Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
793 results about "Reaction layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
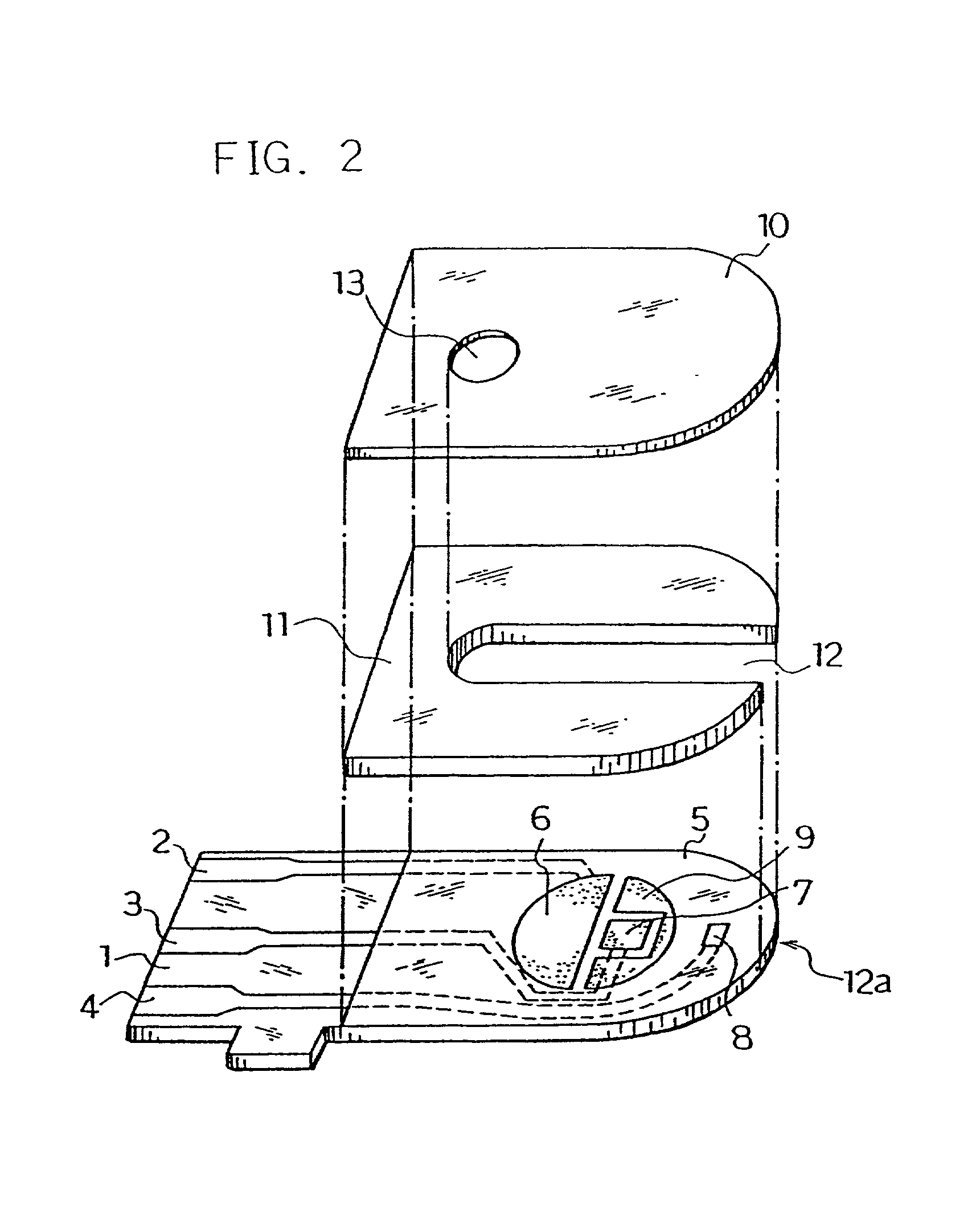
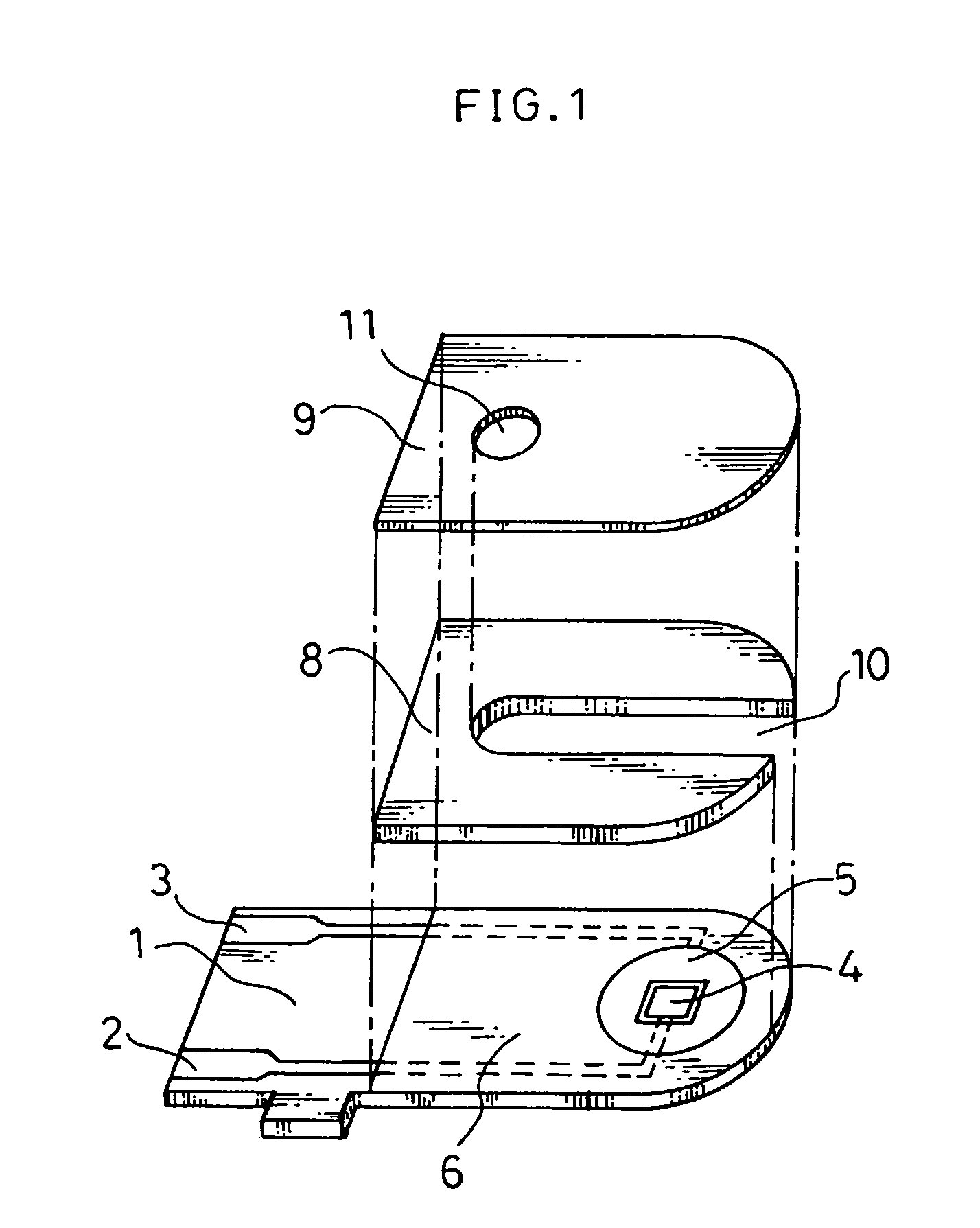
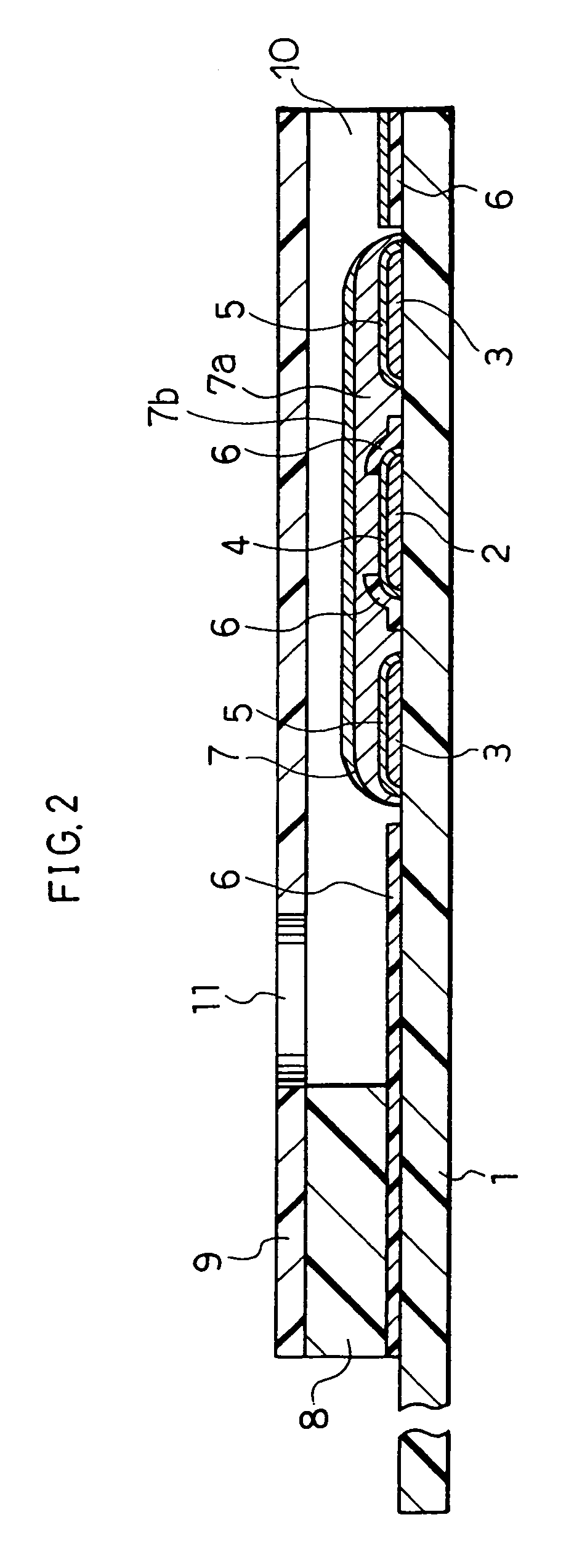
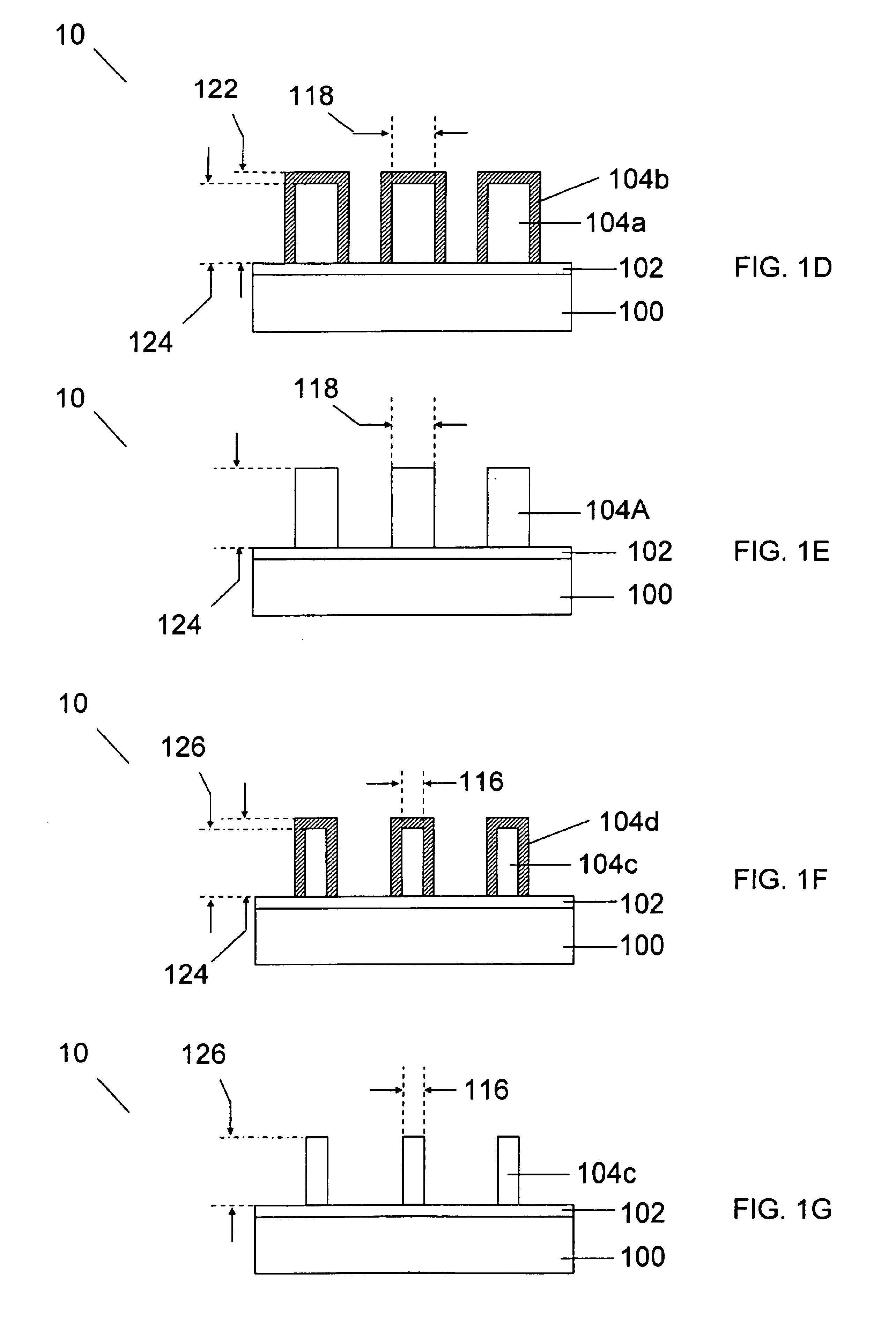
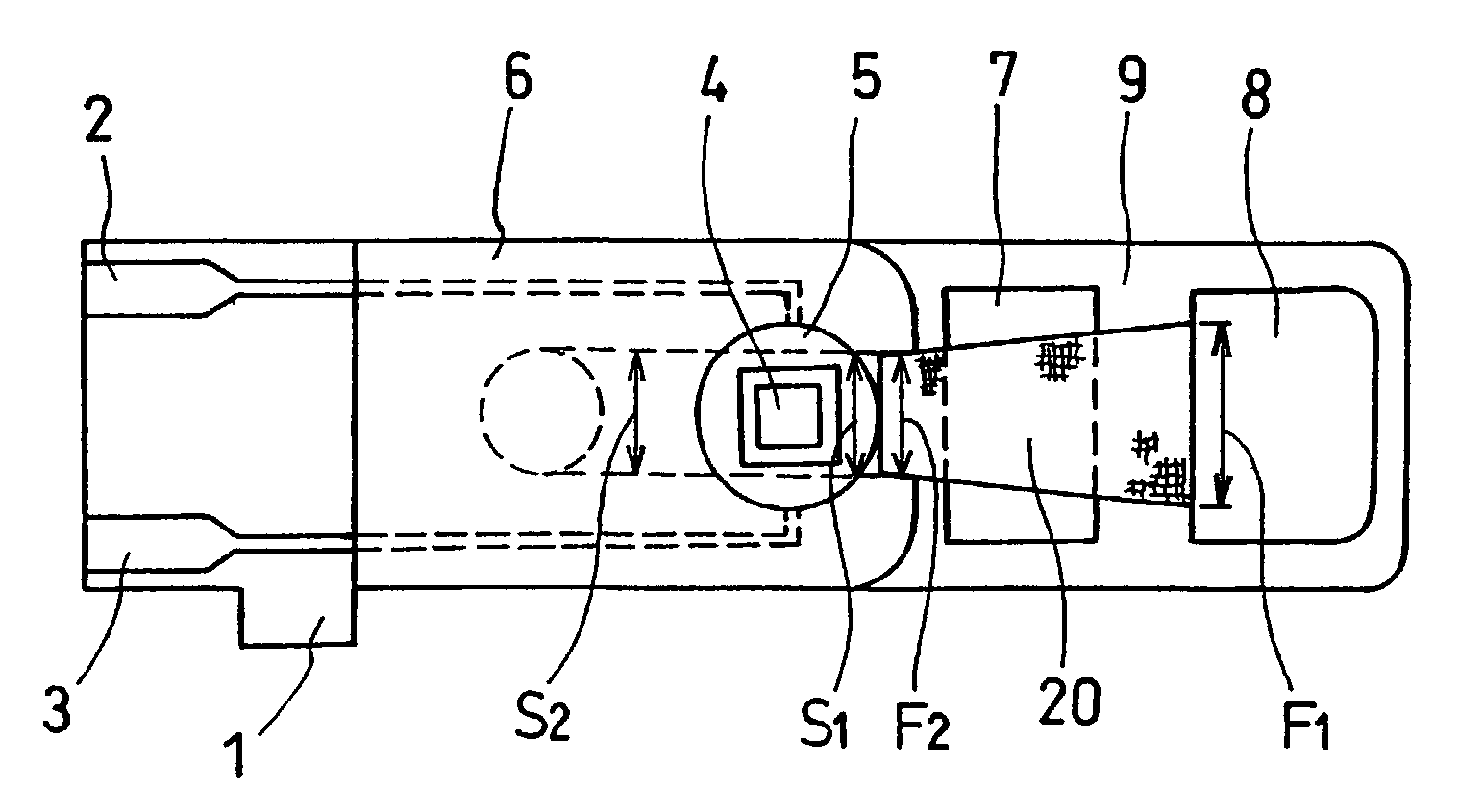
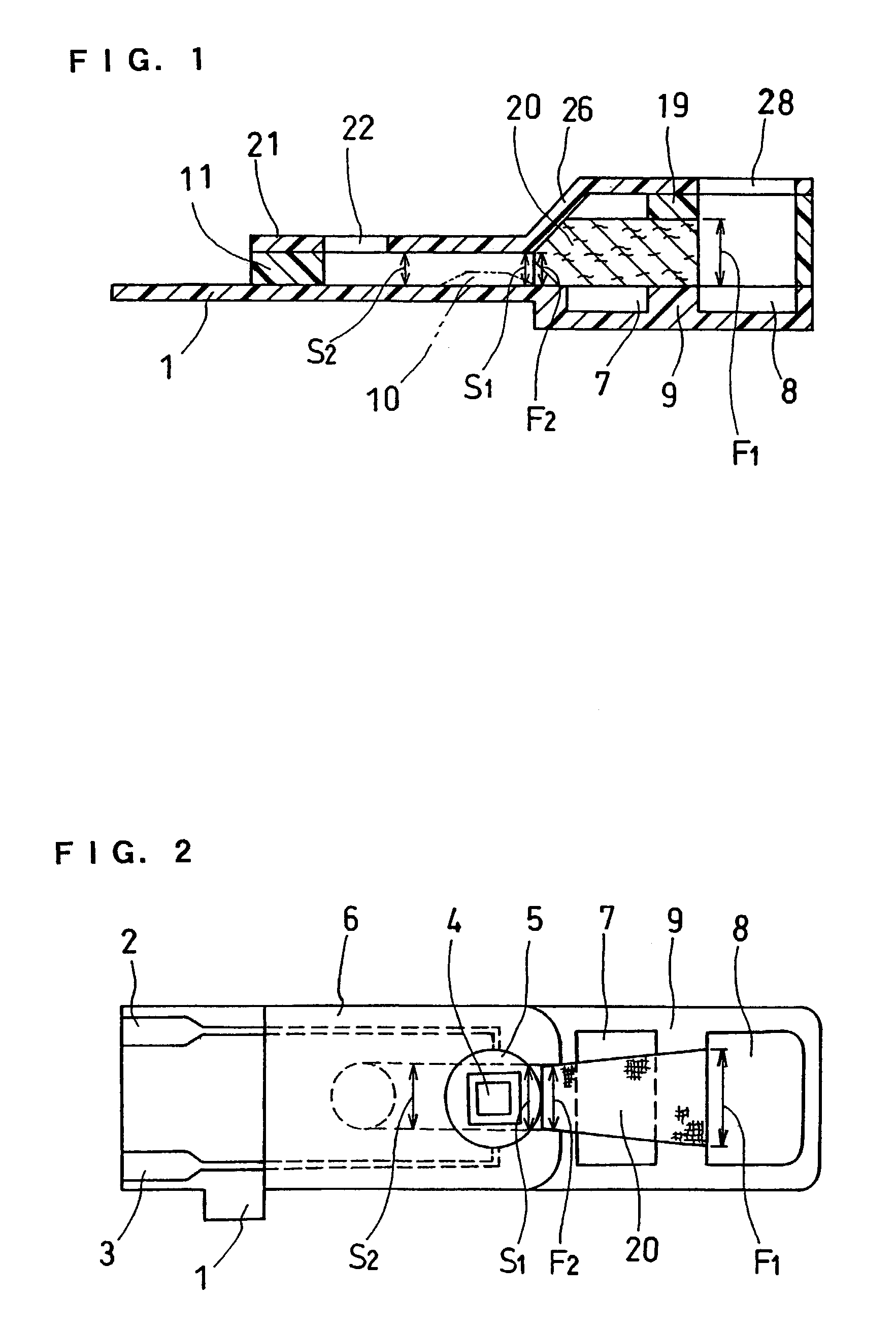
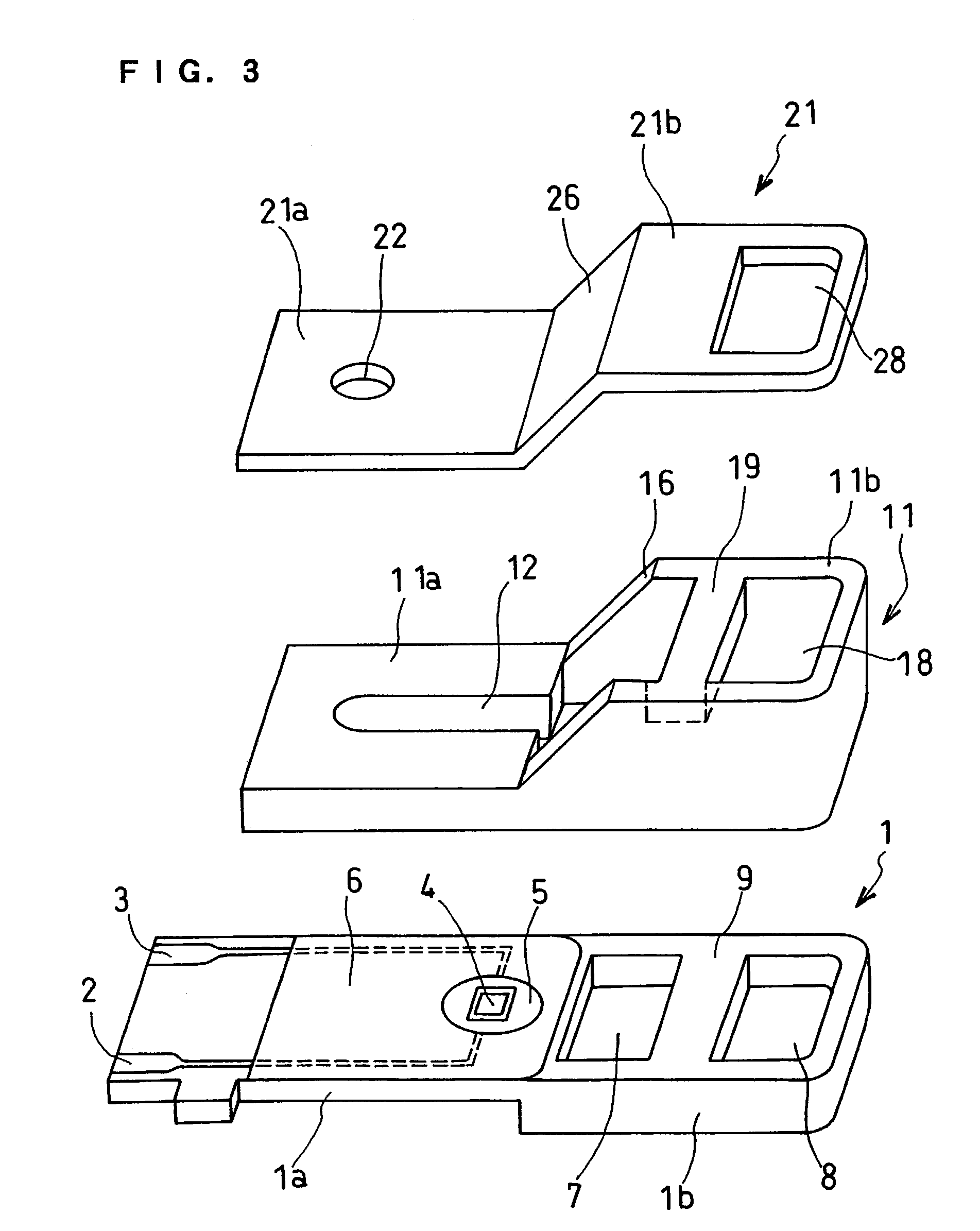
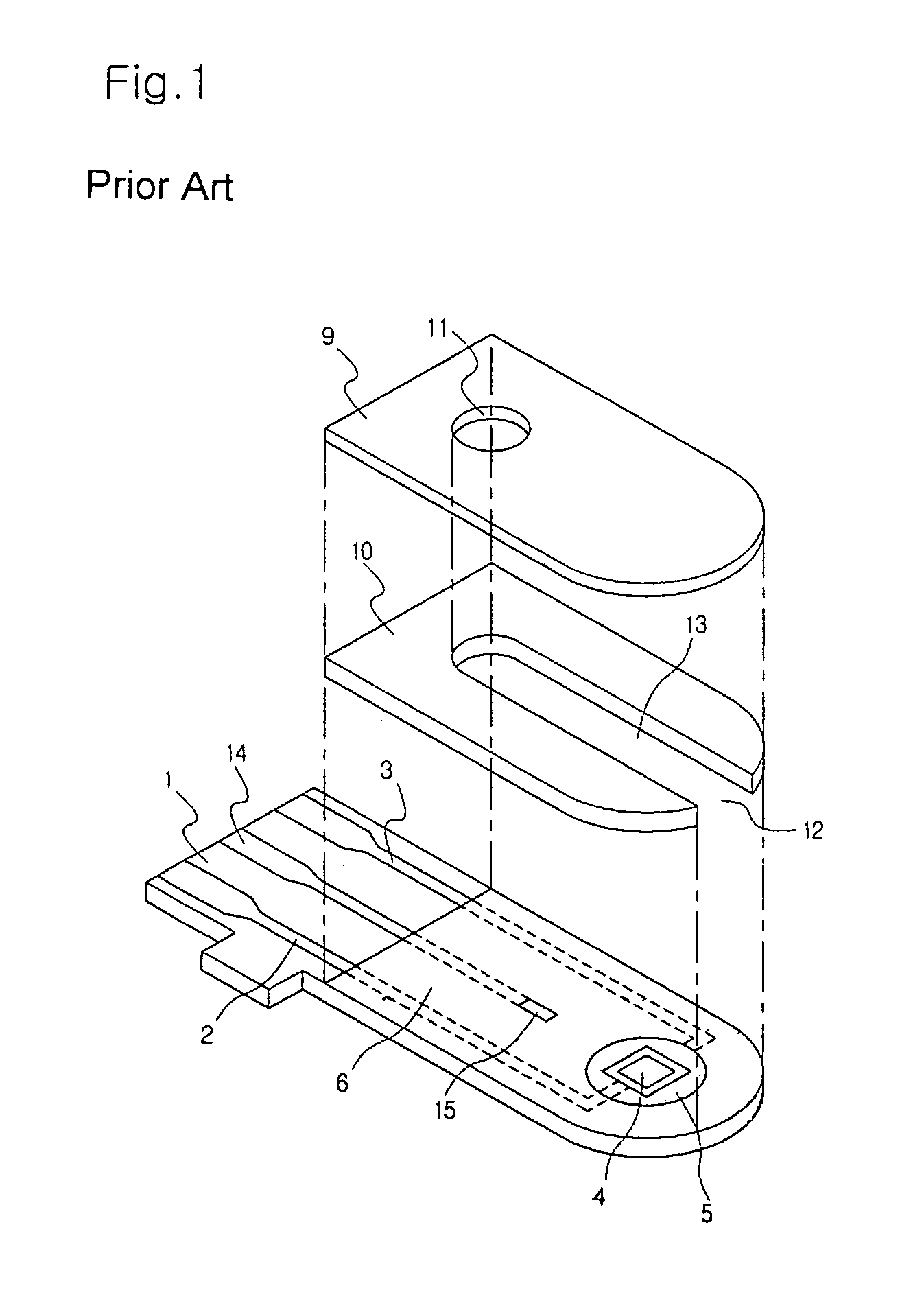
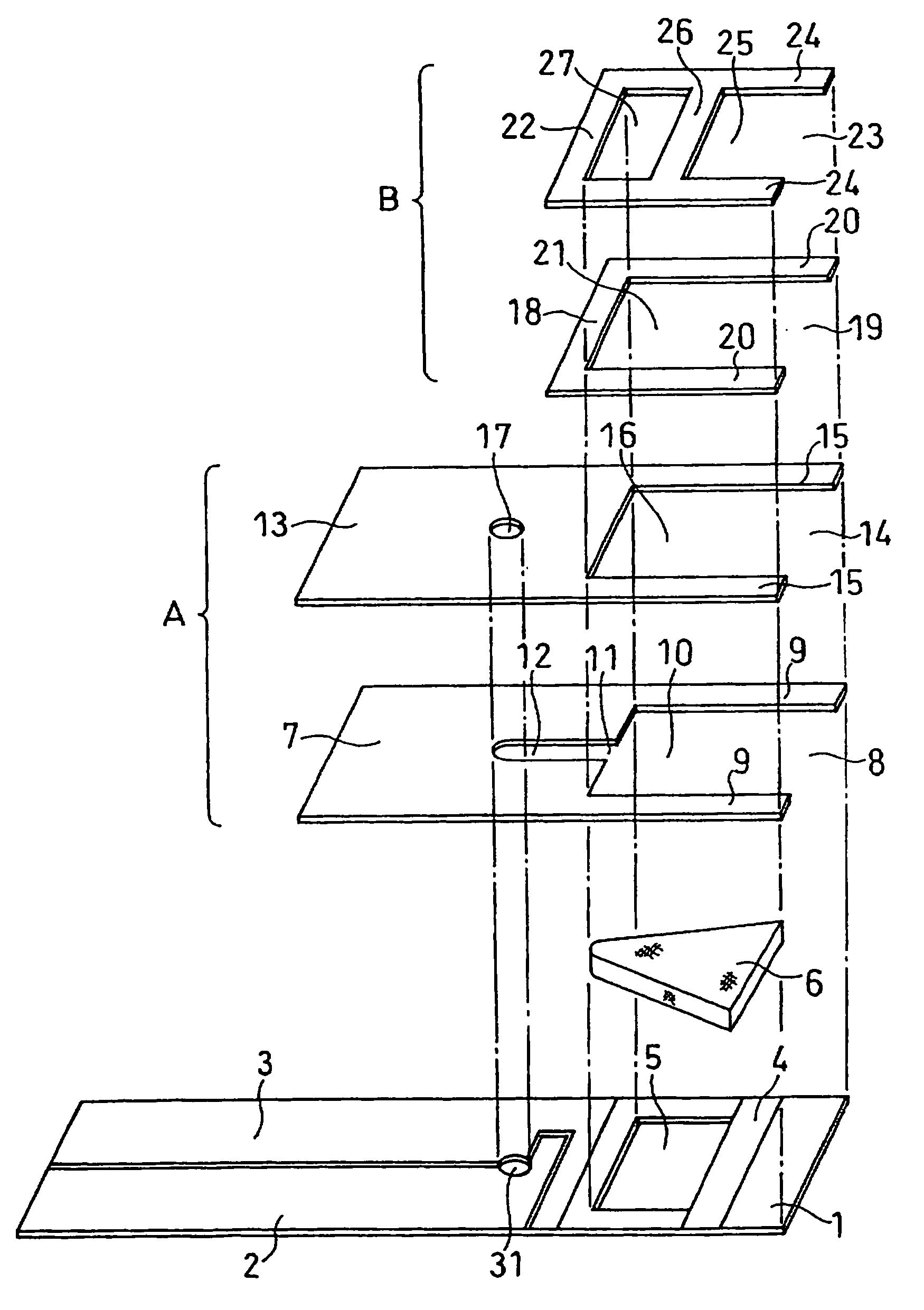
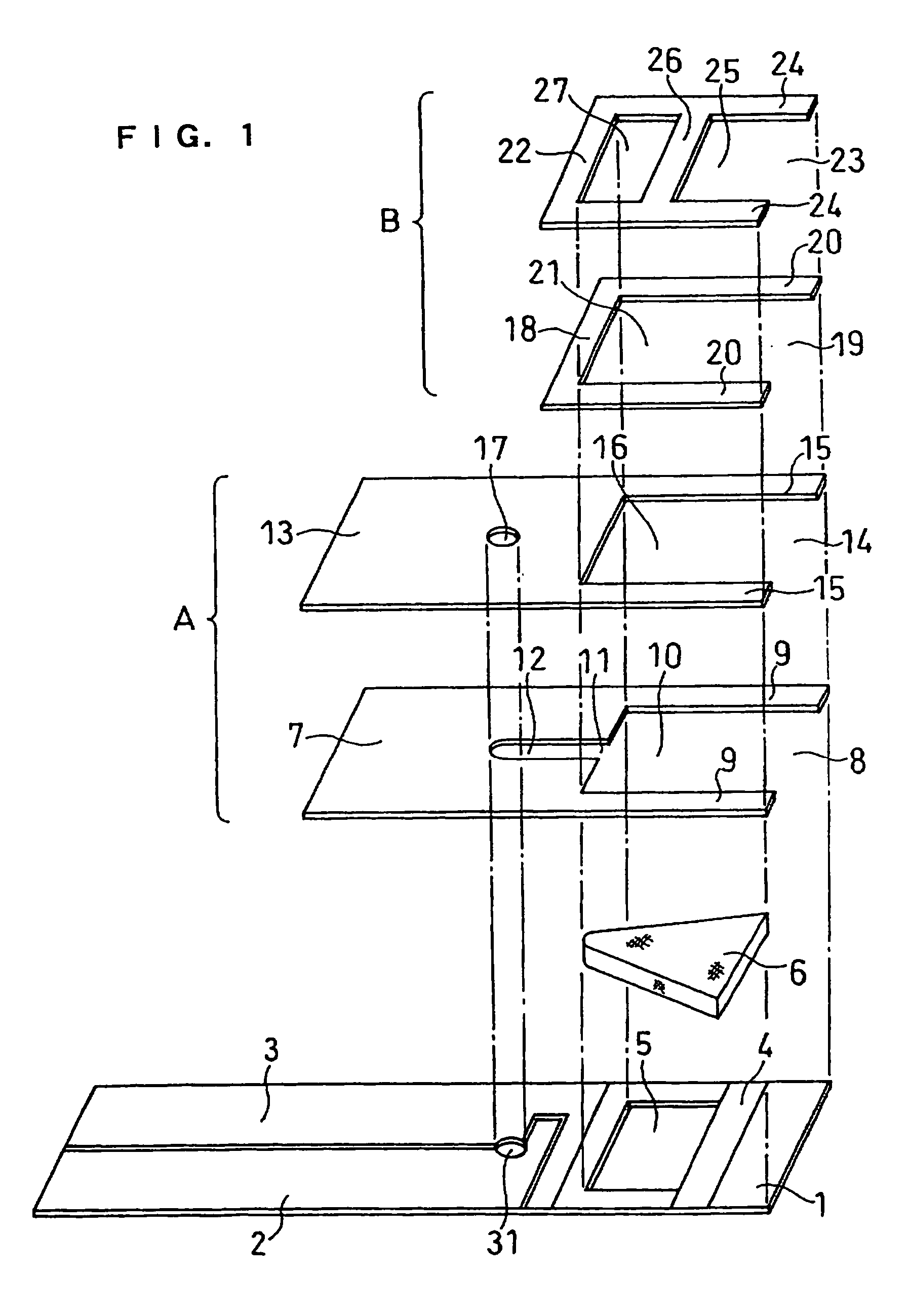
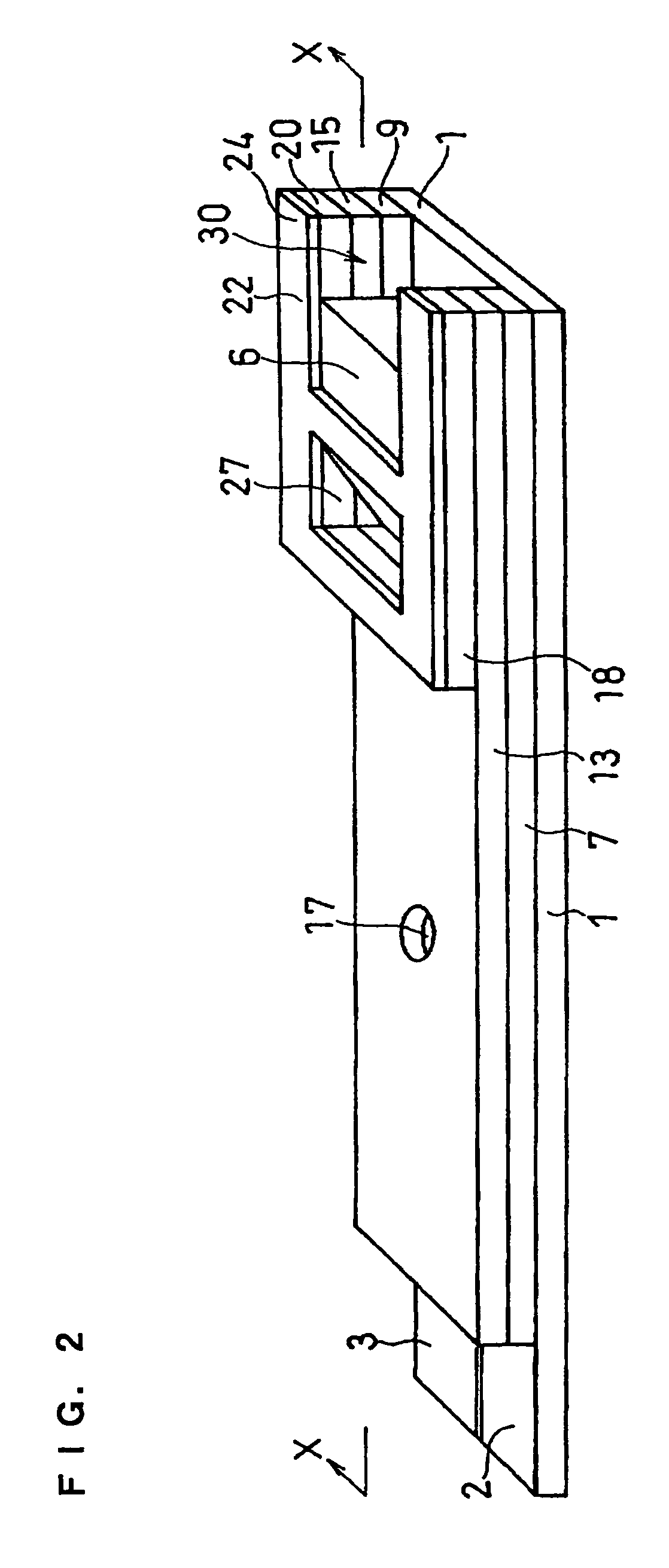
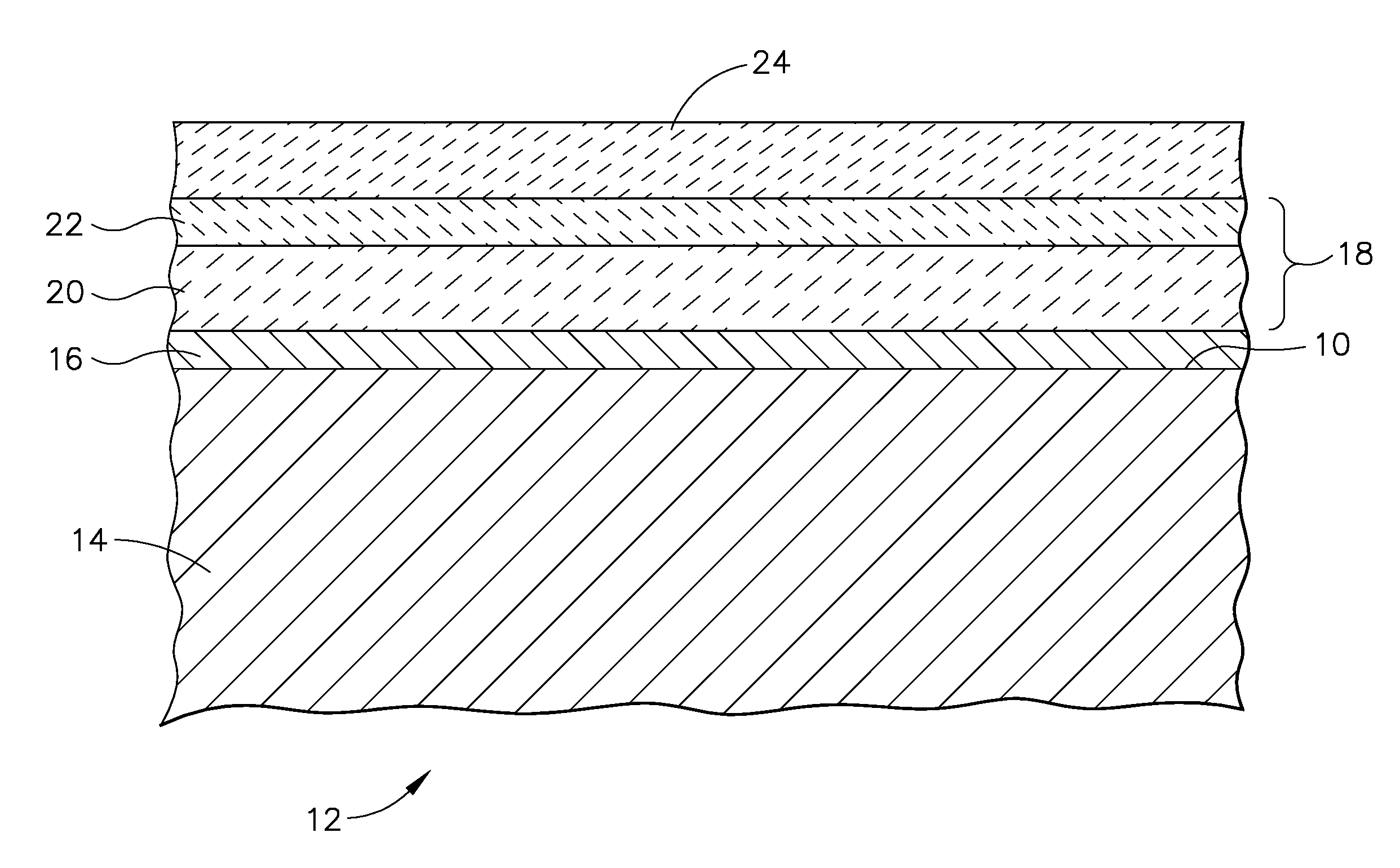
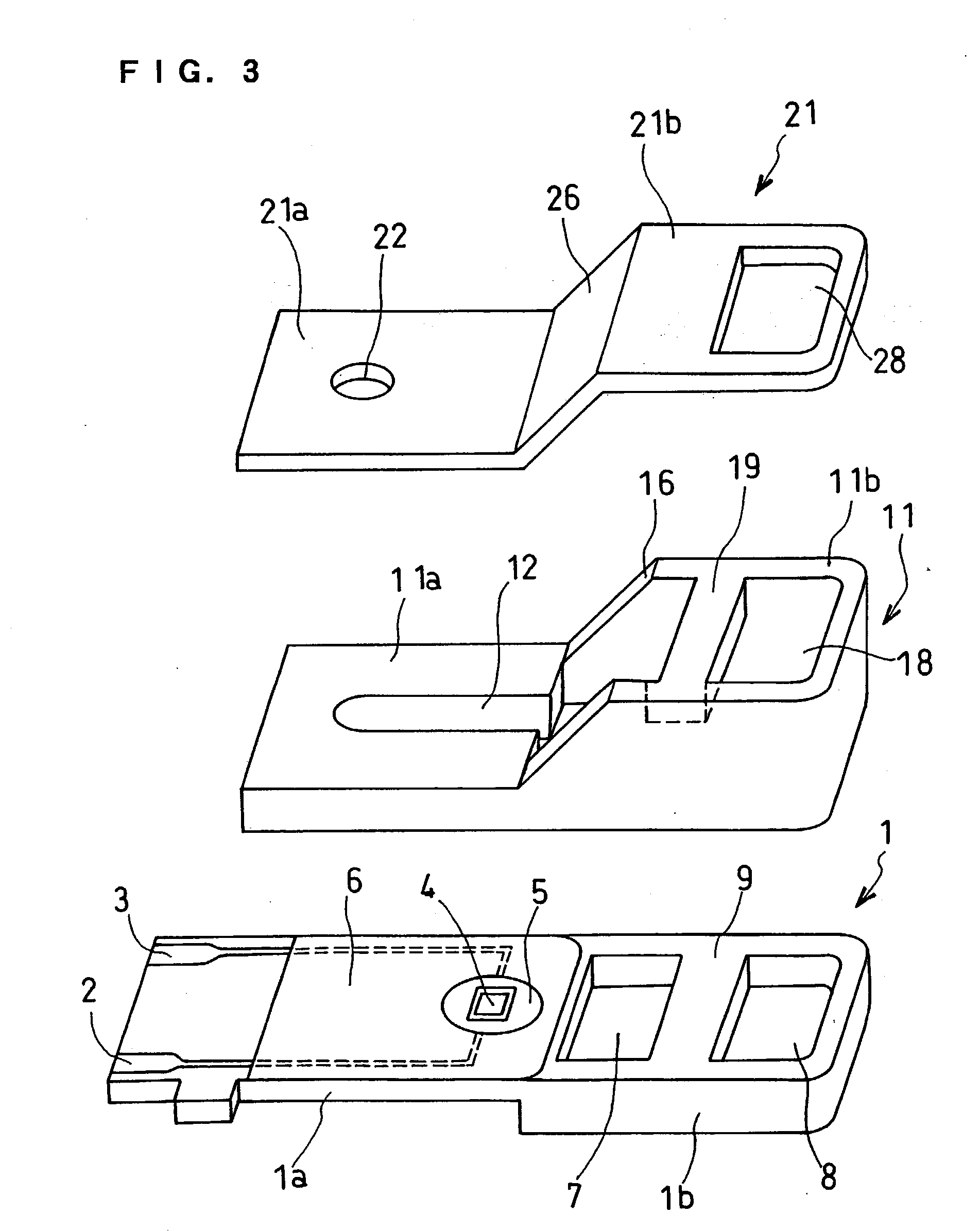
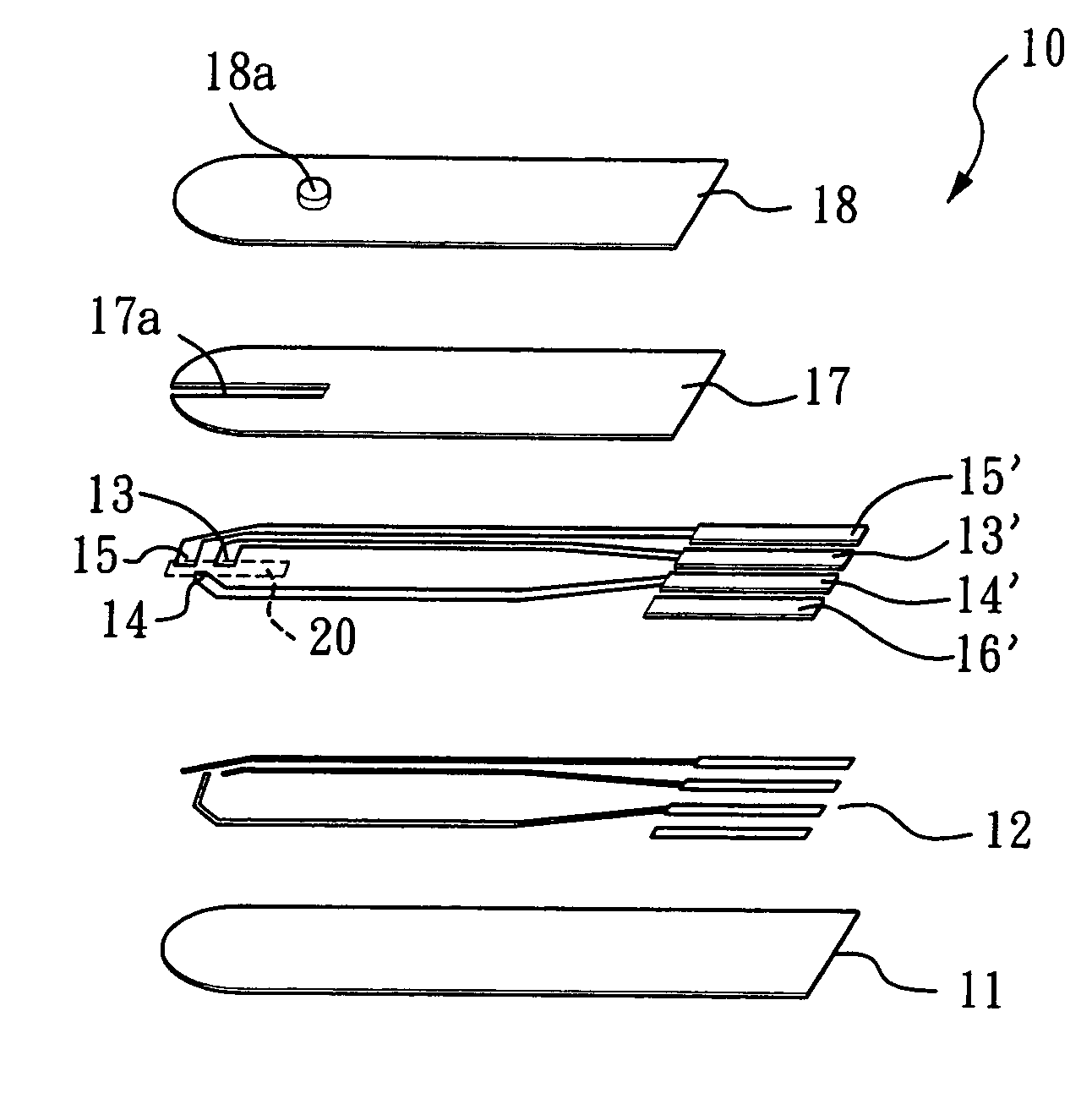
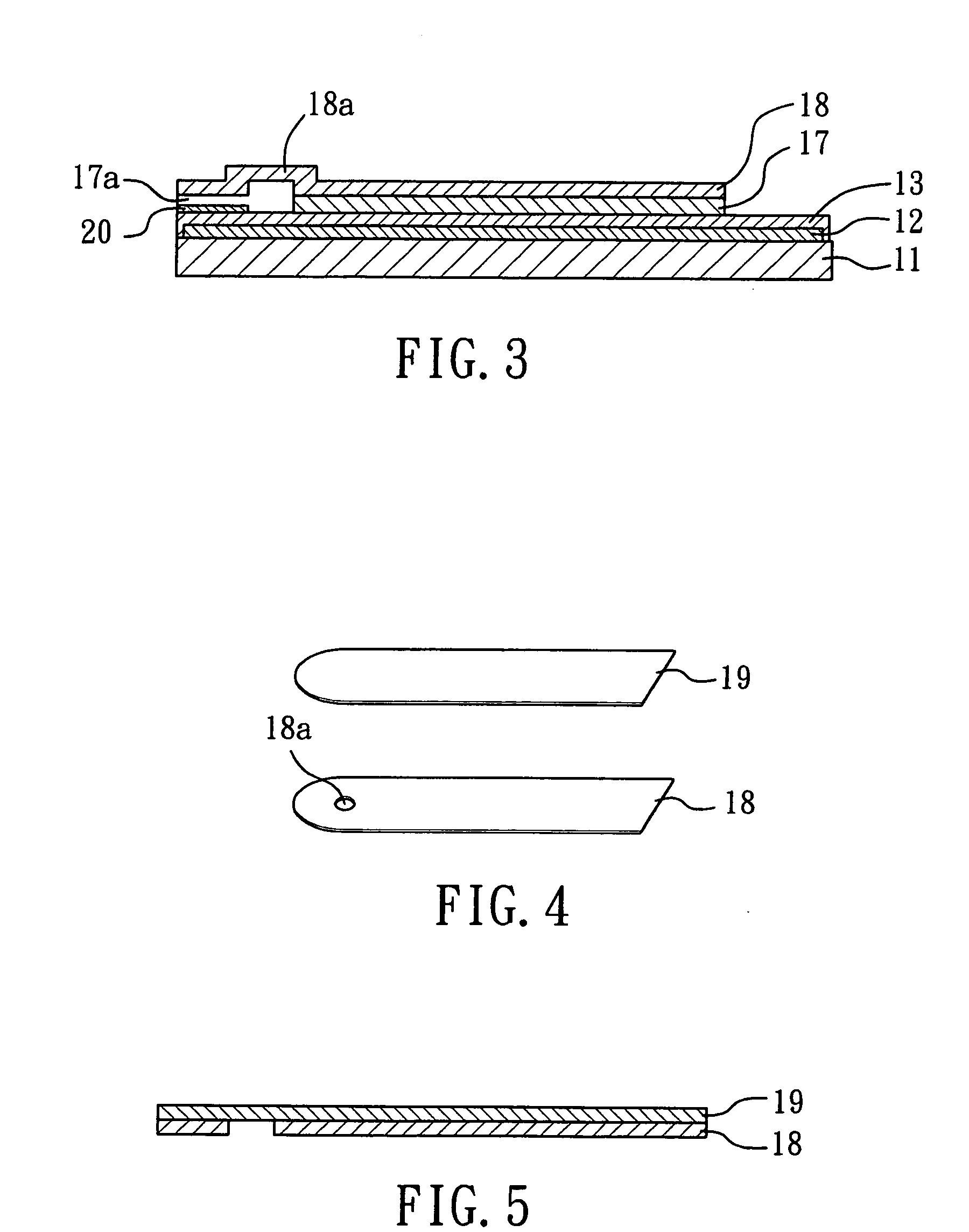
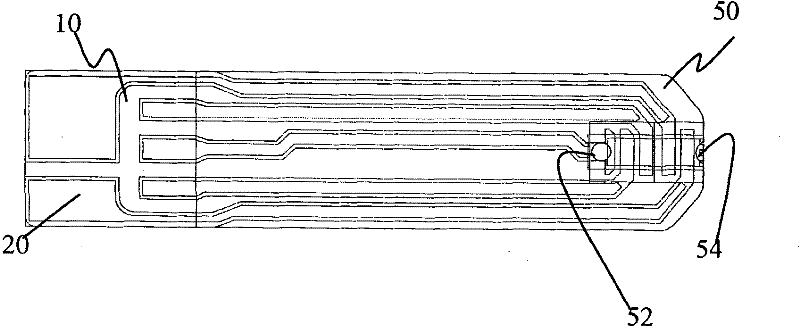
Biosensor and method for producing the same
InactiveUSRE36991E1The way is simple and fastImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerEnzyme
A biosensor for rapid quantification of a specific component contained in various biological samples with high accuracy has an electrically insulating base, an electrode system including a working electrode and a counter electrode formed on one face of the insulating base, and a reaction layer formed on the insulating base in close contact with the electrode system. The reaction layer contains at least a hydrophilic polymer, a buffer and an enzyme which is separated from the buffer.
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
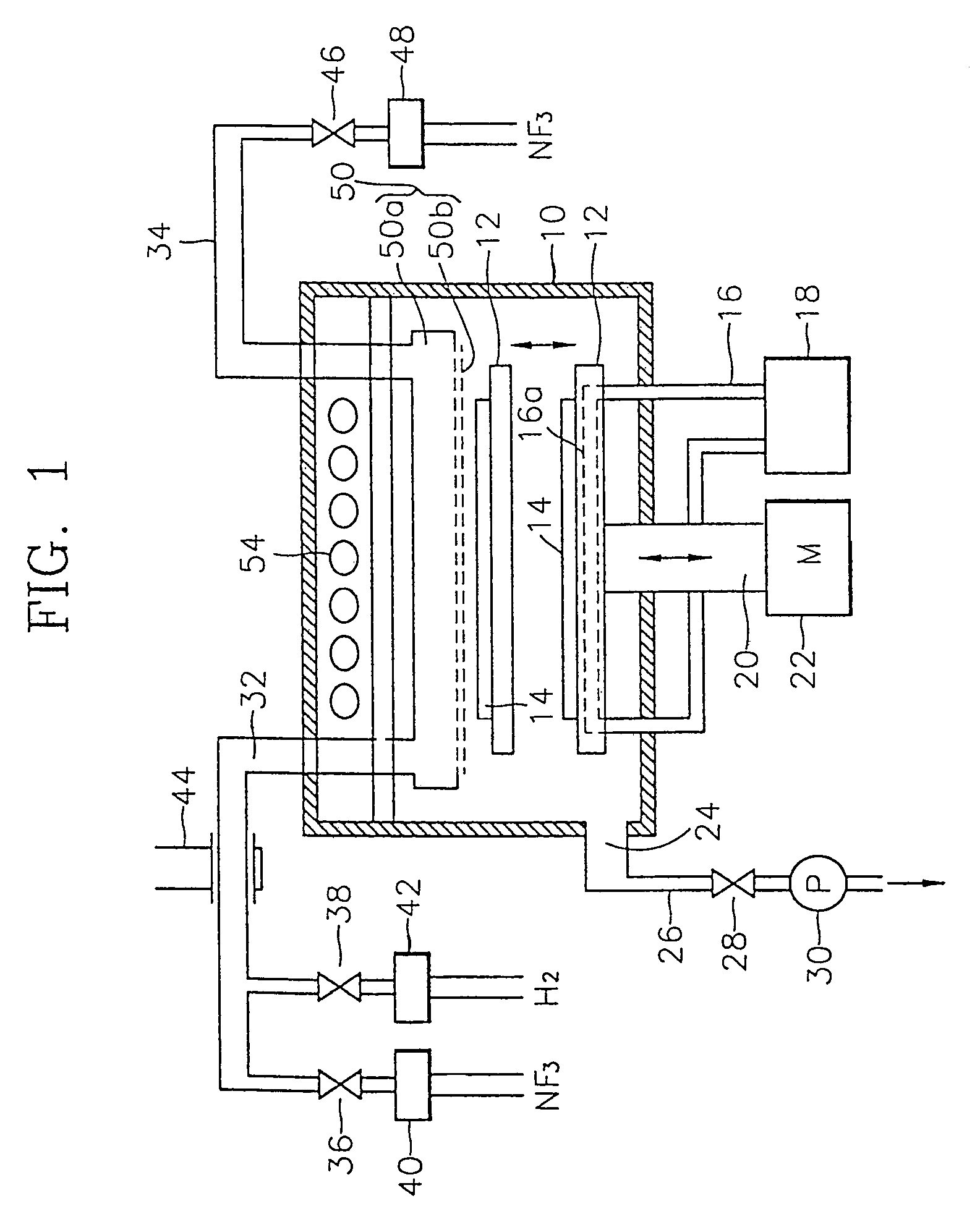
Method of removing oxide layer and semiconductor manufacturing apparatus for removing oxide layer
InactiveUS7488688B2High selectivityEven contactDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReaction layerSusceptor
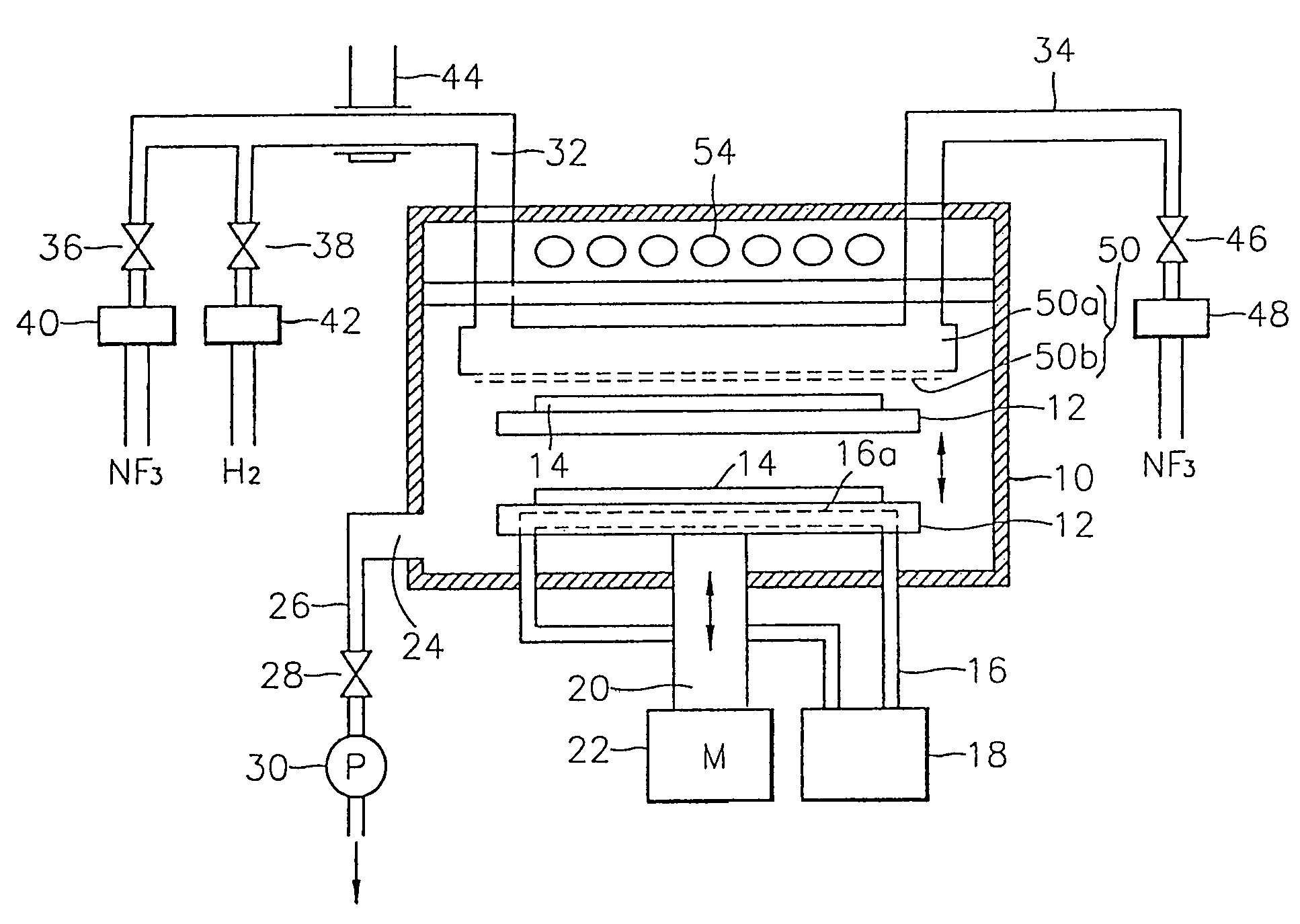
A method for removing an oxide layer such as a natural oxide layer and a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus which uses the method to remove the oxide layer. A vertically movable susceptor is installed at the lower portion in a processing chamber and a silicon wafer is loaded onto the susceptor when it is at the lower portion of the processing chamber. The air is exhausted from the processing chamber to form a vacuum condition therein. A hydrogen gas in a plasma state and a fluorine-containing gas are supplied into the processing chamber to induce a chemical reaction with the oxide layer on the silicon wafer, resulting in a reaction layer. Then, the susceptor is moved up to the upper portion of the processing chamber, to anneal the silicon wafer on the susceptor with a heater installed at the upper portion of the processing chamber, thus vaporizing the reaction layer. The vaporized reaction layer is exhausted out of the chamber. The oxide layer can be removed with a high selectivity while avoiding damage or contamination of the underlying layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device and method for determining the concentration of a substrate
InactiveUS20020043471A1Error in measurement resultExclude influenceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerElectricity
A method for determining the concentration of a substrate in a sample solution using an electrode system comprising a working electrode and a counter electrode, both being formed on an electrically insulating base plate, and a reaction layer which contains at least an oxidoreductase and an electron mediator and is formed on the electrode system to electrochemically measure a reduced amount of the electron mediator resulting from enzyme reaction in the reaction layer, wherein a third electrode is formed as an interfering substance detecting electrode somewhere apart from the reaction layer to detect supply of the sample solution on the basis of an electrical change between the counter electrode and the third electrode. A current flowing between the counter electrode and the third electrode is measured which is taken as a positive error. Subsequently, voltage application between the counter electrode and the third electrode is released and a voltage for oxidizing the reduced form electron mediator is applied between the working electrode and the counter electrode to measure a current flowing between the two electrodes. Influences of any interfering substance such as easy-to-oxidize substance are reduced, whereby a highly reliable value of substrate determination can be obtained.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
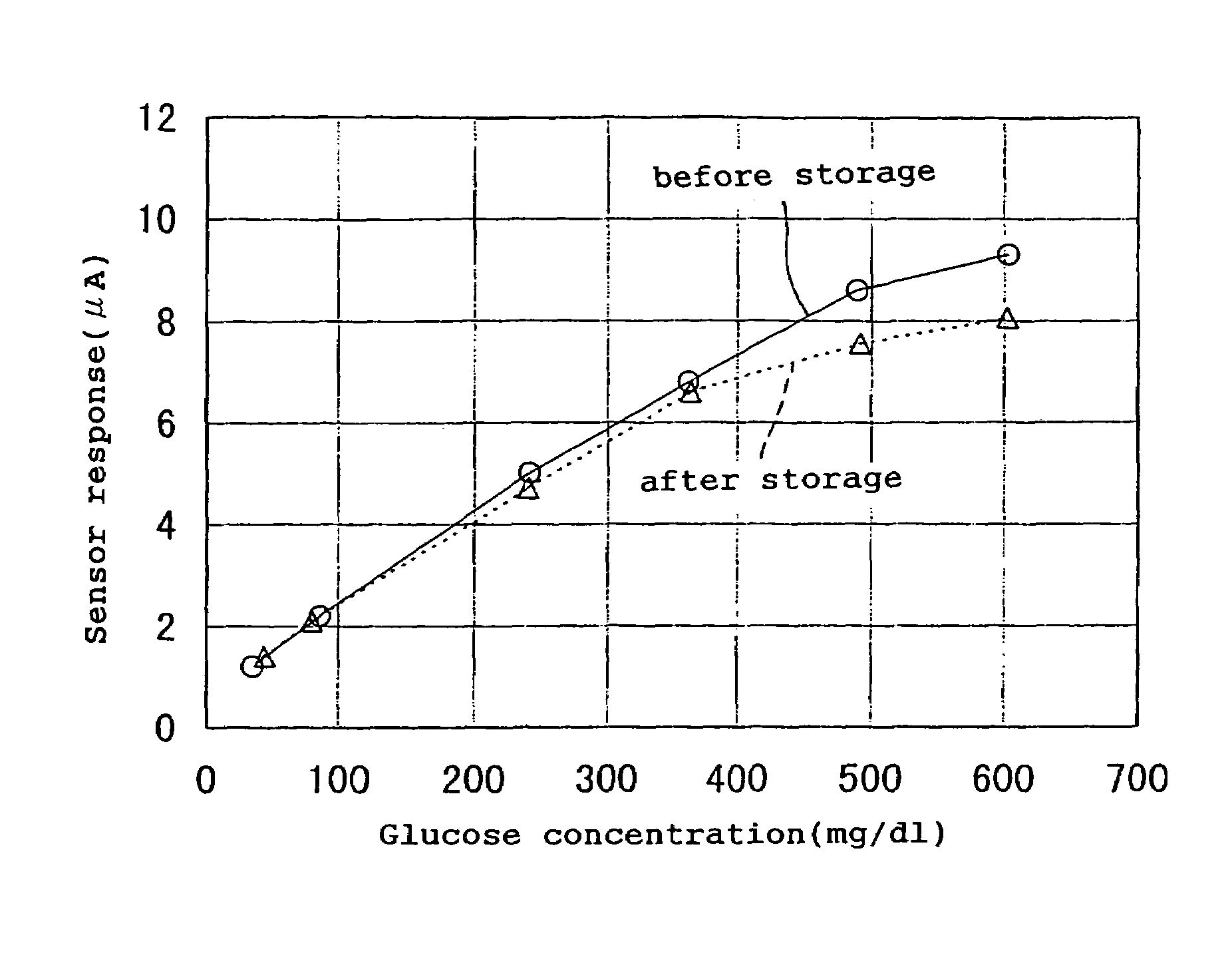
Glucose sensor
InactiveUS7005048B1Avoid separationImprove reliabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerElectricity
The present invention provides a high-performance glucose sensor having excellent storage stability and an improved response characteristic. This sensor comprises: an electrically insulating base plate; an electrode system including at least a working electrode and a counter electrode formed on the base plate; and a reaction layer containing at least pyrrolo-quinoline quinone dependent glucose dehydrogenase, formed in contact with or in the vicinity of the electrode system, and the reaction layer contains at least one kind of additive selected from the group consisting of gluconic acid and salts thereof.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Biosensor
InactiveUS6719887B2Improve solubilityNot easy to dissolveImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerEngineering
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Biosensor with multiple sampling ways
InactiveUS6923894B2Solve the complicated productionEasy to detectImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerOptoelectronics
A biosensor for detecting contents of biochemical components in a sample, comprising an electrically insulating substrate, a working electrode disposed on said substrate, a reference electrode disposed on said substrate, which is spaced from said working electrode, a reaction layer disposed on said working electrode and said reference electrode, wherein said reaction layer and said electrodes form a reaction area for reacting with the sample, an electrically insulating layer disposed on said substrate and having an opening for receiving the sample, wherein said opening exposes a portion of said reaction area and the end of said opening is located at the edge of the biosensor; and a reticular covering layer which covers said opening and the end of said opening of said insulating layer wherein said reticular layer and said insulting layer form a sampling area from said reticular covering area to the edge of said biosensor.
Owner:APEX BIOTECH
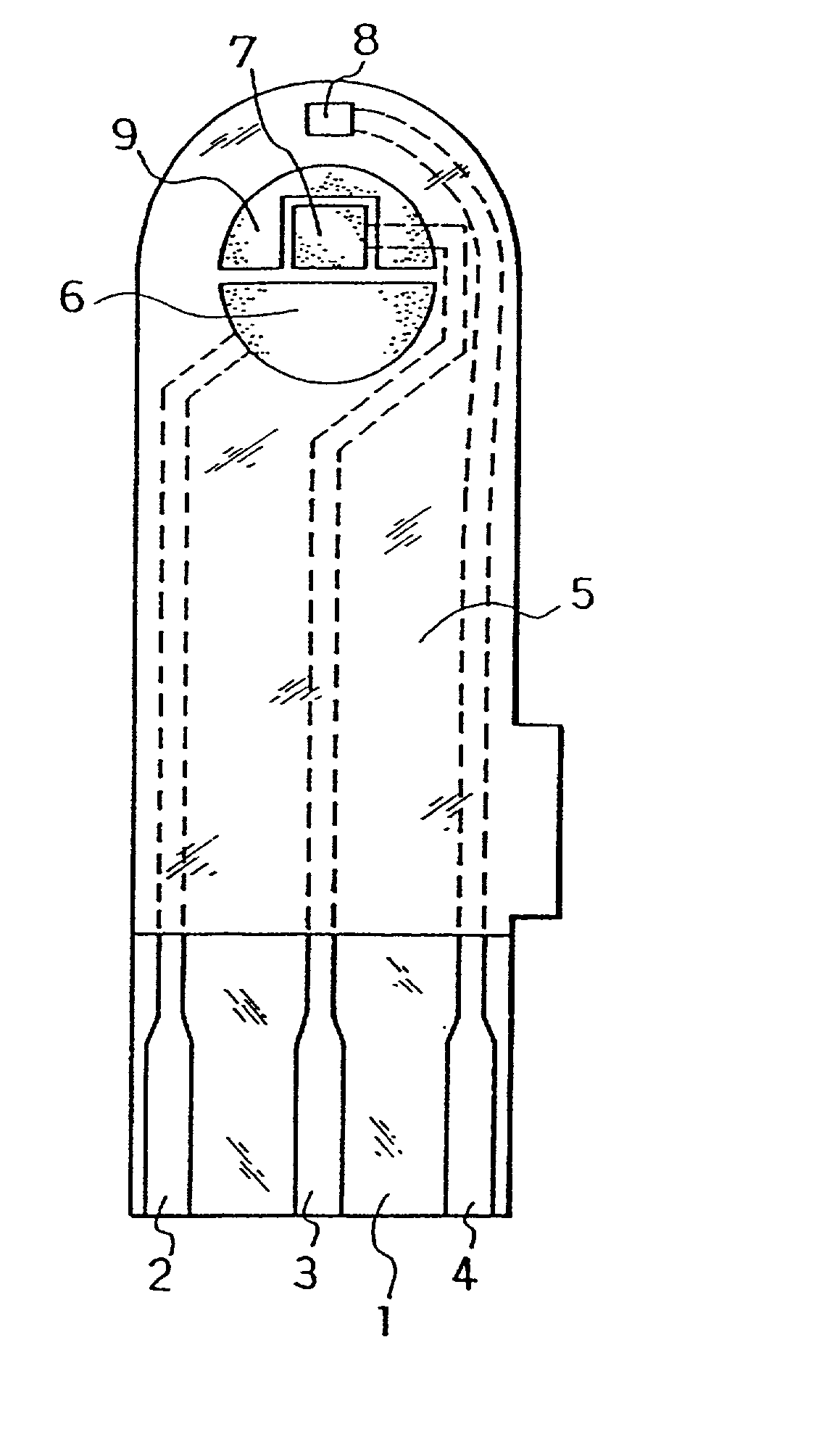
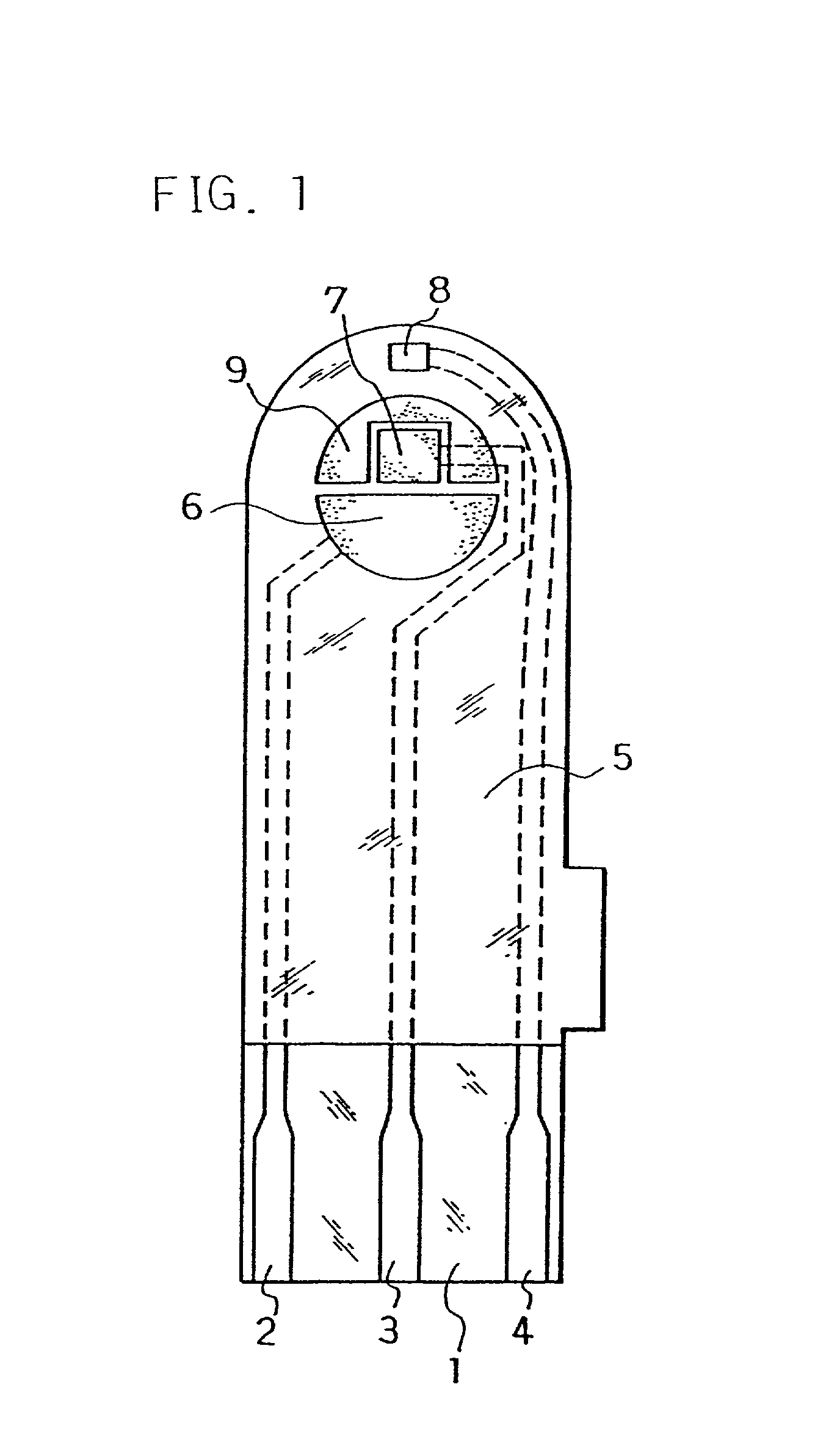
Measuring device using biosensor and biosenor used for it, and dedicated standard liquid
InactiveUS6881322B2Easy to oxidizeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerMeasurement device
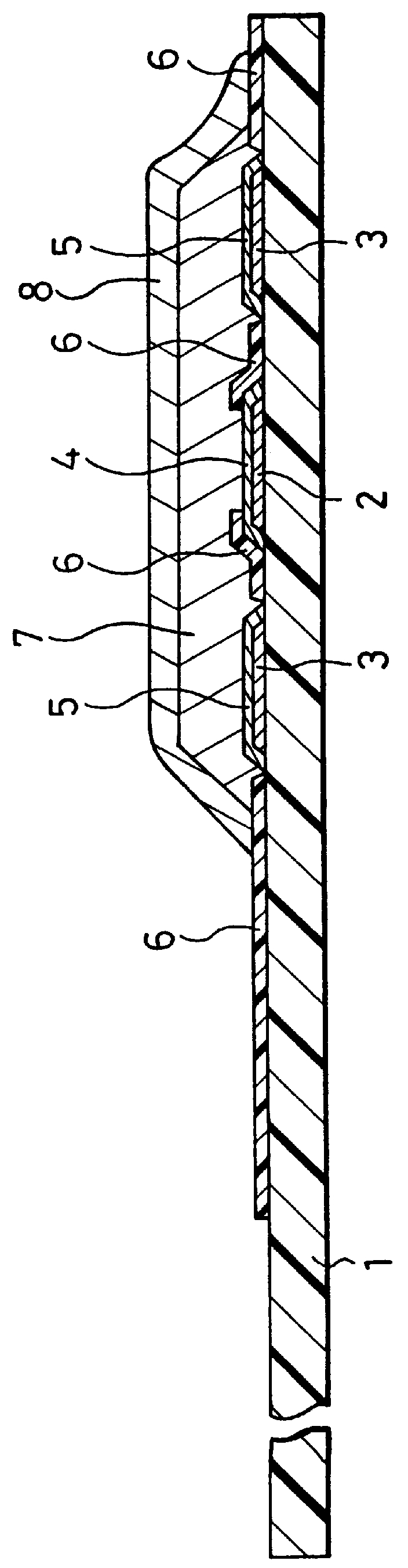
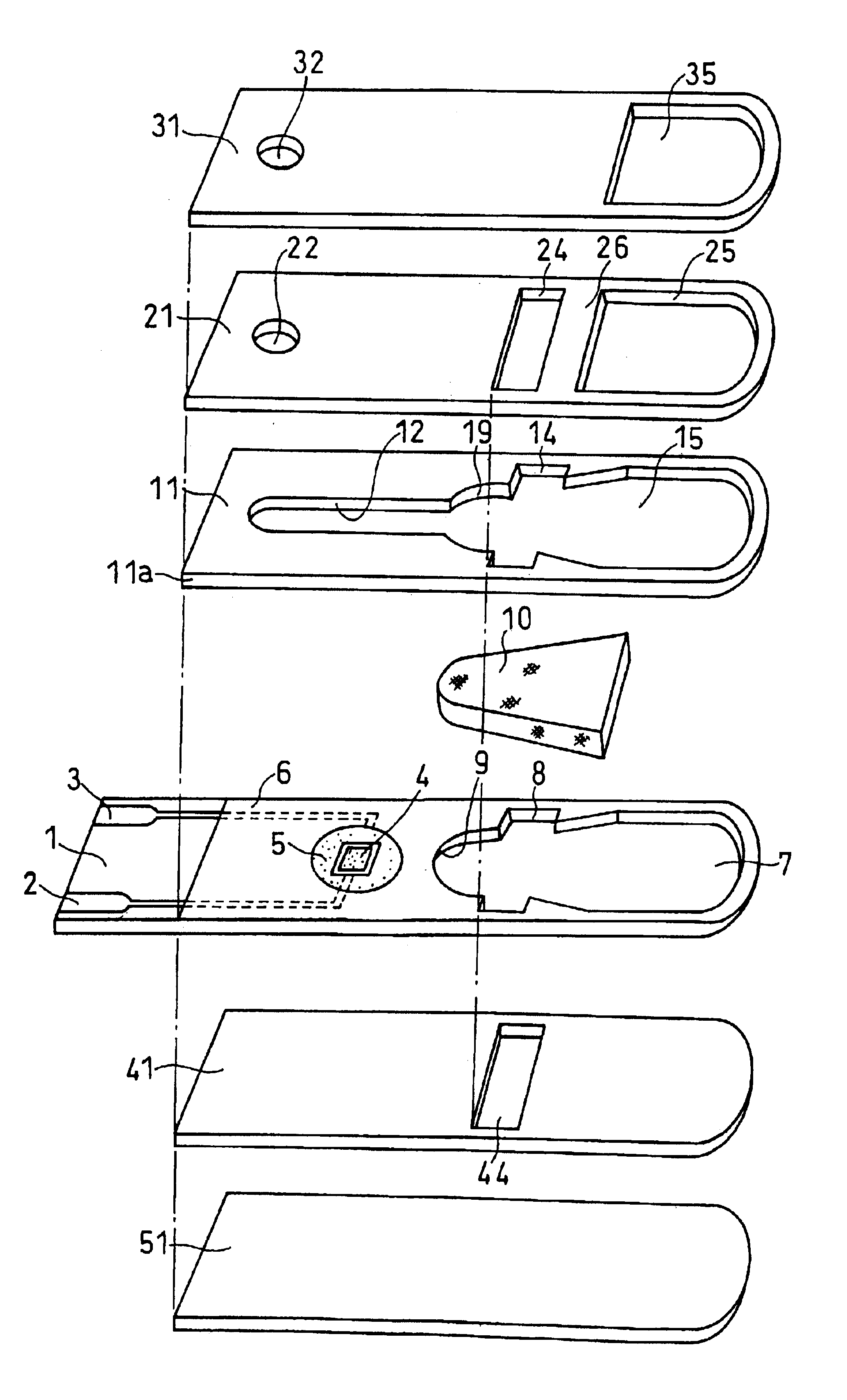
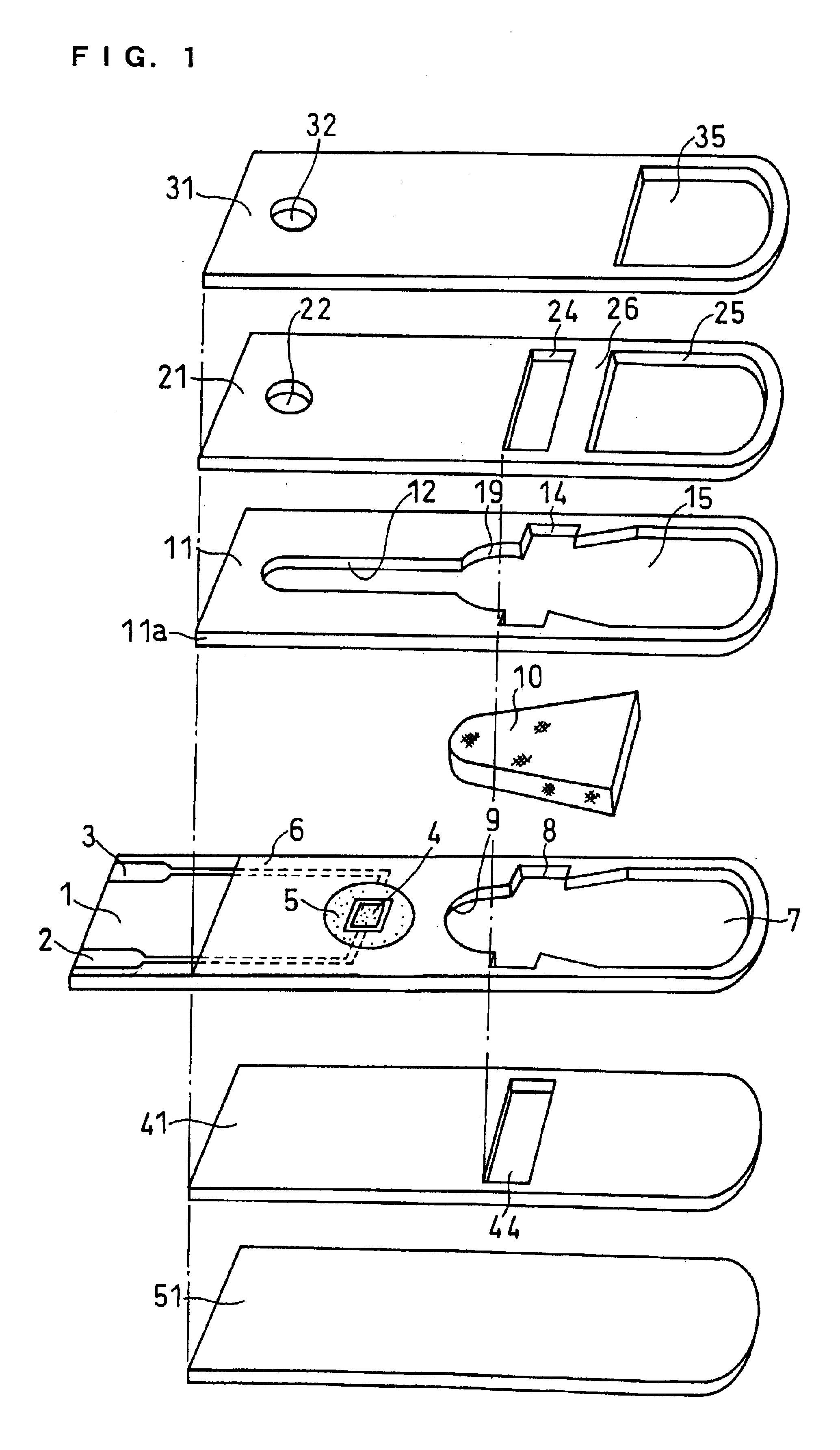
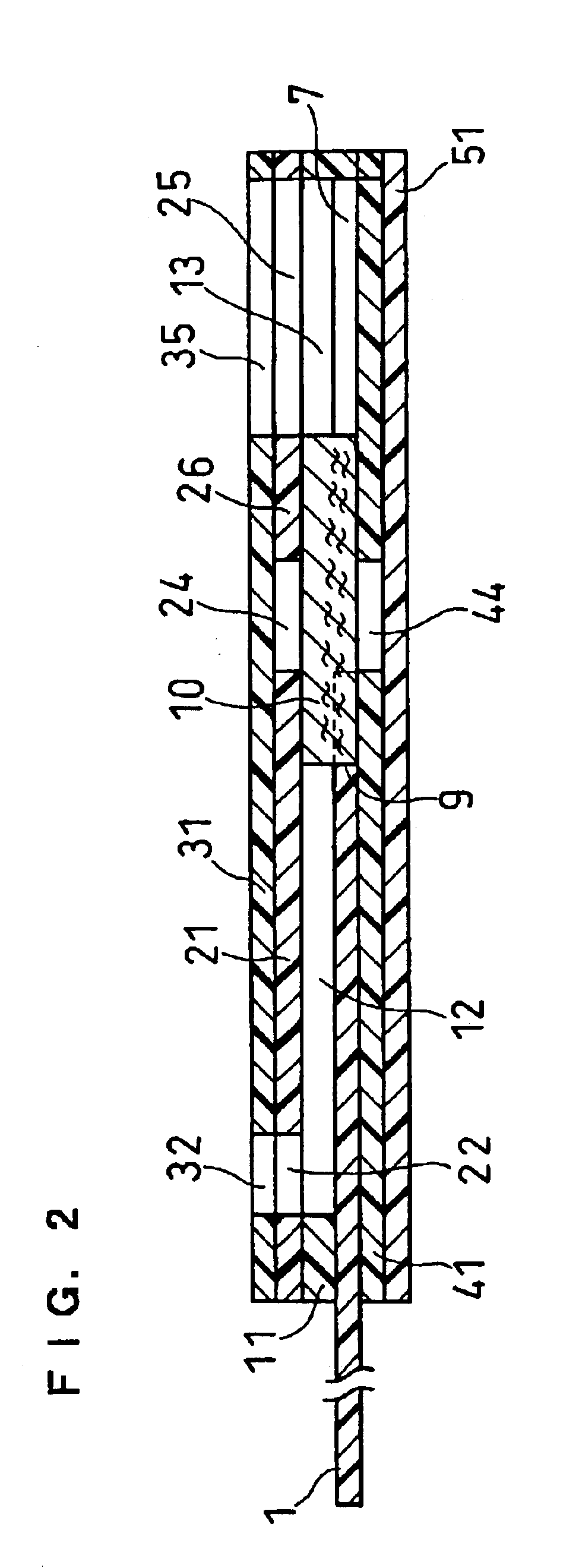
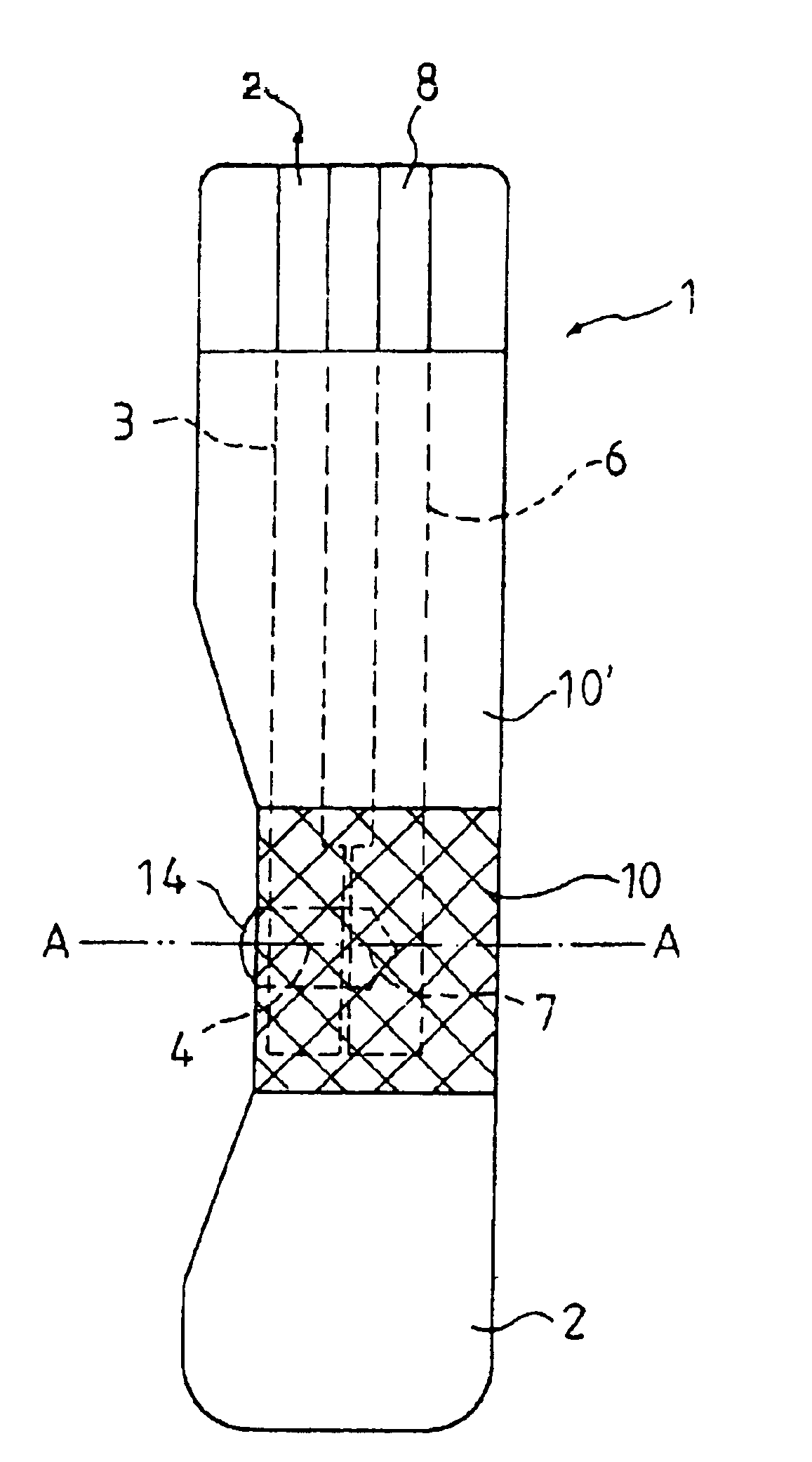
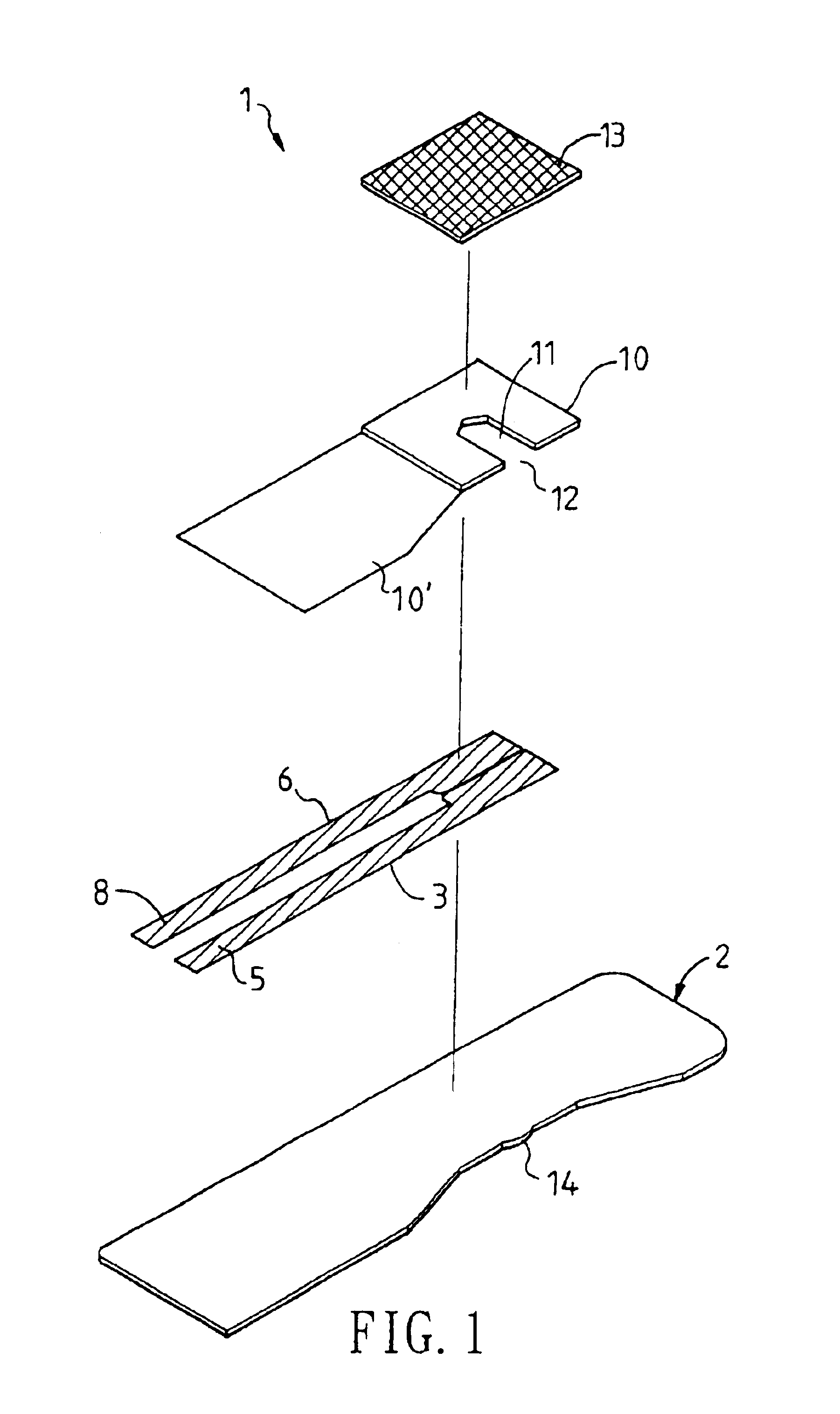
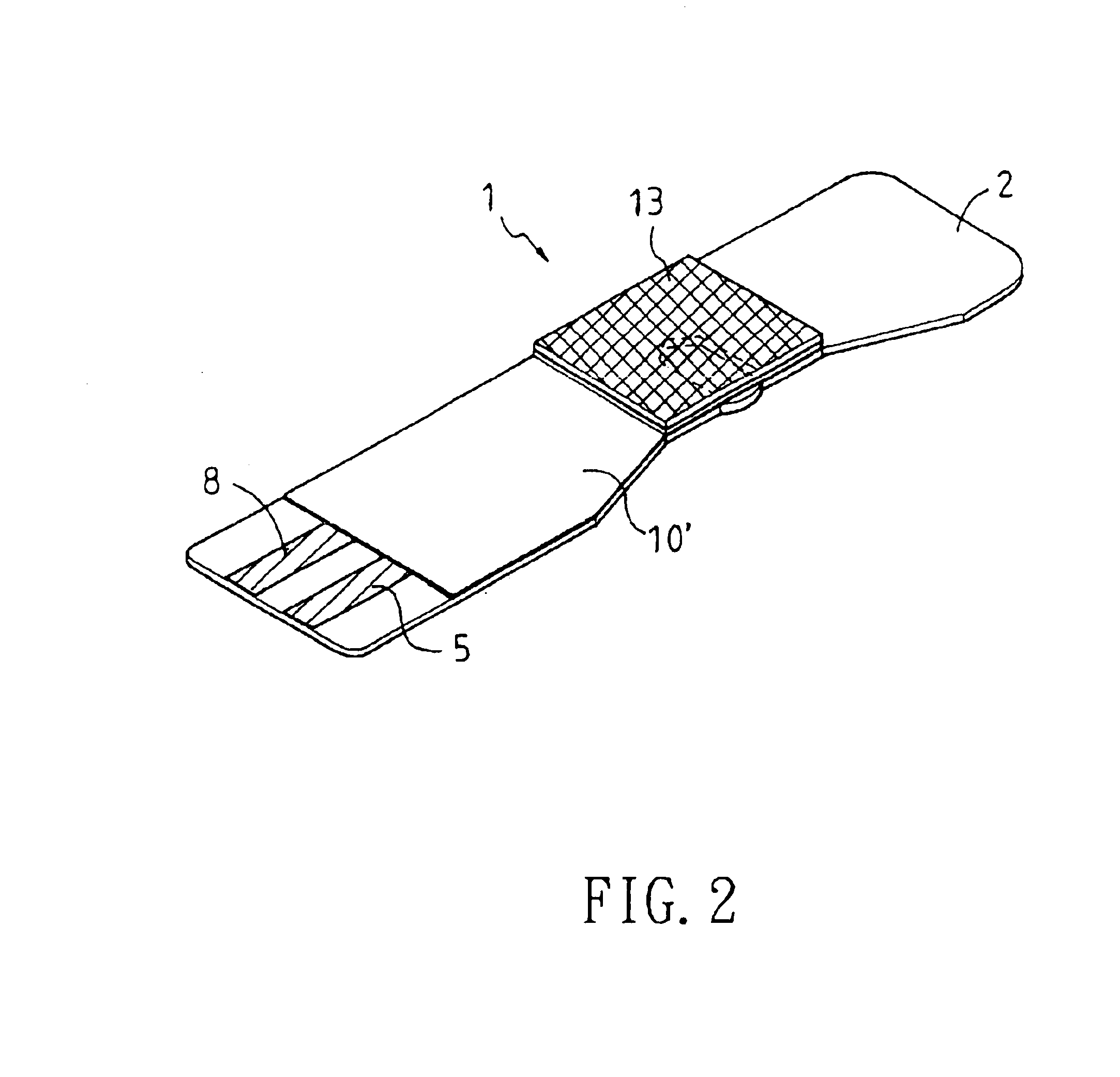
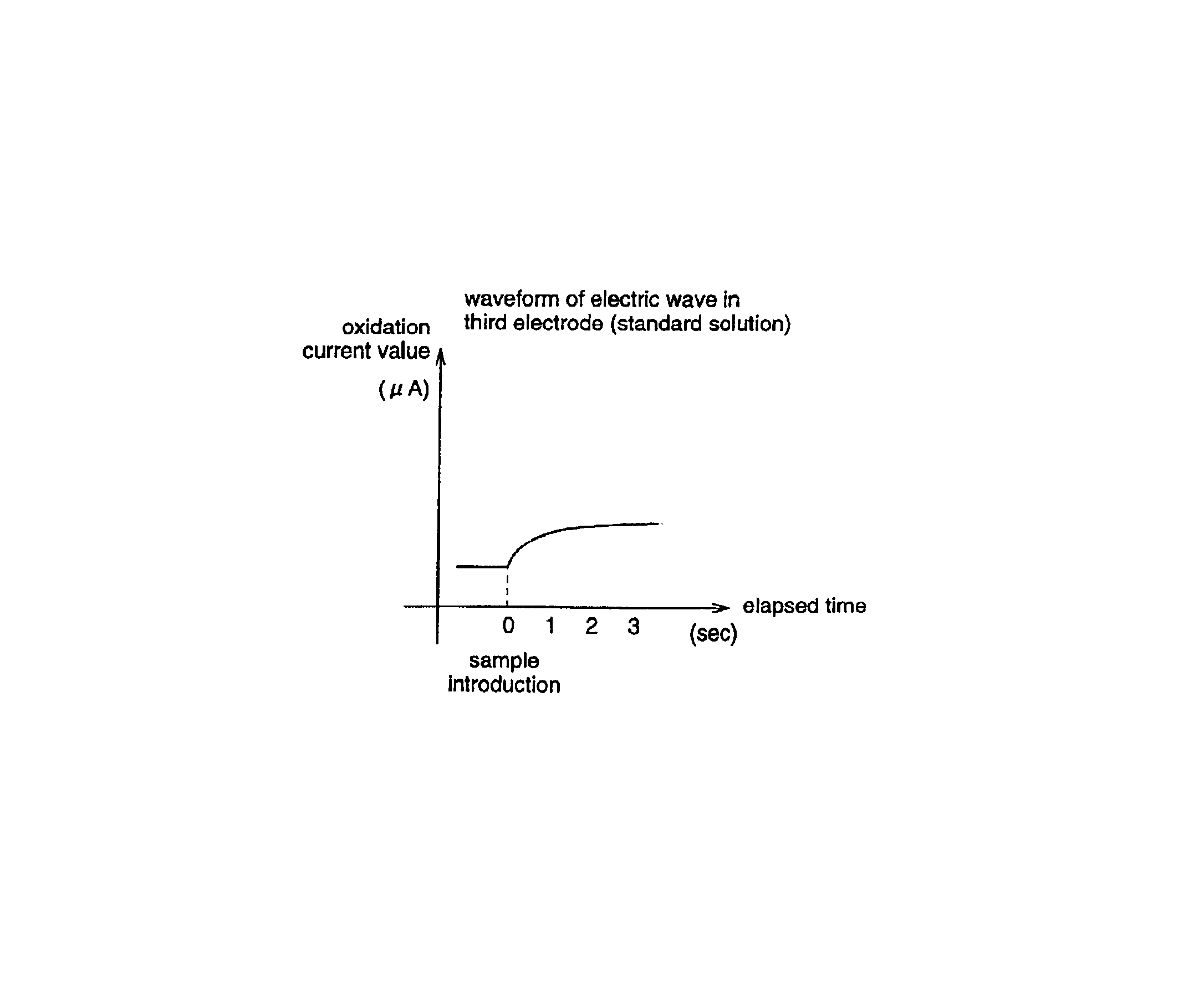
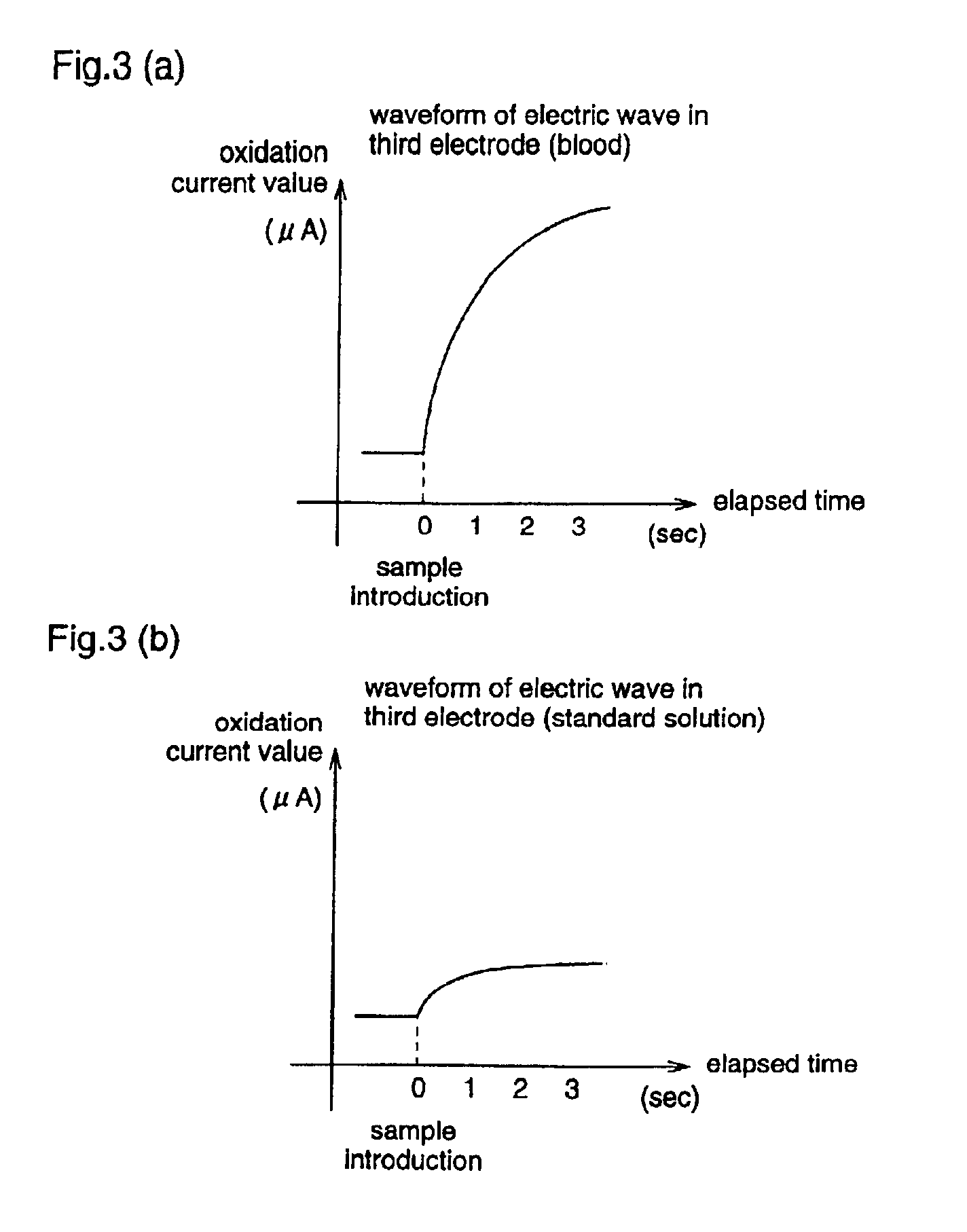
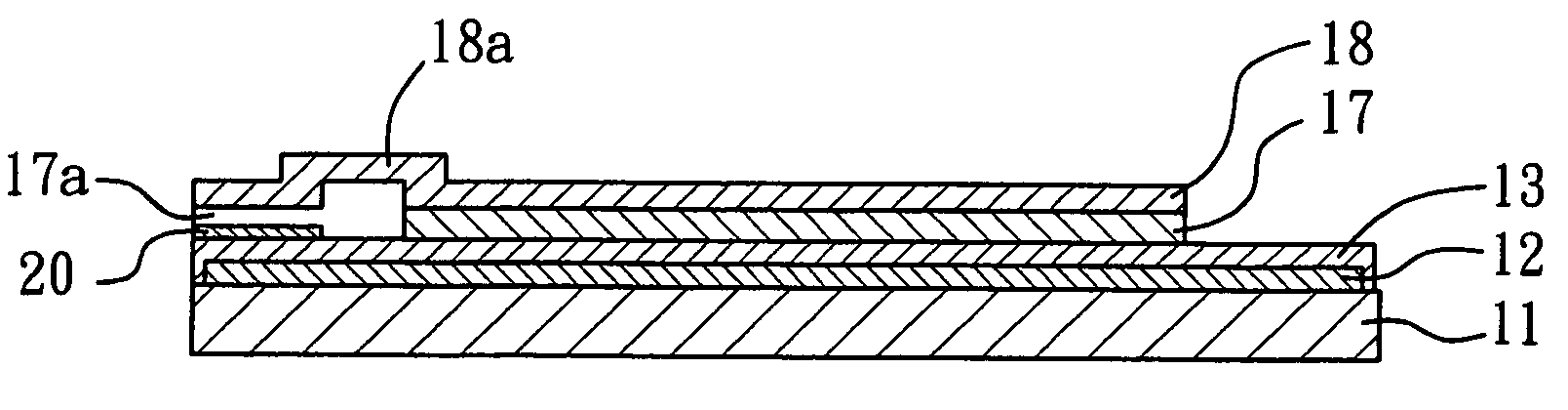
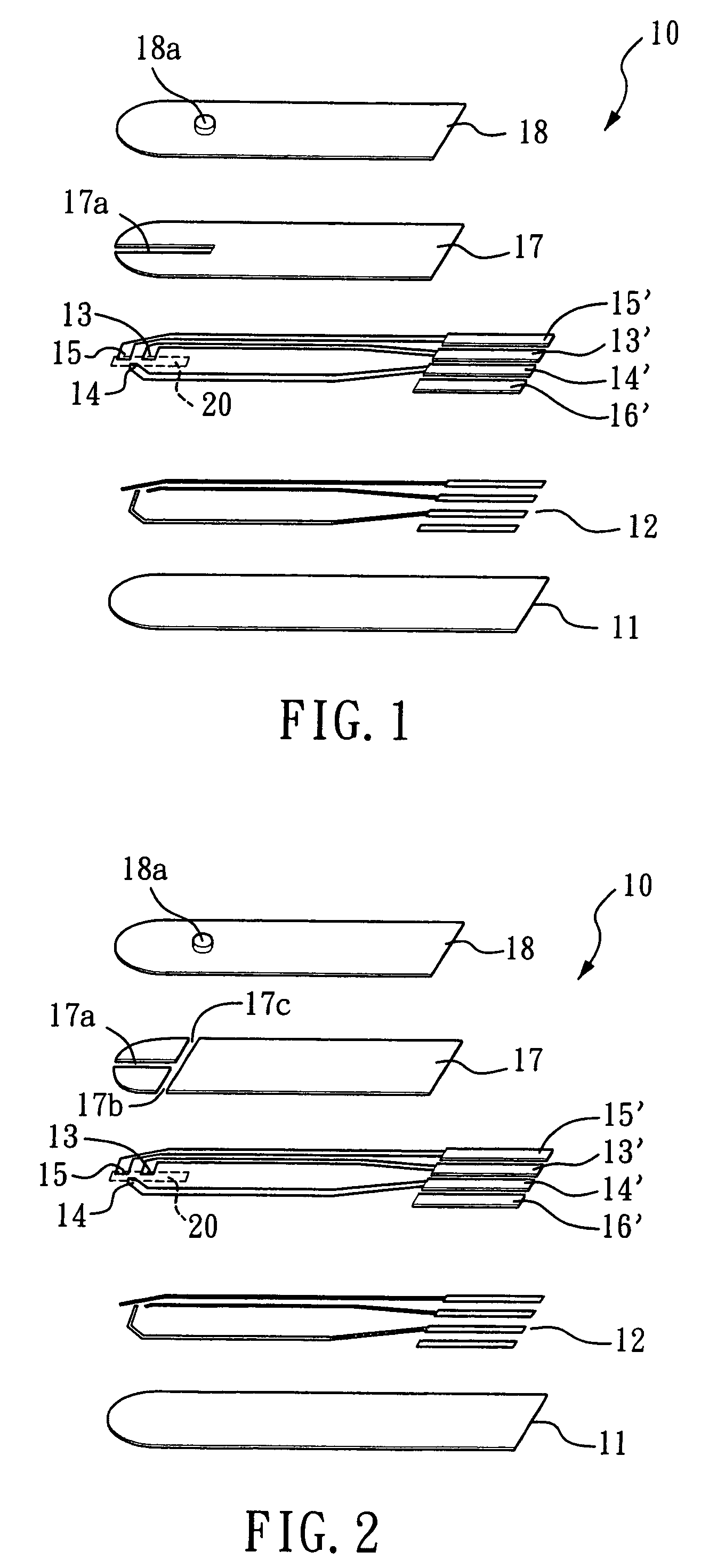
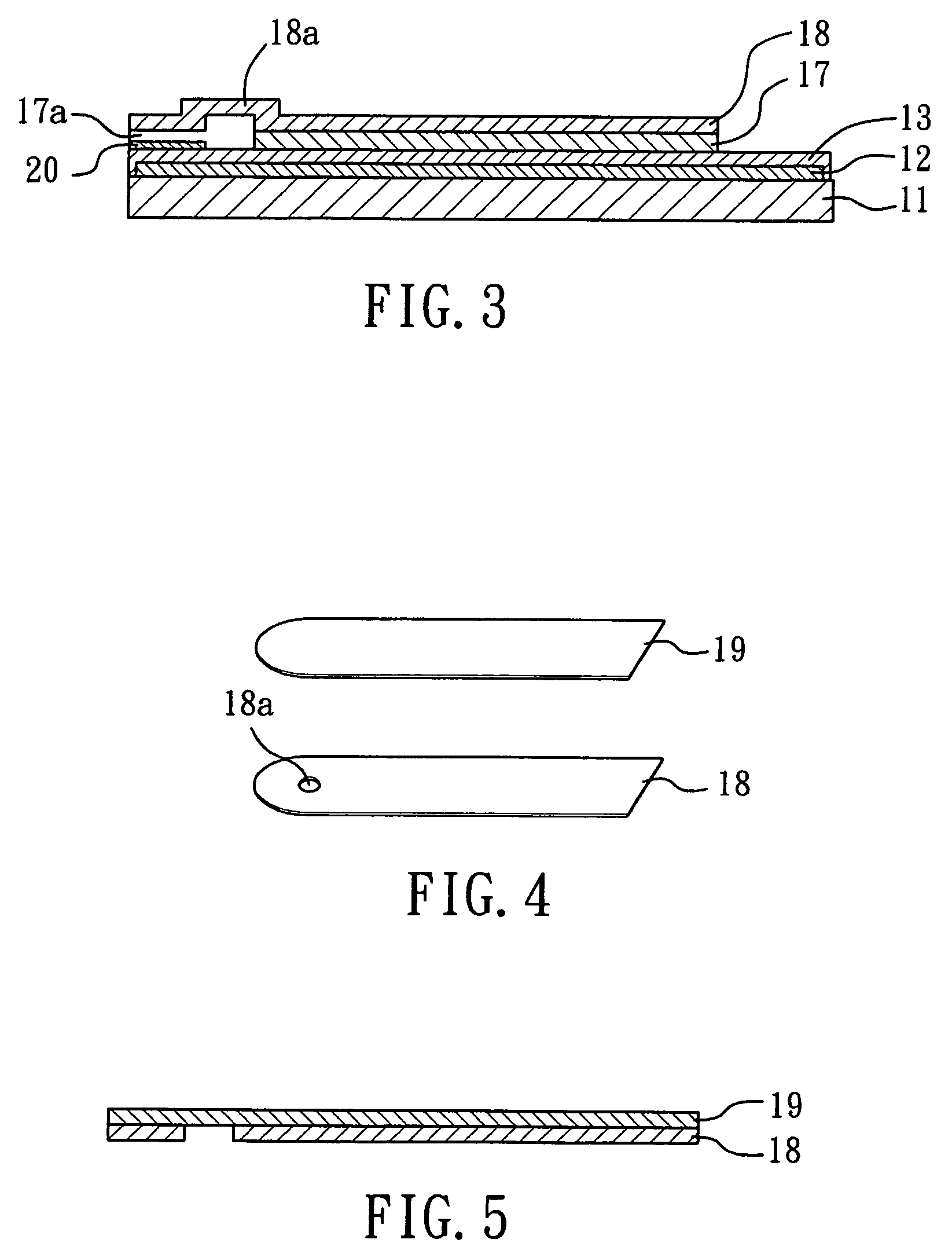
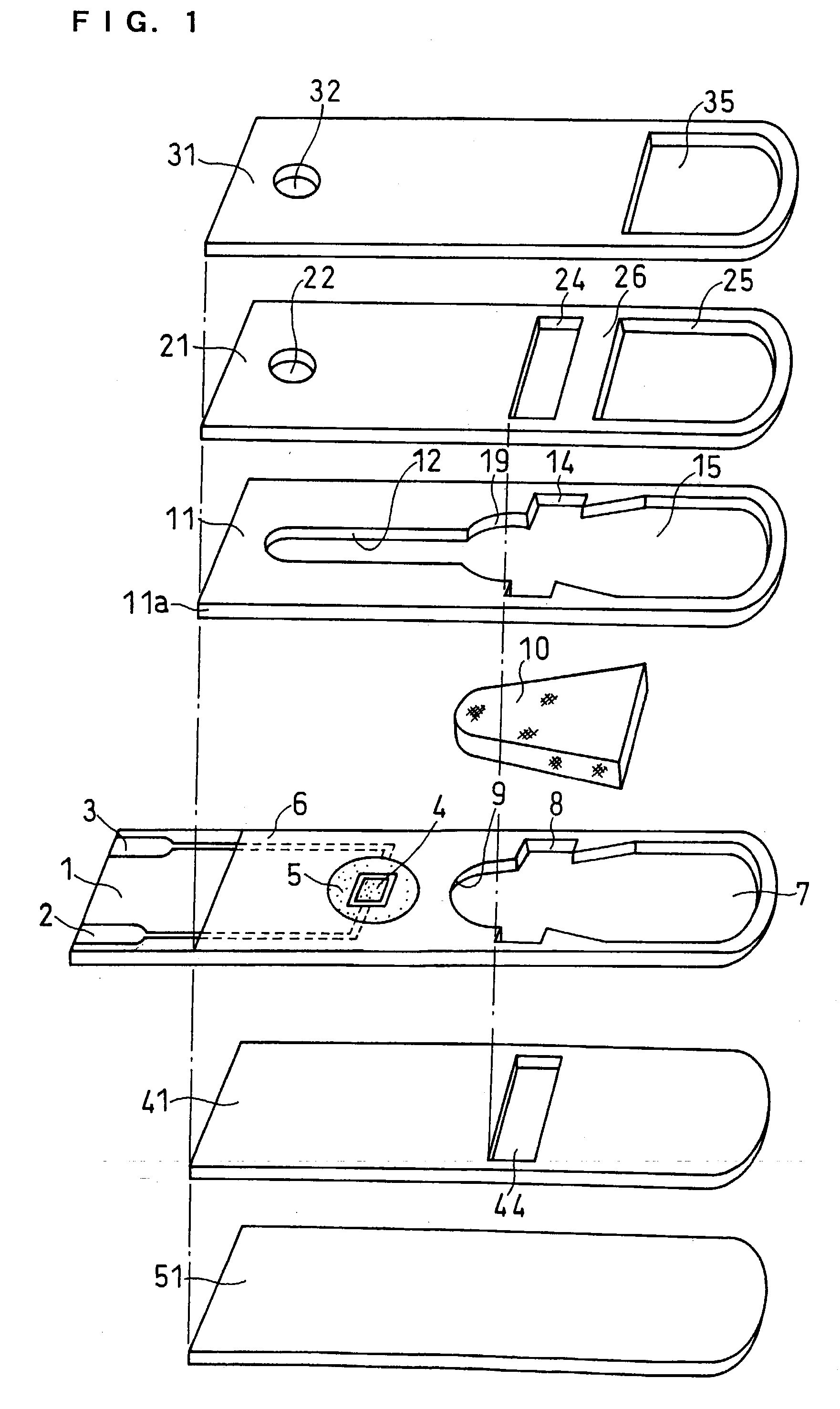
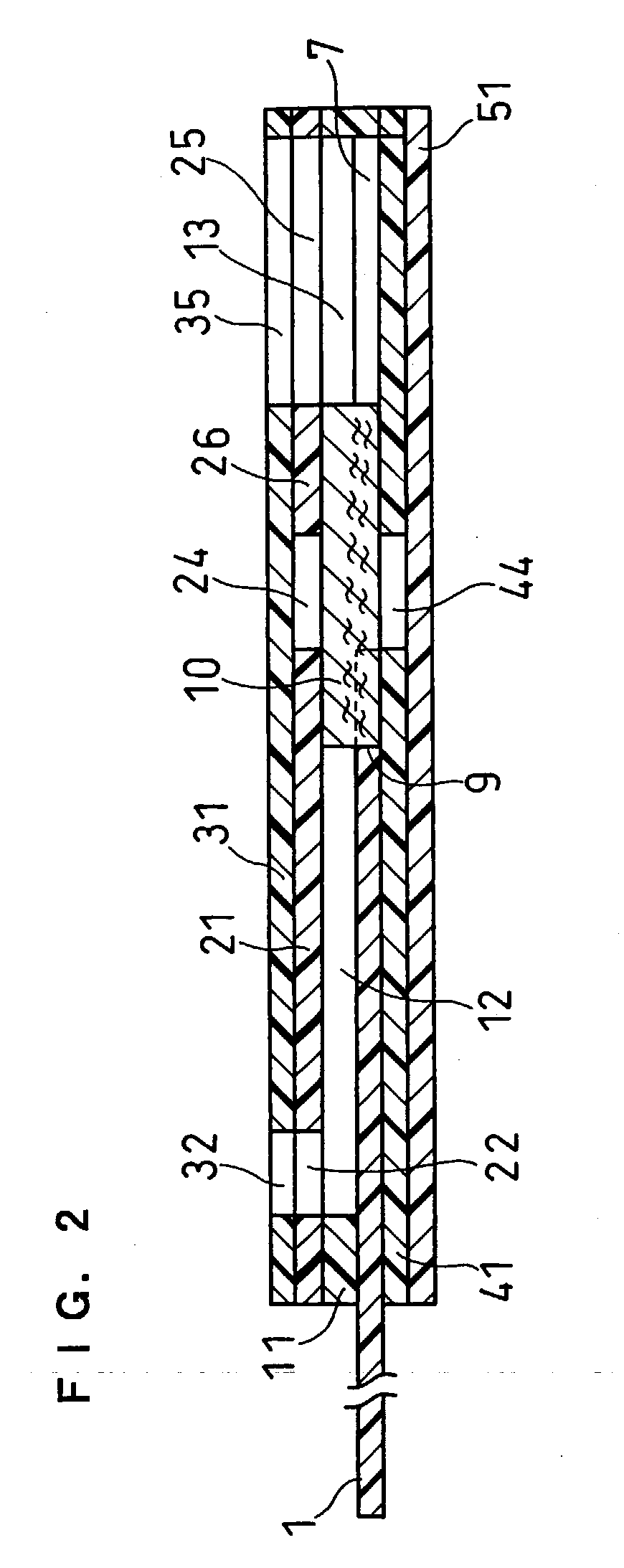
A reaction layer 12 which reacts with a substance to be measured in a sample solution is provided on a working electrode 1, a counter electrode 2, and a third electrode 3 which are provided on an insulating substrate 7 so as to bridge the respective electrodes, the content of the substance to be measured is measured from a current value which reaction is obtained between the working electrode 1 and the counter electrode 2, and the types of sample solution is judged by a difference between oxidation current values or between oxidation current waveforms, which are obtained between the third electrode 3 and the counter electrode 2 or between the third electrode 3 and the working electrode 1, thereby automatically judging the types of sample solution.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Electrochemical biosensor by screen printing and method of fabricating same
ActiveUS7138041B2Rapid sample inflowSmall volumeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerSiphon
An electrochemical biosensor formed by screen printing and method of fabricating such biosensor is disclosed in the present invention. The biosensor can quickly absorb a sample to be measured therein, effectively control volume of the sample fed and “fill-and-position” the sample therein. The biosensor includes an electrode layer (electrode area) comprising two or three electrodes, which are a working electrode, a reference electrode and an auxiliary electrode (tri-electrode) on an insulating substrate. An active reaction layer containing reactant, reaction catalyst, mediator, wetting agent and surfactant is spread on the surface of the electrode layer. A sample inflow area is formed above the electrode area by adding an upper cover on top of a middle insulating layer with a U-shaped opening formed therein. Sample solution with a minute amount about 0.8 to 1 μl can be rapidly introduced into the electrode area and the active reaction layer via the inflow area by siphon or capillary, where the ingredient of the sample can be analysed by measuring reaction between the sample, reaction catalyst and mediator in the reaction layer using electrochemical potentiometric or amperometric method. An upwardly extended closed space formed within the upper cover above the electrode area adjacent to the front of conductive wires can be effectively used to control sample volume and “fill-and-position” the sample.
Owner:GENERAL LIFE BIOTECHNOLGOY
Method of trimming a gate electrode structure
ActiveUS6852584B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSelf limitingReaction layer
A method and processing tool are provided for trimming a gate electrode structure containing a gate electrode layer with a first dimension. A reaction layer is formed through reaction with the gate electrode structure. The reaction layer is the selectively removed from the unreacted portion of the gate electrode structure by chemical etching, thereby forming a trimmed gate electrode structure with a second dimension that is smaller than the first dimension. The trimming process can be carried out under process conditions where formation of the reaction layer is substantially self-limiting. The trimming process can be repeated to further reduce the dimension of the gate electrode structure.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
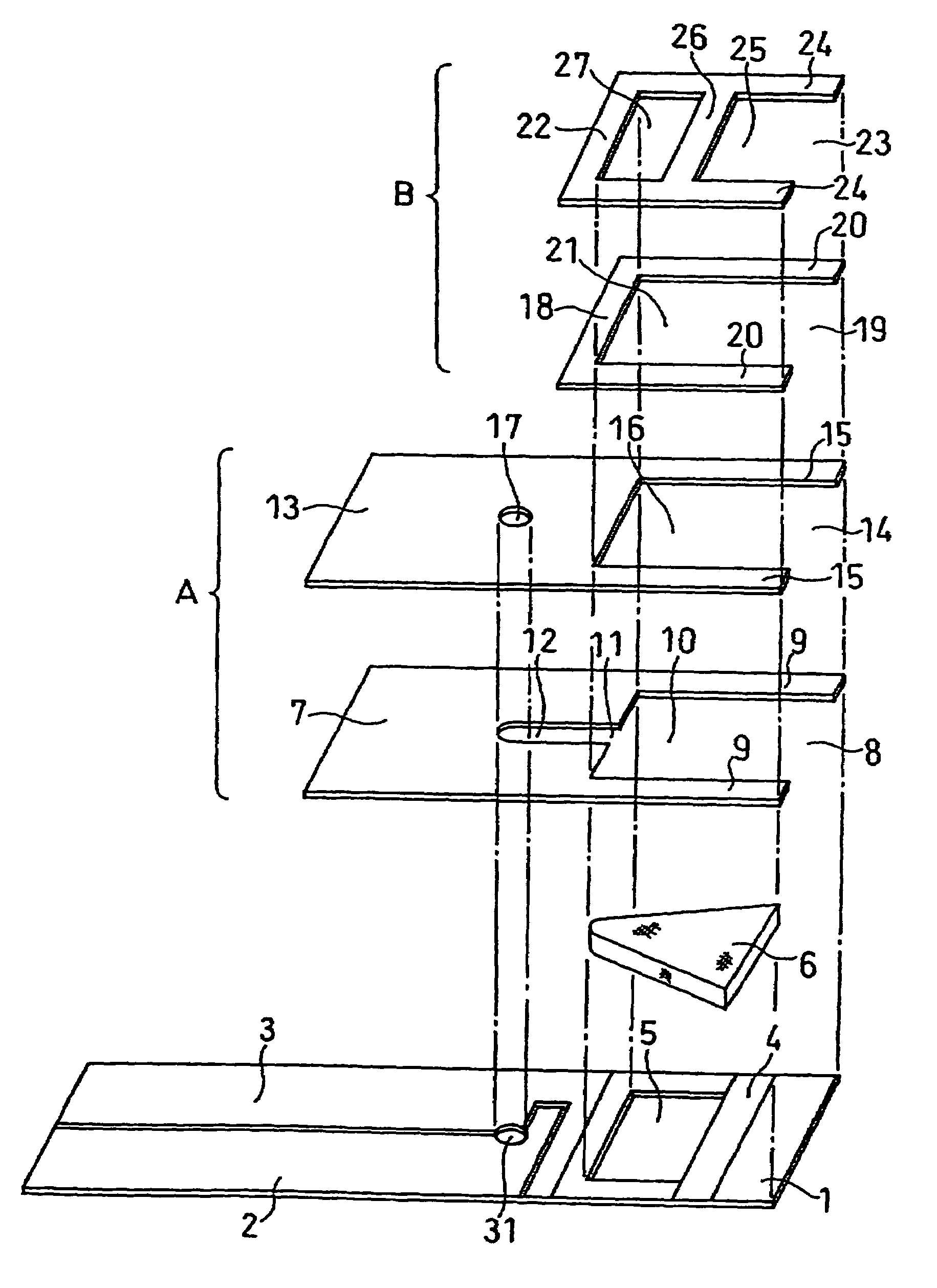
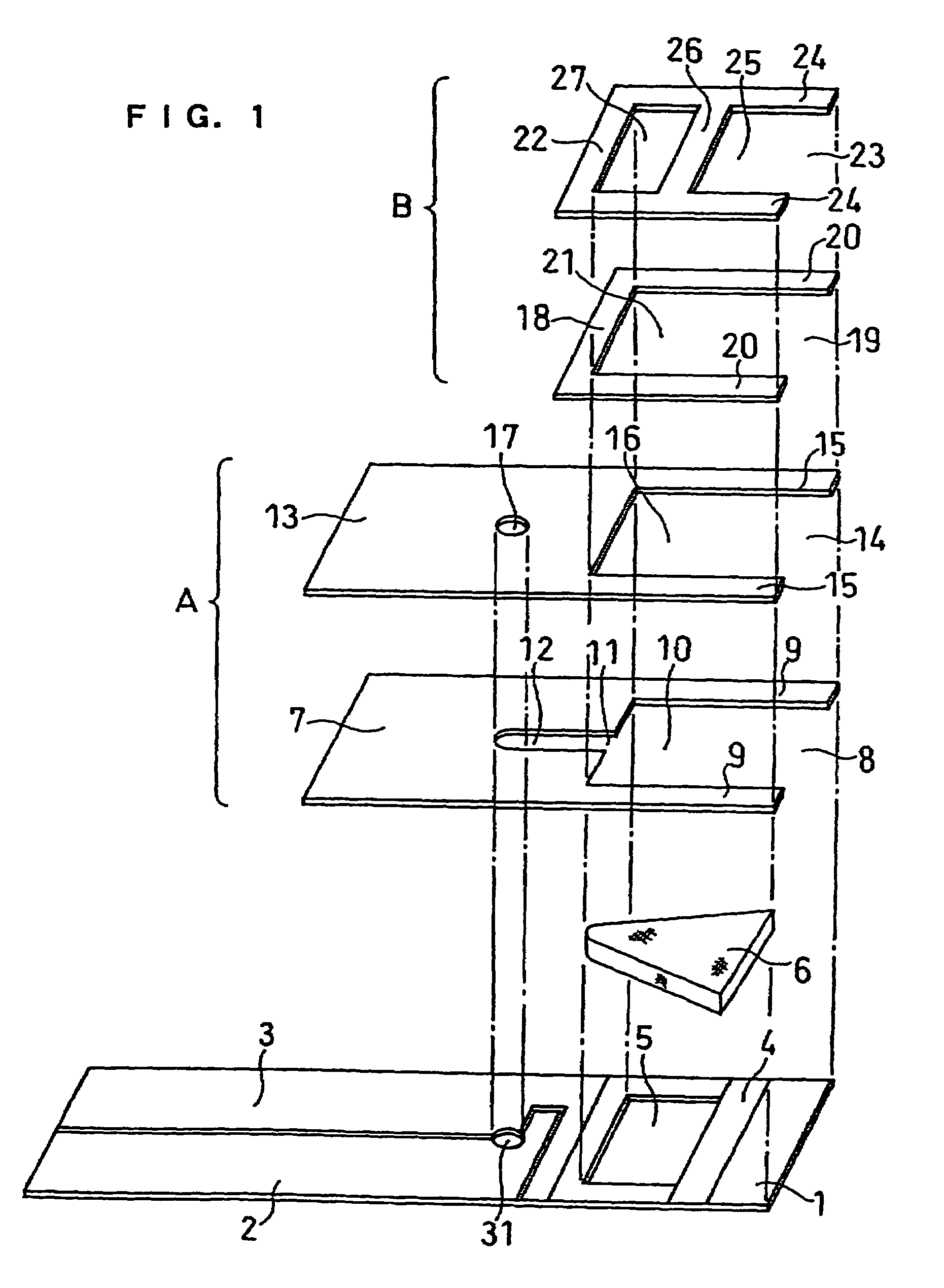
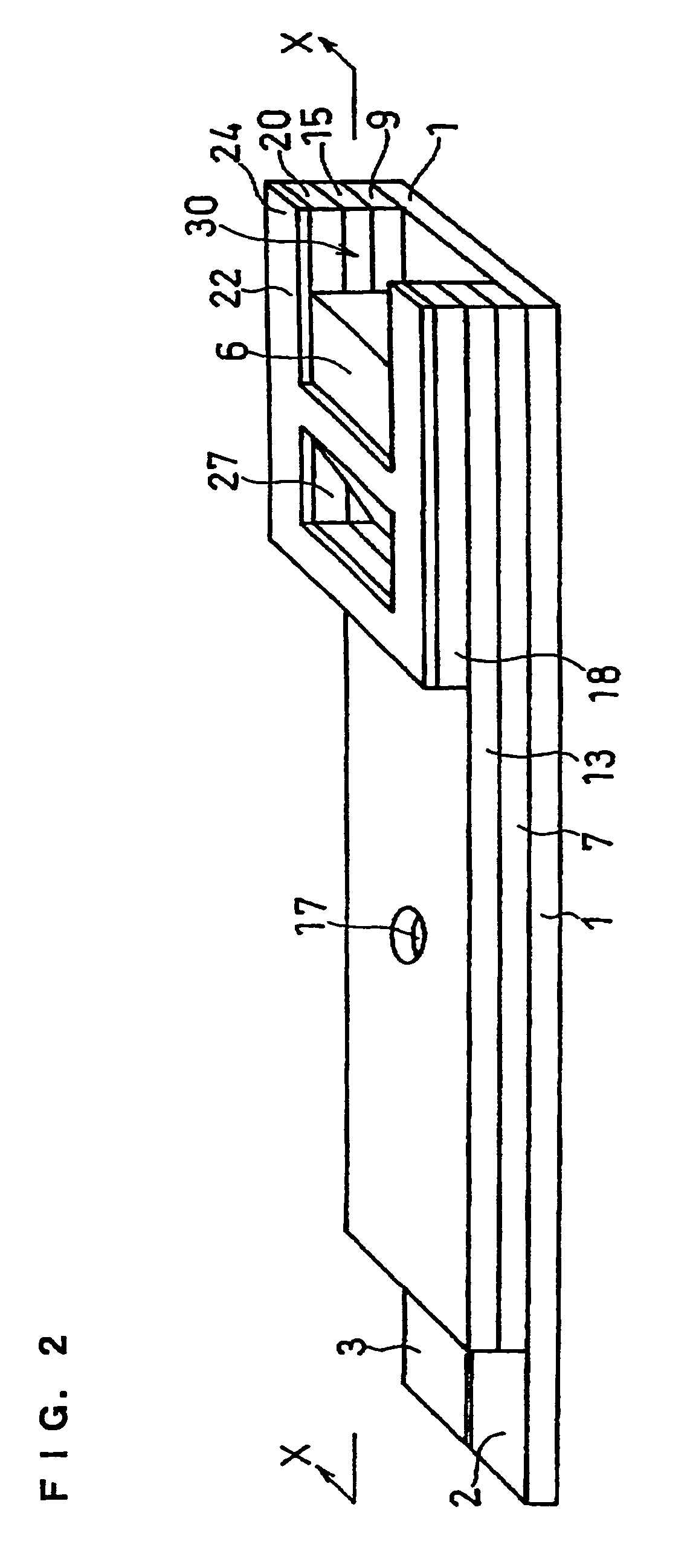
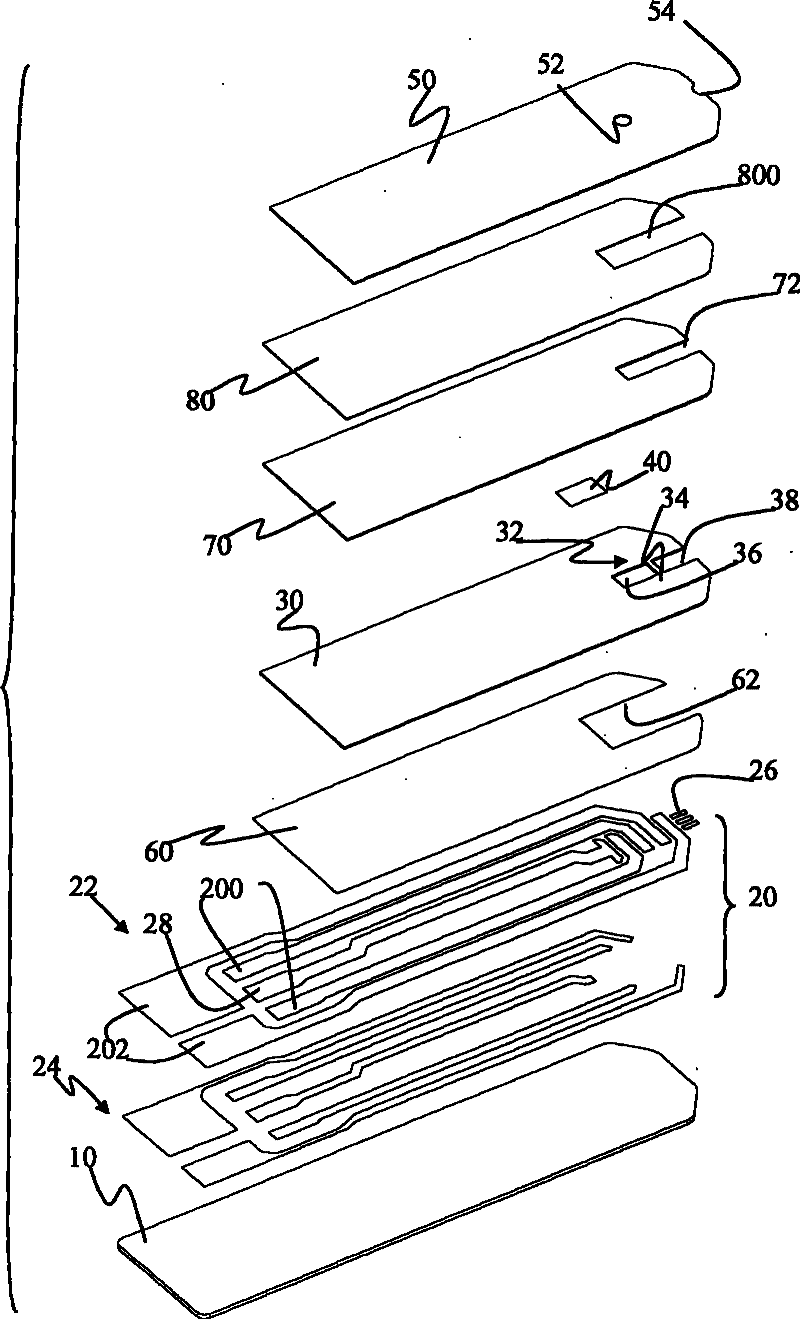
Biosensor
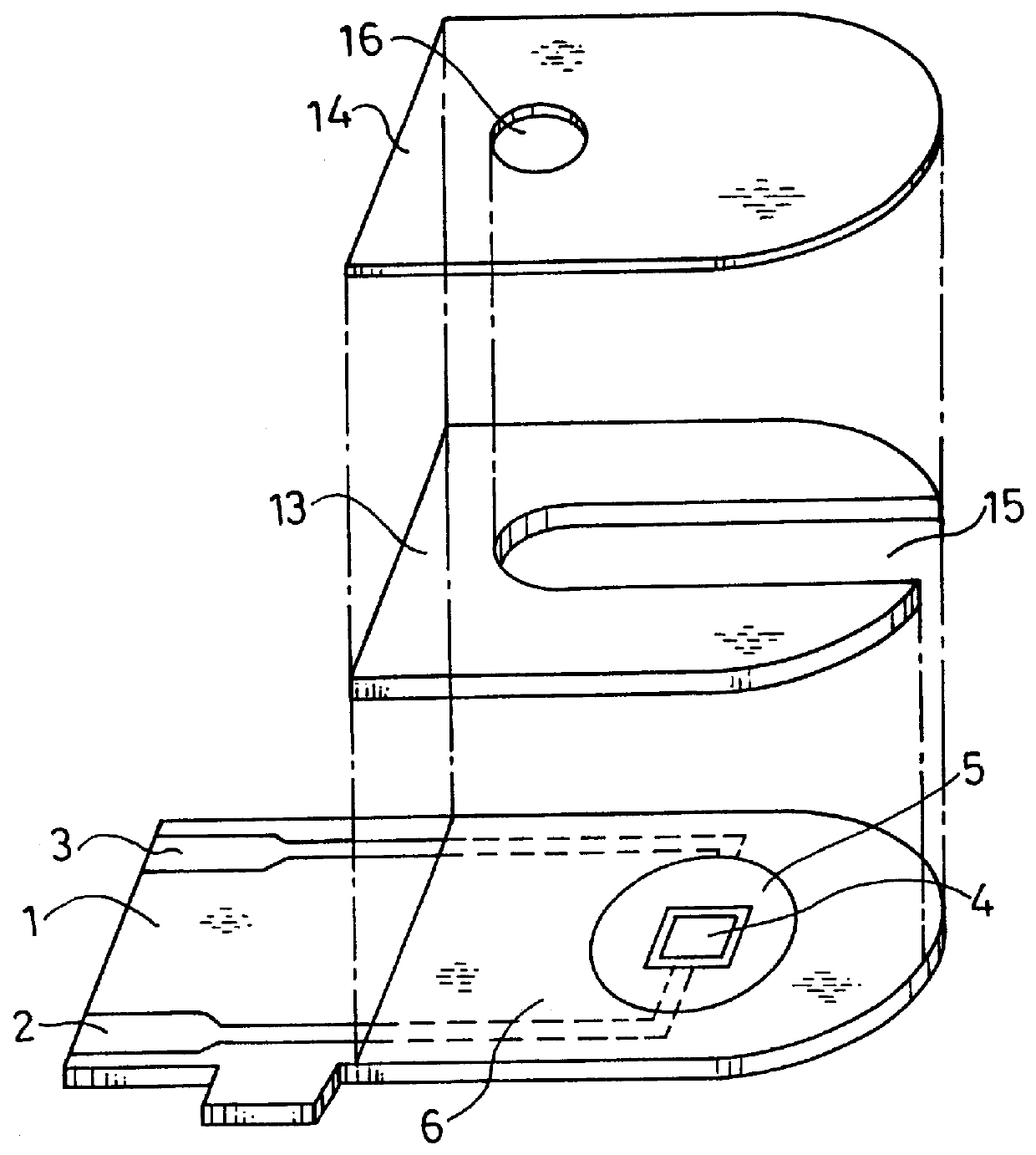
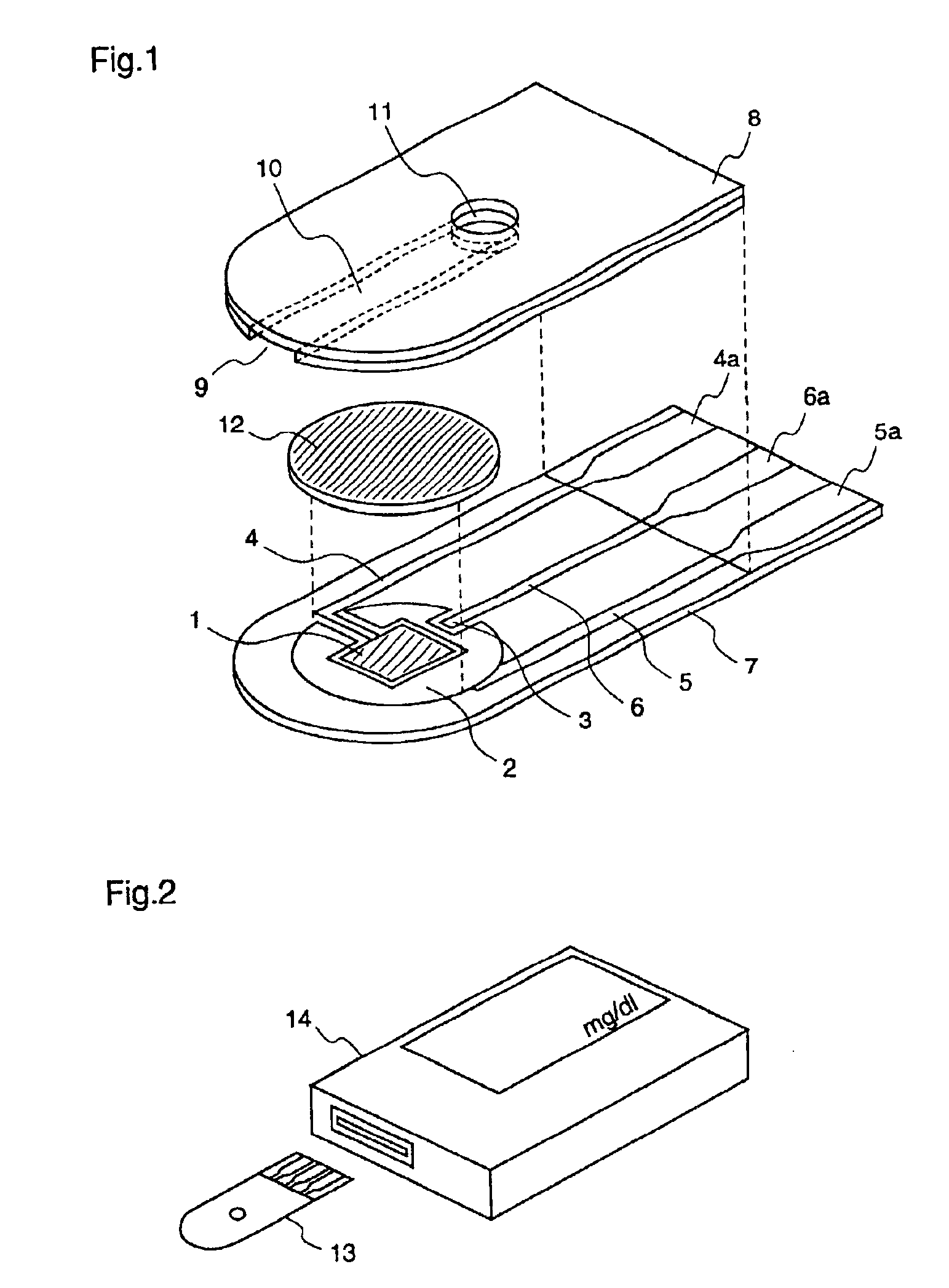
A biosensor including an insulating base plate, an electrode system, a cover for covering the insulating base plate, at least one reaction layer, a sample solution supply pathway communicating with an air aperture at a terminal end side, a sample solution supply part and a filter provided between the sample solution supply pathway and the sample solution supply part to filter hemocytes, an end face and a top face of a primary portion of the filter are exposed and the sample solution supply part is provided adjacently to the primary side portion so as to provide an improved biosensor which allows easy addition of whole blood to the sensor and rapid supply of the added whole blood to a filter even in the case of collecting blood by fingertip centesis for measurement.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Biosensor
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
Biosensor
InactiveUS7070680B2Rapidly inducing absorptionMinimize measurement errorImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerBiochemical engineering
A biosensor for quantifying a specific substance contained in a biological sample includes an electrically insulating base plate, a plurality of lead terminals formed on the base plate, a plurality of lead wires connected to the lead terminals, respectively, an electrode system including two working electrodes and one reference electrode connected to the lead wires, respectively, an insulating layer that insulates the electrodes, an enzyme reaction layer formed on the insulating layer and the electrodes, a spacer formed on the enzyme reaction layer so as to ensure a sufficient space that receives a sample, and a cover formed on the spacer. Further, the spacer has a sample introduction port opened at one side of the spacer, the cover has at least one slit for venting air existing in a sample receiving space defined by the spacer and the cover, and the slit extends to above the electrodes from one end of the cover.
Owner:INFOPIA CO LTD
Biosensor
InactiveUS20050072670A1Low densityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerFiltration
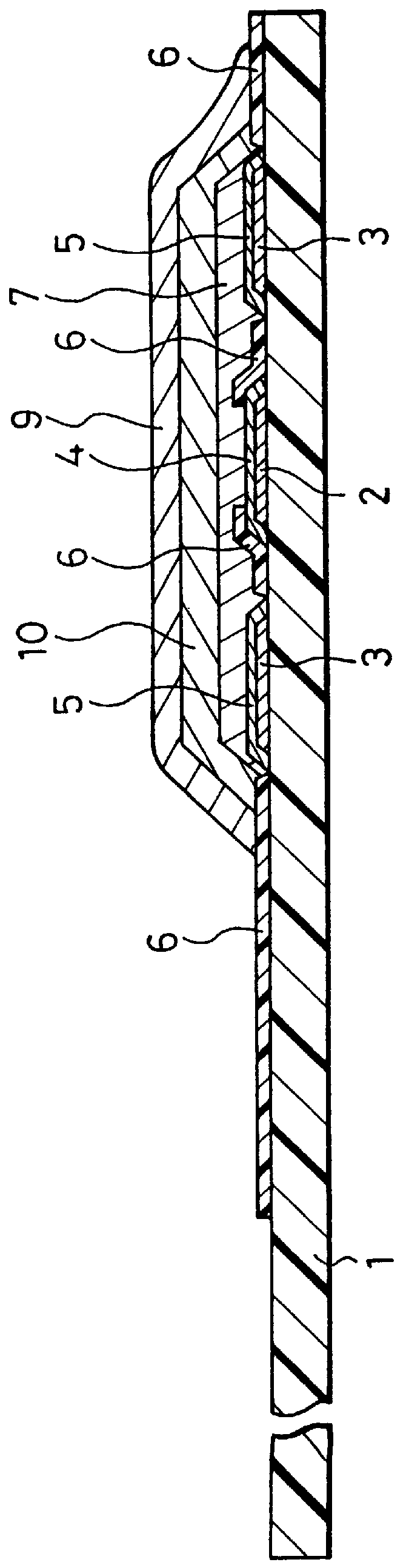
In order to provide a biosensor with high accuracy and excellent response where plasma obtained by filtration of blood rapidly arrives at an electrode system, in a biosensor comprising: an insulating base plate; an electrode system having a working electrode and a counter electrode which are provided on the base plate; a reaction layer including at least oxidoreductase and an electron mediator; a sample solution supply pathway which includes the electrode system and the reaction layer and has an inlet and an air aperture; a sample solution supply part for introducing a sample solution, which is in position apart from the sample solution supply pathway; and a first filter which is disposed between the sample solution supply pathway and the sample solution supply part for filtering the sample solution, where the filtrate filtered with the first filter is supplied into the sample solution supply pathway due to capillary action, the direction in which the sample solution passes through the first filter and the direction in which the filtrate passes through the sample solution supply pathway are made cross at right angles.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Biosensor
InactiveUS7056425B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReaction layerEngineering
To provide an improved biosensor which allows easy addition of whole blood to the sensor and rapid supply of the added whole blood to a filter even in the case of collecting blood by fingertip centesis for measurement, a second air aperture is provided in a sample solution supply pathway including an electrode system and a reaction layer and communicating with a first air aperture on the terminal end side.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Layered thermal barrier coatings containing lanthanide series oxides for improved resistance to CMAS degradation
InactiveUS20070160859A1Avoid damageElimination of expensiveBlade accessoriesEfficient propulsion technologiesReaction layerCerium
A coating applied as a two layer system. The outer layer is an oxide of a group IV metal selected from the group consisting of zirconium oxide, hafnium oxide and combinations thereof, which are doped with an effective amount of a lanthanum series oxide. These metal oxides doped with a lanthanum series addition comprises a high weight percentage of the outer coating. As used herein, lanthanum series means an element selected from the group consisting of lanthanum (La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), lutetium (Lu) and combinations thereof, and lanthanum series oxides are oxides of these elements. When the zirconium oxide is doped with an effective amount of a lanthanum series oxide, a dense reaction layer is formed at the interface of the outer layer of TBC and the CMAS. This dense reaction layer prevents CMAS infiltration below it. The second layer, or inner layer underlying the outer layer, comprises a layer of partially stabilized zirconium oxide.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
MOSFET device with localized stressor
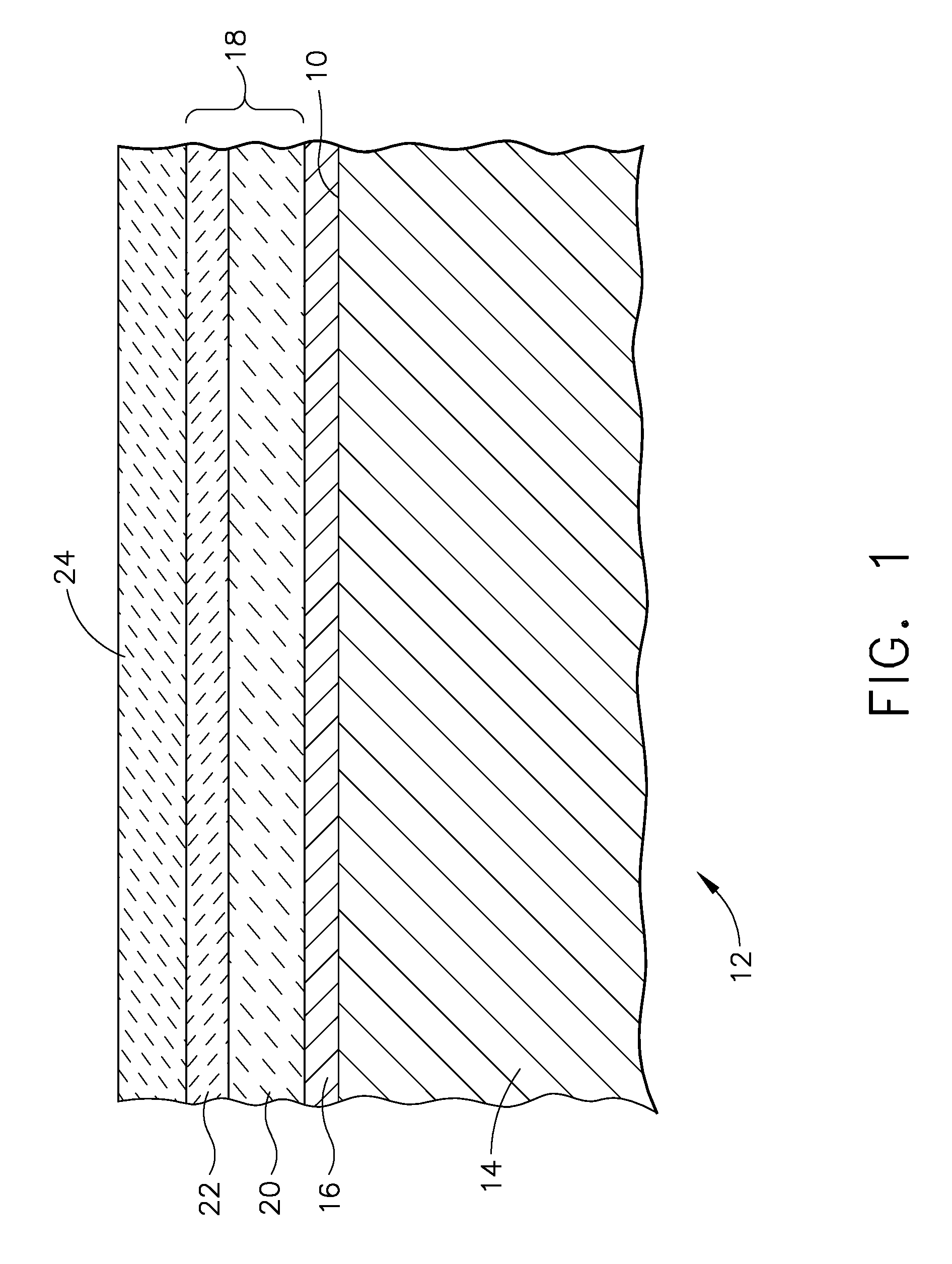
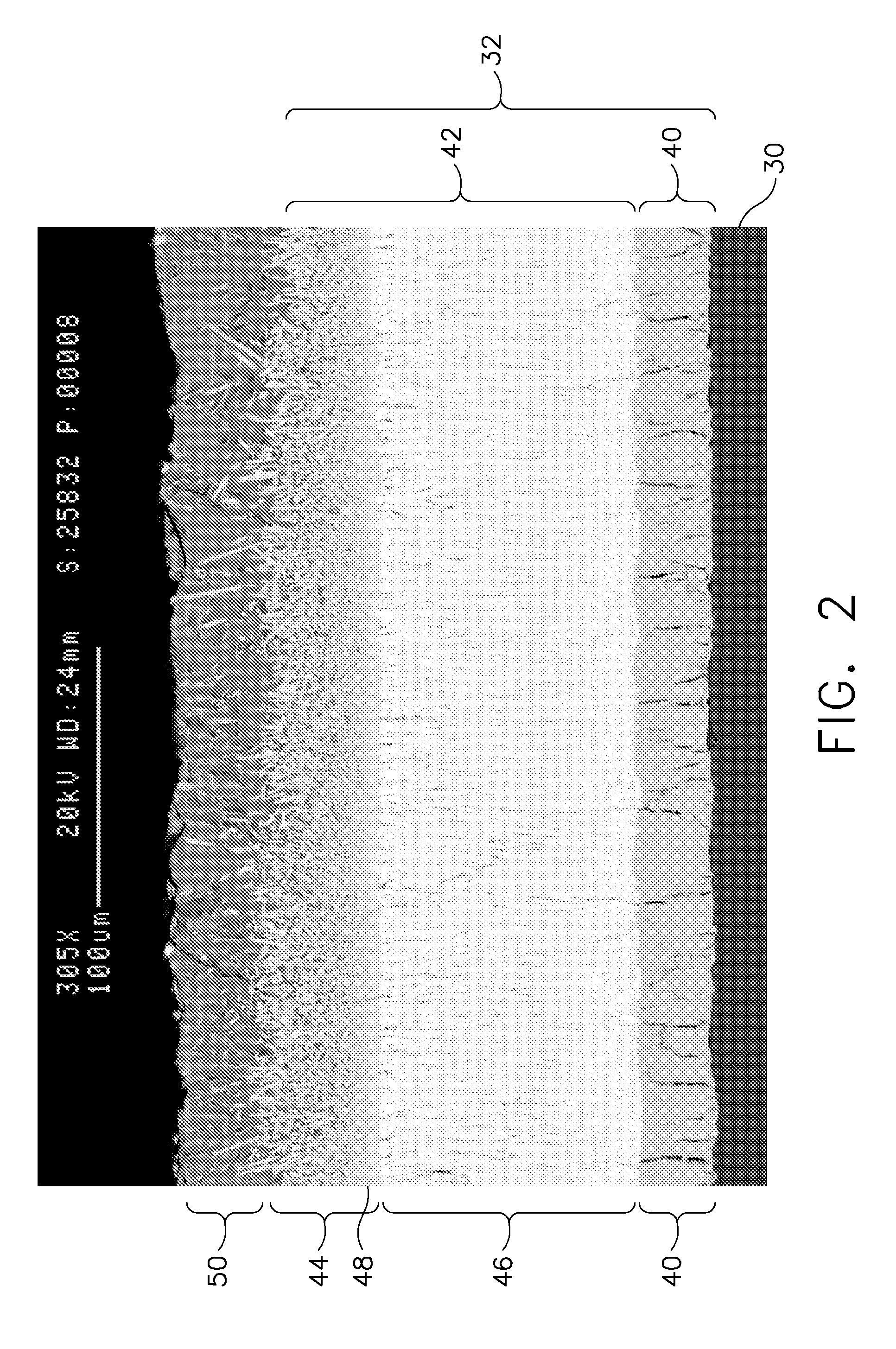
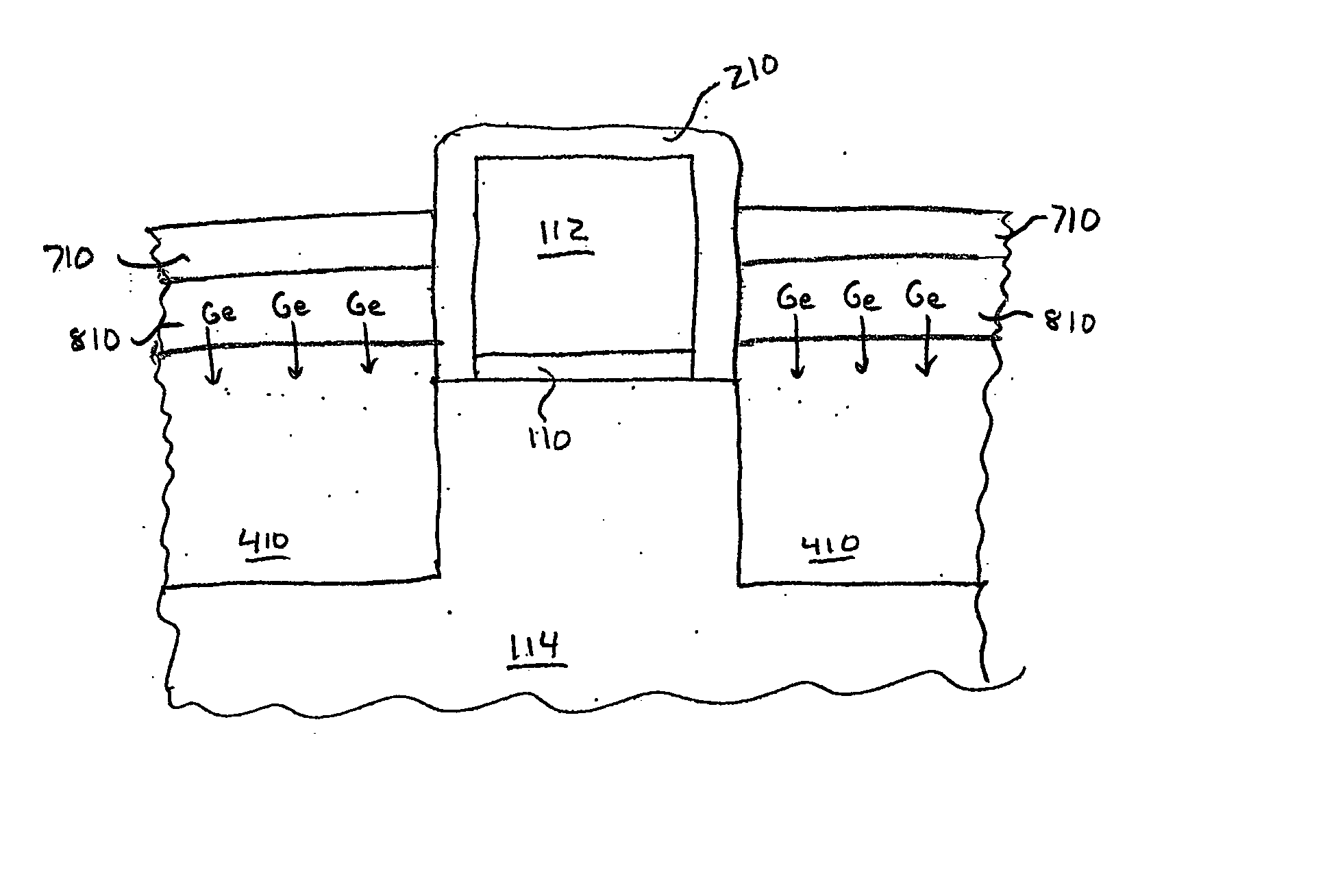
InactiveUS20060151808A1Easy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital video signal modificationMOSFETReaction layer
MOSFETs having localized stressors are provided. The MOSFET has a stress-inducing layer formed in the source / drain regions, wherein the stress-inducing layer comprises a first semiconductor material and a second semiconductor material. A treatment is performed on the stress-inducing layer such that a reaction is caused with the first semiconductor material and the second semiconductor material is forced lower into the stress-inducing layer. The stress-inducing layer may be either a recessed region or non-recessed region. A first method involves forming a stress-inducing layer, such as SiGe, in the source / drain regions and performing a nitridation or oxidation process. A nitride or oxide film is formed in the top portion of the stress-inducing layer, forcing the Ge lower into the stress-inducing layer. Another method embodiment involves forming a reaction layer over the stress-inducing layer and performing a treatment process to cause the reaction layer to react with the stress-inducing layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
A high-density array chip device and application for digital nucleic acid amplification
ActiveCN102277294AReduce consumptionMiniaturizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReaction layerHigh density
The invention provides an integrated flow path chip device used for digital nucleic acid amplification. The device is composed of a vacuum system, a pipeline, a sucker, a sealing cover layer and a reaction layer, wherein two ends of the sealing cover layer are respectively provided with a sample inlet and a sample outlet; a path is formed between the sealing cover layer and the reaction layer; the reaction layer is provided with small reaction chambers; the sucker is arranged on the sample outlet; the vacuum system is connected with the sucker via a pipeline; and the sample inlet and the sample outlet are sealed by adhesive tape paper. According to the integrated flow path chip device, trace reaction samples can be distributed to thousands of small reaction chambers, and mineral oil is led in via a path in the sealing cover layer to separate thousands of small reaction chambers so as to realize the single molecule amplification and precisely quantify the nucleic acid molecules. The device is reasonable to design and is a minitype device used for digital nucleic acid amplification, which has low cost and is easy to operate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
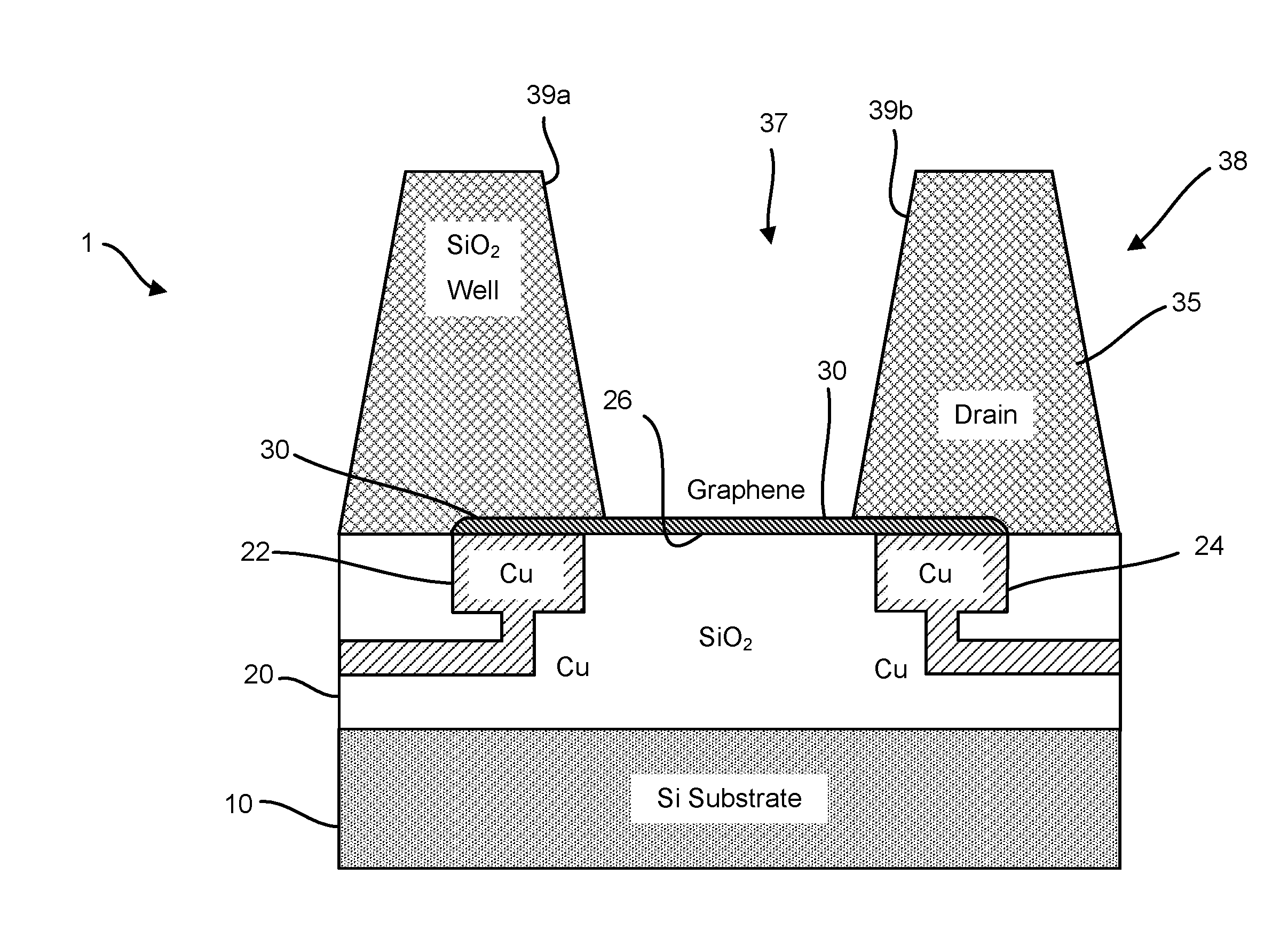
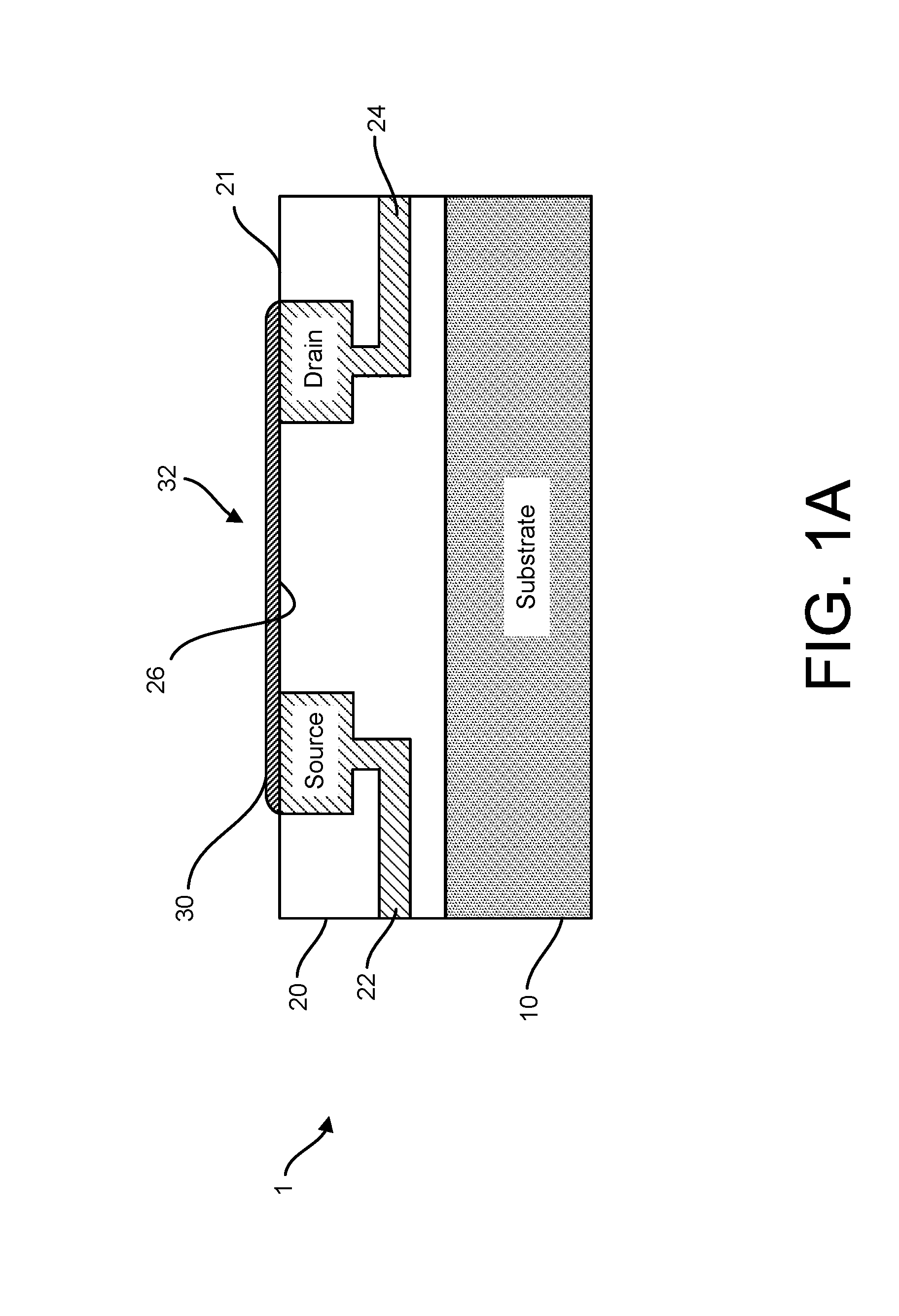
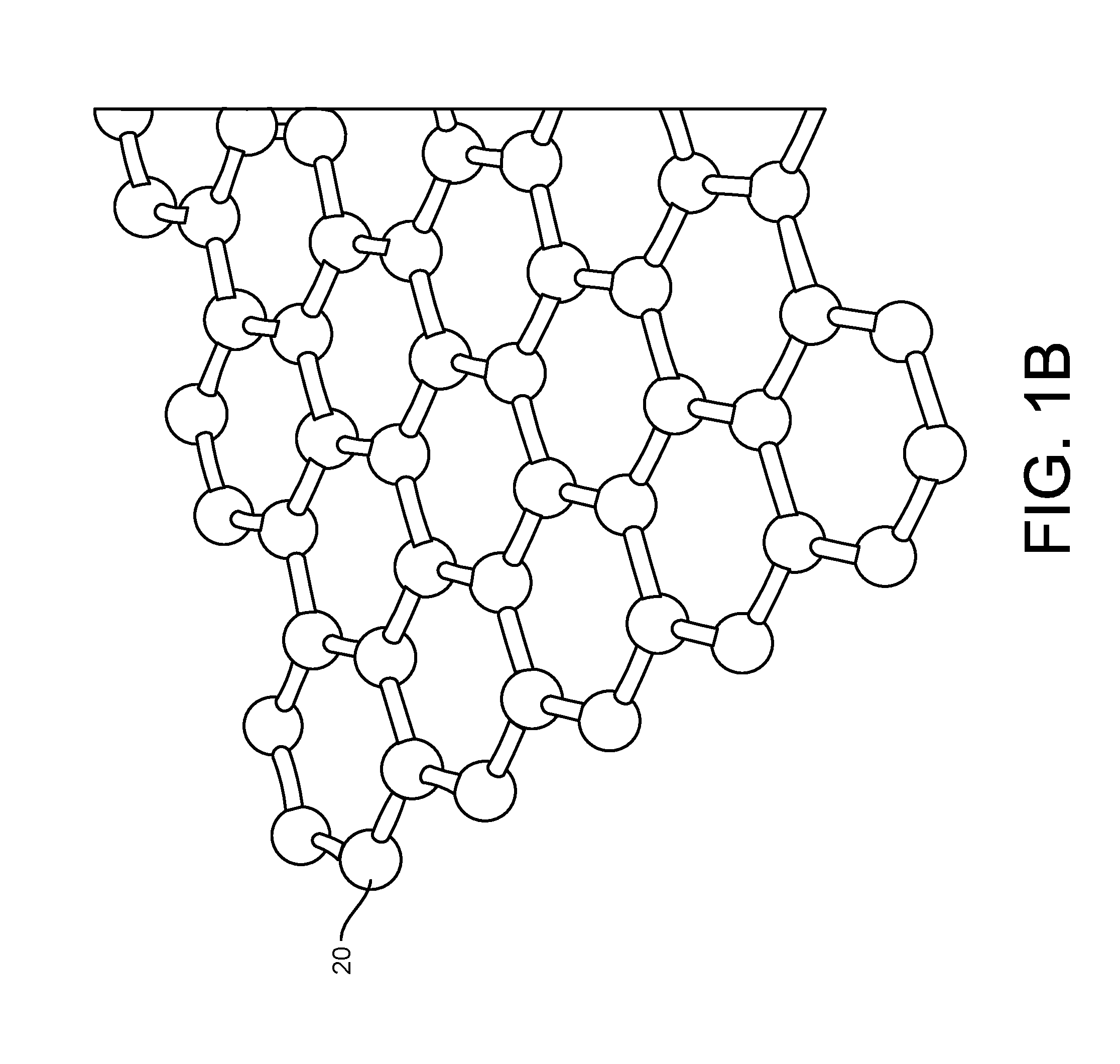
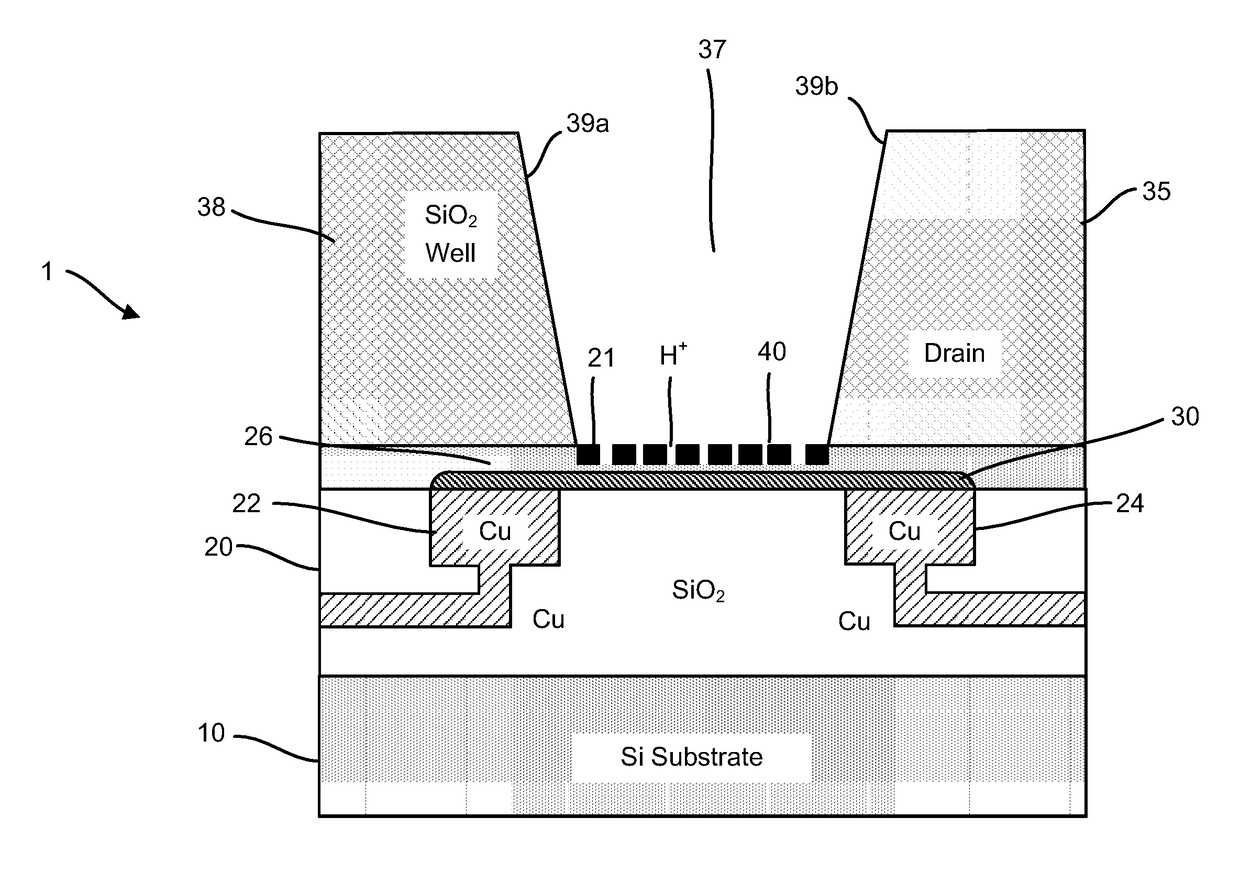
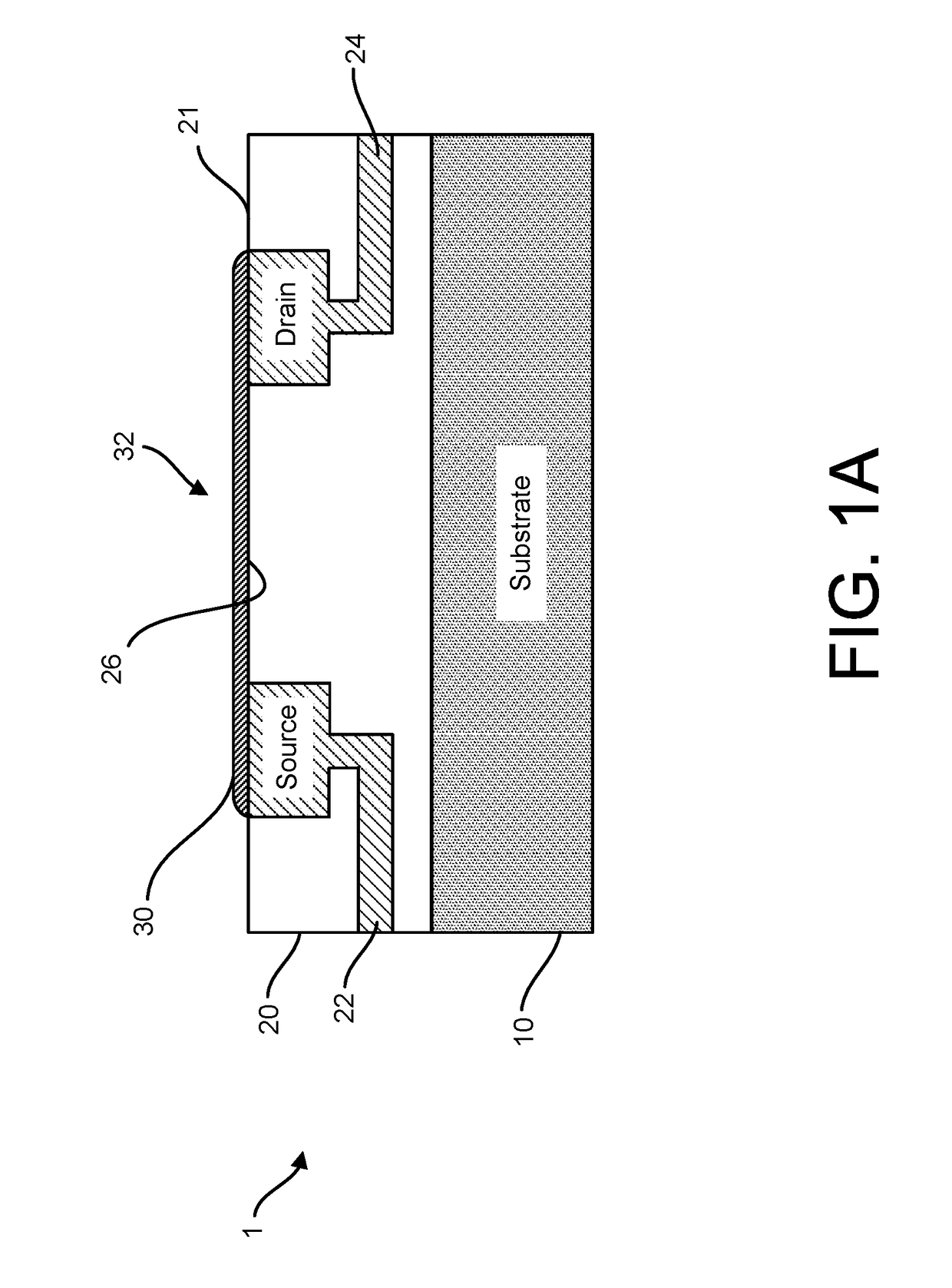
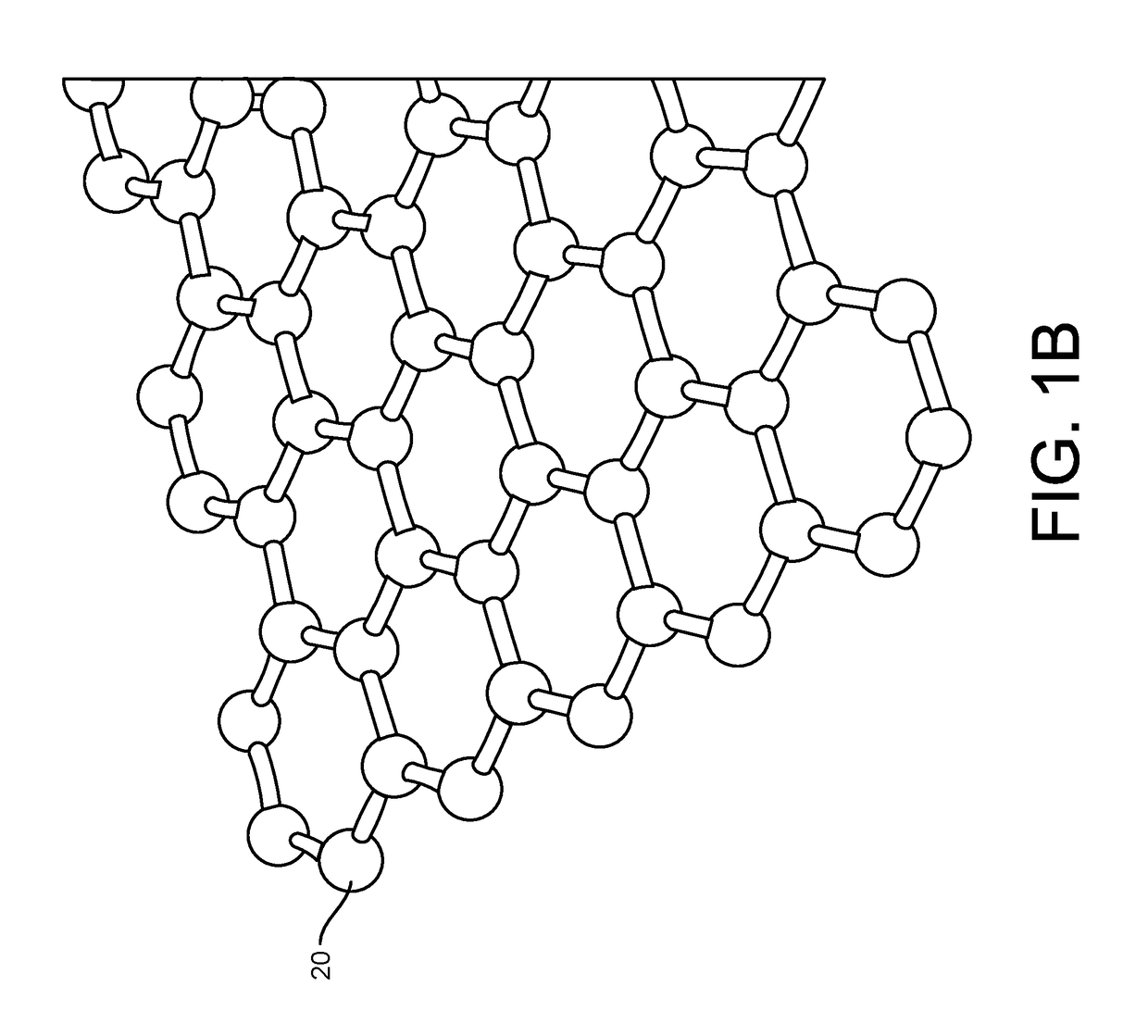
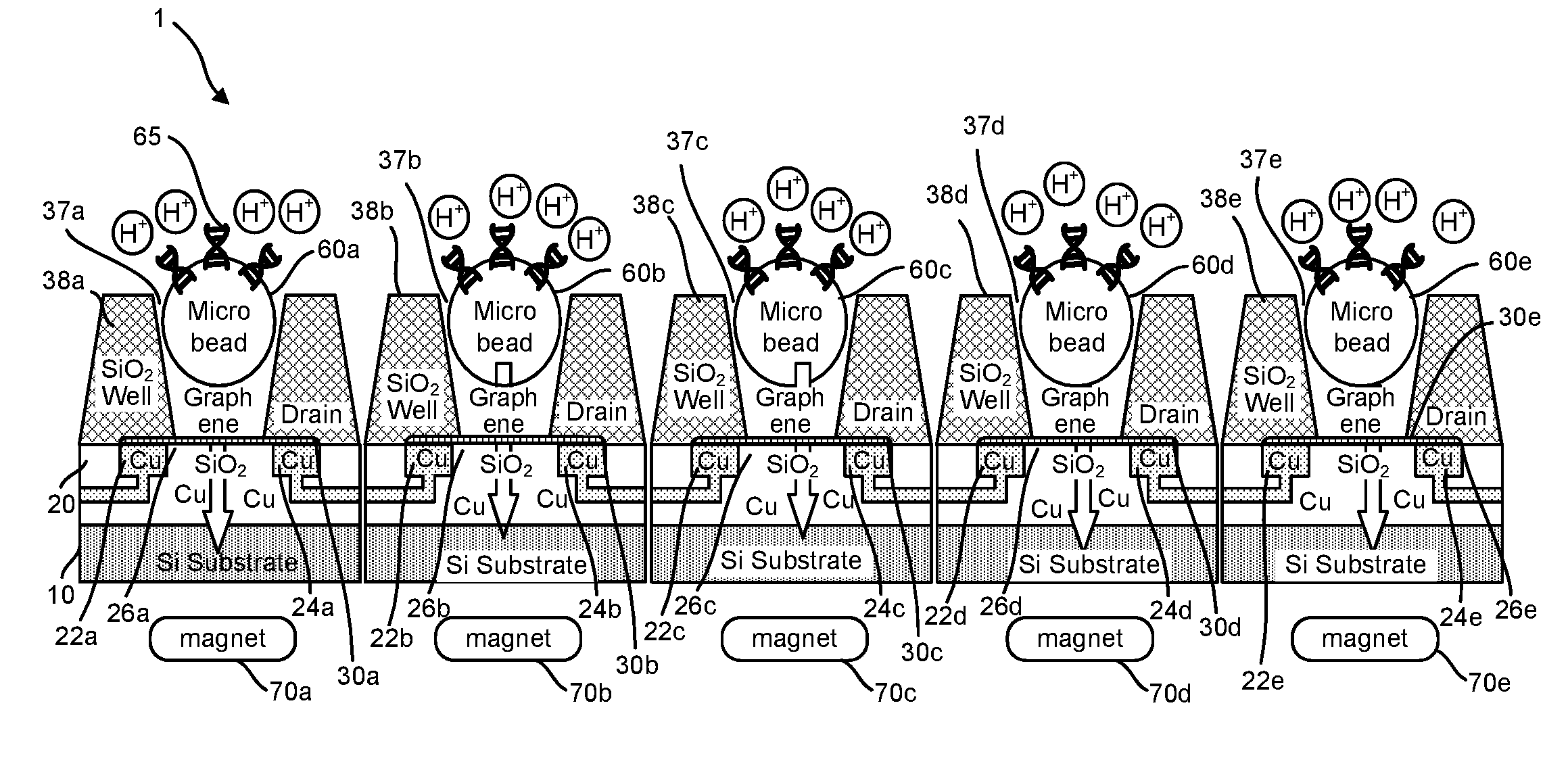
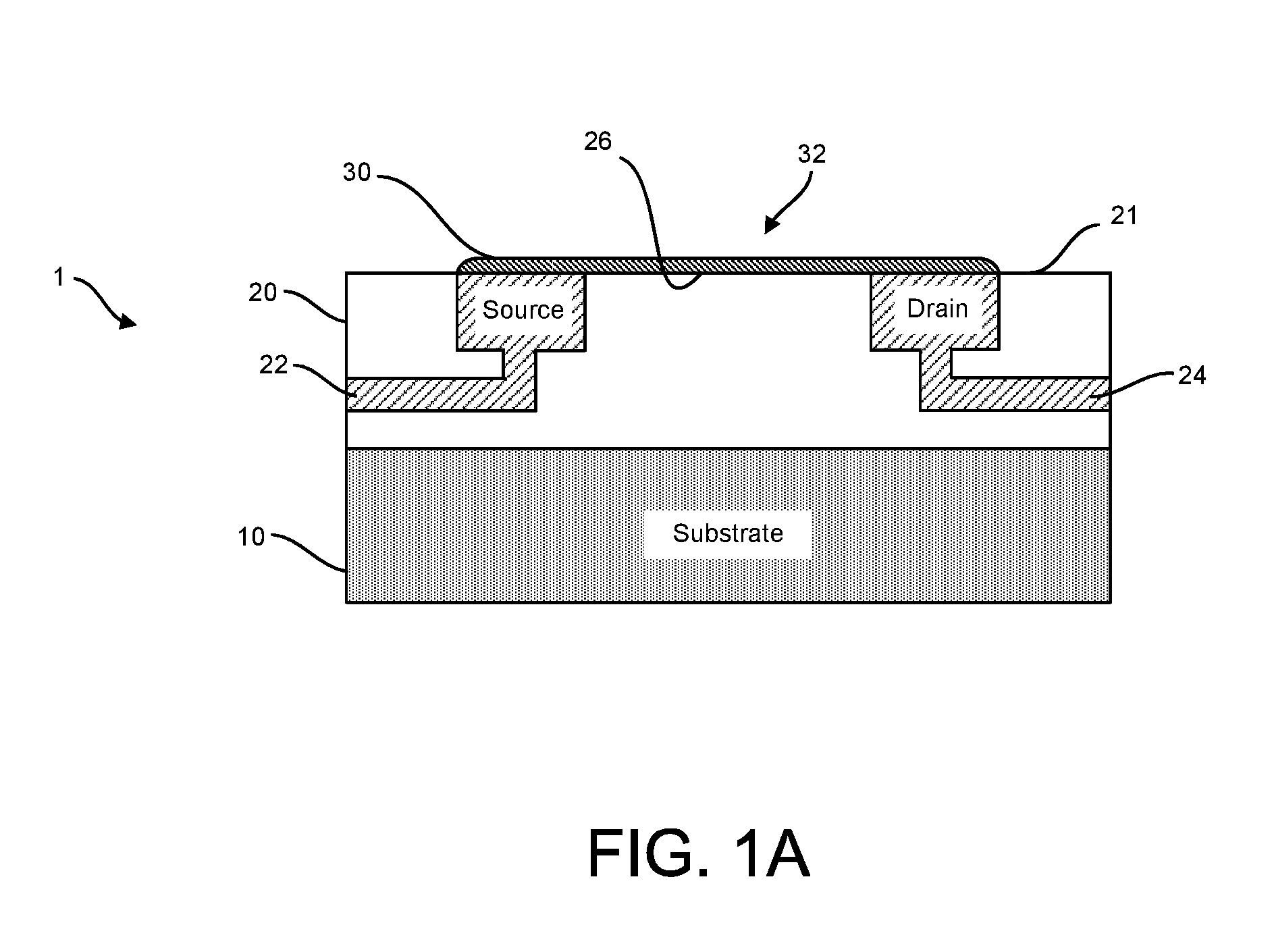
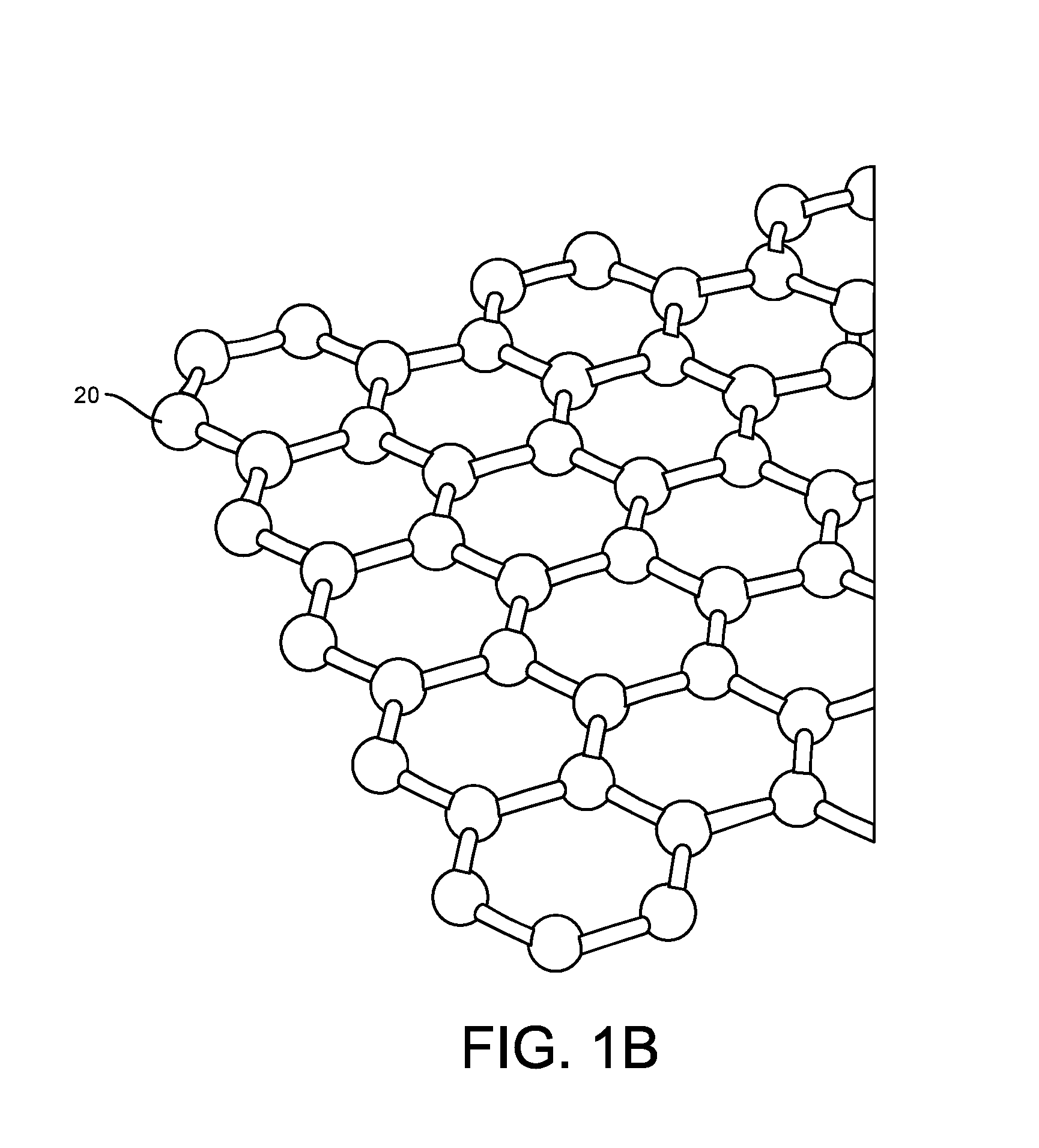
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS20160265047A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementSensor arrayReaction layer
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
Biosensor
InactiveUS20030098234A1Improve solubilityNot easy to dissolveImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerCholesterol
In order to provide a cholesterol sensor capable of measuring whole blood with high accuracy and excellent response, where plasma with hemocytes therein filtered promptly reaches an electrode system, in a biosensor comprising: an insulating base plate; an electrode system which is provided on the base plate and has a measurement electrode and a counter electrode; a reaction layer including at least oxidoreductase and an electron mediator; a sample solution supply pathway which includes the electrode system and the reaction layer and has an air aperture on the termination side thereof; a sample supply portion; and a filter which is disposed between the sample solution supply pathway and the sample supply portion and filters hemocytes, where plasma with the hemocytes therein filtered with the filter is sucked into the sample solution supply pathway due to capillarity, the central part of a secondary side portion of the filter is protruded into the sample solution supply pathway more than both the right and left ends thereof.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
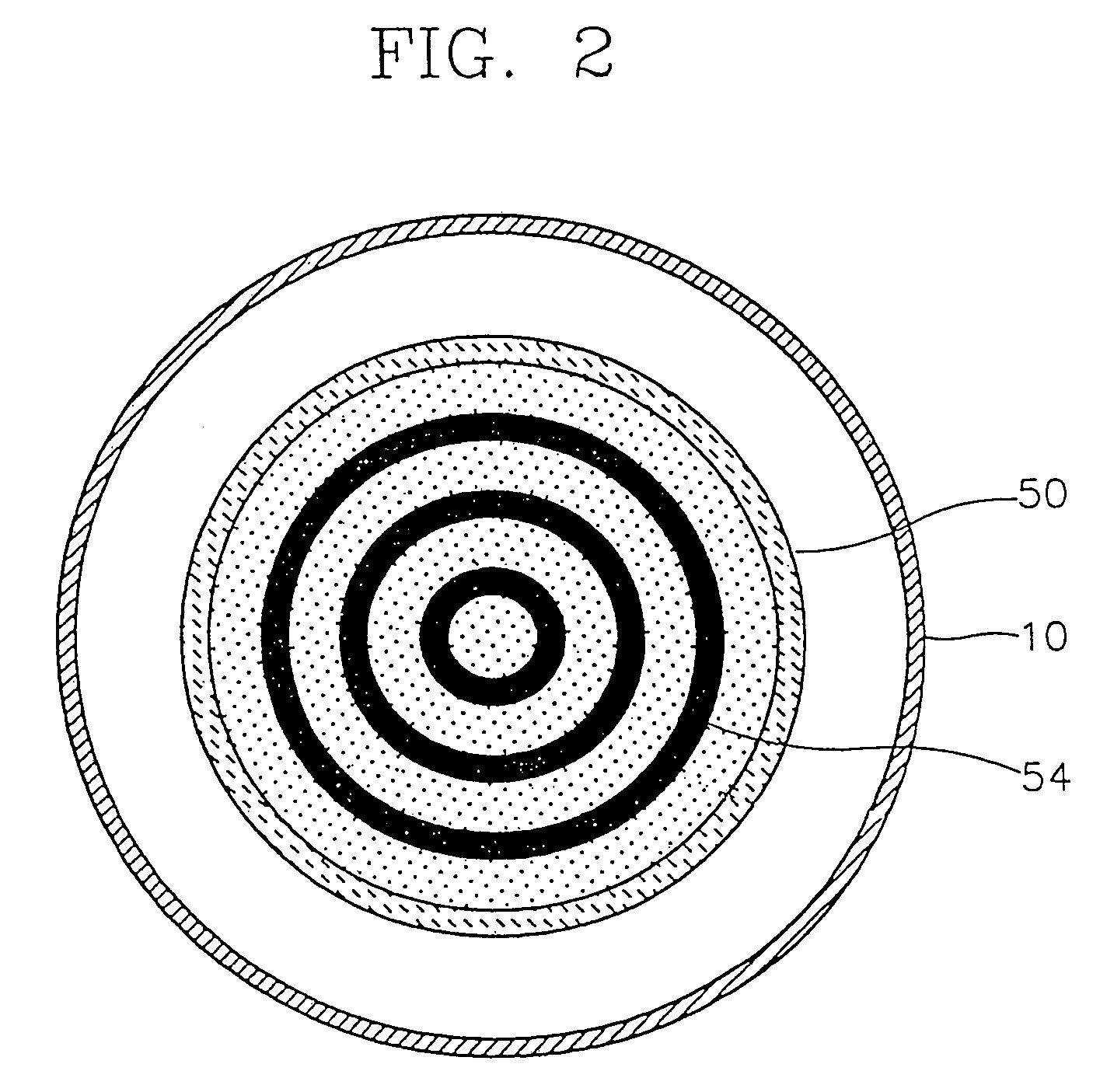
Method and apparatus for improving film deposition uniformity on a substrate
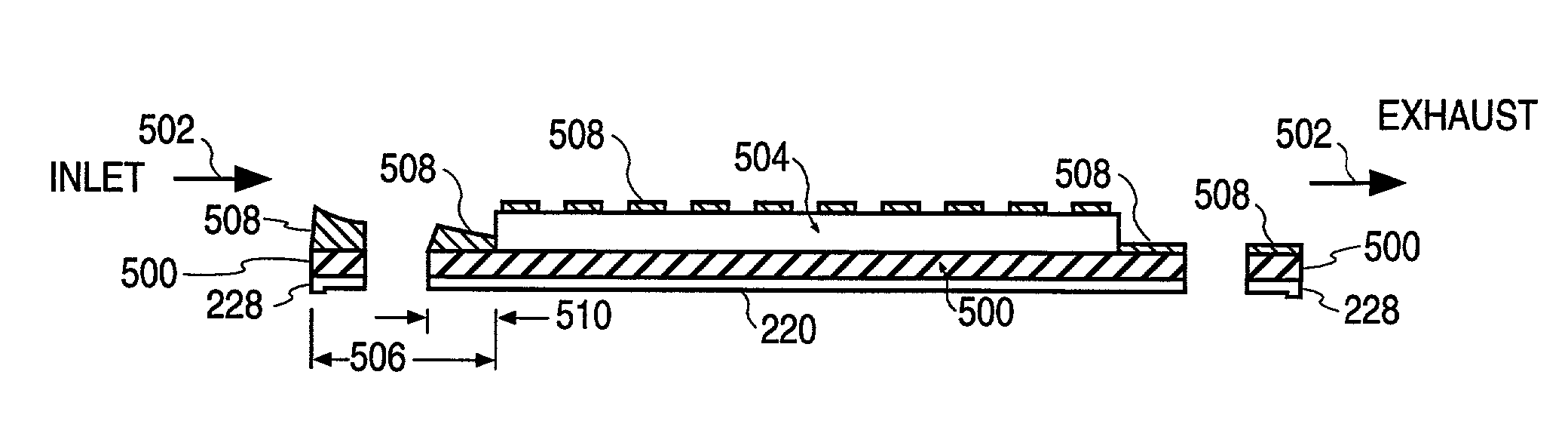
InactiveUS20020020358A1Reduce edge effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingReaction layerSusceptor
A method and apparatus for depositing a film on a substrate. According to the present invention a prewafer reaction layer is deposited onto a susceptor placed in the reaction chamber to form a prewafer reaction layer coated susceptor prior to film deposition. A deposition gas is then fed into the reaction chamber so that it flows over the prewafer reaction layer coated susceptor and the substrate to form a film on the prewafer reaction layer coated susceptor and the substrate.
Owner:HEY H PETER W +2
Fuel electrode of solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell
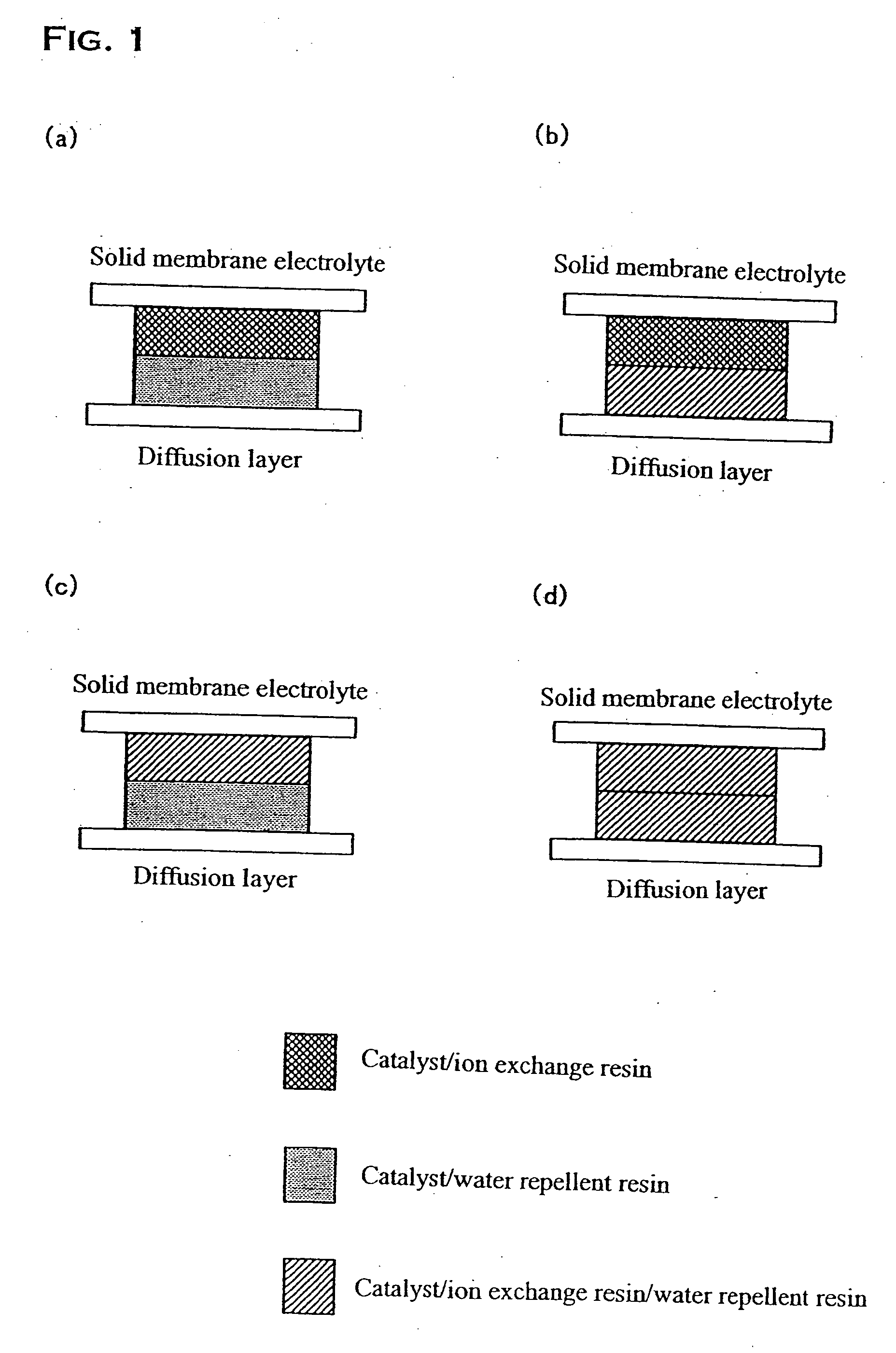
InactiveUS20070042242A1Raise the potentialDifference in densenessFuel cell auxillariesRegenerative fuel cellsReaction layerPolymer electrolytes
The present invention provides a fuel electrode of a solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell for advancing a fuel cell reaction to oxidize the fuel introduced through a diffusion layer, comprising at least one reaction layer which is in contact with a solid polymer electrolyte membrane and advances the fuel cell reaction and at least one water decomposition layer which is in contact with the diffusion layer and electrolyzes the water in the fuel electrode. The layer taking charge of the fuel cell reaction is protected by providing the fuel electrode having a multilayer structure and providing the layer for preferentially performing the electrolysis of the water contained in the fuel or the like. This results in a fuel electrode in which the reduction of the electrode performance will not easily occur even when fuel shortage may be created.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND +1
Light emitting diode having an adhesive layer
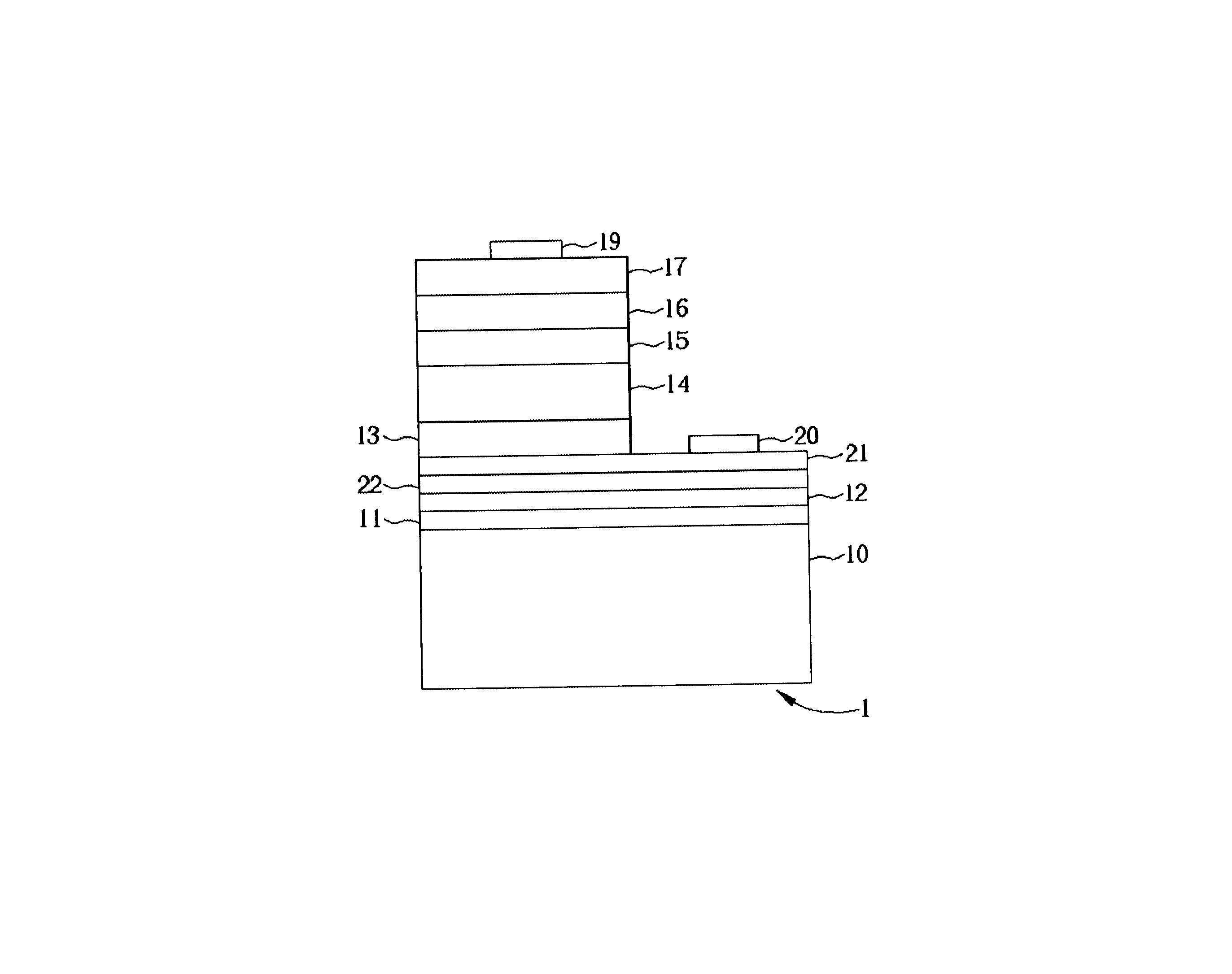
InactiveUS6876005B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReaction layerLight-emitting diode
A method for forming a light emitting diode includes forming a first stack, forming a second reaction layer over the first stack, forming a second stack, forming a first reaction layer over the second stack, and holding together the first reaction layer and the second reaction layer by means of a transparent adhesive layer. The transparent adhesive layer is formed between the first and second reaction layer, therefore the second reaction layer of the first stack will not come off the first reaction layer of the second stack.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Biosensor
InactiveUS20030132110A1Flow fastReduce the cross-sectional areaImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerOxidoreductase
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
Electrochemical biosensor by screen printing and method of fabricating same
ActiveUS20050183953A1Rapid sample inflowSmall volumeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerSiphon
An electrochemical biosensor formed by screen printing and method of fabricating such biosensor is disclosed in the present invention. The biosensor can quickly absorb a sample to be measured therein, effectively control volume of the sample fed and “fill-and-position” the sample therein. The biosensor includes an electrode layer (electrode area) comprising two or three electrodes, which are a working electrode, a reference electrode and an auxiliary electrode (tri-electrode) on an insulating substrate. An active reaction layer containing reactant, reaction catalyst, mediator, wetting agent and surfactant is spread on the surface of the electrode layer. A sample inflow area is formed above the electrode area by adding an upper cover on top of a middle insulating layer with a U-shaped opening formed therein. Sample solution with a minute amount about 0.8 to 1 μl can be rapidly introduced into the electrode area and the active reaction layer via the inflow area by siphon or capillary, where the ingredient of the sample can be analysed by measuring reaction between the sample, reaction catalyst and mediator in the reaction layer using electrochemical potentiometric or amperometric method. An upwardly extended closed space formed within the upper cover above the electrode area adjacent to the front of conductive wires can be effectively used to control sample volume and “fill-and-position” the sample.
Owner:GENERAL LIFE BIOTECHNOLGOY
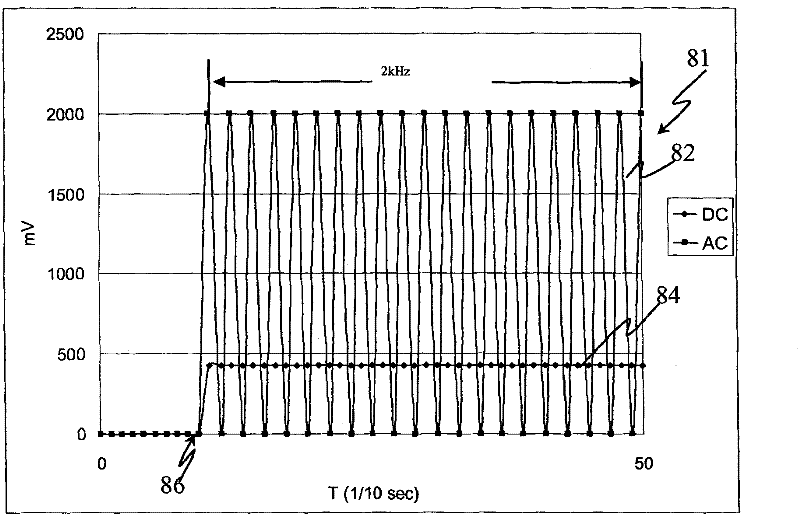
Electrochemical bio-sensing test paper, biosensor device and analyte measuring system
InactiveCN102128932AEasy to useReduced measurement timeBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesReaction layerAnalyte
The invention discloses analyte measuring electrochemical bio-sensing test paper with a blood volume ratio correcting function, a biosensor device, a system and a method. The test paper comprises a first group of electrodes for detecting the concentration of an analyte and a second group of electrodes for detecting a blood volume ratio concentration, wherein the first group of electrodes and the second group of electrodes correspond to different reaction regions respectively; a reaction layer reacting with a substance to be measured is only covered on the first group of electrodes; and first signals including a direct current signal are supplied to the first group of electrodes and second signals including a fixed-frequency alternating current signal are supplied to the second group of electrodes, so that an analyte concentration and a blood volume ratio which are not corrected are further measured respectively and a more accurate analyte concentration corrected by a blood volume ratio is obtained.
Owner:TAIDOC TECH CORP
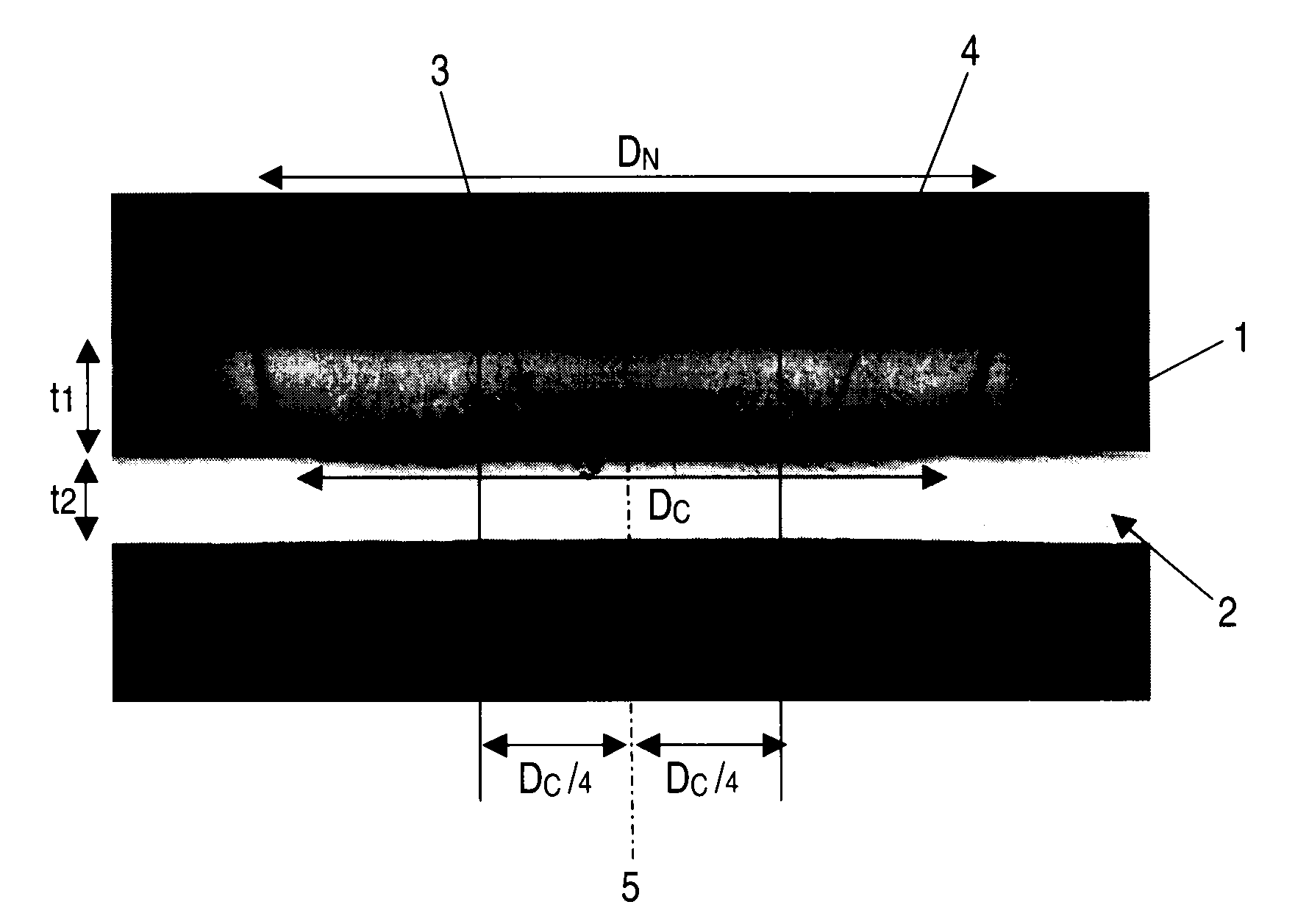
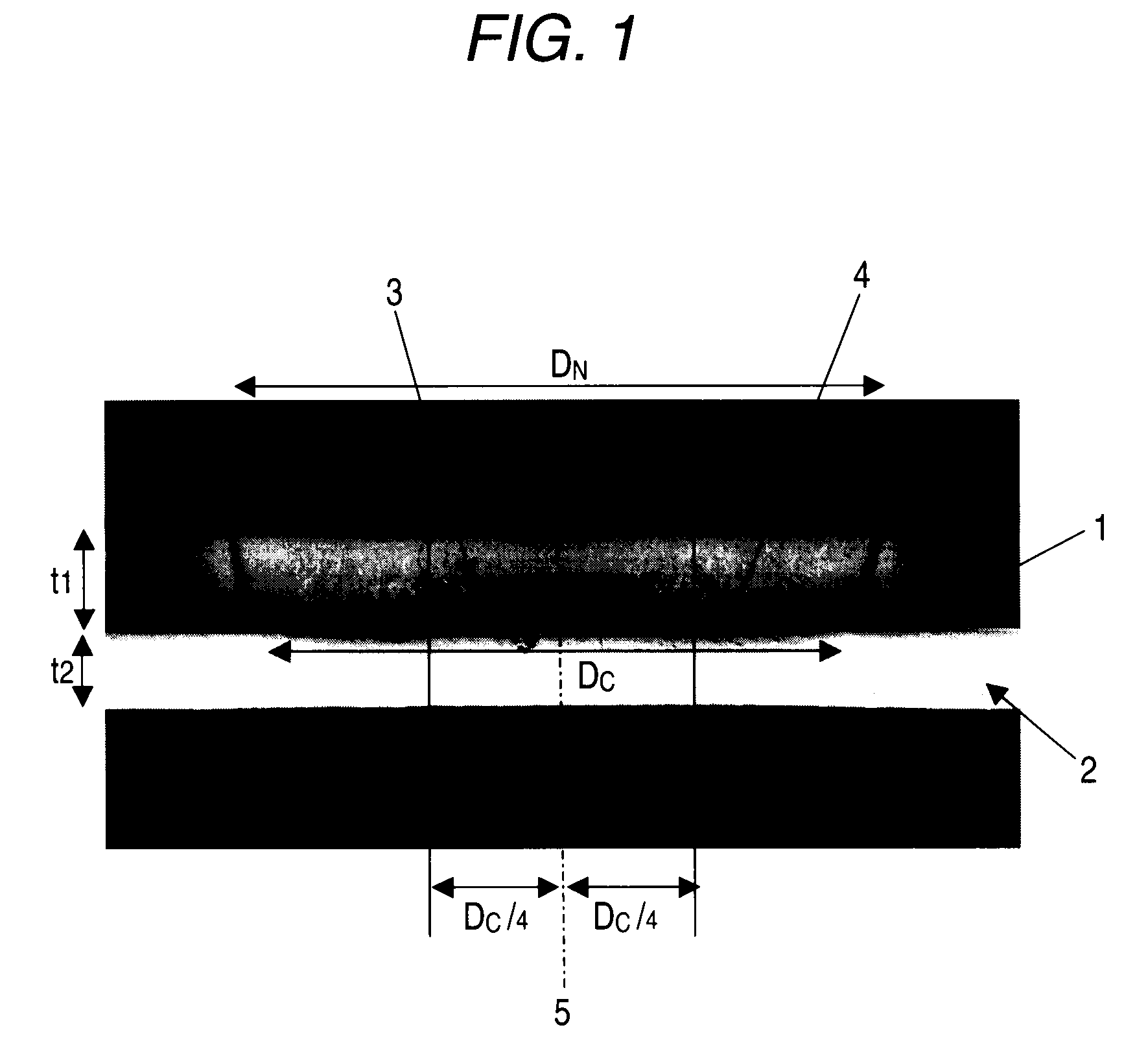
Joint product between steel product and aluminum material, spot welding method for the joint product, and electrode chip for use in the joint product
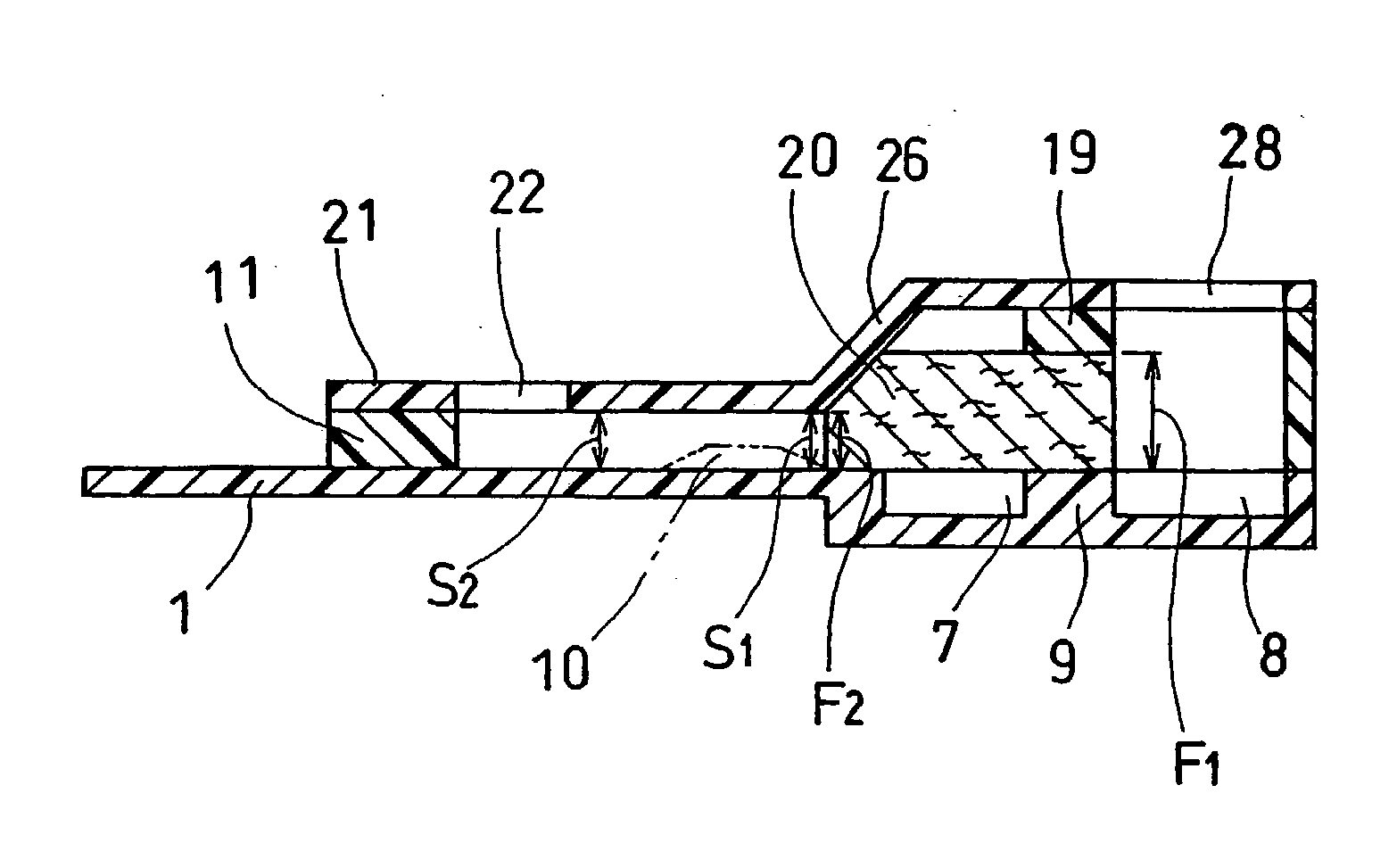
InactiveUS20090011269A1High bonding strengthLow costOhmic-resistance electrodesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsReaction layerSpot welding
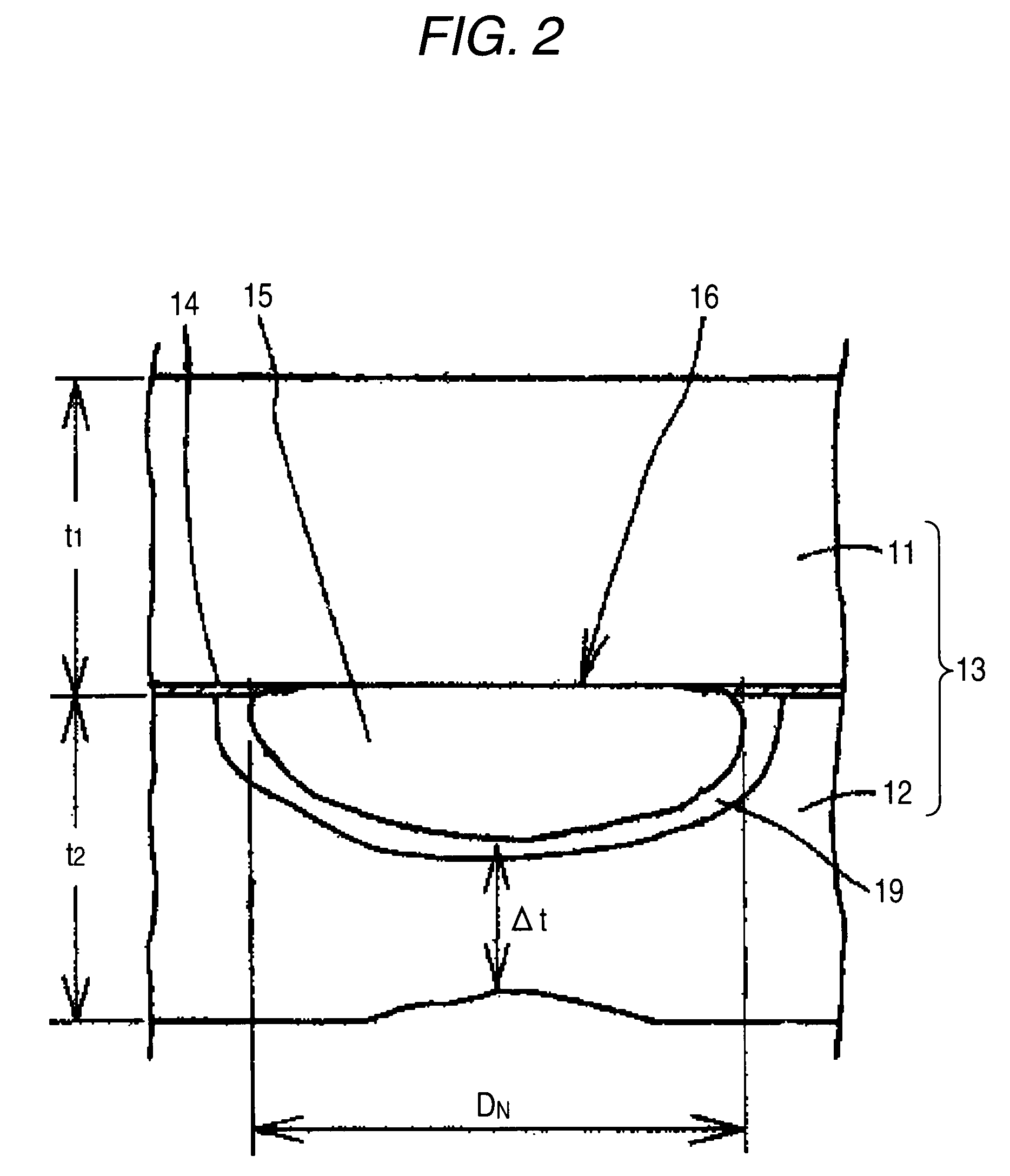
To provide a joint product of a steel product and an aluminum material, and a spot welding method for the joint product, ensuring that spot welding with high bonding strength can be performed. In one embodiment, a steel product 1 having a sheet thickness t1 of 0.3 to 3.0 mm and an aluminum material 2 having a sheet thickness t2 of 0.5 to 4.0 mm are joined together by spot welding to form a joint product of a steel product and an aluminum produce. In this joint product, the nugget area in the joint part is from 20×t20.5 to 100×t20.5 mm2, the area of a portion where the thickness of the interface reaction layer is from 0.5 to 3 μm is 10×t20.5 mm2 or more, and the difference between the interface reaction layer thickness at the joint part center and the interface reaction layer thickness at a point distant from the joint part center by a distance of one-fourth of the joint diameter Dc is 5 μm or less. According to this construction, there can be provided a dissimilar material joint product with excellent bonding strength, which can be formed by an existing spot welding apparatus at a low cost without newly using other materials such as clad material or without newly adding a separate step, and a spot welding method for the dissimilar material joint product.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Method for determining HDL concentration from whole blood or plasma
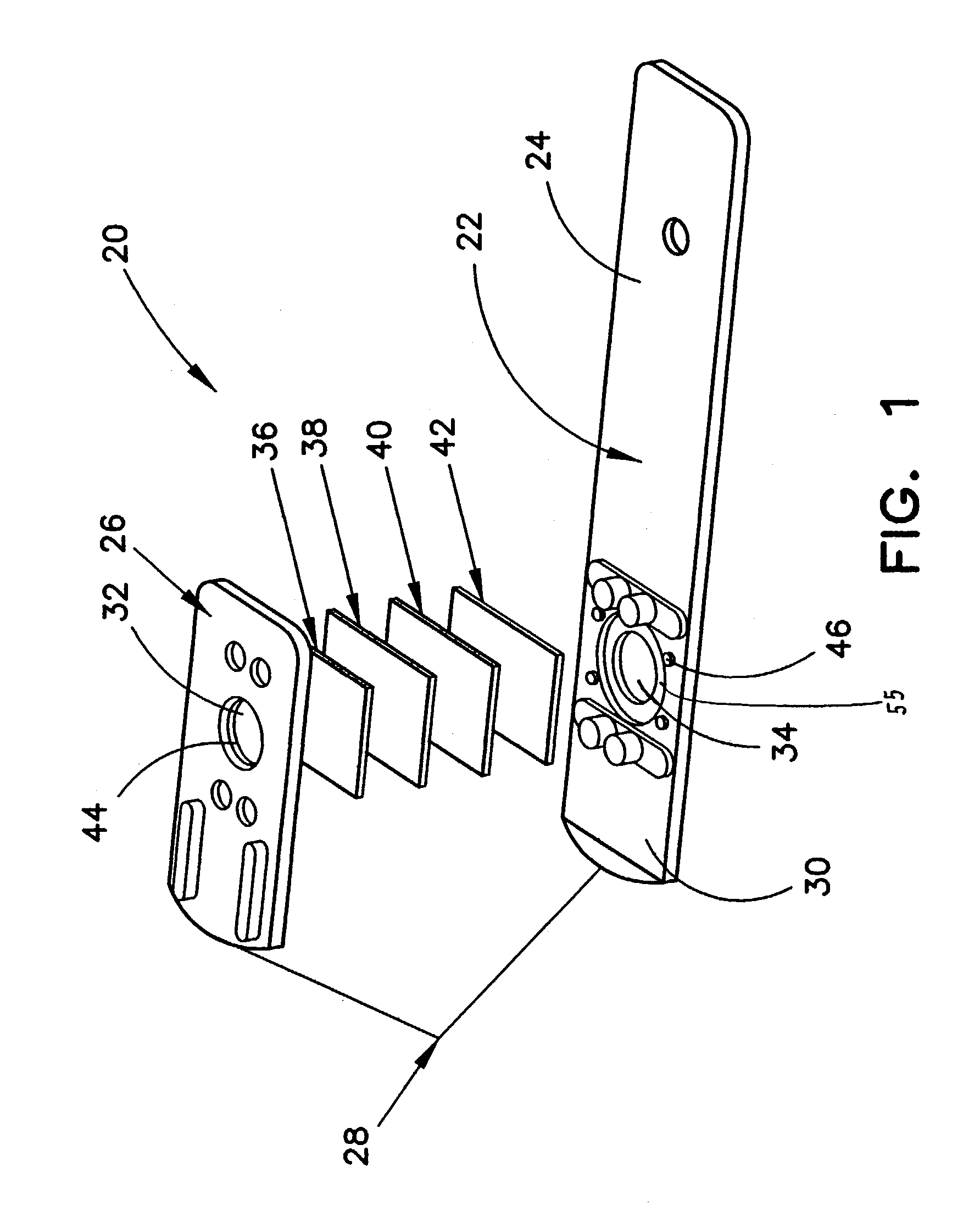
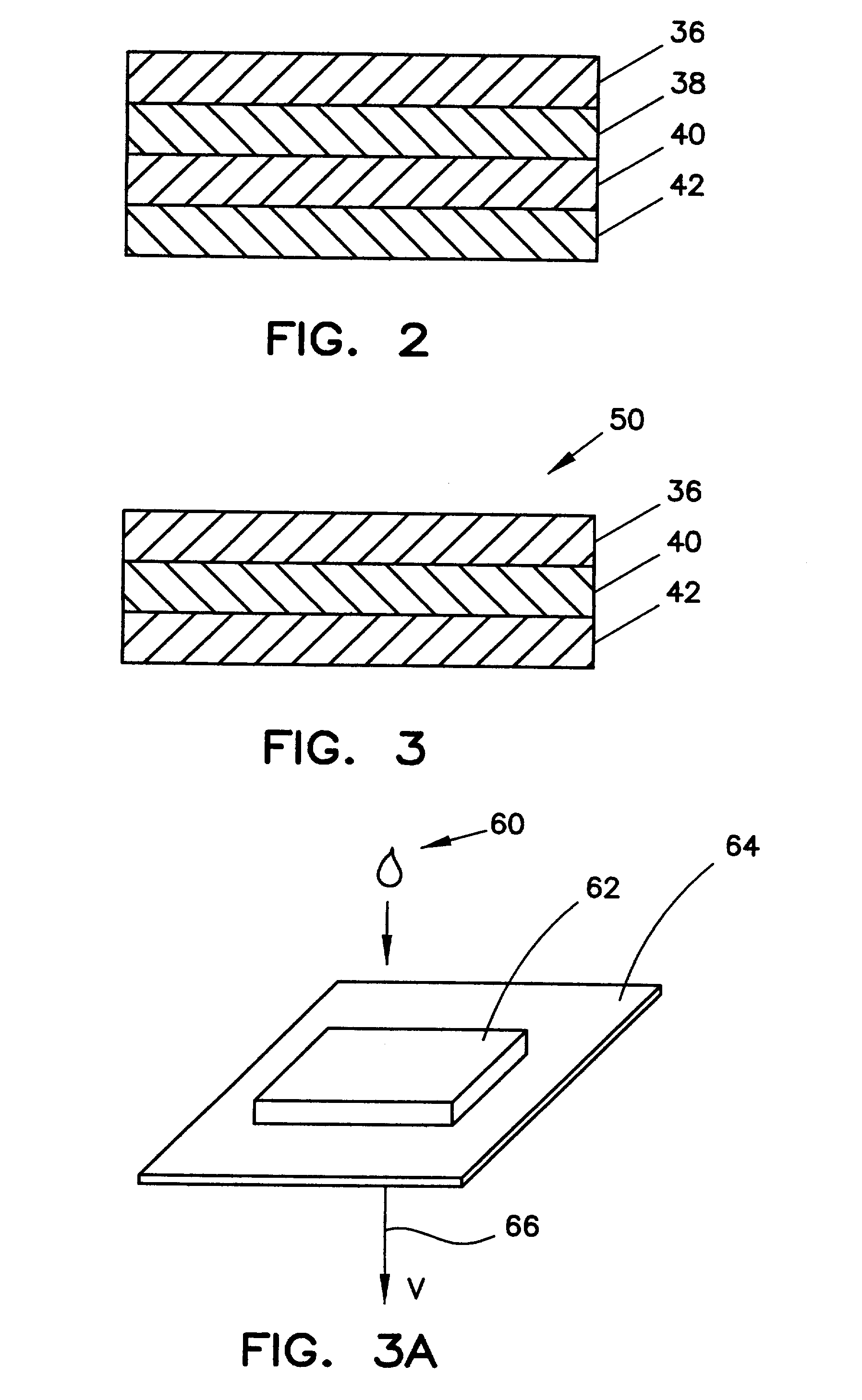
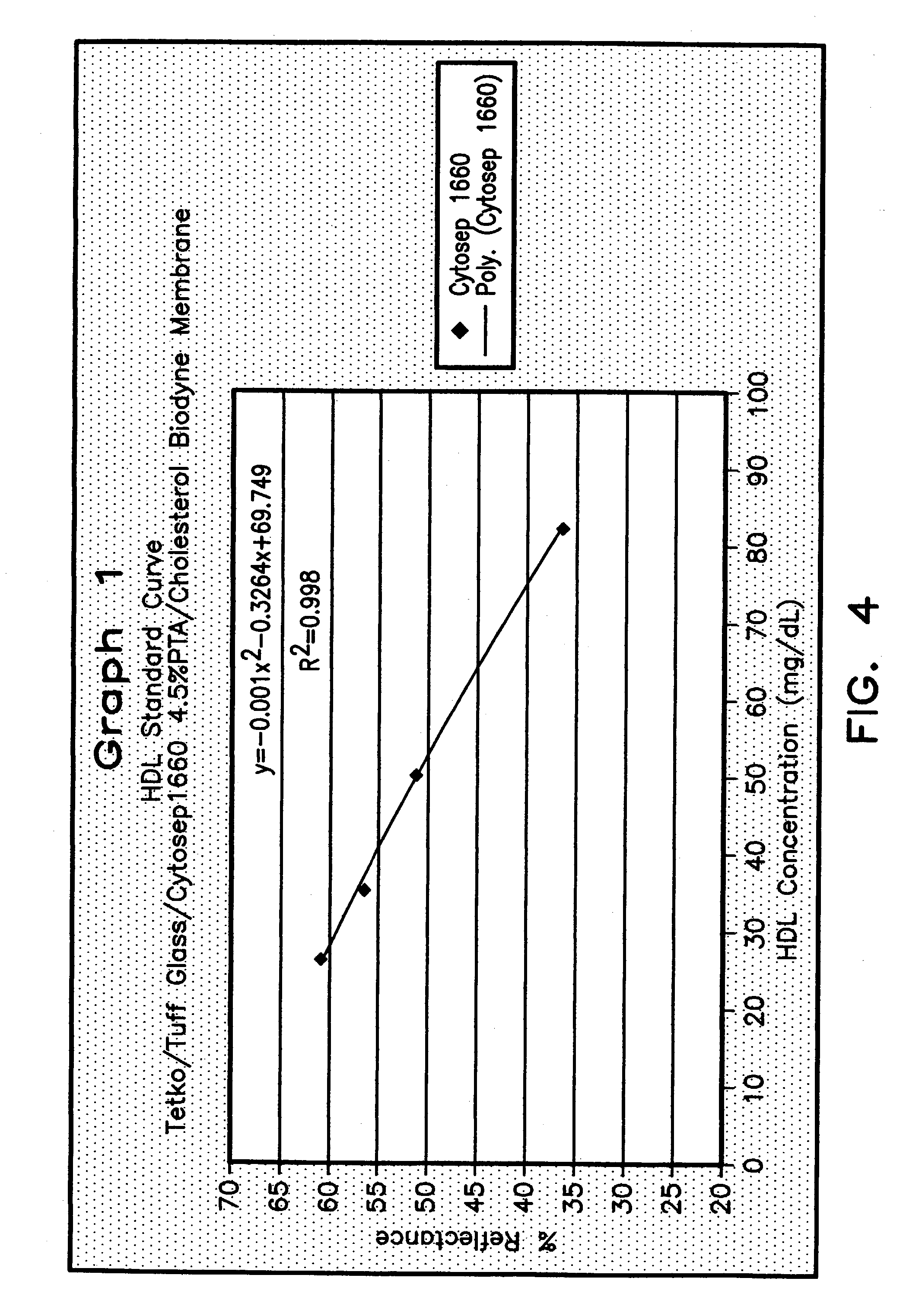
ActiveUS7087397B2Avoid flowEasy and fast assemblyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerCholesterol
A multilayer test strip and method of using the test strip for determining concentration of HDL cholesterol in a whole blood sample. The inventive test strip includes a two-stage blood separation mechanism, including a first glass fiber matrix which separates most of the blood cells and an adjacent, second matrix preferably also containing glass fibers that separates the remainder of the blood cells. The second layer also precipates and retains non-HDL cholesterol, thereby providing plasma that is substantially free of red blood cells and substantially free of non-HDL cholesterol to a reaction layer. Precipitation and retention on non-HDLs takes place by a vertical or dead-end filtration in a single layer. The reaction layer produces a color, the intensity of which is proportional to the concentration of HDL cholesterol in the blood sample which is applied to the test strip. Advantageously, the inventive test strip is a vertical flow device, which can be made more compact and operates more efficiently than a lateral flow device.
Owner:POLYMER TECH SYST
Method for connecting Cf/SiC composite material and Ni-based high-temperature alloy
The invention relates to a method for connecting a Cf / SiC composite material and an Ni-based high-temperature alloy, belonging to the field of heterologous material connecting. The technical process comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out reaction pretreatment on the welding surface of a composite material by utilizing alloying metal liquid; and (2) vacuum brazing connecting. The method is characterized in that the pre-reaction is carried out by applying the welding surface of the titanium-contained metal liquid and the composite material to form a welding surface with raised carbon fibers so as to improve the bonding strength of a subsequent brazing connected interface, and a stable reaction layer containing Ti is formed on the welding surface SiC of the composite material so as to prevent the graphitization reaction of SiC and Ni in the composite material in the subsequent brazing connecting process. A powder containing W and SiC is added to a brazing material, which can prevent the Ni element from diffusing to the composite material in the brazing connecting process, reduce the thermal stress of joints and strengthen the joints. The invention can be conveniently applied to practical work; and the joints have good high-temperature strength and gas tightness. The invention is also suitable for connecting carbon fiber reinforced SiC composite materials and other metals.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Graphene FET devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS9618474B2Faster data acquisitionImprove accuracyTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerSensor array
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS20170018626A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerSensor array
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com