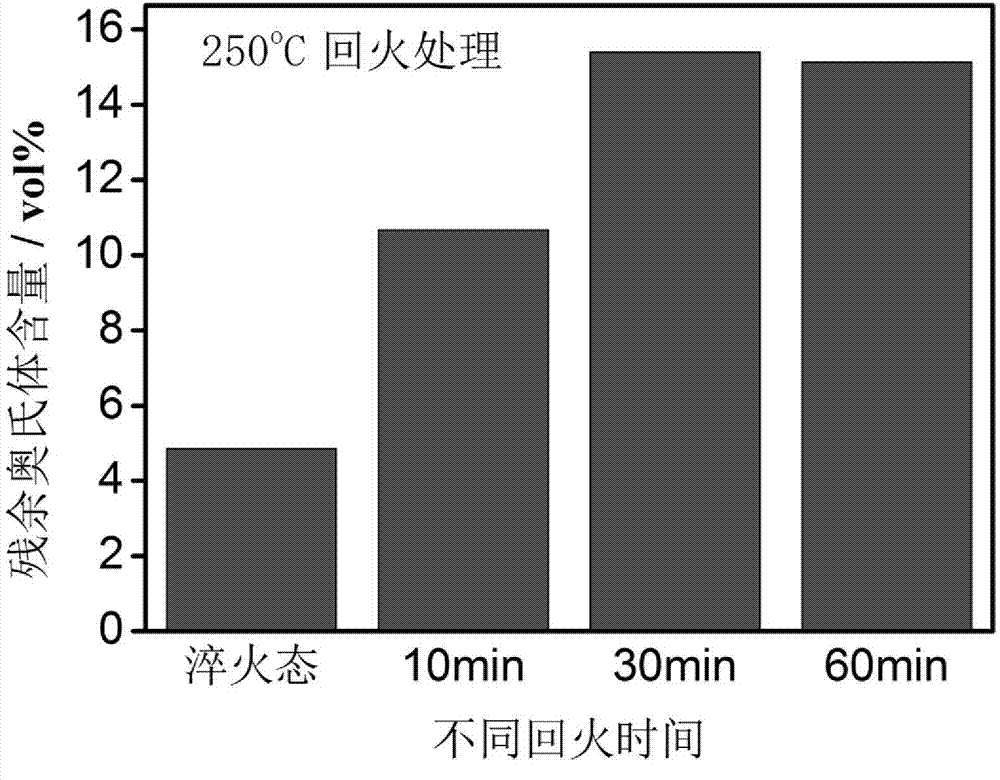
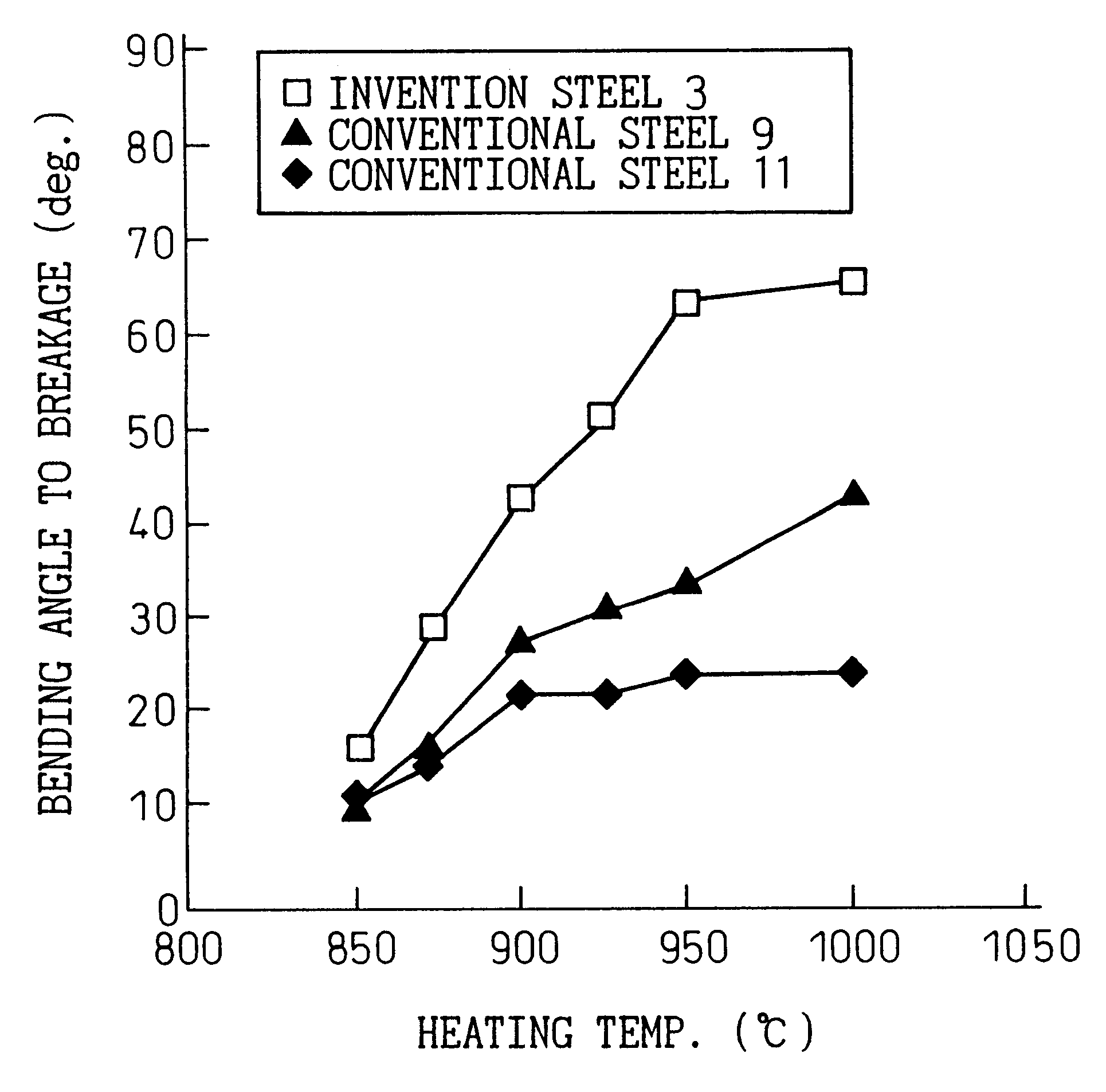
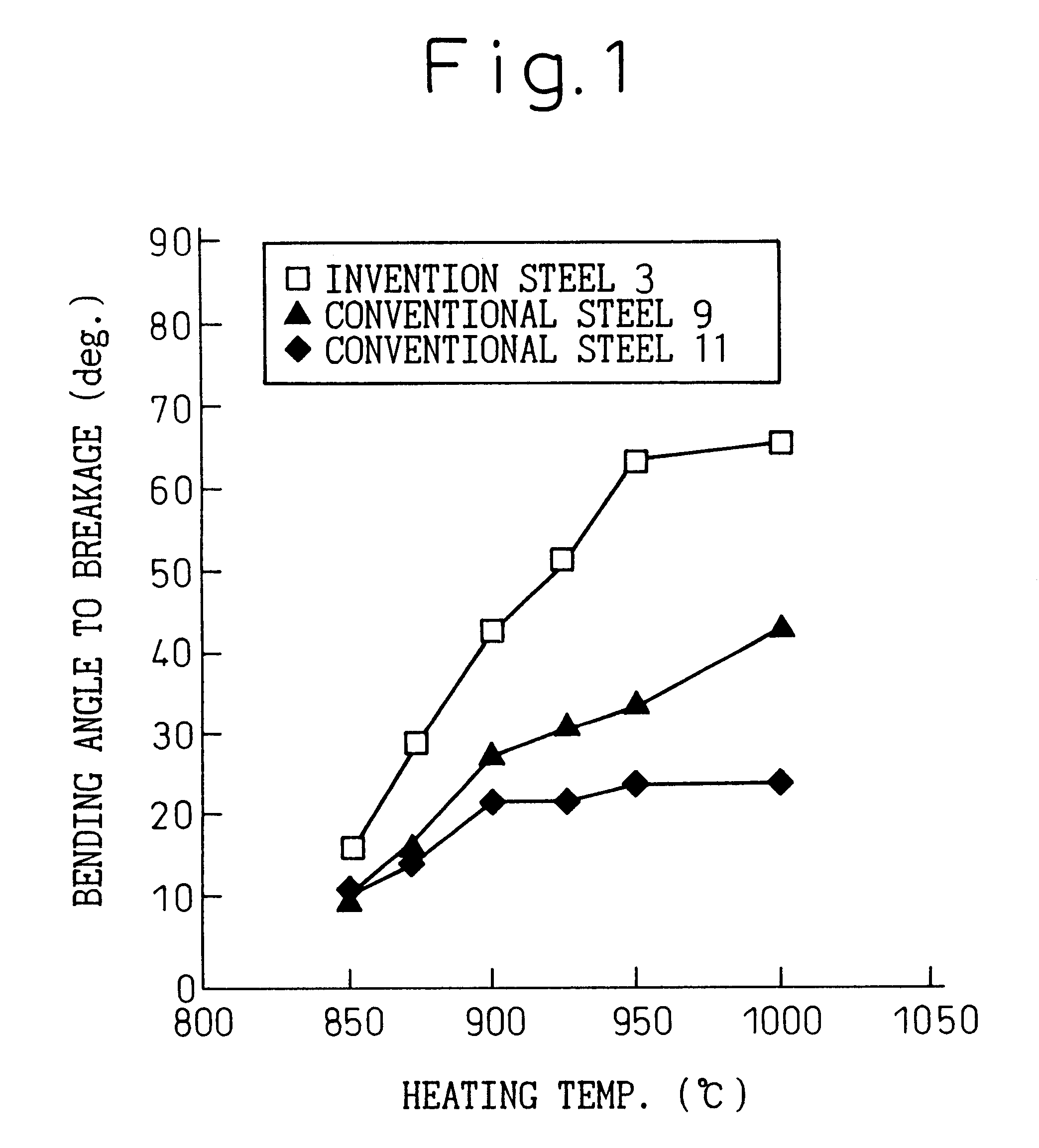
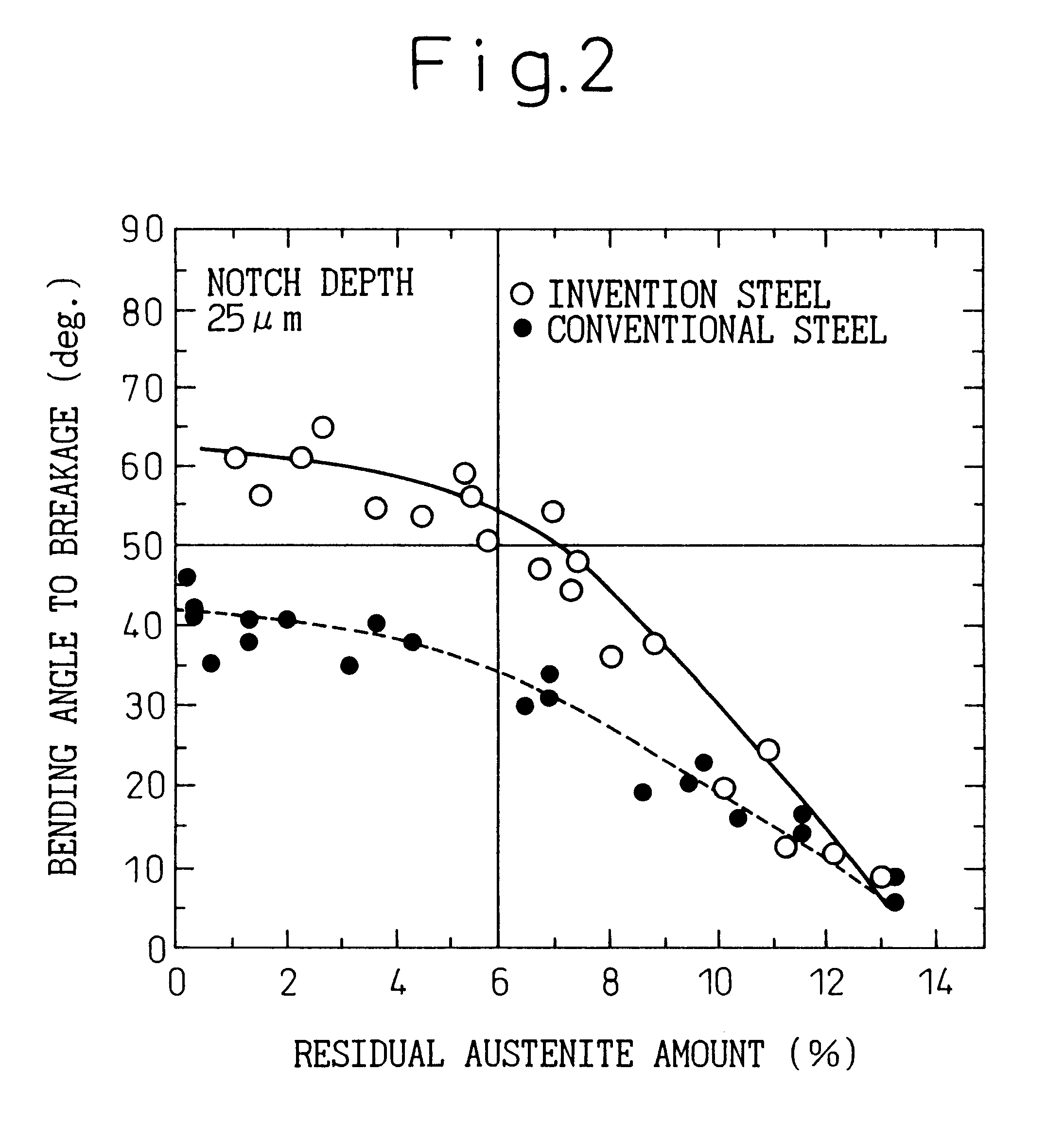
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37004results about "Heat treatment furnaces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
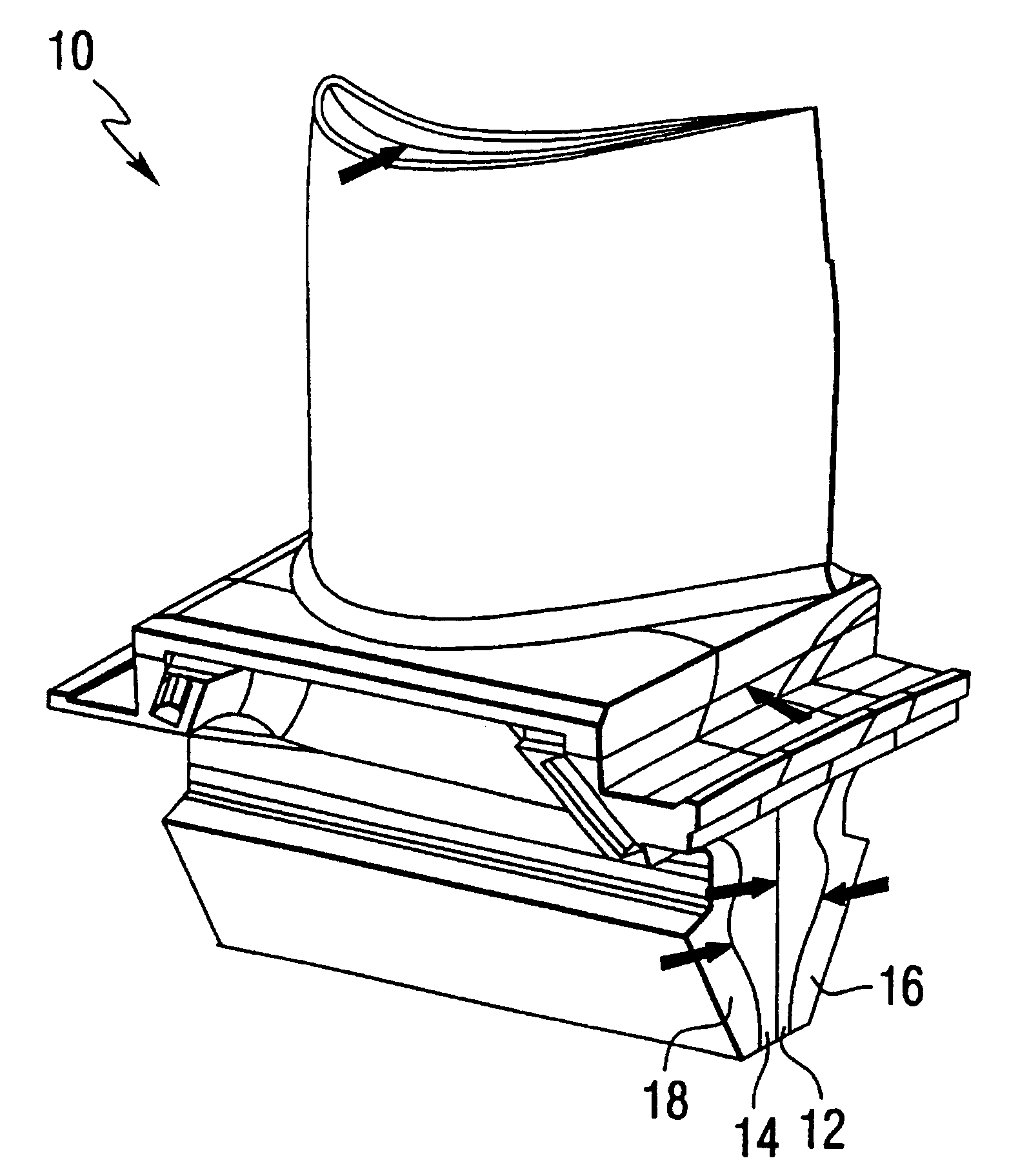
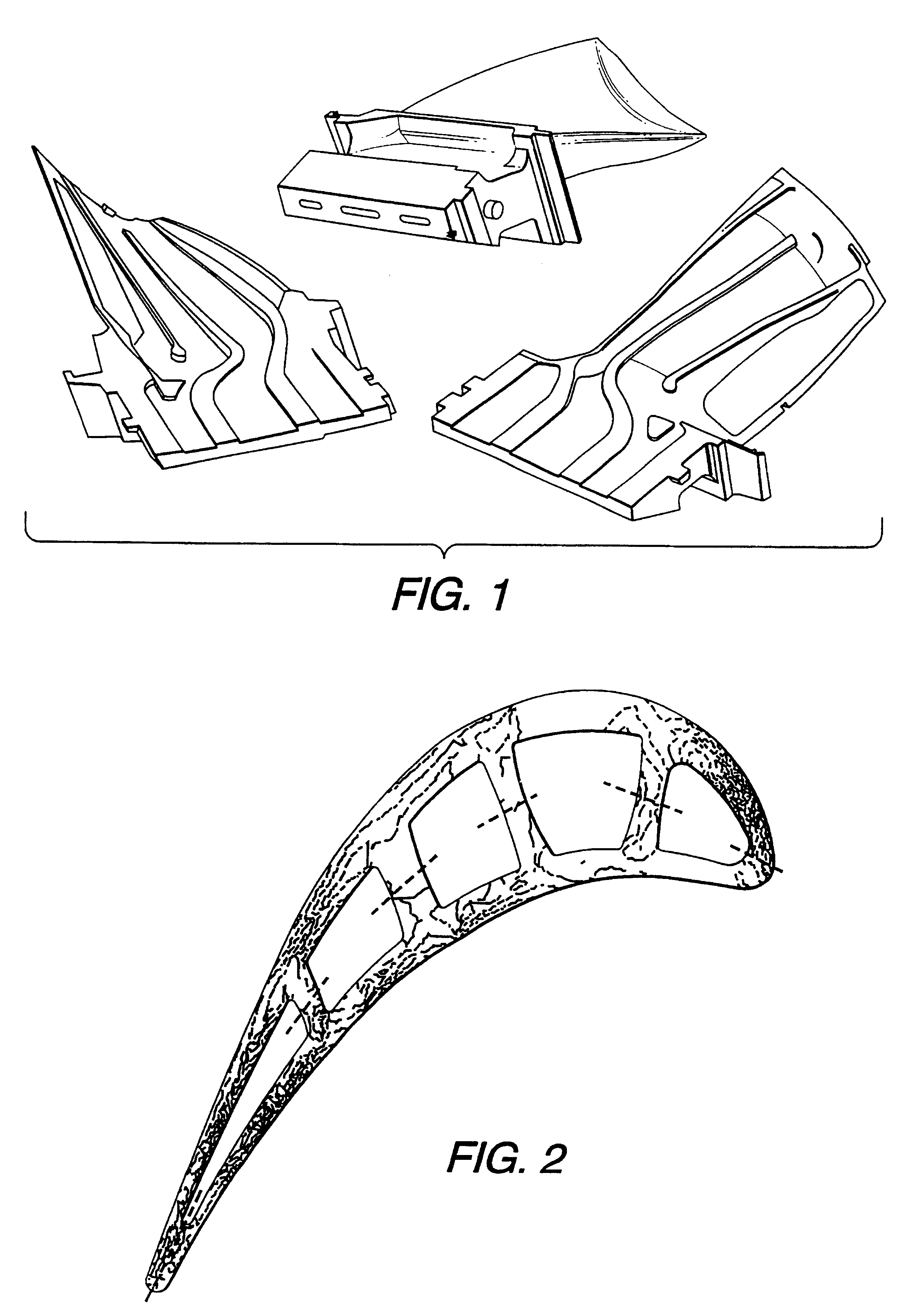
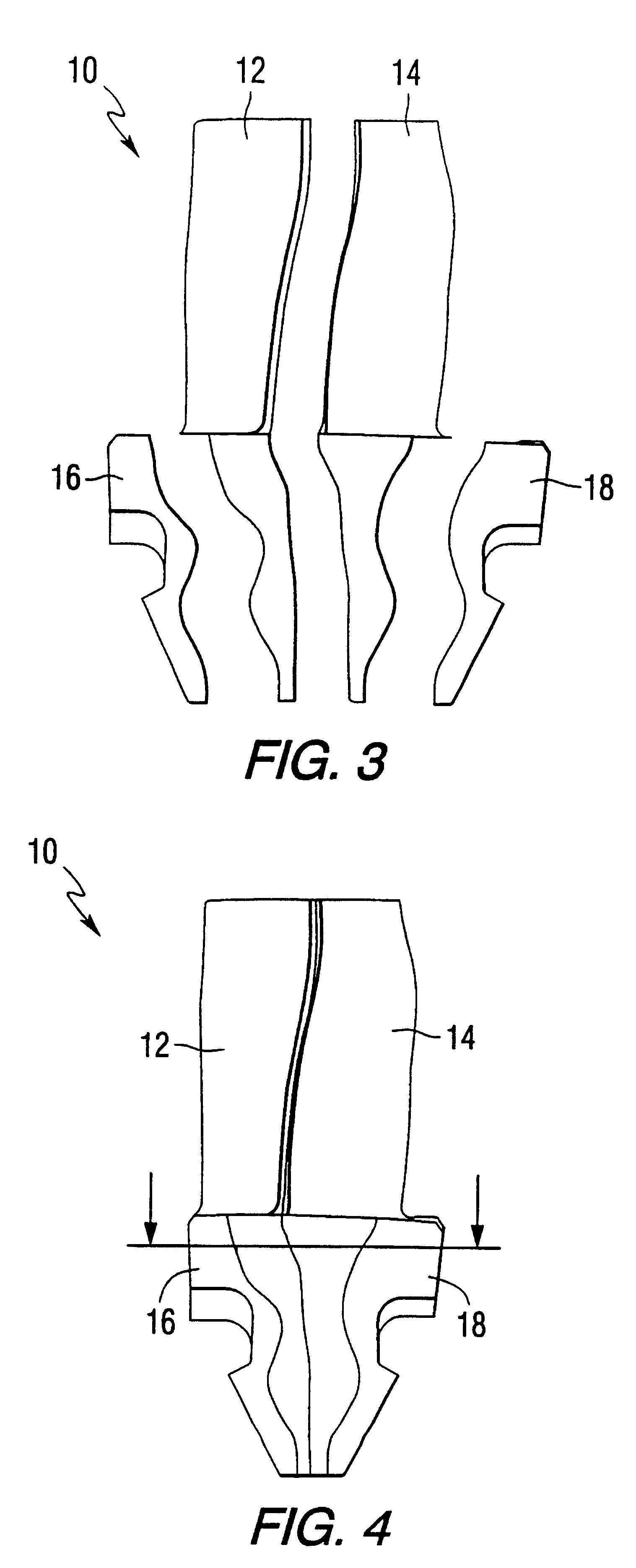
Systems for percutaneous bone and spinal stabilization, fixation and repair
InactiveUS6127597ASize of wire can be enlarged and reducedEnlarging and reducing sizeInternal osteosythesisFluid pressure measurement using pistonsSpinal columnProsthesis
Systems for bone and spinal stabilization, fixation and repair include intramedullar nails, intervertebral cages and prostheses, remotely activatable prostheses, tissue extraction devices, and electrocautery probes. The intramedullar nails, intervertebral cages and prostheses, are designed for expansion from a small diameter for insertion into place to a larger diameter which stabilizes, fixates or repairs the bone, and further can be inserted percutaneously. Remotely activatable prostheses can be activated from an external unit to expand and treat prosthesis loosening. Tissue extraction devices, and electrocautery probes are used to remove tissue from desired areas.
Owner:KYPHON
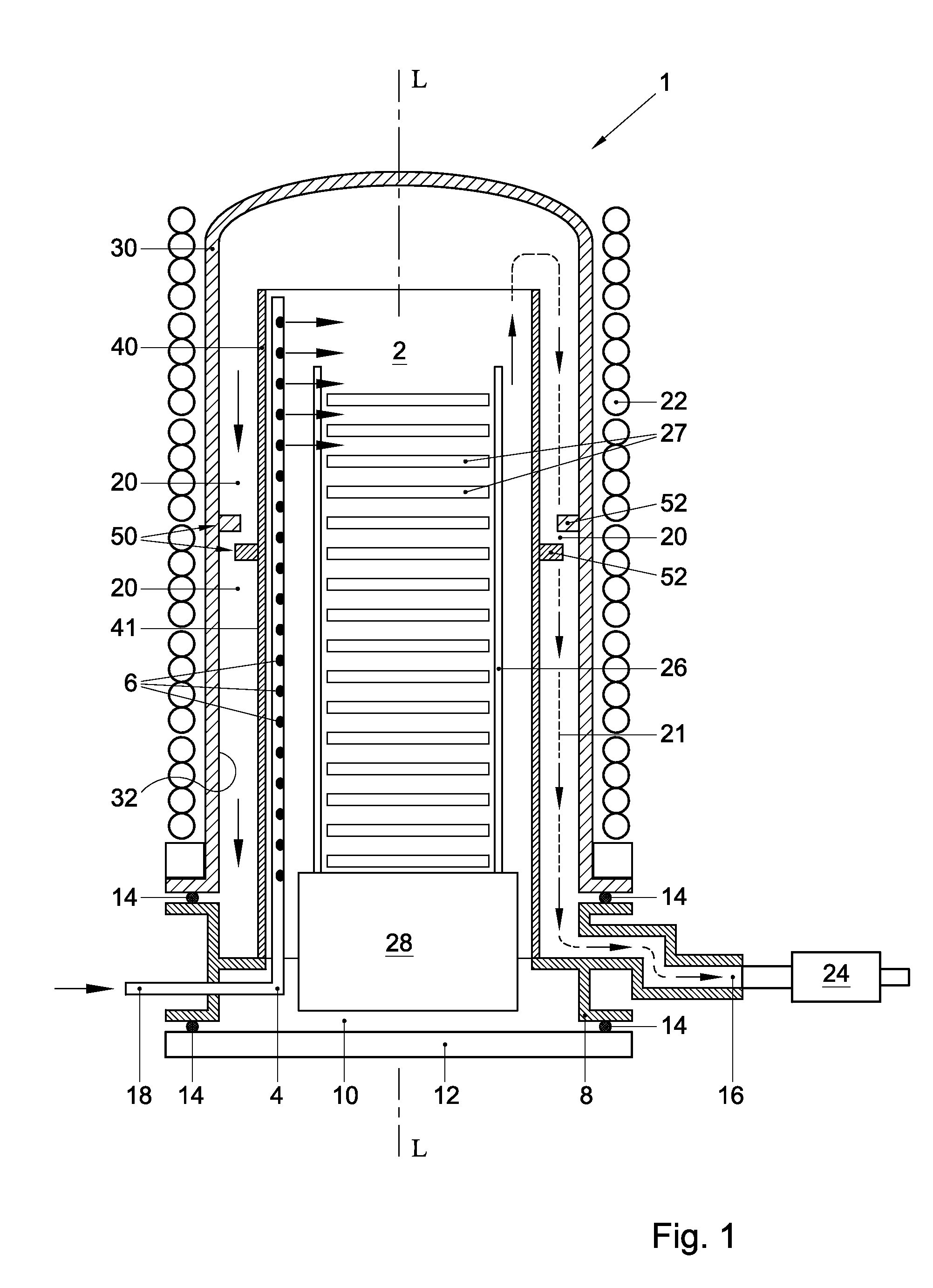
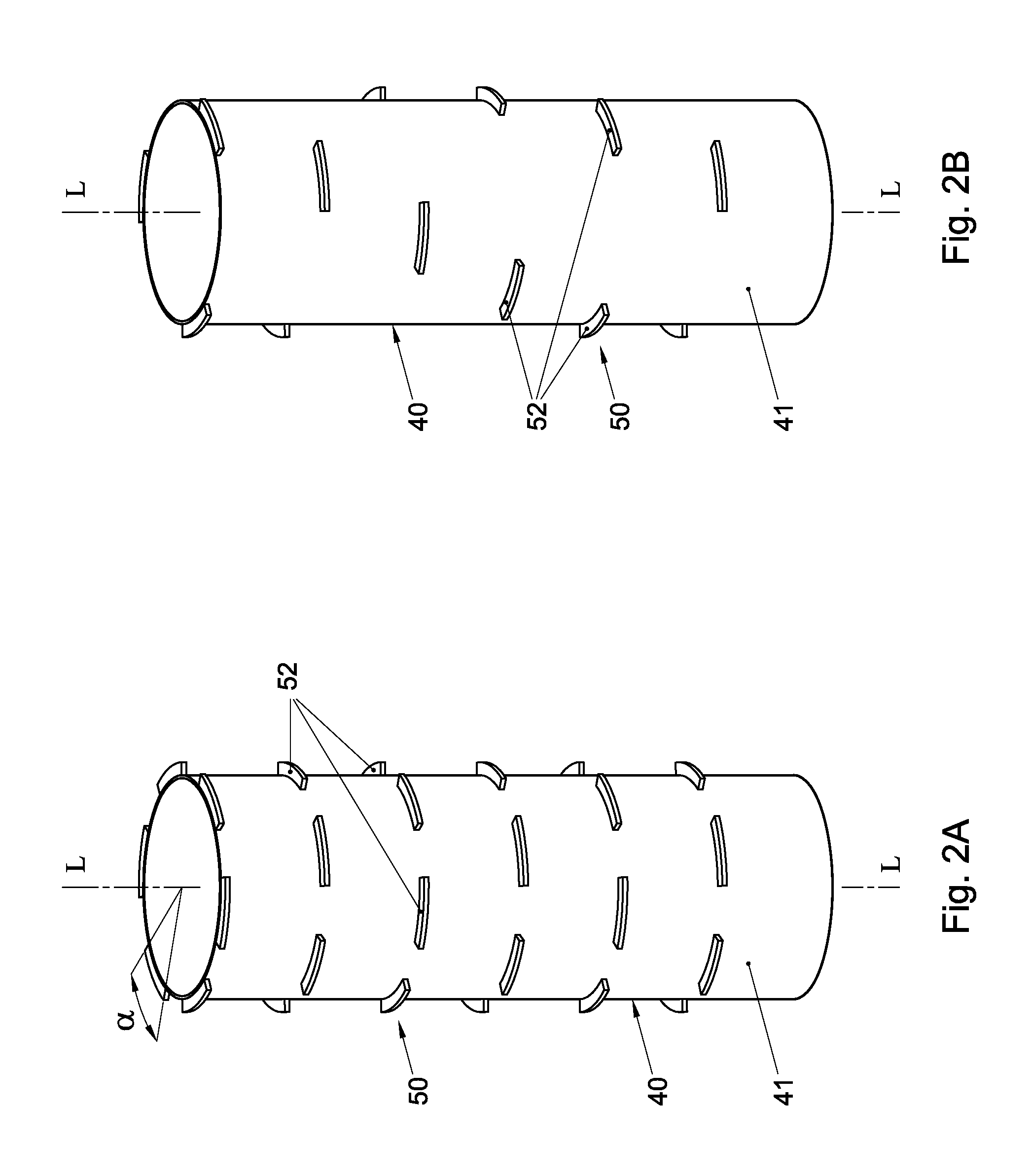
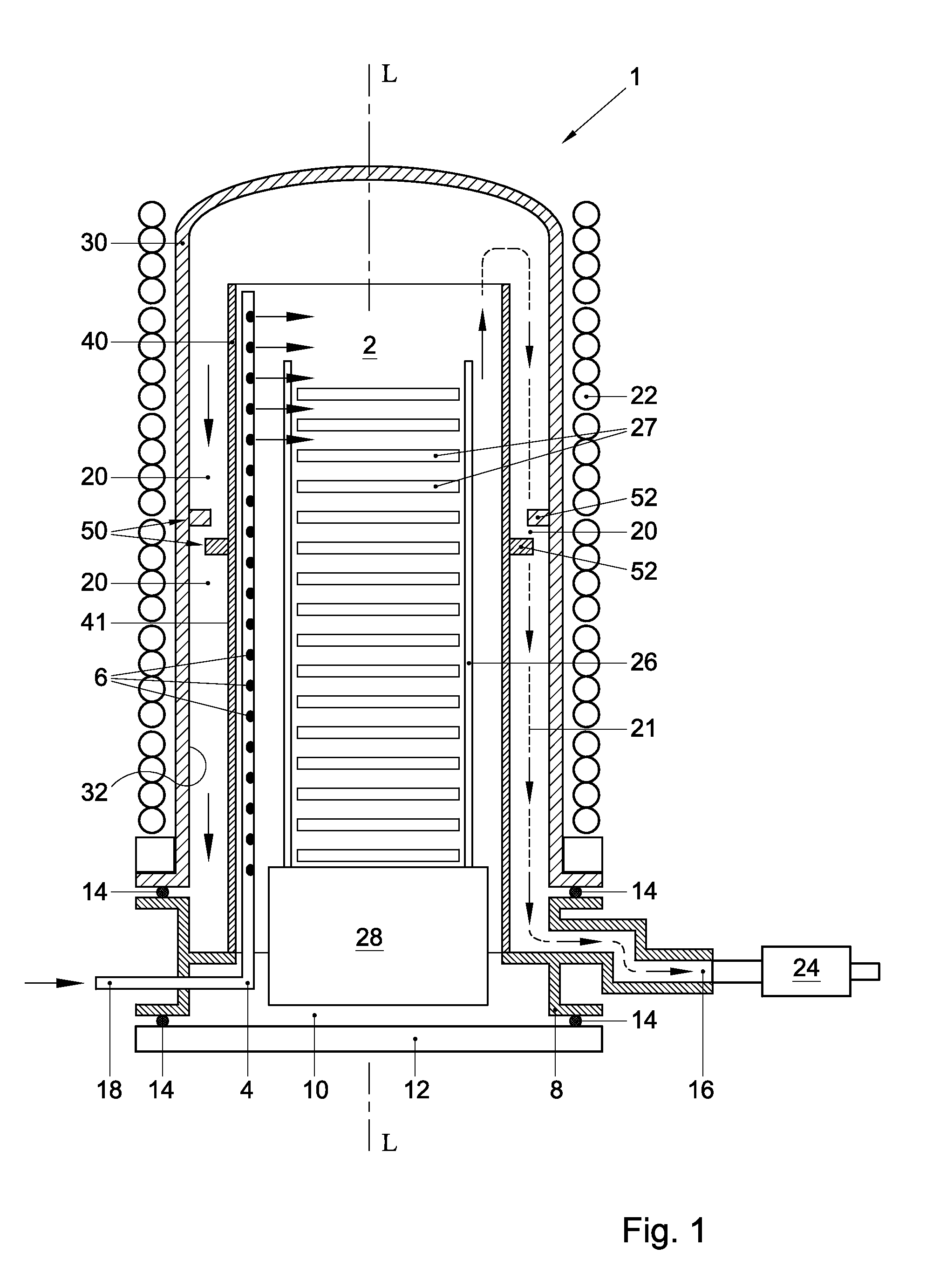
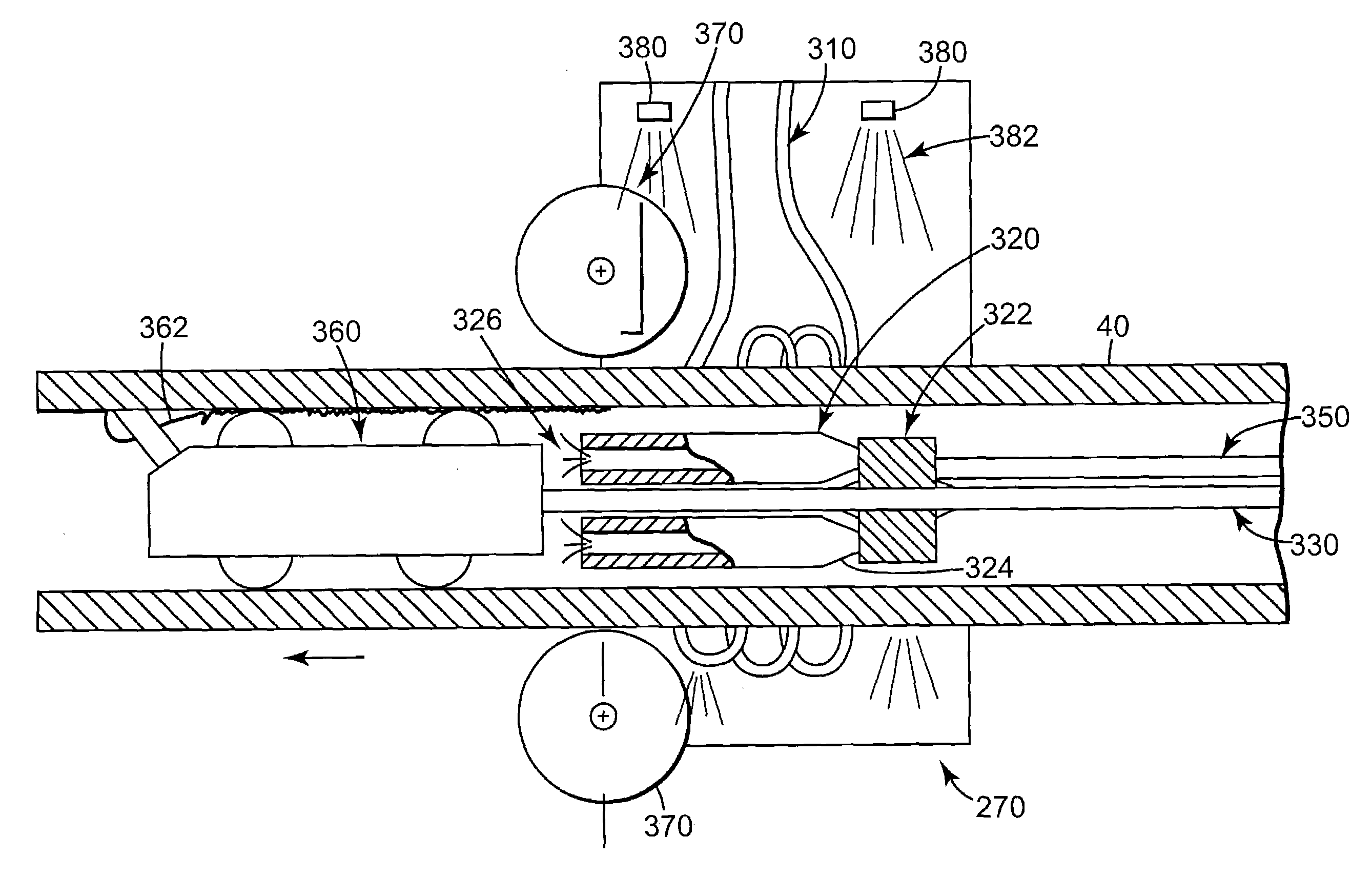
Thermal processing furnace and liner for the same
ActiveUS8398773B2Easy to transportMinimized in sizeDomestic stoves or rangesRotary drum furnacesEngineeringReaction tube
A thermal processing furnace, comprising:a generally bell jar-shaped outer reaction tube having a central axis; andan open-ended inner reaction tube for accommodating a wafer boat holding a plurality of substrates, which inner reaction tube is substantially coaxially disposed within the outer reaction tube, thereby defining a gas passage between an outer wall of the inner reaction tube and an inner wall of the outer reaction tube,wherein at least one of the outer wall of the inner reaction tube and the inner wall of the outer reaction tube is provided with a flow deflector that protrudes radially from the respective wall into the gas passage.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
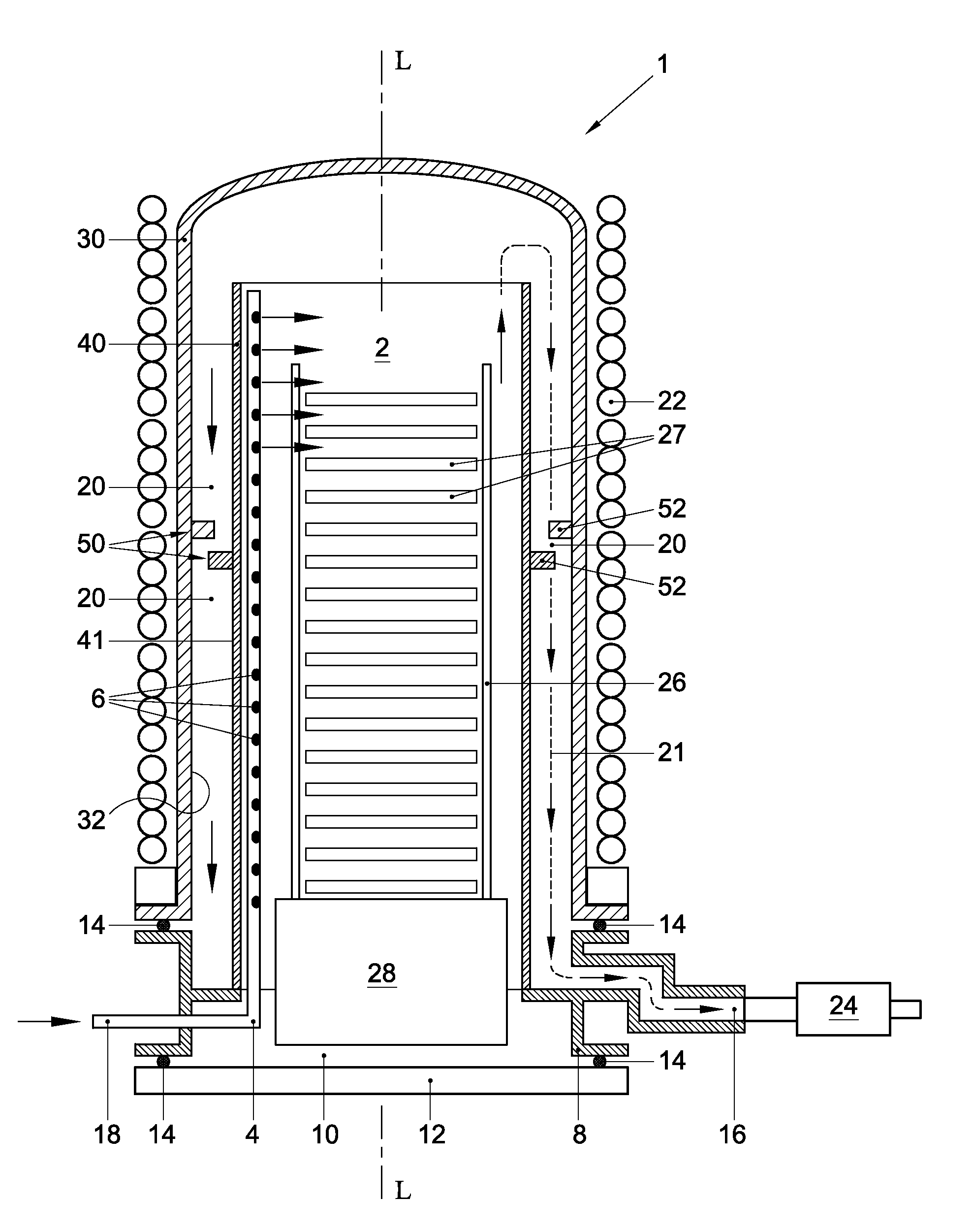
Thermal processing furnace and liner for the same
ActiveUS20120186573A1Easy to transportReduce decreaseDomestic stoves or rangesRotary drum furnacesEngineeringBell jar
A thermal processing furnace, comprising:a generally bell jar-shaped outer reaction tube having a central axis; andan open-ended inner reaction tube for accommodating a wafer boat holding a plurality of substrates, which inner reaction tube is substantially coaxially disposed within the outer reaction tube, thereby defining a gas passage between an outer wall of the inner reaction tube and an inner wall of the outer reaction tube,wherein at least one of the outer wall of the inner reaction tube and the inner wall of the outer reaction tube is provided with a flow deflector that protrudes radially from the respective wall into the gas passage.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
High-strength hot-rolled steel sheet having excellent stretch flangeability, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6364968B1Easy to stretchImprove uniformityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesHigh intensityMechanical property
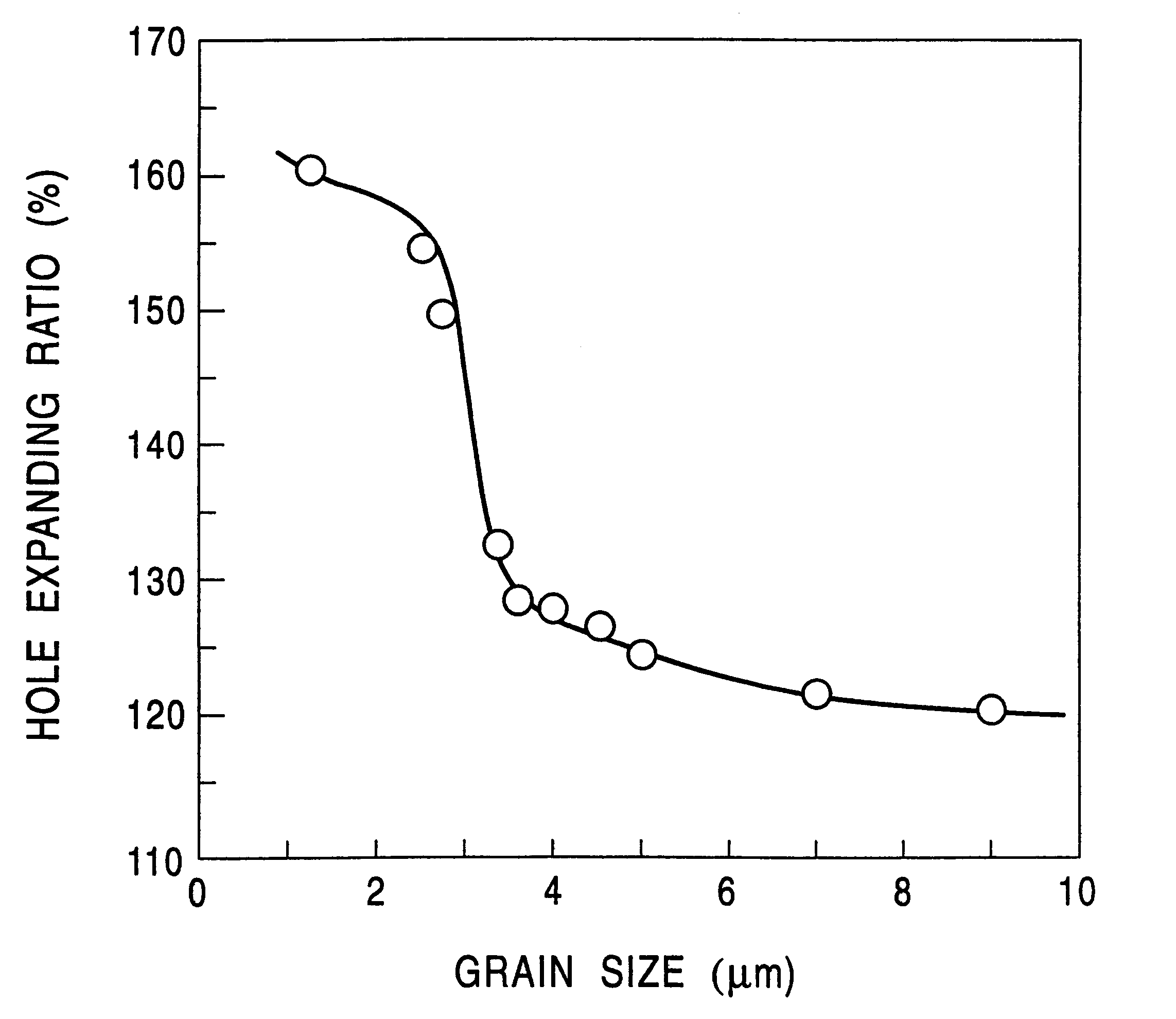
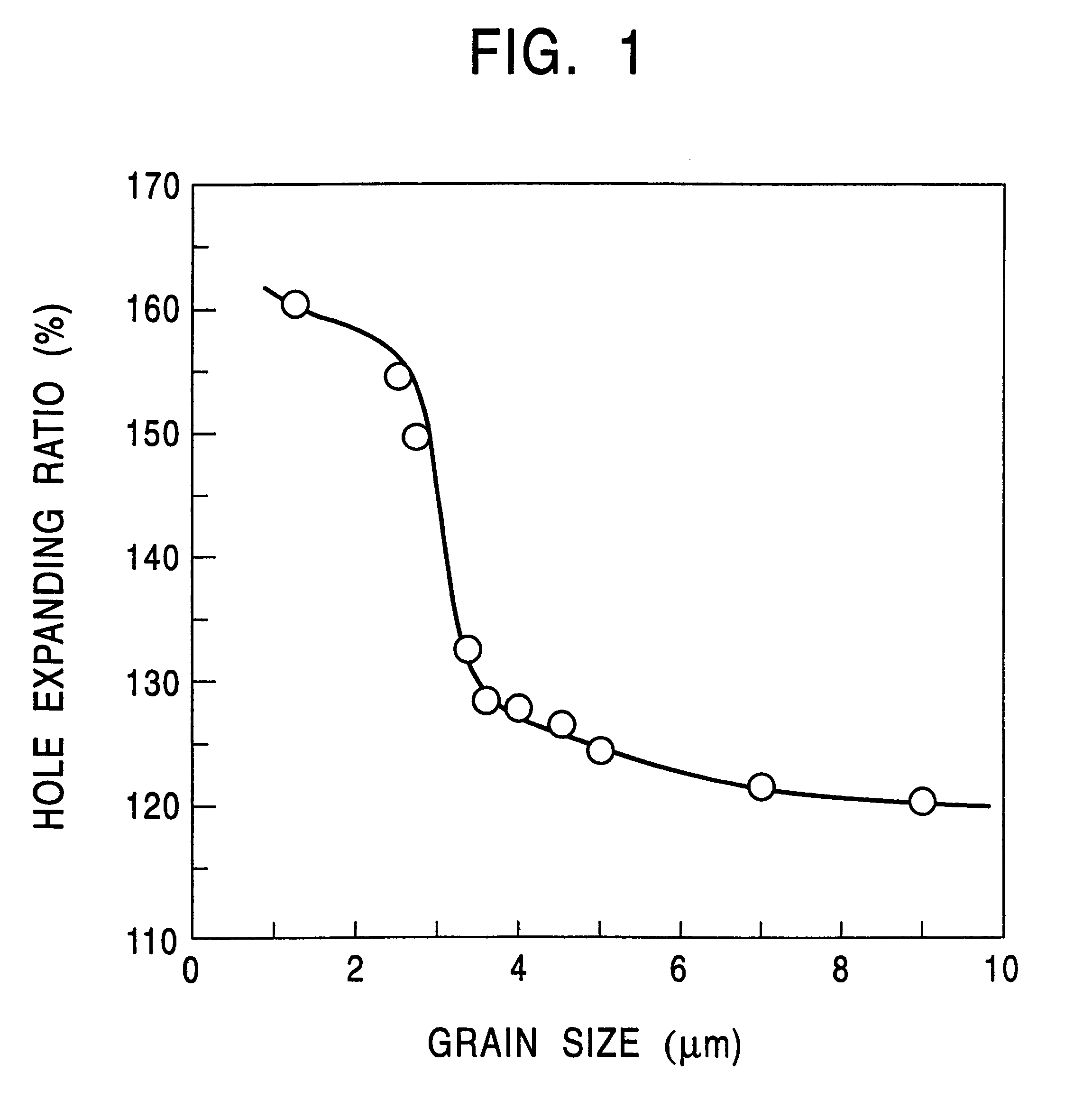
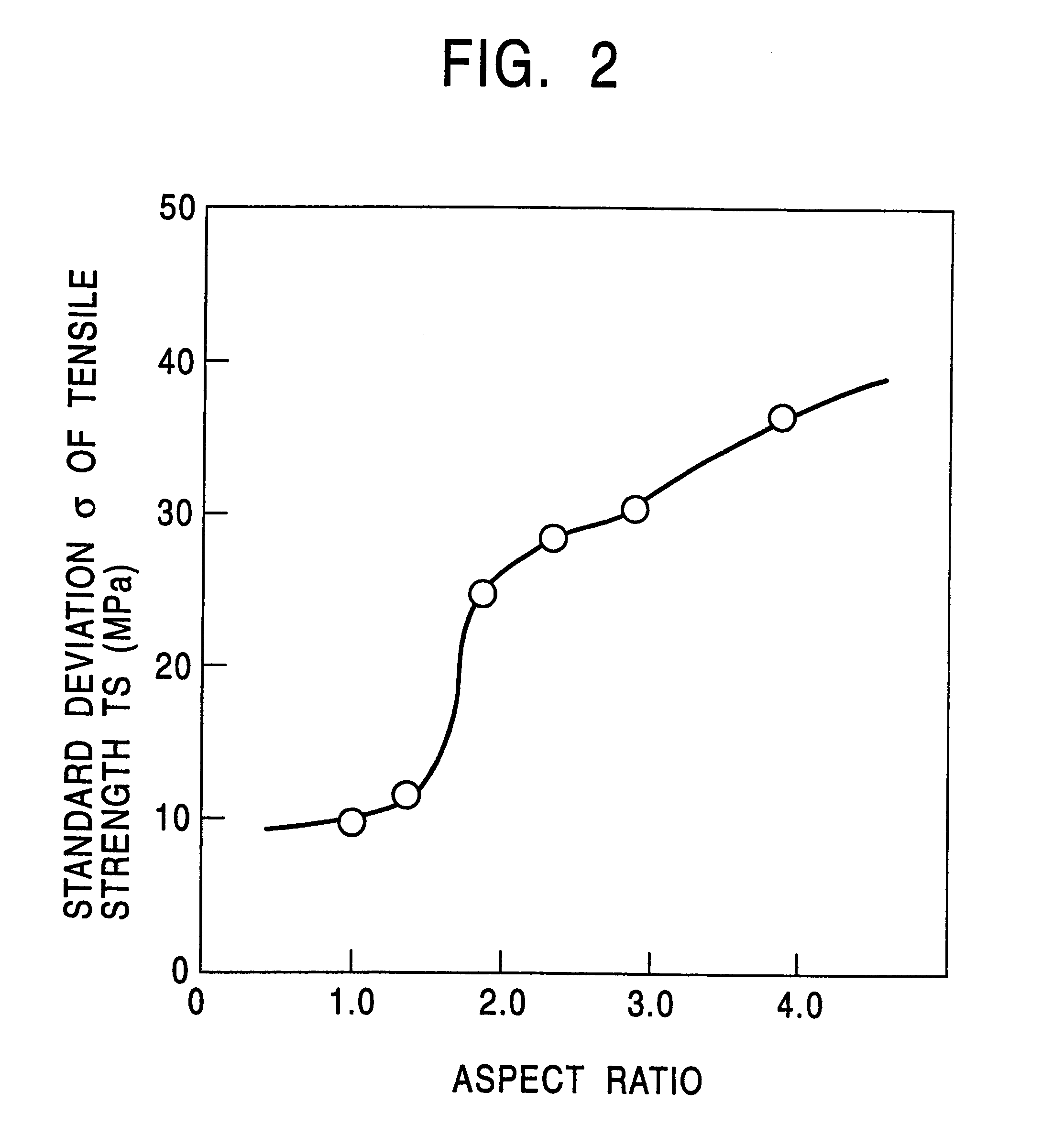
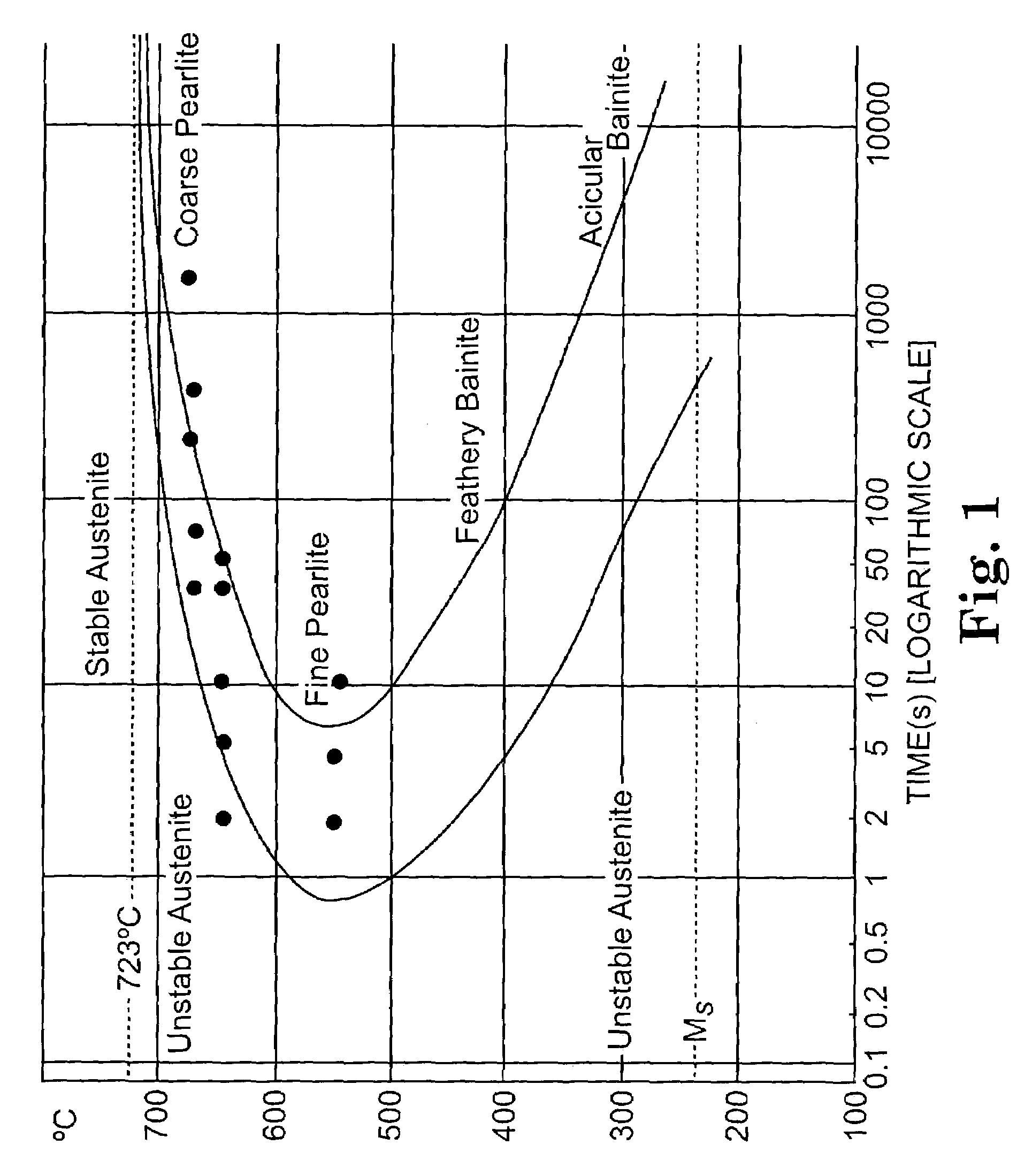
The invention provides a thin high-strength hot-rolled steel sheet with a thickness of not more than 3.5 mm which has excellent stretch flangeability and high uniformity in both shape and mechanical properties of the steel sheet, as well as a method of producing the hot-rolled steel sheet. A slab containing C: 0.05-0.30 wt %, Si: 0.03-1.0 wt %, Mn: 1.5-3.5 wt %, P: not more than 0.02 wt %, S: not more than 0.005 wt %, Al: not more than 0.150 wt %, N: not more than 0.0200 wt %, and one or two of Nb: 0.003-0.20 wt % and Ti: 0.005-0.20 wt % is heated at a temperature of not higher than 1200° C. The slab is hot-rolled at a finish rolling end temperature of not lower than 800° C., preferably at a finish rolling start temperature of 950-1050° C. A hot-rolled sheet is started to be cooled within two seconds after the end of the rolling, and then continuously cooled down to a coiling temperature at a cooling rate of 20-150° C. / sec. The hot-rolled sheet is coiled at a temperature of 300-550° C., preferably in excess of 400° C. A fine bainite structure is obtained in which the mean grain size is not greater than 3.0 mum, the aspect ratio is not more than 1.5, and preferably the maximum size of the major axis is not greater than 10 mum.
Owner:KAWASAKI STEEL CORP
Turbine blades made from multiple single crystal cast superalloy segments
InactiveUS6331217B1Improve bindingQuality improvementPropellersFrom frozen solutionsTurbine bladeSingle crystal
Large gas turbine blades made from separate cast segments of superalloys are disclosed. The turbine blade is designed such that bond lines between adjacent segments are placed in low stress regions of the blade. The cast superalloy segments of the blades are aligned and fitted together with specified tolerances. The turbine blade segments are then joined by transient liquid phase bonding, followed by a controlled heat treatment which produces the desired microstructure in the bond region. The method allows for the production of large, high quality turbine blades by joining small, high quality cast superalloy sections, in comparison with prior attempts to cast large turbine blades as single pieces which have produced very low yields and high individual component costs.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Seam-welded metal pipe and method of making the same without seam anneal
InactiveUS7032809B1Efficient processingEliminates annealing stepArc welding apparatusFurnace typesSufficient timeWeld seam
An apparatus and method for making a seam-welded steel pipe free of untempered martensite without seam anneal. The method includes selecting a steel containing a carbon concentration below a predetermined level, for example, 0.14% or 0.12% by weight. The method also includes flooding both outside and inside of the strip with a coolant while the weld seam is being formed, and continuing to immerse the welded strip for a sufficient time after the weld seam is formed to prevent the formation of untempered martensite. The apparatus includes a heater capable of heating the strip to a temperature sufficient to form a welded seam, a cooling module configured to supply a coolant to the welded seam both inside and outside of the strip as the weld seam is being formed, and another cooling module configured to immerse the welded strip in a coolant after the weld seam is formed for a sufficient length of time to prevent the formation of untempered martensite.
Owner:STEEL VENTURES
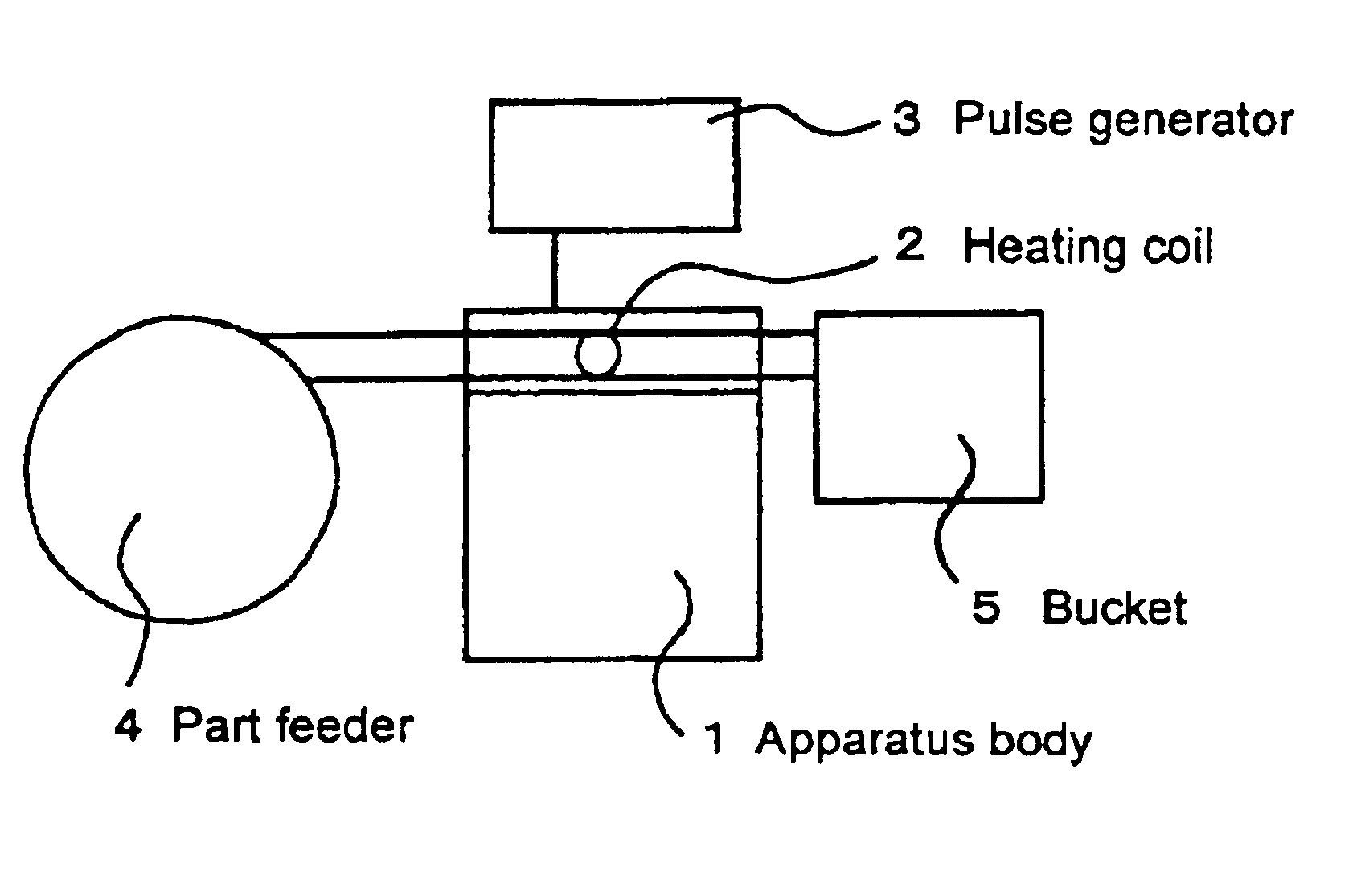
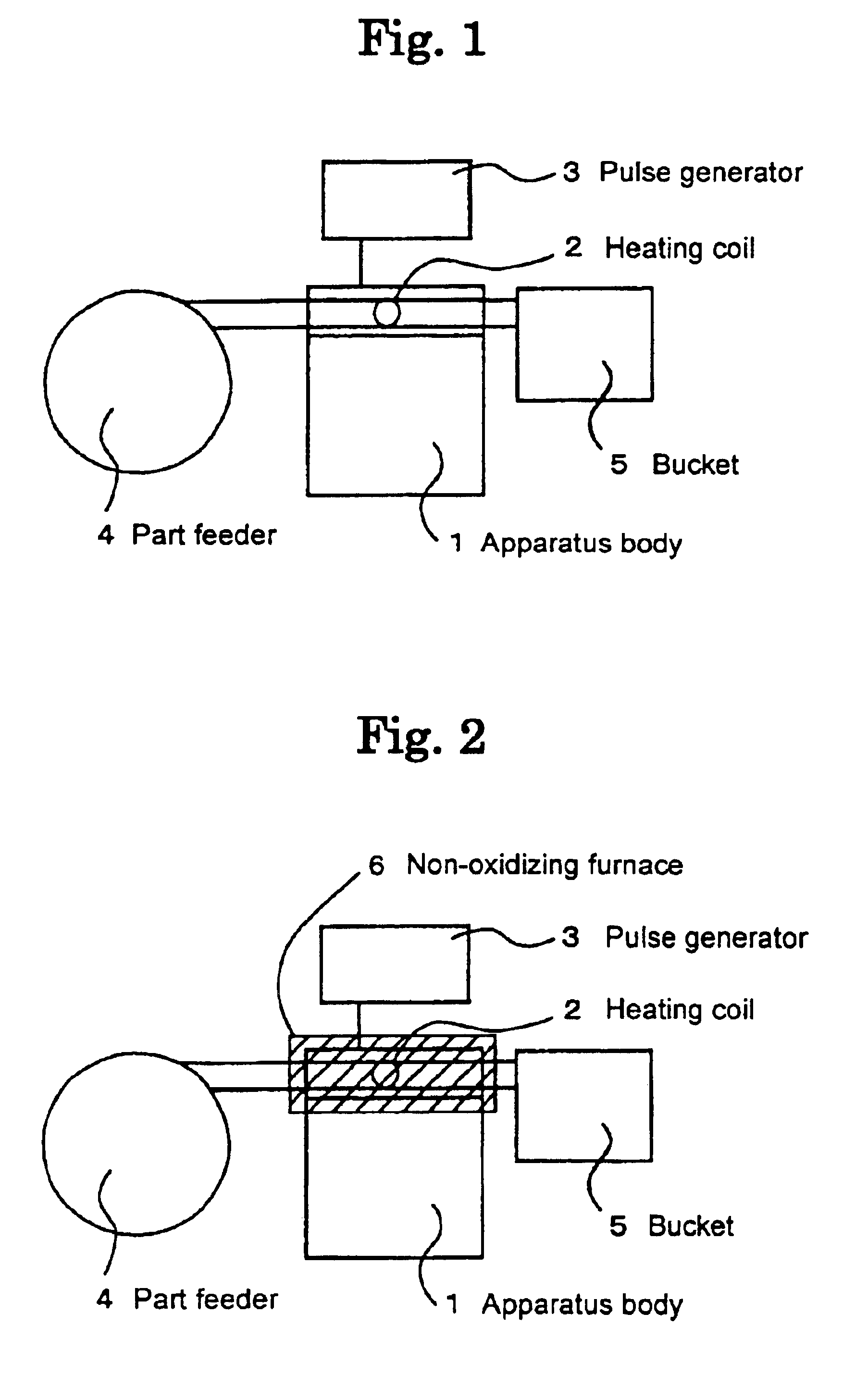
Heat-treating boat for semiconductor wafers
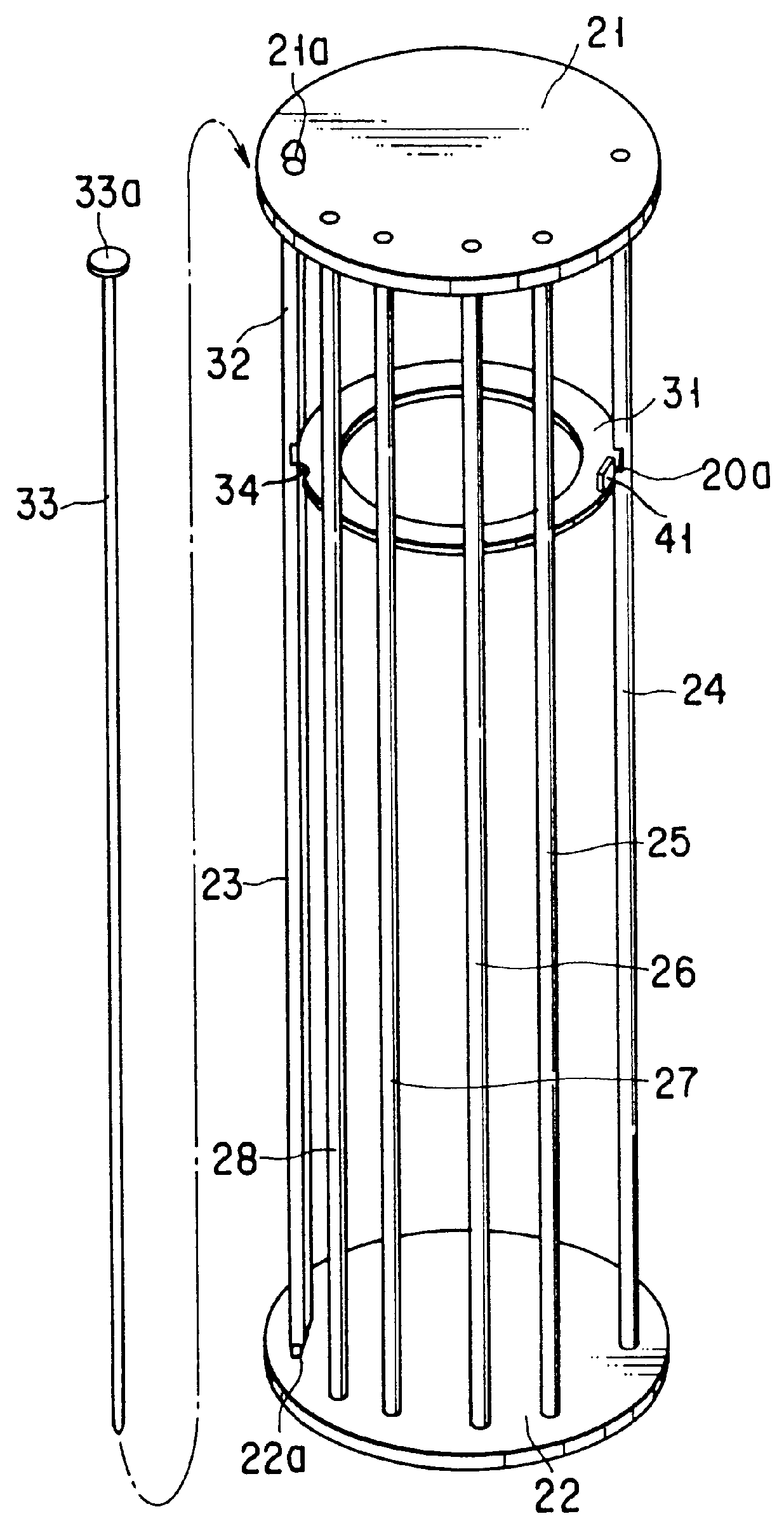
InactiveUS6062853ASimple structureEasy to manufactureDrying solid materials with heatCharge supportsEngineeringSemiconductor
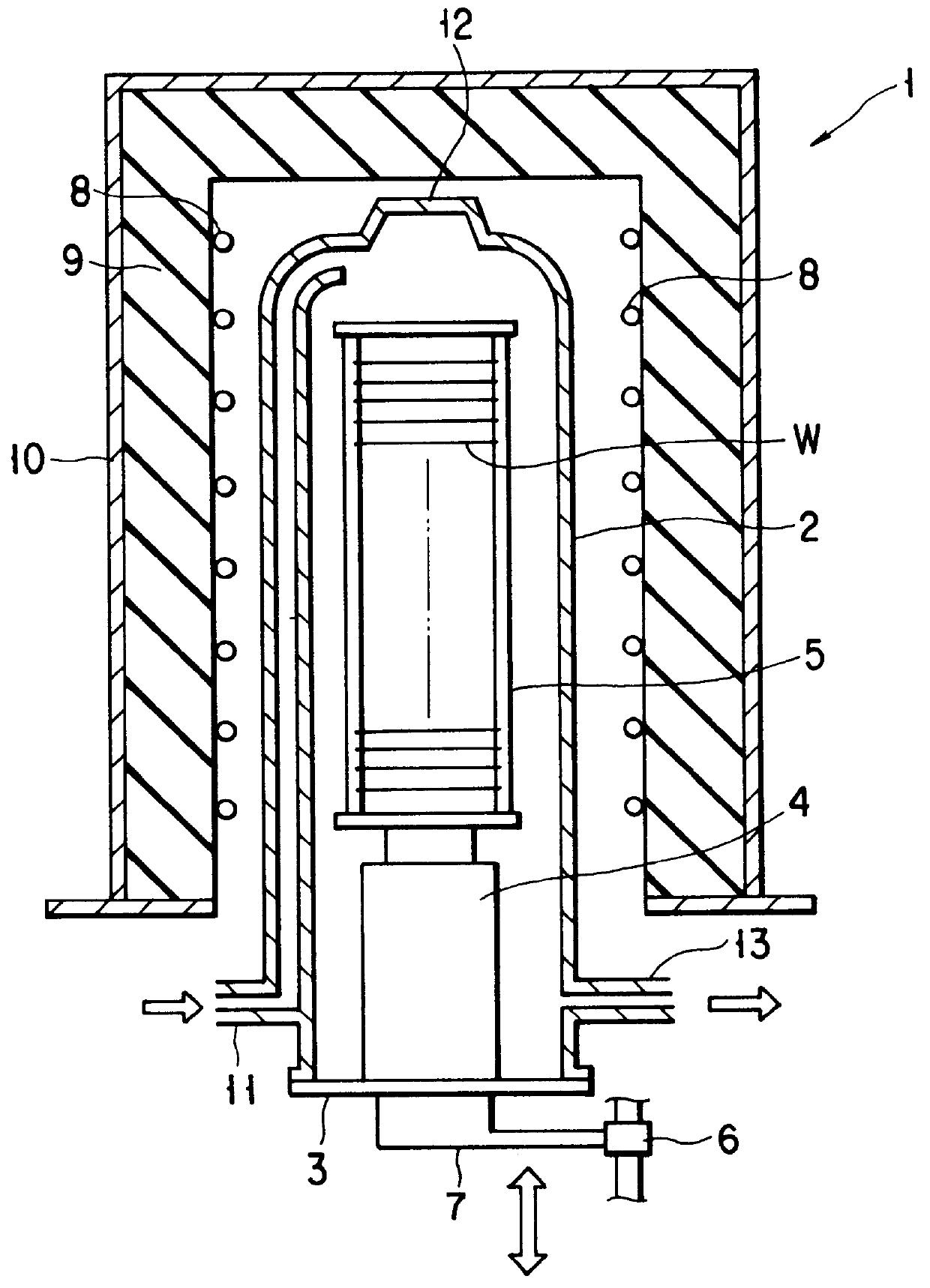
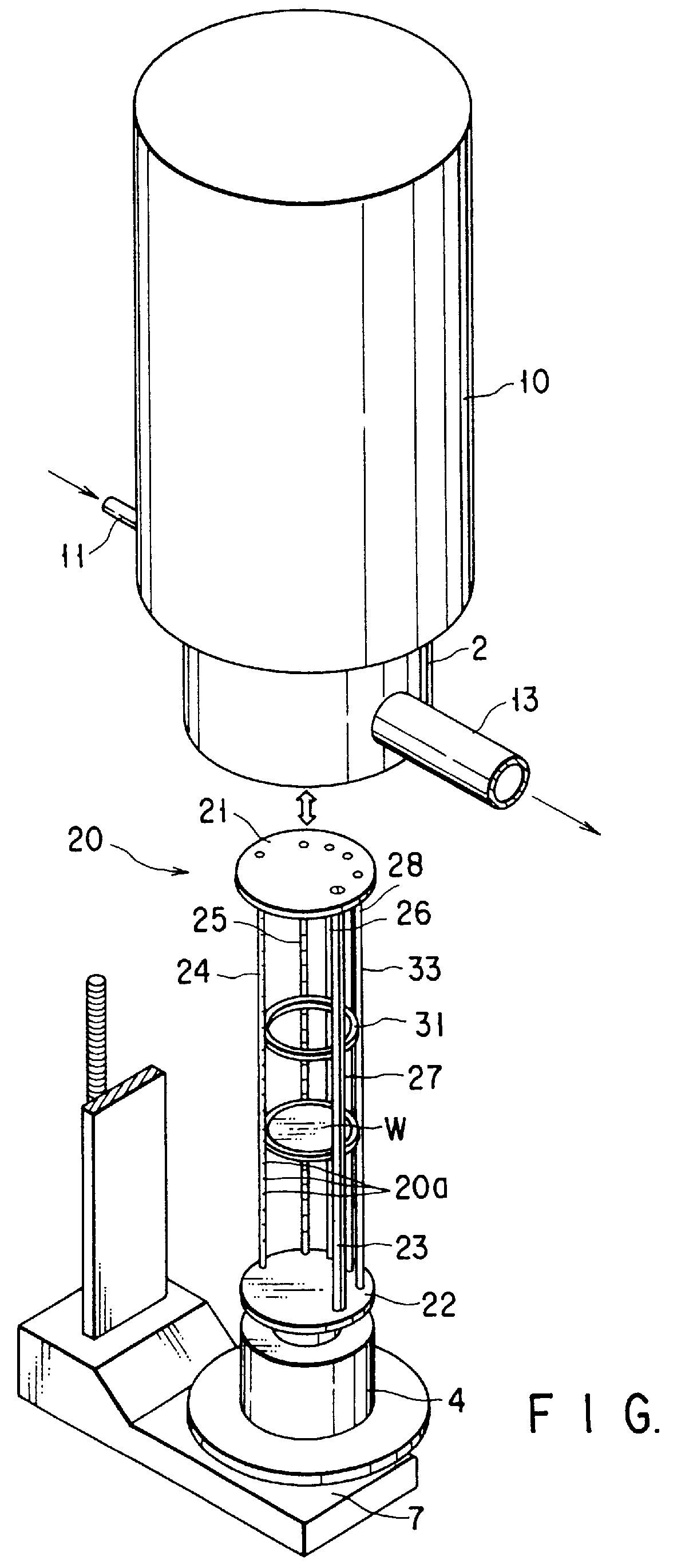
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 00526 Sec. 371 Date Aug. 31, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Aug. 31, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 25, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 32339 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 4, 1997An heat-treating ring boat (20) for semiconductor wafers (W) has a top plate (21), a bottom plate (22), six columns (23-28), and 63 ring trays (31). The trays (31) are mounted in grooves (20a) of the columns (23-28). To fix the trays (31), a fixing rod (33) is detachably mounted between the top plate (21) and bottom plate (22). A through hole (21a) and a recessed portion (22a) to mount the fixing rod (33) therein are formed in the top plate (21) and bottom plate (22). Notches (34) to engage with the fixing rod (33) are formed in the trays (31). A notch (32) to engage with the fixing rod (33) is formed in the column (23). A projection (41) is formed on each tray (31) to abut against the side surface of the column (24).
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
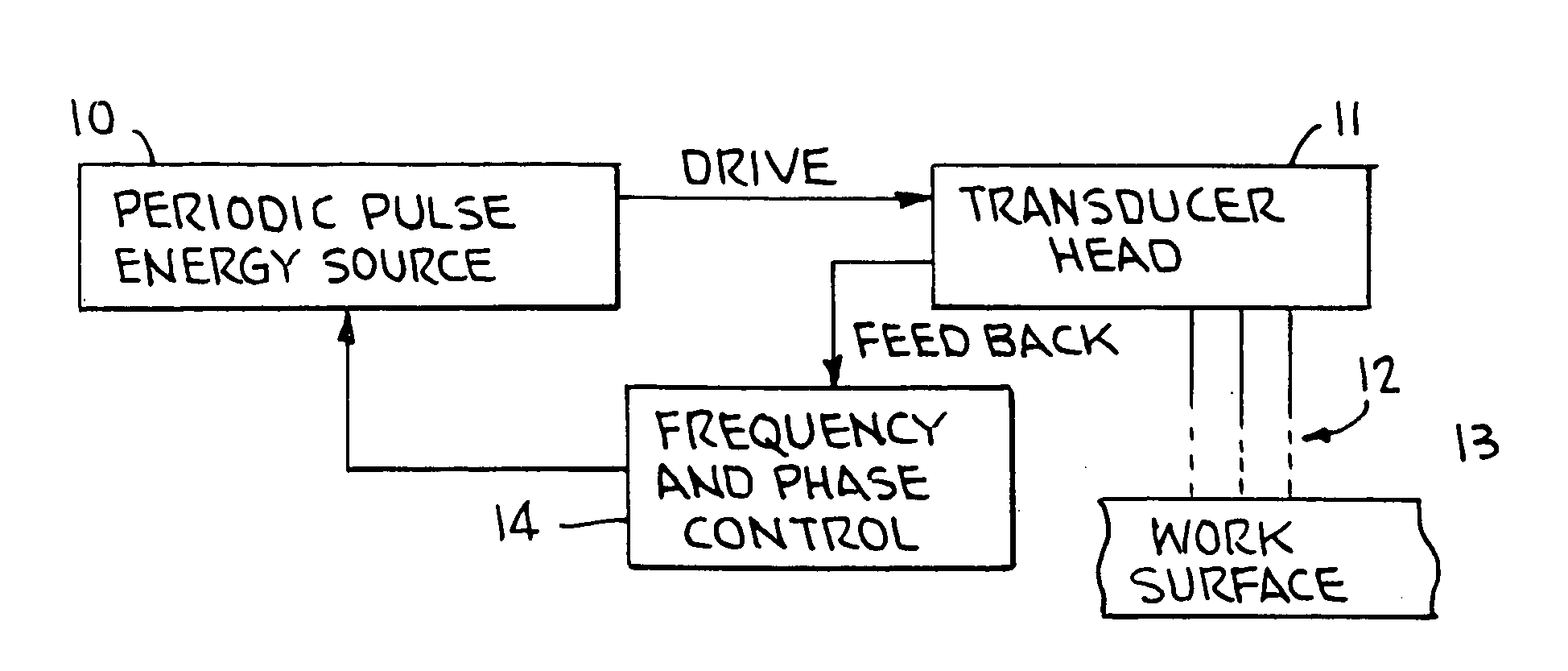
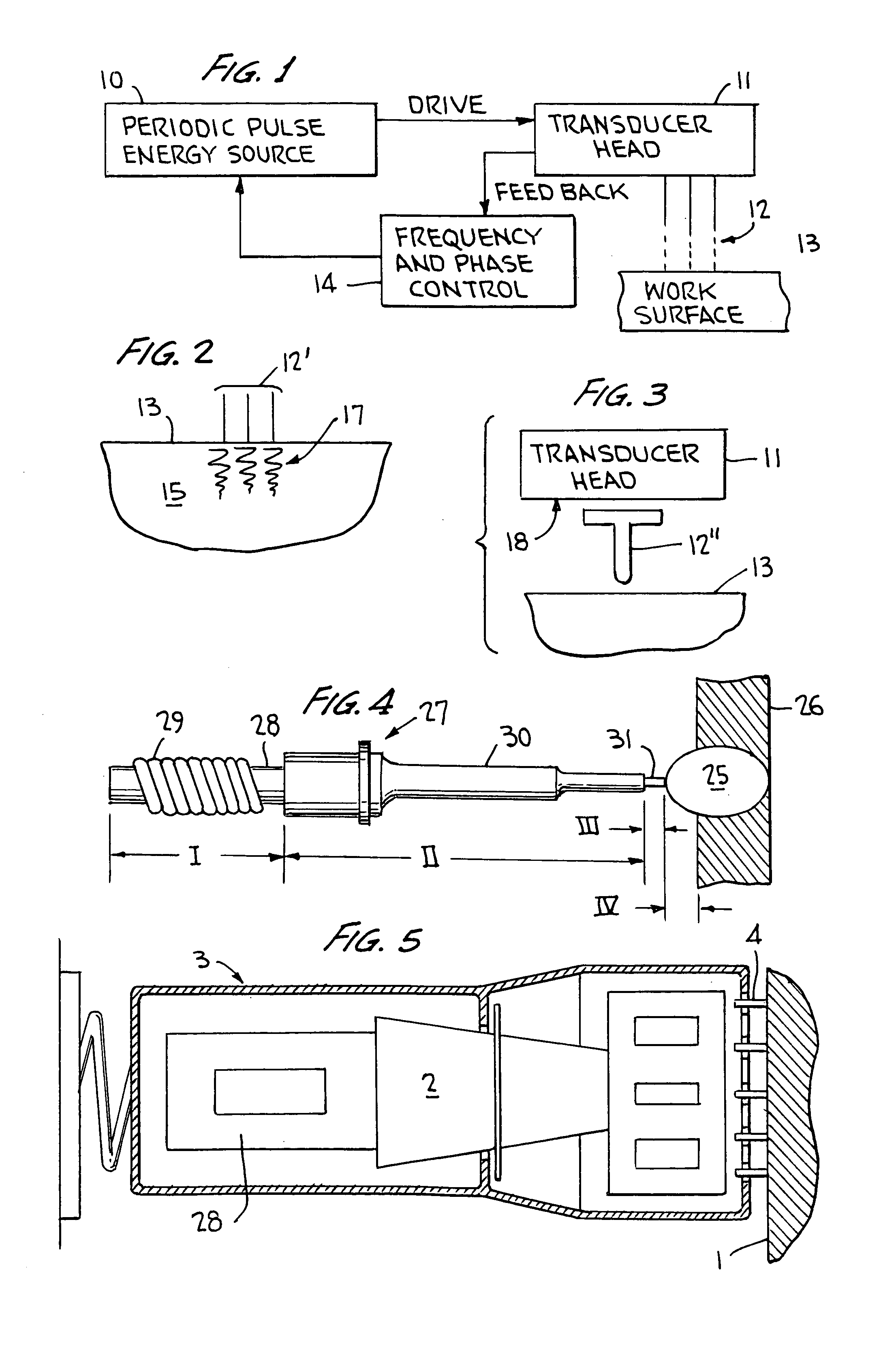
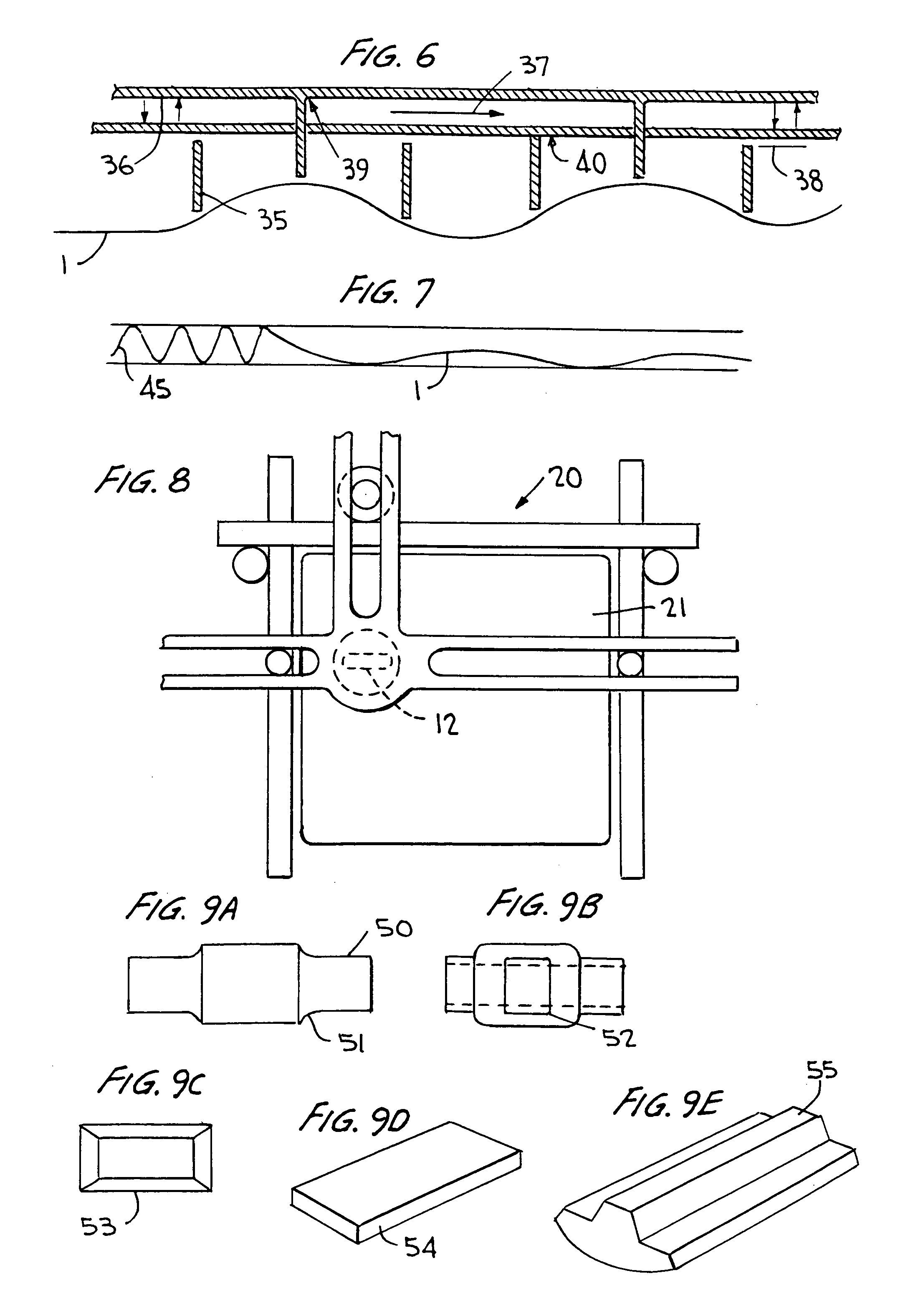
Ultrasonic impact machining of body surfaces to correct defects and strengthen work surfaces
InactiveUS6932876B1Improve power transfer efficiencyEfficient transferMechanical vibrations separationFurnace typesUltrasonic sensorPeriodic oscillation
Metallic workpieces of diverse shapes having work surfaces which are deformed at the surface and adjacent sub-surface layers by surface impact from ultrasonic transducers employing freely axially moving impacting elements propelled and energized by a transducer oscillating surface vibrating periodically at an ultrasonic frequency. The impacting elements are propelled in a random aperiodic and controlled impact mode at different phases of the periodic oscillation cycles. The transducer may be portable and provides a series of mechanically interconnected stages having mechanical resonances harmonically related as a multiple of the primary ultrasonic frequency and have matched stage resistances under instantaneous loading when the impact elements are driven by the transducer oscillating surface into the surface of the workpiece. This mode of operation produces Q-factor amplification of the input ultrasonic power oscillator energy at the impact needles and high propulsion velocities making it possible to machine metallic workpiece bodies to greater depths for compressing the metal to increase compressive strength of the workpiece work surfaces to substantially the ultimate material strength. The impact machining is done at ambient temperatures.
Owner:PROGRESS RAIL SERVICES
High strength steel sheet having excellent formability and method for production thereof
InactiveUS7090731B2Good molding effectHigh strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesHigh intensityHardness
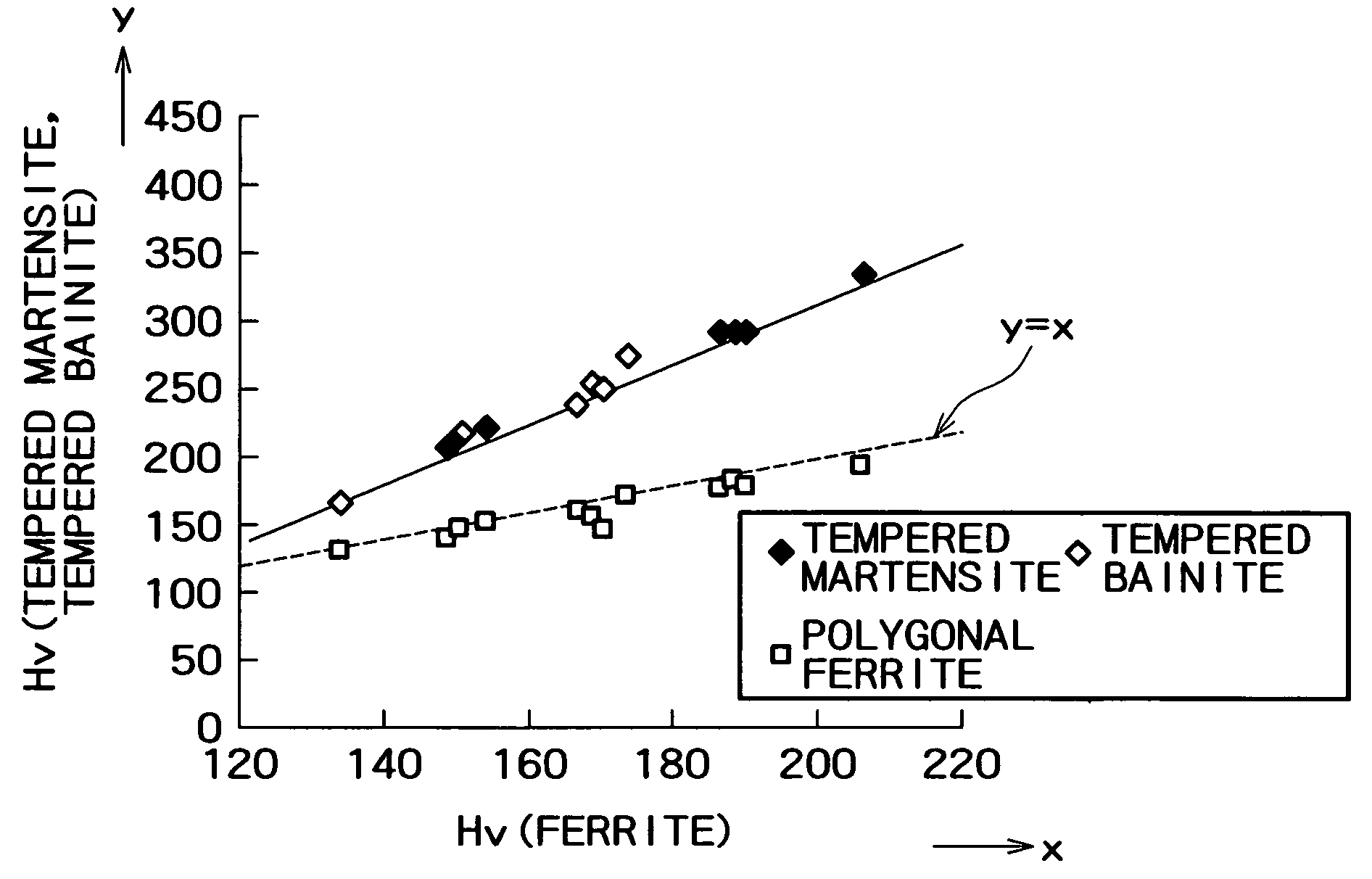
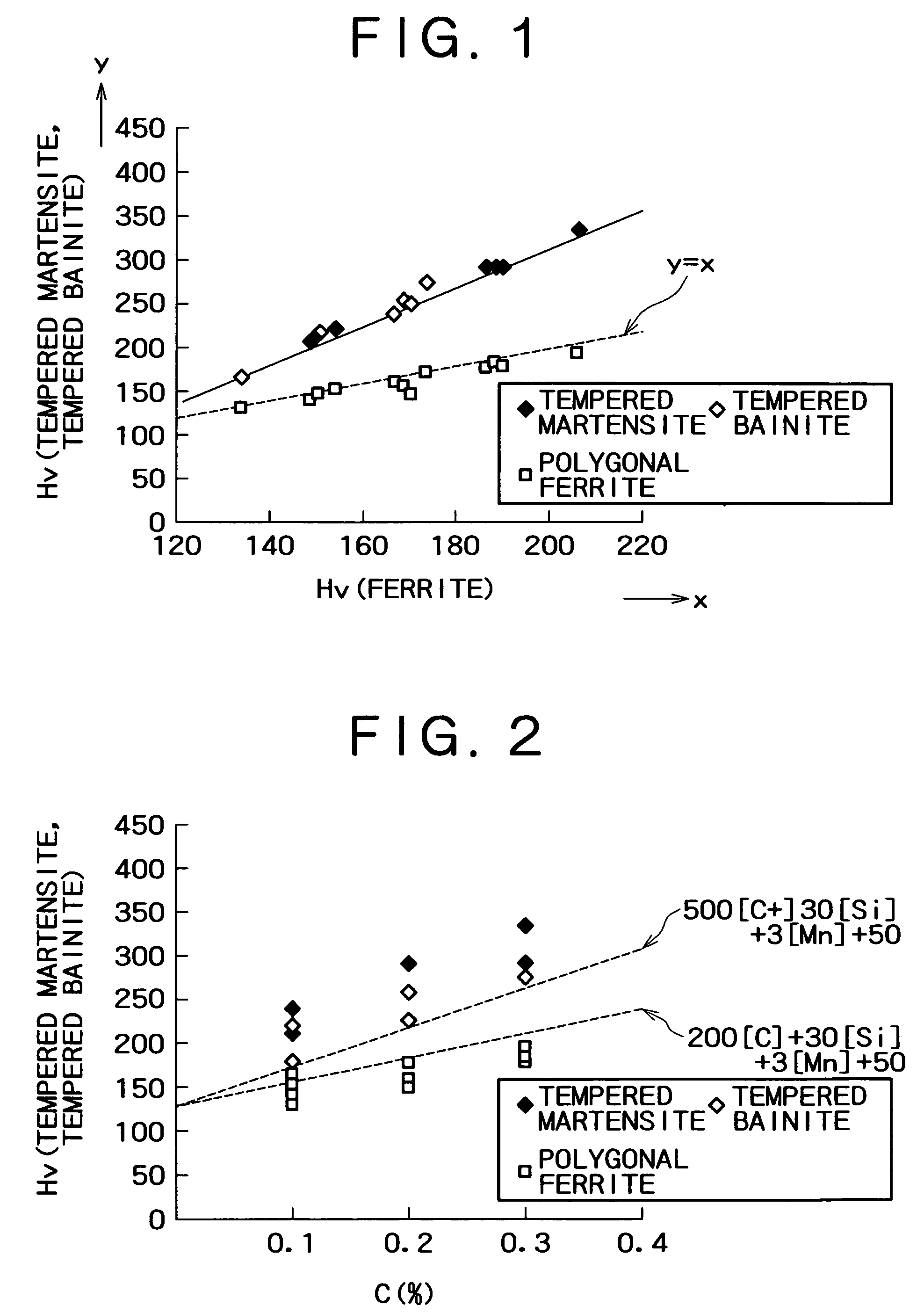
A high strength steel sheet having (2-1) a base phase structure, the base phase structure being tempered martensite or tempered bainite and accounting for 50% or more in terms of a space factor relative to the whole structure, or the base phase structure comprising tempered martensite or tempered bainite which accounts for 15% or more in terms of a space factor relative to the whole structure and further comprising ferrite, the tempered martensite or the tempered bainite having a hardness which satisfies the relation of Vickers hardness (Hv)≧500[C]+30[Si]+3[Mn]+50 where [ ] represents the content (mass %) of each element, and (2-2) a second phase structure comprising retained austenite which accounts for 3 to 30% in terms of a space factor relative to the whole structure and optionally further comprising bainite and / or martensite, the retained austenite having a C concentration (CγR) of 0.8% or more.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
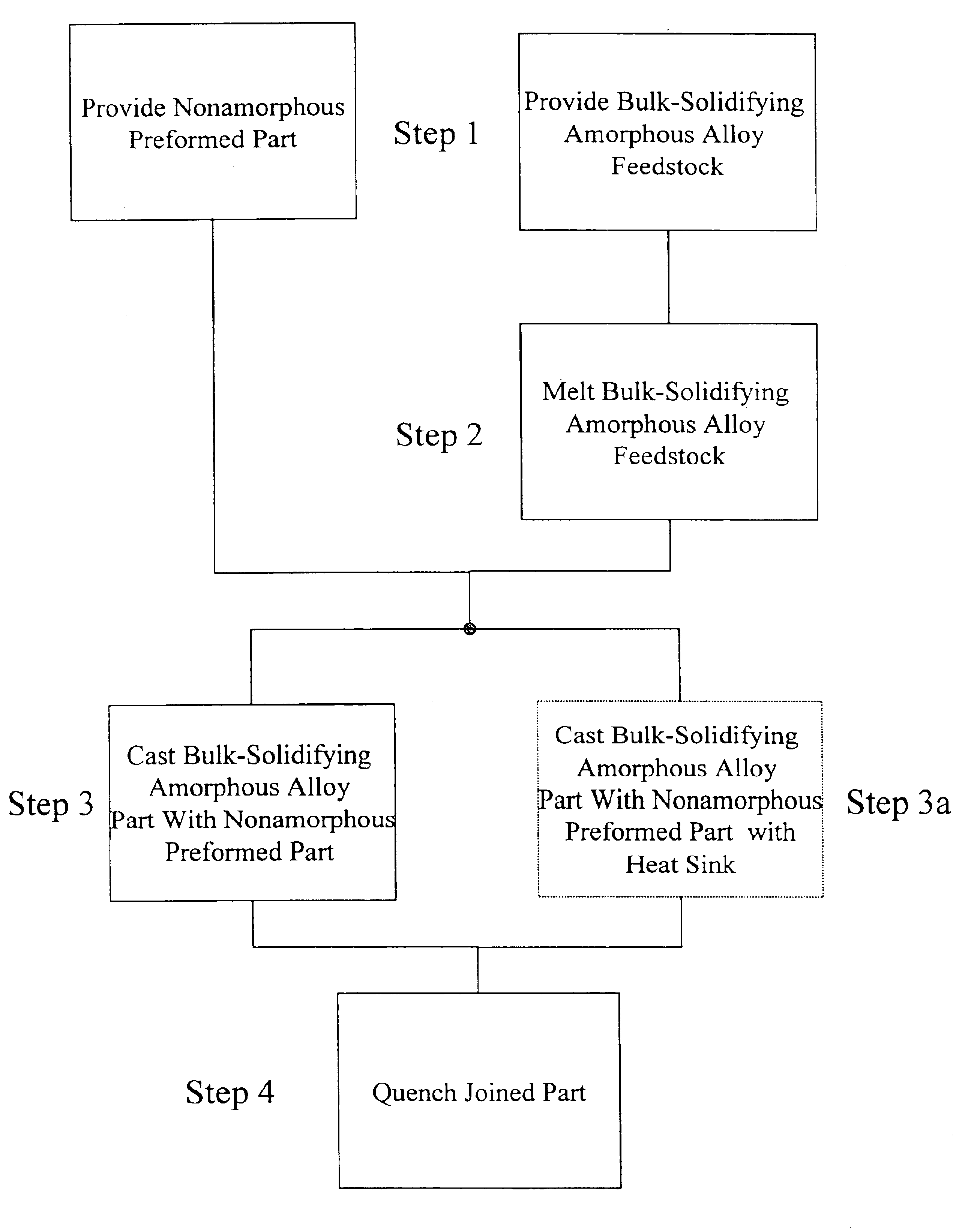
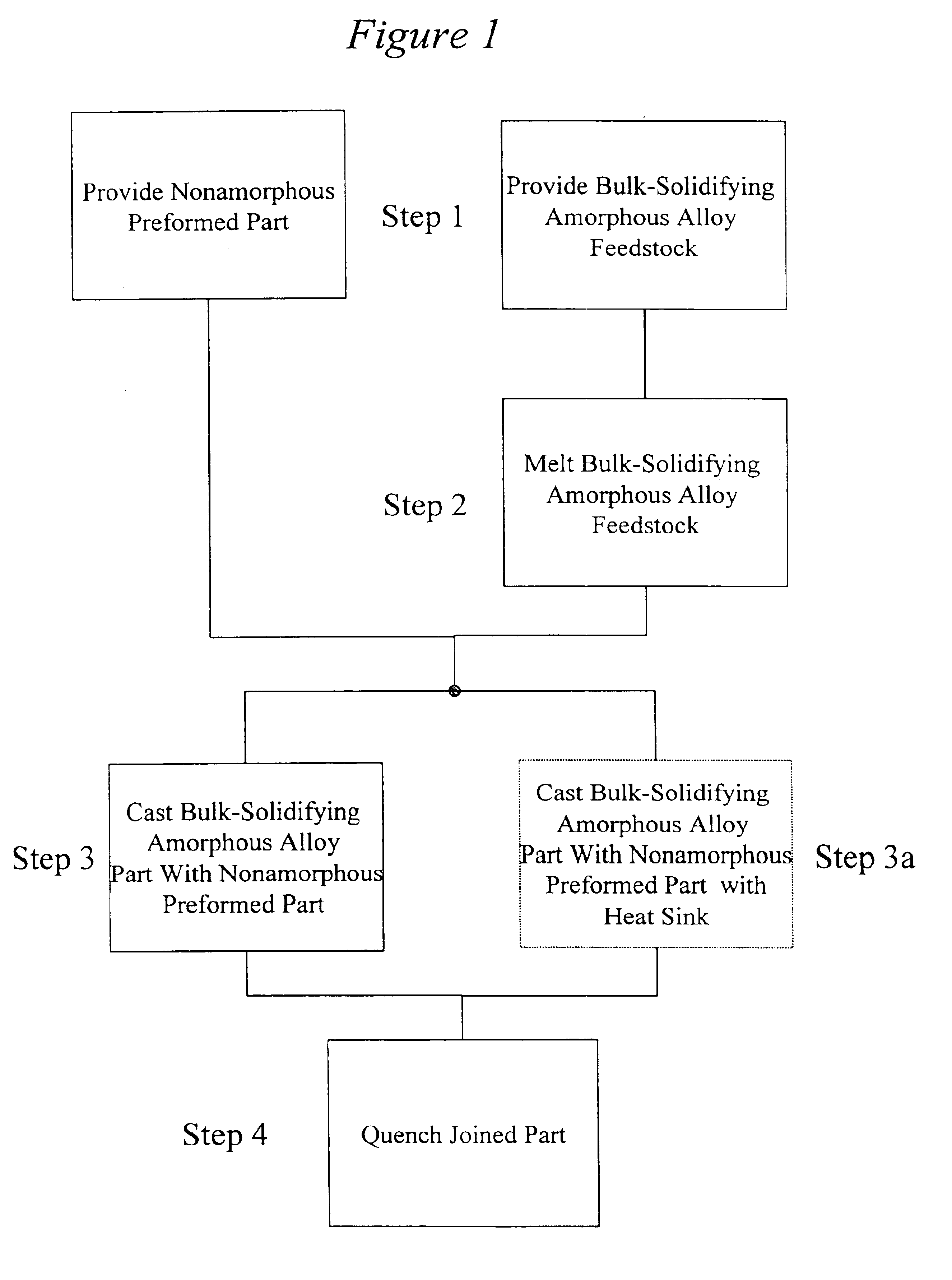
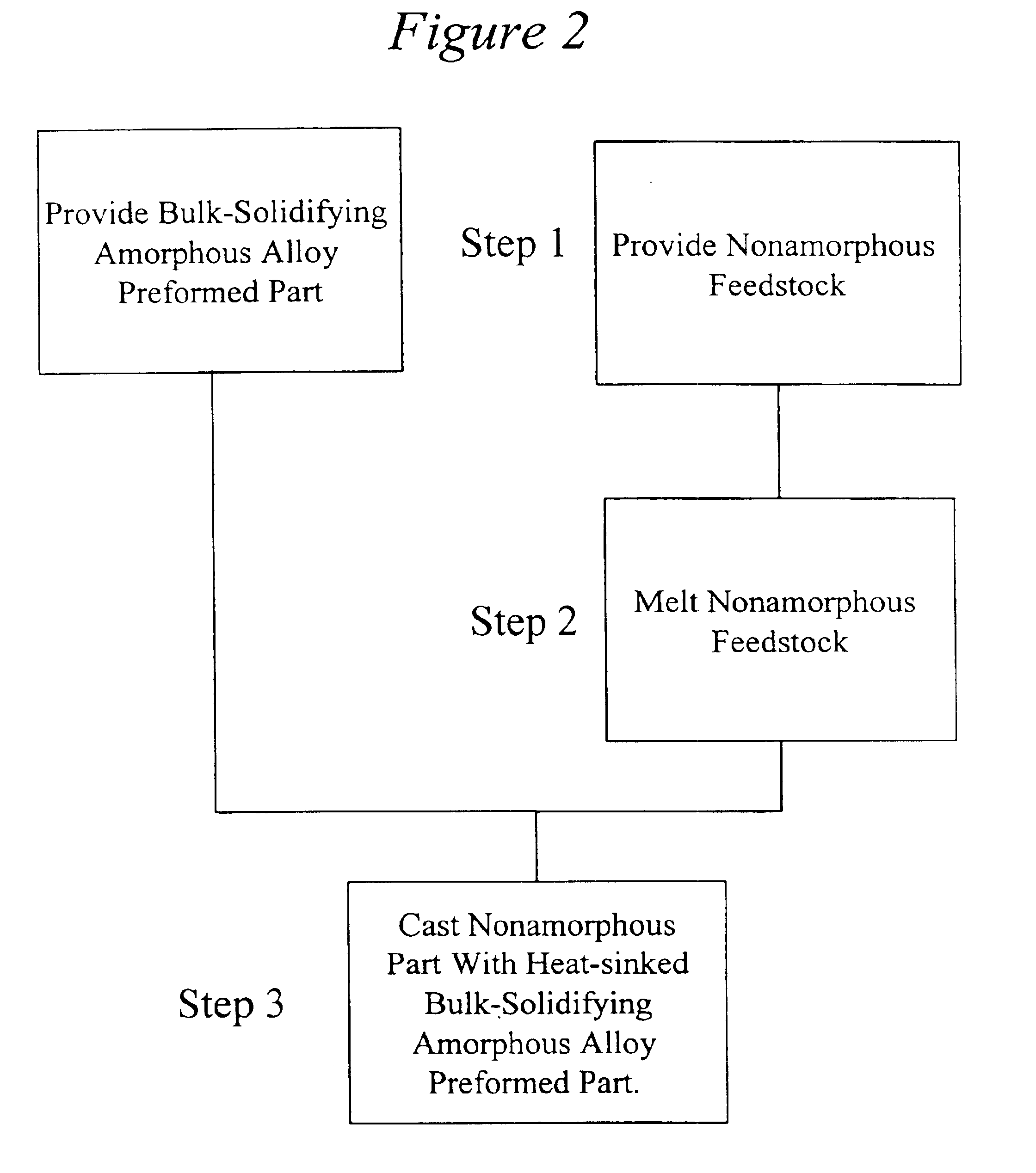
Joining of amorphous metals to other metals utilzing a cast mechanical joint
The present invention is directed to a method of joining an amorphous material to a non-amorphous material including, forming a cast mechanical joint between the bulk solidifying amorphous alloy and the non-amorphous material.
Owner:CRUCIBLE INTPROP LLC
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and production thereof
InactiveUS6312536B1High strengthGood formabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelHigh intensity
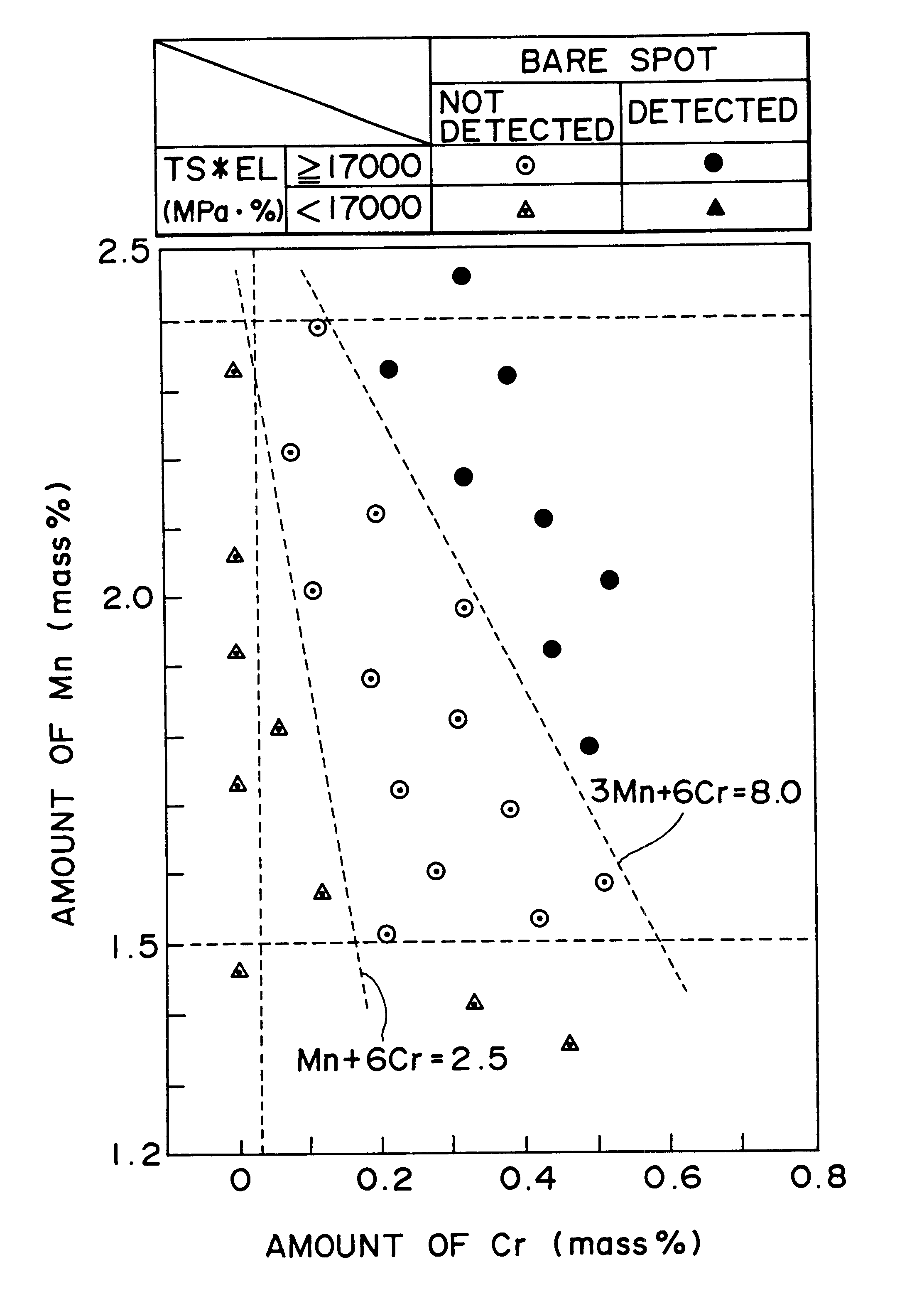
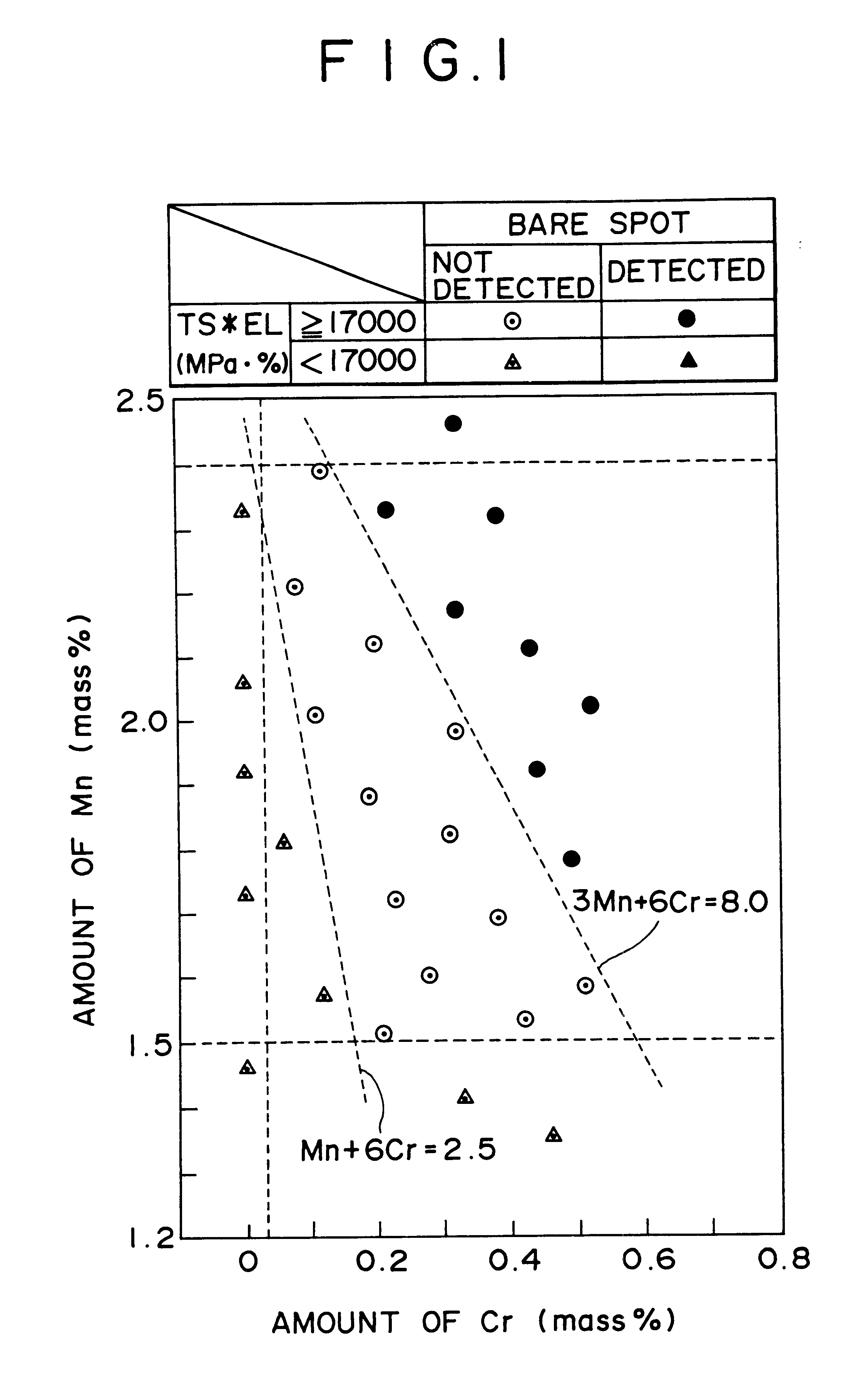
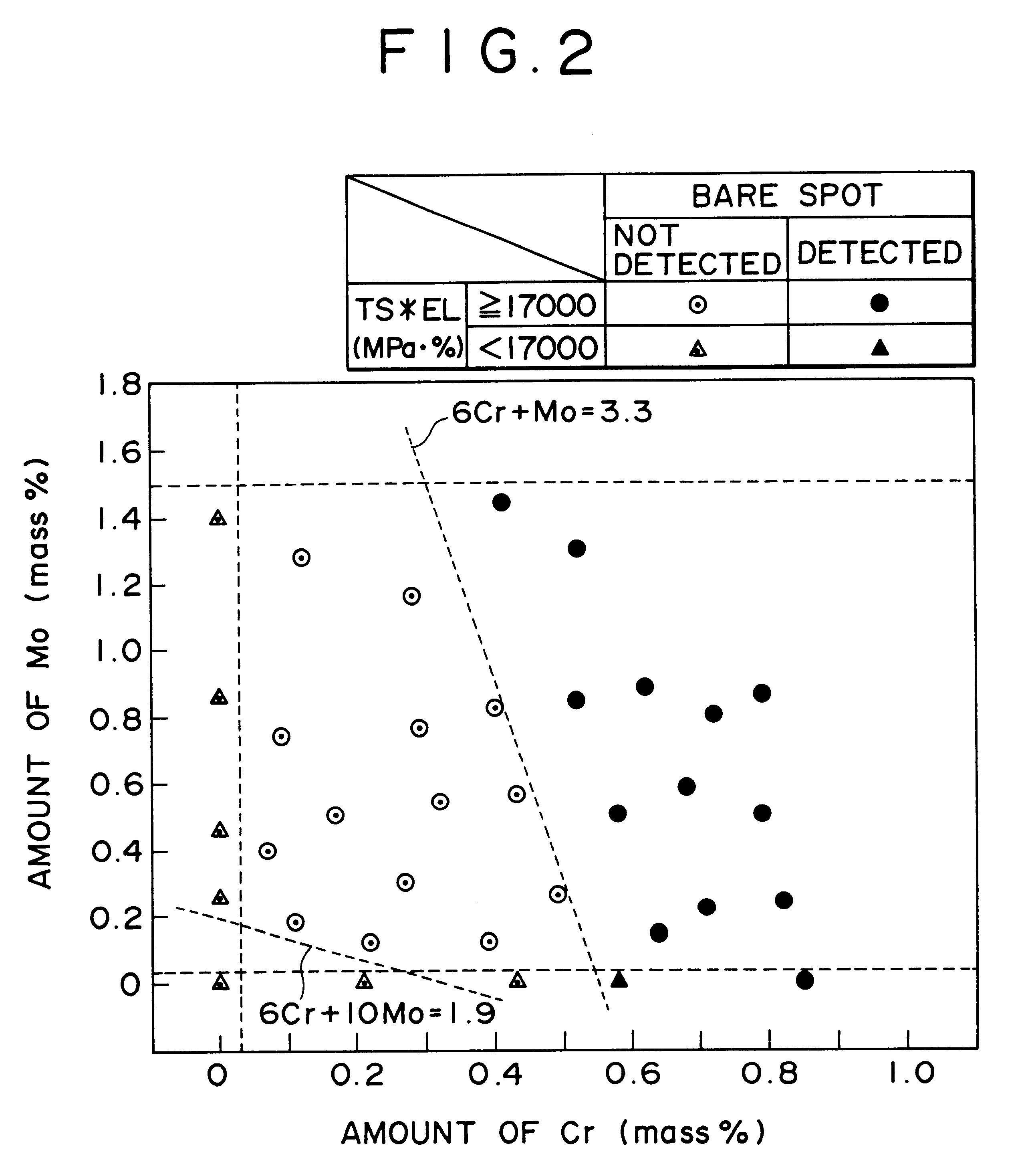
A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet having both high strength and good formability. A process for producing said hot-dip galvanized steel sheet without requiring additional steps of surface grinding and pre-plating.The hot-dip galvanized steel sheet is produced by forming a hot-dip galvanizing layer on a base cold-rolled steel sheet composed of C (0.02-0.20 mass %), Mn (1.50-2.40 mass %), Cr (0.03-1.50 mass %), Mo (0.03-1.50 mass %), 3Mn+6Cr+Mo (no more than 8.1 mass %), Mn+6Cr+10 Mo (no less than 3.5 mass %), Al (0.010-0.150 mass %), and Fe as the principal component, with Ti limited to 0.01 mass % or less, Si limited to 0.04 mass % or less, P limited to 0.060 mass % or less, and S limited to 0.030 mass % or less, and said base steel sheet having the composite microstructure composed mainly of ferrite and martensite.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Method for welding workpieces made of highly heat-resistant superalloys, including a particular mass feed rate of the welding filler material
InactiveUS20120267347A1Improve cooling effectIncrease chanceTurbinesEngine manufactureHeat resistanceRelative motion
A welding method for welding workpieces made of highly heat-resistant superalloys is provided. The method includes generating a heat input zone on the workpiece surface by means of a heat source, feeding welding filler material into the heat input zone by means of a feeding device, and generating a relative motion between the heat source and the feeding device on one hand and the workpiece surface on the other hand by means of a conveying device. Furthermore, according to the welding method, the mass feed rate is ≦350 mg / min.
Owner:SIEMENS AG +1
Oil country tubular goods excellent in collapse characteristics after expansion and method of production thereof
InactiveUS20050217768A1Excellent in collapse characteristicSmall rate of dropFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMethods of productionSteel belt
The present invention provides a method of production of oil country tubular goods having a small drop in collapse pressure after expansion and having a collapse pressure recovering by low temperature ageing at about 100° C. and oil country tubular goods obtained by this method of production. This method of production comprises hot rolling a steel slab having amounts of addition of C, Mn, P, S, Nb, Ti, Al, and N in specific ranges and having a balance of iron and unavoidable impurities and shaping the steel strip coiled at a temperature of not more than 300° C. as it is into a tube. Alternatively, it comprises heating steel pipe having amounts of addition of C, Mn, P, S, Nb, Ti, Al, and N in specific ranges and having a balance of iron and unavoidable impurities to a temperature of the Ac3 [° C.] to 1150° C., then cooling it in a range of 400 to 800° C. at a rate of 5 to 50° C. / second.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Low carbon alloy steel tube having ultra high strength and excellent toughness at low temperature and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050076975A1High strengthImprove toughnessFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesNiobiumManganese
A low carbon alloy steel tube and a method of manufacturing the same, in which the steel tube consists essentially of, by weight: about 0.06% to about 0.18% carbon; about 0.5% to about 1.5% manganese; about 0.1% to about 0.5% silicon; up to about 0.015% sulfur; up to about 0.025% phosphorous; up to about 0.50% nickel; about 0.1% to about 1.0% chromium; about 0.1% to about 1.0% molybdenum; about 0.01% to about 0.10% vanadium; about 0.01% to about 0.10% titanium; about 0.05% to about 0.35% copper; about 0.010% to about 0.050% aluminum; up to about 0.05% niobium; up to about 0.15% residual elements; and the balance iron and incidental impurities. The steel has a tensile strength of at least about 145 ksi and exhibits ductile behavior at temperatures as low as −60° C.
Owner:TENARIS CONNECTIONS
Superhigh strength steel plate with yield strength more than 960Mpa and method for producing same
ActiveCN1840724AEasy to implementEasy to controlFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAusteniteForeign substance
The invention provides a super-strength steel plate comprising the following constituents (by weight percent): C 0.08-0.18%, Si<=0.6%, Mn 0.5-2.0%, Al <=0.018%, N<=0.008%, B<=0.0025%, Ca 0-0.006%, P<=0.015%, S<=0.005%, Ni <=1.0%, Cr<=0.8%, Cu<=0.5%, Mo<=0.6%, Ti 0.01-0.03%, V<=0.1%, Nb 0.01-0.1%, balancing Fe and unavoidable foreign substance. The invention also provides the preparing process.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High toughness steel material and method of producing steel pipes using same
InactiveUS6958099B2Improve toughnessReduce hardenabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesProduction rateAustenite grain
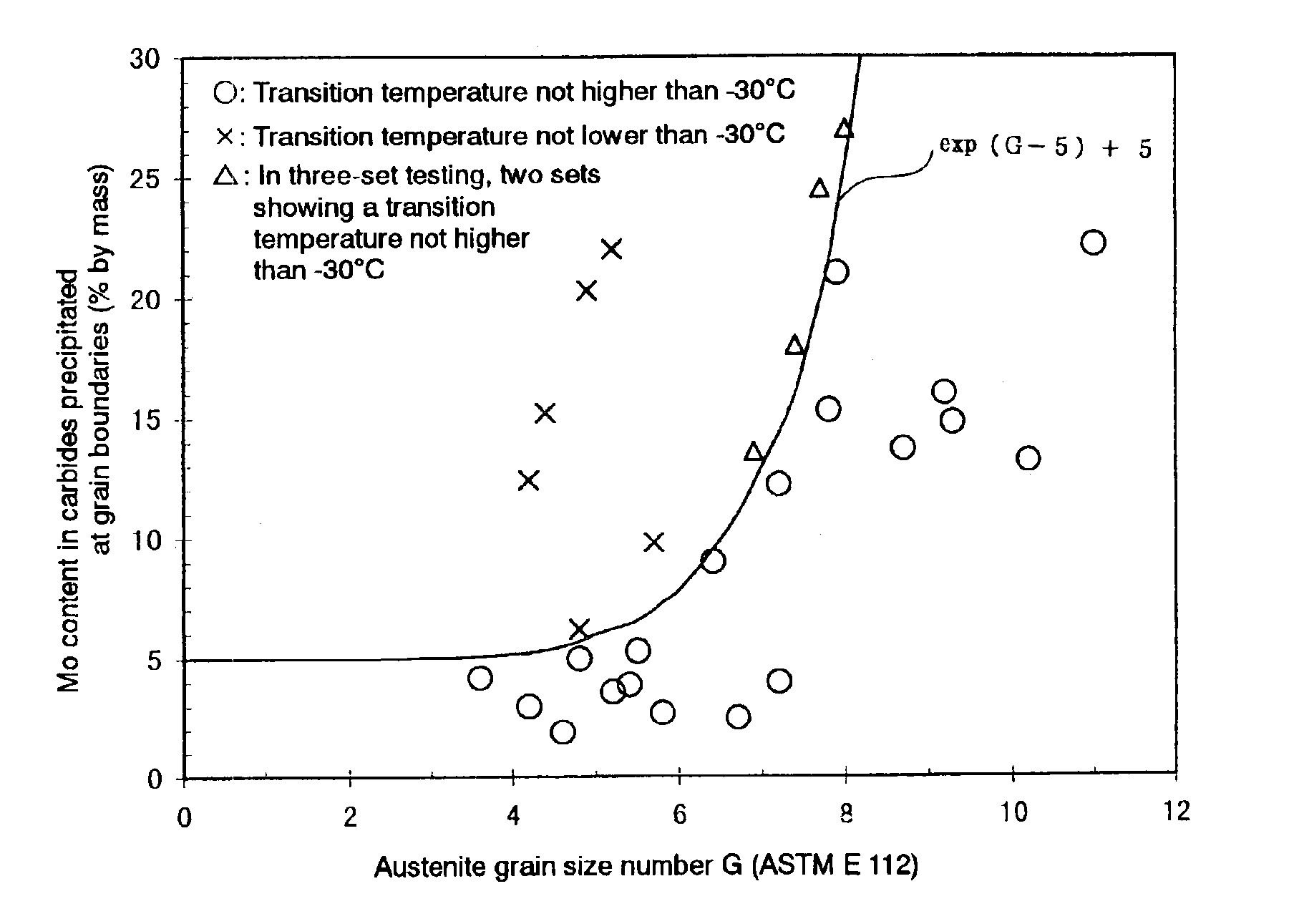
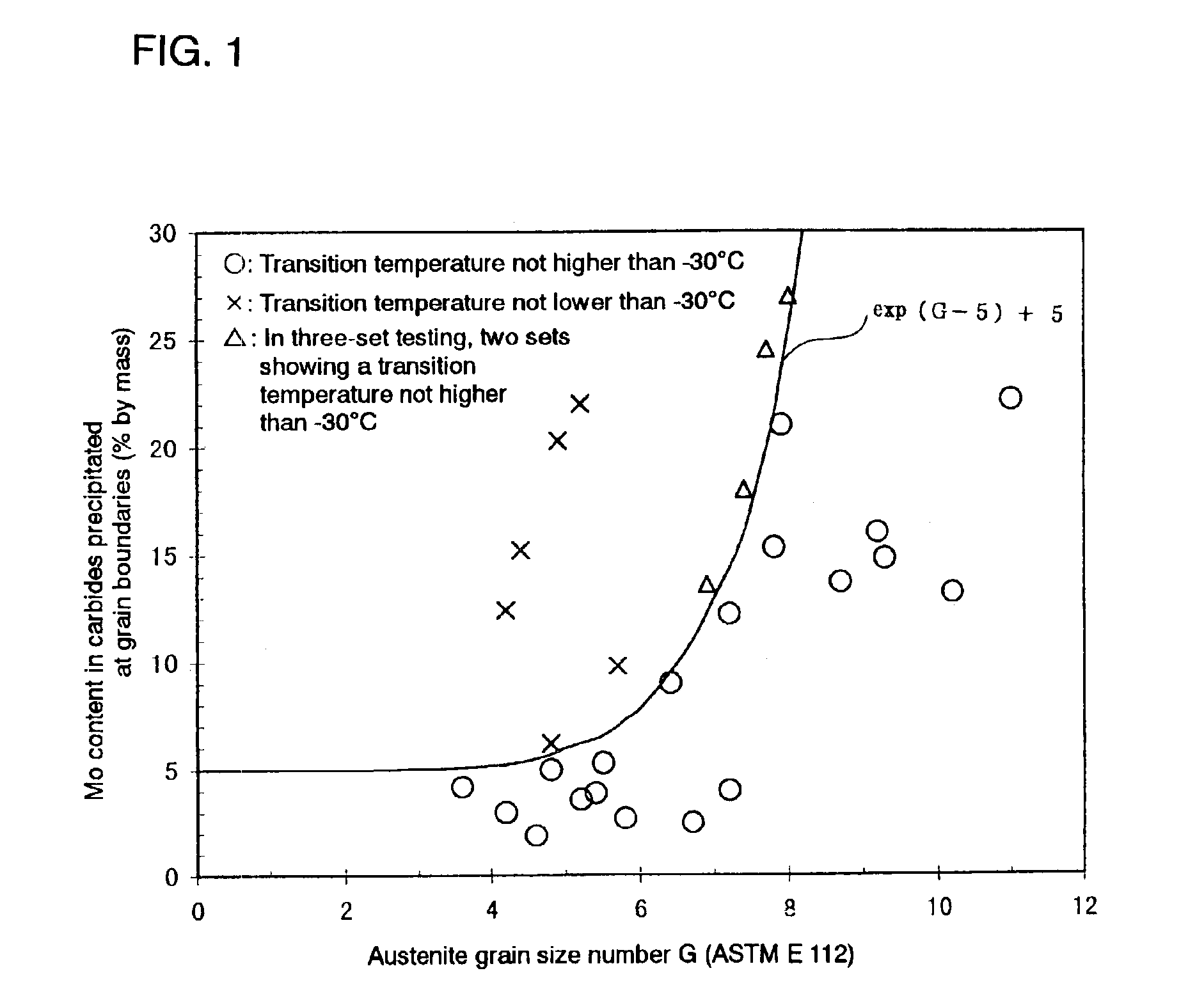
A steel material and a steel pipe made by using the same are provided which are to be used in severe oil well environments. Such a highly tough oil well steel pipe can be produced by rolling the base material, quenching the rolling product from the austenite region and tempering the same so that the relationship between the content of Mo [Mo] in the carbides precipitated at austenite grain boundaries and the austenite grain size (according to ASTM E 112) can be defined by the formula (a) given below. In this manner, steel pipes suited for use even under oil well environments becoming more and more severe can be produced while satisfying the requirements that the cost should be rationalized, the productivity improved and energy saved.[Mo]≦exp(G−5)+5 (a)
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Expandable rotating device and method for tissue aspiration
InactiveUS20080208230A1Relieve pressureVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsExcision instrumentsTissue remodelingControl system
An apparatus and method for removing tissue and / or other material from a patient includes a shaft and a tissue disrupting mechanism operatively coupled to the shaft. The shaft may be coupled to a handpiece or a robotic or remote-controlled system. The mechanism may comprise a rotatable or other movable element having a distal portion with fixed or adjustable radial dimensions. The mechanism may have one or more tissue cutting, chopping, grinding, emulsifying or disrupting features with an adjustable outer diameter for removing substantial tissues. The apparatus may be configured to urge or draw substantial material into the device upon rotation or other movement of the shaft and / or tissue, and may optionally be coupled to sources of suction or aspiration. A radiofrequency or other energy source is optionally included for tissue ablation or other tissue remodeling effects, and / or to enhance coagulation.
Owner:SPINE VIEW INC
Method of forming a tubular blank into a structural component and die therefor
InactiveUS6322645B1Quick upgradeImprove mechanical propertiesShaping toolsFurnace typesElectrical conductorEngineering
A method of forming an elongated tubular blank into a tubular structural component having a predetermined outer configuration, the method comprising: providing a shape imparting shell formed from a low permeability, rigid material which includes an inner surface defining the predetermined shape, plugging the open ends of the tubular blank, placing the plugged blank into the shell, and forming the tubular blank into the tubular component by inductively heating axial portions of the blank by axially spaced conductors adjacent the shell while or before forcing gas at a high pressure into the plugged blank until the blank conforms to at least a portion of the inner surface of the shell to form the structural component.
Owner:TEMPER IP
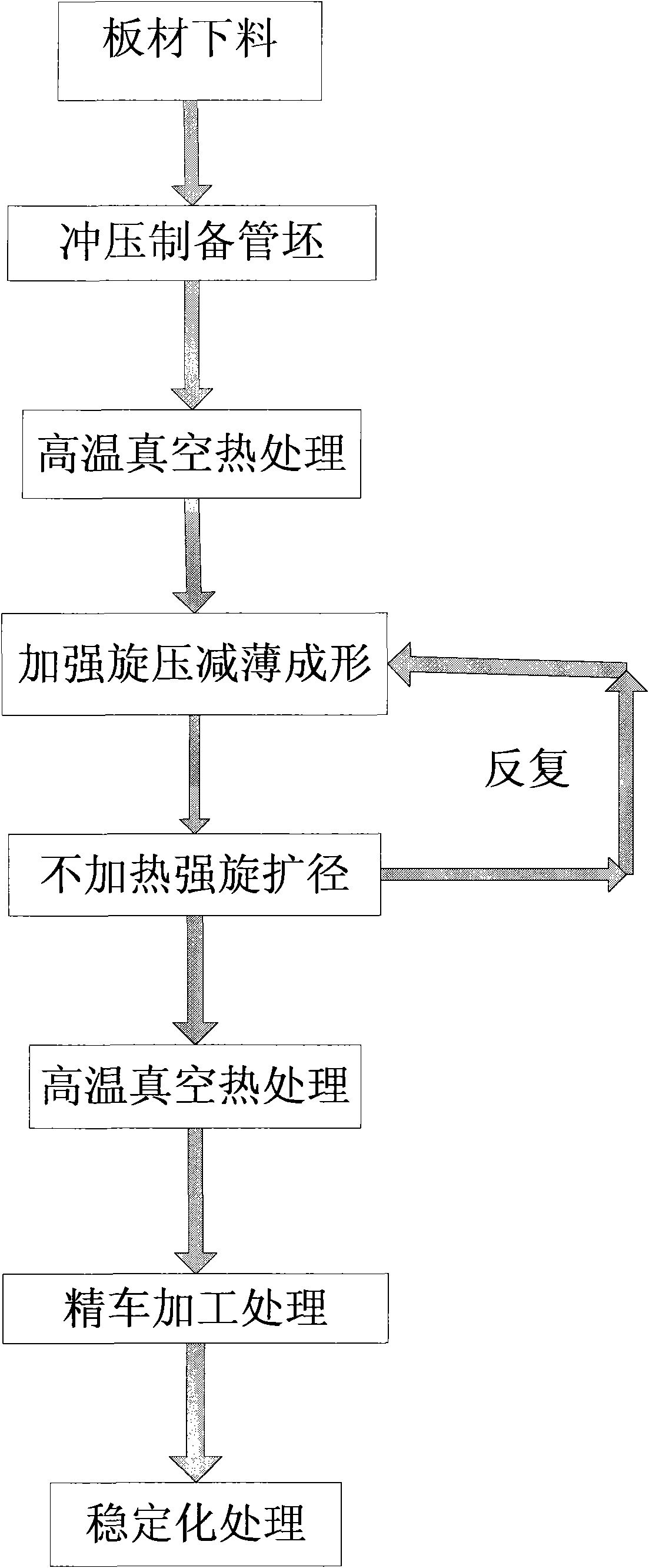
Integral forming method of large size thin-walled titanium alloy cylindrical part without welding line
ActiveCN101579804ASolve UtilizationSolving with longitudinal weldsFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesThinningLarge size
The invention provides an integral forming method of a large size thin-walled titanium alloy cylindrical part without a welding line. The integral forming method comprises the following steps of: (1) tube blank preparation by stamping; (2) high-temperature vacuum heat treatment; (3) heating power spinning thinning; (4) unheating power spinning diameter expanding; (5) repetitive and alternate conduction of steps (3) and (4) for 2-3 times; (6) high-temperature vacuum heat treatment; (7) finish turning treatment; and (8) stabilizing treatment. The integral forming method prepares the large size thin-walled titanium alloy cylindrical part without the welding line (wall thickness is 1-7mm) which has high precision and high performance by utilizing titanium alloy plates and adopting a composite technique combining a stamping method, a spinning method and a stabilizing treatment method, and solves the problems of low material utilization ratio, having longitudinal welding lines, low precision of tube performance and the like in the forging and roll bending welding forming of the large size titanium alloy thin-walled tubes.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH
Steel for machine structure use attaining excellent cutting-tool life and method for cutting same
InactiveCN102209798AImprove the lubrication effectSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesChemical compositionFree energies
Provided is a steel for machine structure use which attains an excellent cutting-tool life at cutting speeds in a wide range regardless of the mode of cutting, such as continuous or intermittent cutting, and in various cutting environments such as an environment using a cutting oil, a dry or semi-dry environment, and an oxygen-enriched environment. Also provided is a method for cutting the steel. The steel has a chemical composition containing, in terms of mass%, 0.01-1.2% C, 0.005-3.0% Si, 0.05-3.0% Mn, 0.0001-0.2% P, 0.0001-0.35% S, 0.0005-0.035% N, and 0.05-1.0% Al and satisfying [Al%]-(27 / 14)[N%]=0.05%, with the remainder being Fe and incidental impurities. The steel is characterized in that when the steel is cut with a cutting tool in which the surface to come into contact with the work material has been coated with a metal oxide having a higher value of standard free energy of formation at 1,300 C than Al2O3, then an Al2O3 coating film is formed on the surface of the cutting tool.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Method of straightening wire rods of titanium and titanium alloy
InactiveUS6077369ALow costImprove production yieldFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesWire rodTitanium
PCT No. PCT / JP95 / 01897 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 19, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 19, 1997 PCT Filed Sep. 20, 1995A method of straightening a wire rod of titanium or titanium alloy wherein the rod is hot-straightened to a straight rod at the straightening temperature T and elongation epsilon satisfying the expression (1) or (2). The method includes hot rolling a titanium billet of beta titanium alloy, ( alpha + beta ) titanium alloy or a near alpha titanium alloy into a wire rod, winding the hot rolled wire rod into a coil, cold drawing the wire rod, cutting the wire rod to obtain a bent wire rod, heating the bent wire rod to a straightening temperature T while both end portions of the bent wire rod are fixed, applying a predetermined elongation epsilon to the wire rod, maintaining a straightening temperature T, hot-straightening the wire in accordance with the expression (2) epsilon (T-400)> / =400(1) epsilon (T-500)> / =200(2) and cooling the wire rod while applying tension. The method is suitable for preparing a straight rod for use in an engine valve.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
HIGH STRENGTH STEEL PLATE WITH ULTIMATE TENSILE STRENGTH OF 900 MPa OR MORE EXCELLENT IN HYDROGEN EMBRITTLEMENT RESISTANCE AND METHOD OF PRODUCTION OF SAME
ActiveUS20120222781A1Reduce resistanceImprove plasticityHot-dipping/immersion processesSurface reaction electrolytic coatingCarbideUltimate tensile strength
High strength steel plate with an ultimate tensile strength of 900 MPa or more which is excellent in hydrogen embrittlement resistance characterized in that, in the structure of the steel plate, (a) by volume fraction, ferrite is present in 10 to 50%, bainitic ferrite and / or bainite in 10 to 60%, and tempered martensite in 10 to 50%, and (b) iron-based carbides which contain Si or Si and Al in 0.1% or more are present in 4×108 (particles / mm3) or more.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Method of baking treatment of steel product parts
InactiveUS6855217B2Shorten the timeImprove facilitiesIncreasing energy efficiencyFurnace typesSurface layerMetallurgy
The present invention relates to a method of baking treatment of steel product parts using a high frequency or ultra-high frequency for preventing delayed fracture from occurring due to diffusive hydrogen occluded in steel parts, for example, screws, bolts and the like, or for heating surface layers of the steel parts to generate a difference in temperature between the surface layers and interiors of the steel parts, thereby causing distortion in lattices, wherein the surface layers of the steel parts are rapidly heated to 100 to 300° C. with a high frequency or ultra-high frequency at 10 KHz or higher to remove the diffusive hydrogen which is involved in hydrogen embrittlement, or to transfer an existing state to non-diffusive hydrogen which is not involved in the hydrogen embrittlement.
Owner:AOYAMA SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
Reciprocating cutting blade having laser-hardened cutting edges and a method for making the same with a laser
InactiveUS6857255B1Minimize occurrenceAdds additional timeMowersFurnace typesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A reciprocating cutting blade includes a body portion having an top surface, a bottom surface, a longitudinal axis, a first working portion extending at an angle to the longitudinal axis and defining a first cutting surface, a second working portion extending at an angle to the longitudinal axis and defining a second cutting surface. A laser-hardened region extends along at least part of one of the first and second working portions, and preferably along at least part of both of the first and second working portions. The working portions can be serrated to include alternating teeth and roots. The teeth can be laser hardened more than the roots.
Owner:FISHER BARTON
High strength aluminium alloy brazing sheet, brazed assembly and method for producing same
ActiveUS20050079376A1Good brazing propertyGood formability characteristicFurnace typesWelding/cutting media/materialsSiluminManganese
The present invention a high strength aluminium alloy brazing sheet, comprising an Al—Zn core layer and at least one clad layer, the core layer including the following composition (in weight percent): Zn1.2 to 5.5Mg0.8 to 3.0Mn0.1 to 1.0Cu<0.2Si <0.35Fe<0.5optionally one or more of: Zr<0.3Cr<0.3V<0.3Ti<0.2Hf<0.3Sc<0.5,the balance aluminium and incidental elements and impurities. The clad layer includes an Al—Si based filler alloy and is applied on at least one side of the core layer. The invention relates furthermore to a brazed assembly including such brazing sheet, to the use of such brazing sheet and to method for producing an aluminium alloy brazing sheet.
Owner:ALERIS ALUMINUM KOBLENZ GMBH
Steel sheet for hot press forming having low-temperature heat treatment property, method of manufacturing the same, method of manufacturing parts using the same, and parts manufactured by the same
ActiveUS20090238715A1Reduced strengthHigh yield strengthMetal rolling stand detailsFurnace typesManganeseHeat treated
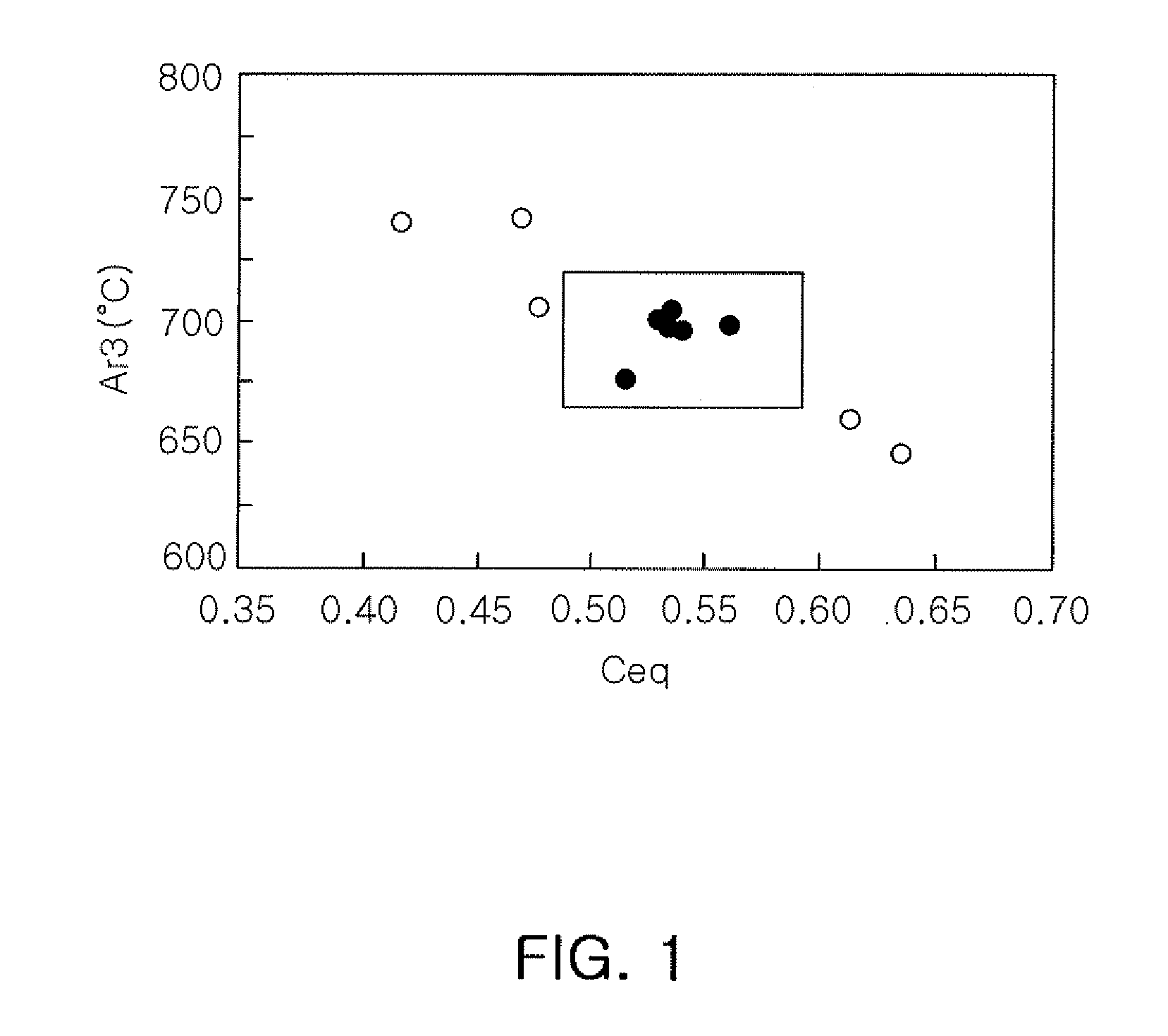
A steel sheet for forming having low-temperature heat treatment property, in which heat treatment is performed within a range of lower temperature than a conventional steel sheet in the event of hot press forming or post-heat treatment after cold forming, a method of manufacturing the same, and a method of manufacturing parts using the same. The steel sheet has a composition of, by weight, carbon (C): 0.15 to 0.35%, silicon (Si): 0.5% or less, manganese (Mn): 1.5 to 2.2%, phosphorus (P): 0.025% or less, sulfur (S): 0.01% or less, aluminum (Al): 0.01 to 0.05%, nitrogen (N): 50 to 200 ppm, titanium (Ti): 0.005 to 0.05%, tungsten (W): 0.005 to 0.1%, and boron (B): 1 to 50 ppm, wherein Ti / N: less than 3.4, where Ti / N is the atomic ratio of the corresponding elements, Ceq expressed by the following formula ranges from 0.48 to 0.58, and temperature Ar3 ranges from 670° C. to 725° C. Wherein Ceq=C+Si / 24+Mn / 6+Ni / 40+Cr / 5+V / 14 where C, Si, Mn, Ni, Cr and V indicate the contents (wt %) of the respective elements.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
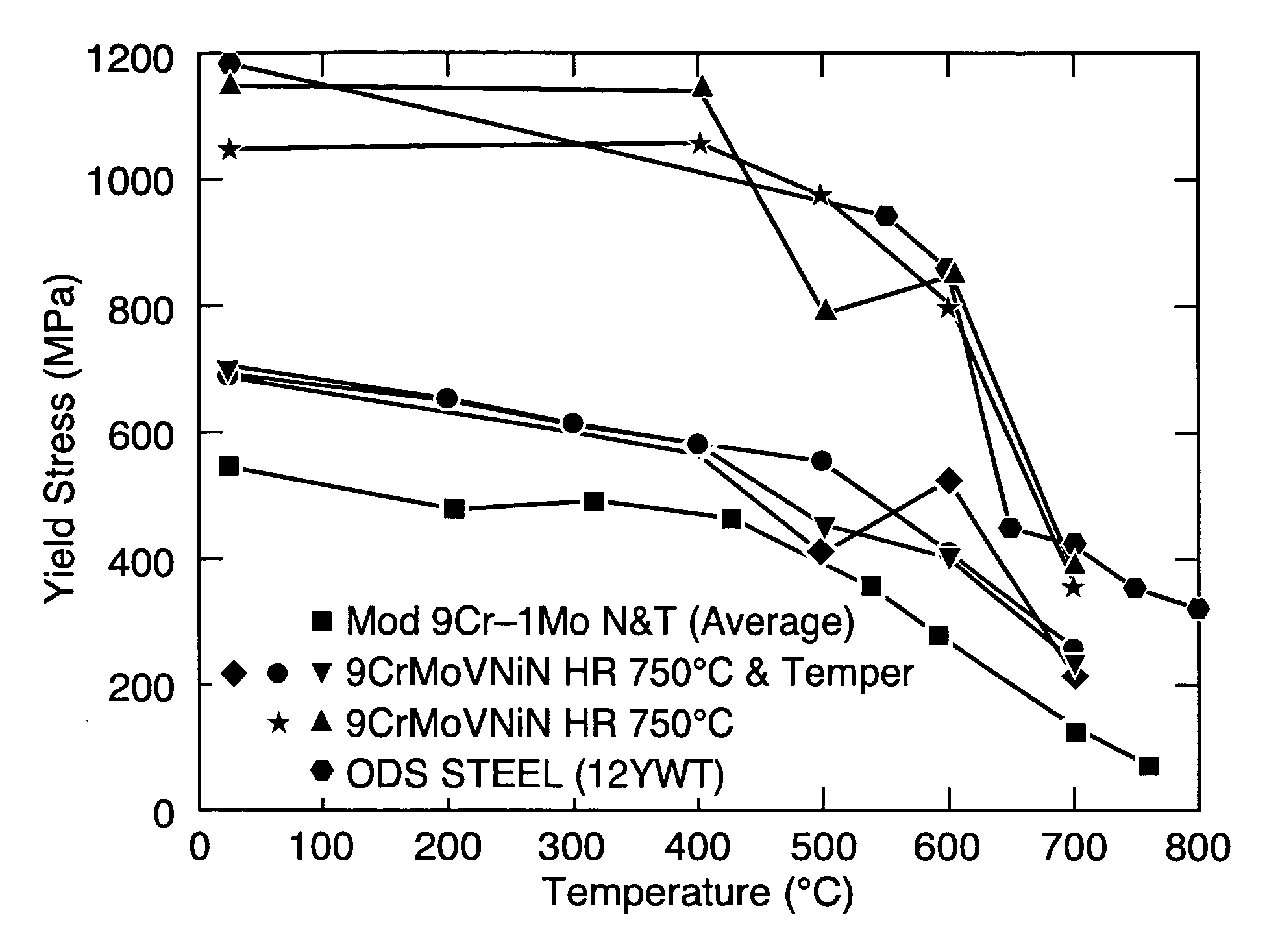
Nano-scale nitride-particle-strengthened high-temperature wrought ferritic and martensitic steels
InactiveUS20060060270A1Improved elevated-temperature strength propertyImprove strength propertiesFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesHot workingNitride
A method of making a steel composition includes the steps of: a. providing a steel composition that includes up to 15% Cr, up to 3% Mo, up to 4% W, 0.05-1% V, up to 2% Si, up to 3% Mn, up to 10% Co, up to 3% Cu, up to 5% Ni, up to 0.3% C, 0.02-0.3% N, balance iron, wherein the percentages are by total weight of the composition; b. austenitizing the composition at a temperature in the range of 1000° C. to 1400° C.; c. cooling the composition of steel to a selected hot-working temperature in the range 500° C. to 1000° C.; d. hot-working the composition at the selected hot-working temperature; e. annealing the composition for a time period of up to 10 hours at a temperature in the range of 500° C. to 1000° C.; and f. cooling the composition to ambient temperature to transform the steel composition to martensite, bainite, ferrite, or a combination of those microstructures.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Steel plate for hot stamping, hot stamping process and hot-stamped member
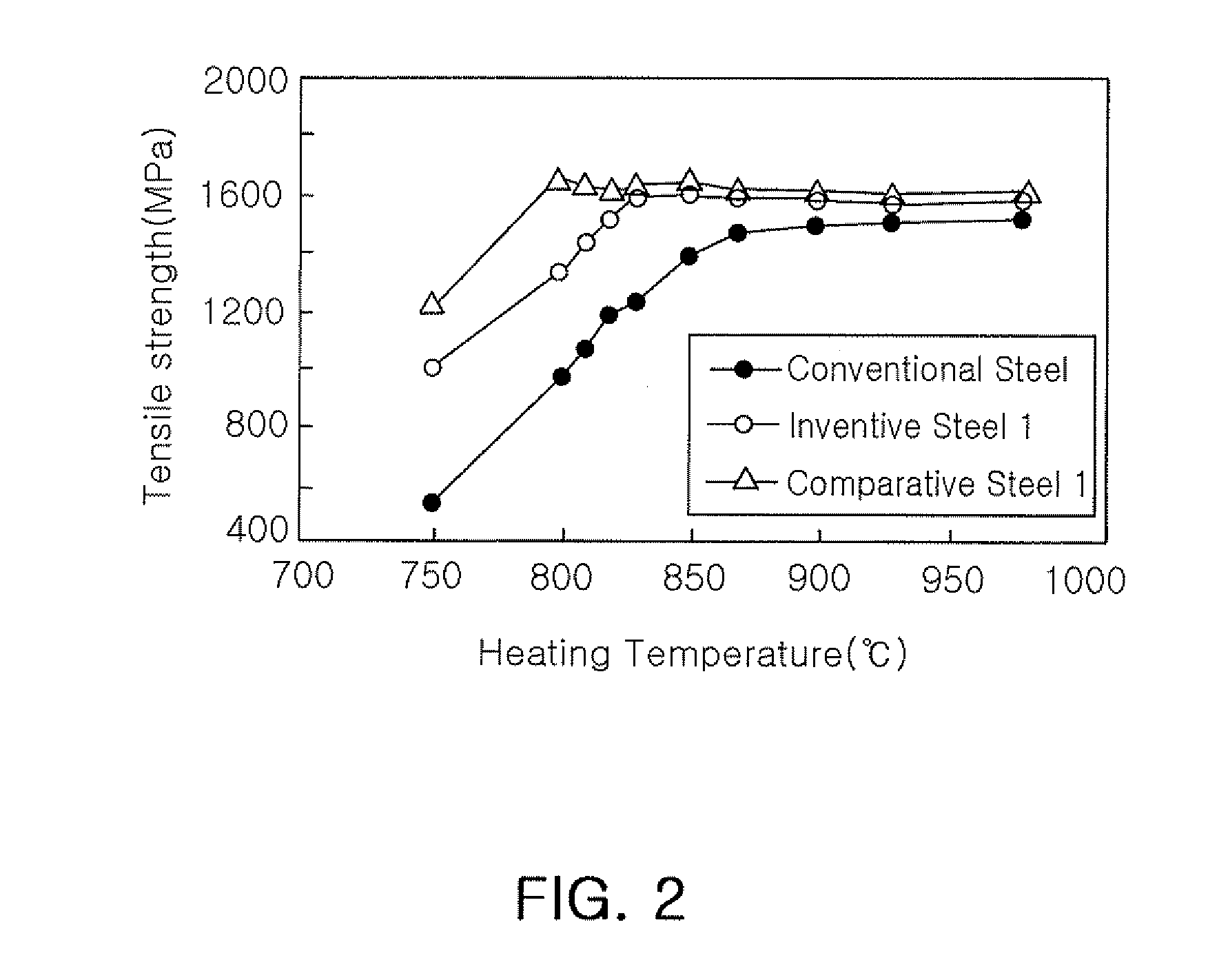
ActiveCN104846274ALow austenitizing temperatureQuenching temperature is lowShaping toolsFurnace typesHot stampingMartensite transformation
The invention relates to a steel plate for hot stamping, a hot stamping process and a hot-stamped member. The steel plate for hot stamping is characterized by comprising, by weight, 0.18 to 0.42% of C, 4 to 8.5% of Mn and 0.8 to 3.0% of Si and Al, with the balance being Fe and avoidable impurities, wherein the alloy component of the steel plate satisfy the condition that the actual measured value of martensite phase transformation beginning temperature is no more than 280 DEG C. A manufacturing method for the hot-stamped member comprises the following steps: heating a material to 700 to 850 DEG C and carrying out stamping; then carrying out cooling in a die or air cooling or cooling in other manners to 150 to 260 DEG C below the martensite phase transformation beginning temperature; and heating the stamped member to 160 to 450 DEG C, maintaining the temperature for 1 to 100,000 s, carrying out tempering heat treatment and cooling the stamped member to room temperature. The hot-stamped member prepared in the invention has yield strength of no less than 1200 MPa, tensile strength of no less than 1600 MPa and total elongation percentage of no less than 10%.
Owner:EASYFORMING STEEL TECH CO LTD
Steel wire for high-strength springs and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6338763B1Reduce contentReduce sizeFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesNon-metallic inclusionsHigh intensity
This invention provides an oil-tempered wire having high strength (tensile strength of not less than 1960 MPa) and excellent workability and specifically provides a steel wire for high-strength springs comprising as steel components, in weight percent,the balance being Fe and unavoidable impurities, the steel wire having no nonmetallic inclusions of a size greater than 15 mum, a tensile strength of not less than 1960 MPa, and a yield ratio (sigma0.2 / sigmaB) of not less than 0.8 and not greater than 0.9 or a yield ratio (sigma0.2 / sigmaB) of not less than 0.8 and an amount of residual austenite of not greater than 6%. This invention also provides a method of producing the steel wire.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +1
Method of bonding cast superalloys
A method of bonding cast superalloys is disclosed. The method includes the steps of casting separate superalloy component parts, machining the mating surfaces of the separate parts in a controlled manner to avoid recrystallization of the material and to ensure a tight fit between the parts, bonding the parts together, and thermally treating the bonded component. In a preferred embodiment, the component is a turbine blade for a land-based gas turbine.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com