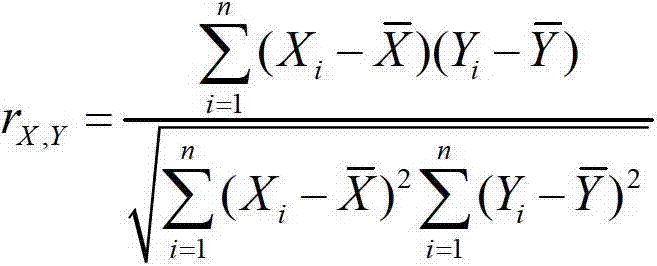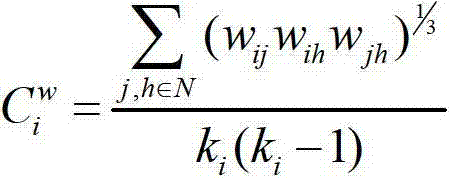Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1061 results about "Tensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
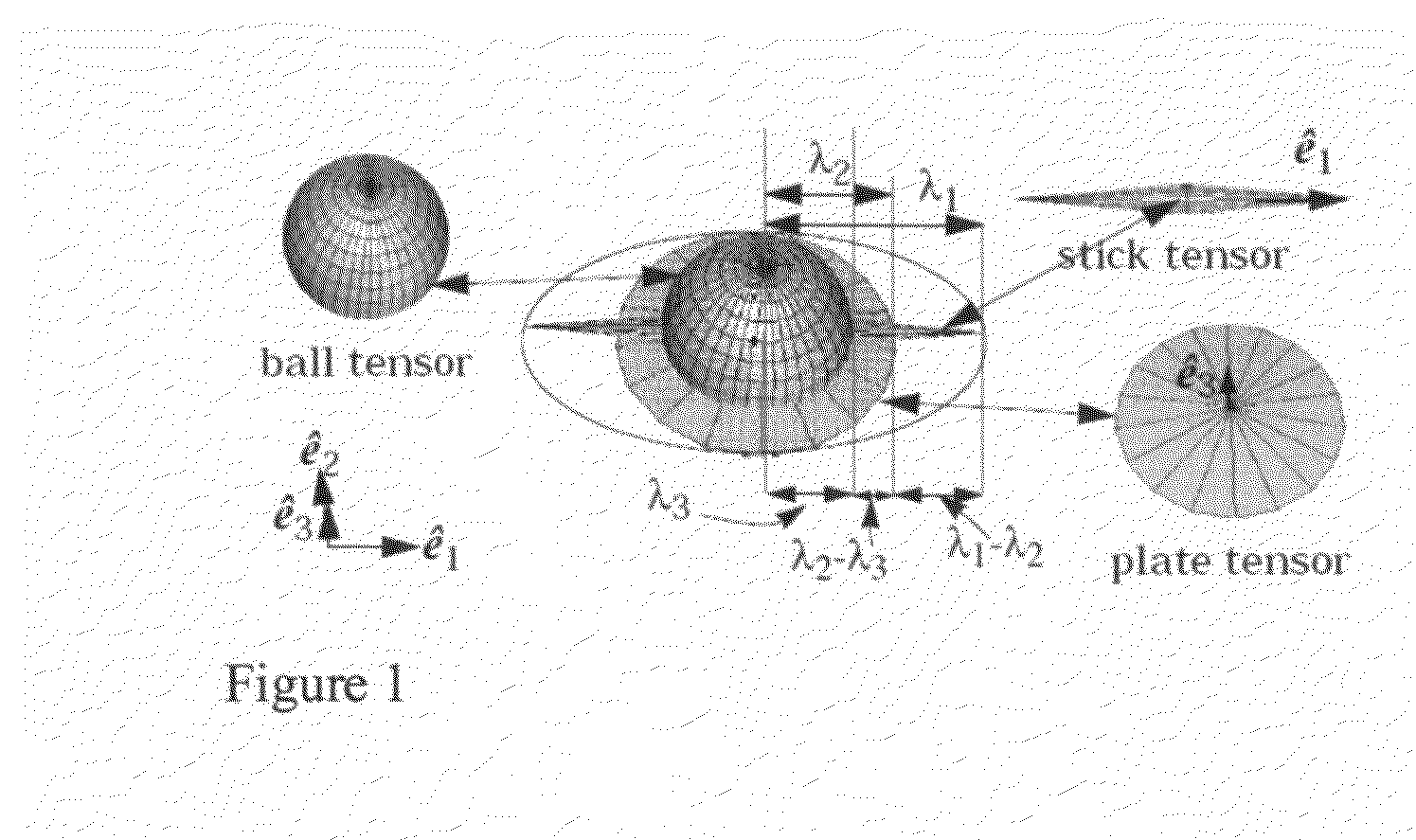
In mathematics, a tensor is an algebraic object that describes a linear mapping from one set of algebraic objects to another. Objects that tensors may map between include, but are not limited to vectors and scalars, and, recursively, even other tensors (for example, a matrix is a map between vectors, and is thus a tensor. Therefore a linear map between matrices is also a tensor). Tensors are inherently related to vector spaces and their dual spaces, and can take several different forms – for example: a scalar, a tangent vector at a point, a cotangent vector (dual vector) at a point, or a multi-linear map between vector spaces.
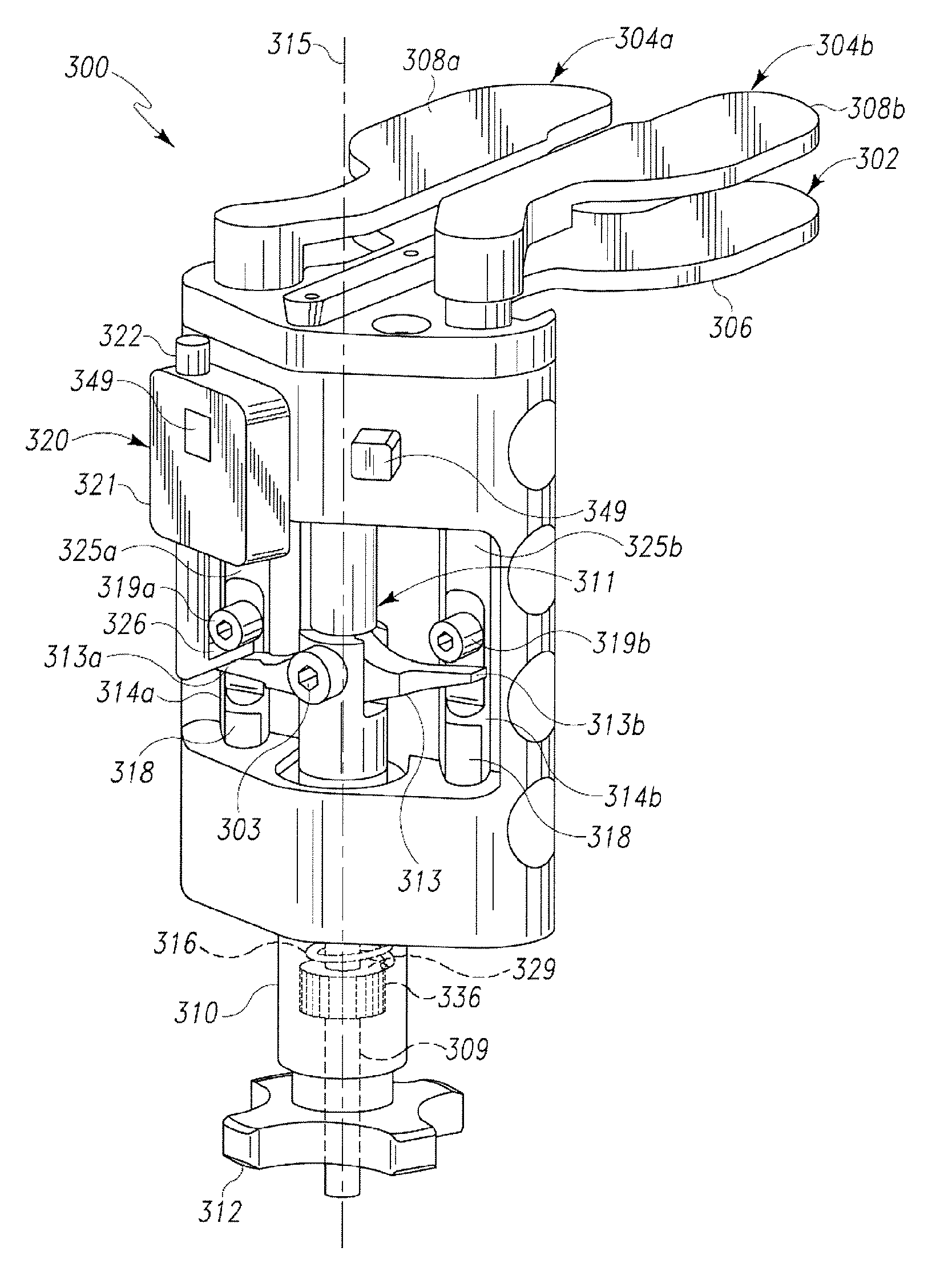
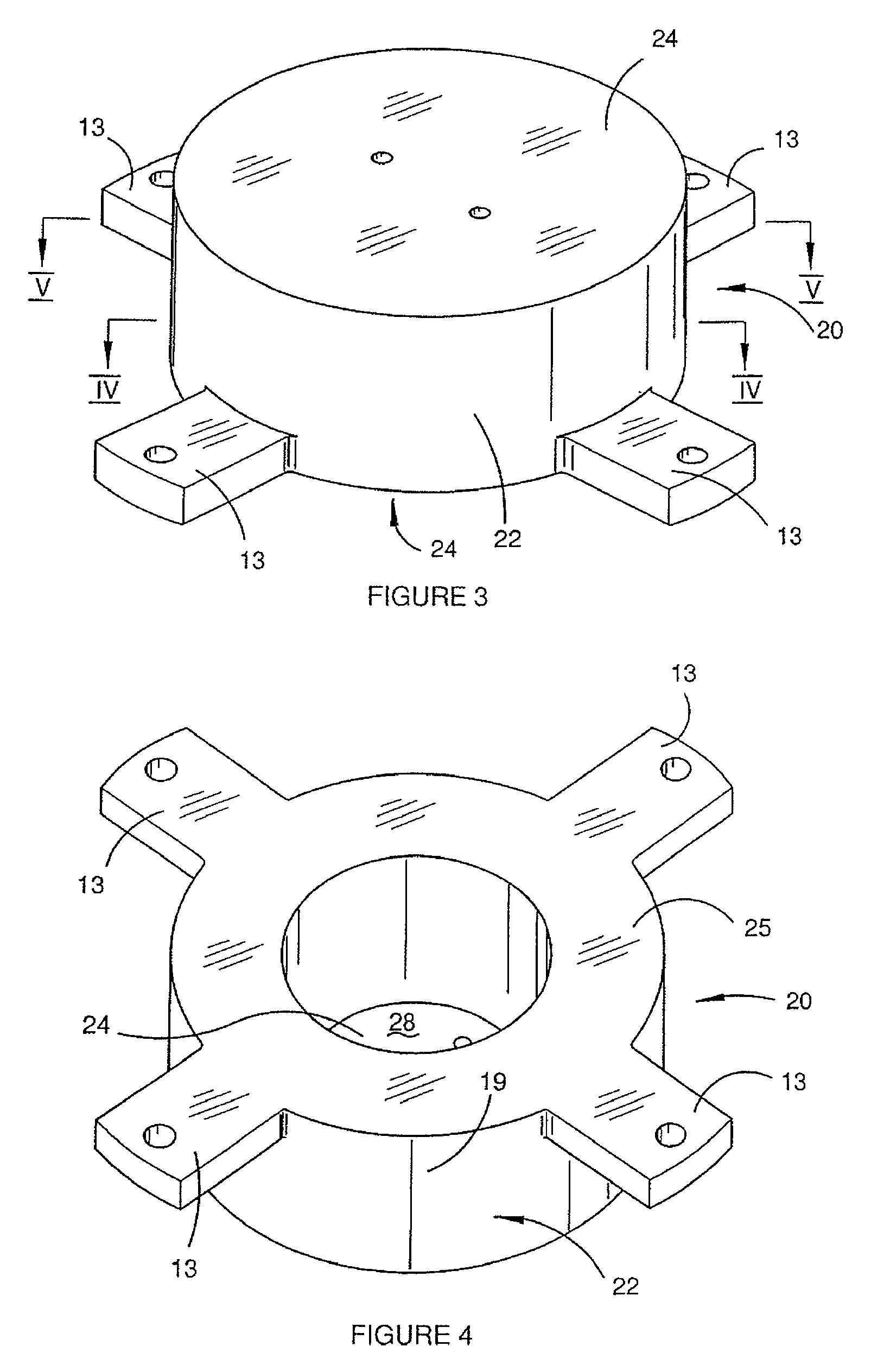
Tensor for use in surgical navigation
A tensor for use with a surgical navigation system is provided. The tensor comprises a first bone engaging member engageable with a first bone and a second bone engaging member engageable with a second bone. A force-applying mechanism is configured to forcibly move the first and second bone engaging members relative to one another and a sensor detects the value of the force applied by the force-applying mechanism. A transmitter communicates a parameter associated with the tensor to the surgical navigation system.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
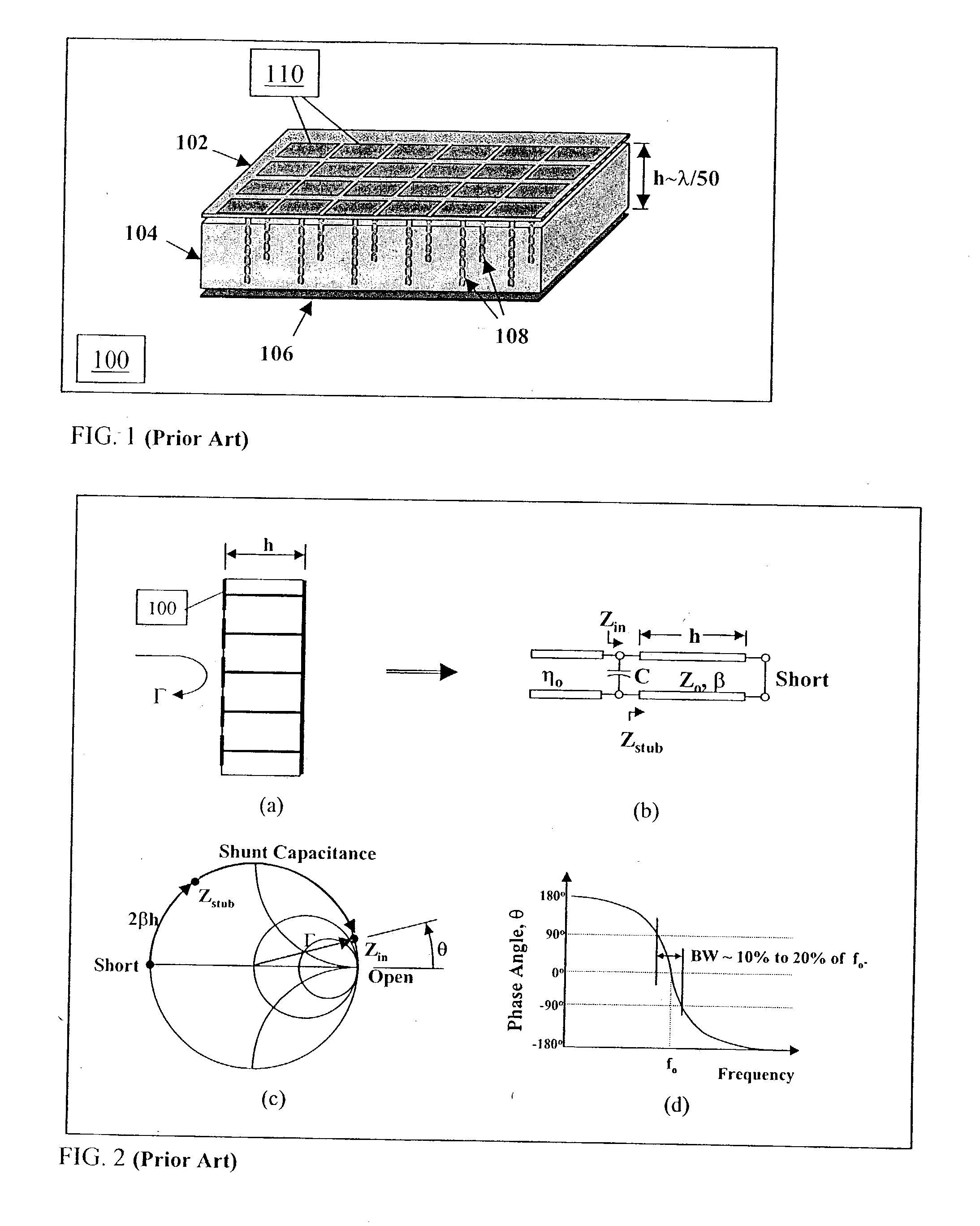
Multi-resonant, high-impedance electromagnetic surfaces
An artificial magnetic conductor is resonant at multiple resonance frequencies. The artificial magnetic conductor is characterized by an effective media model which includes a first layer and a second layer. Each layer has a layer tensor permittivity and a layer tensor permeability having non-zero elements on the main tensor diagonal only.
Owner:E TENNA CORP
Multi-resonant, high-impedance electromagnetic surfaces
An artificial magnetic conductor is resonant at multiple resonance frequencies. The artificial magnetic conductor is characterized by an effective media model which includes a first layer and a second layer. Each layer has a layer tensor permittivity and a layer tensor permeability having non-zero elements on the main tensor diagonal only.
Owner:WEMTEC
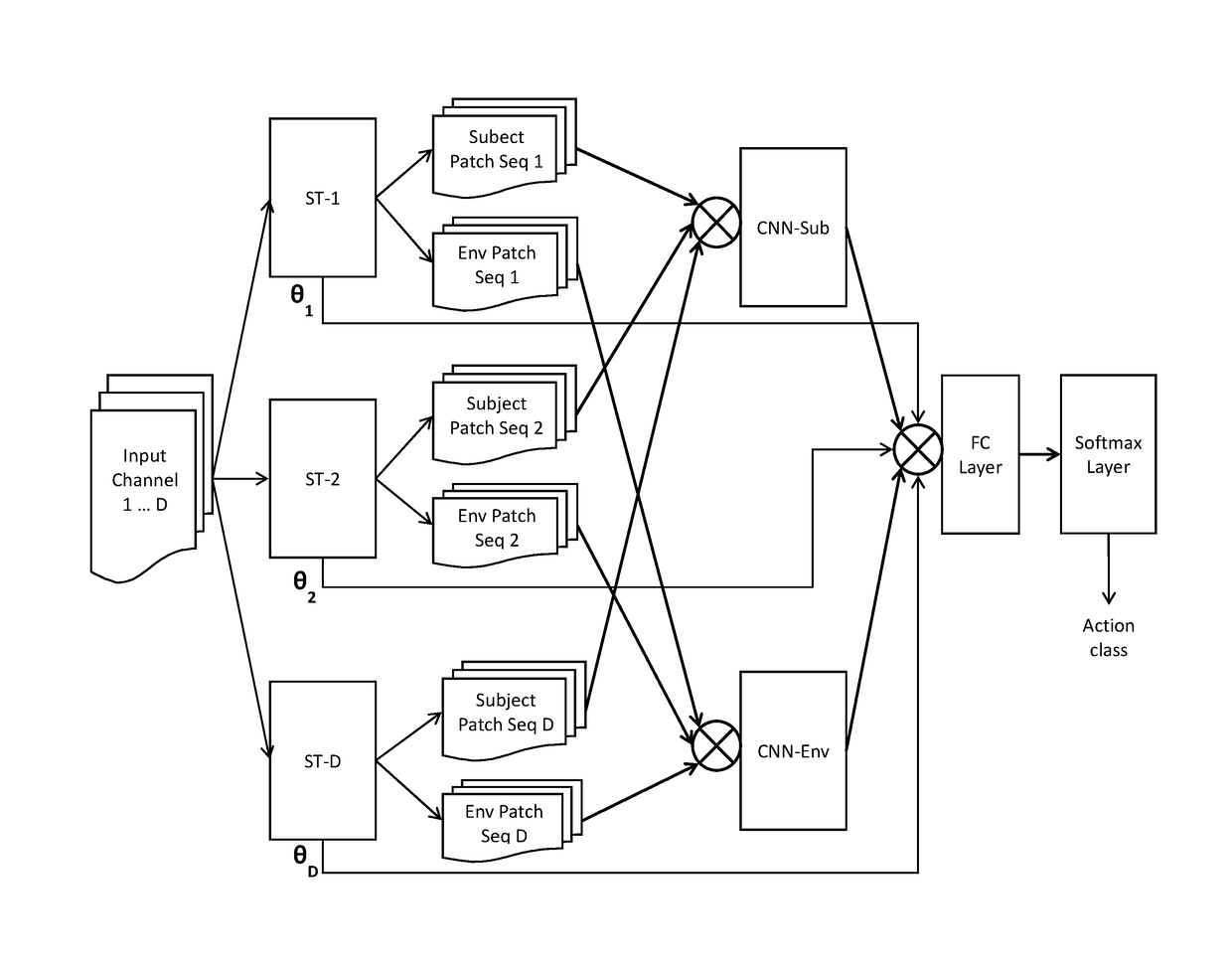
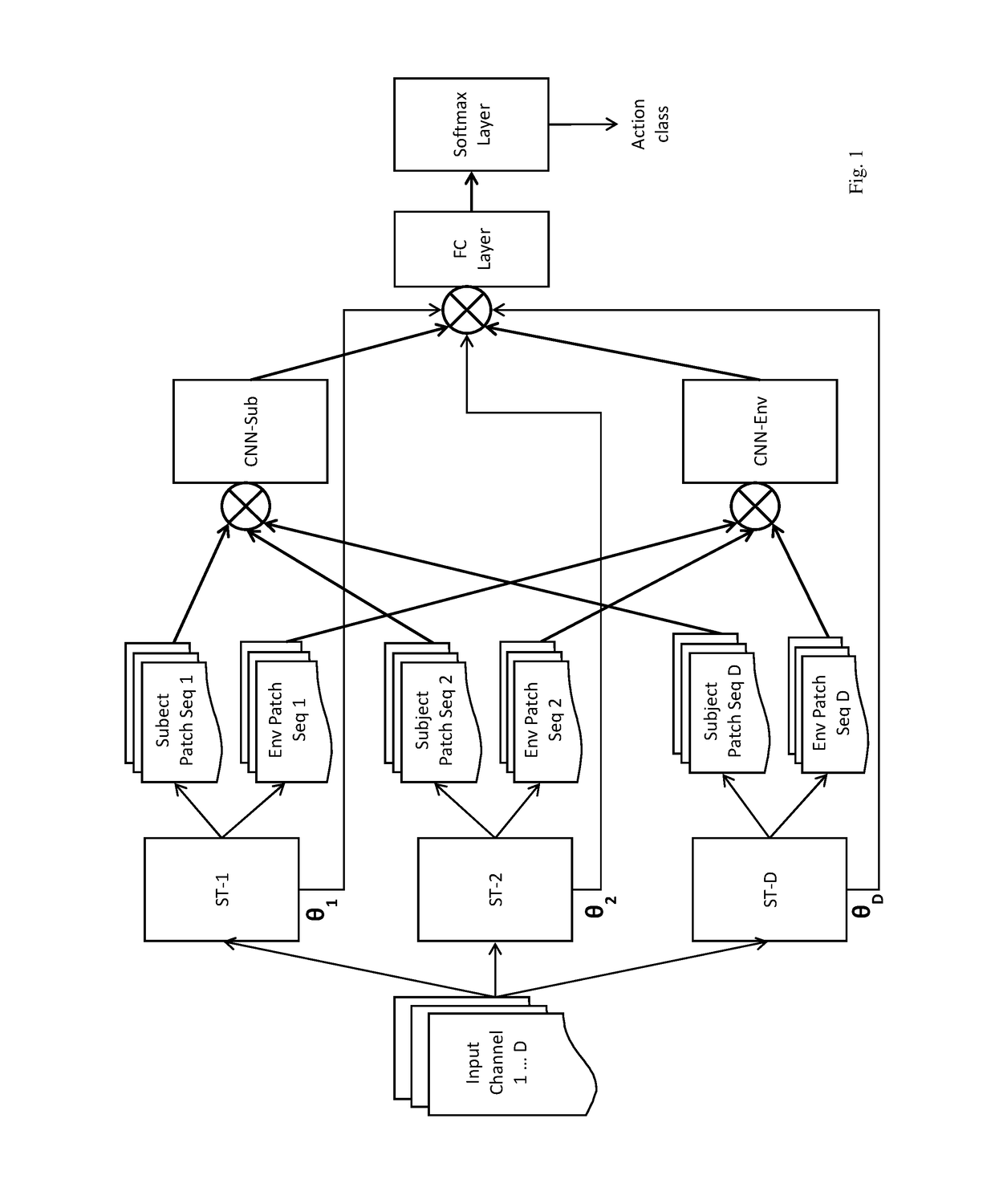
Self-attention deep neural network for action recognition in surveillance videos
An artificial neural network for analyzing input data, the input data being a 3D tensor having D channels, such as D frames of a video snippet, to recognize an action therein, including: D spatial transformer modules, each generating first and second spatial transformations and corresponding first and second attention windows using only one of the D channels, and transforming first and second regions of each of the D channels corresponding to the first and second attention windows to generate first and second patch sequences; first and second CNNs, respectively processing a concatenation of the D first patch sequences and a concatenation of the D second patch sequences; and a classification network receiving a concatenation of the outputs of the first and second CNNs and the D sets of transformation parameters of the first transformation outputted by the D spatial transformer modules, to generate a predicted action class.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA LAB U S A INC
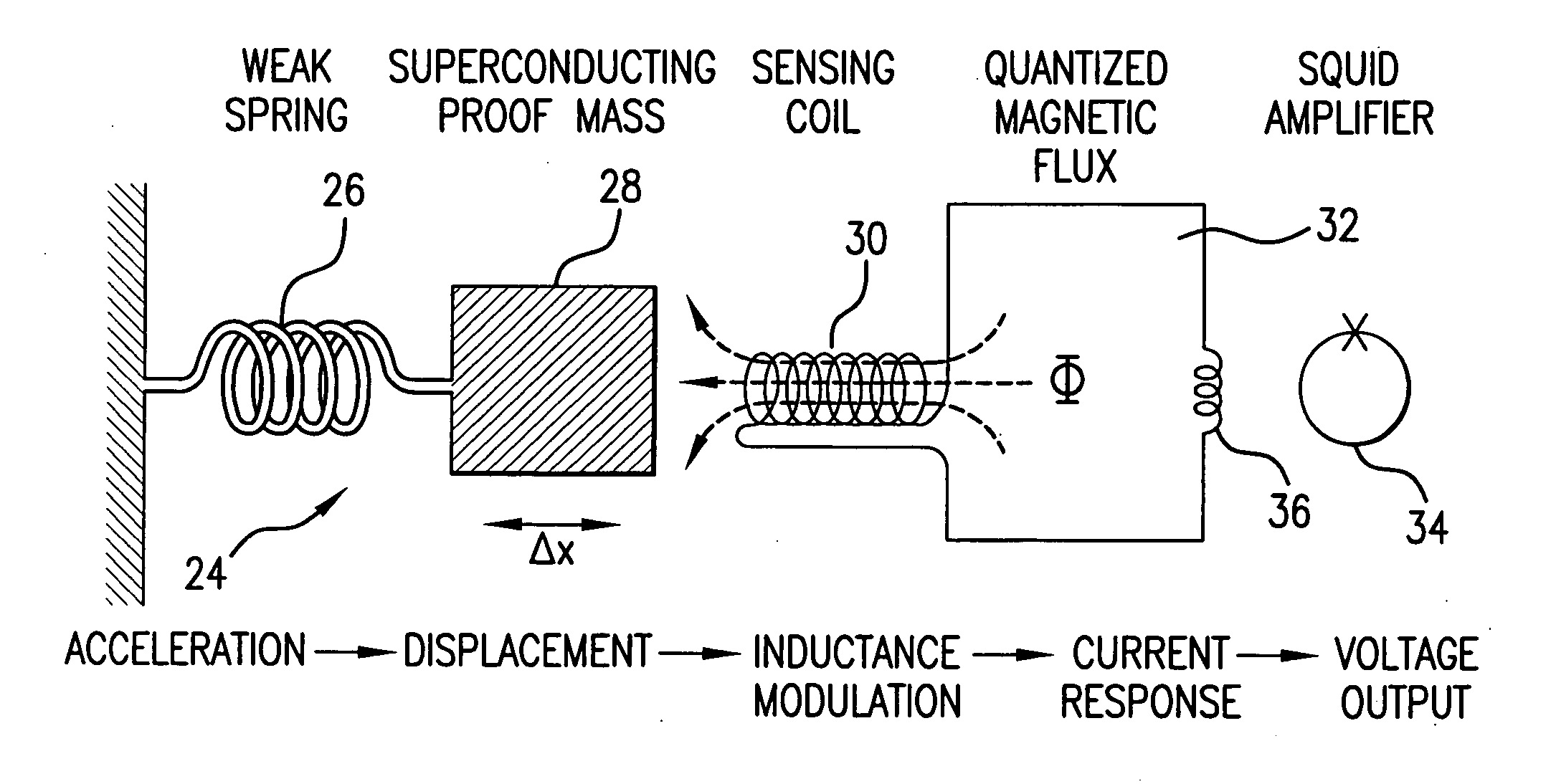
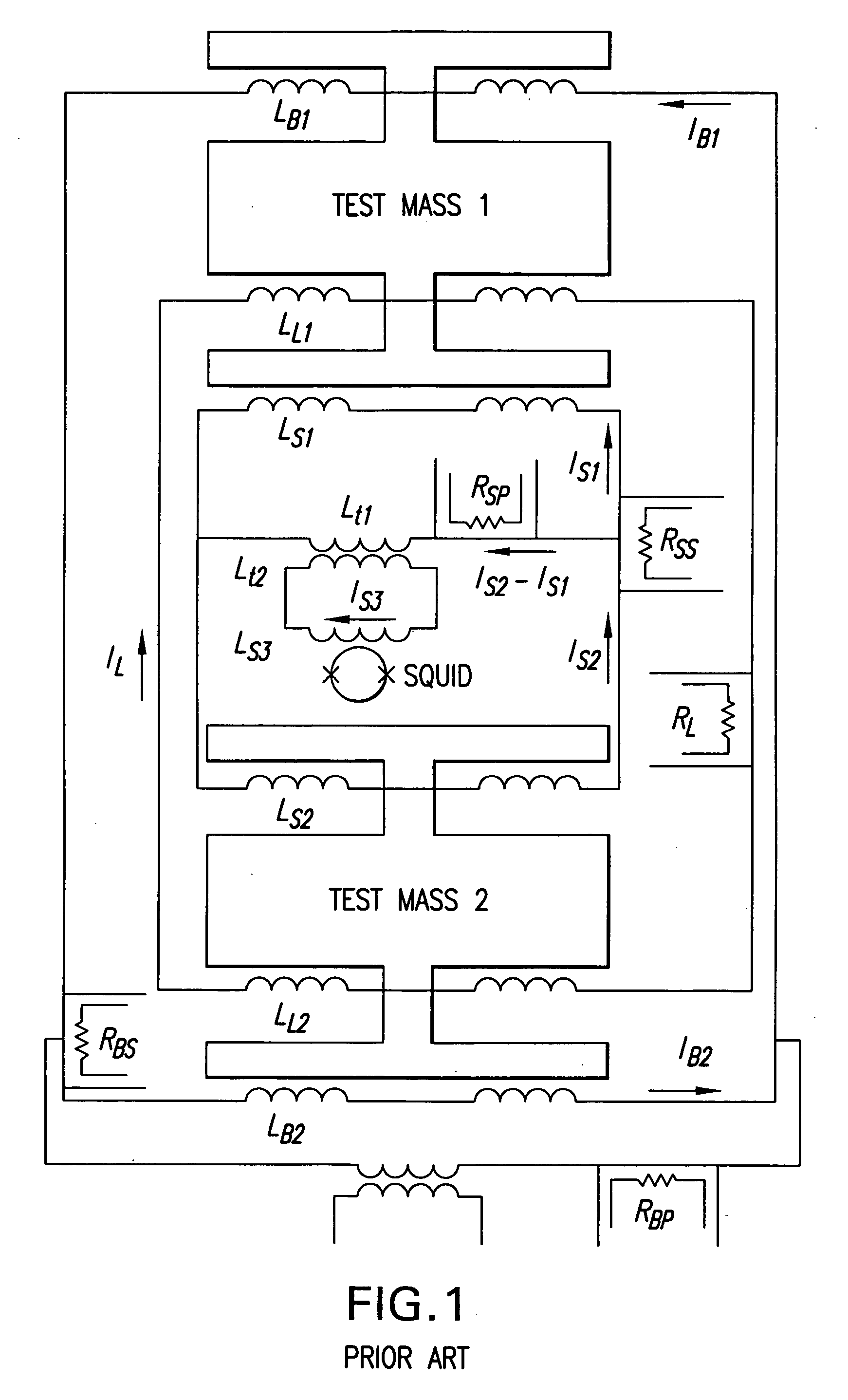
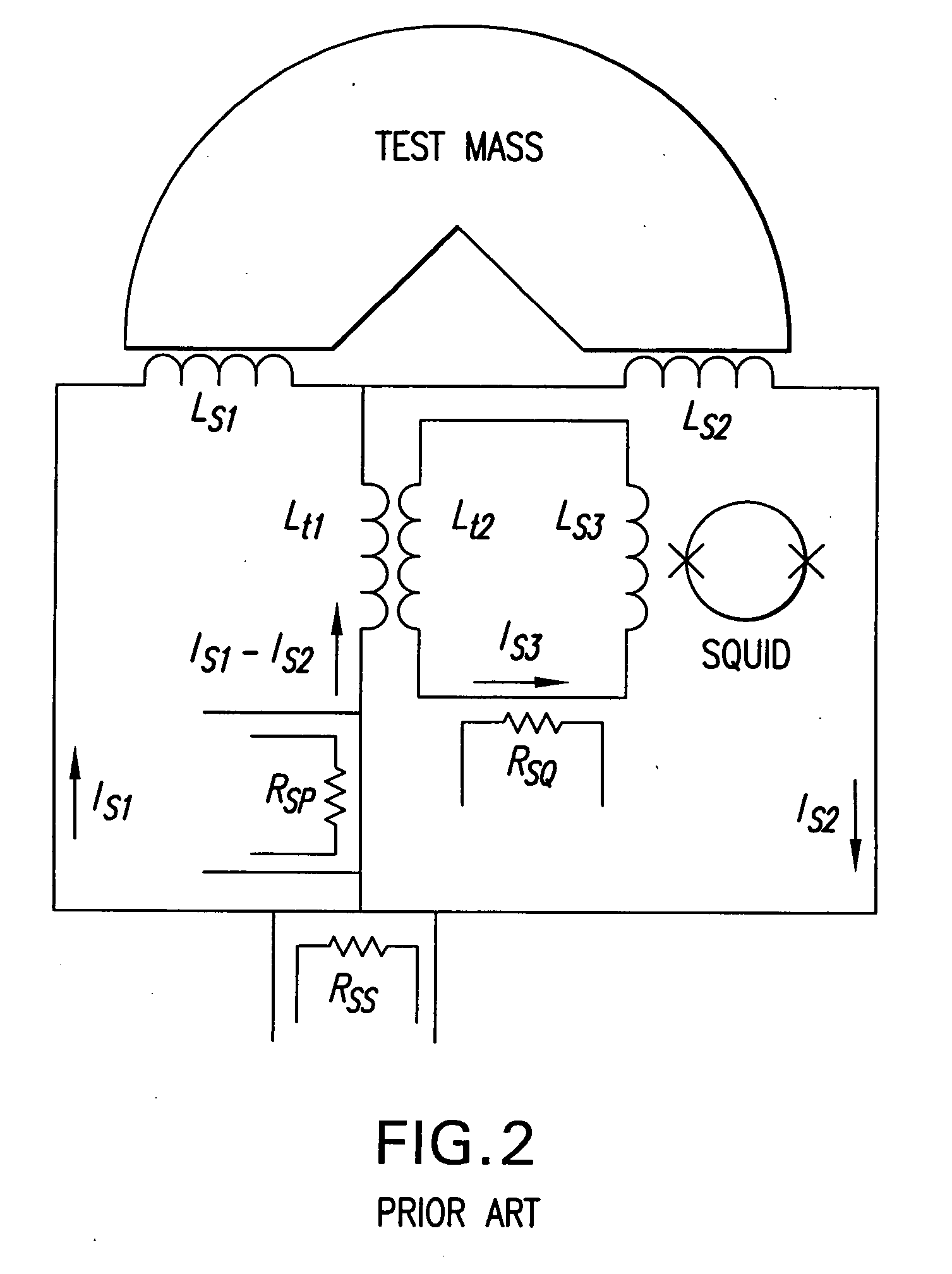
Cross-component superconducting gravity gradiometer with improved linearity and sensitivity and method for gravity gradient sensing
ActiveUS20060207326A1Improve linearityReduce sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesGravitational wave measurementAccelerometerOperability
A cross-component superconducting gravity gradiometer sensitive to off-diagonal components of the gradient tensor includes, for each gradient axis, a pair of closely matched angular accelerometers coupled by superconducting circuitry, including sensing circuits designed to minimize the sensitivity of the instrument to angular acceleration of the platform at which the angular accelerometers are mounted; and a mode-splitting circuitry designed to reduce a nonlinear coupling of angular acceleration to the output of the gravity gradiometer and to attain the operability of the instrument in a broader range in the frequency domain.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
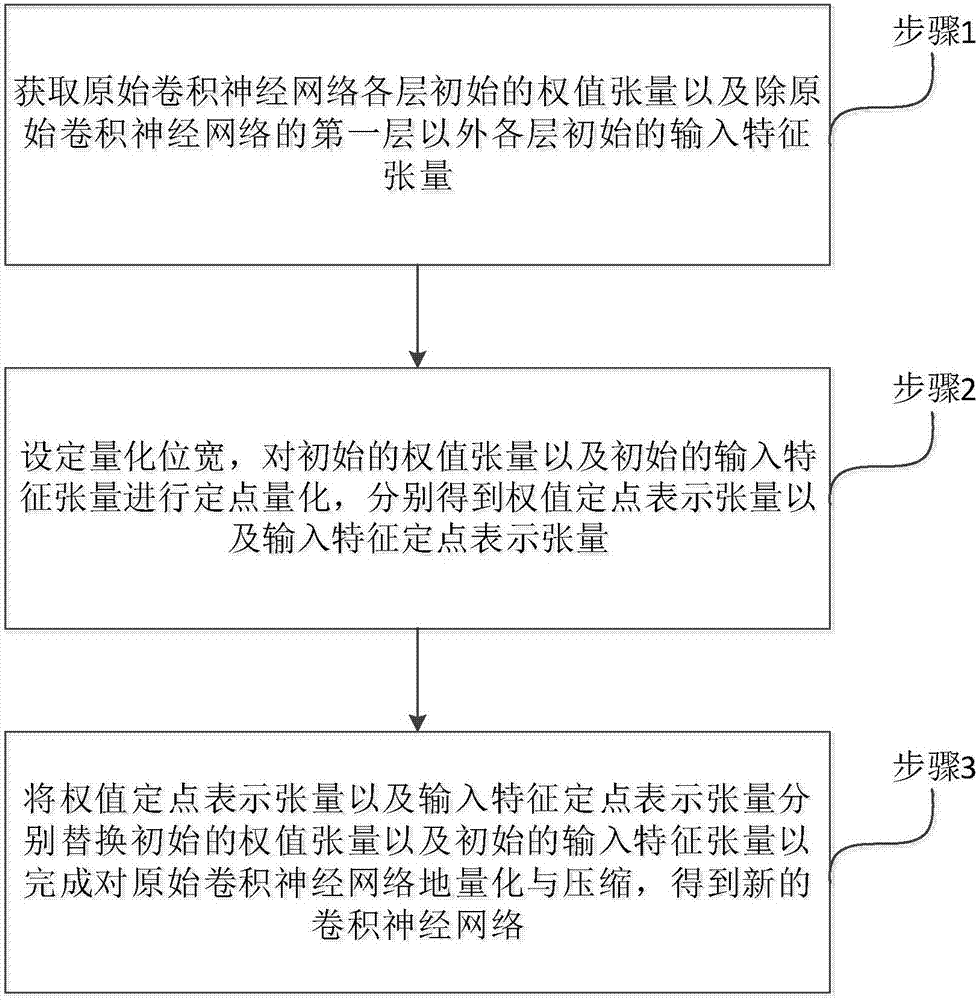
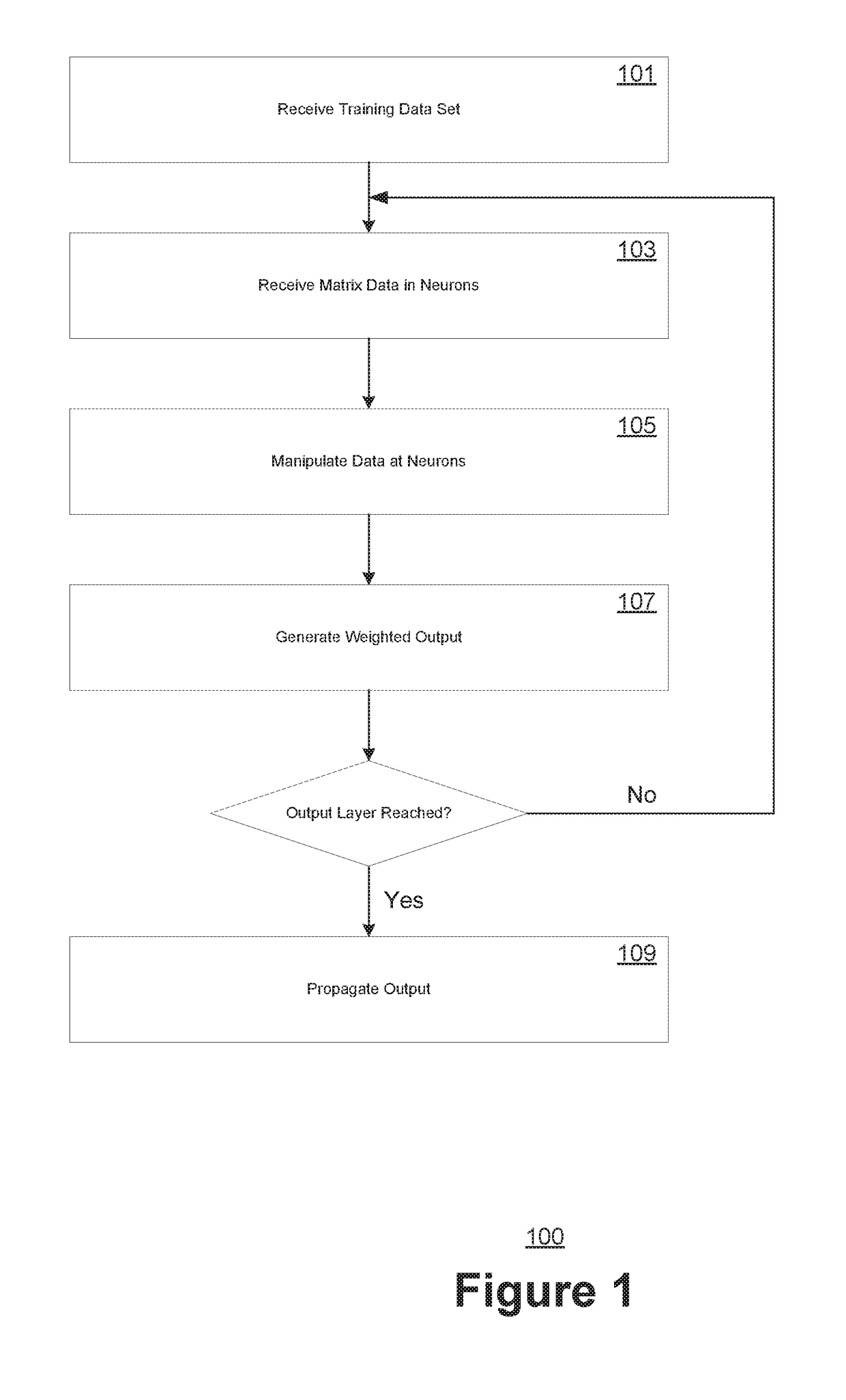
Method and apparatus for quantizing and compressing neural network with adjustable quantization bit width
ActiveCN107480770AReduce occupancyReduce transfer timeNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsNetwork structureTensor
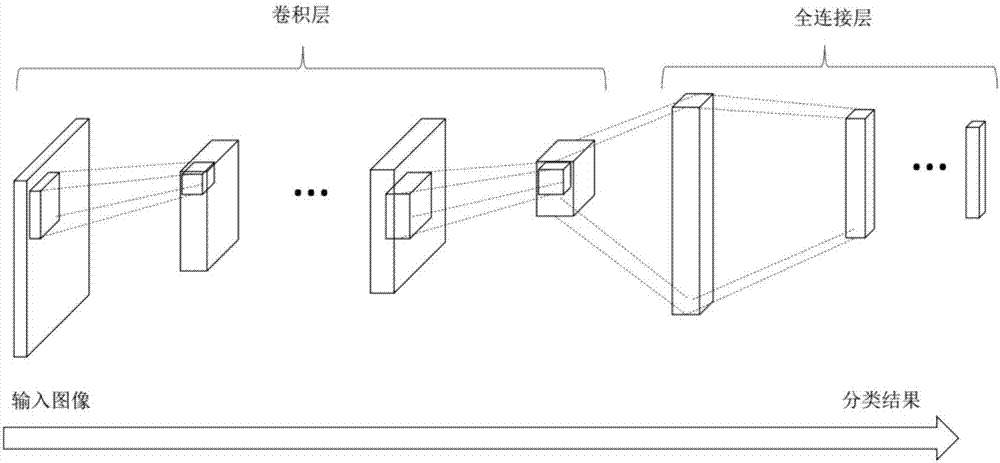
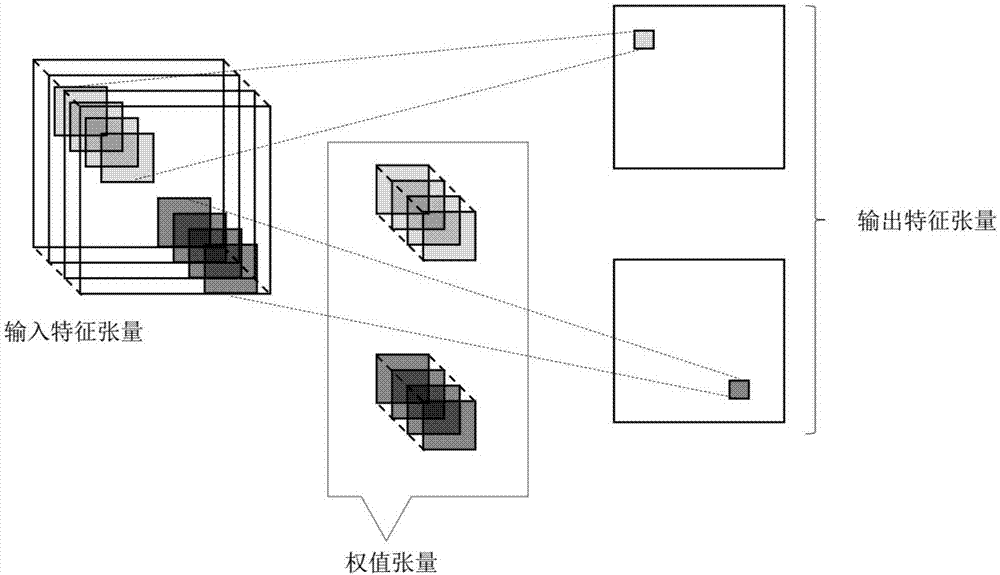
The invention relates to the technical field of neural networks, and specifically provides a method and apparatus for quantifying and compressing a convolutional neural network. The invention aims to solve the existing problem of large loss of network performance caused by an existing method for quantifying and compressing a neural network. The method of the invention comprises the steps of obtaining a weight tensor and an input eigen tensor of an original convolutional neural network; performing fixed-point quantization on the weight tensor and the input eigen tensor based on a preset quantization bit width; and replacing the original weight tensor and the input eigen tensor with the obtained weight fixed-point representation tensor and the input feature fixed-point representation tensor to obtain a new convolutional neural network after quantization and compression of the original convolutional neural network. The method of the invention can flexibly adjust the bit width according to different task requirements and can realize quantization and compression of the convolutional neural network without adjusting the algorithm structure and the network structure so as to reduce the occupation of memory and storage resources. The invention further provides a storage apparatus and a processing apparatus, which have the above beneficial effects.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
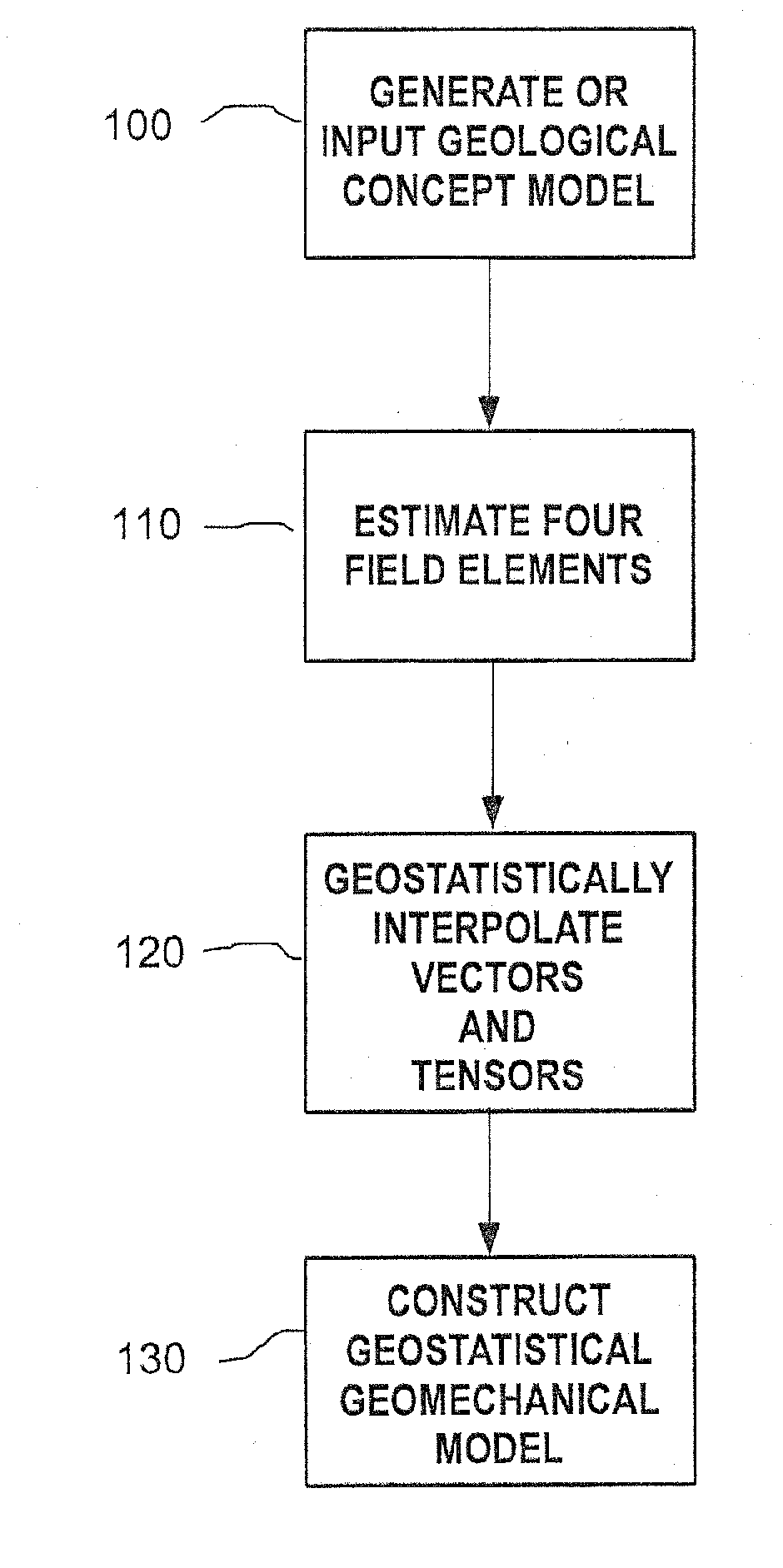
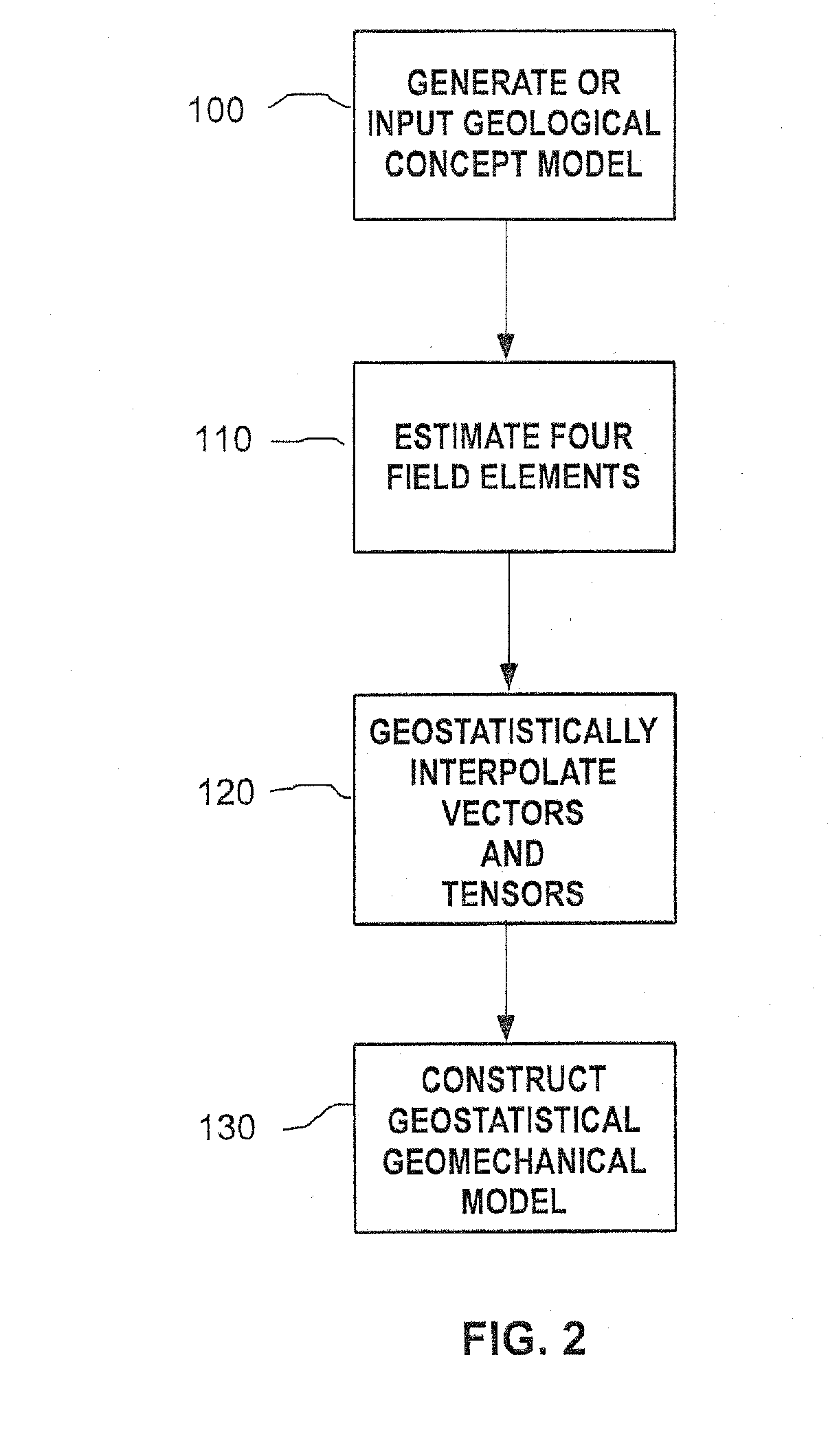
Methods and systems for constructing and using a subterranean geomechanics model spanning local to zonal scale in complex geological environments
ActiveUS20100121623A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingGeomodellingSoil scienceSubsurface geology
In an exemplary embodiment, a method and system is disclosed for developing a subterranean geomechanics model of a complex geological environment. The method can include estimating a pore pressure field, a stress field, a geomechanics property field, and a geological structure field from a geological concept model; geostatistically interpolating vectors and tensors from the estimated fields; and combining the results from the estimated fields and the geostatistically interpolated vectors and tensors to derive a geostatistical geomechanical model of the geological environment.
Owner:YOWAREN ELAN
Tensor for use in surgical navigation
A tensor for use with a surgical navigation system is provided. The tensor comprises a first bone engaging member engageable with a first bone and a second bone engaging member engageable with a second bone. A force-applying mechanism is configured to forcibly move the first and second bone engaging members relative to one another and a sensor detects the value of the force applied by the force-applying mechanism. A transmitter communicates a parameter associated with the tensor to the surgical navigation system.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Encoding and error suppression for superconducting quantum computers
The present invention involves a quantum computing structure, comprising: one or more logical qubits, which is encoded into a plurality of superconducting qubits; and each of the logical qubits comprises at least one operating qubit and at least one ancilla qubit. Also provided is a method of quantum computing, comprising: performing encoded quantum computing operations with logical qubits that are encoded into superconducting operating qubits and superconducting ancilla qubits. The present invention further involves a method of error correction for a quantum computing structure comprising: presenting a plurality of logical qubits, each of which comprises an operating physical qubit and an ancilla physical qubit, wherein the logical states of the plurality of logical qubits are formed from a tensor product of the states of the operating and ancilla qubits; and wherein the states of the ancilla physical qubits are suppressed; and applying strong pulses to the grouping of logical qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC +1
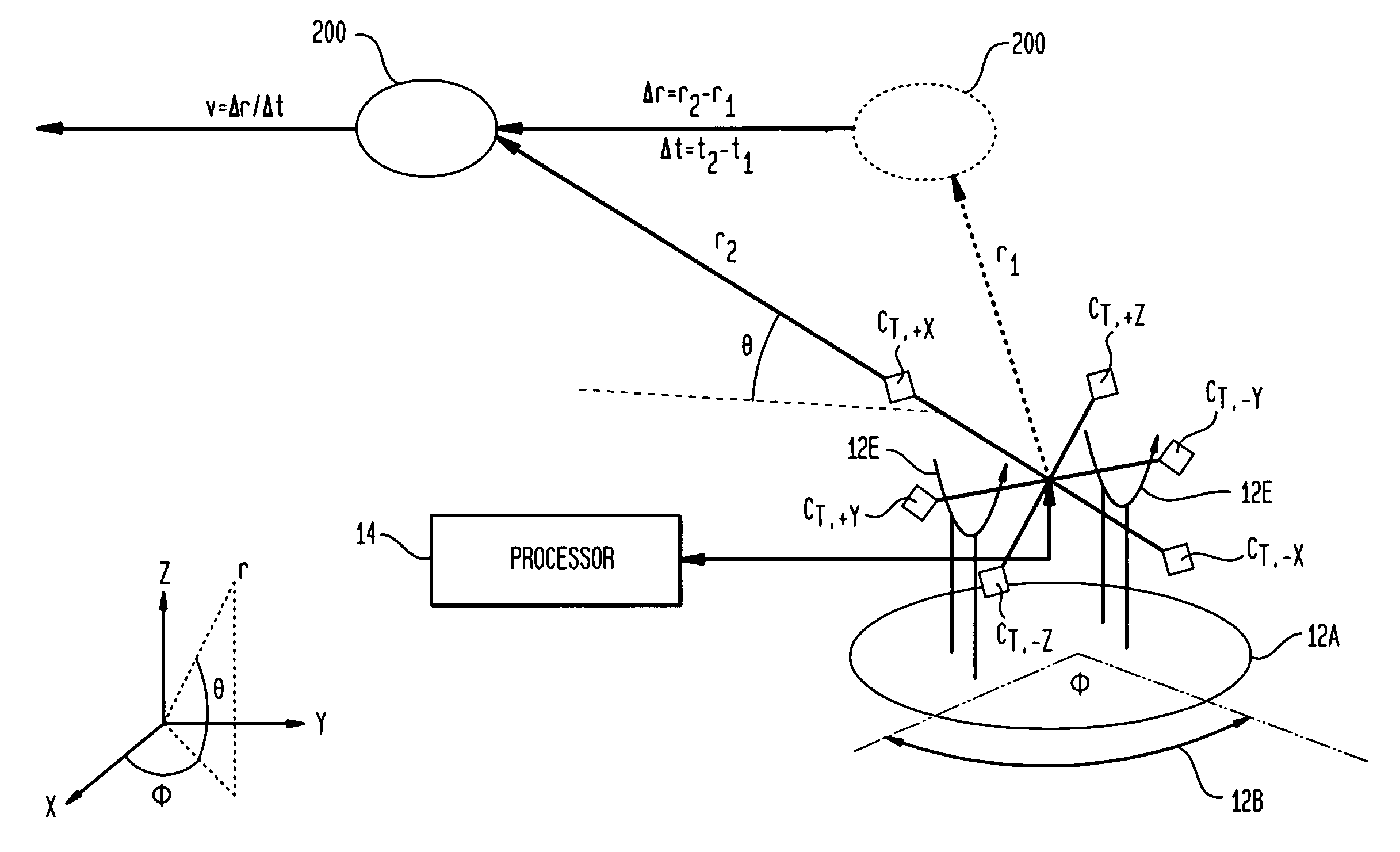
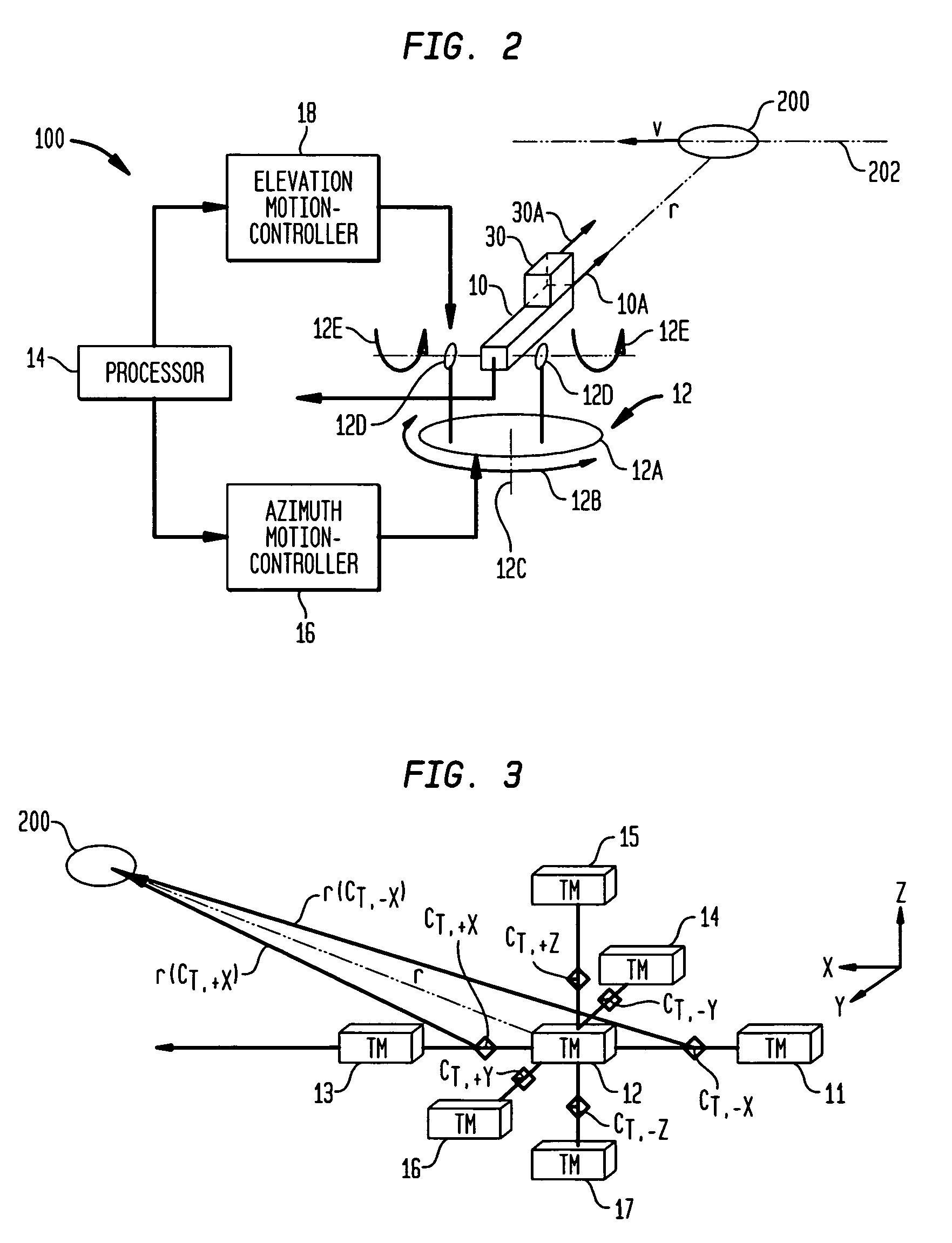
Magnetic anomaly sensing-based system for tracking a moving magnetic target
InactiveUS7342399B1Accurately determineUsing electrical meansDevices using time traversedMagnetic gradientSystem usage
A system for tracking a moving magnetic target uses a magnetic anomaly sensing system to continually determine magnetic gradient tensors associated with the target and converts the magnetic gradient tensors to gradient contraction scalars. A processor uses the magnetic gradient tensors and gradient contraction scalars to determine a minimum of bearing and range to the target. A velocity of the target is determined using the determined bearing and range at two points in time as the target is moving. To continually track with the moving target, the processor determines adjustments in elevation and azimuth using the magnetic gradient tensors and gradient contraction scalars along with bearing, range and determined velocities of the target. The processor can include a routine that determines range while accounting for asphericity errors introduced by the aspherical nature of constant magnetic gradient contours associated with the target.
Owner:NAVY USA AS REPRESENED BY THE SEC OF THE
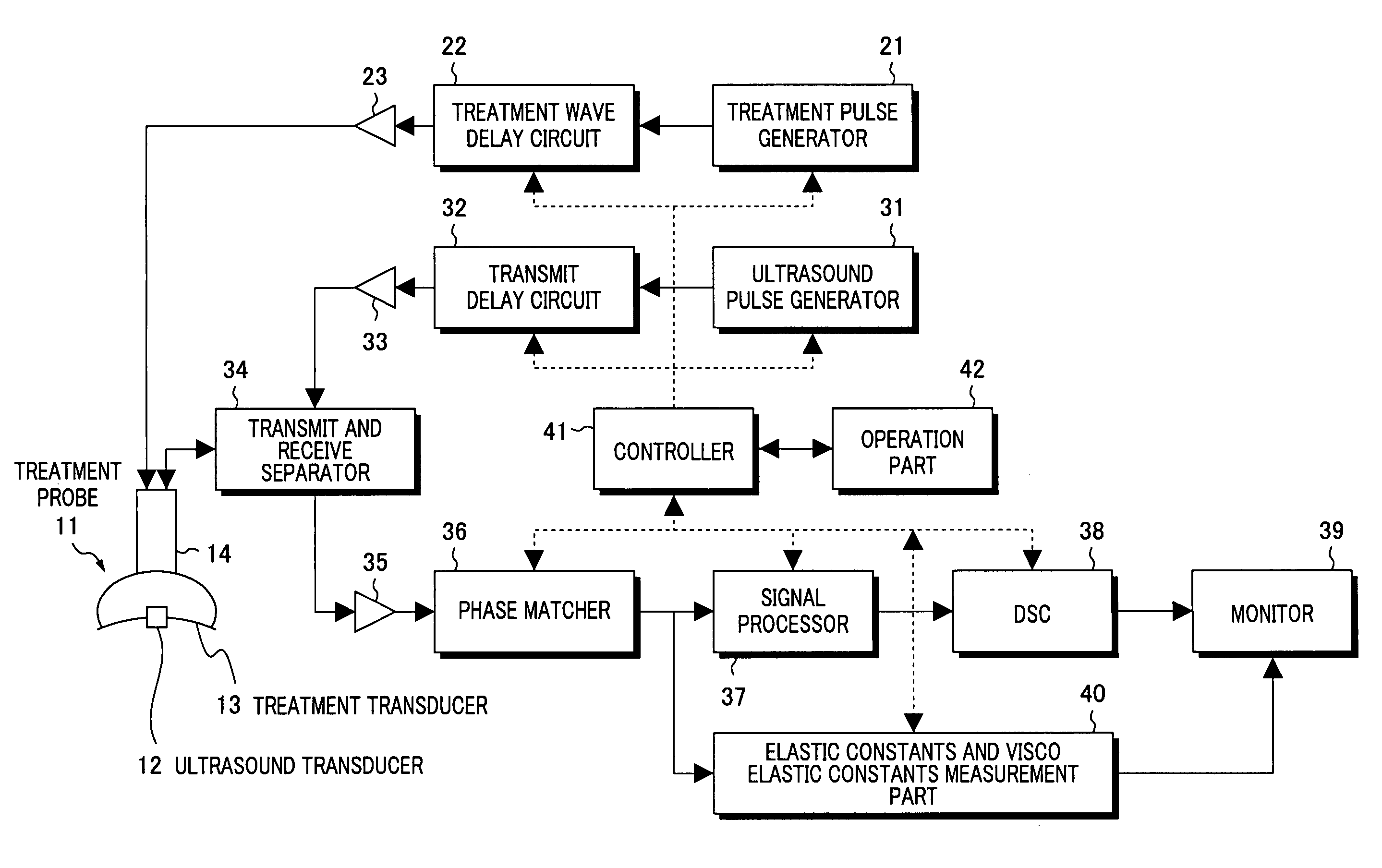
Clinical apparatuses
ActiveUS20060173319A1High measurement accuracySimple calculationDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionShear modulusEngineering
Owner:SUMI CHIKAYOSHI
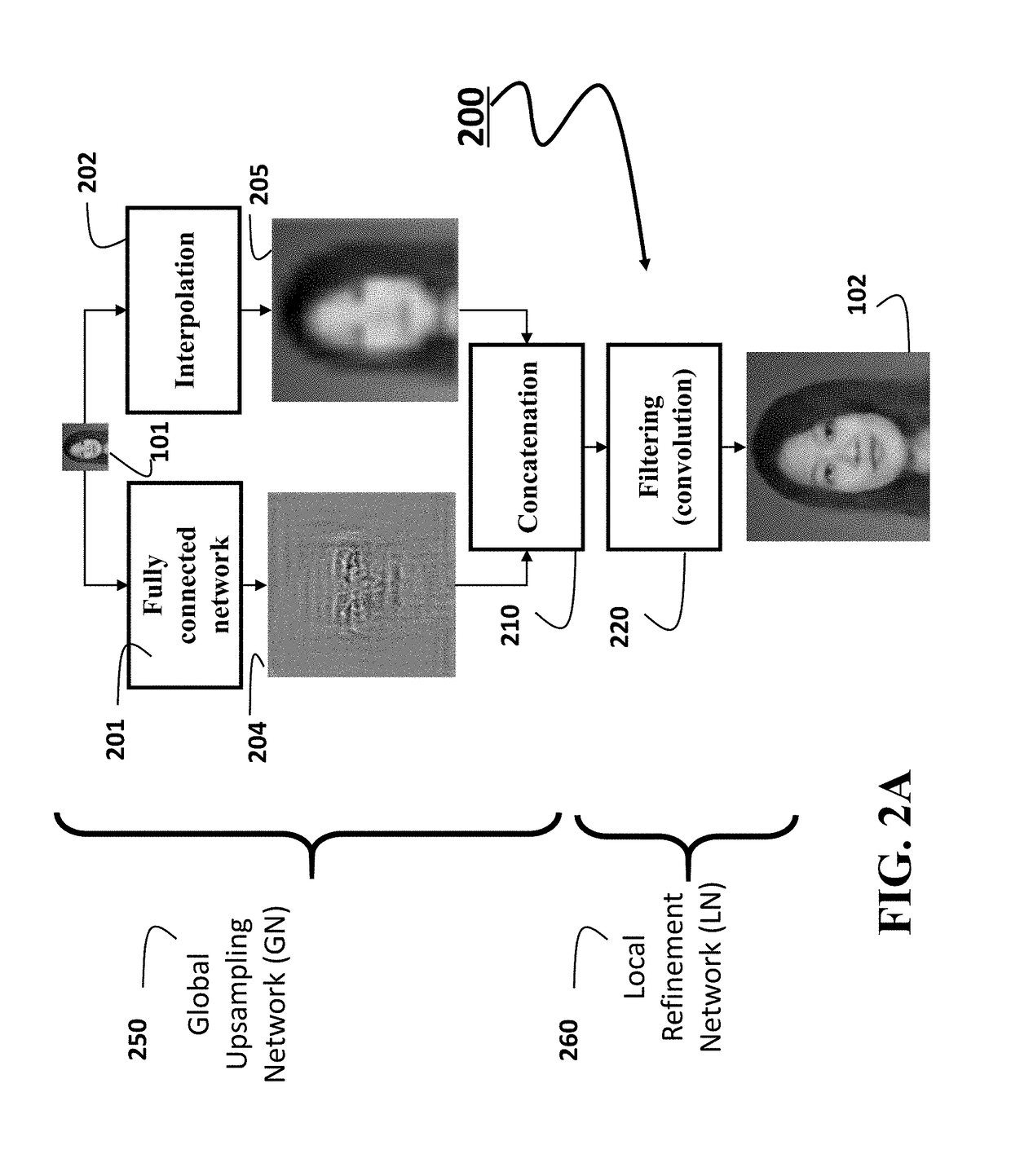
Image Upsampling using Global and Local Constraints
ActiveUS20170256033A1Accurate recoveryHigh-resolution imageImage enhancementImage analysisTensorConvolution
A method upsamples an image using a non-linear fully connected neural network to produce only global details of an upsampled image and interpolates the image to produce a smooth upsampled image. The method concatenates the global details and the smooth upsampled image into a tensor and applies a sequence of nonlinear convolutions to the tensor using a convolutional neural network to produce the upsampled image.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
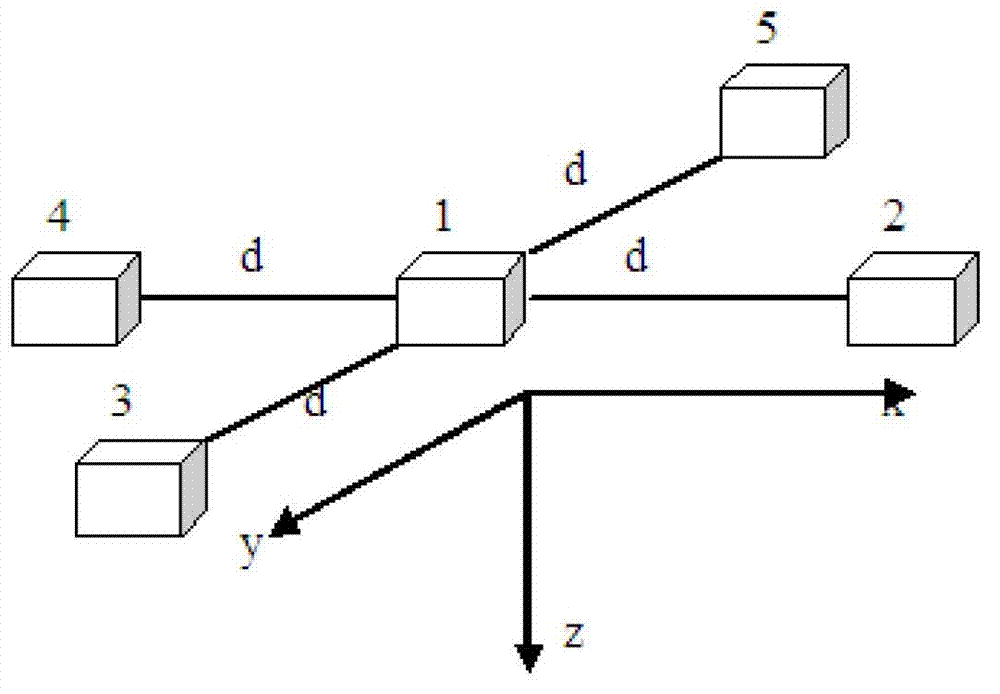
Method of locating magnetic target based on tri-axial vector magnetic sensor array
InactiveCN102927981AThe positioning method is simpleThe positioning method is practicalNavigation instrumentsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientSensor array
The invention discloses a method of locating a magnetic target based on a tri-axial vector magnetic sensor array. According to the method, the magnetic target is located by a magnetic gradient tensor measuring array formed by five tri-axial vector magnetic sensors at high locating precision. The specific scheme of the method comprises the following steps of: at first, measuring the magnetic gradient tensor of any point on the periphery of the magnetic target by utilizing the magnetic gradient tensor measuring array; secondly, resolving a relative distance between the magnetic target and the magnetic measuring array and relative coordinates by utilizing the magnetic tensor; and at last, locating the magnetic target according to the resolved relative distance and the relative position coordinates. The locating method has the advantages of simplicity, practicability and high locating precision.
Owner:710TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
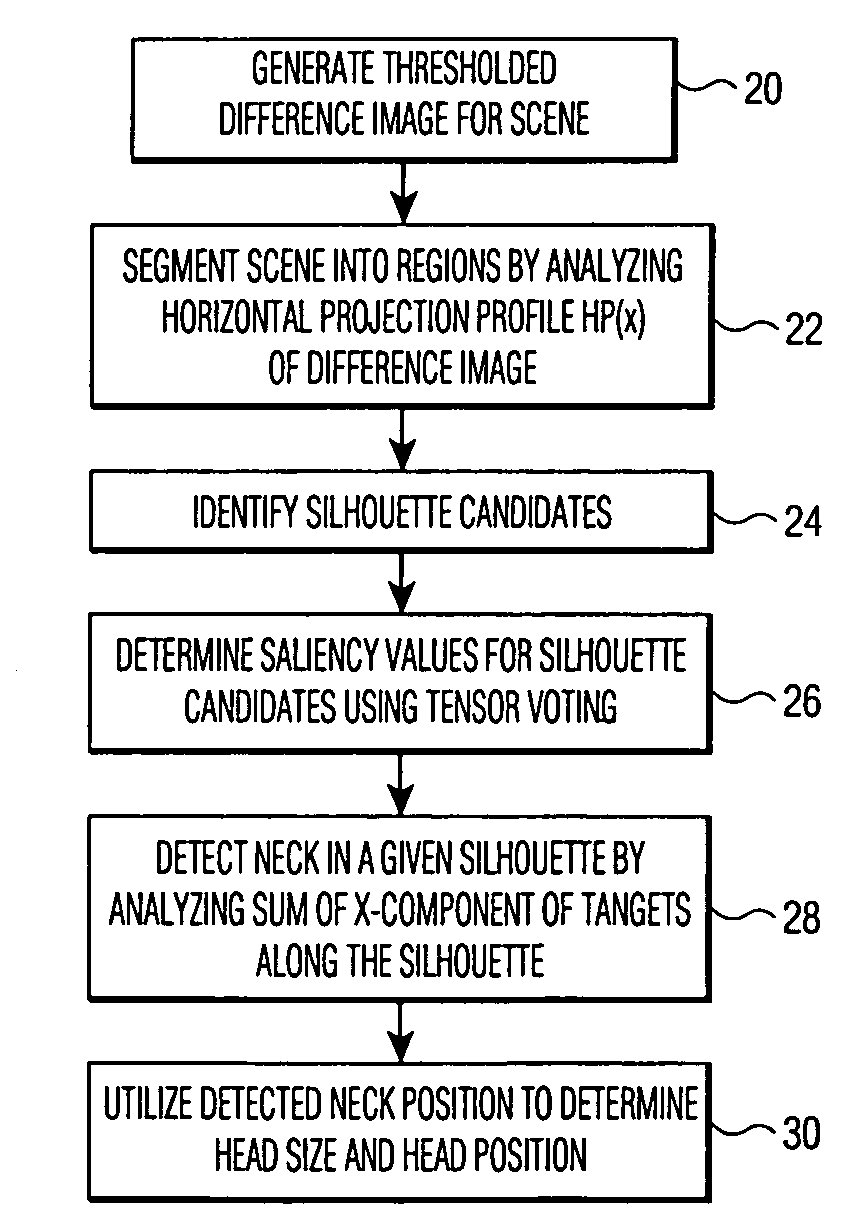
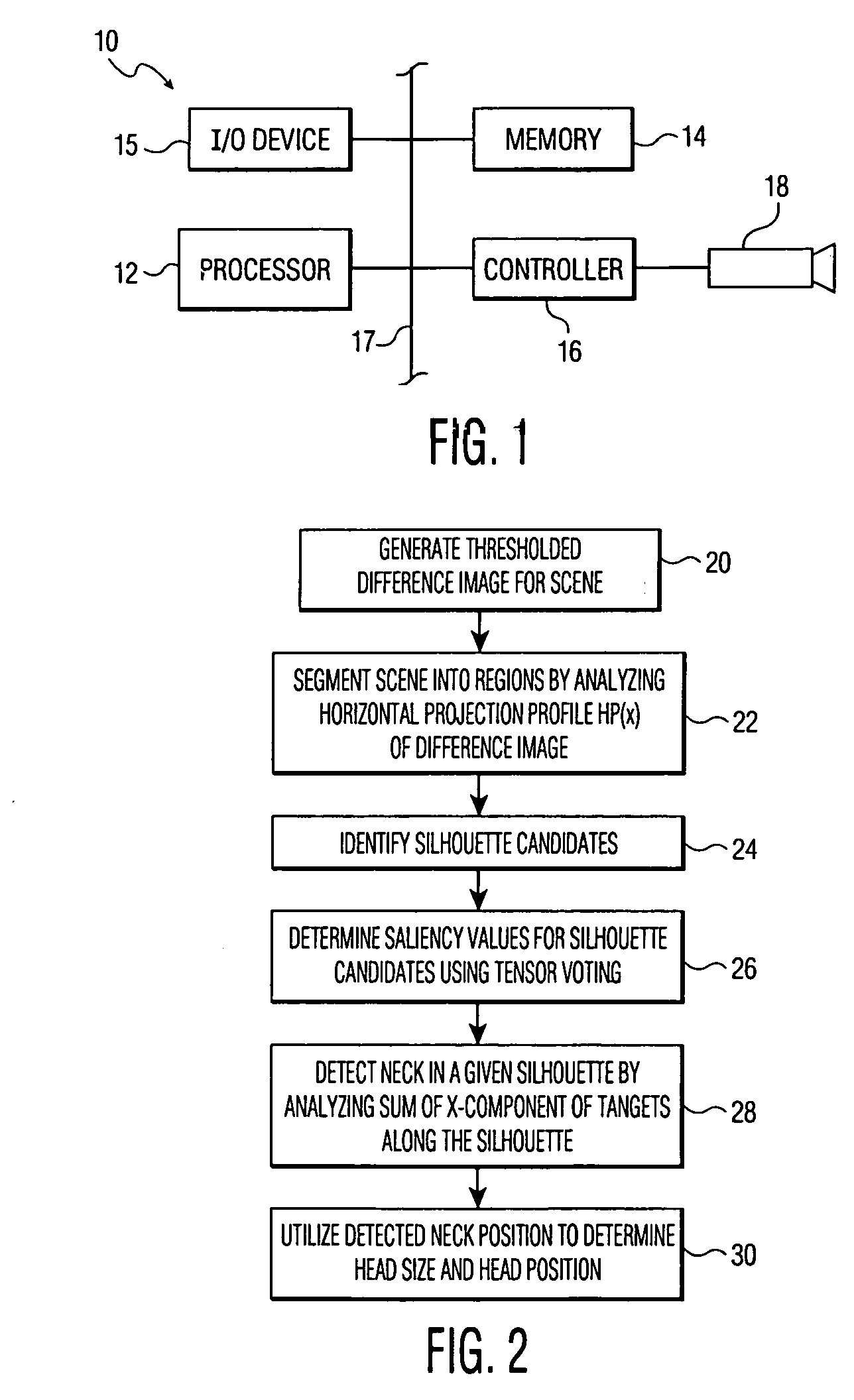
Method and apparatus for detecting moving objects in video conferencing and other applications
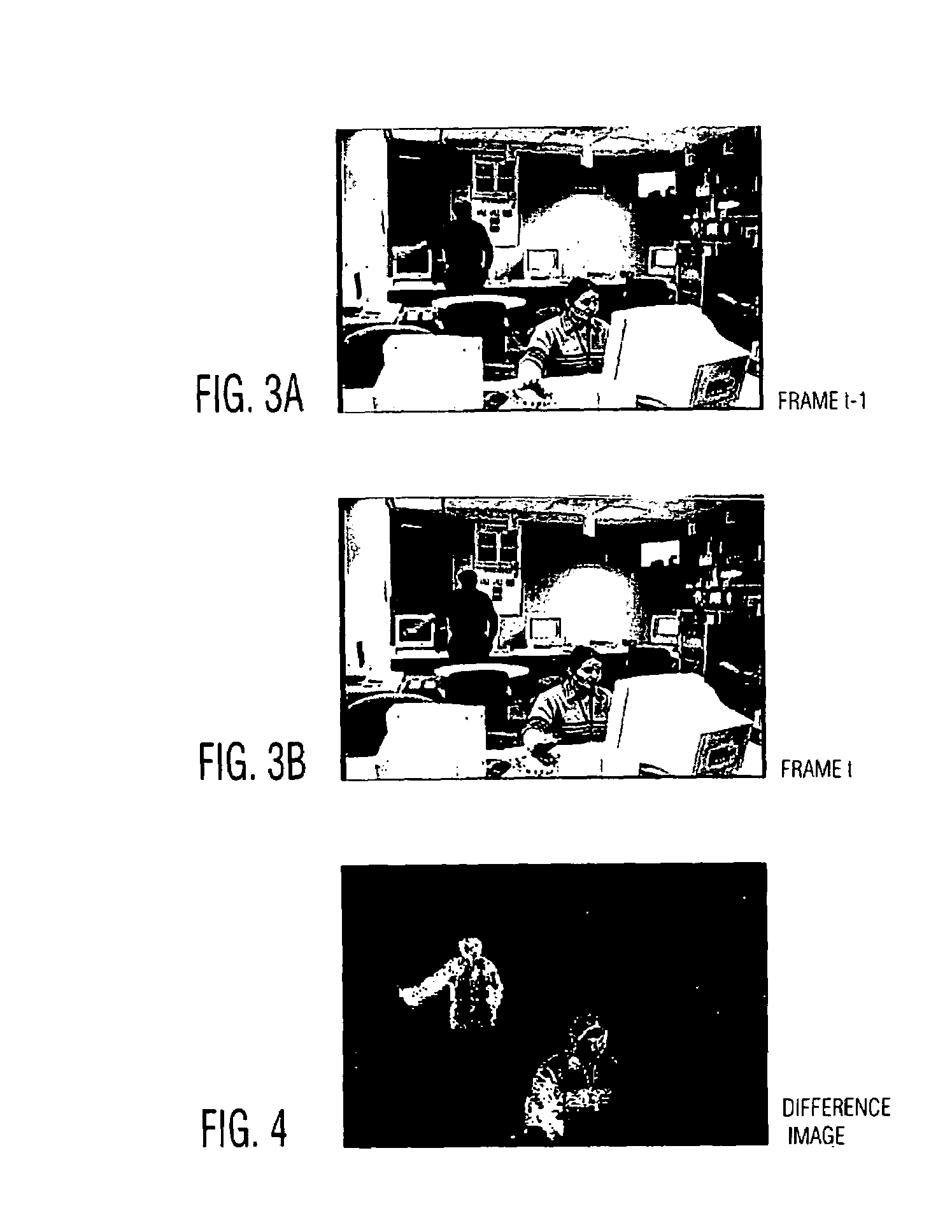
InactiveUS7123745B1Noise robustLess computationally expensiveImage enhancementTelevision system detailsHead sizeImaging processing
An image processing system detects a moving person or other object of interest. The system generates a thresholded difference image by processing a video signal or other type of image signal received from a camera. The difference image is then segmented into regions bounded by vertical lines passing through the image, and silhouette candidates are identified in one or more of the regions. Tensor voting is used to determine saliency values and corresponding tangents for each of the silhouette candidates, and the resulting values and tangents are used to detect the object of interest. In an embodiment in which the object of interest is a moving person, a neck position of the moving person may be detected by analyzing a sum of x-components of tangents along a corresponding silhouette. The detected neck position may then be utilized to determine a head position and a head size for the moving person.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Determining Properties of Earth Formations Using the Electromagnetic Coupling Tensor
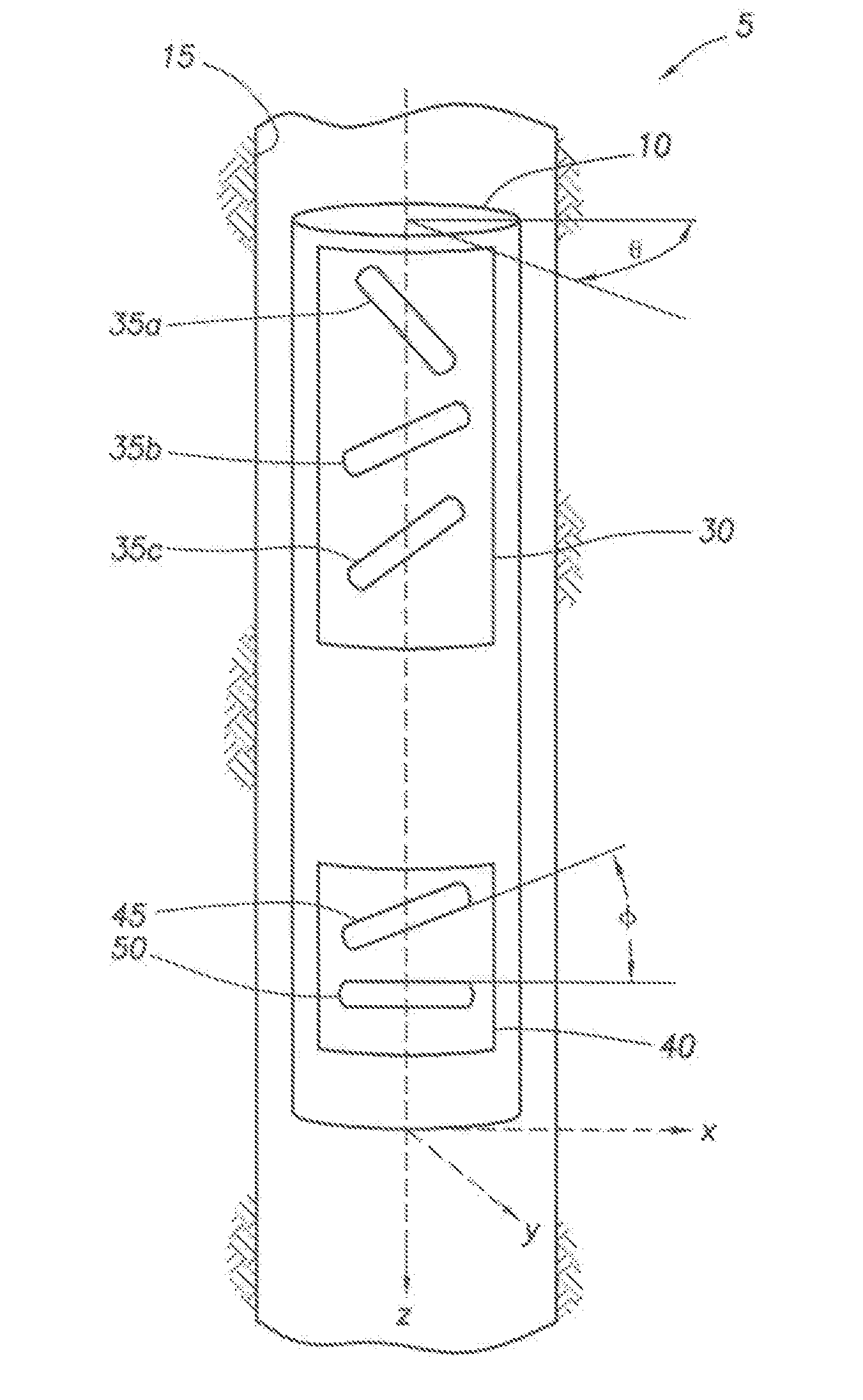
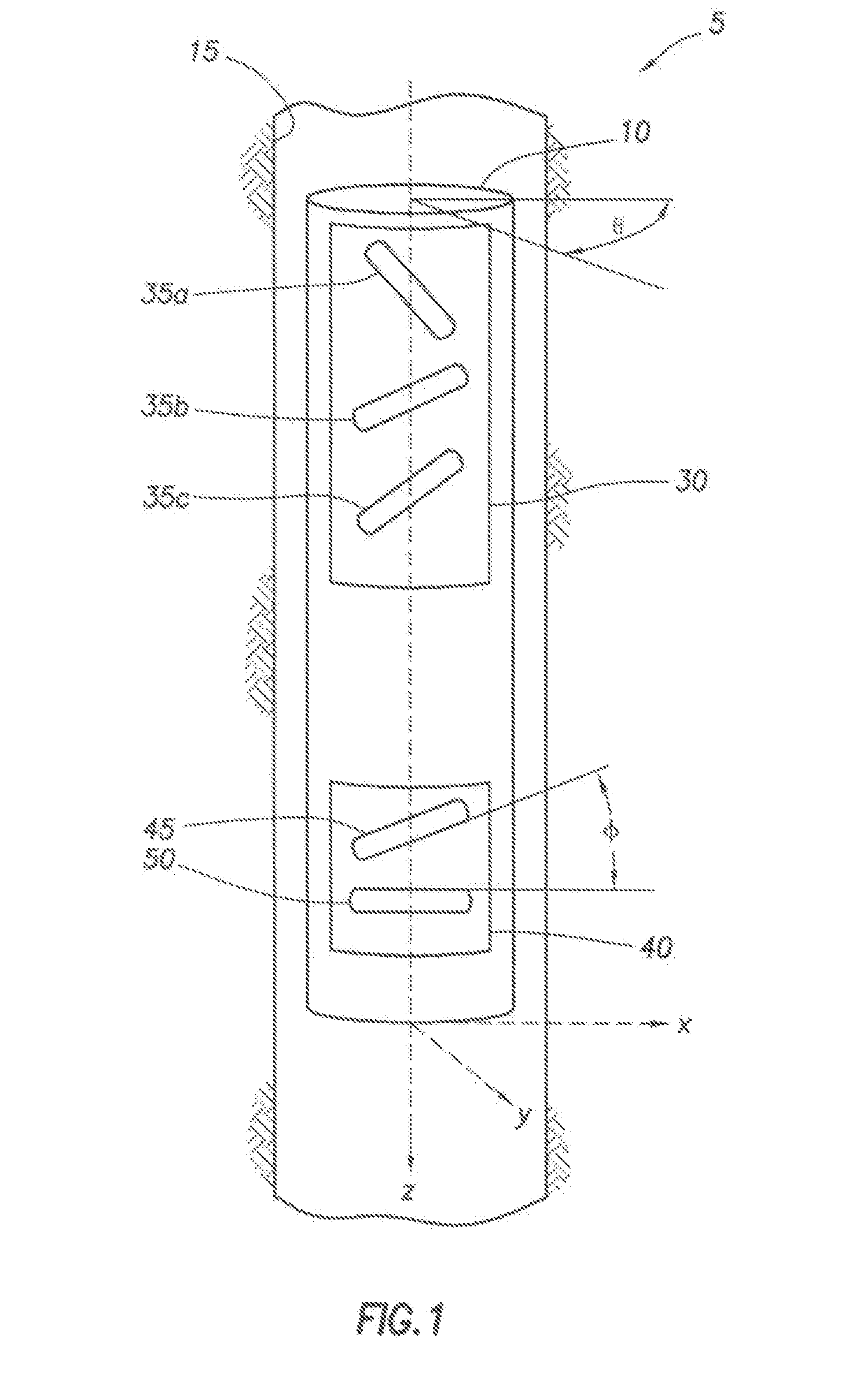
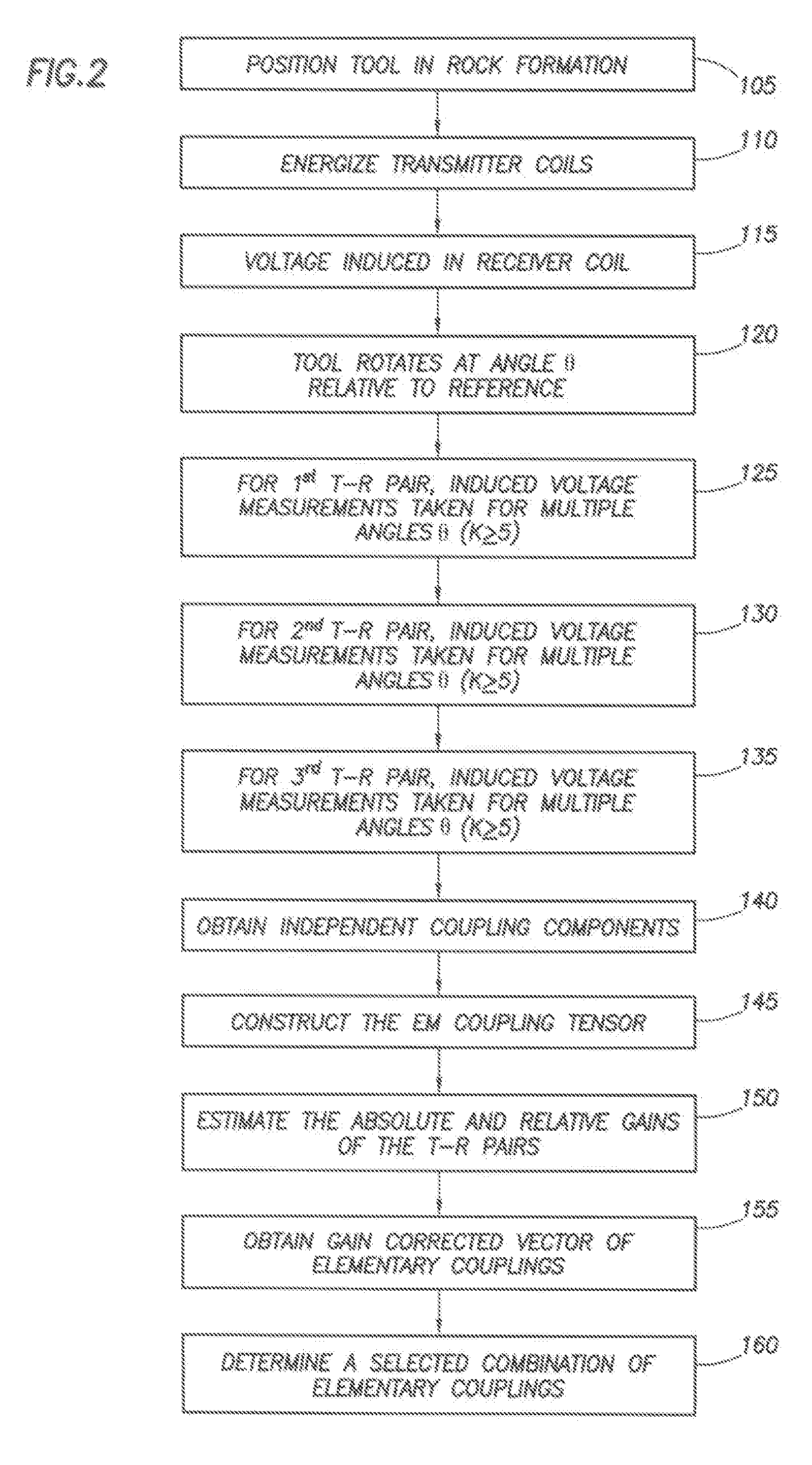
ActiveUS20080143336A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationElectromagnetic couplingReceiver coil
A system and method to determine earth formation properties by positioning a logging tool within a wellbore in the earth formation, the logging tool having a tool rotation axis and a first, a second, and a third tilted transmitter coil, and a tilted receiver coil; rotating the logging tool about the tool rotation axis; energizing each transmitter coil; measuring a coupling signal between each transmitter coil and the receiver coil for a plurality of angles of rotation; determining a coupling tensor; and determining the earth formation properties using the coupling tensor.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Magnetic anomaly sensing system for detection, localization and classification of magnetic objects
InactiveUS6841994B1Magnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsElectric/magnetic detection for transportSystem usageMagnetic dipole
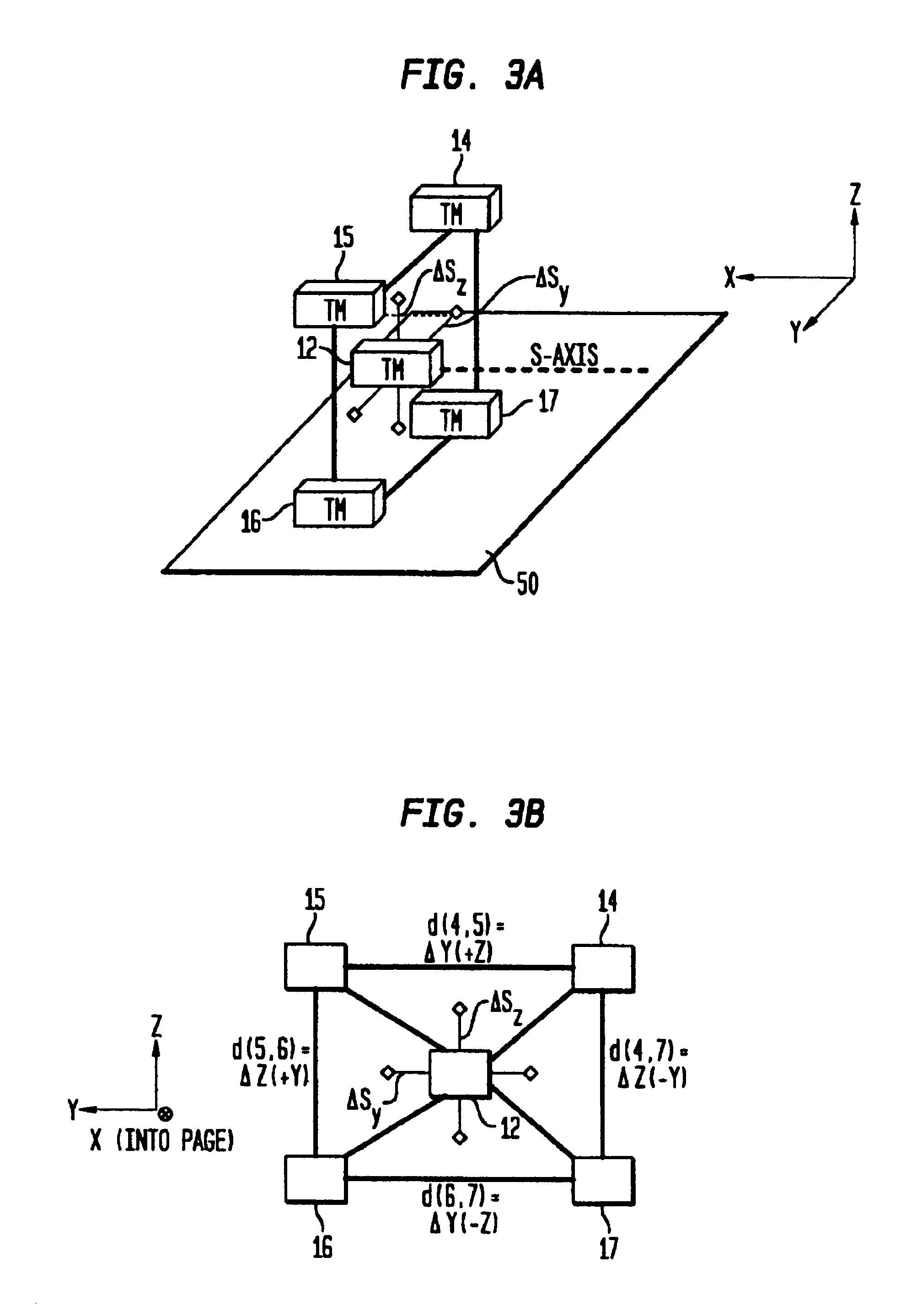
A magnetic anomaly sensing system uses triaxial magnetometer (TM) sensors arranged in a three-dimensional array. A processor coupled to the TM sensors generates partial gradient contraction data, and complete gradient tensor data and corresponding complete gradient contraction data. The generated data can be used to align the three-dimensional array with a magnetic target. Once the three-dimensional array is aligned with the magnetic target, the generated data can be used to uniquely determine (i) distance to the magnetic target, (ii) position of the magnetic target relative to the three-dimensional array, and (iii) the magnetic dipole moment of the magnetic target.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Automated generation of local grid refinement at hydraulic fractures for simulation of tight gas reservoirs
ActiveUS20130073268A1Reasonable computational complexityLow costComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationHorizontal wellsHydraulic fracturing
A computer system and method of automatically generating a Local Grid Refinement (LGR) gridded model of a gas reservoir. A geologic file includes information identifying the locations of one or more wells according to root grid cells within a volume of the earth to be modeled. User inputs specify the number of hydraulic fractures from each well, and such parameters as the fracture length, etc. User inputs also specify the number of “splits” of the root grid cells containing hydraulic fractures; those root grid cells are then split into finer resolution grid cells of increasing width within the root grid cells containing the fractures. For horizontal wells, user inputs indicate the number of splits of root grid cells containing the lateral portions of the wellbore. Non-orthogonal and complex fractures are processed by a“nested” LGR approach. Geologic properties are assigned to each grid cell, with a tensorial adjustment included for non-orthogonal fractures, and the resulting model is available for simulation.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Focal noninvasive stimulation of the sensory cortex of a subject with cerebral palsy
InactiveUS20110270345A1Restore levelRegain healthInternal electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsCerebral paralysisNon invasive
Disclosed are methods and related devices for use with subjects with cerebral palsy or periventricular leukomalacia. In preferred embodiments, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is used to identify neural areas and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is used to stimulate neural pathways.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Image processing apparatus and method, data processing apparatus and method, and program and recording medium
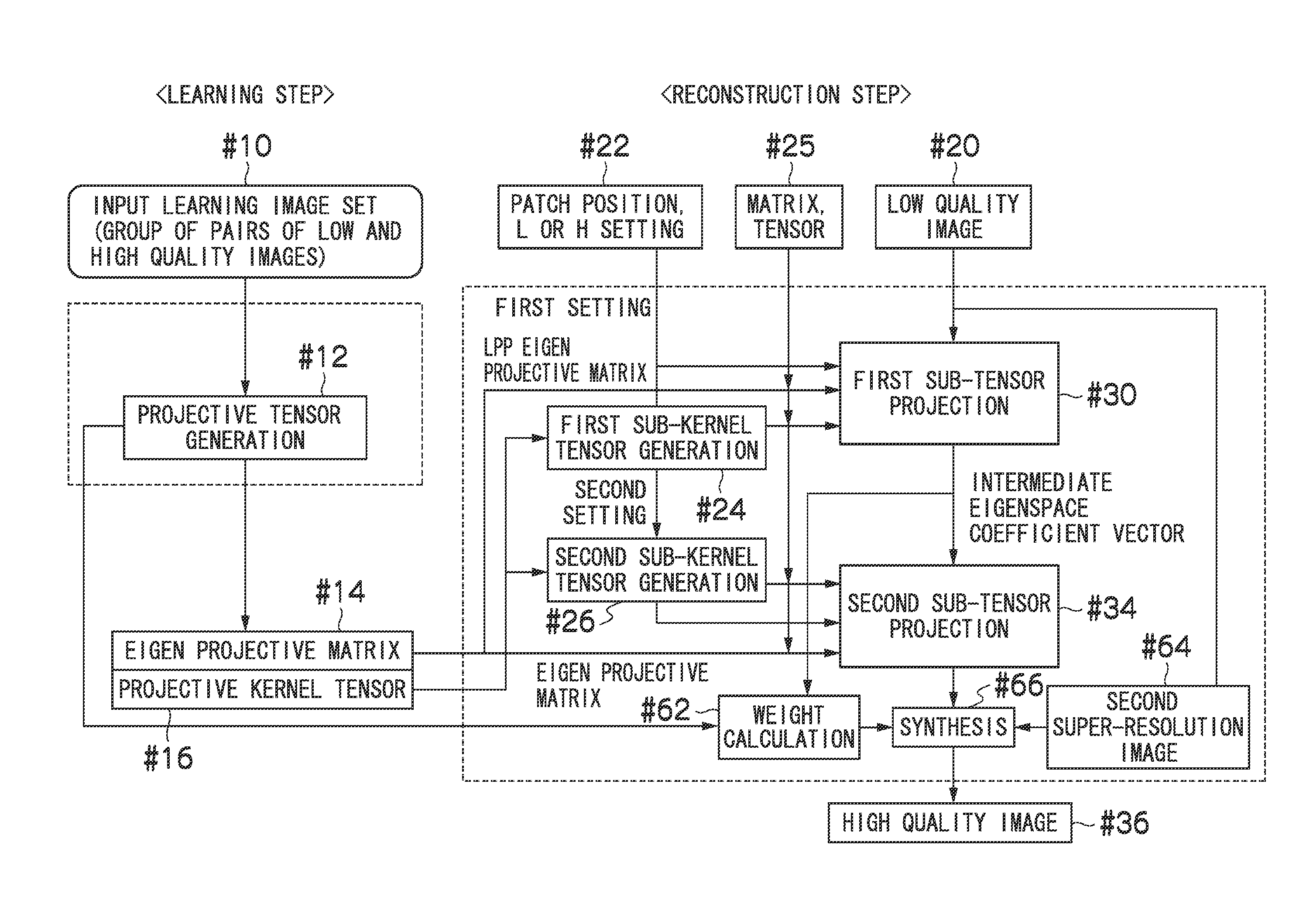
InactiveUS20110026849A1Satisfactory reconstruction imageInhibit deteriorationGeometric image transformationAcquiring/recognising facial featuresImaging processingWeight coefficient
The present invention determines the adopting ratio (weight coefficient) between the high image quality processing using the tensor projection method and the high image quality processing using another method according to the degree of deviation of the input condition of the input image, and combines these processes as appropriate. This allows a satisfactory reconstruction image to be acquired even in a case of deviation from the input condition, and avoids deterioration of the high quality image due to deterioration of the reconstruction image by the projective operation.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
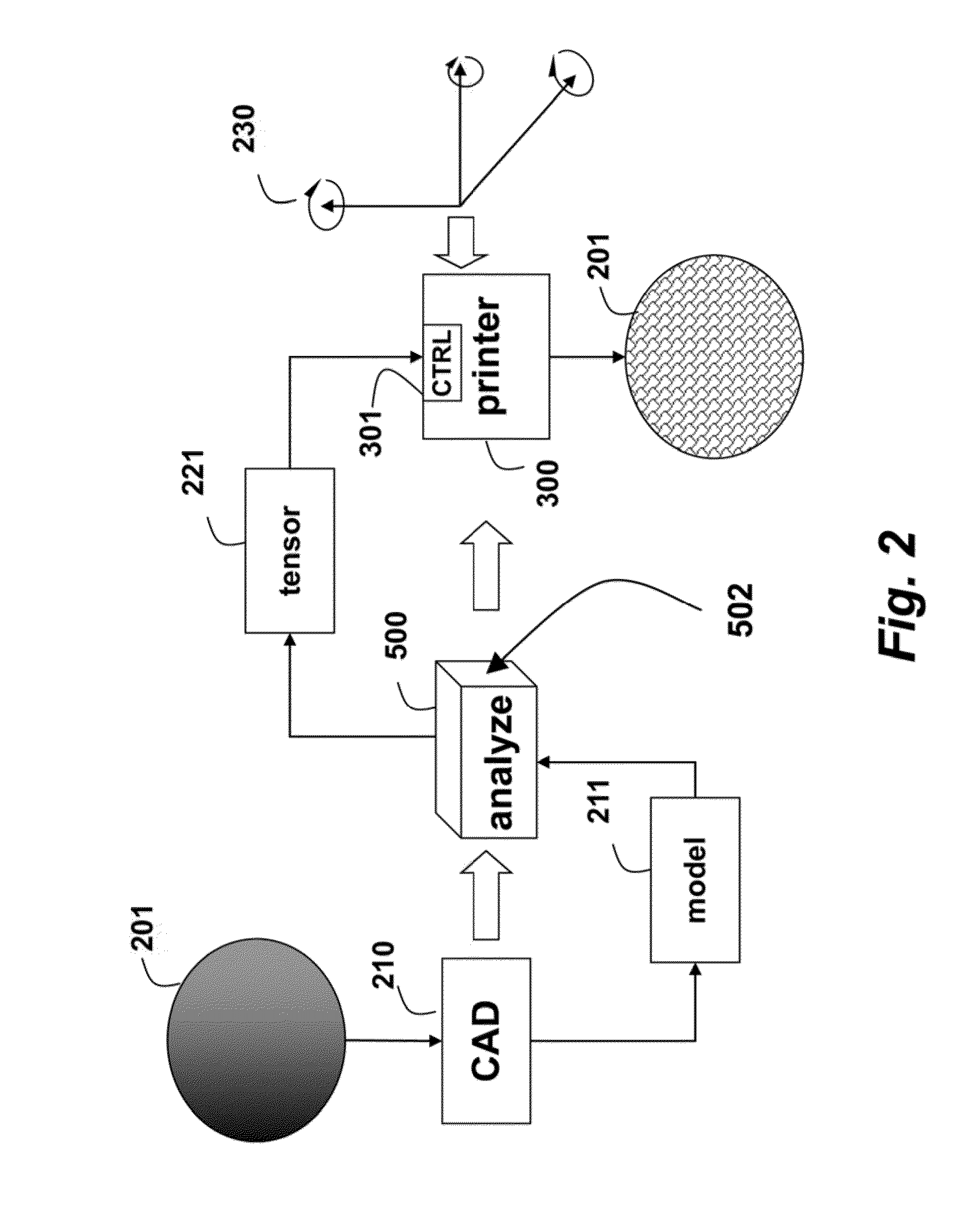
Method and Apparatus for Additively Manufacturing of Objects Based on Tensile Strength
InactiveUS20150021832A1High tensile strengthCeramic shaping apparatusMechanical vibrations separationObject basedEngineering
A 5D printer, which additively manufactures an object, includes an extruder that can move linearly along three orthogonal axes and rotationally around at least one of the axes with respect to the object while depositing a material. A gantry is movable along X, Y and Z axes, and a trunnion table movable about A and B axes is mounted on the gantry. A platen is mounted on the trunnion table, and the extruder deposits the material on the platen while moving the gantry and trunnion table. A model of the object is analyzed to produce a stress tensor for the object, and the depositing is according, to the stress tensor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Cross-component superconducting gravity gradiometer with improved linearity and sensitivity and method for gravity gradient sensing
ActiveUS7305879B2Improve linearityReduce sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesGravitational wave measurementAccelerometerOperability
A cross-component superconducting gravity gradiometer sensitive to off-diagonal components of the gradient tensor includes, for each gradient axis, a pair of closely matched angular accelerometers coupled by superconducting circuitry, including sensing circuits designed to minimize the sensitivity of the instrument to angular acceleration of the platform at which the angular accelerometers are mounted; and a mode-splitting circuitry designed to reduce a nonlinear coupling of angular acceleration to the output of the gravity gradiometer and to attain the operability of the instrument in a broader range in the frequency domain.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
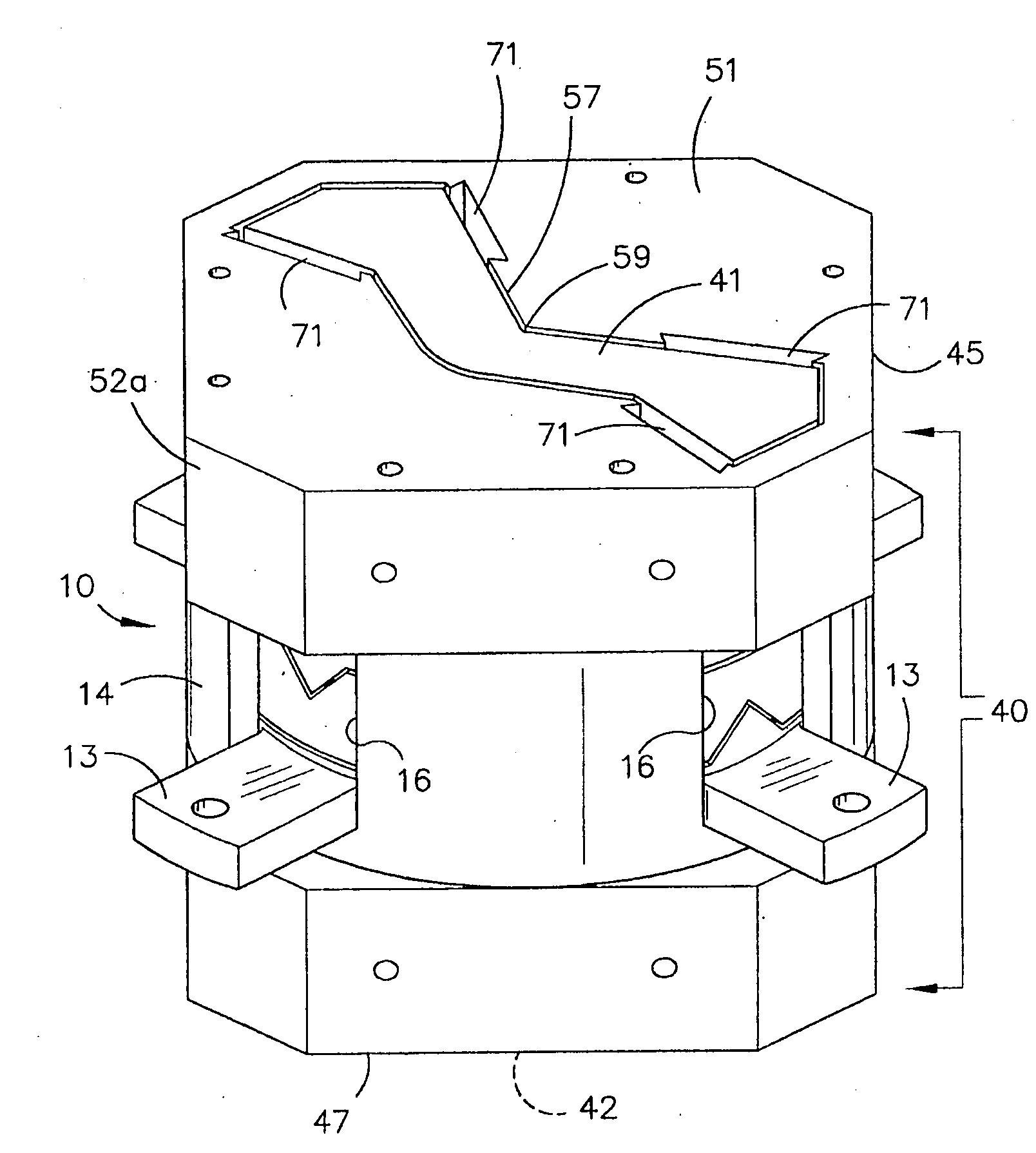
Gravity Gradiometer
InactiveUS20080122435A1Save spaceInaccurate spacingUsing electrical meansPlumb lines for surveyingTransducerEngineering
A gradiometer is disclosed which has a pair of sensor bars 41, 43 supported in housings 45, 47. Transducers 71 are located adjacent the bars 41, 43 to detect movement of the bars in response to the gravity gradient tensor. At least one of the transducers 71 comprises a first coil 510 and a second coil 516 arranged in parallel and a switch 362 for proportioning current between the coils 510 and 516 so as to create a virtual coil at a position D between the coils 510 and 516.
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
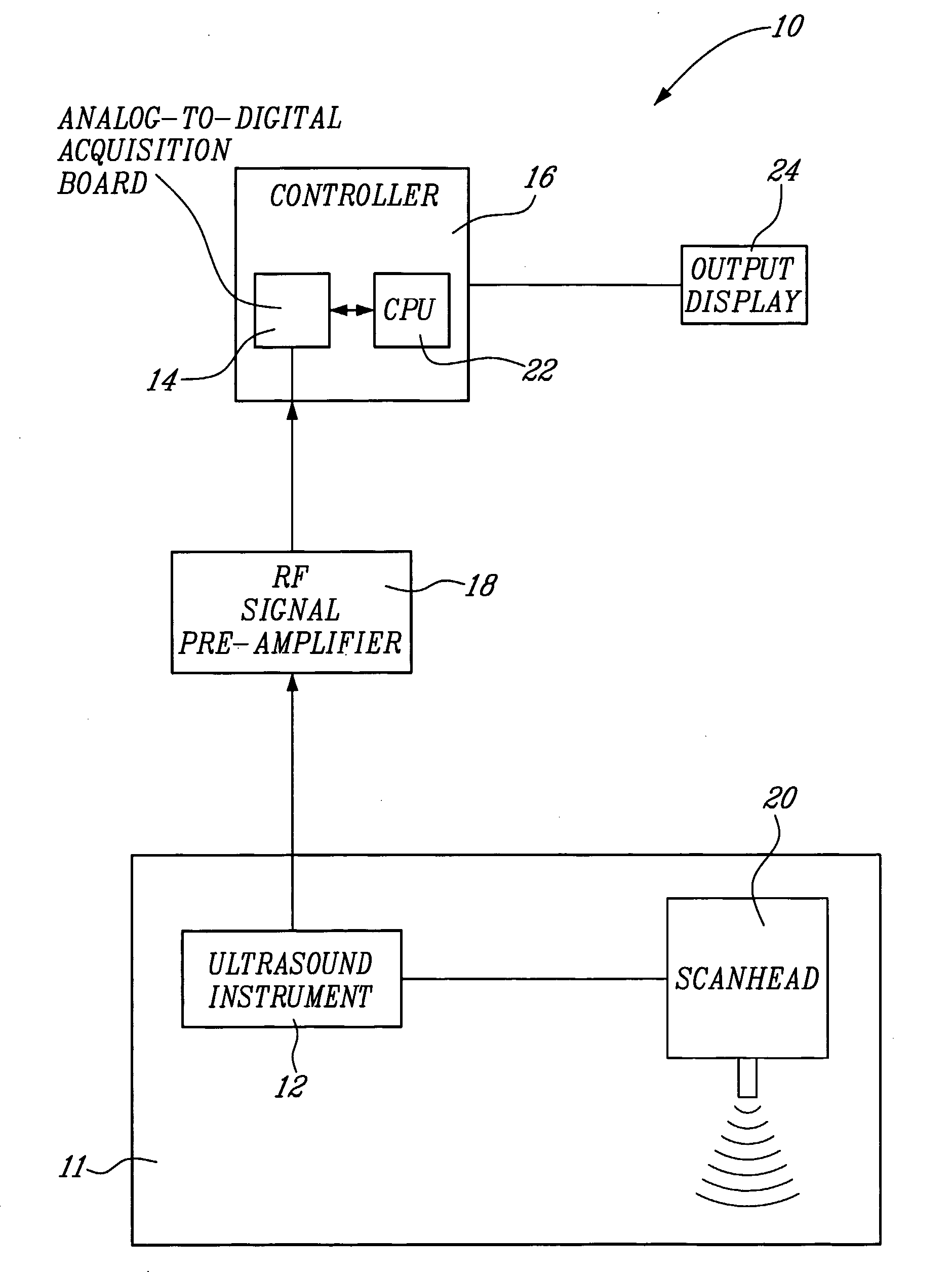
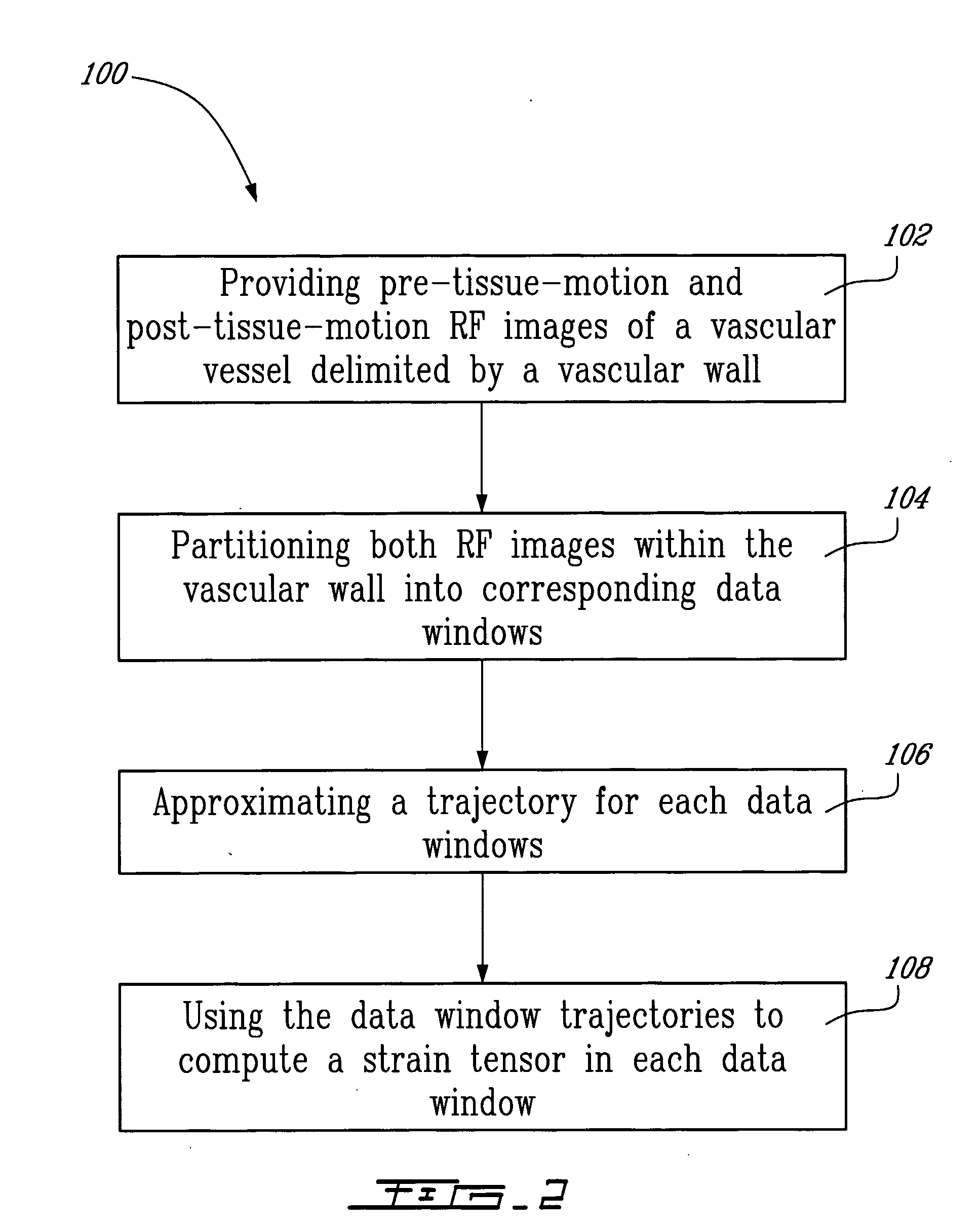
Method And System For Vascular Elastography
The method for vascular elastography comprises: i) obtaining a sequence of radio-frequency (RF) images including pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images in digital form of a vessel delimited by a vascular wall; the pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images being representative of first and second time-delayed configuration, of the whole vessel; ii) partitioning both the pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images within the vascular wall into corresponding data windows; approximating a trajectory between the pre- and post-tissue-motion for corresponding data windows; and using the trajectory for each data window to compute the full strain tensor in each data window, which allow determining the Von Mises coefficient. The method can be adapted for non-invasive vascular elastography (NIVE), for non-invasive vascular micro-elastography (MicroNIVE) on small vessels, and for endovascular elastography (EVE).
Owner:UNIV JOSEPH FOURIER +1
Method for fracture surface extraction from microseismic events cloud
InactiveUS20110029291A1SeismologyComputation using non-denominational number representationOil fieldComputer science
Embodiments of this invention relate to a method for analysing data related to subterranean formations including collecting data from microseismic observations of a subterranean formation that is stored on a device, analysing the data using a tensor voting method, and providing an estimate of a surface of a subterranean formation. Embodiments of this invention relate to a method for analysing data related to subterranean formations including collecting data from microseismic observations of a subterranean formation, analysing the data using a tensor voting method, providing an estimate of a surface of a subterranean formation, and tailoring an aspect of an oil field service in response to the estimate.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Gravity Gradiometer
A gravity gradiometer is disclosed which has a sensor in the form of bars (41 and 42) which are supported on a mounting (5) which has a first mount section (10) and a second mount section (20). A first flexure web (33) pivotally couples the first and second mount sections about a first axis. The second mount has a first part (25), a second part (26) and a third part (27). The parts (25 and 26) are connected by a second flexure web (37) and the parts (26 and 27) are connected by a third flexure web (35). The bars (41 and 42) are located in housings (45 and 47) and form a monolithic structure with the housings (45 and 47) respectively. The housings (45 and 47) are connected to opposite sides of the second mount section 20. The bars (41 and 42) are connected to their respective housings by flexure webs (59). Transducers (71) are located in proximity to the bars for detecting movement of the bars to in turn enable the gravitational gradient tensor to be measured. A calibration sensor is provided for sensing whether the masses are balanced at room temperature so the balance of the masses can be adjusted by adjustable screws to balance the masses for cryogenic operation of the gradiometer. The calibration sensor comprises a resonant circuit (400, 410) and an oscillator (414). The resonant circuit includes a capacitor (400) which is formed by part of the sensor mass and a space plate (405).
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Gravity Gradiometer
ActiveUS20080115376A1Promote sportsAcceleration measurementPlumb lines for surveyingCouplingGradiometer
The present invention provides a gravity gradiometer for measuring components of the gravity gradient tensor. The gravity gradiometer comprises at least one sensor mass for movement in response to a gravity gradient and a pivotal coupling enabling the movement of the at least one sensor mass about an axis. Further, the gravity gradiometer comprises a constant charge capacitor that is arranged so that the movement of the at least one sensor mass generates a change in a voltage across the constant charge capacitor.
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Tensor processing using low precision format
PendingUS20170372202A1Accelerated trainingOperation accuracyNeural architecturesPhysical realisationMatrix additionAlgorithm
Aspects of the present invention are directed to computer-implemented techniques for improving the training of artificial neural networks using a reduced precision (e.g., float16) data format. Embodiments of the present invention rescale tensor values prior to performing matrix operations (such as matrix multiplication or matrix addition) to prevent overflow and underflow. To preserve accuracy throughout the performance of the matrix operations, the scale factors are defined using a novel data format to represent tensors, wherein a matrix is represented by the tuple X, where X=(a, v[.]), wherein a is a float scale factor and v[.] are scaled values stored in the float16 format. The value of any element X[i] according to this data format would be equal to a*v[i].
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
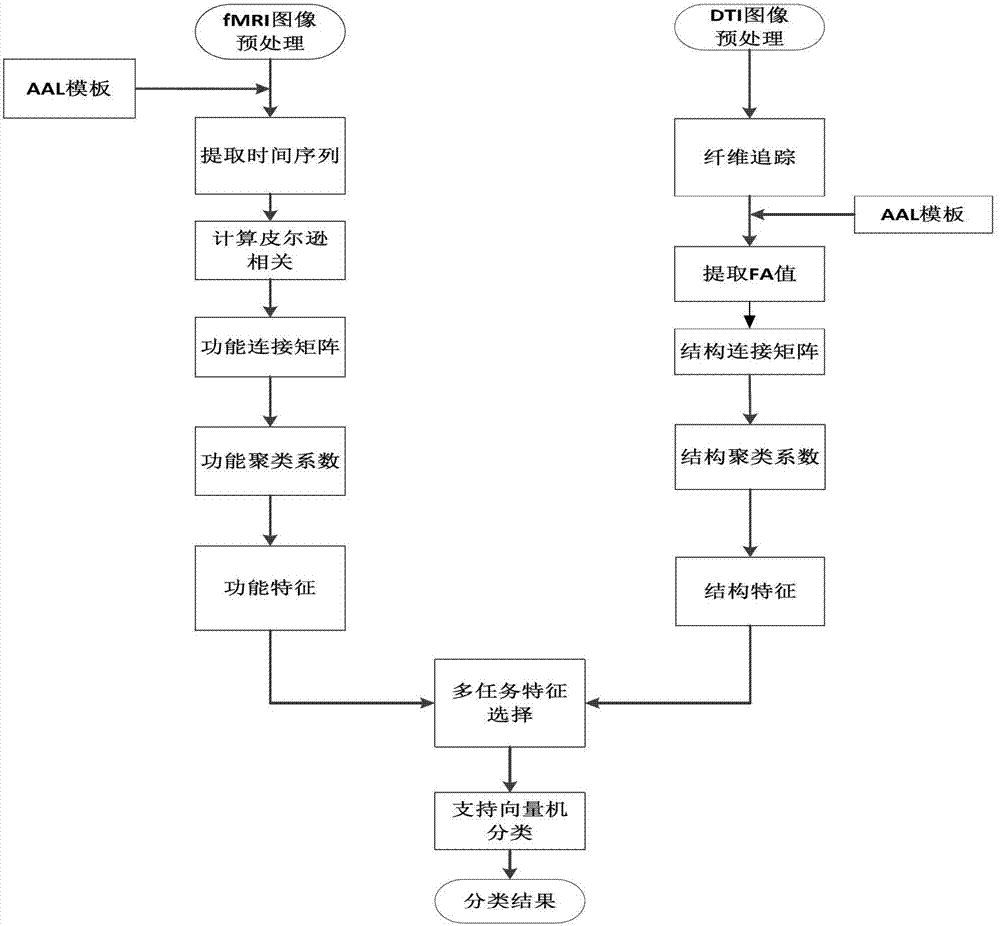
Multimodal brain network feature fusion method based on multi-task learning
InactiveCN103093087ACustomer Service RelevanceImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsFiberDiagnostic Radiology Modality
The invention discloses a multimodal brain network feature fusion method based on multi-task learning, and the multimodal brain network feature fusion method based on the multi-task learning includes the steps of preprocessing the obtained functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) images and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) images, registrating the preprocessed fMRI image to the standard AAL template, carrying out a fiber tracking for preprocessed DTI images, calculating fiber anisotropy (FA) value, and constructing structure connection matrix through the AAL template. Clustering coefficient of each brain area in a function connection matrix and the structure connection matrix is calculated to be regarded as function features and structure features. As two different tasks, the function features and the structure features assess an optimal feature set by solving the problem of multi-task learning optimization. The method uses information with multiple modalities complementing each other to learn simultaneously and to classify, improves the classification accuracy, solves the problems that a single task feature does not consider the correlation between features, and the fact that only one modality feature is used for pattern classification can bring to insufficient amount of information.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Gravity Gradiometer
ActiveUS20080116905A1Reduce noiseResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present invention provides a gravity gradiometer for measuring components of the gravity gradient tensor. The gravity gradiometer comprises at least one sensor mass for movement in response to a gravity gradient and a sensor and actuator unit for generating an electrical signal in response to the movement of the at least one sensor mass and for influencing the movement of the at least one sensor mass. The gravity gradiometer also comprises an electronic circuit for simulating an impedance. The electrical circuit is arranged for amplifying the electrical signal received from the sensor and actuator unit and for directing an actuating signal to the sensor and actuator unit. The electronic circuit comprises a differential amplifiers having first and second amplifier input terminals and an amplifier output terminal and impedances Z1, Z2, Z3, at least one of the impedances have an imaginary impedance component.
Owner:TECH RESOURCES PTY LTD
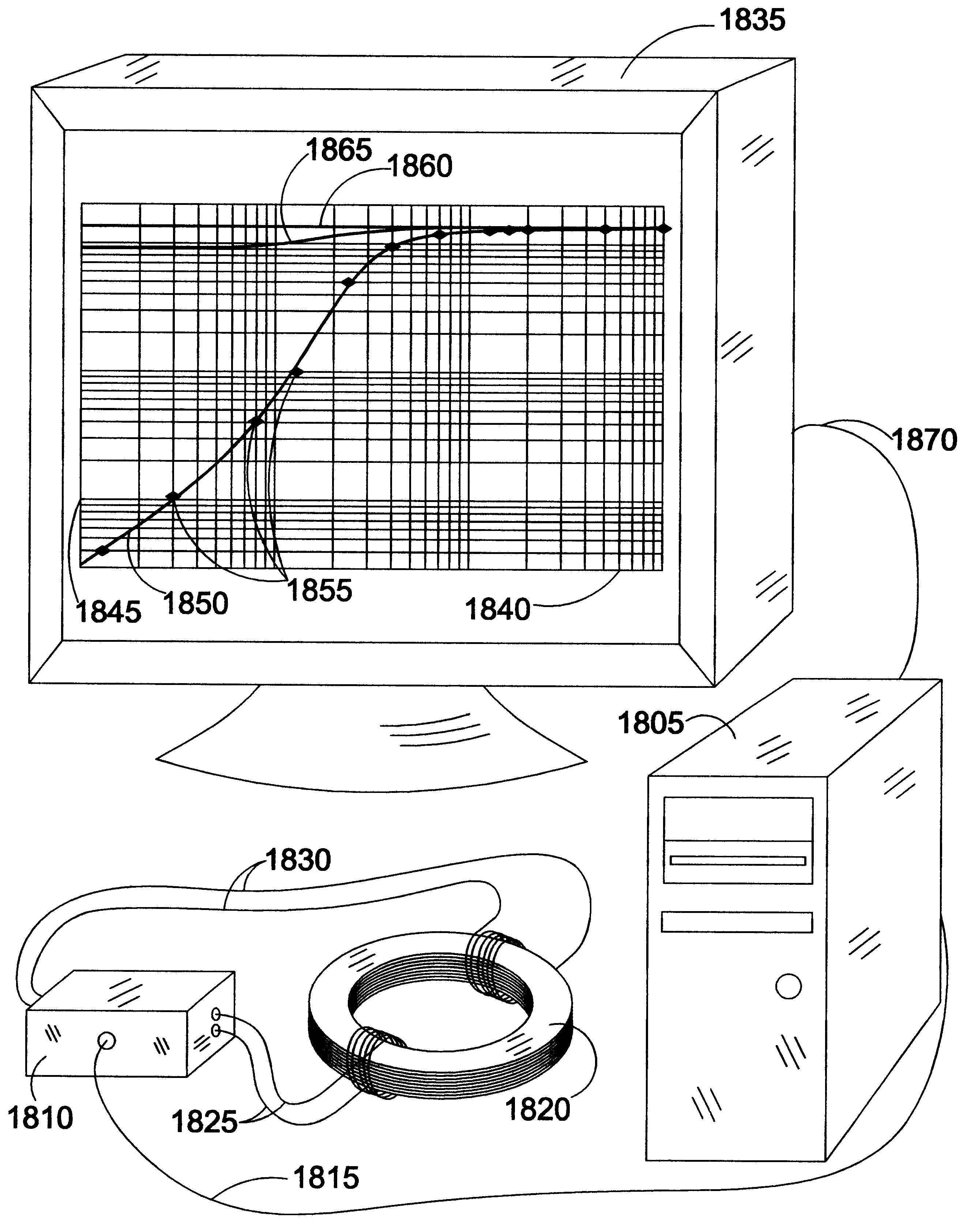
System and method for quantifying material properties
InactiveUS6631647B2Optimize overall economy and utilityThe testing process is simpleForce measurementMeasurement arrangements for variableHysteresisModel dynamics
A materials characterization method models dynamic, non-linear, temperature-dependent stress, strain, hysteresis, creep, and loss of elasticity at high strain, both in test samples and in Finite Element Analysis (FEA). Incorporating universal properties of statistical mechanics and adapting domain models from ferromagnetics to the higher-dimensional realm of stress tensors, the model is applicable to polymers, rubbers, liquids, and metals in elastic and plastic deformation. The model quantifies the dynamics of both plastic and brittle failure. Apparatus and methods are shown for testing material samples and matching the computational model to sample characteristics, leading to a set of characterizing parameters and predictive simulations using those parameters. Though apparatus and testing protocols of the invention yield optimum characterizations, pre-existing data from conventional testing yield useful results.< / PTEXT>
Owner:SEALE JOSEPH B
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com