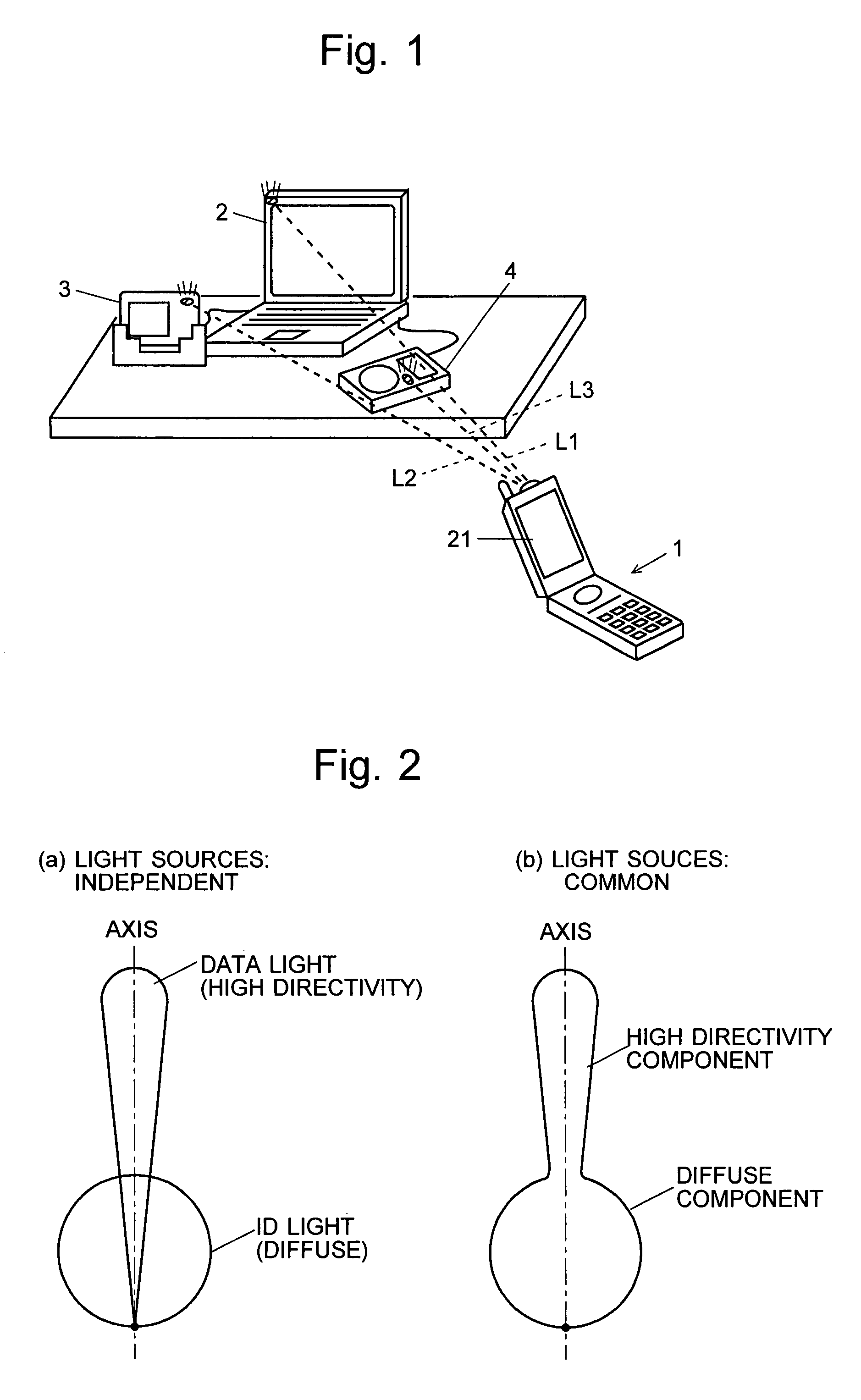
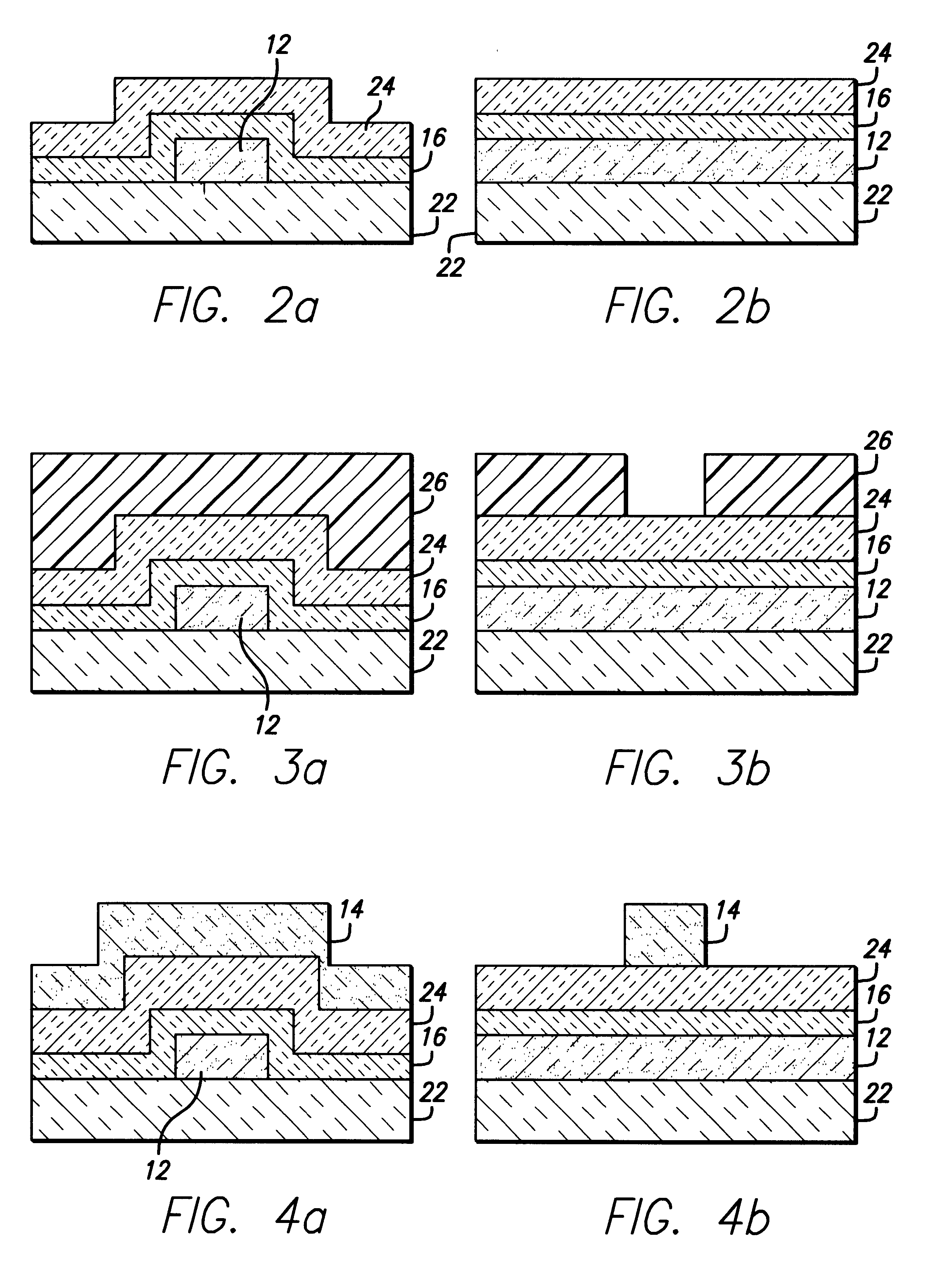
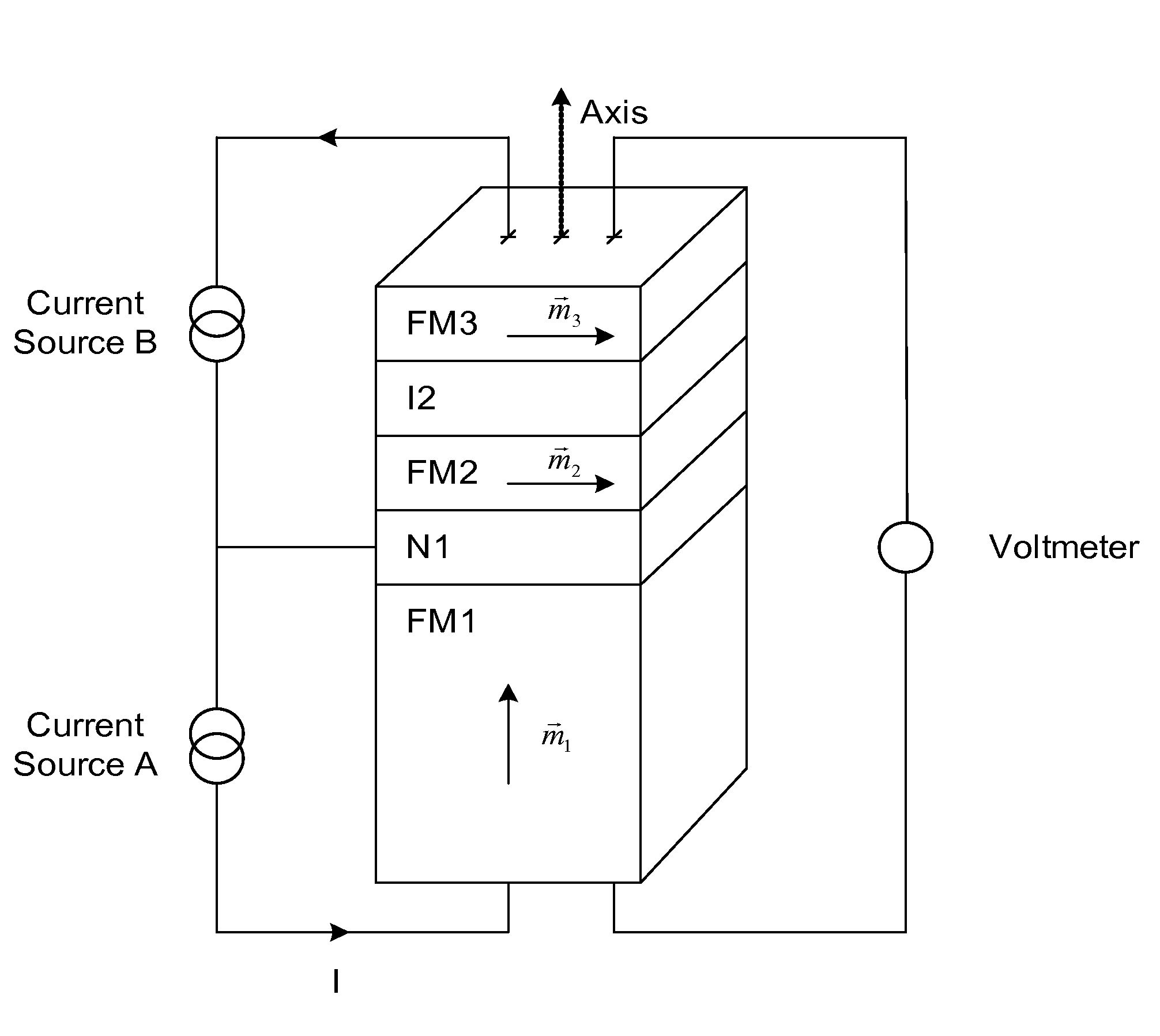
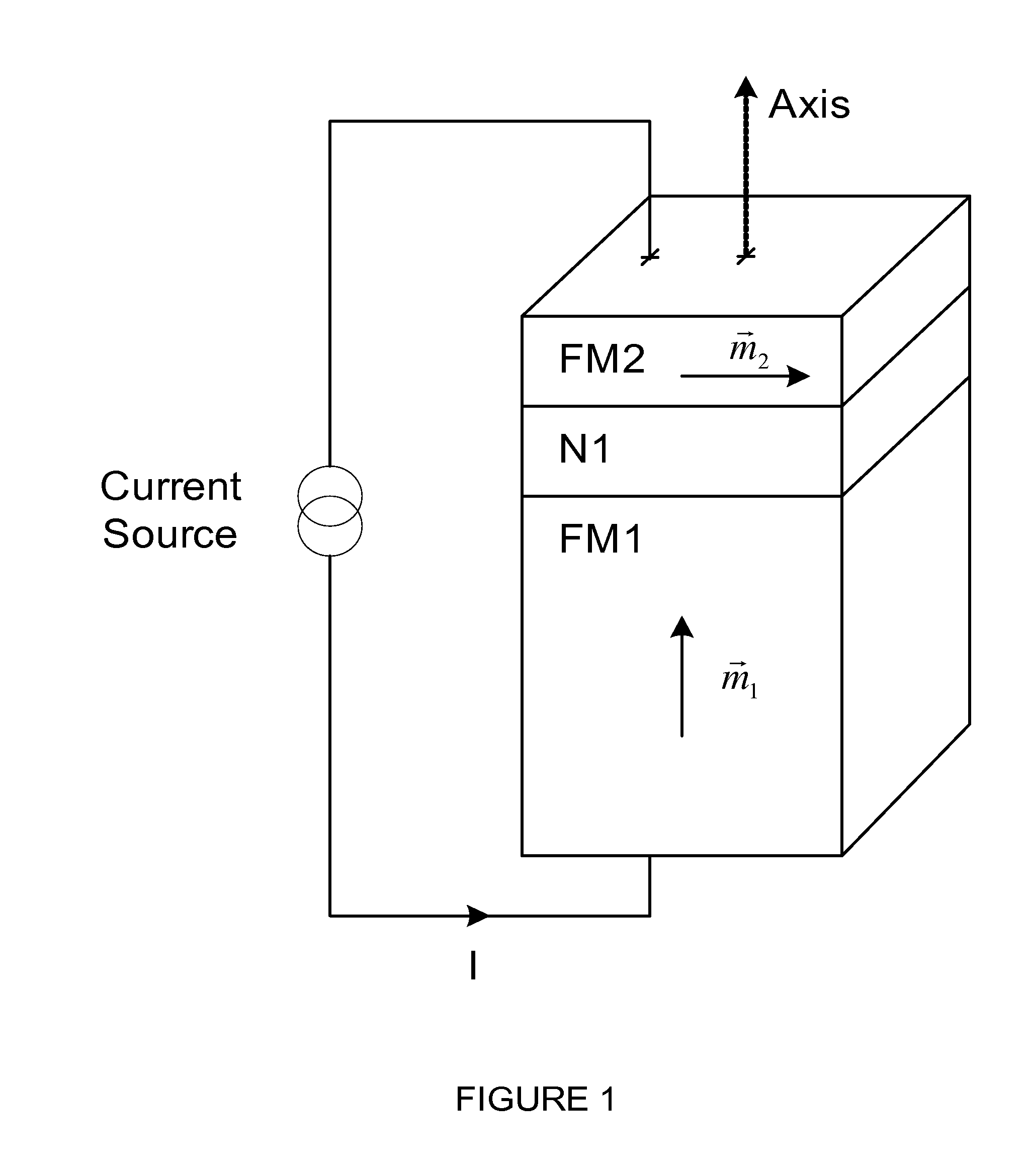
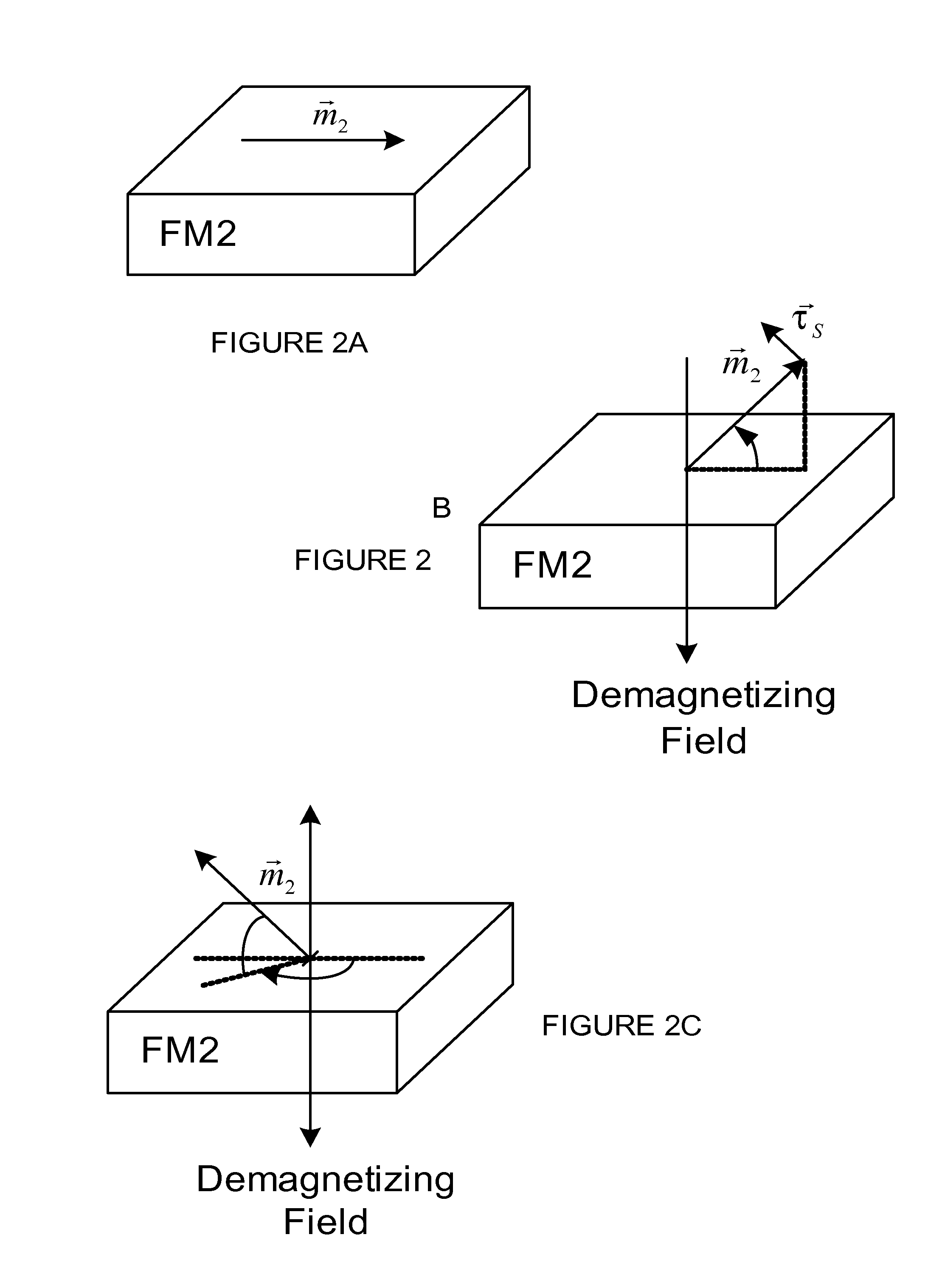
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7347 results about "High velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Projectile firing device using liquified gas propellant
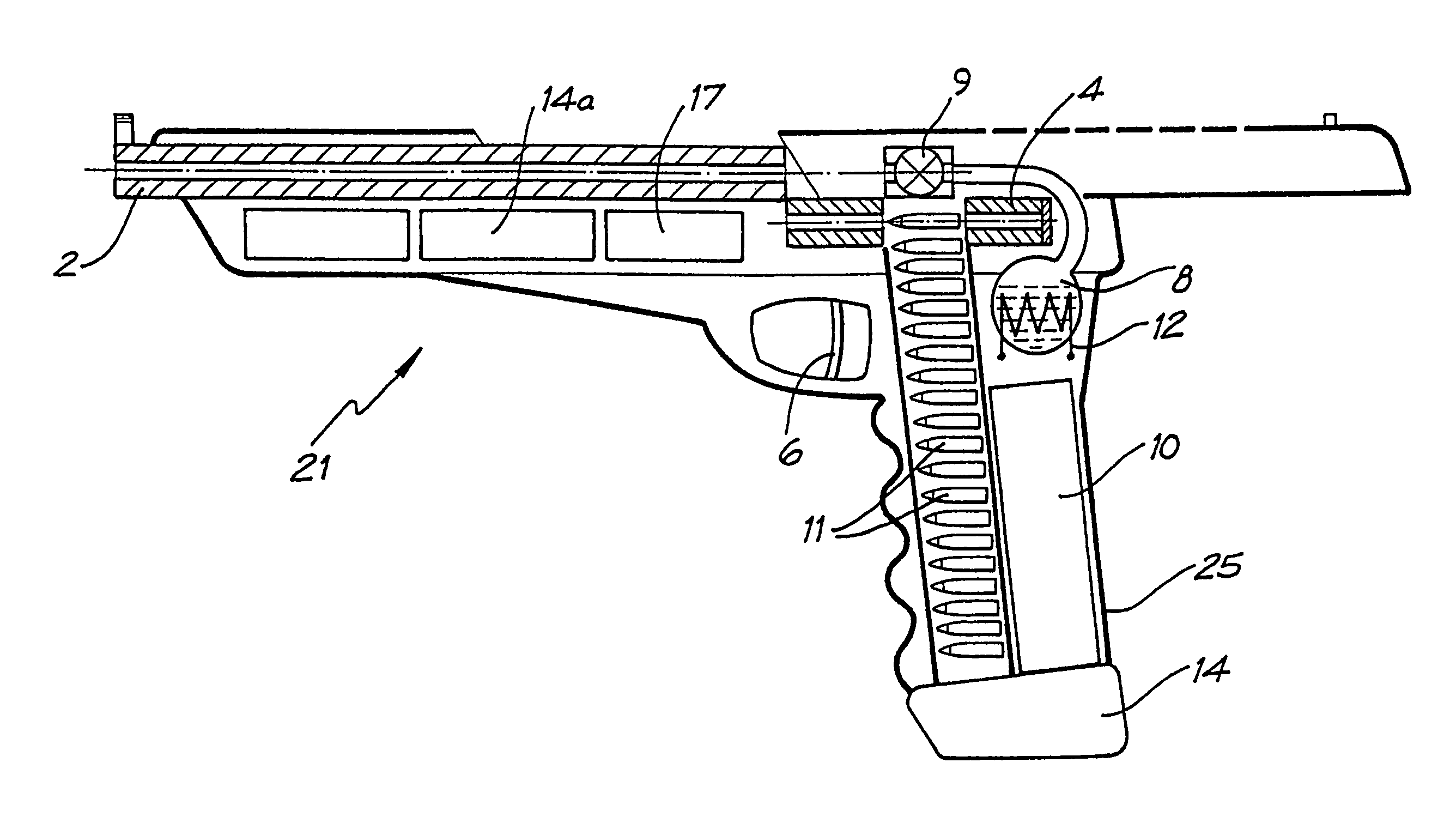
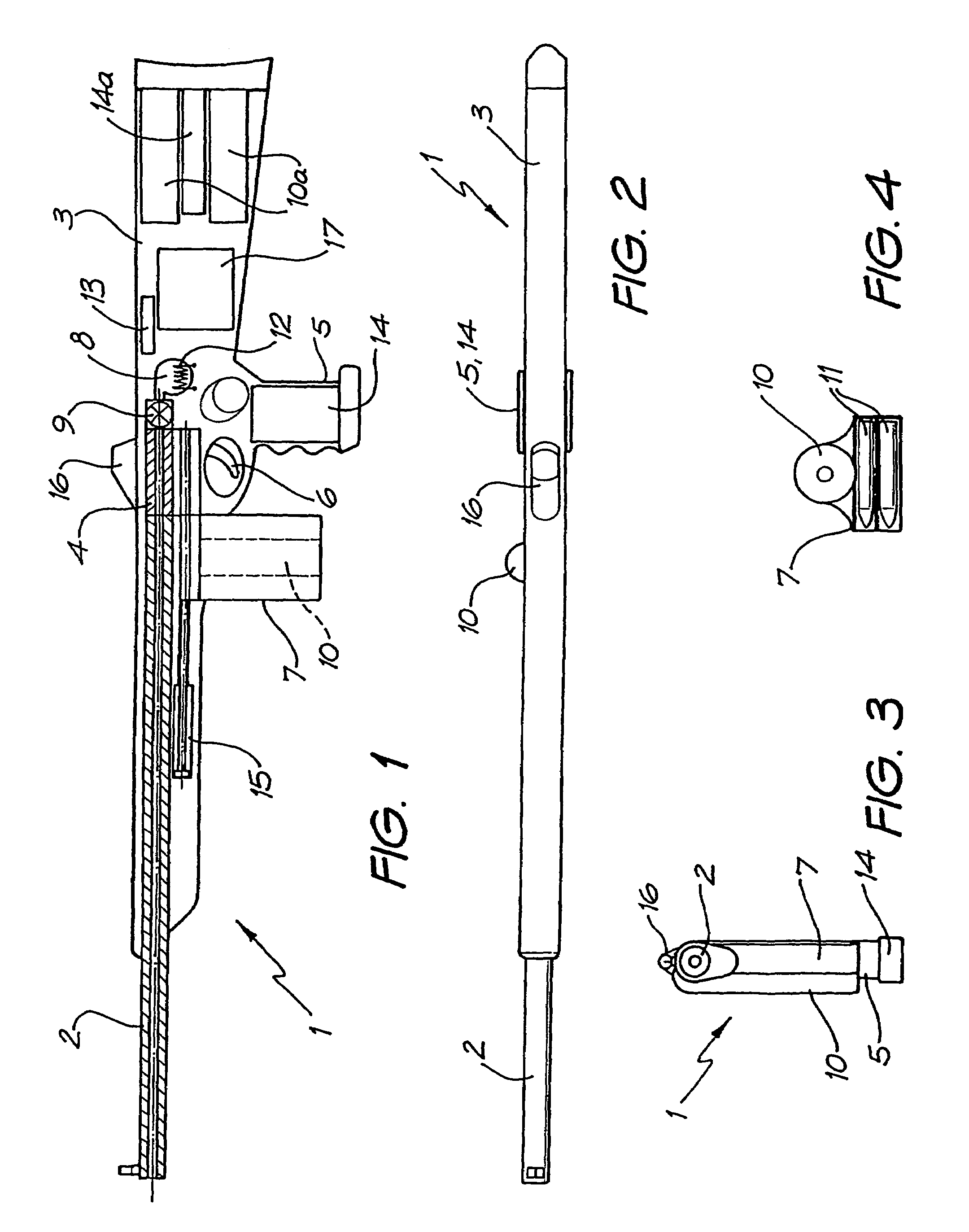
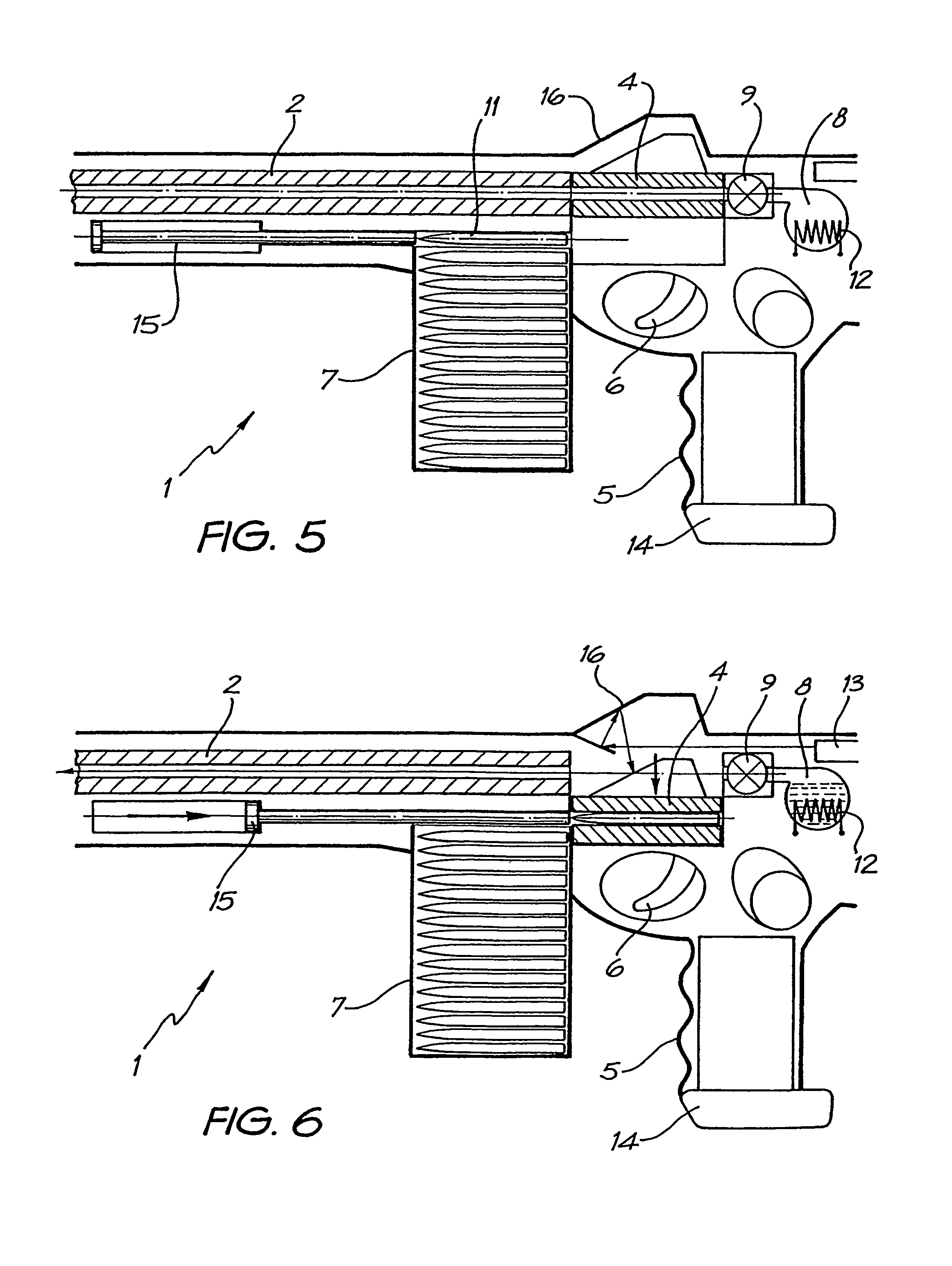
Rifle (1) comprises barrel (2) and loading means (15) for introducing a projectile from magazine (7) into breech (4). The projectile is propelled by a compressed gas propellant initially stored as a liquid in canister (10). The liquid is heated to a super critical state in chamber (8) by heating element (12) to induce a phase change such that the liquid becomes a highly dense gas. The phase change from liquid to gas provides the energy required to expel the projectile at high velocity from rifle (1), regardless of the ambient temperature. The propellant is preferably CO2 which is heated to 31.06° C. Rifle (1) produces minimal noise and no heat signature, making it suitable for military and stealth purposes. A pistol and launchers for grenades or mortar bombs are also disclosed. Another version can launch low earth orbit satellites or payloads.
Owner:POLY SYST PTY LTD
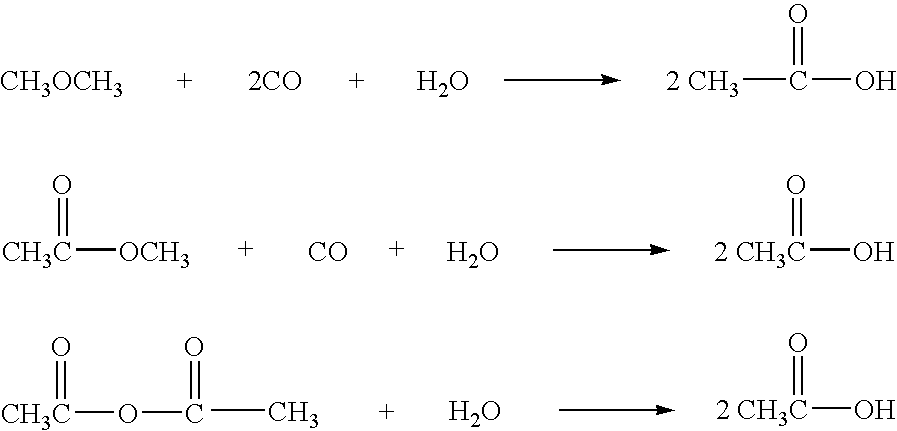
Low water methanol carbonylation process for high acetic acid production and for water balance control
ActiveUS7005541B2High acetic acid production rateIncrease chanceOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionWater methanolAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to a process for the production of acetic acid by carbonylation of methanol, and reactive derivatives thereof, in a reaction mixture using a rhodium-based catalyst in low water conditions. The process is used to achieve reaction rates of at least 15 g mol / l / hr. The high rate reactions proceed at water concentrations of less than 2.0 wt. %. Under certain conditions, the water concentration in the reaction mixture of the process is maintained at a desired concentration by at least one process step including adding a compound such as methyl acetate, dimethyl ether, acetic anhydride, or mixtures of these compounds to the reaction system. The process step of adding the components to the reaction mixture may be combined with other process steps for controlling water concentrations in reaction mixtures for the carbonylation of methanol.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
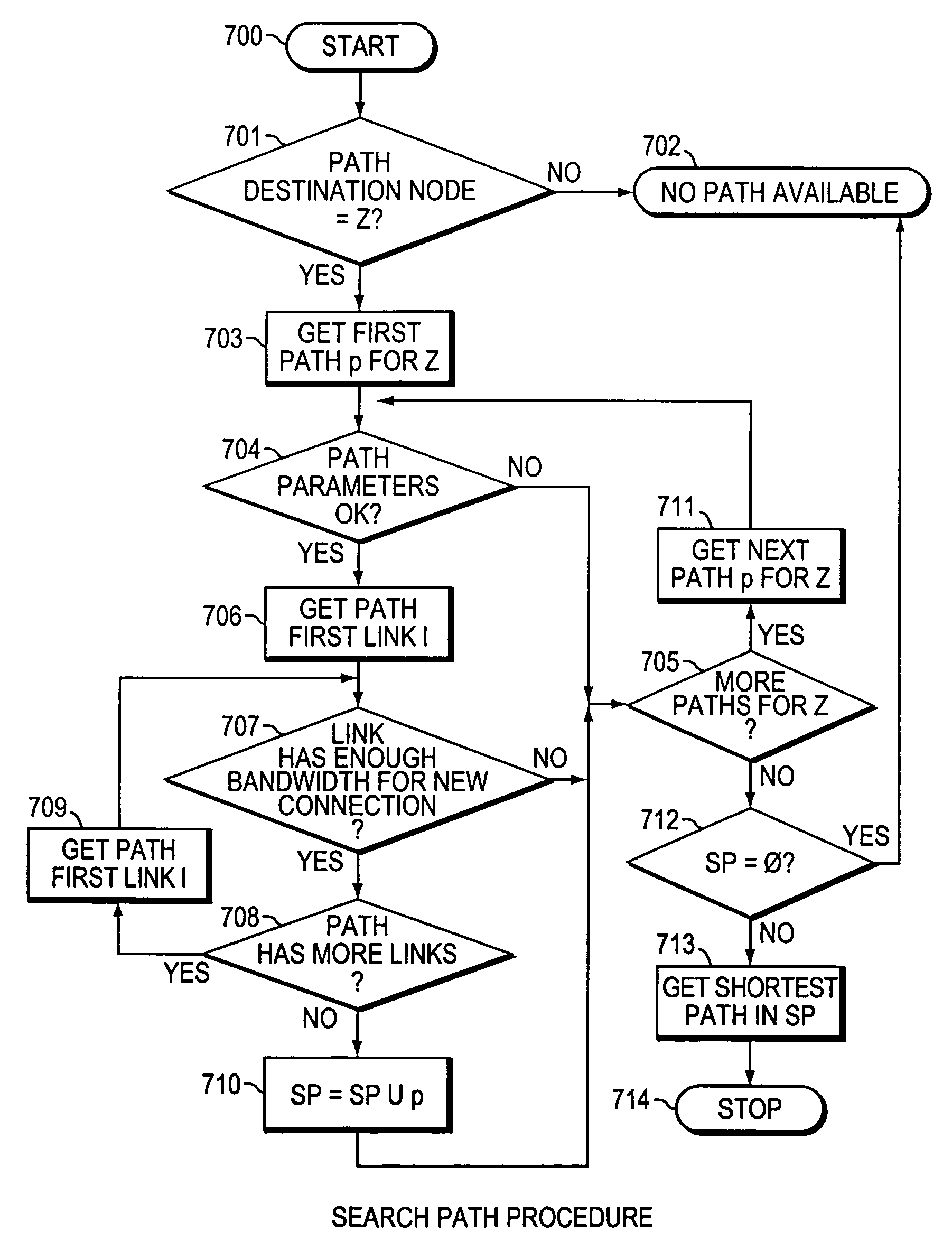
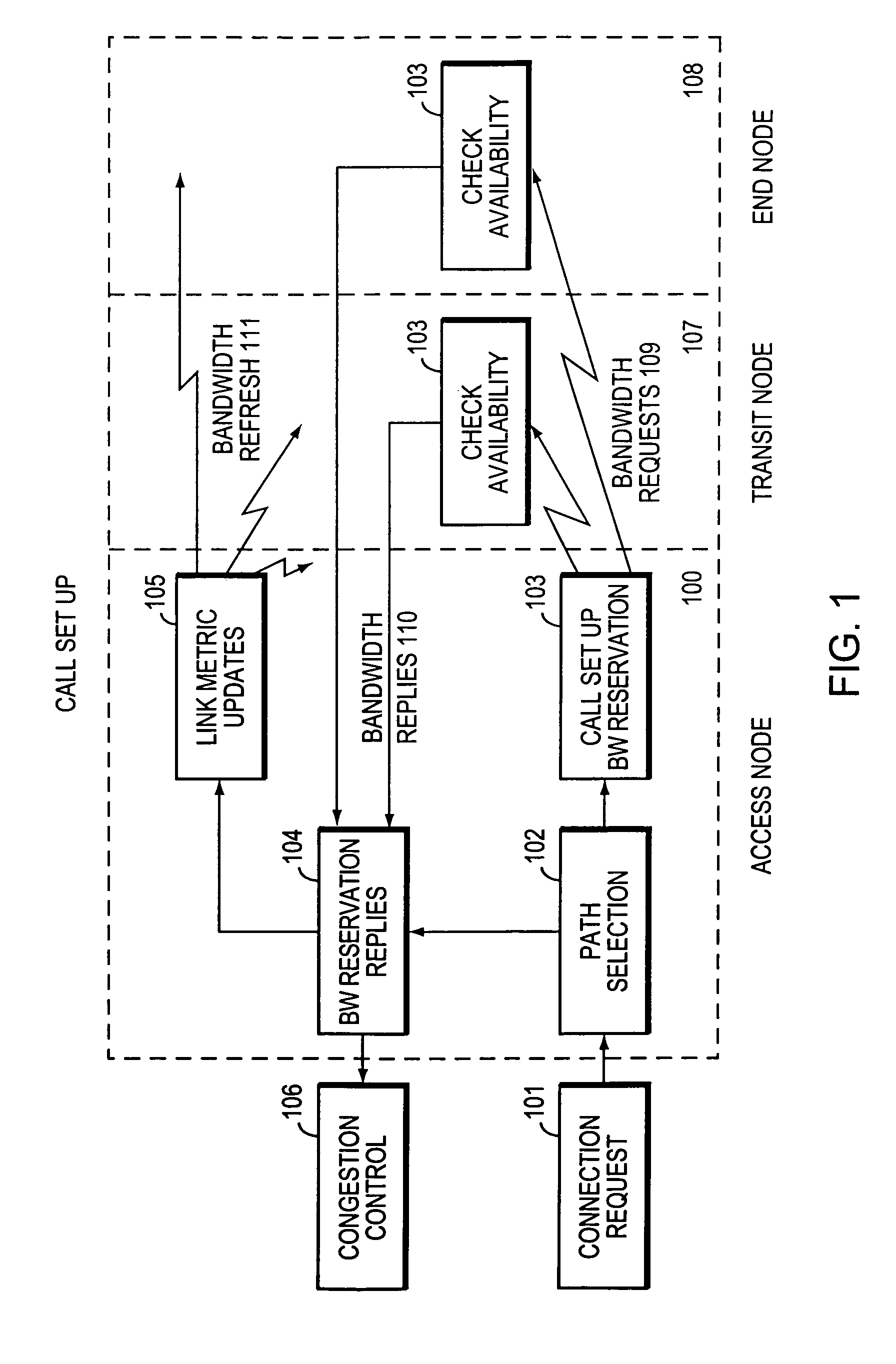
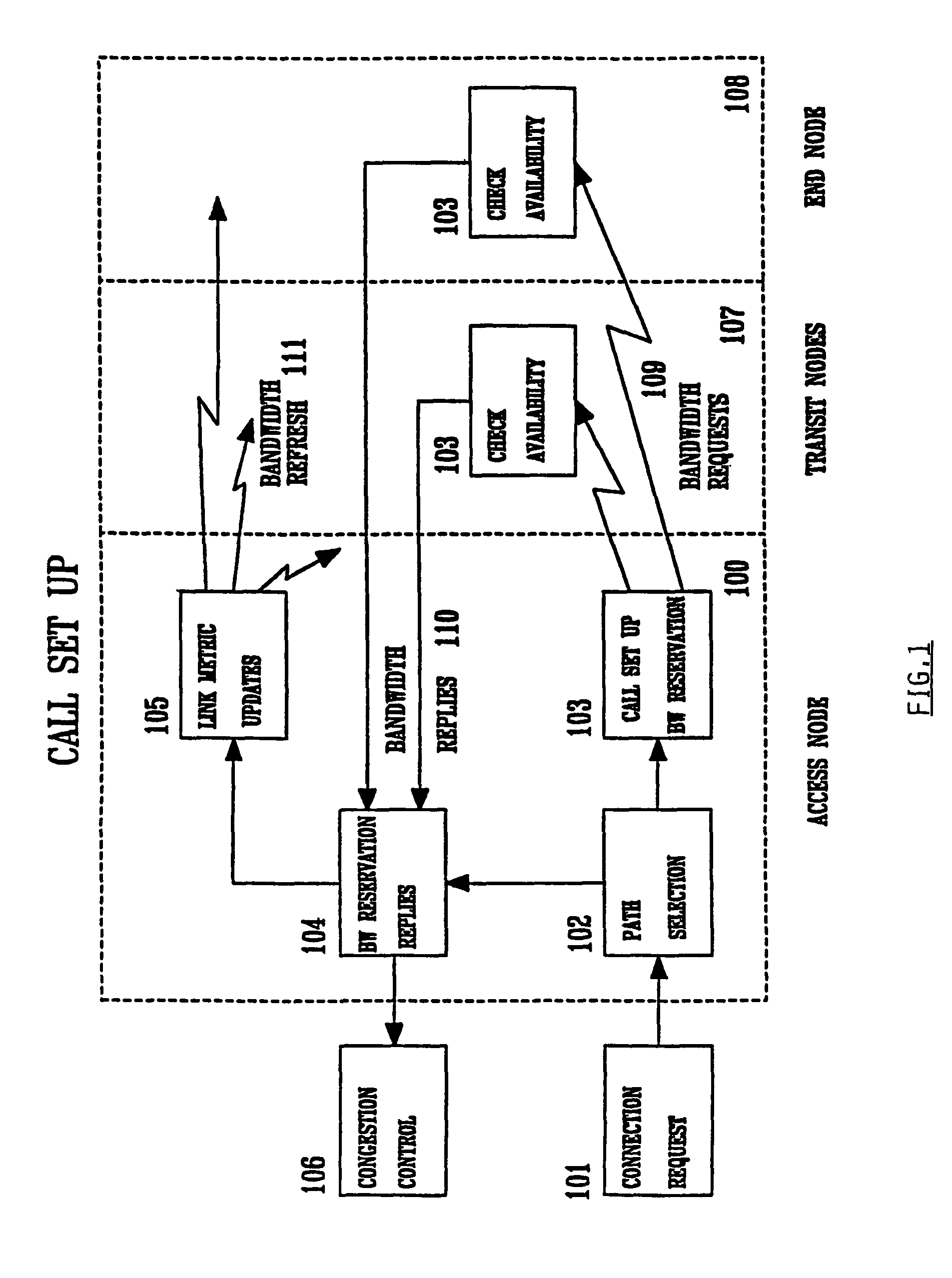
Method and system for minimizing the connection set up time in high speed packet switching networks
InactiveUS6934249B1Minimize delayMinimize in in to selectError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPacket switched
The present invention is directed to a high speed packet switching network and, in particular to a method and system for minimizing the time to establish a connection between an origin and a destination node. Due to high dynamicity of the traffic on transmission links, it is important to select a routing path according to a fully up-to-date information on all network resources. The simpler approach is to calculate a new path for each new connection request. This solution may be very time consuming because there are as many path selection operations as connection set up operations. On another hand, the calculation of paths based on an exhaustive exploration of the network topology, is a complex operation which may also take an inordinate amount of resources in large networks. Many of connections originated from a network node flow to the same destination network node. It is therefore possible to take a serious benefit in reusing the same already calculated paths for several connections towards the same node. The path calculated at the time the connection is requested is recorded in a Routing Database and updated each time a modification occurs in the network. Furthermore, alternate paths for supporting non-disruptive path switch on failure or preemption, and new paths towards potential destination nodes can be calculated and stored when the connection set up process is idle. These last operations are executed in background with a low processing priority and in absence of connection request.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
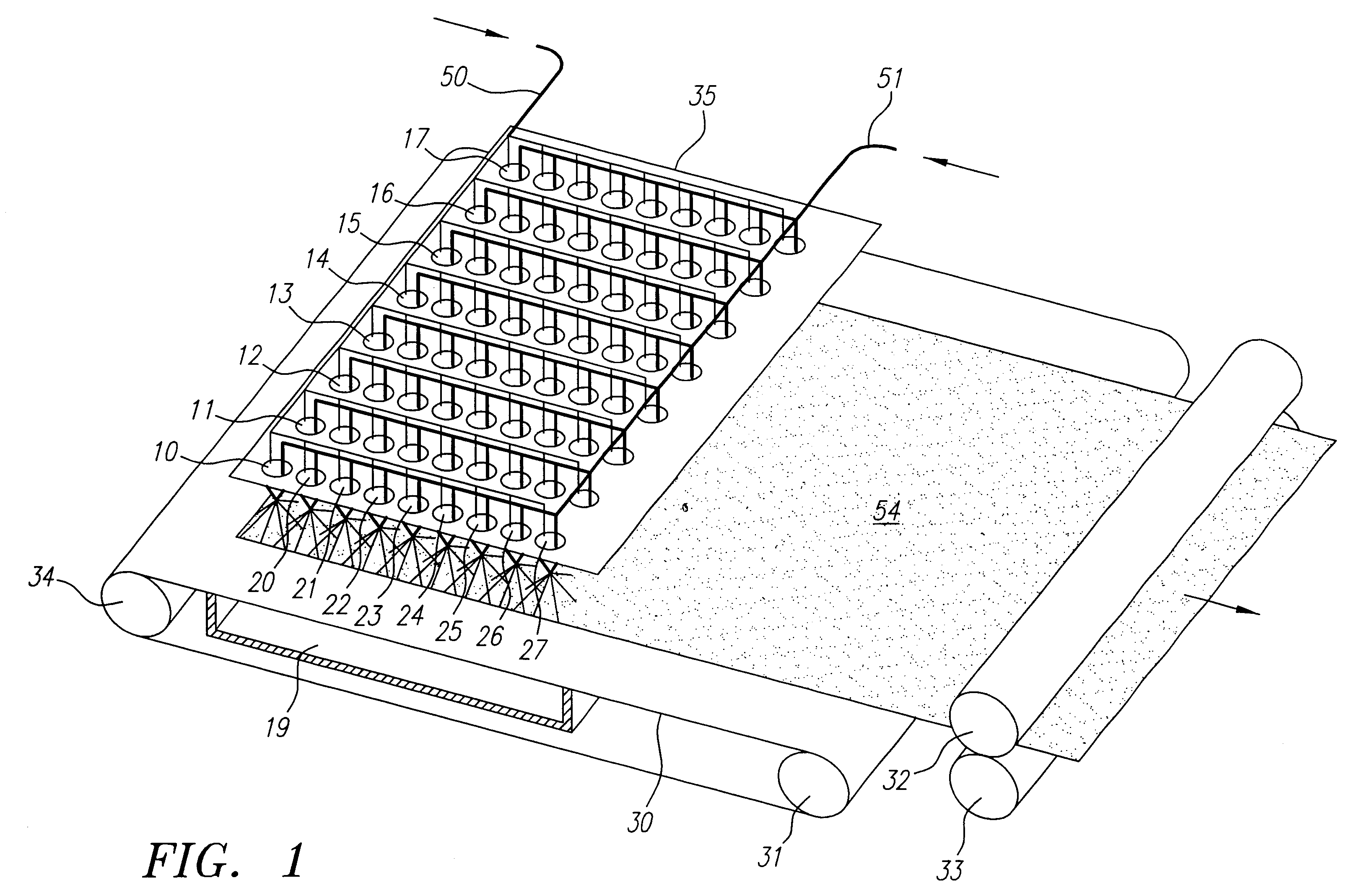
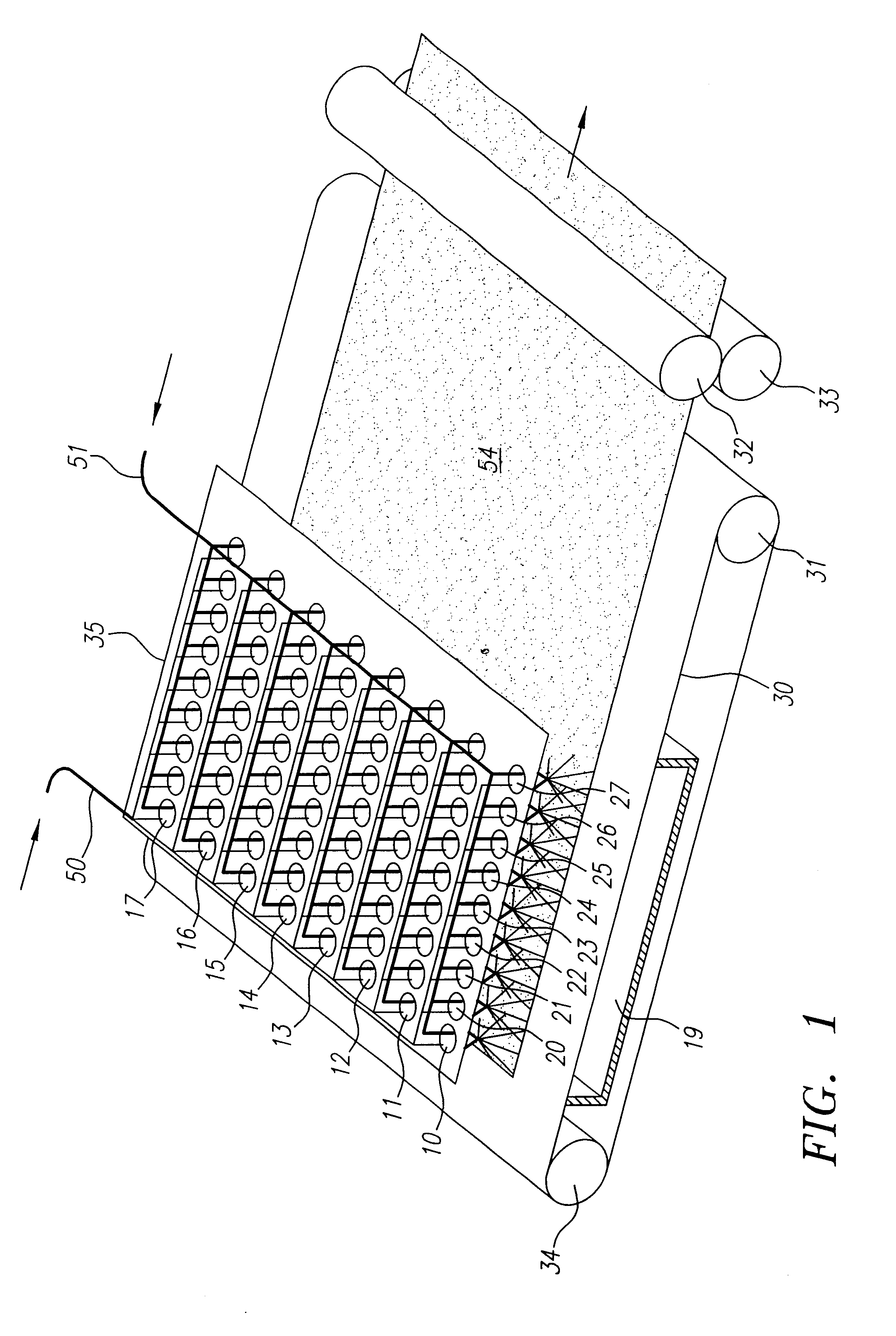
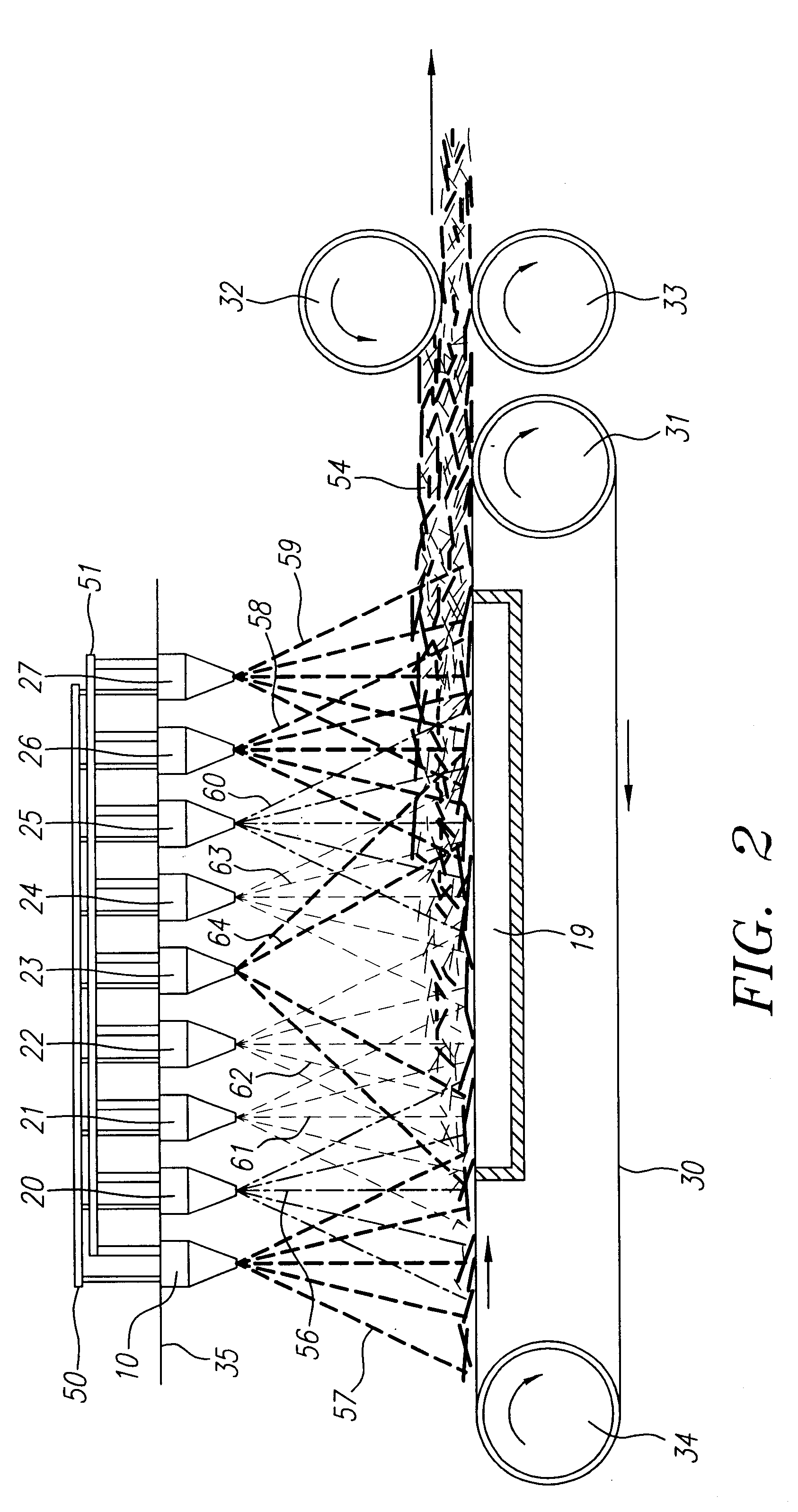
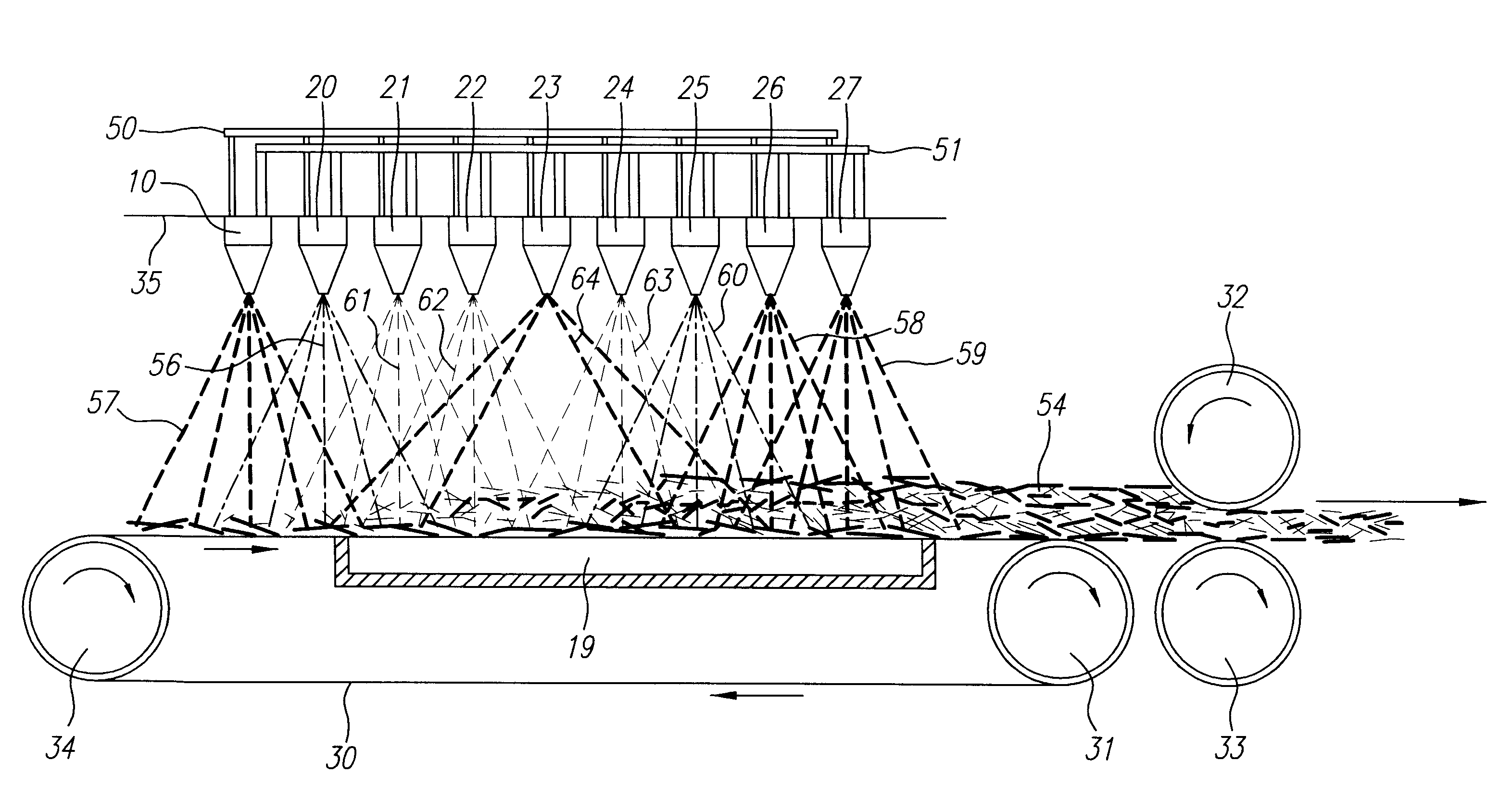
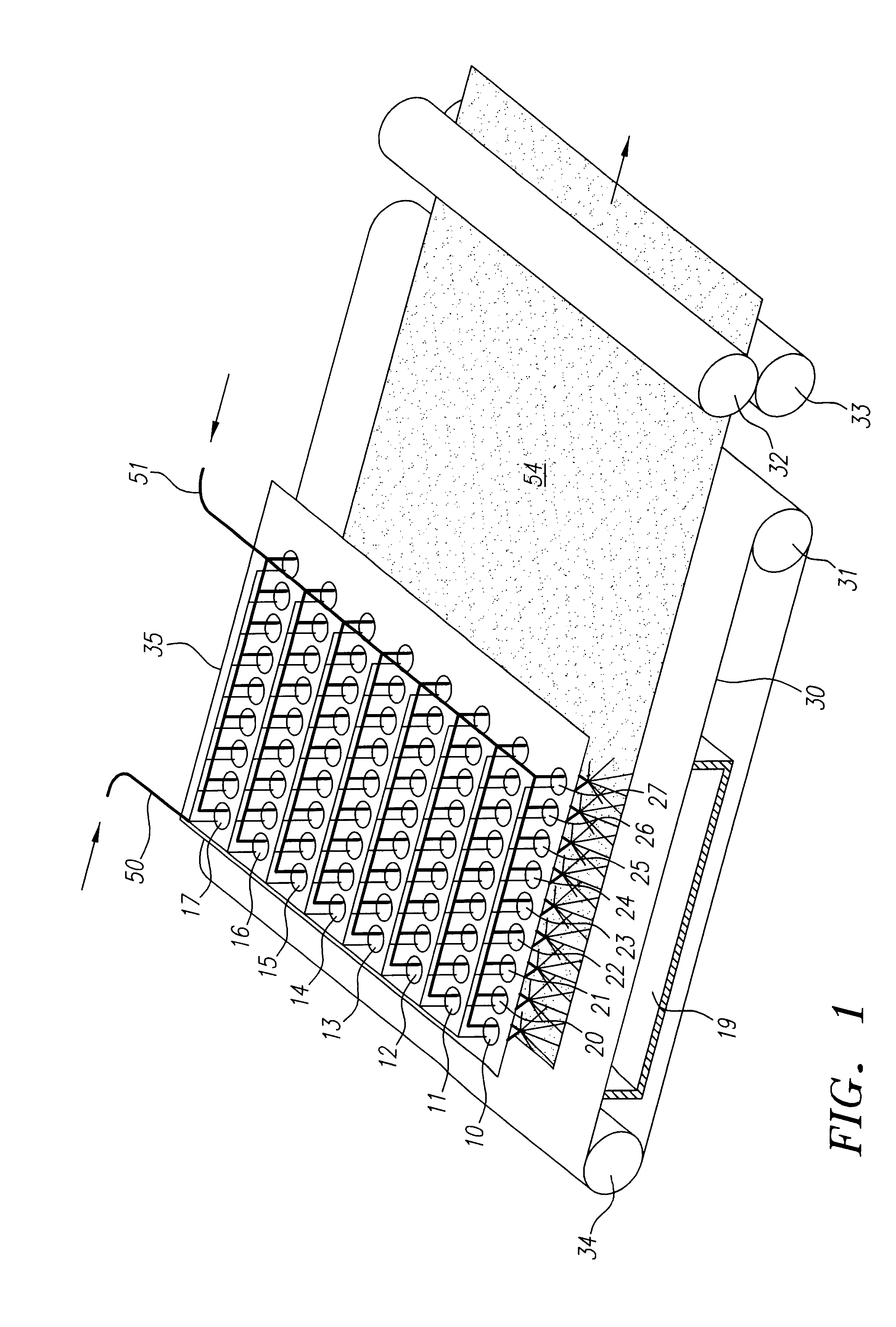
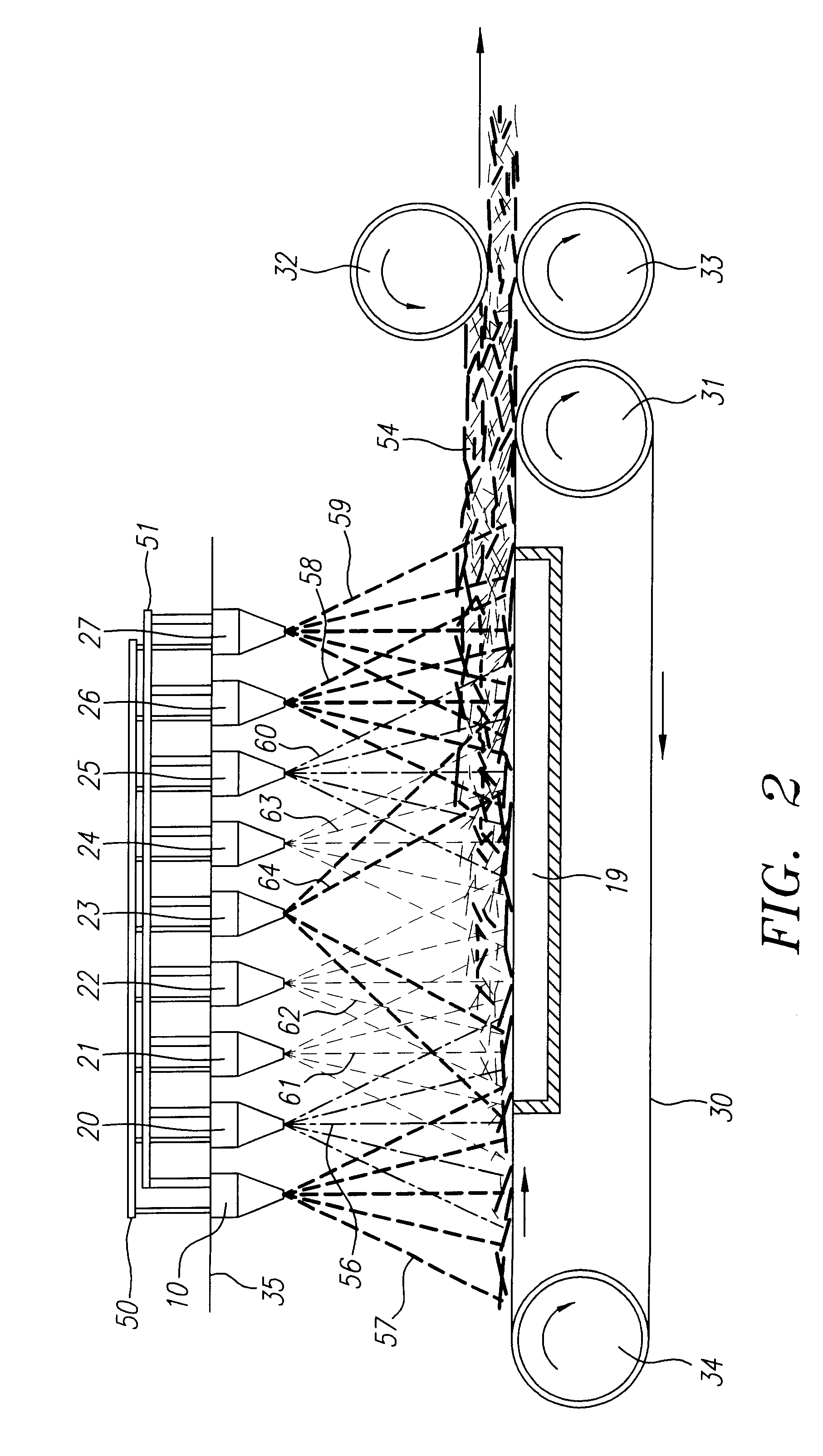
Method and apparatus for producing high efficiency fibrous media incorporating discontinuous sub-micron diameter fibers, and web media formed thereby
InactiveUS6315806B1Increase distanceReduce resistanceFilament/thread formingLoose filtering material filtersMean diameterFiber
A composite filtration medium web of fibers containing a controlled dispersion of a mixture of sub-micron and greater than sub-micron diameter polymeric fibers is described. The filtration medium is made by a two dimensional array of cells, each of which produces a single high velocity two-phase solids-gas jet of discontinuous fibers entrained in air. The cells are arranged so that the individual jets are induced to collide in flight with neighboring jets in their region of fiber formation, to cause the individual nascent fibers of adjacent jets to deform and become entangled with and partially wrap around each other at high velocity and in a localized fine scale manner before they have had an opportunity to cool to a relatively rigid state. The cells are individually adjusted to control the mean diameters, lengths and trajectories of the fibers they produce. Certain cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of fibers having diameters less than one micron diameter, and which are relatively shorter in length and certain other cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of structure-forming reinforcing fibers having diameters greater than one micron diameter which are relatively longer in length. By employing appropriate close positioning and orientation of the cells in the array, the sub-micron fibers are caused to promptly entangle with and partially wrap around the larger reinforcing fibers. The larger fibers thereby trap and immobilize the sub-micron diameter fibers in the region of formation, to minimize the tendency of sub-micron diameter fibers to clump, agglomerate, or rope together in flight. Also, the larger fibers in flight are made to form a protective curtain to prevent the sub-micron fibers from being carried off by stray air currents.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
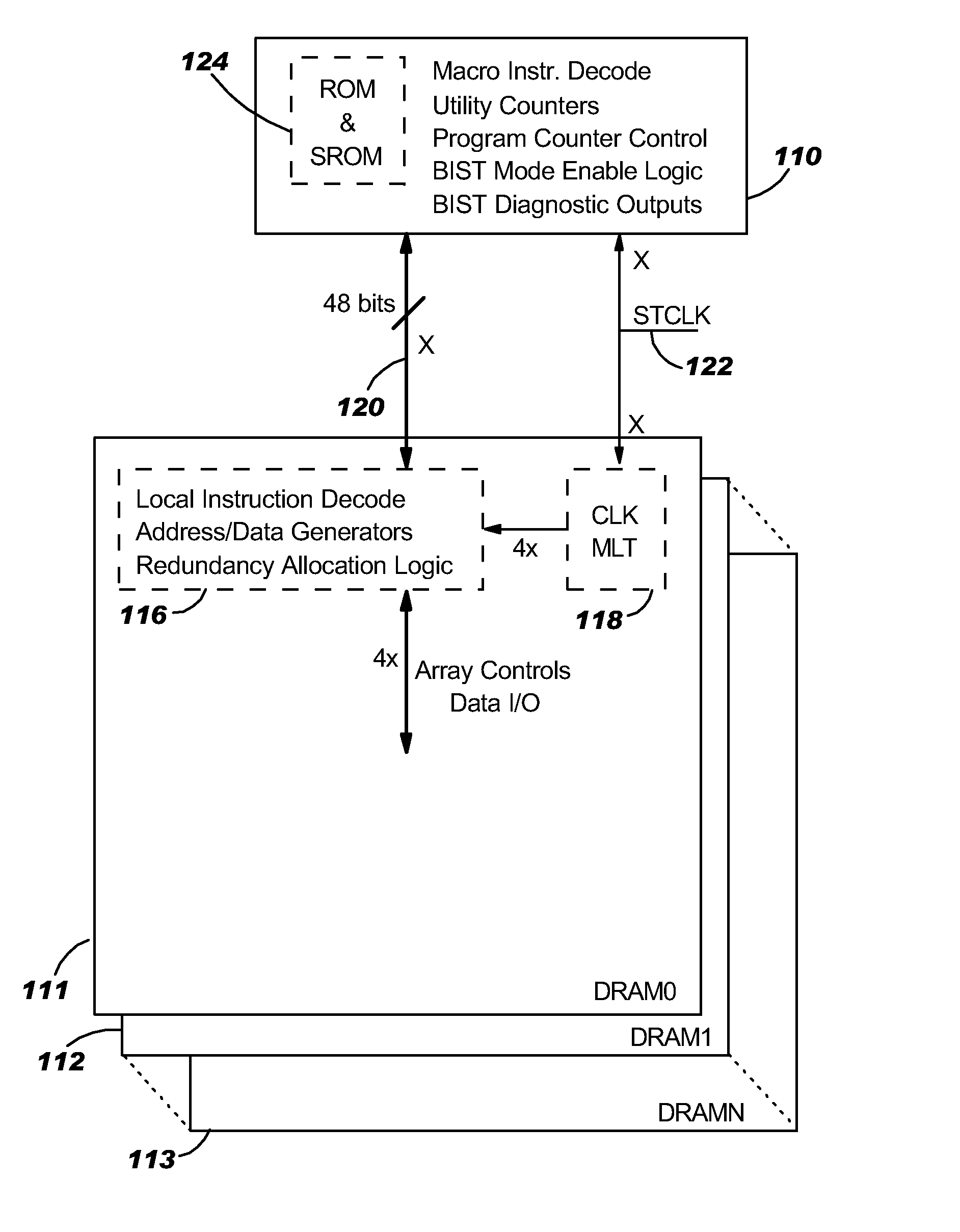
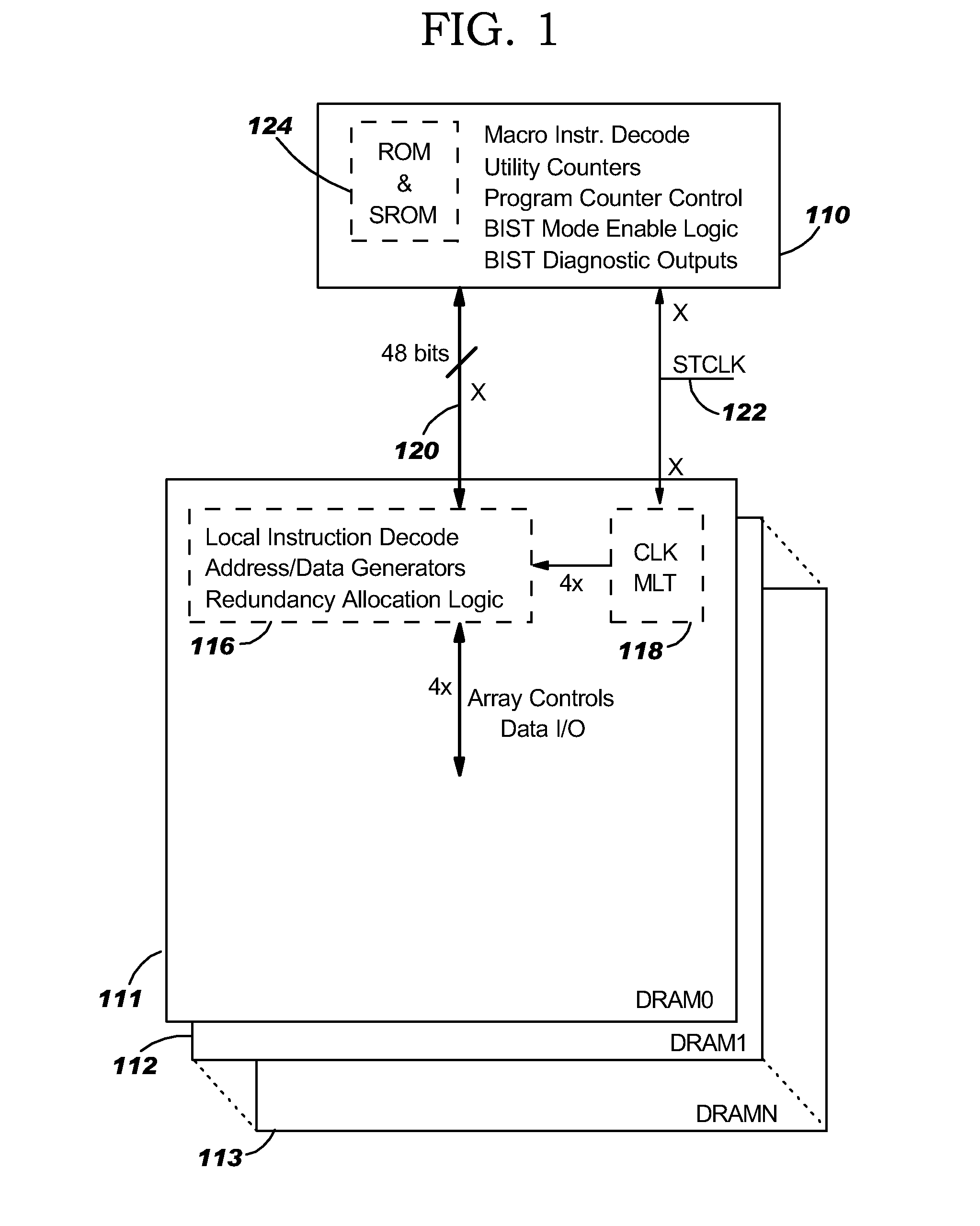
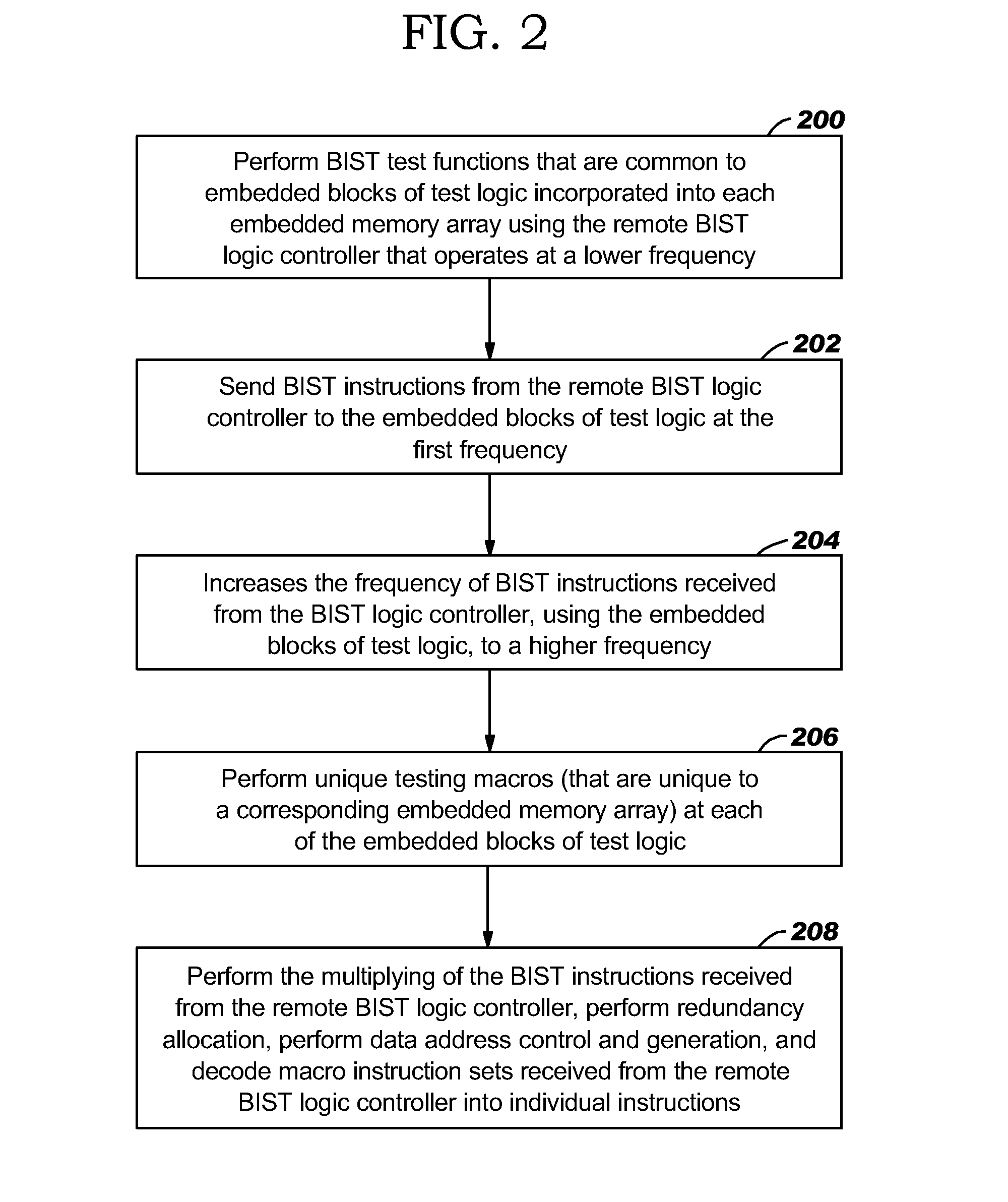
Remote bist for high speed test and redundancy calculation
InactiveUS20080215937A1Reduce frequencyIncrease processing frequencyDigital circuit testingFunctional testingLow speedSpeed test
Disclosed in a hybrid built-in self test (BIST) architecture for embedded memory arrays that segments BIST functionality into remote lower-speed executable instructions and local higher-speed executable instructions. A standalone BIST logic controller operates at a lower frequency and communicates with a plurality of embedded memory arrays using a BIST instruction set. A block of higher-speed test logic is incorporated into each embedded memory array under test and locally processes BIST instructions received from the standalone BIST logic controller at a higher frequency. The higher-speed test logic includes a multiplier for increasing the frequency of the BIST instructions from the lower frequency to the higher frequency. The standalone BIST logic controller enables a plurality of higher-speed test logic structures in a plurality of embedded memory arrays.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Method and apparatus for processing wafer surfaces using thin, high velocity fluid layer
InactiveUS20050145265A1Efficient processingReducing unwanted fluidElectrolysis componentsDrying solid materials without heatHigh velocityBiomedical engineering
Among the many embodiment, in one embodiment, a method for processing a substrate is disclosed which includes generating a fluid layer on a surface of the substrate, the fluid layer defining a fluid meniscus. The generating includes moving a head in proximity to the surface, applying a fluid from the head to the surface while the head is in proximity to the surface of the substrate to define the fluid layer, and removing the fluid from the surface through the proximity head by a vacuum. The fluid travels along the fluid layer between the head and the substrate at a velocity that increases as the head is in closer proximity to the surface.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
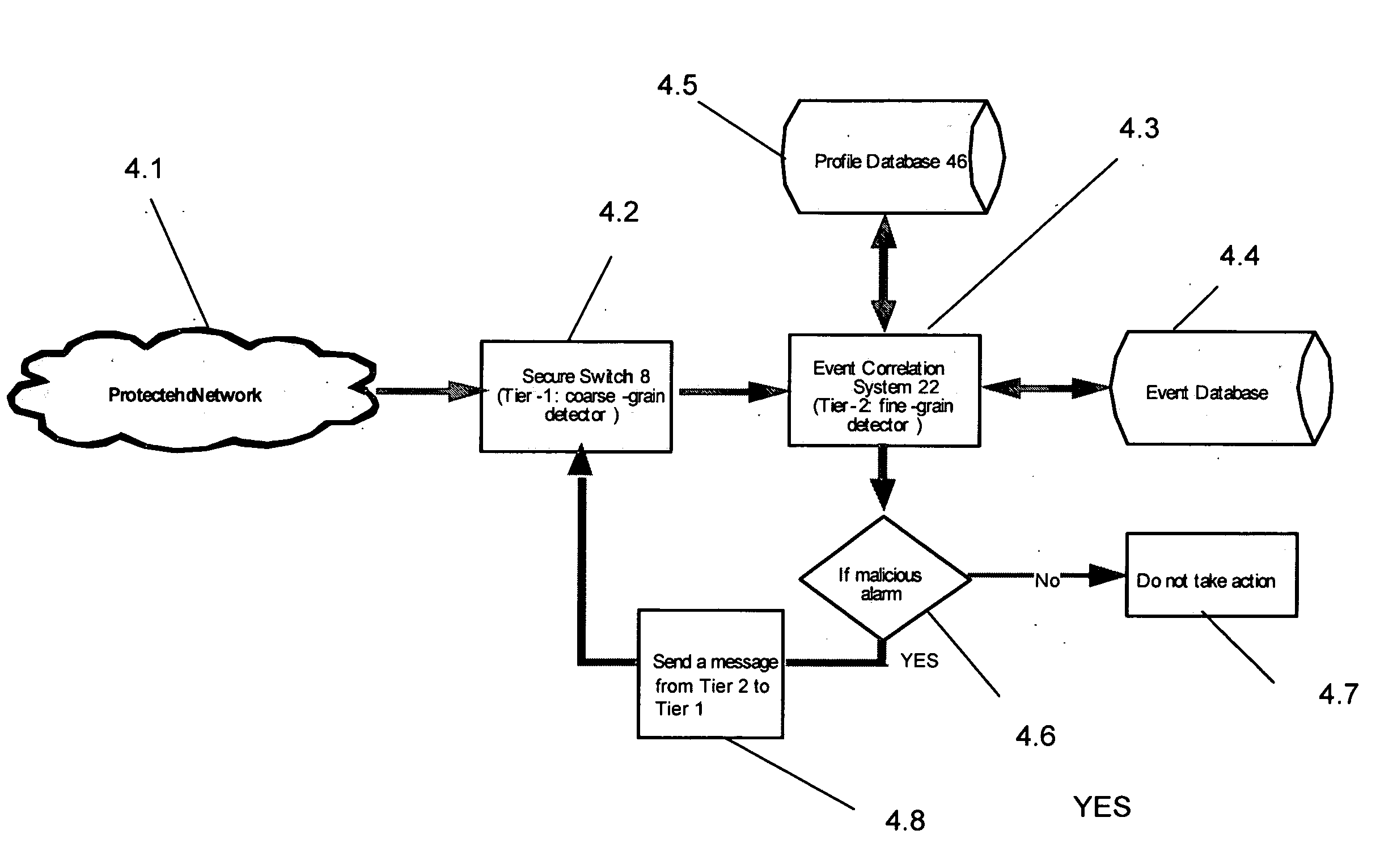
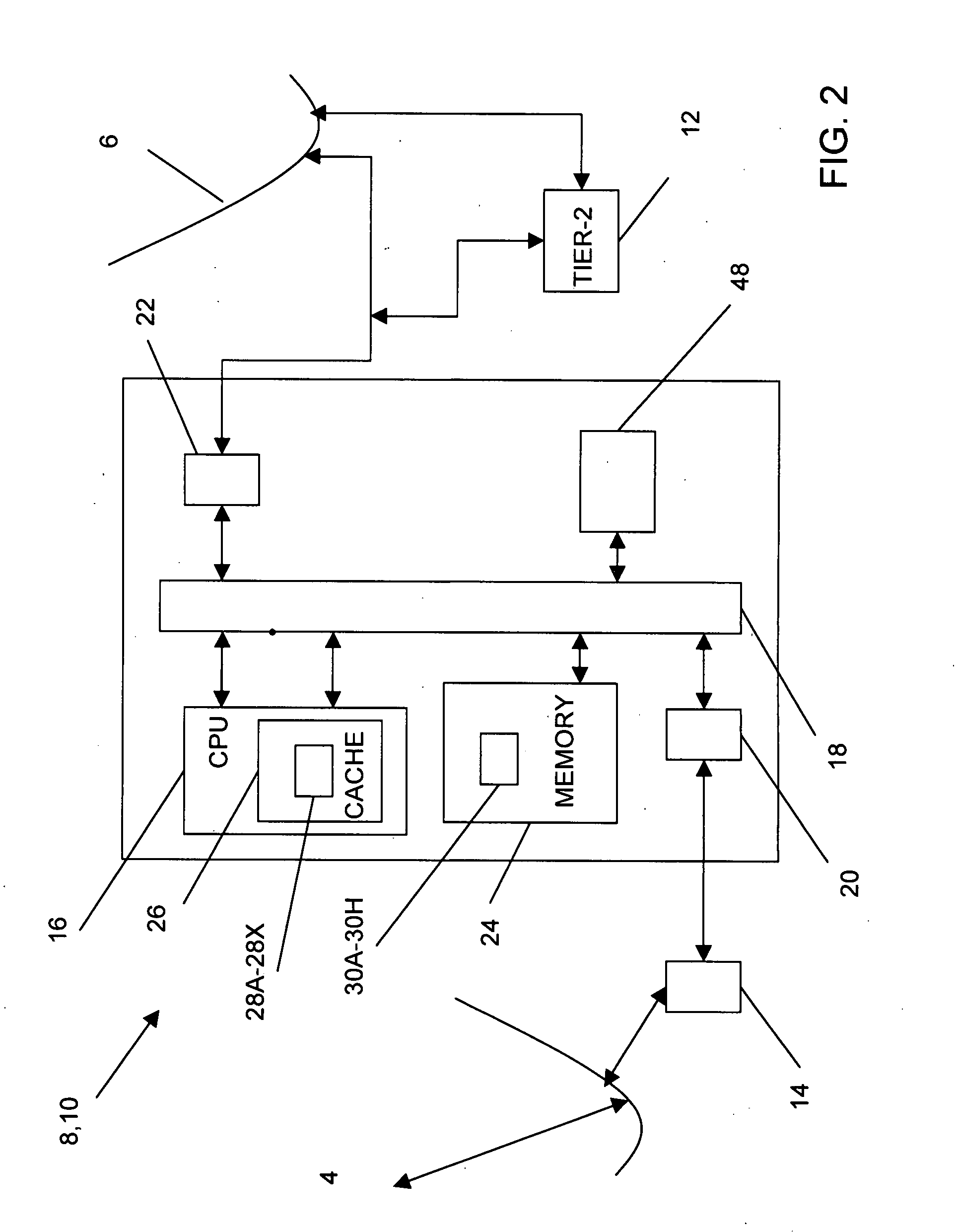
Method, system and computer-readable media for reducing undesired intrusion alarms in electronic communications systems and networks
InactiveUS20080295172A1Reduce probabilityHigh speed detectionMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionCommunications systemElectronic communication
A method, system and computer-readable media that enable the employment of an intrusion detection process are provided. This present invention is able to differentiate between certain malicious and benign incidents by means of a two-stage anomaly-based intrusion detection and prevention system. The invented system works at high-speed and with low-memory resources requirements. In particular, the invented method is implemented in a two-stage detector that performs coarse grain detection using sub-profiles 30A-30H (key features extracted from a profile) at one stage and fine grain (detailed behavioral profile) detection at another stage to eliminate unwanted attacks and false positives. Furthermore, in order to suppress specific alarms, the invented system allows the administrator to specify detailed profiles 32A-32H. By using a sub-profile extractor, a sub-profile is extracted, which is then downloaded into the coarse grain detector.
Owner:NEVIS NETWORLS INC
Method and apparatus for producing high efficiency fibrous media incorporating discontinuous sub-micron diameter fibers, and web media formed thereby
InactiveUS6183670B1Increase collisionImprove compactionFilament/thread formingAuxillary shaping apparatusMean diameterFiber
A composite filtration medium web of fibers containing a controlled dispersion of a mixture of sub-micron and greater than sub-micron diameter polymeric fibers is described. The filtration medium is made by a two dimensional array of cells, each of which produces a single high velocity two-phase solids-gas jet of discontinuous fibers entrained in air. The cells are arranged so that the individual jets are induced to collide in flight with neighboring jets in their region of fiber formation, to cause the individual nascent fibers of adjacent jets to deform and become entangled with and partially wrap around each other at high velocity and in a localized fine scale manner before they have had an opportunity to cool to a relatively rigid state. The cells are individually adjusted to control the mean diameters, lengths and trajectories of the fibers they produce. Certain cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of fibers having diameters less than one micron diameter, and which are relatively shorter in length and certain other cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of structure-forming reinforcing fibers having diameters greater than one micron diameter which are relatively longer in length. By employing appropriate close positioning and orientation of the cells in the array, the sub-micron fibers are caused to promptly entangle with and partially wrap around the larger reinforcing fibers. The larger fibers thereby trap and immobilize the sub-micron diameter fibers in the region of formation, to minimize the tendency of sub-micron diameter fibers to clump, agglomerate, or rope together in flight. Also, the larger fibers in flight are made to form a protective curtain to prevent the sub-micron fibers from being carried off by stray air currents.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Apparatus and method for mounting photovoltaic power generating systems on buildings
InactiveUS7435897B2Preserve integrity and waterproof characteristicBenefit annual energy productionPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyComputer moduleEffective height
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
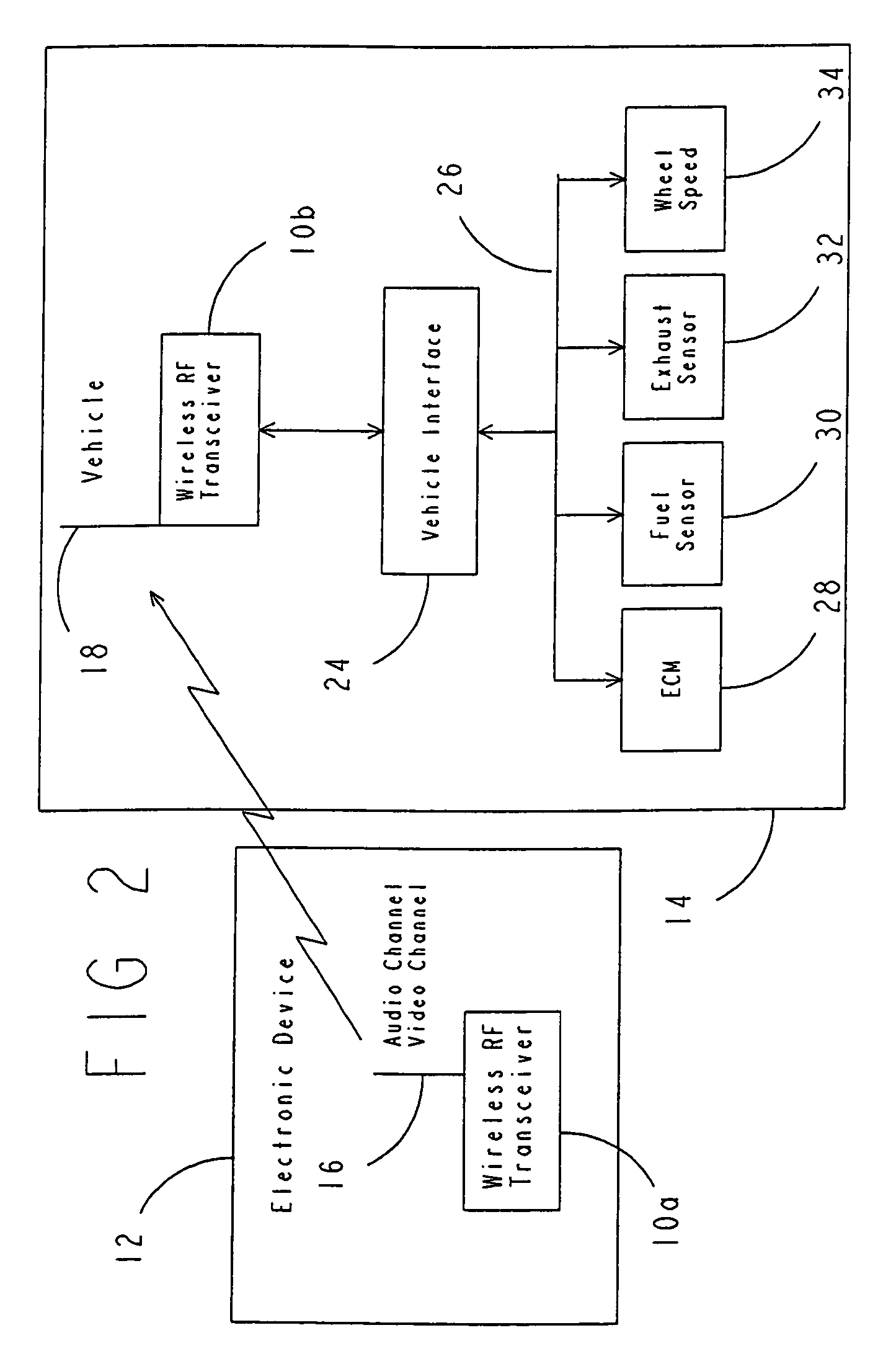
Wireless communications systems and method
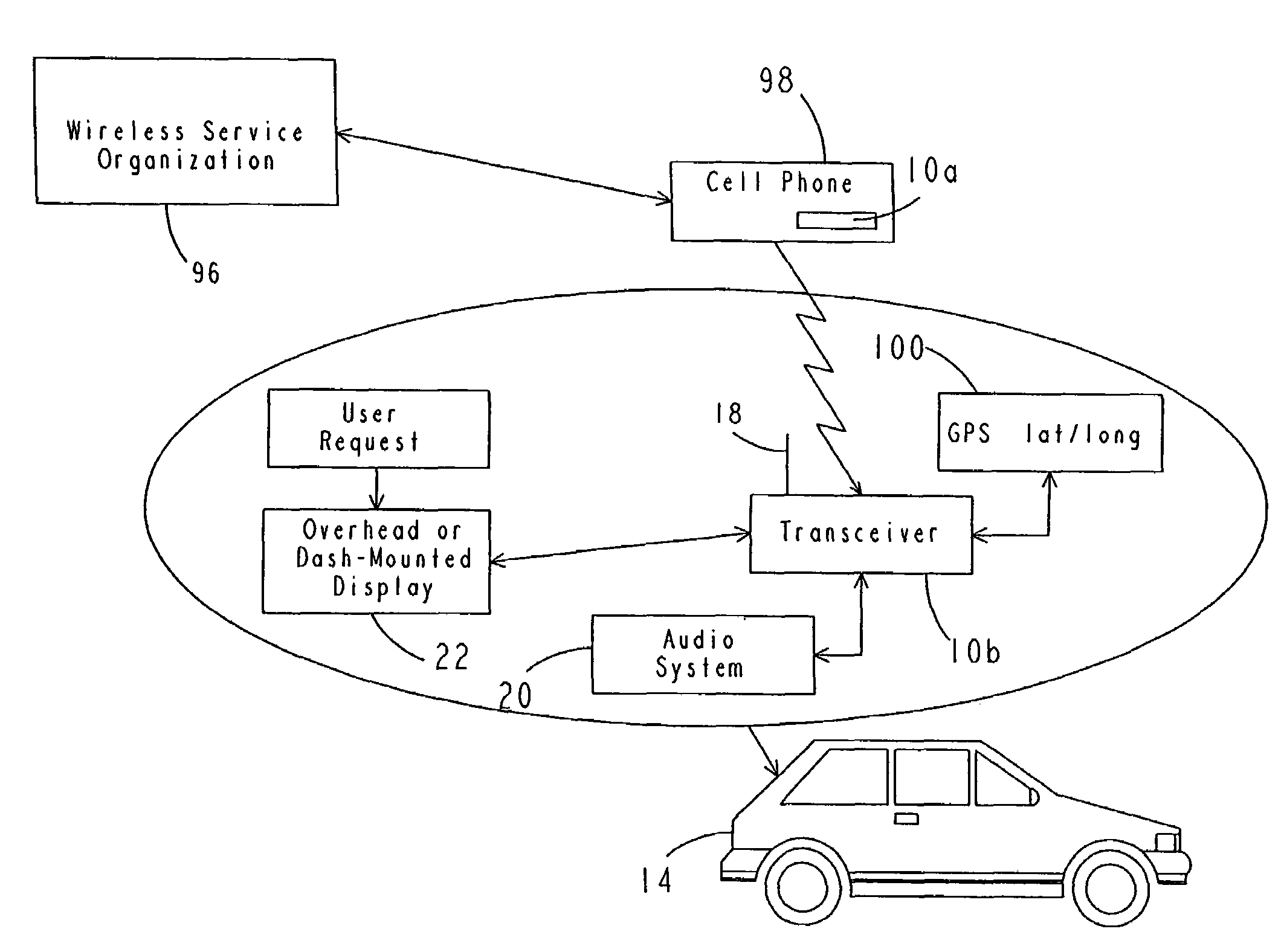
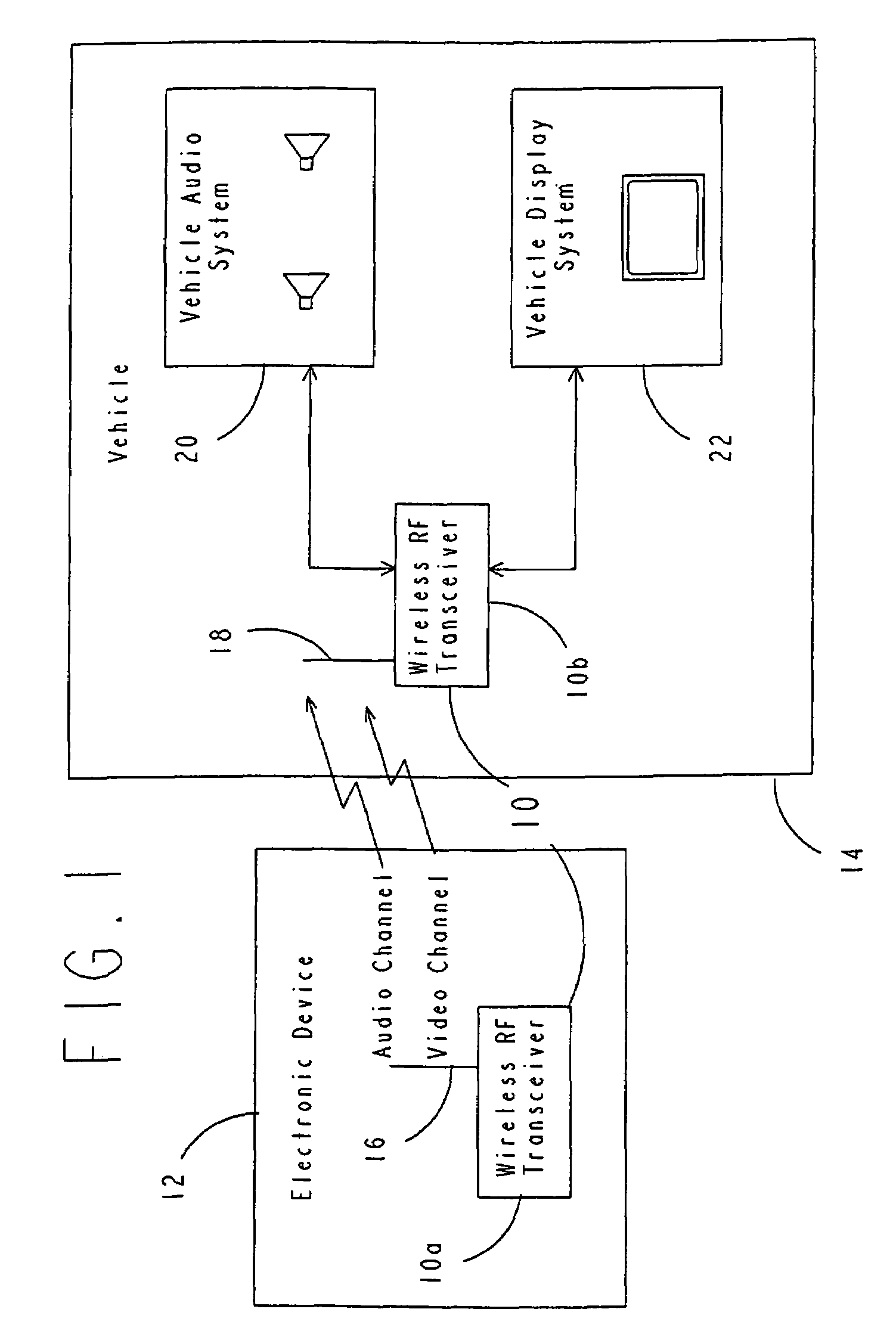
InactiveUS7257426B1Increased security measuresNegligible power consumptionRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesSubstation speech amplifiersTelecommunications linkTransceiver
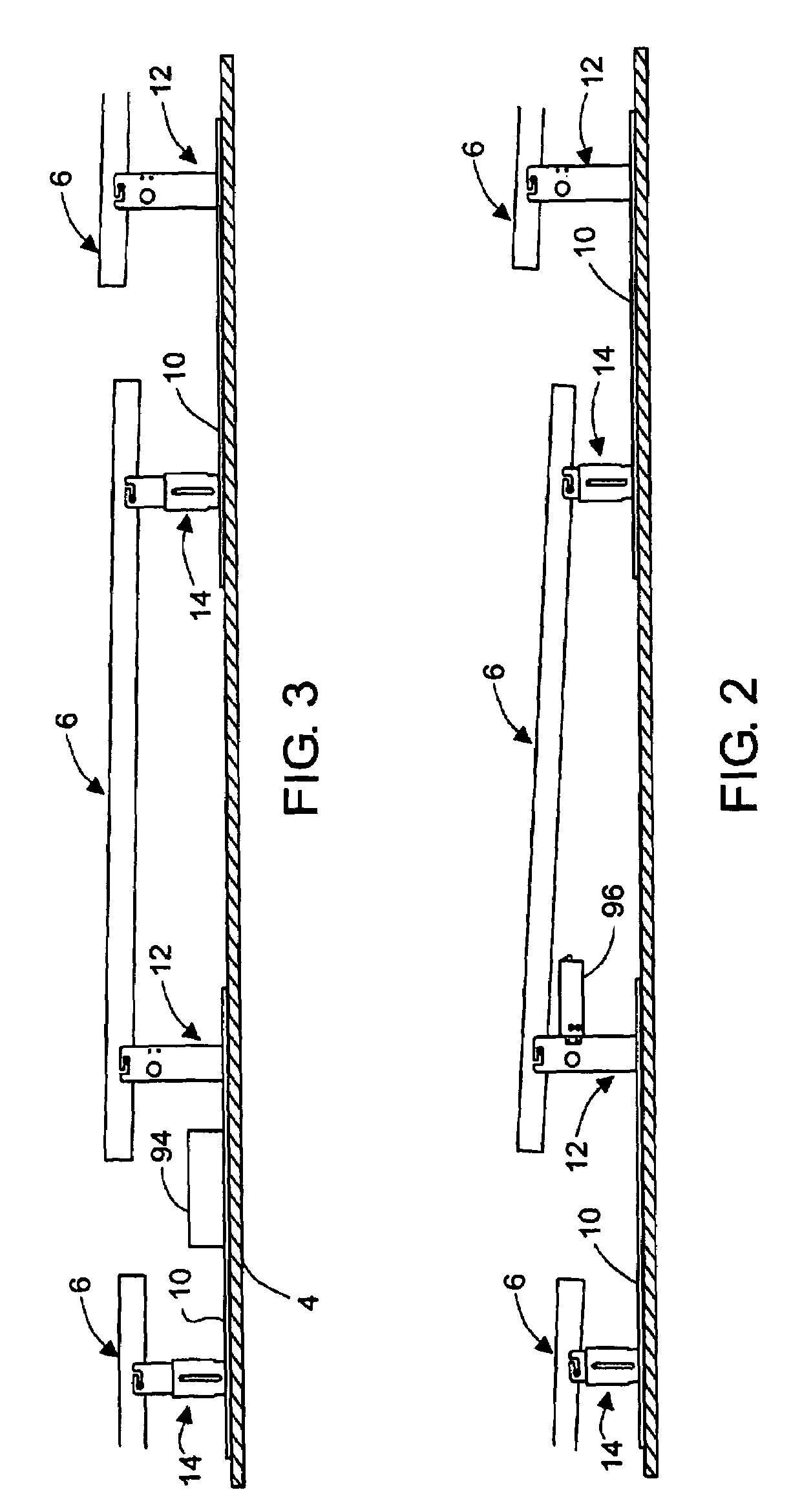
A wireless communications system and method adapted for use in automotive applications for enabling automatic, high-speed, wireless voice and / or data communications link to be established between a wide variety of external devices and various electronic subsystems of a vehicle. The apparatus includes first and second RF transceivers which are operated in accordance with a communications specification to enable a seamless, automatic communications link to be created when the two RF transceivers come within a pre-determined proximity of one another, for example, within up to 100 meters of one another. Information from one device is then automatically transmitted over the wireless communications link to the other device. In various implementations the apparatus is used to obtain information from a home PC, a work PC, a notebook PC and various other electronic devices, as well as information from the Internet, which is displayed and / or played back for the user by various subsystems of the vehicle while traveling in the vehicle. Other applications involving retail and manufacturing applications are disclosed by which the apparatus is used to facilitate and / or expedite manufacturing processes or retail transactions via one or more high-speed, secure, wireless communications links which are created automatically and seamlessly between the RF transceivers of the apparatus of the invention.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
Web of biocomponent blown fibers
InactiveUS6057256AEasy to produceImprove filtering effectBreathing filtersFilament/thread formingFiberPolymer science
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
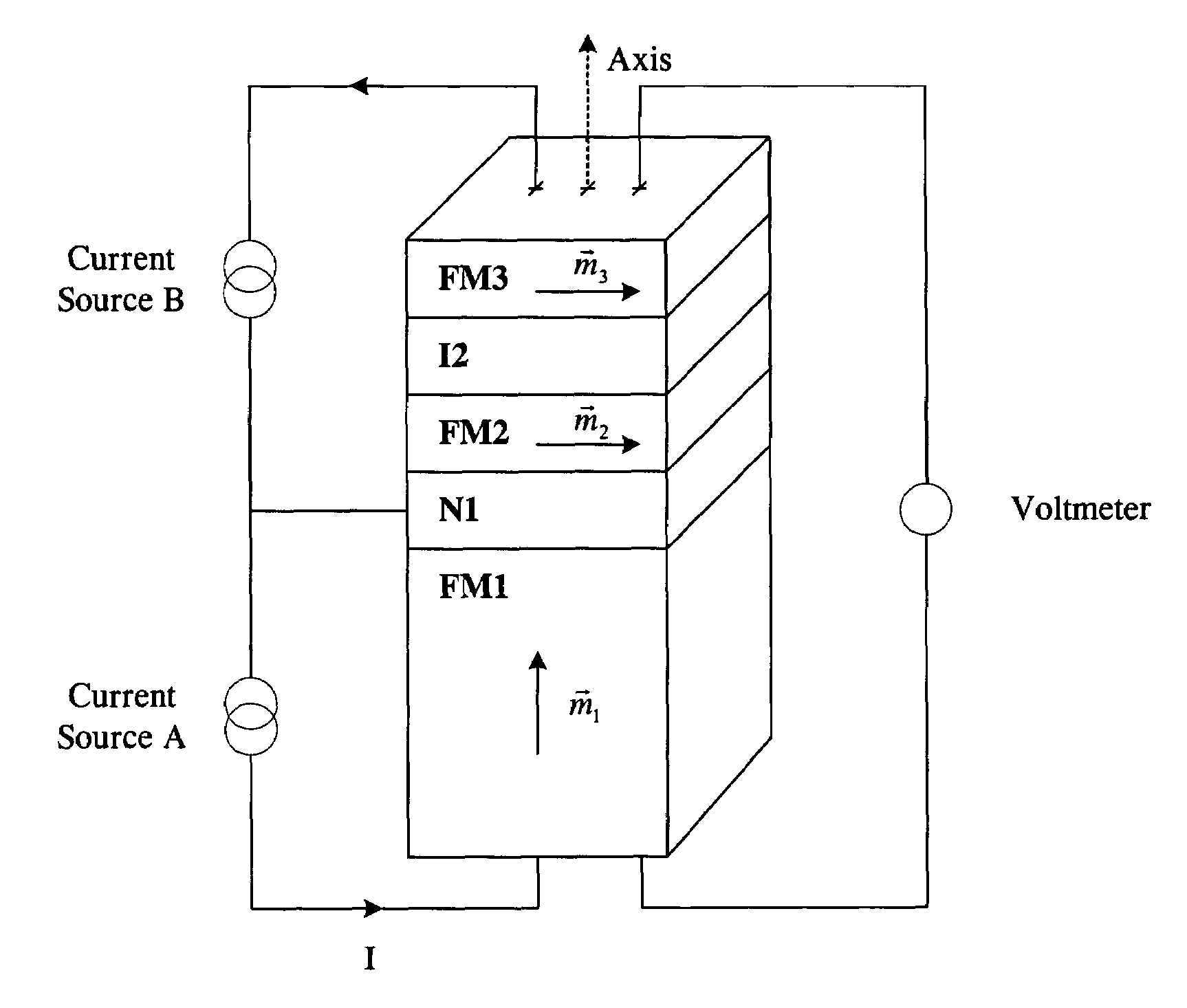
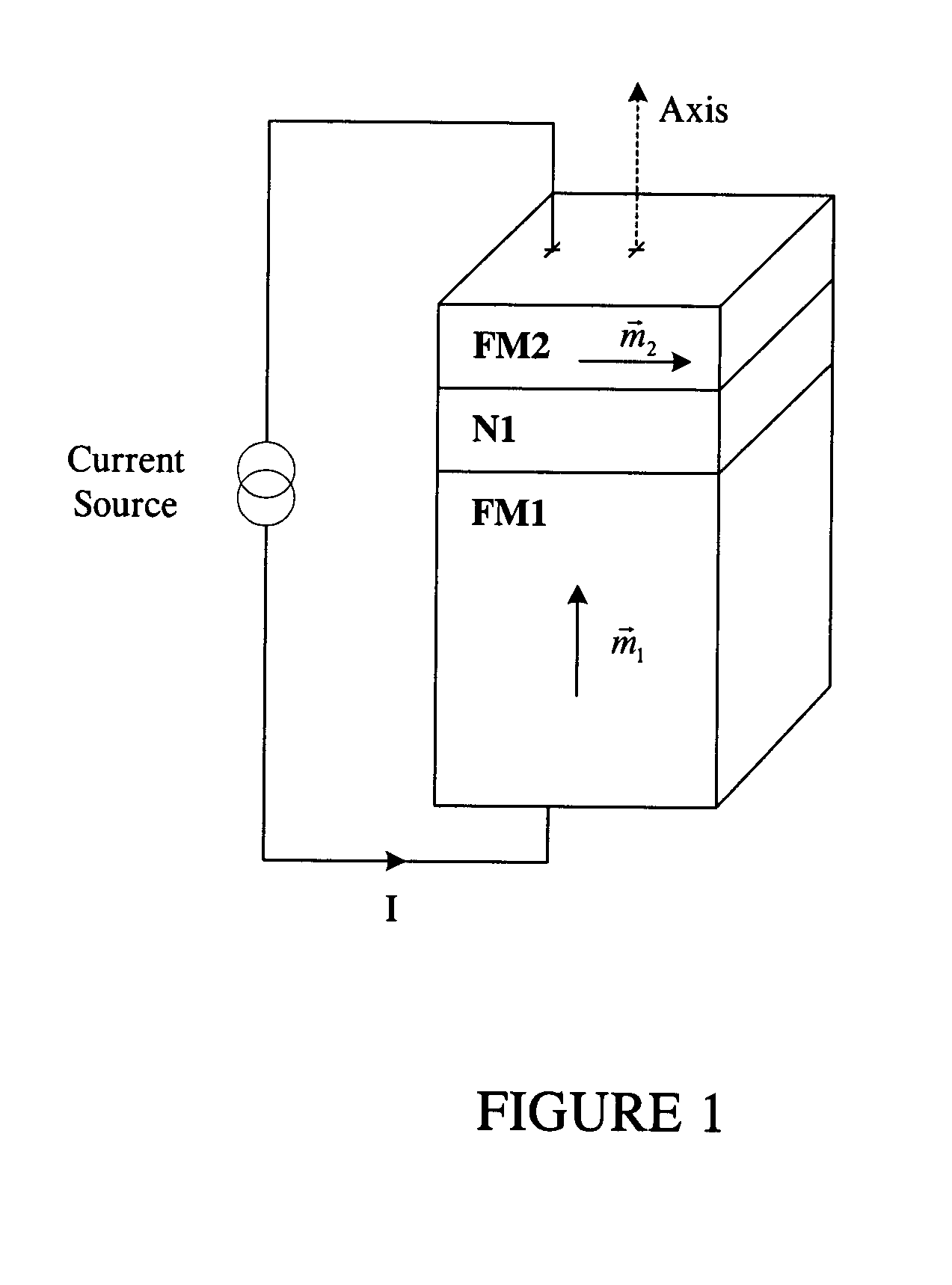
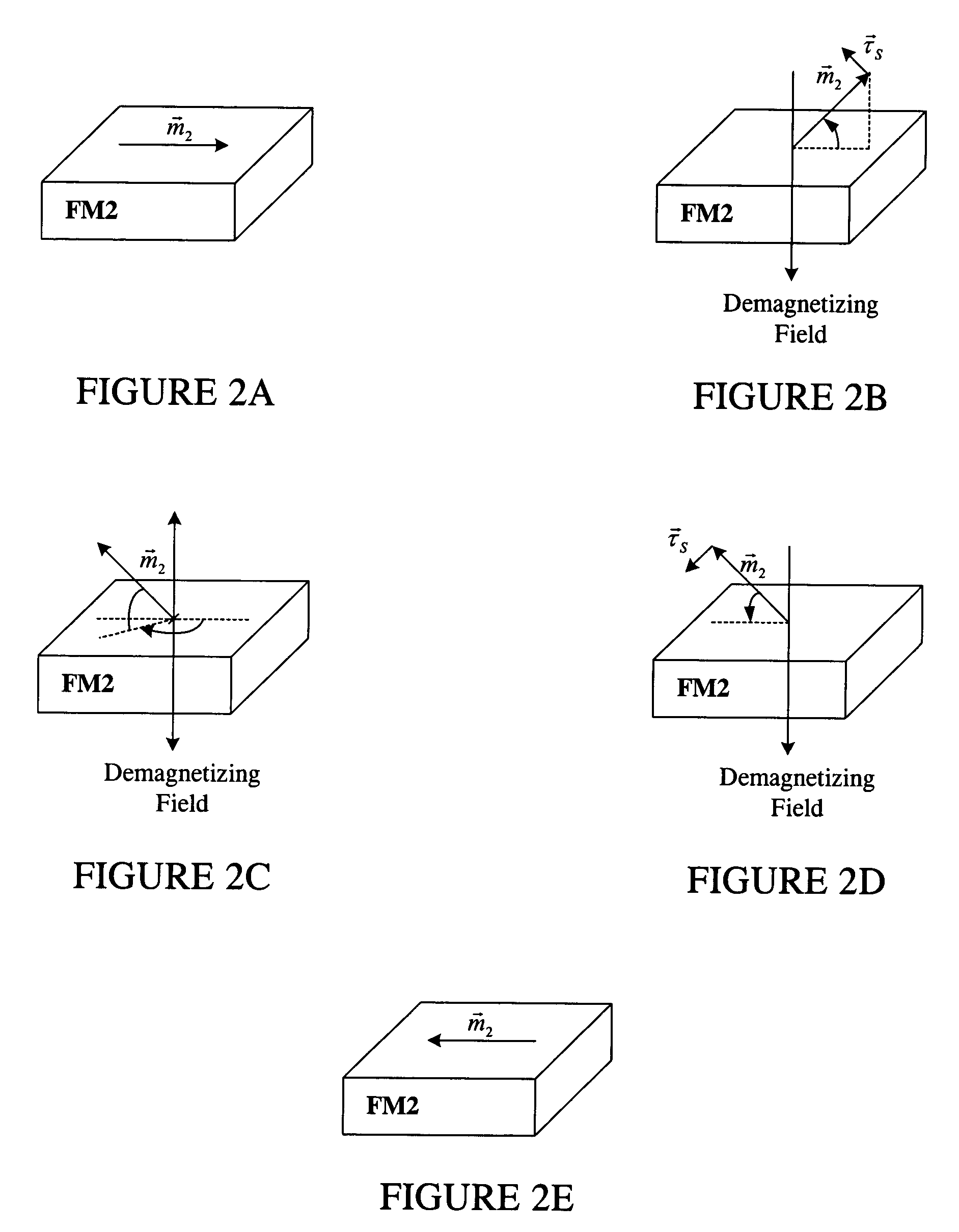
High speed low power magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS6980469B2Operational advantageReduce the required powerNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic memoryMagnetization
The present invention generally relates to the field of magnetic devices for memory cells that can serve as non-volatile memory. More specifically, the present invention describes a high speed and low power method by which a spin polarized electrical current can be used to control and switch the magnetization direction of a magnetic region in such a device. The magnetic device comprises a pinned magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction, a free magnetic layer with a free magnetization direction, and a read-out magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction. The pinned magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the free magnetic layer and the read-out magnetic layer are separated by another non-magnetic layer. The magnetization directions of the pinned and free layers generally do not point along the same axis. The non-magnetic layers minimize the magnetic interaction between the magnetic layers. A current is applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
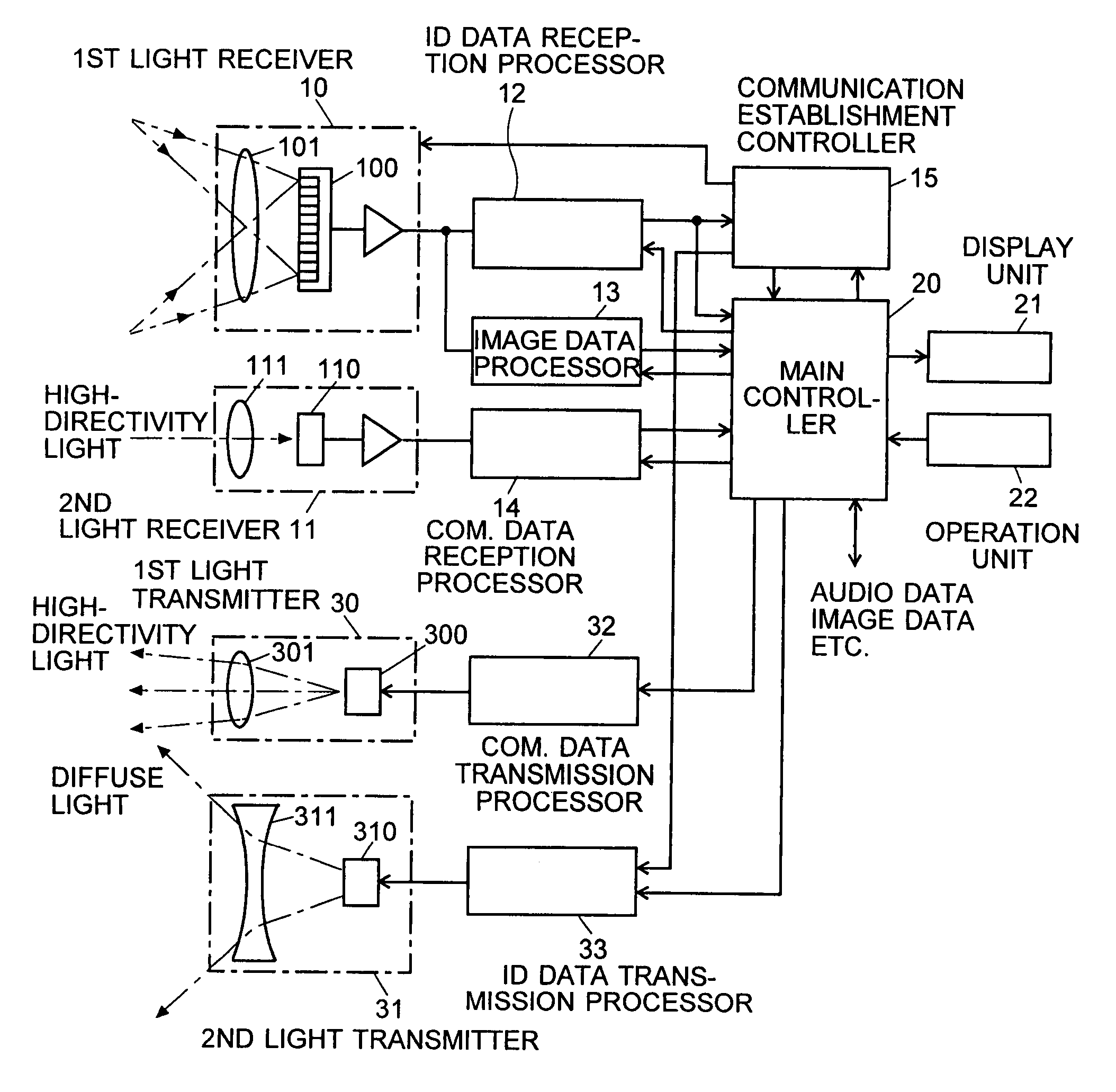
Information-processing system using free-space optical communication and free-space optical communication system
InactiveUS7715723B2Suppress power consumptionSmall sizeNetwork topologiesConnection managementInformation processingImaging data
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
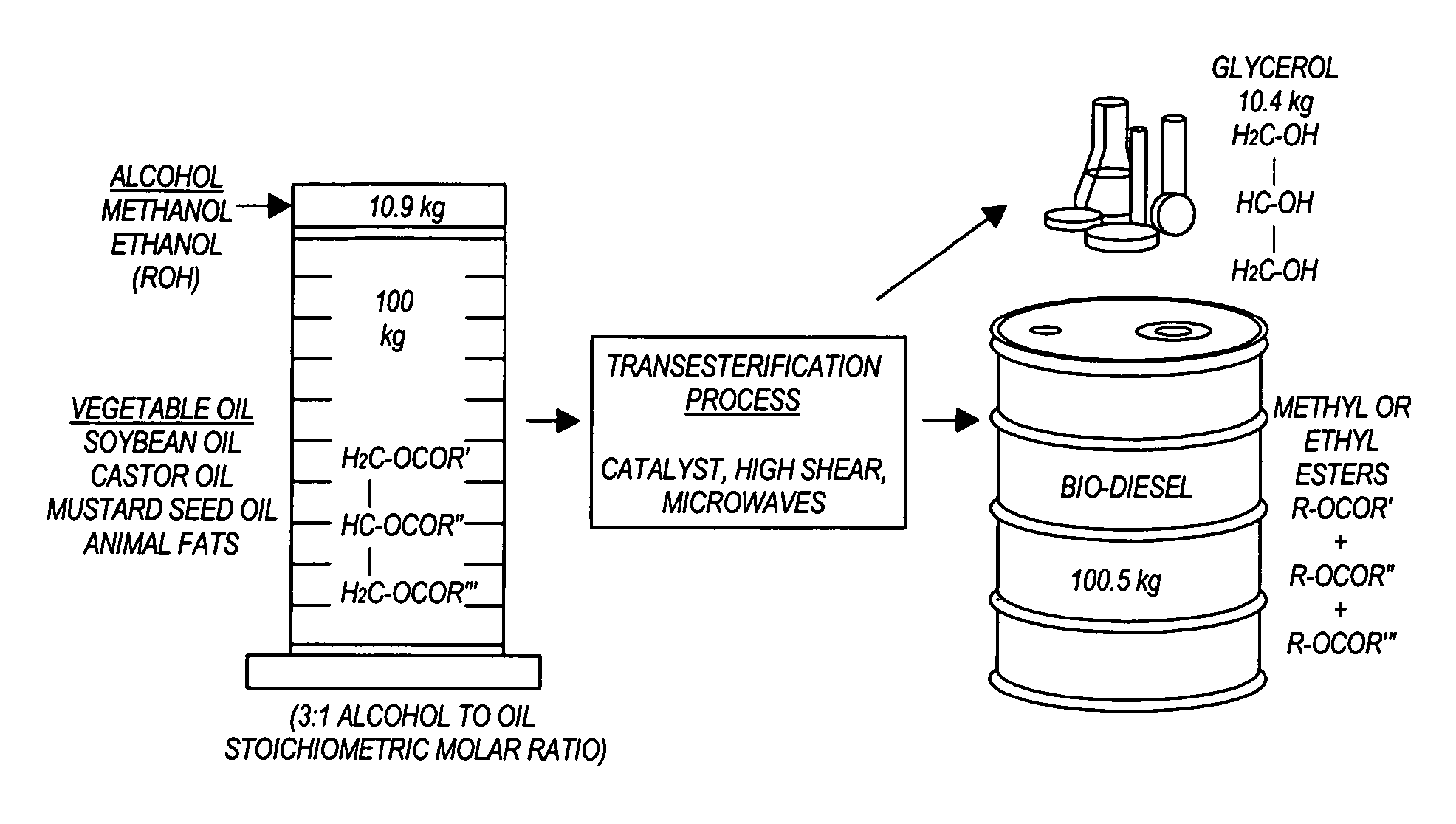
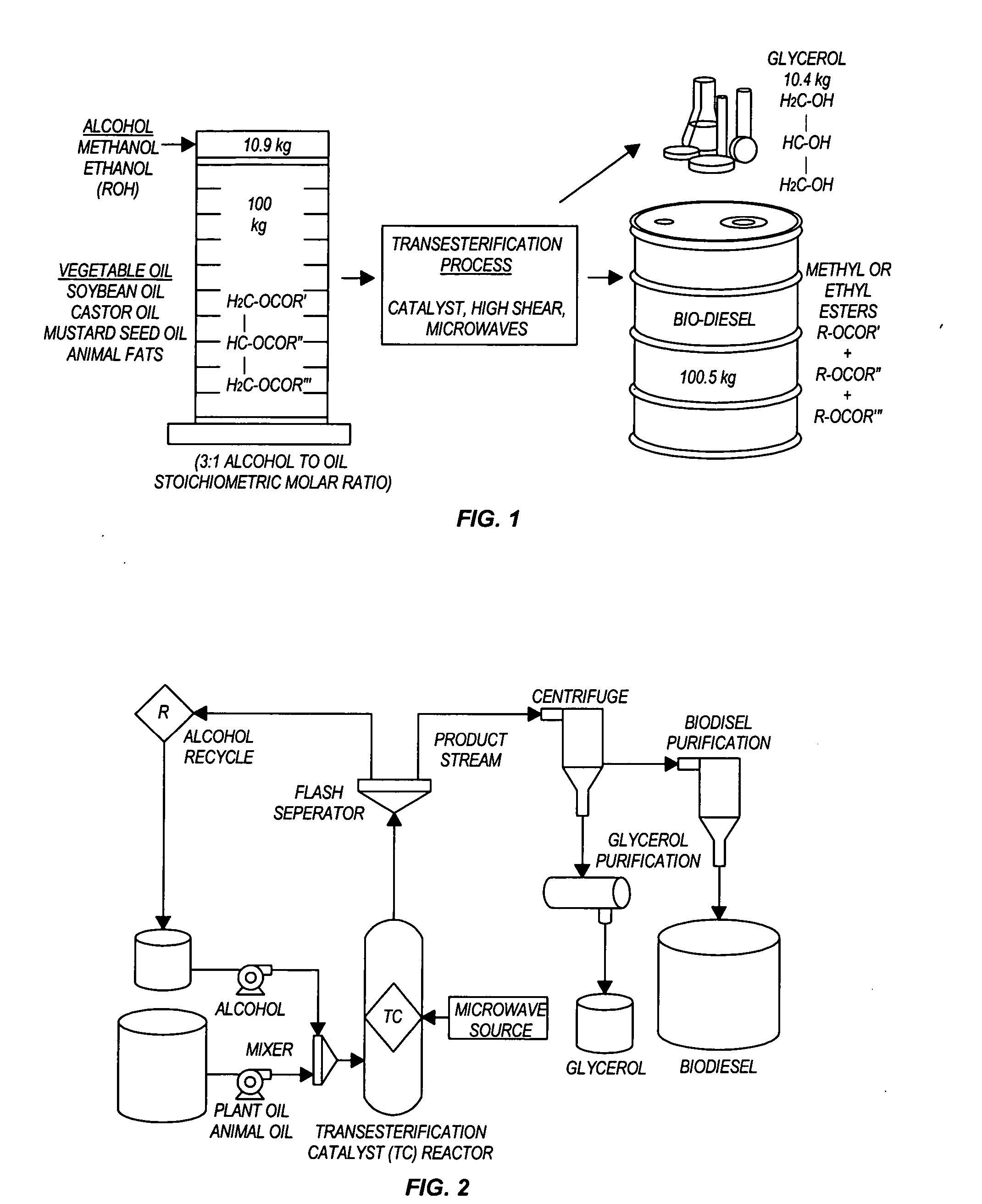
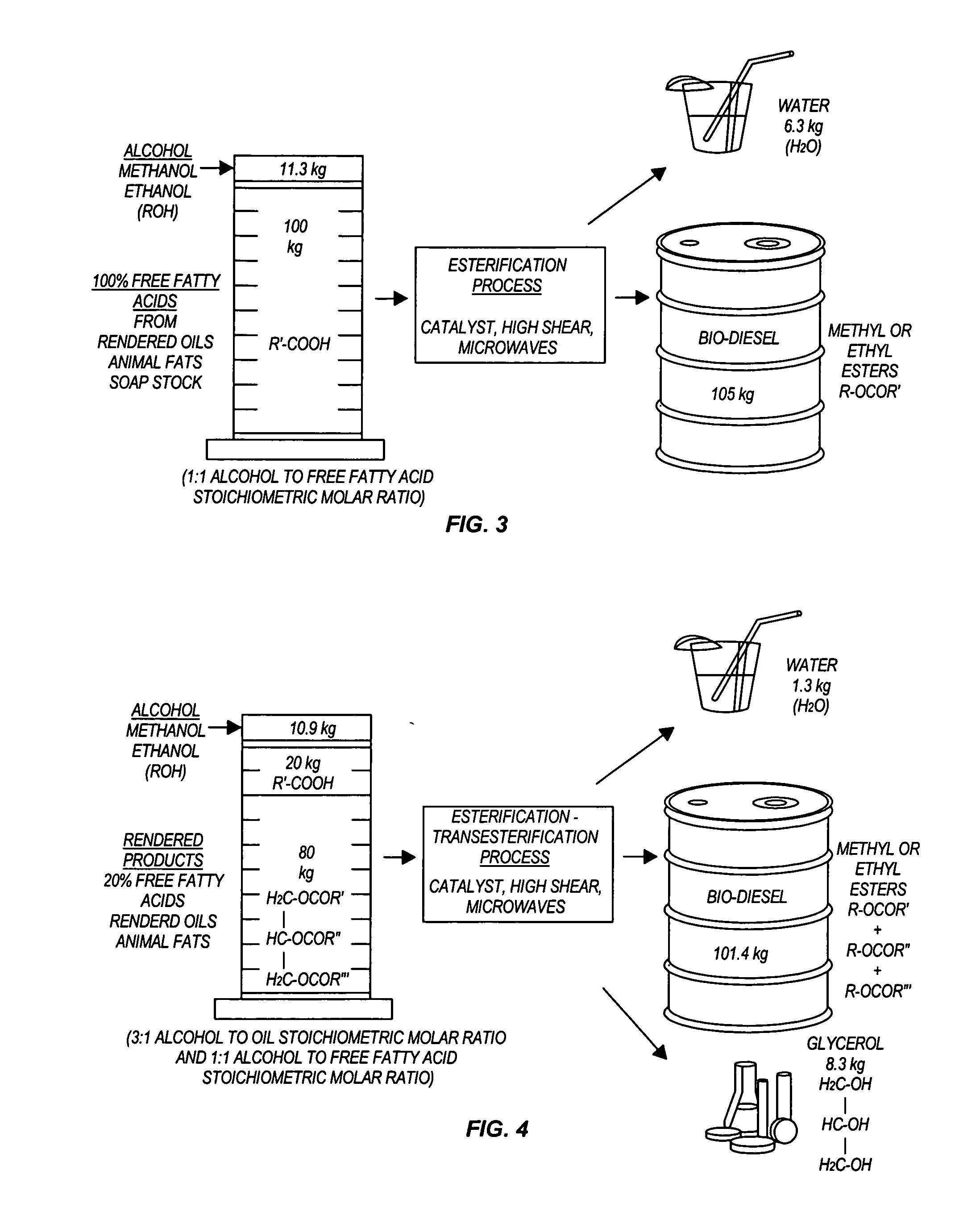
Methods for producing biodiesel
InactiveUS20050274065A1Fatty acid esterificationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionMicrowaveTransesterification
Transesterification, esterification, and esterification-transesterification (both one-step and two-step) for producing biofuels. The process may be enhanced by one or more of the following: 1) applying microwave or RF energy; 2) passing reactants over a heterogeneous catalyst at sufficiently high velocity to achieve high shear conditions; 3) emulsifying reactants with a homogeneous catalyst; or 4) maintaining the reaction at a pressure at or above autogeneous pressure. Enhanced processes using one or more of these steps can result in higher process rates, higher conversion levels, or both.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
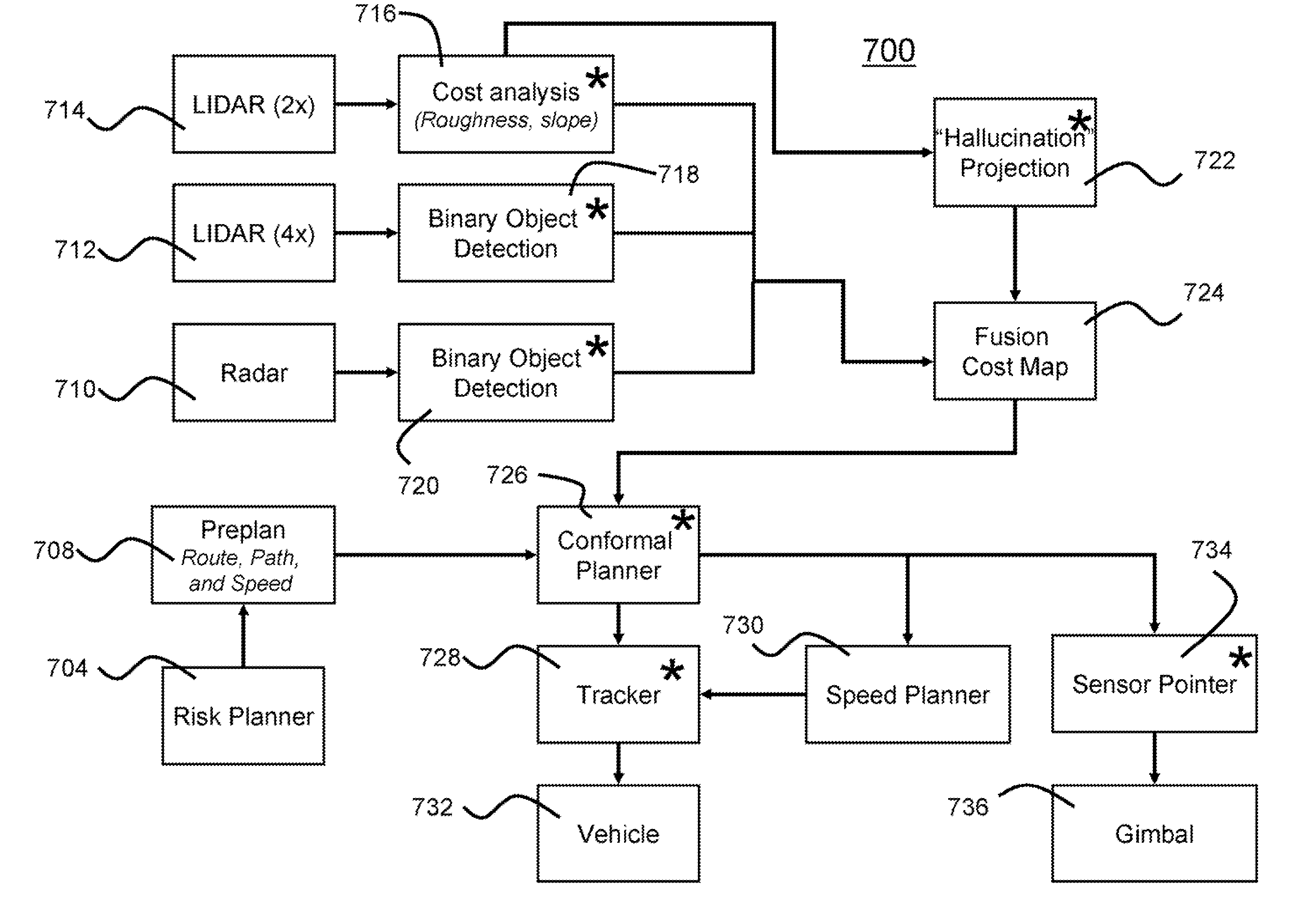
Software architecture for high-speed traversal of prescribed routes
InactiveUS20080059015A1Reduce computing loadImprove abilitiesPlatooningVehicle position/course/altitude controlTerrainLocal environment
Systems, methods, and apparatuses for high-speed navigation. The present invention preferably encompasses systems, methods, and apparatuses that provide for autonomous high-speed navigation of terrain by an un-manned robot. By preferably employing a pre-planned route, path, and speed; extensive sensor-based information collection about the local environment; and information about vehicle pose, the robots of the present invention evaluate the relative cost of various potential paths and thus arrive at a path to traverse the environment. The information collection about the local environment allows the robot to evaluate terrain and to identify any obstacles that may be encountered. The robots of the present invention thus employ map-based data fusion in which sensor information is incorporated into a cost map, which is preferably a rectilinear grid aligned with the world coordinate system and is centered on the vehicle. The cost map is a specific map type that represents the traversability of a particular environmental area using a numeric value. The planned path and route provide information that further allows the robot to orient sensors to preferentially scan the areas of the environment where the robot will likely travel, thereby reducing the computational load placed onto the system. The computational ability of the system is further improved by using map-based syntax between various data processing modules of the present invention. By using a common set of carefully defined data types as syntax for communication, it is possible to identify new features for either path or map processing quickly and efficiently.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
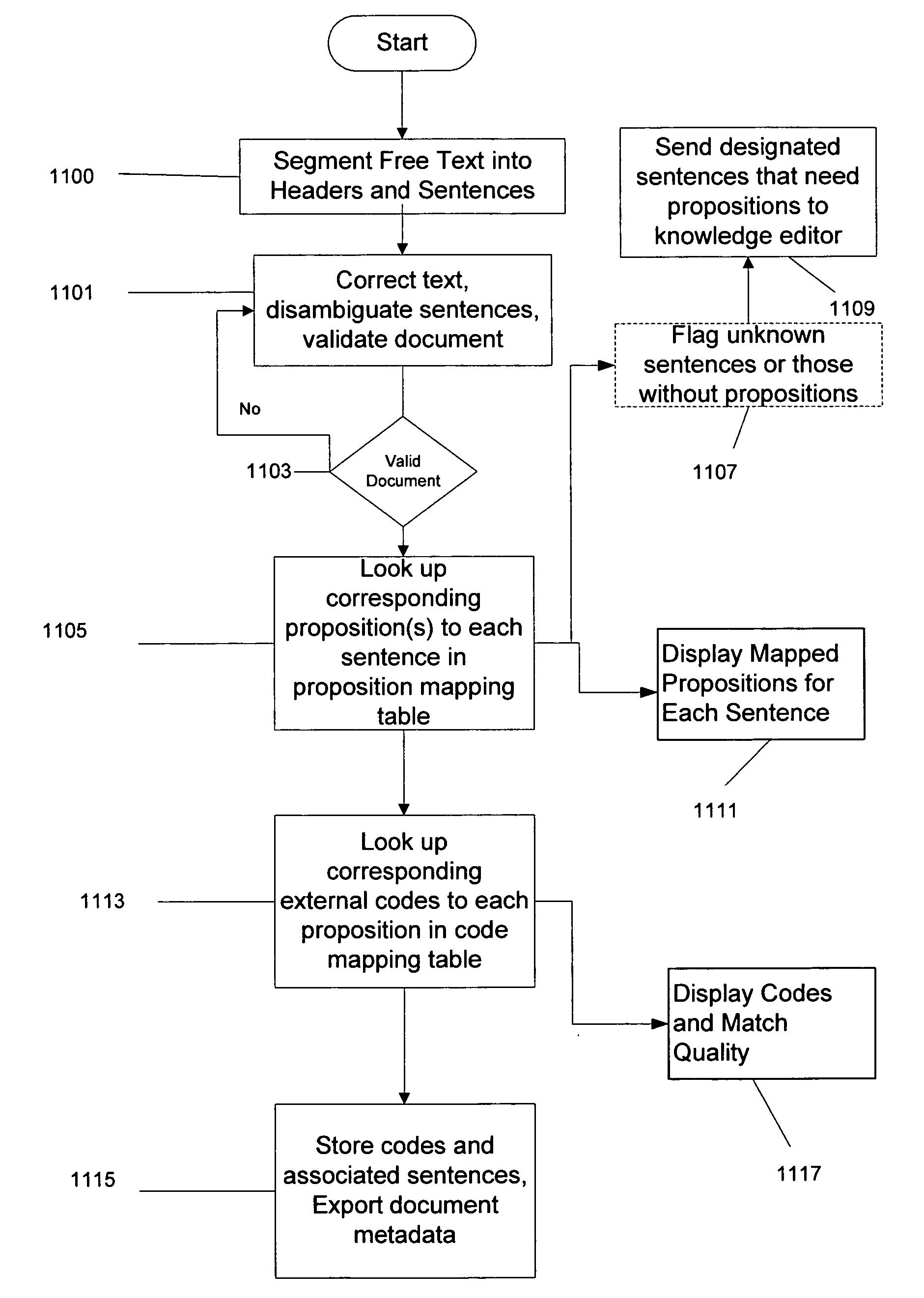
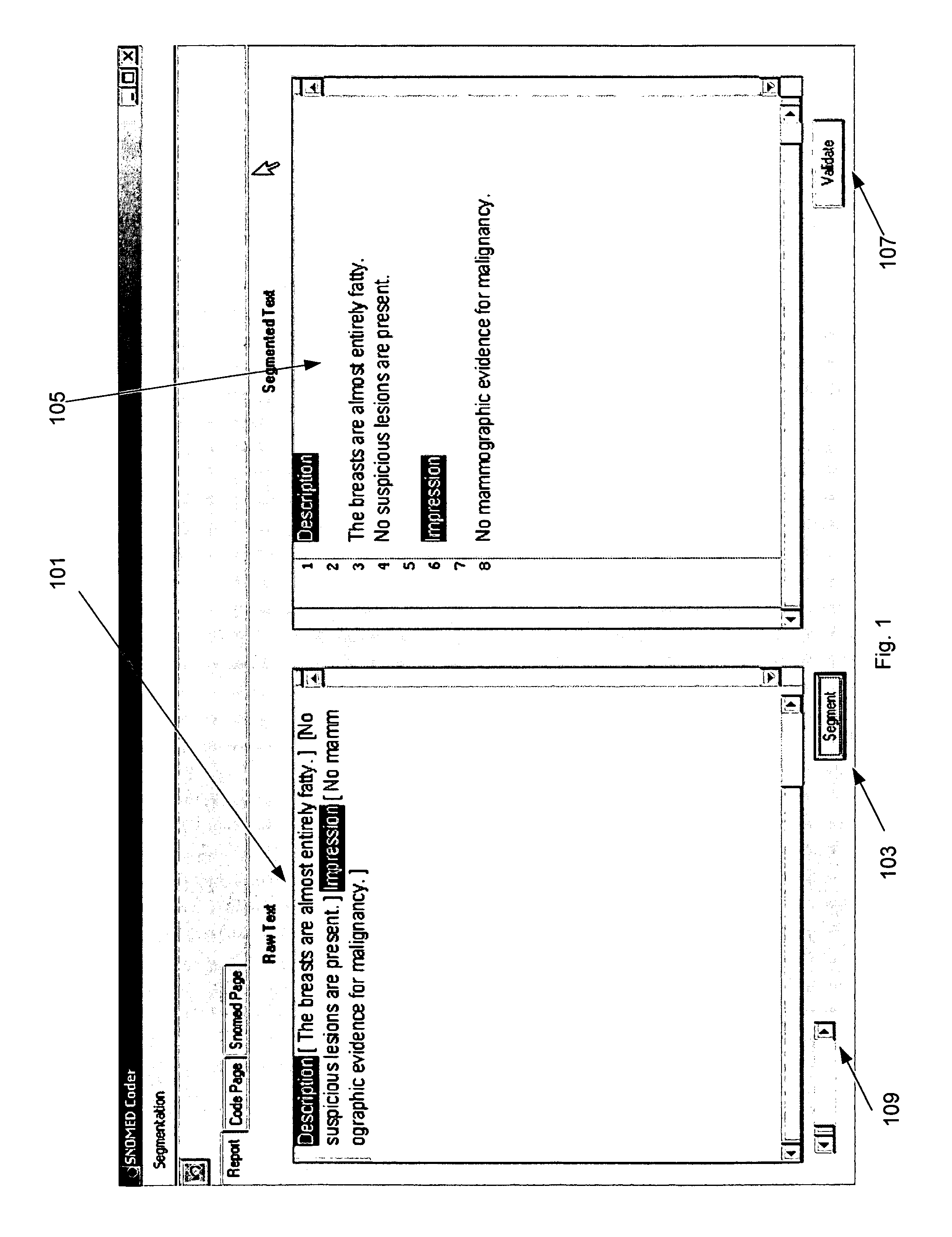
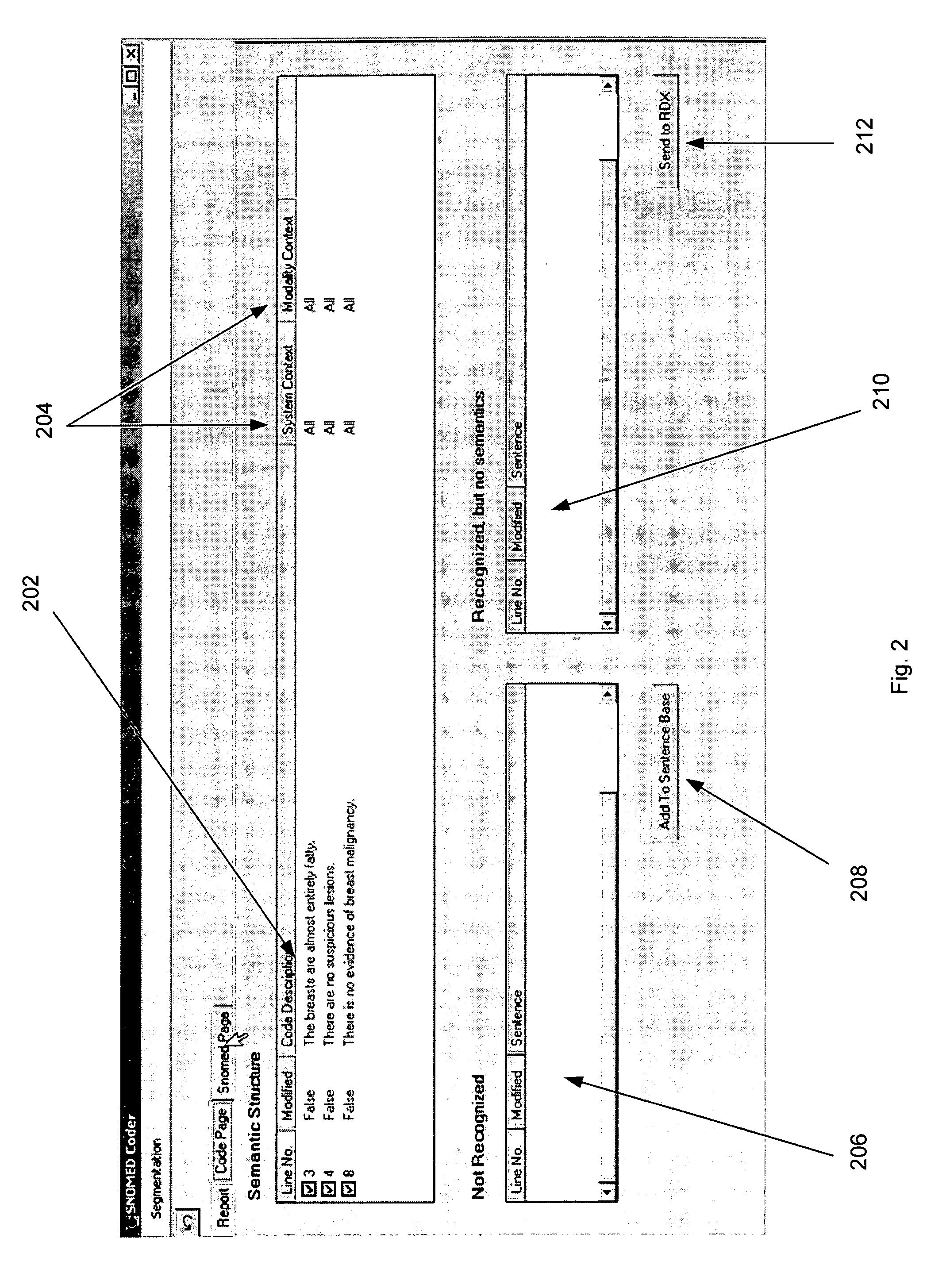
Process and system for high precision coding of free text documents against a standard lexicon
InactiveUS7610192B1Minimal effortFinanceDigital data processing detailsMedical recordElectronic medical record
Coding free text documents, especially in medicine, has become an urgent priority as electronic medical records (EMR) mature, and the need to exchange data between EMRs becomes more acute. However, only a few automated coding systems exist, and they can only code a small portion of the free text against a limited number of codes. The precision of these systems is low and code quality is not measured. The present invention discloses a process and system which implements semantic coding against standard lexicon(s) with high precision. The standard lexicon can come from a number of different sources, but is usually developed by a standard's body. The system is semi-automated to enable medical coders or others to process free text documents at a rapid rate and with high precision. The system performs the steps of segmenting a document, flagging the need for corrections, validating the document against a data type definition, and looking up both the semantics and standard codes which correspond to the document's sentences. The coder has the option to intervene at any step in the process to fix mistakes made by the system. A knowledge base, consisting of propositions, represents the semantic knowledge in the domain. When sentences with unknown semantics are discovered they can be easily added to the knowledge base. The propositions in the knowledge base are associated with codes in the standard lexicon. The quality of each match is rated by a professional who understands the knowledge domain. The system uses this information to perform high precision coding and measure the quality of the match.
Owner:JAMIESON PATRICK WILLIAM
Intravascular Tissue Disruption
InactiveUS20120116438A1Reduce high blood pressureSmall volumeGuide needlesStentsNovel agentsTarget tissue
Owner:SHIFAMED HLDG
Fabrication of molecular electronic circuit by imprinting
A method of fabricating a molecular electronic device or crossbar memory device is provided. The device comprises at least one pair of crossed wires and a molecular switch film therebetween. The method comprises: (a) forming at least one bottom electrode on a substrate by first forming a first layer on the substrate and patterning the first layer to form the bottom electrode by an imprinting technique; (b) forming the molecular switch film on top of the bottom electrode; (c) optionally forming a protective layer on top of the molecular switch film to avoid damage thereto during further processing; (d) coating a polymer layer on top of the protective layer and patterned the polymer layer by the imprinting method to form openings that expose portions of the protective layer; and (e) forming at least one top electrode on the protective layer through the openings in the polymer layer by first forming a second layer on the polymer layer and patterning the second layer. The imprinting method can be used to fabricate nanoscale patterns over a large area at high speeds acceptable in industrial standards. Consequently, it can be used to fabricate nanoscale molecular devices, e.g., crossbar memory circuits.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
High speed low power annular magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS20080112094A1Operational advantageReduce the required powerRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetization
A high speed and low power method to control and switch the magnetization direction and / or helicity of a magnetic region in a magnetic device for memory cells using spin polarized electrical current. The magnetic device comprises a reference magnetic layer with a fixed magnetic helicity and / or magnetization direction and a free magnetic layer with a changeable magnetic helicity. The fixed magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are preferably separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the reference layer includes an easy axis perpendicular to the reference layer. A current can be applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Tunable laser light source
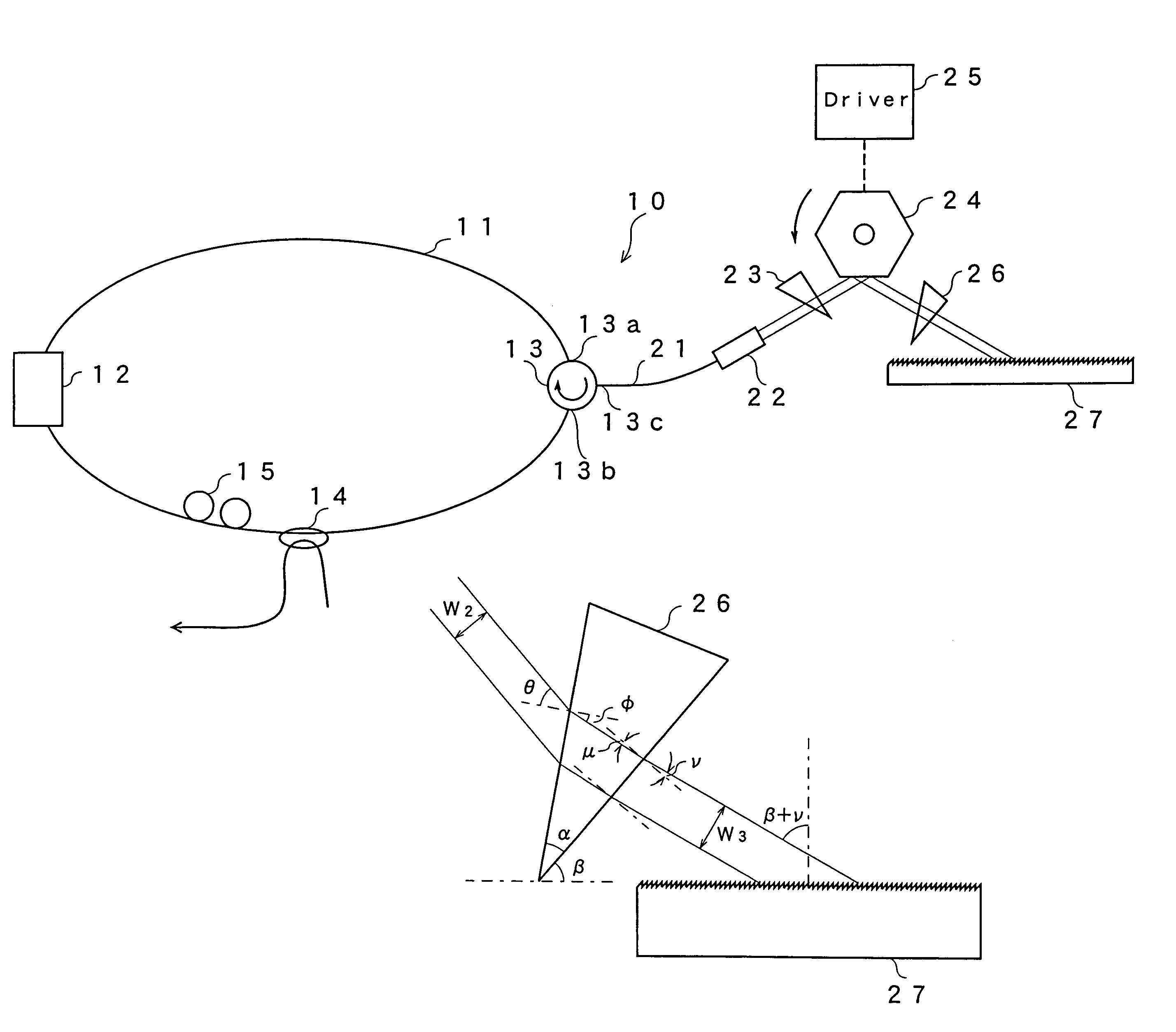
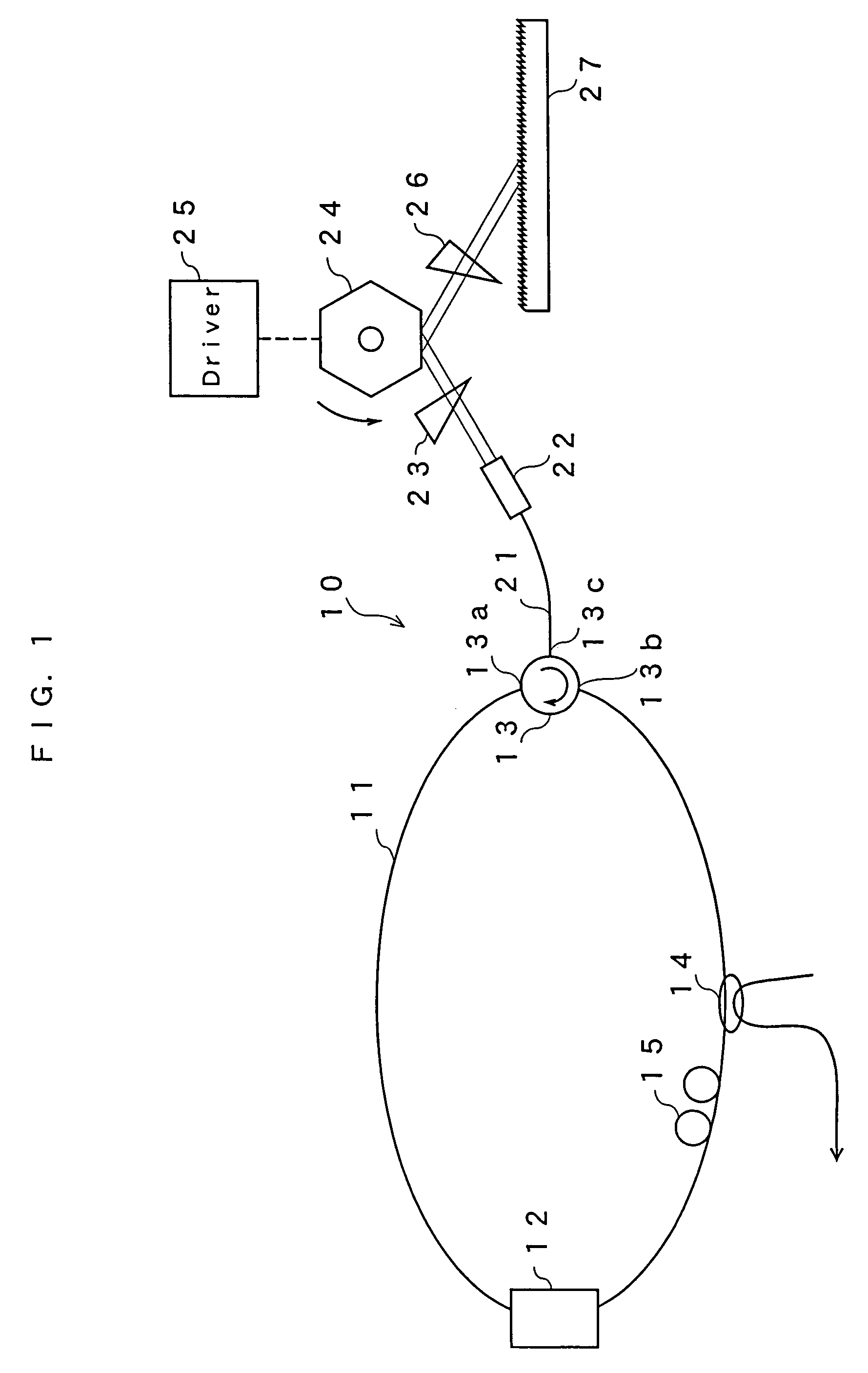
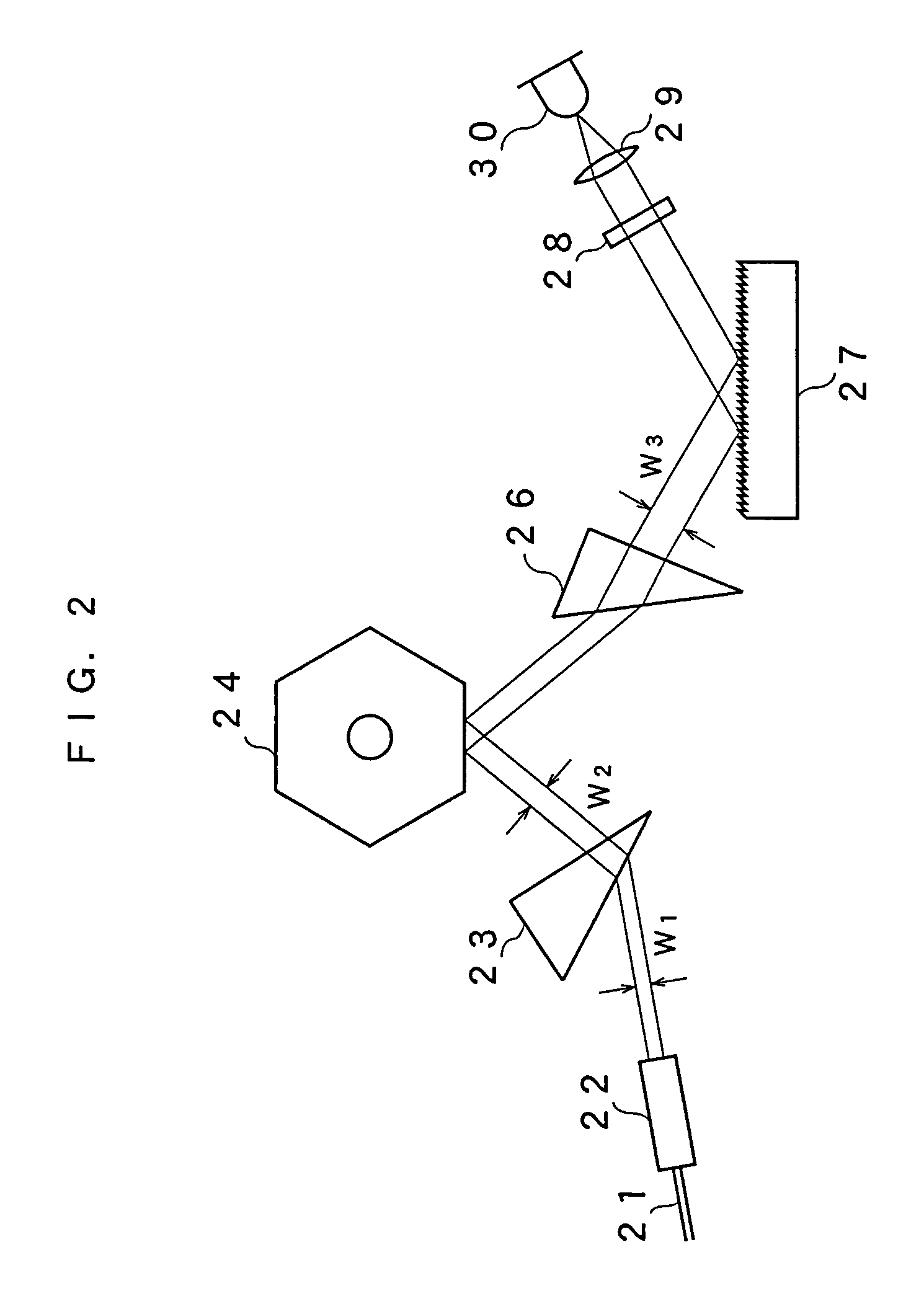
ActiveUS7099358B1Small distortionLittle noiseOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersLight beamPrism
A gain medium 12 and a tunable filter are provided in an optical path of laser oscillation. The tunable filter has an optical beam deflector for periodically changing an optical beam at a constant angular speed, a prism 26 on which deflected light is made incident, and a diffraction grating 27. Appropriate selection of the apex angle α of the prism 26 and an angle β formed by the prism 26 and the diffraction grating 27 can provide a tunable laser light source for changing the oscillation frequency at high speed and a constant variation rate.
Owner:SANTEC
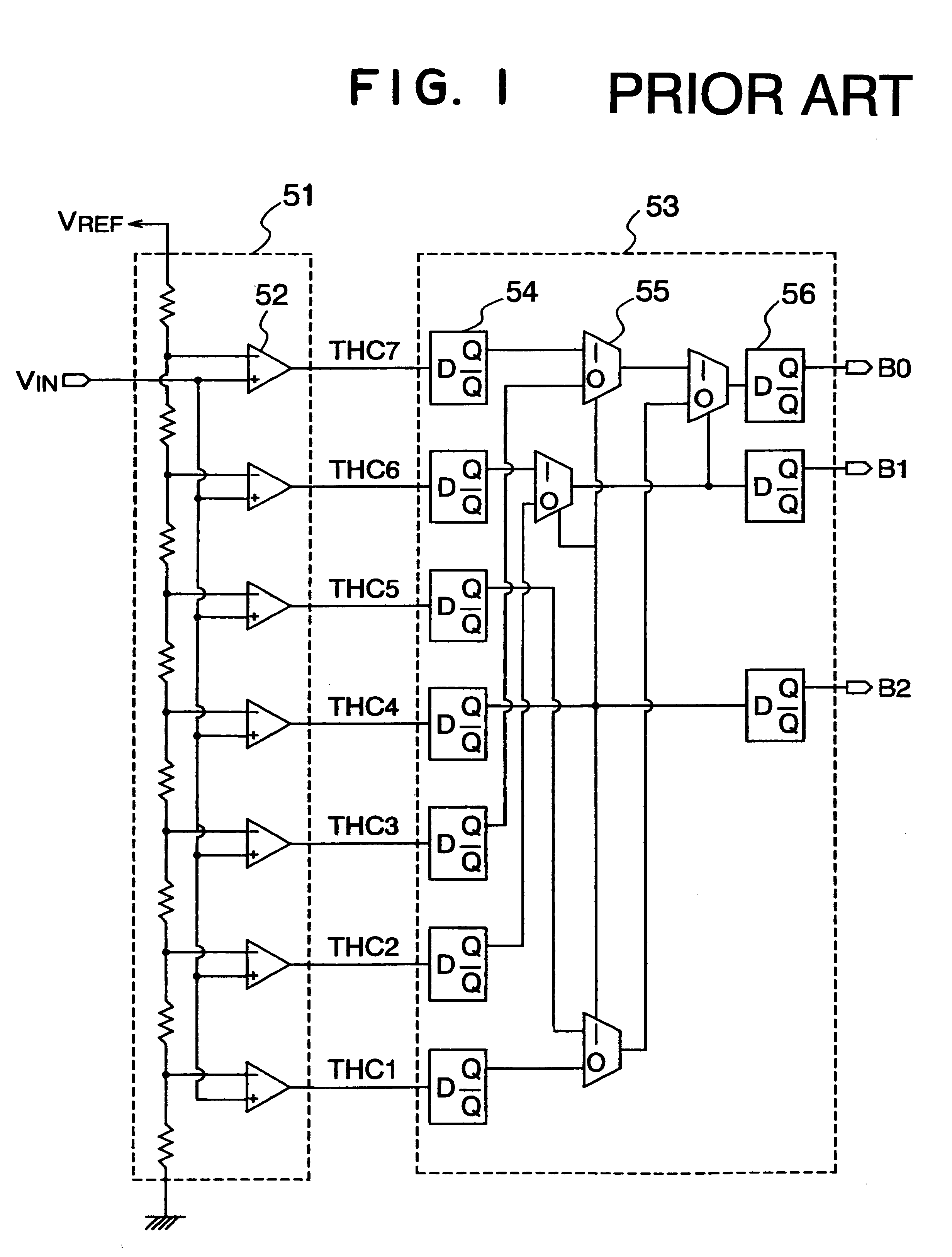
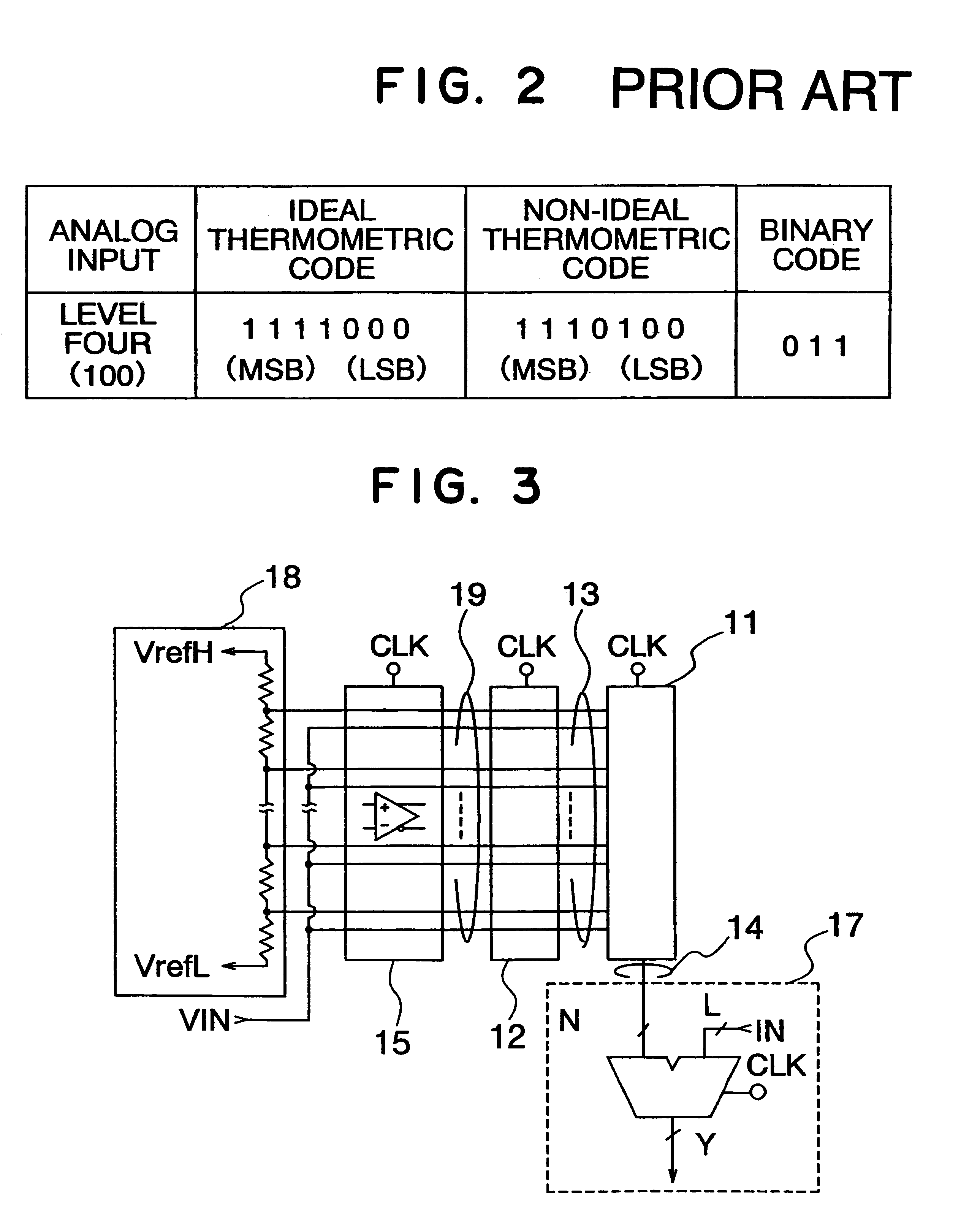
A/D converter having a dynamic encoder
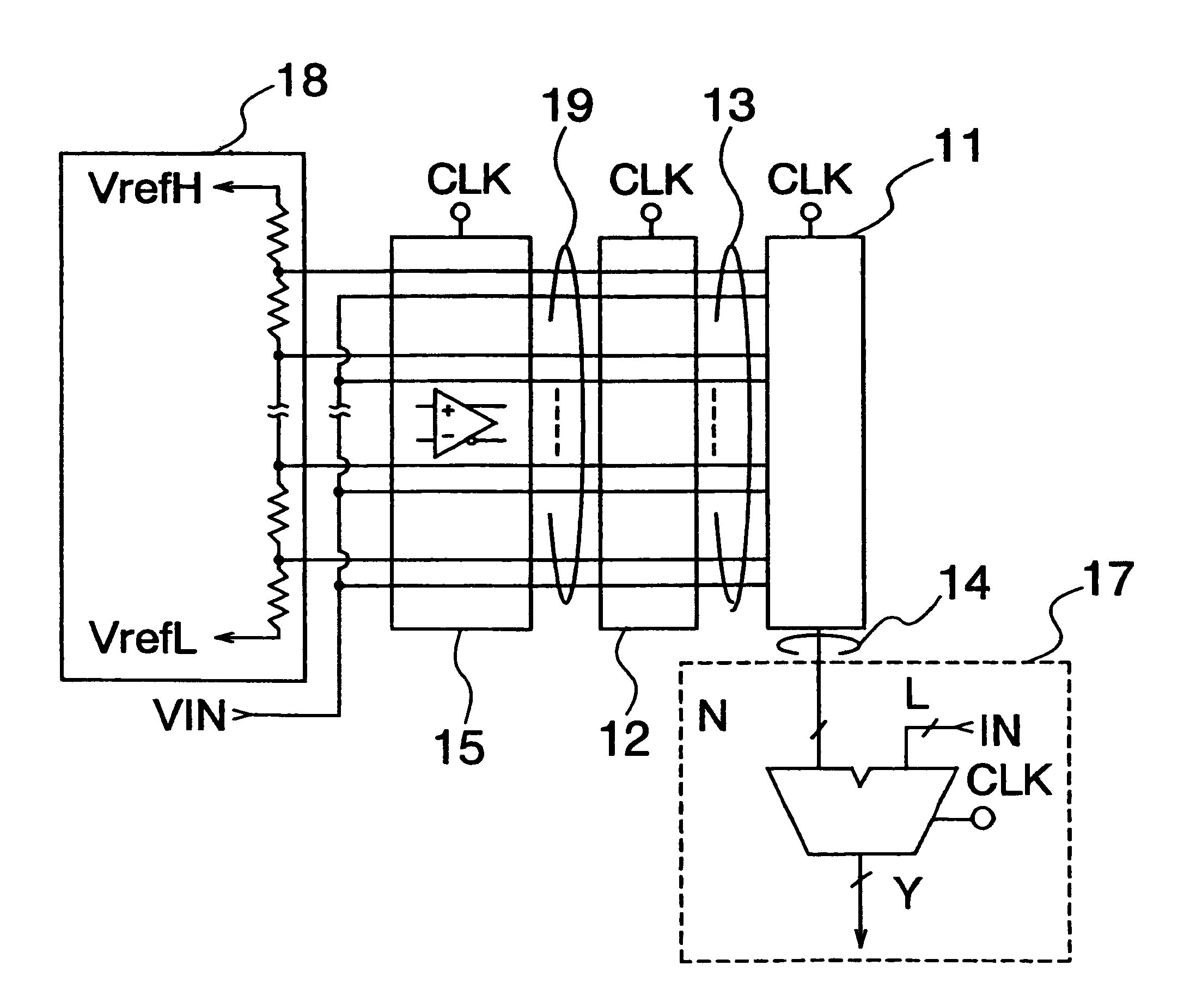
InactiveUS6232908B1Increase speedReduce circuit sizeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersBuck converterA d converter
An A / D converter includes a resistor ladder for generating a plurality of reference potentials, a comparing section for comparing each of the reference potentials against an input analog signal to output a thermometric code, and a dynamic encoder composed of a combinational circuit to encode the thermometric code to a binary code by responding a clock signal. The A / D conversion is finished in a single clock cycle at a high speed, with a reduced number of elements and reduced power dissipation.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Beamforming method, measurement and imaging instruments, and communication instruments
ActiveUS20160157828A1Increase speedImprove accuracyProcessing detected response signalCatheterEngineeringWavenumber
Beamforming method that allows a high speed and high accuracy beamforming with no approximate interpolations. This beamforming method includes step (a) that generates reception signals by receiving waves arrival from a measurement object; and step (b) that performs a beamforming with respect to the reception signals generated by step (a); and step (b) including without performing wavenumber matching including approximate interpolation processings with respect to the reception signals, and the reception signals are Fourier's transformed in the axial direction and the calculated Fourier's transform is multiplied to a complex exponential function expressed using a wavenumber of the wave and a carrier frequency to perform wavenumber matching in the lateral direction and further, the product is Fourier's transformed in the lateral direction and the calculated result is multiplied to a complex exponential function, from which an effect of the lateral wavenumber matching is removed, to perform wavenumber matching in the axial direction, by which an image signal is generated.
Owner:CHIKAYOSHI SUMI
Voltage buck-boost switching regulator
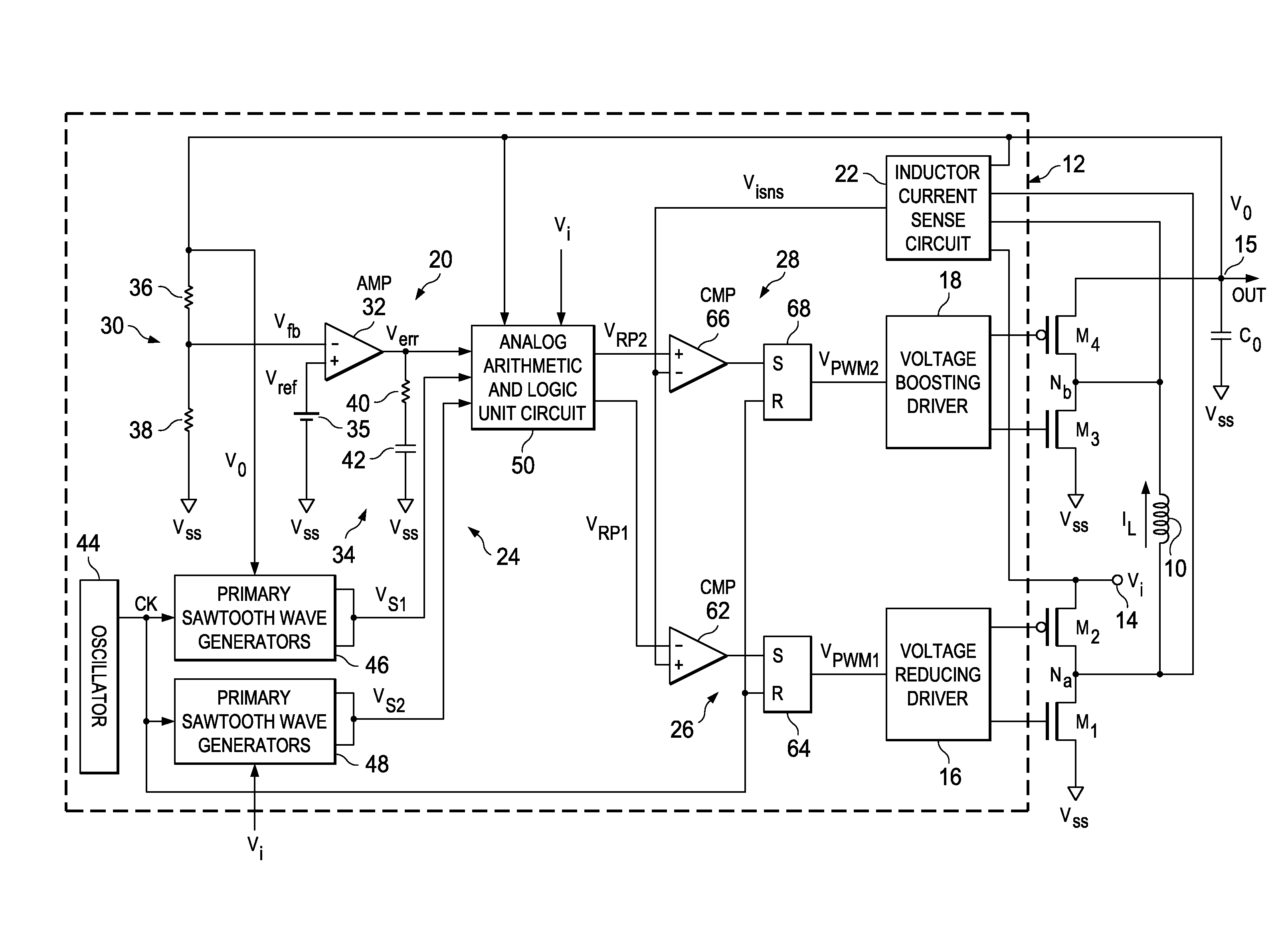
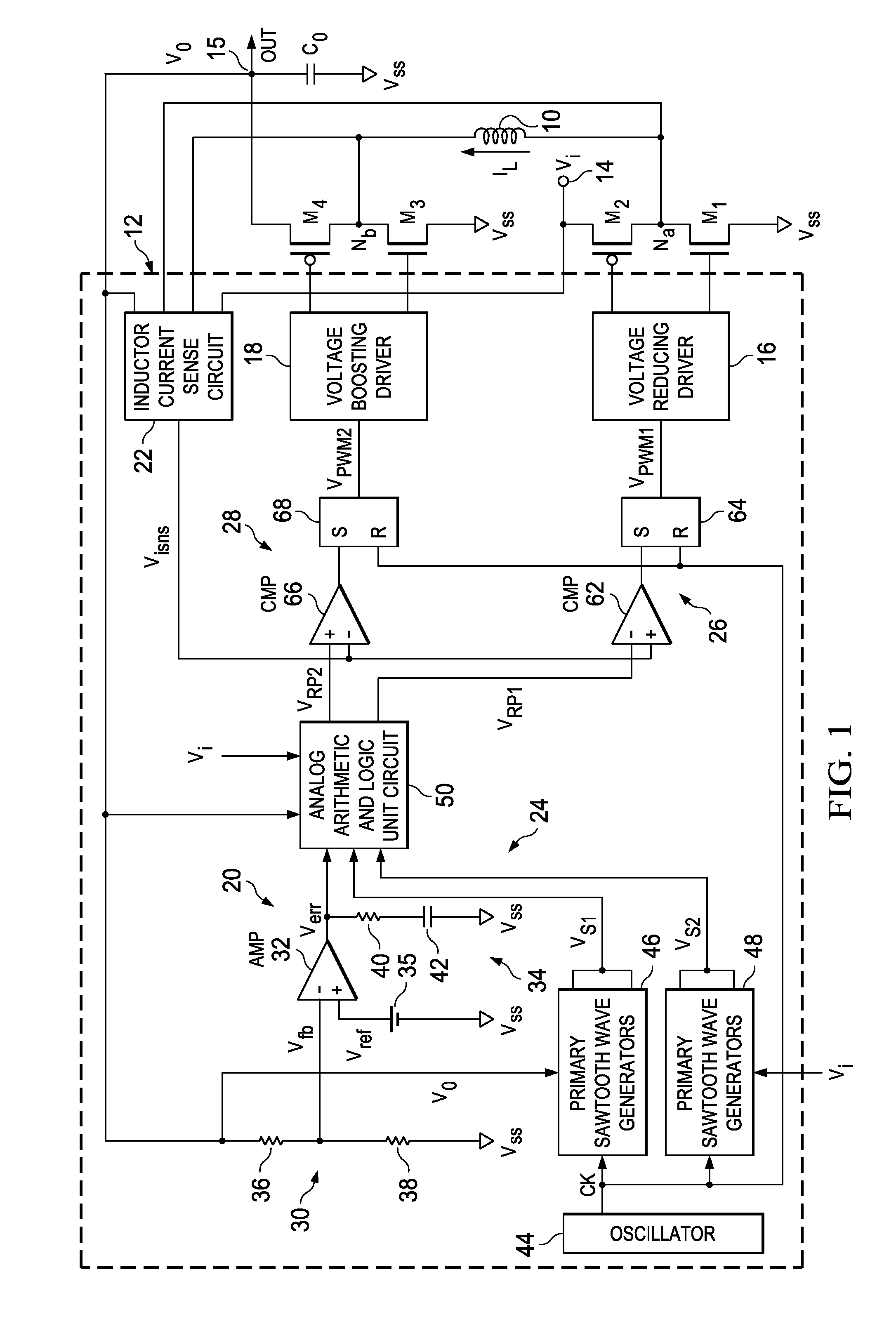
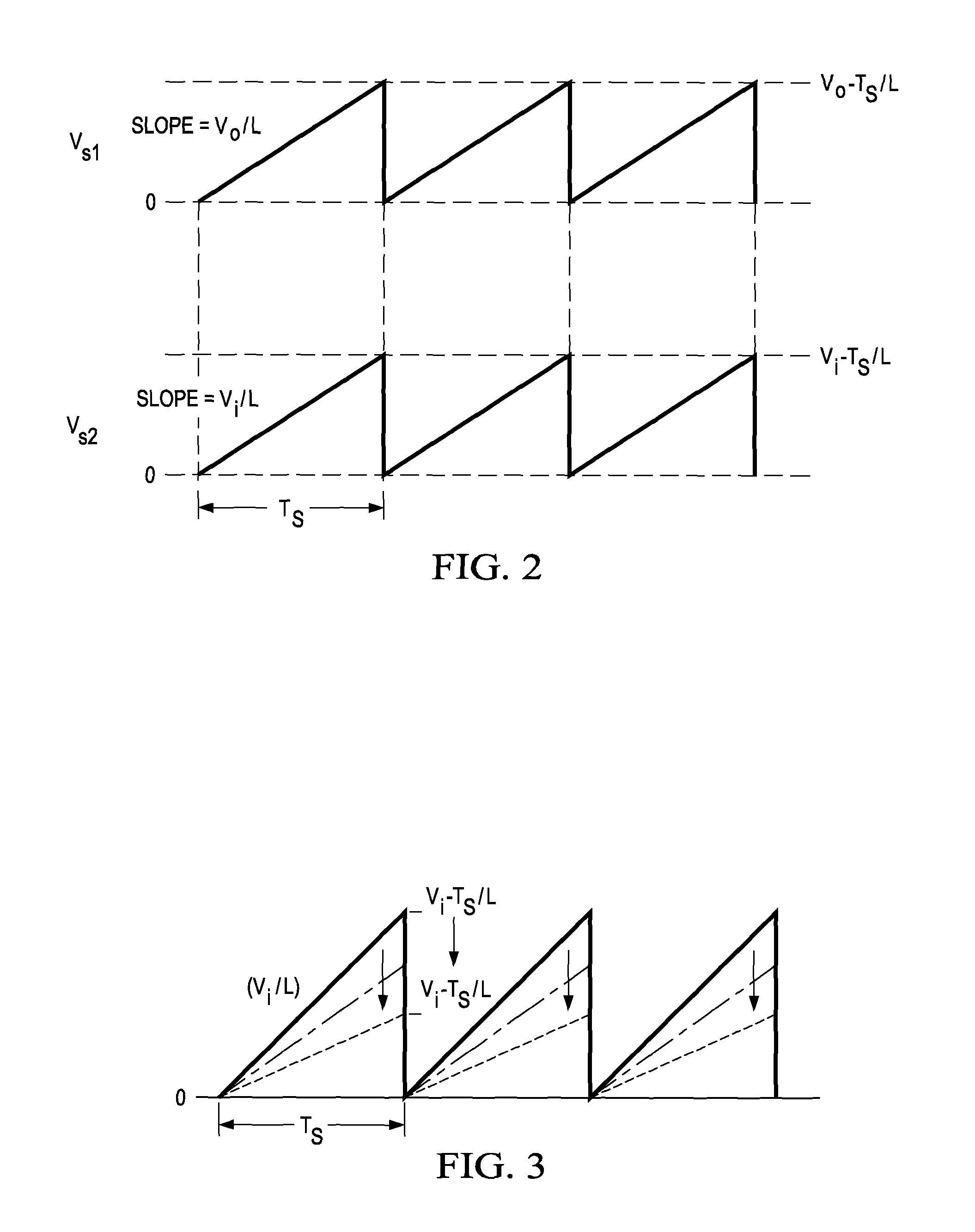
ActiveUS8436592B2Stable, high-speed, high-efficiency constant-voltage output operationStop operationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceEngineering
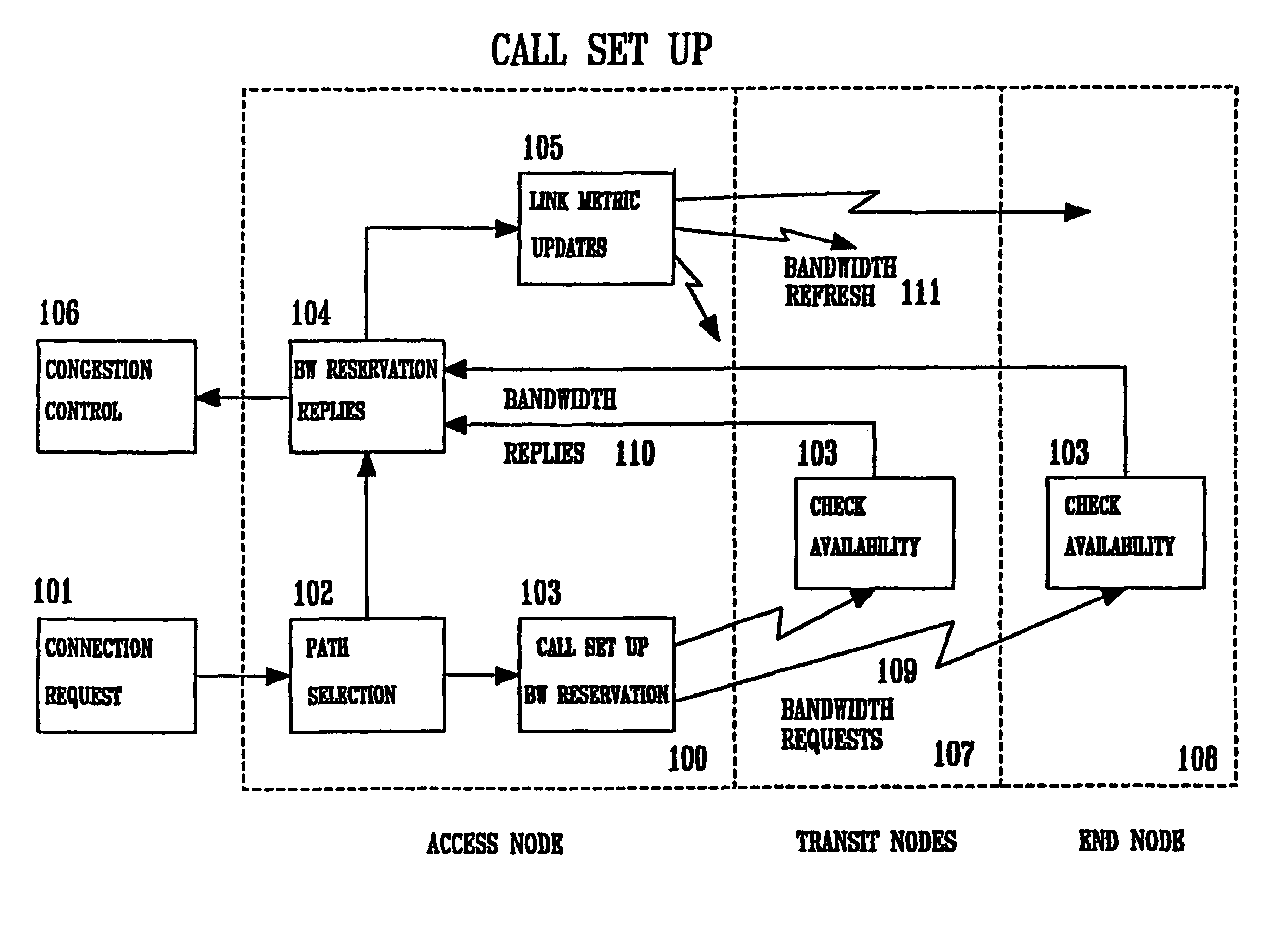
A stable, high-speed, high-efficiency constant voltage is provided without a complicated, large-scale, high-cost phase compensation circuit over a wide range of operating conditions. This voltage buck-boost switching regulator consists of a pair of voltage reducing transistors, a pair of voltage boosting transistors, inductance coil, output capacitor and controller. The controller has the following parts for performing PWM control of constant voltage for voltage reducing transistors and voltage boosting transistors: an output voltage feedback circuit, an inductor current sense circuit, a variable sawtooth wave signal generator, switching controllers, and a voltage boosting driver.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
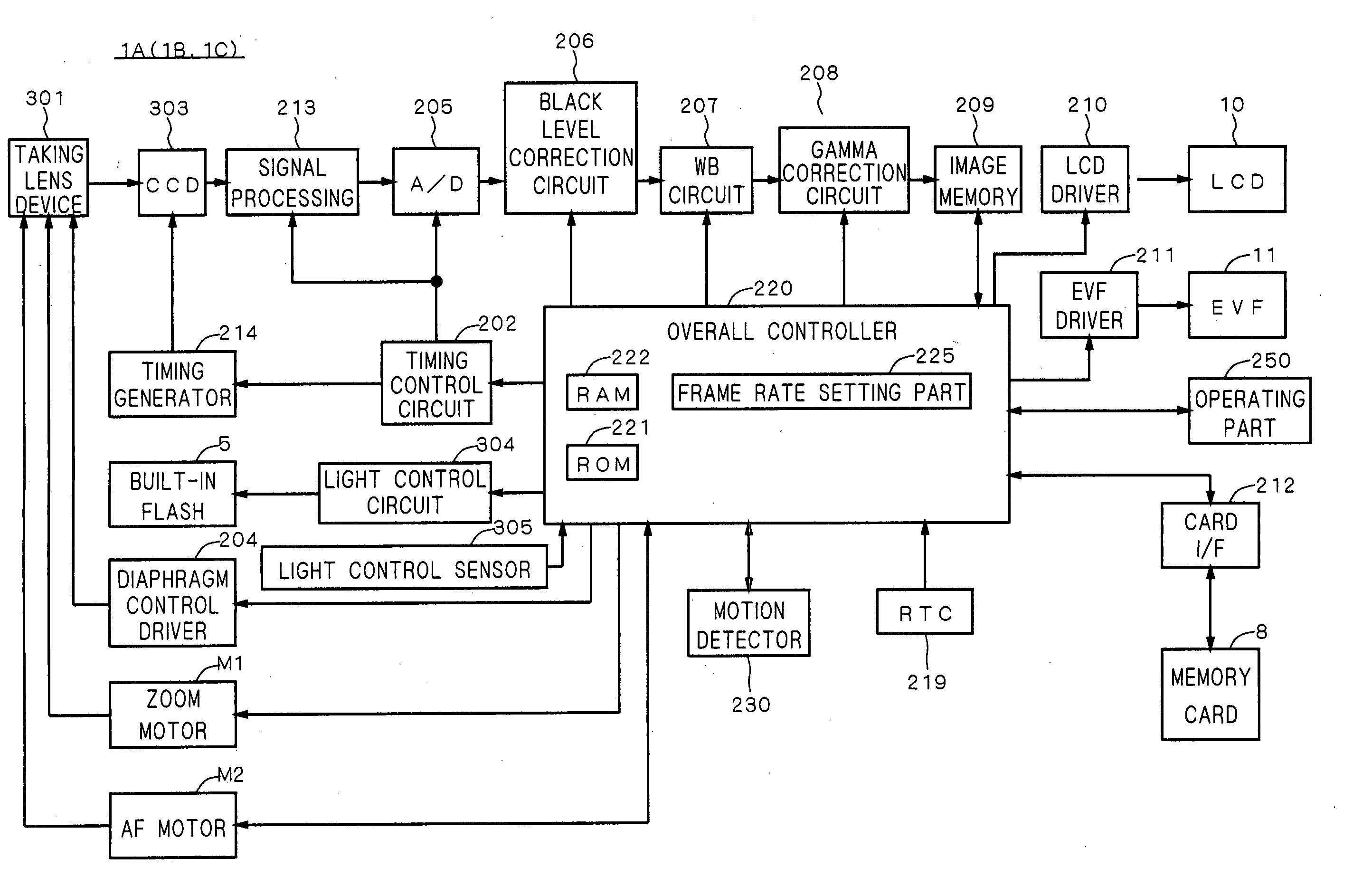
Image capturing apparatus
InactiveUS20050052553A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsHigh velocityComputer science
A digital camera capable of capturing, displaying and recording images at appropriate frame rates is provided. When a current shooting scene mode is a non-sport mode, a current readout mode and a current display mode are set to a high-definition readout mode and a high-definition display mode, respectively, at the same time. Additionally, when a current operating mode is a moving image capturing mode, a current recording mode is also set to a high-definition recording mode at the same time. When the current shooting scene mode is a sport mode, on the other hand, the current readout mode and the current display mode are set to a high-speed readout mode and a high-speed display mode, respectively, at the same time. Additionally, when the current operating mode is the moving image capturing mode, the current recording mode is also set to a high-speed recording mode. The digital camera increases the image-capturing frame rate, the display frame rate and the recording frame rate in synchronism with each other in response to a change of the current shooting scene mode from the non-sport mode to the sport mode.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA CAMERA
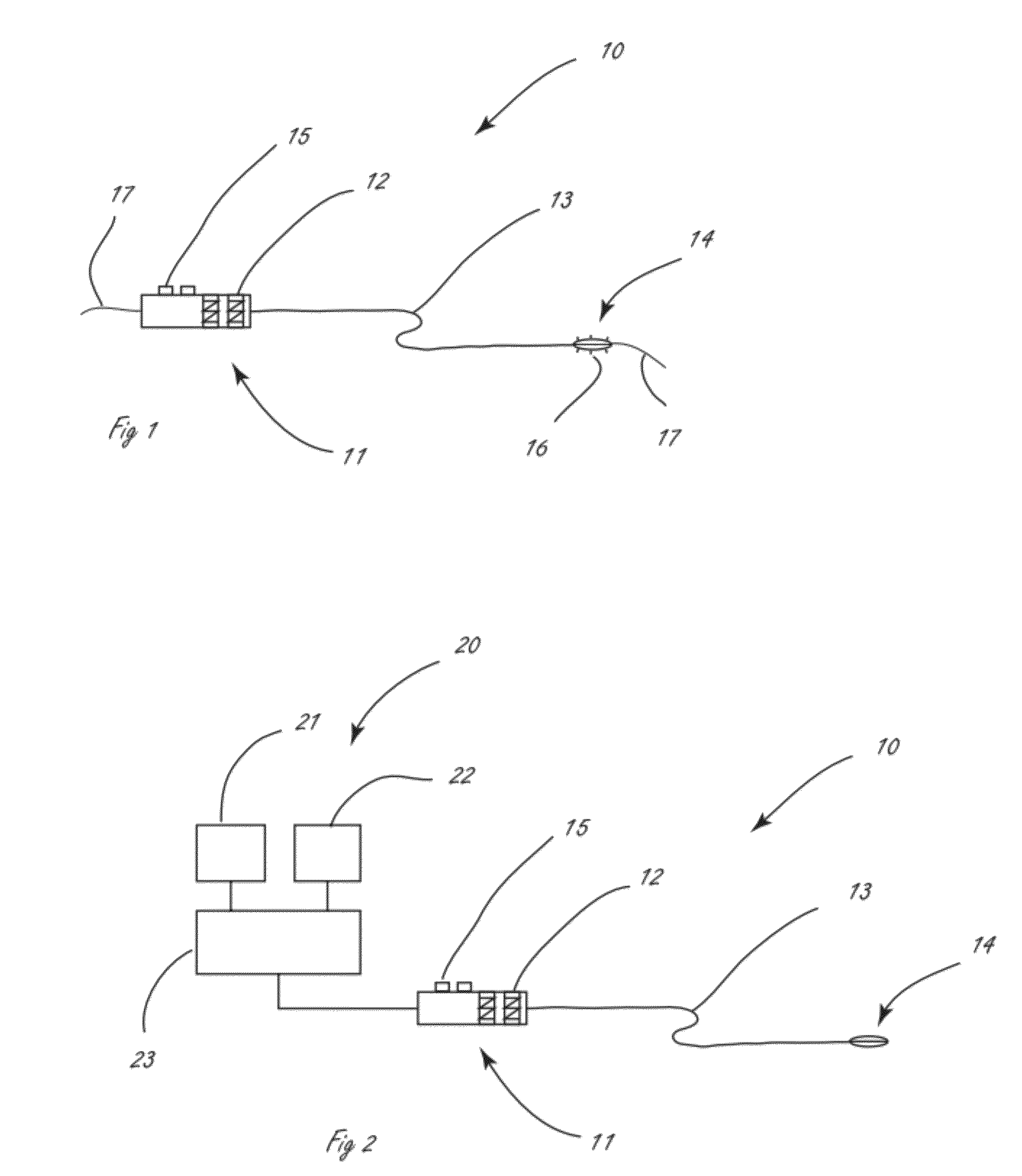
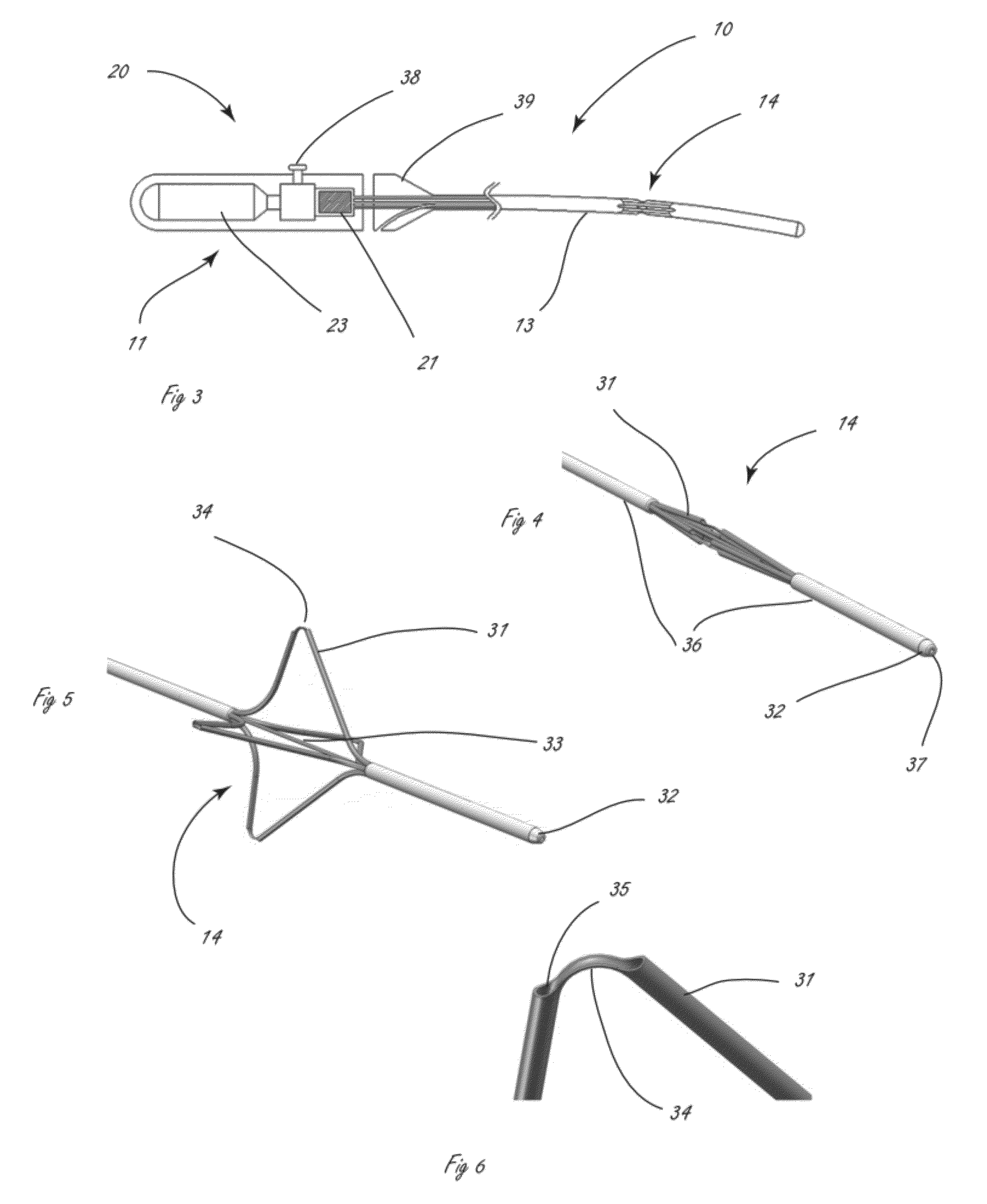
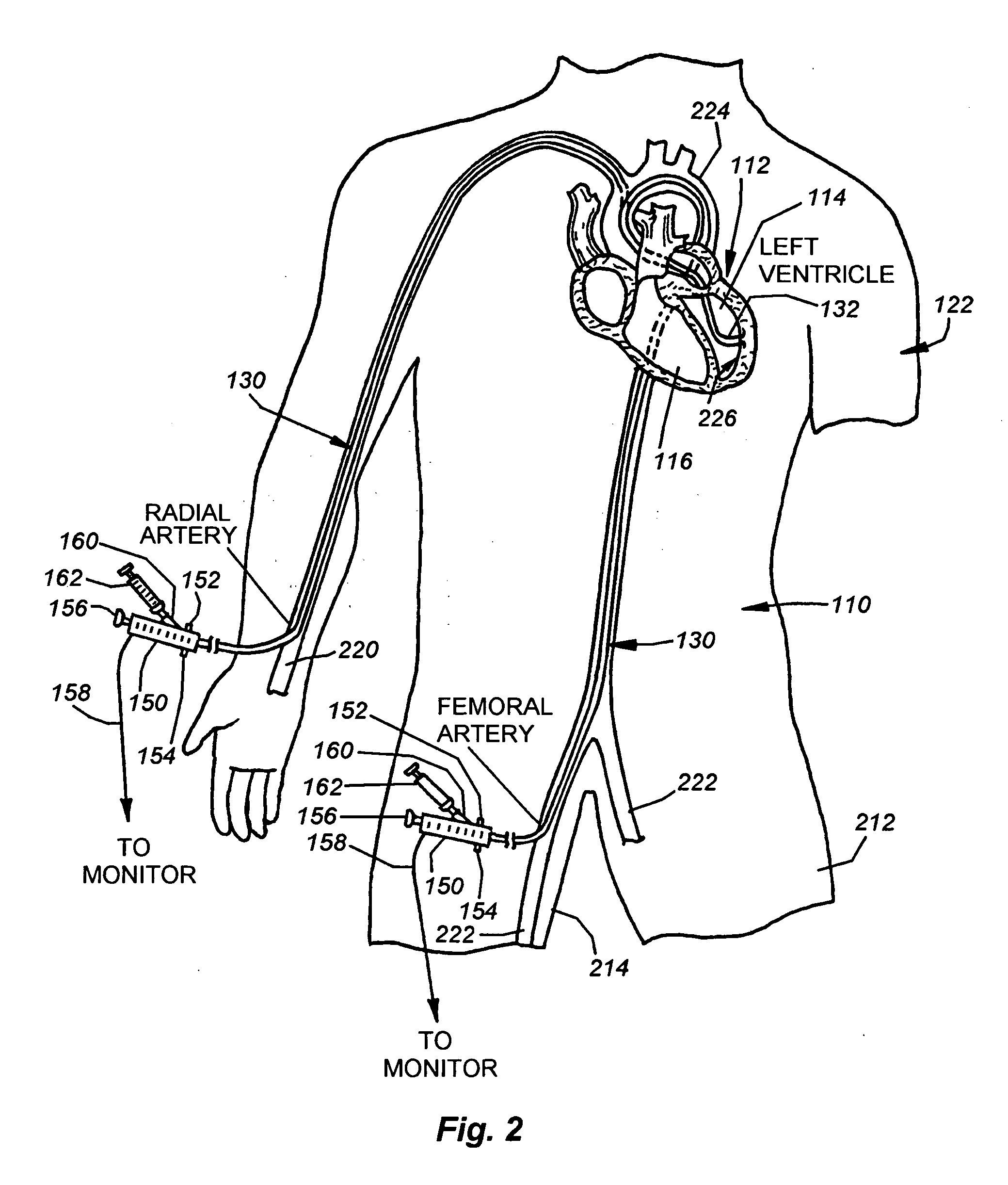
Catheter for introduction of medications to the tissues of a heart or other organ
ActiveUS20070005018A1Shorten the lengthOvercome disadvantagesMulti-lumen catheterInfusion syringesOrgan wallTreatment delivery
This invention overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art by providing a positionable, direct-injection catheters that can access a specific region of the heart or other organ. The catheter is provided with one or two needle shafts, which may be located within respective sheaths that extend axially along the interior of the lumen of a main catheter shaft. Each needle shaft carries, at a distal end thereof a penetrable element or “needle” that is normally retracted within the distal tip of the main shaft during travel to the target organ, but is subsequently deployed by action of a handle-mounted trigger mechanism to extend the needles into the organ's wall. Each extended needle is curved to relative to the shaft's axis to enter the organ wall in a flattened trajectory that both reduces the chance of puncture through the wall and anchors the needles into the wall during injection (for reduced chance of pullout under pressure). A plurality of apertures which provide for more complete agent delivery rapidly, while maintaining a low delivery velocity to effect treatment delivery in as short a period of time as possible without the problems caused by high velocity delivery. The needles are typically arranged to exit the tip at contralateral orientations relative to each other
Owner:TKEBUCHAVA TENGIZ
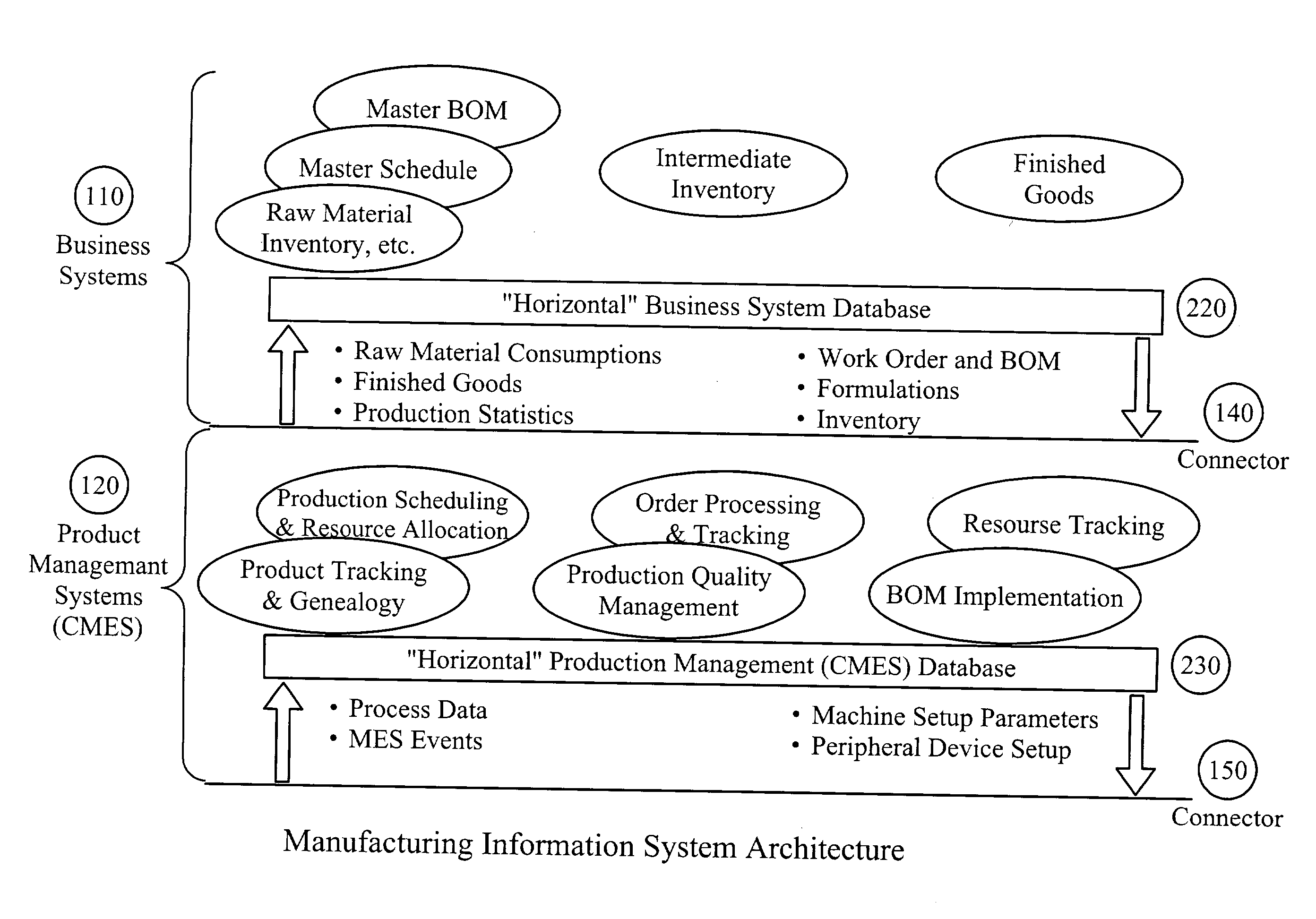
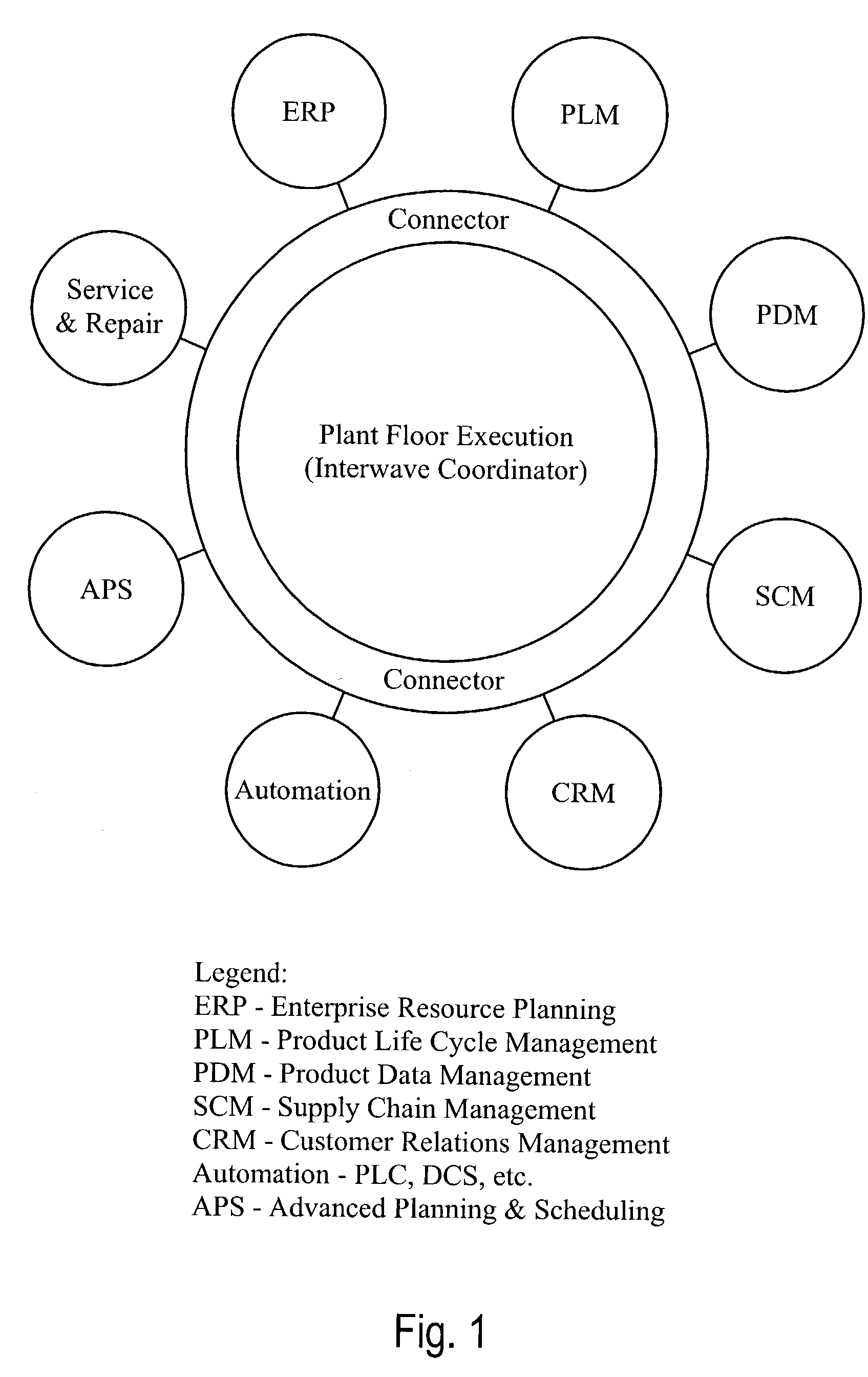
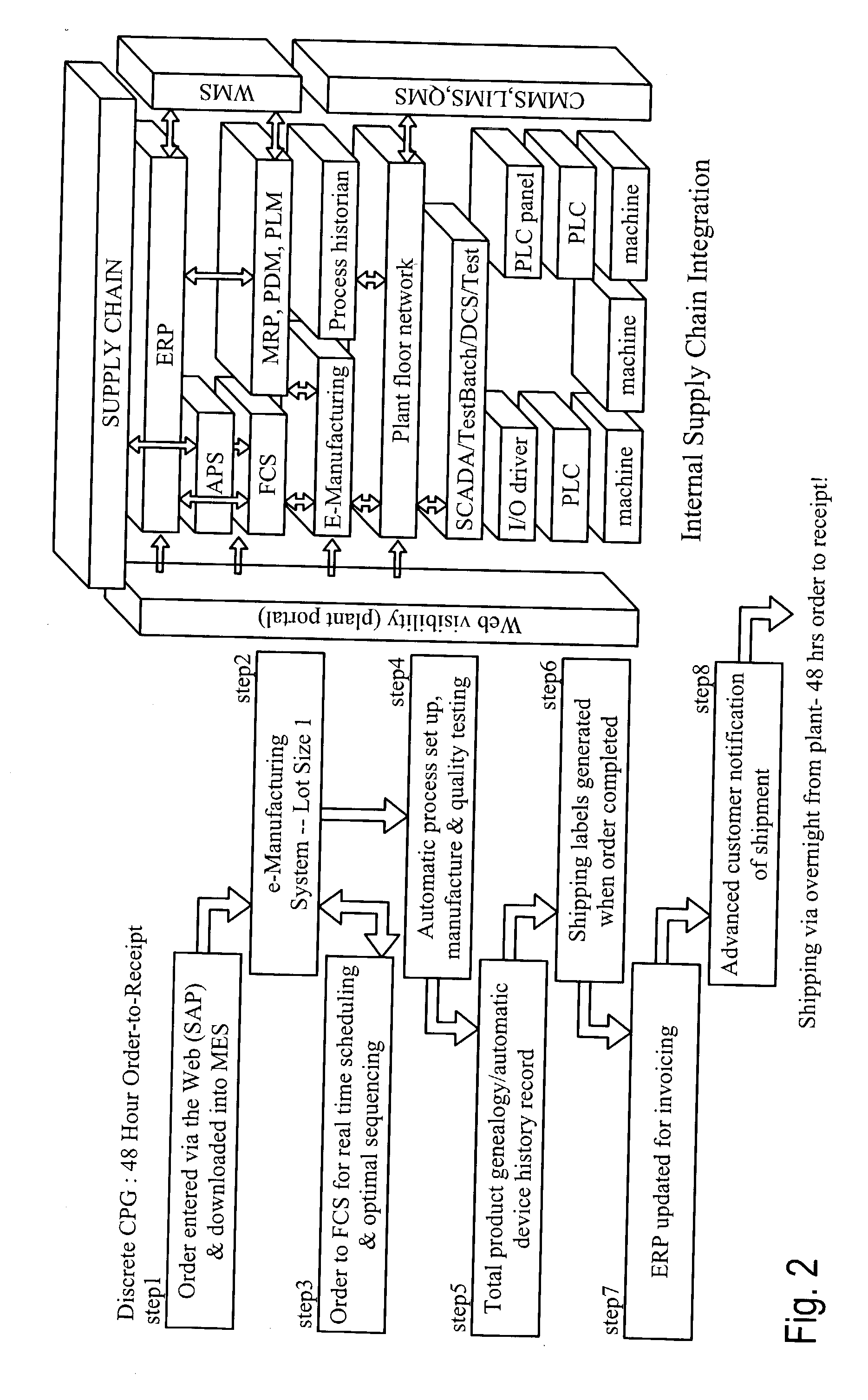
Suite of configurable supply chain infrastructure modules for deploying collaborative e-manufacturing solutions
ActiveUS20030200130A1ResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsManufacturing execution systemE-commerce
A suite of configurable supply chain infrastructure modules provides the "collective manufacturing management infrastructure" necessary to support a high velocity e-business initiative. At the core of the collaboration scheme is the Business Process Modeling Module. The Business Modeling Module consists of two components: Business Process Event Coordinator, and Business Process Modeler. To further support the collaborative scheme, a suite of highly configurable application templates and pre-configured industry applications provide an interface or wrapper around the business rules. The application templates are designed to be used as stand-alone components, or can be assembled / configured into a cohesive solution to provide a basic foundation layer for a Collaborative Manufacturing Execution System (CMES). To address the connectivity of the CMES layer to the business layer and the shop floor automation layer, an Extensible Markup Language (XML) Business Connector and Optical Photo Conductor (OPC) Shop Floor Connector fulfill the interface needs required to support a collaborative infrastructure.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Knowledge-intensive data processing system
ActiveUS20150254330A1Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsData processing systemReal-time data
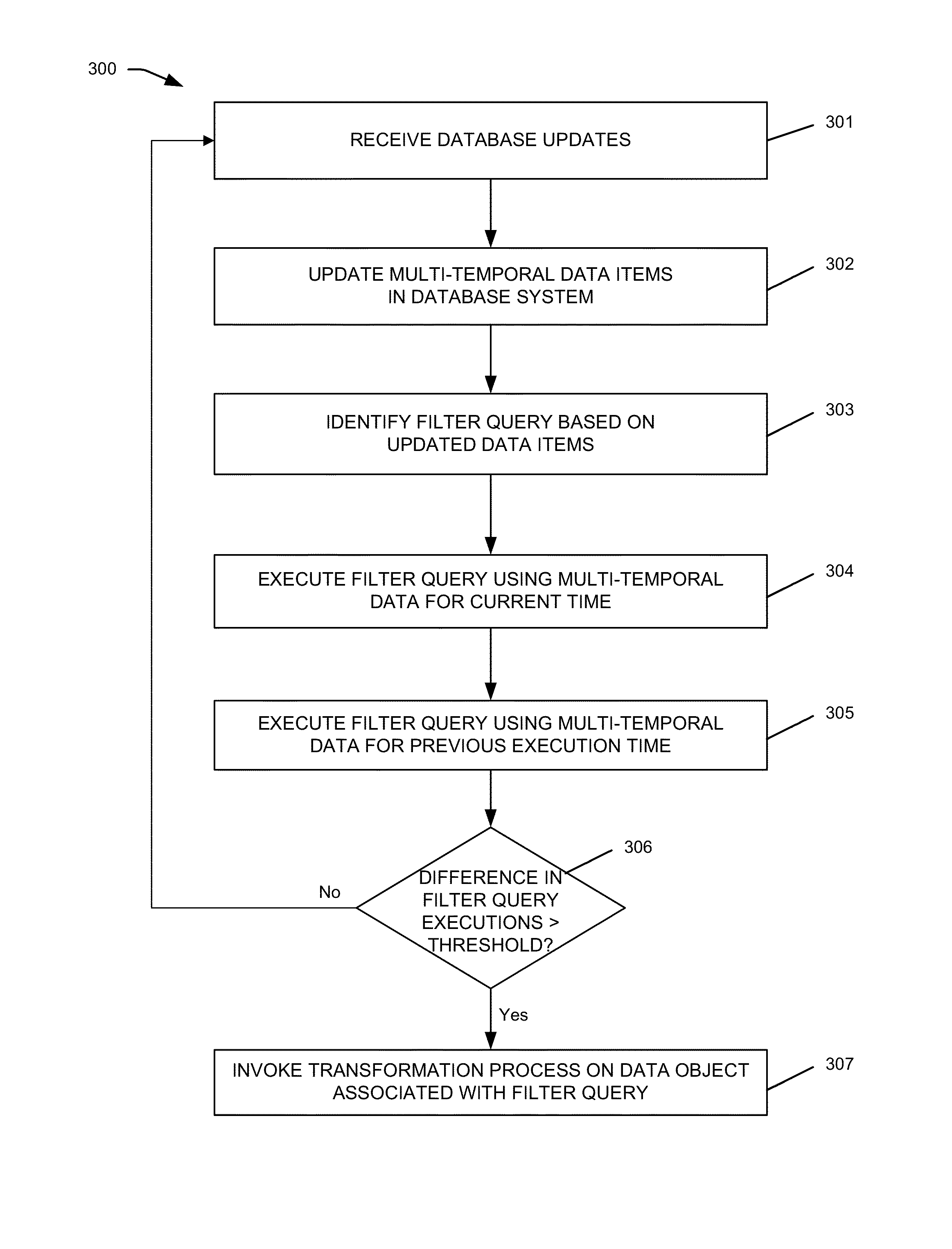
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for managing and processing large amounts of complex and high-velocity data by capturing and extracting high-value data from low value data using big data and related technologies. Illustrative database systems described herein may collect and process data while extracting or generating high-value data. The high-value data may be handled by databases providing functions such as multi-temporality, provenance, flashback, and registered queries. In some examples, computing models and system may be implemented to combine knowledge and process management aspects with the near real-time data processing frameworks in a data-driven situation aware computing system.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for providing broadband content to high-speed access subscribers
InactiveUS6286049B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksClient dataData traffic
Systems and methods for providing broadband content to high-speed access subscribers with layer 4-7 switching are disclosed. The system generally comprises an enhanced services complex (ESC) having at least one content server having Internet content stored or cached therein and a broadband access gateway (BAG) in communication with the ESC and to at least one Internet service provider (ISP), where the BAG is configured to transmit and receive data traffic to and from a client premise equipment (CPE) at a client premise, respectively. The BAG is configured to selectively route data traffic received from the CPE to an ESC content server or the ISP based on multiple instances of the content destination address. The method generally comprises routing client data packets from a CPE to a BAG in communication with at least one ISP and an ESC having at least one content server, selectively routing each client data packet from the BAG to the ESC or the Internet, and routing content data packets from the Internet content or the content server to the CPE.
Owner:GC PIVOTAL LLC
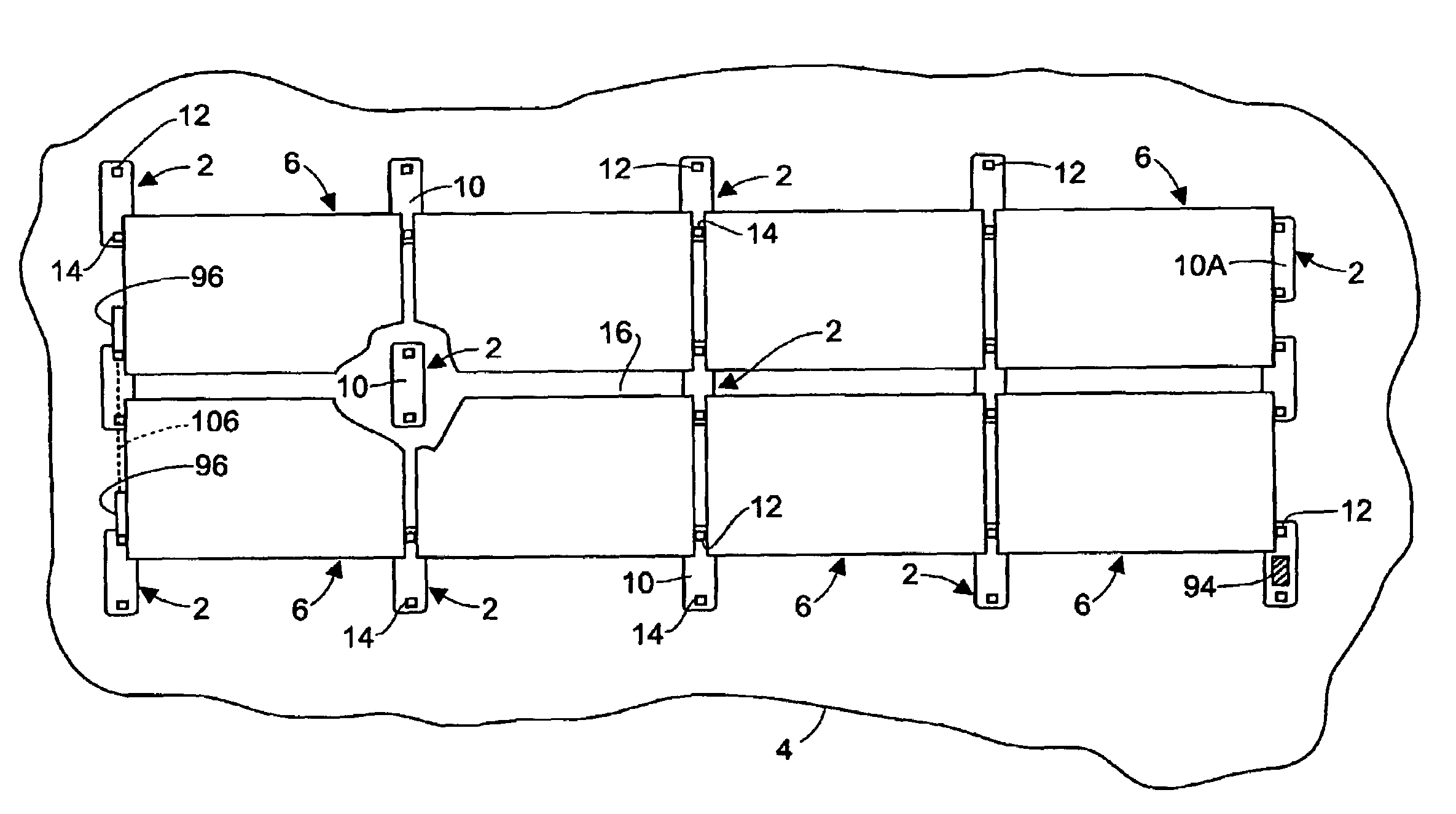
Apparatus and method for mounting photovoltaic power generating systems on buildings
InactiveUS20050115176A1Preserve integrityPreserve waterproof characteristicPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEffective heightEngineering
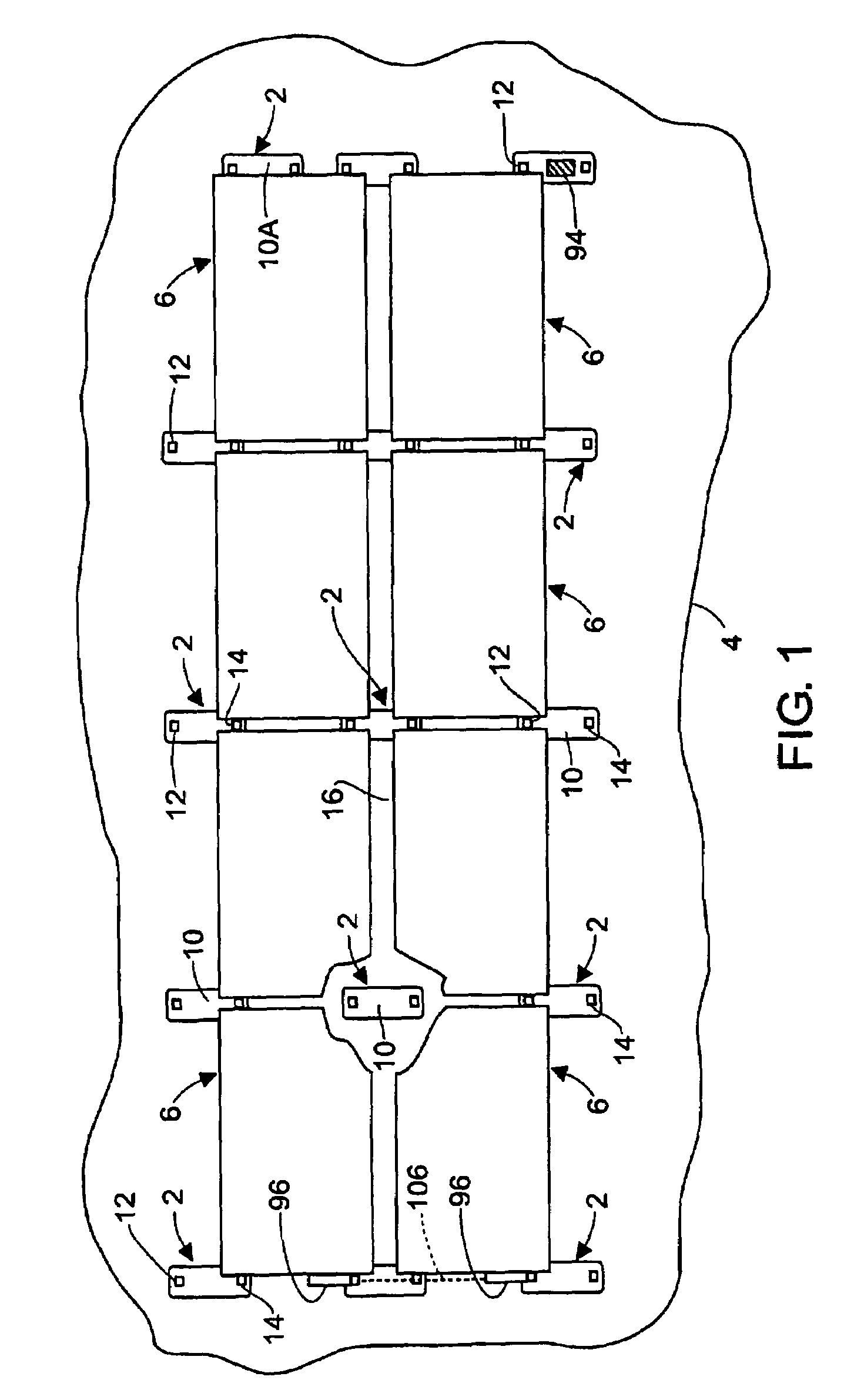
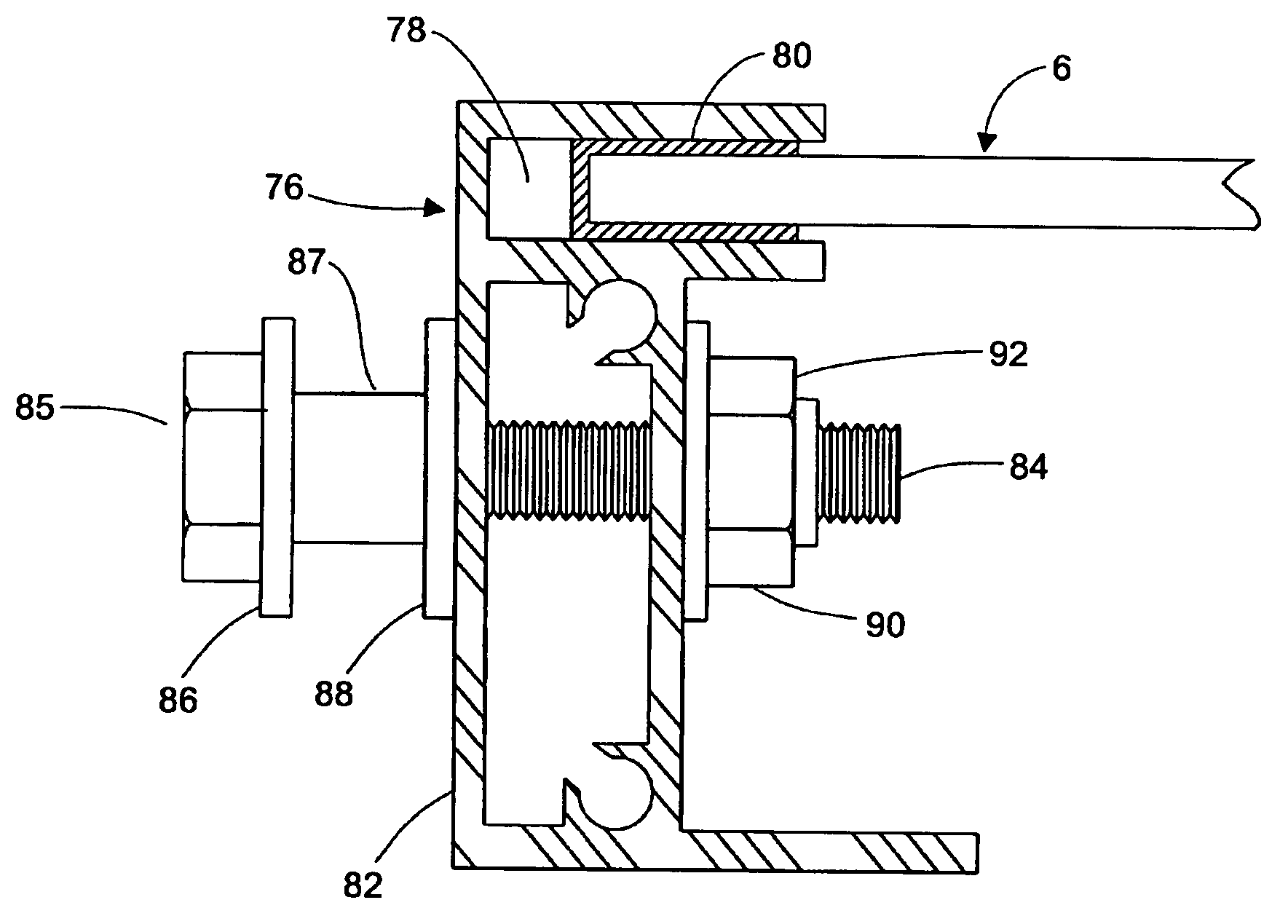
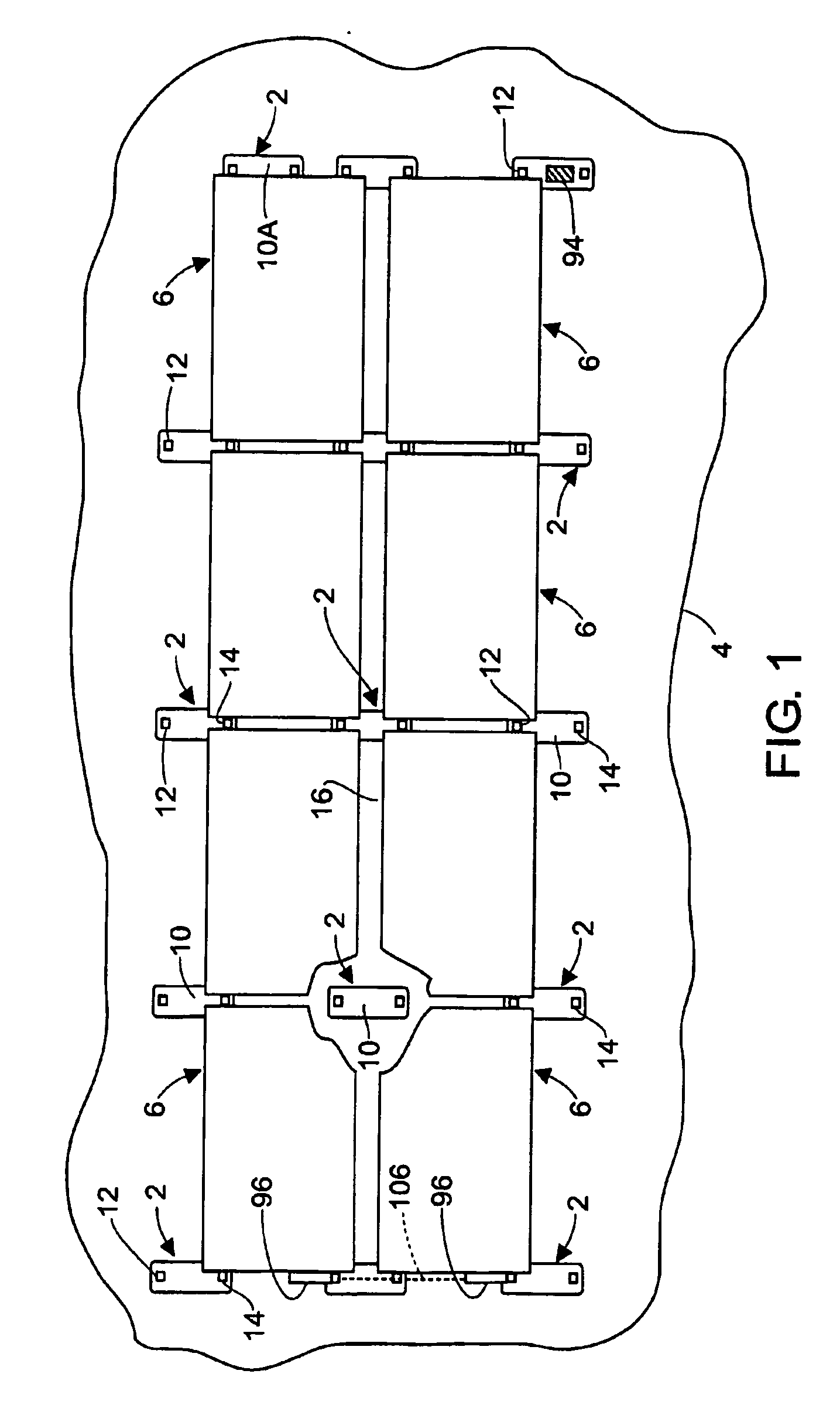
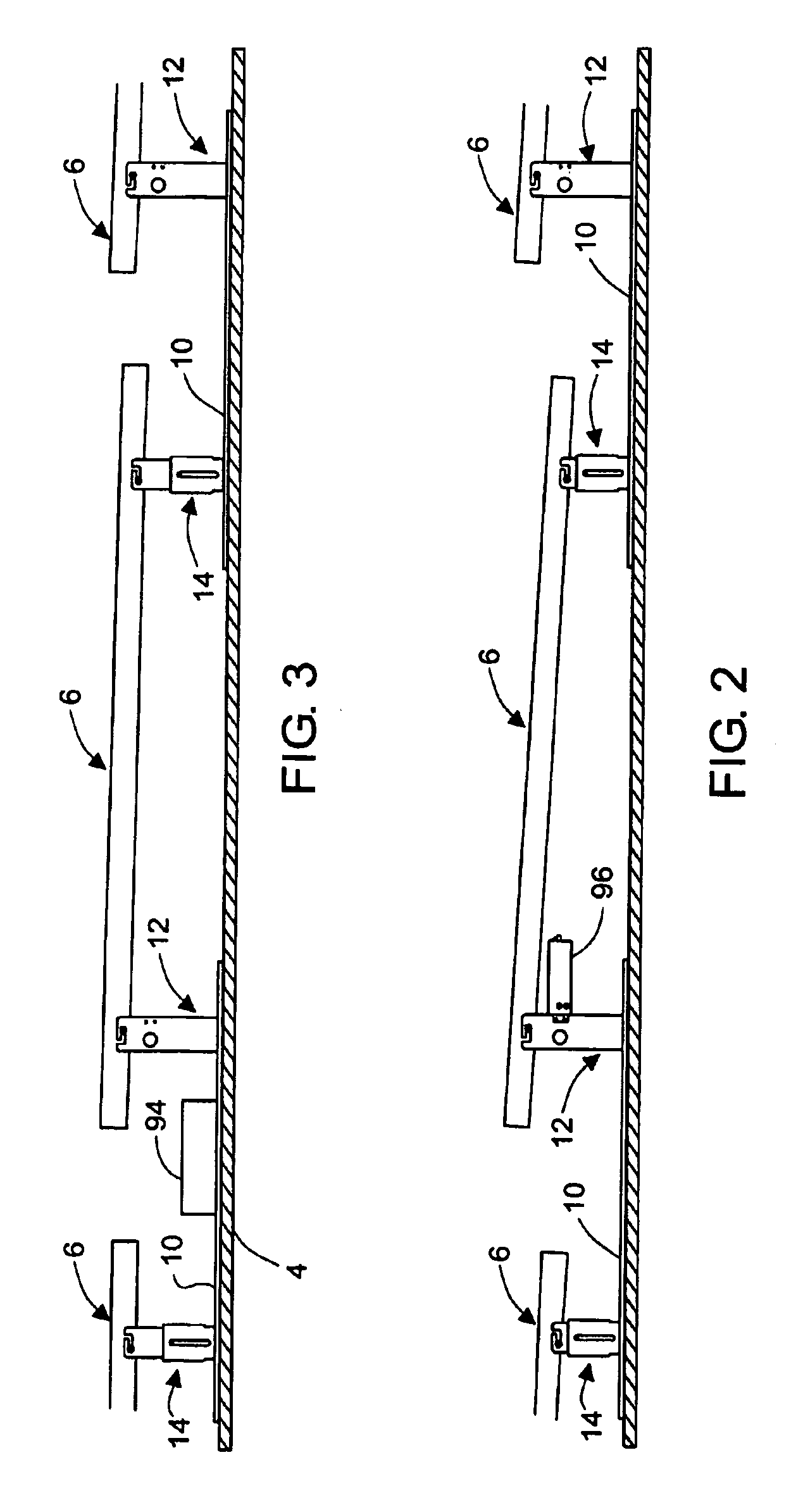
Rectangular PV modules (6) are mounted on a building roof (4) by mounting stands that are distributed in rows and columns. Each stand comprises a base plate (10) that rests on the building roof (4) and first and second brackets (12, 14) of different height attached to opposite ends of the base plate (10). Each bracket (12, 14) has dual members for supporting two different PV modules (6), and each PV module (6) has a mounting pin (84) adjacent to each of its four corners. Each module (6) is supported by attachment of two of its mounting pins (84) to different first brackets (12), whereby the modules (6) and their supporting stands are able to resist uplift forces resulting from high velocity winds without the base plates (10) being physically attached to the supporting roof structure (4). Preferably the second brackets (14) have a telescoping construction that permits their effective height to vary from less than to substantially the same as that of the first brackets (12).
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Method and system for a local and fast non-disruptive path switching in high speed packet switching networks
InactiveUS7593321B2Increase the number ofError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityExchange network
A method for operating a node in a computer network is disclosed, where the network is made up of nodes connected by links. The method has the steps: determining an alternate path for one or more links; reserving resources for the alternate path; and rerouting traffic on the alternate path in case of a link failure. The alternate path may be periodically updated. A plurality of alternate paths may be maintained. The alternate paths may not have any links in common. User traffic may be rerouted substantially simultaneously to each link of the alternate path in the event of failure of a primary path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com