Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
566results about "Cam-followers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
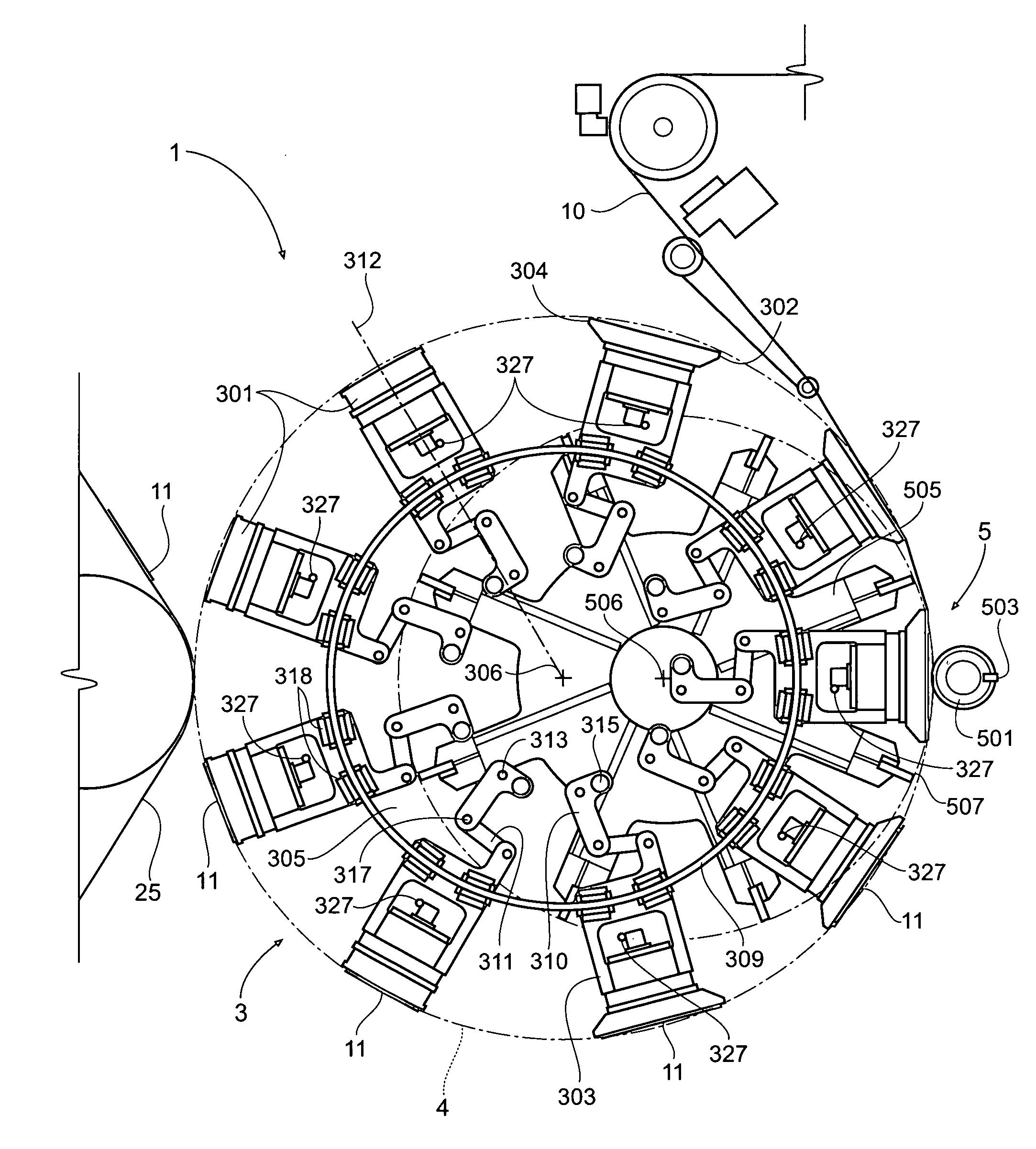
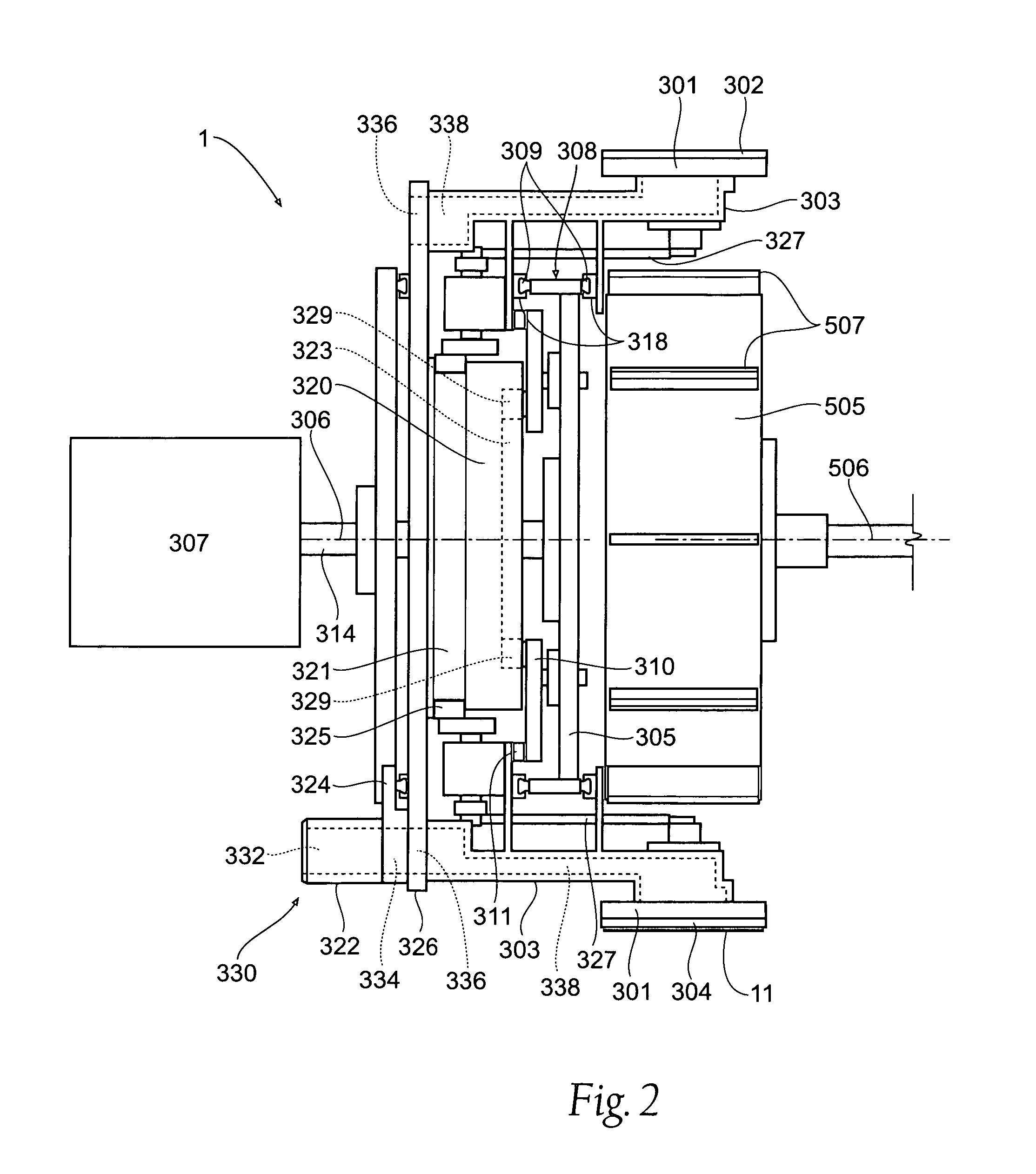
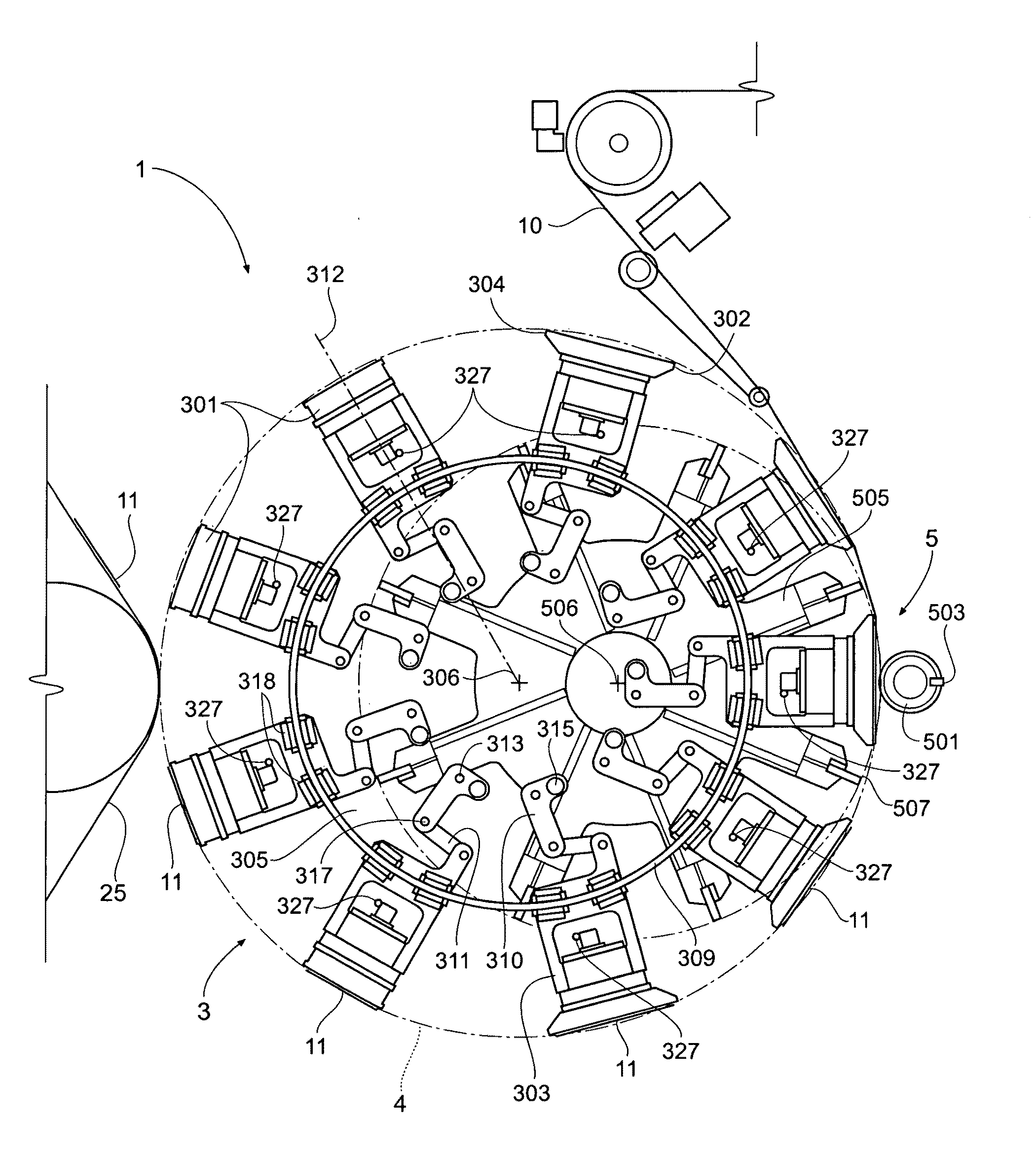
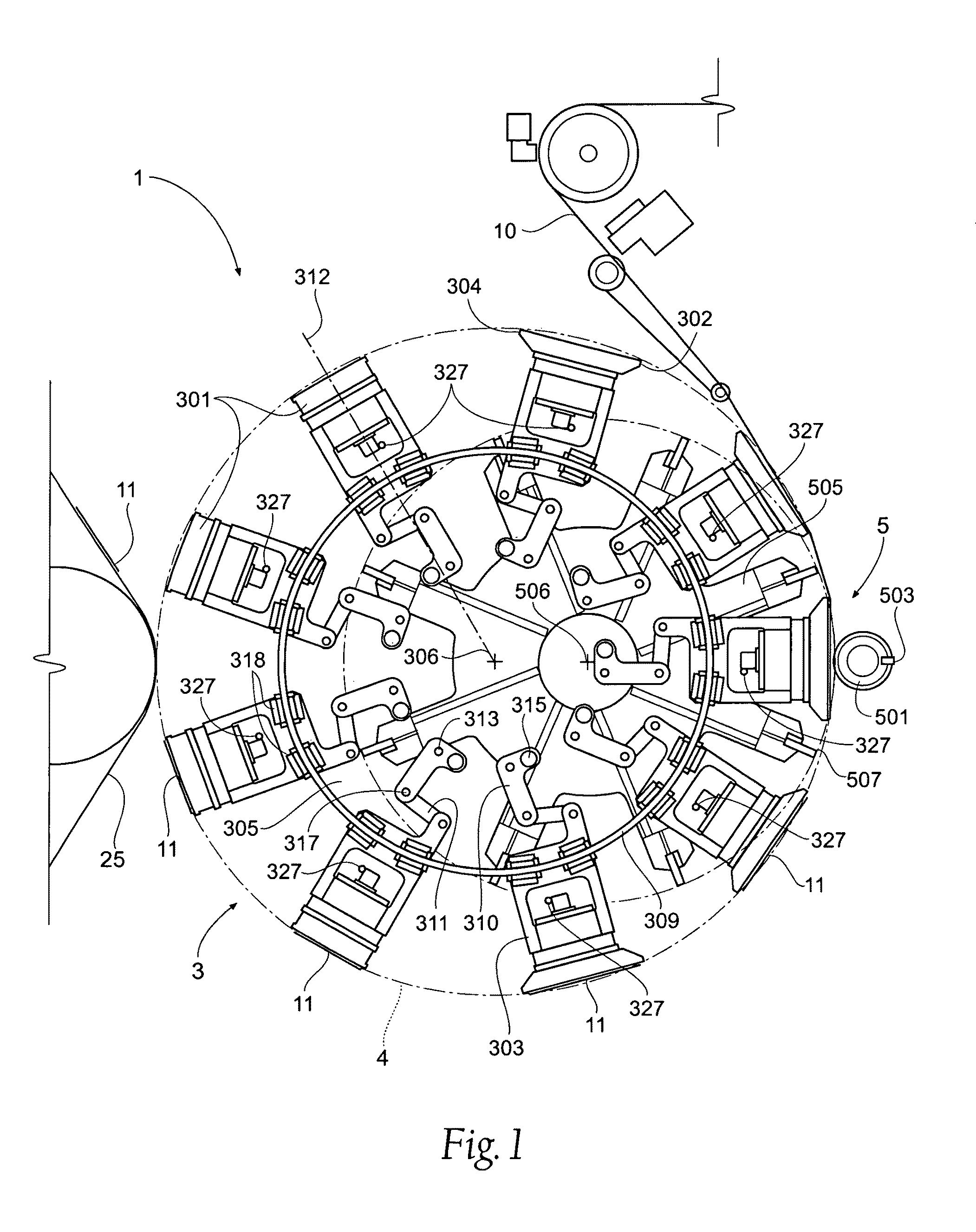
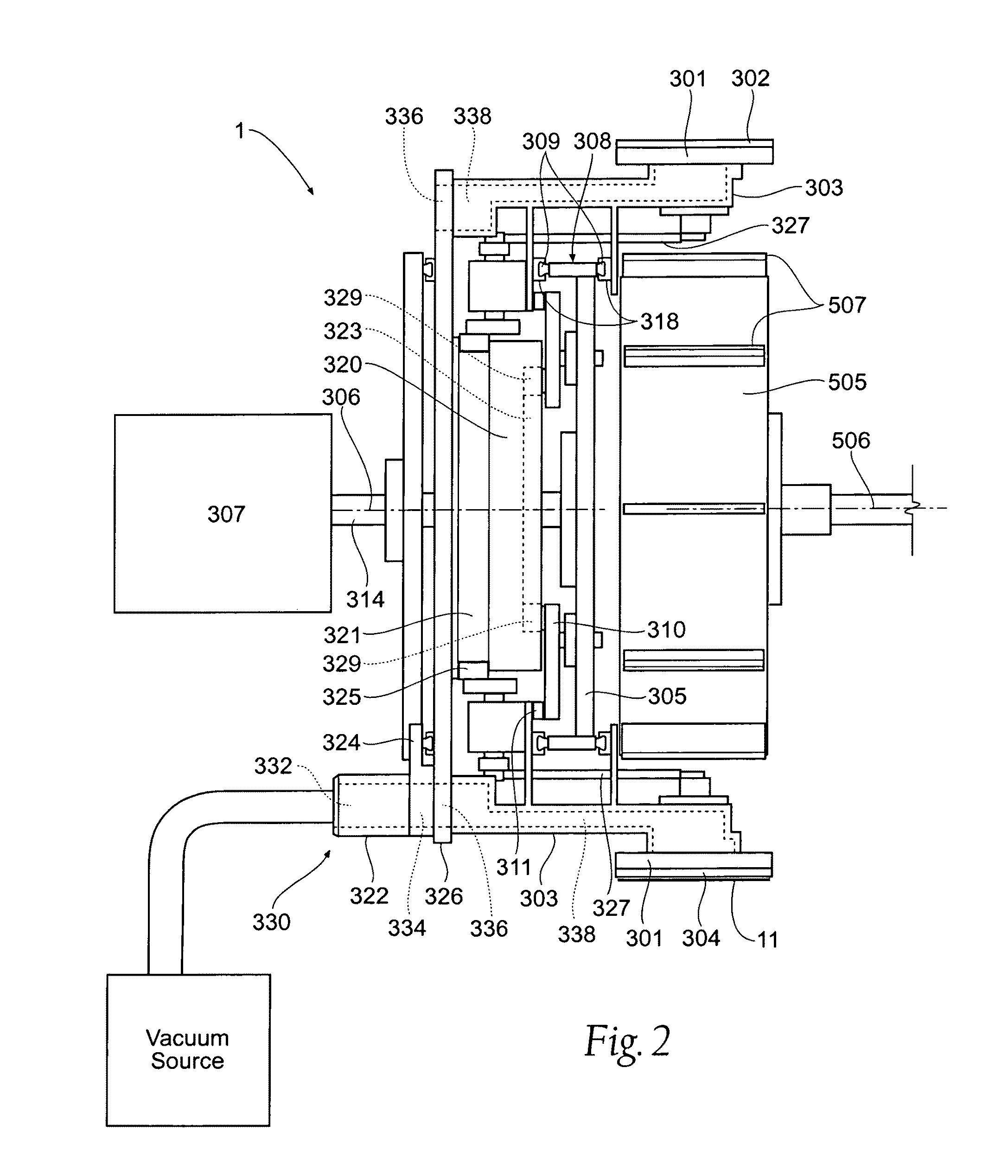
Single transfer insert placement method and apparatus
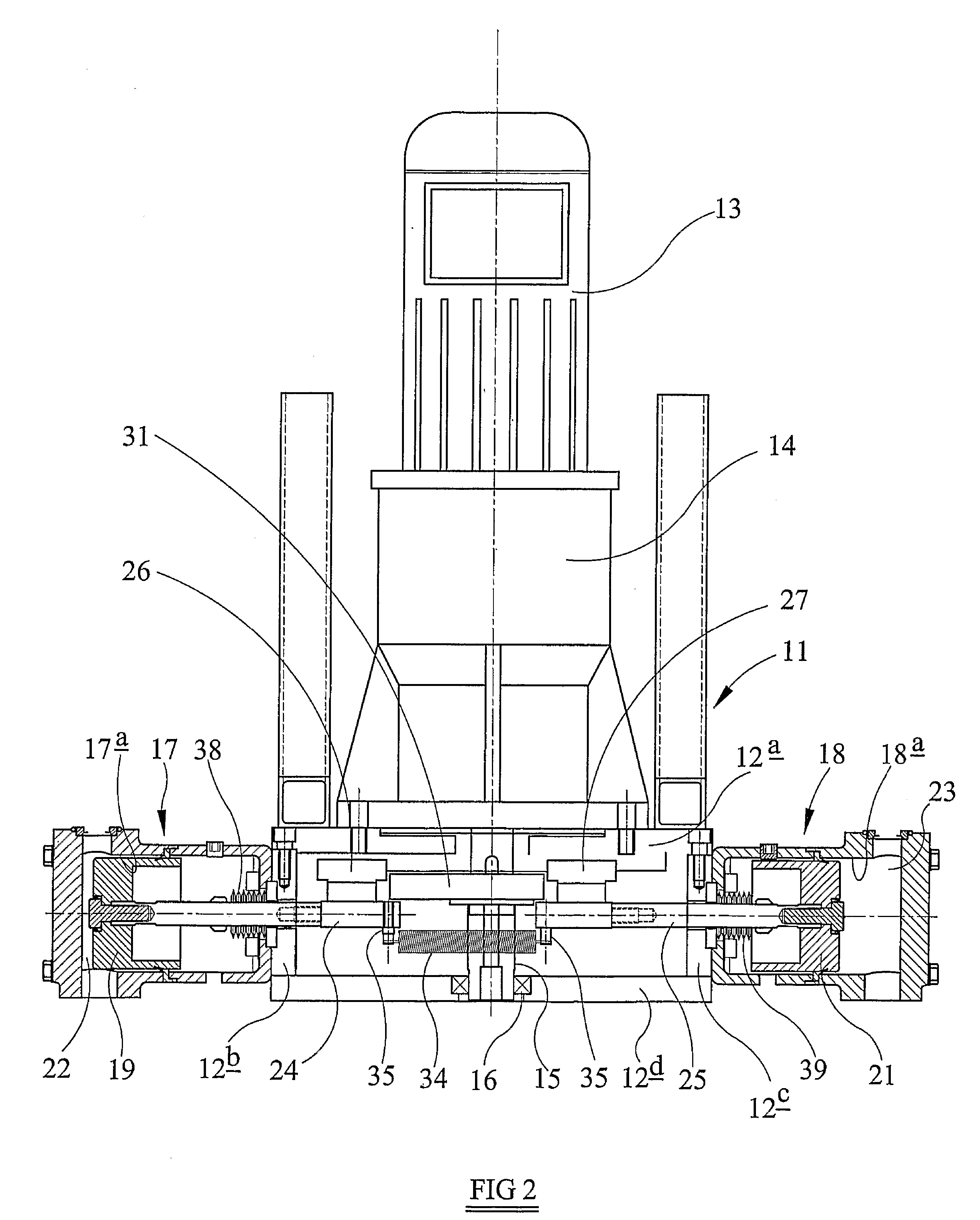
ActiveUS20080196564A1Cam-followersWrapper folding/bending apparatusMechanical engineeringPlacement method
Owner:CURT G JOA
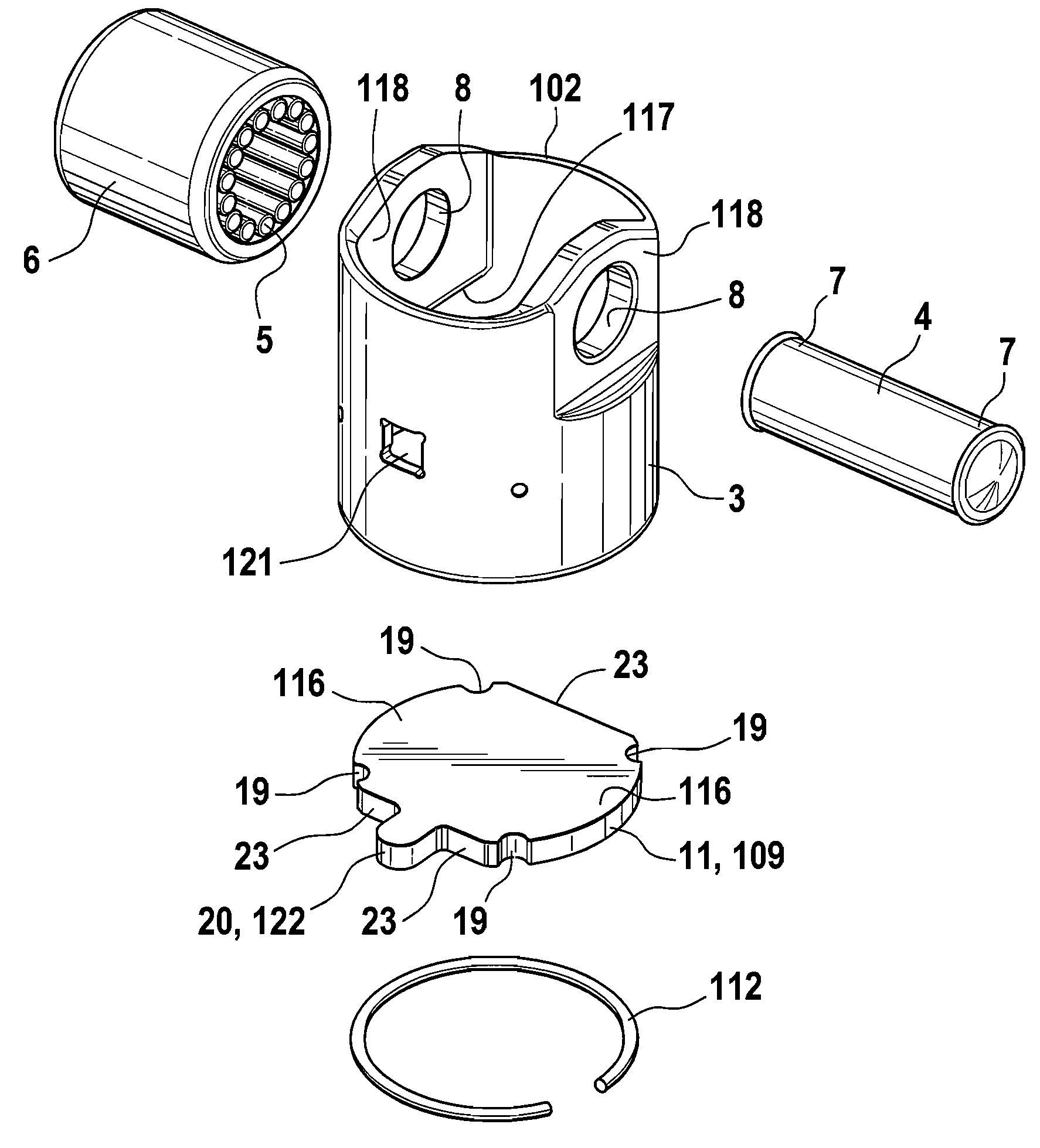
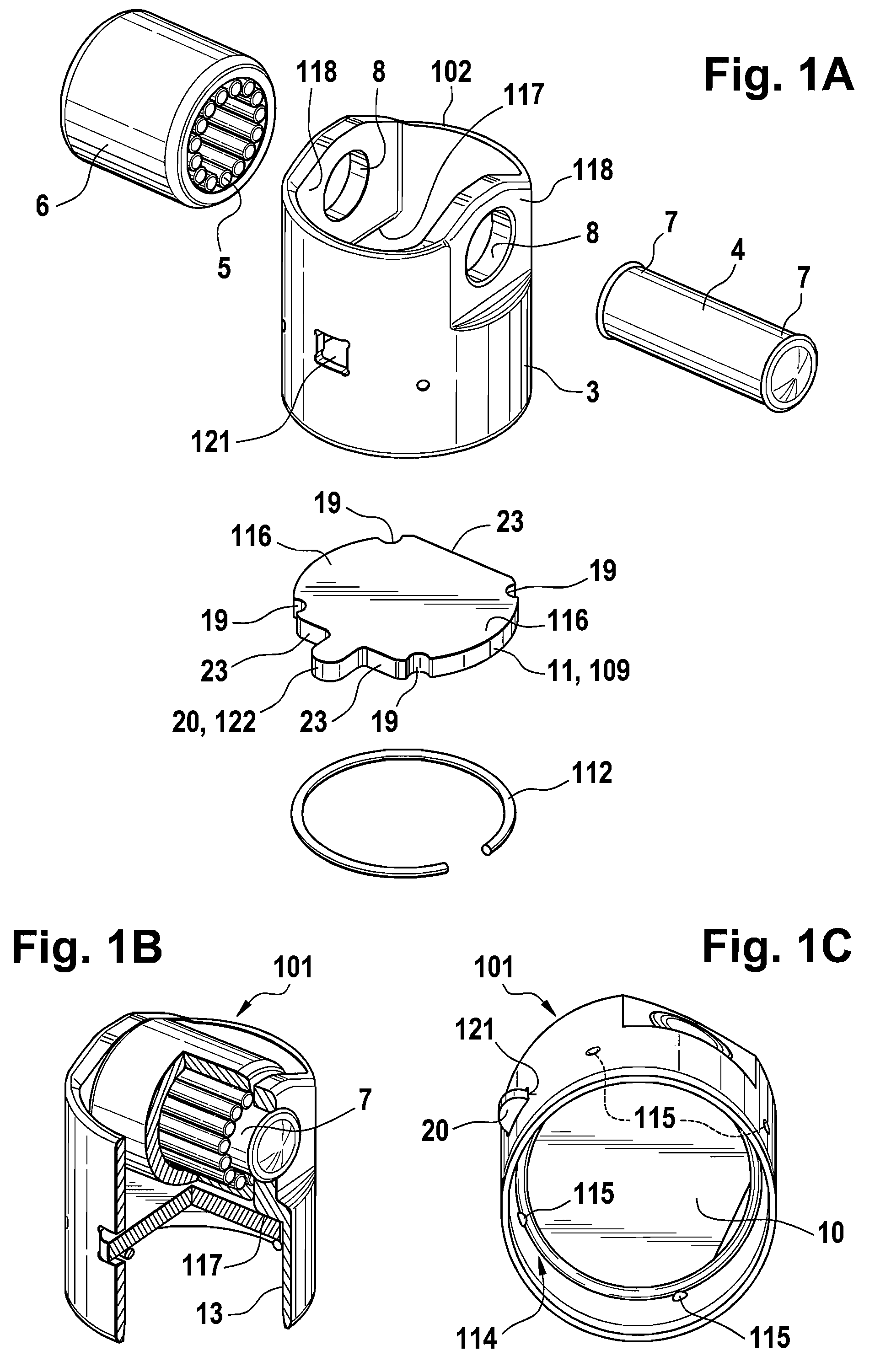
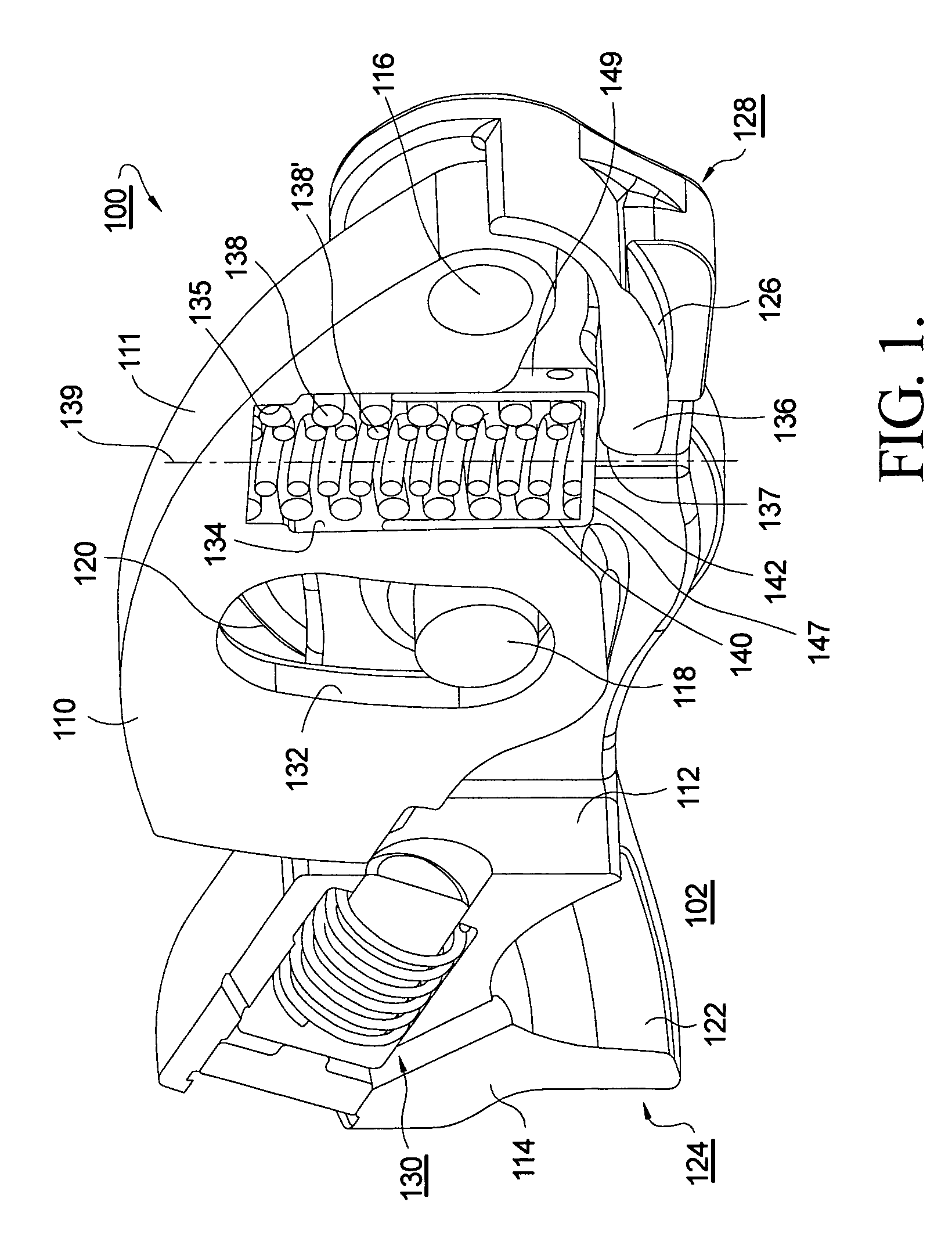
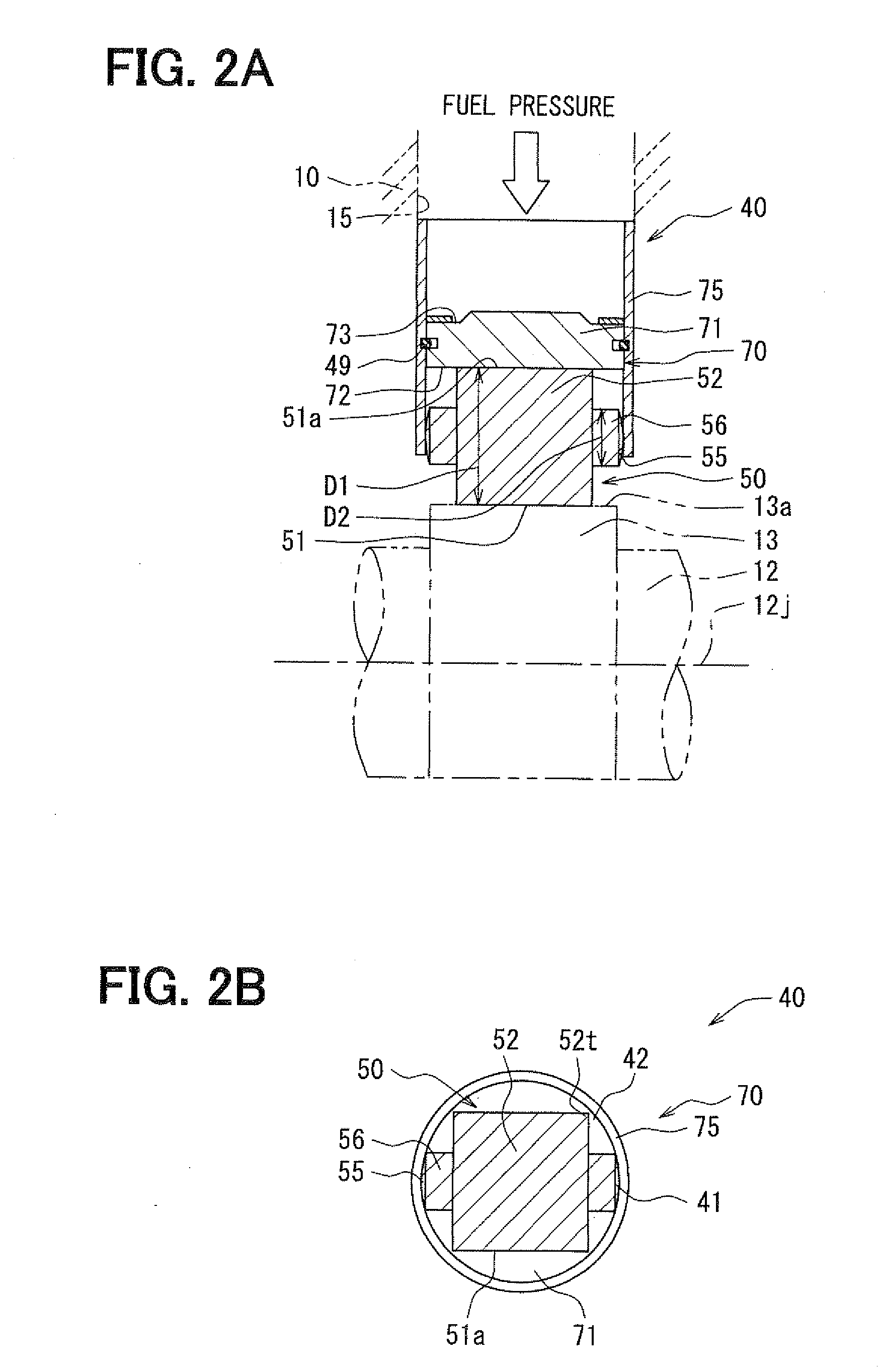
Mechanical tappet in particular for a fuel pump of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7793583B2High potential lightweight constructionSave on high costsValve arrangementsEngine sealsInternal combustion engineTappet
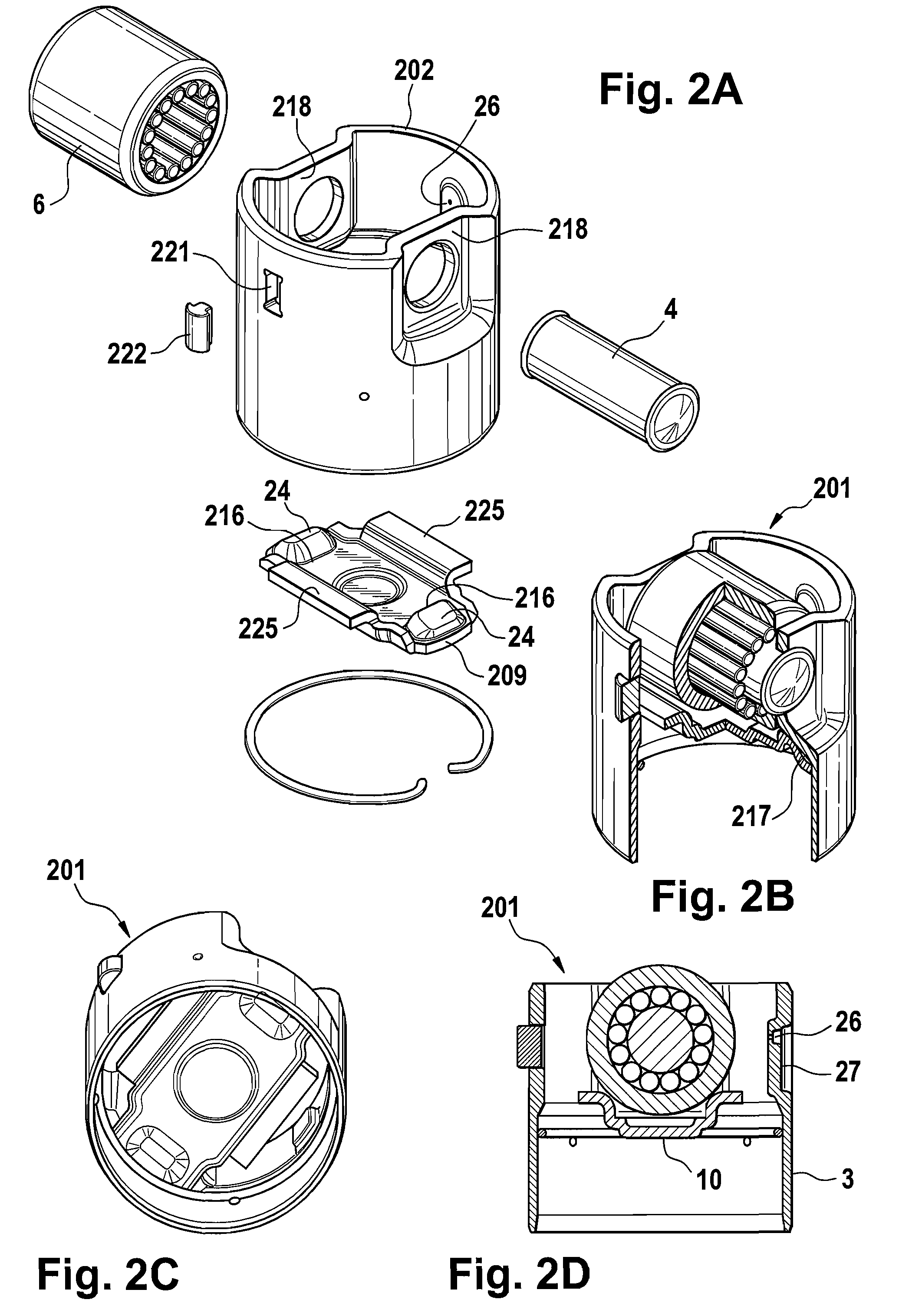
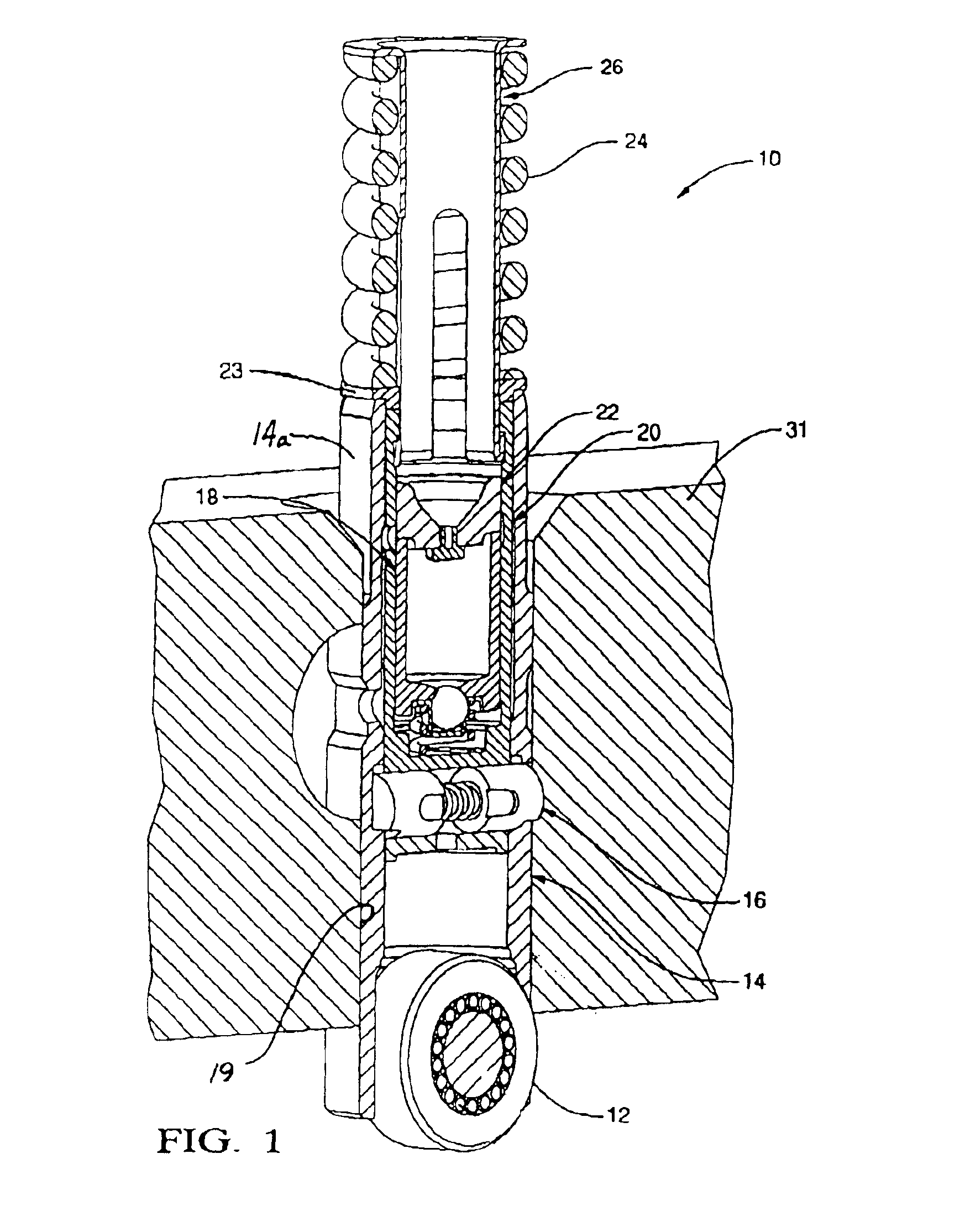
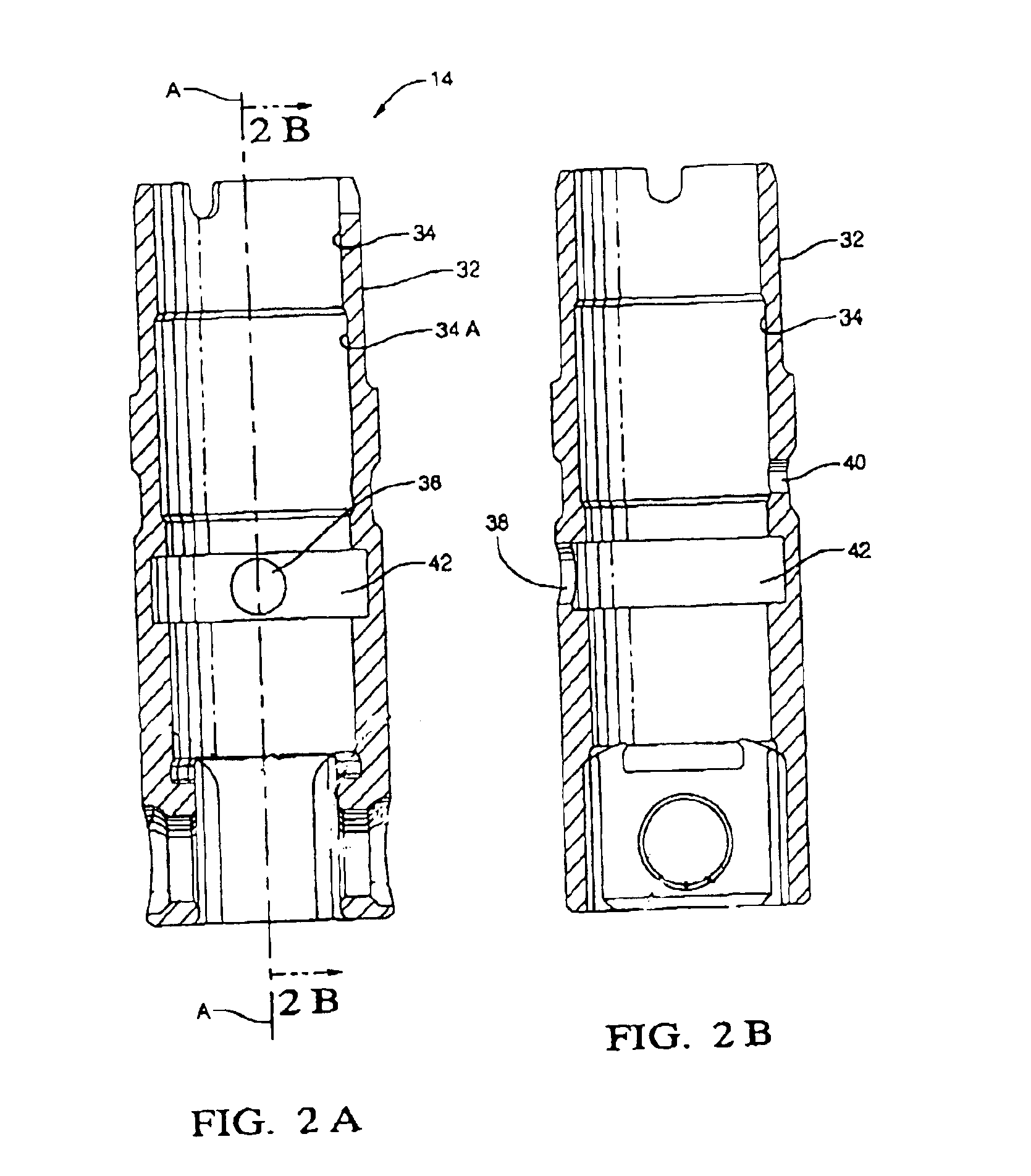
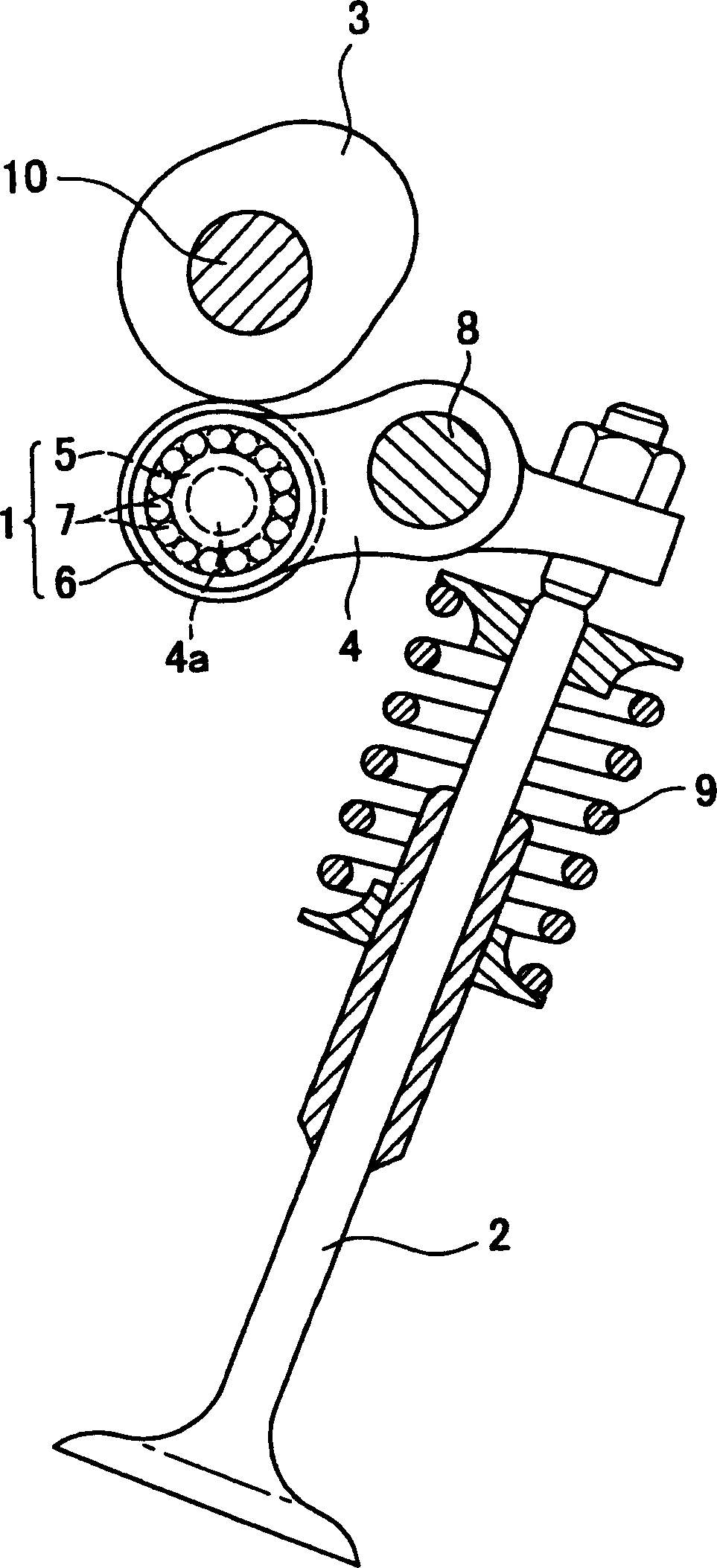
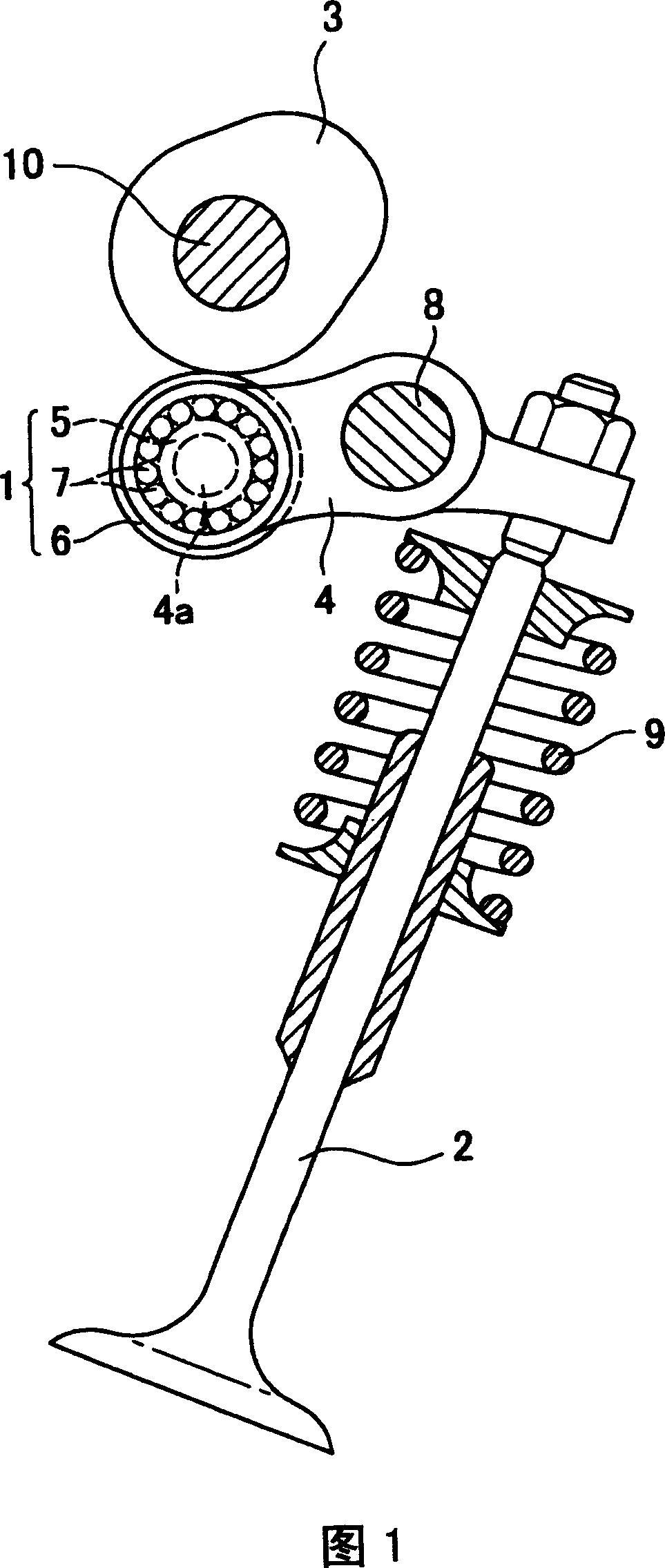
A mechanical tappet (101, 201, 301, 401, 501, 601, 701, 801, 901, 1001) is provided, in particular for actuating the lifting of a pump piston (39) of a fuel pump of an internal combustion engine, with a sleeve-shaped tappet housing (102, 202, 302, 402, 502, 602, 702, 902, 1002) constructed as a shaped sheet-metal part and with a driving roller (6) supported so that it can rotate. Here, a bolt (4) supports the driving roller so that it is centered, and end sections (7) of the bolt projecting from the driving roller are supported in bolt eyes (8) of the tappet housing.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Single transfer insert placement method and apparatus
ActiveUS7975584B2Cam-followersWrapper folding/bending apparatusPlacement methodMechanical engineering
Owner:CURT G JOA
Ice maker control system and method
Provided is an ice maker that includes a mold including a plurality of cavities for receiving water to be frozen into ice pieces, a driver operatively connected to the mold for adjusting a position of the mold to a plurality of different locations during an ice making cycle, and a controller. A limit switch is located at a plurality of different positions along a range of travel of the mold to be actuated and transmit a signal indicative of the mold's arrival at the different locations. The mold can travel along path including first portion having a first axis of rotation and a substantially vertical portion, and can be driven by a motor with a drive shaft rotatable about a single axis of rotation. The motor can drive both the mold and a bail arm, and the mold can be leveled upon reaching a predetermined location. The ice maker can perform a Dry Cycle in response to detecting an anomaly during ice making.
Owner:ELECTROLUX HOME PROD CORP NV
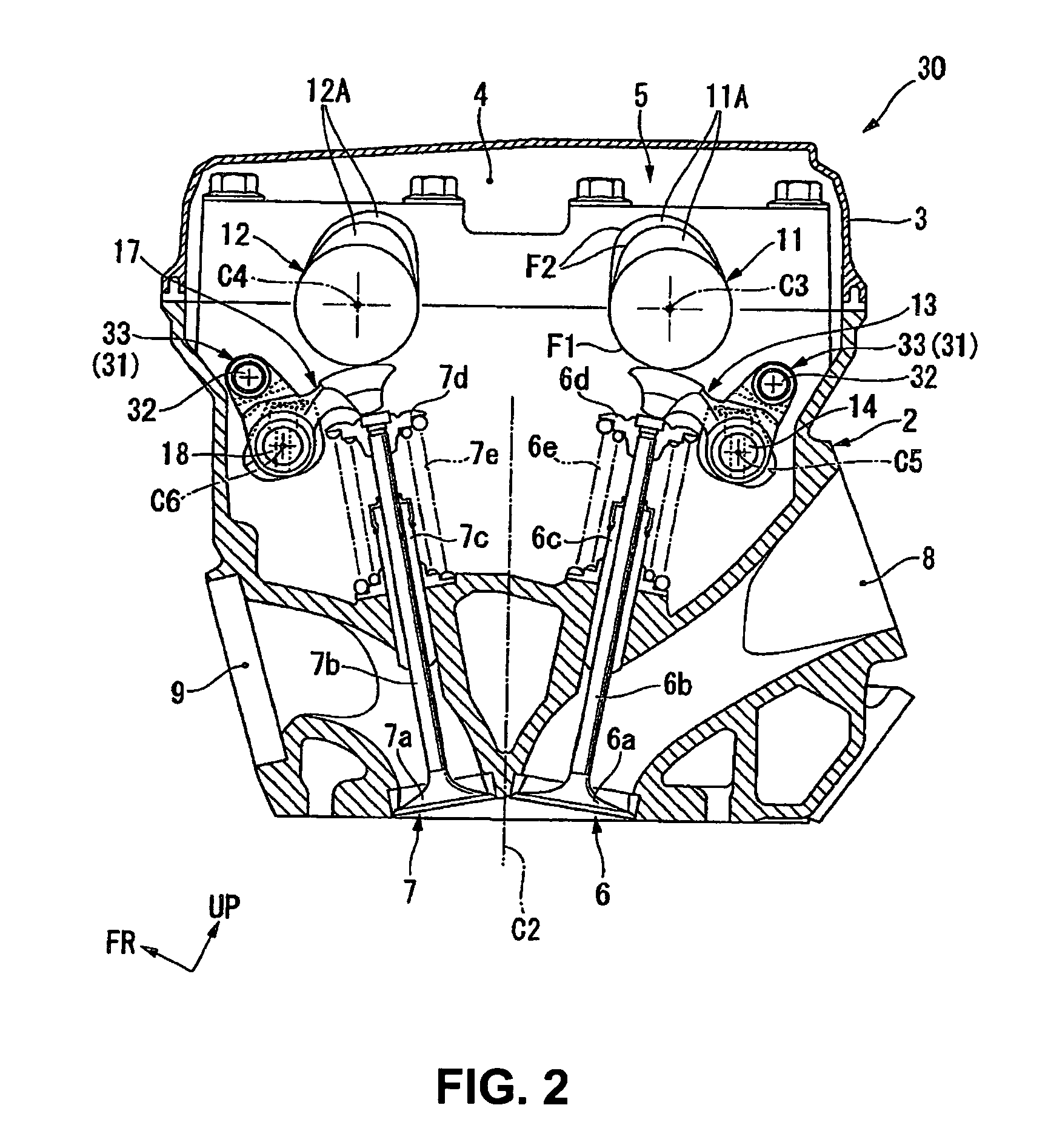
Two-step roller finger follower
A two-step roller finger follower having a high-lift follower portion that rotates relative to a low-lift follower portion about a pivot shaft, including a lost-motion compression spring disposed in a linear bore formed in the high-lift portion to exert force against an curved pad on the back side of the valve pallet of the low-lift portion. The spring is retained and guided in its bore by a spring retainer having a planar bottom for engaging the curved pad. Preferably the retainer is a cup positioned in the spring bore such that the stroke of the cup is limited, to prevent leak-down of the associated hydraulic lash adjuster. Driving the spring by a linear-acting retainer in a linear bore causes the spring to be compressed linearly, resulting in a highly stable and predictable spring rate.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Variable displacement reciprocating pump
A variable displacement reciprocating pump with pumping rate that is adjustable from zero to maximum stroke while the pump is running. Stroke is varied by changing relative position of pairs of eccentric inner and outer cams that drive the pump's plungers. The pump's input drive shaft drives two gear trains: a first gear train that turns the inner cams and a second gear train that turns the outer cams. These cams normally revolve together with no relative motion occurring between them. A rotary actuator is positioned in the first gear train to rotate the inner cams relative to the outer cams and thereby changes the pump's stroke. A computerized system of sensors and control valves allows the pump to be automatically controlled or limited to any one or combination of desired output flow, pressure and horsepower.
Owner:SERVA CORP
Piston pump with cam follower arrangement
A pump primarily for liquid paint includes first and second pistons reciprocable rectilinearly in respective first and second cylinders. The first and second pistons are moved relative to their respective pistons by operation of an A. C. electric motor the rotary output shaft of which is coupled to the first and second pistons by a constant velocity cam and a cam follower mechanism converting rotary motion of the output shaft into reciprocatory motion of the first and second pistons 180° out of phase with one another.
Owner:CARLISLE FLUID TECH UK LTD
Valve bridge with integrated lost motion system
A system and method of actuating one or more engine valves is disclosed. In one embodiment, the system comprises: a valve train element; a rocker arm pivotally mounted on a shaft and adapted to rotate between a first position and a second position, the rocker arm selectively receiving motion from the valve train element; a valve bridge disposed above the one or more engine valves; and a lost motion system disposed in the valve bridge.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Slidably movable member and method of producing same
InactiveUS6844068B1Improve wear resistanceLow friction propertiesValve arrangementsCam-followersHydrogenNitrogen
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Valve guide for rocker arm assembly
ActiveUS20050016480A1Shorten assembly timeLow costValve arrangementsCam-followersControl systemCylinder head
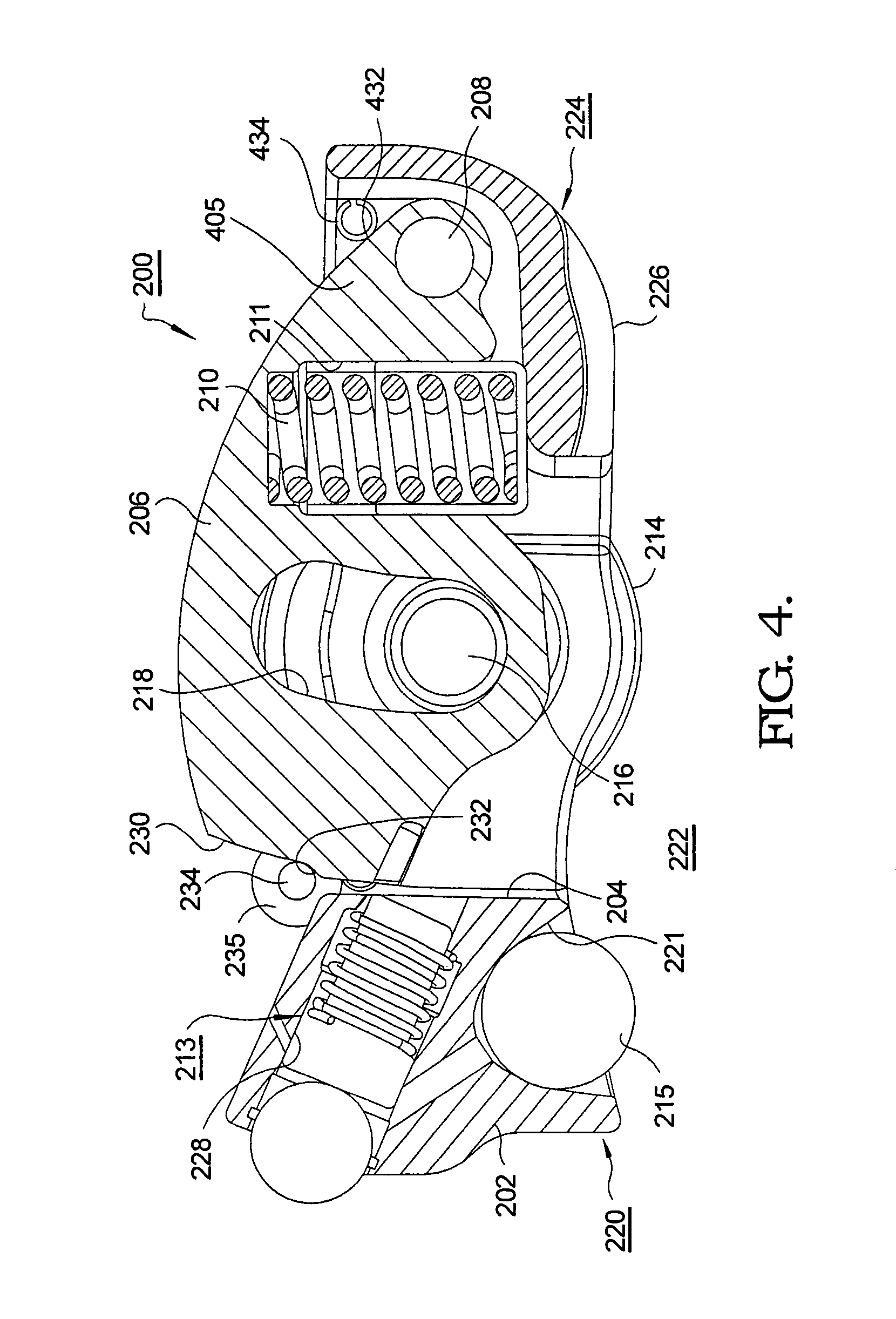
A rocker arm assembly (55) for a valve control system in an internal combustion engine including a cylinder head (11), and a poppet valve (15). The valve control system comprises an HLA (41) having a ball plunger portion (39). The assembly (55) comprises a rocker arm (57) including axially spaced apart side walls (59,61) and a portion (63) for engagement with the ball plunger (39). The rocker arm assembly (55) further comprises a cam follower (29) disposed about a mounting shaft (31) extending into shaft openings (65) defined by the side walls (59,61), and a pin member (67) defining a valve pad for engagement with a stem tip portion (17), the pin member extending into pin openings (71) defined by the side walls. The assembly (55) includes a clip member (75) including spaced apart clip side walls (77,79) disposed on the outside of the side walls of the rocker arm (57). A connection portion (81) interconnects the clip side walls to restrain axial movement of the mounting shaft (31) and of the pin member (67). The clip side walls (77,79) include retention portions (85,87) engaging the adjacent side walls (59,61) of the rocker arm and extending therebetween and include terminal portions (91) adjacent the pin member (67) to limit rotation of the pin member about its axis, relative to said rocker arm (57).
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Rocker arm
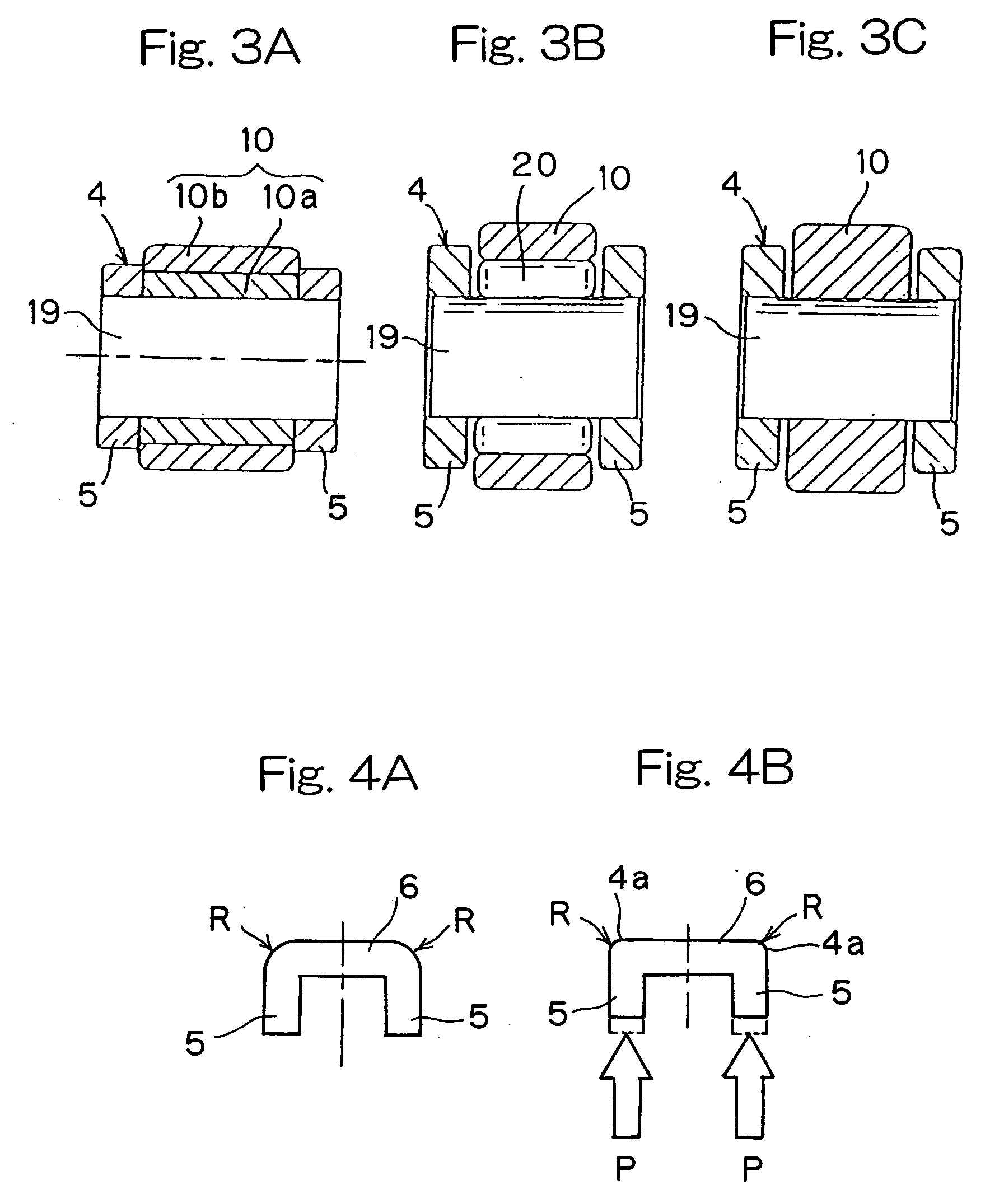
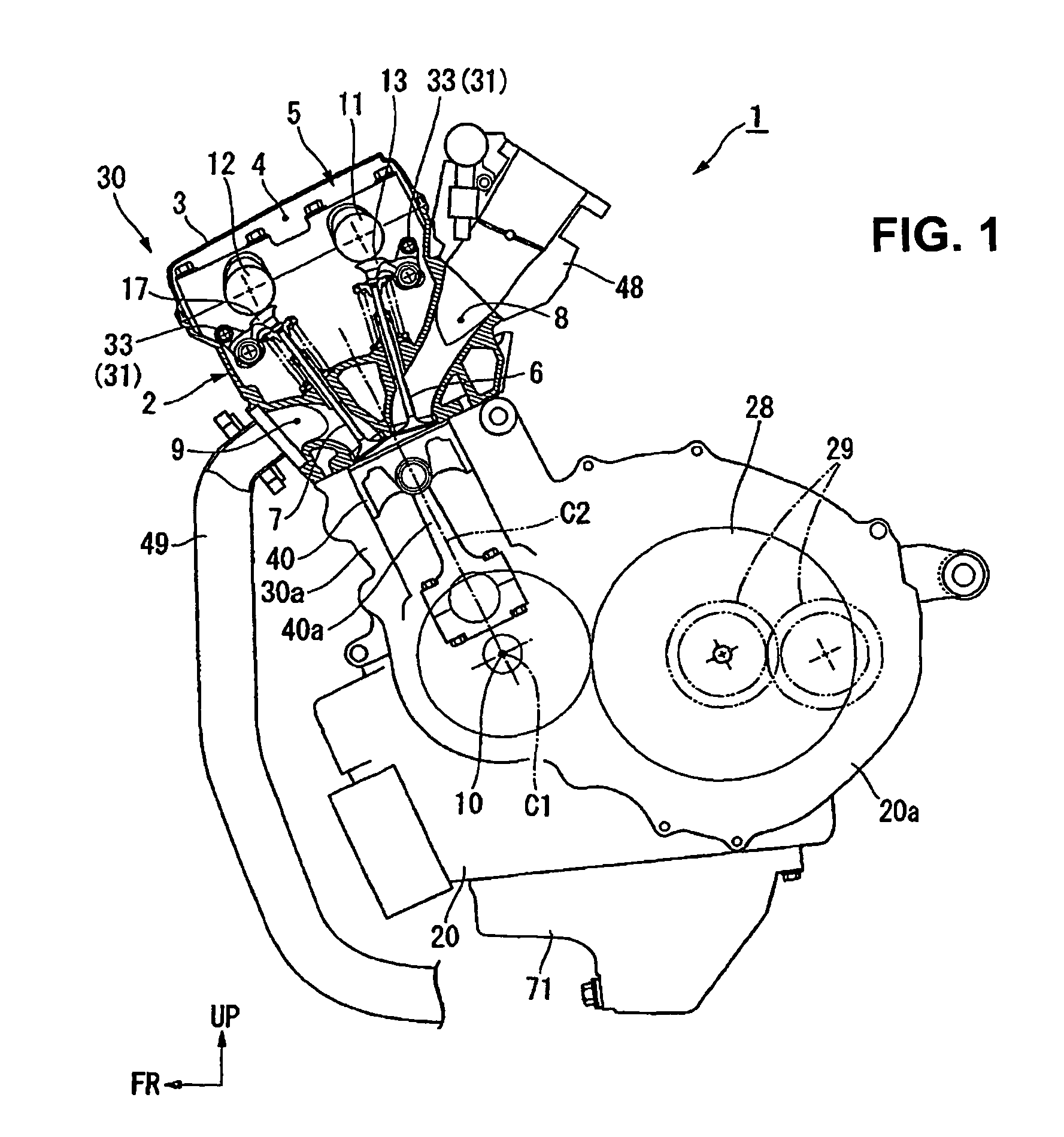
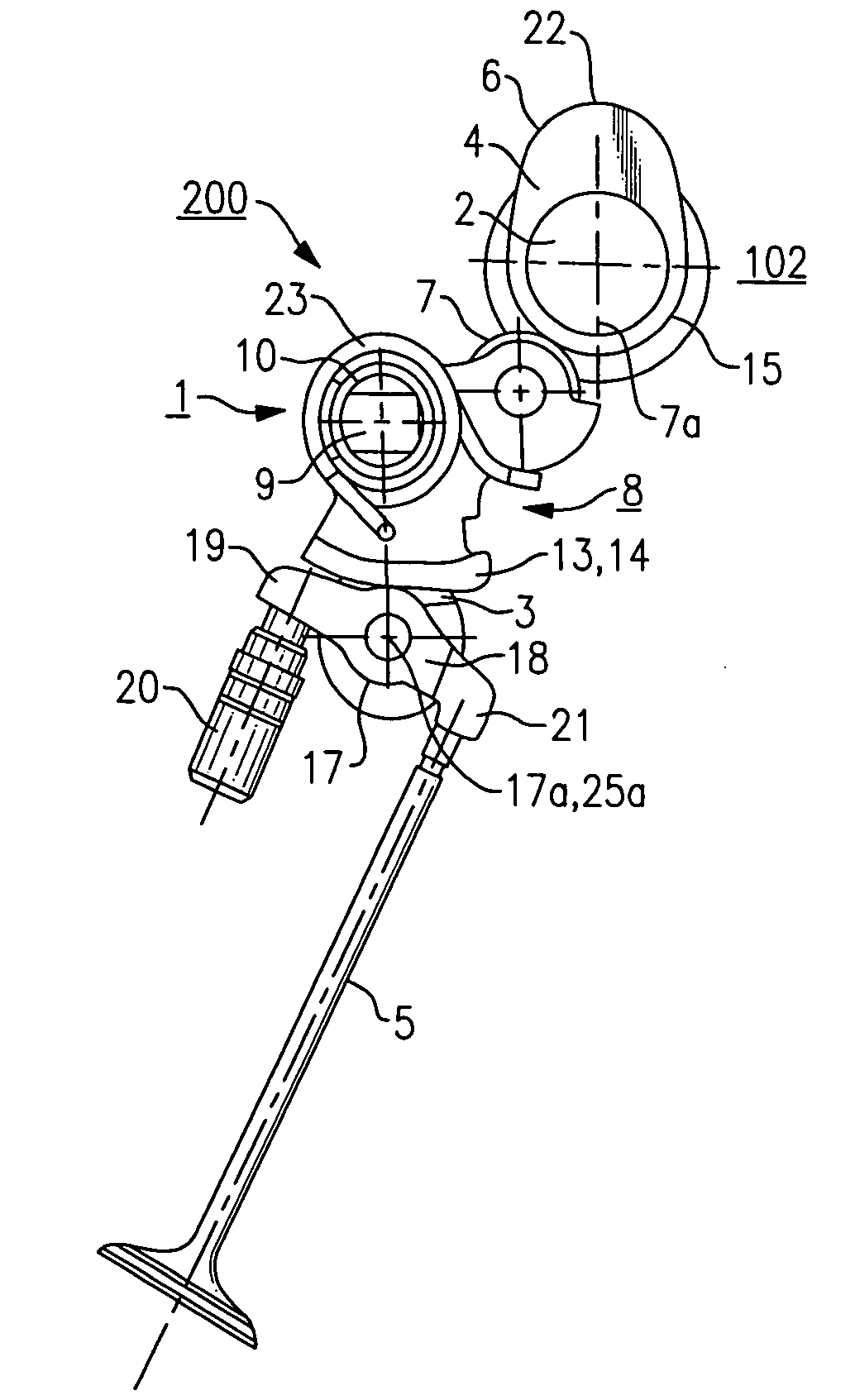
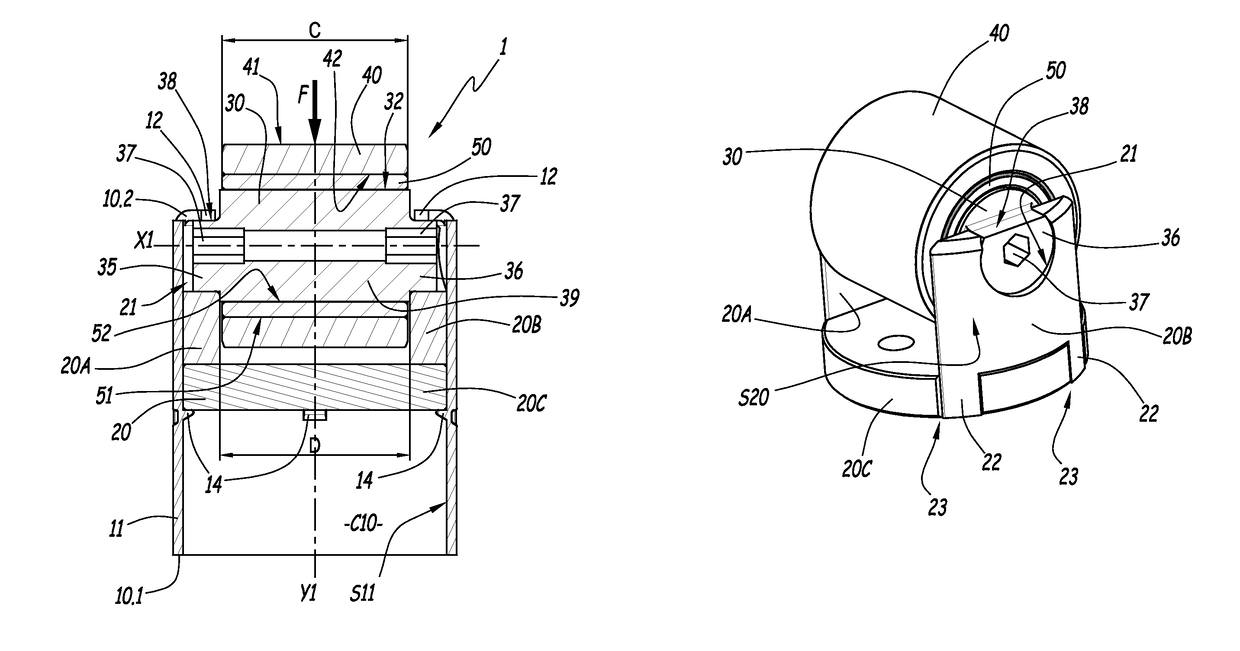
There is provided a rocker arm of a kind in which even though the rocker arm is manufactured by the use of a press working technique the arm width can be minimized while the flat outer surface region of a required width is secured on an outer surface of the connecting wall, thereby contributing to reduction in size and weight of the rocker arm. This rocker arm 1 is capable of being driven by a cam 2 for selectively opening and closing a valve 3 of an internal combustion engine. This rocker arm 1 includes an arm body 4 prepared by bending a single plate material to represent a generally inverted U-shaped section including opposite side walls 5 and a connecting wall 6 bridging between the opposite side walls 5. A roller 10 engageable with the cam 2 is rotatably mounted on a portion of the arm body 4 generally intermediate of the length thereof. A valve drive element 8 is mounted on one end of the arm body 4 for driving the valve 4, while an end portion of the connecting wall 6 adjacent the other end of the arm body 4 is formed with an internally helically threaded hole 12 for threadingly receiving therein an externally helically threaded pivot member 7. An outer chamfered corner delimited between an outer surface of the connecting wall 6 and an outer surface of each of the opposite side walls and formed by bending is deformed to represent a plastically deformed portion 4a so formed by means of a plastic deformation technique that the outer chamfered corner represents a small radius of curvature R.
Owner:NTN CORP
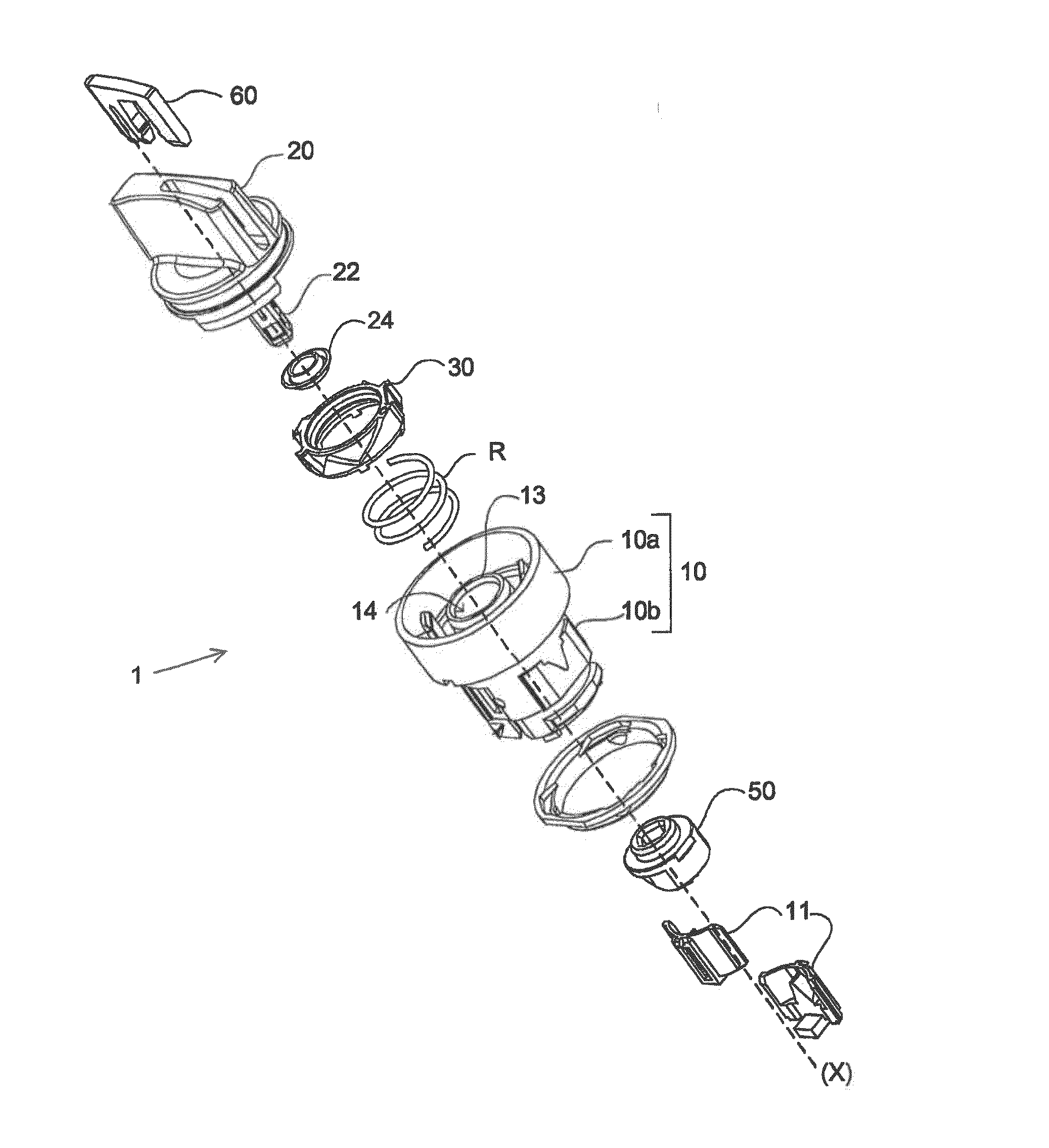
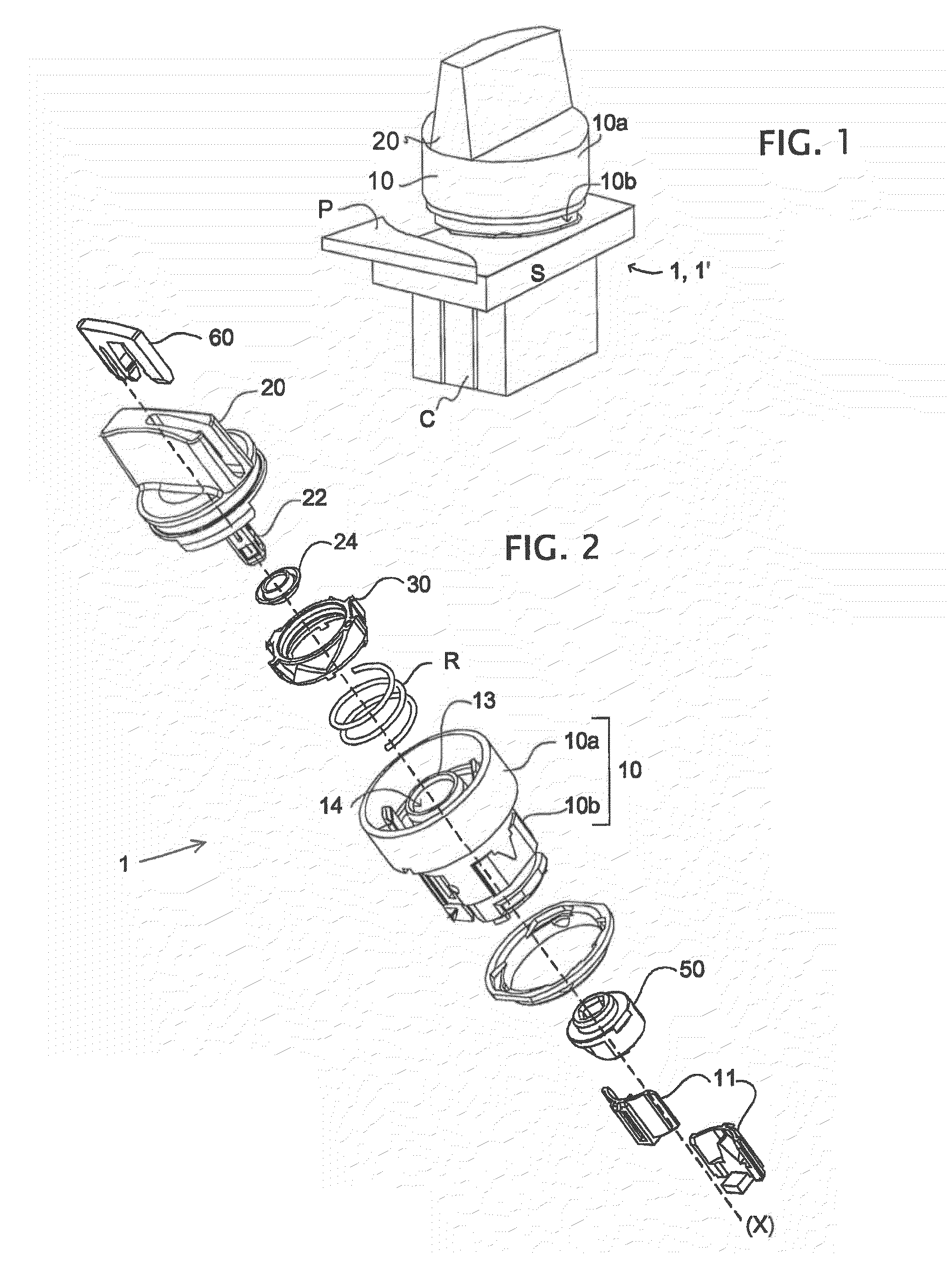
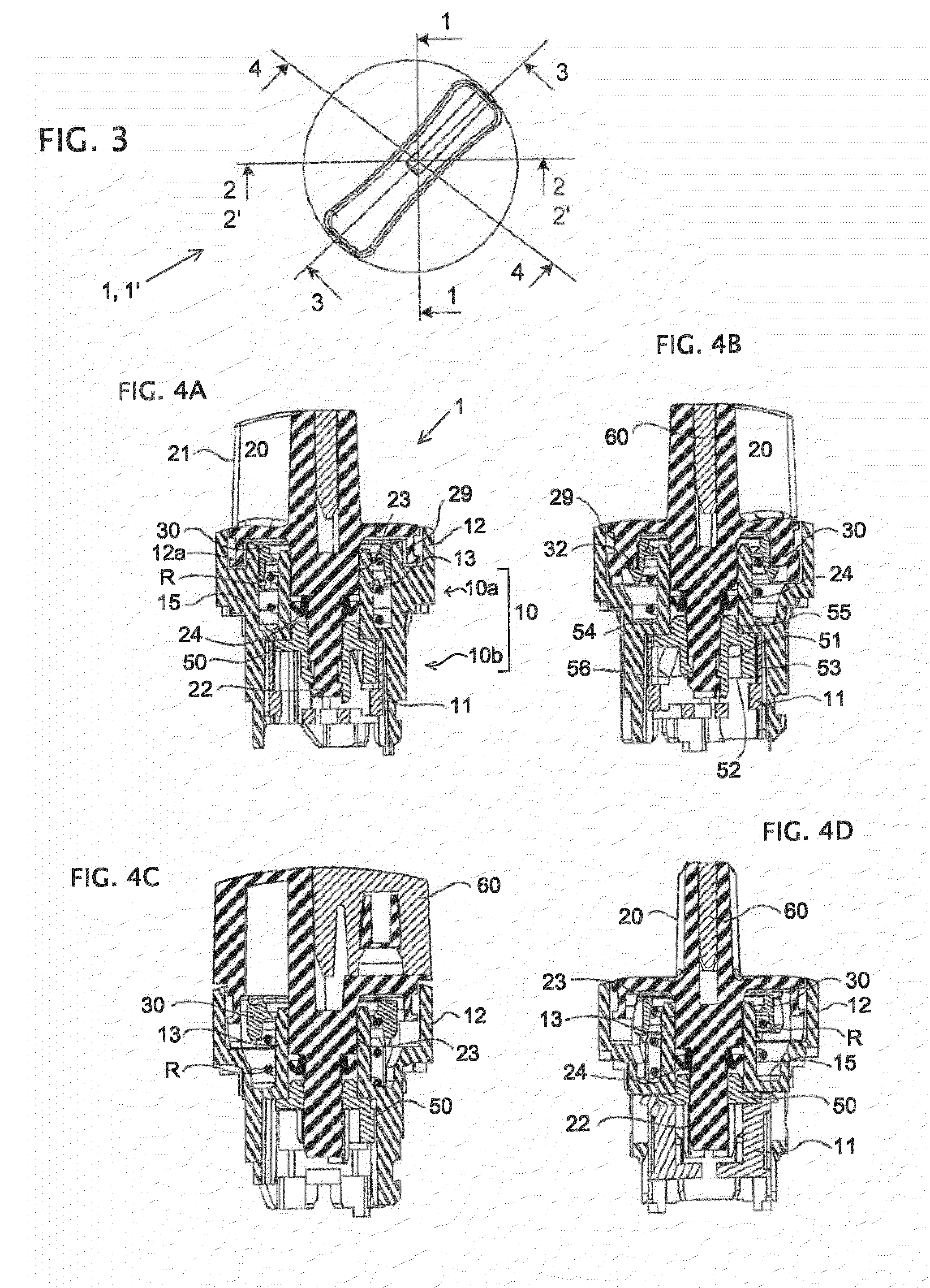
Rotary knob for electrical system
A rotary knob for an electrical system includes a body containing a rotary maneuvering member which actuates a cam-driving part and bears one or more electrical units. A cup is defined between an outer cylindrical flange of the body and an inner cylindrical sleeve, and contains a spring either of a helical type for urging a sliding ring separate from the driving part, or of a torsion type to return the maneuvering member. The ring provides a sensitivity function. The cylindrical sleeve defines in a central opening thereof a centering seat of the shank of the maneuvering member.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Cam follower roller device
The present invention proposes a cam follower roller device, in particular for a fuel injection pump of an internal combustion engine, including a tappet with a sleeve having an opening for partially accommodating a roller, a roller mounted rotatably in the sleeve and having a portion which protrudes axially from the opening of the sleeve provided to cooperate with a cam, and a roller support body housed in the sleeve. The roller includes a cylindrical spindle and a cylindrical body, the ends of the spindle projecting from the lateral faces of the body.It is proposed that the support body includes supports open towards the opening of the sleeve and supporting the ends of the spindle.
Owner:AB SKF
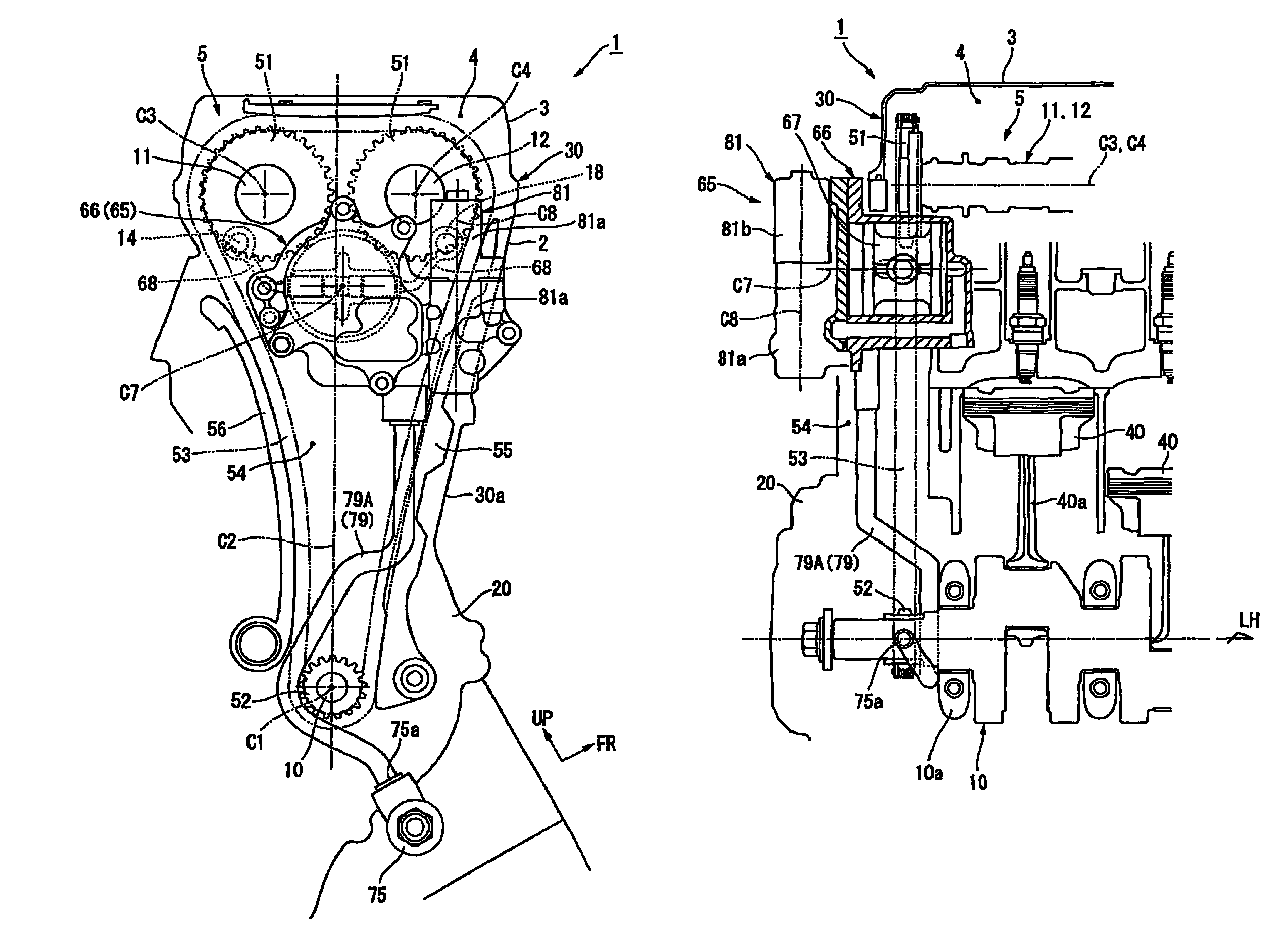
Internal combustion engine having a hydraulically-actuated variable valve control system, and motorcycle incorporating same
InactiveUS7975662B2Small sizeEfficient disposalControlling membersCam-followersHydraulic cylinderVehicle frame
An internal combustion engine is equipped with a variable valve controlling system, in which the single actuator is disposed in a cylinder head on one side where one ends of the rocker-arm shafts are disposed, while enabling the single actuator to activate the rocker arms irrespective of the arrangement of the rocker-arm shafts. In the internal combustion engine, a hydraulic cylinder of a hydraulic actuator is disposed so as to transverse a timing chamber. Operation elements extend respectively from sidewalls of a plunger in the hydraulic cylinder, and activate respective rocker-arm shafts. In a motorcycle on which the engine is mounted, a frame member of a vehicle frame is disposed outside the hydraulic actuator.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Systems and methods for providing a dynamically adjustable reciprocating fluid dispenser
Systems and methods for providing a dynamically adjustable, synchronously and / or asynchronously reciprocating fluid dispenser. A pump drive motor is coupled to the reciprocating fluid pump to actuate a pump shaft within a pump cylinder, wherein the pump shaft includes a duct that allows fluid to selectively pass thereby within the pump cylinder. As the pump shaft rotates within the pump cylinder, fluid is allowed to enter into a pump bore defined by a portion of the pump cylinder through a pump ingress port. As the pump shaft rotates, it blocks the pump ingress port. Further rotation allows the duct to allow the fluid in the pump bore to be dispensed through a pump egress port. An adjustment motor is coupled to an adjustment mechanism, which selectively adjusts the volume of the pump bore. A controller is coupled to the adjustment motor to dynamically control the adjustment motor, to cause the adjustment mechanism to be precisely and repeatably modified, and / or to control the particular waveform. As such, the volume of fluid dispensed is extremely accurate, repeatable, and dynamic.
Owner:ZAXIS
Variable lost motion valve actuator and method
A lost motion engine valve actuation system and method of actuating an engine valve are disclosed. The system may comprise a valve train element, a pivoting lever, a control piston, and a hydraulic circuit. The pivoting lever may include a first end for contacting the control piston, a second end for transmitting motion to a valve stem and a means for contacting a valve train element. The amount of lost motion provided by the system may be selected by varying the position of the control piston relative to the pivoting lever. Variation of the control piston position may be carried out by placing the control piston in hydraulic communication with a control trigger valve and one or more accumulators. Actuation of the trigger valve releases hydraulic fluid allowing for adjustment of the control piston position. Means for limiting valve seating velocity, filling the hydraulic circuit upon engine start up, and mechanically locking the control piston / lever for a fixed level of valve actuation are also disclosed.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Valve lash adjuster having electro-hydraulic lost-motion capability
InactiveUS20070204818A1Small sizeReduced strengthValve arrangementsCam-followersSolenoid valveElectro hydraulic
In a Type 2 engine, a valve deactivation hydraulic lash adjuster (DHLA) in accordance with the invention replaces a conventional hydraulic lash adjuster in the train of a gas-exchange valve in a compression-ignited engine. In a Type 3 engine, a similar DHLA is disposed within an articulated rocker arm which is made selectively competent (valve activating) or incompetent (valve deactivating) thereby. A solenoid valve within the assembly diverts hydraulic fluid between support and non-support of a piston slidably disposed in a housing and terminating in a ball head. The valve is force-balanced. The preferred hydraulic fluid is diesel fuel, allowing for smaller diameter passages and cleaner operation than in prior art systems, eliminating the need for an accumulator chamber and accumulator piston as in the prior art. An alternate version of a type 3 engine having a DHLA, in accordance with the invention, is also shown.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Pedal apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20090000418A1Reduce effortEasily know maximum operational position of pedal armControlling membersCam-followersDriver/operatorControl theory
Owner:DONG HEE IND
Cam follower with polycrystalline diamond engagement element
A cam follower is provided. The cam follower includes a polycrystalline diamond element, including an engagement surface. The engagement surface of the polycrystalline diamond element is positioned on the cam follower for sliding engagement with an opposing engagement surface of a cam. The cam includes at least some of a diamond reactive material.
Owner:XR RESERVE LLC
Pedal reaction force device
ActiveUS20050172753A1Improve mounting efficiencyEasy to set upControlling membersCam-followersDegrees of freedomCam
In the pedal reaction force device 10, a pedaling reaction force is applied to the operating pedal 16 on the basis of a displacement magnitude and a variation speed of the displacement magnitude by the damper device 18 and spring member 20 which are mechanically displaced in accordance with a pedaling operation of the operating pedal 16, and the variation pattern of the displacement magnitude, that is, variation characteristics of the pedaling reaction force are mechanically set by the cam 22. Therefore, a higher degree of freedom in setting the reaction force characteristics close to a conventional mechanical type pedal device and excellent response performance can be obtained, and construction of the pedal reaction force device 10 can be inexpensively achieved.
Owner:TOYODA IRON WORKS CO LTD
Two-step roller finger cam follower assembly having a follower travel limiter
ActiveUS7798113B2Preventing excessive leak down of an associated hydraulic lash adjusterTravel can be limitedValve arrangementsCam-followersEngineeringCam
A two-step roller finger follower assembly for use in conjunction with a camshaft of an internal combustion engine, wherein the camshaft has at least one first lobe and at least one second lobe. The roller finger follower assembly comprises a follower body for engaging the first cam lobe and having a central aperture, a follower pivotably disposed on the follower body in the central aperture for engaging the second cam lobe, and a limiting stop disposed on the follower body for engaging a feature on the follower to limit travel of the follower body with respect to the follower. The limiting stop prevents overtravel of the follower body during valve-deactivation mode of the assembly, thus preventing excessive leak down of an associated hydraulic lash adjuster.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Anti-rotation guide for a deactivation hydraulic valve lifter
InactiveUS6866014B2Minimal frictional resistanceValve arrangementsCam-followersReciprocating motionEngineering
An anti-rotation guide for a deactivation hydraulic valve lifter for an internal combustion engine. The guide includes a through bore accommodating of a hydraulic valve lifter and is sized such that the outer end of the lifter may be inserted into the through bore of the guide. The guide is securable to the engine such that the lifter is reciprocable within the guide. The guide is provided with two opposing keepers for mating with corresponding flats on the lifter to prevent rotation of the lifter. Further, a keyway means is provided in the guide and lifter to prevent the lifter being inserted into the guide 180° from the correct orientation.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
System for variable valvetrain actuation
InactiveUS20070125330A1Simplifies taskReduce in quantityCam-followersValve drivesGear driveCylinder head
An electromechanical VVA system for controlling the poppet valves in the cylinder head of an internal combustion engine. The system varies valve lift, duration, and phasing in a dependent manner for one or more banks of engine valves. A rocker subassembly for each valve is pivotably disposed in roller bearings on a rocker pivot shaft between the camshaft and a roller follower. A control shaft supports the rocker pivot shaft for controlling a plurality of rocker subassemblies mounted in roller bearings for a plurality of engine cylinders. The control shaft rotates about its axis to displace the rocker pivot shaft and change the angular relationship of the rocker subassembly to the camshaft, thus changing the valve opening, closing, lift and duration. An actuator attached to the control shaft includes a worm gear drive for positively rotating the control shaft.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Sliding bearing
InactiveUS20060251348A1High dimensional accuracyHigh rotation accuracyCam-followersRolling contact bearingsMetallic materialsCam
A cam follower includes a shaft member which is cantilevered at one end and a slide bearing fitted onto the outer periphery of the other end of the shaft member. The slide bearing is composed of a cylindrical matrix made of an Fe-based sintered metal material having an Fe content of 90 wt % or more and a slide layer formed from the inner peripheral surface to the both end faces of the matrix. The slide layer is made of a slide material composition having a base material such as polyethylene resin blended with a lubricant such as silicone oil and a globular porous silica impregnated with this lubricant.
Owner:NTN CORP
Valve lash adjuster having electro-hydraulic lost-motion capability
InactiveUS7509933B2Small sizeReduced strengthValve arrangementsCam-followersSolenoid valveElectro hydraulic
In a Type 2 engine, a valve deactivation hydraulic lash adjuster (DHLA) in accordance with the invention replaces a conventional hydraulic lash adjuster in the train of a gas-exchange valve in a compression-ignited engine. In a Type 3 engine, a similar DHLA is disposed within an articulated rocker arm which is made selectively competent (valve activating) or incompetent (valve deactivating) thereby. A solenoid valve within the assembly diverts hydraulic fluid between support and non-support of a piston slidably disposed in a housing and terminating in a ball head. The valve is force-balanced. The preferred hydraulic fluid is diesel fuel, allowing for smaller diameter passages and cleaner operation than in prior art systems, eliminating the need for an accumulator chamber and accumulator piston as in the prior art. An alternate version of a type 3 engine having a DHLA, in accordance with the invention, is also shown.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Apparatus for applying a reaction force to a pivotally supported pedal member upon depression thereof
ActiveUS20050145057A1Easy to buildImprove pedal maneuverabilityControlling membersCam-followersCoil springEngineering
To provide a pedal reaction force applying apparatus which is easy and inexpensive to manufacture and which is capable of obtaining a pedal reaction force which is close to that of a conventional brake booster. A compression coil spring 22 is compressively deformed upon depression of a pedal member 16, whereby the pedal reaction force is applied to the pedal member 16. The pedal reaction force can be suitably established depending upon amount of pivot motion of a cam member 20 caused by a transmission mechanism 26 as a result of the depression of the pedal member 16, or depending upon projection amount and projection shape of a lobe portion 34 of the cam member 20. Further, the cam member 20 is mechanically pivoted by the transmission mechanism 26 upon depression of the pedal member 16, and the number of the compression coil spring 22 to be provided in the apparatus may be one. Therefore, the apparatus can be constructed more inexpensively than an apparatus in which a desired reaction characteristic is established by rotating the cam member 20 with an electric motor, or in which a plurality of spring members are used. Further, the apparatus can be compact in construction, and can be installed in the bracket 12 which is located in a front side of a driver's seat, with a high degree of freedom in designing the arrangement of the apparatus.
Owner:TOYODA IRON WORKS CO LTD
Rolling bearing
Owner:NTN CORP
Material treatments for diamond-on-diamond reactive material bearing engagements
ActiveUS20200056659A1Improve carrying capacityIncrease speedCam-followersDrilling accessoriesMaterials scienceComposite material
An apparatus is provided that includes a diamond bearing surface positioned in sliding engagement with an opposing bearing surface of a diamond reactive material. The opposing bearing surface is hardened via a material treatment.
Owner:XR RESERVE LLC
Fuel supply pump
ActiveUS20100024779A1Reduce facial stressHigh pressurizationValve arrangementsCam-followersEngineeringCam
A fuel supply pump includes a housing, a shaft in a case, a cam in the case formed eccentrically with respect to the shaft to rotate with the shaft, a tappet on an outer circumferential side of the cam movable in a vertical direction, and a plunger reciprocating with the tappet to pressurize fuel in a chamber. The tappet includes a roller and a supporting member rotatably supporting the roller in its thrust direction. The roller slidingly contacts outer circumference of the cam. The member includes an end face supporting the plunger, a surface at its end on an opposite side from the face and slidingly contacting outer circumference of the roller, and an inner wall supporting the roller in the thrust direction. The roller includes a middle section slidingly contacting the surface along its longitudinal direction, and a contact part at both ends of the section contacting the wall.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com