Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4581results about How to "Inhibited Diffusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
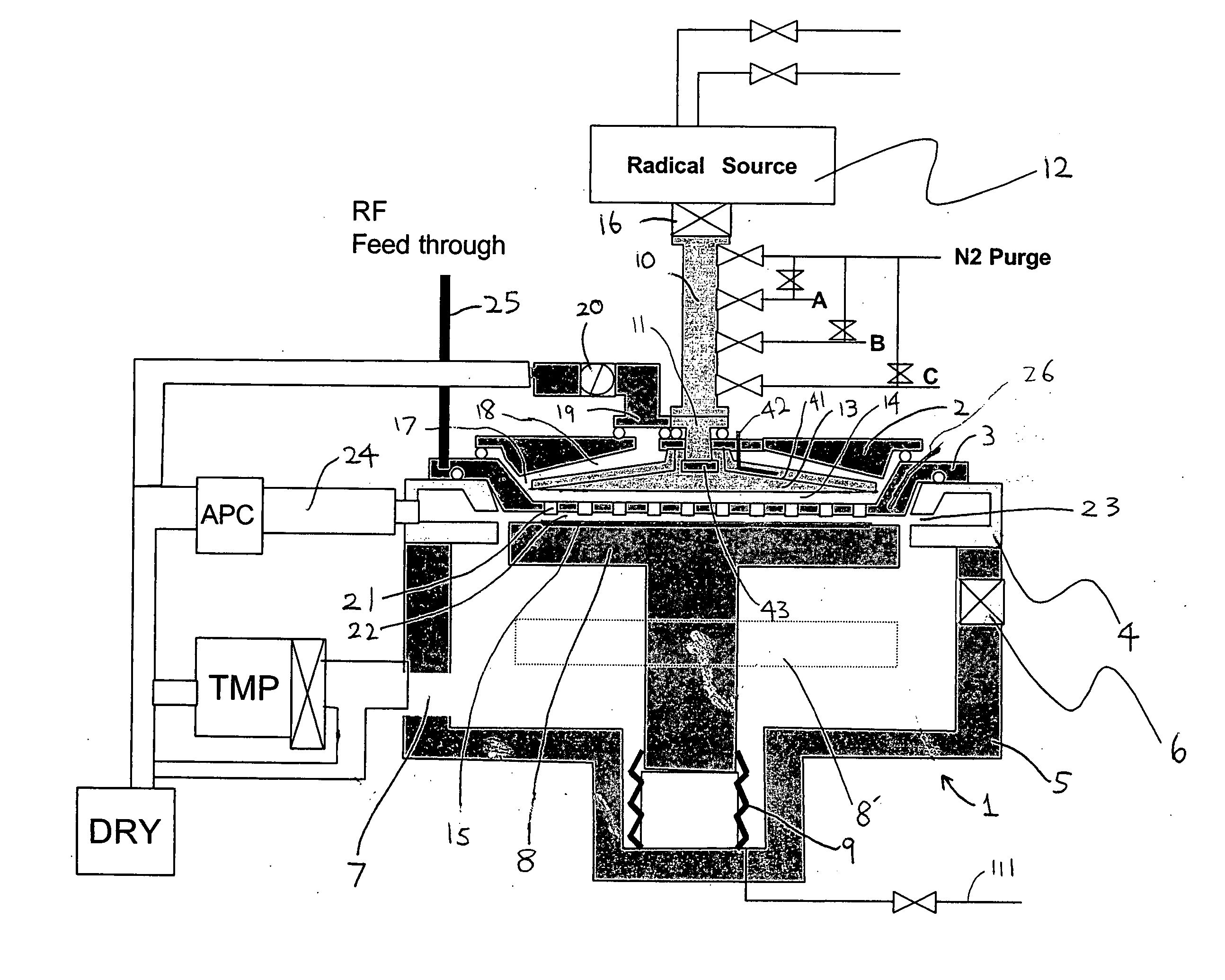
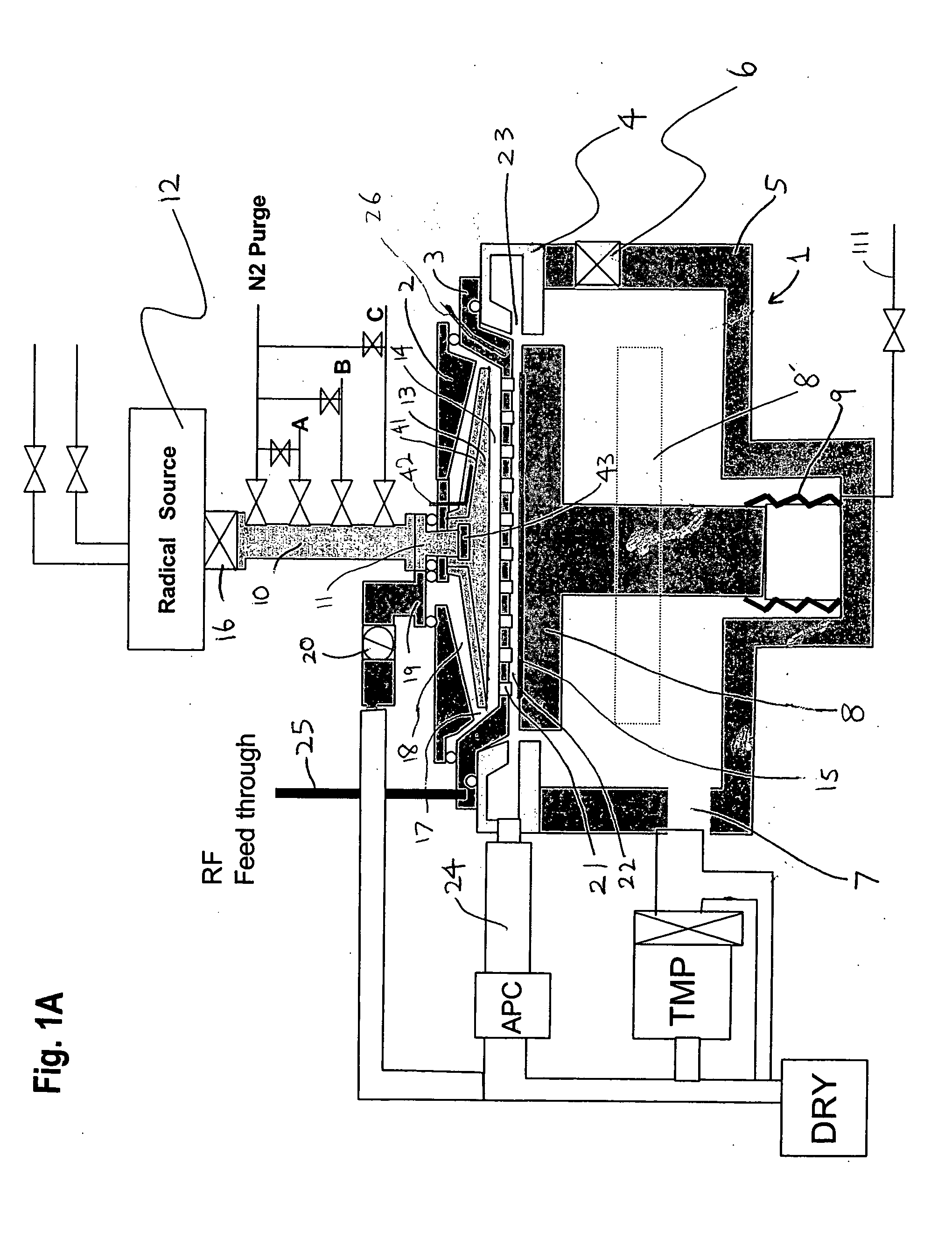
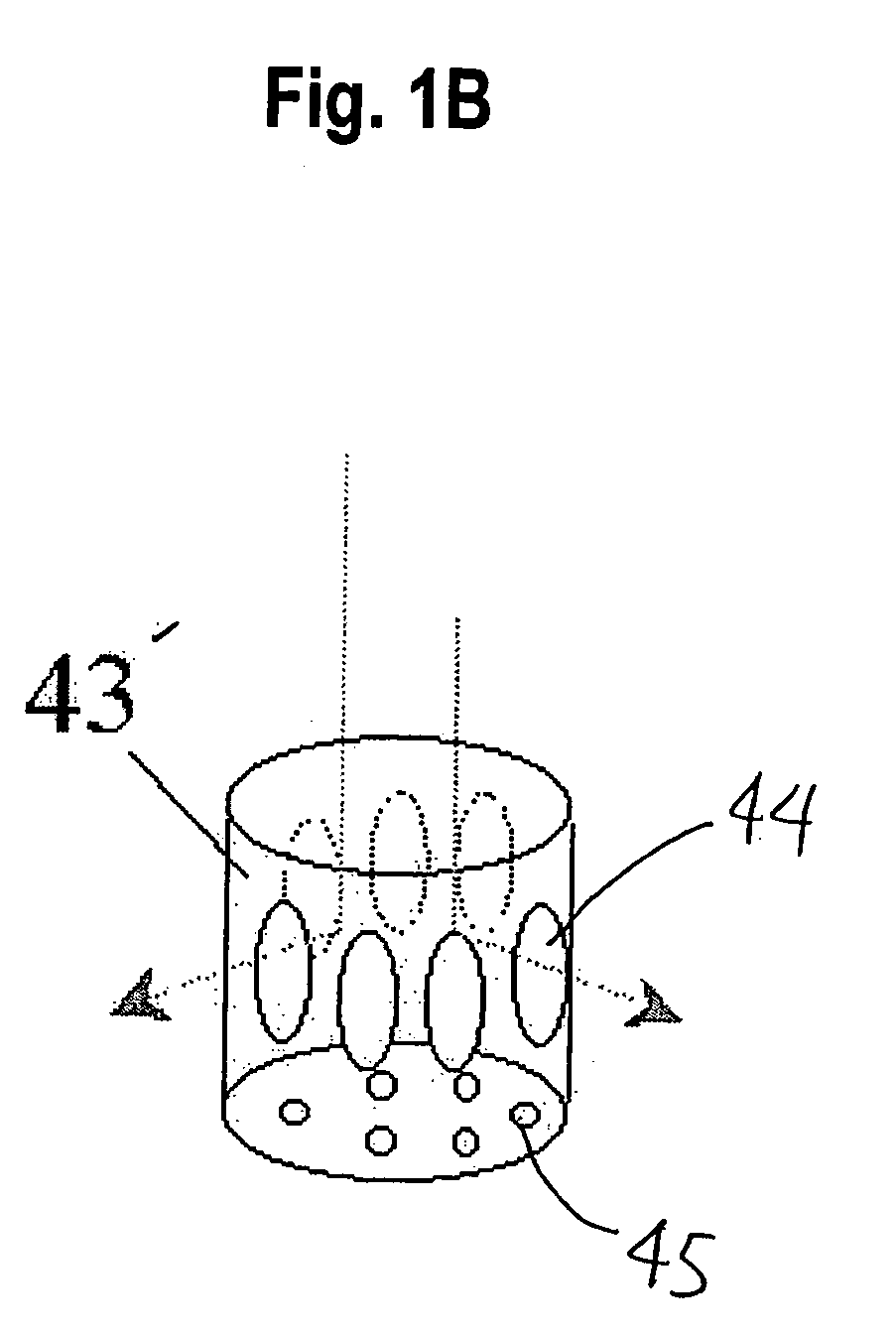
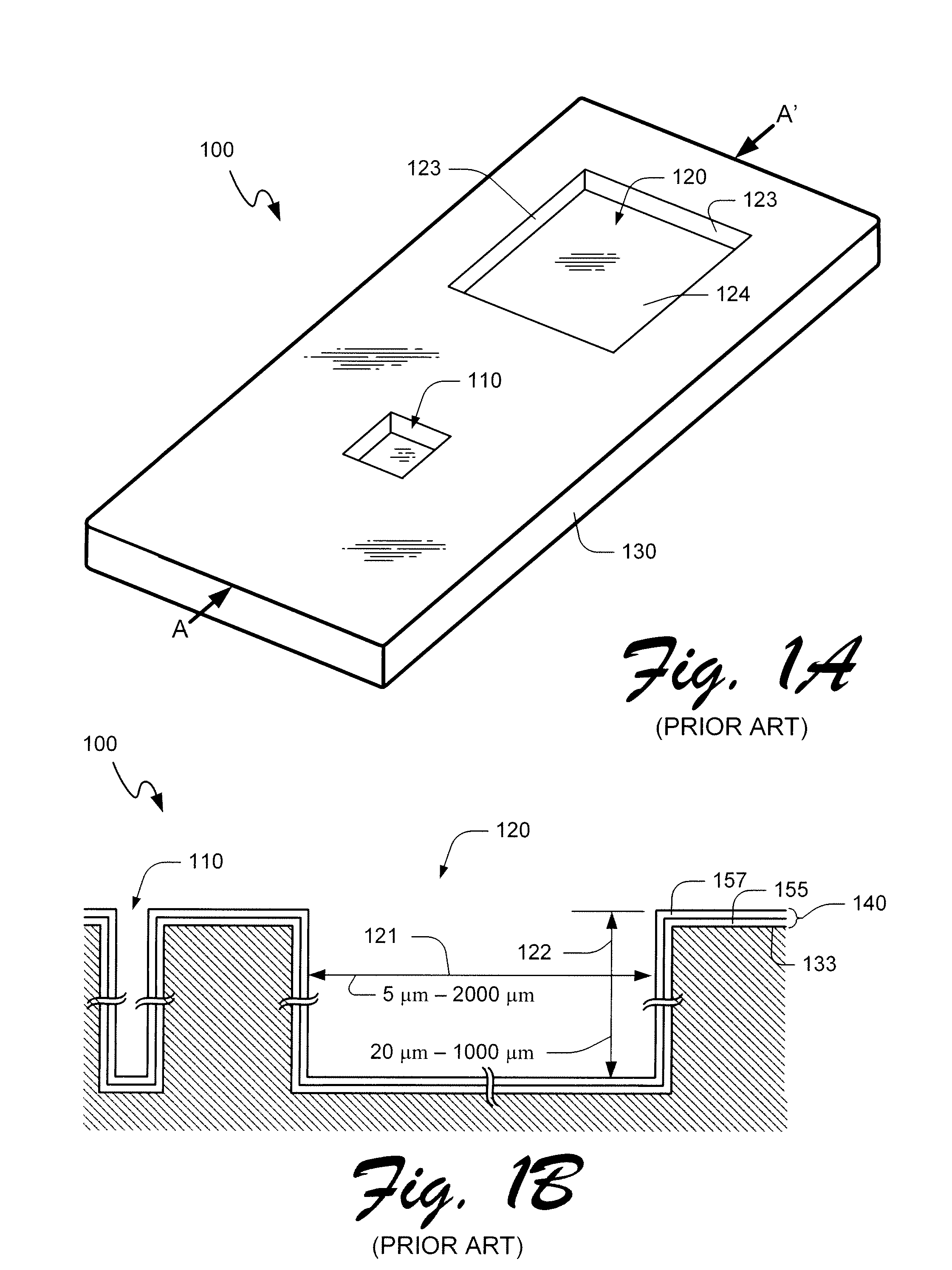
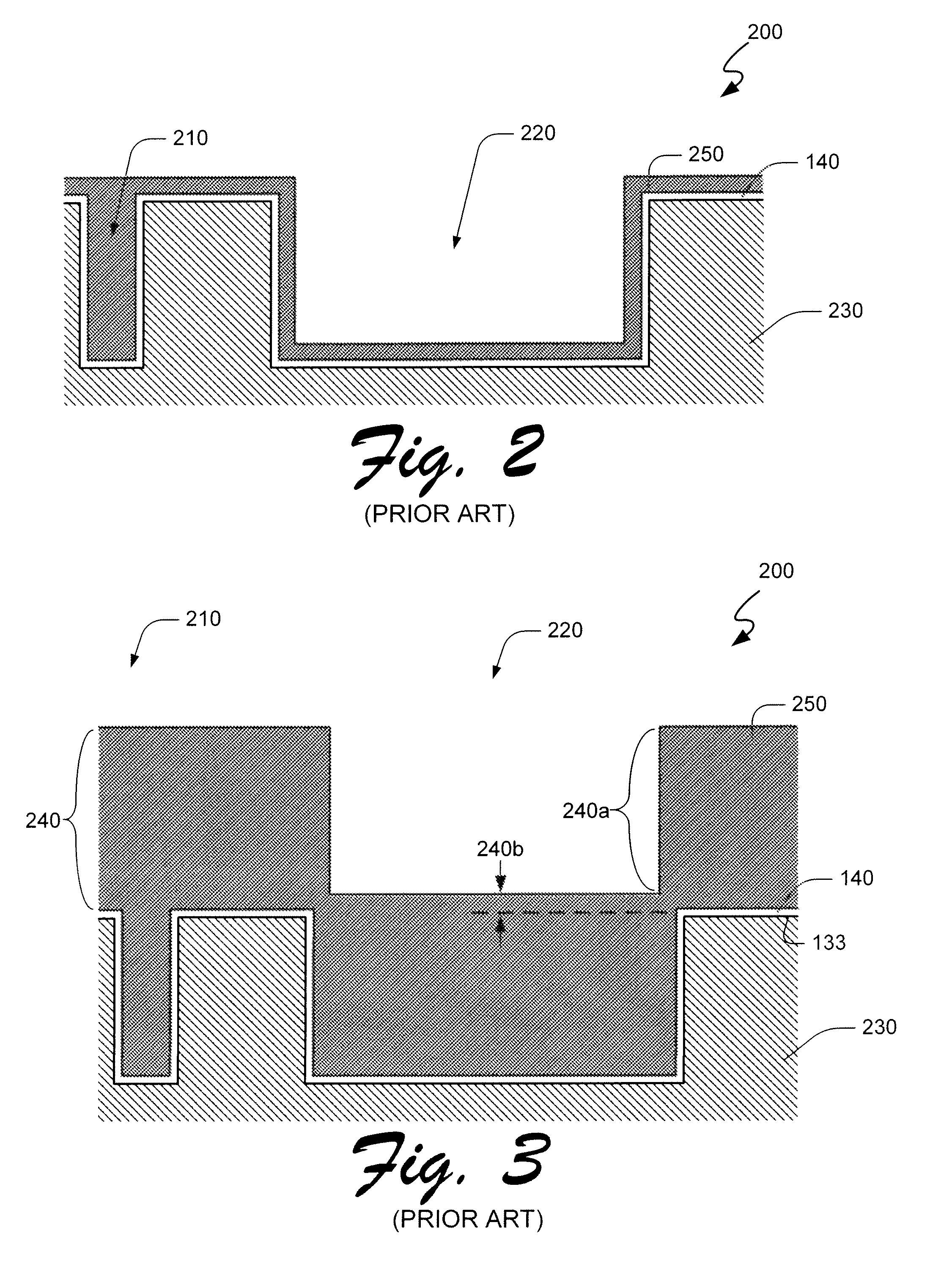
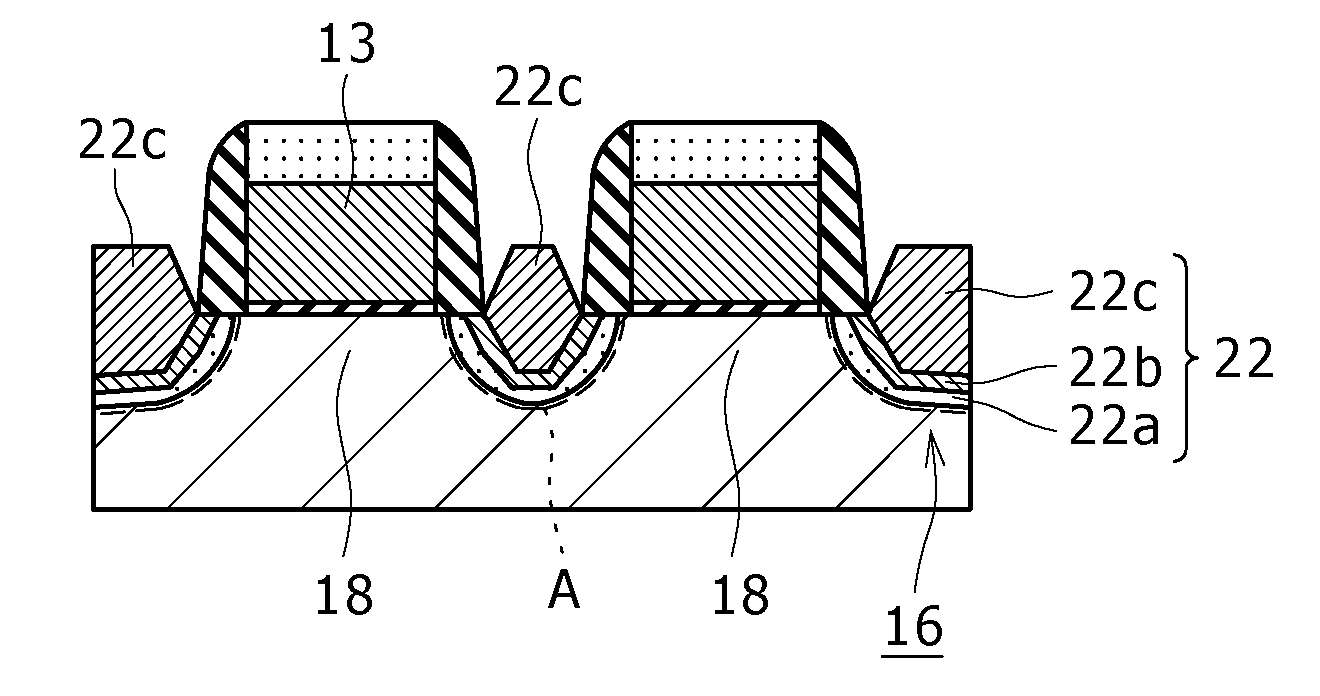
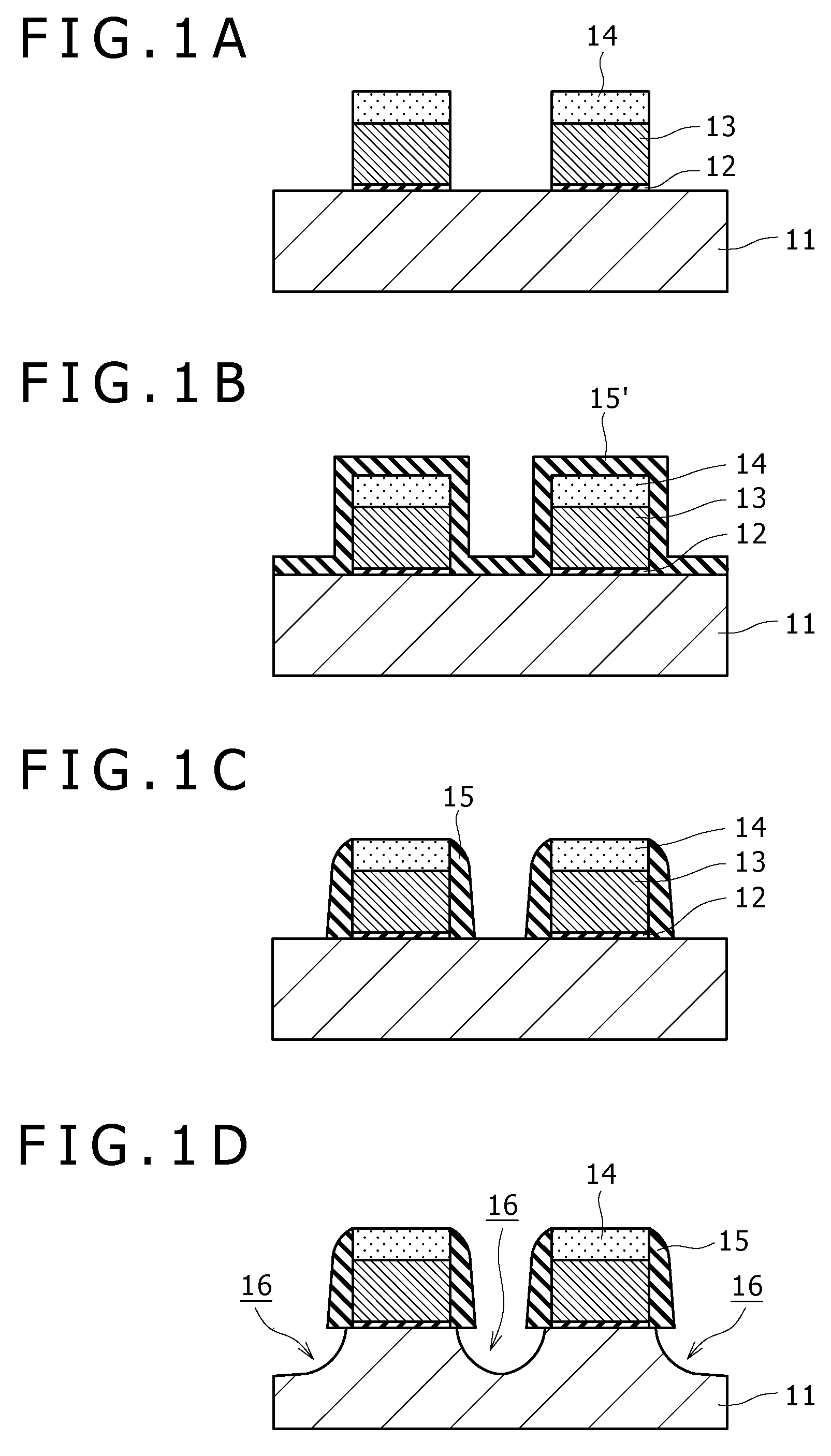
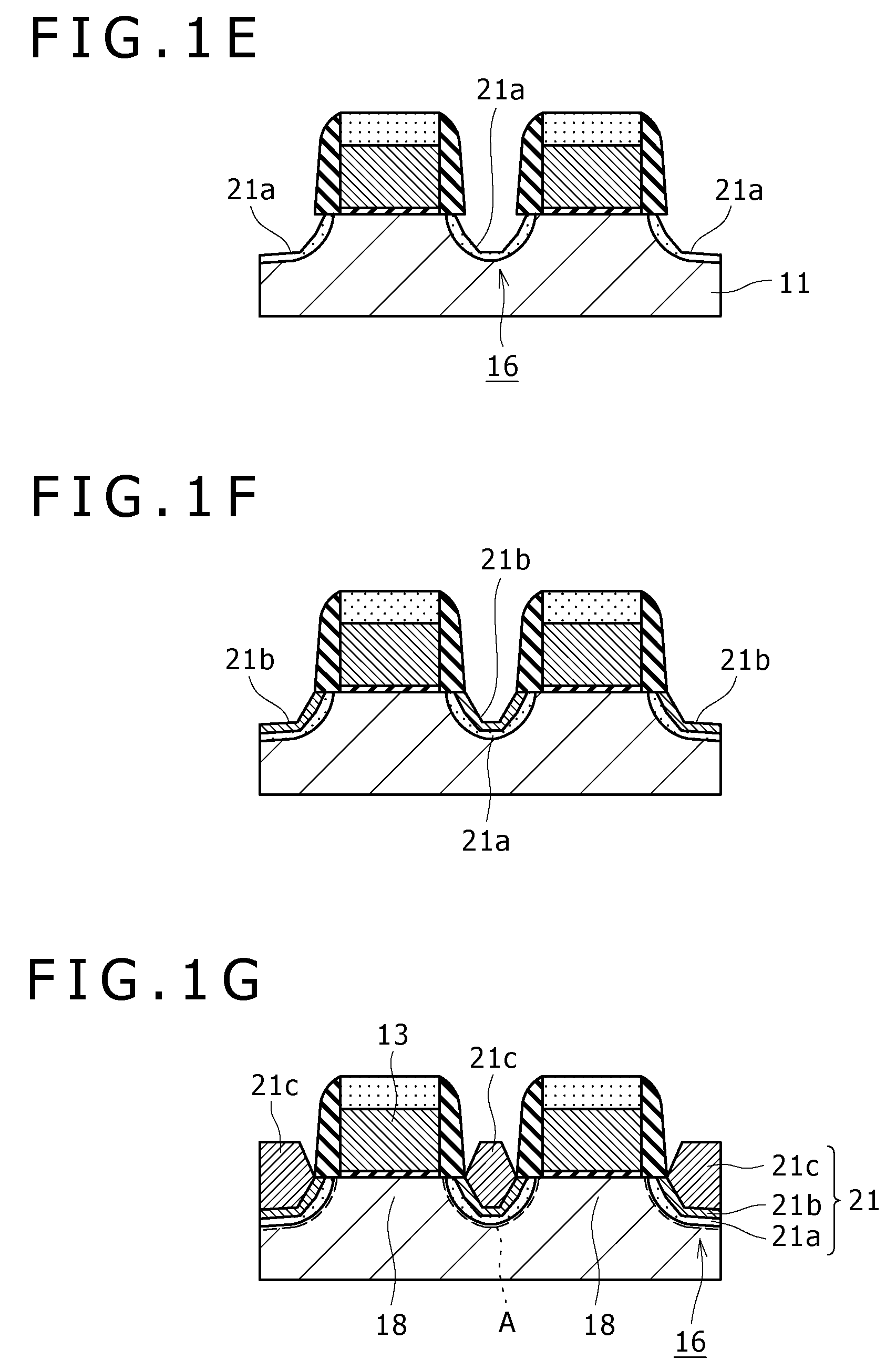
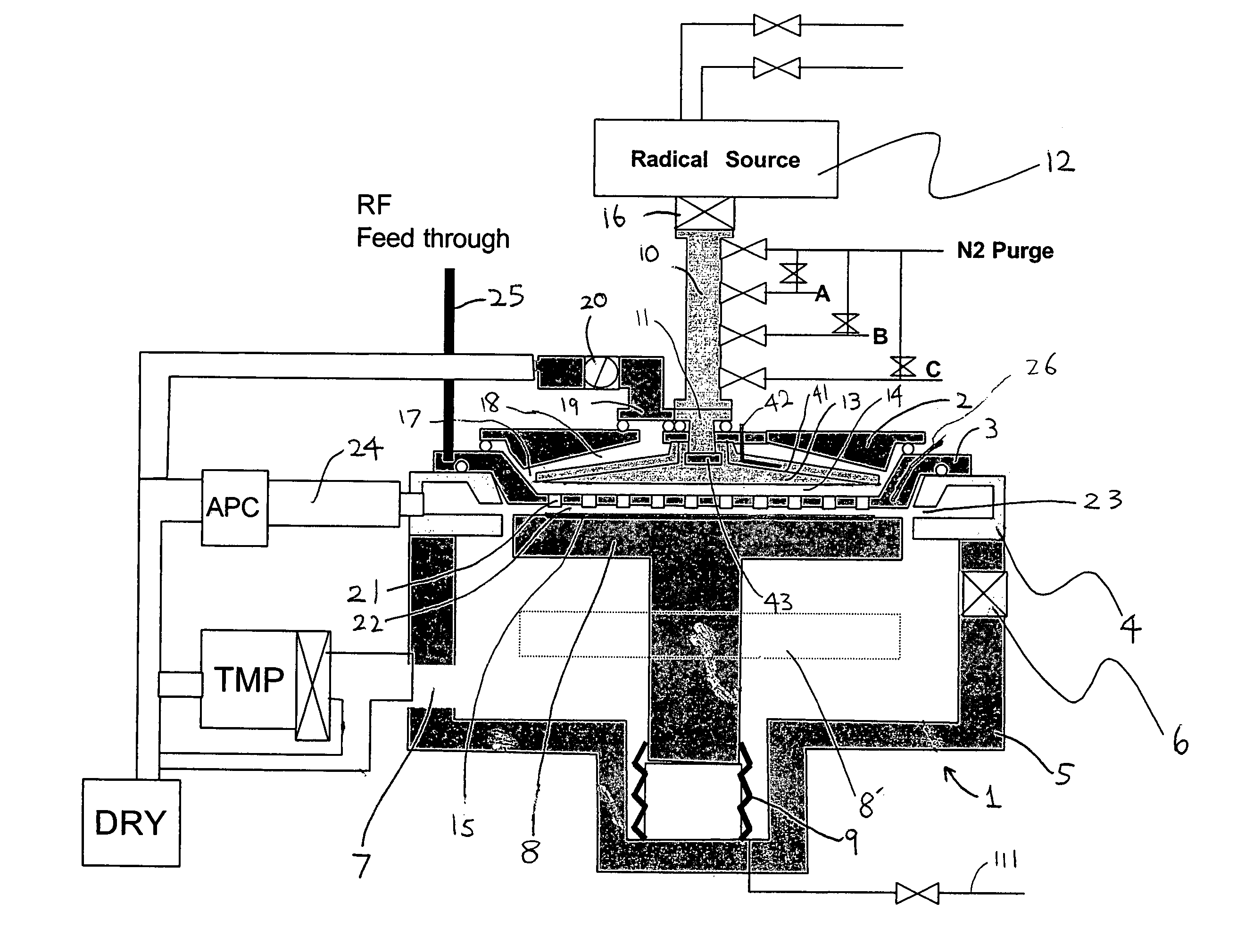
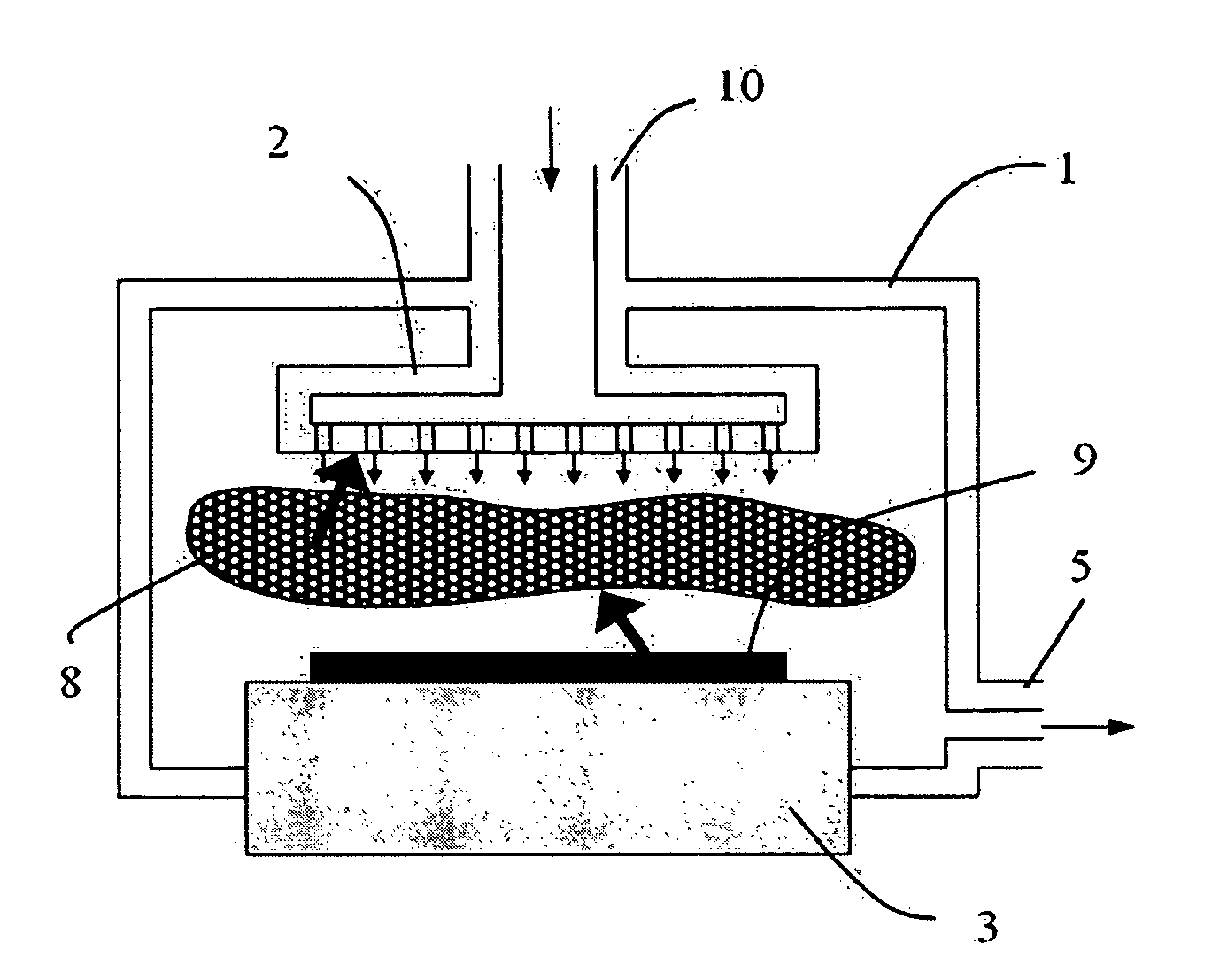
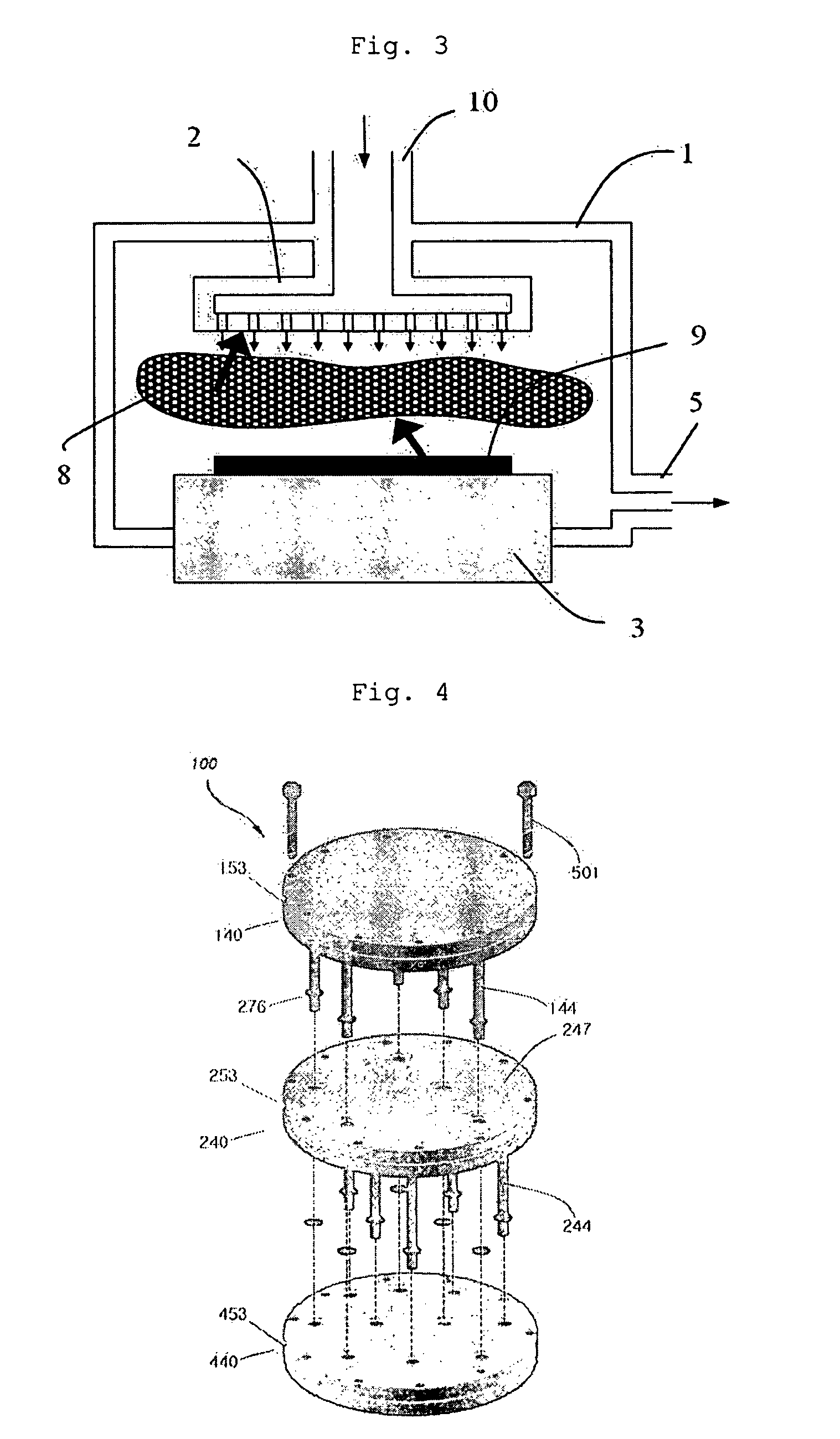
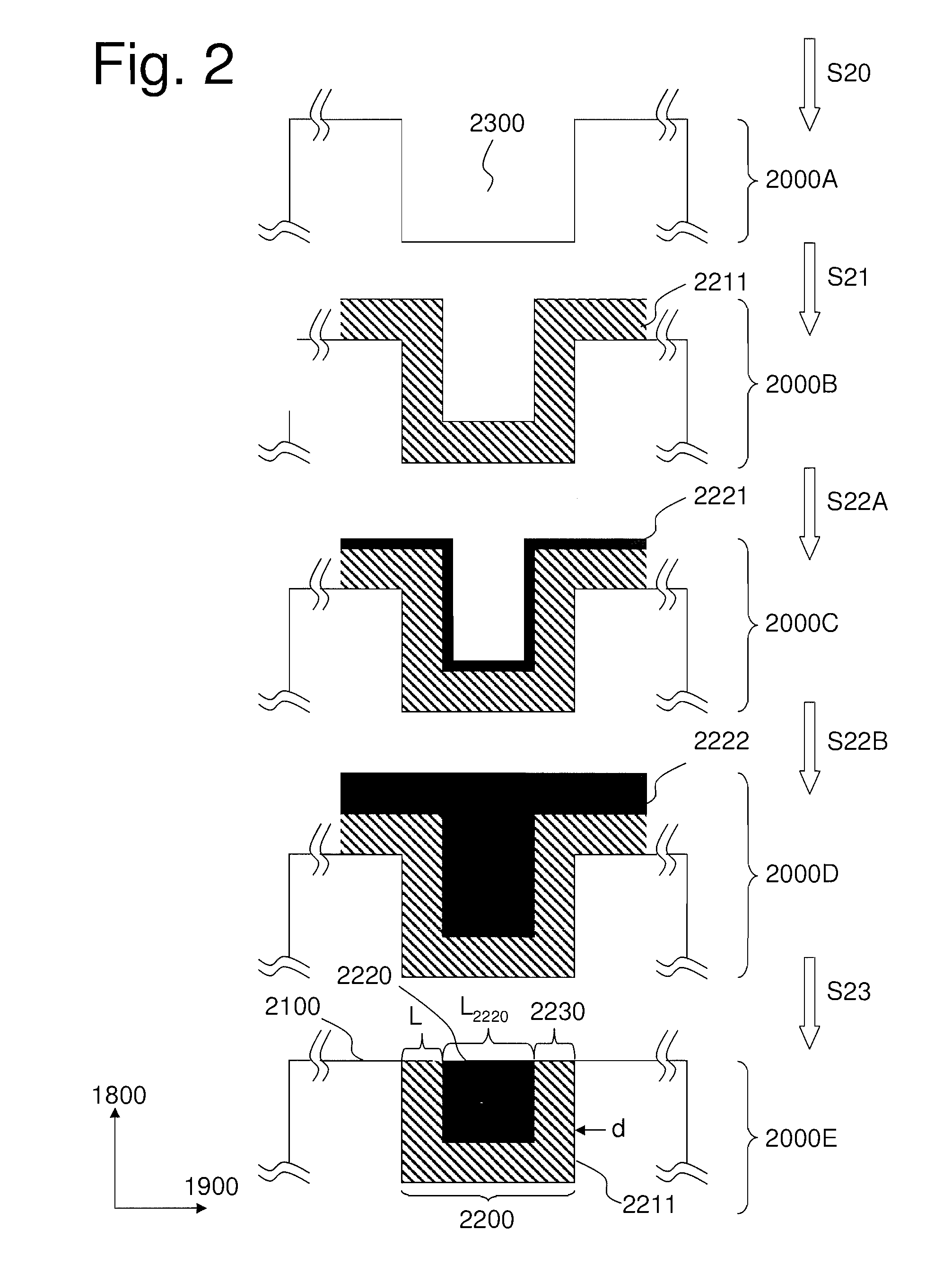
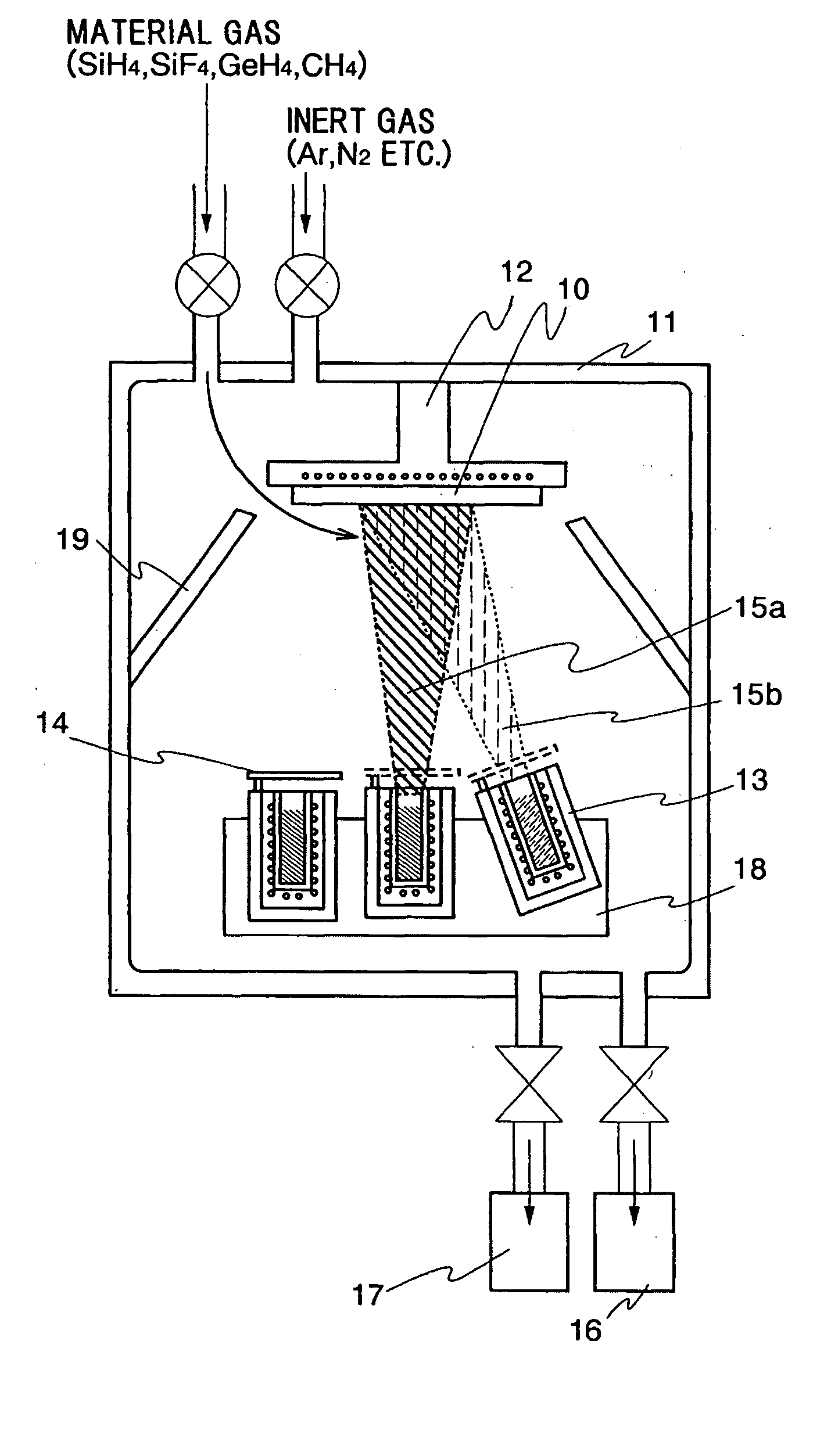
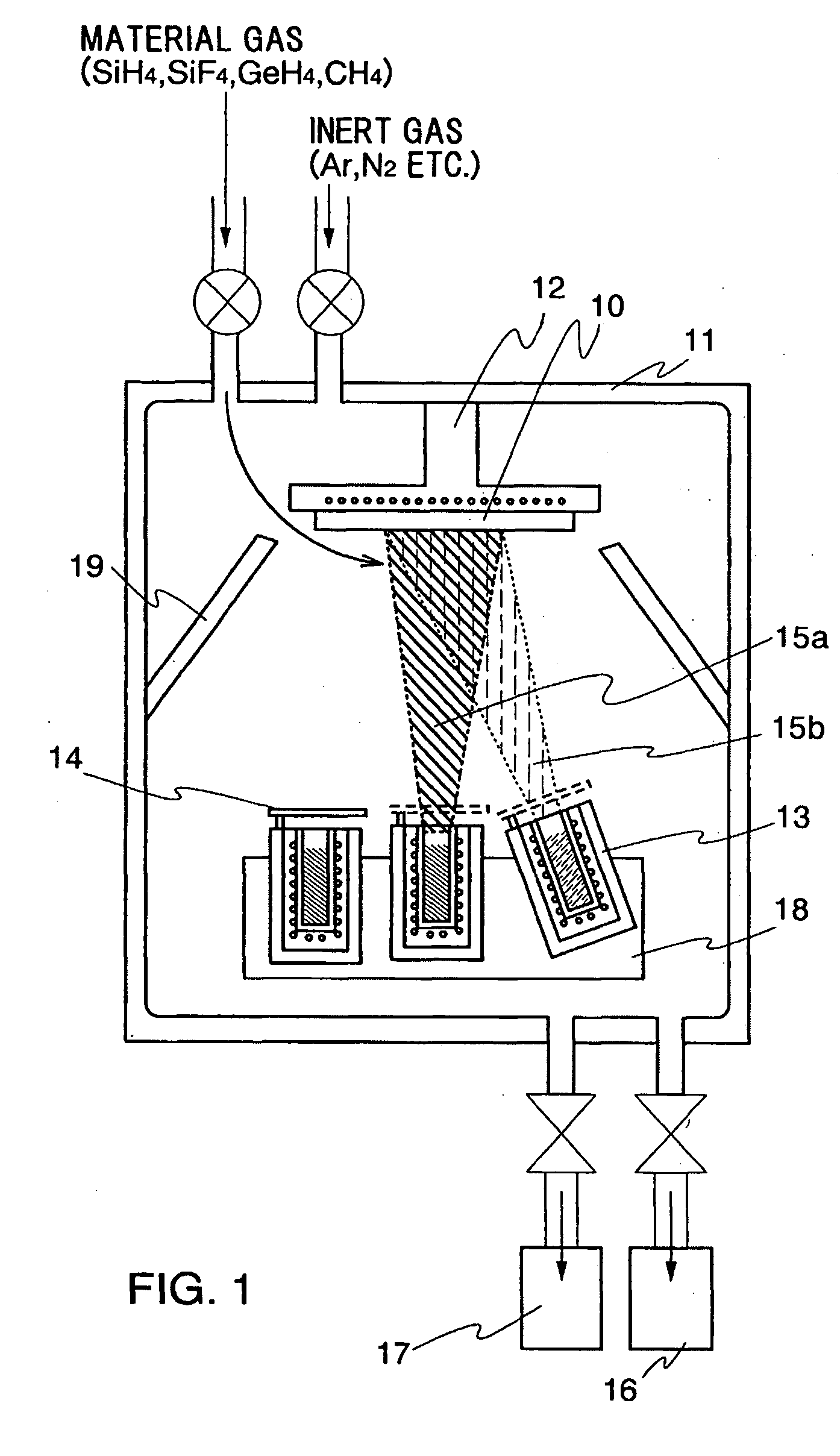
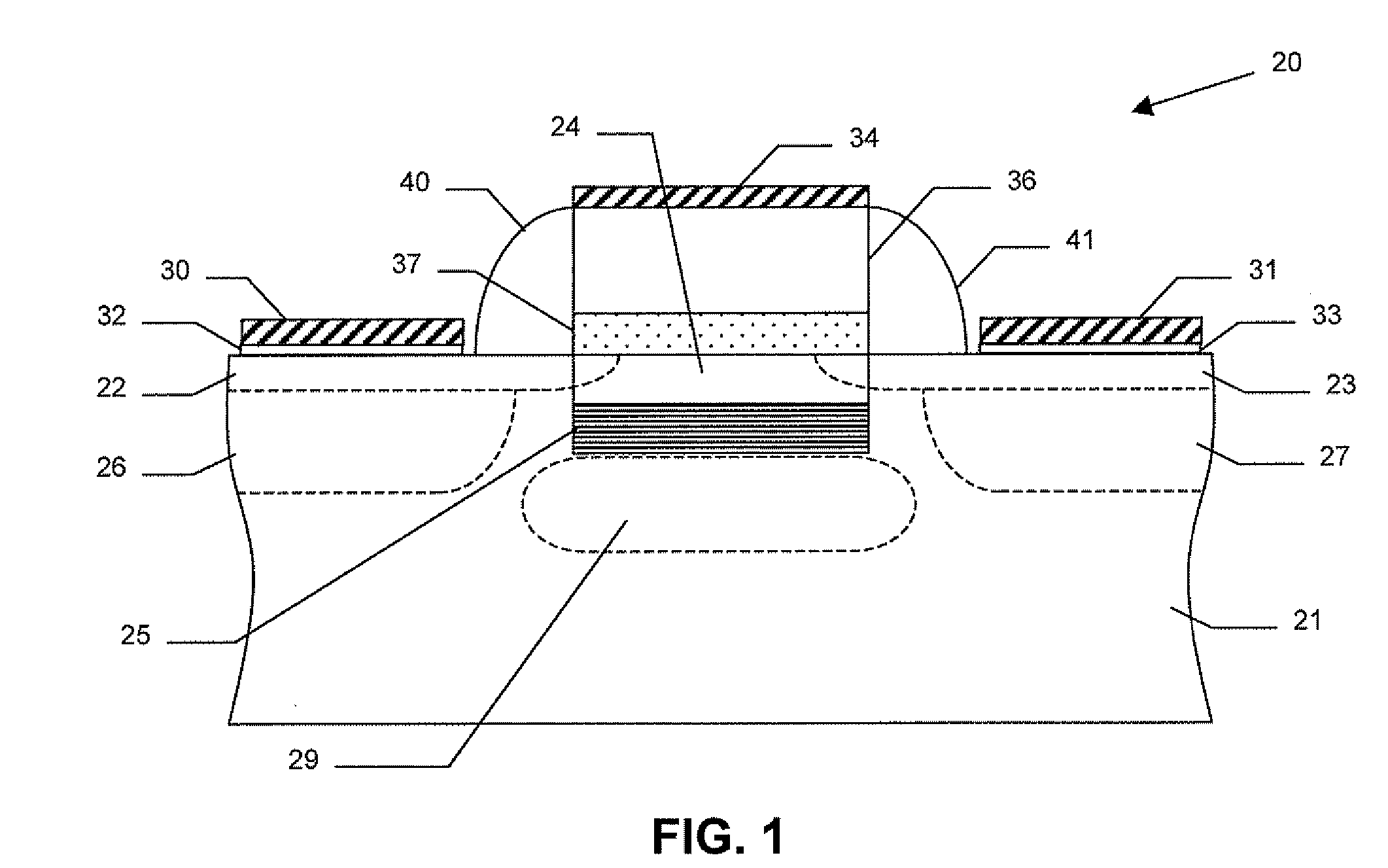
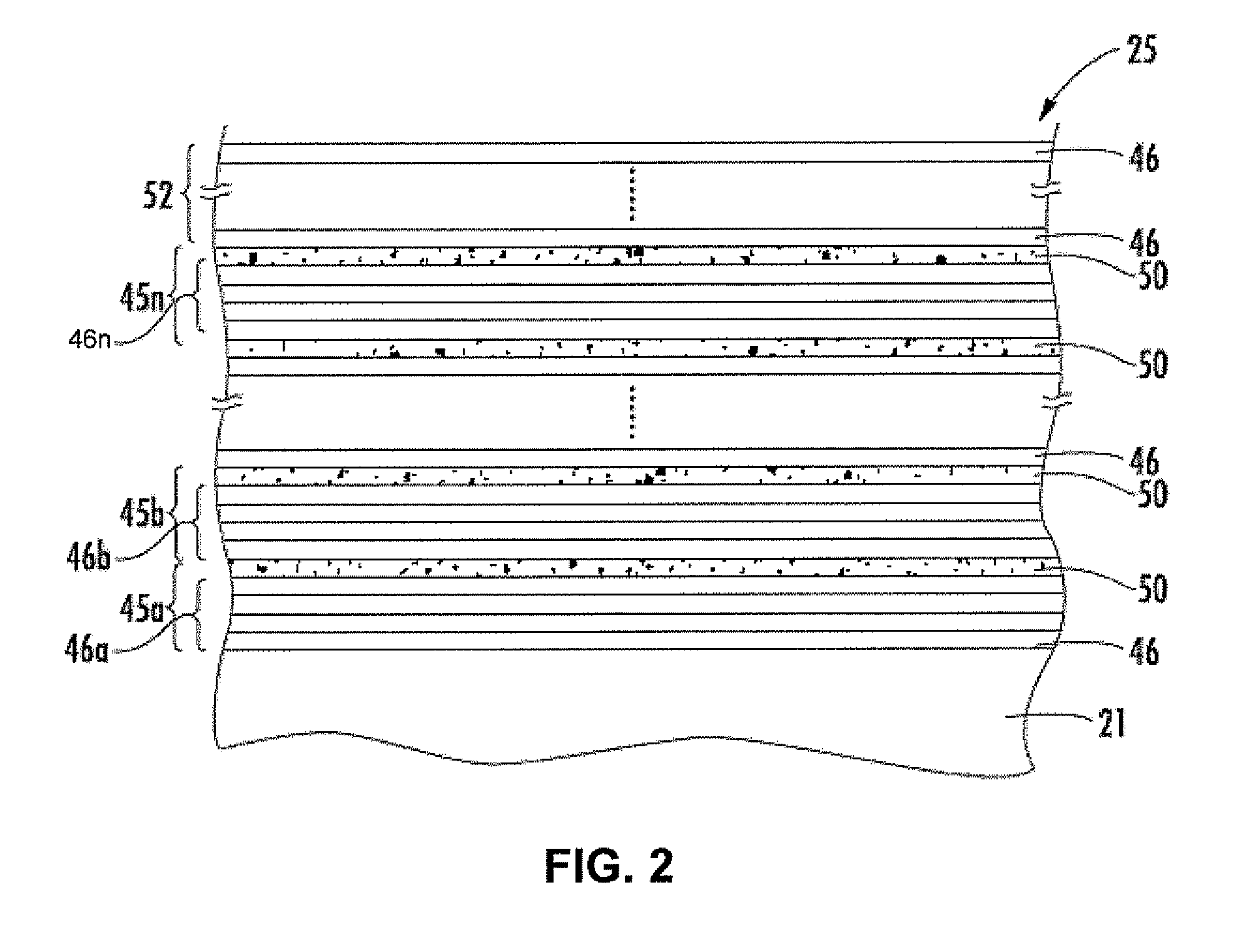
Apparatus and method for forming thin film using upstream and downstream exhaust mechanisms
ActiveUS20050208217A1Improve throughputUniform supplyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGas supplySubstrate surface
A thin-film formation apparatus possesses a reaction chamber to be evacuated, a placing portion on which a substrate is placed inside the reaction chamber, a gas-dispersion guide installed over the placing portion for supplying a gas onto a substrate surface, a gas-supply port for introducing the gas into the gas-dispersion guide, a gas-dispersion plate disposed on the side of the substrate of the gas-dispersion guide and having multiple gas-discharge pores, a first exhaust port for exhausting, downstream of the gas-dispersion plate, the gas supplied onto the substrate surface from the gas-dispersion plate, and a second exhaust port for exhausting, upstream of the gas-dispersion plate, a gas inside the gas-dispersion guide via a space between the gas-dispersion guide and the gas-dispersion plate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method and apparatus for 3D interconnect
ActiveUS8076237B2Improve adhesionInhibited DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsConductive materialsEngineering
The present invention discloses methods for depositing a material, particularly a conductive material, in cavities of a substrate and forming bonding contacts or pads thereon. An intracavity structure may be utilized in conjunction with embodiments of the present invention to provide efficient filling of diverse cavities within the substrate. Also provided are embodiments for interconnection structures using filled cavities, along with electrically conductive or reactive structures which may include capacitors fabricated within a substrate.
Owner:ASM NUTOOL
Method for repairing damage of dielectric film by cyclic processes
ActiveUS20130337583A1Enhanced barrier functionInhibited DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCyclic processMaterials science
A method for repairing process-related damage of a dielectric film includes: (i) adsorbing a first gas containing silicon on a surface of the damaged dielectric film without depositing a film in the absence of reactive species, (ii) adsorbing a second gas containing silicon on a surface of the dielectric film, followed by applying reactive species to the surface of the dielectric film, to form a monolayer film thereon, and (iii) repeating step (ii). The duration of exposing the surface to the first gas in step (i) is longer than the duration of exposing the surface to the second gas in step (ii).
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Substrate Processing Apparatus
InactiveUS20100058984A1Inhibited DiffusionPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess engineeringVacuum pump
Process gas discharged from a bypass pipe to a gas exhaust system can be prevented from diffusing back to the inside of a process chamber without having to install a dedicated vacuum pump at the downstream side of the bypass pipe. The substrate processing apparatus includes a process chamber accommodating a substrate, a gas supply system supplying process gas from a process gas source to the process chamber for processing the substrate, a gas exhaust system configured to exhaust the process chamber, two or more vacuum pumps installed in series at the gas exhaust system, and a bypass pipe connected between the gas supply system and the gas exhaust system. The most upstream one of the vacuum pumps is a mechanical booster pump, and the bypass pipe is connected between the mechanical booster pump and the rest vacuum pumps located at a downstream side of the mechanical booster pump.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device, and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070254414A1Sufficient carrier mobilityImpurity will diffuseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSurface layerConcentration gradient
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes: the first step of forming a gate electrode over a silicon substrate, with a gate insulating film; and the second step of digging down a surface layer of the silicon substrate by etching conducted with the gate electrode as a mask. The method of manufacturing the semiconductor device further includes the third step of epitaxially growing, on the surface of the dug-down portion of the silicon substrate, a mixed crystal layer including silicon and atoms different in lattice constant from silicon so that the mixed crystal layer contains an impurity with such a concentration gradient that the impurity concentration increases along the direction from the silicon substrate side toward the surface of the mixed crystal layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and method for forming thin film using upstream and downstream exhaust mechanisms
ActiveUS7408225B2Reduce impactEvenly distributedElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGas supplySubstrate surface
A thin-film formation apparatus possesses a reaction chamber to be evacuated, a placing portion on which a substrate is placed inside the reaction chamber, a gas-dispersion guide installed over the placing portion for supplying a gas onto a substrate surface, a gas-supply port for introducing the gas into the gas-dispersion guide, a gas-dispersion plate disposed on the side of the substrate of the gas-dispersion guide and having multiple gas-discharge pores, a first exhaust port for exhausting, downstream of the gas-dispersion plate, the gas supplied onto the substrate surface from the gas-dispersion plate, and a second exhaust port for exhausting, upstream of the gas-dispersion plate, a gas inside the gas-dispersion guide via a space between the gas-dispersion guide and the gas-dispersion plate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
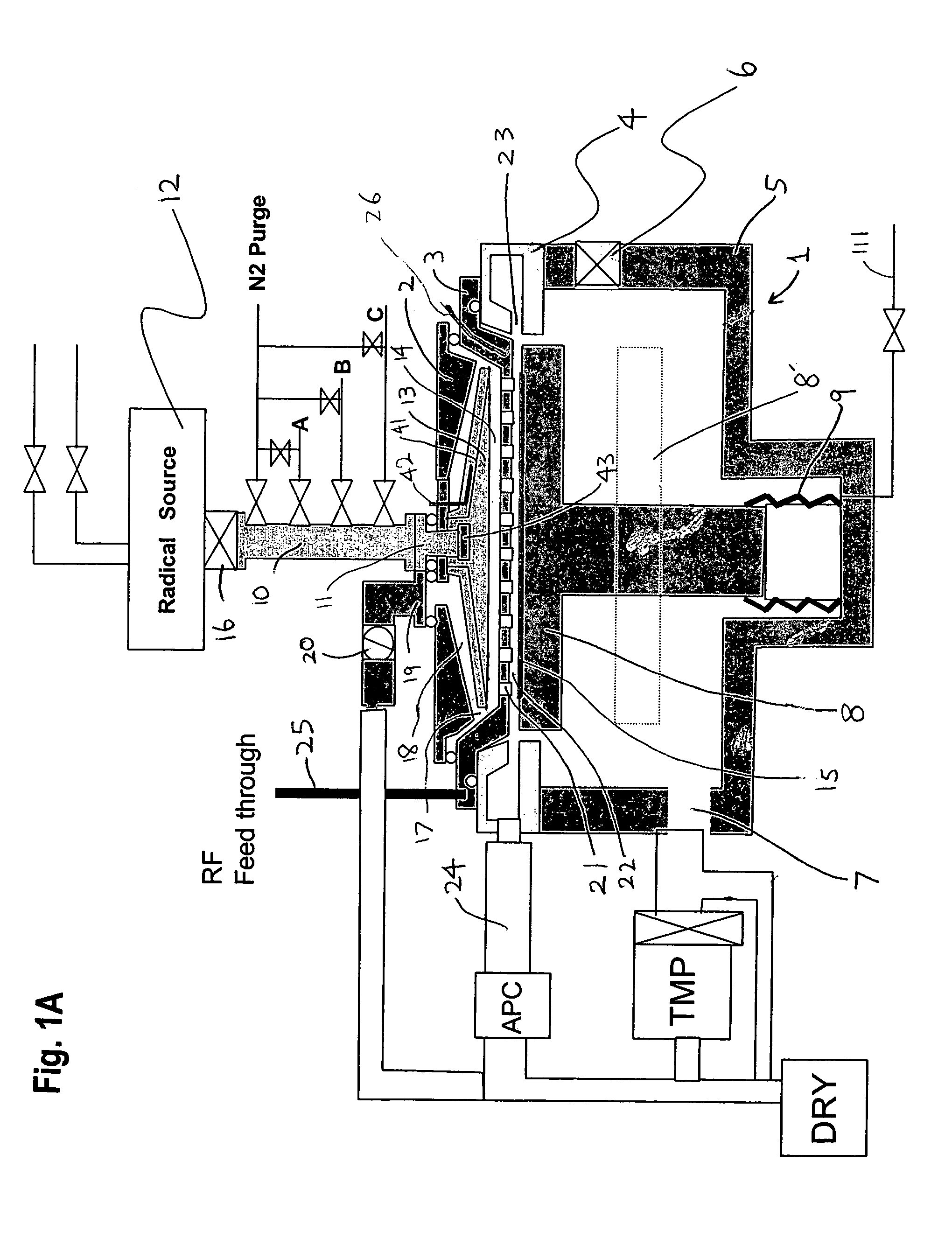
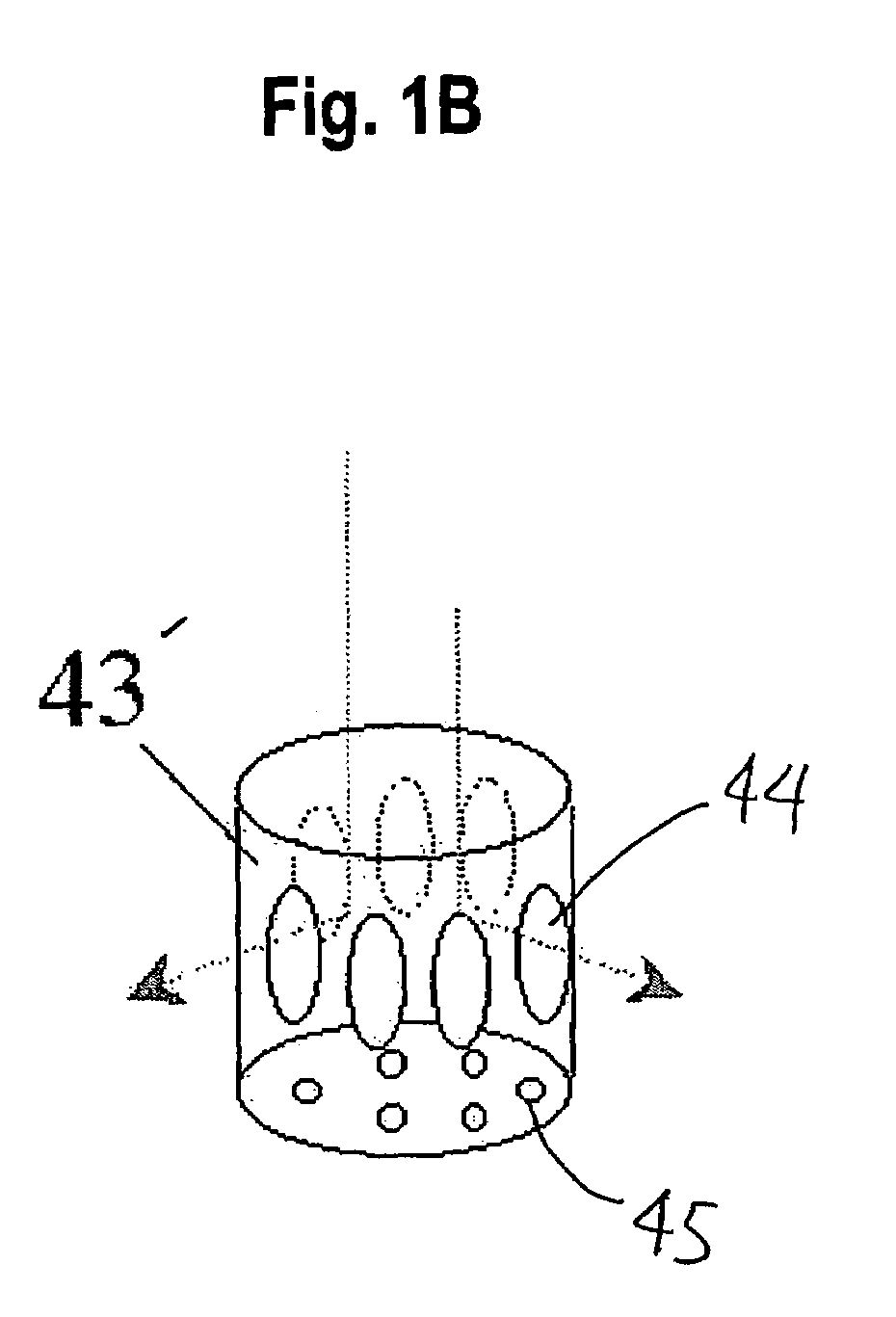
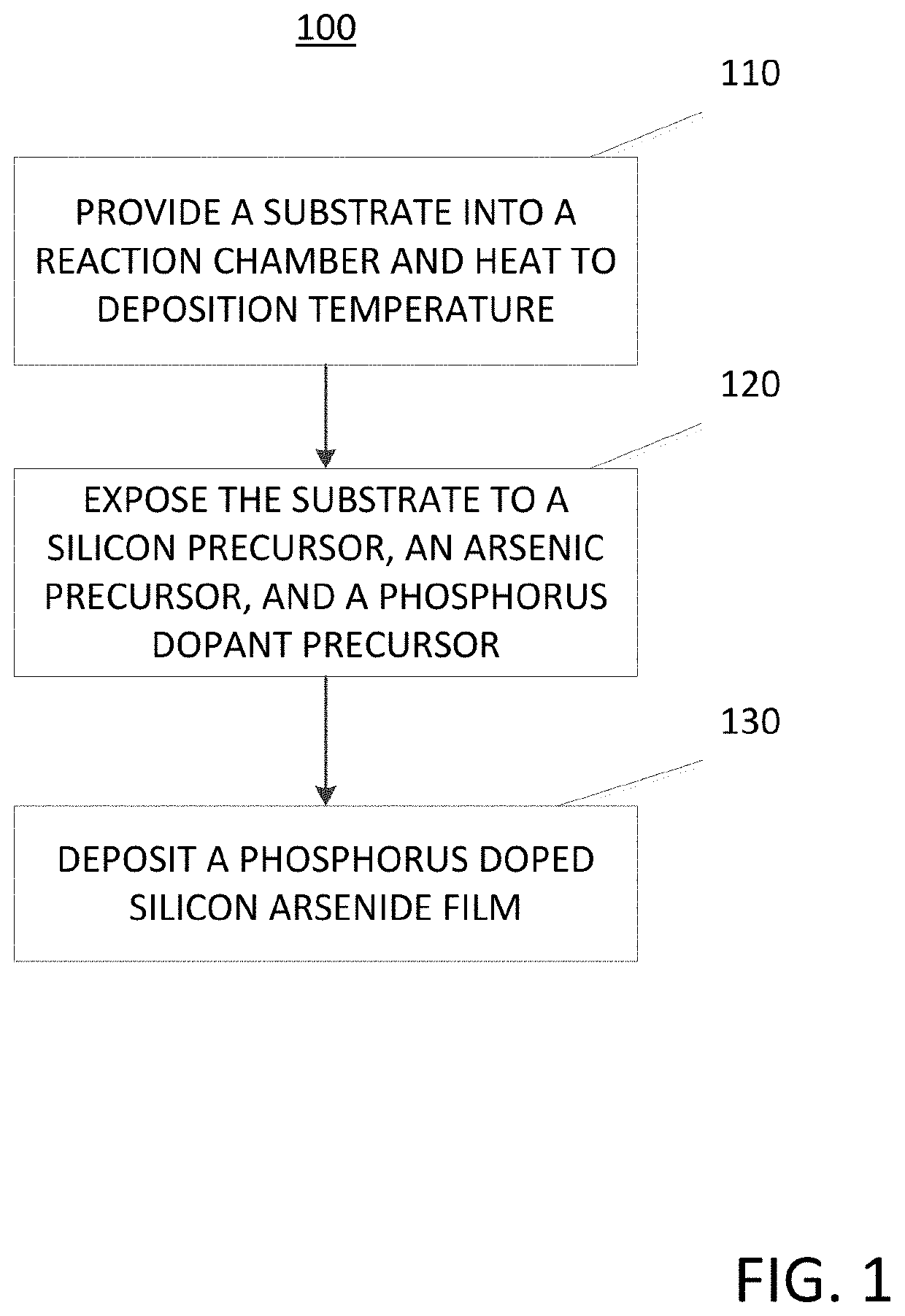
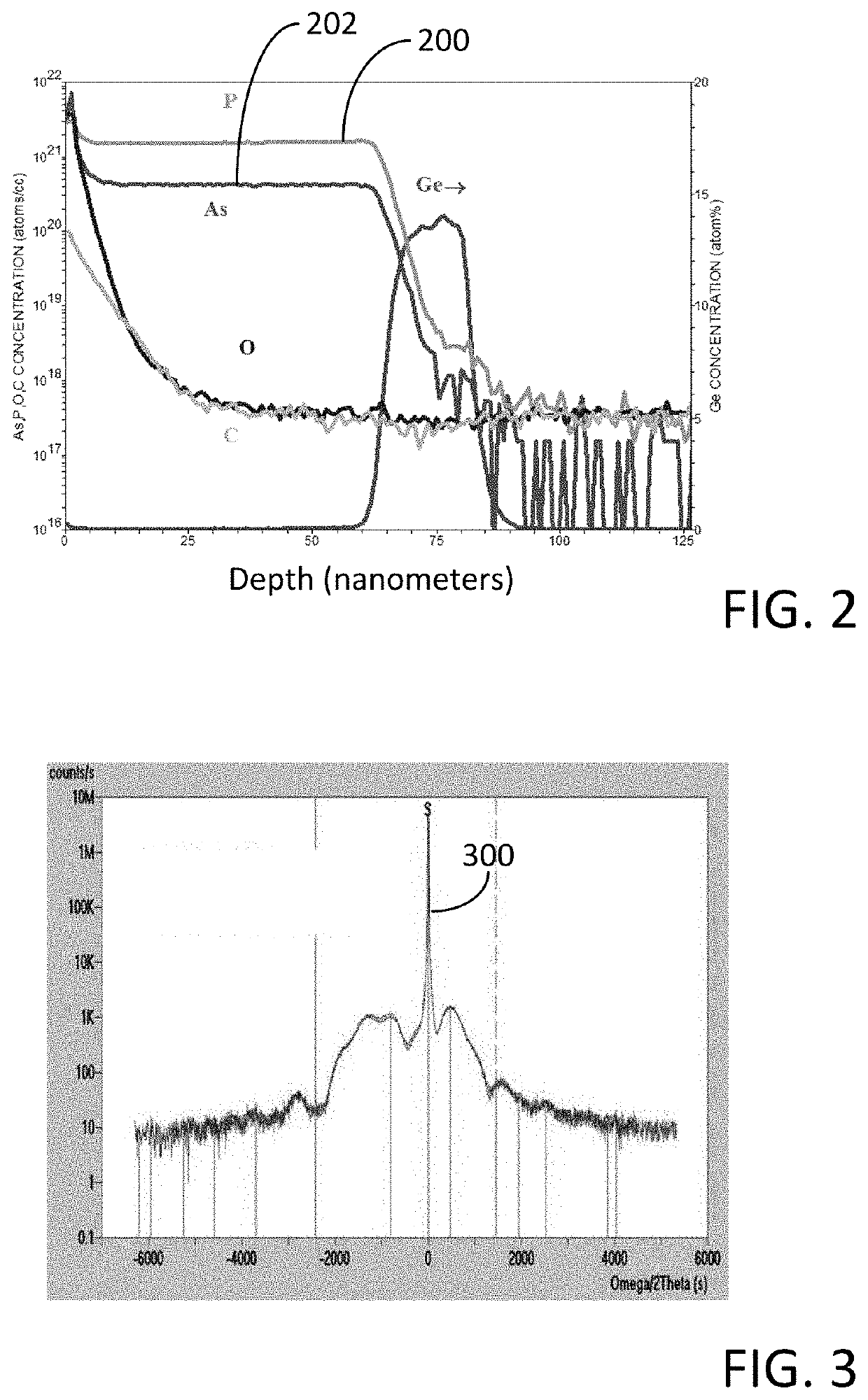
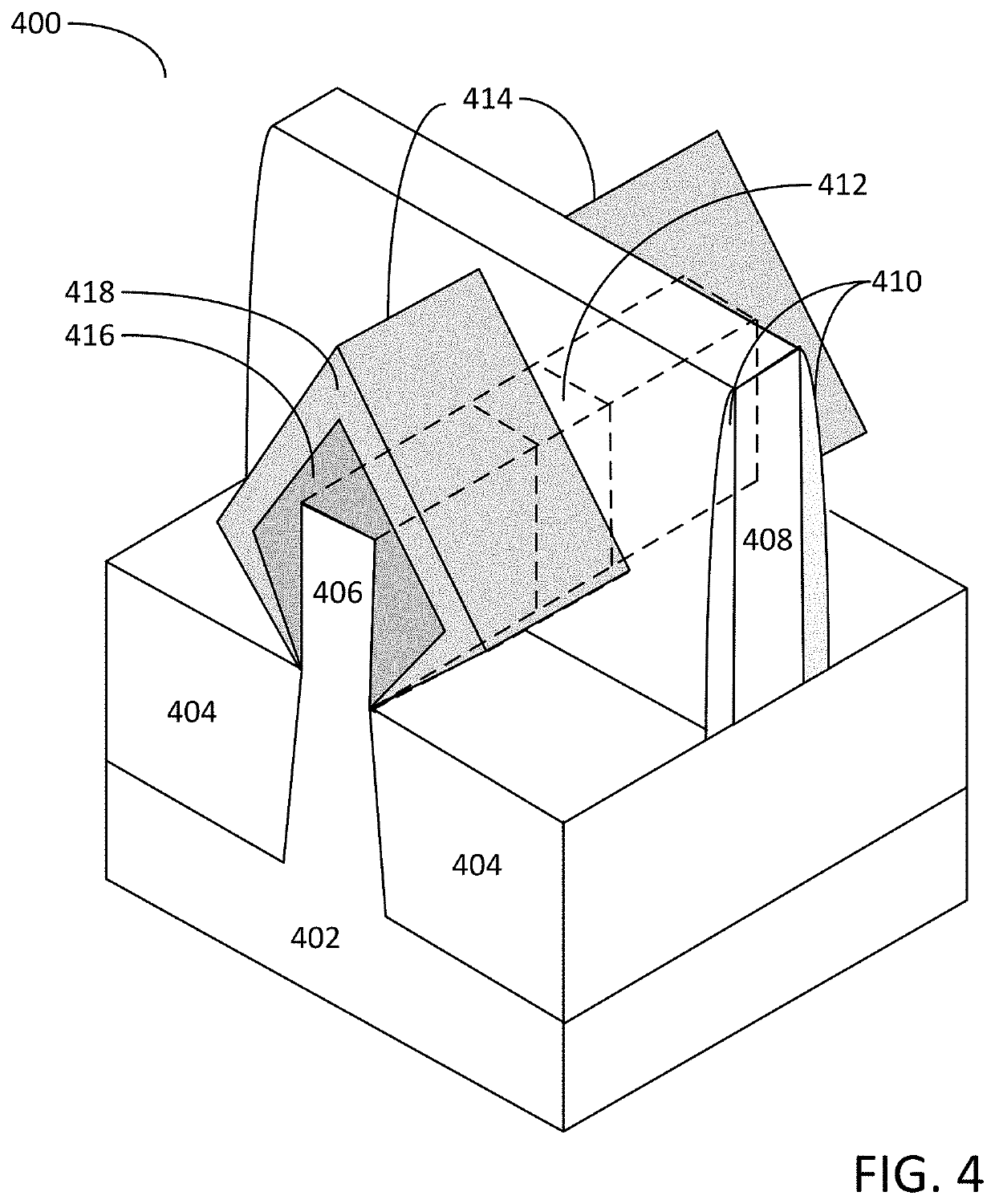
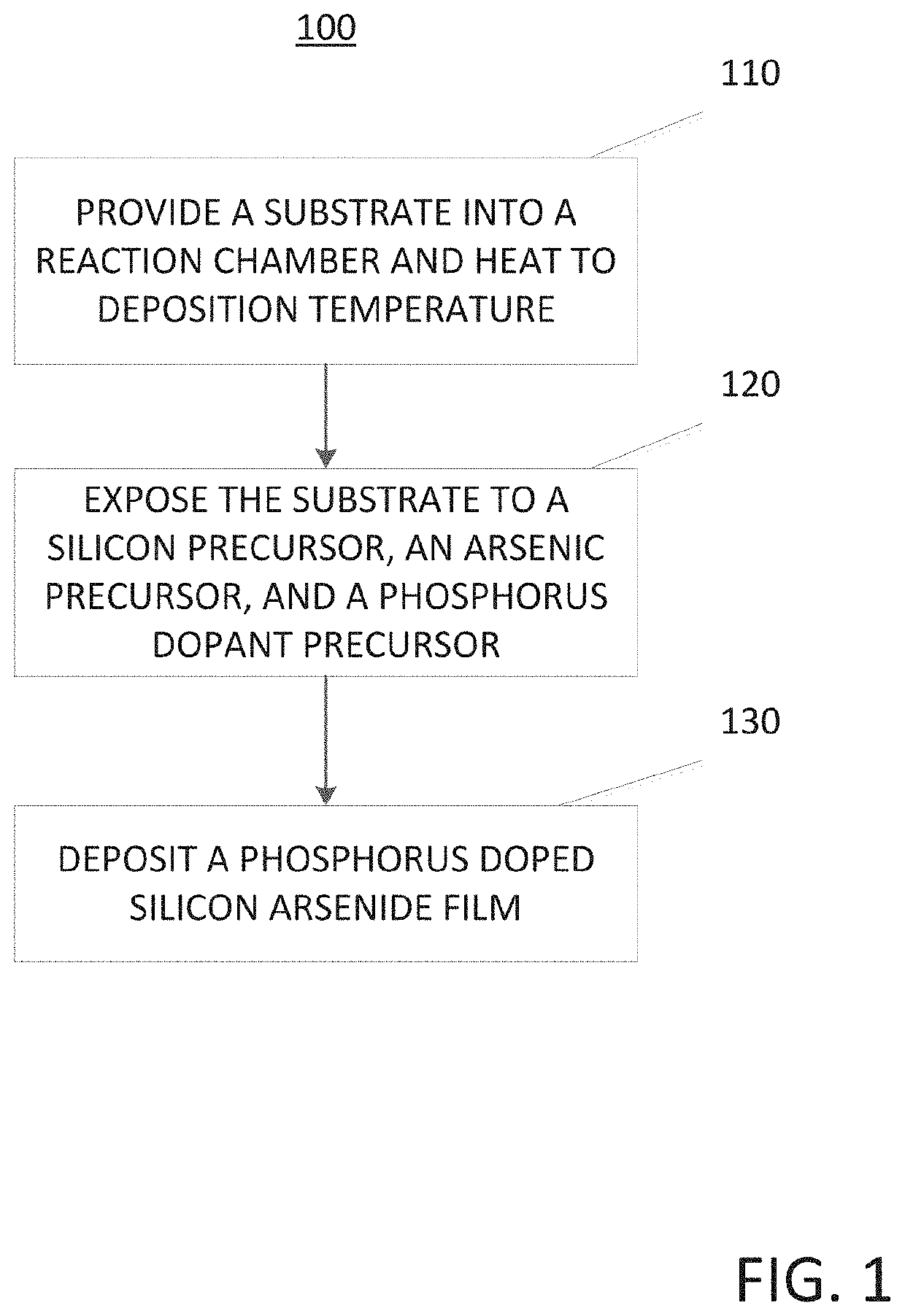
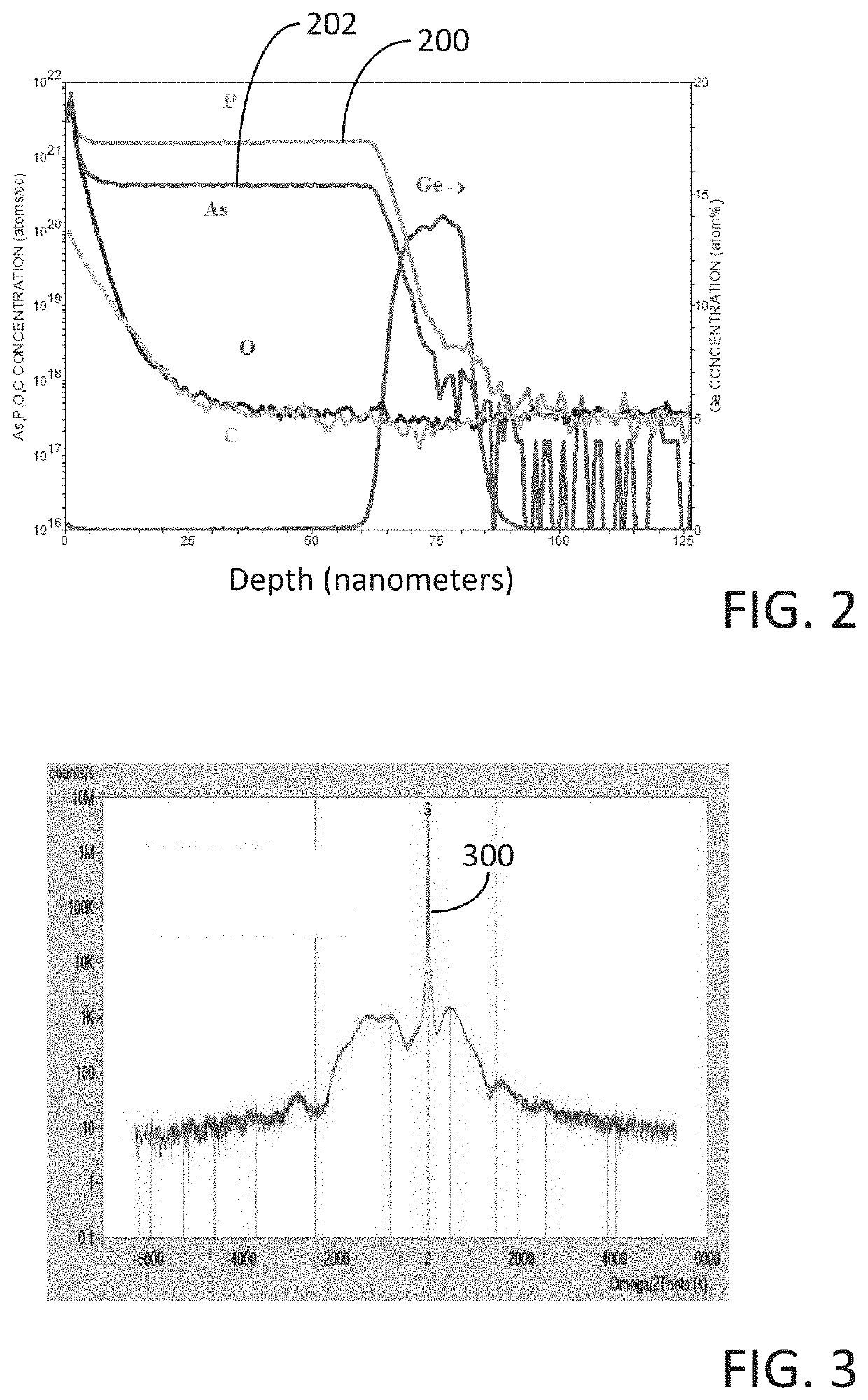
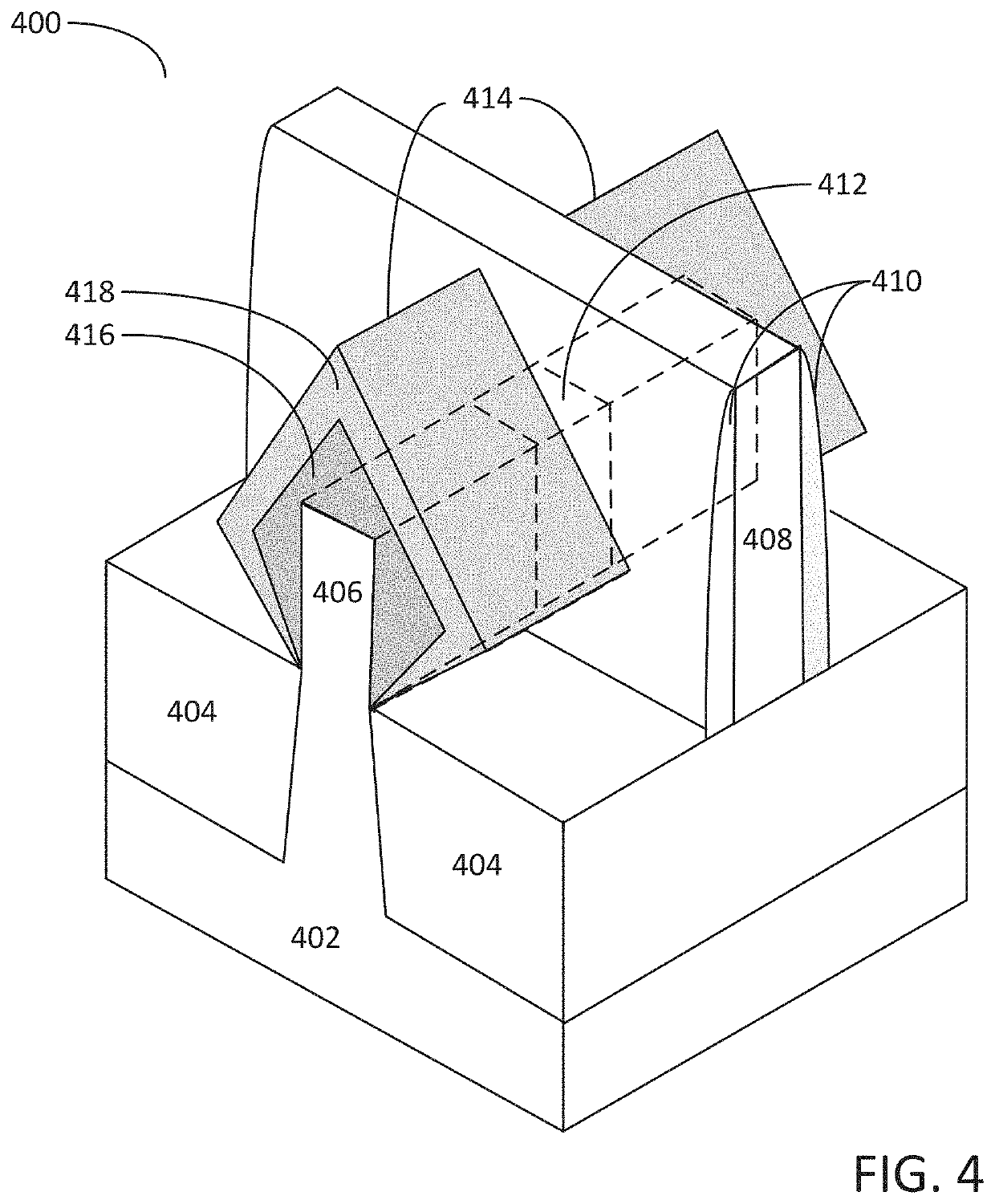
Method for depositing a phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20190393308A1Inhibited DiffusionTransistorPolycrystalline material growthDopantDeposition temperature
A method for depositing a phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film is disclosed. The method may include, providing a substrate within a reaction chamber, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature, exposing the substrate to a silicon precursor, an arsenic precursor, and a phosphorus dopant precursor, and depositing the phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film over a surface of the substrate. Semiconductor device structures including a phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film deposited by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for depositing a phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20200395444A1Inhibited DiffusionTransistorPolycrystalline material growthDevice materialSilicon thin film
A method for depositing a phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film is disclosed. The method may include, providing a substrate within a reaction chamber, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature, exposing the substrate to a silicon precursor, an arsenic precursor, and a phosphorus dopant precursor, and depositing the phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film over a surface of the substrate. Semiconductor device structures including a phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film deposited by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of forming silicon-on-insulator (SOI) semiconductor substrate and SOI semiconductor substrate formed thereby
InactiveUS7183172B2Inhibited DiffusionImpurity diffusion coefficientSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImpurity diffusionDiffusion barrier
A method of forming an SOI semiconductor substrate and the SOI semiconductor substrate formed thereby, is provided. The method includes forming sequentially buried oxide, diffusion barrier and SOI layers on a semiconductor substrate. The diffusion barrier layer is formed by an insulating layer having a lower impurity diffusion coefficient as compared with the buried oxide layer. The diffusion barrier layer serves to prevent impurities implanted into the SOI layer from being diffused into the buried oxide layer or the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
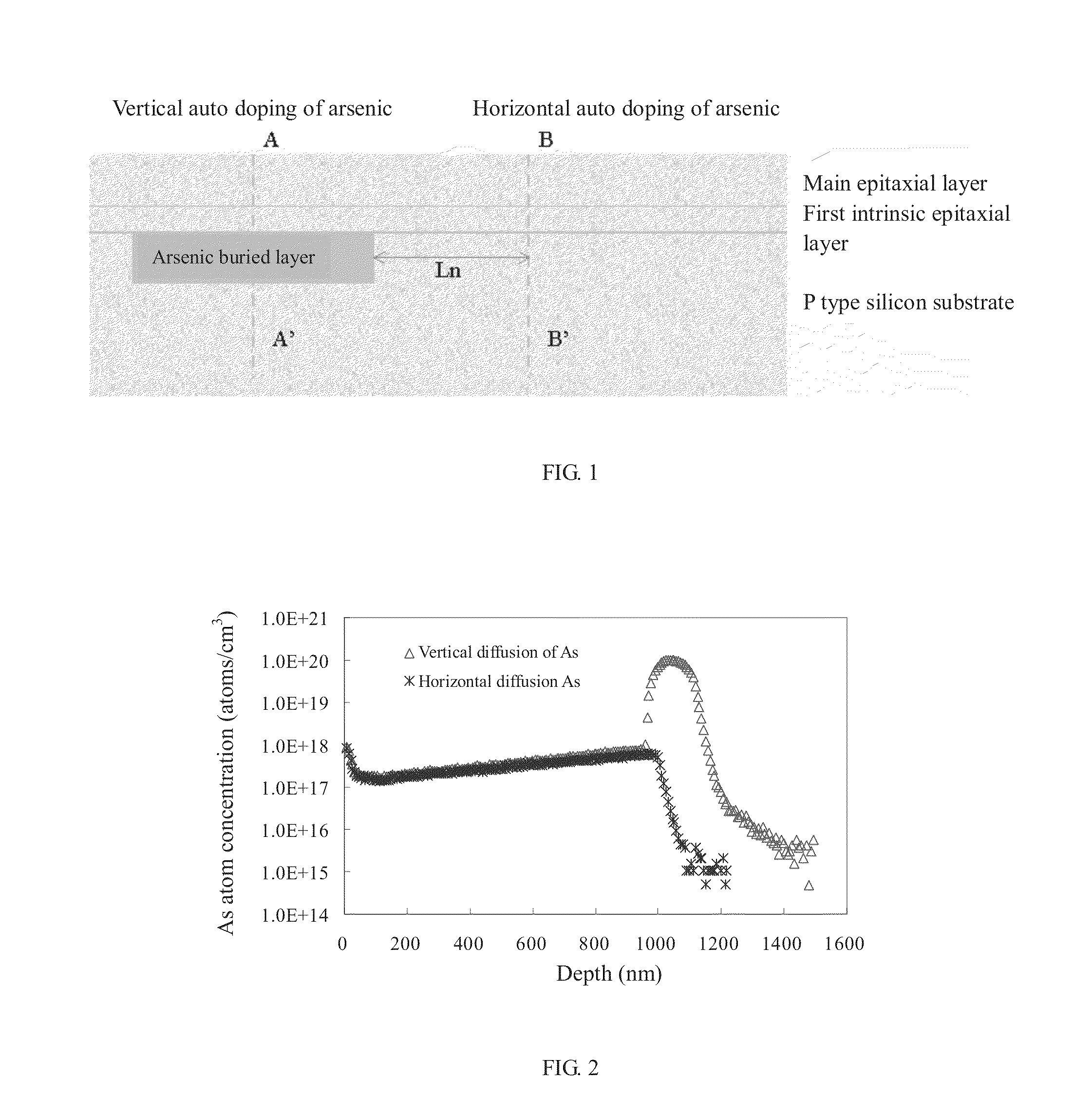
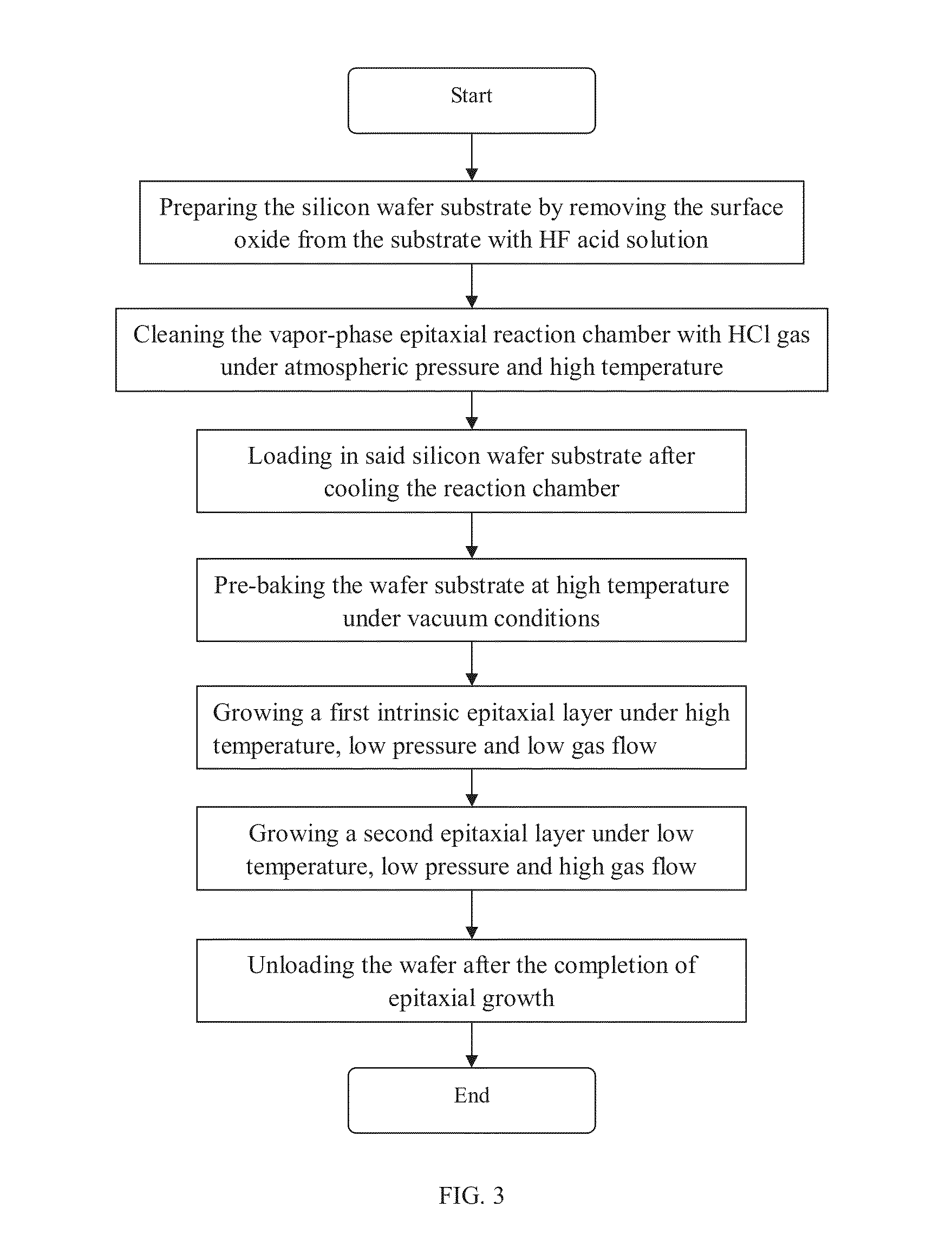
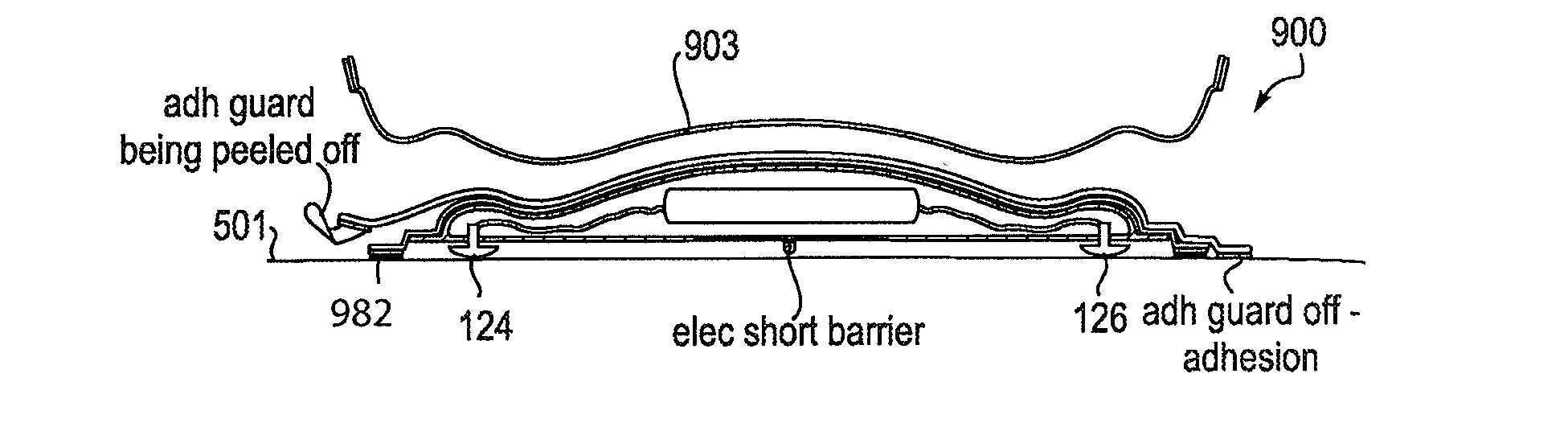
Method of epitaxial growth effectively preventing auto-doping effect
ActiveUS20130145984A1Improve equipment reliabilityInhibited DiffusionPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantMoisture
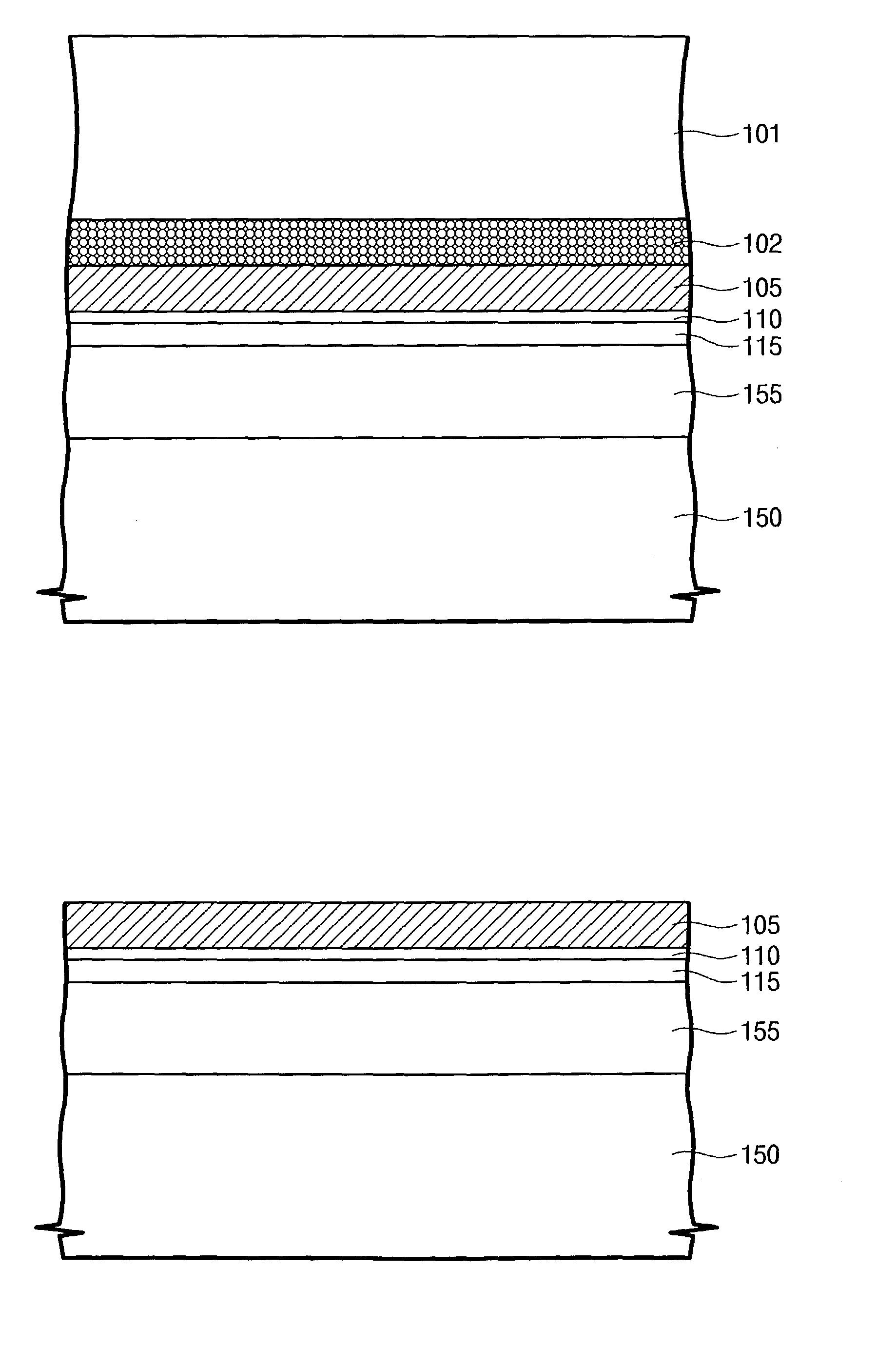
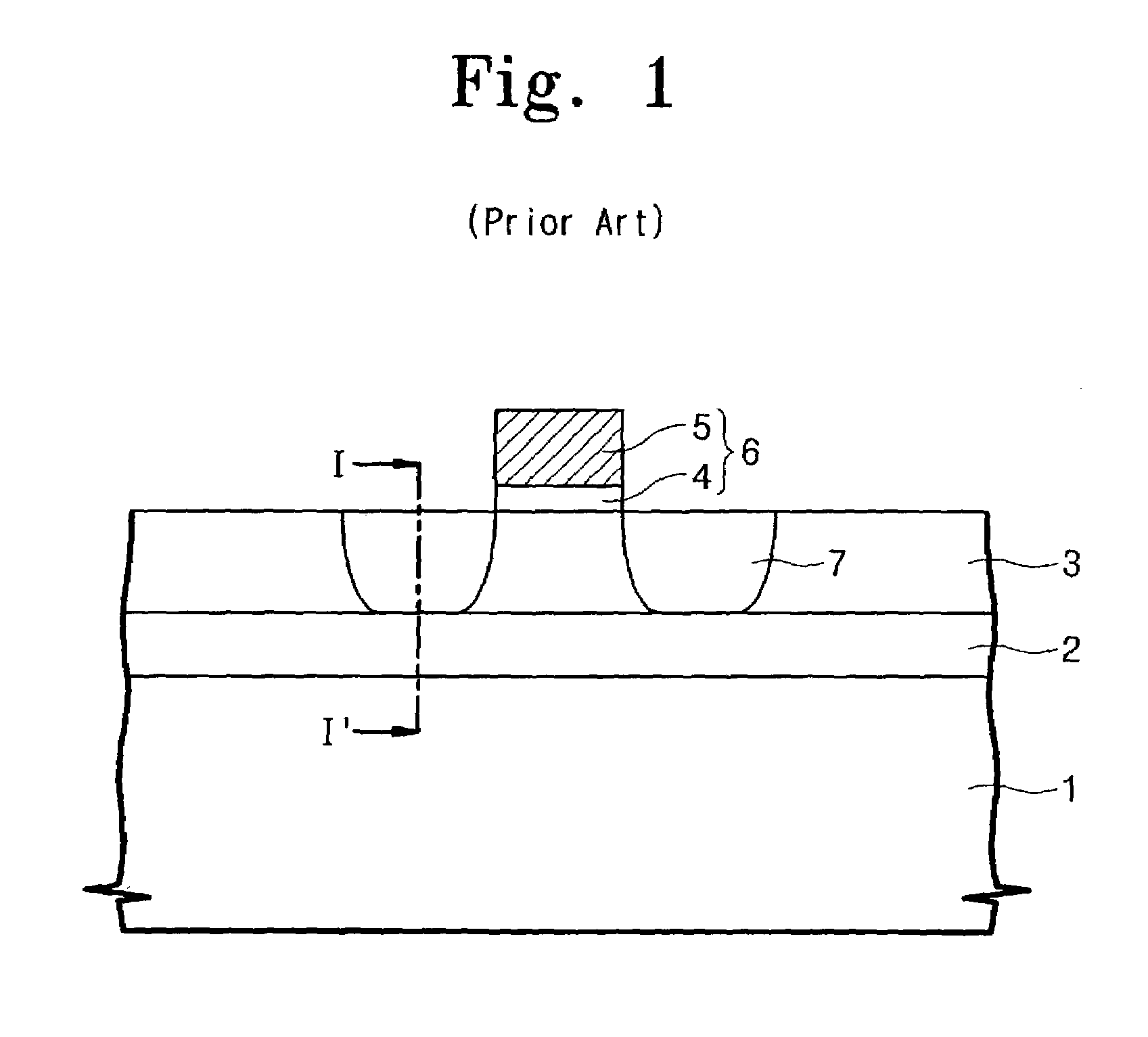
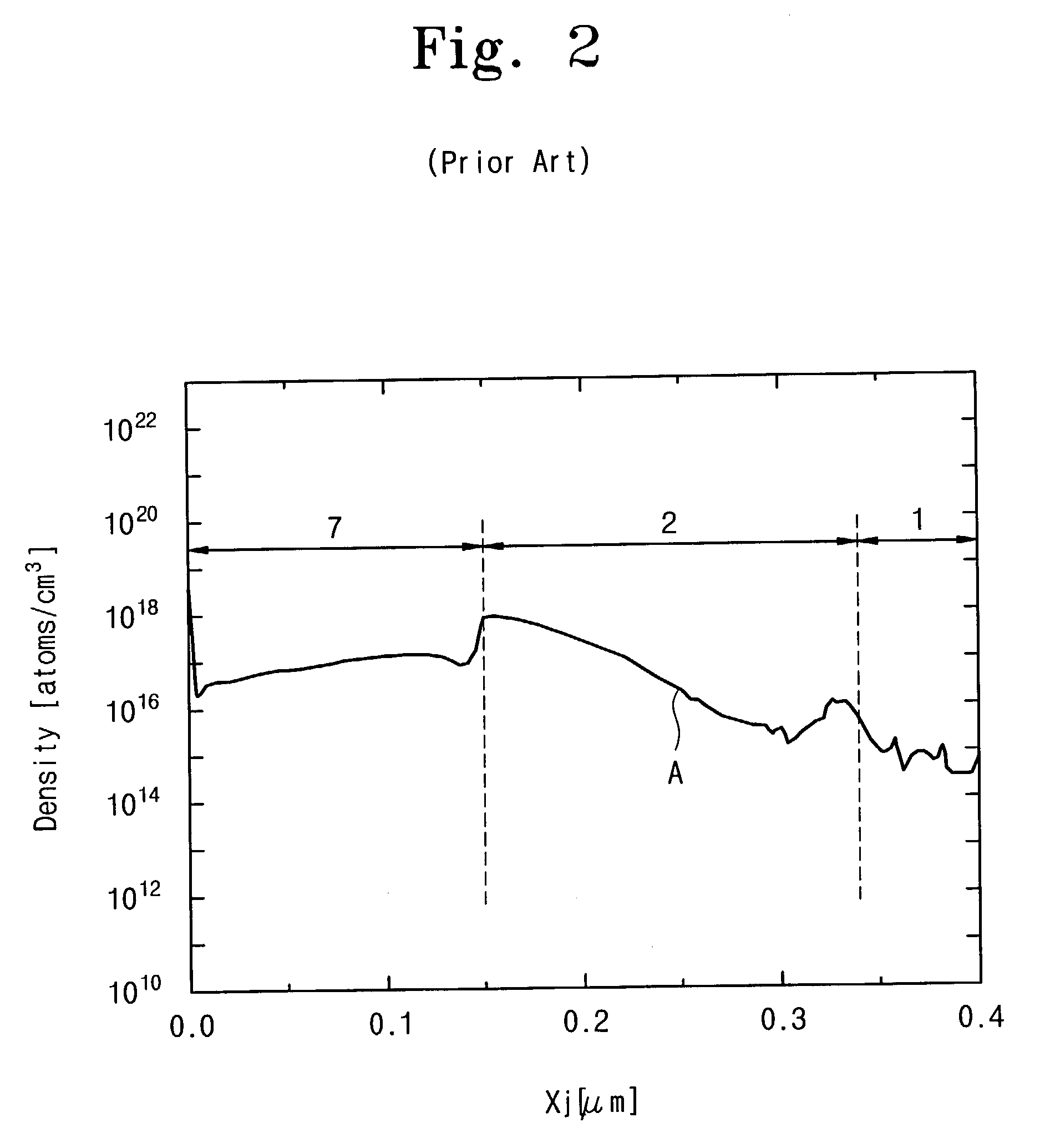
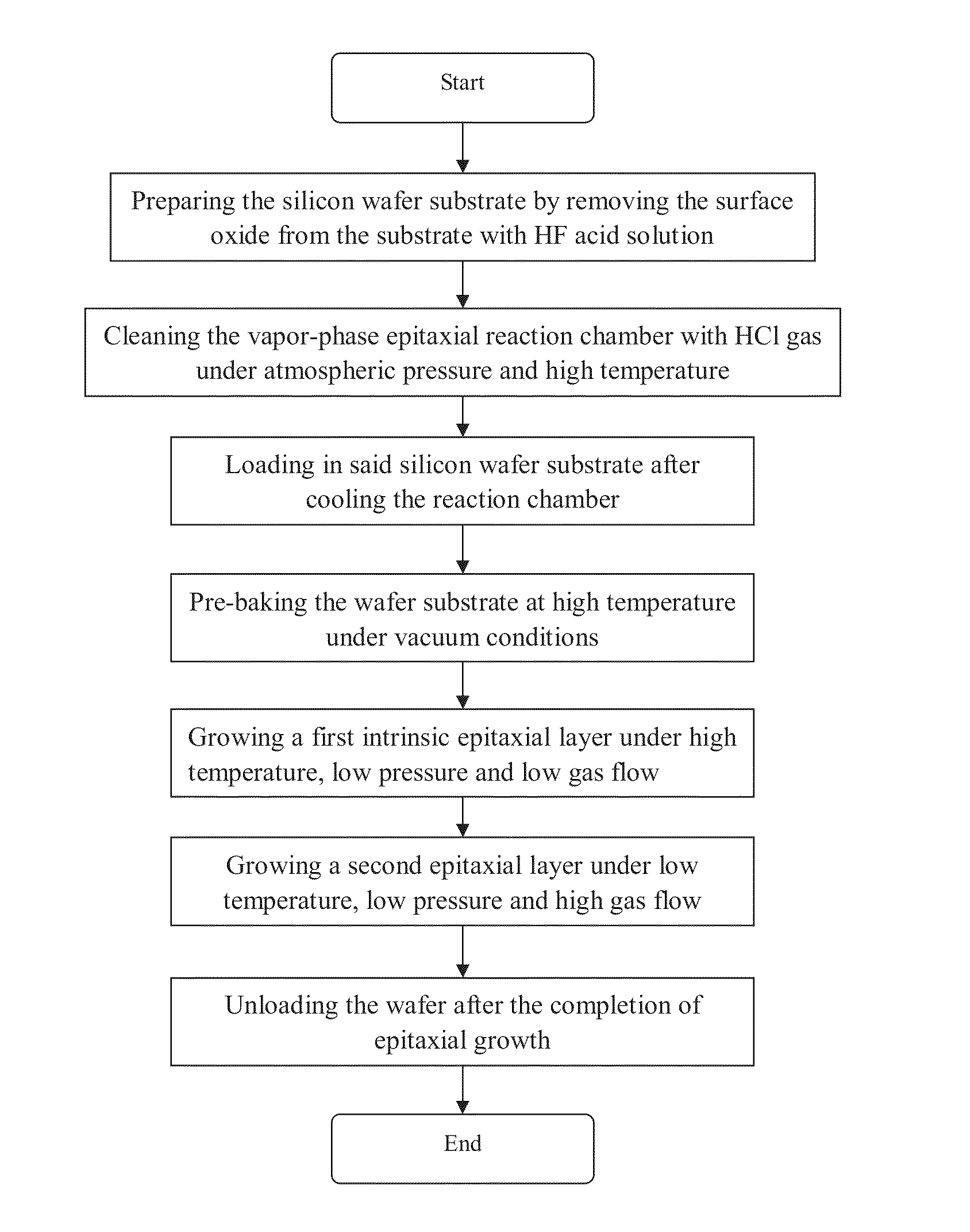
This invention relates to a method of epitaxial growth effectively preventing auto-doping effect. This method starts with the removal of impurities from the semiconductor substrate having heavily-doped buried layer region and from the inner wall of reaction chamber to be used. Then the semiconductor substrate is loaded in the cleaned reaction chamber to be pre-baked under vacuum conditions so as to remove moisture and oxide from the surface of said semiconductor substrate before the extraction of the dopant atoms desorbed from the surface of the semiconductor substrate. Next, under high temperature and low gas flow conditions, a first intrinsic epitaxial layer is formed on the surface of said semiconductor substrate where the dopant atoms have been extracted out. Following this, under low temperature and high gas flow conditions, a second epitaxial layer of required thickness is formed on the structural surface of the grown intrinsic epitaxial layer. Last, silicon wafer is unloaded after cooling. This method can prevent auto-doping effect during the epitaxial growth on semiconductor substrate and thus ensure the performance and enhance the reliability of the devices in peripheral circuit region.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
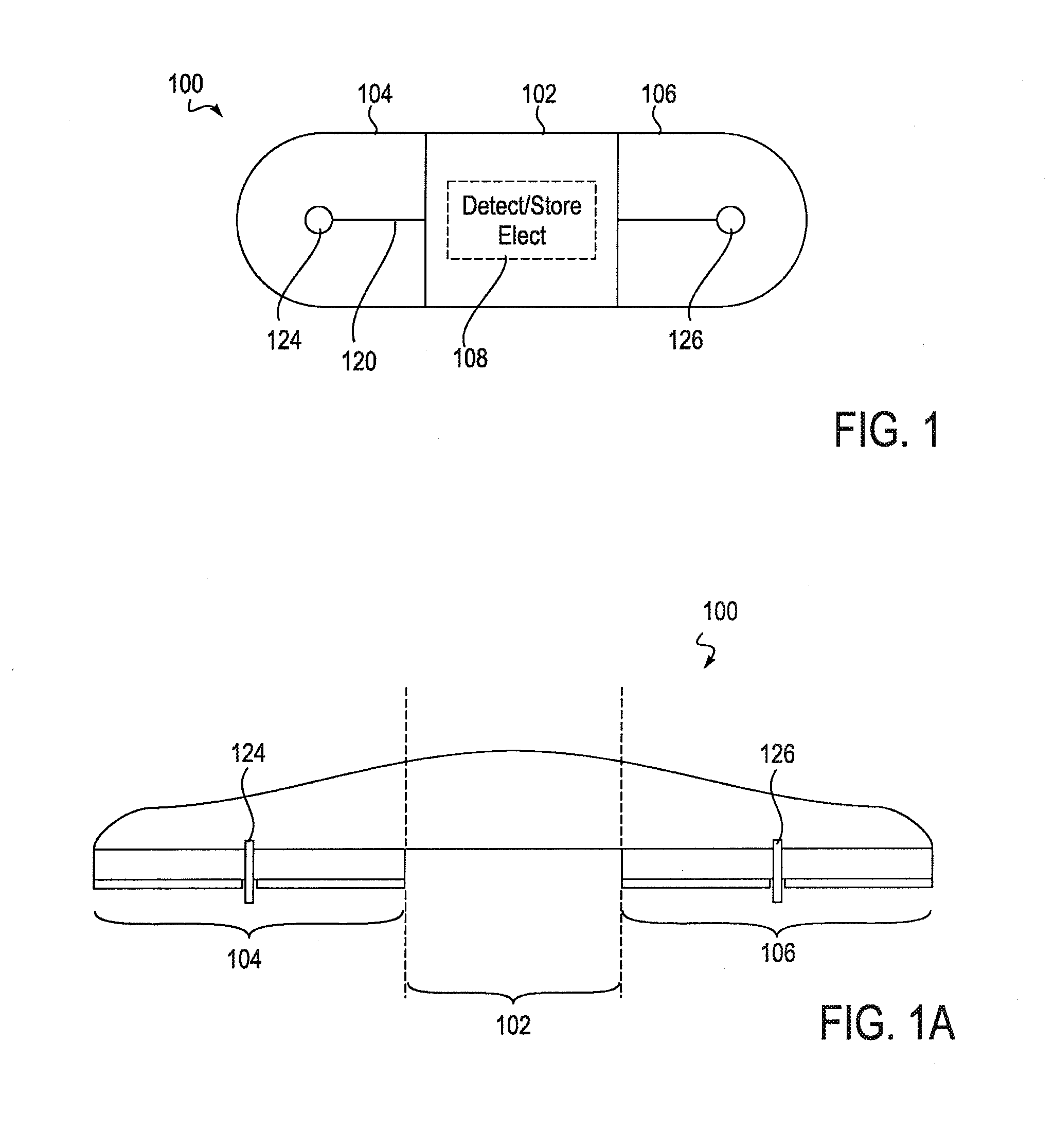
Device features and design elements for long-term adhesion
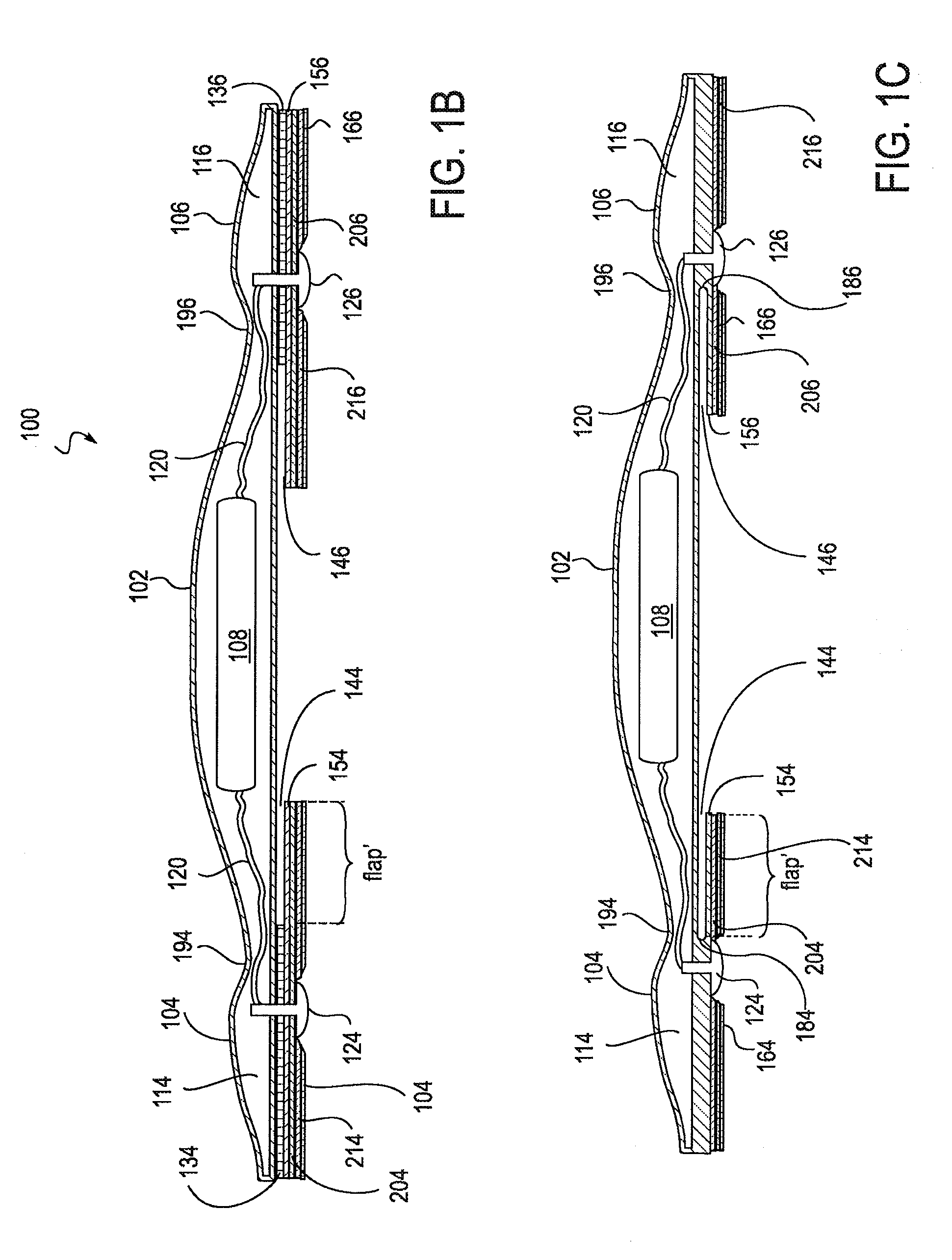
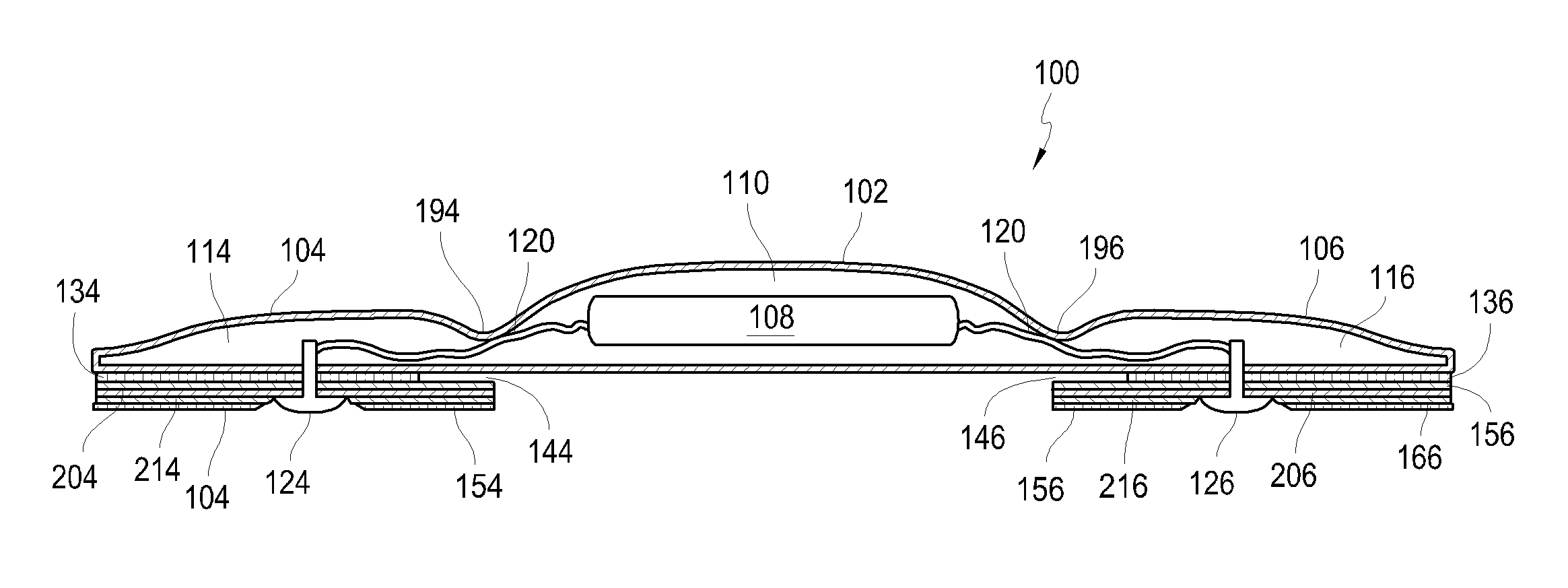
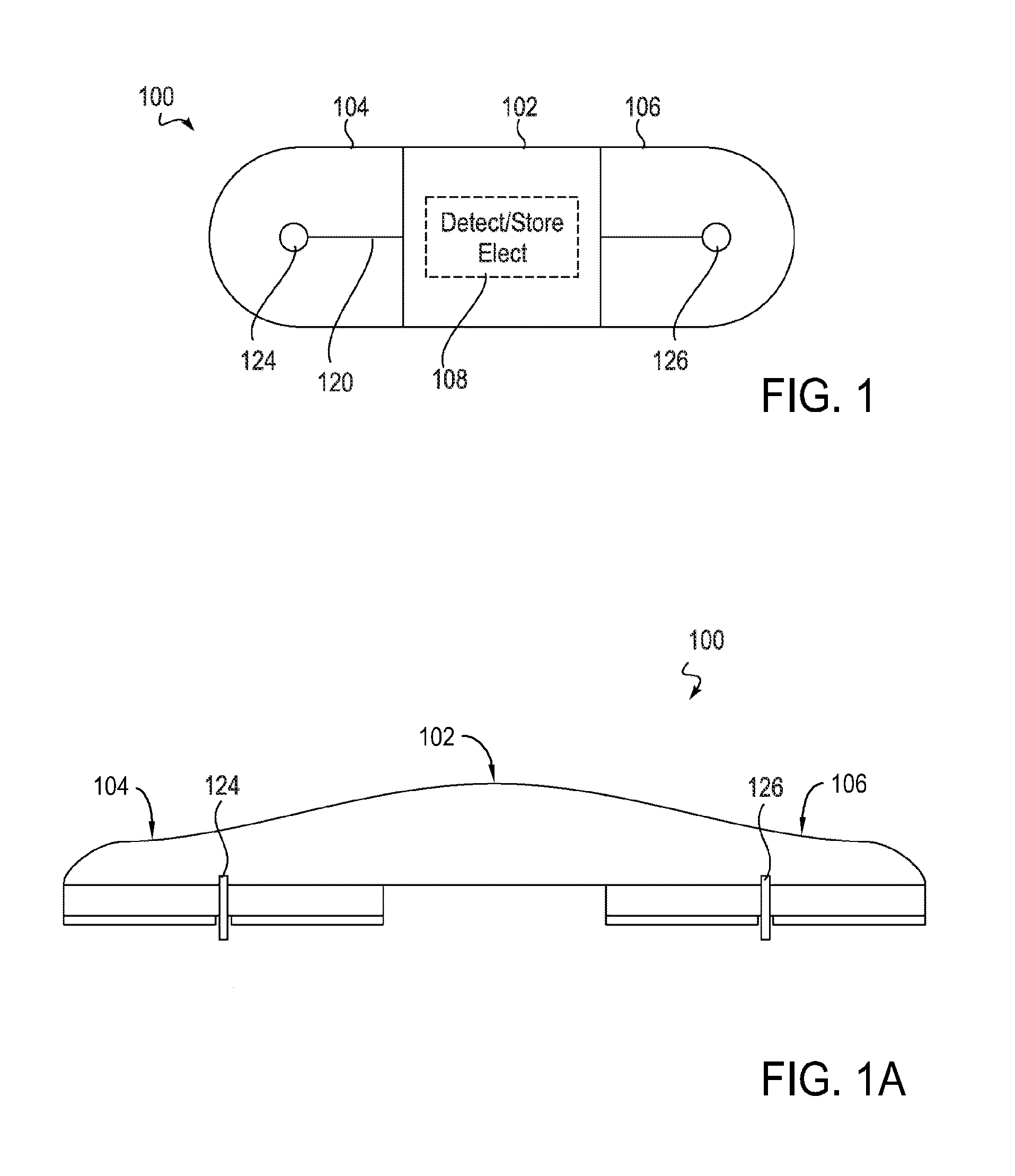
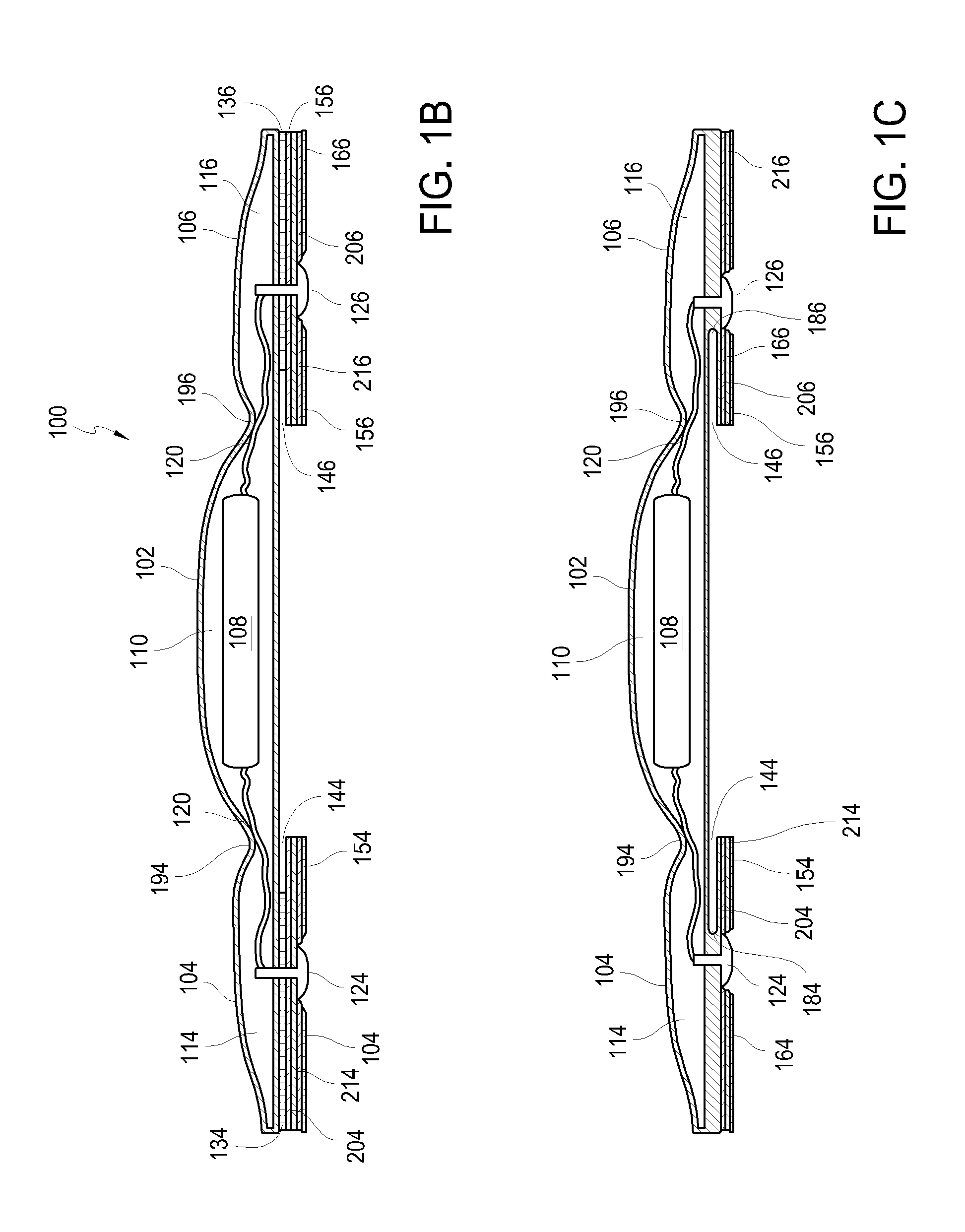
An electronic device for long-term adhesion to a mammal includes a housing with an electronic component. The electronic device may include a first wing and a second wing, each being integrally formed with the housing. An electrode is positioned on a bottom surface of each of the wings, the electrodes electrically connected to the electronic component. An adhesive layer is provided for adhesion to a surface of the mammal. The adhesive layer may cover a portion of the bottom surfaces of the wings but generally does not cover the electrode or a bottom surface of the housing. A method of applying an electronic device to a mammal includes removing first and second adhesive covers from first and second wings of the electronic device to expose an electrode and an adhesive coated on a bottom surface of each wing.
Owner:IRHYTHM TECH
Method and apparatus for enhancing the integrity of an implantable sensor device
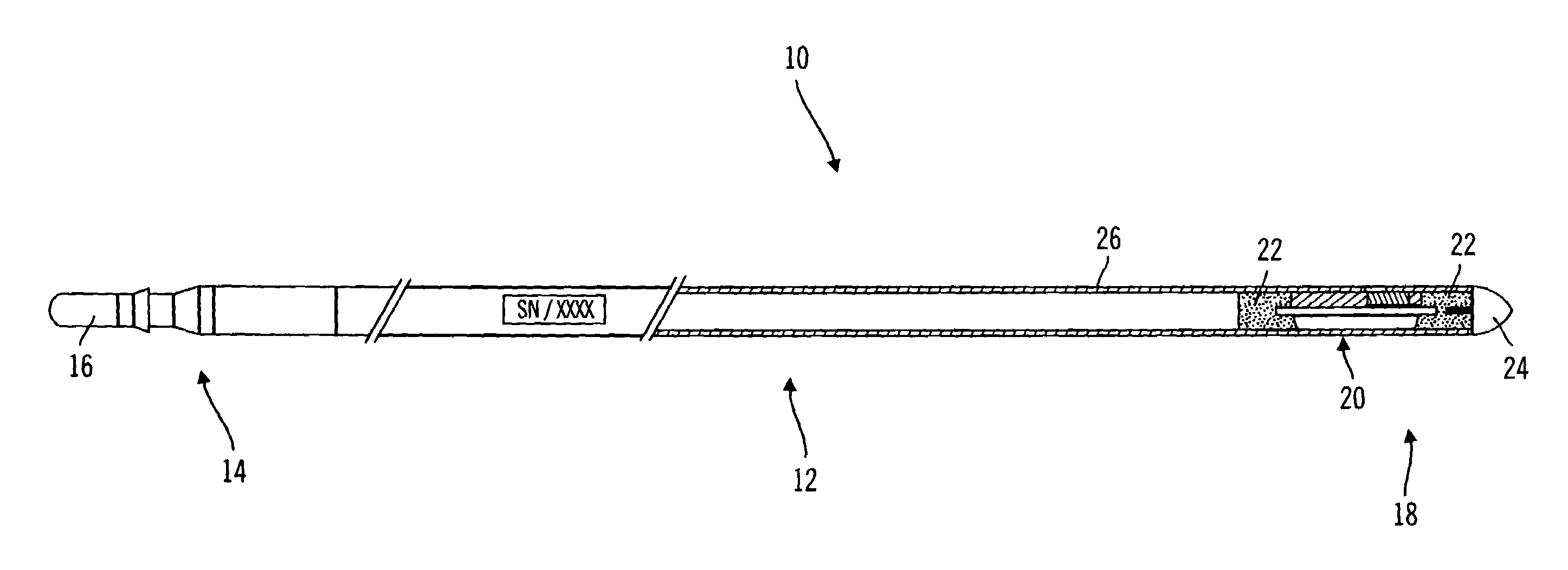
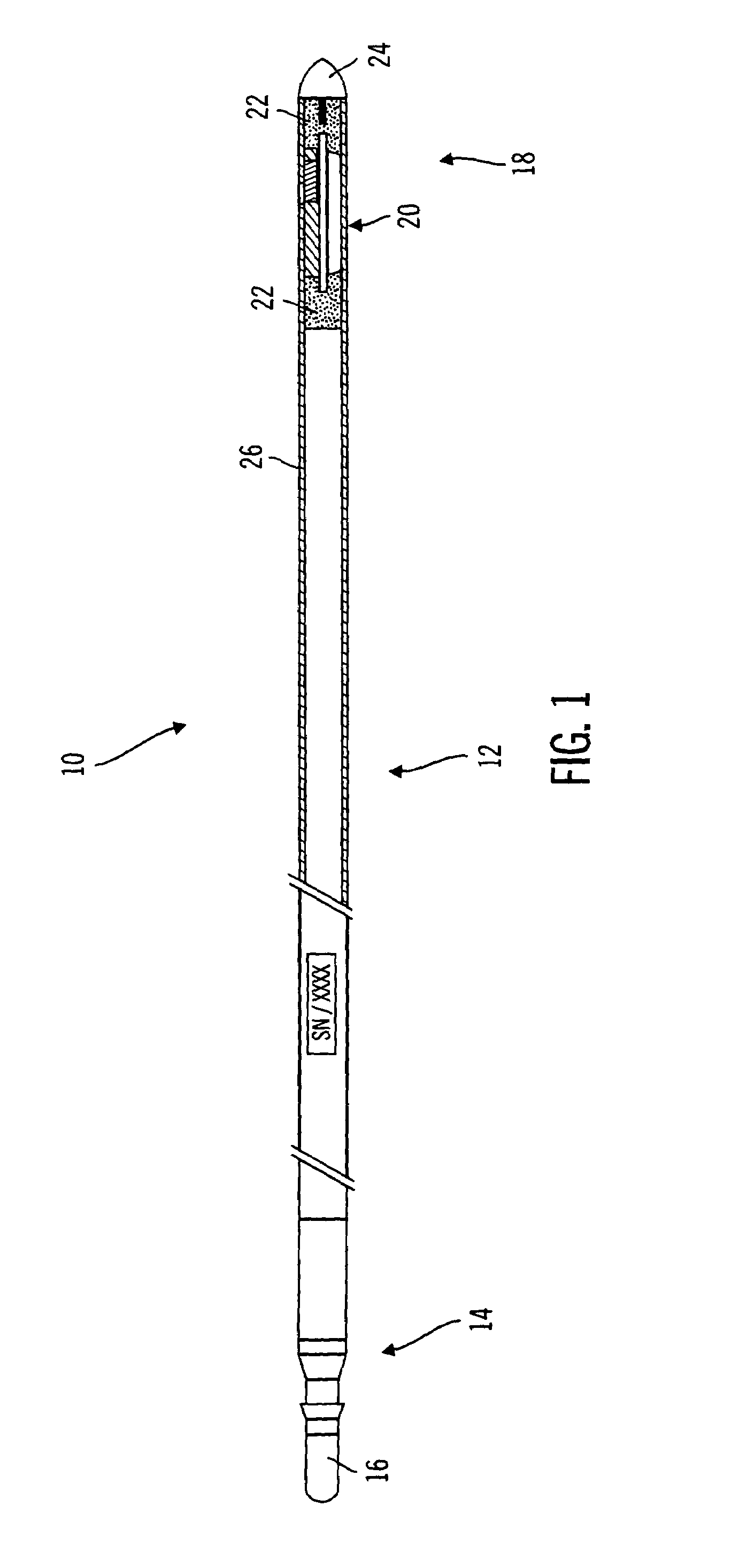
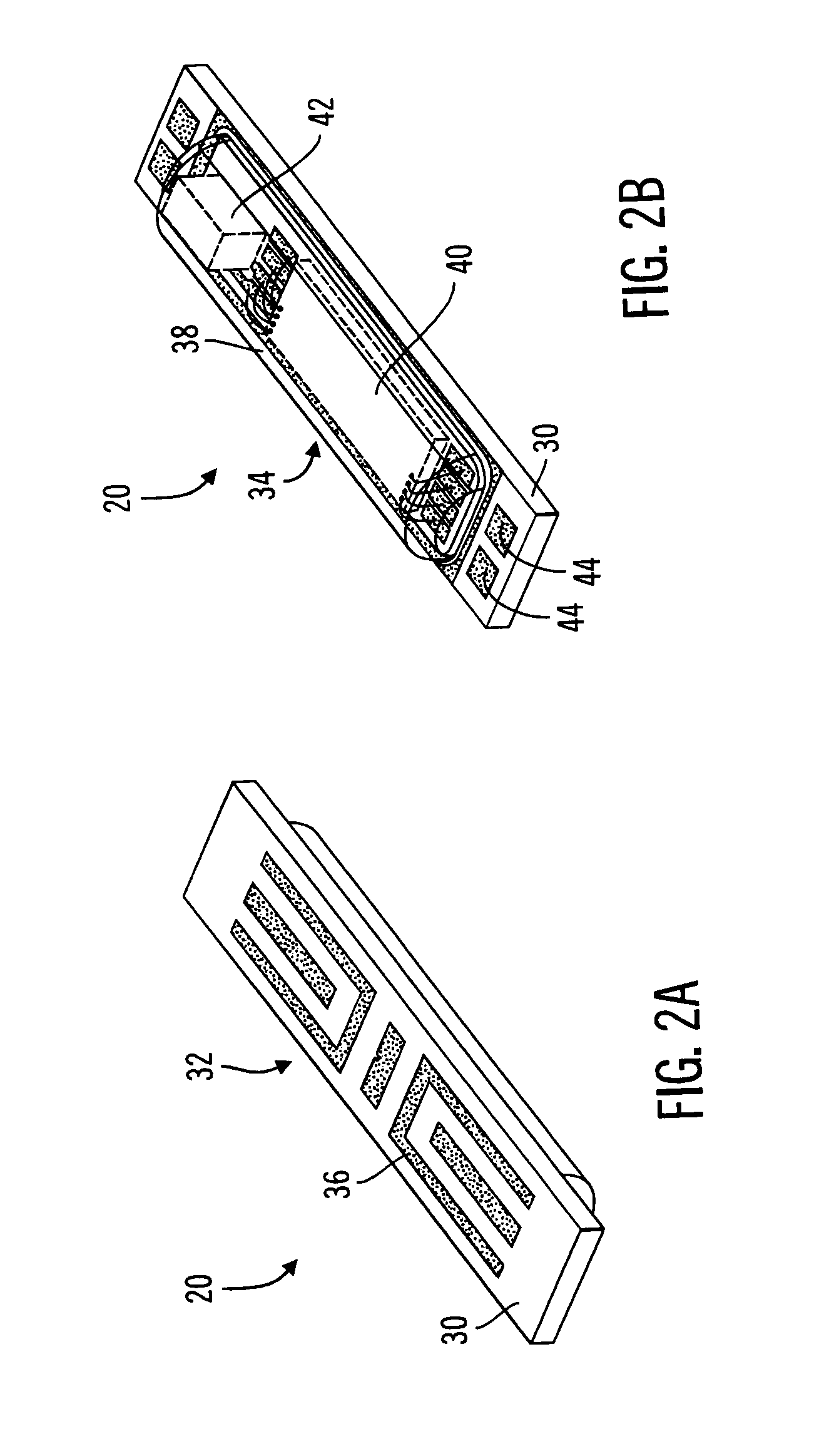
InactiveUS7162289B2Inhibited DiffusionExtended service lifeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProtein materialsLubrication
A method and apparatus for enhancing the integrity of an implantable sensor. Voids formed between an outer tubing and a sensor substrate or spacing element may be back-filled with a curable, implantable material, minimizing the extent to which unwanted fluids diffuse within the sensor. An enzyme or protein matrix pellet below the sensor window may be pre-treated with a reducing agent to enhance its bond stability, and to reduce undesired swelling that may cause the sensor window to detach or leak. The bonding between the enzyme pellet and a hydrogel layer may be reinforced by application of an intervening bonding layer of a protein material, such as human serum albumin (HSA). The size of the window may be minimized by minimizing the size of an underlying electrode, providing reduced flux and lengthening sensor. A coating may be deposited on the surface of the sensor leads, providing stiffening and lubrication.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Device features and design elements for long-term adhesion
An electronic device for long-term adhesion to a mammal includes a housing with an electronic component. The electronic device may include a first wing and a second wing, each being integrally formed with the housing. An electrode is positioned on a bottom surface of each of the wings, the electrodes electrically connected to the electronic component. An adhesive layer is provided for adhesion to a surface of the mammal. The adhesive layer may cover a portion of the bottom surfaces of the wings but generally does not cover the electrode or a bottom surface of the housing. A method of applying an electronic device to a mammal includes removing first and second adhesive covers from first and second wings of the electronic device to expose an electrode and an adhesive coated on a bottom surface of each wing.
Owner:IRHYTHM TECH
Biosensor
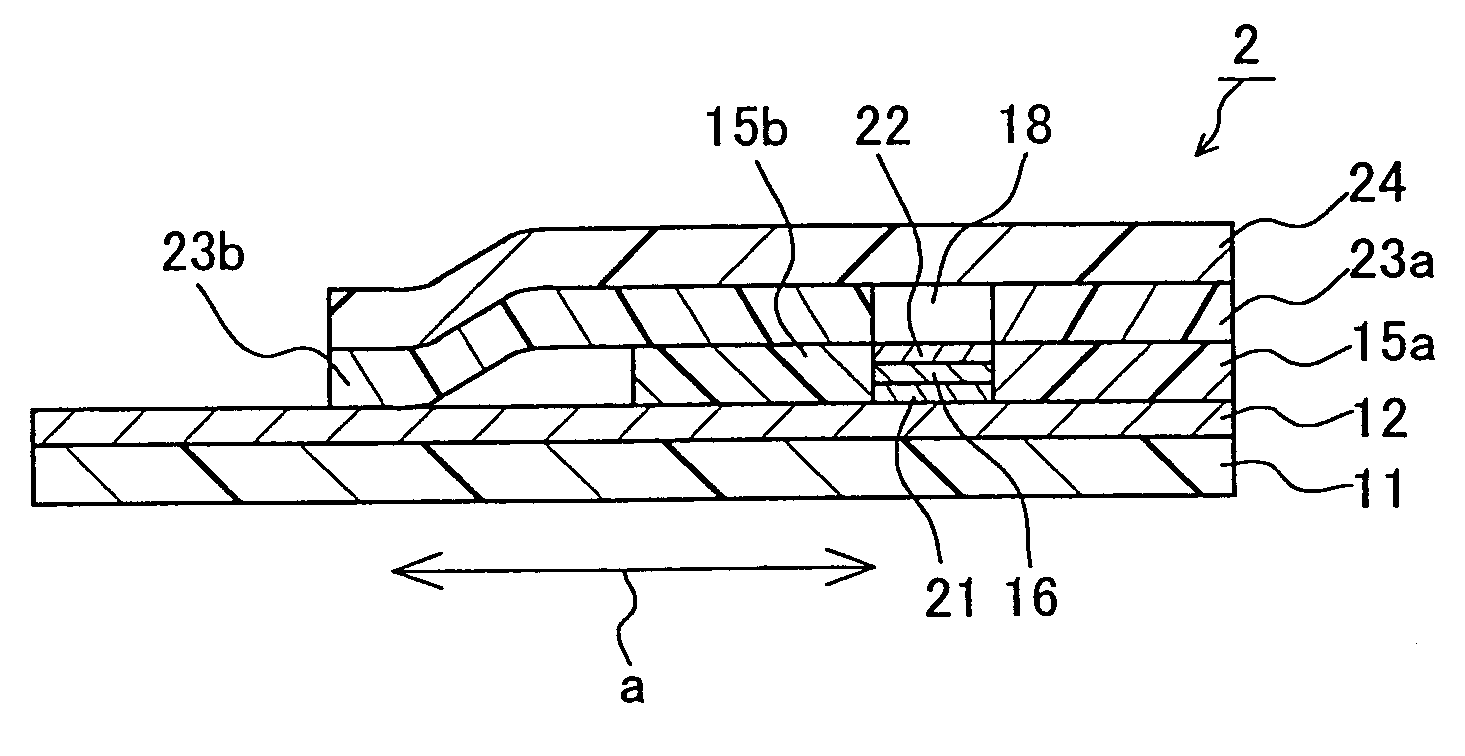
InactiveUS6982027B2Improve accuracyHigh precision measurementImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsParticulatesAnalyte
A biosensor is provided, which can measure an analyte in a sample with high precision. The biosensor is produced by disposing a electrode system including a working electrode 12 and a counter electrode 13 on a substrate 11, and then forming a reagent layer 16 containing a reagent and particulates on the electrode system. The influence of the impurities in the sample on the electrode system can be eliminated by the particulates. The average particle diameter of the particulates preferably is in the range from 0.1 to 45 μm.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20090166677A1Increase the number ofIncrease the areaTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorTransistor
A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor substrate; a diode having a cathode formed on a first surface side of the semiconductor substrate and an anode formed on a second surface side of the semiconductor substrate; and a transistor formed over the semiconductor substrate. The transistor includes a semiconductor layer laminate formed over the semiconductor substrate, a source electrode and a drain electrode that are formed spaced apart from each other over the semiconductor layer laminate, and a gate electrode formed between the source electrode and the drain electrode. The source electrode is electrically connected to the anode, and the drain electrode is electrically connected to the cathode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110084267A1Excellent electrical propertiesEasy to displaySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceSemiconductor
By using a conductive layer including Cu as a long lead wiring, increase in wiring resistance is suppressed. Further, the conductive layer including Cu is provided in such a manner that it does not overlap with the oxide semiconductor layer in which a channel region of a TFT is formed, and is surrounded by insulating layers including silicon nitride, whereby diffusion of Cu can be prevented; thus, a highly reliable semiconductor device can be manufactured. Specifically, a display device which is one embodiment of a semiconductor device can have high display quality and operate stably even when the size or definition thereof is increased.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
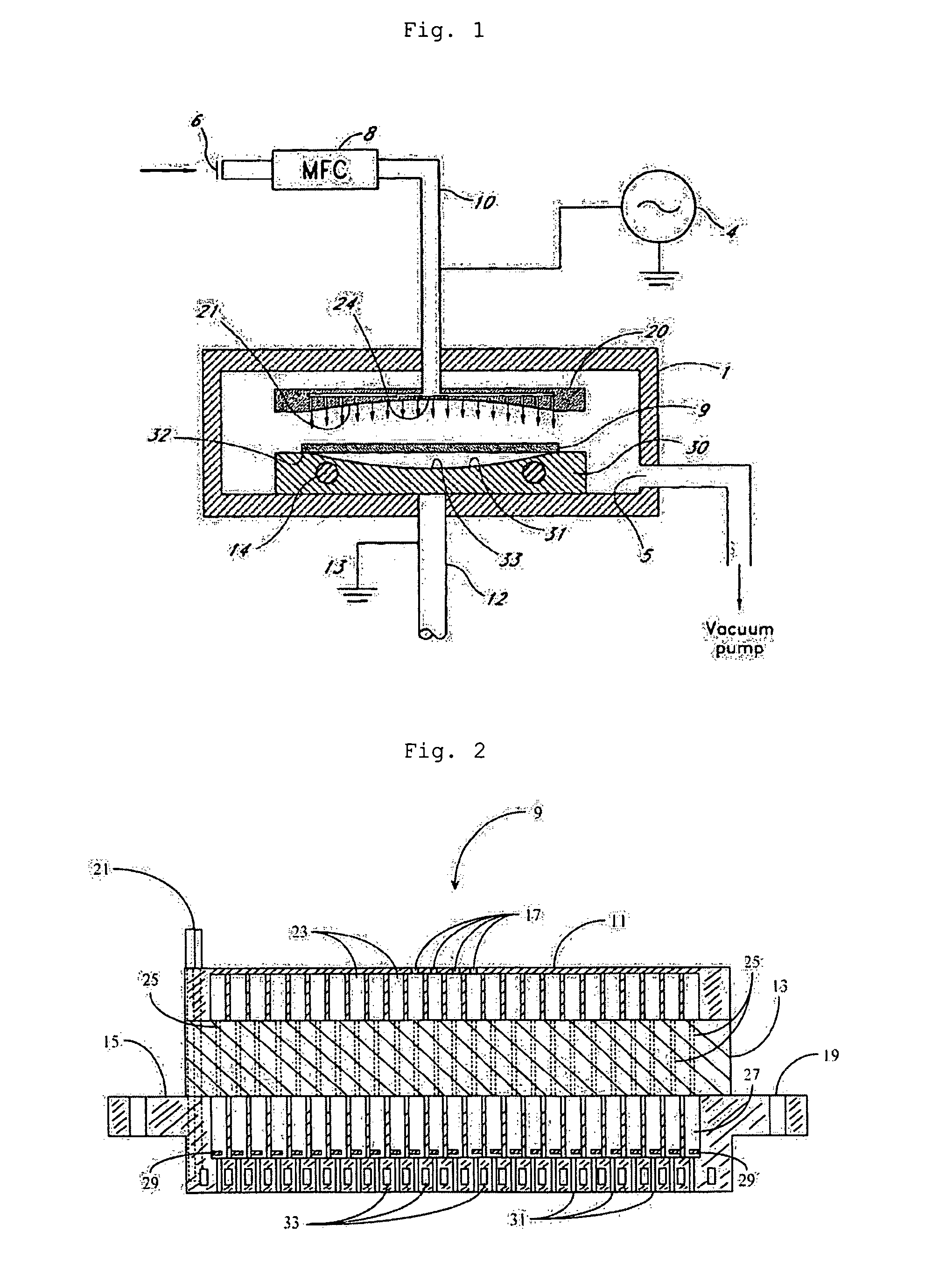
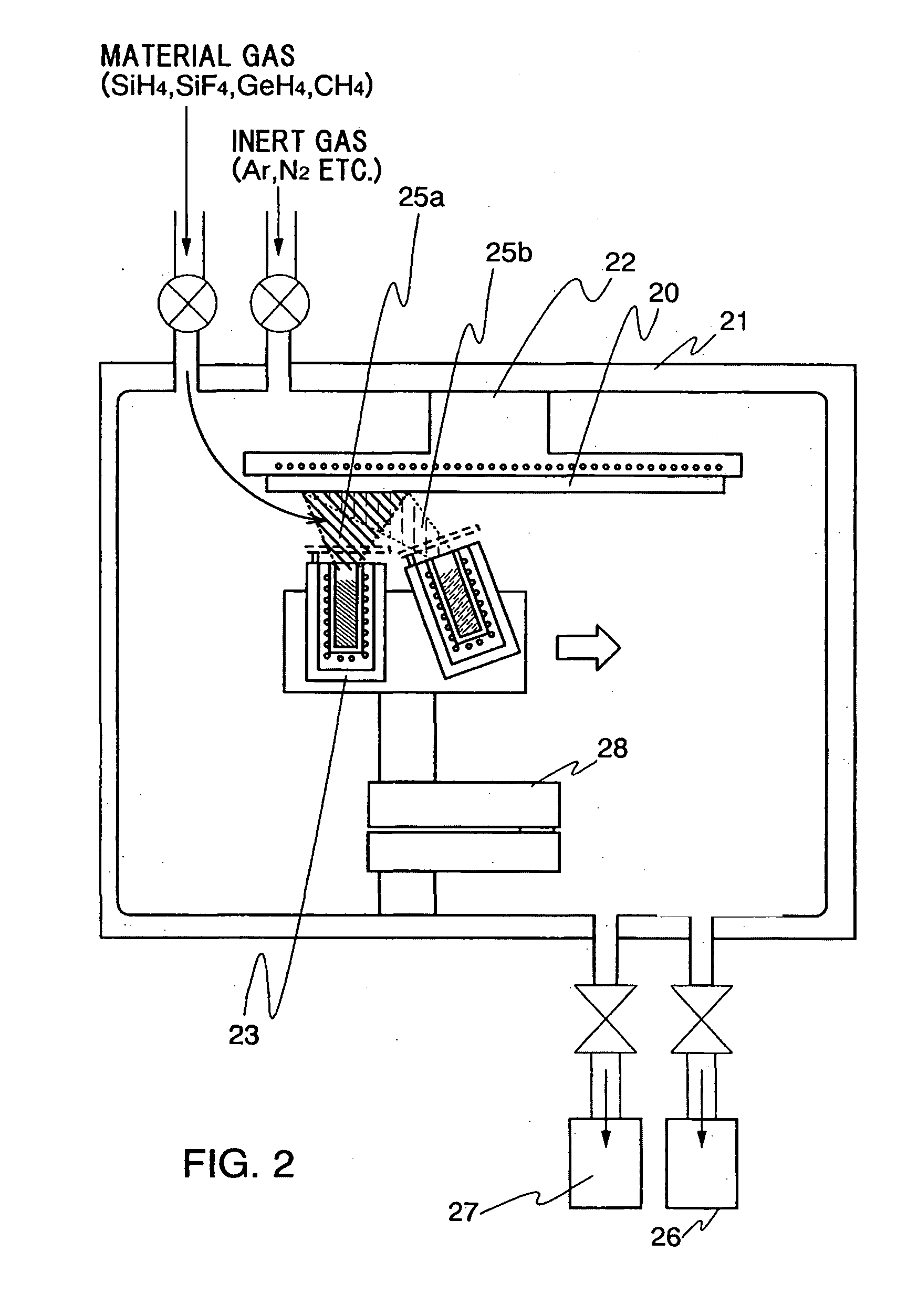
Method for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) with showerhead and method thereof
ActiveUS7479303B2Unwanted chemical reactionInhibited DiffusionFrom chemically reactive gasesChemical vapor deposition coatingSource materialReactive gas
Disclosed is a method of chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The method provides for use of a showerhead through which a source material gas including a reactive gas of at least one kind and a purge gas is injected over a substrate located in a reaction chamber to deposit a film on the substrate. The showerhead has reactive gas outlets surrounded by purge gas outlets. The bottom surface of the showerhead is spaced apart from the substrate by a predetermined distance. Reactive gases of different kinds are injected into compartments formed inside the showerhead so that each compartment of the showerhead is filled with the reactive gas of only one kind, and a purge gas of the source material gas is supplied into another compartment formed inside the showerhead. The reactive gas and the purge gas are discharged through the reactive gas outlets and purge gas outlets. Preferably, there are more purge gas outlets than reactive gas outlets.
Owner:KOREA INST OF IND TECH +1
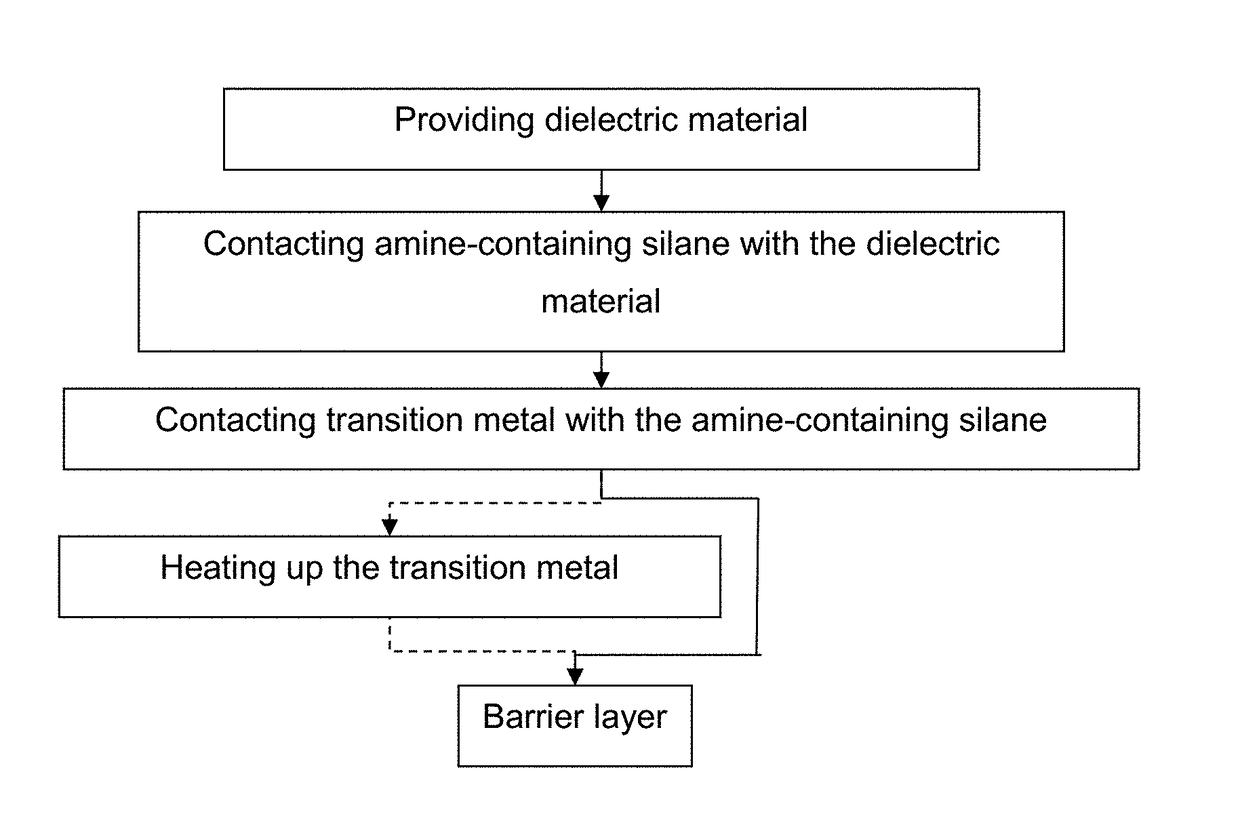
Formation of a transition metal nitride
ActiveUS20180047621A1Inhibited DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilanesNitrogen
A use of an amine-containing silane for forming a transition metal nitride is provided. In this use, the amine of the amine-containing silane is the source of at least some, preferably most and most preferably all of the nitrogen present in the transition metal nitride.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
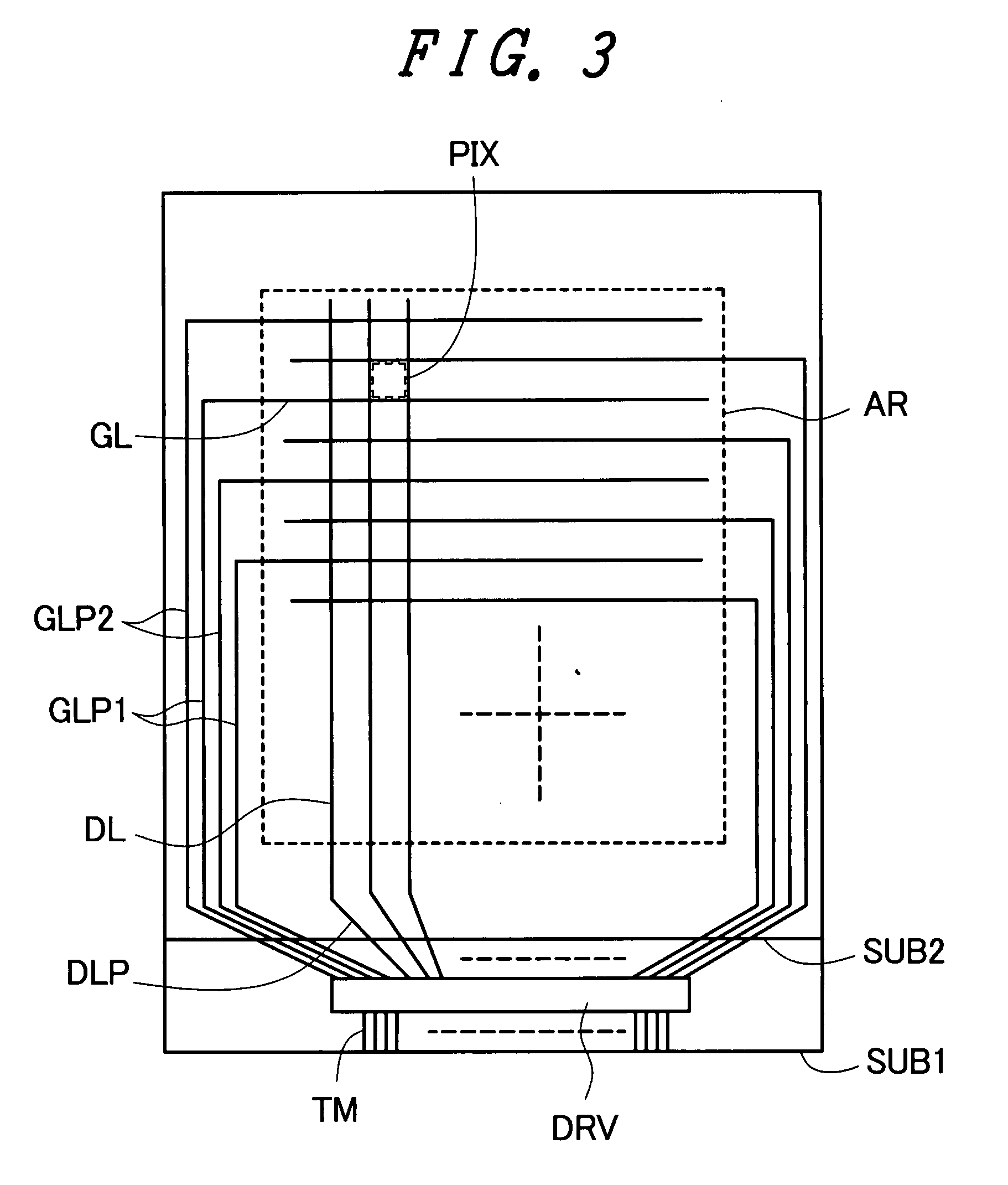
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20080137022A1Reduce sealing defectSuppressing spreadingNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayElectrical and Electronics engineering
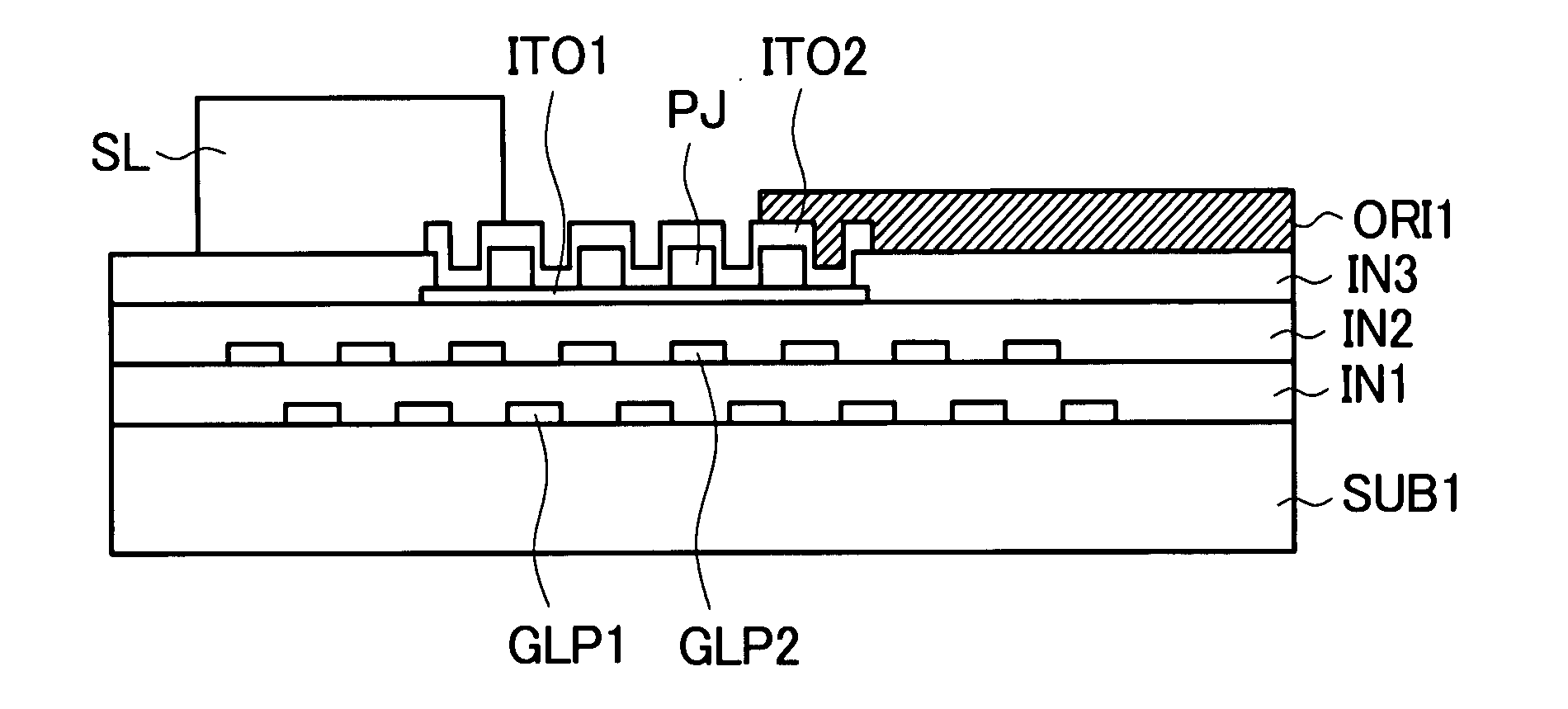
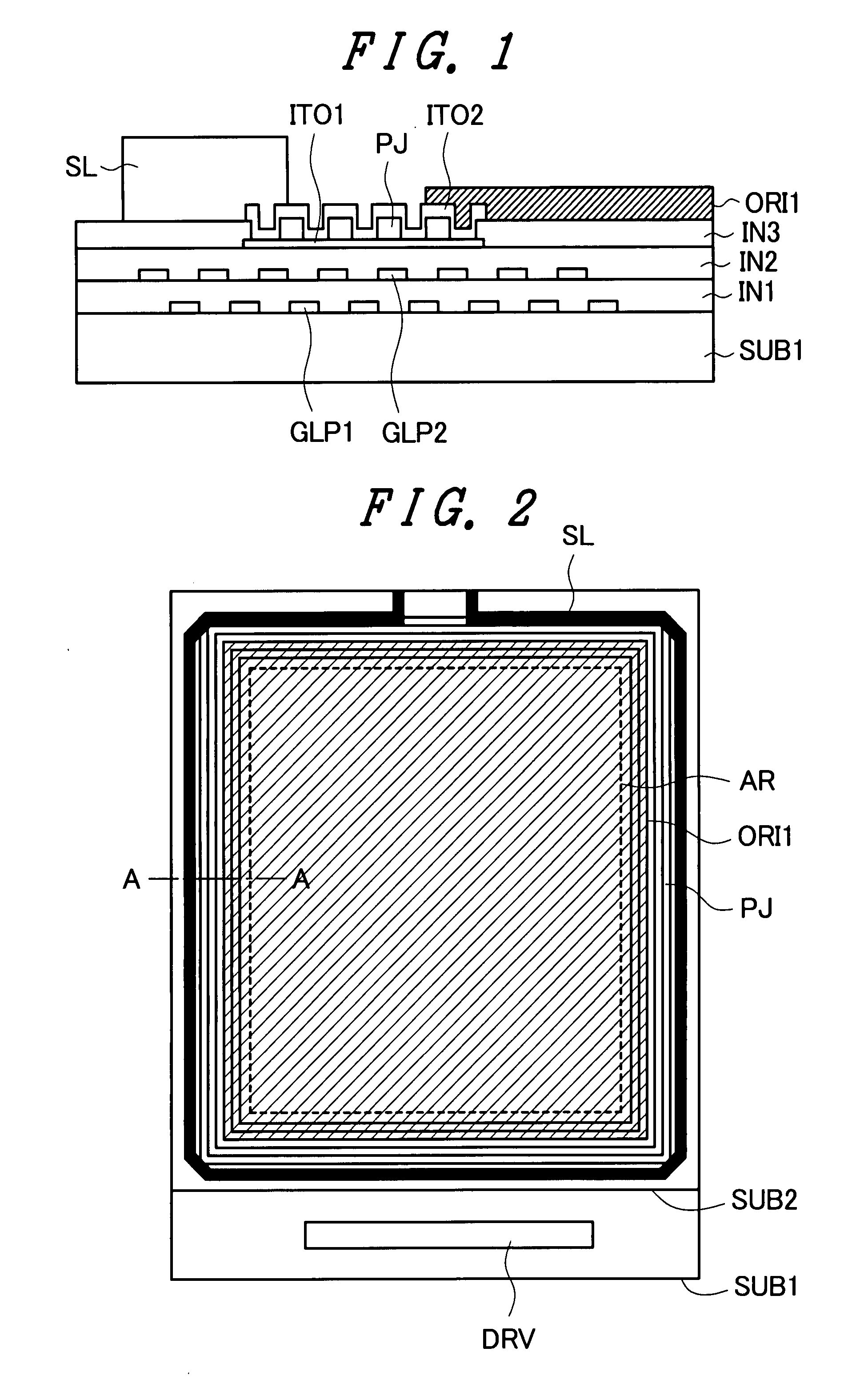
The present invention provides a liquid crystal display device with a narrow picture frame which reduces a sealing defect by suppressing spreading of an orientation film. In a region inside a sealing material and outside a display region, an uneven surface for suppressing spreading of the orientation film is formed. It is preferable that the uneven surface is formed using an insulation film and, at the same time, an etching stopper layer is formed below the insulation film which forms the uneven surface. It is more preferable that the uneven surface and the stopper layer are simultaneously formed with a layer used for forming pixels in a step for forming such a layer thus preventing the increase of manufacturing steps.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus for protein manipulation
InactiveUS6649419B1Avoid problemsAvoid deformationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAvidityAnalytical chemistry
A method and apparatus for extracting, identifying, and manipulating proteins or peptides from a solution uses paramagnetic beads having a coating with an affinity for the target component. In one embodiment, paramagnetic beads coated with C18 are used to adsorb proteins and peptides. The beads can be used to purify, immobilize and assay antibodies. By cycling the beads, many times greater molar amount of binding partner may be separated from a solution. A magnetic probe is used to capture the beads and transfer the beads to selected processing stages.
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
Methods and system for processing a microelectronic topography
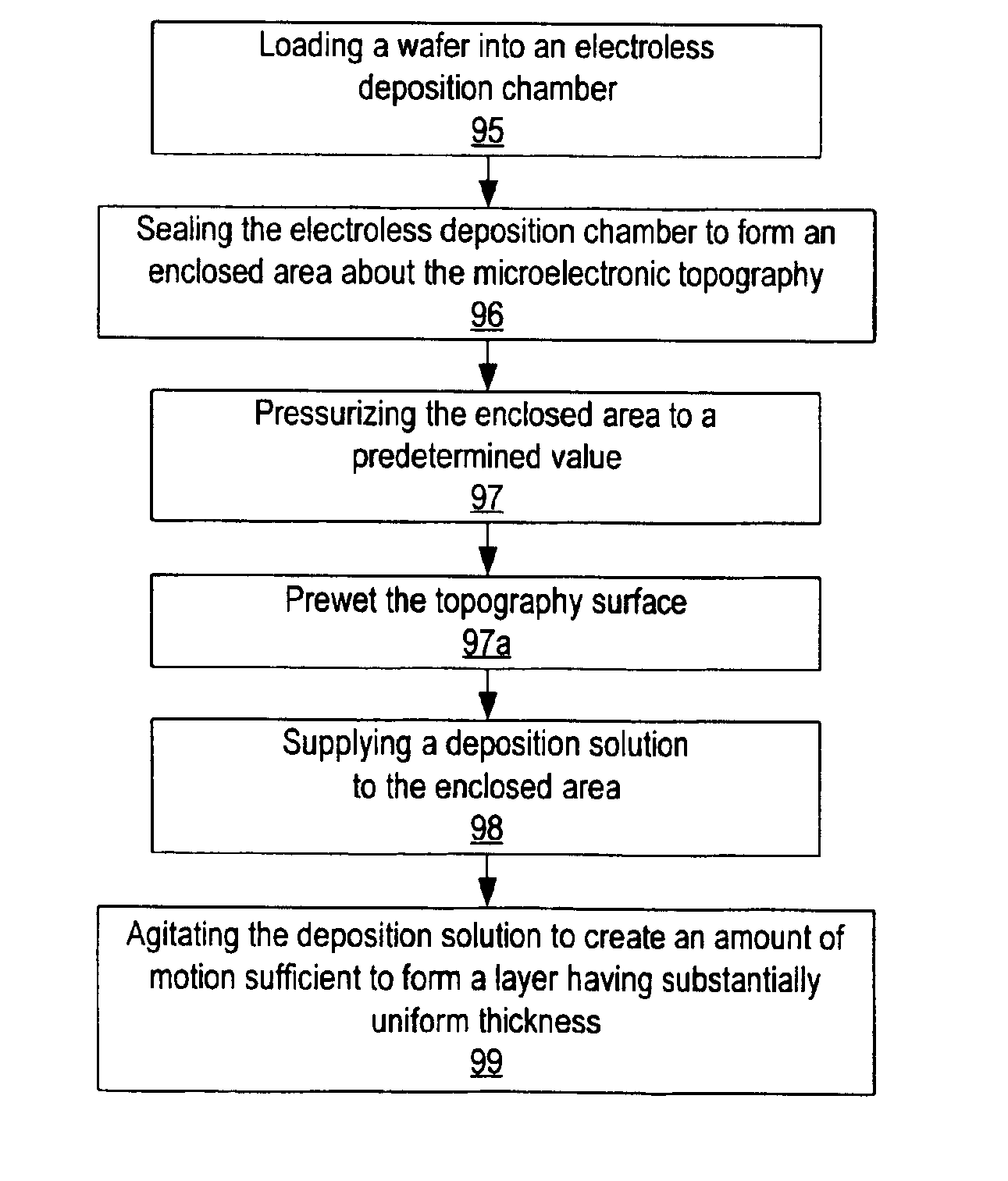
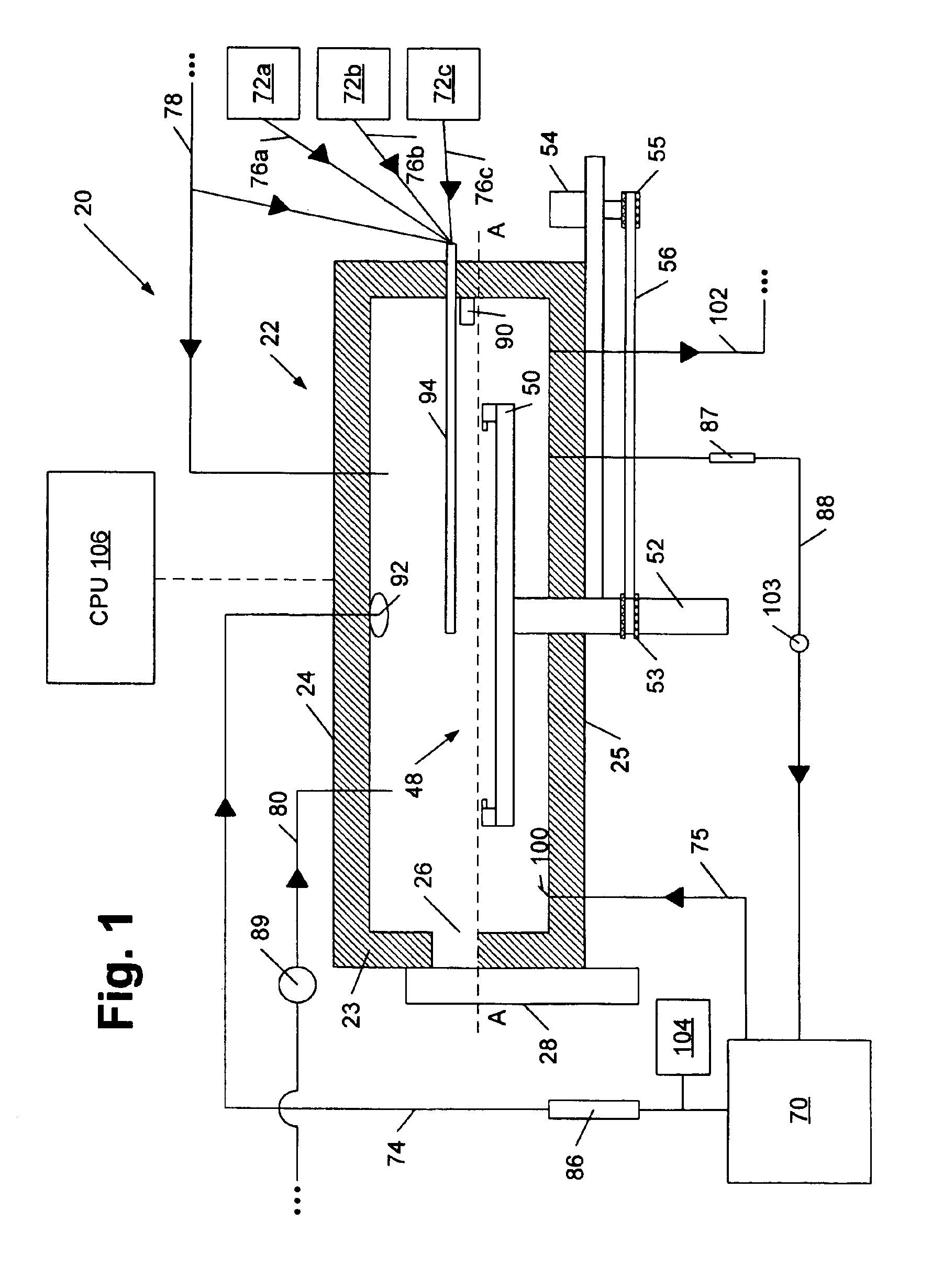
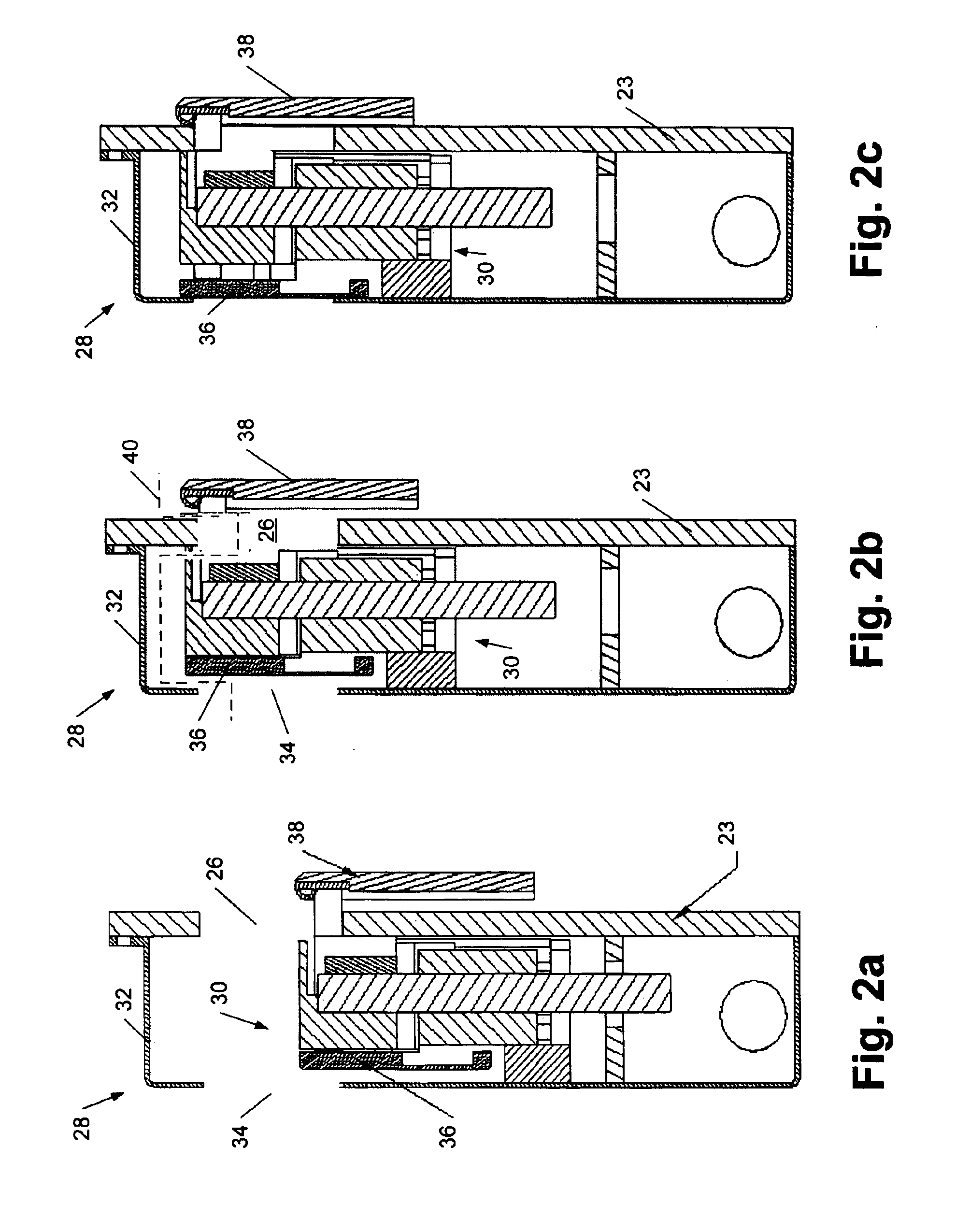
InactiveUS6881437B2Avoid flowHigh boiling pointSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesElectroless depositionTopography
Methods and systems are provided which are adapted to process a microelectronic topography, particularly in association with an electroless deposition process. In general, the methods may include loading the topography into a chamber, closing the chamber to form an enclosed area, and supplying fluids to the enclosed area. In some embodiments, the fluids may fill the enclosed area. In addition or alternatively, a second enclosed area may be formed about the topography. As such, the provided system may be adapted to form different enclosed areas about a substrate holder. In some cases, the method may include agitating a solution to minimize the accumulation of bubbles upon a wafer during an electroless deposition process. As such, the system provided herein may include a means for agitating a solution in some embodiments. Such a means for agitation may be distinct from the inlet / s used to supply the solution to the chamber.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
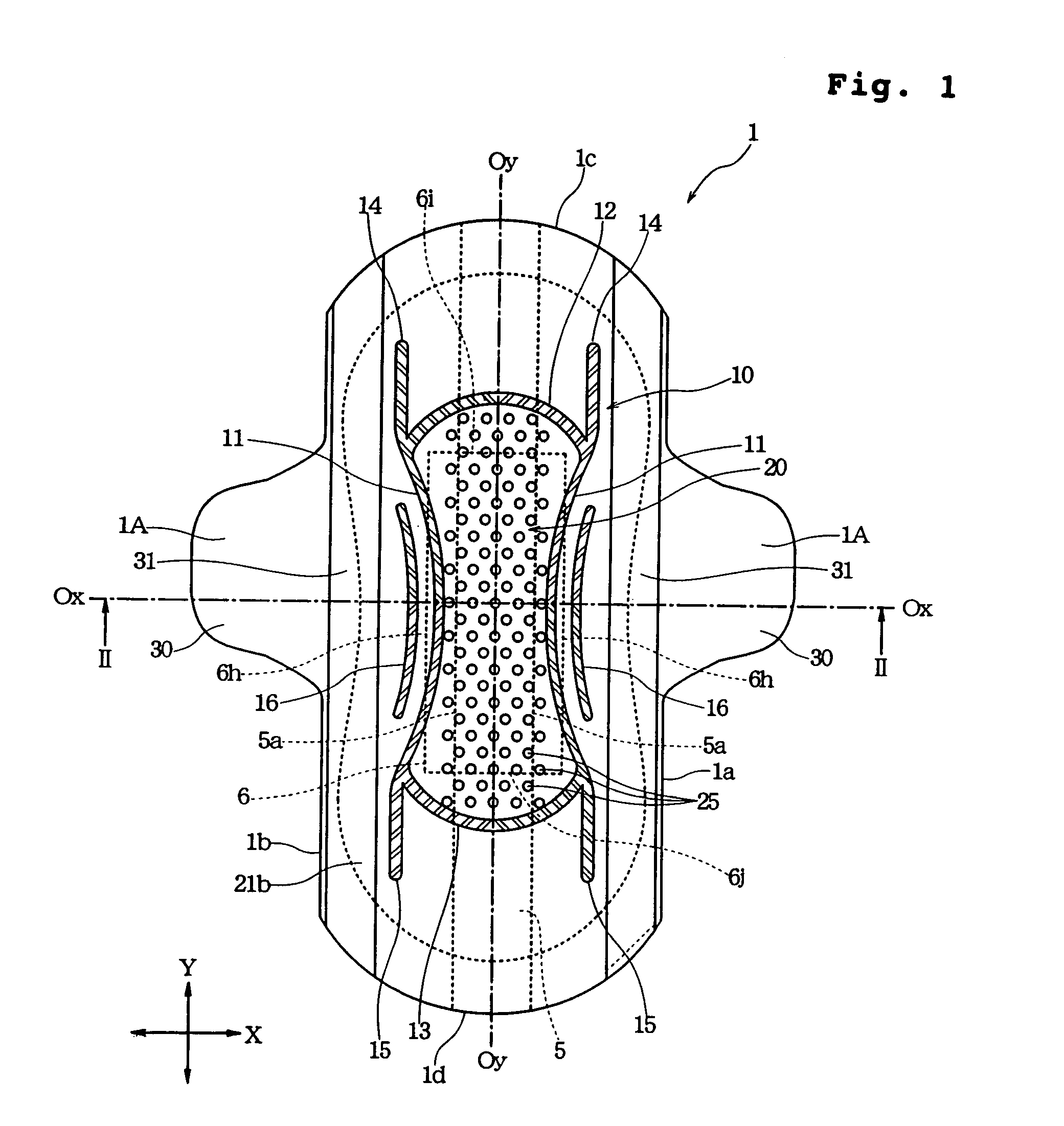
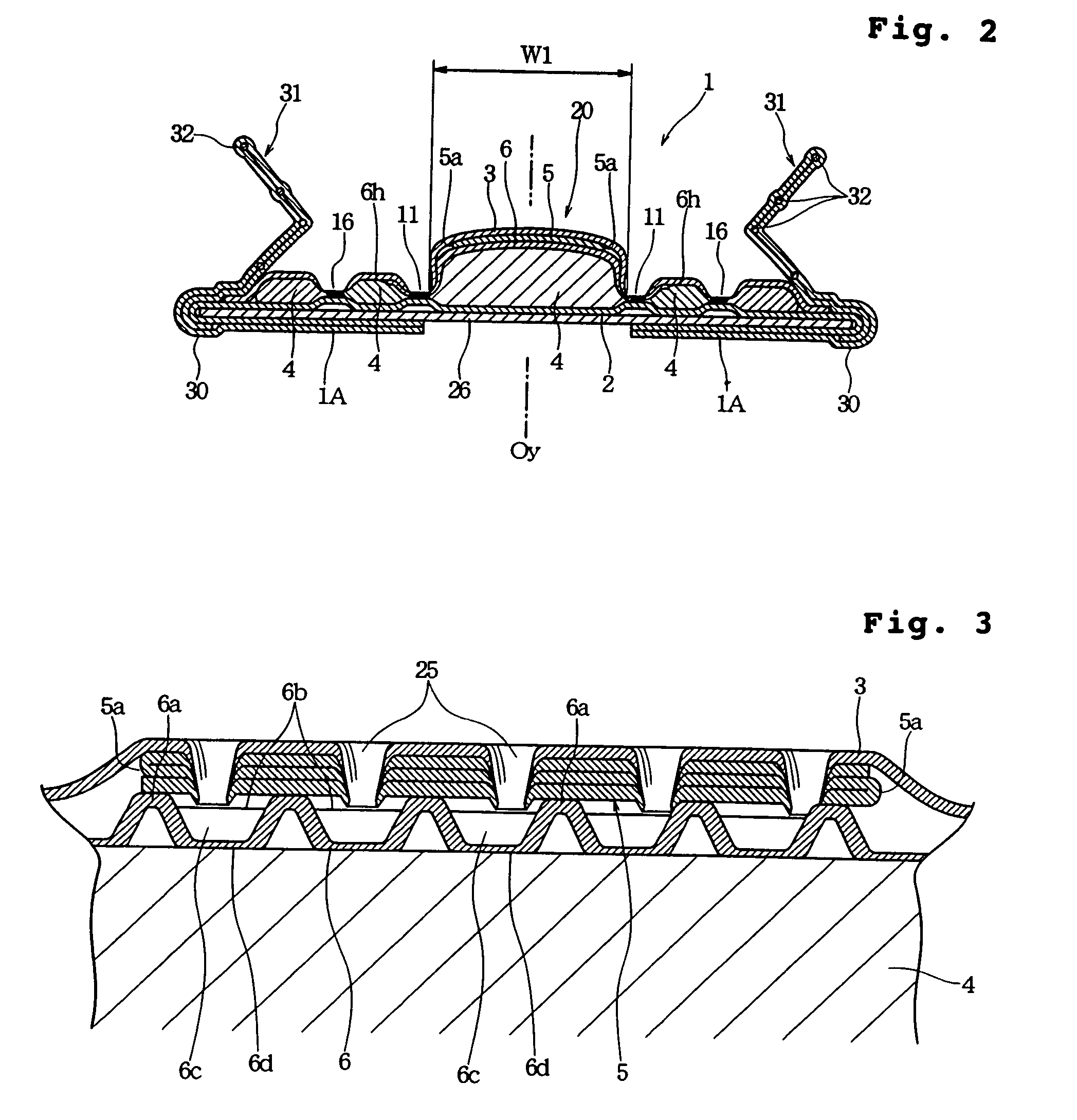
Absorbent article with liquid acquisition layer
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
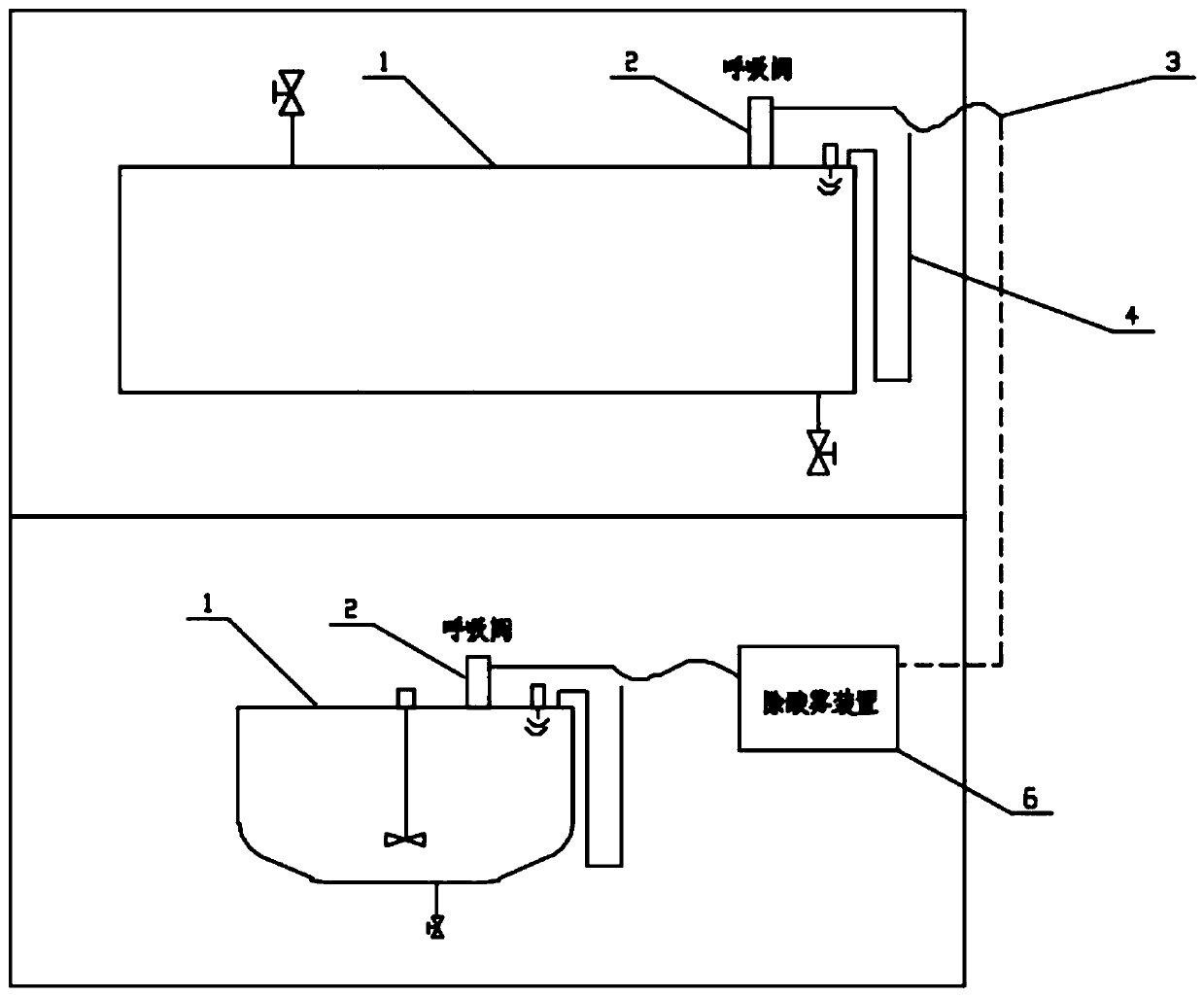
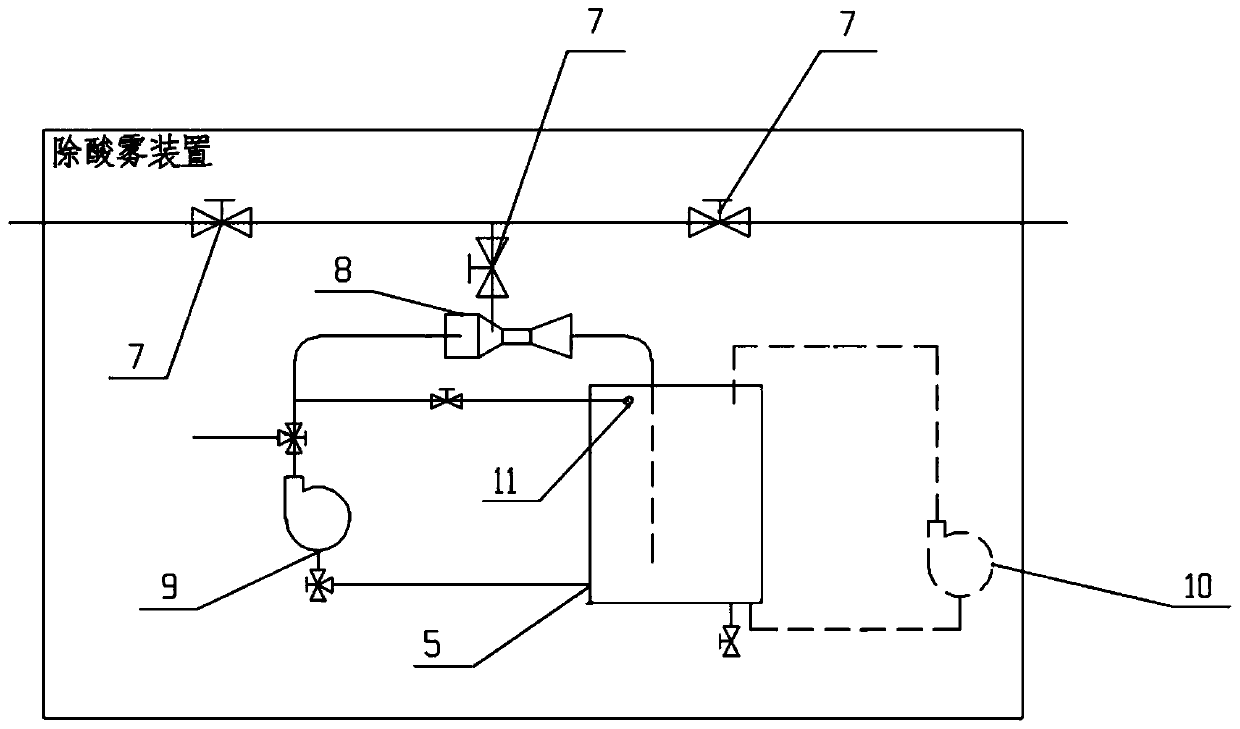
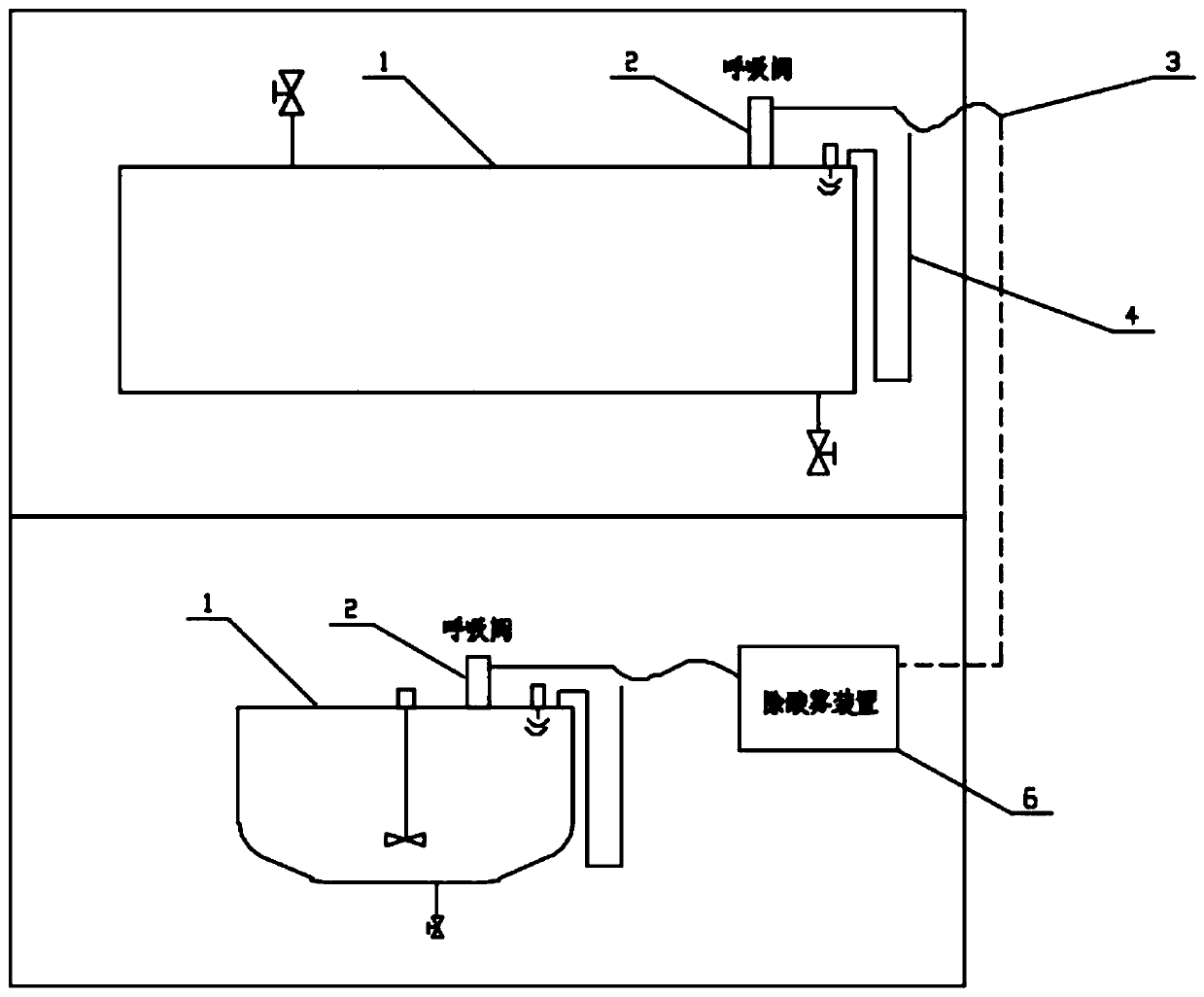
Acid tank sealing treatment system
PendingCN111169833AImprove single processingImprove processing efficiencyLarge containersProcess engineeringEnvironmental geology
The invention discloses an acid tank sealing treatment system. The acid tank sealing treatment system comprises connecting pipes, an acid mist removing device and a plurality of acid tanks, wherein the acid tanks are connected into the acid mist removing device through the connecting pipes for acid mist treatment. The acid tank sealing treatment system has the beneficial effects that acid mist ofthe acid tanks on an operation site can be treated in a centralized mode, single treatment in the prior art is improved, and the treatment efficiency is improved. The acid tanks are connected into theacid mist removing device through the connecting pipes for acid mist treatment, acid tank sealing on the operation site is achieved, and acid mist diffusion on the operation site is avoided.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH PETROLEUM EQUIP & TECH
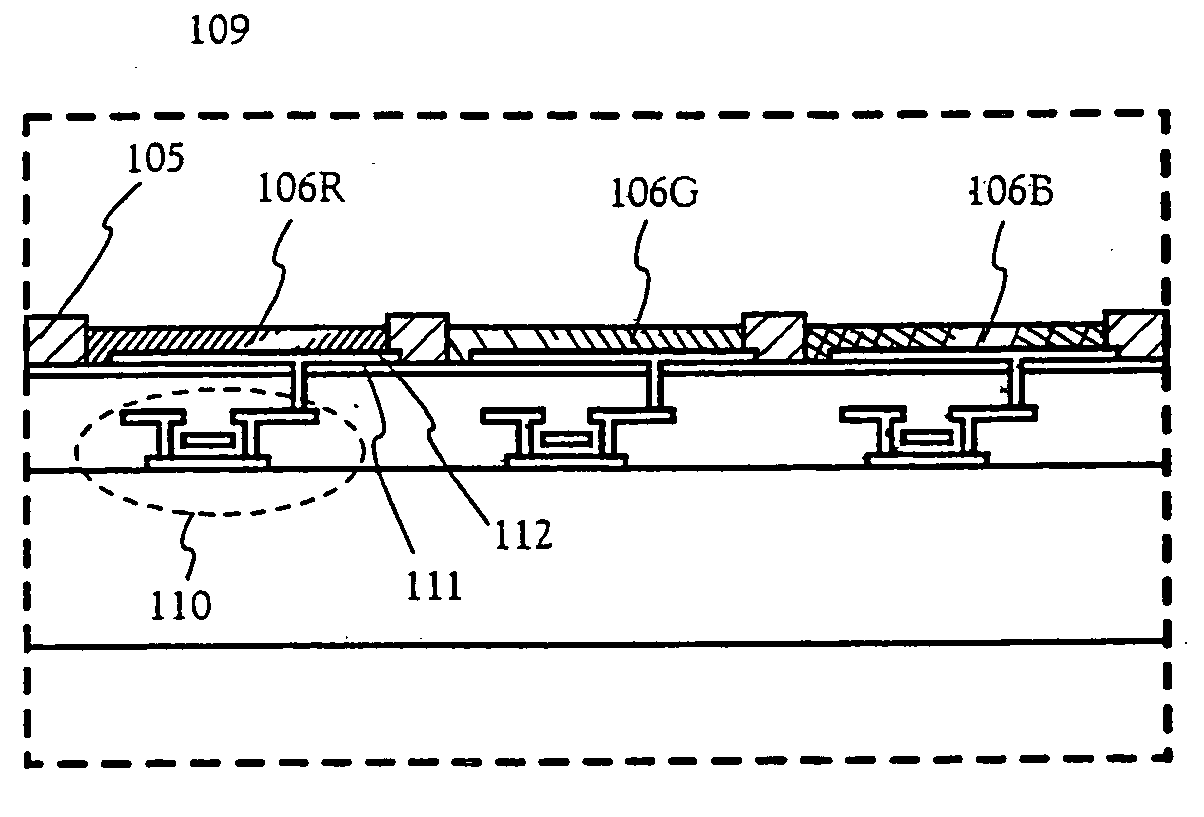
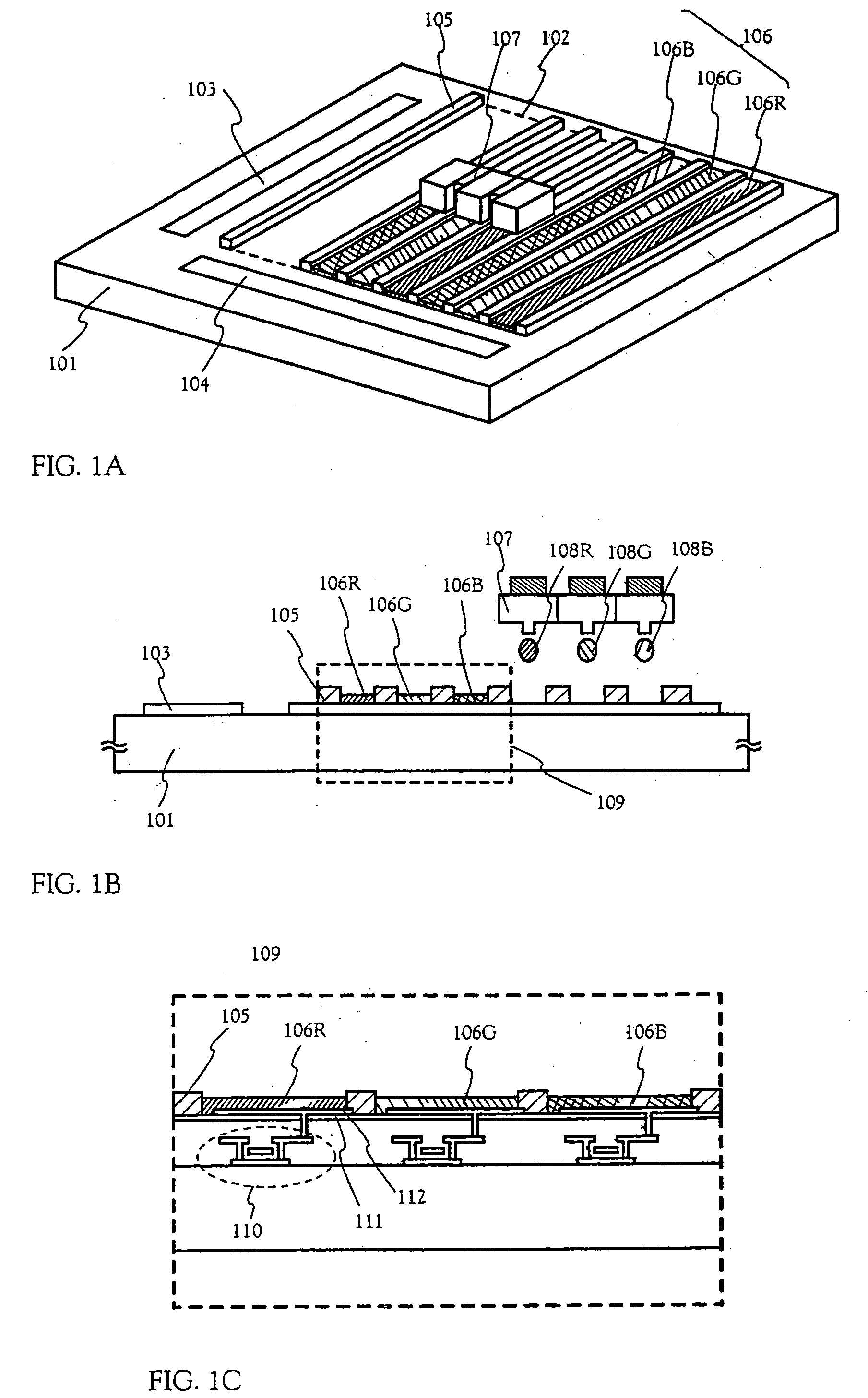
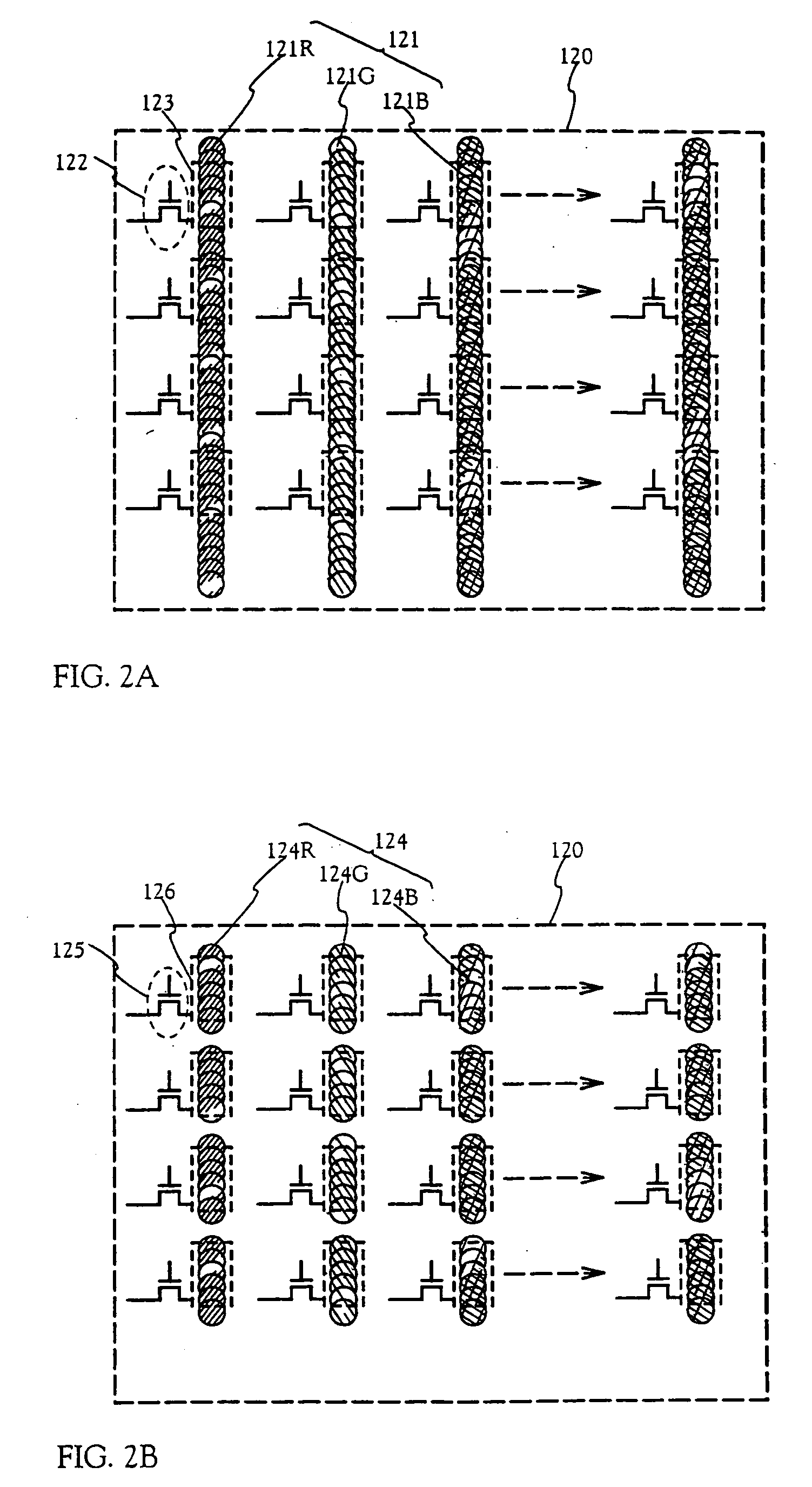
Electro-optical device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050035708A1Simple formatEasy to operateVacuum tubesDischarge tube luminescnet screensDisplay deviceEngineering
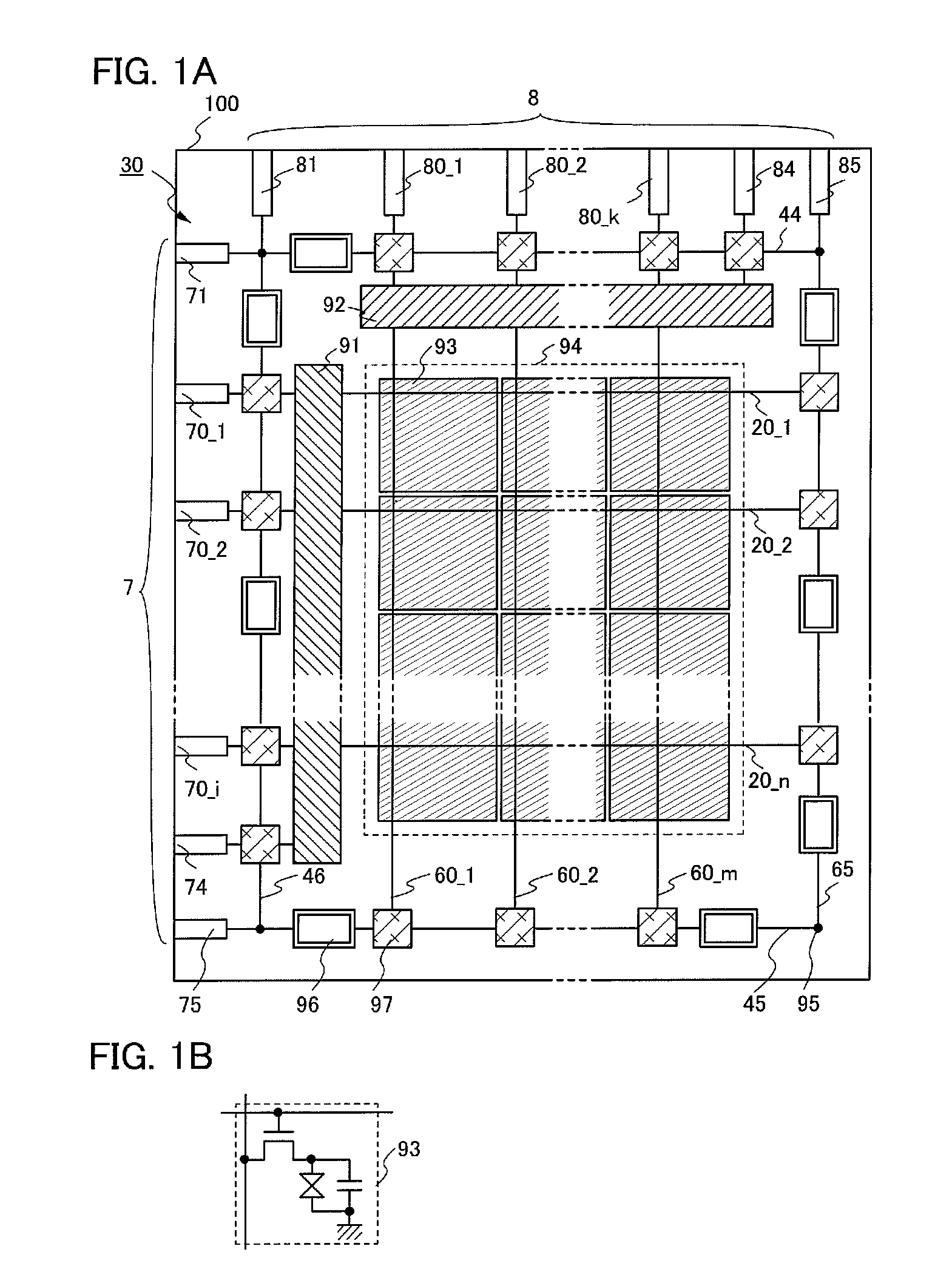
The present invention aims to provide simple, high-speed processing for the formation of an EL layer by an ink-jet method. A method of manufacturing an electro-optical device having good operation performance and high reliability, and in particular, a method of manufacturing an EL display device, is provided. The present invention forms EL layers continuously across a plurality of pixels when the EL layers are formed by the ink-jet method. Specifically, with respect to m columns and n rows of pixel electrodes arranged in a matrix state, the EL layers are formed so as to form stripes with respect to one certain selected row or one column. The EL layers may also be formed having an oblong shape or a rectangular shape with respect to each pixel electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
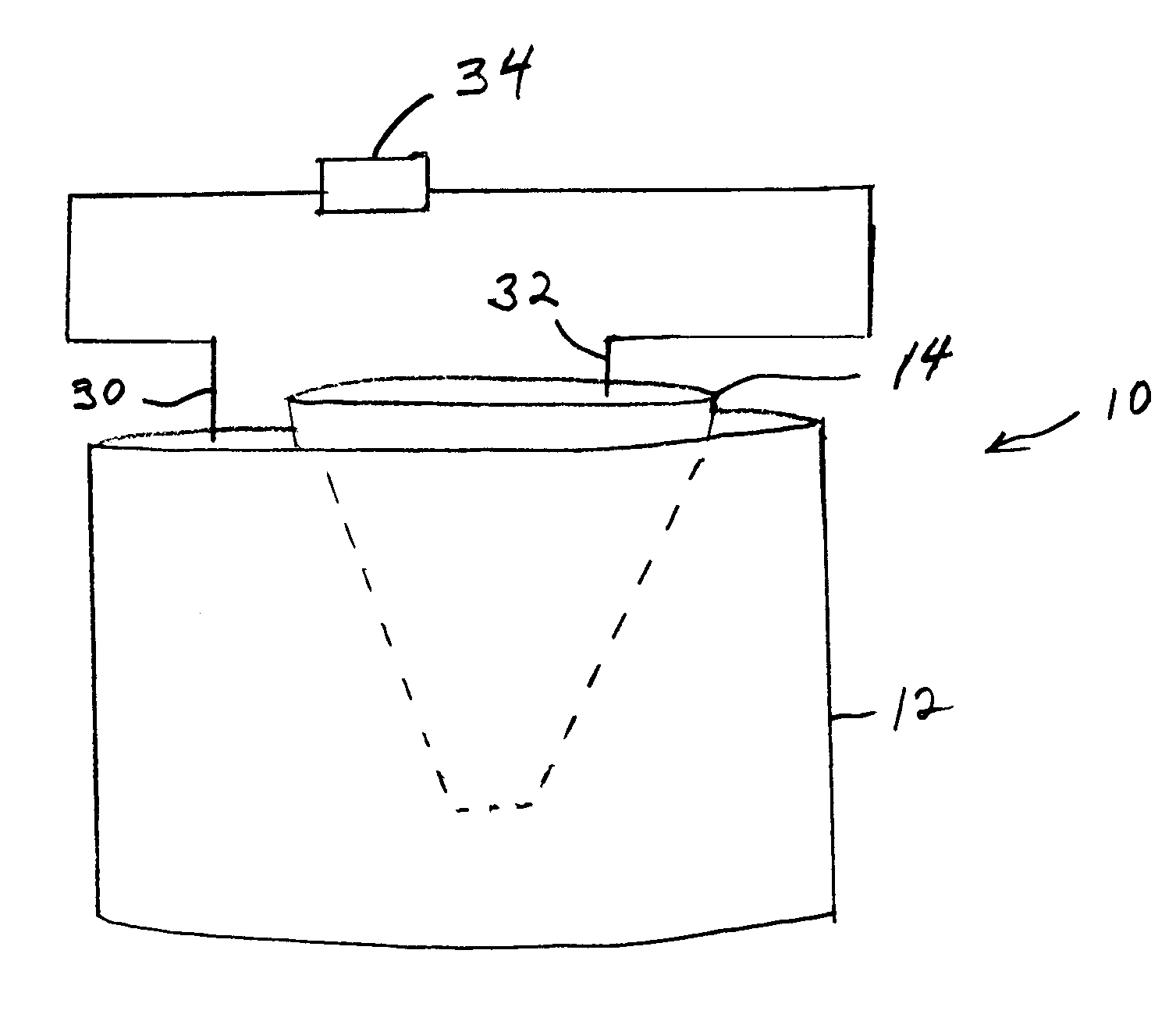
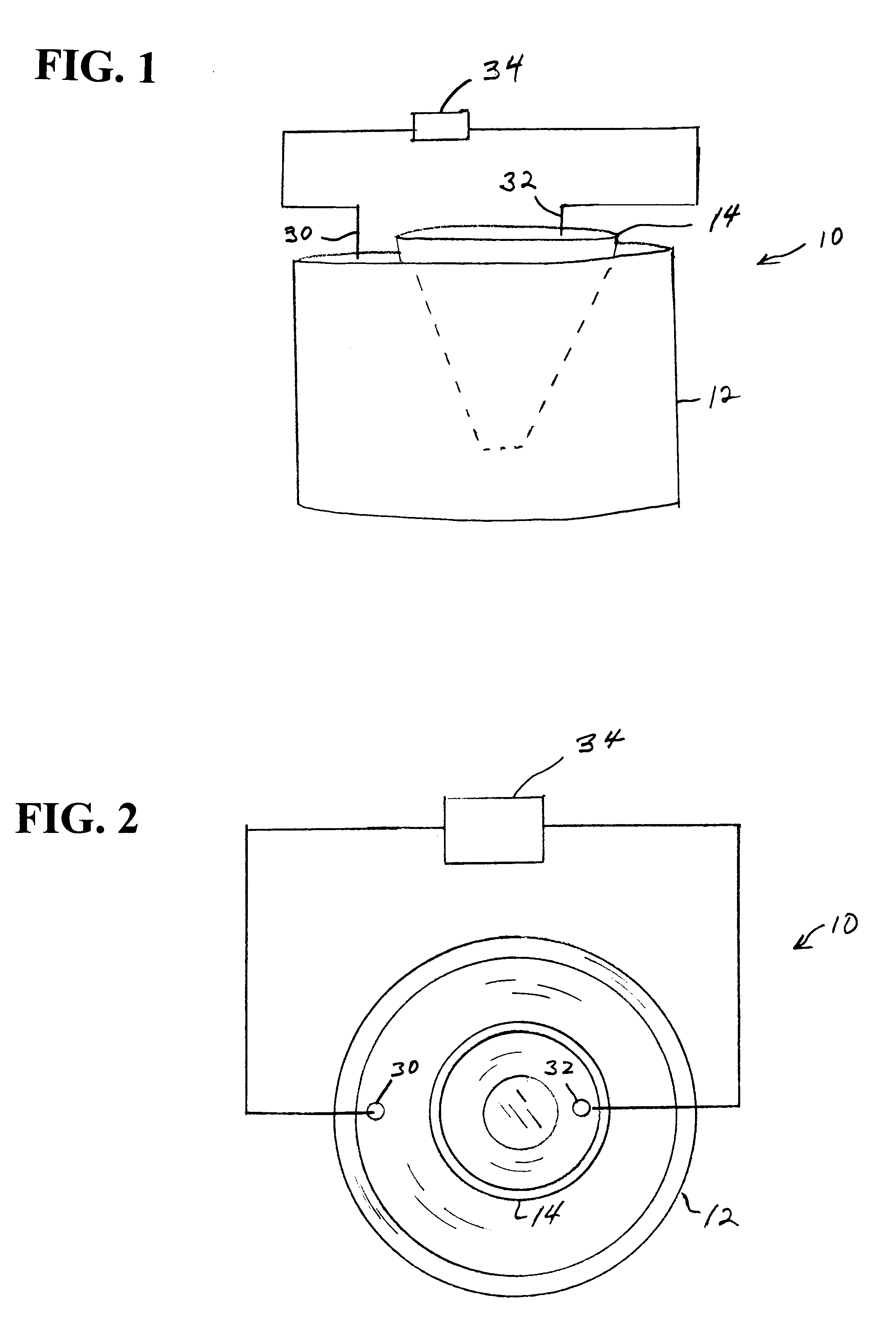
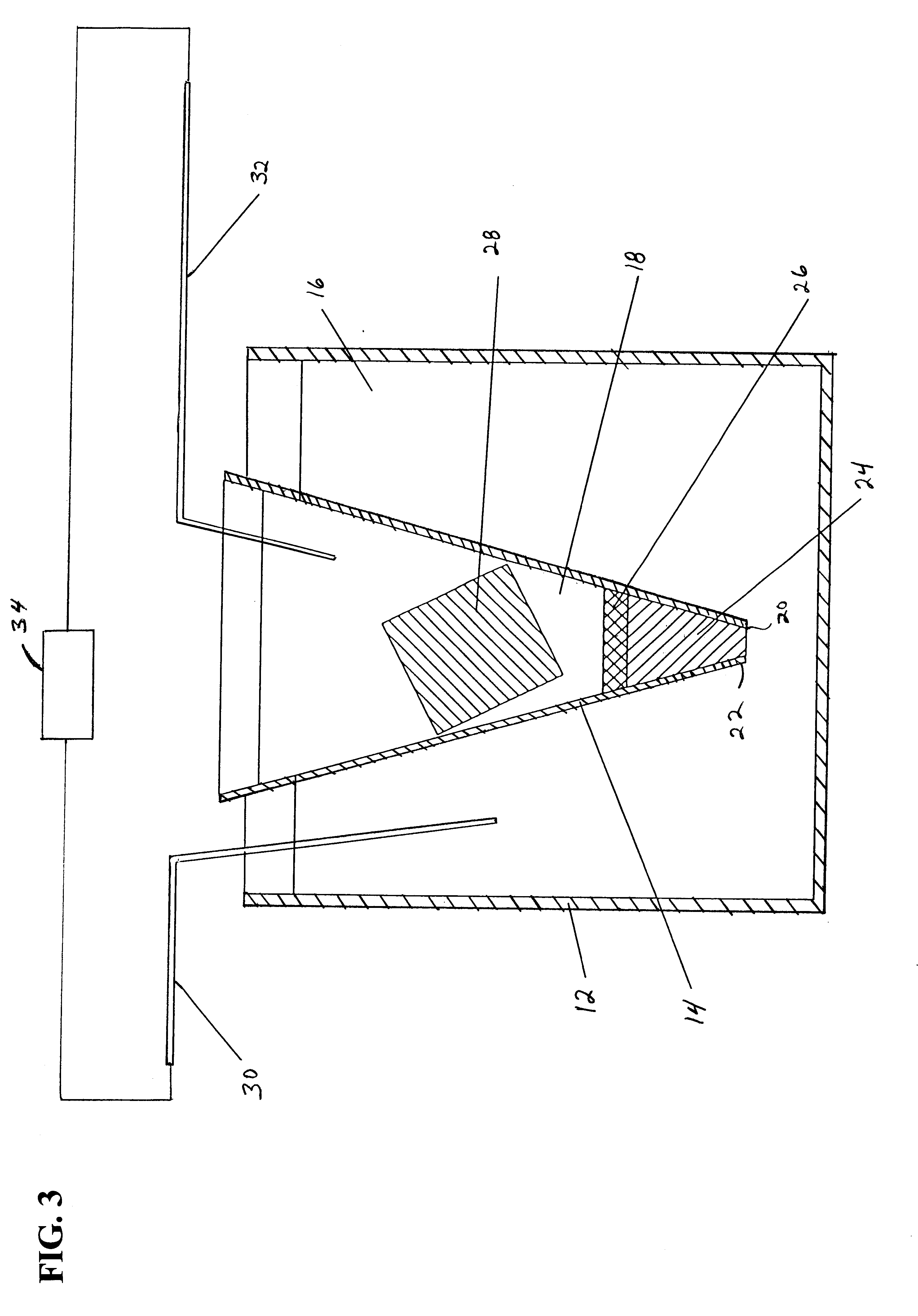
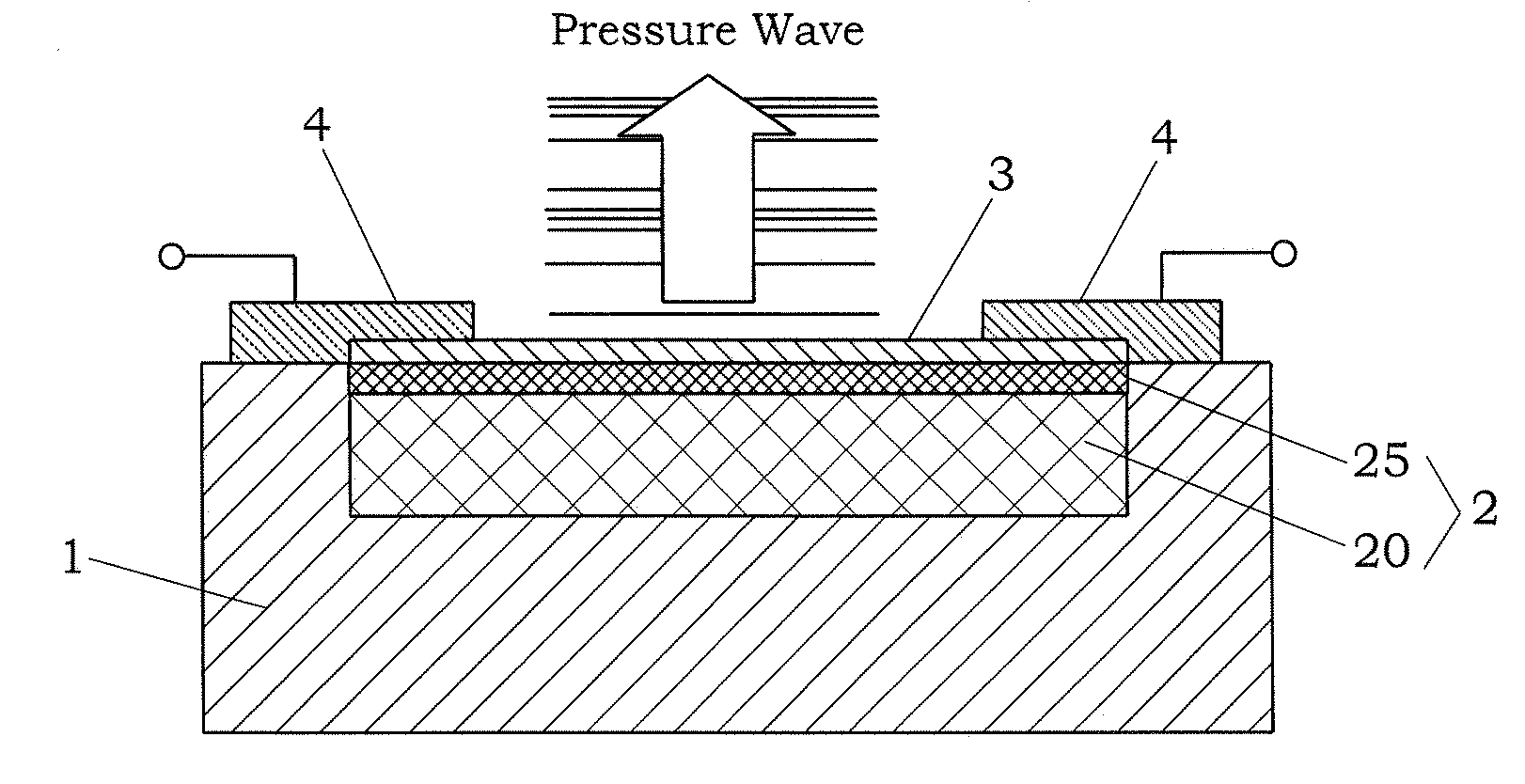
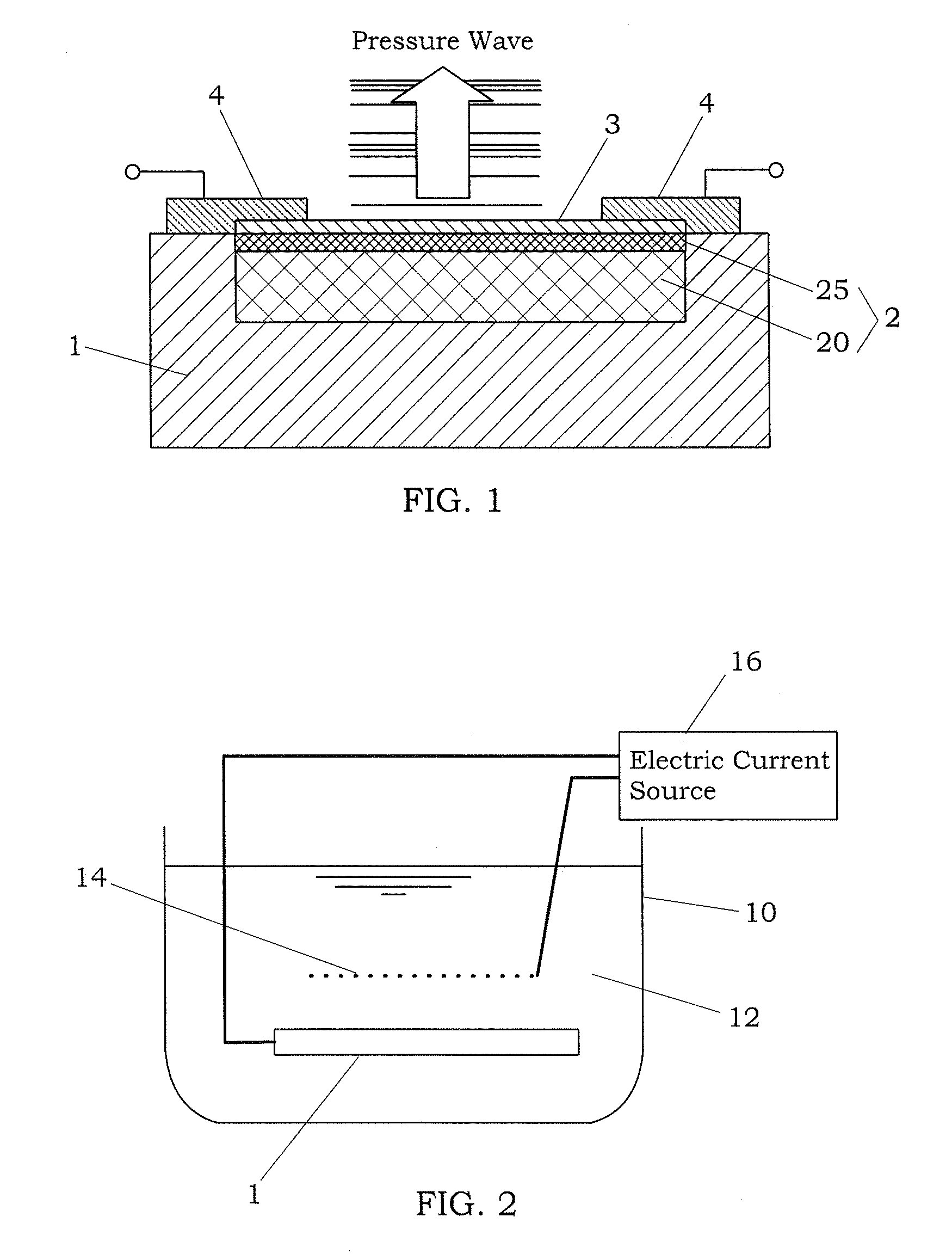
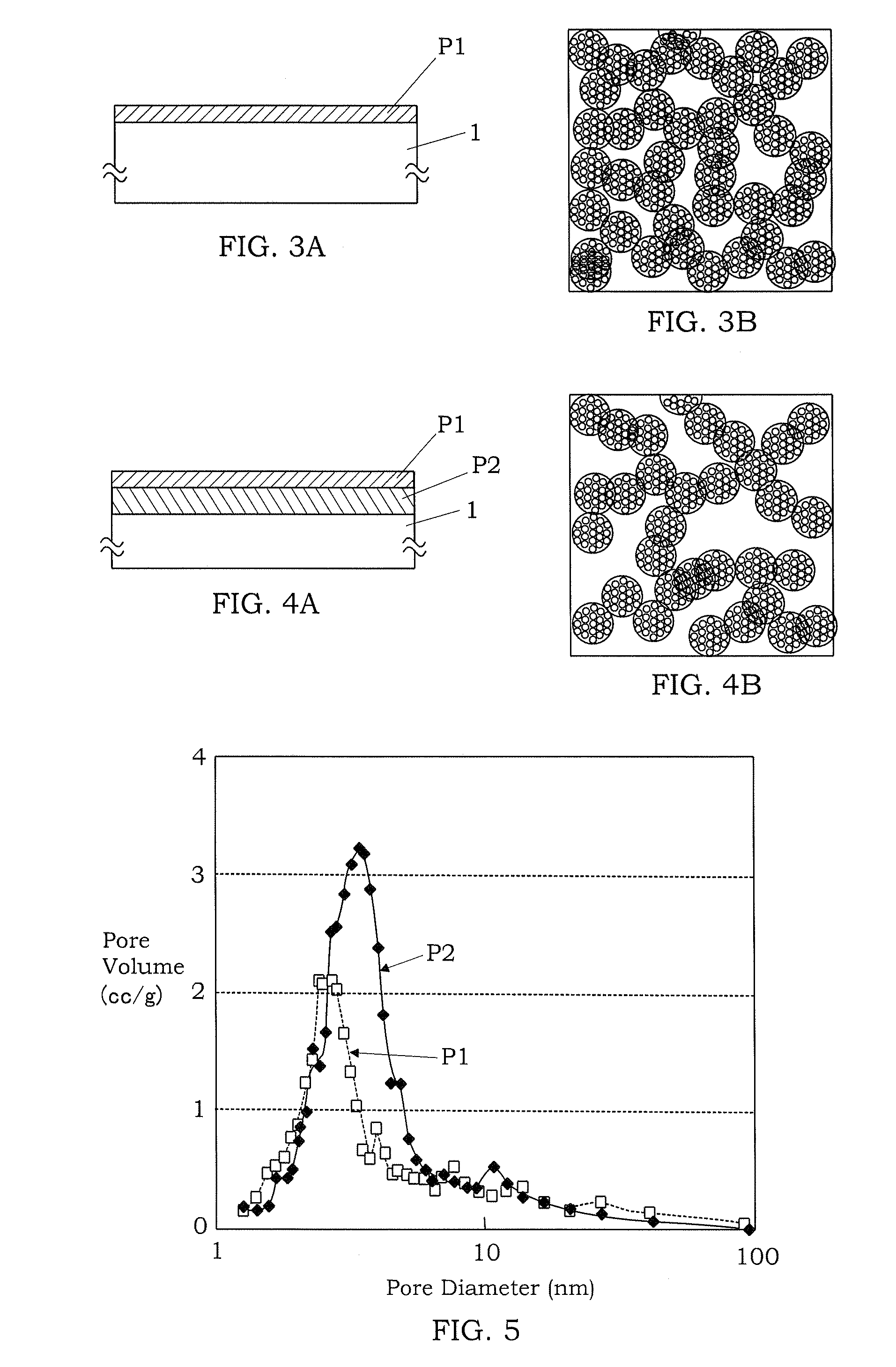
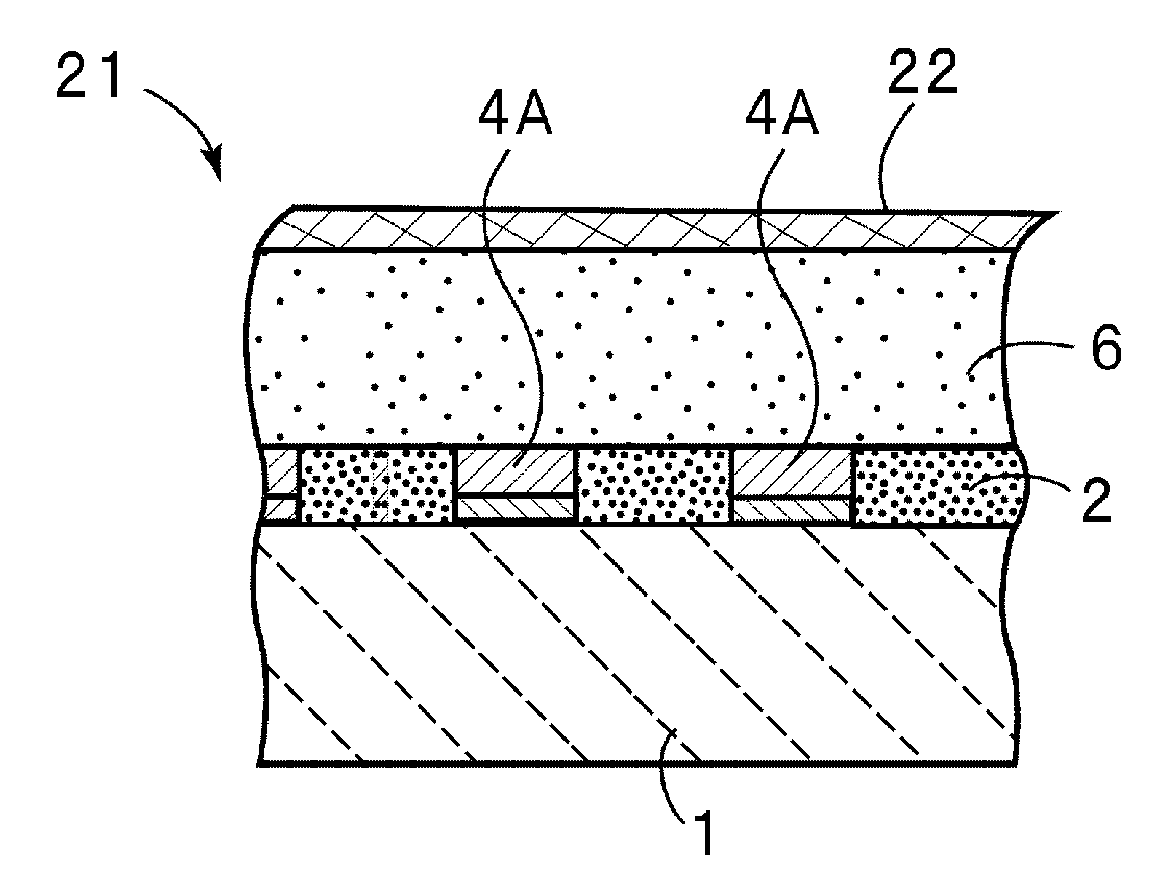
Pressure wave generator and production method therefor
InactiveUS20090145686A1Avoid production cutsInhibited DiffusionElectrothermic-effect transistorSemiconductor electrostatic transducersPorous layerEngineering
A pressure wave generator is provided, which has excellent output stability over time. This pressure wave generator comprises a substrate, a heat generating layer, and a heat insulating layer formed between the substrate and the heat generating layer. A pressure wave is generated in a surrounding medium (air) by a change in temperature of the heat generating layer, which is caused upon energization of the heat generating layer. The heat insulating layer comprises a porous layer and a barrier layer formed between the porous layer and the heat generating layer to prevent diffusion of reactive substances such as oxygen and moisture in the air and impurities into the porous layer. By the formation of the barrier layer, it is possible to prevent a reduction in output of the pressure wave generator caused by a change over time of the porous layer.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
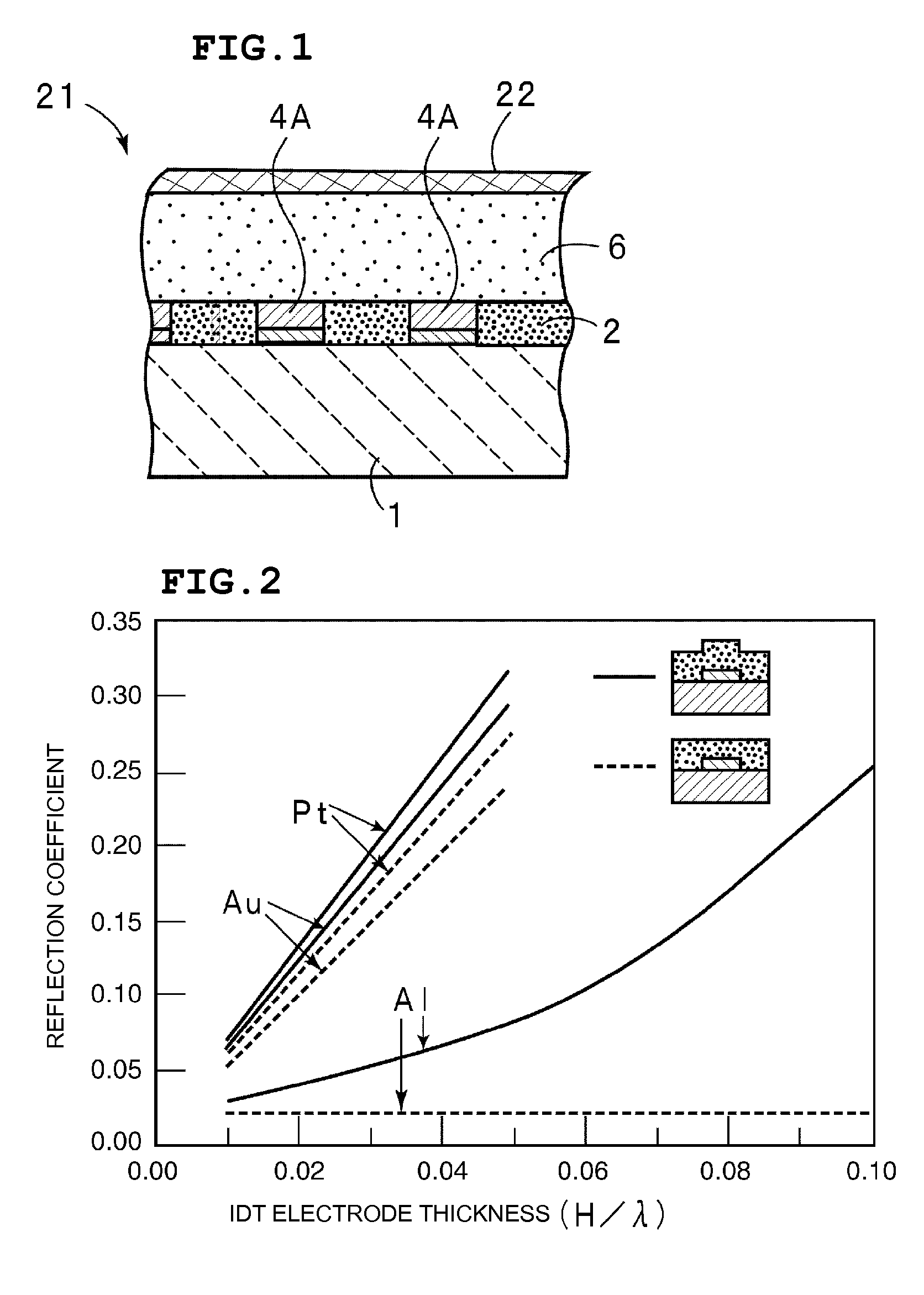
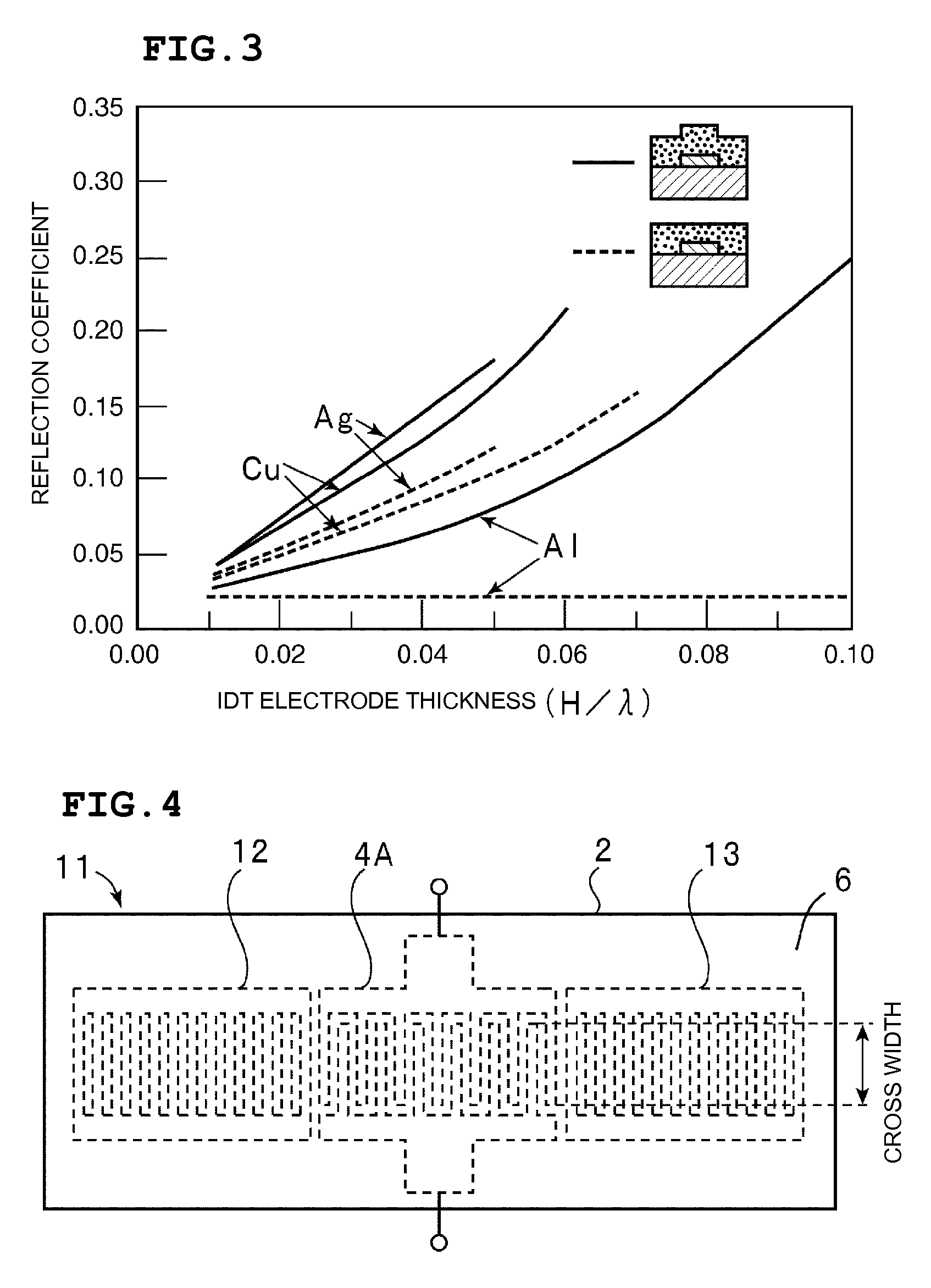
Surface acoustic wave device
ActiveUS7327071B2Improve filtering effectRipples are prevented and minimizedImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAlloyAcoustic wave
A surface acoustic wave device includes a piezoelectric substrate made of LiTaO3 or LiNbO3 having an electromechanical coefficient of about 15% or more, at least one electrode which is disposed on the piezoelectric substrate and which is a laminate film having a metal layer defining a primary metal layer primarily composed of a metal having a density higher than that of Al or an alloy of the metal and a metal layer which is laminated on the primary metal layer and which is composed of another metal, and a first SiO2 layer which is disposed in a remaining area other than that at which the at least one electrode is located and which has a thickness approximately equivalent to that of the electrode. In the surface acoustic wave device described above, the density of the electrode is at least about 1.5 times that of the first SiO2 layer. In addition, a second SiO2 layer disposed so as to cover the electrode and the first SiO2 layer and a silicon nitride compound layer disposed on the second SiO2 layer are further provided.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Process for realizing a connecting structure
ActiveUS9224704B2Prevent metal diffusionInhibited DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringDiffusion barrier
The present invention relates to a process for realizing a connecting structure in a semiconductor substrate, and the semiconductor substrate realized accordingly. The semiconductor substrate has at least a first surface, and is foreseen for a 3D integration with a second substrate along the first surface, wherein the 3D integration is subject to a lateral misalignment in at least one dimension having a misalignment value. This process includes growing a diffusion barrier structure for preventing diffusion of elements out of a conductive layer into the rest of the semiconductor substrate, wherein a first end surface, being the most outward surface of the diffusion barrier structure and being substantially parallel to the first surface, along a direction perpendicular to the first surface and going from the substrate toward the first surface, of the diffusion barrier structure can have a length, in the direction of the lateral misalignment, the length being dependent on the misalignment value, wherein the length of the diffusion barrier structure is chosen such that in a 3D integrated structure a diffusion of elements out of a conductive layer of the second substrate is prevented in the integrated state.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Light-emitting device, film-forming method and manufacturing apparatus thereof, and cleaning method of the manufacturing apparatus
InactiveUS20050016462A1Small surface areaGas discharge is preventedElectroluminescent light sourcesVacuum evaporation coatingSilanesMetallurgy
This invention provides a new film forming method in which, on the occasion that pressure is decreased by pressure decreasing means which was connected to a film forming chamber, and a film is formed by evaporating an organic compound material from a deposition source in the film forming chamber, minute amounts of gas (silane series gas) which comprises smaller particles than particles of the organic compound material, i.e., a material with a smaller atomic radius are flowed, and the material with a small atomic radius is made to be included in an organic compound film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device including a dopant blocking superlattice
InactiveUS20060220118A1Reduce channel degradationReduce degradationNanoinformaticsSemiconductor devicesMOSFETField-effect transistor
A semiconductor device may include at least one metal oxide field-effect transistor (MOSFET). The at least one MOSFET may include a body, a channel layer adjacent the body, and a dopant blocking superlattice between the body and the channel layer. The dopant blocking superlattice may include a plurality of stacked groups of layers. Each group of layers of the dopant blocking superlattice may include a plurality of stacked base semiconductor monolayers defining a base semiconductor portion, and at least one non-semiconductor monolayer constrained within a crystal lattice of adjacent base semiconductor portions.
Owner:MEARS TECH
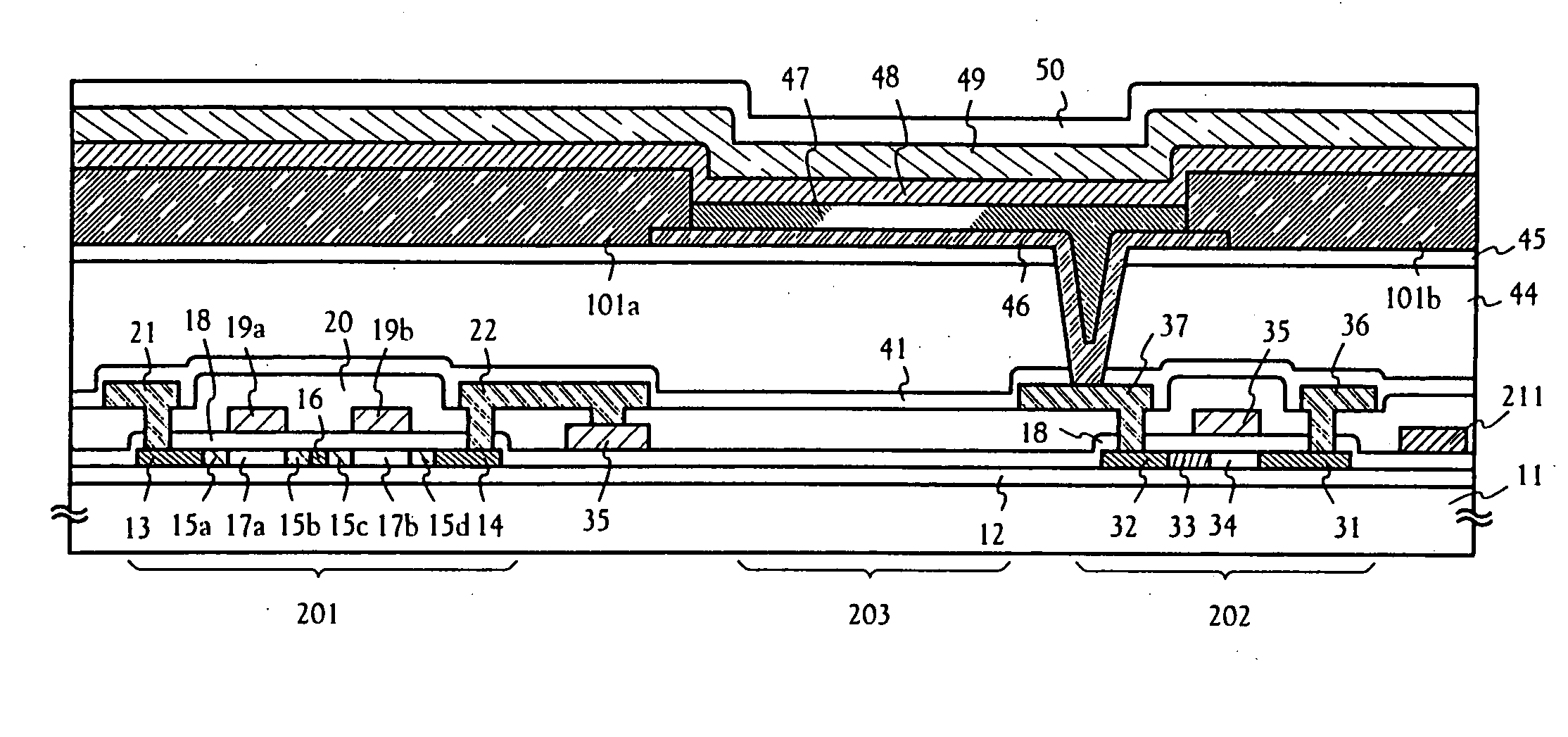
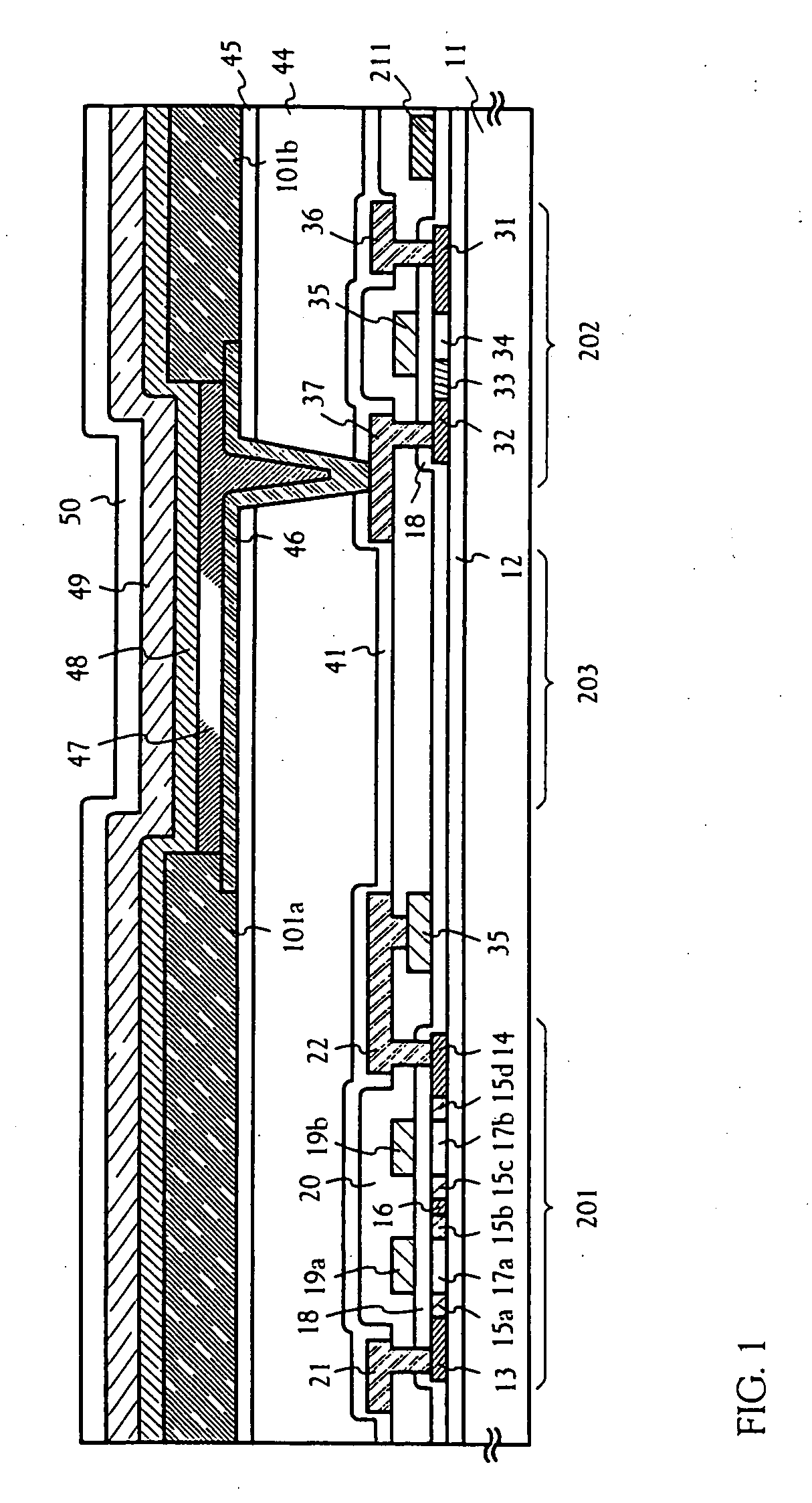
Method for manufacturing an electro-optical device
InactiveUS20050197031A1Guaranteed uptimeImprove reliabilityTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceEngineering
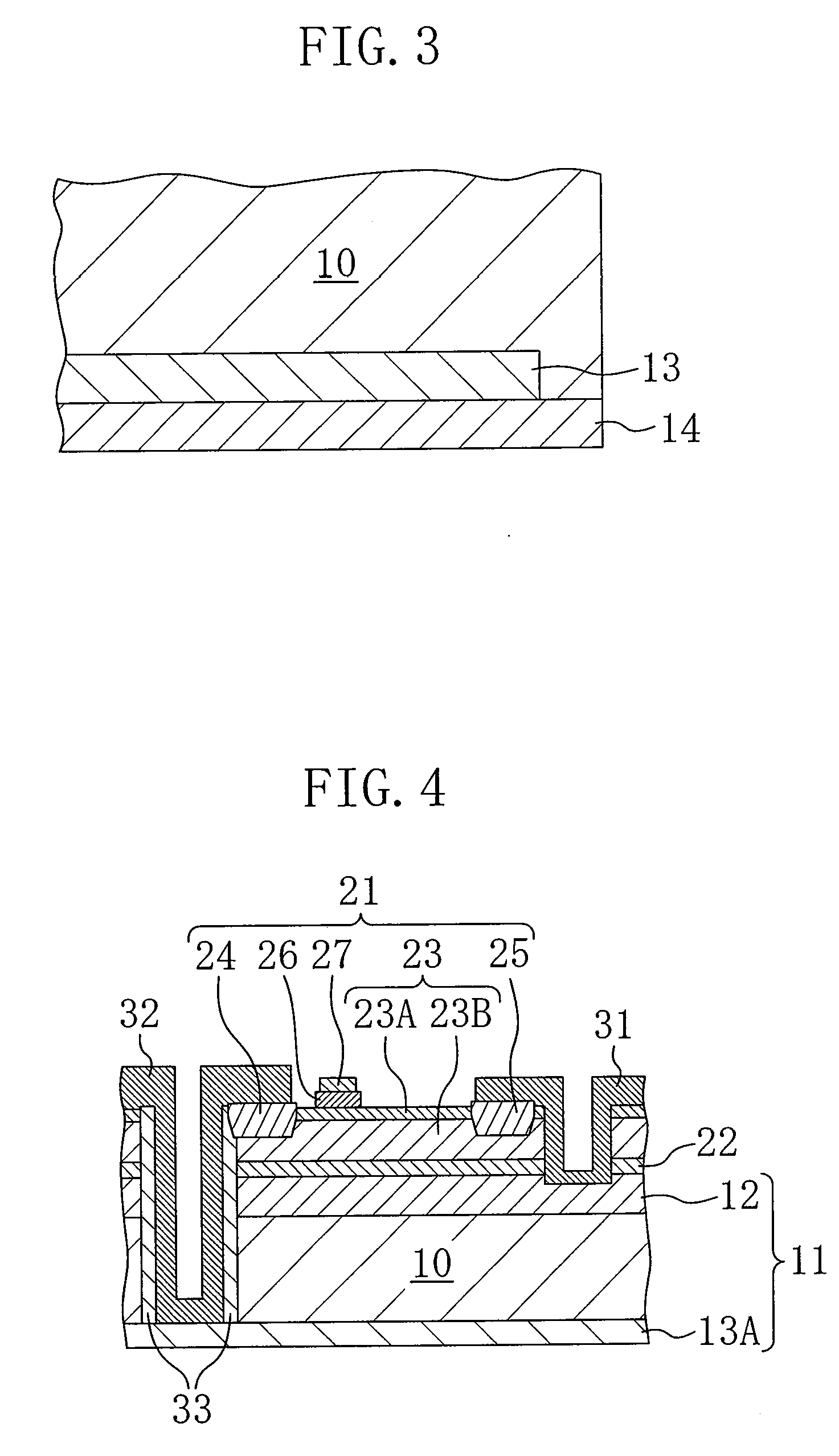
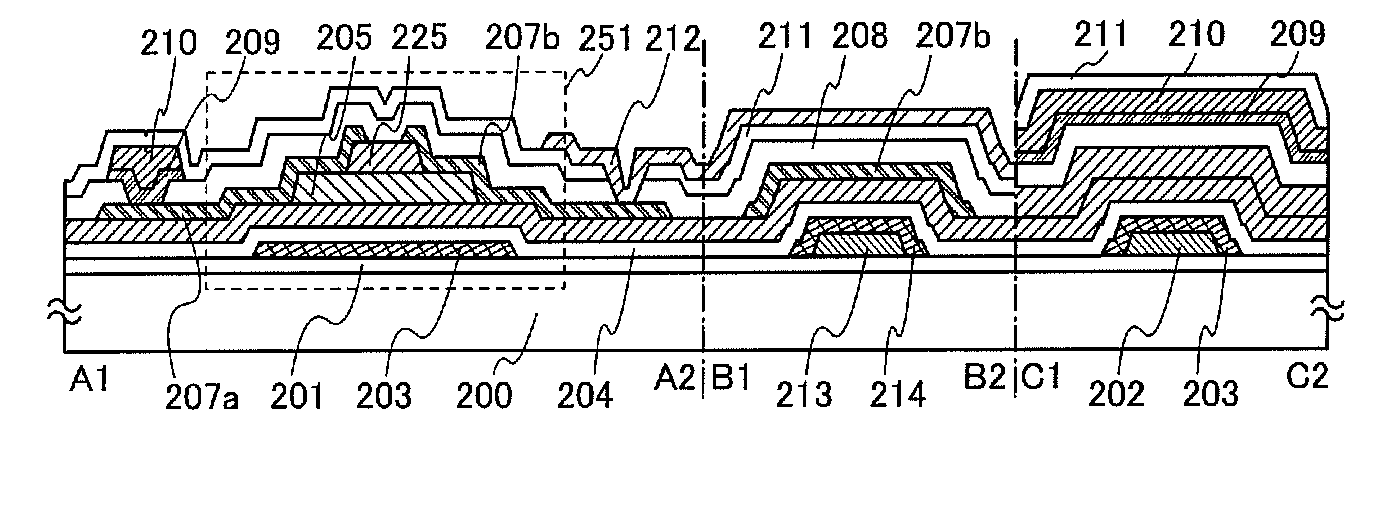
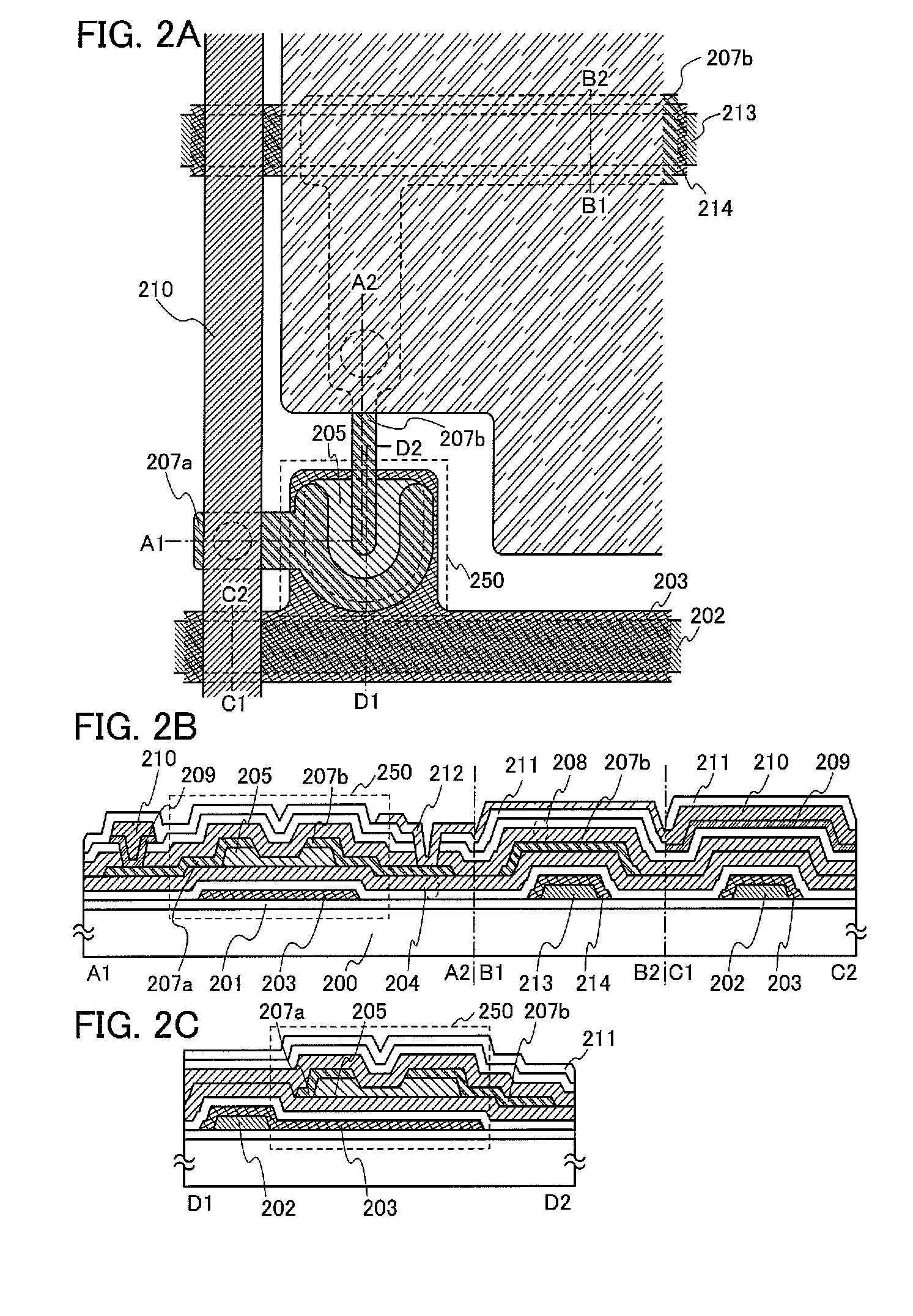
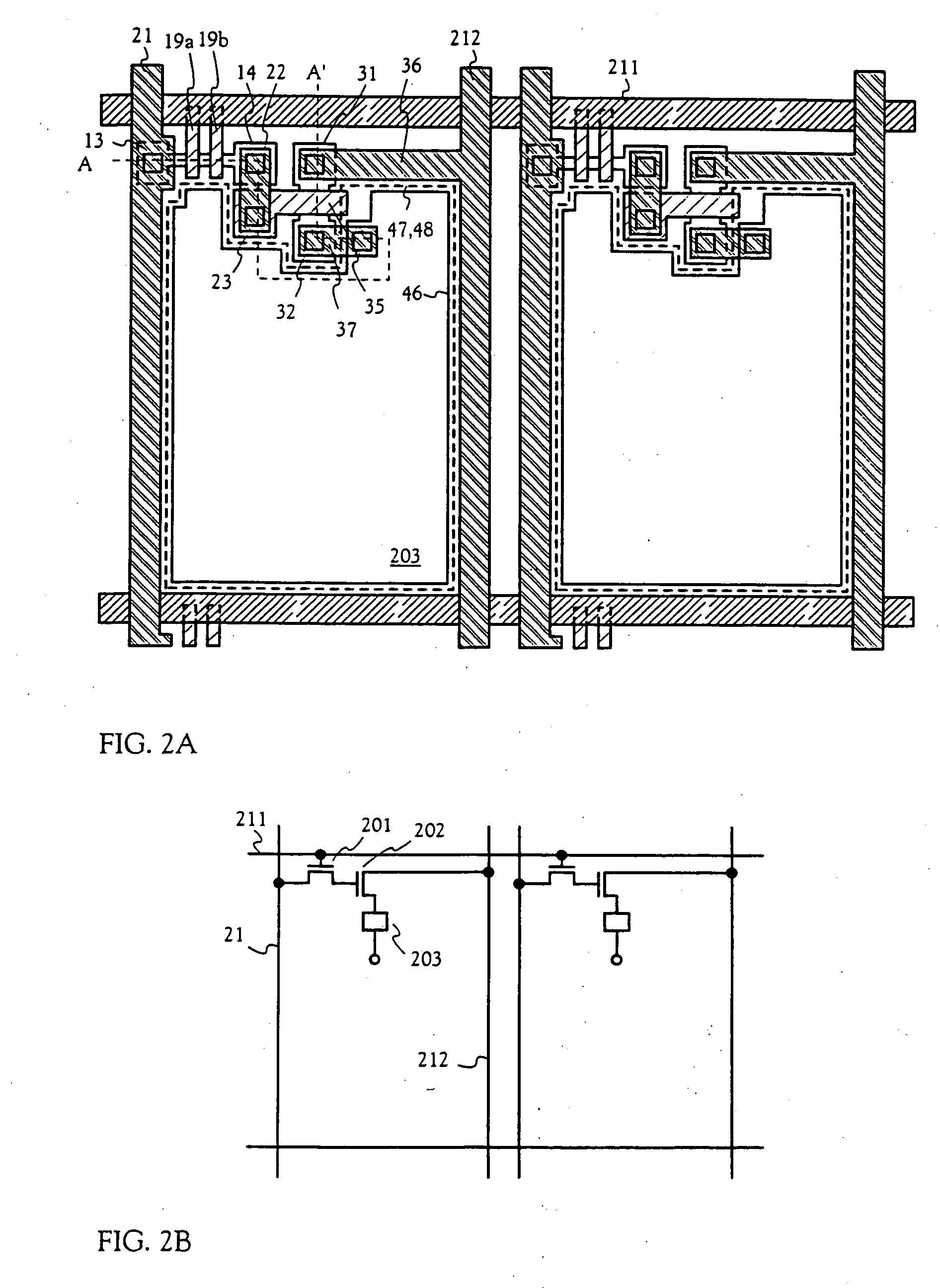
An object of the present invention is to provide an EL display device having high operation performance and reliability. A third passivation film 45 is disposed under the EL element 203 comprising a pixel electrode (anode) 46, an EL layer 47 and a cathode 48, and diffusion of alkali metals from the EL element 203 formed by ink jet method into TFTs is prevented. Further, the third passivation film 45 prevents penetration of moisture and oxygen from the TFTs, and suppress degradation of the EL element 203 by dispersing the heat generated by the EL element 203.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com