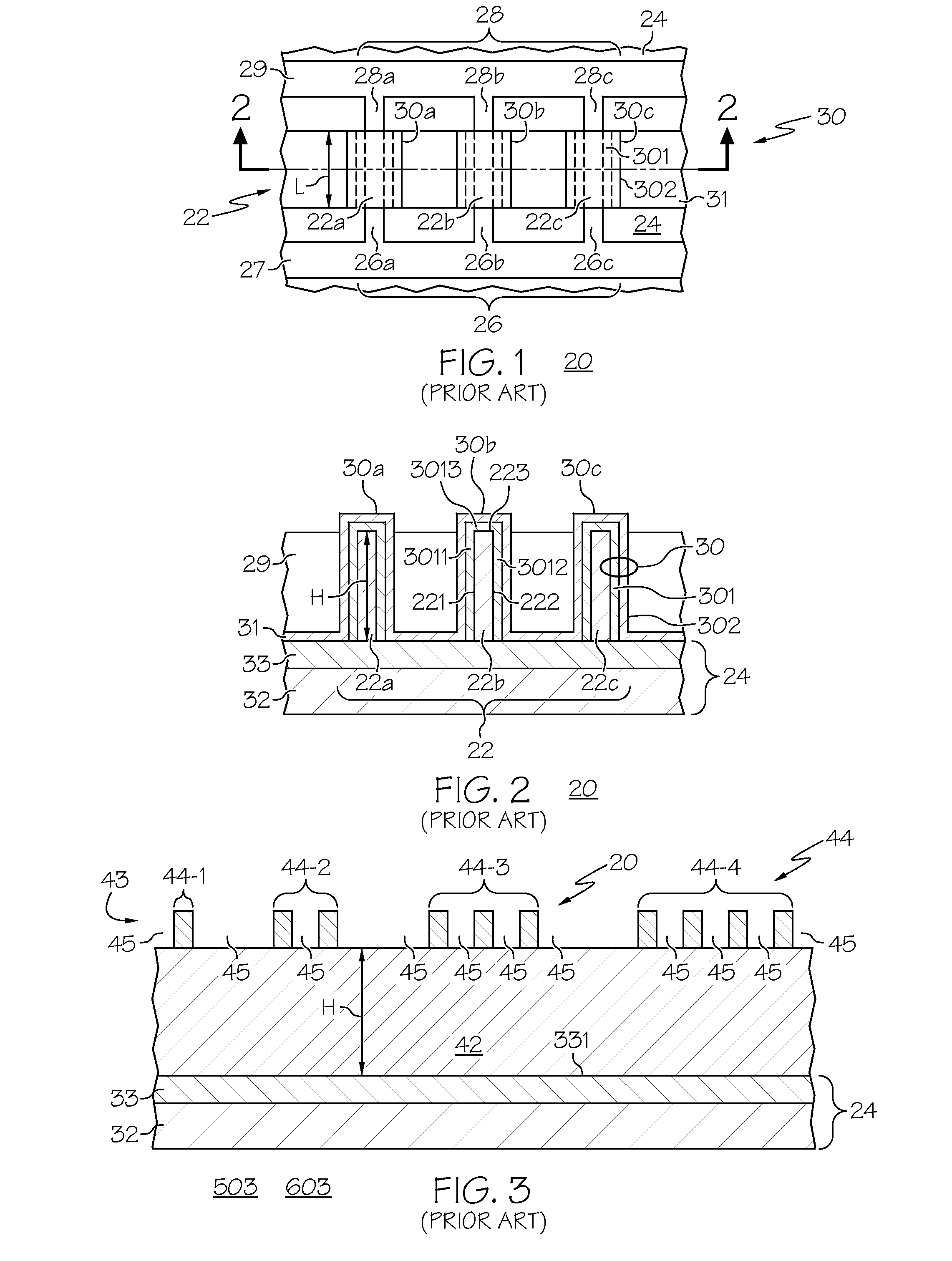
A drain-extended metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor (40) with improved robustness in breakdown characteristics is disclosed. Field oxide isolation structures (29c) are disposed between the source region (30) and drain contact regions (32a, 32b, 32c) to break the channel region of the transistor into parallel sections. The gate electrode (35) extends over the multiple channel regions, and the underlying well (26) and thus the drift region (DFT) of the transistor extends along the full channel width. Channel stop doped regions (33) underlie the field oxide isolation structures (29c), and provide conductive paths for carriers during breakdown. Parasitic bipolar conduction, and damage due to that conduction, is therefore avoided.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Light-emitting device
InactiveUS7262556B2Simple opening portionCurrent densityStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitanceDrain current
A light-emitting device which realizes a high aperture ratio and in which the quality of image is little affected by the variation in the characteristics of TFTs. A large holding capacitor Cs is not provided in the pixel portion but, instead, the channel length and the channel width of the driving TFTs are increased, and the channel capacitance is utilized as Cs. The channel length is selected to be very larger than the channel width to improve current characteristics in the saturated region, and a high VGS is applied to the driving TFTs to obtain a desired drain current. Therefore, the drain currents of the driving TFTs are little affected by the variation in the threshold voltage. In laying out the pixels, further, wiring is arranged under the partitioning wall and the driving TFTs are arranged under the wiring in order to avoid a decrease in the aperture ratio despite of an increase in the size of the driving TFT. In the case of the 3-transistor pixels, the switching TFT and the erasing TFT are linearly arranged to further increase the aperture ratio.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Fin-fet device and method and integrated circuits using such
InactiveUS20120313169A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesEngineeringFin height
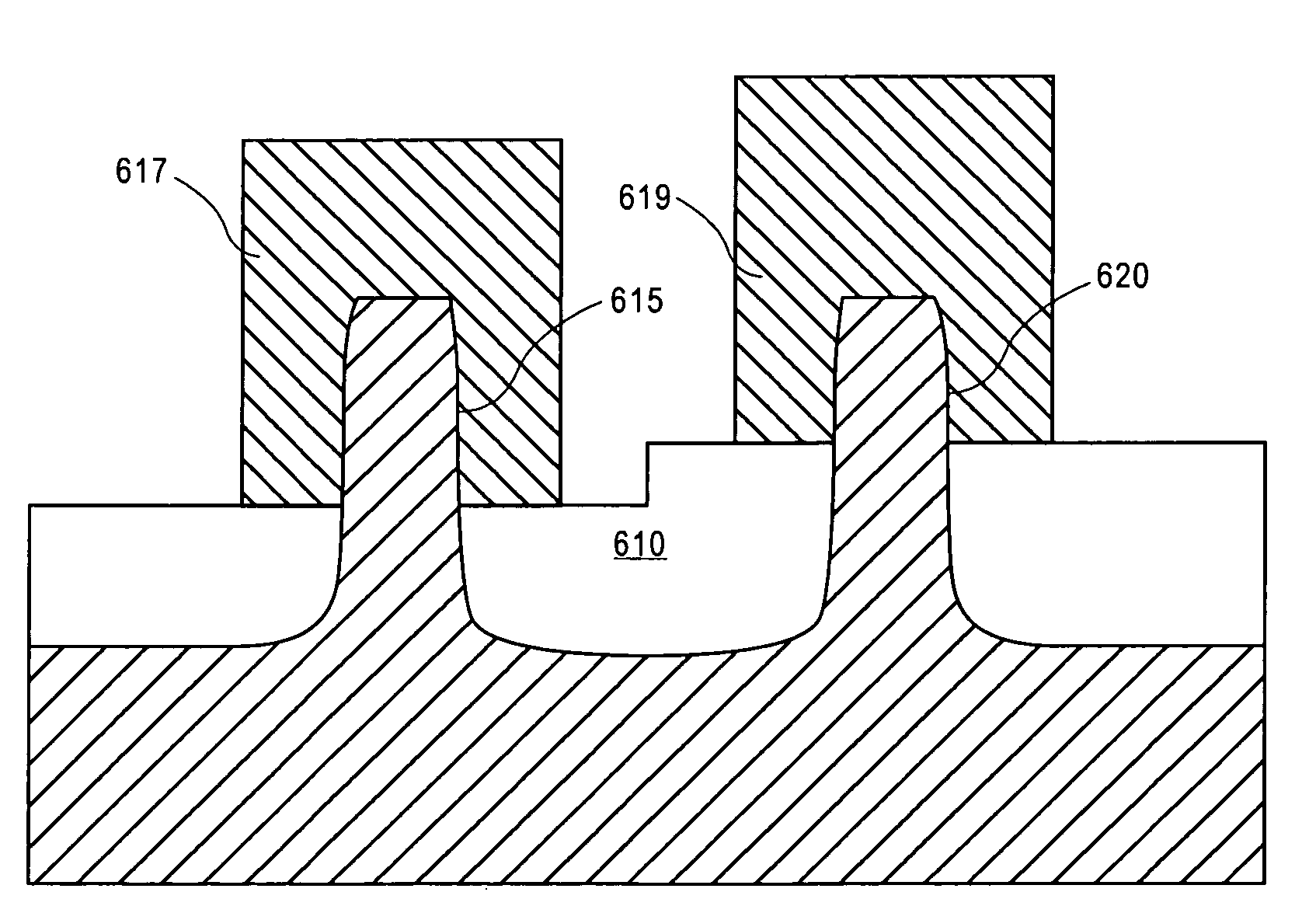
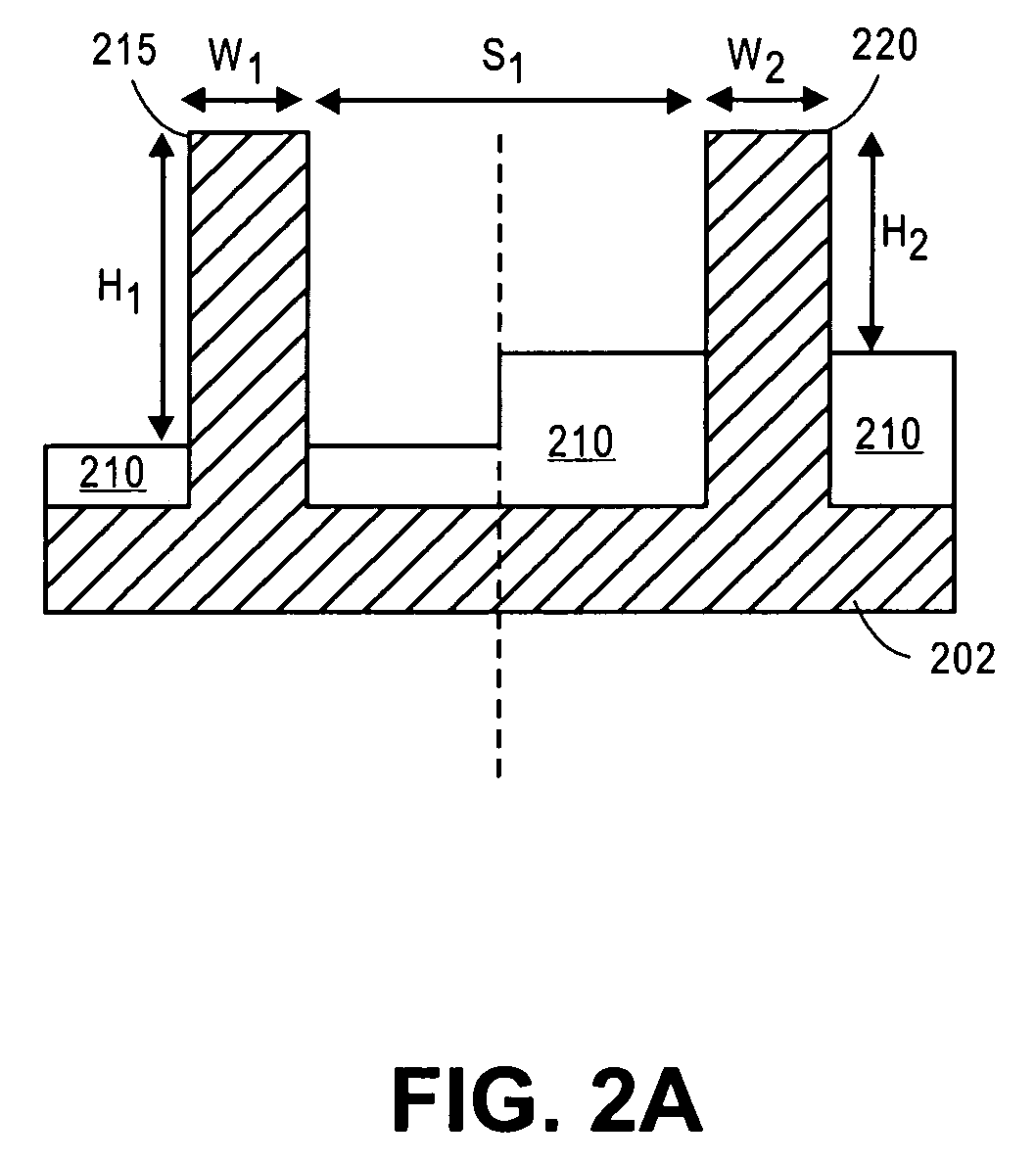
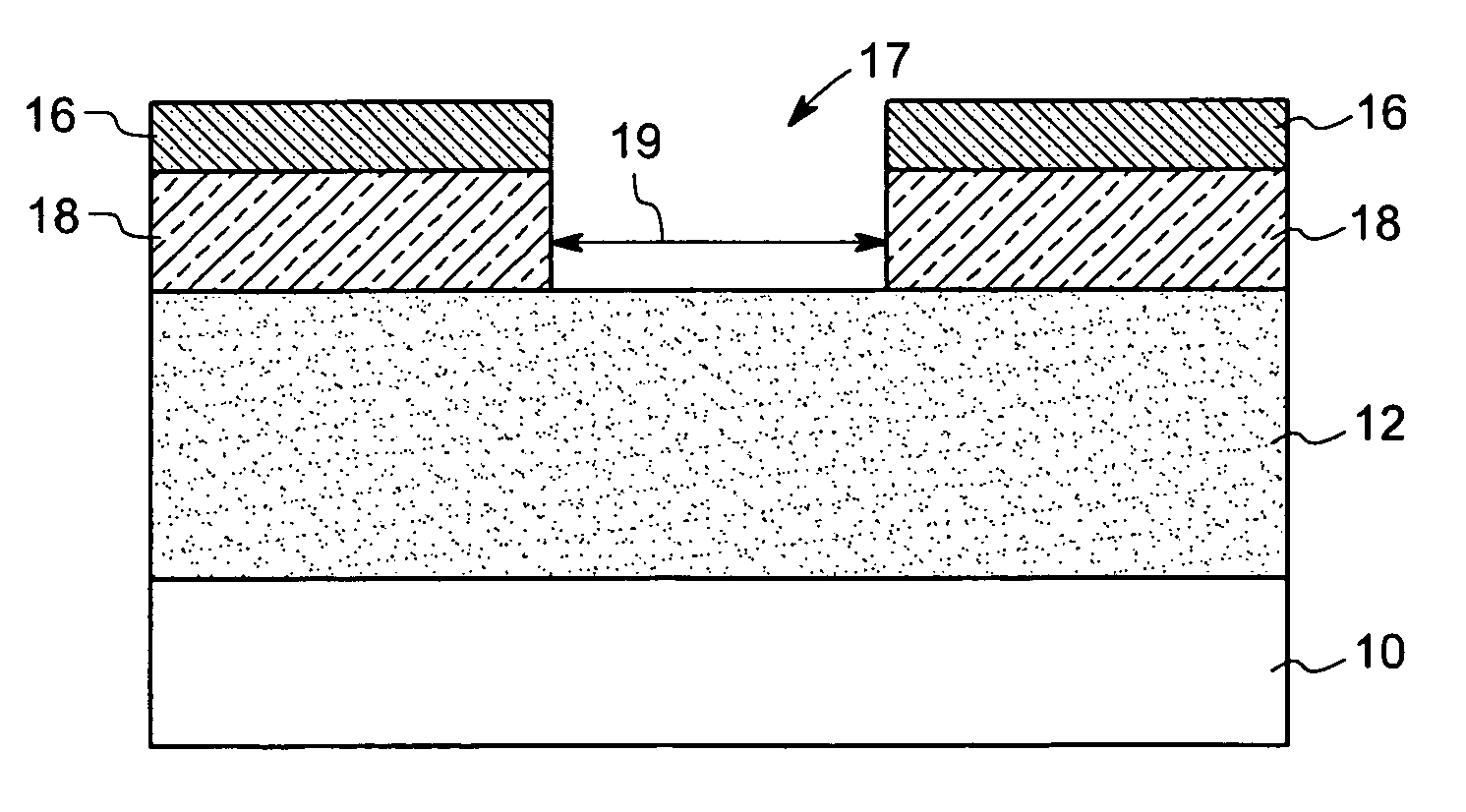
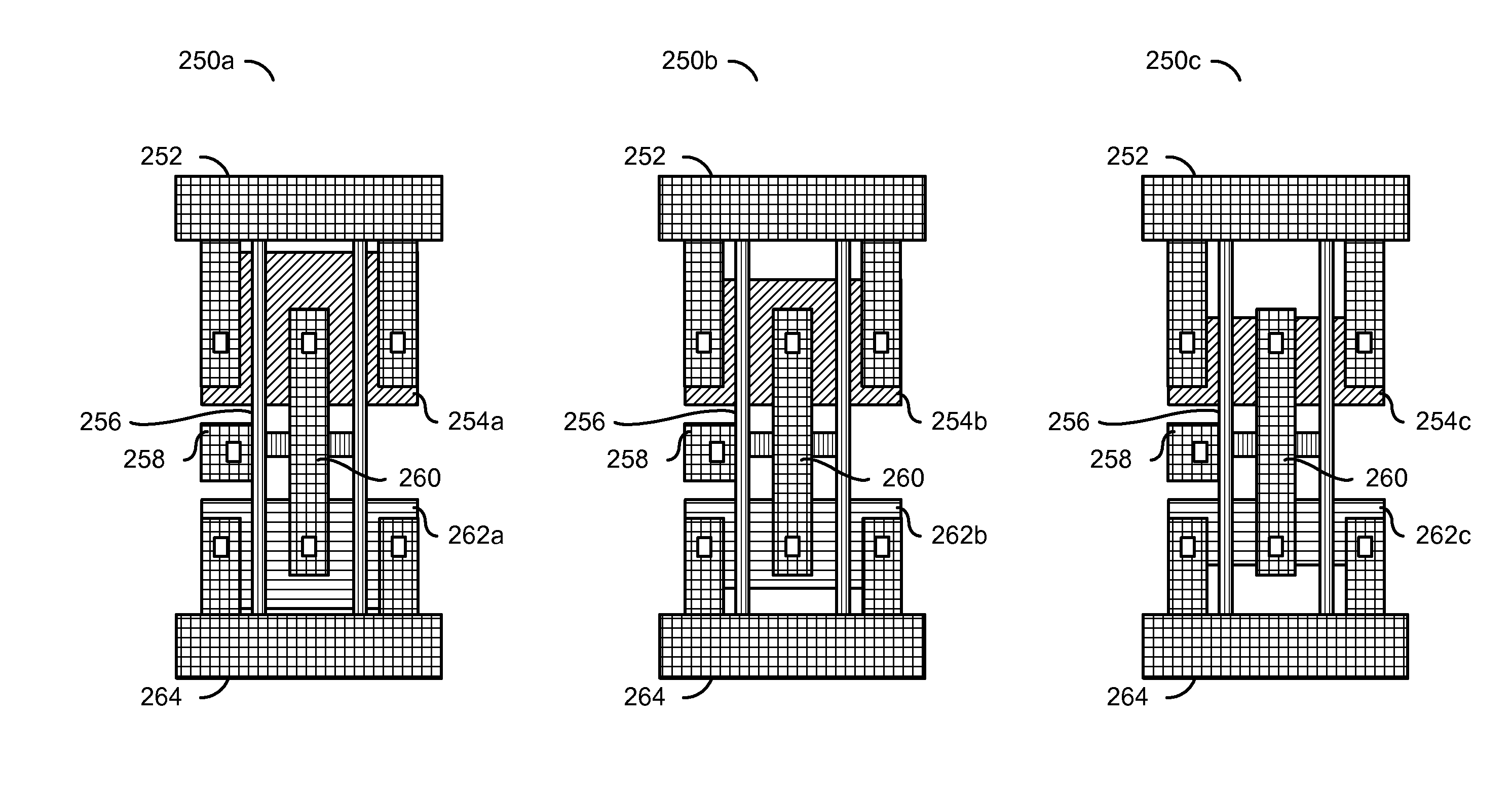
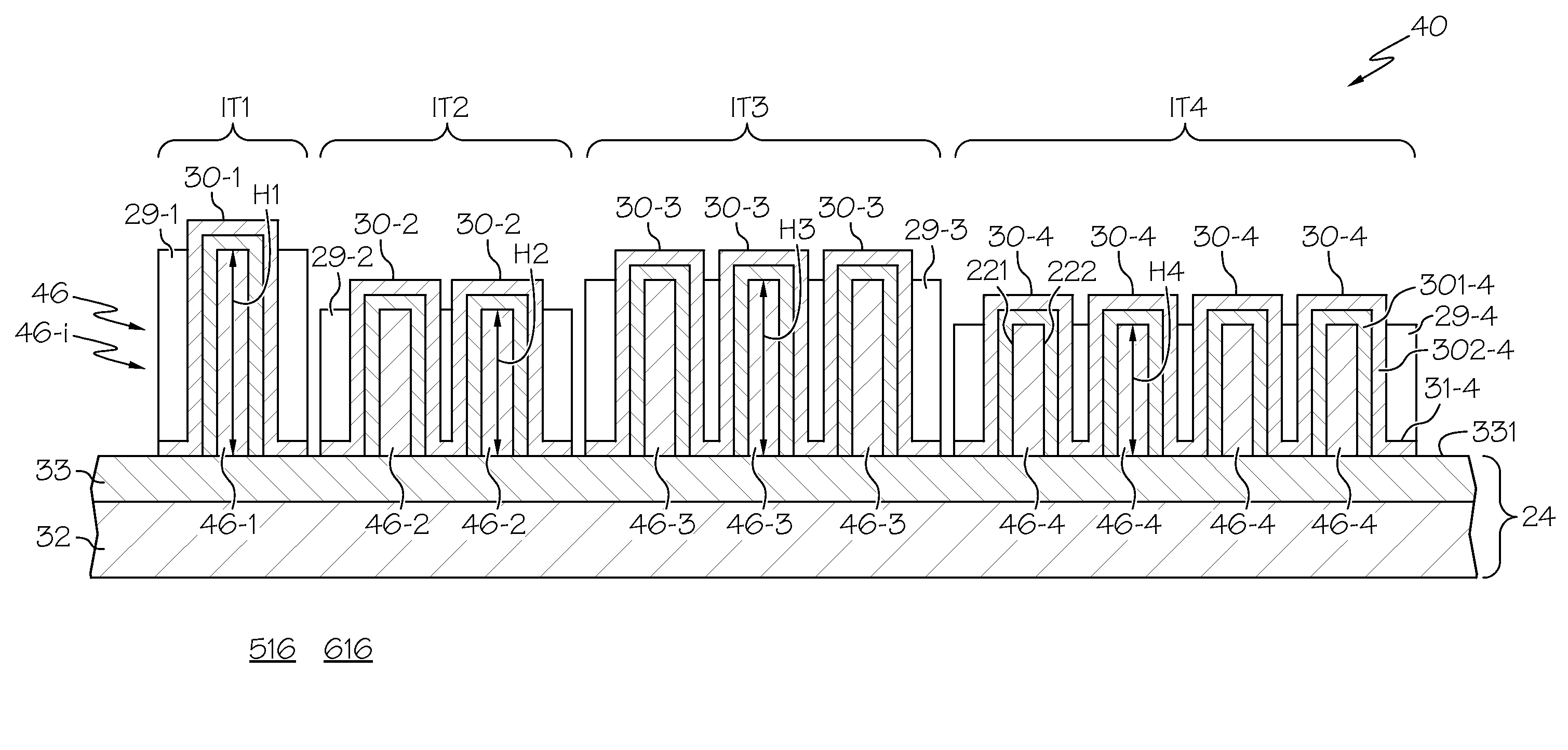
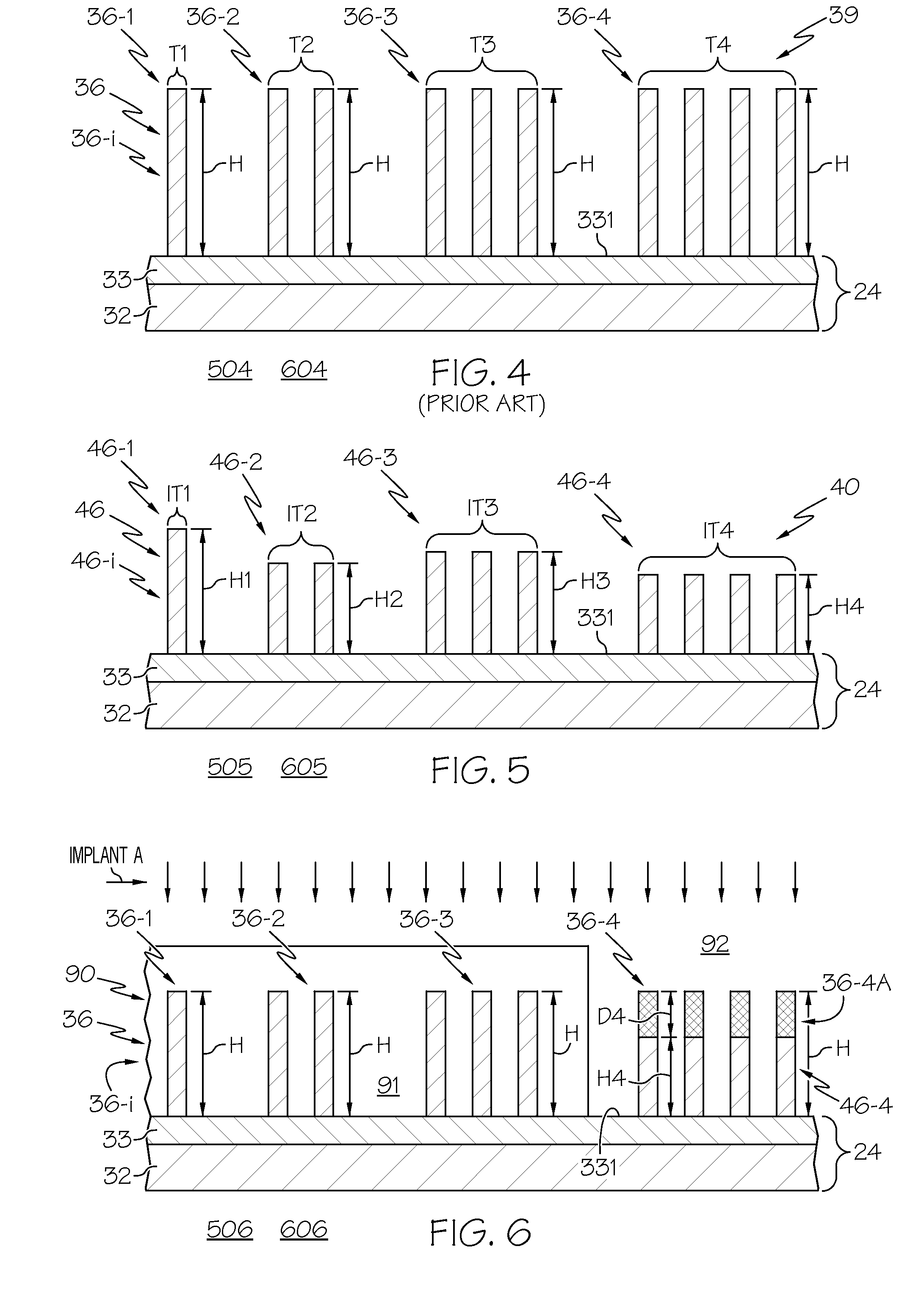
FIN-FET ICs with adjustable FIN-FET channel widths are formed from a semiconductor layer (42). Fins (36) may be etched from the layer (42) and then some (46) locally shortened or the layer (42) may be locally thinned and then fins (46) of different fin heights etched therefrom. Either way provides fins (46) and FIN-FETs (40) with different channel widths W on the same substrate (24). Fin heights (H) are preferably shortened by implanting selected ions (A, B, C, etc.) through a mask (90, 90′, 94, 94′, 97, 97′) to locally enhance the etch rate of the layer (42) or some of the fins (36). The implant(s) (A, B, C, etc.) is desirably annealed and then differentially etched. This thins part(s) (42-i) of the layer (42) from which the fins (46) are then etched or shortens some of the fins (46) already etched from the layer (42). For silicon, germanium is a suitable implant ion. Having fins (42) with adjustable fin heights Hi on the same substrate (24) enables such FIN-FET ICs (40) to avoid channel-width quantization effects observed with prior art uniform fin height FIN-FETs (20).
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
Semiconductor display device
An active matrix semiconductor device is provided which is free of unevenness in image. The analog switch and buffer in a drive circuit are structured by a plurality of parallel-connected analog switches and buffers each formed by a TFT with a small channel width. The carrier moving direction of these TFTs are oblique relative to a scanning direction of a linear laser used for laser crystallization. By doing so, the analog switch and the buffer are decreased in characteristic variation with deterioration suppressed. Thus an active matrix semiconductor device is realized which is free of unevenness in image.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
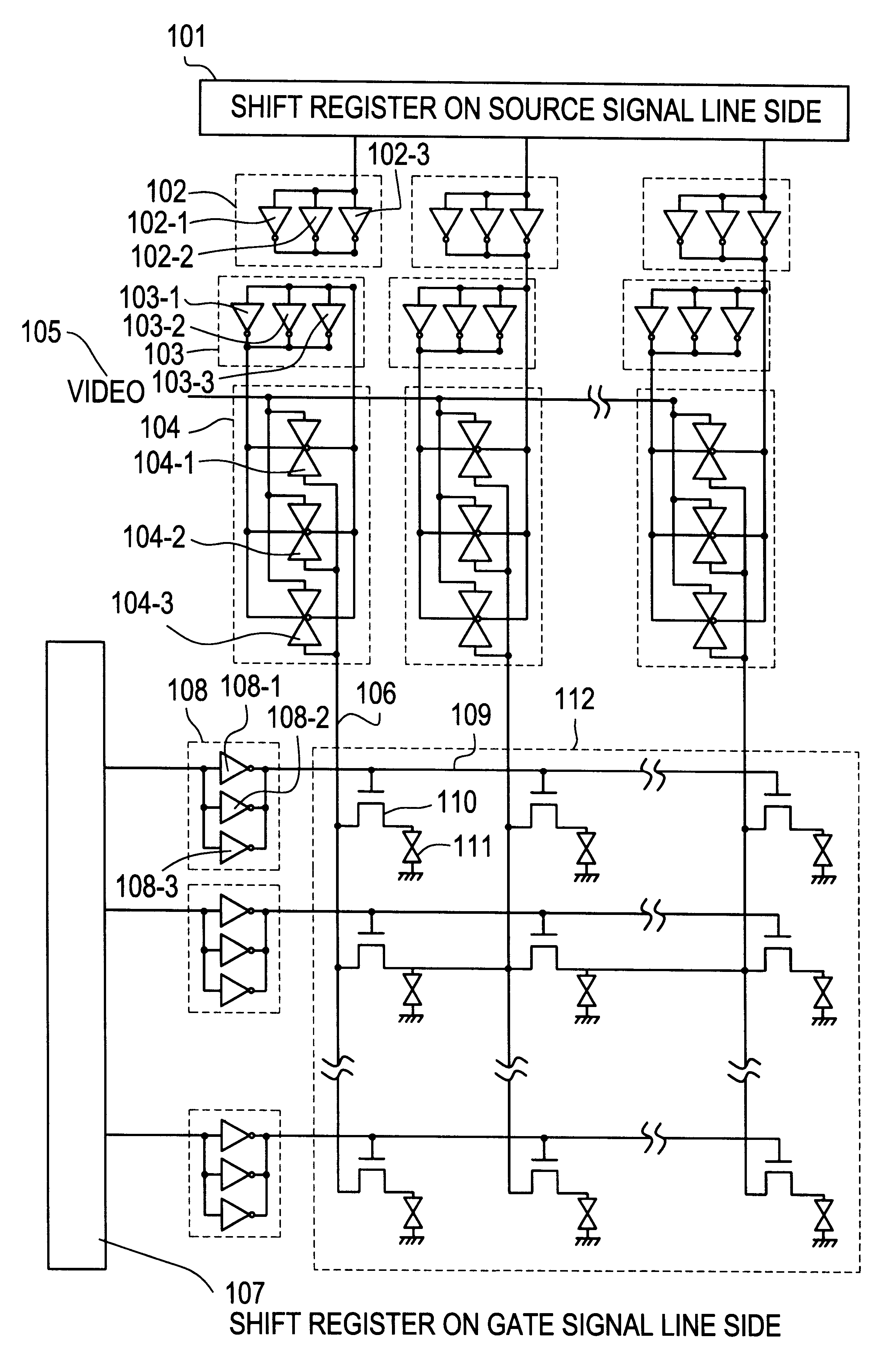
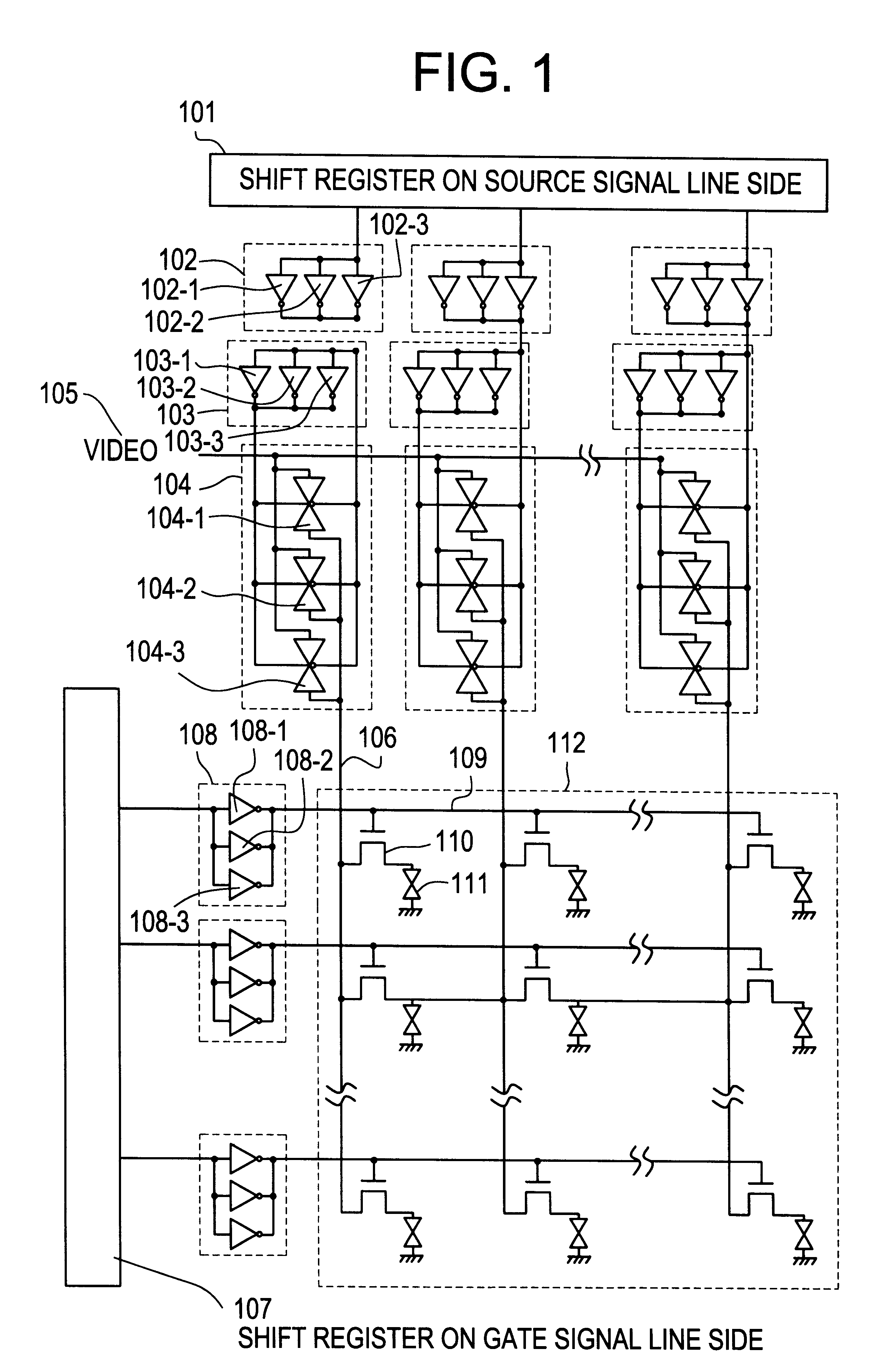
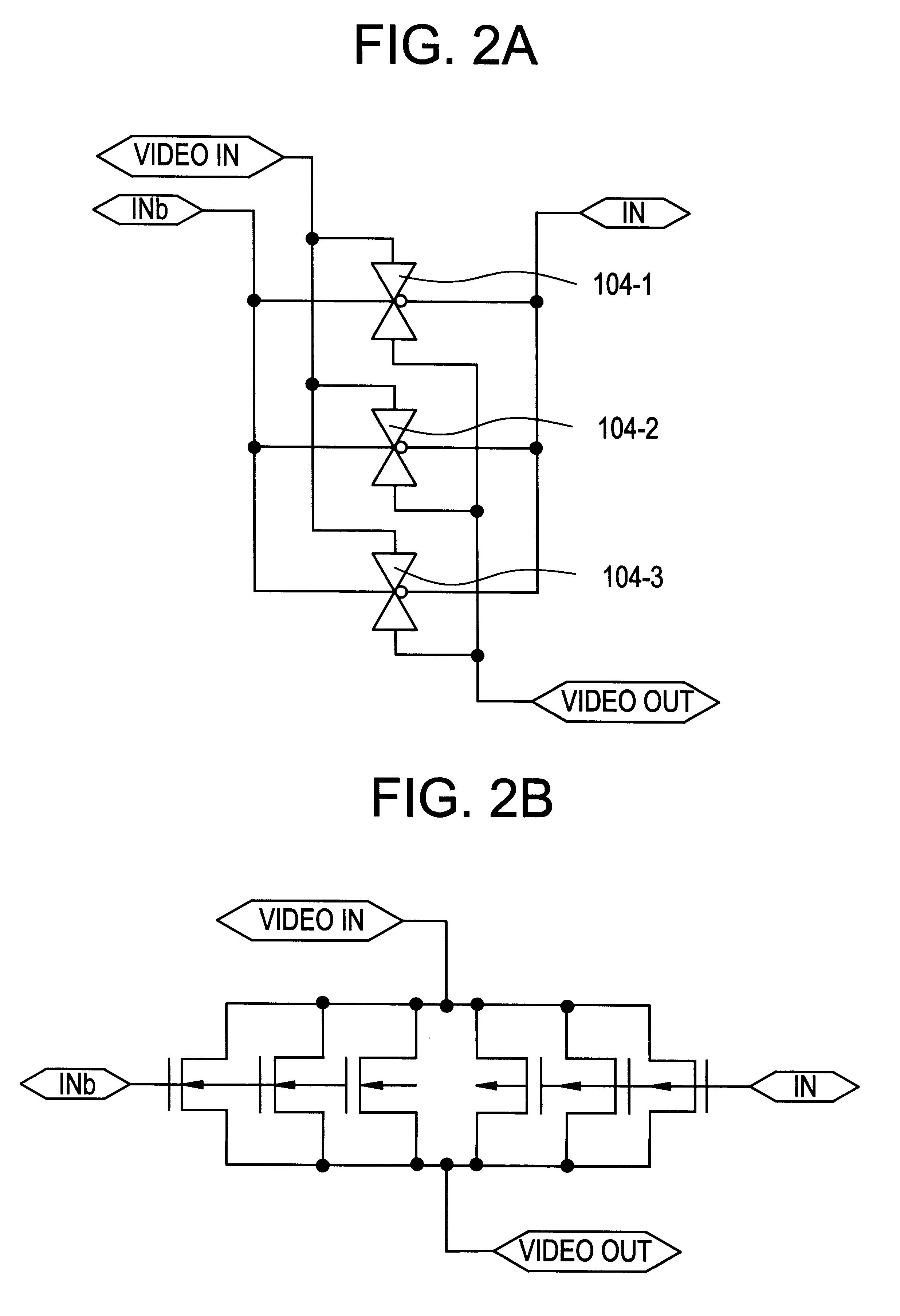
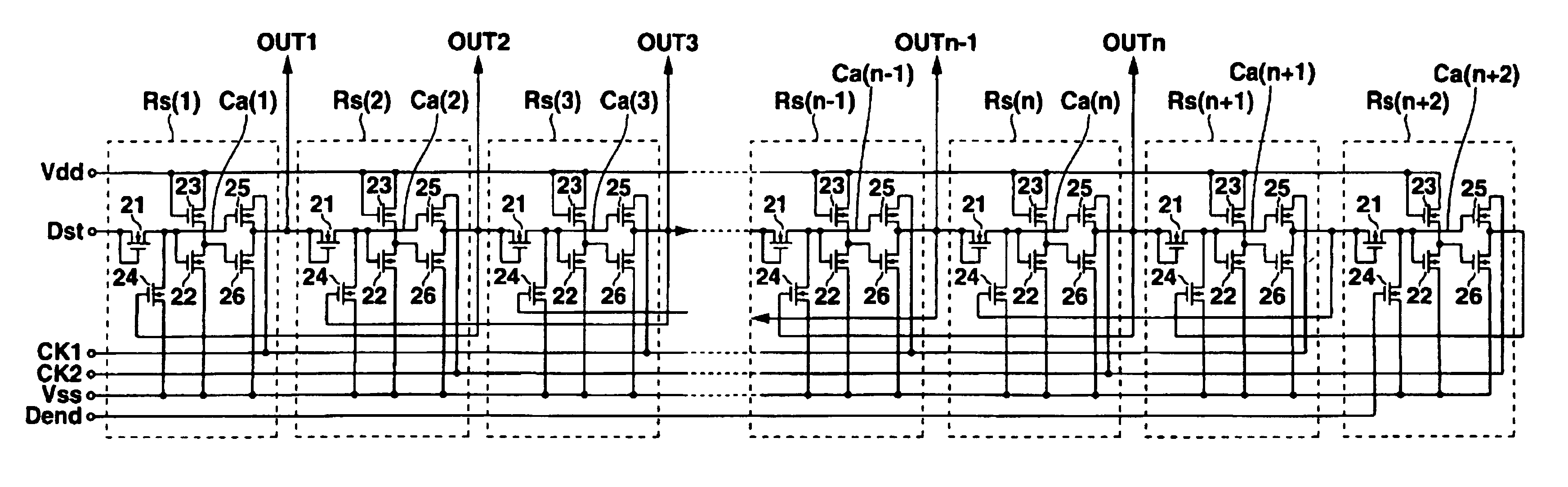
Shift register and electronic apparatus
InactiveUSRE40673E1Correct operation of circuitGuaranteed uptimeCounting chain synchronous pulse countersPower supply linesShift registerTelecommunications
Each of stages RS(1), RS(2), . . . of a shift register is constituted by six TFTs. A ratio of a channel width and a channel length (W / L) of each of these TFTs 1 to 6 is set in accordance with a transistor characteristic of each TFT in such a manner that the shift register normally operates for a long time even at a high temperature.
Owner:ORTUS TECH
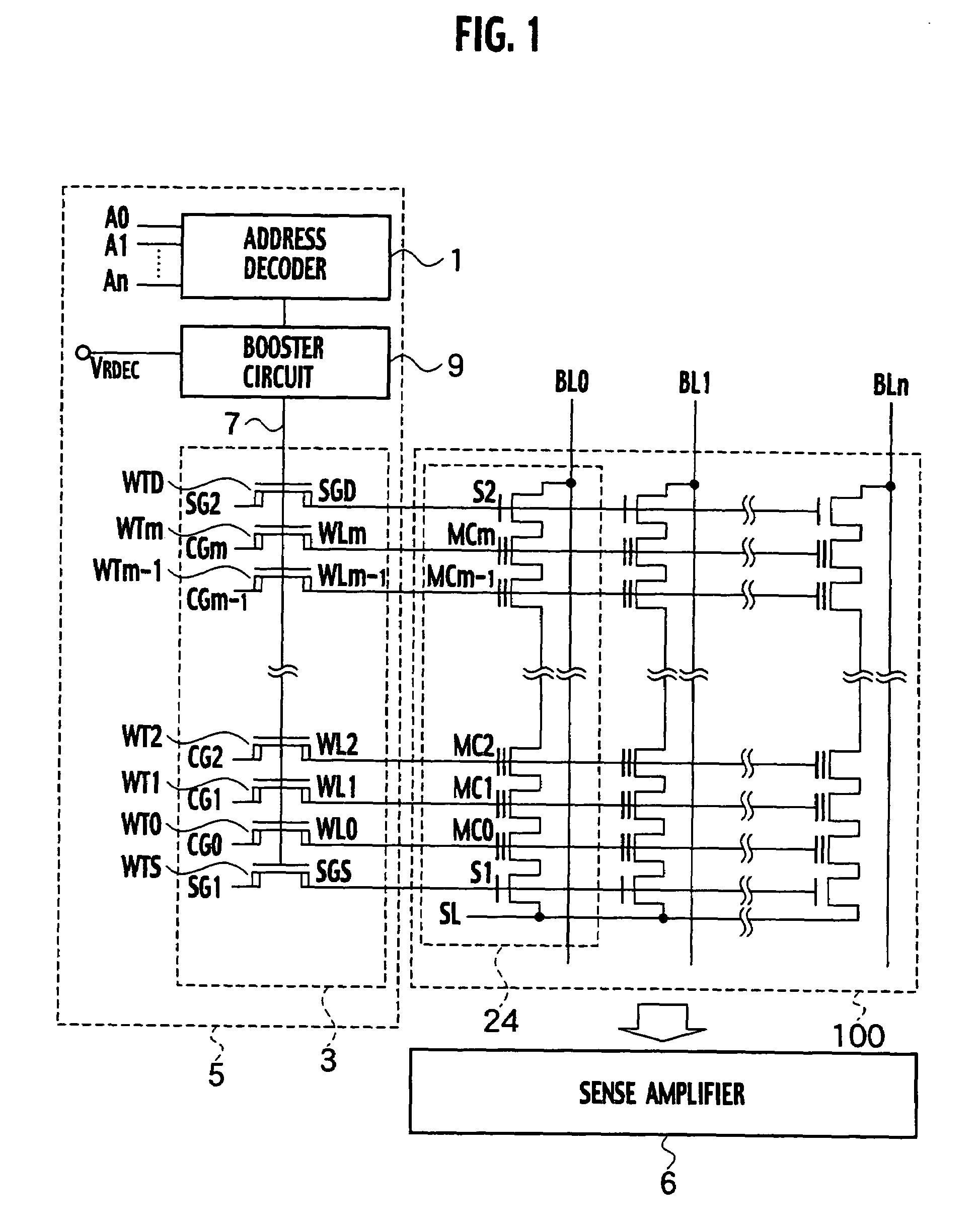
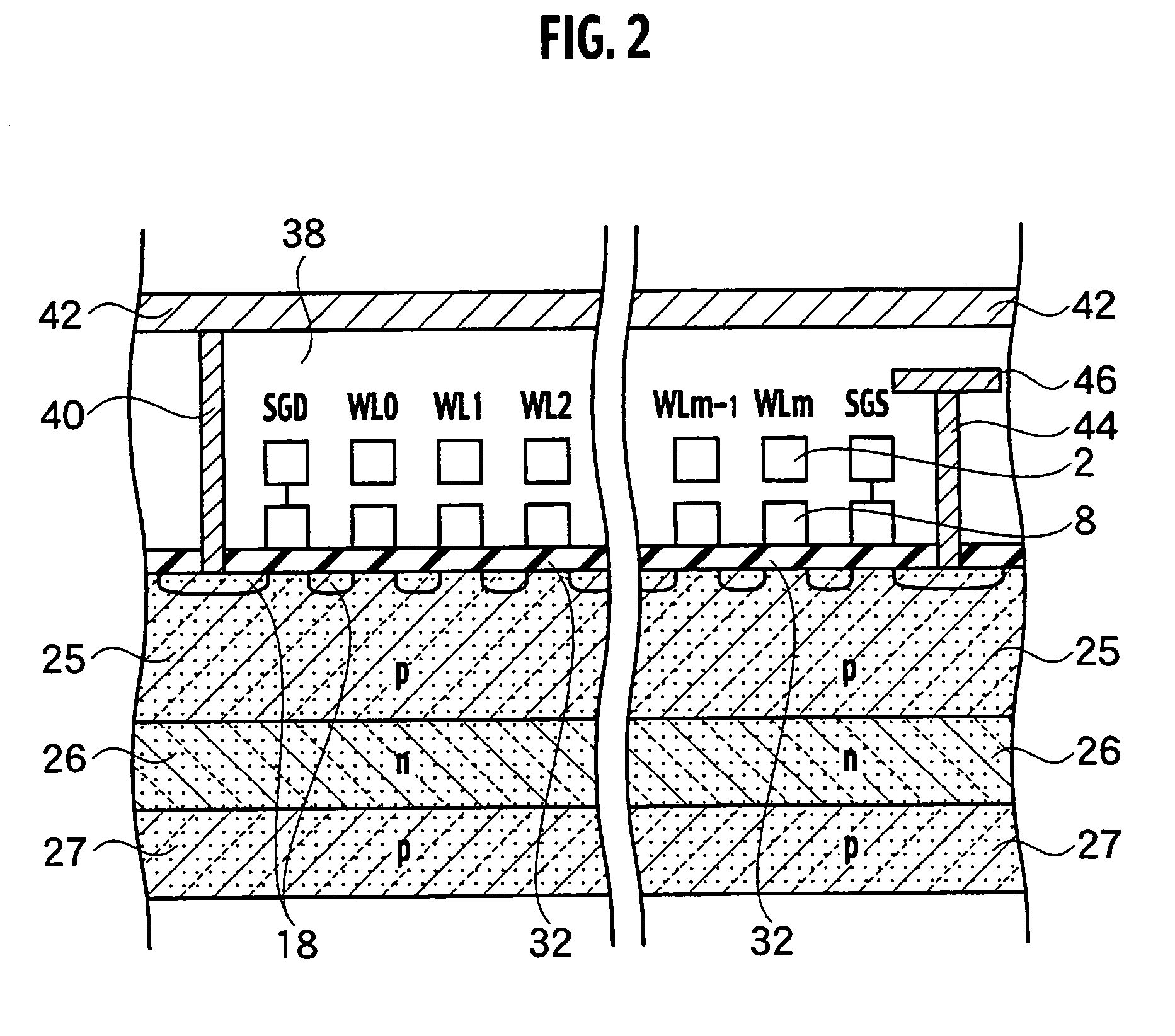
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory includes: a memory cell array constituted by word lines, bit lines, and electrically erasable / rewritable memory cell transistors, which have respective tunnel insulating films and are arranged at the intersections of the word lines and the bit lines; and a word line transfer transistor, which is separated by an element isolation region, has a source diffusion layer, a channel region, a gate insulating film on the channel region, and a drain diffusion layer, and is connected to a word line and a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film via a word line contact plug formed in the drain diffusion layer. The channel width of the word line transfer transistor is at least six times width of the word line contact plug, and the distance in a second direction between the word line contact plug and corresponding element isolation region is greater than distance in a first direction between the word line contact plug and corresponding element isolation region where, the first direction denotes a direction from the source diffusion layer towards the drain diffusion layer, and the second direction denotes a direction perpendicular to the first direction.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com