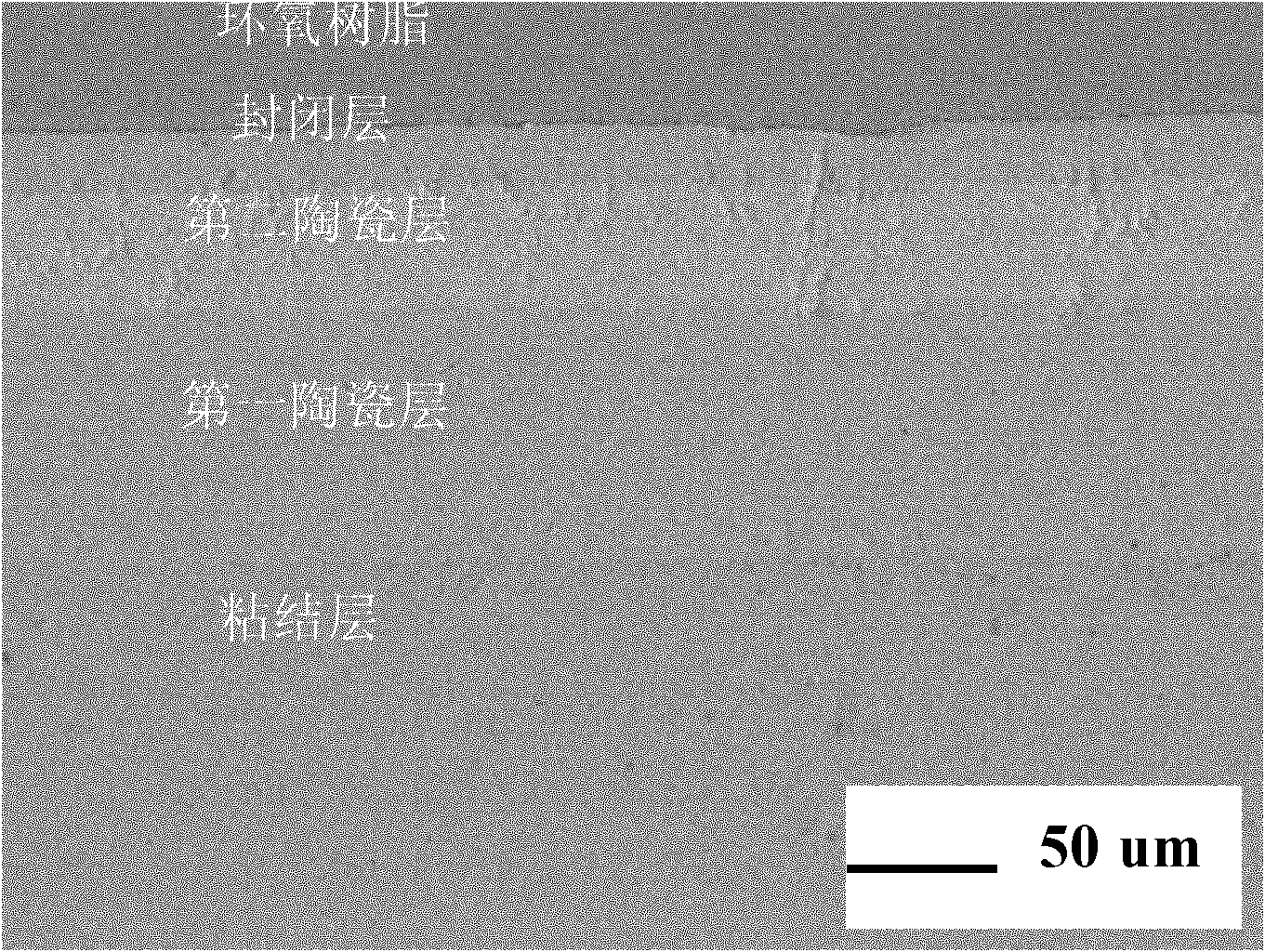Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1845 results about "Thermal barrier coating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
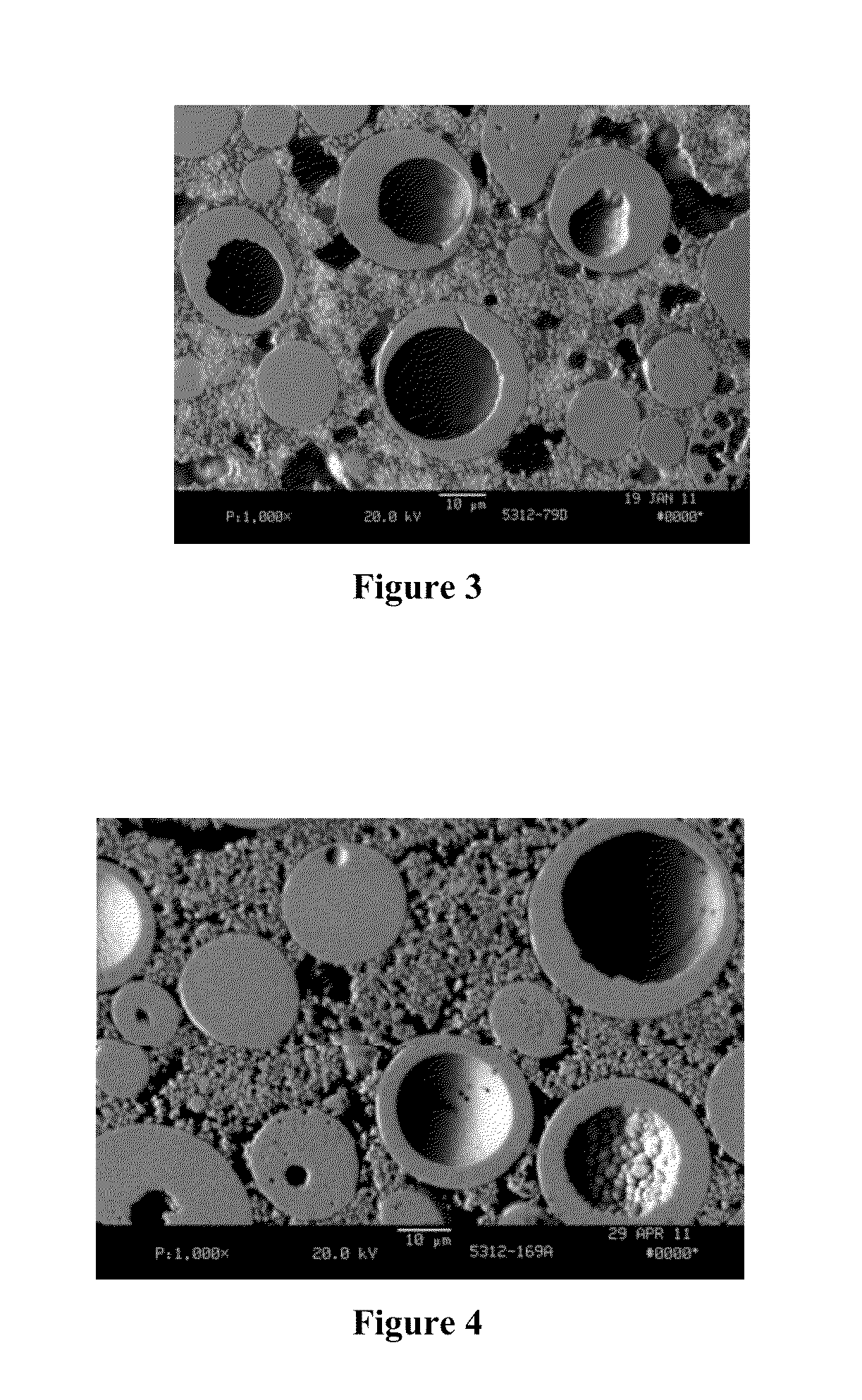
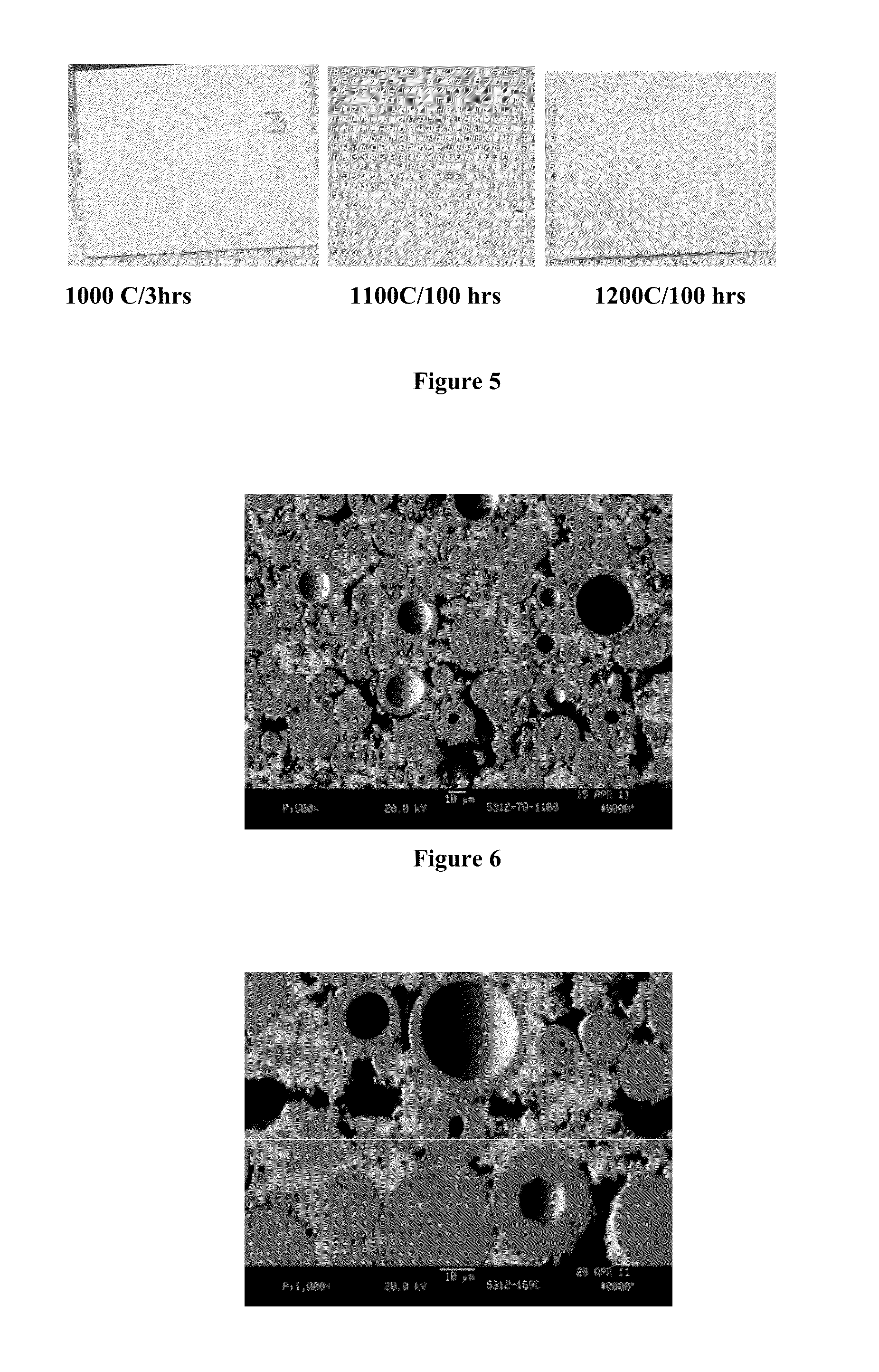
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) are advanced materials systems usually applied to metallic surfaces operating at elevated temperatures, such as gas turbine or aero-engine parts, as a form of exhaust heat management. These 100 μm to 2 mm thick coatings of thermally insulating materials serve to insulate components from large and prolonged heat loads and can sustain an appreciable temperature difference between the load-bearing alloys and the coating surface. In doing so, these coatings can allow for higher operating temperatures while limiting the thermal exposure of structural components, extending part life by reducing oxidation and thermal fatigue. In conjunction with active film cooling, TBCs permit working fluid temperatures higher than the melting point of the metal airfoil in some turbine applications. Due to increasing demand for more efficient engines running at higher temperatures with better durability/lifetime and thinner coatings to reduce parasitic mass for rotating/moving components, there is significant motivation to develop new and advanced TBCs. The material requirements of TBCs are similar to those of heat shields, although in the latter application emissivity tends to be of greater importance.
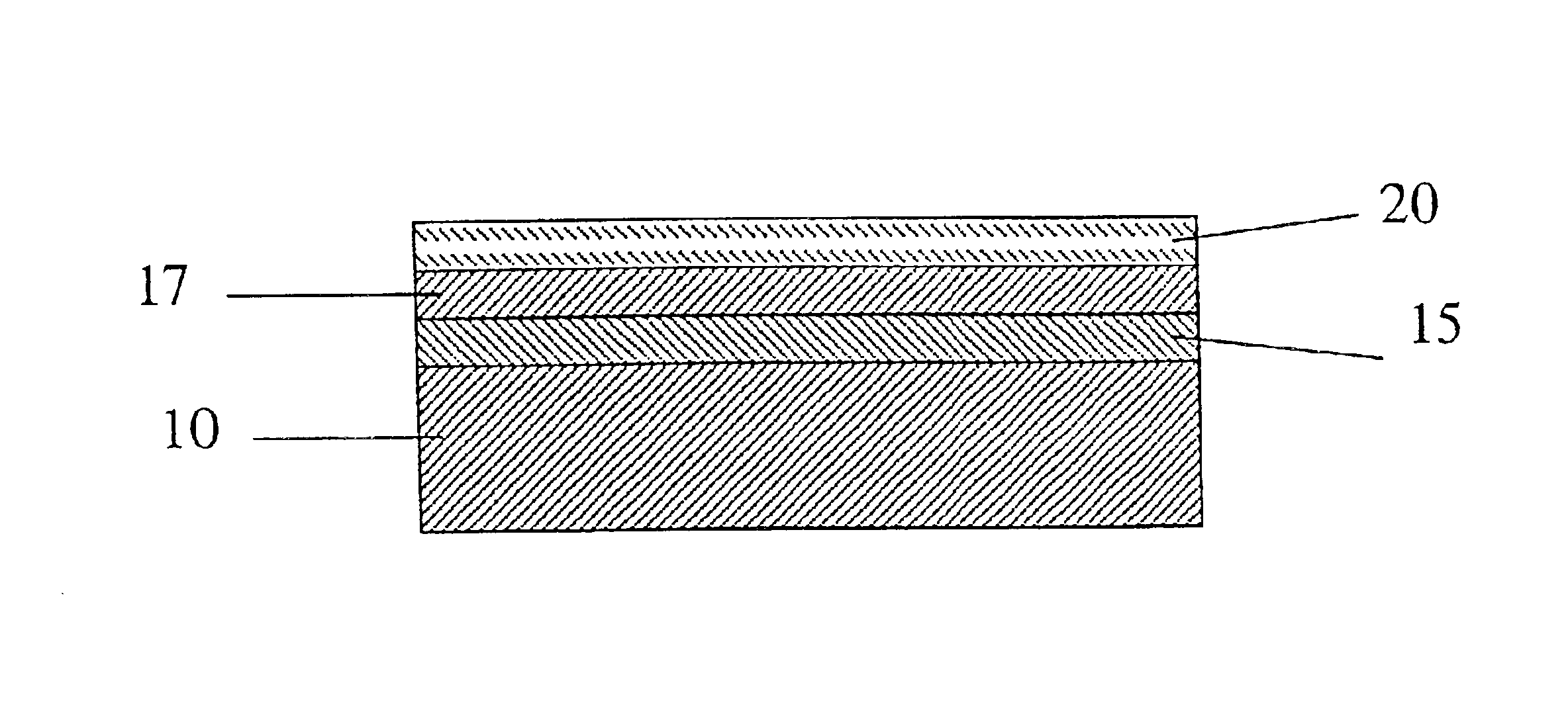
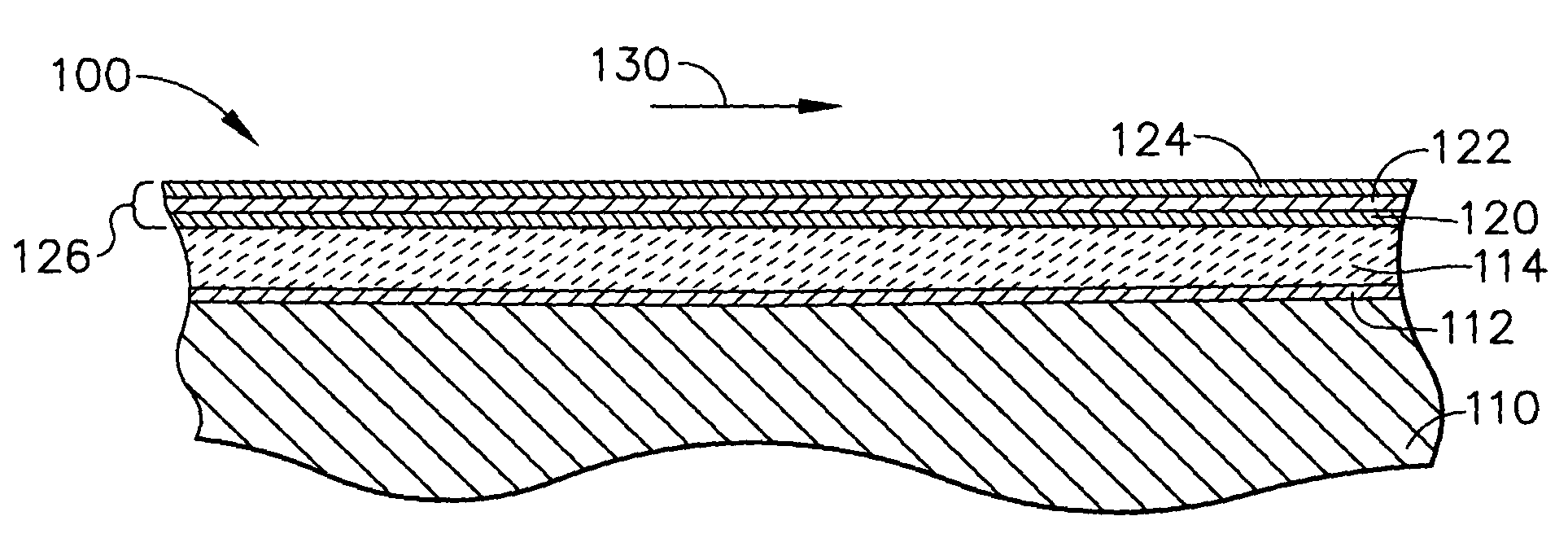
Multilayer thermal barrier coating
InactiveUS20090324989A1Improved thermal barrier coatingAttackLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingThermal barrier coatingZirconium oxide
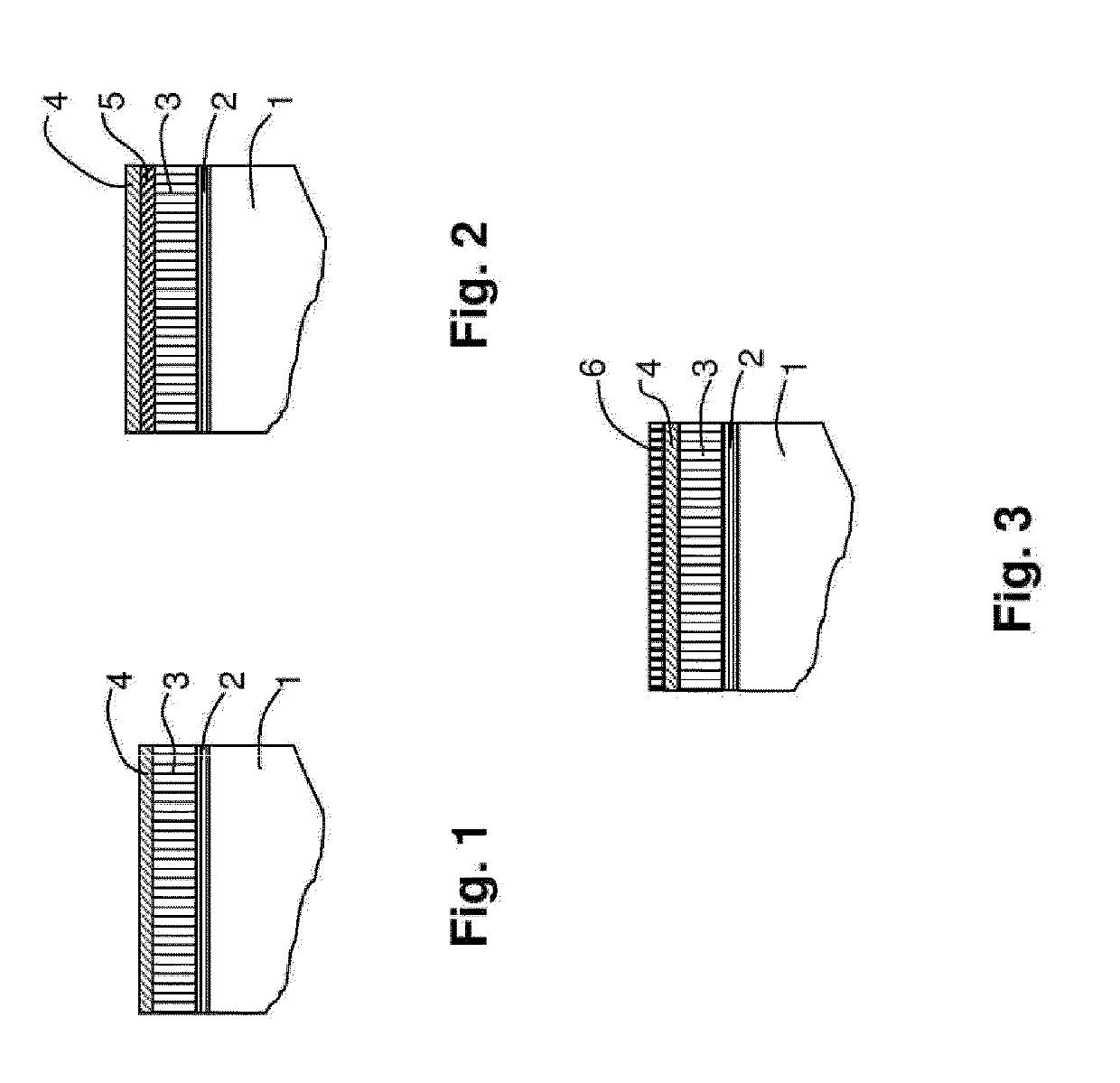
Components (1) have a thermal barrier coating (2-6) on the surface thereof, wherein the thermal barrier coating includes at least one layer (3) having chemically stabilized zirconia, and wherein at least indirectly adjacent to the layer (3) with chemically stabilized zirconia and on its surface facing side, there is provided a protective layer (4) and / or a infiltration zone (5) which does not react with environmental contaminant compositions that contain oxides of calcium and which does not react with the material of the layer (3) having chemically stabilized zirconia. Methods for making such components as well as to uses of specific systems for coating thermal barrier coatings, can prevent CMAS.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD +1
High temperature erosion resistant, abradable thermal barrier composite coating
InactiveUS6235370B1Improve wear resistanceImprove adhesionMolten spray coatingPump componentsCombustorHoneycomb
A composite thermal barrier coating system includes a honeycomb metallic structure filled with high thermal expansion ceramic hollow spheres in a phosphate bonded matrix. The composite thermal barrier coating system may be manufactured to thicknesses in excess of current thermal barrier coating systems, thereby imparting greater thermal protection. Superior erosion resistance and abrasion properties are also achieved. The composite thermal barrier coating is useful on combustion turbine components such as ring seal segments, vane segment shrouds, transitions and combustors.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
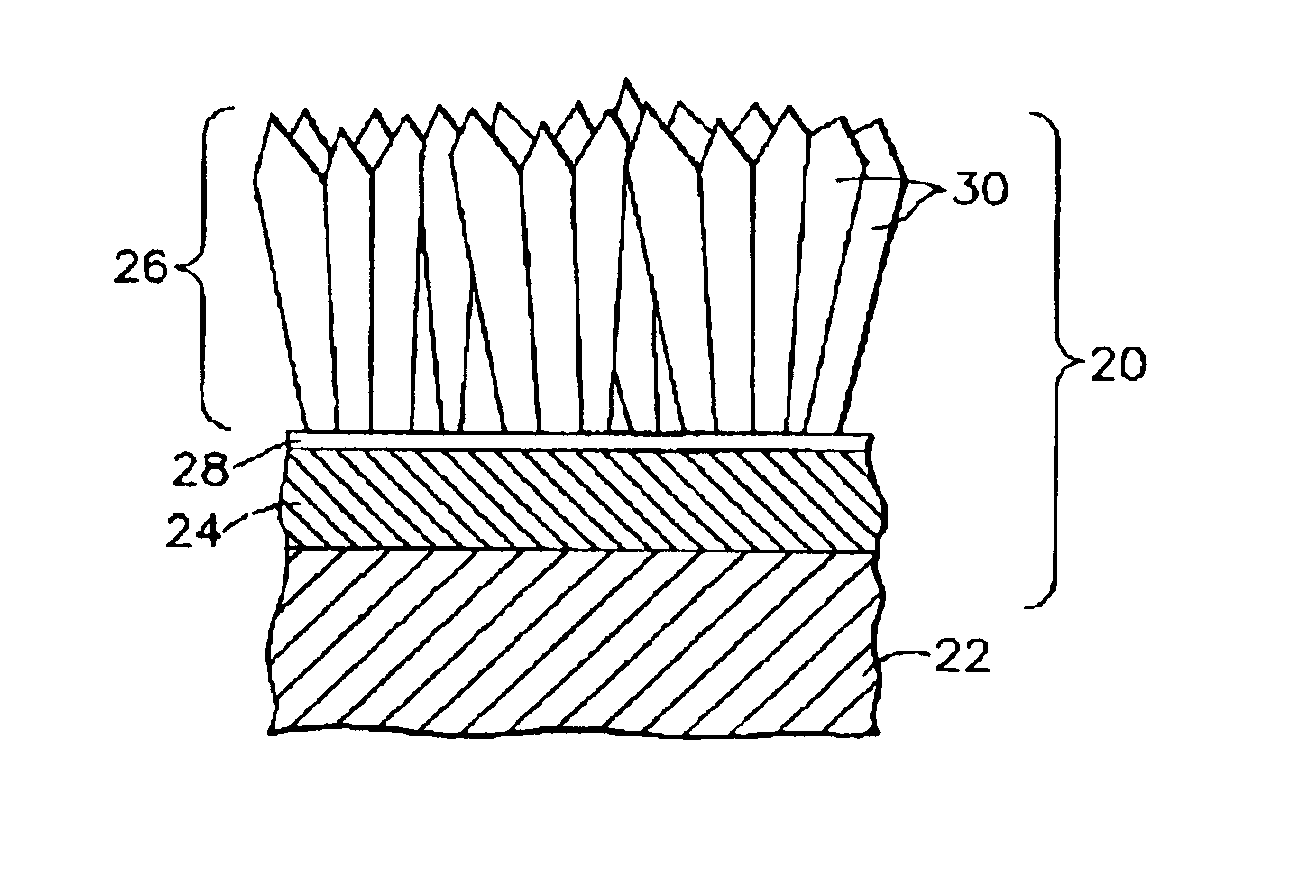
Segmented thermal barrier coating
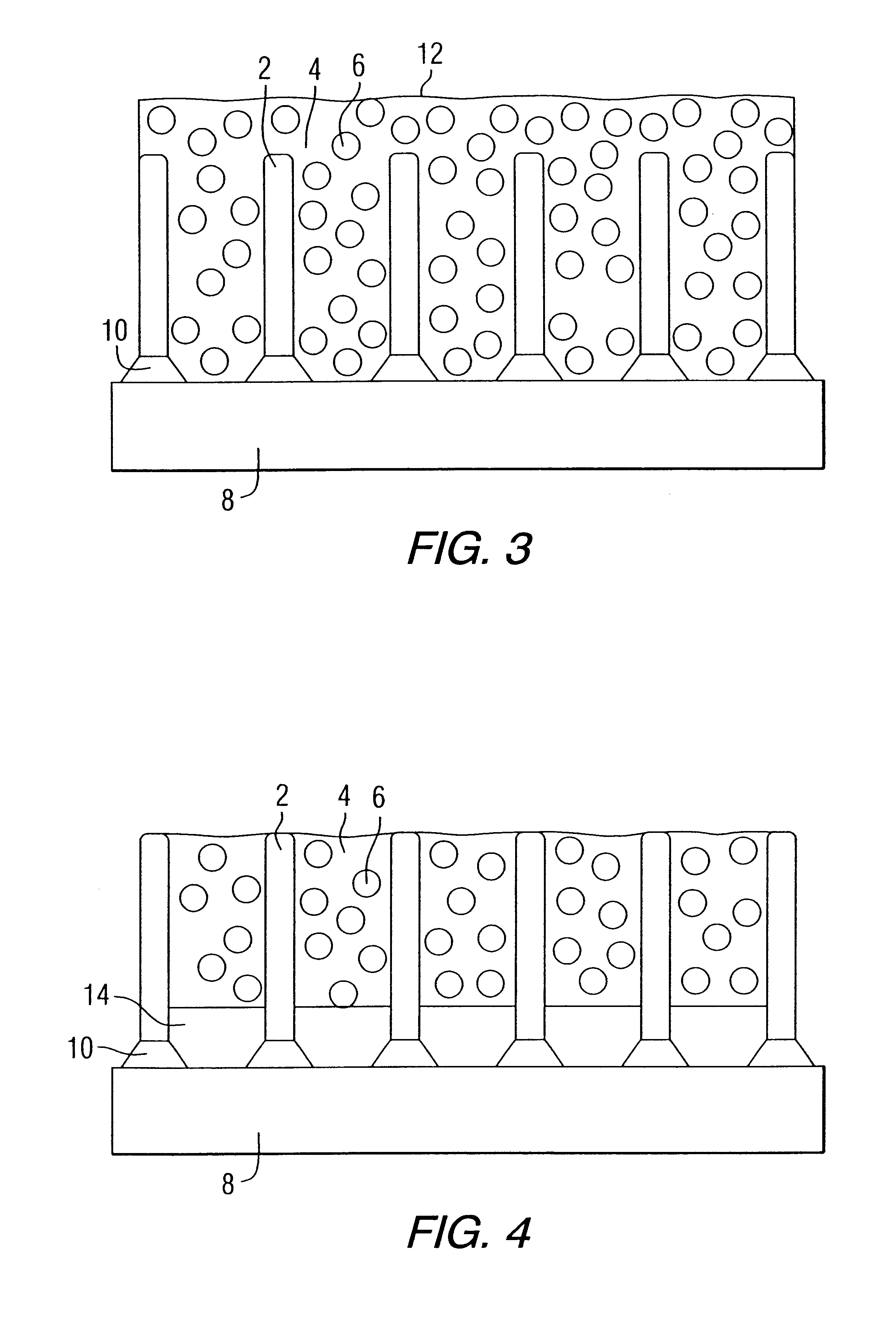
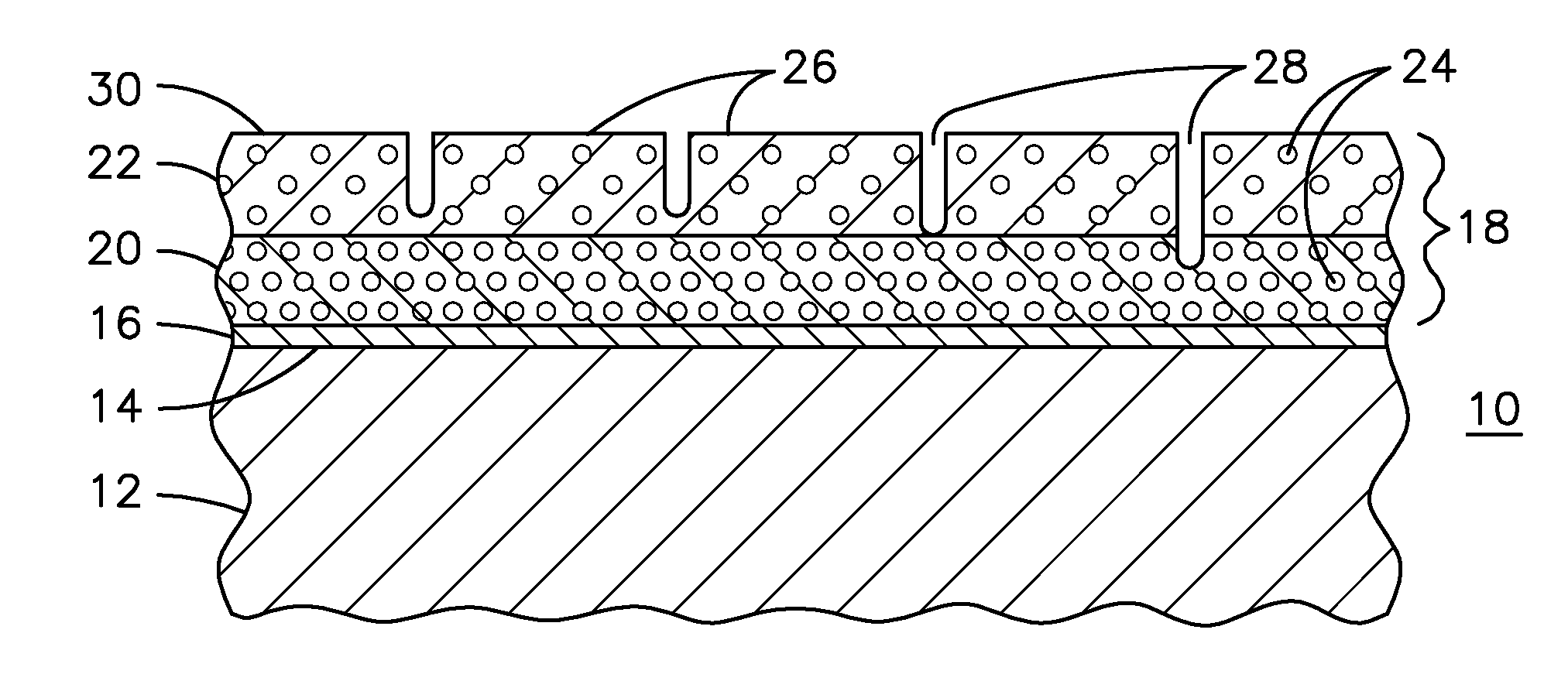
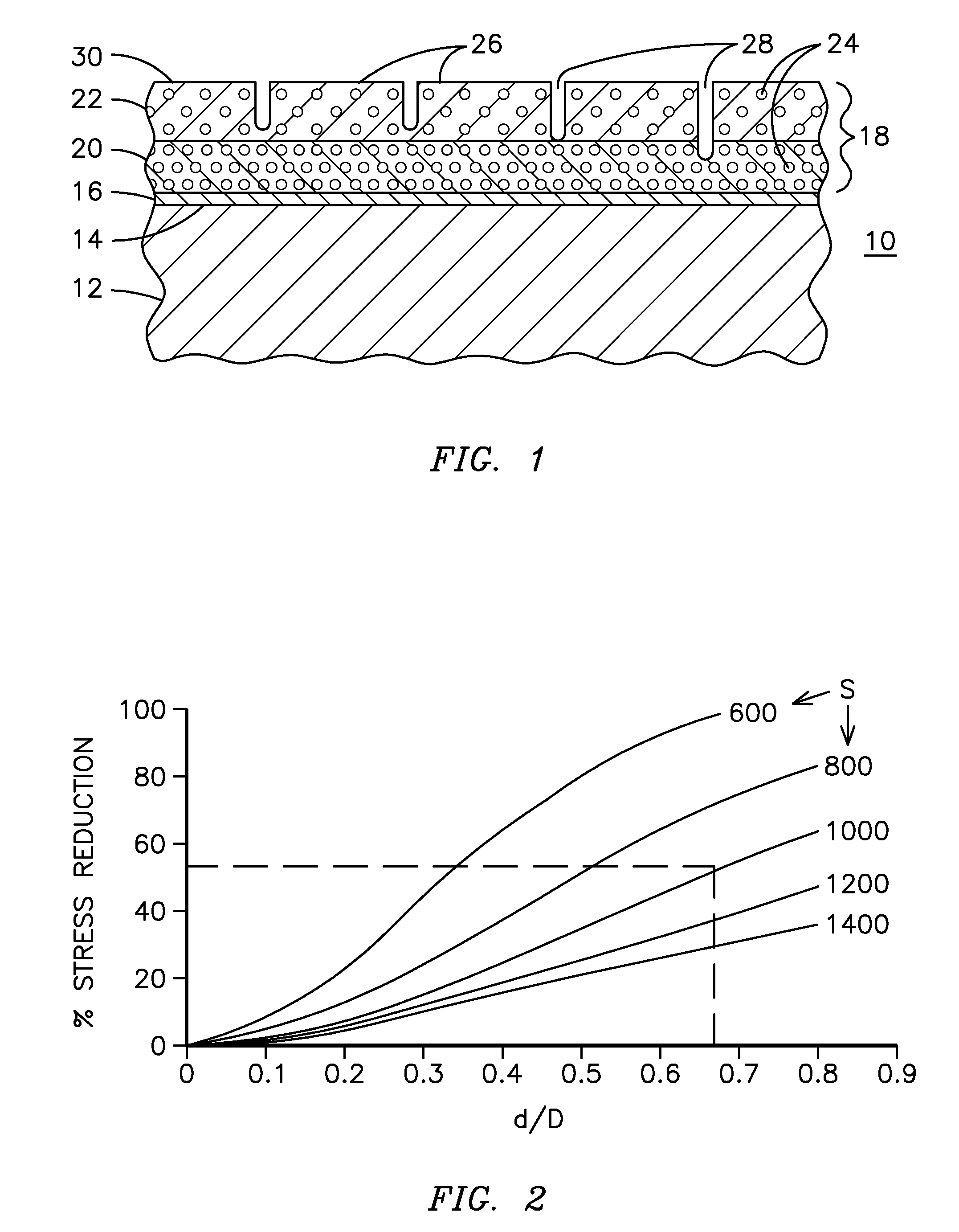
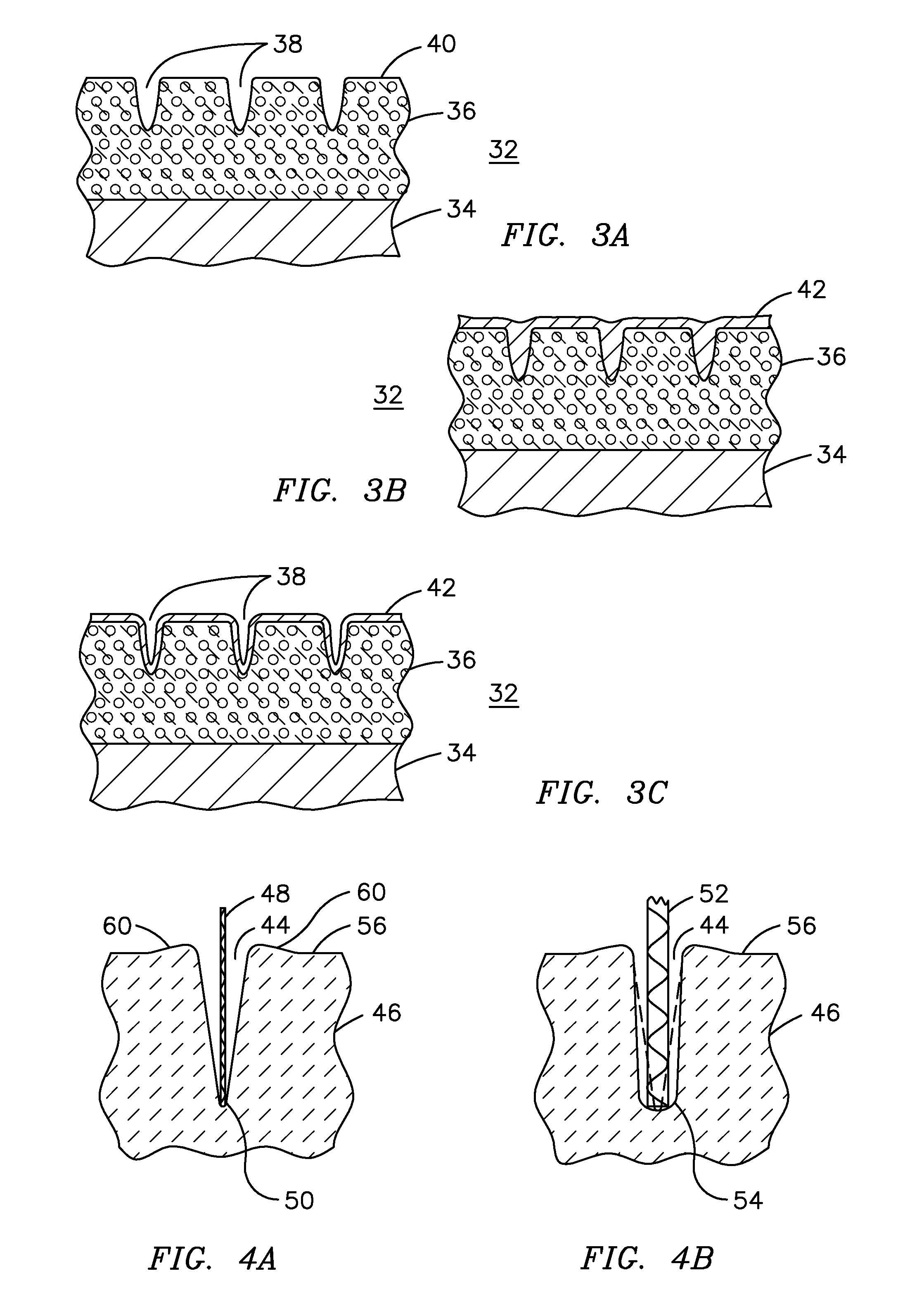
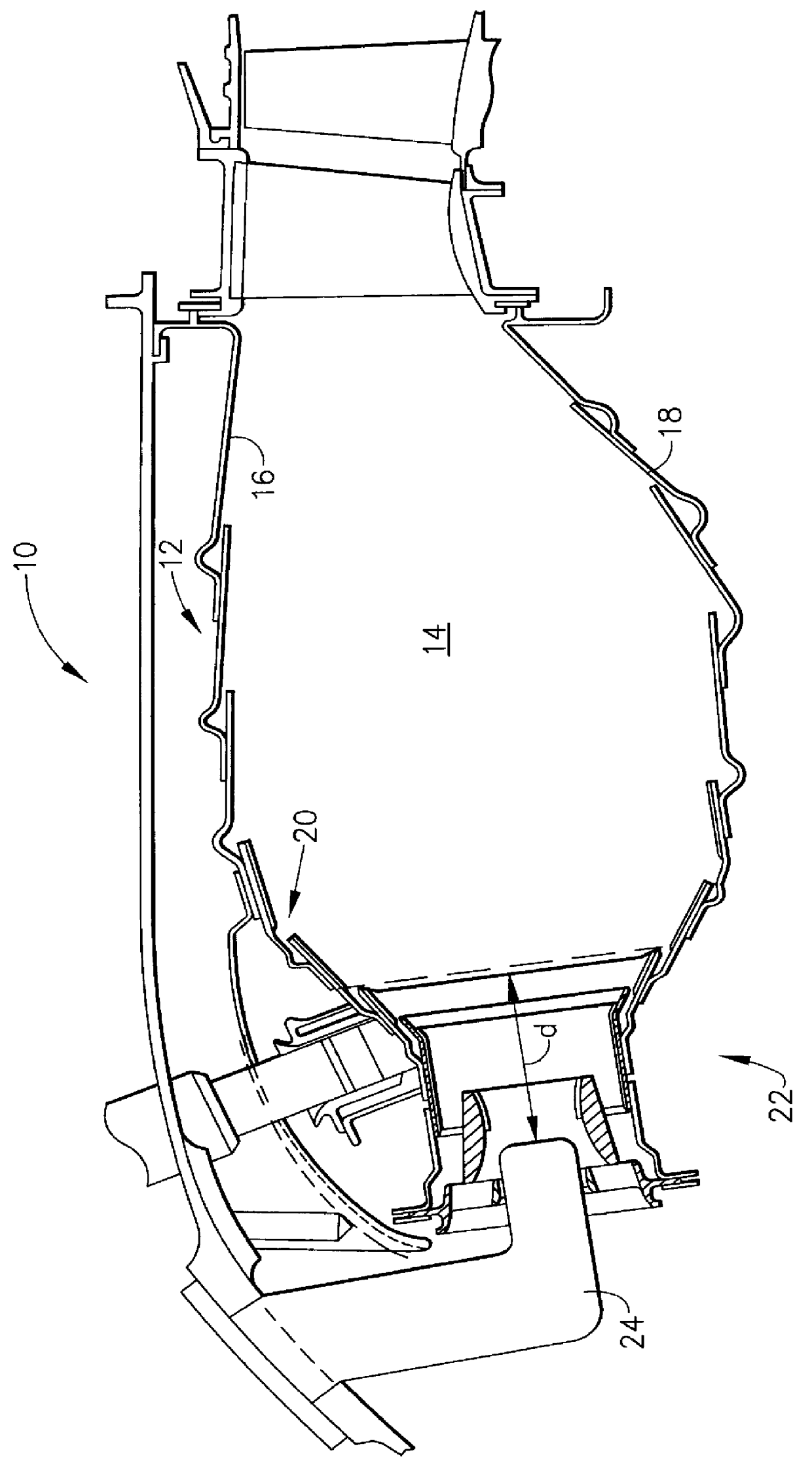
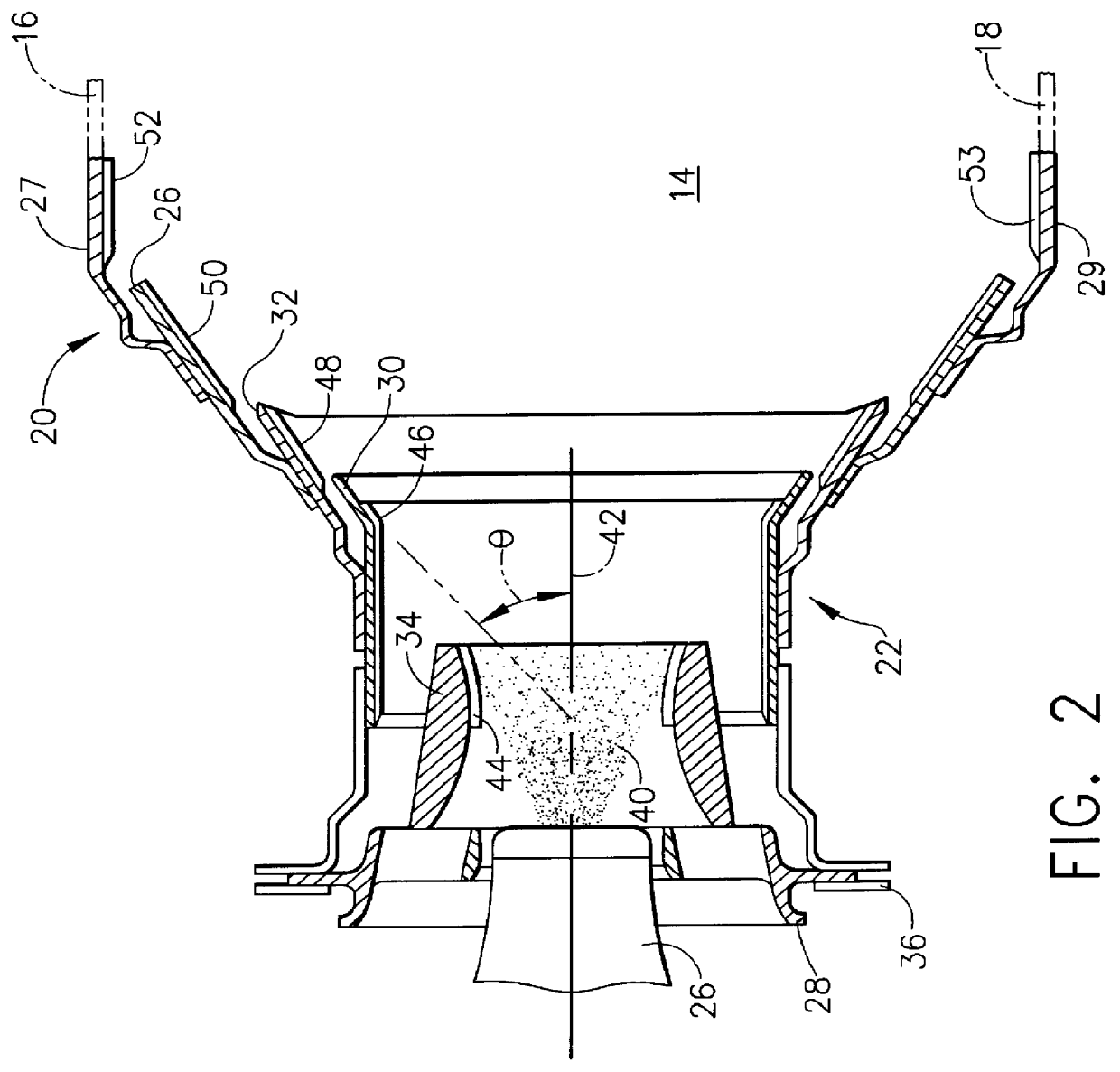
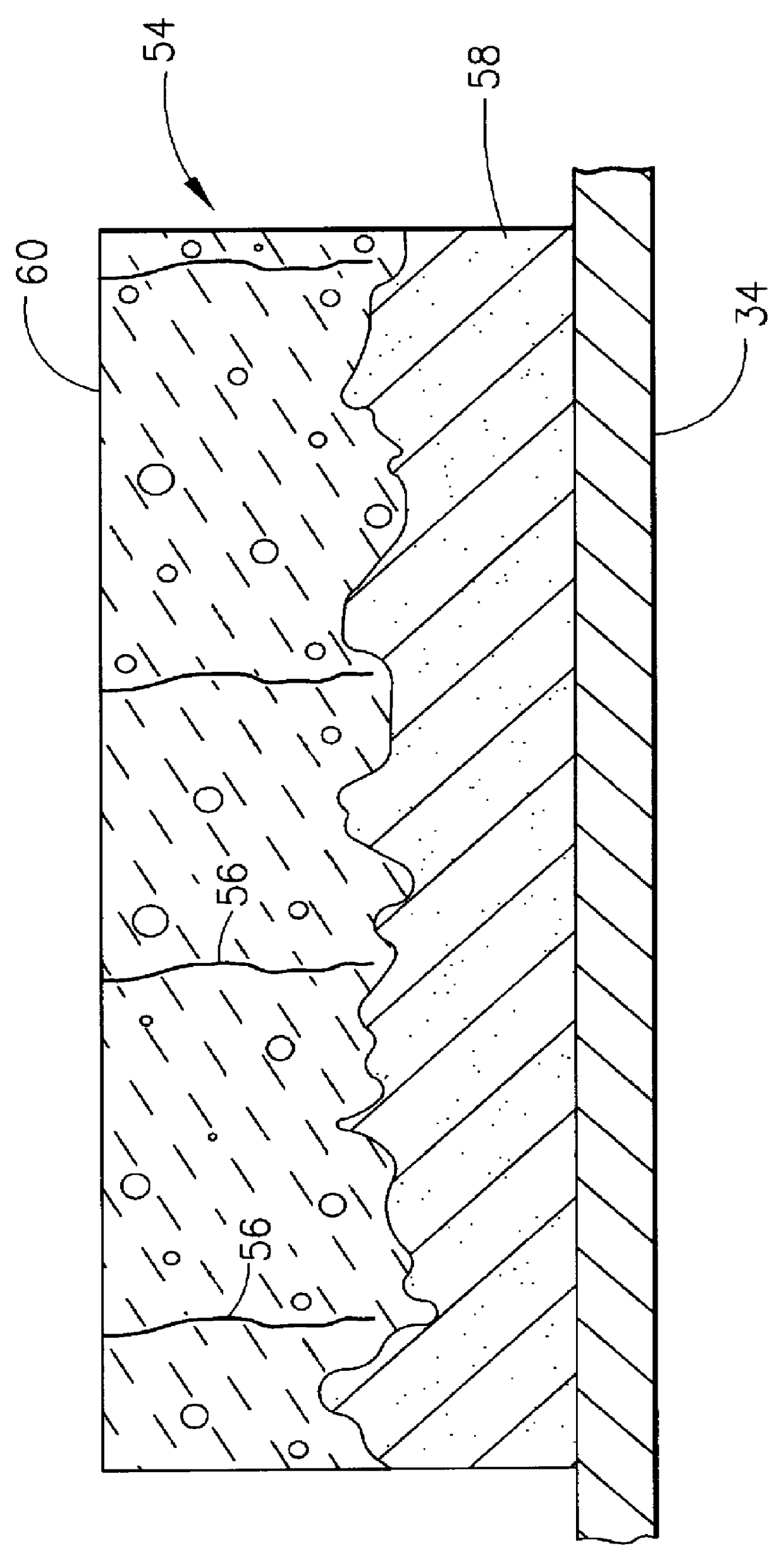
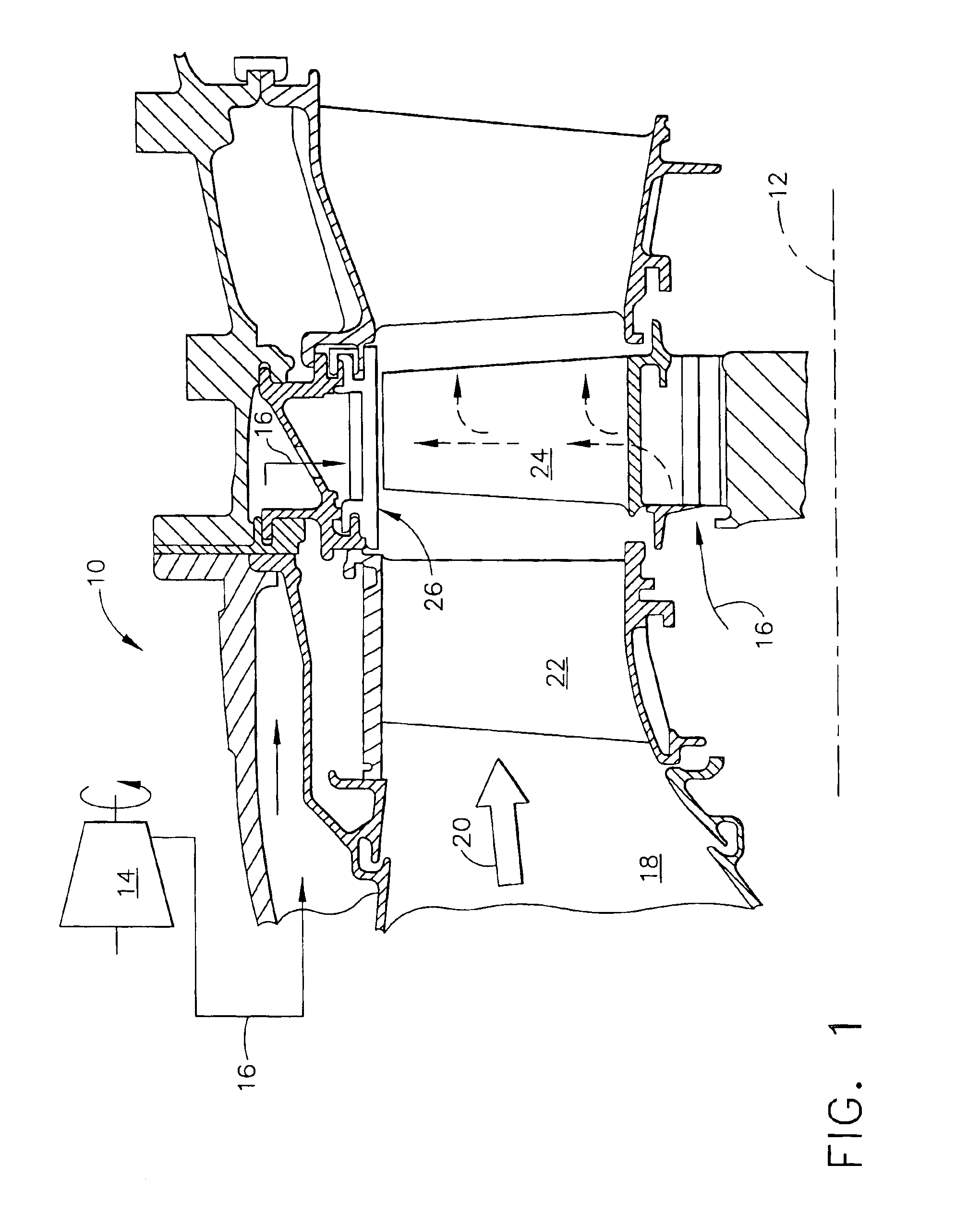
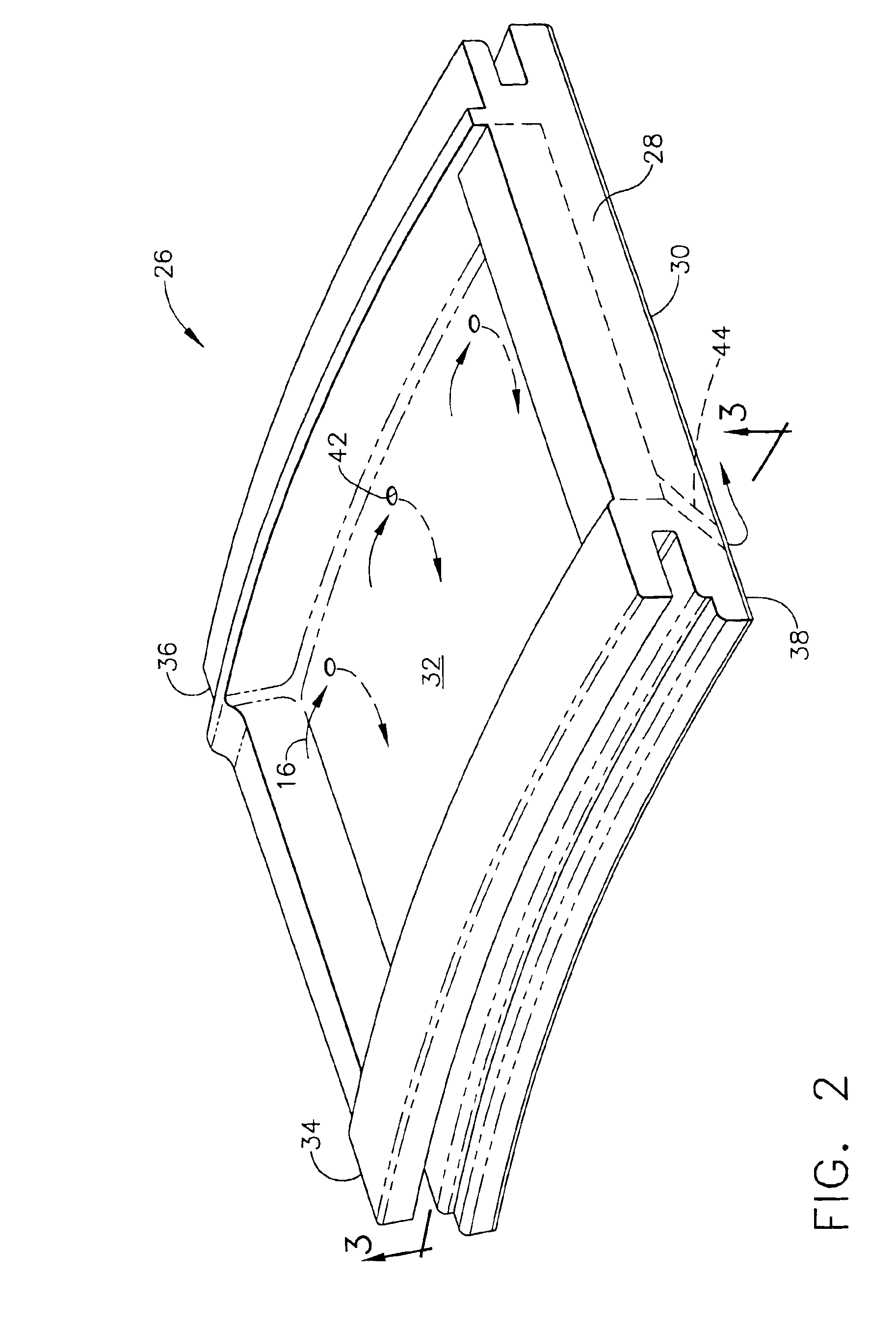
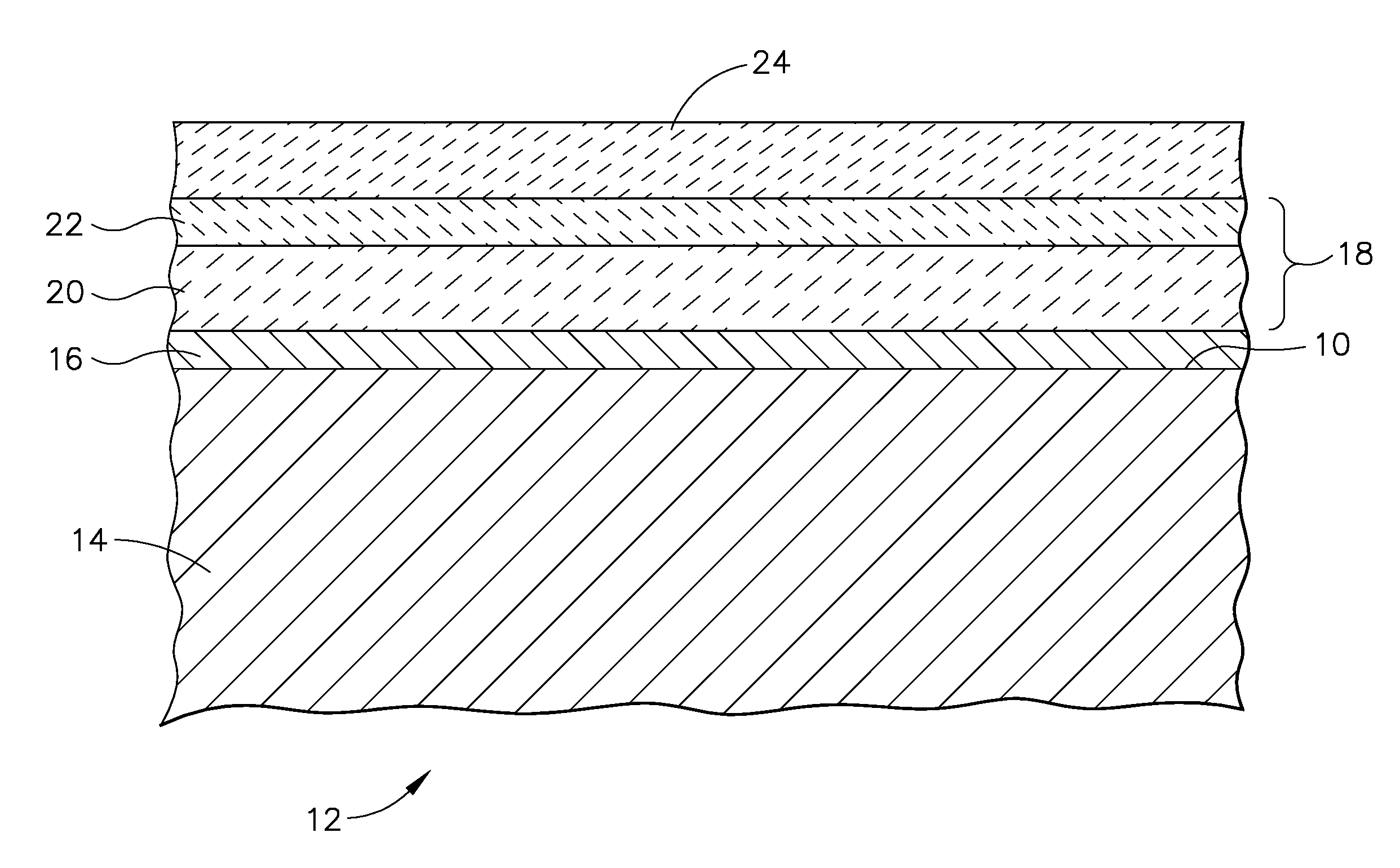
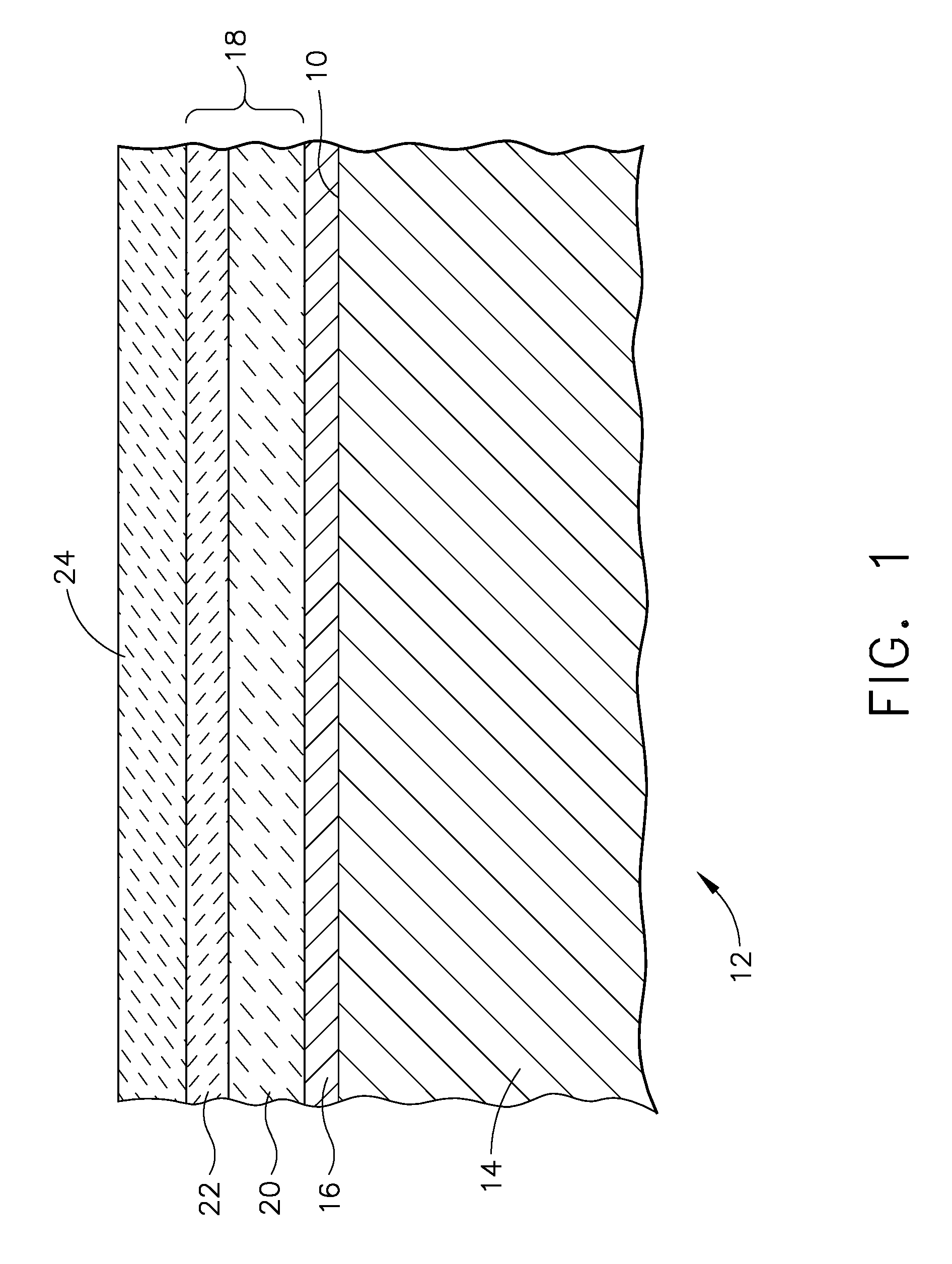
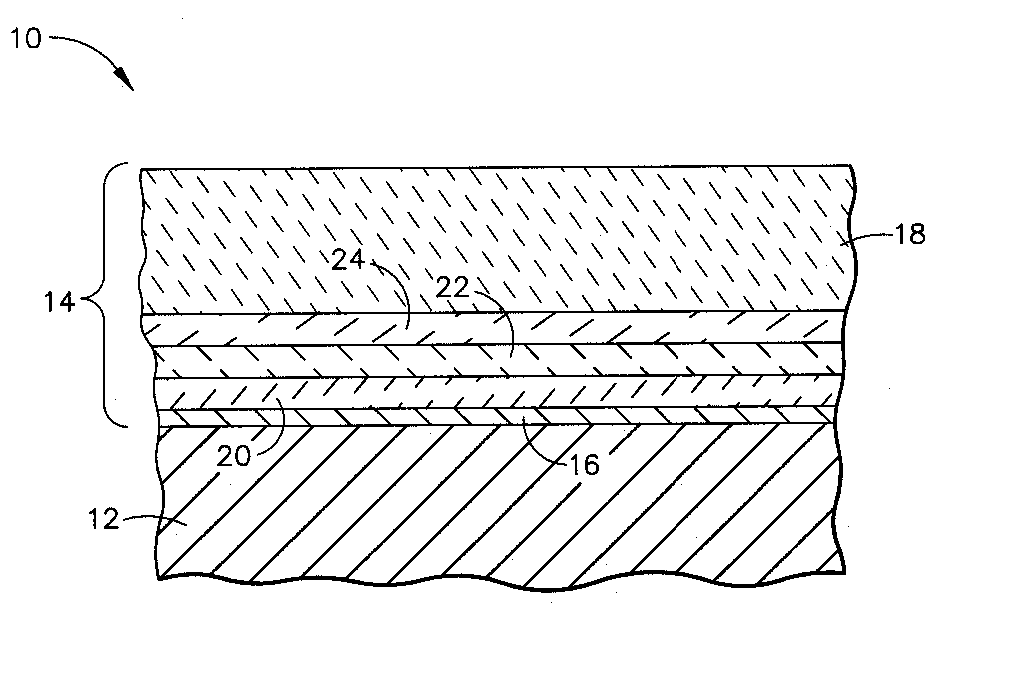
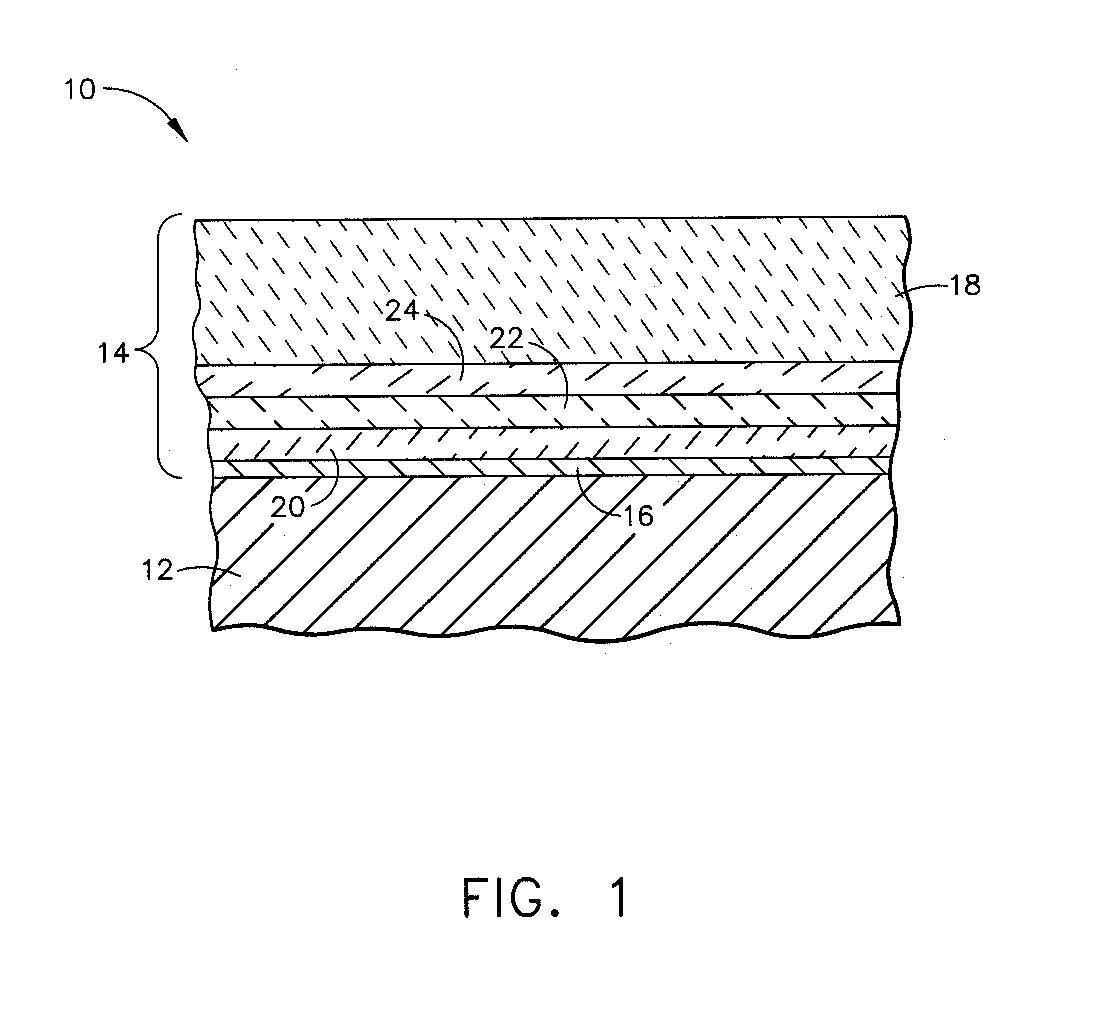
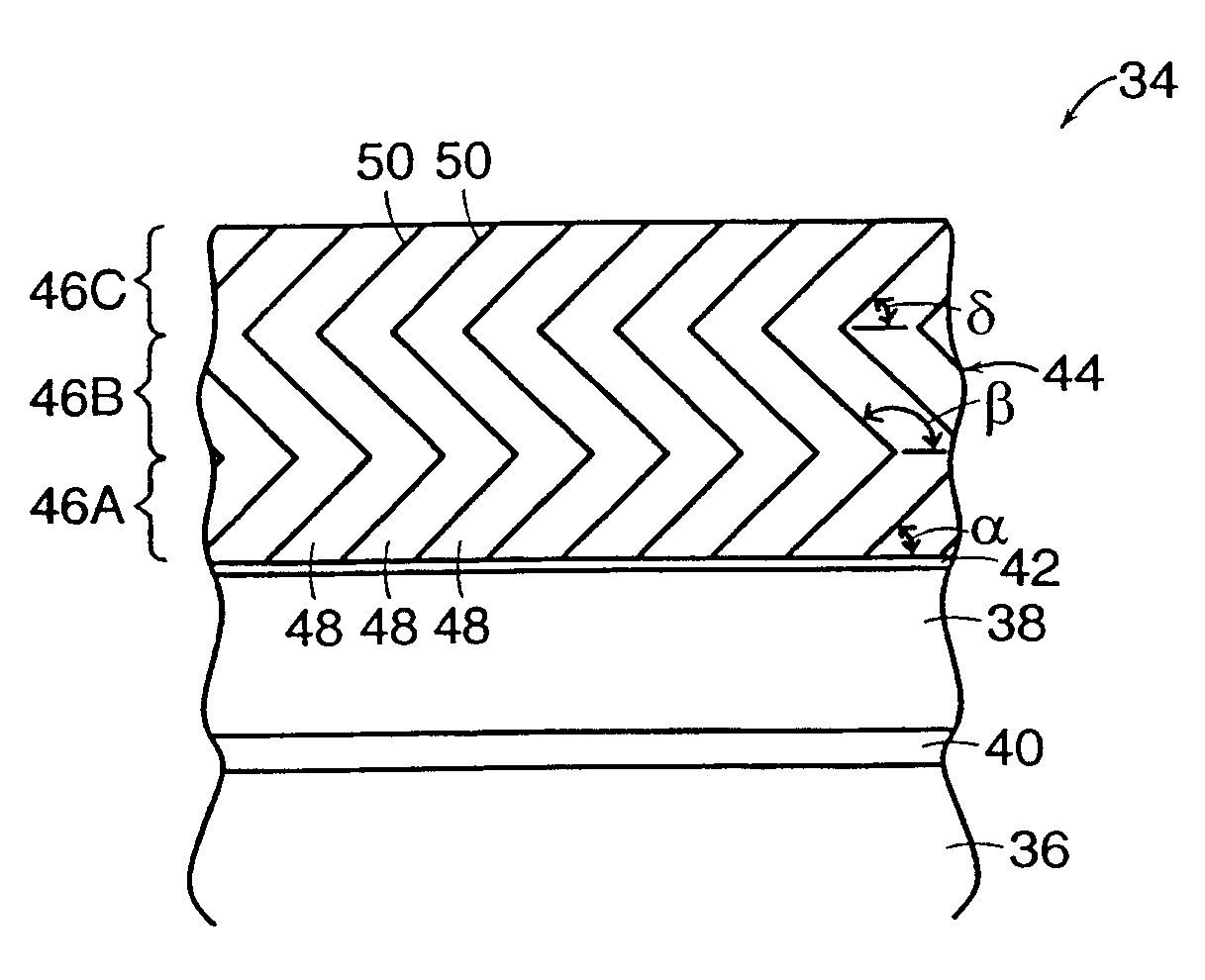
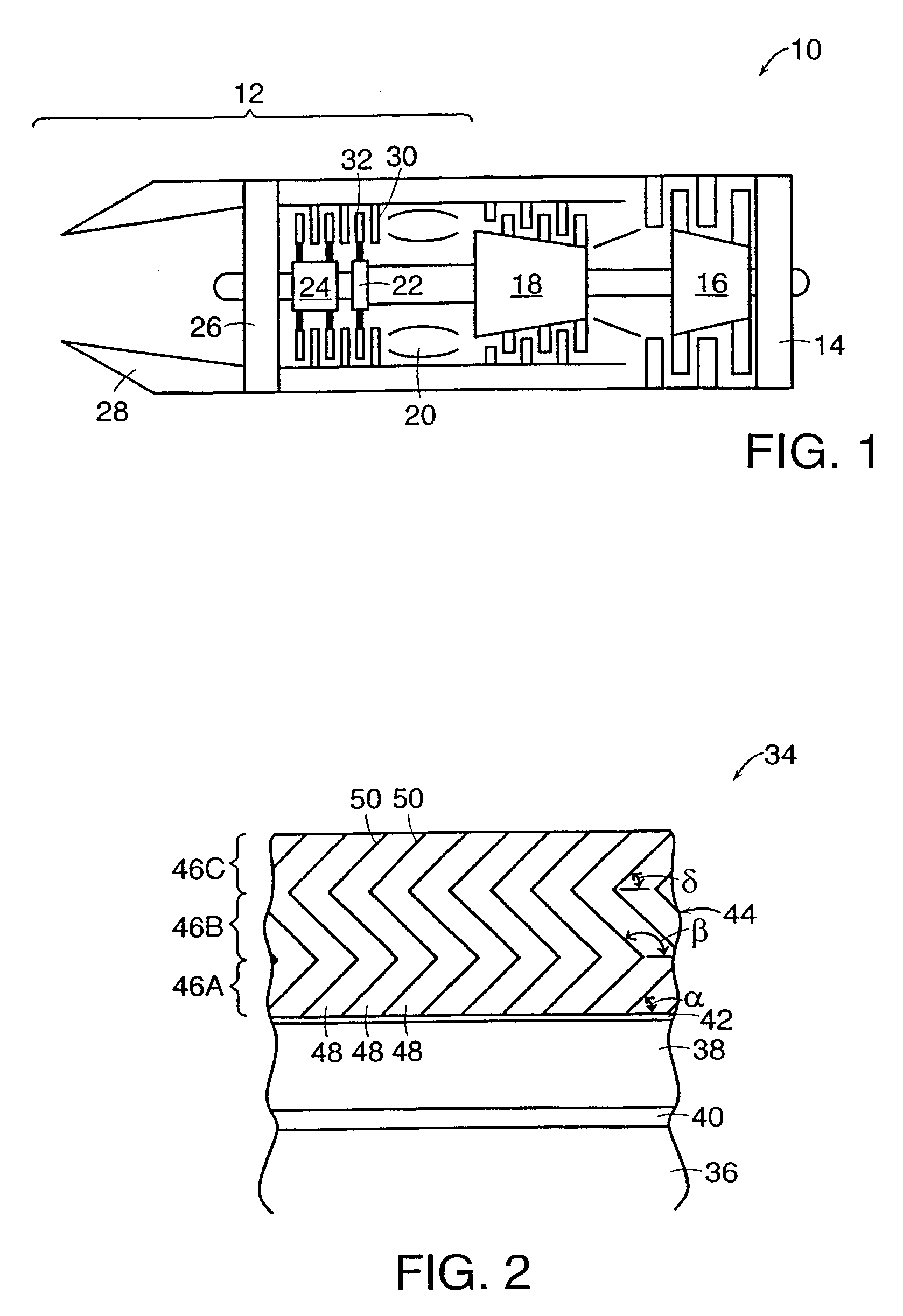
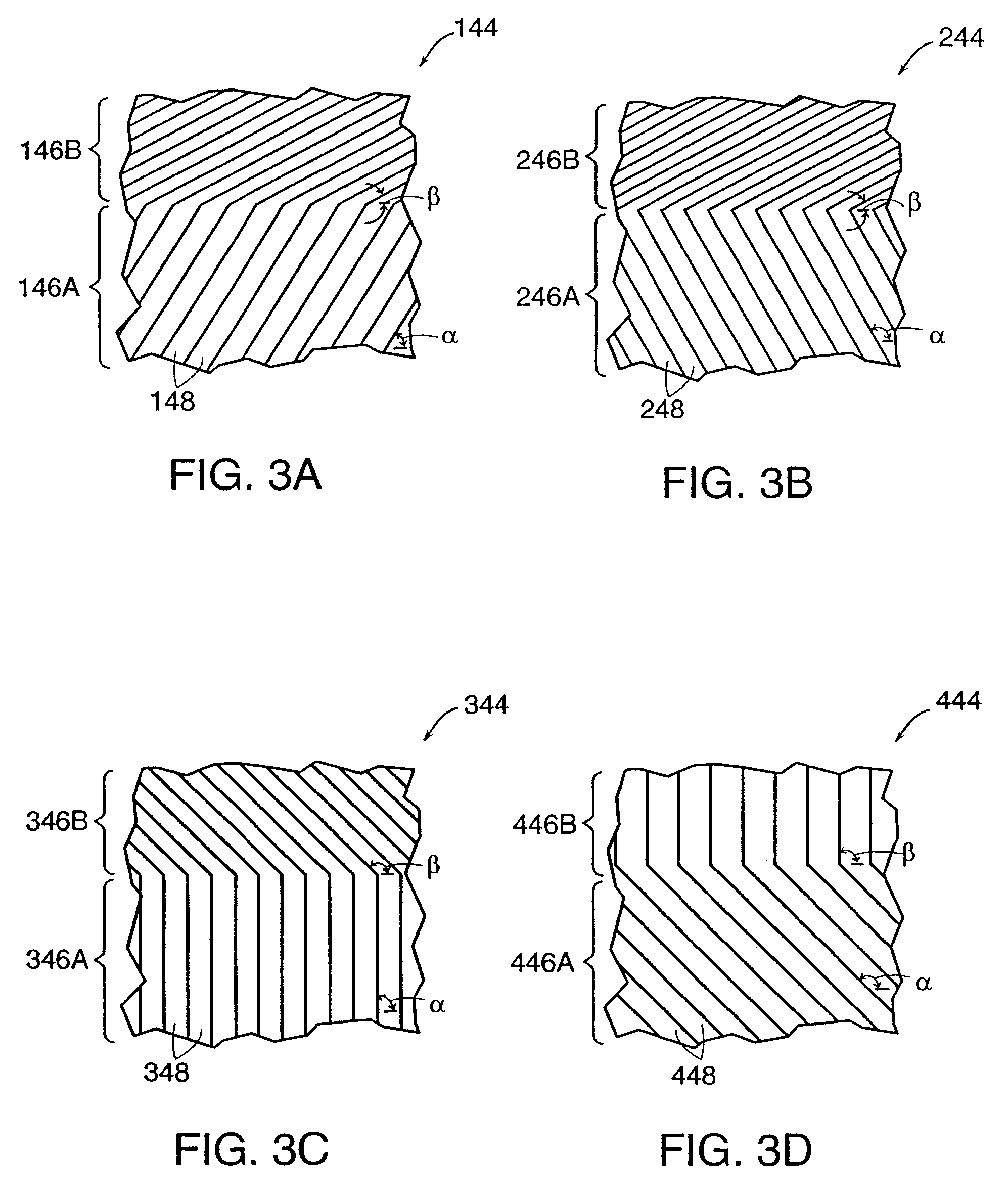
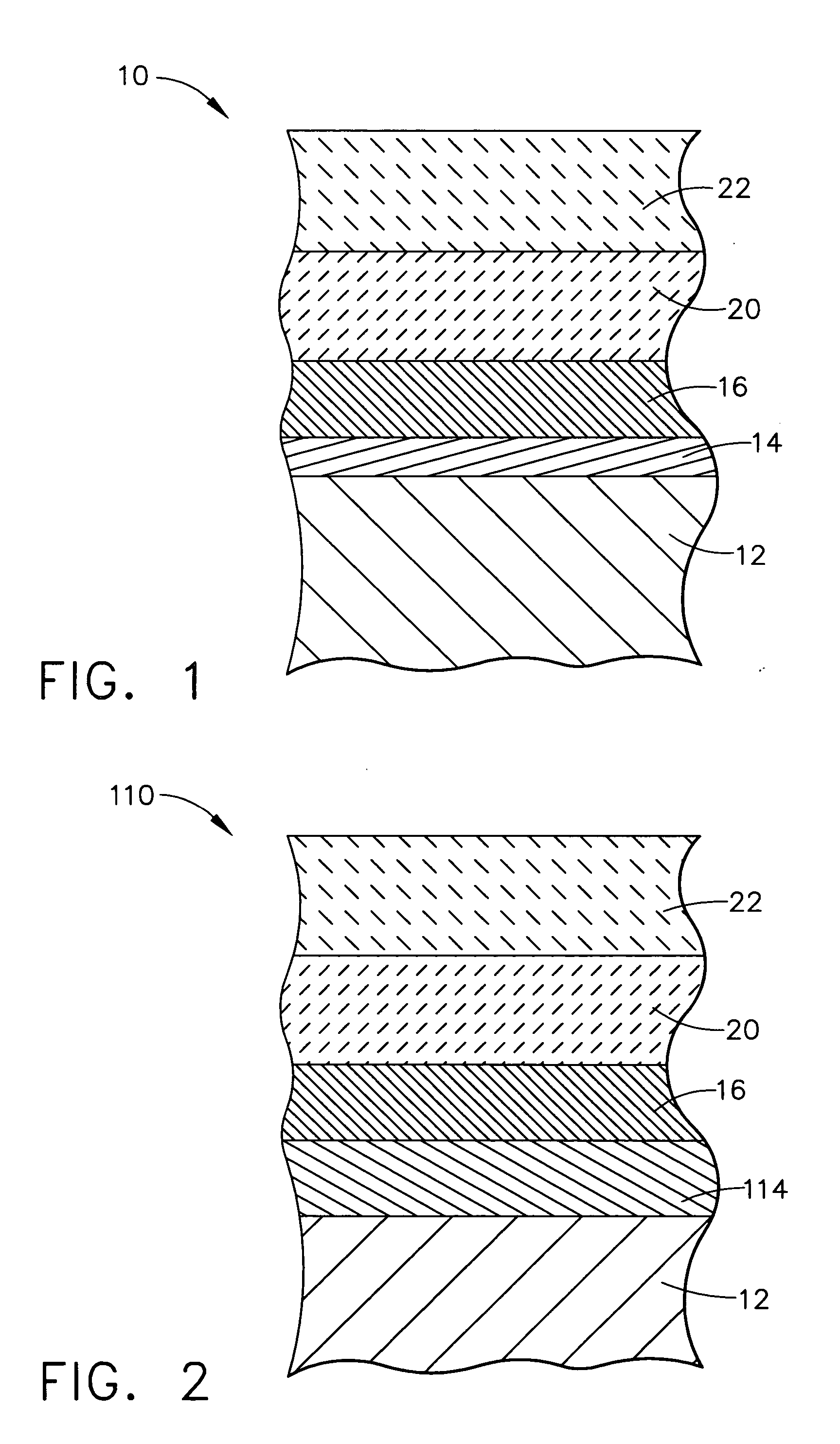
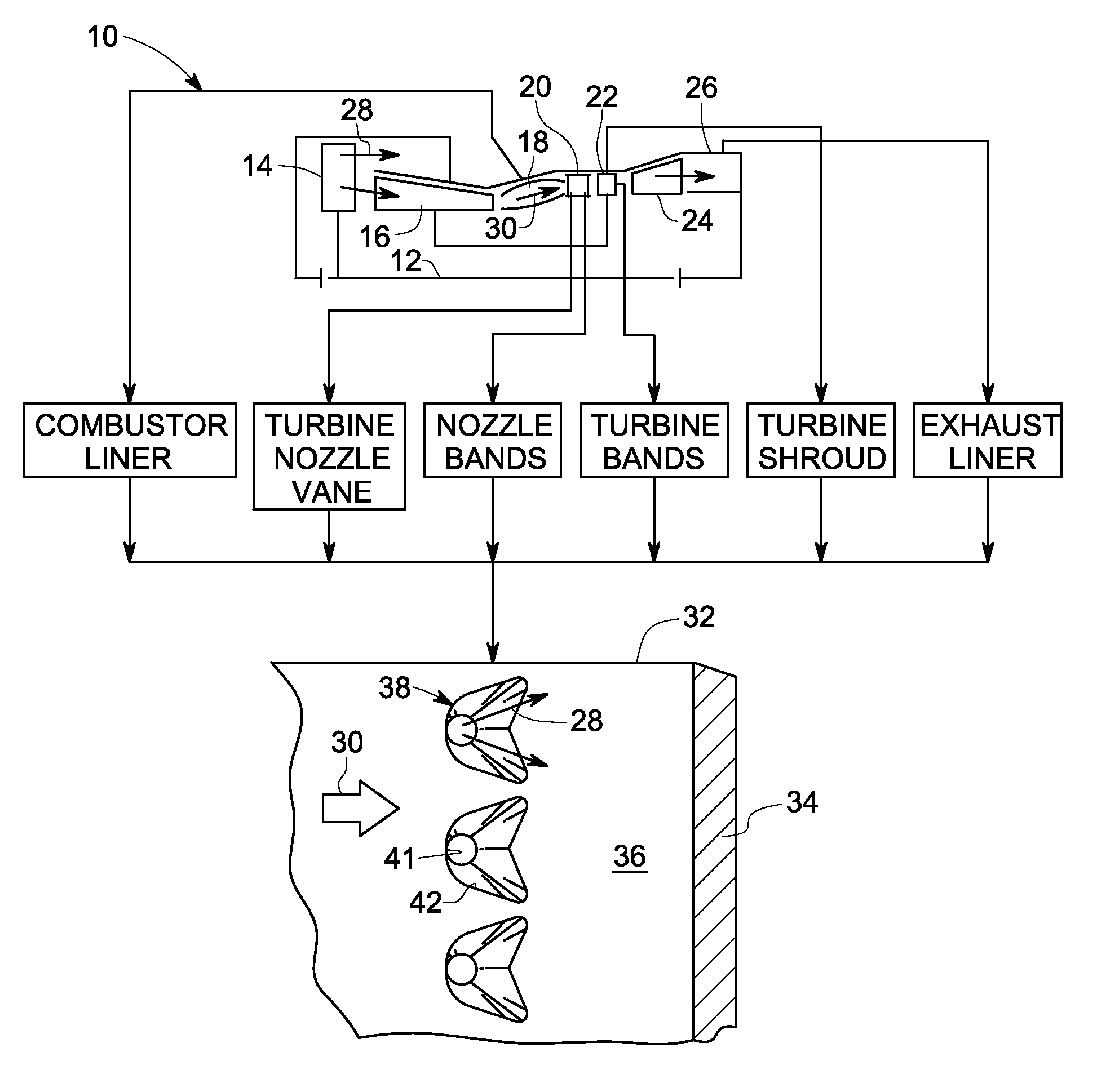
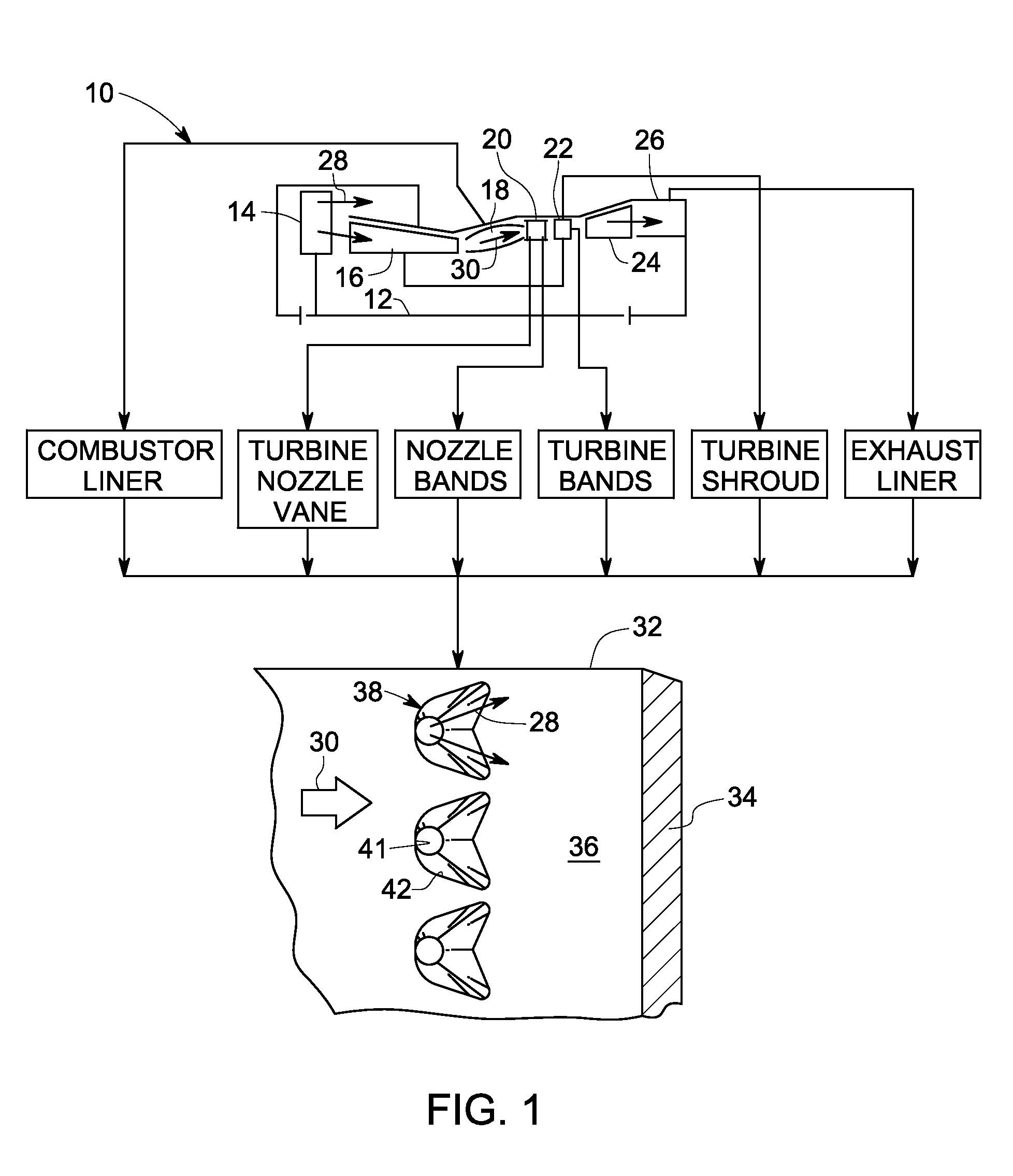
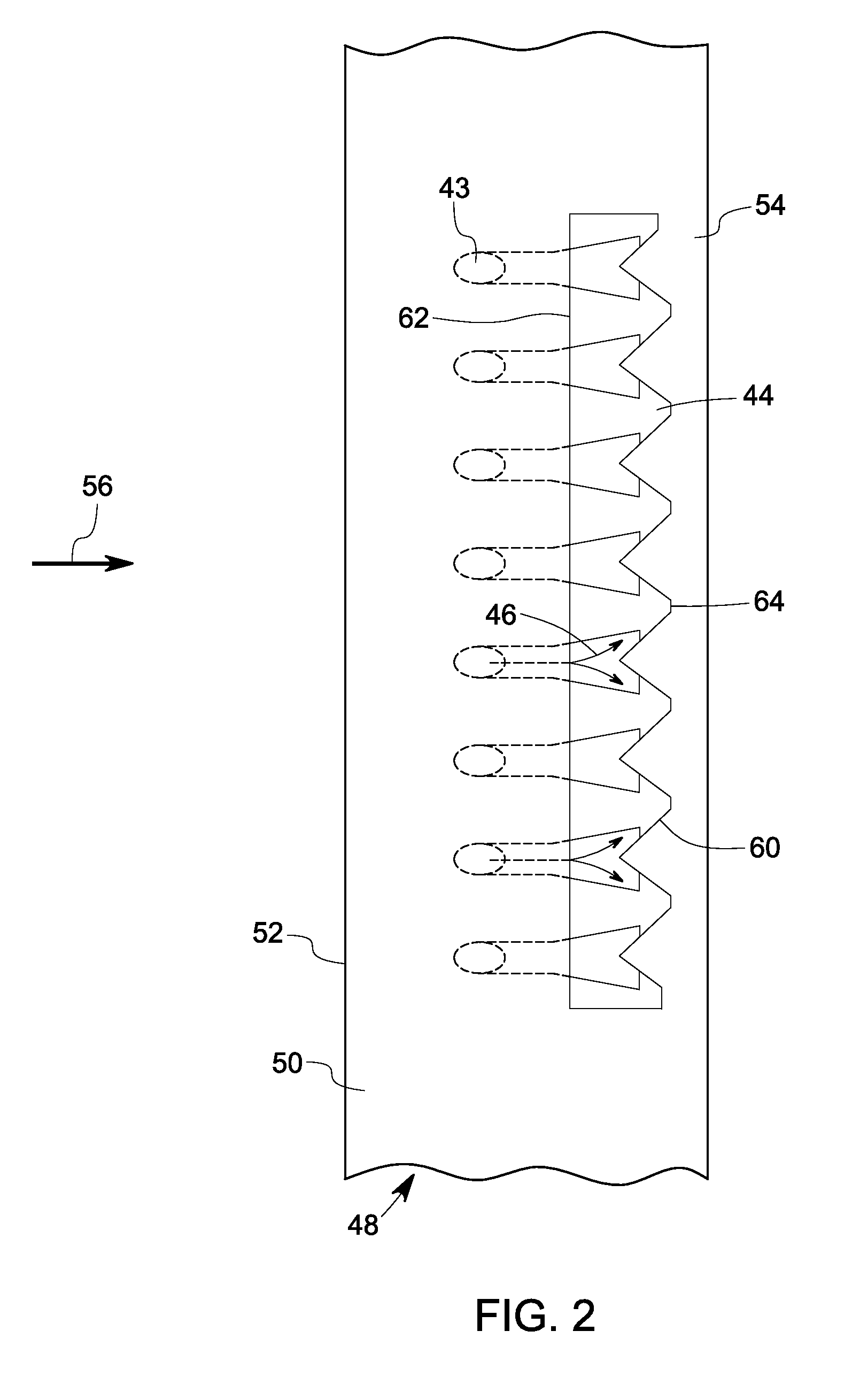
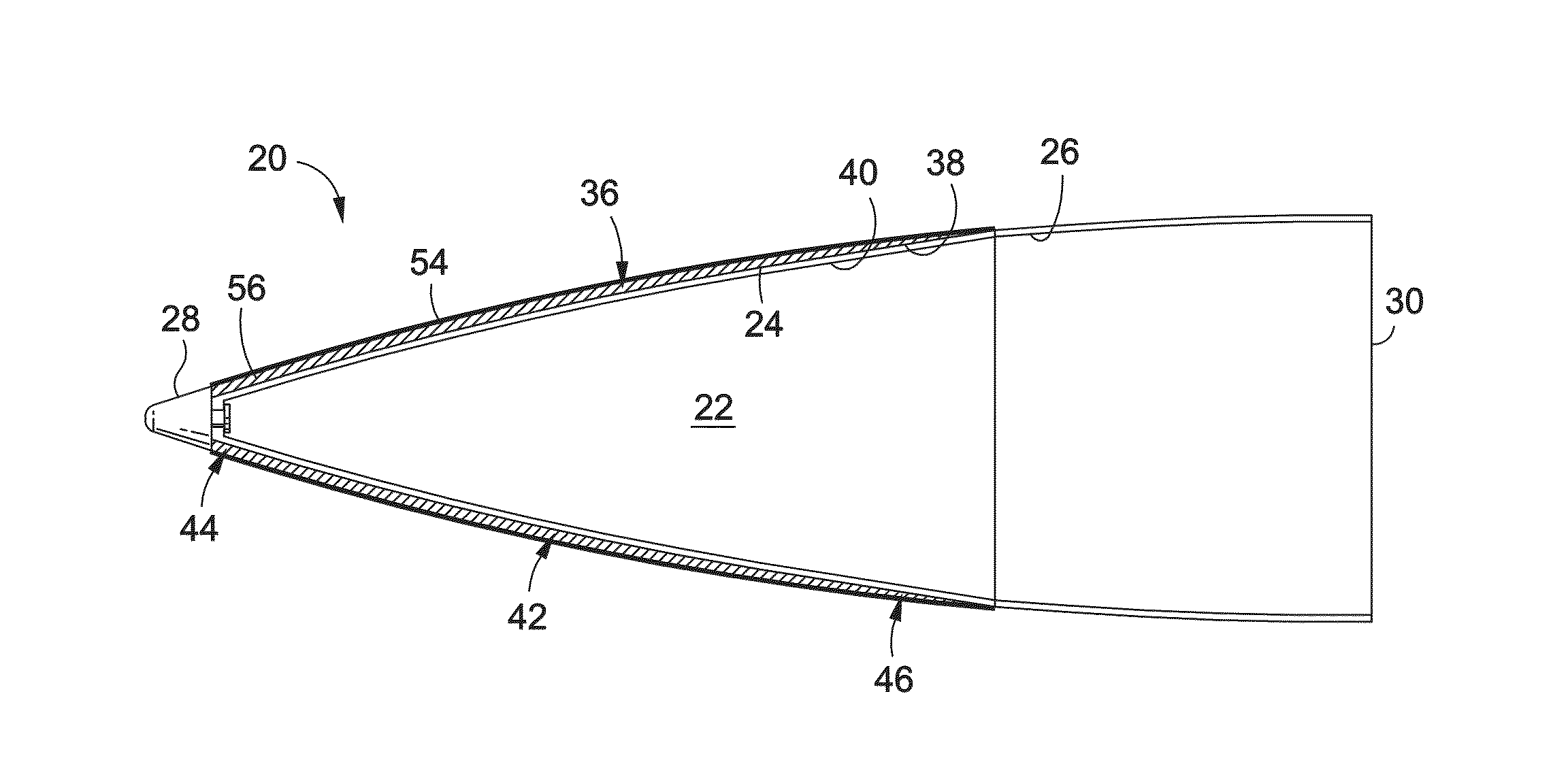
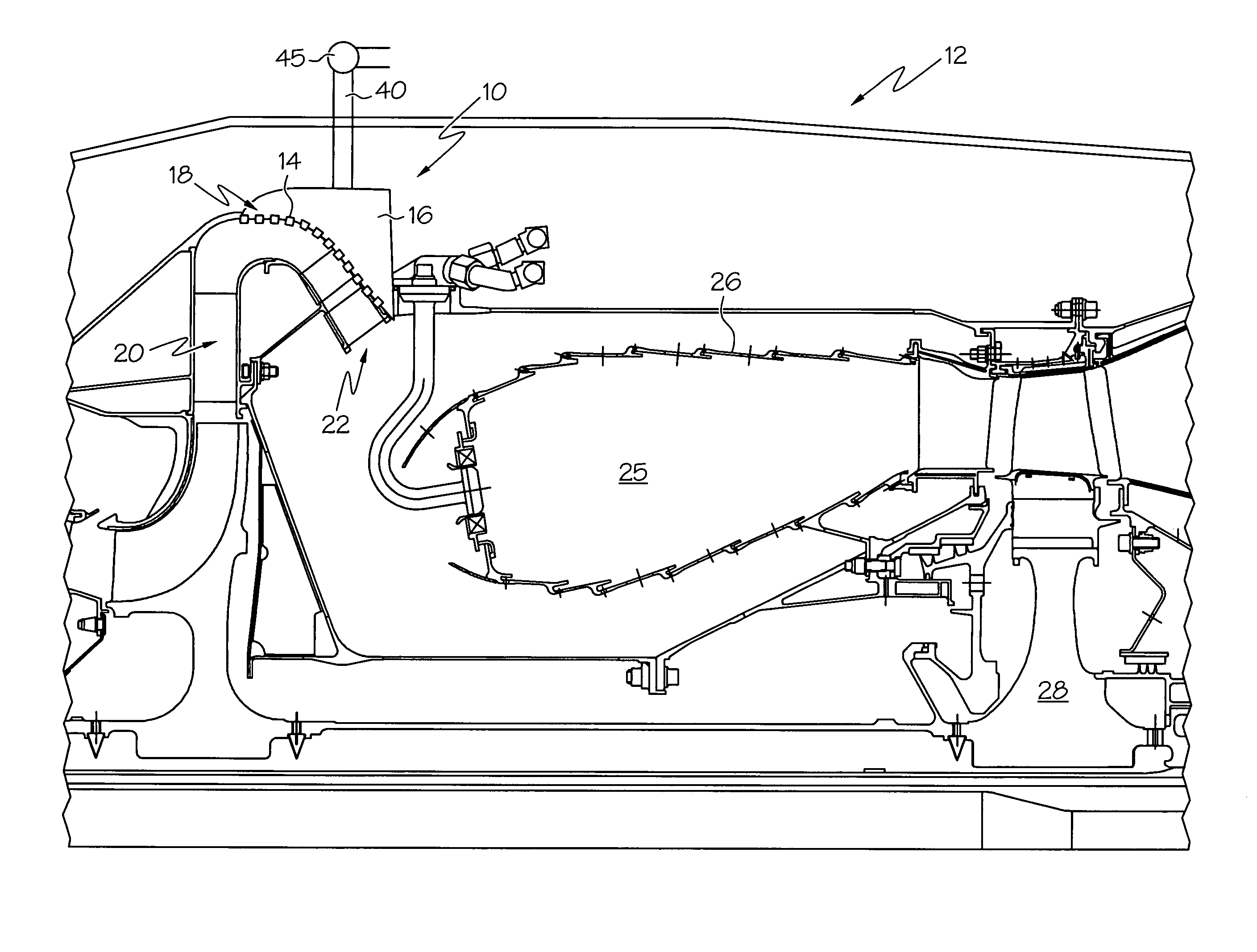
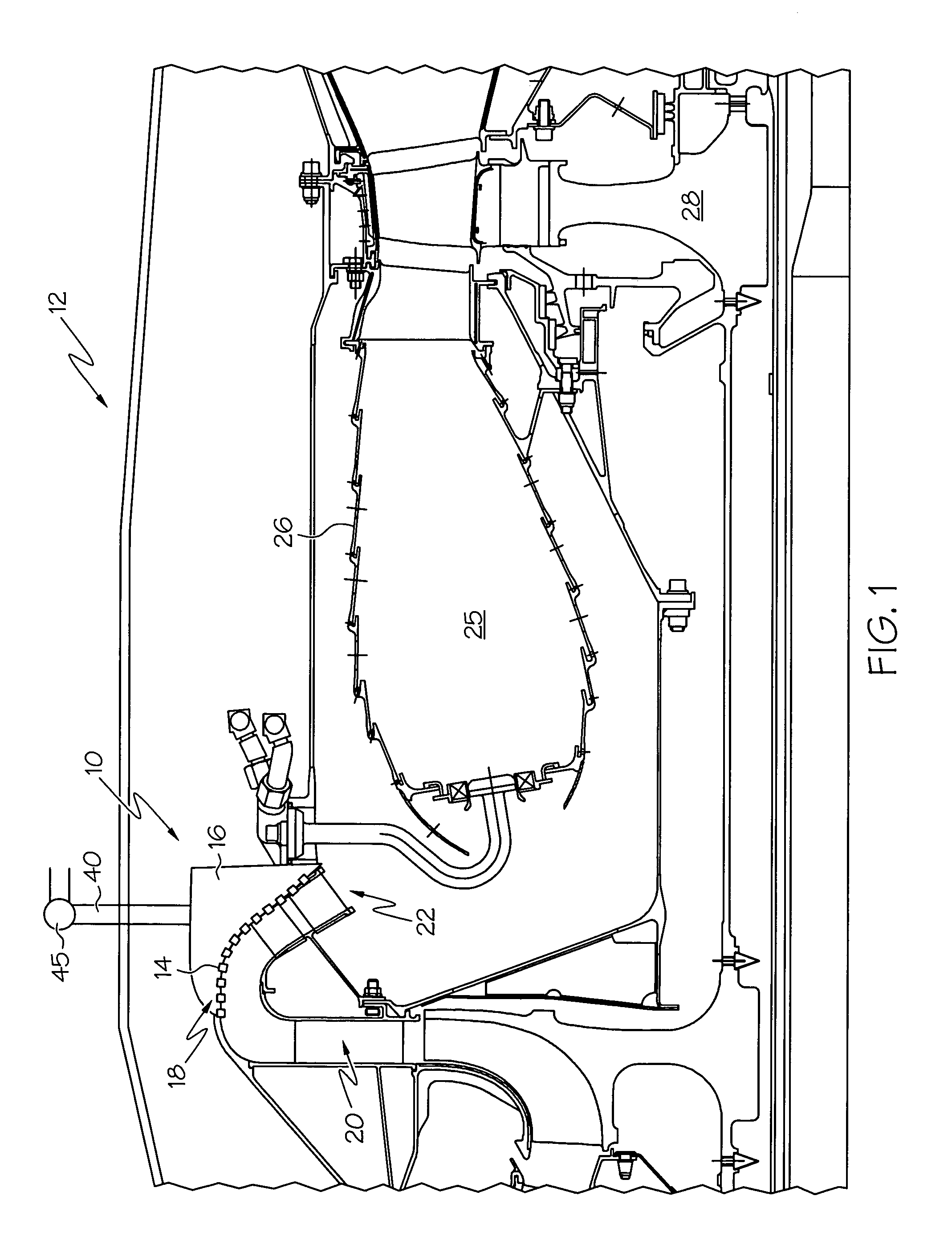
A ceramic thermal barrier coating (TBC) (18) having first and second layers (20, 22), the second layer (22) having a lower thermal conductivity than the first layer for a given density. The second layer may be formed of a material with anisotropic crystal lattice structure. Voids (24) in at least the first layer (20) make the first layer less dense than the second layer. Grooves (28) are formed in the TBC (18) for thermal strain relief. The grooves may align with fluid streamlines over the TBC. Multiple layers (84, 86,88) may have respective sets of grooves (90), Preferred failure planes parallel to the coating surface (30) may be formed at different depths (A1, A2, A3) in the thickness of the TBC to stimulate generation of a fresh surface when a portion of the coating fails by spalling. A dense top layer (92) may provide environmental and erosion resistance.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Method of protecting gas turbine combustor components against water erosion and hot corrosion
A method of preventing water erosion and hot corrosion in a combustor of a gas turbine engine, wherein water is injected into said combustor for NOx abatement, which involves the step of applying a dense vertically cracked thermal barrier coating to certain components thereof The dense vertically cracked thermal barrier coating has a porosity of less than approximately 8% and a tensile strength in the range of approximately 4-7 ksi. The dense vertically cracked thermal barrier coating is applied to such combustor components so as to produce a segmented ceramic structure having macrocracks formed therein which are oriented substantially perpendicular to an interface of the combustor component and the segmented ceramic structure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
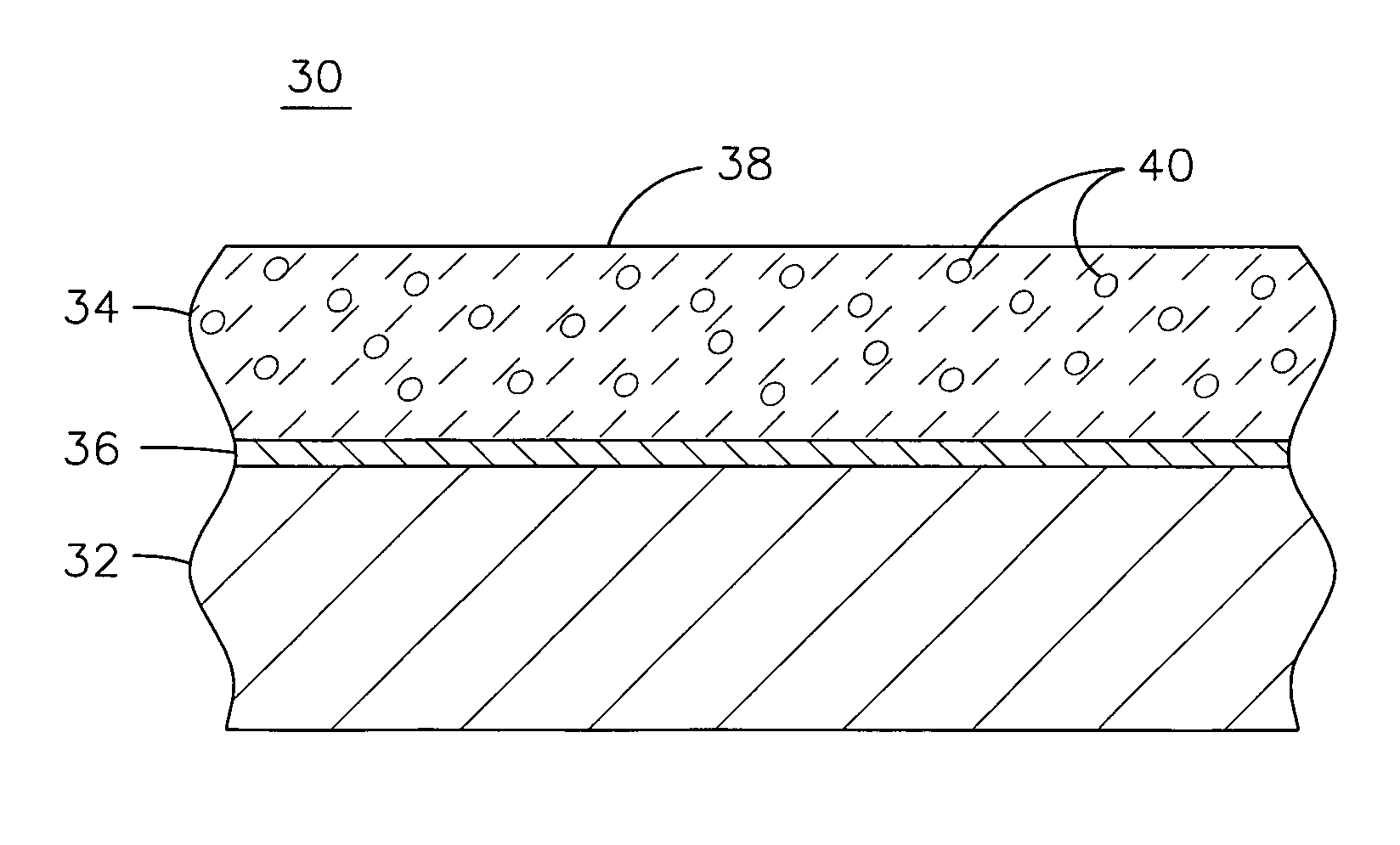
Network cooled coated wall
A turbine wall includes a metal substrate having front and back surfaces. A thermal barrier coating is bonded atop the front surface. A network of flow channels is laminated between the substrate and the coating for carrying an air coolant therebetween for cooling the thermal barrier coating.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
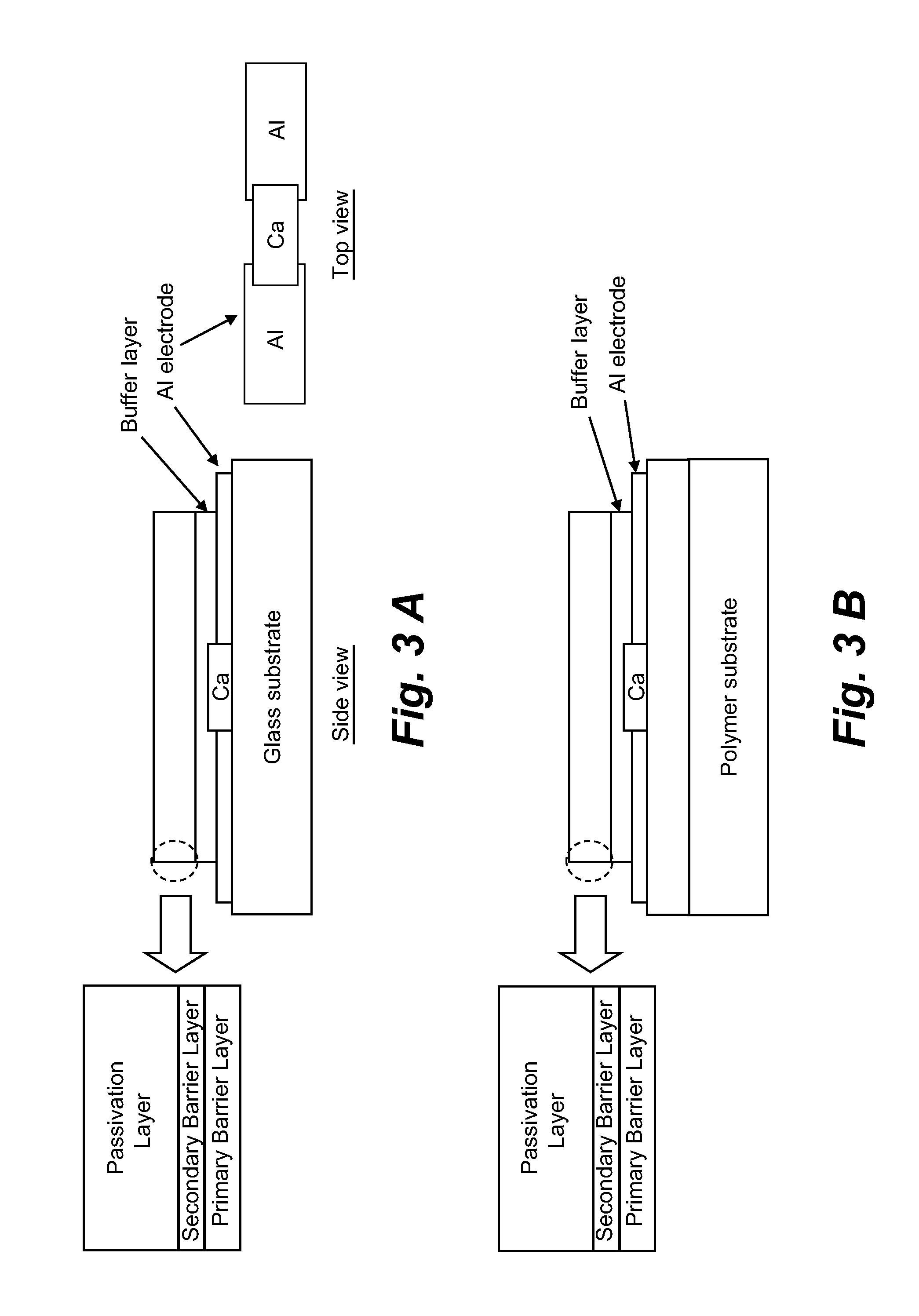
Environmental barrier coating for organic semiconductor devices and methods thereof
InactiveUS20100132762A1Reduce exposurePV power plantsSolid-state devicesOrganic semiconductorThermal barrier coating
Improved environmental barrier coatings and improved organic semiconductor devices employing the improved environmental barrier coatings are disclosed herein. Methods of making and using the improved coatings and devices are also described. An improved environmental barrier coating generally includes a primary barrier layer, a secondary barrier layer disposed on the primary barrier layer, and a passivation layer disposed on the secondary barrier layer. The secondary barrier layer is formed using atomic layer deposition.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
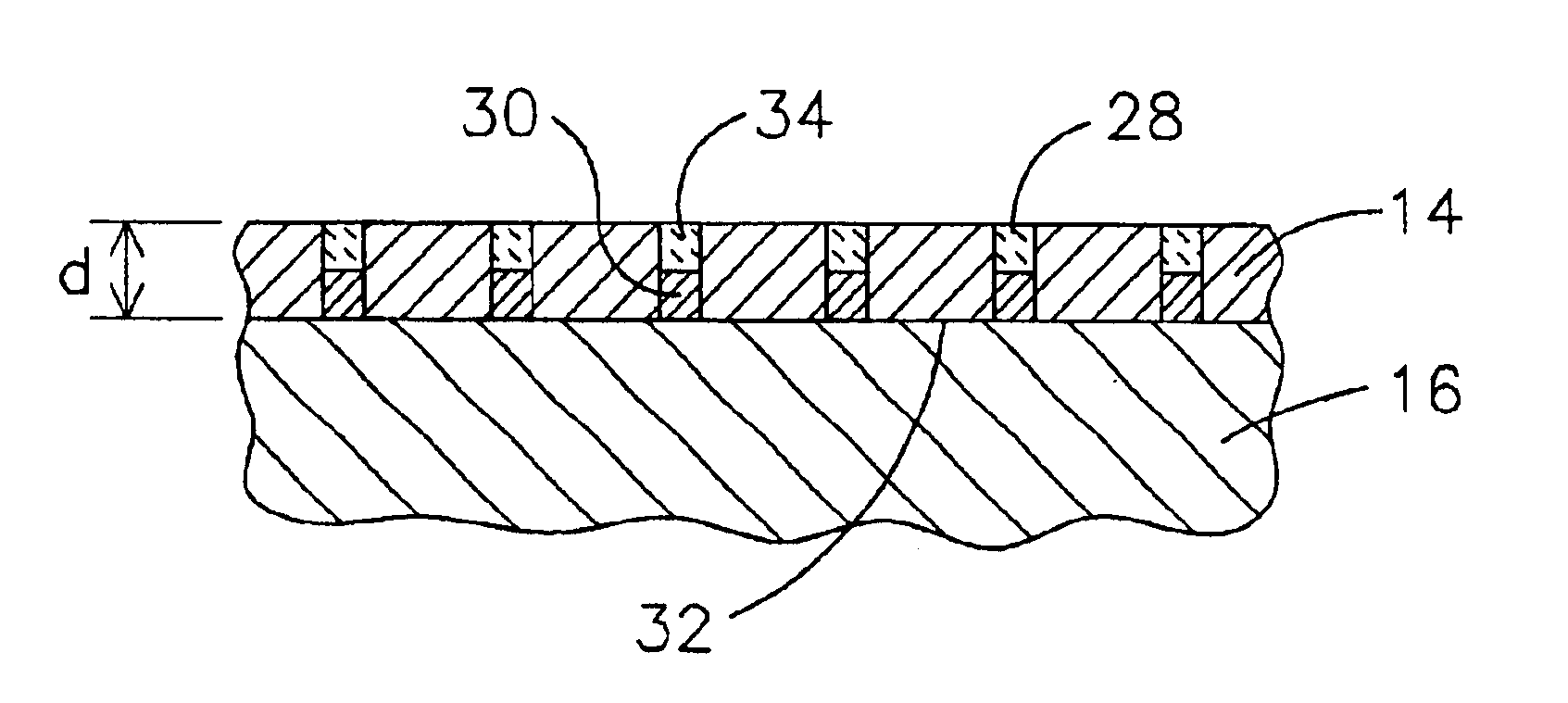
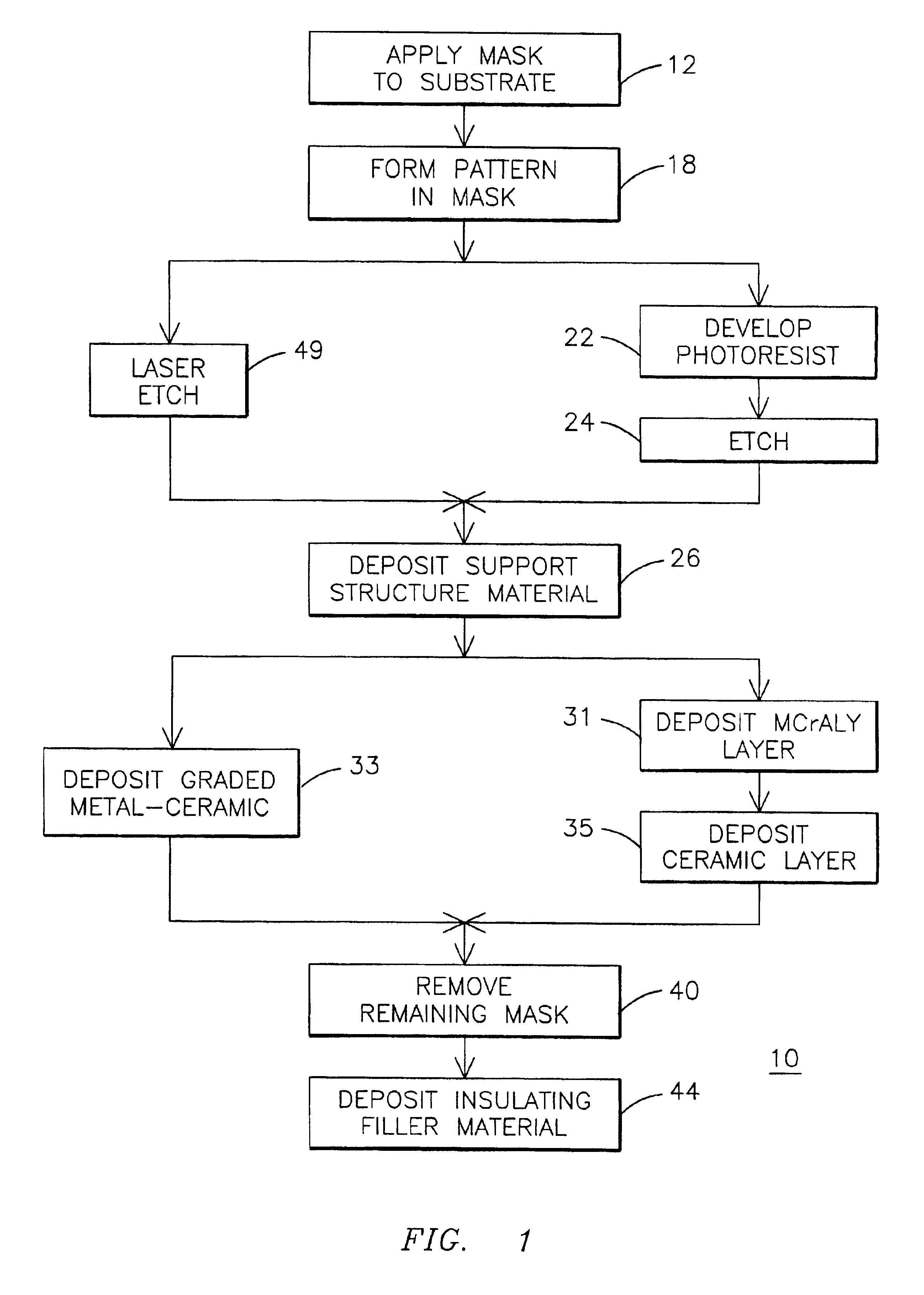
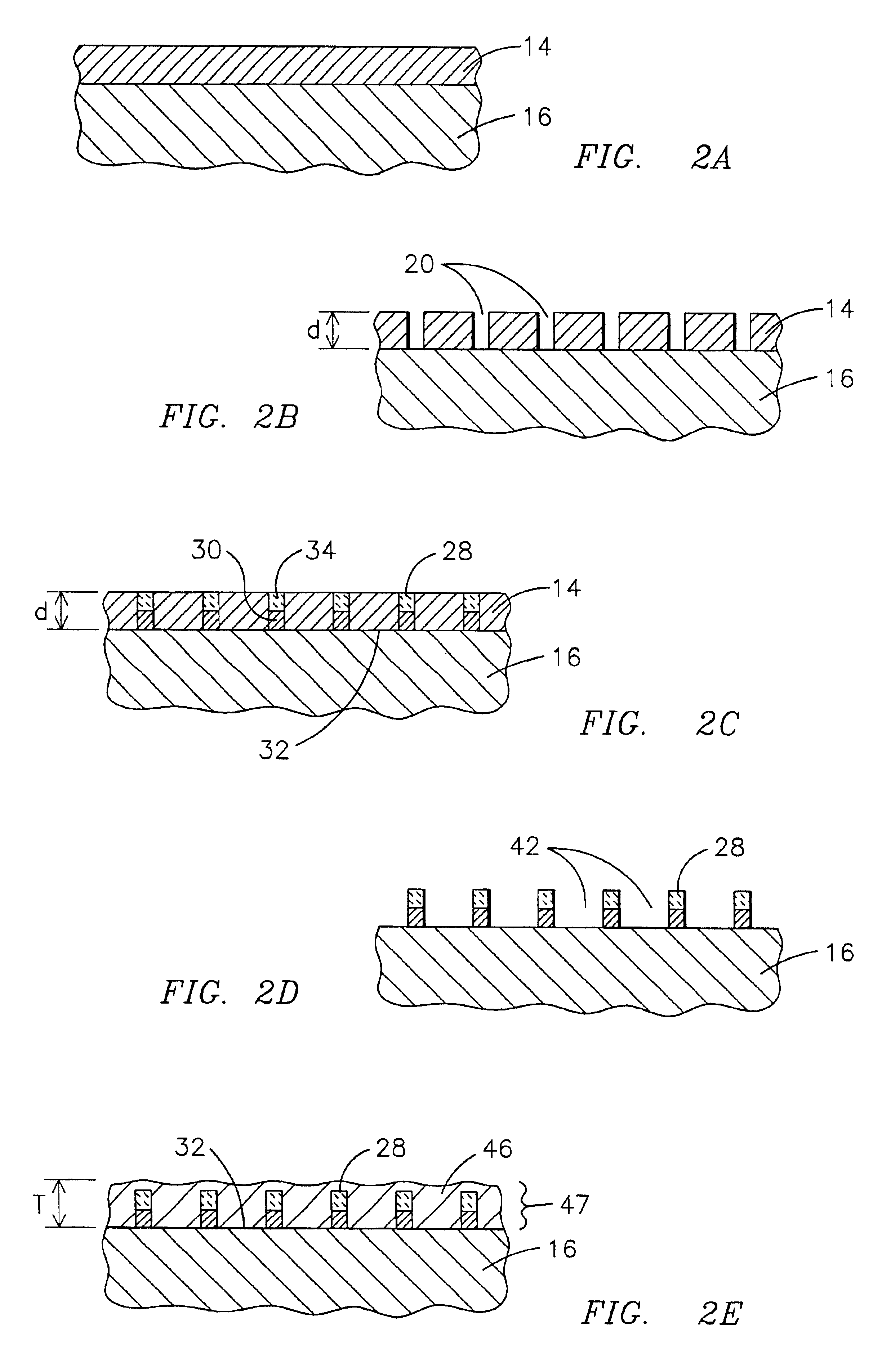
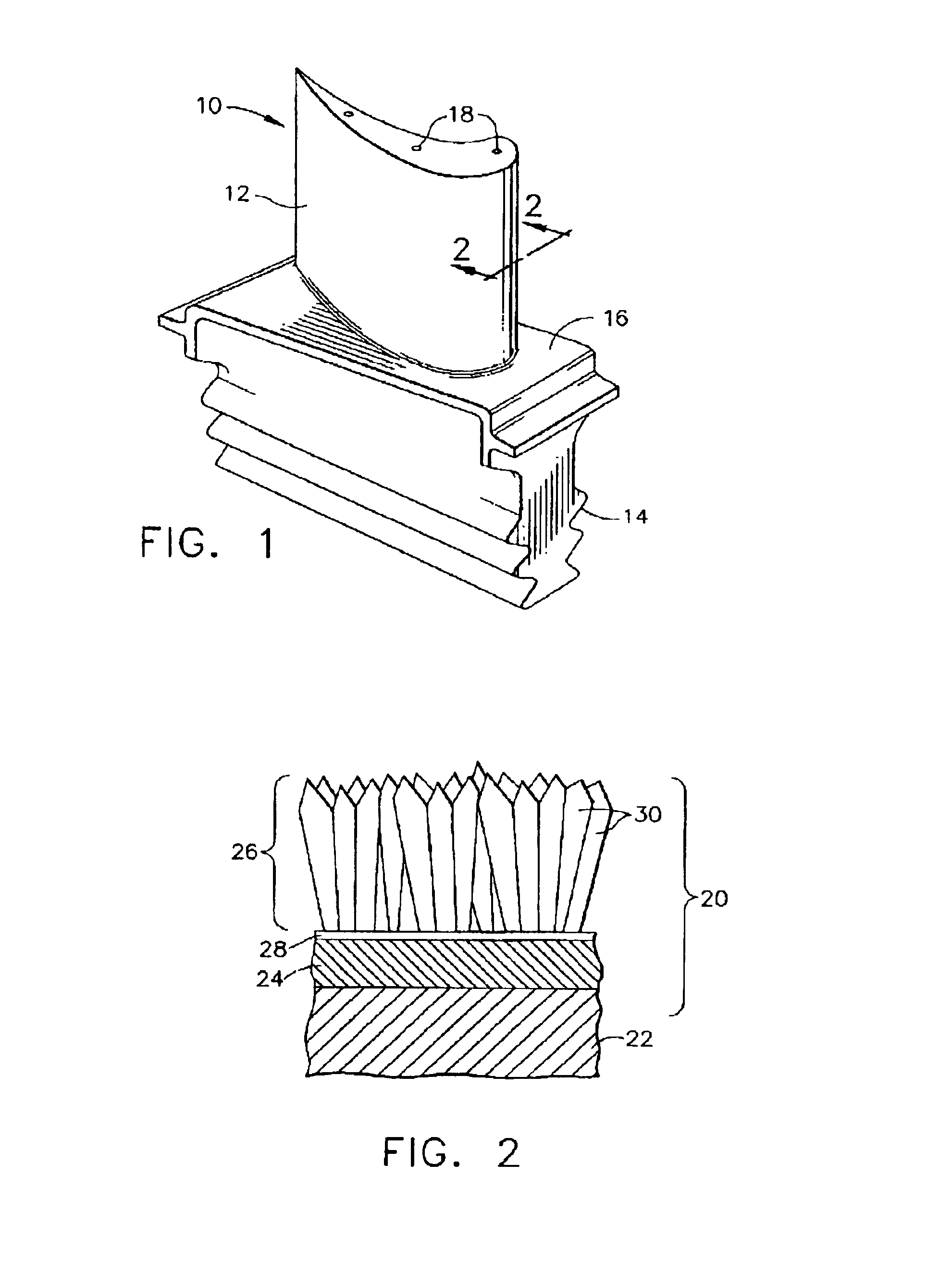
Honeycomb structure thermal barrier coating
InactiveUS6846574B2Minimize heat transfer rateConvenient coatingMolten spray coatingRecord information storageForeign matterLaser etching
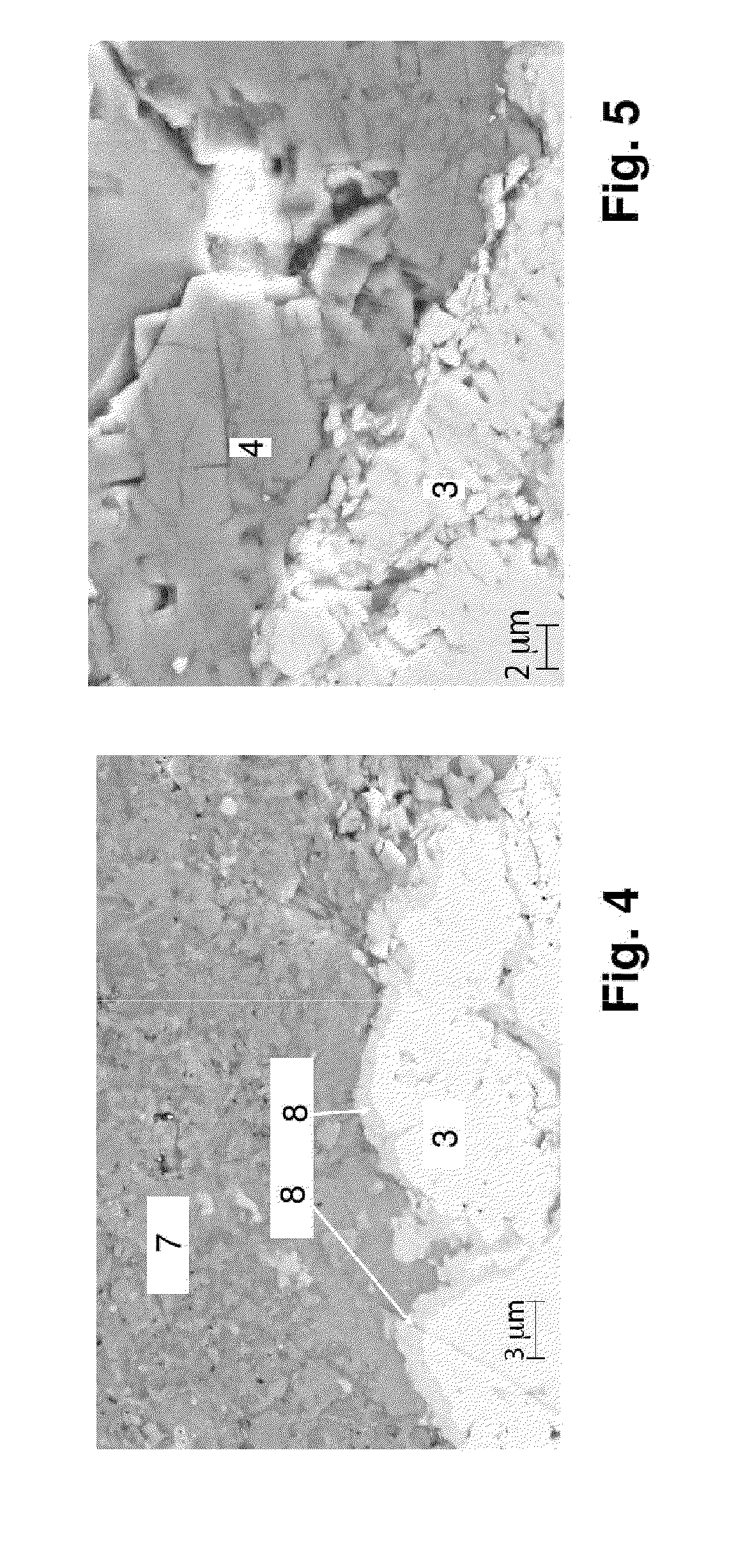
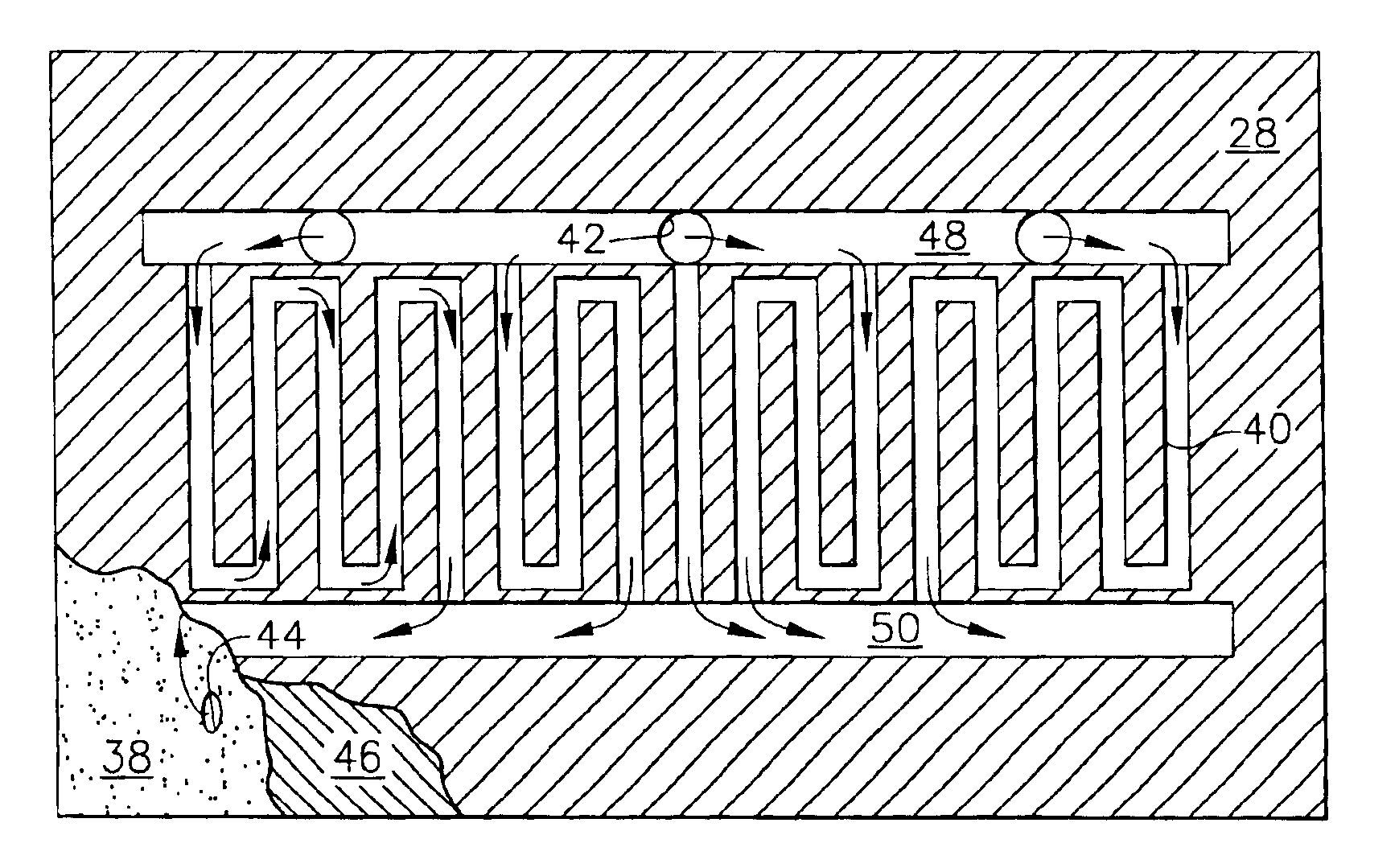
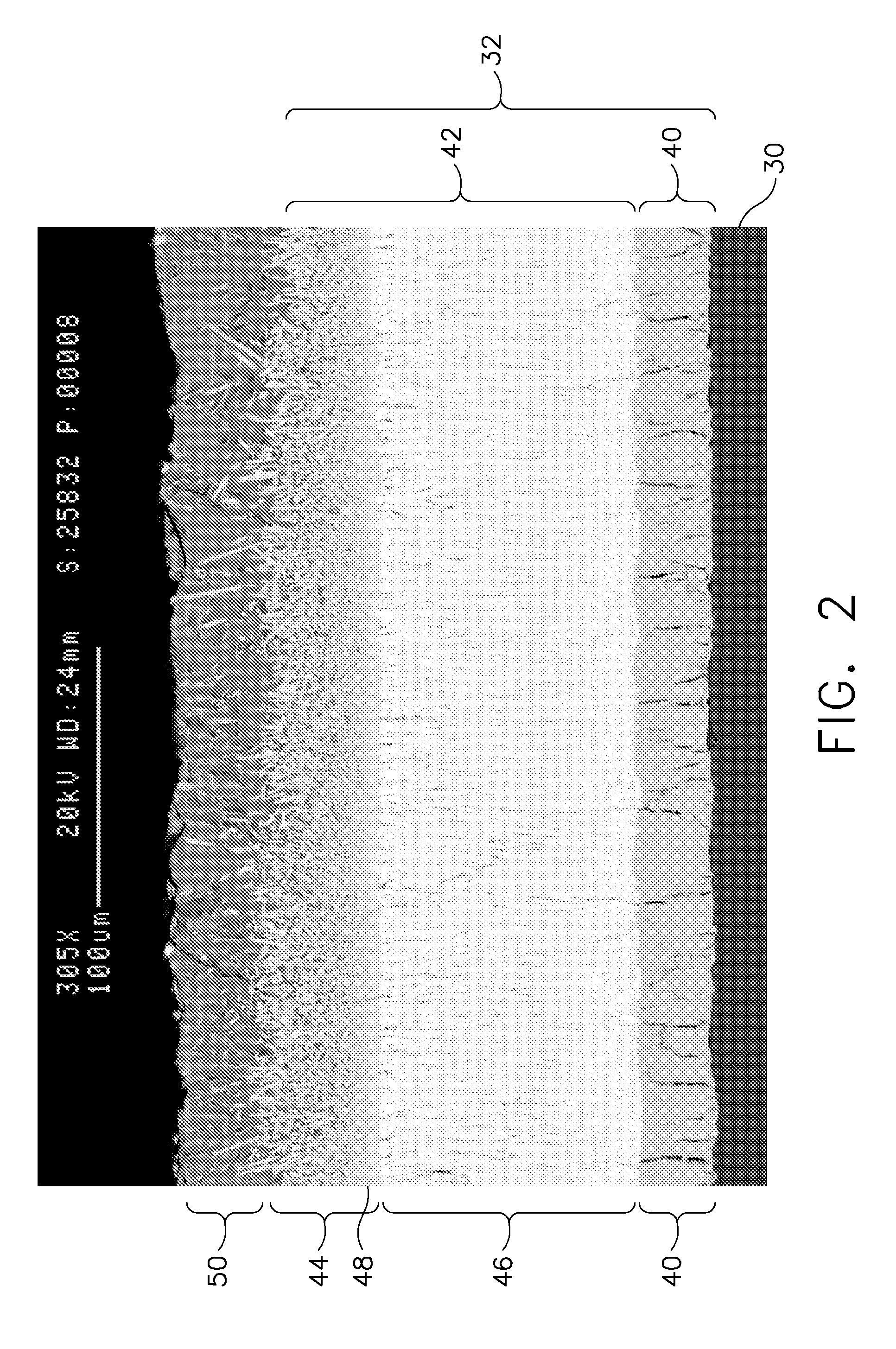
A device having an improved thermal barrier coating (46) and a process for manufacturing the same. A support structure (28) for retaining a ceramic insulating material (46) on a substrate (16) is formed by the deposition of a support structure material through a patterned masking material (14). The support structure can define cells into which the ceramic insulating material is deposited following removal of the masking material. The masking material may be patterned by known photolithographic techniques (22,24) or by laser etching (48). The support structure (28) may be a composite metal-ceramic material having either discreet layers (30,34) or a graded composition and may be deposited by an electro-desposition process followed by a heat treatment to form a solid state diffusion bond with the substrate. The ceramic filler material may be deposited (44) by the electrophoretic deposition of ceramic particles coated with a bonding material that is subsequently heated to oxidize and to bond the particles together. The support structure may be provided with included walls in order to improve its resistance to foreign object impact damage.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Layered thermal barrier coatings containing lanthanide series oxides for improved resistance to CMAS degradation
InactiveUS20070160859A1Avoid damageElimination of expensiveBlade accessoriesEfficient propulsion technologiesReaction layerCerium
A coating applied as a two layer system. The outer layer is an oxide of a group IV metal selected from the group consisting of zirconium oxide, hafnium oxide and combinations thereof, which are doped with an effective amount of a lanthanum series oxide. These metal oxides doped with a lanthanum series addition comprises a high weight percentage of the outer coating. As used herein, lanthanum series means an element selected from the group consisting of lanthanum (La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), lutetium (Lu) and combinations thereof, and lanthanum series oxides are oxides of these elements. When the zirconium oxide is doped with an effective amount of a lanthanum series oxide, a dense reaction layer is formed at the interface of the outer layer of TBC and the CMAS. This dense reaction layer prevents CMAS infiltration below it. The second layer, or inner layer underlying the outer layer, comprises a layer of partially stabilized zirconium oxide.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
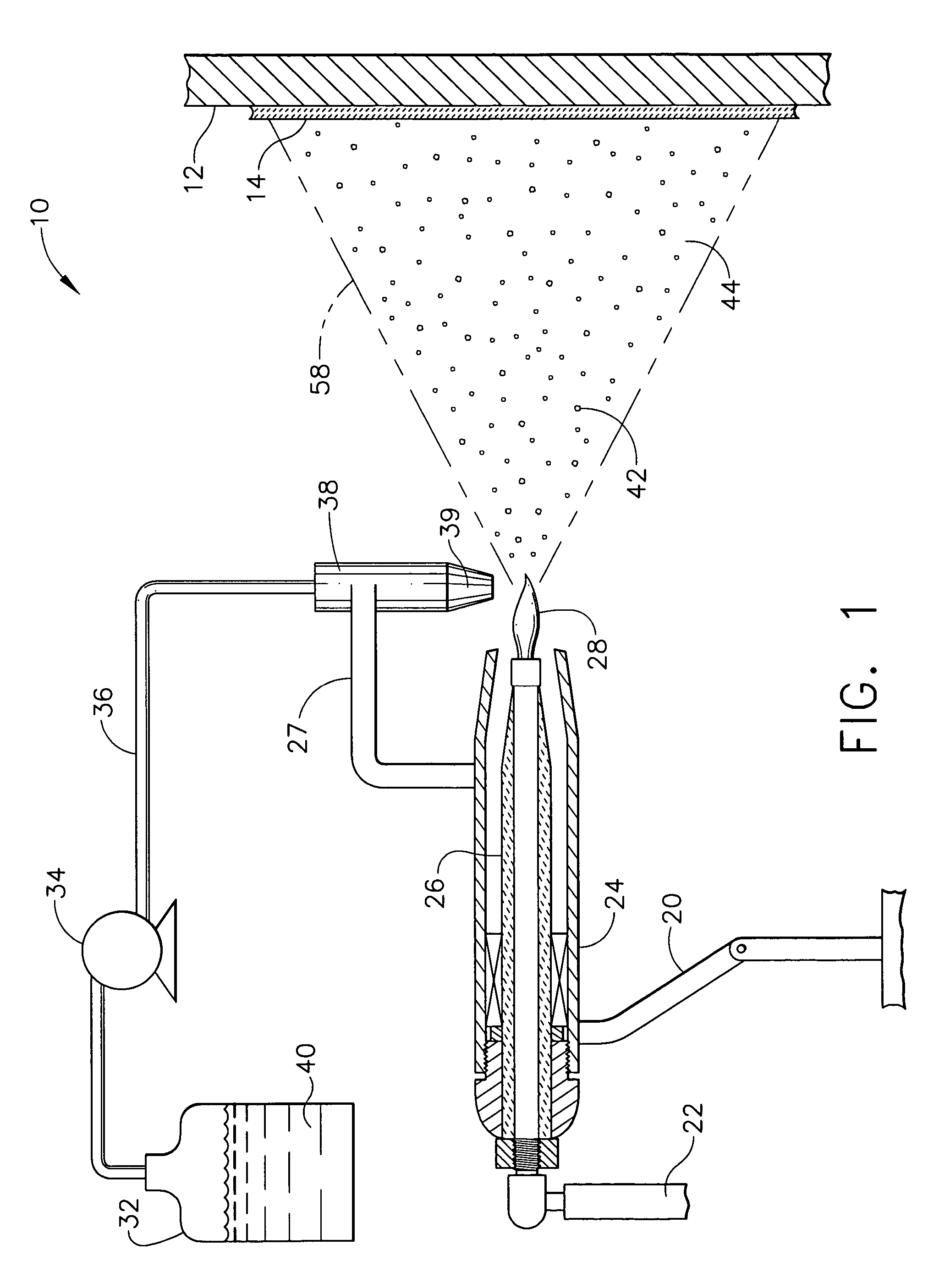
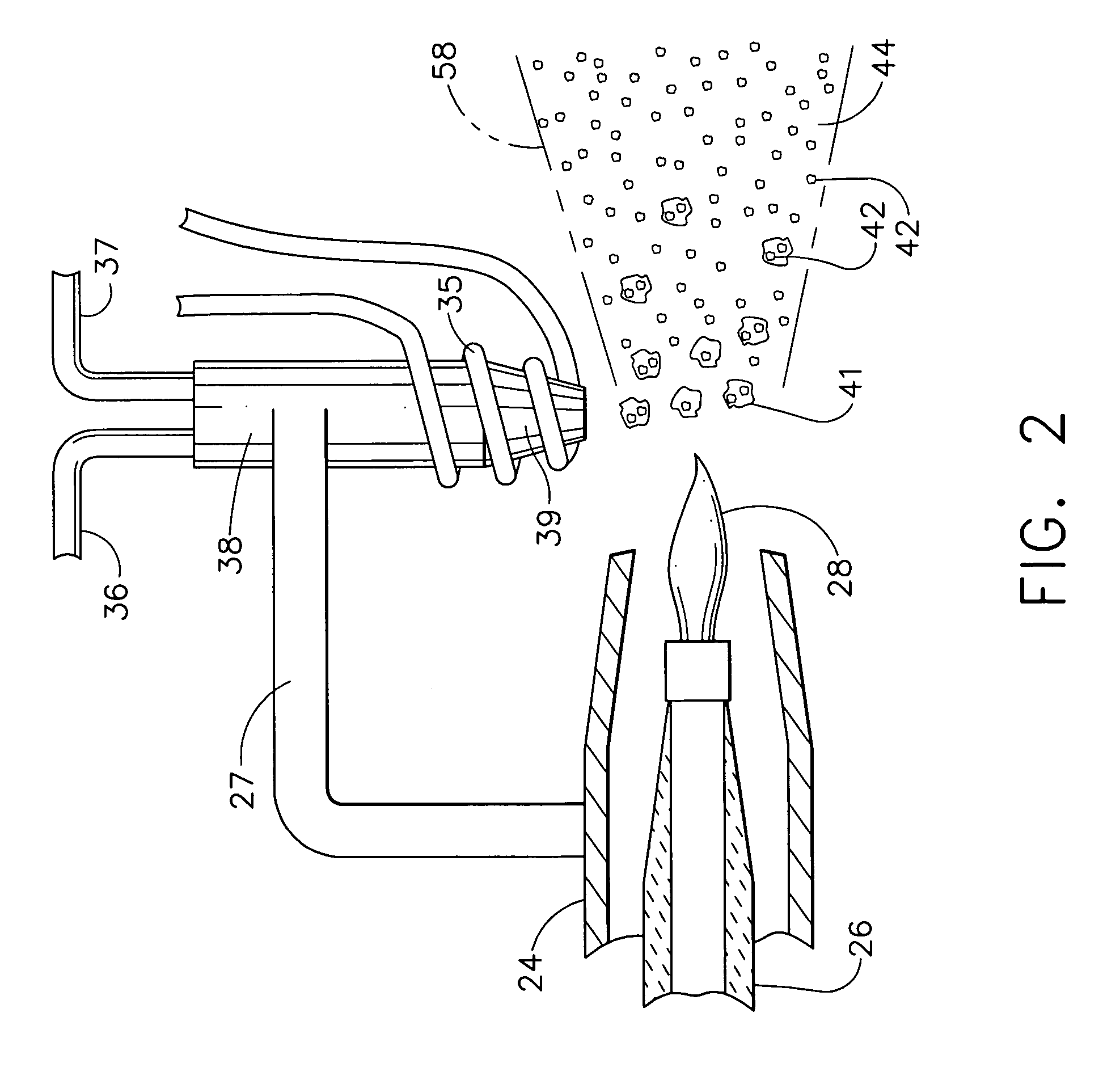
Method for applying a plasma sprayed coating using liquid injection
InactiveUS20060222777A1Improve processing efficiencyReduce the amount requiredLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingPlasma jetPlasma sprayed coating
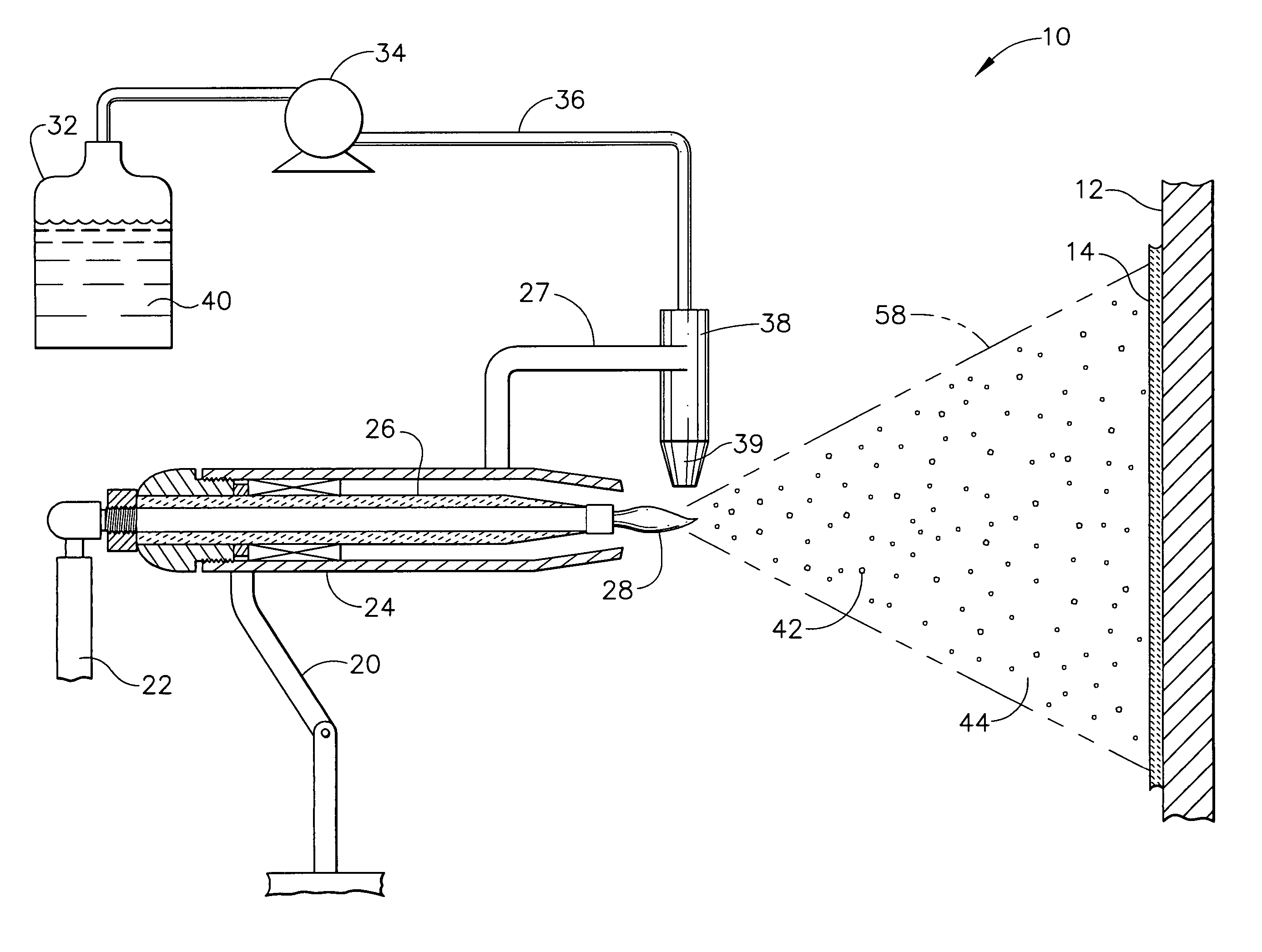
A method for applying a plasma prayed coating using liquid injection is disclosed. The method includes providing a mixture of a liquid and solid particles. The solid particles are constituents of a thermal barrier coating. The mixture is injected into a plasma jet of a plasma spray device and the plasma jet is directed toward a substrate to deposit a gradient film formed from the constituents onto the substrate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
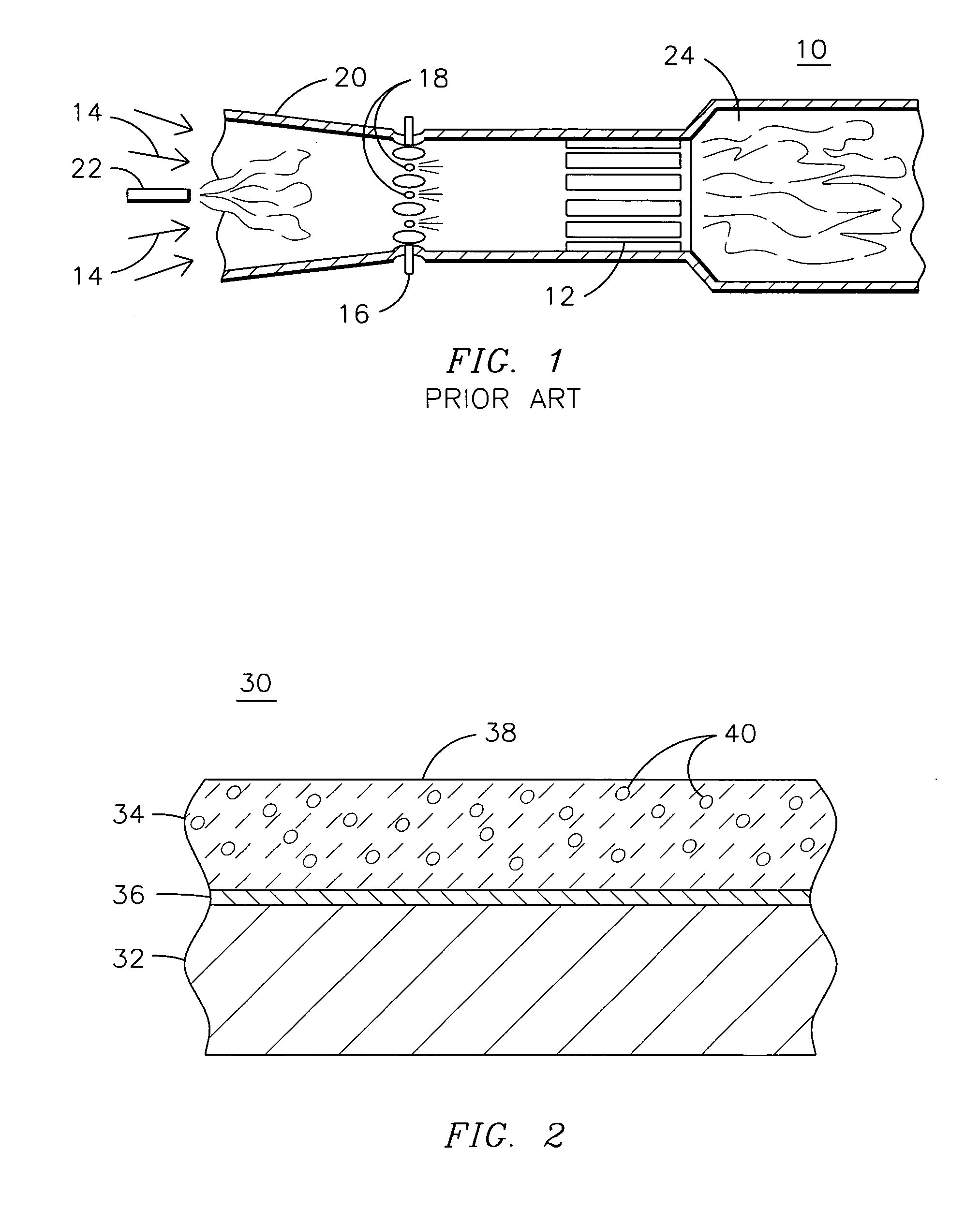
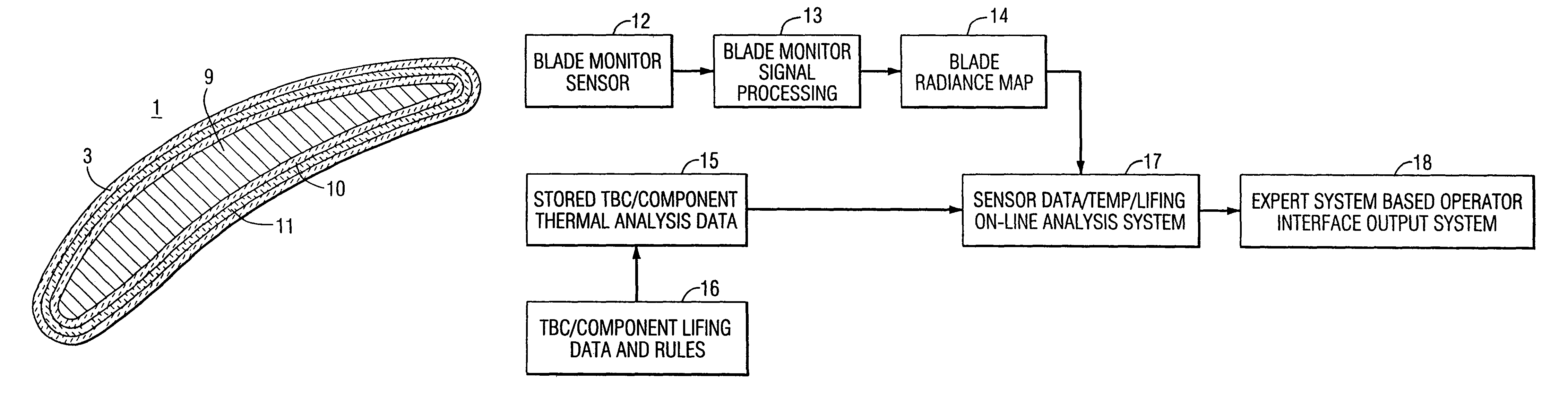
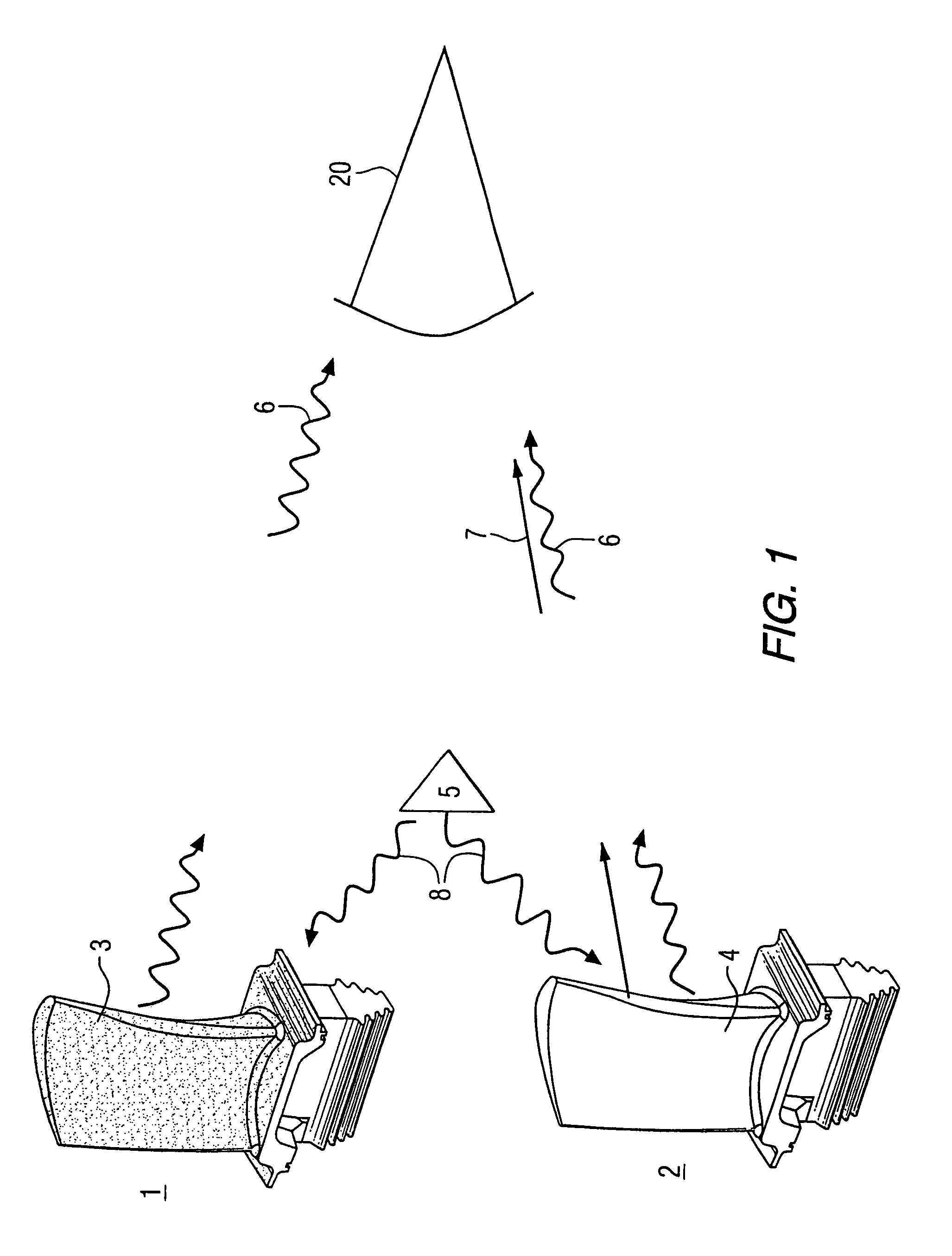
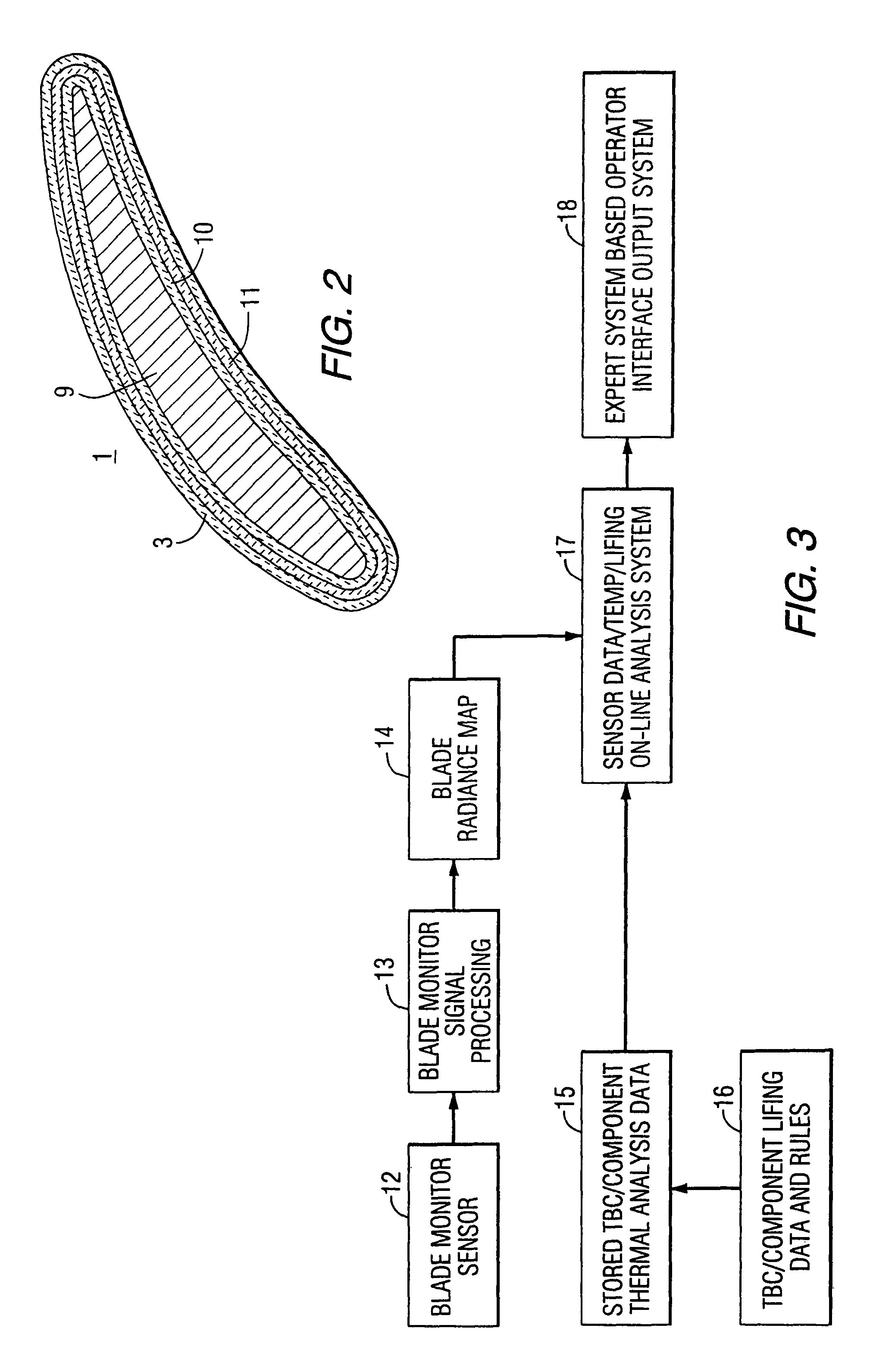
Method and apparatus for measuring on-line failure of turbine thermal barrier coatings
InactiveUS20090312956A1Detect degradationAvoid severe repairThermometer detailsPlug gaugesTurbine bladeEngineering
A method of remotely monitoring the radiant energy (6) emitted from a turbine component such as a turbine blade (1) having a low-reflective surface coating (3) which may be undergoing potential degradation is used to determine whether erosion, spallation, delamination, or the like, of the coating (3) is occurring.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Thermal barrier coating material
InactiveUS6890668B2Promote thermal cycle fatigue lifeLow thermal conductivityMolten spray coatingPropellersThermal barrier coatingZirconium oxide
A coating material for a component intended for use in a hostile thermal environment. The coating material has a cubic microstructure and consists essentially of either zirconia stabilized by dysprosia, erbia, gadolinium oxide, neodymia, samarium oxide or ytterbia, or hafnia stabilized by dysprosia, gadolinium oxide, samarium oxide, yttria or ytterbia. Up to five weight percent yttria may be added to the coating material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Thermal/environmental barrier coating system for silicon-containing materials
ActiveUS20060280963A1Prolong lifeImprove protectionFireproof paintsBlade accessoriesAluminateCoating system
A coating system for Si-containing materials, particularly those for articles exposed to high temperatures. The coating system exhibits improved resistance to corrosion from sea salt and CMAS as a result of using aluminate compounds to protect silicate-containing layers of the coating system. The coating system includes an environmental barrier coating, a thermal barrier coating overlying the environmental barrier coating and formed of a thermal-insulating material, and a transition layer between the environmental barrier coating and thermal barrier coating, wherein the transition layer contains at least one aluminate compound and / or alumina.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Thermal barrier coating ceramic structure
InactiveUS6455173B1PropellersSurface reaction electrolytic coatingElectron beam physical vapor depositionVapor cloud
A multilayered ceramic topcoat of a thermal barrier coating system is useful for high temperature corrosive applications such as hot section components in gas turbine engines. The ceramic topcoat includes at least two layers, each having generally columnar grain microstructures with different grain orientation directions. A preferred method of producing the multilayered ceramic topcoat includes positioning a superalloy substrate at a first angled orientation relative to a ceramic vapor cloud in an electron beam physical vapor deposition apparatus for a time sufficient to grow a first ceramic layer. The substrate is then reoriented to a second, different angled orientation for a time sufficient to grow a second ceramic layer. The ceramic layers exhibit columnar microstructures having respective grain orientation directions which are related to the first and second substrate orientations. For uniformly coating a complex contoured surface such as a turbine blade airfoil, the blade can be rotated during coating deposition at each angled orientation. Alternatively, the article may be continuously reoriented according to a predetermined speed cycle to produce generally arcuate, sinusoidal, helical, or other columnar grain microstructures.
Owner:MARIJNISSEN GILLION HERMAN +4
Thermal barrier coating systems and materials
InactiveUS6924040B2Molten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingThermal stabilityThermal barrier coating
A ceramic material has particular utility as a thermal insulating or thermal barrier coating on metallic substrates. The ceramic material includes gadolinia and hafnia, preferably forming gadolinia-hafnia. This material exhibits chemical stability, thermal stability and thermal insulating properties superior to those of currently used thermal barrier ceramics, and also provides resistance to sintering and erosion comparable to currently used ceramics. A preferred material has between about 3-70 mol. % hafnia, balance hafnia.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Aqueous slurry for the production of thermal and environmental barrier coatings and processes for making and applying the same
ActiveUS20130156958A1Low thermal conductivityConvenient coatingBlade accessoriesPretreated surfacesPorosityMetallurgy
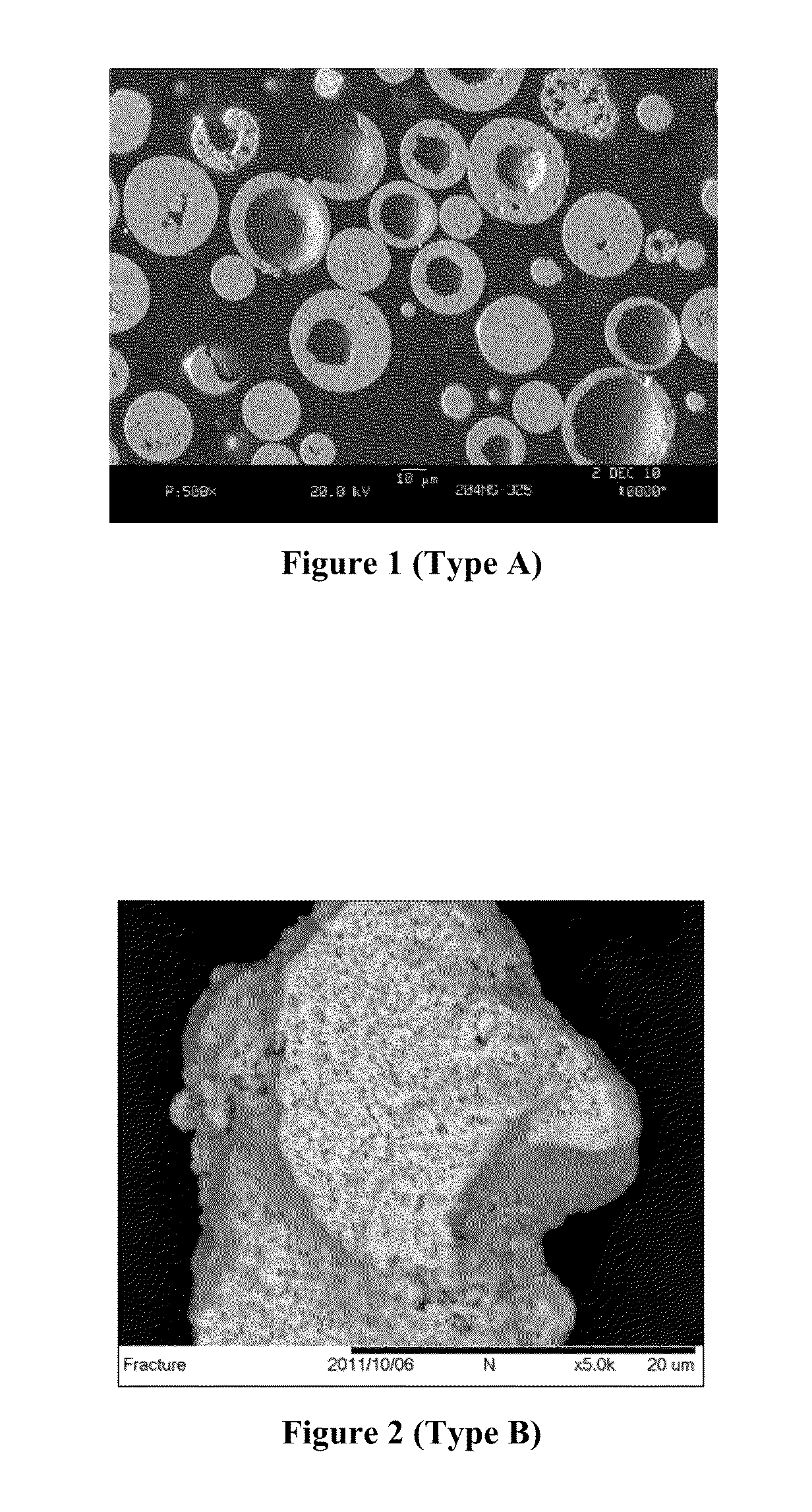
An improved slurry formulation for the production of a thermal and environmental barrier coatings are provided which can withstand high temperature applications. The slurry includes a combination of a coarse ceramic powder fraction having close porosity particles and a fine ceramic powder fraction. The combination of the two powders produces a bimodal particle size distribution having a controlled amount of closed porosity that imparts desirable properties to the coating produced. The finer solid particles are interdispersed within an aqueous binder to produce a ceramic matrix with sufficient mechanical strength. The closed porosity containing coarse particles are embedded within the resultant ceramic matrix and do not disintegrate under high temperature conditions to impart a temperature resistant, non-collapsing closed porosity to the coating which can also act as an environmental barrier.
Owner:PRAXAIR ST TECH INC
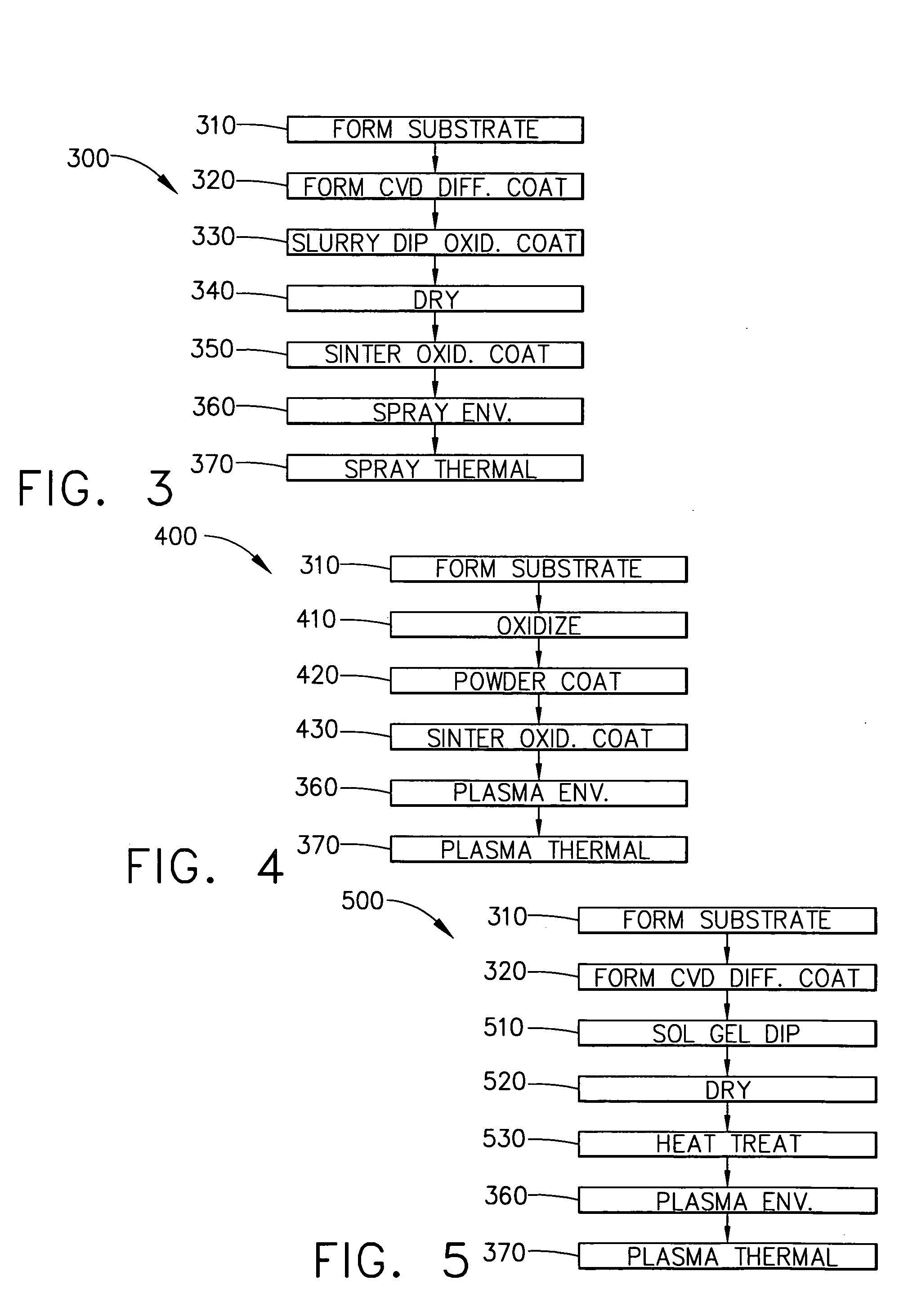
Oxidation barrier coatings for silicon based ceramics
ActiveUS20050112381A1Avoid Explosion HazardsContinuous combustion chamberBlade accessoriesElectron beam physical vapor depositionGas phase
A protective barrier coating system including a diffusion barrier coating and an oxidation barrier coating and method for use in protecting silicon-based ceramic turbine engine components. A complete barrier coating system includes a thermal barrier coating of stabilized zirconia and an environmental barrier coating of an alloyed tantalum oxide. The oxidation barrier coating includes a layer of metallic silicates formed on a substrate of silicon nitride or silicon carbide to be protected. The oxidation barrier coating can include silicates of scandium, ytterbia or yttrium. The oxidation barrier coating may also include an inner layer of Si2ON2 between the diffusion barrier and the metallic silicate layer. The oxidation barrier coating can be applied to the substrate by spraying, slurry dipping and sintering, by a sol-gel process followed by sintering, by plasma spray, or by electron beam-physical vapor deposition. The diffusion layer of essentially pure Si3N4 can be applied to the substrate to prevent the migration of damaging cations from the protective layers to the substrate and is preferably formed by chemical vapor deposition. A method for protecting silicon based substrates can comprise a step of forming an oxidation barrier coating on a substrate, where a step of forming the oxidation barrier includes a step of sintering the oxidation barrier and substrate in a wet gas containing hydrogen.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
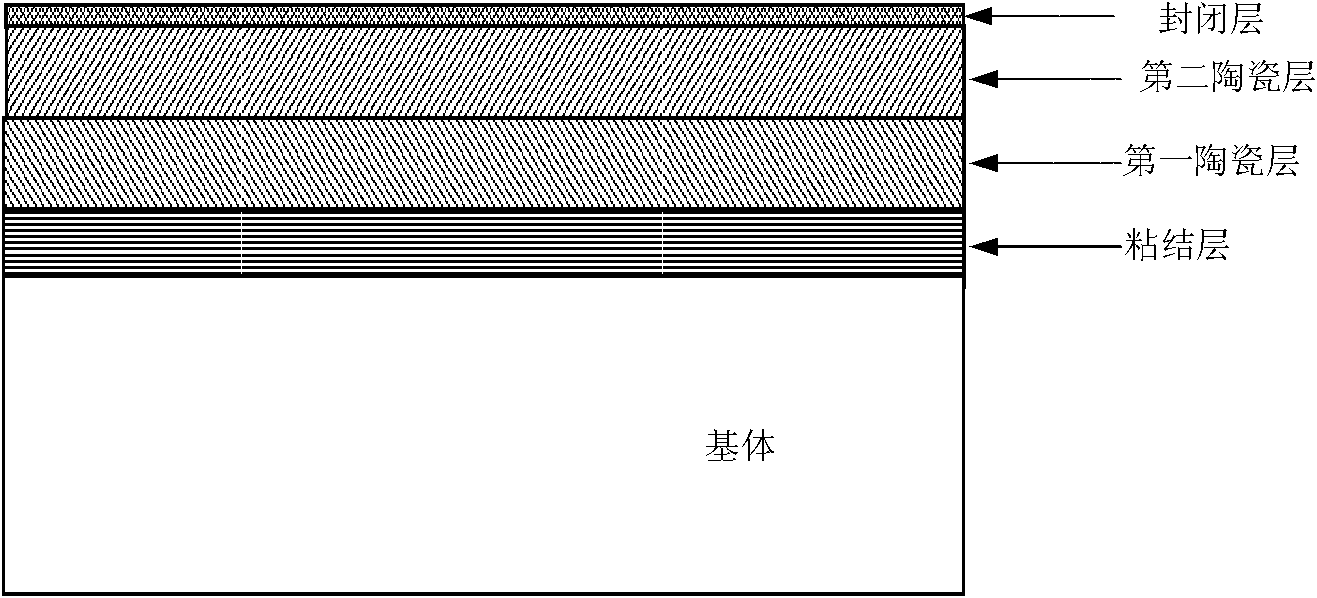
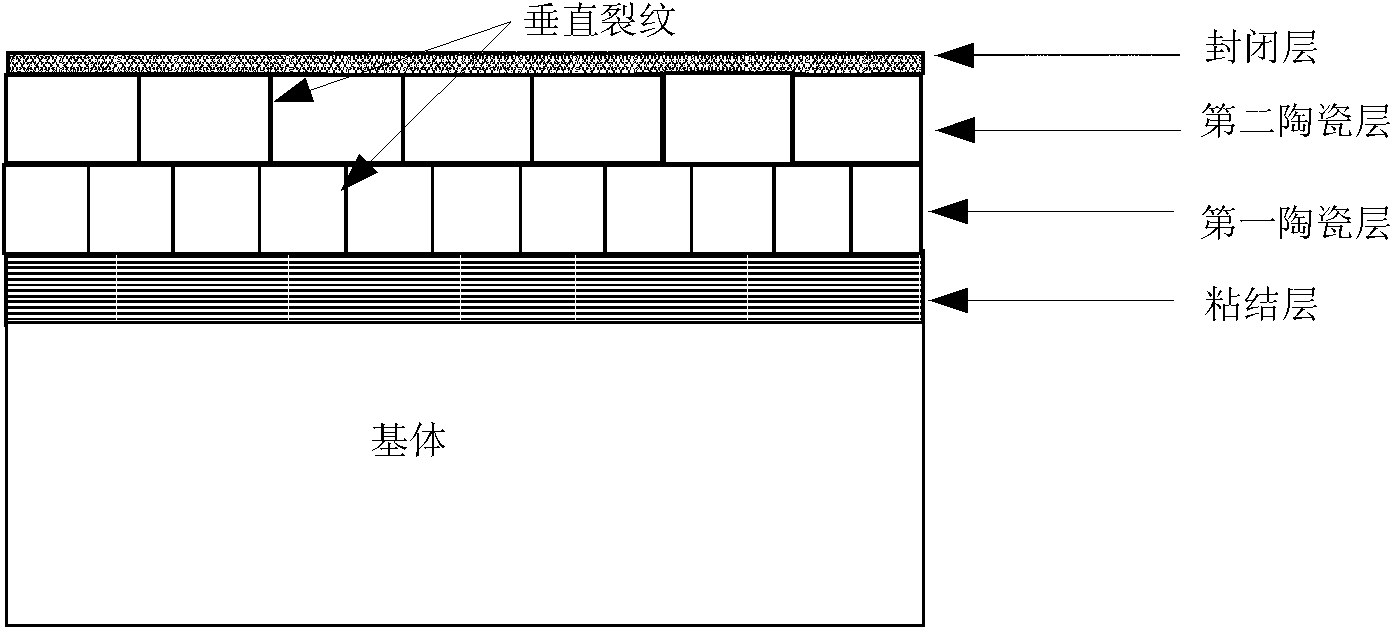
Multilayer thermal barrier coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102127738ANo layer peeling phenomenon occursImprove hot corrosion resistanceMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingPorosityElectron beam physical vapor deposition
The invention provides a multilayer thermal barrier coating and a preparation method thereof. The multilayer thermal barrier coating sequentially comprises an adhesion layer, a first ceramic layer, a second ceramic layer and a closing layer from bottom to top, wherein the closing layer has the thickness of 10-30 micros and the porosity of 2-8 percent and is made from the Al2O3. The thermal barrier coating can be prepared by adopting an electron beam physical gas-phase deposition technology or a plasma spraying method. The multilayer thermal barrier coating provided by the invention can avoid the stripping of the ceramic layers in a thermal circulating process, the thermal erosion resistance of the thermal barrier coating is greatly improved than the dual ceramic layers; and vertical crackles are introduced in the ceramic layer through improving a conventional plasma spraying process so that the thermal shock life of the thermal barrier coating is greatly prolonged.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Thermal barrier coating compositions, processes for applying same and articles coated with same
Owner:RTX CORP
Thermal barrier layer for integrated circuit manufacture
InactiveUS20100075459A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringThermal barrier coating
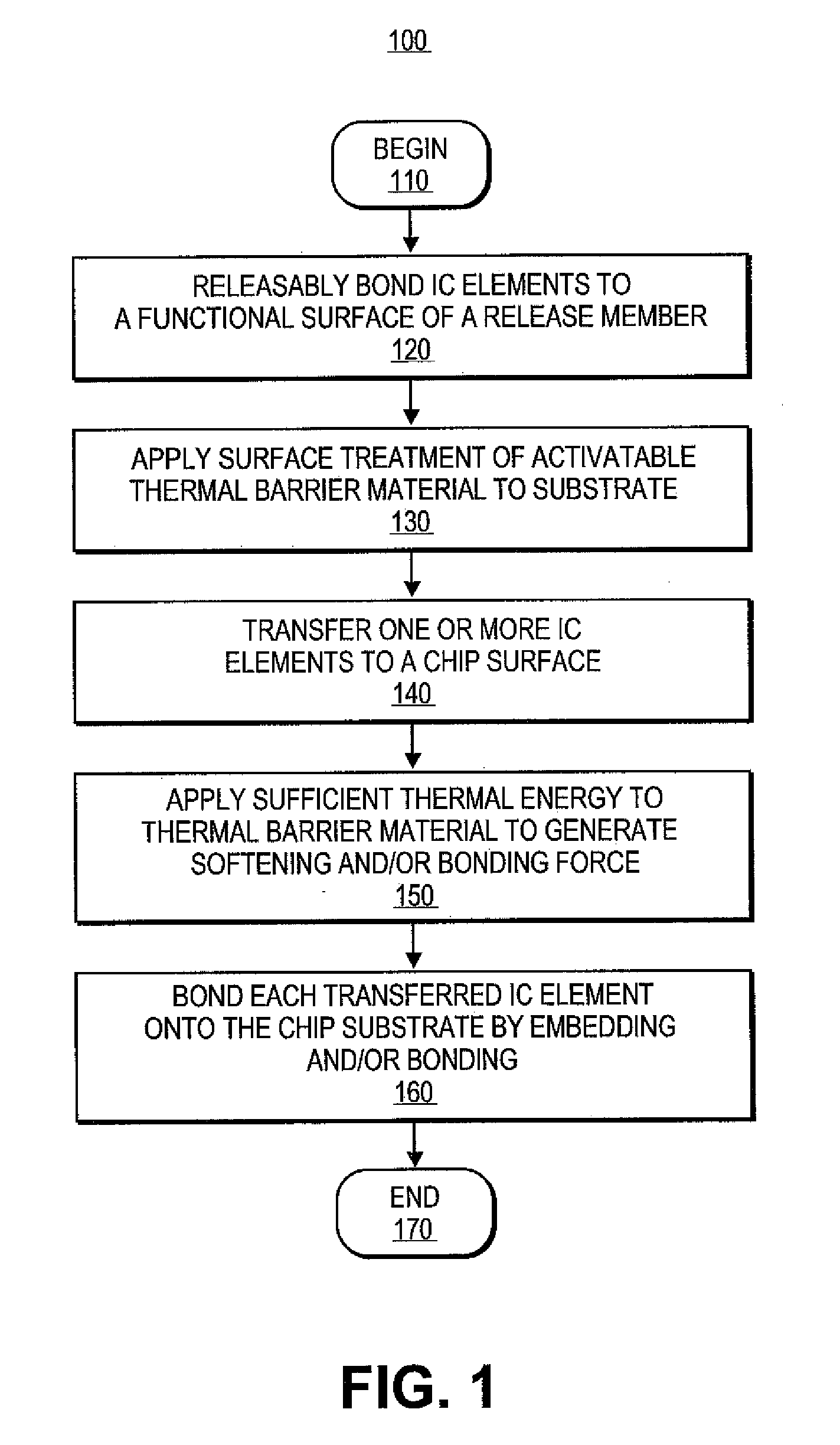
Exemplary embodiments provide methods and systems for assembling electronic devices, such as integrated circuit (IC) chips, by selectively and scalably embedding or seating IC elements onto / into a receiving substrate, such as a chip substrate. Preparing of the chip substrate can be performed by depositing or patterning an activatable thermal barrier material on a surface of the substrate. The IC chips are secured on the prepared substrate by activating the thermal barrier material between the chip substrate and IC chips. Securing can include softening of the chip substrate with the activated thermal barrier material to an amount suitable for embedding the IC chips. Securing can also include adhesively bonding the IC chips to the substrate with the activated thermal barrier material in the case of a non-pliable substrate.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Catalytic thermal barrier coatings
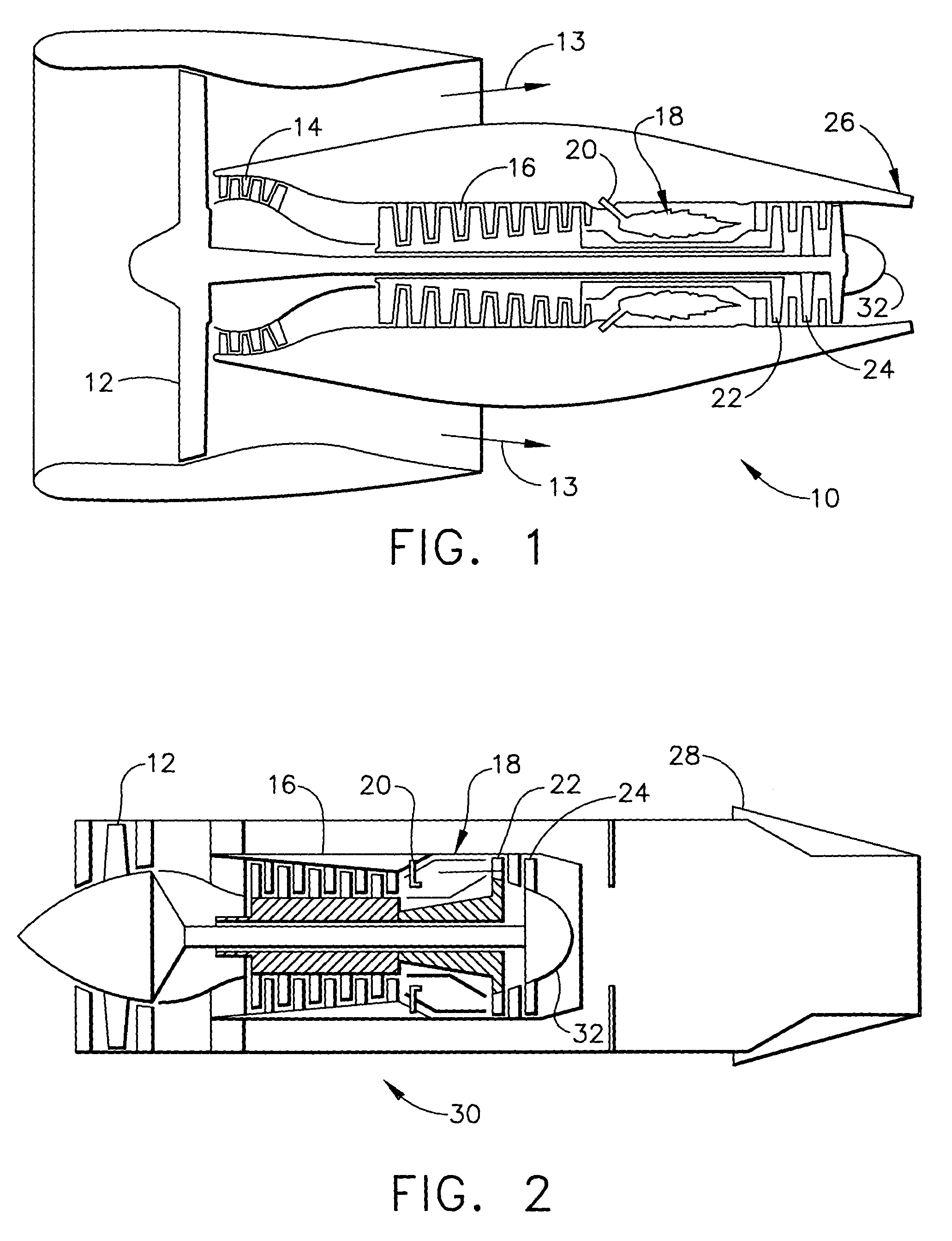
A catalyst element (30) for high temperature applications such as a gas turbine engine. The catalyst element includes a metal substrate such as a tube (32) having a layer of ceramic thermal barrier coating material (34) disposed on the substrate for thermally insulating the metal substrate from a high temperature fuel / air mixture. The ceramic thermal barrier coating material is formed of a crystal structure populated with base elements but with selected sites of the crystal structure being populated by substitute ions selected to allow the ceramic thermal barrier coating material to catalytically react the fuel-air mixture at a higher rate than would the base compound without the ionic substitutions. Precious metal crystallites may be disposed within the crystal structure to allow the ceramic thermal barrier coating material to catalytically react the fuel-air mixture at a lower light-off temperature than would the ceramic thermal barrier coating material without the precious metal crystallites.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
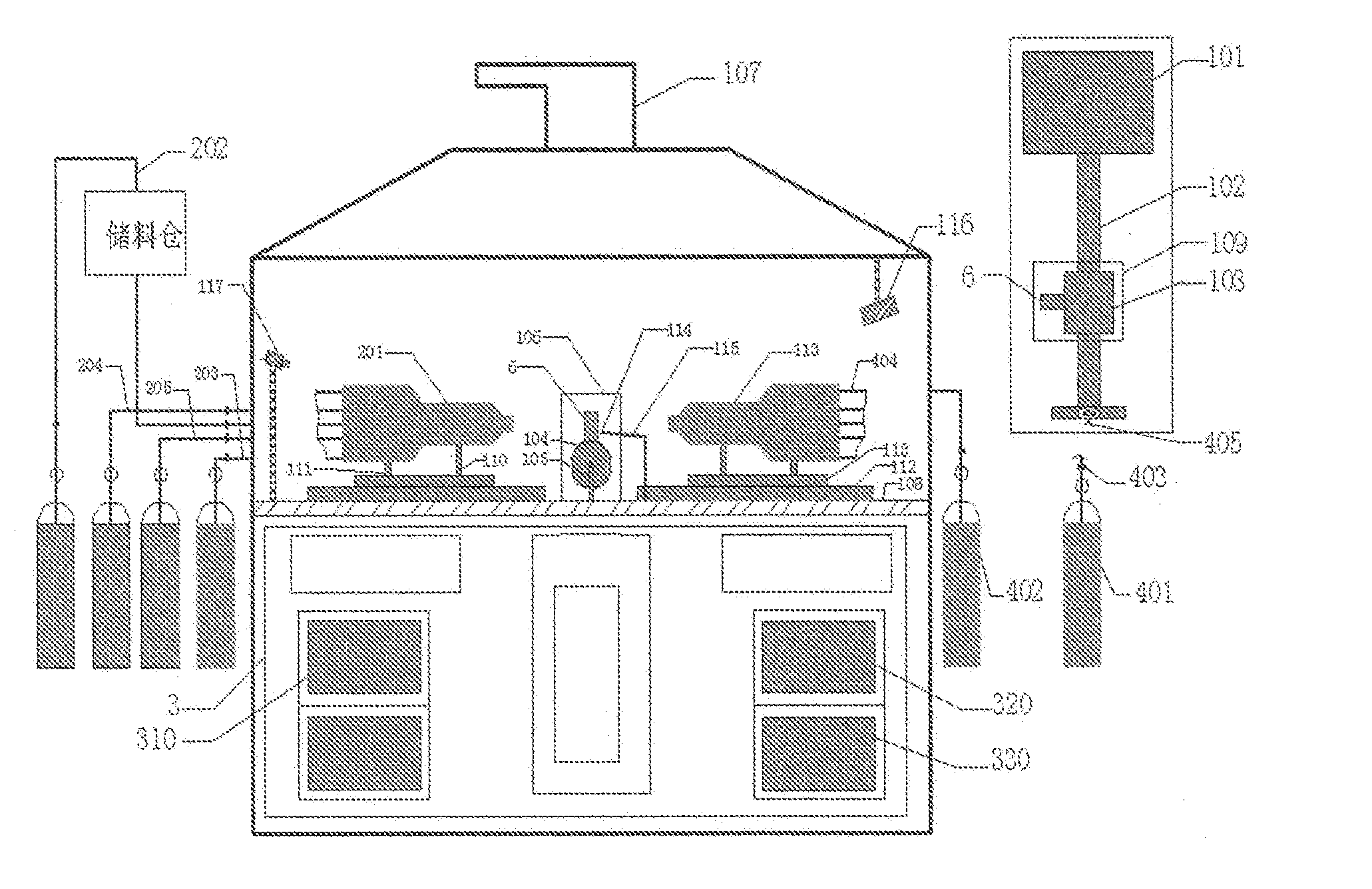
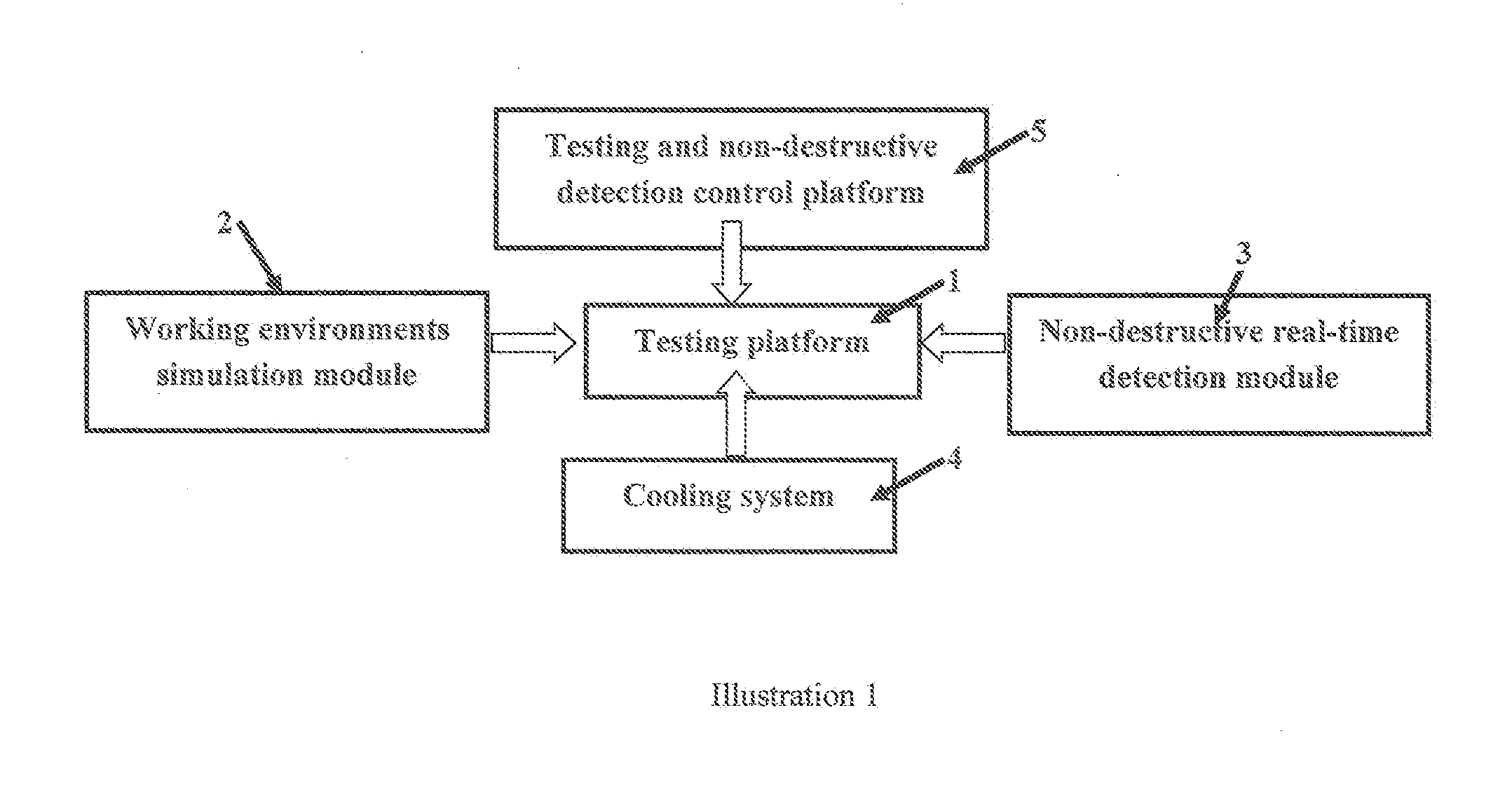
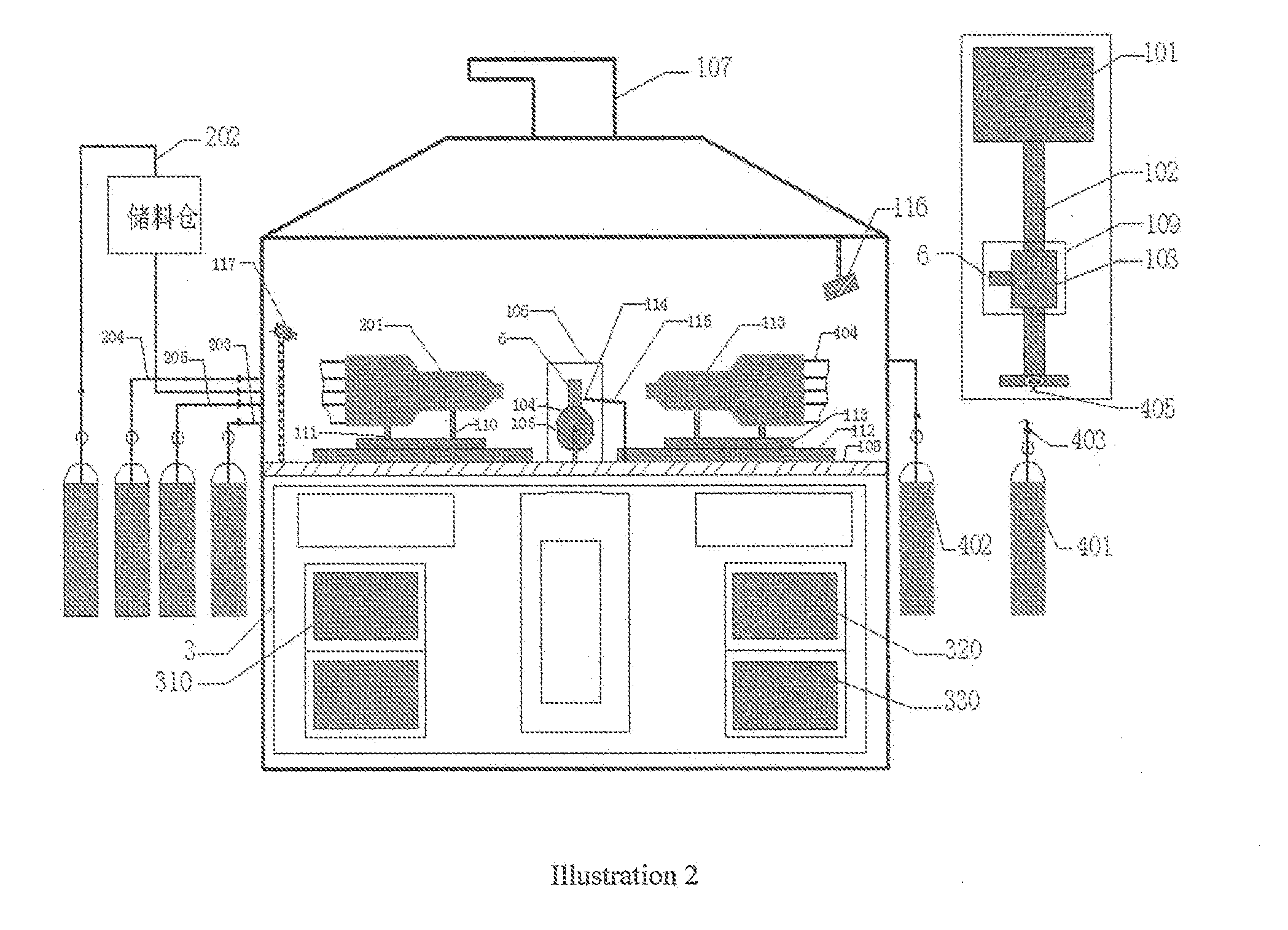
Type of testing equipment for detecting the failure process of thermal barrier coating in a simulted working environment
ActiveUS20150355074A1Better understandingReliable assessmentWeather/light/corrosion resistanceEngine testingSurface oxidationTurbine blade
A type of testing equipment for detecting the failure process of thermal barrier coating in a simulated working environment; it belongs to the field of simulated special working environment equipment. Testing equipment includes testing platform equipped with static or dynamic specimen holding apparatus, simulated module of working environment, real-time detection module, control panel. This invention is capable of simulating a high temperature, erosive, corrosive working environment for thermal barrier coated turbine blade of aero-engines; simulate high speed spinning working environment for thermal coated blade, simulate static working environment for guiding blade; perform real-time testing of temperature field, 3-D displacement field, crack initiation and expansion, surface oxidation, etc. This invention has achieved complete integration of high temperature, erosive, corrosive working environment for thermal barrier coating and complete integration static or dynamic working environment, complete integration of simulated working environment and real-time testing, thus providing a crucial testing platform and reference data to properly understand the failure mechanism of thermal barrier coated blade and to improve relevant designs; strong applicability.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
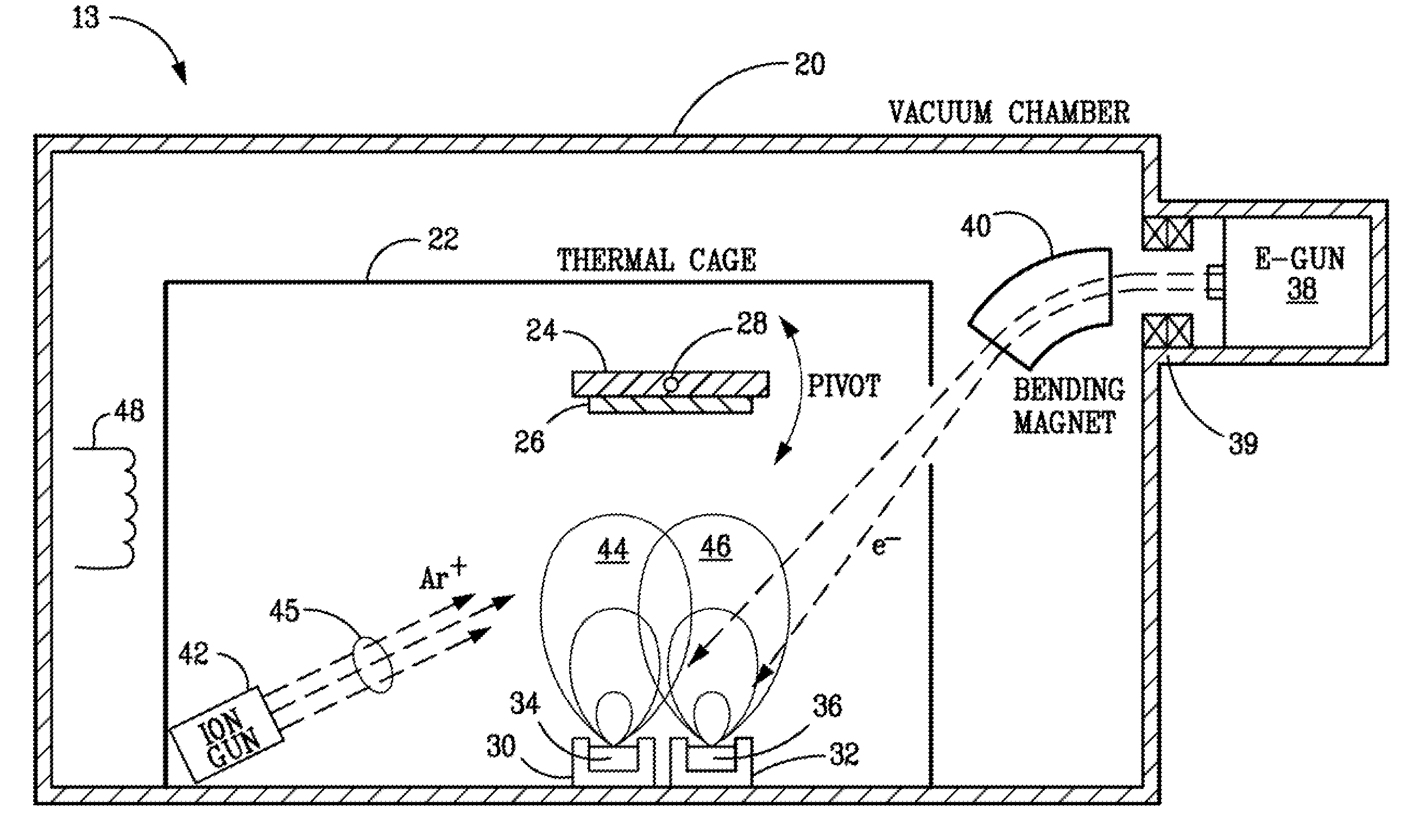
Ion beam assisted deposition of thermal barrier coatings
InactiveUS7838083B1Engine manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingElectron beam physical vapor depositionIon beam-assisted deposition
Methods and apparatus for depositing thermal barrier coatings on gas turbine blades and vanes using Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition (EBPVD) combined with Ion Beam Assisted Deposition (IBAD).
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method and apparatus for measuring on-line failure of turbine thermal barrier coatings
InactiveUS7690840B2Improve efficiencyAvoid maintenanceThermometer detailsPlug gaugesTurbine bladeEngineering
A method of remotely monitoring the radiant energy (6) emitted from a turbine component such as a turbine blade (1) having a low-reflective surface coating (3) which may be undergoing potential degradation is used to determine whether erosion, spallation, delamination, or the like, of the coating (3) is occurring.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
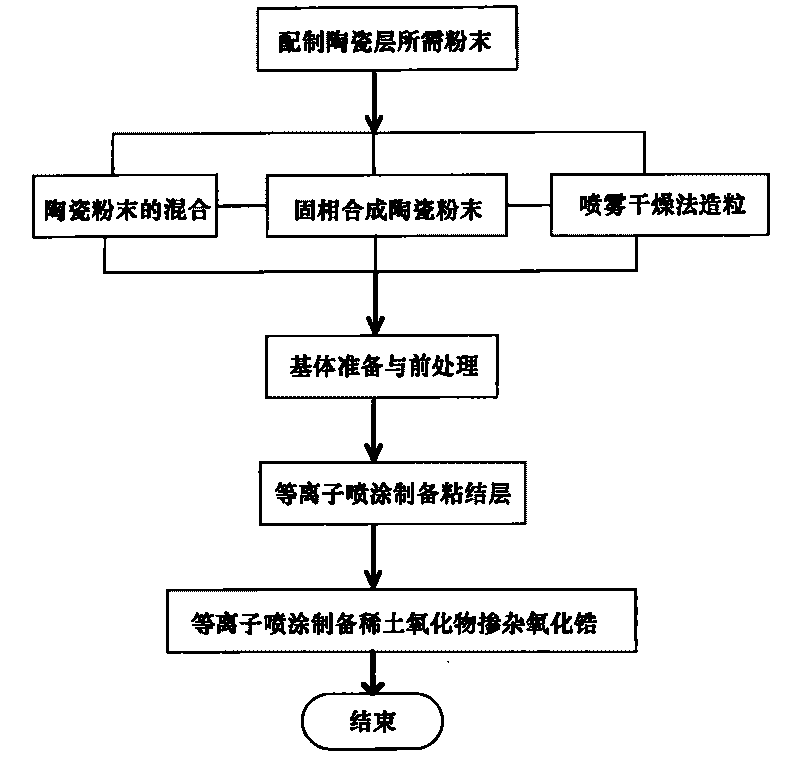
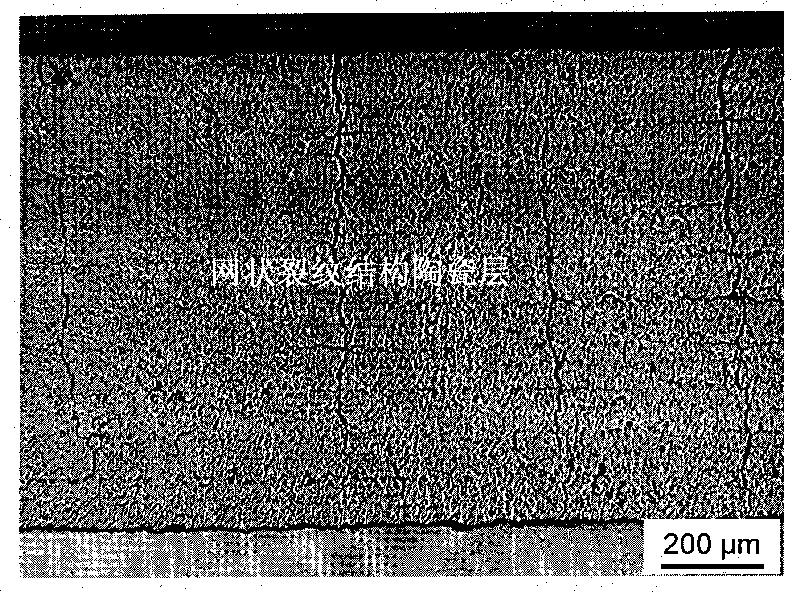
Multielement rare earth oxide doped zirconia thermal barrier coating with craze crack structure and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101723667AGood phase stability at high temperatureLow temperature for long-term useMolten spray coatingEfficient propulsion technologiesThermal insulationRare earth
The invention discloses a method for preparing a rare earth oxide doped zirconia thermal barrier coating with a craze crack structure, which solves the problems of low thermal shock resistance property, difficult further thermal conductivity reduction and the like of the thermal coating prepared by conventional plasma spraying. Under the condition of the plasma spraying technology, the preheating temperature of a base body, the moving speed of a plasma spraying gun and a powder delivery rate are adjusted, then a rare earth oxide doped zirconia thermal barrier coating (BH-TBCO1) with a craze crack structure and stable thermodynamics is prepared. The rare earth oxide doped zirconia thermal barrier coating with a craze crack structure has good high-temperature phase stability at the temperature below 1300 DEG C; the thermal insulation property of the thermal barrier coating is further enhanced, and the thermal insulation temperature achieves more than 150 DEG C and is enhanced by more than 50% when compared with the coating prepared by the conventional plasma spraying; the thermal shock life of the coating exceeds 4000 cycles and is enhanced by more than 1 time when compared with the coating prepared by the conventional plasma spraying.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and method for improved film cooling
ActiveUS20100282721A1Prolongs effectiveness of coolerSimple technologyEngine fuctionsEfficient propulsion technologiesLight beamSystem configuration
A system for producing at least one trench to improve film cooling in a sample is provided. The system includes at least one laser source outputting at least one pulsed laser beam. The pulsed laser beam includes a pulse duration including a range less than about 50 μs, an energy per pulse having a range less than about 0.1 Joule, and a repetition rate with a range greater than about 1000 Hz. The system also includes a control subsystem coupled to the laser source, the control subsystem configured to synchronize a position of the sample with the pulse duration and energy level in order to selectively remove at least one of a thermal barrier coating, a bondcoat and a substrate metal in the sample to form the at least one trench.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Turbine blade tip and shroud clearance control coating system
A turbine blade tip and shroud clearance control coating system comprising an abrasive blade tip coating and an abradable shroud coating are provided. The abrasive layer may comprise abrasive particles of cubic zirconia, cubic hafnia or mixtures thereof, and the abradable layer may be a nanolaminate thermal barrier coating that is softer than the abrasive layer. The invention further provides an alternate coating system comprising an abradable blade tip coating and an abrasive shroud coating.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Thermal barrier coated RF radomes and method
ActiveUS8765230B1Improve performanceLow costLiquid surface applicatorsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio frequencyThermal barrier coating
Thermal barrier coated RF radomes and a method for making the same are provided. In an embodiment of the disclosure, there is provided a method for making a thermal barrier coated radio frequency (RF) radome. The method comprises providing a radio frequency (RF) radome. The method further comprises applying a thermal barrier coating having a dielectric constant less than about 2.0 onto a surface of the radome to form a thermal barrier coated RF radome. The thermal barrier coating reduces a structure temperature of the radome by greater than 300 degrees Fahrenheit to enhance thermo-mechanical properties and performance of the RF radome.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Diffusion barrier and protective coating for turbine engine component and method for forming
A turbine engine component comprising a substrate made of a nickel-base or cobalt-base superalloy, a non-metallic oxide or nitride diffusion barrier layer overlying the substrate, and a protective coating overlying the barrier layer, the protective coating comprising at least one platinum group metal selected from the group consisting of platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium and iridium. The diffusion barrier layer may be a deposited or thermally grown oxide material, especially aluminum oxide. The protective coating may be heat treated to increase homogeneity of the coating and adherence with the substrate. The component typically further comprises a ceramic thermal barrier coating overlying the protective coating. Also disclosed are methods for forming a protective coating system on the turbine engine component by forming the non-metallic oxide or nitride diffusion barrier layer on the substrate and then depositing the platinum group metal on top of the barrier layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Diffuser particle separator
A diffuser particle separator may be integrated into a gas turbine engine to remove corrosive dust and salt particles from the engine's core air flow. The air flow may pass over a series of particle accumulator entrance orifices, trapping particles in a particle accumulator while allowing the air flow to continue unimpeded. Since dust deposits may become molten at high temperatures, removal of dust from the core and secondary airflow may be critical for long-life superalloy and ceramic components, particularly those with small diameter air-cooling holes and thermal barrier coatings.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Optical reflector for reducing radiation heat transfer to hot engine parts
InactiveUS7208230B2Prolong lifeLess mean timePropellersMagnetic materialsOptical reflectionCoating system
A high temperature gas turbine component for use in the gas flow path that comprises a specular optical reflector coating system. A thin specular optical reflector coating system is applied to the gas flow path of the component, that is, the surface of the component that forms a boundary for hot combustion gases. The component typically includes a thermal barrier coating overlying the high temperature metallic component that permits the component to operate at elevated temperatures. The thermal barrier coating must be polished in order to provide a surface that can suitably reflect the radiation into the gas flow path. The thin reflector coating system comprises a thin high temperature and corrosion resistant refractory stabilizing layer, which is applied over a thin reflective metal layer, which is applied over a thin high temperature and corrosion resistant refractory sealing layer. The coating system is applied over the polished thermal barrier coating by a process that can adequately adhere the reflector to the polished surface without increasing the roughness of the surface. The coating system reflects radiation back into the hot gas flow path or into the atmosphere. The reflected radiation is not focused onto any other hardware component. The design of the component is such that the radiation is returned to the gas flow path or sent to the atmosphere rather than absorbed into a component that only serves to increase the temperature of such a component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com