Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3756 results about "Compression method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compression methods are otherwise known as algorithms, which are calculations that are used to compress files. Organisations that create file formats create their own algorithms and compete with each other to create the best format.
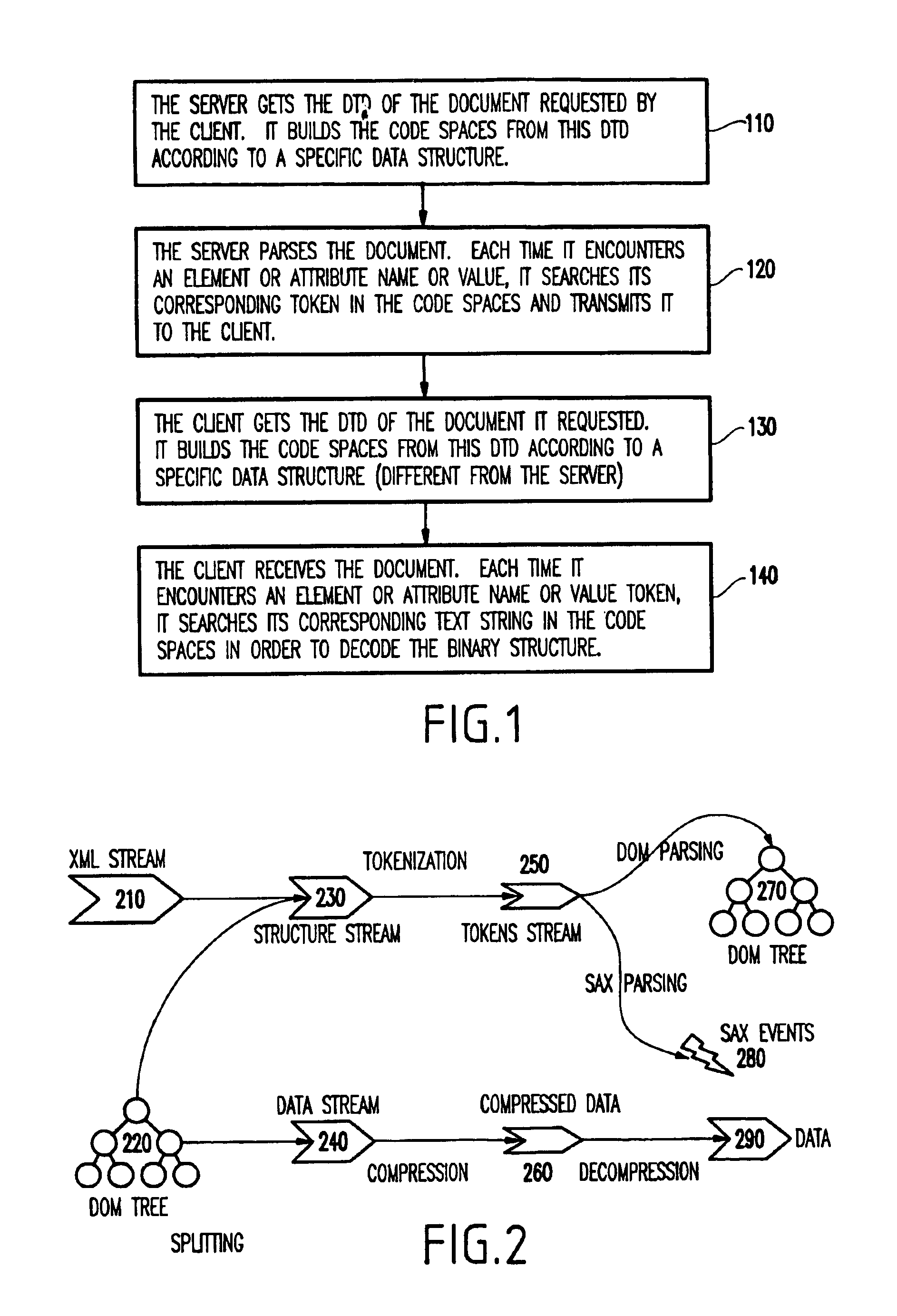
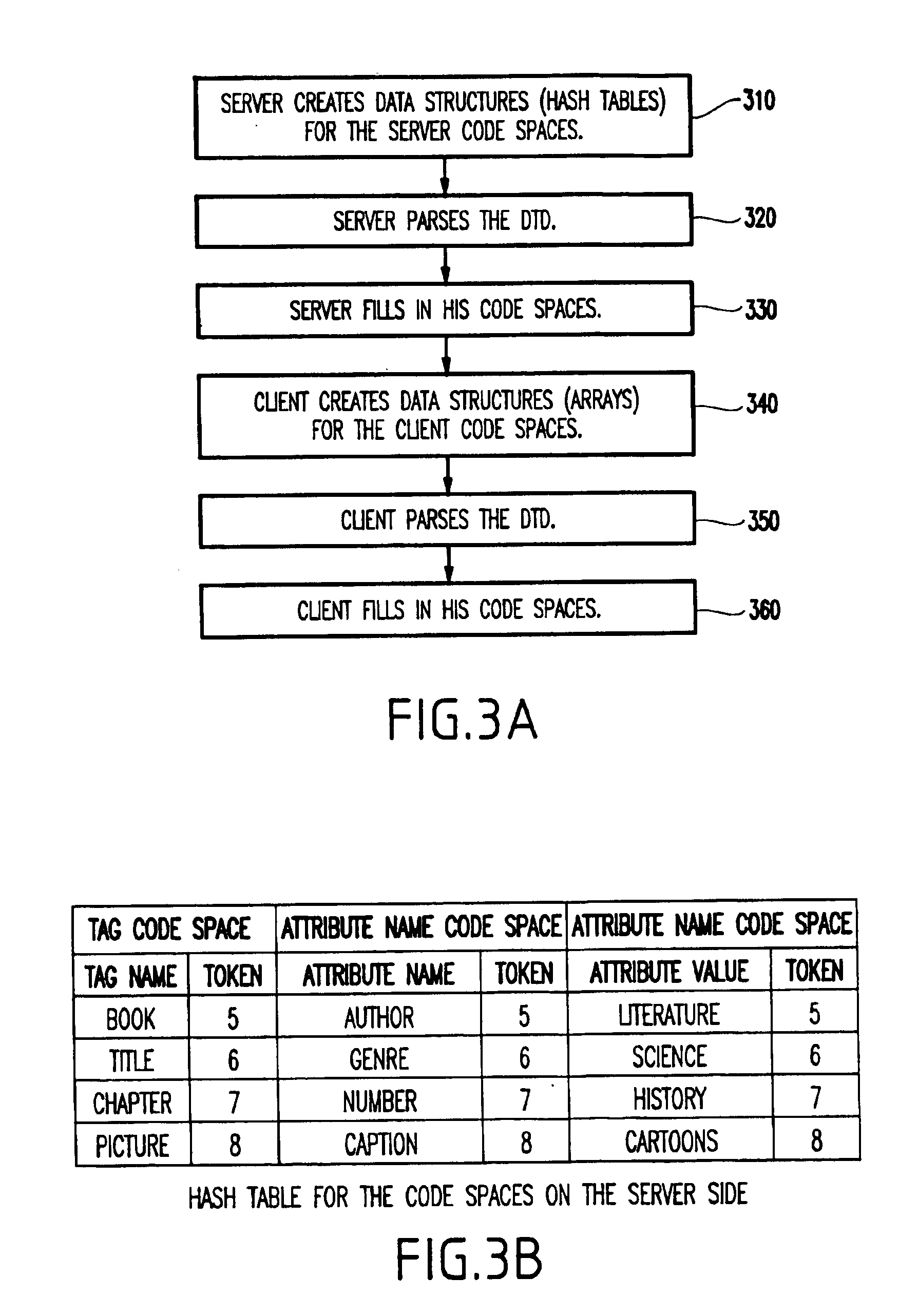
System and method for schema-driven compression of extensible mark-up language (XML) documents
InactiveUS6883137B1Easy to rebuildEfficient compressionDigital computer detailsCode conversionExtensible markupDocumentation
A method (and system) for compressing an extensible markup language (XML) document, includes compressing an XML document such that information in a markup portion therein is maintained in a compressed form to allow the document to be reconstructed. During the compressing, the markup portion and a non-markup portion of the document are separated, and the non-markup component is compressed using a first compression method and the markup component is compressed using a second compression method.
Owner:PENDRAGON NETWORKS
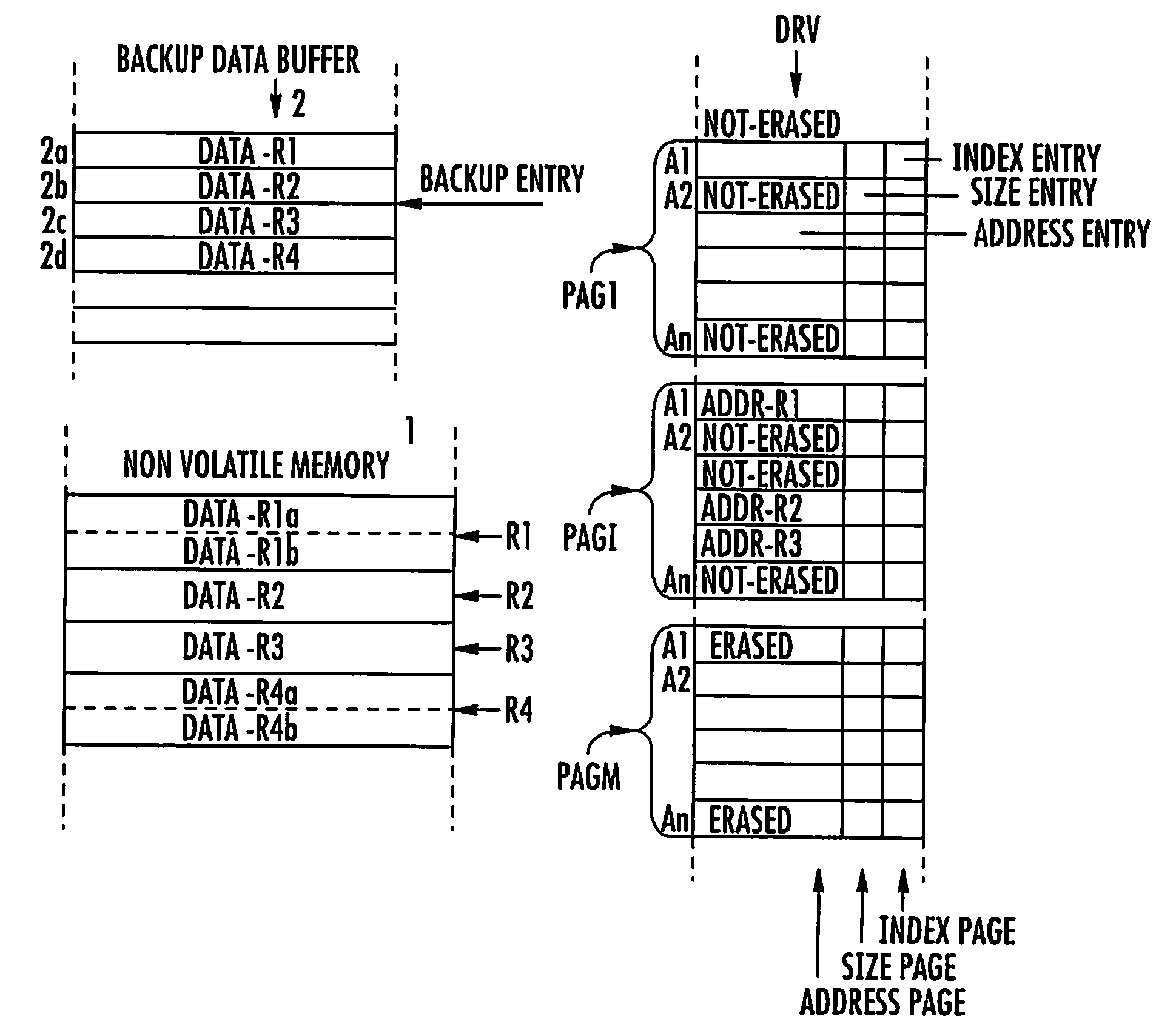
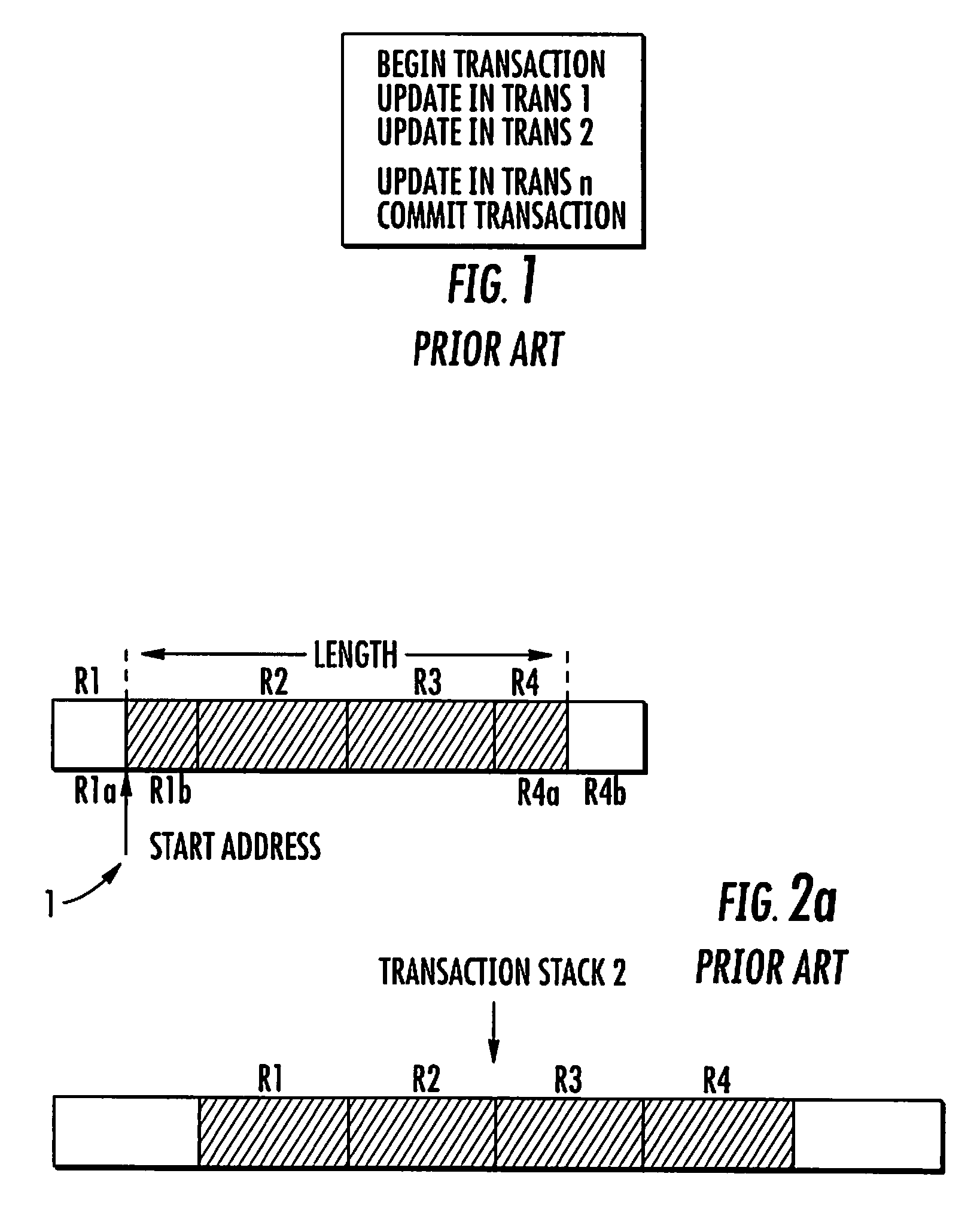
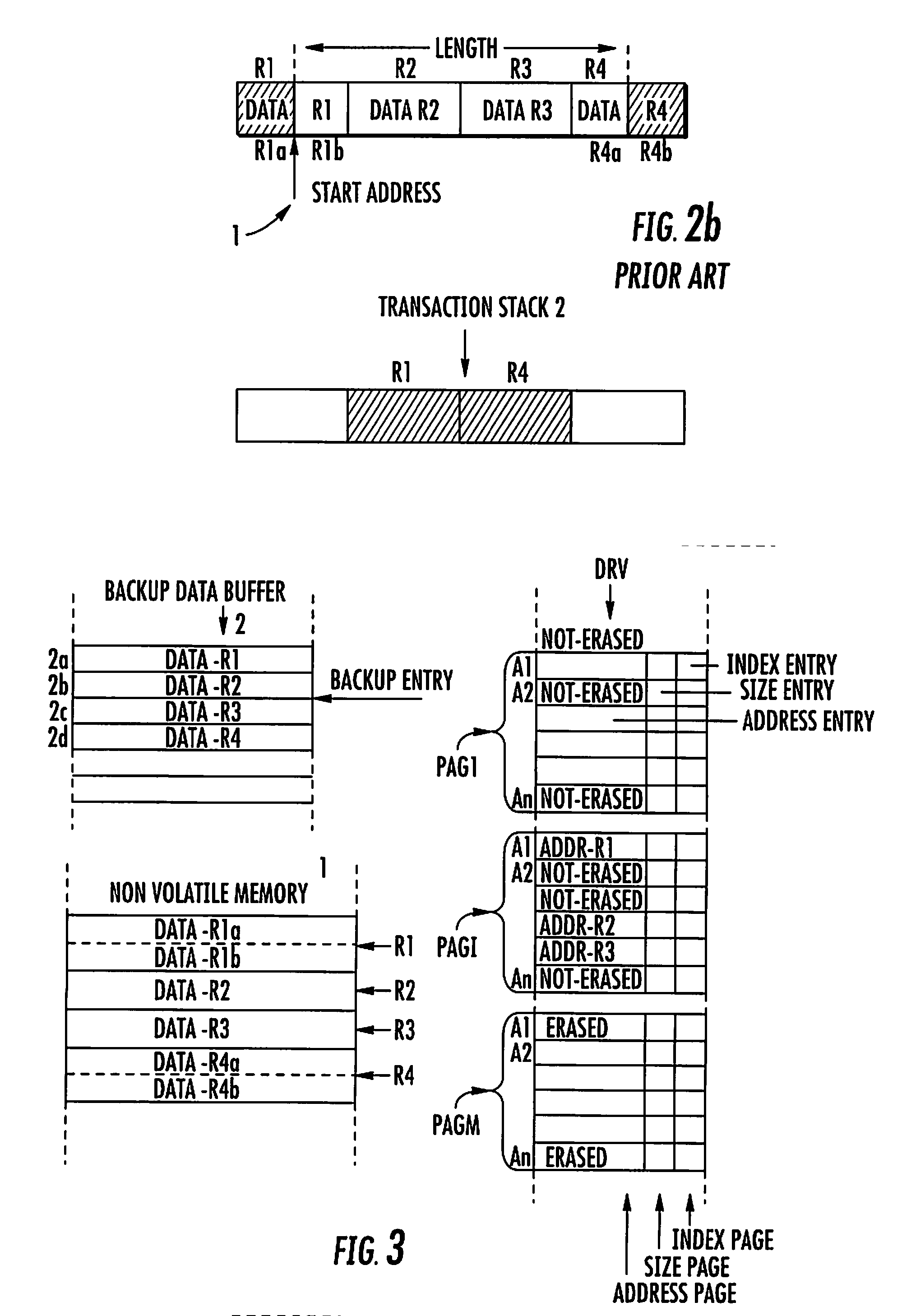
Compression Method for Managing the Storing of Persistent Data From a Non-Volatile Memory to a Backup Buffer
InactiveUS20080005510A1Avoid dataPrevent overflowMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionCompression methodData store
A compression method for a backup data buffer includes a plurality of backup entries for storing persistent data of a non-volatile memory device during at least one update operation. An address of the persistent data in the non-volatile memory device is stored in a driver buffer including address pages. Each address page includes address entries. The compression method includes the functions for marking as erasable an address entry included in a first address page of the driver buffer when the at least one update operation on the persistent data is completed. Address entries not marked as erasable or non-erasable are copied from the first address page to a second address page of the driver buffer. The second address page contains address entries not marked as erasable. The first address page is erased for rendering it ready to be written. The content of the second address page is written to the first, and the second address page is for future writings.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
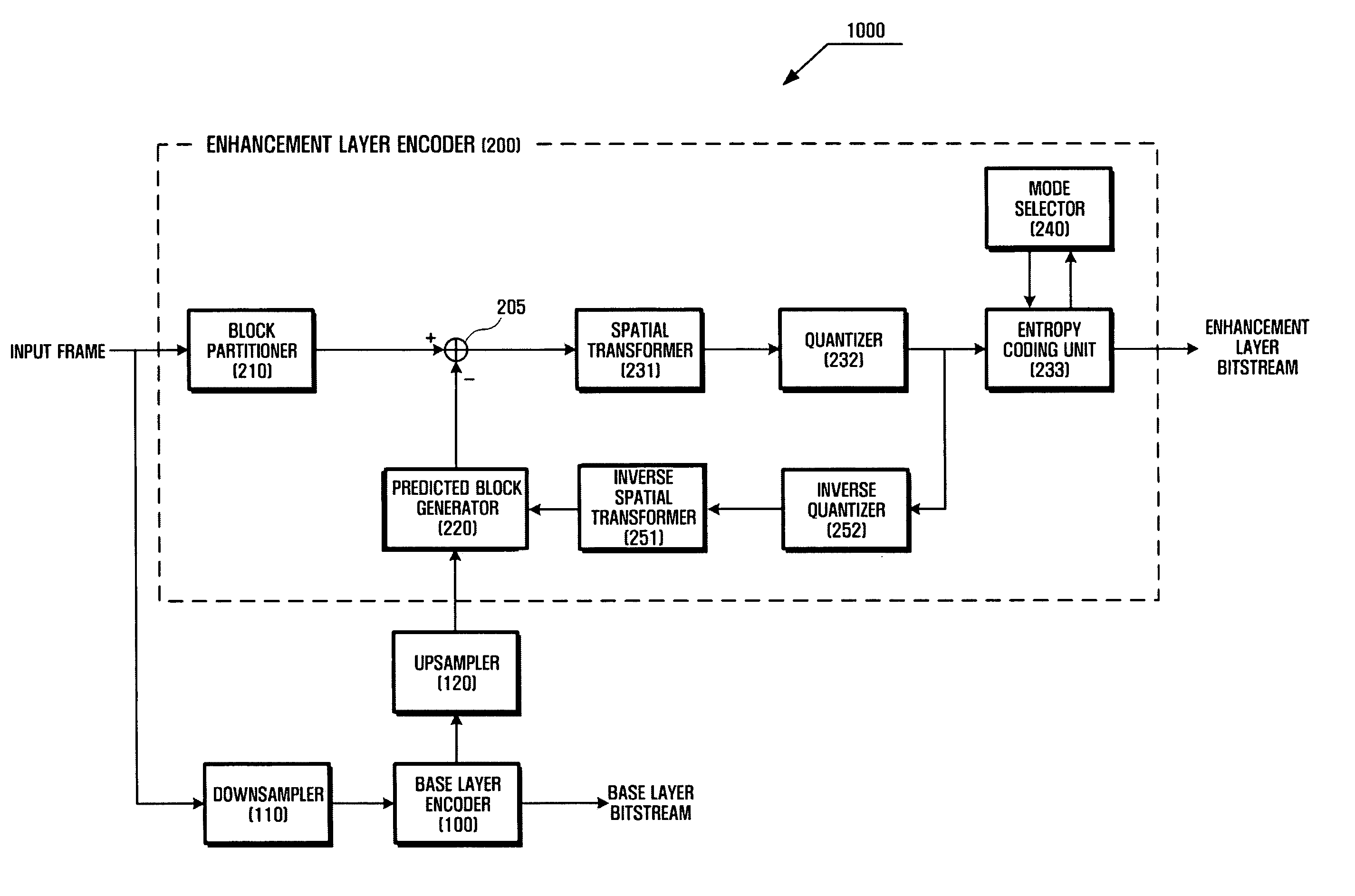
Method and apparatus for multi-layered video encoding and decoding
InactiveUS20060120450A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationSewerage structuresVideo encodingCompression method
A video compression method, and more particularly, a prediction method for efficiently eliminating redundancy within a video frame, and a video compression method and an apparatus using the prediction method are provided. There is provided a method for encoding video based on a multi-layer structure, including performing intra-prediction on a current intra-block using images of neighboring intra-blocks of the current intra-block to obtain a prediction residual, performing prediction on the current intra-block using an image of a lower layer region corresponding to the current intra-block to obtain a prediction residual, selecting one of the two prediction residuals that offers higher coding efficiency, and encoding the selected prediction residual.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
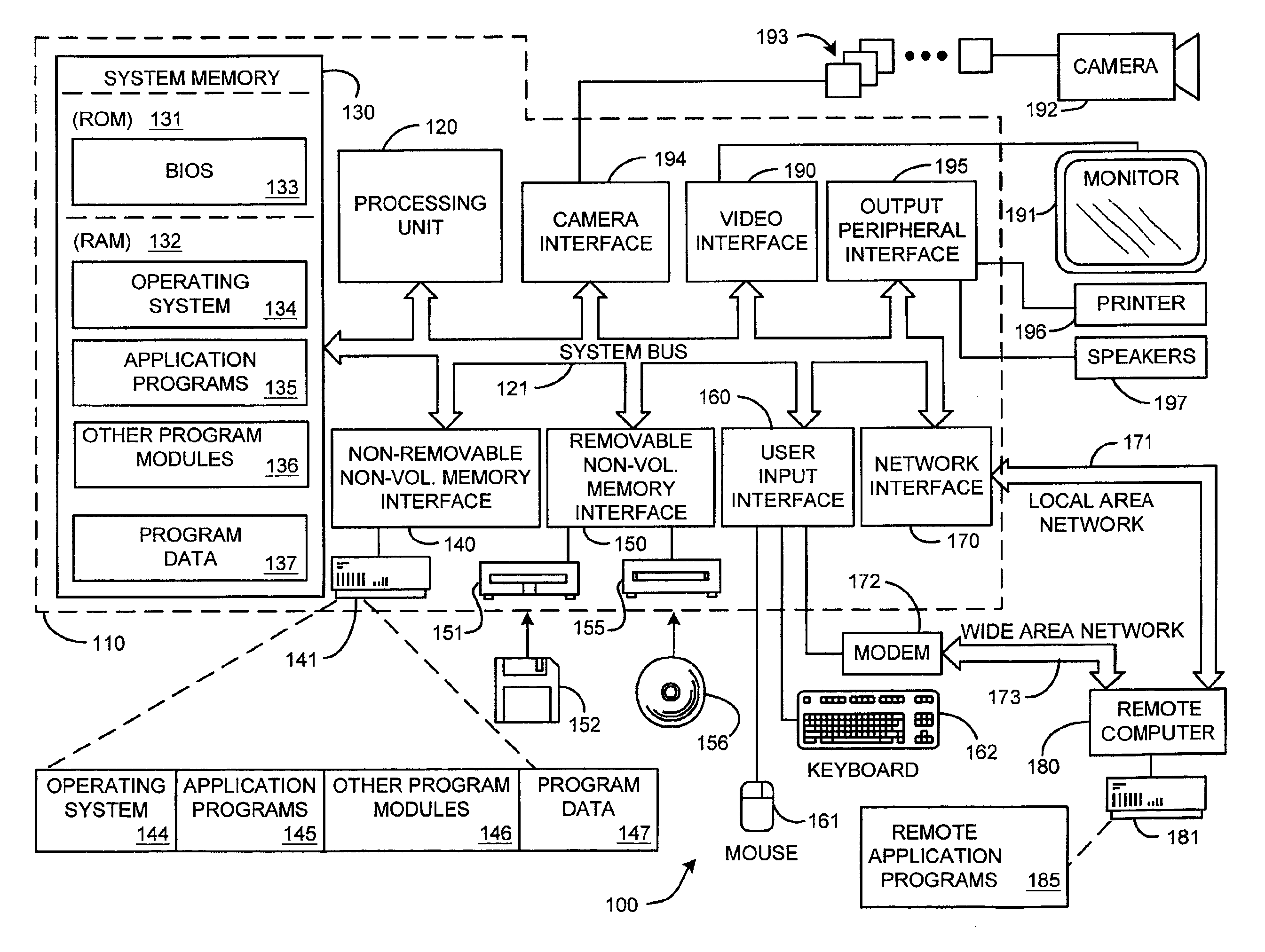
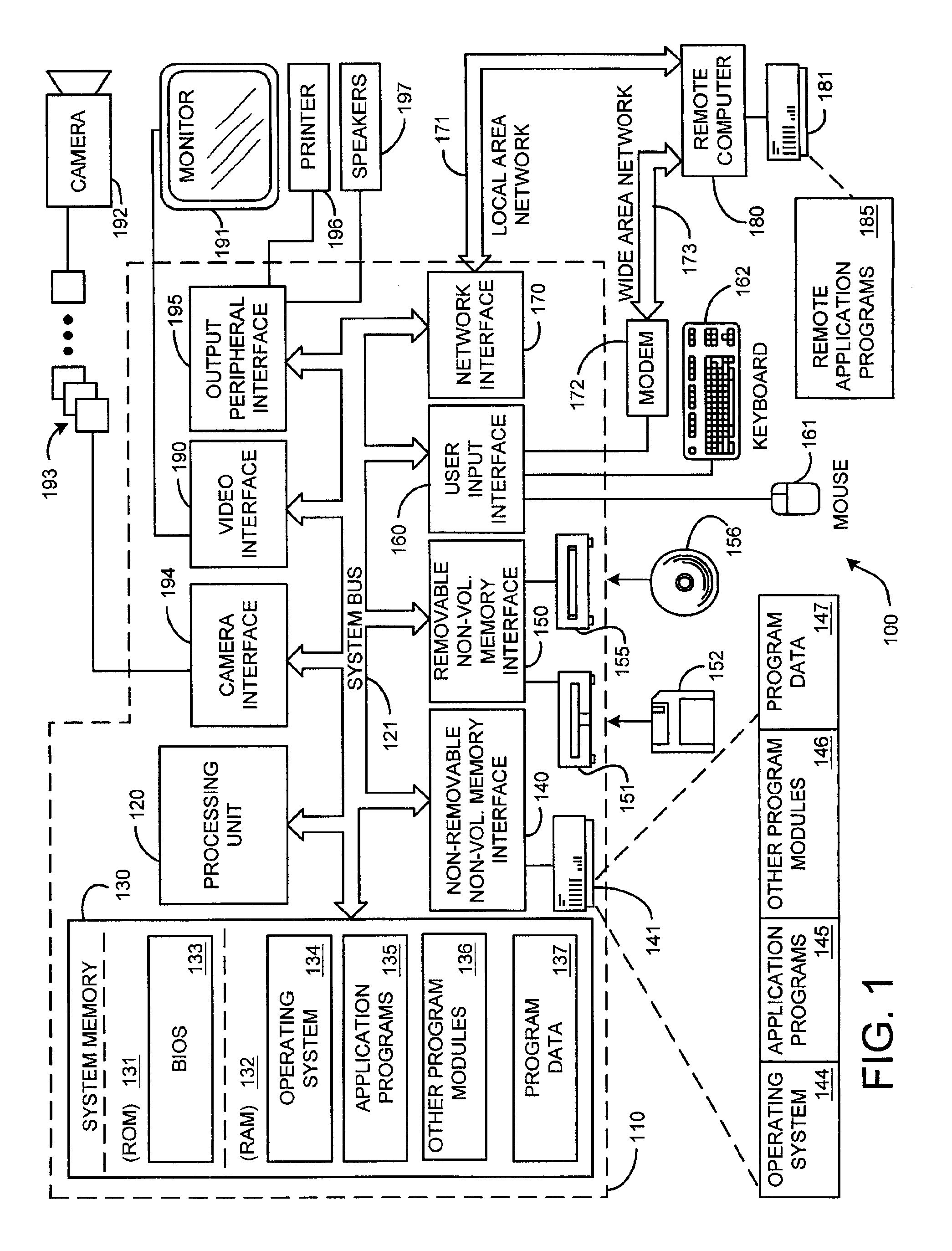
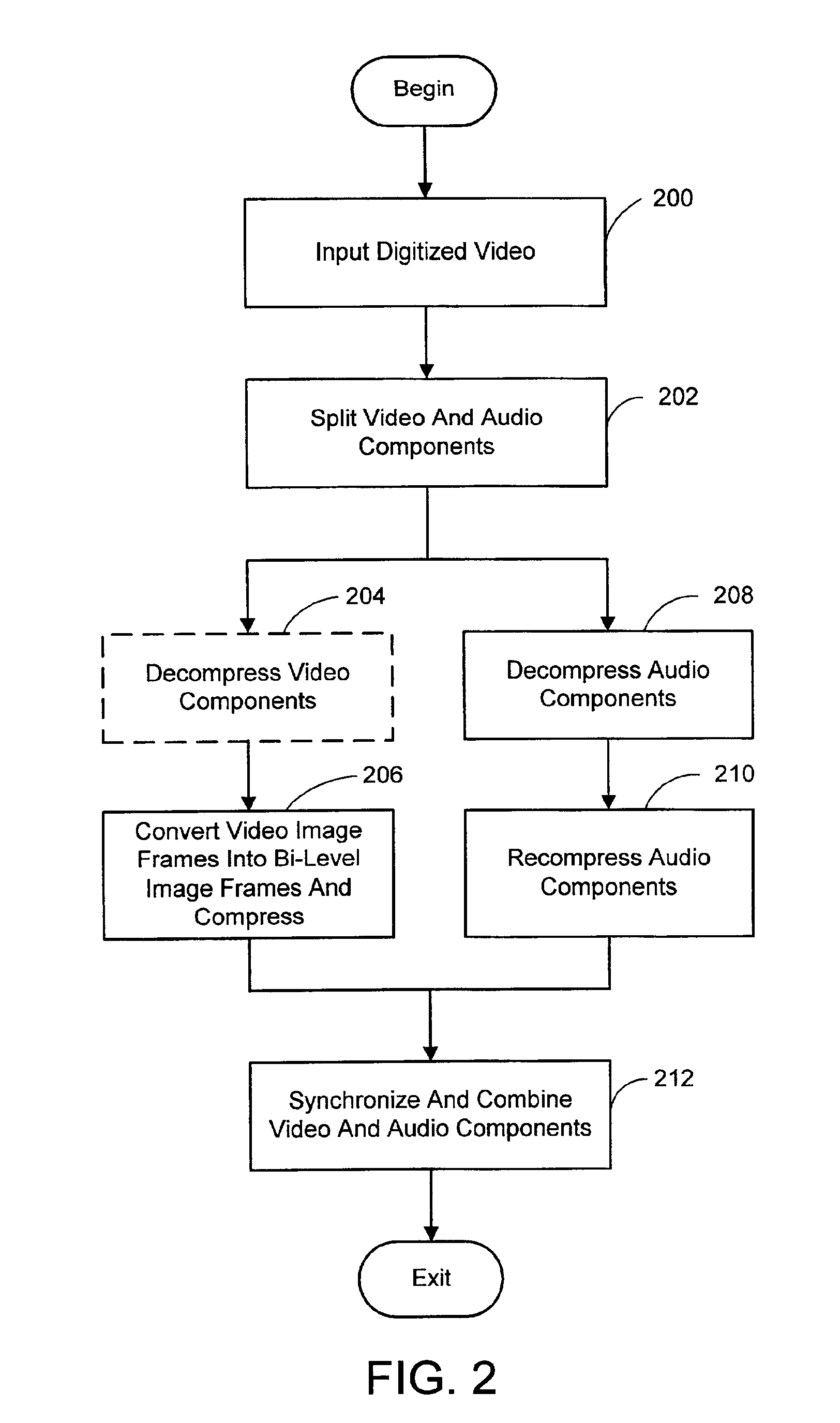
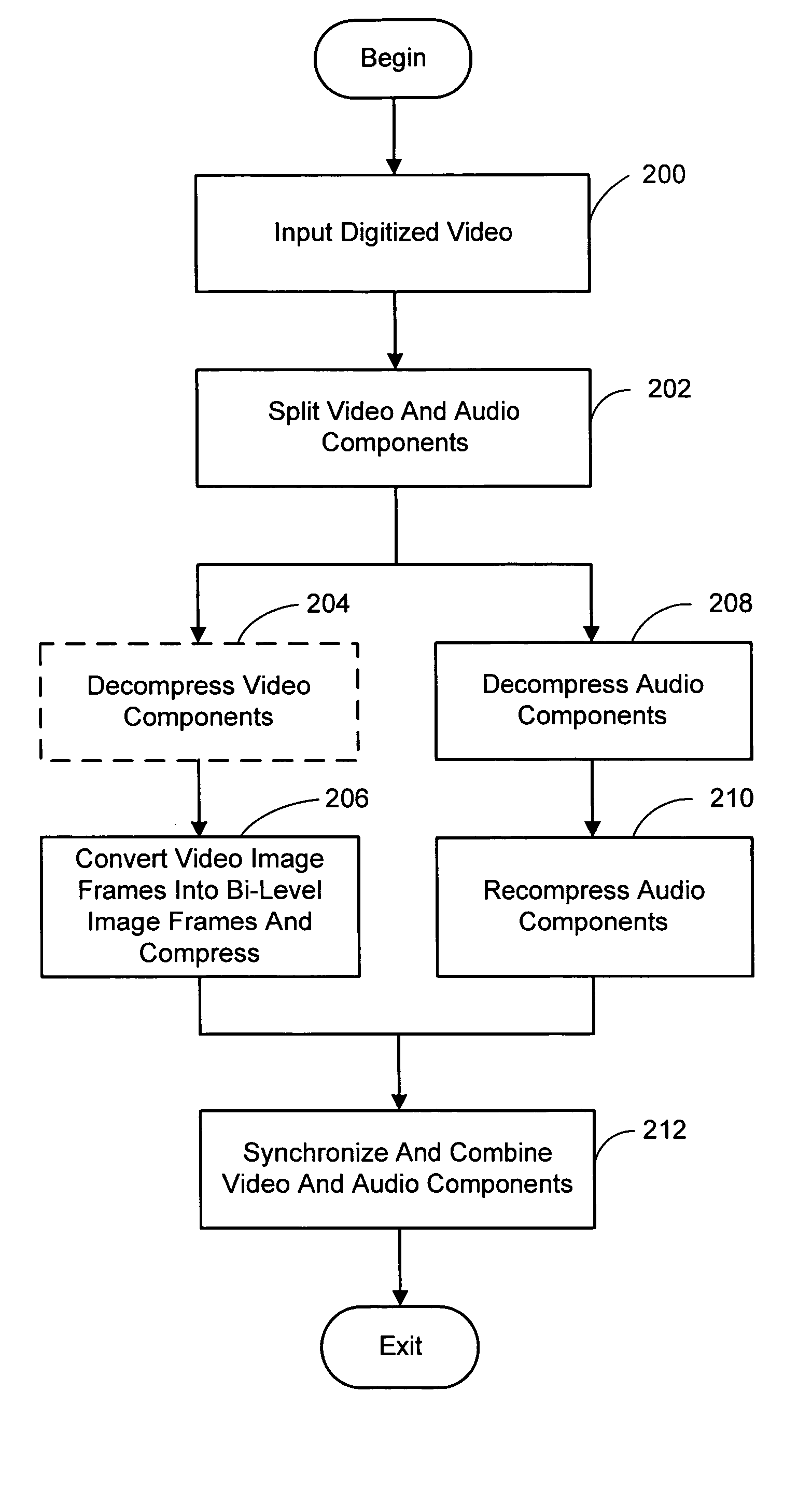
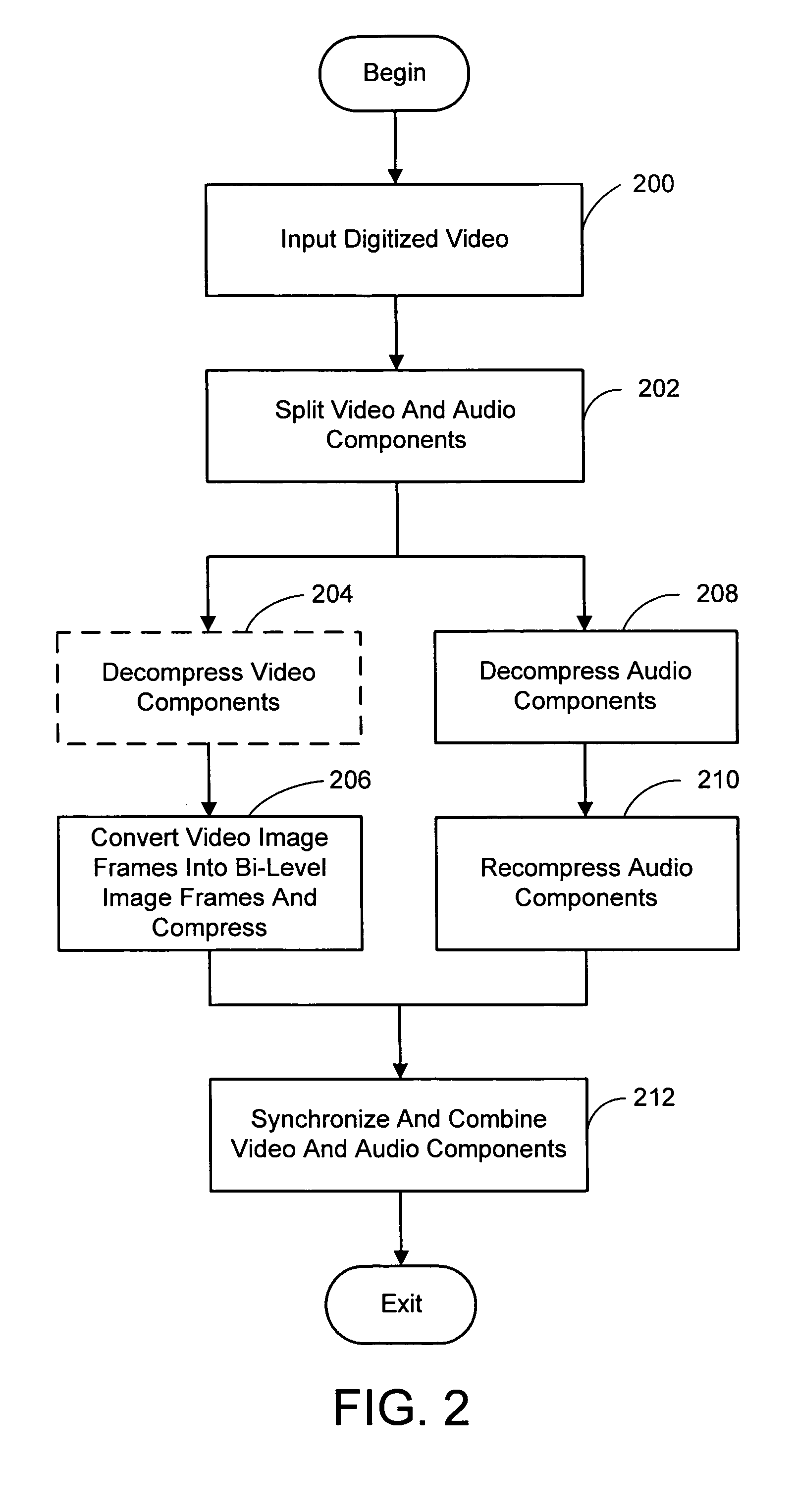
System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video
InactiveUS6888893B2Clear imagingLow bandwidthPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputer graphics (images)Arithmetic coding
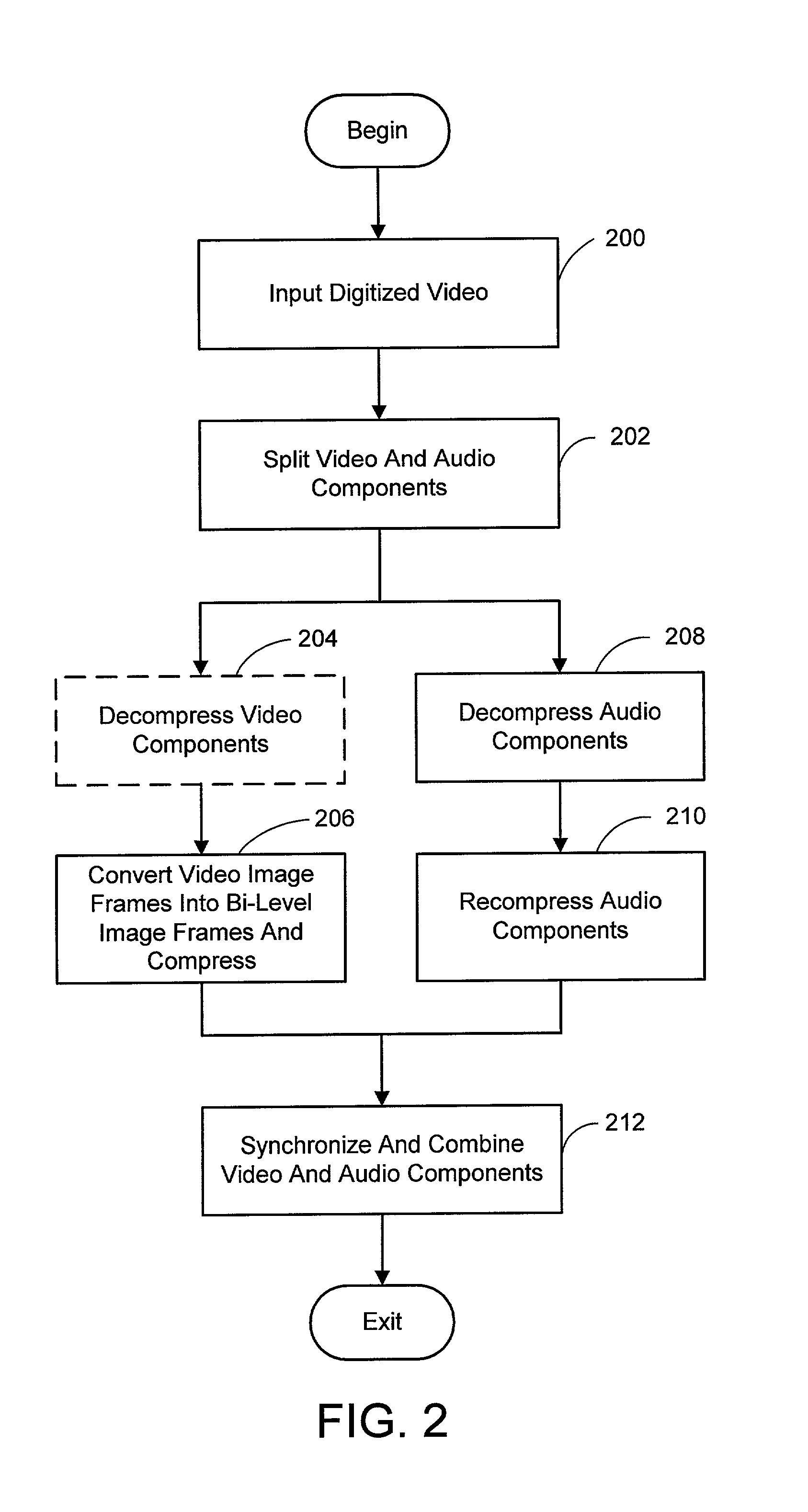
A system and process for broadcast and communication with bi-level or sketch video at extremely low bandwidths is described. Essentially, bi-level and sketch video presents the outlines of the objects in a scene being depicted. Bi-level and sketch video provides a clearer shape, smoother motion, shorter initial latency and cheaper computational cost than do conventional DCT-based video compression methods. This is accomplished by converting each color or gray-scale image frame to bi-level or sketch image frame using adaptive thresholding method, compressing bi-level or sketch image frames into bi-level or sketch video using adaptive context-based arithmetic coding method. Bi-level or sketch video is particularly suitable to such small devices as Pocket PCs and mobile phones that possess small display screen, low bandwidth connection, and light computational power.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
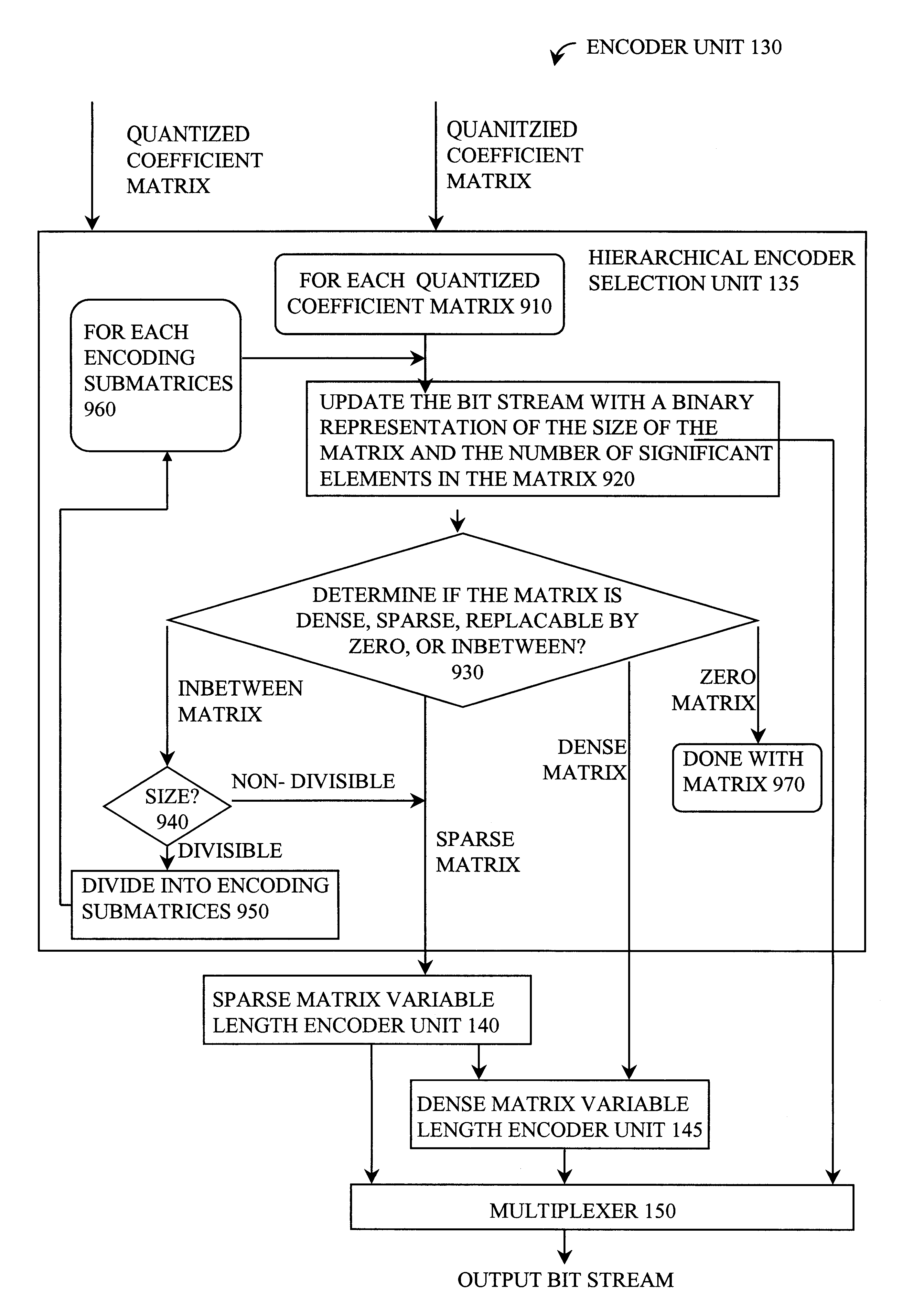
Video compression and decompression using dynamic quantization and/or encoding
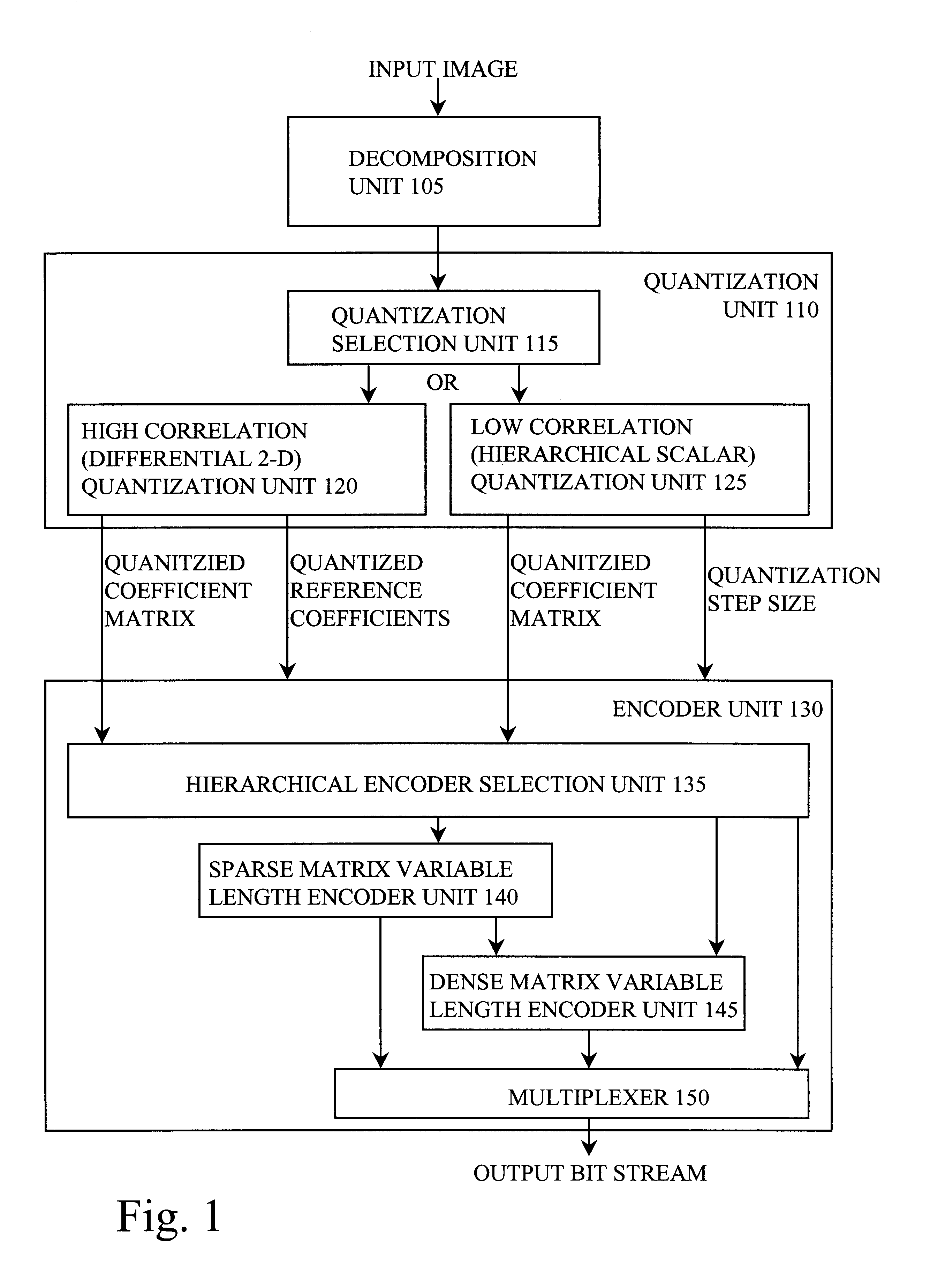
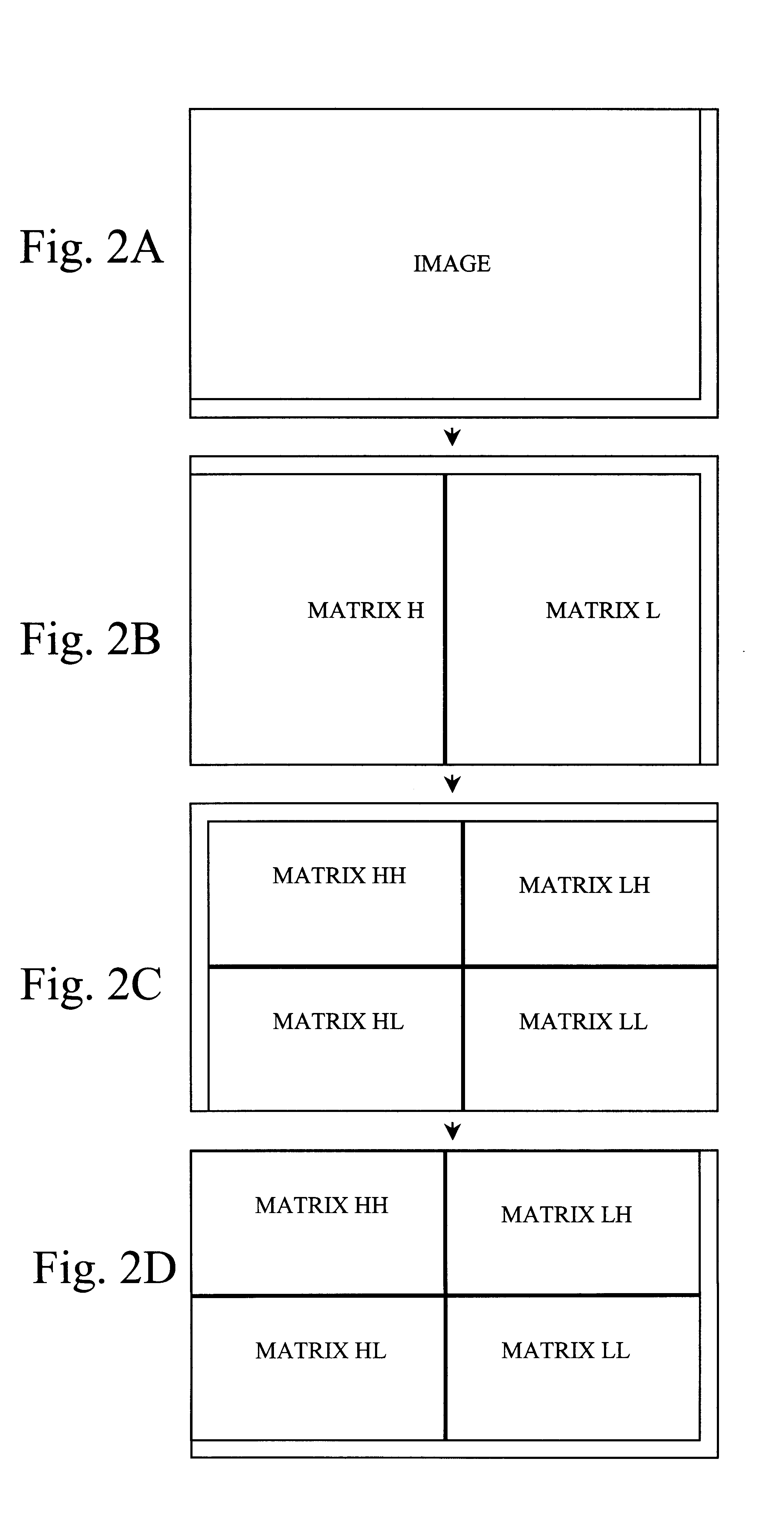
InactiveUS6249614B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionQuantization matrix
A method and apparatus for performing video compression and decompression using dynamic quantization and / or encoding. According to one aspect of the compression method, an image is recursively filtered into its constituent components each represented by a matrix of coefficients. Next, the level of correlation of a first of the matrices of coefficients is determined. Based on the level of correlation of this first coefficient matrix, one of a first quantization technique and a second quantization technique is selected. The first coefficient matrix is then quantized using the selected quantization technique.According to another aspect of the compression method, an image is digitally filtered into its constituent components, each represented by a matrix of coefficients. At least certain matrices are quantized to generated a first quantized matrix. The first quantized matrix is then recursively divided until the first quantized matrix or each of the resulting submatrices is sufficiently dense or sufficiently sparse. Each of the sufficiently dense matrices are encoded using a first technique, while each of the sufficiently sparse matrices are encoded a second technique.
Owner:XVD TECH HLDG LTD IRELAND
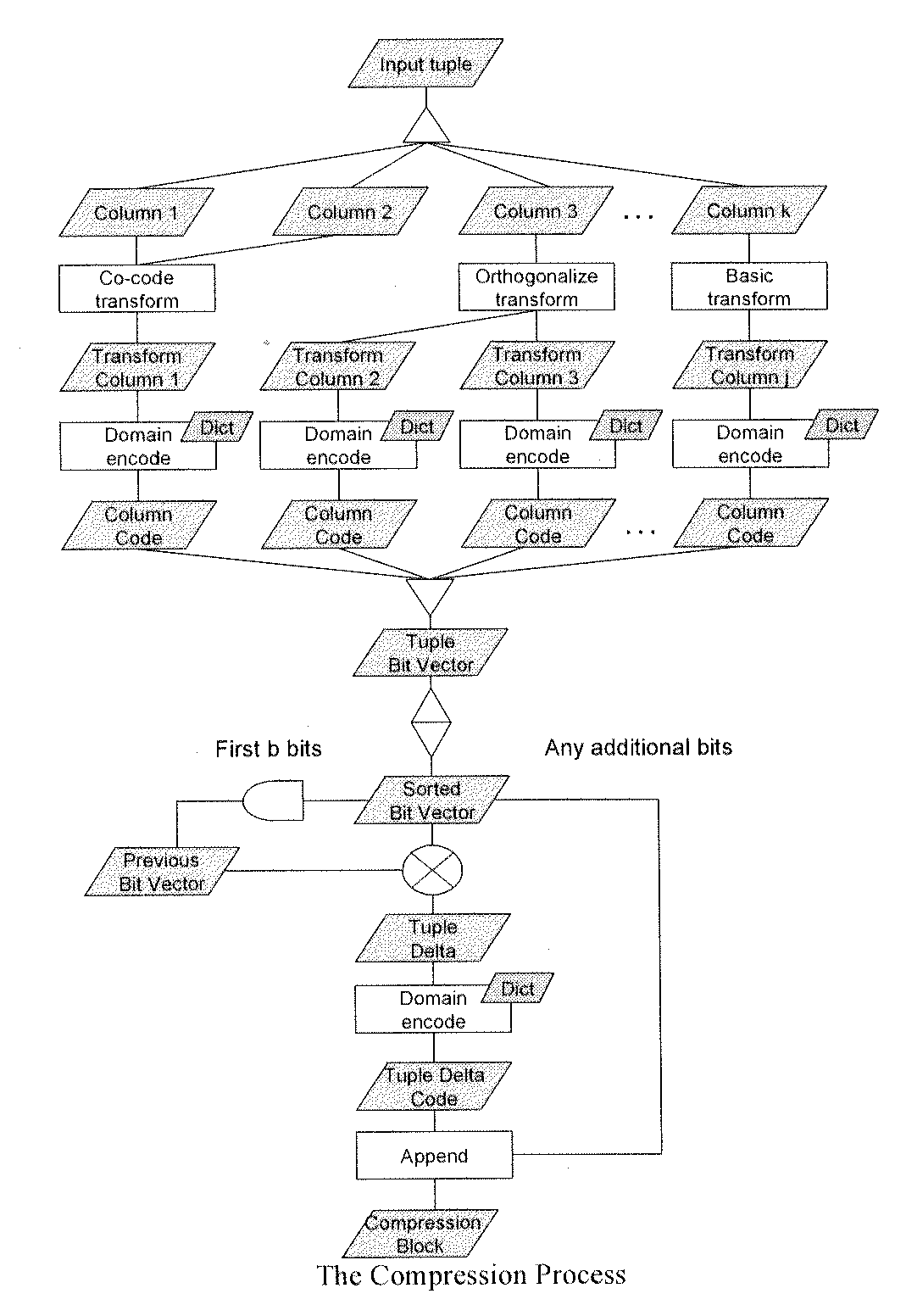
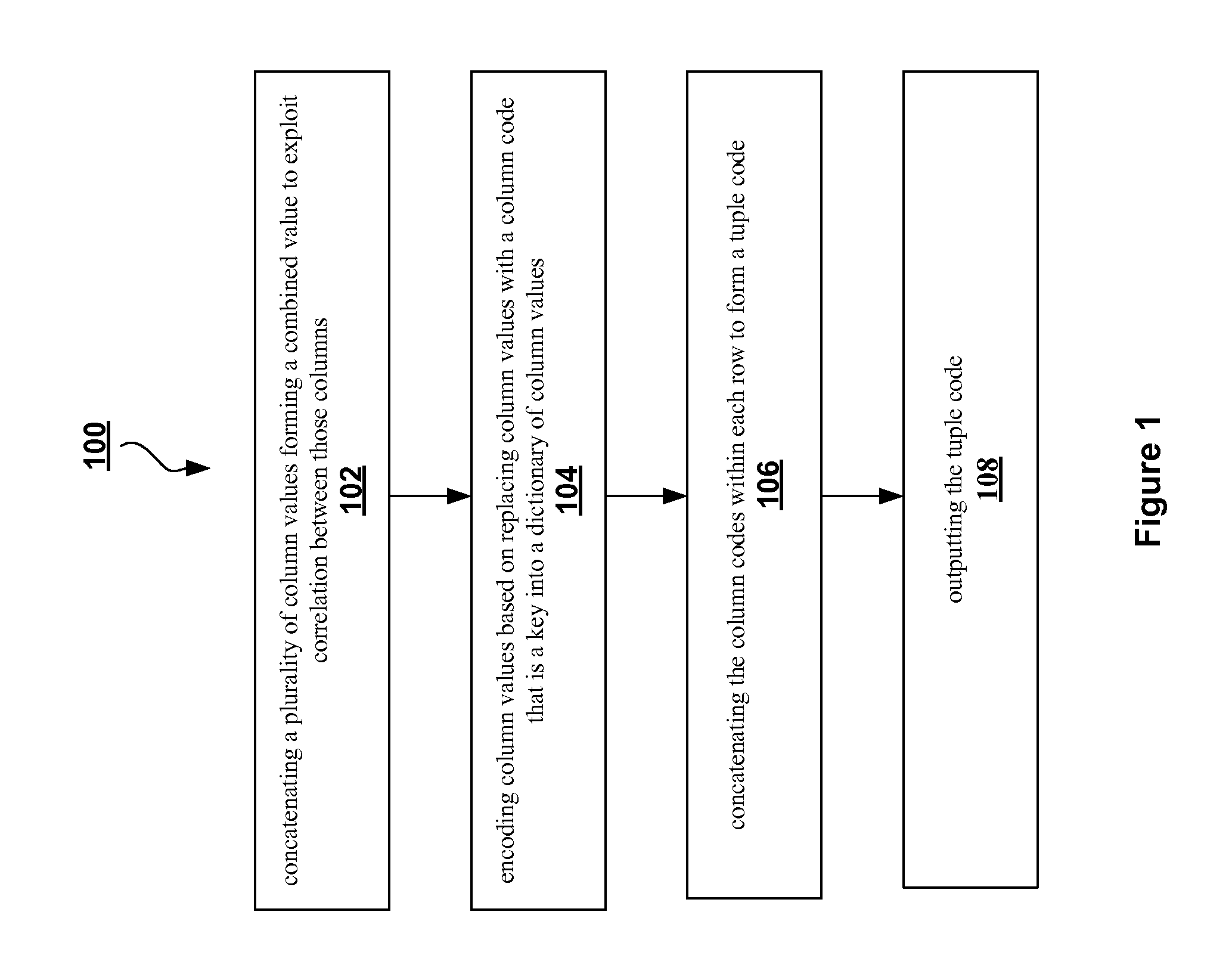
Compression method for relational tables based on combined column and row coding
InactiveUS20090006399A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsVariable-length codeTheoretical computer science
A robust method to compress relations close to their entropy while still allowing efficient queries. Column values are encoded into variable length codes to exploit skew in their frequencies. The codes in each tuple are concatenated and the resulting tuplecodes are sorted and delta-coded to exploit the lack of ordering in a relation. Correlation is exploited either by co-coding correlated columns, or by using a sort order that can leverage the correlation. Also presented is a novel Huffman coding scheme, called segregated coding, that preserves maximum compression while allowing range and equality predicates on the compressed data, without even accessing the full dictionary. Delta coding is exploited to speed up queries, by reusing computations performed on nearly identical records.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and apparatus for a portable toy video/audio visual program player device - "silicon movies" played on portable computing devices such as pda (personal digital assistants) and other "palm" type, hand-held devices
InactiveUS20060148569A1Reduce in quantityLow costDigital video signal modificationVideo gamesData compressionDigital data
A portable audio / visual program player comprising a video display, electrical-audio transducer, a central processing unit and associated logic and memory circuits. The portable audio / visual player is able to play pre-recorded programs from a memory device, which includes compress digital audio and video program information and a decoder program. The digital compression method comprises a series of compression methods to greatly reduce the amount of digital data. The data compression method is particularly suitable for motion video comprising cartoons and similar images, but is also suitable for other applications.
Owner:BECK STEPHEN C
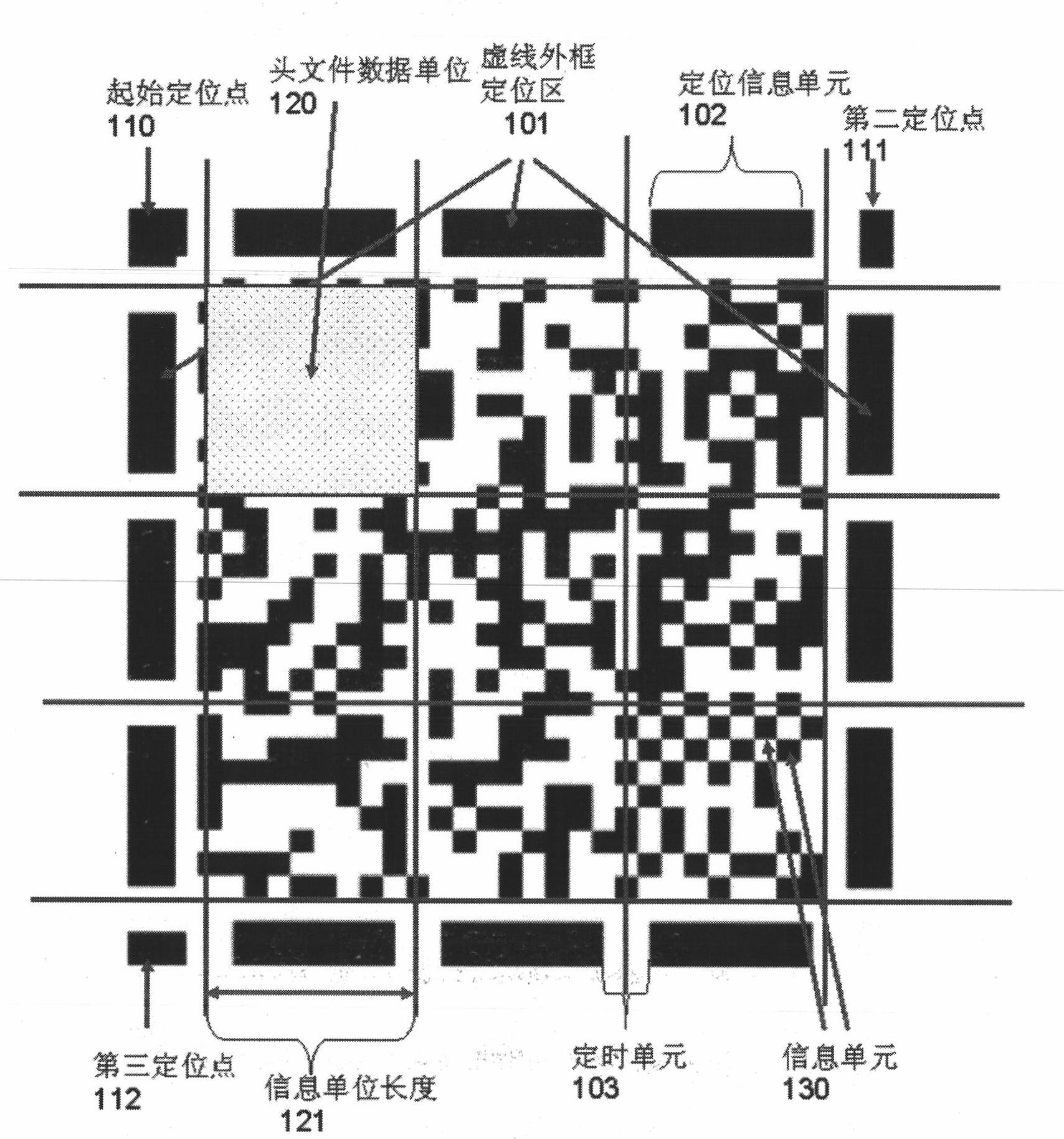
Novel high-capacity two-dimensional barcode and system, encoding and decoding methods and applications thereof
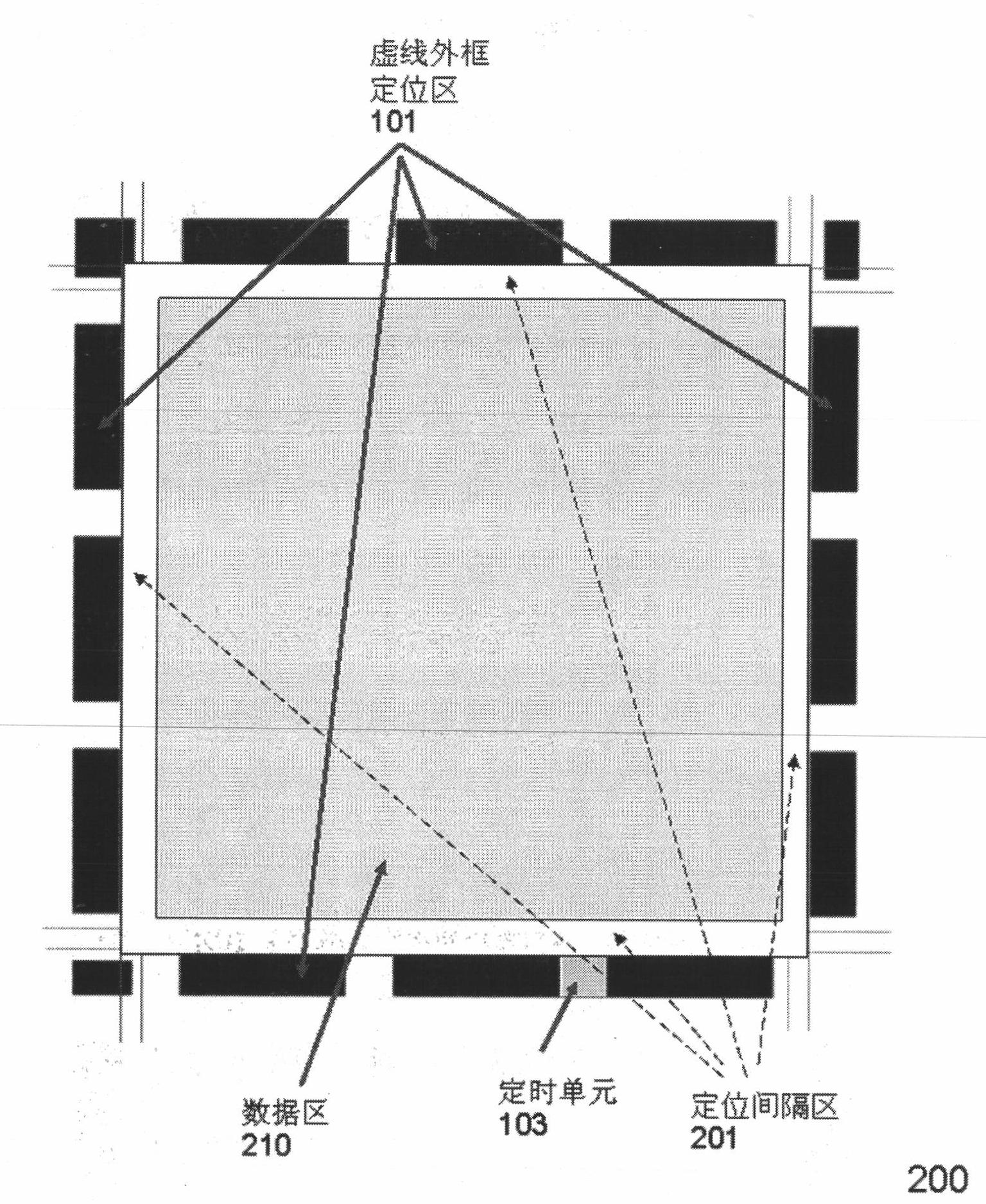
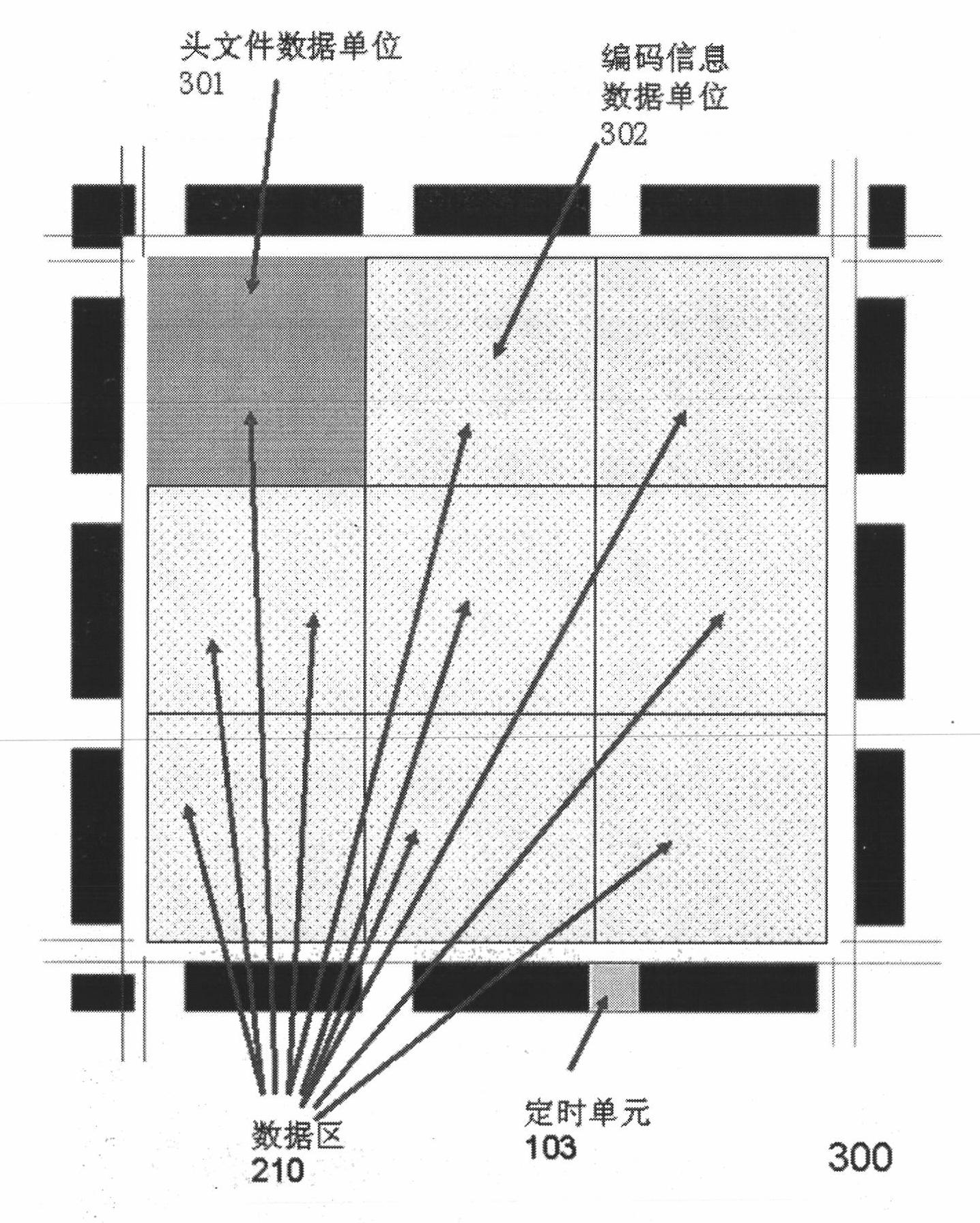
InactiveCN102034127ALarge capacityRapid positioningRecord carriers used with machinesSensing by electromagnetic radiationDecoding methodsBarcode
The invention discloses a novel high-capacity two-dimensional barcode and a system suitable for mobile phones and special equipment, and encoding and decoding methods and applications thereof. The high-capacity two-dimensional barcode is composed of a positioning area, a positioning interval area and a data area, wherein the positioning area is composed of a positioning dotted outline border, positioning points, a positioning information unit and a timing unit; the data area is composed of a header file area and a code information area; the information compression technology, the information coding technology and the information encryption technology are used in the two-dimensional barcode; the two-dimensional barcode can control the error correction level of error correction encoding, the amount of encoding information, the compression method of the information and the encryption method of the information; and in the process of decoding, the dynamic decoding can be performed according to the header file information of the two-dimensional barcode. The two-dimensional barcode is high in capacity, can be positioned quickly so as to carry out all-round code reading, can encrypt information, and can read the information of the two-dimensional barcode by designated special decryption keys or designated decryption devices.
Owner:上海易悠通信息科技有限公司
Flash-based data archive storage system
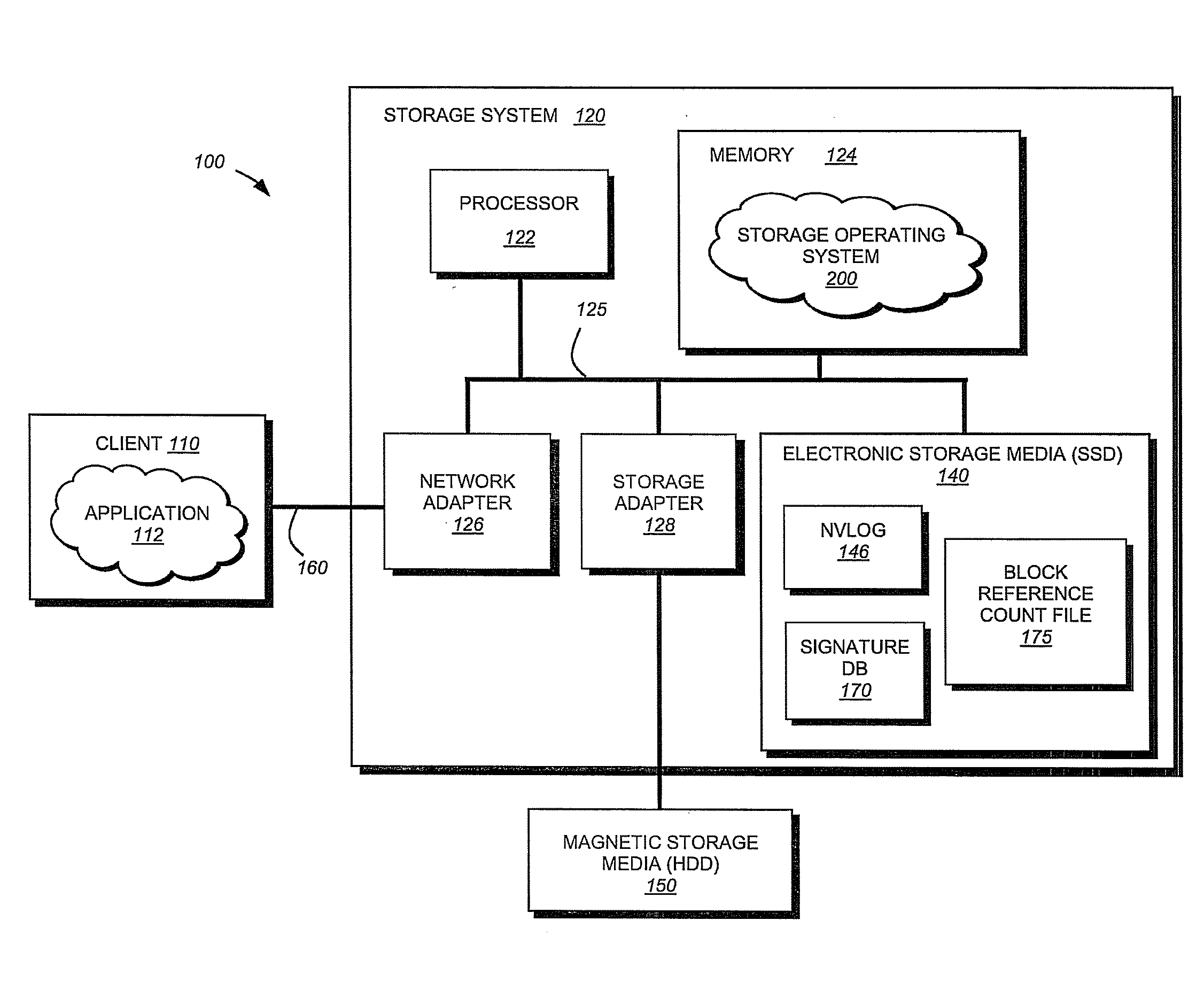
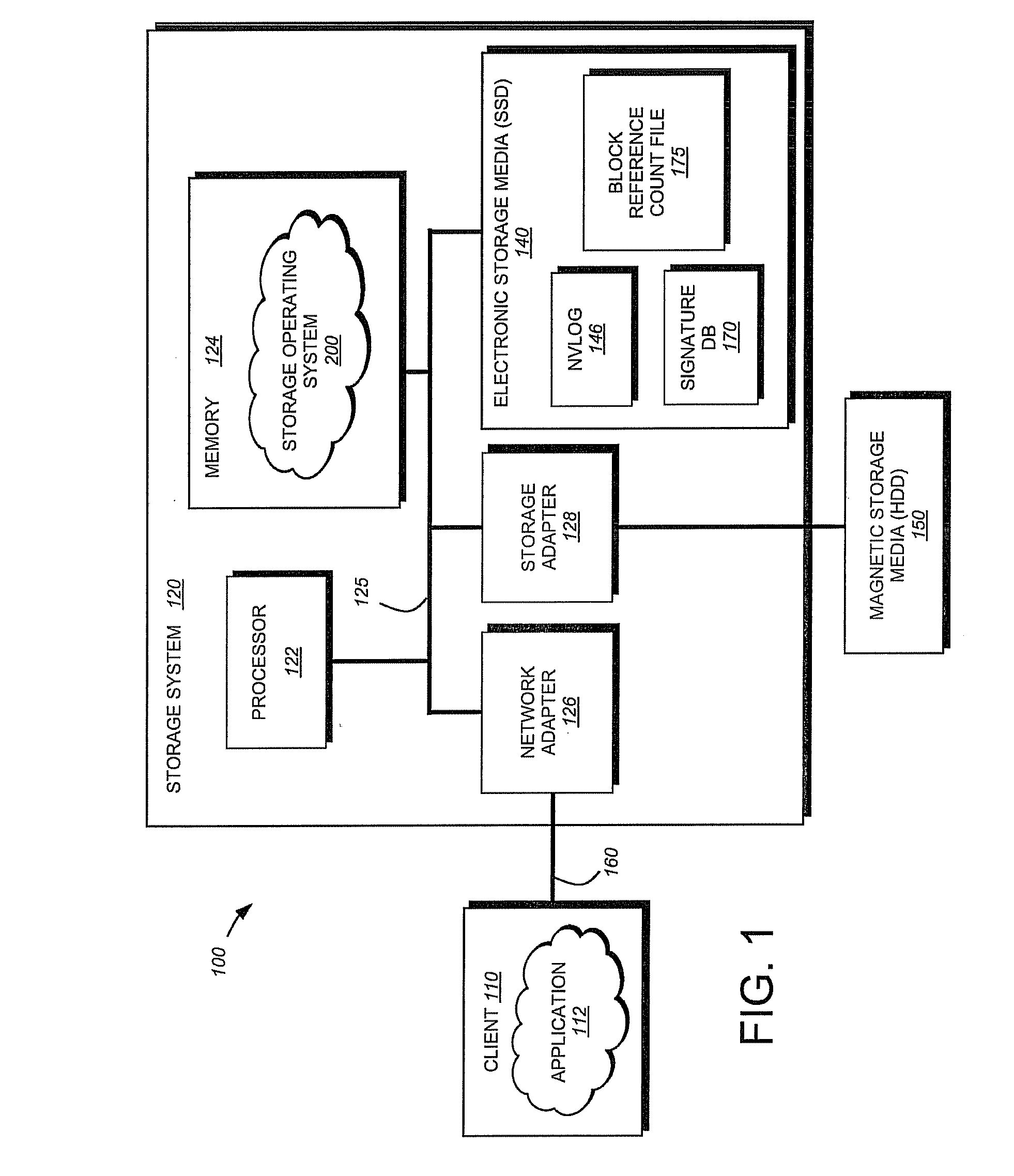
InactiveUS20100281207A1Large capacityMore capacityEnergy efficient ICTMemory loss protectionMass storageMagnetic tape
A flash-based data archive storage system having a large capacity storage array constructed from a plurality of dense flash devices is provided. The flash devices are illustratively multi-level cell (MLC) flash devices that are tightly packaged to provide a low-power, high-performance data archive system having substantially more capacity per cubic inch than more dense tape or disk drives. The flash-based data archive system may be adapted to employ conventional data de-duplication and compression methods to compactly store data. Furthermore, the flash-based archive system has a smaller footprint and consumes less power than the tape and / or disk archive system.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
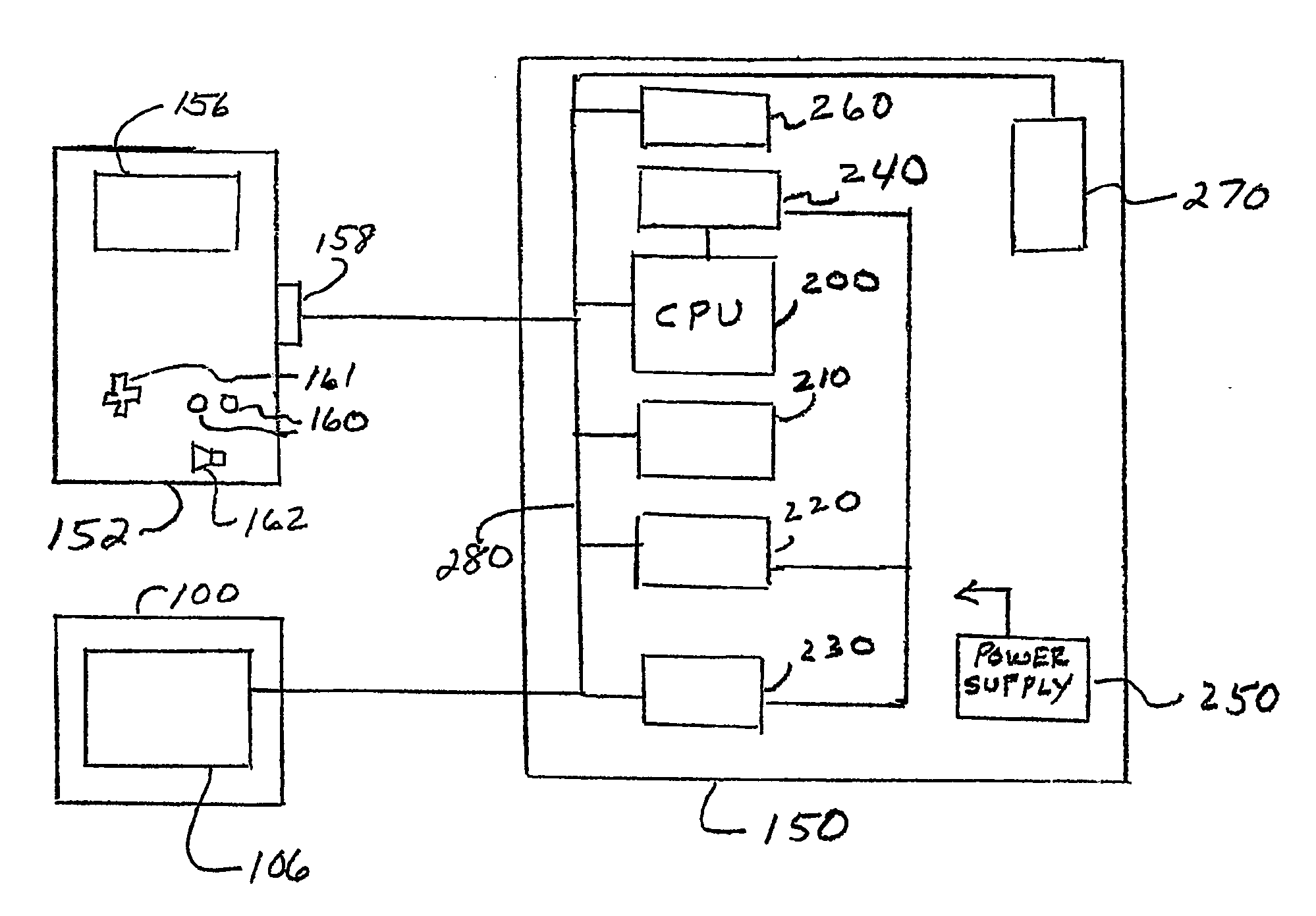
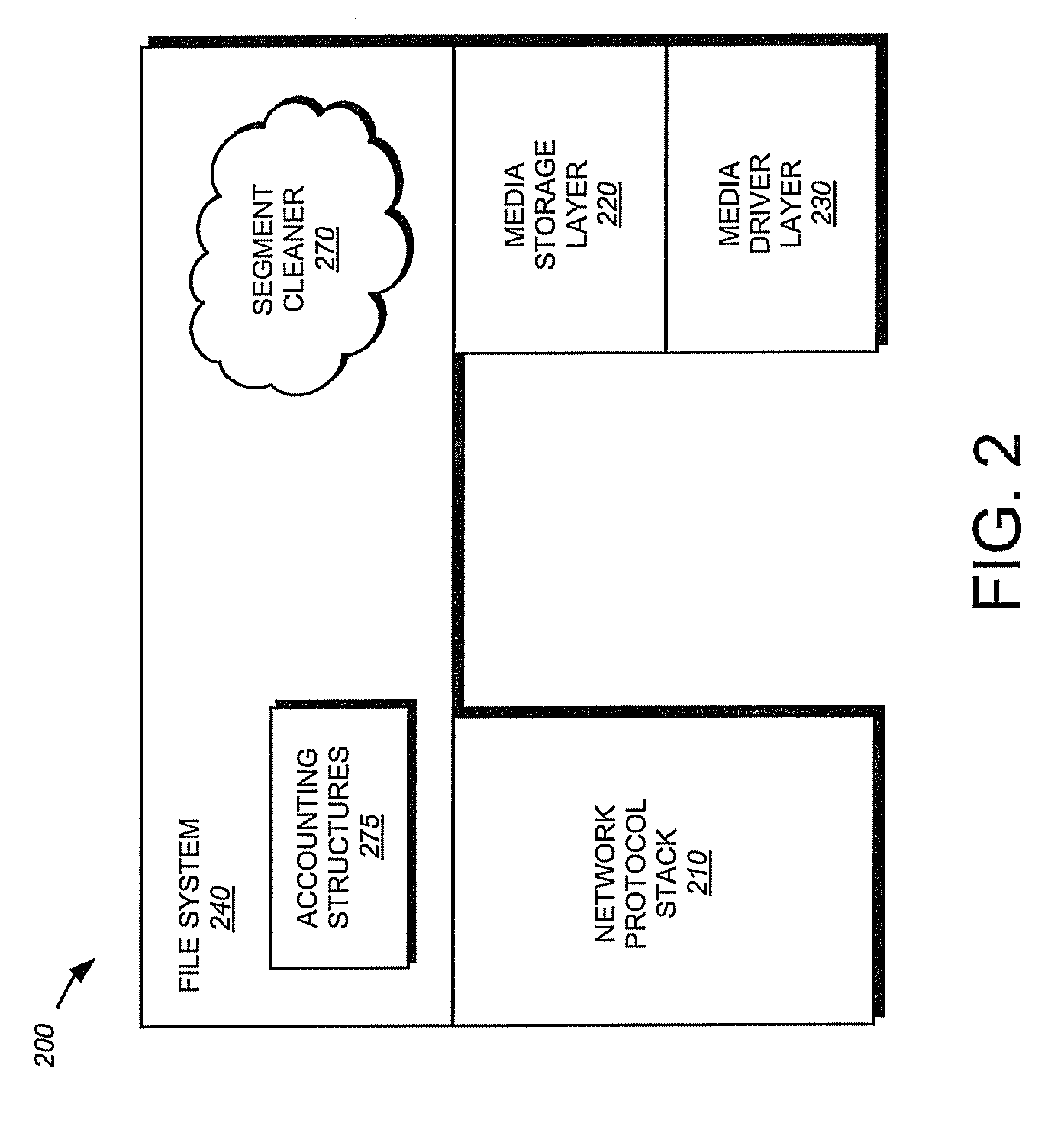
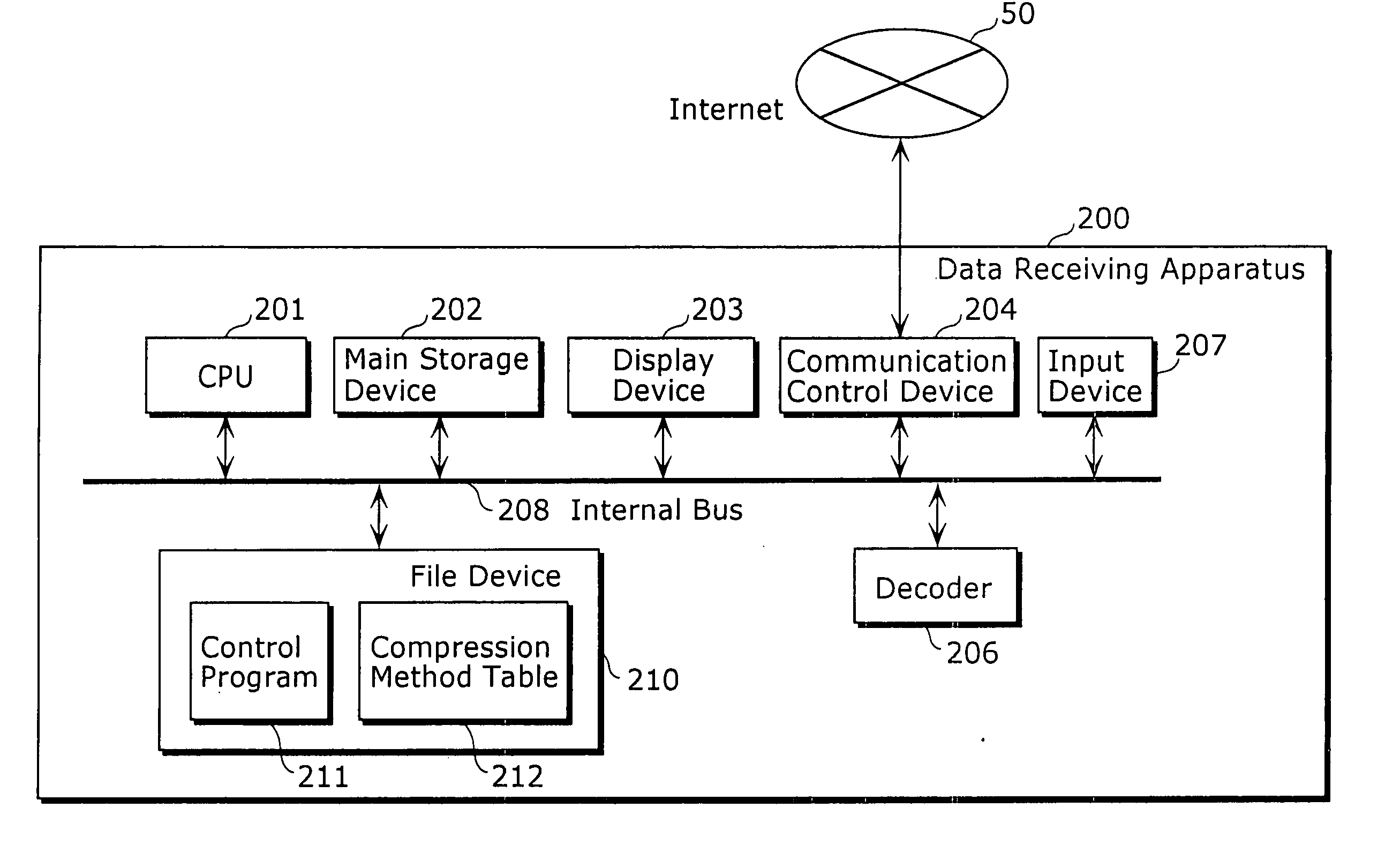
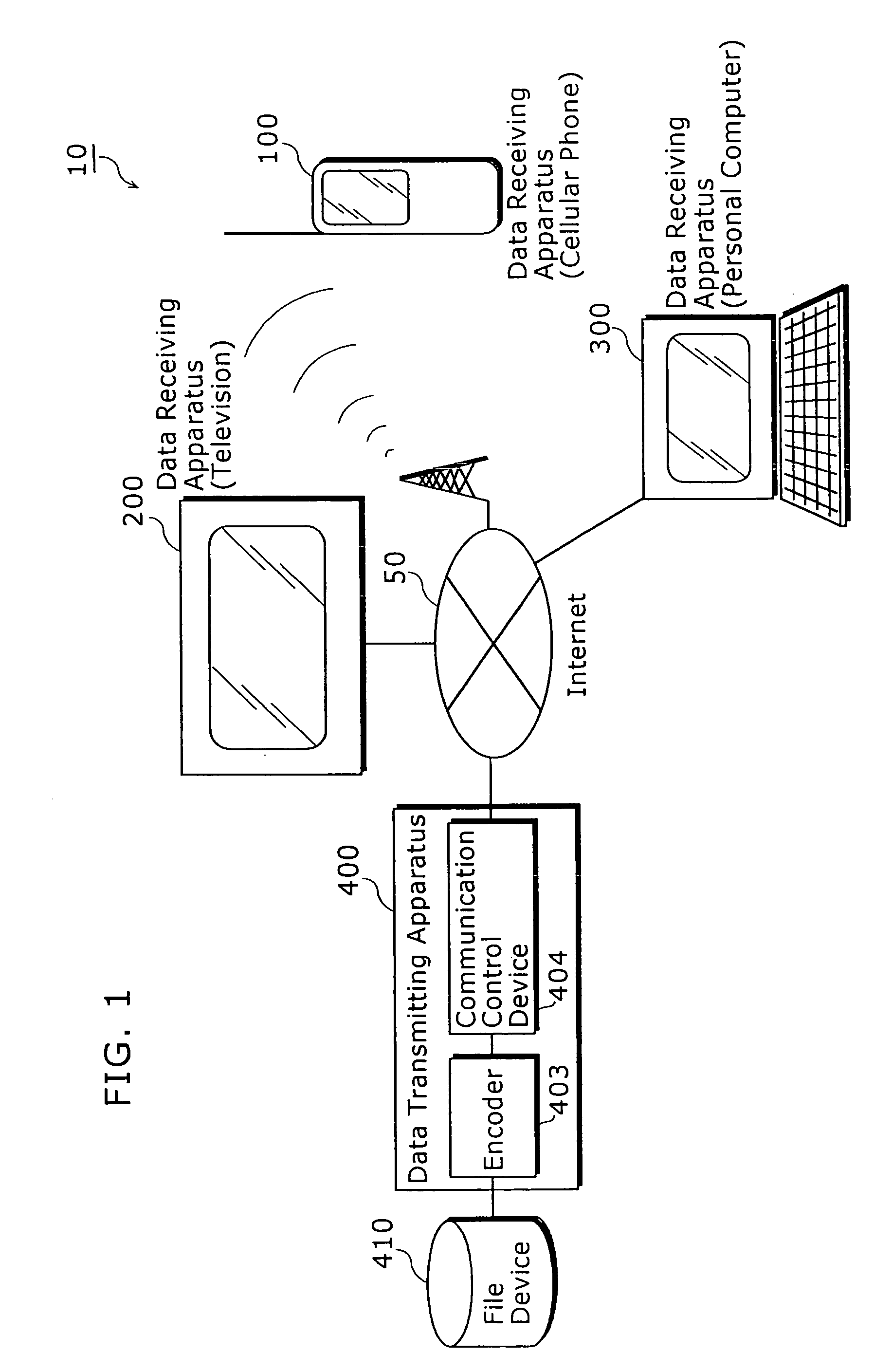
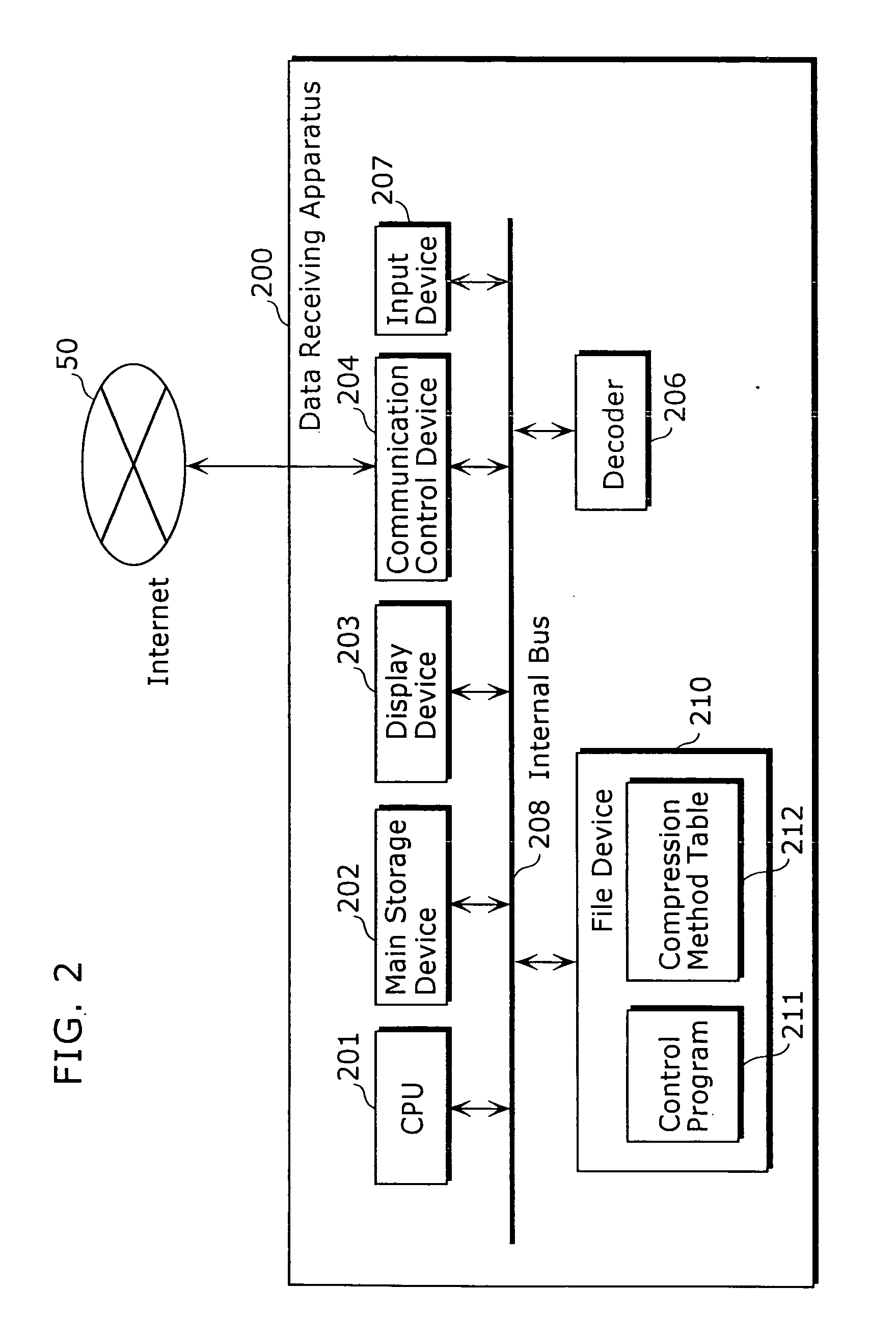
Data transmitting apparatus, data receiving apparatus, data transmitting manner, and data receiving manner
InactiveUS20050204046A1Reduce storage areaGuaranteed normal transmissionMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsComputer hardwareContent distribution
A data receiving apparatus 200 transmits, to a data transmitting apparatus 400, a content ID, a compression method and an extent of a bit rate (S1201). The data transmitting apparatus 400 specifies the compression method and the bit rate and replies to the data receiving apparatus 200 (S1202). The data transmitting apparatus 400 performs decoding of content by the compression method and starts a distribution of content at the bit rate (S1207). During this time, when receiving a “bit rate change request” from the data receiving apparatus 200 (S1208), the data transmitting apparatus 400 notifies, to the data receiving apparatus 200, by determining a new bit rate (S1210) and restarts the content distribution at the changed bit rate (S1213 to S1215).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video
ActiveUS20050041739A1Eliminating the unwanted backgroundColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionBi layerComputer graphics (images)
A system and process for broadcast and communication with bi-level or sketch video at extremely low bandwidths is described. Essentially, bi-level and sketch video presents the outlines of the objects in a scene being depicted. Bi-level and sketch video provides a clearer shape, smoother motion, shorter initial latency and cheaper computational cost than do conventional DCT-based video compression methods. This is accomplished by converting each color or gray-scale image frame to bi-level or sketch image frame using adaptive thresholding method, compressing bi-level or sketch image frames into bi-level or sketch video using adaptive context-based arithmetic coding method. Bi-level or sketch video is particularly suitable to such small devices as Pocket PCs and mobile phones that possess small display screen, low bandwidth connection, and light computational power.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Direct compression metformin hydrochloride tablets
InactiveUS6117451AGood compressibilityImproved flowabilityPowder deliveryBiocideMetformin HydrochlorideHigh doses
Metformin Hydrochloride (herein referred to as metformin HCl) that may be 98.5%-100% pure is a high dose drug capable of being directly compressed with specific excipients into tablets having desired, hardness, disintegrating ability, and acceptable dissolution characteristics. Metformin HCl is not inherently compressible and thus presents formulation problems. Excipients used in the formulation enhance the flow and compaction properties of the drug and tableting mix. Optimal flow contributes to uniform die fill and weight control. The binder used ensures sufficient cohesive properties that allow metformin HCl to be compressed using the direct compression method. The tablets produced provide an acceptable in-vitro dissolution profile.
Owner:PHARMALOGIX
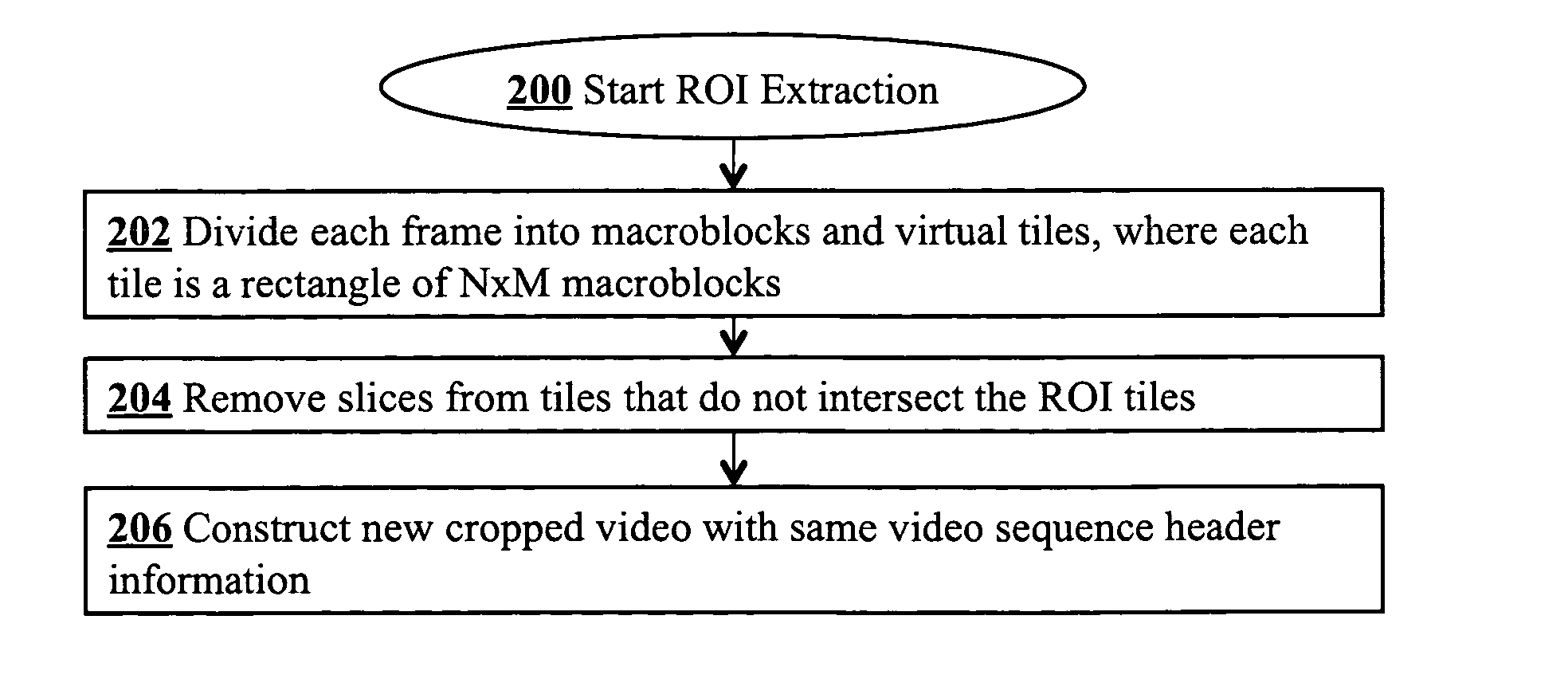
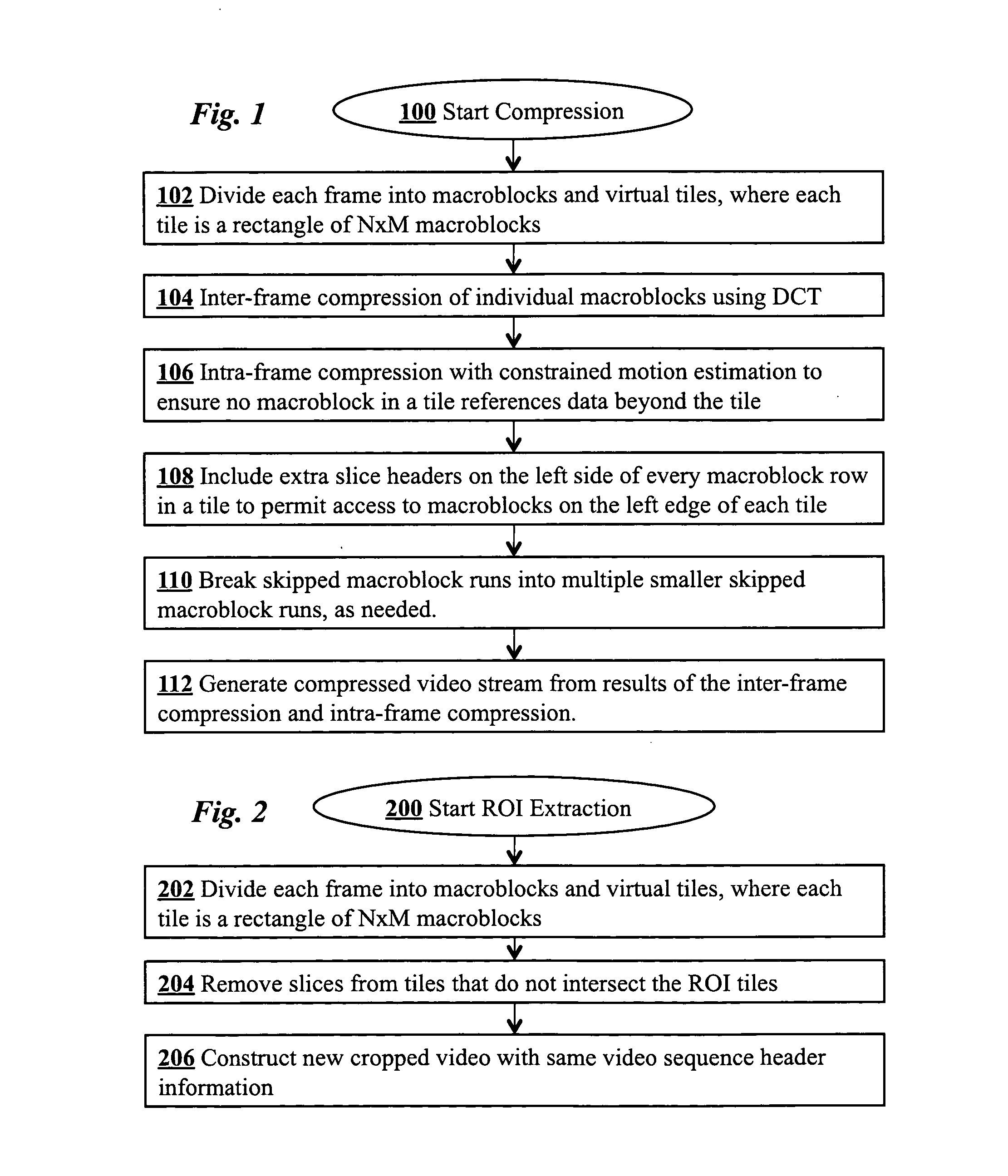
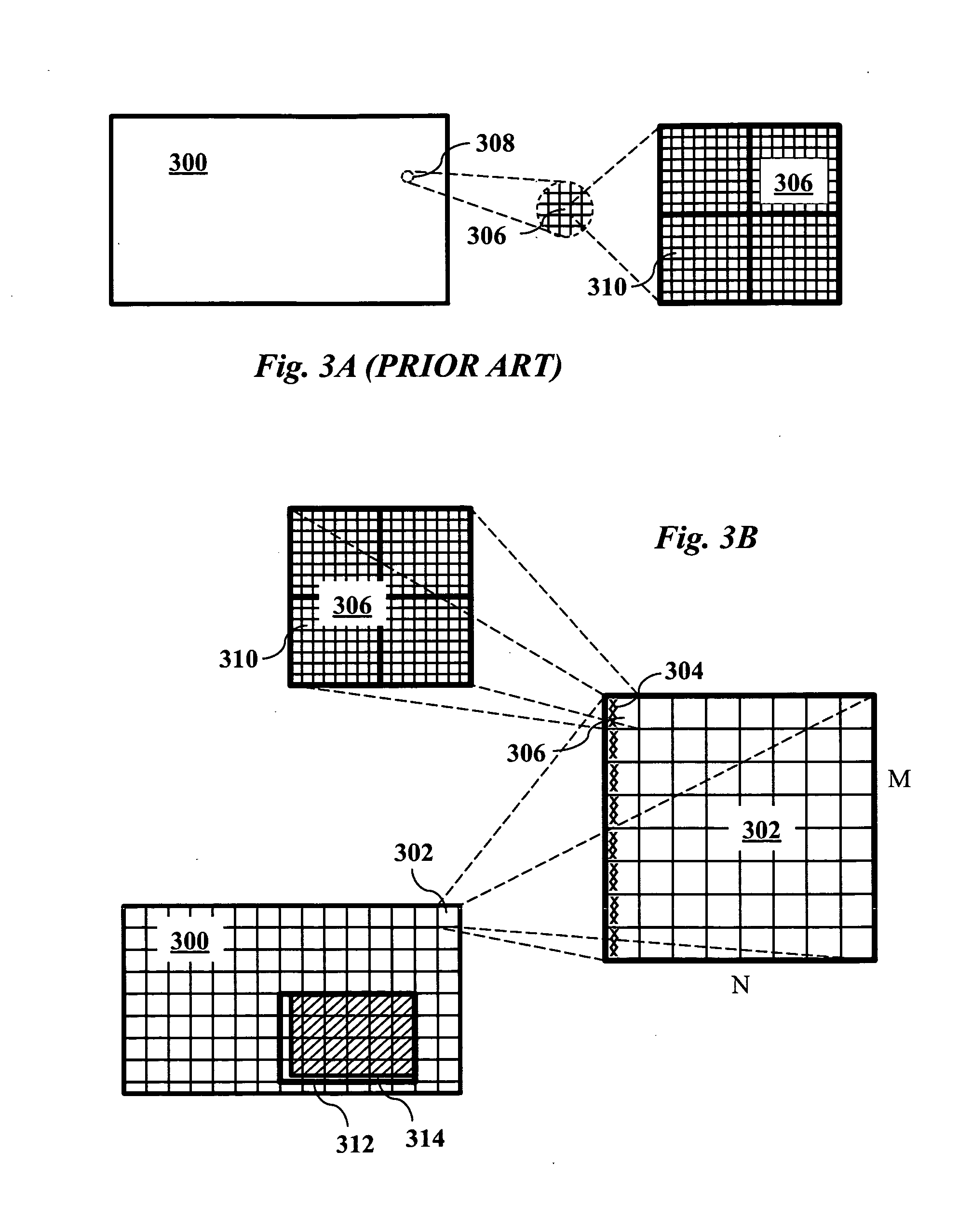
Supporting region-of-interest cropping through constrained compression
InactiveUS20100232504A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
Region-of-interest cropping of high-resolution video is supported video compression and extraction methods. The compression method divides each frame into virtual tiles, each containing a rectangular array of macroblocks. Intra-frame compression uses constrained motion estimation to ensure that no macroblock references data beyond the edge of a tile. Extra slice headers are included on the left side of every macroblock row in the tiles to permit access to macroblocks on the left edge of each tile during extraction. The compression method may also include breaking skipped macroblock runs into multiple smaller skipped macroblock runs. The extraction method removes slices from virtual tiles that intersect the region-of-interest to produce cropped frames. The cropped digital video stream and the compressed digital video stream have the same video sequence header information.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV
Routing loop detecting method and system based on SDN
ActiveCN105721297AImprove detection efficiencyImprove detection accuracyData switching networksTheoretical computer scienceStructure of Management Information
The invention discloses a routing loop detecting method based on a SDN. The routing loop detecting method comprises the following steps of: obtaining routing table information and routing event information of each node in a network in real time; constructing a real-time topological structure of the network according to the obtained routing table information and routing event information; constructing a multi-routing-form prefix tree matched with the longest prefix by adopting a hierarchical compression method according to the real-time topological structure, and storing a forwarding subnet segment in the routing table of each node; generating a routing next-hop table for each subnet node in the prefix tree in the subnet segment, in which the loop is necessary to judge, and traversing each subnet node of the prefix tree to generate a node forwarding figure; and judging whether the routing loop exists or not according to the node forwarding figure. The invention further discloses a routing loop detecting system based on the SDN. By means of the routing loop detecting method and system based on the SDN, the routing loop detection efficiency and accuracy are increased; and simultaneously, the storage space and the calculation time are reduced.
Owner:BEIJING CHINA POWER INFORMATION TECH +4
System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video
InactiveUS20020126755A1Clear imagingLow bandwidthColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Arithmetic coding
A system and process for broadcast and communication with bi-level or sketch video at extremely low bandwidths is described. Essentially, bi-level and sketch video presents the outlines of the objects in a scene being depicted. Bi-level and sketch video provides a clearer shape, smoother motion, shorter initial latency and cheaper computational cost than do conventional DCT-based video compression methods. This is accomplished by converting each color or gray-scale image frame to bi-level or sketch image frame using adaptive thresholding method, compressing bi-level or sketch image frames into bi-level or sketch video using adaptive context-based arithmetic coding method. Bi-level or sketch video is particularly suitable to such small devices as Pocket PCs and mobile phones that possess small display screen, low bandwidth connection, and light computational power.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
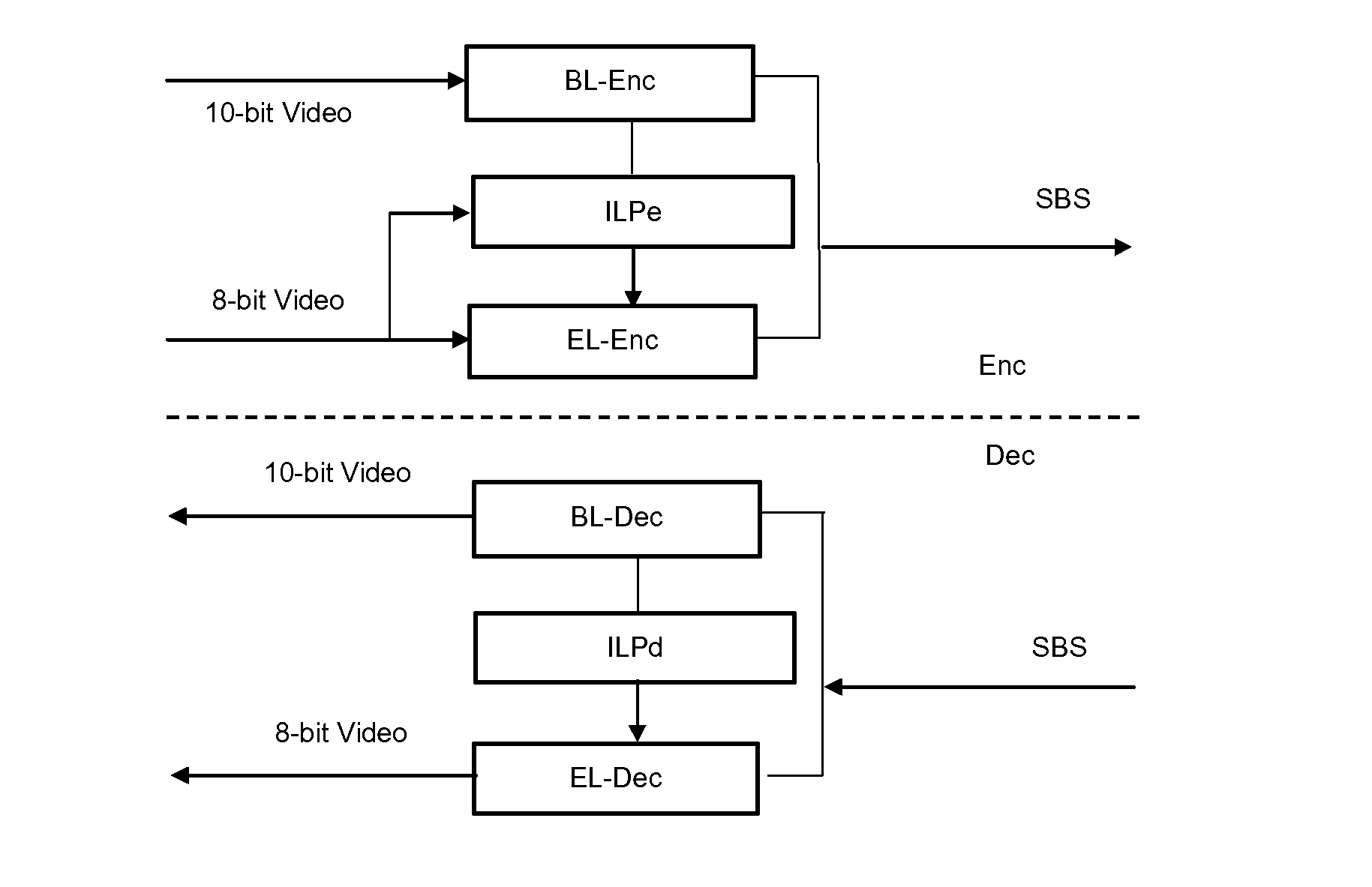
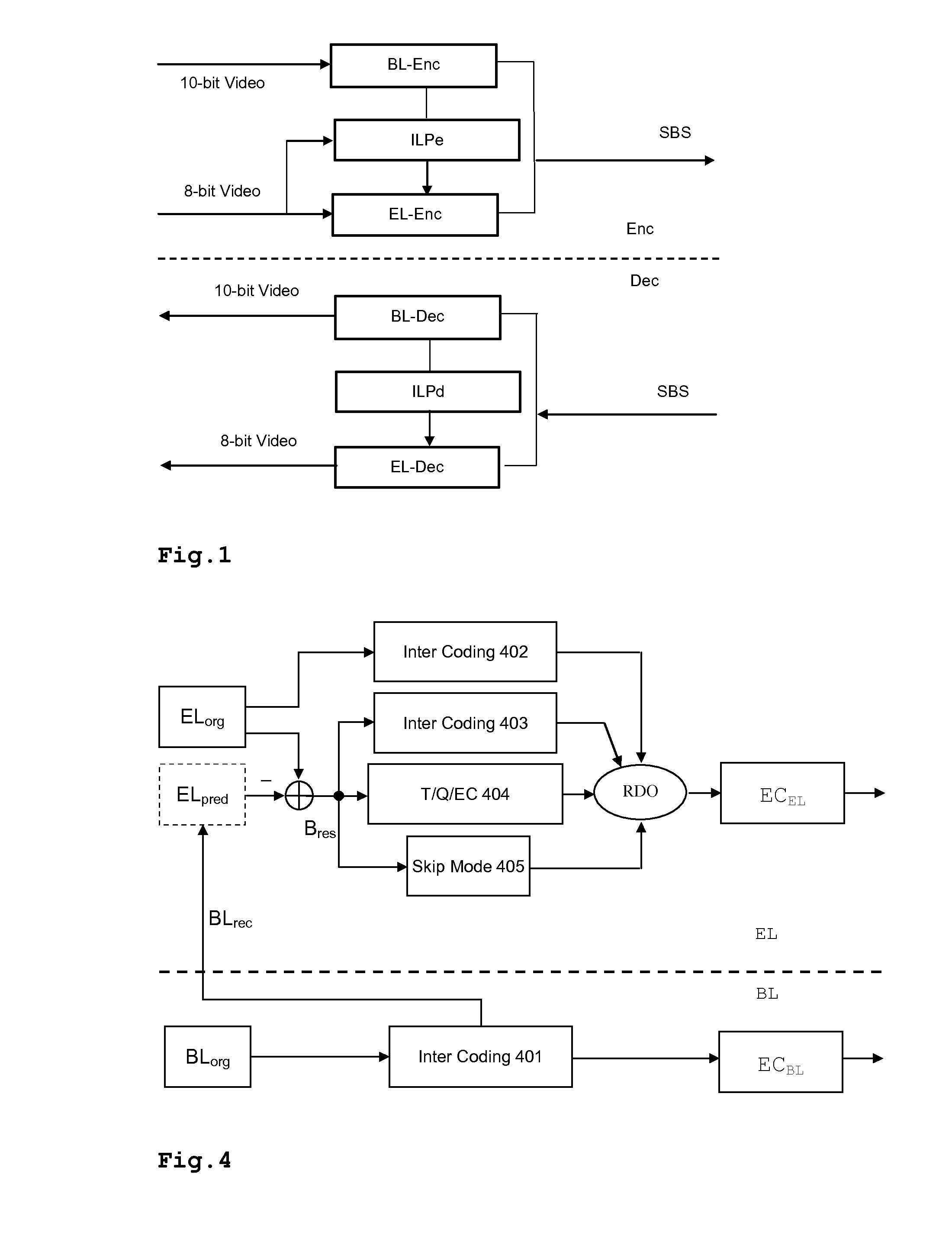
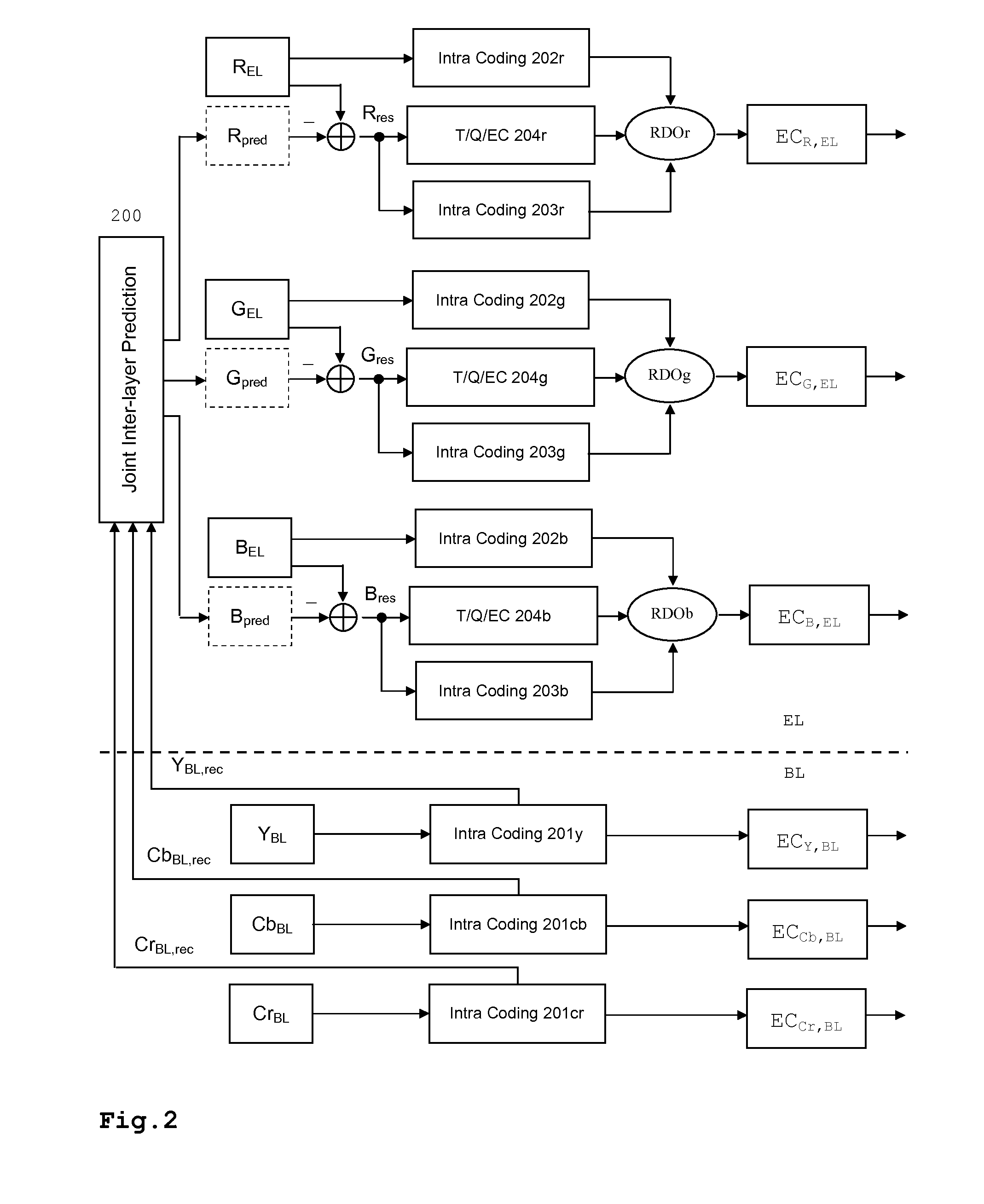
Method and apparatus for encoding video data, method and apparatus for decoding encoded video data and encoded video signal
InactiveUS20100128786A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTone mappingInter layer
For two or more versions of a video with different spatial, temporal or SNR resolution, scalability can be achieved by generating a base layer and an enhancement layer. When a version of a video is available that has higher color bit depth than can be displayed, a common solution is tone mapping. A more efficient compression method is proposed for the case where the two or more versions with different color bit depth use different color encoding. The present invention is based on joint inter-layer prediction among the available color channels. Thus, color bit depth scalability can also be used where the two or more versions with different color bit depth use different color encoding. In this case the inter-layer prediction is a joint prediction based on all color components. Prediction may also include color space conversion and gamma correction.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
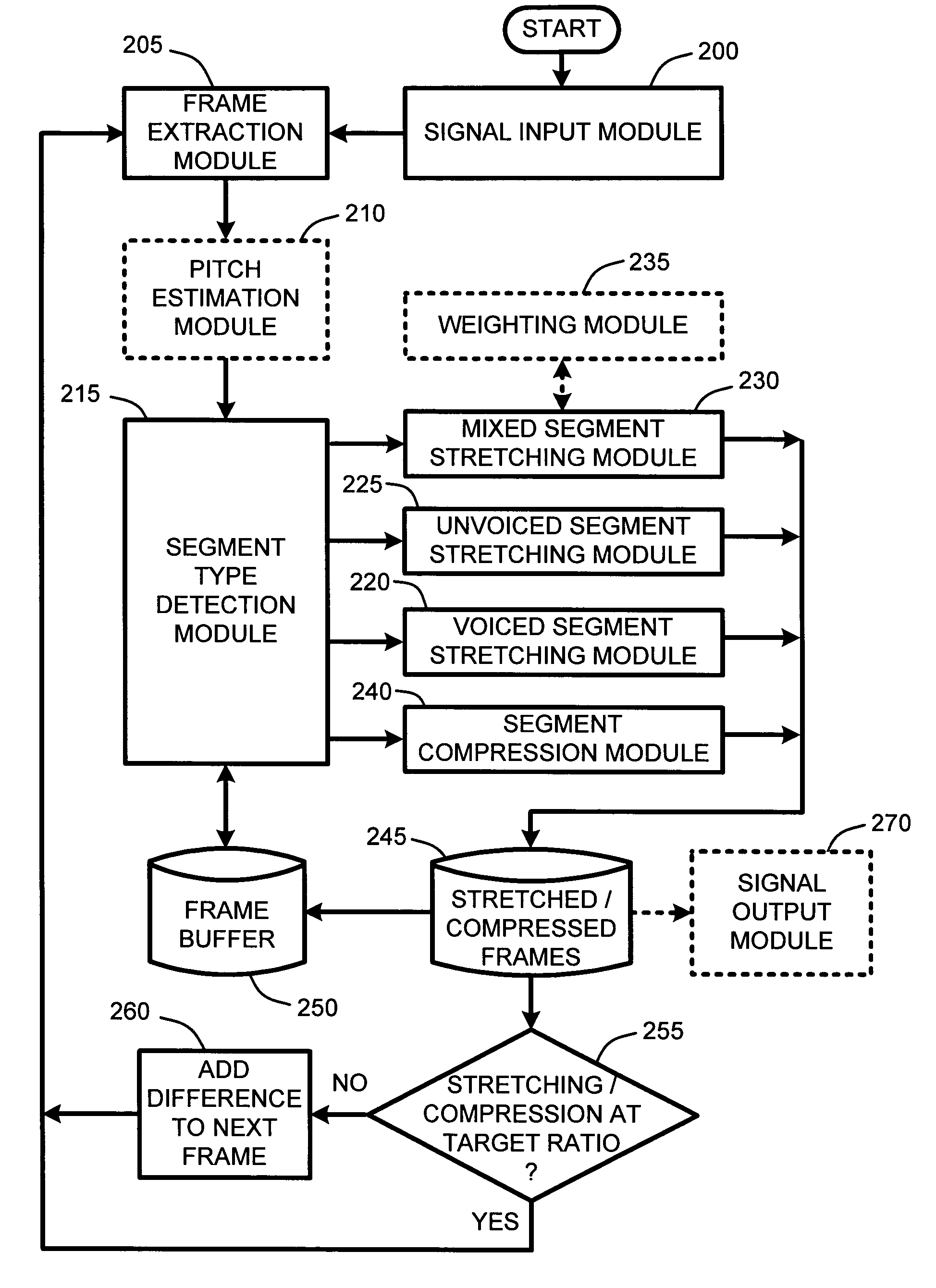
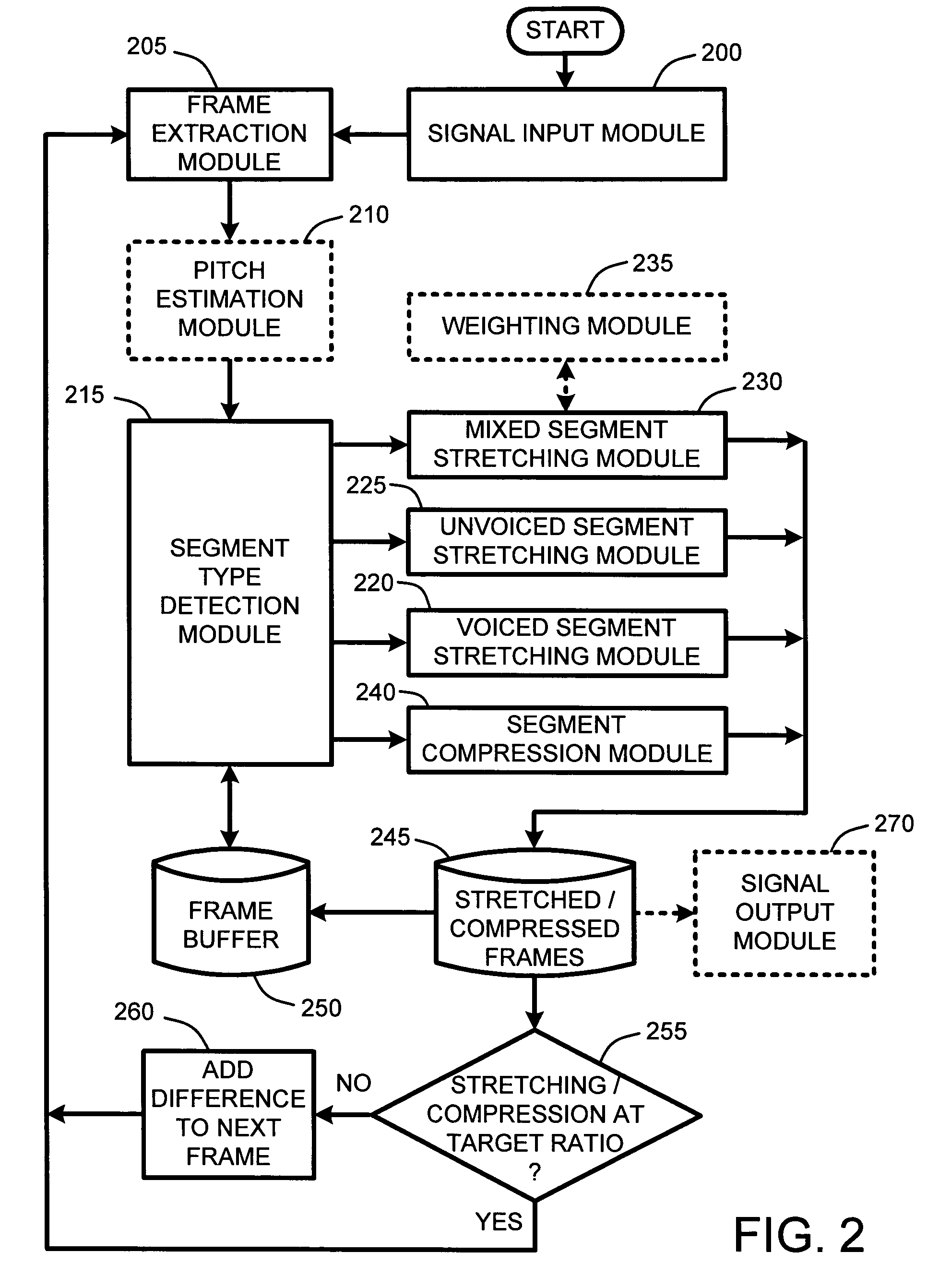
System and method for providing high-quality stretching and compression of a digital audio signal
InactiveUS7337108B2Quality improvementImprove intelligibilitySpeech analysisCode conversionCompression methodSelf adaptive
An adaptive “temporal audio scaler” is provided for automatically stretching and compressing frames of audio signals received across a packet-based network. Prior to stretching or compressing segments of a current frame, the temporal audio scaler first computes a pitch period for each frame for sizing signal templates used for matching operations in stretching and compressing segments. Further, the temporal audio scaler also determines the type or types of segments comprising each frame. These segment types include “voiced” segments, “unvoiced” segments, and “mixed” segments which include both voiced and unvoiced portions. The stretching or compression methods applied to segments of each frame are then dependent upon the type of segments comprising each frame. Further, the amount of stretching and compression applied to particular segments is automatically variable for minimizing signal artifacts while still ensuring that an overall target stretching or compression ratio is maintained for each frame.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
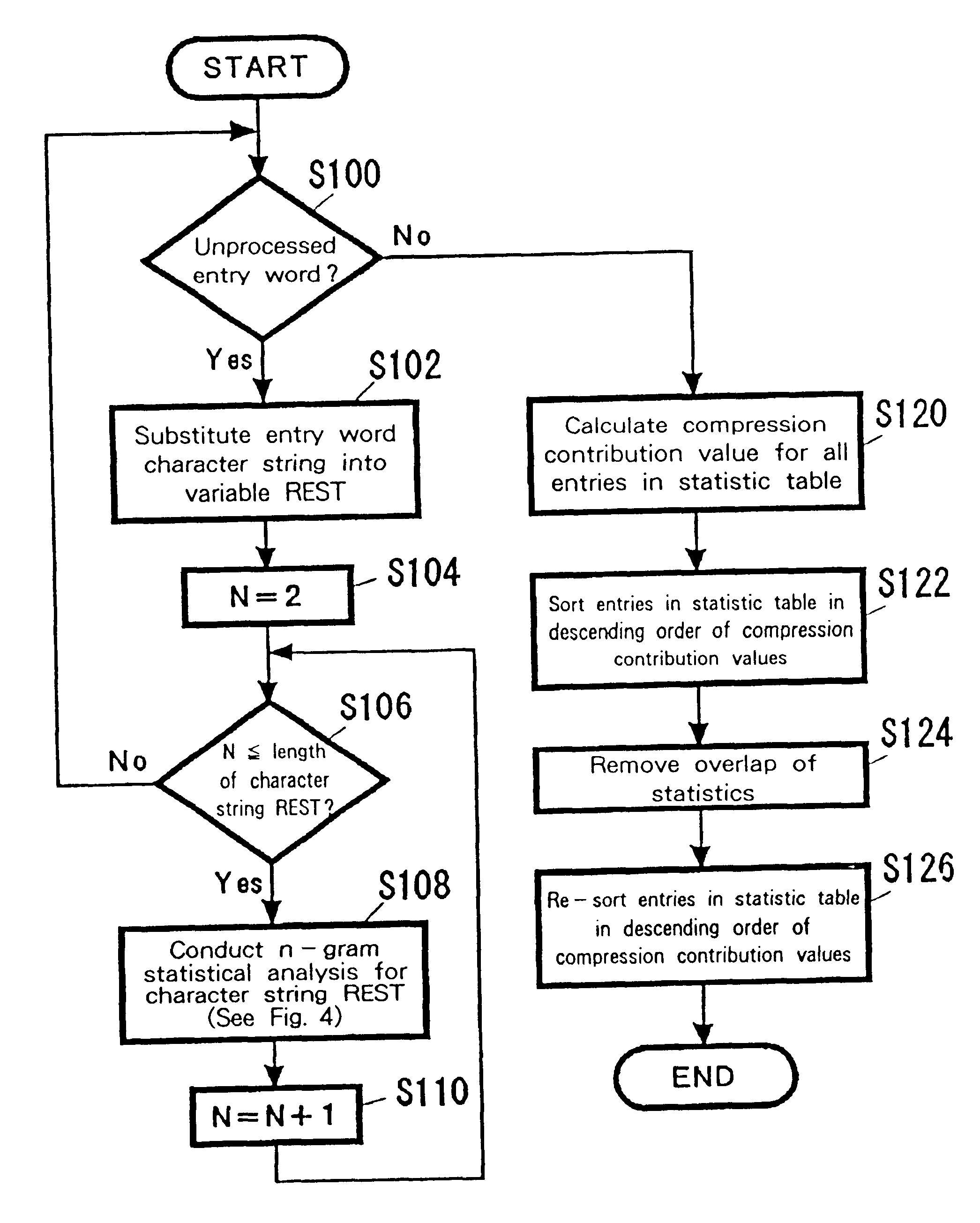
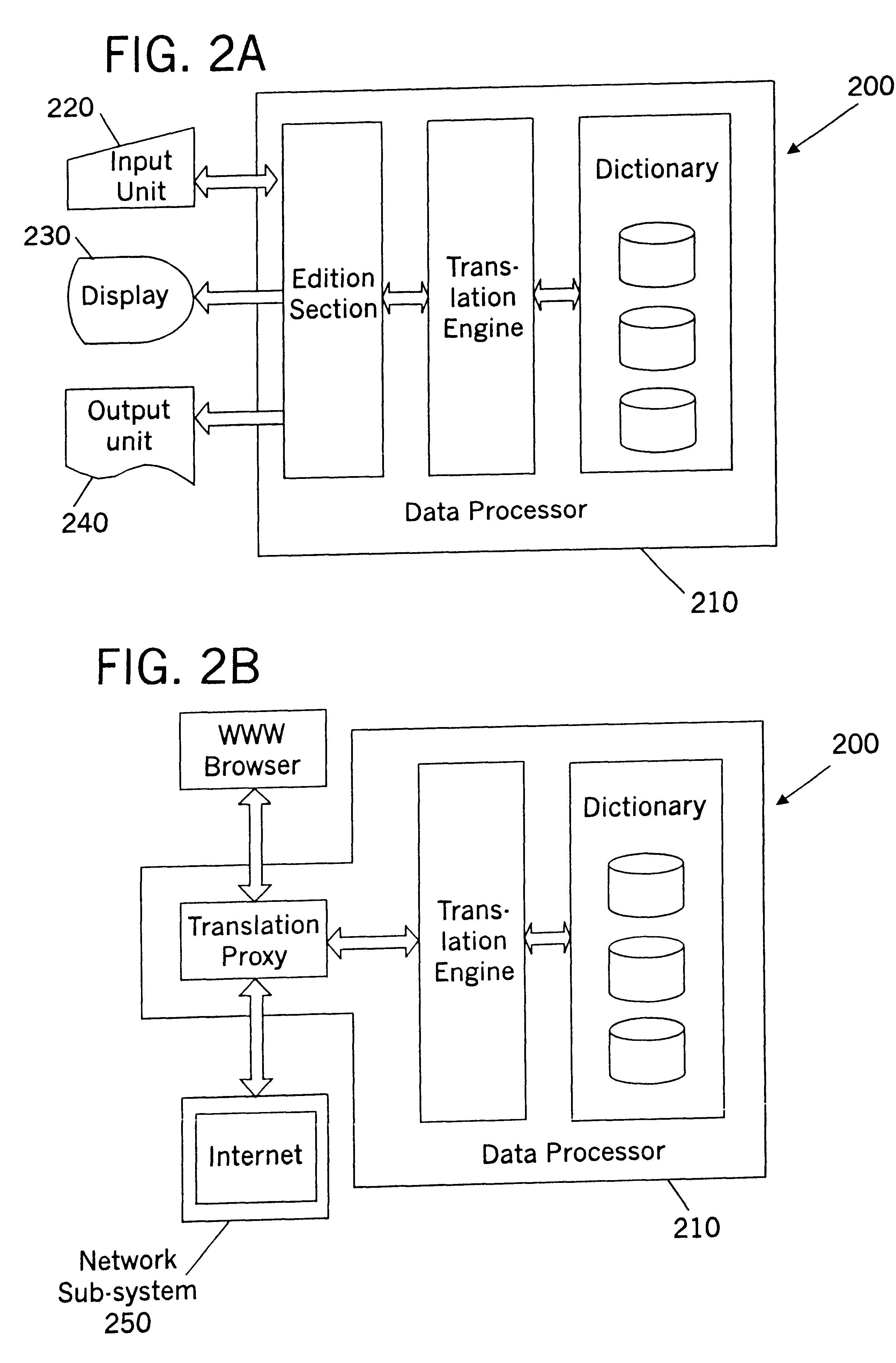
Compression method, method for compressing entry word index data for a dictionary, and machine translation system
A n-gram statistical analysis is employed to acquire frequently appearing character strings of n characters or more, and individual character strings having n characters or more are replaced by character translation codes of 1 byte each. The correlation between the original character strings having n characters and the character translation codes is registered in a character translation code table. Assume that a character string of three characters, i.e., a character string of three bytes, "sta," is registered as 1-byte code "e5" and that a character string of four characters, i.e., a character string of four bytes, "tion," is registered as 1-byte code "f1." Then, the word "station," which consists of a character string of seven characters, i.e., seven bytes, is represented by the 2-byte code "e5 f1," so that this contributes to a compression of five bytes.
Owner:IBM CORP
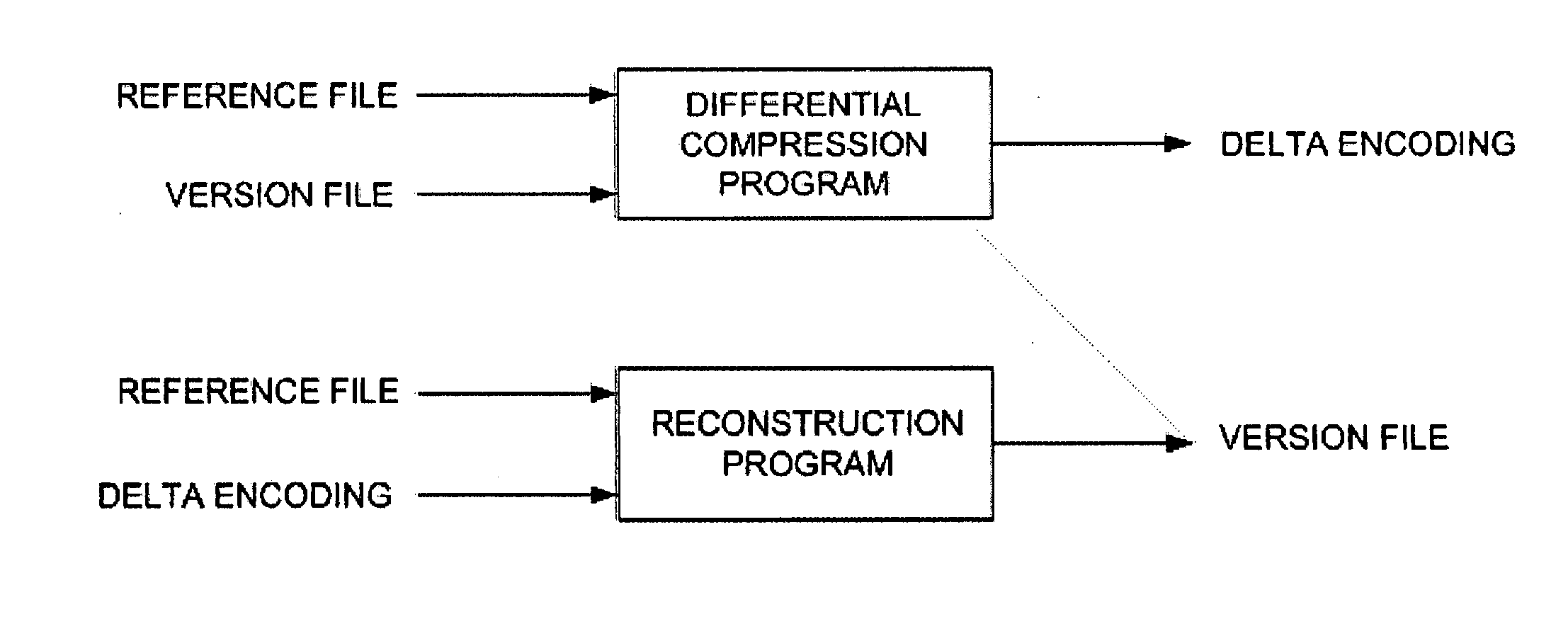
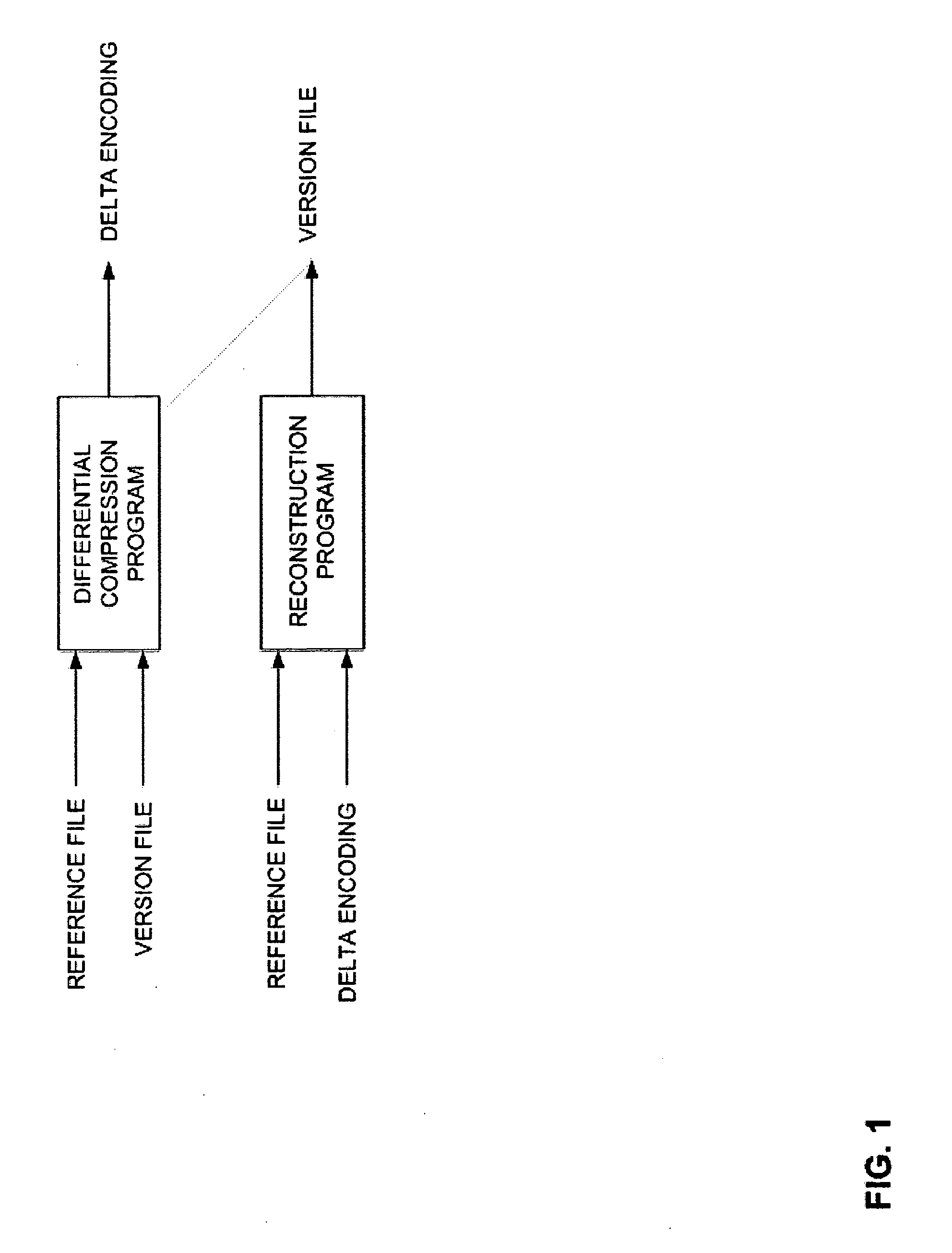
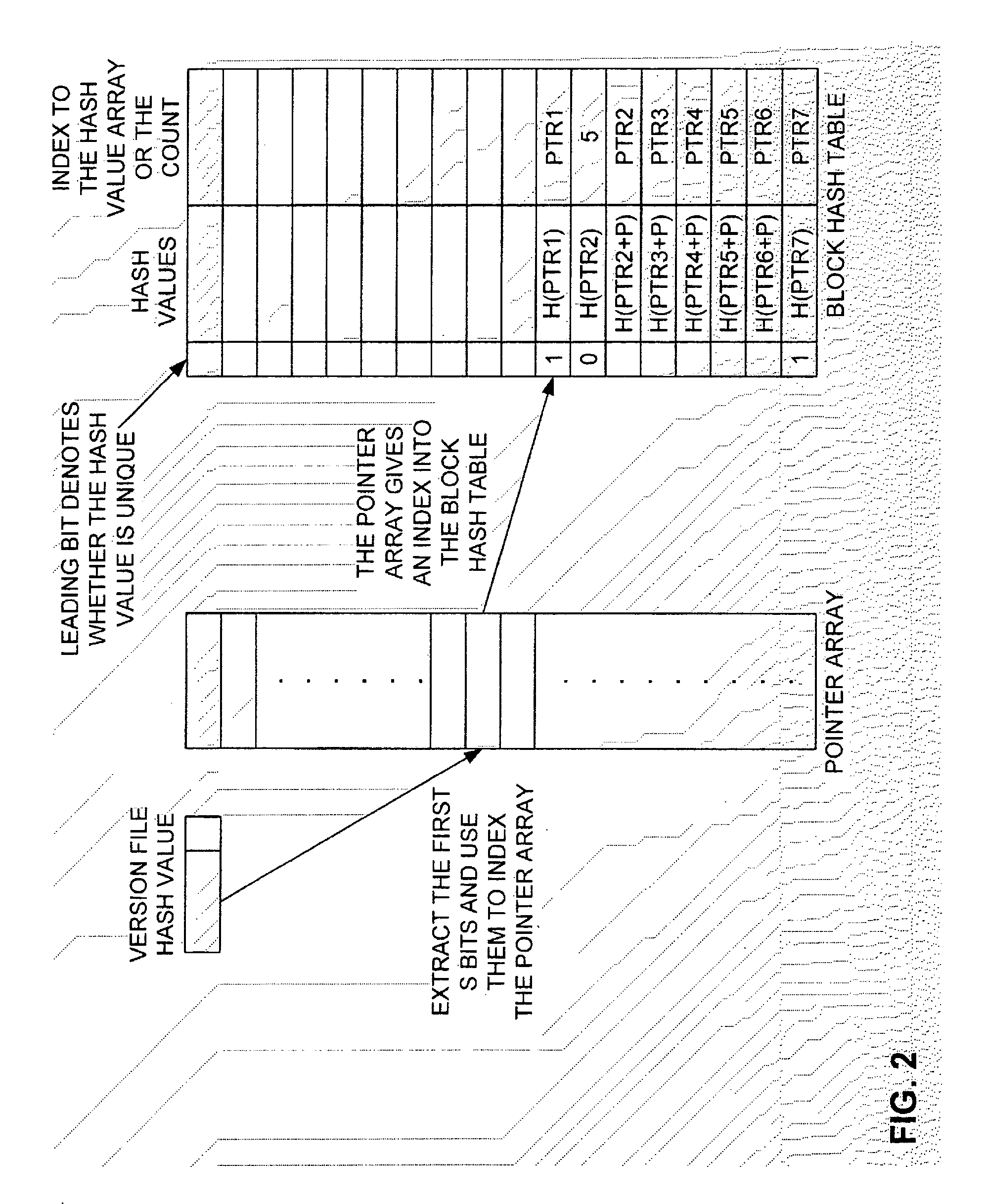
Method and Computer Program Product for Finding the Longest Common Subsequences Between Files with Applications to Differential Compression
InactiveUS20060112264A1Improve I/O performanceLow costCode conversionSecuring communicationLongest common subsequence problemGreedy algorithm
A differential compression method and computer program product combines hash value techniques and suffix array techniques. The invention finds the best matches for every offset of the version file, with respect to a certain granularity and above a certain length threshold. The invention has two variations depending on block size choice. If the block size is kept fixed, the compression performance of the invention is similar to that of the greedy algorithm, without the expensive space and time requirements. If the block size is varied linearly with the reference file size, the invention can run in linear-time and constant-space. It has been shown empirically that the invention performs better than certain known differential compression algorithms in terms of compression and speed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Bi-level iso-surface compression
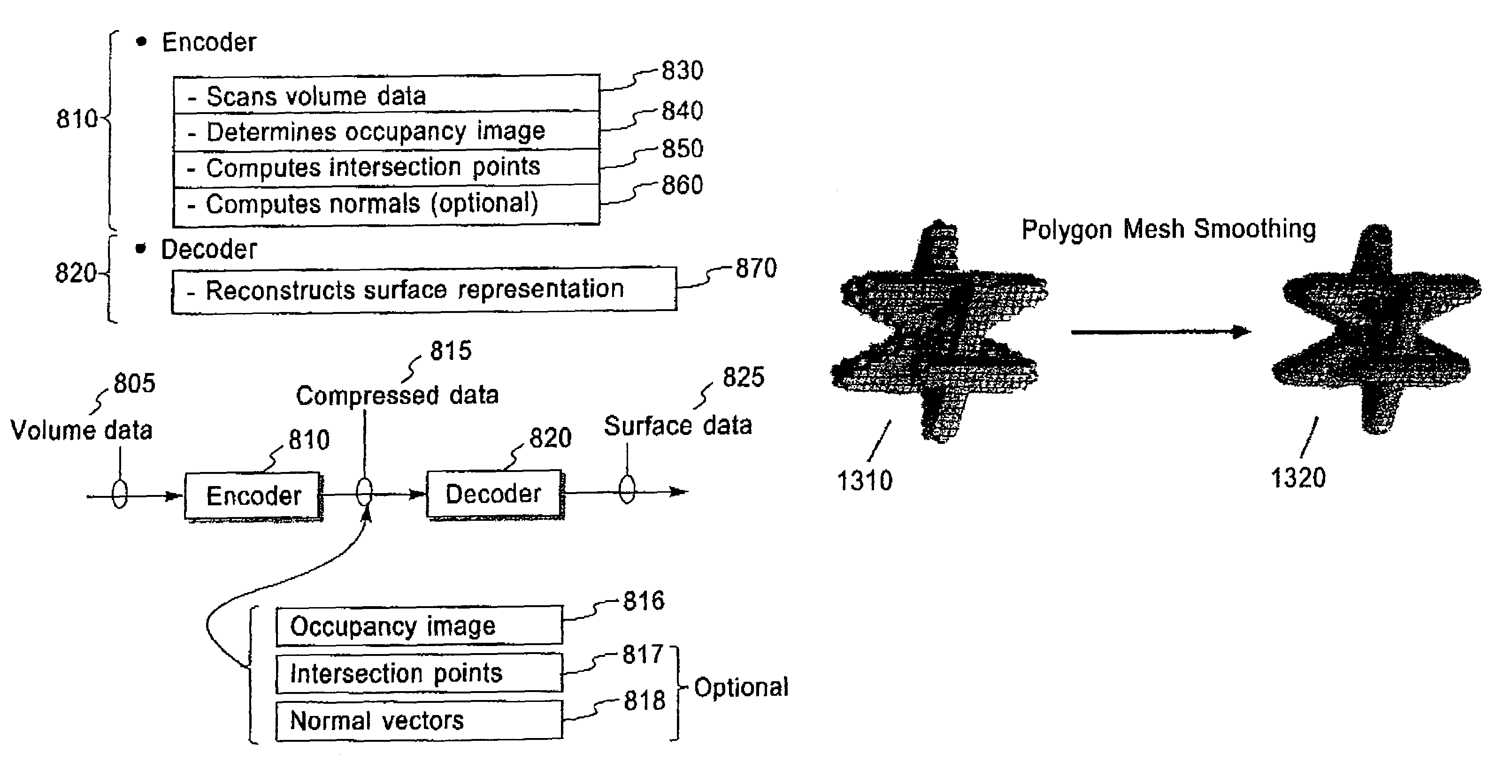
InactiveUS7847799B2Extreme simplicityIncrease the compression ratioImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionRemote computerContext based
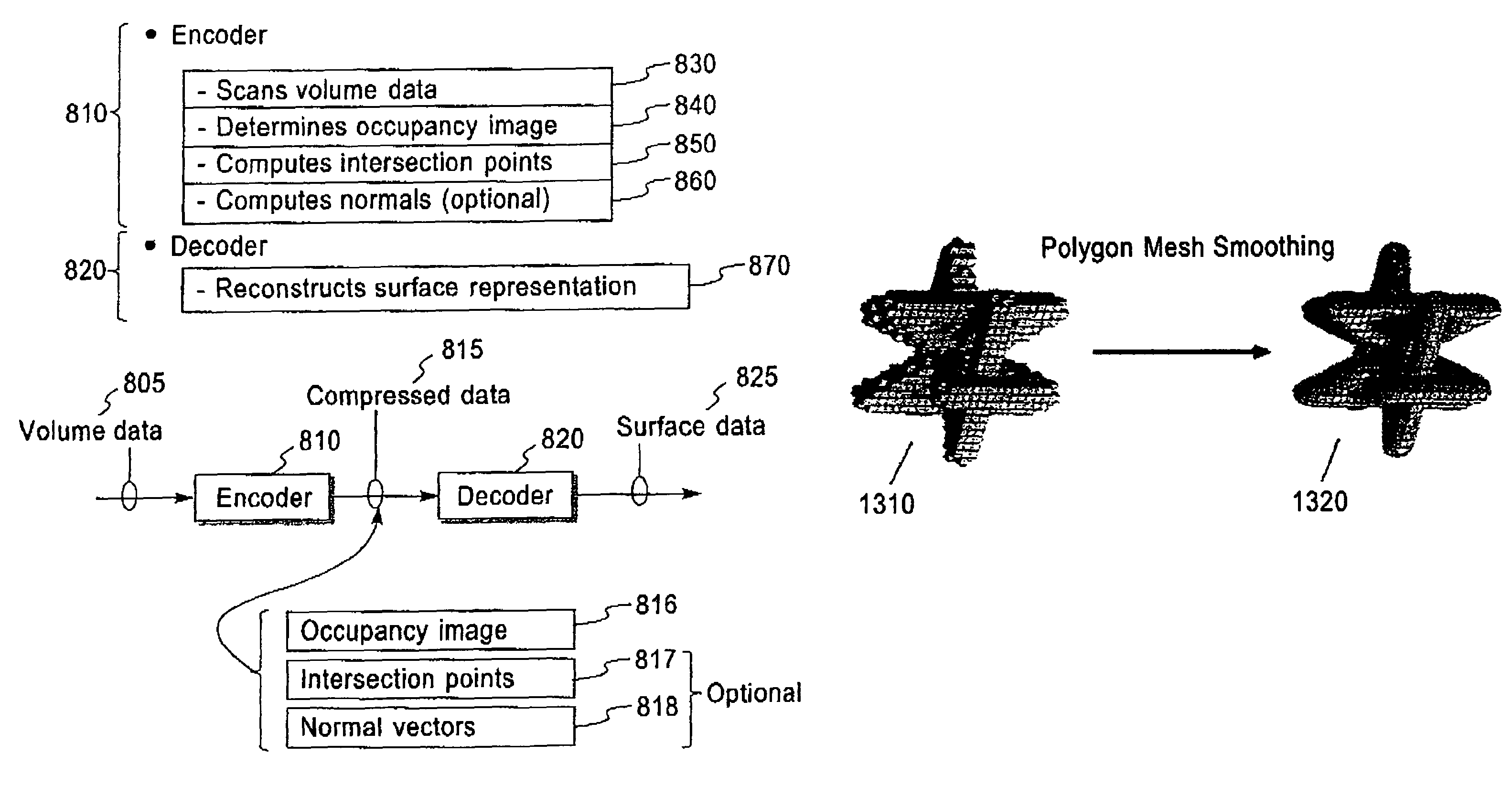
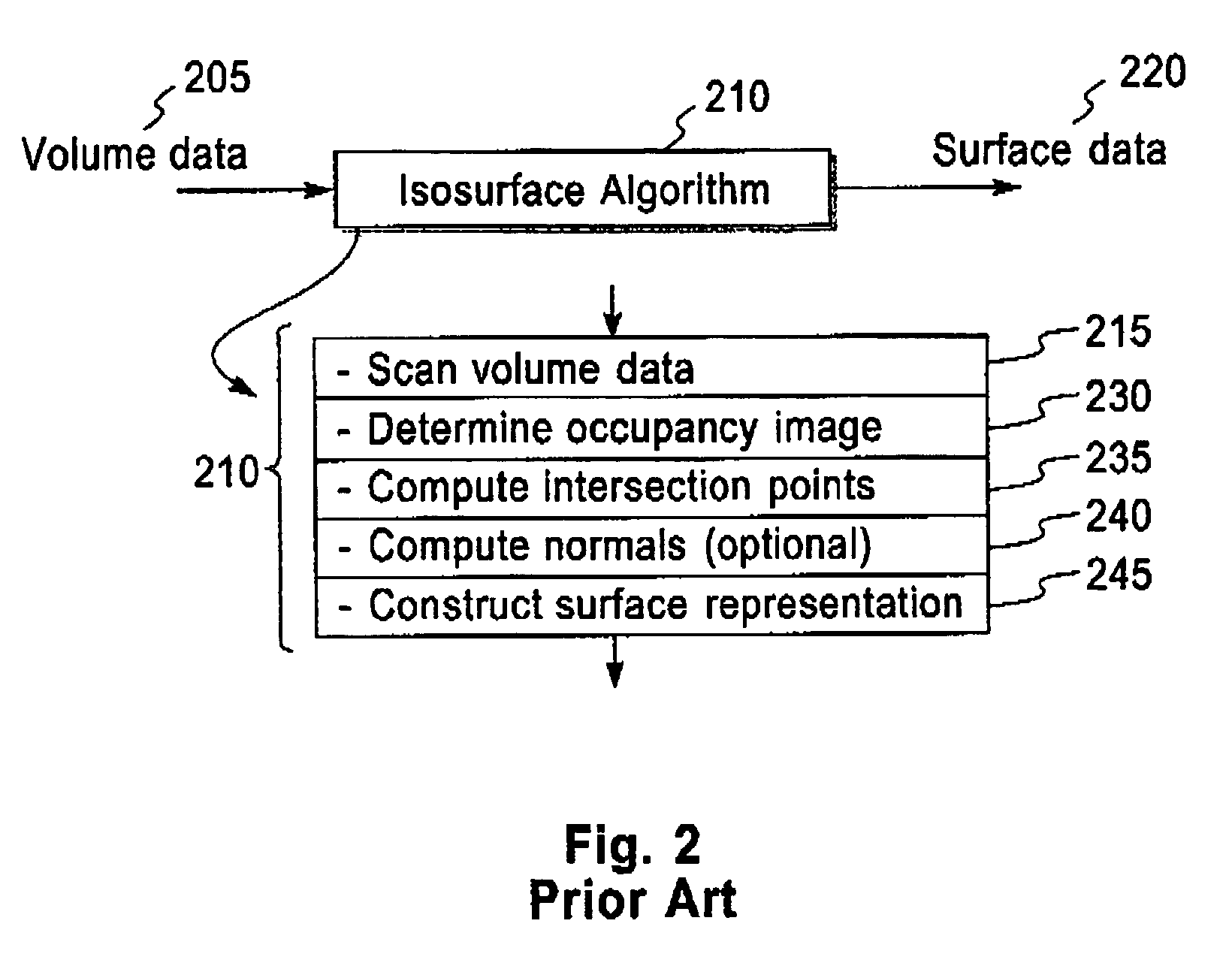
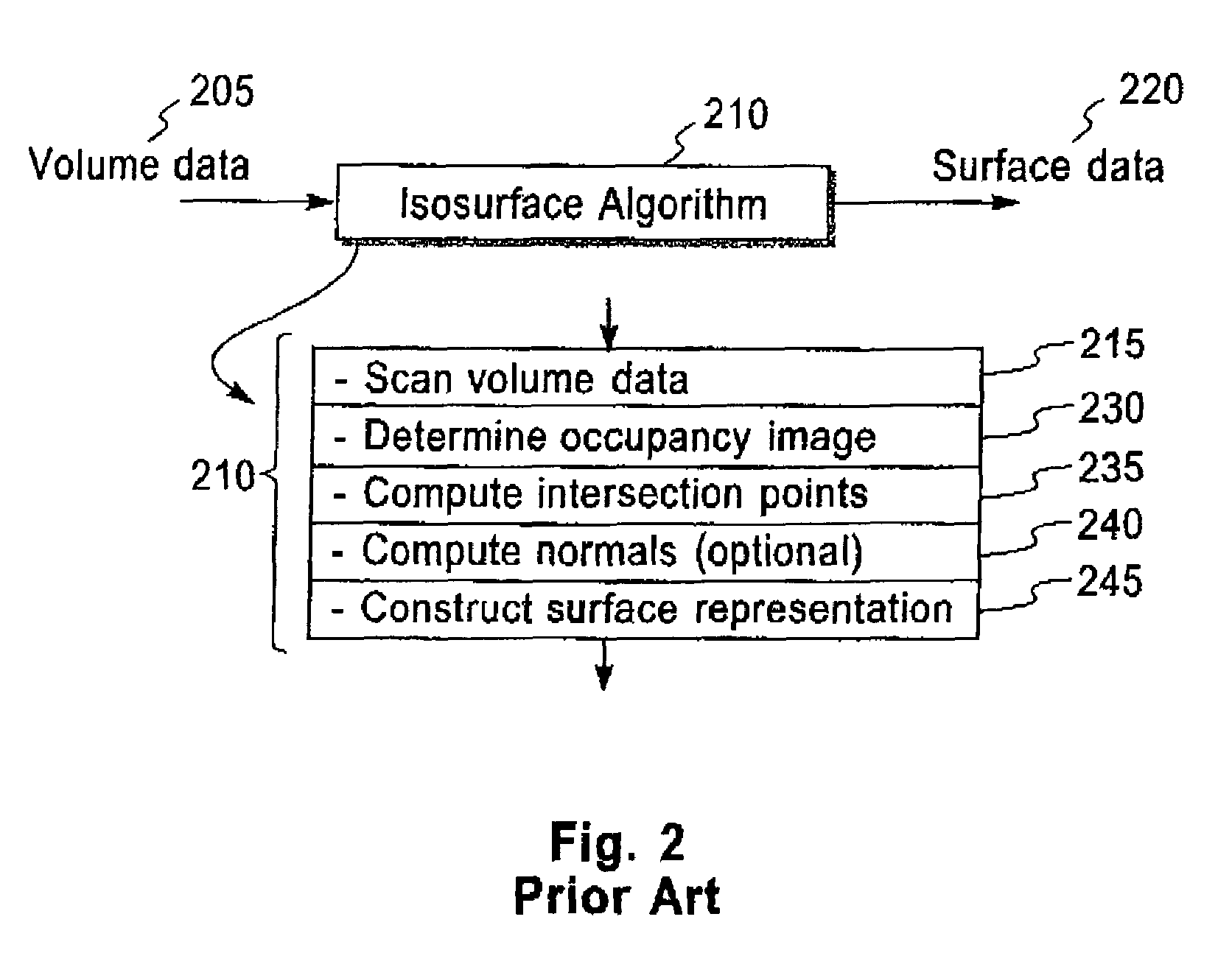
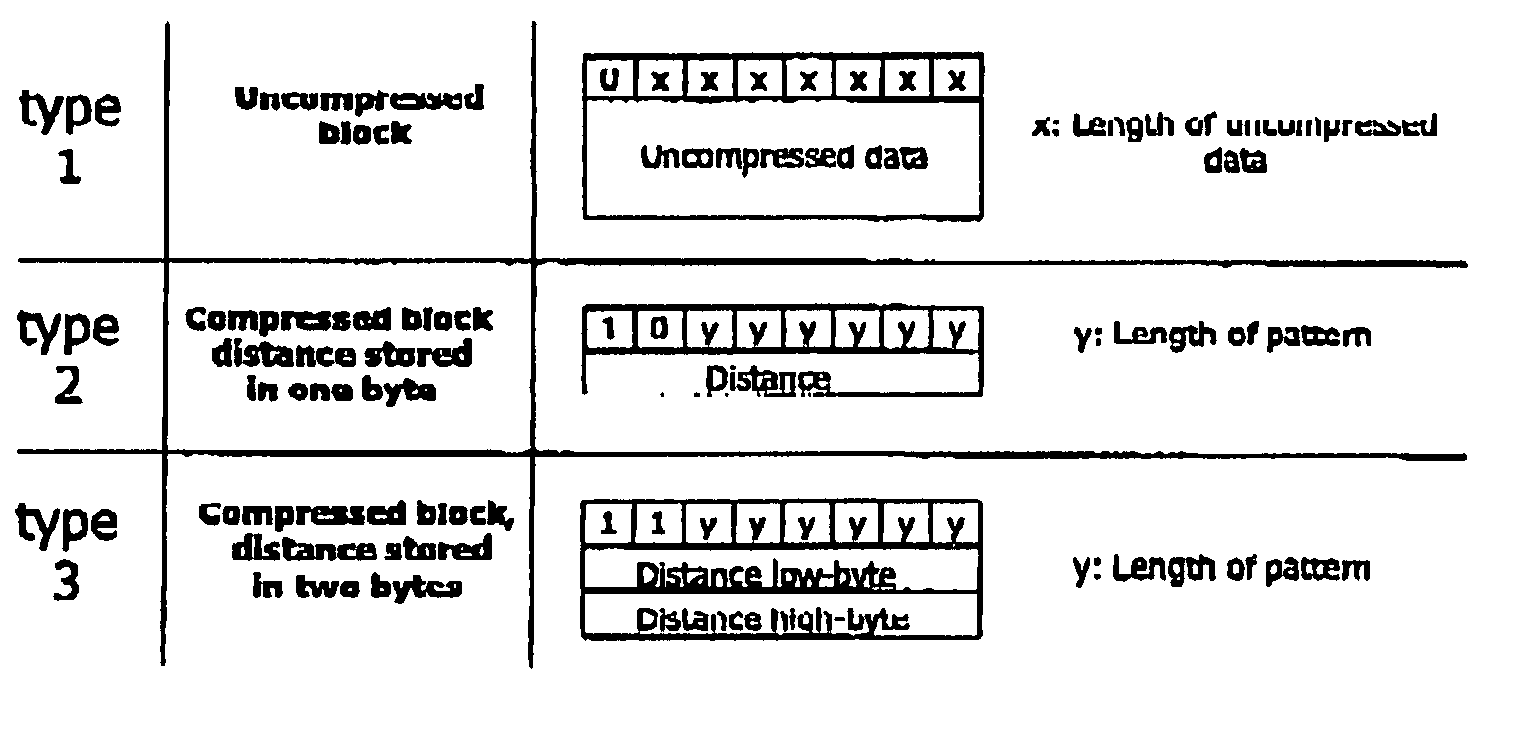
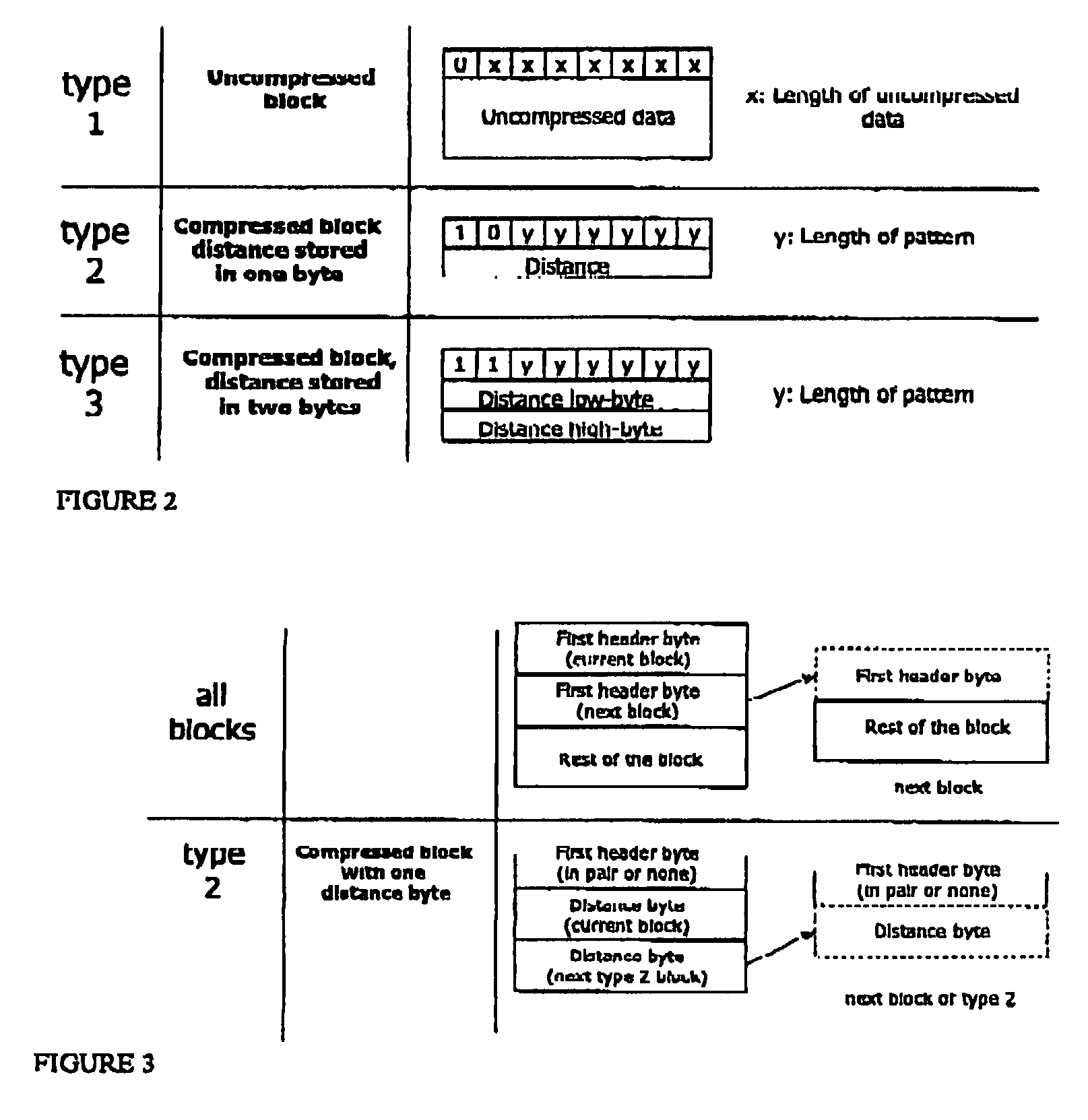
Methods, structures and systems for encoding and decoding isosurface data. An encoder process takes volume data and an isolevel as input and produces compressed isosurface data as output. The compressed isosurface data produced by an encoder process is composed of an occupancy image record, an optional intersection points record, and an optional normal vectors record. An occupancy image is compressed with a context-based arithmetic encoder. Compressed isosurface data can be stored in a data storage device or transmitted through a communication medium to a remote computer system, where the decoder process is executed. The decoder processes take compressed surface data as input and produce surface data as output. The decoder processes first reconstructs the occupancy image by decoding the occupancy image record. An in-core isosurface decoder process produces a polygon mesh as a surface representation. An out-of-core isosurface decoder process produces a set of oriented points as a surface representation.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
Adaptive time/frequency-based audio encoding and decoding apparatuses and methods
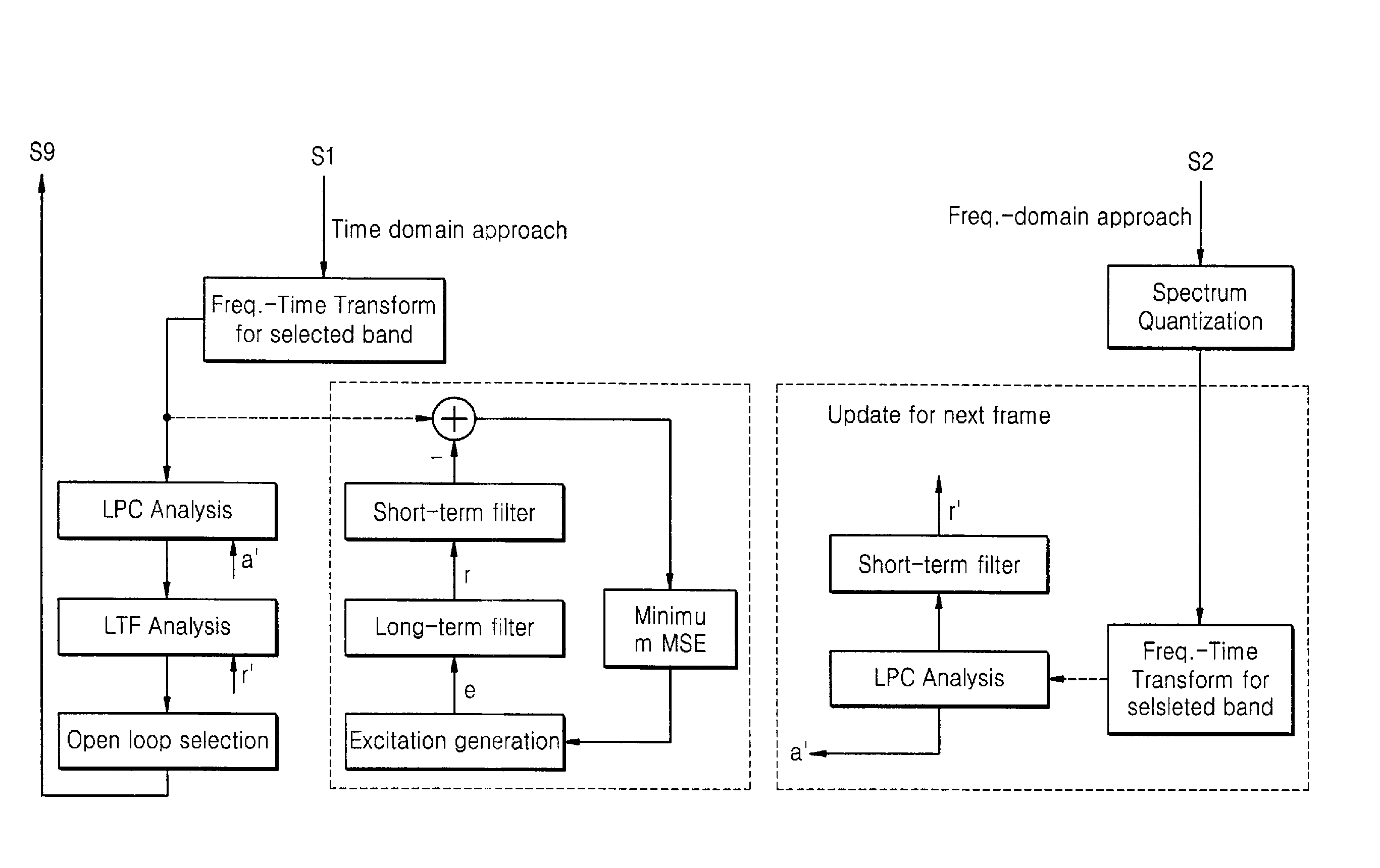
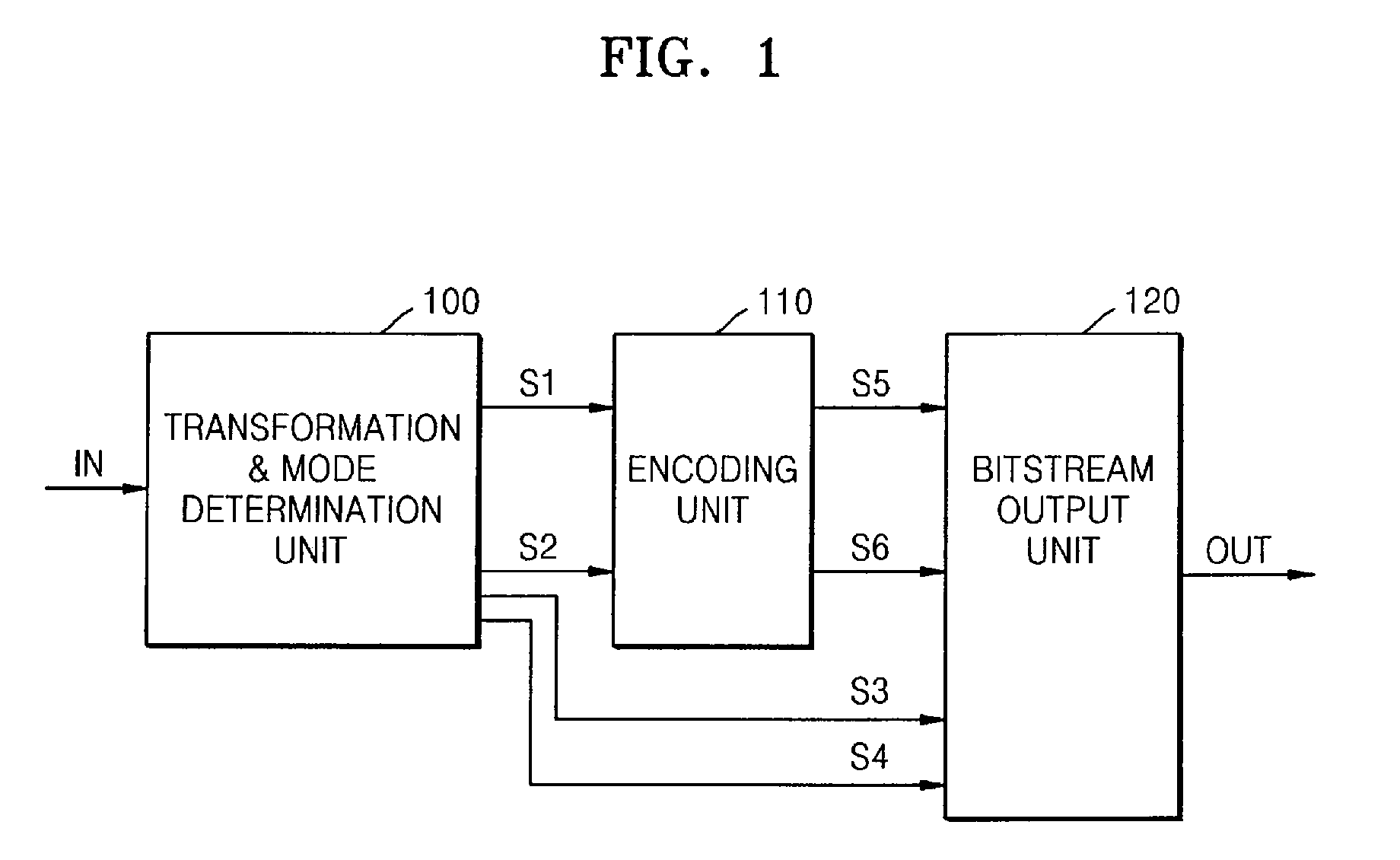
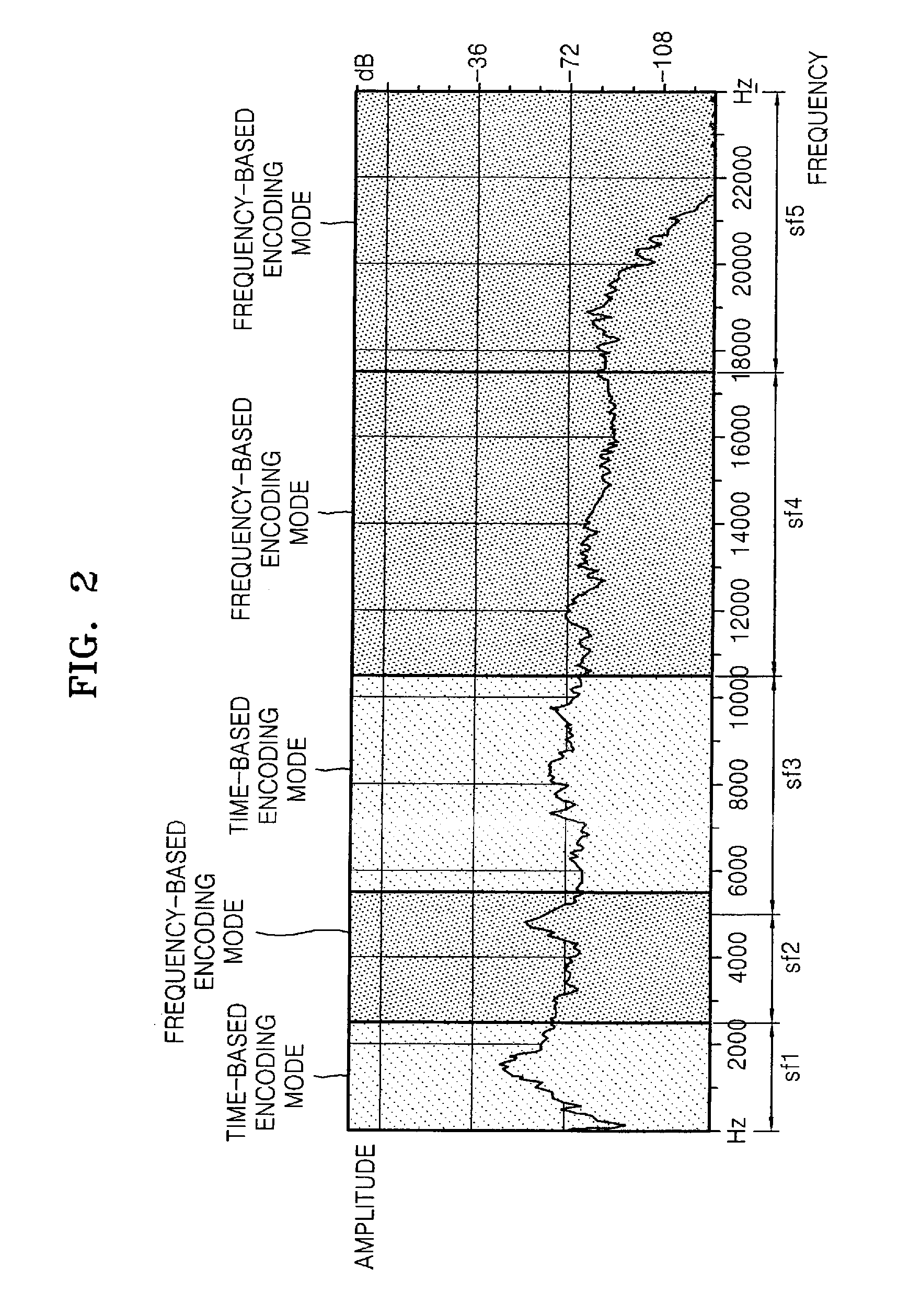
InactiveUS20070106502A1Improve compression efficiencySpeech analysisDigital computer detailsEngineeringProcessing element
Adaptive time / frequency-based audio encoding and decoding apparatuses and methods. The encoding apparatus includes a transformation & mode determination unit to divide an input audio signal into a plurality of frequency-domain signals and to select a time-based encoding mode or a frequency-based encoding mode for each respective frequency-domain signal, an encoding unit to encode each frequency-domain signal in the respective encoding mode, and a bitstream output unit to output encoded data, division information, and encoding mode information for each respective frequency-domain signal. In the apparatuses and methods, acoustic characteristics and a voicing model are simultaneously applied to a frame, which is an audio compression processing unit. As a result, a compression method effective for both music and voice can be produced, and the compression method can be used for mobile terminals that require audio compression at a low bit rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Bi-level iso-surface compression
InactiveUS7230616B2Extreme simplicityIncrease the compression ratioImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmImage compression
Methods, structures and systems for encoding and decoding isosurface data. An encoder process takes volume data and an isolevel as input and produces compressed isosurface data as output. The compressed isosurface data produced by an encoder process is composed of an occupancy image record, an optional intersection points record, and an optional normal vectors record. An occupancy image is compressed with a context-based arithmetic encoder. Compressed isosurface data can be stored in a data storage device or transmitted through a communication medium to a remote computer system, where the decoder process is executed. The decoder processes take compressed surface data as input and produce surface data as output. The decoder processes first reconstructs the occupancy image by decoding the occupancy image record. An in-core isosurface decoder process produces a polygon mesh as a surface representation. An out-of-core isosurface decoder process produces a set of oriented points as a surface representation.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
Data compression/decompression method and apparatus
InactiveUS20020116424A1Improved data compression/decompression arrangementReduce usageDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsData compressionOperational system
The present invention relates to a data compression techniques and is of particular relevance to embedded devices having a flash-prom. Data compression techniques have been known for many years. Devices such as mobile telecommunications handsets, personal digital assistants and vehicular navigation systems do not support access to data storage systems such as hard or floppy devices and their operating system and applications are typically stored on a flash-PROM that is associated with the embedded device. Flash-proms, suffer, in the main, from being rather slow. Flash-proms are also expensive. The present invention seeks to provide a data compression / decompression arrangement which can reduce flash-PROM usage without increasing boot-up time and provides a method for processing information in a data processor operable to process data to provide a sequence of uncompressed and compressed data blocks, whereby each block comprises an even number of bytes. The invention can enable a reduction in boot-up time for systems.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
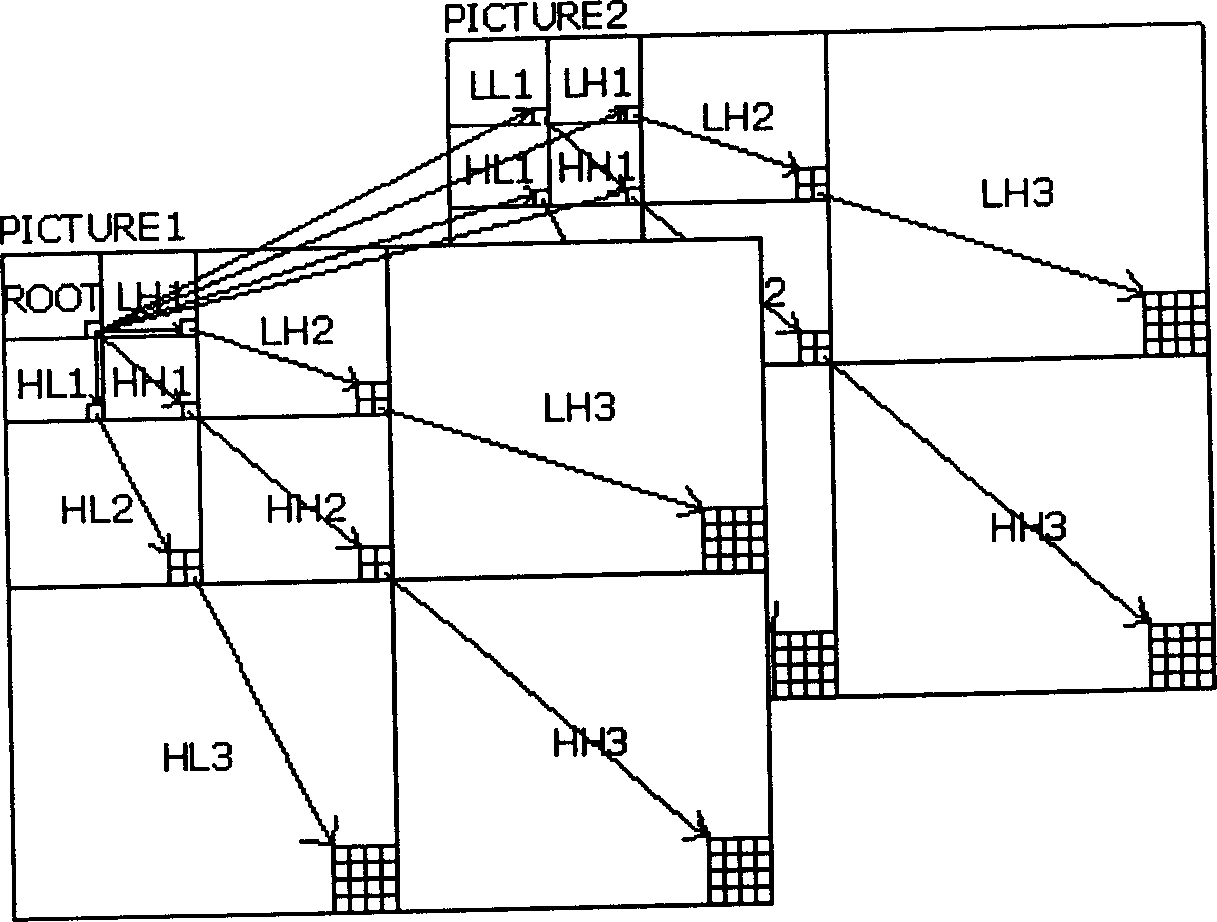
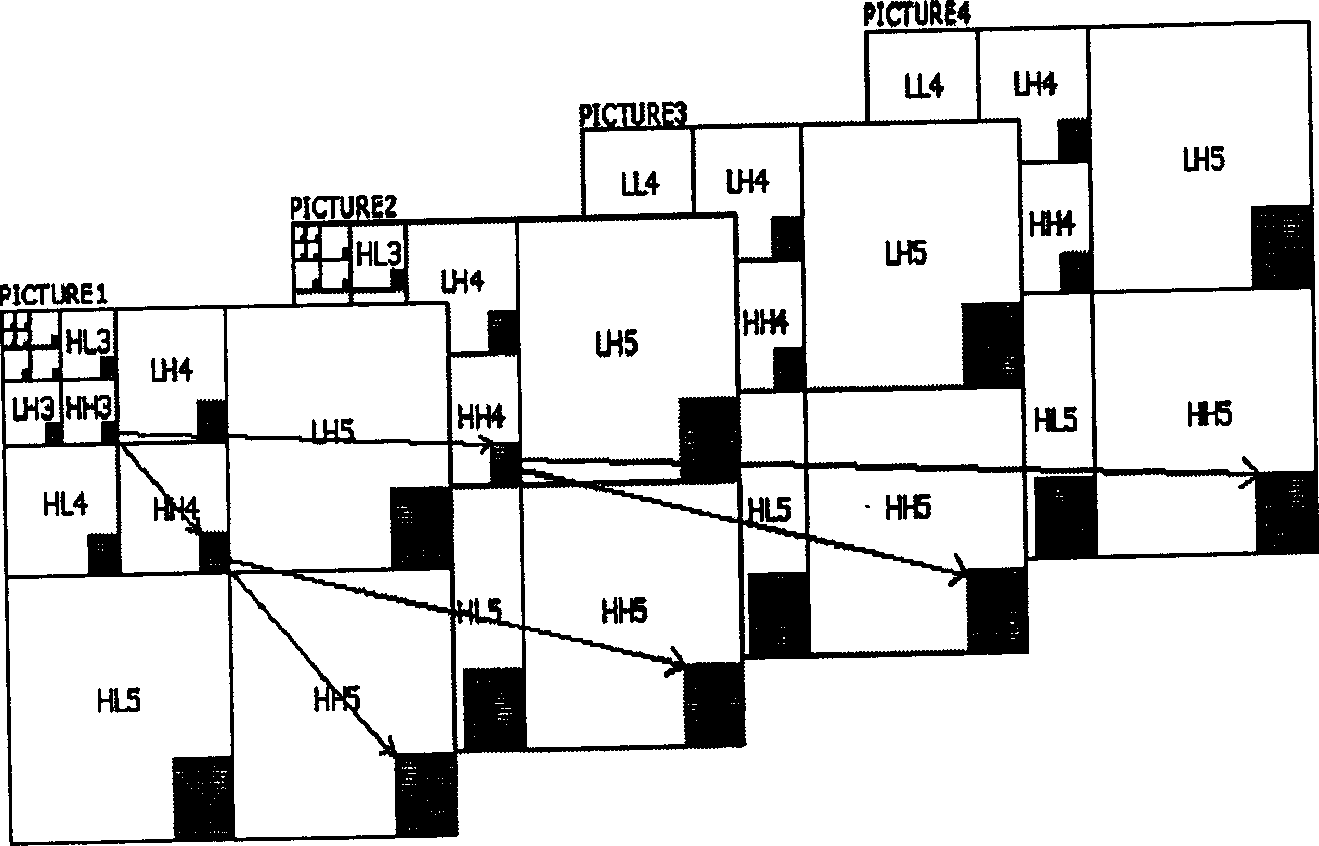
Tree-structure-based grade tree aggregation-divided video image compression method
InactiveCN1581977ASolve the amount of image dataSolve lengthImage codingTelevision systemsCompression methodVideo image
The method includes steps: first at encoding end, obtaining distribution of image energy on time and frequency domain through discrete wavelet transform; based on correlation between wavelet coefficient, wavelet coefficient in each order is divided according to tree structure; SPIHT encoding is carried out for wavelet coefficient of each tree; encoding result is deposited on encoding end momentarily; finally, results of encoding each tree are synthesized as a code stream in use for storing or transferring. The invention realizes video compression in high compression ratio and low degree of distortion by using less memory space, particular suitable to dedicated system realized through hardware.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
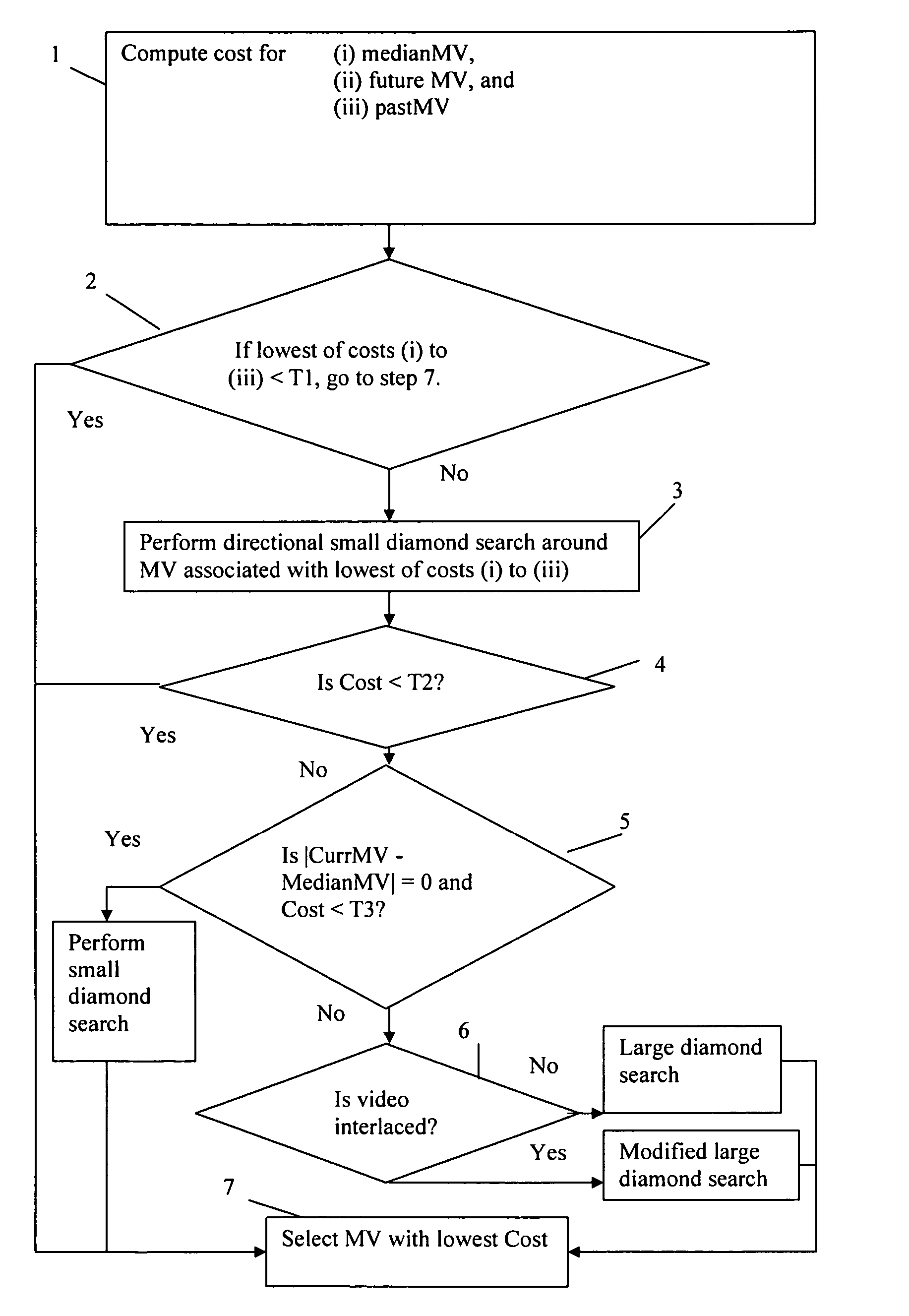
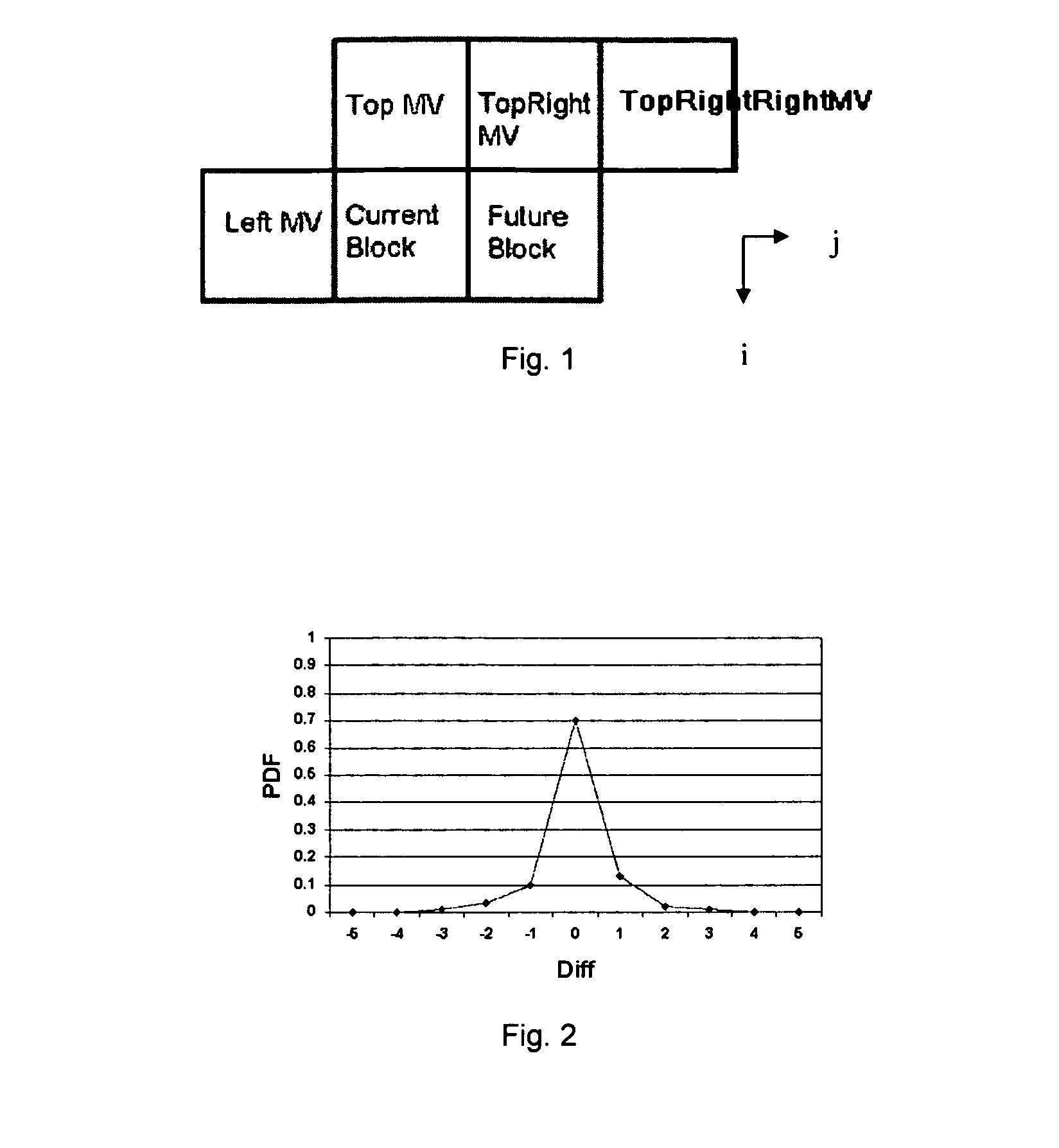
Enhanced block-based motion estimation algorithms for video compression
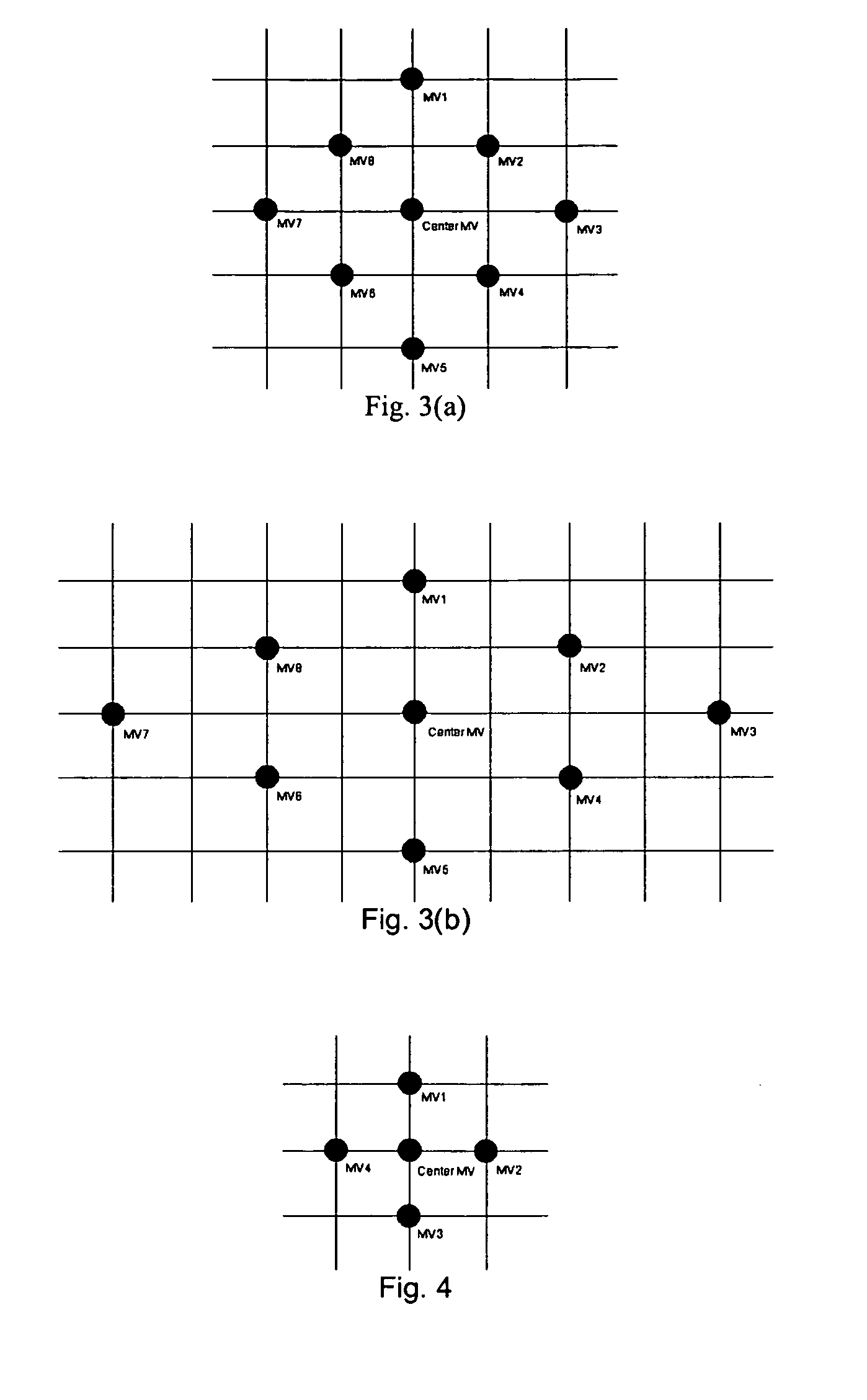
InactiveUS20070154103A1Improve smoothnessGood compensationCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Motion vector
Method, systems and software are proposed for obtaining for blocks of a first image similar blocks of a second image (the “reference image”). The blocks of the first image are processed sequentially, for each block trying out a number of candidate locations in the second image and evaluating a cost function for each. Each candidate location in the second image is displaced by a respective motion vector from the block of the first image. In a first aspect of the invention the cost function is a function of a predicted motion vector for future blocks of the first image (i.e. blocks of the first image which have not yet been processed). In a second aspect of the invention the motion vectors are given by location values which are not all whole pixel spacings, halves of the pixel spacing, or quarters of the pixel spacing.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
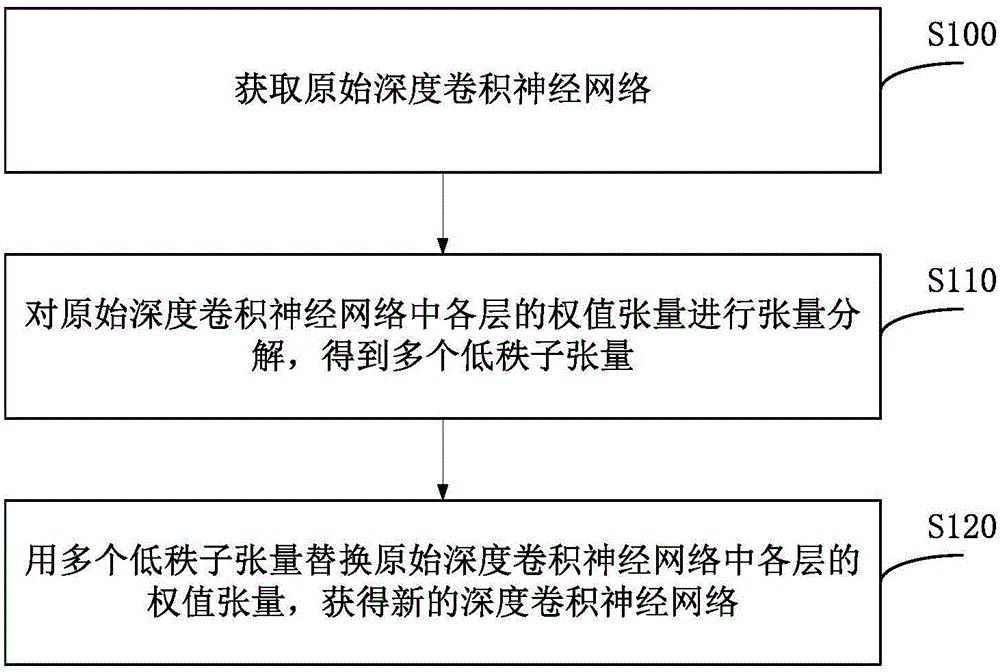
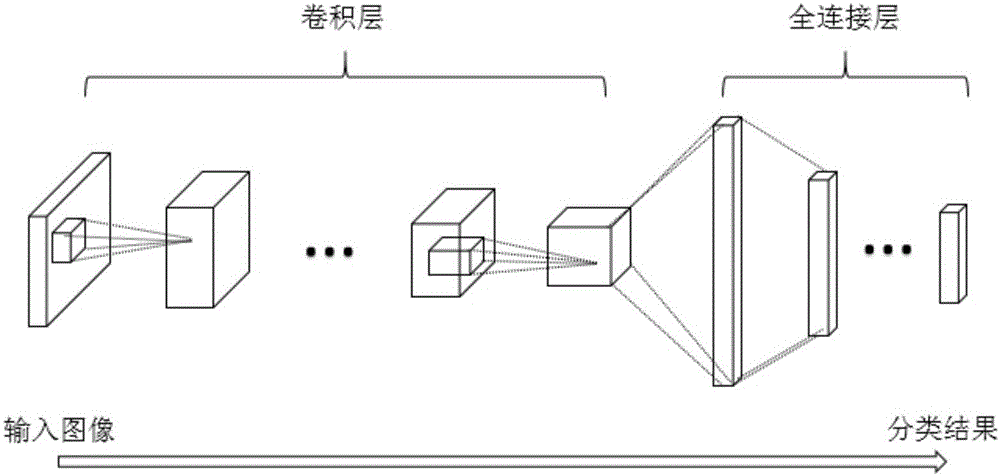
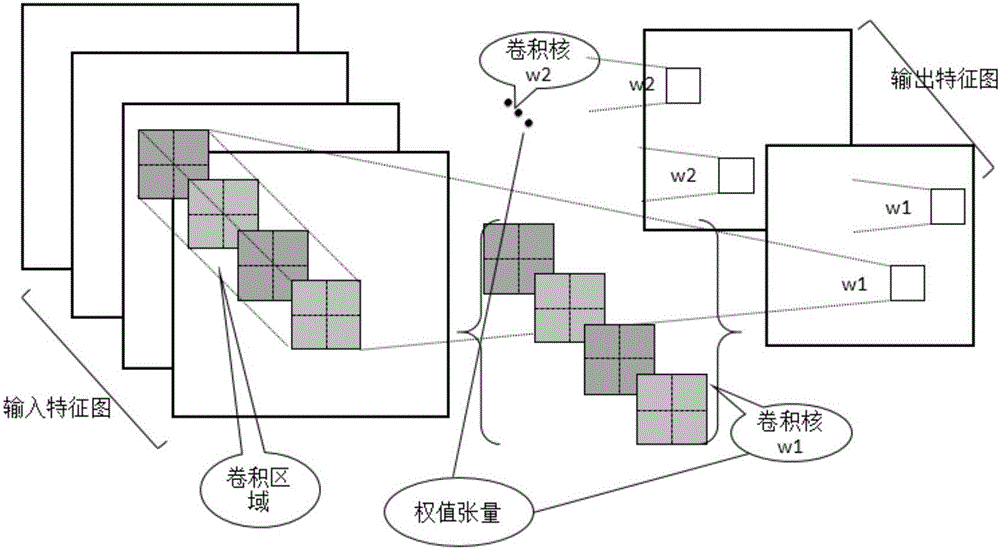
Tensor decomposition-based acceleration and compression method for deep convolutional neural network
ActiveCN106127297AAchieve accelerationAchieve compressionNeural architecturesPhysical realisationNerve networkTensor decomposition
The invention discloses a tensor decomposition-based acceleration and compression method for a deep convolutional neural network. The method at least comprises the steps of 1: obtaining an original deep convolutional neural network; 2: performing tensor decomposition on a weight tensor of each layer in the original deep convolutional neural network to obtain a plurality of low-rank sub-tensors; and 3: replacing the weight tensor of each layer in the original deep convolutional neural network with the low-rank sub-tensors to obtain a new deep convolutional neural network. Through an embodiment of the method, the acceleration and compression of a large deep convolutional neural network are realized.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mono and multi-layer articles and compression methods of making the same
Owner:CONCENTRATE MFG OF IRELAND
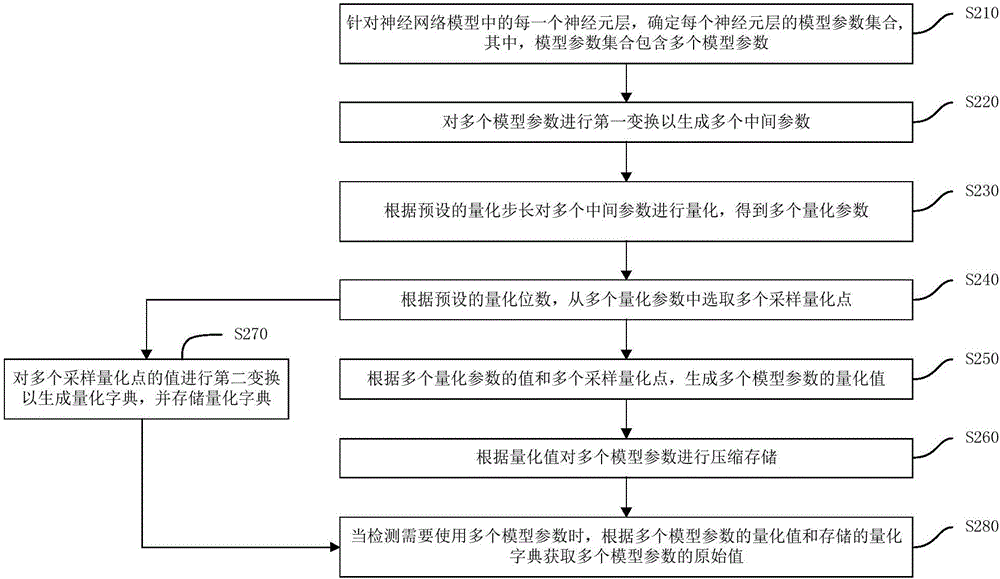
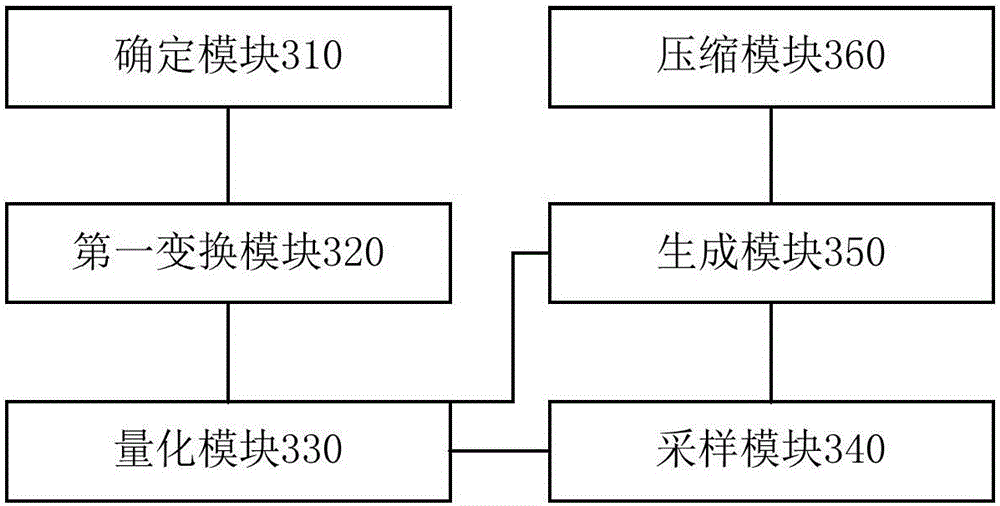
Neural network model compression method and device
ActiveCN106485316AReduce sizeReduce occupancyAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCompression deviceModel parameters
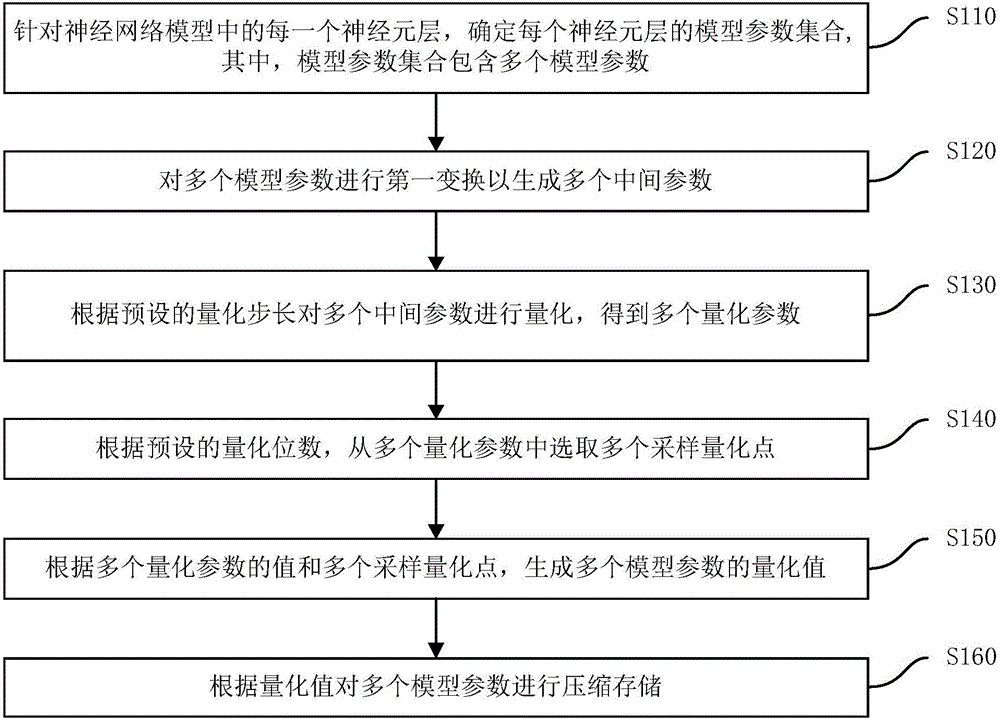
The invention discloses a neural network model compression method and a neural network model compression device. The neural network model compression method comprises the steps of: determining a model parameter set of each neuron layer for each neuron layer in a neural network model, wherein the model parameter set includes a plurality of model parameters; carrying out first transformation on the plurality of model parameters to generate a plurality of intermediate parameters; quantizing the plurality of intermediate parameters according to a preset quantization step size to obtain a plurality of quantization parameters; selecting a plurality of sampling quantization points from the plurality of quantization parameters according to a preset quantization bit number; generating quantized values of the plurality of model parameters according to values of the plurality of quantization parameters and the plurality of sampling quantization points; and compressing and storing the plurality of model parameters according to the quantized values. The neural network model compression method can better maintain the effect of the model, greatly reduces the size of the neural network model, and reduces the occupation of computing resources, especially memory resources.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
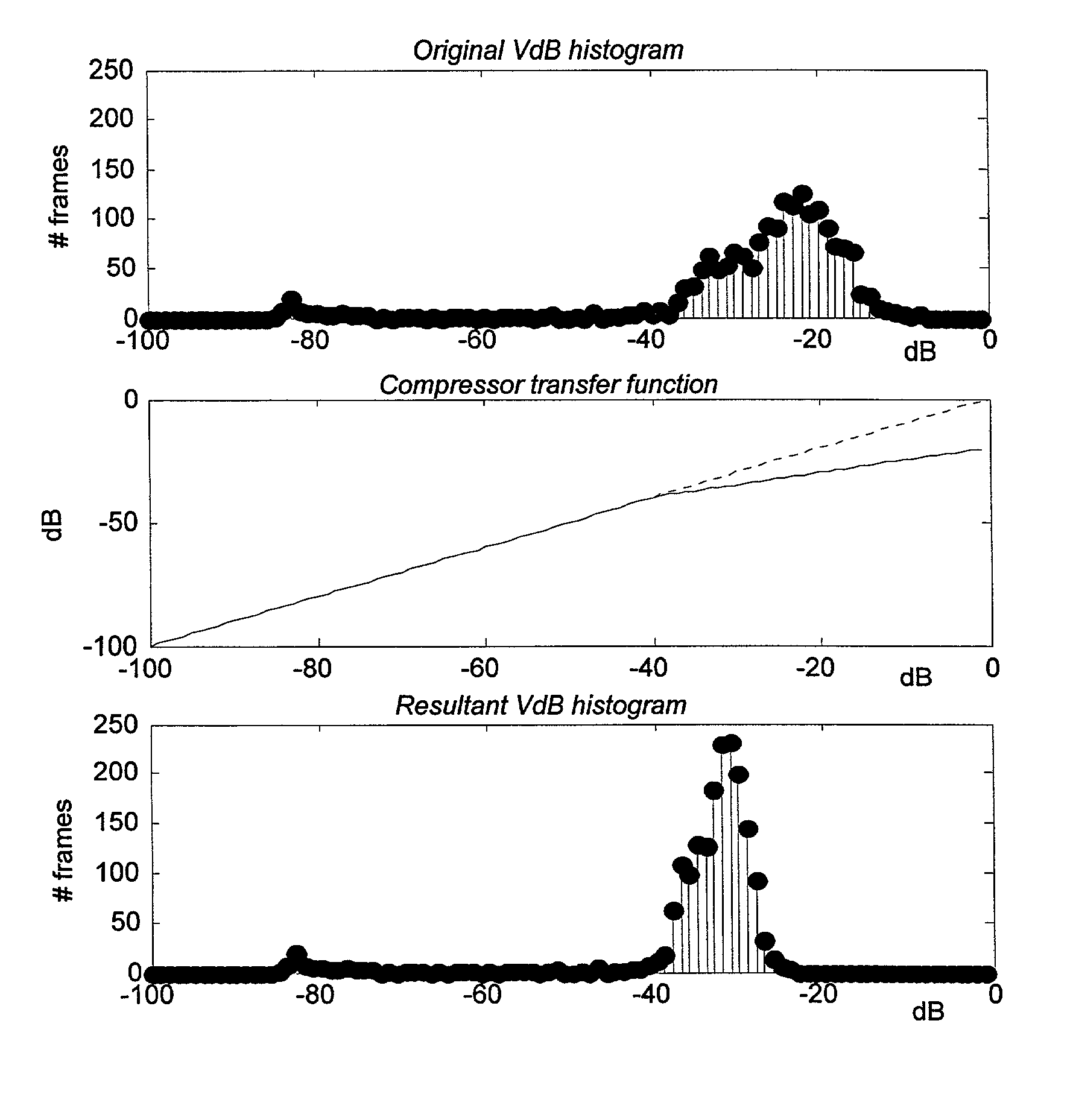
Method and apparatus for audio loudness and dynamics matching
ActiveUS7848531B1Prevent overcompressionLimited dynamicGain controlVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersEngineeringCompression method
The overall loudness of an audio track is calculated by combining a number of weighted loudness measures for segments of the audio track, where the weight applied to each individual loudness measure is a function of the loudness measure. By comparing the original overall loudness measure to a desired overall loudness measure, a gain can be determined that will adjust the loudness level to the desired value. Also disclosed is a dynamic compression method that analyzes the dynamic characteristics of an audio track and determines appropriate compressor parameters. Additionally, the loudness of a post-compressor audio track can be estimated for any given compressor parameters, thus permitting post-compression loudness matching to be done even if the compression is performed in real-time.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for data compression of heart signals
InactiveUS6599242B1Easy to compressReliable choiceElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyData compressionElectrical polarity
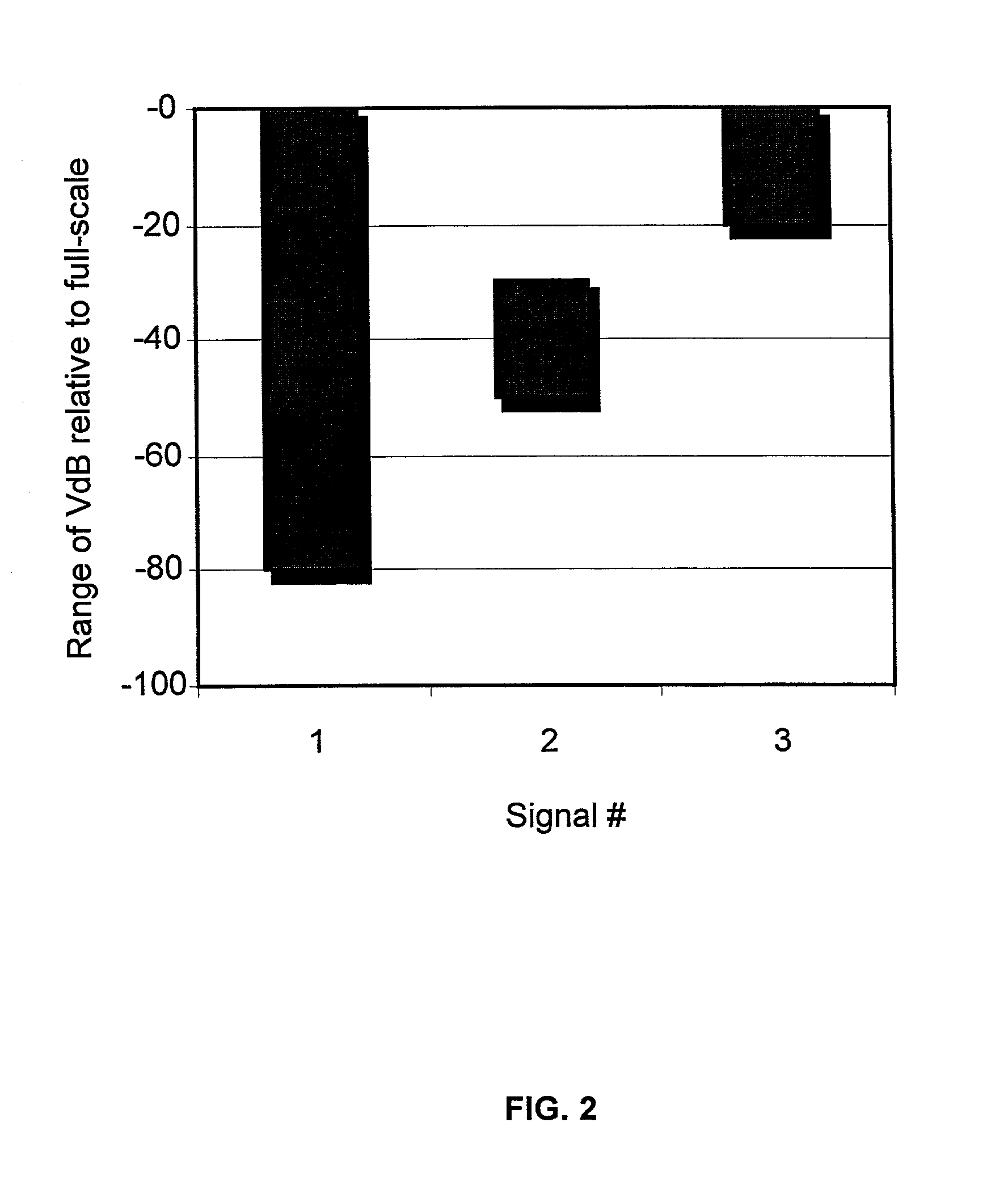
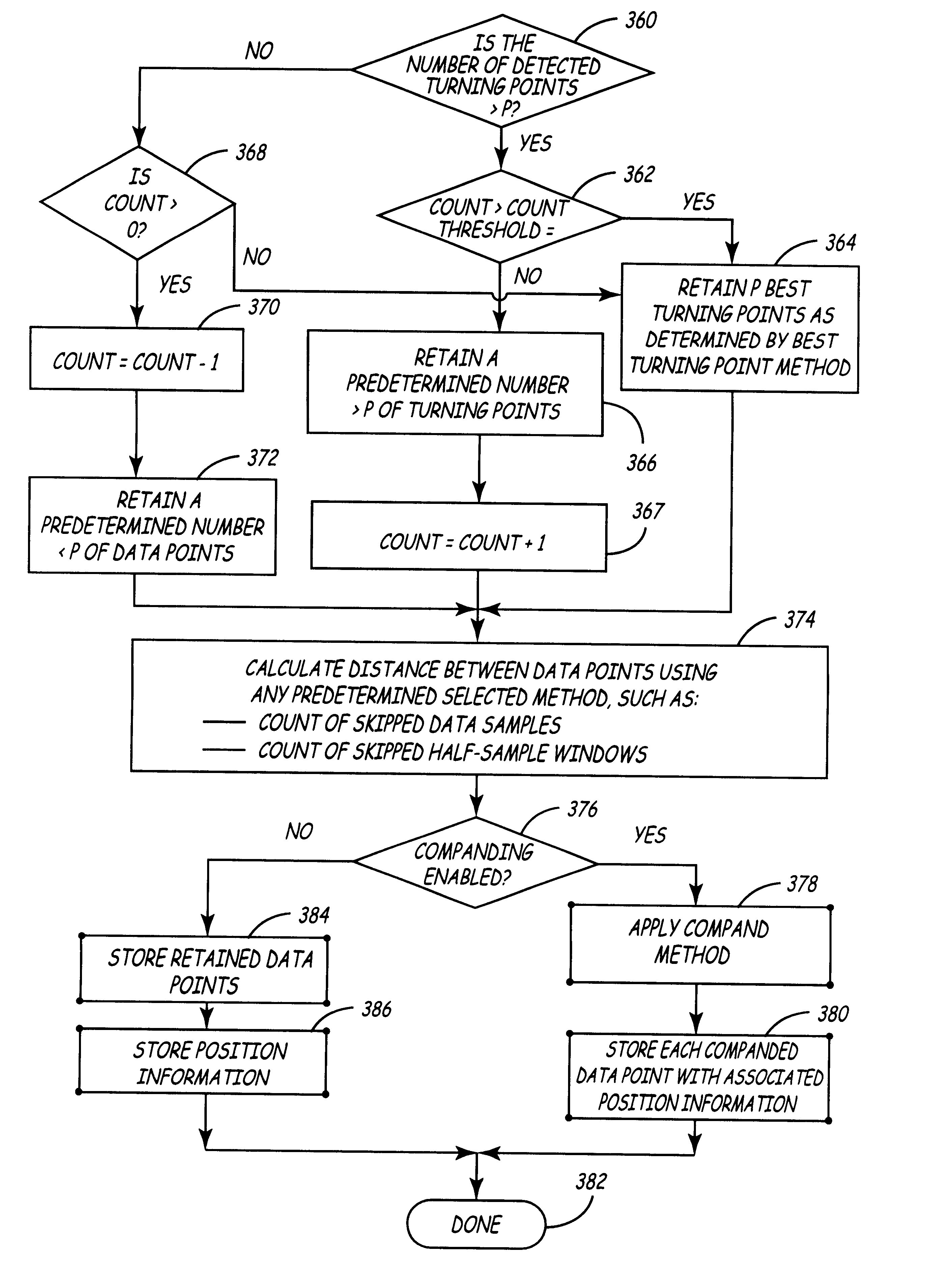
An improved turning point system and method for performing data compression is disclosed. The system improves the conventional turning point compression method by selecting a predetermined number of the "best" turning points in the sample window including data samples X0 and XN. From this sample-window, ones of the data samples X1 through X(N-1) will be identified as turning points using a selected one of a disclosed set of turning point detection methods. In one embodiment, a turning point is identified by determining that the slopes in the lines interconnecting adjacent data points have different polarities. In an alternative embodiment, a data sample XM is considered a turning point if the slope of the line between the data samples XM and X(M+1) has a different polarity as compared to the slope of the last waveform segment that was encountered that did not have a slope of zero. According to one mechanism, amplitude thresholding is used to detect whether an identified turning point is likely the result of noise such that the turning point status of the data sample should be disregarded. After data samples are identified as turning points, ones of the identified turning points are identified as the "best" turning points to be selected for retention. The best turning points may be identified by determining which waveform segment included within a sample window has the largest change of amplitude. An alternative embodiment detects which of the turning points has the greatest signal amplitude compared to a reference value. Yet another embodiment selects as the best turning point that point having an amplitude that differs the most from the amplitude of the first data sample in the sample window. Still other embodiments retain the turning point having an amplitude which is more positive, or alternatively, more negative, than the other data samples. According to one aspect of the invention, the compression ratio varies based on the frequency of the input waveform. In another embodiment, position data is retained to indicate the relative position of retained data samples as compared to the position of other retained data samples. This position data may be calculated at a frequency that is less than the frequency of the sampled data.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com