Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2528 results about "Macroblock" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
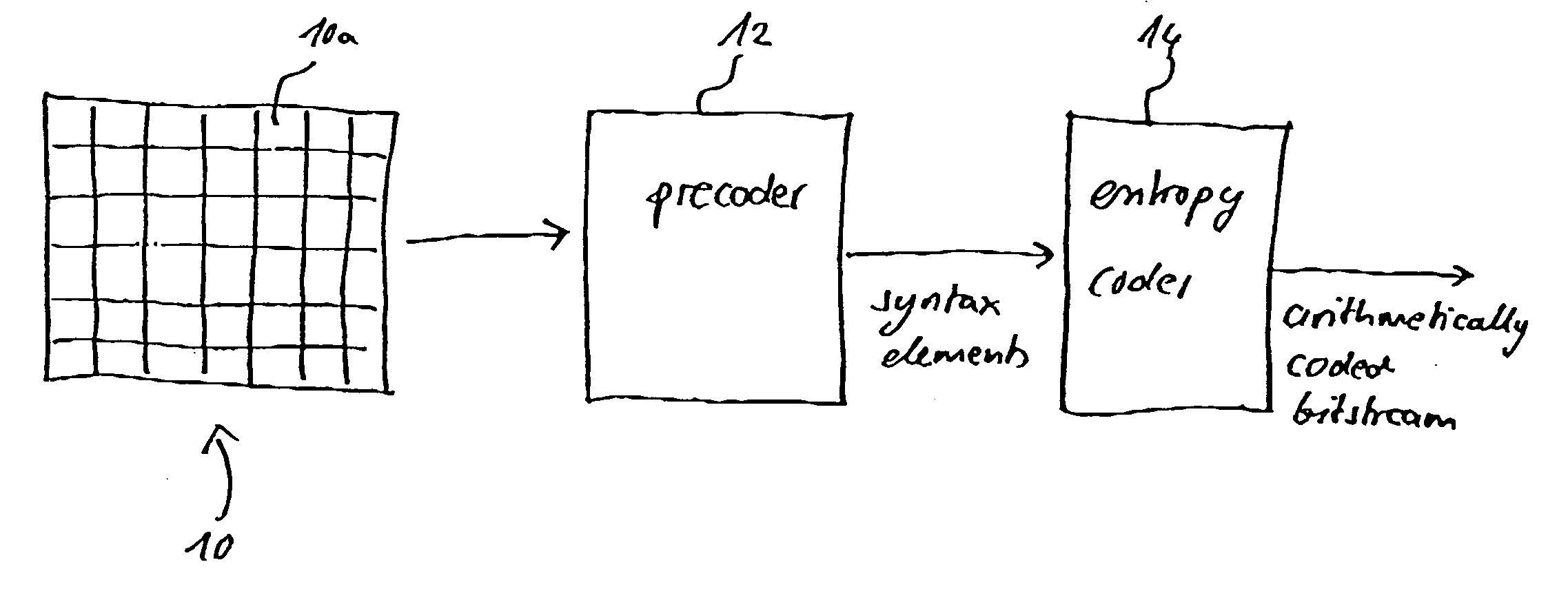
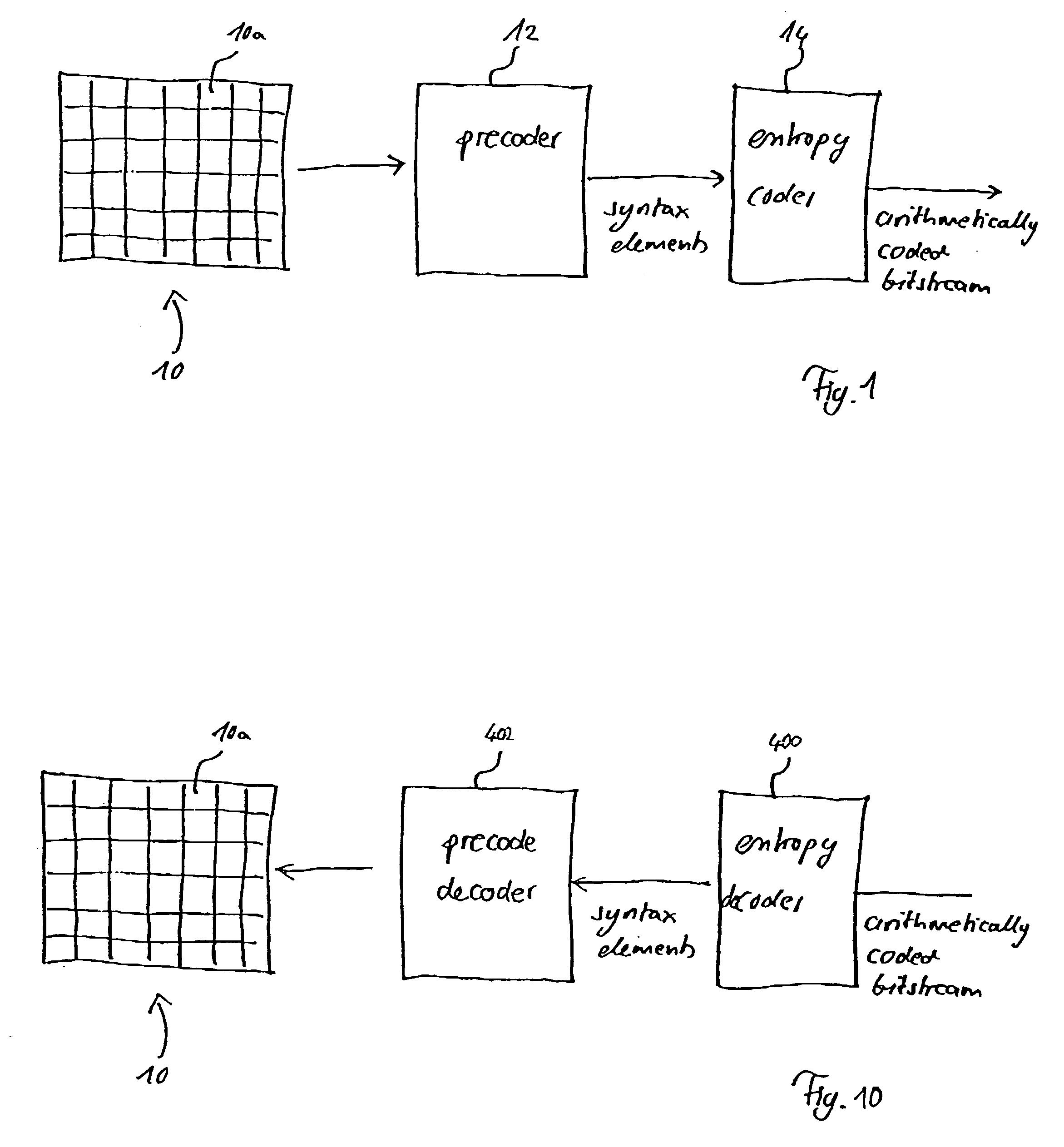
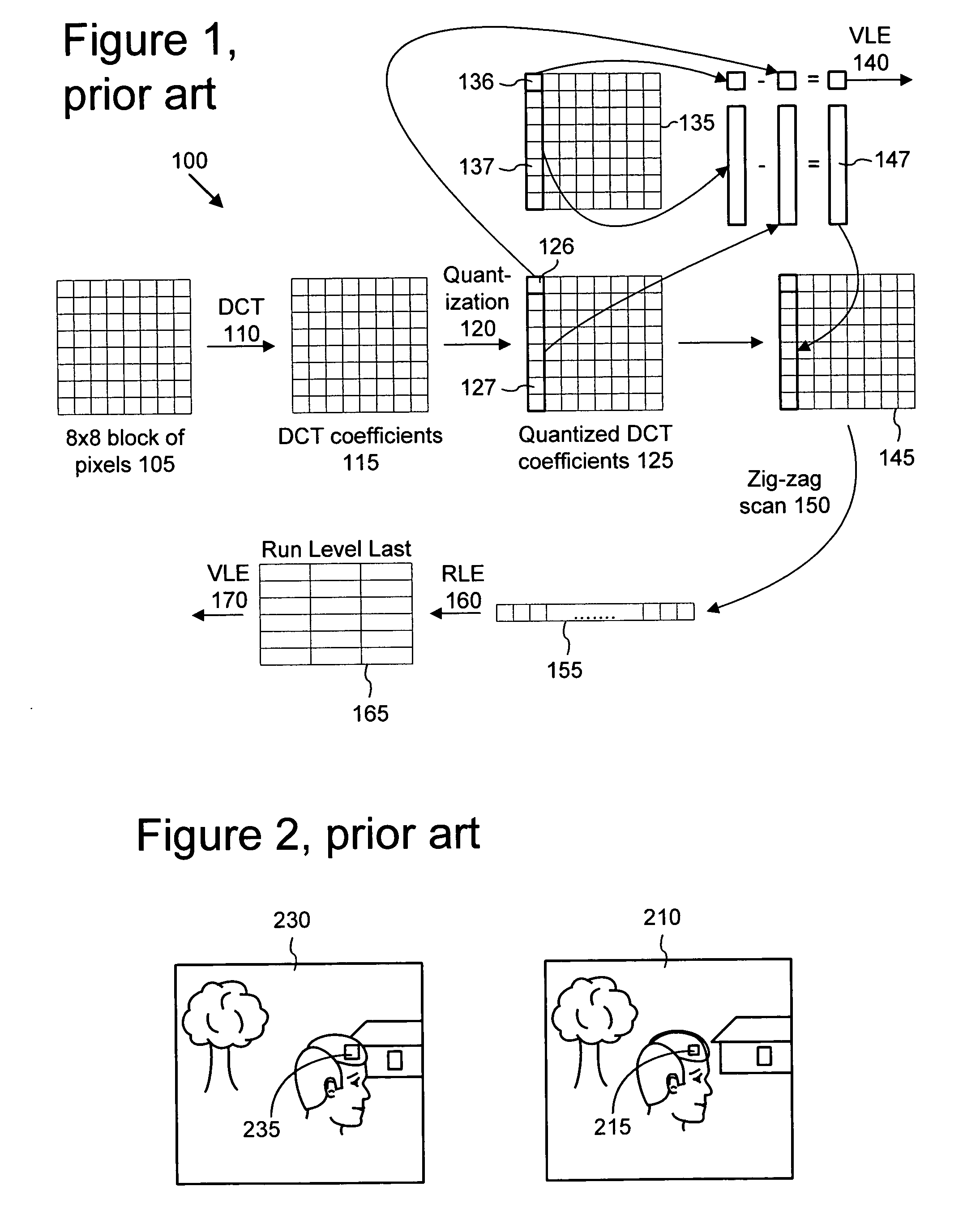
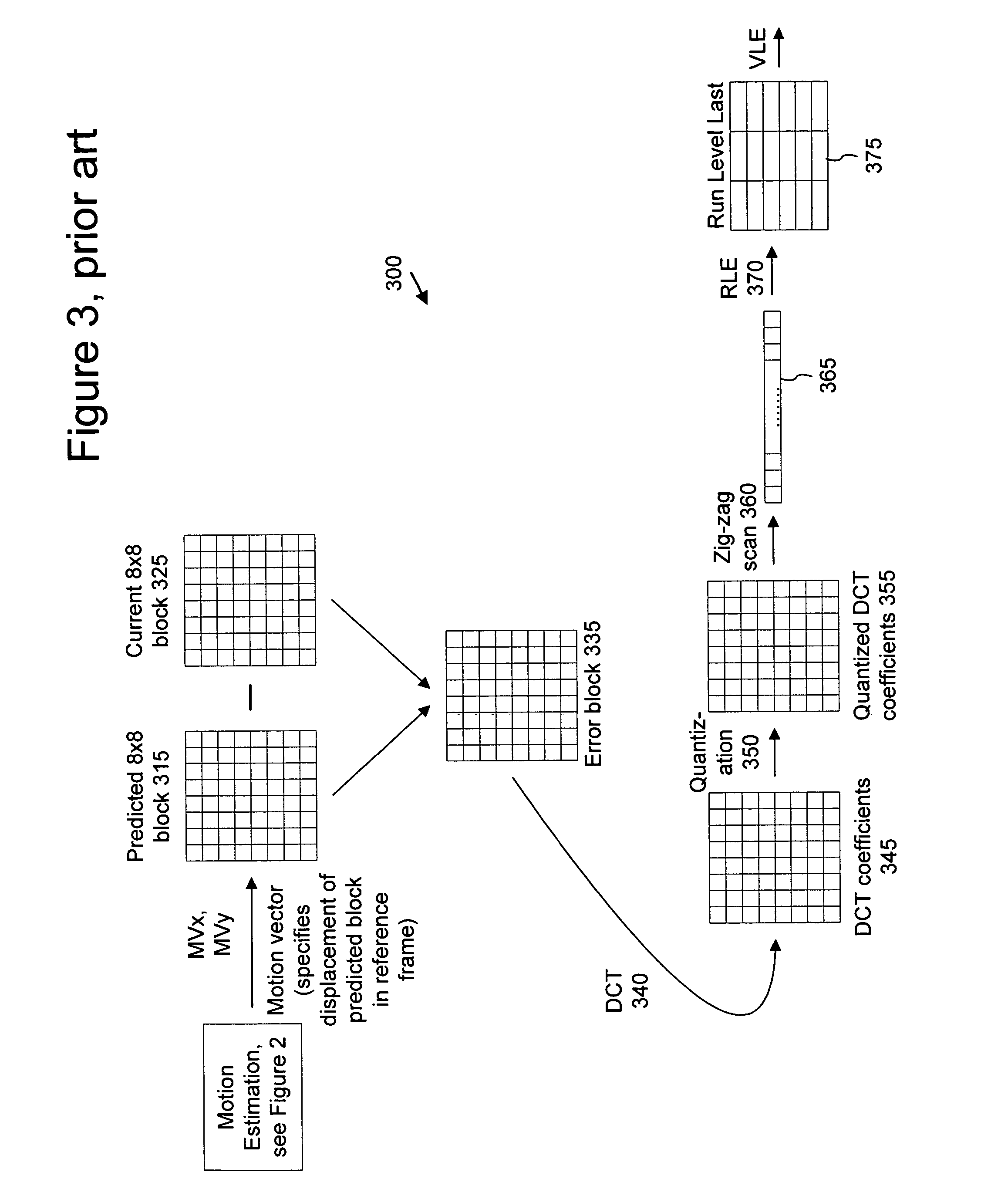
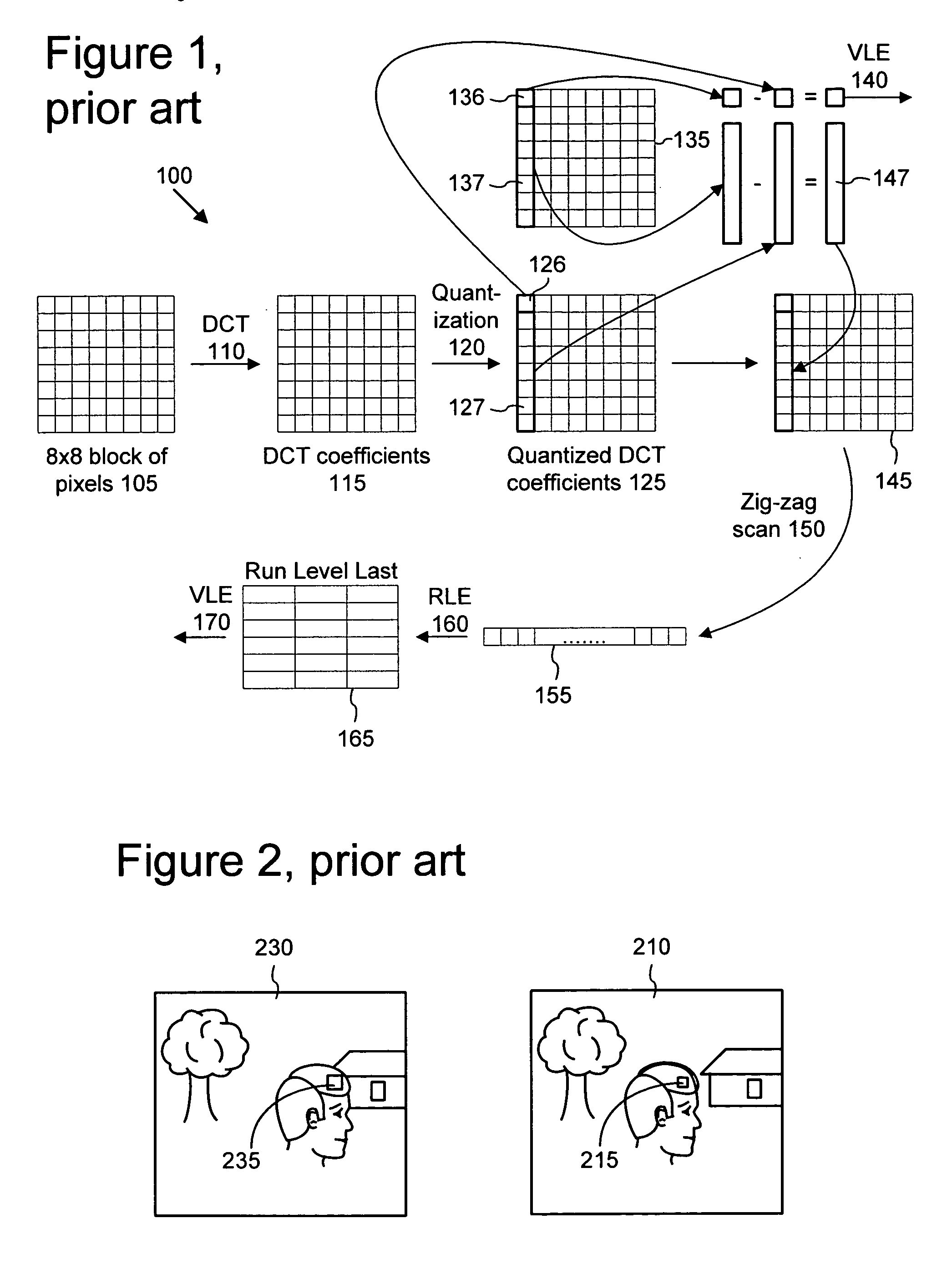
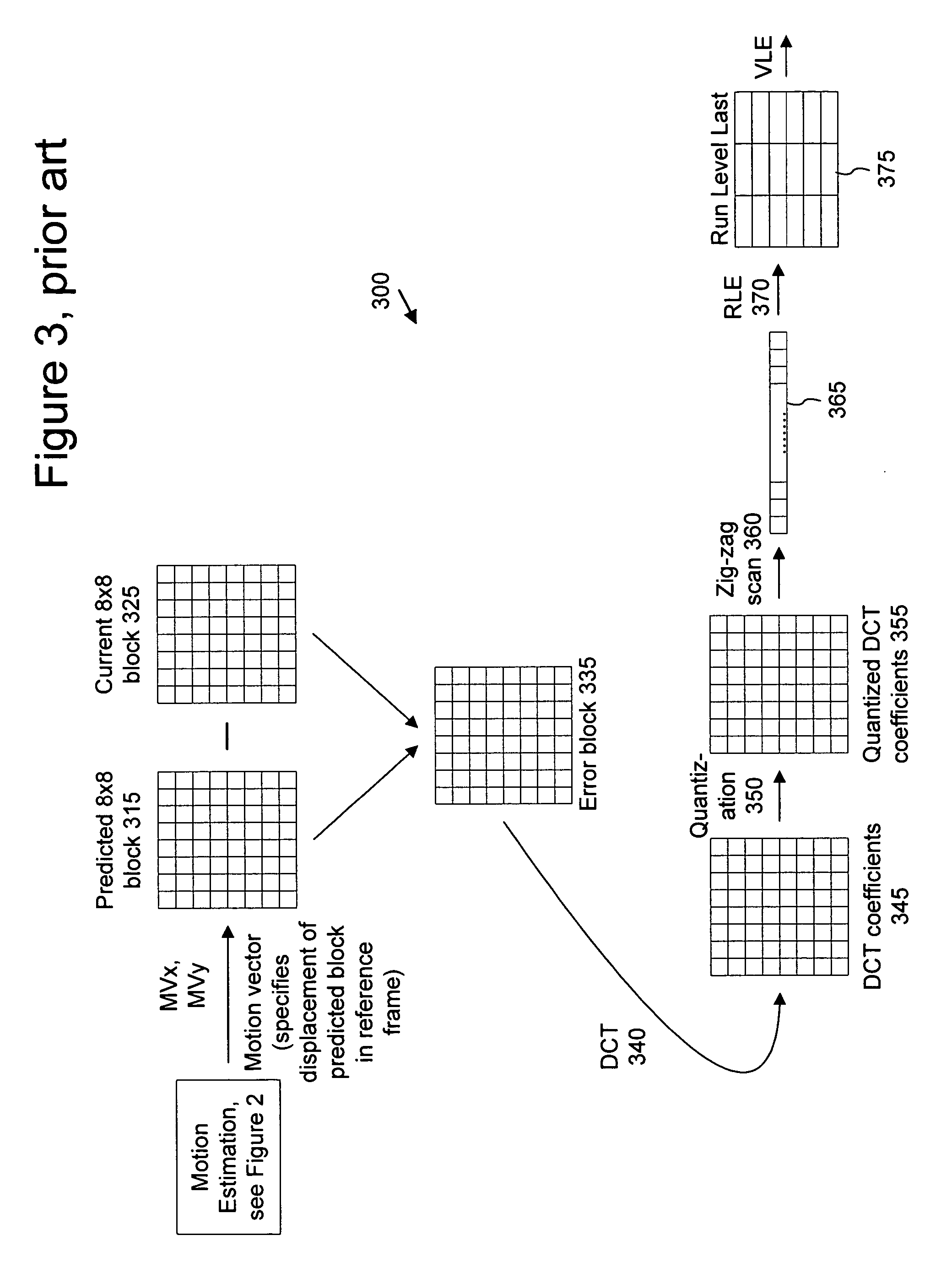
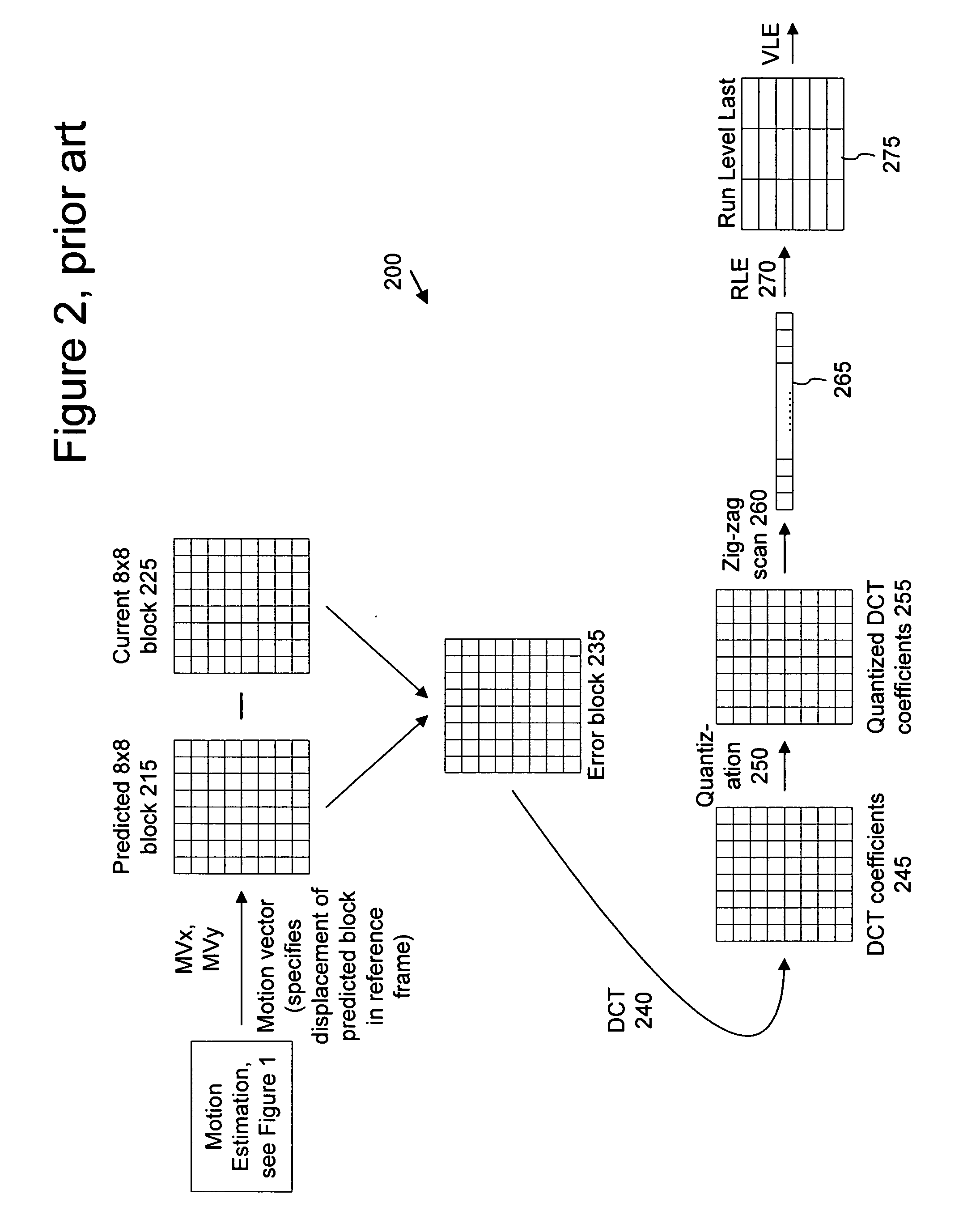
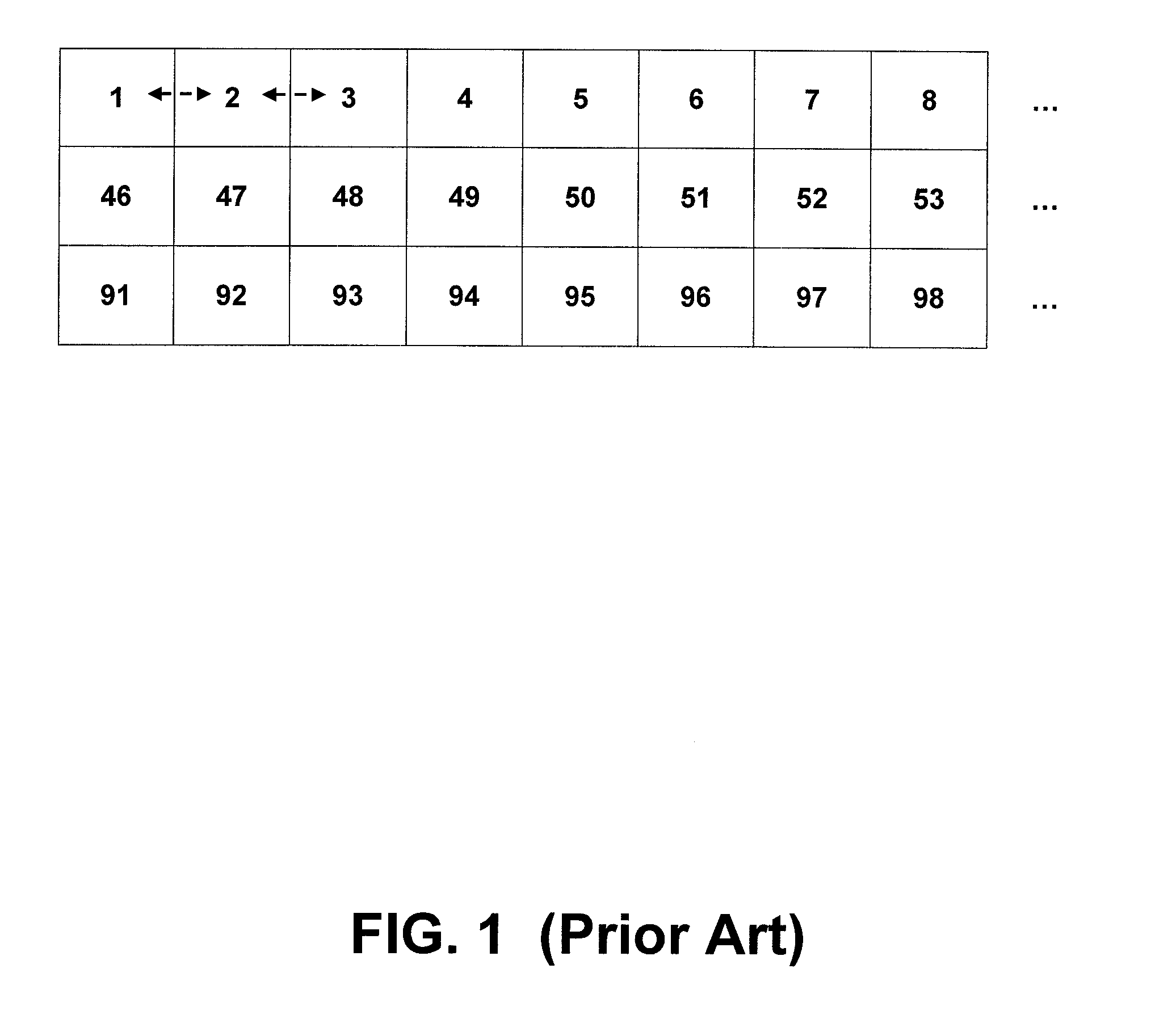
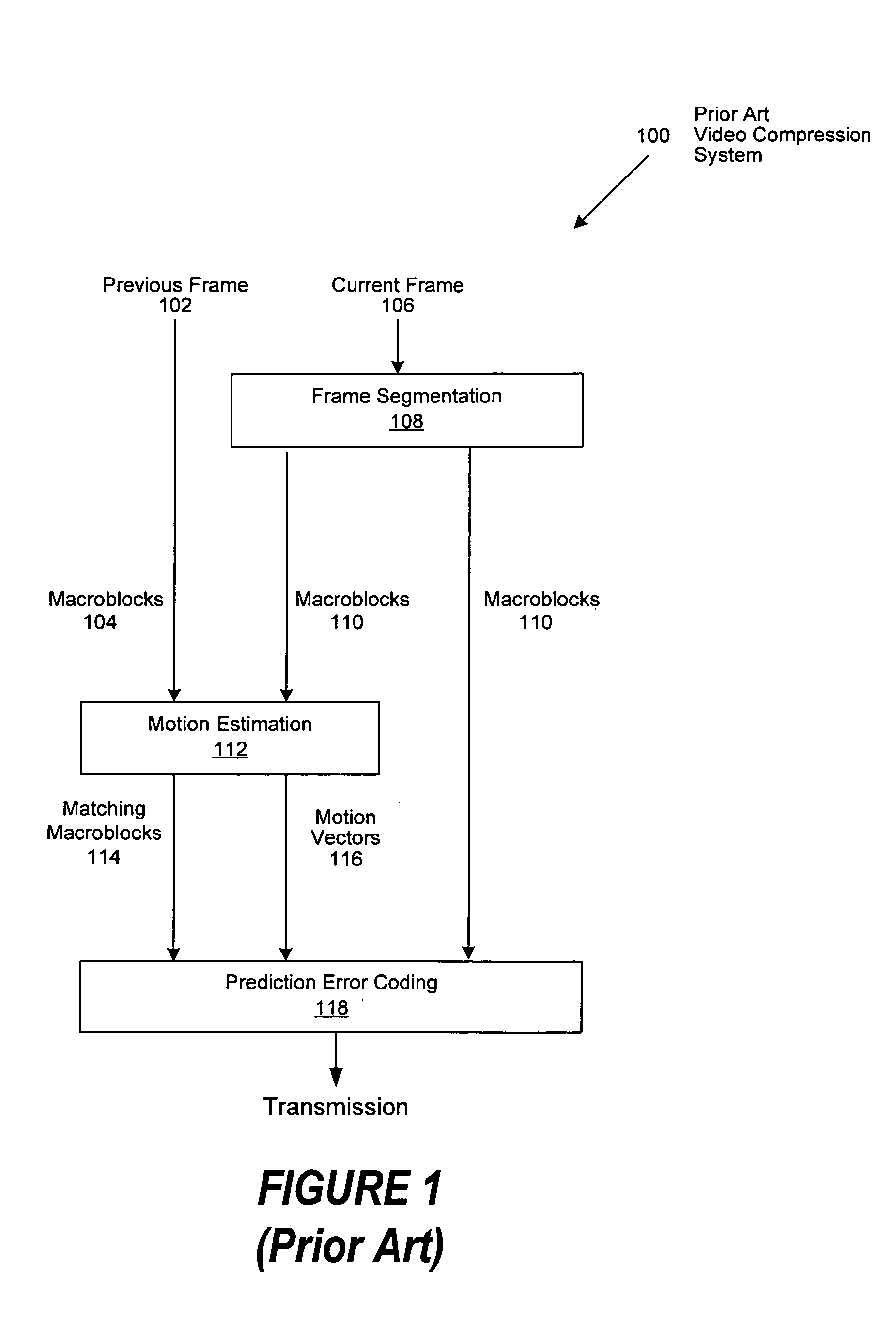
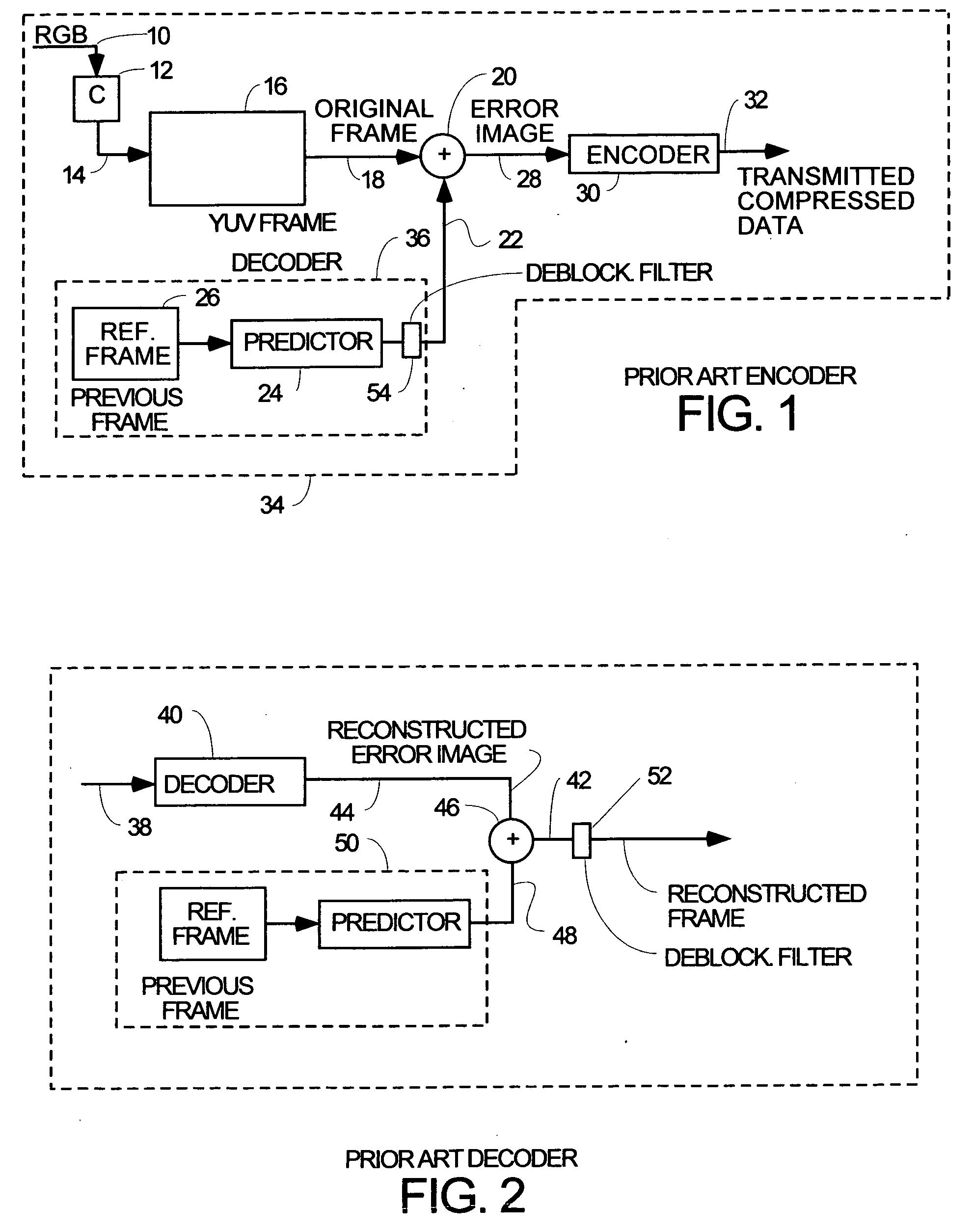
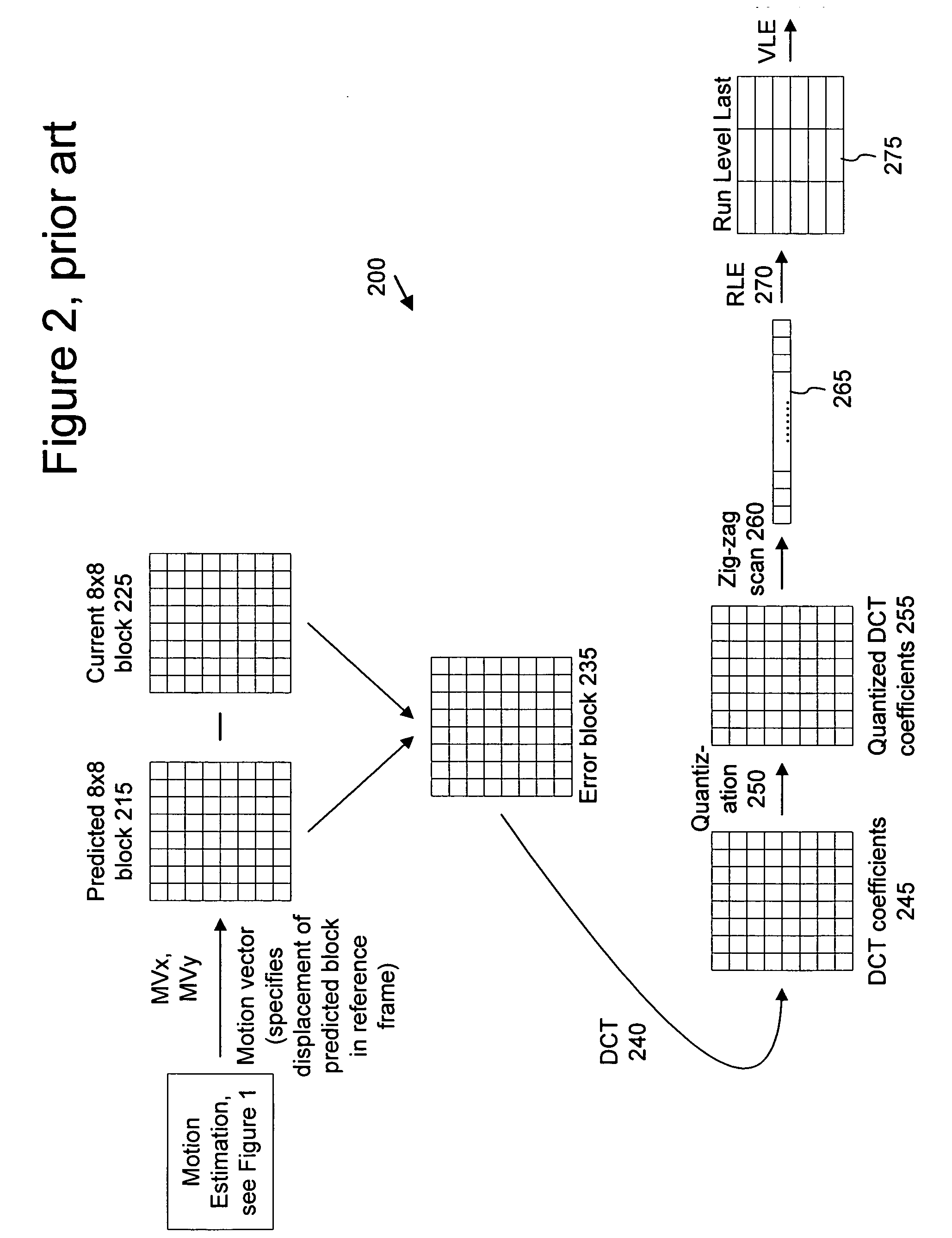
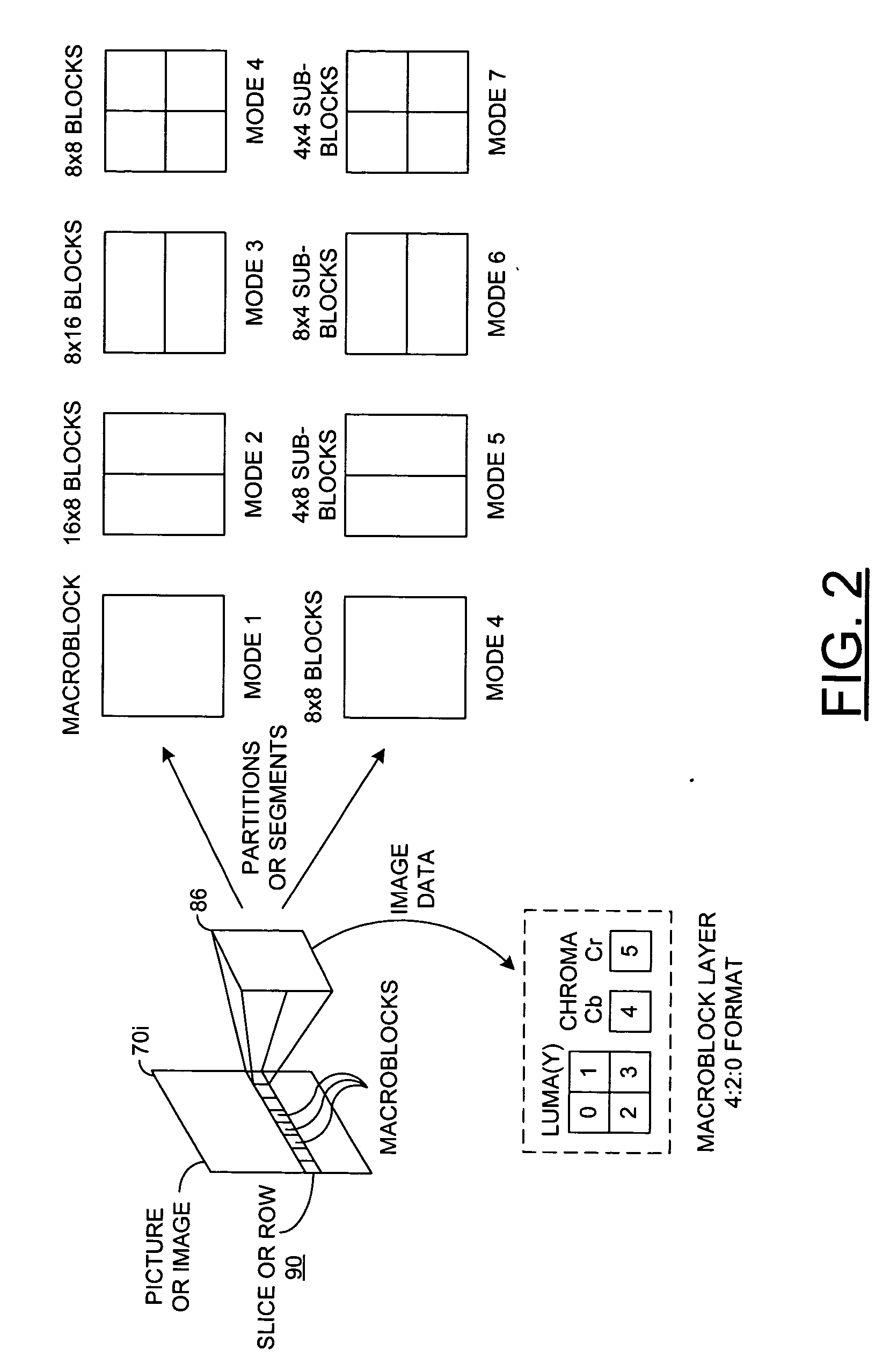
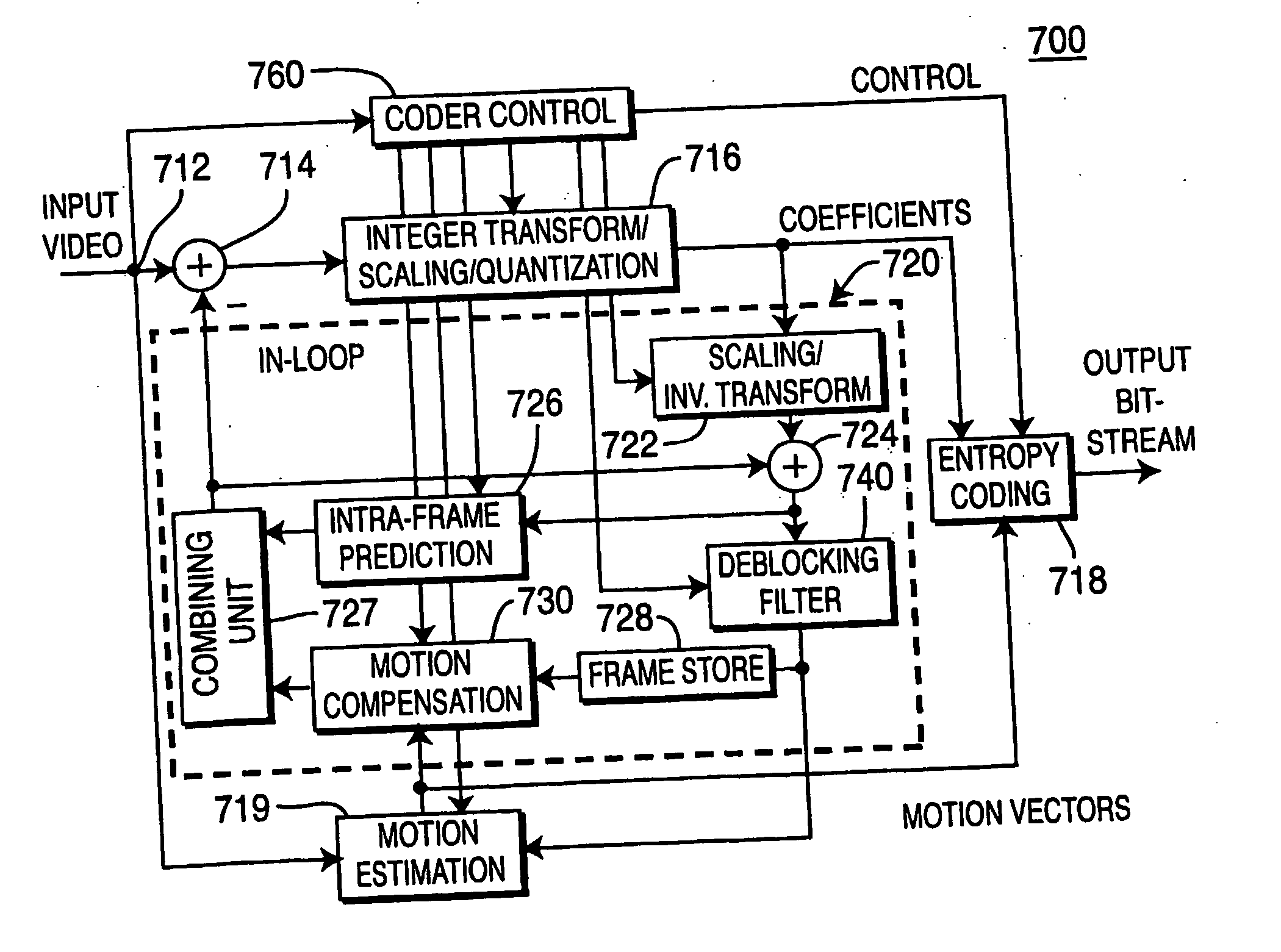
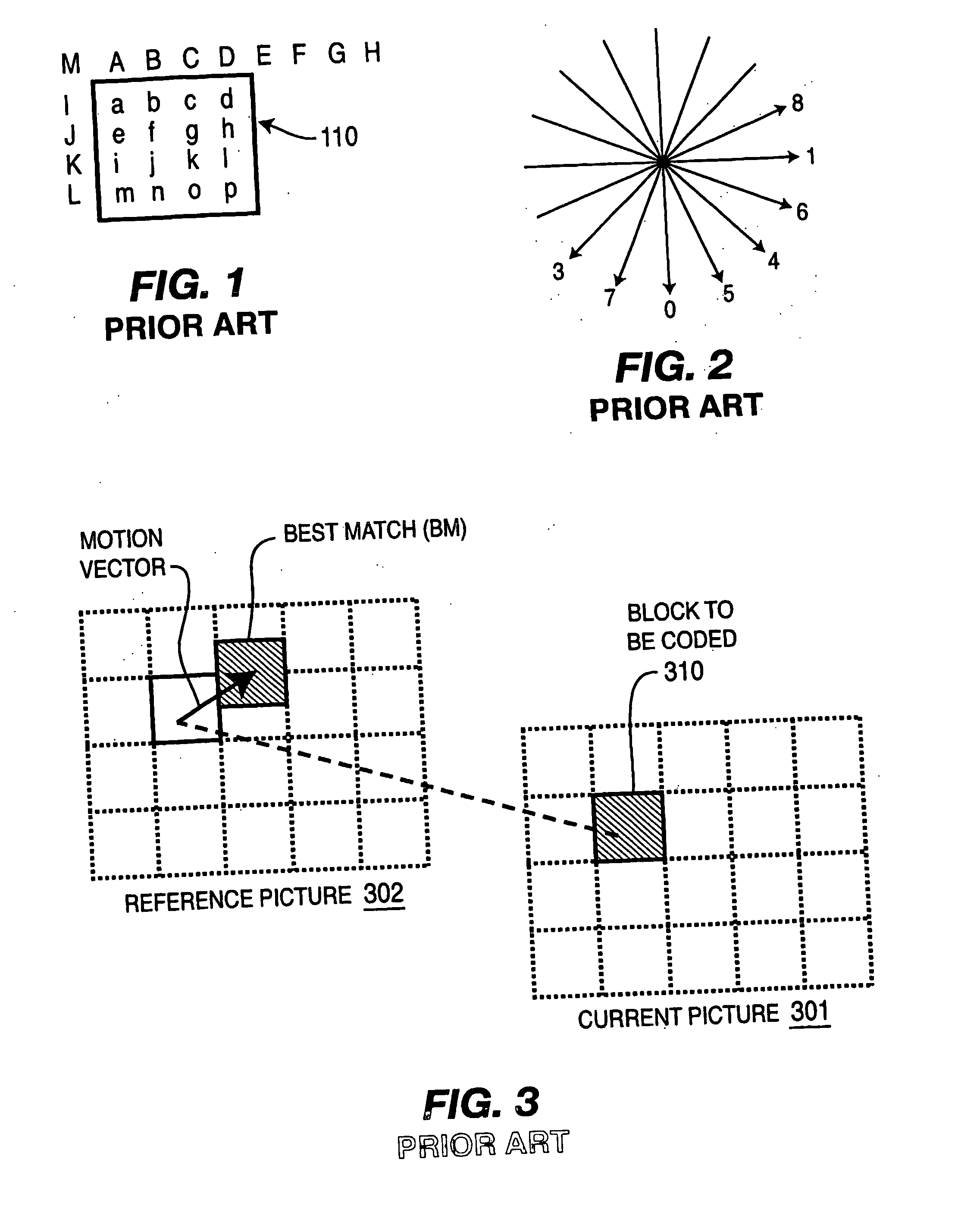
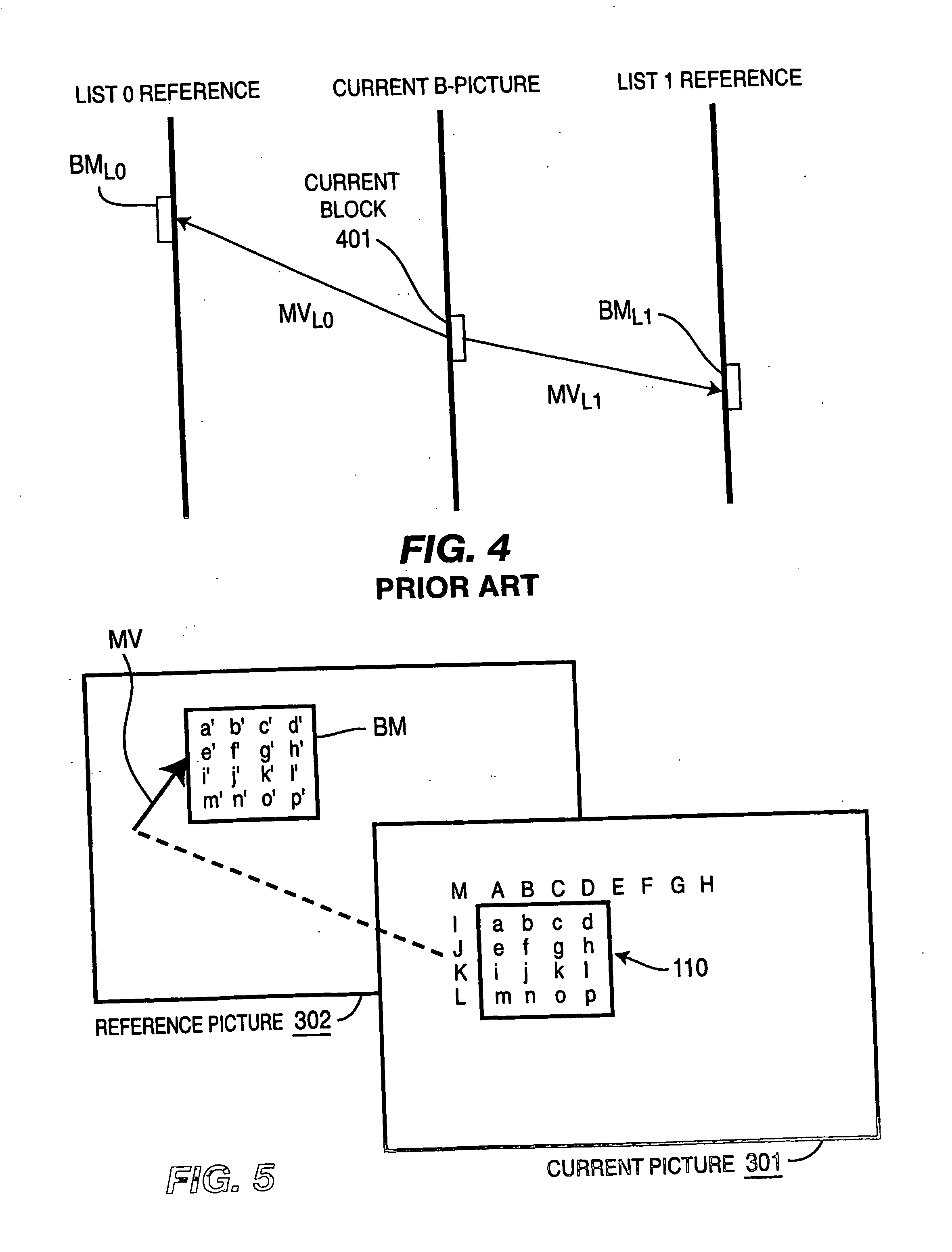
Macroblock is a processing unit in image and video compression formats based on linear block transforms, such as the discrete cosine transform (DCT). A macroblock typically consists of 16×16 samples, and is further subdivided into transform blocks, and may be further subdivided into prediction blocks. Formats which are based on macroblocks include JPEG, where they are called MCU blocks, H.261, MPEG-1 Part 2, H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2, H.263, MPEG-4 Part 2, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. In H.265/HEVC, the macroblock as a basic processing unit has been replaced by the coding tree unit.
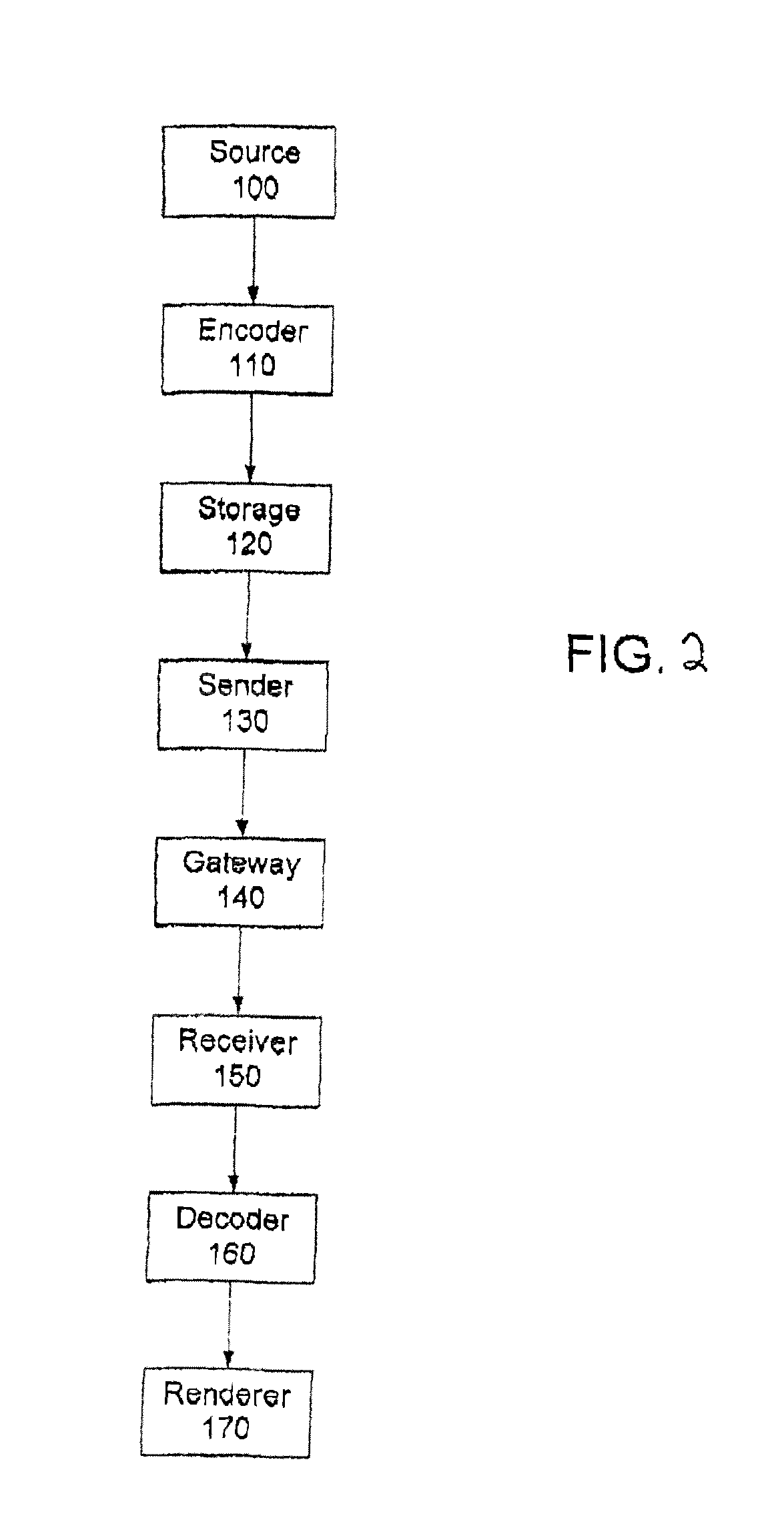
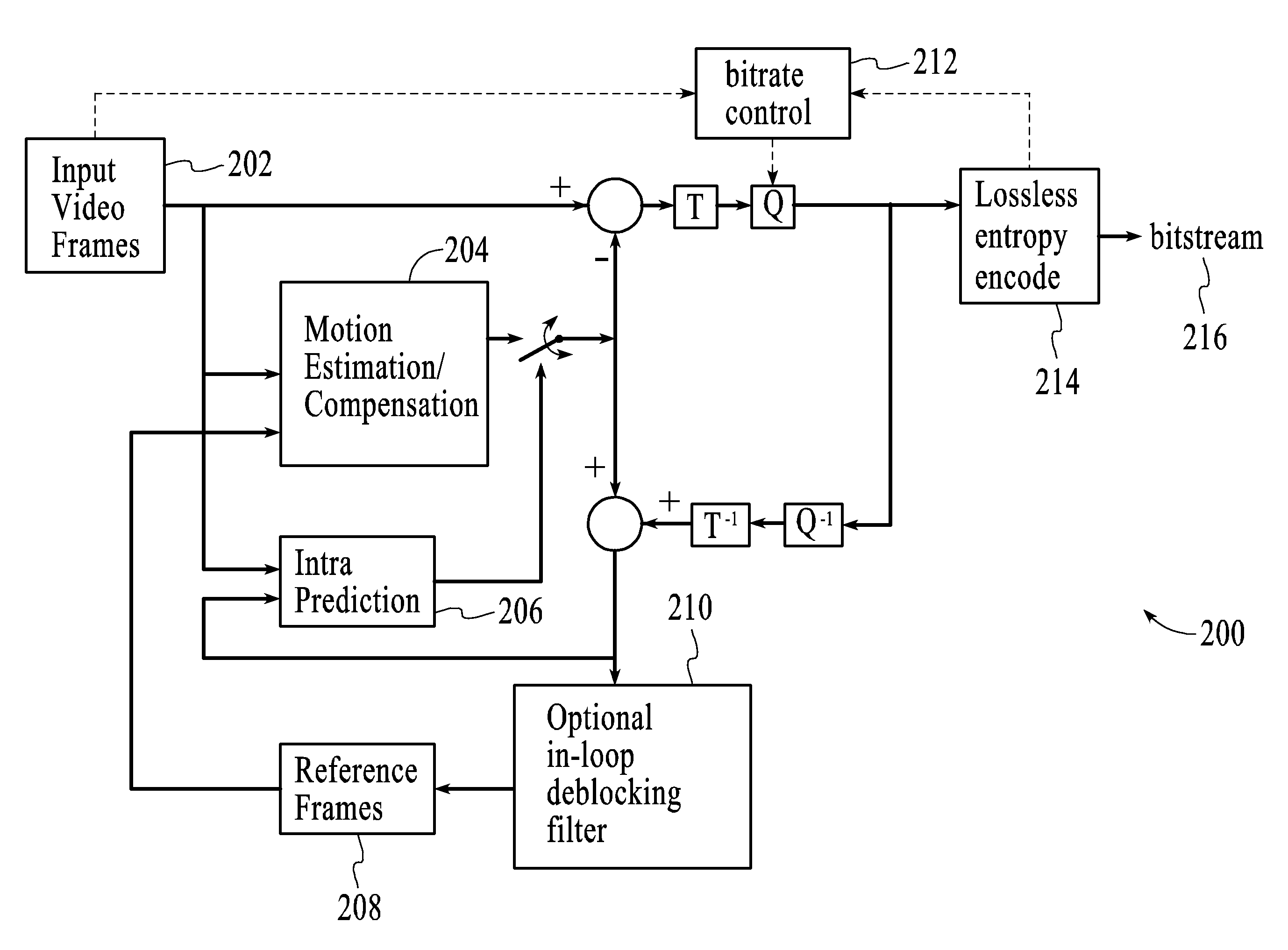
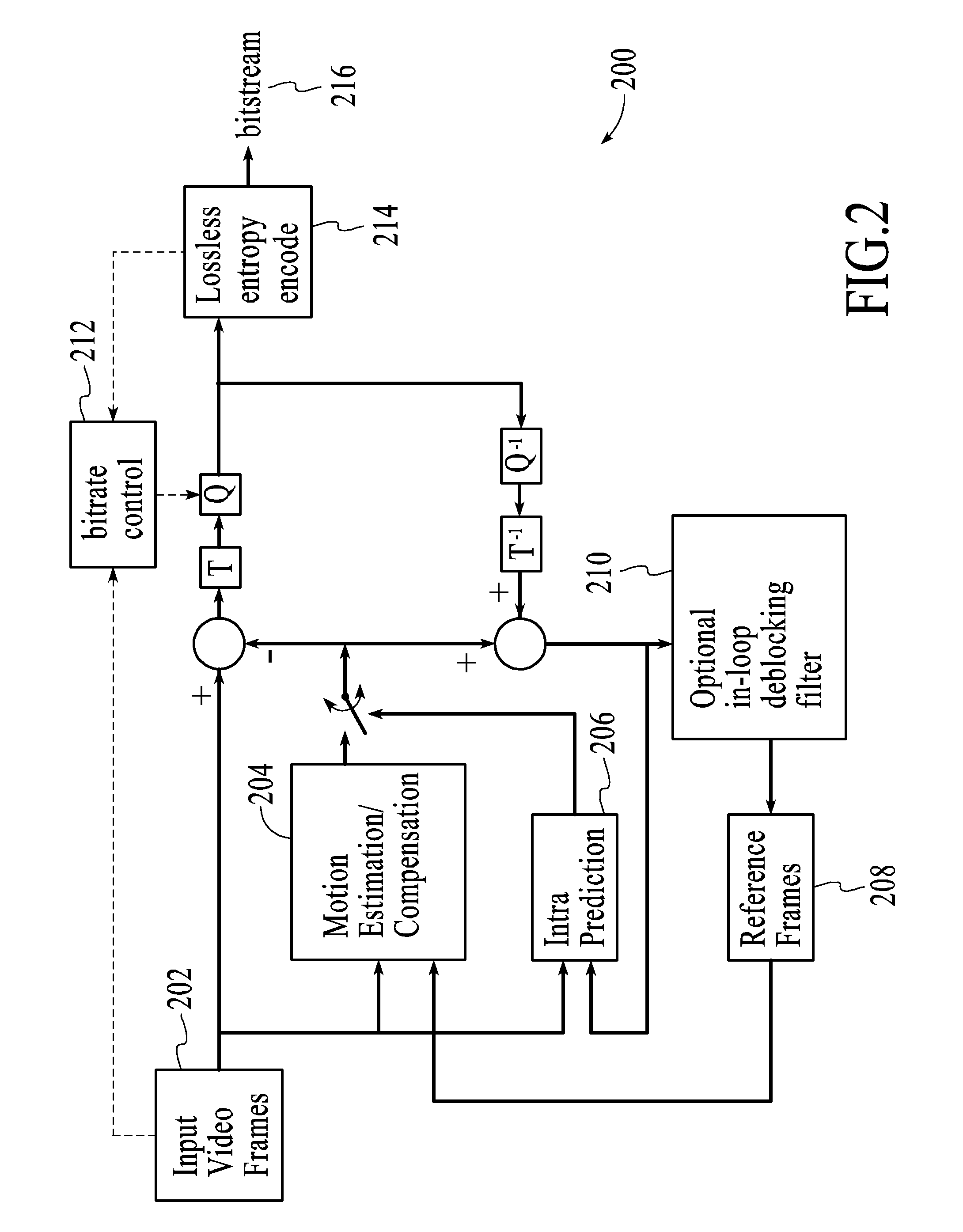
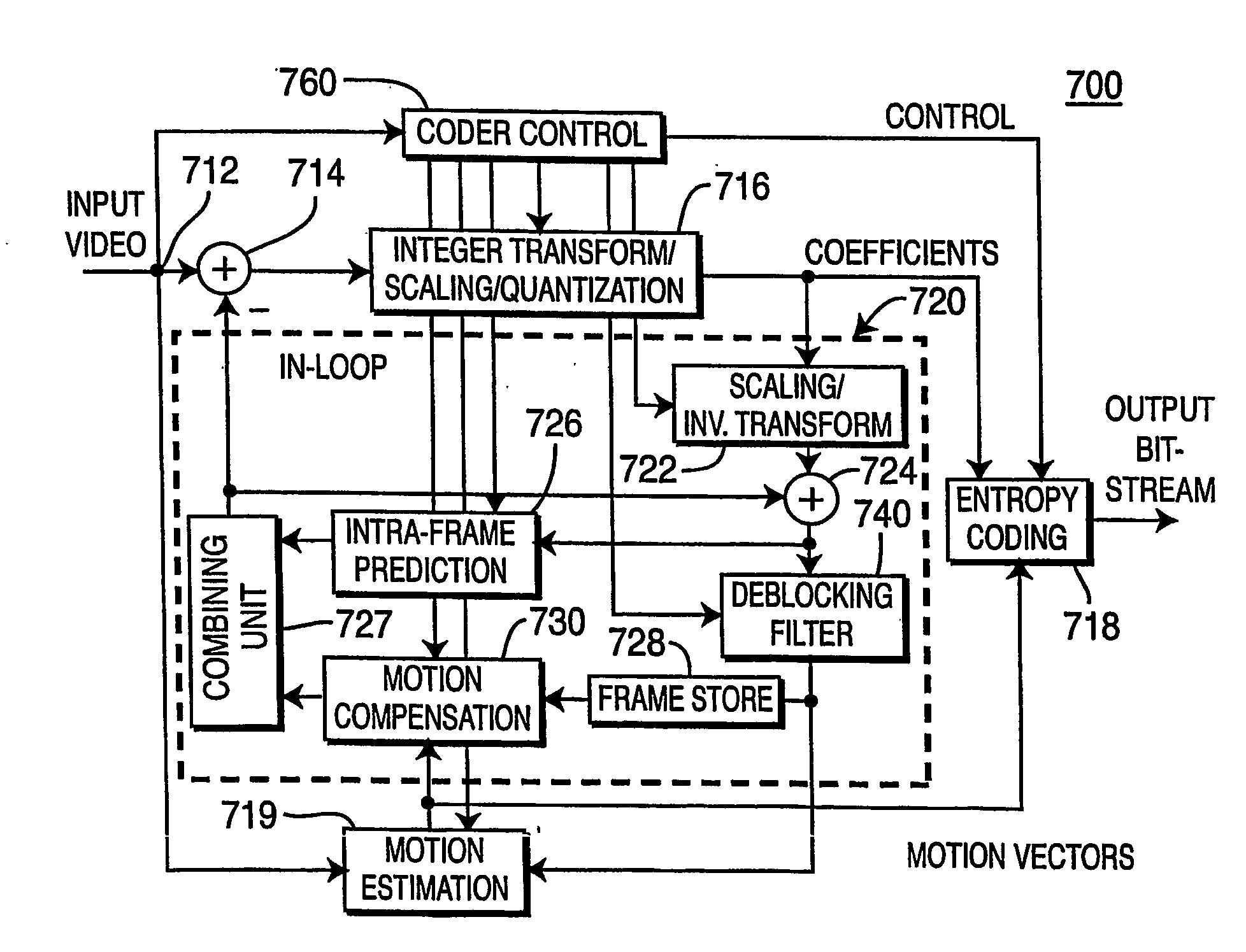
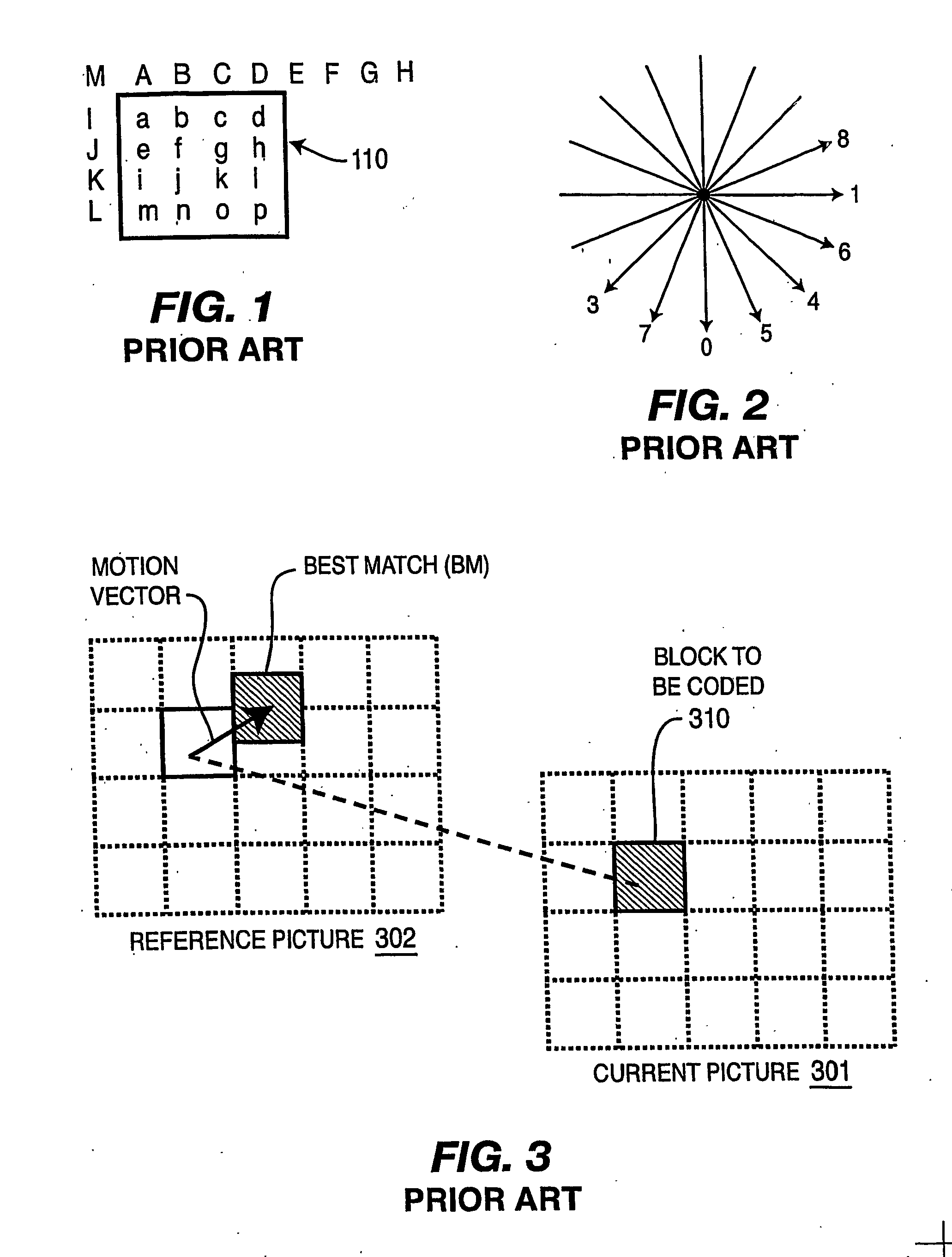
Video frame encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20050169374A1Improve effectivenessDecrease in code efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAdaptive encodingContext model
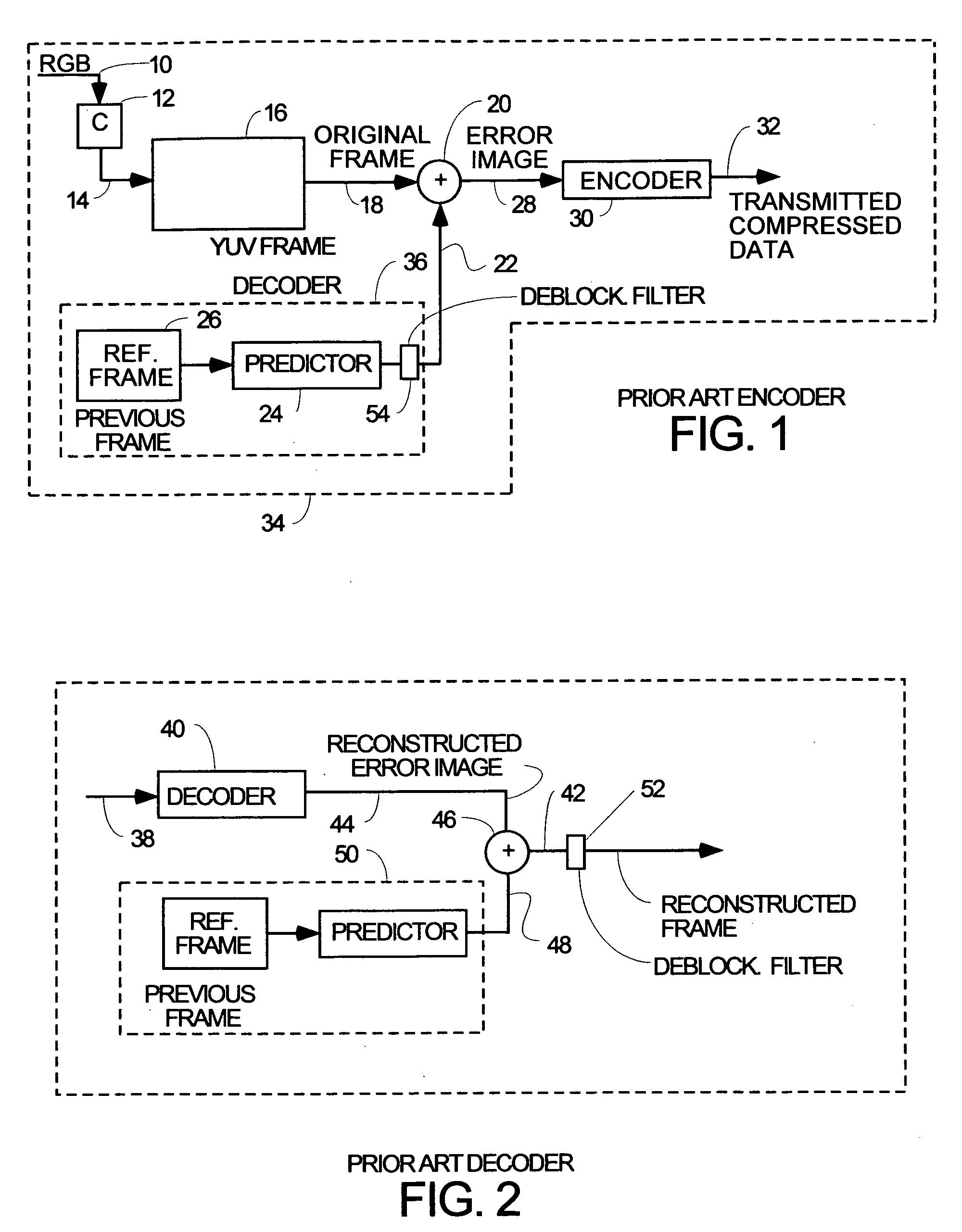
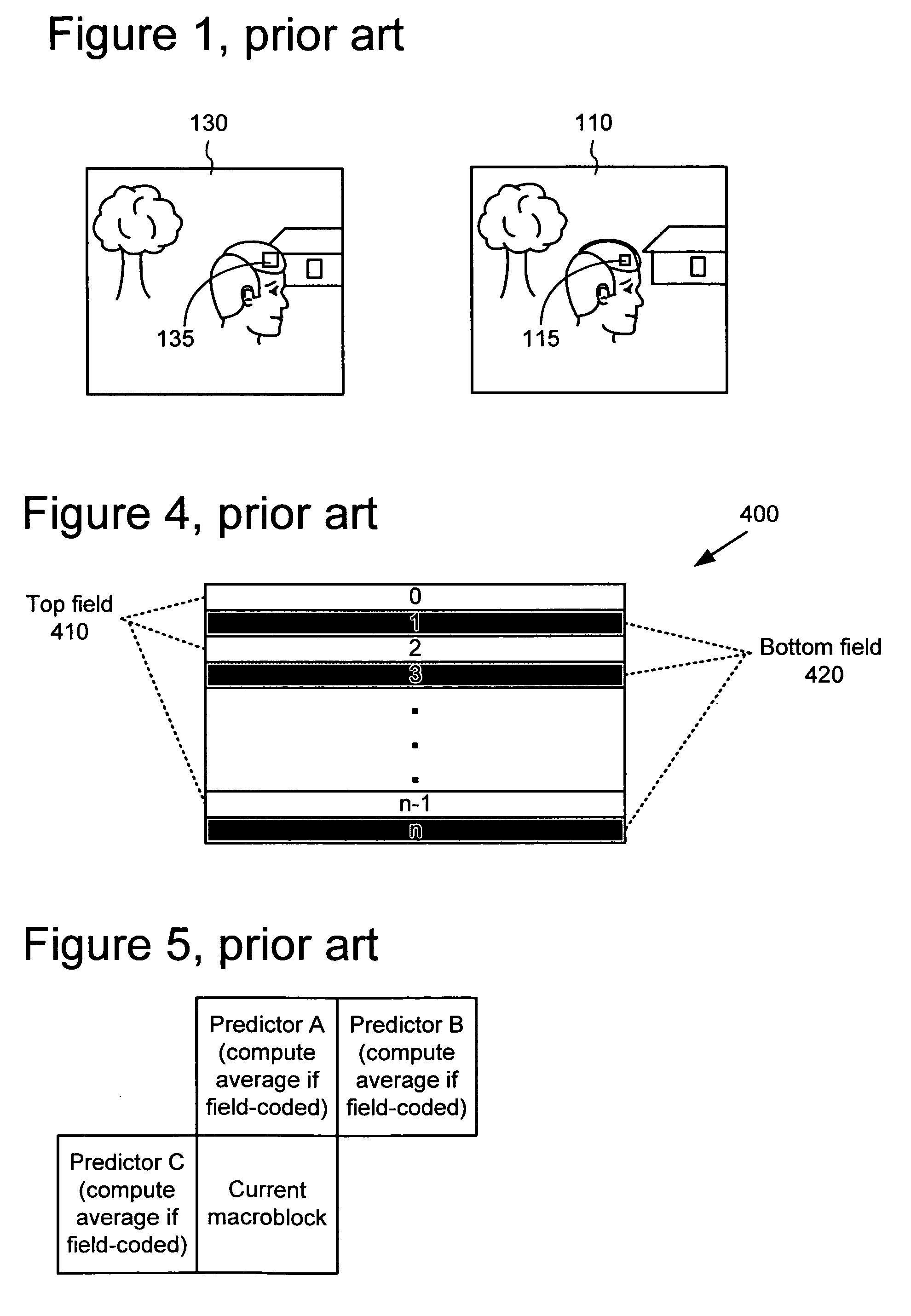
A video frame arithmetical context adaptive encoding and decoding scheme is presented which is based on the finding, that, for sake of a better definition of neighborhood between blocks of picture samples, i.e. the neighboring block which the syntax element to be coded or decoded relates to and the current block based on the attribute of which the assignment of a context model is conducted, and when the neighboring block lies beyond the borders or circumference of the current macroblock containing the current block, it is important to make the determination of the macroblock containing the neighboring block dependent upon as to whether the current macroblock pair region containing the current block is of a first or a second distribution type, i.e., frame or field coded.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Coding of motion vector information
InactiveUS20050013498A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionEncoder decoder
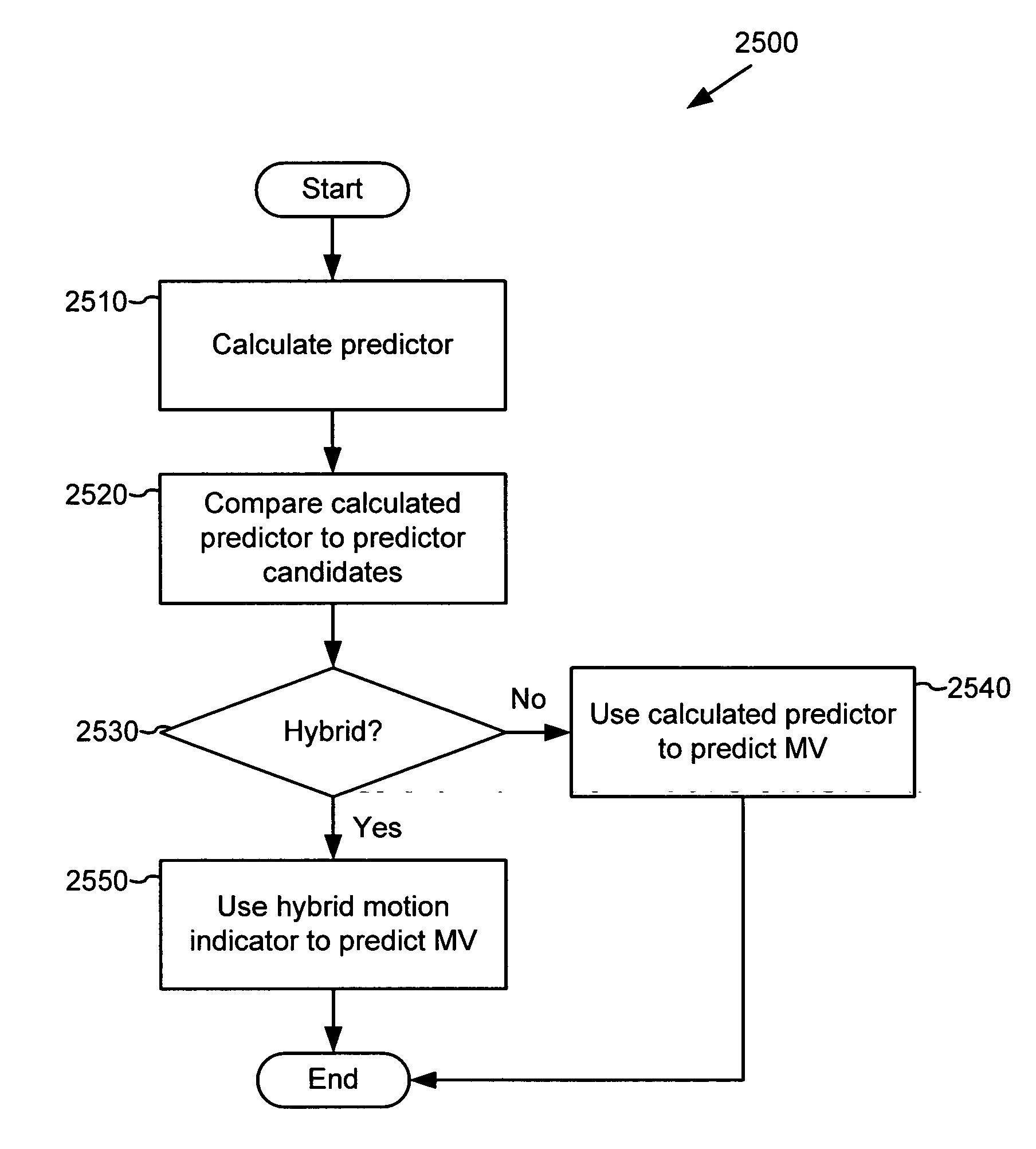
Techniques and tools for encoding and decoding motion vector information for video images are described. For example, a video encoder yields an extended motion vector code by jointly coding, for a set of pixels, a switch code, motion vector information, and a terminal symbol indicating whether subsequent data is encoded for the set of pixels. In another aspect, an encoder / decoder selects motion vector predictors for macroblocks. In another aspect, a video encoder / decoder uses hybrid motion vector prediction. In another aspect, a video encoder / decoder signals a motion vector mode for a predicted image. In another aspect, a video decoder decodes a set of pixels by receiving an extended motion vector code, which reflects joint encoding of motion information together with intra / inter-coding information and a terminal symbol. The decoder determines whether subsequent data exists for the set of pixels based on e.g., the terminal symbol.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Intraframe and interframe interlace coding and decoding
ActiveUS20050013497A1Facilitate decodingCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsInterlaced videoMotion vector
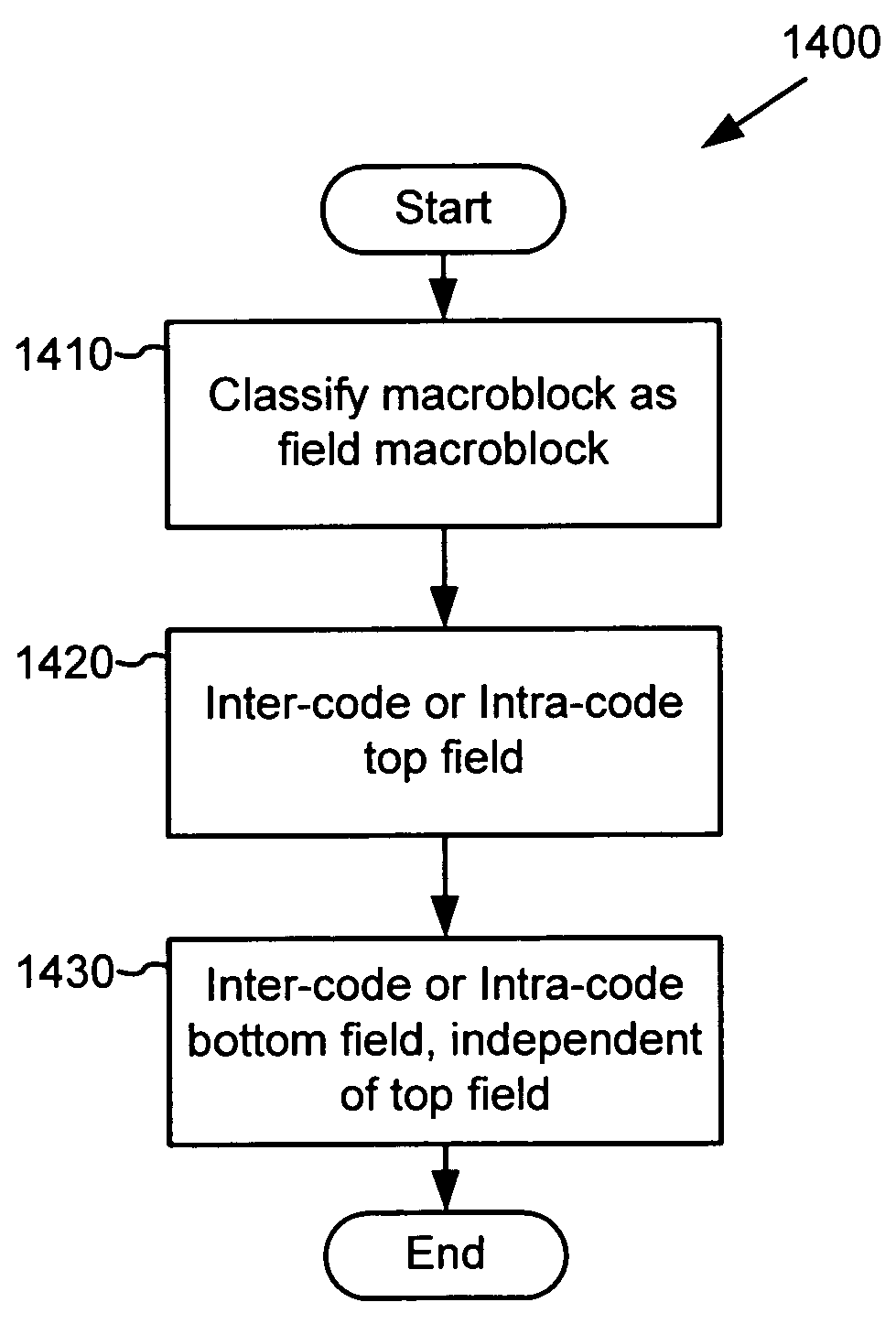
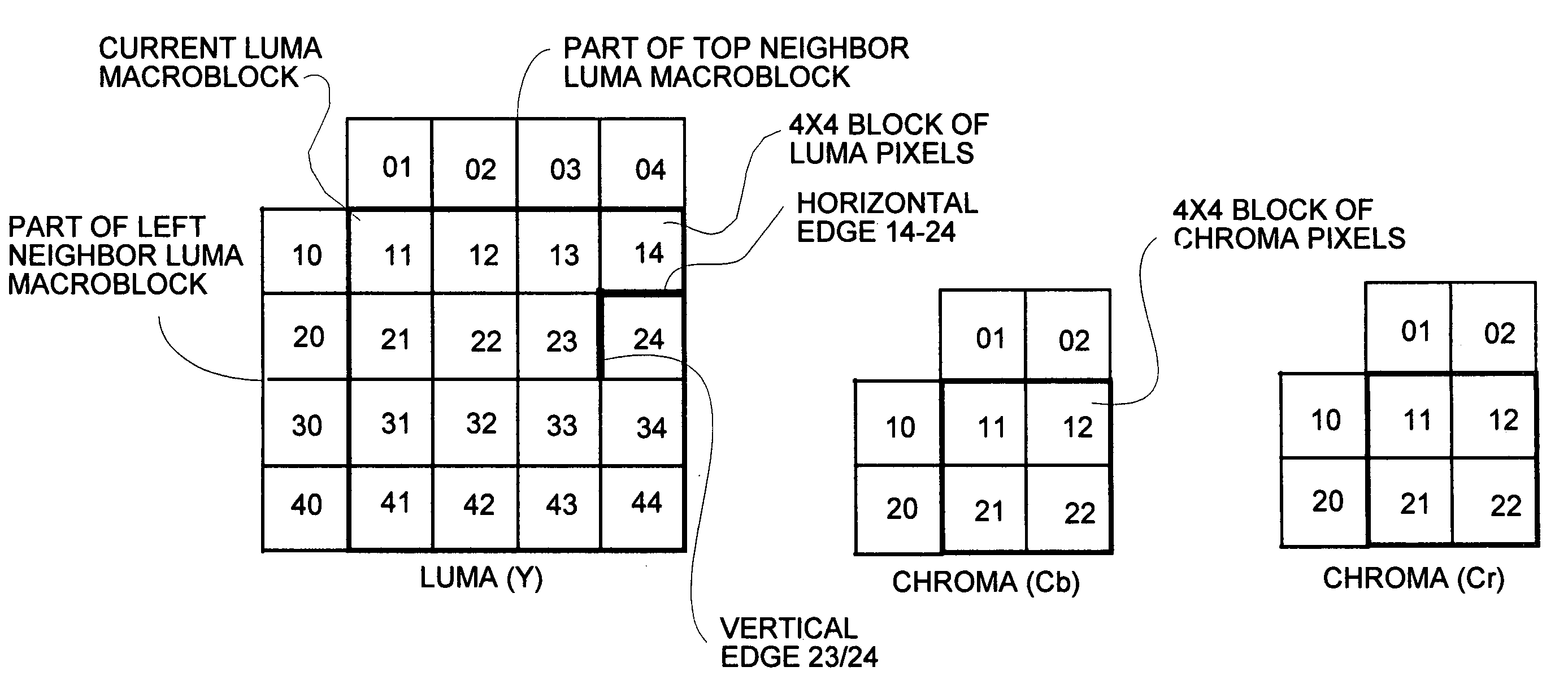
Techniques and tools for encoding and decoding video images (e.g., interlaced frames) are described. For example, a video encoder or decoder processes 4:1:1 format macroblocks comprising four 8×8 luminance blocks and four 4×8 chrominance blocks. In another aspect, fields in field-coded macroblocks are coded independently of one another (e.g., by sending encoded blocks in field order). Other aspects include DC / AC prediction techniques and motion vector prediction techniques for interlaced frames.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
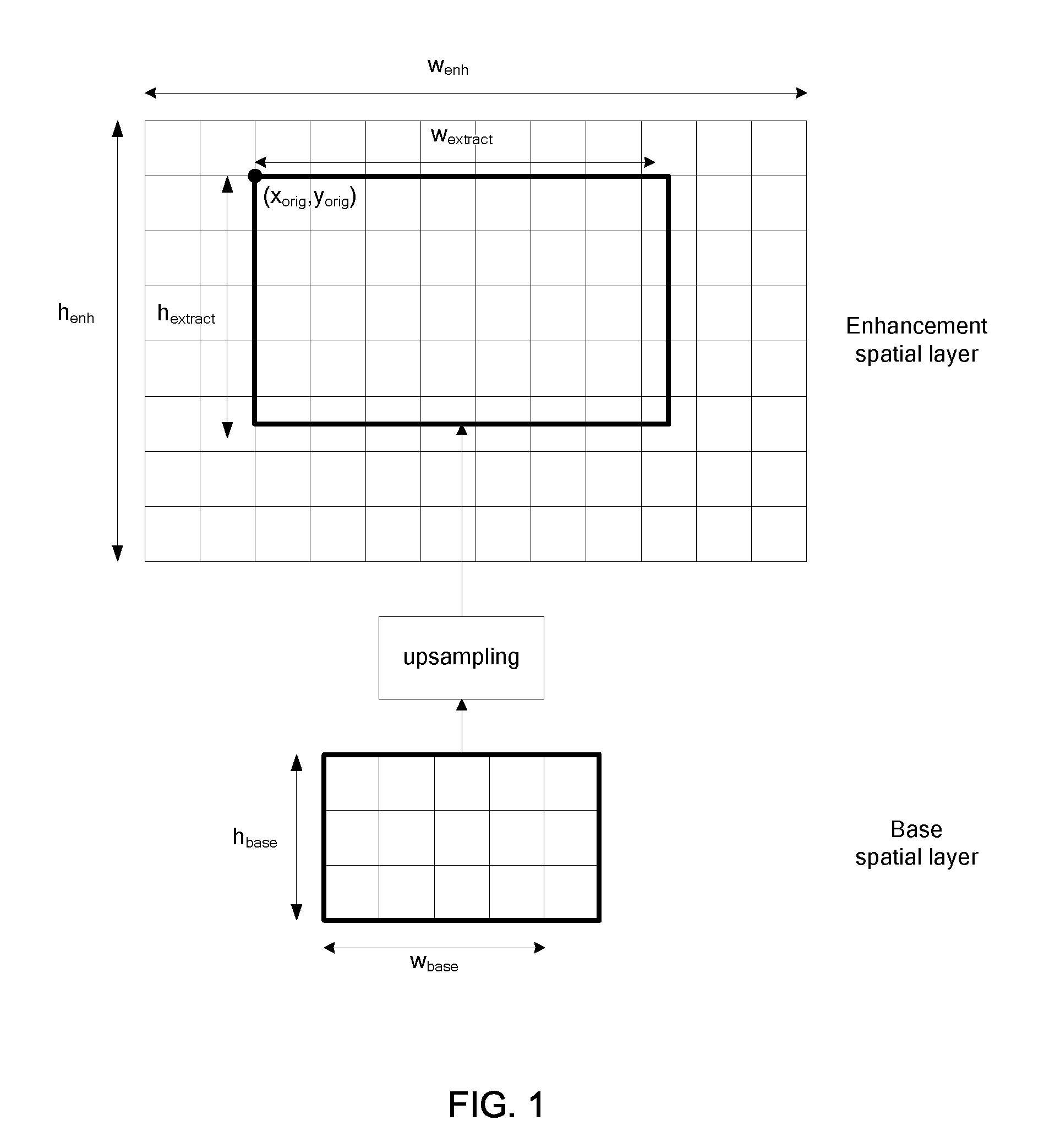
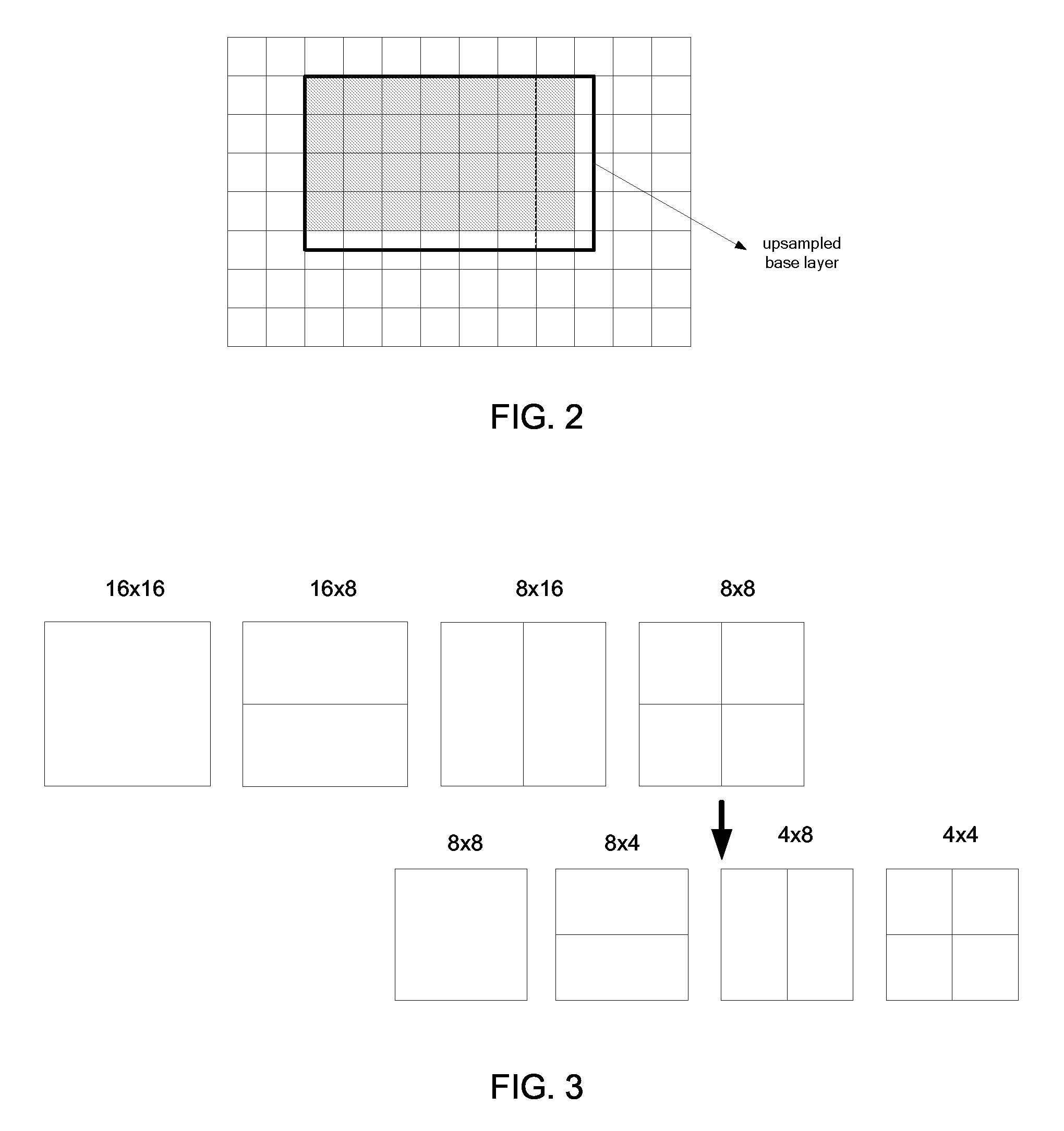
Inter-layer prediction for extended spatial scalability in video coding
ActiveUS20080165855A1Improving inter-layer predictionReduce computational complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInter layerMotion vector
An improved system and method for providing improved inter-layer prediction for extended spatial scalability in video coding, as well as improving inter-layer prediction for motion vectors in the case of extended spatial scalability. In various embodiments, for the prediction of macroblock mode, the actual reference frame index and motion vectors from the base layer are used in determining if two blocks should be merged. Additionally, multiple representative pixels in a 4×4 block can be used to represent each 4×4 block in a virtual base layer macroblock. The partition and motion vector information for the relevant block in the virtual base layer macroblock can be derived from all of the partition information and motion vectors of those 4×4 blocks.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Parallel deblocking filter for H.264 video codec
InactiveUS20080123750A1Speed up deblocking processSpeed advantageColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDeblocking filterMacroblock
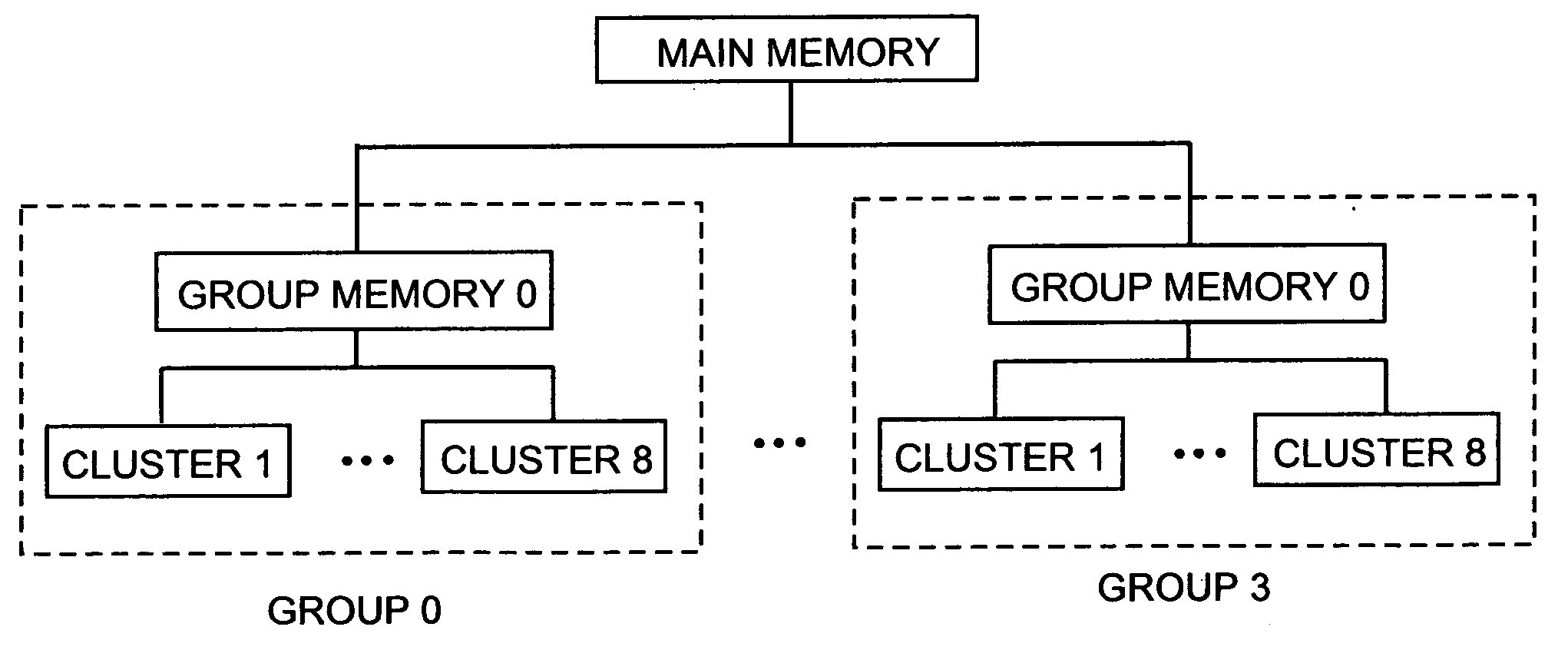
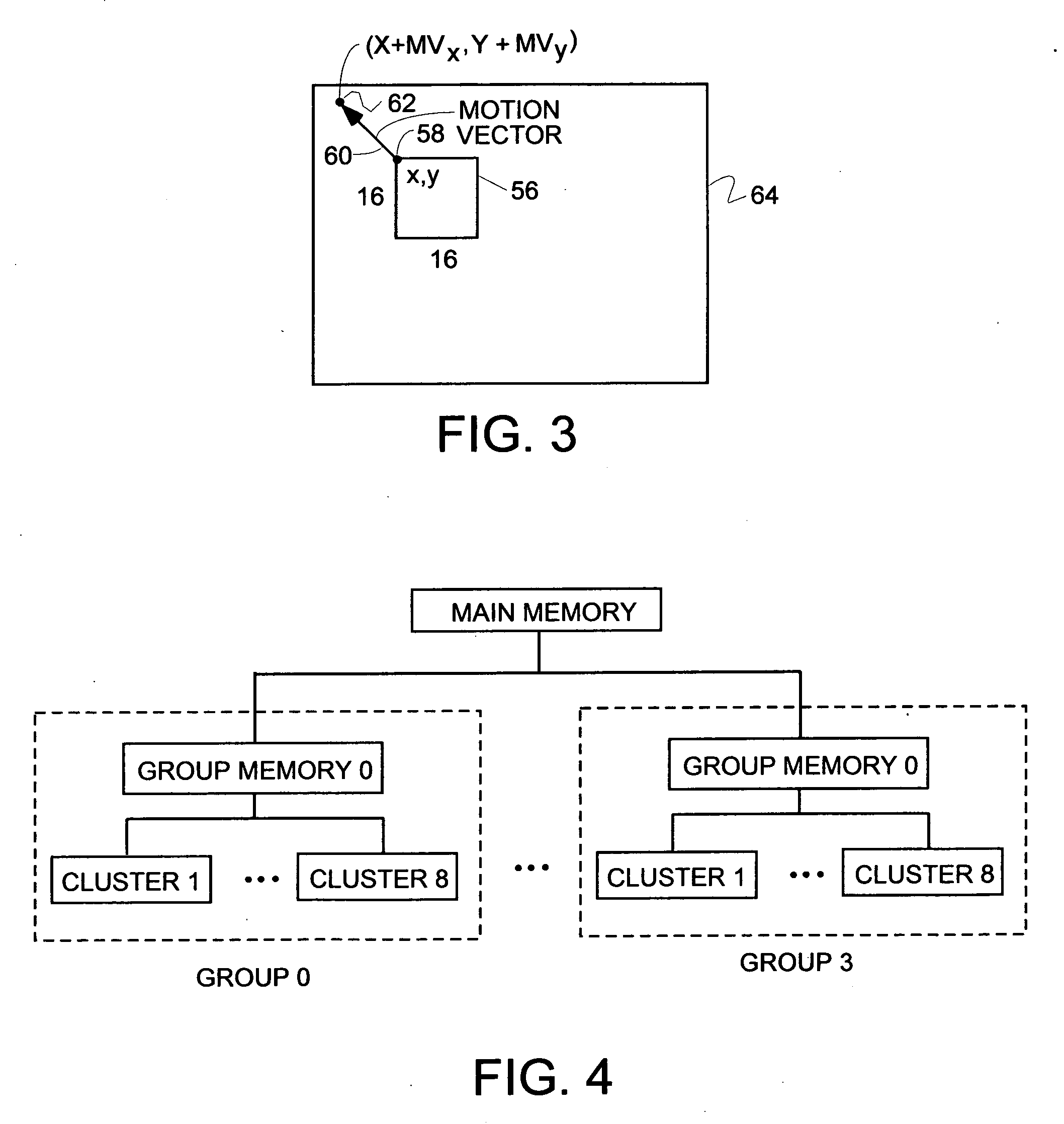
A process and apparatus for implementing parallelization in deblocking filter used in a an H.264 codec are disclosed. In the preferred embodiment, the process is carried out on a parallel architecture consisting of a plurality of groups, each consisting of eight clusters, wherein each cluster is a separate processor capable of tensor operations in SIMD or MIMD or mode on 4×4 matrix data. All eight clusters of one group are used to simultaneously deblock both luma and chroma vertical and horizontal edges between 4×4 blocks of pixels in a macroblock in a total of eight iterations, utilizing in the best way the data dependency between the edges. Processes to deblock these same luma and chroma edges in more iterations on four cluster and two cluster parallel architectures are also disclosed. A comparison of the maximum parallelization achievable with the invention and the amount of parallelization with various species within the prior art is also disclosed.
Owner:NOVAFORA
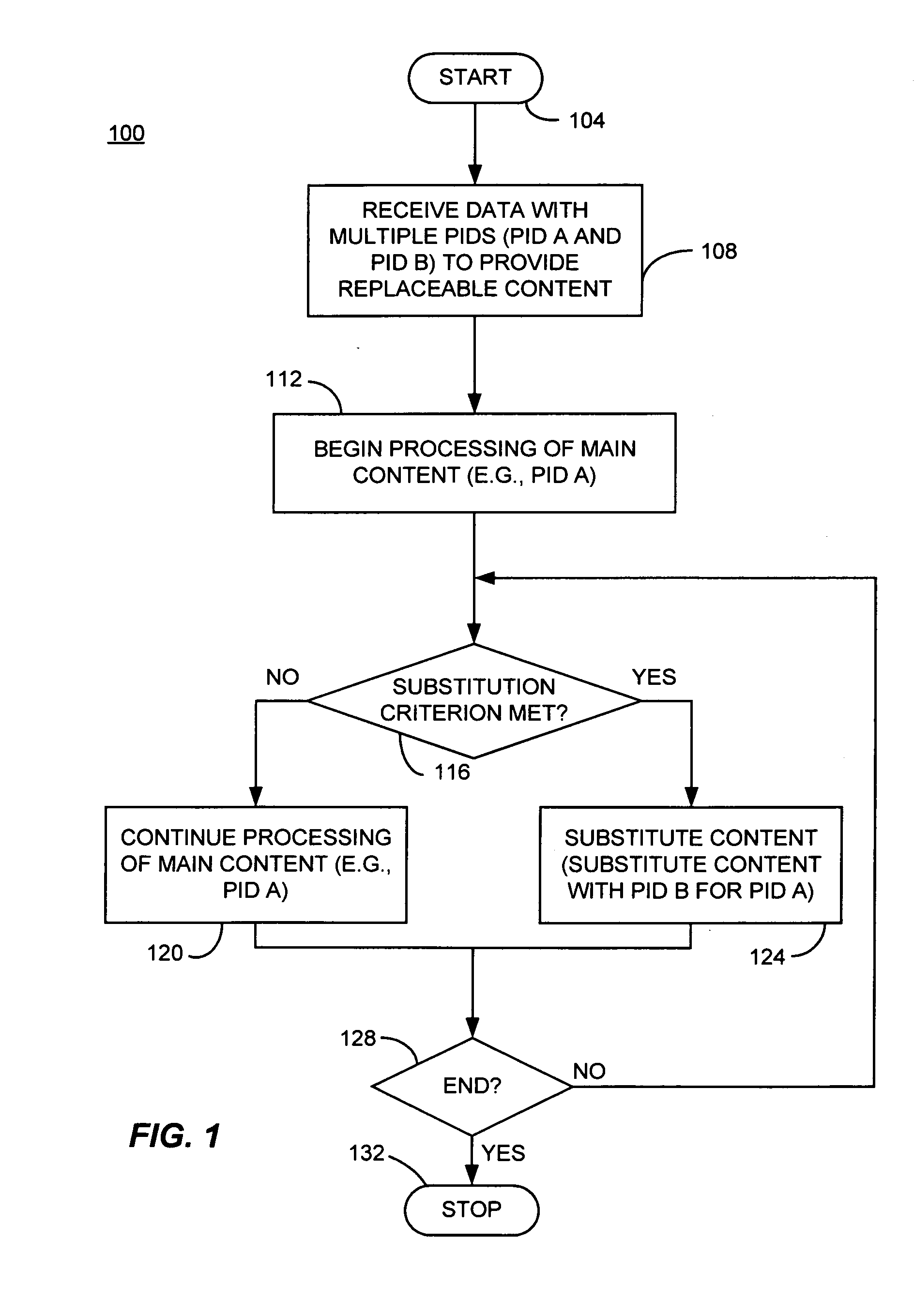
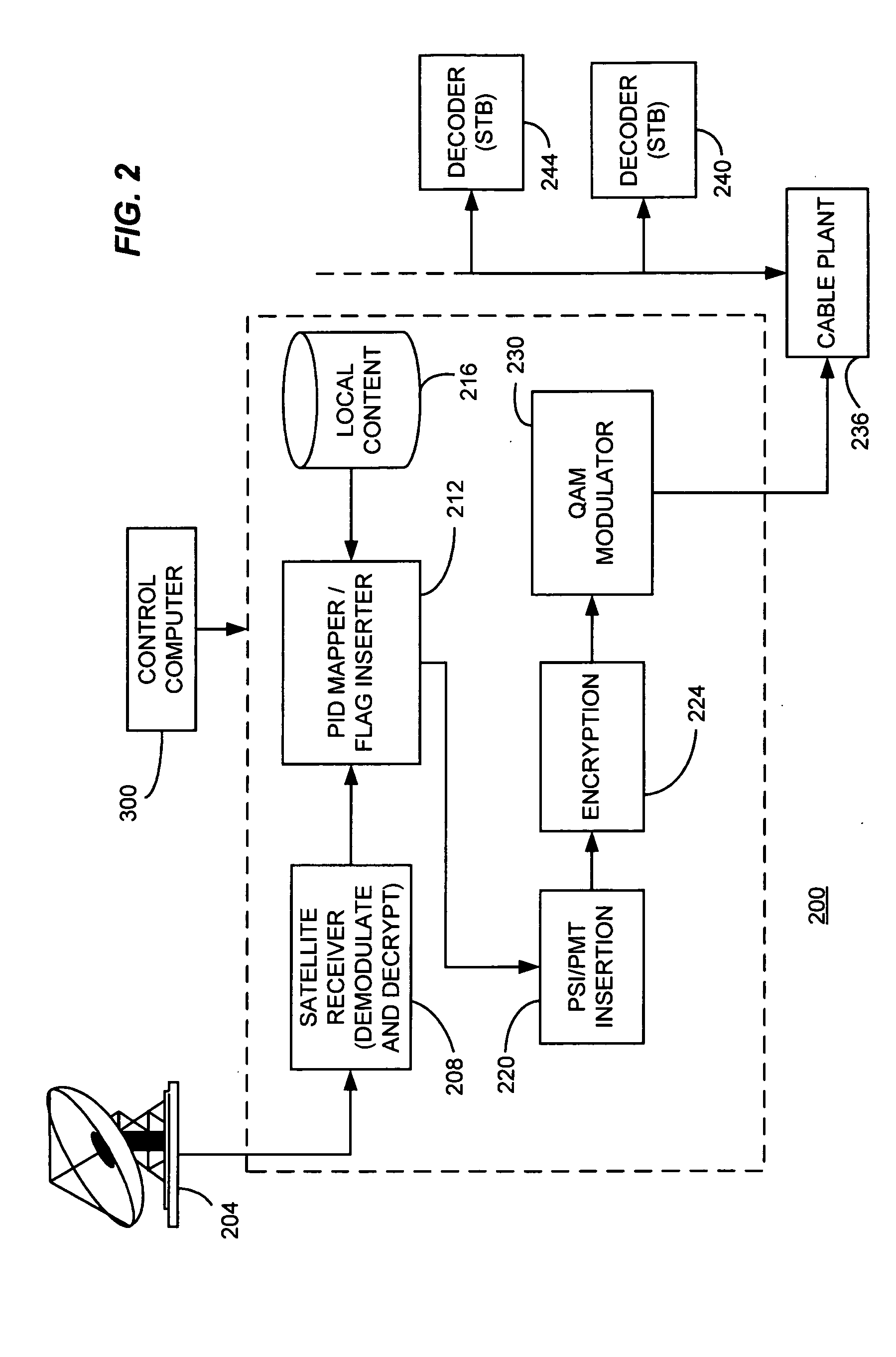
Macro-block based content replacement by PID mapping
InactiveUS20050028193A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMacroblockMultiple view
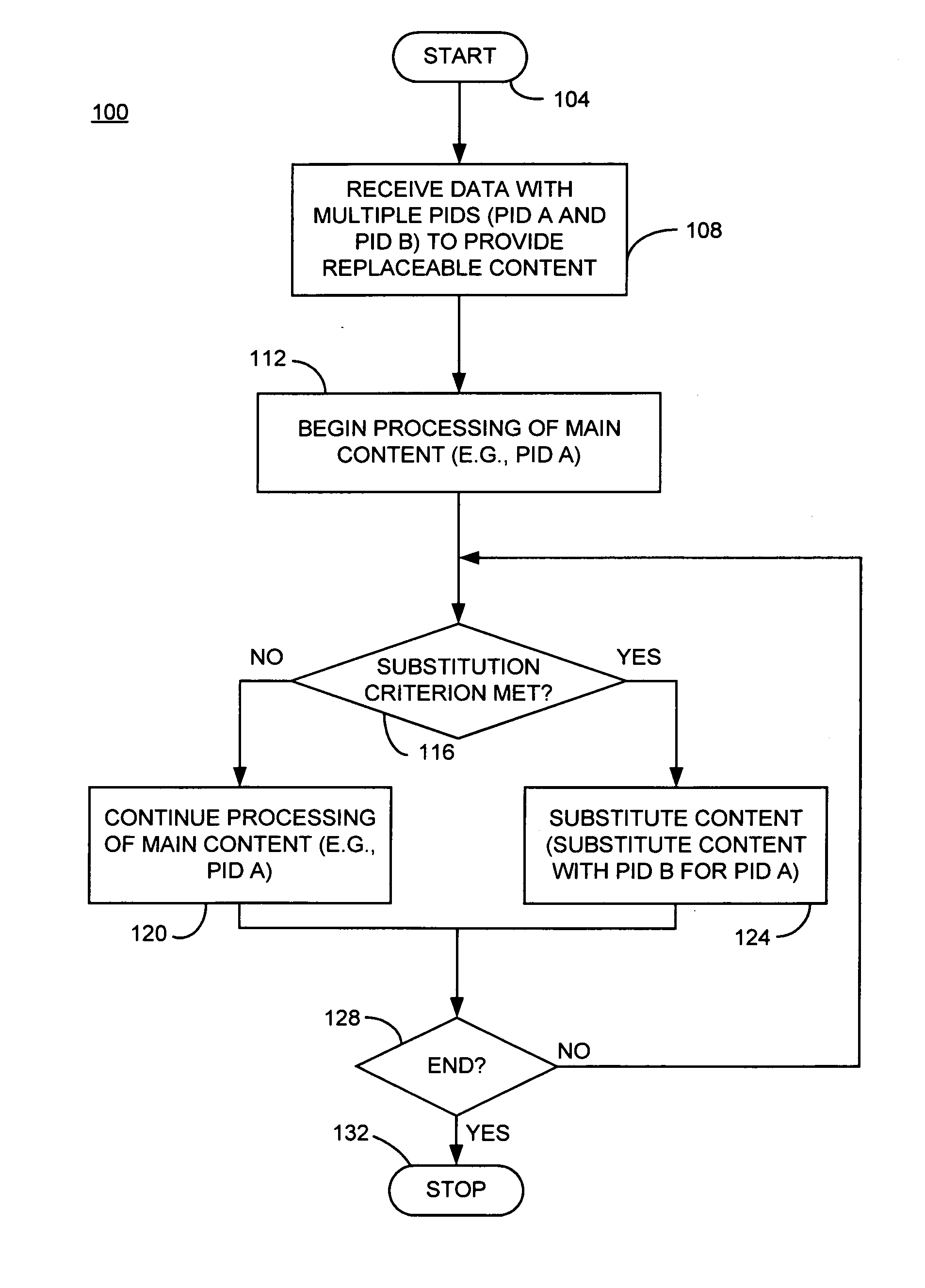
A method and apparatus for content substitution, consistent with certain embodiments of the present invention involves receiving data representing one or more macroblocks of content, the data having at least first and second packet identifiers (PIDs) associated with first and second portions of content. The content having the first PID is placed into a data stream. An initiation flag is received indicating initiation of a PID mapping operation. The substitute macroblocks of content having the second PID is then mapped to the first PID and the mapped content is placed into the data stream. A termination flag is received indicating termination of the PID mapping operation at which point the process returns to placing content having the first PID into the data stream. The content substitution process can be used to replace advertisements, provide multiple plots, multiple endings, multiple views as well as other applications. This abstract should not be considered limiting, since other embodiments may incorporate more, fewer or different elements that those described in this abstract.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
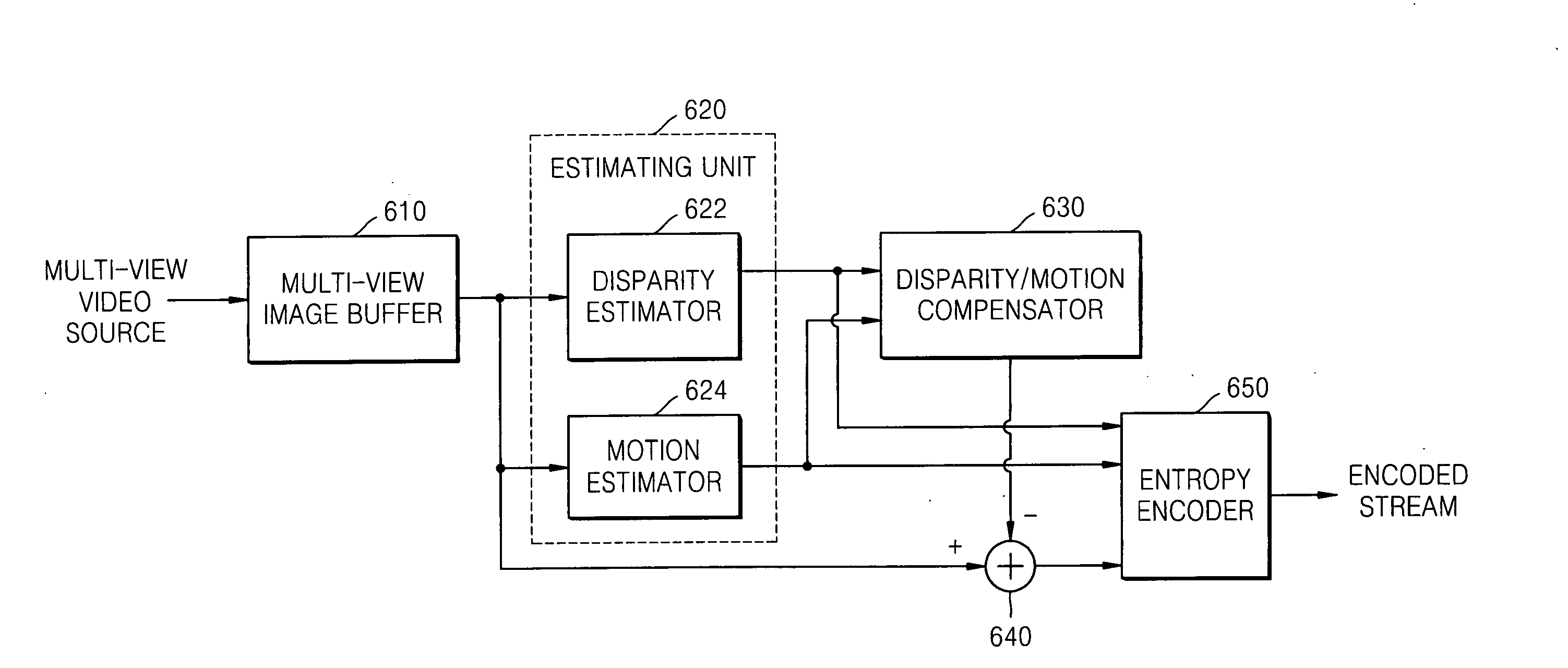
Motion skip and single-loop encoding for multi-view video content
InactiveUS20090116558A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallaxMotion vector
A system, method and computer program tangibly embodied in a memory medium for implementing motion skip and single-loop decoding for multi-view video coding. In various embodiments, a more efficient motion skip is used for the current JMVM arrangement by 8×8 or 4×4 pel disparity motion vector accuracy, while maintaining the motion compensation process that is compliant with the H.264 / AVC design regarding hierarchical macroblock partitioning. Adaptive referencing merging may be used in order achieve a more accurate motion skip from one inter-view reference picture. In order to indicate whether a picture is to be used for motion skip, a new syntax element or syntax modification in the NAL unit header may be used.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Real-time video coding/decoding
ActiveUS20050276323A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMotion vectorDownscaling
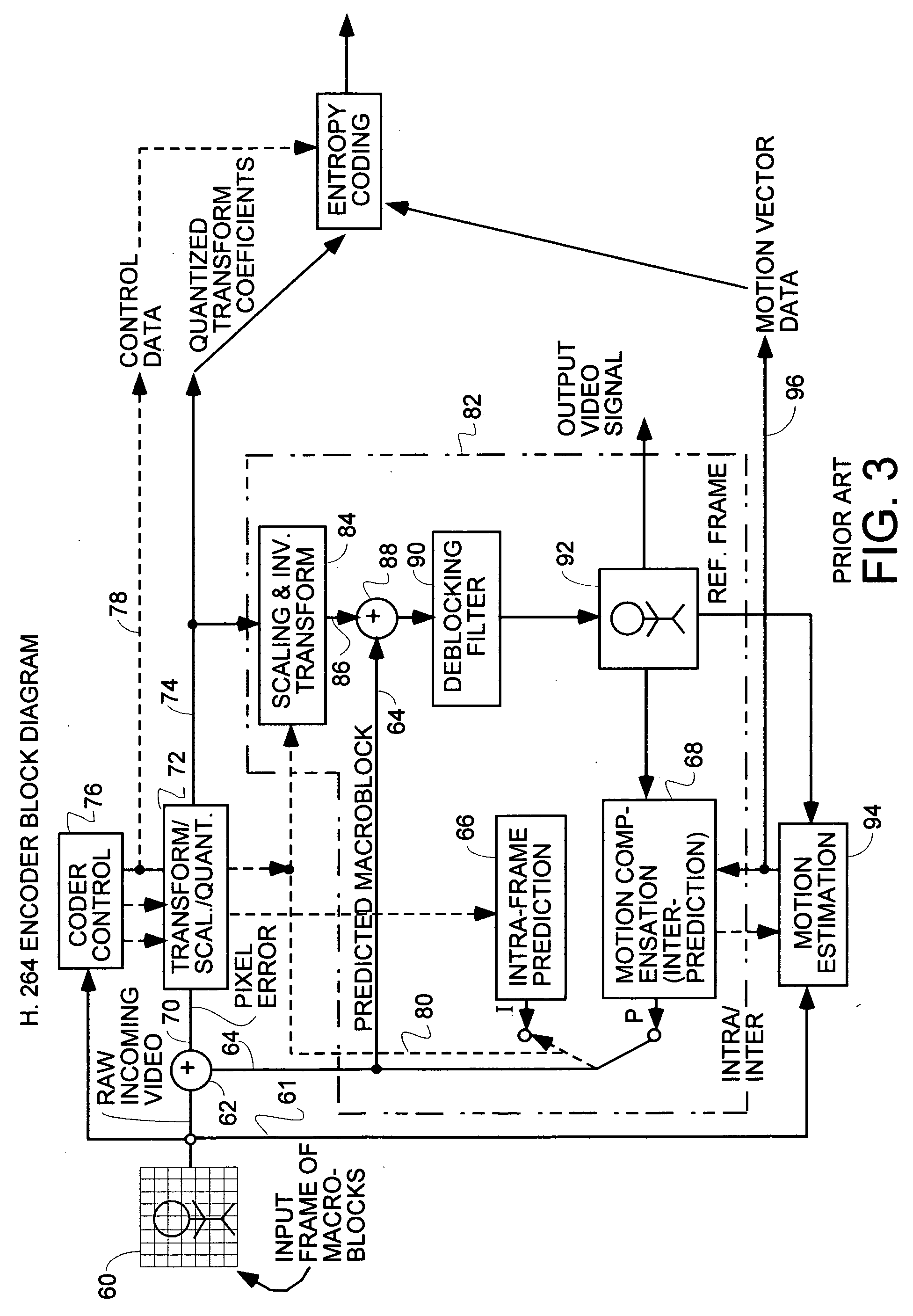
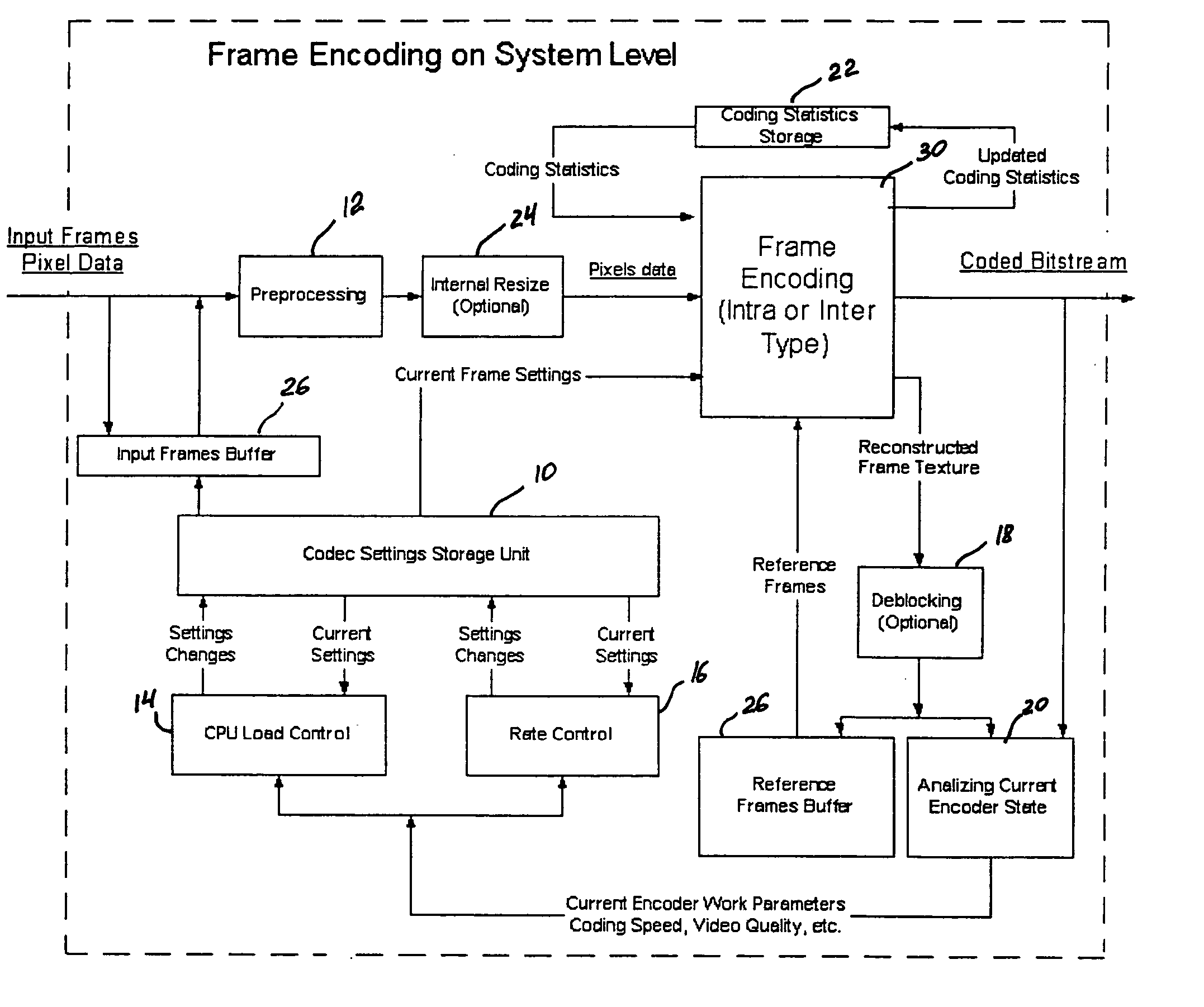
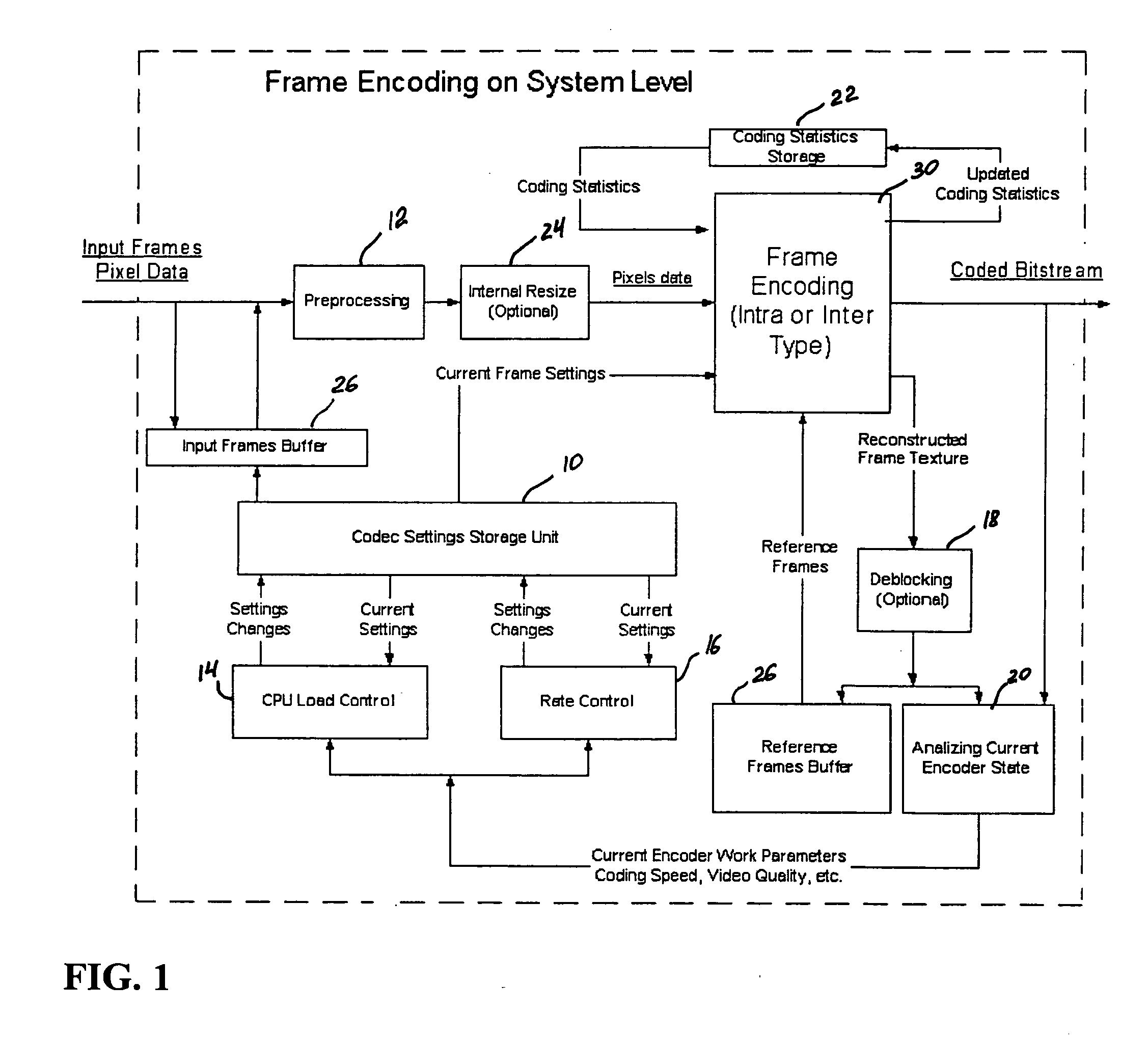
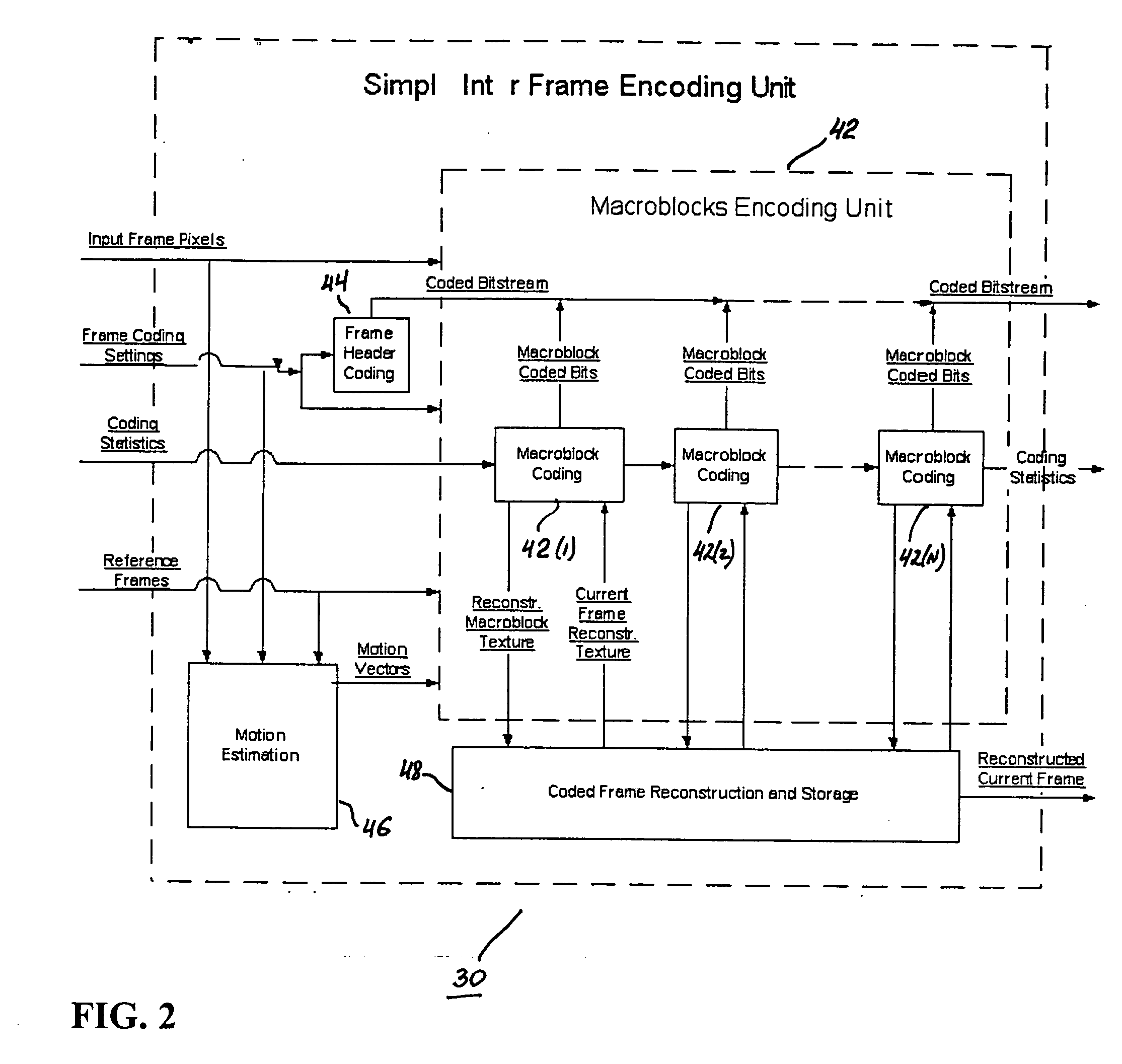
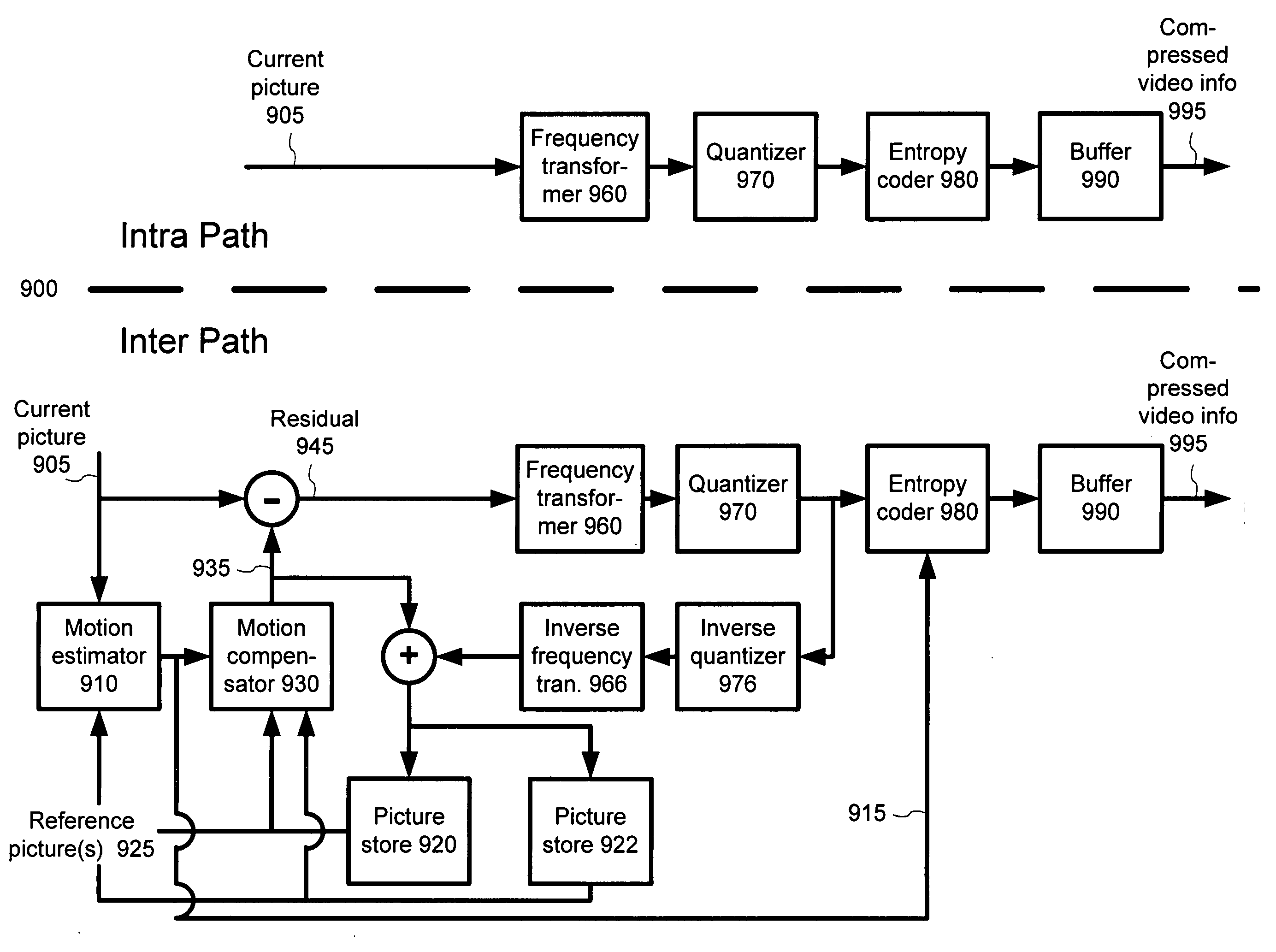
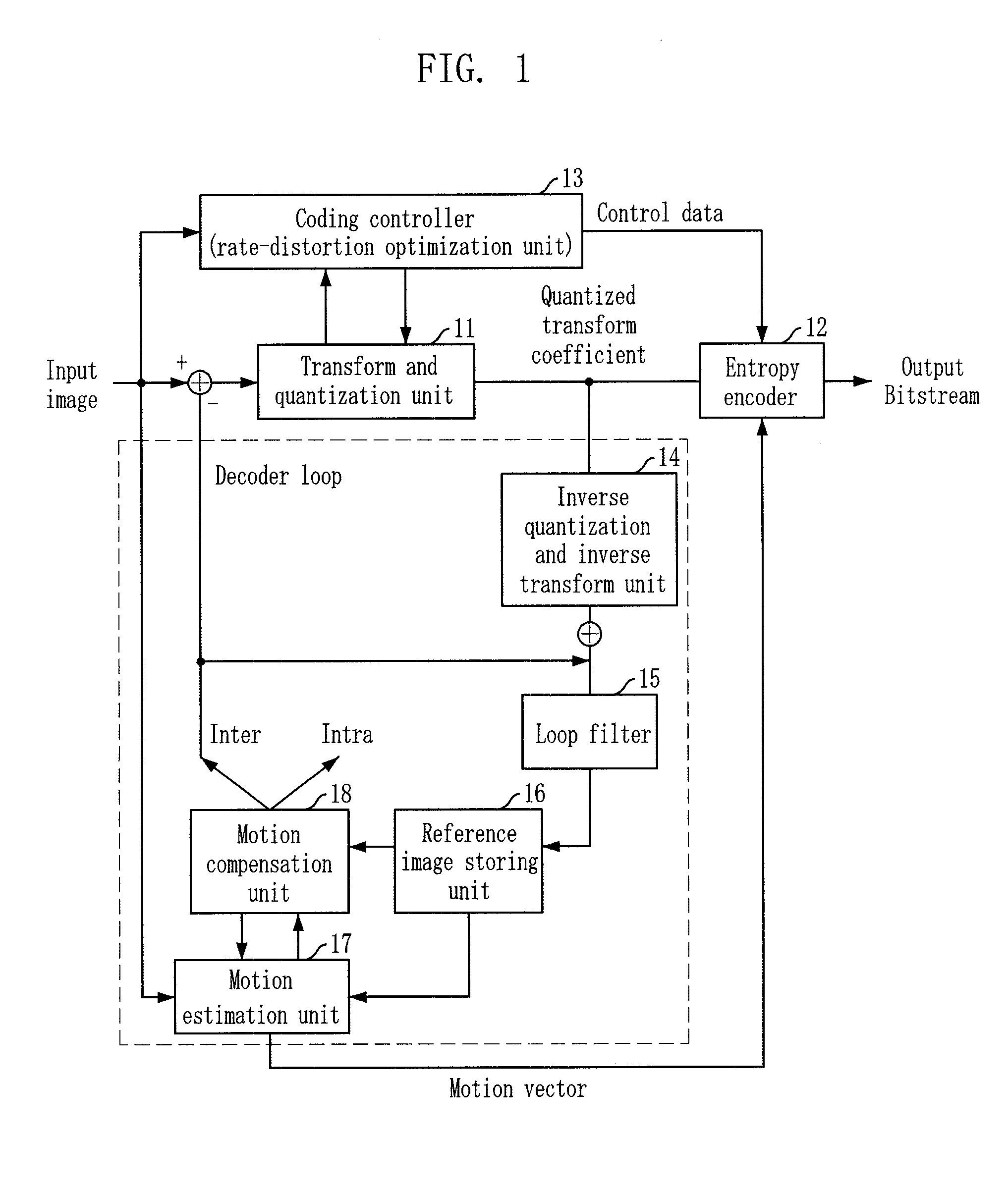
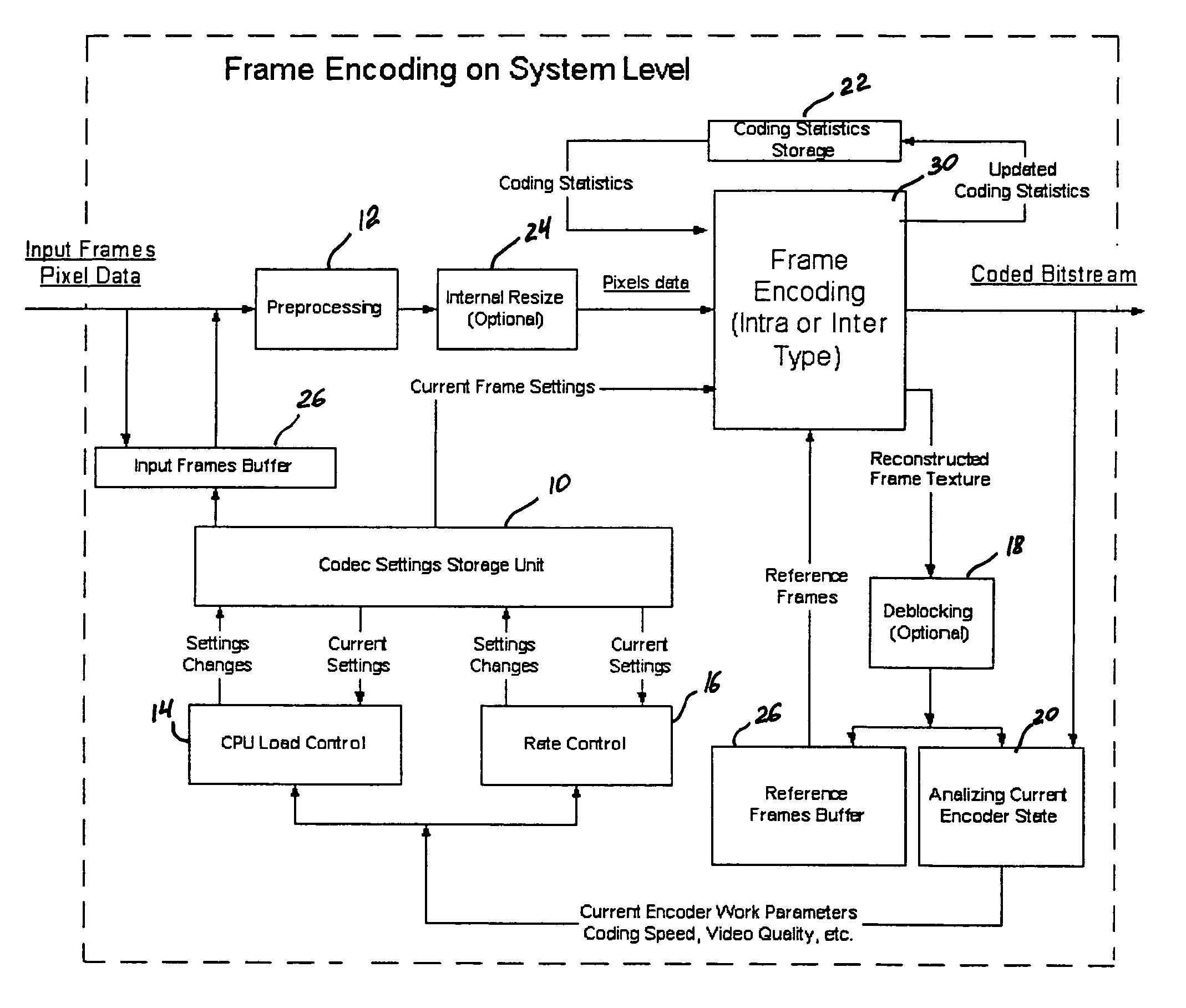
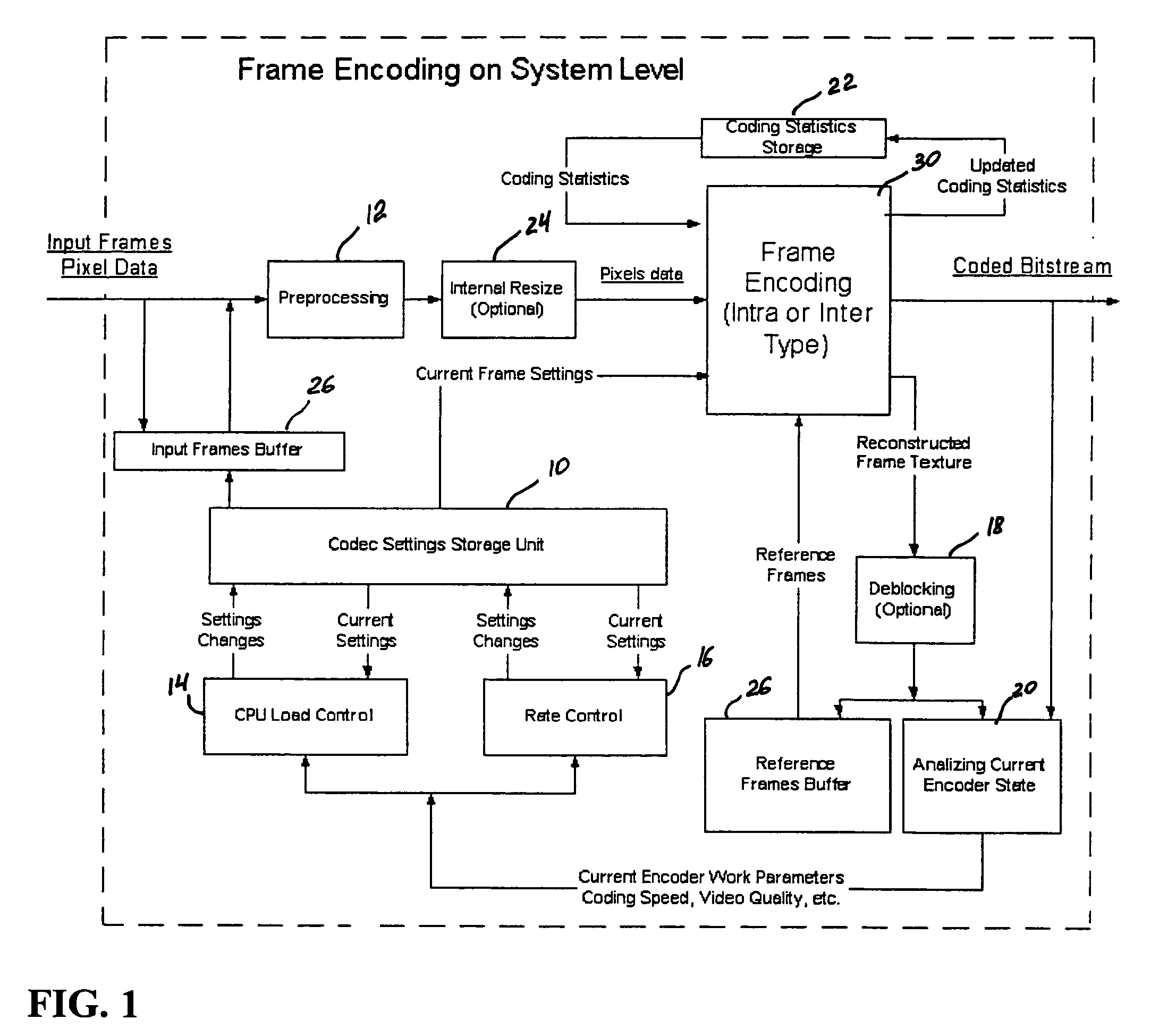
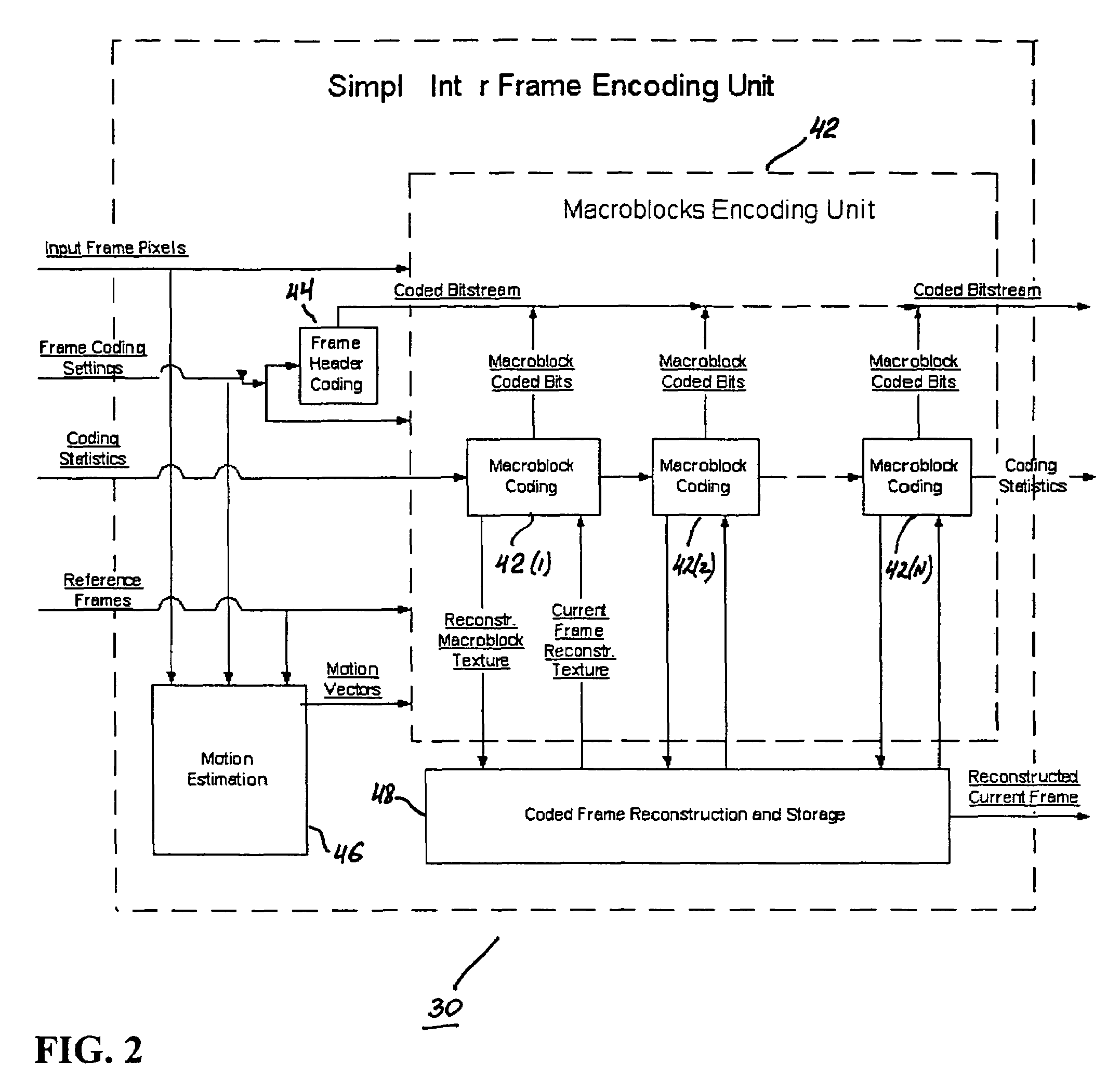
A video codec for real-time encoding / decoding of digitized video data with high compression efficiency, comprising a frame encoder receiving input frame pixels; a codec setting unit for setting and storing coding setting parameters; a CPU load controller for controlling desired frame encoding time and CPU loading; a rate controller for controlling frame size; a coding statistics memory for storing frequency tables for arithmetic coding of bitstream parameters and a reference frame buffer for storing reference frames. The frame encoder comprises a motion estimation unit, a frame head coding unit, a coded frame reconstruction and storage unit and a macroblock encoding unit. The macroblock encoding unit provides calculation of texture prediction and prediction error, transforming texture prediction error and quantization of transform coefficient, calculation of motion vector prediction and prediction error and arithmetic context modeling for motion vectors, header parameters and transform coefficients. The codec also includes a deblocking unit for processing video data to eliminate blocking effect from restored data encoded at high distortion level, which may be a part of encoder or decoder, an internal resize unit, providing matching downscaling of a frame before encoding and upscaling of decoded frame according to the coding setting parameters, and a noise suppression unit.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
Chroma motion vector derivation for interlaced forward-predicted fields
Techniques and tools for deriving chroma motion vectors for macroblocks of interlaced forward-predicted fields are described. For example, a video encoder or decoder determines a prevailing polarity among luma motion vectors for a macroblock. The encoder or decoder then determines a chroma motion vector for the macroblock based at least in part upon one or more of the luma motion vectors having the prevailing polarity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
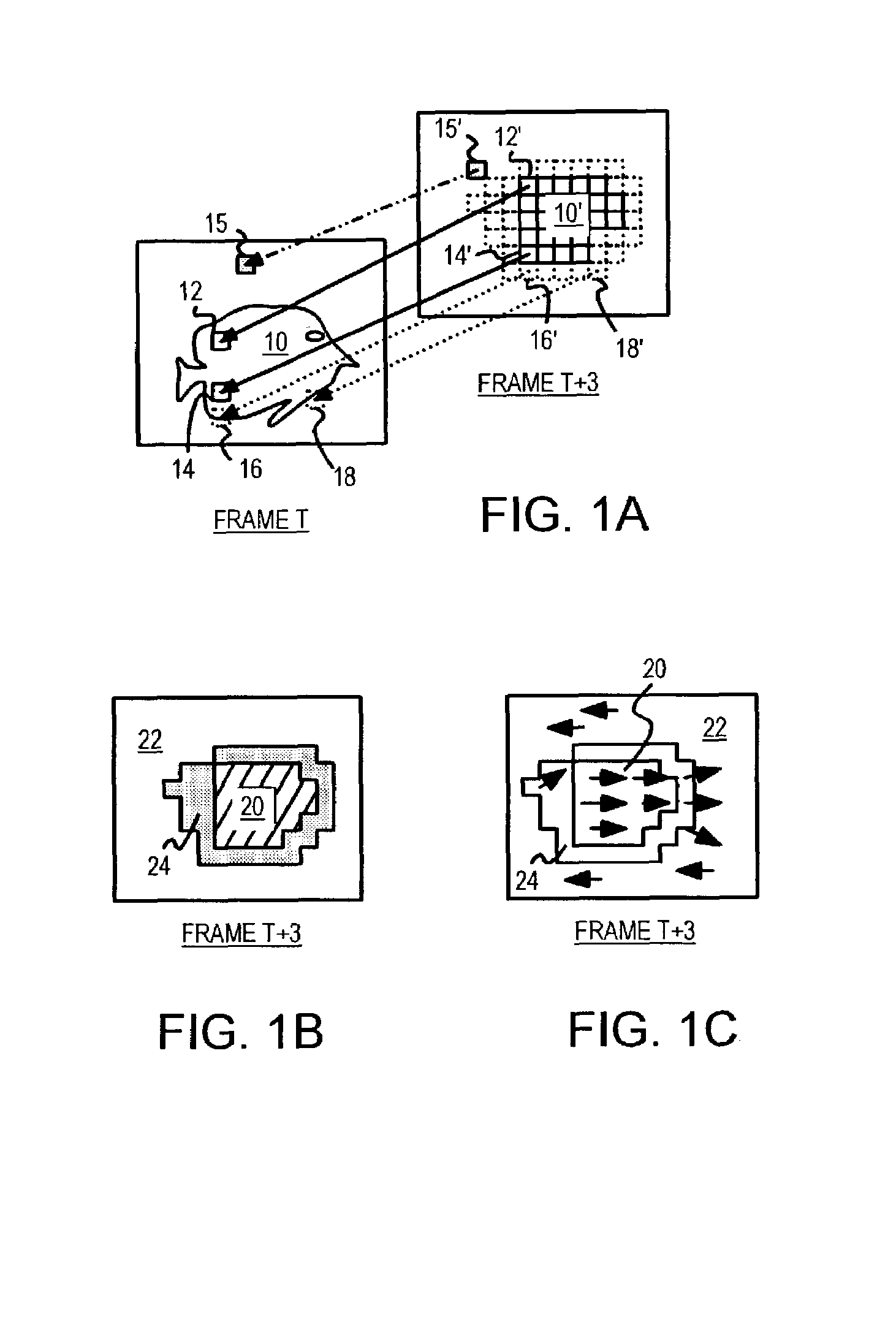
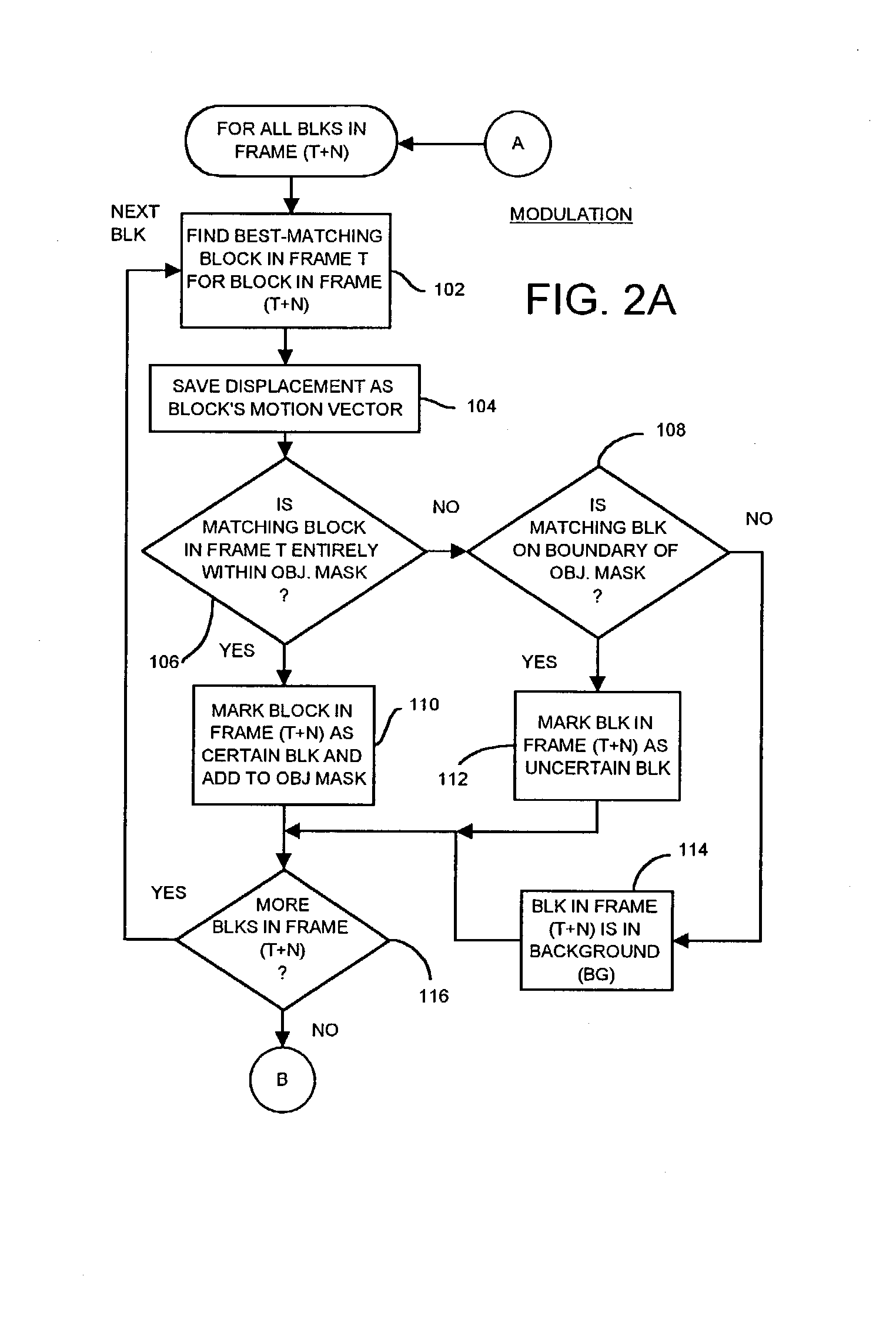
Occlusion/disocclusion detection using K-means clustering near object boundary with comparison of average motion of clusters to object and background motions
ActiveUS7142600B1Reduce varianceAccurate representationColor television with pulse code modulationImage analysisMotion vectorVideo sequence
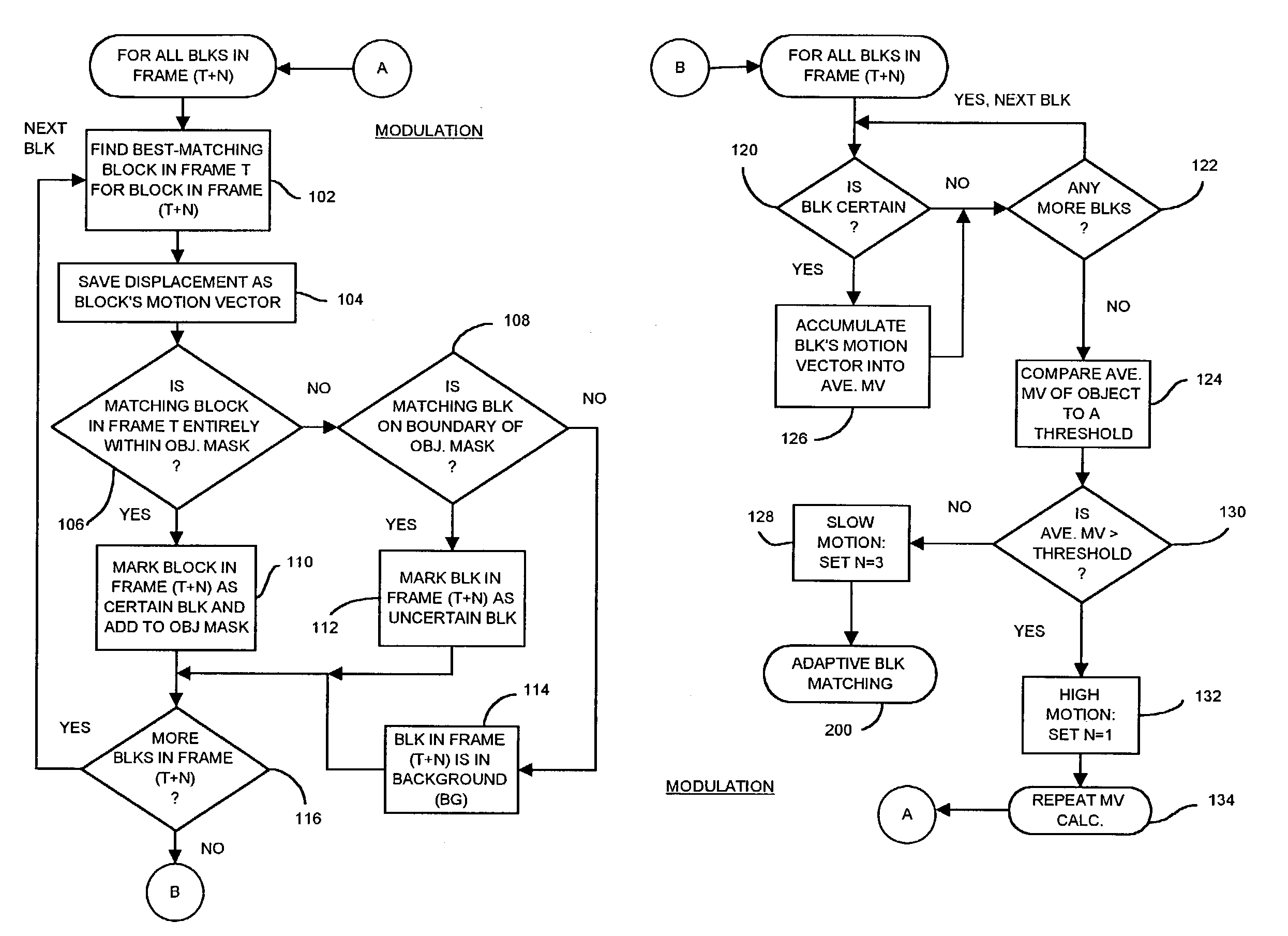
An object in a video sequence is tracked by object masks generated for frames in the sequence. Macroblocks are motion compensated to predict the new object mask. Large differences between the next frame and the current frame detect suspect regions that may be obscured in the next frame. The motion vectors in the object are clustered using a K-means algorithm. The cluster centroid motion vectors are compared to an average motion vector of each suspect region. When the motion differences are small, the suspect region is considered part of the object and removed from the object mask as an occlusion. Large differences between the prior frame and the current frame detect suspected newly-uncovered regions. The average motion vector of each suspect region is compared to cluster centroid motion vectors. When the motion differences are small, the suspect region is added to the object mask as a disocclusion.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
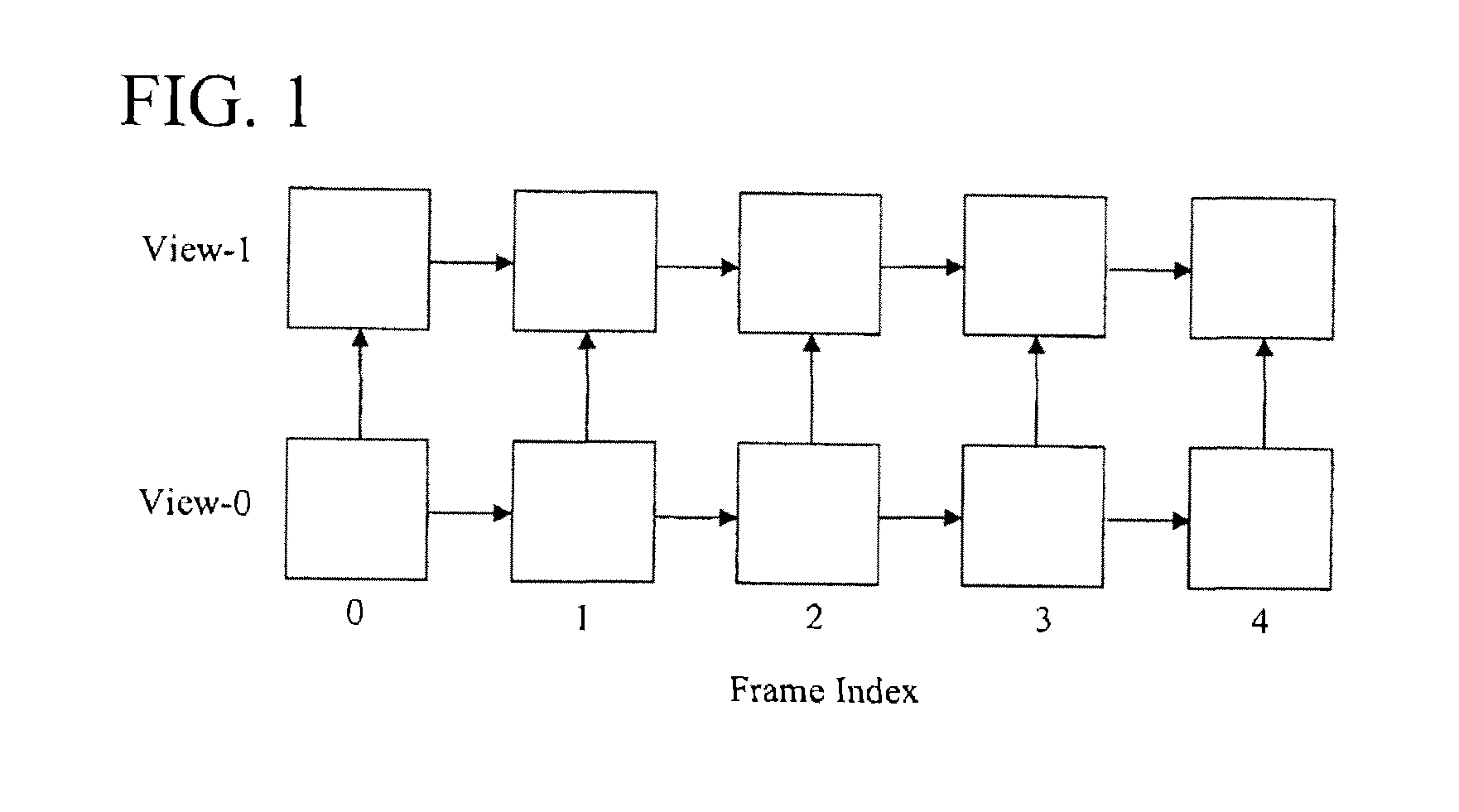
System and method for using parallelly decodable slices for multi-view video coding
ActiveUS20080089412A1Reduce delaysPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVideo encodingComputer engineering
A system and method for enabling parallel decoder implementation for different views, even when there are existing dependencies between views. In various embodiments of the present invention, information is signaled to a decoder that slices are coded using certain constraints, so that parallel decoding of slices is possible. This signaling can be performed at a sequence parameter set level, or it could be performed at picture parameter set level, slice header level or macroblock header level. Additionally, the delay between various views is also signaled to the decoder, at the same location as the constraint information in various embodiments. Various algorithms can also be used to improve the coding efficiency of the system.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
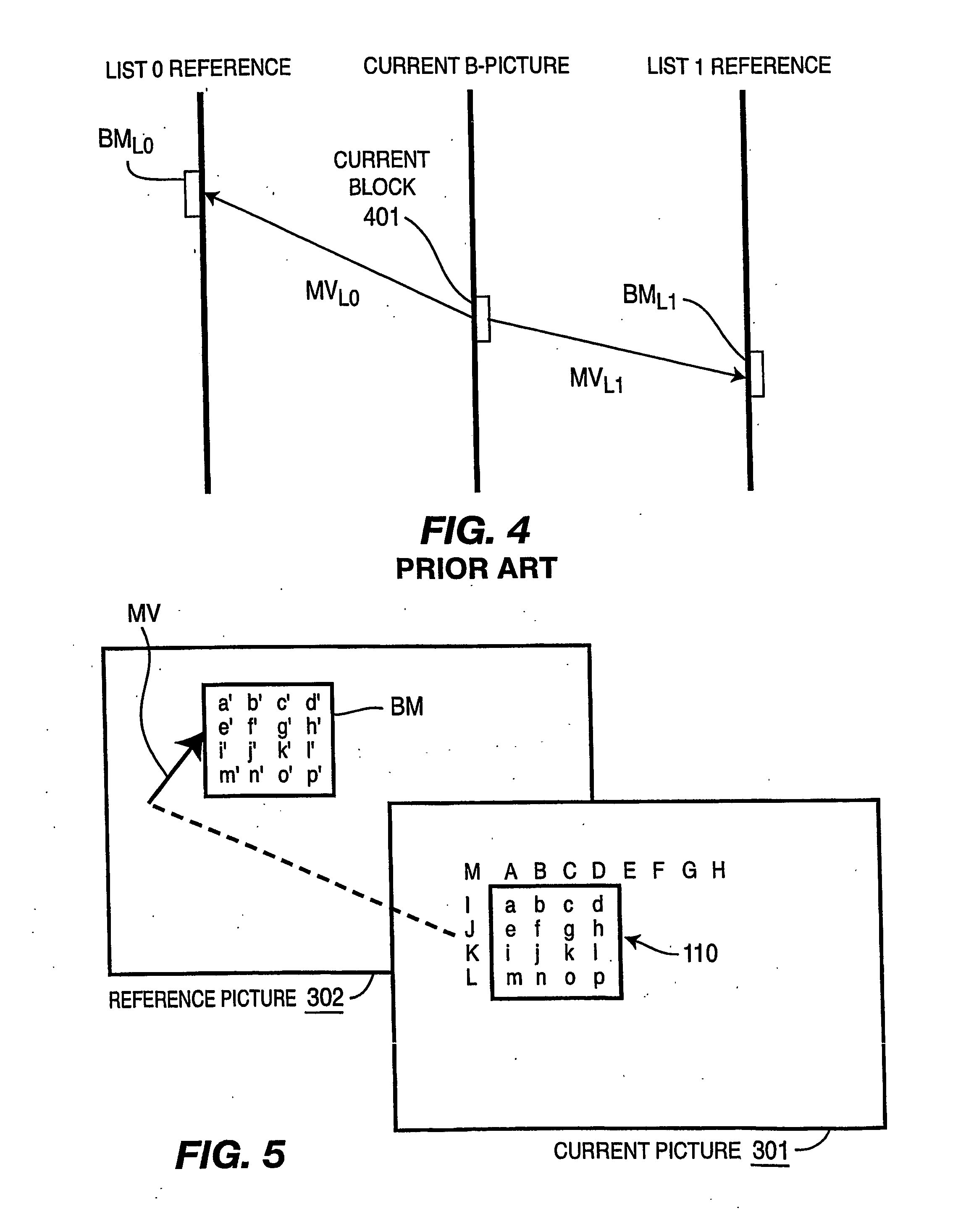
Predicting motion vectors for fields of forward-predicted interlaced video frames
ActiveUS20050053137A1Improve accuracyReduce bitratePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionInterlaced videoEncoder decoder
Techniques and tools for encoding and decoding predicted images in interlaced video are described. For example, a video encoder or decoder computes a motion vector predictor for a motion vector for a portion (e.g., a block or macroblock) of an interlaced P-field, including selecting between using a same polarity or opposite polarity motion vector predictor for the portion. The encoder / decoder processes the motion vector based at least in part on the motion vector predictor computed for the motion vector. The processing can comprise computing a motion vector differential between the motion vector and the motion vector predictor during encoding and reconstructing the motion vector from a motion vector differential and the motion vector predictor during decoding. The selecting can be based at least in part on a count of opposite polarity motion vectors for a neighborhood around the portion and / or a count of same polarity motion vectors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative converter accoding to the correlation of residual signal
InactiveUS20090238271A1Increase the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareRate distortion
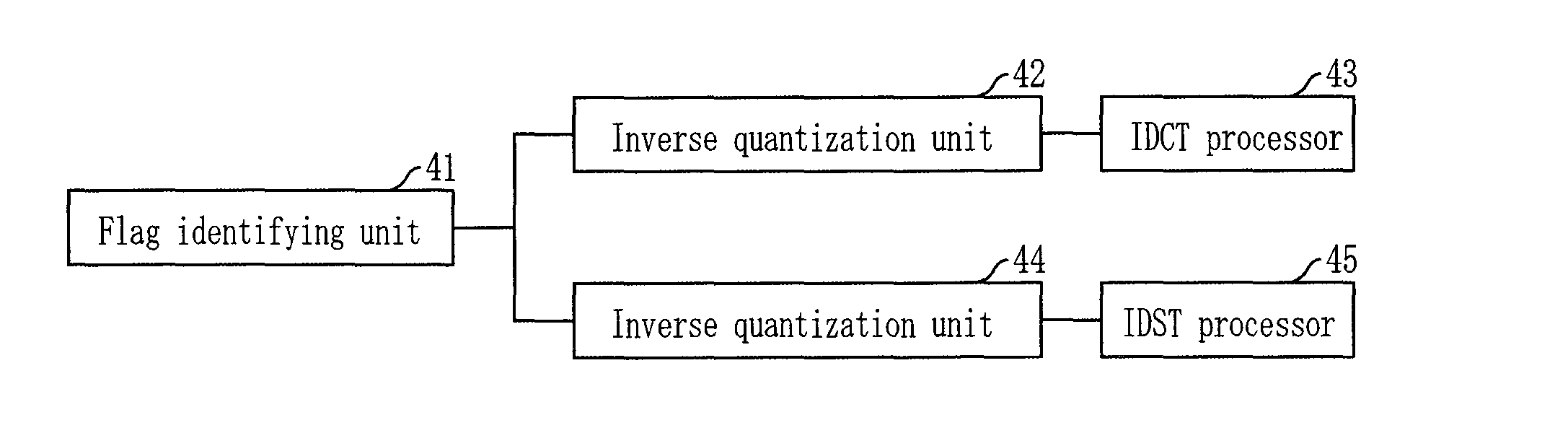
Provided is an apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative transform units according to the correlation of residual signals. The video encoding apparatus includes a first transforming unit for performing discrete cosine transform (DCT), first quantization, first inverse quantization, and inverse DCT on a block basis onto residual coefficients generated after intra frame prediction or inter frame prediction; a second transforming unit for performing discrete sine transform (DST), second quantization, second inverse quantization, and inverse DST on a block basis onto the residual coefficients; a selecting unit for selecting one having a high compression rate between the first and second transforming units for each block through performing rate-distortion optimization; and a flag marking unit for recording information about the selected transforming unit at a flag bit provided on a macroblock basis.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +2
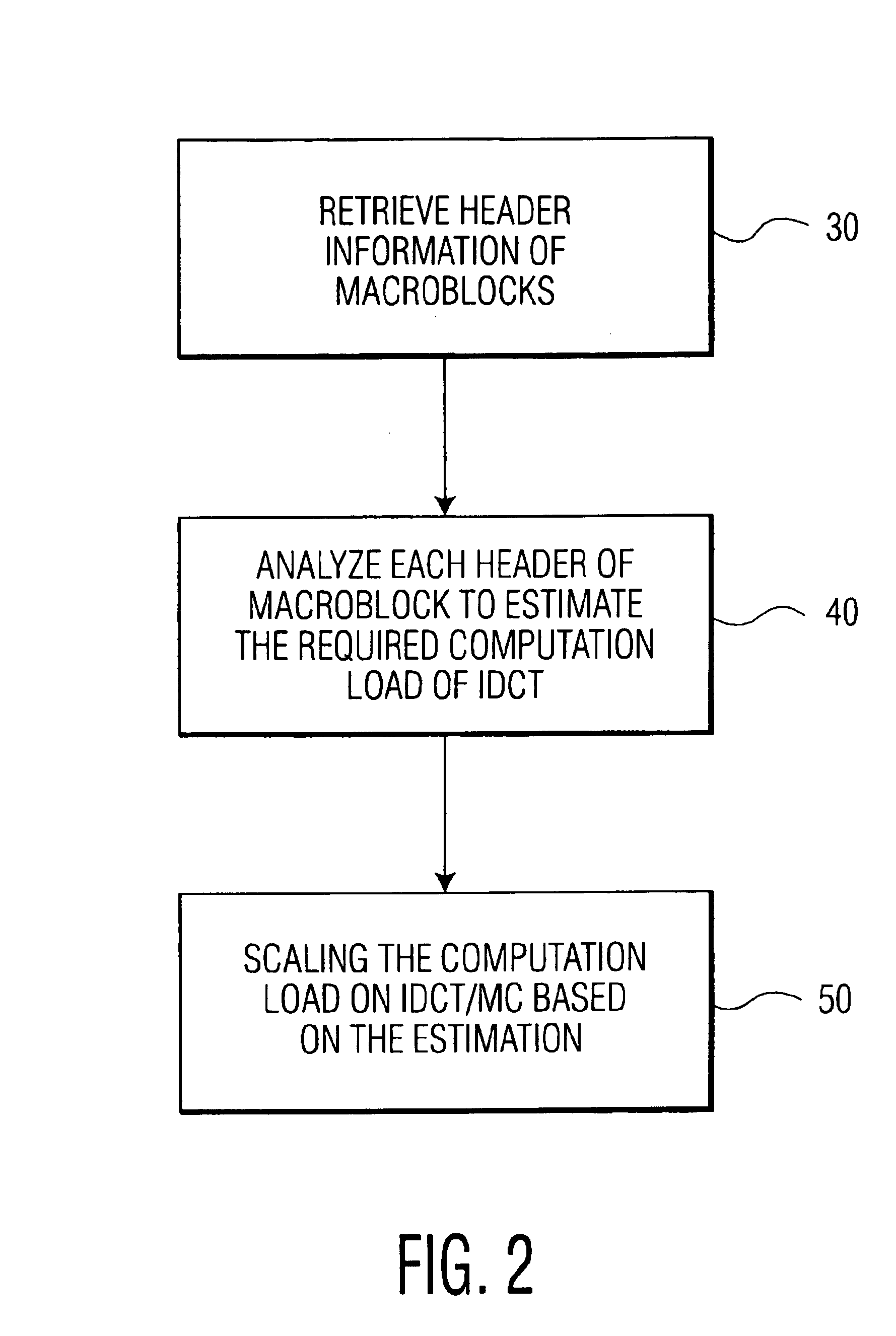
Dynamic complexity prediction and regulation of MPEG2 decoding in a media processor
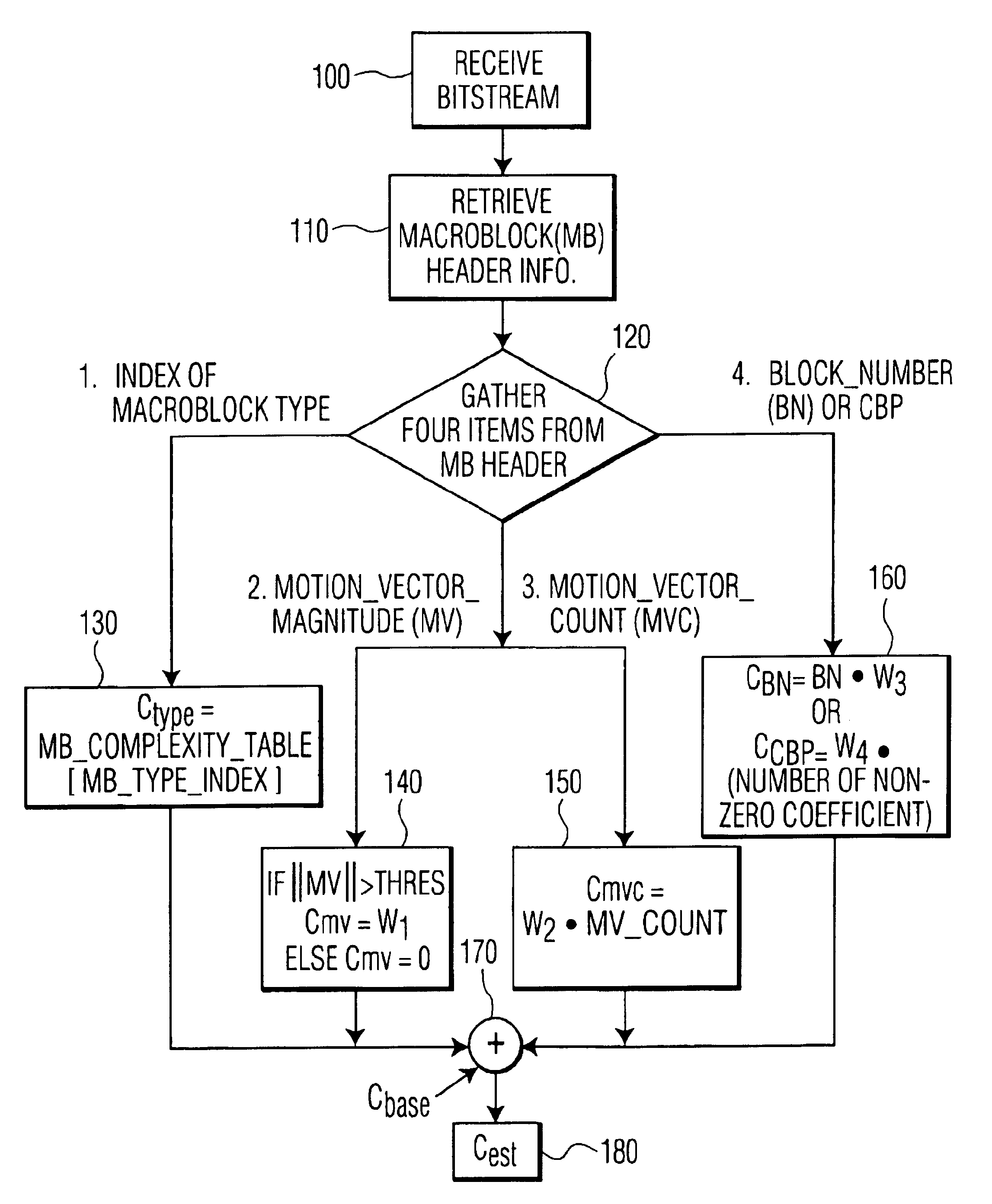
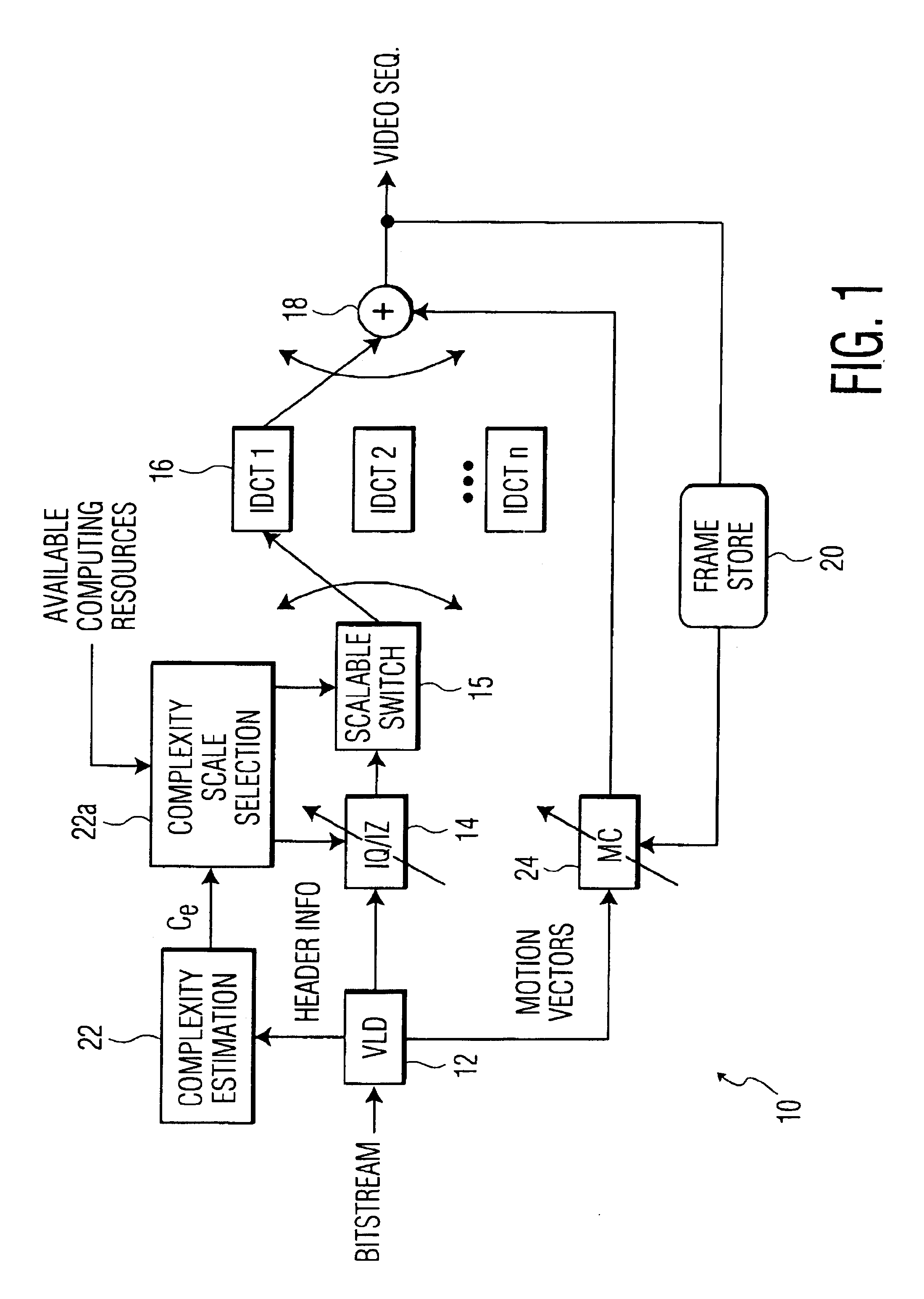
InactiveUS6925126B2Improve decoding efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData streamMotion vector
A method and system of regulating the computation load of an MPEG decoder in a video processing system are provided. The video processing system processes the header information of a compressed video data stream including a plurality of macroblocks with a motion vector associated therewith. Then, the computation load of each functional block of the MPEG decoder is adjusted according to predetermined criteria; thus, substantial computational overhead is desirably avoided.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Linear system based, qualitative independent motion detection from compressed mpeg surveillance video
InactiveUS8164629B1Shorten the timeExtra computationImage enhancementImage analysisIndependent motionMotion vector
The present invention features a qualitative method to detect independent motion revealed in successive frames of a compressed surveillance MPEG video stream using linear system consistency analysis without decompression of the stream, identifying the segments containing independent motion in a real-time or faster manner, for the retrieval of these segments. The linear system is constructed using the macroblocks of MPEG compressed video frames. The normal flow value of the macroblock is obtained by taking the dot product between the macroblock gradient vector, computed by averaging the four block gradient vectors, and the motion vector of this macroblock. The normal flow value is filtered for inclusion in the linear system, and the statistic of the matrices of the resulting linear system is determined, filtered to screen out false negatives and outliers, and used to determine the presence or absence of independent motion.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Digital video fingerprinting
ActiveUS20130208942A1Low efficiencyHigh residual energyDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDigital video
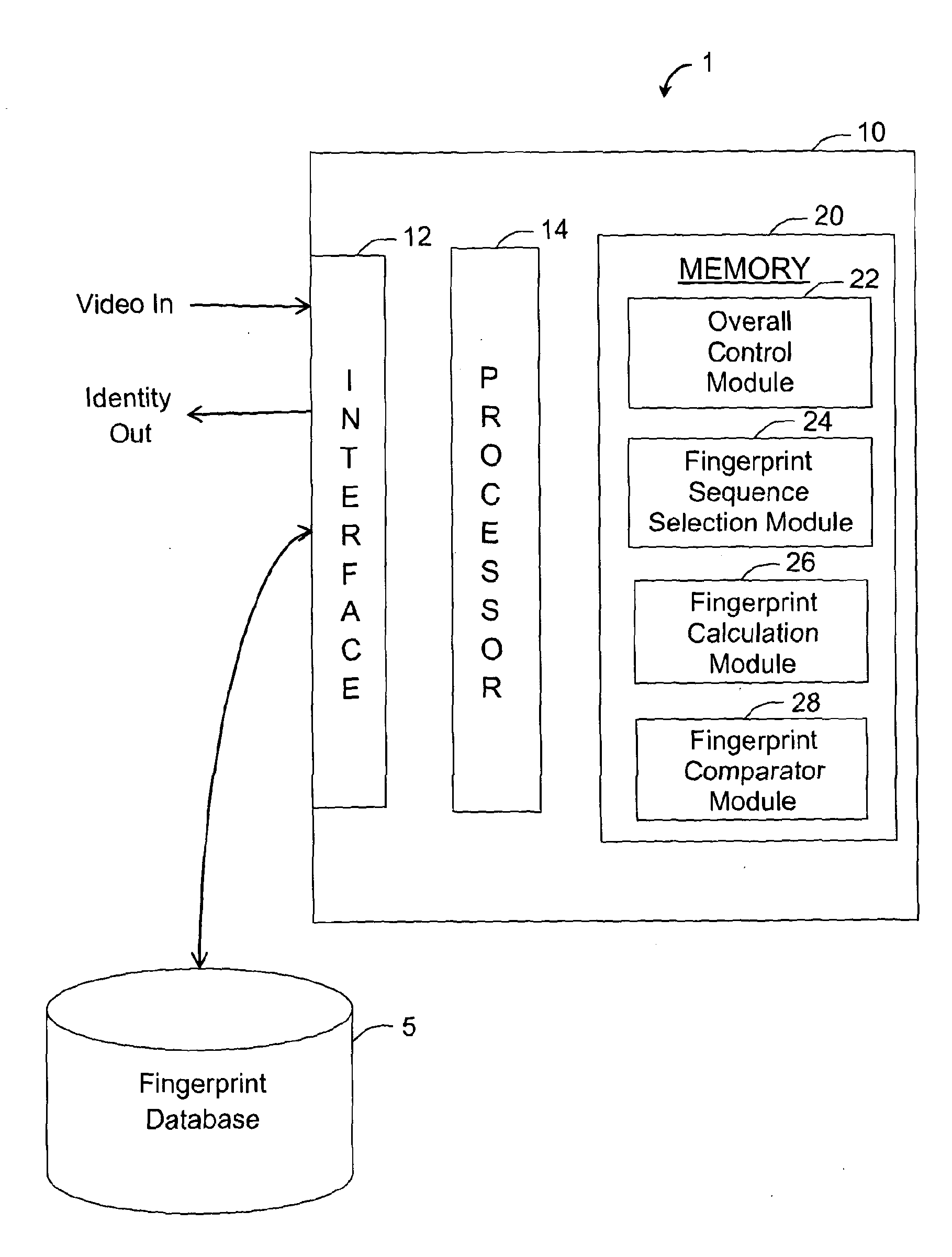
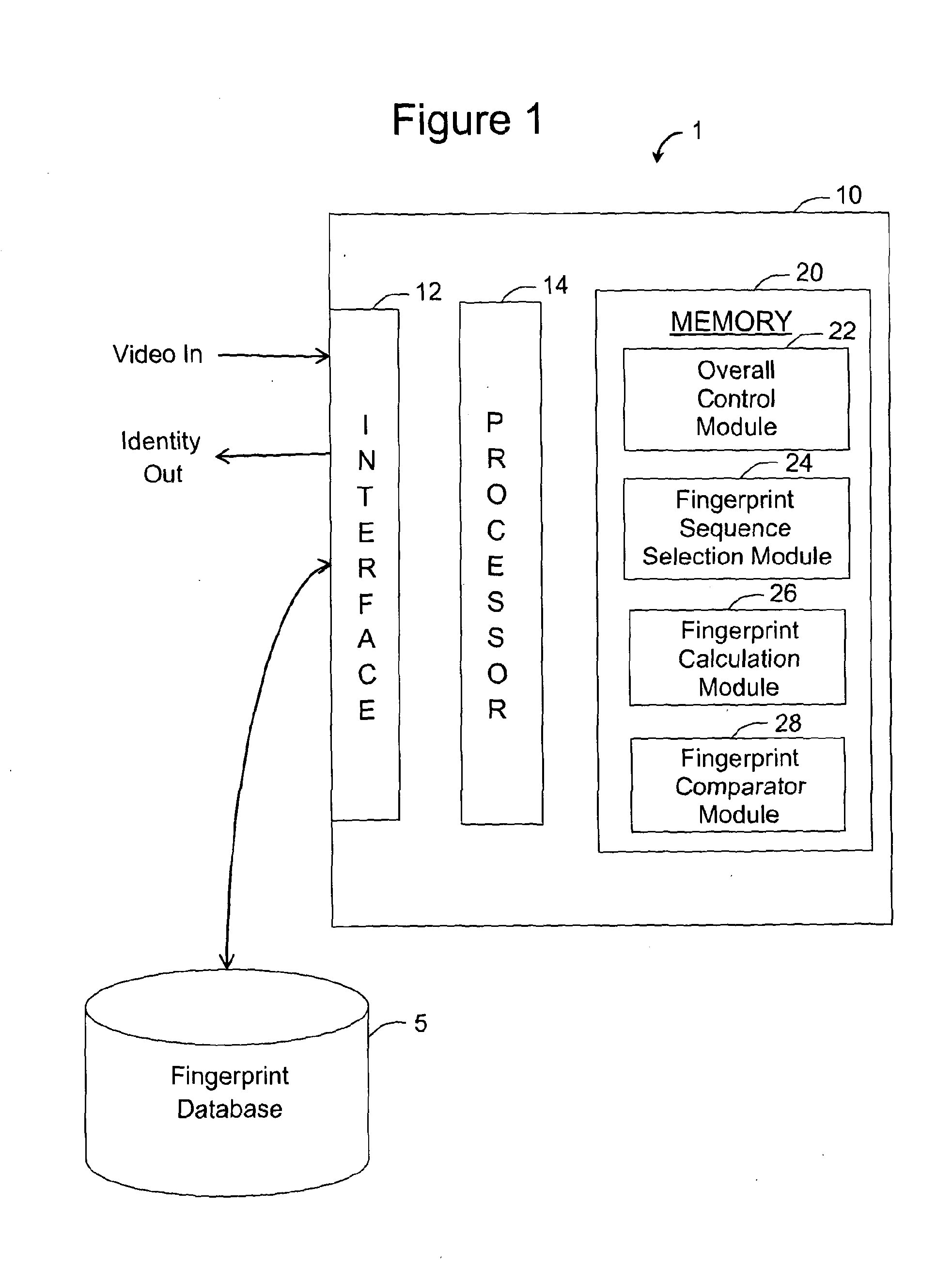
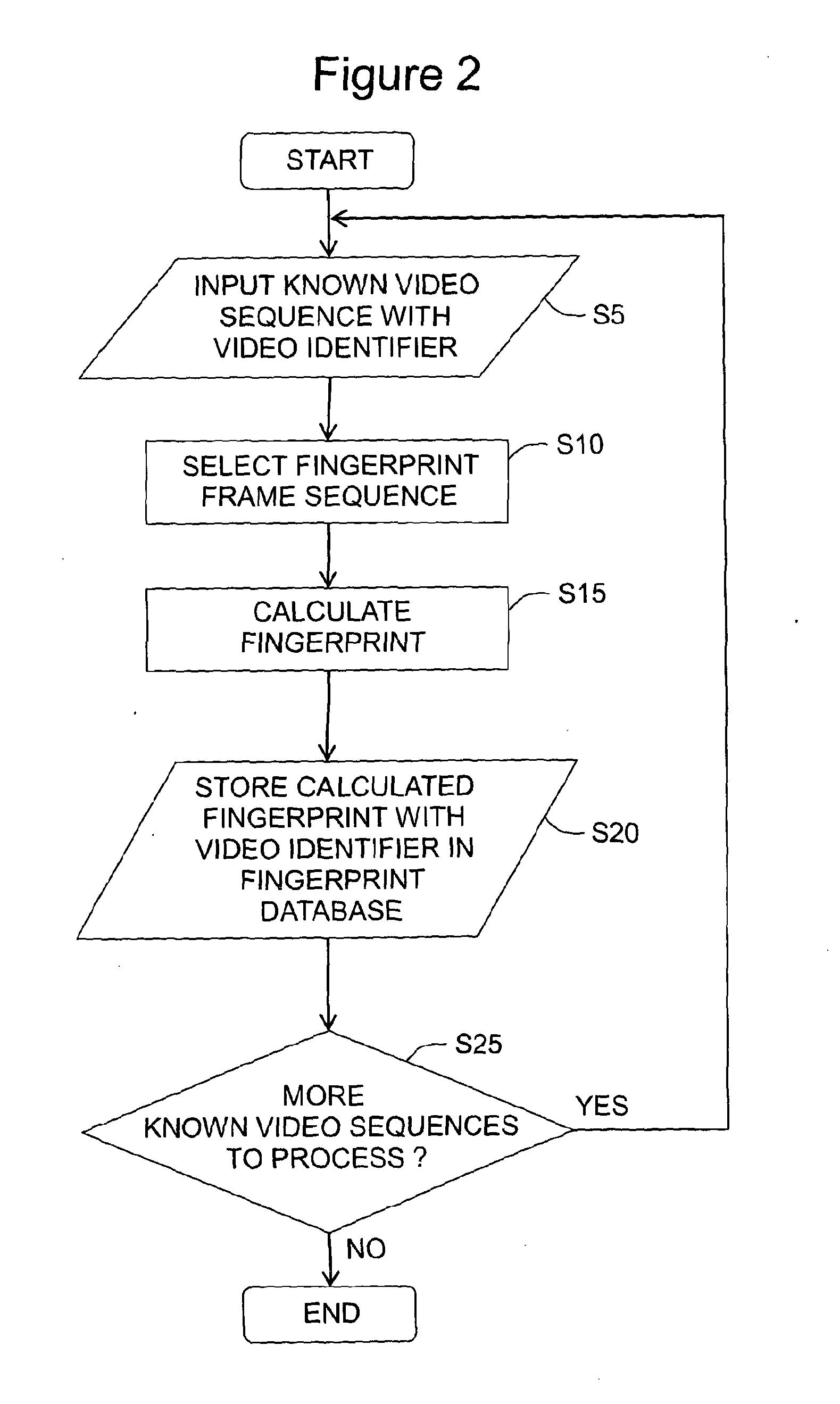
A digitally encoded video fingerprinting system for generating and comparing / matching finger-prints from digitally encoded video which has been encoded according to an encoding method which involves the generation of residual macroblocks of pixels and the generation of quantized transform coefficients of the residual macroblocks, or of portions of the residual macroblocks, comprises a fingerprint database (5) and a video processing subsystem (10). The video processing subsystem (10) includes a fingerprint sequence selection module (14, 24) which is operable to select one or more sets of frames from input video content to be processed in order to generate a fingerprint; a fingerprint calculation module (14, 26) which is operable to generate a fingerprint based on a set of frames selected by the fingerprint sequence selection module; and a fingerprint comparator module (14, 28) which is operable to compare two fingerprints and to output a similarity score of the compared fingerprints. The method used by the fingerprint selection and fingerprint calculation modules includes selecting a group of frames of the encoded video content; processing the digitally encoded video content to obtain a set of quantized transform coefficients of residual macroblocks or portions of residual macroblocks associated with each of the selected frames; identifying a set of residual macroblocks per frame whose transform coefficients satisfy a threshold criterion; and generating a digital video fingerprint for the encoded video content in dependence upon the identified macroblocks or some property thereof within each of the selected frames.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Method for Deriving Coding Information for High Resolution Images from Low Resolution Images and Coding and Decoding Devices Implementing Said Method
InactiveUS20080267291A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureBlock code
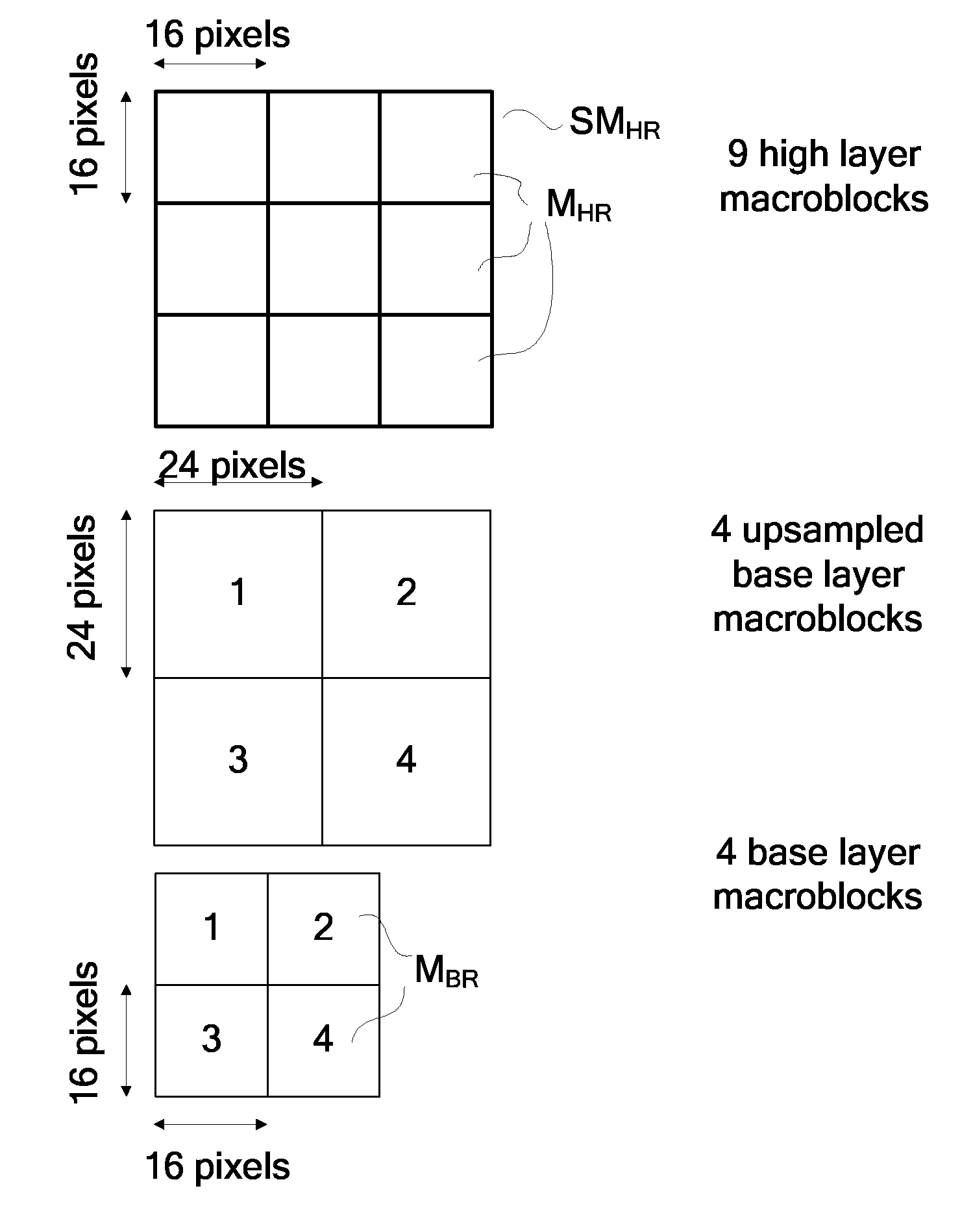
The invention relates to spatially scalable encoding and decoding processes using a method for deriving coding information. More particularly, it relates to a method for deriving coding information used to encode high resolution images from coding information used to encode low resolution images when the ratio between high resolution and low resolution images dimensions is a multiple of 3 / 2. The method mainly comprises the following steps:deriving a block coding mode for each 8×8 blocks of a prediction macroblock MBi_pred from the macroblock coding mode of the associated base layer macroblocks on the basis of the macroblock class of MBi and an the basis of the position of the 8×8 block within MBi_pred;deriving a macroblock coding mode for MBi_pred from the coding modes of the associated base layer macroblocks; andderiving motion information for each macroblock MBi_pred from the motion information of the associated base layer macroblocks.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
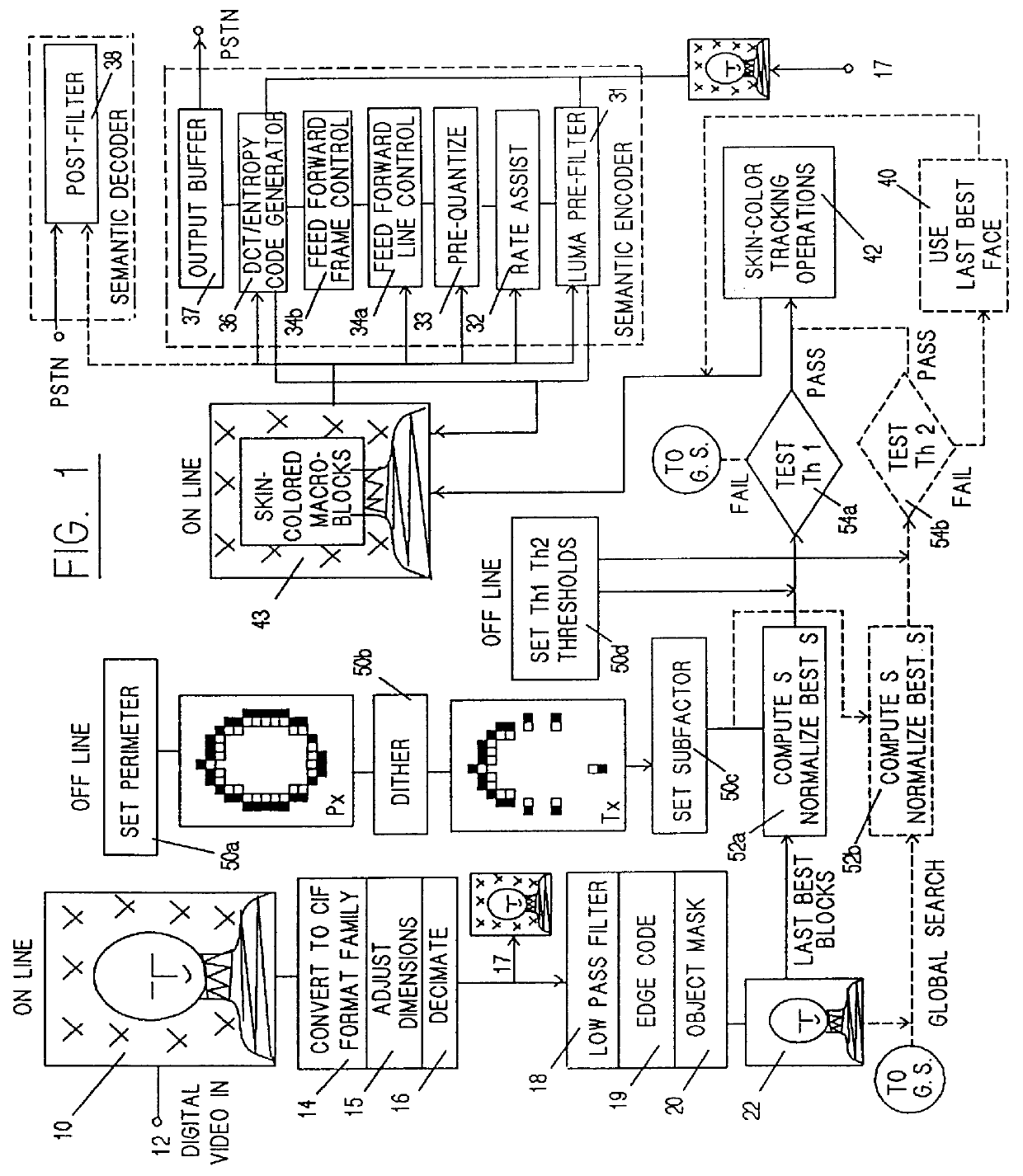
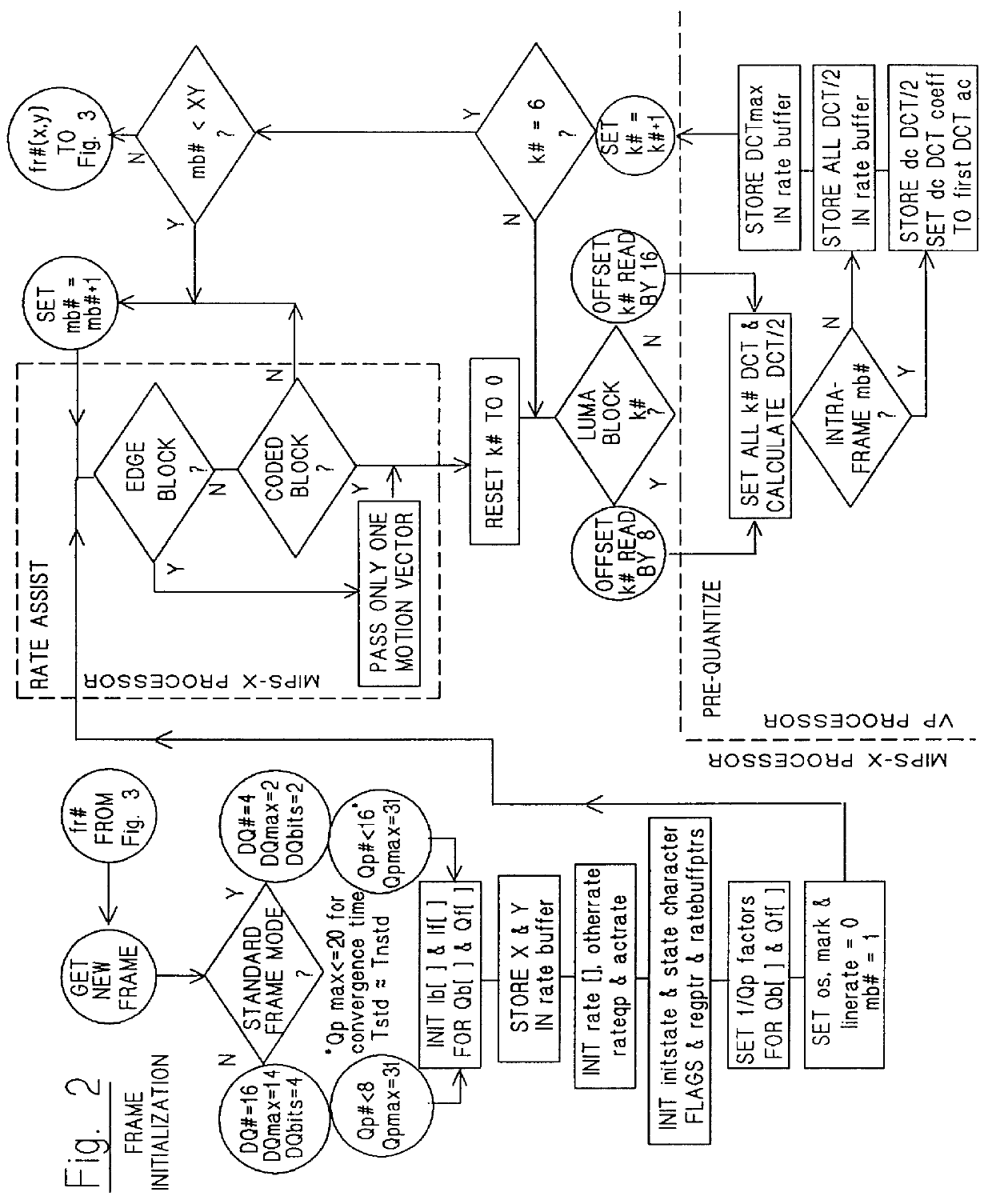
Bit rate coder for differential quantization
InactiveUS6088392AColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionControl systemMotion vector
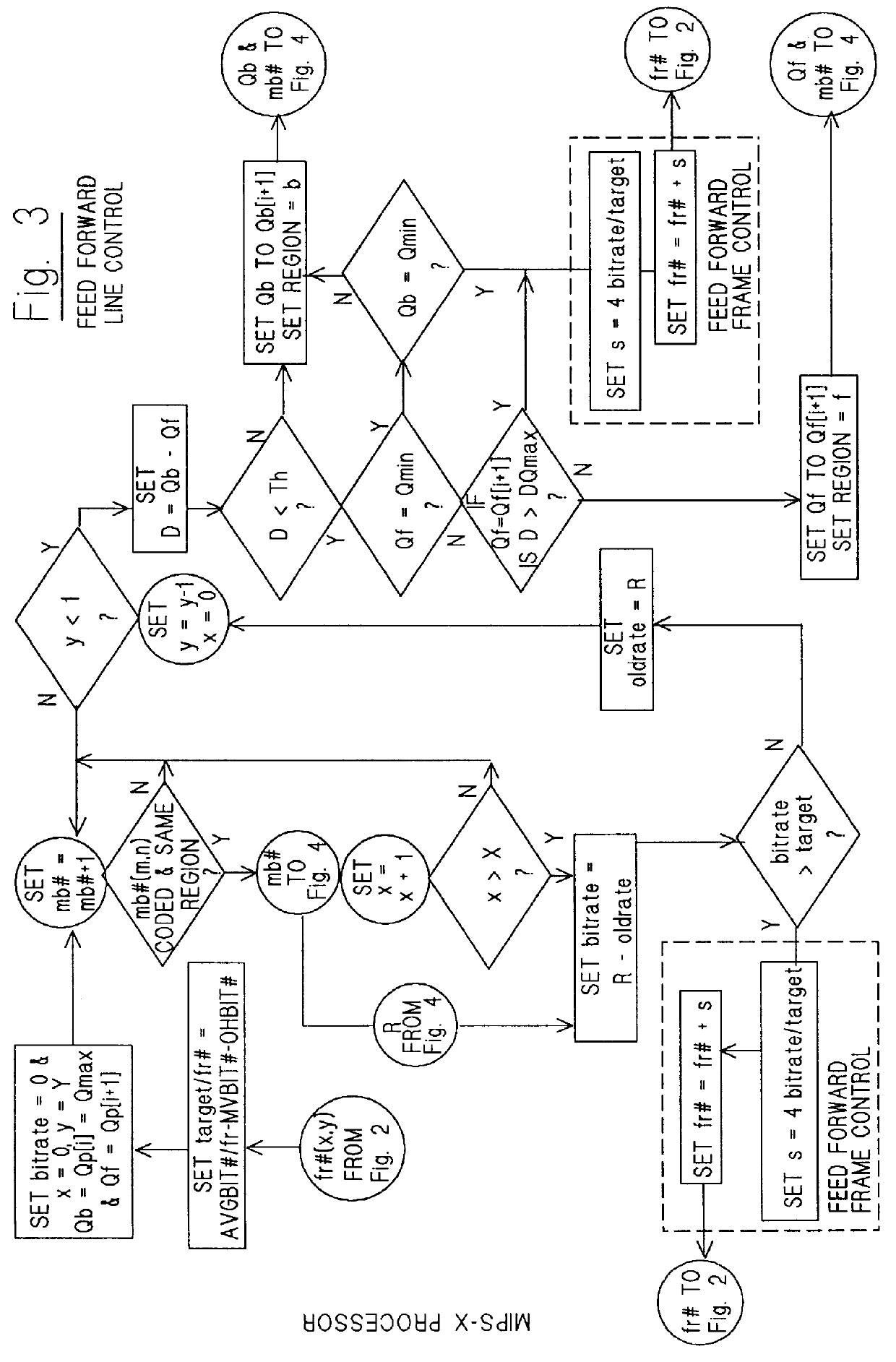
A feed-forward bit-rate control system that selects and formats DQUANT values in real time for optimal semantically-encoded image transmission by video-compression codecs complying with the ITU-T standards H.263 or H.263E. The system uses a prequantization process to reduce the computational load imposed by the quantizer optimization calculations required for feed-forward semantic coding bit-rate control. The H.263 CBPY and MCBPC coding tables are reordered so as to be indexed using an orthogonal flag-based index values and the RLA coding table is block-indexed using clipped amplitude values, for faster access into these tables. The system also uses a rate-assist process to assure that DQUANT values are provided in each edge macroblock that follows a transition to and from each semantically-defined region when the edge macroblocks have four motion vectors by reducing the number of motion vectors in the macroblock to one.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
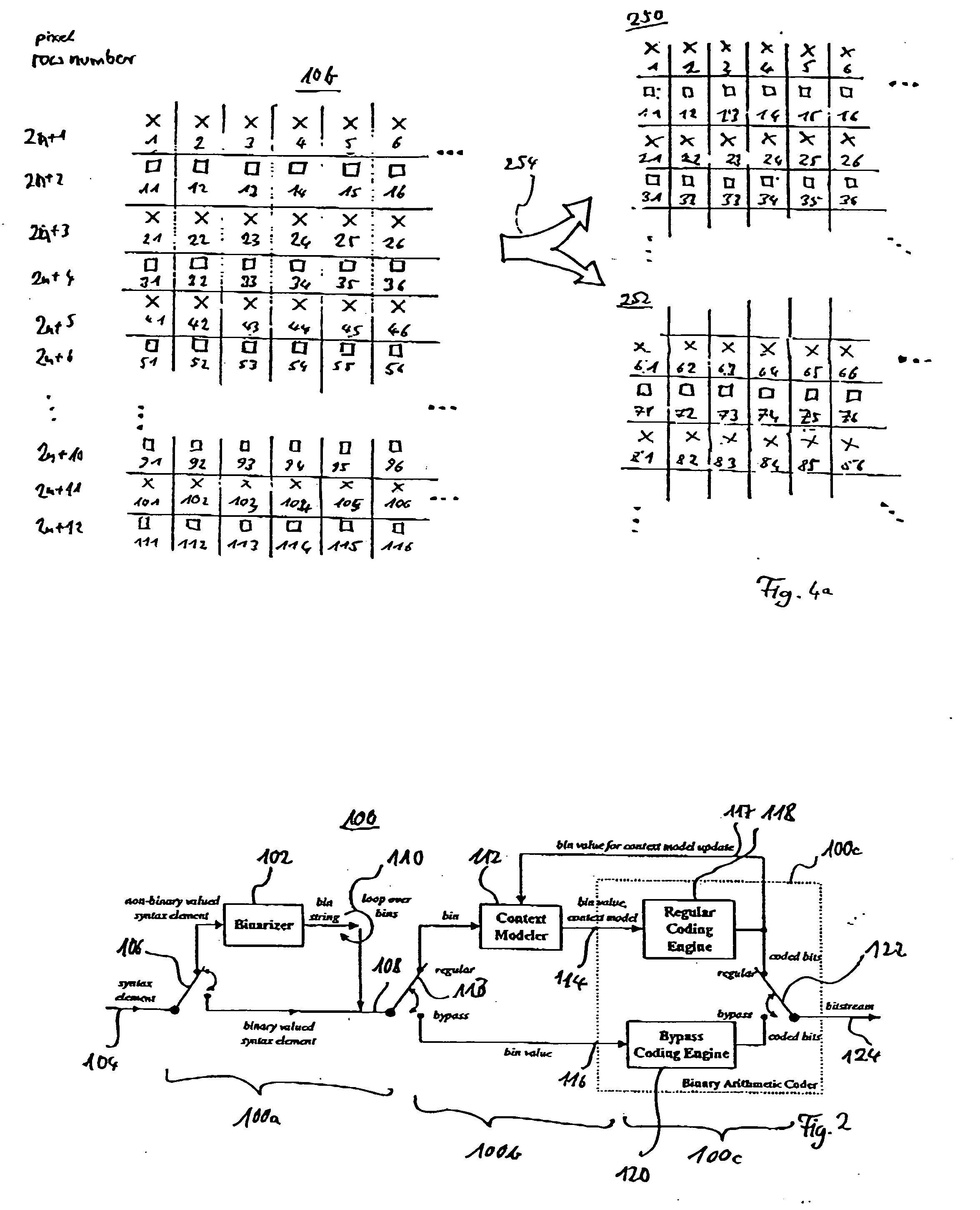
Context adaptive binary arithmetic decoding for high definition video
ActiveUS20070183491A1Faster access to dataEasy accessColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareHigh-definition video
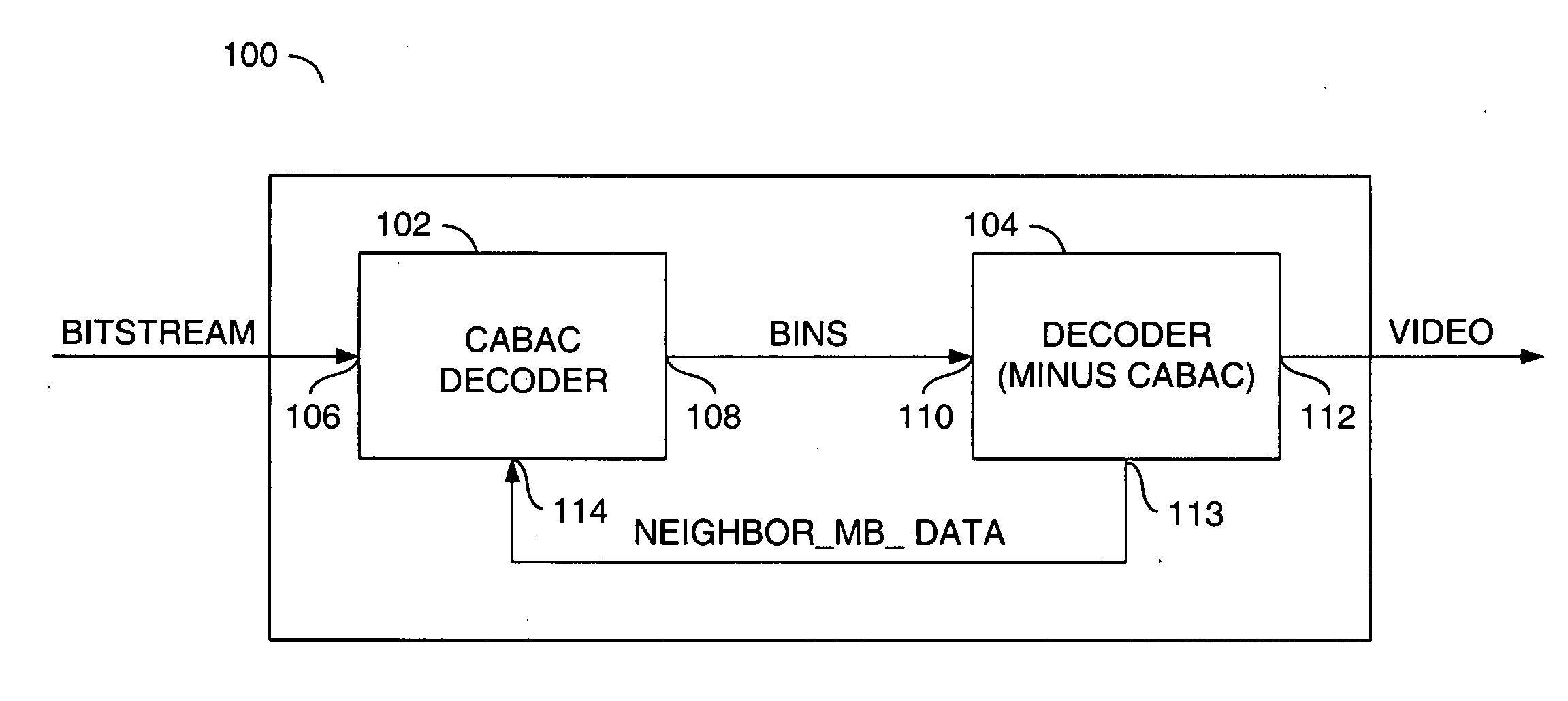
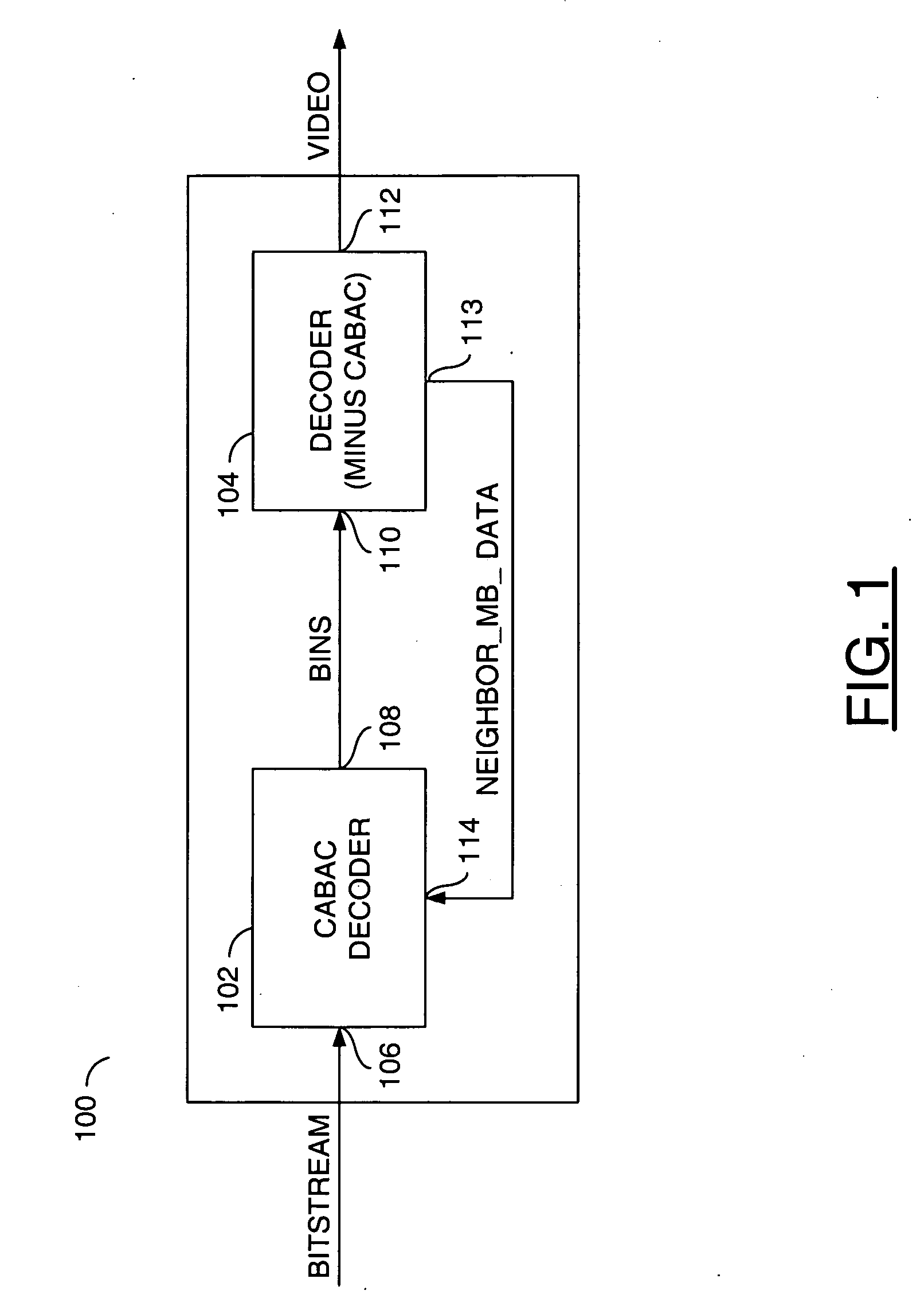
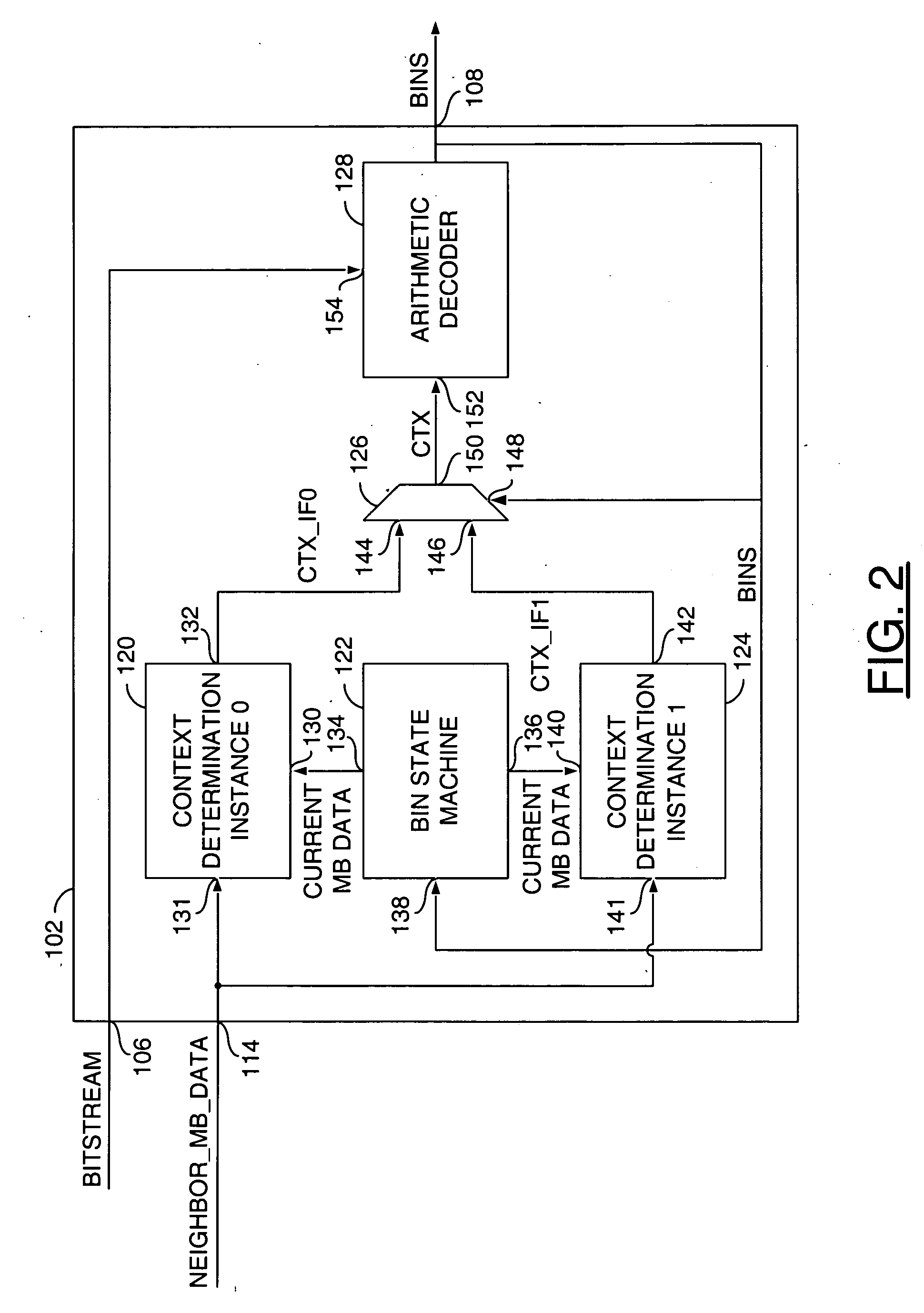
An apparatus comprising a first circuit and a second circuit. The first circuit may be configured to present a video signal and macroblock data in response to decoding one or more bins on a binary signal. The second circuit may be configured to, in parallel (i) generate the binary signal in response to a bitstream signal and an initial context information and (ii) calculate subsequent context information.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multiple-Candidate Motion Estimation With Advanced Spatial Filtering of Differential Motion Vectors
InactiveUS20100166073A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorEuclidean vector
Embodiments include a motion estimation method performed in a parallel processing system that determines a list of several candidate motion vectors for a macroblock of a video image and retains them through multiple computation passes. All candidate motion vectors are used as potential neighboring predictors, so that the best combination of differential vectors rises to the top of the candidate list. Numerous combinations of differential motion vectors are considered during the process that compares motion vectors among up to eight neighboring macroblocks, instead of simply between pairs of macroblocks. The motion estimation system is configured to use a large number of compute engines, such as on a highly parallel GPU platform. This is achieved by having no dependencies between macroblocks except one per pass. This allows the number of calculations per pass to be very large.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
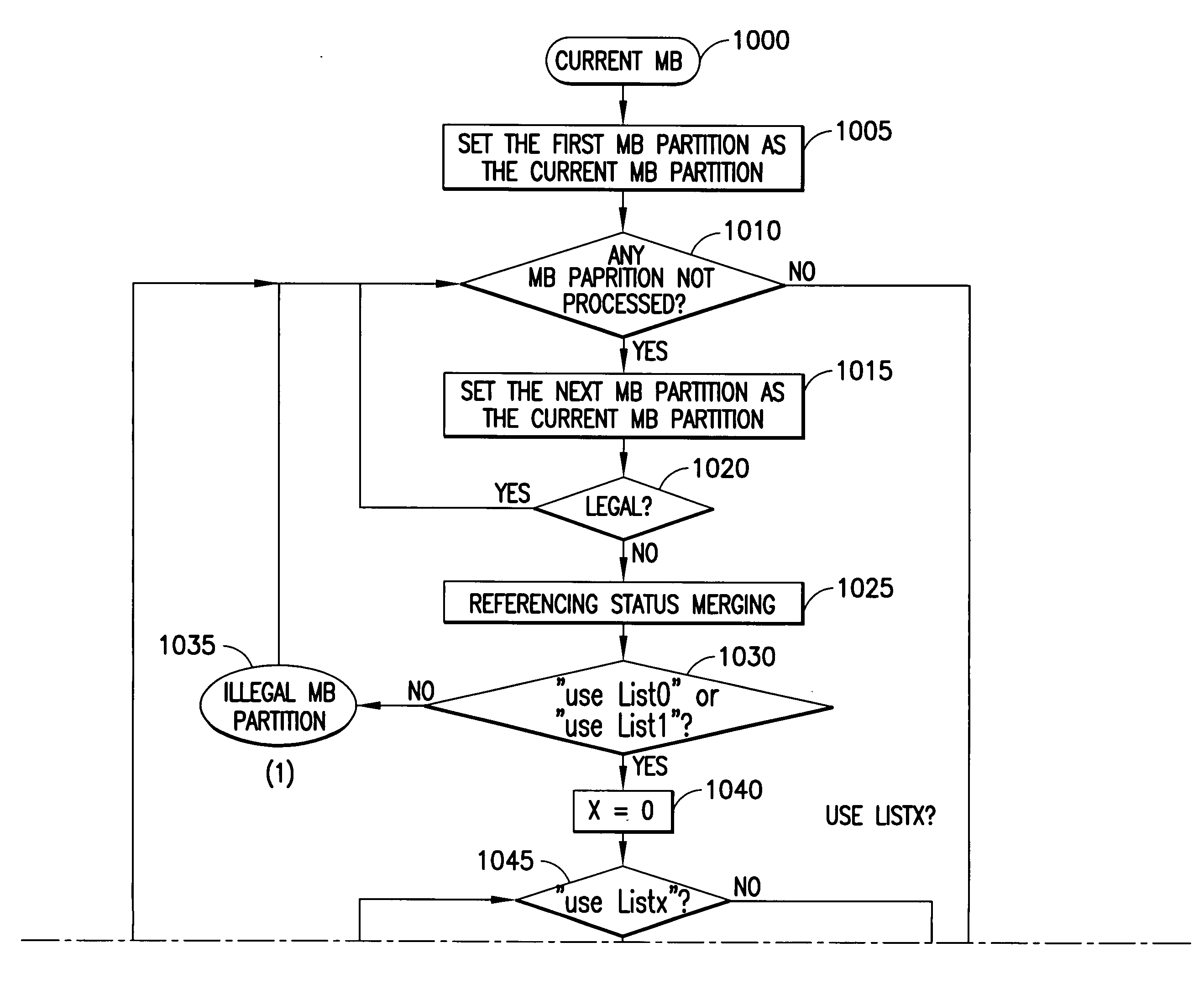
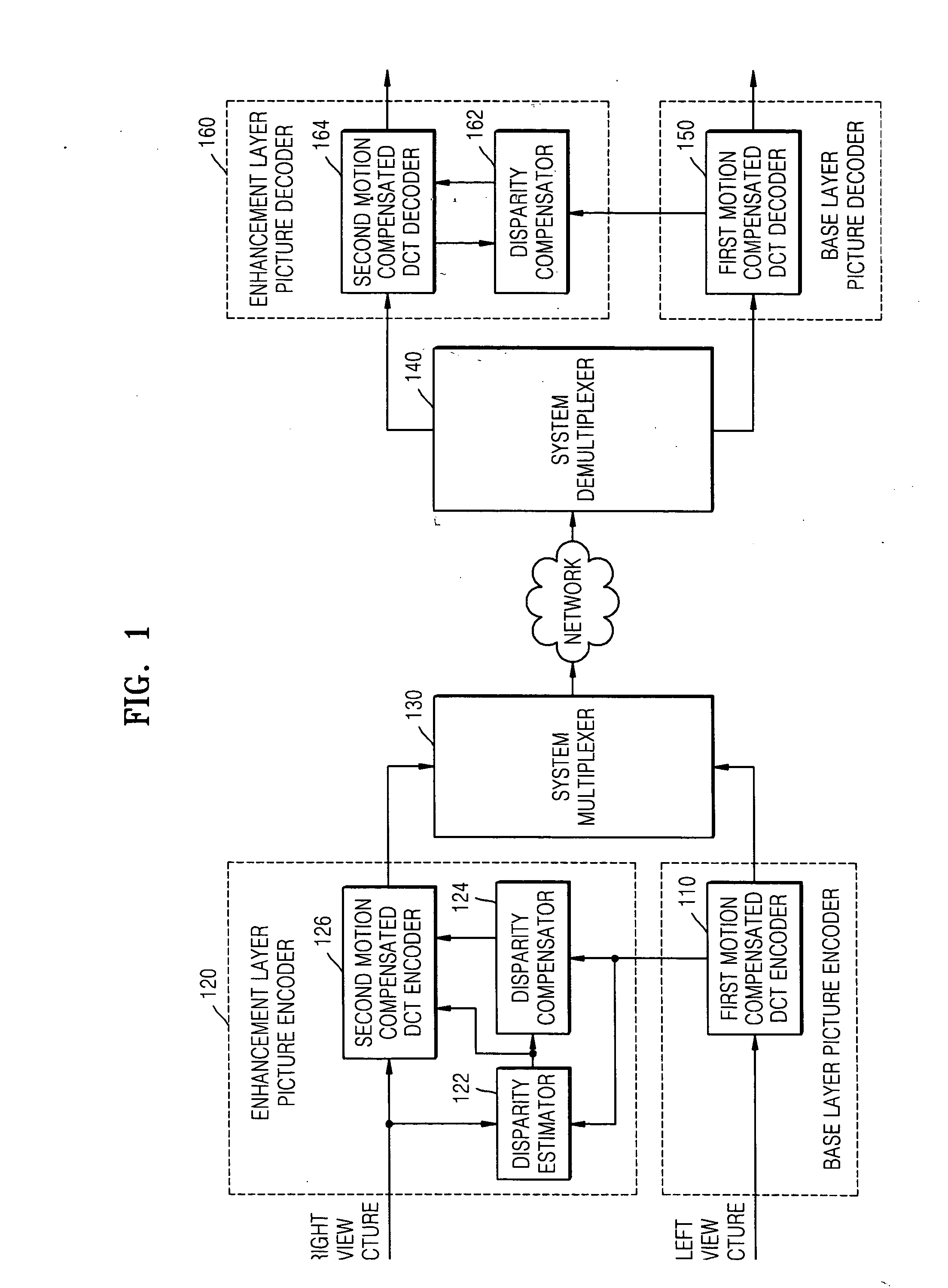
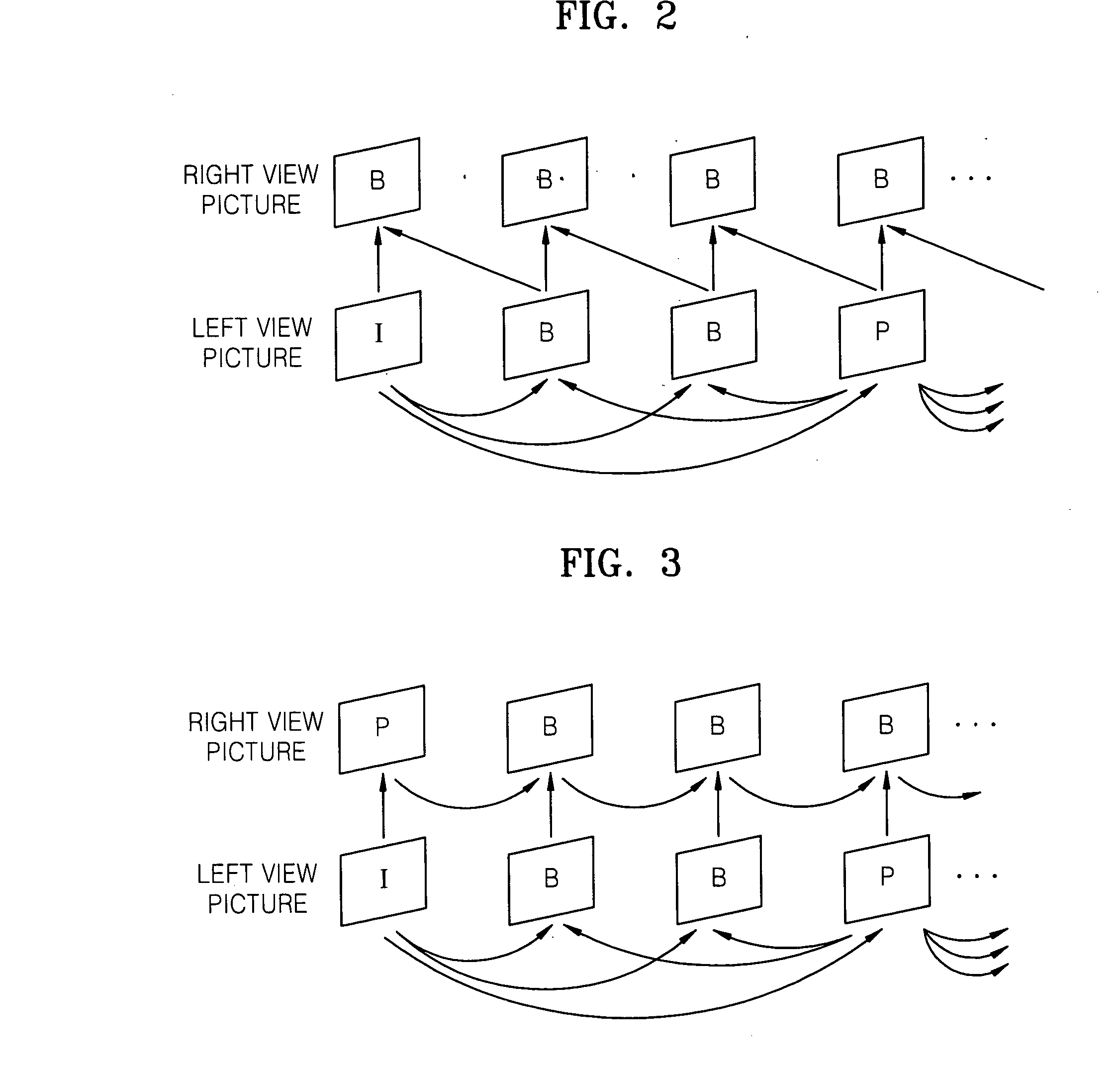
Method of estimating disparity vector, and method and apparatus for encoding and decoding multi-view moving picture using the disparity vector estimation method
InactiveUS20070064800A1Improve compression performanceAddressing slow performanceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallaxEstimation methods
A method and apparatus are provided for encoding and decoding a multi-view moving picture. A method of estimating a disparity vector to encode a multi-view moving picture includes: estimating disparity vectors for a predetermined number of encoded macroblocks; and calculating disparity vectors of macroblocks adjacent to the encoded macroblocks using the estimated disparity vectors. Therefore, it is possible to quickly perform encoding of a multi-view moving picture and enhance compressibility of the multi-view moving picture.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
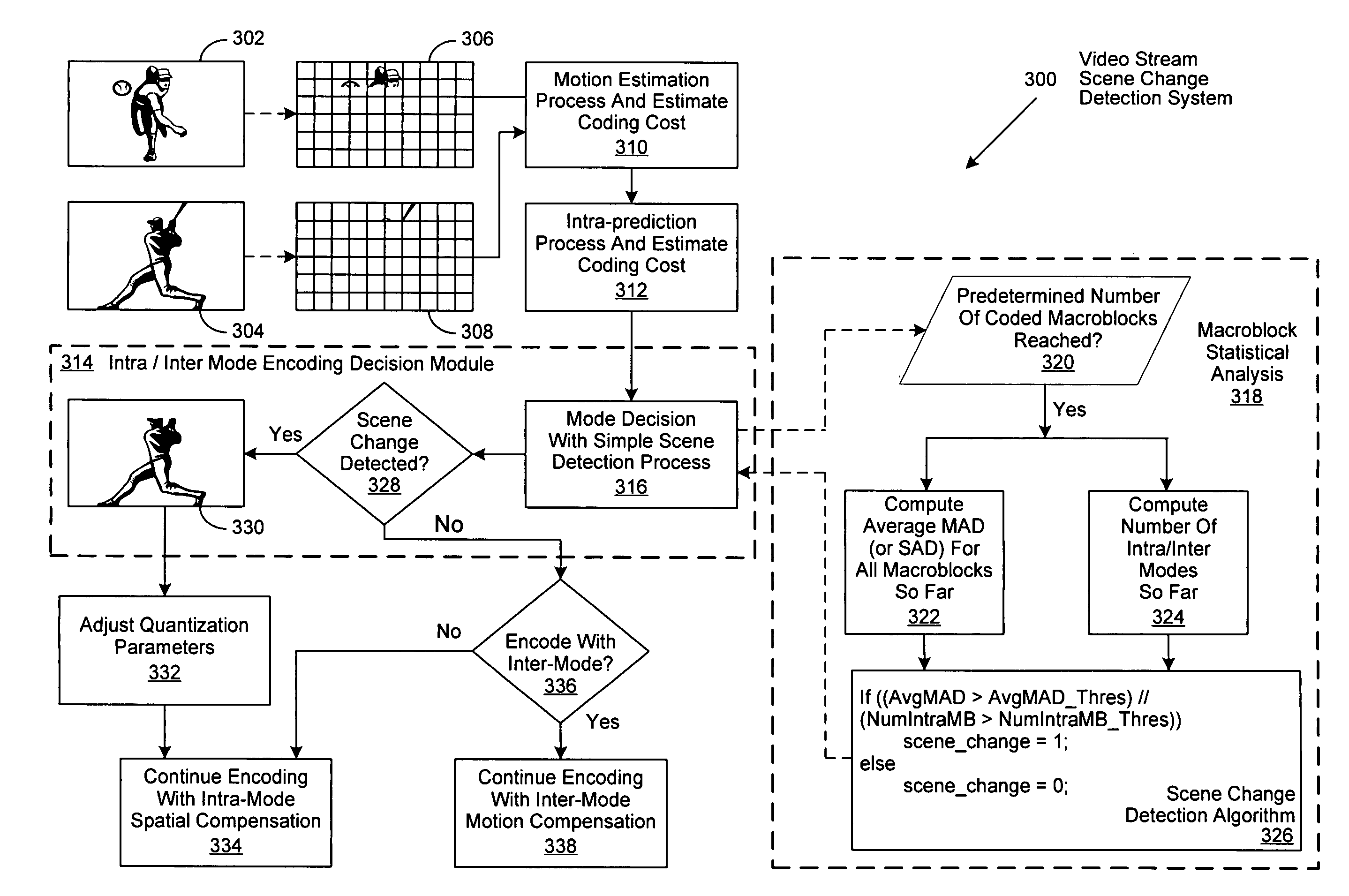
Method of increasing coding efficiency and reducing power consumption by on-line scene change detection while encoding inter-frame
InactiveUS20070274385A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationPattern recognitionComputation complexity
A system and method for on-the-fly detection of scene changes within a video stream through statistical analysis of a portion of the macroblocks comprising each video frame as they are processed using inter-frame coding. If the statistical analysis of the selected macroblocks of the current frame differs from the previous frame by exceeding predetermined thresholds, the current video frame is assumed to be a scene change. Once a scene change is detected, the remainder of the video frame is encoded as an intra-frame, intra-macroblocks, or intra slices, through implementation of one or more predetermined or adaptively adjusted quantization parameters to reduce computational complexity, decrease power consumption, and increase the resulting video image quality. As decoding is the inverse of encoding, these improvements are similarly recognized by a decoder as it decodes a resulting encoded video stream.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and system for rate distortion optimization
ActiveUS20080253457A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionCost MeasuresMotion vector
Method, video encoders, and digital systems are provide in which motion vector determination includes selecting a plurality of candidate motion vectors for a macroblock using a cost function including both a block distortion measure and a motion vector cost measure for single-partition motion vectors in the plurality of candidate motion vectors and using a cost function including a distortion measure without a motion vector cost measure for multi-partition motion vectors in the plurality of candidate motion vectors, and refining the plurality of candidate motion vectors to obtain a refined plurality of candidate motion vectors, wherein multi-partition motion vectors of the plurality of candidate motion vectors are refined using a cost function including a distortion measure without a motion vector cost measure and single-partition motion vectors of the plurality of candidate motion vectors are refined using a cost function including both a block distortion measure and a motion vector cost measure.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Real-time video coding/decoding
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
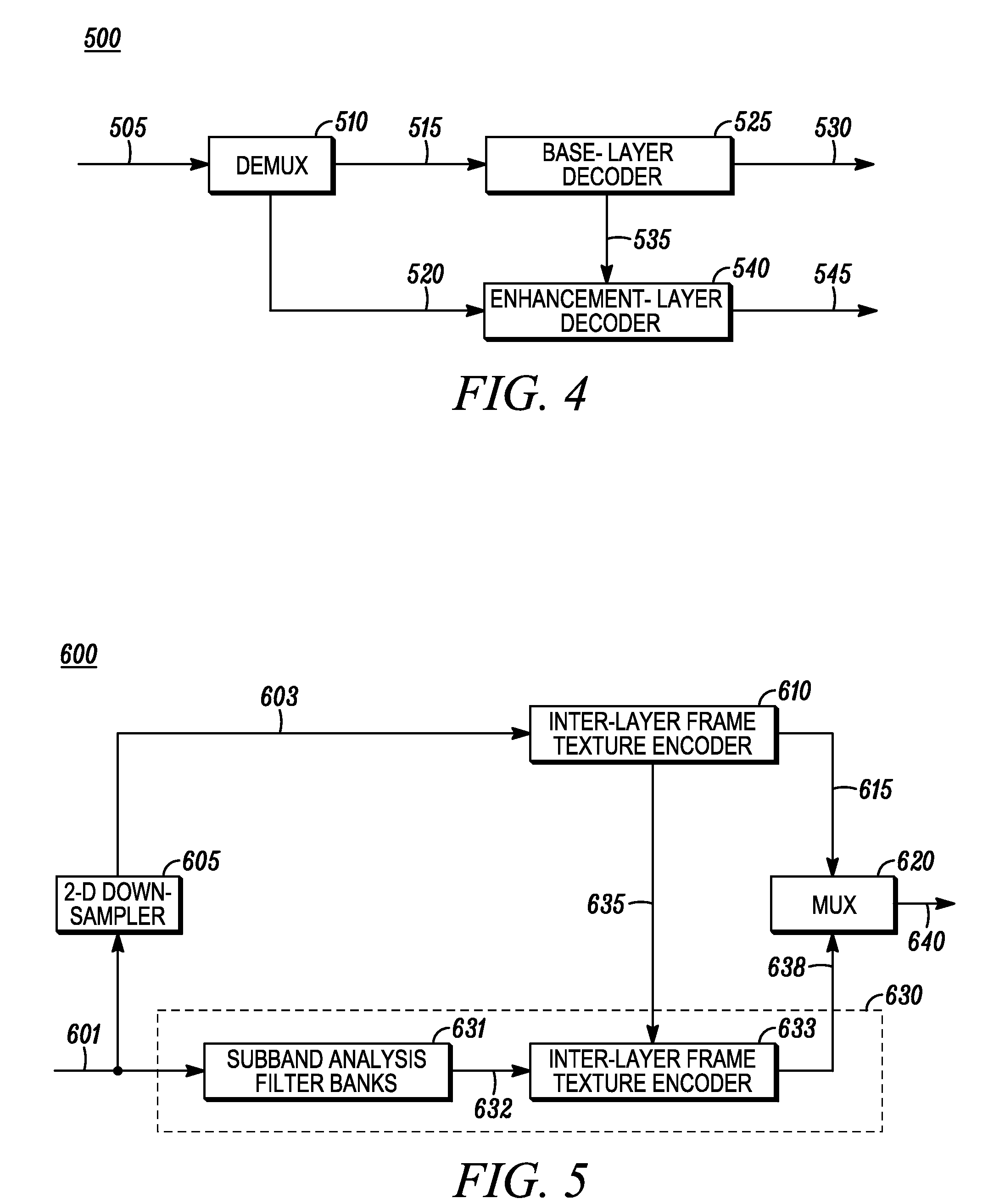
Method and apparatus for highly scalable intraframe video coding
ActiveUS20090175333A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureInter layer
An apparatus and method is provided for highly scalable intraframe video coding. The conventional macroblock DCT tools are integrated with the subband filter banks for the improved efficiency of scalable compression. The enhancement layers are represented in a subband domain and coded by an inter-layer frame texture coder utilizing inter-layer prediction signal formed by the decoded previous layer. Each quality enhancement layer is additionally scalable in resolution.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for decoding hybrid intra-inter coded blocks
ActiveUS20070009044A1High gainImproved encoding efficiencyTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationCoding blockData stream
A hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive (or multi-predictive) coding mode allows both intraframe (intra) and interframe (inter) predictions to be combined together for hybrid-encoding a current macroblock or a subblock. Bi-prediction may be used also in I-pictures, combining two intra predictions that use two different intra prediction directions. A video encoder processes data representing a two-dimensional video image which has been produced by a conventional commercially available video camera. The video encoder is adapted to select, for coding a current macroblock, between an intra encoding mode, an P-frame inter encoding mode, a B-frame bi-predictive inter mode, and a hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive encoding mode. A video decoder receives and decodes a data stream that may contain a block / macroblock encoded in accordance with the hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive encoding mode.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Parallel processing motion estimation for H.264 video codec
InactiveUS20080126278A1Low costMinimize the numberImage enhancementImage analysisMotion vectorMotion estimate
A genus of motion estimation processes is disclosed which is characterized by the following characteristics which all species in the genus will share 1) a process within this genus does not perform the motion estimation separately for each of the partitions and subpartitions defined in the H.264 standard; 2) a process within the genus computes for each motion vector in the search region the partial costs for all macroblock partitions and sub-partitions, compares them to the best partial costs found so far, and for partitions and sub-partitions having lower costs updates the corresponding best partial costs and records the current motion vectors as the one realizing them. 3) a process within the genus after finishing scanning the motion vectors in the search region, computes from the best partial costs the total costs for all possible macroblock partitioning modes and selects the one with the lowest total cost as the best macroblock partitioning mode, with the best motion vectors corresponding to each of the selected macroblock partitions and sub-partitions.
Owner:NOVAFORA
Advanced bi-directional predictive coding of interlaced video
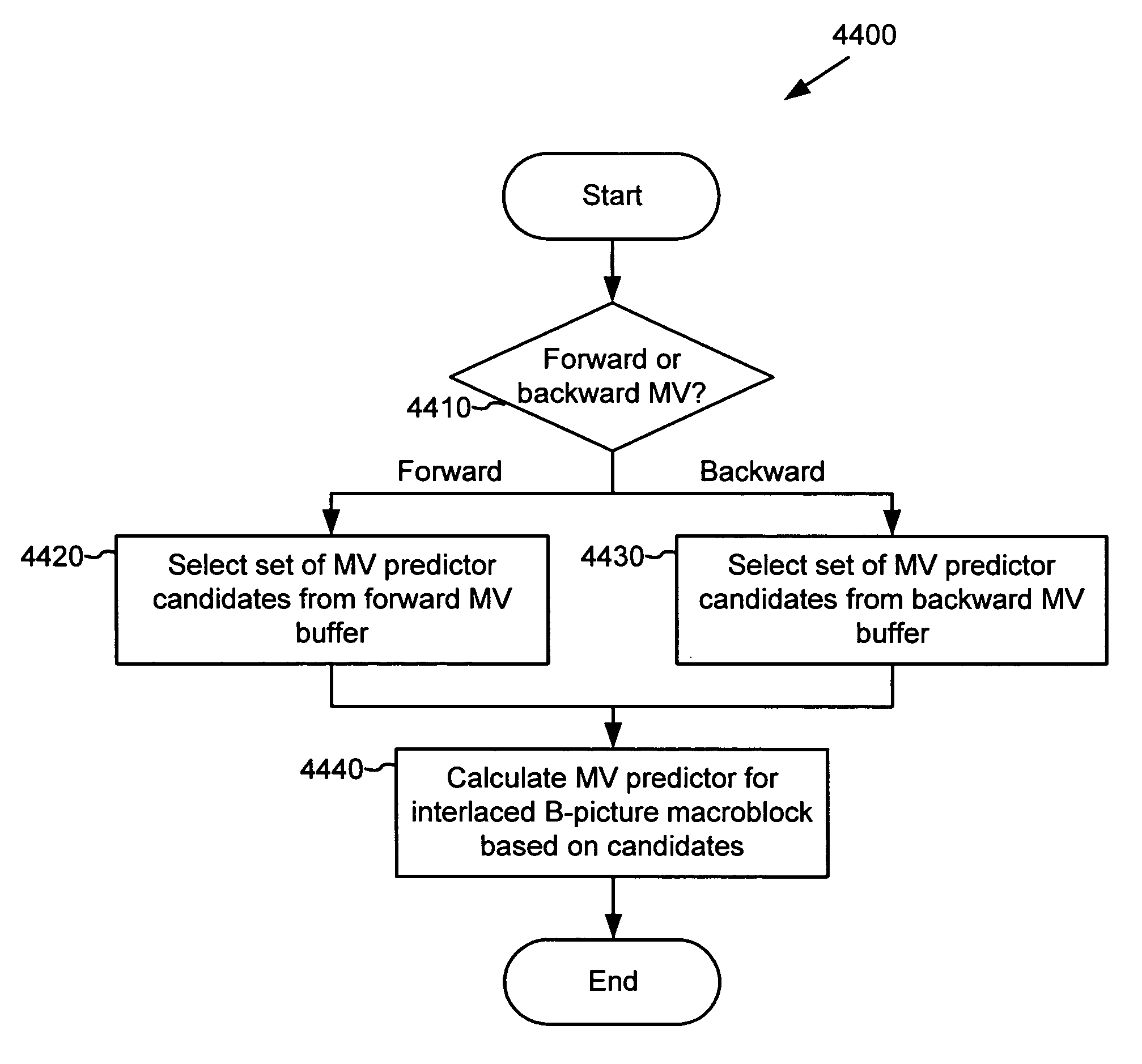
ActiveUS20050053292A1Accurate compensationReduce encoding overheadPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionInterlaced videoMotion vector
For interlaced B-fields or interlaced B-frames, forward motion vectors are predicted by an encoder / decoder using forward motion vectors from a forward motion vector buffer, and backward motion vectors are predicted using backward motion vectors from a backward motion vector buffer. The resulting motion vectors are added to the corresponding buffer. Holes in motion vector buffers can be filled in with estimated motion vector values. An encoder / decoder switches prediction modes between fields in a field-coded macroblock of an interlaced B-frame. For interlaced B-frames and interlaced B-fields, an encoder / decoder computes direct mode motion vectors. For interlaced B-fields or interlaced B-frames, an encoder / decoder uses 4 MV coding. An encoder / decoder uses “self-referencing” B-frames. An encoder sends binary information indicating whether a prediction mode is forward or not-forward for one or more macroblocks in an interlaced B-field. An encoder / decoder uses intra-coded B-fields [“BI-fields”].
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Intra 4 x 4 modes 3, 7 and 8 availability determination intra estimation and compensation
InactiveUS20050013376A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionElectrical and Electronics engineeringReal-time computing
An apparatus comprising a first processing circuit and a second precessing circuit. The first processing circuit may be configured to generate a plurality of reconstructed samples in response to one or more macroblocks of an input signal. The second processing circuit may be configured to determine availability of intra 4×4 prediction modes for each luma sub-block of a current macroblock in response to available reconstructed samples adjacent to the current macroblock.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and apparatus for encoding hybrid intra-inter coded blocks
ActiveUS20070047648A1High gainImproved encoding efficiencyTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationCoding blockData stream
A hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive (or multi-predictive) coding mode allows both intraframe (intra) and interframe (inter) predictions to be combined together for hybrid-encoding a current macroblock or a subblock Bi-prediction may be used also in I-pictures, combining two intra predictions that use two different intra prediction directions. A video encoder processes data representing a two-dimensional video image which has been produced by a conventional commercially available video camera. The video encoder is adapted to select, for coding a current macroblock, between an intra encoding mode, an P-frame inter encoding mode, a B-frame bi-predictive inter mode, and a hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive encoding mode. A video decoder (800) receives and decodes a data stream that may contain a block / macroblock encoded in accordance with the hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive encoding mode.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com