Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
417 results about "Spin polarization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spin polarization is the degree to which the spin, i.e., the intrinsic angular momentum of elementary particles, is aligned with a given direction. This property may pertain to the spin, hence to the magnetic moment, of conduction electrons in ferromagnetic metals, such as iron, giving rise to spin-polarized currents. It may refer to (static) spin waves, preferential correlation of spin orientation with ordered lattices (semiconductors or insulators).
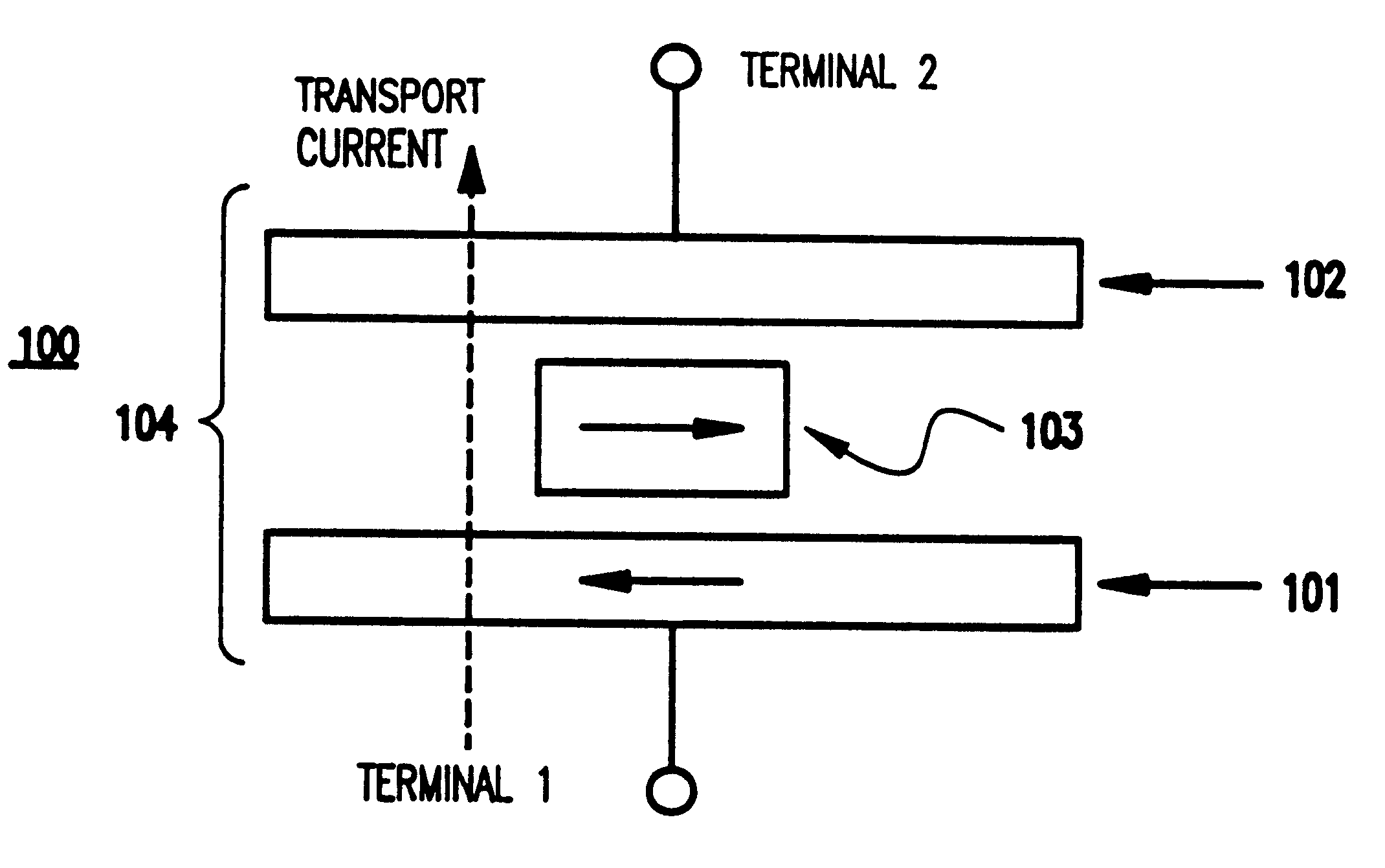
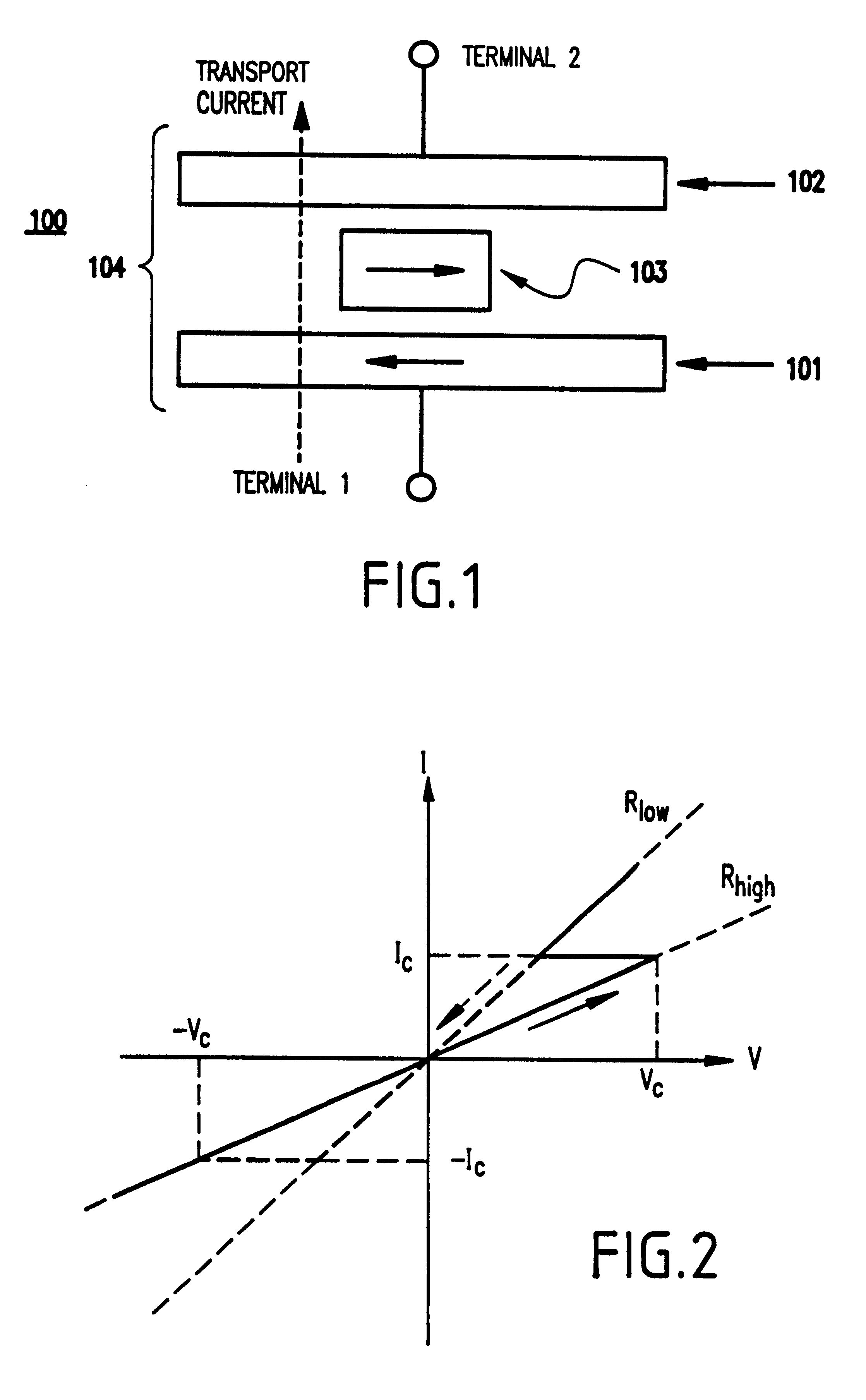
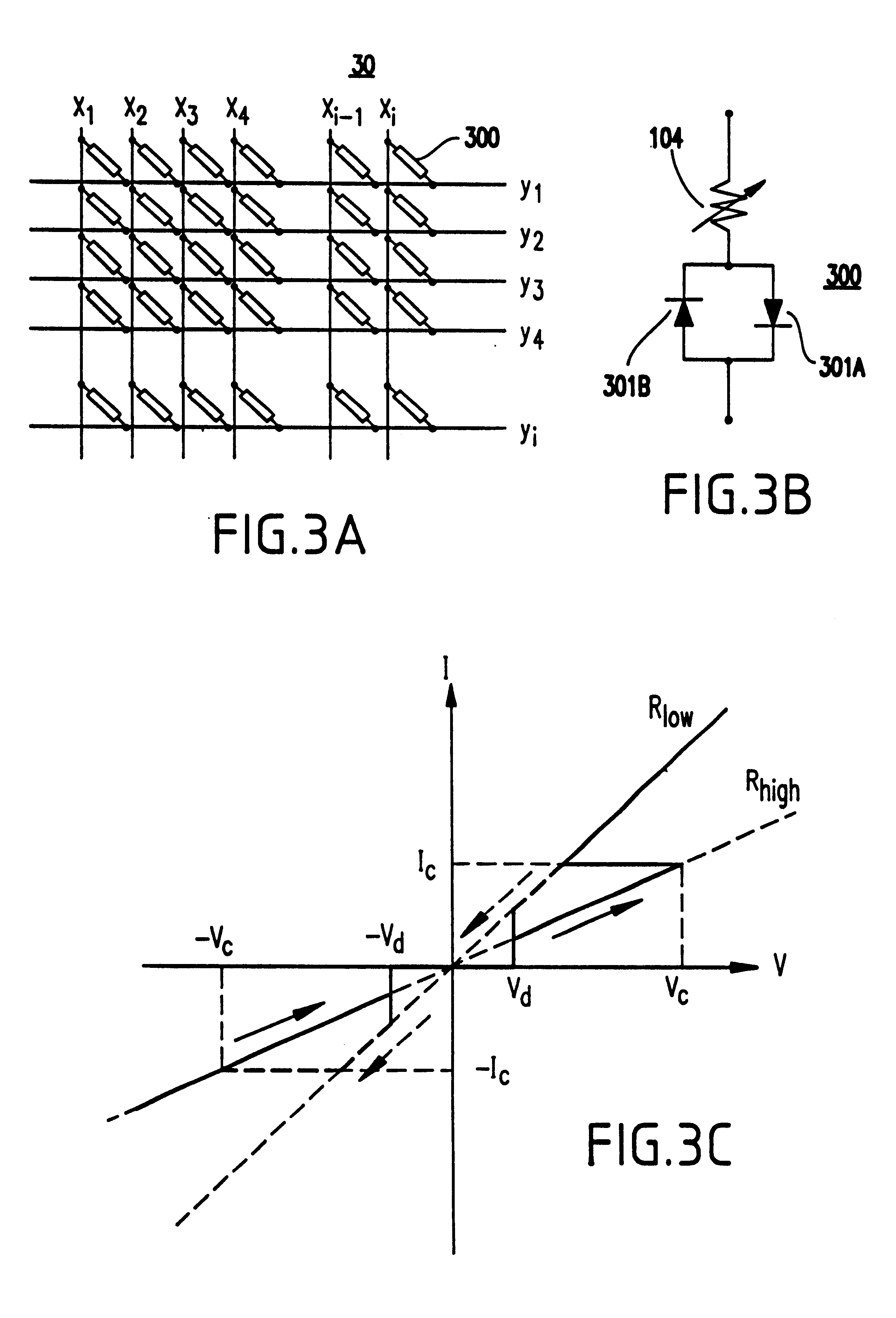
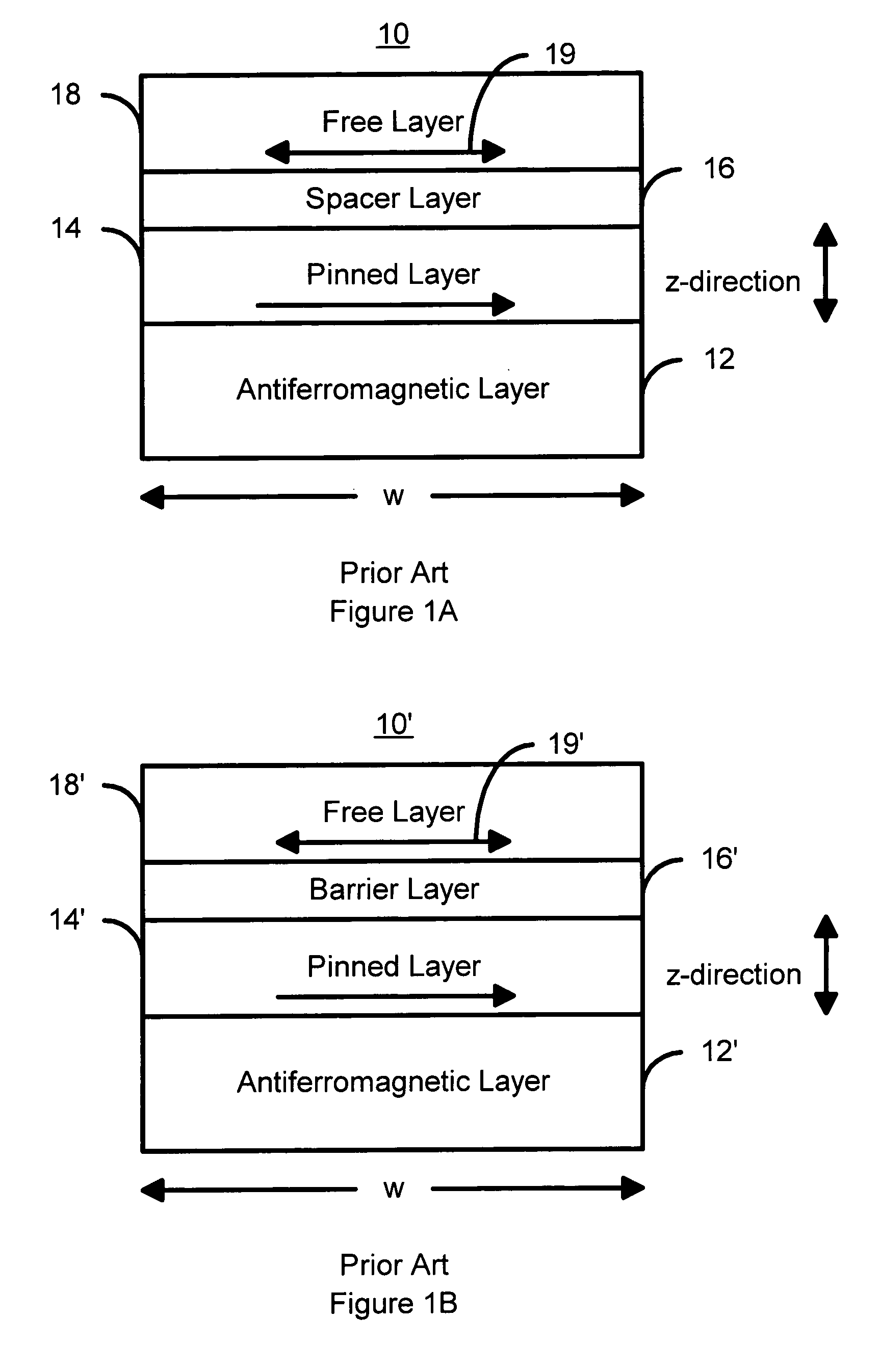
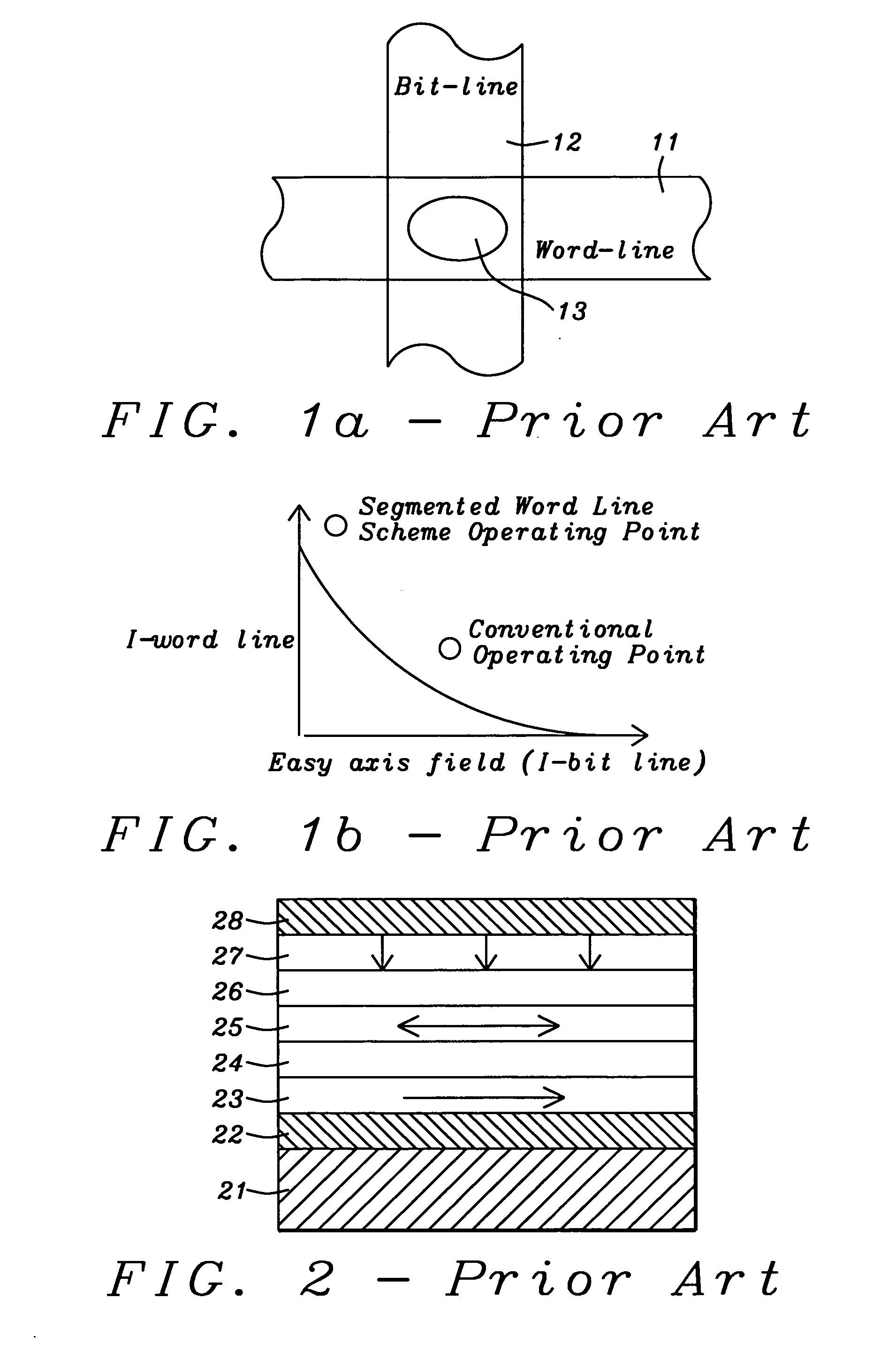
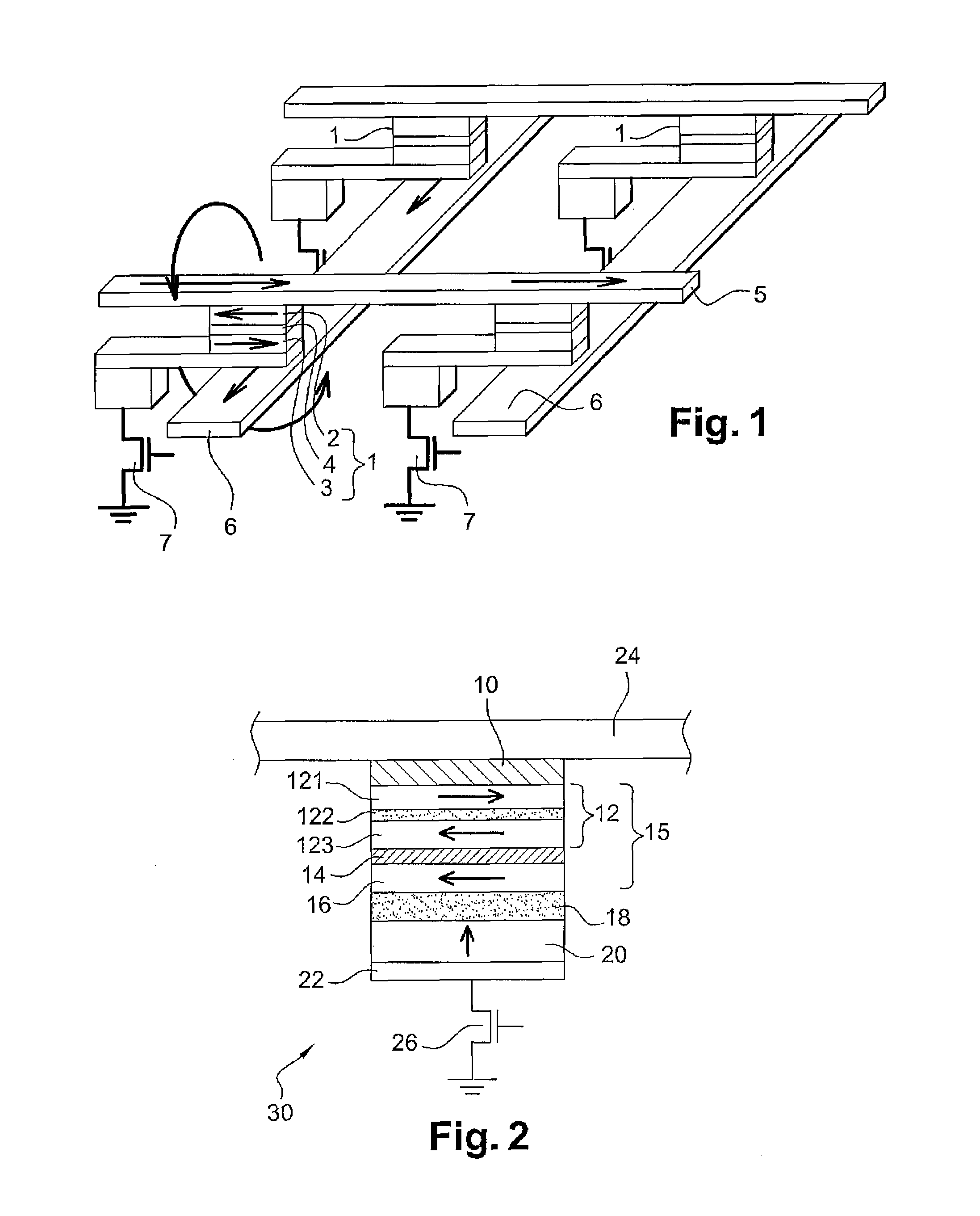
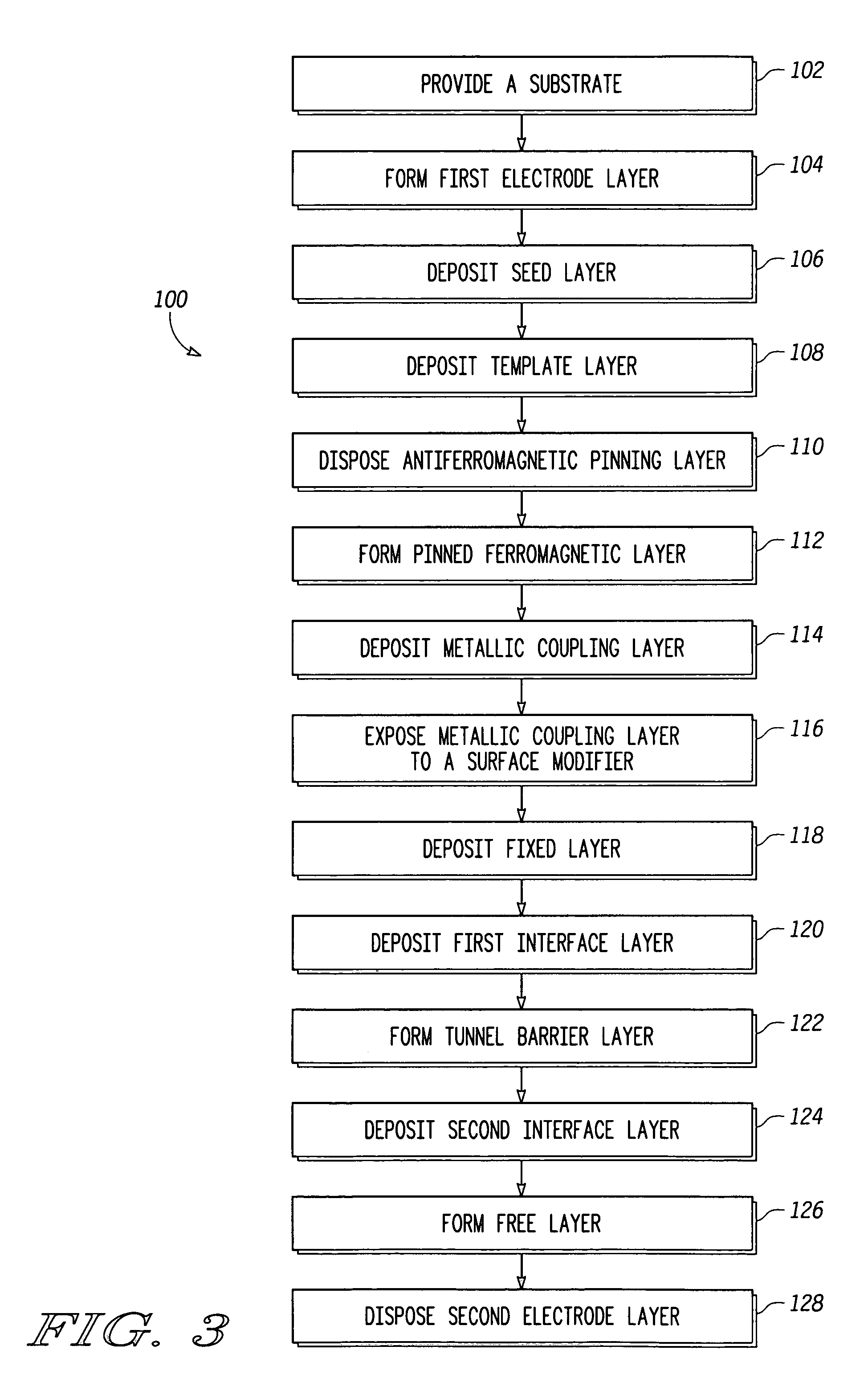
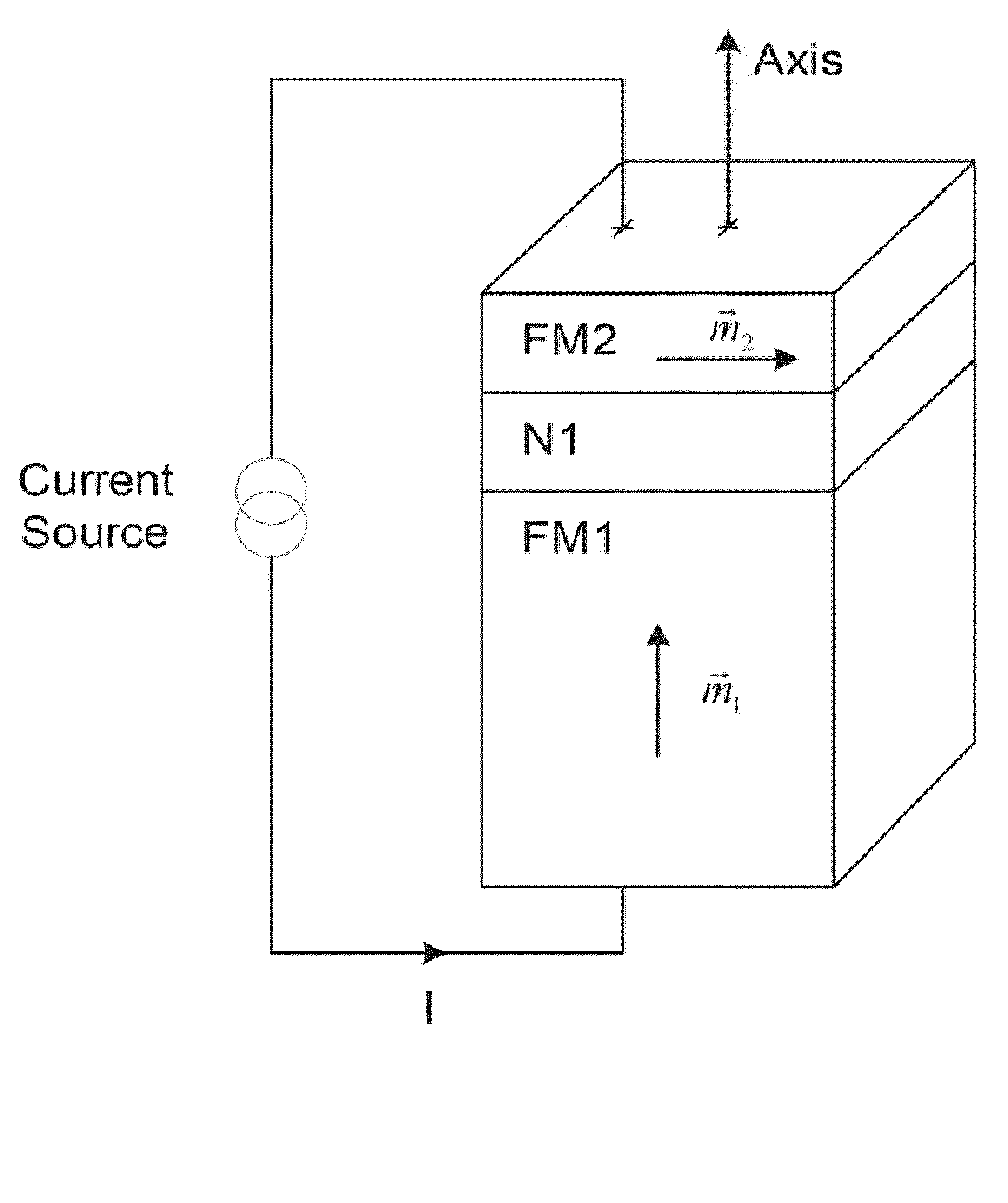
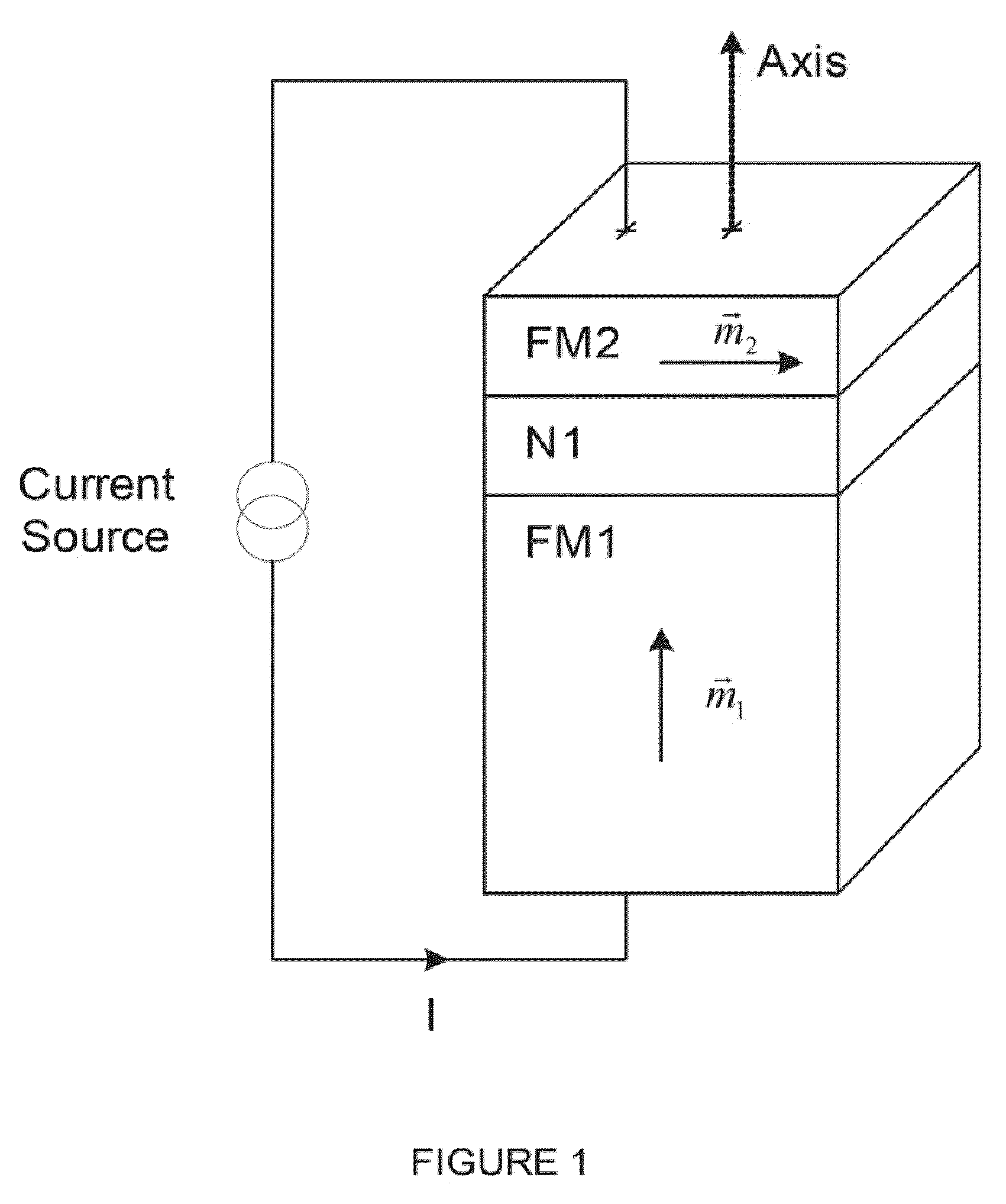
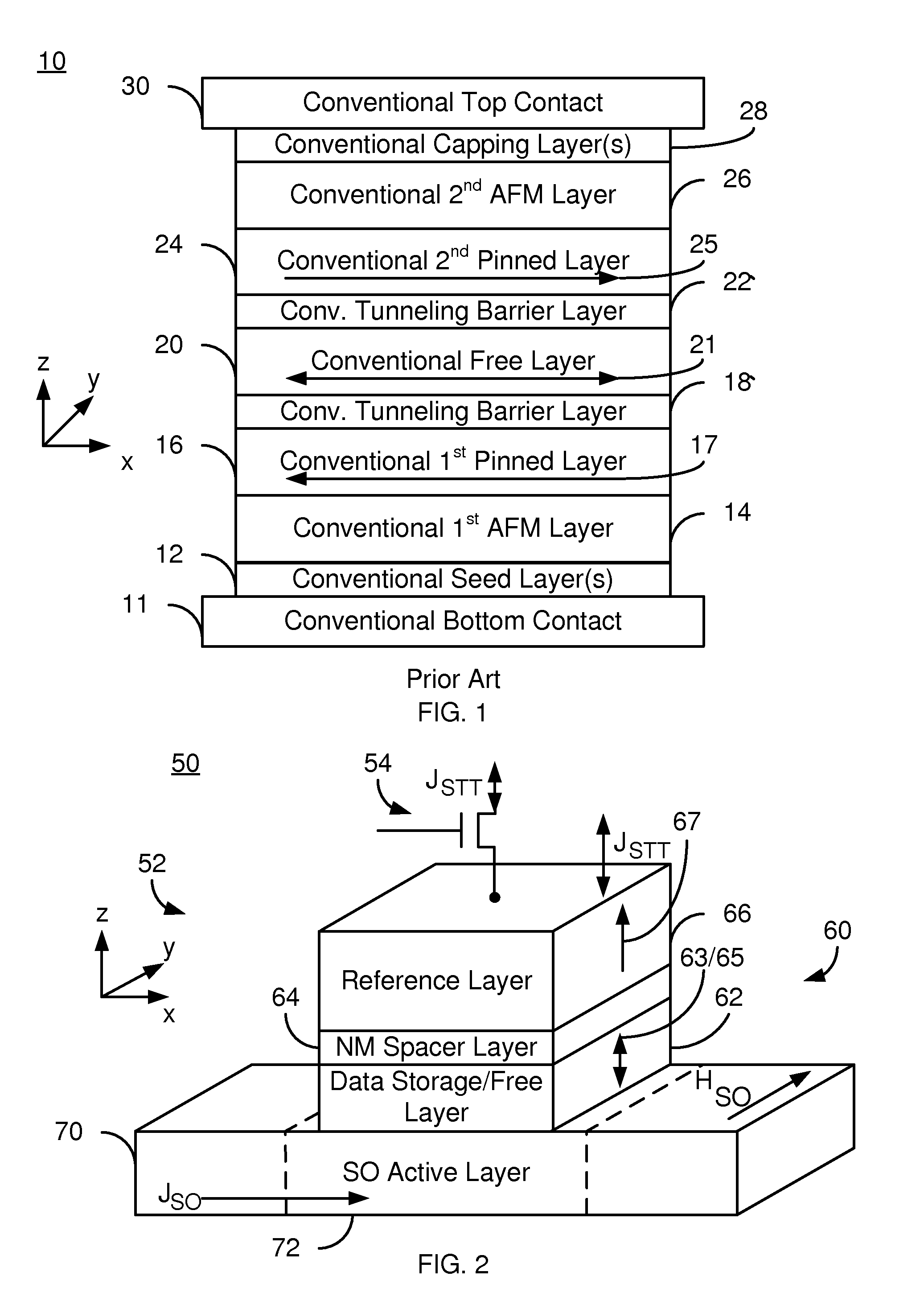
Current-induced magnetic switching device and memory including the same
InactiveUS6256223B1High bulk densitySimpler driving circuitsNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsNanoparticleConduction band
A magnetic switching device, includes a first electrode, a second electrode, and a nanoparticle having a magnetic moment and being disposed between the first and second electrodes. At least one of the first electrode and the second electrode includes a magnetic material which has a net spin polarization in its conduction band for injecting, into the nanoparticle, an electrical current including a net spin polarization for overcoming the magnetic moment of the nanoparticle upon selection of a predetermined magnitude for the electrical current.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
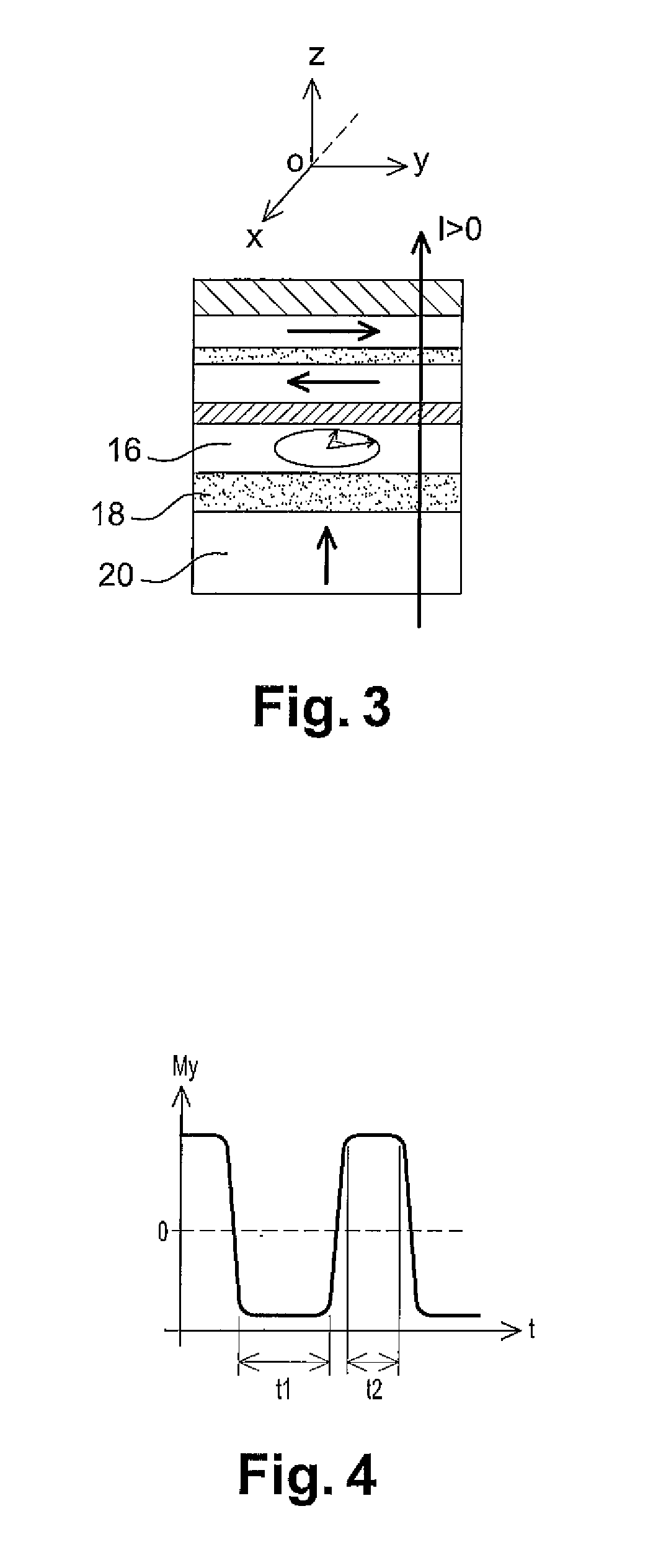
Magnetoresistive element
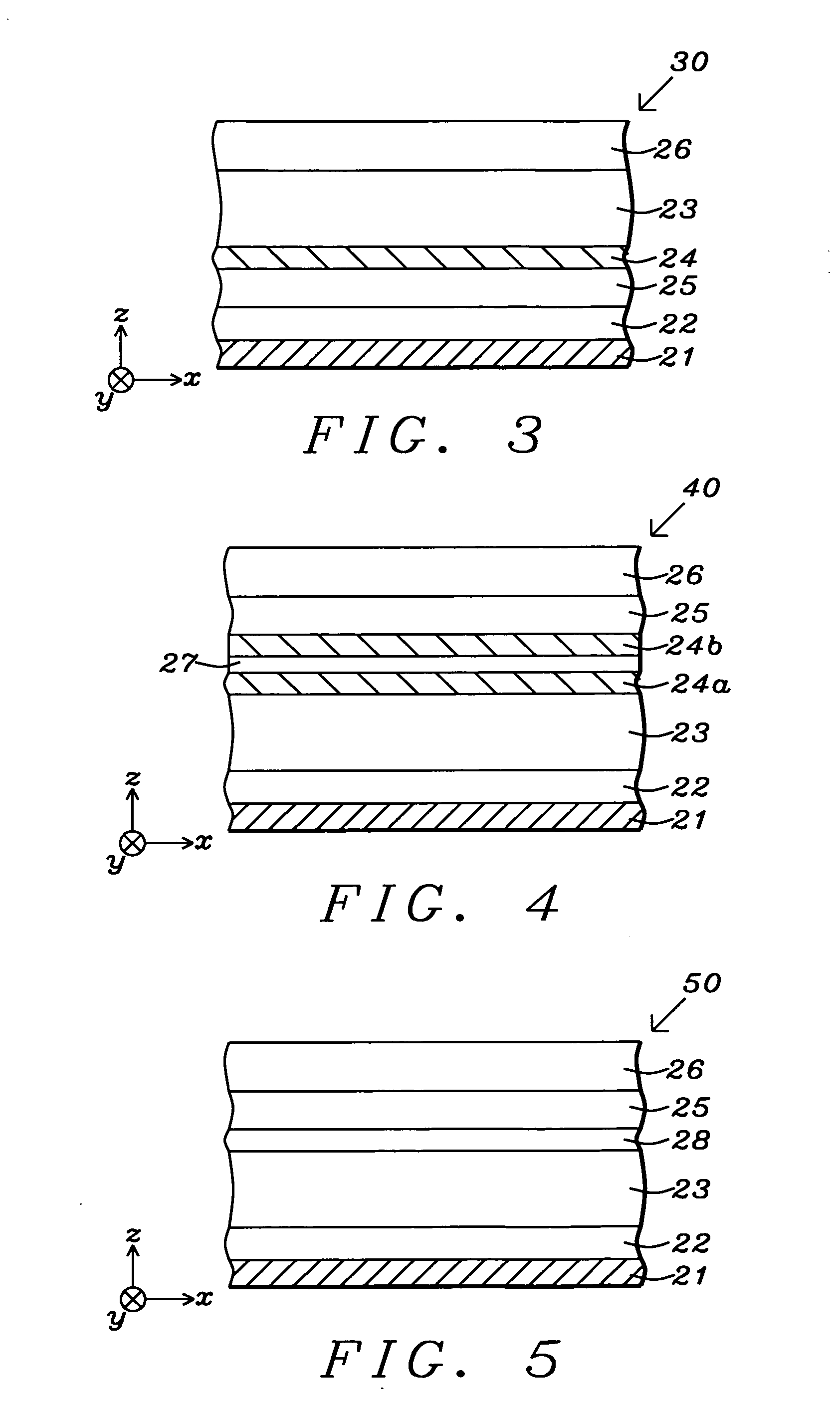
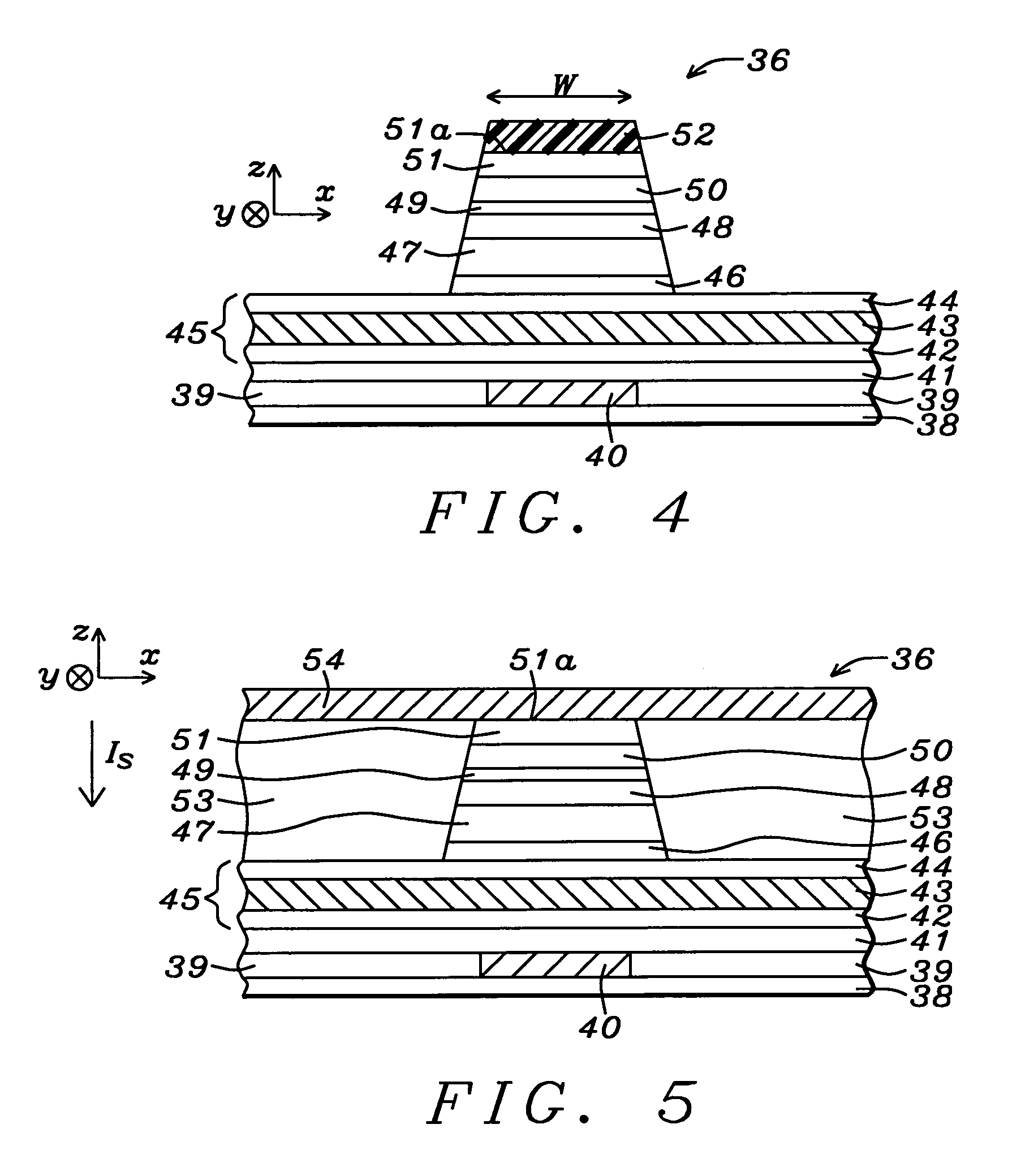
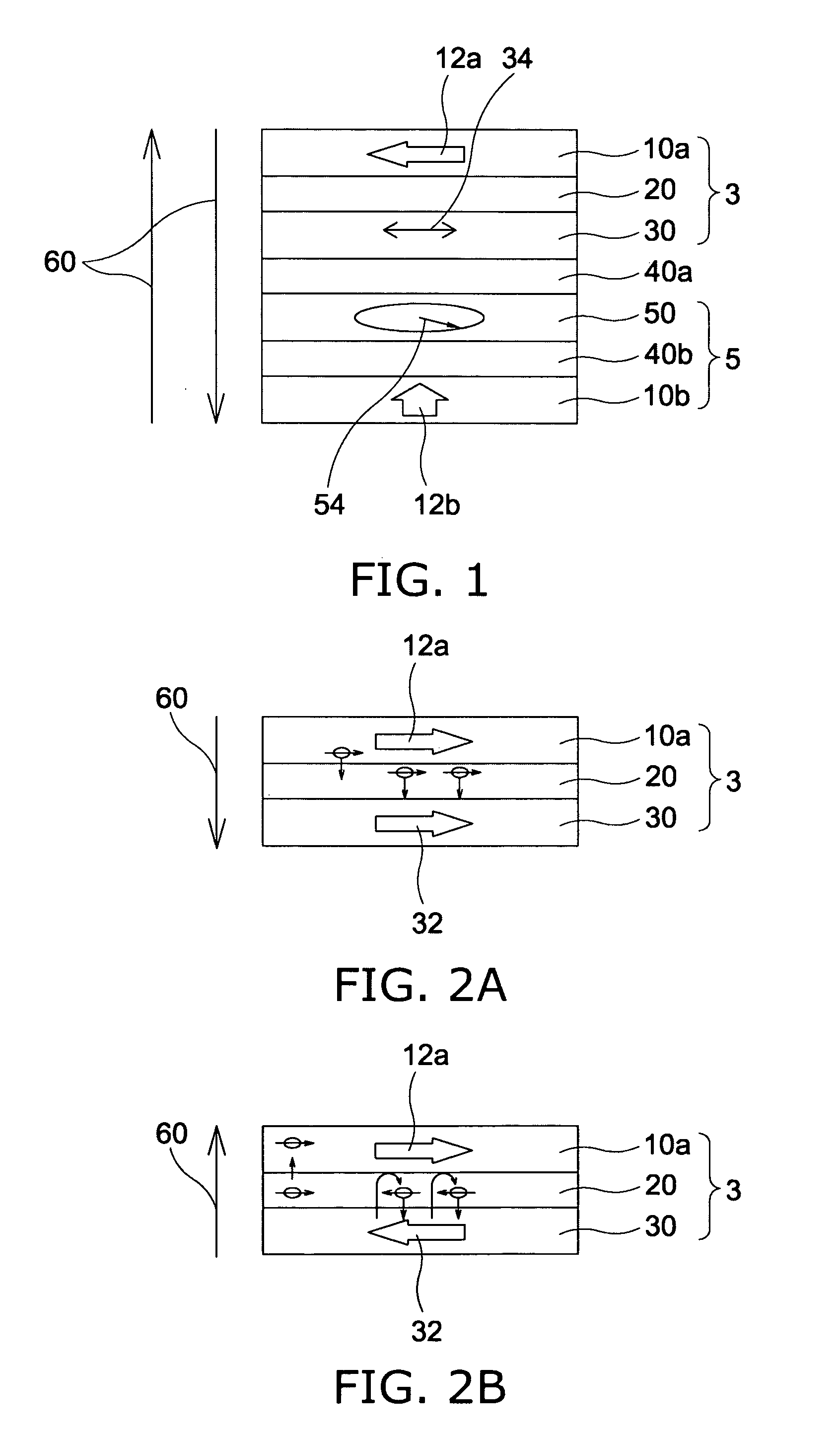
A magnetoresistive element which records information by supplying spin-polarized electrons to a magnetic material, includes a first pinned layer which is made of a magnetic material and has a first magnetization directed in a direction perpendicular to a film surface, a free layer which is made of a magnetic material and has a second magnetization directed in the direction perpendicular to the film surface, the direction of the second magnetization reversing by the spin-polarized electrons, and a first nonmagnetic layer which is provided between the first pinned layer and the free layer. A saturation magnetization Ms of the free layer satisfies a relationship 0≧Ms<√{square root over ( )}{Jw / (6nAt)}. Jw is a write current density, t is a thickness of the free layer, A is a constant.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Thin seeded Co/Ni multilayer film with perpendicular anisotropy for spintronic device applications
ActiveUS20090257151A1Raise the ratioNot to damageMagnetic measurementsVacuum evaporation coatingPerpendicular anisotropySpins
A spin valve structure for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a composite seed layer made of at least Ta and a metal layer having a fcc(111) or hcp(001) texture to enhance perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying (Co / Ni)x multilayer. The (Co / Ni)x multilayer is deposited by a low power and high Ar pressure process to avoid damaging Co / Ni interfaces and thereby preserving PMA. As a result, only a thin seed layer is required. PMA is maintained even after annealing at 220° C. for 10 hours. Examples of GMR and TMR spin valves are described and may be incorporated in spin transfer oscillators and spin transfer MRAMs. The free layer is preferably made of a FeCo alloy including at least one of Al, Ge, Si, Ga, B, C, Se, Sn, or a Heusler alloy, or a half Heusler alloy to provide high spin polarization and a low magnetic damping coefficient.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
InactiveUS20070297220A1Easily magnetizedNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsIn planeInter layer
A magnetoresistive includes a first magnetic reference layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a magnetic free layer having a magnetization direction which is changeable by being supplied with spin polarized electrons, a second magnetic reference layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a first intermediate layer provided between the first magnetic reference layer and the magnetic free layer, and a second intermediate layer provided between the magnetic free layer and the second magnetic reference layer. The magnetic free layer and the first magnetic reference layer have directions of easy magnetization perpendicular or parallel to an in-plane direction. The first magnetic reference layer and the second magnetic reference layer have directions of easy magnetization perpendicular to each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
MTJ elements with high spin polarization layers configured for spin-transfer switching and spintronics devices using the magnetic elements
ActiveUS20060141640A1Write currentEnhanced signalNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin transferSpin polarization
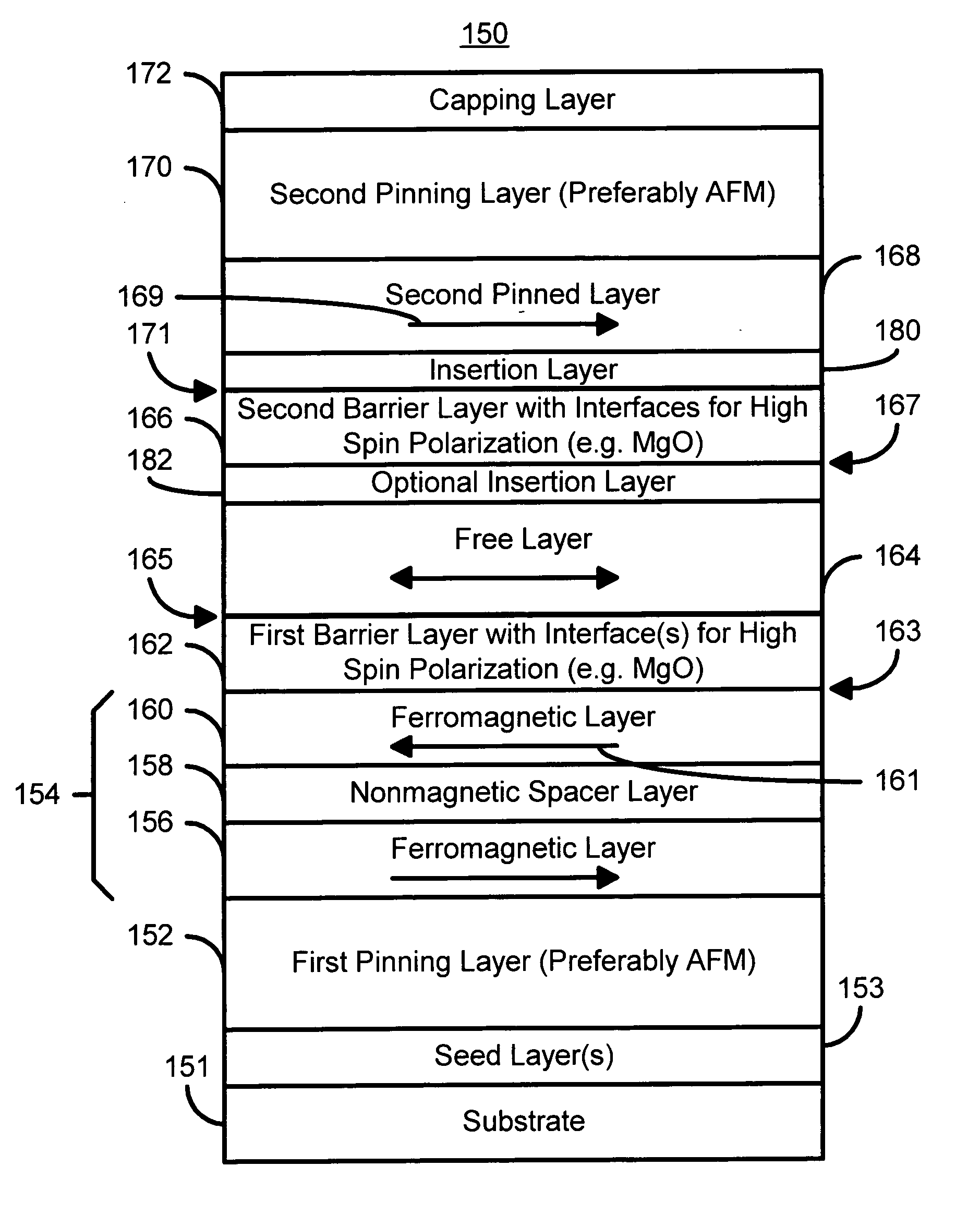
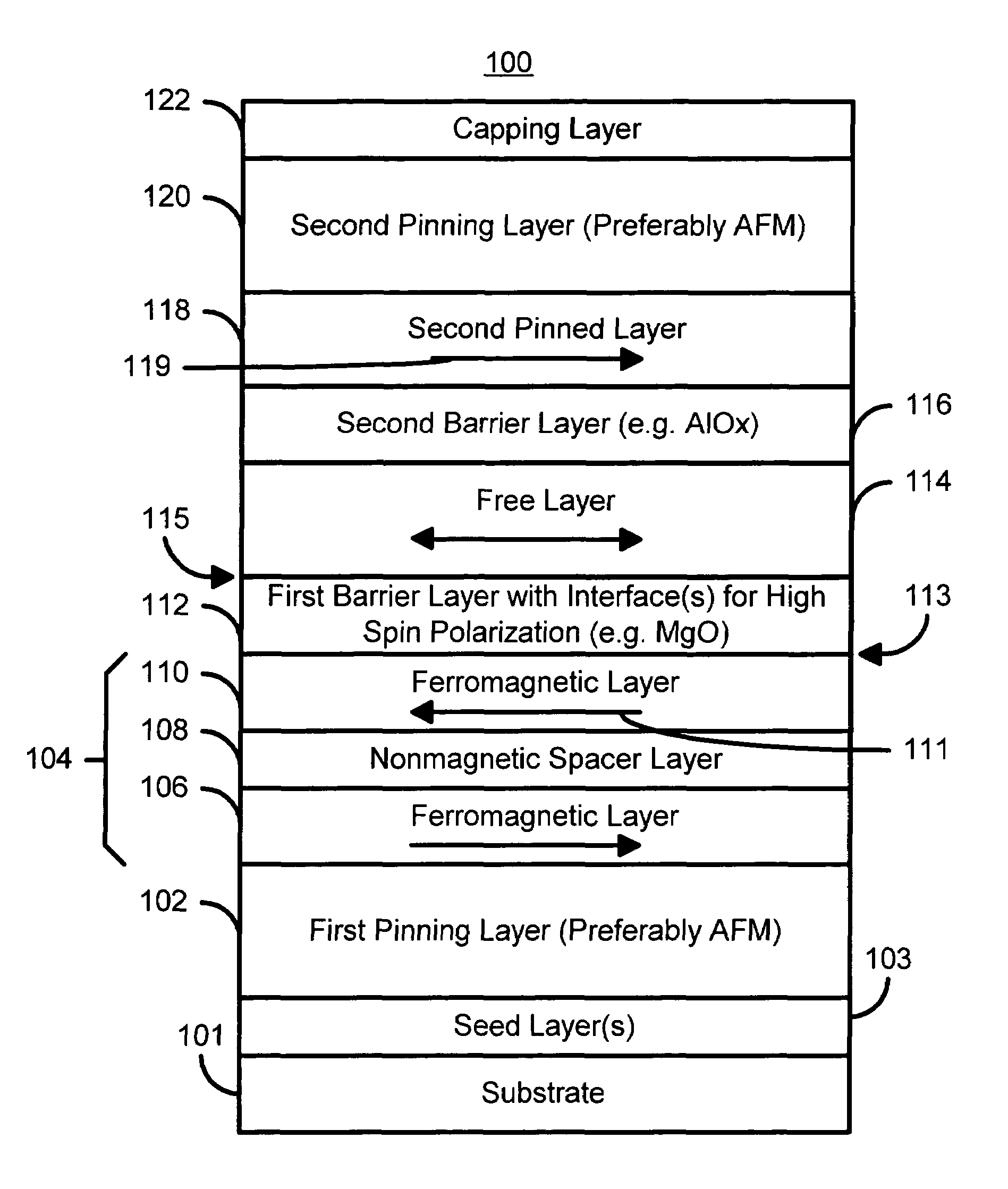
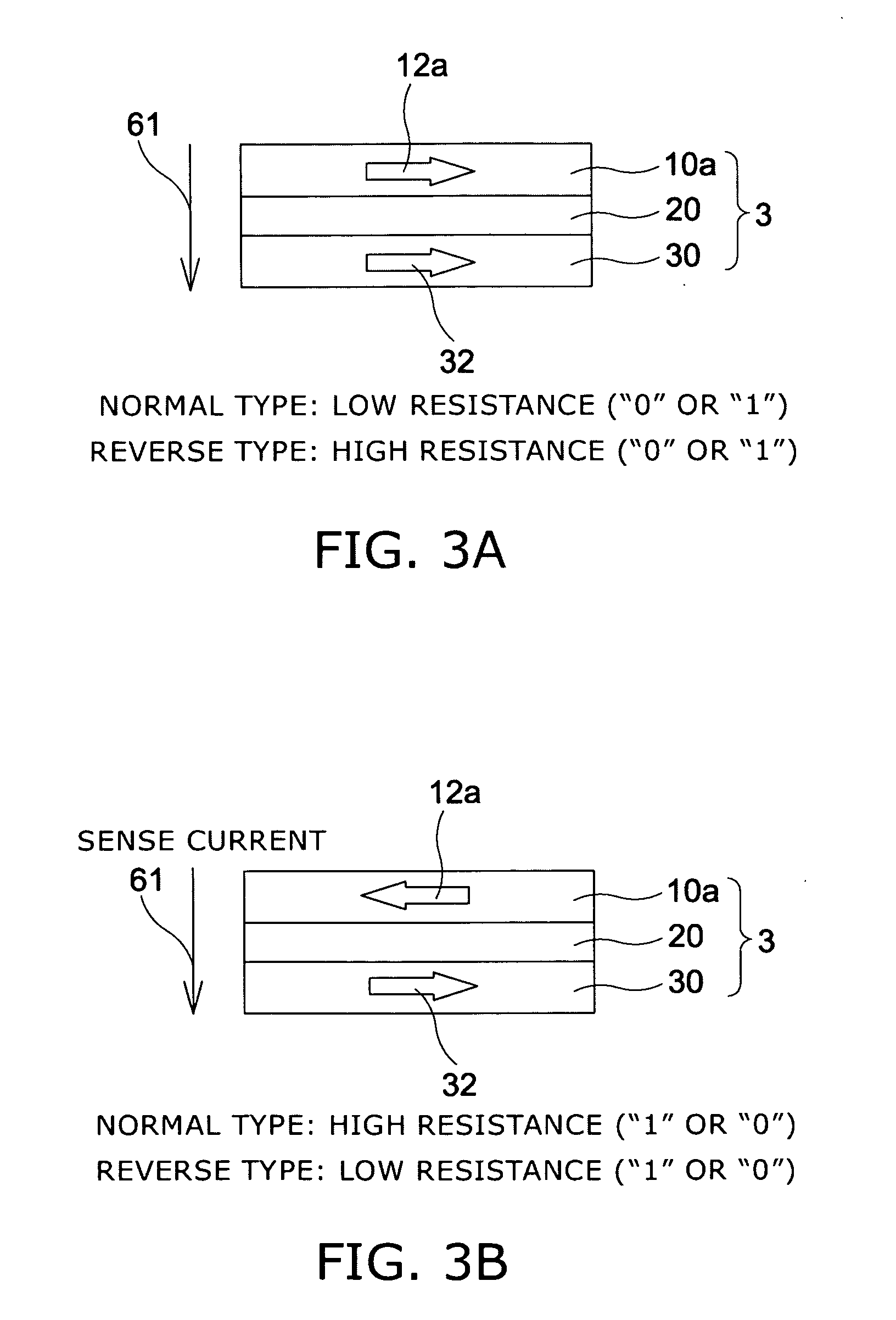
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are disclosed. The method and system include providing first and second pinned layers, a free layer, and first and second barrier layers between the first and second pinned layers, respectively, and the free layer. The first barrier layer is preferably crystalline MgO, which is insulating, and configured to allow tunneling through the first barrier layer. Furthermore, the first barrier layer has an interface with another layer, such as the free layer or the first pinned layer. The interface has a structure that provides a high spin polarization of at least fifty percent and preferably over eighty percent. The second barrier layer is insulating and configured to allow tunneling through the second barrier layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
MTJ elements with high spin polarization layers configured for spin-transfer switching and spintronics devices using the magnetic elements
ActiveUS7241631B2Write currentEnhanced signalNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin transferSpin polarization
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are disclosed. The method and system include providing first and second pinned layers, a free layer, and first and second barrier layers between the first and second pinned layers, respectively, and the free layer. The first barrier layer is preferably crystalline MgO, which is insulating, and configured to allow tunneling through the first barrier layer. Furthermore, the first barrier layer has an interface with another layer, such as the free layer or the first pinned layer. The interface has a structure that provides a high spin polarization of at least fifty percent and preferably over eighty percent. The second barrier layer is insulating and configured to allow tunneling through the second barrier layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
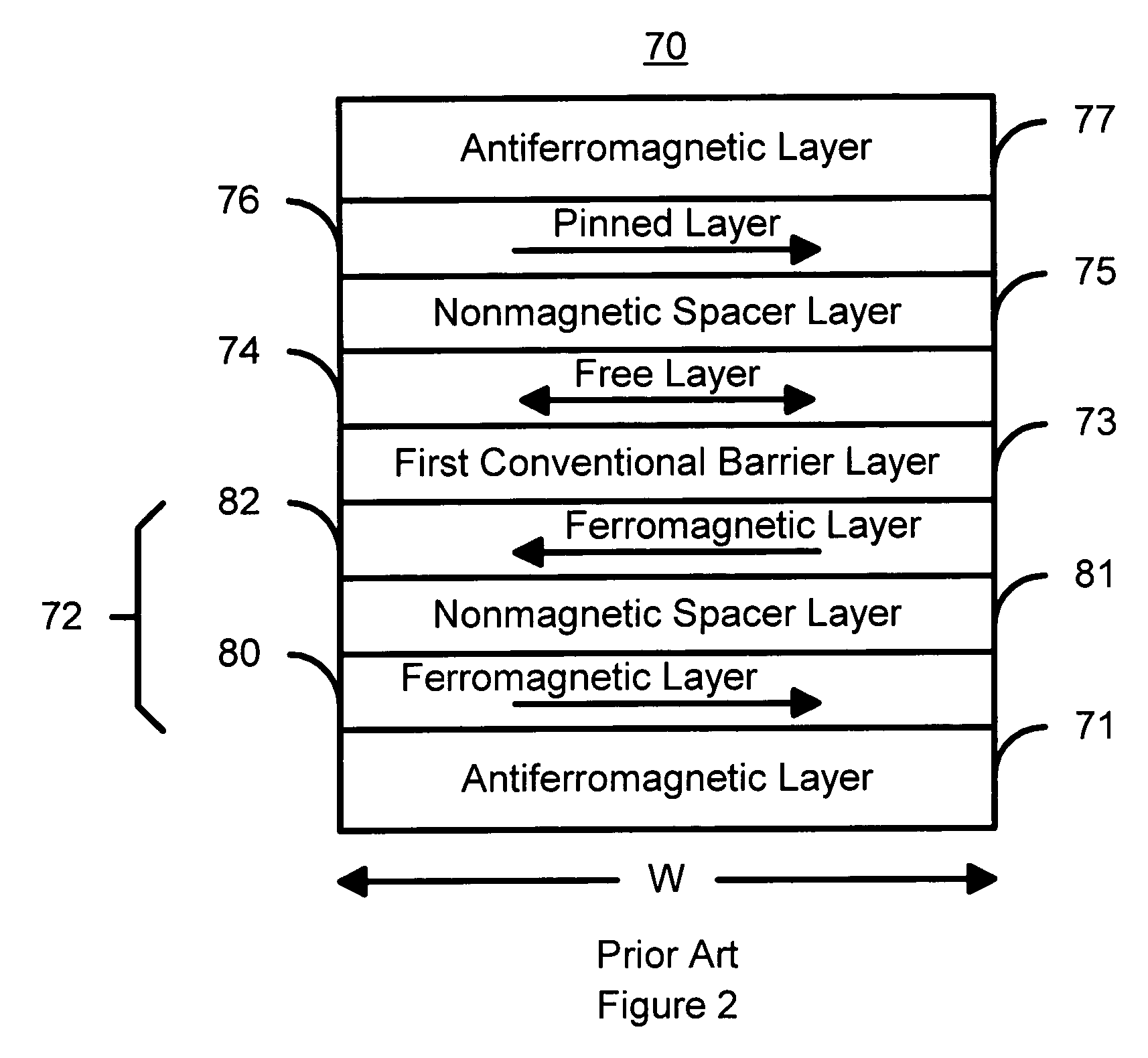
Novel capping structure for enhancing dR/R of the MTJ device
InactiveUS20050276099A1Well controlled magnetizationWell controlled switching characteristicNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsElectrical conductorOxygen
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC +1
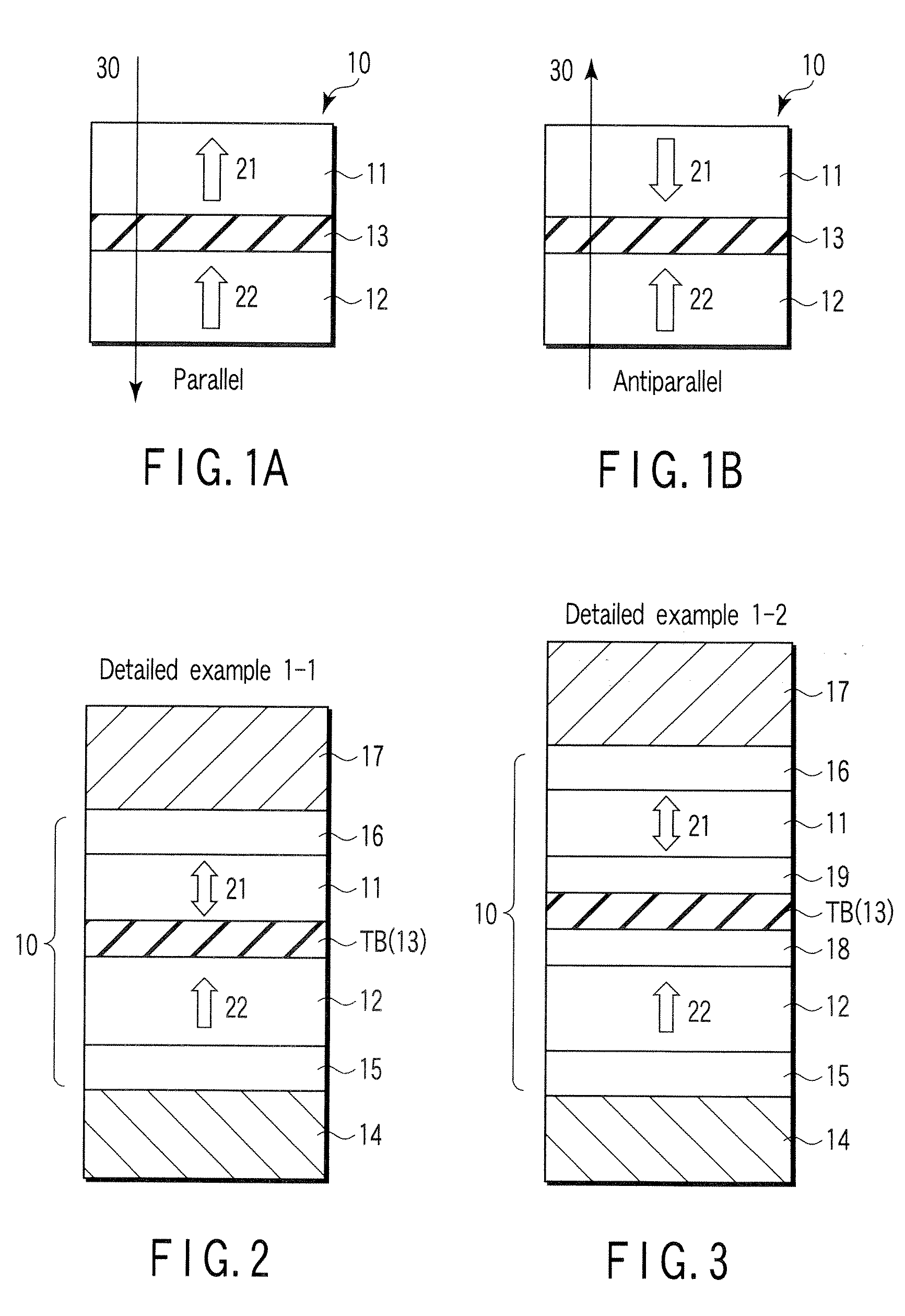
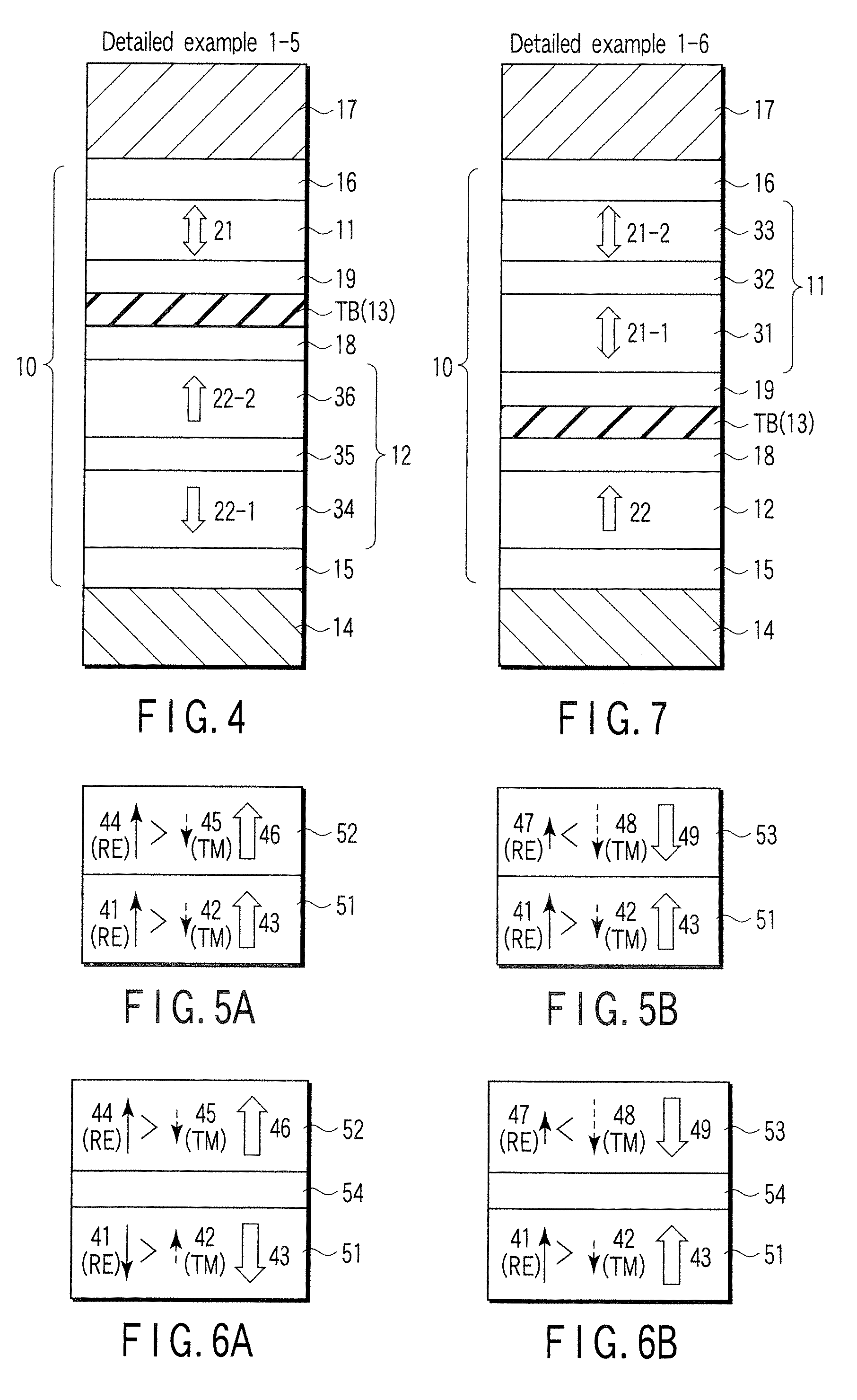
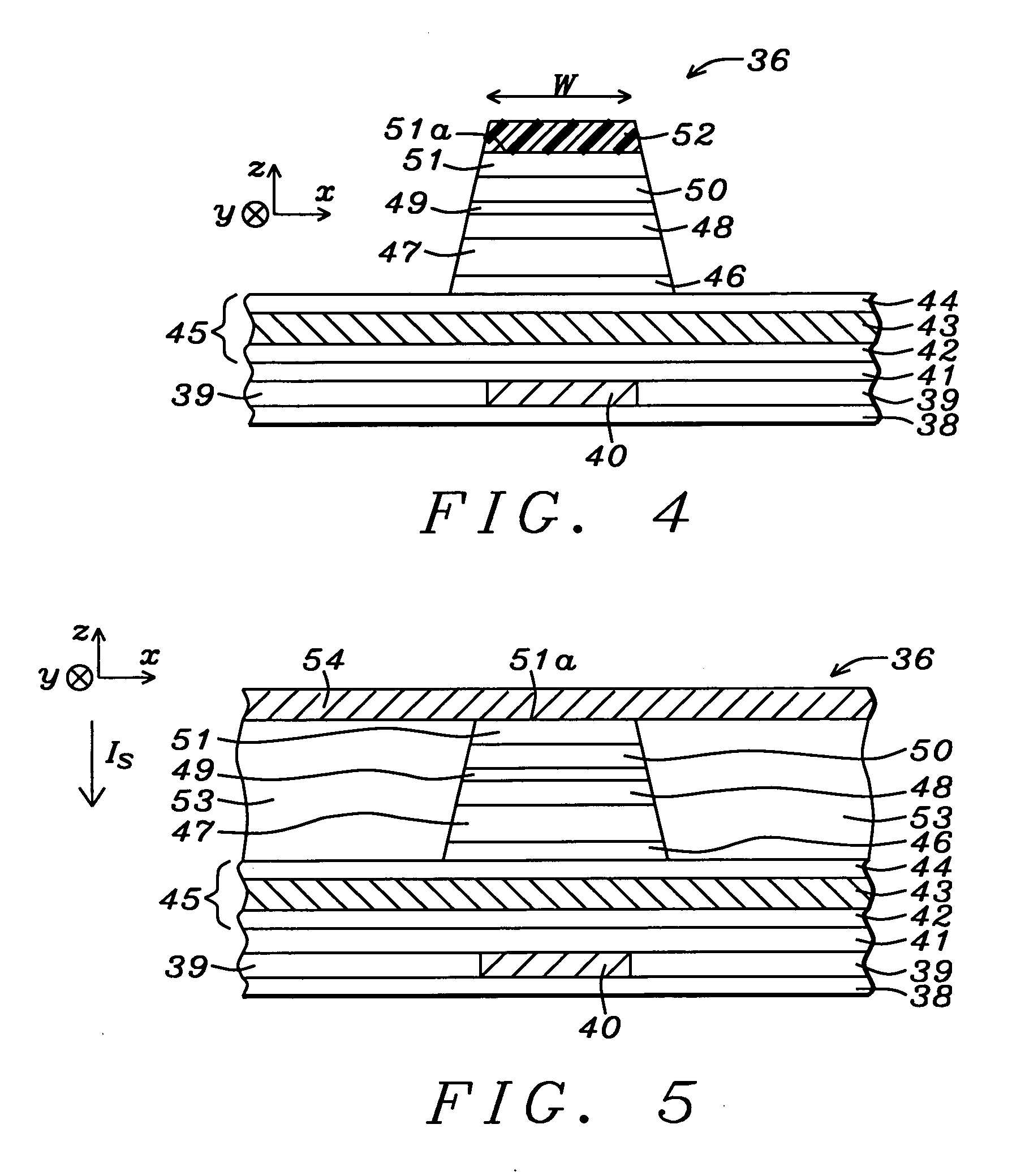
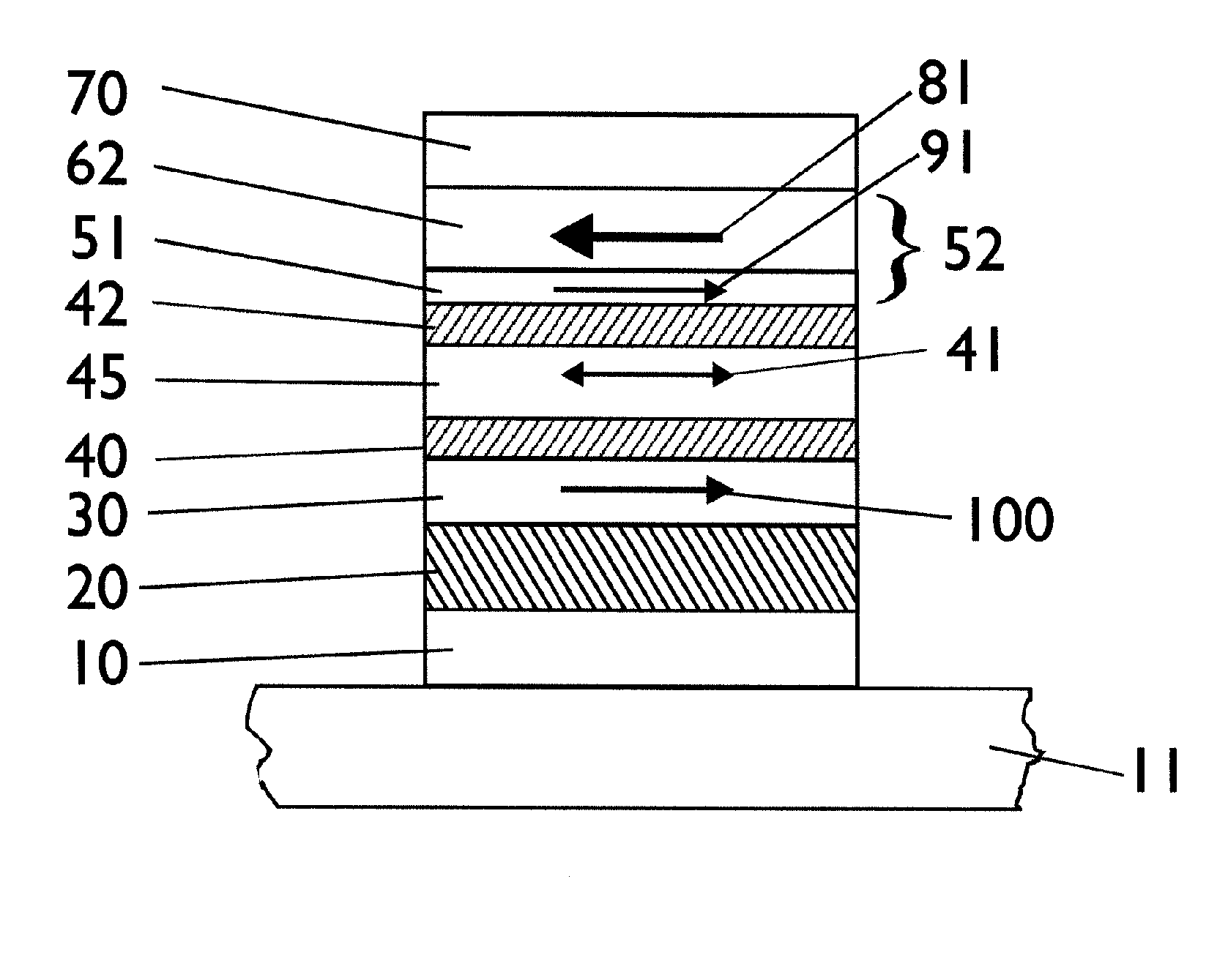
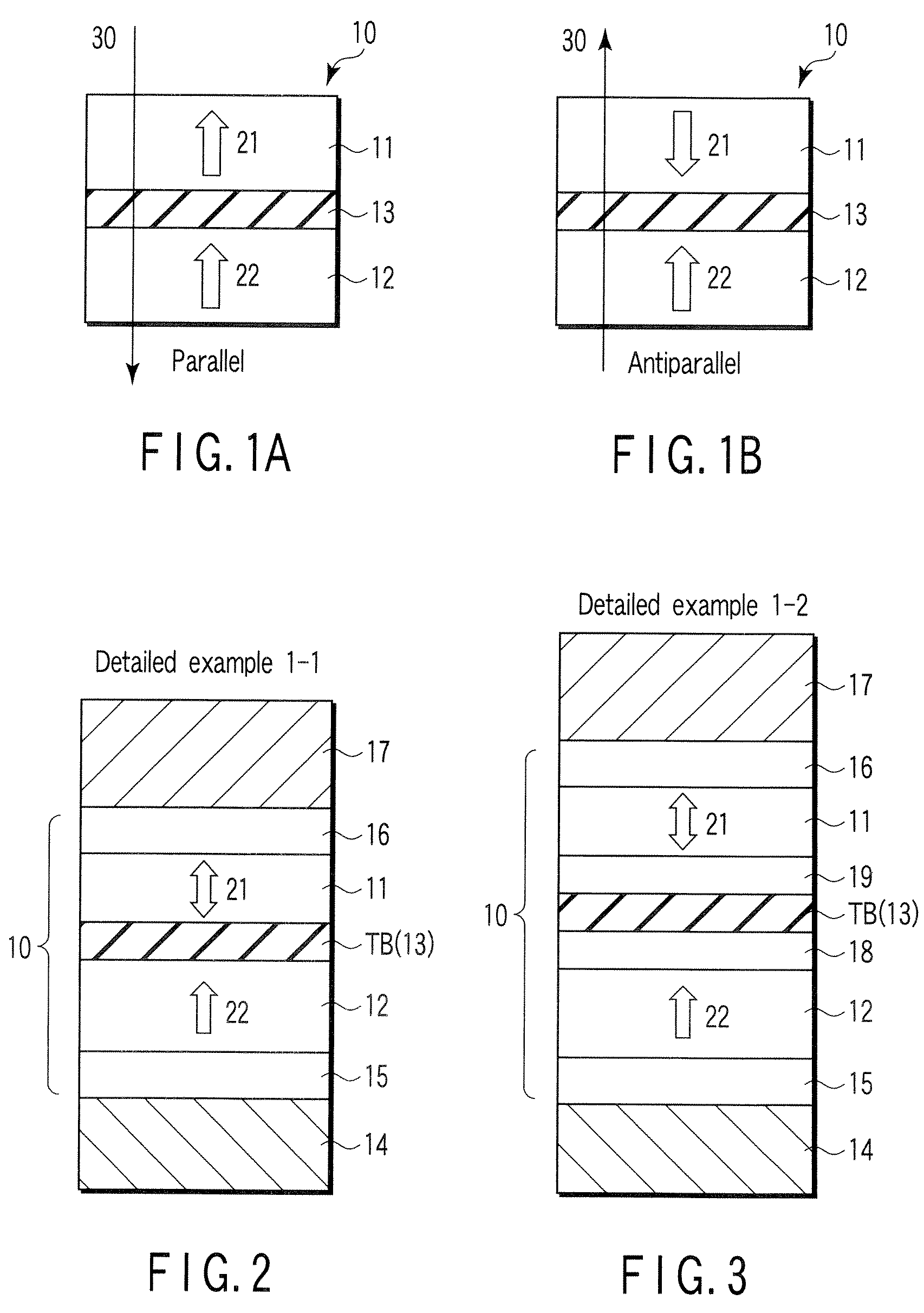
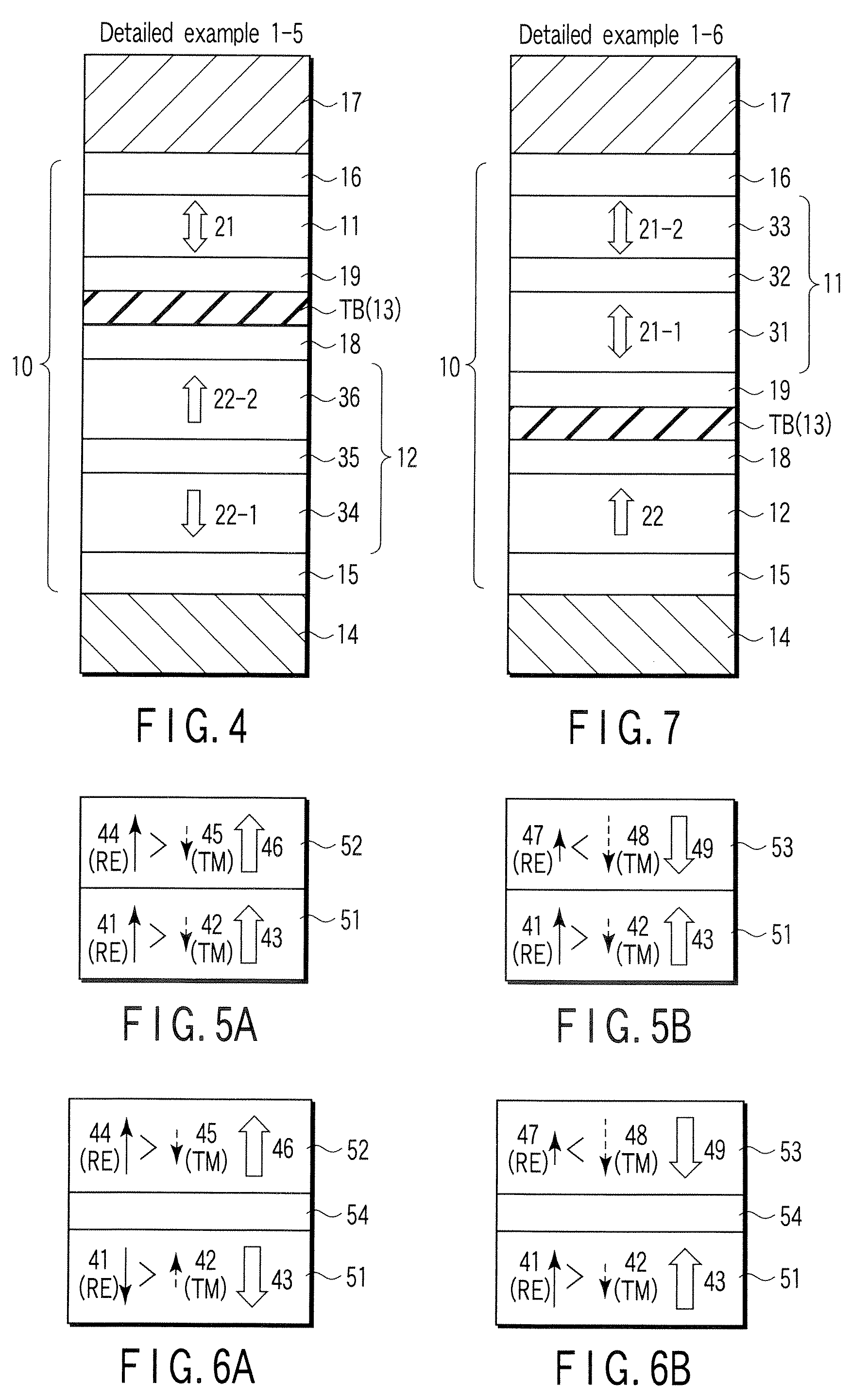
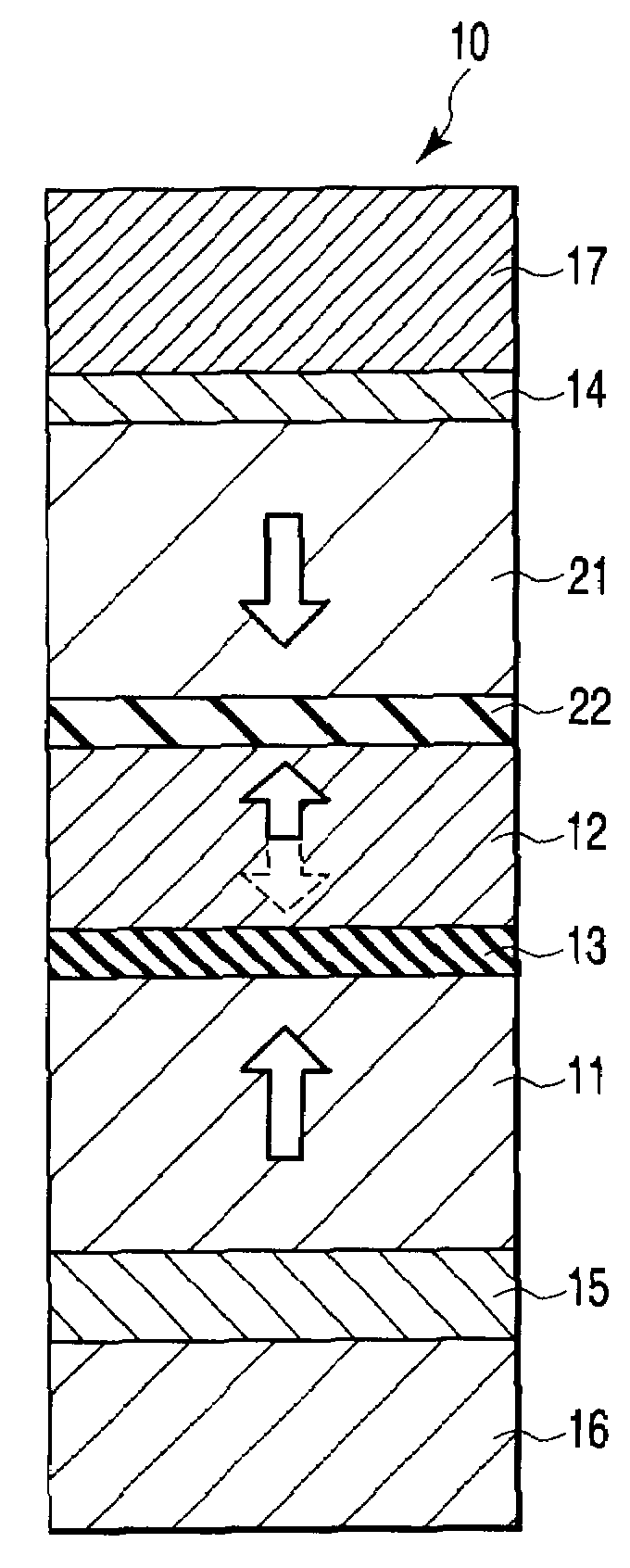
Spin-polarization devices using rare earth-transition metal alloys
ActiveUS7230265B2Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionRare-earth elementMetal alloy
A tunnel barrier in proximity with a layer of a rare earth element-transition metal (RE—TM) alloy forms a device that passes negatively spin-polarized current. The rare earth element includes at least one element selected from the group consisting of Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, and Yb. The RE and TM have respective sub-network moments such that the absolute magnitude of the RE sub-network moment is greater than the absolute magnitude of the TM sub-network moment. An additional layer of magnetic material may be used in combination with the tunnel barrier and the RE—TM alloy layer to form a magnetic tunnel junction. Still other layers of tunnel barrier and magnetic material may be used in combination with the foregoing to form a flux-closed double tunnel junction device.
Owner:IBM CORP
High speed low power annular magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS20080112094A1Operational advantageReduce the required powerRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetization
A high speed and low power method to control and switch the magnetization direction and / or helicity of a magnetic region in a magnetic device for memory cells using spin polarized electrical current. The magnetic device comprises a reference magnetic layer with a fixed magnetic helicity and / or magnetization direction and a free magnetic layer with a changeable magnetic helicity. The fixed magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are preferably separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the reference layer includes an easy axis perpendicular to the reference layer. A current can be applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
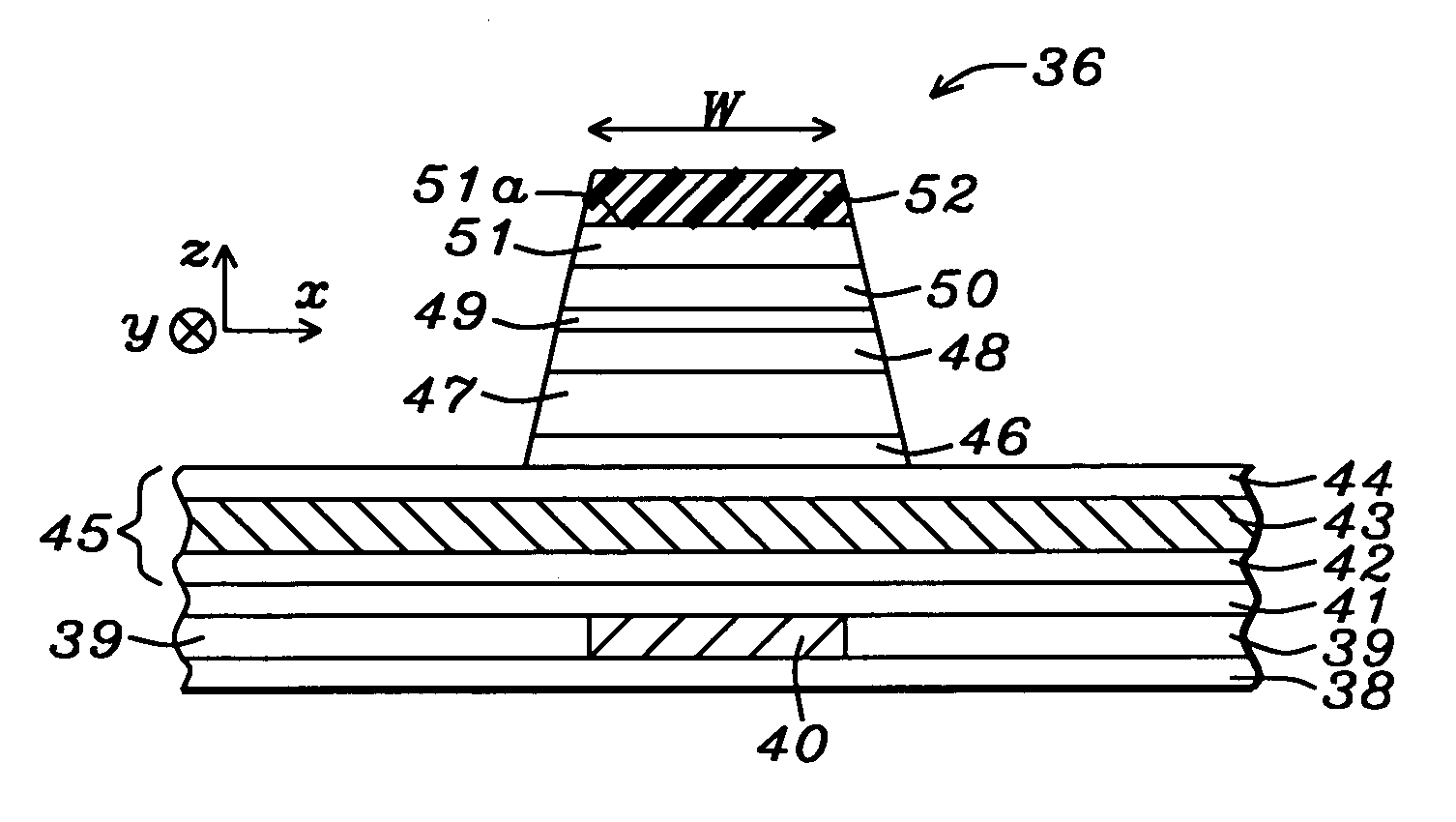
Magnetoresistive sensors having an improved free layer
ActiveUS8498084B1Reduce thicknessGilbert damping constantMagnetic measurementsRecord information storageSpin polarizationCobalt
A magnetoresistive sensor having a novel free layer and a method of producing the same are disclosed. The magnetoresistive sensor comprises a pinned layer, a barrier layer disposed over the pinned layer, and a free layer disposed over the barrier layer. The free layer comprises a first magnetic layer disposed over the barrier layer. The first magnetic layer has a positive spin polarization, a positive magnetostriction, and a polycrystalline structure. The free layer further comprises a second magnetic layer disposed over the first magnetic layer. The second magnetic layer has a negative magnetostriction and comprises at least cobalt (Co) and boron (B).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Capping structure for enhancing dR/R of the MTJ device
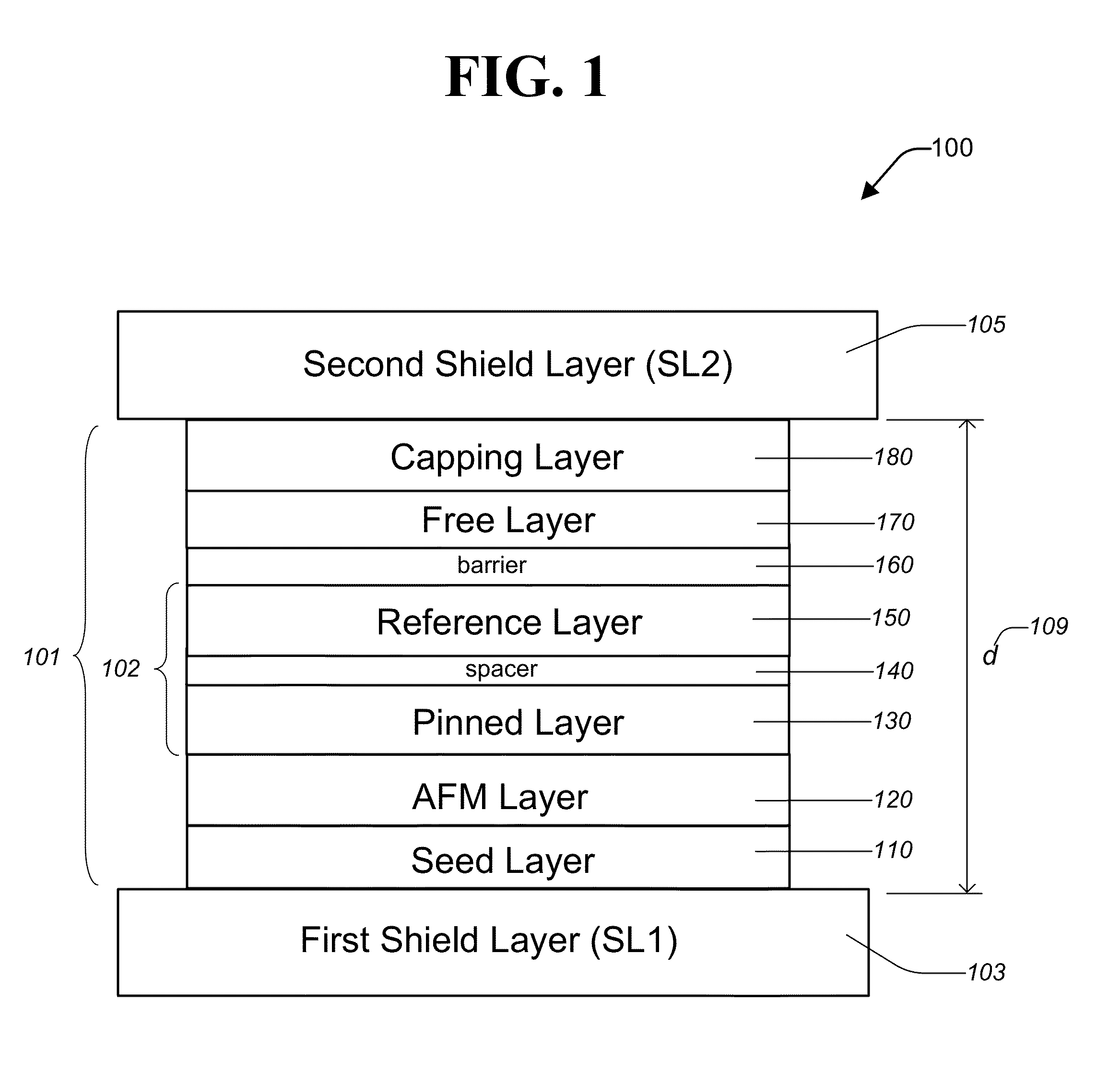
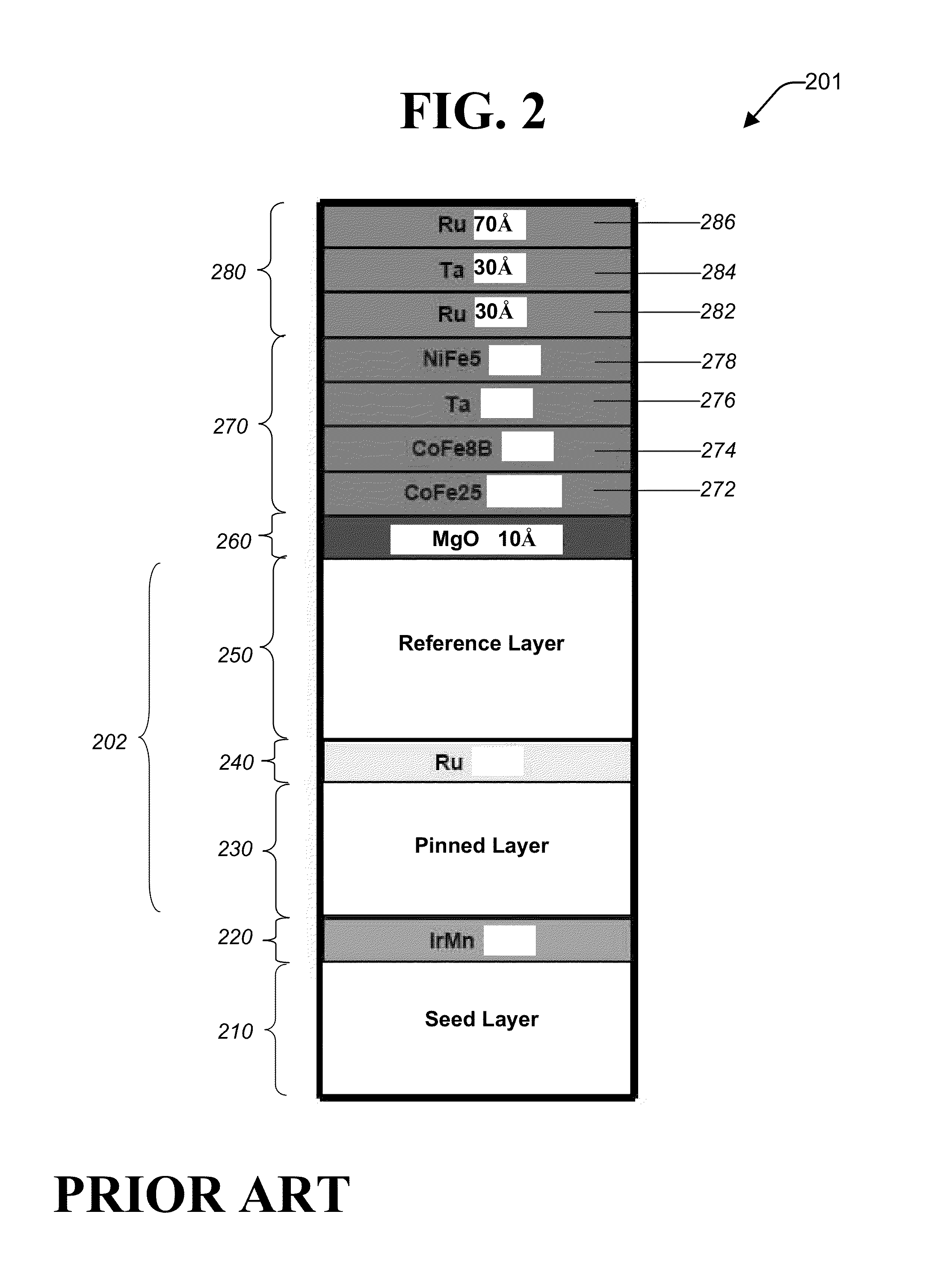
An MTJ in an MRAM array or in a TMR read head is comprised of a capping layer with a lower inter-diffusion barrier layer, an intermediate oxygen gettering layer, and an upper metal layer that contacts a top conductor. The composite capping layer is especially useful with a moderate spin polarization free layer such as a NiFe layer with a Fe content of about 17.5 to 20 atomic %. The capping layer preferably has a Ru / Ta / Ru configuration in which the lower Ru layer is about 10 to 30 Angstroms thick and the Ta layer is about 30 Angstroms thick. As a result, a high dR / R of about 40% is achieved with low magnetostriction less than about 1.0 E−6 in an MTJ in an MRAM array. Best results are obtained with an AlOx tunnel barrier layer formed by an in-situ ROX process on an 8 to 10 Angstrom thick Al layer.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC +1
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
A magnetoresistive element includes a free layer which contains a magnetic material and has an fct crystal structure with a (001) plane oriented, the free layer having a magnetization which is perpendicular to a film plane and has a direction to be changeable by spin-polarized electrons, a first nonmagnetic layer and a second nonmagnetic layer which sandwich the free layer and have one of a tetragonal crystal structure and a cubic crystal structure, and a fixed layer which is provided on only one side of the free layer and on a surface of the first nonmagnetic layer opposite to a surface with the free layer and contains a magnetic material, the fixed layer having a magnetization which is perpendicular to a film plane and has a fixed direction.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
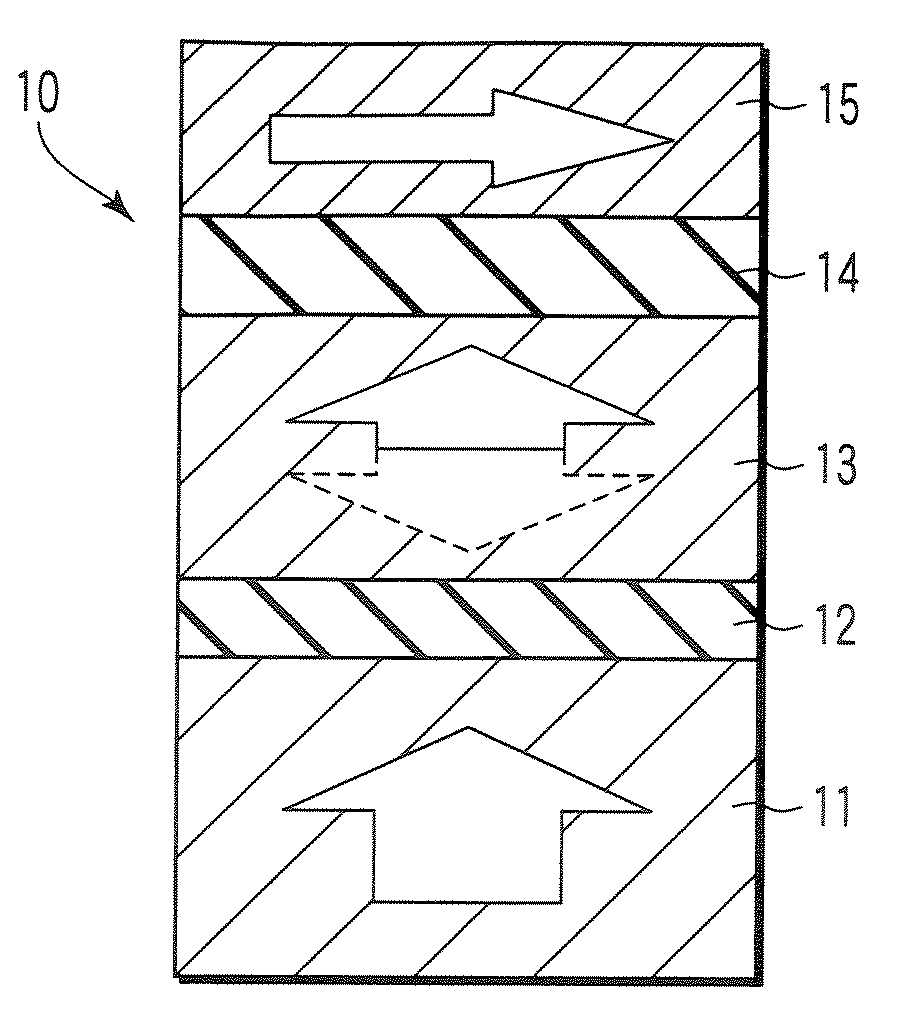
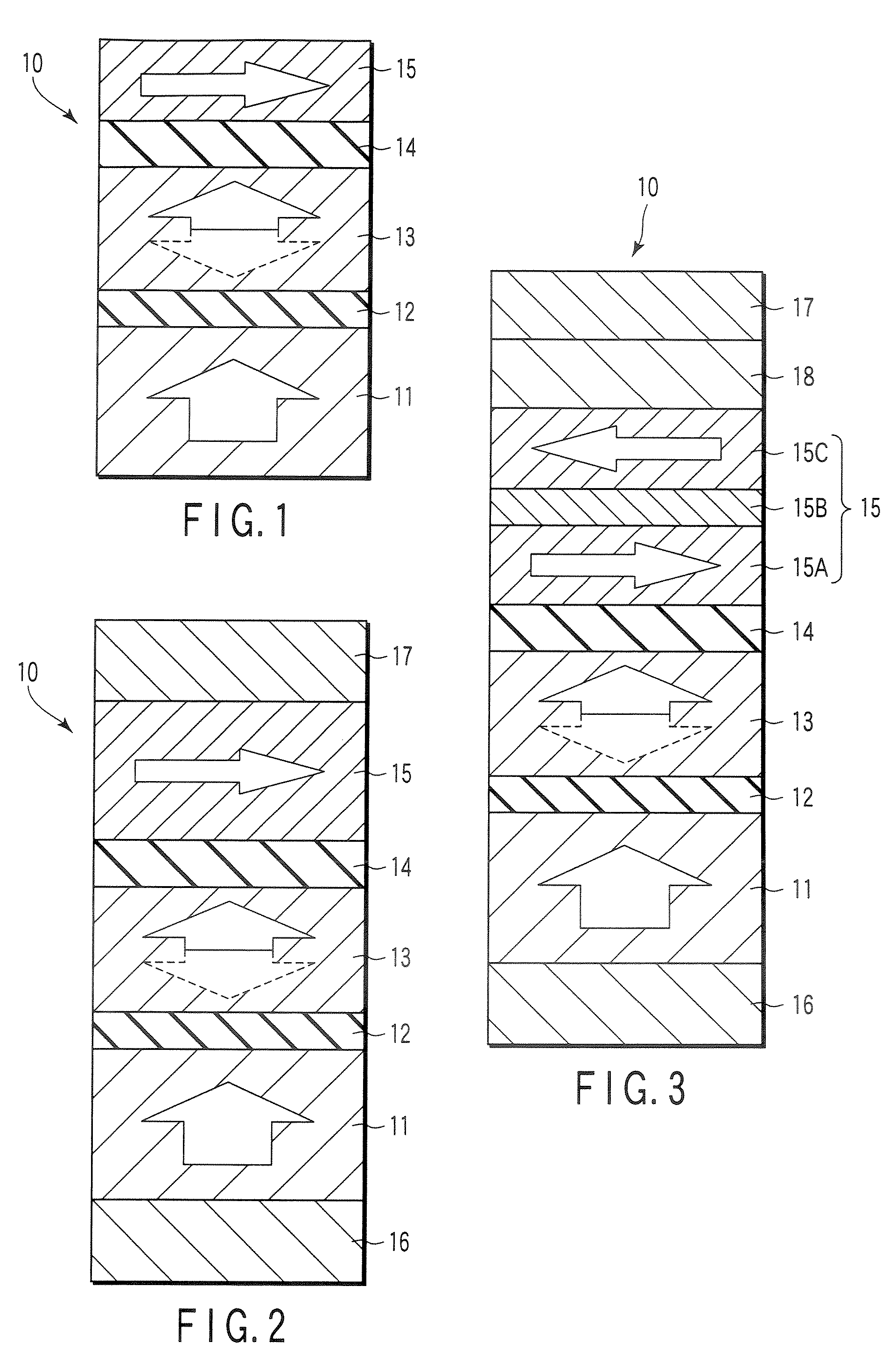
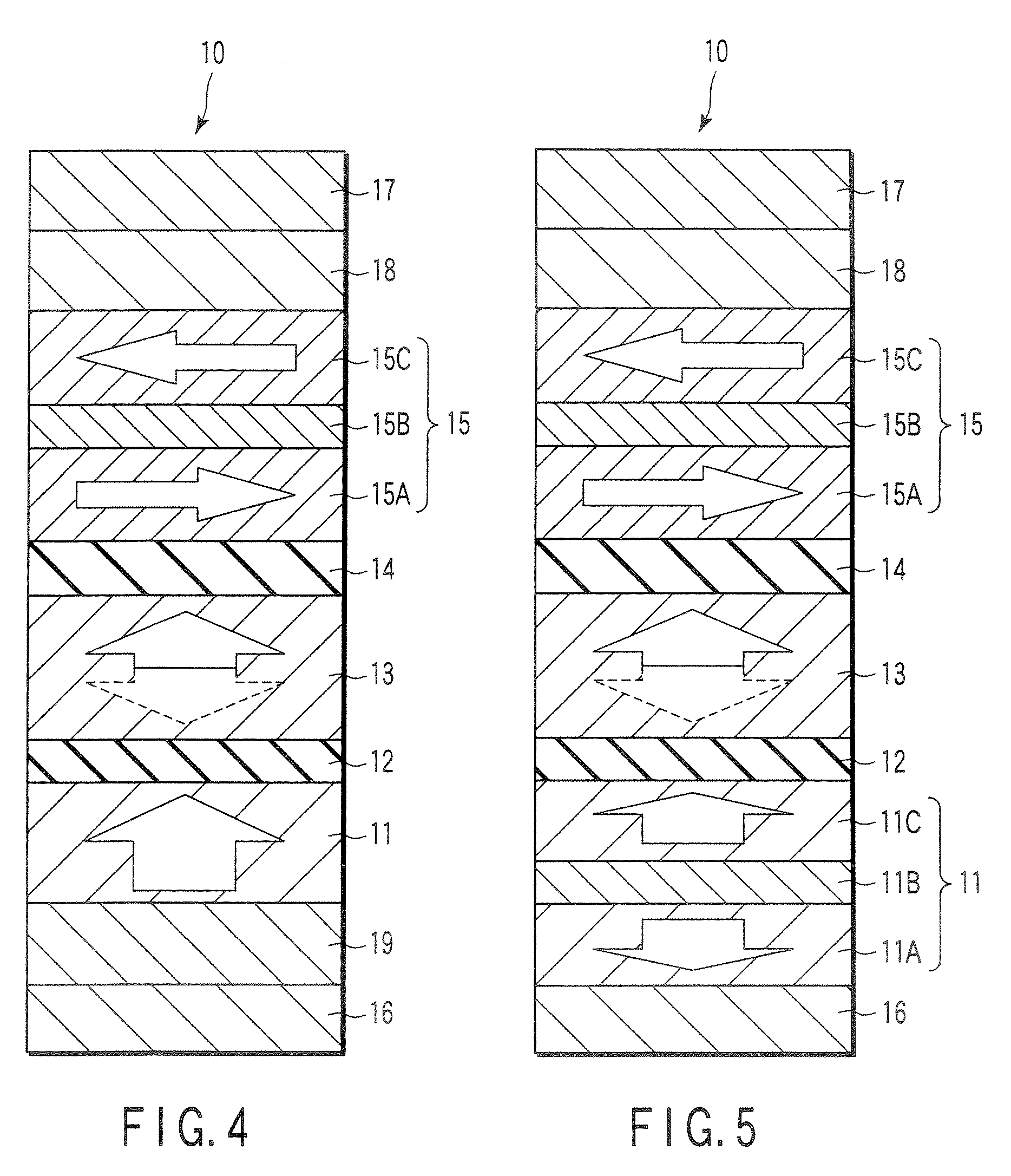
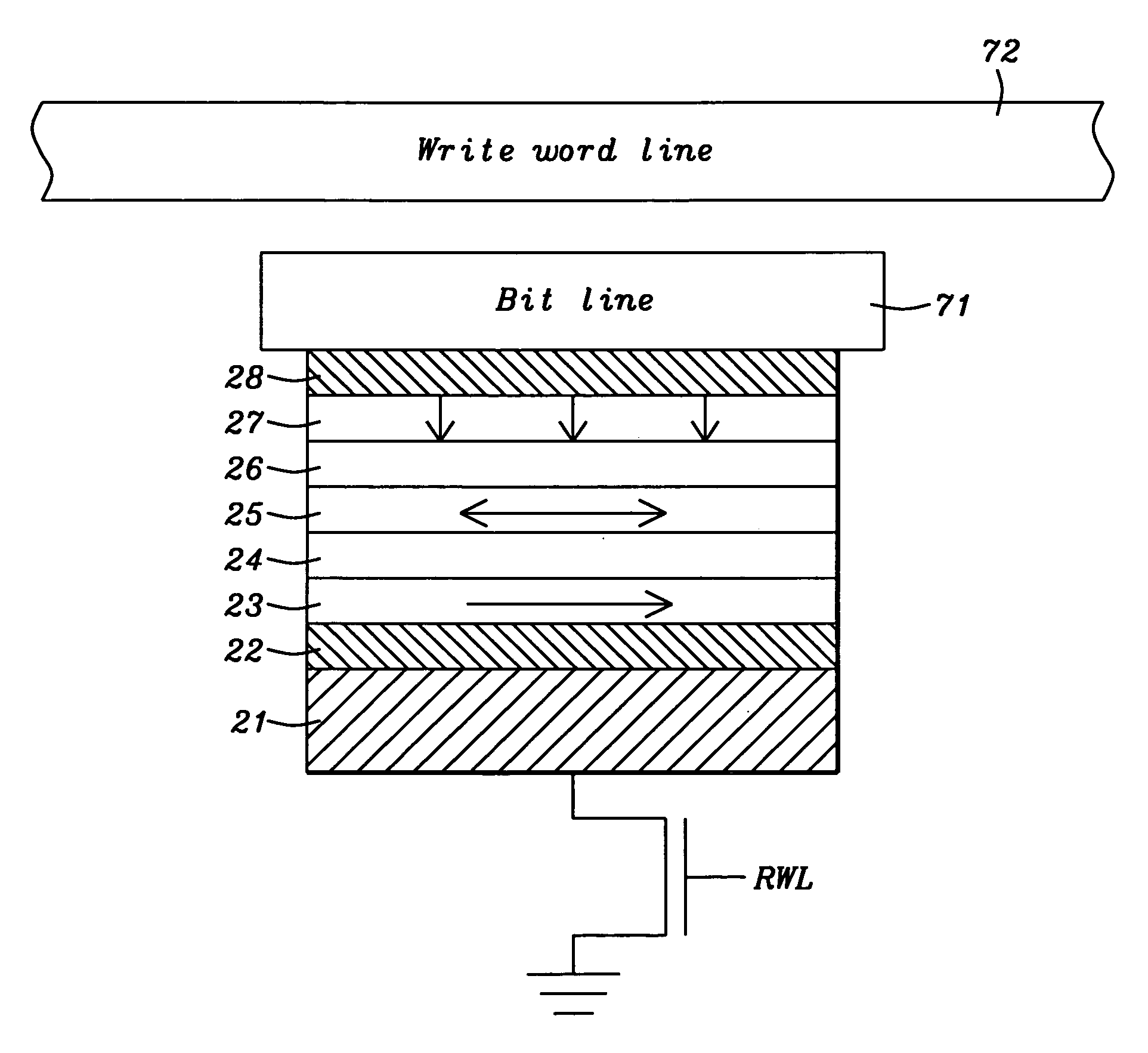
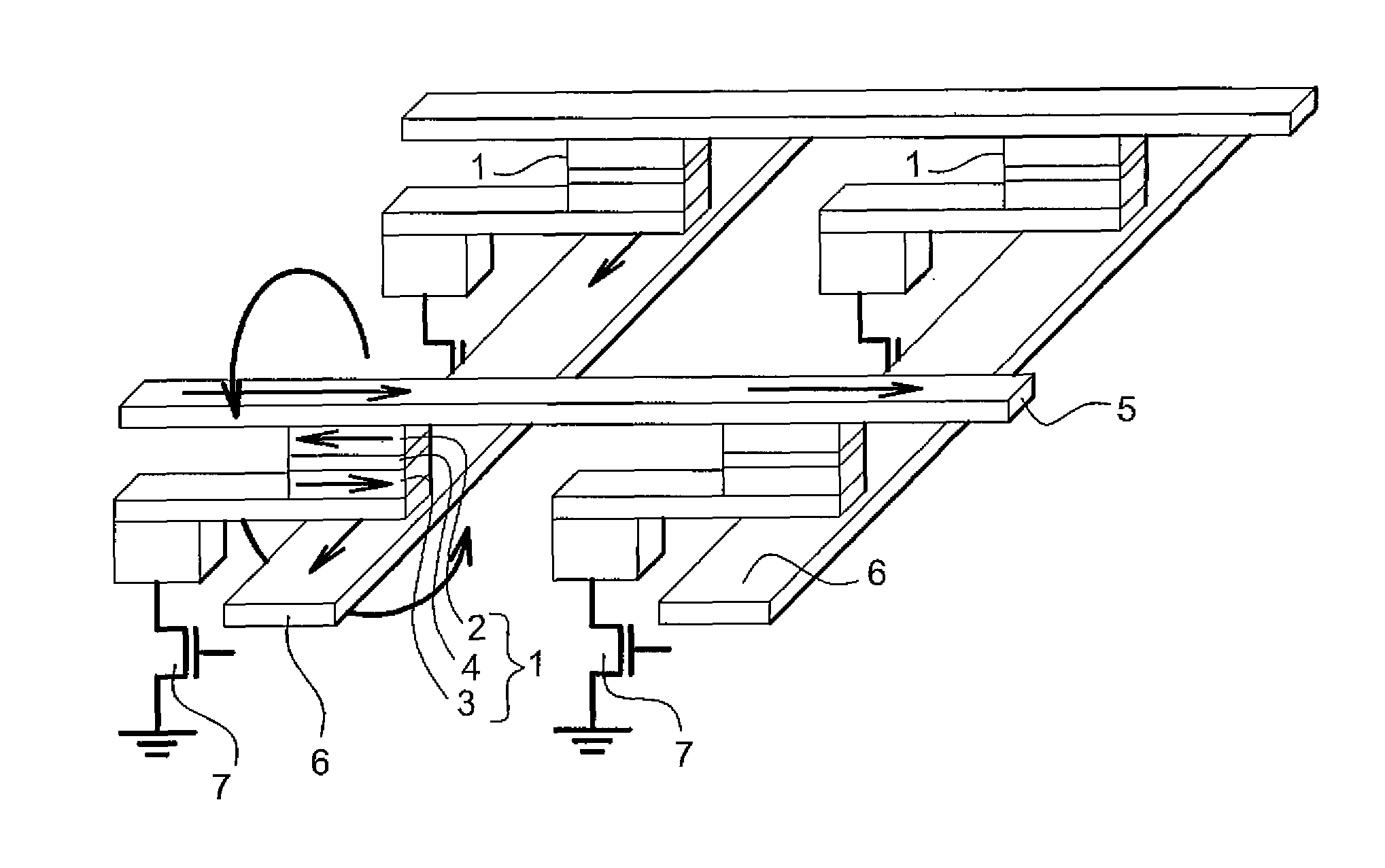
Spin transfer MRAM device with magnetic biasing
ActiveUS20080151614A1Strict controlSignificant power savingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpinsSpin transfer
The addition of segmented write word lines to a spin-transfer MRAM structure serves to magnetically bias the free layer so that the precessional motion of the magnetization vector that is set in play by the flow of spin polarized electrons into the free layer allows said magnetic vector to be switched rather than to oscillate between two easy axis directions.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
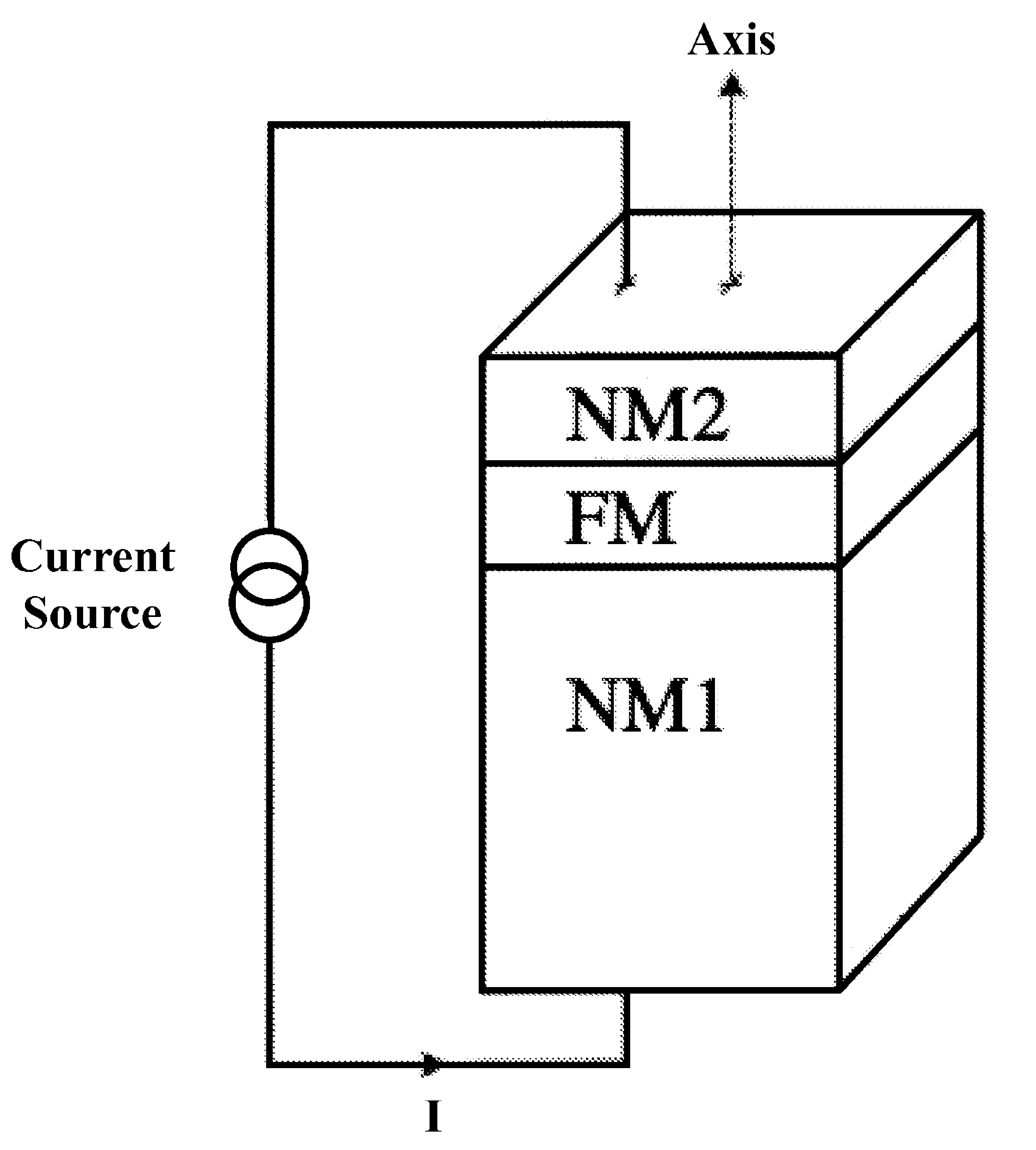
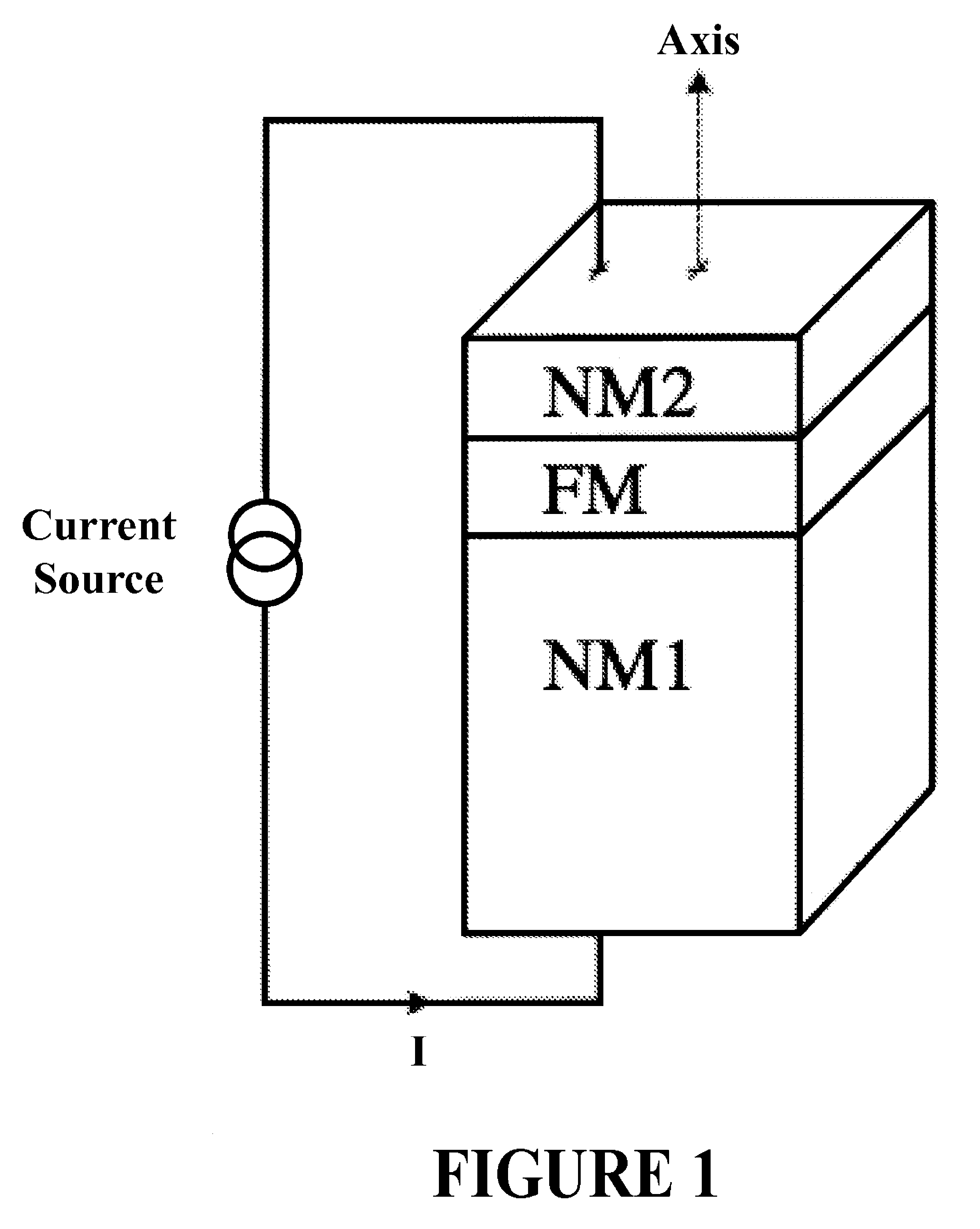
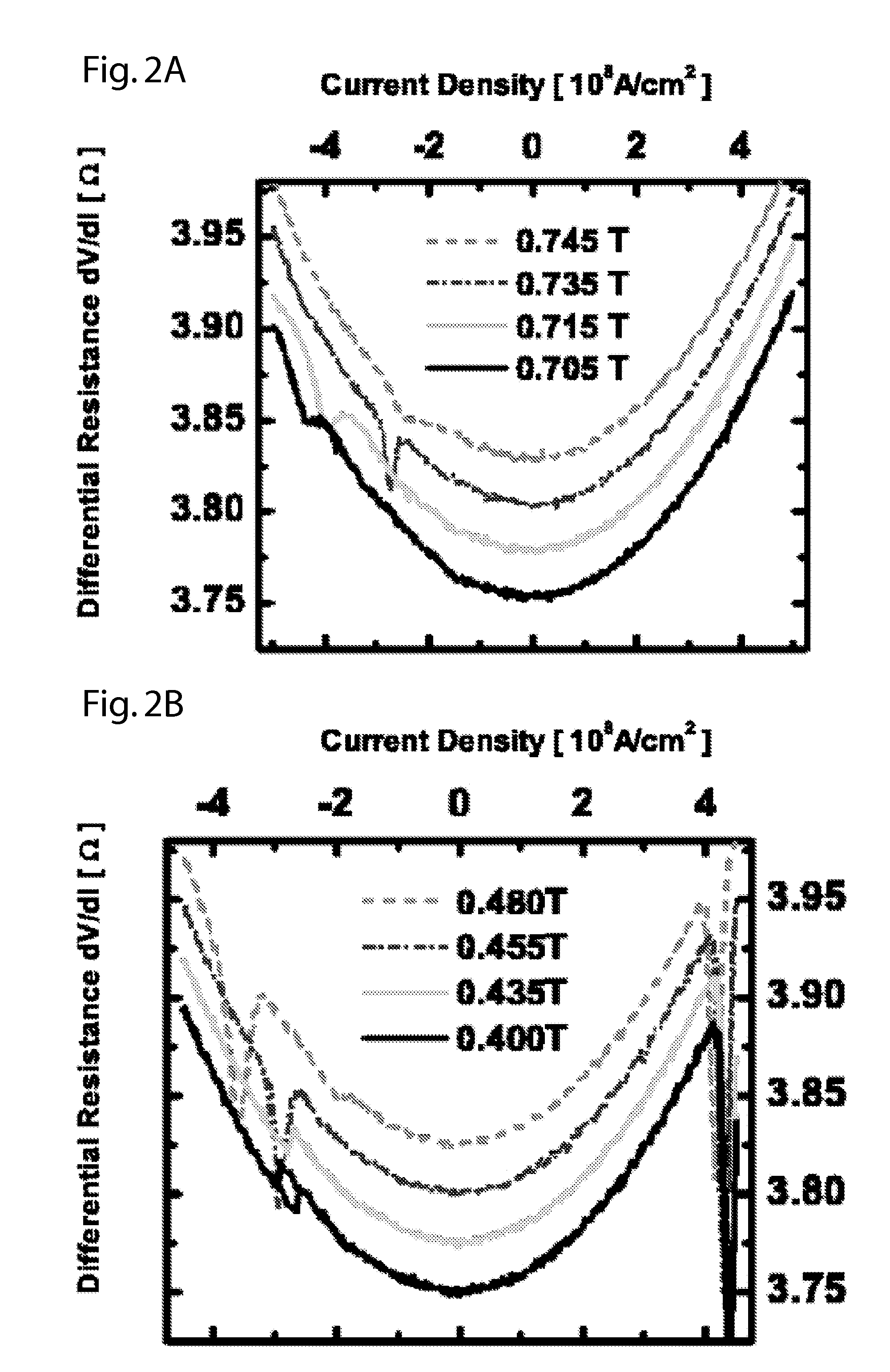
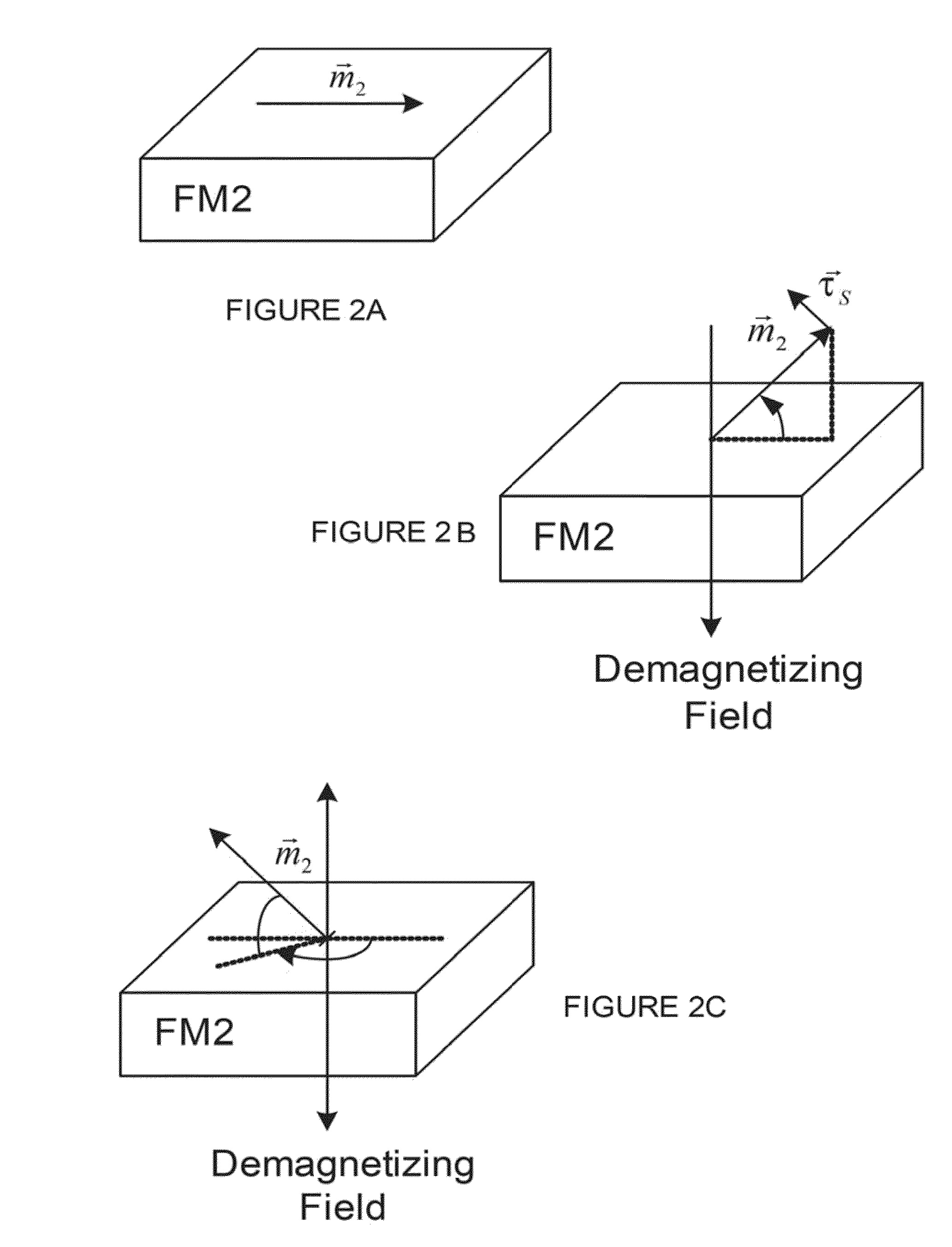
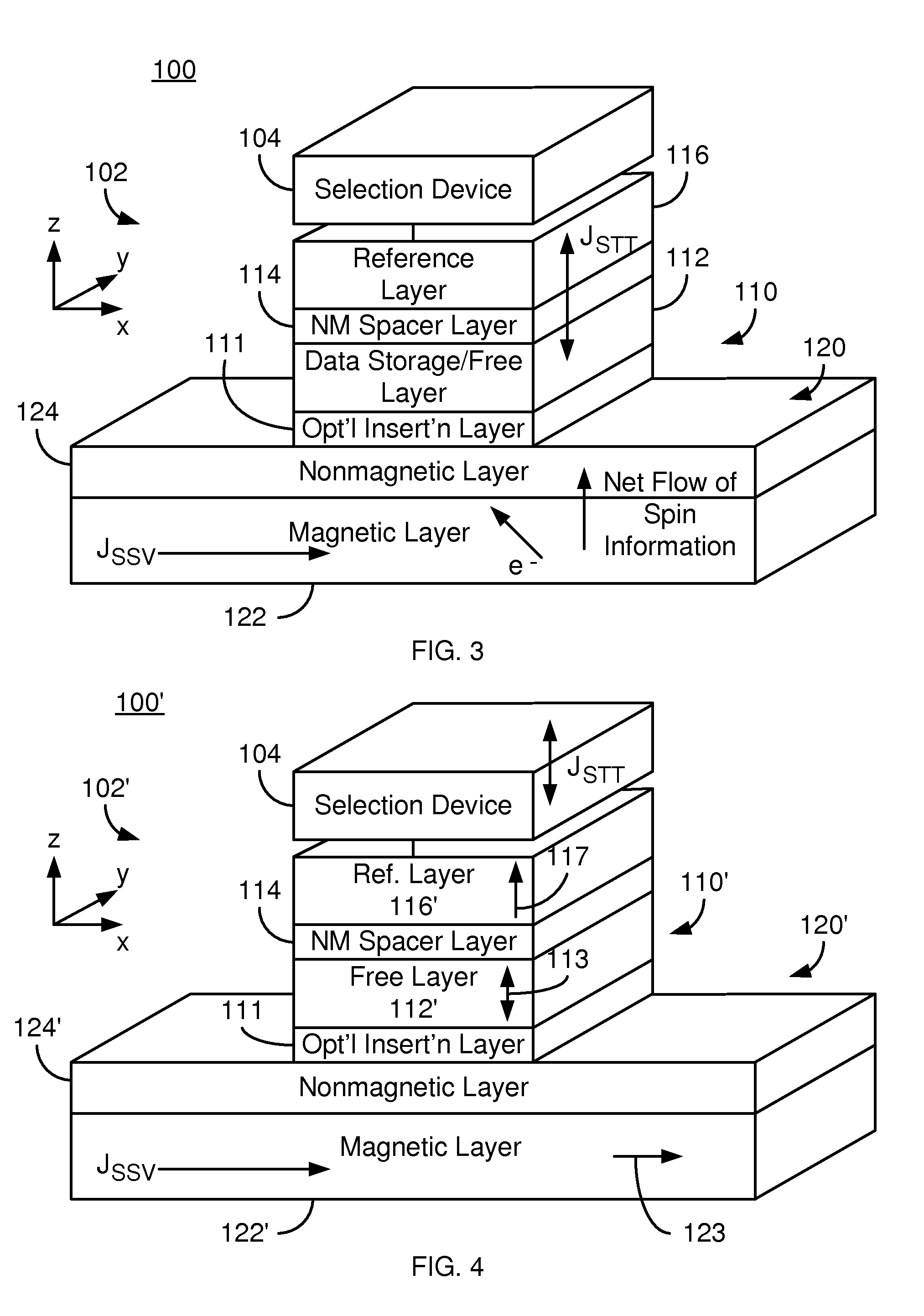
Spin polarised magnetic device
ActiveUS8279666B2Reducing the stochastic fluctuations in the magnetisation reversal timeTotal current dropNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic storageSpins
A magnetic device includes a magnetic reference layer with a fixed magnetization direction located either in the plane of the layer or perpendicular to the plane of the layer, a magnetic storage layer with a variable magnetization direction, a non-magnetic spacer separating the reference layer and the storage layer and a magnetic spin polarizing layer with a magnetization perpendicular to that of the reference layer, and located out of the plane of the spin polarizing layer if the magnetization of the reference layer is directed in the plane of the reference layer or in the plane of the spin polarizing layer if the magnetization of the reference layer is directed perpendicular to the plane of the reference layer. The spin transfer coefficient between the reference layer and the storage layer is higher than the spin transfer coefficient between the spin polarizing layer and the storage layer.
Owner:INSTITUT NAT POLYTECHN DE GRENOBLE +2
Magnetic shift register with shiftable magnetic domains between two regions, and method of using the same
InactiveUS7031178B2Highly localized and large magnetic fieldsComparable in costLiquid applicationDigital storageShift registerProcessor register
A magnetic shift register uses the inherent, natural properties of domain walls in magnetic materials to store data. The shift register uses spin electronics without changing the physical nature of its constituent materials. The shift register comprises a fine track or strip of magnetic materials. Information is stored as domain walls in the track. An electric current is applied to the track to move the magnetic moments along the track past a reading or writing device. In a magnetic material with domain walls, a current passed across the domain wall moves the domain wall in the direction of the current flow. As the current passes through a domain, it becomes “spin polarized”. When this spin polarized current passes through the next domain and across a domain wall, it develops a circle of spin torque. This spin torque moves the domain wall.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Magnetoresistive random access memory cell design
A new magnetic memory cell comprises a perpendicular-anisotropy tunneling magnetic junction (TMJ) and a fixed in-plane spin-polarizing layer, which is separated from the perpendicular-anisotropy data storage layer of tunneling magnetic junction by a non-magnetic layer. The non-magnetic layer can be made of metallic or dielectric materials.
Owner:GE YI +3
High speed low power magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS7573737B2Operational advantageReduce the required powerDigital storageMagnetic memoryMagnetization
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Magnetic recording device and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20090015958A1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsPrecessionFilm plane
A magnetic recording device includes: a laminated body including: a first ferromagnetic layer with a magnetization substantially fixed in a first direction; a second ferromagnetic layer with a variable magnetization direction; a first nonmagnetic layer disposed between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer; and a third ferromagnetic layer with a variable magnetization direction. The magnetization direction of the second ferromagnetic layer is determinable in response to the orientation of a current, by allowing electrons spin-polarized by passing a current in a direction generally perpendicular to the film plane of the layers of the laminated body to act on the second ferromagnetic layer, and by allowing a magnetic field generated by precession of the magnetization of the third ferromagnetic layer to act on the second ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
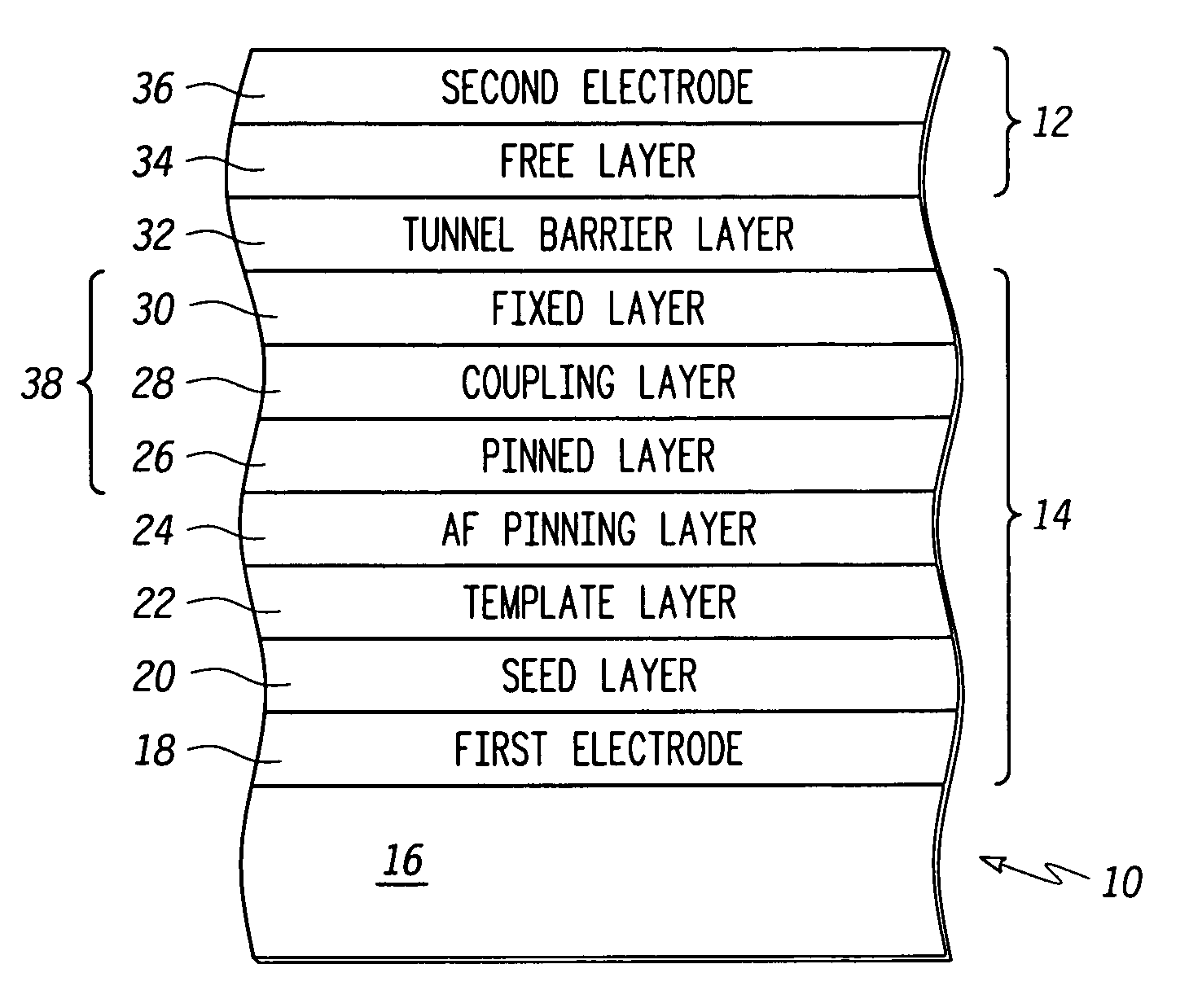
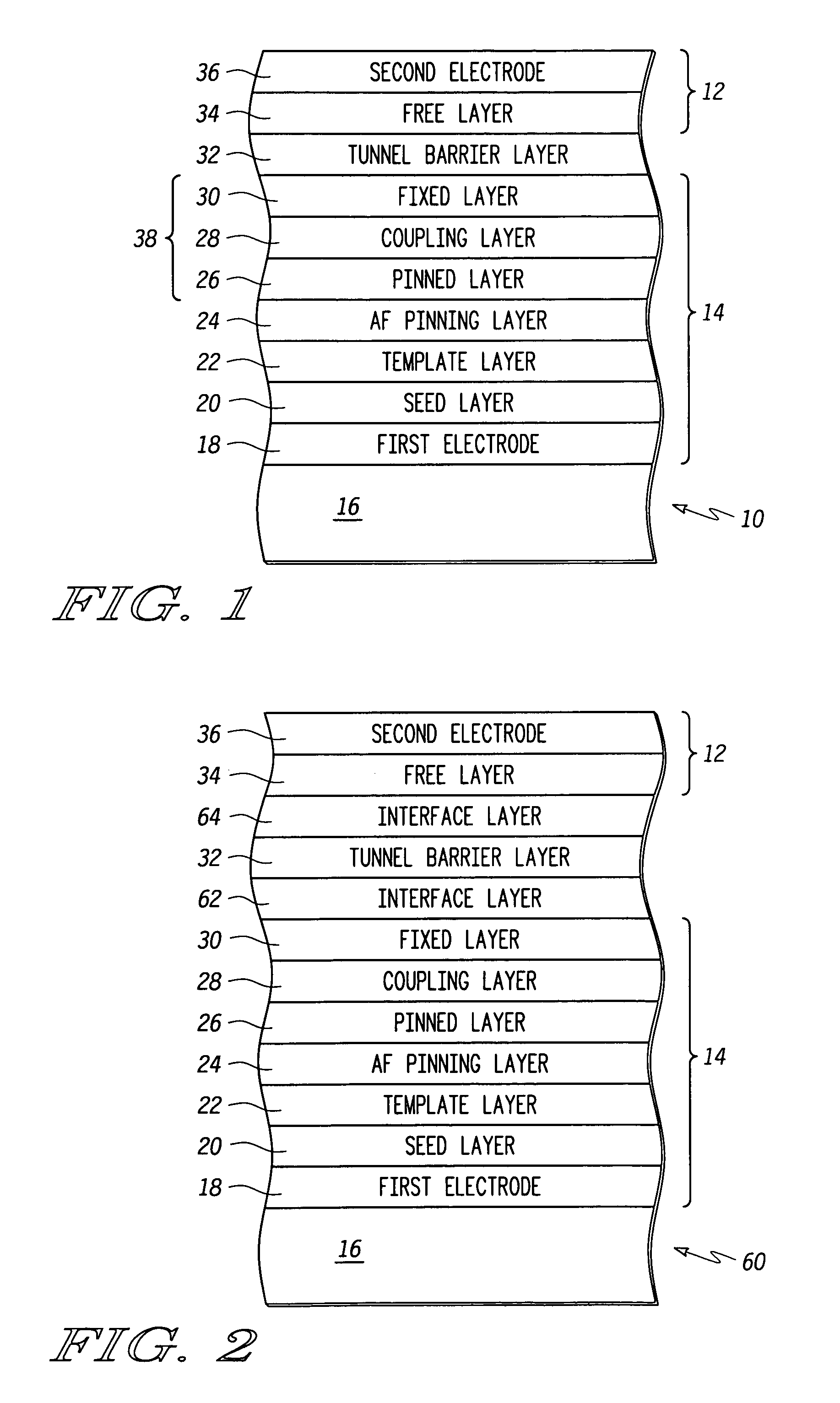
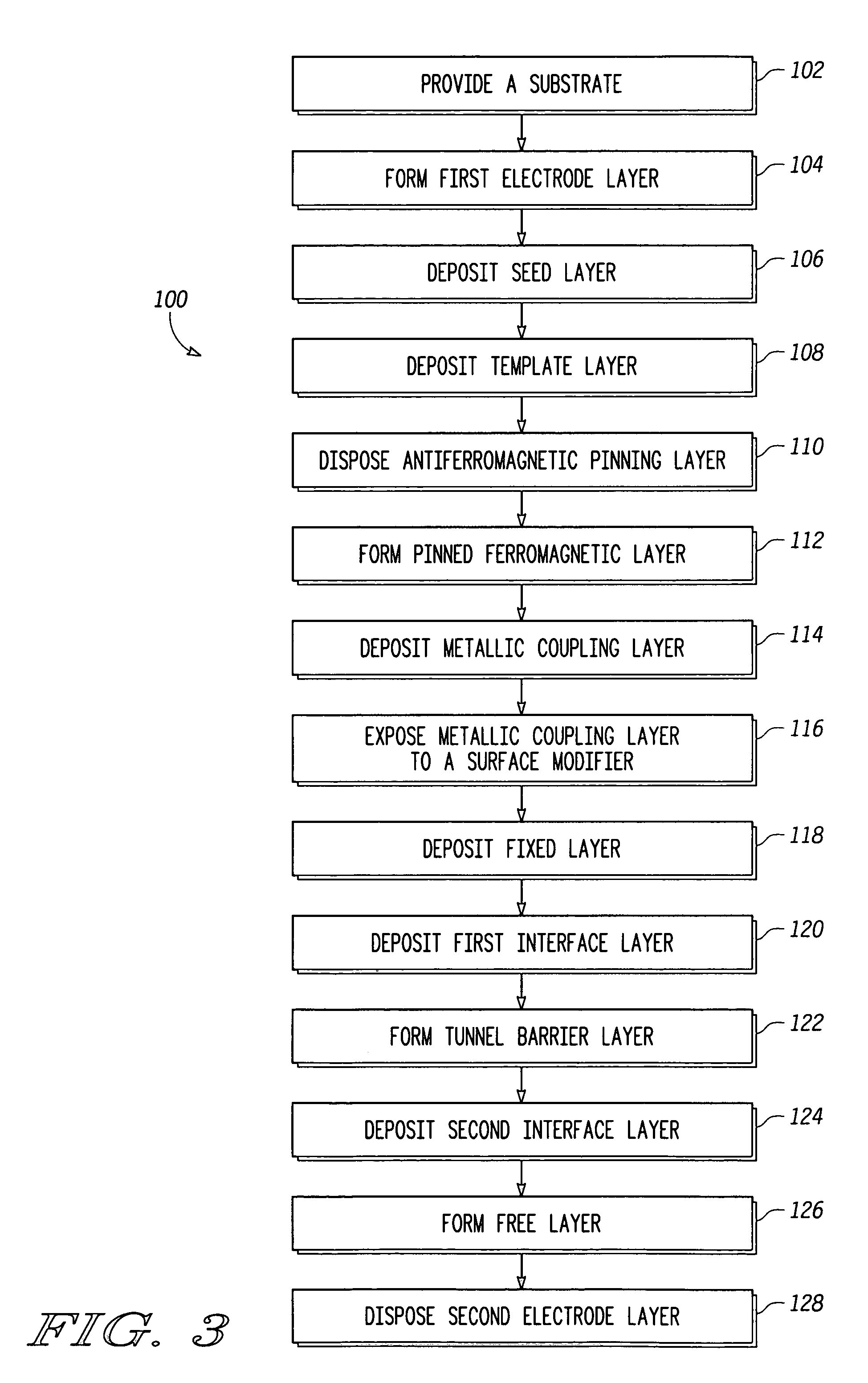
Magnetic tunnel junction element structures and methods for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20060017081A1NanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsAntiferromagnetic couplingInterface layer
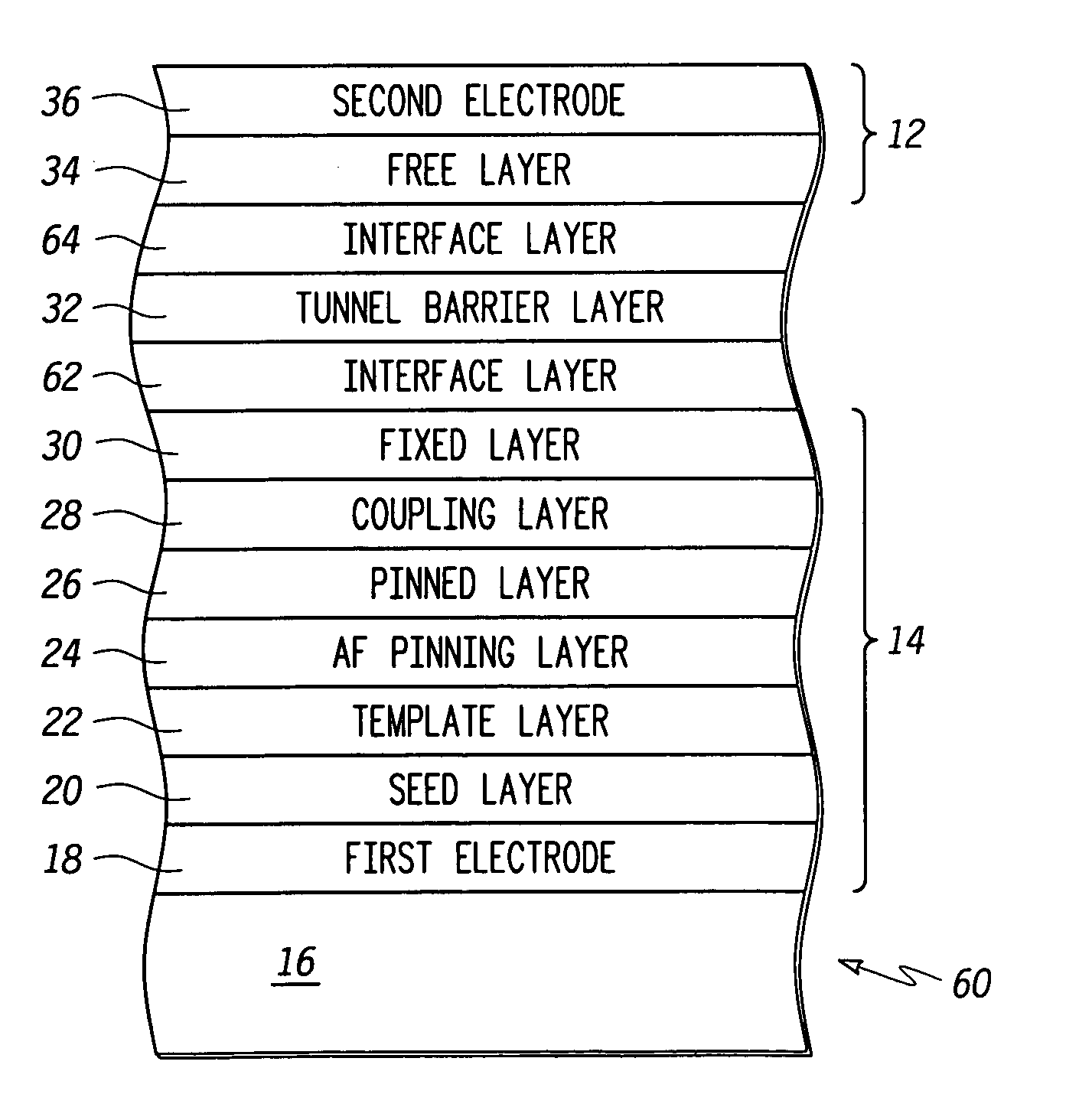
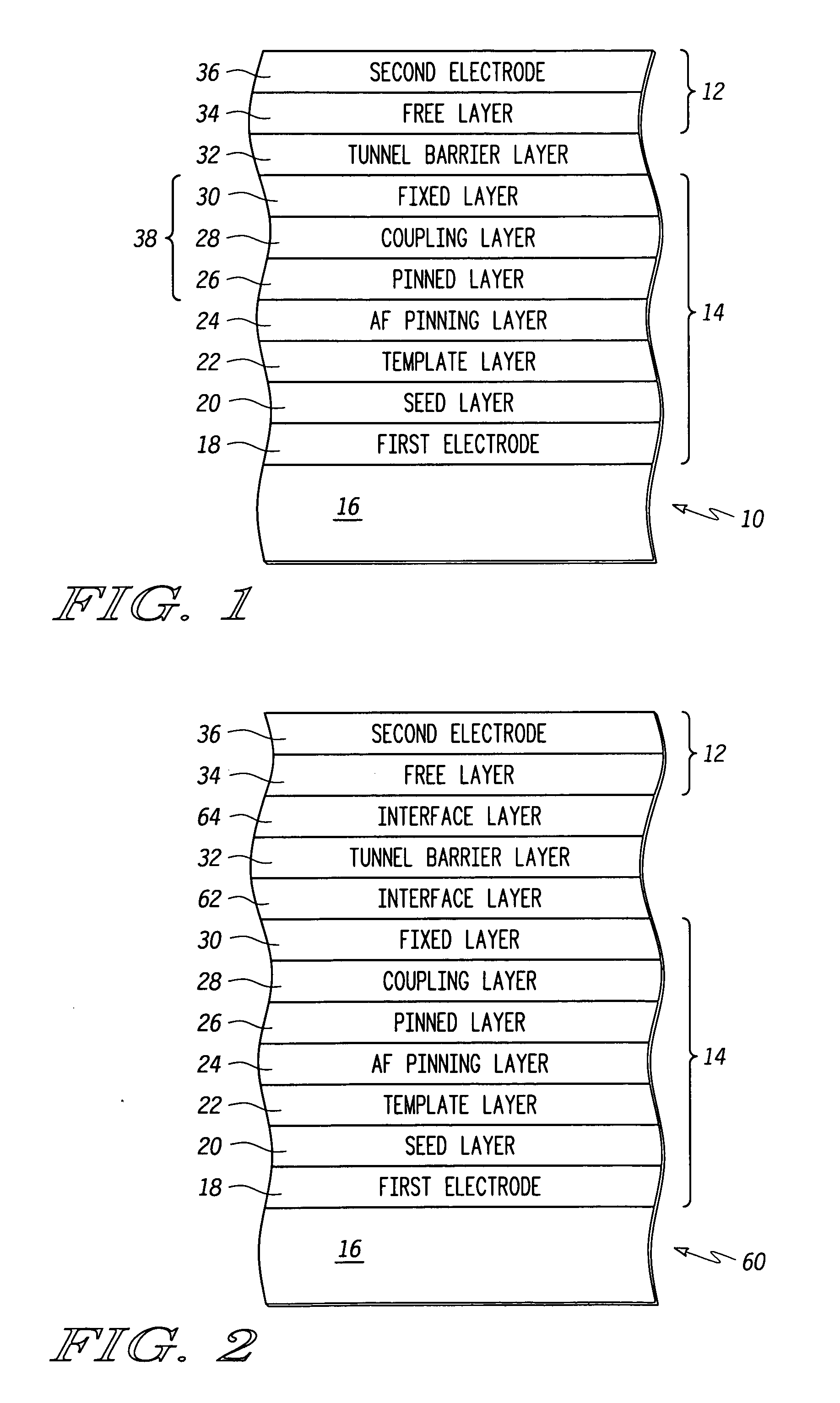
Magnetic tunnel junction (“MTJ”) element structures and methods for fabricating MTJ element structures are provided. An MTJ element structure may comprise a crystalline pinned layer, an amorphous fixed layer, and a coupling layer disposed between the crystalline pinned layer and the amorphous fixed layer. The amorphous fixed layer is antiferromagnetically coupled to the crystalline pinned layer. The MTJ element further comprises a free layer and a tunnel barrier layer disposed between the amorphous fixed layer and the free layer. Another MTJ element structure may comprise a pinned layer, a fixed layer and a non-magnetic coupling layer disposed therebetween. A tunnel barrier layer is disposed between the fixed layer and a free layer. An interface layer is disposed adjacent the tunnel barrier layer and a layer of amorphous material. The first interface layer comprises a material having a spin polarization that is higher than that of the amorphous material.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Electronic devices based on current induced magnetization dynamics in single magnetic layers
InactiveUS7986544B2Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageInformation processingMagnetization dynamics
The present invention generally relates to magnetic devices used in memory and information processing applications, such as giant magneto-resistance (GMR) devices and tunneling magneto-resistance devices. More specifically, the present invention is directed to a single ferromagnetic layer device in which an electrical current is used to control and change magnetic configurations as well as induce high frequency magnetization dynamics. The magnetic layer includes full spin-polarized magnetic material, which may also have non-uniform magnetization. The non-uniform magnetization is achieved by varying the shape or roughness of the magnetic material. The present invention may be used in memory cells, as well as high frequency electronics, such as compact microwave sources, detectors, mixers and phase shifters.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
High speed low power magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS7911832B2Operational advantageReduce the required powerDigital storageMagnetic memoryMagnetization
A high speed and low power method to control and switch the magnetization direction and / or helicity of a magnetic region in a magnetic device for memory cells using spin polarized electrical current. The magnetic device comprises a reference magnetic layer with a fixed magnetic helicity and / or magnetization direction and a free magnetic layer with a changeable magnetic helicity and / or magnetization direction. The fixed magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are preferably separated by a non-magnetic layer. The fixed and free magnetic layers may have magnetization directions at a substantially non-zero angle relative to the layer normal. A current can be applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
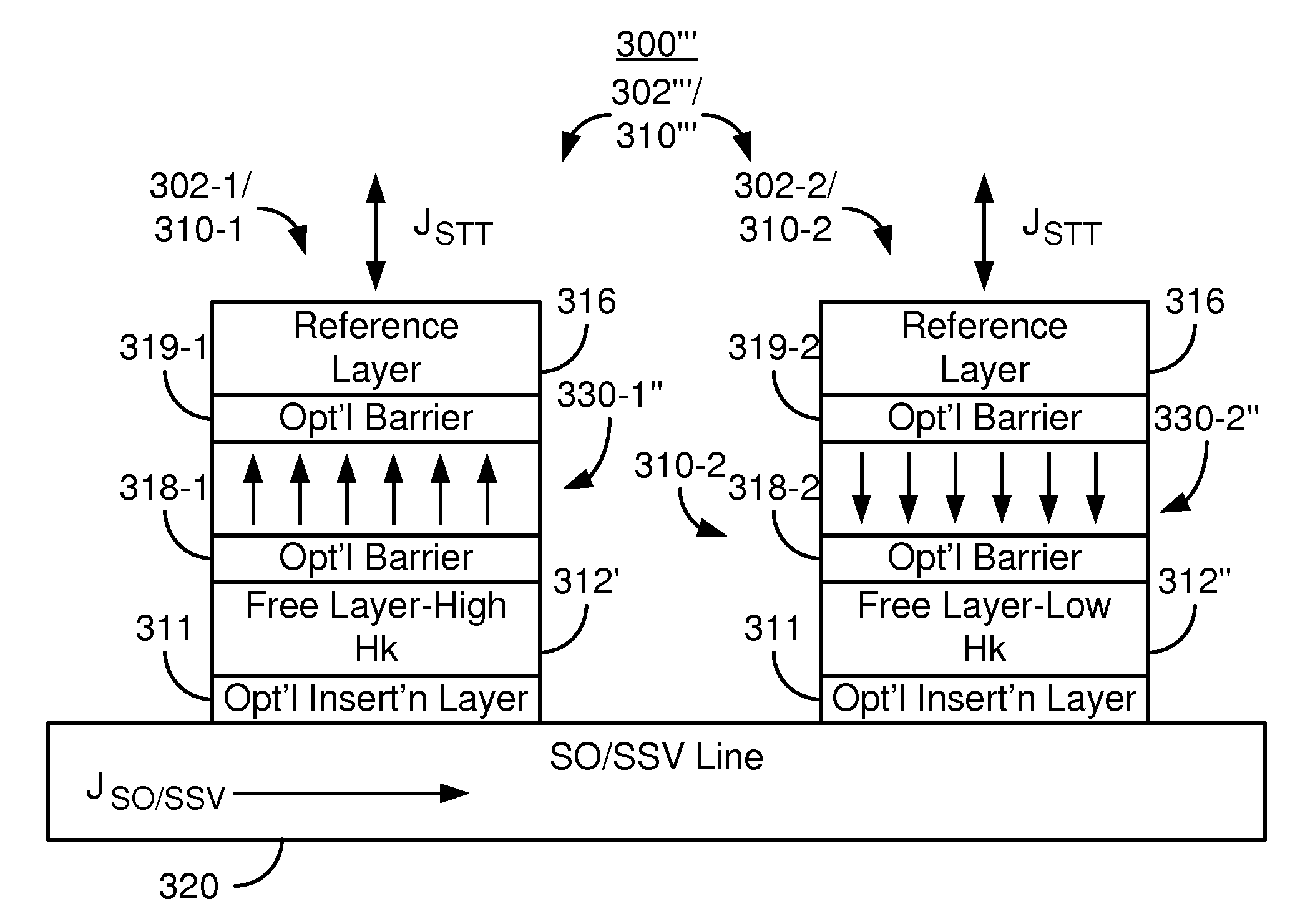
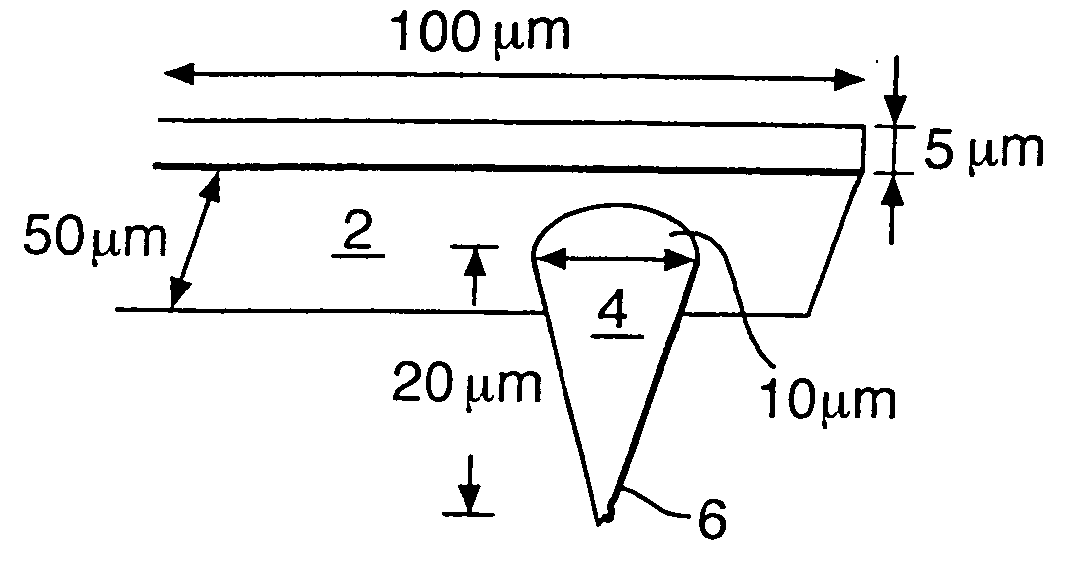
Method and system for providing magnetic memories switchable using spin accumulation and selectable using magnetoelectric devices
A magnetic memory is described. In one aspect, the magnetic memory includes magnetic junctions and at least one semi-spin valve (SSV) line adjacent to the magnetic junctions. Each magnetic junction includes a magnetic free layer. The SSV line(s) include a ferromagnetic layer and a nonmagnetic layer between the ferromagnetic layer and the magnetic junctions. The SSV line(s) are configured to exert a spin accumulation induced torque on at least a portion of the magnetic junctions due to an accumulation of spin polarized current carriers from a current that is substantially in-plane. The free layer is configured to be written using at least the spin accumulation induced torque. In another aspect, the magnetic memory includes magnetic memory cells and at least one spin torque (ST) line that is analogous to the SSV line. Each magnetic memory cell includes magnetic junction(s) analogous to those above and magnetoelectric selection device(s).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
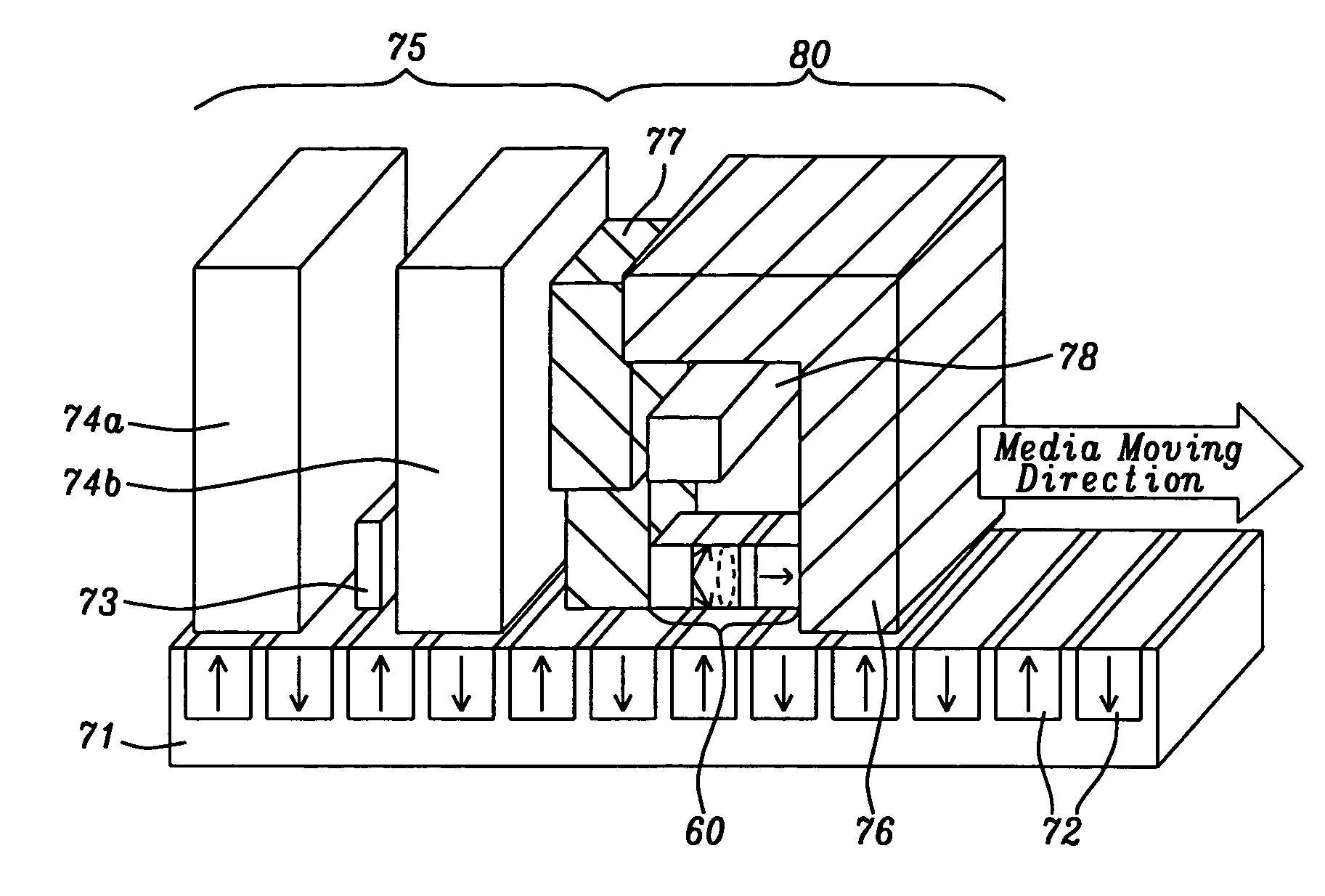
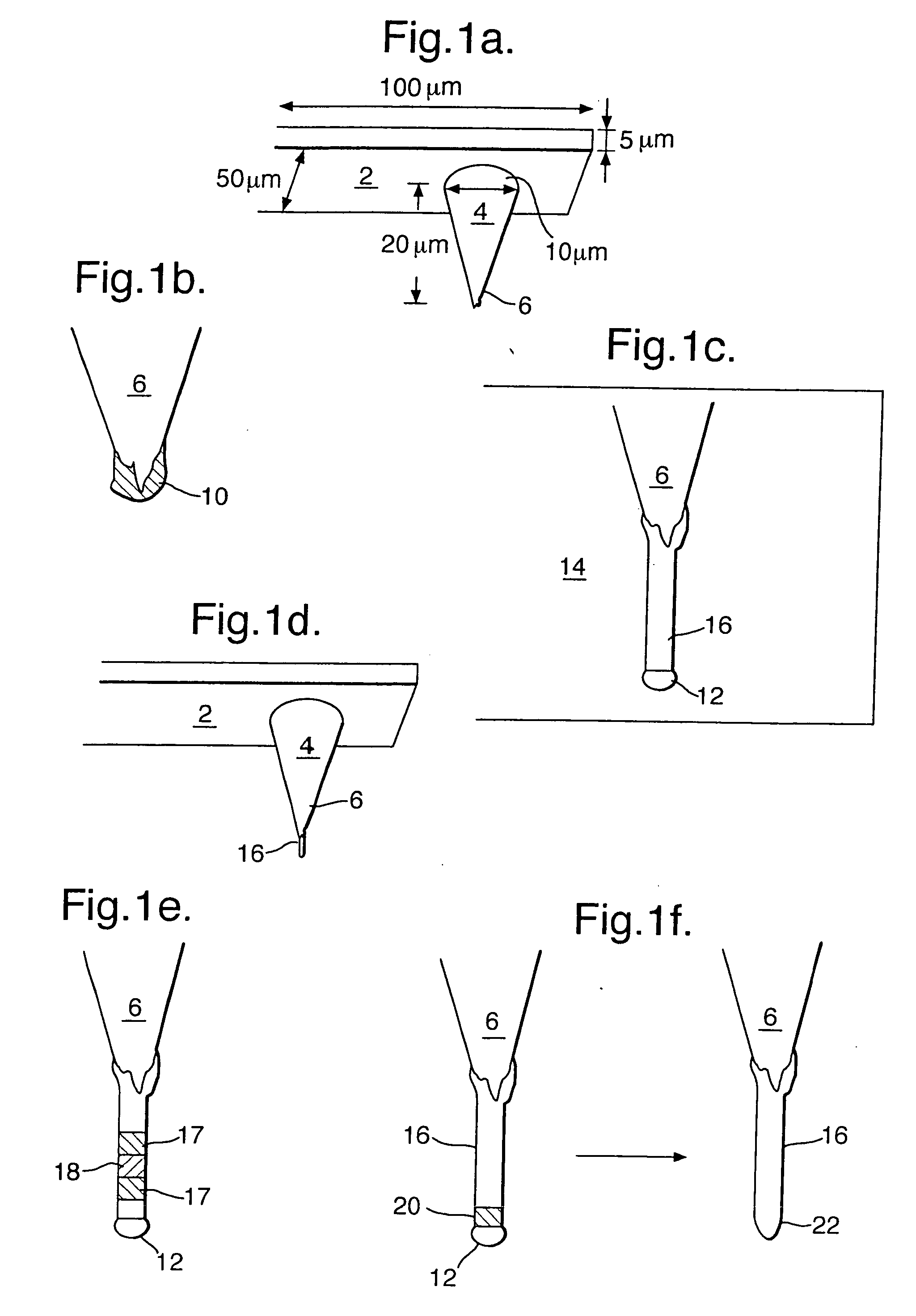
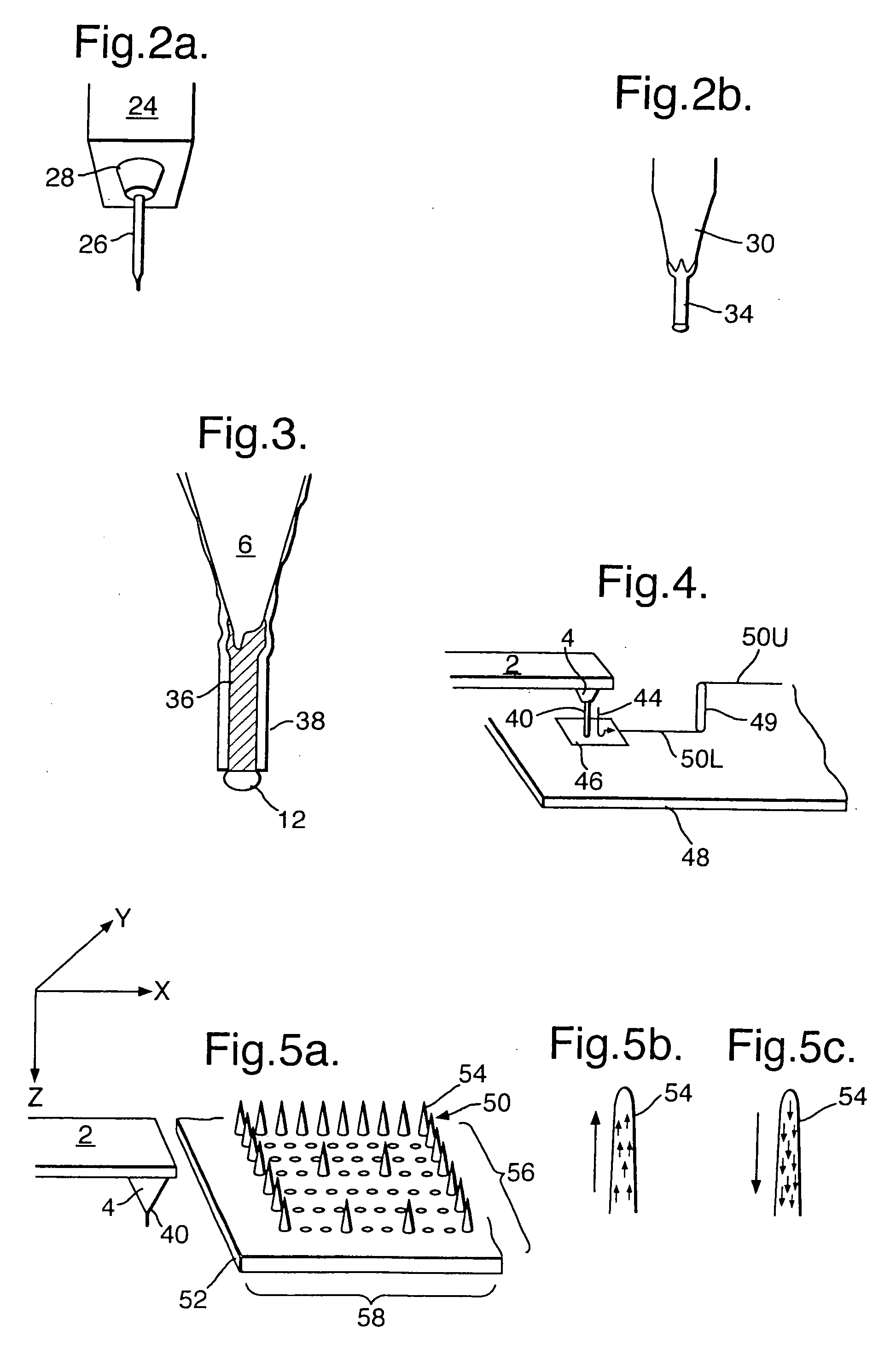
Probe structures incorporating nanowhiskers, production methods thereof and methods of forming nanowhiskers
InactiveUS20050017171A1Small sizeReduce the overall diameterMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationInorganic material artificial filamentsEtchingWhiskers
A probe structure for a scanning probe microscope comprises a nanowhisker (16,34) projecting from a free end of an upstanding tip member (4,26), and being formed integrally with the tip member. In another embodiment, a data storage medium comprises an array of nanowhiskers (54), each nanowhisker being formed from magnetic material, the diameter of the nanowhisker being such that a single ferromagnetic domain exists within the nanowhisker, preferably having a diameter not greater than about 25 nm and more preferably not greater than about 10 nm, and a read / write structure comprising the probe structure for injecting a stream of spin-polarised electrons into a selected nanowhisker of the array, either for sensing the direction of magnetisation in the nanowhisker, or for forcing the nanowhisker into a desired direction of magnetisation. When the probe nanowhisker is formed by a VLS process using a catalytic particle melt, the whisker may be formed with a sacrificial segment to allow for removal of the catalytic material by selective etching of the segment.
Owner:QUNANO
Magnetic tunnel junction element structures and methods for fabricating the same
ActiveUS7098495B2NanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsAntiferromagnetic couplingInterface layer
Magnetic tunnel junction (“MTJ”) element structures and methods for fabricating MTJ element structures are provided. An MTJ element structure may comprise a crystalline pinned layer, an amorphous fixed layer, and a coupling layer disposed between the crystalline pinned layer and the amorphous fixed layer. The amorphous fixed layer is antiferromagnetically coupled to the crystalline pinned layer. The MTJ element further comprises a free layer and a tunnel barrier layer disposed between the amorphous fixed layer and the free layer.Another MTJ element structure may comprise a pinned layer, a fixed layer and a non-magnetic coupling layer disposed therebetween. A tunnel barrier layer is disposed between the fixed layer and a free layer. An interface layer is disposed adjacent the tunnel barrier layer and a layer of amorphous material. The first interface layer comprises a material having a spin polarization that is higher than that of the amorphous material.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Optical Pumping Magnetometer
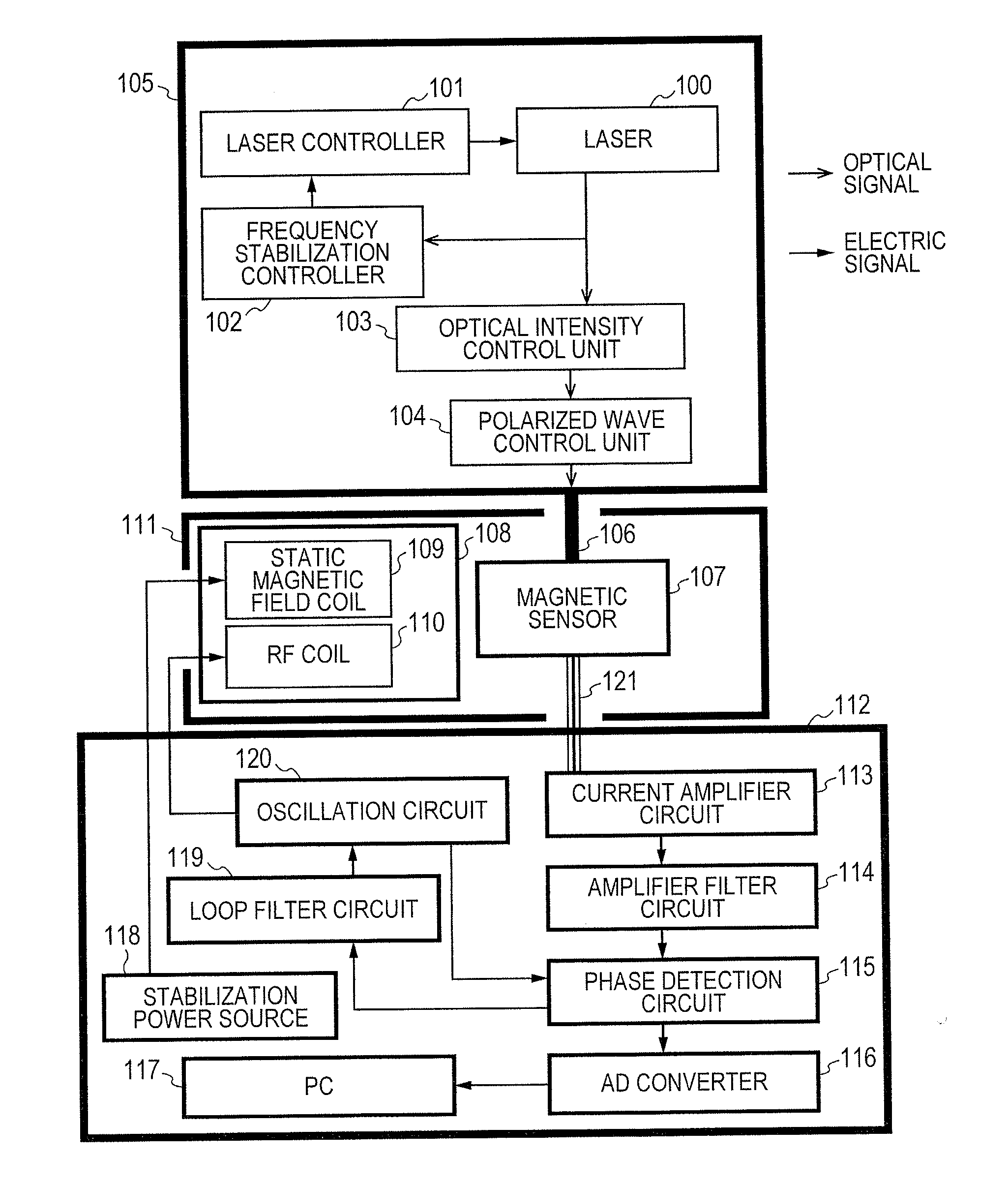
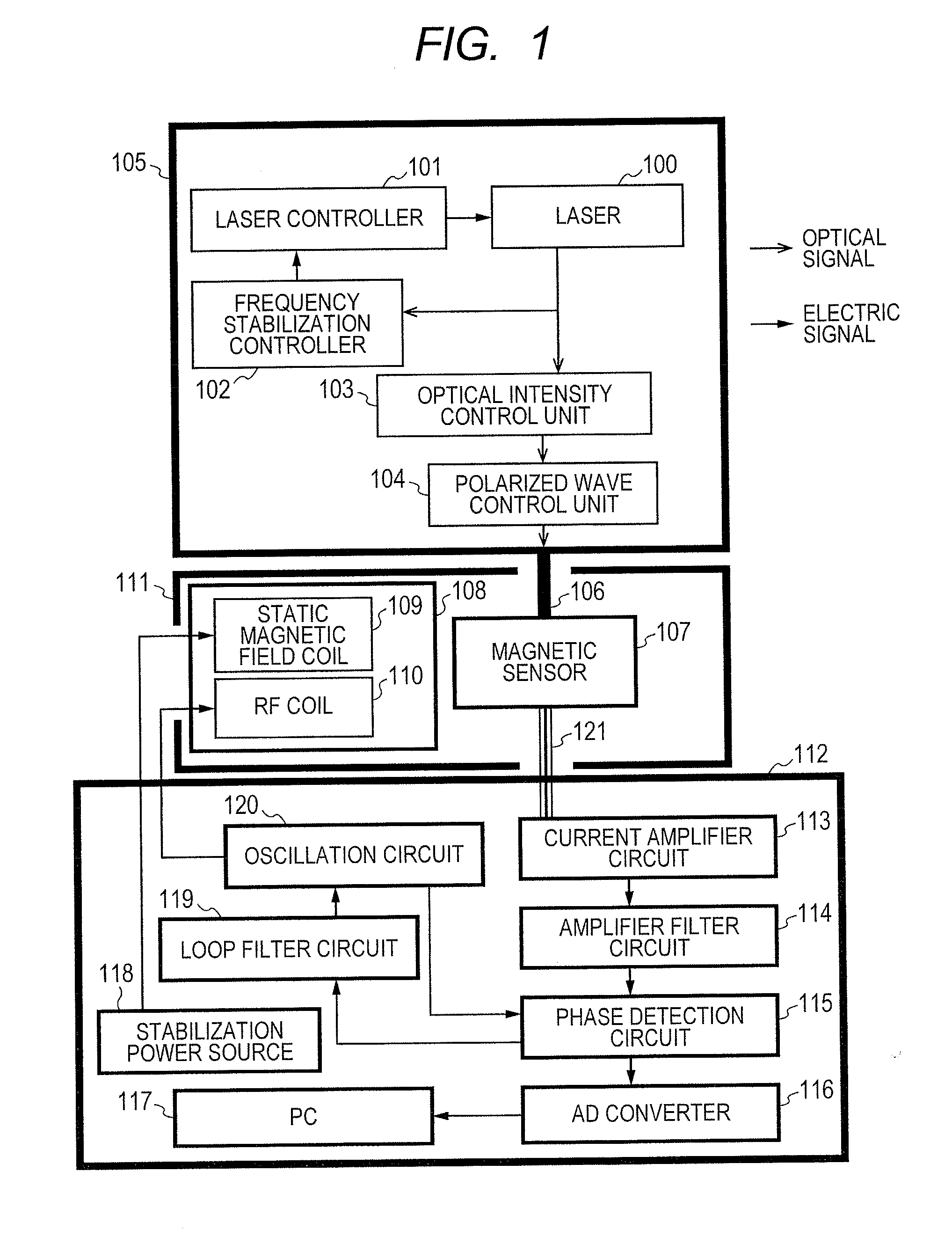
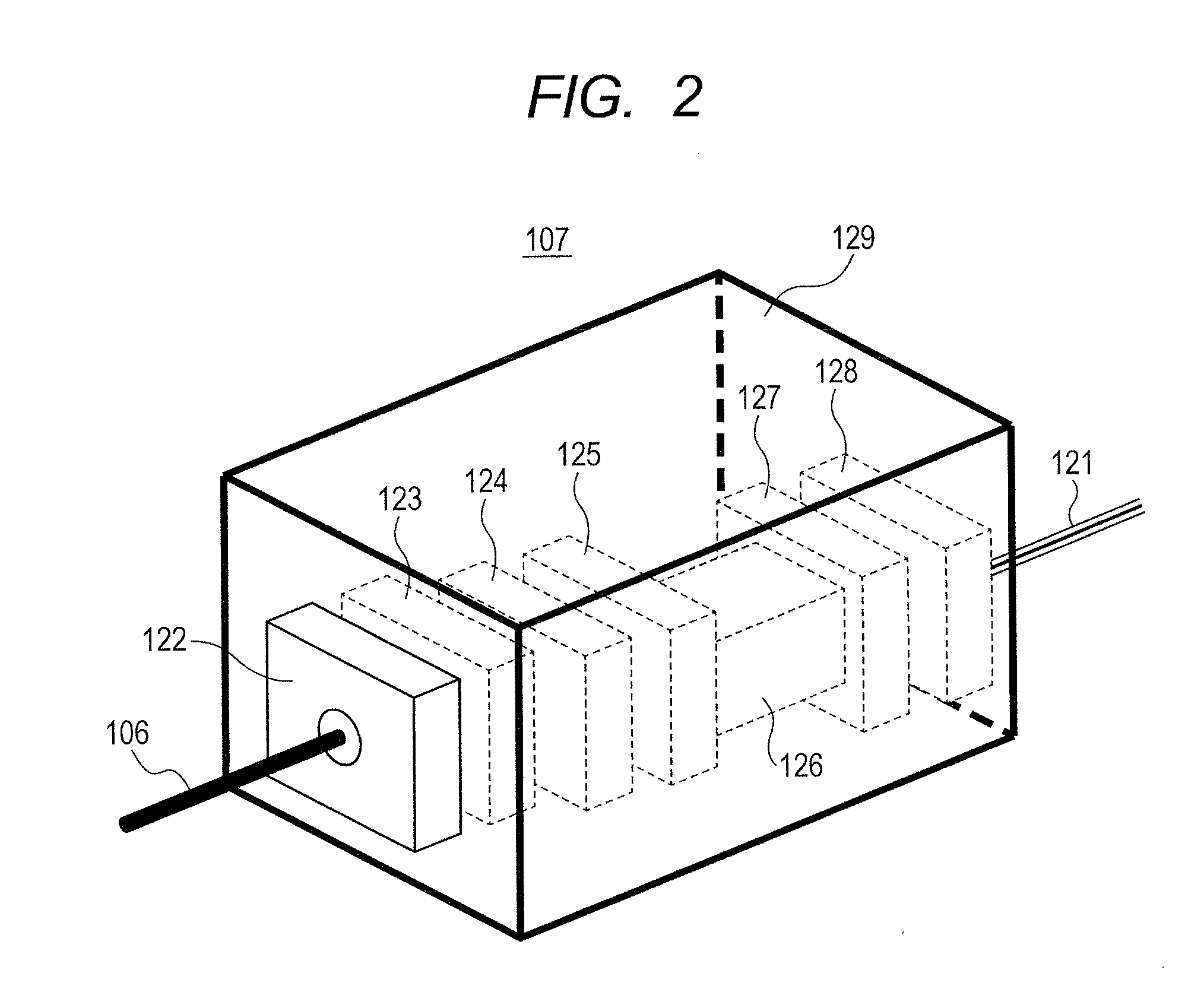
ActiveUS20130265042A1Easy to controlGuaranteed uptimeElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceFrequency stabilizationPhotodetector
Stable magnetic field measurement is enabled without collapse of polarization or fluctuation of intensity of a laser beam incident on a glass cell of an optical pumping magnetic sensor. Excitation light generated with a light source, having optimized light intensity and polarized wave, through frequency stabilization, intensity control and polarized-wave control, is introduced via a polarized wave holding optical fiber to a magnetic sensor provided in a magnetic shield, and magnetic field measurement is performed by optical pumping using magneto-optical properties of spin-polarized alkali metal. The magnetic sensor has a structure where a lens, a polarization optical device, the glass cell and a photodetector, are integrally accommodated in a non-magnetic case.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetoresistive Element and Method of Manufacturing the Same
ActiveUS20120261777A1Magnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic reluctanceMagnetization
A magnetoresistive element (and method of fabricating the magnetoresistive element) that includes a free ferromagnetic layer comprising a first reversible magnetization direction directed substantially perpendicular to a film surface, a pinned ferromagnetic layer comprising a second fixed magnetization direction directed substantially perpendicular to the film surface, and a nonmagnetic insulating tunnel barrier layer disposed between the free ferromagnetic layer and the pinned ferromagnetic layer, wherein the free ferromagnetic layer, the tunnel barrier layer, and the pinned ferromagnetic layer have a coherent body-centered cubic (bcc) structure with a (001) plane oriented, and a bidirectional spin-polarized current passing through the coherent structure in a direction perpendicular to the film surface reverses the magnetization direction of the free ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:SHUKH ALEXANDER MIKHAILOVICH
Magnetoresistive element
A magnetoresistive element which records information by supplying spin-polarized electrons to a magnetic material, includes a first pinned layer which is made of a magnetic material and has a first magnetization directed in a direction perpendicular to a film surface, a free layer which is made of a magnetic material and has a second magnetization directed in the direction perpendicular to the film surface, the direction of the second magnetization reversing by the spin-polarized electrons, and a first nonmagnetic layer which is provided between the first pinned layer and the free layer. A saturation magnetization Ms of the free layer satisfies a relationship 0≧Ms<√{square root over ( )}{Jw / (6πAt)}. Jw is a write current density, t is a thickness of the free layer, A is a constant.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
A magnetoresistive element includes a free layer which contains a magnetic material and has an fct crystal structure with a (001) plane oriented, the free layer having a magnetization which is perpendicular to a film plane and has a direction to be changeable by spin-polarized electrons, a first nonmagnetic layer and a second nonmagnetic layer which sandwich the free layer and have one of a tetragonal crystal structure and a cubic crystal structure, and a fixed layer which is provided on only one side of the free layer and on a surface of the first nonmagnetic layer opposite to a surface with the free layer and contains a magnetic material, the fixed layer having a magnetization which is perpendicular to a film plane and has a fixed direction.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions, magnetic devices including the same and method of manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction
InactiveUS20110149647A1NanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin polarizationTunnel junction
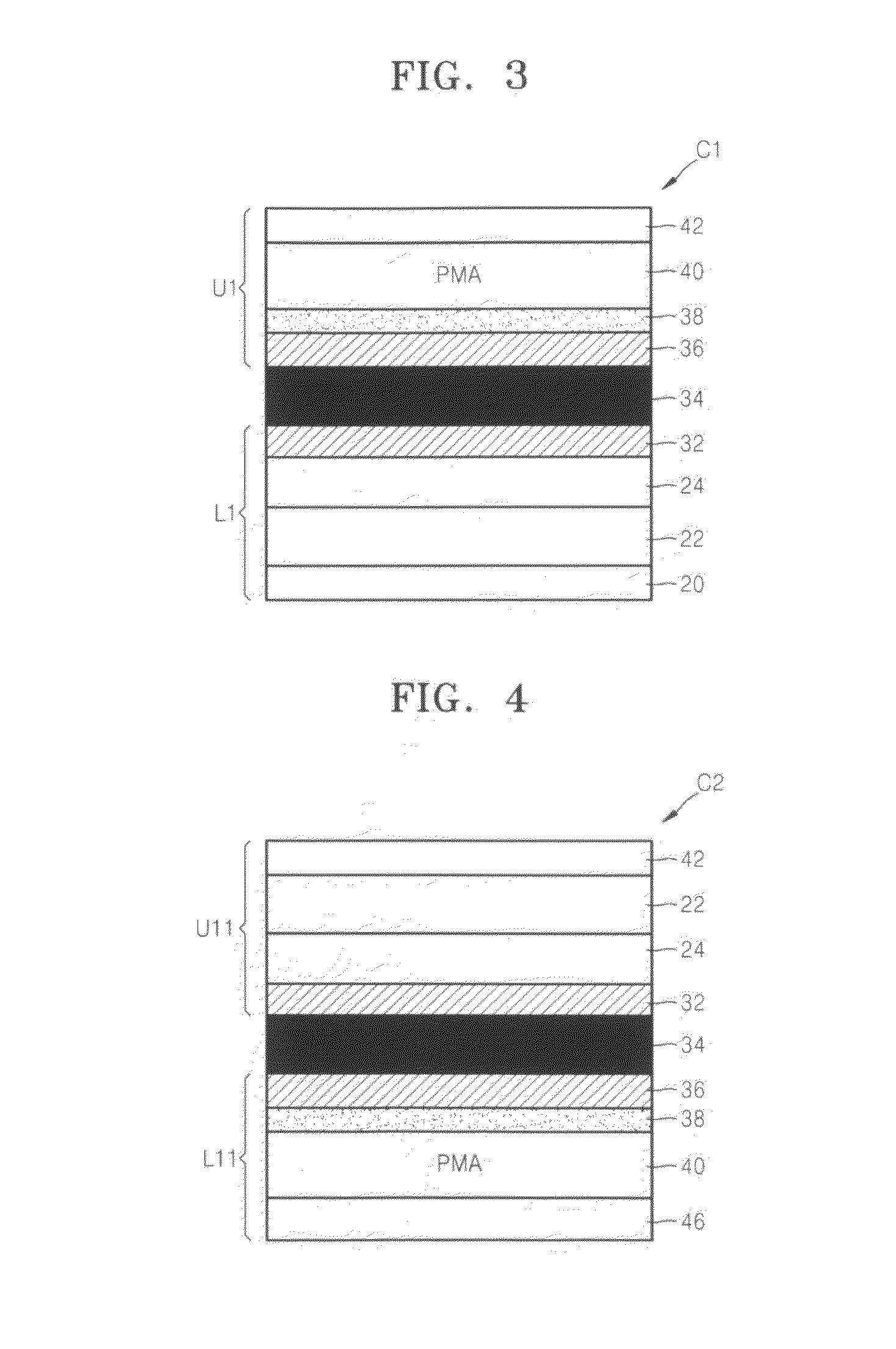
Provided are a perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), a magnetic device including the same, and a method of manufacturing the MTJ, the perpendicular MTJ includes a lower magnetic layer; a tunnelling layer on the lower magnetic layer; and an upper magnetic layer on the tunnelling layer. One of the upper and lower magnetic layers includes a free magnetic layer that exhibits perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, wherein the magnetizing direction of the free magnetic layer is changed by a spin polarization current. A polarization enhancing layer (PEL) and an exchange blocking layer (EBL) are stacked between the tunnelling layer and the free magnetic layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Downhole high resolution NMR spectroscopy with polarization enhancement
InactiveUS7126332B2Increase amplitudeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using double resonanceSignal onProton NMR
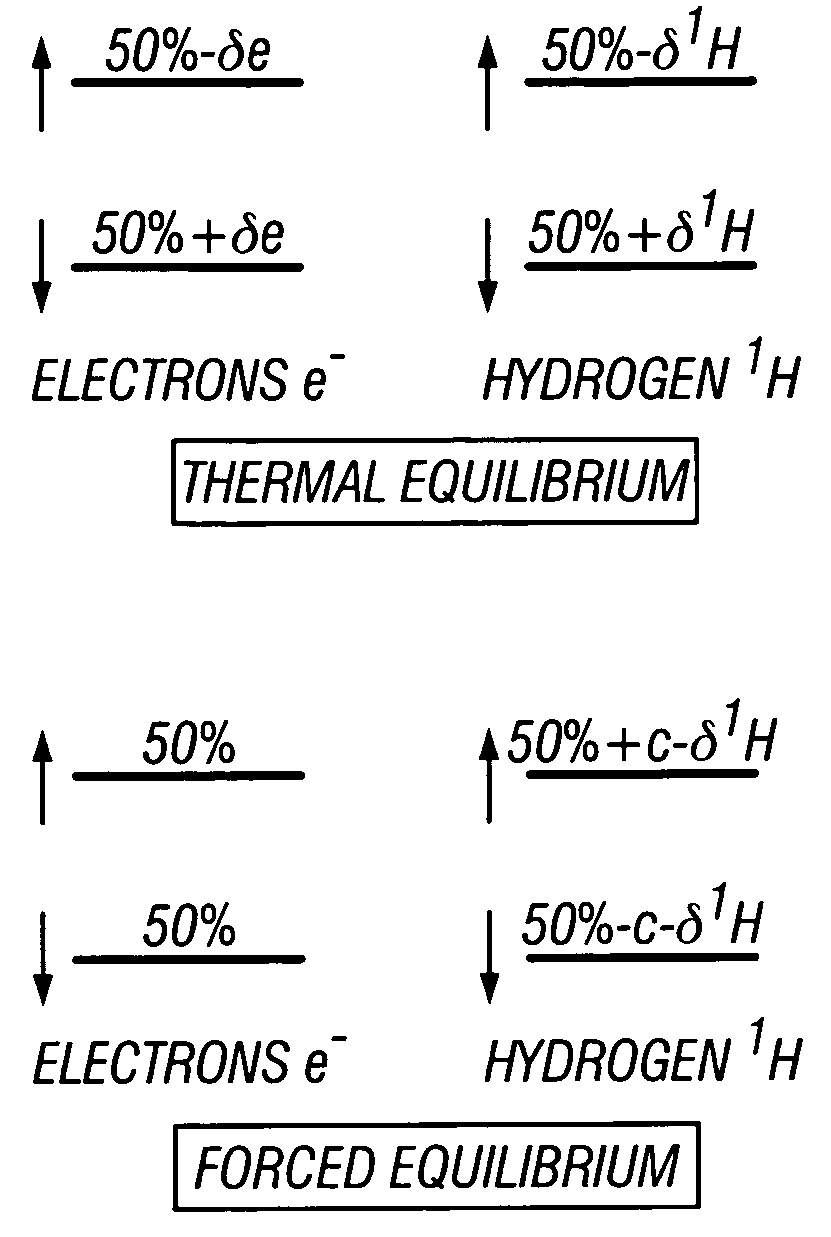
An apparatus and method is discussed for characterizing a fluid sample downhole of aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds, aromatic hydrocarbon compound, or connate mud filtrates containing carbon-13 isotopes using an enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal on a measurement-while-drilling device. To enhance the carbon-13 NMR signal these nuclei are being hyperpolarized. Either the Overhauser Effect (OE) or the Nuclear Overhauser Effect or optical pumping and the Spin Polarization Induced Nuclear Overhauser Effect (SPINOE) can serve as a mechanism for hyperpolarization of the carbon-13 nuclei.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com