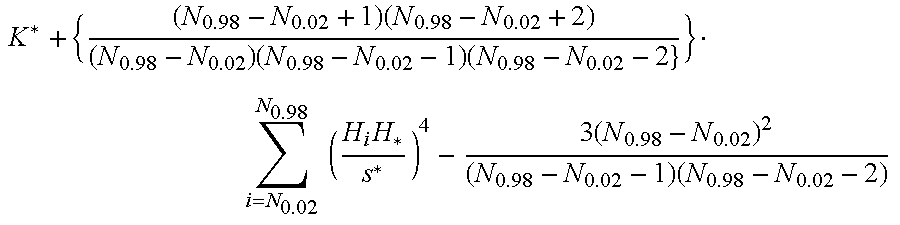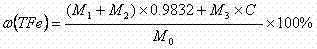Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
493 results about "Fe content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
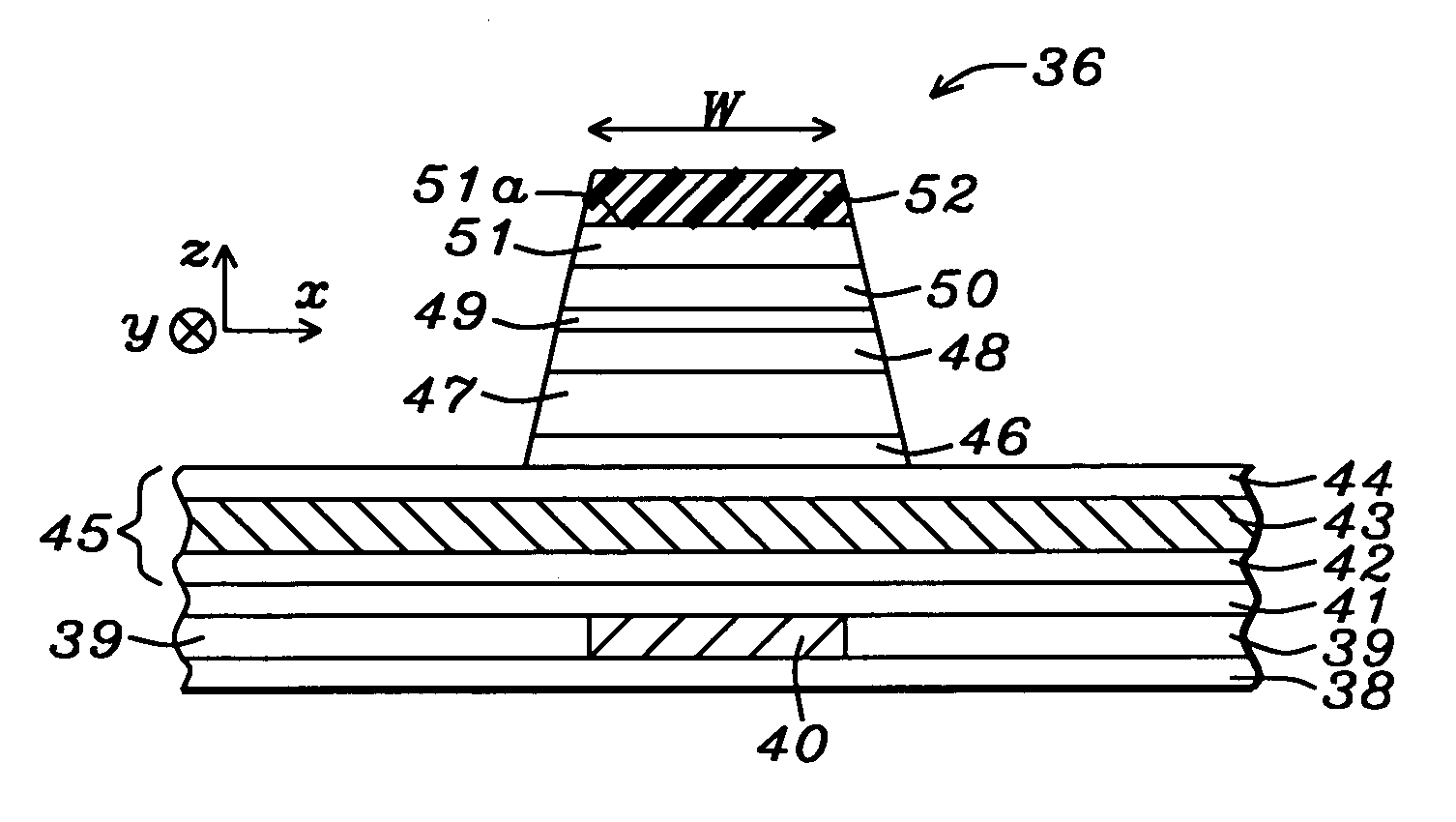
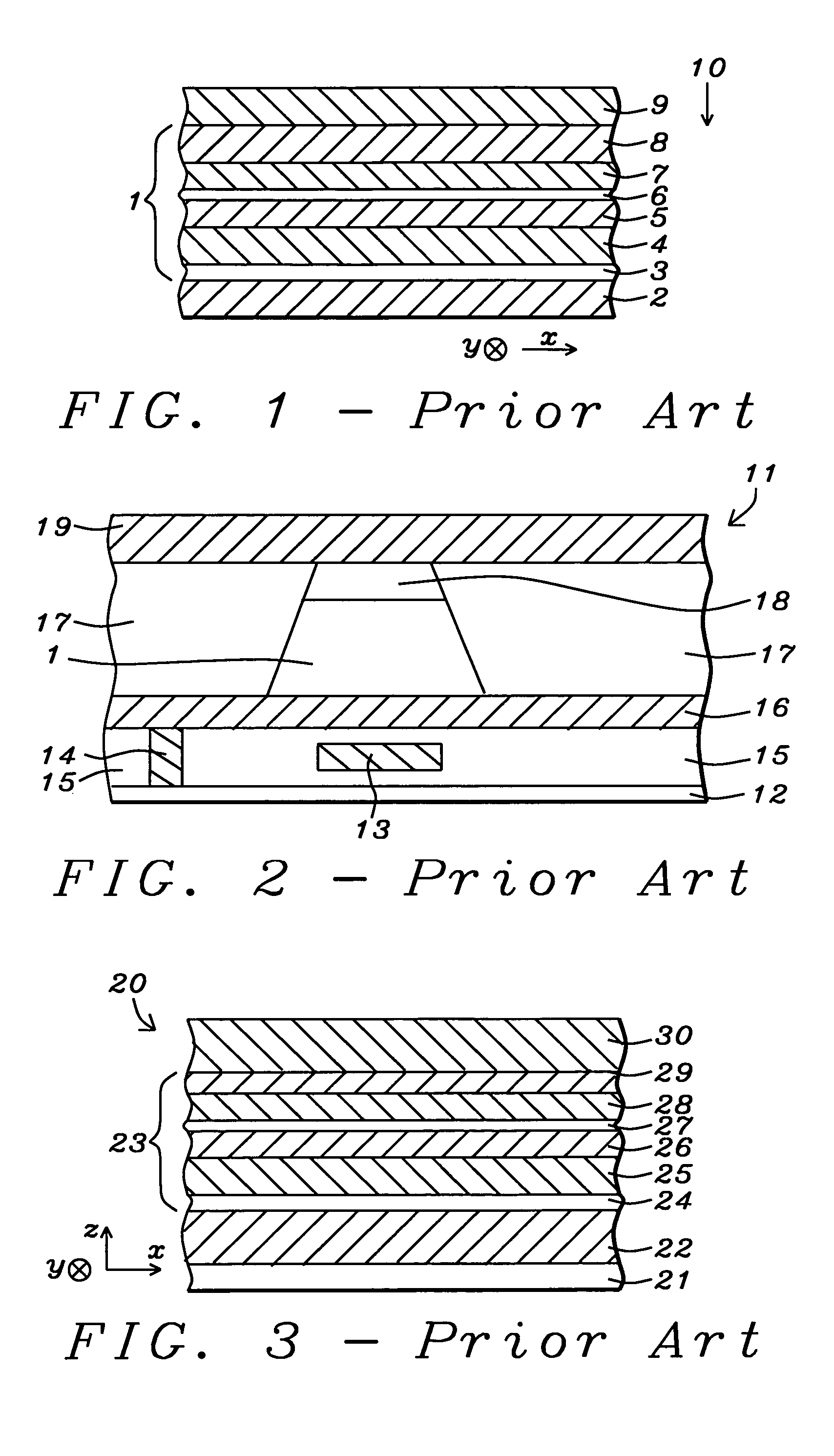
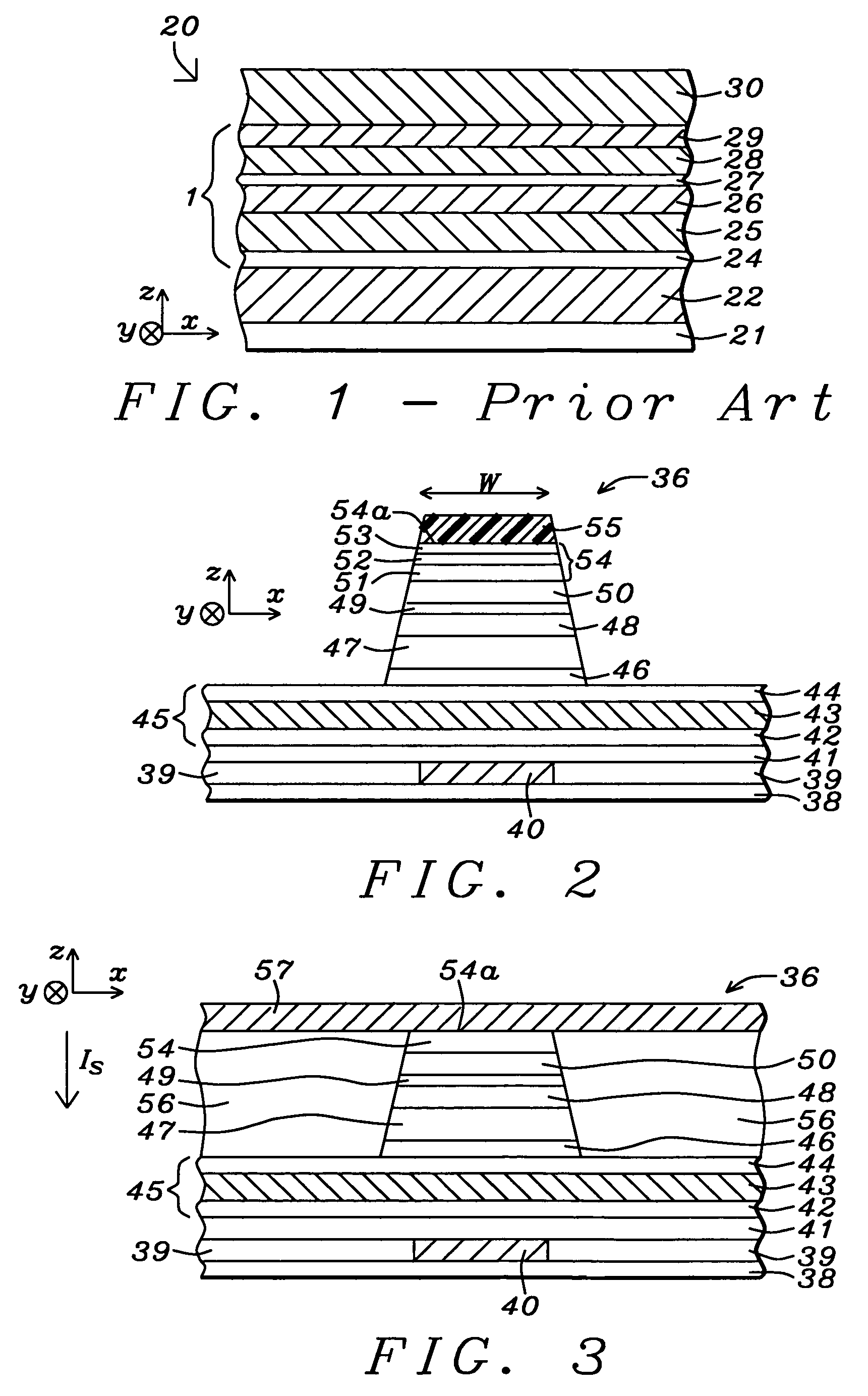
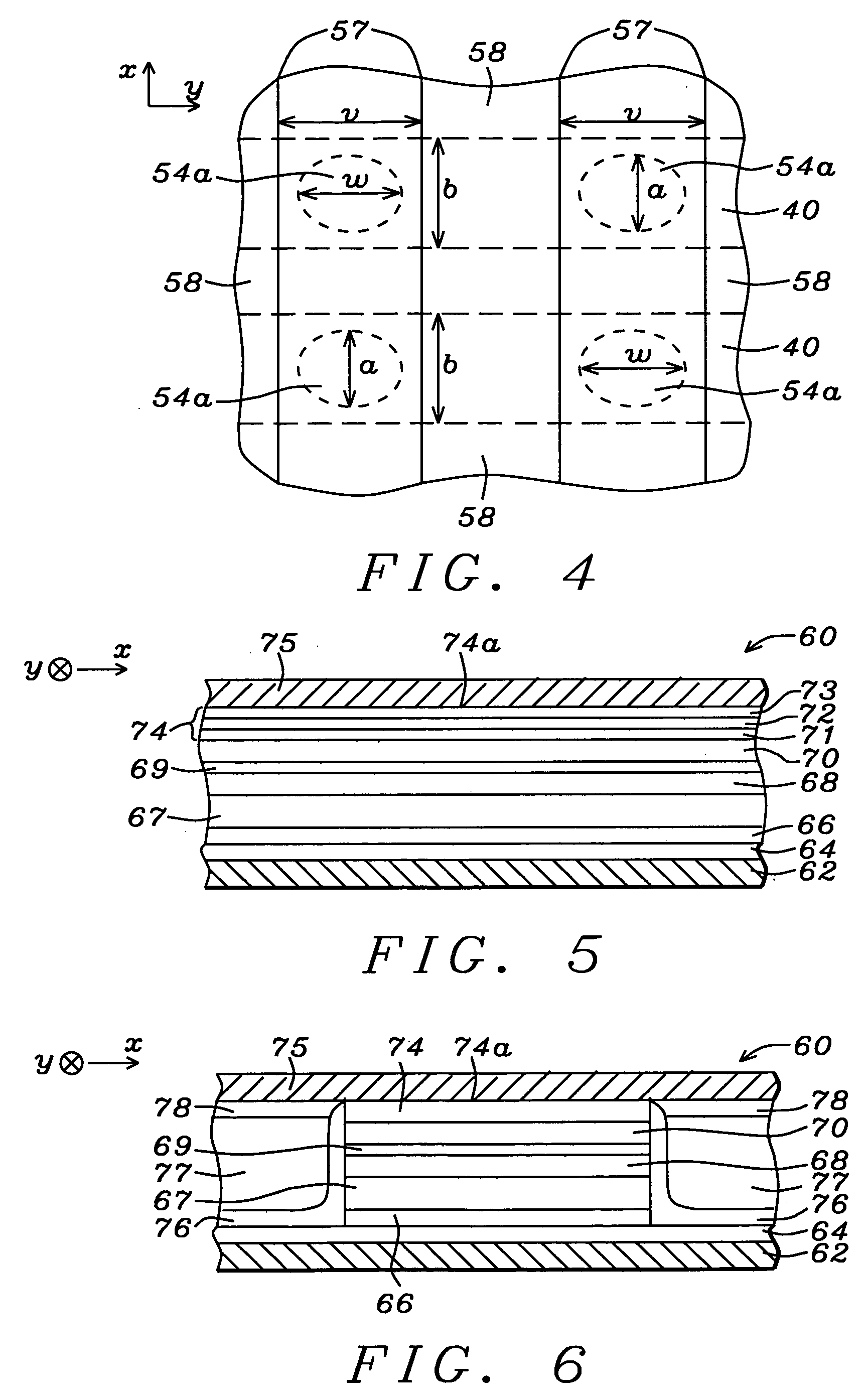
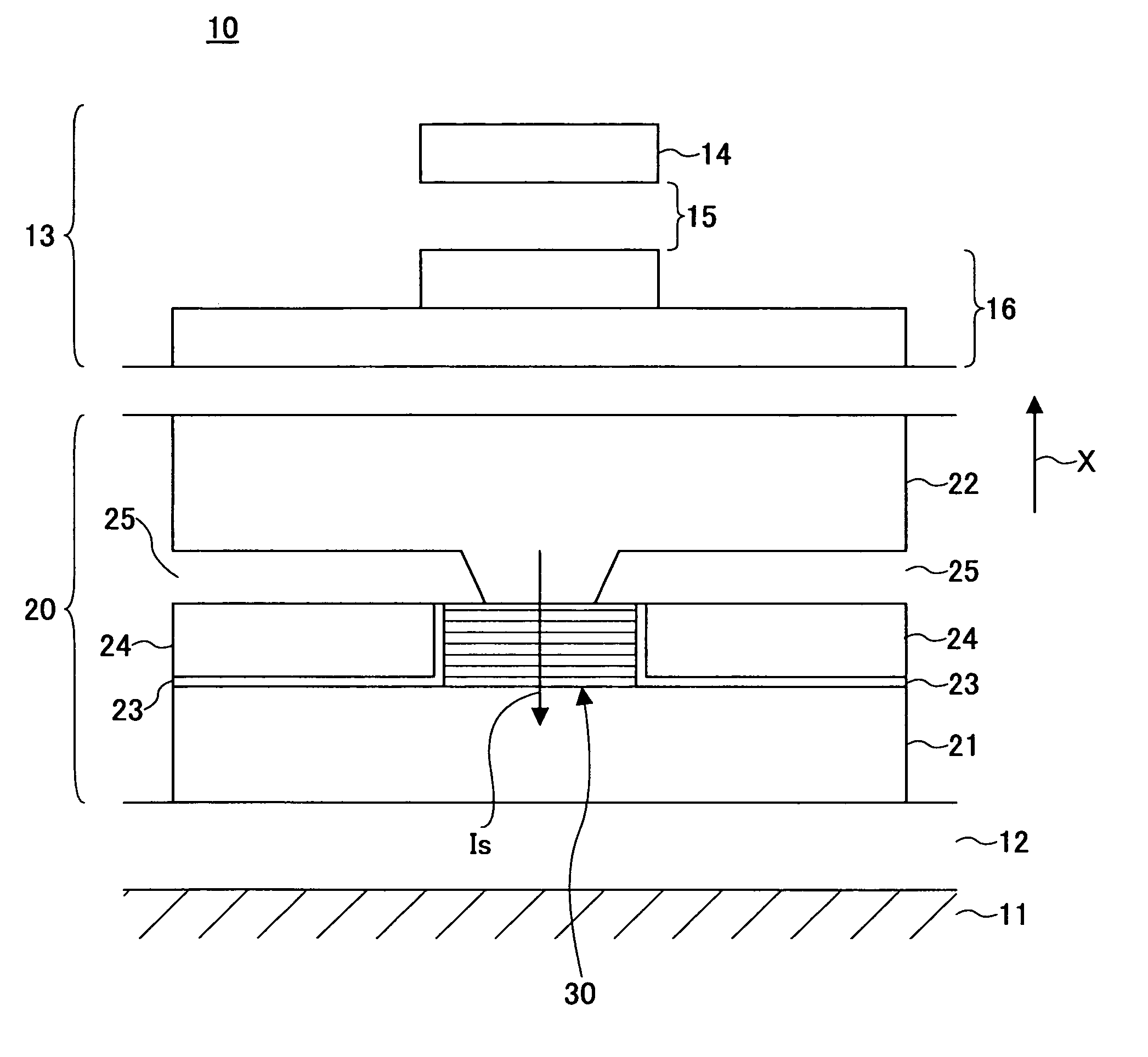
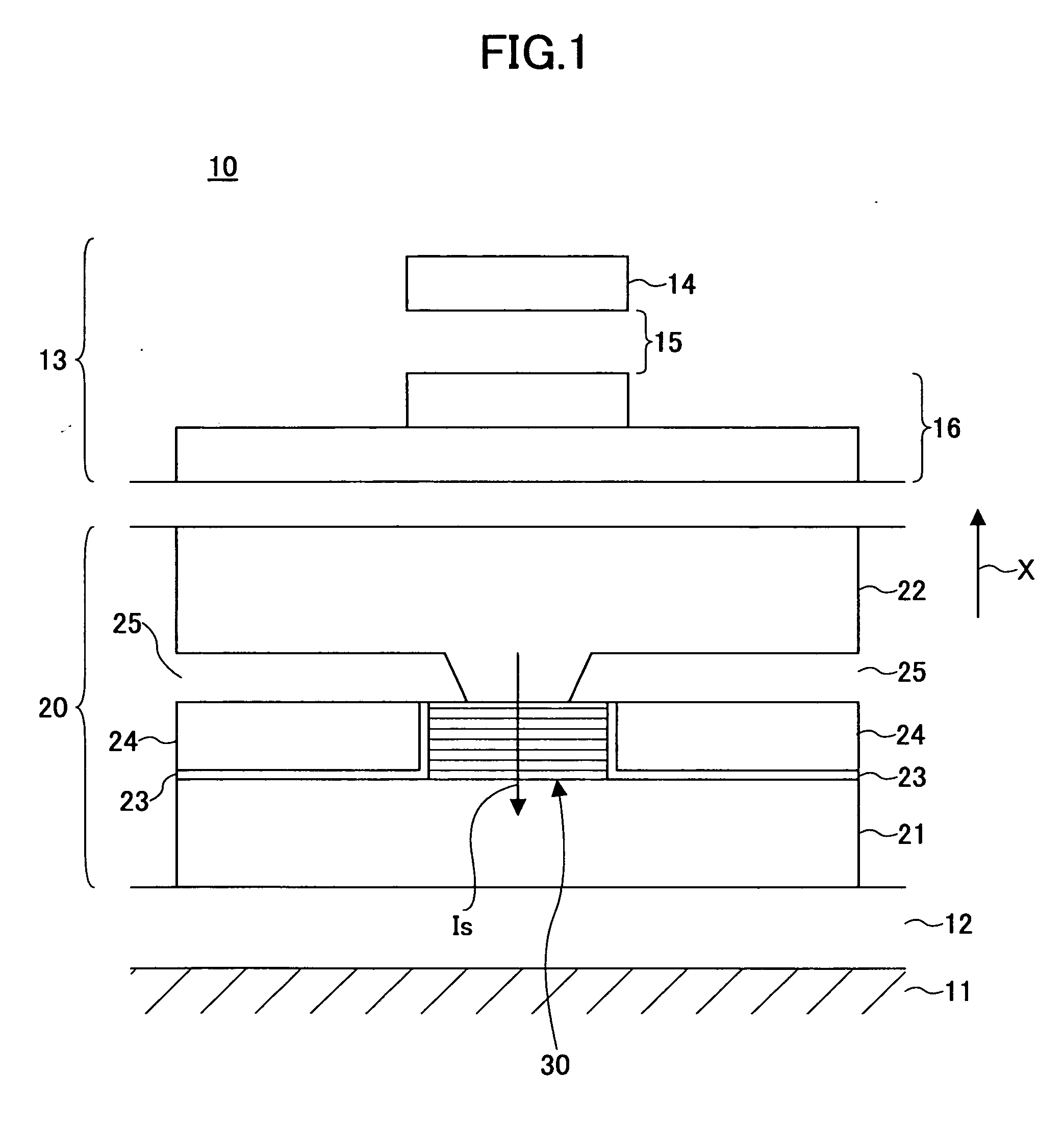
Novel capping structure for enhancing dR/R of the MTJ device
InactiveUS20050276099A1Well controlled magnetizationWell controlled switching characteristicNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsElectrical conductorOxygen
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC +1
Capping structure for enhancing dR/R of the MTJ device
An MTJ in an MRAM array or in a TMR read head is comprised of a capping layer with a lower inter-diffusion barrier layer, an intermediate oxygen gettering layer, and an upper metal layer that contacts a top conductor. The composite capping layer is especially useful with a moderate spin polarization free layer such as a NiFe layer with a Fe content of about 17.5 to 20 atomic %. The capping layer preferably has a Ru / Ta / Ru configuration in which the lower Ru layer is about 10 to 30 Angstroms thick and the Ta layer is about 30 Angstroms thick. As a result, a high dR / R of about 40% is achieved with low magnetostriction less than about 1.0 E−6 in an MTJ in an MRAM array. Best results are obtained with an AlOx tunnel barrier layer formed by an in-situ ROX process on an 8 to 10 Angstrom thick Al layer.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC +1
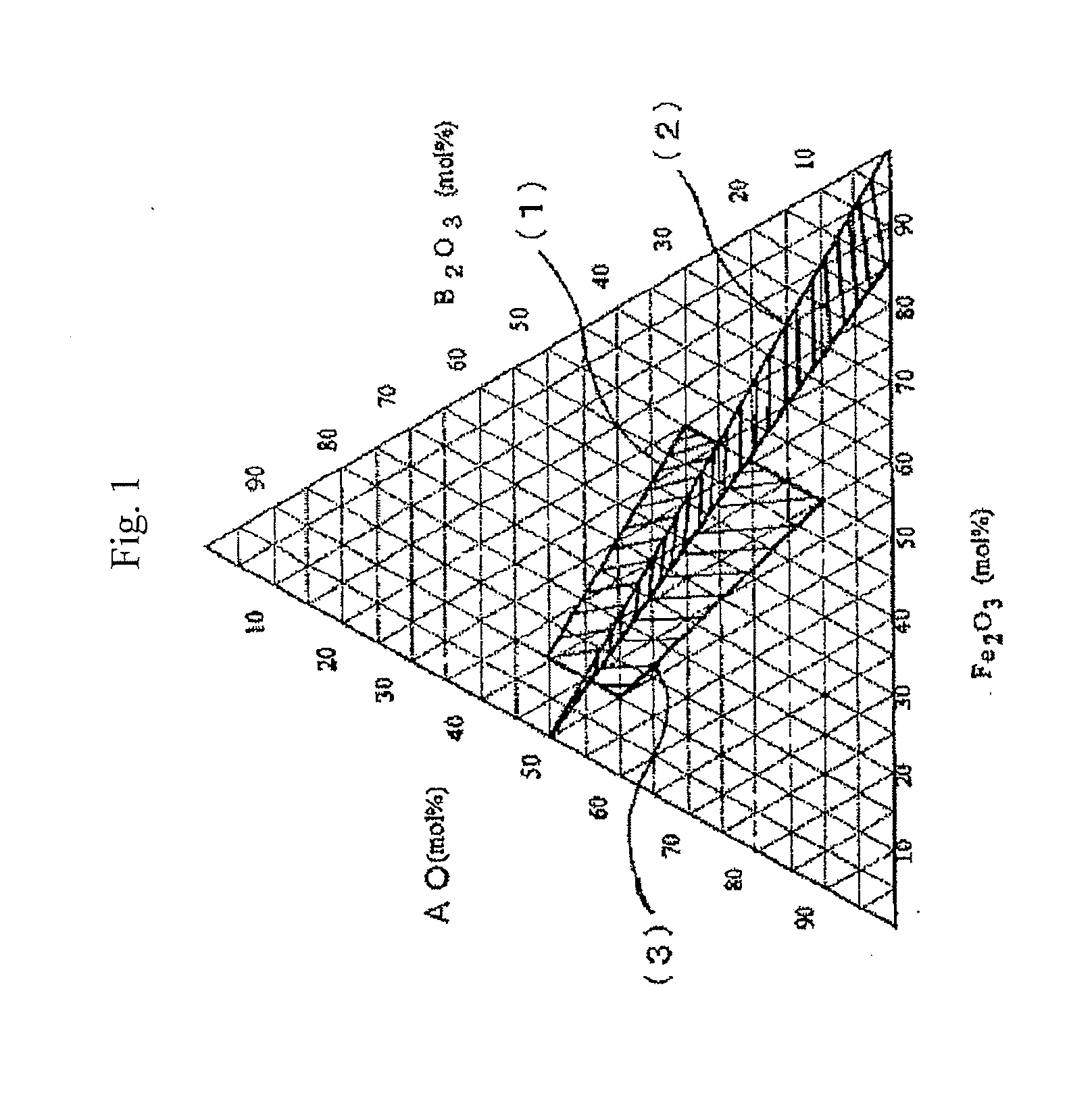
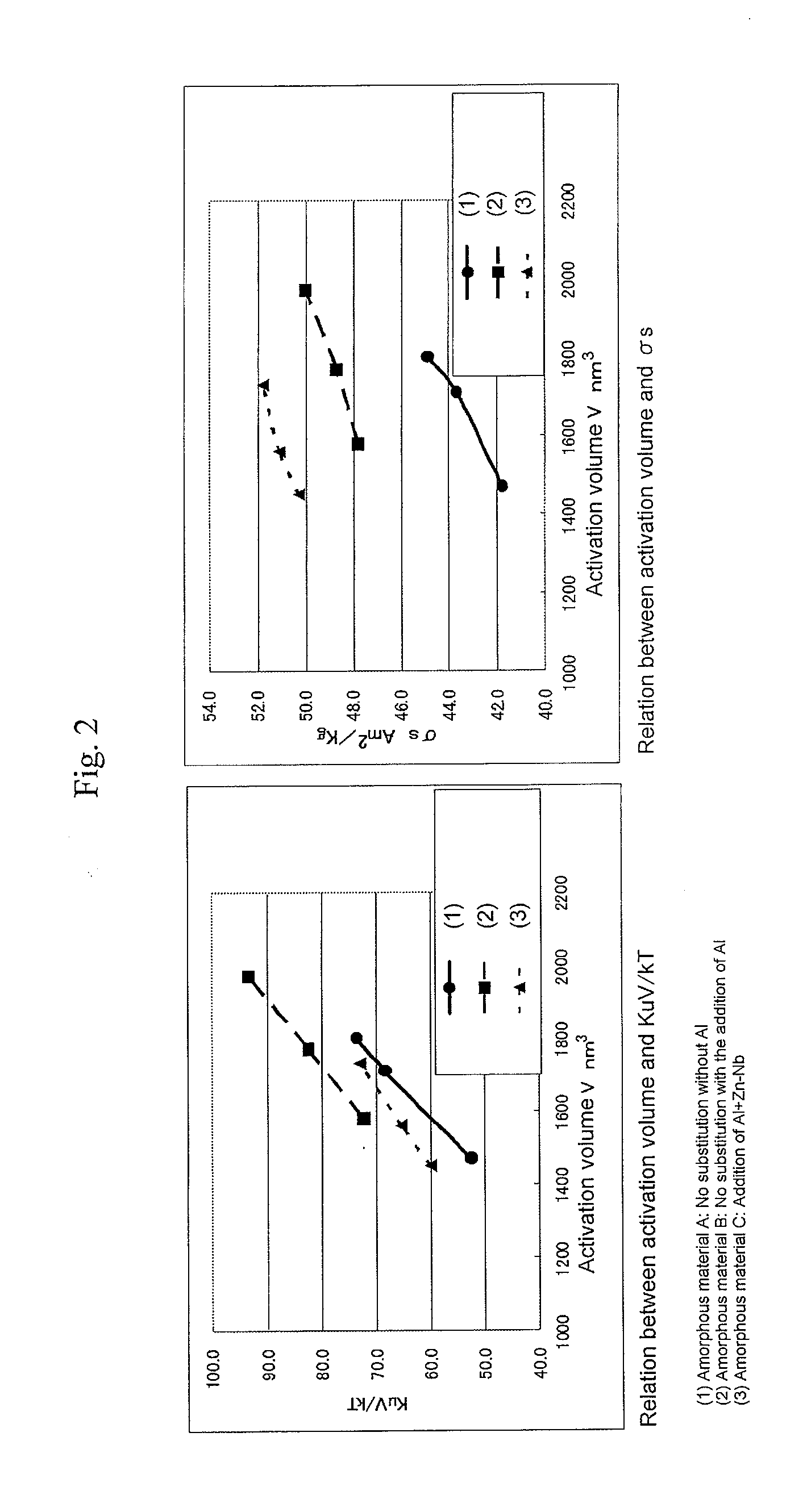
Hexagonal barium ferrite magnetic particle and method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20120177951A1Inhibit drop in thermal stabilityEnsure easeMagnetic materials for record carriersInorganic material magnetismBiological activationMaterials science
An aspect of the present invention relates to a hexagonal barium ferrite magnetic particle, wherein, relative to 100 atom percent of a Fe content, an Al content ranges from 1.5 to 15 atom percent, a combined content of a divalent element and a pentavalent element ranges from 1.0 to 10 atom percent, an atomic ratio of a content of the divalent element to a content of the pentavalent element is greater than 2.0 but less than 4.0, and an activation volume ranges from 1,300 to 1,800 nm3.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method of making iron and steel
InactiveUS6149709AEasy to getLess impurity contentProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceHigh energyRefractory
Molten iron is prepared by (1) providing iron oxide and a carbonaceous reducing agent, (2) preparing a shaped product from the carbonaceous reducing agent and the iron oxide, (3) preparing solid reduced iron from the shaped product, wherein the solid reduced iron has a metallization of at least 60%, a specific gravity of at least 1.7, and a carbon content of at least 50% of the theoretical amount required for reducing the iron oxide remaining in the solid reduced iron, and, (4) before substantial cooling occurs, heating the solid reduced iron in an arc heating-type melting furnace at a high temperature. The molten iron can be prepared efficiently from iron ores of relatively low iron content without causing erosion of refractories, at high energy and high reduction efficiencies, and by a simple operation in a simple facility.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Systems, methods, and catalysts for producing a crude product
Contact of a crude feed with one or more catalysts produces a total product that includes a crude product. The crude feed has a total Ni / V / Fe content of at least 0.00002 grams per gram of crude feed. The crude product is a liquid mixture at 25° C. and 0.101 MPa. At least one of the catalysts has a pore size distribution with a median pore diameter of at least 230 Å. The crude product has a total Ni / V / Fe of at most 90% of the total Ni / V / Fe content of the crude feed. One or more other properties of the crude product may be changed by at least 10% relative to the respective properties of the crude feed.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
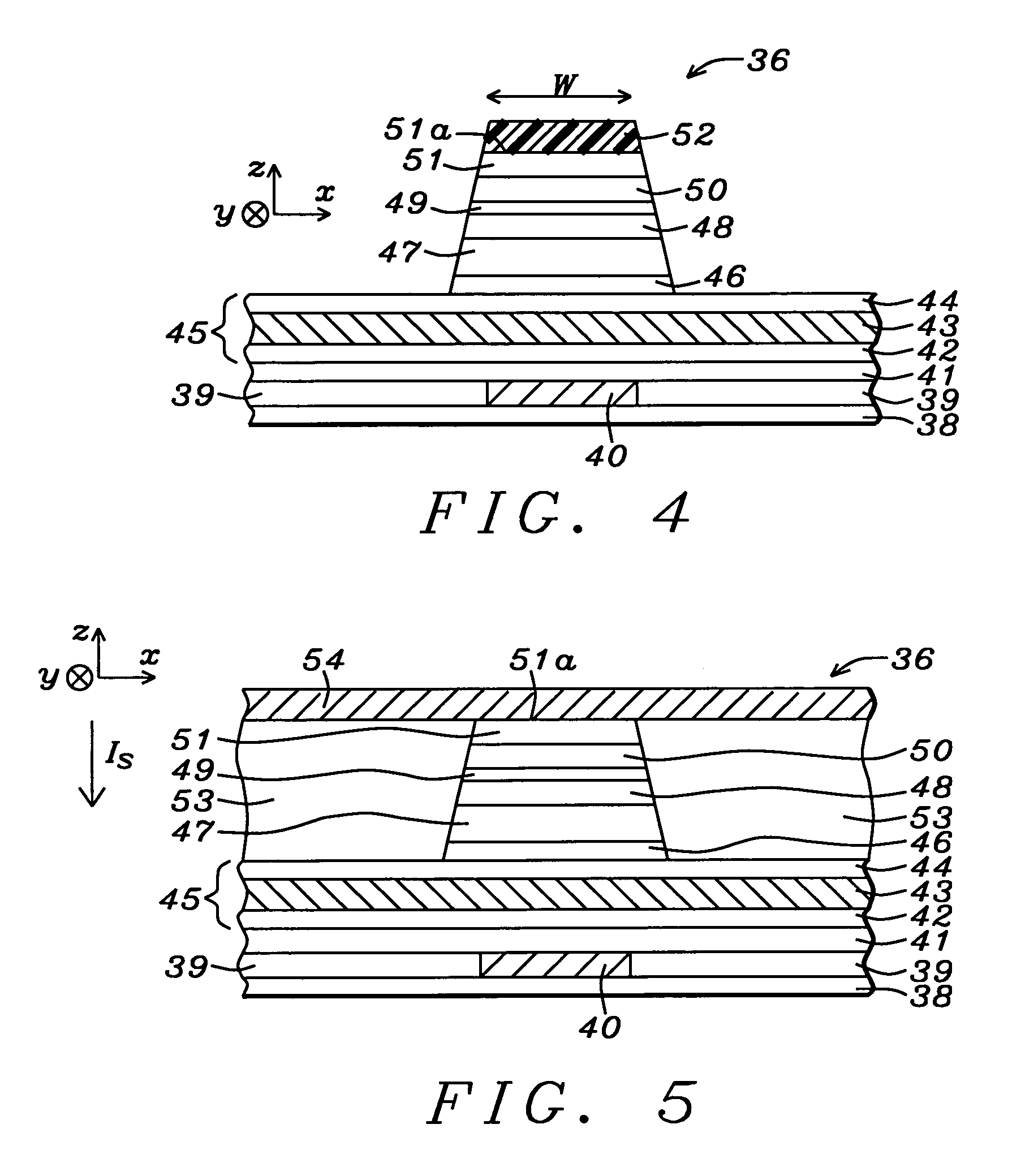
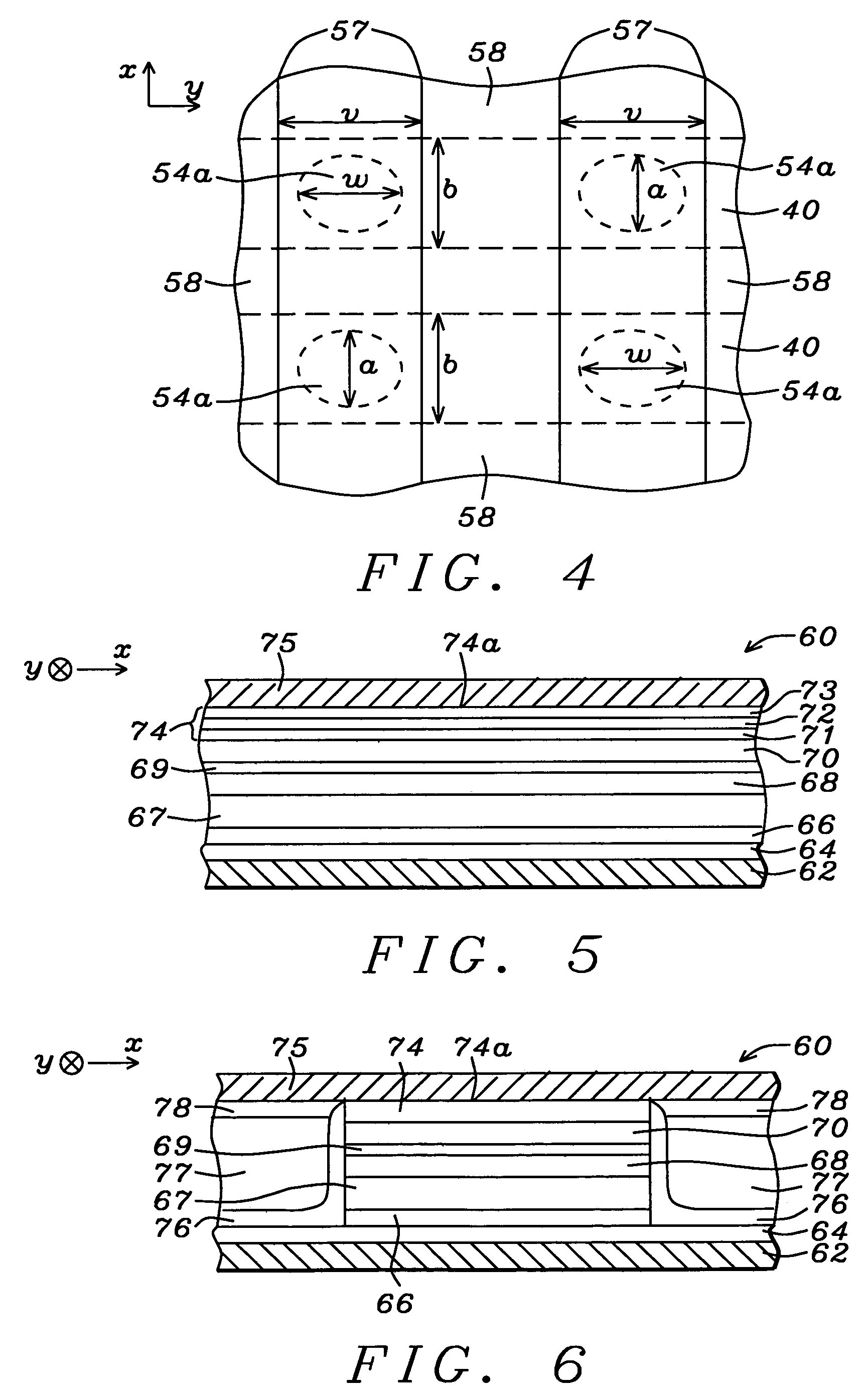
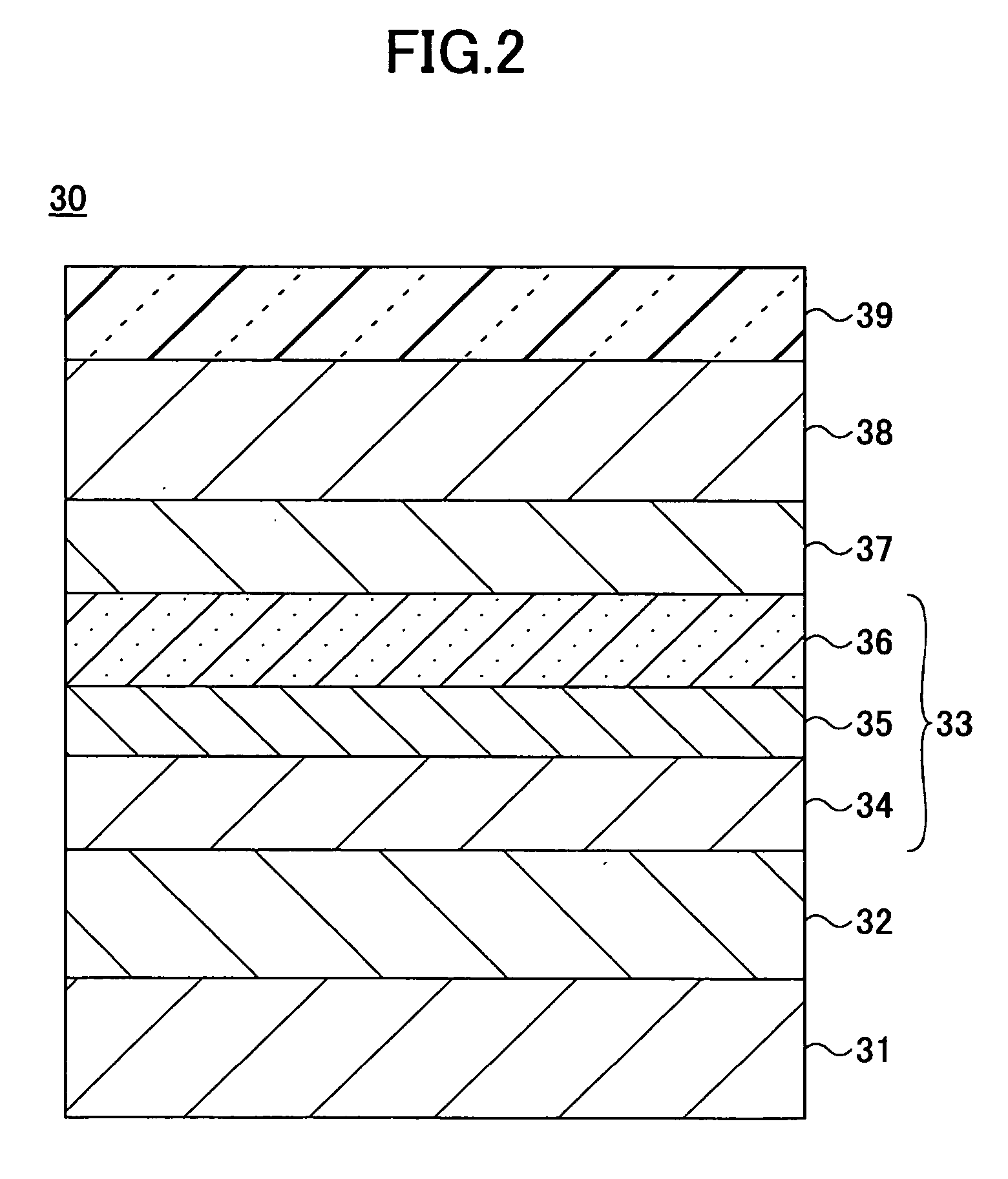
Capping layer for a magnetic tunnel junction device to enhance dR/R and a method of making the same
An MTJ in an MRAM array or TMR read head is disclosed in which a low magnetization capping layer is a composite having a NiFeHf inner layer formed on a NiFe or CoFeB / NiFe free layer, a Ta middle layer, and a Ru outer layer on the Ta layer. For example, a low magnetization NiFeHf layer is achieved by co-sputtering NiFe and Hf targets with a forward power of 400 W and 200 W, respectively. A higher Hf content increases the oxygen gettering power of the NiFeHf layer and the thickness is modified to change dR / R, RA, and magnetostriction values. A so-called dead layer between the free layer and capping layer is restored by incorporating a NiFeHf layer on the free layer to improve lattice matching. The Fe content in the NiFe target used to make the NiFeHf layer is preferably the same as in the NiFe free layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Perpendicular spin transfer torque (STT) memory cell with double MgO interface and CoFeB layer for enhancement of perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
ActiveUS9337415B1Increase contentInhibited DiffusionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionSpin-transfer torqueMagnetic reluctance
A magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) for use in a magnetoresistive random access memory (MRAM) has a CoFeB alloy free layer located between the MgO tunnel barrier layer and an upper MgO capping layer, and a CoFeB alloy enhancement layer between the MgO capping layer and a Ta cap. The CoFeB alloy free layer has high Fe content to induce perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) at the interfaces with the MgO layers. To avoid creating unnecessary PMA in the enhancement layer due to its interface with the MgO capping layer, the enhancement layer has low Fe content. After all of the layers have been deposited on the substrate, the structure is annealed to crystallize the MgO. The CoFeB alloy enhancement layer inhibits diffusion of Ta from the Ta cap layer into the MgO capping layer and creates good crystallinity of the MgO by providing CoFeB at the MgO interface.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
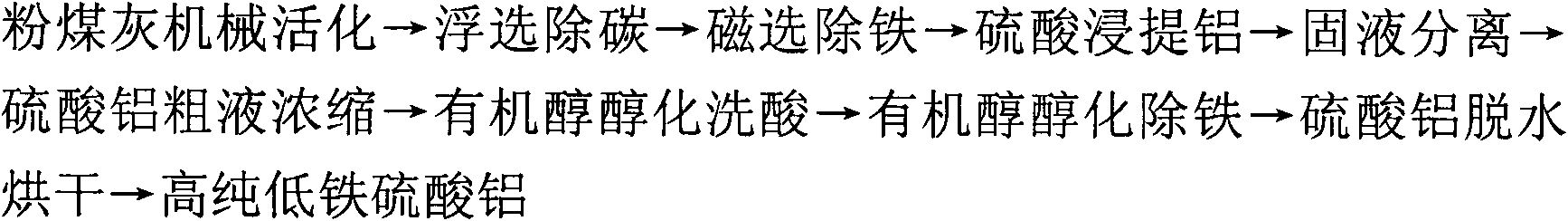
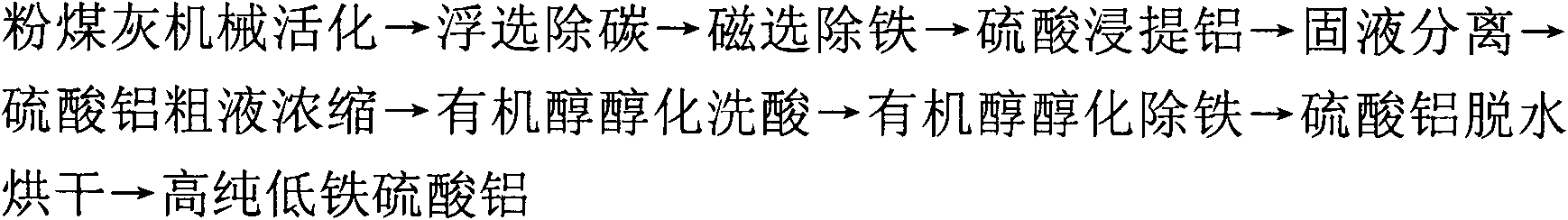
Technological method for producing high-purity low-iron aluminum sulfate by using coal ash and comprehensively utilizing coal ash
InactiveCN102101689AEasy industrial iron removalLow costPigmenting treatmentSolid waste disposalBiological activationCoal
The invention discloses a technological method for producing high-purity low-iron aluminum sulfate by using coal ash and comprehensively utilizing the coal ash, comprising the following steps of: carrying out mechanical activation, flotation decarburization, magnetic separation for deferrization, aluminum extraction with sulfuric acid, solid-liquid separation, concentration of aluminum sulfate crude liquor, organic alcohol alcoholization for acid rinse, organic alcohol alcoholization for deferrization and aluminum sulfate dewatering and drying on the coal ash to obtain the high-purity low-iron aluminum sulfate with low Fe content. The invention solves the problems on impurity removal and purification of the aluminum sulfate in the recycling process of the coal ash, simplifies the process flow, reduces the energy consumption, solves the technical problem of overlarge accumulation of secondary residue quantity, achieves high extraction ratio of aluminum contained in the coal ash, and realizes the recycling of organic alcohol and sulfuric acid and the comprehensive utilization of side products including unburnt black, magnetic iron powder, iron-containing aluminum sulfate crystals, high-silicon-dust active mineral blending materials or novel silicon-magnesium cement, and the like. The technological method has the advantages of simple process, short flow, easiness for control of a production process, high aluminum extraction ratio, low impurity content of products and stable quality.
Owner:内蒙古昶泰资源循环再生利用科技开发有限责任公司 +2
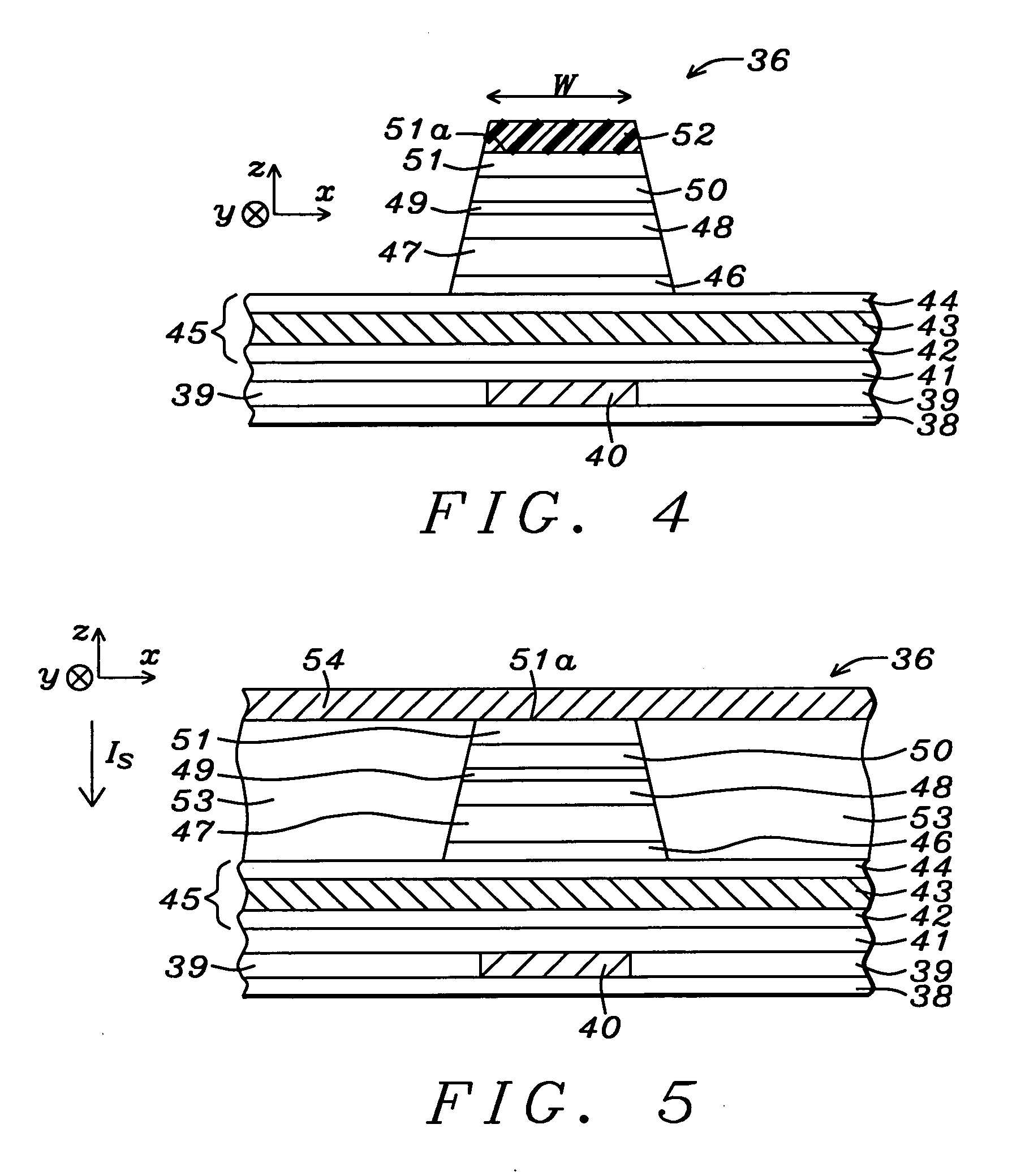
Novel capping layer for a magnetic tunnel junction device to enhance dR/R and a method of making the same
ActiveUS20080023740A1Magnetization is so lowLow layerNanomagnetismSolid-state devicesSputteringMagnetization
An MTJ in an MRAM array or TMR read head is disclosed in which a low magnetization capping layer is a composite having a NiFeHf inner layer formed on a NiFe or CoFeB / NiFe free layer, a Ta middle layer, and a Ru outer layer on the Ta layer. For example, a low magnetization NiFeHf layer is achieved by co-sputtering NiFe and Hf targets with a forward power of 400 W and 200 W, respectively. A higher Hf content increases the oxygen gettering power of the NiFeHf layer and the thickness is modified to change dR / R, RA, and magnetostriction values. A so-called dead layer between the free layer and capping layer is restored by incorporating a NiFeHf layer on the free layer to improve lattice matching. The Fe content in the NiFe target used to make the NiFeHf layer is preferably the same as in the NiFe free layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
High-dispersion iron catalyst by direct coal hydrogenation liquefaction
InactiveCN1778871AHigh activityDifficult to repolymerizeLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionActive componentCoal
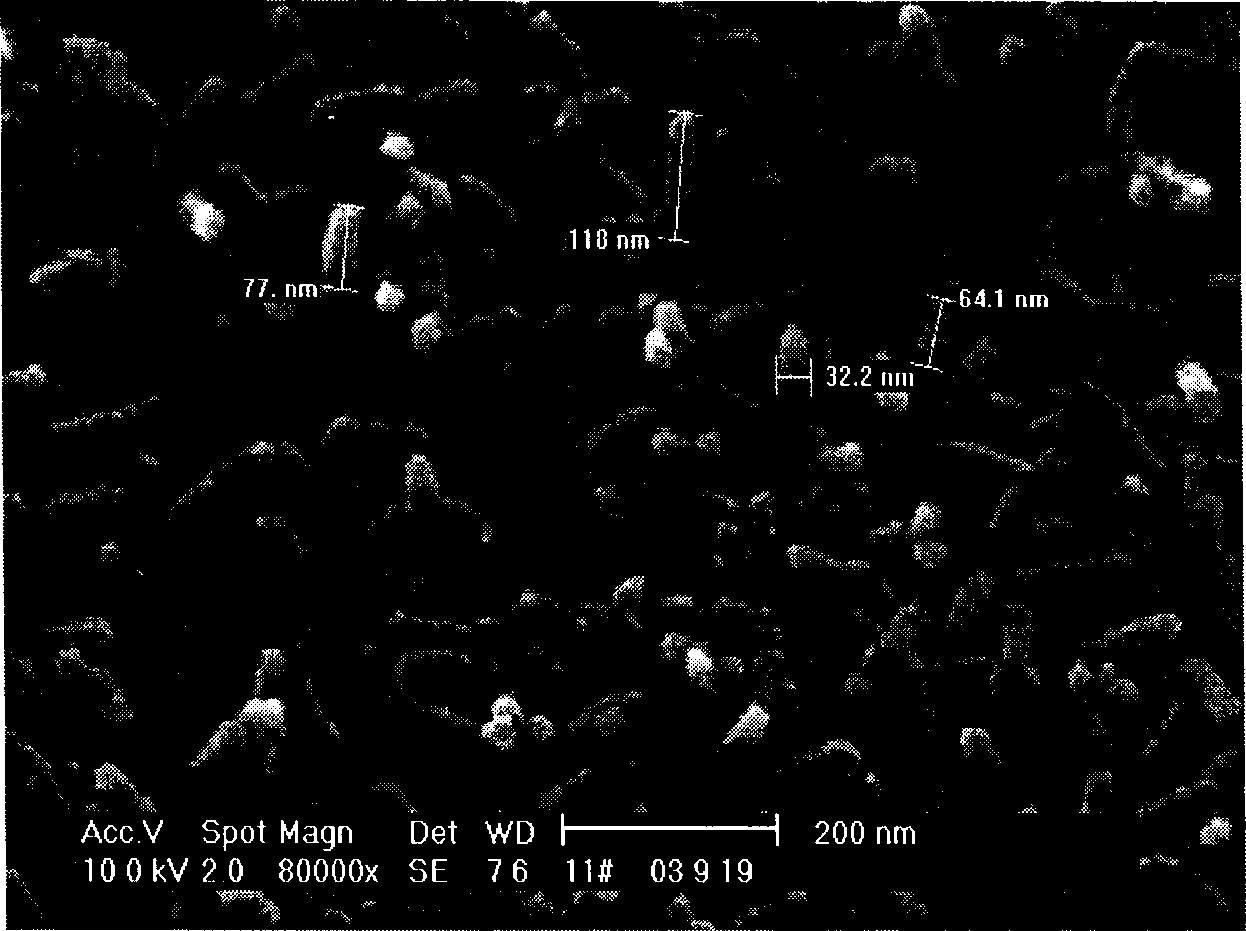
A hydrogenation liquefied high-dispersion iron catalyst from coal consists of active component gamma-FeOOH with Fe content 1í½15wt%(dry base), carrier coal 50í½90wt%(dry base) and impurity water residue. The gamma-FeOOH is distributed in liquefied coal with strip shape, grain size range 60í½200nm and width 20í½100nm. It is cheap, high efficient and easy storage, has small size, high catalyst activity and various resources.
Owner:CHINA COAL RES INST
Smelting technique of novel nickel-iron-base high-temperature alloy GH4169D
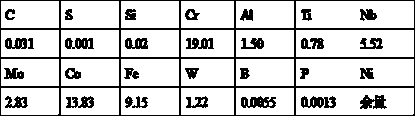
The invention discloses a smelting technique of a novel nickel-iron-base high-temperature alloy GH4169D, which aims to smelt the novel high-temperature alloy GH4169D consumable ingot which has the advantages of lower raw material cost and favorable hot working properties in industrial production as well as high stability at high temperature. The scheme of the smelting technique is as follows: on the basis of the GH4169 alloy composition, the Fe content is lowered, the sum and proportion of Al and Ti are adjusted, and proper P and B are added; and by adopting a triple (VIM+PESR+VAR) smelting technique, proper slag and technological parameters are selected, and the burning loss of Al and Ti in the protective-atmosphere electroslag smelting process is controlled to obtain the precise contents of Al and Ti. The technique enhances the metallurgical quality of the high-temperature alloy, and fills up the blank of the high-temperature alloy in the aspect of the application temperature between 650 DEG C and 750 DEG C; the GH4169D alloy has the high strength, favorable hot working property and weldability of the GH4169 alloy, and has the high application temperature and other comprehensive properties of the GH4738 alloy; and the GH4169D alloy has long-term stability at 700 DEG C.
Owner:FUSHUN SPECIAL STEEL SHARES
Alloyed hot galvanizing bake hardening steel and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN101230437ANot easy to produceImprove PlatabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesTemperature control deviceCooking & bakingSheet steel
The invention relates to an alloyed hot-galvanized baking-hardened steel plate and the manufacturing method thereof, which solves the problems of the anti-pulverization of the galvanized layer, the surface quality and the baking-hardened value. The mass percentage for the chemical components of a baseplate is as follows: C 0.0015 to 0.0025 percent, Si less than or equal to 0.030 percent, Mn 0.50 to 0.60 percent, P 0.050 to 0.060 percent, S less than or equal to 0.015 percent, N less than or equal to 0.003 percent, sol.Al 0.030 to 0.055 percent, Nb 0.004 to 0.015 percent, O less than or equal to 0.0050 percent and the rest are Fe and unavoidable impurities. The weight of the galvanized layer (for a single side) is 30-60g / m2 and the mass percentage for the Fe component of the galvanized layer is 8 to 12 percent. The steel plate of the invention has excellent anti-pulverization performance of the galvanized layer, excellent surface quality and appropriate baking-hardened value.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-strength galvanized steel sheet excellent in bendability and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140212684A1Improve bending performanceHigh tensile strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesAlloyHardness
The present invention provides a high-strength galvanized steel sheet with maximum tensile strength of 900 MPa or more. The high-strength galvanized steel sheet has an alloyed galvanized layer formed on a surface of a base steel sheet containing predetermined amounts of C, Si, Mn, P, S, Al, N, O with a balance being constituted of iron and inevitable impurities, in which in a structure of the base steel sheet, retained austenite is limited to 8% or less in volume fraction, kurtosis K* of the hardness distribution between 2% hardness and 98% hardness is −0.30 or less, a ratio between Vickers hardness of surface layer of the base steel sheet and Vickers hardness of ¼ thickness of the base steel sheet is 0.35 to 0.70, and a content of iron in the alloyed galvanized layer is 8 to 12% in mass %.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Softening-resistant copper alloy and method of forming sheet of the same
InactiveUS20050092404A1Improve softening resistanceReduced strengthMetal rolling arrangementsWork cycleReduction ratio
A softening-resistant copper alloy contains Fe in an Fe content in the range of 0.01 to 4.0% by mass. The copper alloy has a cube orientation density of 50% or below and a mean grain size of 30 μm or below after being annealed at 500° C. for 1 min. A copper alloy sheet forming method of forming a copper alloy sheet comprises, in successive steps: a hot rolling process for hot-rolling a copper alloy sheet of the copper alloy according to any one of claims 1 to 4, at least two working cycles each of a cold rolling process and an annealing process, and a finish cold rolling process. Reduction ratio for each of the cold rolling processes of the working cycles is in the range of 50 to 80%, and reduction ratio for the finish cold rolling process is in the range of 30 to 85%.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
High-damage tolerance type ultrahigh strength aluminum alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-damage tolerance type ultrahigh strength aluminum alloy and a preparation method thereof. The high-damage tolerance type ultrahigh strength aluminum alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 8.5-10.0 percent of Zn, 1.0-2.5 percent of Mg, 1.0-2.0 percent of Cu, 0.06-0.20 percent of Zr, 0.02-0.05 percent of Ti, not more than 0.08 percent of Fe, not more than 0.06 percent of Si and the balance of Al and unavoidable impurities, wherein the Fe content is larger than Si content. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, smelting and casting; then carrying out homogenization on an alloy casting blank by stages, carrying out hot rolling on the homogenized casting blank and carrying out solid dissolution on a hot rolled plate; prestretching the plate in four hours after quenching; and finally immediately carrying out double-stage ageing processing on the prestretched plate. The obtained alloy has higher strength and damage tolerance and is suitable for being applied in an airplane part exposed in the atmospheric environment for a long time.
Owner:CHINA ALUMINUM INT ENG CORP
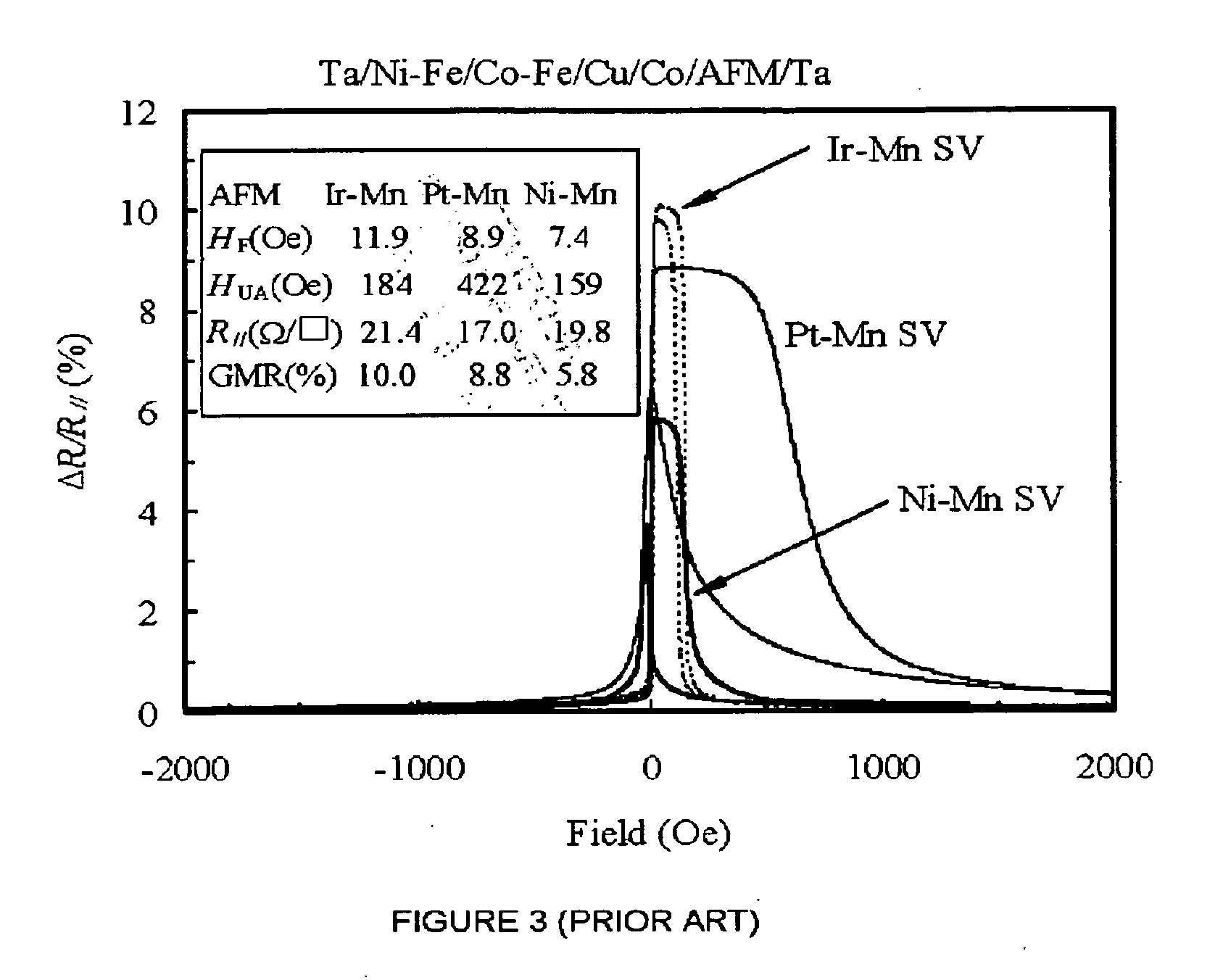
GMR sensors with strongly pinning and pinned layers
InactiveUS20060193089A1Simple designEasy to operateNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsIridiumFerromagnetism
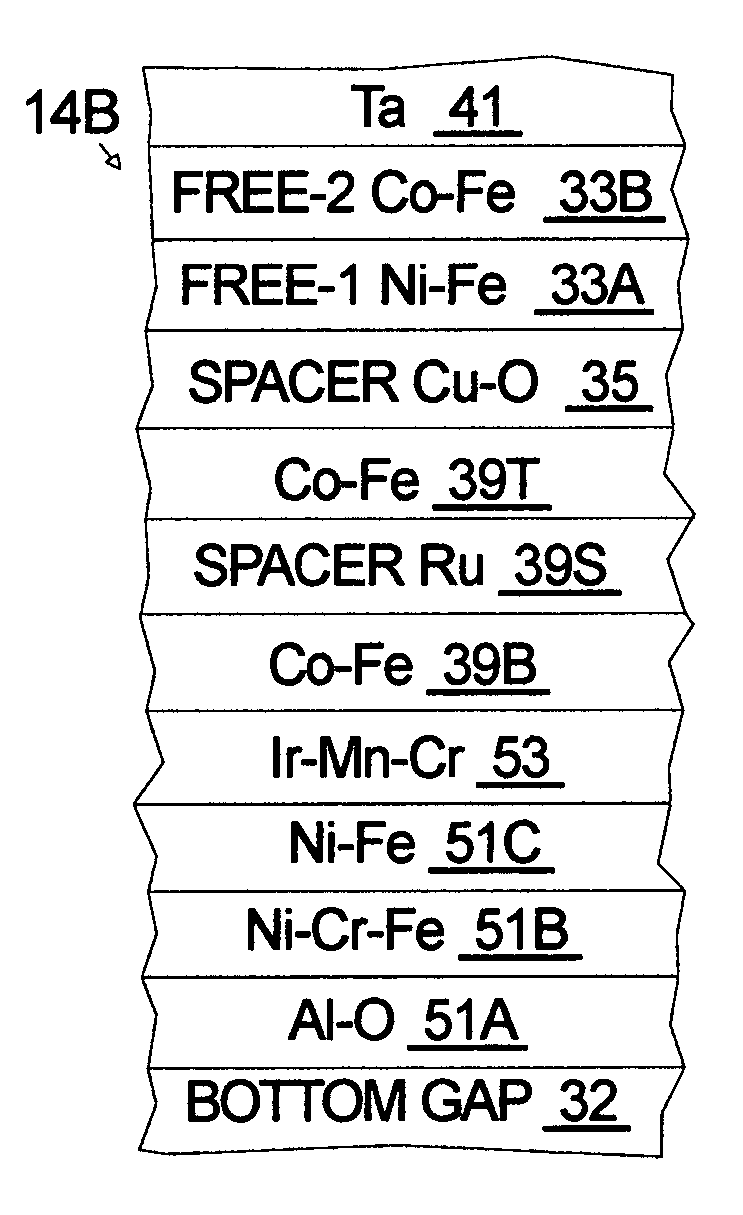
A giant magnetoresistance (GMR) sensor with strongly pinning and pinned layers is described for magnetic recording at ultrahigh densities. The pinning layer is an antiferromagnetic (AFM) iridium-manganese-chromium (Ir—Mn—Cr) film having a Mn content of approximately from 70 to 80 atomic percent and having a Cr content of approximately from 1 to 10 atomic percent. The first pinned layer is preferably a ferromagnetic Co—Fe having an Fe content of approximately from 20 to 80 at % and having high, positive saturation magnetostriction. The second pinned layer is preferably a ferromagnetic Co—Fe having an Fe content of approximately from 0 to 10 atomic percent. The net magnetic moment of the first and second pinned layers is designed to be nearly zero in order to achieve a pinning field of beyond 3,000 Oe.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Alloyed zinc aluminum magnesium alloy coated steel plate and production method thereof
ActiveCN103507324AImprove corrosion resistanceGood formabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesMetal layered productsRare earthAir knife
The invention provides an alloyed zinc aluminum magnesium alloy coated steel plate and a production method thereof. The coating has an Fe content of not more than 5%, the coating surface contains an MgZn2 phase, which has a particle size of not greater than 5 micrometers. The coating surface is in the form of equiaxed grains, and in the coating, Mg accounts for 1.5-8wt%, aluminum accounts for 1.5-15wt%, and rare earth accounts for 0-0.2wt%. According to the production method, cold rolled strip steel is subjected to continuous annealing and hot dipping in a continuous hot dip galvanizing unit, and then alloy treatment is carried out on the hot-dip galvanized zinc aluminum magnesium steel plate. Chemically, a plating solution comprises 1.0-11wt% of Al, 0.5-5wt% of Mg, and the balance Zn and inevitable impurities. After the steel plate undergoes annealing by N2 containing 0.5%-30 vol % of H2, the steel plate is immersed in the plating solution at a temperature of 450-650DEG C, the steel plate enters a zinc pot at 420-580DEG C, and the immersion plating time of the steel plate in the plating solution is 1-10s. After air knife cooling, the zinc aluminum magnesium steel plate enters an alloying furnace to undergo alloying treatment, the alloying temperature is 450-650DEG C, the alloying time is 3-20s, and then the steel plate is cooled at a speed of 10-50DEG C / s. The steel plate provided by the invention ensures that the coating does not fall off in a complex forming process, and after forming, the zinc aluminum magnesium coating can put its excellent corrosion resistance to good use, thus prolonging the service life of components.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
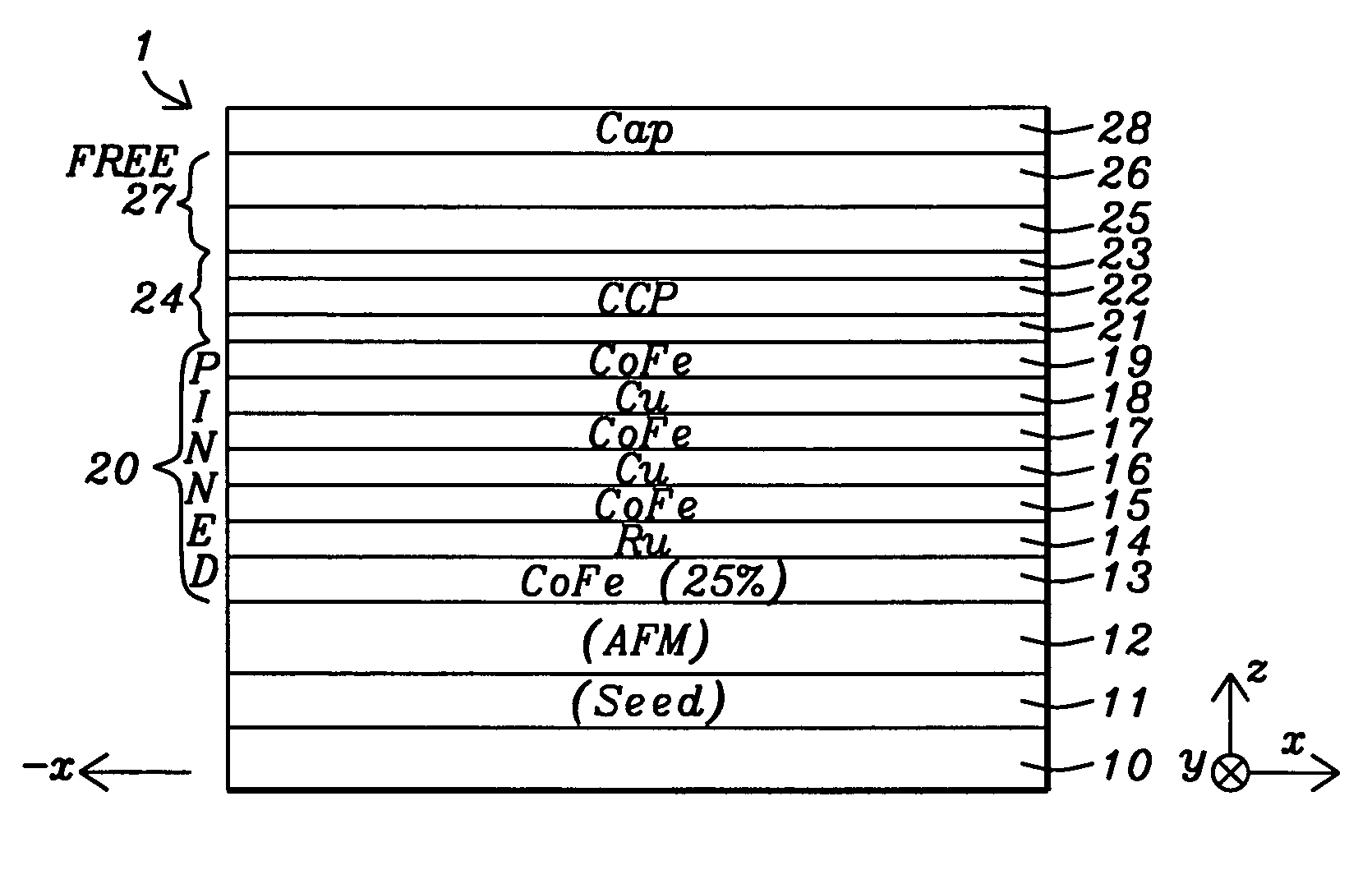
CPP structure with enhanced GMR ratio
InactiveUS20070014054A1Raise the ratioLow coercivityElectrical transducersMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsCopperSpin valve
A CPP-GMR spin valve having a CoFe / NiFe composite free layer is disclosed in which Fe content of the CoFe layer ranges from 20 to 70 atomic % and Ni content in the NiFe layer varies from 85 to 100 atomic % to maintain low Hc and λS values. A higher than normal Fe content in the CoFe layer improves the MR ratio by ≧16% compared with conventional CoFe / NiFe free layers in which the Fe content in CoFe is typically <20 atomic % and the Ni content in NiFe is <85 atomic %. The CPP-GMR performance may also be optimized by incorporating a confining current path layer in the copper spacer between the pinned layer and free layer. For a pinned layer with an AP2 / Ru / AP1 configuration, the spin valve performance is further improved by an AP1 layer comprised of a lamination of CoFe and Cu layers as in [CoFe / Cu]2 / CoFe.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Magnetoresistive effect element, magnetic head, magnetic storage device and magnetic memory device
InactiveUS20070048485A1Increase productionGood sensitivity in detection of magnetic fieldNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic storageMagnetization
A magnetoresistive effect element of a CPP type includes a fixed magnetization layer, a non-magnetic layer and a free magnetization layer formed of CoFeAl. The CoFeAl has a composition falling within a range defined by straight lines connecting points A, B, C, D, E, F and A, in that order, in a ternary composition diagram. The point A is (55, 10, 35), the point B is (50, 15, 35), the point C is (50, 20, 30), the point D is (55, 25, 20), the point E is (60, 25, 15), and the point F is (70, 15, 15), where coordinates of the composition of each point is represented by (Co content, Fe content, Al content). Each content is expressed by atomic percent.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for measuring iron content in steel slag
The invention provides a method for measuring iron content in steel slag. The method includes grinding and screening a steel slag sample by multiple times; completely separating granular metal substances from slag in the steel slag sample; measuring the mass of the granular metal substances by a physical process; measuring iron content of the slag by a titanium trichloride and potassium dichromate volumetric process; and computing the full iron content of the steel slag sample via data of the iron content of the slag and the mass of the granular metal substances. The method has the advantages of convenience in operation, high accuracy of the measured iron content and good stability, repeatability and accuracy of a measuring result. Besides, as proved by tests, the method is reliable and practical, and the requirement on measuring iron content in steel slag in daily life can be met.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
Hot dip galvanizing method for steel pieces
ActiveCN101092682ALong corrosion lifeImprove uniformityHot-dipping/immersion processesRare-earth elementAlloy
This invention discloses a method for hot-dip galvanizing on steel work piece. The method comprises: checking black work piece, suspending, degreasing, rinsing, washing with acid, rinsing, treating with a galvanizing aid, drying with hot air, hot-dip galvanizing and cooling. During the hot-dip galvanizing process, Al, Ni, Si and rare earth element are added into the galvanizing solution. The galvanizing solution comprises: Al 7-9 wt. %, Ni 3-6 wt. %, Si 0.5-0.8 wt. %, rare earth element 0.5-1.0 wt. %, and Zn as balance. The addition of Si can reduce Fe content in the galvanizing solution, and the formation of Zn-Fe alloy residue. The Zn consumption is lowered by nearly 1%, and the surface quality of galvanized steel is improved.
Owner:南京大吉铁塔制造有限公司
Corrosion-resisting surface treatment method for stainless steel in high-corrosion environment
InactiveCN102691059AImprove electrochemical impedanceIncrease Mo element contentChromatisationElectrolytic inorganic material coatingElectrolysisMolybdate
The invention relates to a corrosion-resisting surface treatment method for stainless steel in a high-corrosion treatment. The corrosion-resisting surface treatment method is characterized by comprising a treatment link comprising a washing step, an oxidizing step, an electrolyzing step, a cleaning step and a drying step; carrying out chemical oil removal with thermokalite, and eliminating oil stains of a stainless steel part in a processing process; and carrying out total immersion oxidization passivating treatment on the stainless steel part with oxidizing solution added with molybdate, so as to generate oxide in high oxidization valence state on the surface of the stainless steel, wherein electrolyzing comprises that a metal part is taken as a cathode, the metal part is immersed into an electrolyte containing the molybdate, electrolyzing is carried out for 10 minutes at normal temperature, then washing is carried out for 3-5 times with clear water, and then the metal part is suspended and drained. Through the treatment, a protective film with the thickness of 100-700nm is generated on the surface of the stainless steel, the Cr content in the protective film reaches up to 40-50%, while the Fe content is only 10-20%, and the Mo content is doubled. The method disclosed by the invention adopts common reagents, can be completed on relatively simple equipment, consumes less time and has a simple process while the effect that the stainless steel part with excellent corrosion resistance, heat resistance and scaling resistance can be obtained is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN CANDORTECH INC CO
Copper alloy for use in electric and electronic parts
InactiveUS20020012603A1High strengthPoor in softening resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh intensityLead frame
A copper alloy of high strength and high electroconductivity which is excellent in characteristics such as strength, electroconductivity and bending formability required as copper alloys for use in electric and electronic parts such as lead frames, terminals and connectors, as well as excellent in the characteristics such as softening resistance, shearing formability. Ag plating property and soldering wettability, the copper alloy comprising: Ni: 0.1 to 1.0% (means mass % here and hereinafter), Fe: 0.01 to 0.3%, P: 0.03 to 0.2%, Zn: 0.01 to 1.5%, Si: 0.01% or less; and Mg: 0.001% or less; in which the relation between the P content and the Si content satisfies the relation: P content / Si content>=10, and the relation for the Ni content, the Fe content and the P content can satisfy following relations: 5<=(Ni content+Fe content) / P content<=7 4<=Ni content / Fe content<=9.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Sliding bearing
InactiveUS20060251348A1High dimensional accuracyHigh rotation accuracyCam-followersRolling contact bearingsMetallic materialsCam
A cam follower includes a shaft member which is cantilevered at one end and a slide bearing fitted onto the outer periphery of the other end of the shaft member. The slide bearing is composed of a cylindrical matrix made of an Fe-based sintered metal material having an Fe content of 90 wt % or more and a slide layer formed from the inner peripheral surface to the both end faces of the matrix. The slide layer is made of a slide material composition having a base material such as polyethylene resin blended with a lubricant such as silicone oil and a globular porous silica impregnated with this lubricant.
Owner:NTN CORP
Ordinary brass full-elemental analysis apparatus based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, and method thereof
InactiveCN102359953AFully automatedRealize real-time online sortingSpectrum investigationAnalysis by material excitationElemental analysisLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
The invention relates to an ordinary brass full-elemental analysis apparatus based on a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, and a method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. The apparatus comprises a laser, a spectrometer, a delay generator, a focusing lens, a collecting lens, optical fiber, a sample and a computer. The laser and the spectrometer are respectivelyconnected to the delay generator. The spectrometer is connected with the computer. The optical fiber is connected with the spectrometer. The focusing lens is arranged between the laser and the sample. The collecting lens is connected with the spectrometer by the optical fiber. The analysis method comprises: establishing working curves of Cu, Pb, Fe and Ni, and verifying the working curves. The apparatus and the method are applicable for analyzing the Cu content, the Pb content, the Fe content and the Ni content in the ordinary brass.
Owner:AUTOMATION RES & DESIGN INST OF METALLURGICAL IND
Malted brown rice containing rich nutritive elements, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN1631225APromote absorptionMeet needsFood preservationFood preparationSulfateSodium selenate
The invention provides a malted brown rice containing rich nutritive elements, its preparation method and application, wherein the preparation comprises steeping the husked paddy seeds into nutrient solution, accelerating germination photophygously, finally drying the rice seeds. The nutrient solution comprises ferrous sulfate solution with Fe content of 500-3000 ug / g, zinc sulphate solution with the Zn content of 500-3000ug / g, sodium selenate solution with the Se content of 5-50ug / g, chromium trichloride solution with the Cr content of 50-1000ug / g, and cobaltous chloride solution with the Co content of 5-100ug / g.
Owner:王将克
Current-perpendicular-to-plane sensor with dual keeper layers
InactiveUS20080144234A1Reduce couplingLower junction resistance-area productNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsRough surfaceAmorphous phase
This invention provides a CPP TMR or GMR sensor with an amorphous ferromagnetic lower keeper layer and a crystalline ferromagnetic upper keeper layer. The amorphous ferromagnetic lower keeper layer strongly exchange-couples to an underlying antiferromagnetic pinning layer and planarizes its rough surface. The crystalline ferromagnetic upper keeper layer strongly antiparallel-couples to an adjacent ferromagnetic reference layer across a nonmagnetic spacer layer. The amorphous ferromagnetic lower keeper layer is preferably made of a Co—Fe—B alloy film with an Fe content high enough to ensure strong exchange-coupling to the underlying antiferromagnetic pinning layer, and with a B content high enough to ensure the formation of an amorphous phase for planarizing an otherwise rough surface due to the underlying antiferromagnetic pinning layer. The crystalline ferromagnetic upper keeper layer is preferably made of a Co—Fe alloy film with an Fe content low enough to ensure strong antiparallel-coupling to the adjacent ferromagnetic reference layer across the nonmagnetic spacer layer. The sensor is annealed at temperatures low enough to prevent the amorphous phase from transforming into a polycrystalline phase, but also high enough to maximize TMR.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Kiln slag processing technology of zinc volatilizing kiln
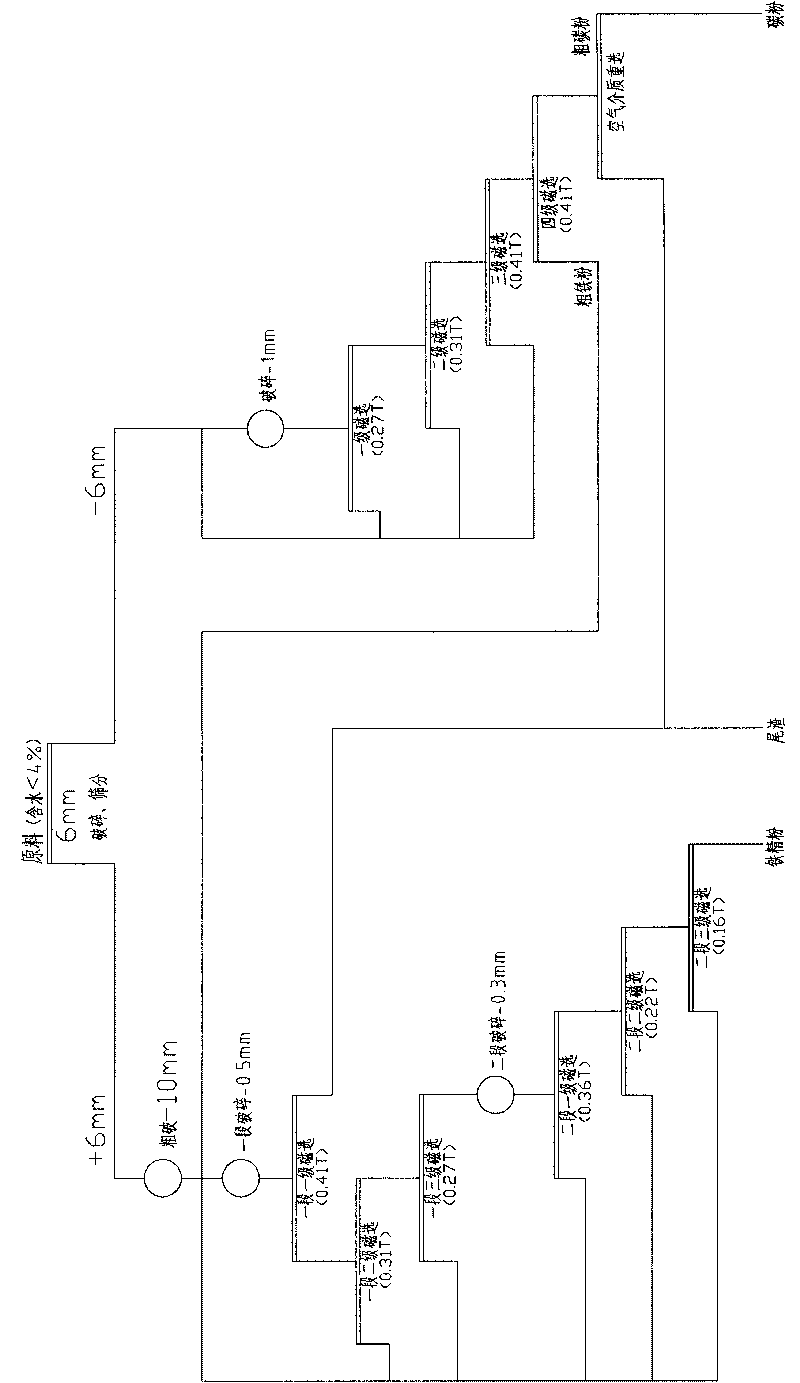
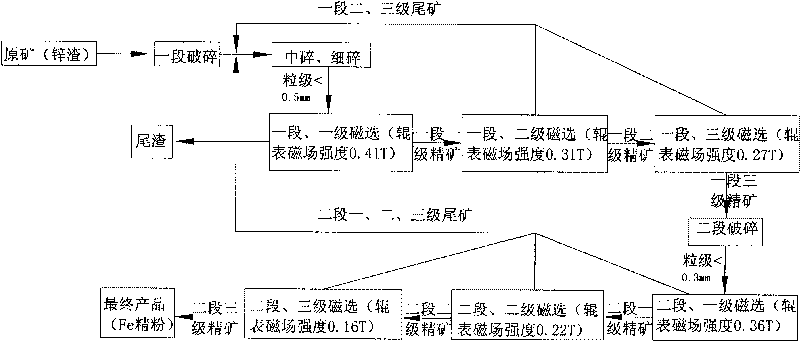
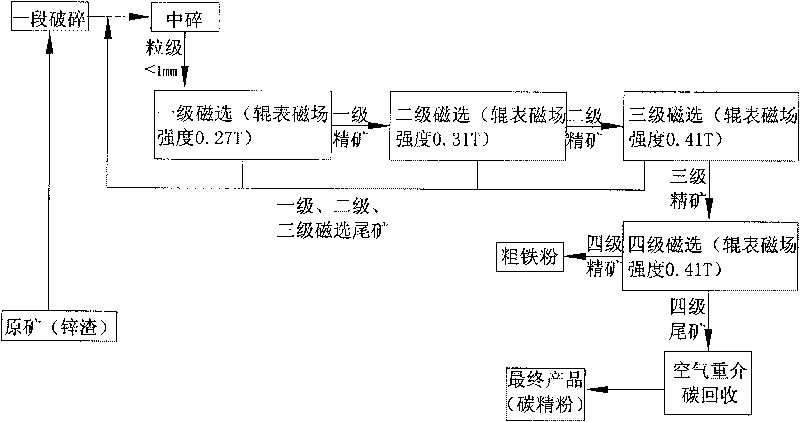
The invention relates to a kiln slag processing technology of a zinc volatilizing kiln, which is characterized by comprising the technological steps of crude crushing and prescreening, medium crushing and fine crushing, two-section and three-stage magnetic separating Fe fined powder, four-stage magnetic separating and re-separating carbon refined powder by an air medium. The invention has the advantages of simple technology, high production efficiency, stable product quality and low energy consumption and enhances the utilization rate of resources, the Fe content of the finally separated Fe refined powder can be about 60%, and the Fe refined powder according with the national requirements can be separated without secondary processing.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
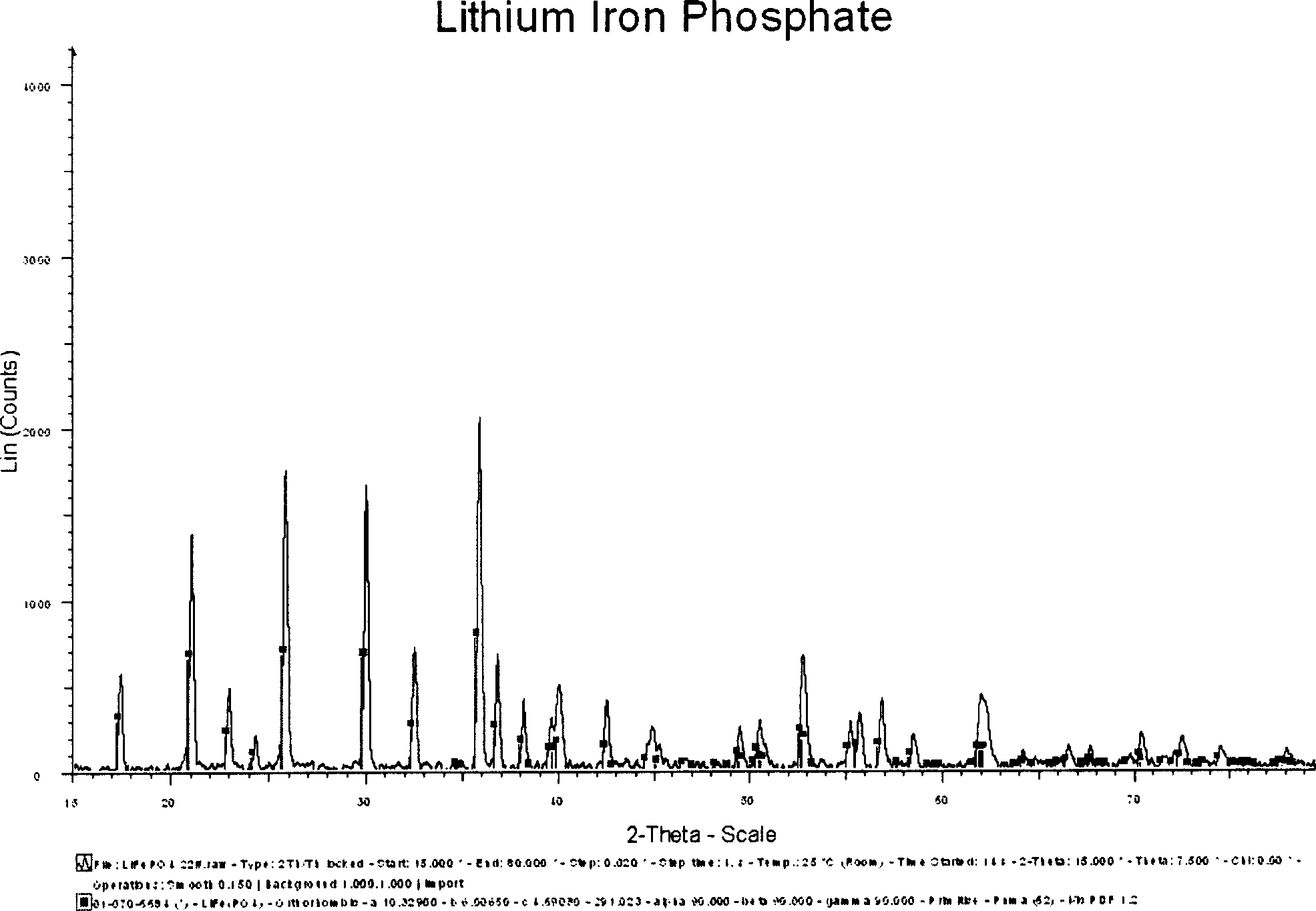
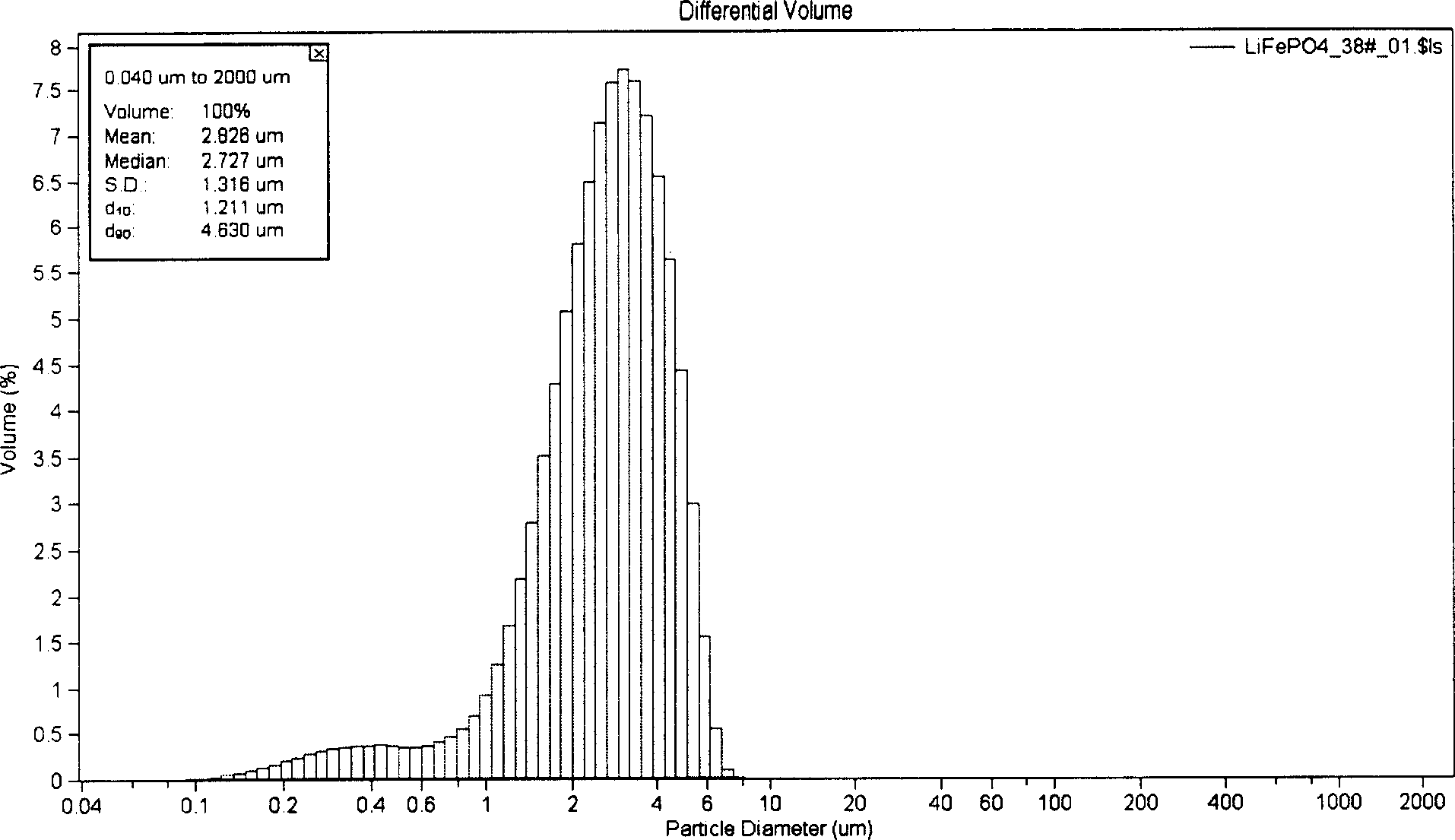
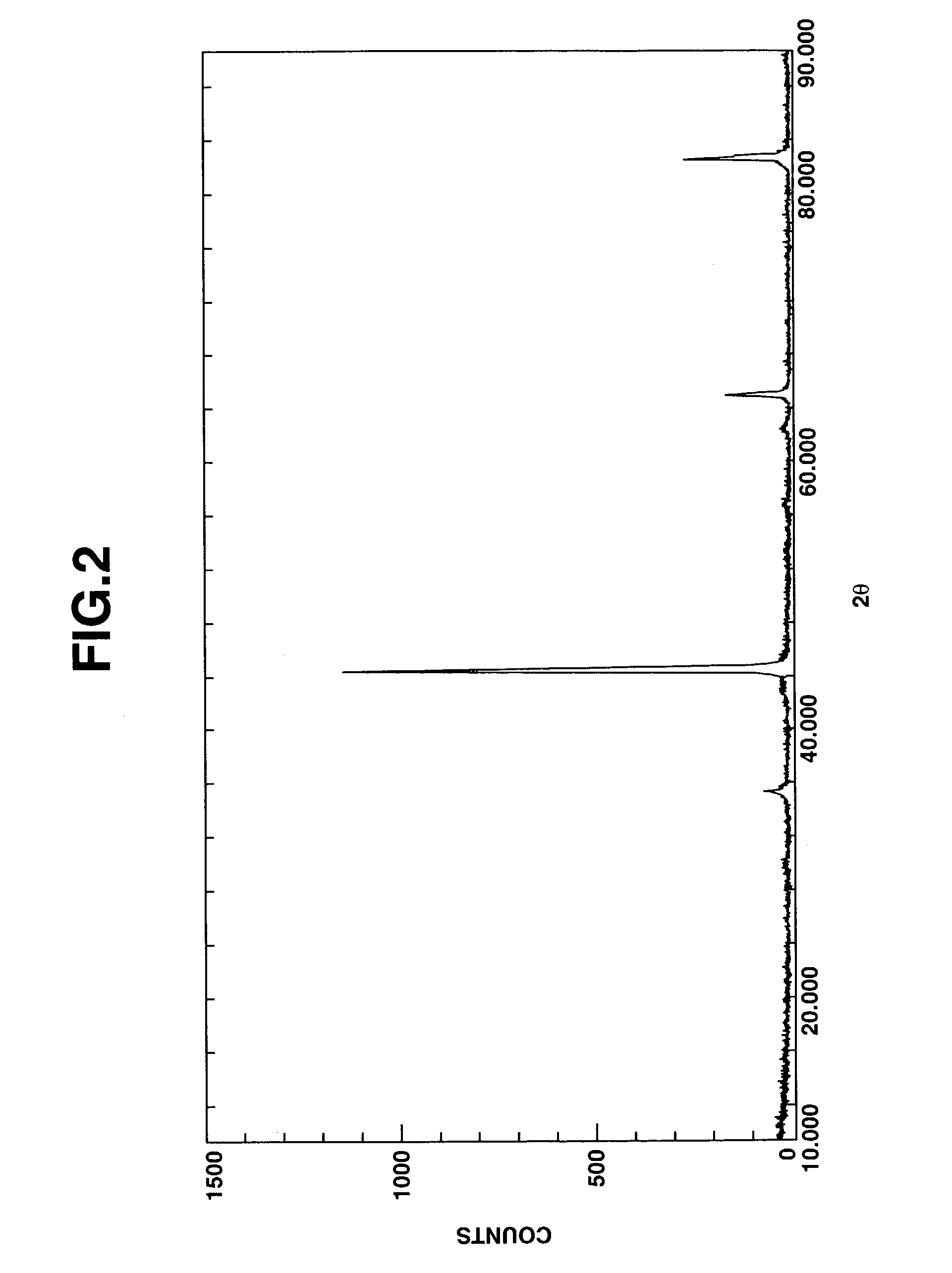
Semiwet method of preparing lithium ferrous phosphate and its prepared lithium ferrous phosphate
InactiveCN1903707AQuality improvementWell mixedCell electrodesPhosphorus compoundsPhosphateWater insoluble
The present invention provides a method for preparing ferrous lithium phosphate by using semi-wet method. Said method includes the following steps: in the compounds containing Li, Fe and P selecting one water-insoluble compound and others are water-soluble, placing the above-mentioned water-insoluble compound into the above-mentioned water-soluble compound solution to obtain a suspension; in said suspension Li content, Fe content and P content must be met with the following formula: [mLi+n(1-m) / n M]:Fe:qPO4=1:1:1(1), in formula (1) n is chemical valence of alloying element M, m is mole number of Li, (1-m) / n is mole number of alloying element M and P and q respectively are mole numbers of Fe and PO4; adding reduction electro-conductive additive, spraying and pyrolyzing suspension so as to obtain precursor powder, roasting said precursor powder and pulverizing to obtain the invented product.
Owner:新乡市华鑫电源材料有限公司
Iron particles for purifying contaminated soil or ground water
InactiveUS7022256B2Material nanotechnologyScale removal and water softeningHalogenHazardous substance
Iron particles for purifying soil or ground water of the present invention comprise a mixed phase of α-Fe phase and Fe3O4 phase, and having a BET specific surface area of 5 to 60 m2 / g, an Fe content of not less than 75% by weight based on the weight of the iron particles and a sulfur content of not less than 1,000 ppm. The iron particles are capable of decomposing or insolubilizing harmful substances such as organohalogen compounds and / or heavy metals, cyanogen, etc. contained in the soil or ground water in efficient, continuous and economical manners.
Owner:TODA IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com