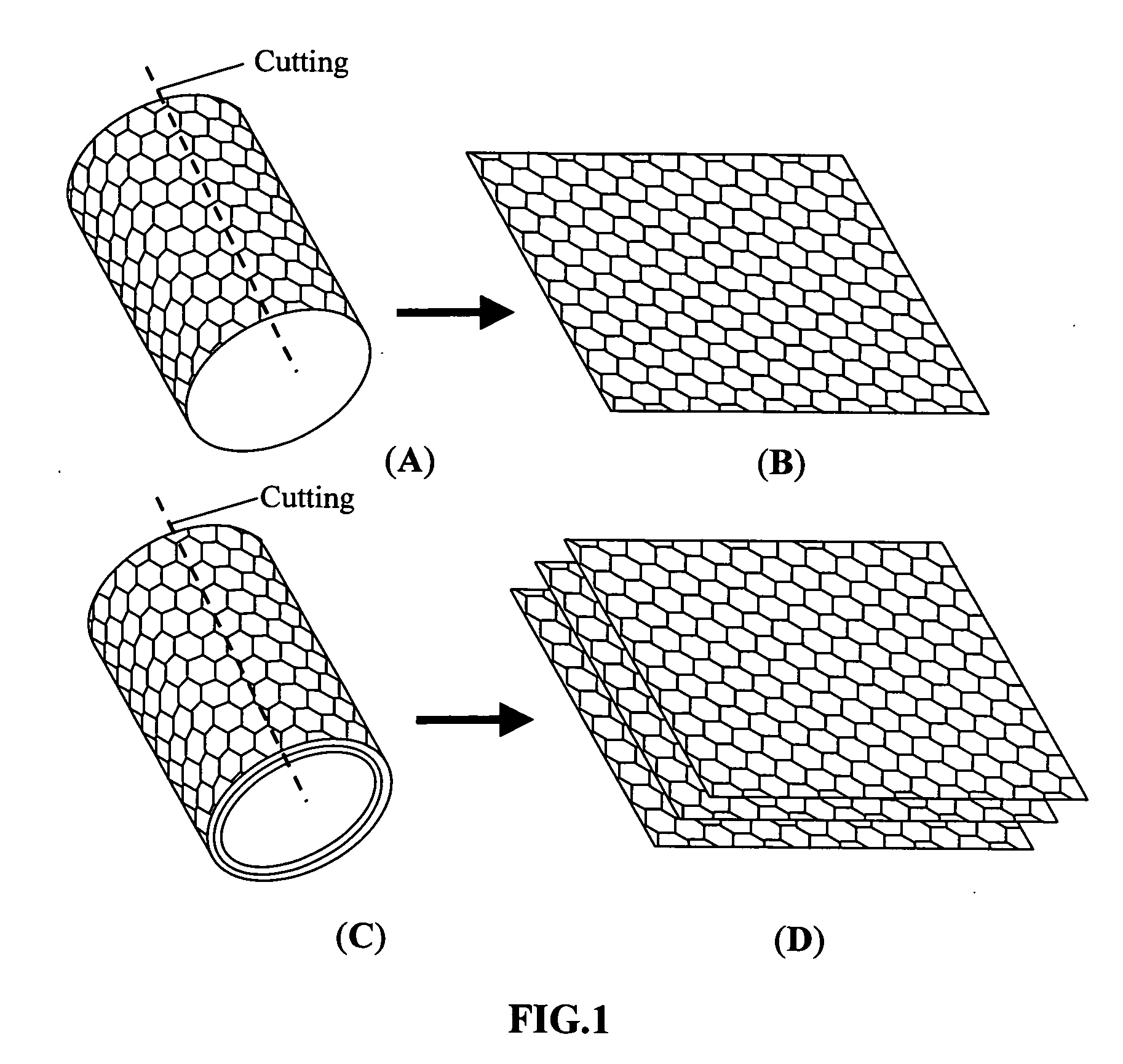
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
20185 results about "Crystallite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
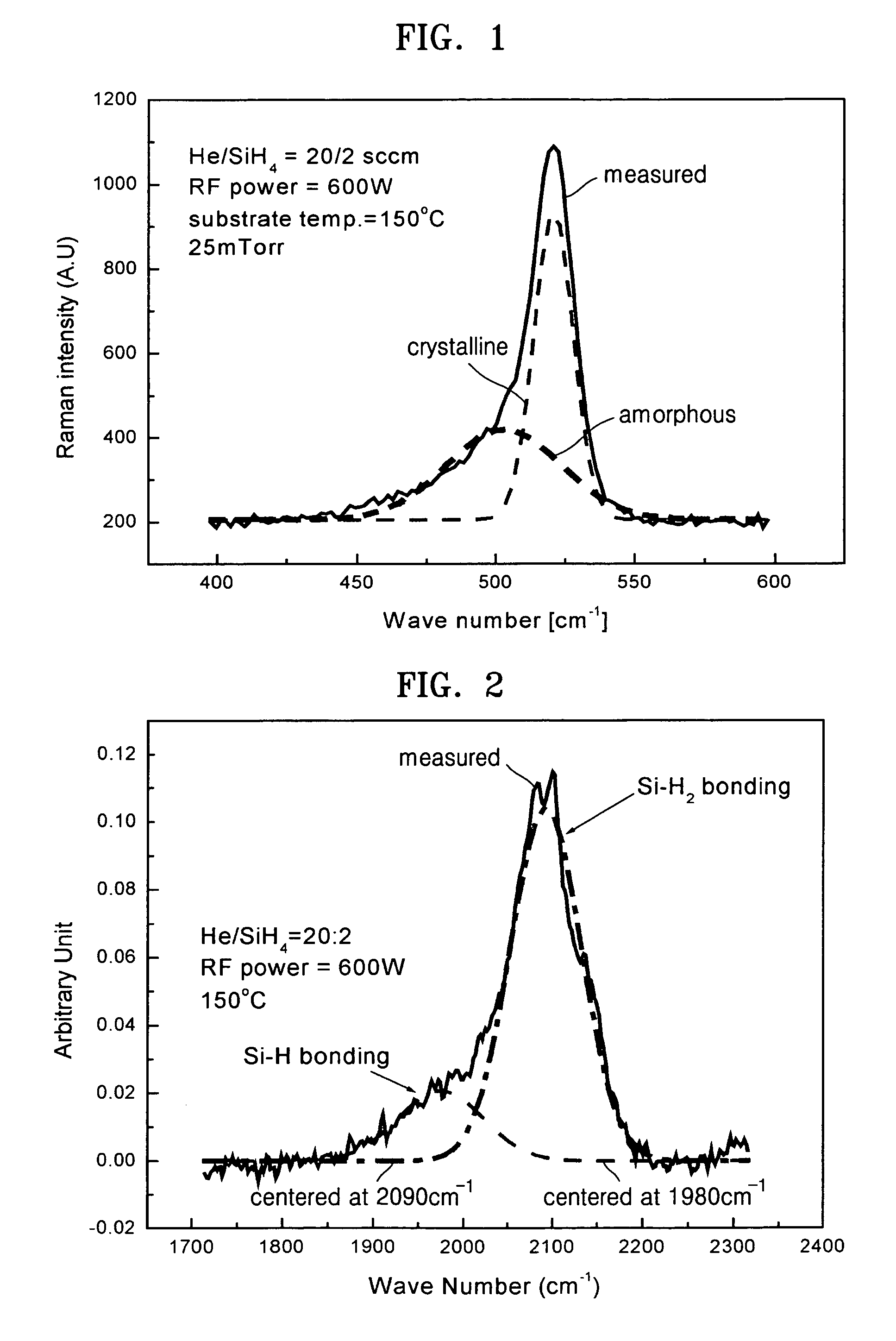
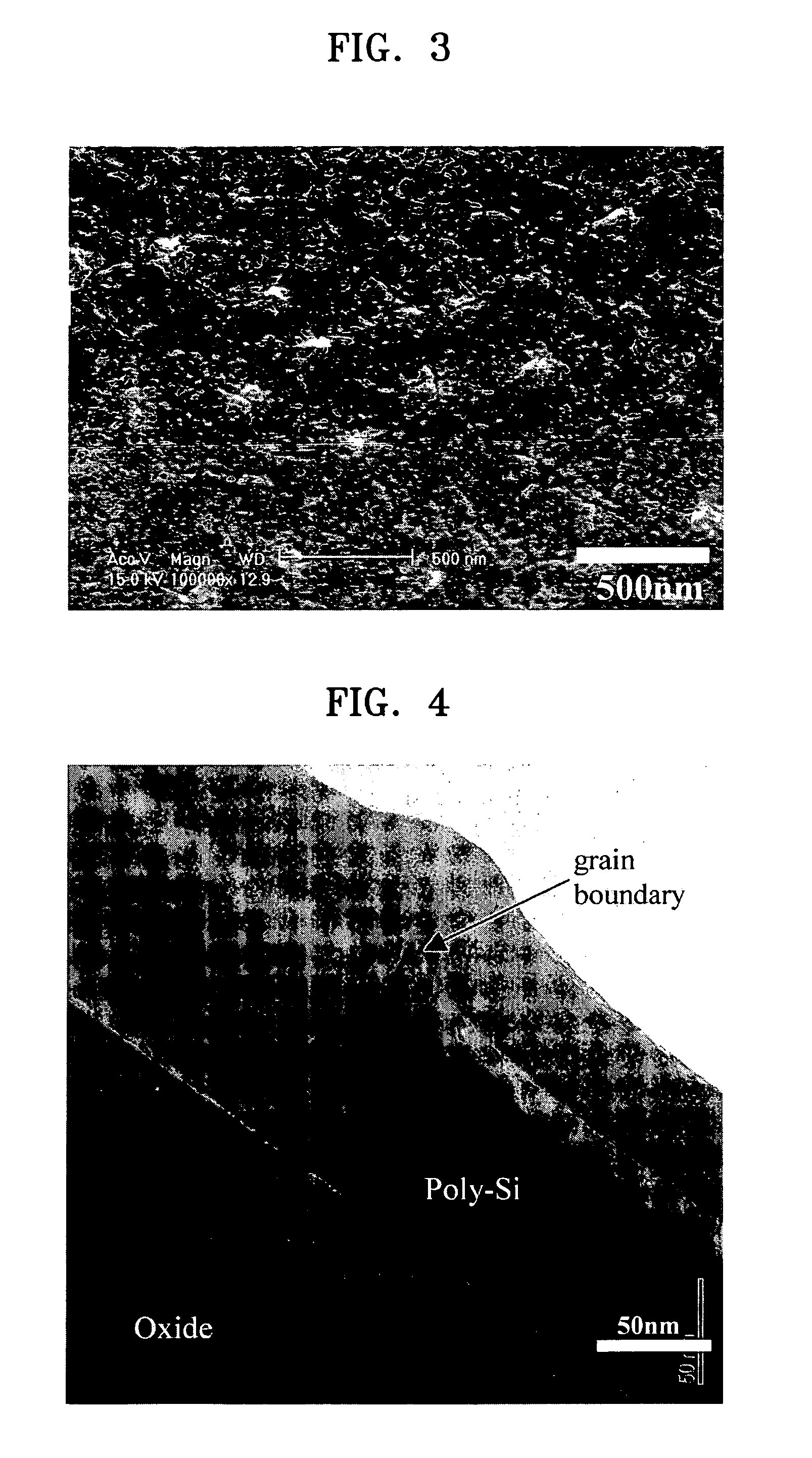
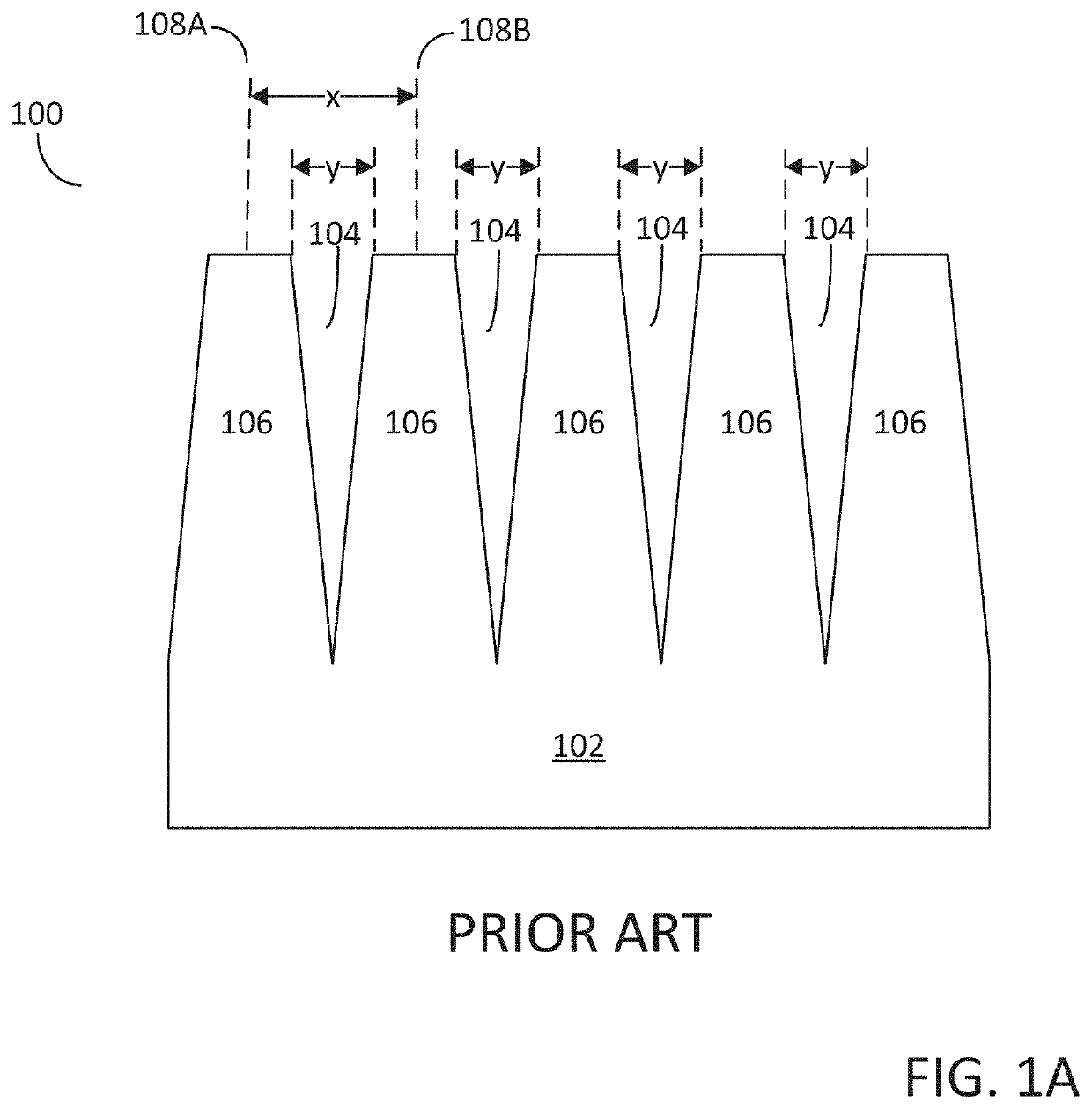
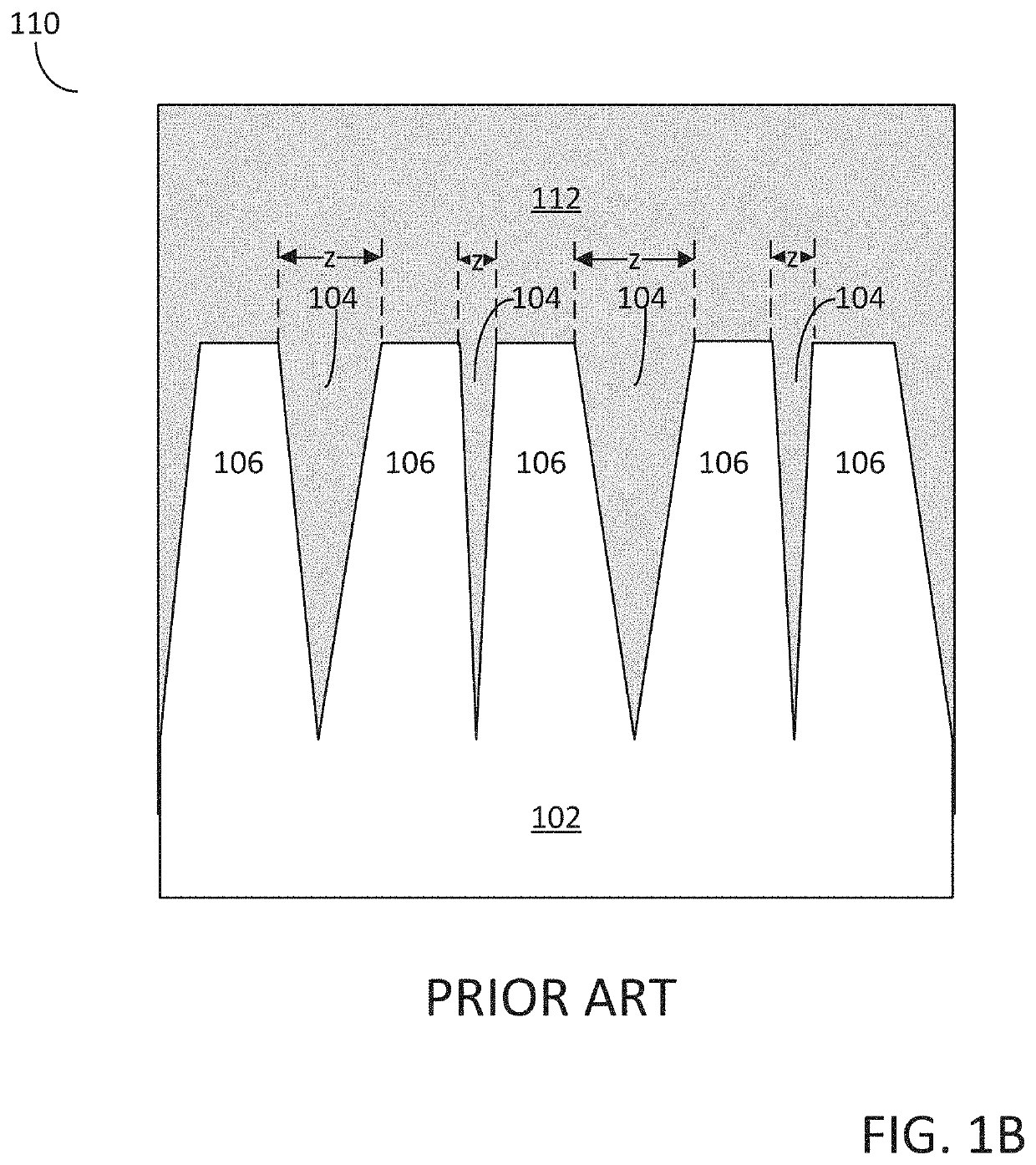
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. The orientation of crystallites can be random with no preferred direction, called random texture, or directed, possibly due to growth and processing conditions. Fiber texture is an example of the latter. Crystallites are also referred to as grains. The areas where crystallites meet are known as grain boundaries. Polycrystalline or multicrystalline materials, or polycrystals are solids that are composed of many crystallites of varying size and orientation.
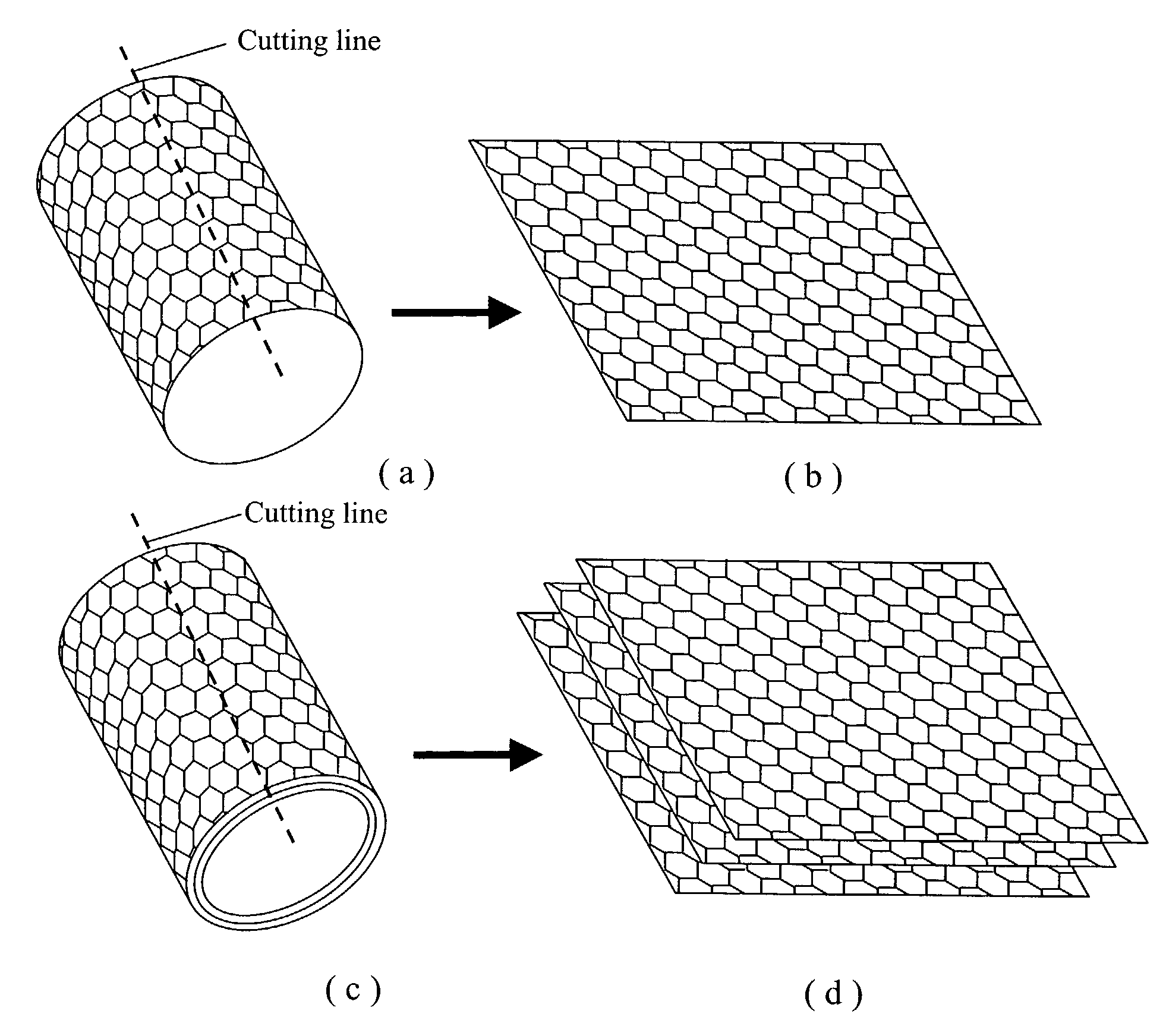
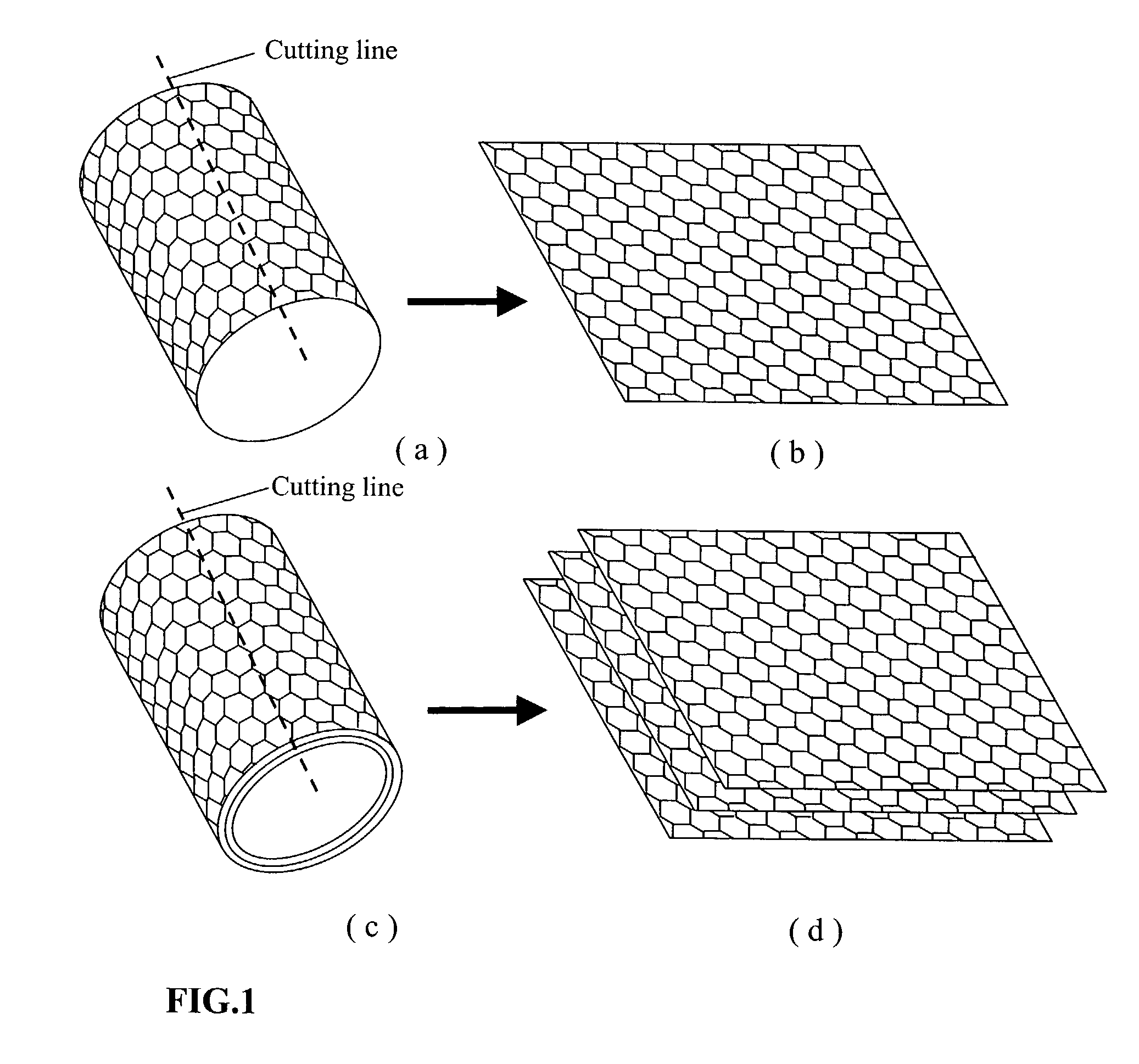
Nano-scaled graphene plates
A nano-scaled graphene plate material and a process for producing this material. The material comprises a sheet of graphite plane or a multiplicity of sheets of graphite plane. The graphite plane is composed of a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms and the plate has a length and a width parallel to the graphite plane and a thickness orthogonal to the graphite plane with at least one of the length, width, and thickness values being 100 nanometers or smaller. The process for producing nano-scaled graphene plate material comprises the steps of: a). partially or fully carbonizing a precursor polymer or heat-treating petroleum or coal tar pitch to produce a polymeric carbon containing micron- and / or nanometer-scaled graphite crystallites with each crystallite comprising one sheet or a multiplicity of sheets of graphite plane; b). exfoliating the graphite crystallites in the polymeric carbon; and c). subjecting the polymeric carbon containing exfoliated graphite crystallites to a mechanical attrition treatment to produce the nano-scaled graphene plate material.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
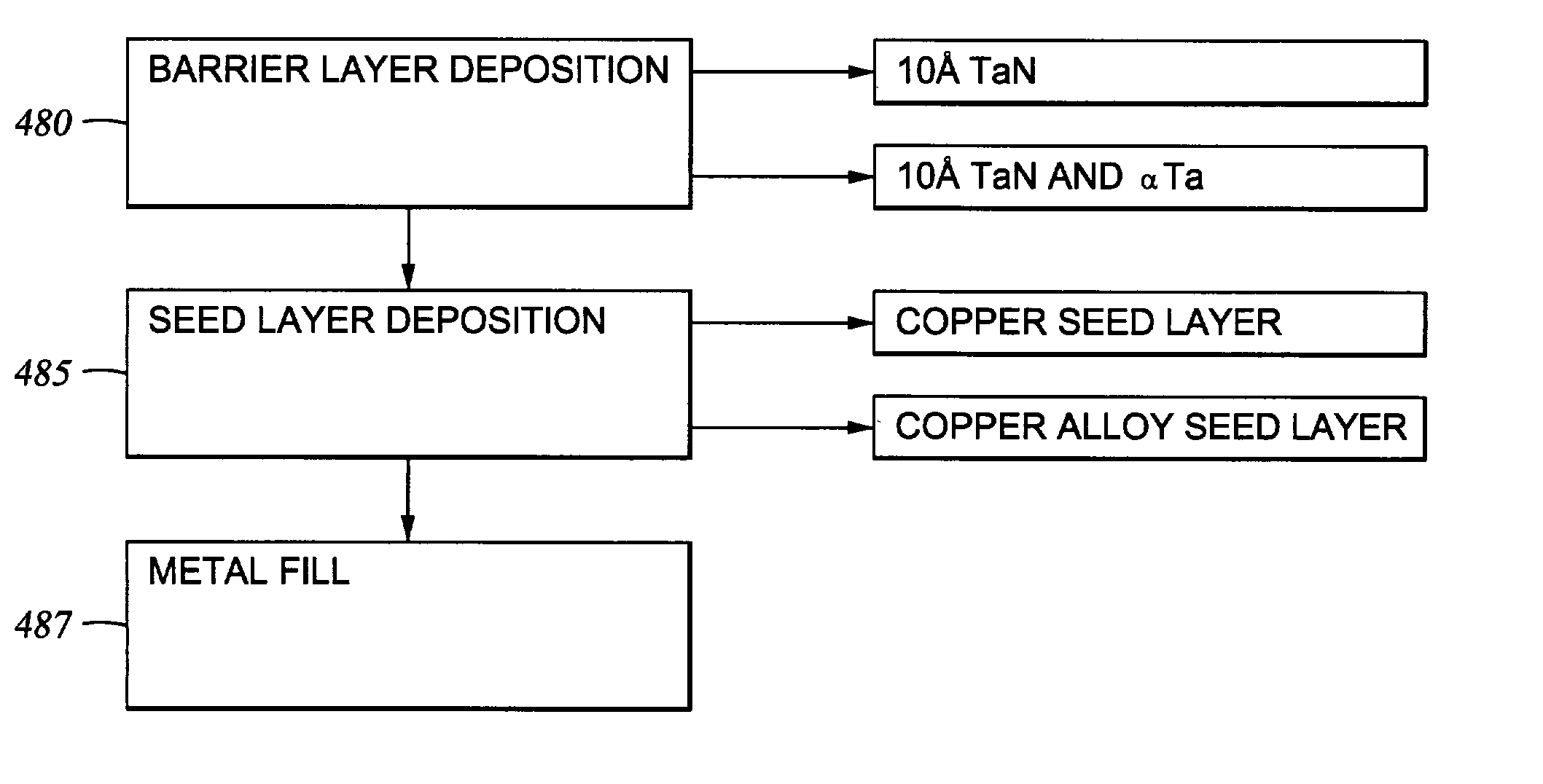
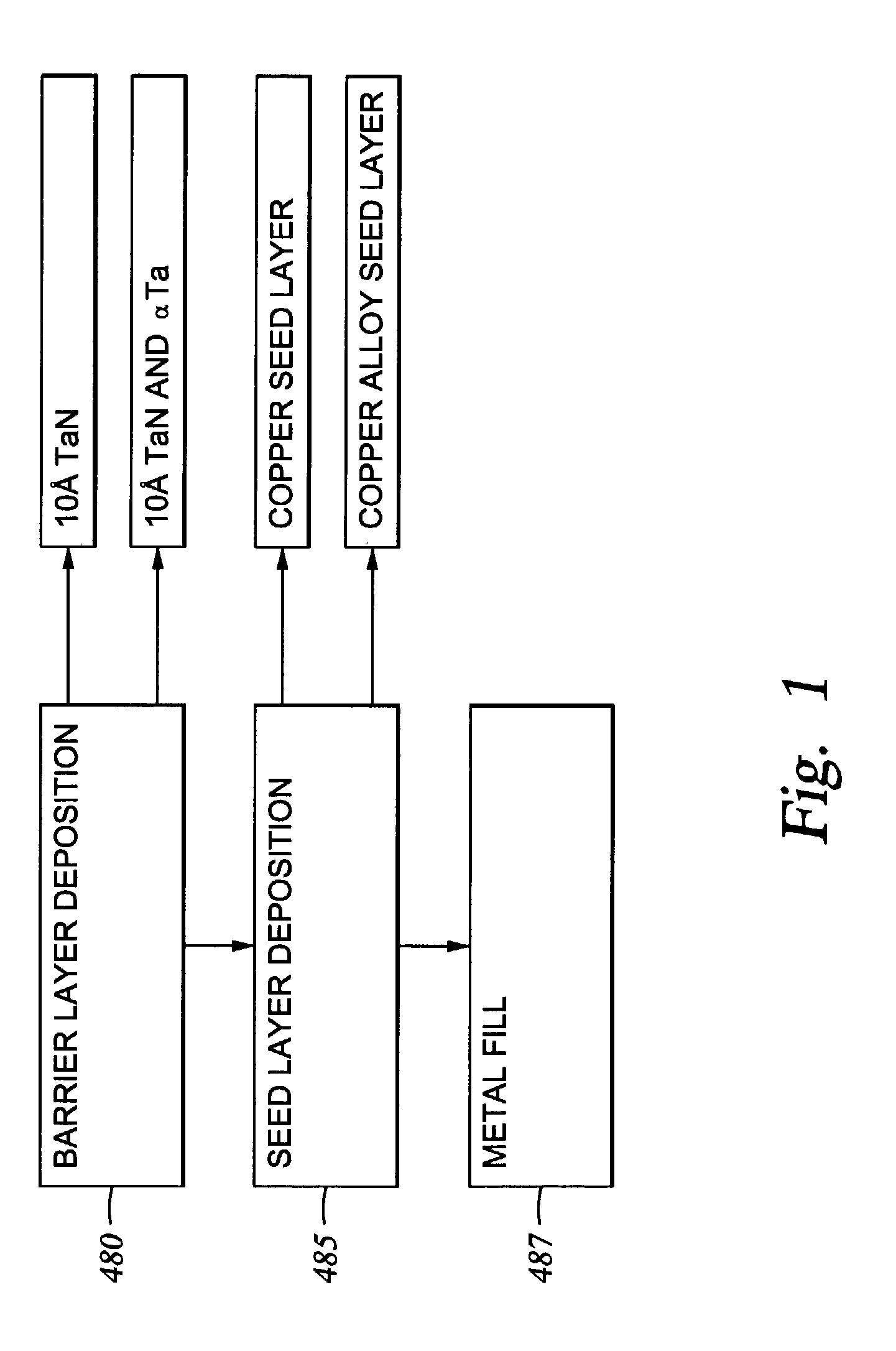
Integration of ALD tantalum nitride and alpha-phase tantalum for copper metallization application
InactiveUS20030082307A1Pretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal interconnectTantalum nitride
A method for forming a metal interconnect on a substrate is provided. The method includes depositing a refractory metal-containing barrier layer having a thickness less than about 20 angstroms on at least a portion of a metal layer by alternately introducing one or more pulses of a metal-containing compound and one or more pulses of a nitrogen-containing compound. The method also includes depositing a seed layer on at least a portion of the barrier layer, and depositing a second metal layer on at least a portion of the seed layer. The barrier layer provides adequate barrier properties and allows the grain growth of the metal layer to continue across the barrier layer into the second metal layer thereby enhancing the electrical performance of the interconnect.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
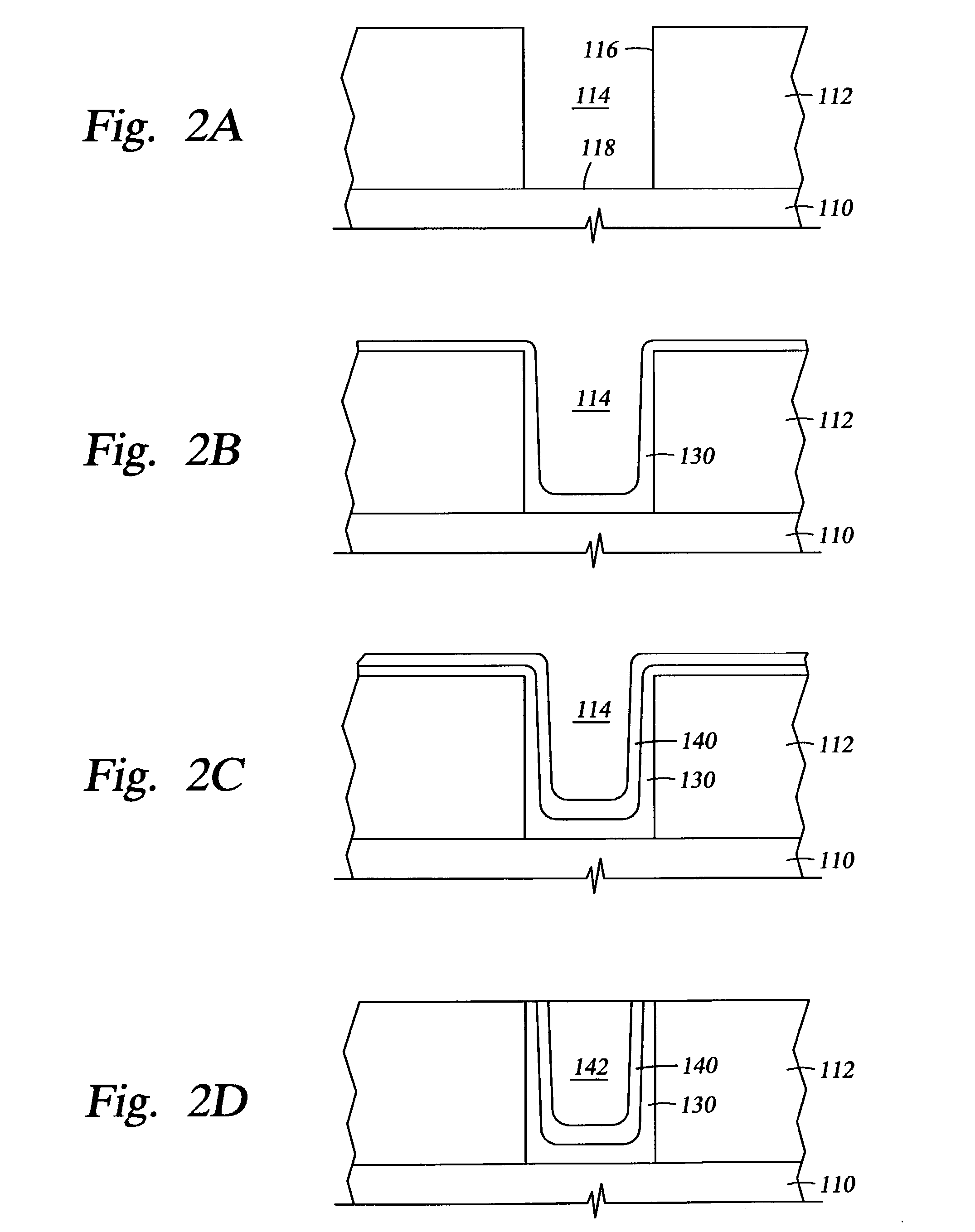
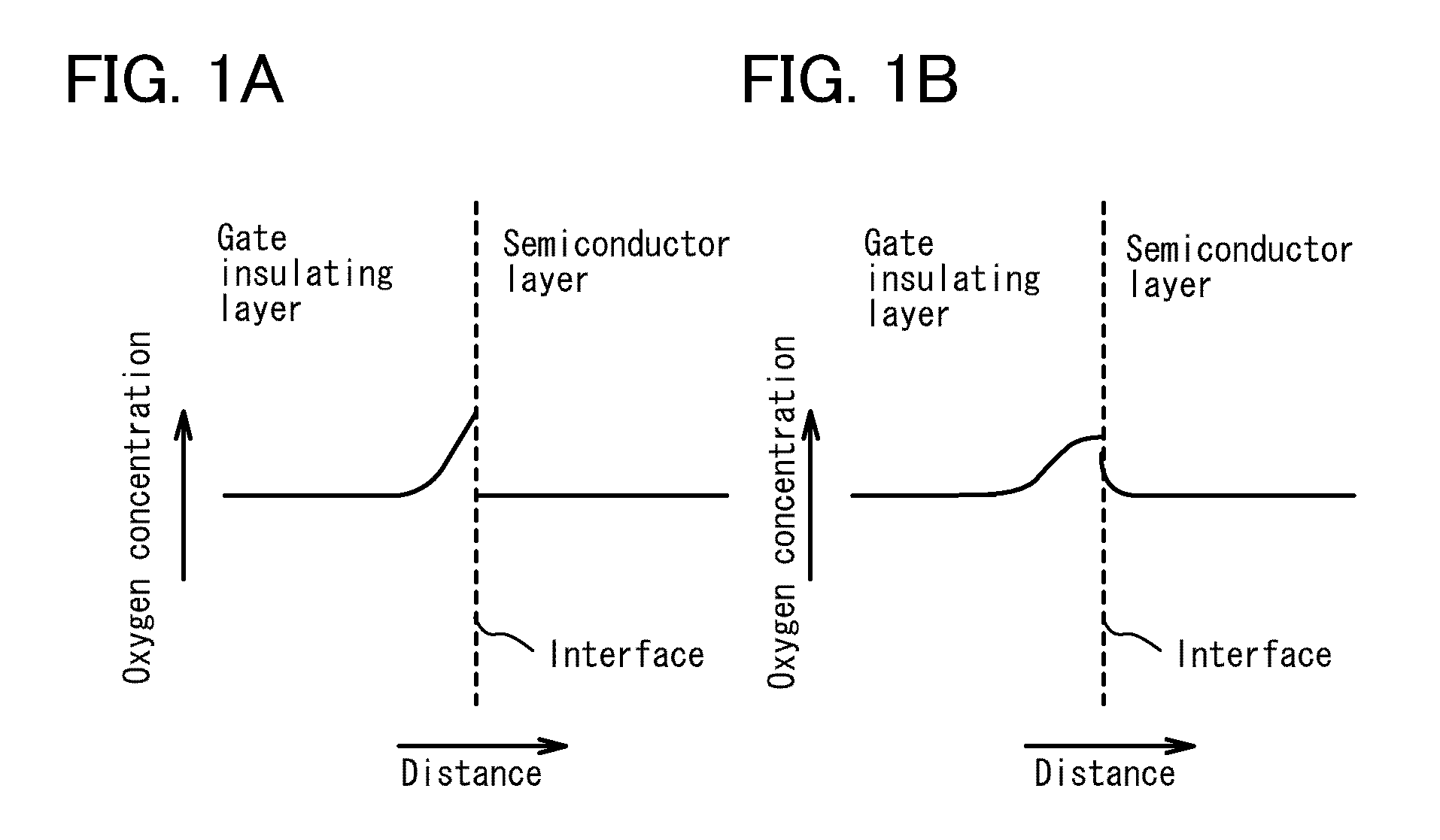
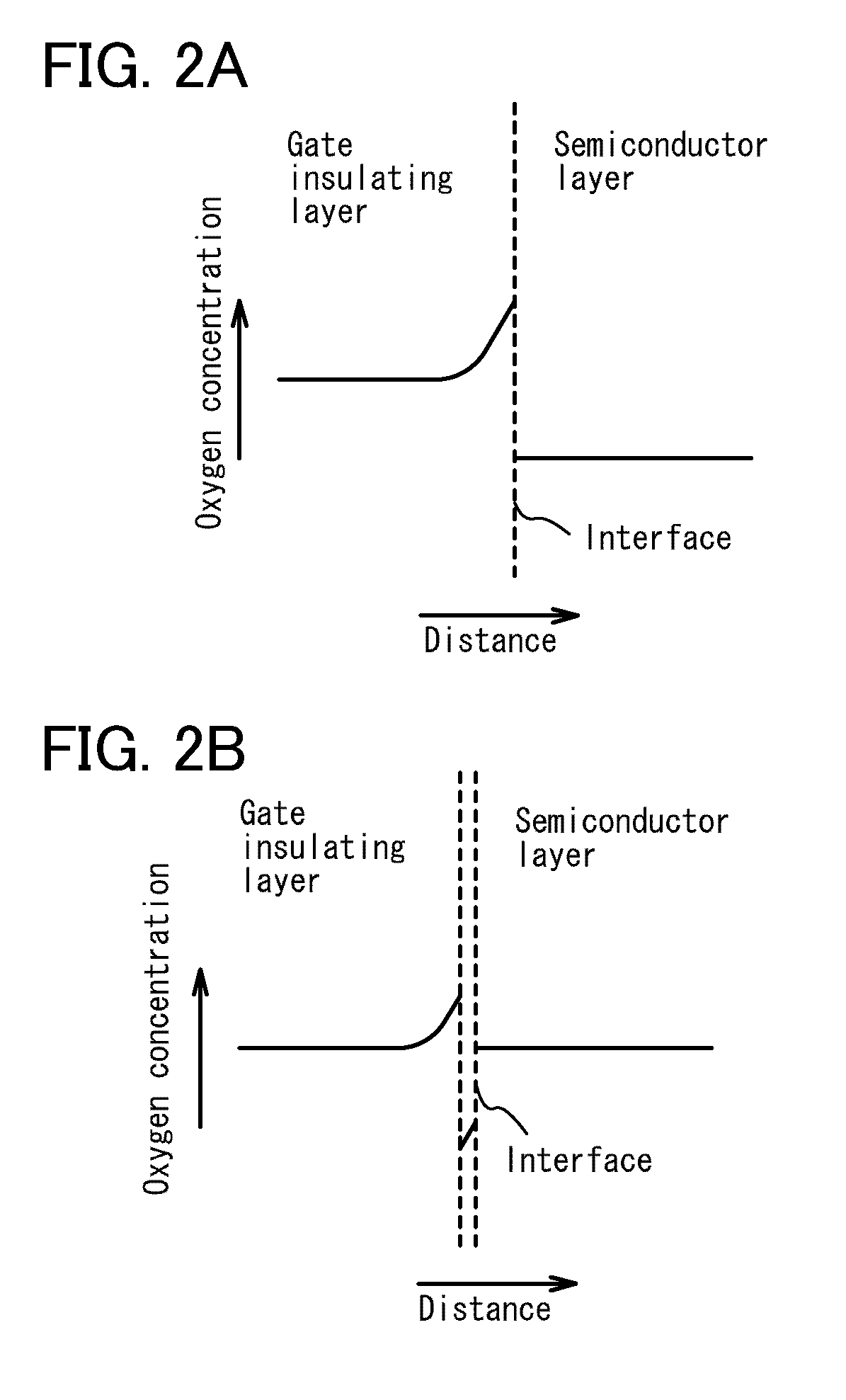
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100051949A1Small currentHigh on-off ratioTransistorStatic indicating devicesMetallic materialsOxygen deficient
A thin film transistor structure in which a source electrode and a drain electrode formed from a metal material are in direct contact with an oxide semiconductor film may lead to high contact resistance. One cause of high contact resistance is that a Schottky junction is formed at a contact plane between the source and drain electrodes and the oxide semiconductor film. An oxygen-deficient oxide semiconductor layer which includes crystal grains with a size of 1 nm to 10 nm and has a higher carrier concentration than the oxide semiconductor film serving as a channel formation region is provided between the oxide semiconductor film and the source and drain electrodes.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Process for producing nano-scaled graphene plates
InactiveUS20050271574A1Faster and cost-effective processHighly cost-effectiveMaterial nanotechnologyGraphiteGrapheneGraphite particle
A process for producing nano-scaled graphene plates with each plate comprising a sheet of graphite plane or multiple sheets of graphite plane with the graphite plane comprising a two-dimensional hexagonal structure of carbon atoms. The process includes the primary steps of: (a) providing a powder of fine graphite particles comprising graphite crystallites with each crystallite comprising one sheet or normally a multiplicity of sheets of graphite plane bonded together; (b) exfoliating the graphite crystallites to form exfoliated graphite particles, which are characterized by having at least two graphite planes being either partially or fully separated from each other; and (c) subjecting the exfoliated graphite particles to a mechanical attrition treatment to further reduce at least one dimension of the particles to a nanometer scale, <100 nm, for producing the nano-scaled graphene plates.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
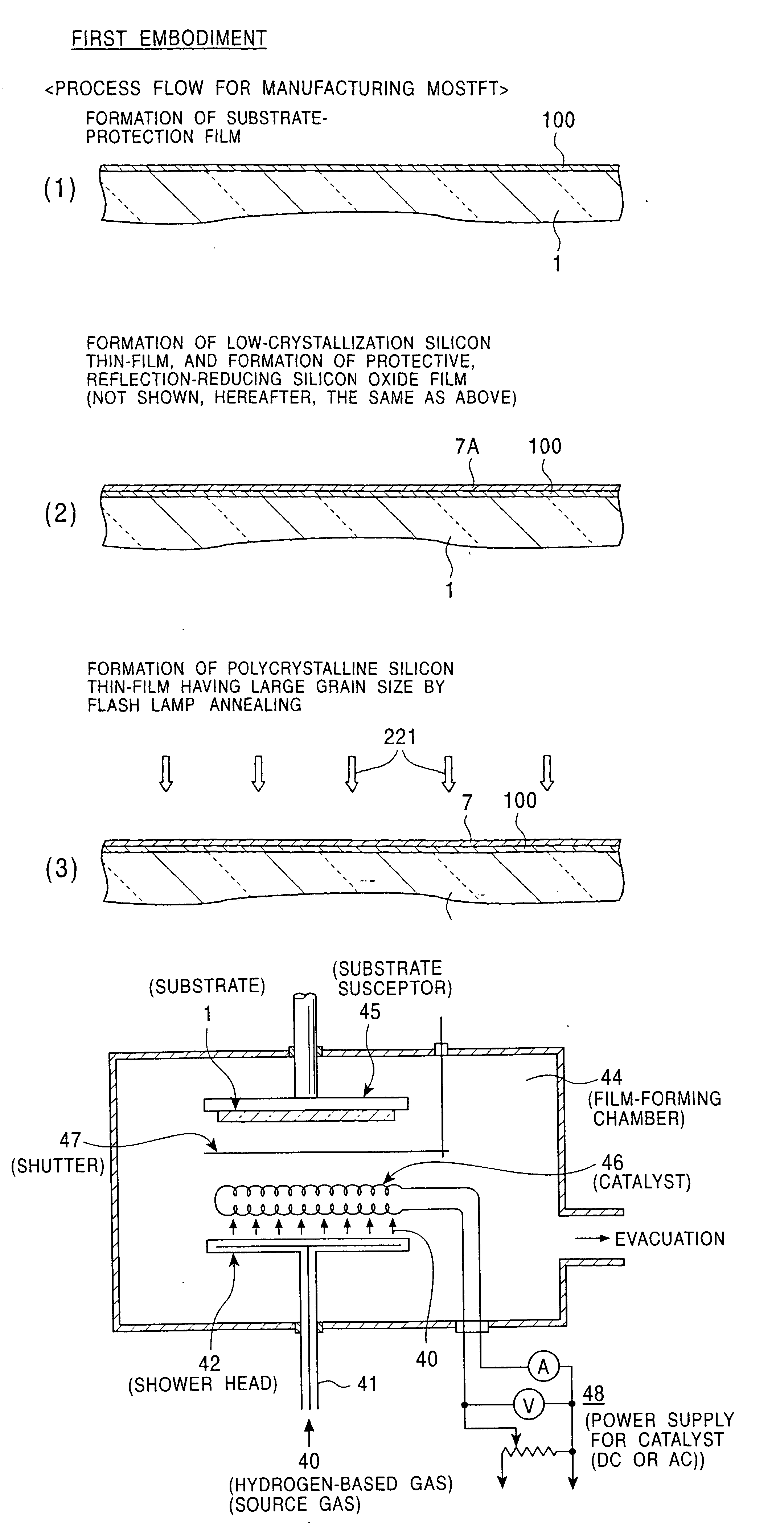
Semiconductor thin film forming method, production methods for semiconductor device and electrooptical device, devices used for these methods, and semiconductor device and electrooptical device
InactiveUS20030013280A1Promote crystallizationTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystalCrystallinity
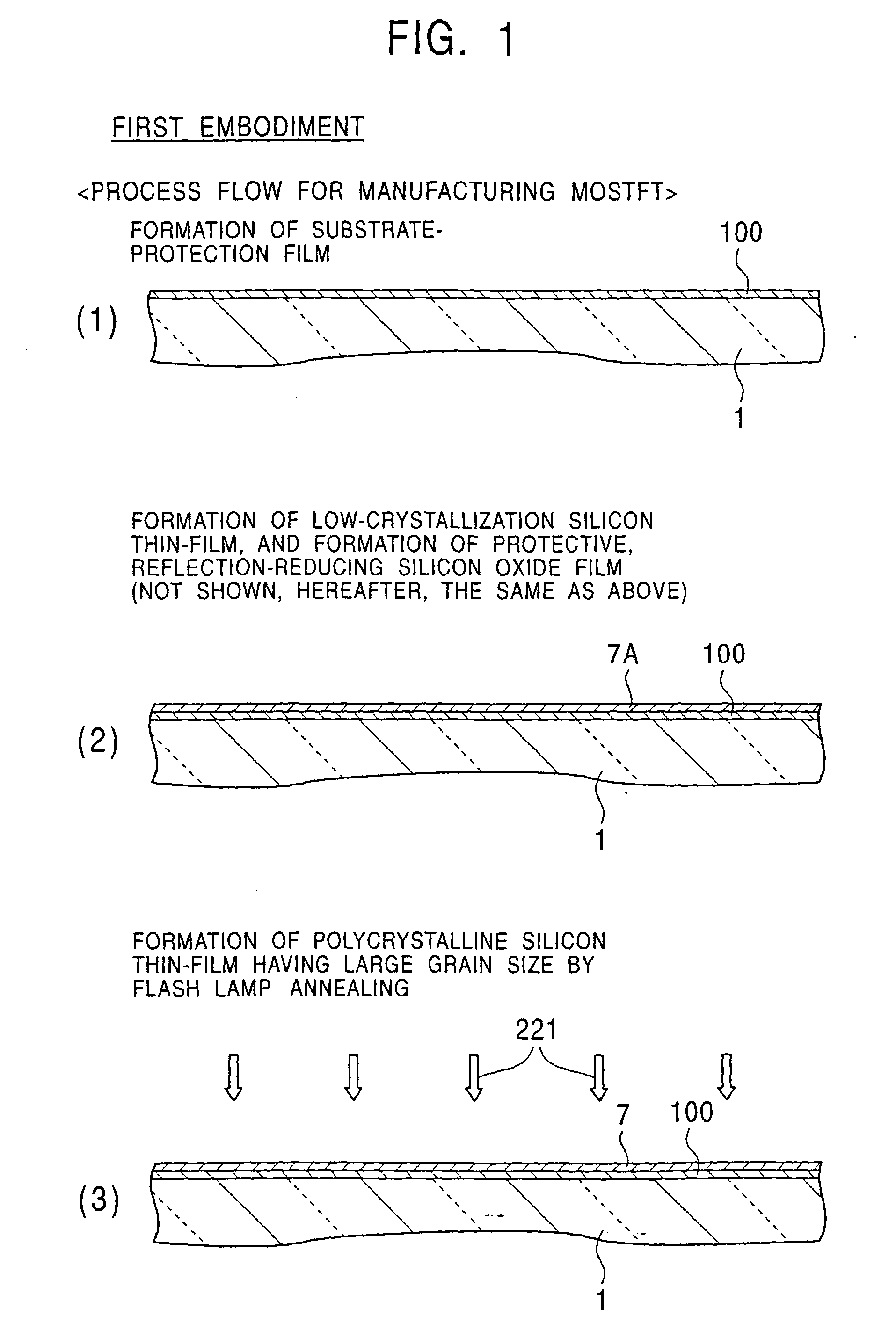
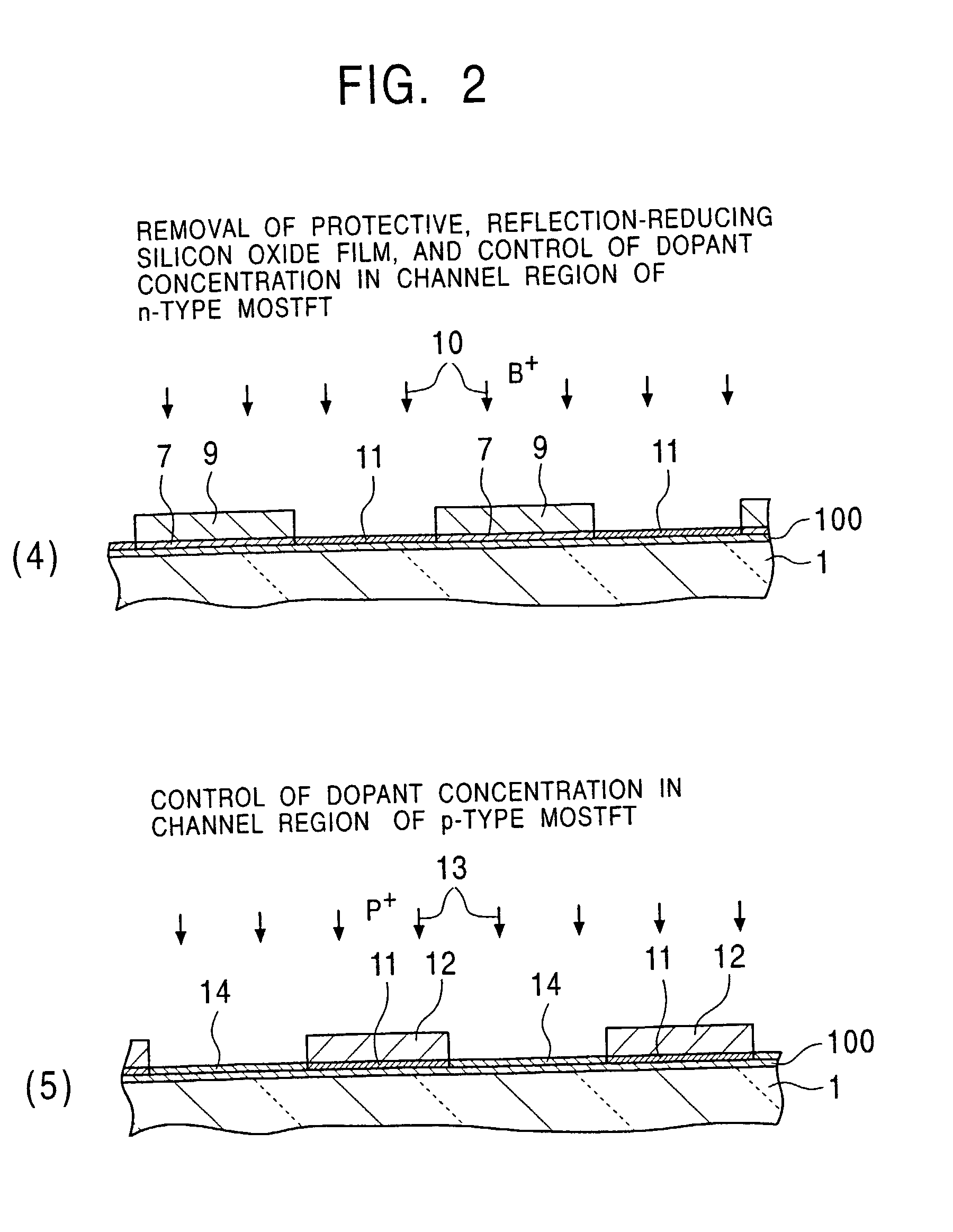
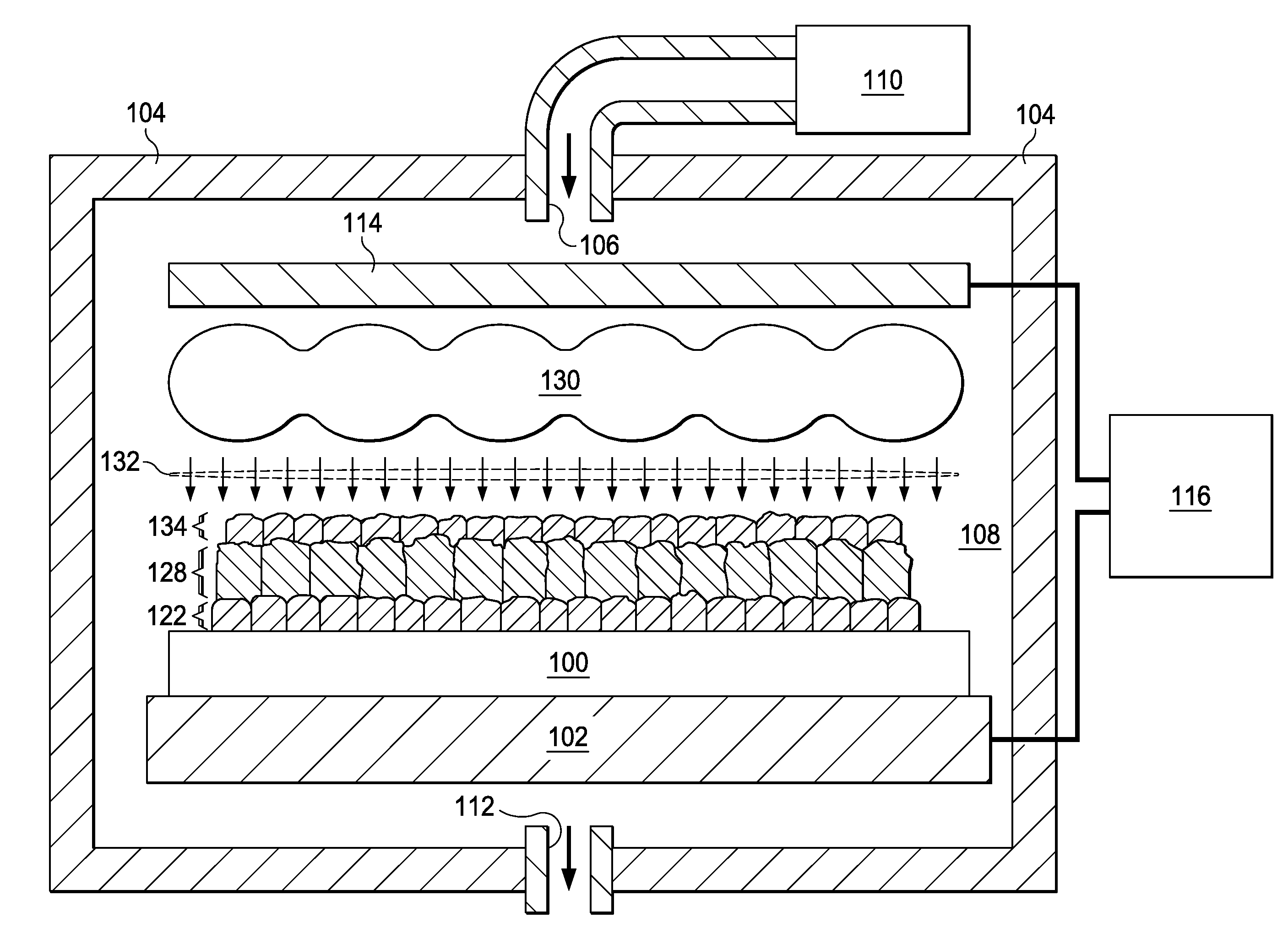
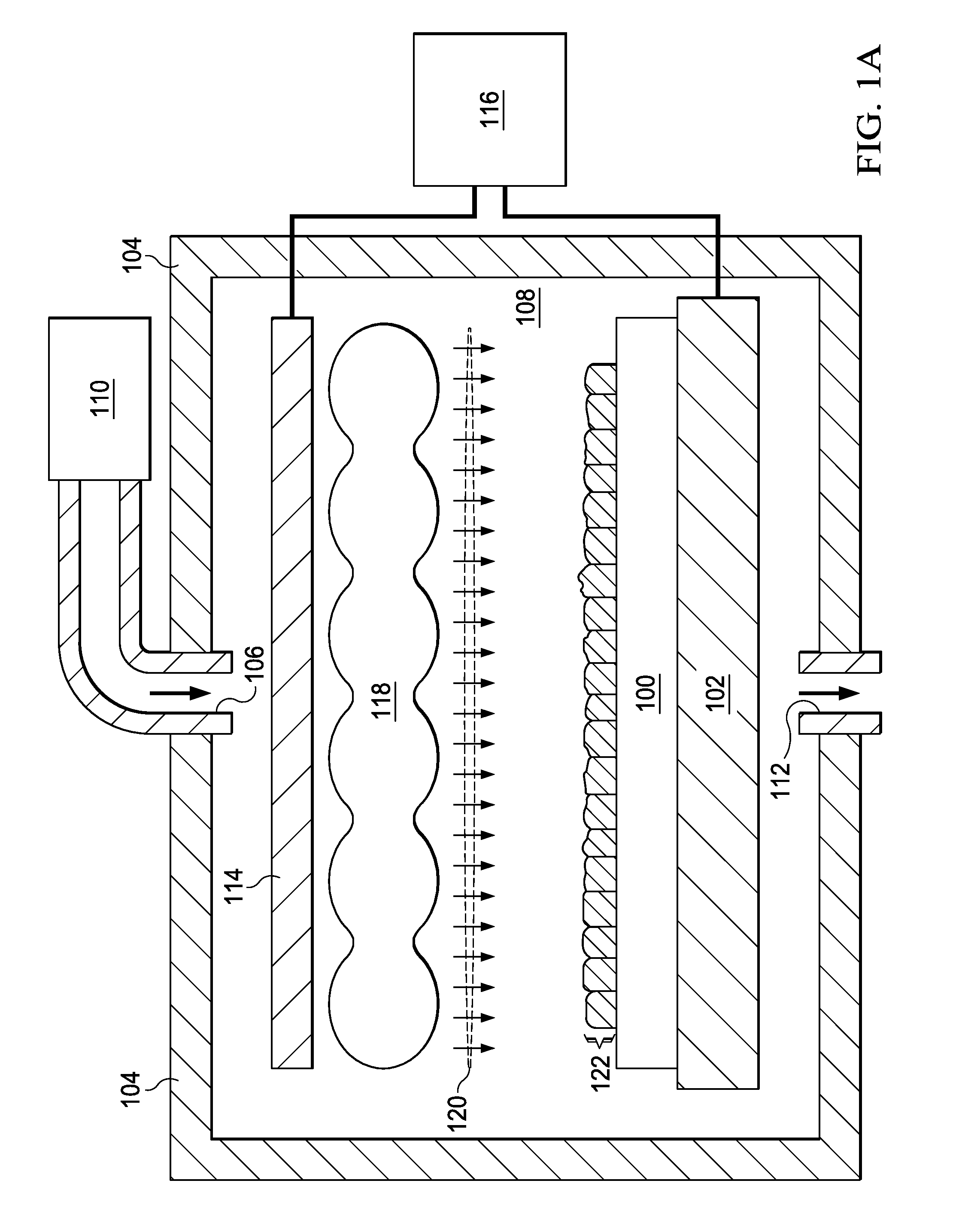
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for easily forming a polycrystalline semiconductor thin-film, such as polycrystalline silicon having high crystallinity and high quality, or a single crystalline semiconductor thin-film at inexpensive cost, the crystalline semiconductor thin-film having a large area, and to provide an apparatus for processing the method described above. In forming a polycrystalline (or single crystalline) semiconductor thin-film (7), such as a polycrystalline silicon thin-film, having high crystallinity and a large grain size on a substrate (1), or in forming a semiconductor device having the polycrystalline (or single crystalline) semiconductor thin-film (7) on the substrate (1), a method comprises forming a low-crystallization semiconductor thin-film (7A) on the substrate (1), and subsequently heating and cooling this low-crystallization semiconductor thin-film (7A) to a fusion, a semi-fusion, or a non-fusion state by flash lamp annealing to facilitate the crystallization of the low-crystallization semiconductor thin-film, whereby a polycrystalline (single crystalline) semiconductor thin-film (7) is obtained. A method for forming the semiconductor device and an apparatus for processing the methods are also disclosed.
Owner:SONY CORP
MODULATED DEPOSITION PROCESS FOR STRESS CONTROL IN THICK TiN FILMS
ActiveUS20100032842A1Liquid surface applicatorsIncorrect coupling preventionNitrogen plasmaDeposition process
A multi-layer TiN film with reduced tensile stress and discontinuous grain structure, and a method of fabricating the TiN film are disclosed. The TiN layers are formed by PVD or IMP in a nitrogen plasma. Tensile stress in a center layer of the film is reduced by increasing N2 gas flow to the nitrogen plasma, resulting in a Ti:N stoichiometry between 1:2.1 to 1:2.3. TiN films thicker than 40 nanometers without cracks are attained by the disclosed process.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of forming polycrystalline silicon layer and atomic layer deposition apparatus used for the same
ActiveUS20110263107A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconOptoelectronics
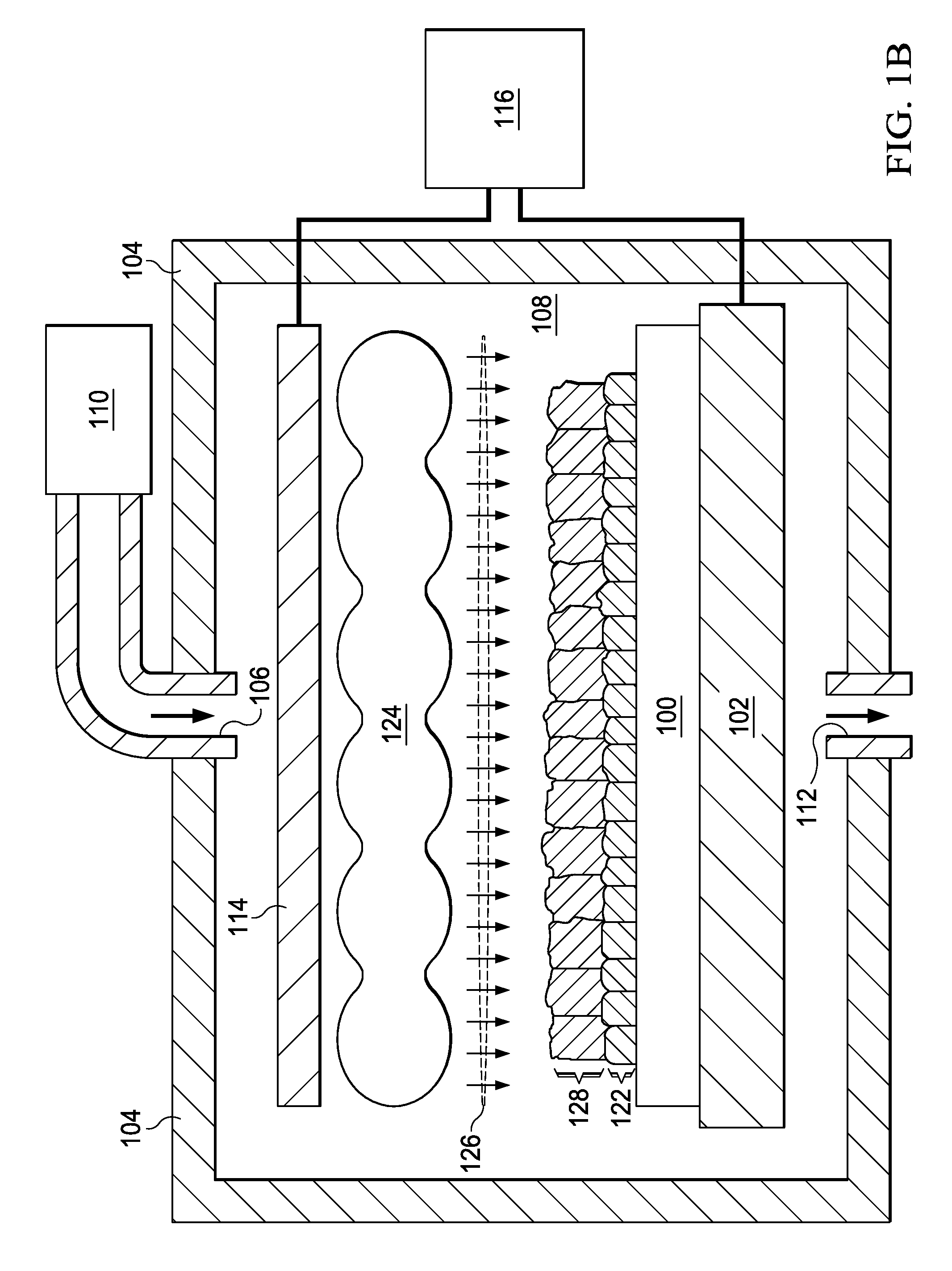
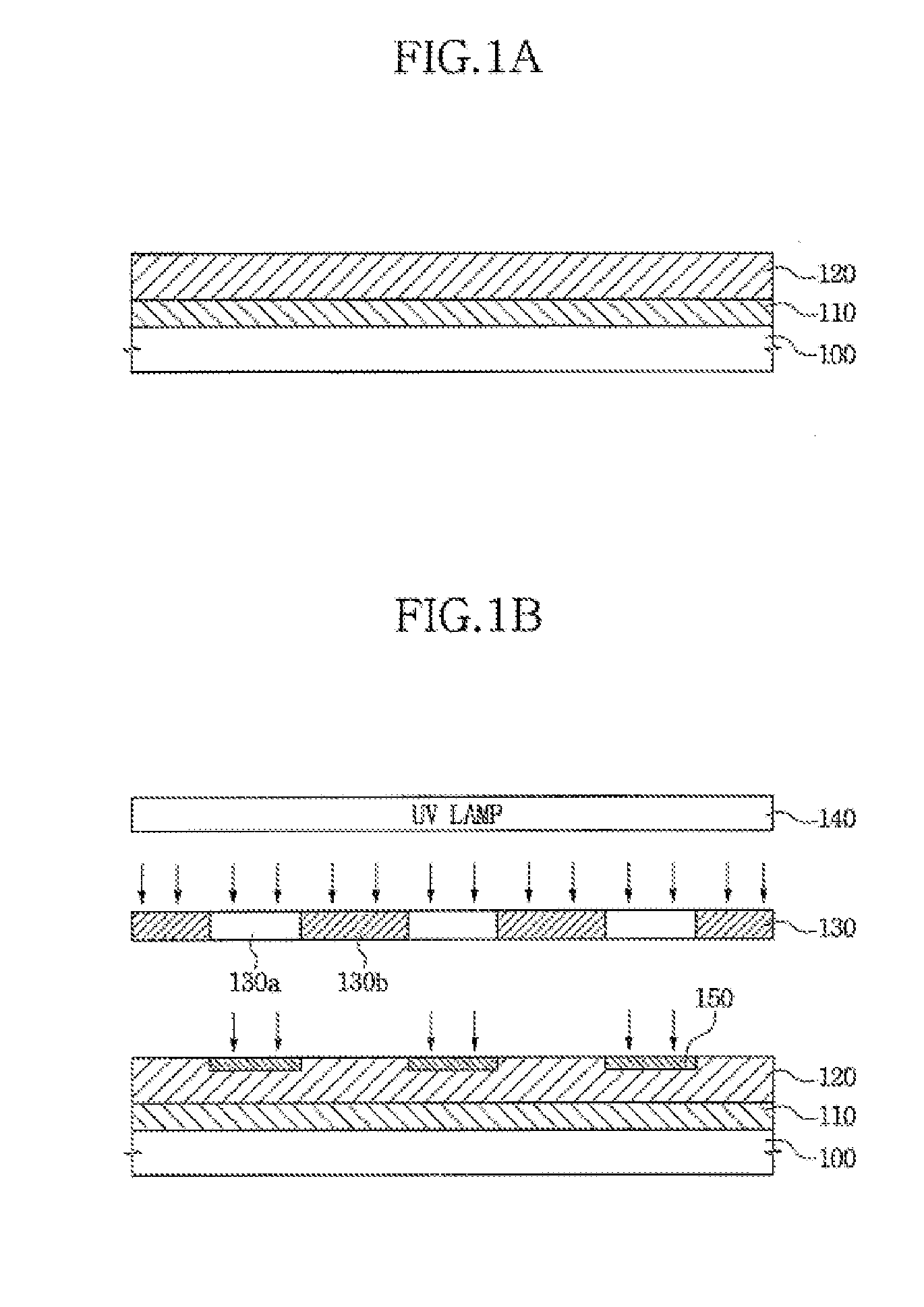
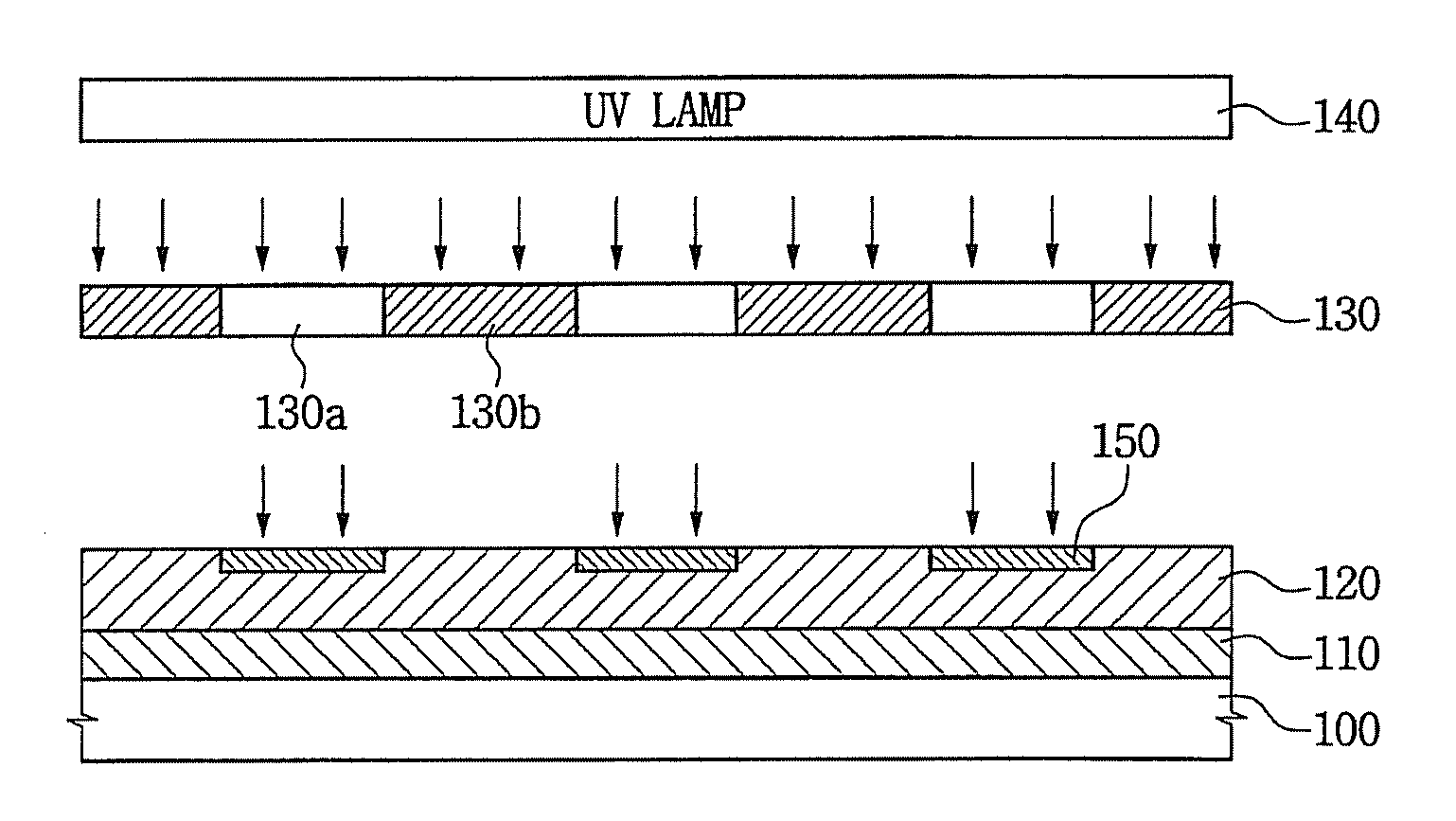
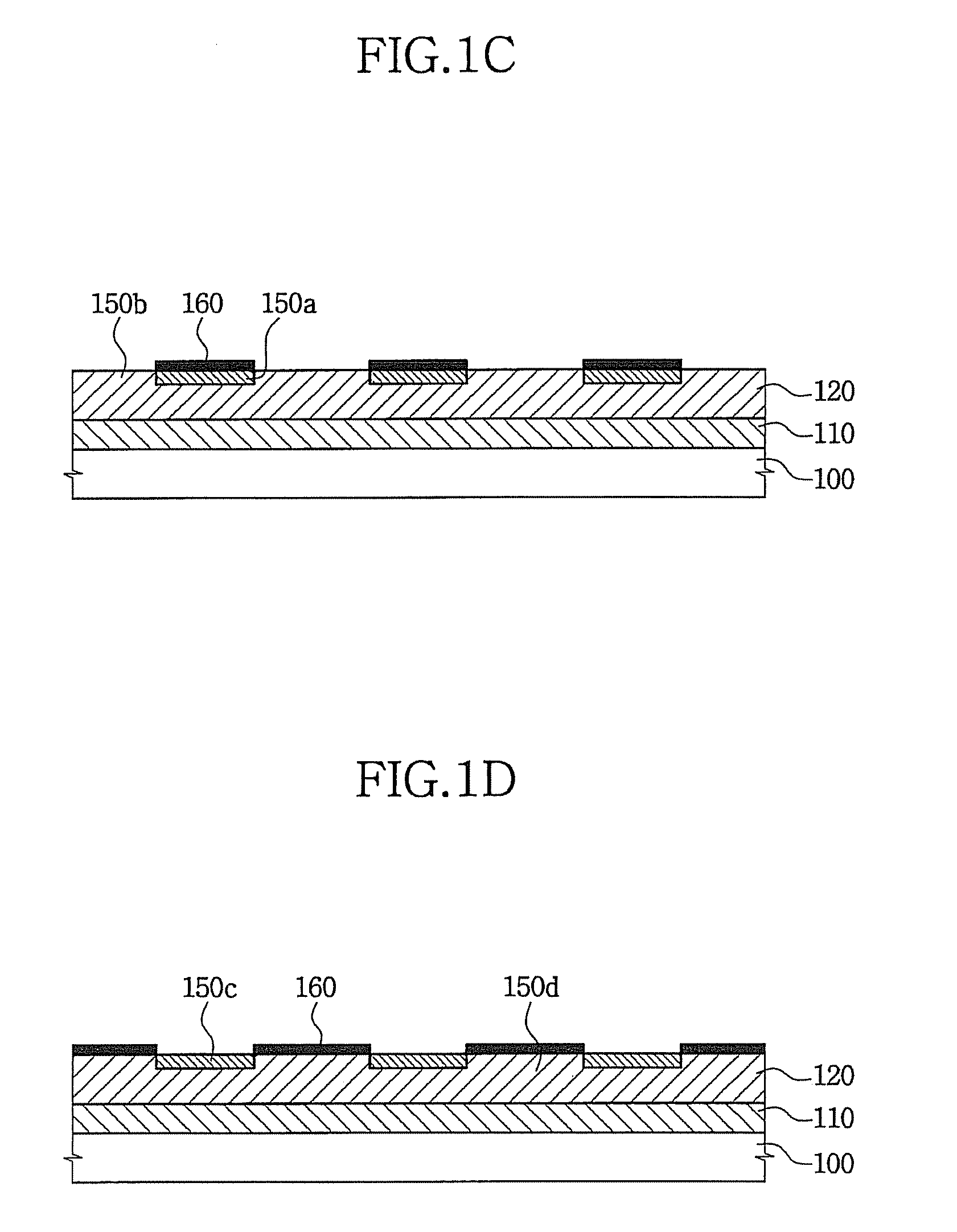
A method of forming a polycrystalline silicon layer and an atomic layer deposition apparatus used for the same. The method includes forming an amorphous silicon layer on a substrate, exposing the substrate having the amorphous silicon layer to a hydrophilic or hydrophobic gas atmosphere, placing a mask having at least one open and at least one closed portion over the amorphous silicon layer, irradiating UV light toward the amorphous silicon layer and the mask using a UV lamp, depositing a crystallization-inducing metal on the amorphous silicon layer, and annealing the substrate to crystallize the amorphous silicon layer into a polycrystalline silicon layer. This method and apparatus provide for controlling the seed position and grain size in the formation of a polycrystalline silicon layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Porous silicon particulates for lithium batteries
An anode structure for lithium batteries includes nanofeatured silicon particulates dispersed in a conductive network. The particulates are preferably made from metallurgical grade silicon powder via HF / HNO3 acid treatment, yielding crystallite sizes from about 1 to 20 nm and pore sizes from about 1 to 100 nm. Surfaces of the particles may be terminated with selected chemical species to further modify the anode performance characteristics. The conductive network is preferably a carbonaceous material or composite, but it may alternatively contain conductive ceramics such as TiN or B4C. The anode structure may further contain a current collector of copper or nickel mesh or foil.
Owner:TIEGS TERRY N
Method of manufacturing a multilayer semiconductor structure with reduced ohmic losses
InactiveUS20070032040A1Reduce and minimiseElectrical losses are reducedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInter layerSemiconductor structure
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a multilayer semiconductor structure featuring reduced ohmic losses with respect to standard multilayer semiconductor structures. The semiconductor structure comprises a high resistivity silicon substrate with resistivity higher than 3 KΩ.cm, an active semiconductor layer and an insulating layer in between the silicon substrate and the active semiconductor layer. The method comprises suppressing ohmic losses inside the high resistivity silicon substrate by increasing, with regard to prior art devices, charge trap density between the insulating layer and the silicon substrate. In particular this may be obtained by applying an intermediate layer in between the silicon substrate and the insulating layer, the intermediate layer comprising grains having a size, wherein the mean size of the grains of the intermediate layer is smaller than 150 nm, preferably smaller than 50 nm.
Owner:UNIV CATHOLIQUE DE LOVAIN
Method of fabricating poly-crystalline silicon thin film and method of fabricating transistor using the same
InactiveUS7563659B2Refined grain sizeHigh energyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInductively coupled plasmaSilicon thin film
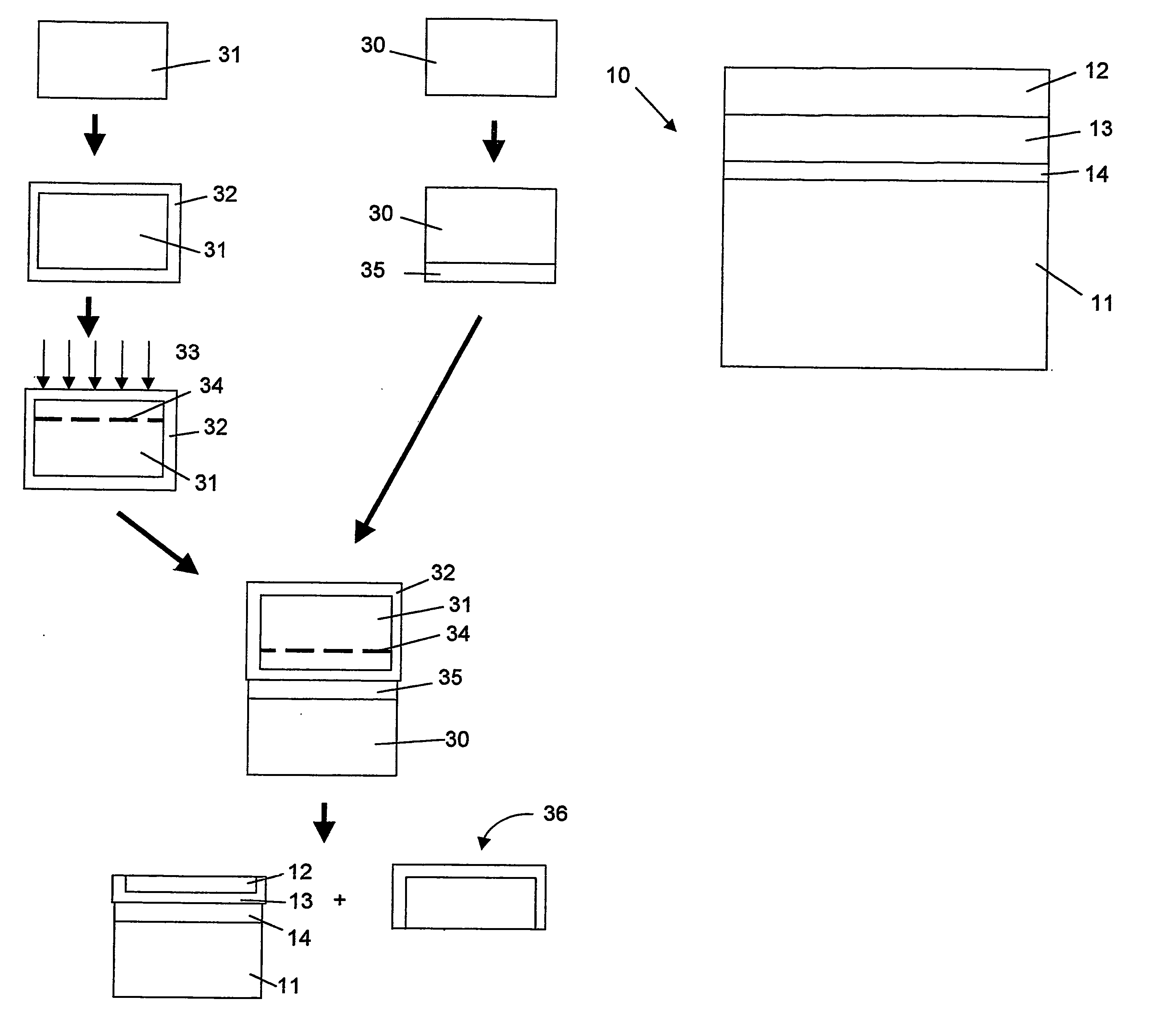
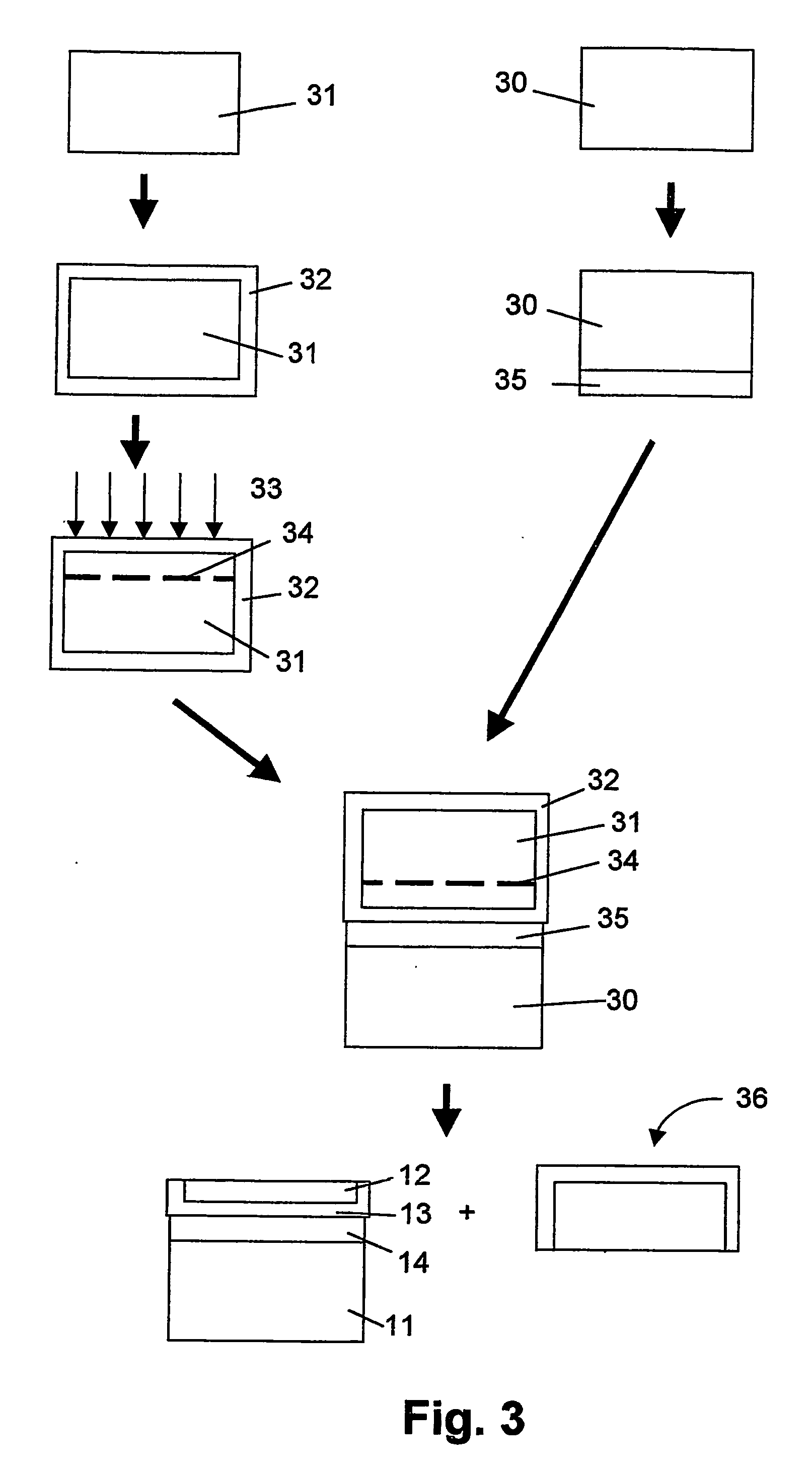
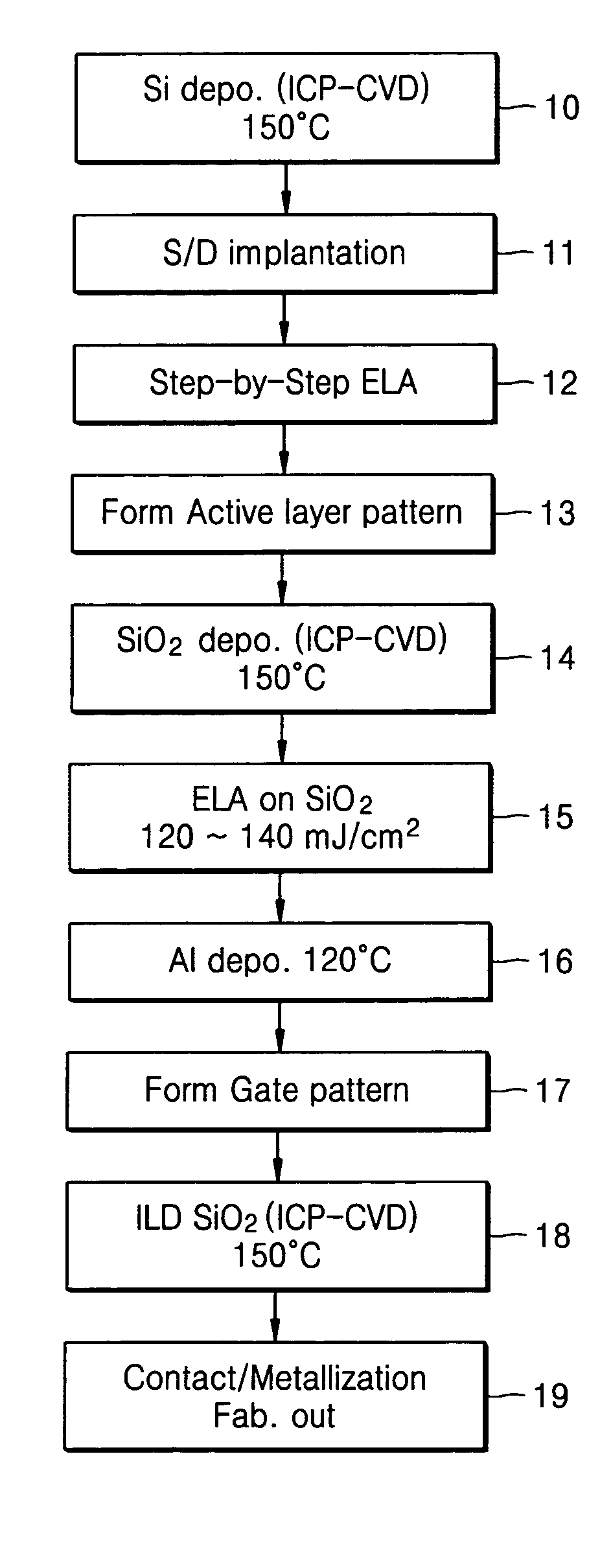
A method of fabricating a poly-Si thin film and a method of fabricating a poly-Si TFT using the same are provided. The poly-Si thin film is formed at a low temperature using inductively coupled plasma chemical vapor deposition (ICP-CVD). After the ICP-CVD, excimer laser annealing (ELA) is performed while increasing energy by predetermined steps. A poly-Si active layer and a SiO2 gate insulating layer are deposited at a temperature of about 150° C. using ICP-CVD. The poly-Si has a large grain size of about 3000 Å or more. An interface trap density of the SiO2 can be as high as 1011 / cm2. A transistor having good electrical characteristics can be fabricated at a low temperature and thus can be formed on a heat tolerant plastic substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
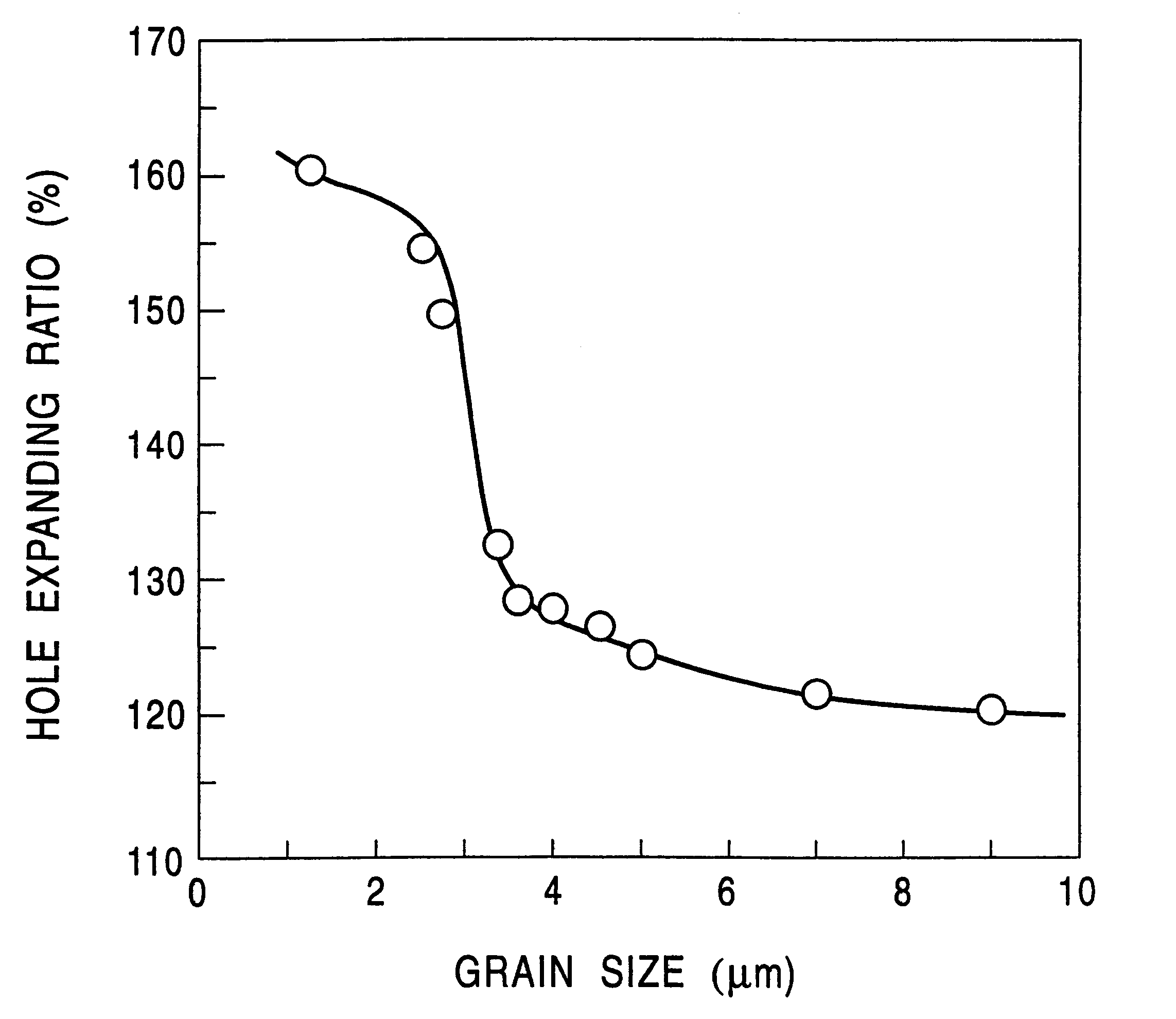
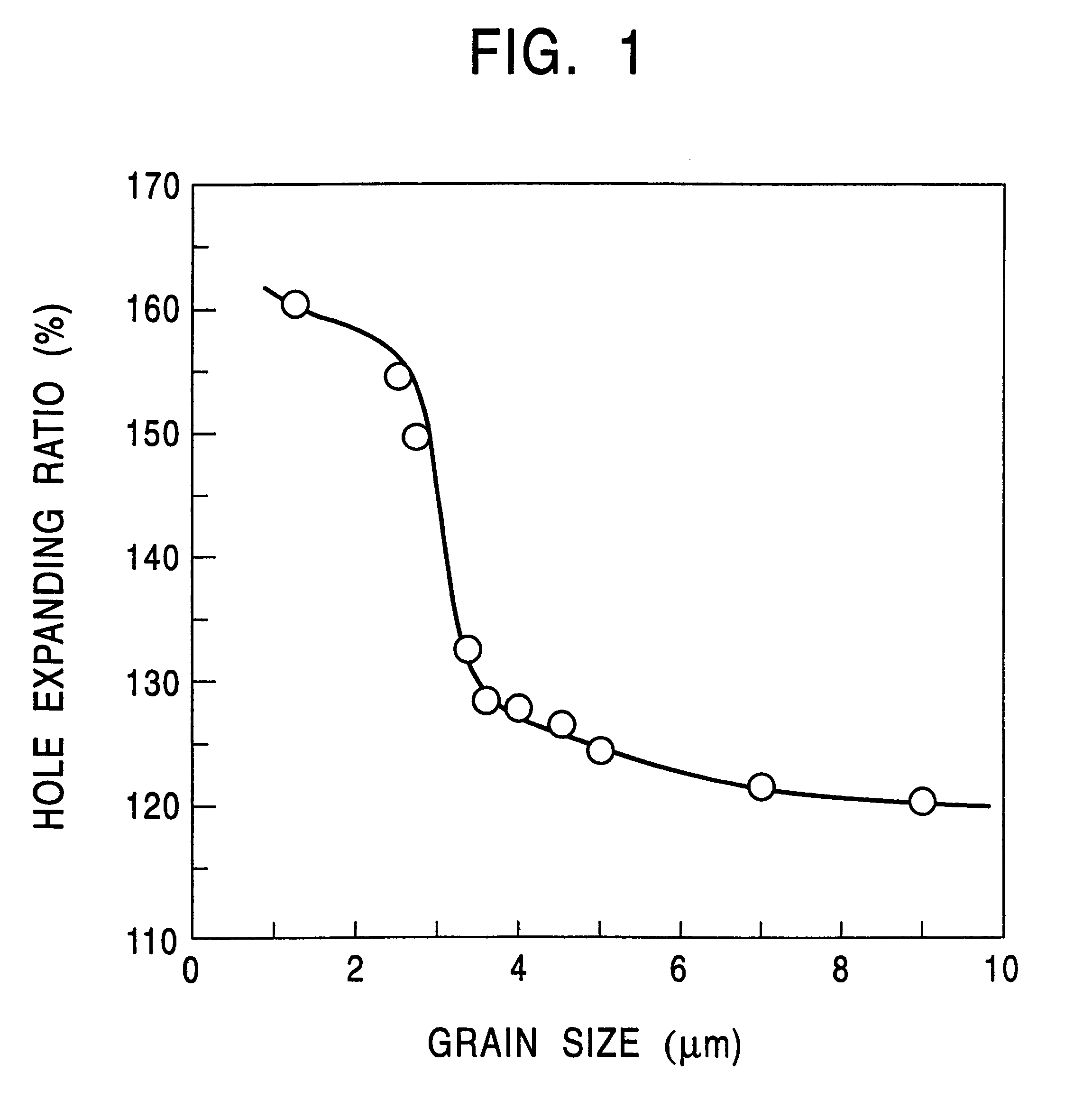
High-strength hot-rolled steel sheet having excellent stretch flangeability, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6364968B1Easy to stretchImprove uniformityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesHigh intensityMechanical property
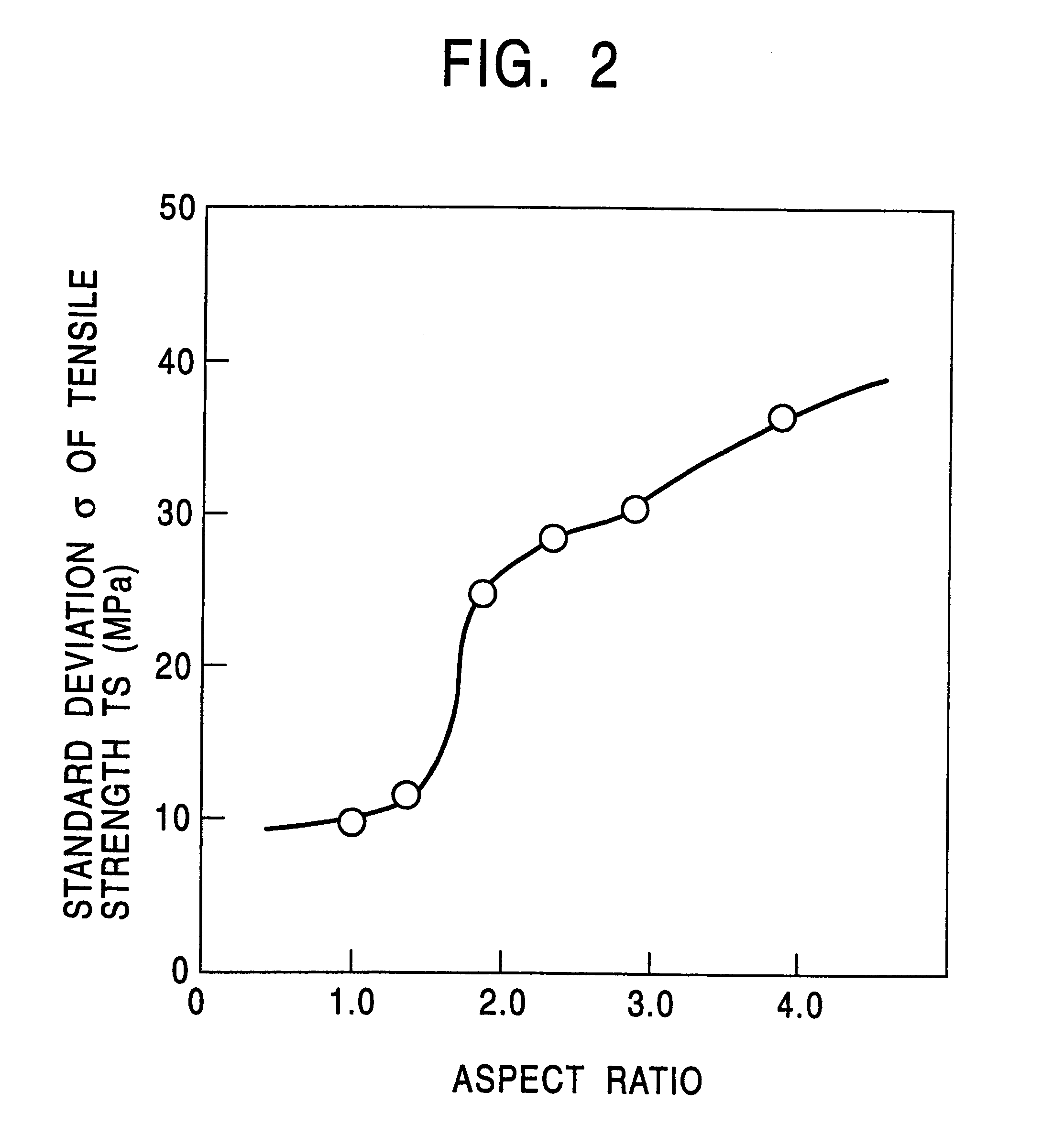
The invention provides a thin high-strength hot-rolled steel sheet with a thickness of not more than 3.5 mm which has excellent stretch flangeability and high uniformity in both shape and mechanical properties of the steel sheet, as well as a method of producing the hot-rolled steel sheet. A slab containing C: 0.05-0.30 wt %, Si: 0.03-1.0 wt %, Mn: 1.5-3.5 wt %, P: not more than 0.02 wt %, S: not more than 0.005 wt %, Al: not more than 0.150 wt %, N: not more than 0.0200 wt %, and one or two of Nb: 0.003-0.20 wt % and Ti: 0.005-0.20 wt % is heated at a temperature of not higher than 1200° C. The slab is hot-rolled at a finish rolling end temperature of not lower than 800° C., preferably at a finish rolling start temperature of 950-1050° C. A hot-rolled sheet is started to be cooled within two seconds after the end of the rolling, and then continuously cooled down to a coiling temperature at a cooling rate of 20-150° C. / sec. The hot-rolled sheet is coiled at a temperature of 300-550° C., preferably in excess of 400° C. A fine bainite structure is obtained in which the mean grain size is not greater than 3.0 mum, the aspect ratio is not more than 1.5, and preferably the maximum size of the major axis is not greater than 10 mum.
Owner:KAWASAKI STEEL CORP
Method of forming polycrystalline silicon layer and atomic layer deposition apparatus used for the same
A method of forming a polycrystalline silicon layer and an atomic layer deposition apparatus used for the same. The method includes forming an amorphous silicon layer on a substrate, exposing the substrate having the amorphous silicon layer to a hydrophilic or hydrophobic gas atmosphere, placing a mask having at least one open and at least one closed portion over the amorphous silicon layer, irradiating UV light toward the amorphous silicon layer and the mask using a UV lamp, depositing a crystallization-inducing metal on the amorphous silicon layer, and annealing the substrate to crystallize the amorphous silicon layer into a polycrystalline silicon layer. This method and apparatus provide for controlling the seed position and grain size in the formation of a polycrystalline silicon layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Magnetic write head with high moment magnetic thin film formed over seed layer
A magnetic write head includes a seed layer and a magnetic layer on the seed layer. The seed layer includes seed-layer grains having either a face-centered cubic (fcc) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [111] direction or a hexagonal-close-packed (hcp) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [0001] direction. The magnetic layer includes magnetic-layer grains having a body-centered-cubic (bcc) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [110] direction.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
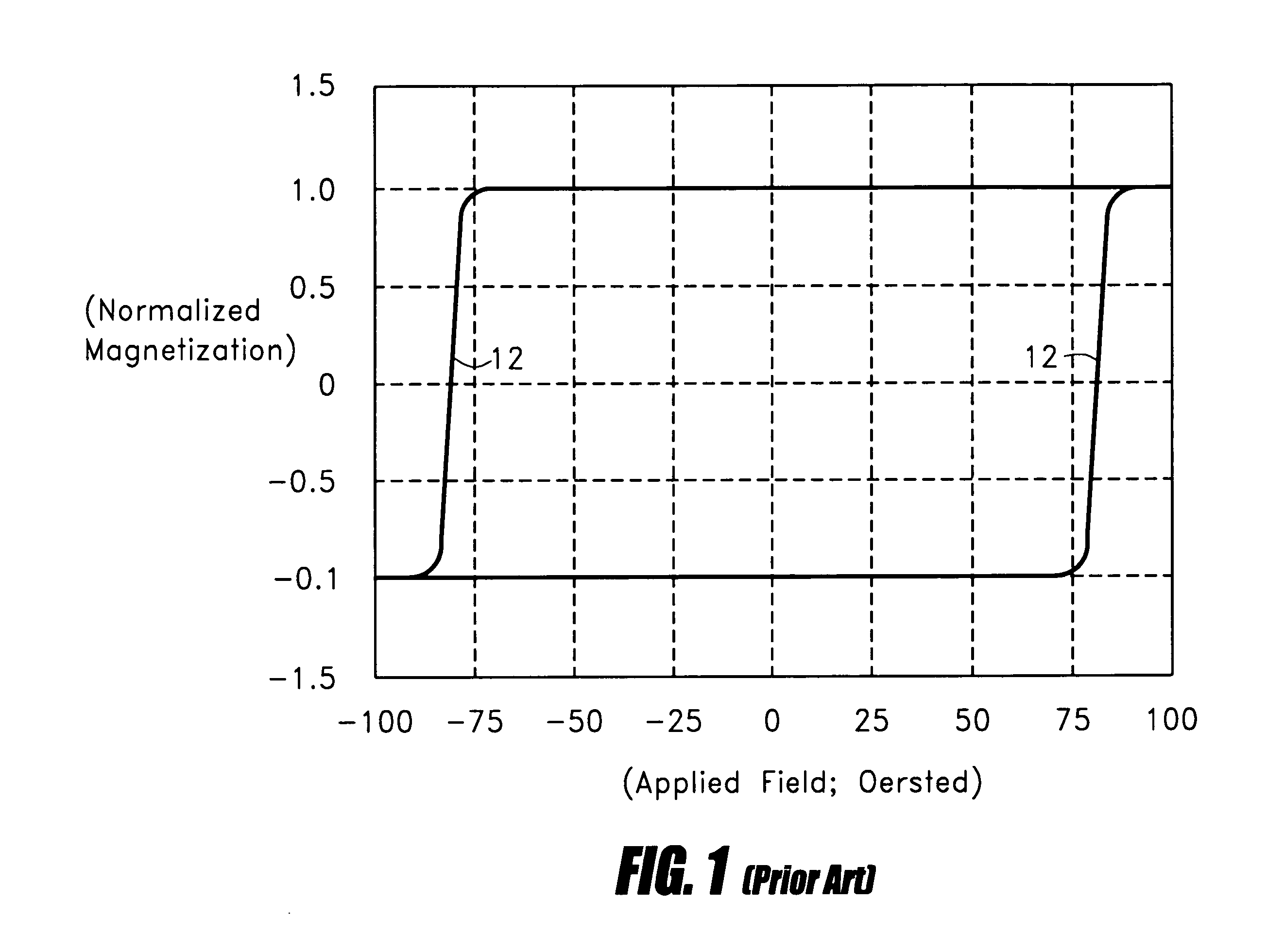
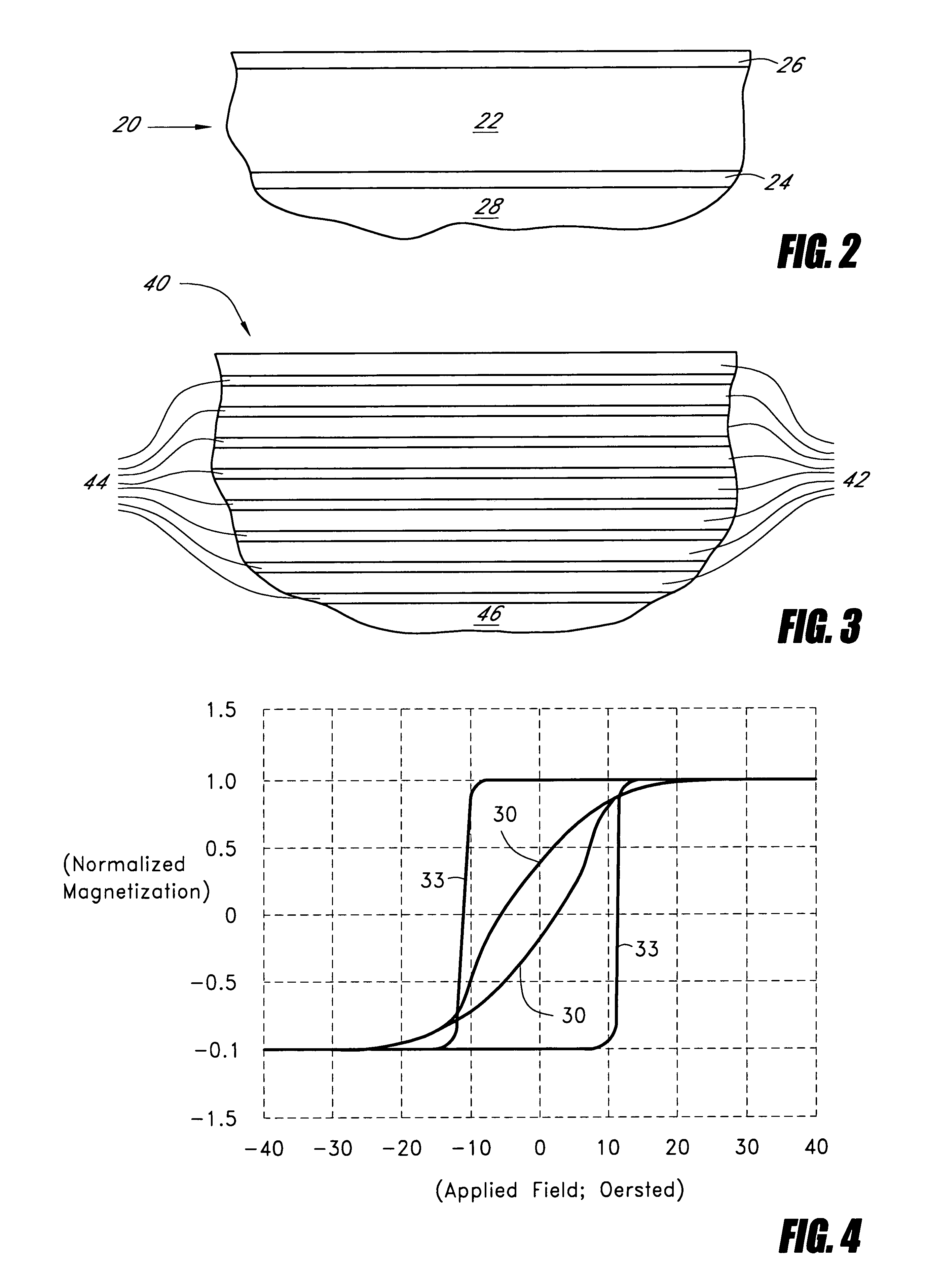
Method for preparing cryomilled aluminum alloys and components extruded and forged therefrom
InactiveUS6902699B2Stable structureHigh strengthTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusNanostructureAluminium alloy
High strength aluminum alloy powders, extrusions, and forgings are provided in which the aluminum alloys exhibit high strength at atmospheric temperatures and maintain high strength and ductility at extremely low temperatures. The alloy is produced by blending about 89 atomic % to 99 atomic % aluminum, 1 atomic % to 11 atomic % of a secondary metal selected from the group consisting of magnesium, lithium, silicon, titanium, zirconium, and combinations thereof, and up to about 10 atomic % of a tertiary metal selected from the group consisting of Be, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra, Sc, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Y, Nb, Mo, Tc, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd, W, and combinations thereof. The alloy is produced by nanostructure material synthesis, such as cryomilling, in the absence of refractory dispersoids. The synthesized alloy is then canned, degassed, consolidated, extruded, and optionally forged into a solid metallic component. Grain size within the alloy is less than 0.5 μm, and alloys with grain size less than 0.1 μm may be produced.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
High purity tantalum, products containing the same, and methods of making the same
InactiveUS6348113B1Fine grain structureUniform textureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMetallic materialsUltimate tensile strength
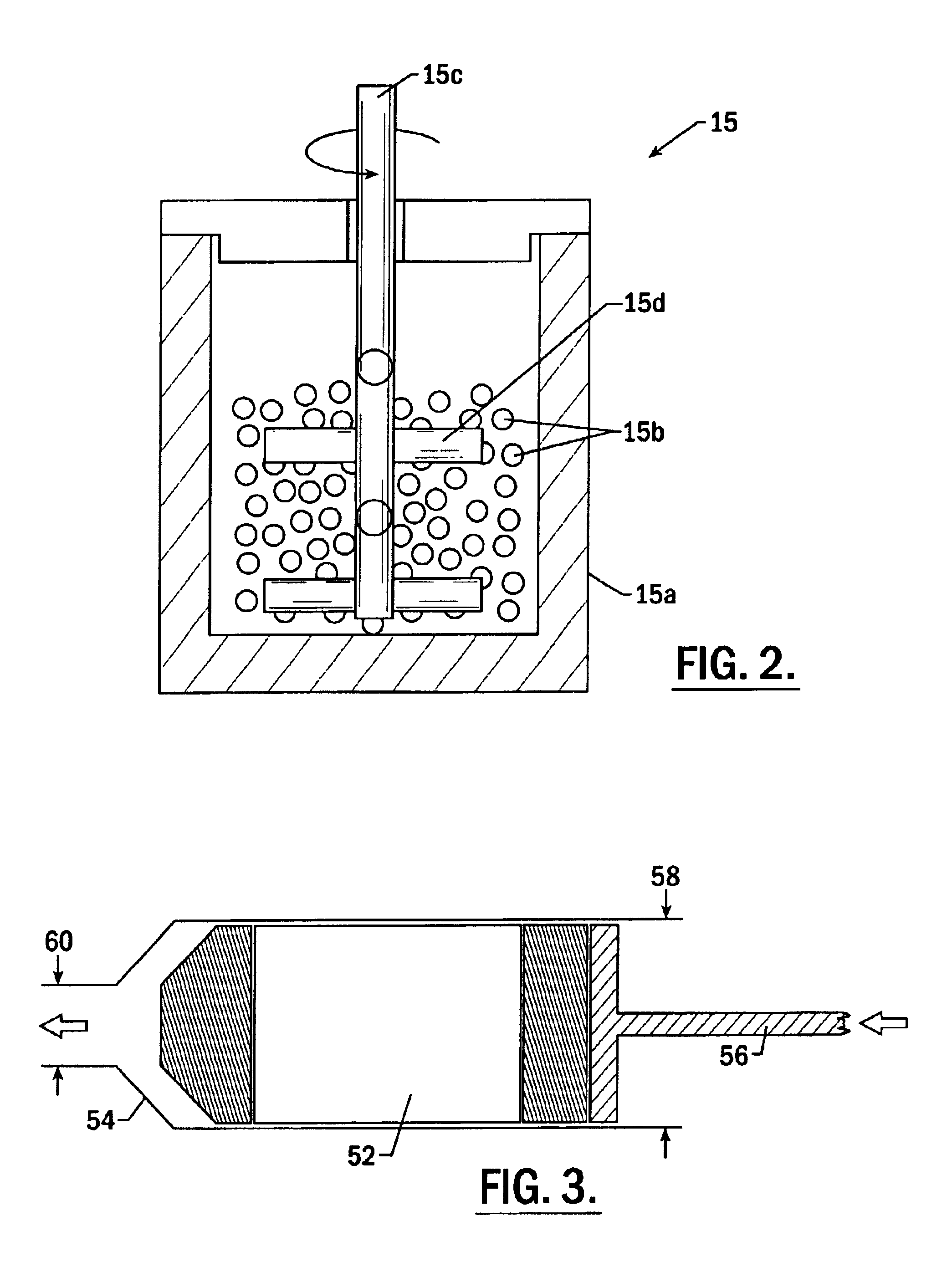
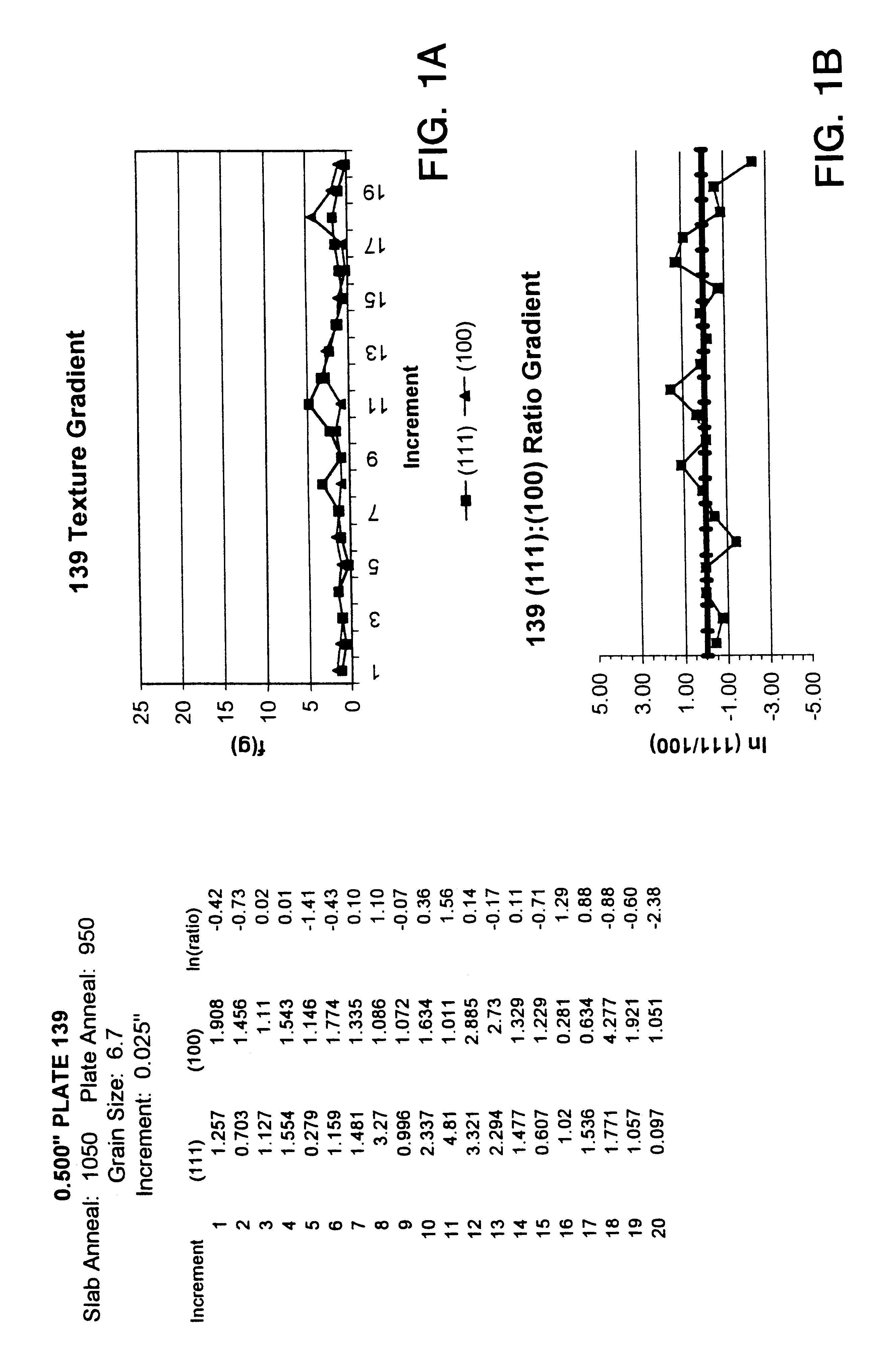
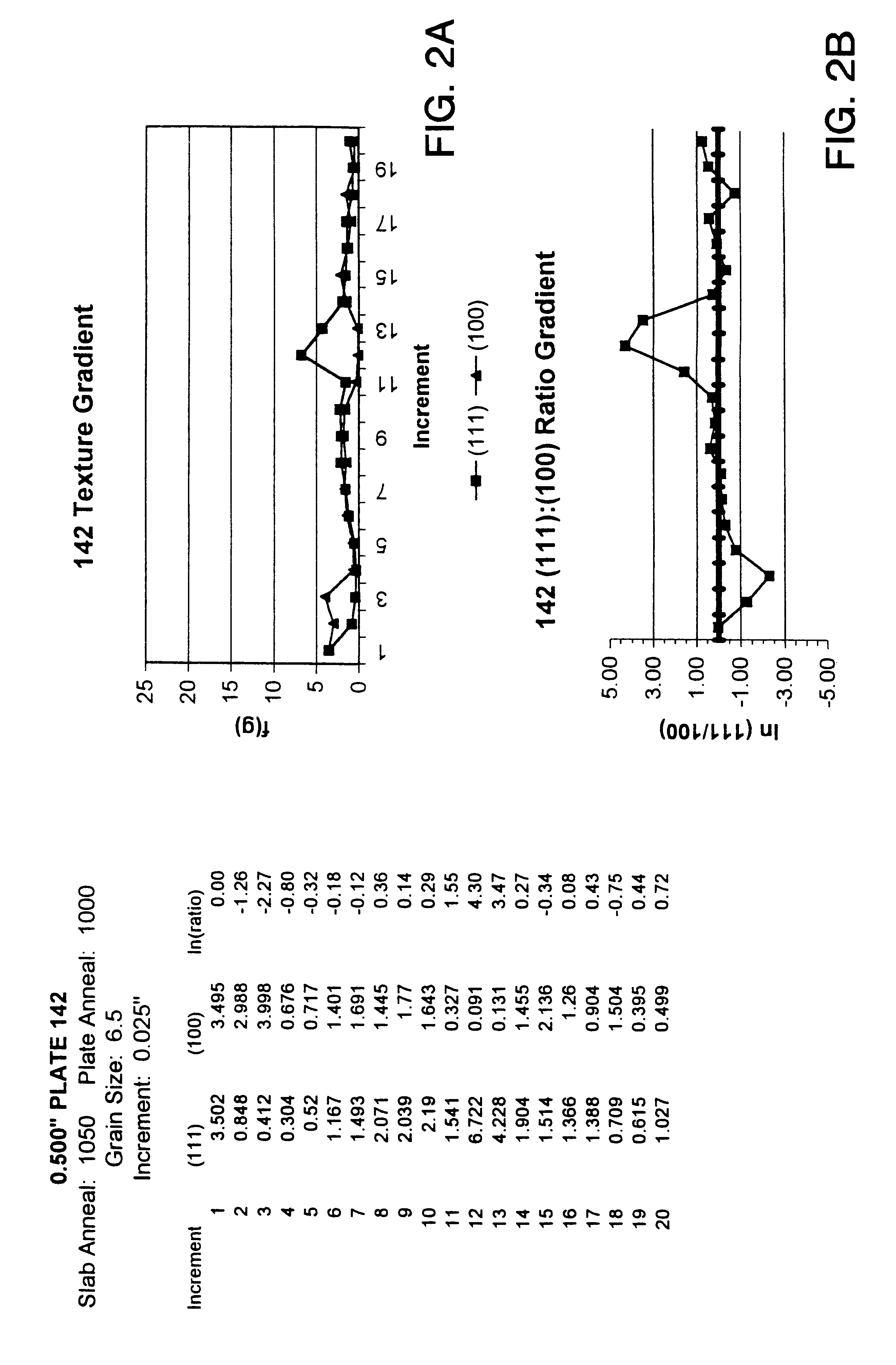
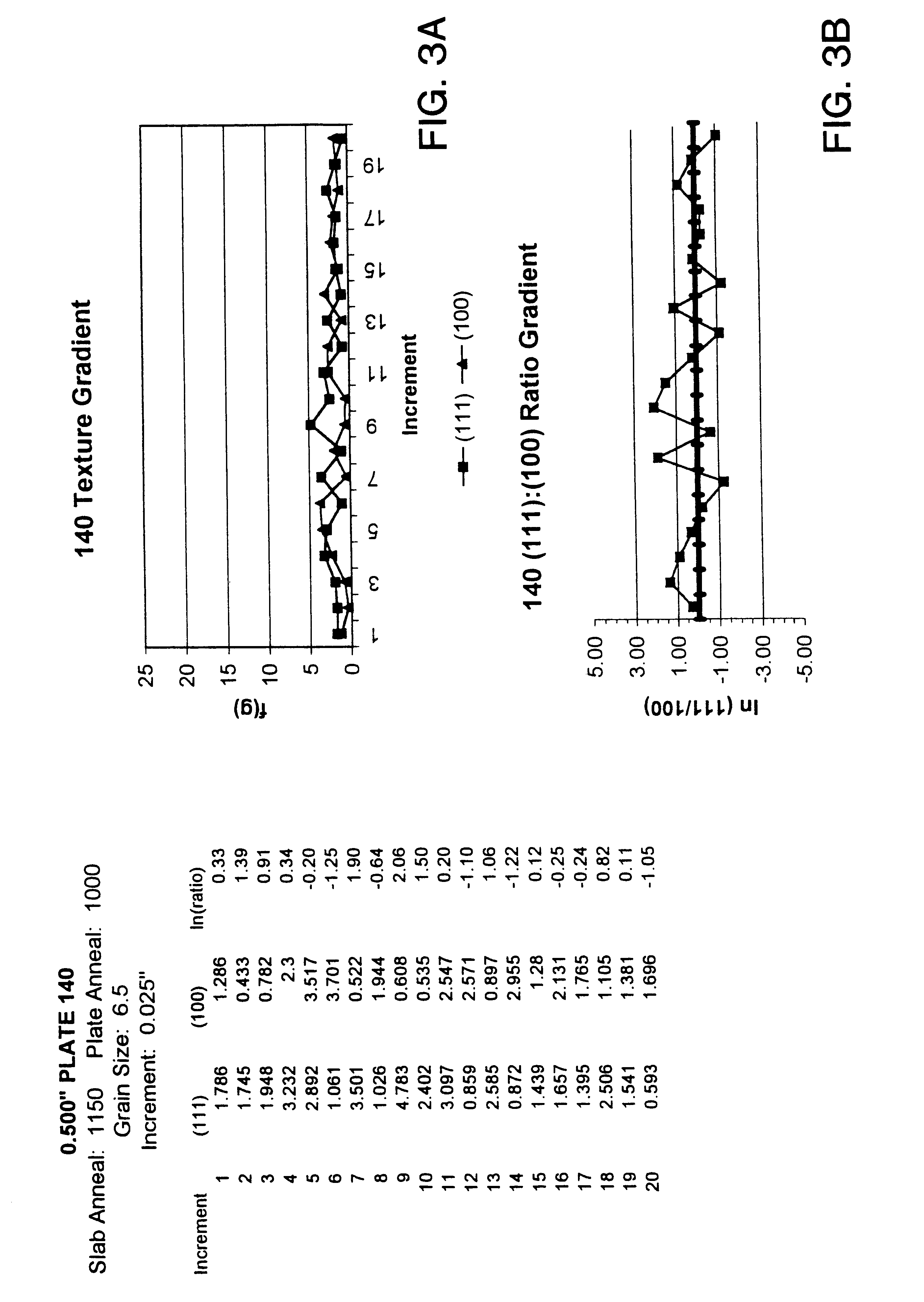
High purity tantalum metals and alloys containing the same are described. The tantalum metal preferably has a purity of at least 99.995% and more preferably at least 99.999%. In addition, tantalum metal and alloys thereof are described, which either have a grain size of about 50 microns or less, or a texture in which a (100) intensity within any 5% increment of thickness is less than about 15 random, or an incremental log ratio of (111):(100) intensity of greater than about -4.0, or any combination of these properties. Also described are articles and components made from the tantalum metal which include, but are not limited to, sputtering targets, capacitor cans, resistive film layers, wire, and the like. Also disclosed is a process for making the high purity metal which includes the step of reacting a salt-containing tantalum with at least one compound capable of reducing this salt to tantalum powder and a second salt in a reaction container. The reaction container or liner in the reaction container and the agitator or liner on the agitator are made from a metal material having the same or higher vapor pressure of melted tantalum. The high purity tantalum preferably has a fine and uniform microstructure.
Owner:GLOBAL ADVANCED METALS USA
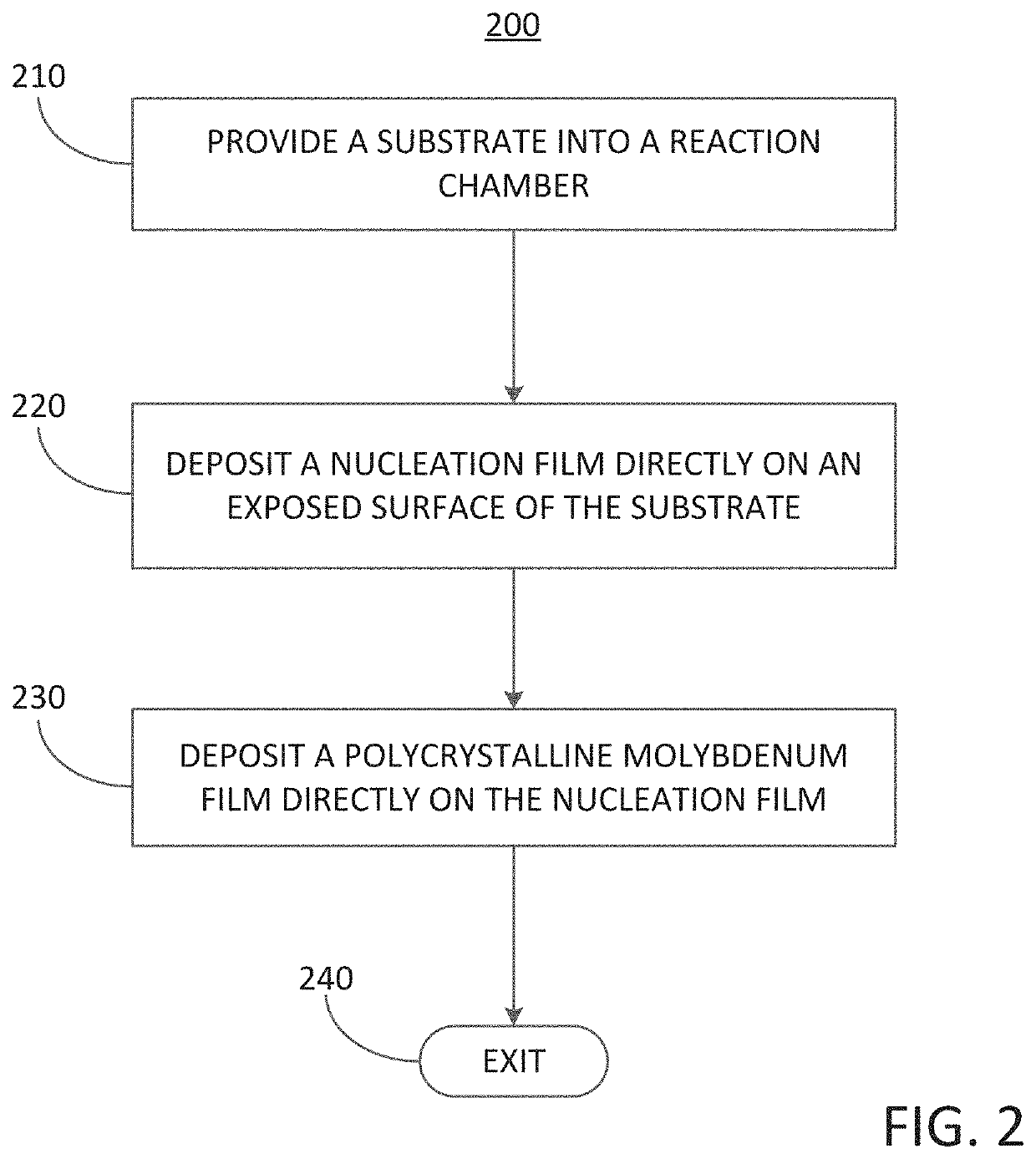
Methods for forming a polycrystalline molybdenum film over a surface of a substrate and related structures including a polycrystalline molybdenum film
Methods for forming a polycrystalline molybdenum film over a surface of a substrate are disclosed. The methods may include: providing a substrate into a reaction chamber; depositing a nucleation film directly on an exposed surface of the substrate, wherein the nucleation film comprises one of a metal oxide nucleation film or a metal nitride nucleation film; and depositing a polycrystalline molybdenum film directly on the nucleation film; wherein the polycrystalline molybdenum film comprises a plurality of molybdenum crystallites having an average crystallite size of less than 80 Å. Structures including a polycrystalline molybdenum film disposed over a surface of a substrate with an intermediate nucleation film are also disclosed.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Carbonaceous material for electrode and non-aqueous solvent secondary battery using this material
InactiveUS6632569B1Large discharge capacityImprove propertiesAlkaline accumulatorsConductive materialX-rayPeak value
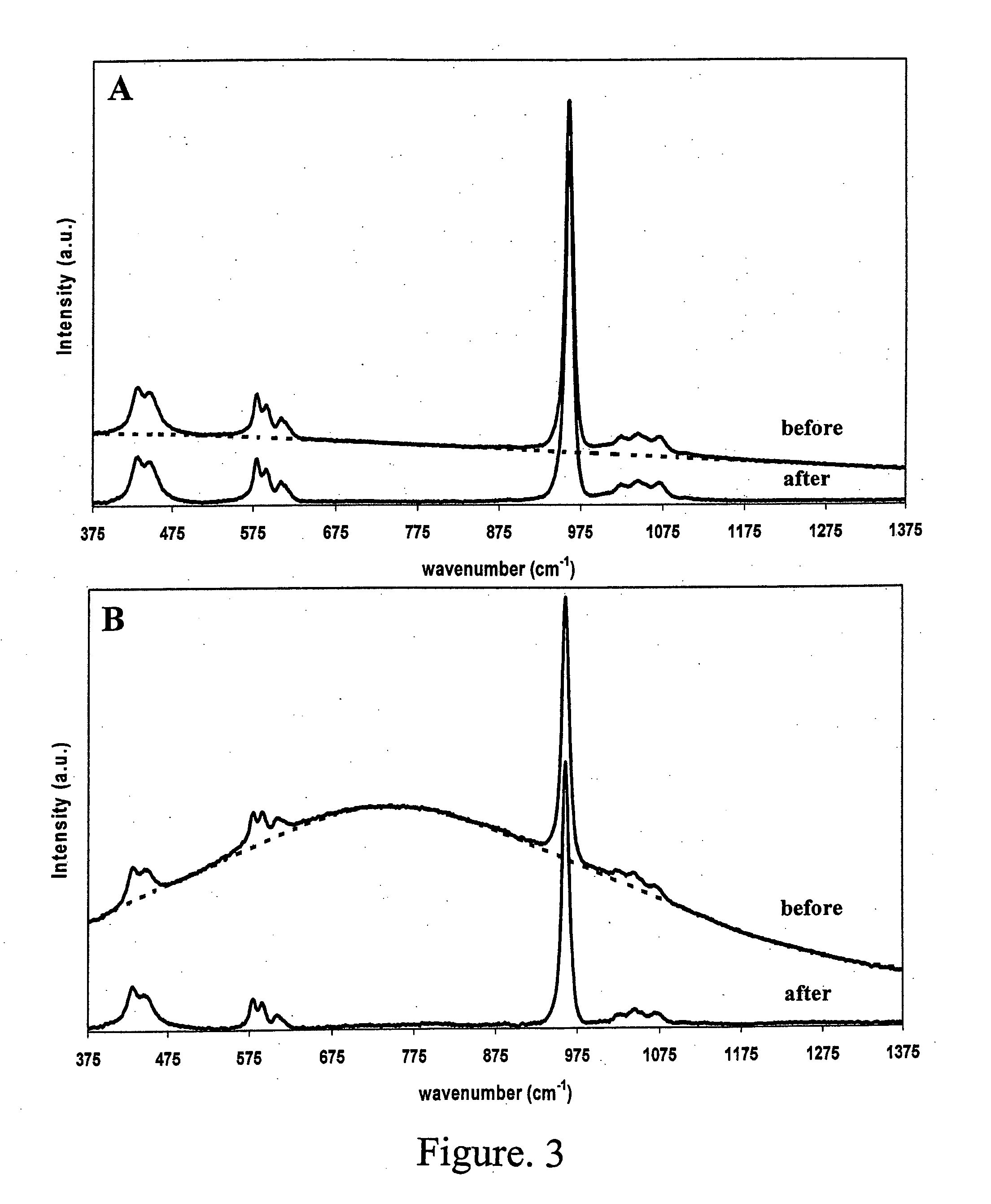
A carbonaceous material has a plane space d002 of a (002) plane less than 0.337 nm in an X-ray wide angle diffraction method, a crystallite size (Lc) of 90 nm or higher, an R value, as a peak intensity ratio of a peak intensity of 1360 cm<HIL><−1 < / SP><PDAT>to a peak intensity of 1580 cm<HIL><−1 < / SP><PDAT>in a Raman spectrum in use of an argon ion laser, of 0.20 or higher, and a tap density of 0.75 g / cm<HIL><3 < / SP><PDAT>or higher. Also disclosed is a multilayer structure carbonaceous material for electrode, which is manufactured by carbonizing some organic compounds where the carbonaceous material for electrode is mixed with the organic compounds. The battery using the carbonaceous material for electrode or the multilayer structure carbonaceous material for electrode has a large capacity, a small irreversible capacity admitted in the initial cycle, excellent capacity maintaining rate of the cycle, and particularly, largely improved quick charging and discharging characteristics.< / PTEXT>
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method for improving performance of 700MPa grade V-N micro-alloying high-strength weathering steel
InactiveCN101161849AImprove low temperature impact toughnessGood formabilityTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionHigh intensity
The invention discloses a method for improving the performance of 700 MPa grade V-N microalloyed high strength weathering steel. The method is specific to the characteristics of the sheet billet continuous casting and tandem rolling technology and metallurgy component, and adopts an electric furnace or a revolving furnace to smelt, refine, continuously cast sheet billet which directly enters into a roller hearth to heat after a casting blank concretes, or soaking furnace, hot rolling, laminar flow cooling and wind-up process flow. The chemical composition of molten steel is :C occupies less than or equal to 0.08Wt. percent, Si occupies from 0.25 to 0.75Wt. percent, Mn occupies from 0.2 to 2.0Wt.percent, P occupies less than or equal to 0.025Wt. percent, S occupies less than or equal to 0.040Wt. percent, Cu occupies from 0.25 to 0.60Wt. percent, Cr occupies from 0.30 to 1.25 Wt.percent, Ni occupies less than or equal to 0.65Wt. percent, V occupies from 0.02 to 0.20Wt. percent and N occupies from 0.015 to 0.030 Wt. percent. The invention takes full advantages of the characteristics of the sheet billet continuous casting and tandem rolling short flow process and adopts the V-N microalloyed technique to produce 700 MPa grade high strength weathering steel under the thinning function of VN and V (C, N) nanometer scale precipitate on crystal grain in casting blank of the sheet billet continuous casting and tandem rolling flow and the theory of precipitation strength. By the optimization design of the metallurgy component of V-N microalloyed 700MPa grade high strength weathering steel, the invention increases the low temperature impact ductility of coil of strip and improves the shaping property.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PEARL RIVER STEEL & IRON
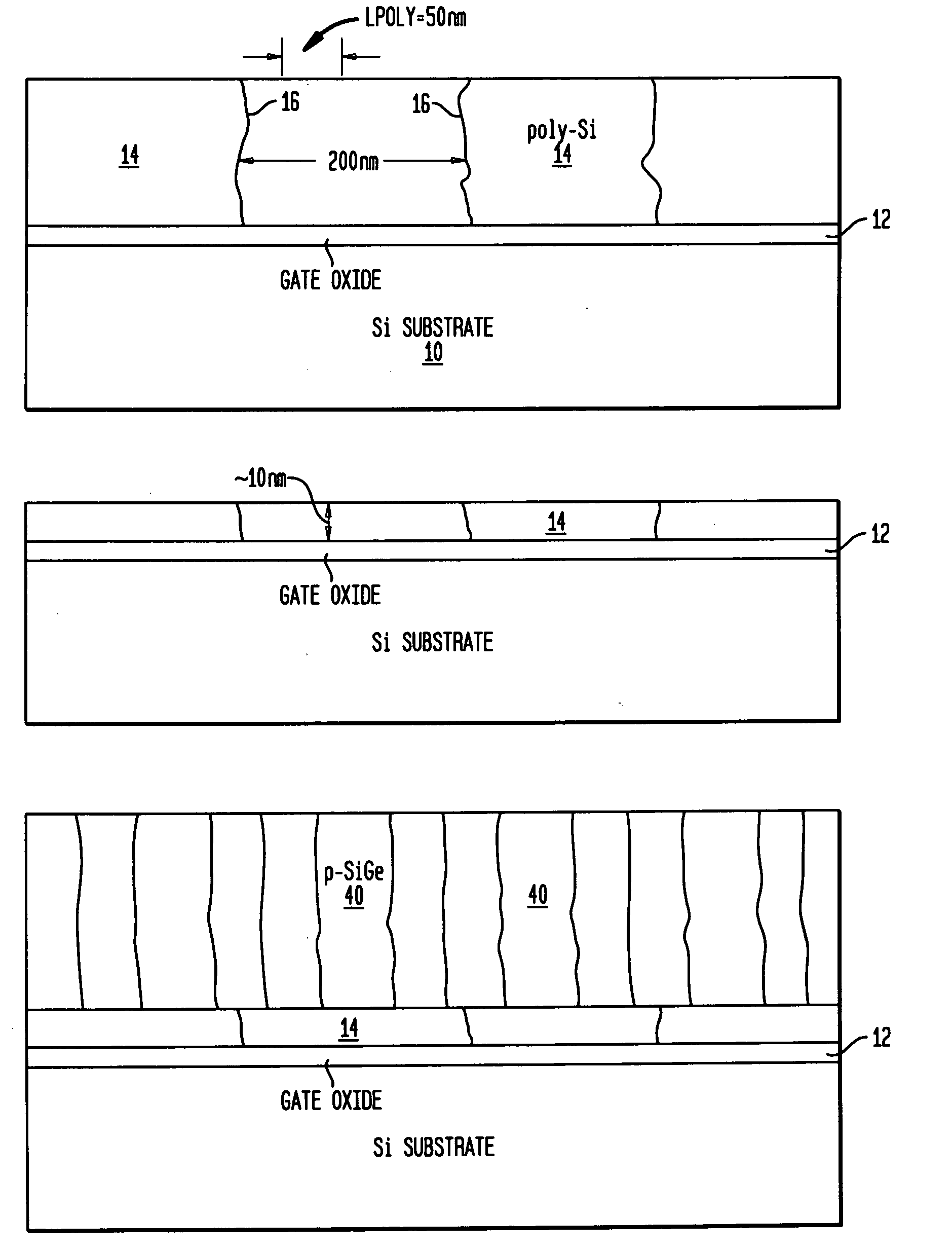
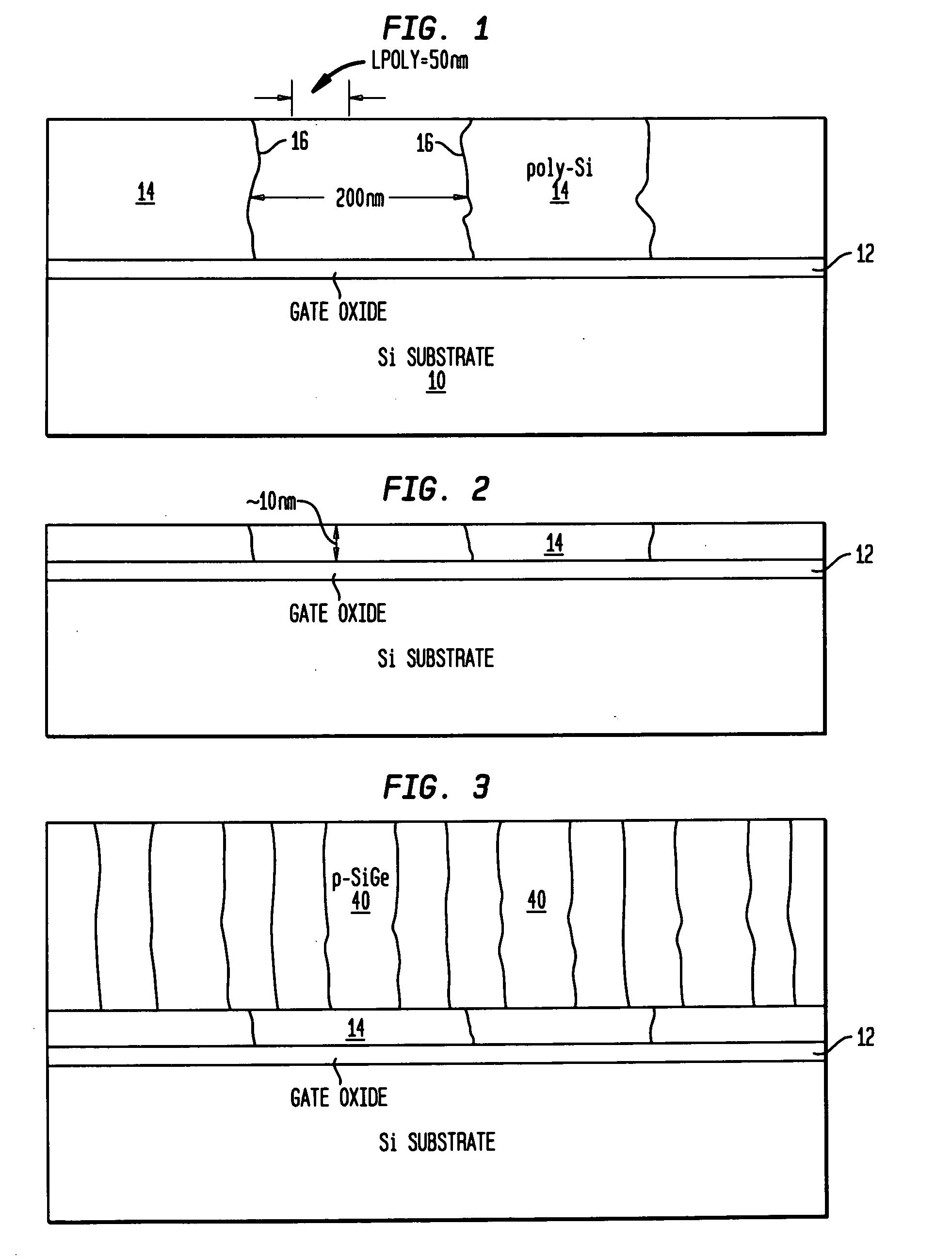
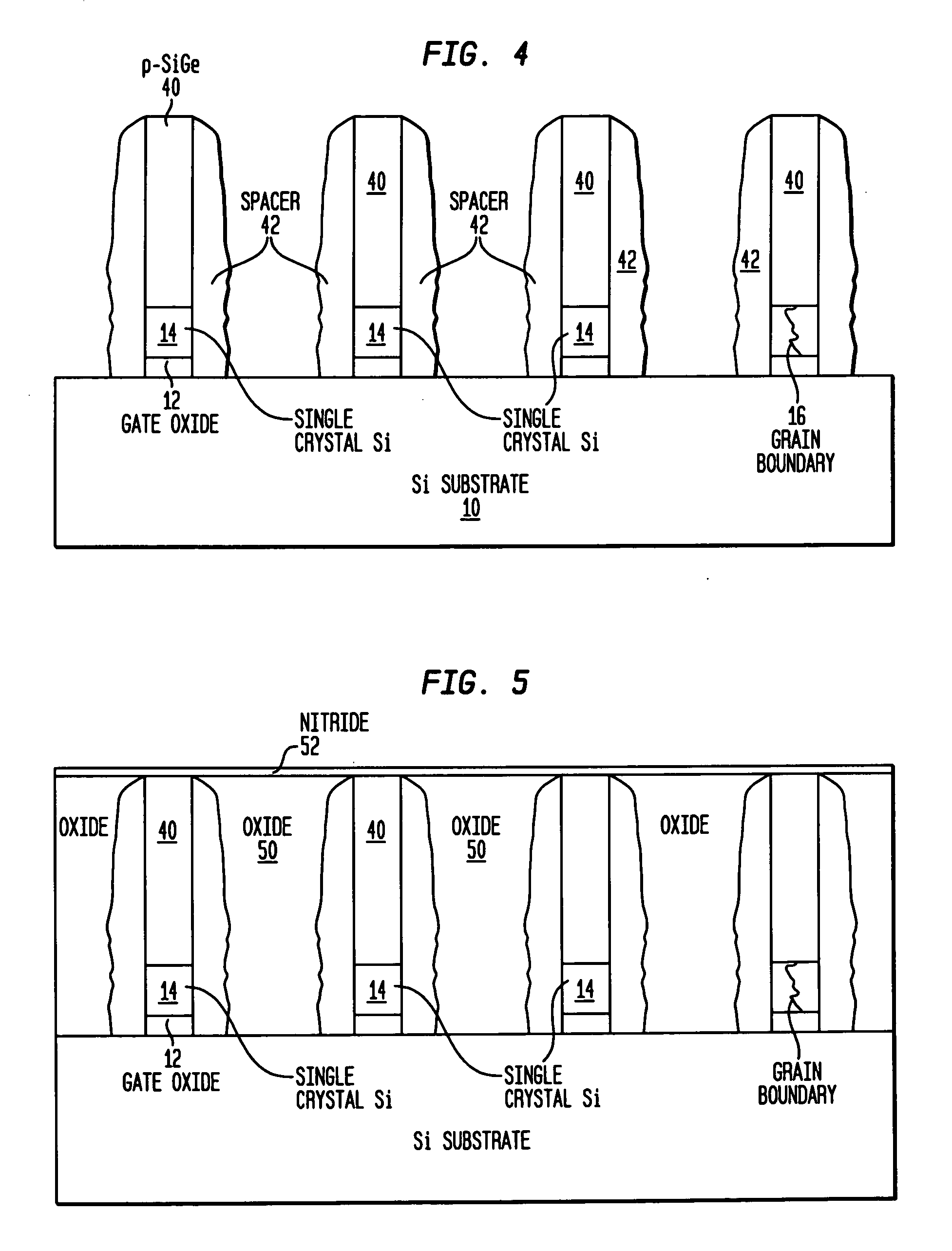
STRUCTURES AND METHODS FOR MANUFACTURING OF DISLOCATION FREE STRESSED CHANNELS IN BULK SILICON AND SOI CMOS DEVICES BY GATE STRESS ENGINEERING WITH SiGe AND/OR Si:C
ActiveUS20050236668A1Avoid misalignmentReduce generationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSoi cmosCMOS
Structures and methods of manufacturing are disclosed of dislocation free stressed channels in bulk silicon and SOI (silicon on insulator) CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) devices by gate stress engineering with SiGe and / or Si:C. A CMOS device comprises a substrate of either bulk Si or SOI, a gate dielectric layer over the substrate, and a stacked gate structure of SiGe and / or Si:C having stresses produced at the interfaces of SSi(strained Si) / SiGe or SSi / Si:C in the stacked gate structure. The stacked gate structure has a first stressed film layer of large grain size Si or SiGe over the gate dielectric layer, a second stressed film layer of strained SiGe or strained Si:C over the first stressed film layer, and a semiconductor or conductor such as p(poly)-Si over the second stressed film layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
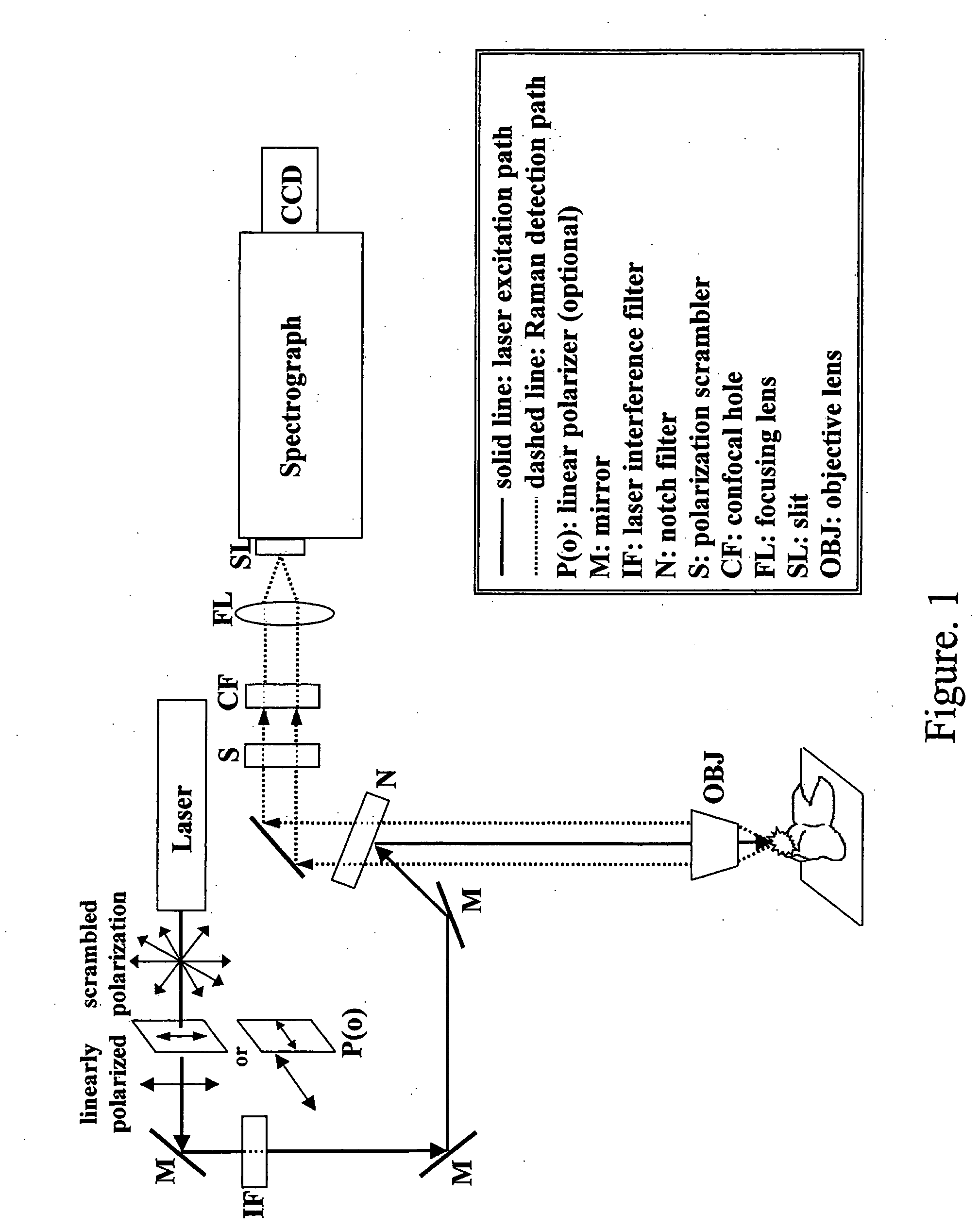
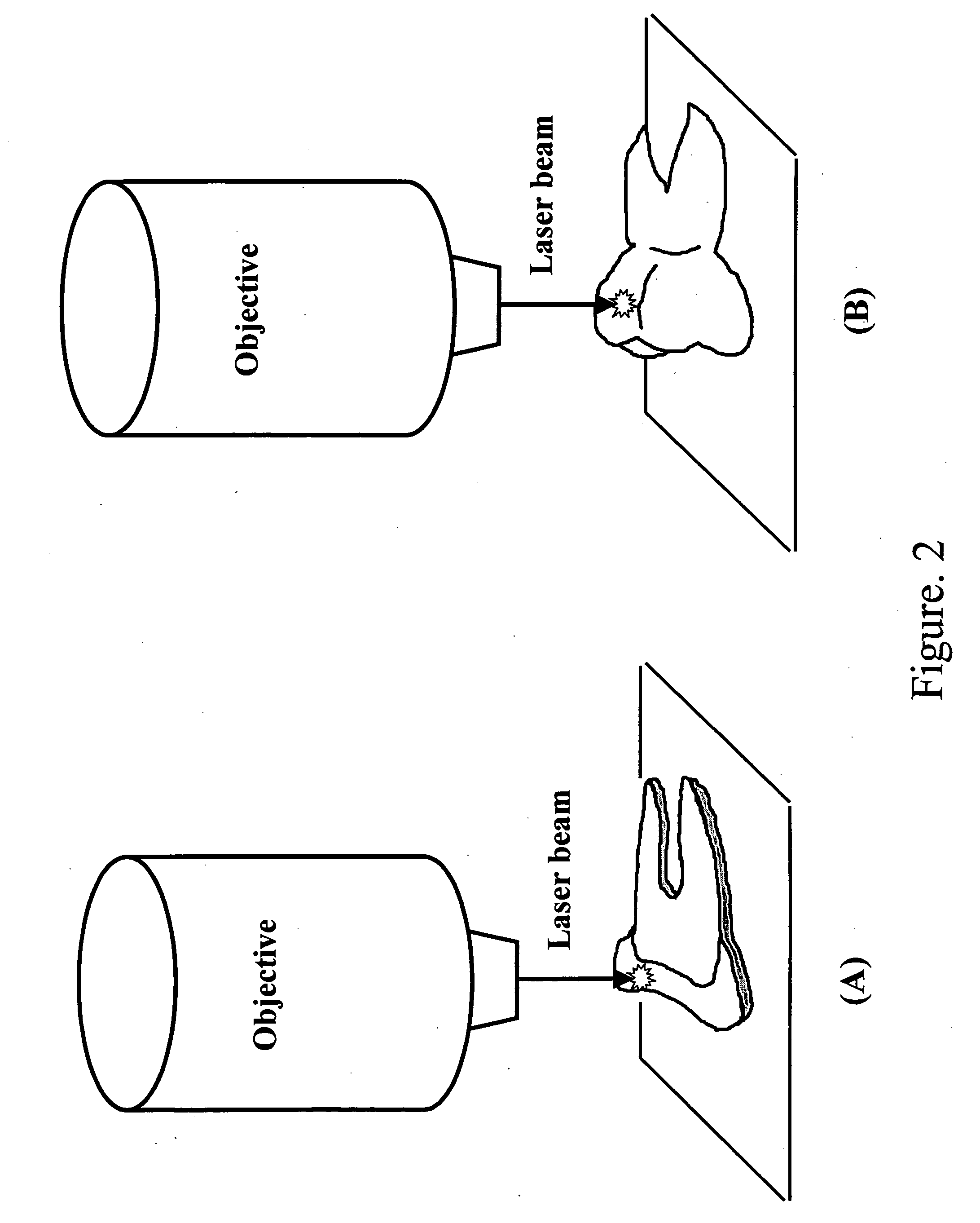
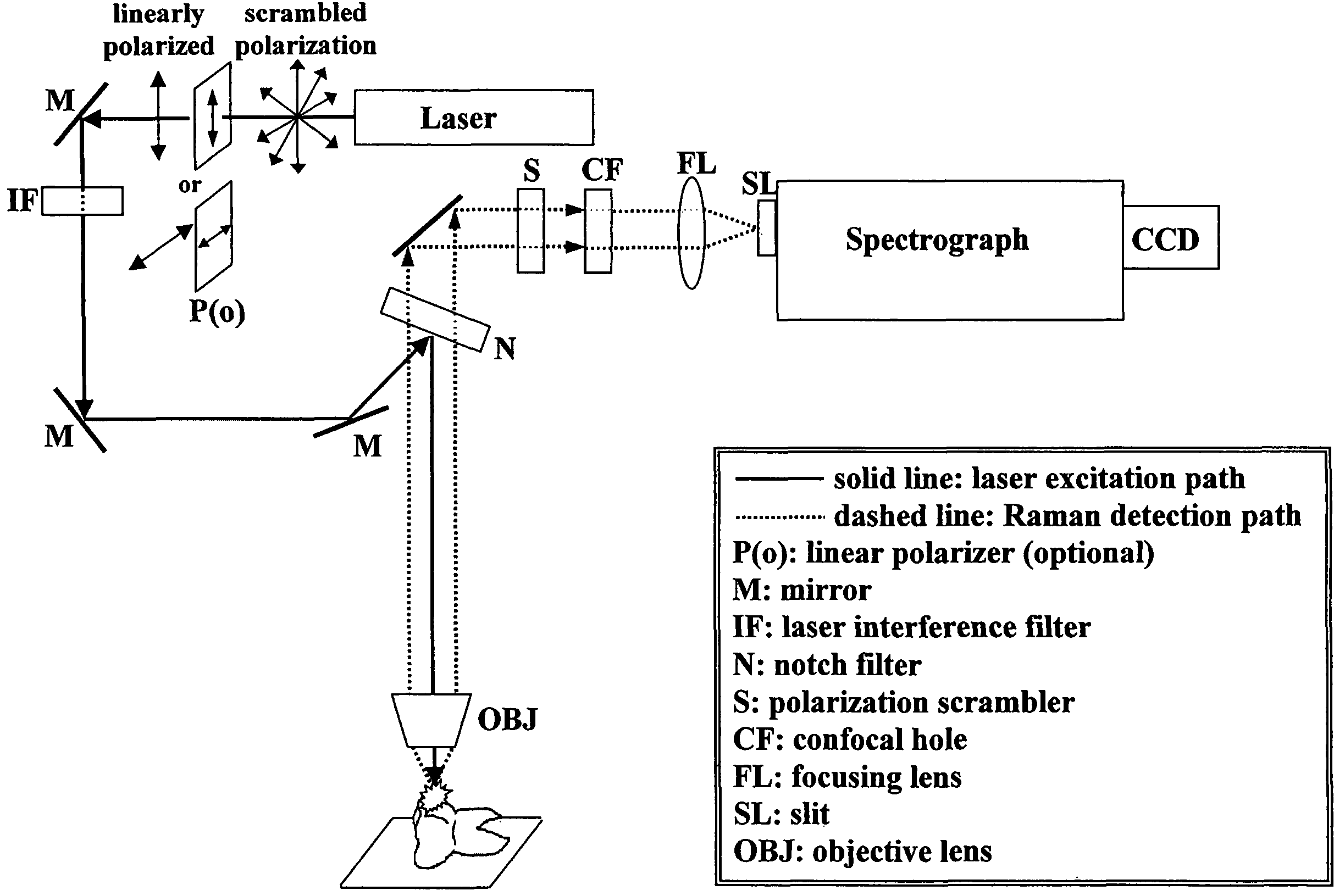
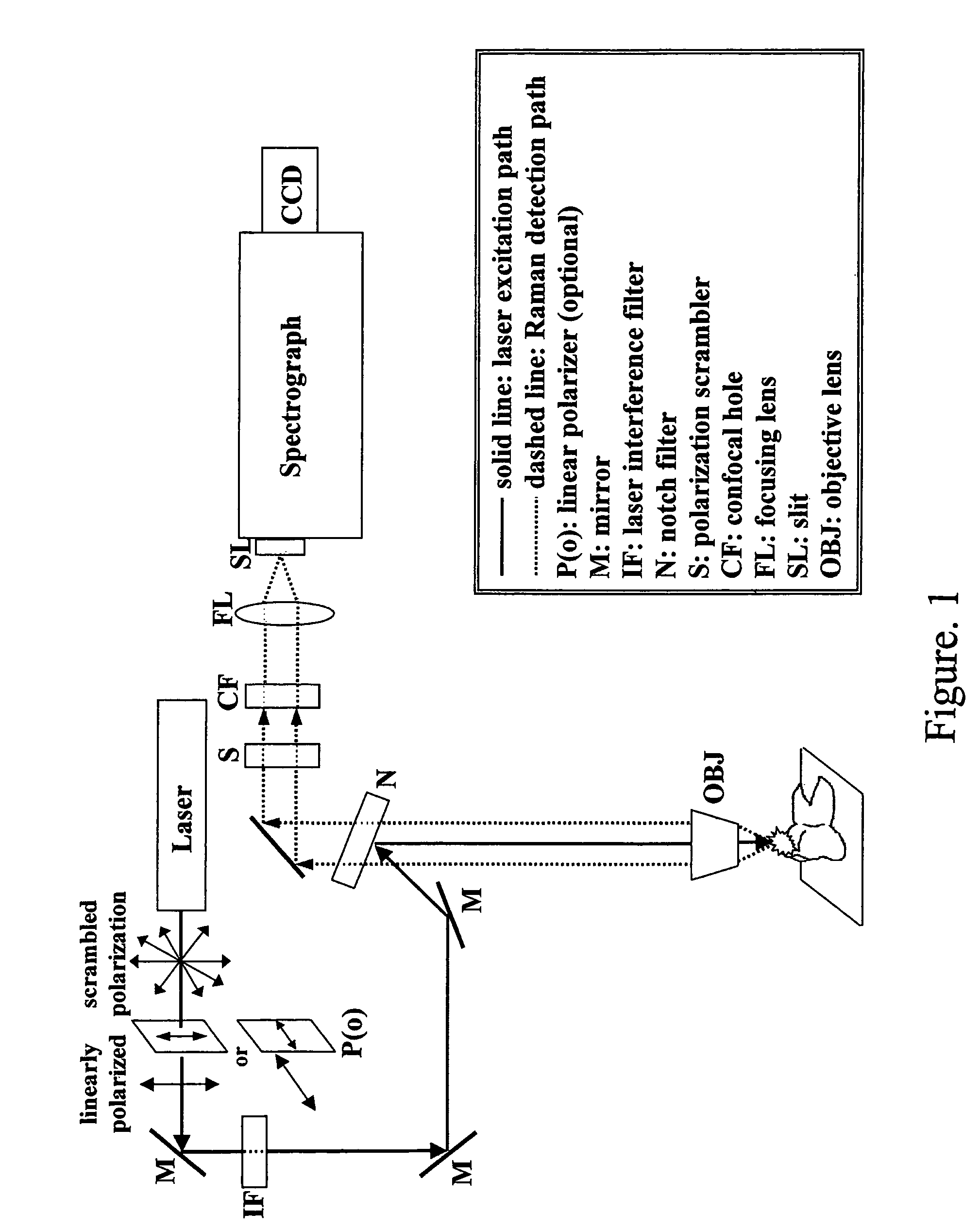
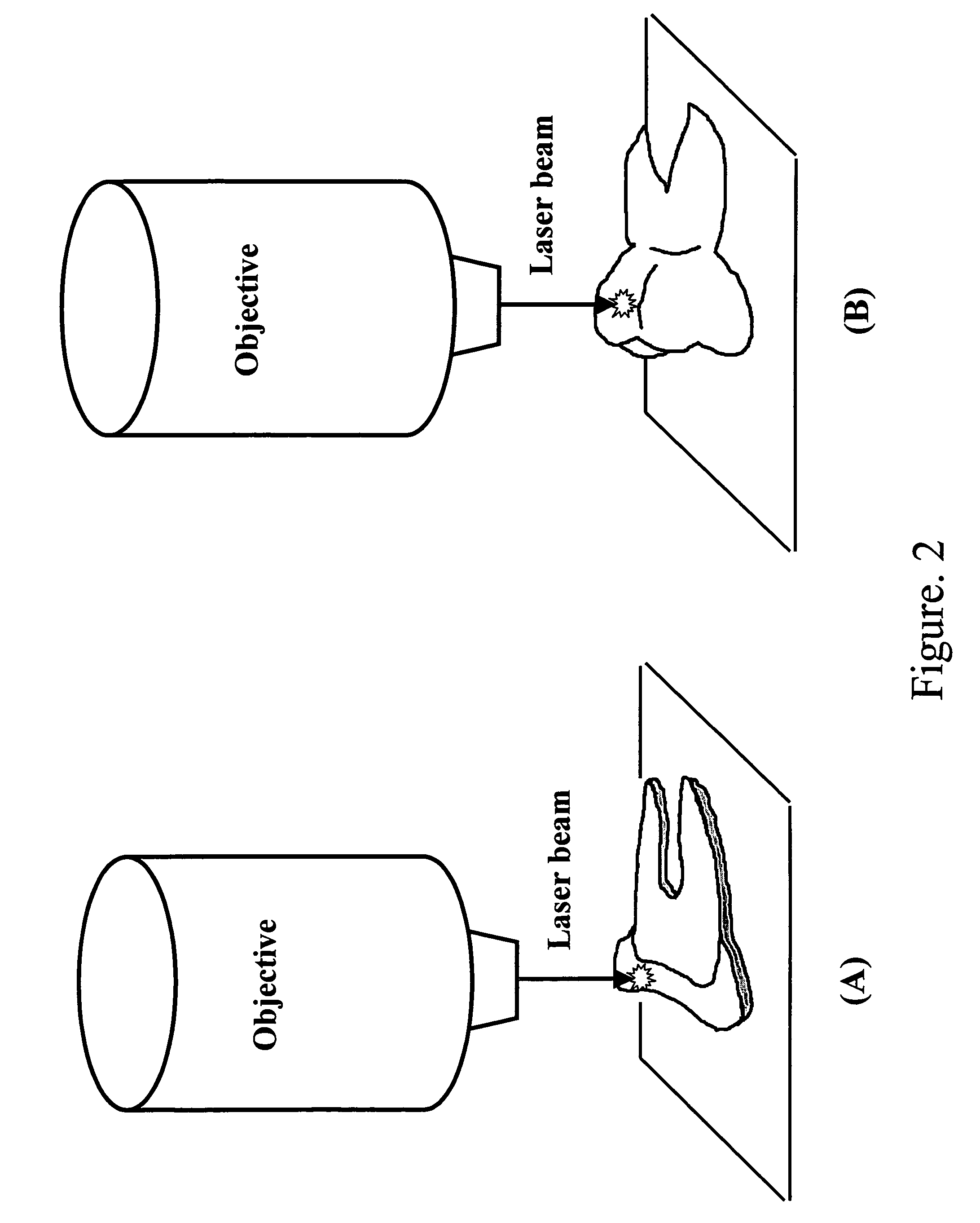
Detection and monitoring of changes in mineralized tissues or calcified deposits by optical coherence tomography and Raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050283058A1Minimal disruptionHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansMedicineCarious lesion
Early dental caries detection is carried out by a method that combines optical coherence tomography (OCT) and Raman spectroscopy to provide morphological information and biochemical specificity for detecting and characterizing incipient carious lesions found in extracted human teeth. OCT imaging of tooth samples demonstrated increased light back-scattering intensity at sites of carious lesions as compared to the sound enamel. Raman microspectroscopy and fibre-optic based Raman spectroscopy are used to characterize the caries further by detecting demineralization-induced alterations of enamel crystallite morphology and / or orientation. OCT imaging is useful for screening carious sites and determining lesion depth, with Raman spectroscopy providing biochemical confirmation of caries. The combination is incorporated into a common probe operable without movement to scan the tooth surface and to provide an output for the dentist.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA +2
Fine Grained, Non Banded, Refractory Metal Sputtering Targets with a Uniformly Random Crystallographic Orientation, Method for Making Such Film, and Thin Film Based Devices and Products Made Therefrom
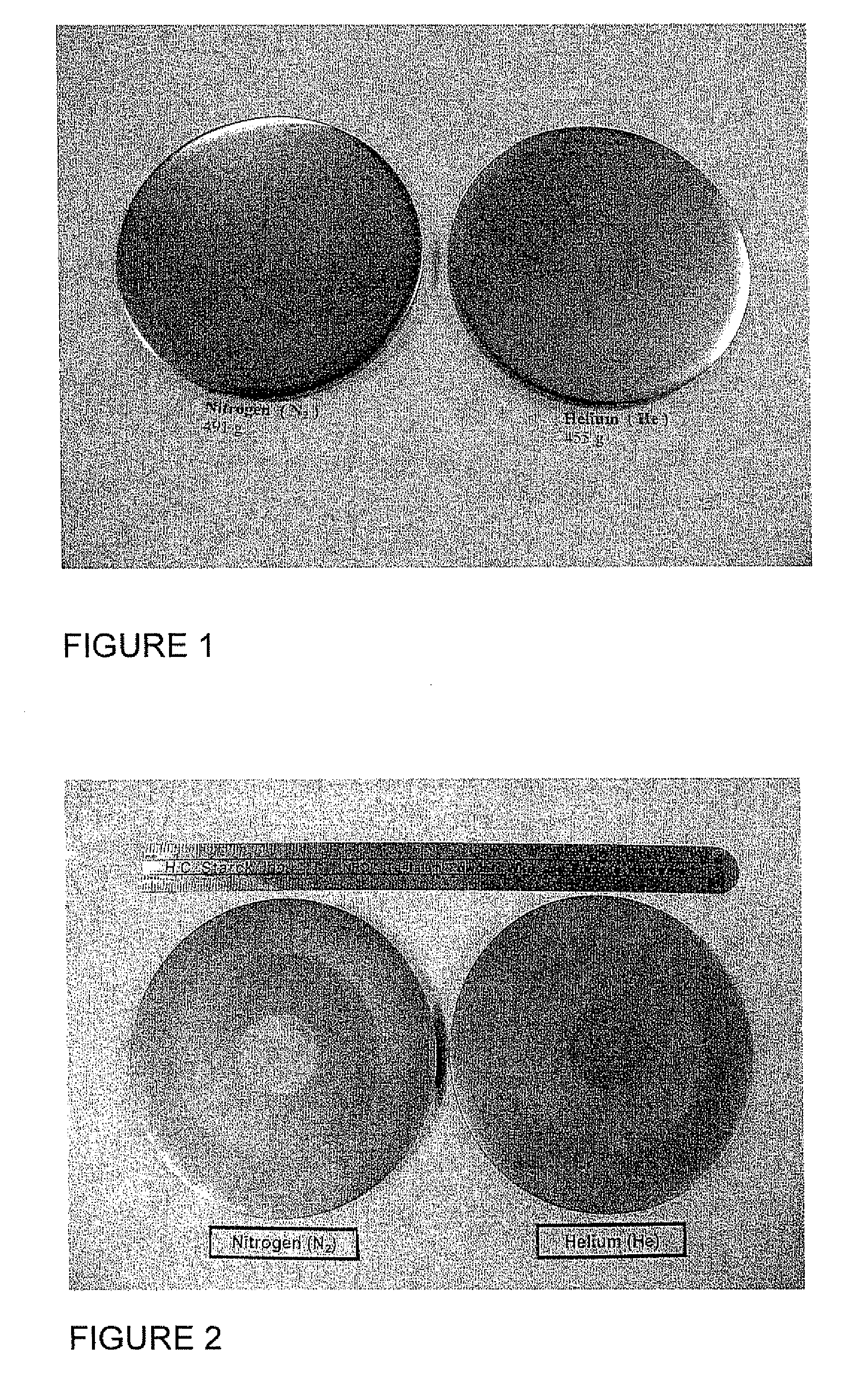
ActiveUS20080271779A1Cost-effectively createCost effectiveLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingFilm baseThermal expansion
The invention relates to a sputtering target which has a fine uniform equiaxed grain structure of less than 44 microns, no preferred texture orientation as measured by electron back scattered diffraction (“EBSD”) and that displays no grain size banding or texture banding throughout the body of the target. The invention relates a sputtering target with a lenticular or flattened grain structure, no preferred texture orientation as measured by EBSD and that displays no grain size or texture banding throughout the body of the target and where the target has a layered structure incorporating a layer of the sputtering material and at least one additional layer at the backing plate interface, said layer has a coefficient of thermal expansion (“CTE”) value between the CTE of the backing plate and the CTE of the layer of sputtering material. The invention also relates to thin films and their use of using the sputtering target and other applications, such as coatings, solar devices, semiconductor devices etc. The invention further relates to a process to repair or rejuvenate a sputtering target.
Owner:H C STARCK GMBH +1
Laser apparatus, laser annealing method, and manufacturing method of a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20020048864A1Solution value is not highIncrease valueSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesLaser lightSolid-state laser
To provide a laser apparatus and a laser annealing method with which a crystalline semiconductor film with a larger crystal grain size is obtained and which are low in their running cost. A solid state laser easy to maintenance and high in durability is used as a laser, and laser light emitted therefrom is linearized to increase the throughput and to reduce the production cost as a whole. Further, both the front side and the back side of an amorphous semiconductor film is irradiated with such laser light to obtain the crystalline semiconductor film with a larger crystal grain size.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Carbon electrode material for a vanadium-based redox-flow battery
The carbon electrode material of the present invention is used for a vanadium redox-flow cell. The carbon electrode material has quasi-graphite crystal structure in which <002> spacing obtained by X-ray wide angle analysis is 3.43 to 3.60 Å, size of a crystallite in c axial direction is 15 to 33 Å and size of crystallite in a axial direction is 30 to 70 Å. In addition, an amount of surface acidic functional groups obtained by XPS surface analysis is 0.1 to 1.2% and total number of surface bound-nitrogen atoms is 5% or smaller relative to total number of surface carbon atoms. The carbon electrode materials formed of a non-woven fabric of a carbonaceouss fiber is preferable.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Structure and method to fabricate high performance MTJ devices for spin-transfer torque (STT)-RAM application
ActiveUS20110014500A1High densityIncreased polarizationNanomagnetismMagnetic materials for record carriersPower flowSpin-transfer torque
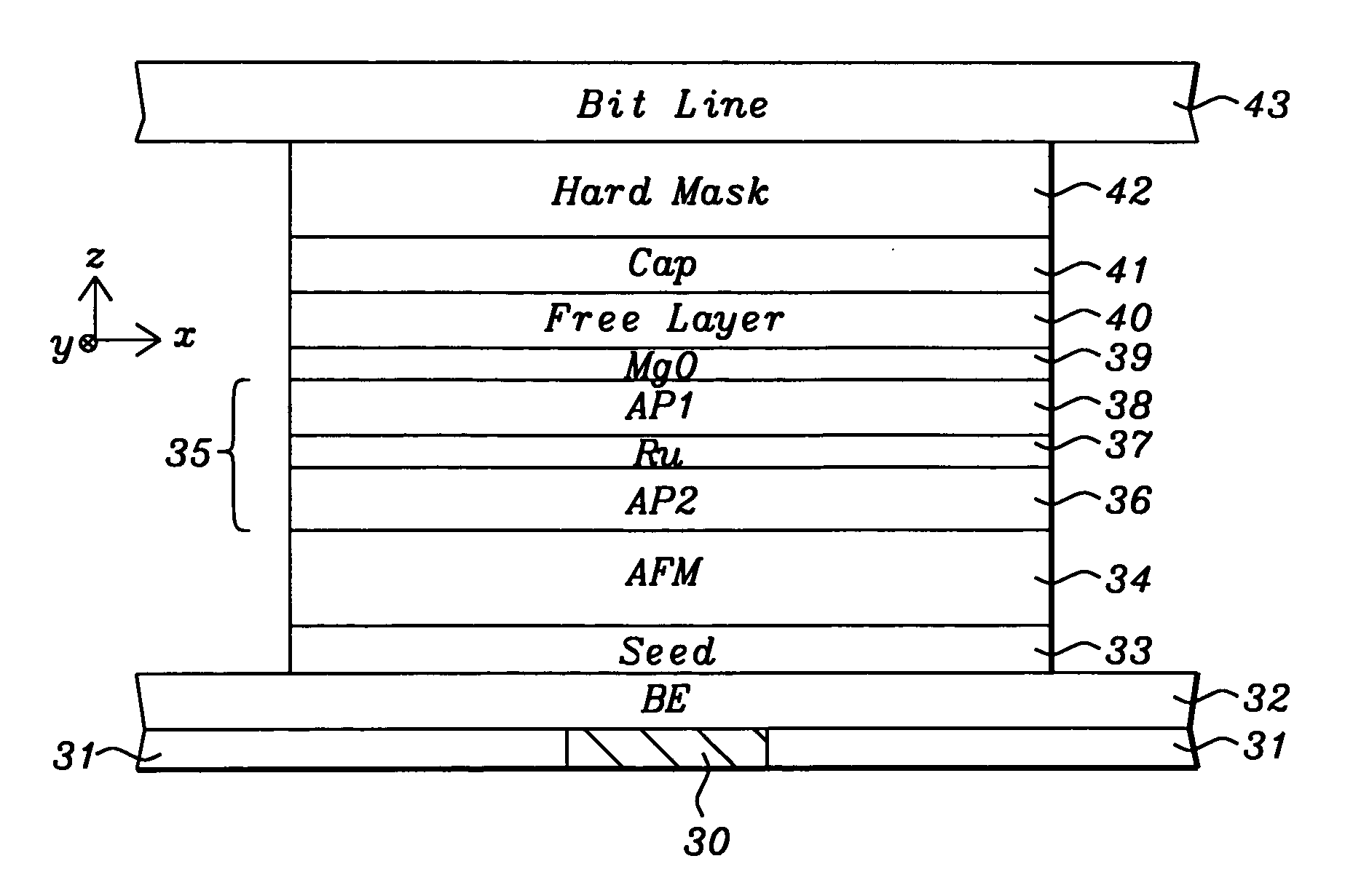
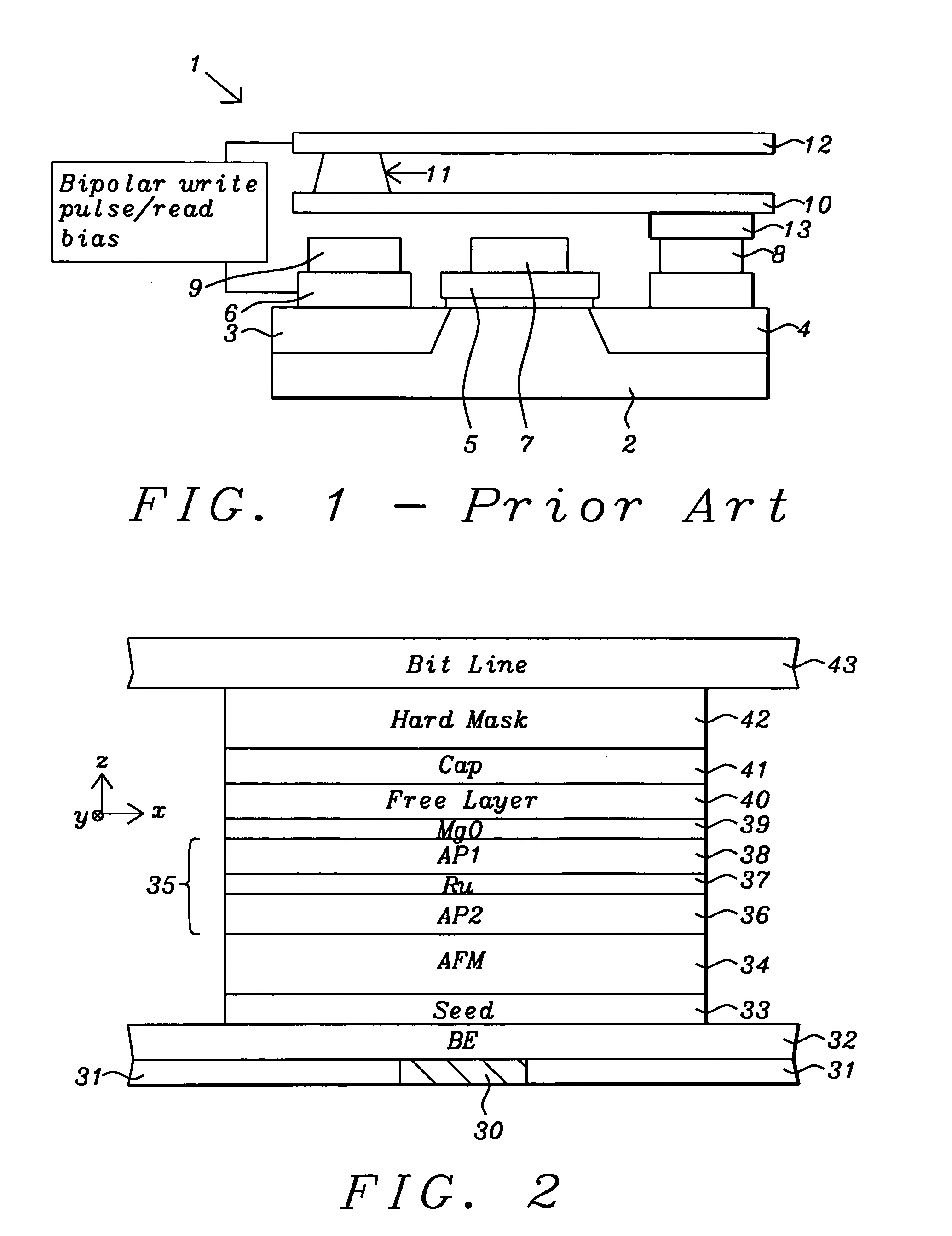
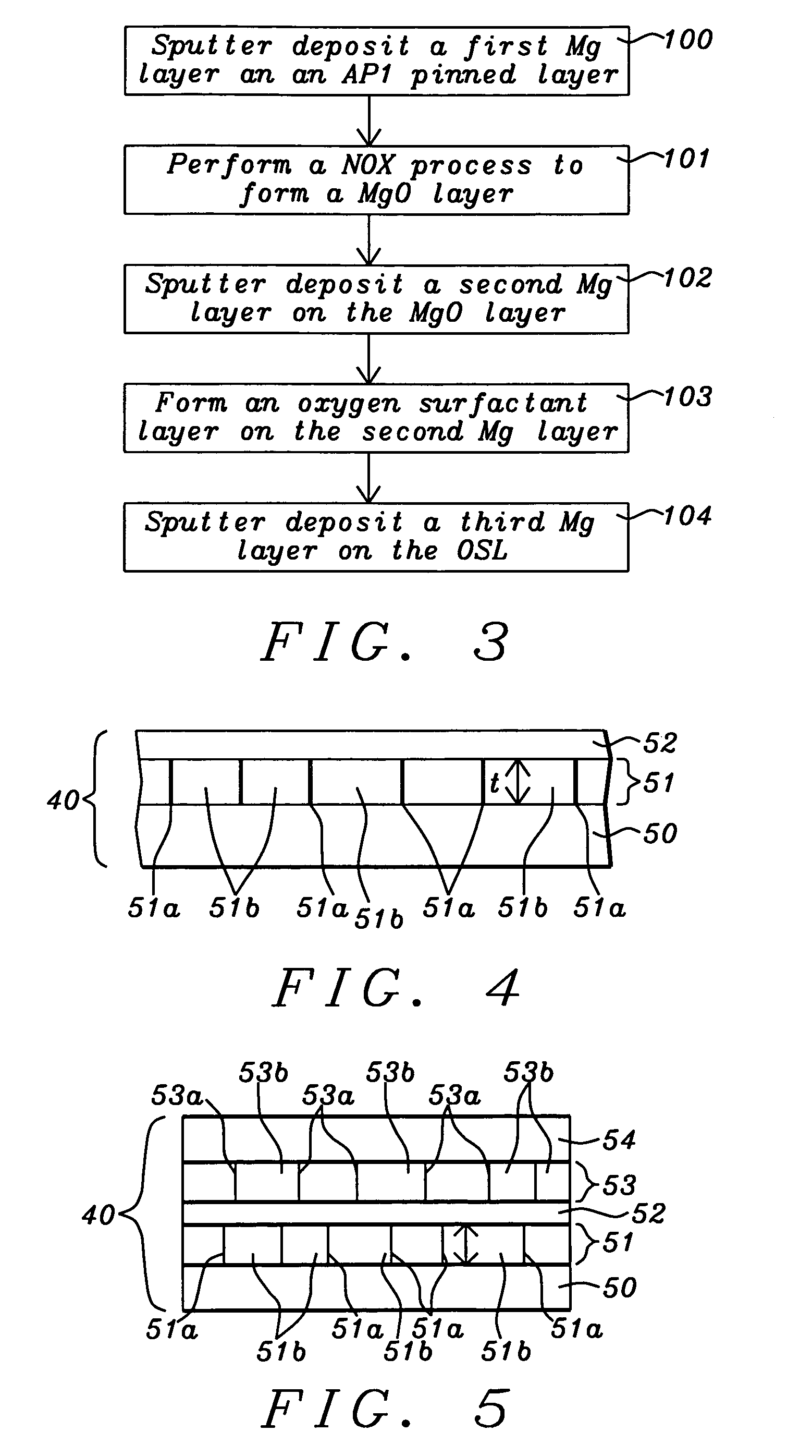
A STT-RAM MTJ is disclosed with a MgO tunnel barrier formed by natural oxidation and containing an oxygen surfactant layer to form a more uniform MgO layer and lower breakdown distribution percent. A CoFeB / NCC / CoFeB composite free layer with a middle nanocurrent channel layer minimizes Jc0 while enabling thermal stability, write voltage, read voltage, and Hc values that satisfy 64 Mb design requirements. The NCC layer has RM grains in an insulator matrix where R is Co, Fe, or Ni, and M is a metal such as Si or Al. NCC thickness is maintained around the minimum RM grain size to avoid RM granules not having sufficient diameter to bridge the distance between upper and lower CoFeB layers. A second NCC layer and third CoFeB layer may be included in the free layer or a second NCC layer may be inserted below the Ru capping layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Dental restorations using nanocrystalline materials and methods of manufacture
Dental articles are produced using relatively low sintering temperatures to achieve high density dental articles exhibiting strengths equal to and greater than about 700 MPa. Ceramic powders comprised of nanoparticulate crystallites are used to manufacture dental articles. The ceramic powders may include sintering agents, binders and other similar additives to aid in the processing of the ceramic powder into a dental article. The ceramic powders may be processed into dental articles using various methods including, but not limited to, injection molding, gel-casting, slip casting, or electroforming, hand, cad / camming and other various rapid prototyping methods. The ceramic powder may be formed into a suspension, pellet, feedstock material or a pre-sintered blank prior to forming into the dental article.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Laser apparatus, laser annealing method, and manufacturing method of a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6974731B2Large grainLow running costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser lightSolid-state laser
To provide a laser apparatus and a laser annealing method with which a crystalline semiconductor film with a larger crystal grain size is obtained and which are low in their running cost. A solid state laser easy to maintenance and high in durability is used as a laser, and laser light emitted therefrom is linearized to increase the throughput and to reduce the production cost as a whole. Further, both the front side and the back side of an amorphous semiconductor film is irradiated with such laser light to obtain the crystalline semiconductor film with a larger crystal grain size.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Silica-alumina catalyst support, catalysts made therefrom and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS7541310B2High activityHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMolecular sieve catalystsCompound (substance)Catalytic metal
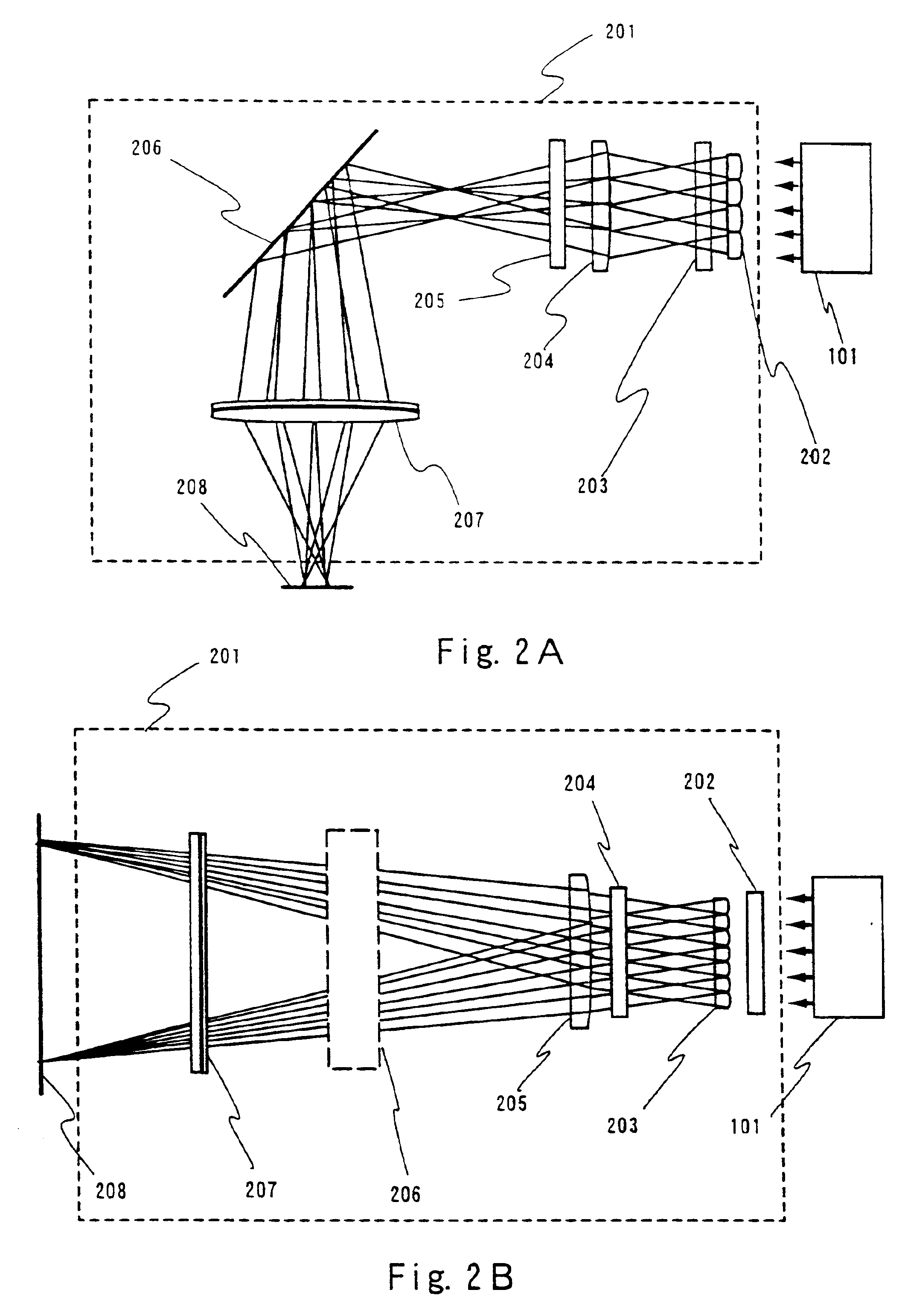
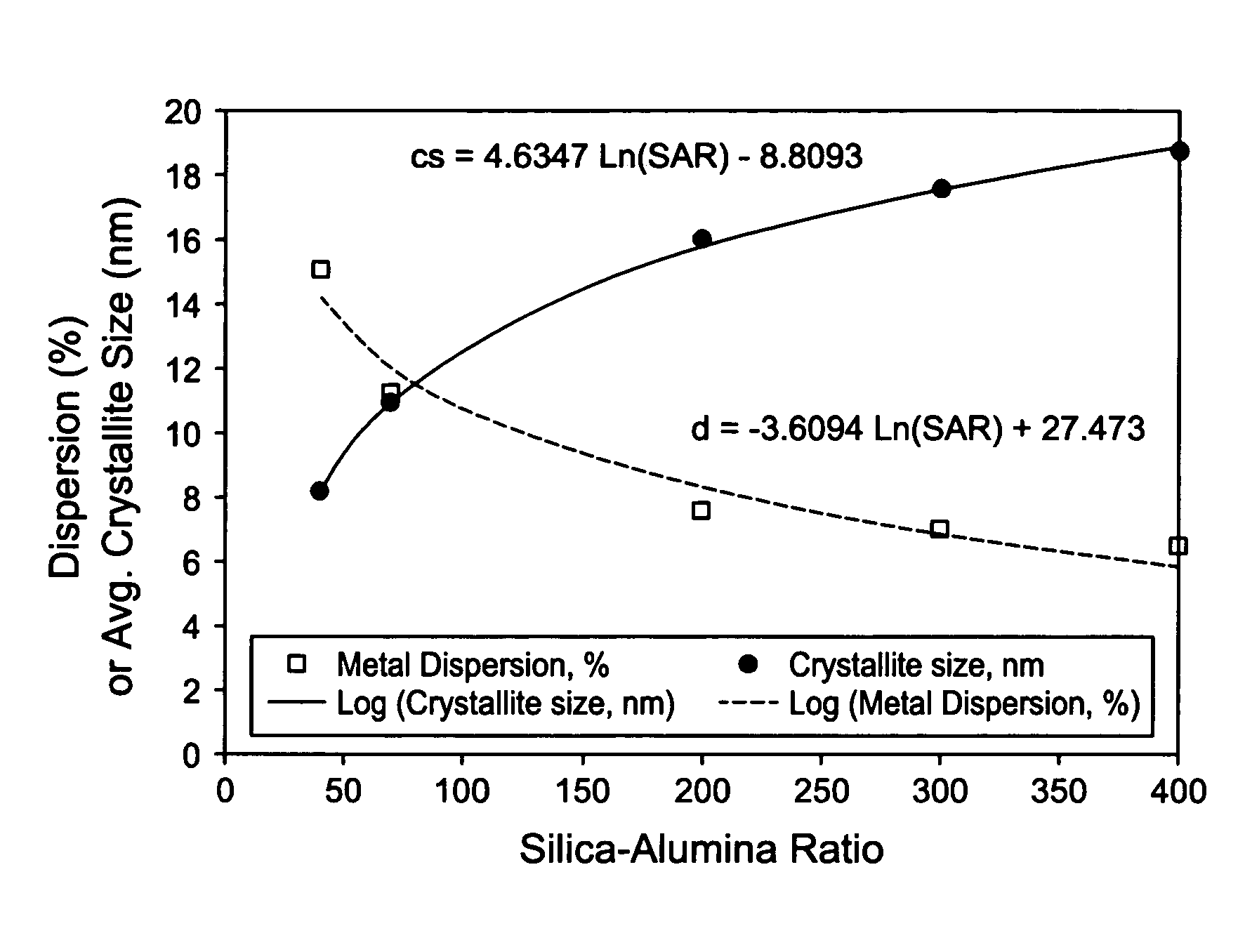
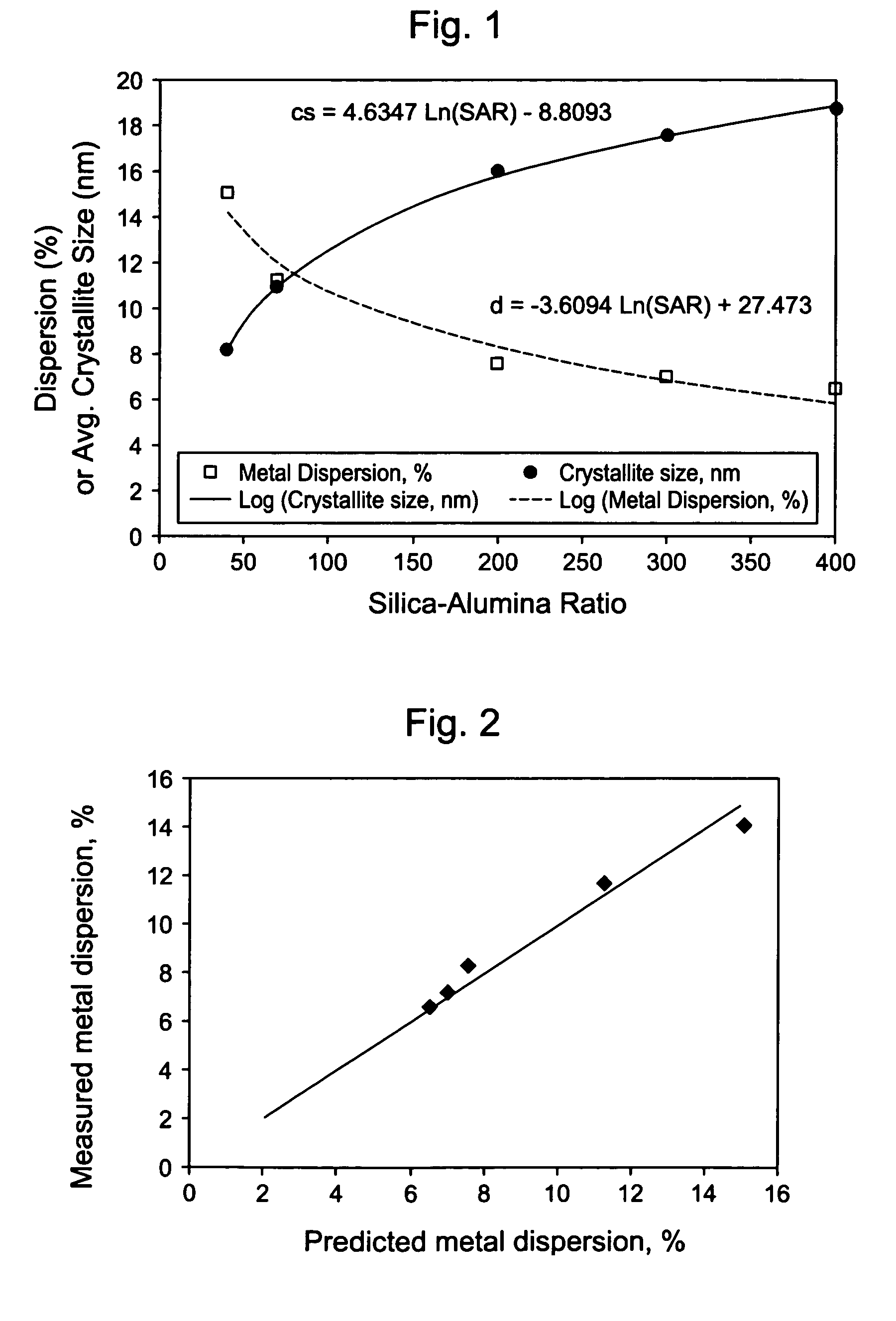
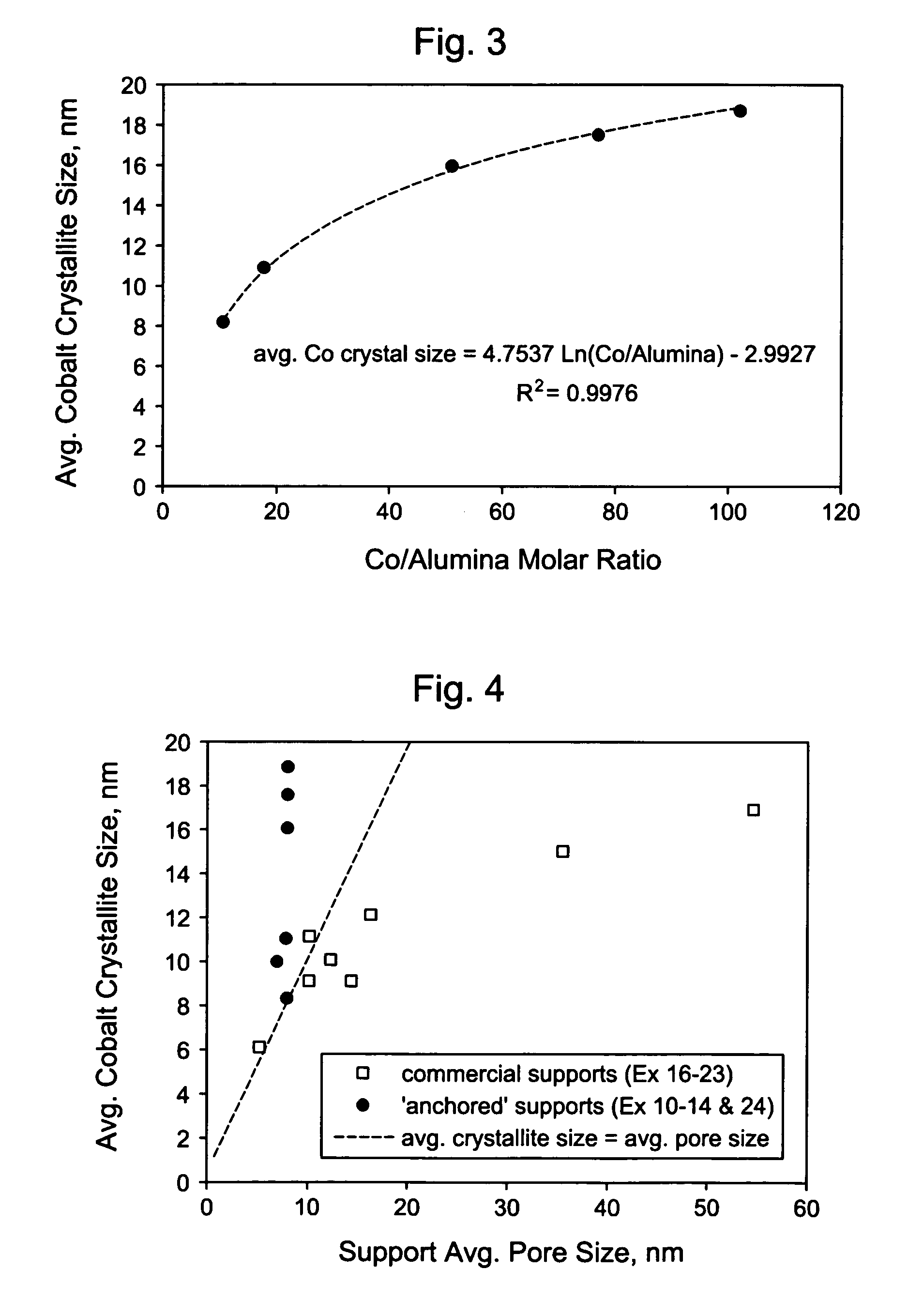
This invention relates to catalysts comprising a catalytic metal deposited on a composite support with well-dispersed chemical “anchor” species acting as nucleation centers for catalytic metal crystallites growth. The catalysts have the advantage that the average catalytic metal crystallite size can be controlled by the molar ratio of catalytic metal to chemical “anchor,” and is not limited by the porous structure of the support. A preferred embodiment comprises a cobalt-based catalyst on a silica-alumina support made by a co-gel method, wherein its average pore size can be controlled by the pH. The alumina species in the support most likely serve as chemical “anchors” to control the dispersion of cobalt species, such that the average cobalt crystallite size can be greater than the average pore size.
Owner:CLARIANT INT LTD
Detection and monitoring of changes in mineralized tissues or calcified deposits by optical coherence tomography and Raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS7796243B2Minimal disruptionHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansCarious lesionTooth Supporting Structures
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA +2
Conductive sintered layer forming composition and conductive coating film forming method and bonding method using the same
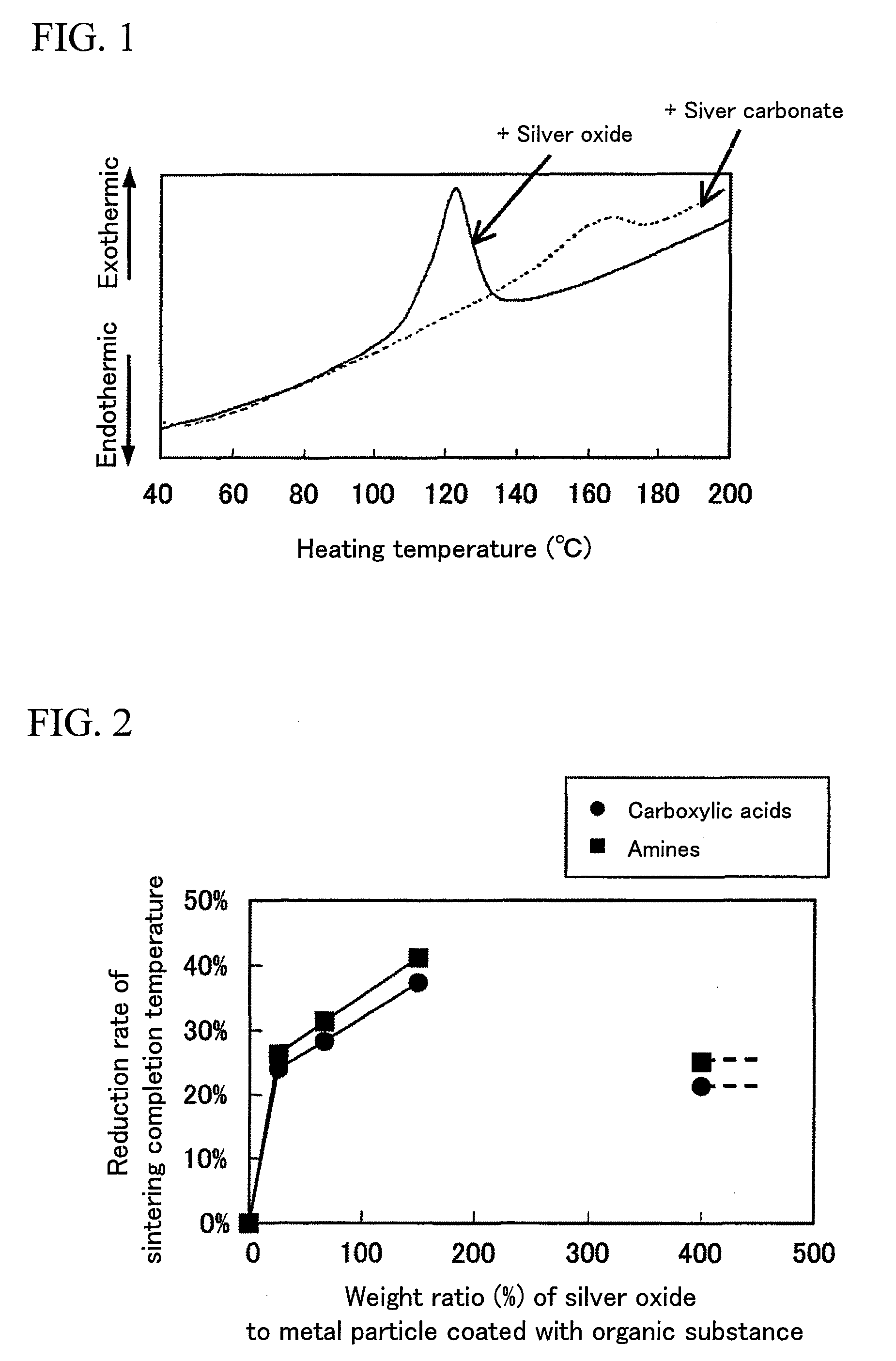
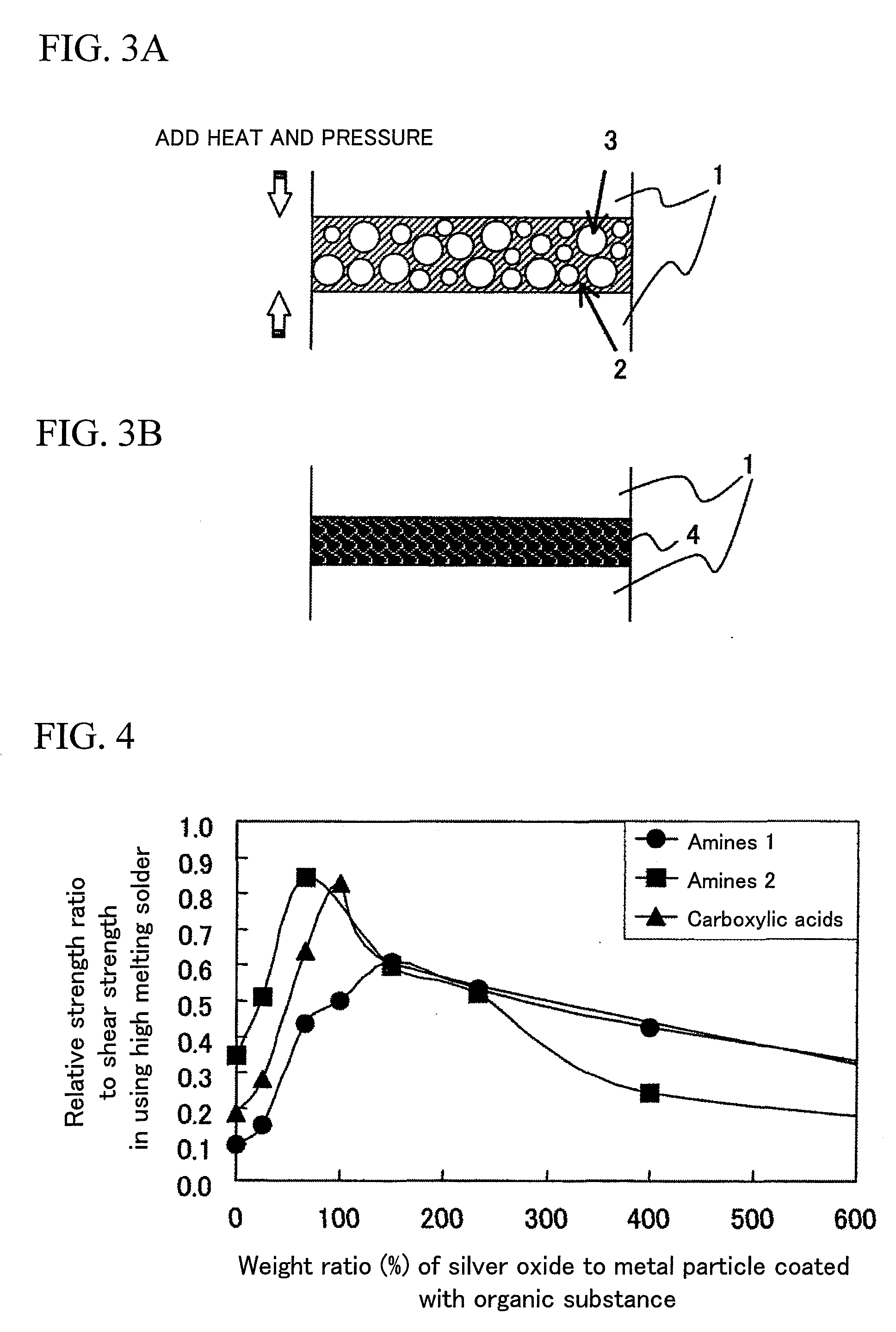
InactiveUS20080160183A1Low heating temperatureShorten heating timeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialHeating timeConductive coating
There is provided a conductive sintered layer forming composition and a conductive sintered layer forming method that can lower heating temperature and shorten heating time for a process of accelerating sintering or bonding by sintering of metal nano-particles coated with an organic substance. The conductive sintered layer forming composition may be obtained by utilizing a phenomenon that particles may be sintered at low temperature by mixing silver oxide with metal particles coated with the organic substance and having a grain size of 1 nm to 5 μm as compared to sintering each simple substance. The conductive sintered layer forming composition of the invention is characterized in that it contains the metal particles whose surface is coated with the organic substance and whose grain size is 1 nm to 5 μm and the silver oxide particles.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Silicon carbide substrate, epitaxial layer provided substrate, semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing silicon carbide substrate
InactiveUS20120119225A1Lower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSingle crystal substrateSingle crystal
The present invention provides a silicon carbide substrate, an epitaxial layer provided substrate, a semiconductor device, and a method for manufacturing the silicon carbide substrate, each of which achieves reduced on-resistance. The silicon carbide substrate is a silicon carbide substrate having a main surface, and includes: a SiC single-crystal substrate formed in at least a portion of the main surface; and a base member disposed to surround the SiC single-crystal substrate. The base member includes a boundary region and a base region. The boundary region is adjacent to the SiC single-crystal substrate in a direction along the main surface, and has a crystal grain boundary therein. The base region is adjacent to the SiC single-crystal substrate in a direction perpendicular to the main surface, and has an impurity concentration higher than that of the SiC single-crystal substrate.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com