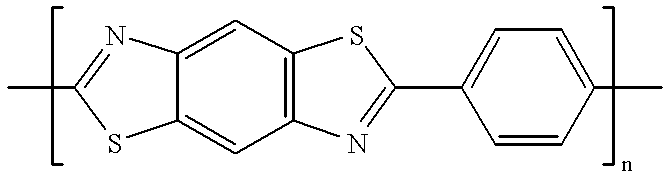
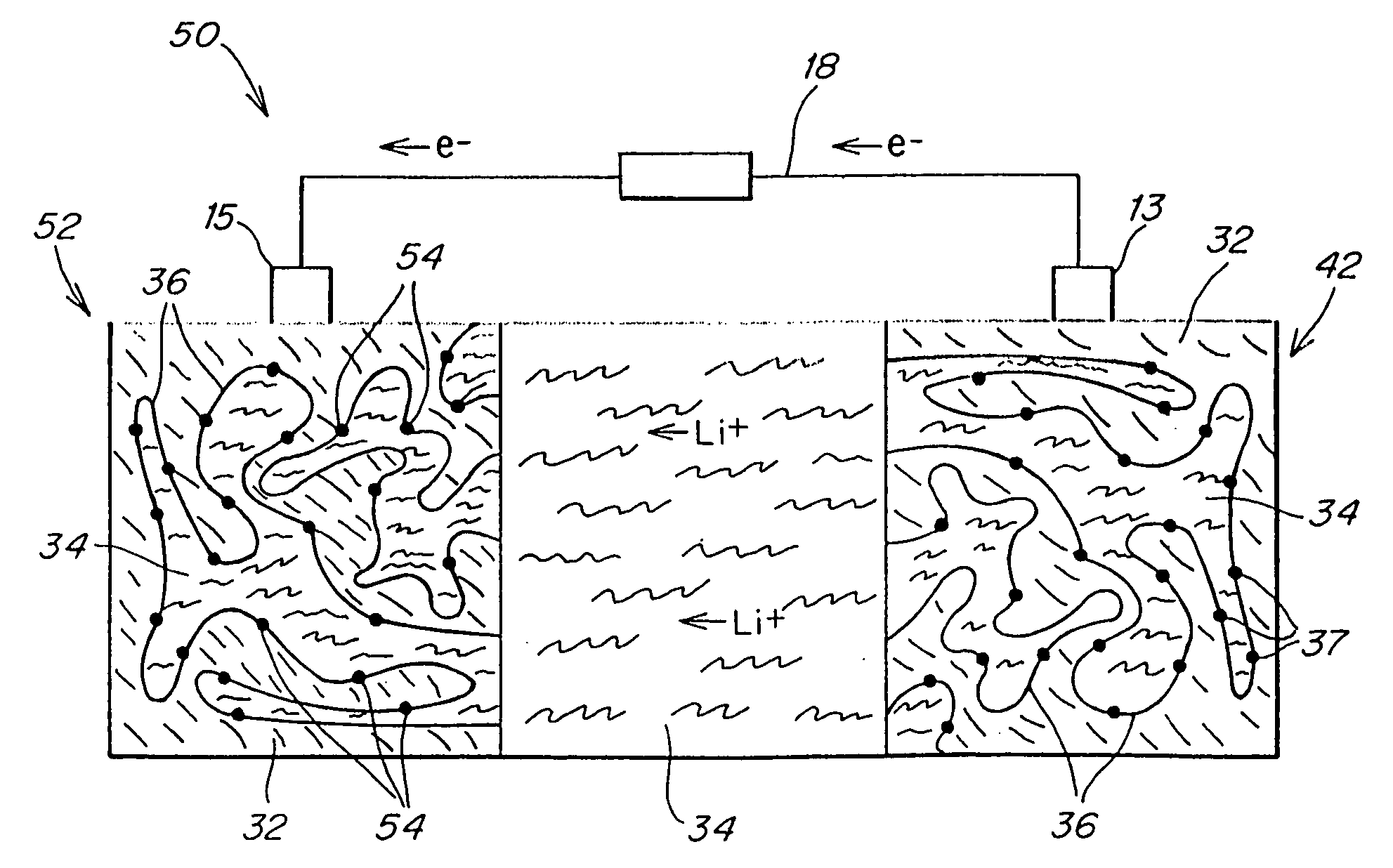
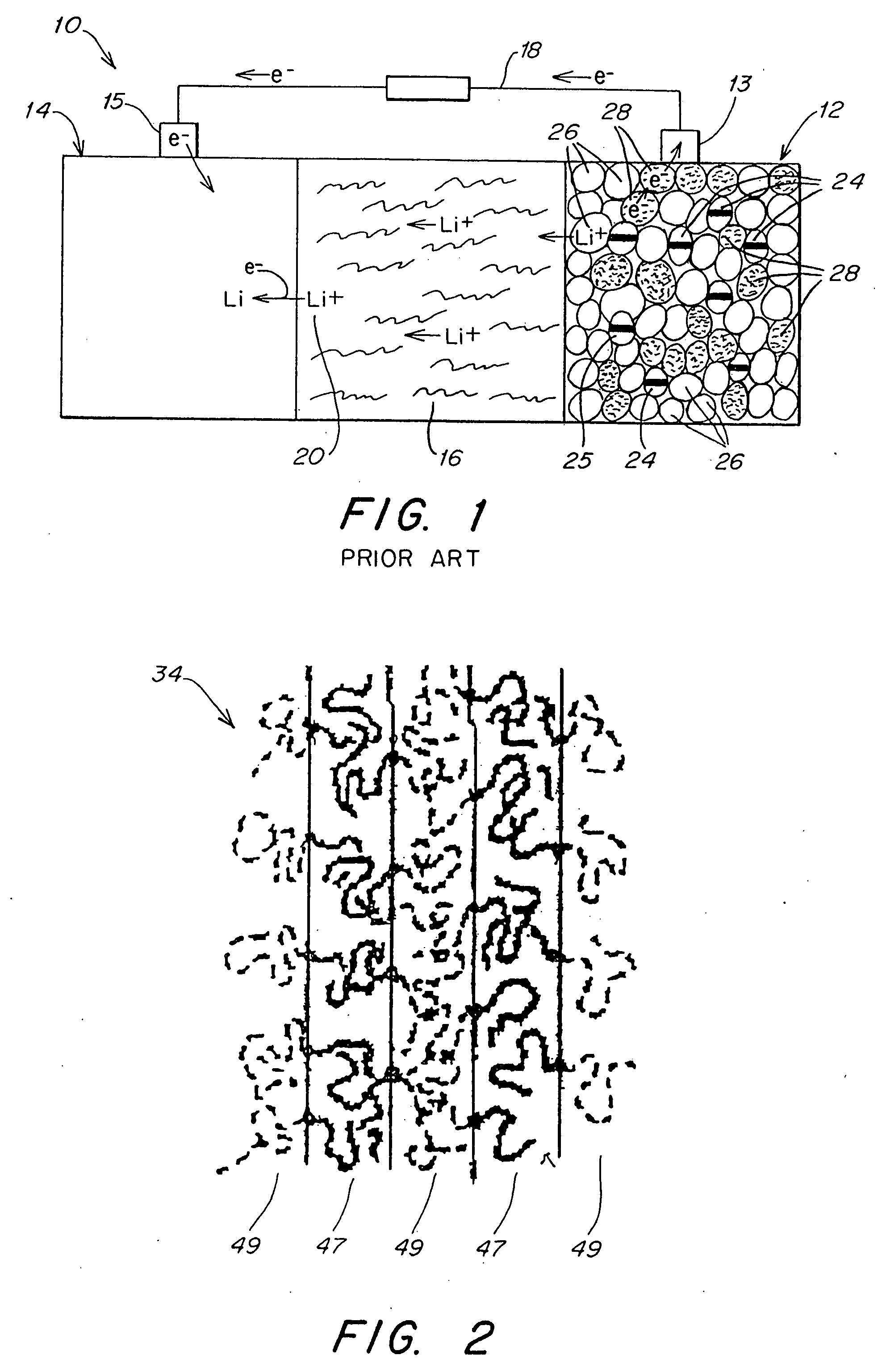
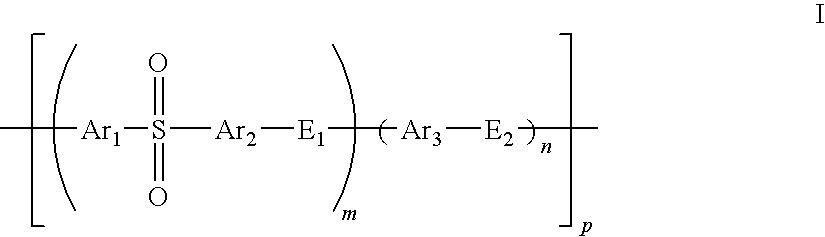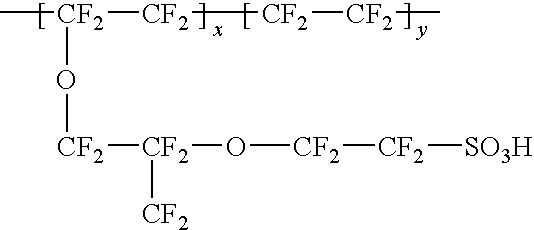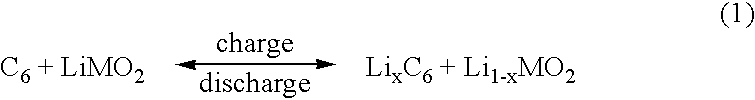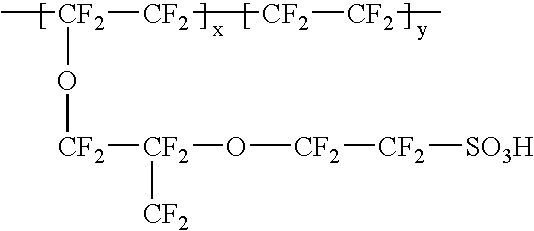Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5048 results about "Polymer electrolytes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
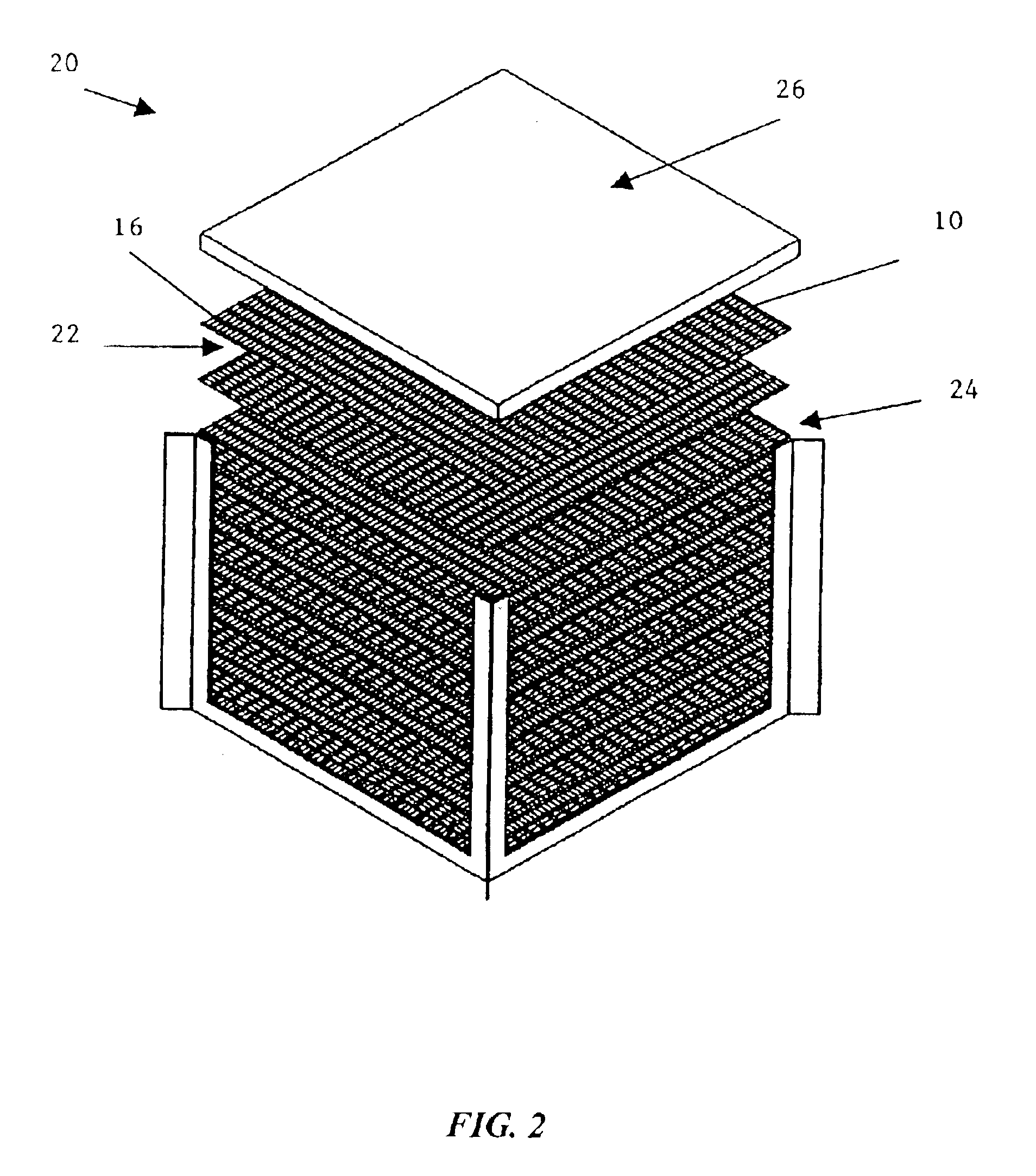
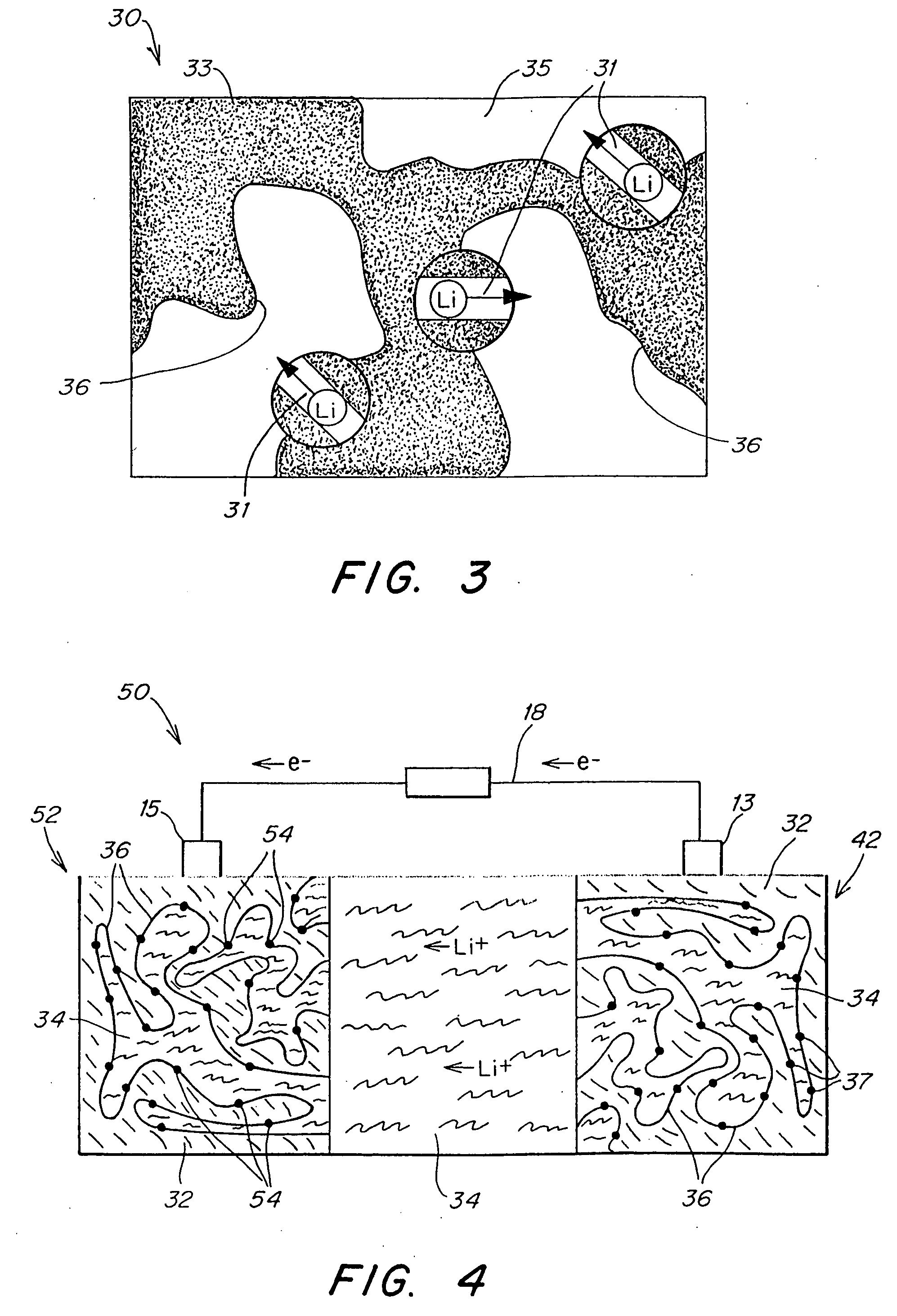
Composite solid polymer electrolyte membranes
InactiveUS7550216B2Improve performanceLow costElectrolyte holding meansMembranesPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
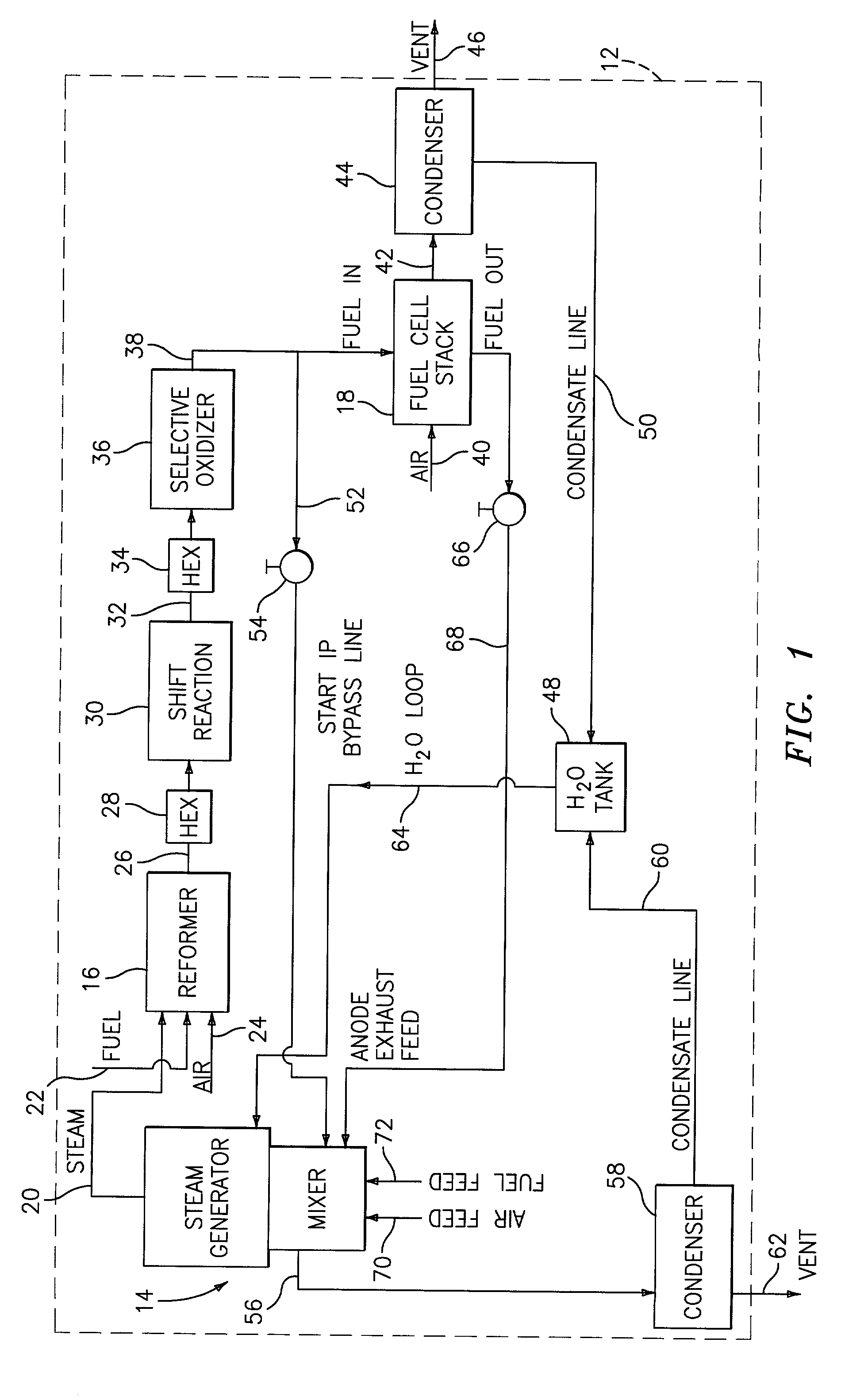
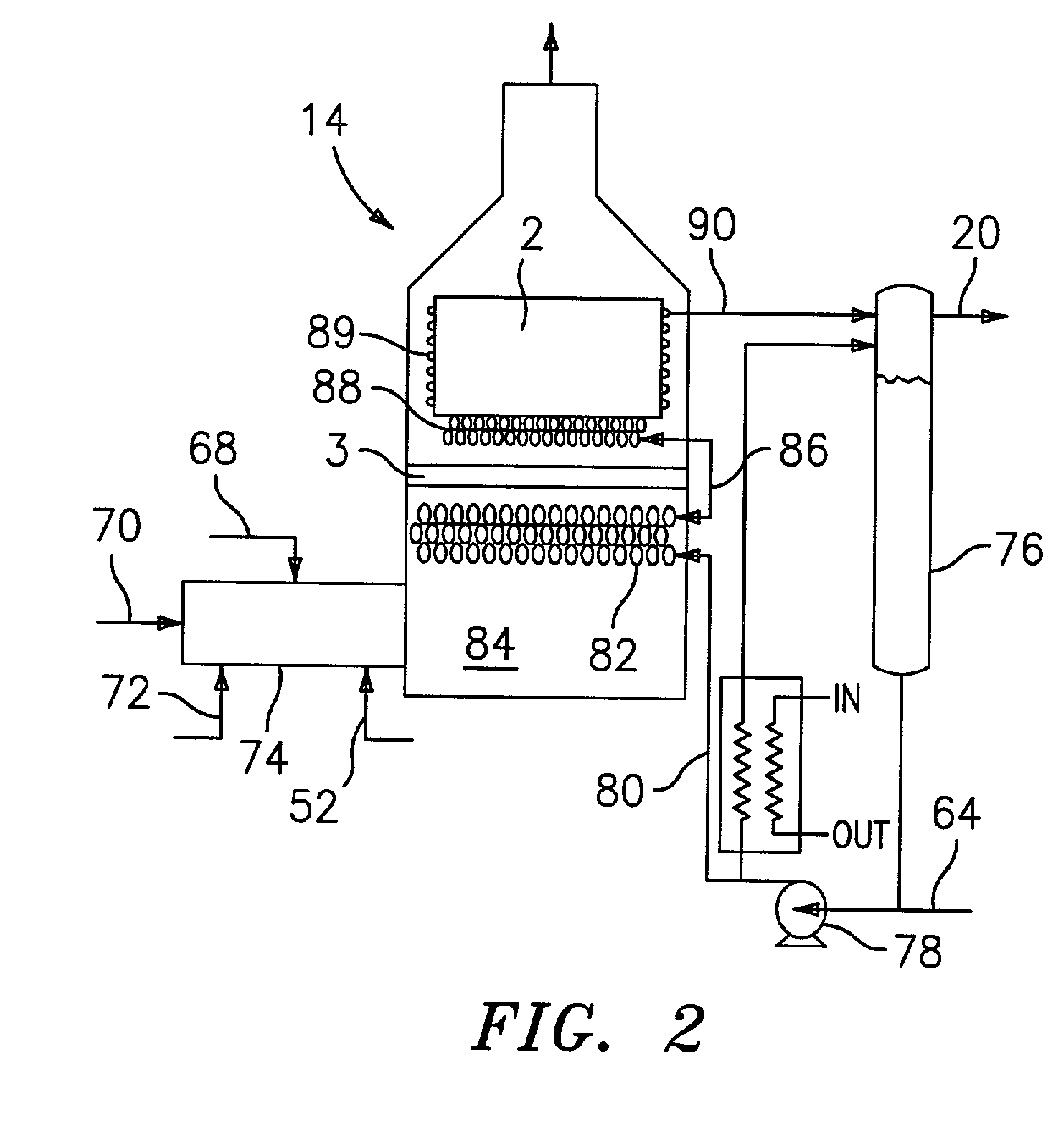
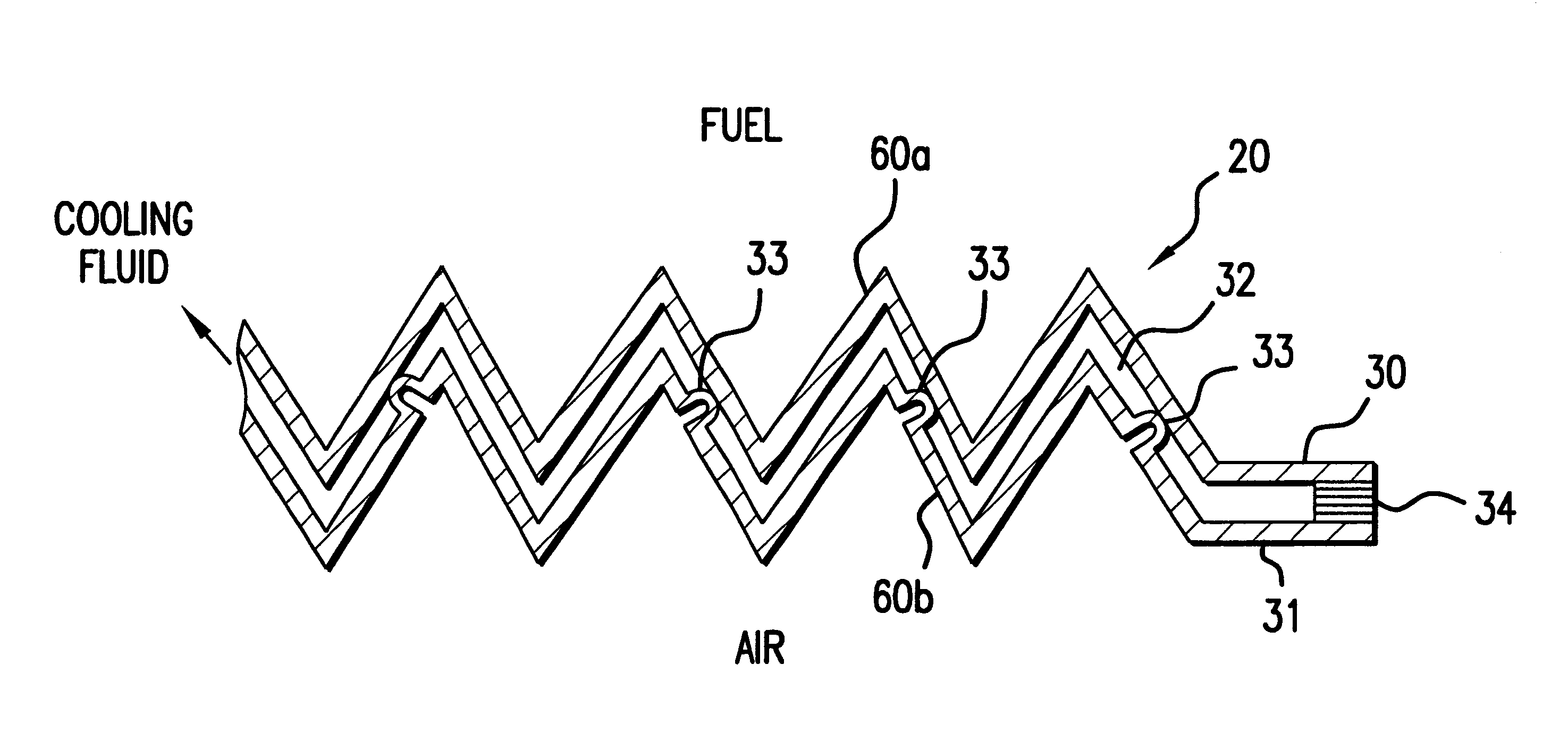
Steam generator for a PEM fuel cell power plant
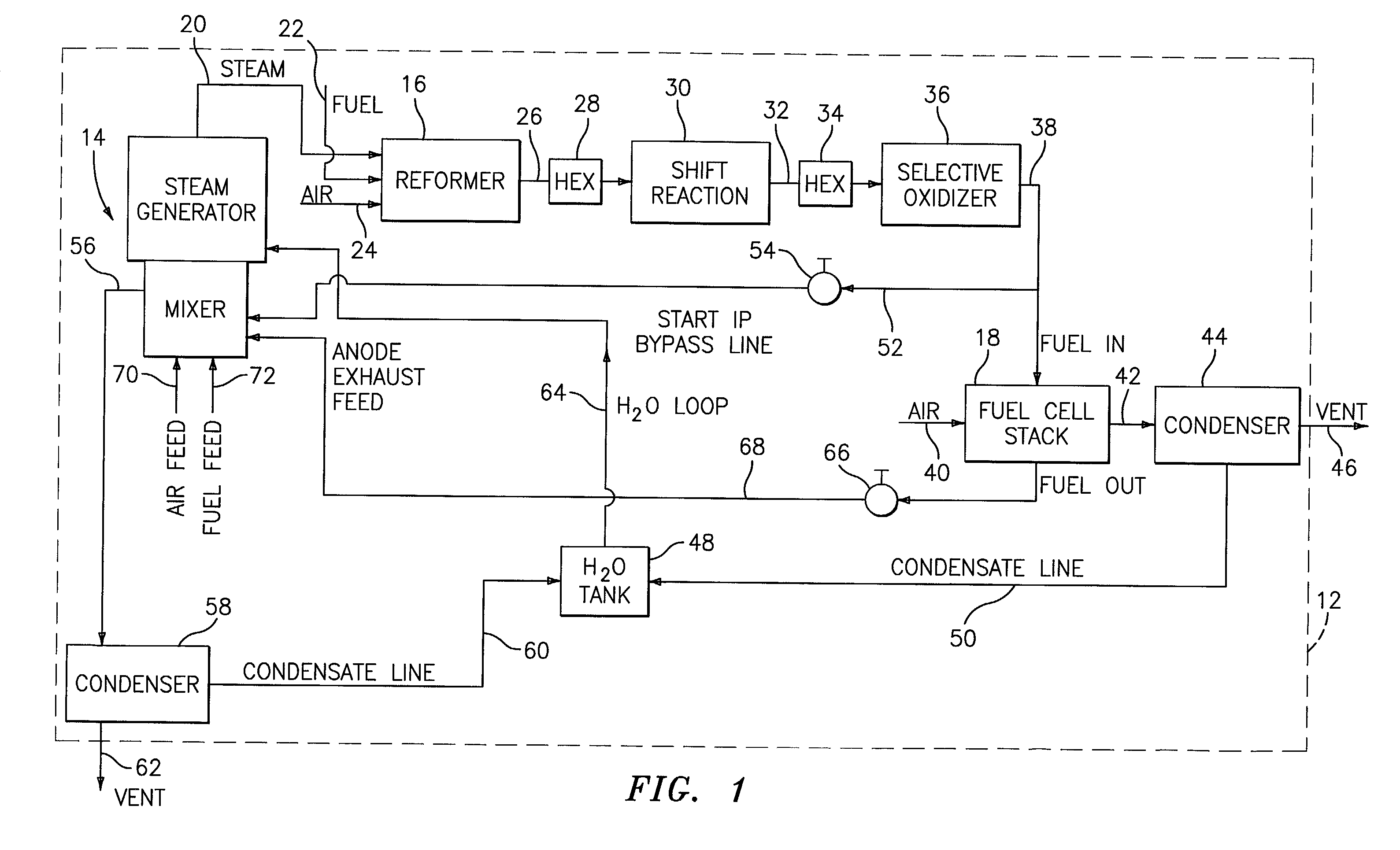
A burner assembly includes a catalyzed burner for combusting an anode exhaust stream from a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cell power plant. The catalysts coated onto the burner can be platinum, rhodium, or mixtures thereof. The burner includes open cells which are formed by a lattice, which cells communicate with each other throughout the entire catalyzed burner. Heat produced by combustion of hydrogen in the anode exhaust stream is used to produce steam for use in a steam reformer in the PEM fuel cell assembly. The catalyzed burner has a high surface area wherein about 70-90% of the volume of the burner is preferably open cells, and the burner has a low pressure drop of about two to three inches water from the anode exhaust stream inlet to the anode exhaust stream outlet . The burner assembly operates at essentially ambient pressure and at a temperature of up to about 1,700° F. (646° C.). The burner assembly can combust anode exhaust during normal operation of the fuel cell assembly. The burner assembly also includes an adjunct burner which can combust gasoline or anode bypass gas (the latter of which is a reformed fuel gas which is tapped off of the fuel cell stack fuel inlet line) during startup of the fuel cell power plant. Once start up of the fuel cell power plant is achieved, the burner assembly will need only combustion of the anode exhaust by the catalytic burner to produce steam for the reformer.
Owner:BALLARD POWER SYSTEMS
Composite solid polymer elecrolyte membranes
InactiveUS20020045085A1Optimize swellingOptimize fuel crossover resistanceElectrolyte holding meansFinal product manufacturePolymer electrolytesPolymer science
The present invention relates to composite solid polymer electrolyte membranes (SPEMs) which include a porous polymer substrate interpenetrated with an ion-conducting material. SPEMs of the present invention are useful in electrochemical applications, including fuel cells and electrodialysis.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
Method of manufacturing solid electrolyte battery
InactiveUS20050132562A1High trafficAvoid excessive power outputNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsFinal product manufacturePolymer electrolytesBattery cell
A method of manufacturing a solid electrolyte battery includes a step of thermally pressing a composite layer including a positive electrode ink layer, an electrolyte ink layer and a negative electrode ink layer that are formed by coating a positive electrode ink, an electrolyte ink and a negative electrode ink. Further, the positive electrode ink, the electrolyte ink and the negative electrode ink contain a polymer electrolyte. By this method, it is possible to improve the flow of ions across respective interlayers of a positive electrode active material layer, a solid electrolyte layer and a negative electrode active material layer.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
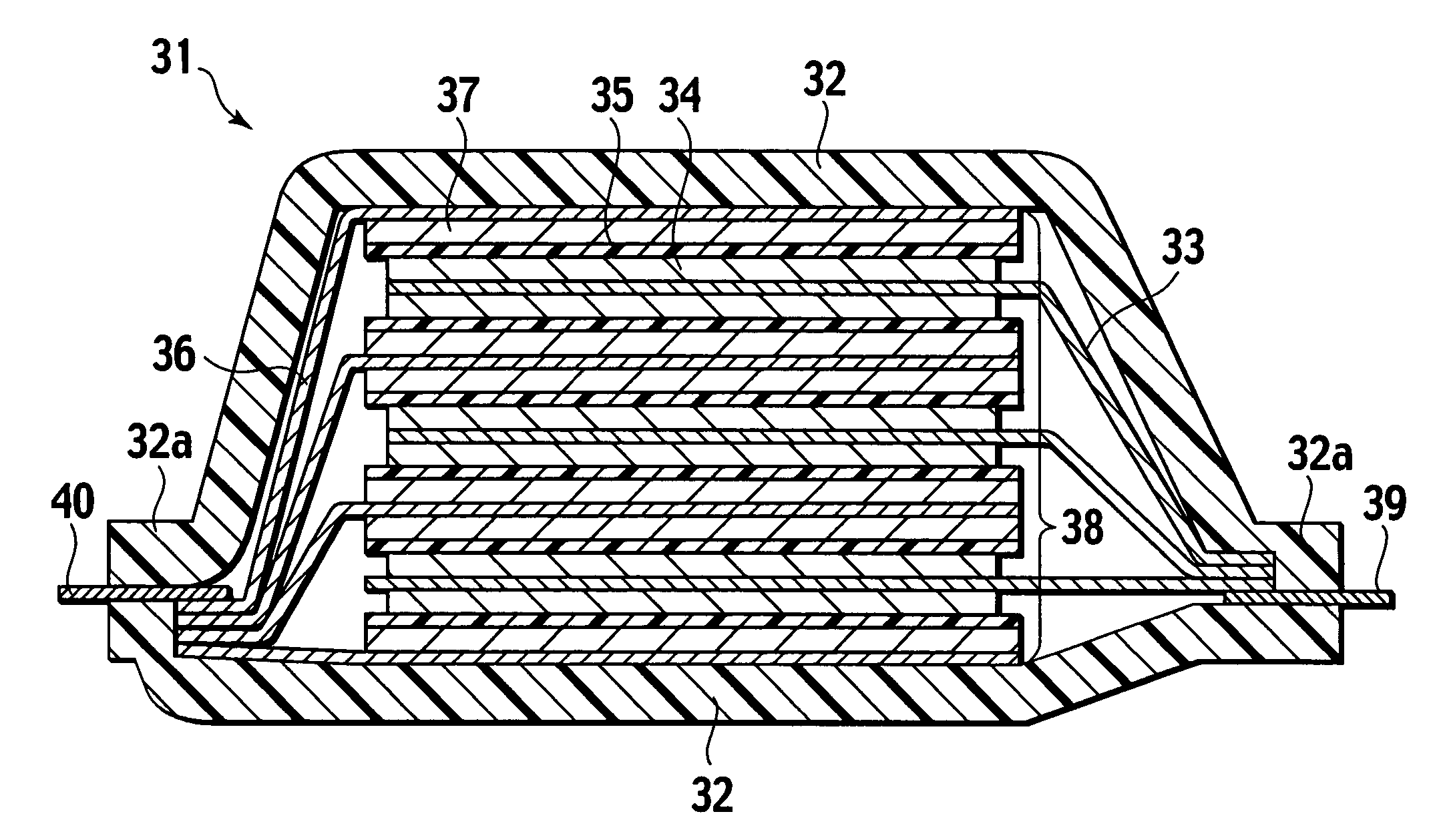
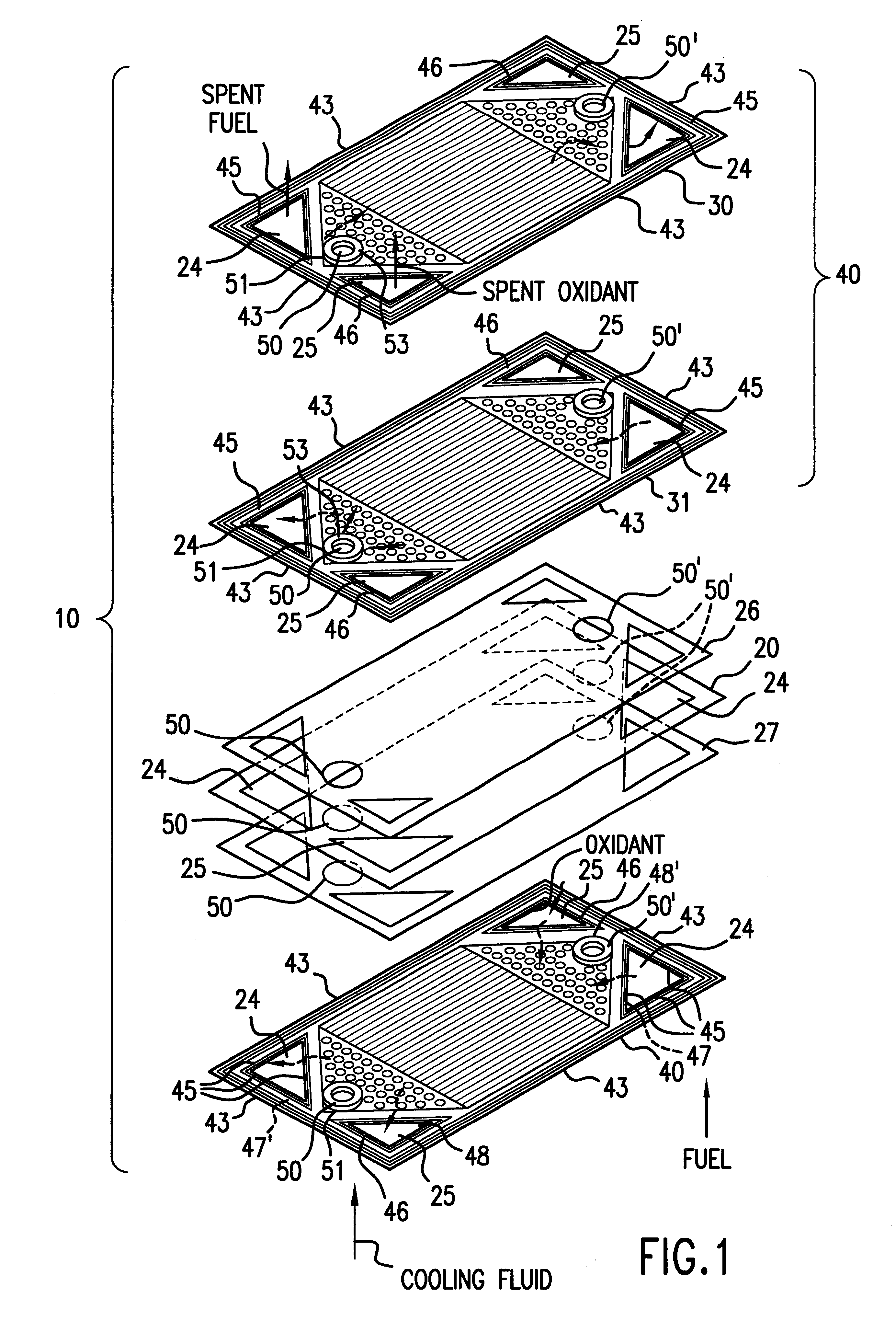
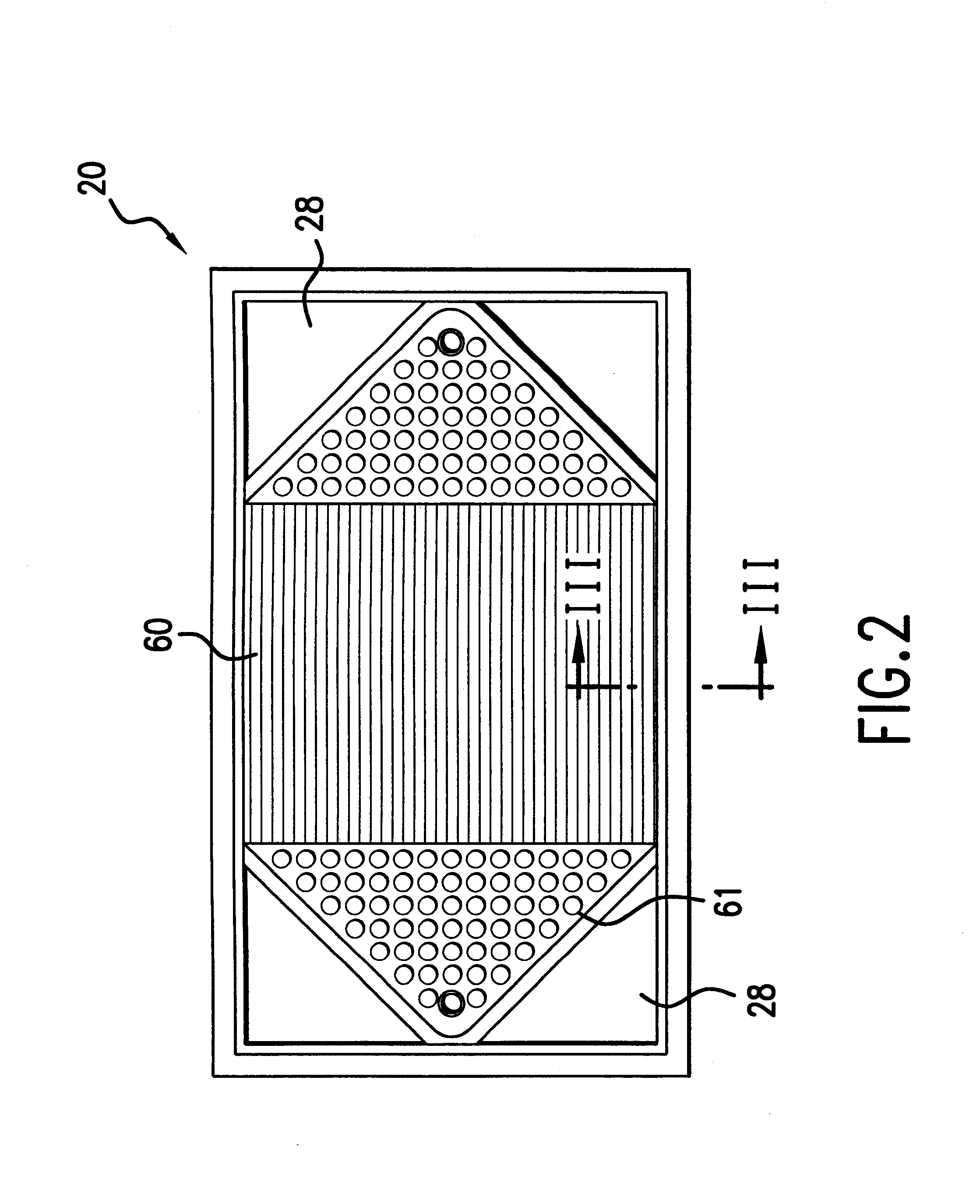
Sheet metal bipolar plate design for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
InactiveUS6261710B1Compact designIncrease the number ofSolid electrolytesFuel cells groupingPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
A separator plate for a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell stack constructed of at least two coextensive sheet metal elements shaped to promote the distribution of reactant gases to the electrodes of the fuel cell units of the fuel cell stack. The coextensive sheet metal elements are nestled together and form a coolant flow space therebetween.
Owner:INST OF GAS TECH
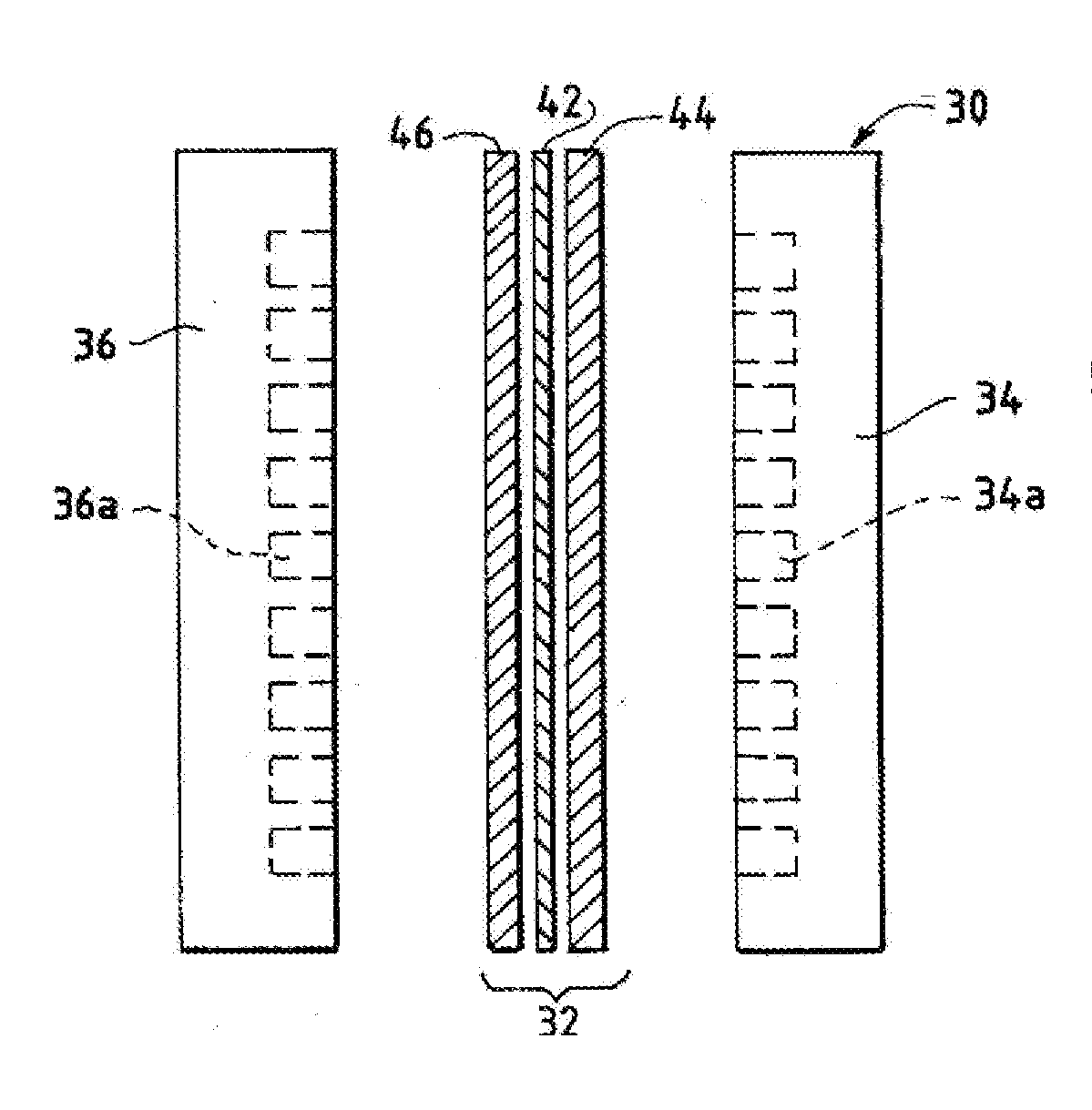
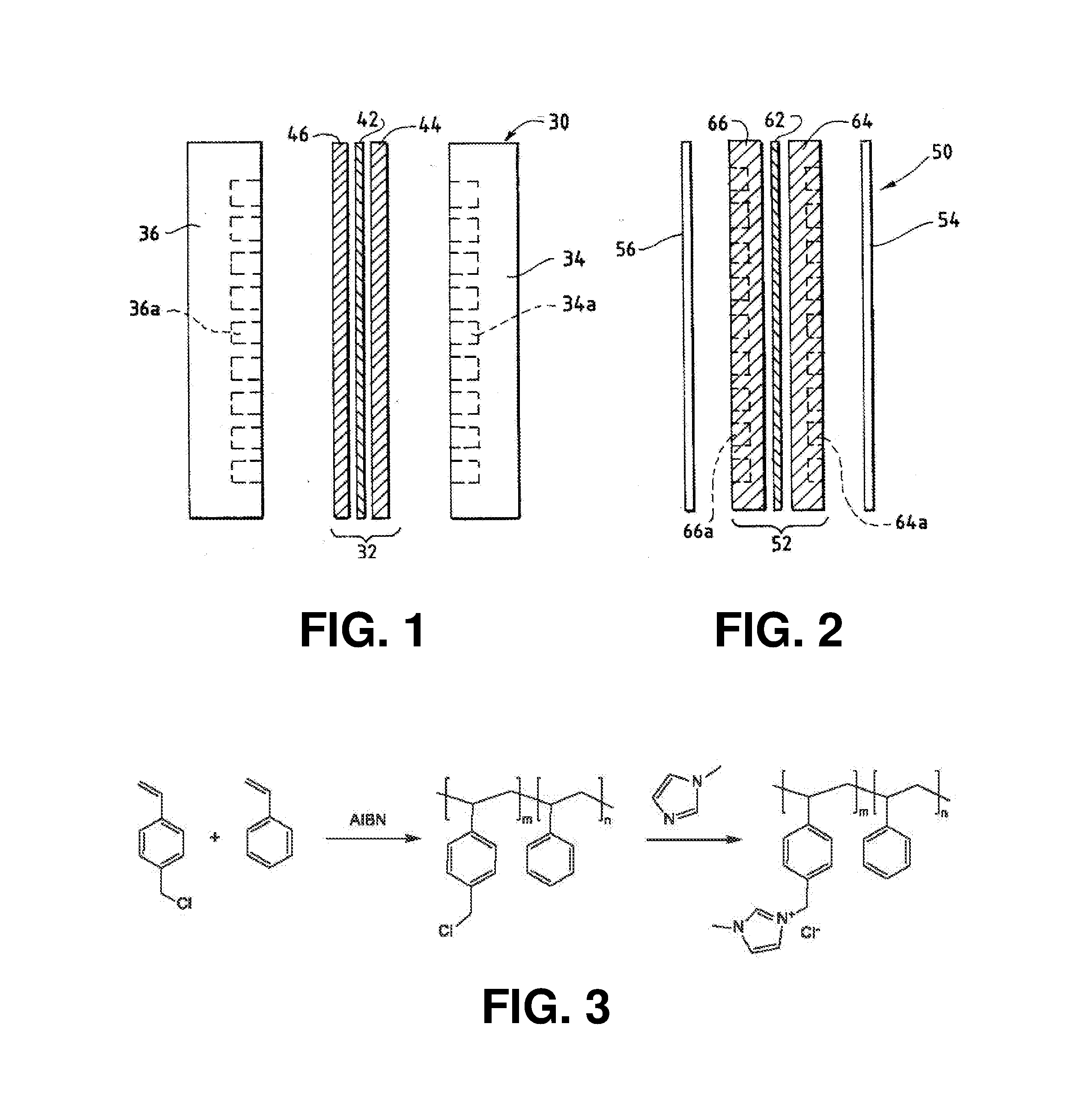
Crosslinked polymer electrolyte membranes for heat and moisture exchange devices
InactiveUS6841601B2Improve permeabilityLow costSpace heating and ventilationIndirect heat exchangersEnergy recoveryMoisture
A unitary humidity exchange cell (HUX) is dislosed that includes at least one composite membrane, disposed between at least one first chamber for flow of the first fluid therethrough and at least one second chamber for flow of the second fluid therethrough. The composite membrane include an at least partially sulfonated humidity-conducting polymer comprising residues derived from at least one arylvinyl monomer; and a reinforcing substrate bonded thereto. The product finds utility in a variety of physical and chemical processes and products whereby moisture or other highly polar liquid or gas transfer, exchange removal or delivery is important. A notable application is the Membrane Energy Recovery Ventilator (MERV) in which both heat, ions and moisture is transferred between two air streams, one intake and one exhaust, from an air-conditioned building.
Owner:TANGREDI PATRICIA
Structurally embedded intelligent power unit
InactiveUS7150938B2Increase capacityImprove power performanceBatteries circuit arrangementsCell temperature controlElectric power systemEngineering
An electrical power system for a spacecraft or other vehicle or structure comprising a structural member containing an integrated solid-state power source is disclosed. The power source includes a solar cell system and an energy storage system that are combined into a single unit or package, and in certain embodiments, are configured into the shape of a flexible aerobot balloon or a rigid nanosat surface panel. The power components of a preferred lightweight power unit, include thinly layered photovoltaic cells, a rechargeable lithium solid polymer electrolyte battery, a capacitor, electronics and thermal management capability.
Owner:LITHIUM POWER TECH
Lithium ion polymer electrolytes
InactiveUS6413676B1Prevent kinkingAvoid deformationElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufacturePorosityCross-link
A dimensionally stable, highly resilient, hybrid copolymer solid-solution electrolyte-retention film for use in a lithium ion battery in one preferred embodiment has a predominantly amorphous structure and mechanical strength despite contact with liquid solvent electrolyte. The film is a thinned (stretched), cast film of a homogeneous blend of two or more polymers, one of which is selected for its pronounced solvent retention properties. A very high surface area inorganic filler dispersed in the blend during formation thereof serves to increase the porosity of the film and thereby enhance electrolyte retention. The film is soaked in a solution of liquid polymer with liquid organic solvent electrolyte and lithium salt, for absorption thereof. Use of a cross-linked liquid polymer enhances trapping of molecules of the electrolyte into pores of the film. The electrolyte film is sandwiched between flexible active anode and cathode layers to form the lithium ion battery. Novel methods are provided for forming the electrodes, the polymer substrate, and other elements of the battery.
Owner:LITHIUM POWER TECH
Anode catalyst for fuel cells with polymer electrolyte membranes
A platinum / ruthenium alloy catalyst that includes finely dispersed alloy particles on a powdery, electrically conductive carrier material. The catalyst is particularly resistant to carbon monoxide poisoning when the alloy particles display mean crystallite sizes of 0.5 to less than 2 nm.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Polymer electrolyte, intercalation compounds and electrodes for batteries
Solid battery components are provided. A block copolymeric electrolyte is non-crosslinked and non-glassy through the entire range of typical battery service temperatures, that is, through the entire range of at least from about 0° C. to about 70° C. The chains of which the copolymer is made each include at least one ionically-conductive block and at least one second block immiscible with the ionically-conductive block. The chains form an amorphous association and are arranged in an ordered nanostructure including a continuous matrix of amorphous ionically-conductive domains and amorphous second domains that are immiscible with the ionically-conductive domains. A compound is provided that has a formula of LixMyNzO2. M and N are each metal atoms or a main group elements, and x, y and z are each numbers from about 0 to about 1. y and z are chosen such that a formal charge on the MyNz portion of the compound is (4-x). In certain embodiments, these compounds are used in the cathodes of rechargeable batteries. The present invention also includes methods of predicting the potential utility of metal dichalgogenide compounds for use in lithium intercalation compounds. It also provides methods for processing lithium intercalation oxides with the structure and compositional homogeneity necessary to realize the increased formation energies of said compounds. An article is made of a dimensionally-stable, interpenetrating microstructure of a first phase including a first component and a second phase, immiscible with the first phase, including a second component. The first and second phases define interphase boundaries between them, and at least one particle is positioned between a first phase and a second phase at an interphase boundary. When the first and second phases are electronically-conductive and ionically-conductive polymers, respectively, and the particles are ion host particles, the arrangement is an electrode of a battery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Structurally embedded intelligent power unit
InactiveUS20030038610A1Batteries circuit arrangementsCell temperature controlElectric power systemEngineering
An electrical power system for a spacecraft or other vehicle or structure comprising a structural member containing an integrated solid-state power source is disclosed. The power source includes a solar cell system and an energy storage system that are combined into a single unit or package, and in certain embodiments, are configured into the shape of a flexible aerobot balloon or a rigid nanosat surface panel. The power components of a preferred lightweight power unit, include thinly layered photovoltaic cells, a rechargeable lithium solid polymer electrolyte battery, a capacitor, electronics and thermal management capability.
Owner:LITHIUM POWER TECH
Ultra thin solid state lithium batteries and process of preparing same
InactiveUS6030421ASimple manufacturing processEasy to operateElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureMetallic lithiumConductive materials
There is provided a mother-battery containing at least the following films: an anode of metallic lithium or sodium, a polymer electrolyte which is conductive towards the alkaline ions of the anode and also acts as a separator between the electrodes, and a composite cathode consisting of a compound which is reducible to lithium or sodium, an additive of electronic conduction and a polymer electrolyte binder. The mother battery also includes an electronically conductive thin coating on the external face of the anode and, possibly of the cathode, in which the conductive material is chemically inert towards the electrode material and which also serves to establish permanent electrical contacts on the external faces. The laminated mother-battery of larger surface area and at least partially charged is thereafter subjected to a sharp mechanical cutting out to give thin polymer electrolyte batteries with lithium or sodium anode. The thus cut out batteries preserve substantially their voltage after mechanical cutting out which is recovered by a mechanism of self-healing.
Owner:BATHIUM CANADA
Solid polymer electrolyte and process for making same
ActiveUS20070072036A1Enhanced release propertiesIon-exchanger regenerationFinal product manufactureFiberIon exchange
A solid polymer electrolyte membrane having a first surface and a second surface opposite the first surface, where the solid polymer electrolyte membrane has a failure force greater than about 115 grams and comprises a composite membrane consisting essentially of (a) at least one expanded PTFE membrane having a porous microstructure of polymeric fibrils, and (b) at least one ion exchange material impregnated throughout the porous microstructure of the expanded PTFE membrane so as to render an interior volume of the expanded PTFE membrane substantially occlusive; (c) at least one substantially occlusive, electronically insulating first composite layer interposed between the expanded PTFE membrane and the first surface, the first composite layer comprising a plurality of first carbon particles supporting a catalyst comprising platinum and an ion exchange material, wherein a plurality of the first carbon particles has a particle size less than about 75 nm, or less than about 50 nm, or less than about 25 nm.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Fuel cell
InactiveUS6083638AEfficient humidificationSolid electrolytesFuel cells groupingPorous substratePolymer electrolytes
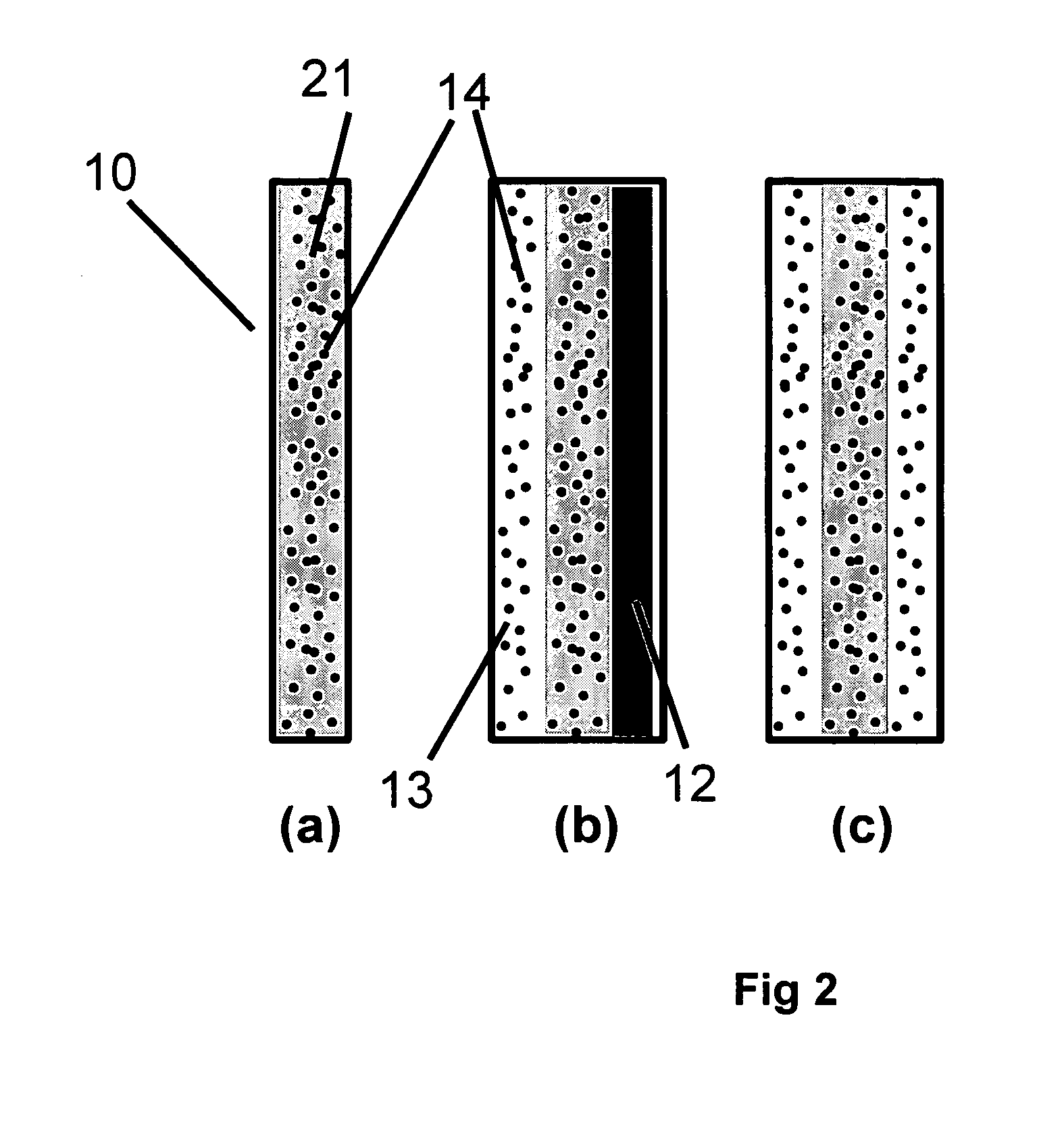
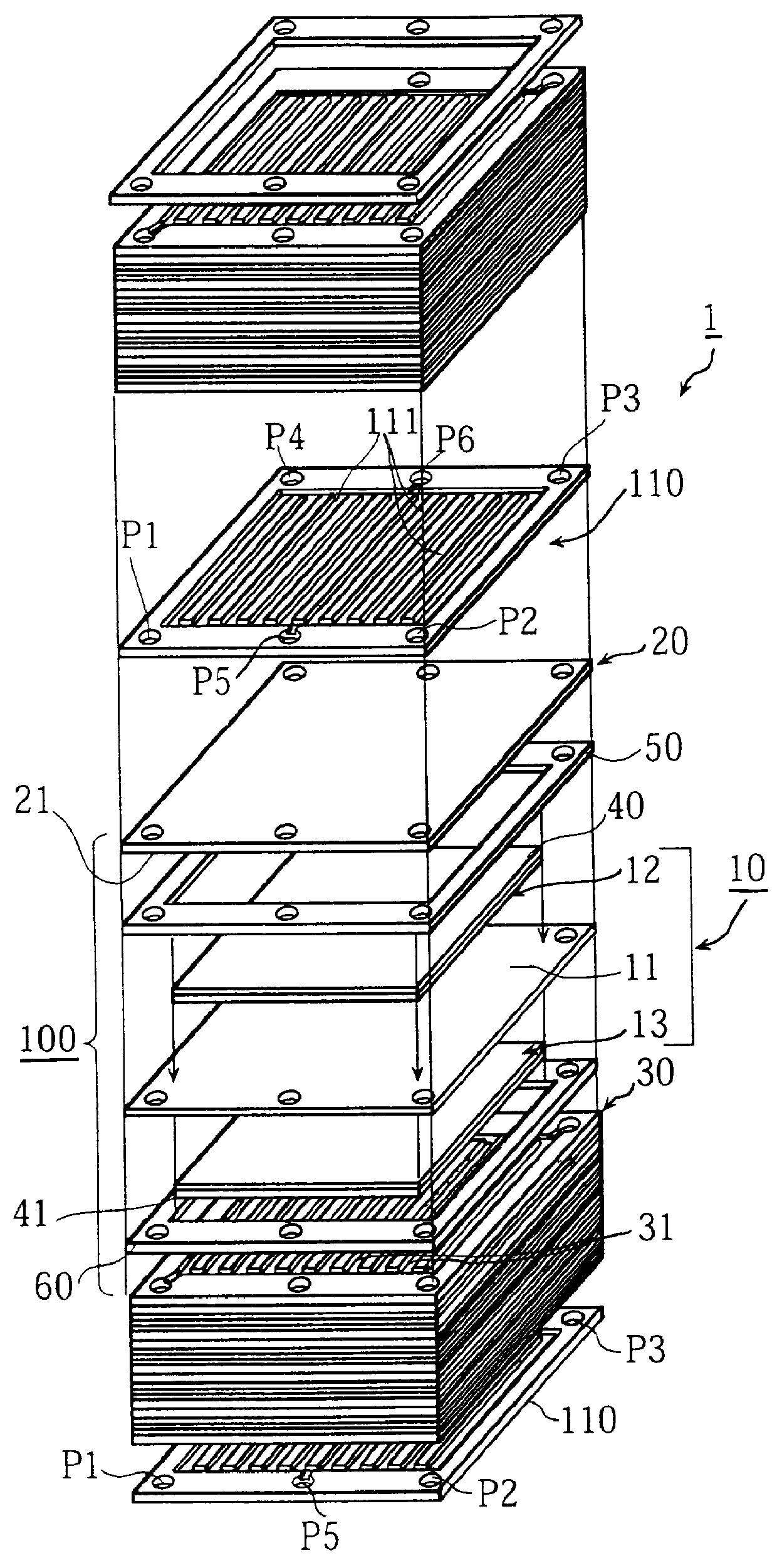
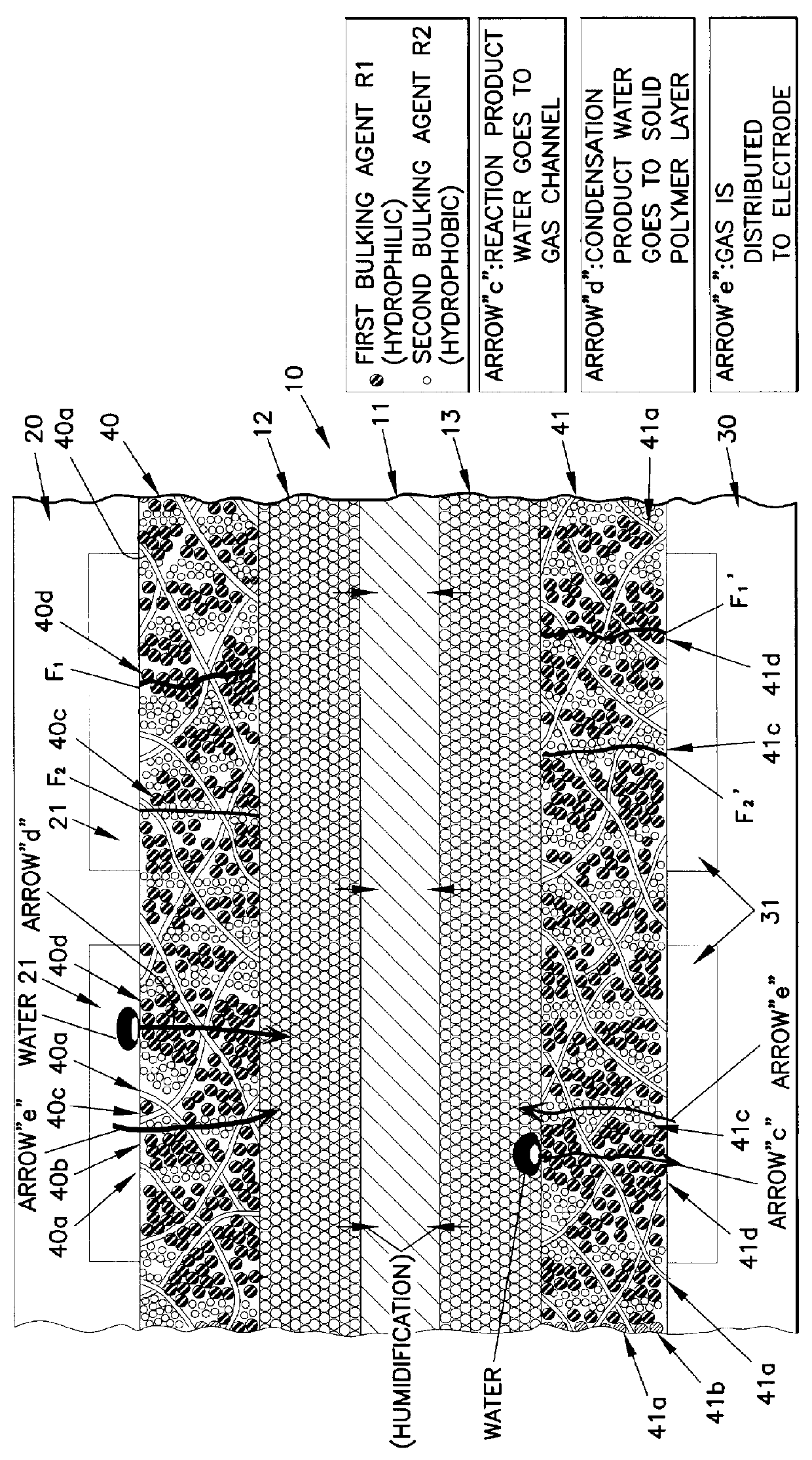
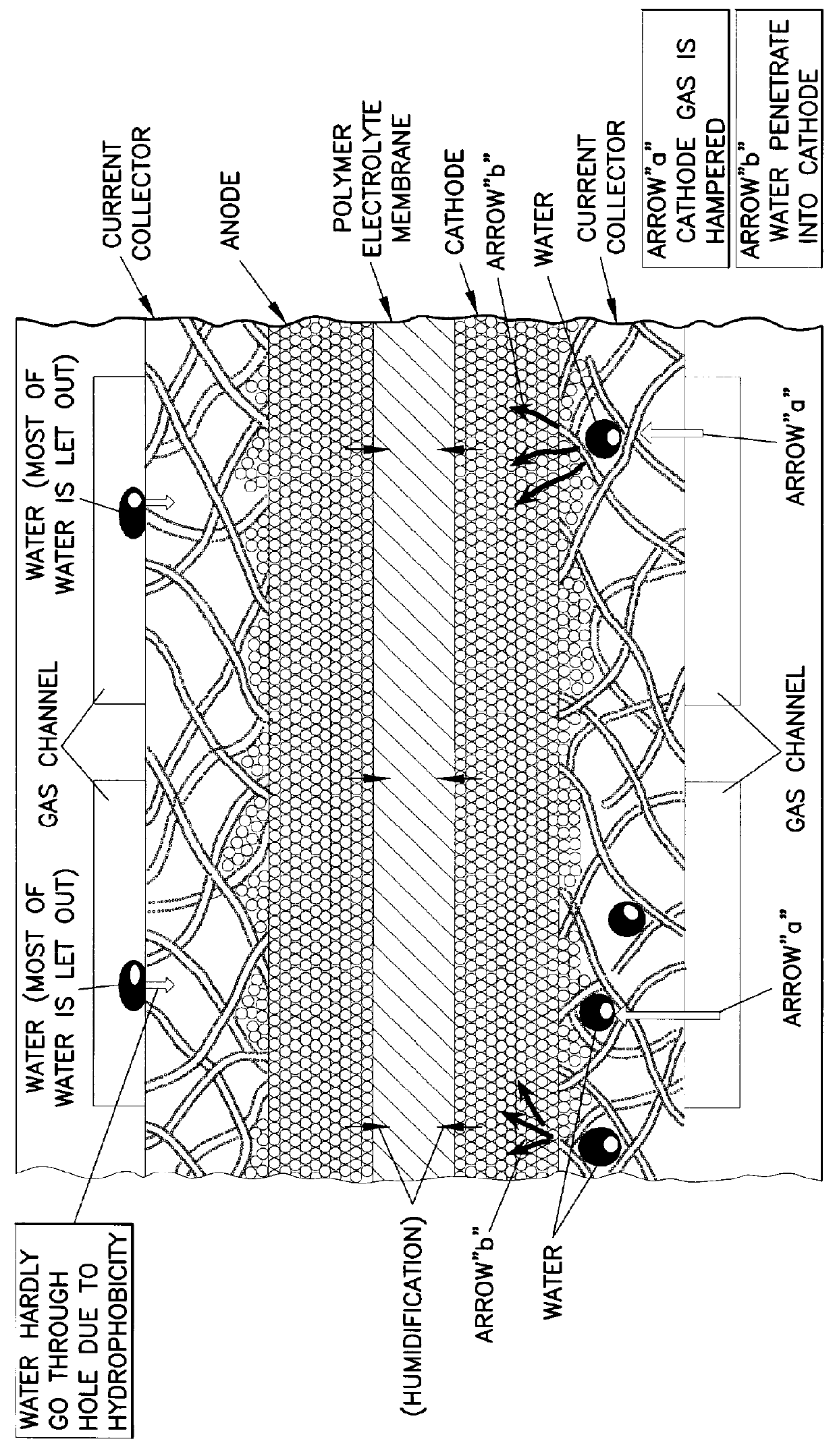
A current collector includes a thin porous substrate and a hydrophilic material, where the hydrophilic material is provided to holes of the thin porous substrate or surfaces of skeleton elements of the porous substrate so that hydrophilic areas formed by the hydrophilic material successively pass through the thin porous substrate between both surfaces of the thin porous substrate. In the current collector, water is let out through the hydrophilic areas and does not stay on an interface between an electrode and the current collector so that reaction gas is not hampered and is supplied, unlike a conventional current collector. When the current collector is applied to a polymer electrolyte fuel cell, water is supplied with reliability through the hydrophilic areas to a polymer electrolyte membrane so that the polymer electrolyte membrane is effectively humidified. The current collector applied to a cathode achieves a profound effect because reaction product water tends to stay around a cathode of any types of fuel cells. The current collector also includes gas flow paths which are surrounded by particles of a hydrophobic material and pass through the thin porous substrate between both surfaces of the thin porous substrate. As a result, gas permeability of the current collector is maintained with reliability.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
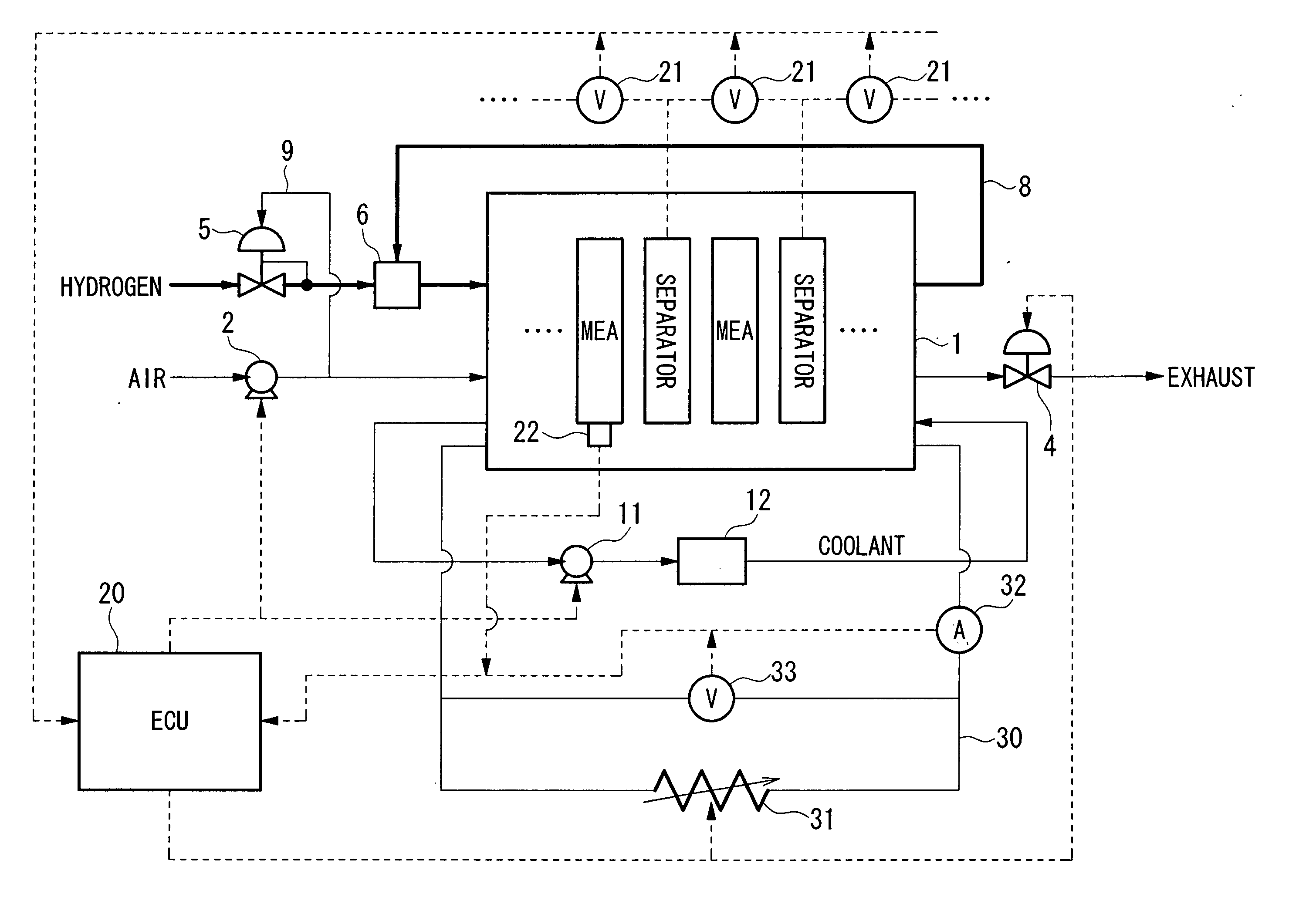
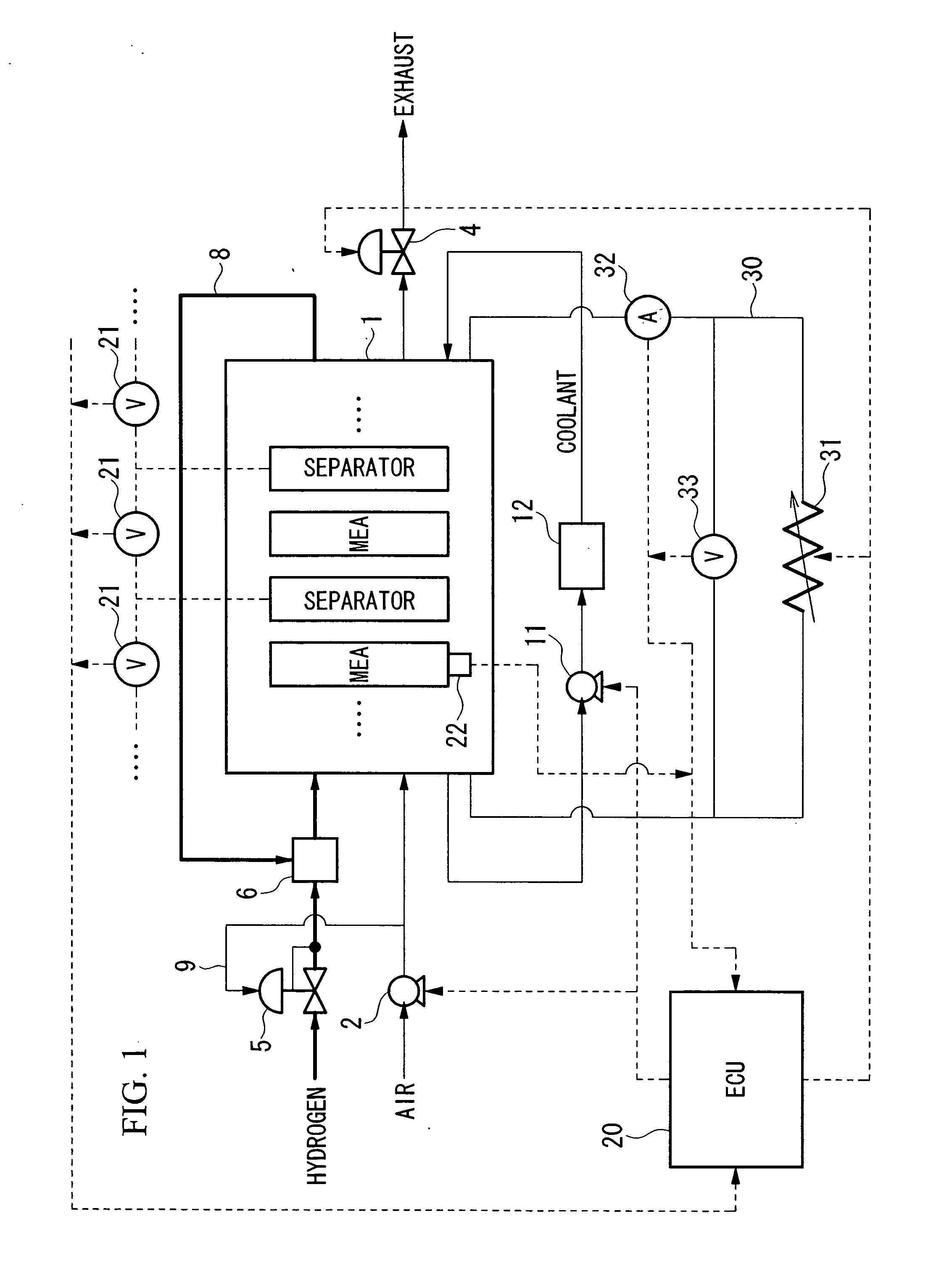
Method and system for starting up fuel cell stack at subzero temperatures, and method of designing fuel cell stack
InactiveUS20050053810A1Shorten warm-up timeSmall heat capacityFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
A method of starting up at a subzero temperature a solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell stack that is formed by stacking a plurality of layers of separators and membrane electrode assemblies having a solid polymer electrolyte membrane and electrodes. The method includes a step of using a solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell stack in which the separators are made from metal and have a cross-sectional waveform structure, and a space that is formed between at least a portion of the separators and separators that are placed adjacent to this portion of the separators is used as a coolant flow passage.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Manufacturing method of all solid state power lithium ion battery
ActiveCN108232318AReduce interface resistanceImprove securitySolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureHigh energyAdhesive
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of an all solid state power lithium ion battery. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of dissolving an anode active material, a conductive agent,an adhesive and a polymer electrolyte in a solvent, so as to prepare an anode sizing agent, applying the anode sizing agent to an anode current collector, performing thermal treatment and rolling treatment so as to obtain an anode piece; then dissolving a cathode material, a conductive agent, an adhesive and a polymer electrolyte in a solvent, so as to prepare a cathode sizing agent, applying thecathode sizing agent to a cathode current collector, and performing thermal treatment and rolling treatment so as to obtain a cathode piece; dissolving a polymer electrolyte, a filler and lithium salt in a solvent, so as to prepare an electrolyte solution; applying the electrolyte solution to the surface of the anode piece or the cathode piece, and performing thermal treatment to obtain an anodepiece or a cathode piece with an electrolyte layer; and finally, assembling the anode piece and the cathode piece in a winding or superposing manner, so as to prepare the all solid state lithium ion battery. The all solid state lithium battery prepared by the method has the advantages of lower interface resistance, higher energy density, high security and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI COAL & CHEM TECH INST
Process for producing a modified electrolyte and the modified electrolyte
InactiveUS20020160272A1Increased durabilityIncrease resistanceSemi-permeable membranesSolid electrolytesPolymer electrolytesSide chain
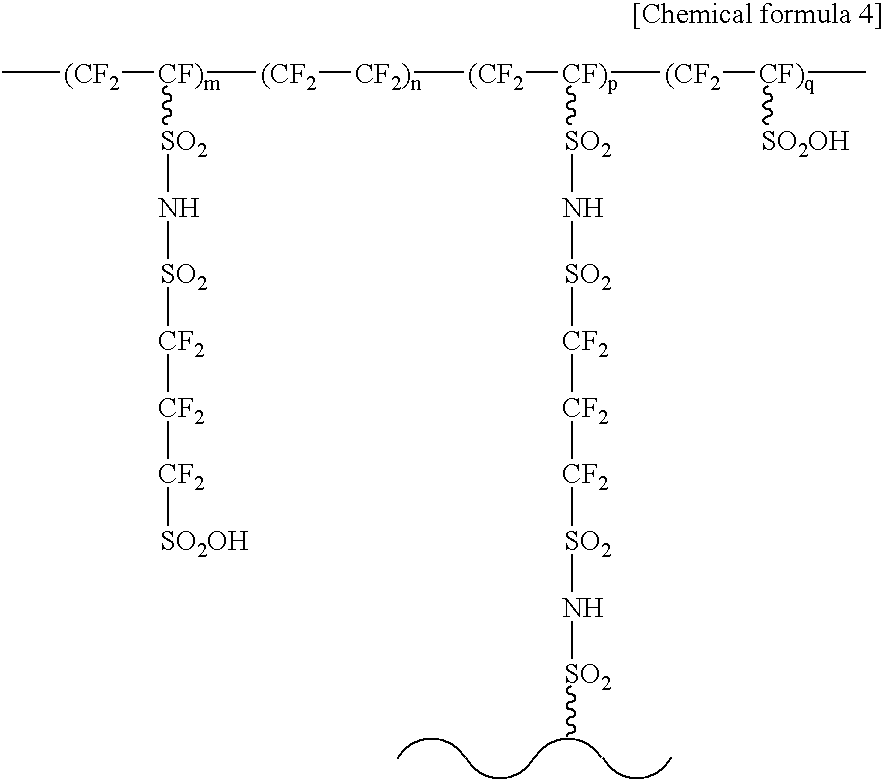
A first process for producing a modified electrolyte consistent with the present invention comprises an amine treatment step of contacting a solid polymer electrolyte or a precursor thereof with an amine compound. Further, a first modified electrolyte consistent with the present invention consists essentially of what is obtained in such a process. A second process for producing the modified electrolyte consistent with the present invention includes a step of introducing, to a solid polymer compound having a functional group A, a first modifying agent comprising at least one functional group B capable of reacting with the functional group A thereby forming a first intermediate acid group; and the step also includes reacting the functional group A and the functional group B. Further, a second modified electrolyte consistent with the present invention comprises a solid polymer compound having side chains, at least one terminal acid group present at terminals of the side chains, and at least one intermediate acid group and / or reformed acid group present within the side chains identical with the side chains containing the terminal acid group.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
High polymer electrolyte fuel cell and electrolyte film-gasket assembly for the fuel cell
InactiveUS6840969B2Prevent gas leakageImprove sealingFuel cells groupingPrimary cellsPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
An electrolyte membrane-gasket assembly for a fuel cell, including a polymer electrolyte membrane and a gasket, made of a seal material, covering the peripheral portion of the electrolyte membrane, in which the electrolyte membrane has a sequence of a plurality of through-holes in the peripheral portion, and a portion of the gasket covering one surface of the electrolyte membrane and a portion covering the other surface are connected to each other through the through-holes of the electrolyte membrane. This assembly provides a polymer electrolyte fuel cell free from gas cross leakage caused by a detachment of the gasket from the polymer electrolyte membrane. It is preferable to further include catalyst layers carried on both surfaces of the polymer electrolyte membrane, respectively, and protective films covering, respectively, sections spanning from the peripheral portion of each of the catalyst layers to the peripheral portion of the polymer electrolyte membrane.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method And System For Electrochemical Production Of Formic Acid From Carbon Dioxide
An electrochemical device converts carbon dioxide to a formic acid reaction product. The device includes an anode and a cathode, each comprising a quantity of catalyst. The anode and cathode each have reactant introduced thereto. Two membranes, a cation exchange polymer electrolyte membrane and an anion exchange polymer electrolyte membrane, are interposed between the anode and the cathode, forming a central flow compartment where a carbon dioxide reduction product, such as formic acid, can be recovered. At least a portion of the cathode catalyst is directly exposed to gaseous carbon dioxide during electrolysis. The average current density at the membrane is at least 20 mA / cm2, measured as the area of the cathode gas diffusion layer that is covered by catalyst, and formate ion selectivity is at least 50% at a cell potential difference of 3.0 V. In some embodiments, at least one polymer electrolyte membrane comprises a polymer in which a constituent monomer is (p-vinylbenzyl)-R, where R is selected from the group consisting of imidazoliums, pyridiniums and phosphoniums. In some embodiments, the polymer electrolyte membrane is a Helper Membrane comprising a polymer containing an imidazolium ligand, a pyridinium ligand, or a phosphonium ligand.
Owner:DIOXIDE MATERIALS
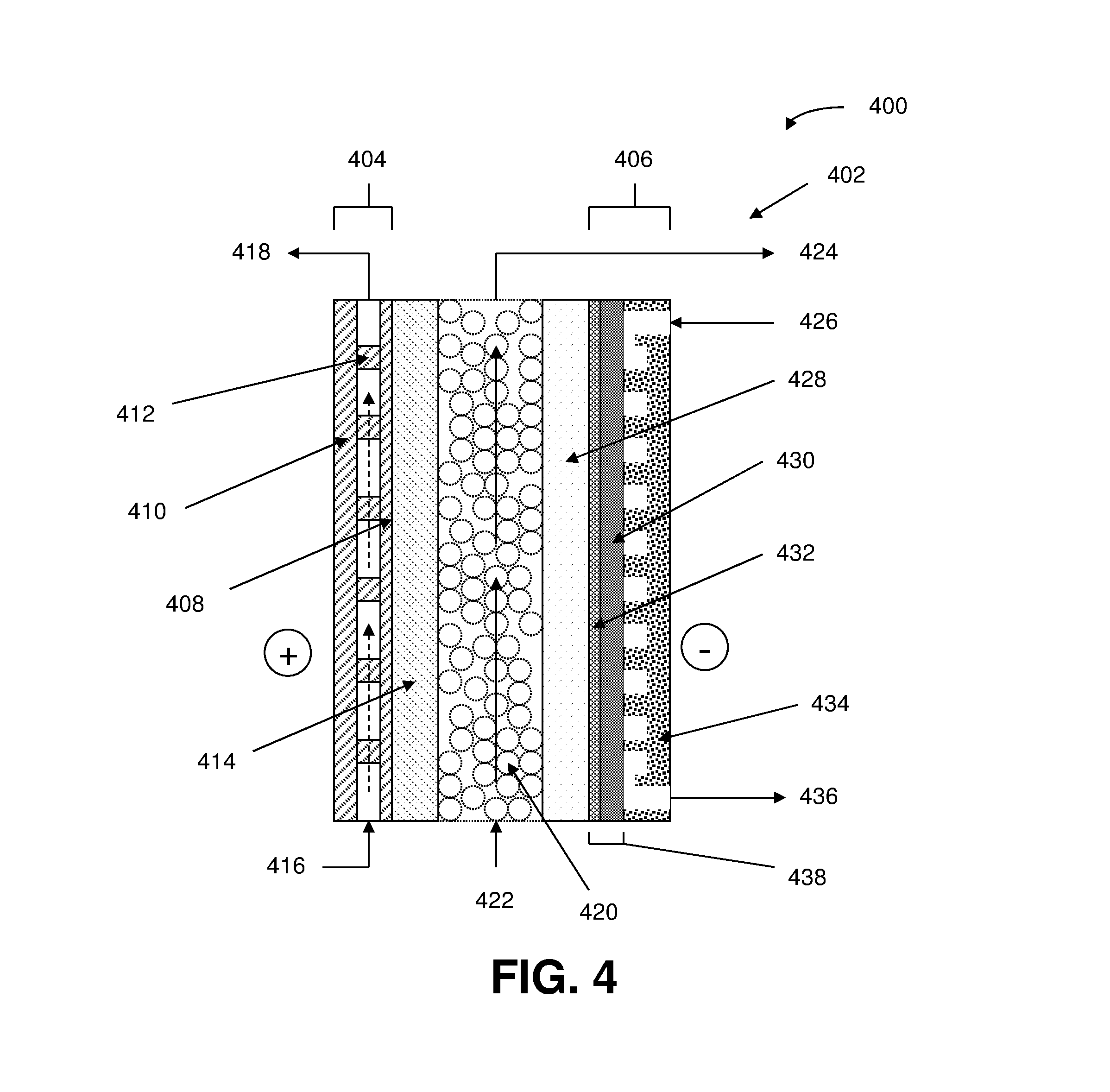
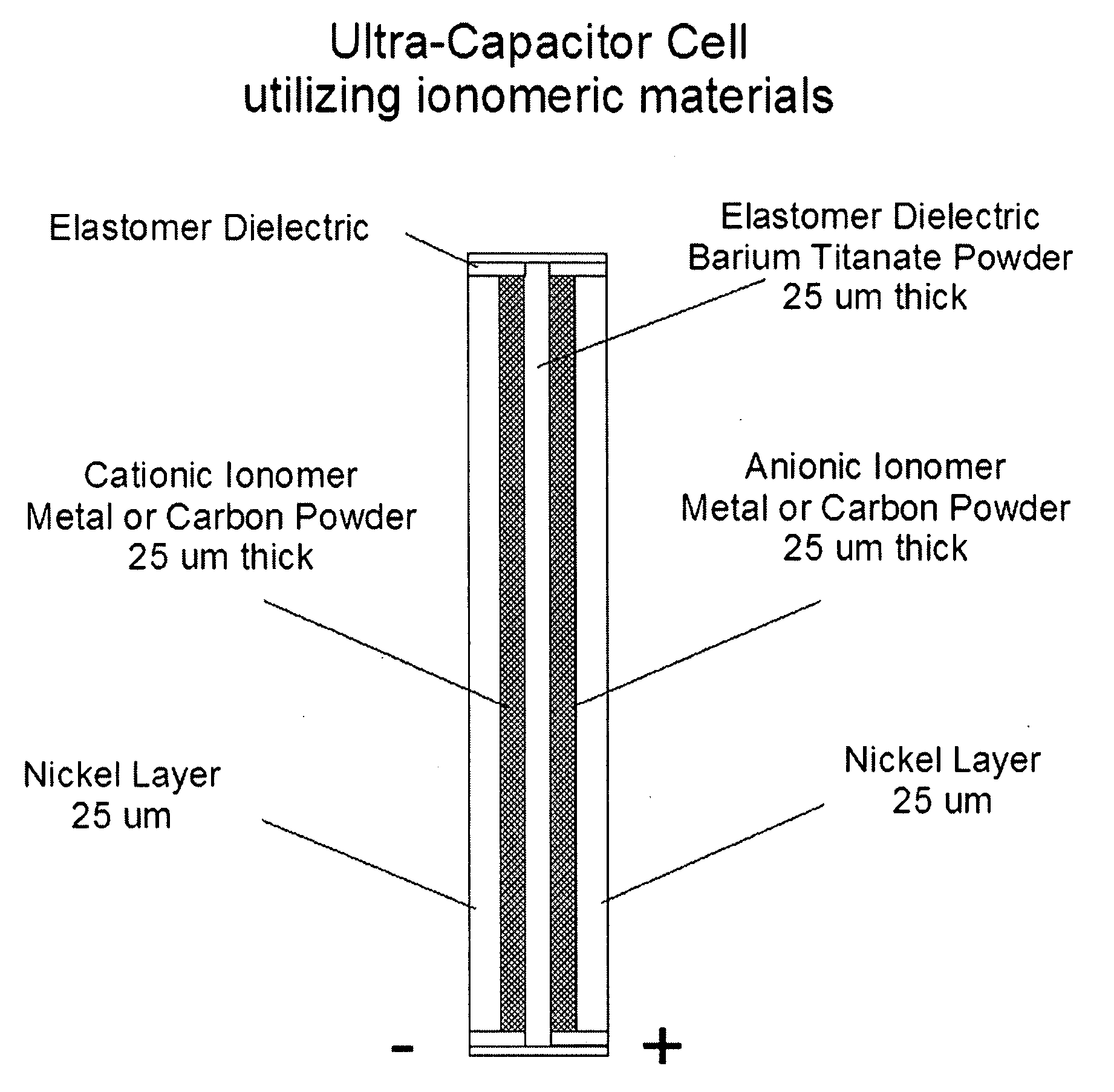
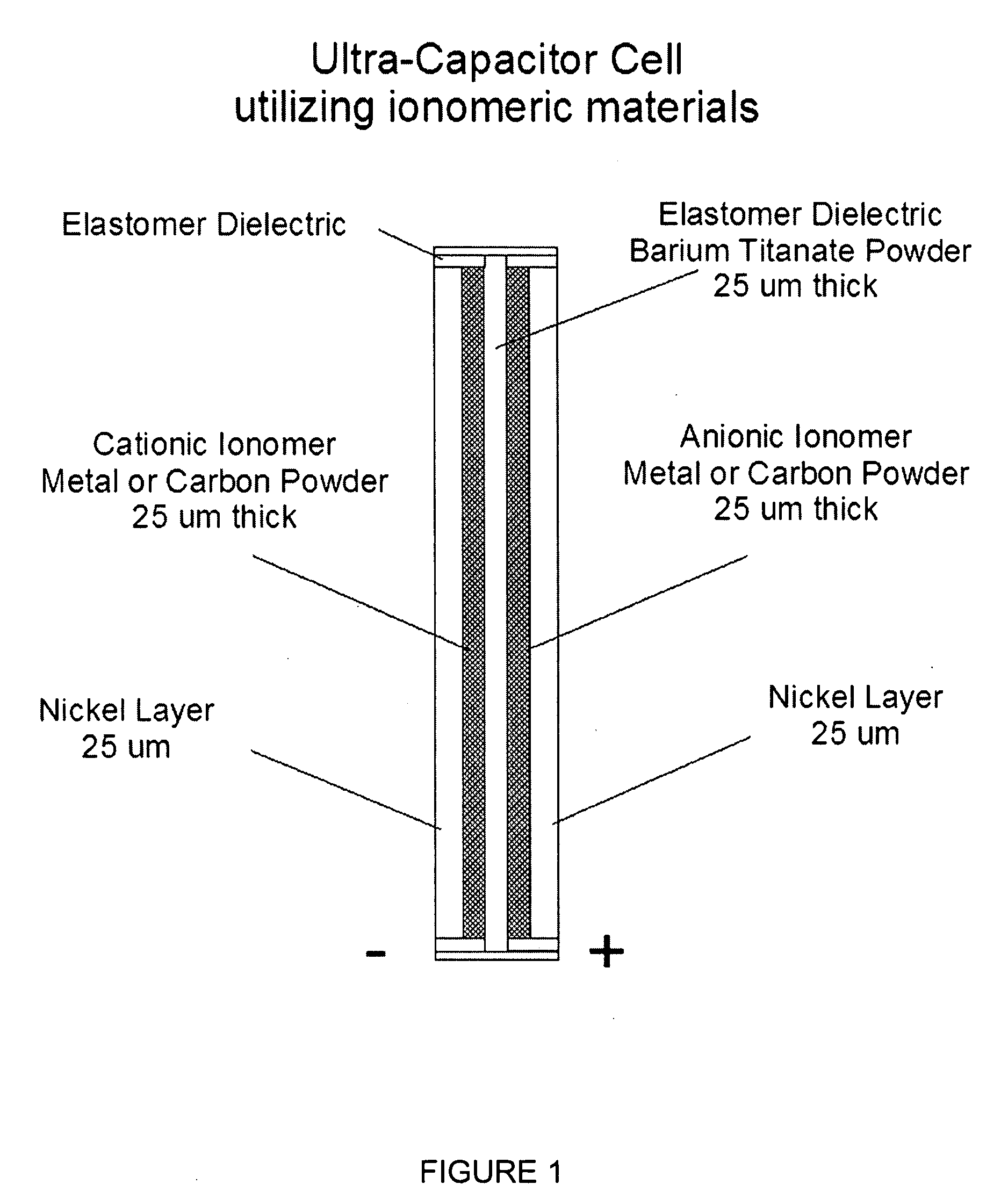
Nanoparticle ultracapacitor
InactiveUS20080316678A1Hybrid capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricCapacitancePolymer science
Particular aspects provide capacitors, and particularly ultracapacitors, comprising molecules suitable to substantially increasing the capacitance of the capacitor, and methods for making same Particular aspects provide ultracapacitors that include nanoparticles optionally coated with molecules, such as polymer electrolytes. Certain aspects provide an energy storage device or capacitor, comprising at least three layers sealed in a fluid-tight covering, wherein a first layer comprises at least one electrolytic polymer molecule of positive charge and at least one nanoparticle; a second dielectric layer comprising at least one insulative polymer; a third layer comprising at least one electrolytic polymer molecule of negative charge and at least one nanoparticle. In certain aspects, the electrolytic polymer of the first layer comprises at least one high charge density polymer electrolyte of positive charge, and wherein the electrolytic polymer of the third layer comprises at least one high charge density polymer electrolyte of negative charge.
Owner:TANGREDI PATRICIA
Composite solid polymer electrolyte membranes
InactiveUS20050031925A1Improve performanceLow costElectrolyte holding meansSemi-permeable membranesPolymer electrolytesPolymer science
The present invention relates to composite solid polymer electrolyte membranes (SPEMs) which include a porous polymer substrate interpenetrated with a water soluble ion-conducting material. SPEMs of the present invention are useful in electrochemical applications, including fuel cells and electrodialysis.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
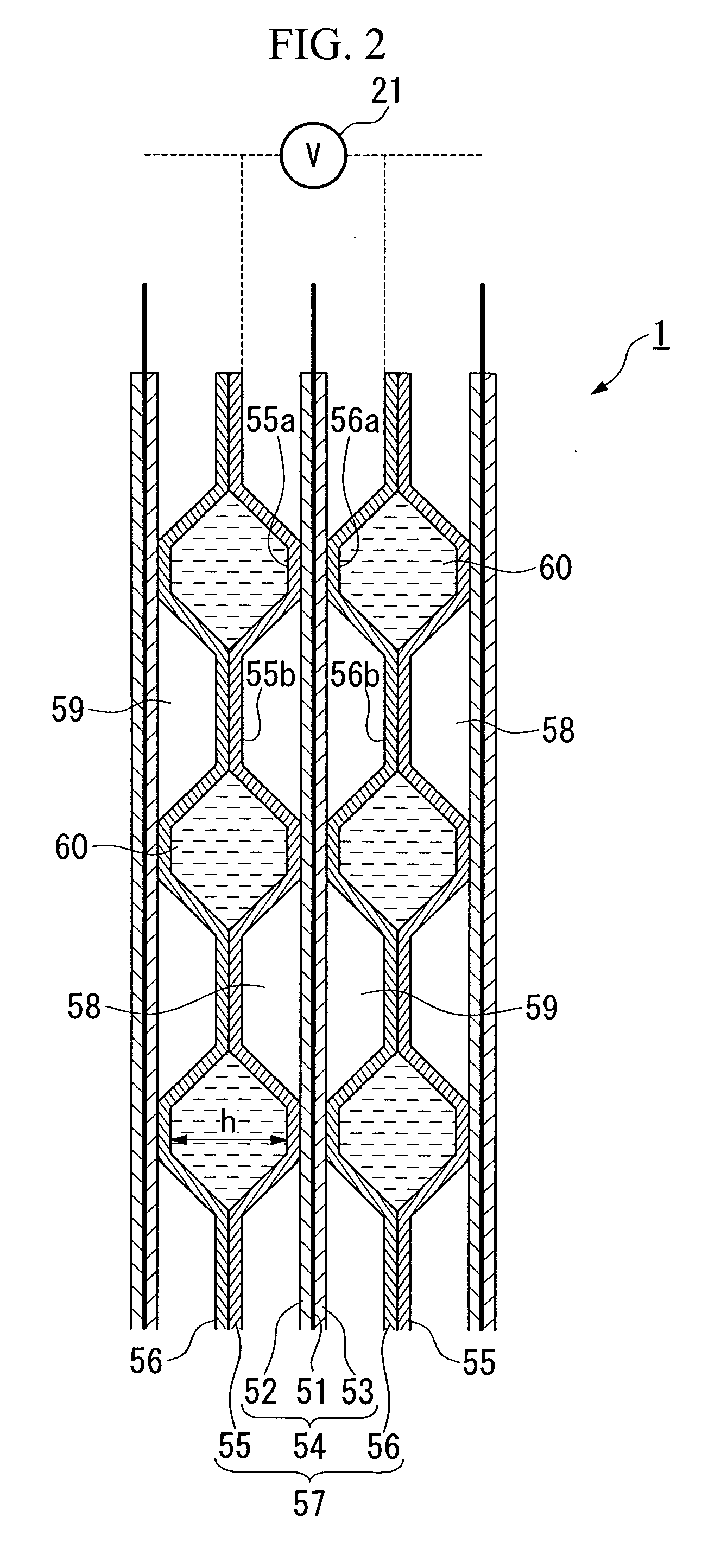
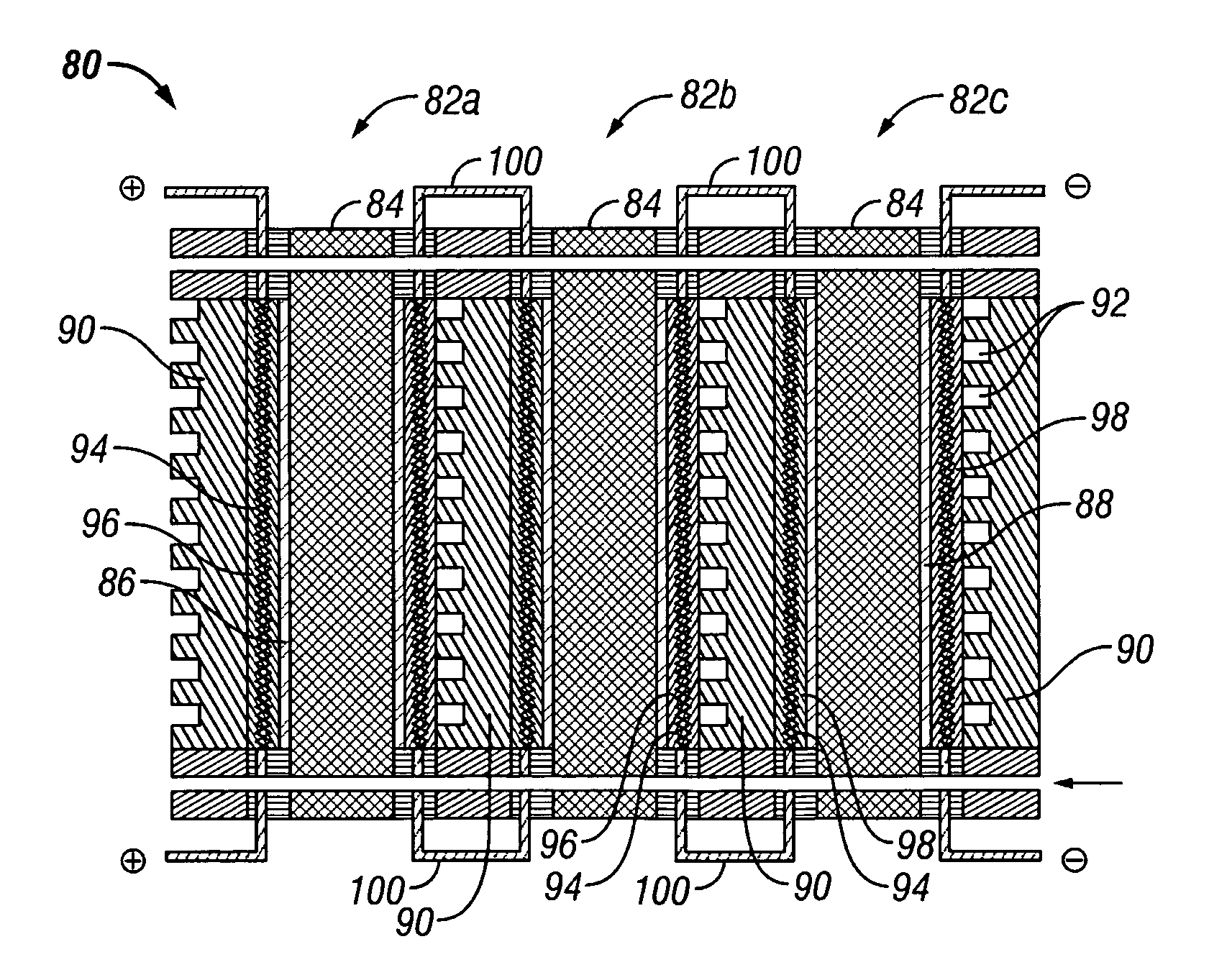
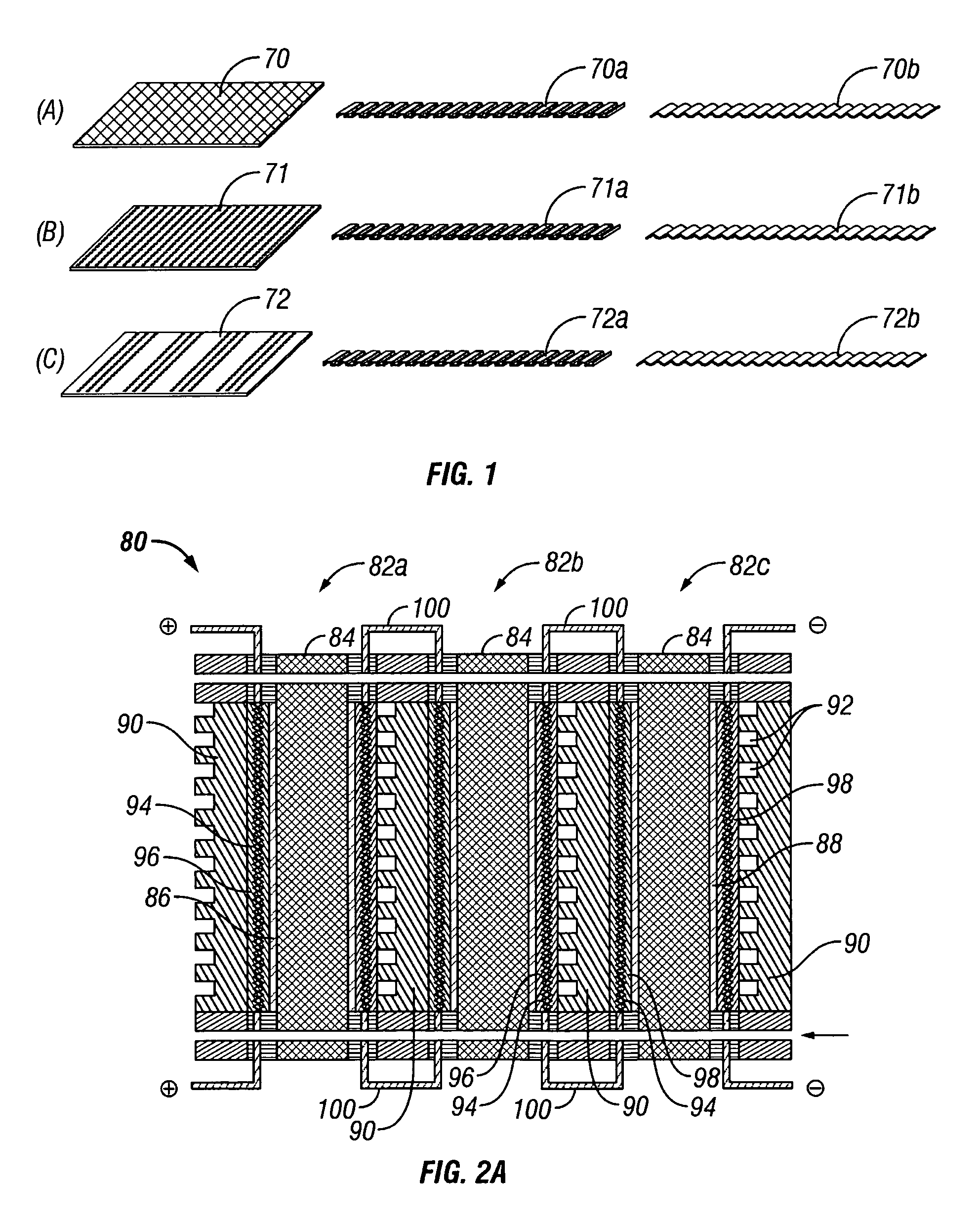
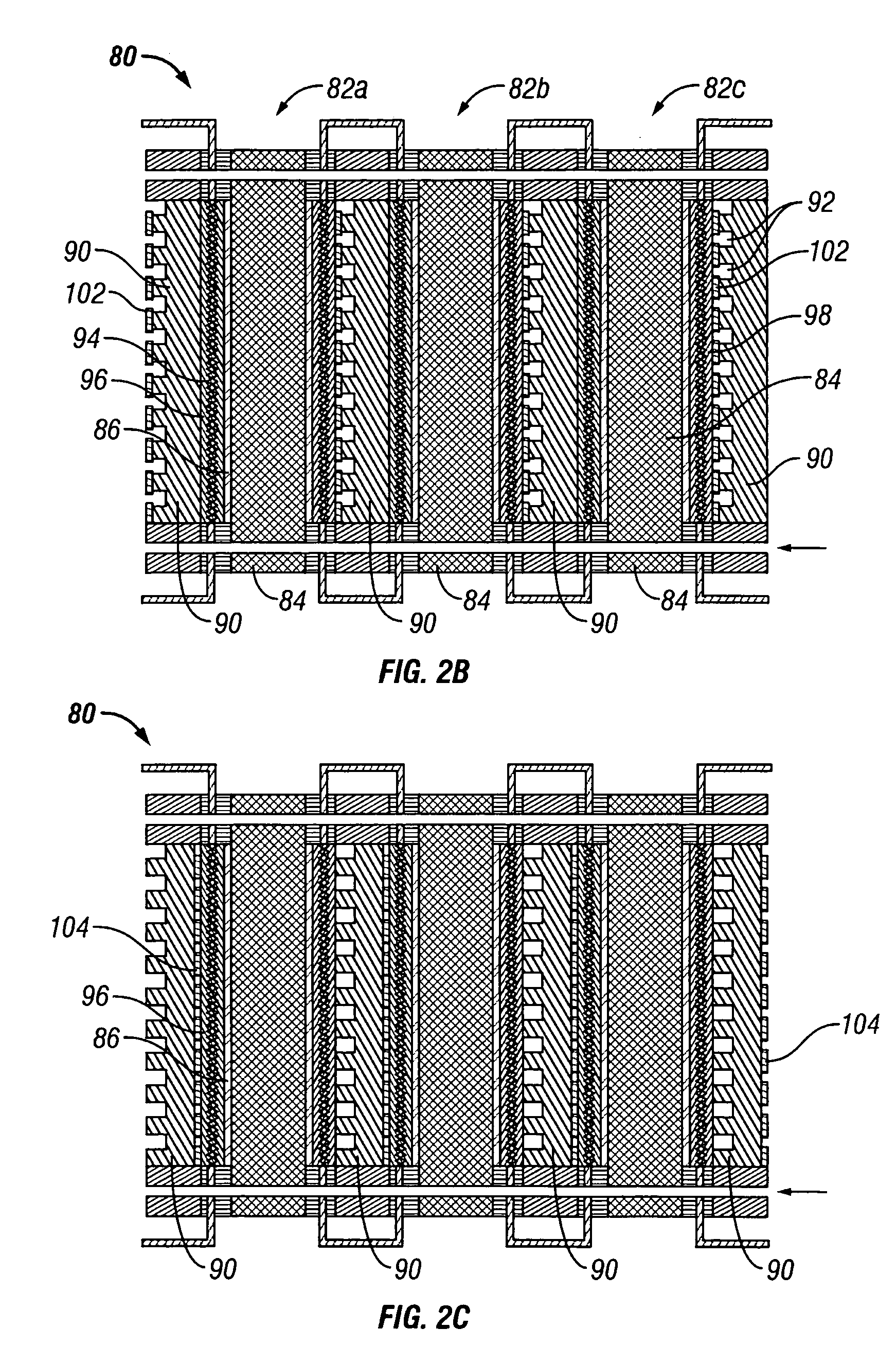
Water management in bipolar electrochemical cell stacks
InactiveUS20060199061A1Reduce probabilityPromote loss of waterFuel cells groupingWater management in fuel cellsPolymer electrolytesLiquid water
A bipolar, filter press-like electrochemical cell stack comprising a plurality of electrochemical cells, where each electrochemical cell is supplied with a gaseous anodic reactant and either supplied with a gaseous cathodic reactant or produces a gaseous cathodic product, and where each electrochemical cell avoids drying out the ion exchange membrane polymer electrolyte, avoids flooding at the cathode, facilitates recovery of liquid water at the anode, and reduces water losses from at least one of the electrodes. A water retention barrier is variously positioned, such as between a gas diffusion electrode and a fluid flow field. The barrier may be either: (i) a thin, gas permeable, liquid water impermeable membrane; (ii) a thin, porous sheet of material; or (iii) a thin, substantially solid sheet of material except for a plurality of small through-holes that penetrate from one side of the sheet to an opposing side of the same sheet. The barrier is advantageously used at the cathode and facilitates air cooling of the cell.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Solid polymer battery electrolyte and reactive metal-water battery
In one implementation, a reactive metal-water battery includes an anode comprising a metal in atomic or alloy form selected from the group consisting of periodic table Group 1A metals, periodic table Group 2A metals and mixtures thereof. The battery includes a cathode comprising water. Such also includes a solid polymer electrolyte comprising a polyphosphazene comprising ligands bonded with a phosphazene polymer backbone. The ligands comprise an aromatic ring containing hydrophobic portion and a metal ion carrier portion. The metal ion carrier portion is bonded at one location with the polymer backbone and at another location with the aromatic ring containing hydrophobic portion. The invention also contemplates such solid polymer electrolytes use in reactive metal / water batteries, and in any other battery.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
InactiveUS6946211B1Improve performanceImprove toleranceSolid electrolytesPrimary cellsThermoplasticGas diffusion electrode
A method for preparing polybenzimidazole or polybenzimidazole blend membranes and fabricating gas diffusion electrodes and membrane-electrode assemblies is provided for a high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. Blend polymer electrolyte membranes based on PBI and various thermoplastc polymers for high temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells have also been developed. Miscible blends are used for solution casting of polymer membranes (solid electrolytes). High conductivity and enhanced mechanical strength were obtained for the blend polymer solid electrolytes. With the thermally resistant polymer, e.g., polybenzimidazole or a mixture of polybenzimidazole and other thermoplastics as binder, the carbon-supported noble metal catalyst is tape-cast onto a hydrophobic supporting substrate. When doped with an acid mixture, electrodes are assembled with an acid doped solid electrolyte membrane by hot-press. The fuel cell can operate at temperatures up to at least 200° C. with hydrogen-rich fuel containing high ratios of carbon monoxide such as 3 vol % carbon monoxide or more, compared to the carbon monoxide tolerance of 10-20 ppm level for Nafion®-based polymer electrolyte fuel cells.
Owner:DANISH POWER SYST
Highly-stable polymeric electrolyte and use thereof in electrochemical systems
ActiveUS20050234177A1Hybrid capacitor electrolytesHybrid capacitor electrodesPolymer electrolytesElectrolysis
Polymer electrolyte for an electrochemical generator based on at least a four branched polymer, at least a poly(vinylyldienefluoride), a poly(vinyldiene fluoro-co-hexafluoropropene copolymer), a poly(tetrafluoroethylene), a poly(ethylene-co-propylene-co-5-methylene-2-norbornene) or an ethylene propylene-diene copolymer, a polyol, a poly(methylmethacrylate, a poly(acrylonitrile), SiO2Al2O3, or nano TiO2 non coated or coated with an organic material. This electrolyte allows to prepare electrolytic compositions that can be used in high performance electrochemical devices.
Owner:HYDRO QUEBEC CORP
Fuel cell electrode comprising conductive zeolite support material
InactiveUS6117581AReduce resistanceLess ohmic power lossActive material electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsConductive polymerPolymer chemistry
A polymer-electrolyte-membrane fuel cell assembly comprising an ionomeric, conducting polymer membrane, an anode on a first face of the polymer membrane, a cathode on a second face of the polymer membrane, at least one of the anode and the cathode each comprising catalyst support material comprising conductive zeolite particulate material, and noble metal catalysts supported on the catalyst support material.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO +1
Multi-component composite film method for preparing the same
InactiveUS7470488B2Improve wettabilityImprove conductivitySolid electrolyte cellsSolid electrolyte fuel cellsPolymer electrolytesPolymer science
The present invention provides a multi-component composite film comprising a) polymer support layer; and b) porous gellable polymer layer which is formed on one side or both sides of the support layer of a), wherein the support film of a) and the gellable polymer layer of b) are unified without the interface, a method for preparing the same, and a polymer electrolyte system applied the same.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD +1
Double-electrolyte system lithium sulphur battery and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN103531840AImprove stabilityInhibit Corrosion BehaviorFinal product manufactureLi-accumulatorsPolymer electrolytesLithium
The invention relates to a double-electrolyte system lithium sulphur battery and a preparing method thereof. The double-electrolyte system lithium sulphur battery comprises a positive electrode and a negative electrode, wherein solid electrolyte is arranged between the positive electrode and the negative electrode, and the gap between the solid electrolyte and the positive electrode and the gap between the solid electrolyte and the negative electrode are filled with electrolyte solution or polymer electrolyte. The positive electrode and the negative electrode are separated by the solid electrolyte, the gap between the solid electrolyte and the positive electrode and the gap between the solid electrolyte and the negative electrode are filled with the electrolyte solution or the polymer electrolyte, polysulfide is prevented from shuttling between the positive electrode and the negative electrode, the full contact between electrode active materials and electrolyte is guaranteed, and accordingly active materials in electrodes can be well utilized. The lithium sulphur battery of a new structure can fundamentally solve the shuttling effect and can achieve high electrochemical performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polymer electrolyte membrane and solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell using same
InactiveUS6933068B2Improve adhesionHigh mechanical strengthSemi-permeable membranesIon-exchanger regenerationPolymer electrolytesPolymer science
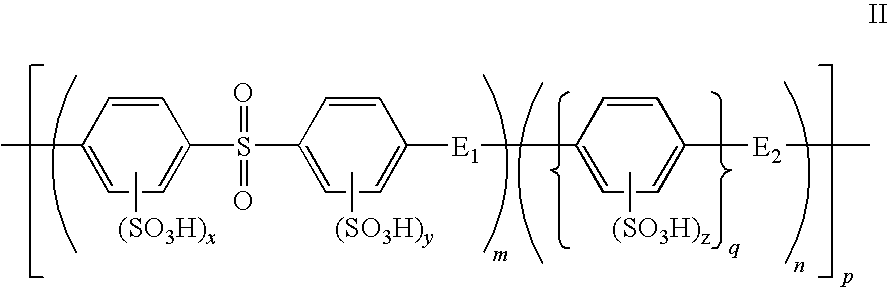
A composite polymer electrolyte membrane is formed from a first polymer electrolyte comprising a sulfonated polyarytene polymer and a second polymer electrolyte comprising another hydrocarbon polymer electrolyte. In the first polymer electrolyte, 2-70 mol % constitutes an aromatic compound unit with an electron-attractive group in its principal chain, while 30-98 mol % constitutes an aromatic compound unit without an electron-attractive group in its principal chain. The second polymer electrolyte is a sulfonated polyether or sulfonated polysulfide polymer electrolyte.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Membrane electrode assembly and fuel cell
InactiveUS20050142397A1Avoid damageDesired performanceFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
A membrane electrode assembly includes an anode, a cathode, and a solid polymer electrolyte membrane interposed between the anode and the cathode. The anode and the cathode include gas diffusion layers and electrode catalyst layers. Mixture layers are provided over predetermined areas H around surfaces of the electrode catalyst layers. The electrode catalyst layers and adhesive layers are mixed in the mixture layers, respectively.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com