Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2824 results about "Memory circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
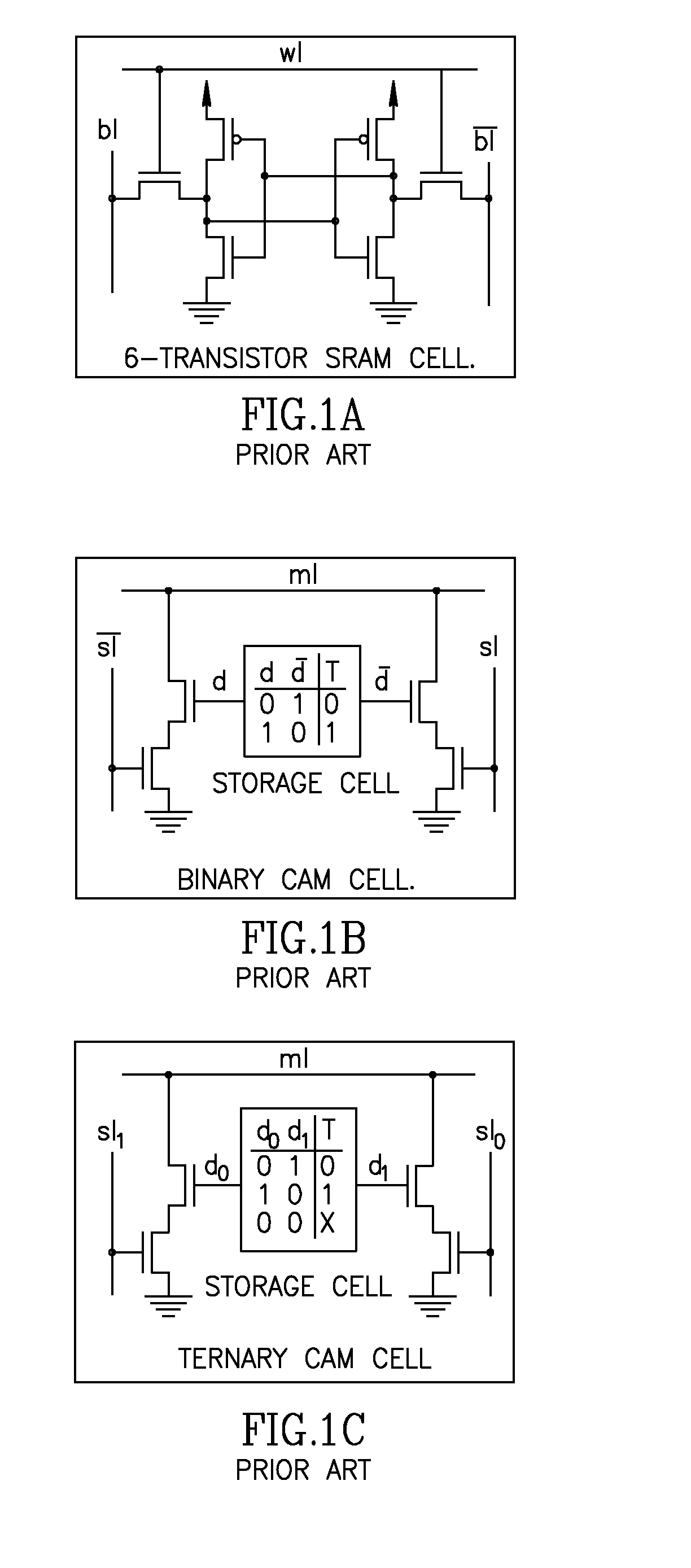
Memory Circuits. Memory circuits function by storing the voltage present on an input signal whenever they are triggered by a control signal. They retain that stored voltage until the next assertion of the control (or trigger) signal.
Processor Arrays Made of Standard Memory Cells
Owner:GSI TECH
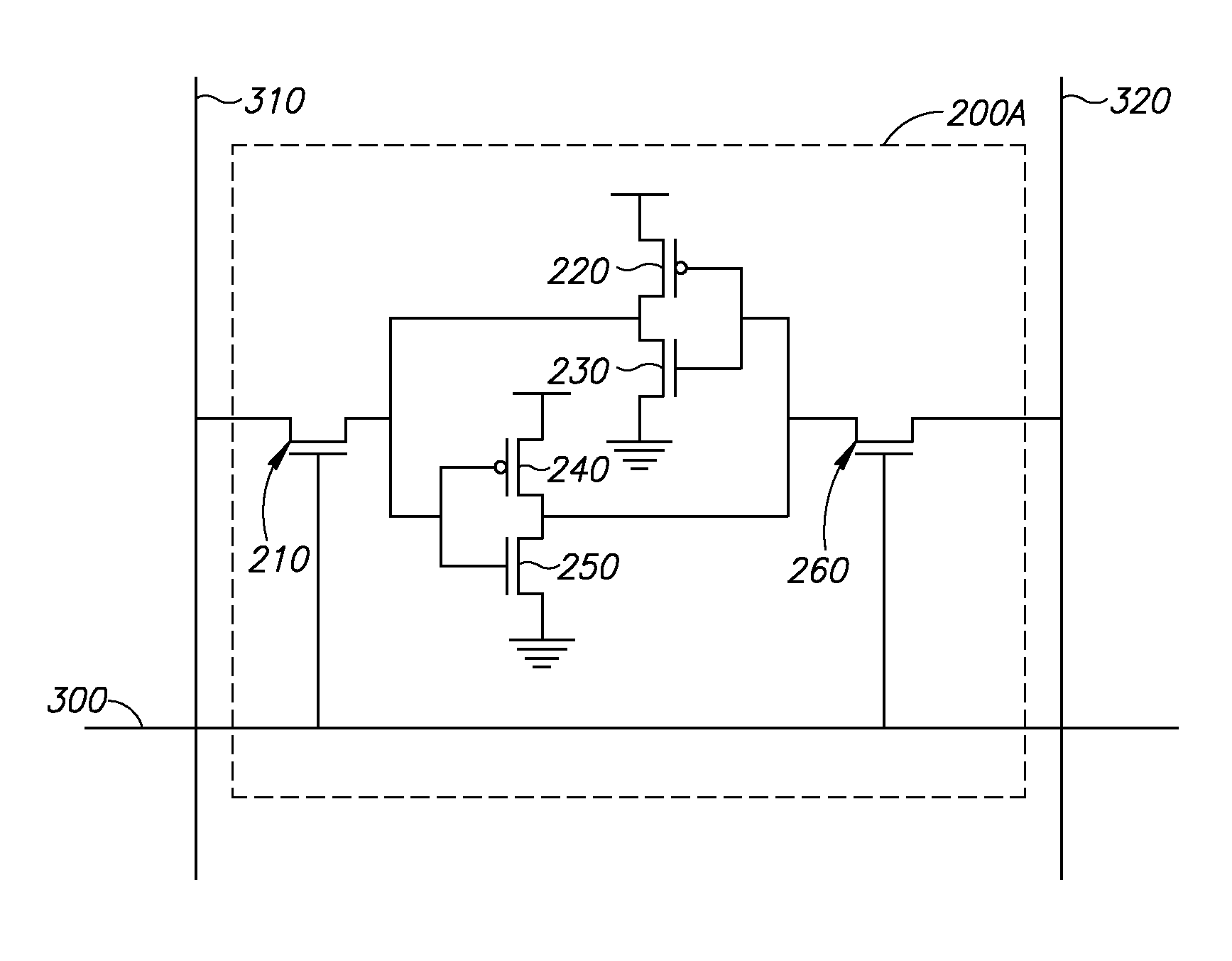
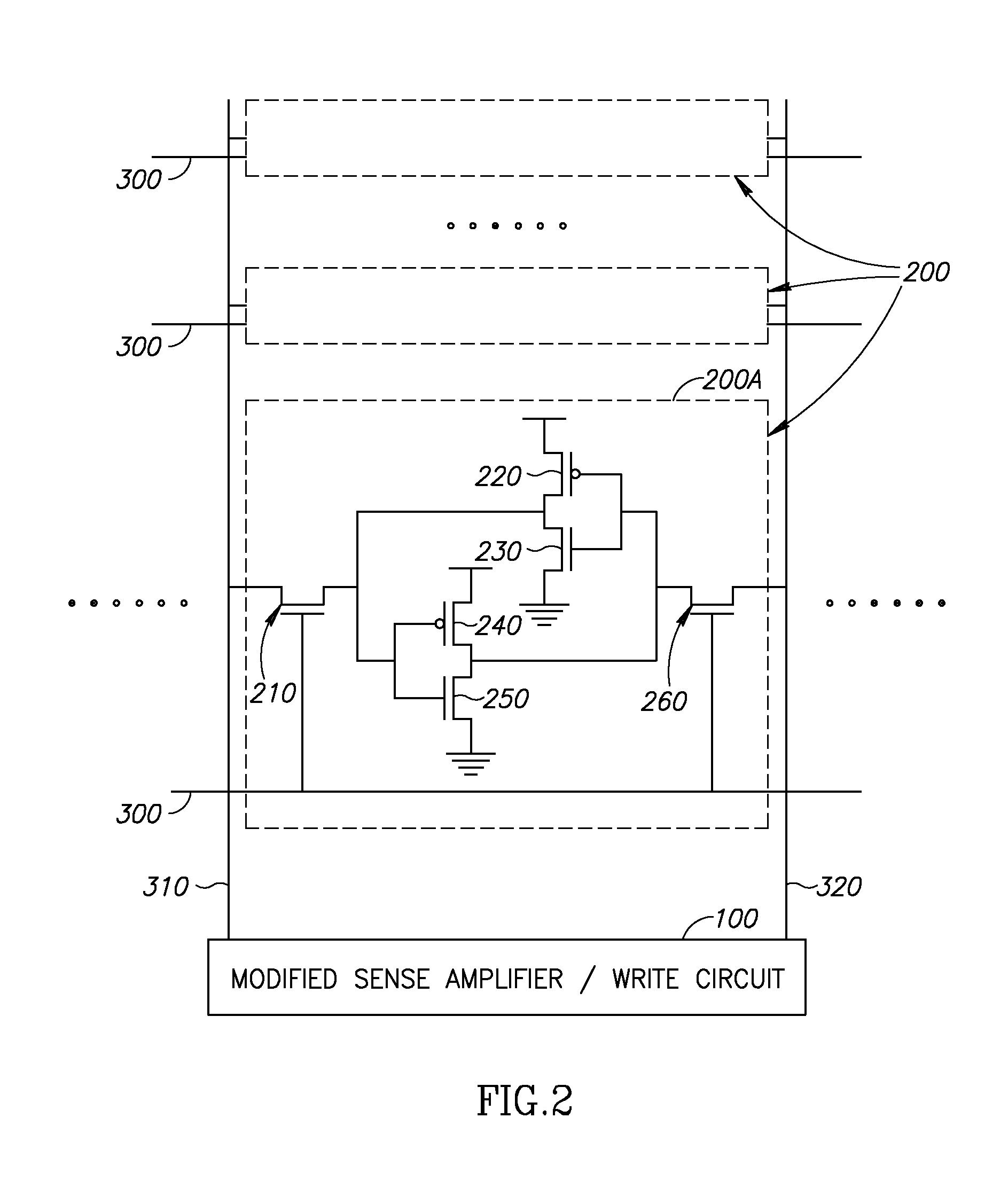
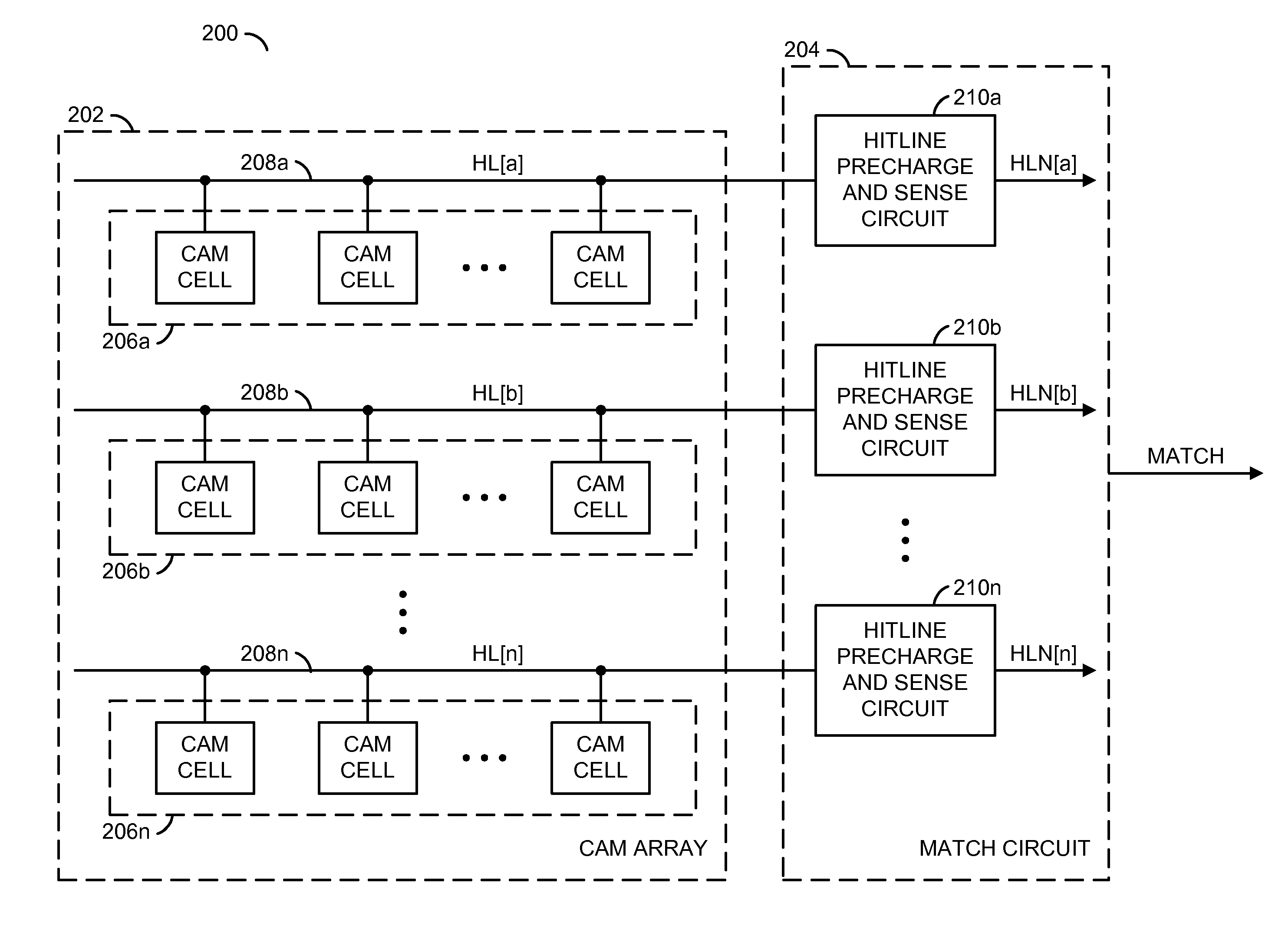
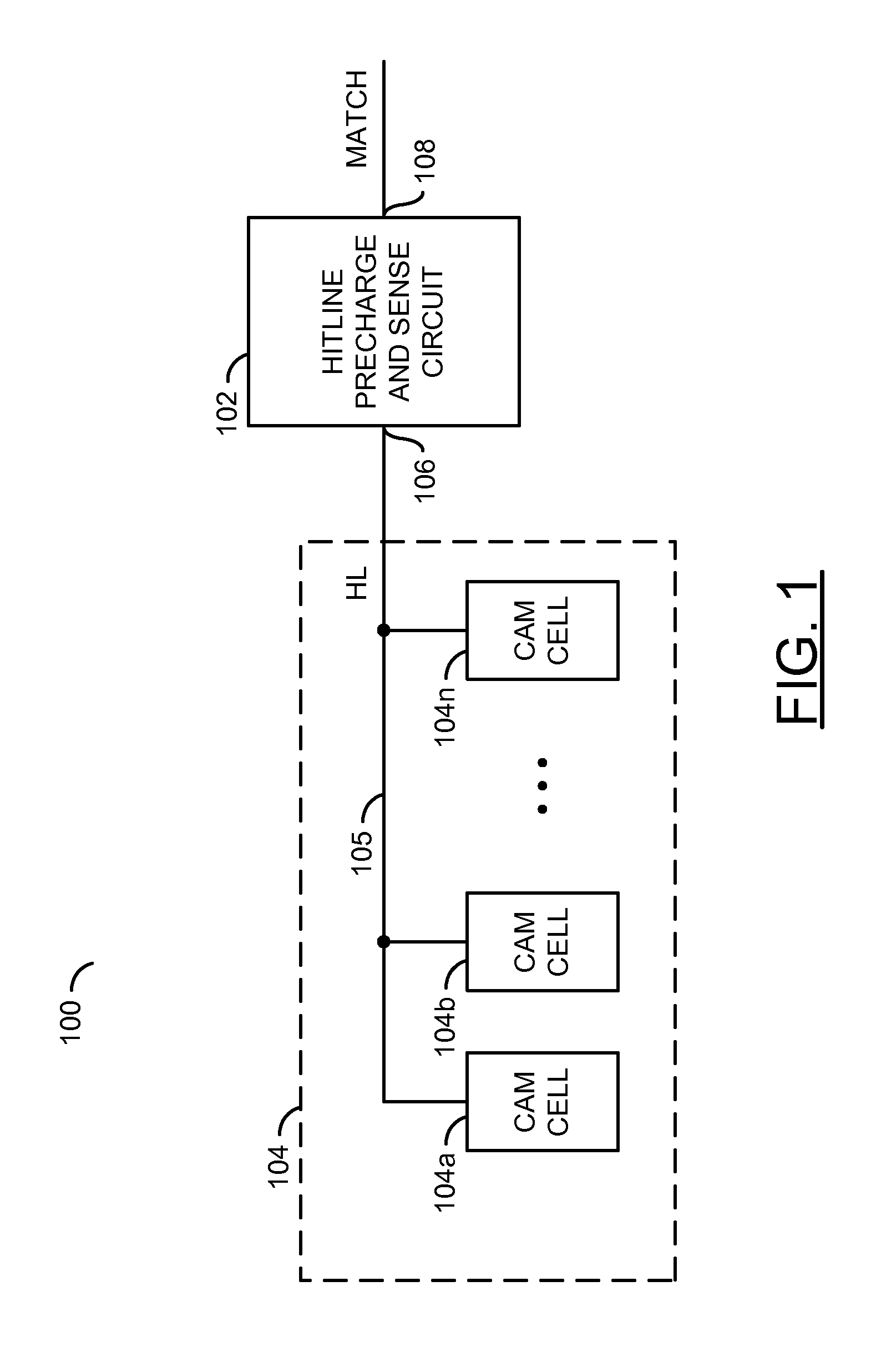
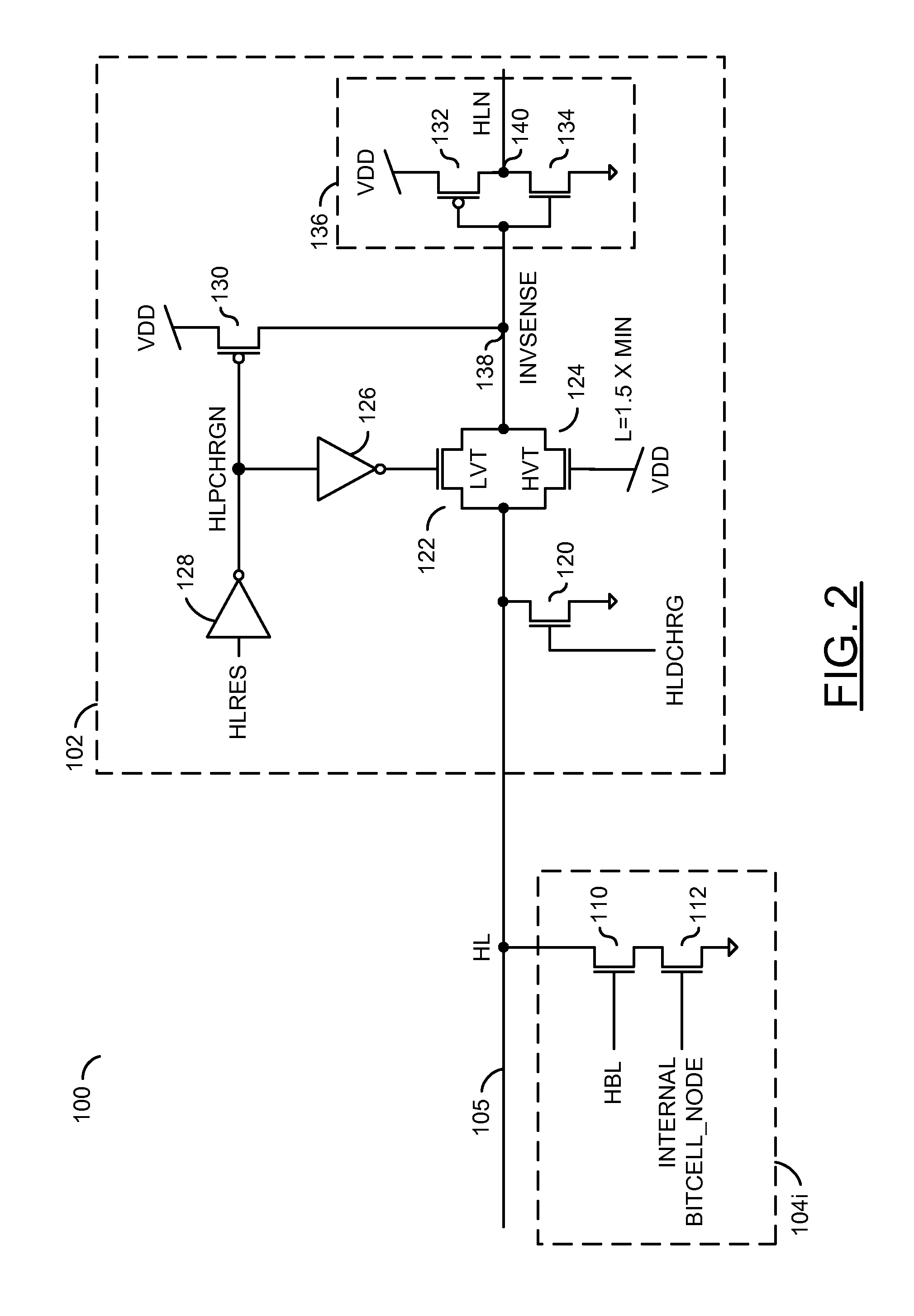
Low power content addressable memory hitline precharge and sensing circuit
An apparatus and a method of operating the apparatus. The apparatus includes a driver circuit and a memory circuit. The driver circuit may be configured to precharge a hitline in response to a predetermined voltage level and a control signal and sense a result of a compare operation based upon a hitline signal on the hitline. The driver circuit generally precharges the hitline to a voltage level lower than the predetermined voltage level and senses the result of the compare operation using the full predetermined voltage level. The memory circuit may be configured to perform the compare operation using the hitline.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Merged logic and memory combining thin film and bulk Si transistors
InactiveUS20010028059A1Compact and economicalTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh densitySingle process
The present invention describes the use of two semiconductor layers, a thin film (TF) layer and a bulk Si wafer layer, to make high density and high speed merged logic and memory IC chips. The memory cells use three-dimensional (3D) SRAM structures. Two kinds of 3D logic cells are disclosed. 3D form of the differential cascode voltage switch (DCVS) architecture, and a 3D form of the DCVS with pass gate (DCVSPG) logic architecture. A high density "system on chip" architecture is described. The high density is achieved by locating large PMOS transistors in the TF Si layer, and the fast NMOS transistors in a bulk Si wafer layer. A single process sequence to simultaneously make the logic and memory circuits on the IC chip is also described.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Body contacted dynamic memory
InactiveUS6111778AEfficiently store and retrieveIncreases magnitudeTransistorSolid-state devicesBody contactMemory circuits
A dynamic memory circuit in which the inherent bipolar transistor effect within a floating body transistor is utilized to store an information bit. A floating body of a storage transistor stores an information bit in the form of an electric charge. The floating body is charged and discharged via an access transistor during data write operations. The inherent bipolar transistor resident within the floating body transistor increases the effective capacitance of the floating body which acts as the storage node, and thereby enhances the magnitude of the discharge current which represents the stored information bit during read operations.
Owner:IBM CORP
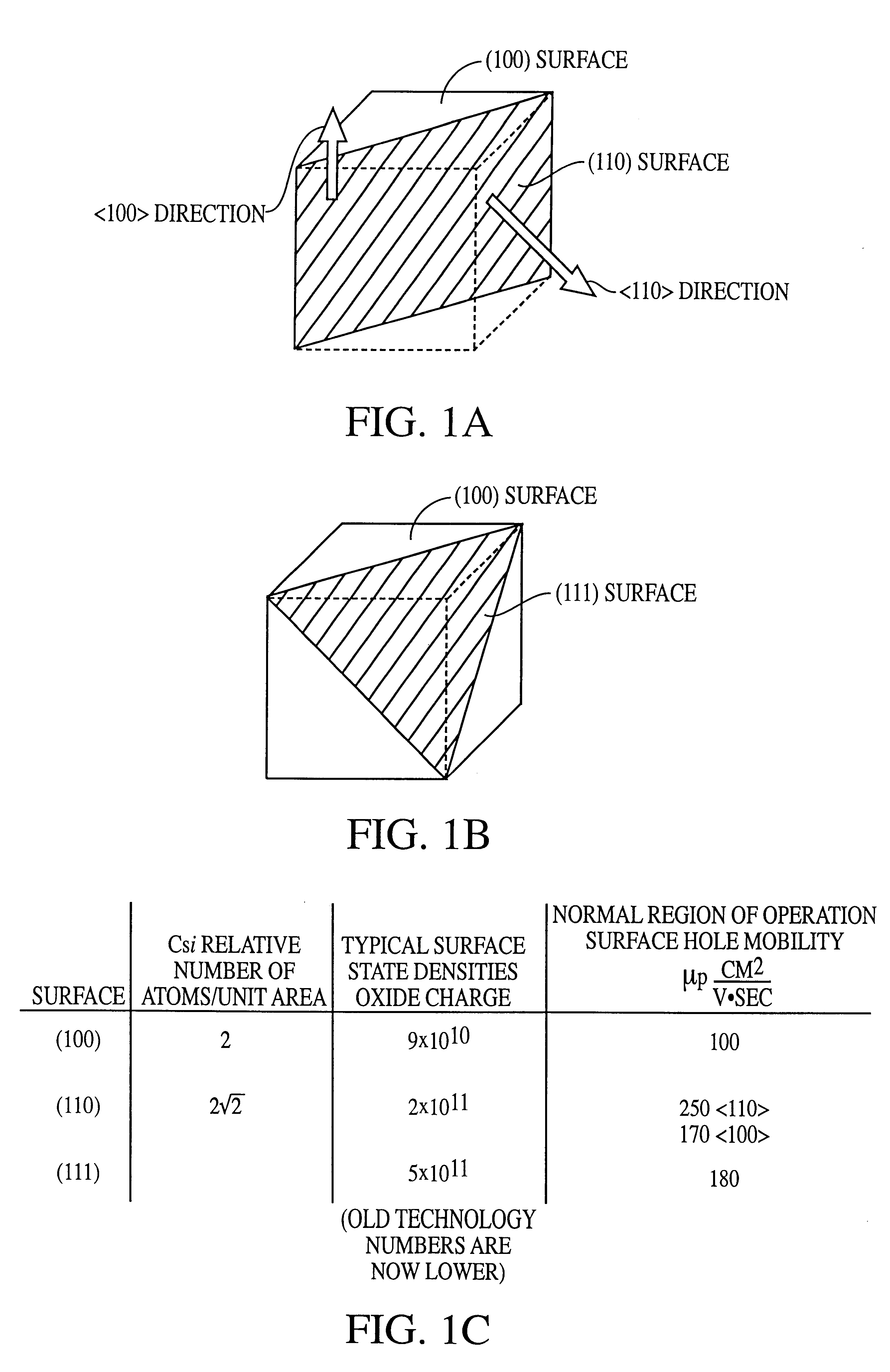
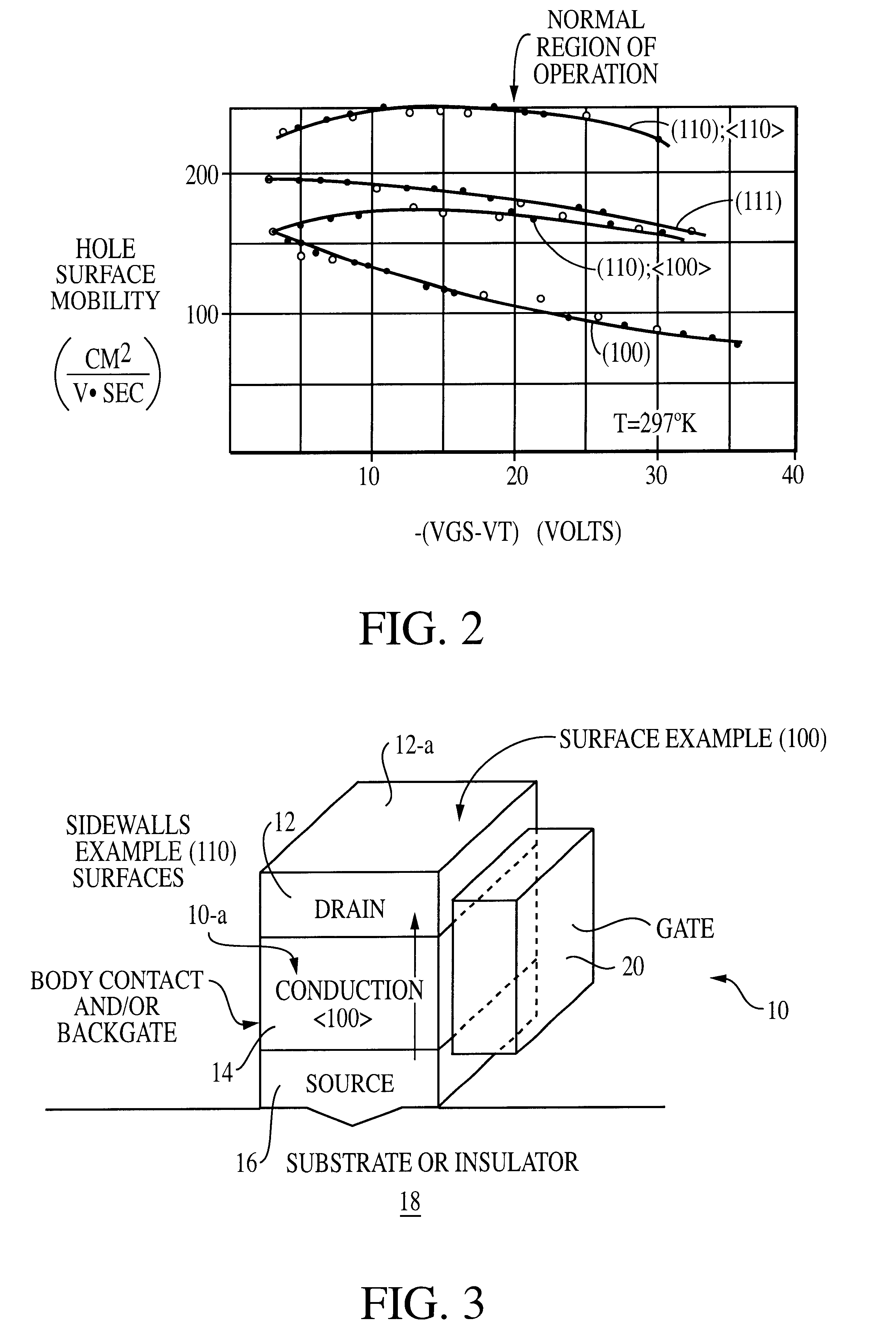
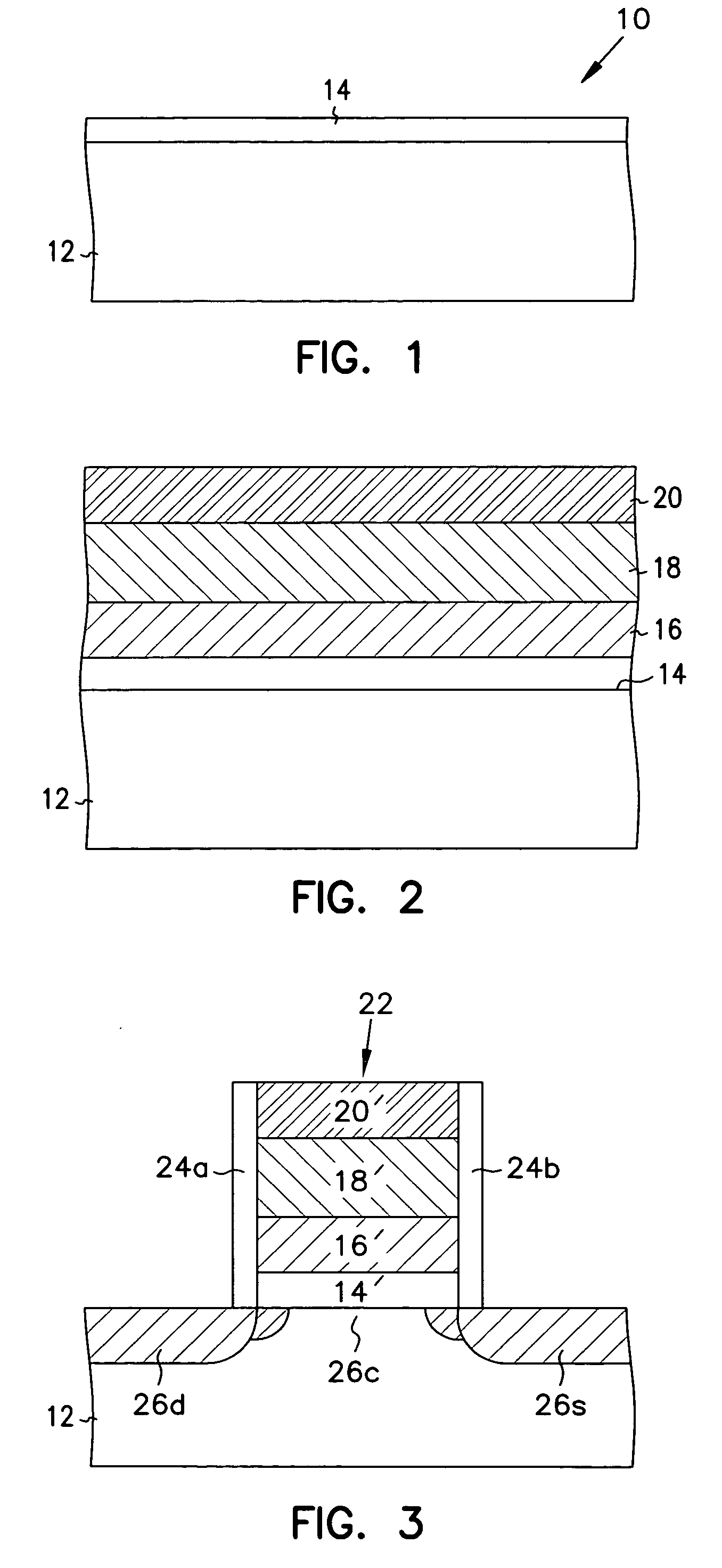
Vertical sub-micron CMOS transistors on (110), (111), (311), (511), and higher order surfaces of bulk, SOI and thin film structures and method of forming same
A method for forming NMOS and PMOS transistors that includes cutting a substrate along a higher order orientation and fabricating deep sub-micron NMOS and PMOS transistors on the vertical surfaces thereof. The complementary NMOS and PMOS transistors form a CMOS transistor pair. The transistors are preferably used in structures such as memory circuits, e.g., DRAMs, which are, in turn, used in a processor-based system. Ideally, the deep sub-micron NMOS and PMOS transistors are operated in velocity saturation for optimal switching operation.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Electronic circuit with embedded memory
InactiveUS20080048327A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory circuitsSemiconductor
Owner:BESANG
Information storage system which includes a bonded semiconductor structure
An information storage system includes a bonded semiconductor structure having a memory circuit region carried by an interconnect region. The memory circuit region includes a memory control device region having a vertically oriented memory control device. The memory circuit region includes a memory device region in communication with the memory control device region. The memory device region includes a memory device whose operation is controlled by the vertically oriented memory control device.
Owner:BESANG
Electronic circuit with embedded memory
InactiveUS7633162B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory circuitsSemiconductor
Owner:BESANG
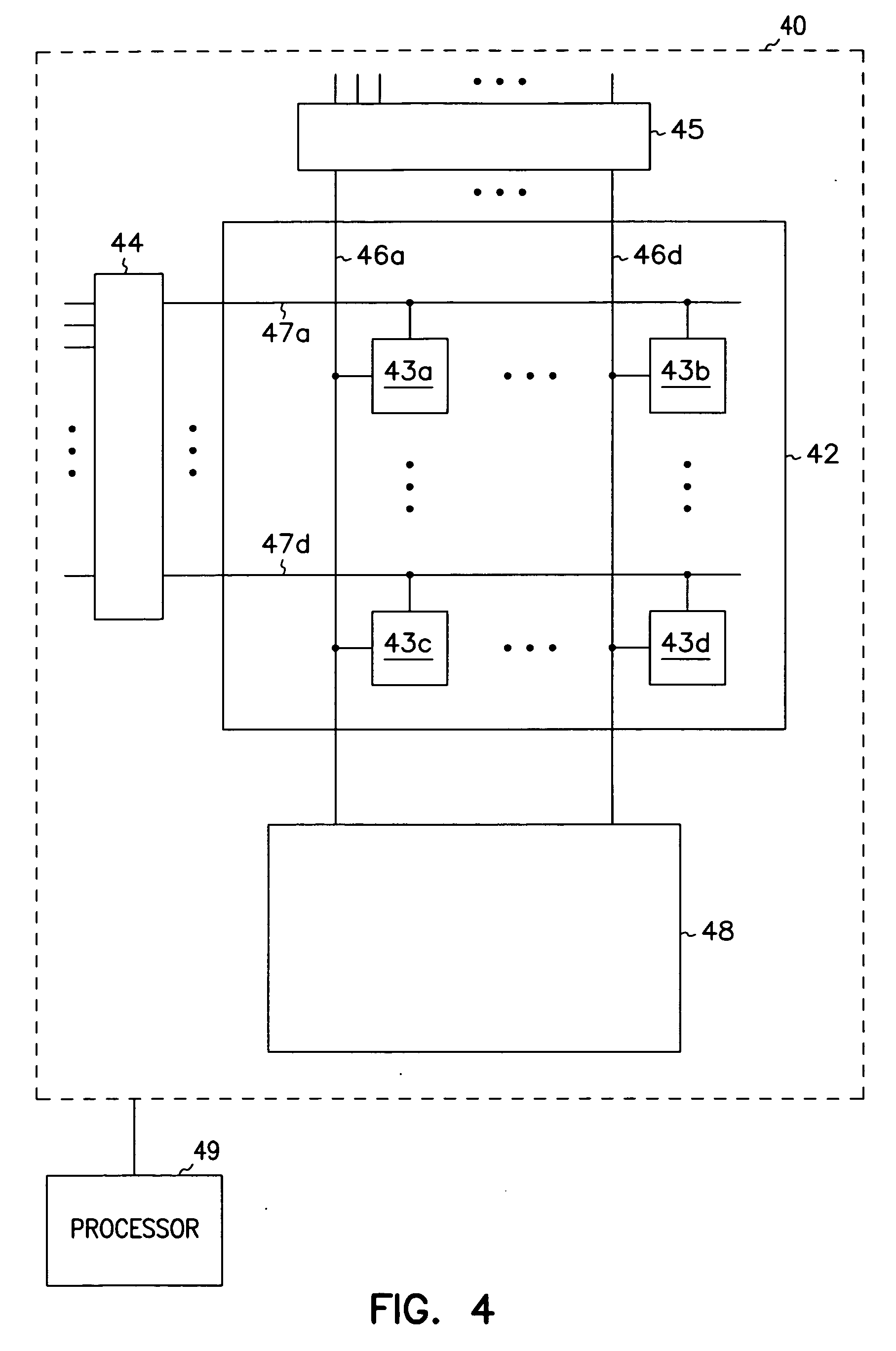
Semiconductor device and method for controlling semiconductor device
ActiveUS20090134468A1Meet high-speed operationGuaranteed uptimeTransistorSolid-state devicesInsulation layerMemory circuits
To provide a semiconductor device having a thin-film BOX-SOI structure and capable of realizing a high-speed operation of a logic circuit and a stable operation of a memory circuit. A semiconductor device according to the present invention includes a semiconductor support substrate, an insulation layer having a thickness of at mast 10 nm, and a semiconductor layer. In an upper surface of the semiconductor layer, a first field-effect transistor including a first gate electrode and constituting a logic circuit is formed. Further, in the upper surface of the semiconductor layer, a second field-effect transistor including a second gate electrode and constituting a memory circuit is formed. At least three well regions having different conductivity types are formed in the semiconductor support substrate. In the presence of the well regions, a region of the semiconductor support substrate below the first gate electrode and a region of the semiconductor support substrate below the second gate electrode are electrically separated from each other.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Electronic circuit with embedded memory
InactiveUS20100133695A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMemory circuits
Circuitry includes first and second circuits spaced apart by an interconnect region. The interconnect region includes a first interconnect, and the second circuit includes a stack of semiconductor layers. The first interconnect extends between the first and second circuits to provide communication therebetween. The second circuit operates as a memory circuit.
Owner:BESANG
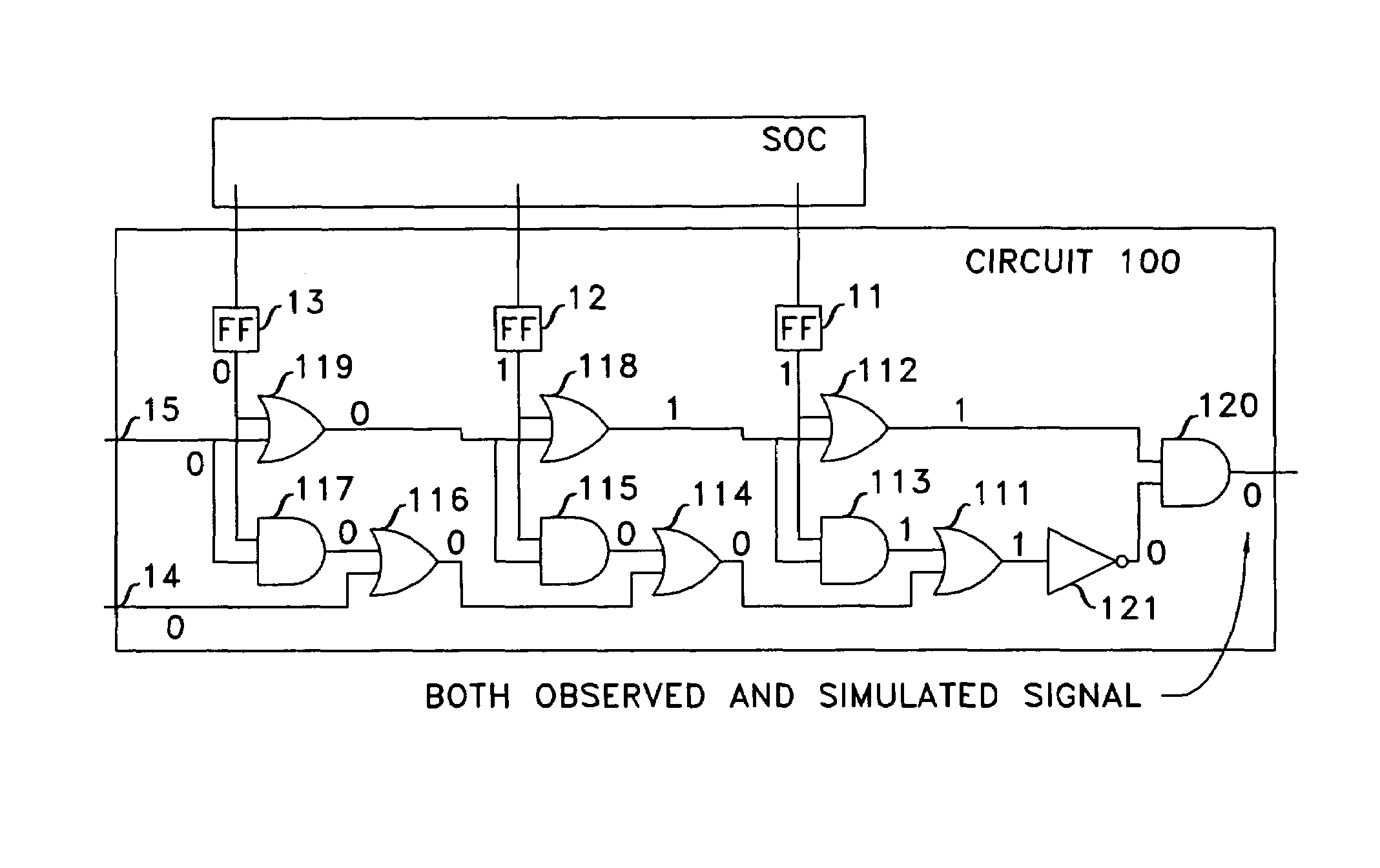
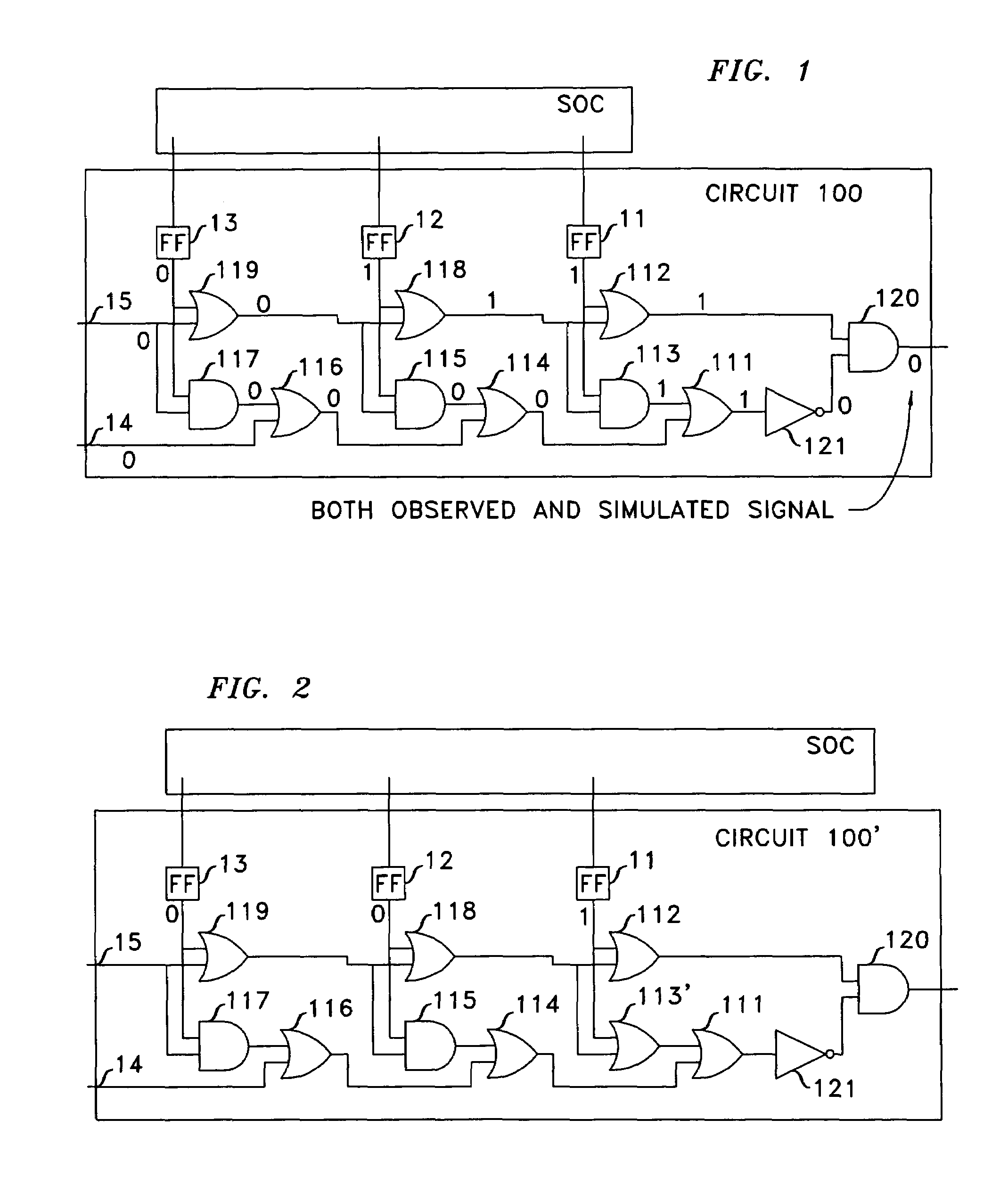
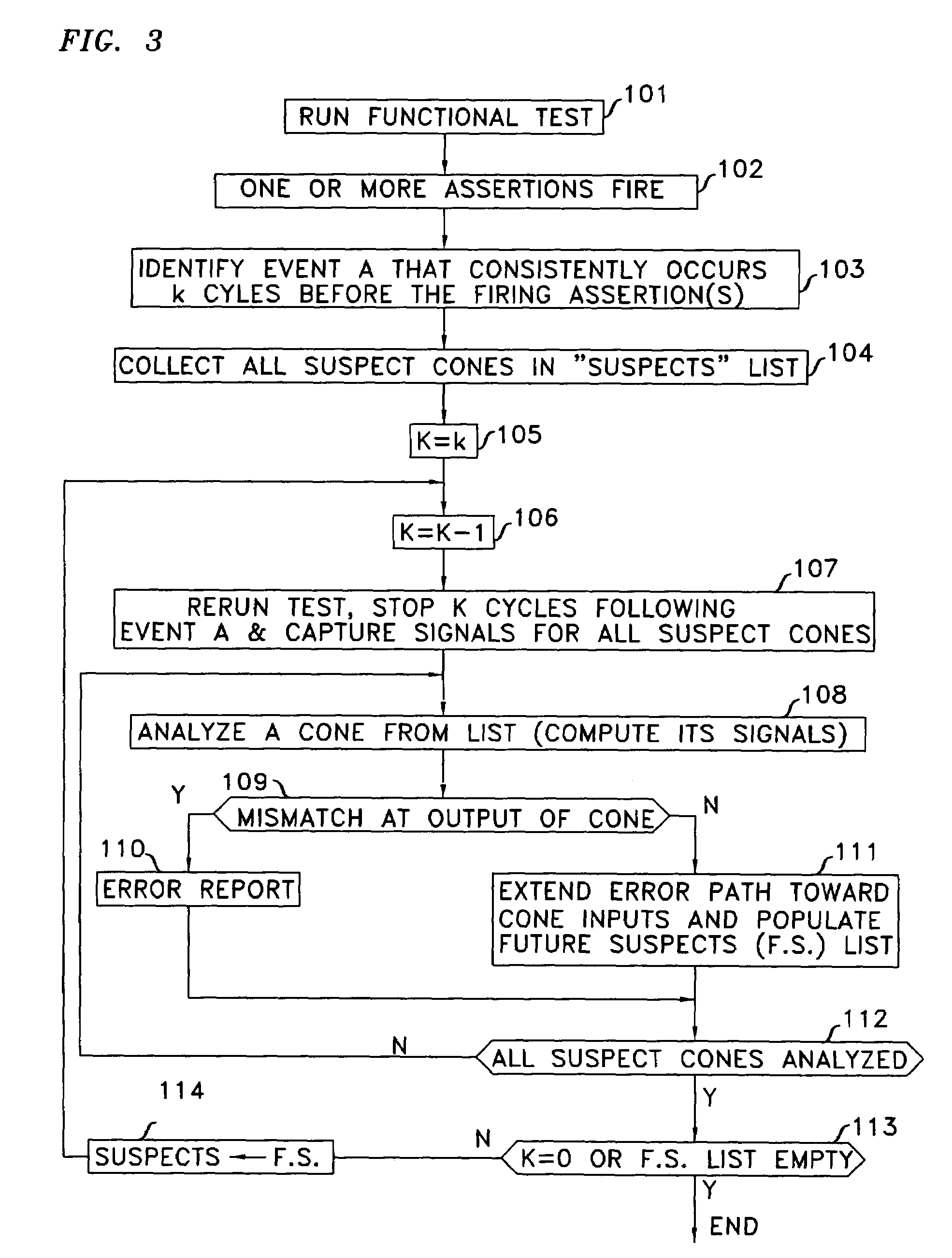
Method to locate logic errors and defects in digital circuits
When, in the course of an integrated circuit's functional test an assertion fires at clock k, the operational clock is stopped, the sequence is reapplied to capture inputs to the assertion circuit that fired, signals within the assertion circuit are computed, and the error is backtraced. Once one or more inputs of the assertion circuit are identified as potentially the source of the error, the process of backtracing is performed for each such input. When the input that is potentially the source of the error emanates from a memory circuit, the fanin cone of the memory circuit is identified and the process of backtracing through the last-identified fanin cone is undertaken for clock k−1. This is repeated iteratively until either a module of the integrated circuit is found to be the source of the error, or the error is extended to inputs of the SoC.
Owner:DAFCA
Electronic circuit with embedded memory
InactiveUS20050218521A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMemory circuits
Circuitry includes first and second circuits spaced apart by an interconnect region. The interconnect region includes a first interconnect and the second circuit includes a stack of semiconductor layers. The first interconnect extends between the first and second circuits to provide communication therebetween. The second circuit operates as a memory circuit.
Owner:BESANG
Self-powered current monitor
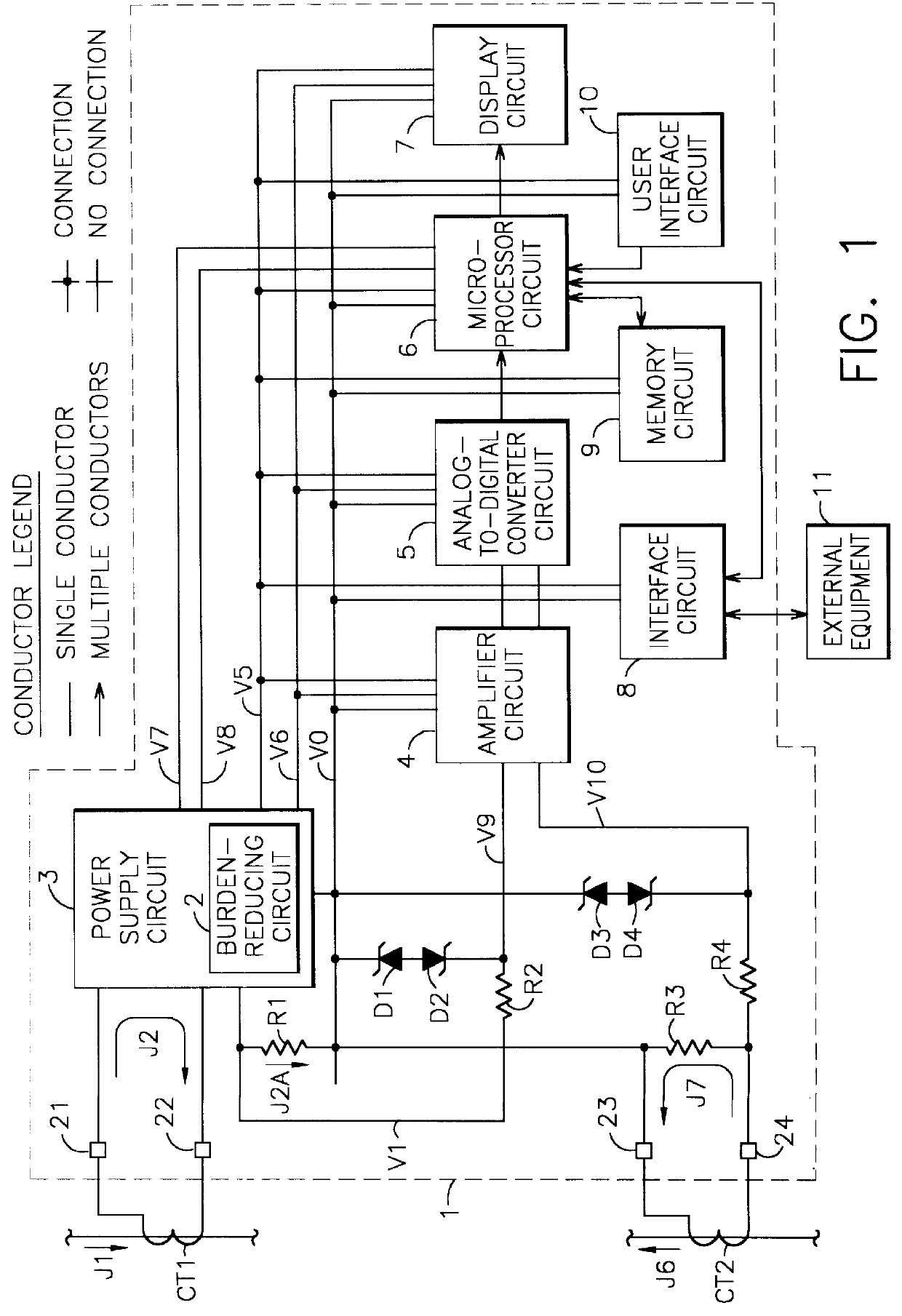
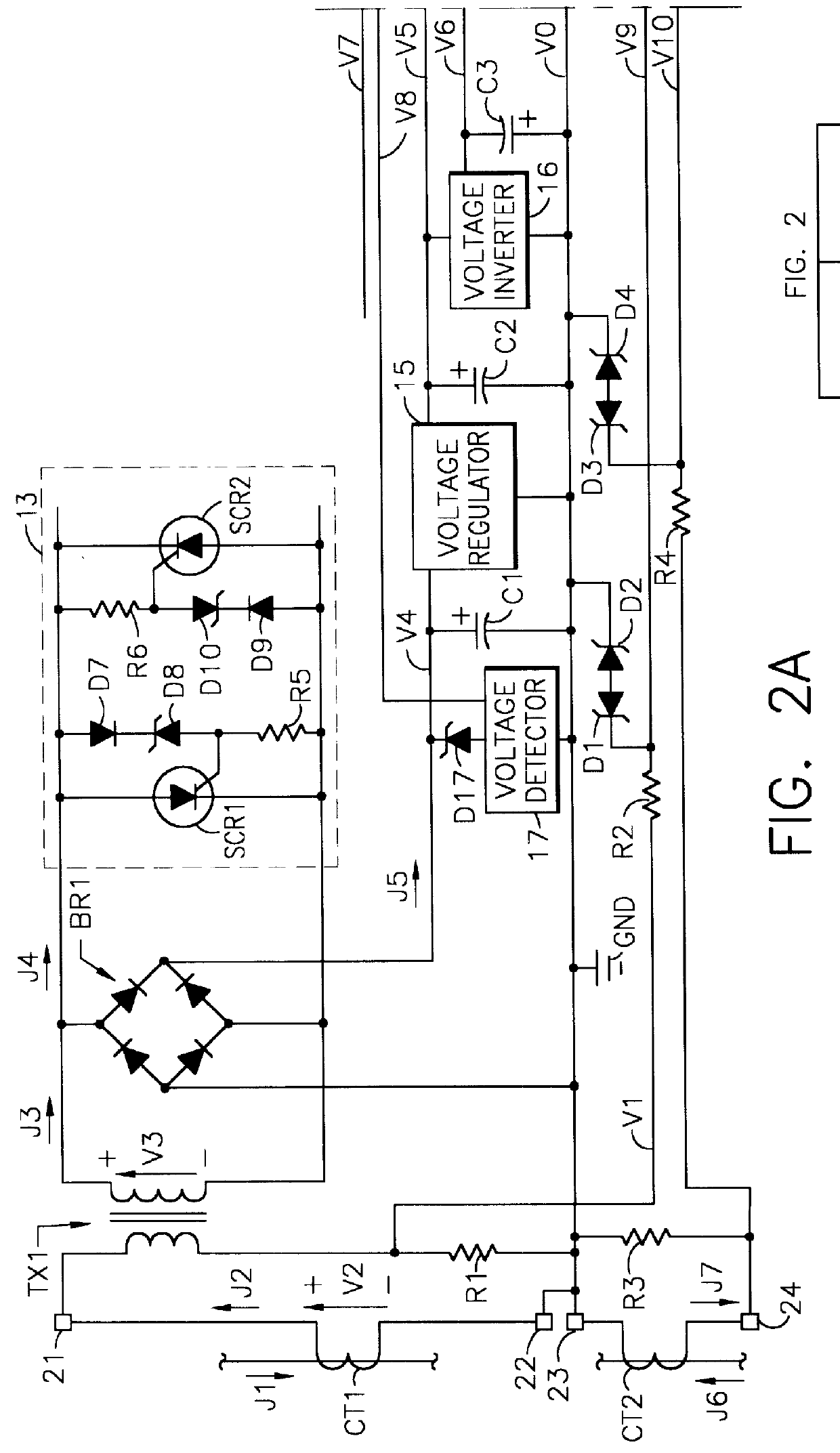
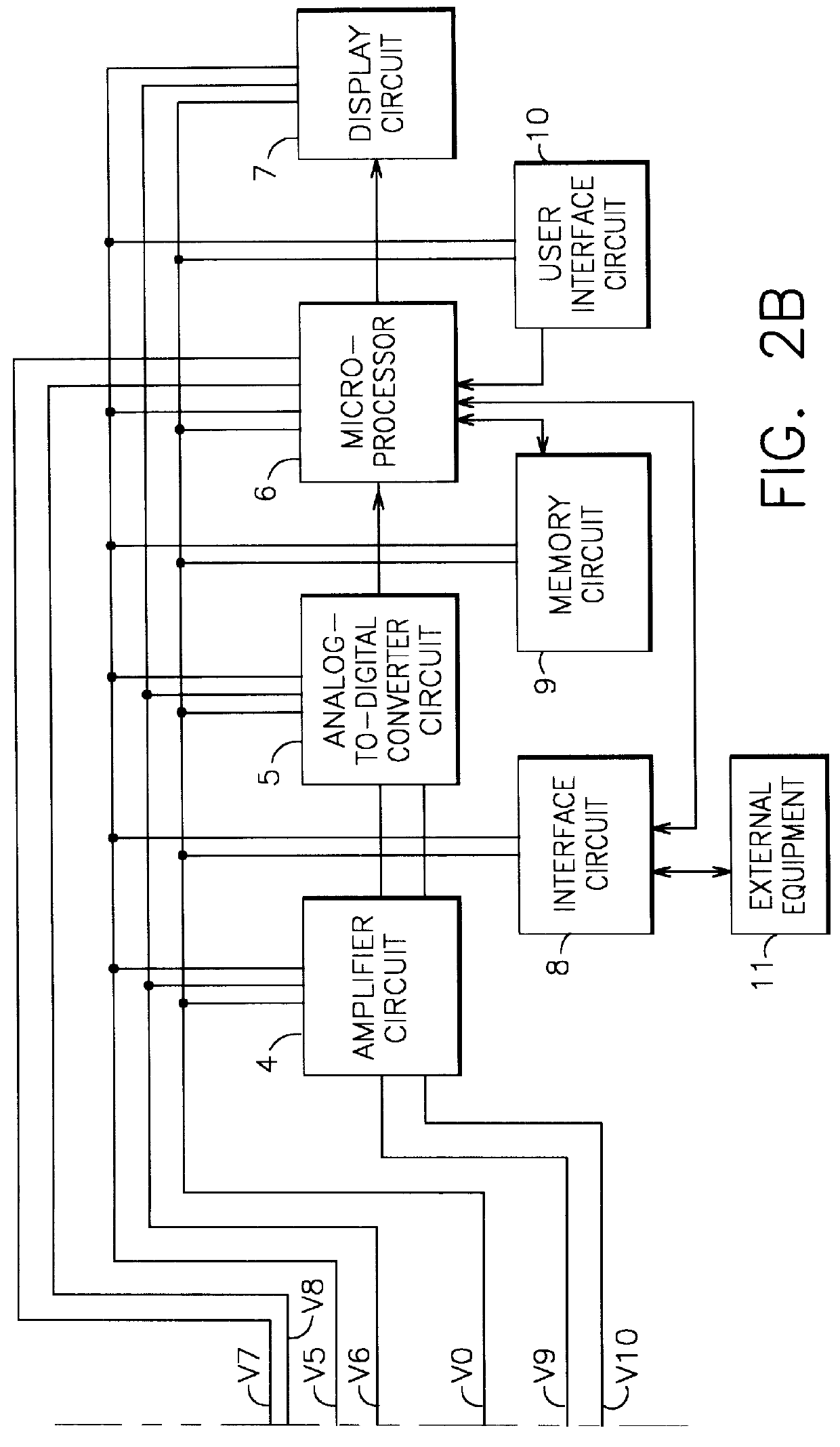
A self-powered current monitor for monitoring current in electric power systems. Various data relating to input currents may be displayed, such as current magnitude, current demand, and harmonics levels. Operating power is derived from one or more of the input currents. The power supply configuration may include a burden-reducing means to reduce the burden on input current sources during sampling of the input currents. The self-powered current monitor (1) includes a power supply section (3), input resistors (R1 and R3), an analog-to-digital converter circuit (5), a microprocessor circuit (6), a memory circuit (9), and a display circuit (7). Optional features include a burden-reducing circuit (2), input circuit protective elements (D1, D2, D3, D4, R2, and R4), an amplifier circuit (4), a user interface circuit (10), and an interface circuit (8) for communication to other equipment.
Owner:EDEL THOMAS G
Fabrication of molecular electronic circuit by imprinting
A method of fabricating a molecular electronic device or crossbar memory device is provided. The device comprises at least one pair of crossed wires and a molecular switch film therebetween. The method comprises: (a) forming at least one bottom electrode on a substrate by first forming a first layer on the substrate and patterning the first layer to form the bottom electrode by an imprinting technique; (b) forming the molecular switch film on top of the bottom electrode; (c) optionally forming a protective layer on top of the molecular switch film to avoid damage thereto during further processing; (d) coating a polymer layer on top of the protective layer and patterned the polymer layer by the imprinting method to form openings that expose portions of the protective layer; and (e) forming at least one top electrode on the protective layer through the openings in the polymer layer by first forming a second layer on the polymer layer and patterning the second layer. The imprinting method can be used to fabricate nanoscale patterns over a large area at high speeds acceptable in industrial standards. Consequently, it can be used to fabricate nanoscale molecular devices, e.g., crossbar memory circuits.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Methods and apparatus for a portable toy video/audio visual program player device - "silicon movies" played on portable computing devices such as pda (personal digital assistants) and other "palm" type, hand-held devices
InactiveUS20060148569A1Reduce in quantityLow costDigital video signal modificationVideo gamesData compressionDigital data
A portable audio / visual program player comprising a video display, electrical-audio transducer, a central processing unit and associated logic and memory circuits. The portable audio / visual player is able to play pre-recorded programs from a memory device, which includes compress digital audio and video program information and a decoder program. The digital compression method comprises a series of compression methods to greatly reduce the amount of digital data. The data compression method is particularly suitable for motion video comprising cartoons and similar images, but is also suitable for other applications.
Owner:BECK STEPHEN C
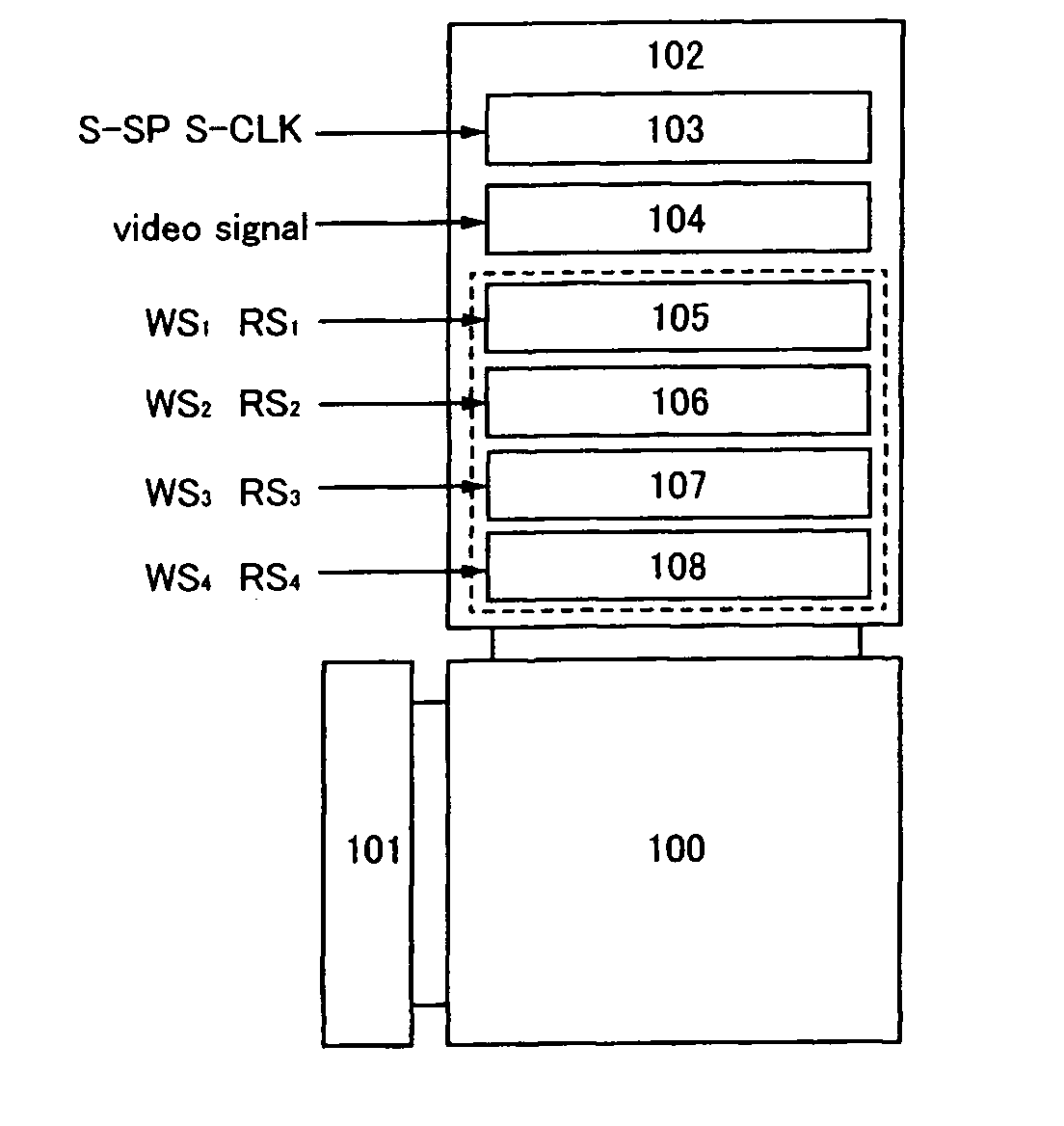
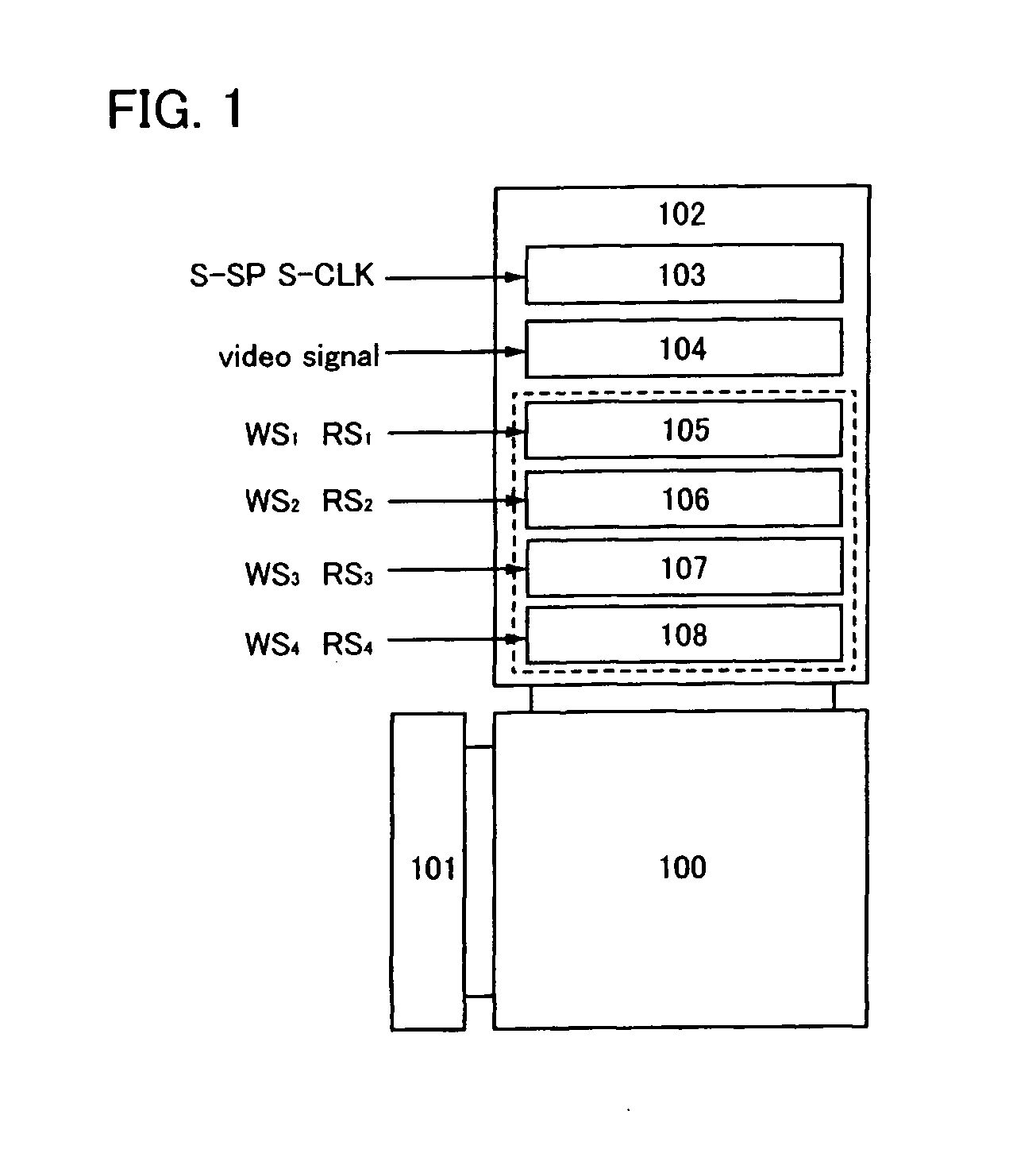
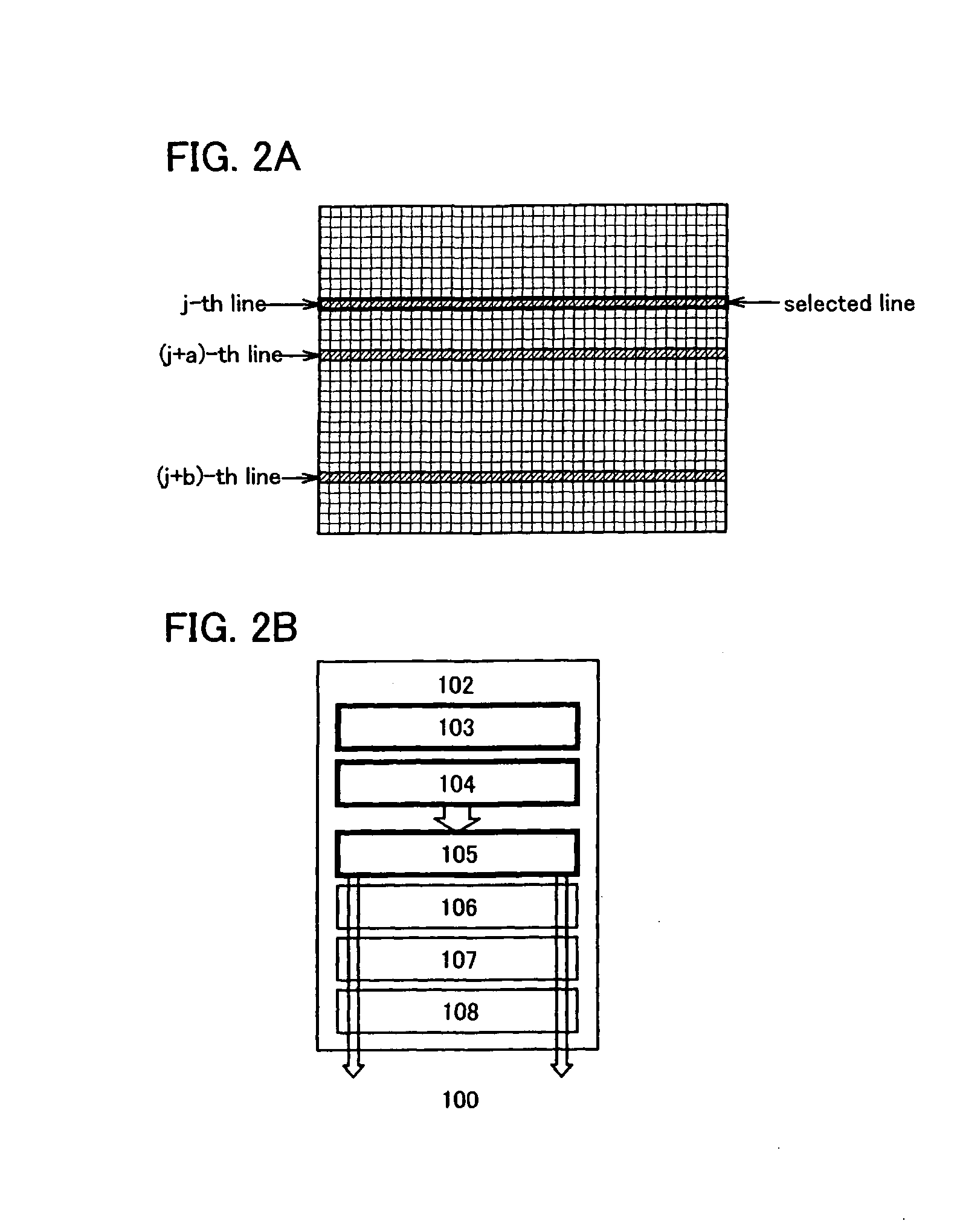
Display device
InactiveUS20080170028A1Suppress power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDriver circuitActive matrix
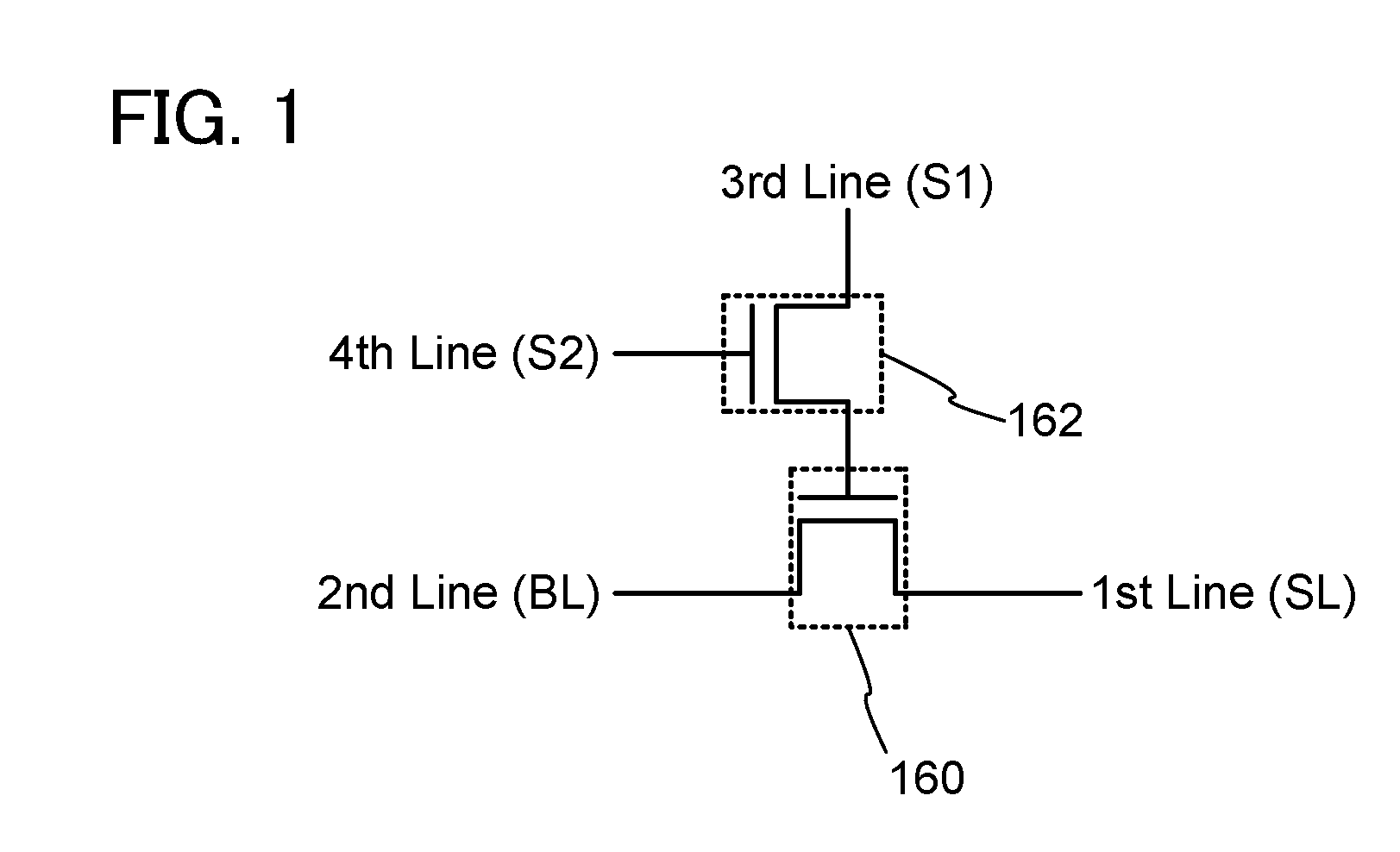
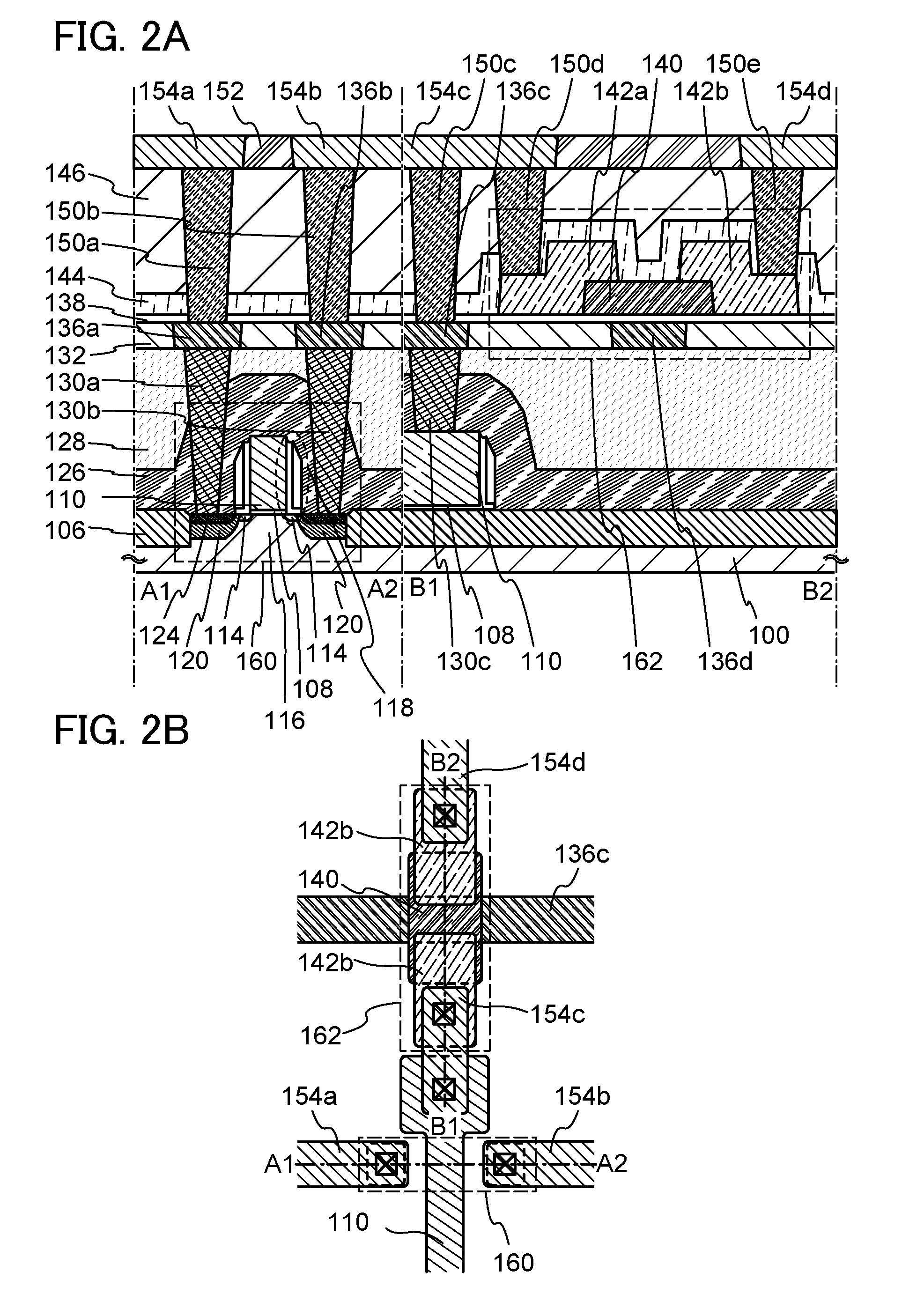
To provide an active matrix display device in which power consumption of a signal line driver circuit can be suppressed, so that power consumption of the entire memory can be suppressed. A plurality of memory circuits which can write data of a video signal input to a pixel in one line period and can hold the data are provided in a signal line driver circuit of a display device. Then, the data held in each memory circuit is input to a pixel of a corresponding line as a video signal. By providing two or more memory circuits in a driver circuit, pieces of data of video signals corresponding to two or more line periods can be concurrently held in the memory circuits.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
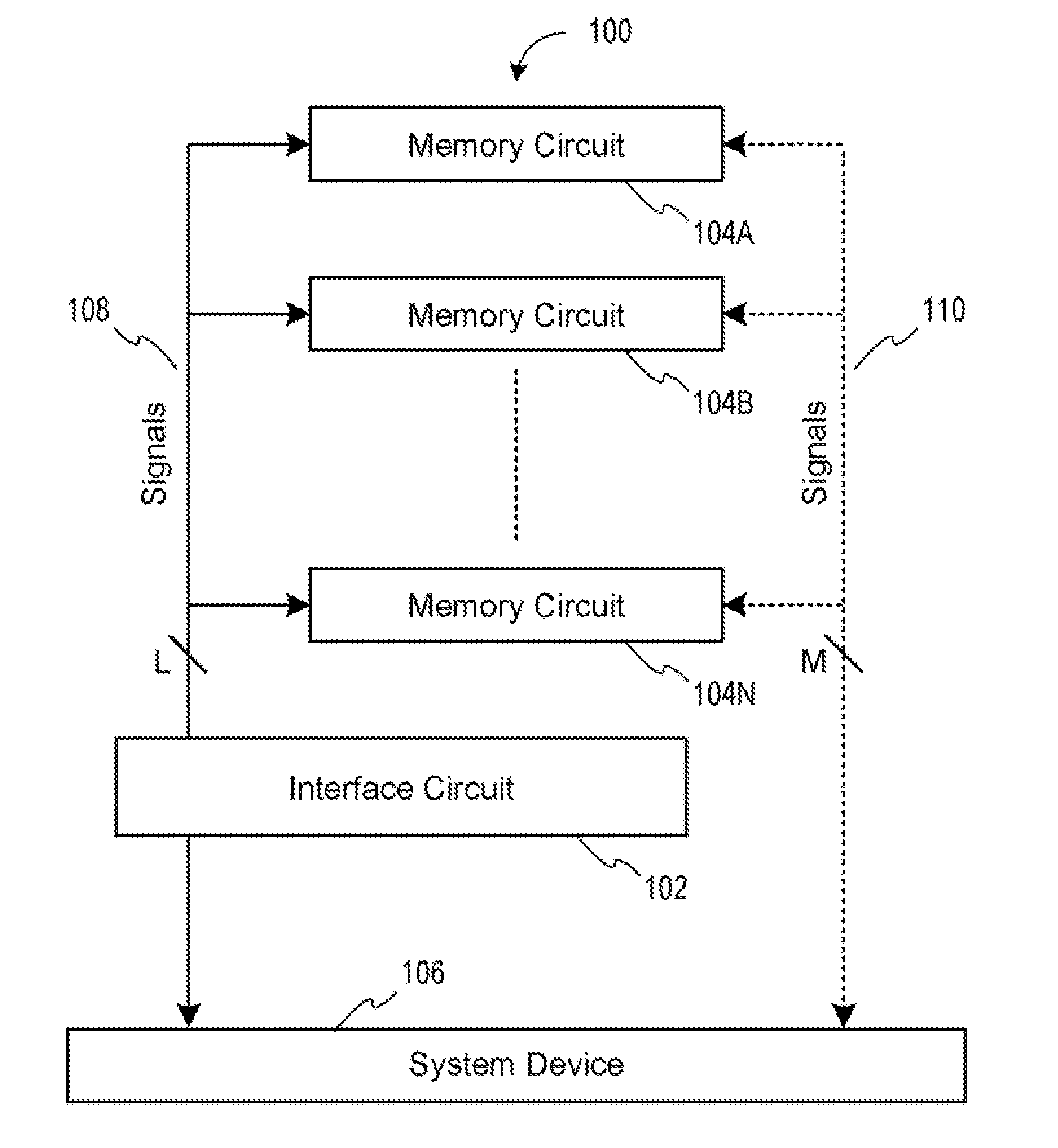
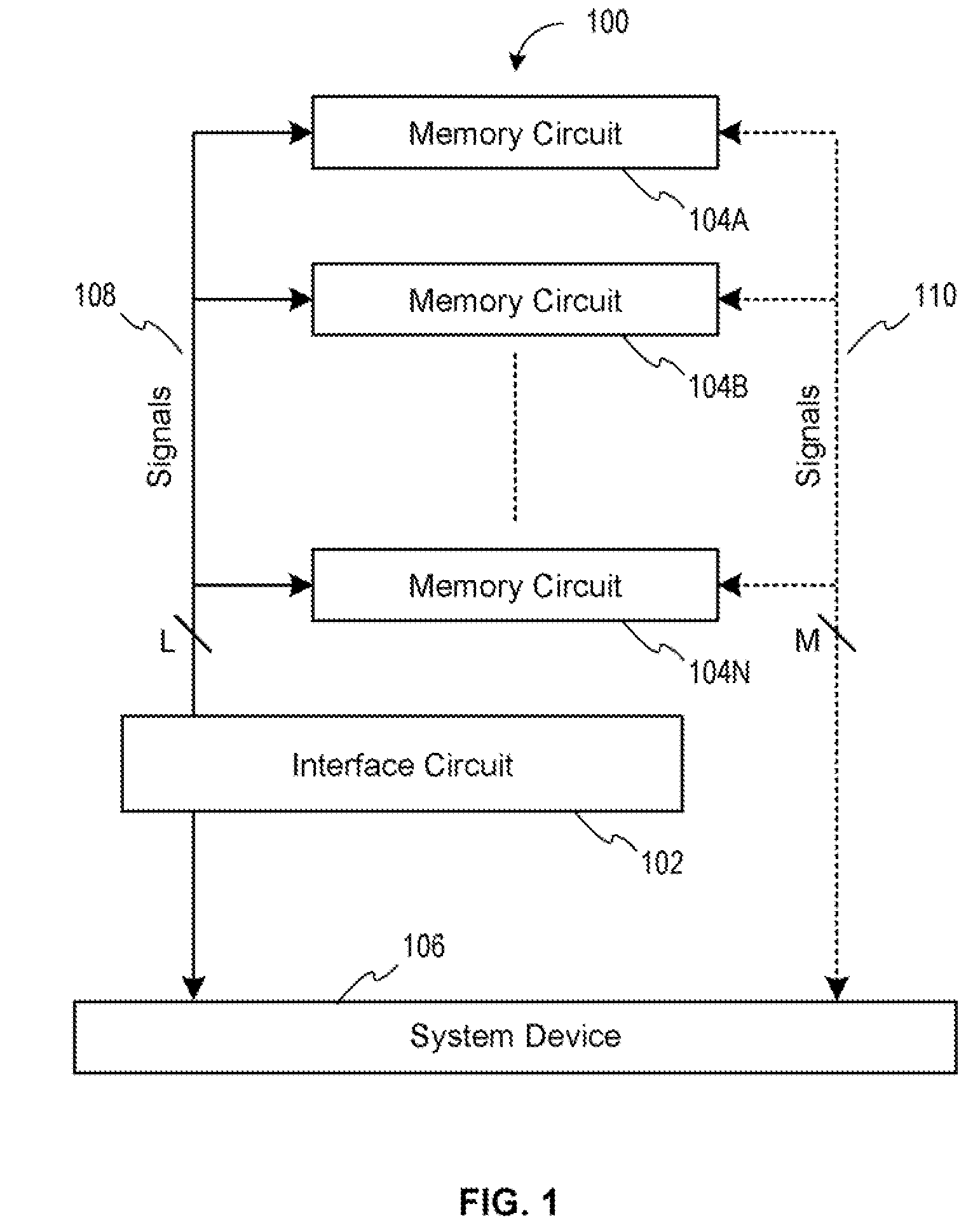
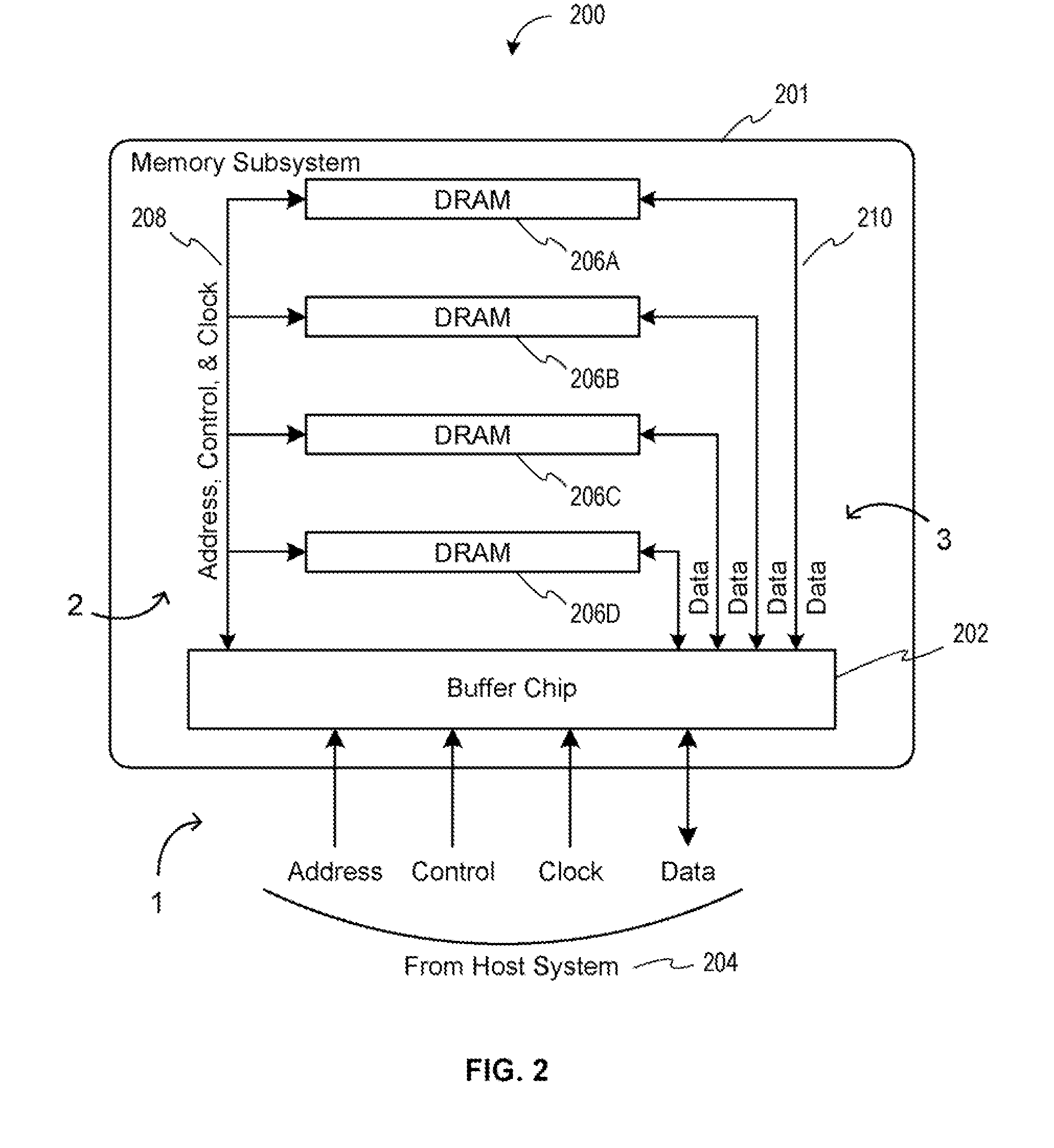
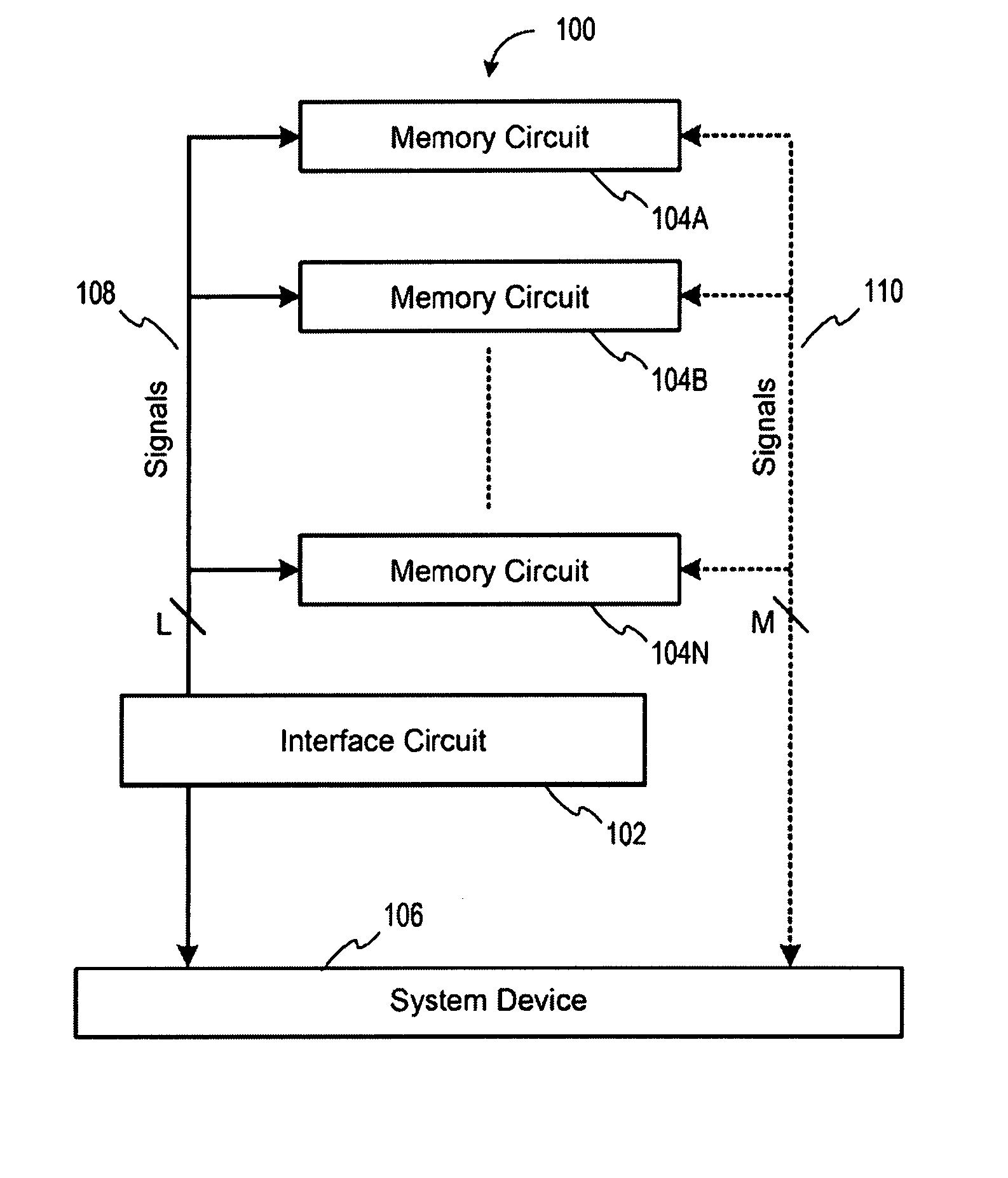
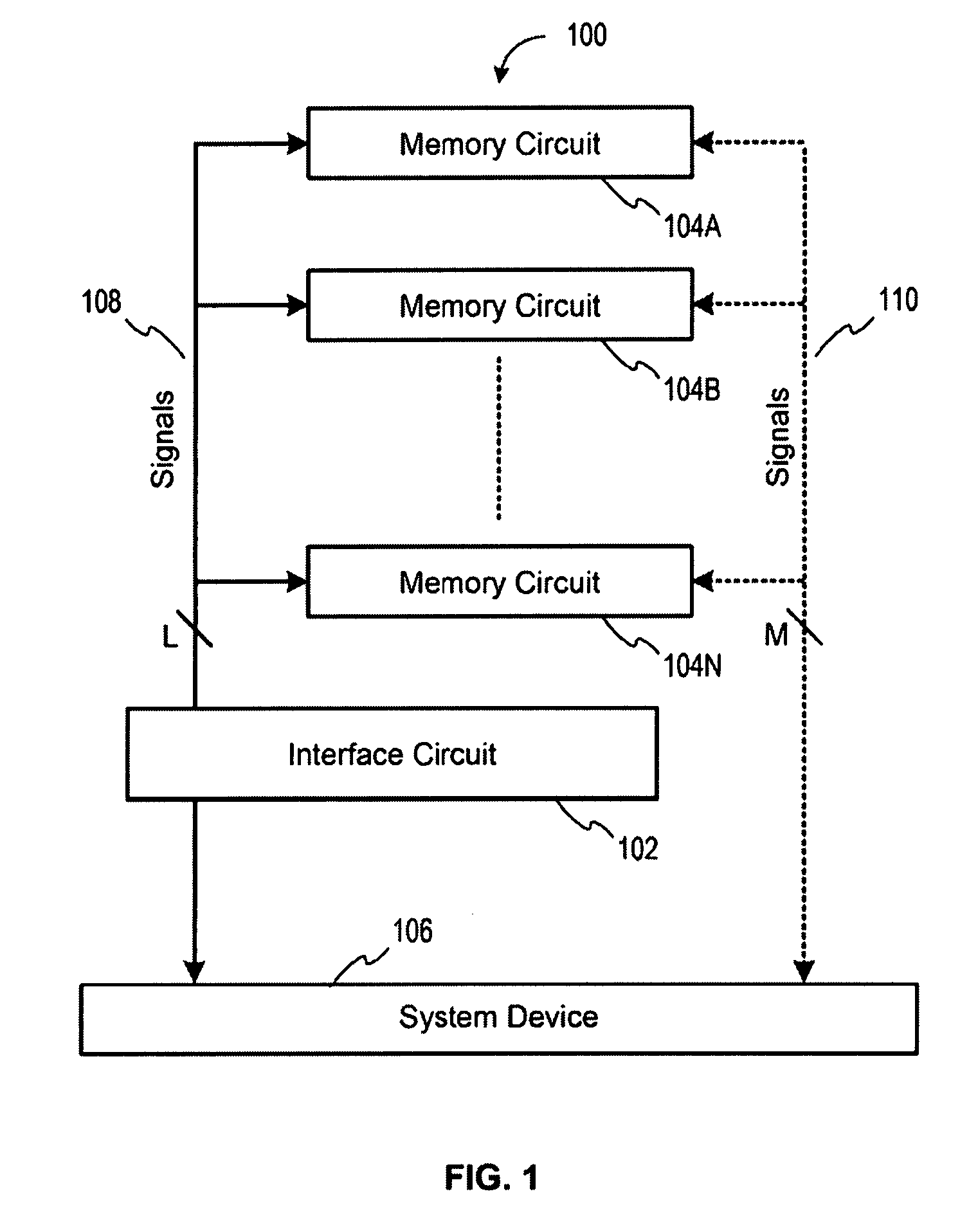
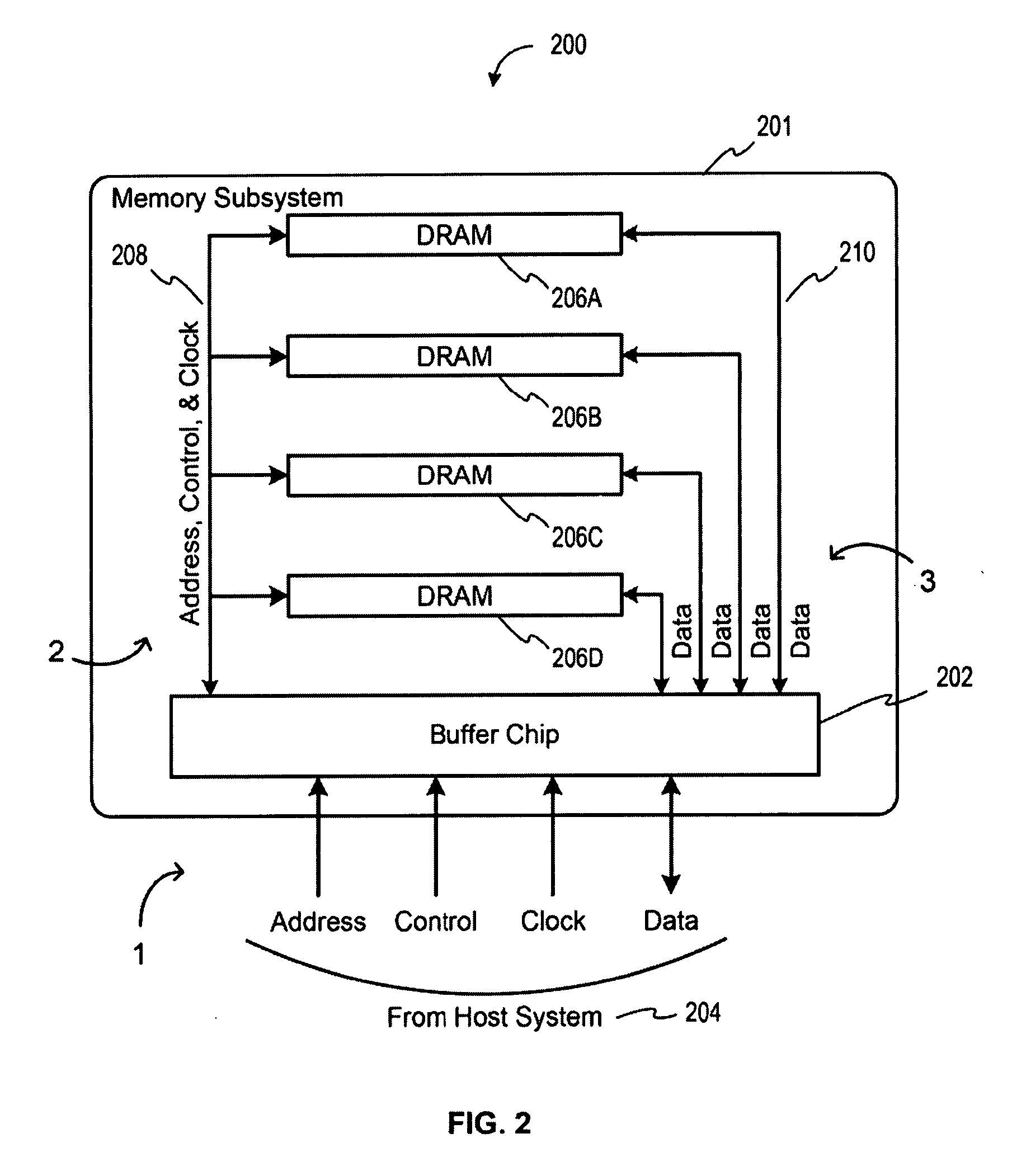
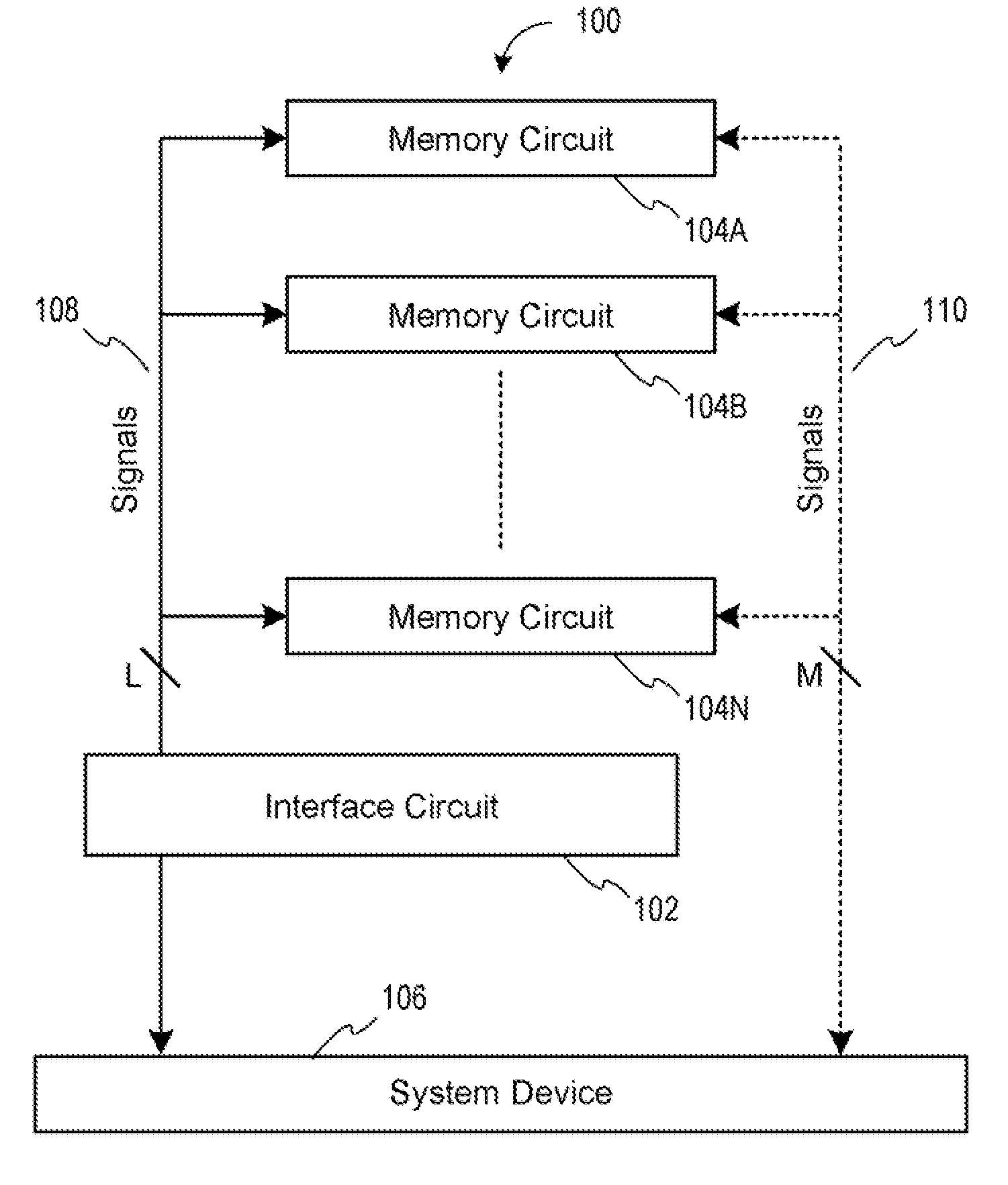
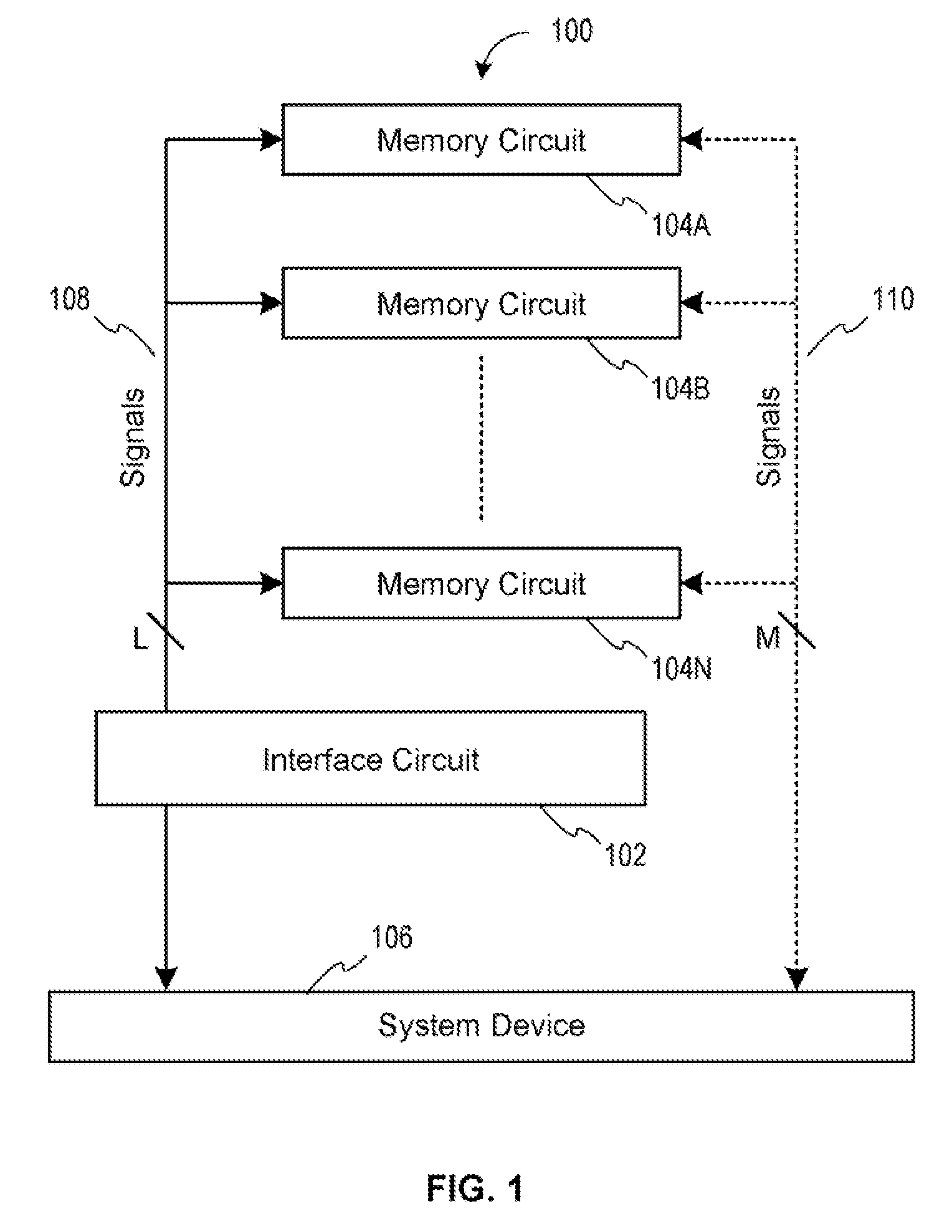
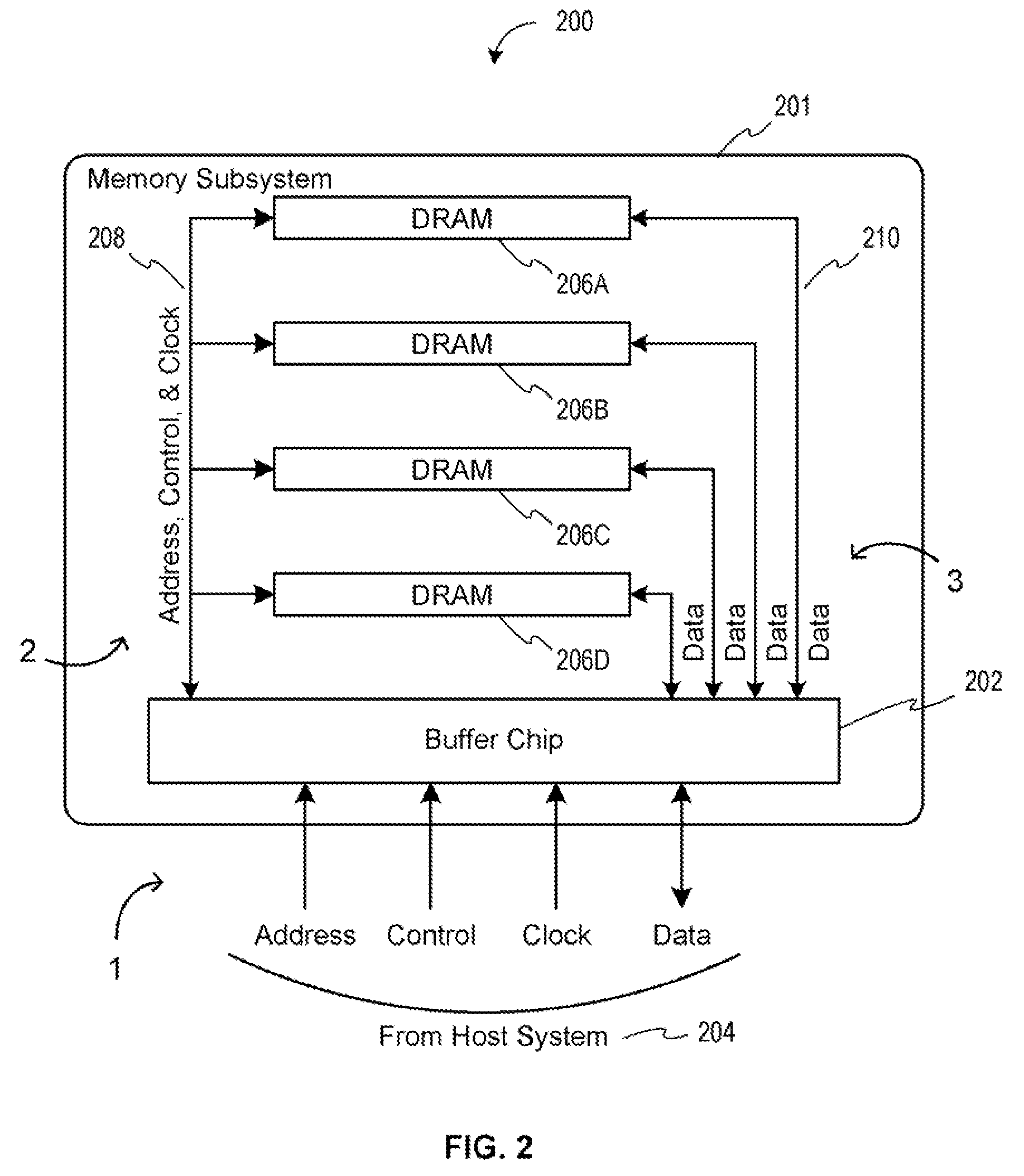
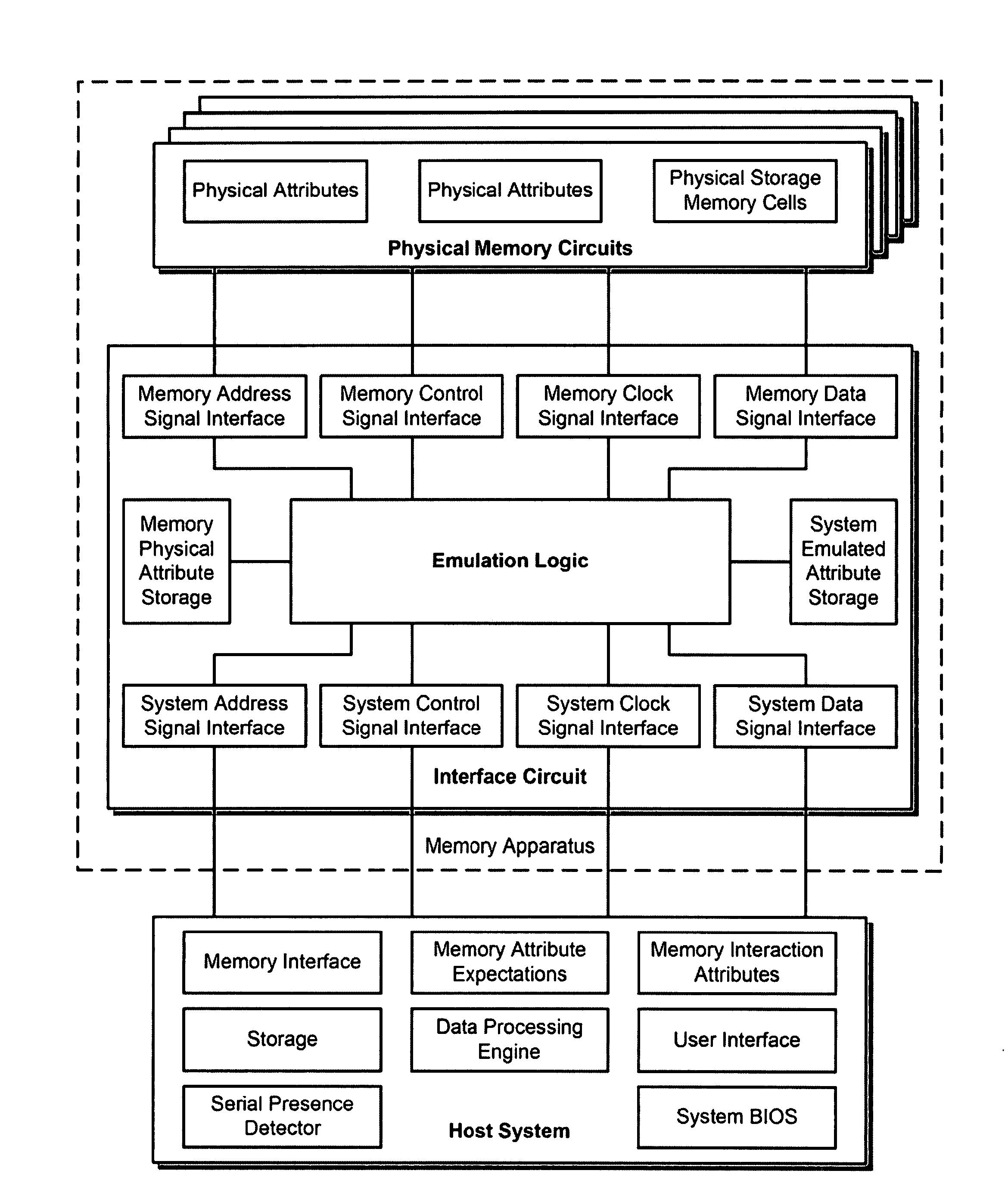
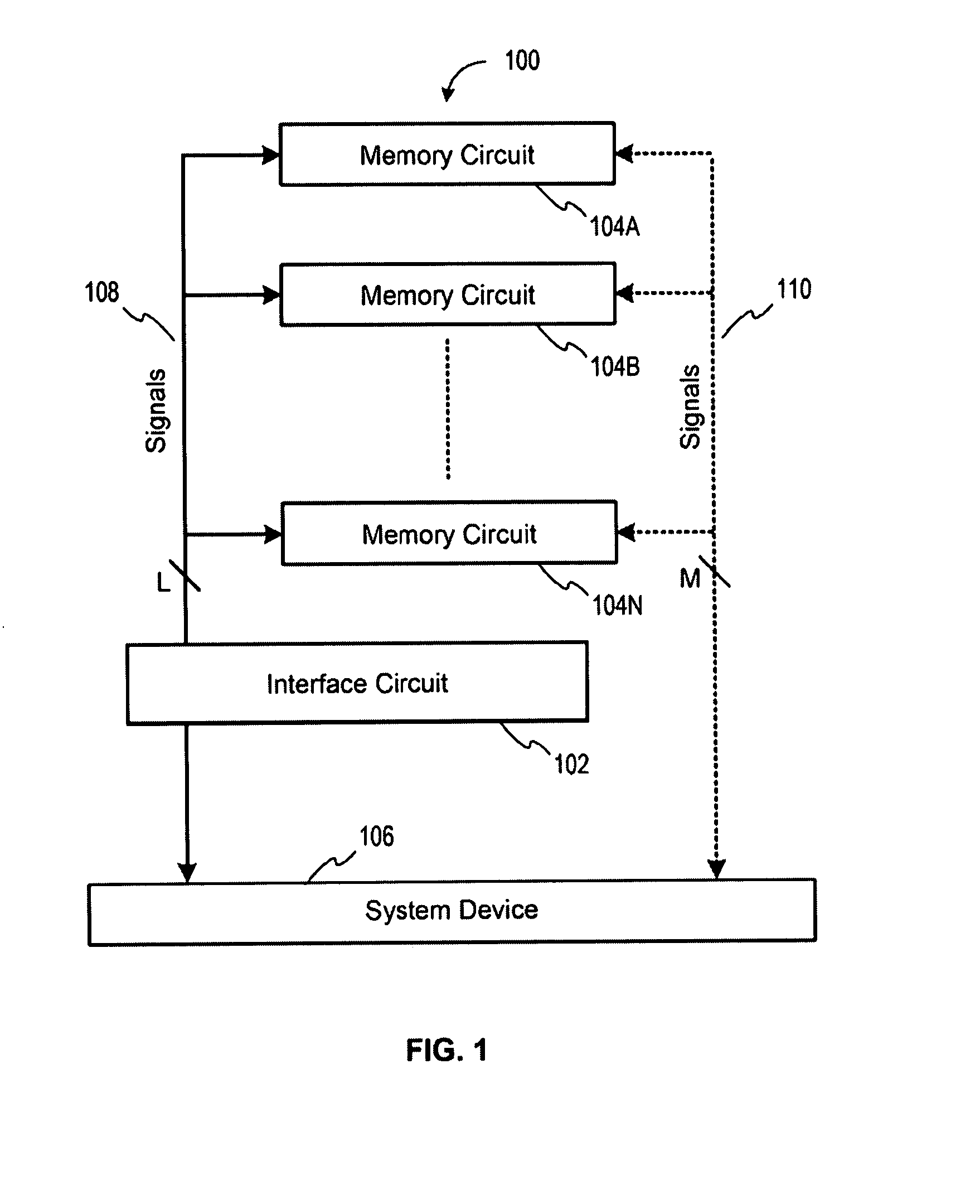
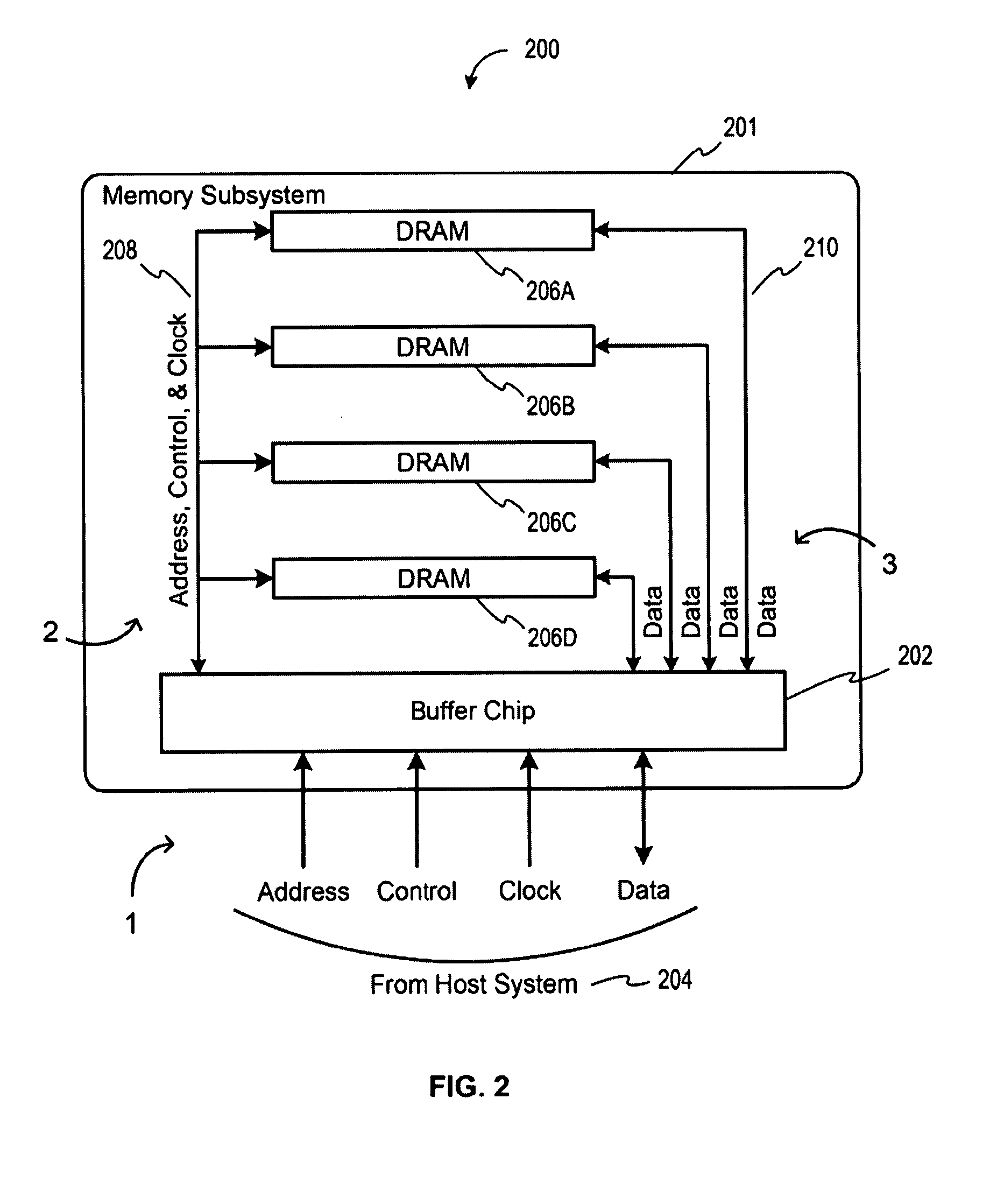
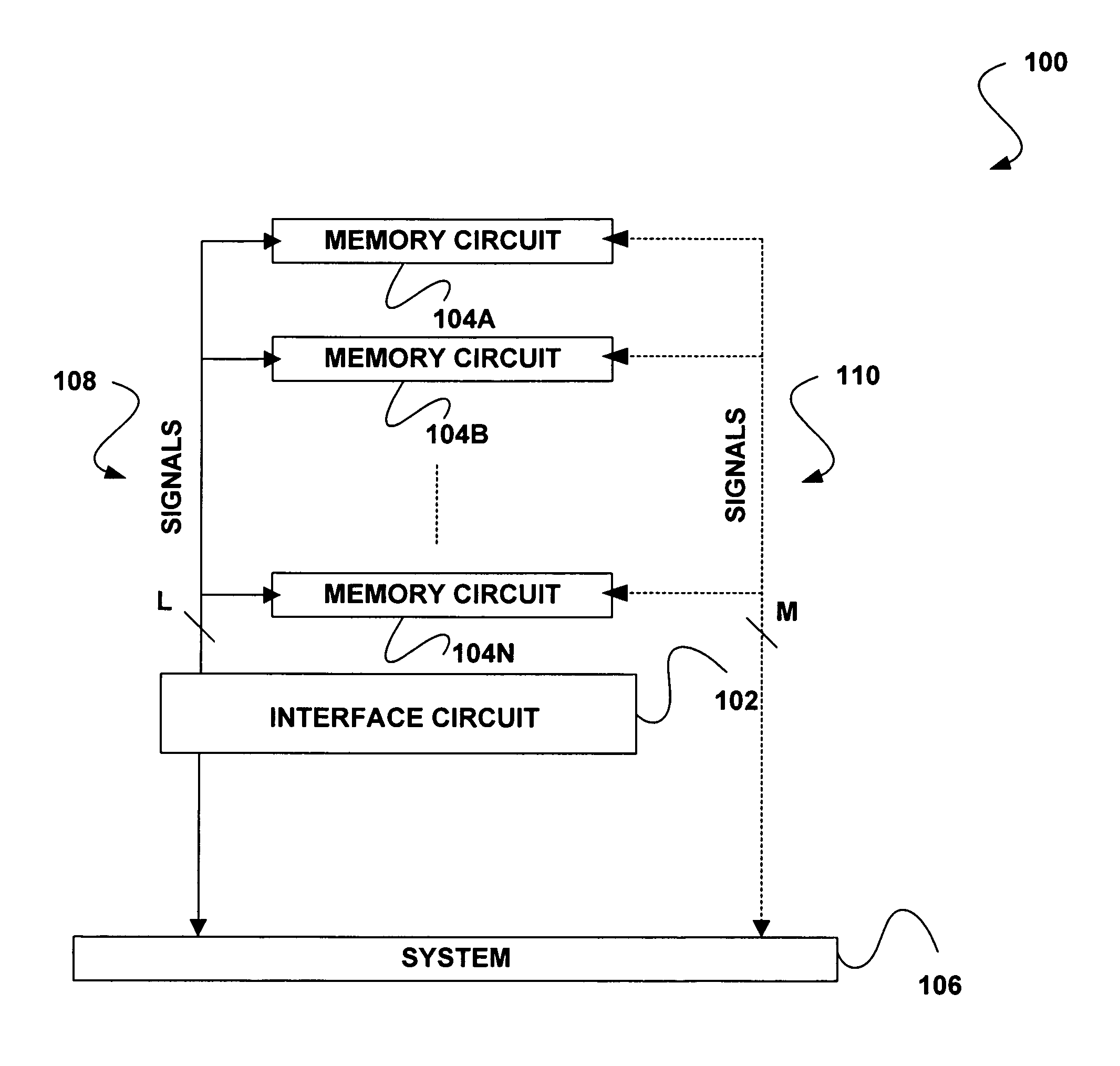
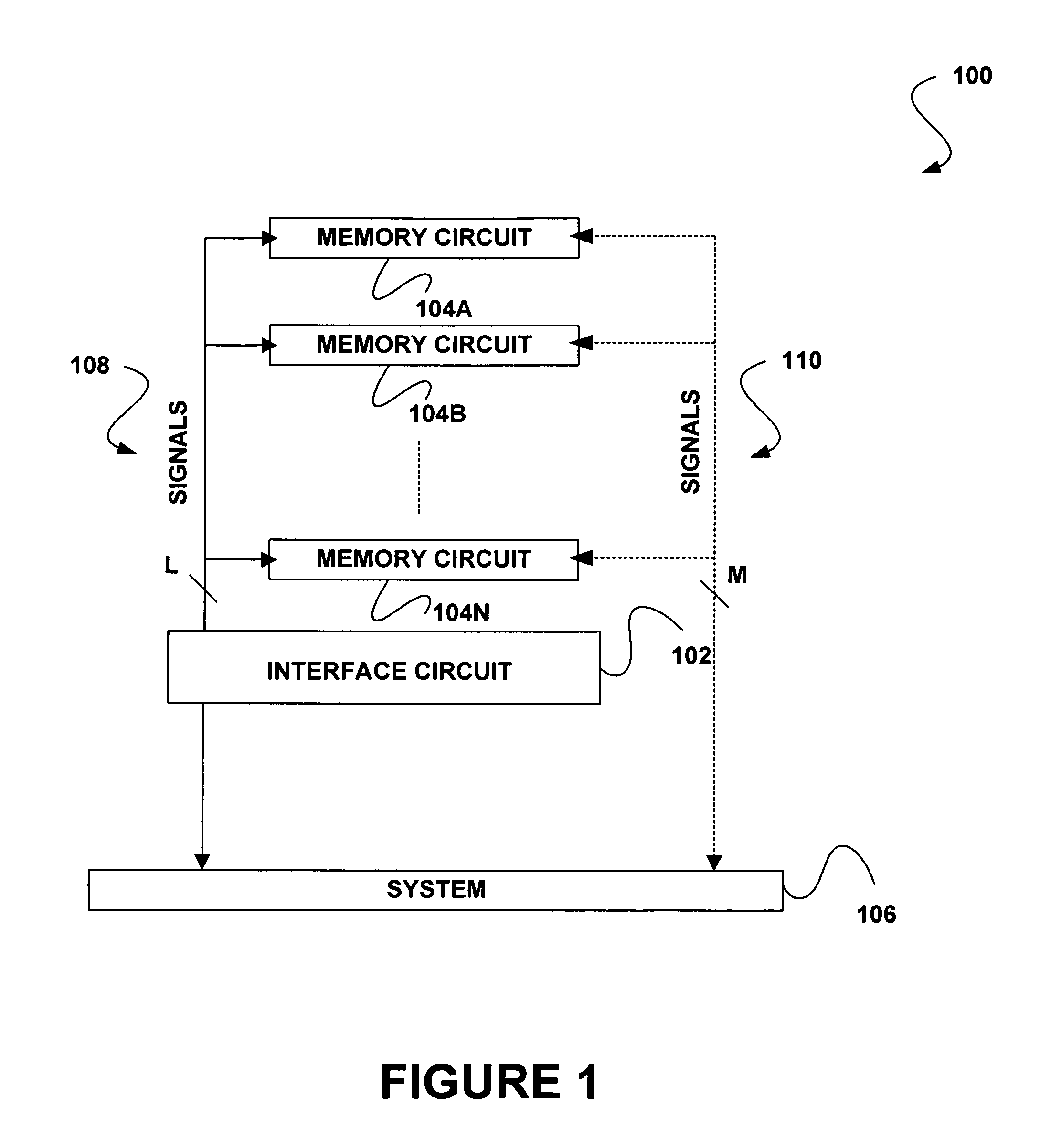
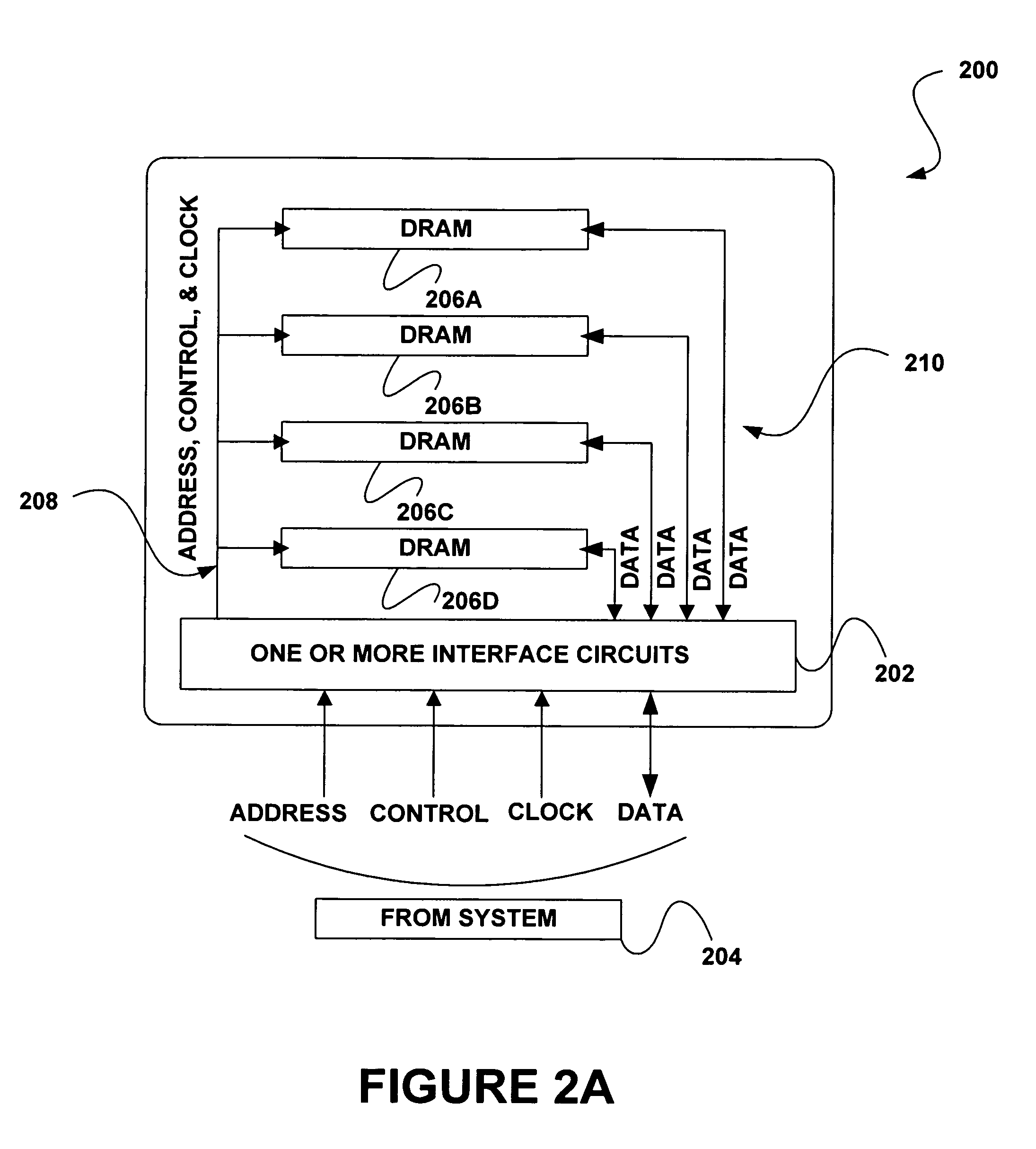
Memory device with emulated characteristics
A memory subsystem is provided including an interface circuit adapted for communication with a system and a majority of address or control signals of a first number of memory circuits. The interface circuit includes emulation logic for emulating at least one memory circuit of a second number.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Memory device with emulated characteristics
A memory subsystem is provided including an interface circuit adapted for communication with a system and a majority of address or control signals of a first number of memory circuits. The interface circuit includes emulation logic for emulating at least one memory circuit of a second number.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
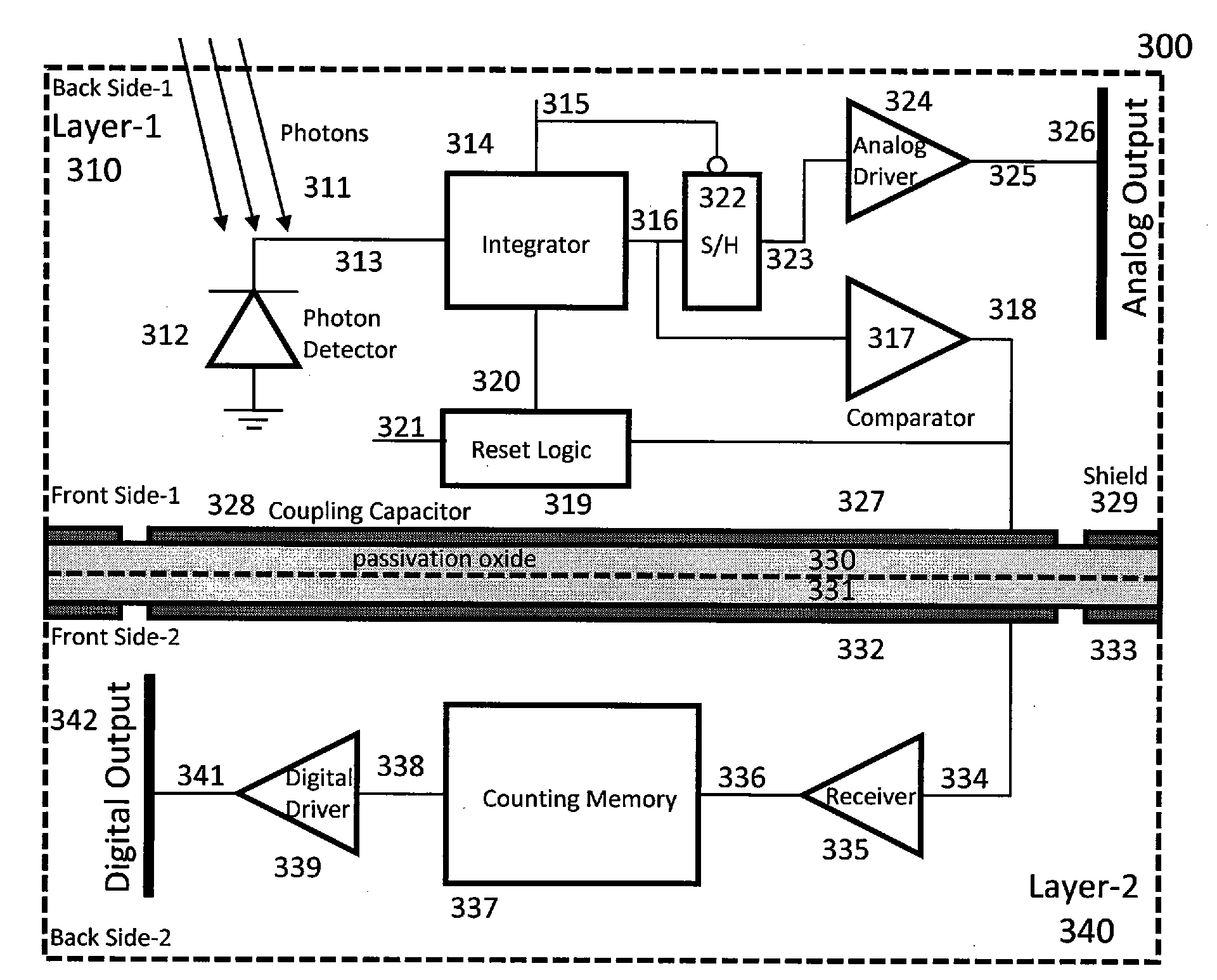
Method and apparatus for backside illuminated image sensors using capacitively coupled readout integrated circuits
InactiveUS20100140732A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove scanning rateTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceIntegrator
The images sensor includes a readout circuit capacitatively coupled to a memory circuit. The readout circuit includes: (i) a photon detector to receive a plurality of photons and to provide a charge signal corresponding to the received photons, (ii) a resettable integrator that is reset multiple times over a single exposure time and provides an analog representation of the incident photons during the last integration cycle, and (iii) a comparator that monitors the integrator output and generates a reset pulse when the integrator reaches a built-in threshold value. The memory circuit includes: (i) a receiver circuit that detects the output of the digital driver in the front-end readout circuit via capacitive coupling and generates a digital voltage pulse for each received signal, and (ii) a digital counting memory to count the received pulses to provide a coarse digital representation of how many times the integrator is reset.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
System and method for simulating an aspect of a memory circuit
A memory subsystem is provided including an interface circuit adapted for coupling with a plurality of memory circuits and a system. The interface circuit is operable to interface the memory circuits and the system for emulating at least one memory circuit with at least one aspect that is different from at least one aspect of at least one of the plurality of memory circuits. Such aspect includes a signal, a capacity, a timing, and / or a logical interface.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20110101334A1Long storageReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesMemory effectMemory circuits
It is an object to provide a semiconductor having a novel structure. In the semiconductor device, a plurality of memory elements are connected in series and each of the plurality of memory elements includes first to third transistors thus forming a memory circuit. A source or a drain of a first transistor which includes an oxide semiconductor layer is in electrical contact with a gate of one of a second and a third transistor. The extremely low off current of a first transistor containing the oxide semiconductor layer allows storing, for long periods of time, electrical charges in the gate electrode of one of the second and the third transistor, whereby a substantially permanent memory effect can be obtained. The second and the third transistors which do not contain an oxide semiconductor layer allow high-speed operations when using the memory circuit.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
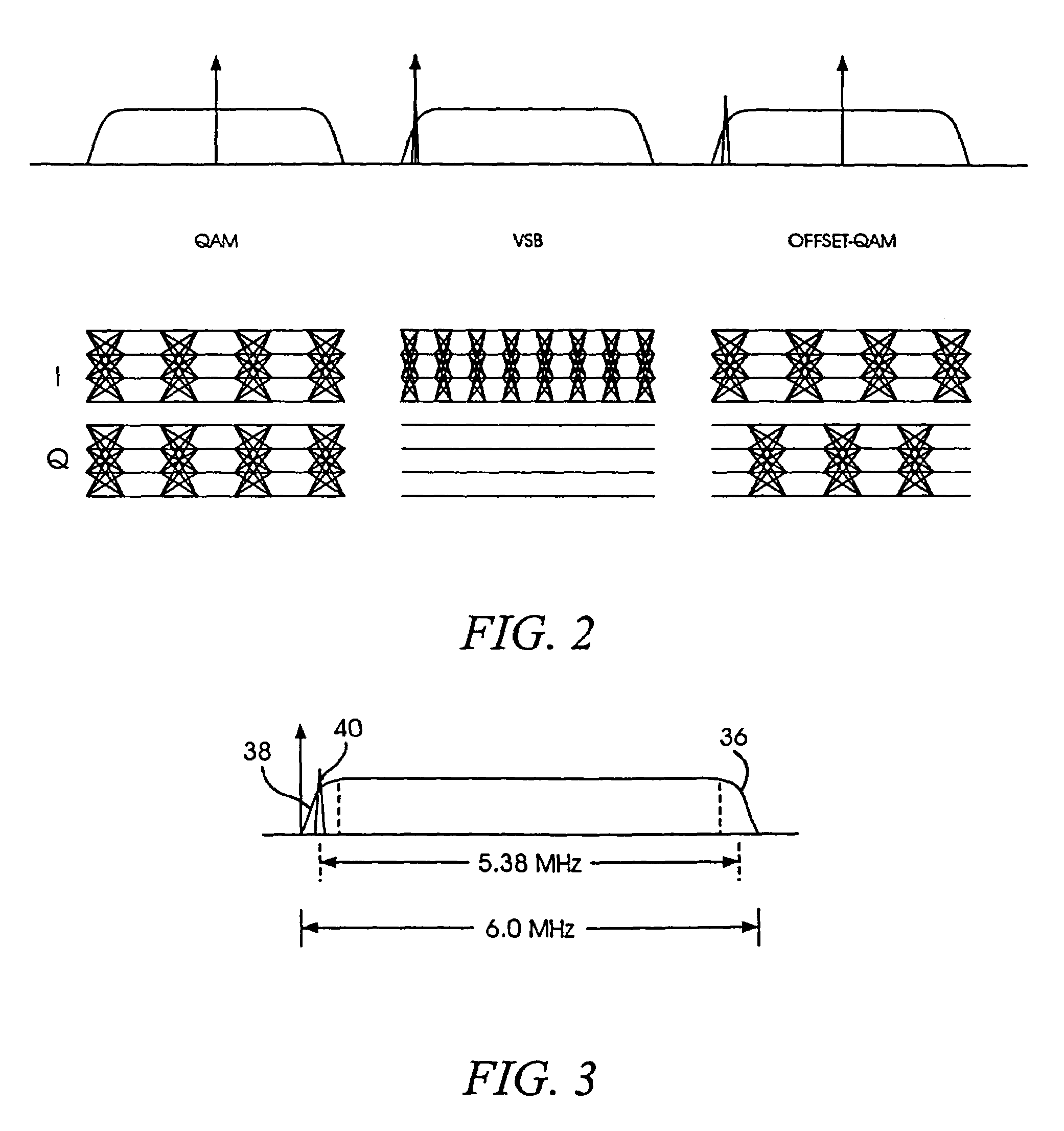
Equalization and decision-directed loops with trellis demodulation in high definition TV
InactiveUS7474695B2Improve reliabilityIncrease delay timeTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksHigh definition tvHigh-definition television
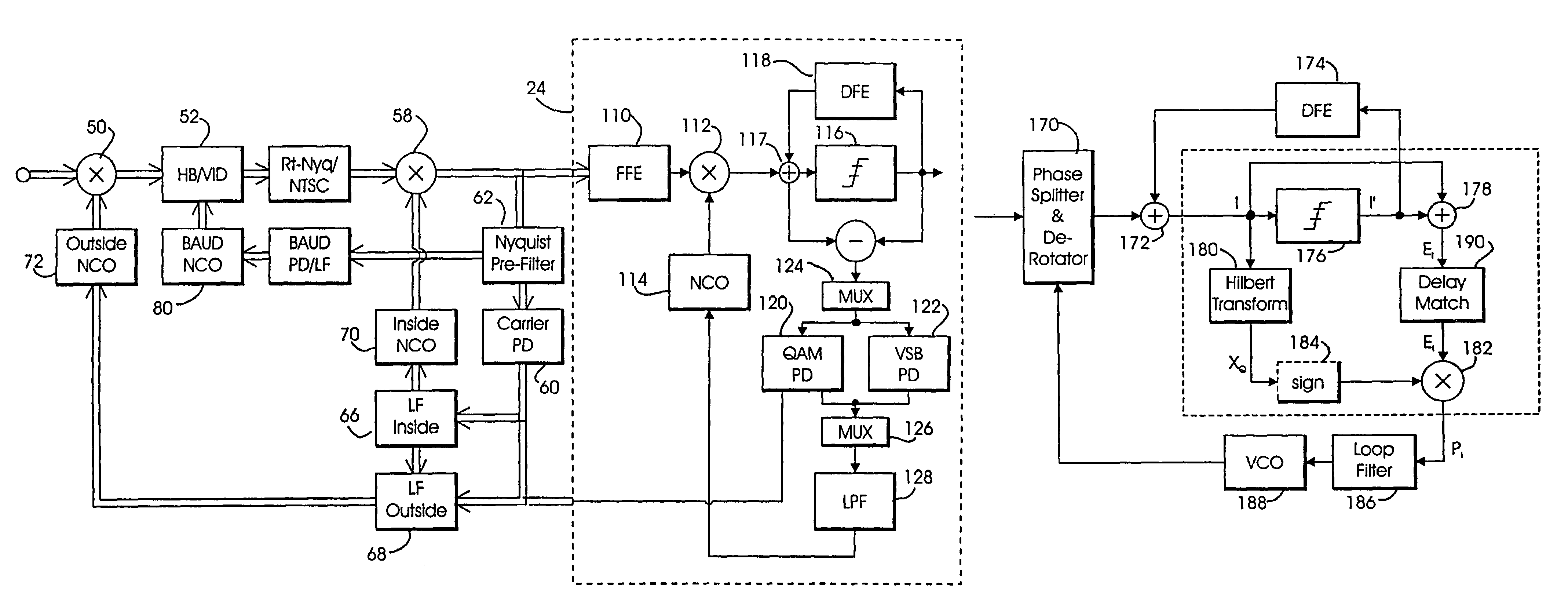
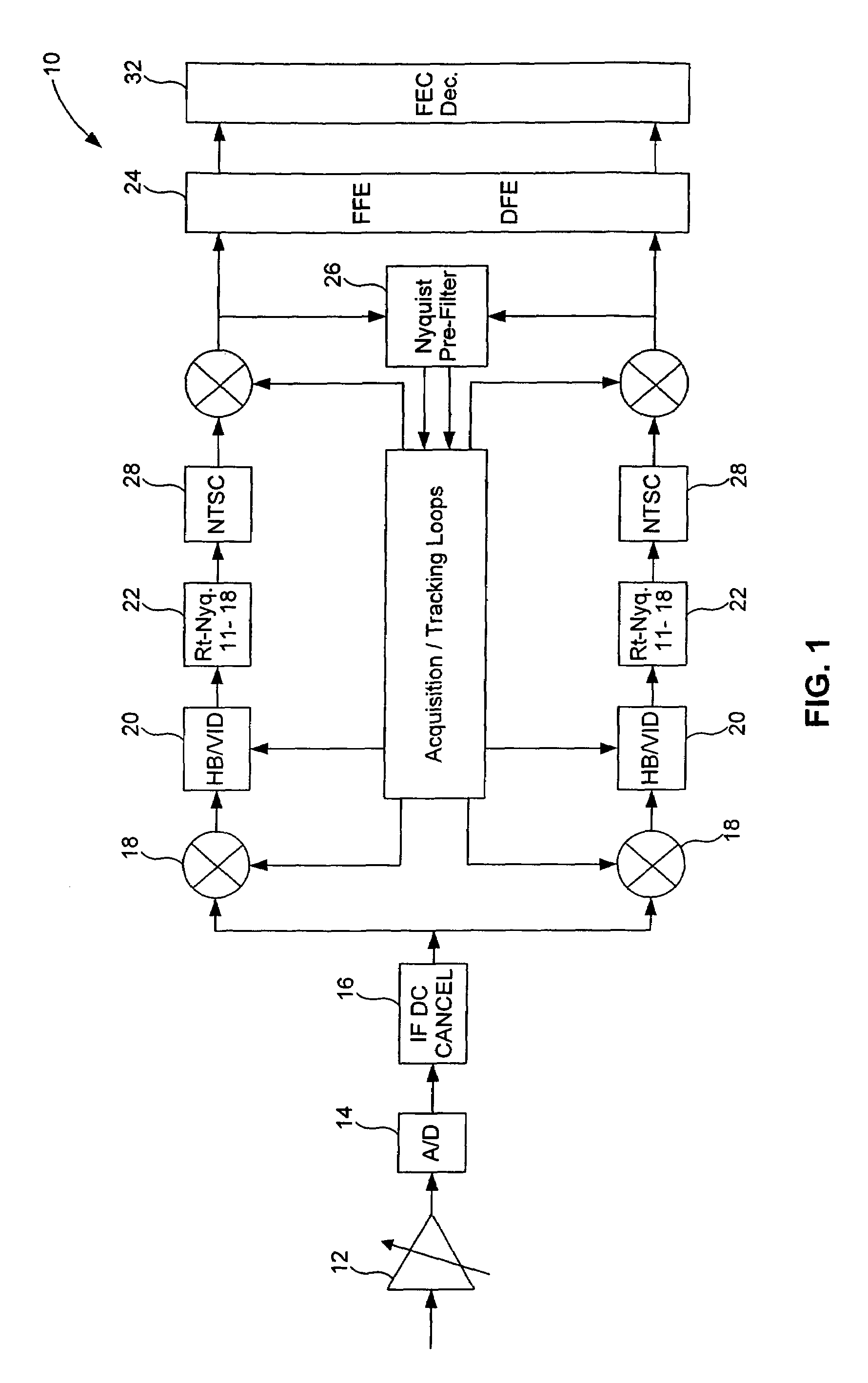
Improved decision feedback equalizer and decision directed timing recovery systems and methods suitable for use in connection with a dual mode QAM / VSB receiver system are disclosed. A trellis decoder operates in conjunction with a decision feedback equalizer circuit on trellis coded 8-VSB modulated signals. The trellis decoder includes a 4-state traceback memory circuit outputting a maximum likelihood decision as well as a number of intermediate decisions based upon the maximum likelihood sequence path. Any number of decisions, along the sequence, may be provided as an input signal to timing recovery system loops, with the particular decision along the sequence chosen on the basis of its delay through the trellis decoder. Variable delay circuitry is coupled to the other input of the timing recovery system loops in order to ensure that both input signals bear the same timestamp. Final decisions are output from the trellis decoder to a DFE in order to enhance the DFE's ability to operate in low SNR environments. A decision sequence estimation error signal is also generated and used to drive the tap updates of both the DFE and an FFE portion of the equalizer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for simulating an aspect of a memory circuit
A memory subsystem is provided including an interface circuit adapted for coupling with a plurality of memory circuits and a system. The interface circuit is operable to interface the memory circuits and the system for emulating at least one memory circuit with at least one aspect that is different from at least one aspect of at least one of the plurality of memory circuits. Such aspect includes a signal, a capacity, a timing, and / or a logical interface.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Interface circuit system and method for performing power saving operations during a command-related latency
A memory circuit power management system and method are provided. In use, an interface circuit is in communication with a plurality of memory circuits and a system. The interface circuit is operable to interface the memory circuits and the system for performing a power management operation in association with at least a portion of the memory circuits. Such power management operation is performed during a latency associated with one or more commands directed to at least a portion of the memory circuits.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
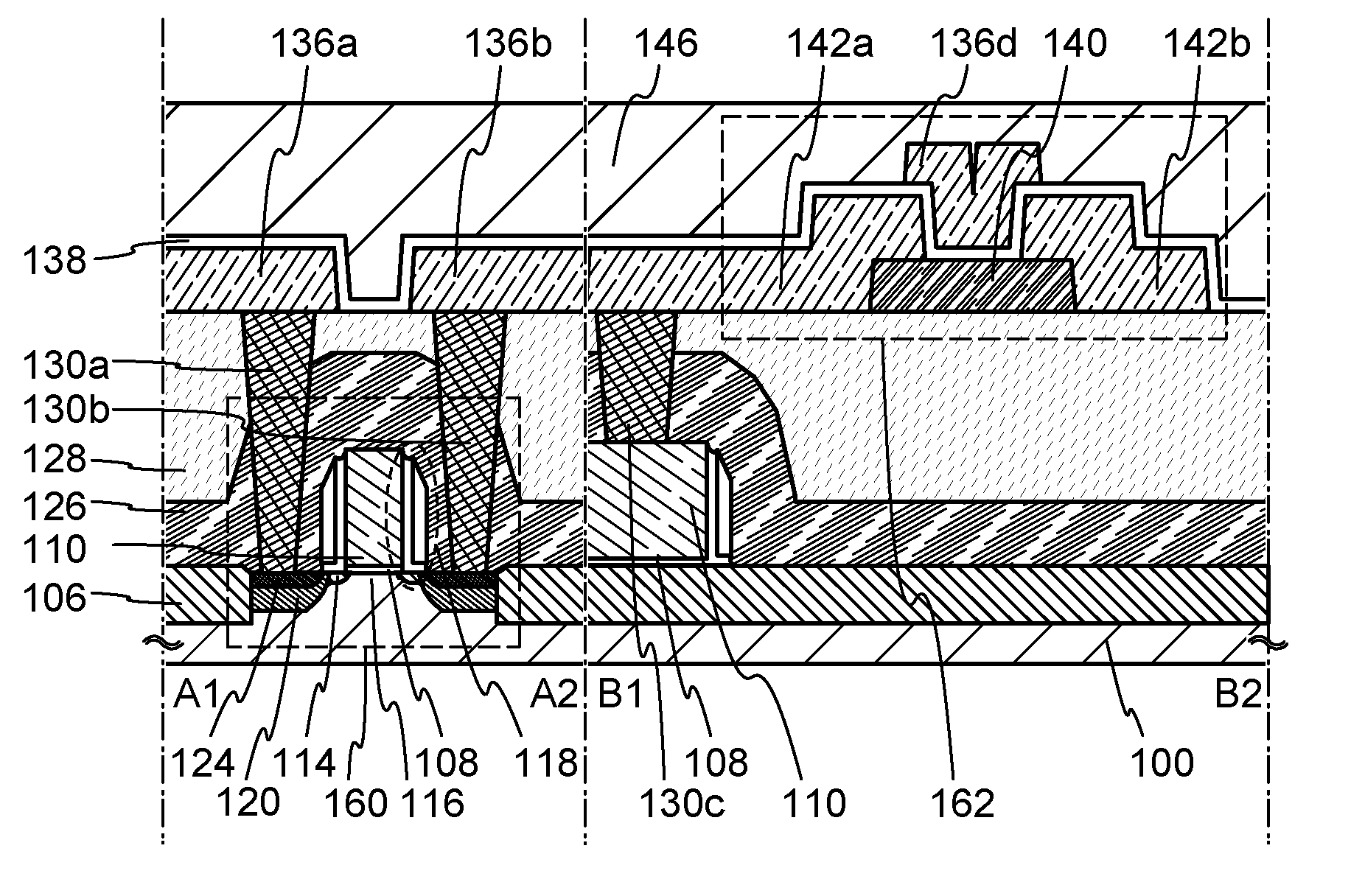
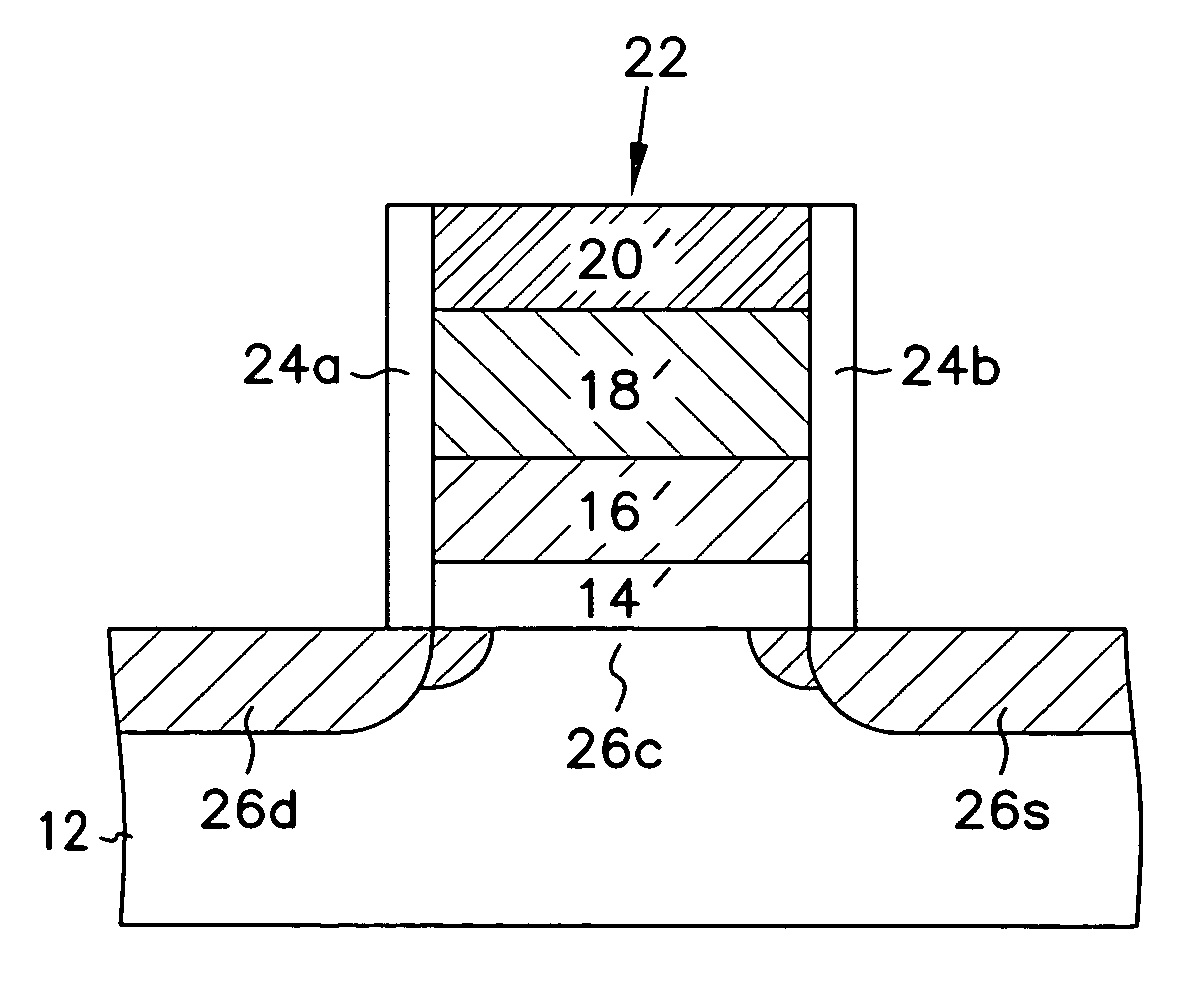
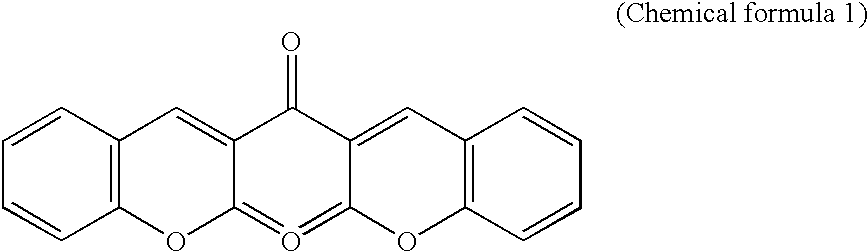
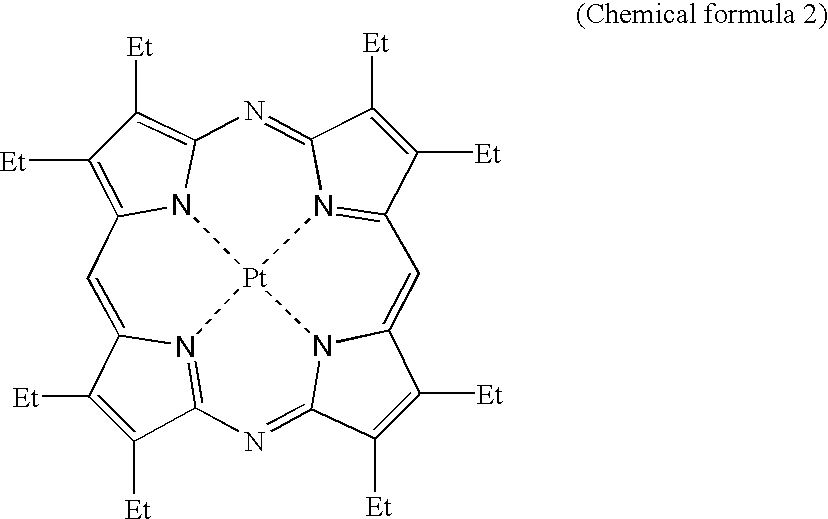
Structures, methods, and systems for ferroelectric memory transistors
InactiveUS20050030825A1Reliability can be promotedReduce layeringSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerPermittivity
Integrated memory circuits, key components in thousands of electronic and computer products, have recently been made using ferroelectric memory transistors, which offer faster write cycles and lower power requirements than over conventional floating-gate transistors. One problem that hinders the continued down-scaling of conventional ferroelectric memory transistors is the vulnerability of their gate insulations to failure at thinner dimensions. Accordingly, the inventors devised unique ferroelectric gate structures, one of which includes a high-integrity silicon-oxide insulative layer, a doped titanium-oxide layer, a weak-ferroelectric layer, and a control gate. The doped titanium-oxide layer replaces a metal layer in the conventional ferroelectric gate structure, and the weak-ferroelectric layer replaces a conventional ferroelectric layer. These replacements reduce the permittivity mismatch found in conventional gate structures, and thus reduce stress on gate insulation layers, thereby improving reliability of ferroelectric memory transistors, particularly those with thinner gate insulation.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Self light emitting device and method of driving thereof
A self light emitting device having a function of correcting drops in brightness in self light emitting elements in a pixel portion, and capable of displaying a uniform image without brightness irregularities, is provided. A specific test pattern is displayed when an electric power source is connected, brightnesses are detected by photoelectric conversion elements arranged in each pixel, and then stored in a memory circuit. A correction circuit then corrects a first image signal based on portions which are insufficient from standard brightnesses (brightnesses of normal self light emitting elements at the same gray stale, stored in advance), and a second image signal is obtained. Display of an image in a display device is performed in accordance with the second image signal.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Gate Level Reconfigurable Magnetic Logic
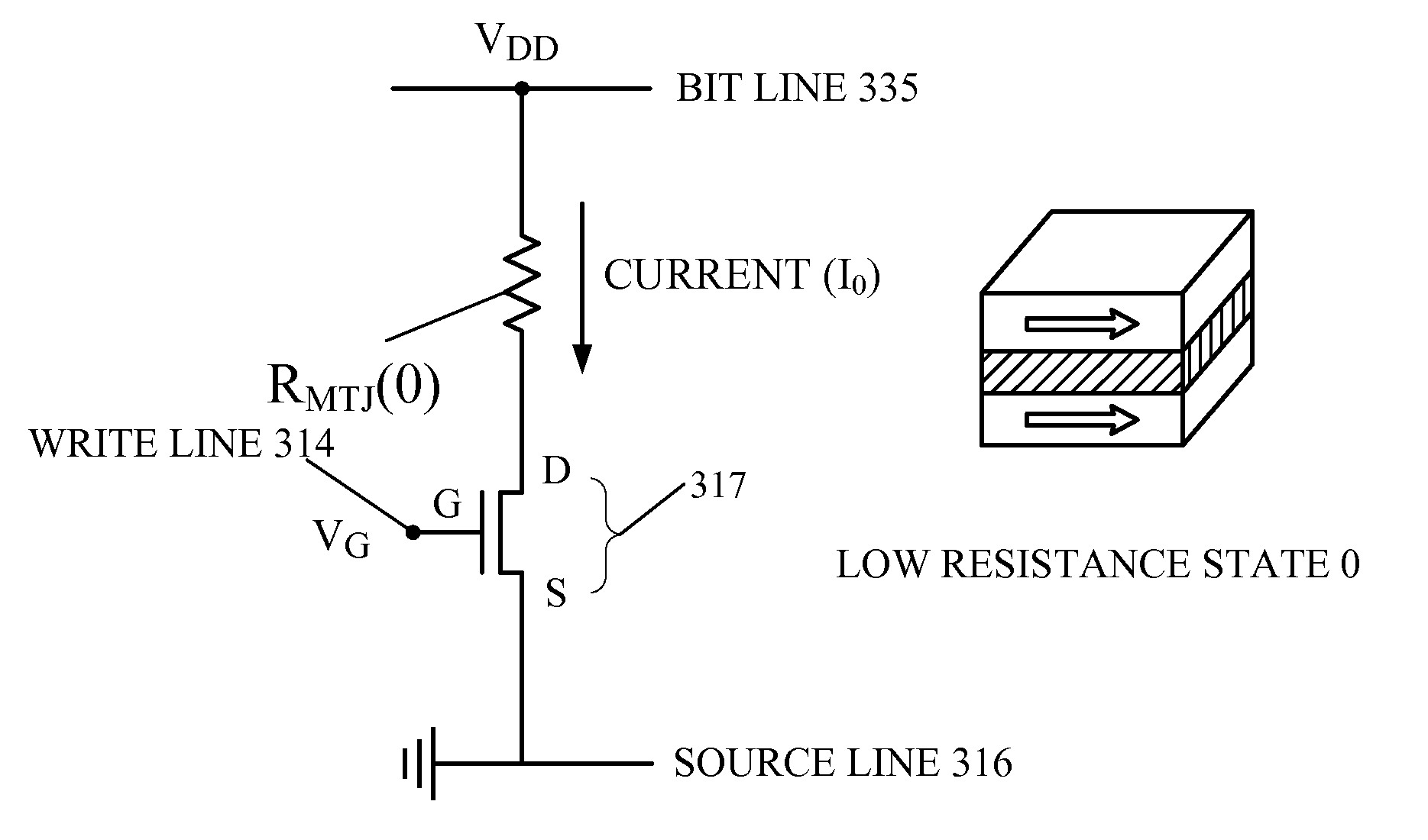
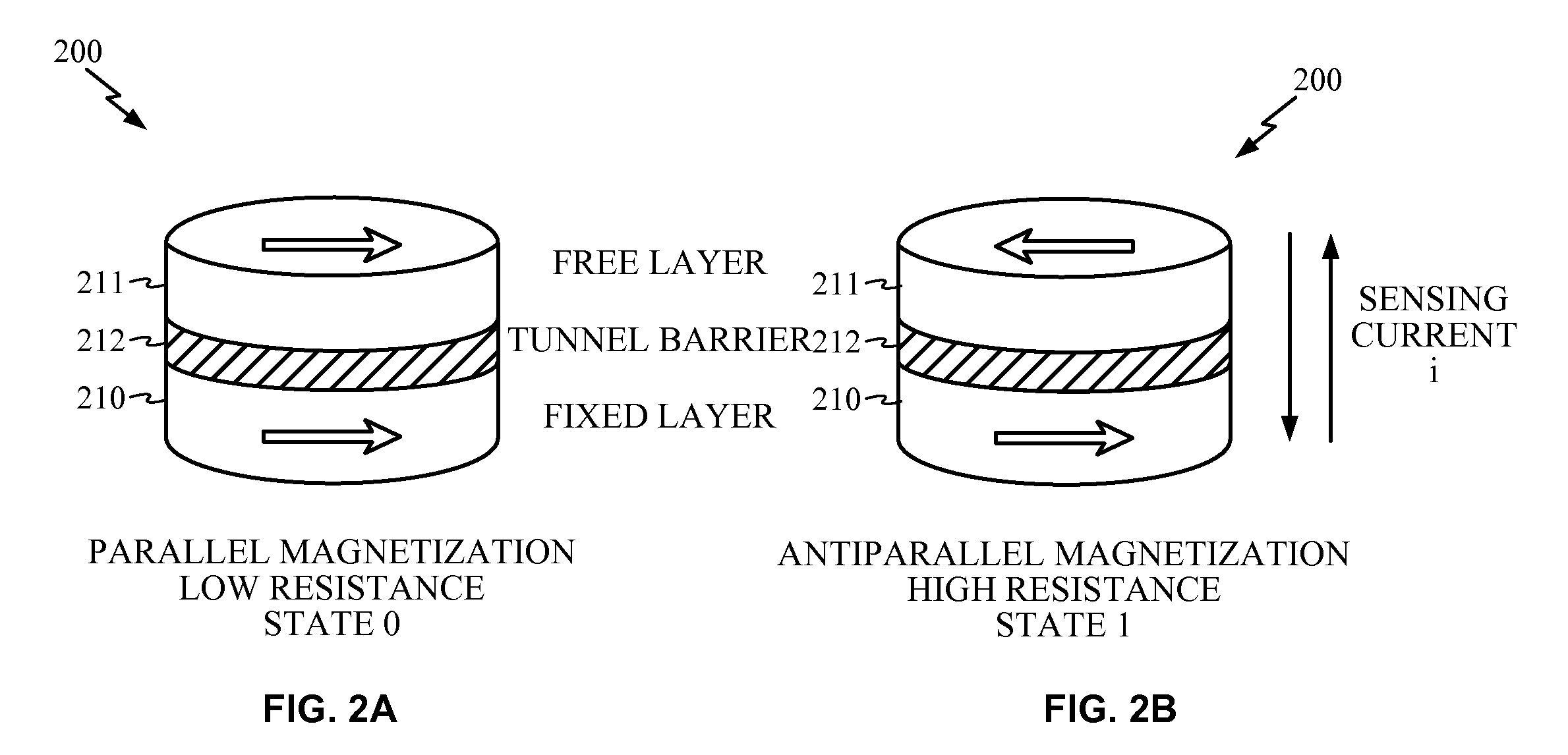
ActiveUS20100039136A1Write currentIncrease current densitySolid-state devicesDigital storageSignal onRandom access memory
A re-programmable gate logic includes a plurality of non-volatile re-configurable resistance state-based memory circuits in parallel, wherein the circuits are re-configurable to implement or change a selected gate logic, and the plurality of non-volatile re-configurable resistance state-based memory circuits are each adapted to receive a logical input signal. An evaluation switch in series with the plurality of parallel non-volatile re-configurable resistance state-based memory circuits is configured to provide an output signal based on the programmed states of the memory circuits. A sensor is configured to receive the output signal and provide a logical output signal on the basis of the output signal and a reference signal provided to the sensor. The reconfigurable logic may be implemented based on using spin torque transfer (STT) magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) magnetoresistance random access memory (MRAM) as the re-programmable memory elements. The logic configuration is retained without power.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and computer program for efficient cell failure rate estimation in cell arrays
InactiveUS7380225B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationFailure rateMemory circuits
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
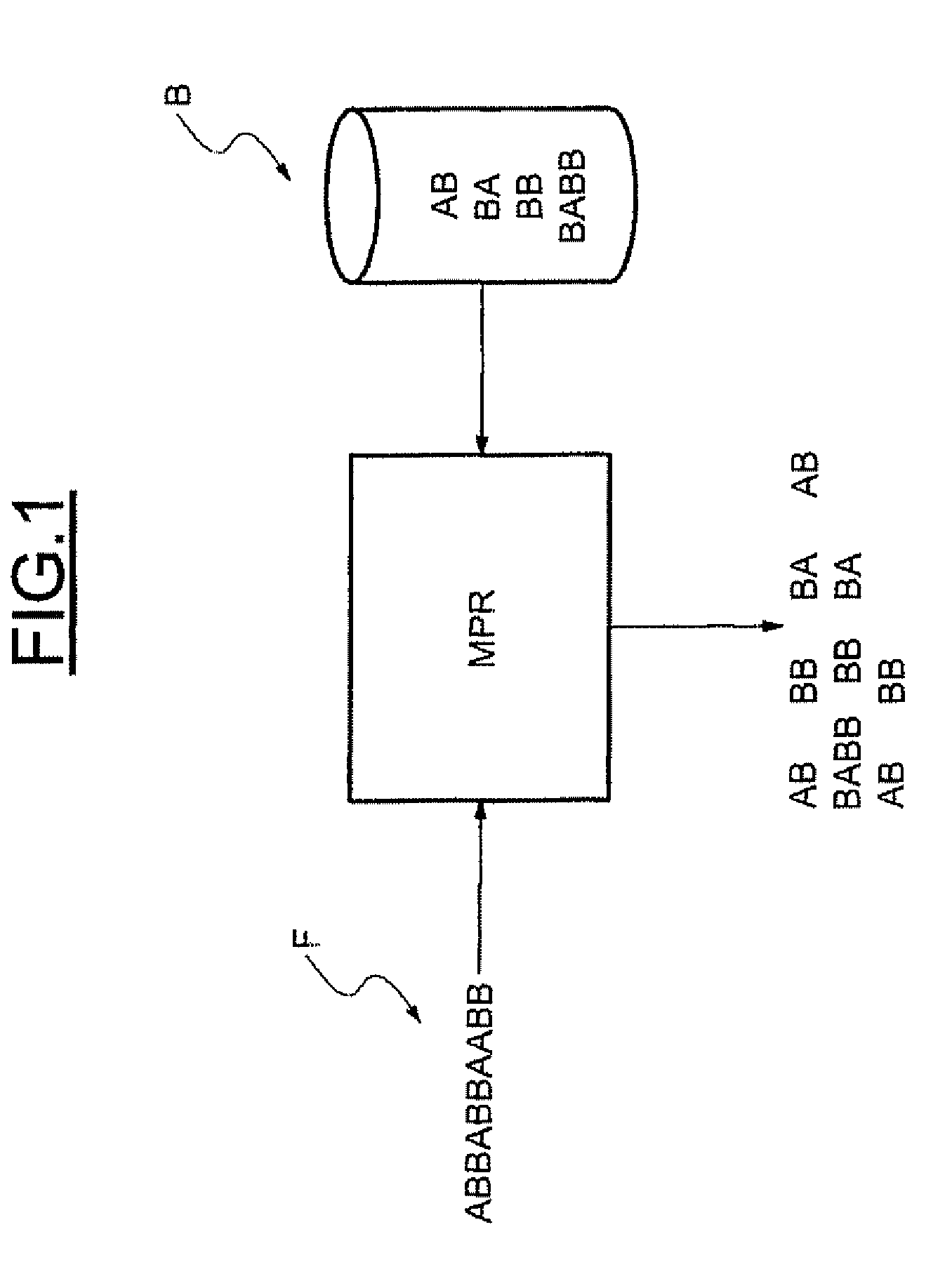
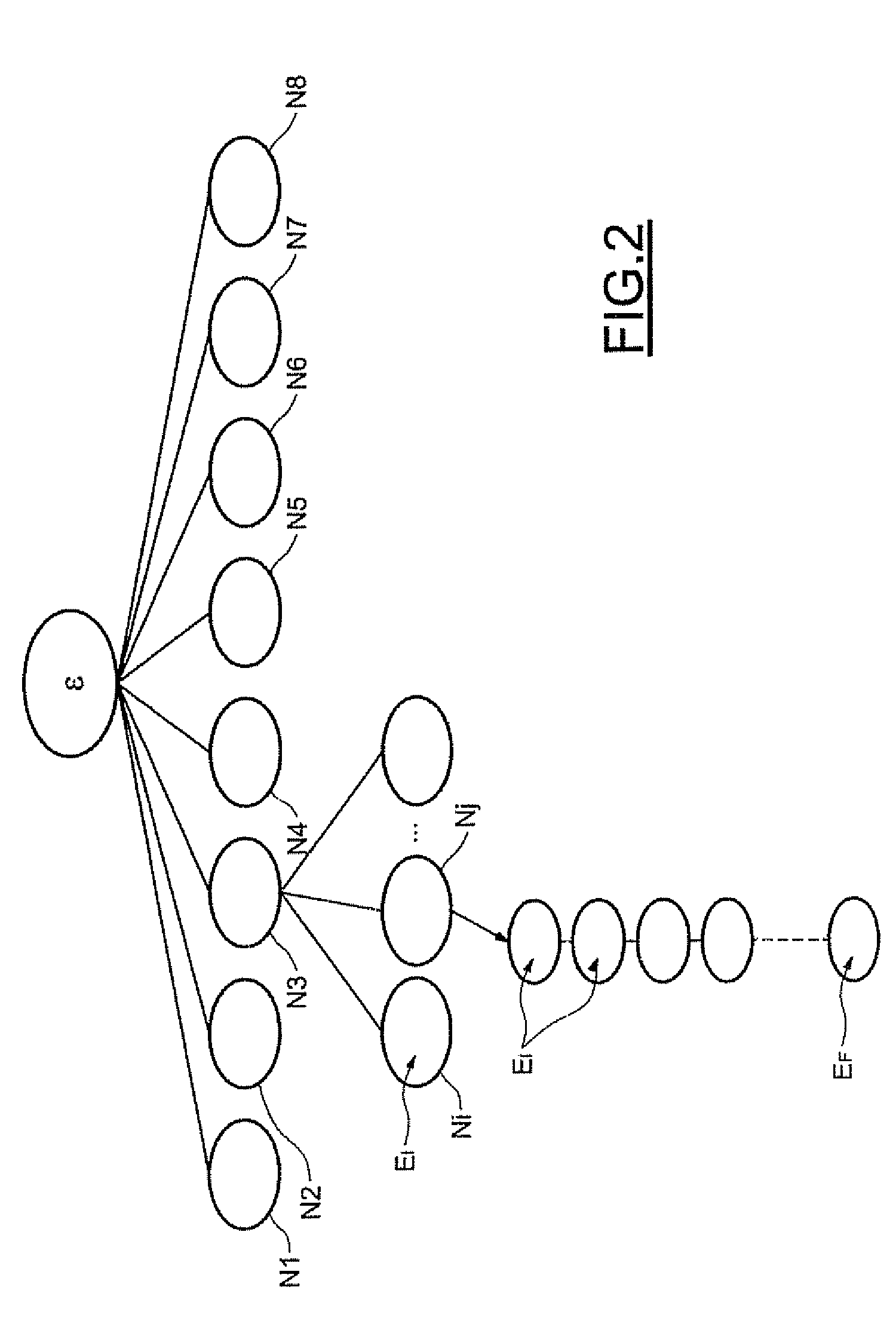
Memory circuit for aho-corasick type character recognition automaton and method of storing data in such a circuit
ActiveUS20070075878A1Number of bitDigital data information retrievalCode conversionMemory addressData stream
A memory circuit for an Aho-Corasick type character recognition automaton uses a node tree for recognizing predetermined strings of characters in an incoming data stream. The recognization is based upon successive transitions in the node tree stored in memory in which each node corresponds to a recognized sequence of a character string. At least part of the nodes are related to a consecutive node by a valid transition, from an initial state to terminal states, with each one corresponding to a recognized character string This memory circuit includes first sets of consecutive memory addresses defining respectively strings of consecutive nodes accessible sequentially during successive transitions to a terminal state, and second sets of memory addresses defining multiple nodes each pointing to several states.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Device with embedded high-bandwidth, high-capacity memory using wafer bonding
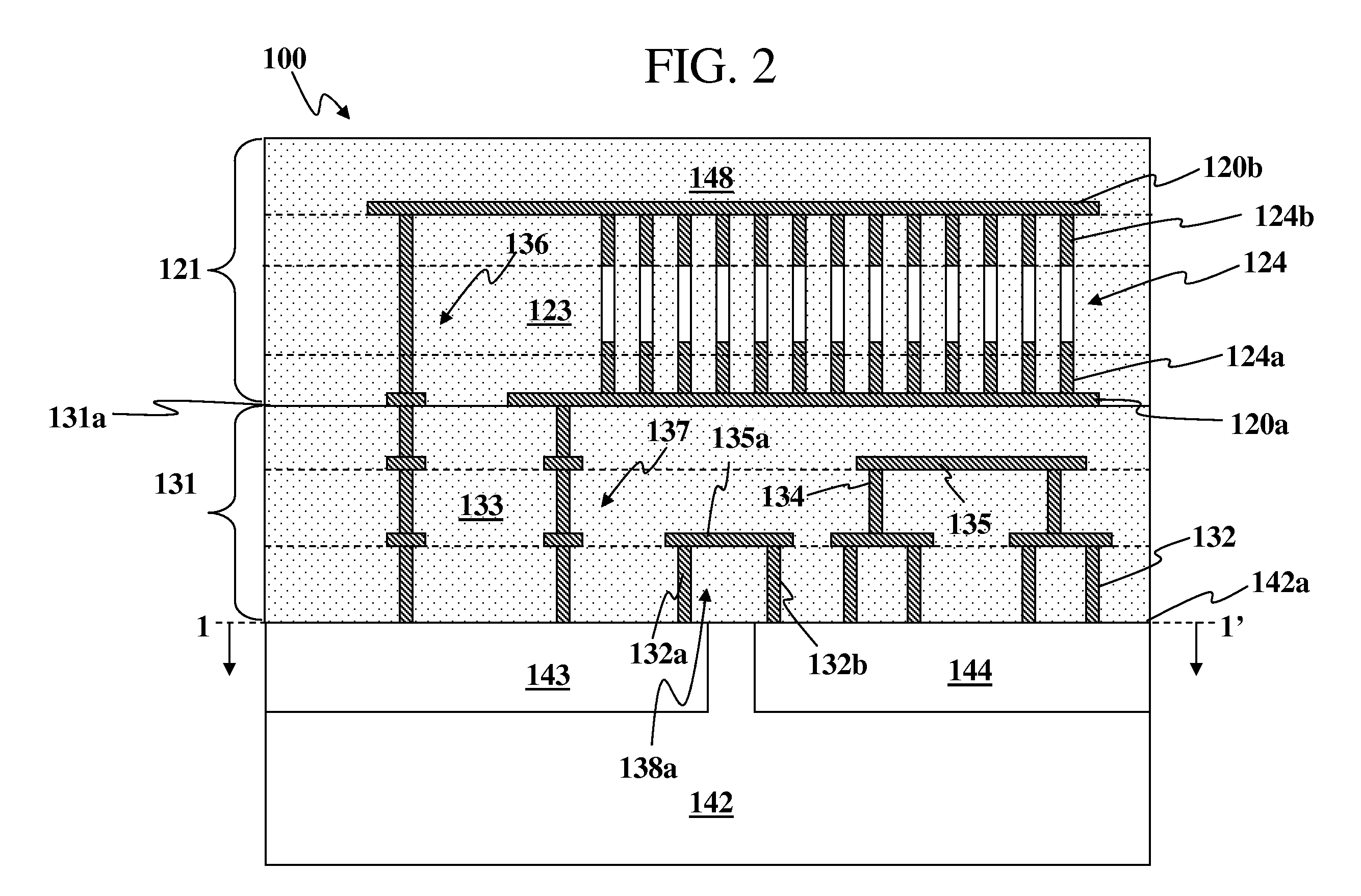
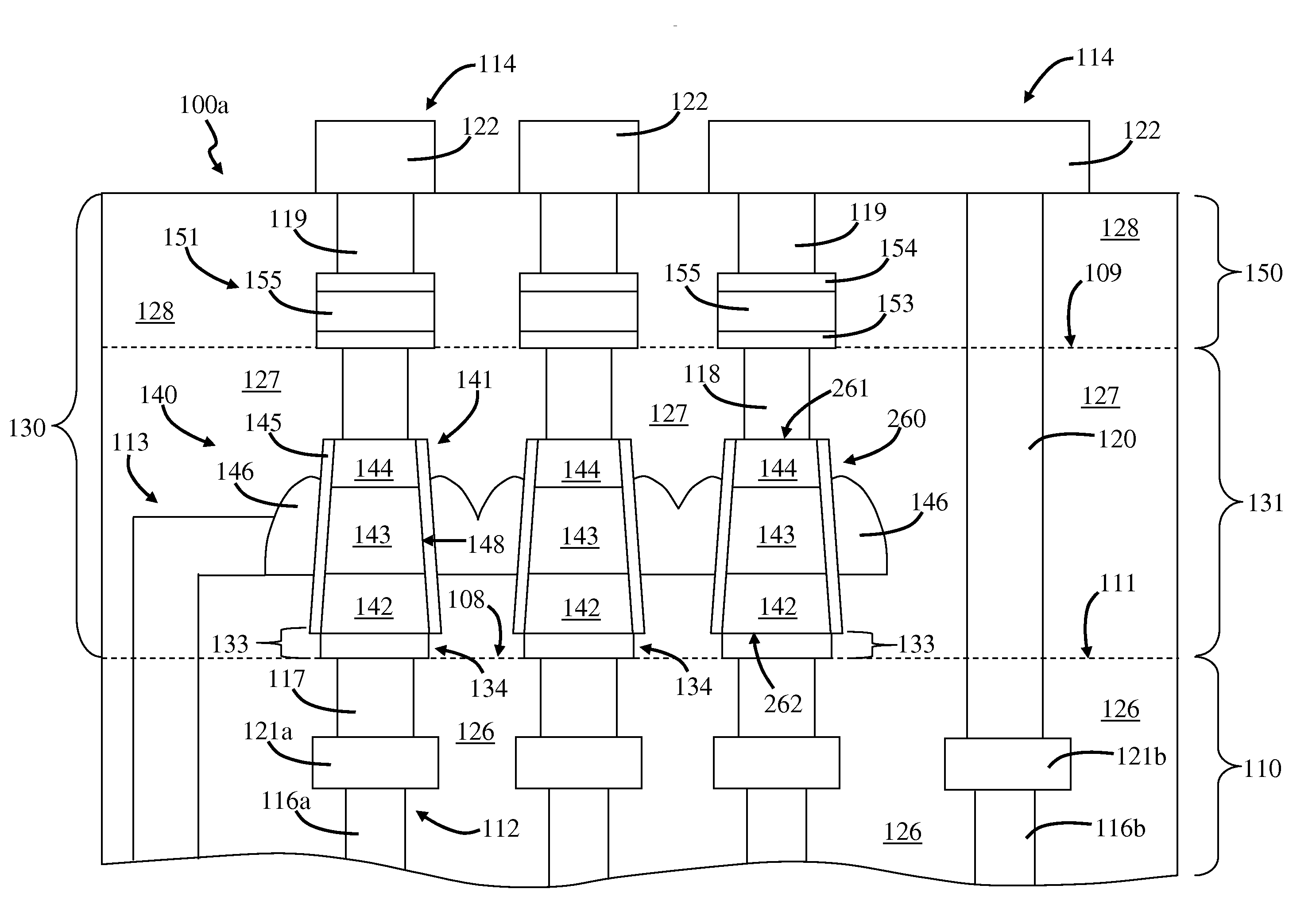
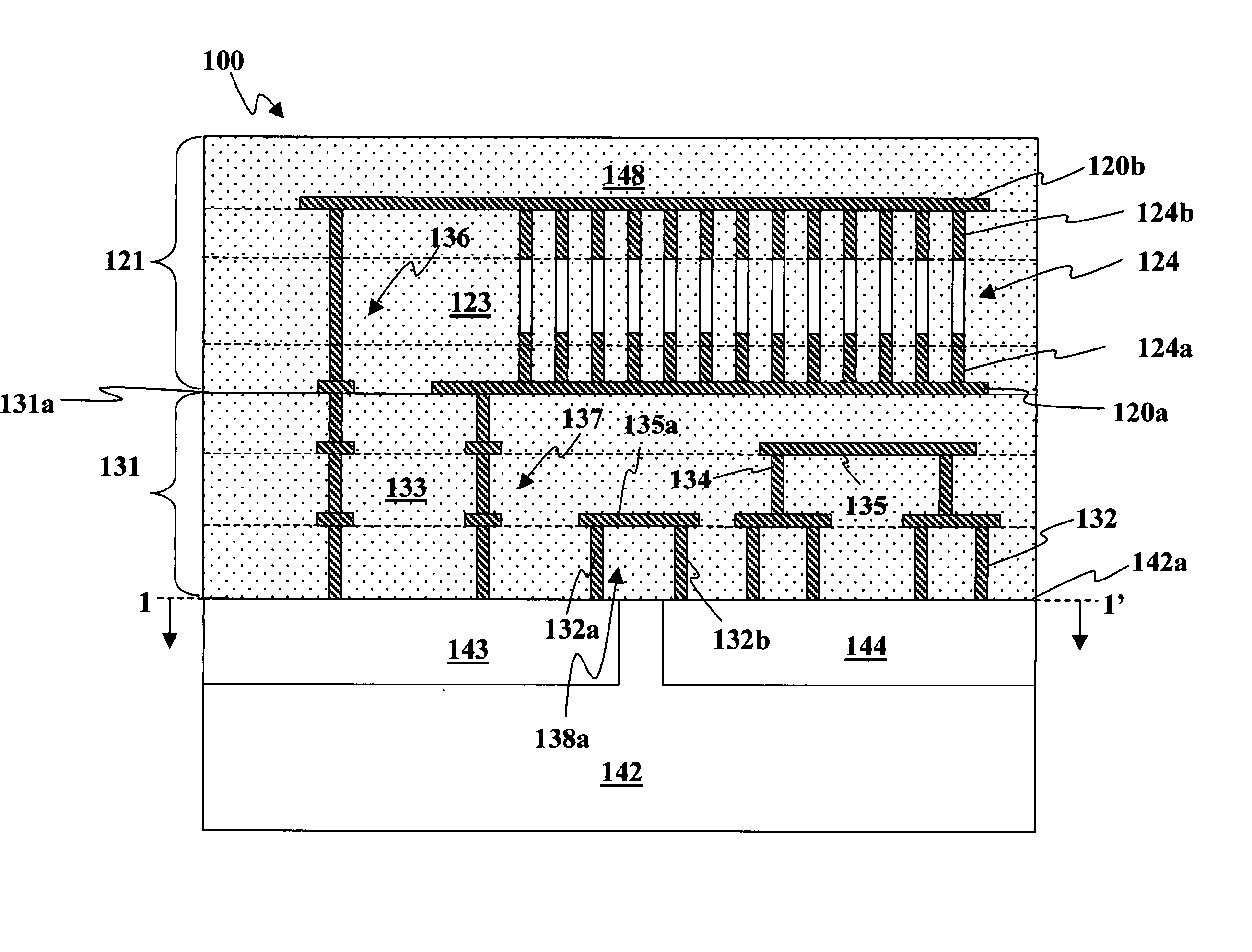
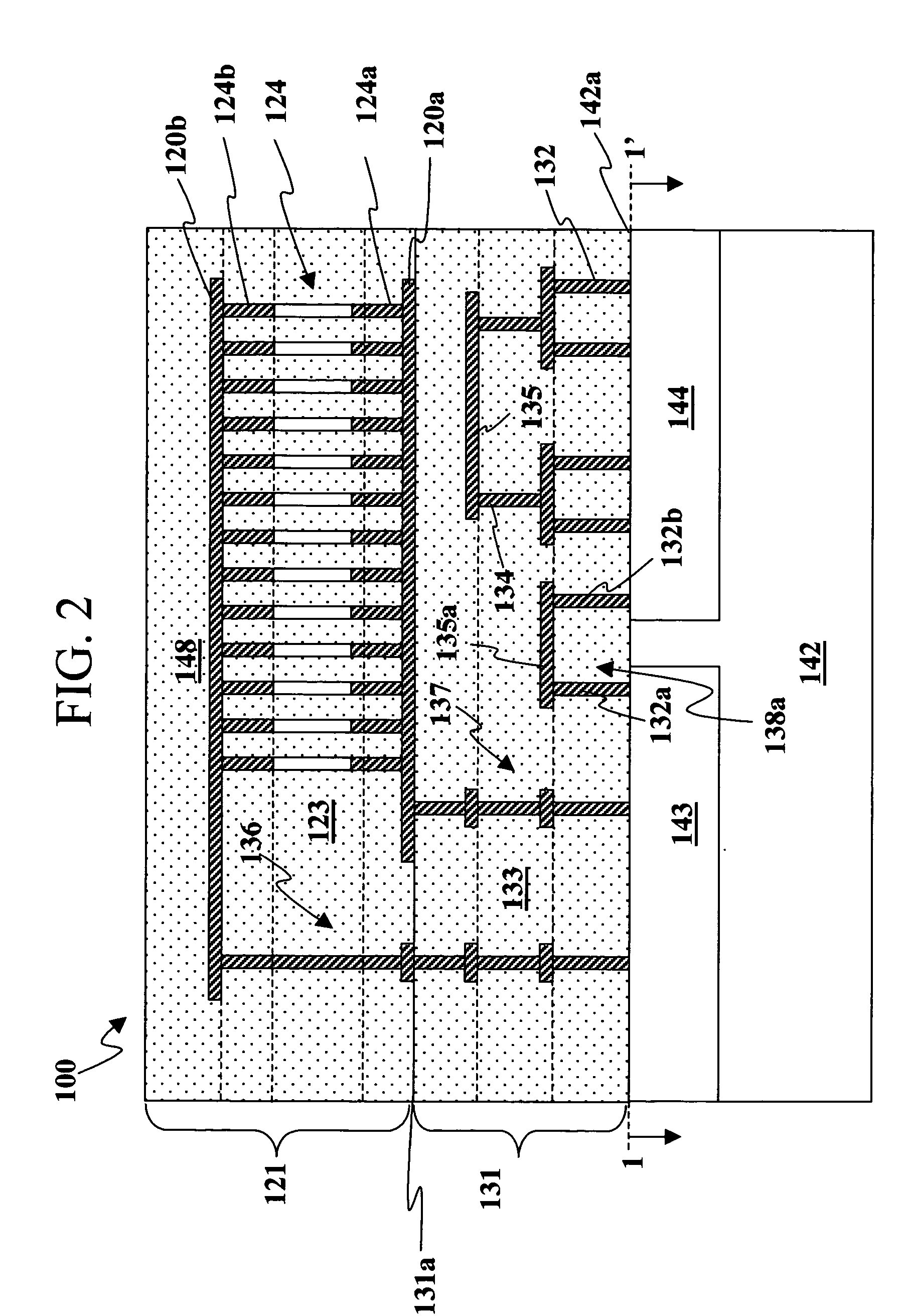
ActiveUS20200243486A1Allowed to operateFast bootMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersComputer architectureElectrical conductor
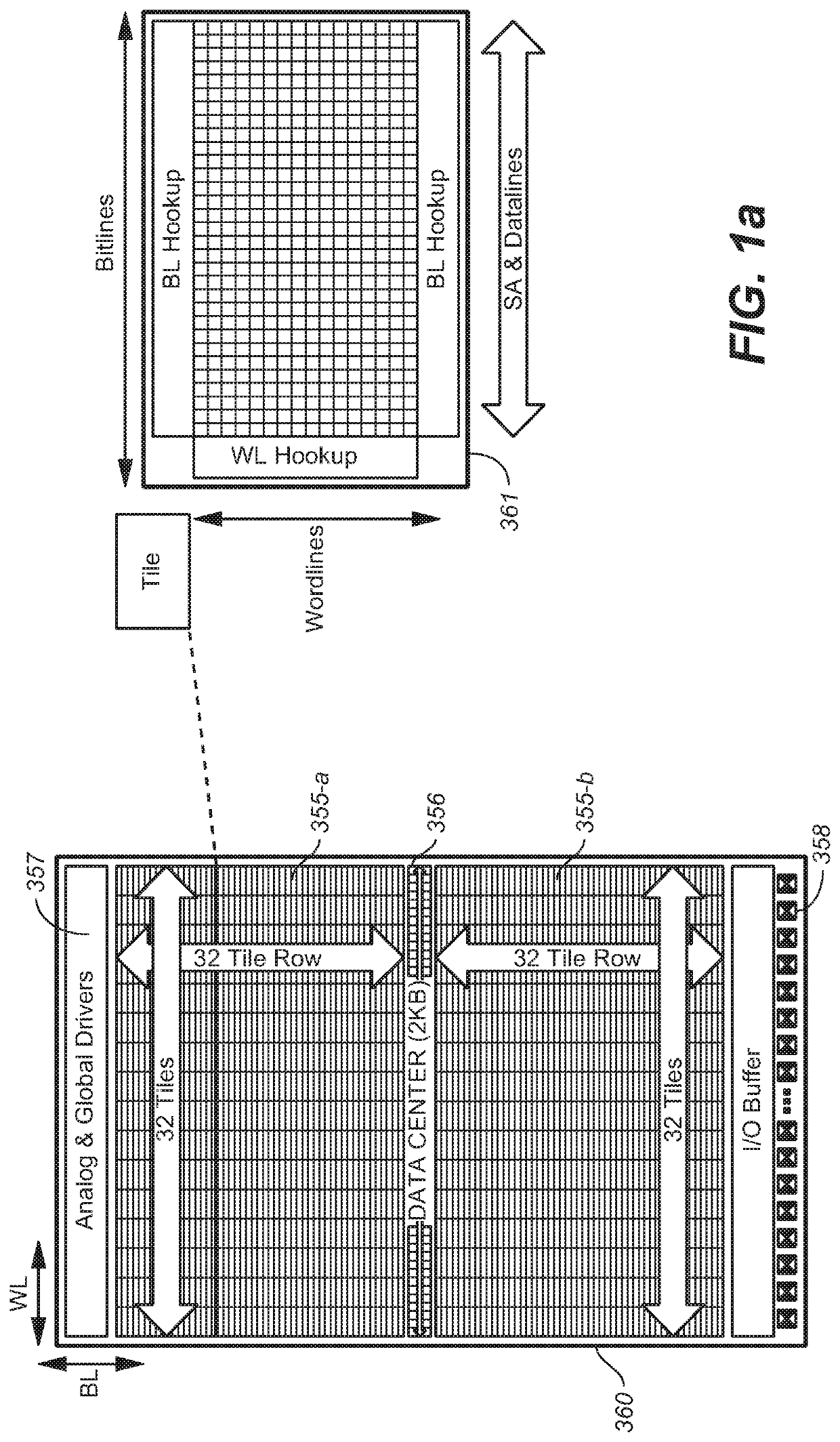
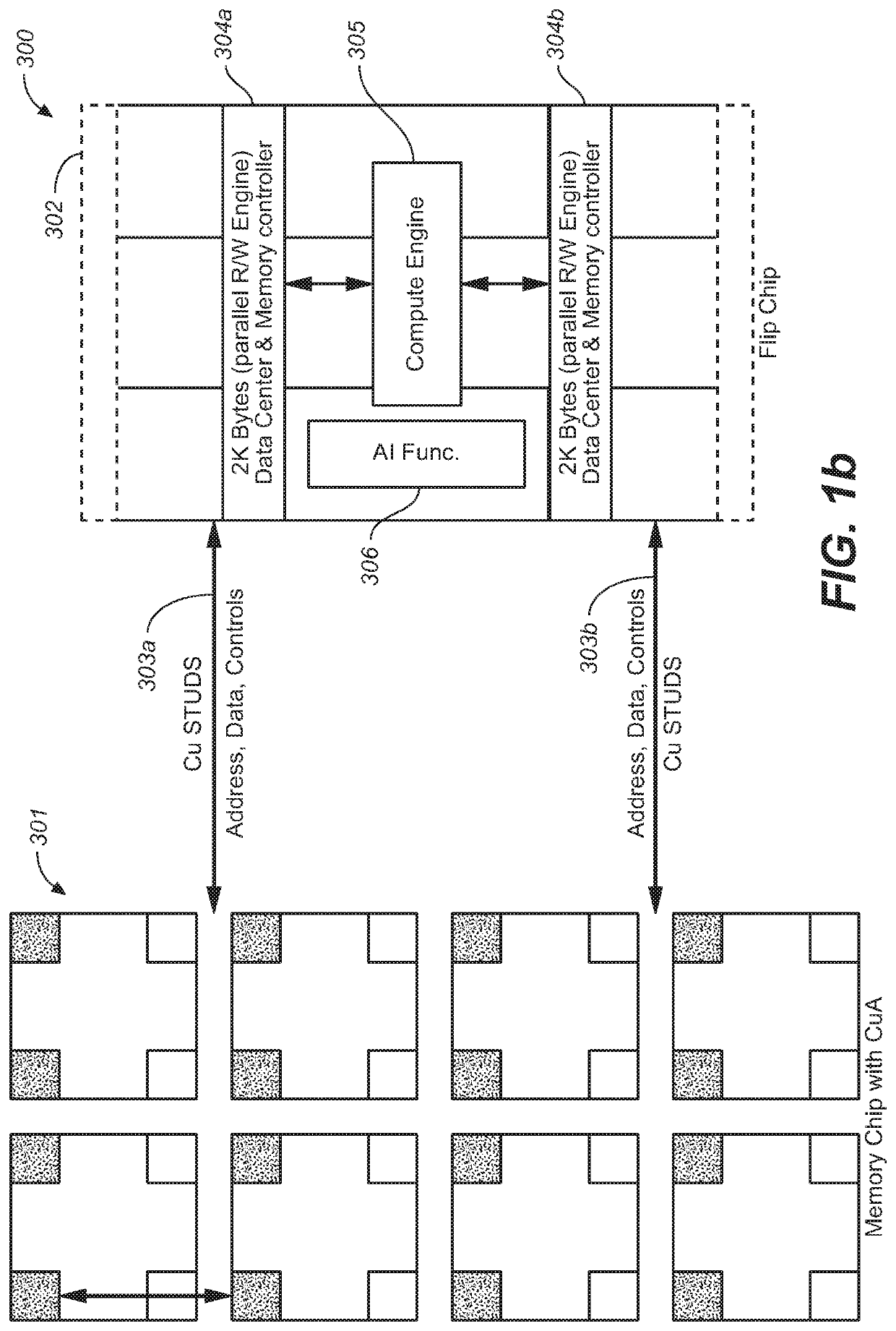
An electronic device with embedded access to a high-bandwidth, high-capacity fast-access memory includes (a) a memory circuit fabricated on a first semiconductor die, wherein the memory circuit includes numerous modular memory units, each modular memory unit having (i) a three-dimensional array of storage transistors, and (ii) a group of conductors exposed to a surface of the first semiconductor die, the group of conductors being configured for communicating control, address and data signals associated the memory unit; and (b) a logic circuit fabricated on a second semiconductor die, wherein the logic circuit also includes conductors each exposed at a surface of the second semiconductor die, wherein the first and second semiconductor dies are wafer-bonded, such that the conductors exposed at the surface of the first semiconductor die are each electrically connected to a corresponding one of the conductors exposed to the surface of the second semiconductor die. The three-dimensional array of storage transistors may be formed by NOR memory strings.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com