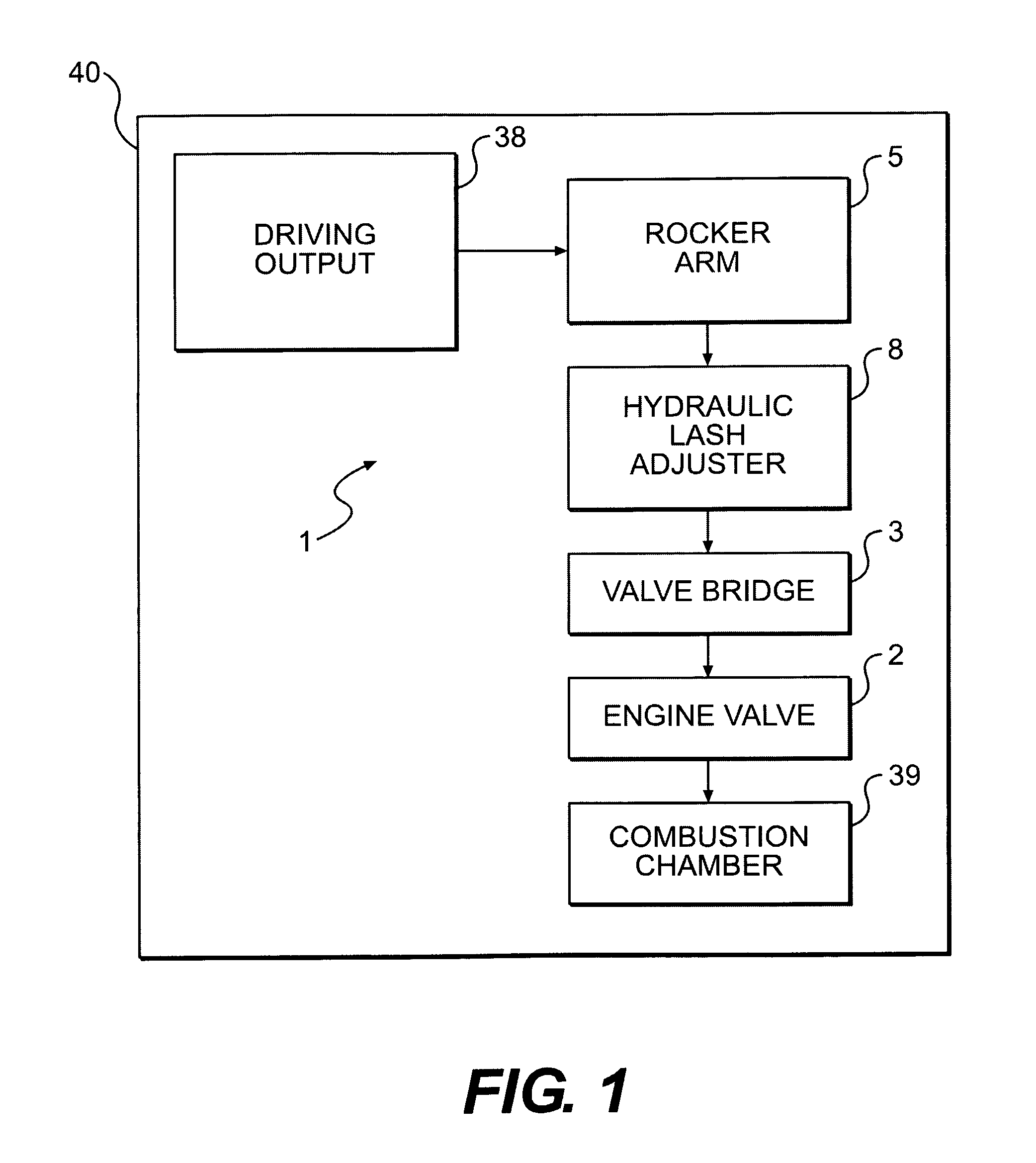
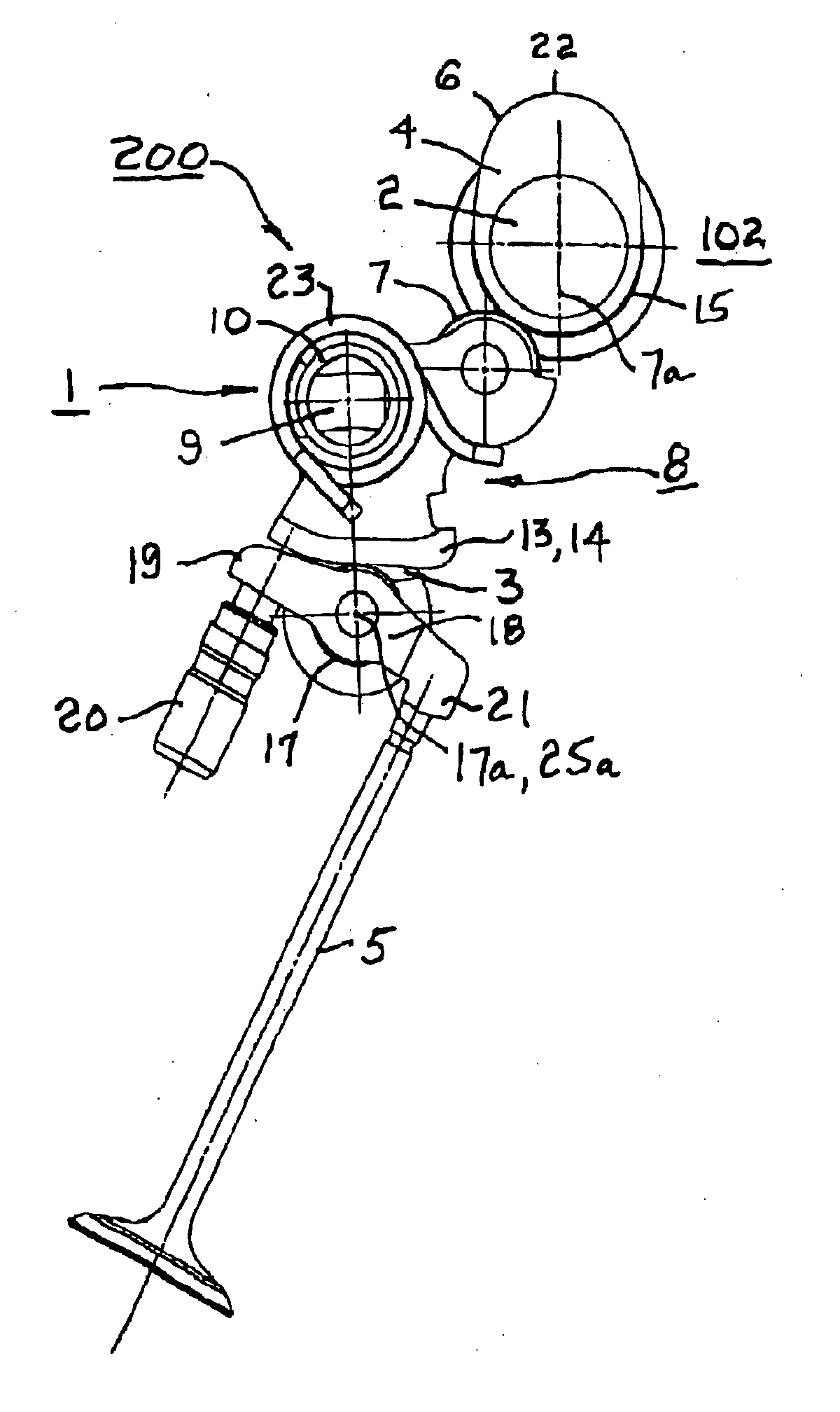
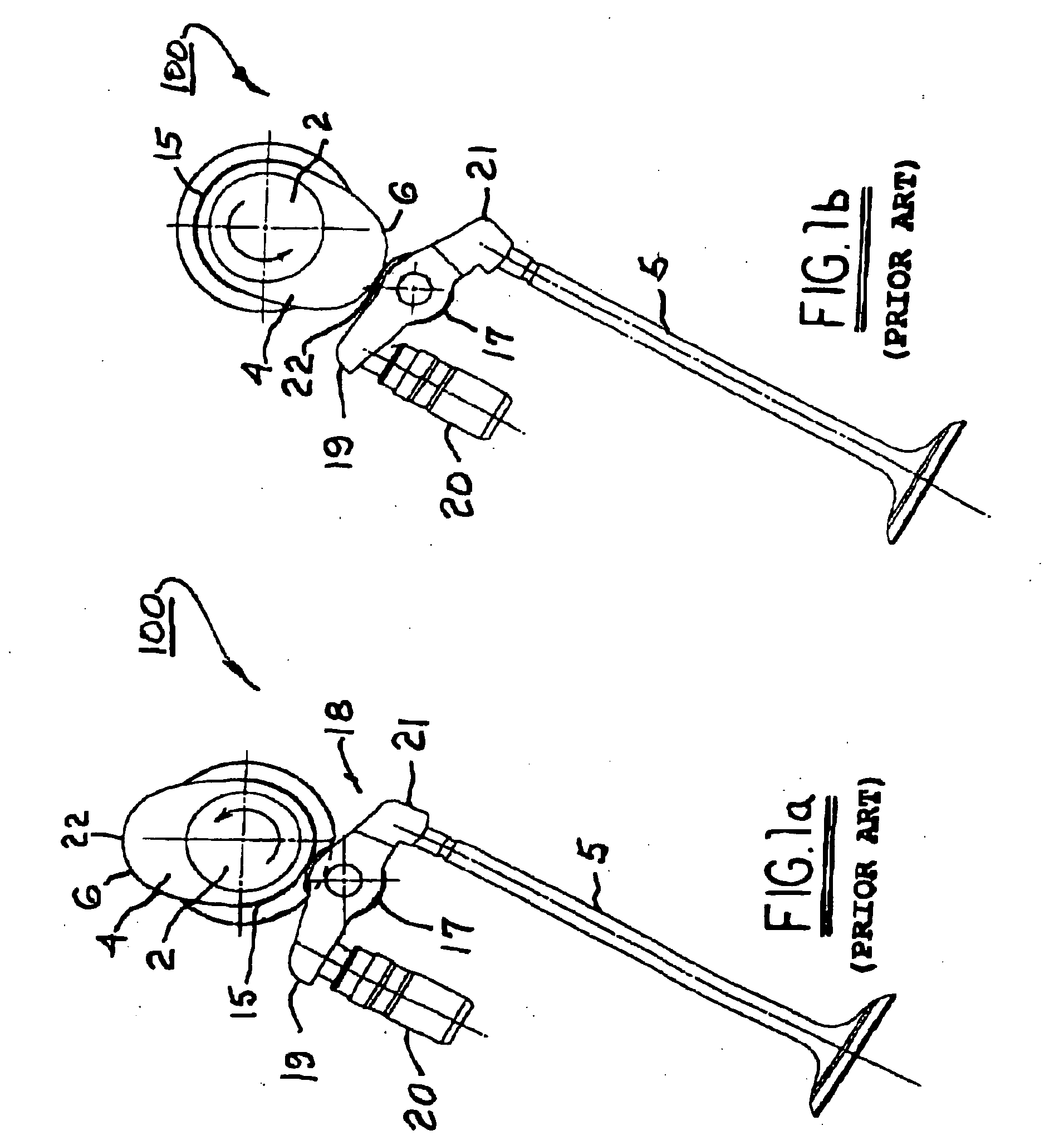
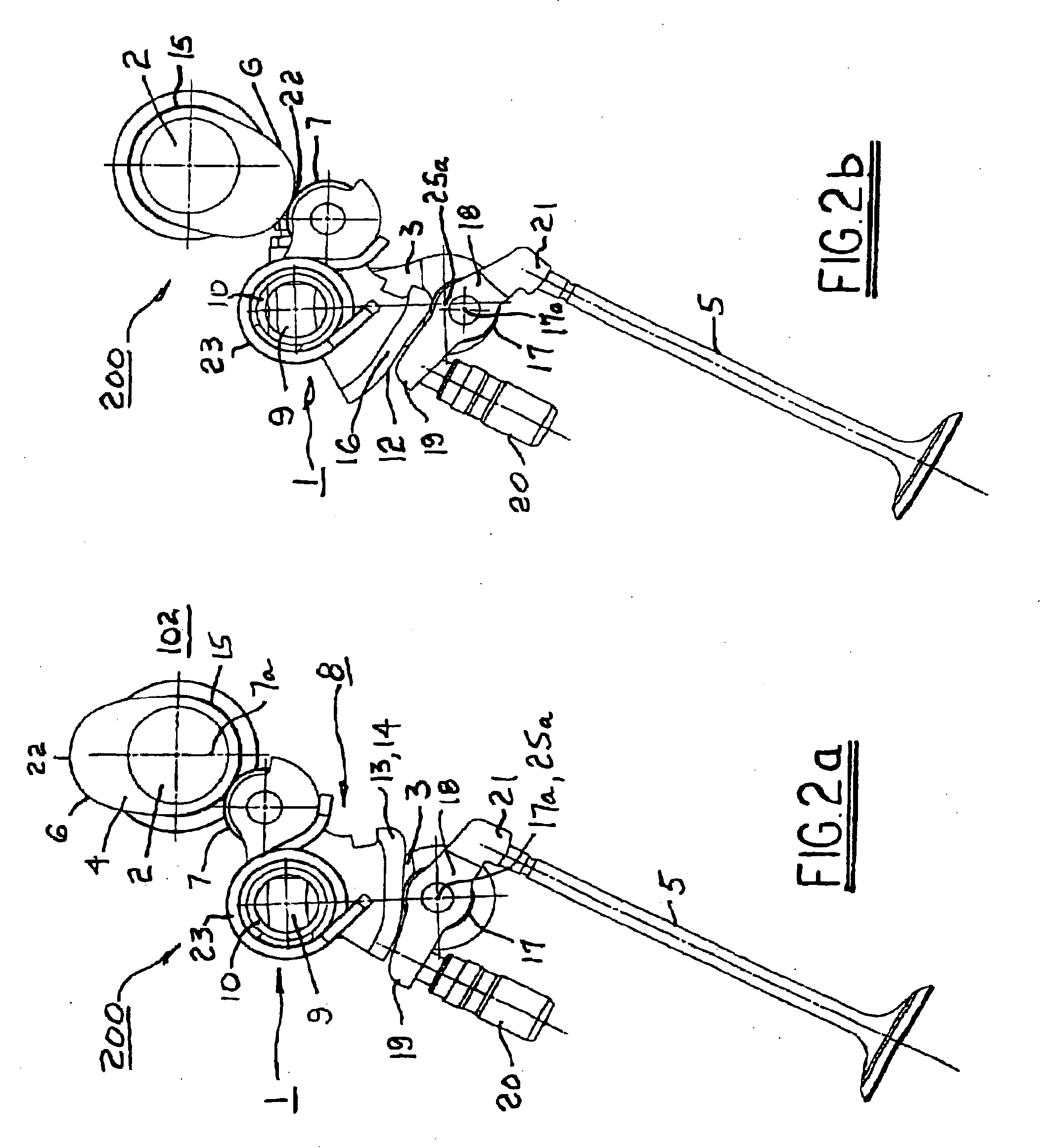
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1665 results about "Engine valve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
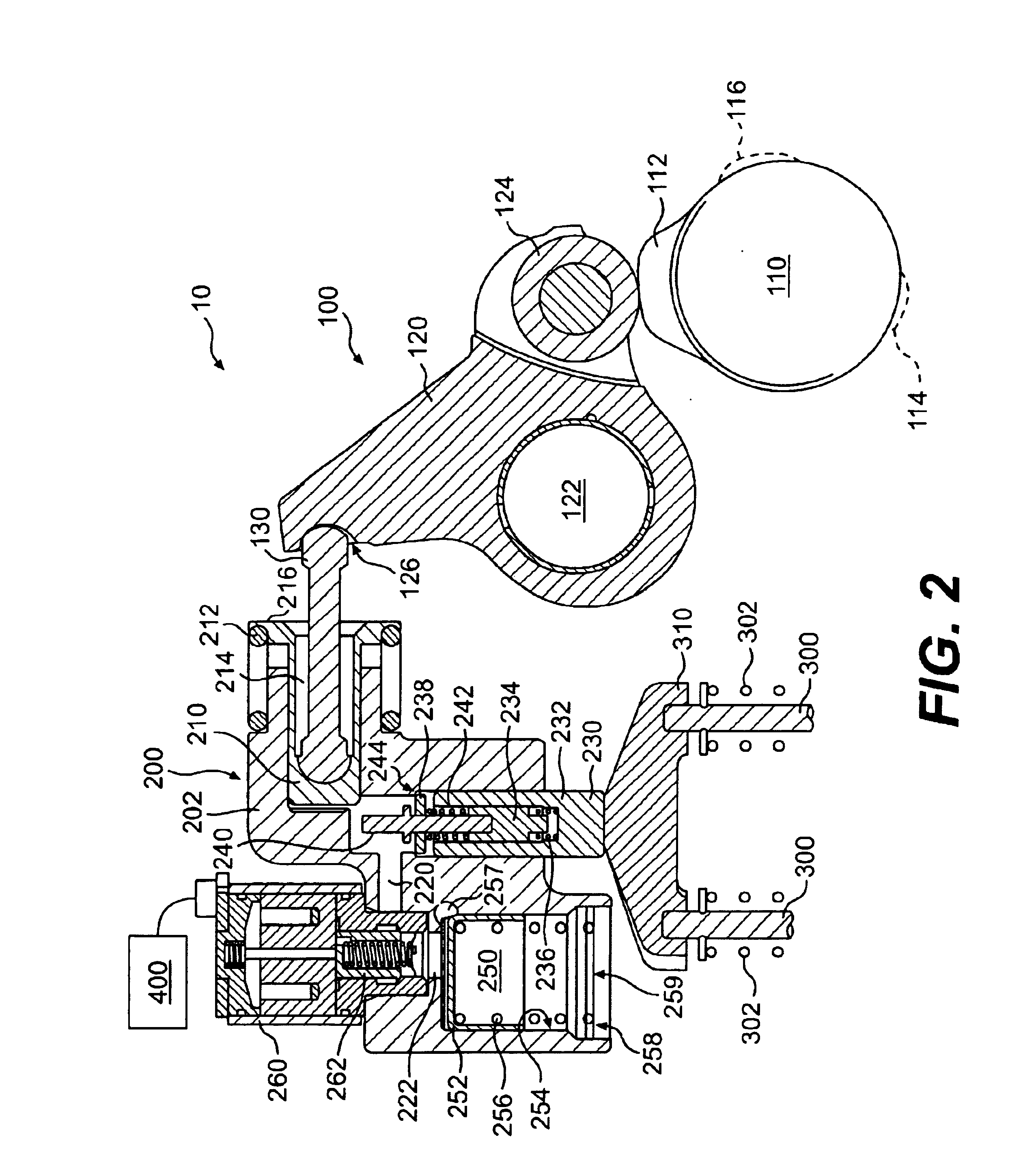
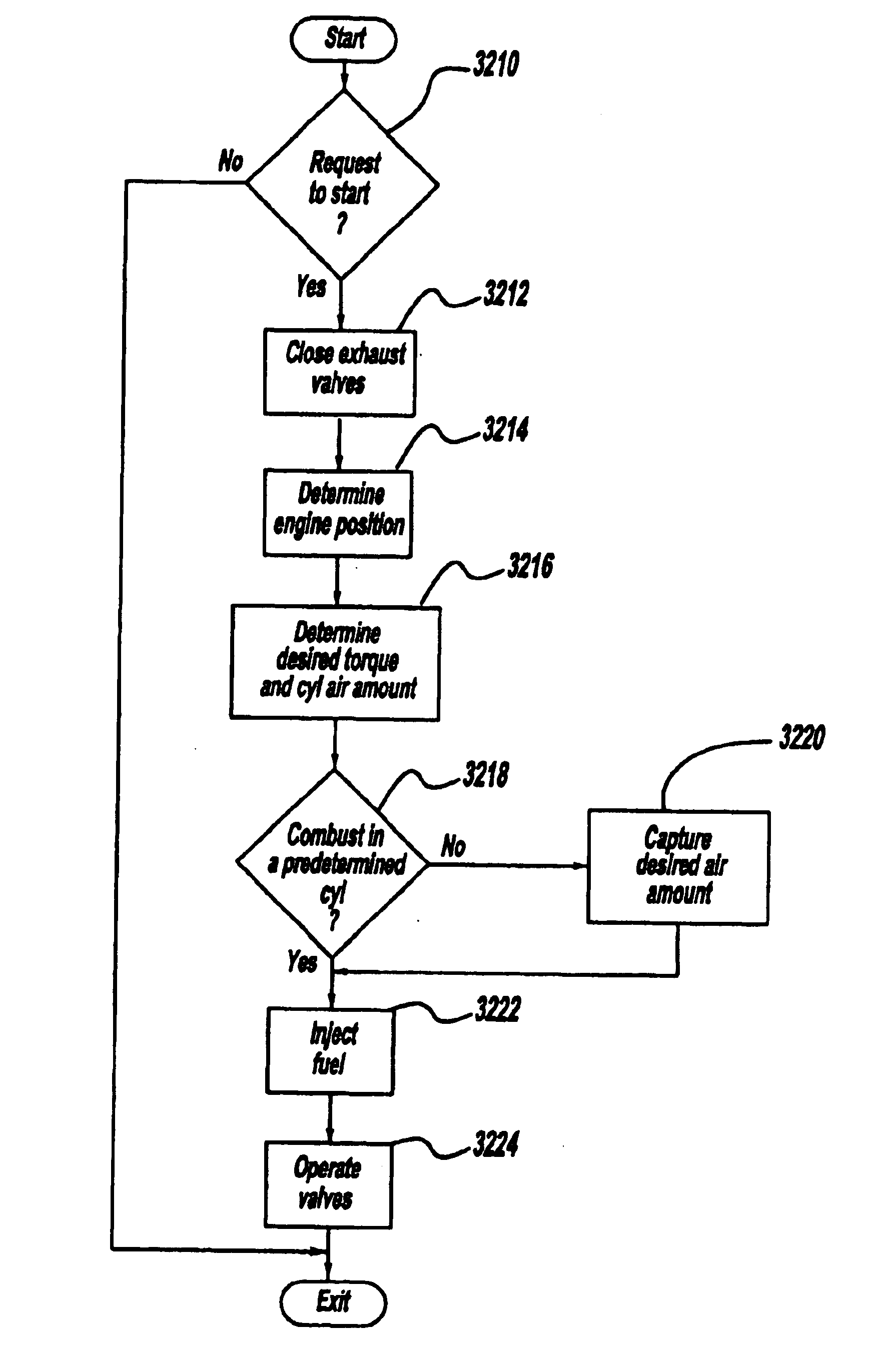
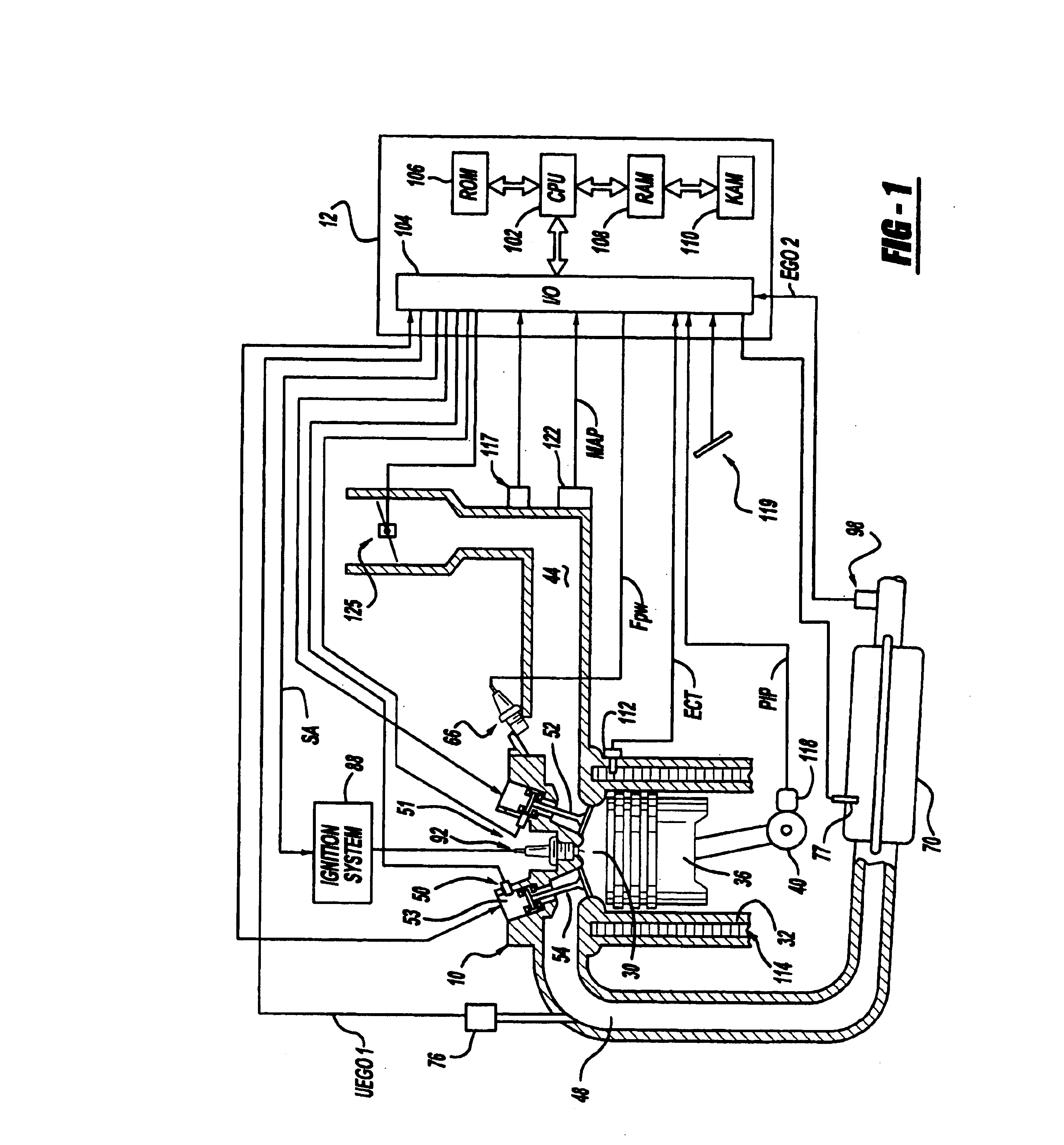
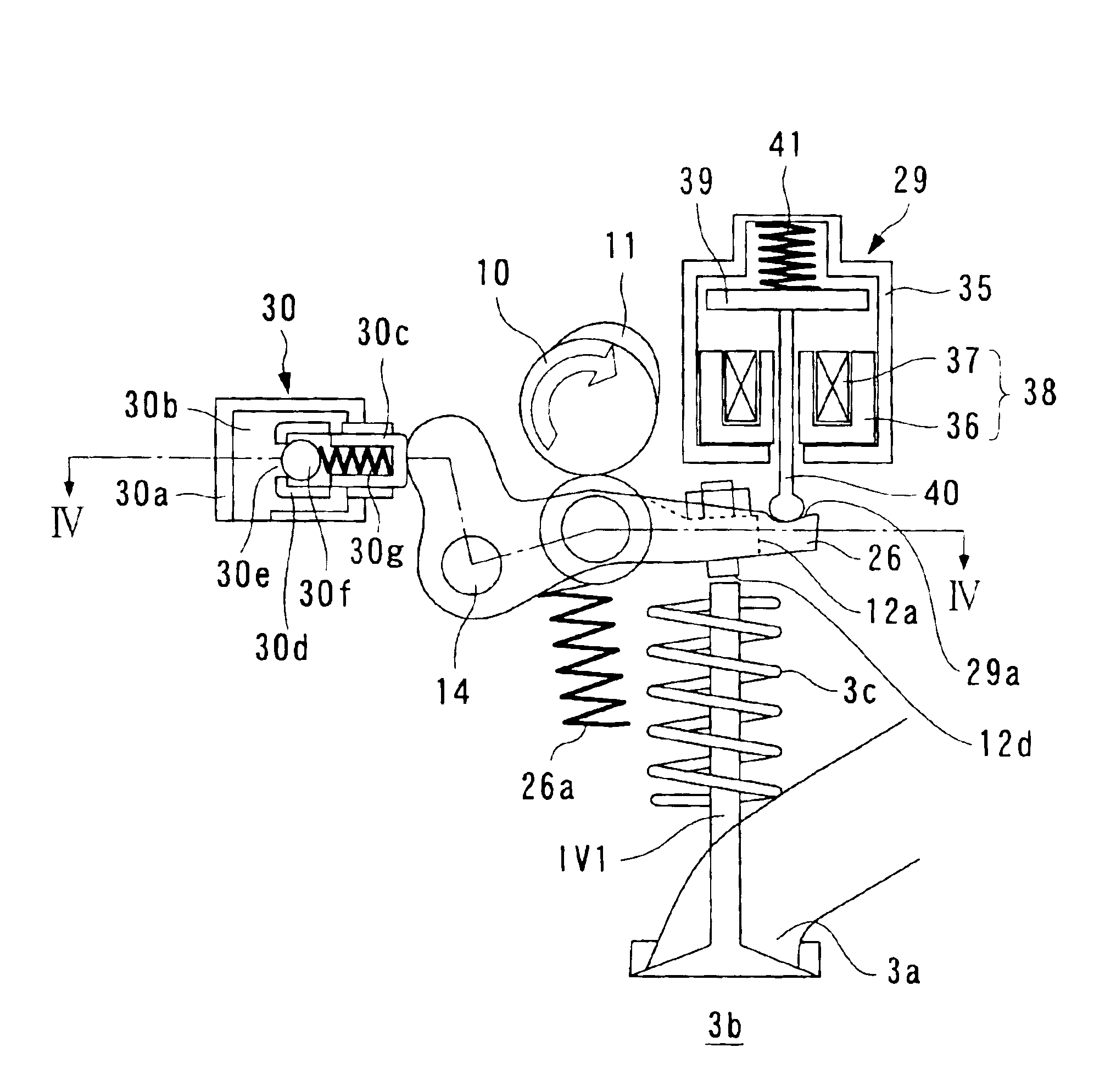
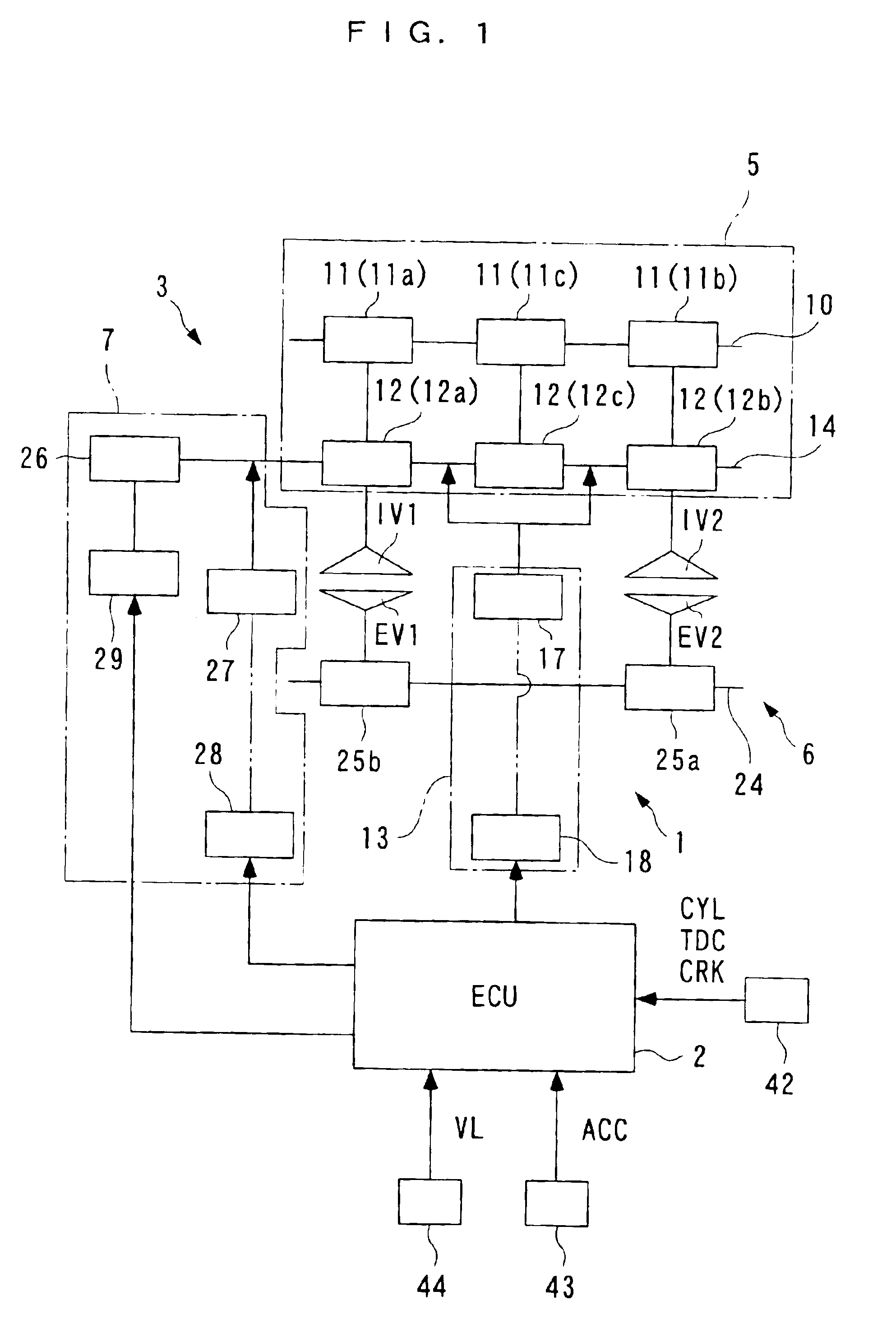
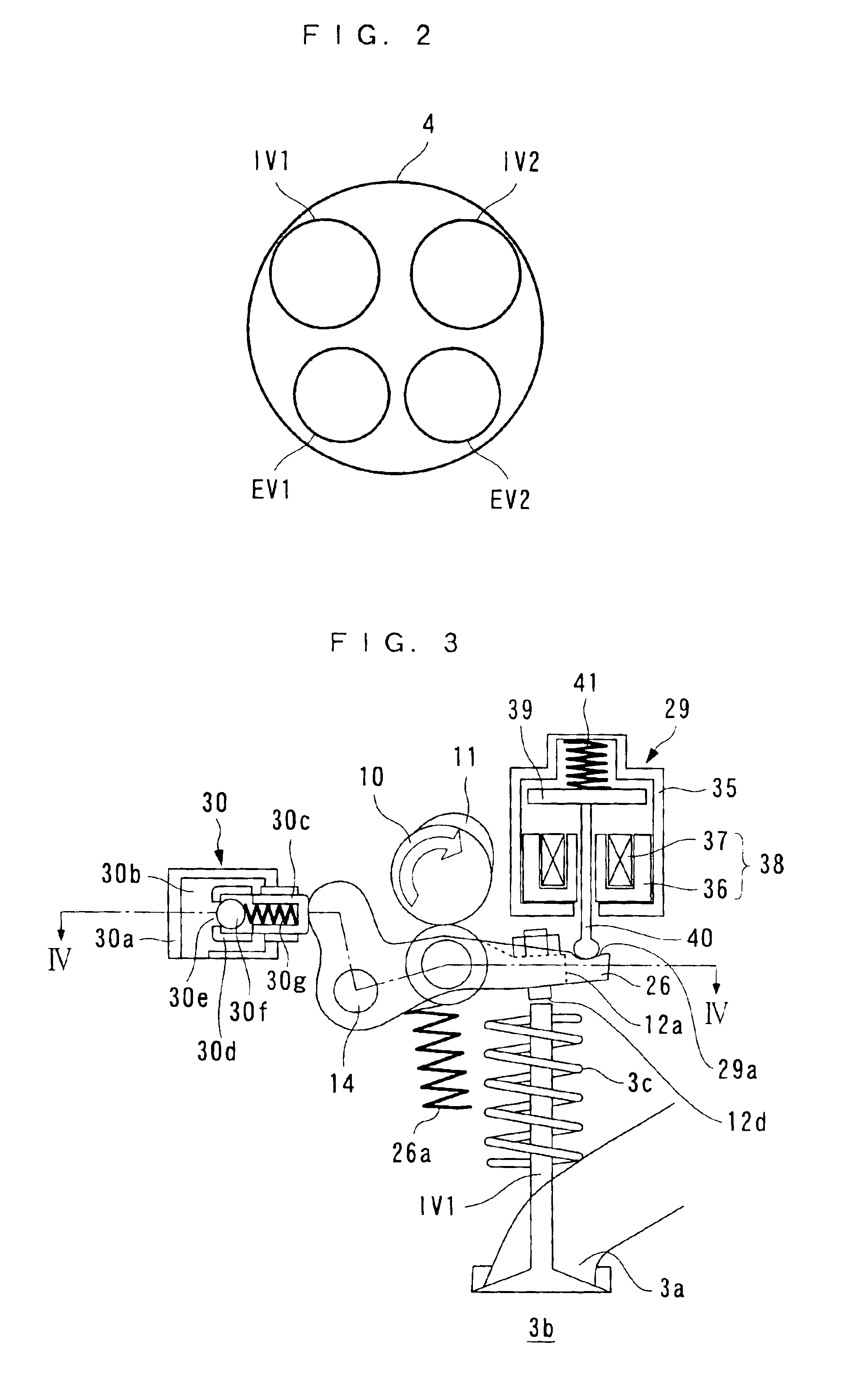
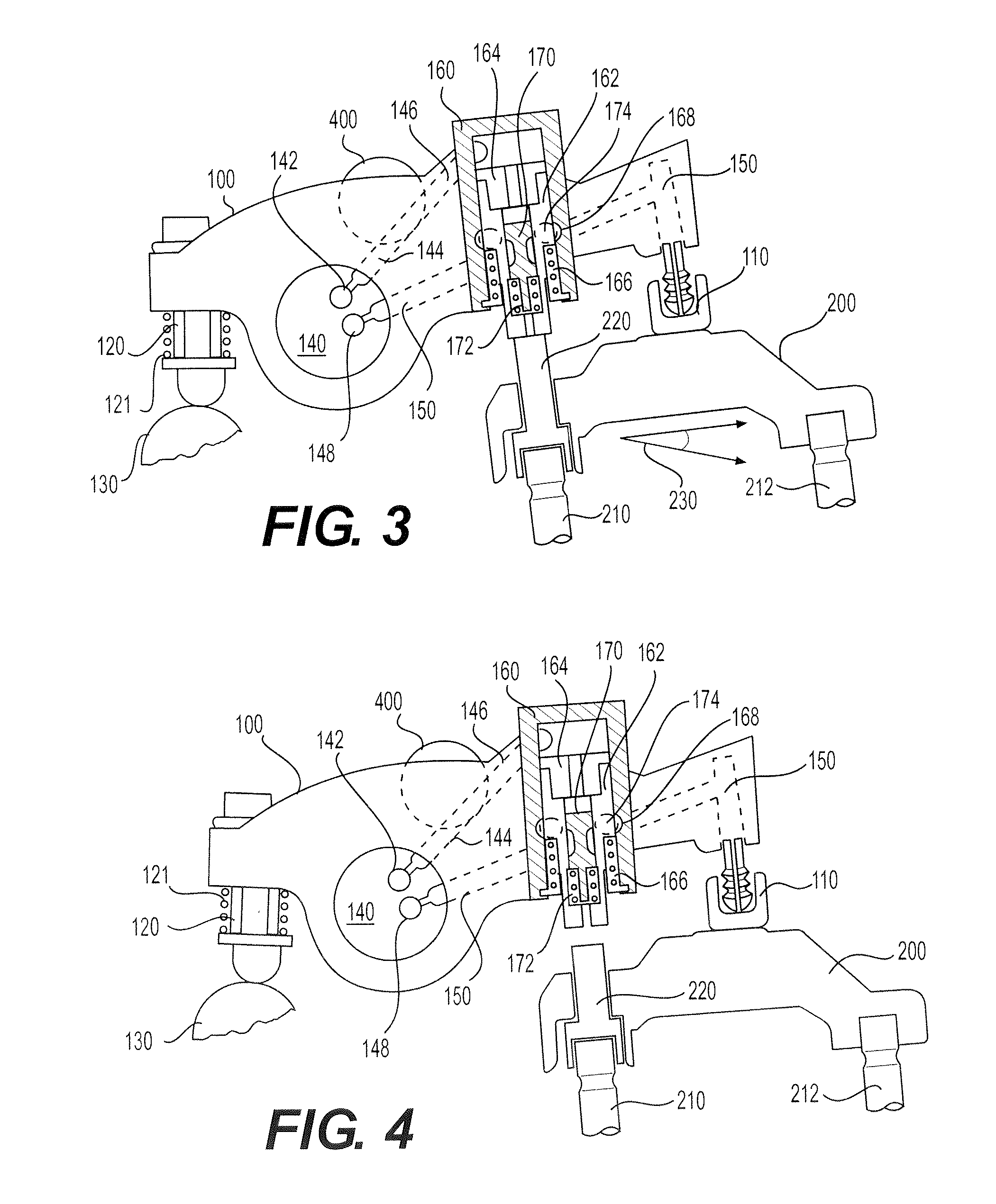
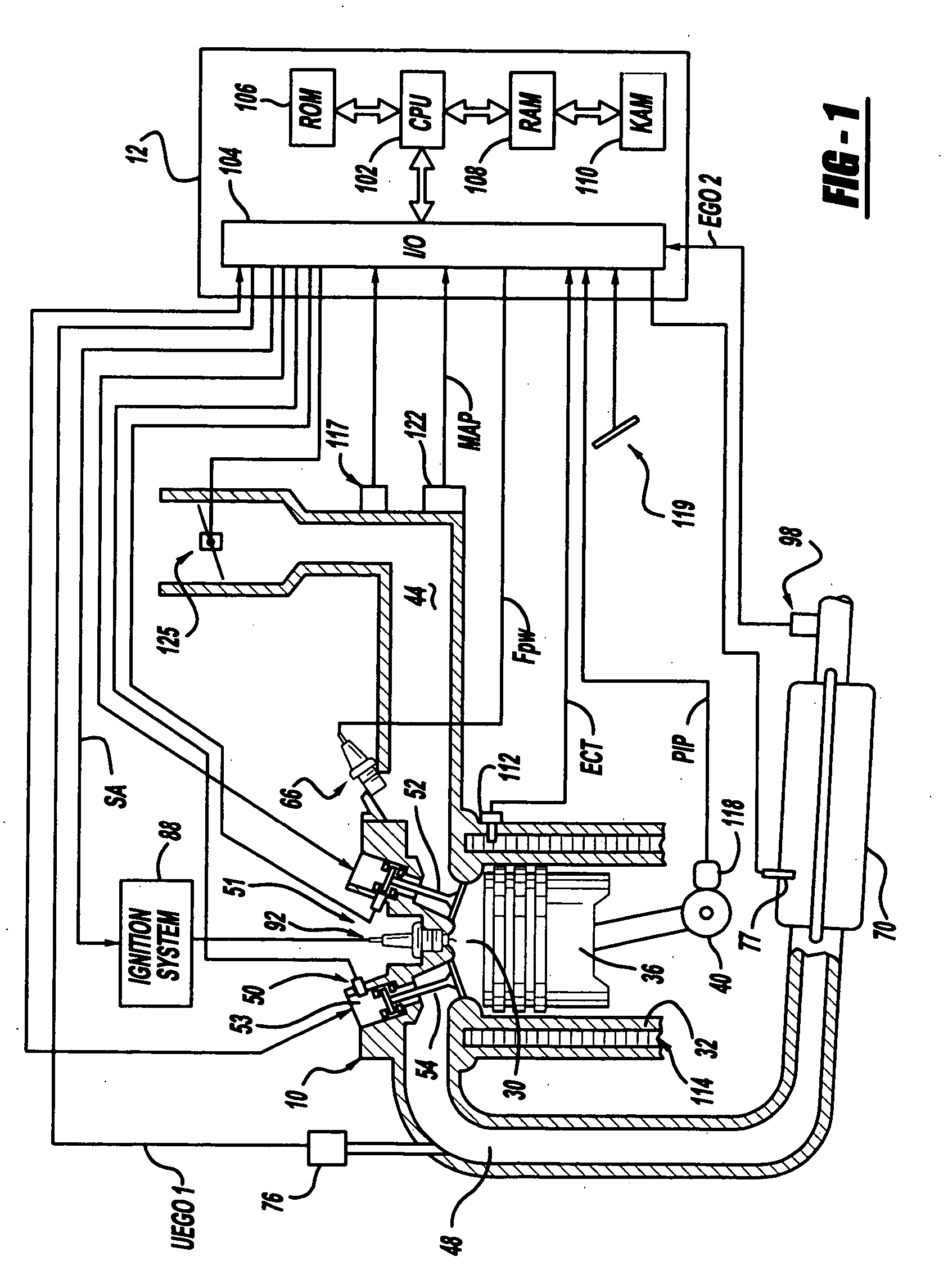
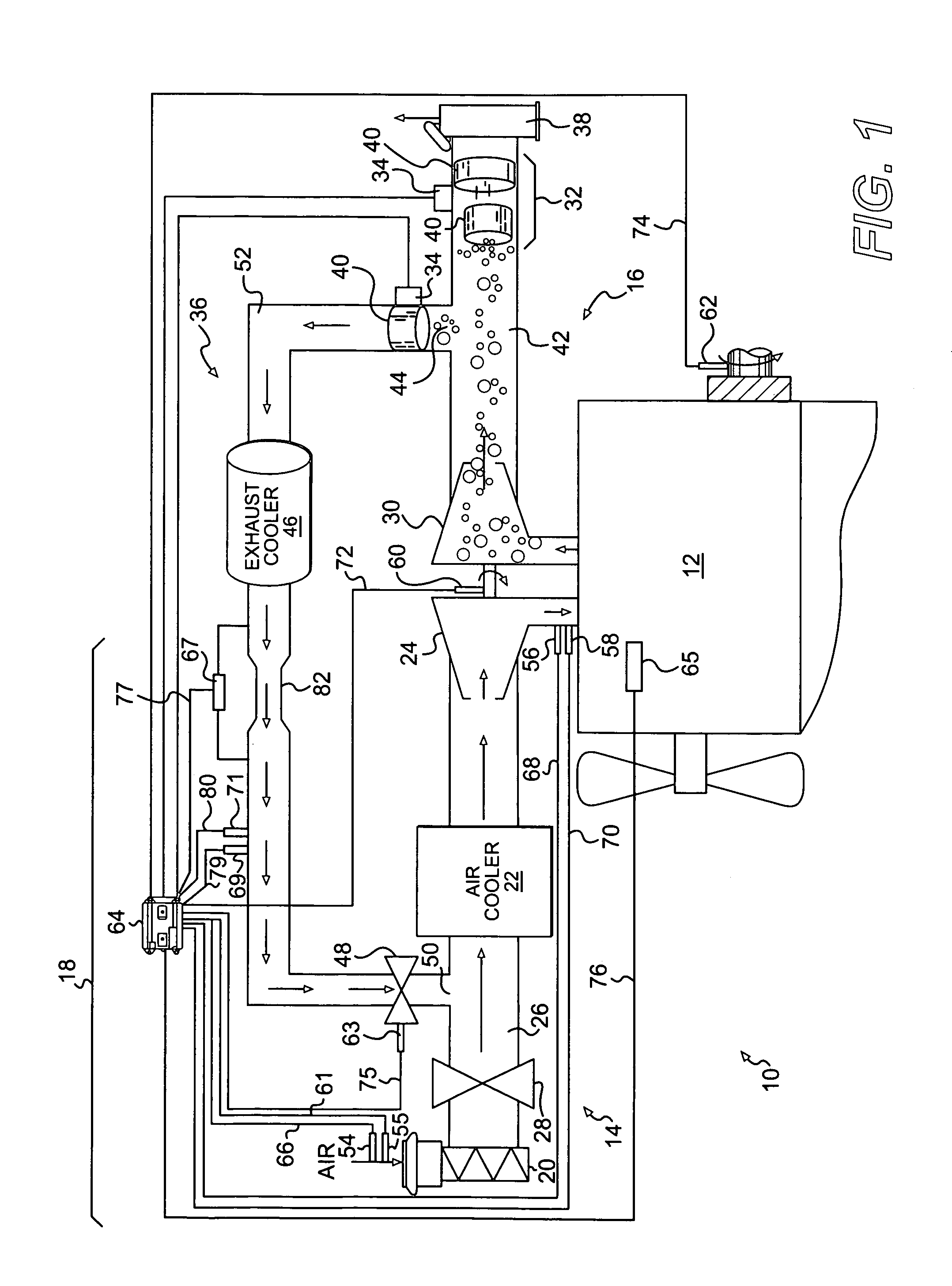
Engine air-fuel control for an engine with valves that may be deactivated
ActiveUS7032581B2Weaken influenceEasy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngine valveAir–fuel ratio
A system and method to control engine valve timing to improve air-fuel control in an engine with valves that may be deactivated. Valves that may be deactivated are controlled in a manner to improve detection of individual cylinder air-fuel ratios.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Compact lost motion system for variable valve actuation
InactiveUS6883492B2Wide rangeNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesVariable valve timingHydraulic circuit
Lost motion systems and methods for providing engine valves with variable valve actuation for engine valve events are disclosed. The system may include a master piston hydraulically linked to a slave piston, and a dedicated cam operatively connected to the master piston. The slave piston may be disposed substantially perpendicular to the master piston in a common housing. The slave piston is adapted to actuate one or more engine valves. The slave piston may incorporate an optional valve seating assembly into its upper end. A trigger valve may be operatively connected to the master-slave hydraulic circuit to selectively release and add hydraulic fluid to the circuit.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Engine valve disabler
A method for improving efficiency and reducing emissions of an internal combustion engine. Variable displacement engine capabilities are achieved by disabling engine valves during load changes and constant load operations. Active cylinders may be operated at minimum BSFC by intermittently disabling other cylinders to provide the desired net torque. Disabling is begun by early closing of the intake valve to provide a vacuum at BDC which will result in no net gas flow across the piston rings, and minimum loss of compression energy in the disabled cylinder; this saving in engine friction losses is significant with multiple disablements.
Owner:MOYER DAVID F
Starting an engine with electromechanical valves
ActiveUS6938598B1VariationLarge emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl mannerFour-stroke engine
A system and method to control engine valve timing to during the start of an internal combustion engine. Electromechanical valves are controlled in a manner to reduce engine vibration and hydrocarbon emissions during the start of an internal combustion engine. The method controls valves without an explicit four-stroke engine cycle during a start.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Process for forging titanium-based material, process for producing engine valve, and engine valve
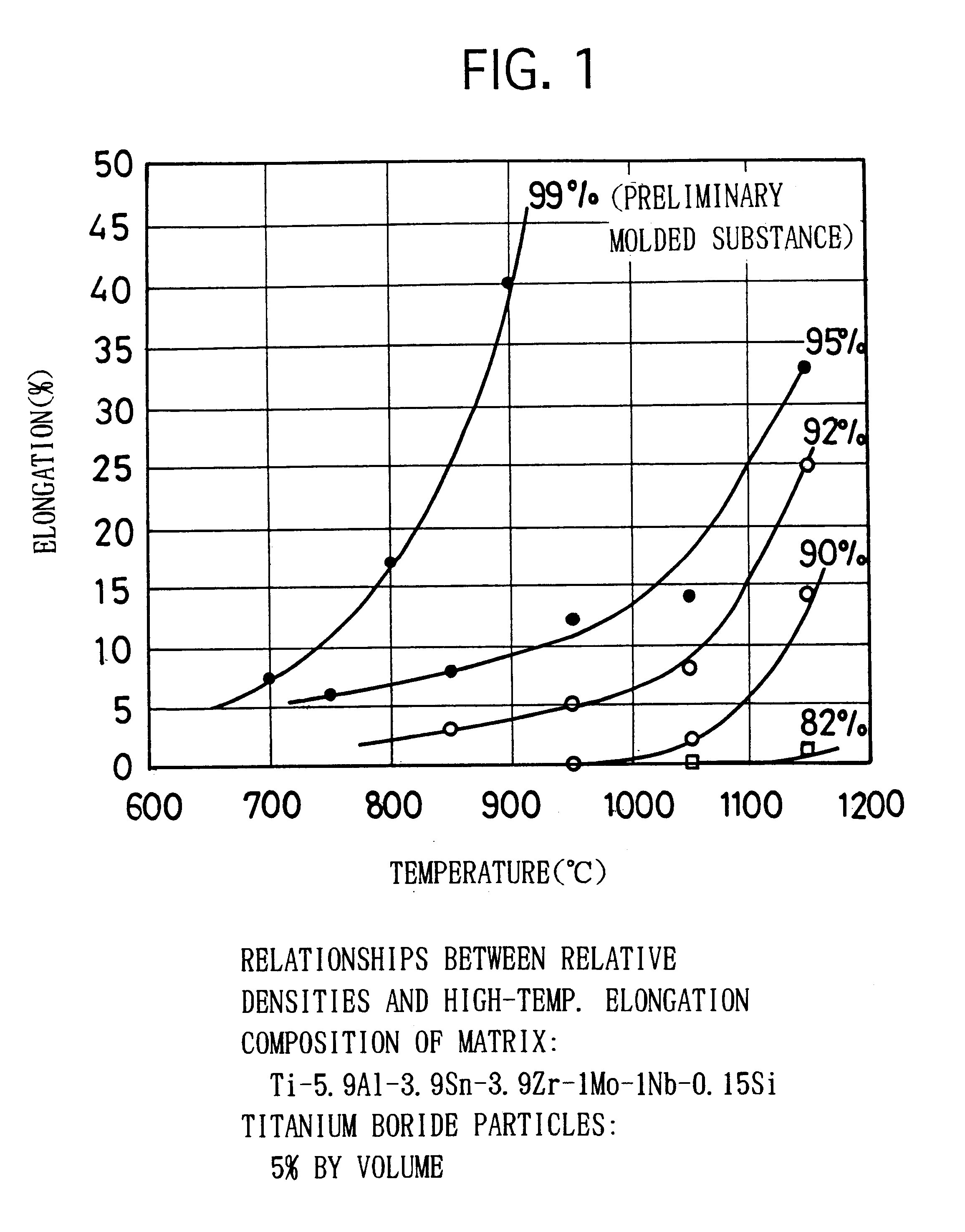
InactiveUS6599467B1Degradation can be suppressedReduced strengthMetal-working apparatusMachines/enginesTitaniumEngine valve
The invention provides a process for forging a titanium-based material comprises the steps of: preparing a titanium-based sintered workpiece including at least one of ceramics particles and pores in a total amount of 1% or more by volume, the ceramics particles being thermodynamically stable in a titanium alloy; and heating the workpiece to a forging temperature and forging the same. In the production process, the pores or the ceramics particles inhibit the grain growth during forging. Accordingly, it is possible to carry out the forging at a relatively high temperature at which the titanium-based material exhibits a small resistance to deformation. Moreover, the titanium-based material can maintain an appropriate microstructure even after the forging. Consequently, the impact value and the fatigue strength are inhibited from decreasing.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
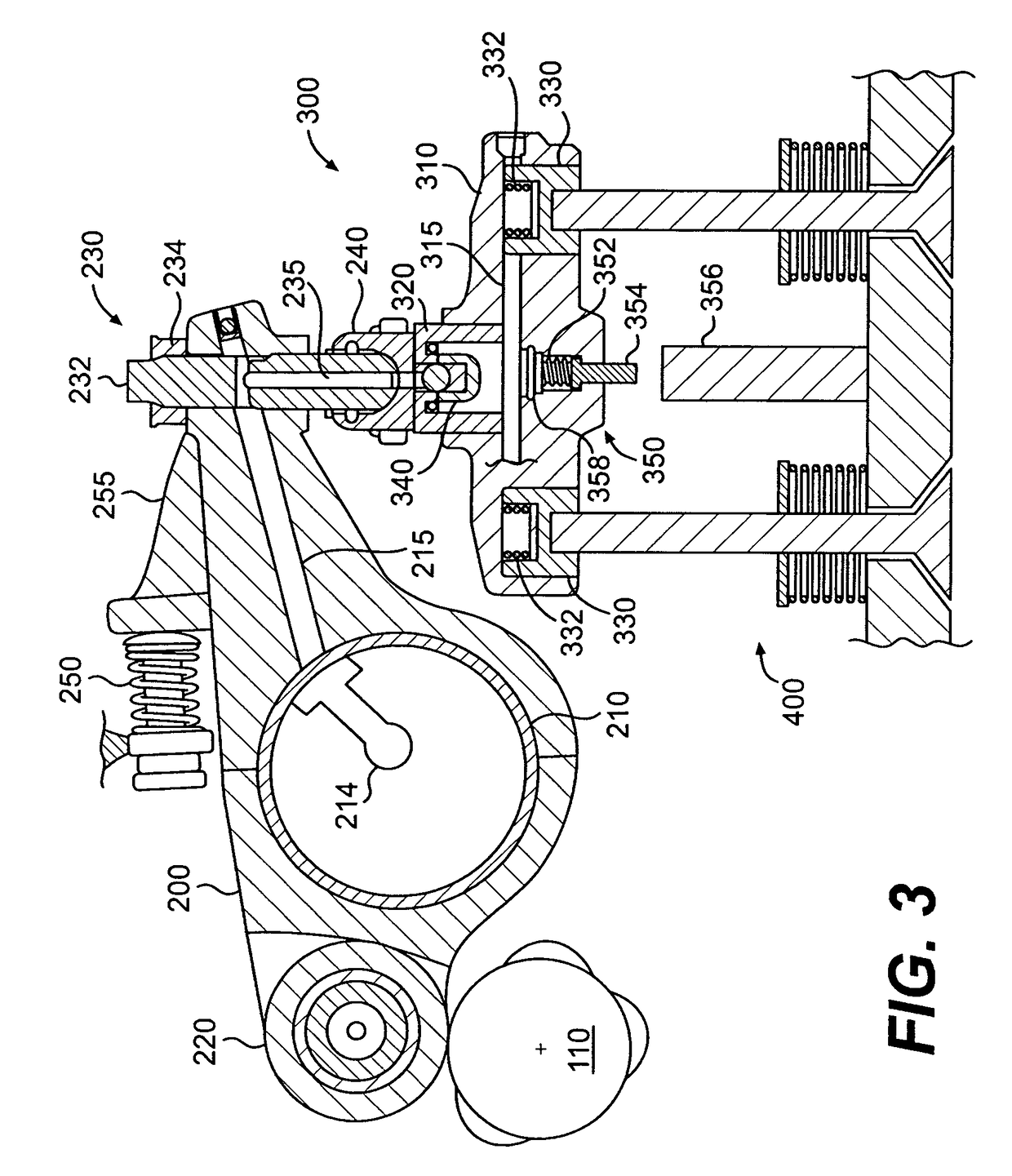
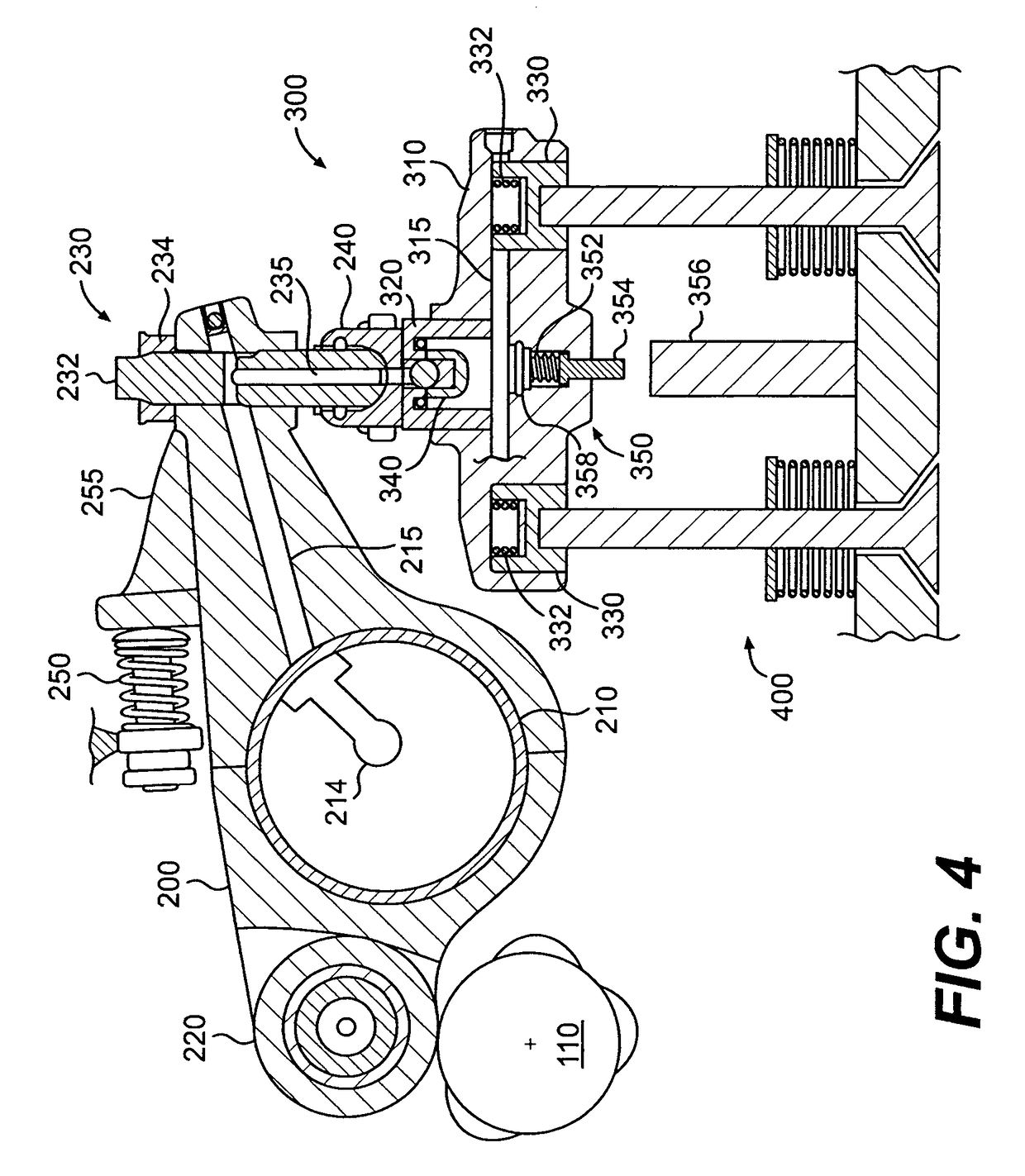
Combined engine braking and positive power engine lost motion valve actuation system
A system for actuating one or more engine valves for positive power operation and engine braking operation is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, an exhaust valve bridge and intake valve bridge each receive valve actuations from two sets of rocker arms. Each valve bridge includes a sliding pin for actuating a single engine valve and an outer plunger disposed in the center of the valve bridge to actuate two engine valves through the bridge. The outer plunger of each valve bridge may be selectively locked to its valve bridge to provide positive power valve actuation. During engine braking, application of hydraulic pressure to the outer plungers may cause the respective valve bridges and outer plungers to unlock so that all engine braking valve actuations are provided from a rocker arm acting on one engine valve through the sliding pin.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Method of straightening wire rods of titanium and titanium alloy
InactiveUS6077369ALow costImprove production yieldFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesWire rodTitanium
PCT No. PCT / JP95 / 01897 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 19, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 19, 1997 PCT Filed Sep. 20, 1995A method of straightening a wire rod of titanium or titanium alloy wherein the rod is hot-straightened to a straight rod at the straightening temperature T and elongation epsilon satisfying the expression (1) or (2). The method includes hot rolling a titanium billet of beta titanium alloy, ( alpha + beta ) titanium alloy or a near alpha titanium alloy into a wire rod, winding the hot rolled wire rod into a coil, cold drawing the wire rod, cutting the wire rod to obtain a bent wire rod, heating the bent wire rod to a straightening temperature T while both end portions of the bent wire rod are fixed, applying a predetermined elongation epsilon to the wire rod, maintaining a straightening temperature T, hot-straightening the wire in accordance with the expression (2) epsilon (T-400)> / =400(1) epsilon (T-500)> / =200(2) and cooling the wire rod while applying tension. The method is suitable for preparing a straight rod for use in an engine valve.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
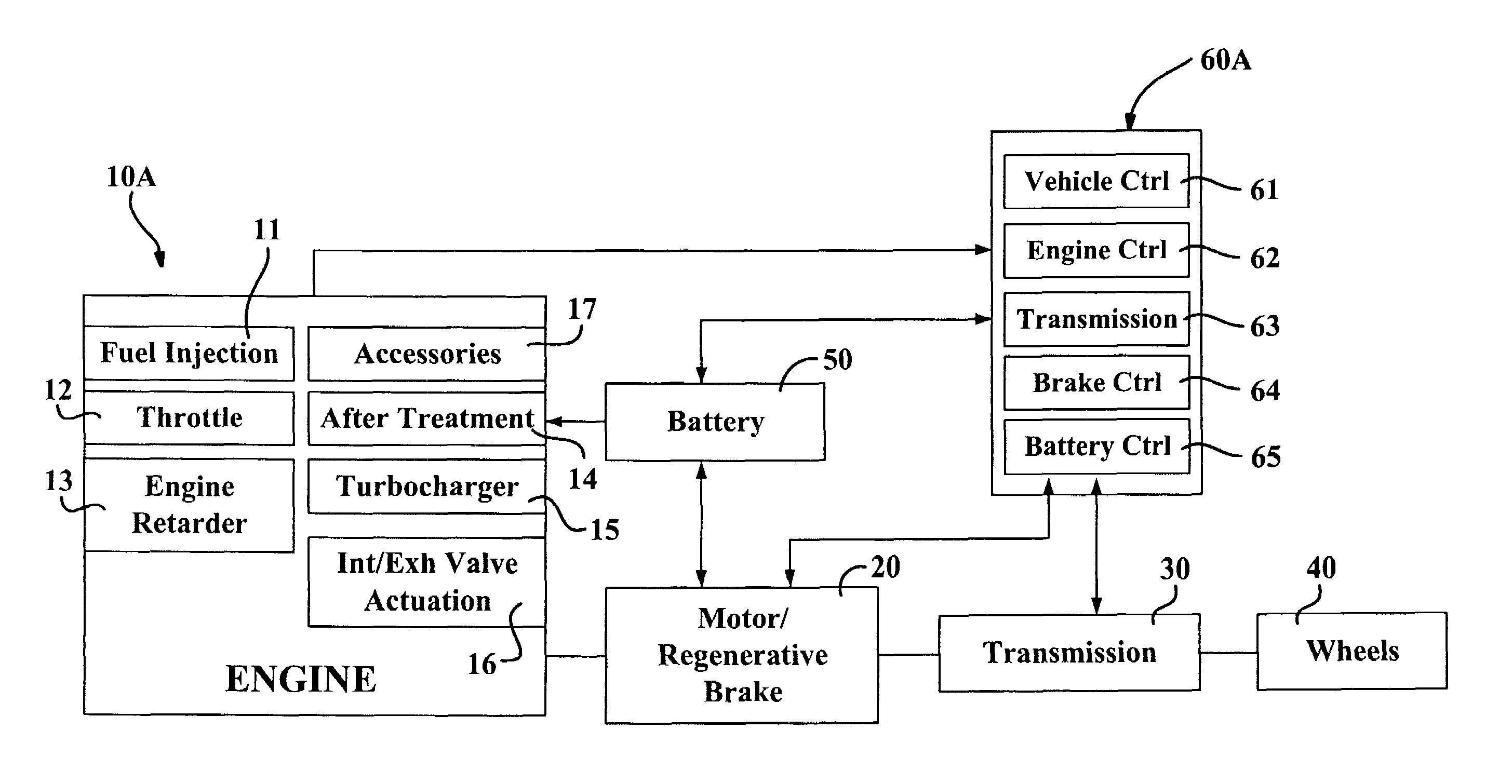
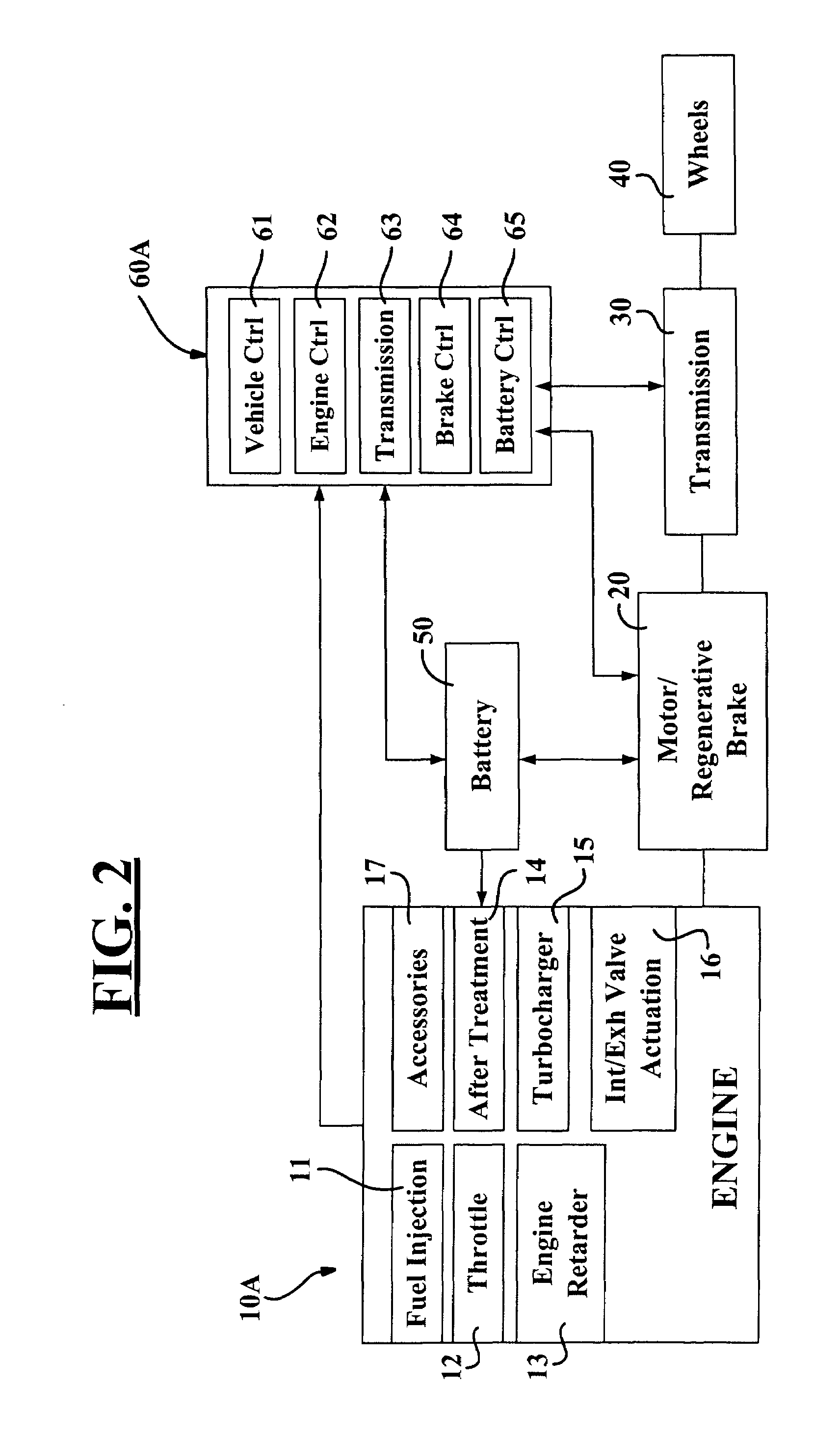
Internal combustion engines for hybrid power train
InactiveUS20060086546A1Improve responsivenessReduce exhaust emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesRegenerative brakeCombustion
Owner:GREEN VISION TECH
Multistage fuel-injection internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20070074702A1Reduce impactReduce outputElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveEngine valve
In a multi-stage fuel-injection internal combustion engine employing a fuel injection system and a variable valve actuation system, engine valve timings are variably controlled depending on engine operating conditions. An electronic engine control unit is configured to execute cooperative control of the timing of sub-injection, injected before main injection, responsively to intake valve closure timing, and also to execute cooperative control of the timing of sub-injection, injected after the-main injection, responsively to exhaust valve open timing.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Internal combustion engines for hybrid powertrain
InactiveUS7028793B2Reduced fuel economyReduce power outputElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionRegenerative brake
A hybrid powertrain and method for operating same in which the operation of the engine is modified to effect an improvement in the fuel economy and / or emissions performance of the hybrid powertrain. In one embodiment, the battery of the powertrain is employed to provide auxiliary heat to an engine aftertreatment system to thereby improve the effectiveness of the aftertreatment system. In another embodiment, various components of the engine, such as a water pump, are wholly or partly operated by electric motors that receive power from the battery of the powertrain. In another embodiment, engine braking can be employed in situations where regenerative braking does not provide sufficient braking torque. In a further embodiment, the engine valves may be selectively opened to reduce pumping losses associated with the back-driving of the engine.
Owner:GREEN VISION TECH
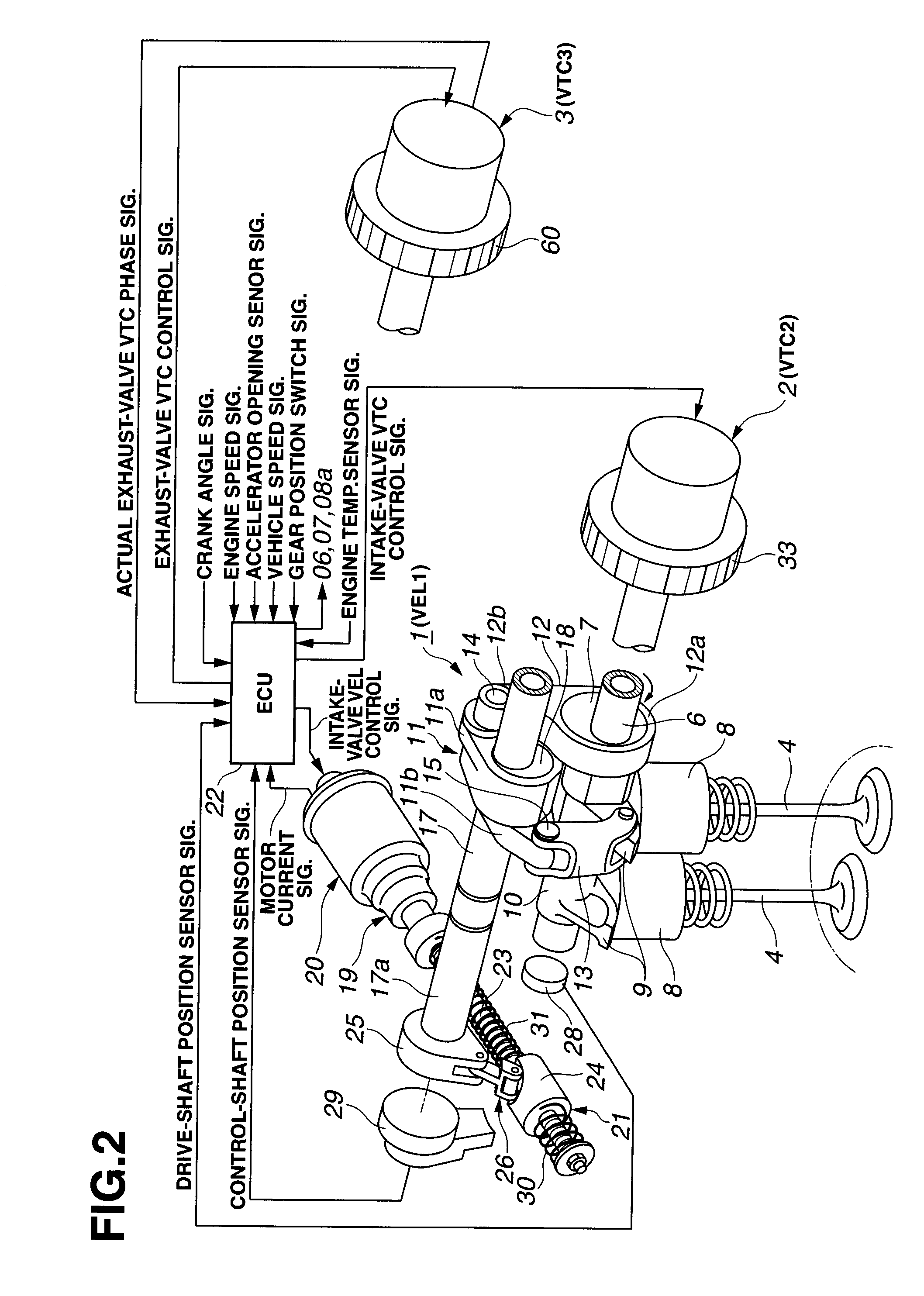
Variable valve actuation system of internal combustion engine and control apparatus of internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20090228187A1Improve responsivenessEngine-torque-increase responsivenessAnalogue computers for vehiclesValve arrangementsExhaust valvePhase shifted
In a control apparatus of a supercharged internal combustion engine, a variable valve actuation system interacts with an engine control system. A controller is configured or programmed to increase an intake-valve lift by a variable valve lift mechanism, which is provided for variably controlling at least the intake-valve lift of engine valves, when starting from a vehicle stand-still state or when accelerating from an idling state or a light load state. The controller is further configured or programmed to increase a valve overlap of intake and exhaust valves by a variable phase control mechanism, which is provided for variably phase-shifting a central phase angle of a valve lift characteristic curve of at least one of the intake and exhaust valves, while increasing a boost pressure of intake air introduced into an engine cylinder by a supercharging device, after the intake-valve lift has been increased.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Valve control apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6955144B2Reduce power consumptionImprove fuel economyElectrical controlOutput powerInertial massExternal combustion engine
A valve control apparatus for an internal combustion engine is provided which is capable of optimally setting the closing timing of an engine valve according to operating conditions of the engine while suppressing an increase in the inertial mass of the engine valve to the minimum, thereby attaining improvement of fuel economy, and realization of higher engine rotational speed and higher power output in a compatible fashion, and reducing costs and weight thereof. The valve control apparatus controls opening and closing operations of an engine valve. A cam-type valve actuating mechanism actuates the engine valve to open and close the engine valve, by a cam which is driven in synchronism with rotation of the engine. An actuator makes blocking engagement with the engine valve having been opened, to thereby hold the engine valve in an open state. An ECU controls operation of the actuator to thereby control closing timing of the engine valve.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
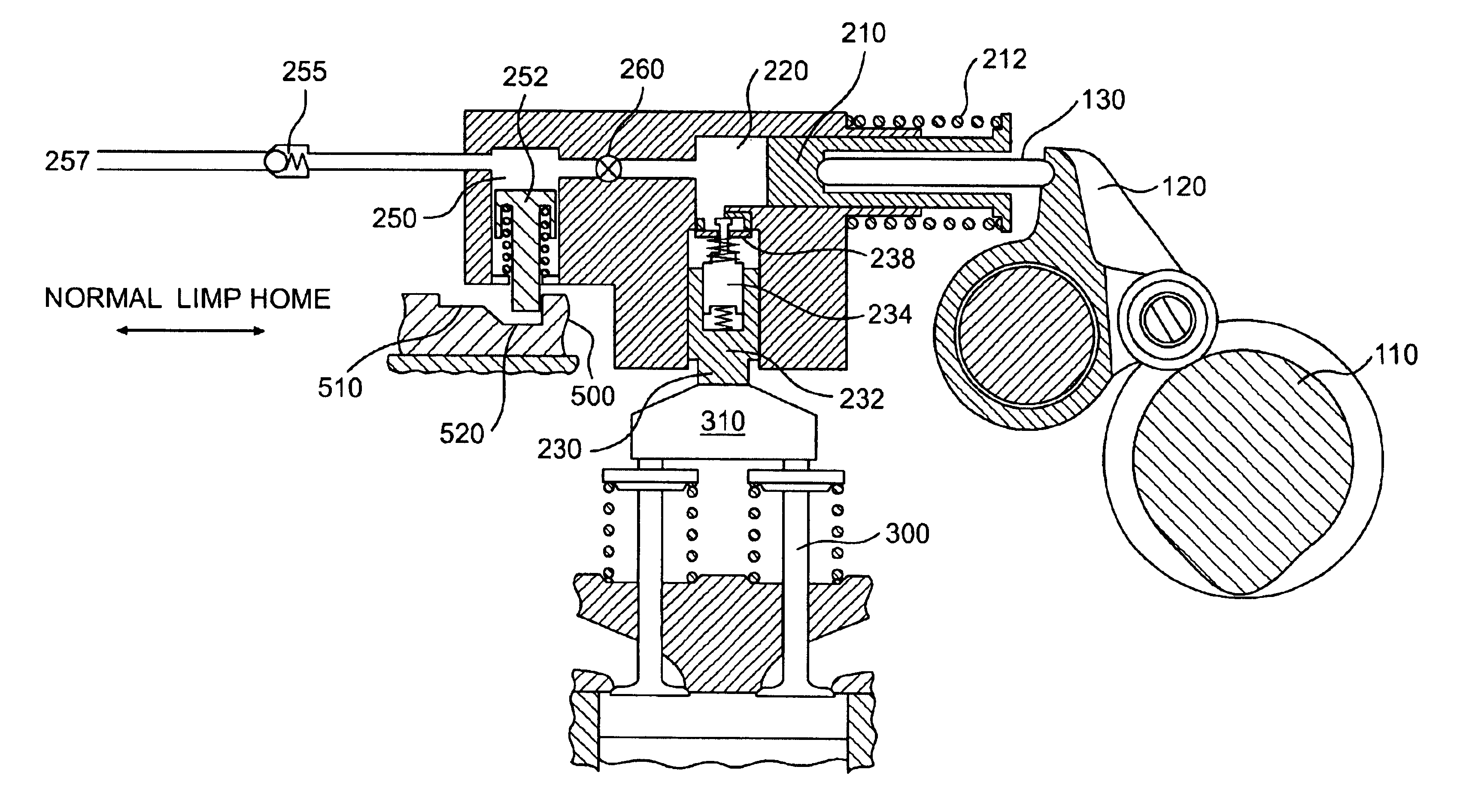
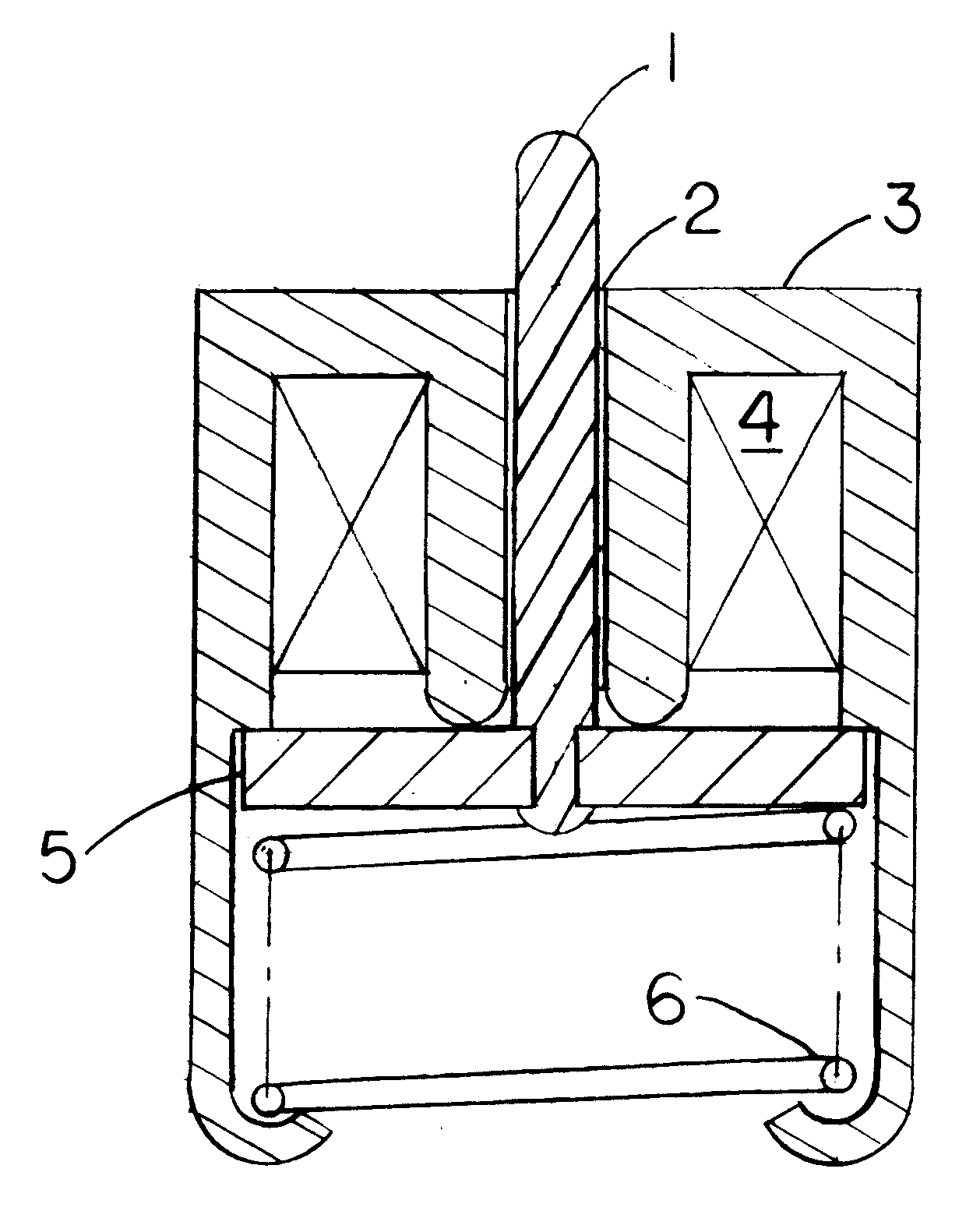
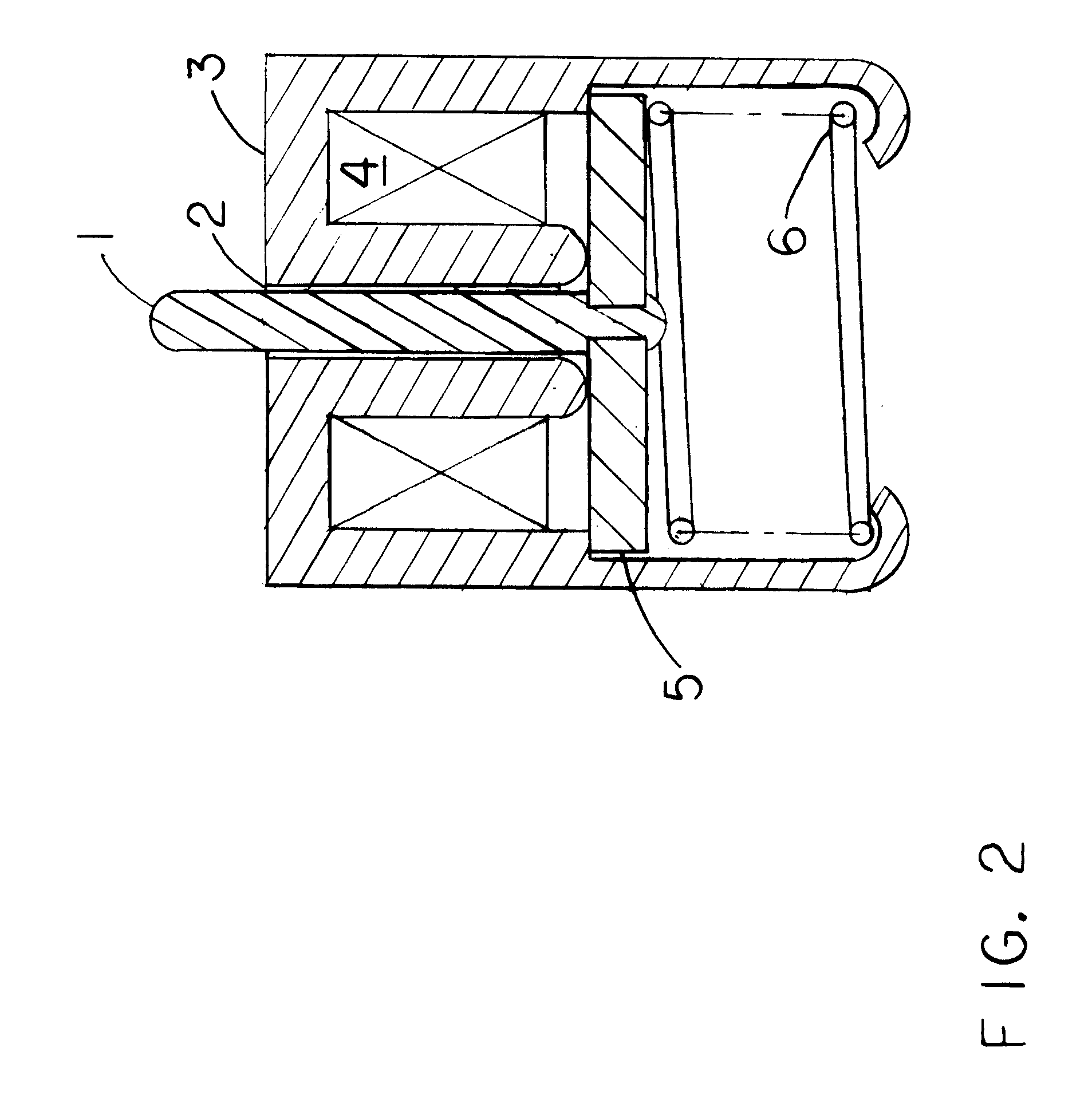
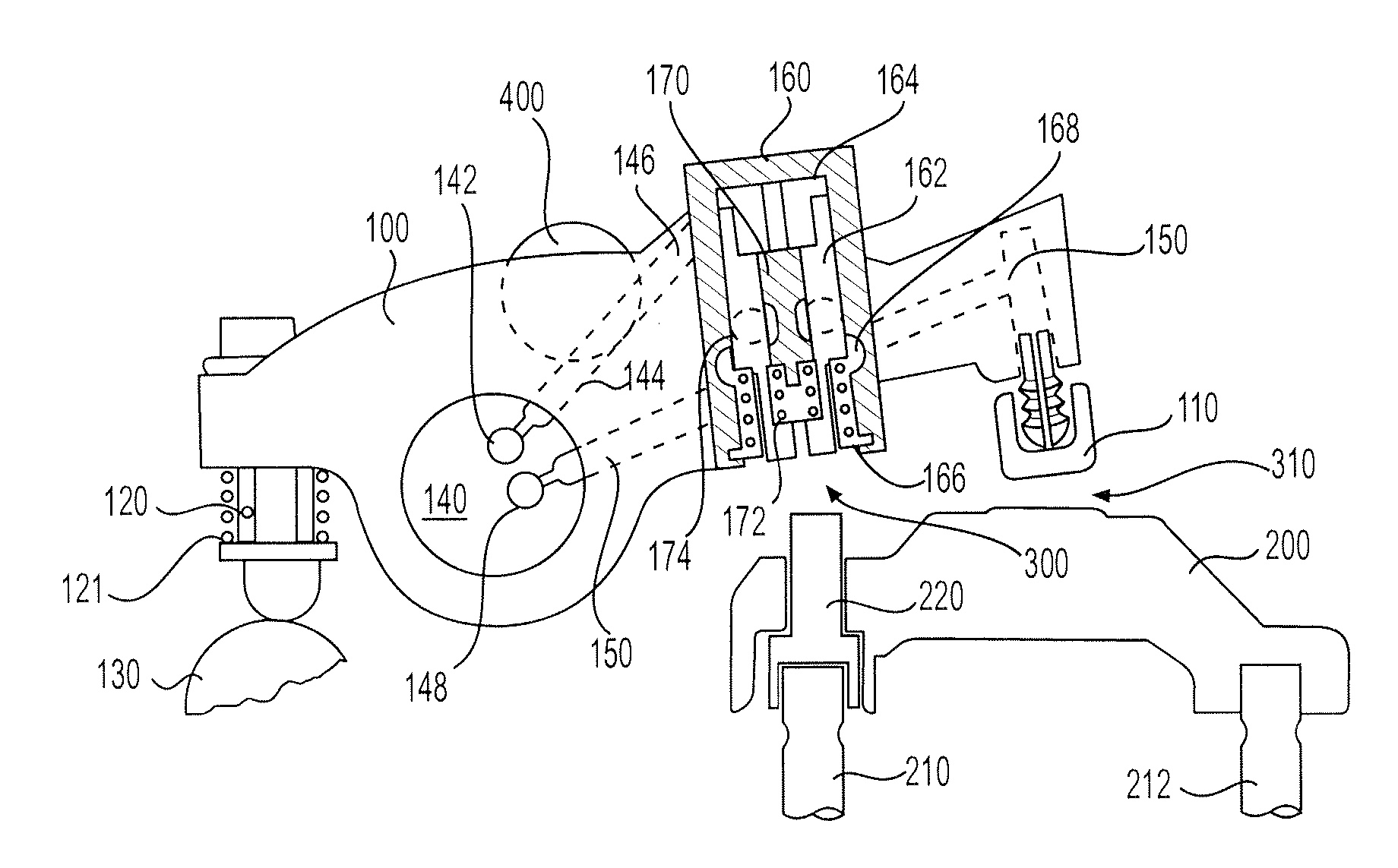
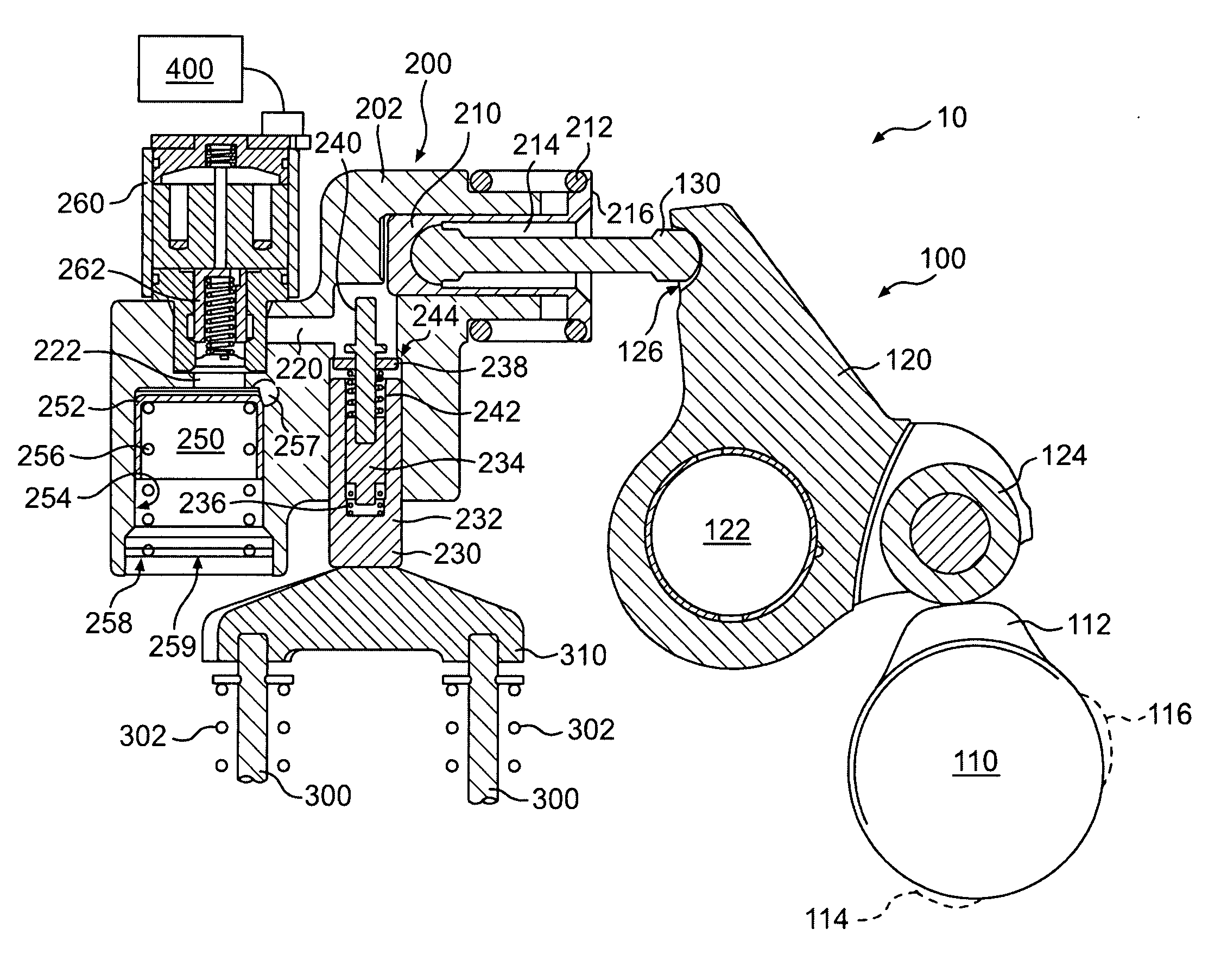
Integrated lost motion rocker brake with automatic reset
Systems and methods for actuating engine valves are disclosed. The systems may include a rocker arm having an adjustable length push tube mounted to a first end and multiple contact surfaces for an engine valve bridge at a second end. An actuator piston assembly may be provided in the rocker arm between the first and second rocker arm ends. The actuator piston assembly is adapted to extend from the rocker arm under the influence of hydraulic pressure and actuate an inboard engine valve through the engine valve bridge when an actuator piston is locked into an extended position.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Valve bridge with integrated lost motion system
A system and method of actuating one or more engine valves is disclosed. In one embodiment, the system comprises: a valve train element; a rocker arm pivotally mounted on a shaft and adapted to rotate between a first position and a second position, the rocker arm selectively receiving motion from the valve train element; a valve bridge disposed above the one or more engine valves; and a lost motion system disposed in the valve bridge.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Compressed air engine electrically driven whole-variable valve actuating system
InactiveCN101149002AReduce throttling lossRealize time adjustmentReciprocating piston enginesNon-mechanical valveEngineeringEngine valve
The present invention relates to compressed air engine, and is especially one kind of variable air valve driving system for compressed air engine. The system includes one air valve spring, one shaft coupler, one piston rod and one piston inside a cylinder, connected successively to the air valve. There are two communication states between the air passage and the air exhaust electromagnetic directional valve based on the final position of the valve. The valve opening time may be controlled by means of controlling the power-on pulse duration. The present invention has the advantages of capacity of decoupling air valve motion and the crankshaft rotation speed of the pneumatic engine to optimize the air distributing phase, capacity of recovering the vehicle braking energy, convenient braking strength regulation, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Modal variable valve actuation system for internal combustion engine and method for operating the same
ActiveUS6925976B2Improve fuel economyImprove power densityValve drivesOutput powerExhaust brakeInlet valve
A variable valve actuation system for providing discrete exhaust and intake valve lift profiles for various operating modes of an internal combustion engine. The variable valve actuation system includes exhaust and intake rocker assemblies, exhaust and intake hydraulic extension devices operatively coupling corresponding rocker assemblies with respective engine valves and exhaust and intake control valves for selectively supplying the pressurized hydraulic fluid to the extension devices so as to independently switch them between a pressurized condition and a depressurized condition. The engine further includes an exhaust brake provided to initiate a small lift of the exhaust valve during the engine braking operation while the exhaust extension device maintains the exhaust valve open during a compression stroke for bleeder-compression release braking. The exhaust and intake valves can be adjusted independently to provide combinations of valve lift modes.
Owner:JENARA ENTERPRISES
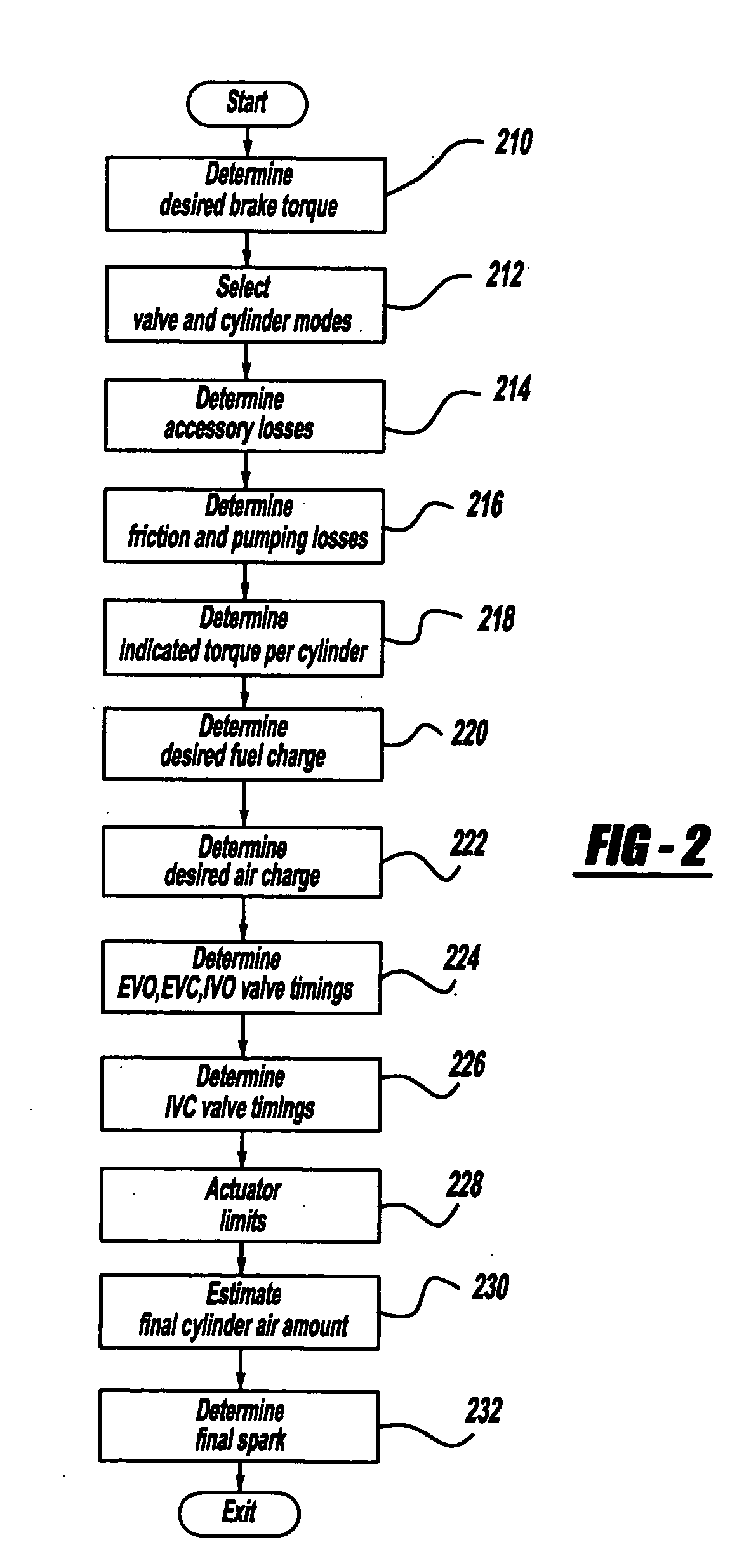
Method and apparatus to control operation of a homogeneous charge compression-ignition engine
InactiveUS7360523B2Weakening rangeReduce environmental stressValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionAmbient pressure
The invention provides a method for operating a multi-cylinder, spark-ignition, direct-injection, four-stroke internal-combustion engine adapted to operate in a controlled auto-ignition mode selectively operative at stoichiometry and lean of stoichiometry. The method comprises adapting an engine valve actuation system to control engine valve opening and closing, and monitoring engine operating conditions and ambient barometric pressure. The engine is operated unthrottled and the engine valve actuation system is controlled to effect a negative valve overlap period when the engine operating conditions are within predetermined ranges. A mass of fuel is injected during the negative valve overlap period. The magnitude of the negative valve overlap period is decreased with decreasing ambient pressure and increased with increasing ambient pressure.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
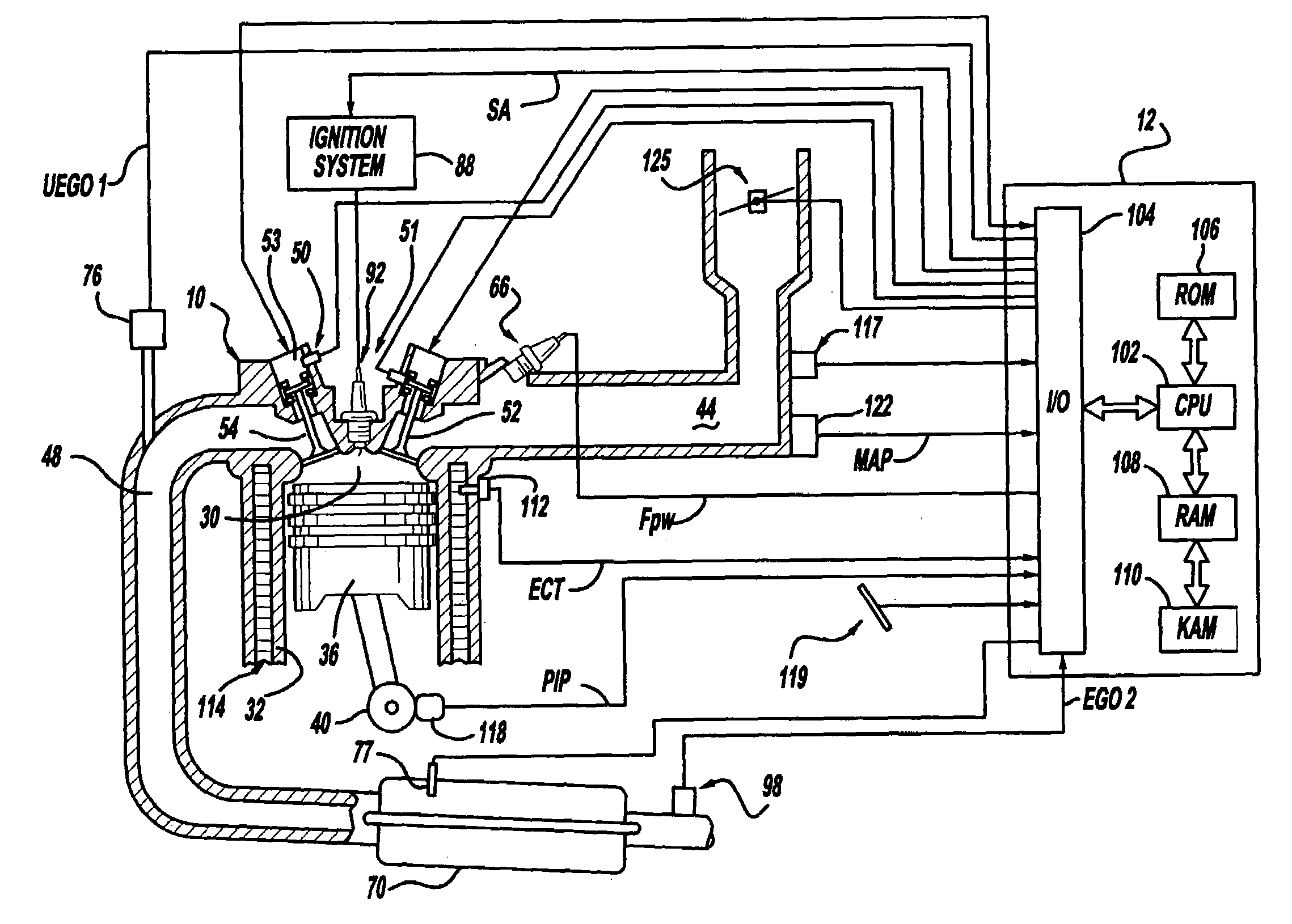
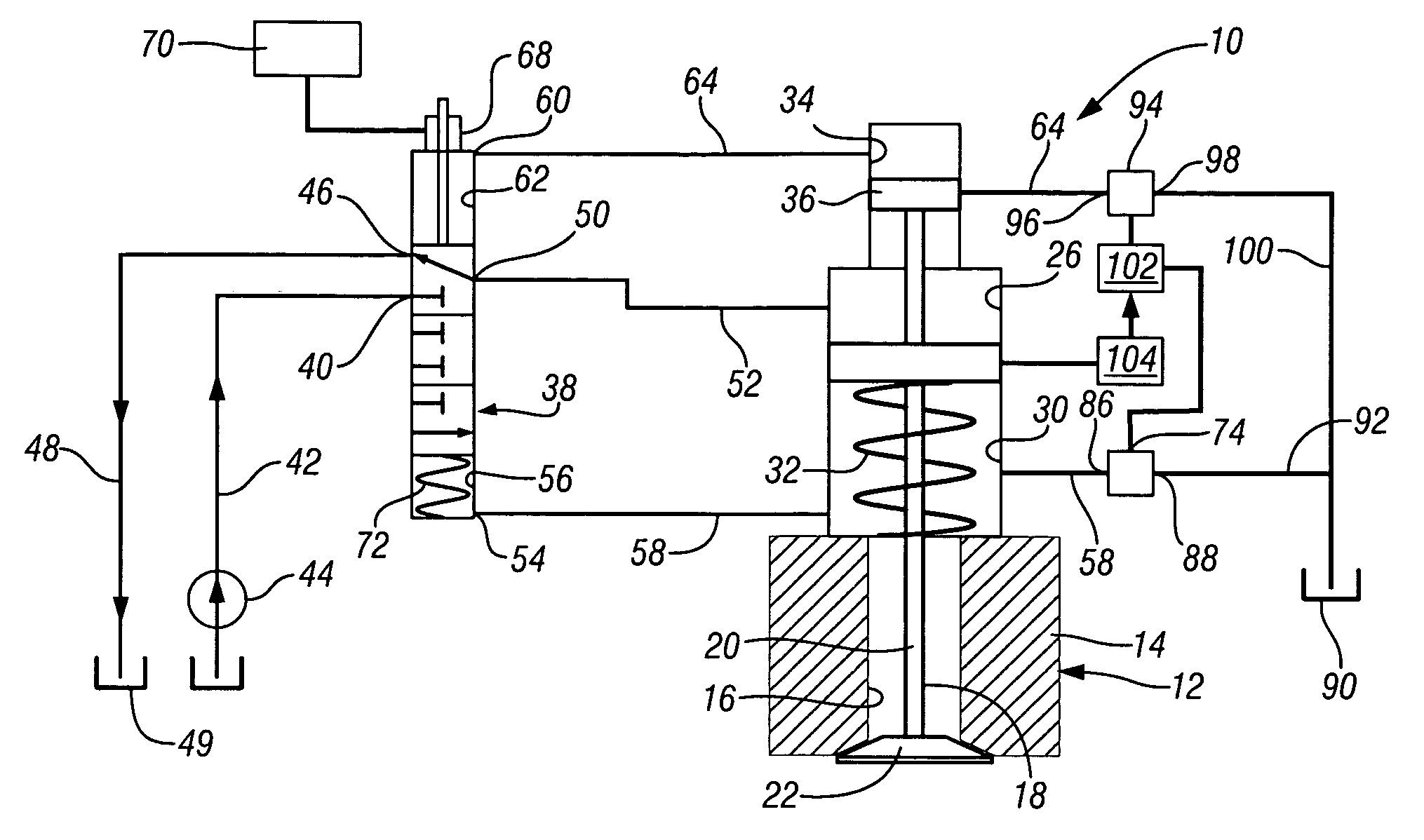
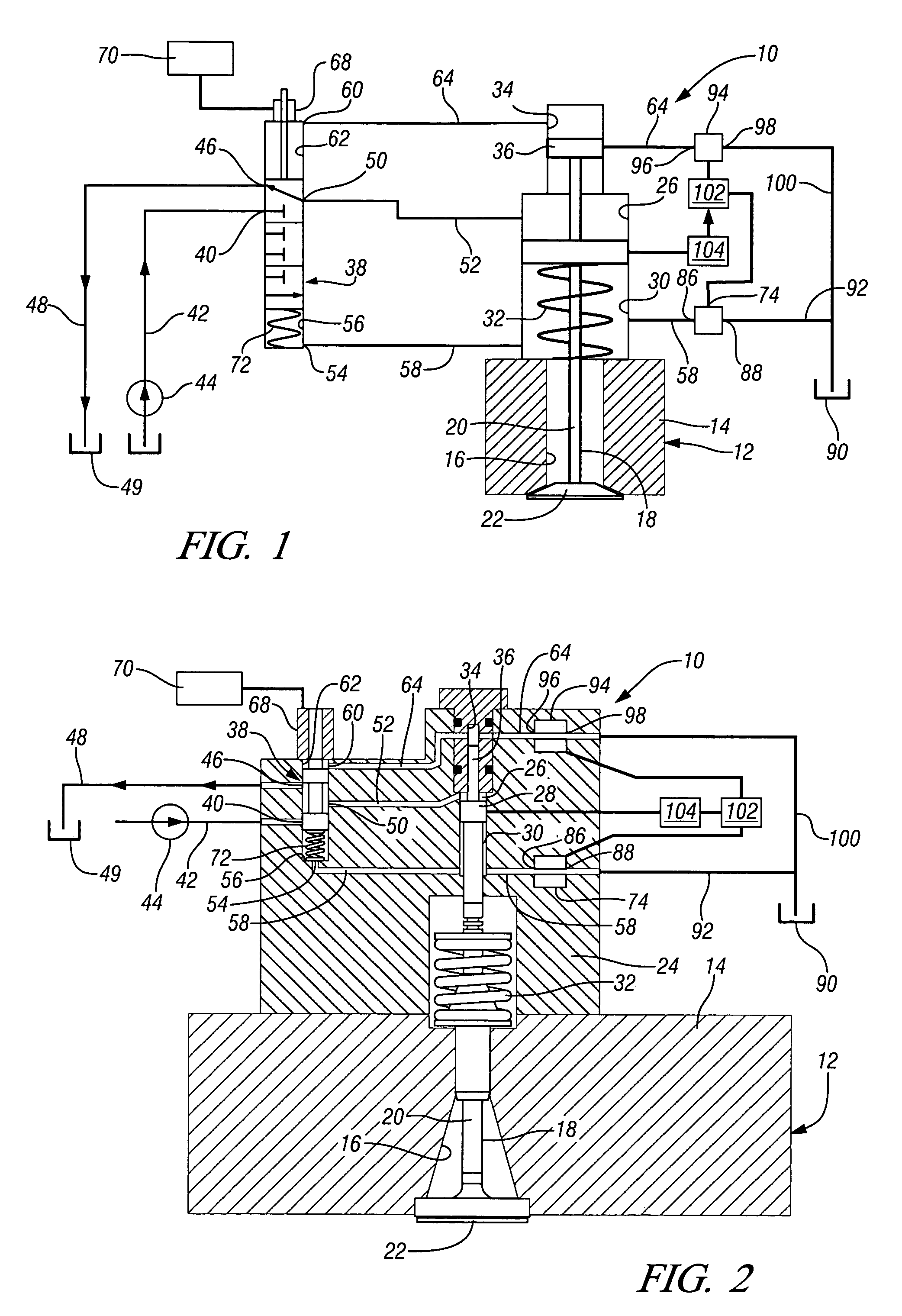
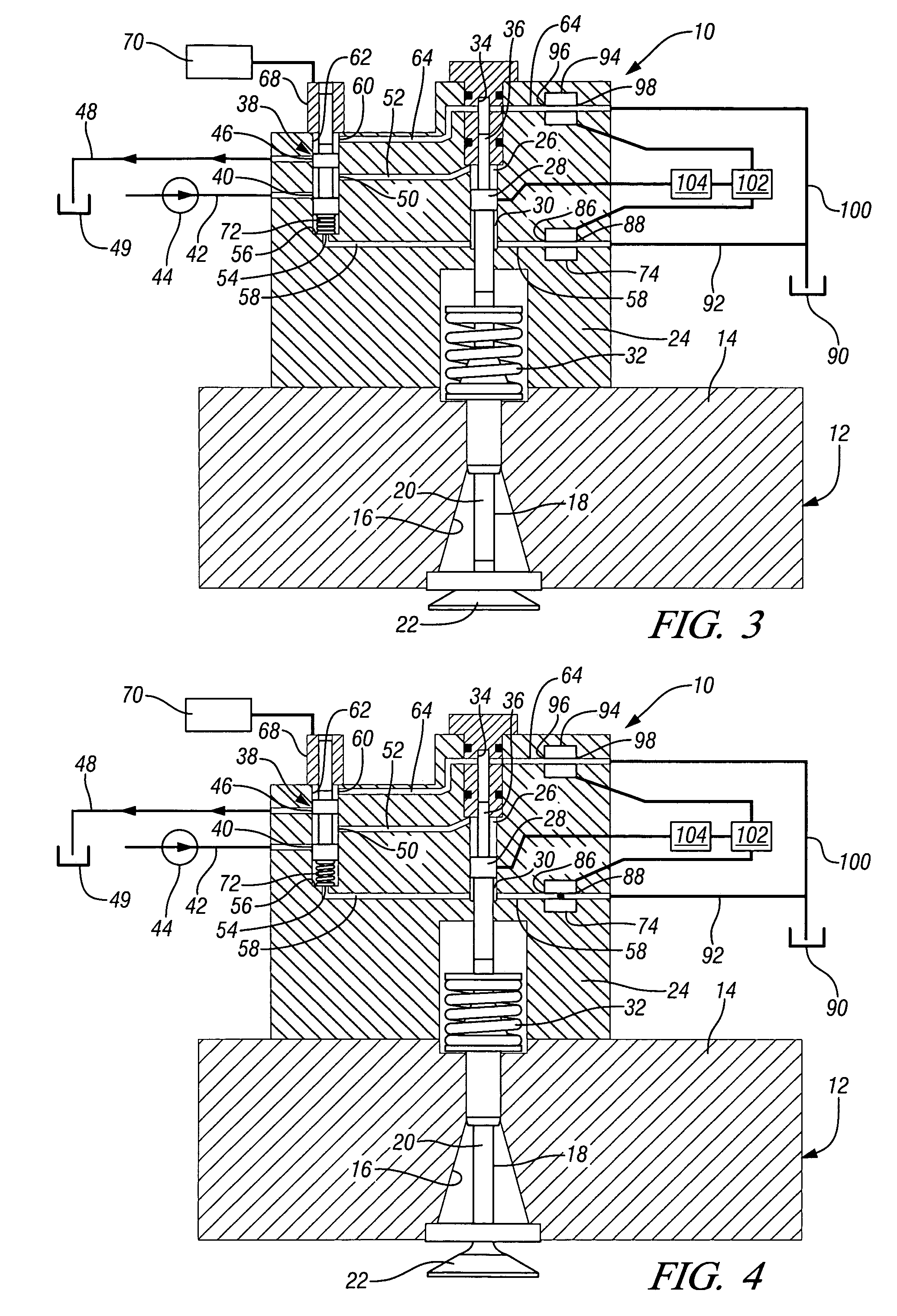
Engine air-fuel control for an engine with valves that may be deactivated
ActiveUS20050205074A1Undesirable influence be greatly reduceImproved individual cylinder air-fuel detectionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngine valveAir–fuel ratio
A system and method to control engine valve timing to improve air-fuel control in an engine with valves that may be deactivated. Valves that may be deactivated are controlled in a manner to improve detection of individual cylinder air-fuel ratios.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Engine valve actuation system
InactiveUS7004122B2Avoid oscillationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInlet valveEngineering
An engine valve actuation system is provided. The engine valve actuation system includes an intake valve that is moveable between a first position to prevent a flow of fluid and a second position to allow a flow of fluid. A cam assembly is configured to move the intake valve between the first position and the second position. A fluid actuator is configured to selectively prevent the intake valve from moving to the first position. A source of fluid is in fluid communication with the fluid actuator. A directional control valve is configured to control a flow of fluid between the source of fluid and the fluid actuator. A fluid passageway connects the directional control valve with the fluid actuator. An accumulator is in fluid communication with the fluid passageway. A restricted orifice is disposed between the accumulator and the fluid passageway to restrict a flow of fluid between the accumulator and the fluid passageway.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Compact lost motion system for variable value actuation
InactiveUS20050252484A1Internal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHydraulic circuitEngineering
Lost motion systems and methods for providing engine valves with variable valve actuation for engine valve events are disclosed. The system may include a master piston hydraulically linked to a slave piston, and a dedicated cam operatively connected to the master piston. The slave piston may be disposed substantially perpendicular to the master piston in a common housing. The slave piston is adapted to actuate one or more engine valves. The slave piston may incorporate an optional valve seating assembly into its upper end. A trigger valve may be operatively connected to the master-slave hydraulic circuit to selectively release and add hydraulic fluid to the circuit.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Variable valve actuator with a pneumatic booster
InactiveUS20080251041A1Large initial opening forceSubstantial seating forceMachines/enginesLift valveValve actuatorHigh pressure
Actuators, and corresponding methods and systems for controlling such actuators, provide independent valve control with a large initial or opening force. In an exemplary embodiment, an actuator includes a driver further including a housing defining a longitudinal axis and first and second directions, an actuation mechanism capable of generating actuation force at least in the first direction, and a rod with one end operably connected with at least one part of the actuation mechanism and with the other end available for an operable connection with a load such as an engine valve; at least one return spring operably connected with the rod through a spring retainer assembly and biasing the rod in the second direction; and a pneumatic booster further including a pneumatic cylinder, a pneumatic piston operably connected with the rod through the spring retainer assembly and biasing the rod in the first direction, a charge mechanism providing a controlled fluid communication between the pneumatic cylinder and a high-pressure gas source, and a bleed mechanism providing a controlled fluid communication between the pneumatic cylinder to a low-pressure gas sink.
Owner:SKADERI GRUP LLC
Valve bridge having a centrally positioned hydraulic lash adjuster
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
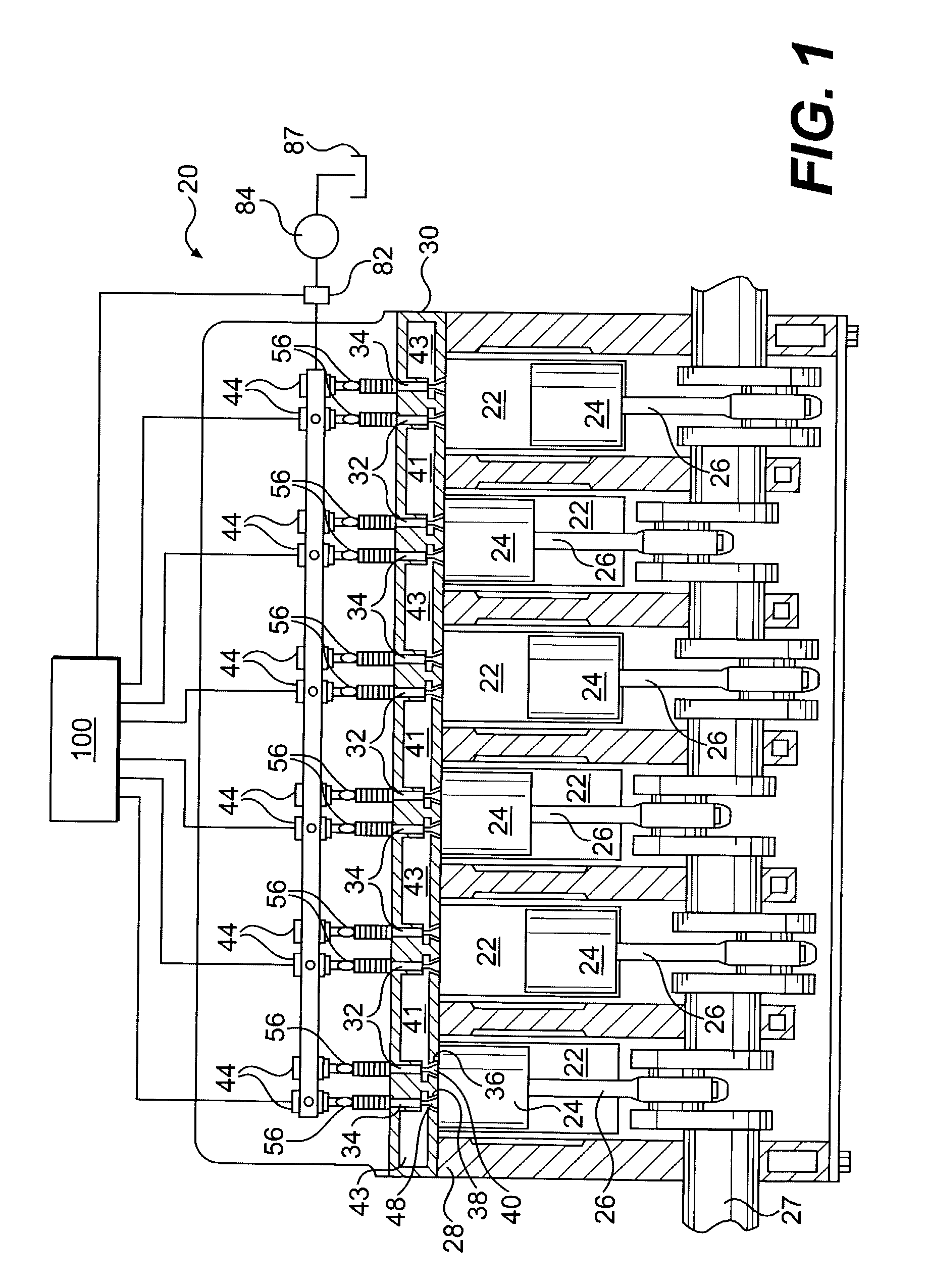
System for variable valvetrain actuation
InactiveUS20070125329A1Simple taskReduce in quantityValve drivesMachines/enginesCylinder headGasoline
An electromechanical VVA system for controlling the poppet valves in the cylinder head of an internal combustion engine. The system varies valve lift, duration, and phasing in a dependent manner for one or more banks of engine valves. A rocker subassembly for each valve or valve pair is pivotably disposed on a control shaft between the camshaft and the roller finger follower. The control shaft may be displaced about a pivot axis outside the control shaft to change the angular relationship of the rocker subassembly to the camshaft, thus changing the valve opening, closing, and lift. A plurality of control shafts for controlling all valvetrains in an engine bank defines a control shaft assembly. The angular positions of the individual control shafts may be tuned to optimize the valve timing of each cylinder. The system is applicable to the intake and exhaust camshafts of diesel and gasoline engines.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Variable valve actuation and engine braking
Systems and methods of actuating two engine valves associated with a common engine cylinder using one or more lost motion systems and one or more control valves are disclosed. The control valves are capable of selectively trapping hydraulic fluid in the lost motion systems for auxiliary engine valve actuations and selectively releasing the hydraulic fluid to default to cam controlled valve seating of the engine valves. The systems may provide a combination of main exhaust, compression release, exhaust gas recirculation and early exhaust valve opening in preferred embodiments.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
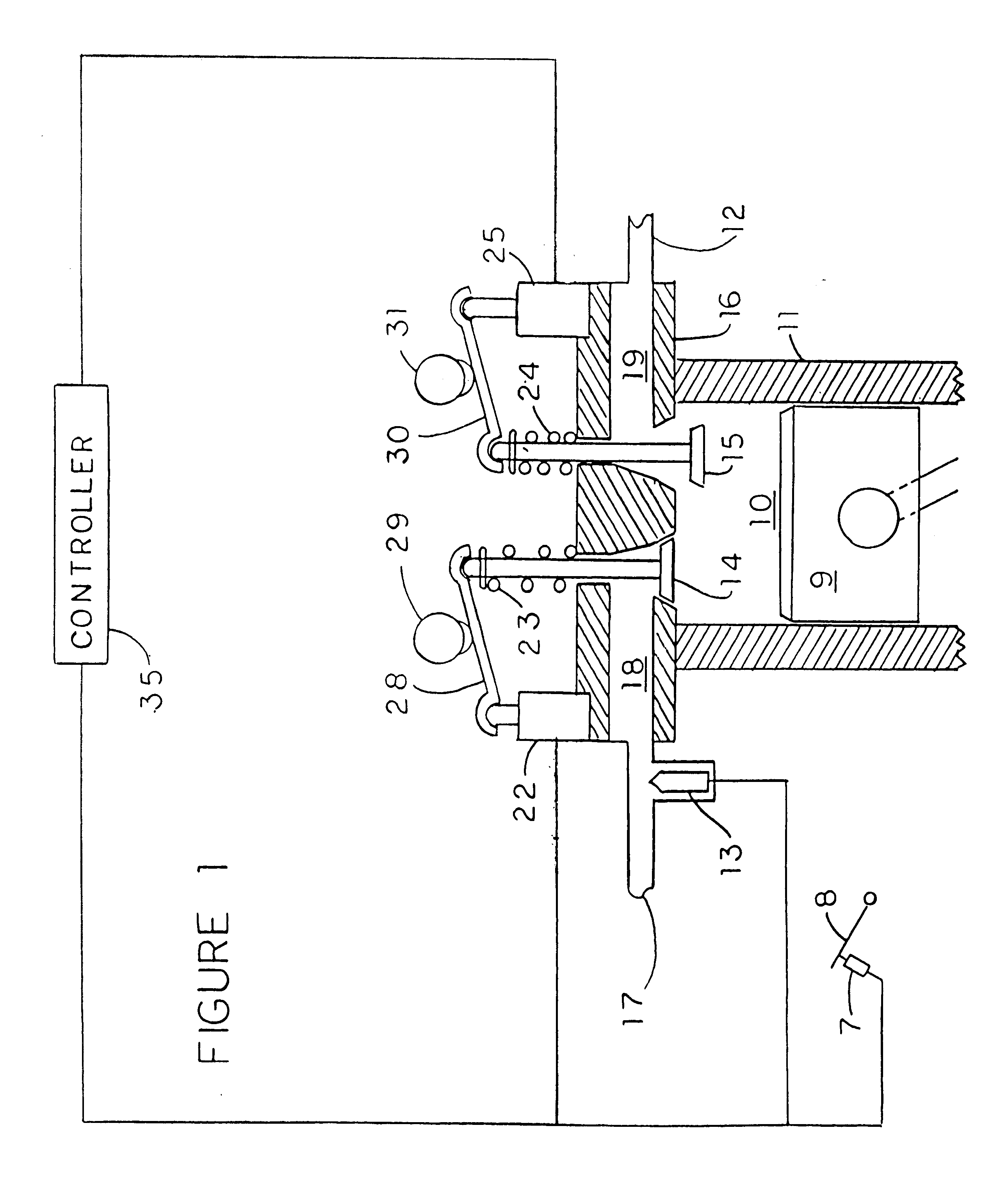
Engine valve actuation control and method
InactiveUS6966285B1Precise engine valve liftPrecise seating velocityOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsValve actuatorEngineering
A valve actuator control monitors engine valve trajectory, lift and seating velocity and varies the timing of internal feedback control channels to correct for engine valve positioning errors to achieve precise engine valve lift, closing timing and desired seating velocity.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Starting an engine with valves that may be deactivated
ActiveUS20050205037A1Reduce engine emissionsReduce vibrationHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlEngine valveInternal combustion engine
A system and method to control engine valve timing to during the start of an internal combustion engine. Valves that may be deactivated are controlled in a manner to reduce hydrocarbon emissions during the start of an internal combustion engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
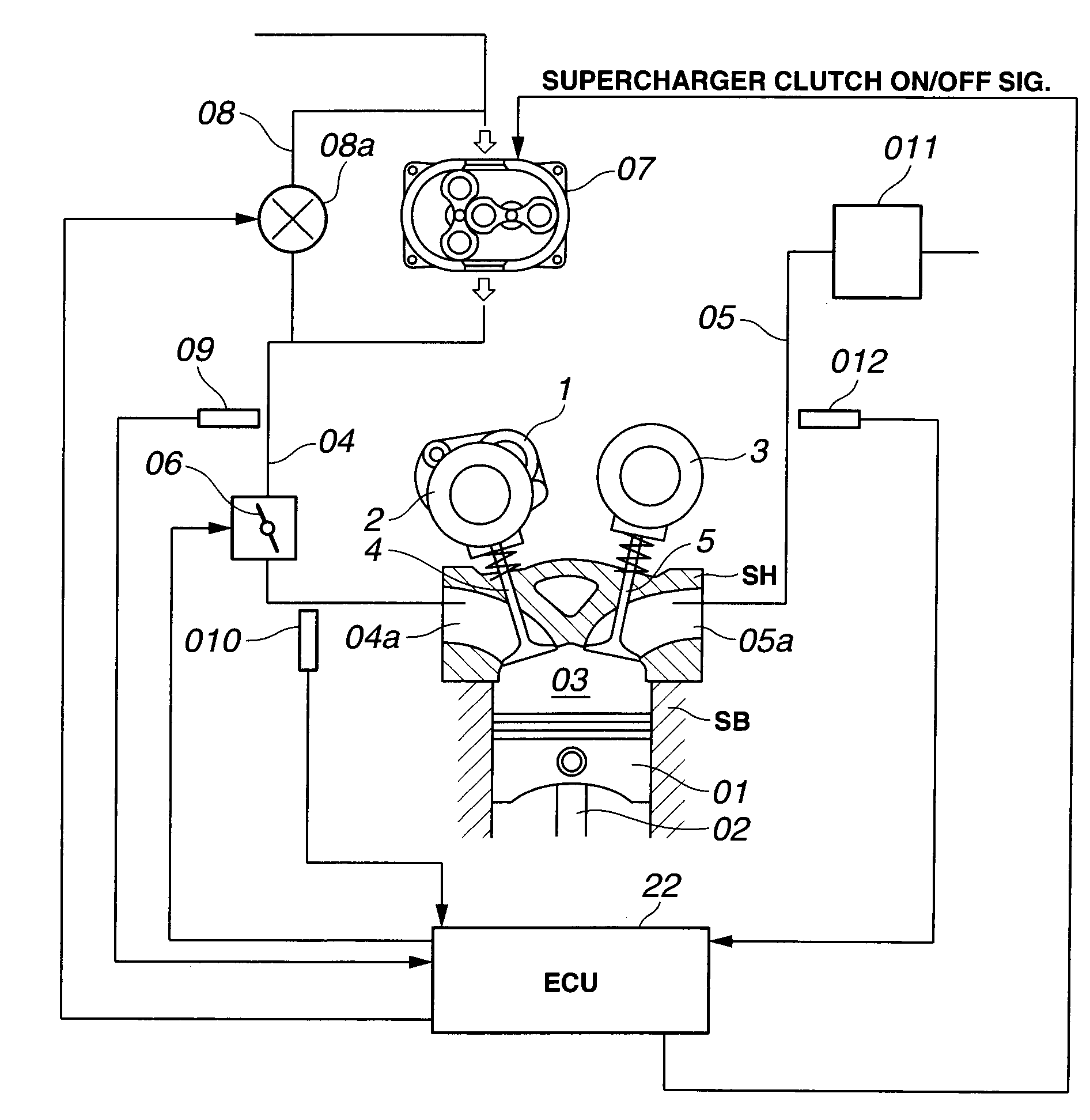
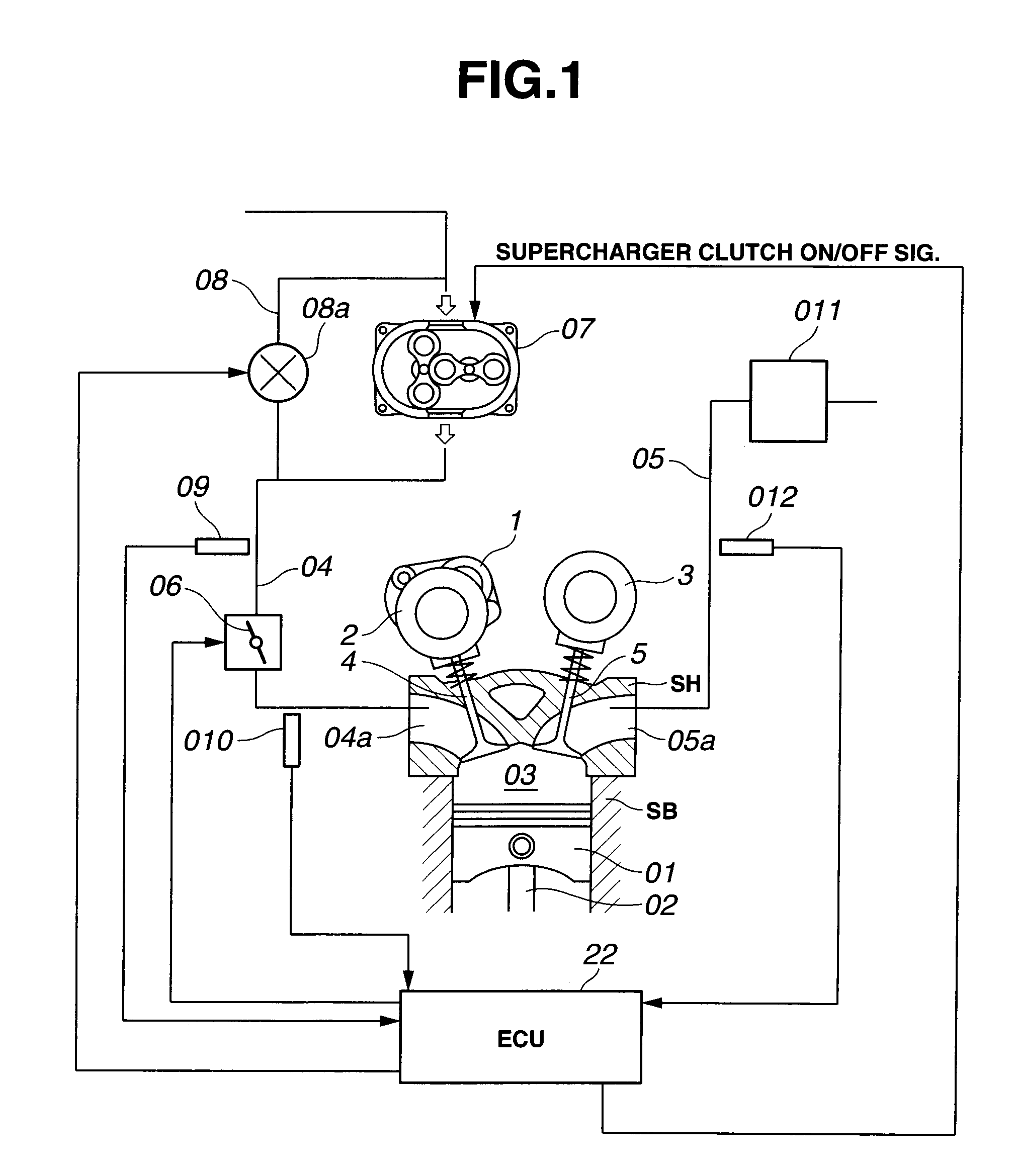
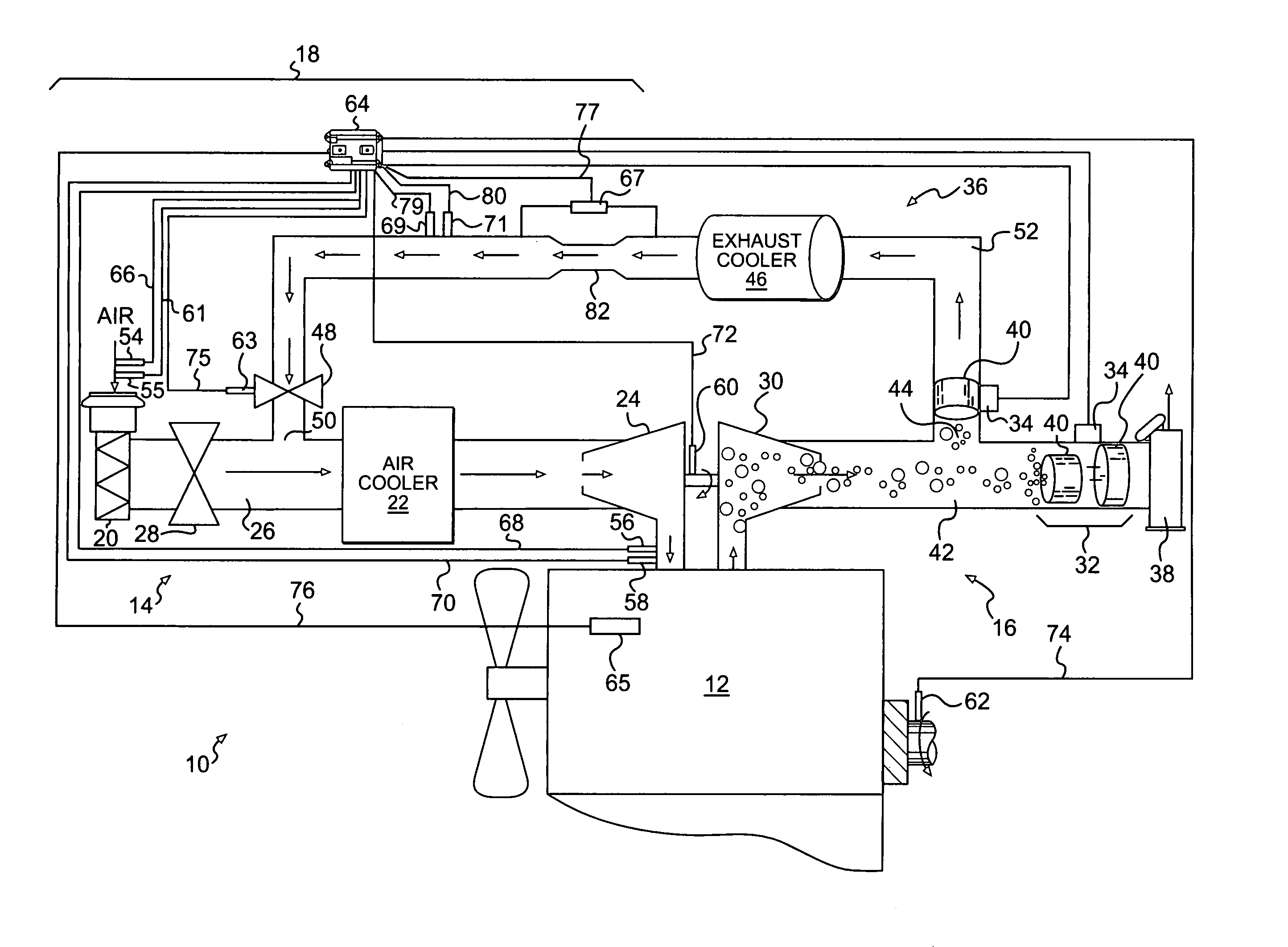
Control system and method for estimating turbocharger performance
A control system for estimating the performance of a compressor is disclosed. The control system has a compressor fluidly connected to an inlet manifold of a power source. The control system also has a power source speed sensor to provide an indication of a rotational speed of the power source, an inlet pressure sensor to provide an indication of a pressure of a fluid within the inlet manifold, an inlet temperature sensor to provide an indication of a temperature of the fluid within the inlet manifold, an atmospheric pressure sensor to provide an indication of an atmospheric pressure, and a control module in communication with each of the sensors. The control module is configured to monitor an engine valve opening duration and an exhaust gas recirculation valve position, and estimate a compressor inlet pressure based on the provided indications, the monitored duration, and the monitored position.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Engine valve actuation system and method
InactiveUS20050051119A1Prevent returnInternal combustion piston enginesNon-mechanical valveEngineeringActuator
An engine valve actuation system is provided. The system includes an engine valve moveable between a closed position and an open position. A spring is operatively connected to the engine valve to bias the engine valve towards the closed position. An actuator is operatively connected to the engine valve and is operable to selectively engage the engine valve to prevent the engine valve from returning to the closed position and to release the engine valve to allow the engine valve to return to the closed position. A sensor is configured to provide information related to the operation of the actuator. A controller is configured to transmit a signal to the actuator to engage the engine valve to prevent the engine valve from returning to the closed position and to release the engine valve to the allow the engine valve to return to the closed position. The controller is further configured to receive a signal from said sensor and to identify when the actuator fails to engage the engine valve in response to the transmitted signal or when the actuator fails to release the engine valve.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Combined engine braking and positive power engine lost motion valve actuation system
A system for actuating one or more engine valves for positive power operation and engine braking operation is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, an exhaust valve bridge and intake valve bridge each receive valve actuations from two sets of rocker arms. Each valve bridge includes a sliding pin for actuating a single engine valve and an outer plunger disposed in the center of the valve bridge to actuate two engine valves through the bridge. The outer plunger of each valve bridge may be selectively locked to its valve bridge to provide positive power valve actuation. During engine braking, application of hydraulic pressure to the outer plungers may cause the respective valve bridges and outer plungers to unlock so that all engine braking valve actuations are provided from a rocker arm acting on one engine valve through the sliding pin.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
System and method for modifying engine valve lift
Devices for modifying engine valve lift during an engine valve event are disclosed. In one embodiment, the device comprises: a housing having a hydraulic fluid dump port formed therein; a sleeve slidably disposed in a bore formed in the housing, the sleeve having a cavity formed therein; a piston slidably disposed in the sleeve cavity; and a clip passage formed in the piston, the clip passage in selective communication with the dump port.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com