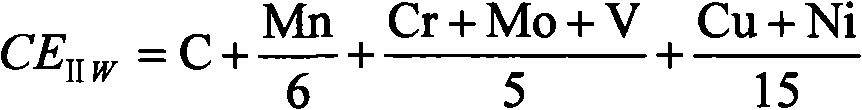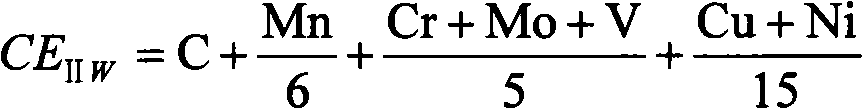Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
633 results about "High strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
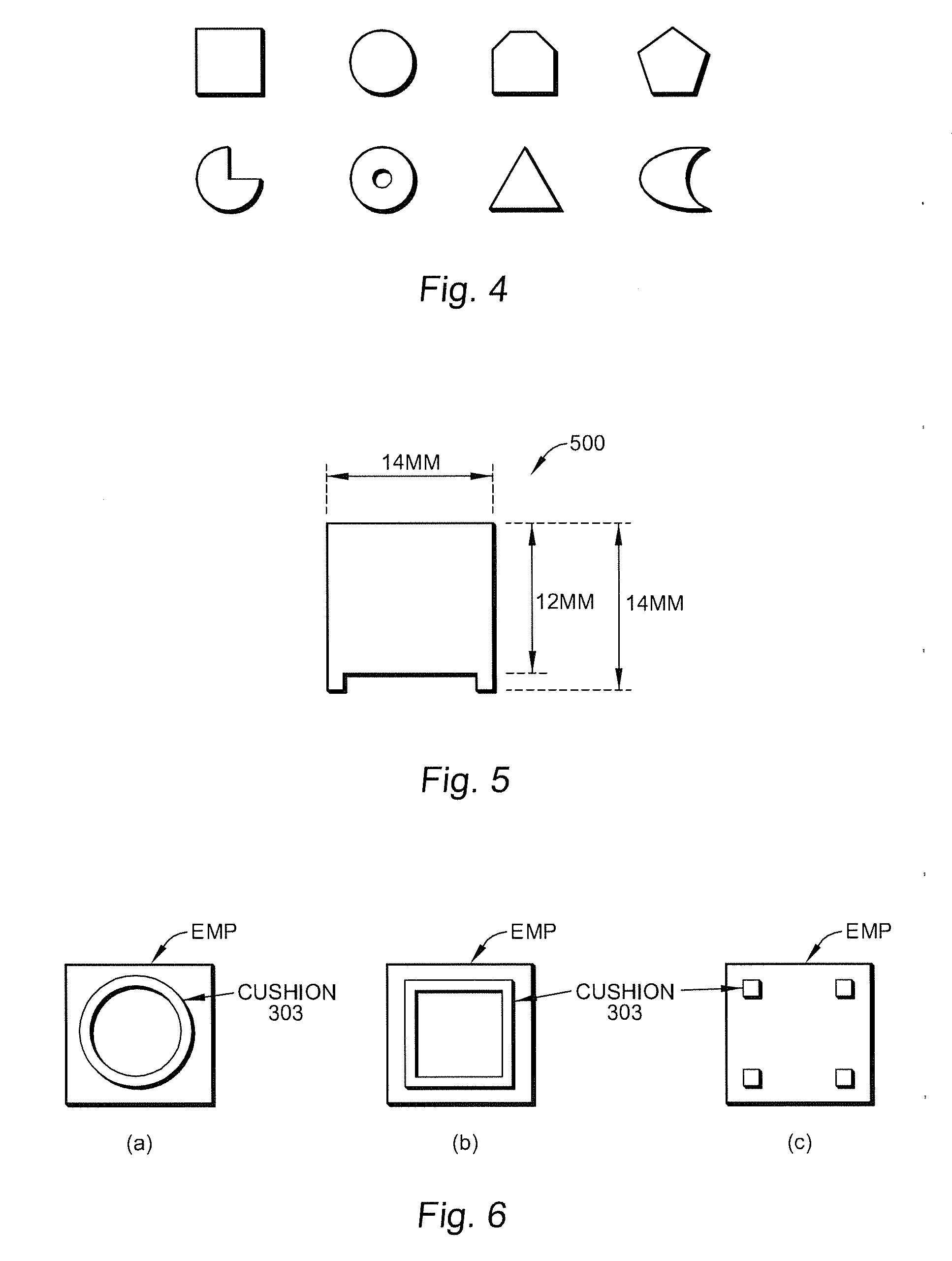
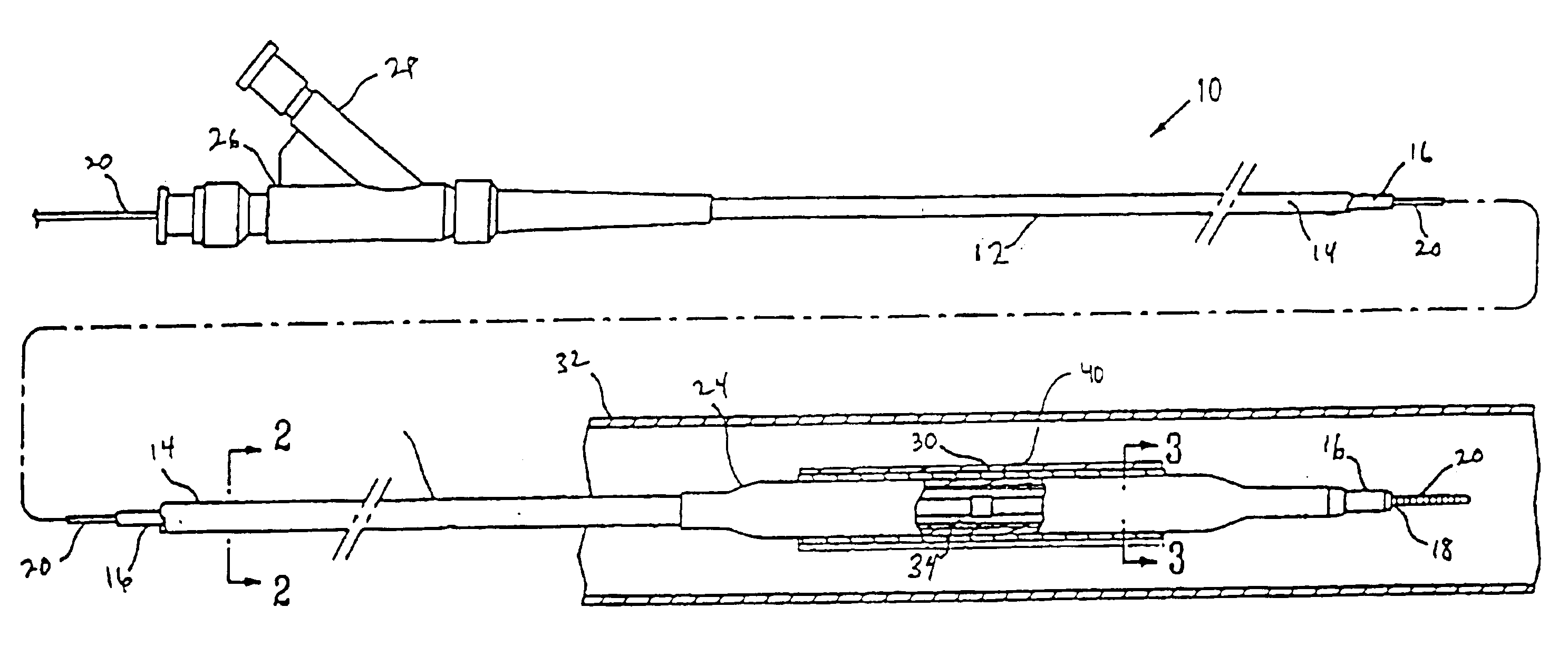
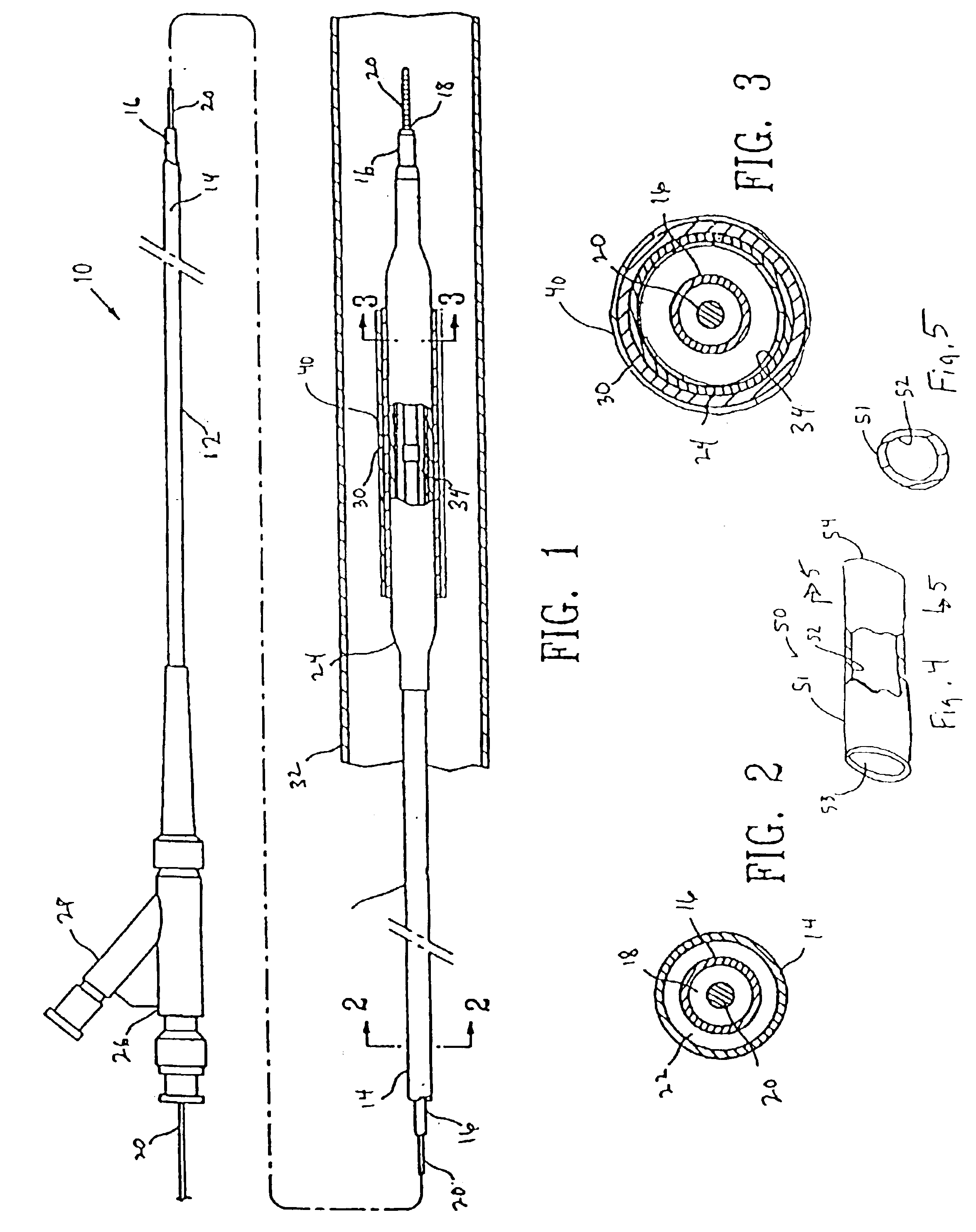
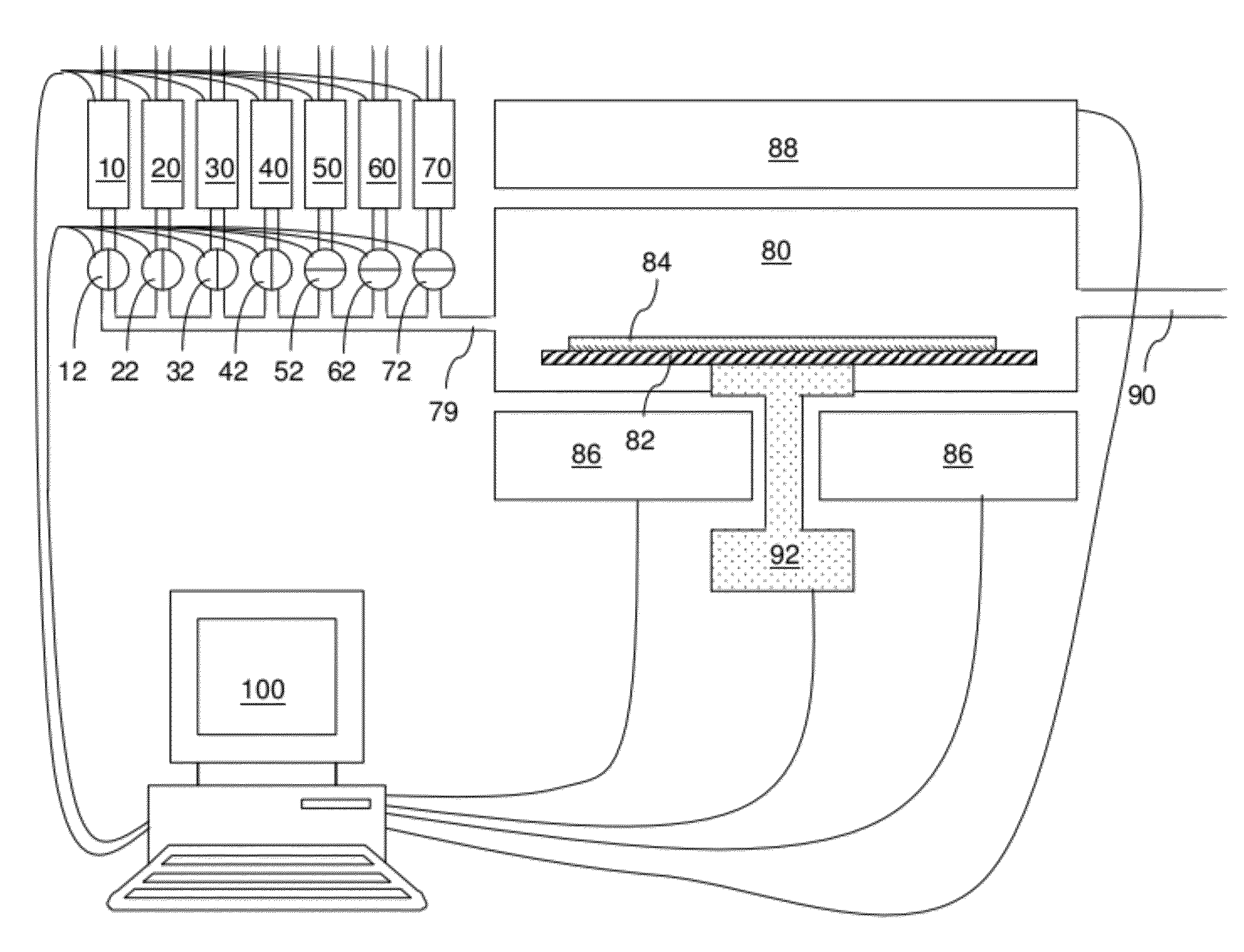
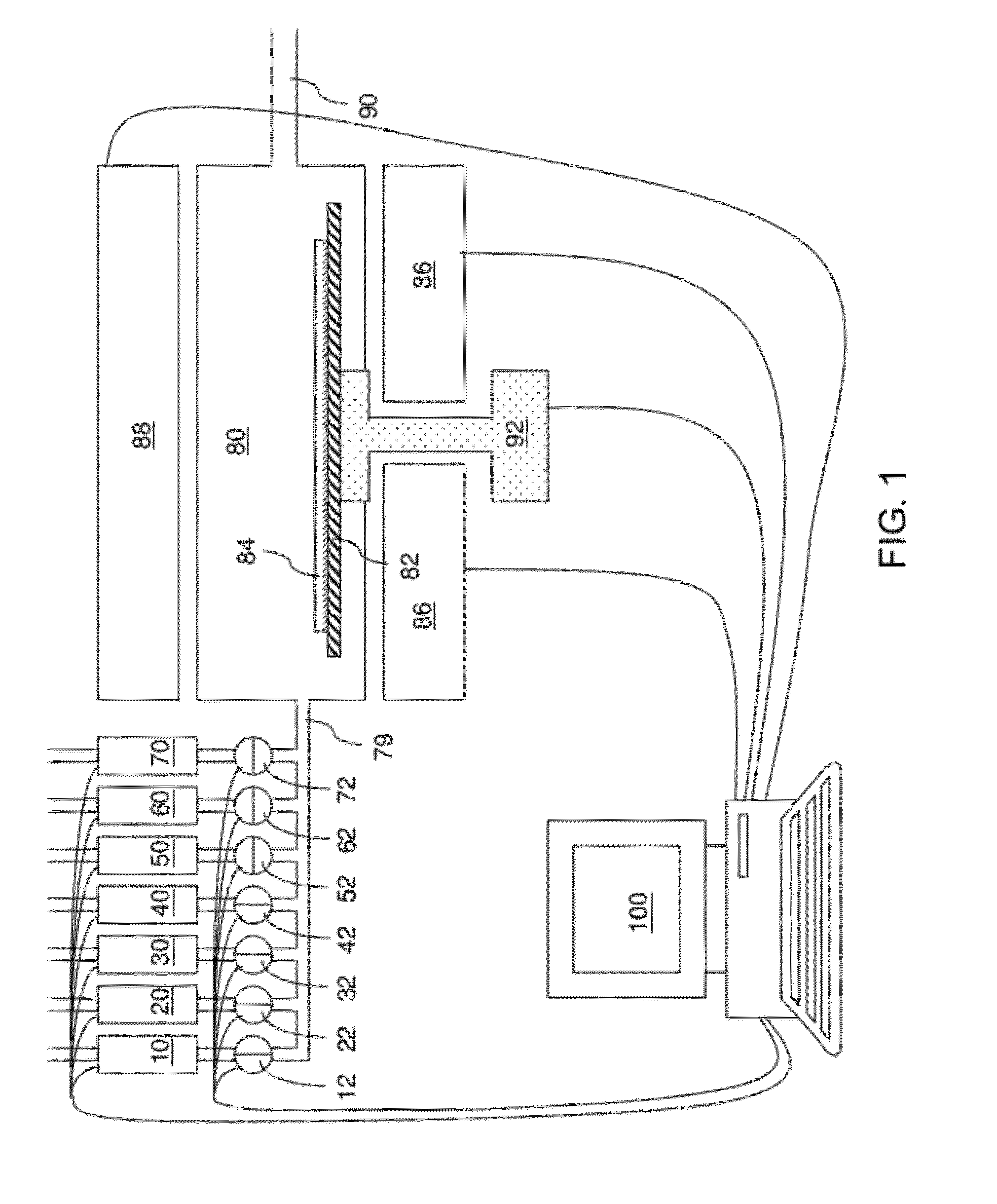
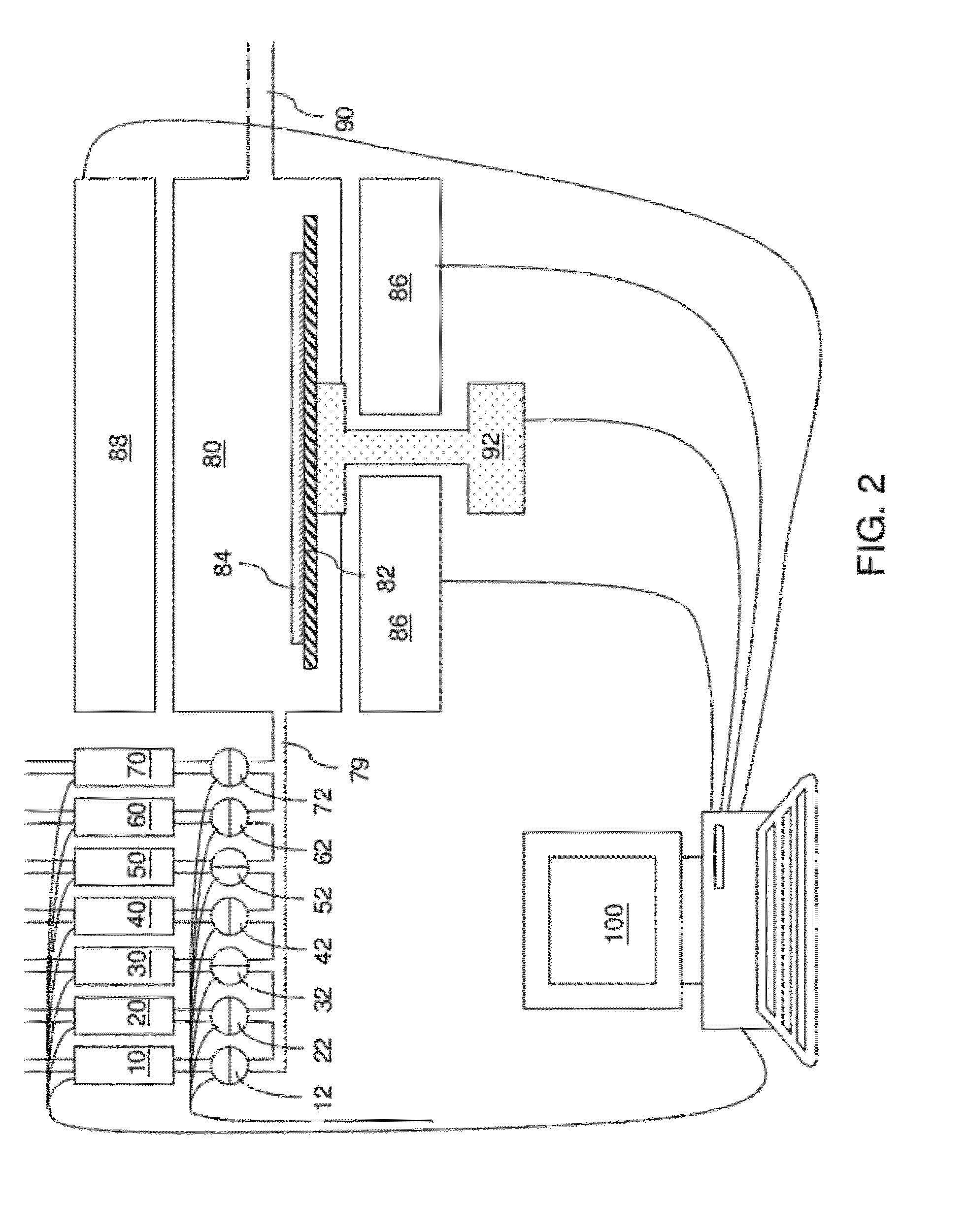
Thin profile user interface device and method providing localized haptic response
ActiveUS20140191973A1Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsGraphicsTransducer
Electromechanical polymer (EMP) actuators are used to create haptic effects on a user interface deface, such as a keyboard. The keys of the keyboard may be embossed in a top layer to provide better key definition and to house the EMP actuator. Specifically, an EMP actuator is housed inside an embossed graphic layer that covers a key of the keyboard. Such a keyboard has a significant user interface value. For example, the embossed key provides the tactile effect of the presence of a key with edges, while allowing for the localized control of haptic vibrations. For such applications, an EMP transducer provides high strains, vibrations or both under control of an electric field. Furthermore, the EMP transducer can generate strong vibrations. When the frequency of the vibrations falls within the acoustic range, the EMP transducer can generate audible sound, thereby functioning as an audio speaker.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
Tissue products having enhanced cross-machine directional properties
ActiveUS20070131366A1Enhanced cross-machine directional propertyHigh peak stretchNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperMedicineUltimate tensile strength
Tissue products are disclosed having desirable strength, stretch and softness properties. In particular, the tissue products exhibit relatively high strength while still having a relatively low stiffness and a significant amount of stretch. The tissue webs generally comprise uncreped through-air dried webs. In accordance with the present disclosure, the webs are formed in a through-air drying process in which the transfer fabric and the through-air drying fabric are both textured fabrics having a substantially uniform high strain distribution in the cross-machine direction. Various improvements in properties in the cross-machine direction are exhibited by deforming or molding a tissue web against one or more of the fabrics during the tissue making process.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Tissue products having enhanced cross-machine directional properties
ActiveUS7972474B2Enhanced cross-machine directional propertyHigh peak stretchNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperMedicineHardness
Tissue products are disclosed having desirable strength, stretch and softness properties. In particular, the tissue products exhibit relatively high strength while still having a relatively low stiffness and a significant amount of stretch. The tissue webs generally comprise uncreped through-air dried webs. In accordance with the present disclosure, the webs are formed in a through-air drying process in which the transfer fabric and the through-air drying fabric are both textured fabrics having a substantially uniform high strain distribution in the cross-machine direction. Various improvements in properties in the cross-machine direction are exhibited by deforming or molding a tissue web against one or more of the fabrics during the tissue making process.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
High strain tear resistant gels and gel composites for use as artificial muscle actuators
InactiveUS6909220B2Improve propertiesImprove tear resistanceCellsSludge treatmentPolymer sciencePlasticizer
Novel gels and articles are formed from one or more copolymers having at least one poly(ethylene) components and high levels of one or more plasticizers, said gels having an amount of crystallinity, glassy components, and selected plasticizers sufficient to achieve improvements in one or more physical properties including improved crack propagation resistance, improved tear resistance, improved resistance to fatigue, resistance to catastrophic failure, and exhibiting high strain under elongations not obtainable in amorphous gels which high strain making the gel suitable for use as film layers for artificial muscles.
Owner:APPLIED ELASTOMERICS
Medical device formed of ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin
Medical devices having at least a component, such as a catheter balloon, stent cover and vascular graft, formed of ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin, such as ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. The device component is formed from ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene that has been processed so that it is microporous and has an oriented node and fibril structure. The device component expands compliantly at low strains and are substantially less compliant at higher strains. The invention also comprises methods for making such medical devices, including the steps of compacting a polyethylene powder and deforming it to impart the oriented structure.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
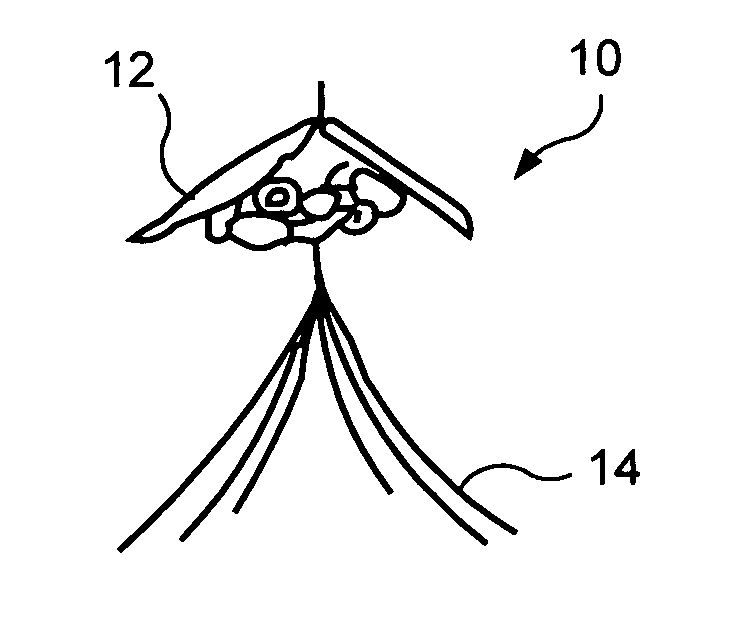
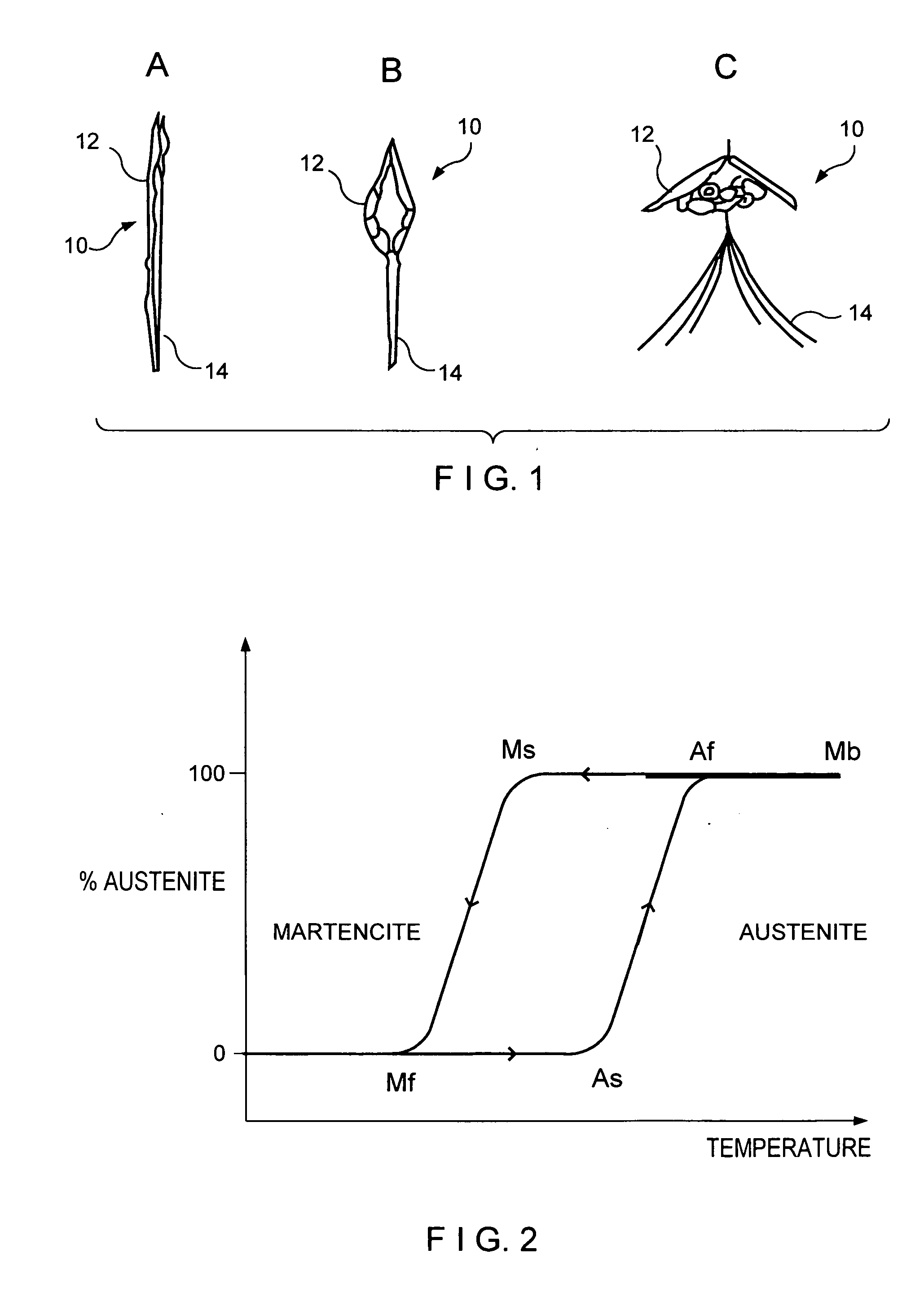
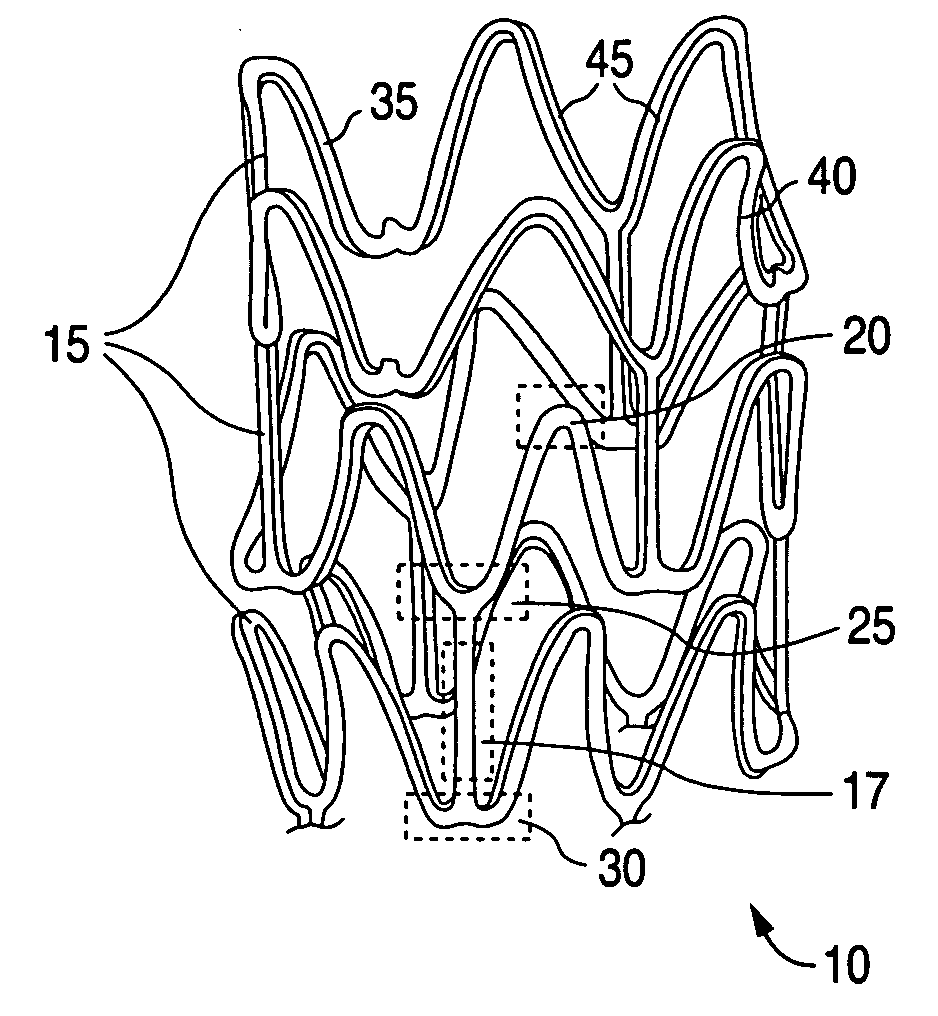
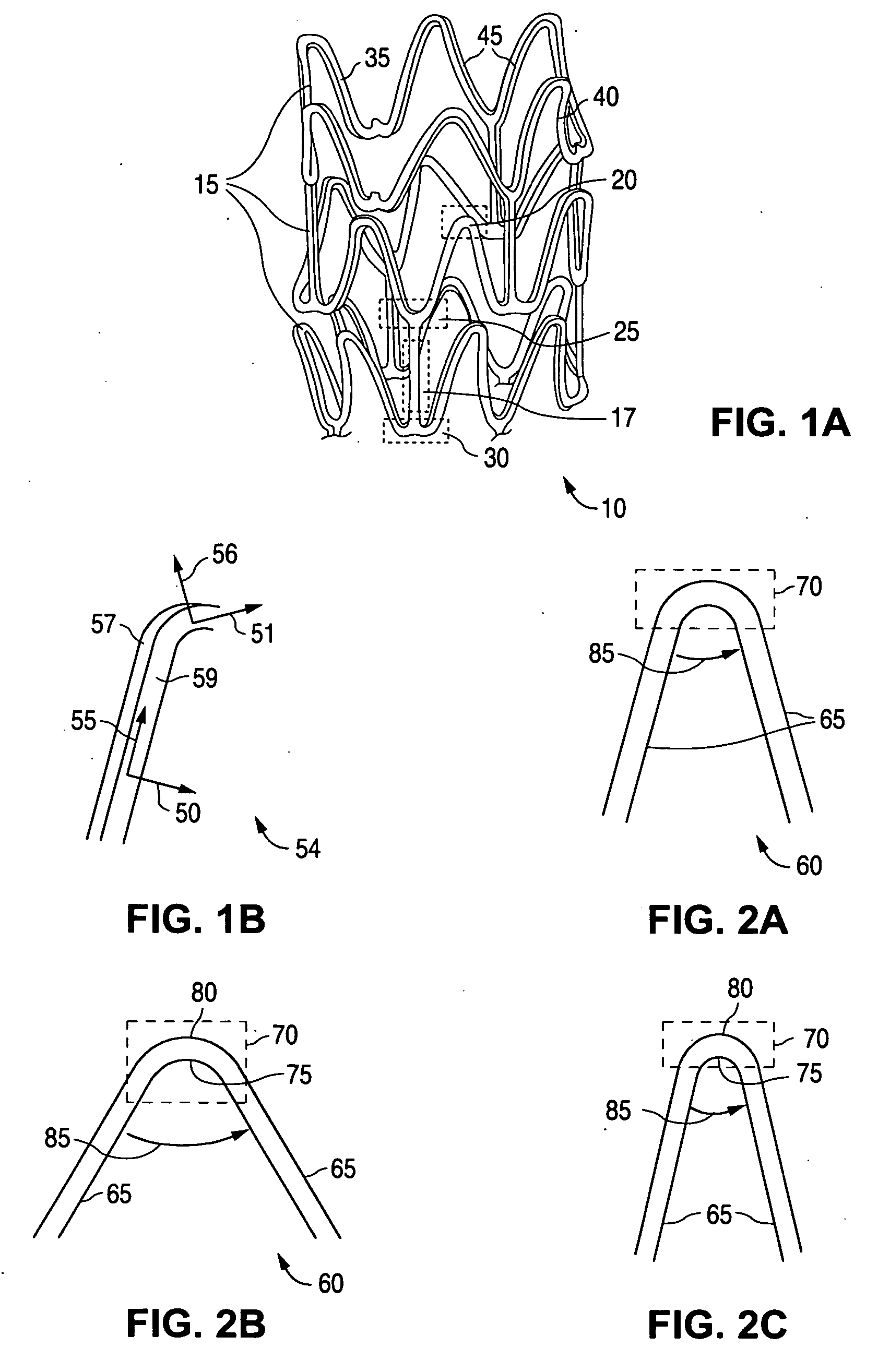
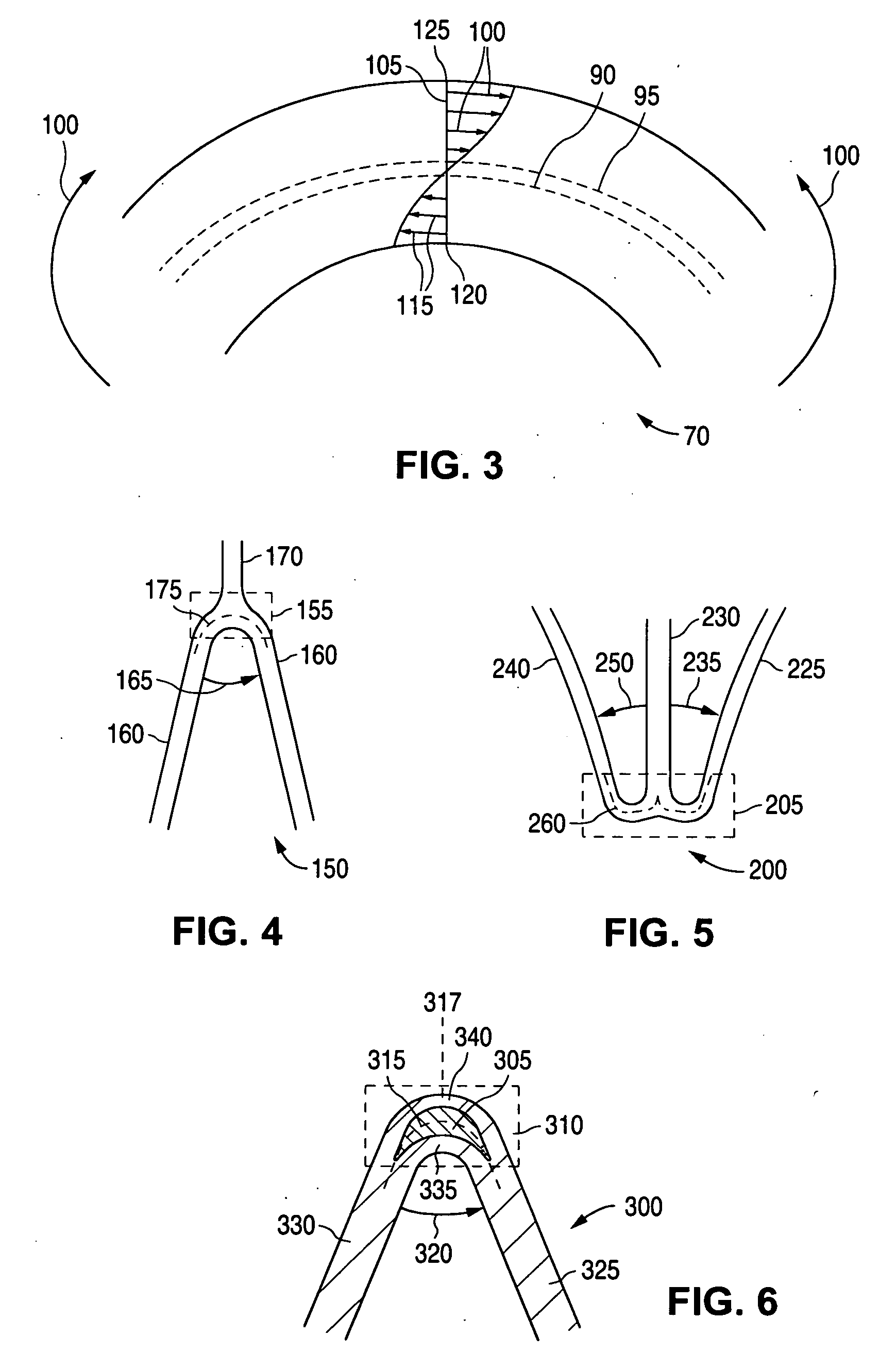
Fatigue resistant medical devices
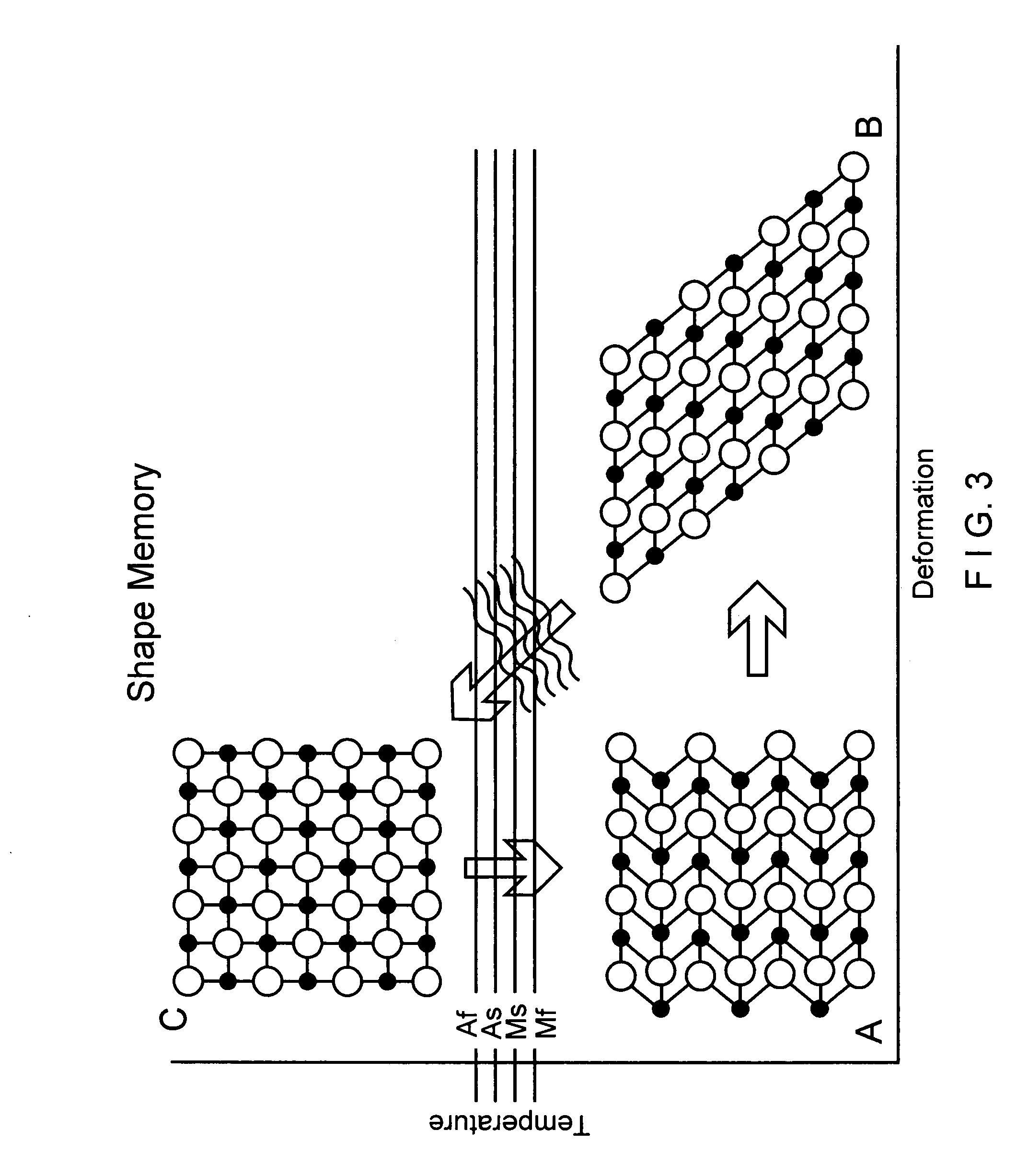
A flexible device comprises a metallic element including high strain portions and lesser strain portions, wherein the high strain portions are to be subjected to levels of strain during use increased with respect to strain levels in the lesser strain portions. The high strain portions comprise a material which, under predetermined operating conditions, is stabilized in a martensite phase and the lesser strain portions comprise a material which, under the predetermined operating conditions, is in an austenite phase. A method of forming an element of a medical device comprises the steps of forming an element of the device of Nitinol and impressing a memorized shape on the element, wherein the memorized shape is a shape the element is to assume when in an operational configuration. A high strain portion of the element is treated so that it is substantially Martensite phase stabilized under expected operating conditions of the device, wherein untreated portions of the element are in a substantially austenitic phase under the expected operating conditions.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
High strain glass/glass-ceramic containing semiconductor-on-insulator structures
InactiveUS20060038228A1Low costMinimized substrate compactionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor structure
The present invention relates to semiconductor-on-insulator structures having strained semiconductor layers. According to one embodiment of the invention, a semiconductor-on-insulator structure has a first layer including a semiconductor material, attached to a second layer including a glass or glass-ceramic, with the strain point of the glass or glass-ceramic equal to or greater than about 800° C.
Owner:CORNING INC
Stent with flexible sections in high strain regions
InactiveUS20060271170A1Good flexibilityImprove the immunityStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentHigh strain
A stent for treating a bodily lumen with a flexible section in a high strain region is disclosed. A flexible section may be selectively positioned to reduce an amount of strain in the high strain region when subjected to the applied stress during use to inhibit or prevent fracturing in the high strain region.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
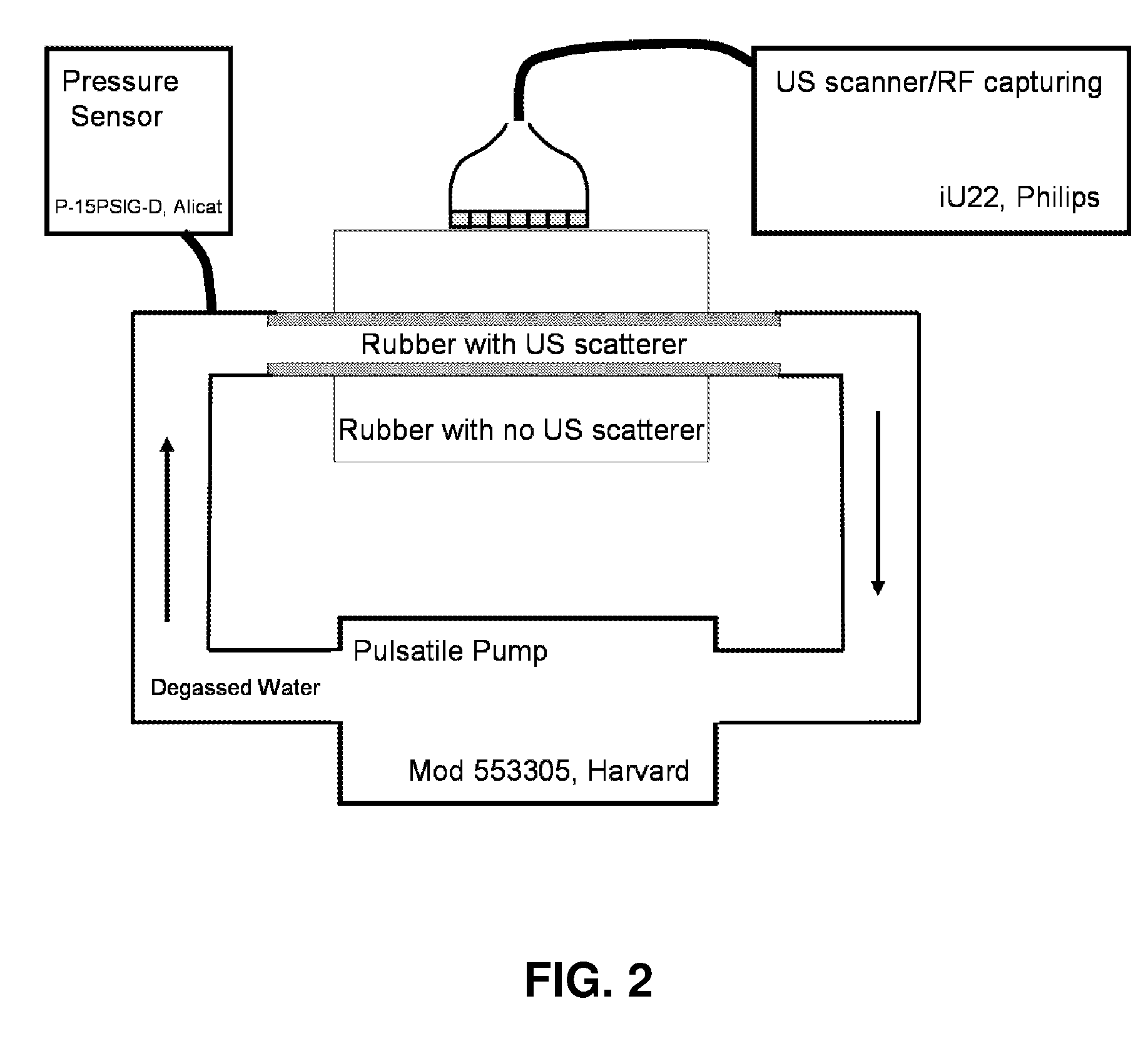
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and method and system for determining health of a vascular structure
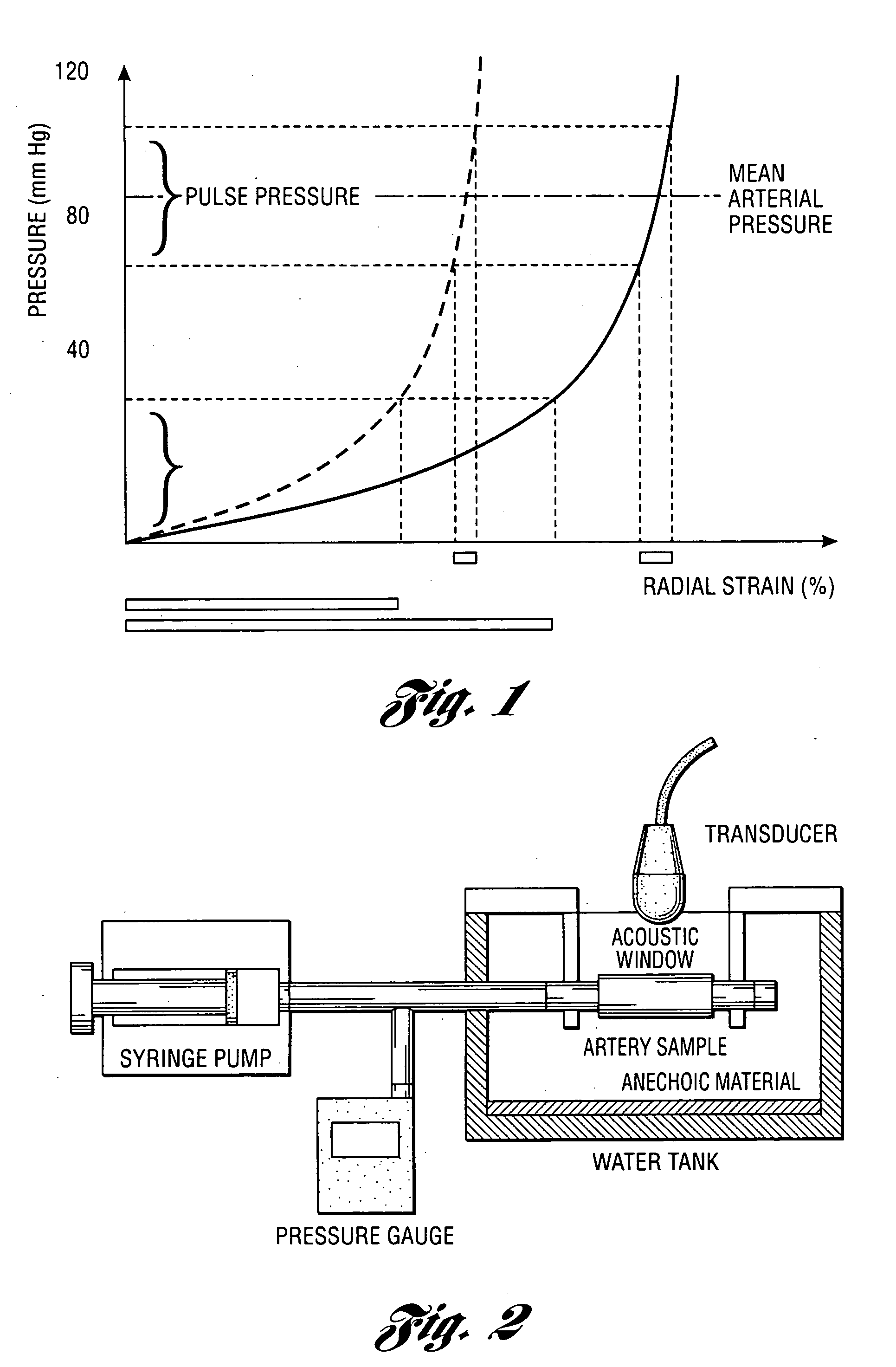
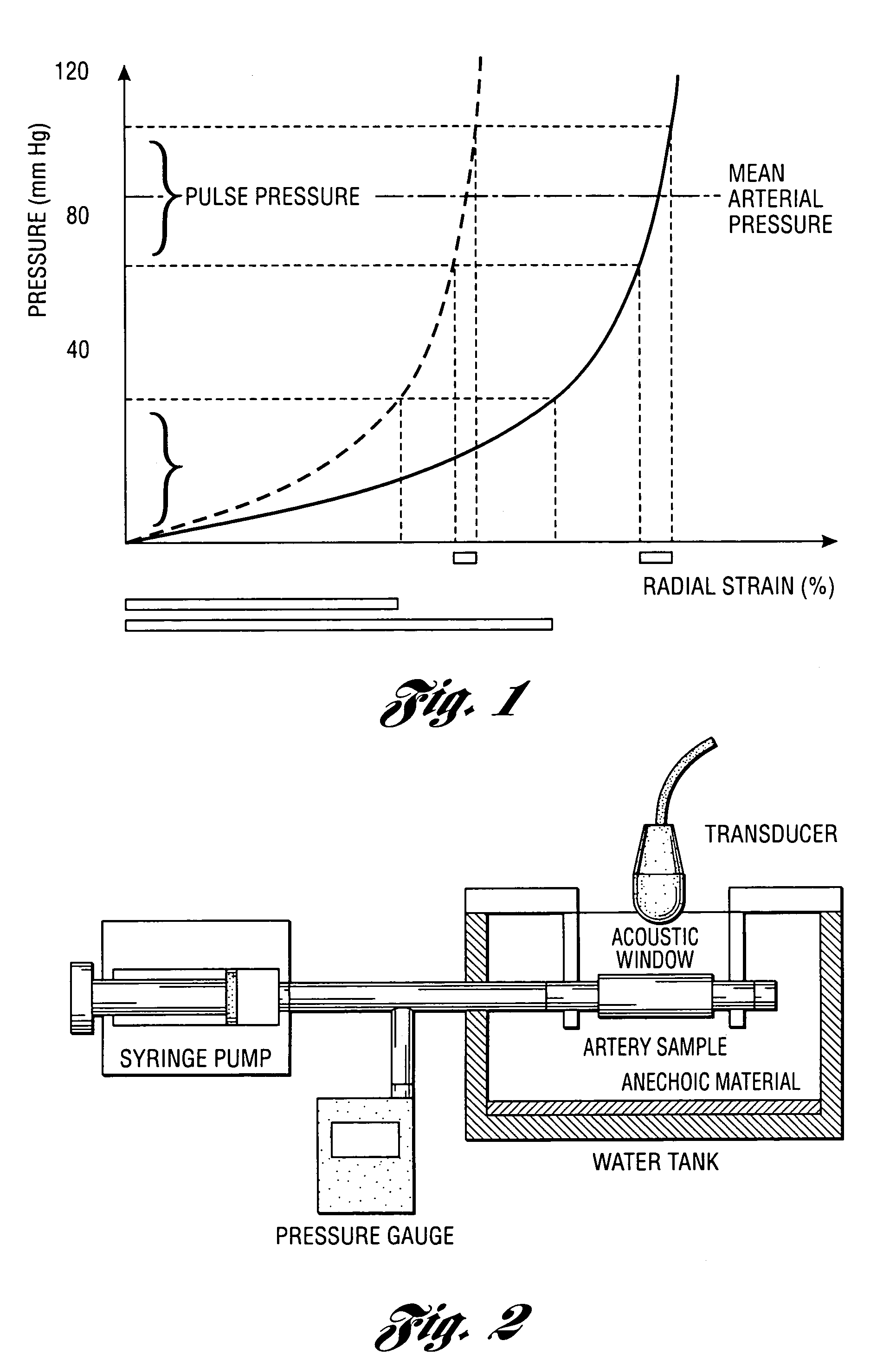
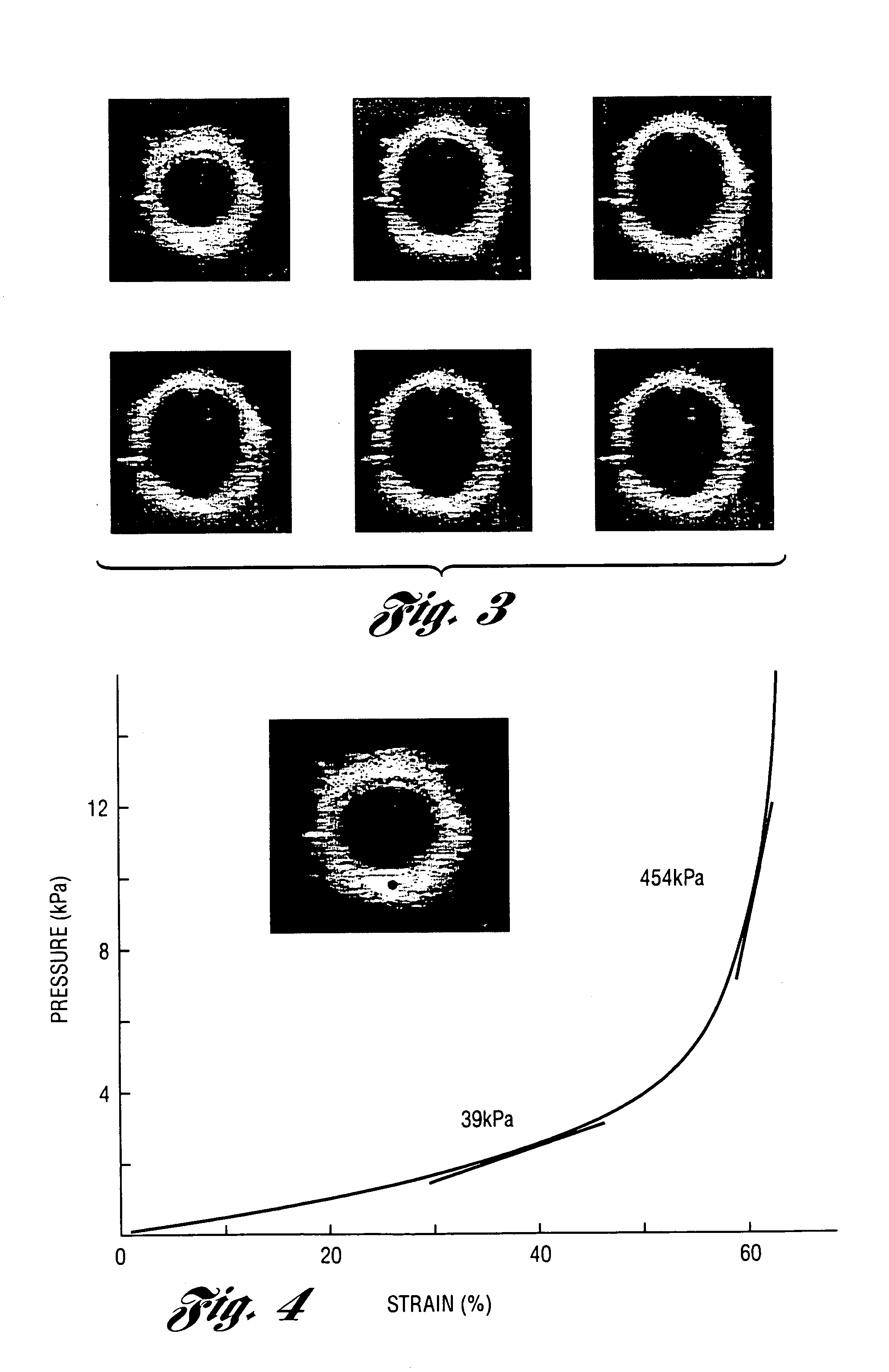
InactiveUS20050124892A1Reduce internal pressureBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionCardiac cyclePhase sensitive
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and a method and system for determining health of a vascular structure are provided wherein local deformation of a vessel wall resulting from physiologic pressures with altered transmural forces is measured. A non-invasive free-hand ultrasound scanning-procedure was performed to apply external force, comparable to the force generated in measuring a subject's blood pressure, to achieve higher strains by equalizing the internal arterial baseline pressure. When the applied pressure matched the internal baseline diastolic pressure, strain and strain rate increased by a factor of 10 over a cardiac cycle. Radial arterial strain was assessed in the vessel wall over the entire deformation procedure using a phase-sensitive, two-dimensional speckle-tracking algorithm. An elastic modulus reconstruction procedure was developed to estimate the non-linear elastic properties of the vascular wall.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
System and method for quantifying material properties
InactiveUS20020157478A1Simple processOptimize economyForce measurementMeasurement arrangements for variableElement analysisComputational model
A materials characterization method models dynamic, non-linear, temperature-dependent stress, strain, hysteresis, creep, and loss of elasticity at high strain, both in test samples and in Finite Element Analysis (FEA). Incorporating universal properties of statistical mechanics and adapting domain models from ferromagnetics to the higher-dimensional realm of stress tensors, the model is applicable to polymers, rubbers, liquids, and metals in elastic and plastic deformation. The model quantifies the dynamics of both plastic and brittle failure. Apparatus and methods are shown for testing material samples and matching the computational model to sample characteristics, leading to a set of characterizing parameters and predictive simulations using those parameters. Though apparatus and testing protocols of the invention yield optimum characterizations, pre-existing data from conventional testing yield useful results.
Owner:SEALE JOSEPH B
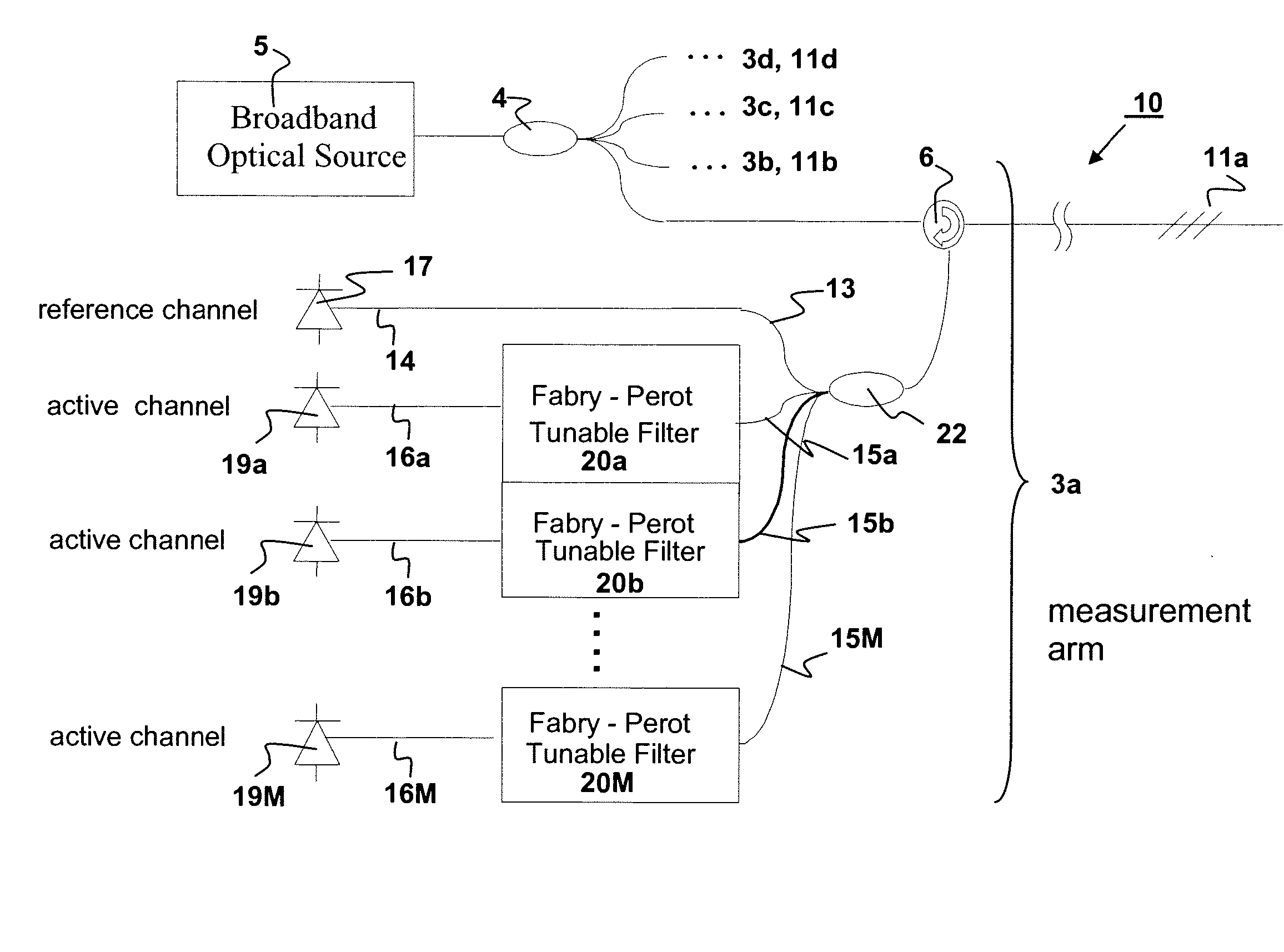
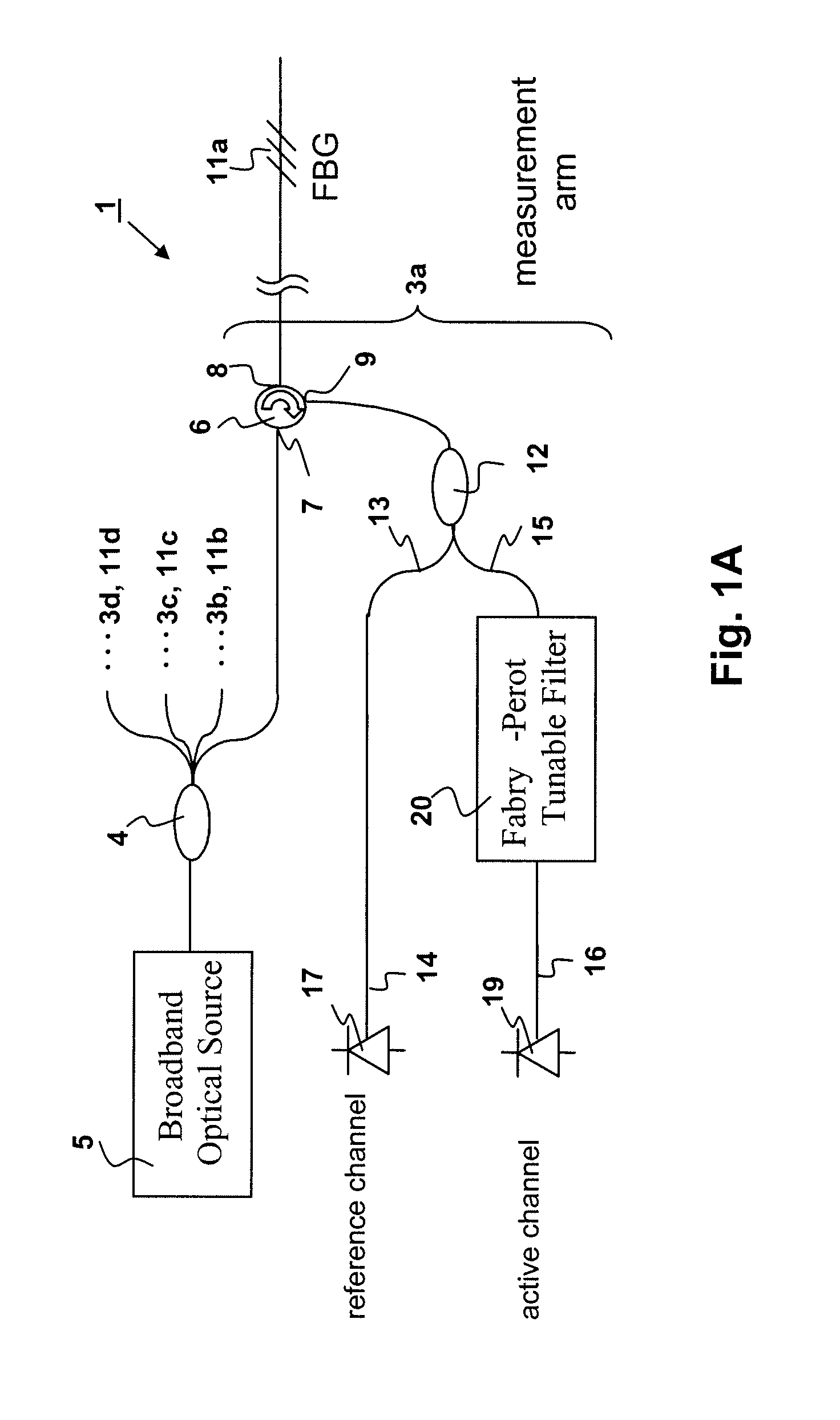
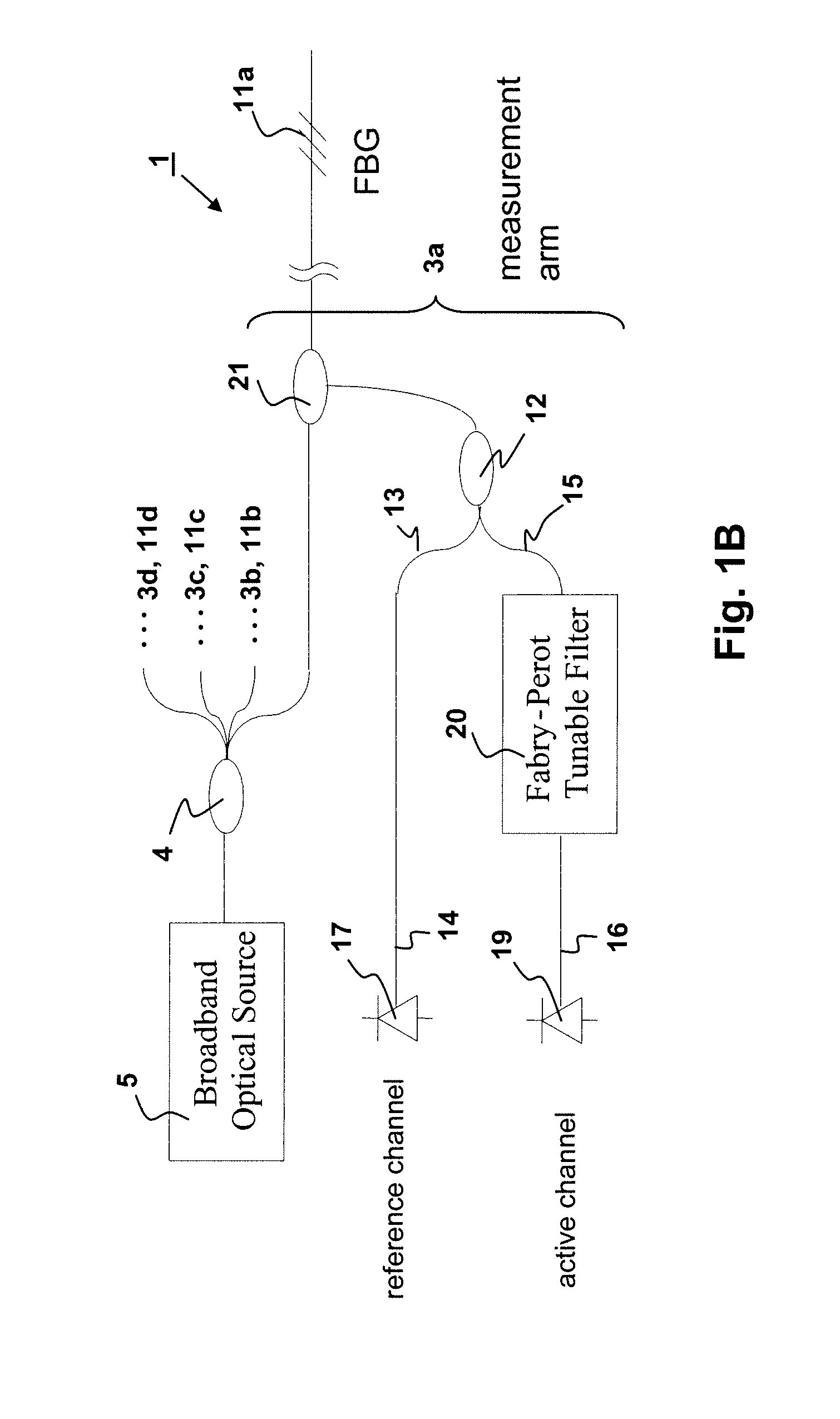
Method and apparatus for high frequency optical sensor interrogation
InactiveUS20080106745A1High sensitivityAccurate resolutionForce measurementUsing optical meansSmall amplitudeHigh strain
Optical sensor measurement methods that convert a wavelength change in an optical sensor to a measurable optical intensity change, which can be calibrated and used to measure optical wavelength change and environmental changes such as temperature or strain which affect sensor wavelength. The current invention makes use of tunable fiber Fabry-Perot filters as the wavelength selective elements for the wavelength to optical intensity conversion. The invention provides high measurement sensitivities to small amplitude, high frequency modulations to the fiber sensor center wavelength, accommodates for system drift from thermal or other perturbations, and enables either frequency mode or time varying resolution of sensor modulation events. Selection of proper Fabry-Perot optics allow for measurement optimization of either high sensitivity or high strain measurement range.
Owner:MICRON OPTICS
Friction material
InactiveUS20050004258A1Good brake feelingImprove effectivenessBraking element arrangementsOther chemical processesMohs scale of mineral hardnessHardness
A friction material is made by molding and curing a composition containing a fibrous base that includes stainless steel fibers but not other steel fibers, a binder, and a friction modifier that includes at least two types of hard particles having a large Mohs hardness, bronze powder and a specific amount of tin sulfide. The friction material has a excellent balance of properties, including a high strain linearity that provides a excellent brake feel, a high torque linearity and a excellent effectiveness, and also minimizes disc rotor attack, disc pad wear and metal pickup. Such friction materials are particularly suitable for automotive applications, such as disc pads.
Owner:NISSHINBO INDDUSTRIES
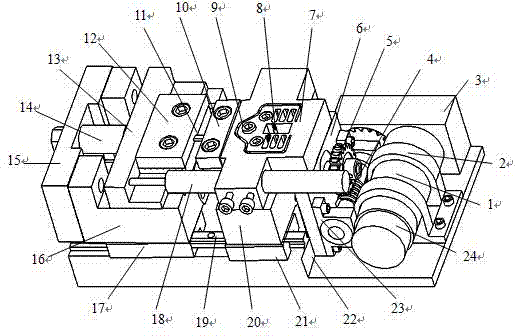
In-situ high-frequency fatigue material mechanical test platform under scanning electron microscope based on stretching/compressing mode
ActiveCN102331370AGood structural compatibilityImprove compatibilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesControl cellEngineering
The invention relates to an in-situ high-frequency fatigue material mechanical test platform under a scanning electron microscope based on a stretching / compressing mode and belongs to the field of machinery and electronics. The test platform comprises a precise loading unit, a precise motion conversion unit, a load / displacement signal acquisition and control unit, a high-frequency driving unit and a test piece clamping and connecting unit. The test platform provided by the invention has the advantages that the structure is compact, the test precision is high, the strain rate and the test frequency are controllable, an in-situ high-frequency test based on the stretching / compressing mode can be performed on a three-dimensional test piece aiming at centimeter-scale or above in characteristicdimension under the condition of observation of various imaging instruments, the on-line monitoring can be carried out on the microcosmic deformation, damage and breaking process of a material under a fatigue stress, and a novel test method for revealing microcosmic deformation behaviors and a damage system of the material is provided.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
System and method for quantifying material properties
InactiveUS6631647B2Optimize overall economy and utilityThe testing process is simpleForce measurementMeasurement arrangements for variableHysteresisModel dynamics
A materials characterization method models dynamic, non-linear, temperature-dependent stress, strain, hysteresis, creep, and loss of elasticity at high strain, both in test samples and in Finite Element Analysis (FEA). Incorporating universal properties of statistical mechanics and adapting domain models from ferromagnetics to the higher-dimensional realm of stress tensors, the model is applicable to polymers, rubbers, liquids, and metals in elastic and plastic deformation. The model quantifies the dynamics of both plastic and brittle failure. Apparatus and methods are shown for testing material samples and matching the computational model to sample characteristics, leading to a set of characterizing parameters and predictive simulations using those parameters. Though apparatus and testing protocols of the invention yield optimum characterizations, pre-existing data from conventional testing yield useful results.< / PTEXT>
Owner:SEALE JOSEPH B
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and method and system for determining health of a vascular structure
InactiveUS7318804B2Reduce internal pressureOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsCardiac cyclePhase sensitive
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and a method and system for determining health of a vascular structure are provided wherein local deformation of a vessel wall resulting from physiologic pressures with altered transmural forces is measured. A non-invasive free-hand ultrasound scanning-procedure was performed to apply external force, comparable to the force generated in measuring a subject's blood pressure, to achieve higher strains by equalizing the internal arterial baseline pressure. When the applied pressure matched the internal baseline diastolic pressure, strain and strain rate increased by a factor of 10 over a cardiac cycle. Radial arterial strain was assessed in the vessel wall over the entire deformation procedure using a phase-sensitive, two-dimensional speckle-tracking algorithm. An elastic modulus reconstruction procedure was developed to estimate the non-linear elastic properties of the vascular wall.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Fusion formable sodium free glass
ActiveUS20100300536A1Improve battery efficiencyImprove film adhesionFinal product manufactureSynthetic resin layered productsSilicate glassThermal expansion
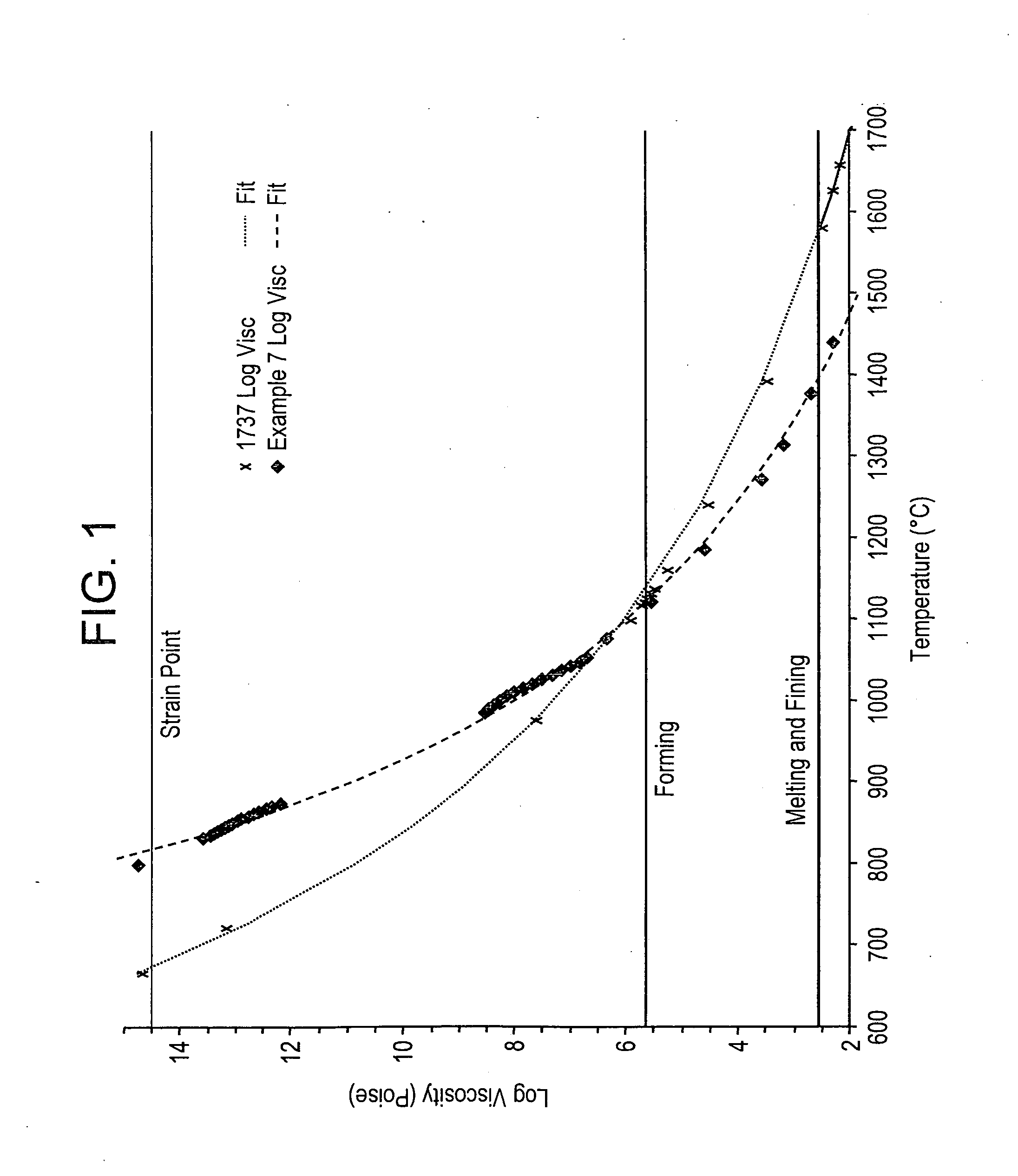
A compositional range of fusion-formable, high strain point sodium free, silicate, aluminosilicate and boroaluminosilicate glasses are described herein. The glasses can be used as substrates for photovoltaic devices, for example, thin film photovoltaic devices such as CIGS photovoltaic devices. These glasses can be characterized as having strain points≧540° C., thermal expansion coefficient of from 6.5 to 10.5 ppm / ° C., as well as liquidus viscosities in excess of 50,000 poise. As such they are ideally suited for being formed into sheet by the fusion process.
Owner:CORSAM TECH
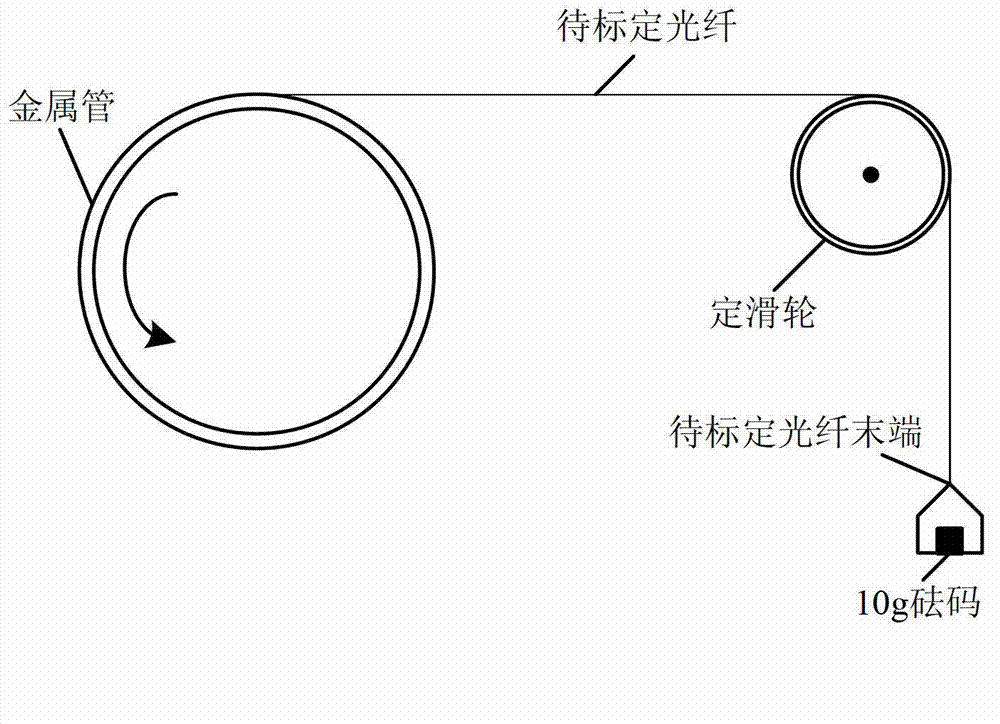
Optical fiber strain and temperature simultaneous calibration device and method based on Brillouin scattering
InactiveCN103115642AControl lengthEnsure consistencyMeasurement devicesPlastic optical fiberHigh strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of distribution-type optical fiber sensing measurement, in particular to an optical fiber strain and temperature simultaneous calibration device and a method based on Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber strain and temperature simultaneous calibration device comprises optical fiber Brillouin sensing measurement equipment, a shockproof support frame, a metal pipe and constant-temperature equipment. According to the method, the metal pipe with large and stable linear expansion coefficient is adopted to manufacture the strain calibration device, and the position of an optical fiber is accurately controlled by curving a thread on the outer wall of the metal pipe. Due to the characteristic that the optical fiber on the metal pipe bears strain and temperature at the same time, and the loose optical fiber only bears temperature, the temperature and the strain are calibrated simultaneously. The constant-temperature equipment is used for applying accurate and controllable strain and temperature on the optical fiber and the loose optical fiber on the metal pipe, and calibration of the strain of the optical fiber and temperature coefficient is carried out by means of detailed calibration steps. By means of the strain and temperature high-accuracy simultaneous calibration device and the method of the optical fiber Brillouin sensor, the problems of high strain calibration error and low efficiency of strain and temperature calibration are resolved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
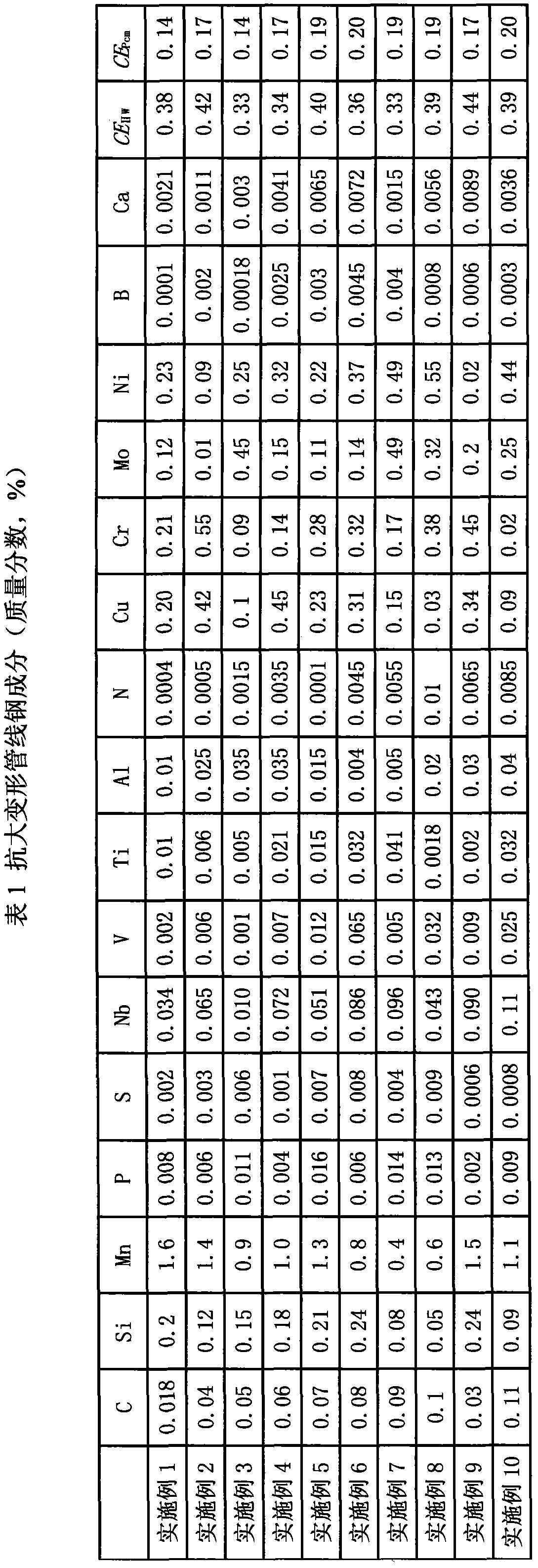
Anti-large-deformation pipe line steel prepared by thermal treatment method and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses anti-large-deformation pipe line steel prepared by a thermal treatment method and a preparation method thereof. The steel comprises the following chemical components of: not less than 0.02% and not greater than 0.12% of C, not less than 0.5% and not greater than 2.0% of Mn, not more than 0.25% of Si, not more than 0.02% of P, not more than 0.01% of S, not more than 0.11% of Nb, not more than 0.08% of V, not more than 0.05% of Ti, not more than 0.06% of Al, not more than 0.012% of N, not more than 0.50% of Cu, not more than 0.60% of Cr, not more than 0.50% of Mo, not more than 0.60% of Ni, not more than 0.005% of B, not more than 0.01% of Ca and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, wherein the CEIIW is not less than 0.3% and not greater than 0.45%, and the CEPcm is not more than 0.2%. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: heating steel at 700-950 DEG C in a thermal treatment furnace, maintaining the temperature for 6-15 min, cooling with the rate of 1-400 DEG C / s to room temperature, and simultaneously tempering from room temperature to 500 DEG C to obtain steel with ferrite as a first phase and bainite, martensite, degenerate perlite or any mixture thereof as a second phase. The steel has the advantages of high tensile strength, low yield strength, low yield ratio, high uniform elongation rate and high strain hardening exponent, thereby having good toughness and deformation performance.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for preparing magnesium alloy section bar by continuous corner shearing and squeezing shaping and mold
InactiveCN101406906AImprove material plasticityImprove plasticityExtrusion diesExtrusion control devicesGrain structureHigh strain
The invention relates to a method for preparing a magnesium alloy section through continuous angle rotation shearing, extrusion and shaping and a mould. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a magnesium alloy blank material is subjected to homogenization treatment; (2) a mould of an extrusion mould with a plurality of angle rotation and molding is preheated; and the inside of a mould passage is evenly coated with lube; (3) an extrusion cylinder is heated to a temperature of between 175 and 325 DEG C; and (4) the homogenized blank material is heated to a temperature of between 200 and 350 DEG C; the extrusion ratio of the extrusion mould is between 4 and 100; and the magnesium alloy blank material is subjected to unidirectional extrusion at an extrusion speed of between 3 and 6 m / min so that the magnesium alloy blank material is subjected to compression and extrusion with high extrusion ratio and equal passage extrusion with a plurality of angle rotation. The magnesium alloy material prepared through the method has an ultrafine crystal grain structure, has the advantages of substantially improving the plasticity, low temperature superplasticity and high strain speed of the magnesium alloy material and has high yield stress.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
High tenacity, high modulus filament
Polyethylene solutions are extruded through a multi-orifice spinneret into a cross-flow gas stream to form a fluid product. The fluid product is stretched at a temperature at which a gel will form at a stretch ratio of at least 5:1 over a length of less than about 25 mm with the cross-flow gas stream velocity at less than about 3m / min. The fluid product is quenched in a quench bath consisting of an immiscible liquid to form a gel. The gel is stretched. The solvent is removed from the gel to form a xerogel and the xerogel product is stretched in at least two stages to produce a polyethylene yarn characterized by a tenacity of at least 35g / d, a modulus of at least 1600 g / d and a work to break of at least 65 J / g. The yarn is further characterized by having greater than about 60 % of a high strain orthorhombic crystalline component and, optionally, a monoclinic crystalline component greater than about 2 % of the crystalline content. Composite panels made with these yarns exhibit excellent ballistic resistance, e.g., SEAC of 300J-m<2> / Kg or higher against .38 caliber bullets using test procedure NILECJ-STD-0101.01. A ballistic resistant composite panel is provided comprising a polyethylene multi-filament yarn having a tenacity of at least about 35 g / d, a modulus of at least 1600 g / d, a work-to-break of at least about 65 J / g wherein the yarn has greater than about 60 % of a high strain orthorhombic crystalline component and the yarn has a monoclinic crystalline component greater than about 2 % of the crystalline content.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Apparatus and method for reducing gaseous inclusions in a glass
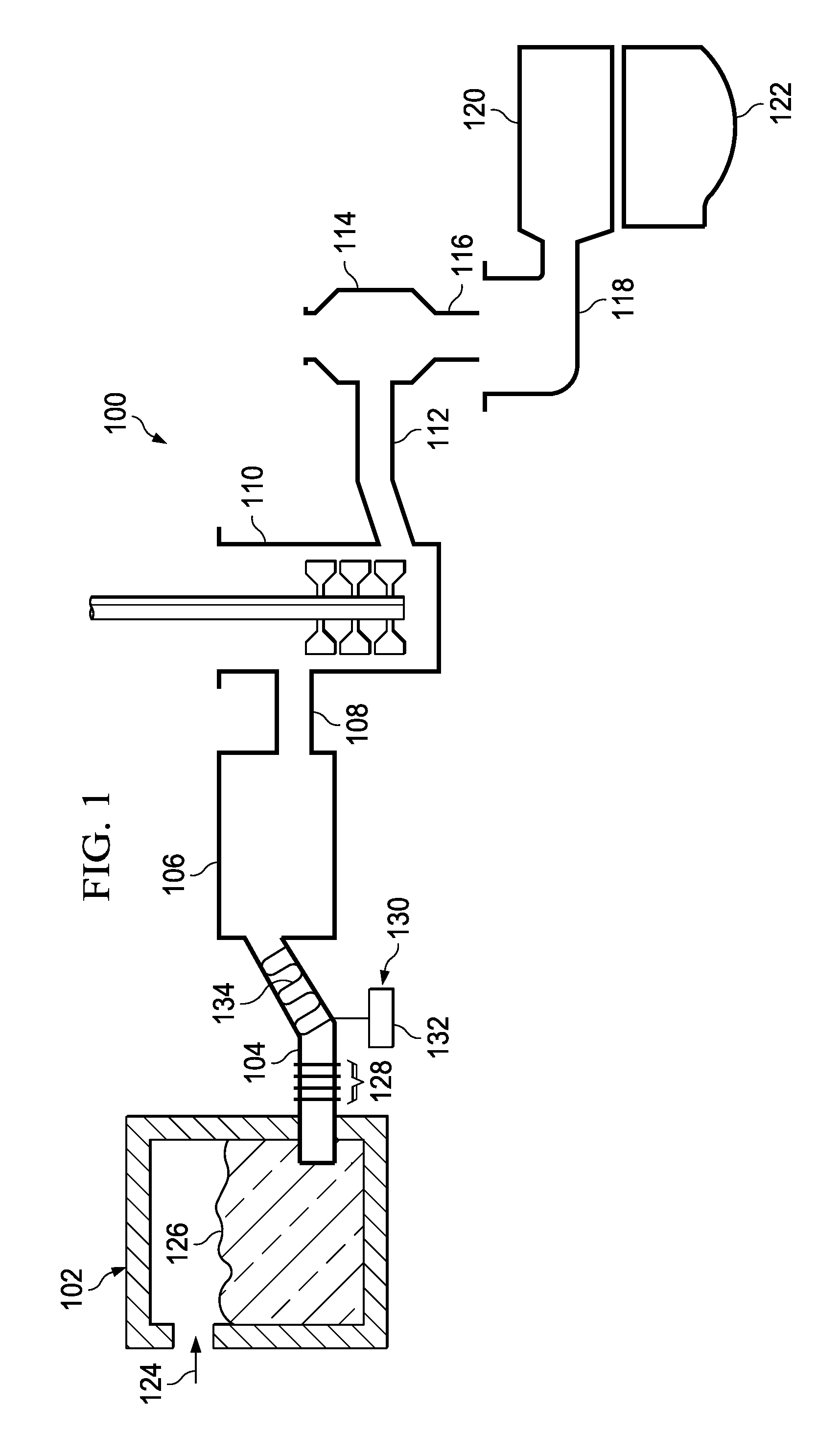
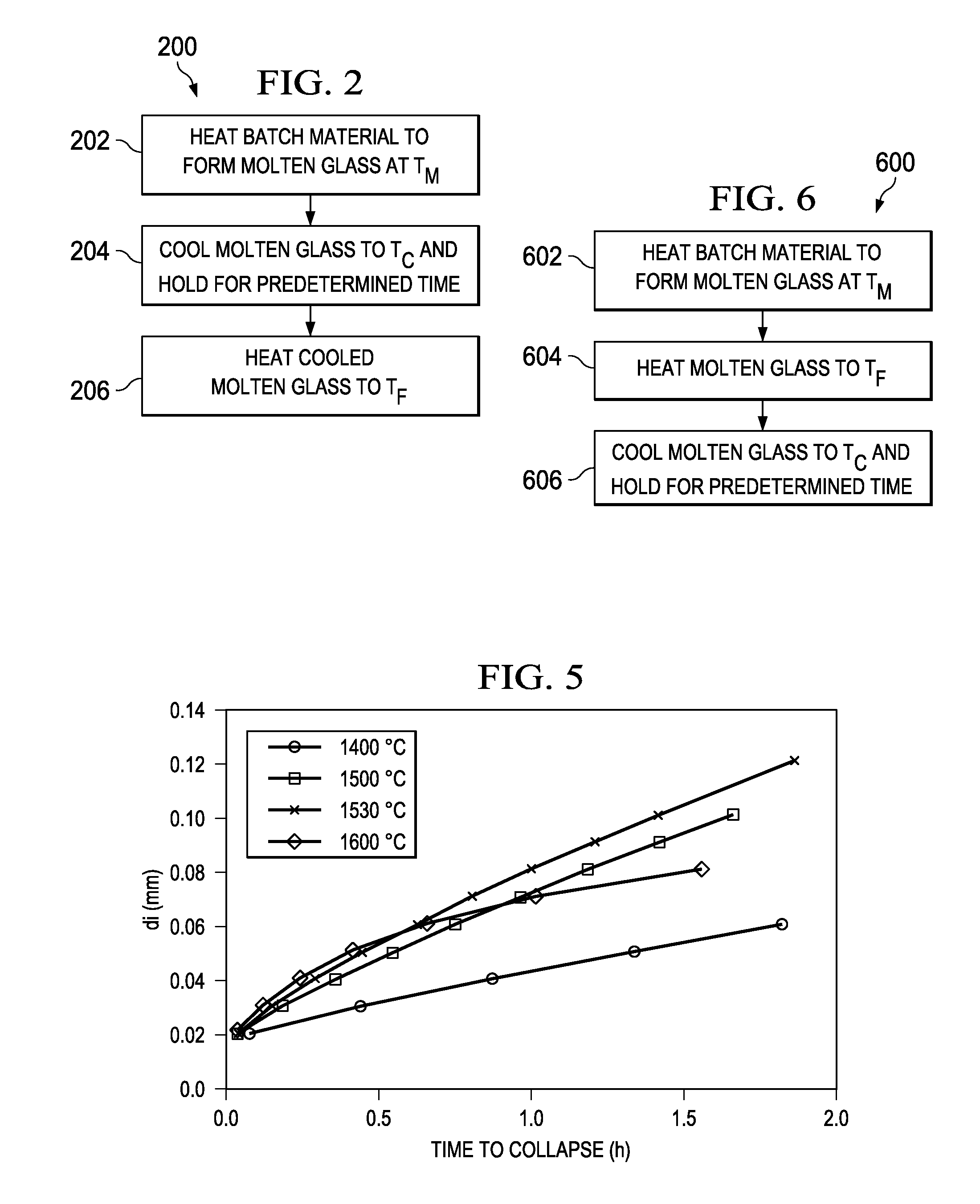
InactiveUS20100199721A1Lower the volumeForehearthsGlass furnace apparatusFlat panel displayGlass manufacturing
A glass manufacturing system and a method are described herein for reducing gaseous inclusions in high melting temperature or high strain point glasses, such as those that are used as glass substrates in flat panel display devices. In one embodiment, the method including the steps of: (a) heating a batch material within a melting vessel to form molten glass at a melting temperature TM, the molten glass comprising a multivalent oxide material; (b) heating the molten glass within a fining vessel to a fining temperature TF≧TM; and (c) cooling the molten glass within a refractory tube after the first heating step or after the second heating step to a cooling temperature TC less than TM, where the molten glass remains within the refractory tube for a predetermined resident time to reduce a volume of the gaseous inclusions in the molten glass and cause gas species to migrate out of the gaseous inclusions into the molten glass such that at least a portion of the gaseous inclusions collapse into the molten glass.
Owner:CORNING INC
Flexible semi-clarity strain sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102353324AIncreased durabilityIncreased sensitivityDecorative surface effectsElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementPolystyreneEngineering
The invention discloses a flexible semi-clarity strain sensor and a preparation method thereof. The sensor is characterized in that: a functional layer is provided on a flexible polymer substrate, the functional layer is a latticed structure which is formed by ZnO and nanofiber, and two sides of the functional layer are titanium and silver electrodes. The invention provides a method for preparinga super-high strain resistance semi-clarity stretching type mechanics sensor based on a zinc oxide nano wire / polystyrene nanofiber hybrid structure on a polydimethylsiloxane substrate. Transmissivities of the sensor before and after zinc oxide growth are represented. The sensor can detect force as high as 50% and has high endurance, rapid response and high sensitivity. A device can be applied to a human body rapid motion test simultaneously. In addition, through driving of a solar energy cell, the device becomes potential application of an outdoor self driven sensor system. The method in the invention has the characteristics of simplicity and a low price, and the sensor has the characteristics of semi-clarity, high strain resistance, high sensitivity, rapid response and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Wear resistant coating for brush seal applications
InactiveUS6186508B1Less stressReduced tendency to crackEngine sealsMolten spray coatingWear resistantCarbide
A metallic coating containing hard carbide particles is described. The coating is applied by an HVOF process using powder particles whose size ranges from about 15 to about 44 microns. The carbide particles are held in a 80% nickel-20% chromium matrix. The coating has a reduced tensile compressive stress relative to similar plasma sprayed coatings and exhibits a high strain to cracking value.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
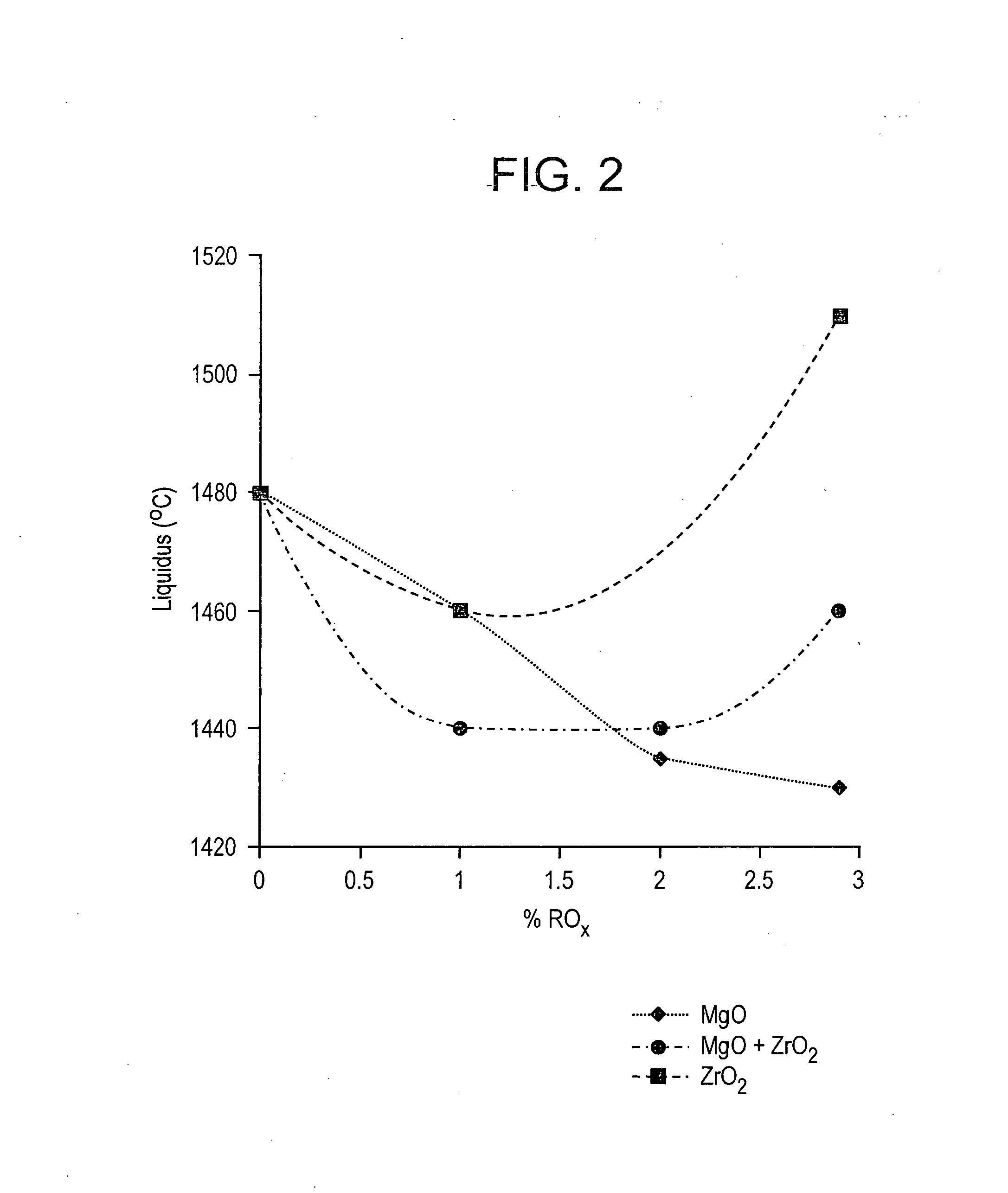
High strain point glasses
A family of glasses from the rare earth alumino-silicate (RE2O3-Al2O3-SiO2) ternary system exhibiting high strain point and low liquidus temperatures; preferably the La2O3 -Al2O3-SiO2 ternary system. The glasses are excellent candidates for electronics applications and have the following composition, expressed in mole percent and calculated from the glass batch on an oxide basis: 60-85% SiO2, 10-25% Al2O3, and 4-15% RE2O3.
Owner:CORNING INC
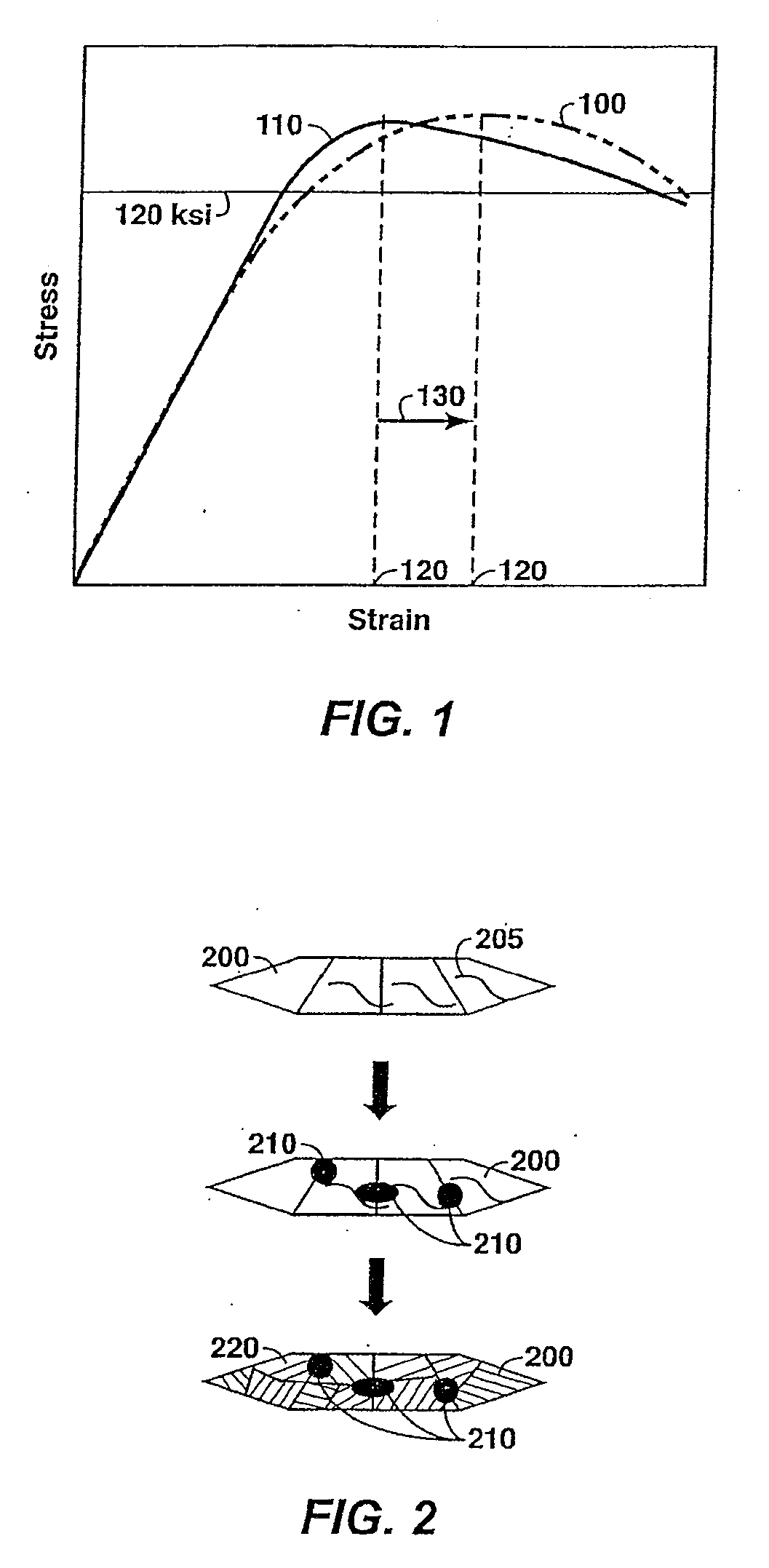
High Strength Dual Phase Steel With Low Yield Ratio, High Toughness and Superior Weldability
A dual phase, high strength steel having a composite microstructure of soft and hard phases providing a low yield ratio, high strain capacity, superior weldability, and high toughness is provided. The dual phase steel includes from about 10% by volume to about 60% by volume of a first phase or constituent consisting essentially of fine-grained ferrite. The first phase has a ferrite mean grain size of about 5 microns or less. The dual phase steel further includes from about 40% by volume to about 90% by volume of a second phase or constituent comprising fine-grained martensite, fine-grained lower bainite, fine-grained granular bainite, fine-grained degenerate upper bainite, or any mixture thereof. Methods for making the same are also provided.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Low temperature selective epitaxy of silicon germanium alloys employing cyclic deposit and etch
ActiveUS20120295421A1Increase etch rateIncrease deposition ratePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesAlloy
Cyclic deposit and etch (CDE) selective epitaxial growth employs an etch chemistry employing a combination of hydrogen chloride and a germanium-containing gas to provide selective deposition of a silicon germanium alloy at temperatures lower than 625° C. High strain epitaxial silicon germanium alloys having a germanium concentration greater than 35 atomic percent in a temperature range between 400° C. and 550° C. A high order silane having a formula of SinH2n+2, in which n is an integer greater than 3, in combination with a germanium-containing precursor gas is employed to deposit the silicon germanium alloy with thickness uniformity and at a high deposition rate during each deposition step in this temperature range. Presence of the germanium-containing gas in the etch chemistry enhances the etch rate of the deposited silicon germanium alloy material during the etch step.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD +1
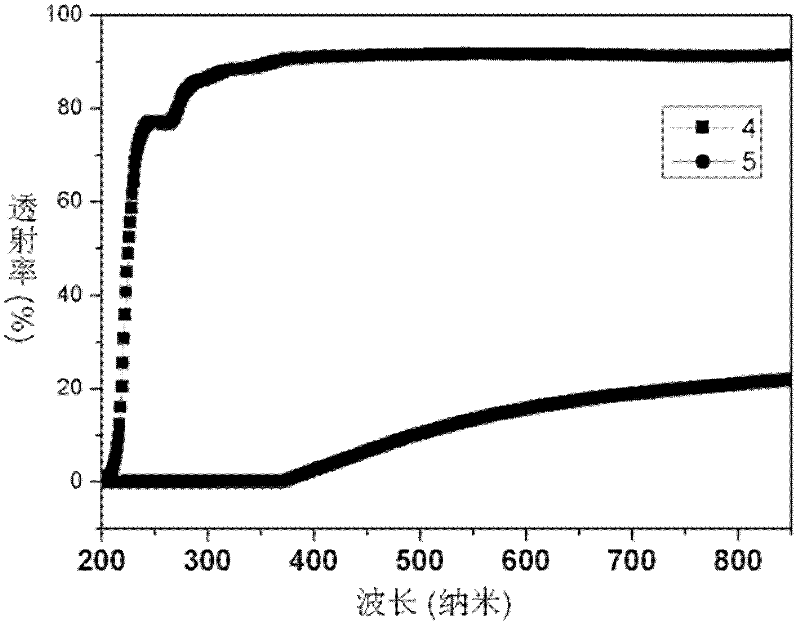
Composition of aluminum boron silicate glass and application
ActiveCN101092280AImprove melting qualityReduce the presence of air bubblesSilicate glassFlat panel display
This invention relates to aluminum borosilicate glass with high elastic modulus and its application. The aluminum borosilicate glass is prepared from: 55-63.5 wt.% SiO2, 8-10.5 wt.% B2O3, 15-21 wt.% Al2O3, 0-3.5 wt.% MgO, 4-10 wt.% CaO, 0-5 wt.% SrO, 1-5.5 wt.% BaO, 0.001-4 wt.% Y2O3, 0-2.5 wt.% La2O3, 0-0.5 wt.% ZnO, 0-0.3 wt.% ZrO2, and 0.005-0.08 wt.% R2O (R = Li, Na or K). The aluminum borosilicate glass has such advantages as high strain point, low expansion coefficient, high elastic modulus and no alkali, and is suitable for flat panel display and TFT-LCD glass substrate.
Owner:HENAN ANCAI HI-TECH +1
Nanometer/columnar-like crystal mixing structure thermal barrier coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103009704ASmall shrinkageGood heat insulationMolten spray coatingCeramic layered productsThermal insulationNanoparticle
The invention relates to a nanometer / columnar-like crystal mixing structure thermal barrier coating and a preparation method thereof. The mixing structure thermal barrier coating is a nanometer / columnar-like crystal mixing structure coating, and comprises a substrate, a metal bonding layer and a ceramic layer, wherein the metal bonding layer and the ceramic layer are sequentially coated on the substrate, the ceramic layer comprises unmelted nanoparticles, nanometer pores, nanometer crystal and ultrafine crystal, and has cracks perpendicular to the substrate, and the cracks form the columnar-like crystal structure. The mixing structure thermal barrier coating preparation method comprises powder selection, a pretreatment step, a substrate pretreatment step, a metal bonding layer preparation step, and a 6-8% YSZ ceramic layer preparation step. The coating disclosed by the present invention has characteristics of high strain tolerance, excellent thermal insulation performance, high bonding strength, high thermal cycle life, and high thermal shock life, such that the thermal barrier coating has a good comprehensive performance.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI MECHANIZATION SCI +1
Measurement of tissue elastic modulus
ActiveUS20080081994A1Easy to measureEasy to quantifyWave based measurement systemsBlood flow measurement devicesArterial velocityMedicine
An optimized elastic modulus reconstruction procedure can estimate the nonlinear elastic properties of vascular wall from intramural strain and pulse wave velocity (PWV) measurements. A noninvasive free-hand ultrasound scanning procedure is used to apply external force, comparable to the force in measuring a subject's blood pressure, to achieve higher strains by equalizing the internal arterial baseline pressure. PWV is estimated at the same location where intramural strain is measured. The reconstructed elastic modulus is optimized and the arterial elastic modulus can be determined and monitored using a simple dual elastic modulus reconstruction procedure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Bioerodible Magnesium Alloy Microstructures for Endoprostheses
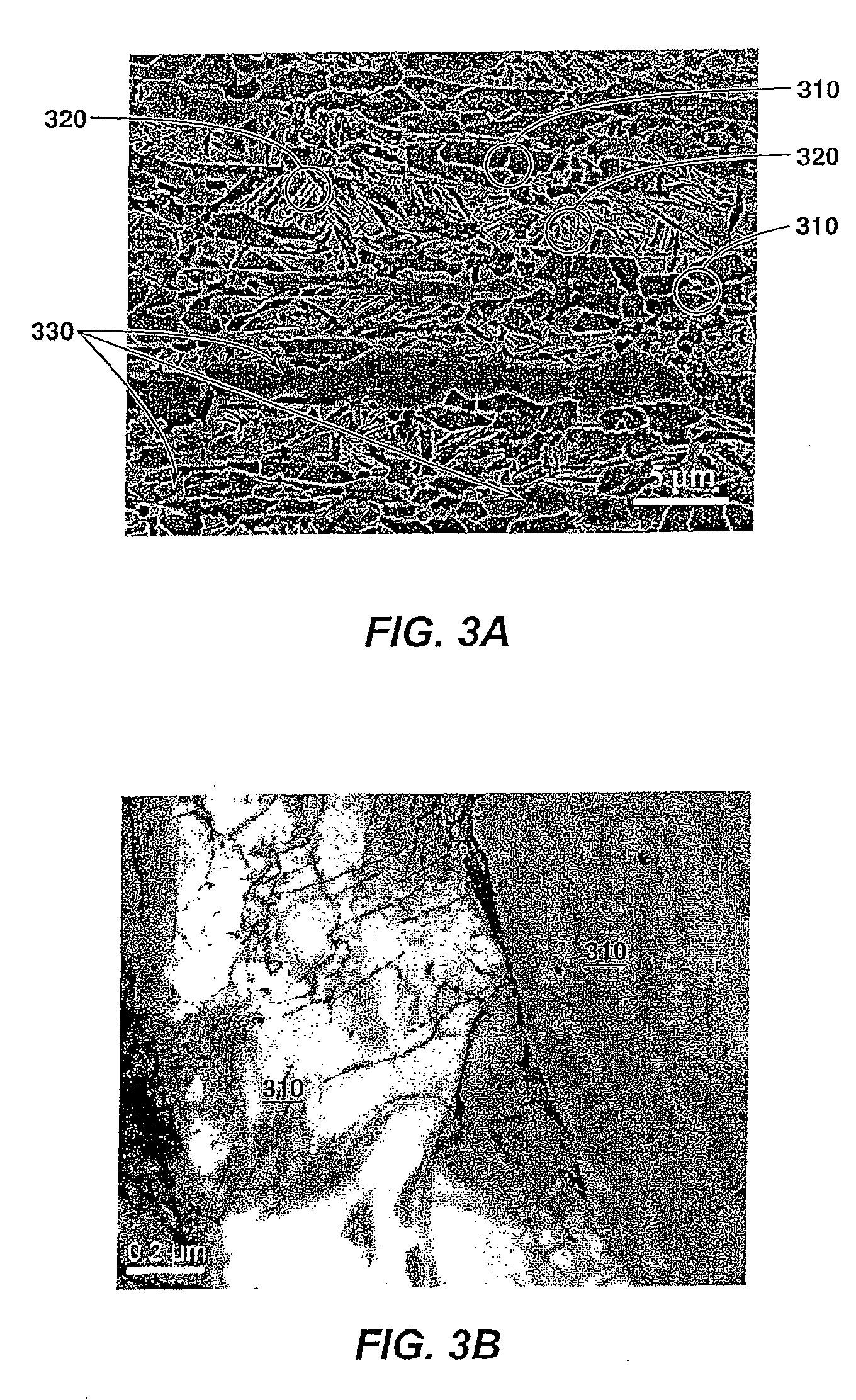
ActiveUS20140236284A1Improve mechanical propertiesIncrease ratingsStentsSurgerySolid solutionGrain boundary
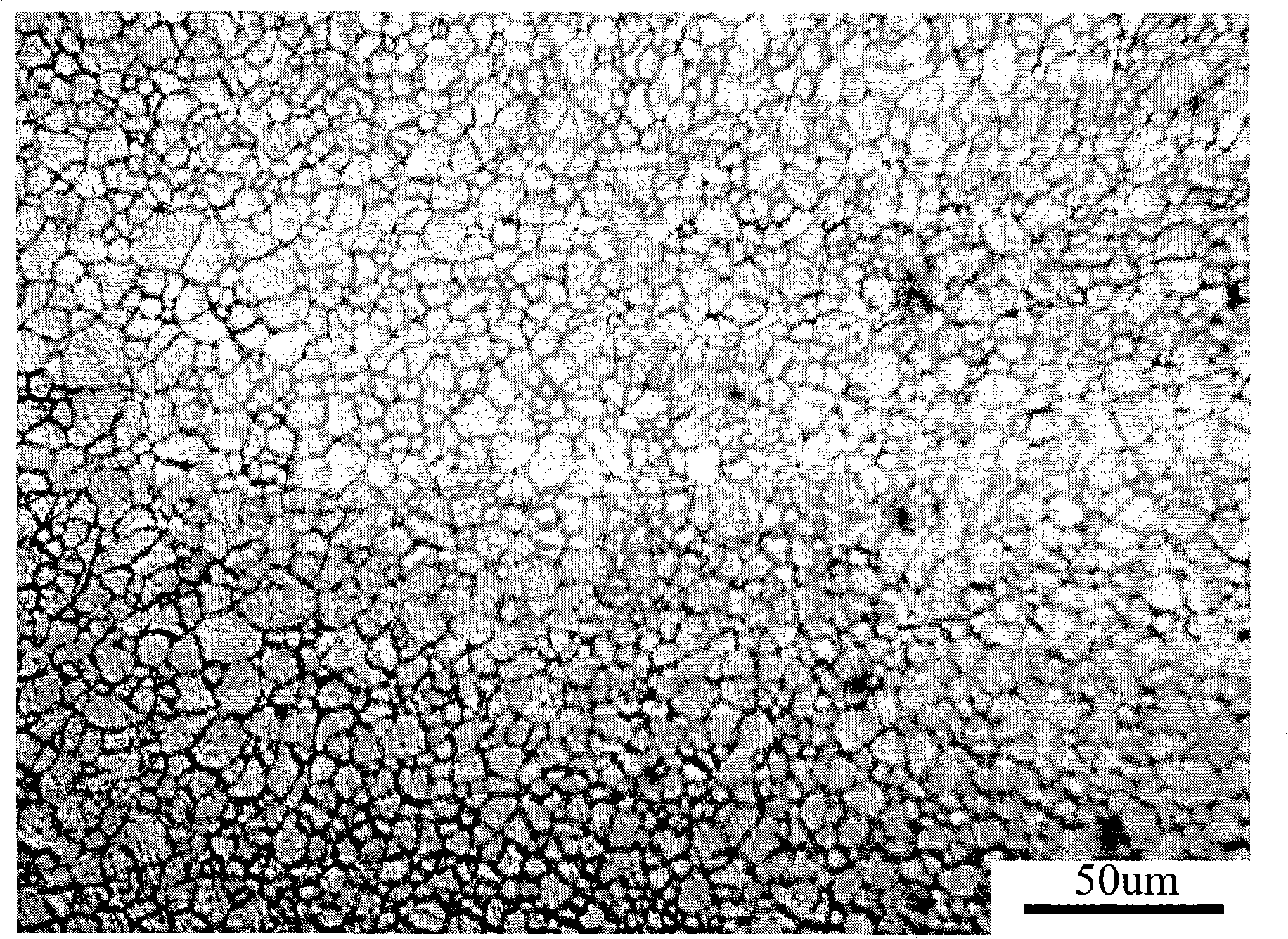
A bioerodible endoprosthesis includes a bioerodible magnesium alloy. The bioerodible magnesium alloy has a microstructure including equiaxed Mg-rich solid solution-phase grains having an average grain diameter of less than or equal to 5 microns and second-phase precipitates in grain boundaries between the equiaxed Mg-rich solid solution-phase grains. The beta-phase precipitates have an average longest dimension of 0.5 micron or less. The microstructure can be produced by one or more equal-channel high-strain processes.
Owner:BIOTRONIK AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com